Patents
Literature
67results about How to "Increased drum strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sintering method for high-chromic vanadium-titanium ferroferrite
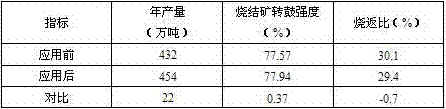
The invention discloses a sintering method of high-chromine typed V-Ti-bearing iron ore, which comprises the following steps: 1) allocating limestone and fined ferric ore to make grain; 2) adding water to wet; 3) putting wet and grained materials into sintering material in the mixer to ball; adding B2O3 in the composite material; 4) adding MgO in the composite material; 5) loading the composite material into sintering cup or sintering machine to sinter over 50 deg.c; increasing the content of calcium ferrite in the sintering ore by 5% and production by 4.2-5.0%.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL
Two-stage type blowing breeze method and apparatus for blast furnace
InactiveCN101492748AOperational Metric ImpactIncreased drum strengthTuyeresBlast furnace detailsProduct gasEngineering
The invention relates to a method for two-stage coal injection in blast furnace ironmaking and a device thereof. The invention is characterized in that the inventive two-stage coal injection device provided with a special distributor, an inert gas special pipeline, a plurality of control valves, a flowmeter and a control meter is utilized, fixed operational programs are executed and partial technological parameters are controlled, thus realizing the two-stage coal injection of the blast furnace; through practical production verification for 40 days, by adopting the device and method, blockage of injection guns is effectively avoided; the average coal ratio of the blast furnace is increased by 11.35kg / tHM; and the coke ratio is reduced by 9.87kg / tHM.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
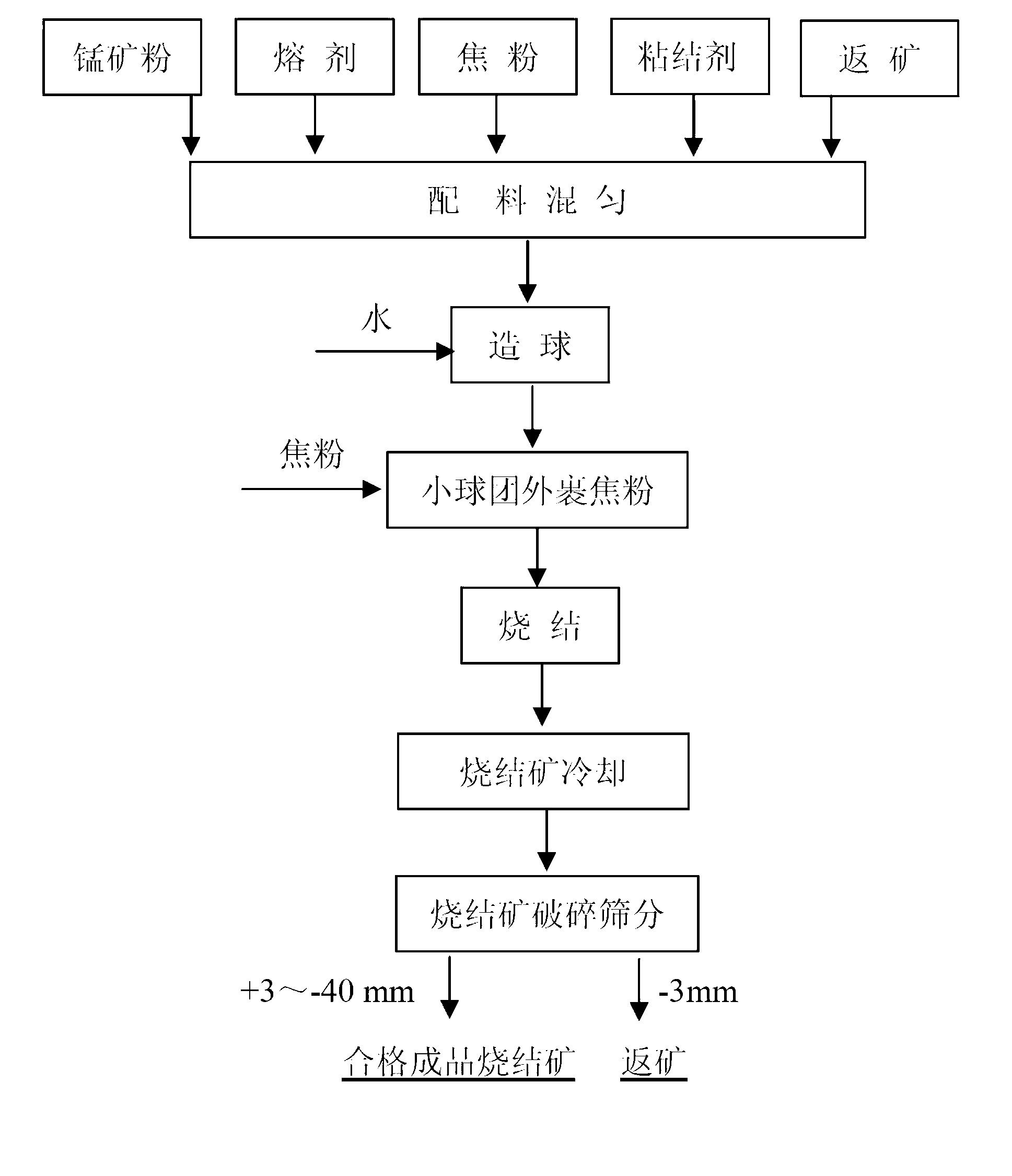
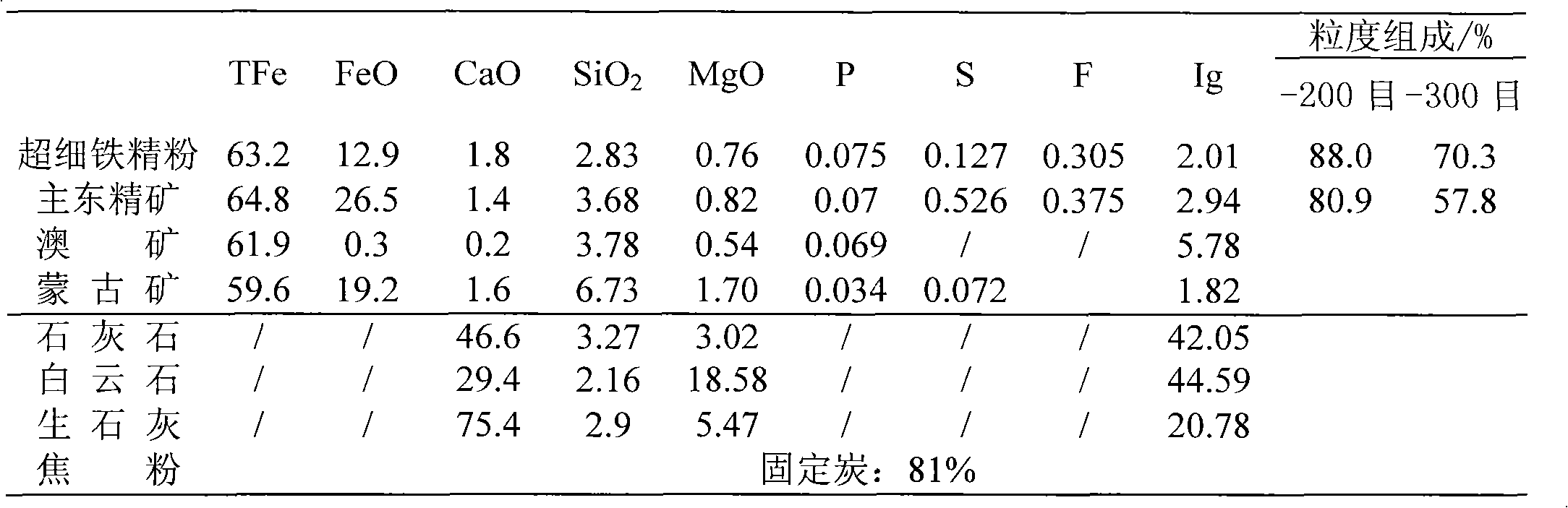
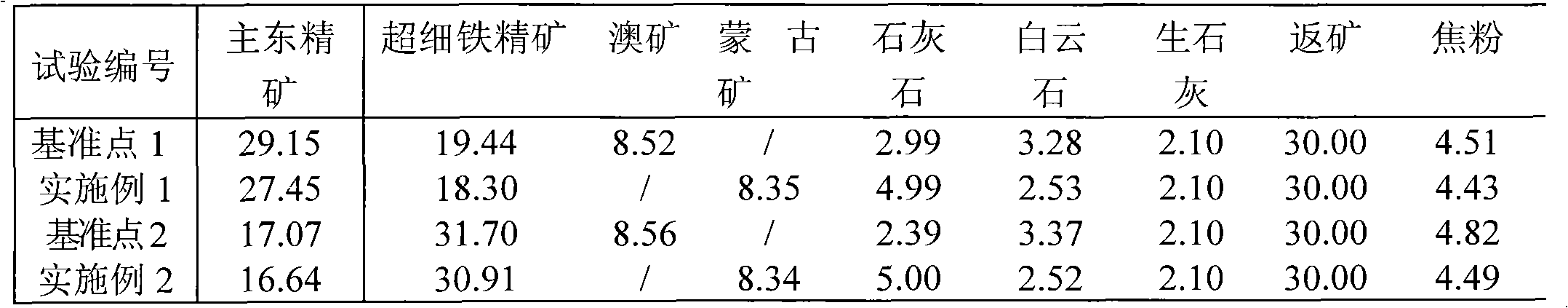
Sintering process of manganese ore powder
The invention discloses a sintering process of manganese ore powder. The process comprises the following steps of: adding water to mix manganese ore powder, a binding agent, fuel, a fluxing agent and return ore as mixed ore, wherein the binding agent is formed by mixing manganese salt and organic matter and counts for 0.6-3.0% of mass of the mixed ore, the fuel counts for 3.0-6.0% of mass of the mixed ore, the fluxing agent counts for 3.0-15.0% of mass of the mixed ore, the return ore counts for 10-30% of mass of the mixed ore and the adding amount of water counts for 5.0-15.0% of mass of the mixed ore; preparing the mixed ore as pellets; and then coating a layer of fuel on the surfaces of the generated pellets, drying and preheating, subsequently firing and sintering as hot-sintered ore; and cooling, breaking and screening the hot-sintered ore to obtain finished product sintered ore and return ore. The sintering process of manganese ore powder disclosed by the invention combines the advantages of the pelleting process and the sintering process, so that the strength and the yield of the finished product sintered ore are greatly enhanced and the energy consumption is obviously reduced.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Method for applying Bayan Obo ore ultra-fine iron powder in sintering
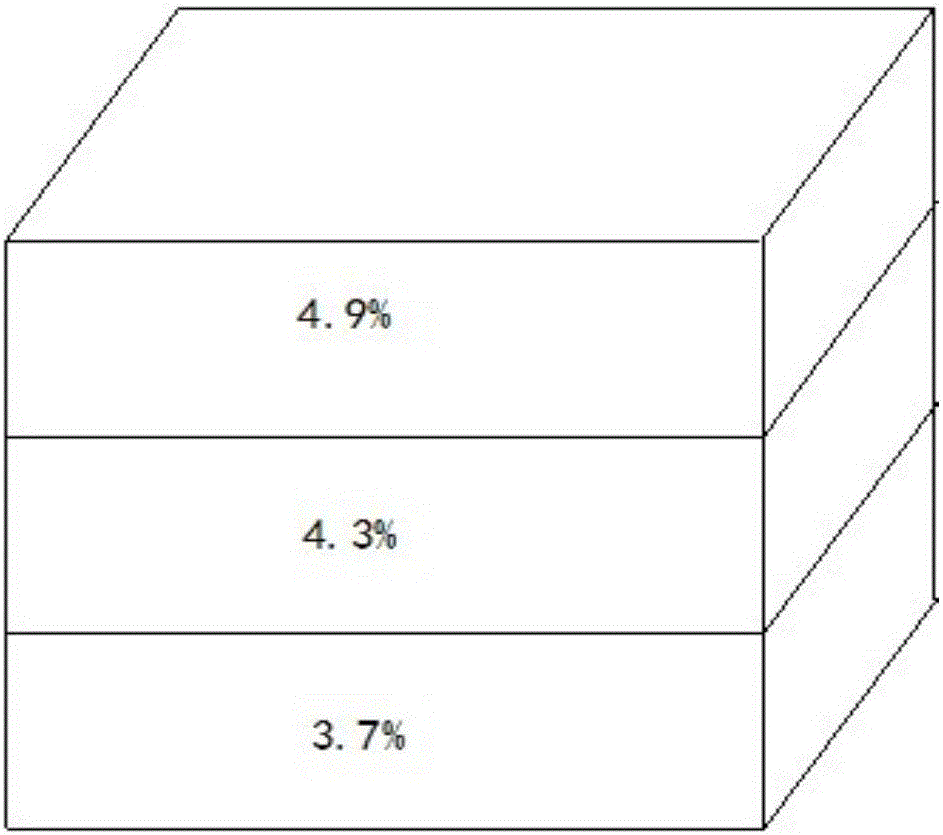
A method for applying Bayan Obo ore ultra-fine iron powder in sintering is a using method in sintering before iron making and belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy sintering. The method for applying the Bayan Obo ore ultra-fine iron powder in sintering is characterized by comprising the steps of evenly mixing and pelletizing Bayan Obo ore main ore concentrate 16%-31%, Bayan Obo oreultra-fine iron ore concentrate 17%-31%, Mongolia ore powder 8.0%-9.0%, limestone 4.9%-5.1%, dolomite 2.4%-2.6%, unslaked lime 2.1%, coke powder 4.4%-4.5% and returned ores 30%, then performing sintering in a sinter pot and supplying sintered finished ores for a blast furnace, wherein the alkalinity of the sintered ores is controlled in a range of 1.90-2.05, and MgO is controlled in a range of 1.9%-2.1%. The Bayan Obo ore ultra-fine iron powder is added into sintering mixed materials, thereby improving air permeability and the yield of the sintered ores. In addition, solid burn-up is reduced remarkably, and the process is simple.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Method for sintering ore blending of Jianshan concentrate fines and limonite
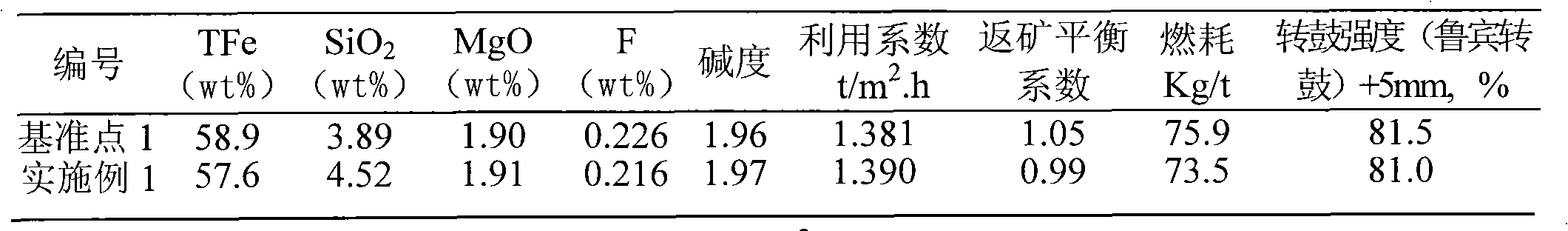
The invention discloses a method for sintering ore blending of Jianshan concentrate fines and limonite, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing materials at a sintering site; (2) pre-humidifying Yangdi fines; (3) preparing iron materials; (4) blending the prepared iron materials, flux and fuel; (5) mixing the materials in a primary mixer; (6) pelletizing in a secondary mixer; (7) forcefully pelletizing in a ternary mixer; (8) distributing and pressing the materials; (9) igniting and keeping temperature; (10) sintering by pumping air; (11) cooling; (12) granulating. The method is mainly characterized in that: when the Yangdi fines are pre-humidified, the pre-humidifying moisture reaches 8.5 to 9.5 percent; in step (3), the iron materials comprise 40 to 50 parts of Jianshan fines, 33.5 to 43.5 parts of humidified Yangdi fines, 10 to 16 parts of pilbarablend (PB) fines and 0 to 4 parts of mixed fines; and in step (4), the mass part ratio of the mixed iron materials to blast-furnace return mine to lime to dolomite to coke powder is 77.8-78.8: 7-8: 4.8-5.7: 6-7: 2-3. In the invention, the ore blending is low in cost and cheap minerals are used rationally.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Blast furnace slag recycling method
InactiveCN103374635AImprove utilization factor of blast furnaceIncreased drum strengthRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementMagnetic powderRaw material
The invention relates to a blast furnace slag recycling method. The blast furnace slag recycling method comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing blast furnace slag to the particle size of below 100mm, and sieving the crushed blast furnace slag to obtain powder with the particle size of less than 20mm and lump materials with the particle size of greater than 20mm; and (2) sequentially grinding and magnetically separating the powder to obtain magnetic powder and non-magnetic powder, wherein the magnetic powder is used as a part of sintering raw material to be sintered, and the lump materials are used as a part of furnace charge to be smelted in a blast furnace. The blast furnace slag recycling method can be used for effectively recycling the blast furnace slag and is particularly suitable for recycling the blast furnace slag with relatively high iron content.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +2
Low-carbon and low-NOx sintering method based on reasonable distribution of fuel
ActiveCN109628733AImprove less heat storageImprove the problem of insufficient heat supplyFlue gasNitrogen
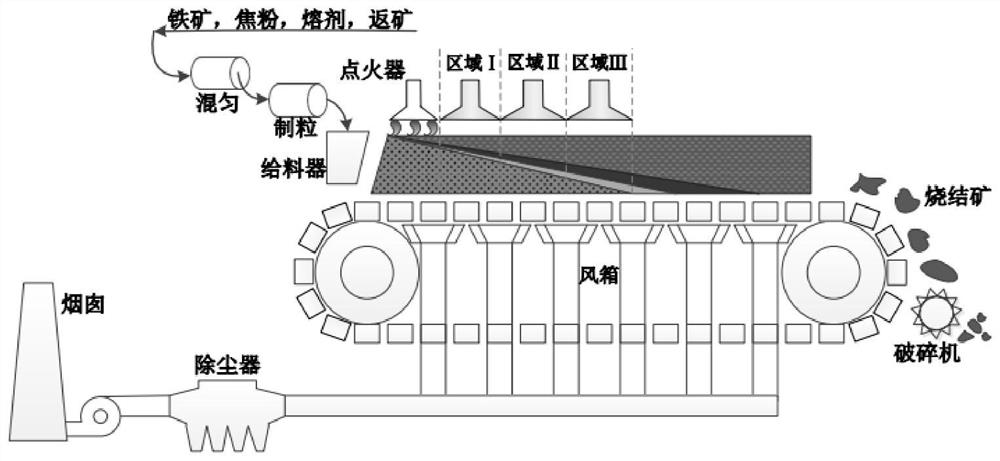
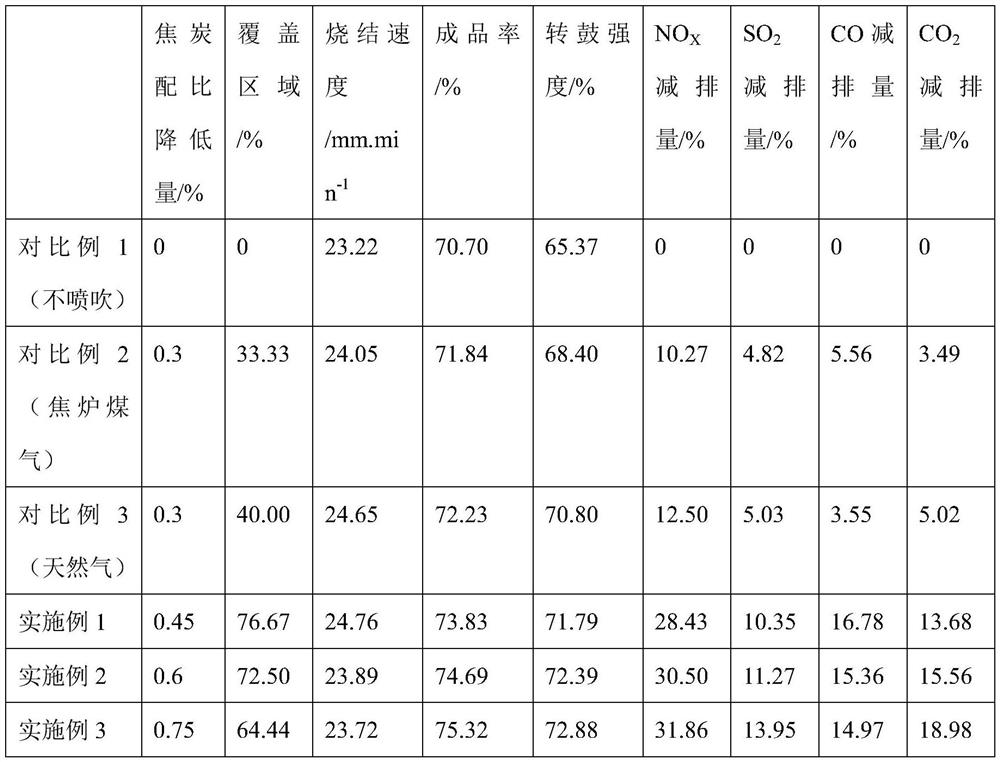
The invention discloses a low-carbon and low-NOx sintering method based on reasonable distribution of fuel. According to the low-carbon and low-NOx sintering method based on reasonable distribution offuel, a lower fuel layer is mainly fed with new fuel which is high in burning speed, relatively low in heat value and low in nitrogen content, an upper fuel layer is fed with fossil fuel which is lowin burning speed and high in heat value, flue gas with high in CO content in an intermediate air bellow of a sintering machine is circulated to a sintered material surface at the same time, and latent heat of the flue gas is fully utilized for further supplementing heat to the upper fuel layer. According to the low-carbon and low-NOx sintering method based on reasonable distribution of fuel, thecharacteristics that the sintering speed changes from low to high from the upper fuel layer to the lower fuel layer, and heat storage changes from low to high, the difference between the burning speedof the new fuel and the fossil fuel, and the difference between the heat value of the new fuel and the fossil fuel are effectively coupled, the CO latent heat in the fuel gas is efficiently utilized,and at the same time of increasing sintering yield and improving quality indexes, solid fuel consumption of each ton of sinter is reduced by 2kgce to 4 kgce, CO emission is reduced by 30% to 50%, NOxemission is reduced by 40% to 60%, and low-carbon and low-NOx sintering is implemented.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for reducing burnup of iron ore powder composite agglomerated solid
The invention discloses a method for reducing burnup of an iron ore powder composite agglomerated solid. An iron ore powder composite agglomeration material comprises a pellet material and a matrix material, wherein the pellet material does not contain fuel, and the matrix material contains solid fuel; the distribution of the matrix material along a material layer is regulated to be matched with a distribution rule of utilizable heat storage capacity at different heights of the material layer, and the content of the solid fuel in the matrix material is controlled, so that the matrix material has sufficient heat for liquid phase solidification, and the pellet material is adequately subjected to solid phase solidification by virtue of stored heat of the material layer. According to the method, the stored heat of the composite agglomeration material layer is adequately utilized, so that the consumption of the solid fuel is reduced, and the rate of finished products and the product quality of the composite agglomeration are improved. Compared with a normal composite agglomeration process, the method has the advantages that the consumption of the solid fuel is reduced by 6.2%-12.6%, the yield is increased by more than or equal to 2%-5%, and the drum strength of the product is improved by 3%-5%; by further producing blast furnace materials by virtue of operation regulations of high material layer and low negative pressure, the yield of the composite agglomeration is increased by 10%-20%, and the electricity consumption of an exhaust fan is decreased by 10% or more.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Low-carbon low-emission sintering method based on coupled injection of multiple gases
The invention discloses a low-carbon low-emission sintering method based on coupled injection of multiple gases. Based on the difference of heat storage capacities of parts at the heights of differentmaterial layers, areas from thermal insulation completion to a waste gas temperature rising point of a material surface of a sintering machine are sequentially divided into a low heat storage capacity area, an intermediate heat storage capacity area and a high heat storage capacity area according to the temperature intervals smaller than 1250 DEG C, 1250-1300 DEG C and 1300-1350 DEG C, and high heating value gas with the injection heating value being larger than 30 MJ / Nm<3>, an intermediate heating value gas with the injection heating value being 15-30 MJ / Nm<3> and low heating value gas withthe injection heating value being smaller than 15 MJ / Nm<3> are separately injected to the three areas. The low-carbon low-emission sintering method effectively couples the differences between the heating capacity requirements and the gas quality of different areas of the sintering material layer, realizes heating capacity balanced distribution of the material layers at different heights, forms a beneficial ore-forming condition, greatly improves the sintering quality and the quality index, meanwhile, effectively expands the coverage area of gas injection, further reduces the solid fuel consumption, increases the emission reduction ratio of pollutants such as NOX, SO2 and COX, and realizes the low-carbon low-emission sintering.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Novel additive for improving tumbler strength of vanadium-titanium magnet sintered ore
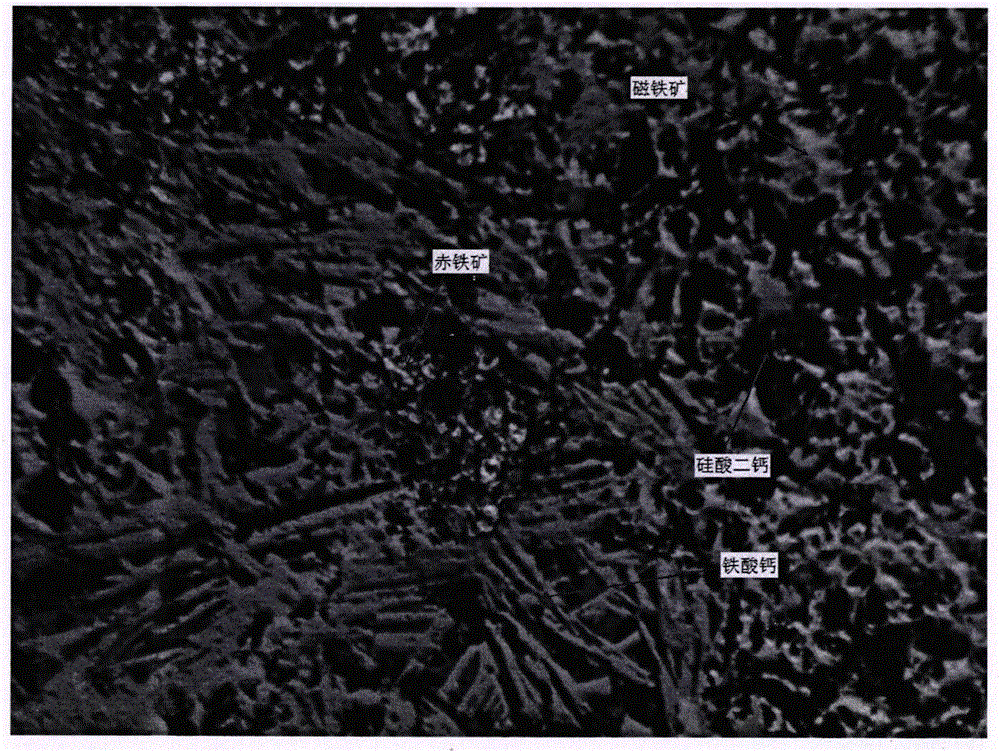
The invention provides a novel additive for improving tumbler strength of vanadium-titanium magnet sintered ore. The novel additive contains, by weight percentage, 10-30% of B2O3, 5-20% of NaCl, 3-9% of NaNO3 and 45-85% of CaCl2, and the addition amount is 0.04-0.06%. The additive is added in a manner that the additive is prepared into a solution, the solution is added to a sintering mixed material when mixing for the first time is conducted, and a sintering test is conducted. It is indicated through test results that the content of magnetite, the content of hematite and the content of perovskite in the sintered ore are decreased; the content of calcium ferrite, the content of dicalcium silicate and the content of vitreous substances are increased; the air hole rate of the sintered ore is reduced; the proportion of maculosus-granular structures which are poor in strength in an ore phase structure is reduced; the proportion of corrosion structures which are good in strength is increased; the ore phase structure becomes more uniform; and furthermore, compared with that of sintered ore with no additive added, tumbler strength is improved by 1.5-3.5%.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
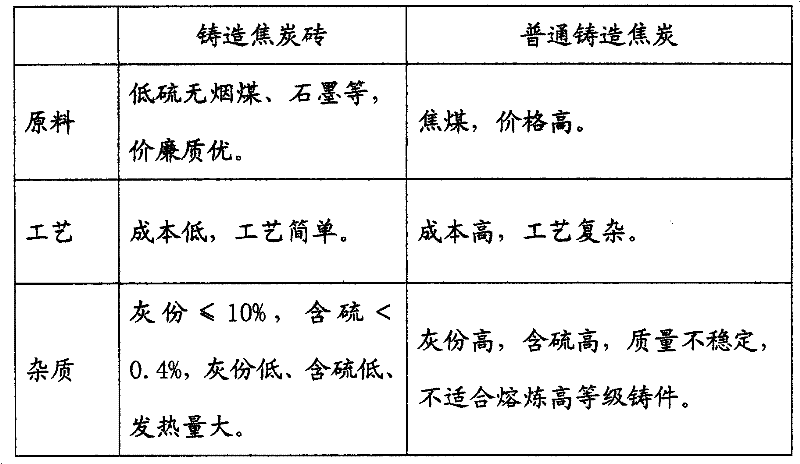
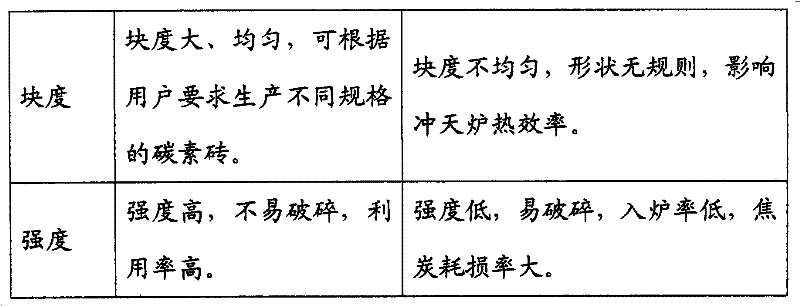
Cast coke brick and its production method
InactiveCN102295944AHigh calorific valueImprove pass rateSpecial form destructive distillationFoundryBrick
The invention discloses casting coke bricks and a production method thereof, which belong to the production technology of coke for industrial use. The product is made of the following raw materials in weight ratio: 60%-72% of low-sulfur anthracite, 10%-15% of graphite, 2.5%-3% of tar, and the balance is waste paper pulp. The low-sulfur anthracite is crushed to a diameter of 0.5-2 mm. After preheating and drying, it is mixed with graphite, tar, and waste paper paddles in a kneading mixer, and then shaped by a pressure molding machine. The temperature of the kiln is raised to 800 Carbonize at ~1000°C for 6-9 days, and cool down to room temperature naturally to obtain cast coke bricks. No need to add coking coal during production, the production cost is low, and the process is simple. Cast coke bricks have high calorific value, fixed carbon can reach more than 85%, volatile content can be controlled below 1.5%, drum strength can reach more than 98%, high density, durable and flame-resistant. Ash content ≤ 10%, sulfur content < 0.4%, less ash content, low sulfur content, full combustion, less exhaust gas emission, and easy transportation.
Owner:吴亚飞
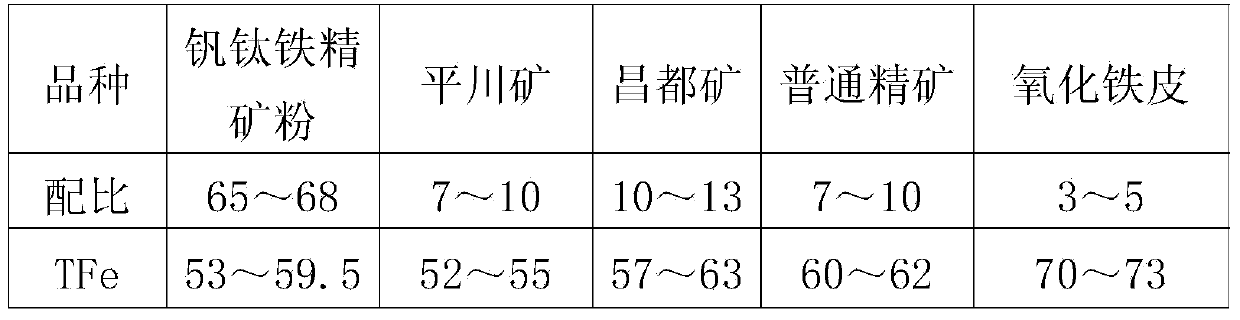
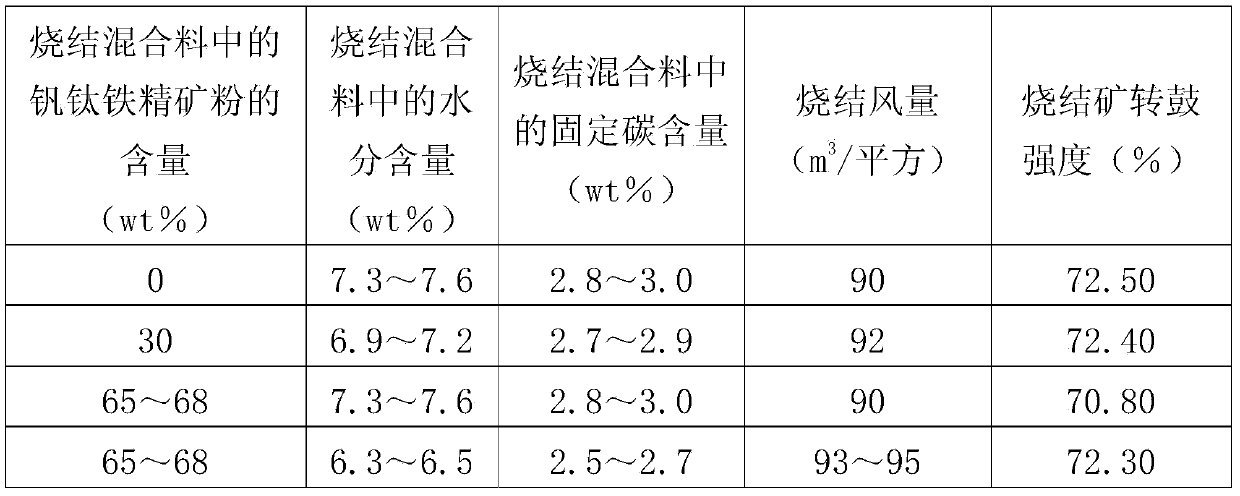
Method for improving drum index of vanadium-titanium magnetite sinter
The invention discloses a method for improving the drum index of vanadium-titanium magnetite sinter. A sinter mixture of the vanadium-titanium magnetite sinter comprises 65-68 percent by weight of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate powder, wherein the moisture content in the sinter mixture is reduced to 6.3-6.5 percent by weight, the sintering air volume is reduced to 93-95m<3> / <m2>, and the fixed carbon content in the sinter fixture is reduced to 2.5-2.7 percent by weight. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that a large change is not made to the overall sintering process, only are control indexes, such as moisture content and fixed carbon content in the sinter mixture and sintering air volume optimized, and the technical effect that the drum strength of the sinter is improved to above the level required by a blast furnace is achieved under the sintering condition of high vanadium-titanium magnetite sinter rate.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP CHENGDU STEEL & VANADIUM
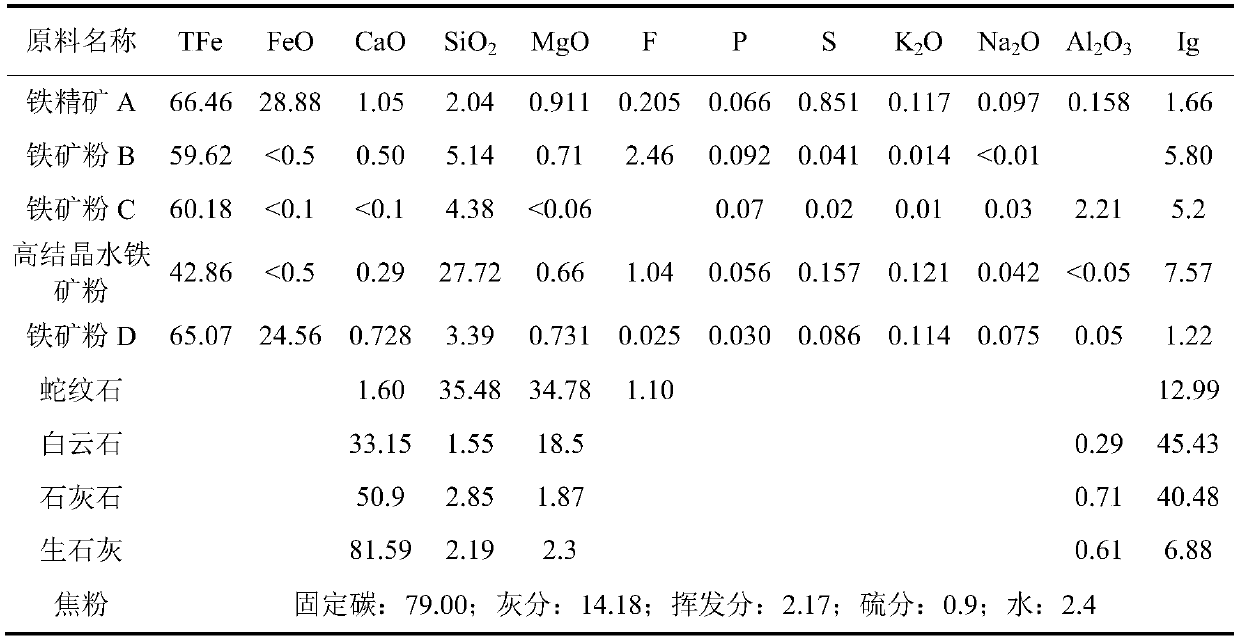
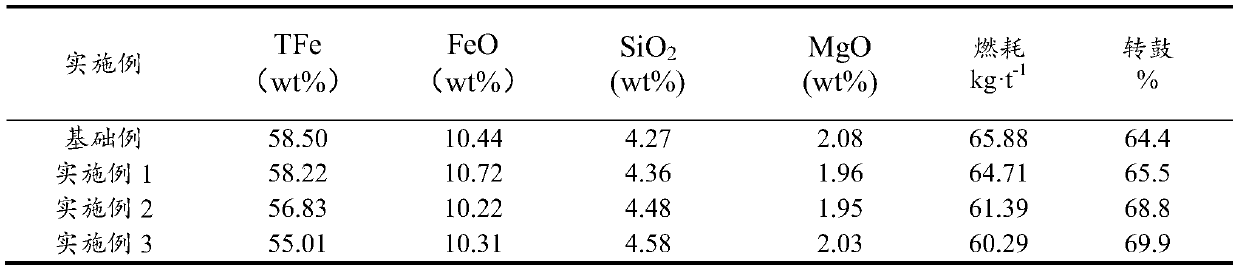
Method for preparing sintering ore from high-crystallite ferrihydrite powder
The invention discloses a method for preparing a sintering ore from high-crystallite ferrihydrite powder. The method includes the following steps of firstly, preparing a raw material from, by mass, 75-90% of iron powder, 3.5-8.5% of limestone, 0-4% of light-burned dolomite, 1.5-2.5% of serpentine, 3.0-4.5% of quick lime and 4.5-6.0% of coke powder; secondly, adding water to the raw material to bemixed to obtain a mixture, and performing granulating to obtain granules; and thirdly, performing distributing, igniting and sintering on the granules to obtain the sintering ore. The obtained sintering ore has the alkalinity of 1.95-2.05, the MgO mass percentage of 1.90-2.10% and the tumbler strength of larger than or equal to 65.8%, can be effectively used for production in a blast furnace, andensures the long-term smoothness of the production in the blast furnace.
Owner:BAOTOU IRON & STEEL GRP
Sintering-mineralizing energy-saving combustion adjuvant and its preparing method
This invention discloses an energy save combustion accelerator and its manufacturing method for agglomerate, which mixes borax 45%-50% boric acid 10%-14%, NaHCO3 24%-30%, NaCl 21%-6% in the proportion of a formula to mix them evenly and put them in bags. The chemical reaction of said accelerator is carried out in the sintering process, which can further increase its smelting strength and reduce the coke ratio.
Owner:刘志伟
Method for preparing sintered ore by using coke drying quenching (CDQ) powder and sintered ore manufactured by method
ActiveCN111500855AImprove hydrophilicityImprove combustion performanceProcess efficiency improvementCokeCalcium ferrite
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered ore by using coke drying quenching (CDQ) powder. The method comprises the steps that firstly, wetting pre-treatment is carried out on the CDQ powder; next, a premix is prepared, wherein the wetted CDQ powder is pre-mixed with a flux with particle size less than or equal to 3mm to prepare the premix, that is C-melting pre-mixed powder; next, ablending material is prepared, and the C-melting pre-mixed powder is evenly mixed with hematite powder and magnetite concentrate powder to prepare the blending material; next, sintering ingredients are prepared; and finally, the sintered ore is prepared. The high-efficiency utilization of the CDQ powder is achieved, the ratio of coke particles and fuel consumption is significantly reduced, and CO2 and NOx emission is reduced; and the content of calcium ferrite in the fine hematite concentrate powder sintered ore obtained according to the method is improved, the drum strength can be improved,and the reducibility can be improved. The invention further discloses sintered ore manufactured by the method for preparing the sintered ore by using the CDQ powder.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
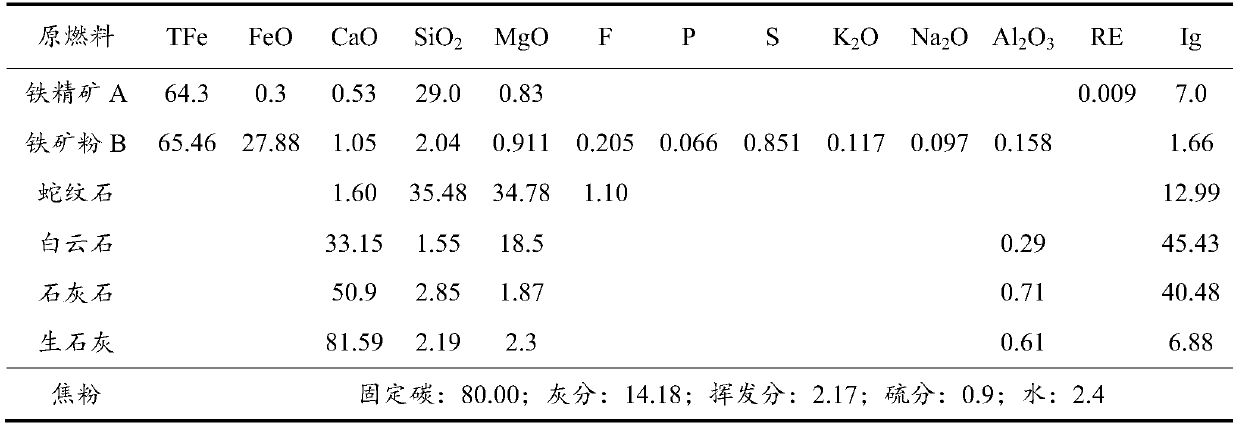
F-containing sintered ore and production method thereof
The invention discloses F-containing sintered ore and a production method thereof. The production method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of 1) proportioning the following components including, by mass, 5%-15% of iron ore concentrate A, 65%-75% of iron ore powder B, 3.5%-8.5% of limestone, 0-4% of light calcined dolomite, 1.5%-2.5% of serpentine, 3.0%-4.5% of quick lime and4.5%-6.0% of coke powder, and obtaining a raw material; 2) adding water into the raw material, performing mixing to obtain a mixture, and performing granulating to obtain granules; and 3) performing distributing, igniting and sintering on the granules to obtain the F-containing sintered ore. The prepared F-containing sintered ore has the drum strength of more than or equal to 65.5%, can be effectively used for blast furnace production, and ensures long-term smooth operation of the blast furnace production.
Owner:BAOTOU IRON & STEEL GRP
Centrifugal extraction machine drum resistant to strong acid corrosion
InactiveCN106267884AIncreased drum strengthEasy to processLiquid solutions solvent extractionAgricultural engineeringStrong acids
The invention provides a centrifugal extraction machine drum resistant to strong acid corrosion. The centrifugal extraction machine drum is used for completing mixing and separating of two kinds of incompatible liquid unequal in density. The problems that a drum is low in strength, complex in structure and nonresistant to strong acid corrosion are solved. The centrifugal extraction machine drum is high in strength, easy to machine, accurate in size and resistant to strong acid corrosion.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TIANYI EXTRACTION TECH
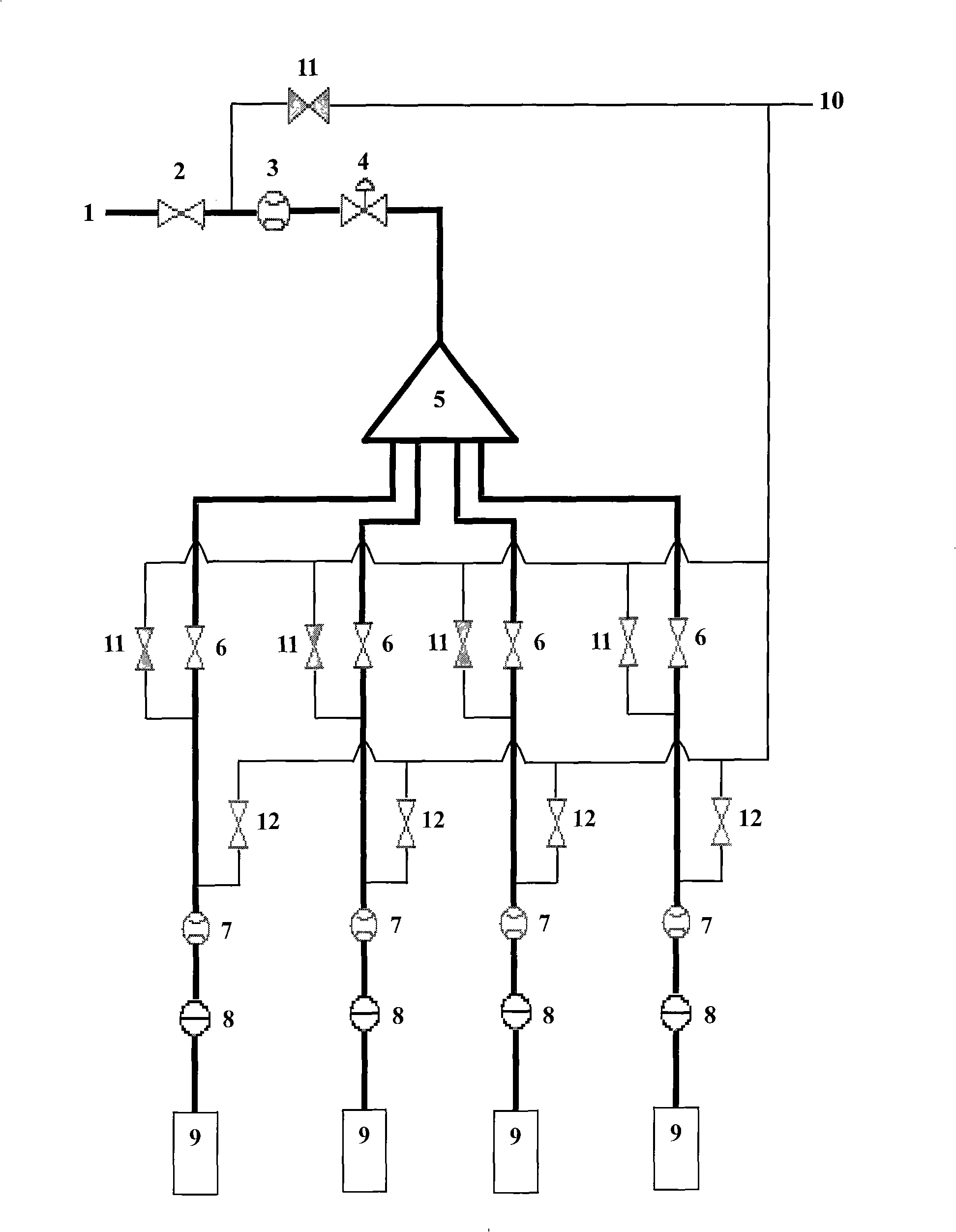
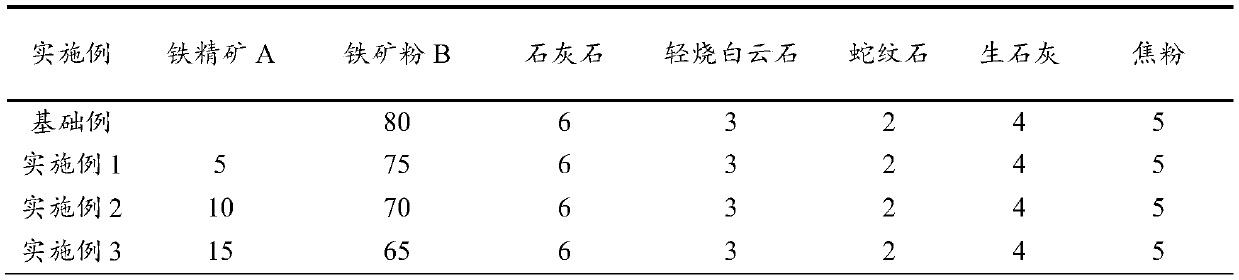
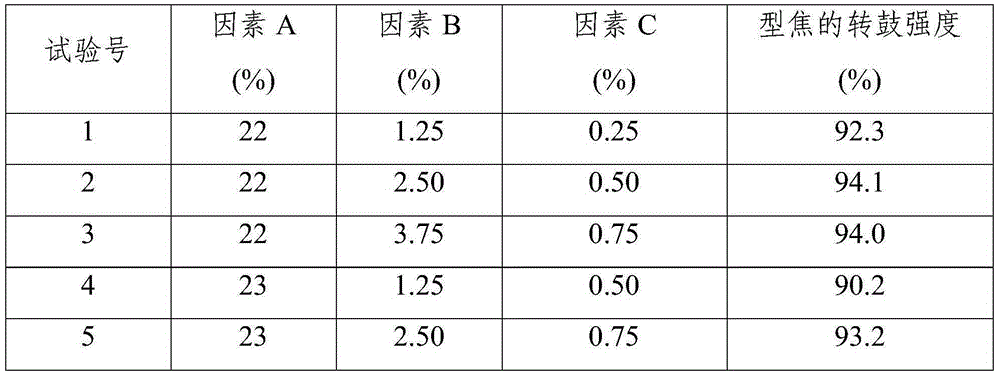
Sintering method for high-chromic vanadium-titanium ferroferrite
The invention provides a sintering method of high-chromium vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate, which can effectively reduce the melting point of high-chromium-type vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate sintering mixture, improve the mineral composition and structure of sintered ore, thereby improving the sintering rate. mine quality and yield. The method comprises the following steps: 1) pre-granulating the iron concentrate with quicklime; 2) pre-wetting the returned ore with water; 3) preparing the sintered material from the pre-granulated material and the pre-wetted returned ore, and placing the sintered material in the Mix and pelletize in a mixer, and add B2O3 to the mixture; 4) Add MgO to the mixture; 5) Put the mixture into a sintering cup or a sintering machine for sintering. After adopting the method of the invention, the melting point of the sinter mixture is lowered by more than 50°C, the content of calcium ferrite in the sintered ore is increased by more than 5 percentage points, the drum strength of the sintered ore is increased by 1.09-1.56 percentage points, the yield is increased by 1.27-3.18 percentage points, and the output is increased. 4.2% to 5.0%.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON AND STEEL
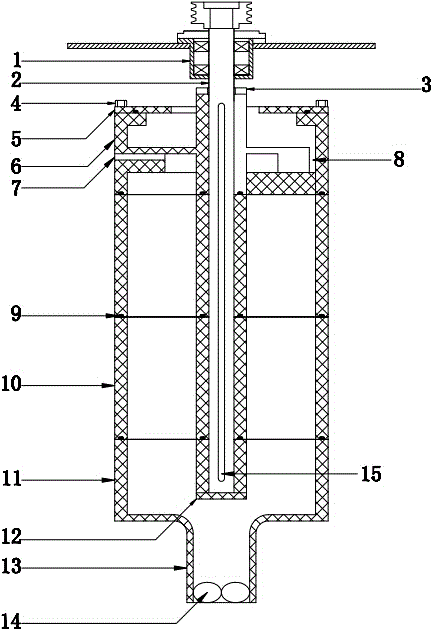
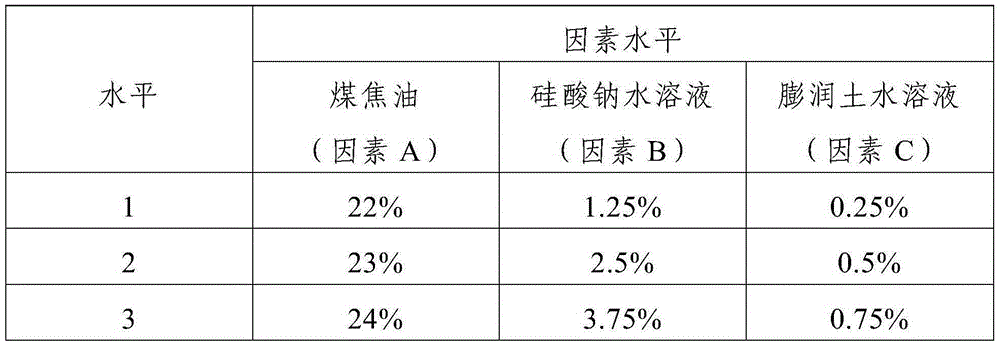
Method for preparing formed coke
The invention provides a method for preparing formed coke. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a sodium silicate aqueous solution and a sodium bentonite aqueous solution; 2, adding coal tar, the sodium silicate aqueous solution and the sodium bentonite aqueous solution into pulverized coal, uniformly mixing, filling a steel mold with the mixture, performing cold press molding by utilizing a hydraulic press, and demolding to obtain a blank material; and 3, drying the blank material in a drying oven, and naturally cooling to obtain the formed coke. The formed coke prepared by adopting the method is an organic-inorganic composite material, and novel formed coke with high cold strength can be produced by adopting the cold press molding method; and the type of coal mines can be selected without strict requirements, and formed coke with high tumbler strength can be prepared by utilizing lean coal, meager lean coal and other weak caking coal.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fuel gradation homoenergetic sintering method
InactiveCN106636618AReduce energy consumptionImprove utilization factorChemical reaction kineticsHigh energy
The invention discloses a fuel gradation homoenergetic sintering method and relates to the field of strand sintering of iron ore powder in the metallurgical production system and chemical reaction kinetics. According to the method, the automatic heat accumulation function in the sintering process of a material bed is considered, the fuel usage amount is gradually reduced in the height direction of the material bed, so that the sintering material bed can keep stable production performance of high temperature and uniformity from top to bottom, and the effects of high quality, high yield and low energy consumption are achieved; the method aims for energy consumption reduction and waste heat recovery in the steel production, has the eyes on the characteristic that automatic heat accumulation can be conducted on a thick material bed in the sintering technique with higher energy consumption and solves the problem that the quality of sintered ores in the height direction of the material bed is uneven, so that the yield of the sintered ores is reduced, and sintering energy consumption is increased, so that the utilization efficiencyof waste heat and the utilization factor, the tumbler strength and the yield of the sintered ores are improved, and the average grain diameters of finished ores are increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Fluctuation treatment method of sinter bed based on master pumping regulation
The invention relates to a sintering production process of a mixed material and particularly relates to a fluctuation treatment method of a sinter bed based on master pumping regulation. The method provided by the invention completes the sintering process in a qualified manner by monitoring the thickness of a bed on a vehicle to determine the master pumping rotating speed and adjusting the sintering time of a skip car if the bed is thick, so that the sinter quality is improved, the drum strength is improved, the rate of return mine of sintering is reduced, and the circular material amount is reduced. The problem of red ores easy to appear when the bed is thick is avoided, and the service life of a product belt is prolonged.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
A Method for Improving the Air Permeability of All-fine Powder Sintered Material Layer
The invention discloses a method for improving the air permeability of a fully refined powder sintered material layer, relates to the field of steel smelting, in particular to the field of fully refined powder sintered ore. The method comprises the steps that sintering return mines are adopted as granulating balls, are subjected to primary fully refined powder batching mixing, secondary fully refined powder batching mixing, and tertiary fully refined powder batching mixing sequentially, then enter a material loosening device, come out of the material loosening device, and then enter a sintering process. Before being subjected to the primary fully refined powder batching mixing, the sintering return mines are subjected to pre-wetting with atomized water till the water content reaches 4-6%.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
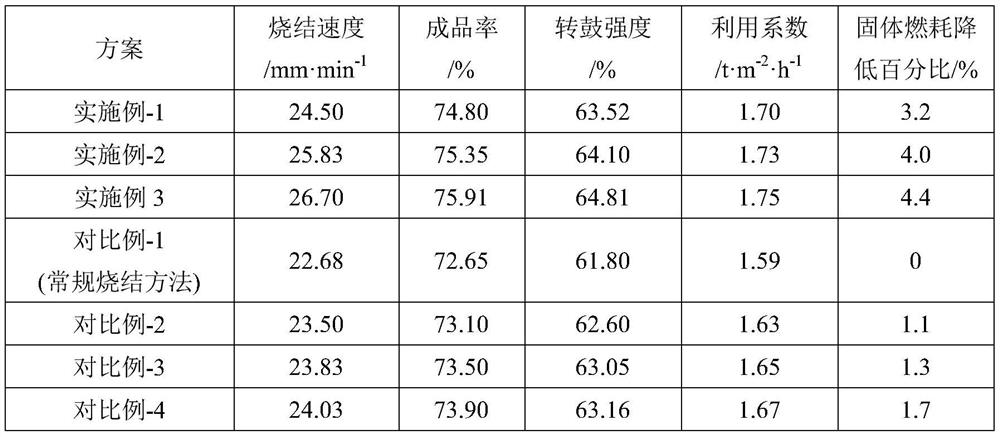
Method for strengthening sintering of high-proportion fine-grained material through multi-medium gas injection
The invention discloses a method for strengthening sintering of a high-proportion fine-grained material through multi-medium gas injection. The method comprises the following steps that uniform mixing, granulation, distribution, ignition and sintering are sequentially conducted on raw materials such as fine-grained iron ore, a fluxing agent, high-combustion-activity fuel, conventional fossil fueland return mines, and a mixed gas medium formed by fuel gas and water vapor is sprayed to the surface of a sintered material in the sintering process. According to the method, the permeability and thethermal state of a material layer are optimized by regulating and controlling the characteristic parameters and the addition proportion of the high-combustion-reaction-activity fuel and regulating and controlling the injection concentration and the coverage range of multi-medium gas and the relative volume percentage of fuel gas and water vapor in a coupling manner, so that the sintering of high-proportion fine-grained material is strengthened.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
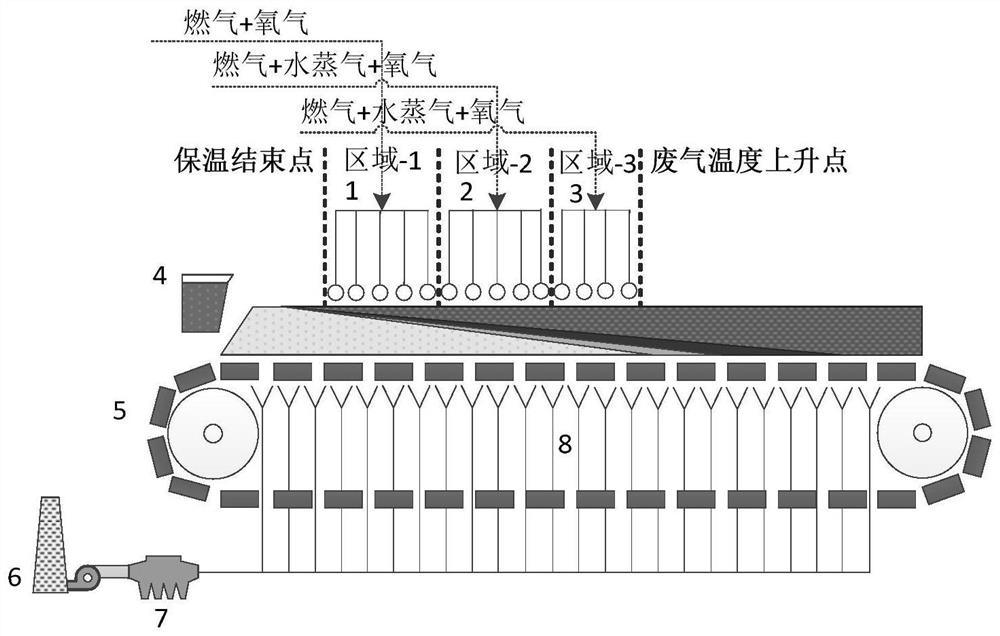
Low-energy-consumption and low-emission sintering method for multi-component gas medium composite injection
The invention discloses a low-energy-consumption and low-emission sintering method for multi-component gas medium composite injection. The method comprises the following steps: sequentially dividing a region, from an ignition end point to a waste gas temperature rising start point, of a sintering material surface in a sintering machine into a region 1, a region 2 and a region 3; and in the sintering process, blowing a multi-component gas medium with a high fuel gas ratio to the region 1, a multi-component gas medium with a medium fuel gas ratio to the region 2, and a multi-component gas medium with a low fuel gas ratio to the region 3. By means of the method, the limitation of different heat requirements at different heights of a material layer can be met to a greater extent, the combustion efficiency of fuel is improved synergistically, the solid fossil fuel consumption is further reduced, the solid fuel consumption can be reduced by 6-10 kg, and the emission of CO2 is reduced by 18-30%, the emission of CO is reduced by 25-40%, and the emission of dioxin is reduced by 40-70%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A sintering method for sintering base material
The invention discloses a sintering bedding material, and a manufacturing method and sintering method thereof, relating to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy. The sintering bedding material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 48-52 parts of sintering dust, 20-24 parts of gas ash, 14-16 parts of gas sludge, 11-12.8 parts of converter dust and 1.0-1.2 parts of bentonite. The particle size of the sintering bedding material is 7-20mm, and the thickness of the sintering bedding material is 25-35mm. The technique can save abundant finished sinter and lump ore resources, greatly enhance the sintered ore yield and output and lower the fuel consumption and production cost. The sintering bedding material can sufficiently utilize various iron-containing dust and sludge generated in the steel production process, thereby changing wastes into valuable substances and reducing the environmental pollution. The technique has favorable effect, is simple and easy to implement, only needs to add one iron-containing dust and sludge pelletizer, and has the advantages of high feasibility for popularization and application and high practical value.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Economical method for preparing carbon-containing pellet, carbon-containing pellet prepared through method and smelting process of carbon-containing pellet
InactiveCN108384947AEliminates tendency to popAvoid poor heat transfer conditionsSmelting processMass ratio
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy, and particularly relates to an economical method for preparing a carbon-containing pellet, a carbon-containing pellet prepared through the method and a smelting process of the carbon-containing pellet. The economical method for preparing the carbon-containing pellet comprises the following steps that 1, hematite powders used for preparingthe carbon-containing pellet are divided into first hematite powders and second hematite powders by the mass ratio of 0.8:1.2; 2, Fe2O3 in the first hematite powders is converted into Fe3O4 to obtainmagnetite powders; and 3, the magnetite powders obtained in the step 2, the second hematite powders in the step 1 and coal powders are mixed to obtain the carbon-containing pellet, and the mass ratioof the mass sum of the magnetite powders and the second hematite powders to the coal powders is (6-8):3. The economical method for preparing the carbon-containing pellet can effectively improve the DRI metallization rate of carbon-containing pellets, enhances the drum strength, and is capable of saving energy and economical, and the carbon-containing pellet is convenient to transport and store.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
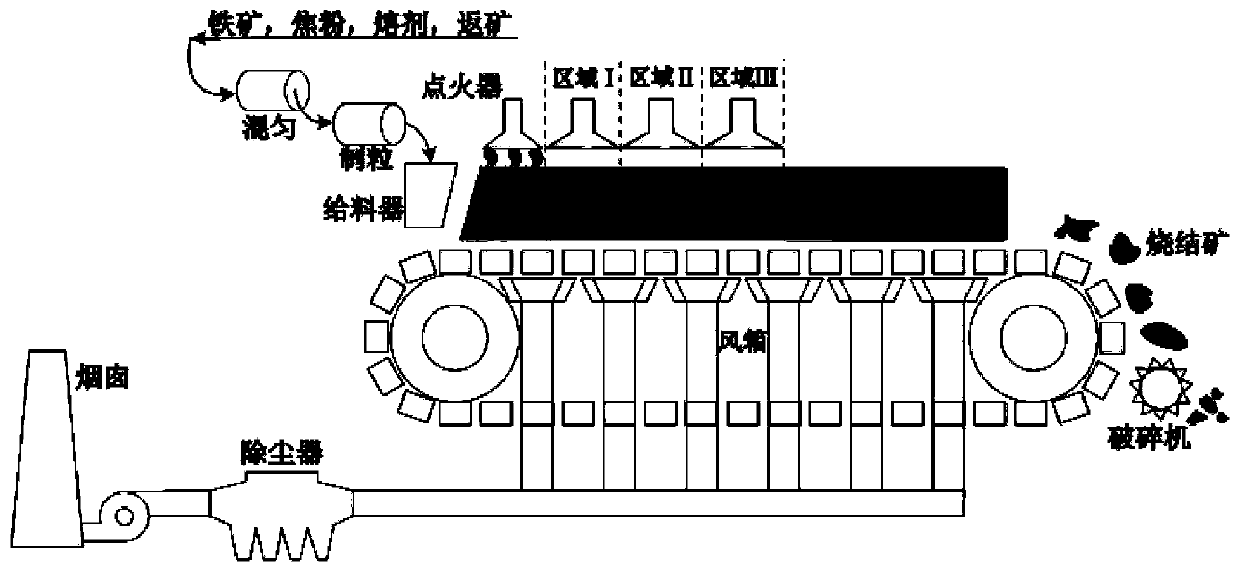
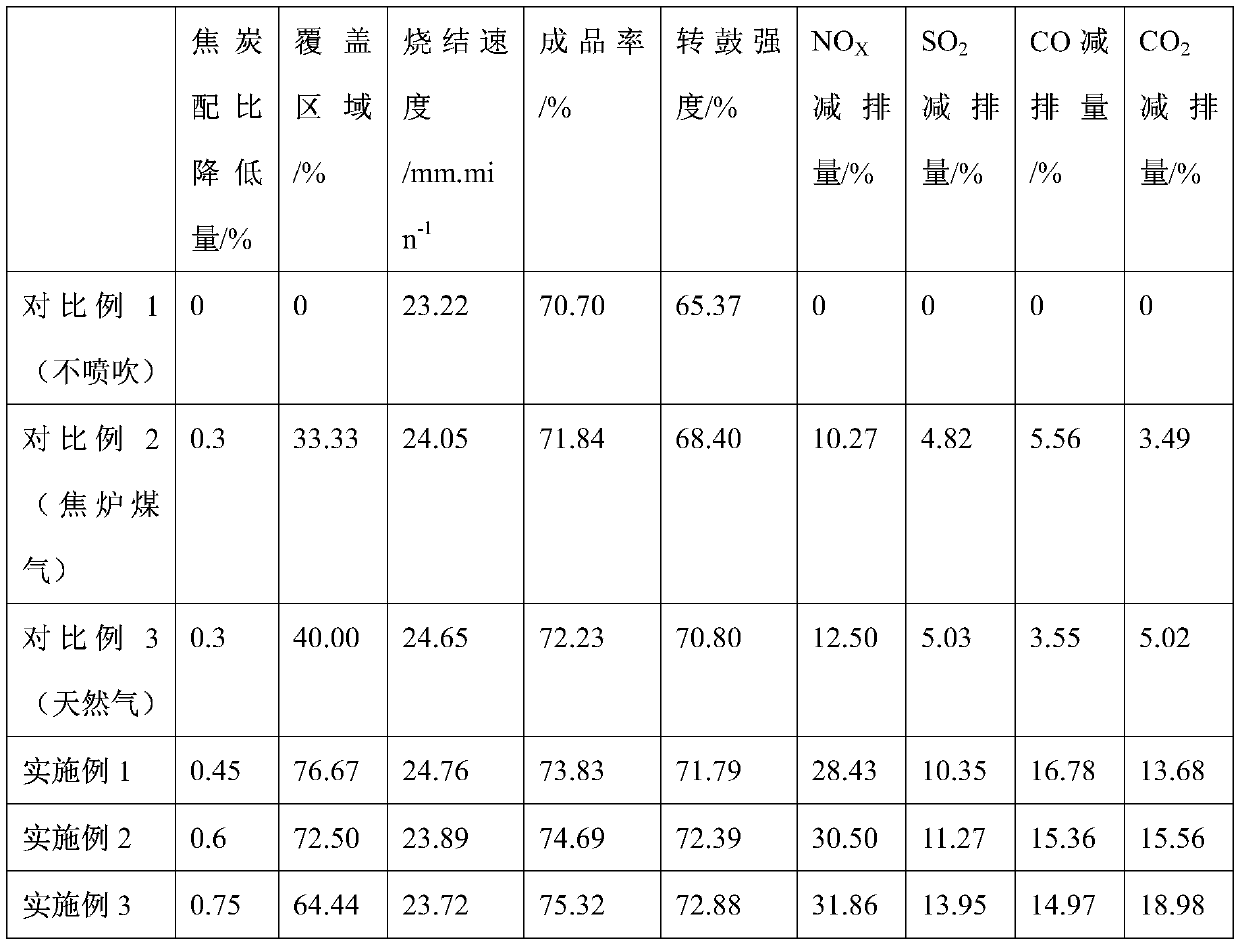
A low-carbon and low-emission sintering method based on multi-type gas coupling injection
The invention discloses a low-carbon low-emission sintering method based on coupled injection of multiple gases. Based on the difference of heat storage capacities of parts at the heights of differentmaterial layers, areas from thermal insulation completion to a waste gas temperature rising point of a material surface of a sintering machine are sequentially divided into a low heat storage capacity area, an intermediate heat storage capacity area and a high heat storage capacity area according to the temperature intervals smaller than 1250 DEG C, 1250-1300 DEG C and 1300-1350 DEG C, and high heating value gas with the injection heating value being larger than 30 MJ / Nm<3>, an intermediate heating value gas with the injection heating value being 15-30 MJ / Nm<3> and low heating value gas withthe injection heating value being smaller than 15 MJ / Nm<3> are separately injected to the three areas. The low-carbon low-emission sintering method effectively couples the differences between the heating capacity requirements and the gas quality of different areas of the sintering material layer, realizes heating capacity balanced distribution of the material layers at different heights, forms a beneficial ore-forming condition, greatly improves the sintering quality and the quality index, meanwhile, effectively expands the coverage area of gas injection, further reduces the solid fuel consumption, increases the emission reduction ratio of pollutants such as NOX, SO2 and COX, and realizes the low-carbon low-emission sintering.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for improving utilization efficiency of solid fuel and application of solid fuel in production process of sintered ore
InactiveCN106090978AIncrease the calorific value of combustionPromote generationLump/pulverulent fuel feeder/distributionLump/pulverulent fuel preparationSolid fuelEngineering
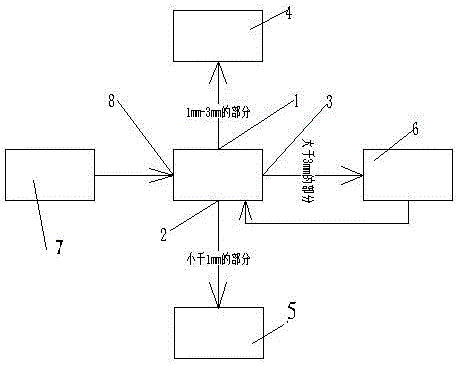
The invention discloses a method for improving the utilization efficiency of solid fuel and belongs to the technical field of iron making and briquetting. The difference of the method from a conventional solid fuel processing procedure is that a solid fuel winnowing device is additionally arranged on a solid fuel crushing machining procedure, solid fuel smaller than 1.0 mm is winnowed, and the solid fuel is conveyed to a blast furnace procedure to be used as blast furnace injection coal. According to the solid fuel crushing machining process, on the one hand, the grain composition of the solid fuel for sintering can be improved, the drum strength and average grain size of the sintered ore can be improved, and the sinter return rate of a blast furnace is reduced; on the other hand, the winnowed solid fuel smaller than 1 mm is used for blast furnace injection, best use is achieved, and the utilization efficiency of the solid fuel is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for manufacturing ultra-low alkalinity high-strength sintered ore
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing ultra-low alkalinity high-strength sintered ore. The technical problem of low iron grade of sintered ore produced by using iron ore with the high SiO2 content in the prior art is mainly solved. According to the technical scheme, the method for manufacturing the ultra-low alkalinity high-strength sintered ore comprises the steps that (1) a magnesium flux is prepared; (2) burdening is carried out, and the iron ore and the magnesium flux used for sintering are weighed according to the proportion, the binary alkalinity R2 of the sintered ore is controlled to be 1.70-1.80, the weight percentage of SiO2 in the sintered ore is 5.0%-5.7%, and the weight percentage of MgO is 1.0%-1.2%; (3) mixing and granulating are carried out, a primary mixing material is transferred into a secondary mixing drum for mixing and granulating, and a secondary mixing material is obtained after granulating; and (4) air extracting and sintering are carried out on the secondary mixing material, and after sintering, the finished sintered ore is obtained. The high-strength sintered ore produced by the iron ore with the high SiO2 content is obtained, and the significant benefit is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Pressurized densification sintering method for laterite nickel ore
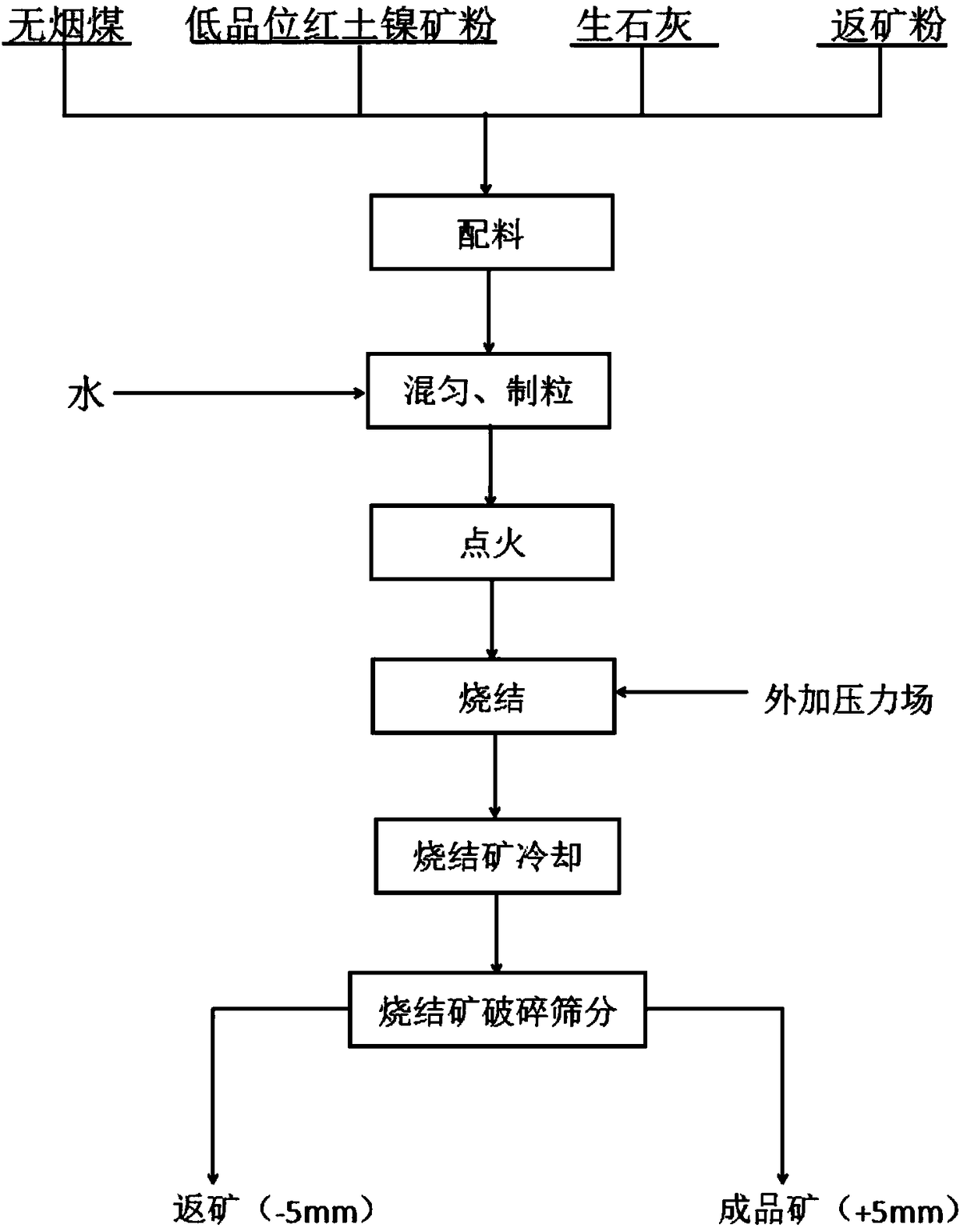
The invention discloses a pressurized densification sintering method for laterite nickel ore, which includes steps of: 1) mixing laterite nickel ore, return mine powder, a fuel, and quicklime to obtain a mixture material; 2) regulating water content of the mixture material to 16-18 wt%, and performing mixing granulation to obtain a sintering material; 3) loading the sintering material in a sintering machine and igniting the sintering machine; 4) applying an external force field to the surface of the sintering material and sintering the sintering material to obtain thermo-sintered ore; 5) removing the external force field and cooling the thermo-sintered ore, and crushing and sieving the product to obtain a sintered ore finish product. In the method, by applying a certain pressure to the surface of the laterite nickel ore sintering material, loosen sintered ore from the surface layer to the middle layer can be auto-densified, so that strength and yield of the sintered laterite nickel orecan be improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com