Method for reducing burnup of iron ore powder composite agglomerated solid
A technology of composite agglomeration and iron ore powder, which is applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve problems such as the difficulty in the development of the furnace charge preparation process, earth damage, fine particle size, etc., and achieve the effects of increased output, reduced emissions, and improved drum strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
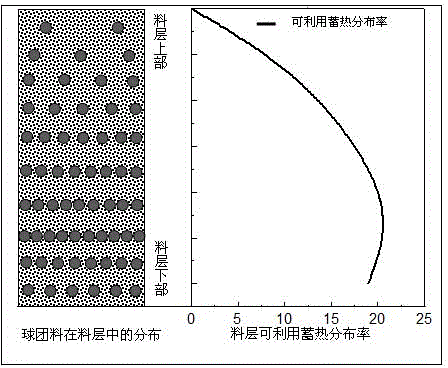
[0021] Add 2% binder (bentonite or other) to the fine-grained iron concentrate accounting for 40% of the sintering raw material to prepare pellets of 10~12mm, and mix the rest of the raw materials (iron ore powder, solid fuel, flux and returned ore) to prepare Into the base material. Among them, the solid fuel content in the base material is 6.7% (the average fuel content of the sinter mixture is 4.0%). The sintering mixture is divided into 6 layers and distributed in the sintering cup. From top to bottom, the weight of pellets in each layer accounts for the percentage of the weight of the layer of mixture: 12%, 25.2%, 40.8%, 48%, 52.8% and 48%, the material layer height is 800 mm, the sintering suction negative pressure is 9kPa for sintering, and the utilization coefficient is 1.67 t m -2 h -1 , yield rate 79.55%, drum index 66.23%, solid fuel consumption 53.09 kg·t -1 index of.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Add 2% binder (bentonite or other) to the fine-grained iron concentrate accounting for 30% of the sintering raw material to prepare pellets of 10~12mm, and mix the rest of the raw materials (iron ore powder, solid fuel, flux and returned ore) Into the base material. Among them, the solid fuel content in the base material is 5.71% (the average fuel content of the sinter mixture is 4.0%). The sintering mixture is divided into 6 layers and distributed in the sintering cup. From top to bottom, the weight of pellets in each layer accounts for the percentage of the weight of the layer of mixture: 12%, 25.2%, 40.8%, 48%, 52.8% and 48%, the material layer height is 800 mm, the sintering suction negative pressure is 9kPa for sintering, and the utilization coefficient is 1.56 t m -2 h -1 , yield rate 77.89%, drum index 65.38%, solid fuel consumption 53.88 kg·t -1 index of.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Add 2% binder (bentonite or other) to the fine-grained iron concentrate accounting for 40% of the sintering raw material to prepare pellets of 10~12mm, and mix the rest of the raw materials (iron ore powder, solid fuel, flux and returned ore) to prepare Into the base material. Among them, the solid fuel content in the base material is 6.7% (the average fuel content of the sinter mixture is 4.0%). The sintering mixture is divided into 6 layers and distributed in the sintering cup. From top to bottom, the weight of pellets in each layer accounts for the percentage of the weight of the layer of mixture: 24%, 36%, 36%, 48%, 52.8% and 43.2%, the material layer height is 800 mm, the sintering suction negative pressure is 9kPa for sintering, and the utilization coefficient is 1.61 t m -2 h -1 , yield rate 78.57%, drum index 65.71%, solid fuel consumption 53.25 kg·t -1 index of.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com