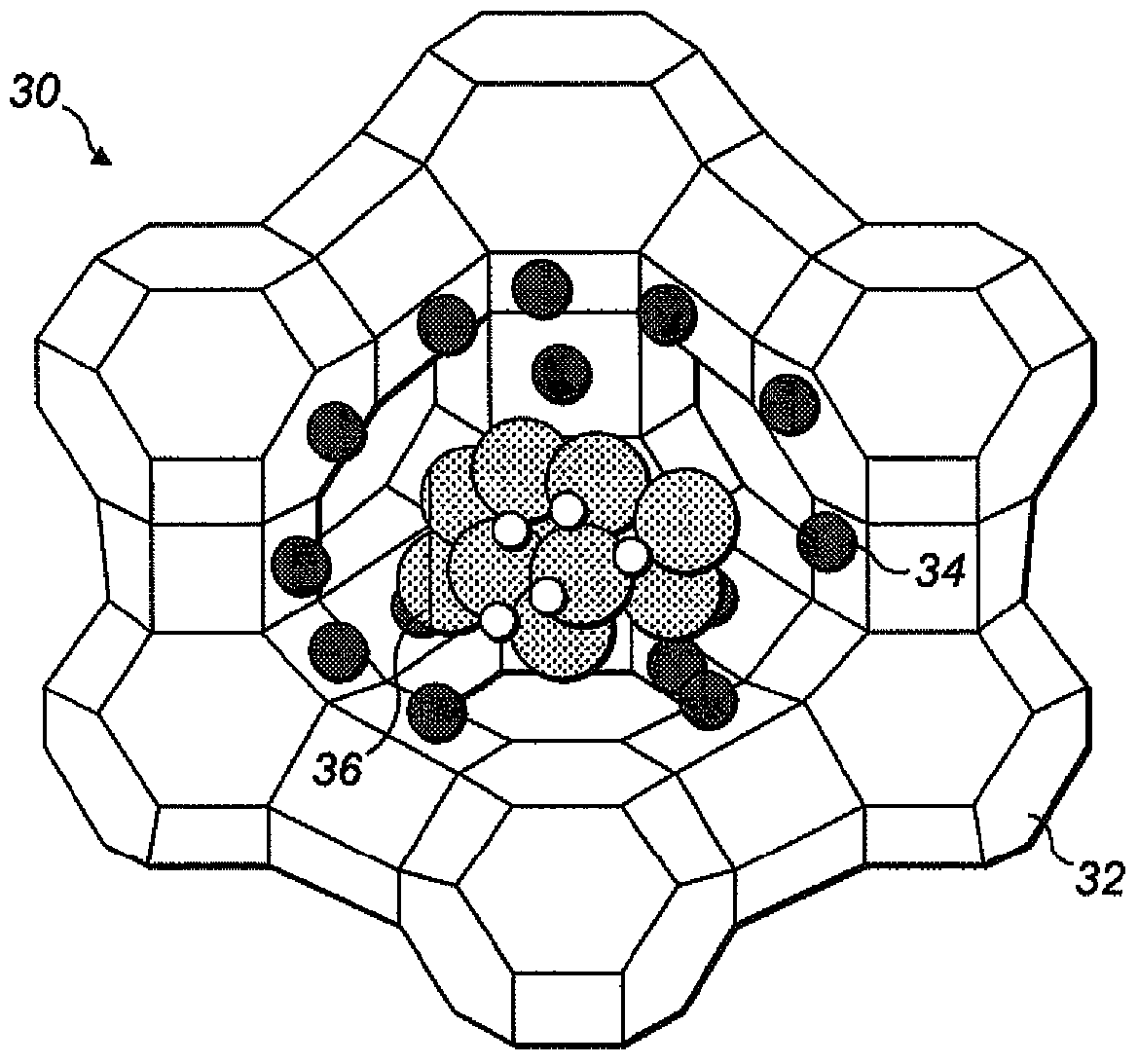
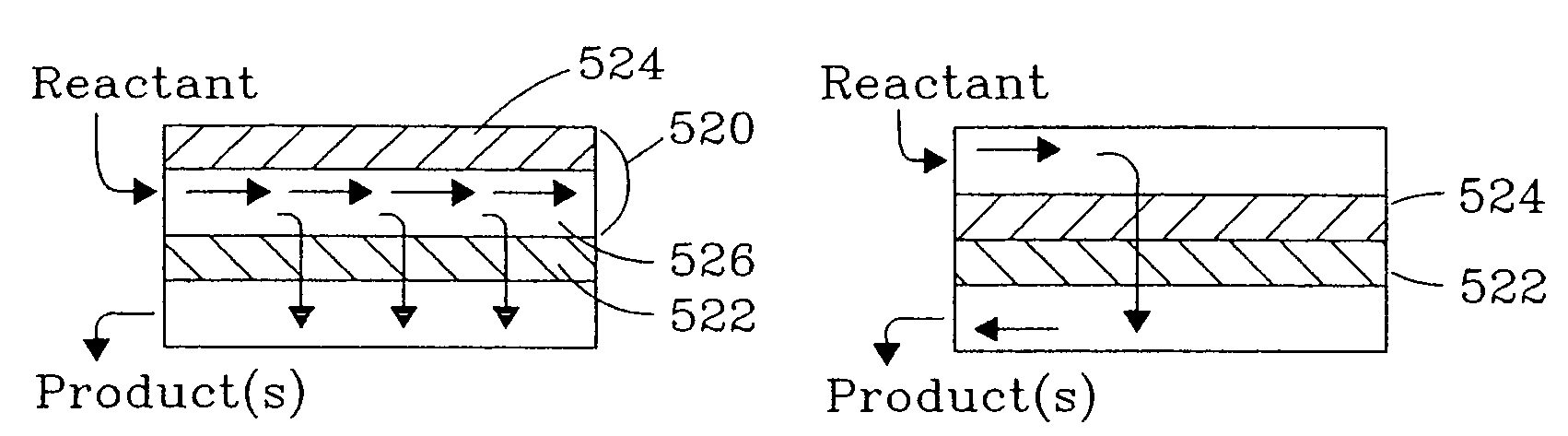
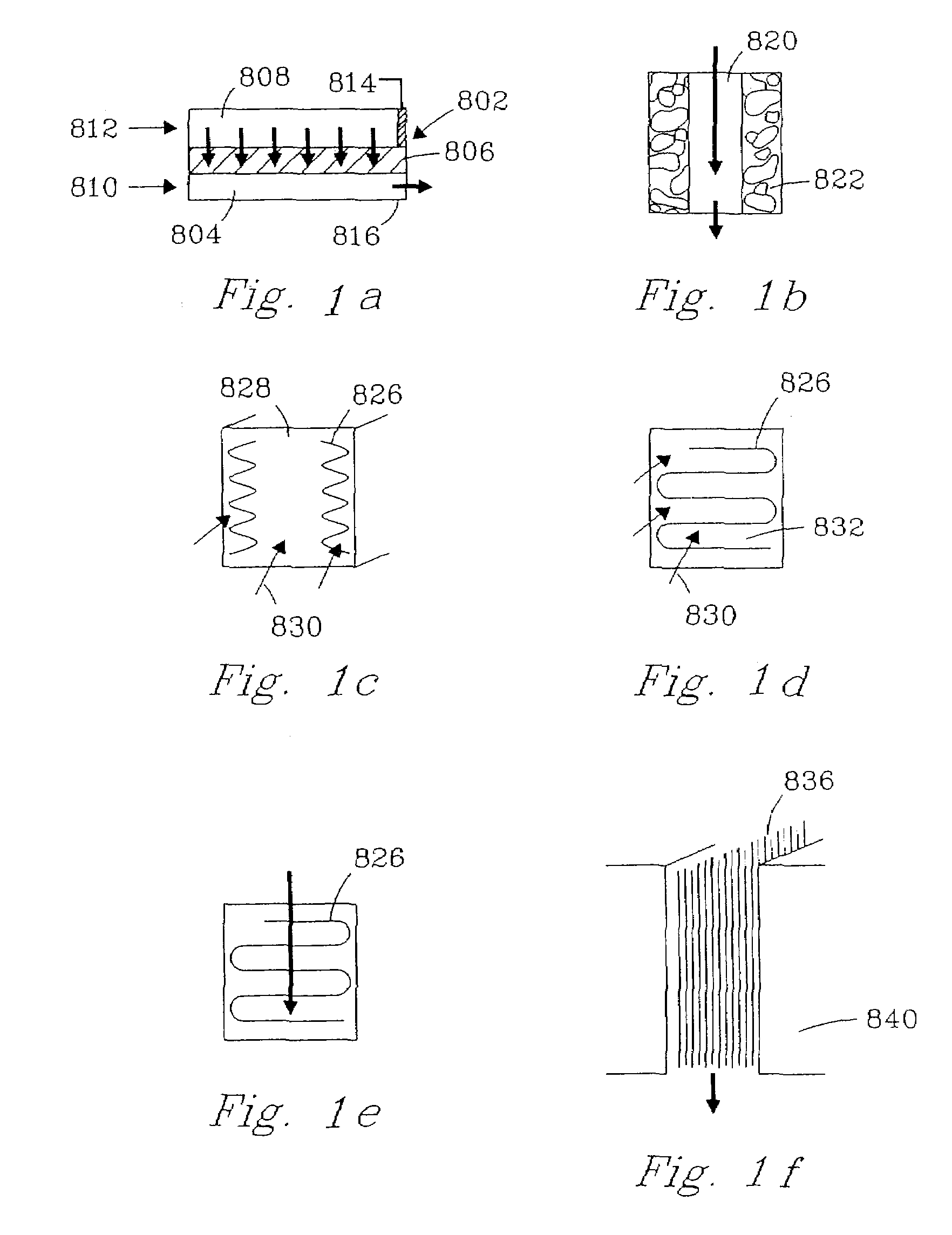
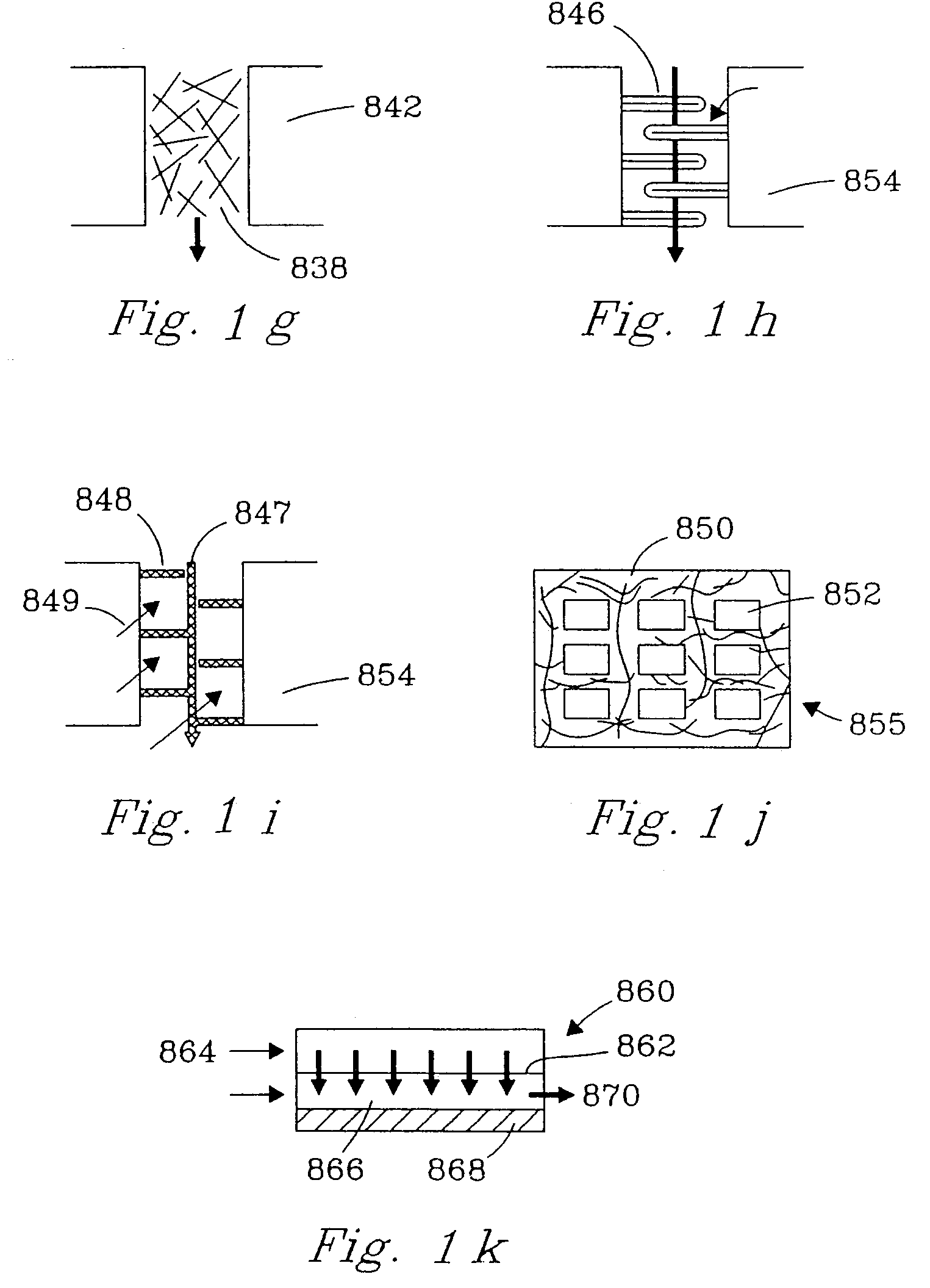
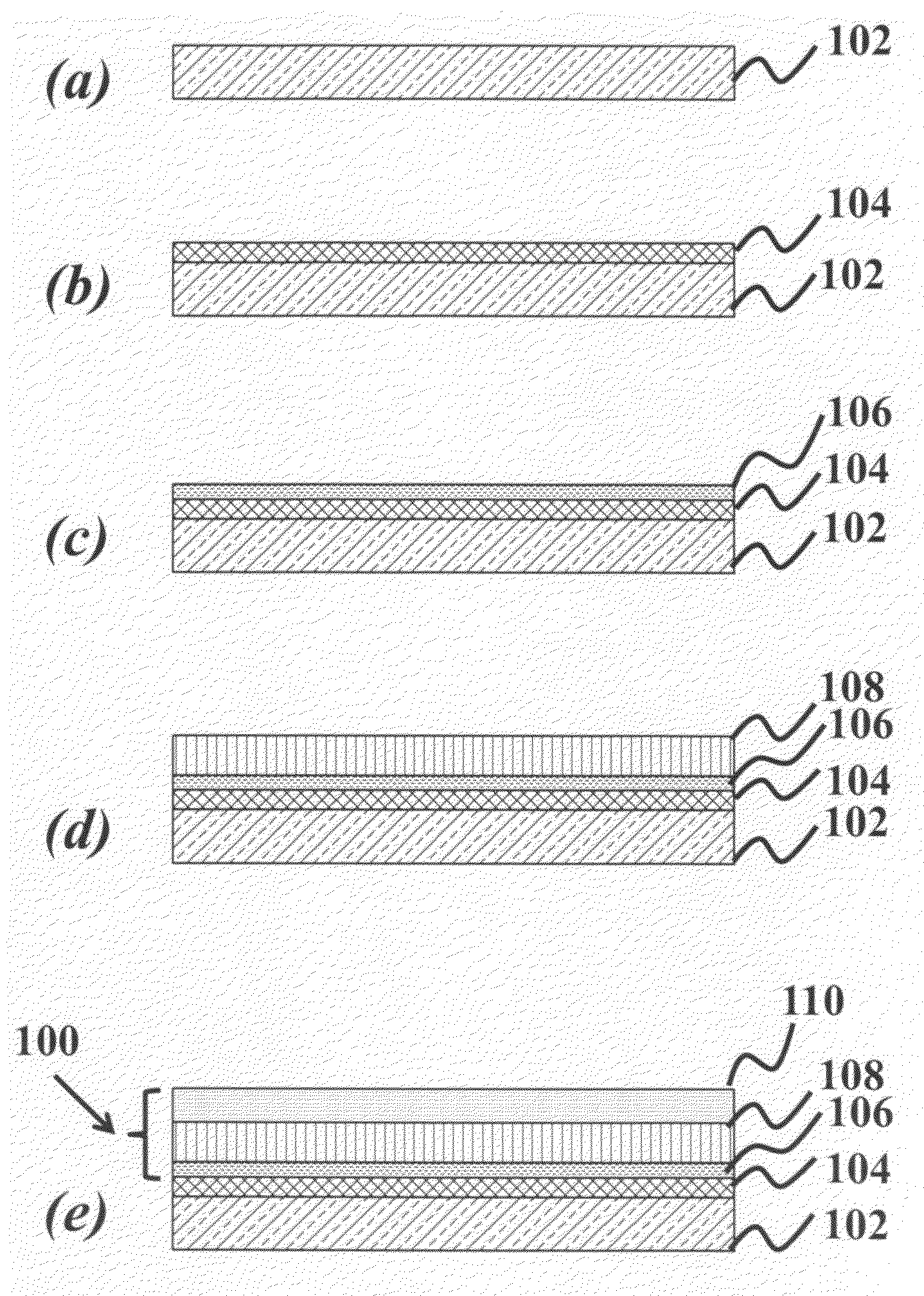
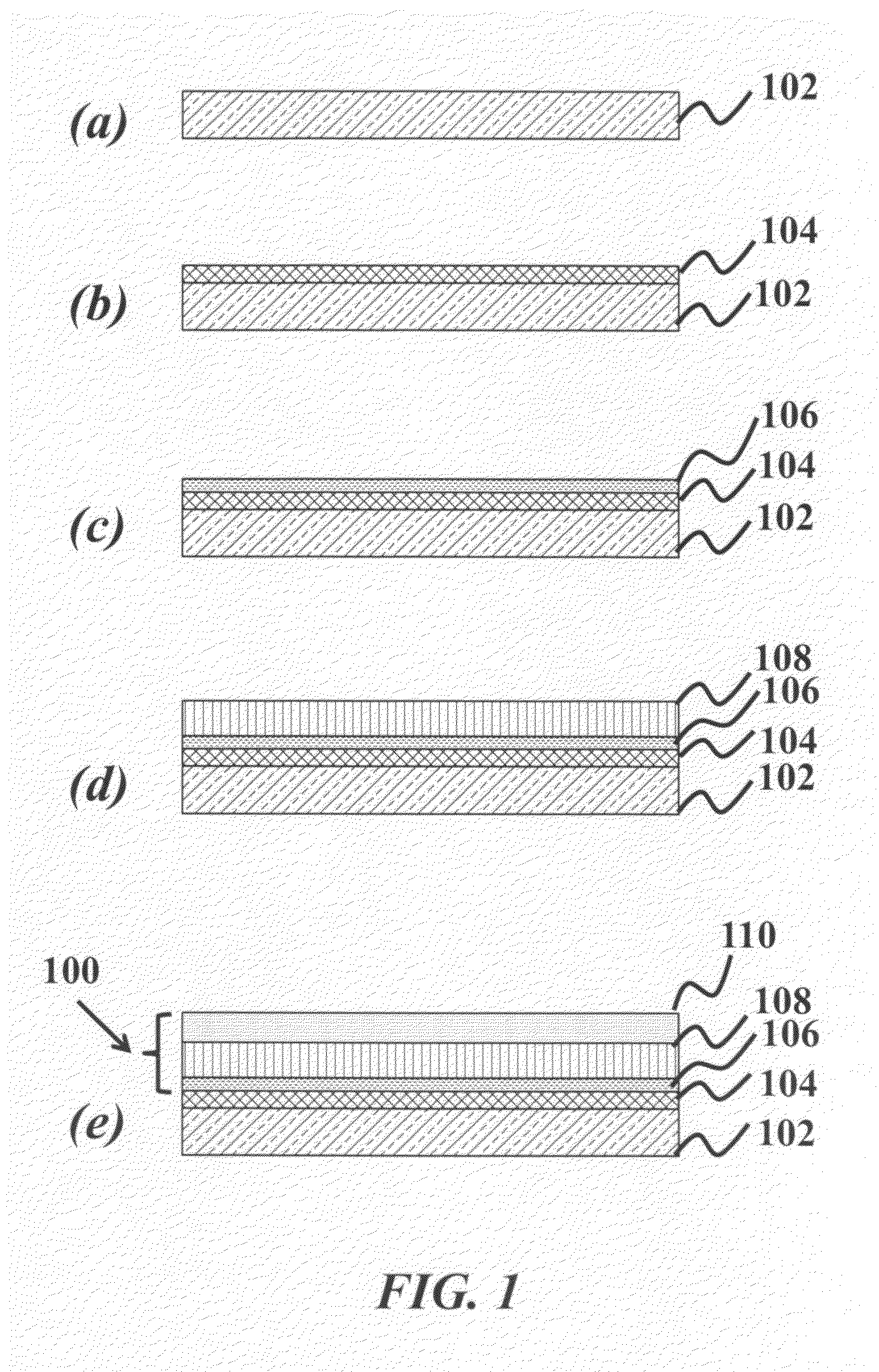
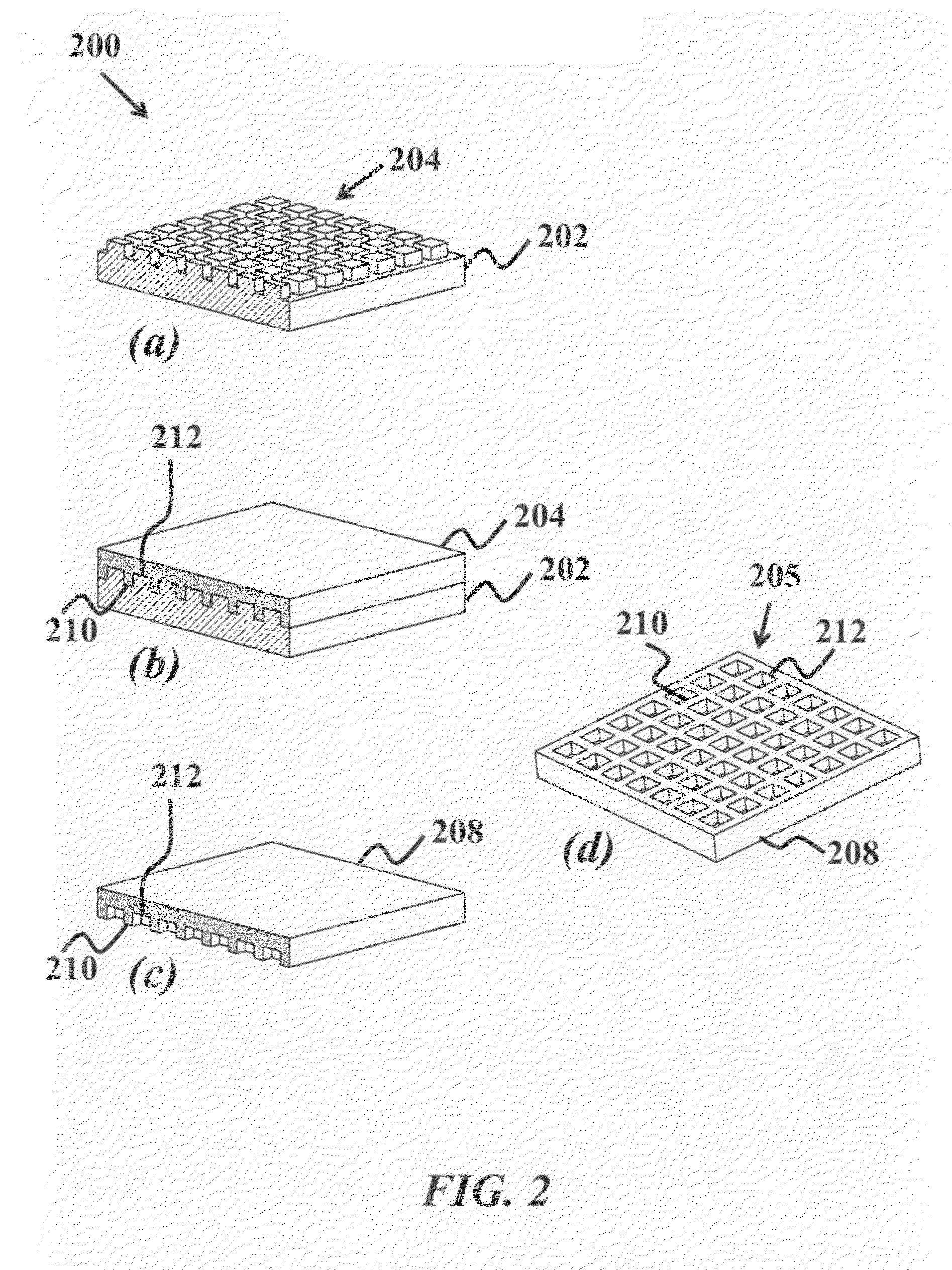
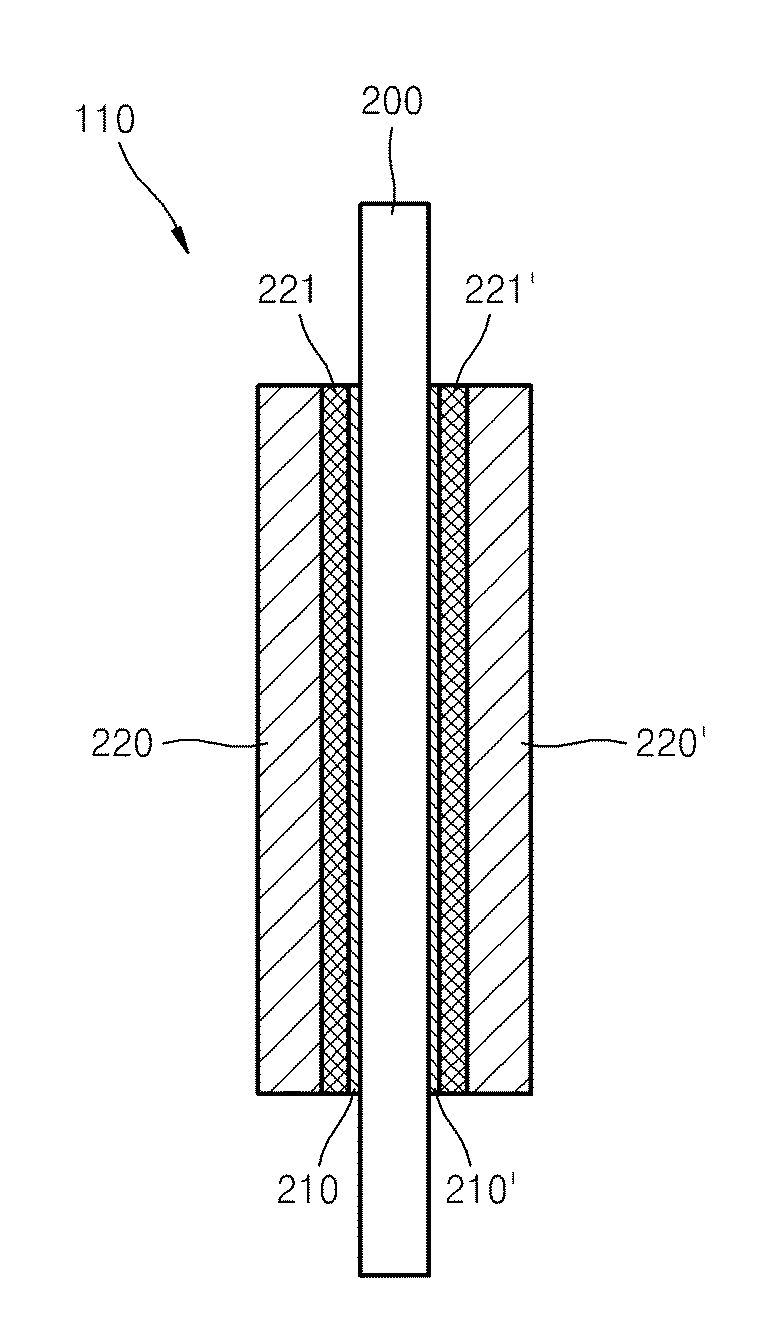
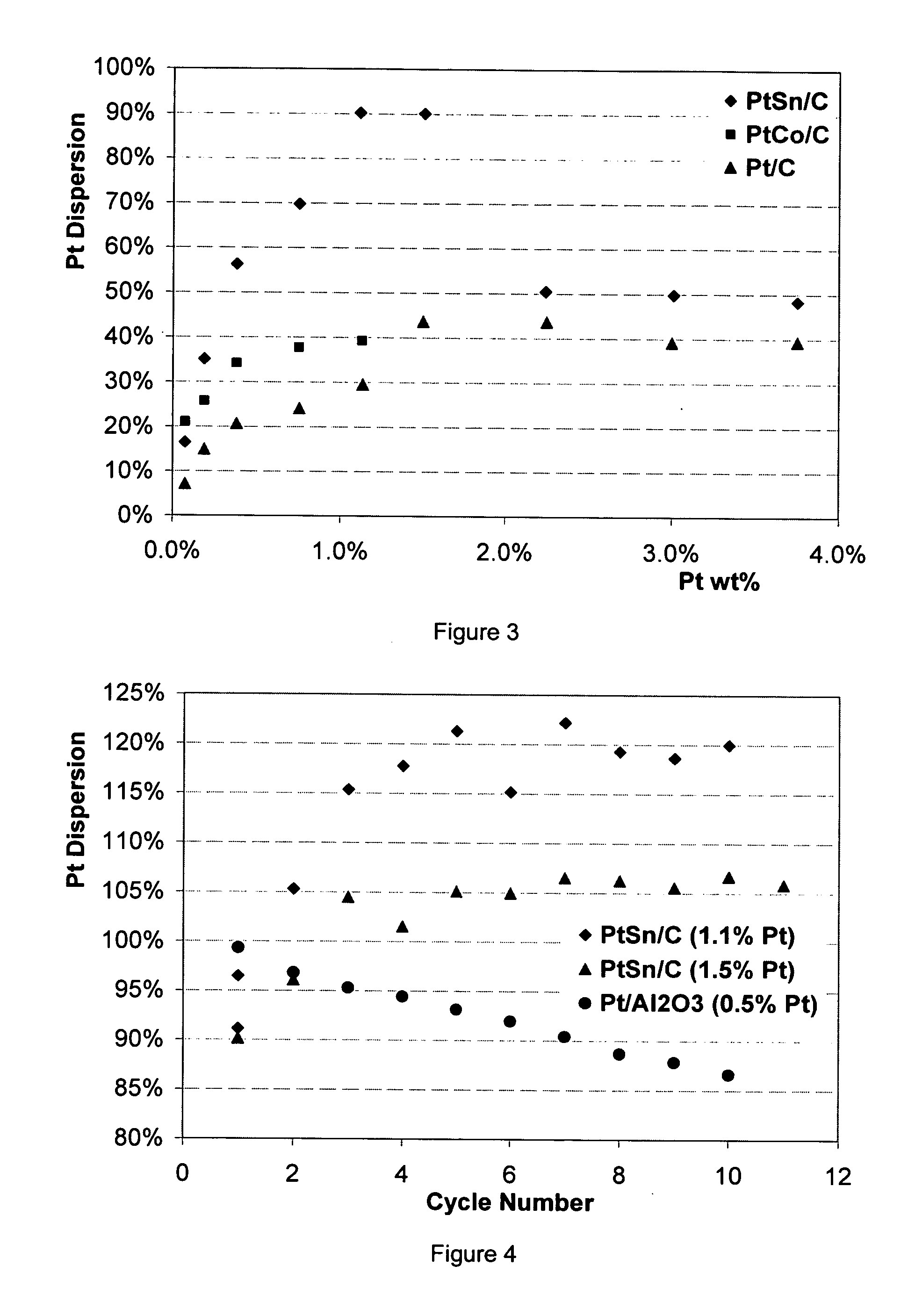
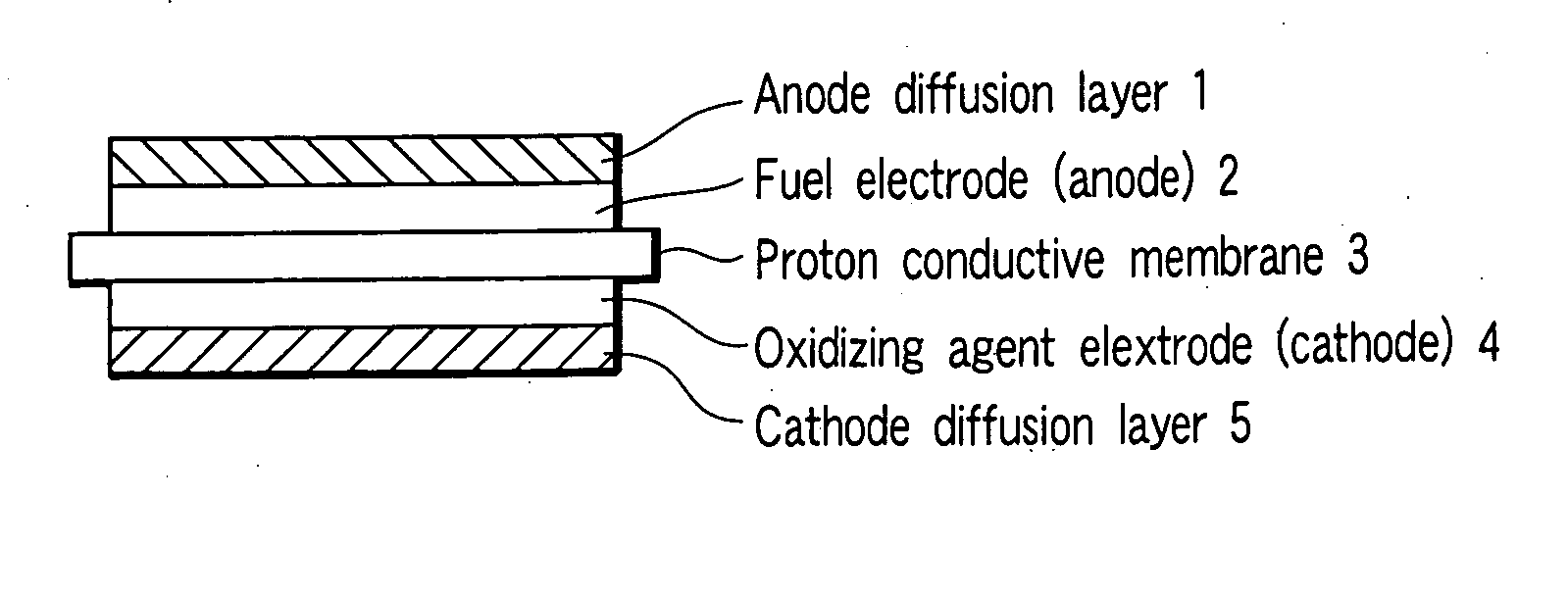
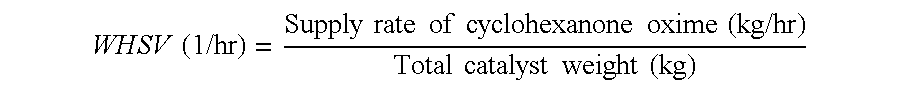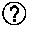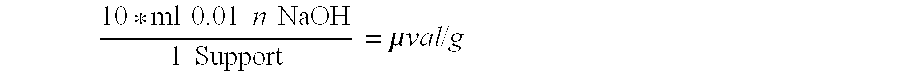Patents
Literature
268 results about "Porous catalyst" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
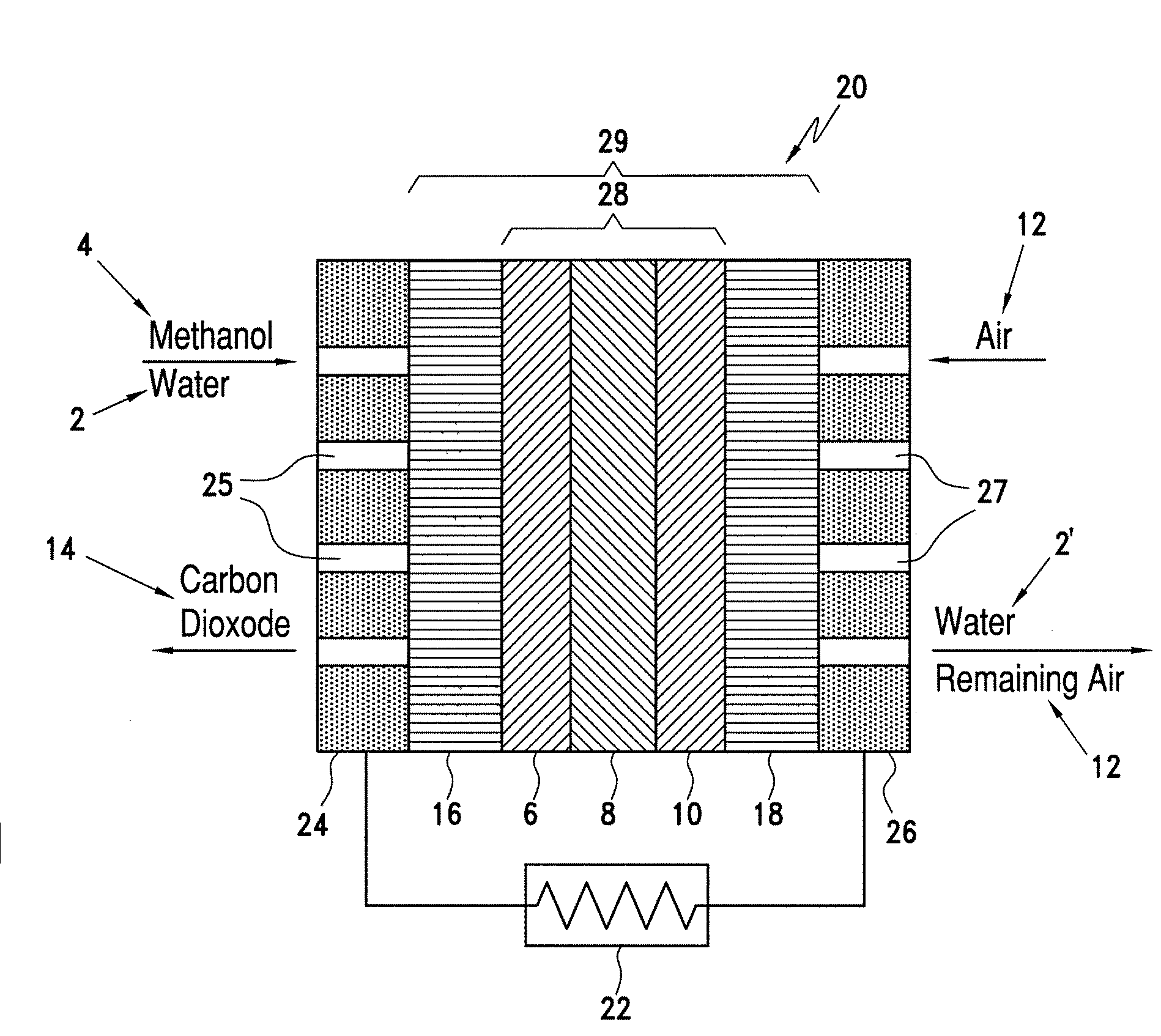
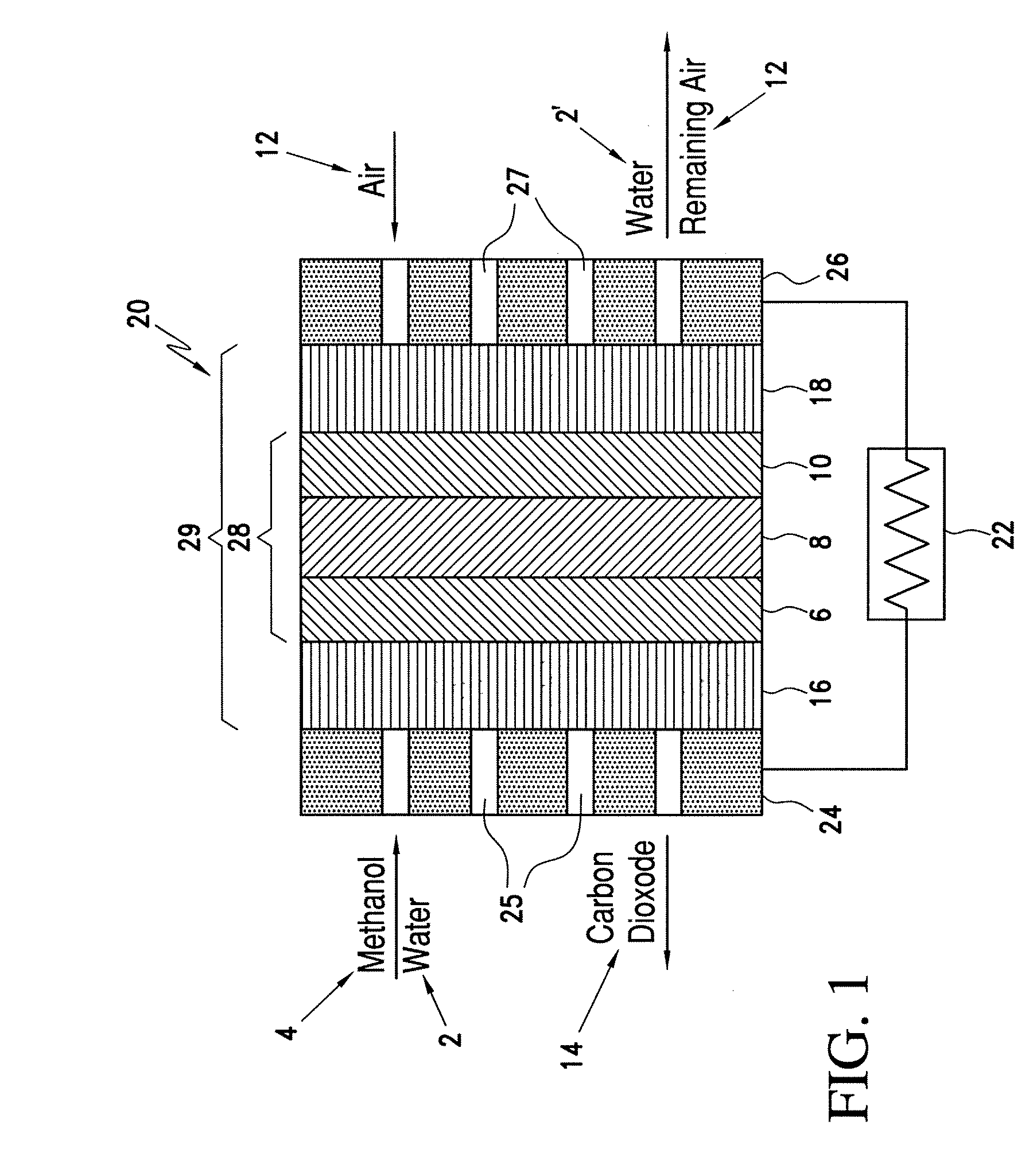
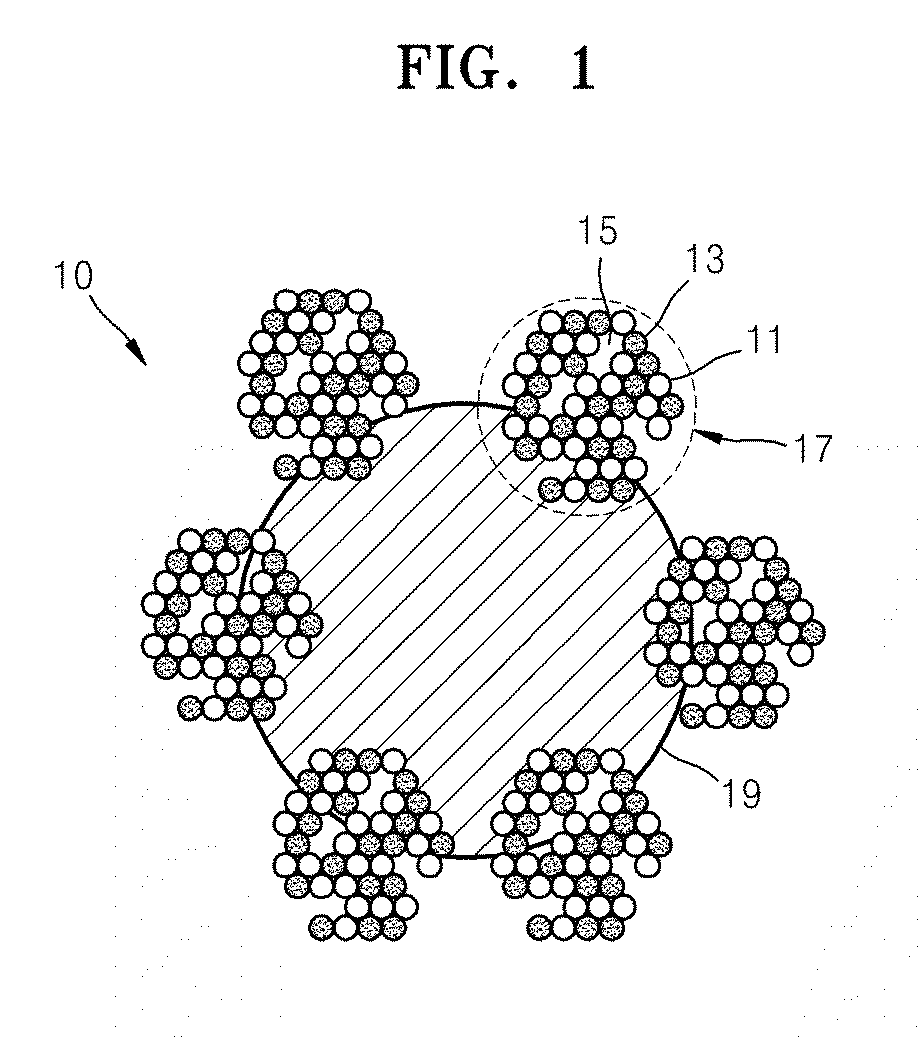
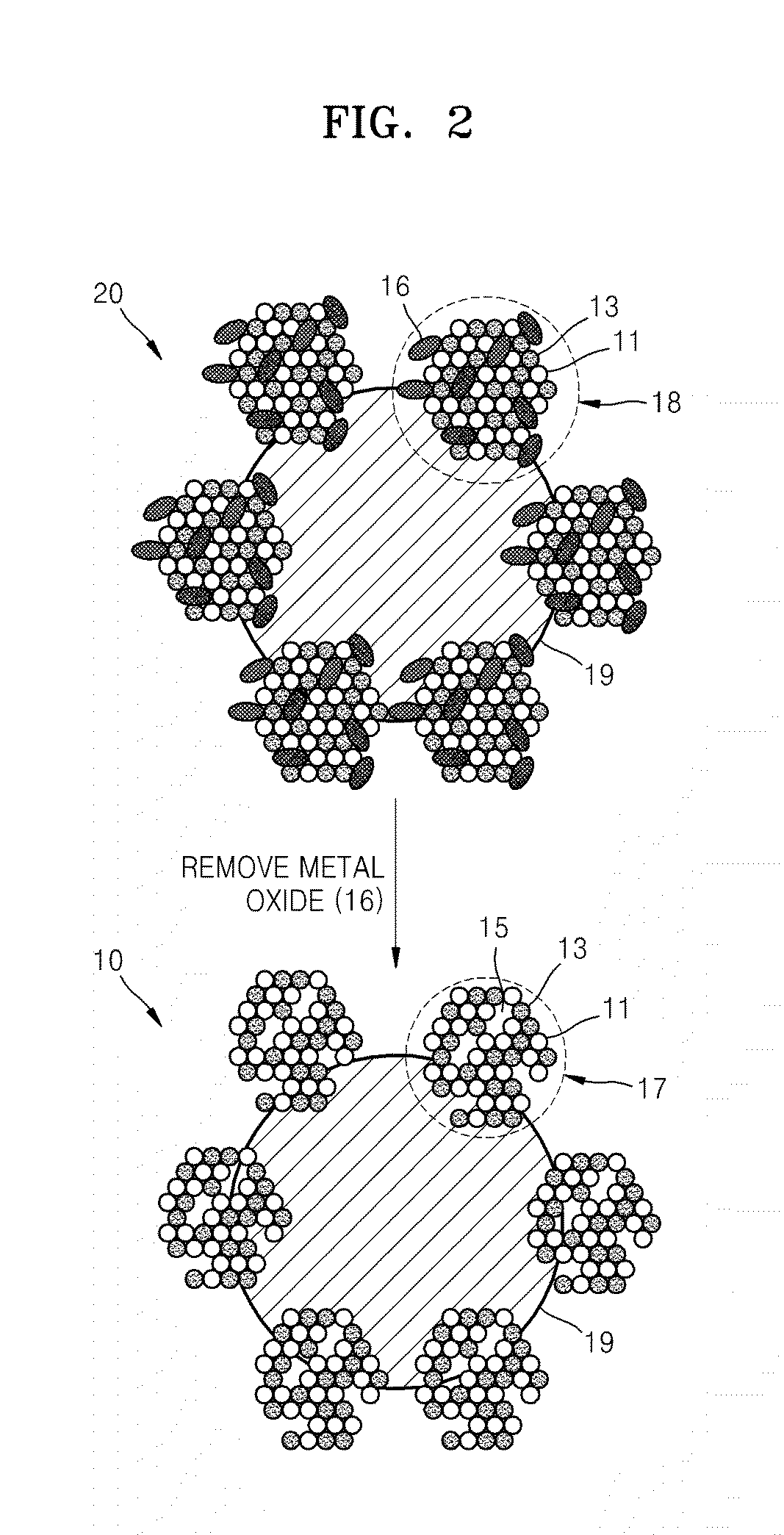
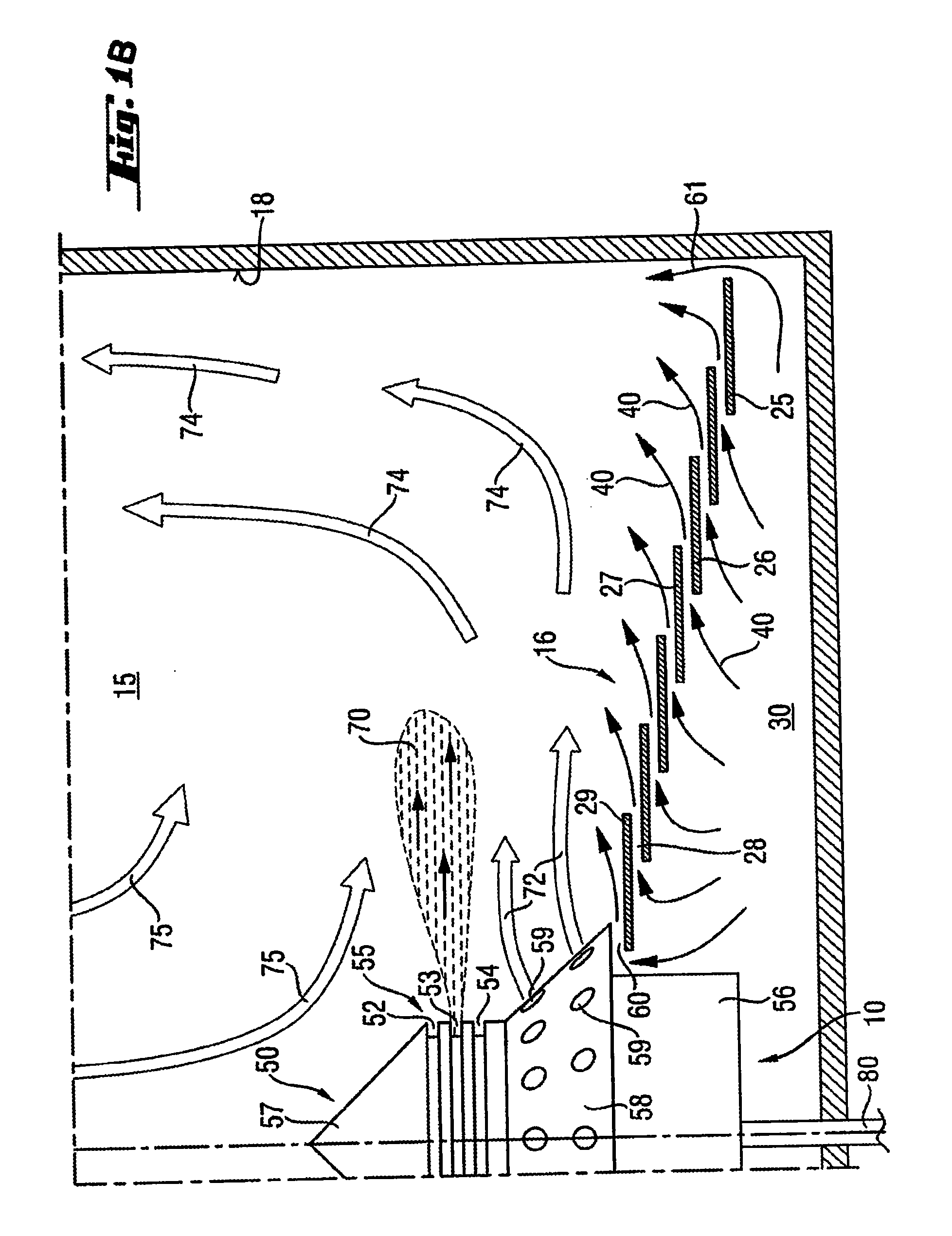
Catalyst coated membranes and sprayable inks and processes for forming same
The invention is directed to highly porous catalyst coated membranes and to sprayable inks and processes for forming catalyst coated membranes. In one aspect, the invention is to a sprayable ink, comprising catalyst particles, polymer electolyte ionomer, and a vehicle for dispersing the catalyst particles and polymer electolyte ionomer. In another aspect, the process comprises the steps of depositing an ink comprising catalyst particles and a vehicle onto a membrane and vaporizing from 40 to 95 weight percent of the vehicle from the sprayed ink under conditions effective to form a catalyst layer on the membrane. Preferably, the depositing and vaporizing steps are alternated to form multiple stacked catalyst layers on the membrane.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Catalytic reaction method
InactiveCN1507940AReduce dosageIncrease profitChemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactorsPorous catalystMulti phase
The present invention discloses a catalytic reaction method. Said method can make the catalytic reaction be implemented in the supergravitational field. Said method utilizes the rotary bed supergravitational field equipment as reactor, on the rotor of said rotary bed supergravitational field equipment a porous catalyst layer and / or a porous filler layer are fixed, and the described catalytic reaction is homogeneous reaction or heterogeneous reaction. Said invention cal reduce catalyst consumption, raise utilization rate of catalyst, raise stability of catalyst and can reduce denergy consumption, etc.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Method and apparatus for obtaining enhanced production rate of thermal chemical reactions
InactiveUS7045114B2Reduce formationReaction is slowOrganic chemistry methodsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsSteam reformingChemical reaction
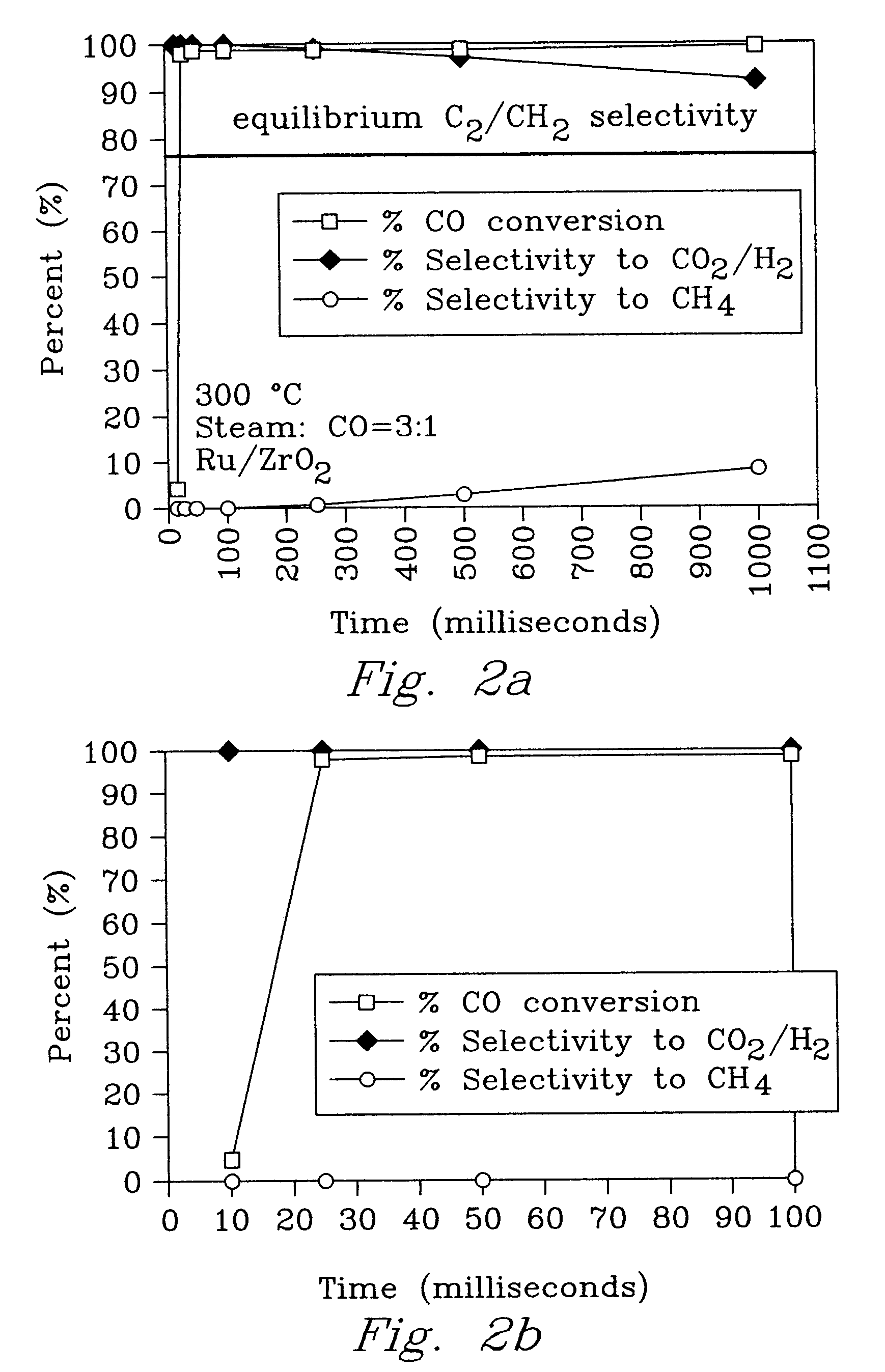
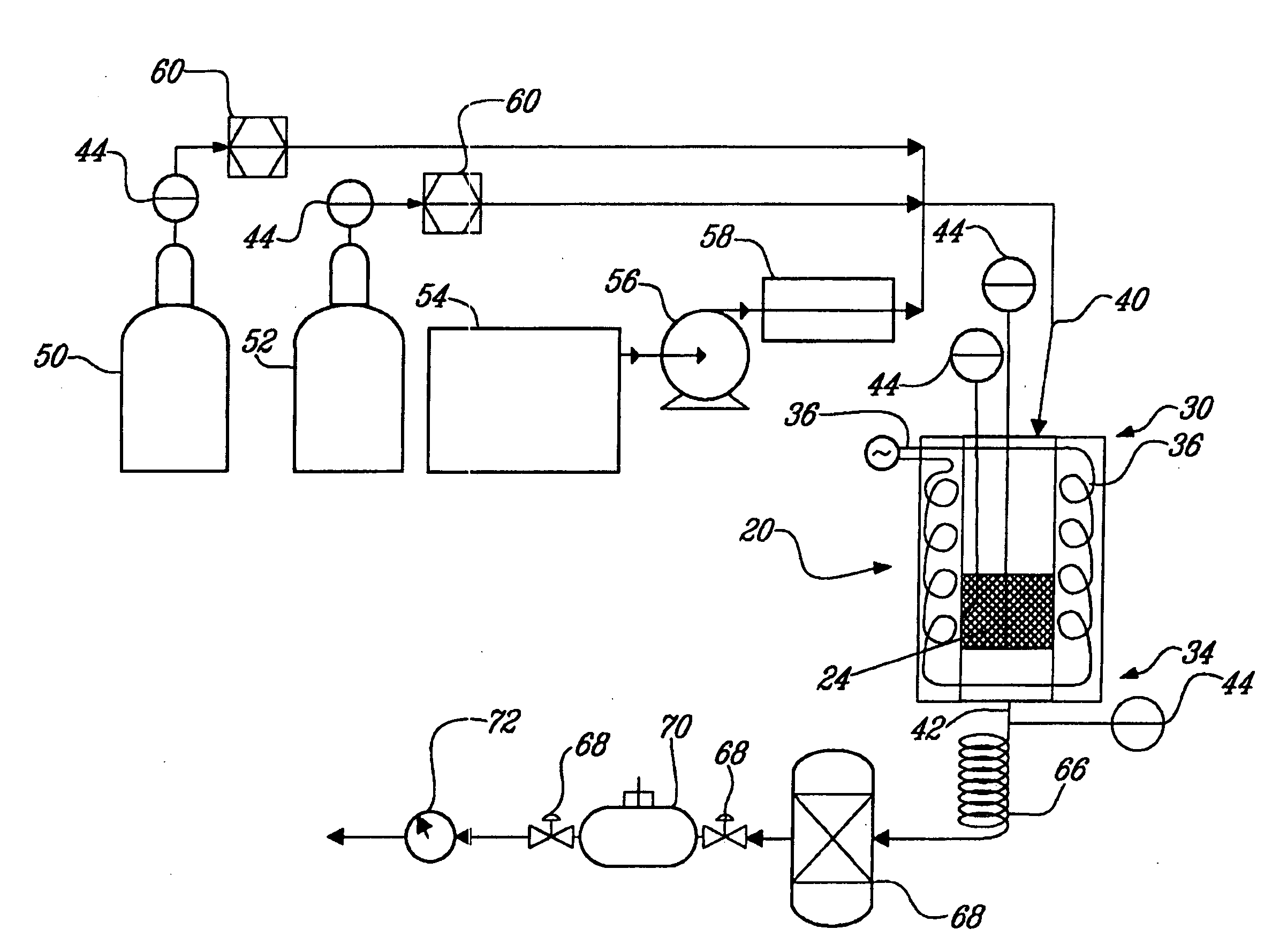
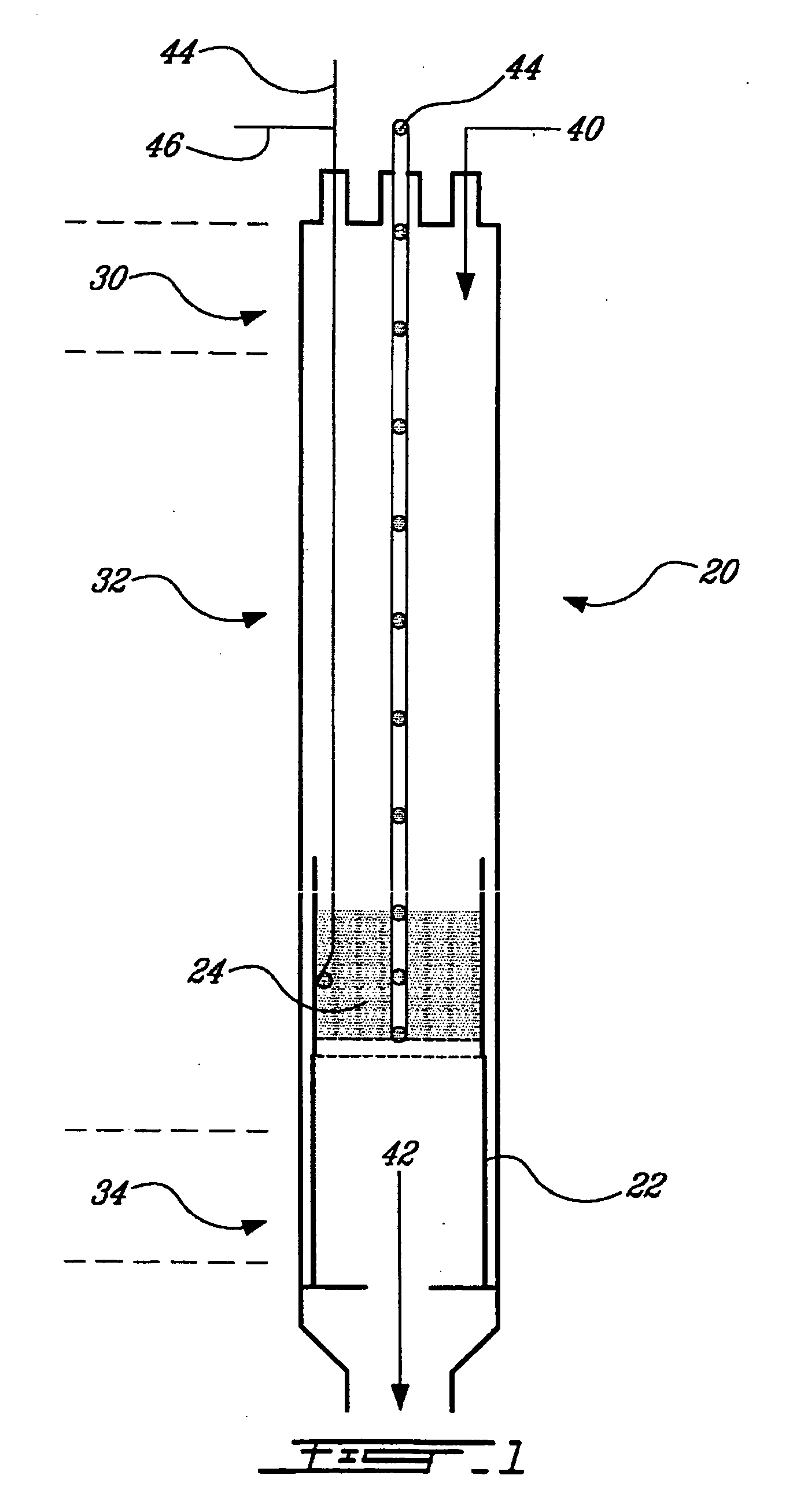
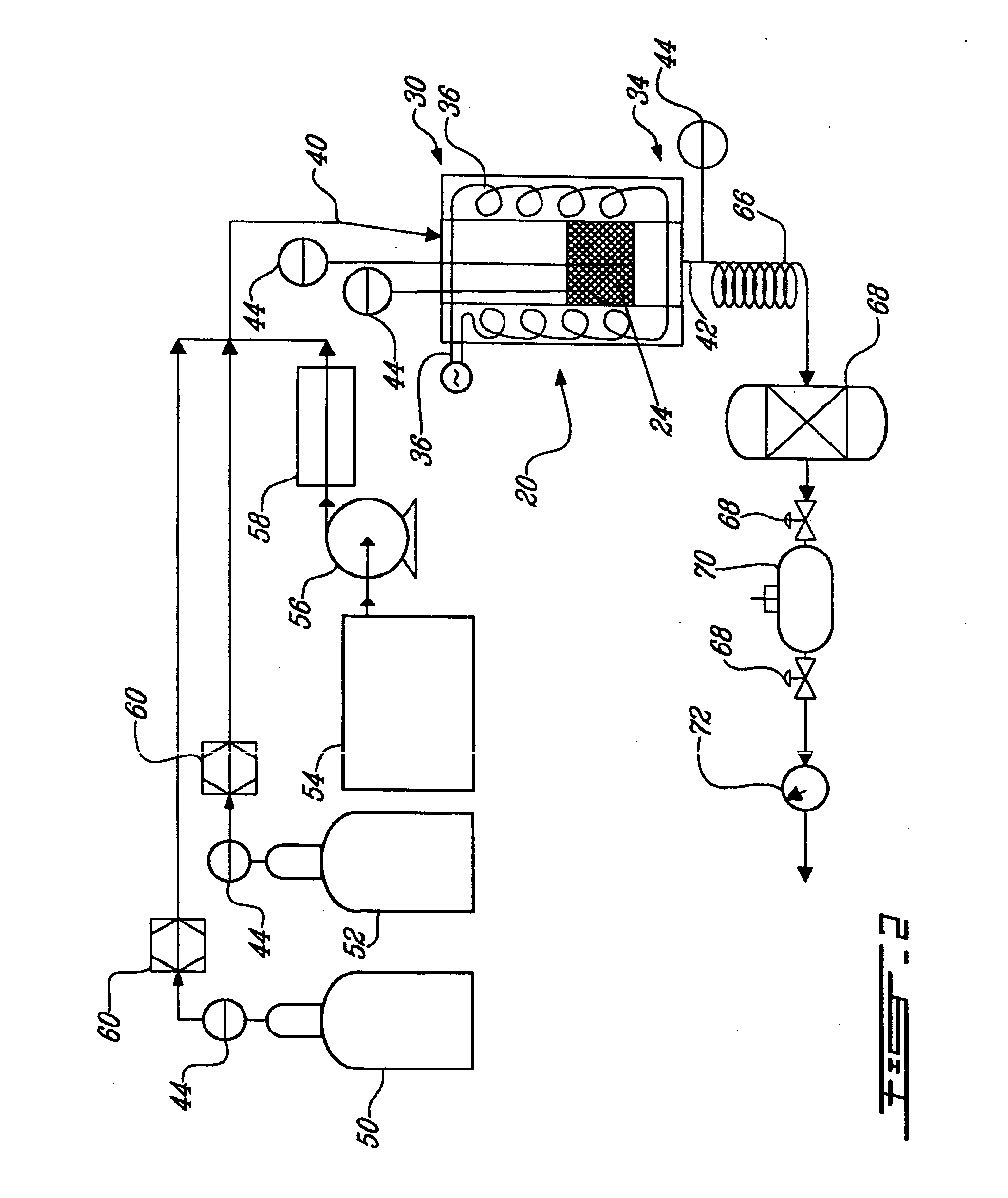
Reactors and processes are disclosed that can utilize high heat fluxes to obtain fast, steady-state reaction rates. Porous catalysts used in conjunction with microchannel reactors to obtain high rates of heat transfer are also disclosed. Reactors and processes that utilize short contact times, high heat flux and low pressure drop are described. Improved methods of steam reforming are also provided.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Non-porous catalysts for co2 sequestration through dry reforming
InactiveUS20090203519A1Reduce gas emissionsMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenPorous catalystCarbon dioxide production
A carbon sequestration and dry reforming process for the production of synthesis gas and sequestered carbon from carbon dioxide. Two-dimension (non-porous) catalysts for sequestering carbon are also disclosed and a process to produce same as well as a method for activating two dimension catalysts.
Owner:UNIV DE SHERBROOKE +1
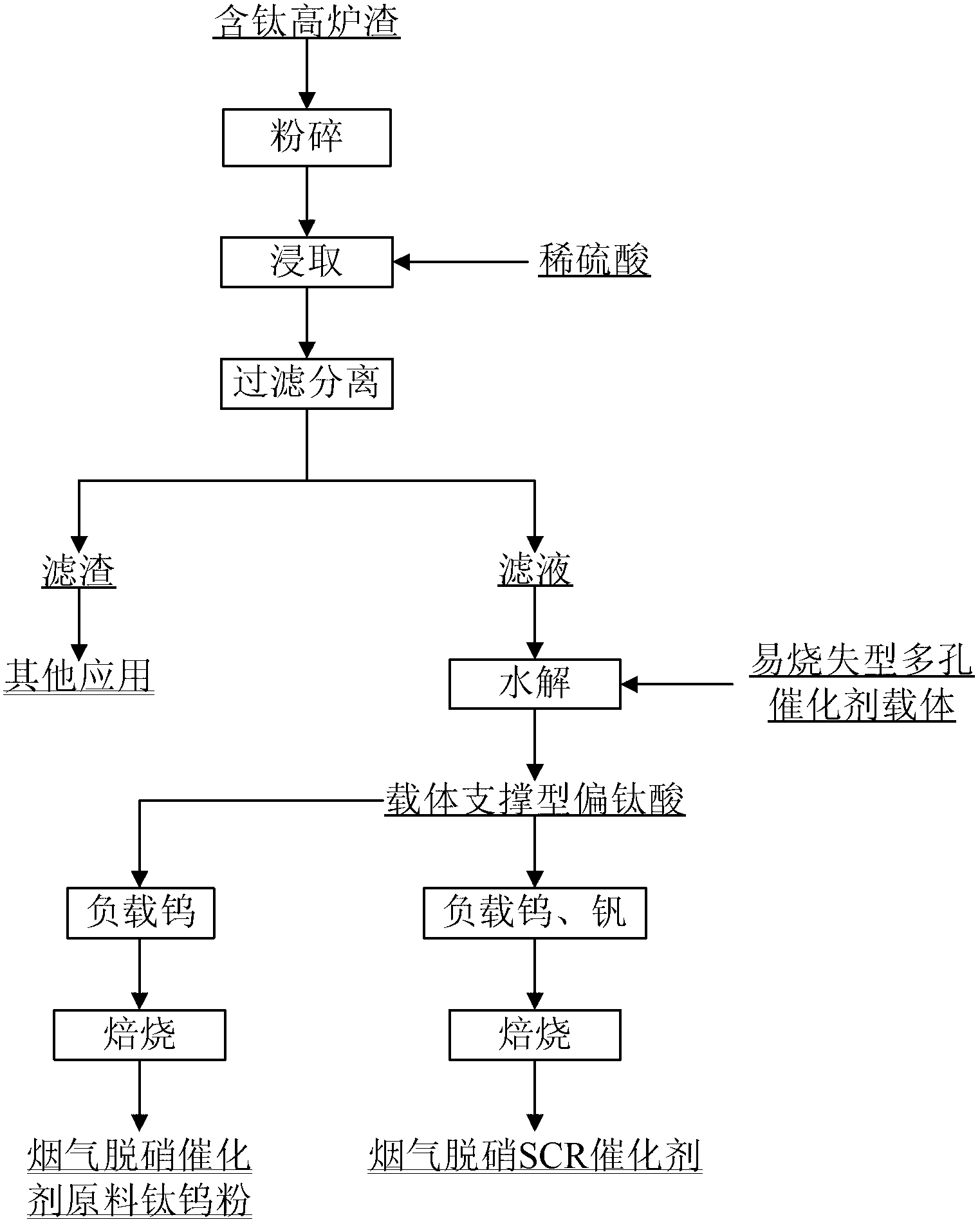
Method for preparing selective catalytic reduction SCR flue gas denitration catalyst and method for preparing raw material titanium-tungsten powder of SCR flue gas denitration catalyst
ActiveCN102698737AReduce manufacturing costAlleviate the pricey situationDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPorous catalystSlag
The invention relates to a method for preparing a selective catalytic reduction SCR flue gas denitration catalyst and a method for preparing a raw material titanium-tungsten powder of the SCR flue gas denitration catalyst. The method for preparing the SCR flue gas denitration catalyst comprises the followings: smashing titanium-bearing blast furnace slag, leaching TiO2 in the smashed titanium-bearing blast furnace slag with dilute sulphuric acid, filtering and separating the mixture to obtain residues and titanium solution, adding a porous catalyst carrier which is easy to be burnt off into the titanium solution and hydrolyzing the mixture; filtering, washing and drying the hydrolyzed product to obtain a carrier supported metatitanic acid, and further loading tungsten and vanadium on the metatitanic acid, and baking the obtained product to obtain a vanadium-tungsten-titanium SCR denitration catalyst. The method not only effectively utilizes valuable elements in blast furnace slag, solves the problems that the titanium dioxide product is extracted, separated and purified difficultly from the blast furnace slag, and the quality of the product cannot meet the standard easily, and also greatly reduces the production cost of the vanadium-tungsten-titanium SCR denitration catalyst and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
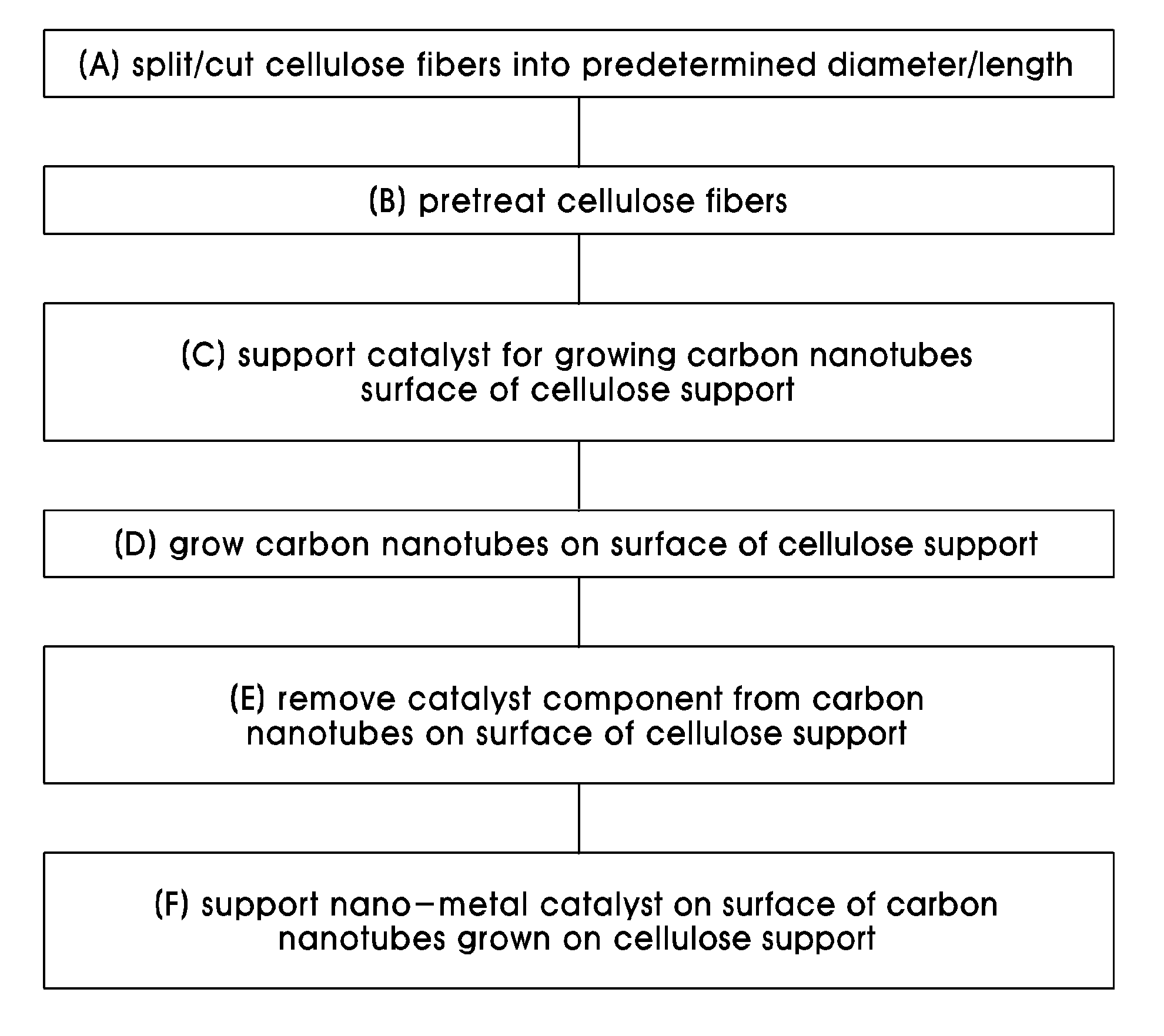
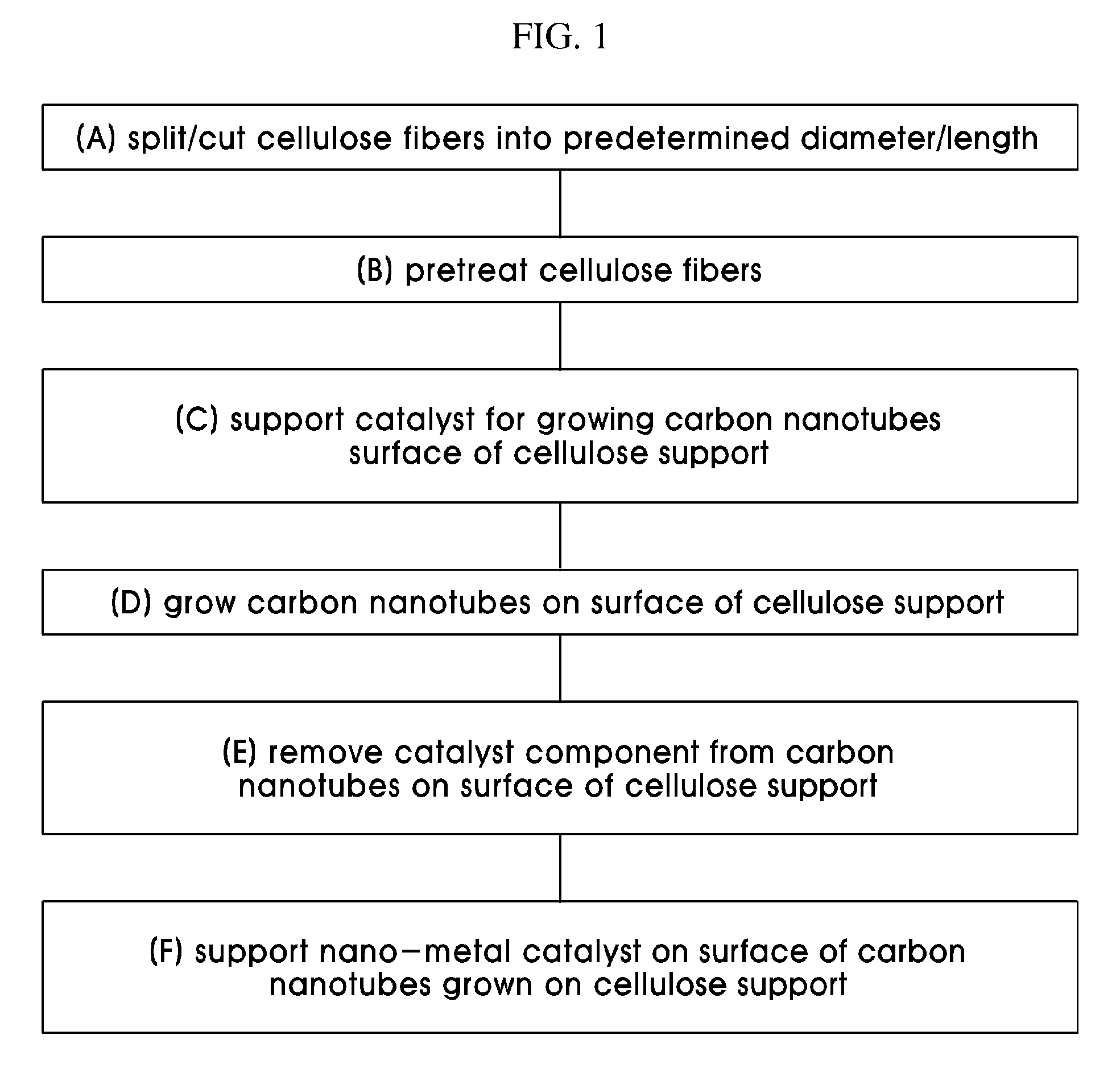
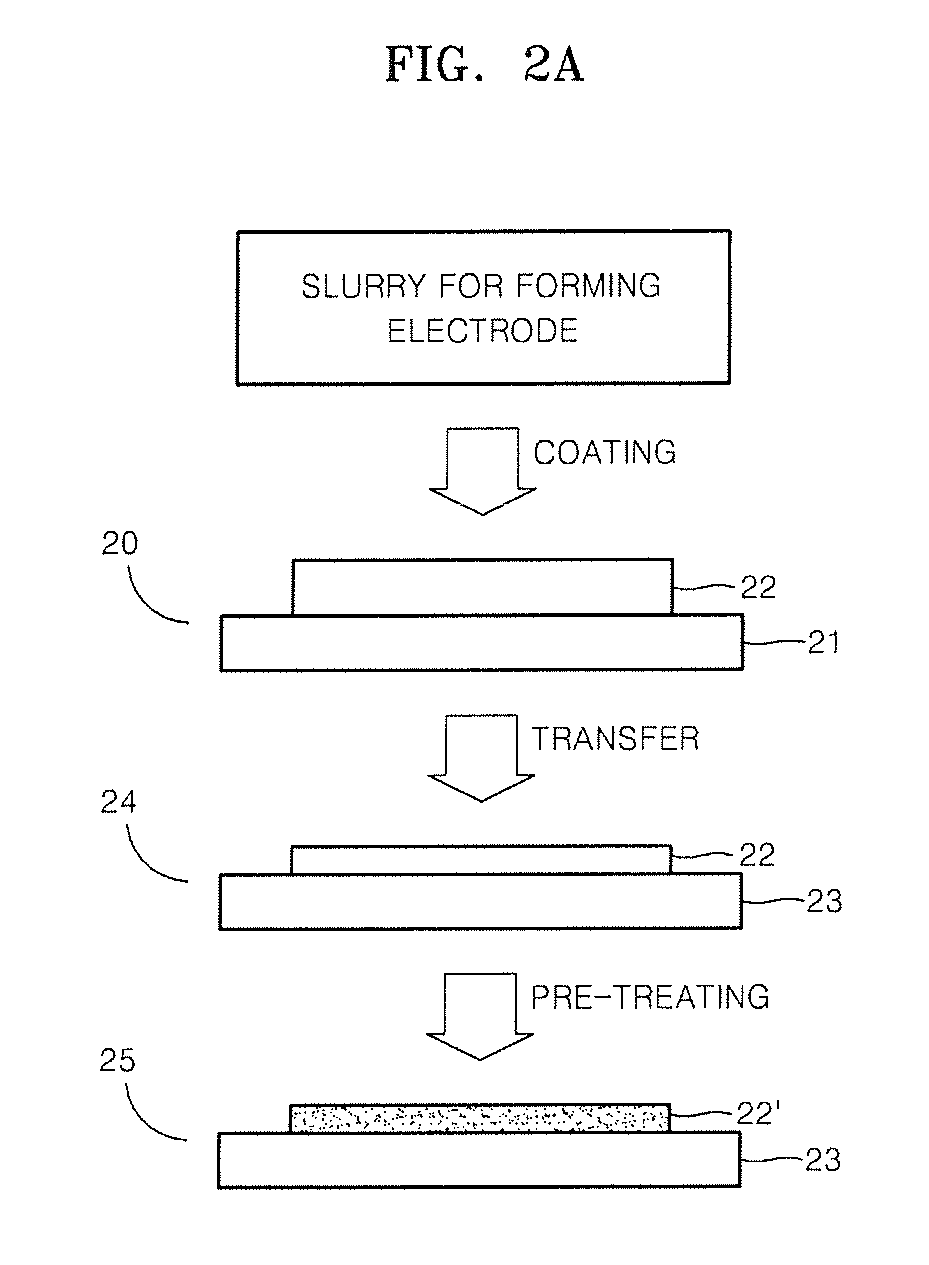
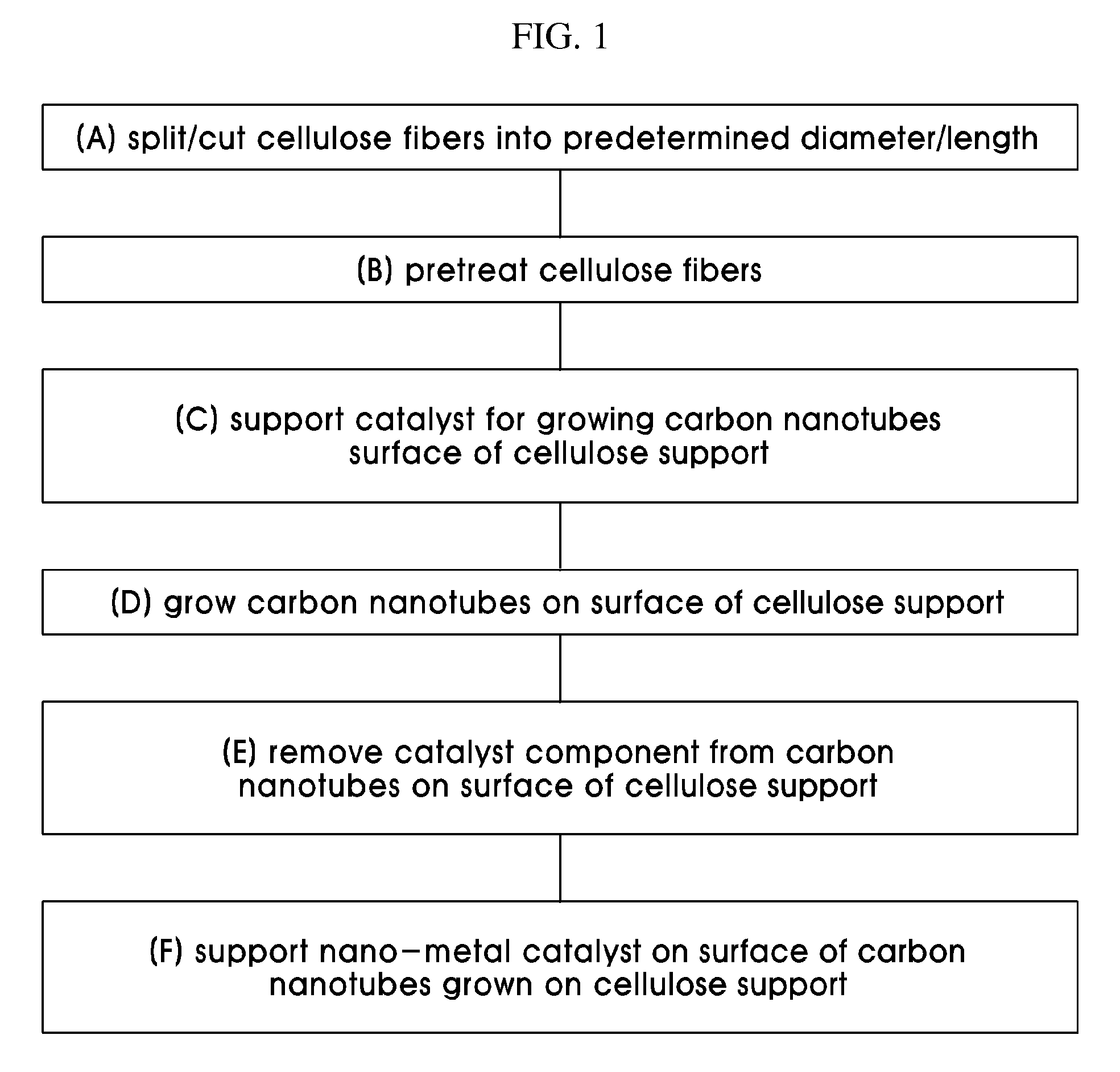
Catalyst support using cellulose fibers, preparation method thereof, supported catalyst comprising nano-metal catalyst supported on carbon nanotubes directly grown on surface of the catalyst support, and method of preparing the supported catalyst
ActiveUS7776777B2Easy to collectReduce manufacturing costMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufacturePorous catalystMetal catalyst
The present invention is directed to a porous catalyst support for maximizing an increase in catalytic reaction activity and a method of preparing a nano-metal-supported catalyst using the same. The method includes splitting cellulose fibers, thus preparing a catalyst support, growing carbon nanotubes on the prepared catalyst support, and supporting a nano-metal catalyst on the catalyst support having the carbon nanotubes grown thereon.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Methods of preparation and forming supported active metal catalysts and precursors
ActiveCN103889577AReduce or eliminate inactivationMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPorous catalystChemical reaction
The invention relates to a method of preparing a supported catalyst, which method comprises the steps of; (i) providing a porous catalyst support comprising a framework having an internal pore structure comprising one or more pores which internal pore structure comprises a precipitant; (ii) contacting the catalyst support with a solution or colloidal suspension comprising a catalytically active metal such that, on contact with the precipitant, particles comprising the catalytically active metal are precipitated within the internal pore structure of the framework of the catalyst support. The invention also relates to supported catalysts made according to the above method, and to use of the catalysts in catalysing chemical reactions, for example in the Fischer Tropsch synthesis of hydrocarbons.
Owner:IGTL TECH
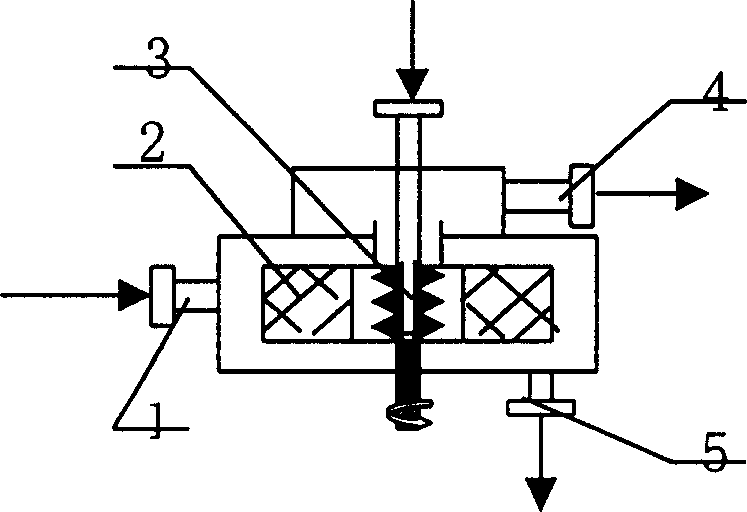
Chemical reactor and method for gas phase reactant catalytic reactions
InactiveUS7288231B2High yieldReduce contact timeCombination devicesExhaust apparatusPorous catalystChemical reaction
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Layer-structured fuel cell catalysts and current collectors
InactiveUS20090218311A1Improve adhesionElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufacturePolymer electrolytesPorous catalyst
A method of fabricating a layer-structured catalysts at the electrode / electrolyte interface of a fuel cell is provided. The method includes providing a substrate, depositing an electrolyte layer on the substrate, depositing a catalyst bonding layer to the electrolyte layer, depositing a catalyst layer to the catalyst bonding layer, and depositing a microstructure stabilizing layer to the catalyst layer, where the bonding layer improves adhesion of the catalyst onto the electrolyte. The catalyst and a current collector is a porous catalyst and a fully dense current collector, or a fully dense catalyst and a fully dense current collector structure layer. A nano-island catalyst and current collector structure layer is deposited over the catalyst and current collector or over the bonding layer, which is deposited over the electrolyte layer. The fuel cell can be hydrogen-fueled solid oxide, solid oxide with hydrocarbons, solid sensor, solid acid, polymer electrolyte or direct methanol.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Exhaust gas treatment catalyst and exhaust gas treatment system
ActiveUS8202481B2Reduce thicknessReduce leak rateCombination devicesCatalyst activation/preparationPt elementDecreased thickness
Provided are an exhaust gas treatment catalyst capable of reducing ammonia leakage rate while keeping a sufficient NOx removal efficiency, said catalyst comprising a coating layer and a catalyst base material, wherein said coating layer has a decreased thickness relative to that of a catalyst base material; and an exhaust gas treatment system using the same. In the exhaust gas treatment catalyst for catalytically removing nitrogen oxides from an exhaust gas by using ammonia as a reducing agent and simultaneously decomposing and removing unreacted ammonia, a coating layer comprising platinum supported on titania is formed on a surface of a porous catalyst base material comprising titania and at least one compound selected from oxides of vanadium (V), oxides of tungsten (W) and oxides of molybdenum (Mo).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Electrode catalyst for a fuel cell, method of preparing the same, and membrane electrode assembly and fuel cell including the electrode catalyst
InactiveUS20130149632A1High catalytic activityActive material electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsPorous catalyst
An electrode catalyst for a fuel cell including porous catalyst particles including a noble metal having oxygen-reduction activity and a carbonaceous support, wherein the porous catalyst particles are disposed on the carbonaceous support, and an electrochemical specific surface area of the porous catalyst particles is about 70 m2 / g or more.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
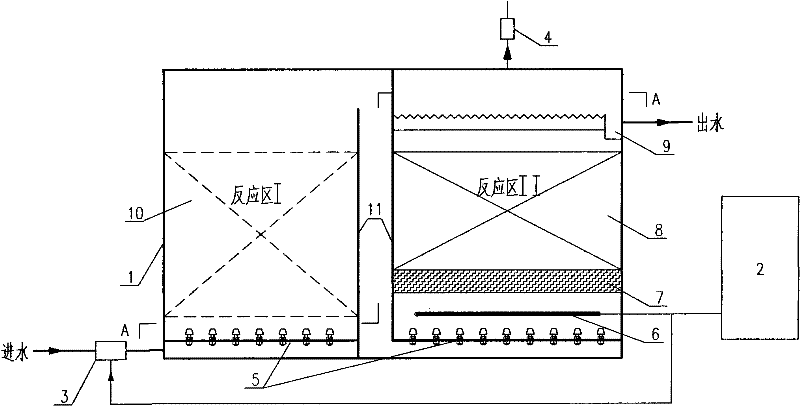
A method and device for advanced treatment of wastewater by heterogeneous catalytic ozonation
The invention provides a heterogeneous catalysis and ozone oxidation method, and an apparatus thereof. The apparatus is characterized in that: with adopting a coupling method of sectional ozone oxidation and catalytic oxidation, most organic matters can be removed through the ozone oxidation reaction in a ozone oxidation zone, wherein the most organic matters can be oxidized by the ozone; the generated organisms hard to be oxidized by the ozone from the reaction and the original refractory organic matters in the waste water react with hydroxyl radicals generated through the catalysis in a catalytic oxidation zone to generate low molecular weight compounds, carbon dioxide and water, such that the organic matters in the waste water are substantially reduced, and the biodegradability is improved; the catalytic oxidation zone adopts two catalysts of a regular catalyst and a porous catalyst such that a uniform water distribution effect and a uniform gas distribution effect are provided, the degradation of the organic matter can be efficiently catalytically oxidized. According to the method and the apparatus provided by the present invention, the refractory organic matters in the waste water can be removed, the utilization efficiency of the ozone is improved, the apparatus has characteristics of simple structure and easy operation, the method is an efficient and low-cost waste waterdeep treatment method.
Owner:BEIJING CYCLE COLUMBUS ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
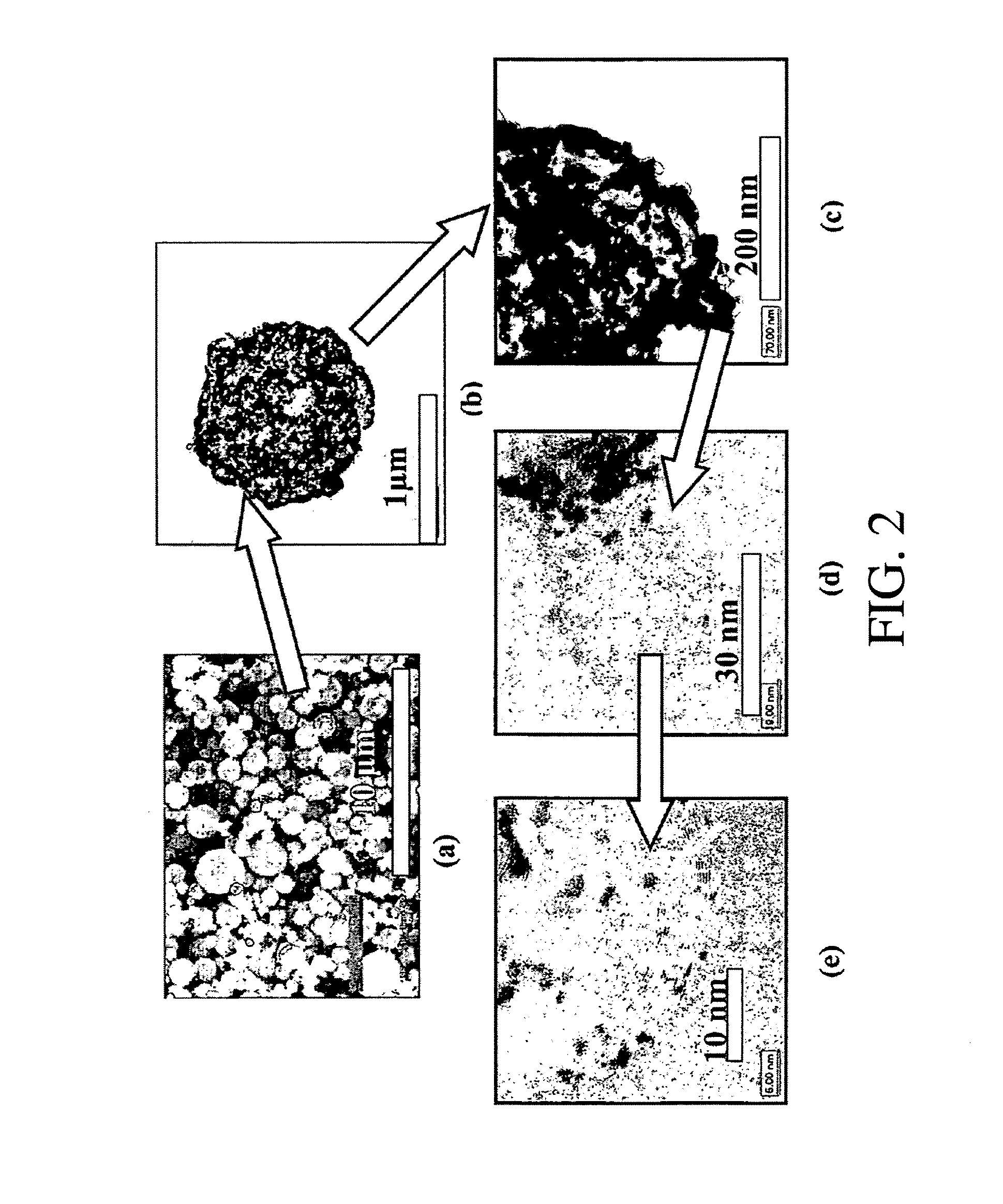
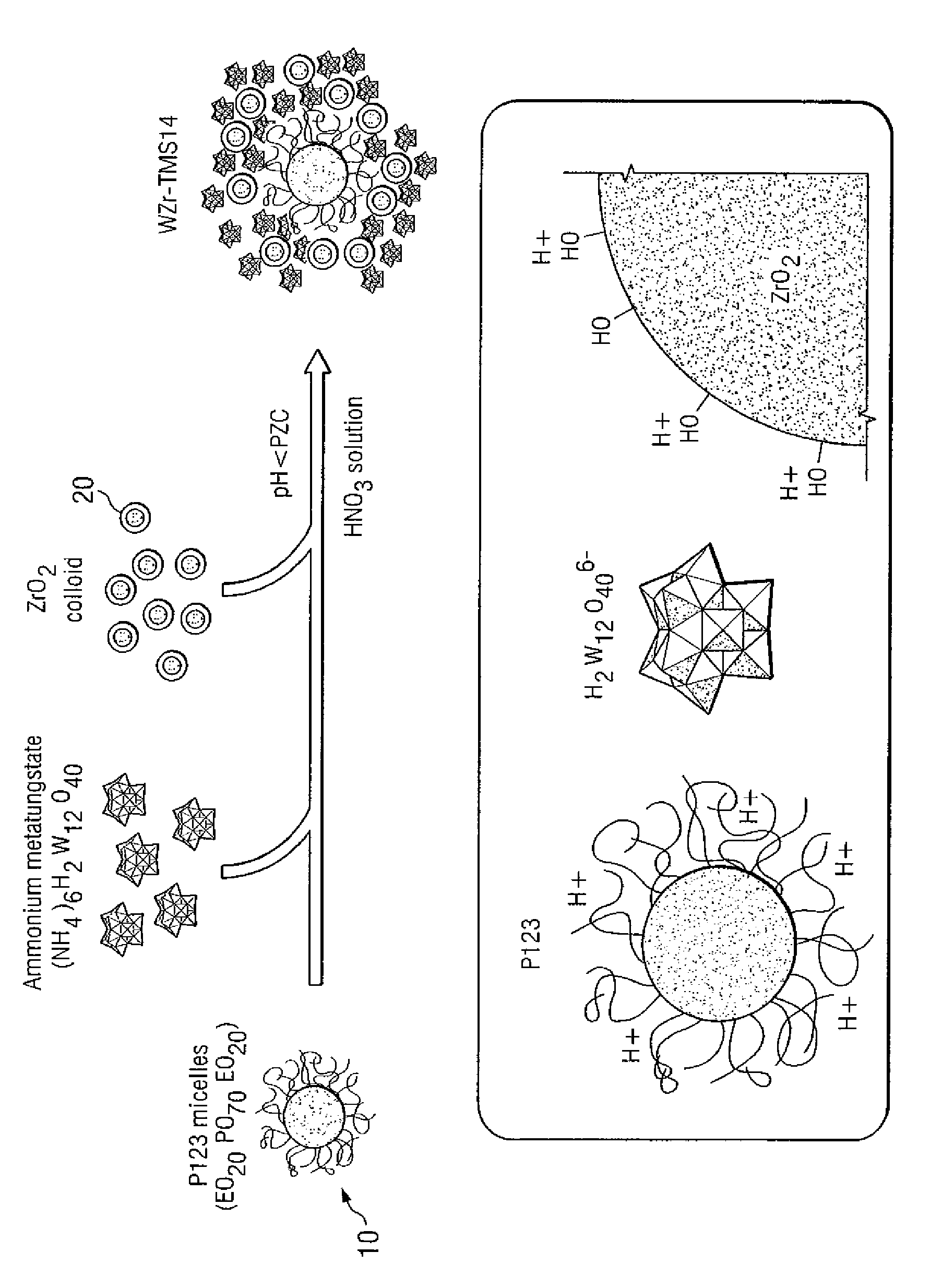
Supported catalysts using nanoparticles as the support material
A process for making a porous catalyst, comprises a) providing an aqueous solution containing a nanoparticle precursor, b) forming a composition containing nanoparticles, c) adding a first catalytic component or precursor thereof and a pore-forming agent to the composition containing nanoparticles and allowing the first catalytic component, the pore-forming agent, and the nanoparticles form an organic-inorganic structure, d) removing water from the organic-inorganic structure; and e) removing the pore-forming agent from the organic-inorganic structure so as to yield a porous catalyst.
Owner:RICE UNIV
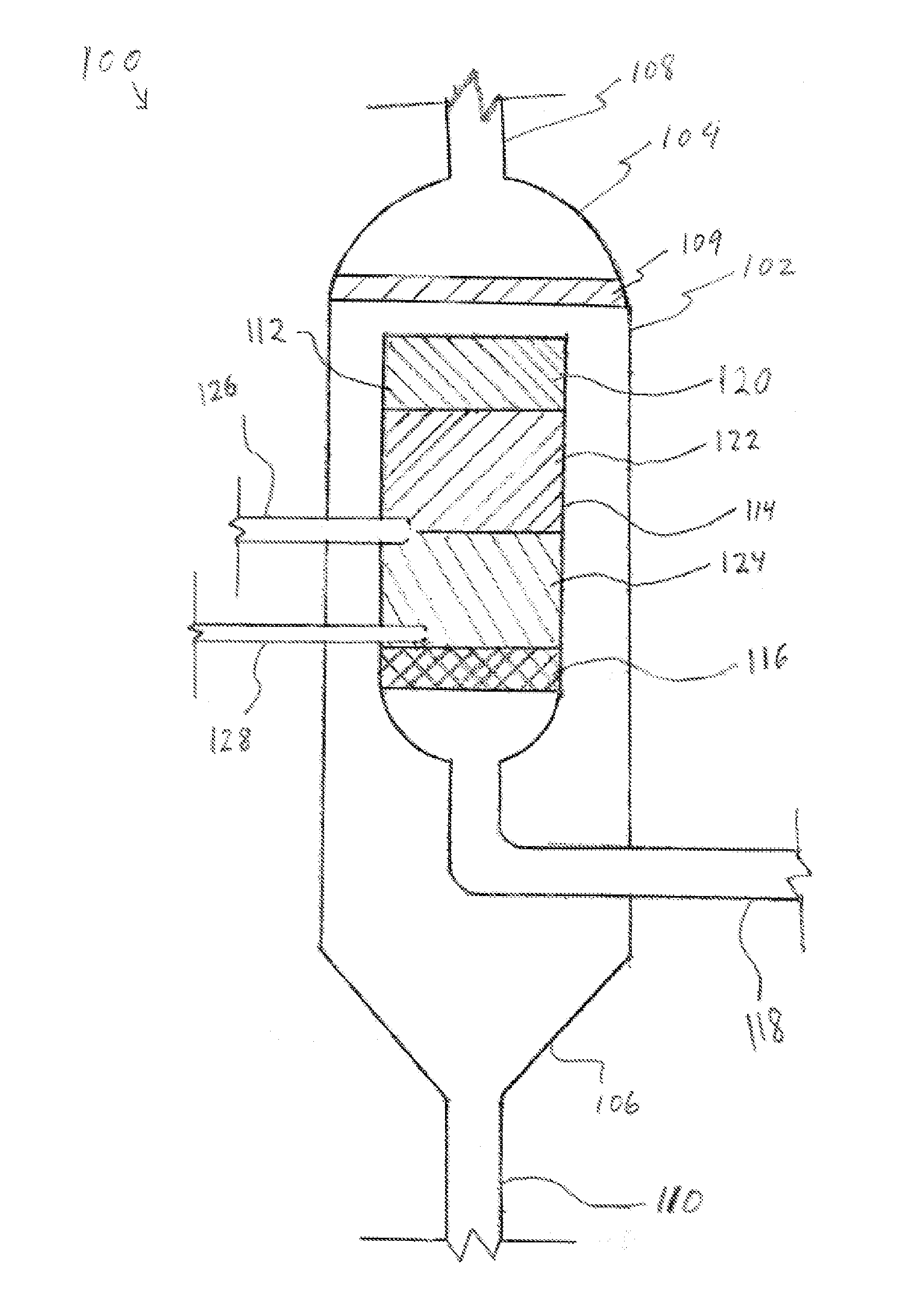
Method for producing a shell catalyst and corresponding shell catalyst
ActiveUS20100197488A1Uniform concentrationUniform shell thicknessOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationFluidized bedProduct gas
The present invention relates to a method for producing a shell catalyst which comprises a porous shaped catalyst support body with an outer shell in which at least one catalytically active species is present. In order to provide a shell catalyst production method by means of which shell catalysts can be produced, said shell catalysts having, over a comparatively large region of their shell thickness, a substantially uniform concentration of catalytically active species and having a substantially uniform shell thickness, what is proposed is a method using an device which is designed to generate, by means of a process gas, a fluid bed of shaped catalyst support bodies in which the shaped catalyst support bodies circulate elliptically or toroidally, preferably toroidally, comprising the steps of charging the device with shaped catalyst support bodies and generating a shaped catalyst support body fluid bed by means of a process gas, the shaped catalyst support bodies circulating elliptically or toroidally in the fluid bed, preferably toroidally; impregnating an outer shell of the shaped catalyst support body with a catalytically active species or precursor thereof by spraying the shaped catalyst support bodies circulating elliptically or toroidally in the fluid bed with a solution comprising a catalytically active species or a precursor thereof; drying the shaped catalyst support bodies sprayed with the solution.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD
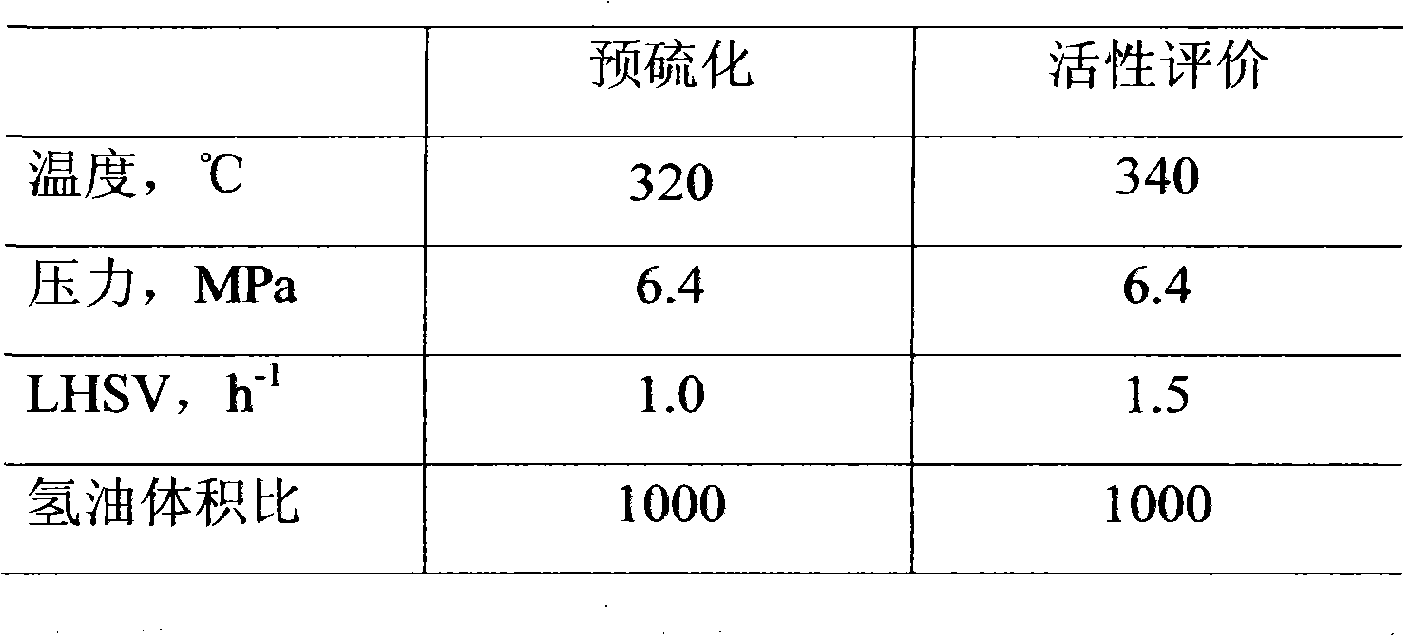
Preparation method of hydrogenation catlayst
ActiveCN101279291AEasy to useInhibit aggregationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsPorous catalystSulfur
The present invention relates to a preparation method for a hydrotreating catalyst, which induces organic additives before, in the middle of or after inducing the active metal components on a porous catalyst carrier; wherein, at least one organic additive is an organic additive containing sulfur; then carries out one or a plurality of drying steps after inducing the active metals or the organic additives with a drying temperature lower than 300 DEG C but without baking processes in the preparation process of the catalyst. The use property of the hydrotreating catalyst prepared by the method of the present invention can be further improved and the method can be applied to various hydrotreating catalyst processes.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
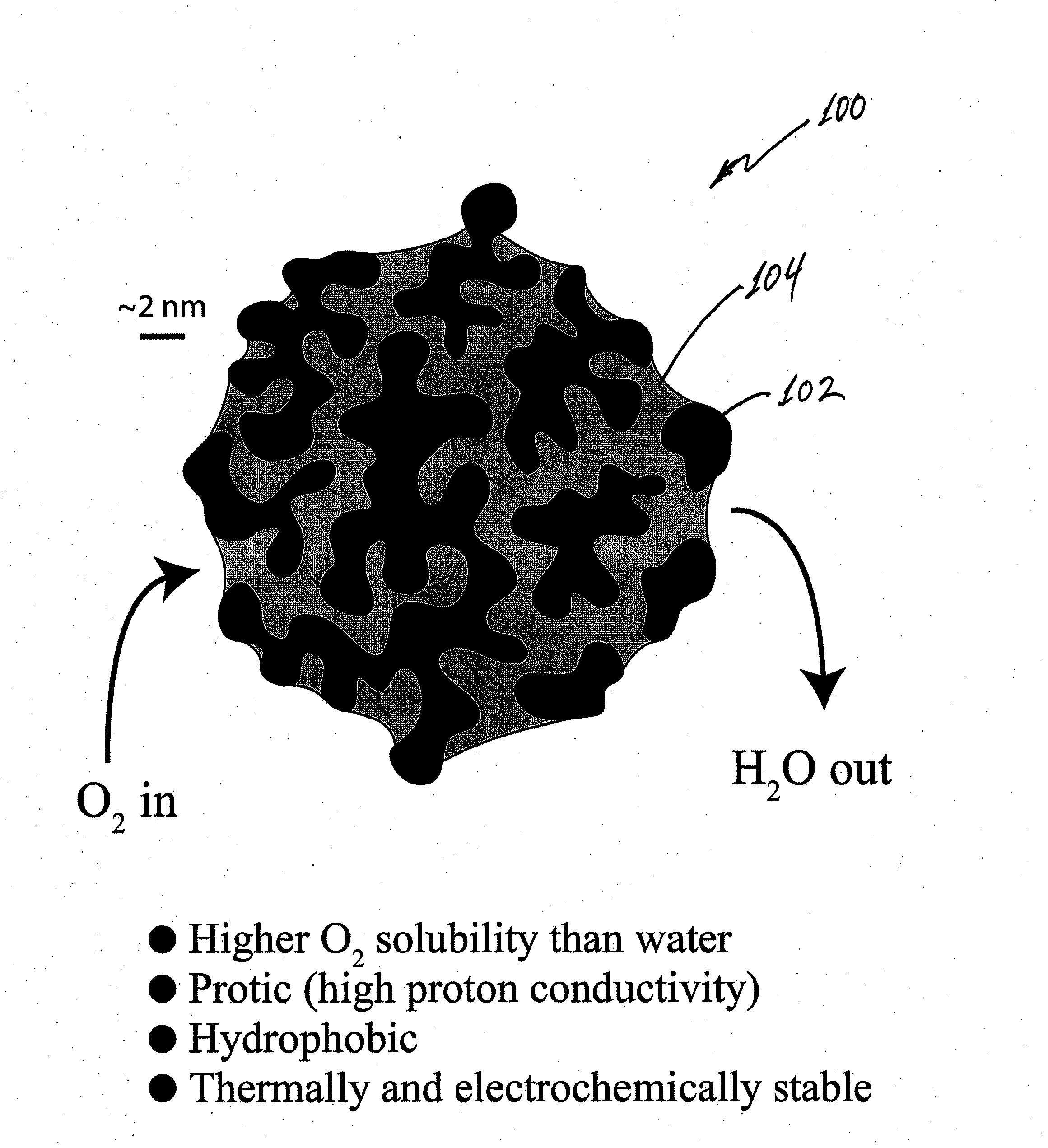
Composite porous catalysts
InactiveUS20110189589A1Increase attractivenessEnhances expulsionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsActive material electrodesFuel cellsPorous catalyst
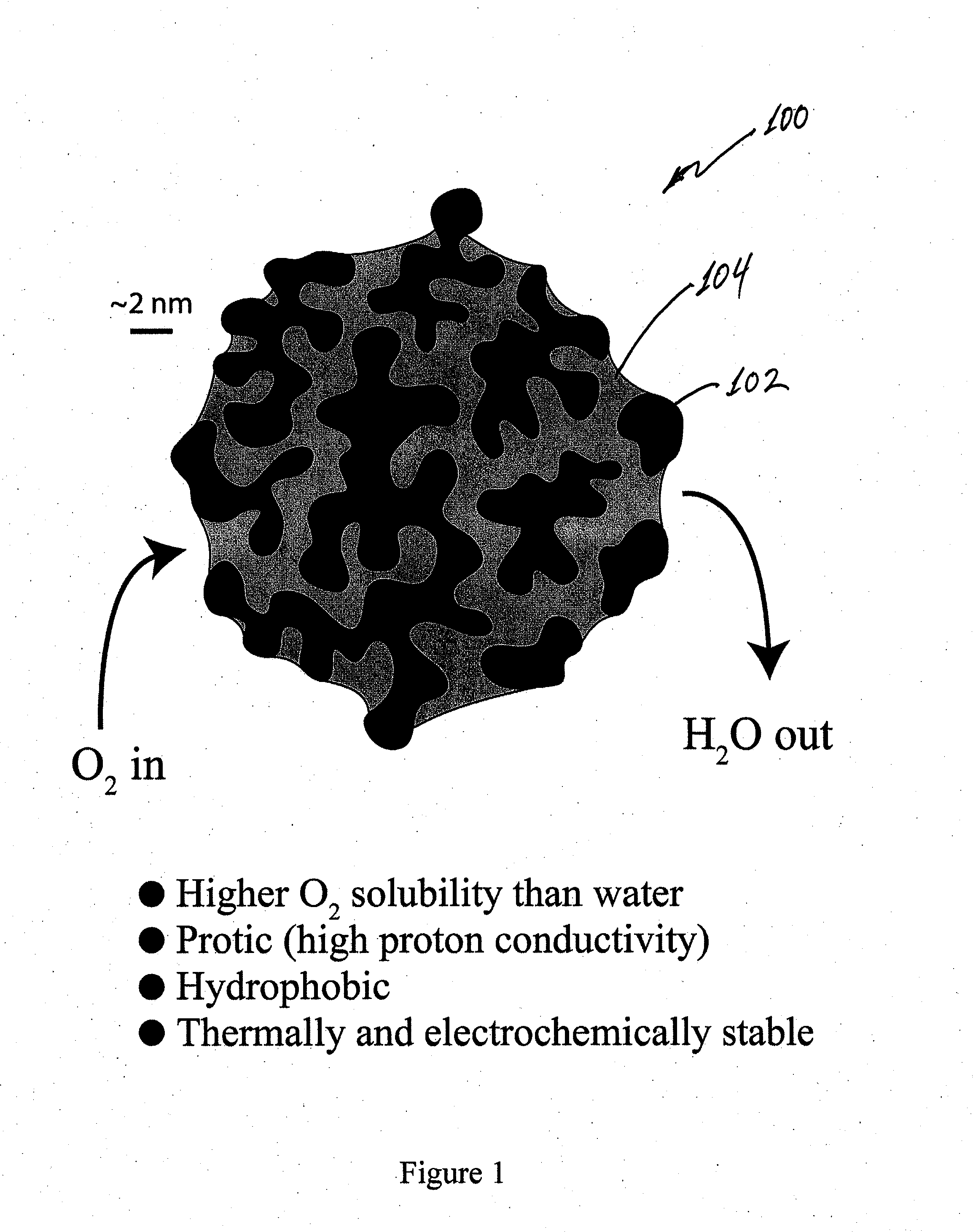
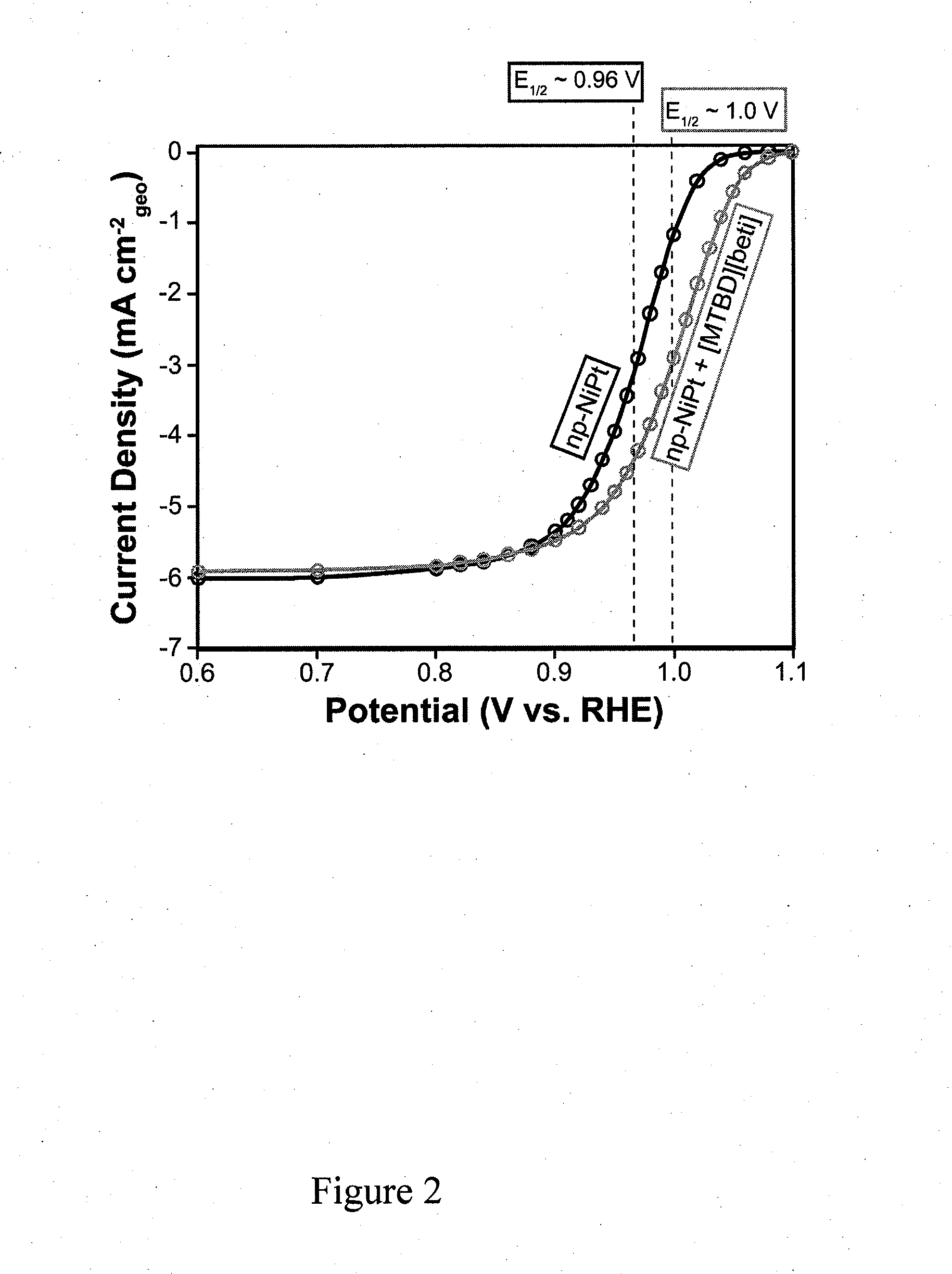
A composite catalyst for a chemical reaction includes a porous metal catalyst that catalyzes a plurality of reactants to provide a reaction product, and a reaction-enhancing material disposed within pores defined by the porous metal catalyst. The reaction-enhancing material enhances attraction of at least one reactant of the plurality of reactants into the pores defined by the porous metal catalyst and enhances expulsion of the reaction product from the pores defined by the porous metal catalyst. A fuel cell according to an embodiment of the current invention has a first electrode, a second electrode spaced apart from the first electrode, and an electrolyte arranged between the first and the second electrodes. The at least one of the first and second electrodes is at least one of coated with or comprises a composite catalyst. A method of producing a composite catalyst includes providing a metal alloy, de-alloying the metal alloy to provide a porous metal catalyst that catalyzes a plurality of reactants to provide a reaction product, and adding a reaction-enhancing material to the porous metal catalyst such that the reaction-enhancing material is disposed within pores defined by the porous metal catalyst.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Layered silicate catalysts pillared with metal oxide
InactiveUS6703501B1Speed up the conversion processHigh selectivityLactams preparationMolecular sieve catalystsPorous catalystCyclohexanone oxime
The present invention relates to porous catalysts comprising layered silicate and metal oxides, and a method of preparing epsilon-caprolactam from cyclohexanone oxime using the catalyst. This new catalyst can resolve the environmental and safety problems arising from conventional liquid acid process. Also the present catalyst solves the problem of short lifetime of current solid acid catalysts. Moreover, the present catalyst provides higher selectivity and yield.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Reactors, systems, and methods for forming solid products
ActiveUS20160016800A1Easy to set upLow costCarbon nanotubesCarbon preparation/purificationPorous catalystPtru catalyst
A reactor includes a vessel, a gas inlet, a solid outlet, a catalyst support configured to at least partially retain a catalyst material and allow a tail gas to pass therethrough, and a tail gas outlet. The gas inlet is in fluid communication with the solid outlet. A system for producing a solid product includes a reactor, a compressor, a heater, a make-up reactive gas inlet, and a solids discharge means for removing the solid product from the solid outlet of the reactor. Methods of forming solid products include providing a catalyst material in a vessel having a porous catalyst support, delivering a reactive gas to the vessel, reacting the reactive gas to form a solid product and a tail gas in the vessel, passing the tail gas through a portion of the catalyst material to separate the solid product from the tail gas, and removing the solid product.
Owner:SEERSTONE
Membrane electrode assembly including porous catalyst layer and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080292942A1Improve efficiencyEfficient transferCell electrodesFinal product manufactureFuel cellsPorous catalyst
A membrane electrode assembly for a fuel cell including a porous catalyst layer, and a method of manufacturing the same in which an electrode includes a catalyst layer formed adjacent to a surface of an electrolyte membrane, and the catalyst layer has a uniform porosity as pluralities of pores are uniformly distributed on the catalyst layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Catalyst support using cellulose fibers, preparation method thereof, supported catalyst comprising nano-metal catalyst supported on carbon nanotubes directly grown on surface of the catalyst support, and method of preparing the supported catalyst
ActiveUS20090176646A1Decreasing catalyst preparation costHigh reactivityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufacturePorous catalystMetal catalyst
Disclosed are a porous catalyst support for maximizing an increase in catalytic reaction activity and a method of preparing a nano-metal-supported catalyst using the same. The method includes splitting cellulose fibers, thus preparing a catalyst support, growing carbon nanotubes on the prepared catalyst support, and supporting a nano-metal catalyst on the catalyst support having the carbon nanotubes grown thereon. A nano-metal-supported catalyst including the cellulose catalyst support and the use of cellulose fibers as the catalyst support for supporting the nano-metal catalyst are also provided. When porous cellulose fibers having a plurality of micropores are used as material for the catalyst support for supporting a nano-metal catalyst, the preparation cost of the catalyst is reduced and the increase in catalytic reaction activity is maximized even with the use of a small amount thereof in various catalytic reactions. A technique for directly growing carbon nanotubes is applied, thereby controlling the electrical conductivity of the catalyst and increasing the surface area, and further, an expensive nano-metal catalyst component can be easily collected after the reaction, resulting in eco-friendly properties.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Graphene oxide composite aerogel and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105536774AImprove adsorption catalytic activityHigh mechanical strengthWaste water treatment from plant processingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFreeze-dryingOxide composite
The present invention belongs to the field of porous catalyst materials, and specifically discloses a graphene oxide composite aerogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method is as follows: mixing graphene oxide powder and water in solid-liquid ratio of 1: 2 to 1: 6 for ultrasonic dispersion; under stirring conditions, adding nanoscale MnO2 powder, performing hydrothermal reaction, after the reaction is stopped, cooling to room temperature, filtering, washing a filter cake with water, and drying; placing an obtained solid material in an alcohol solution for substitution reaction to obtain a graphene oxide composite hydrogel; finally freeze-drying the graphene oxide hydrogel, and then cooling to obtain the graphene oxide composite aerogel. The catalyst preparation method is simple and easy to operate, the graphene oxide composite aerogel is high in stability, and the catalytic ozonation treatment effect of the graphene oxide composite aerogel is good, and an effective method is provided for advanced treatment of papermaking wastewater.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Highly dispersed metal catalyst
ActiveUS20120004098A1Small particle sizeRaise the ratioCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationPorous catalystMetal catalyst
A supported catalyst having an atomic level single atom structure is provided such that substantially all the catalyst is available for catalytic function. A process of forming a single atom catalyst unto a porous catalyst support is also provided.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS +1
DOPED Pd/Au SHELL CATALYST, METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE SAME AND USE THEREOF
InactiveUS20100273644A1High VAM activity and selectivityLow costMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesMischmetalPorous catalyst
A shell catalyst for producing vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), comprising an oxidic porous catalyst support, formed as a shaped body, with an outer shell in which metallic Pd and Au are contained. To provide a shell catalyst for producing VAM which has a relatively high activity and can be obtained at relatively low cost, the catalyst support is doped with at least one oxide of an element selected from the group consisting of Li, P, Ca, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Sr, Nb, Ta, W, La and the rare-earth metals.
Owner:SUED CHEM IP GMBH & CO KG
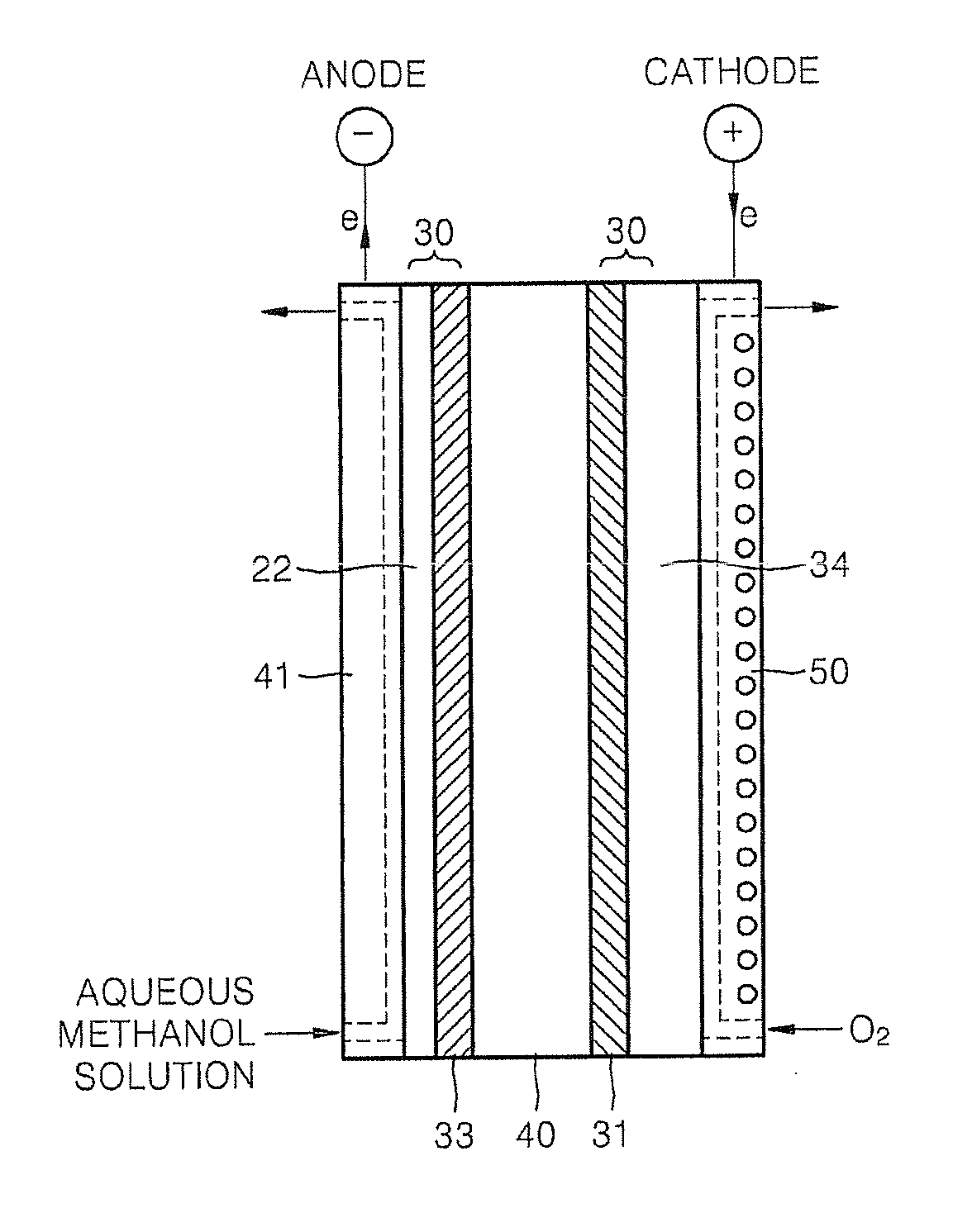
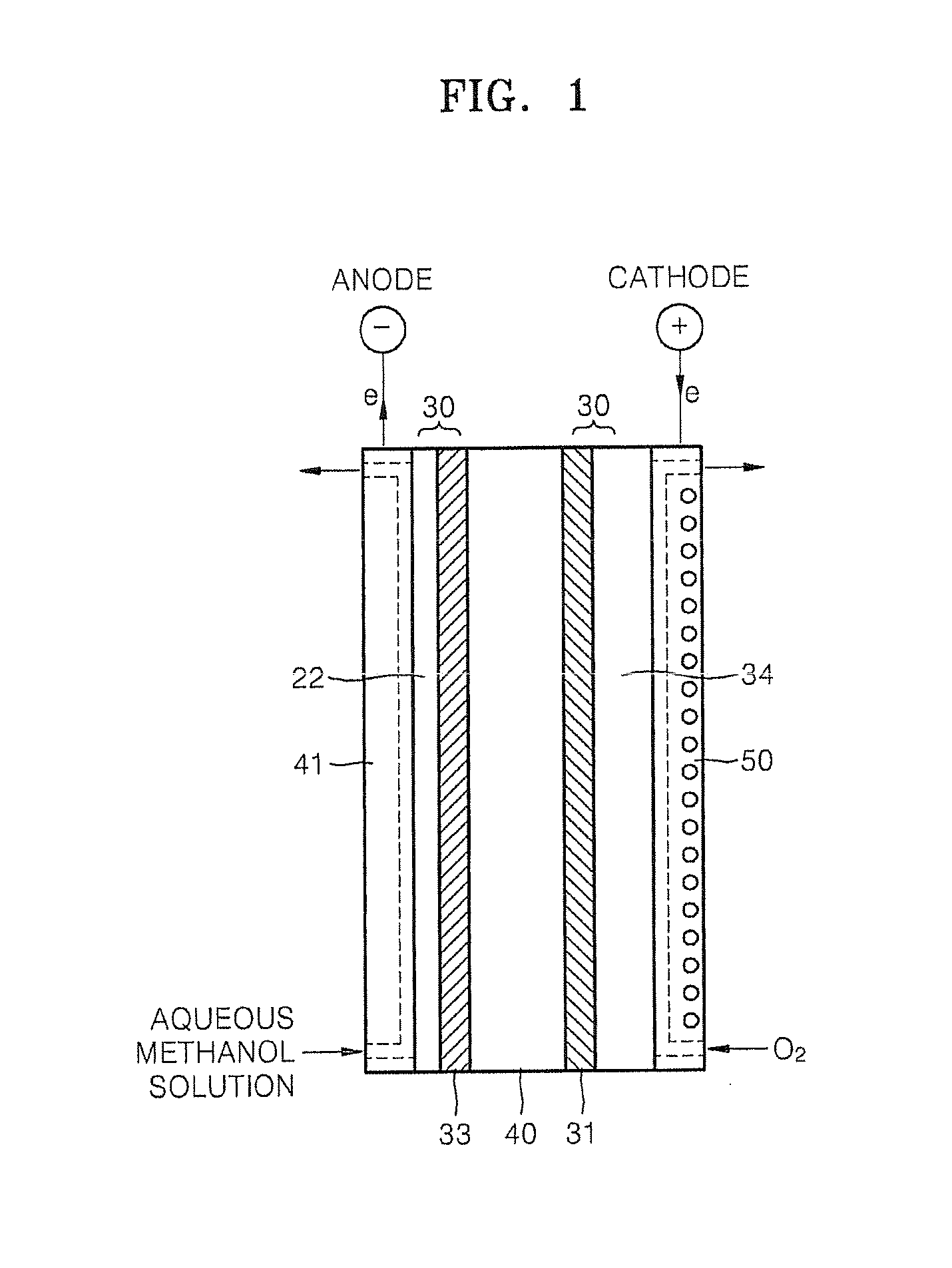
Liquid fuel cell, membrane electrode assembly and cathode
InactiveUS20060204832A1Excellent low air performanceActive material electrodesAqueous electrolyte fuel cellsFiberPorous catalyst
A cathode includes a diffusion layer, and a porous catalyst layer provided on the diffusion layer. The porous catalyst layer has a thickness not greater than 60 μm, a porosity of 30 to 70% and a pore diameter distribution including a peak in a range of 20 to 200 nm of a pore diameter. A volume of pores having a diameter of 20 to 200 nm is not less than 50% of a pore volume of the porous catalyst layer. The porous catalyst layer contains a supported catalyst comprising 10 to 30% by weight of a fibrous supported catalyst and 70 to 90% by weight of a granular supported catalyst. The fibrous supported catalyst includes a carbon nanofiber having a herringbone structure or a platelet structure. The granular supported catalyst includes a carbon black having 200 to 600 mL / 100 g of a dibutyl phthalate (DBP) absorption value.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Preparation method of hydroprocessing catalyst
ActiveCN102463150AAvoid enteringIncrease profitCatalyst activation/preparationRefining to eliminate hetero atomsSimple Organic CompoundsPorous catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of hydroprocessing catalyst, comprising the following steps of: (1) preparing a porous catalyst carrier; (2) impregnating the catalyst carrier with organic compound solution; (3) carrying out heat treatment by utilizing the organic compound additive supported carrier obtained by the step (2); (4) supporting active metal component onto the organic matter supported carrier, so as to obtain a catalyst precursor; and (5) roasting the catalyst precursor obtained by the step (4), so as to obtain the hydroprocessing catalyst. In the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the organic matter is uniformly supported onto surface of the catalyst carrier, and then the active metal is supported, operational performance of the catalyst is improved, especially aggregation of the catalyst in a roasting process is reduced, and dispersion of the active metal of the catalyst is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Combustible gas sensor
InactiveUS20100221148A1High measurement sensitivityHigh bonding strengthChemical analysis using combustionMaterial resistancePorous catalystThermopile
The present invention provides a combustible gas sensor that can realize a considerable improvement in the measurement sensitivity and the measurement precision by increasing the contact area between the measurement object gas and the oxidation catalyst particles, increasing the amount of heat generation of oxidation reaction in accordance therewith, and improving the transference of the oxidation reaction heat, while reducing the scale of the whole.In this invention, a temperature measurement element such as a thermopile obtained by joining different kinds of metals is formed on a top surface of a Si substrate; a porous catalyst layer made by allowing a porous material layer to carry oxidation catalyst particles such as Pt or a chain-form catalyst layer made by linking and bonding numerous oxidation catalyst particles in a chain form is provided on a heat-sensitive part of this temperature measurement element; and this porous catalyst layer or the chain-form catalyst layer is integrally bonded with the heat-sensitive part of this temperature measurement element.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
Cobalt catalysts
InactiveUS20030144367A1Enhanced and superior initialHigh activityHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalyst protectionParticulatesPorous catalyst
A process for preparing a cobalt based catalyst precursor includes in a first support impregnation / drying / calcination stage, impregnating a particulate porous catalyst support with a cobalt salt, partially drying the impregnated support, and calcining the partially dried impregnated support to obtain a calcined material. The calcined material is partially reduced. Thereafter, in a second support impregnation / drying / calcination stage, the partially reduced material is impregnated with a cobalt salt, partially dried and calcined, to obtain the cobalt based catalyst precursor.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD +1
Preparation method for natural calcium base porous solid alkaline catalyst for catalysis in interesterification
ActiveCN102430400AImprove catalytic performanceLow costFatty acid esterificationBiofuelsPorous catalystPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method for a natural calcium base porous solid alkaline catalyst for catalysis in interesterification. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: simply heating and stirring cheap calcium carbonate-enriched natural calcium base materials serving as a raw material and C12-C22 fatty acid as a modifier to form a fatty acid compound; and baking to form a porous catalyst with a larger surface area. The preparation method is simple, low in cost and high in operability. The catalyst prepared by applying the method shows higher catalytic performance compared with the catalyst prepared by the conventional method (direct baking); and the catalytic efficiency can be increased by over 25 percent under the same condition.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Hydrocarbon-decomposing porous catalyst body and process for producing the same, process for producing hydrogen-containing mixed reformed gas from hydrocarbons, and fuel cell system
ActiveUS20110038775A1Increase contact areaHigh catalytic activityMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenDecompositionComposite oxide
The present invention aims at providing a catalyst as a porous catalyst body for decomposing hydrocarbons which comprises at least magnesium, aluminum and nickel, wherein the catalyst has an excellent catalytic activity for decomposition and removal of hydrocarbons, an excellent anti-sulfur poisoning property, an excellent anti-coking property even under a low-steam condition, a sufficient strength capable of withstanding crushing and breakage even when coking occurs within the catalyst, and an excellent durability. The above aim of the present invention can be achieved by a porous catalyst body for decomposing hydrocarbons which comprises at least magnesium, aluminum and nickel in such a manner that the magnesium and aluminum are present in the form of a composite oxide of magnesium and aluminum, and the nickel is present in the form of metallic nickel; and which porous catalyst body has a magnesium element content of 10 to 50% by weight, an aluminum element content of 5 to 35% by weight and a nickel element content of 0.1 to 30% by weight, a pore volume of 0.01 to 0.5 cm3 / g, an average pore diameter of not more than 300 Å and an average crushing strength of not less than 3 kgf.
Owner:TODA IND
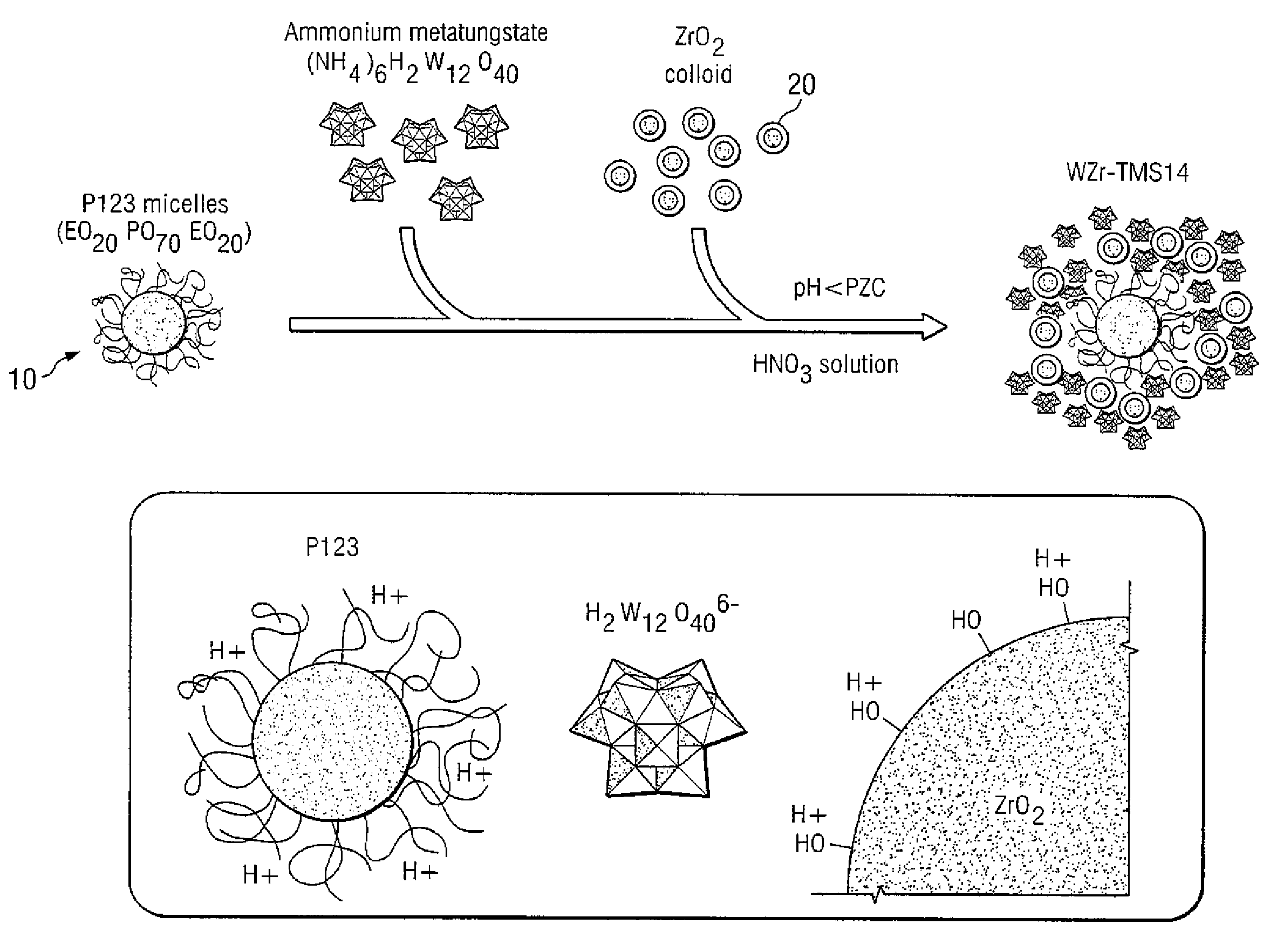
Supported catalysts using nanoparticles as the support material
InactiveUS20070009417A1Improve distributionHigh catalytic activityNitrogen compoundsZirconium compoundsPorous catalystNanoparticle
A process for making a porous catalyst, comprises a) providing an aqueous solution containing a nanoparticle precursor, b) forming a composition containing nanoparticles, c) adding a first catalytic component or precursor thereof and a pore-forming agent to the composition containing nanoparticles and allowing the first catalytic component, the pore-forming agent, and the nanoparticles form an organic-inorganic structure, d) removing water from the organic-inorganic structure; and e) removing the pore-forming agent from the organic-inorganic structure so as to yield a porous catalyst.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com