Patents
Literature
335 results about "Highly porous" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
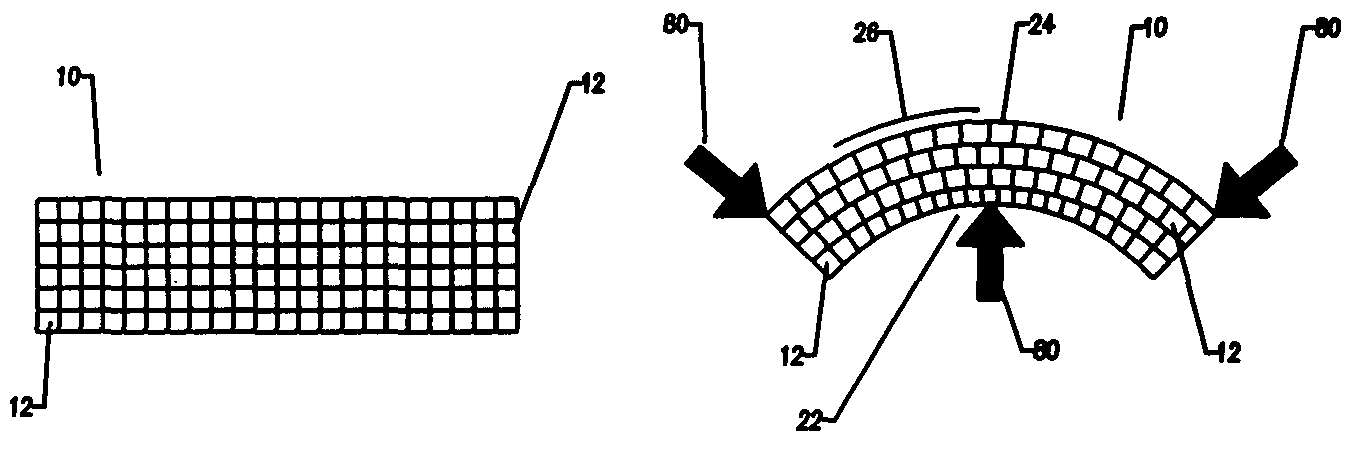
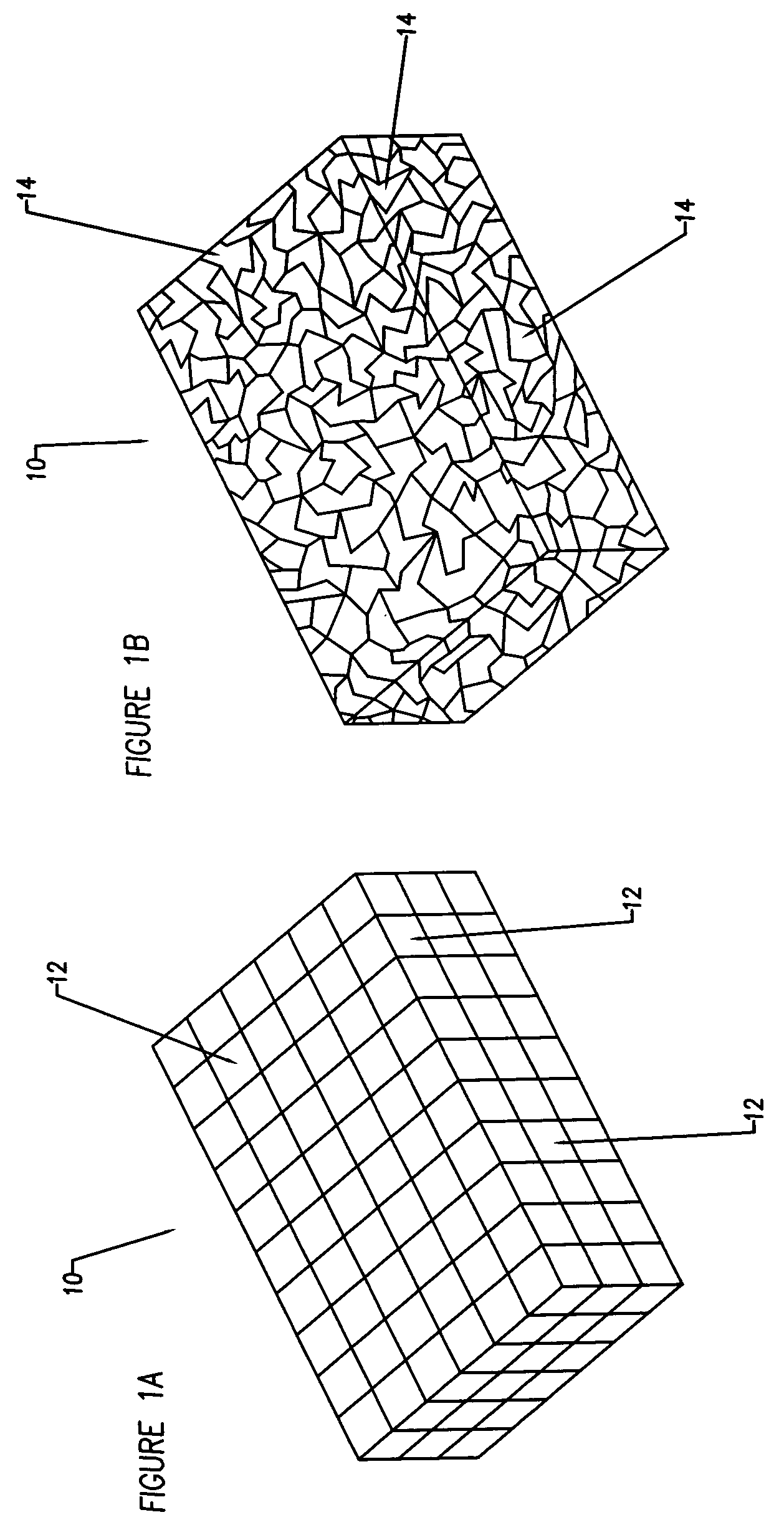
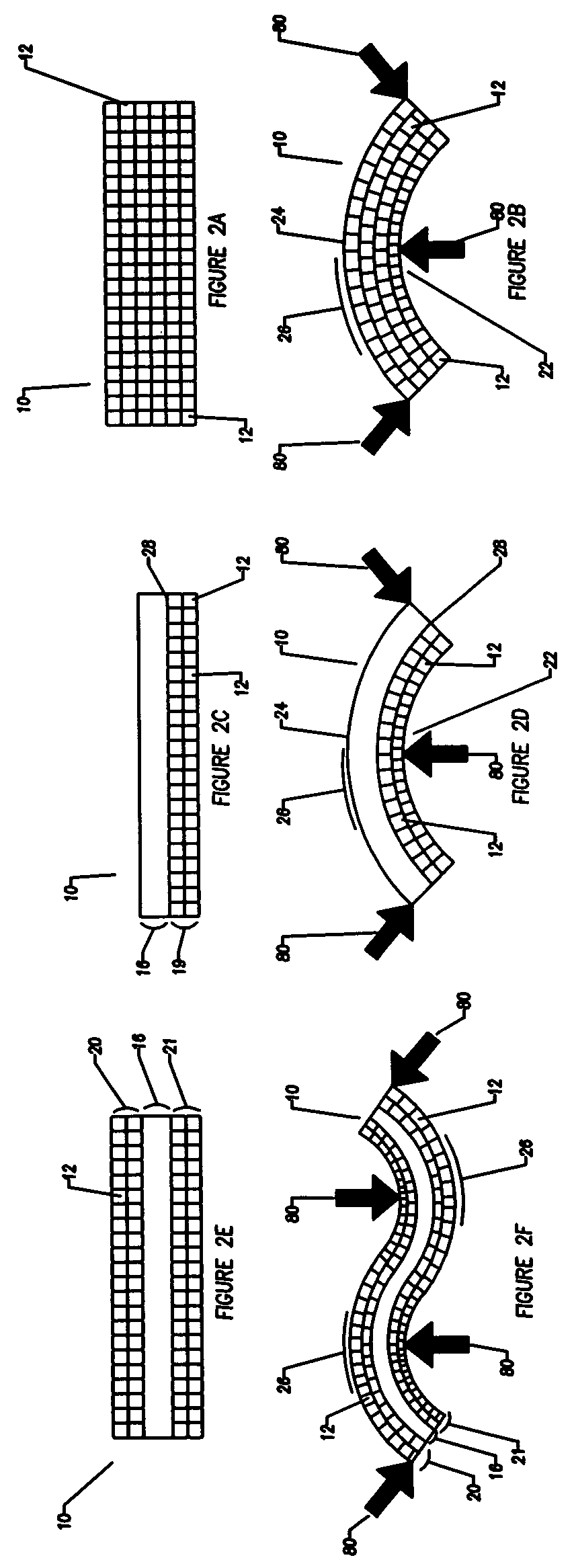
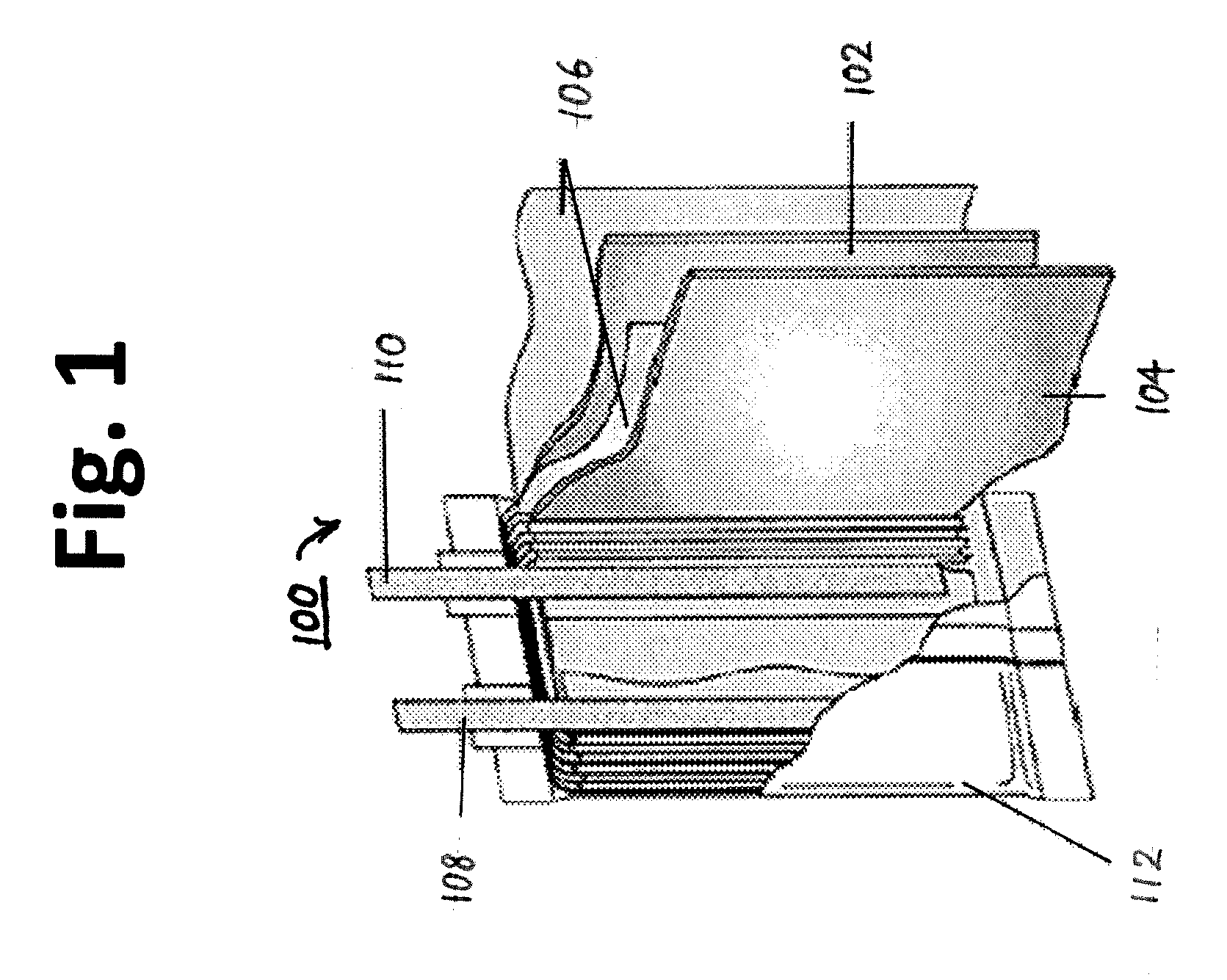
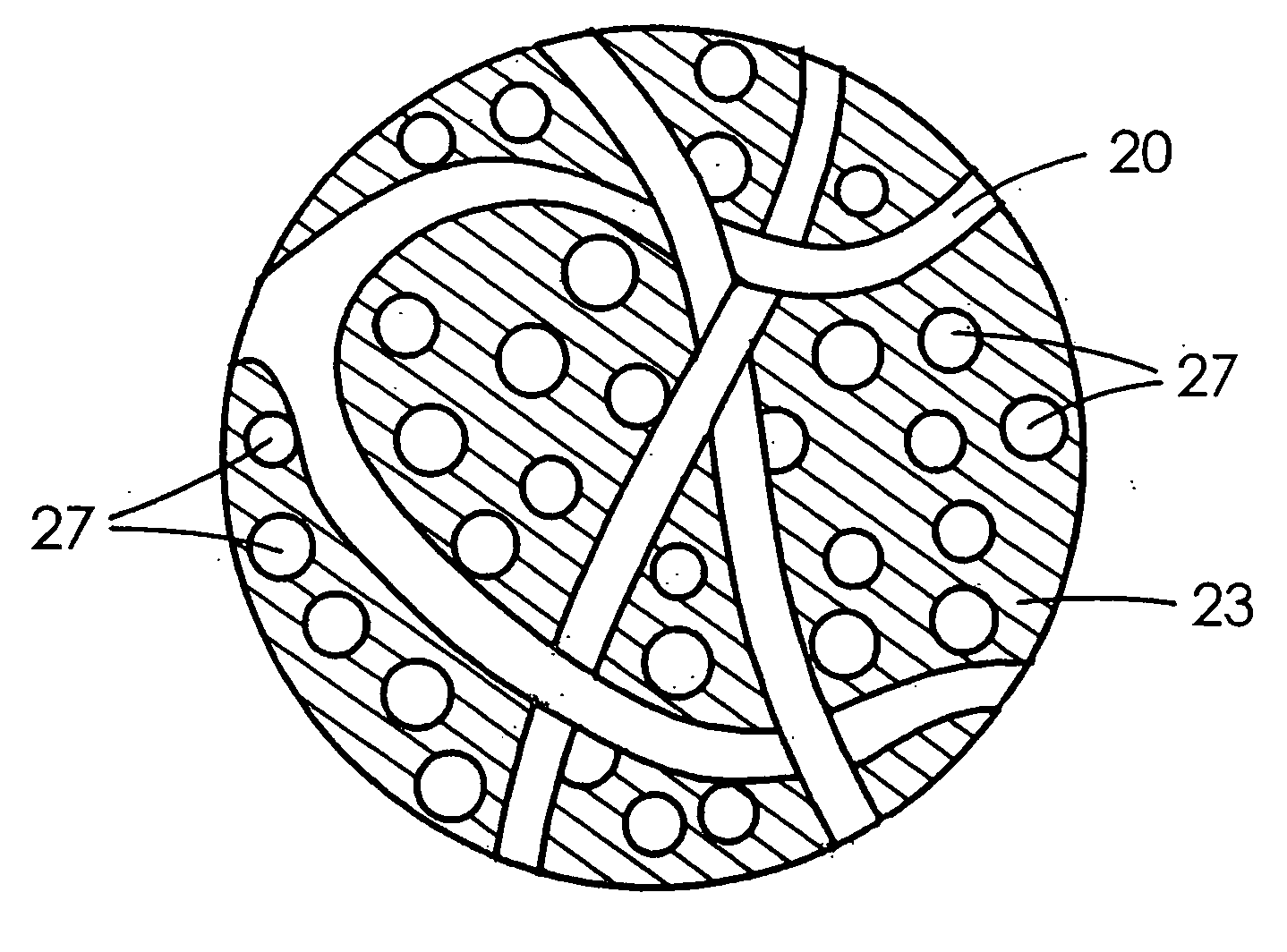
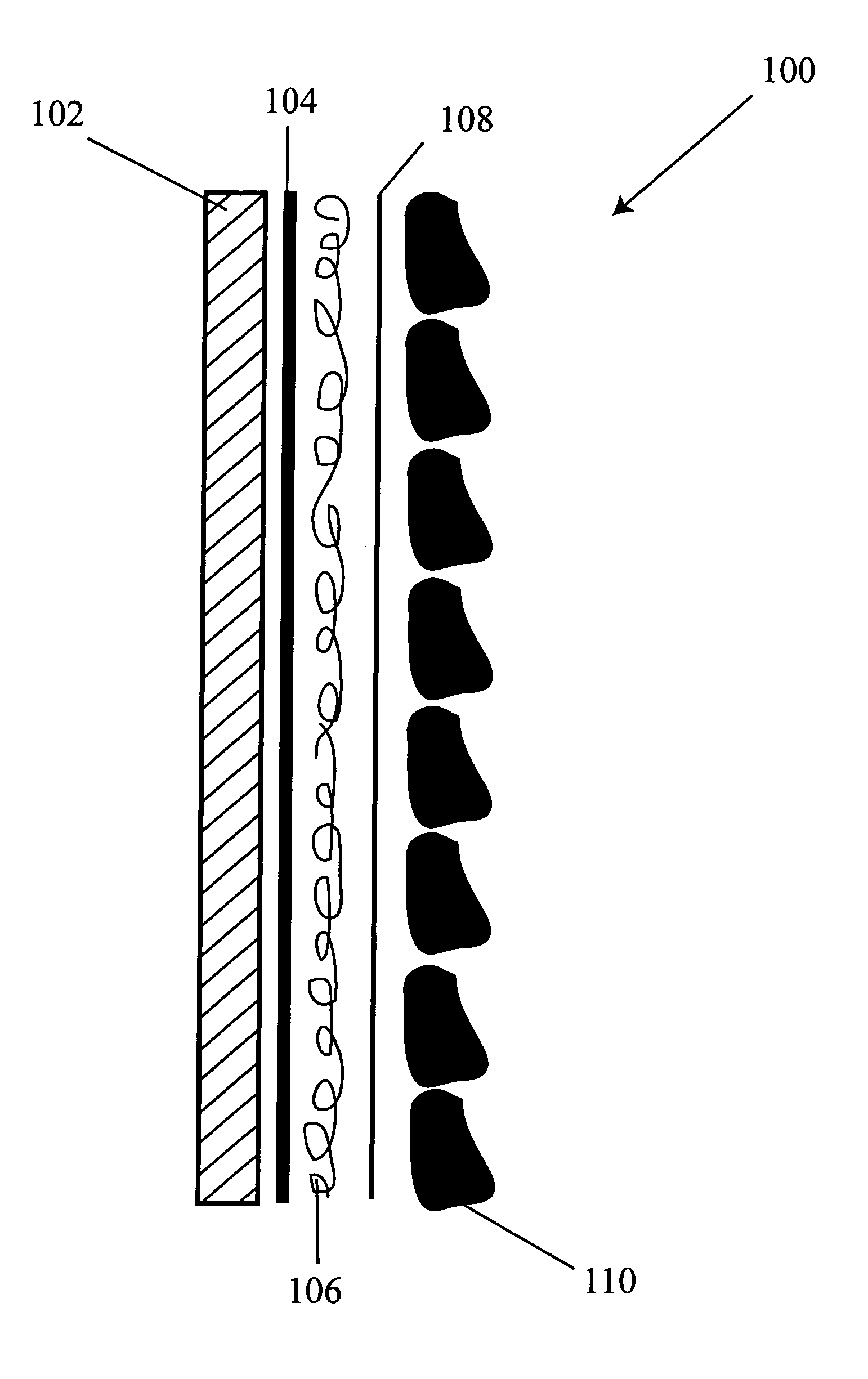
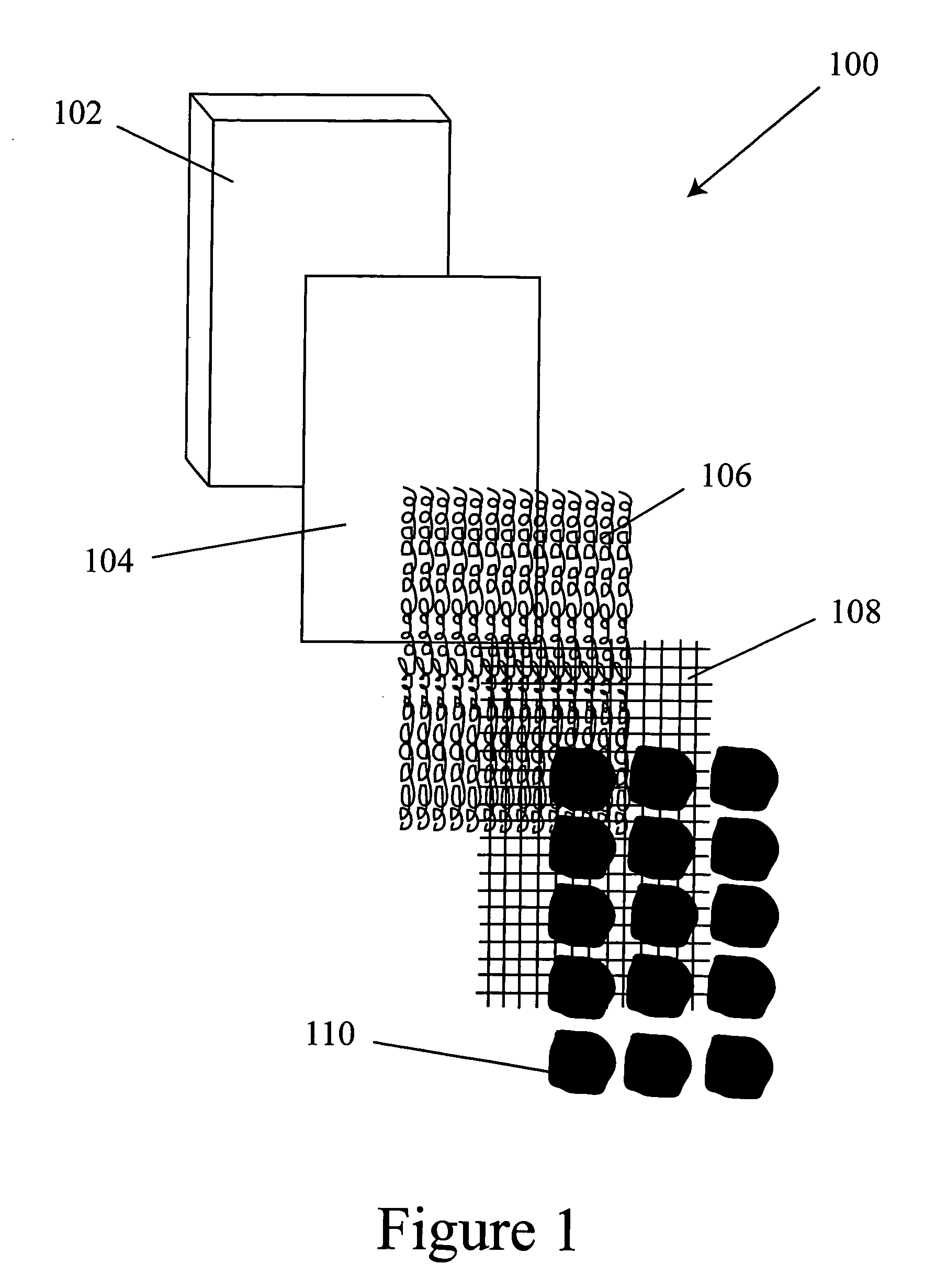
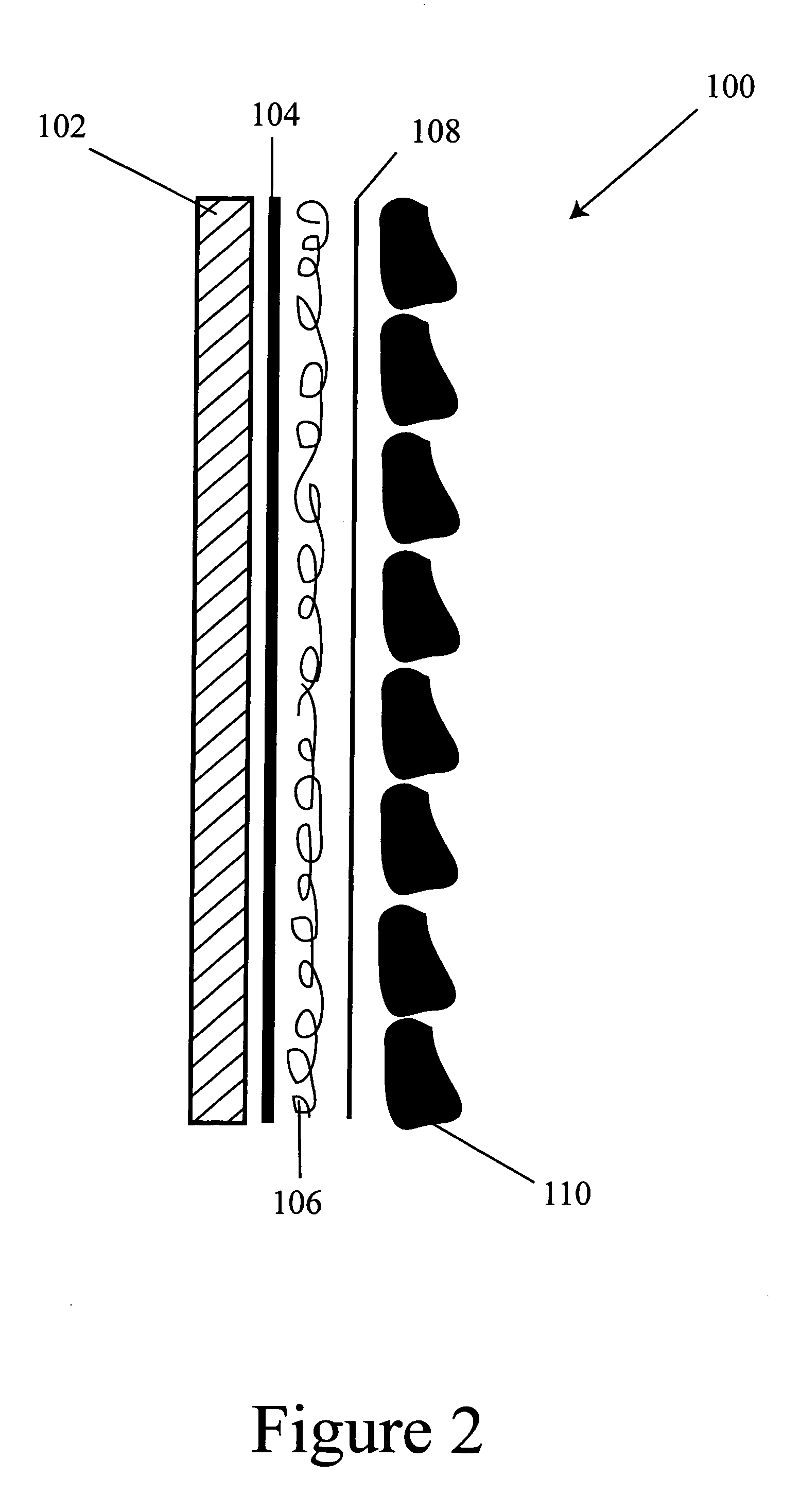
Compliant osteosynthesis fixation plate
ActiveUS7931695B2Maintaining structural rigidityBending stabilityBone implantBone platesMedicineLiving body
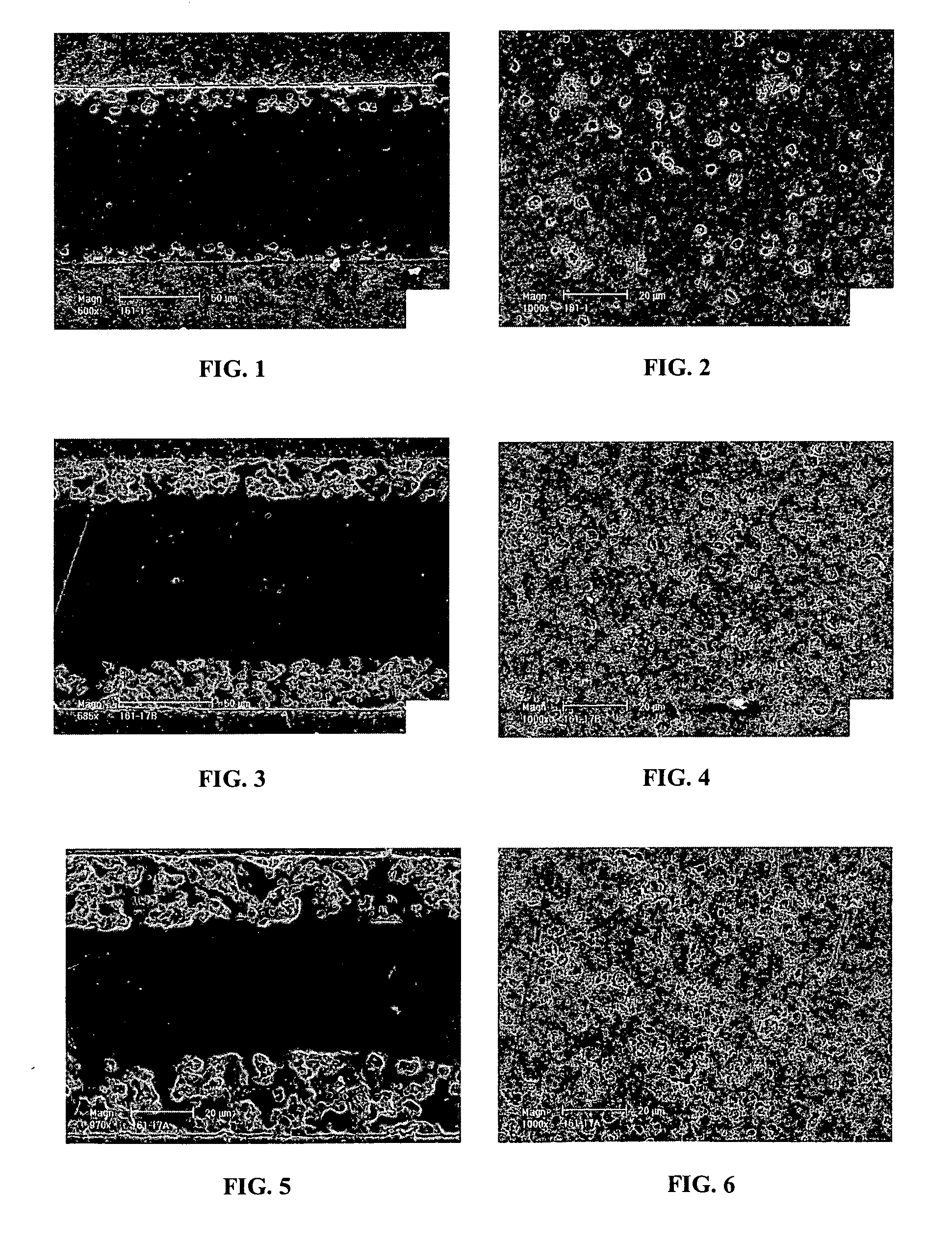
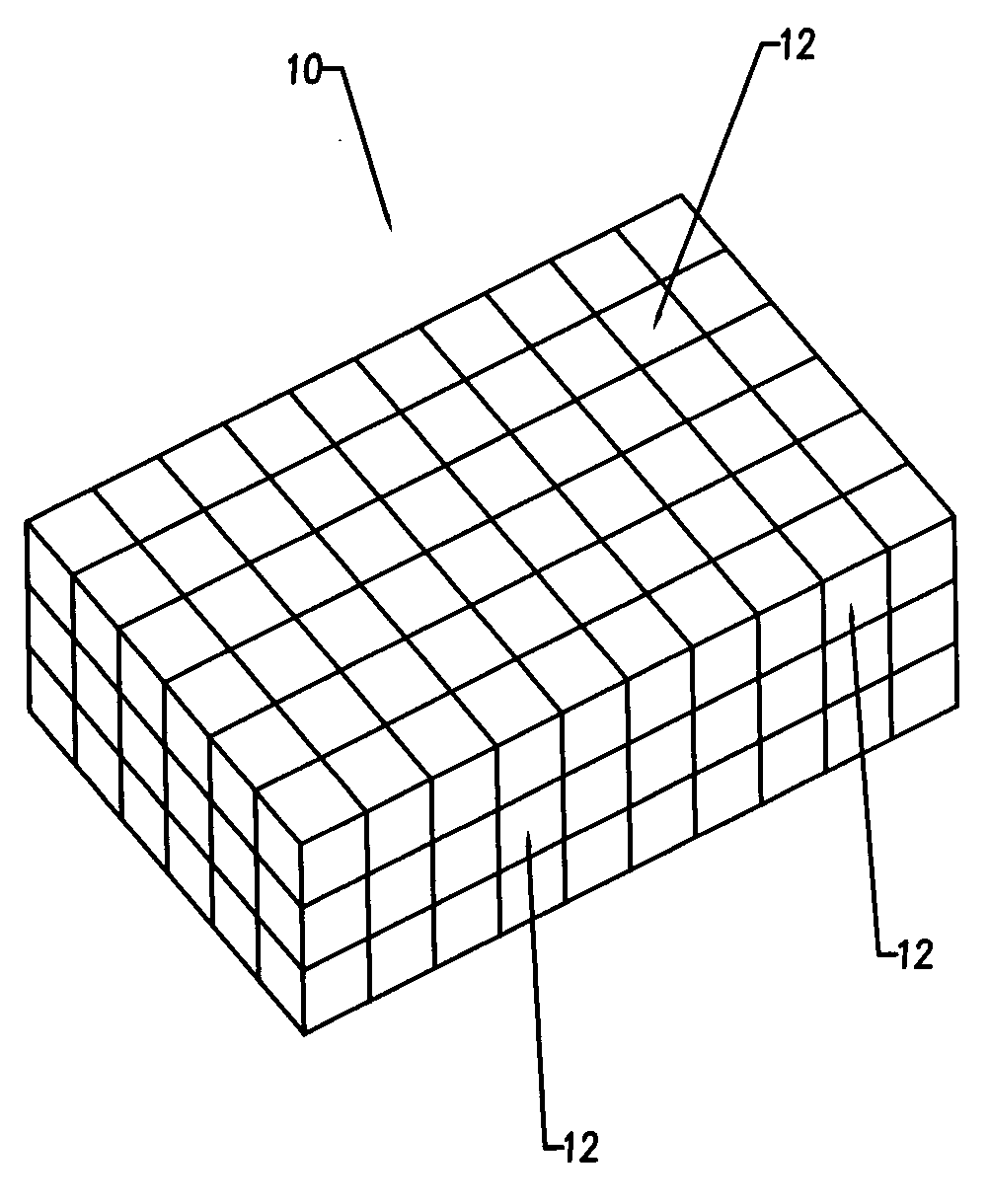
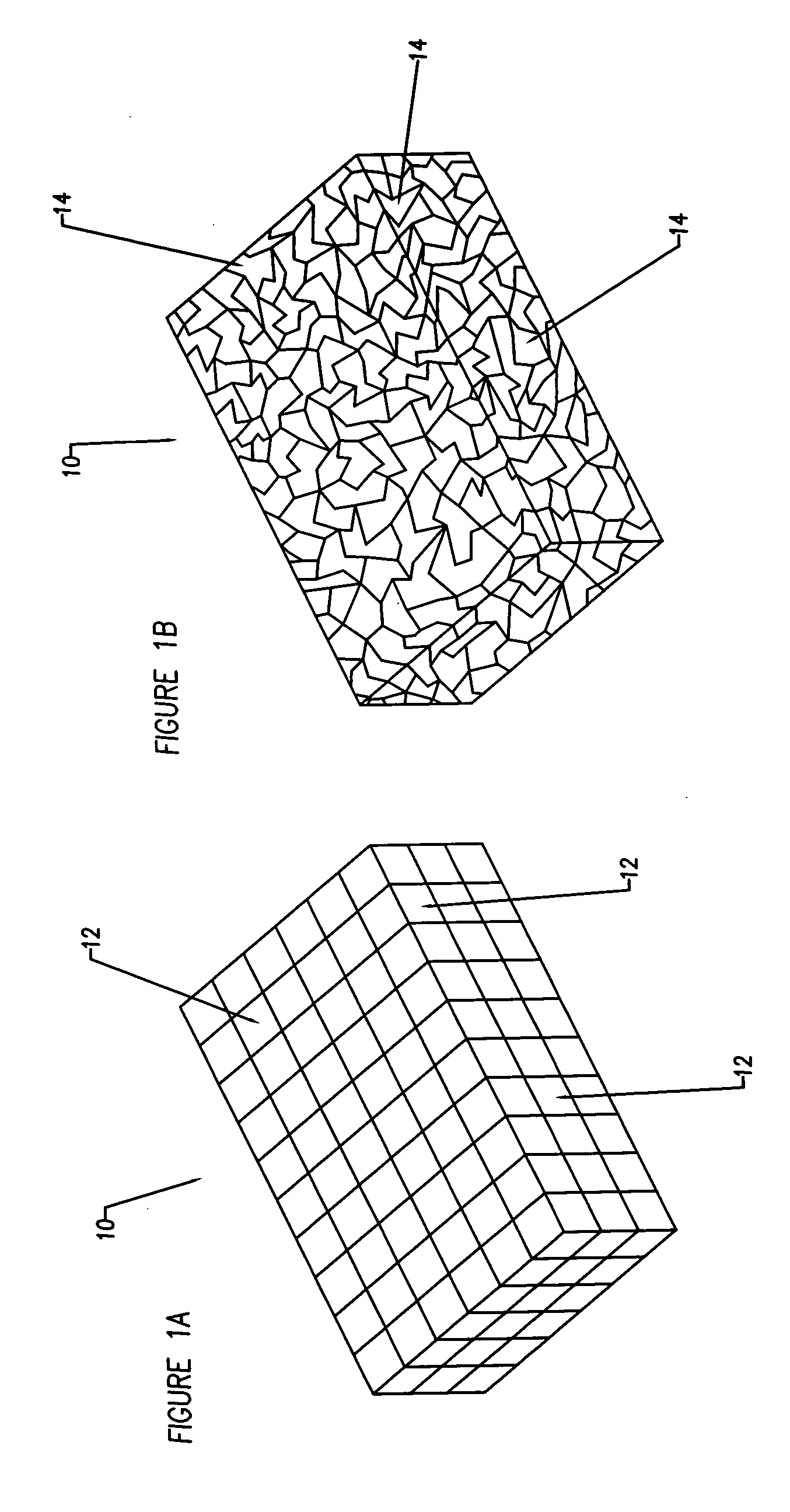
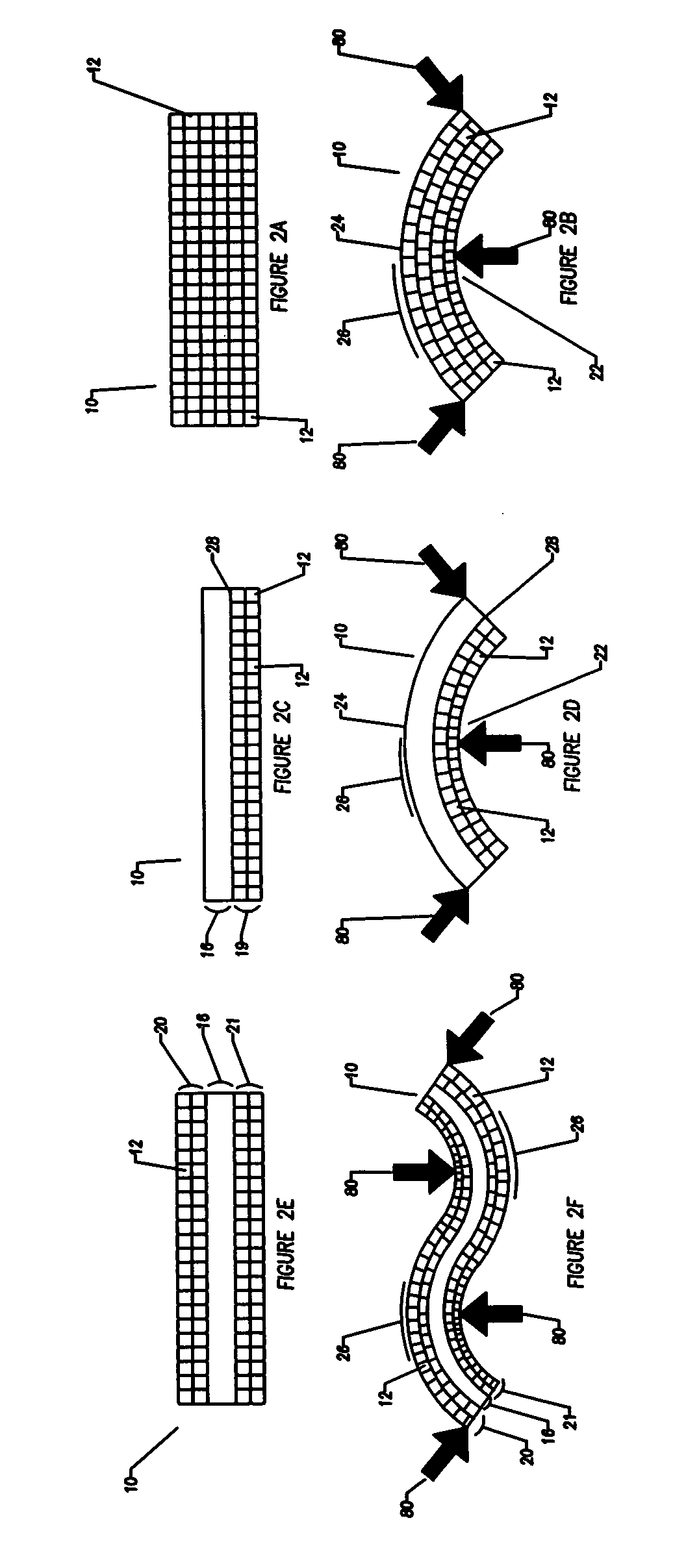
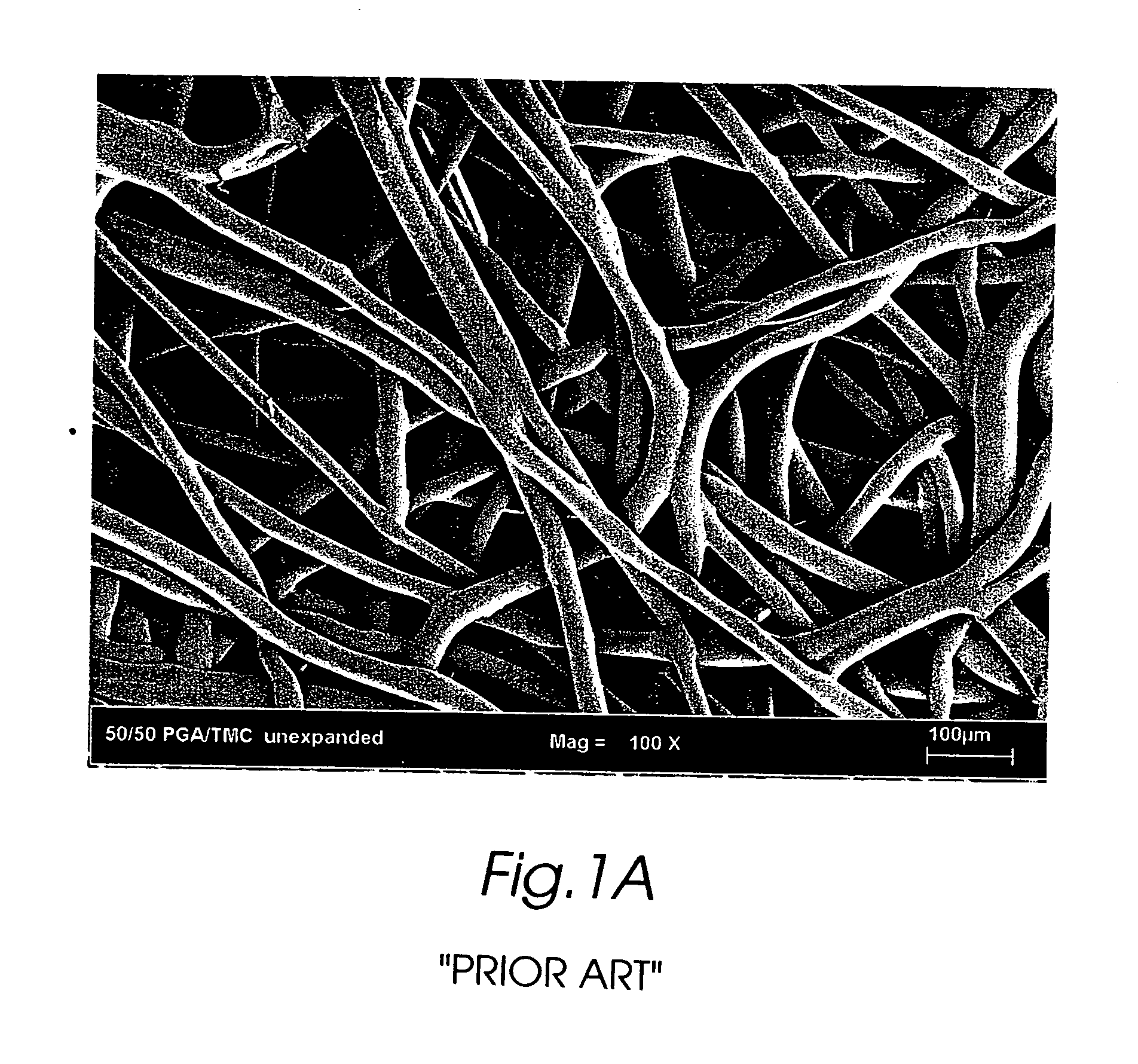
A bendable polymer tissue fixation device suitable to be implanted into a living body, comprising a highly porous body, the porous body comprising a polymer, the porous body comprising a plurality of pores, the porous body being capable of being smoothly bent, wherein the bending collapses a portion of the pores to form a radius curve, the polymer fixation device being rigid enough to protect a tissue from shifting. In a preferred embodiment the polymer fixation device may be capable of being gradually resorbed by said living body. In one embodiment, the polymer fixation device comprises a plurality of layers distinguishable by various characteristics, such as structural or chemical properties. In another embodiment, the polymer fixation device may comprise additional materials; the additional materials serving to reinforce or otherwise alter the structure or physical characteristics of the device, or alternatively as a method of delivering therapy or other agents to the system of a living being.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
High energy lithium ion batteries with particular negative electrode compositions
ActiveUS20090305131A1Degree of crystallinity of will decreaseAlkaline accumulatorsElectrode manufacturing processesHigh energyMetal alloy
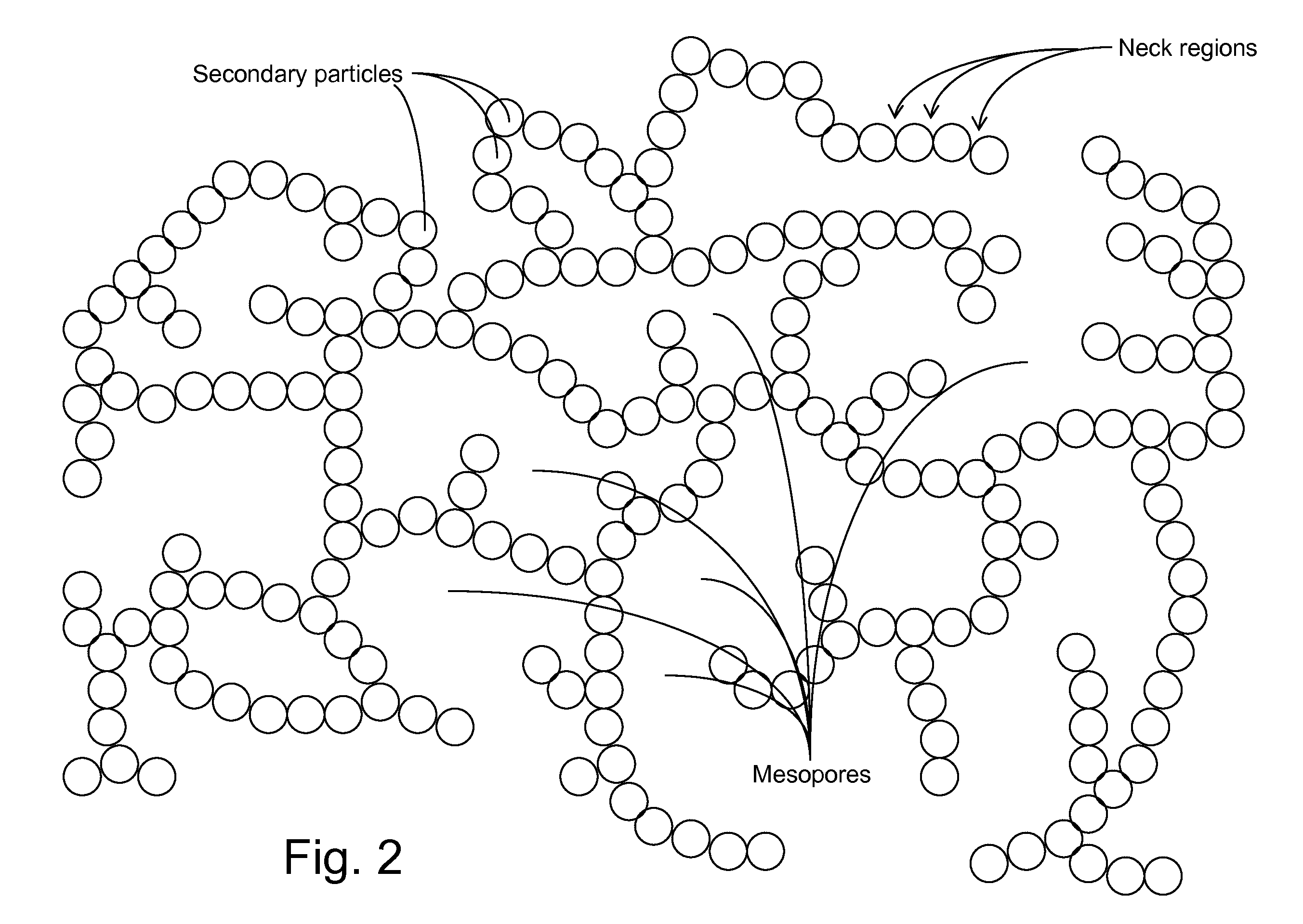
Combinations of materials are described in which high energy density active materials for negative electrodes of lithium ion batteries. In general, metal alloy / intermetallic compositions can provide the high energy density. These materials can have moderate volume changes upon cycling in a lithium ion battery. The volume changes can be accommodated with less degradation upon cycling through the combination with highly porous electrically conductive materials, such as highly porous carbon and / or foamed current collectors. Whether or not combined with a highly porous electrically conductive material, metal alloy / intermetallic compositions with an average particle size of no more than a micron can be advantageously used in the negative electrodes to improve cycling properties.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
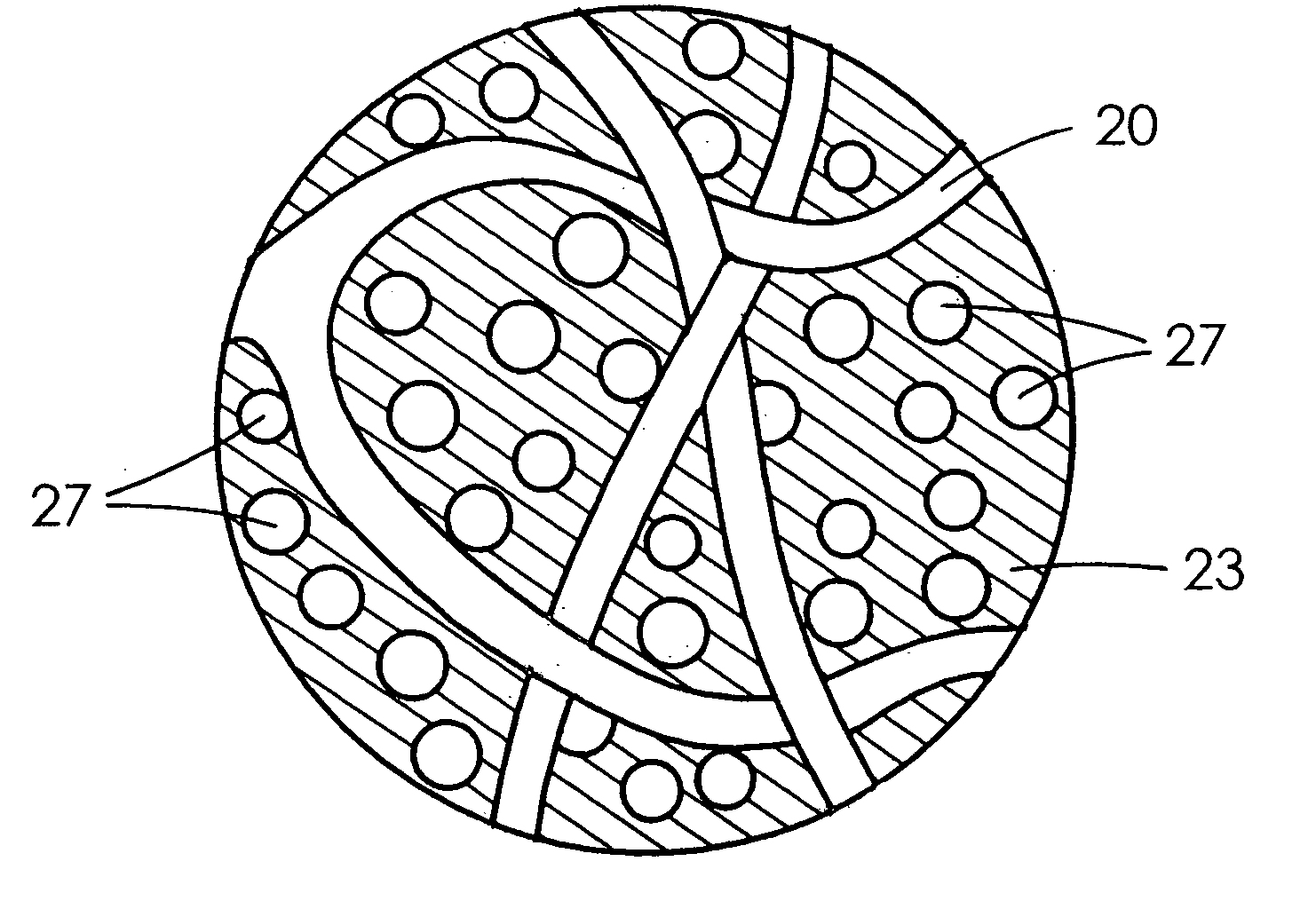
Highly porous self-cohered web materials
ActiveUS20070027553A1Increased void spaceImprove featuresWoven fabricsNon-woven fabricsUltimate tensile strengthMedical device
The present invention is directed to implantable bioabsorbable non-woven self-cohered web materials having a very high degree of porosity. The web materials are very supple and soft, while exhibiting proportionally increased mechanical strength in one or more directions. The web materials often possess a high degree of loft. The web materials can be formed into a variety of shapes and forms suitable for use as implantable medical devices or components thereof. In some embodiments, the web materials exhibit significant thrombogenic properties.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Dust filter bag including a highly porous backing material ply
InactiveUS6706086B2Simple and cost-effective productionCleaning filter meansCombination devicesBursting strengthCellulose fiber
A dust filter bag having a highly porous backing material ply and a method for producing the dust filter bag. The dust filter bag includes at least one filter material ply and at least one backing material ply, the backing material ply possessing an air permeability of at least 900 l / m<2 >x s, a burst strength of at least 70 kPa, a rupture strength longitudinally better than 10 and transversely better than 3 N, a flexural rigidity longitudinally better than 0.5 cN cm<2 >and transversely better than 0.25 cN cm<2>, a basis weight of 30-80 g / m<2 >and a droplet sink-in time of less than 10 minimum. The dust filter bag can be produced by the following steps: mixing fibers including cellulose fibers and fusible fibers into a homogenous fiber mix, processing the fiber mix into a fiber web by wet laying, drying the fiber web, curing the dried fiber web by thermofusion into a backing material ply, processing the backing material ply with a filter material ply into a raw bag, and finishing the raw bag into a dust filter bag.
Owner:NEENAH GESSNER GMBH
Catalyst coated membranes and sprayable inks and processes for forming same
The invention is directed to highly porous catalyst coated membranes and to sprayable inks and processes for forming catalyst coated membranes. In one aspect, the invention is to a sprayable ink, comprising catalyst particles, polymer electolyte ionomer, and a vehicle for dispersing the catalyst particles and polymer electolyte ionomer. In another aspect, the process comprises the steps of depositing an ink comprising catalyst particles and a vehicle onto a membrane and vaporizing from 40 to 95 weight percent of the vehicle from the sprayed ink under conditions effective to form a catalyst layer on the membrane. Preferably, the depositing and vaporizing steps are alternated to form multiple stacked catalyst layers on the membrane.
Owner:CABOT CORP
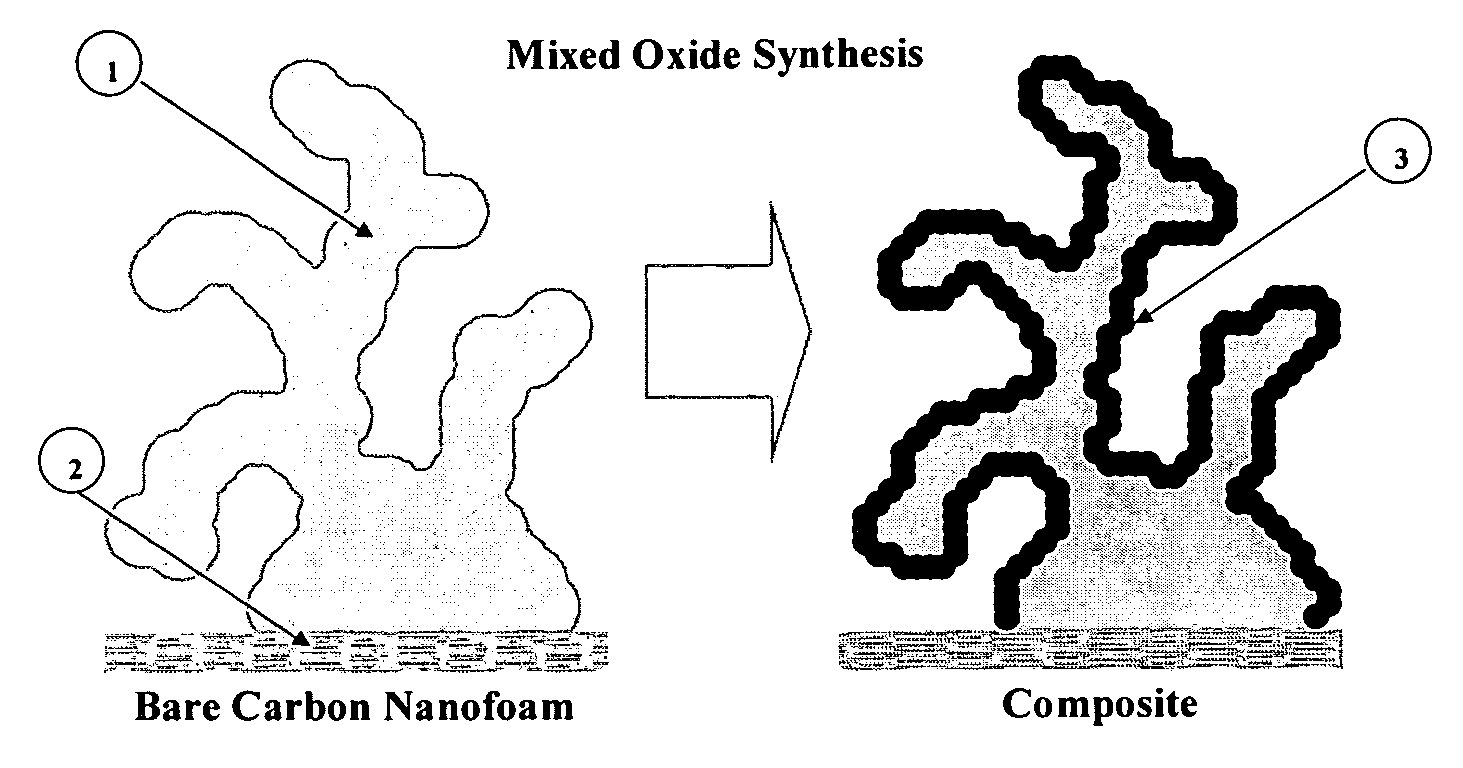
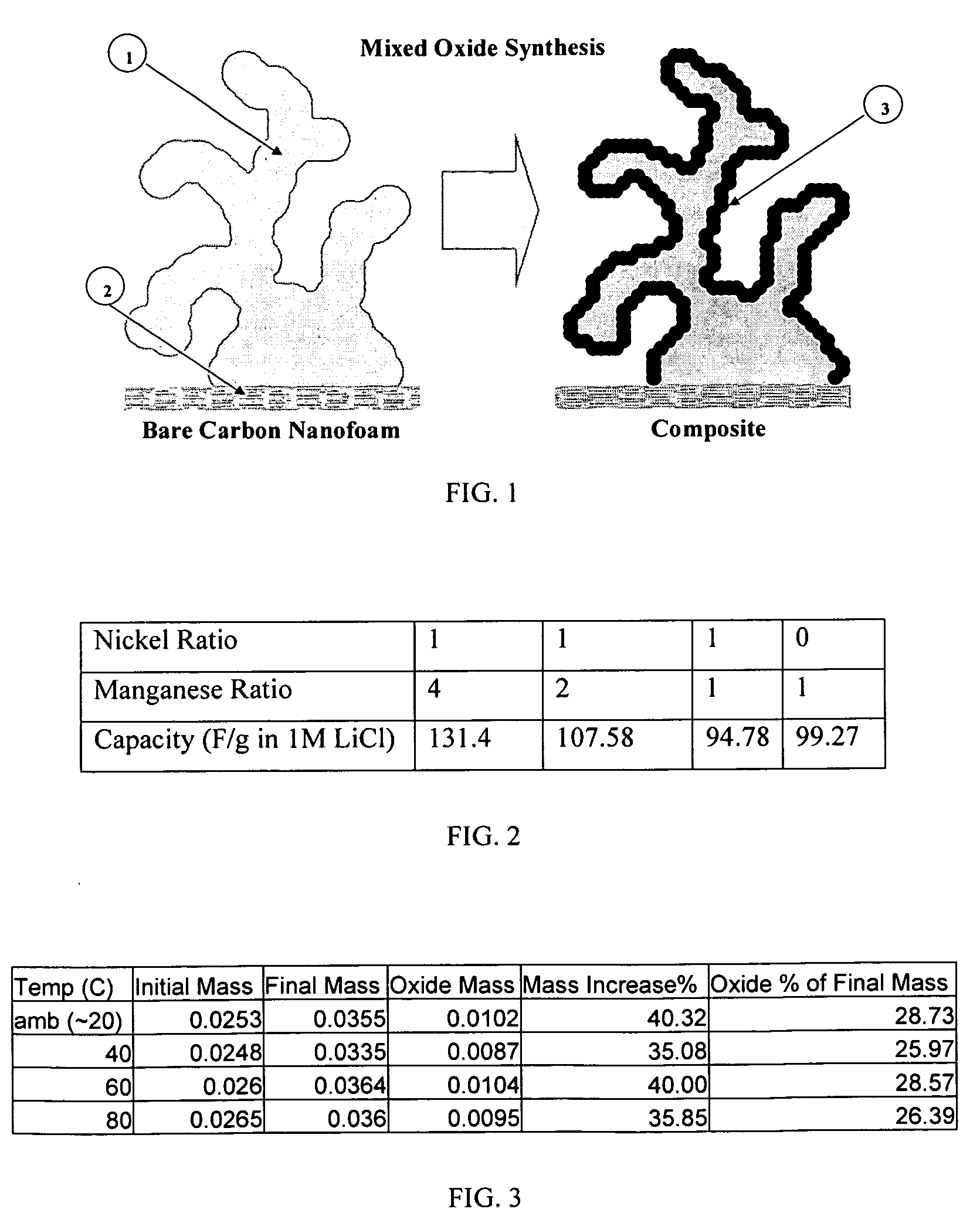
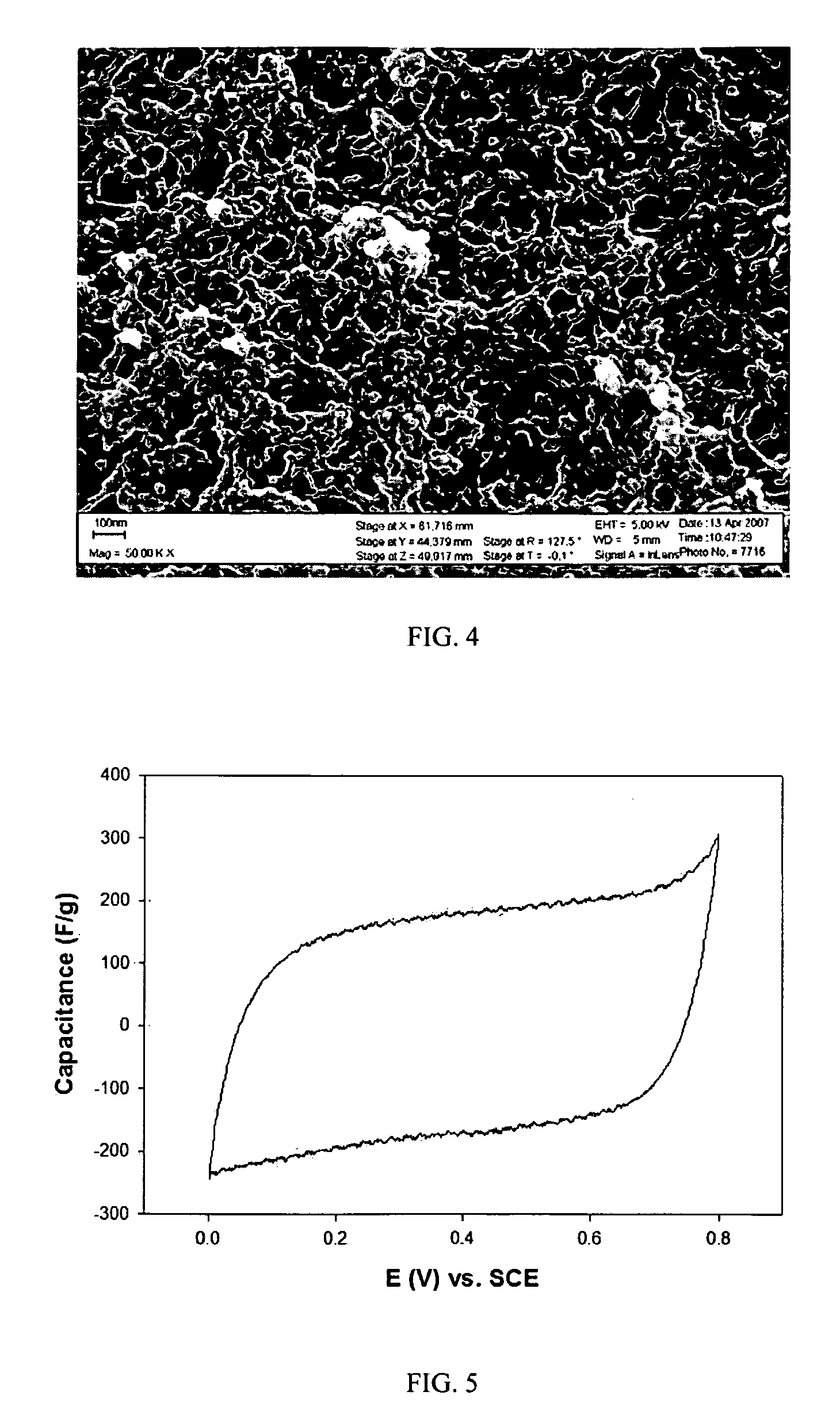
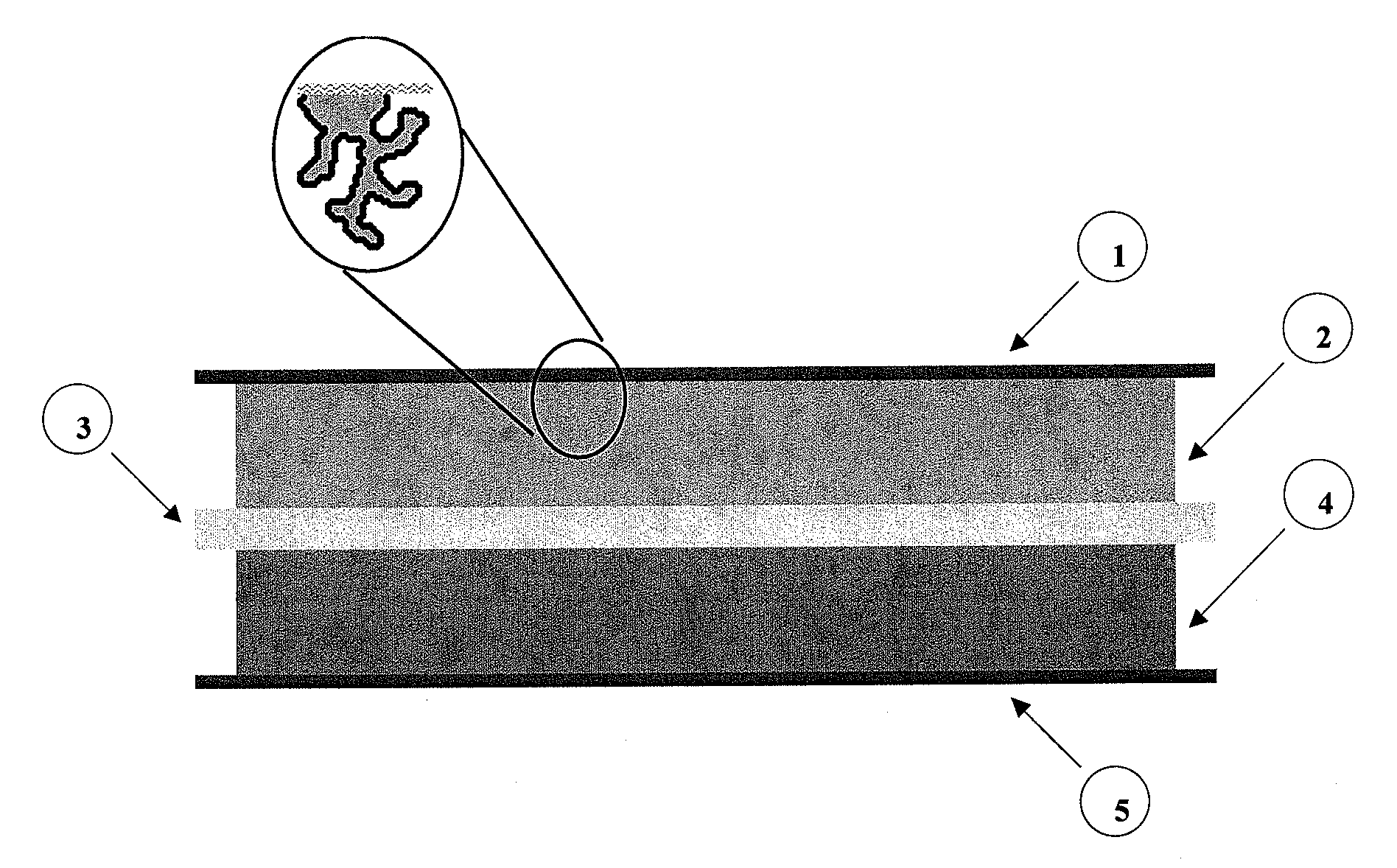
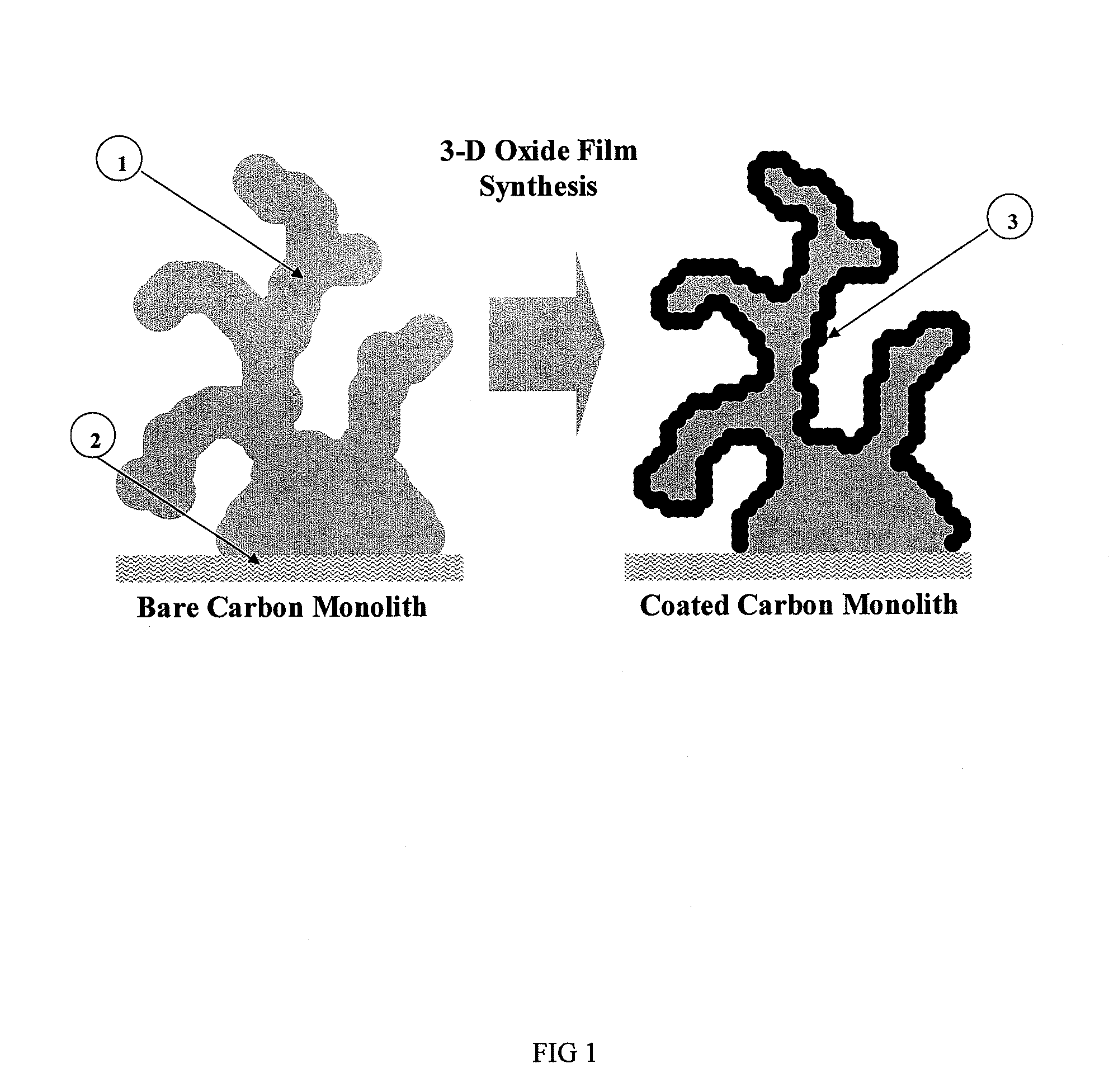
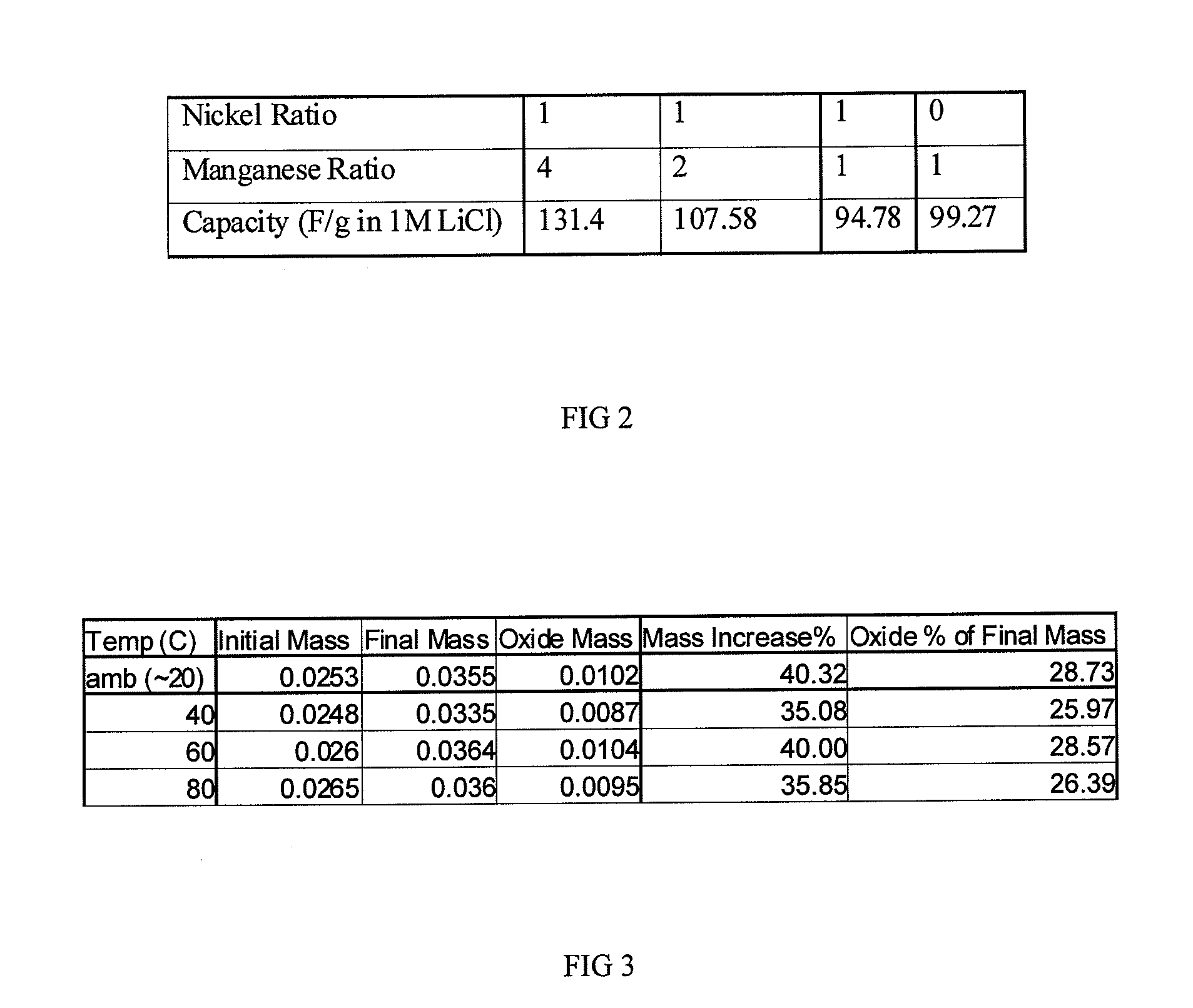
Composite electrode comprising a carbon structure coated with a thin film of mixed metal oxides for electrochemical energy storage
InactiveUS20090185327A1Increase capacityProlong lifeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufactureComposite electrodeMixed oxide
A composite electrode is created by forming a thin conformal coating of mixed metal oxides on a highly porous carbon structure. The highly porous carbon structure performs a role in the synthesis of the mixed oxide coating and in providing a three-dimensional, electronically conductive substrate supporting the thin coating of mixed metal oxides. The metal oxide mixture shall include two or more metal oxides. The composite electrode, a process for producing said composite electrode, an electrochemical capacitor and an electrochemical secondary (rechargeable) battery using said composite electrode are disclosed.
Owner:SEYMOUR FRASER WADE
Highly Porous Ceramic Oxide Aerogels Having Improved Flexibility
Ceramic oxide aerogels having improved flexibility are disclosed. Preferred embodiments exhibit high modulus and other strength properties despite their improved flexibility. The gels may be polymer cross-linked via organic polymer chains to further improve strength properties, without substantially detracting from the improved flexibility. Methods of making such aerogels are also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT ADMINISTRATOR OF NASA +1
Large pore volume composite mineral oxide beads, their preparation and their applications for adsorption and chromatography
InactiveUS6613234B2Good chemical stabilityEasy to packIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesPhysical chemistryHafnia
The present invention provides porous mineral oxide beads which have large pore volumes and enhanced stability. The beads are based on a tetravalent metal oxide, such as zirconia, titania or hafnia. These highly porous beads are produced from a mixture of tetravalent mineral oxides, mineral pore inducing agents which are oxides or salts of trivalent metals, and optional binders. The porous mineral beads can be filled with a polymer gel and used for adsorption and chromatography applications.
Owner:PALL CORP
High energy lithium ion batteries with particular negative electrode compositions
Combinations of materials are described in which high energy density active materials for negative electrodes of lithium ion batteries. In general, metal alloy / intermetallic compositions can provide the high energy density. These materials can have moderate volume changes upon cycling in a lithium ion battery. The volume changes can be accommodated with less degradation upon cycling through the combination with highly porous electrically conductive materials, such as highly porous carbon and / or foamed current collectors. Whether or not combined with a highly porous electrically conductive material, metal alloy / intermetallic compositions with an average particle size of no more than a micron can be advantageously used in the negative electrodes to improve cycling properties.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Method of making an anti-reflection coating
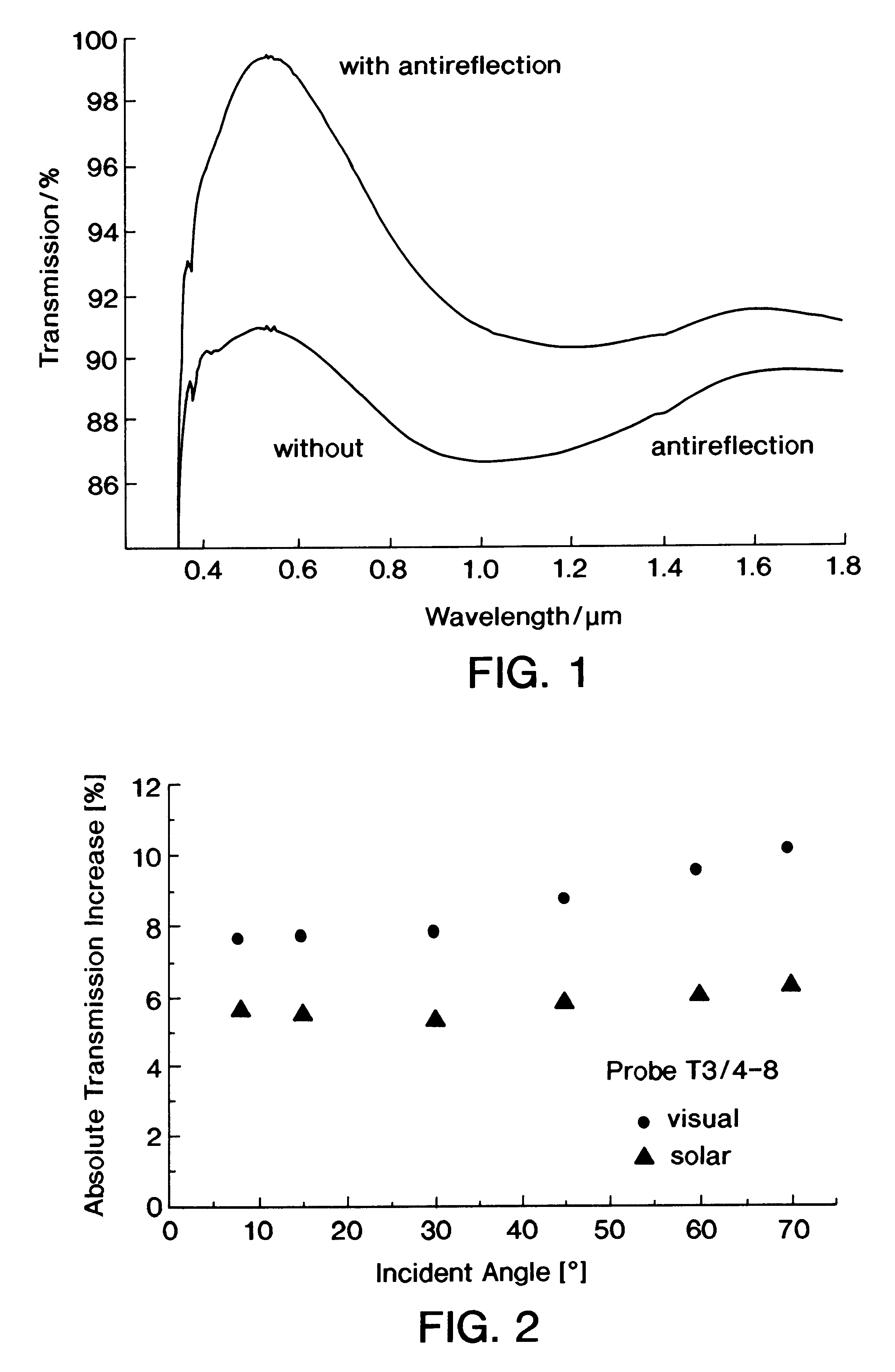
InactiveUS6177131B1Reducing and eliminating reflectionReduce and even reflectionSolar heat devicesPretreated surfacesSilanesRefractive index
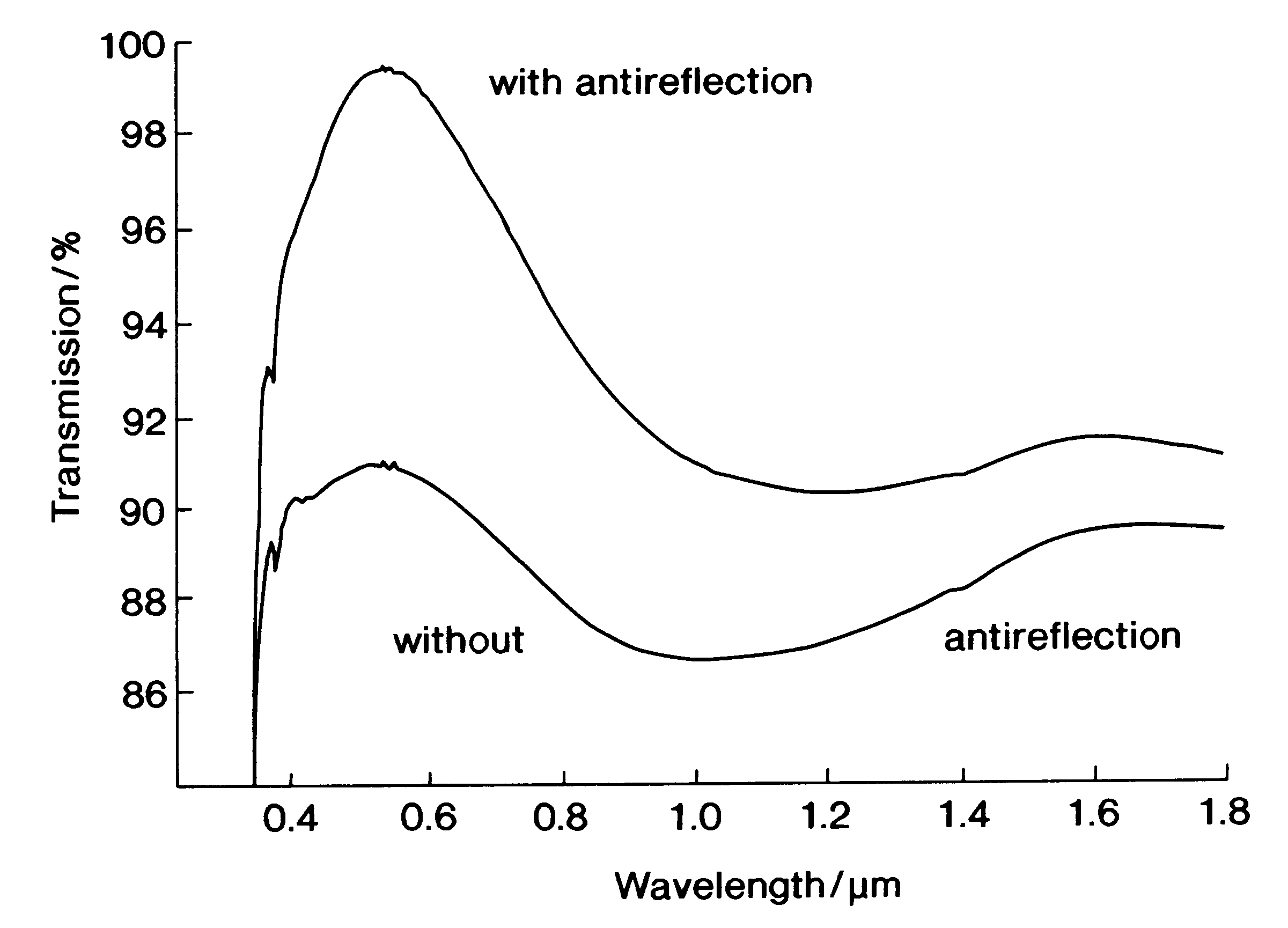
A method of and a solution for making a highly porous optical antireflection coating of a selectively designed index of refraction, by applying a colloidal dispersion derived from hydrolytically condensing, in the presence of water and a catalyst, one or more silicon compounds of the general formula RaSiX4-a, or precondensates derived therefrom, to a substrate. In the formula, R is an organic group having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms which may be interrupted by oxygen atoms and / or sulfur atoms and / or amino groups, X is hydrogen, halogen, hydroxy, alkoxy, acyloxy, alkylcarbonyl, alkoxycarbonyl or NR'2, R' being hydrogen, alkyl or aryl and a being 0, 1 or 2. The solution also contains colloidally dispersed organic polymers at a molar ratio, relative to the silane, between 0.1 mmol / mol silane and 100 mmol / mol silane, the median molecular mass of the polymer being between 200 and 500,000. Sol-vents, preferably alcohol, may also be present in the solution. After being applied to an optical substrate, the solution is dried and organic components are removed from it to leave a porous coating of predetermined index of refraction.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Supported ceramic membranes and electrochemical cells and cell stacks including the same
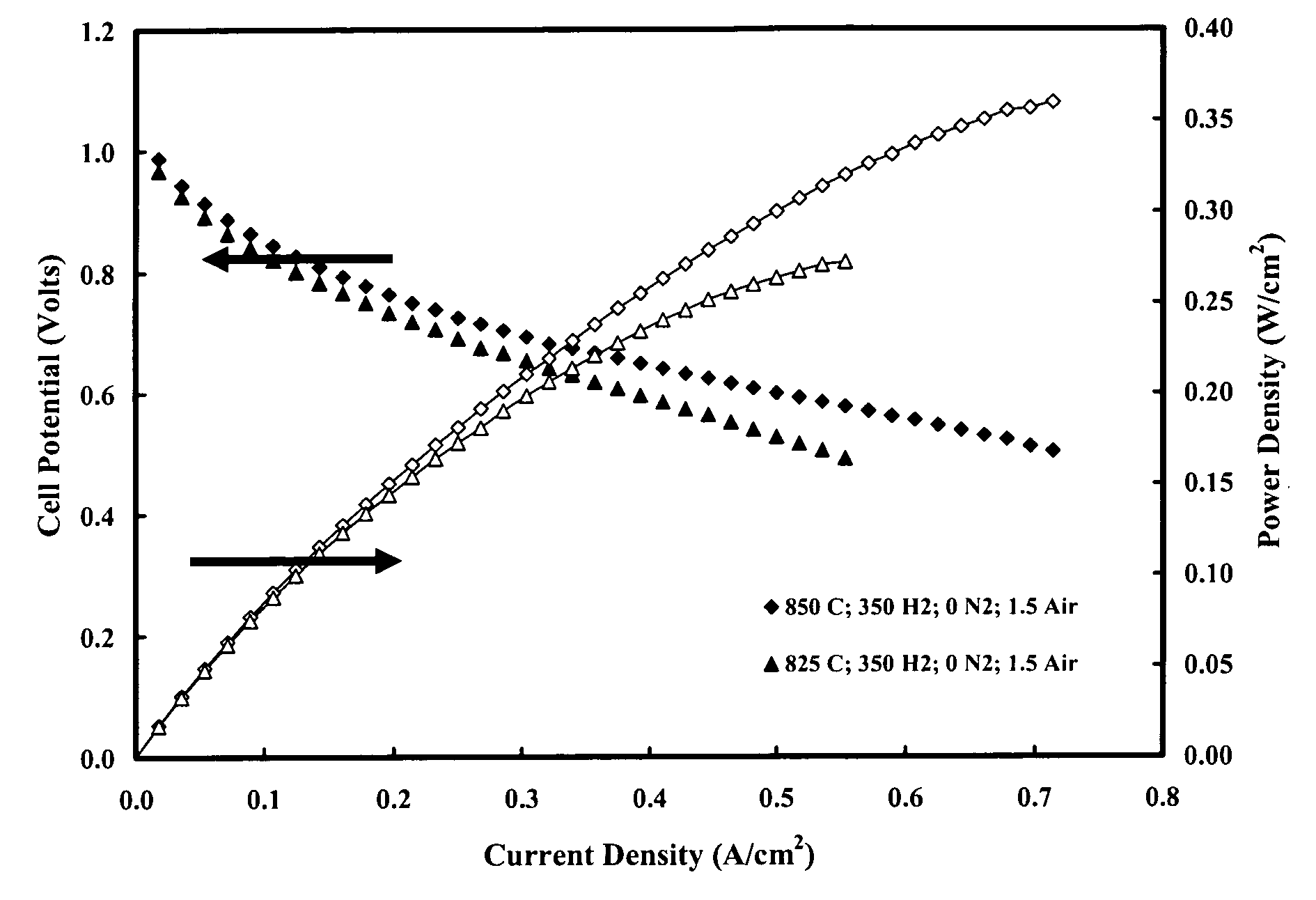
InactiveUS20060269813A1Advantage in processingAdvantage in mechanical integrityFuel cells groupingFinal product manufacturePorous ceramicsMaterials science
A dense ceramic electrolyte membrane supported by symmetrical porous ceramic electrolyte layers. The thin (t<100 microns) electrolyte layer is sandwiched between two fugitive-containing electrolyte support layers that become highly porous after firing. The heat treated fugitive-containing support layers form a skeletal structure of strongly adhered electrolyte with an interpenetrating network of pores that extends well always from the electrolyte surface. The porous layers can be infiltrated with a range of electrode materials or precursors to form a solid oxide fuel cell or other electrochemical cell as well as electrochemical cell stacks. The supported ceramic membrane provides electrochemical performance advantages and reduces warpage during sintering compared to conventional structures.
Owner:NEXTECH MATERIALS
Large pore volume composite mineral oxide beads, their preparation and their applications for adsorption and chromatography
InactiveUS20020005383A1Good chemical stabilityHigh porosityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesPhysical chemistryHafnia
The present invention provides porous mineral oxide beads which have large pore volumes and enhanced stability. The beads are based on a tetravalent metal oxide, such as zirconia, titania or hafnia. These highly porous beads are produced from a mixture of tetravalent mineral oxides, mineral pore inducing agents which are oxides or salts of trivalent metals, and optional binders. The porous mineral beads can be filled with a polymer gel and used for adsorption and chromatography applications.
Owner:PALL CORP
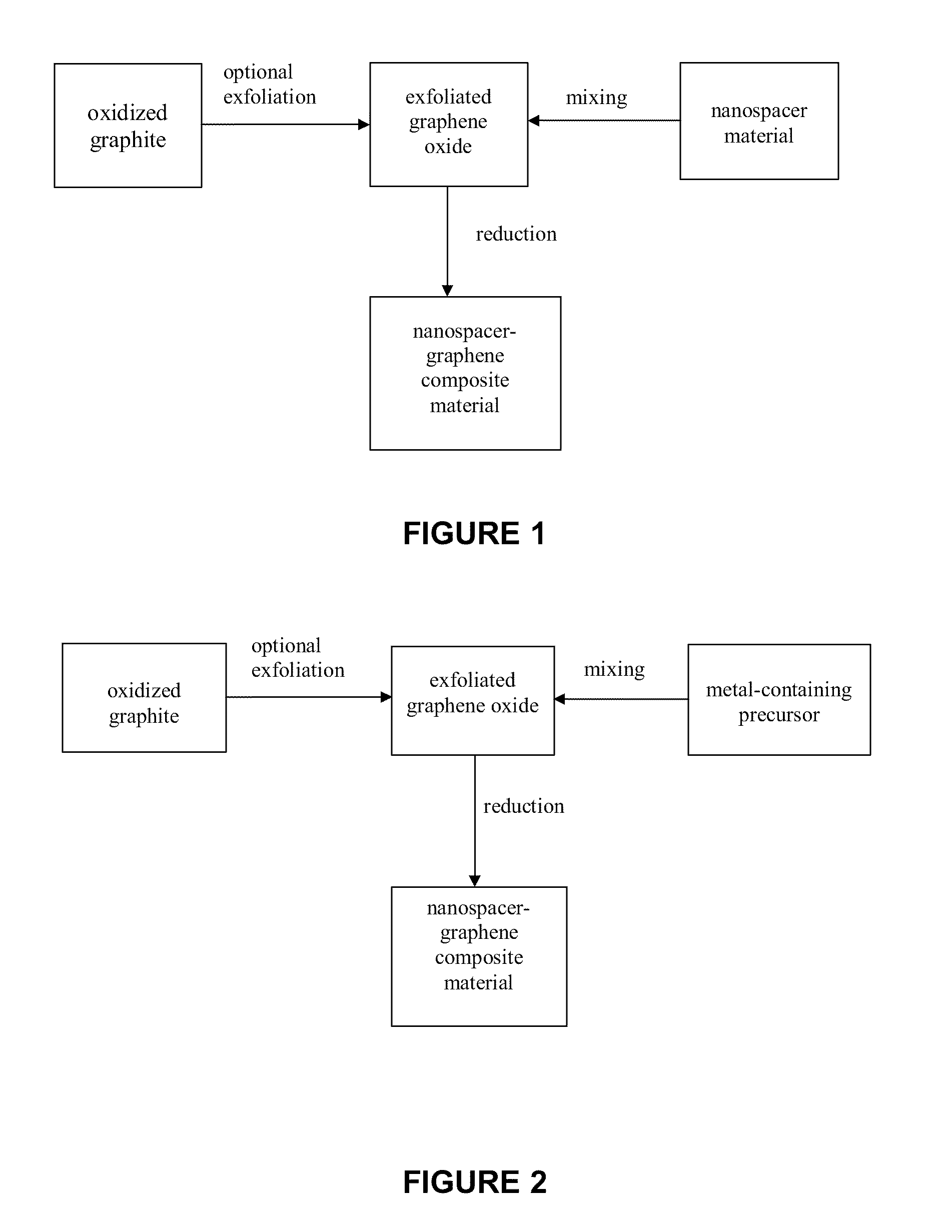
Production of mechanically exfoliated graphene and nanoparticle composites comprising same
InactiveUS20110284805A1Minimizing aggregationMaterial nanotechnologyNon-metal conductorsNanoparticleGraphene
A method for producing nanospacer-graphene composite materials (i.e., mechanically-exfolitated graphene), wherein the graphene sheets are interspersed with nanospacers, thereby maintaining the 2D characteristics of the graphene sheets. The nanospacer-graphene composite material is highly porous, has a high surface area and is highly electrically conductive and may be optically transparent.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Compliant osteosynthesis fixation plate
ActiveUS20050015088A1Maintaining structural rigidityBending stabilityProsthesisBone platesLiving bodyTissue fixing
A bendable polymer tissue fixation device suitable to be implanted into a living body, comprising a highly porous body, the porous body comprising a polymer, the porous body comprising a plurality of pores, the porous body being capable of being smoothly bent, wherein the bending collapses a portion of the pores to form a radius curve, the polymer fixation device being rigid enough to protect a tissue from shifting. In a preferred embodiment the polymer fixation device may be capable of being gradually resorbed by said living body. In one embodiment, the polymer fixation device comprises a plurality of layers distinguishable by various characteristics, such as structural or chemical properties. In another embodiment, the polymer fixation device may comprise additional materials; the additional materials serving to reinforce or otherwise alter the structure or physical characteristics of the device, or alternatively as a method of delivering therapy or other agents to the system of a living being.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
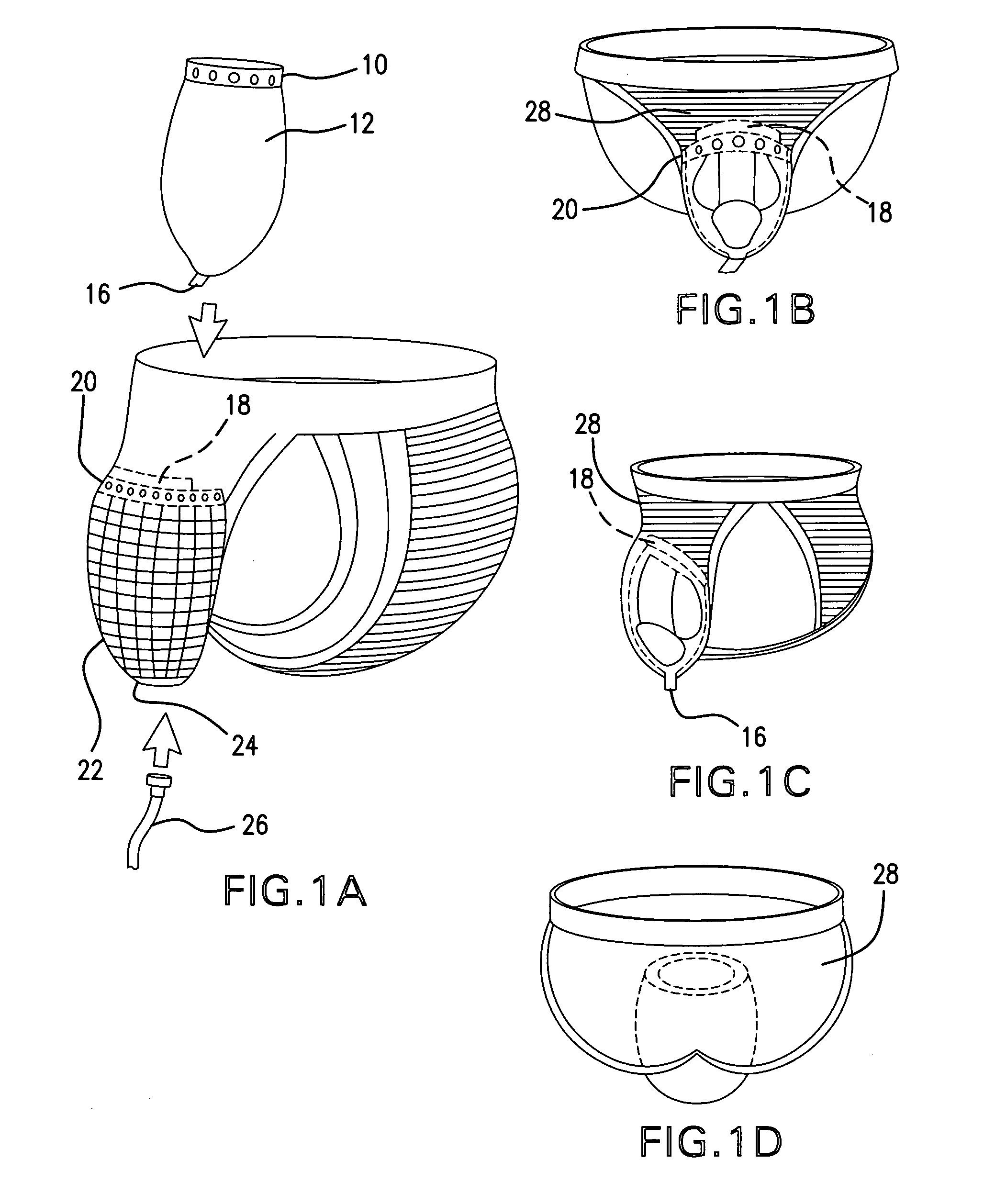
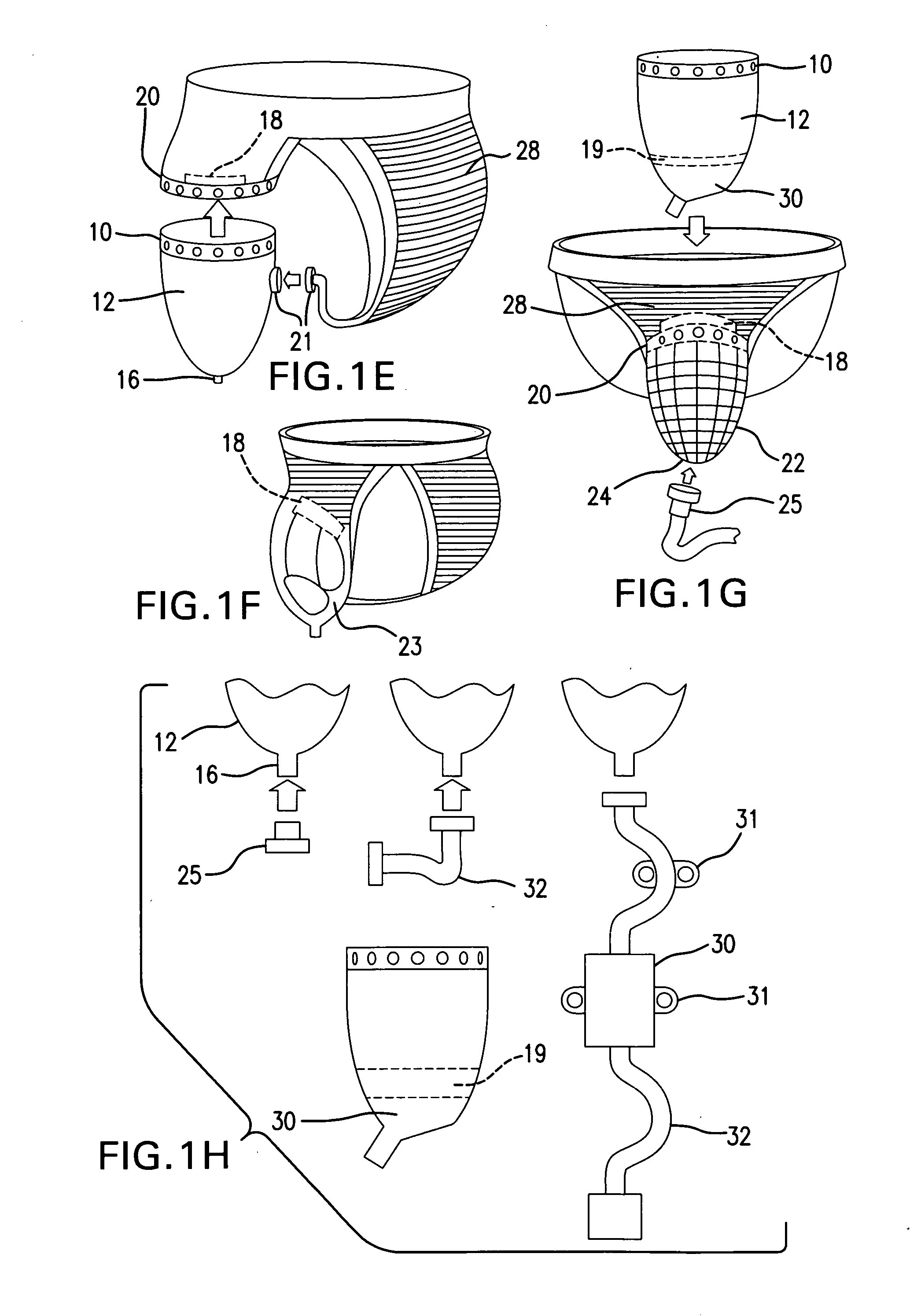
Holder
InactiveUS20090270822A1Facilitated releaseTrousersNon-surgical orthopedic devicesGravitationTriggering device
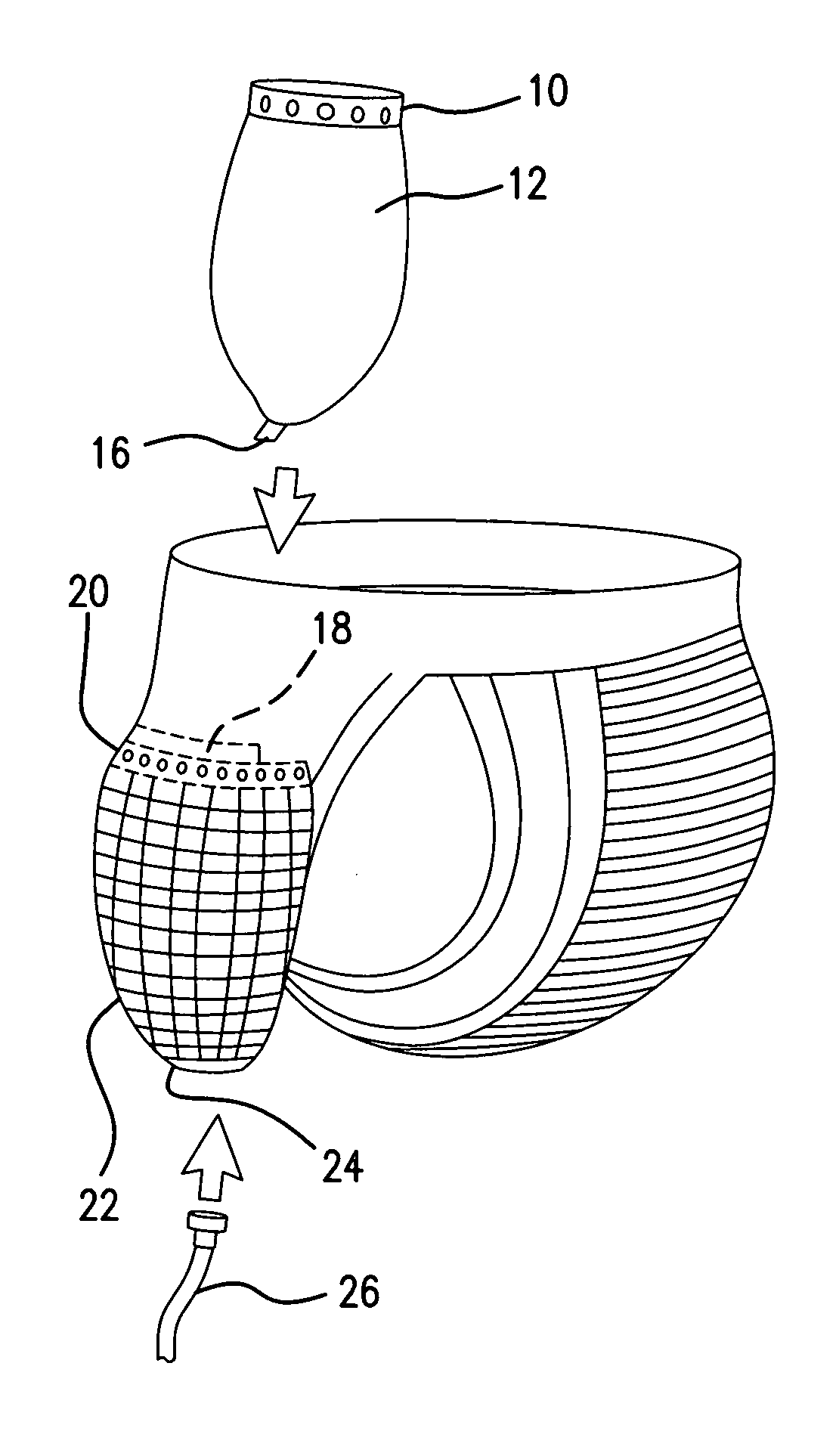
The present invention is a solution for continence problems. A supporting structure can be in the form of a modified jock strap or biker's shorts. It includes a male version (bag) and a unisex version (wicking pad). The male model can do alright with gravity alone. The unisex model uses wicking through micro channels to a trigger device in a small bag. This is made of highly porous hydrophilic material that allows flow to drain downward for disposal but not wet backwardsIt would be advantageous to provide a solution whereas the users would have a comfortable and efficient way to dispose of their urine without getting their garments wet without having to throw something away like absorption pad. It would also be convenient and cost effective to provide a way of using the same device without changing anything all day long.
Owner:MEDEIROS LESTER WILLIAM
Hydrogen storage composition and method
InactiveUS6528441B1Maximize surface area and catalyzing activityLarge specific surface areaHydrogenOther chemical processesHigh pressureHYDROSOL
A hydrogen storage composition based on a metal hydride dispersed in an aerogel prepared by a sol-gel process. The starting material for the aerogel is an organometallic compound, including the alkoxysilanes, organometals of the form M(OR)x and MOxRy, where R is an alkyl group of the form CnH2n+1, M is an oxide-forming metal, n, x, and y are integers, and y is two less than the valence of M. A sol is prepared by combining the starting material, alcohol, water, and an acid. The sol is conditioned to the proper viscosity and a hydride in the form of a fine powder is added. The mixture is polymerized and dried under supercritical conditions. The final product is a composition having a hydride uniformly dispersed throughout an inert, stable and highly porous matrix. It is capable of absorbing up to 30 moles of hydrogen per kilogram at room temperature and pressure, rapidly and reversibly. Hydrogen absorbed by the composition can be readily be recovered by heat or evacuation.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS
Plastic films containing a fragrance and an odor barrier material within and a method for their production
InactiveUS6921581B2Extended shelf lifePrevents the fragrance from dissipatingFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsChemical compositionPlastic film
A plastic film comprised of a polymer material, fragrance, and a waxy chemical composition for imparting to the film substantial impermeability to odors. A method for producing such films including the steps of: adding a liquid fragrance to highly porous polymer pellets; adding a waxy chemical composition to the fragrance and polymer; blending the polymer, fragrance, and waxy composition mixture; adding additional polymer to the blended mixture; extruding the resultant composition, thereby forming pellets; mixing the pellets with additional polymer; and forming a film therefrom. A plastic film, produced according to this method, for packaging or for masking unpleasant odors, comprising polyethylene or polypropylene, a fragrance, and a bis fatty-acid amide is also disclosed.
Owner:SAKIT
Highly porous mullite particulate filter substrate
A typically monolithic particulate filter including a highly porous block made primarily of intertangled polycrystalline mullite fibers, a set of channels formed through the block, and a set of porous walls separating adjacent channels. Exhaust gas is flowed through the channels and interacts with the walls such that particulate matter carried in the exhaust gas, such as soot particles, is screened out by porous fibrous mullite walls.
Owner:GE02 TECH INC
Bio-artificial organ containing a matrix having hollow fibers for supplying gaseous oxygen
InactiveUS6372495B1Practical to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHollow fibreFiber
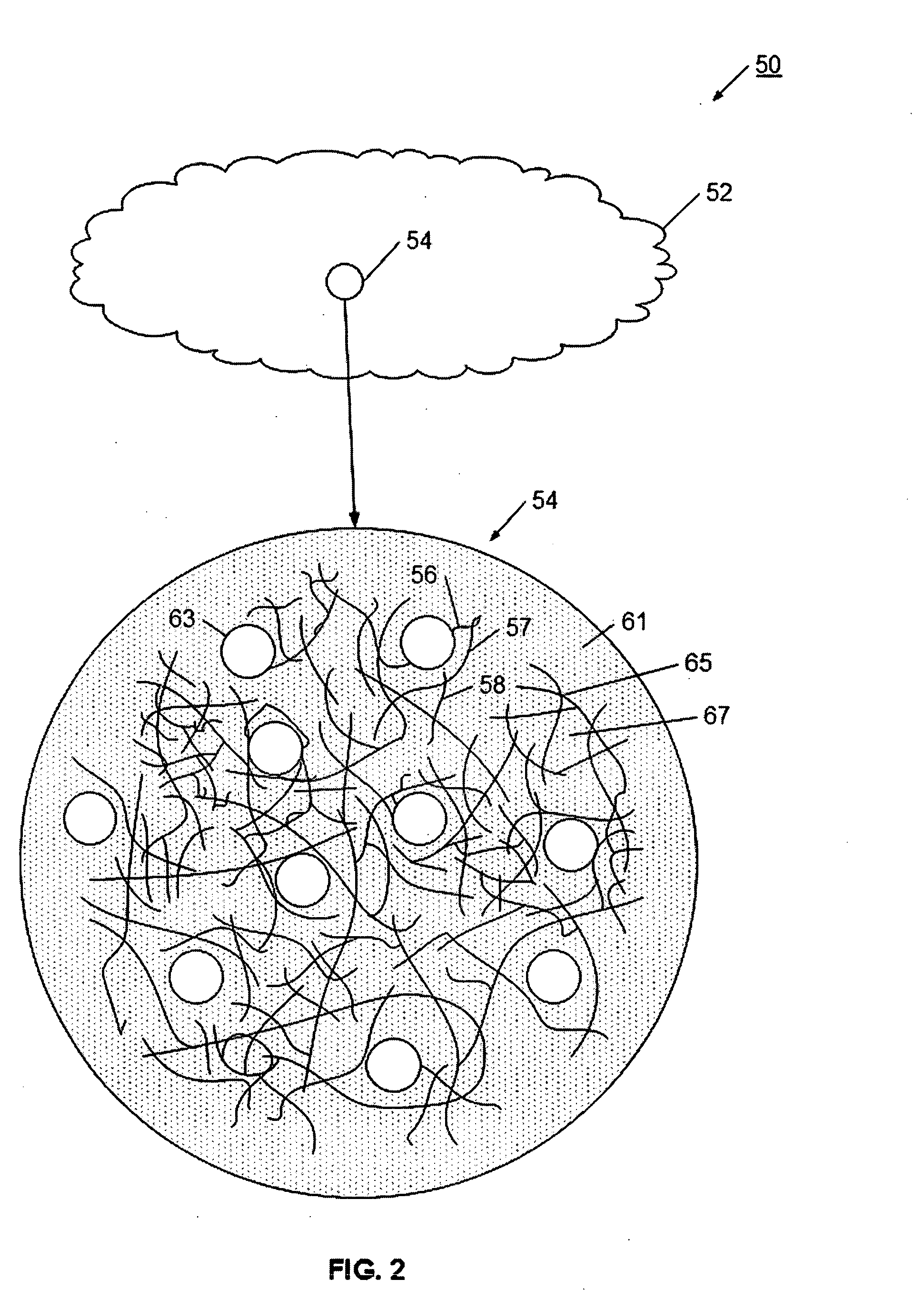
A bio-artificial organ system is provided comprising a wall surrounding a space which has a solid support for cell cultivation. The space includes a there dimensional matrix in the form of a highly porous sheet or mat and including a physiologically acceptable network of fibers or an open-pore foam structure; hydrophobic hollow fibers permeable to gaseous oxygen or gaseous carbon dioxide evenly distributed through the three dimensional matrix material and arranged in parallel running from one end of the matrix material to the other end of the matrix material. Cells obtained from organs are present in the extra fiber space for culture wherein the cells are provided with sufficient oxygenation and are maintained as small aggregates with three dimensional attachment.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT +1
Highly porous self-cohered web materials having haemostatic Properties
ActiveUS20070027554A1High porositySuitable for useSynthetic resin layered productsWoven fabricsUltimate tensile strengthMedical device
The present invention is directed to implantable bioabsorbable non-woven self-cohered web materials having a high degree of porosity. The web materials are very supple and soft, while exhibiting proportionally increased mechanical strength in one or more directions. The web materials often possess a high degree of loft. The web materials can be formed into a variety of shapes and forms suitable for use as implantable medical devices or components thereof. The web materials possess hemostatic properties.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Removing compounds from blood products with porous particles immobilized in a matrix
InactiveUS7037642B2Reduce concentrationMaintain biological activityImmobilised enzymesOther blood circulation devicesWhole blood productSorbent
Methods and devices are provided for reducing the concentration of low molecular weight compounds in a biological composition containing cells while substantially maintaining a desired biological activity of the biological composition. The device comprises highly porous adsorbent particles, and the adsorbent particles are immobilized by an inert matrix.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Extruded porous substrate and products using the same
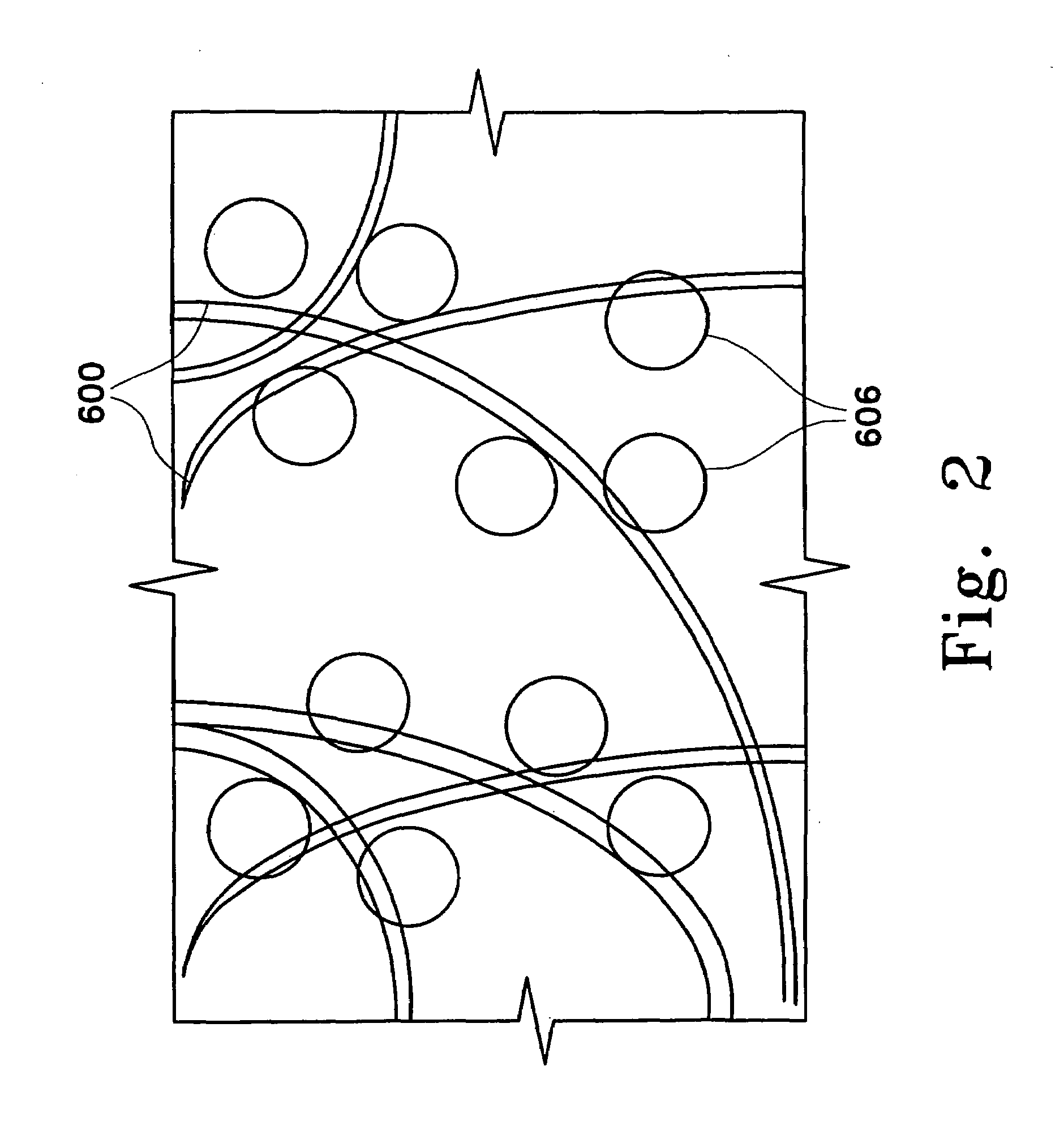
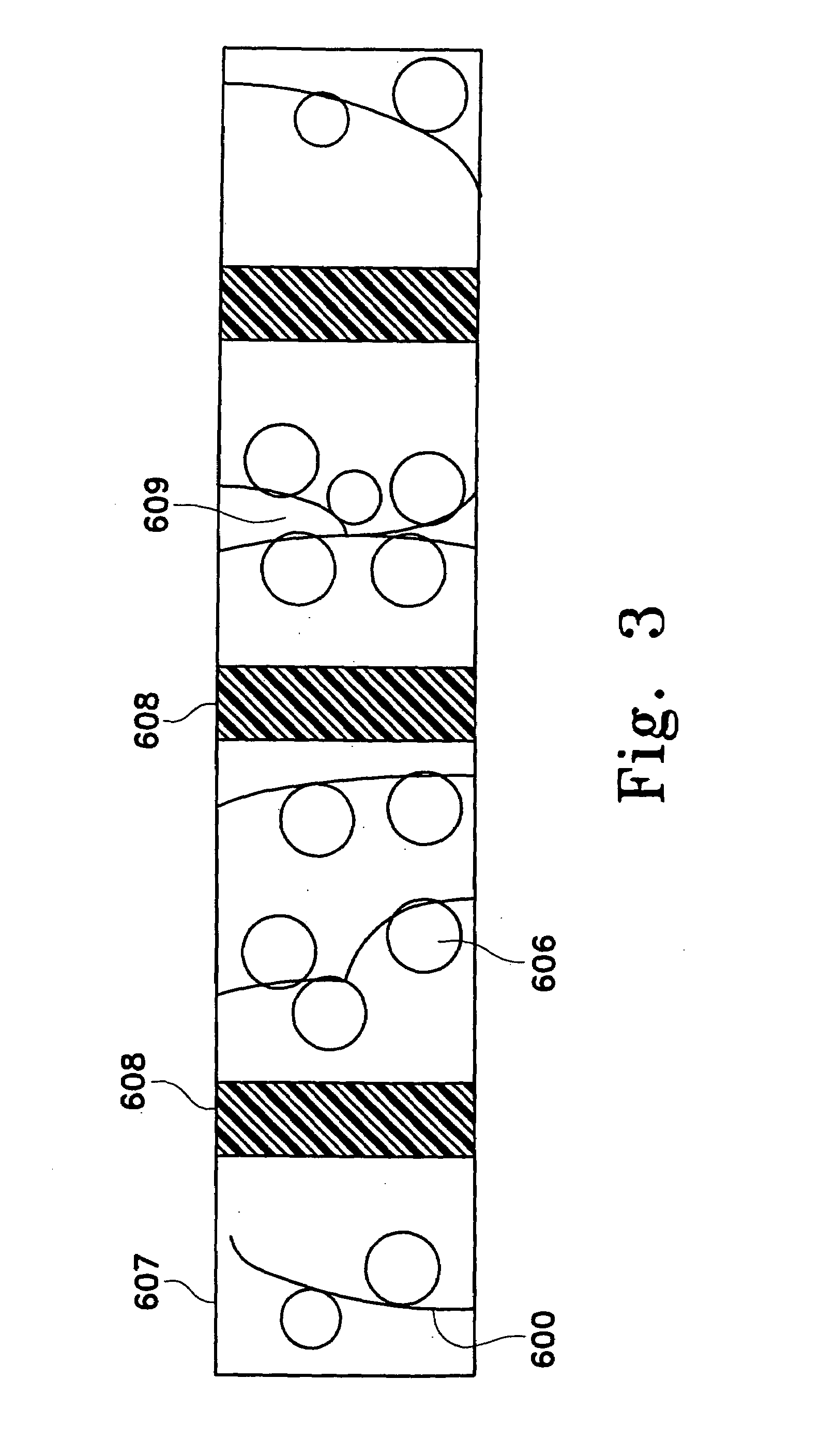
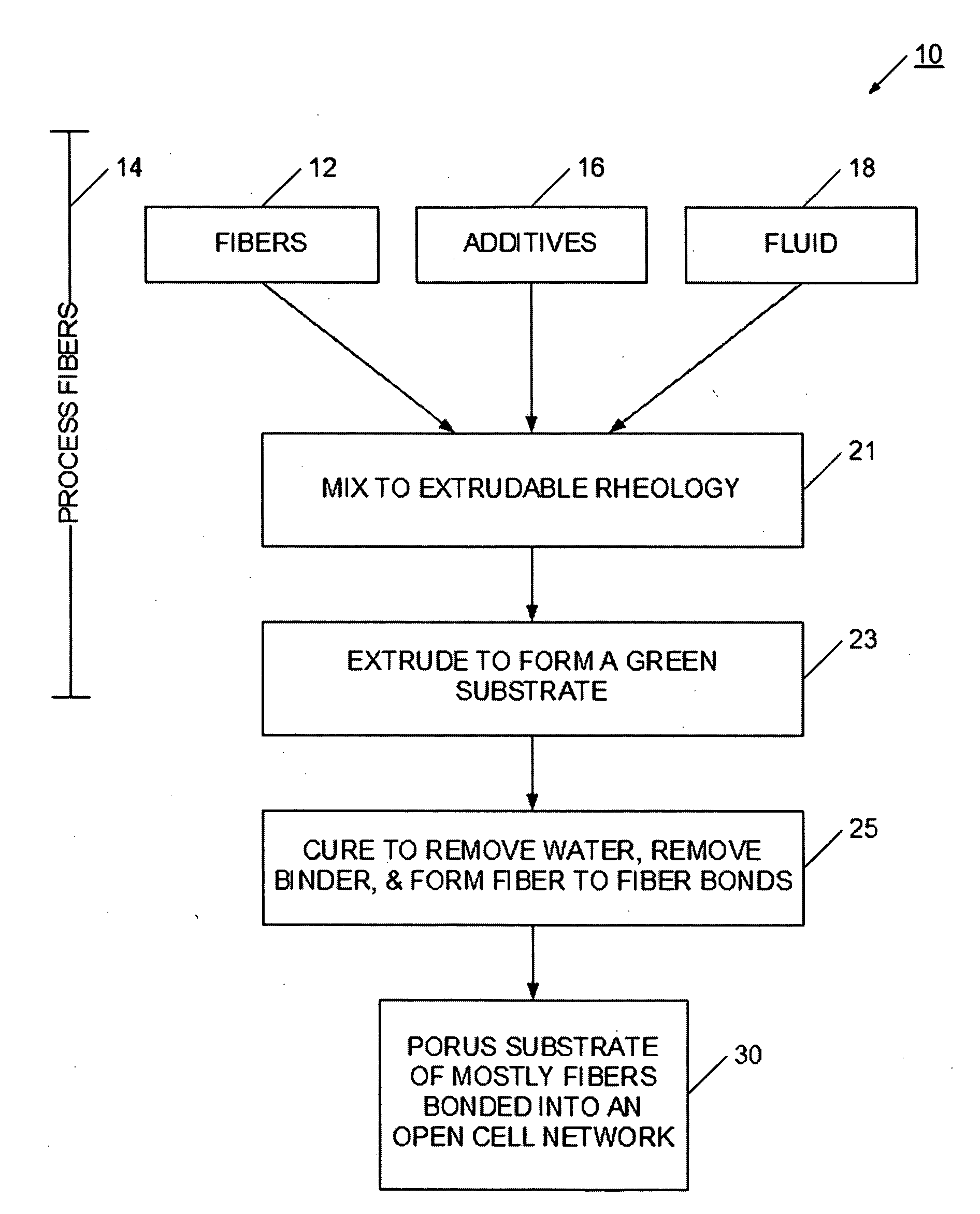
InactiveUS20070107395A1Highly porousHigh porosityDispersed particle filtrationExhaust apparatusPorous substrateFiber
A highly porous substrate is provided using an extrusion system. More particularly, the present invention enables the production of a highly porous substrate. Depending on the particular mixture, the present invention enables substrate porosities of about 60% to about 90%, and enables advantages at other porosities, as well. The extrusion system enables the use of a wide variety of fibers and additives, and is adaptable to a wide variety of operating environments and applications. Fibers, which have an aspect ratio greater than 1, are selected according to substrate requirements, and are typically mixed with binders, pore-formers, extrusion aids, and fluid to form a homogeneous extrudable mass. The homogeneous mass is extruded into a green substrate. The more volatile material is preferentially removed from the green substrate, which allows the fibers to form interconnected networks. As the curing process continues, fiber to fiber bonds are formed to produce a structure having a substantially open pore network. The resulting porous substrate is useful in many applications, for example, as a substrate for a filter or catalyst host, or catalytic converter.
Owner:GE02 TECH INC
Syngas conversion system using asymmetric membrane and anaerobic microorganism
InactiveUS20090215163A1Increase productionLess permeabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid productMetabolite
A stable system for producing liquid products such as ethanol, butanol and other chemicals from syngas components contacts CO or a mixture of CO2 and H2 with a highly porous side of an asymmetric membrane under anaerobic conditions and transferring these components into contact with microorganisms contained within bio-pores of the membrane. The membrane side of the membrane utilizes a dense layer to control hydration of the bio-pores with a liquid phase. The gas feed directly contacts the microorganisms in the bio-pores and maximizes their utilization of the syngas. Metabolic products produced by the microorganisms leave the membrane through the side opposite the entering syngas. This system and method establishes a unitary direction across the membrane for the supply of the primary feed source to the microorganisms and the withdrawal of metabolically produced products. The feed and product flow improves productivity and performance of the microorganism and the membrane.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Monolithic electrode, related material, process for production, and use thereof
InactiveUS20110281174A1Increase capacityProlong lifeAlkaline accumulatorsHybrid capacitor electrodesRechargeable cellConformal coating
An electrode material is created by forming a thin conformal coating of metal oxide on a highly porous monolithic carbon structure. The highly porous carbon structure performs a role in the synthesis of the oxide coating and in providing a three-dimensional, electronically conductive substrate supporting the thin coating of metal oxide. The metal oxide includes one or more metal oxides. The electrode material, a process for producing said electrode material, an electrochemical capacitor and an electrochemical secondary (rechargeable) battery using said electrode material is disclosed.
Owner:SEYMOUR FRASER W
Absorbing pathogen-inactivating compounds with porous particles immobilized in a matrix
InactiveUS6951713B2Reduce risk of leakageReduce decreaseImmobilised enzymesOther blood circulation devicesWhole blood productSorbent
Methods and devices are provided for reducing the concentration of low molecular weight compounds in a biological composition, while substantially maintaining a desired biological activity of the biological composition. The device comprises highly porous adsorbent particles, and the adsorbent particles are immobilized by an inert matrix. The matrix containing the particles is contained in a housing, and the particles range in diameter from about 1 μm to about 200 μm. The matrix can be fibrous, and the particles can have a surface area greater than 750 m2 / g and a pore diameter between about 25 and 800 Å. The device can be used to adsorb and remove a pathogen-inactivating compound that is a nucleic acid-binding compound such as psoralen, an acridine derivative or a dye from a biological composition such as a blood product.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Highly porous self-cohered web materials
ActiveUS20070027550A1High porositySuitable for useClosuresLayered productsUltimate tensile strengthMedical device
The present invention is directed to implantable bioabsorbable non-woven self-cohered web materials having a high degree of porosity. The web materials are very supple and soft, while exhibiting proportionally increased mechanical strength in one or more directions. The web materials often possess a high degree of loft. The web materials can be formed into a variety of shapes and forms suitable for use as implantable medical devices or components thereof.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Absorbing pathogen-inactivating compounds with porous particles immobilized in a matrix
InactiveUS20050142542A1Reduce risk of leakageEasy to manufactureImmobilised enzymesOther blood circulation devicesWhole blood productSorbent
Methods and devices are provided for reducing the concentration of low molecular weight compounds in a biological composition, while substantially maintaining a desired biological activity of the biological composition. The device comprises highly porous adsorbent particles, and the adsorbent particles are immobilized by an inert matrix. The matrix containing the particles is contained in a housing, and the particles range in diameter from about 1 μm to about 200 μm. The matrix can be fibrous, and the particles can have a surface area greater than 750 m2 / g and a pore diameter between about 25 and 800 Å. The device can be used to adsorb and remove a pathogen-inactivating compound that is a nucleic acid-binding compound such as psoralen, an acridine derivative or a dye from a biological composition such as a blood product.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Devices and methods for the regeneration of bony defects
This invention relates to methods for producing a composite bone graft material that can regenerate bony defects in the body. The invention further relates to methods that allow for the production of bioactive glass particles used in the composite that have been surface treated to allow for the production of a highly porous composite that can hold significant amounts of body fluid or other molecules that will aid in the regenerative process. The method of surface treatment allows for the manufacture of a suitable implantable composite while retaining the unique osteostimulative properties that are associated with bioactive glass particles.
Owner:NOVABONE PRODS
Dust filter bag including a highly porous backing material ply
InactiveUS20020083690A1Simple and cost-effective productionCleaning filter meansCombination devicesBursting strengthCellulose fiber
The invention relates to a dust filter bag having a highly porous backing material ply and to a method for producing the dust filter bag The dust filter bag comprises at least one filter material ply and at least one backing material ply, the backing material ply featuring an air permeability of at least 900 l / m2xs, a burst strength of at least 70 kPa, a rupture strength longitudinally better than 10 N and transversely better than 3 N, a flexural rigidity longitudinally better than 0.5 cN cm2 and transversely better than 0.25 cN cm2, a basis weight of 30-80 g / m2 and a droplet sink-in time of less than 10 minimum. The dust filter bag can be produced by the following steps: mixing fibers including cellulose fibers and fusible fibers into a homogenous fiber mix, processing the fiber mix into a fiber web by wet laying, drying the fiber web, curing the dried fiber web by thermofusion into a backing material ply, processing the backing material ply with a filter material ply into a raw bag, finishing the raw bag into a dust filter bag.
Owner:NEENAH GESSNER
Building facade construction system and methods therefor
A building façade system adapted to be installed onto an exposed surface of a building and provide a substrate for installation of façade elements (e.g., stone, stucco and the like). The system preferably provides a corrosion-resistant structure adapted to withstand extended environmental exposure. In general, the system includes a highly porous three dimensional matrix filamentous polymeric mat and a fiberglass mesh layer associated therewith. Collectively, the polymeric mat and fiberglass mesh layer are adapted to be installed onto an exposed building wall and provide a substrate onto which desired façade elements may be installed.
Owner:KEENE BUILDING PRODS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com