Patents
Literature
127results about How to "Reduce gas emissions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
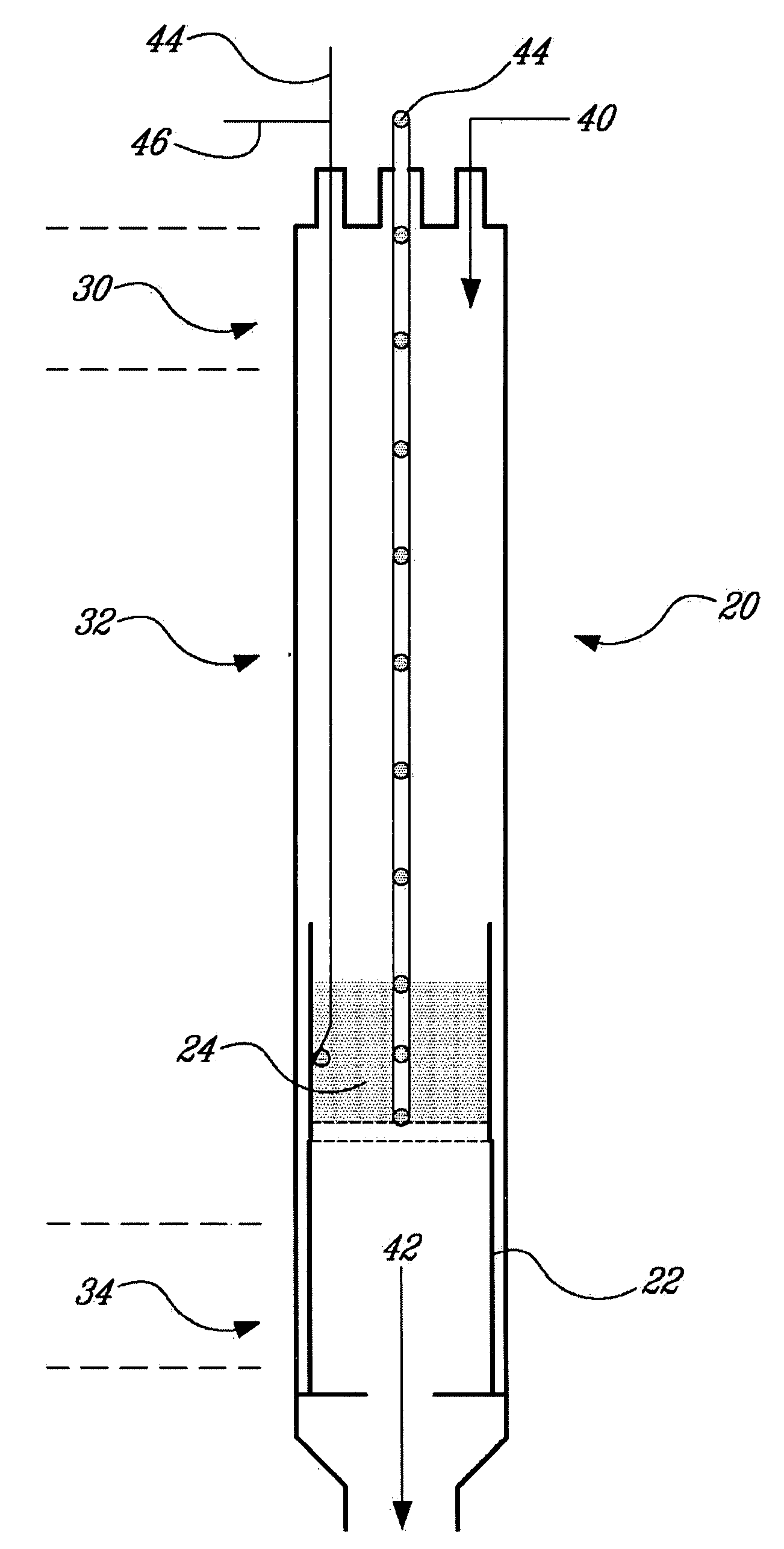
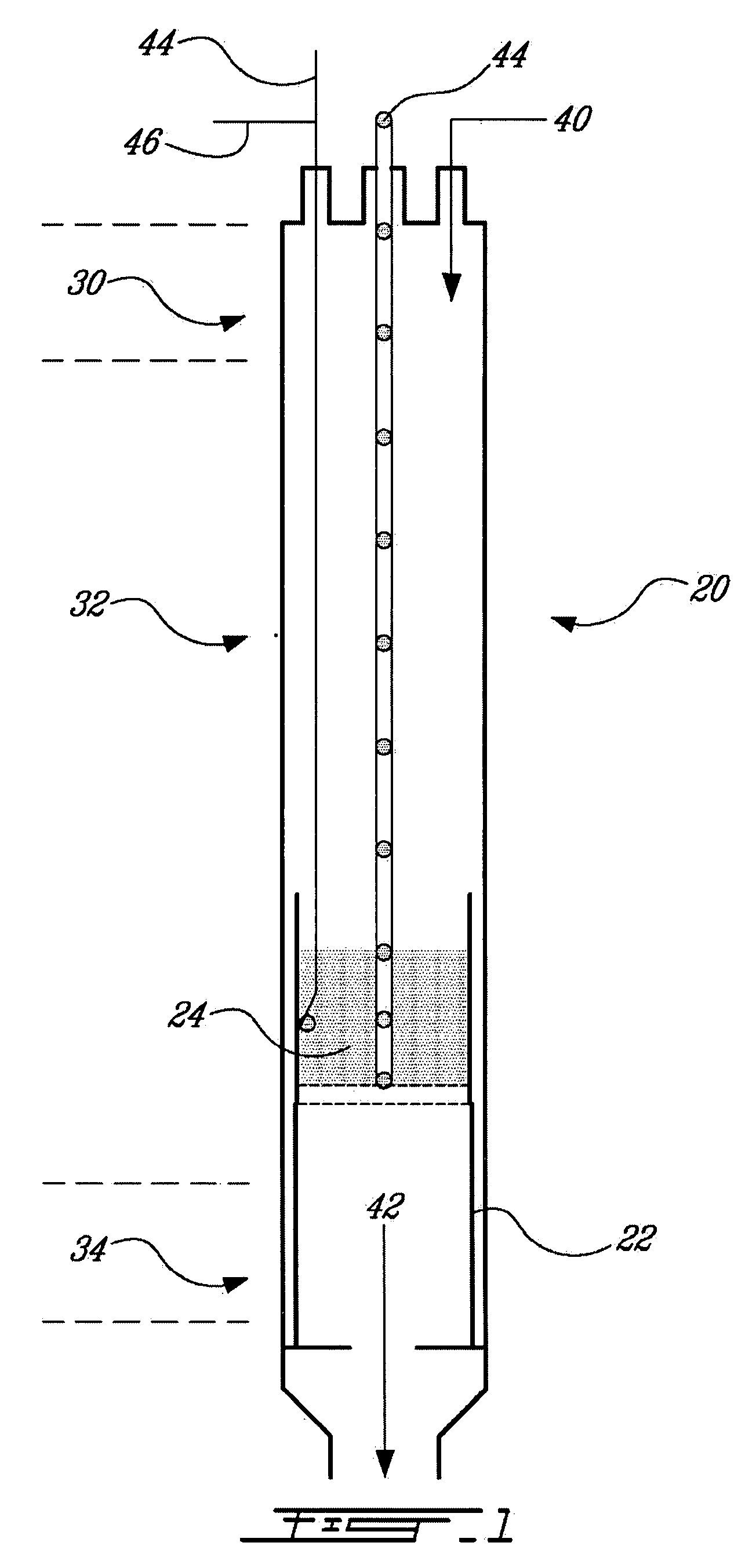
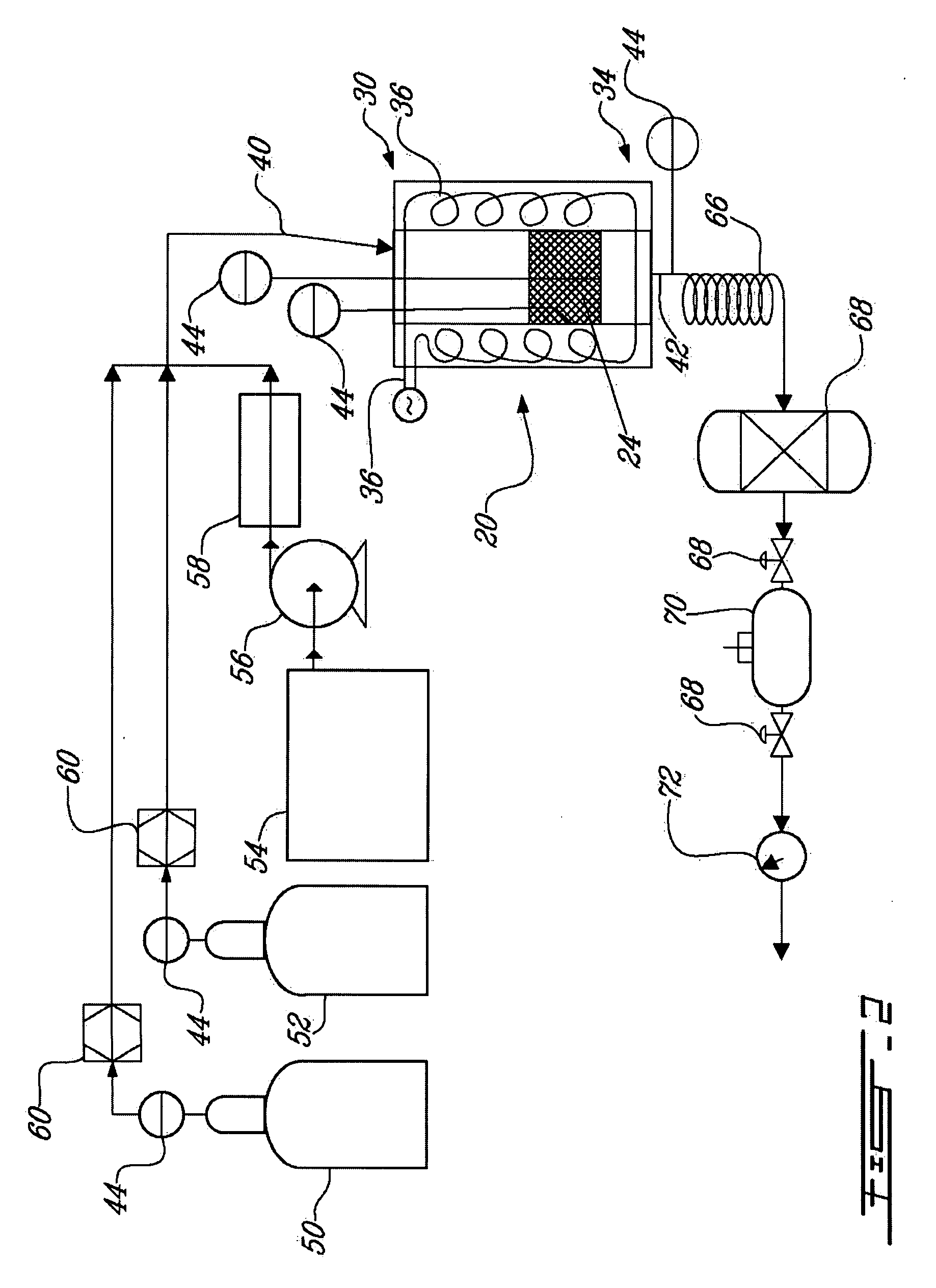
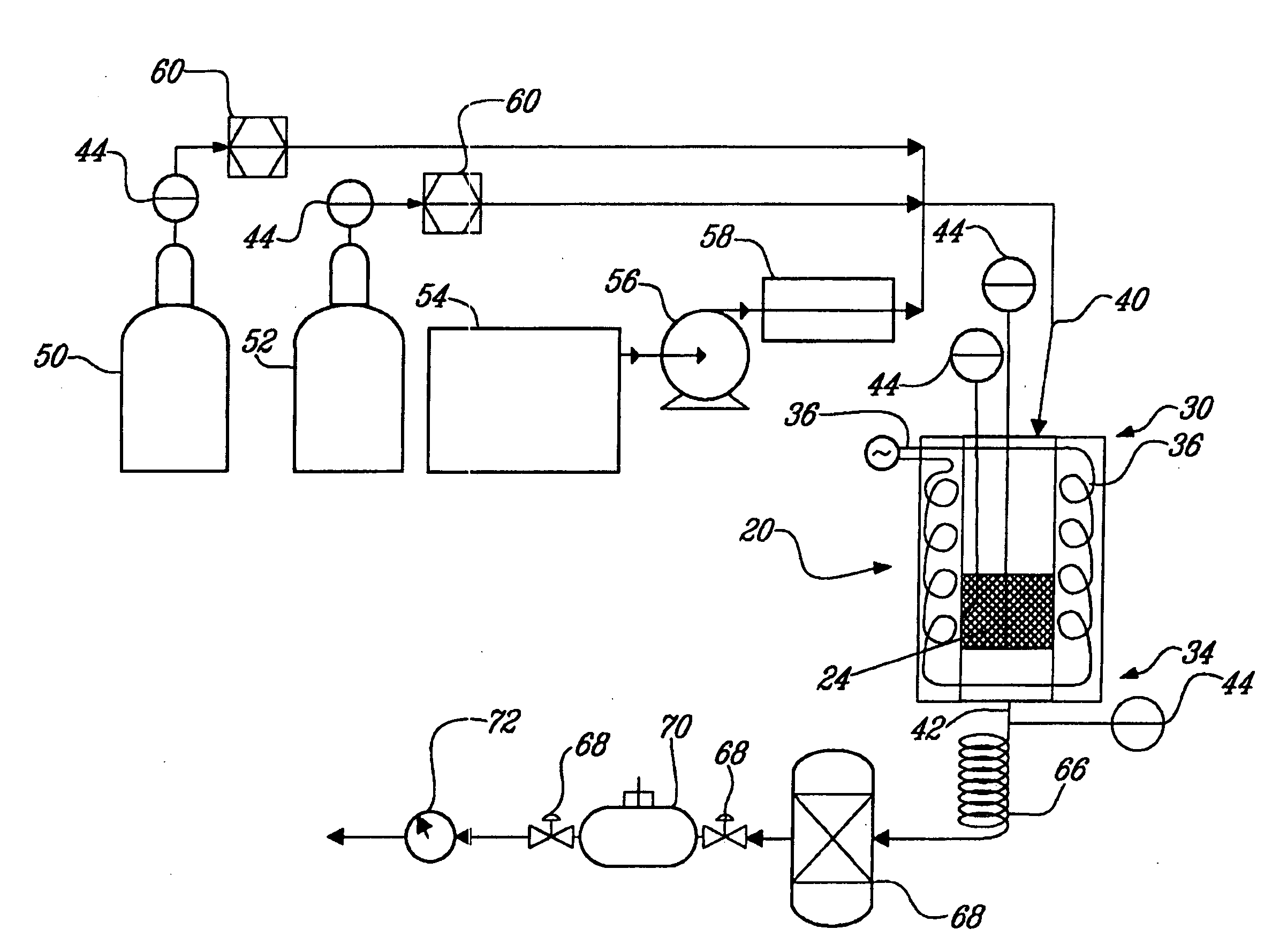
Carbon sequestration and dry reforming process and catalysts to produce same
ActiveUS20050220695A1Reduce emissionReduce gas emissionsCatalyst carriersHydrogen production carbon captureSyngasChemistry
A carbon sequestration and dry reforming process for the production of synthesis gas and sequestered carbon from carbon dioxide. Two-dimension catalysts for sequestering carbon and a process to produce same. A method for activating two dimension catalysts.
Owner:SCOPRA SCI & GENIE SEC
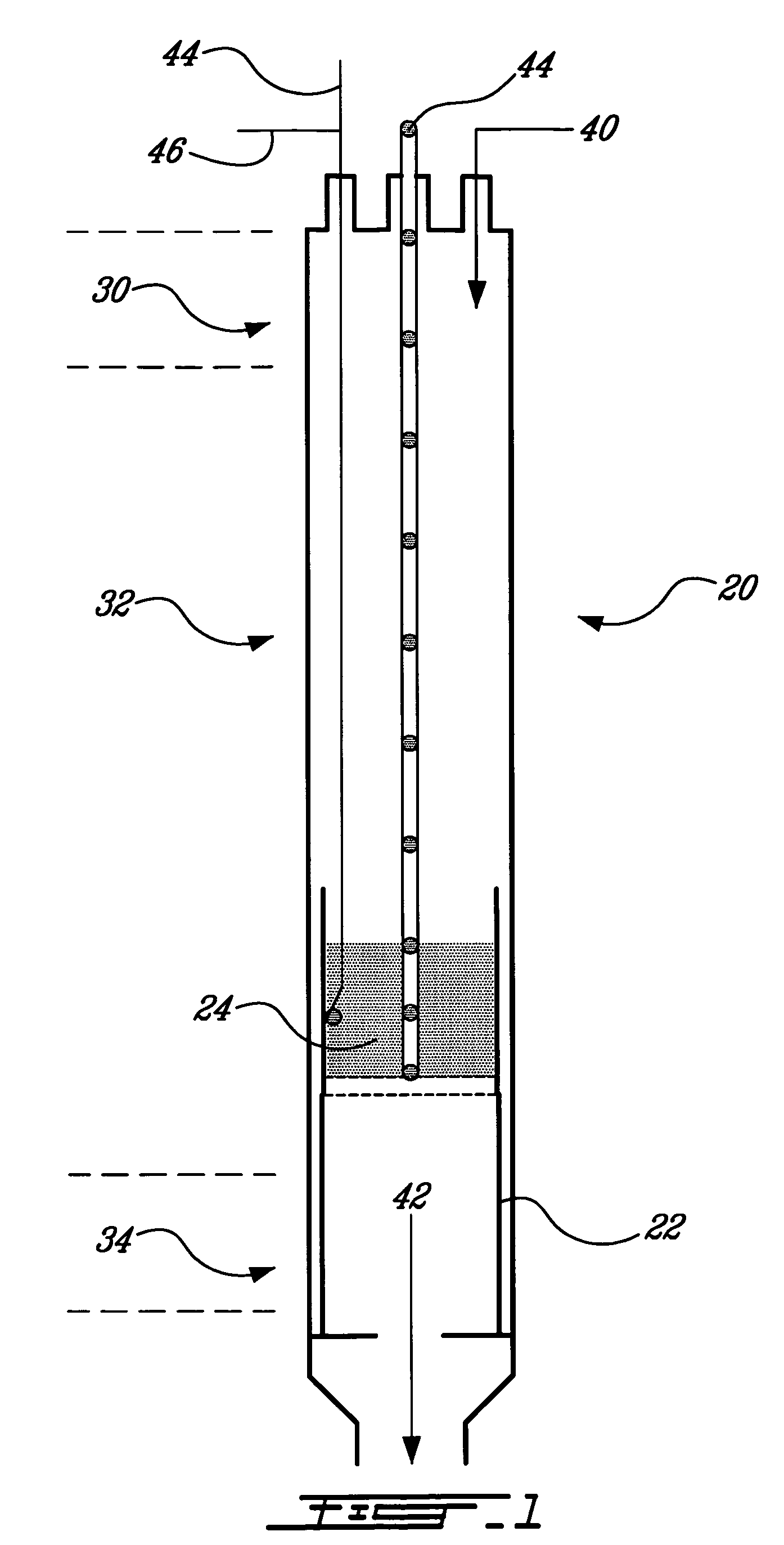
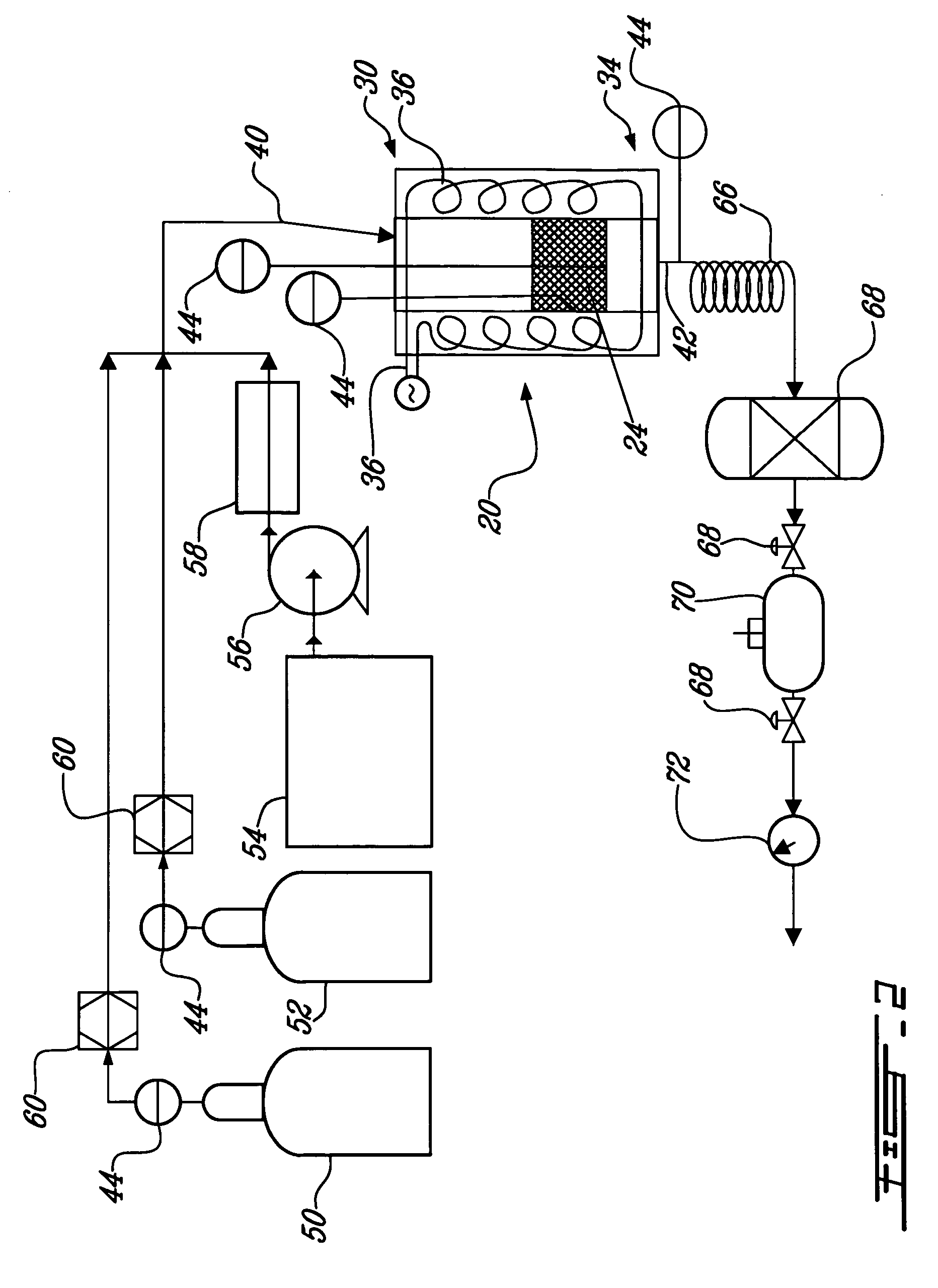
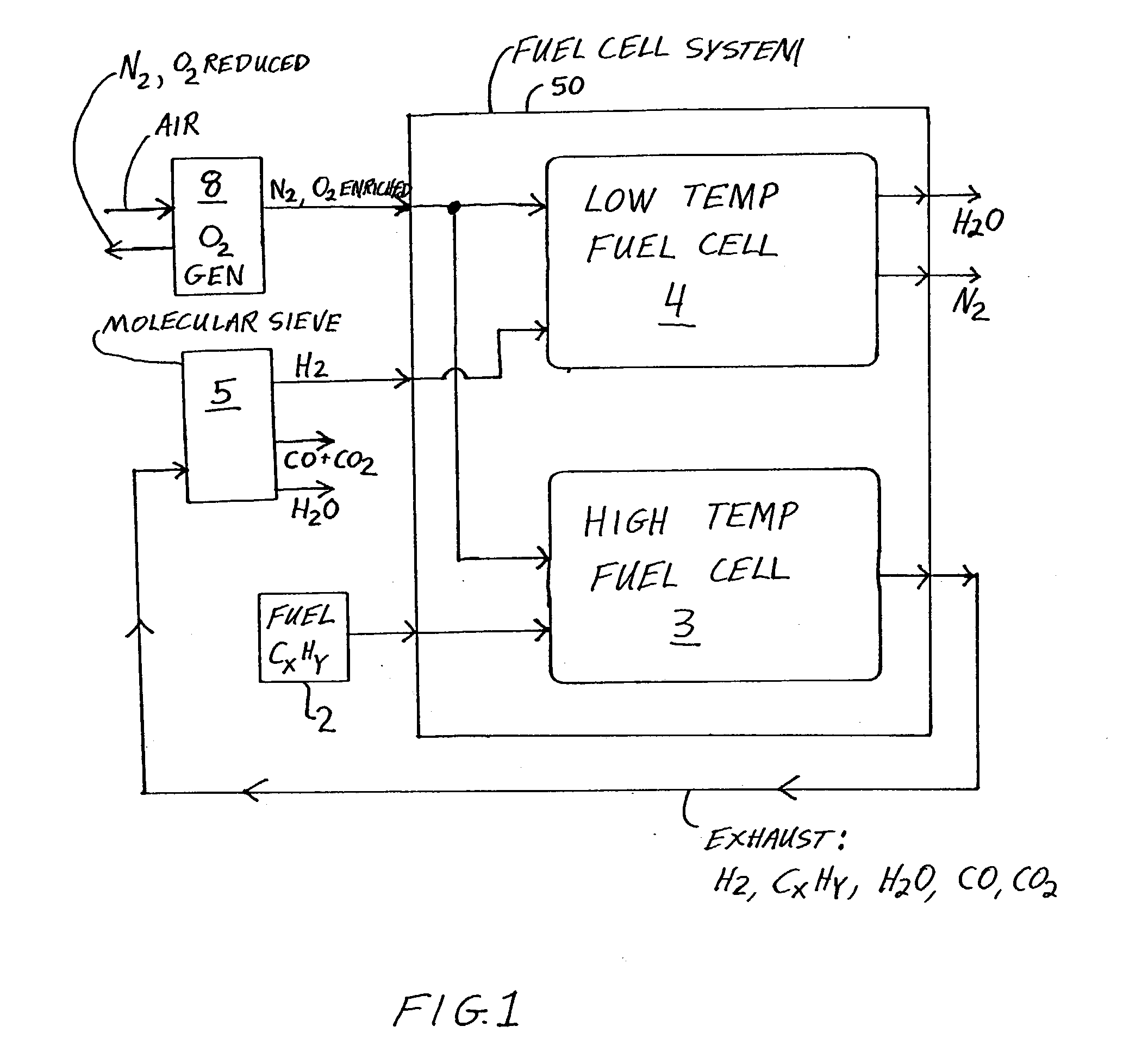
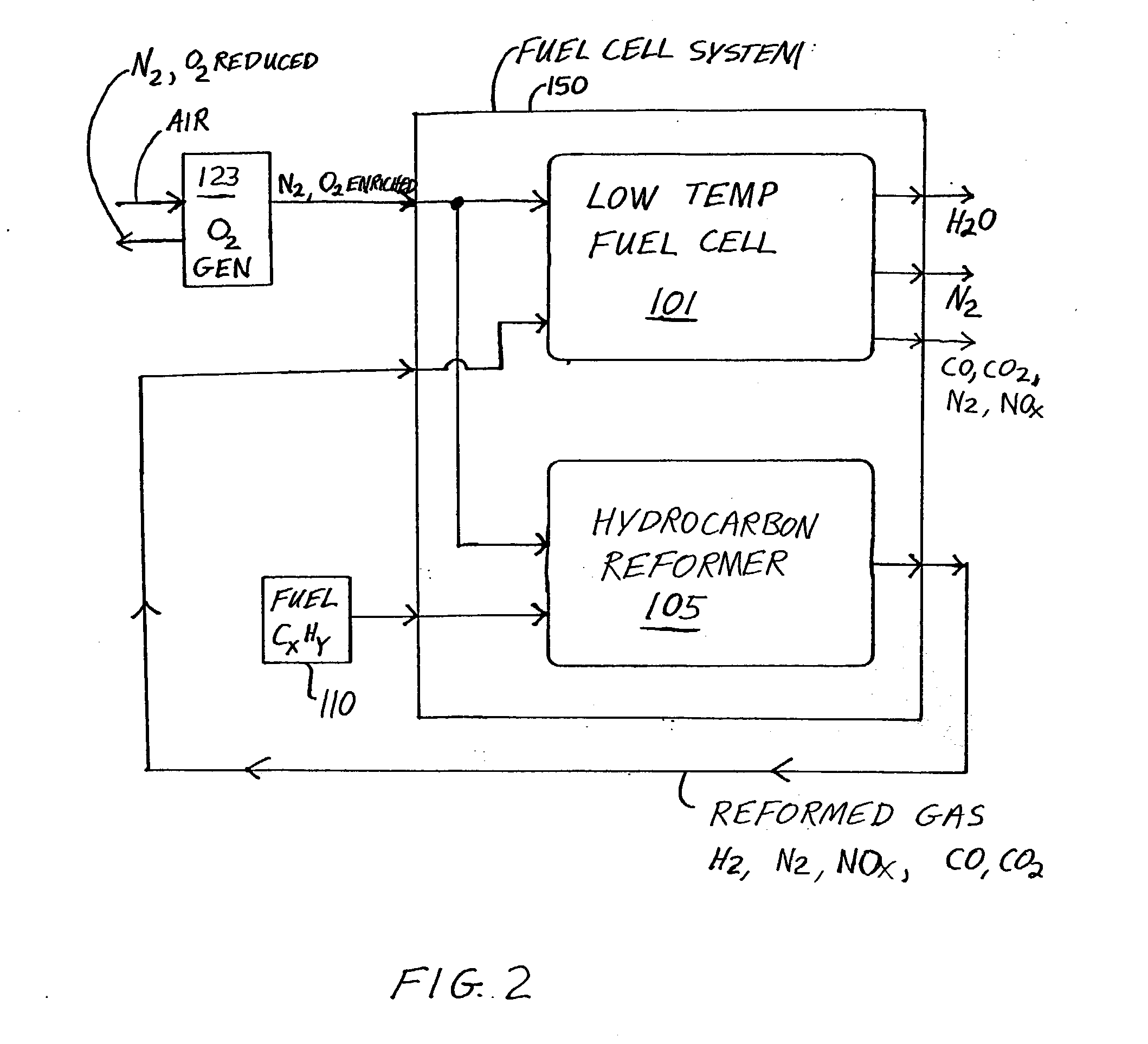
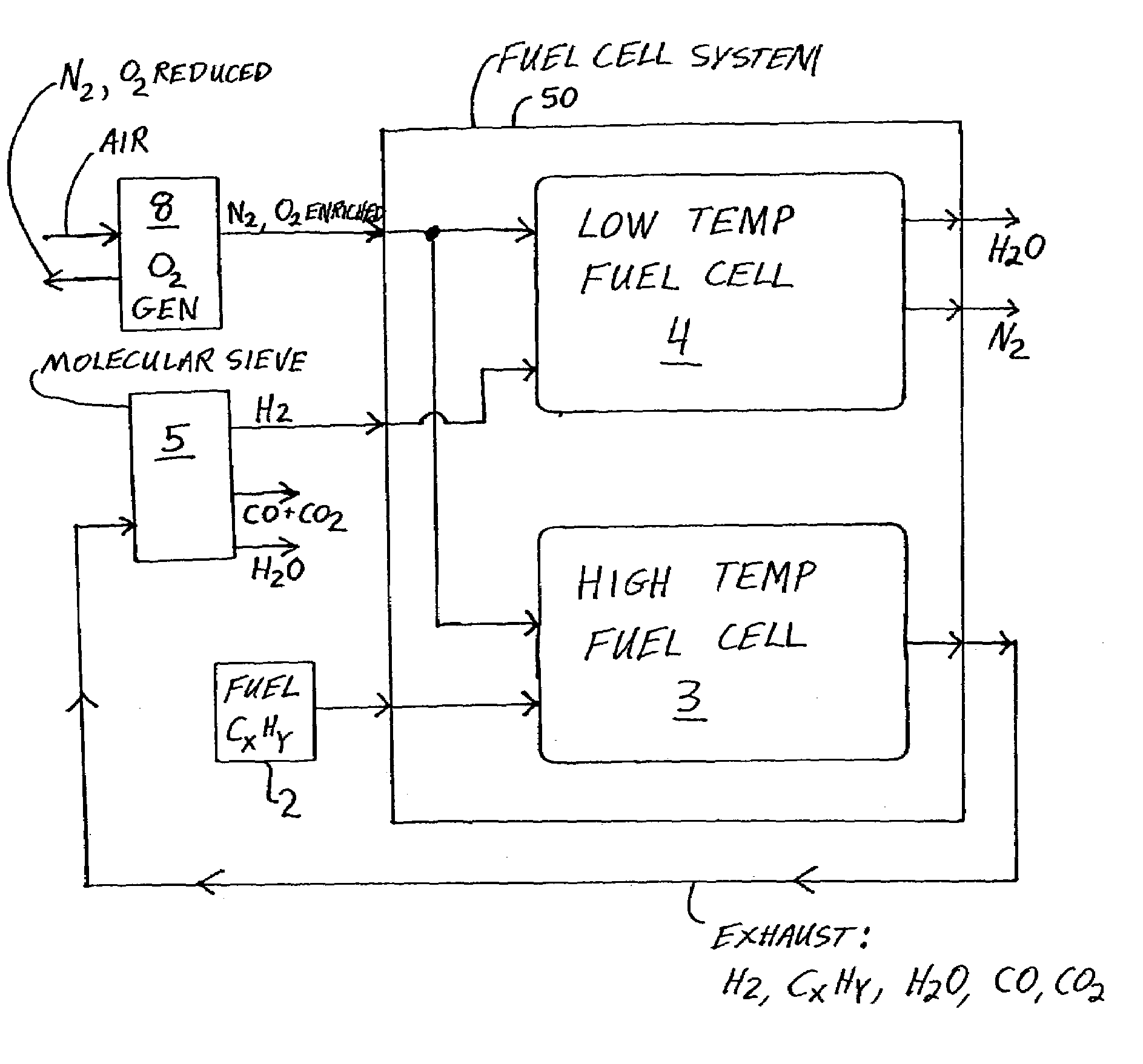
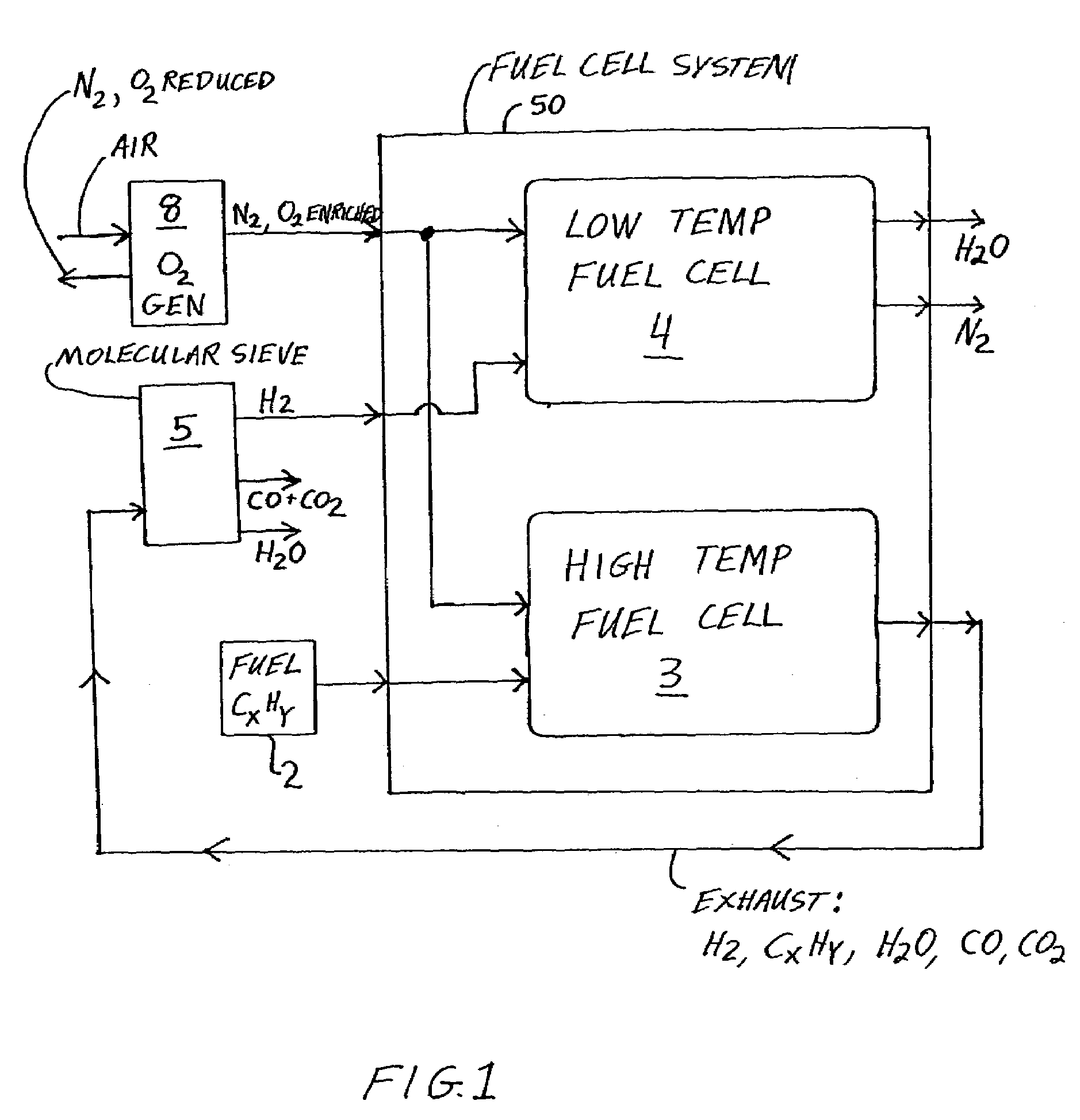
Fuel cell system and method with increased efficiency and reduced exhaust emissions
InactiveUS20040043276A1Improve efficiencyEfficient and effective usePower installationsFuel cells groupingAtmospheric airNitrogen gas
An apparatus includes a low temperature fuel cell, a high temperature fuel cell or a hydrocarbon reformer, a hydrocarbon fuel supply, an oxygen generator, and a molecular sieve. The oxygen generator separates air to provide oxygen enriched air to the fuel cells and the reformer. Hydrocarbon fuel is provided to the high temperature fuel cell or the reformer, and the exhaust gas thereof may be separated through the molecular sieve, to provide hydrogen enriched gas to the low temperature fuel cell, water, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. The low temperature fuel cell outputs nitrogen gas and high purity water. The emitted carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides are catalytically converted to nitrogen and carbon dioxide being returned to the atmosphere. The process and apparatus are very efficient, produce high purity water and electrical energy, and are environmentally friendly.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Carbon sequestration and dry reforming process and catalysts to produce same
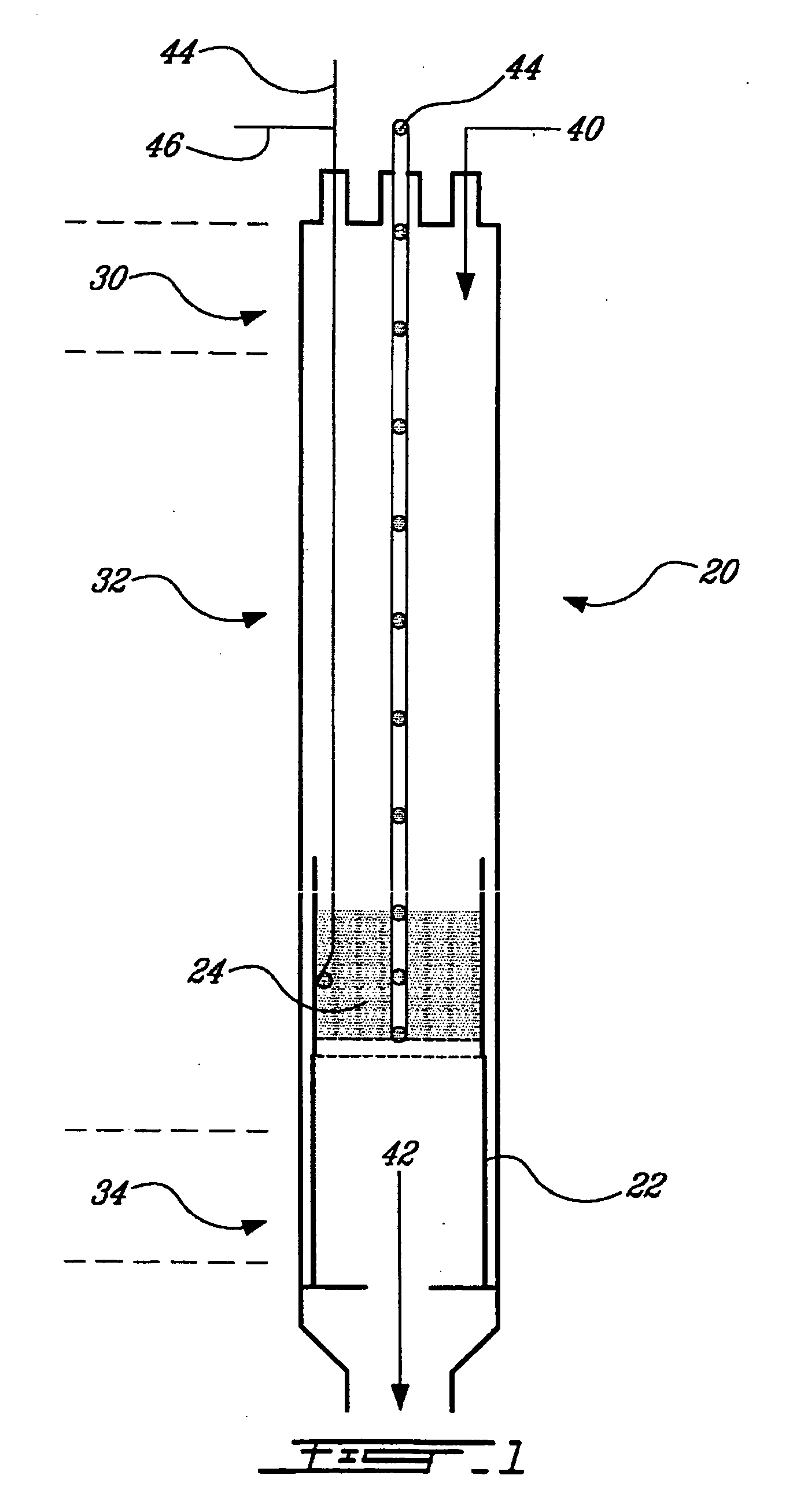
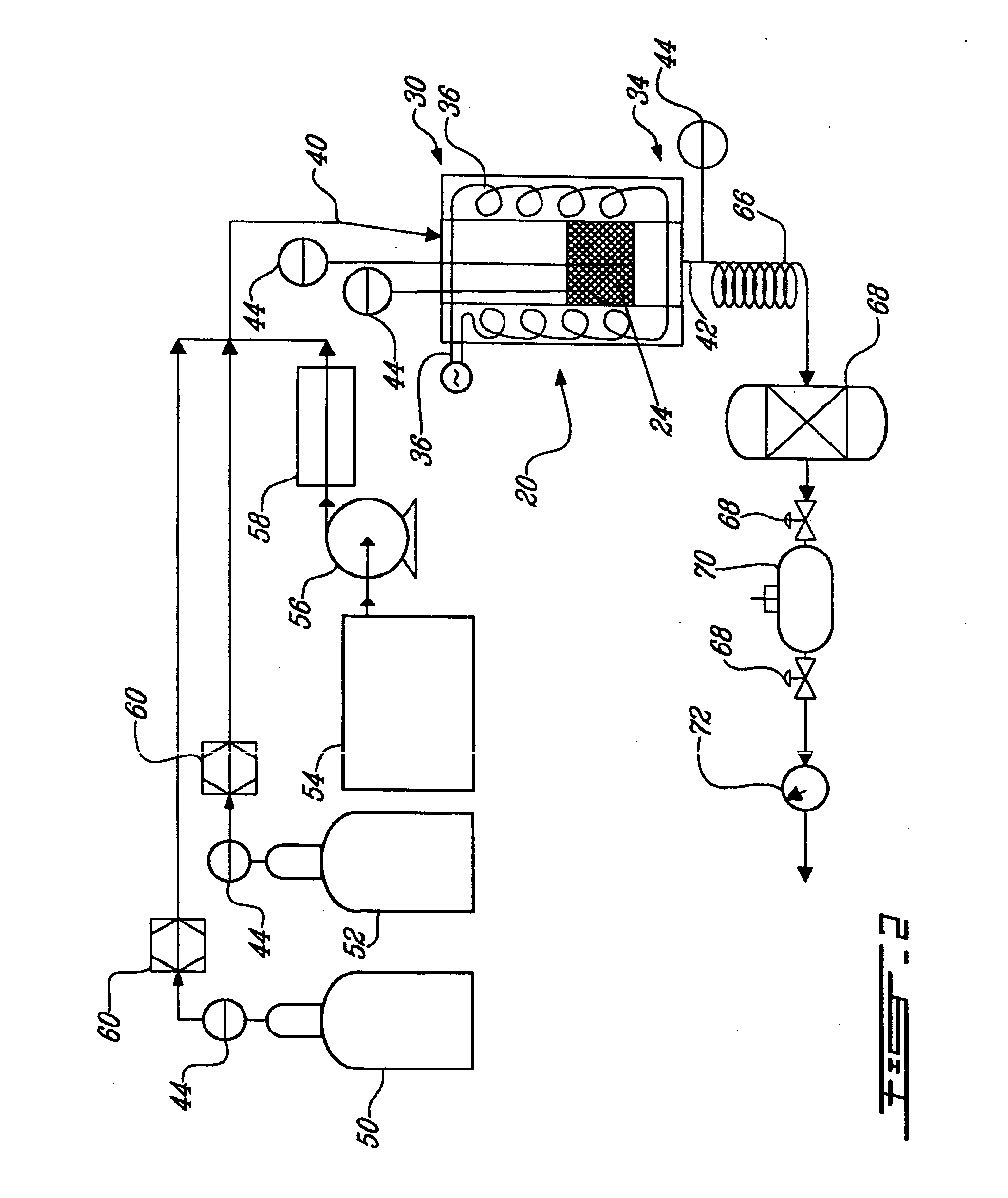
ActiveUS7794690B2Reduce gas emissionsCatalyst carriersHydrogen productionCarbon dioxide productionCarbon sequestration
A carbon sequestration and dry reforming process for the production of synthesis gas and sequestered carbon from carbon dioxide. Two-dimension catalysts for sequestering carbon and a process to produce same. A method for activating two dimension catalysts.
Owner:SCOPRA SCI & GENIE SEC
Carbon sequestration and dry reforming process and catalysts to produce same
InactiveUS20070253886A1Reduce gas emissionsMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenSyngasCarbon sequestration
A carbon sequestration and dry reforming process for the production of synthesis gas and sequestered carbon from carbon dioxide. Two-dimension (non-porous) catalysts for sequestering carbon are also disclosed and a process to produce same as well as a method for activating two dimension catalysts.
Owner:SCOPRA SCI & GENIE SEC
Non-porous catalysts for co2 sequestration through dry reforming
InactiveUS20090203519A1Reduce gas emissionsMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenPorous catalystCarbon dioxide production
A carbon sequestration and dry reforming process for the production of synthesis gas and sequestered carbon from carbon dioxide. Two-dimension (non-porous) catalysts for sequestering carbon are also disclosed and a process to produce same as well as a method for activating two dimension catalysts.
Owner:UNIV DE SHERBROOKE +1
Fire resistant material
InactiveUS20070194289A1Improve compatibilityImprove rheologySilicon compoundsTextile shapingPolyamideMaterials science
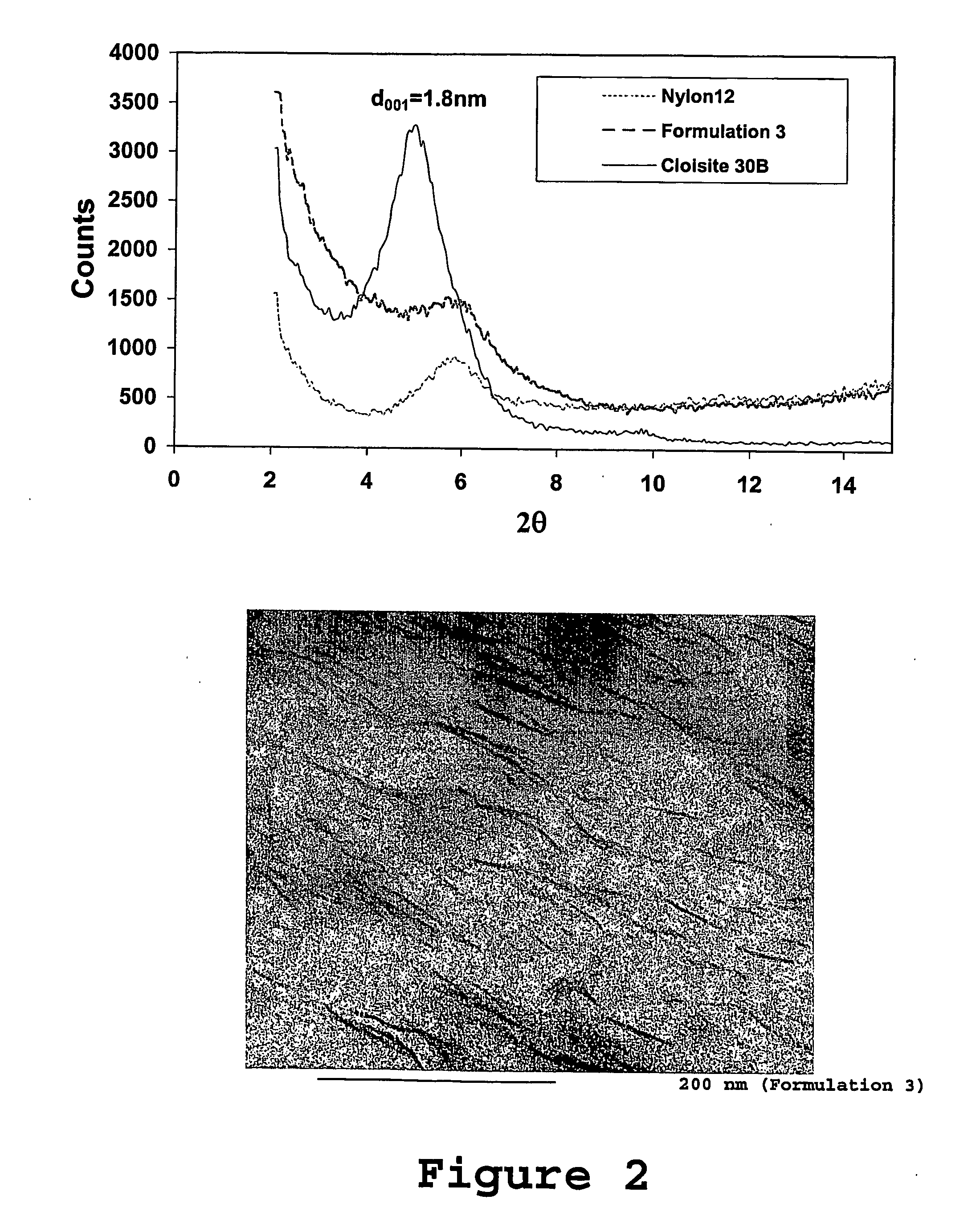
The present invention relates to inorganic-organic hybrids (IOHs), methods for their preparation and their use as fire resistant materials or components of fire resistant materials. More specifically, the invention relates to polyamide fire resistant formulations containing IOHs which have application in the production of fire resistant articles or parts thereof for use in the transportation, building, construction and electrical or optical industries.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Internal combustion engine with auto ignition
InactiveUS20060037563A1Prevent wettingMinimize wettingElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
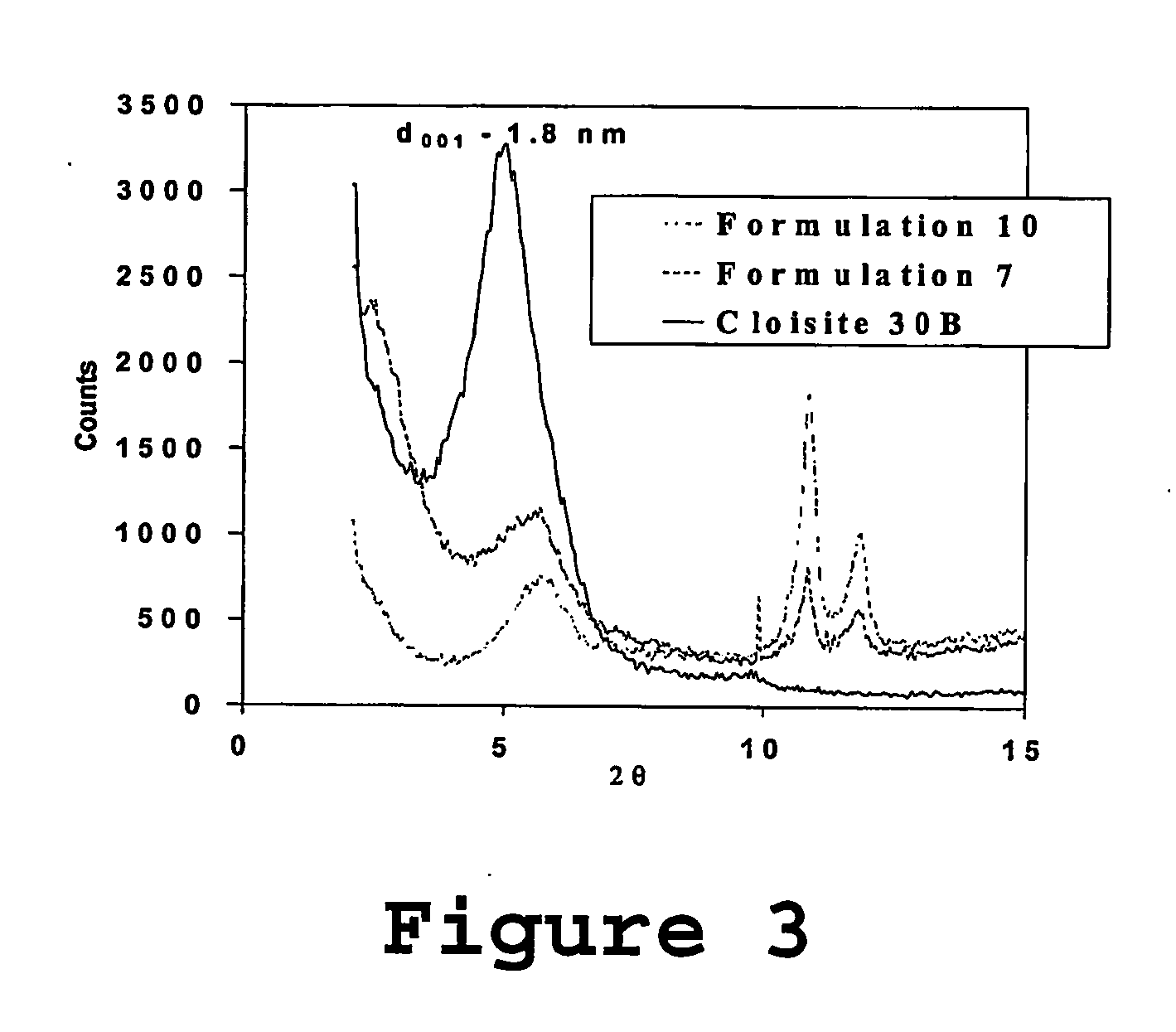
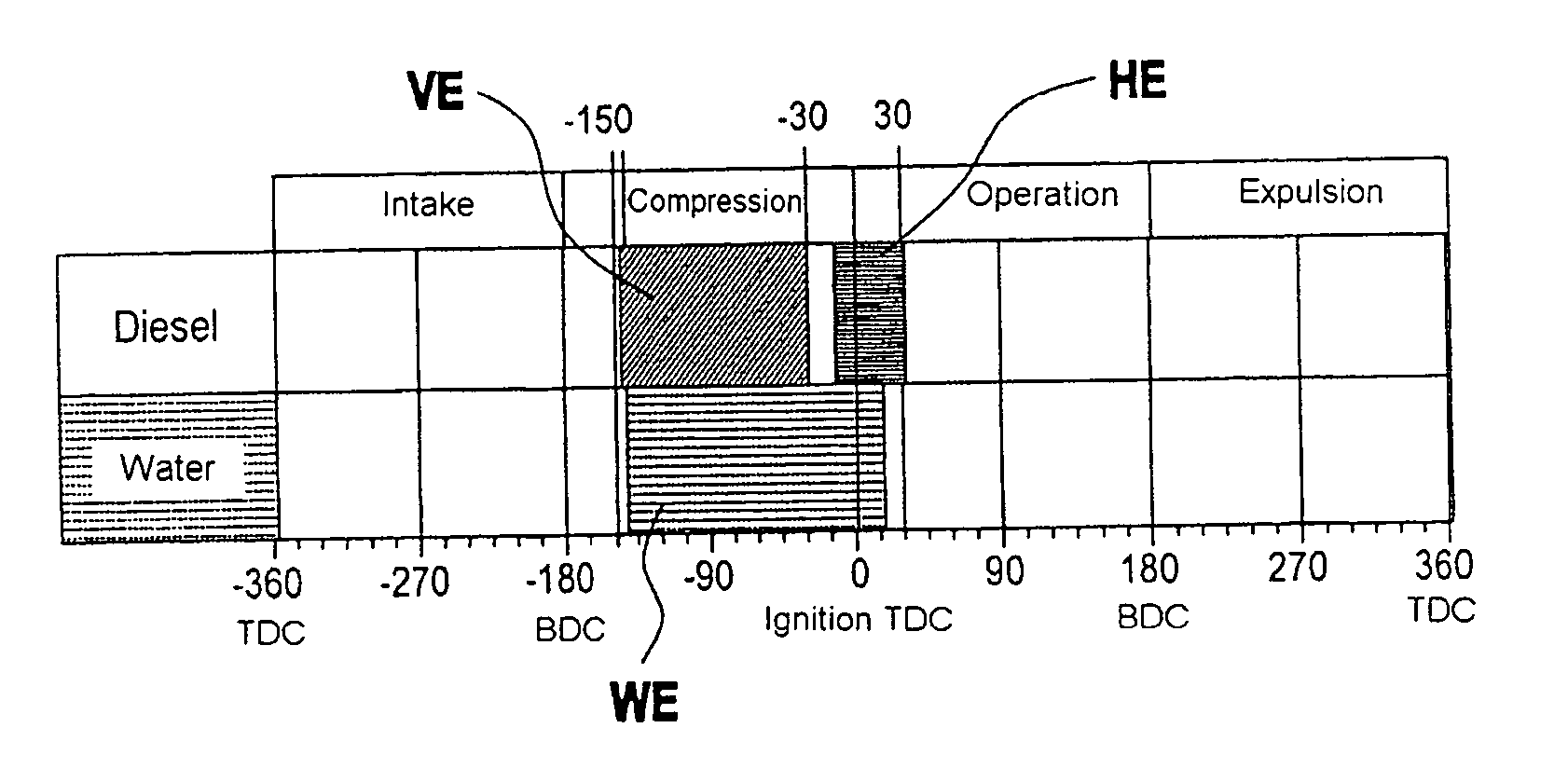
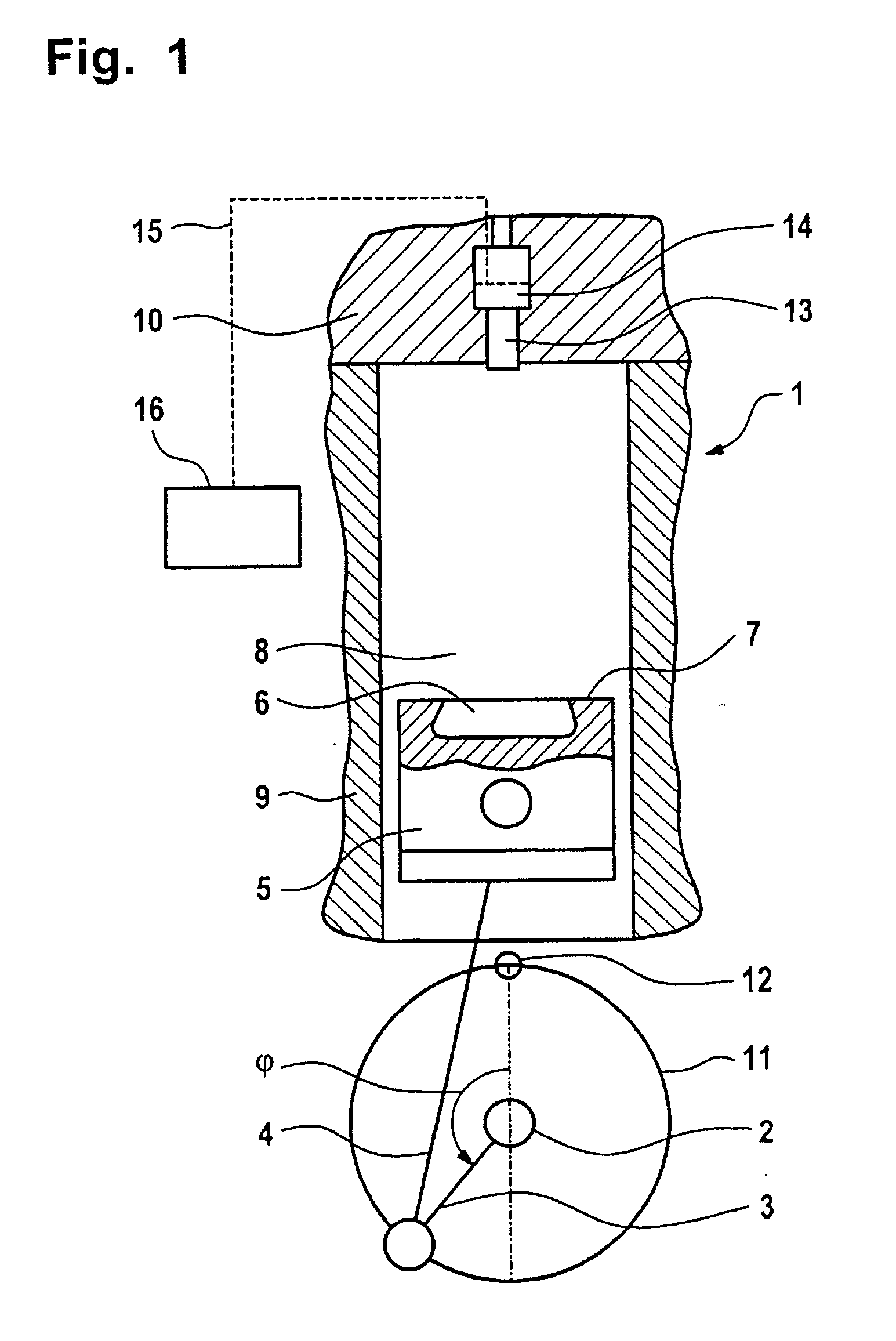
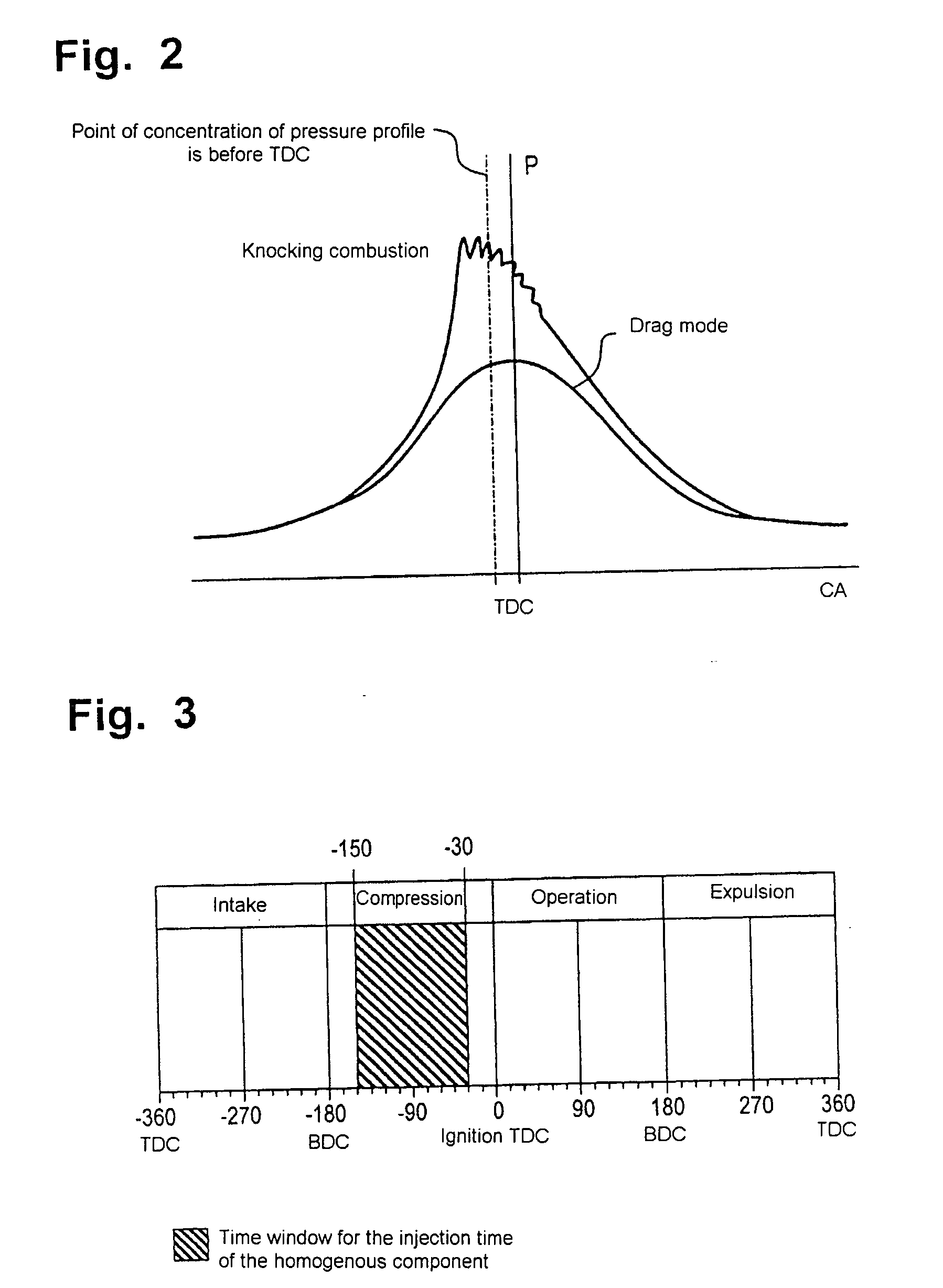
In a method for operating an internal combustion engine in which fuel is injected directly into a combustion chamber in a pre-injection and a main fuel injection step, and, if appropriate, also in a post-injection step by means of an injection nozzle with a plurality of injection bores, the injection of fuel takes place in a timed fashion and, to limit pressure and temperature during combustion of the fuel in the combustion chamber, a quantity of water is introduced into the combustion chamber during or after the pre-injection step.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Light emitting device
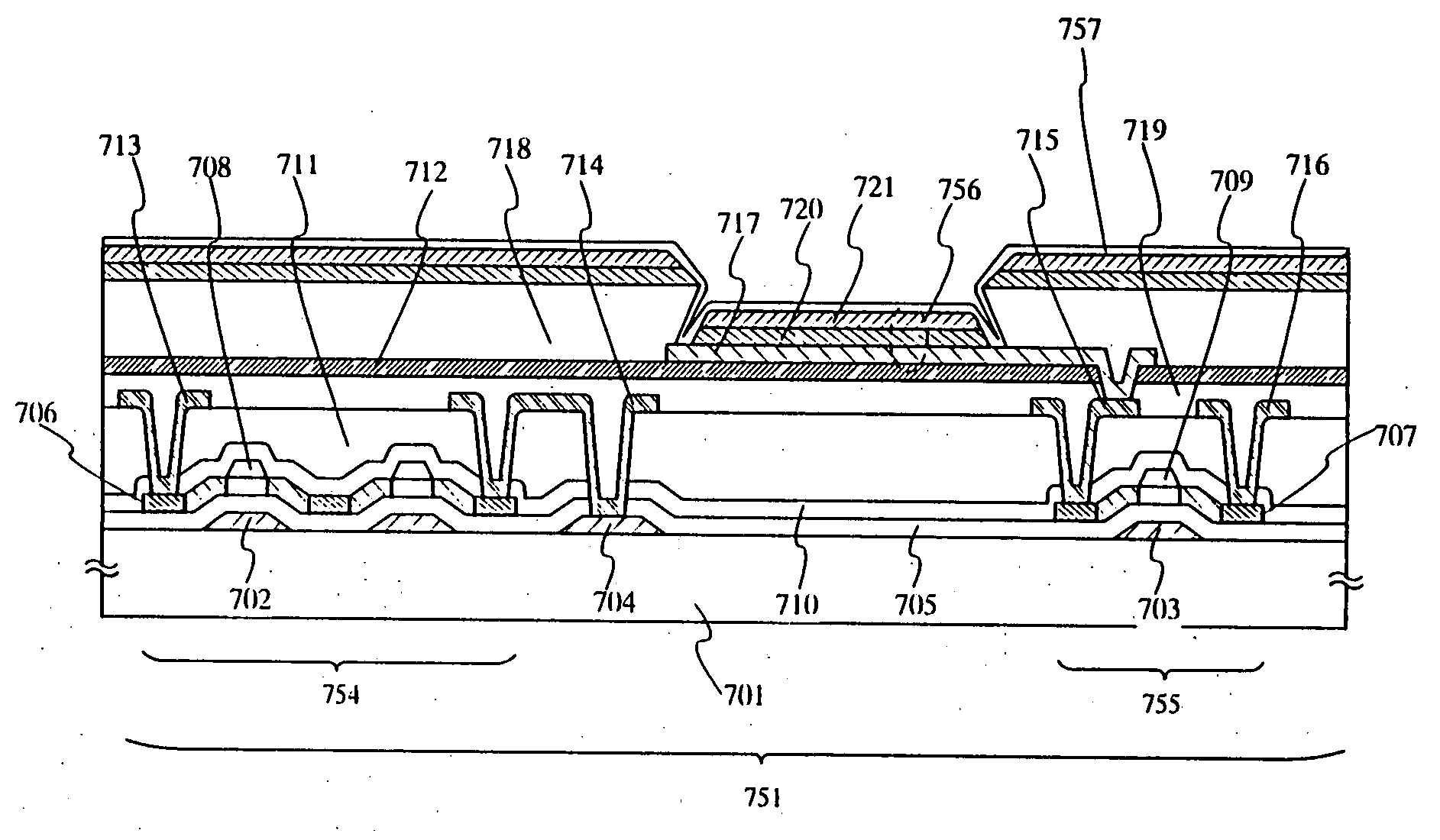
InactiveUS20050093436A1Inhibit deteriorationImprove reliabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsActive matrix
In an active matrix drive light emitting device, above a thin film transistor, a light emitting element having an anode, a layer comprised of an organic compound and a cathode containing an alkali metal is formed between a third insulating layer comprised of silicon nitride or silicon oxynitride and a fourth insulating layer containing carbon as its main constituent. The light emitting element is formed between partition layers that are formed of an insulating material and have an inverse tapered shape.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
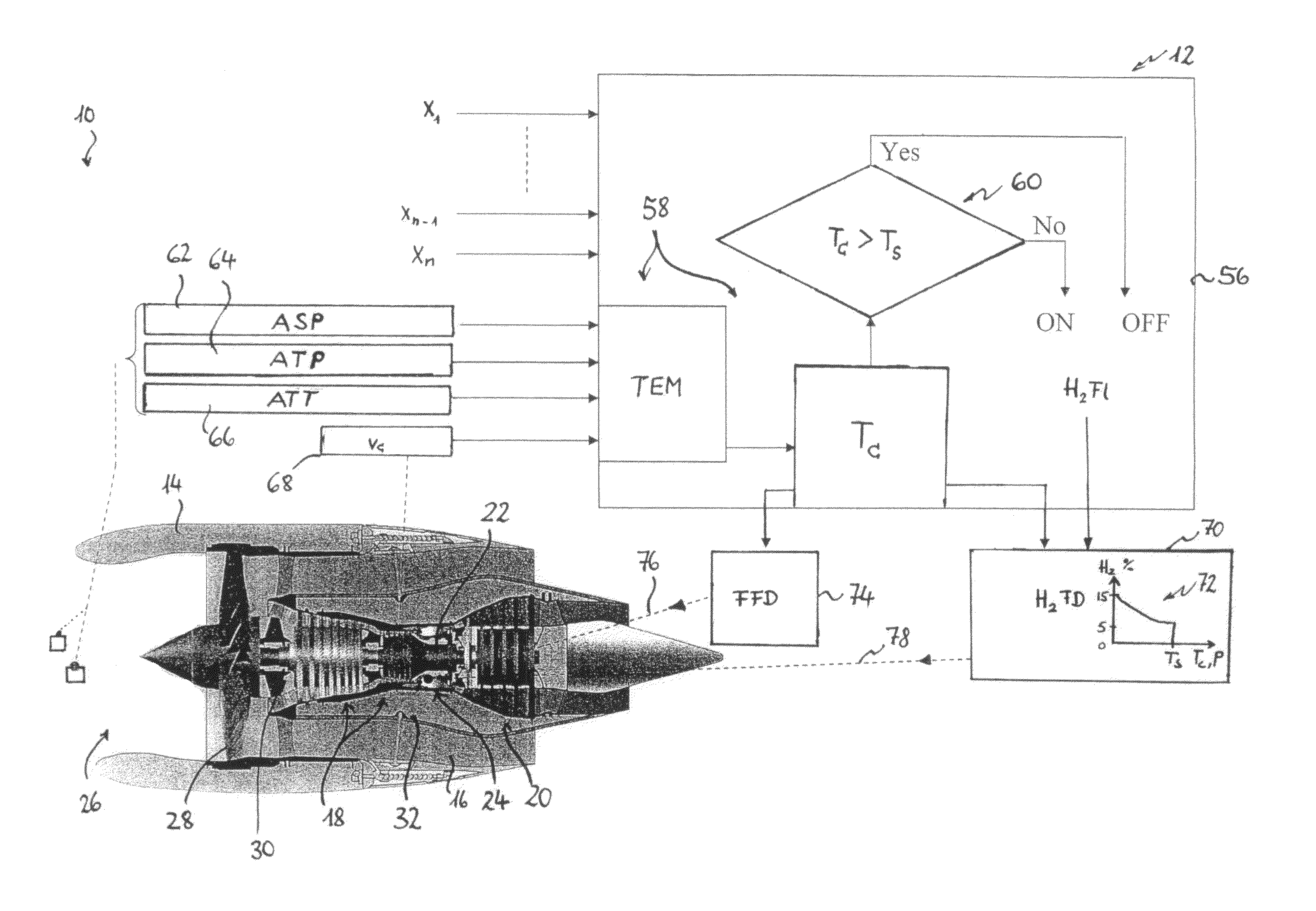
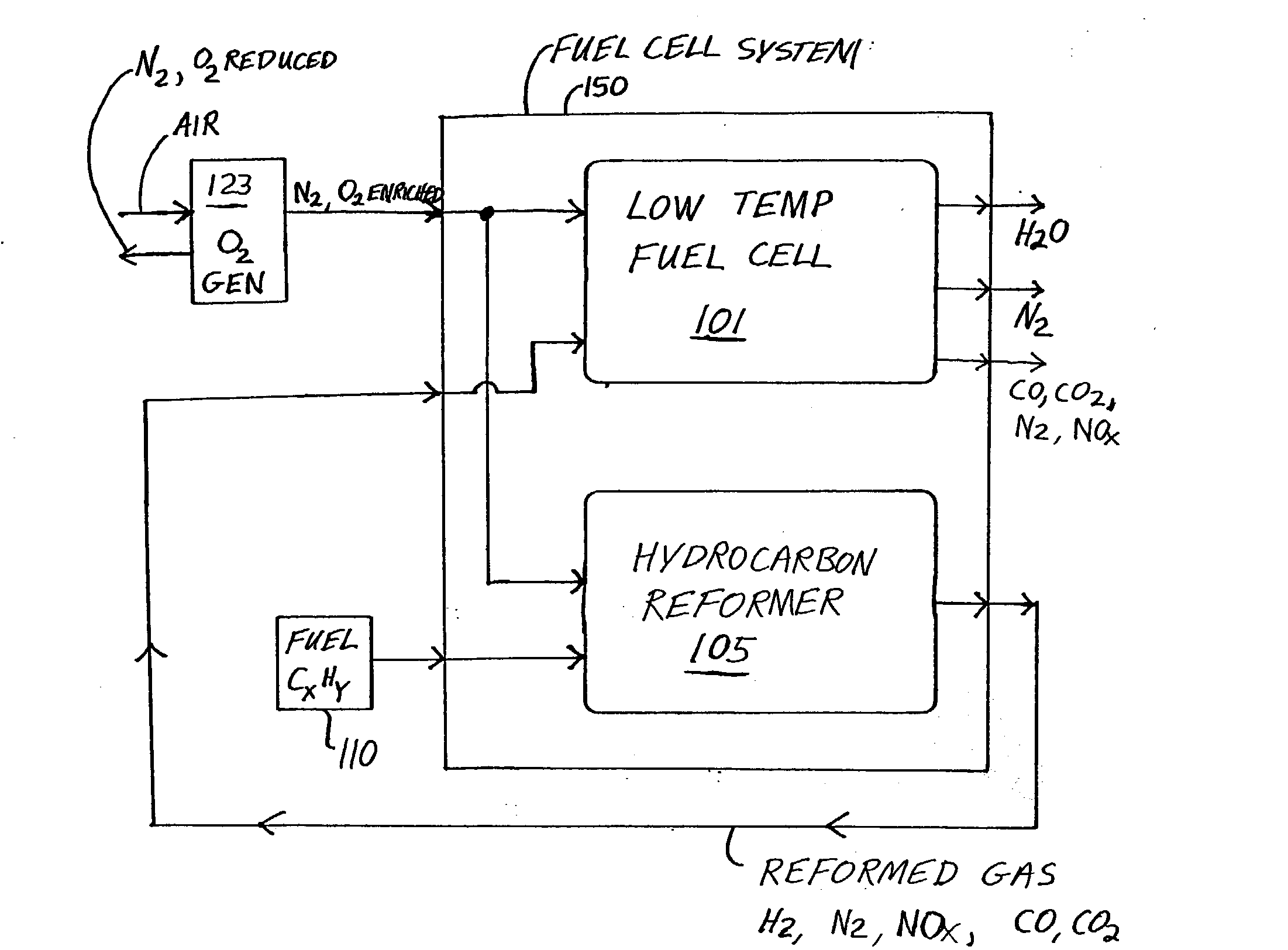
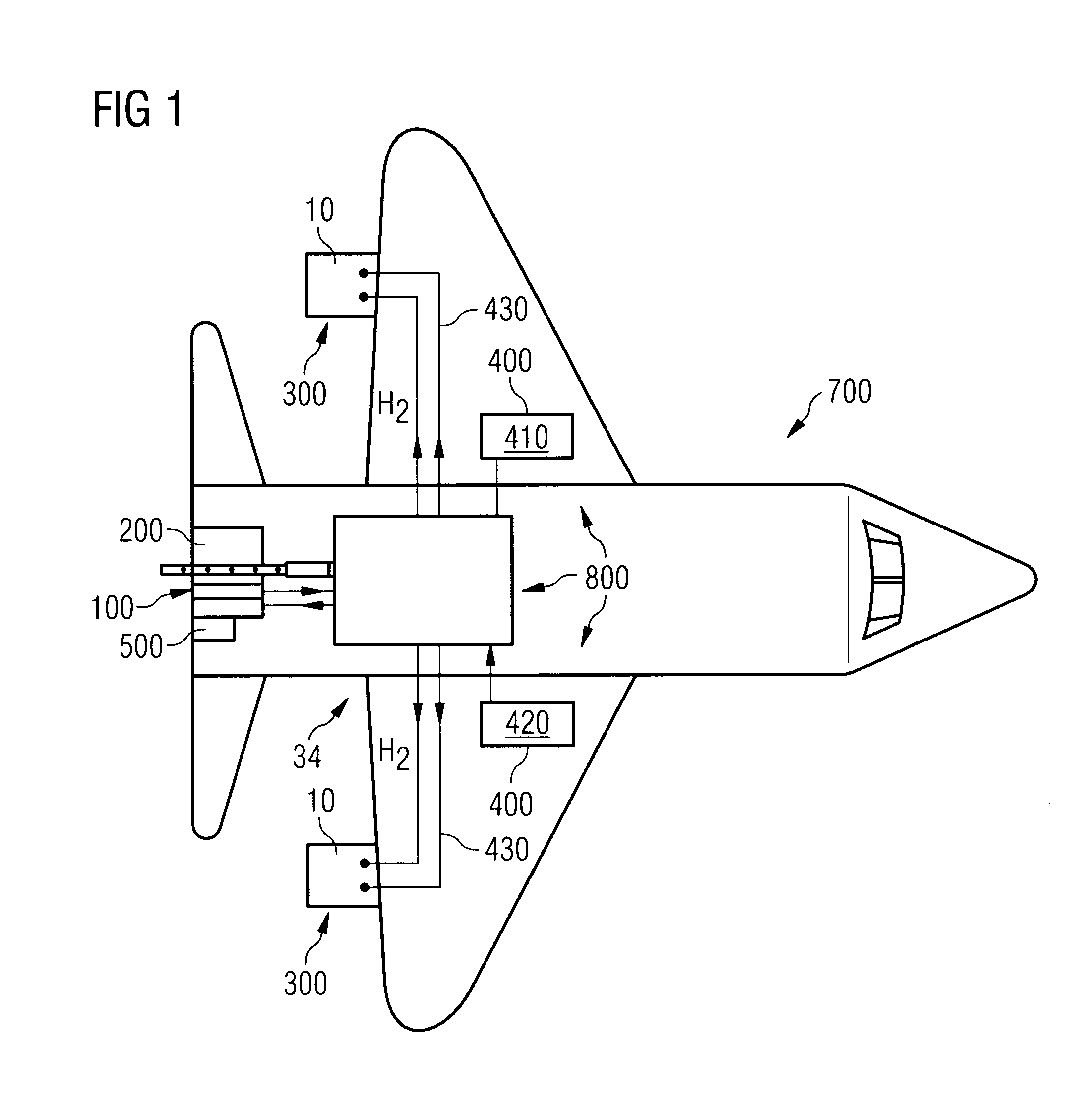
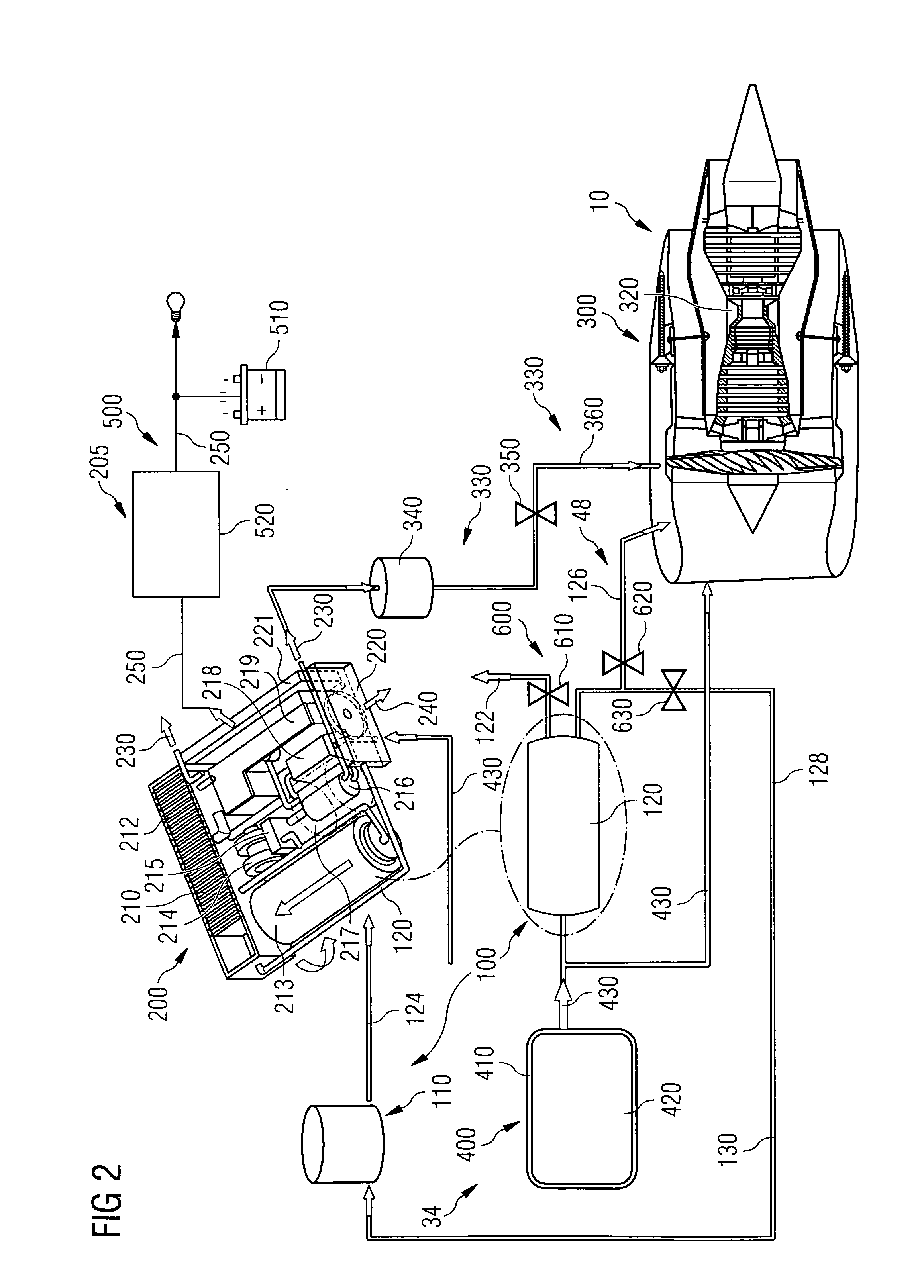
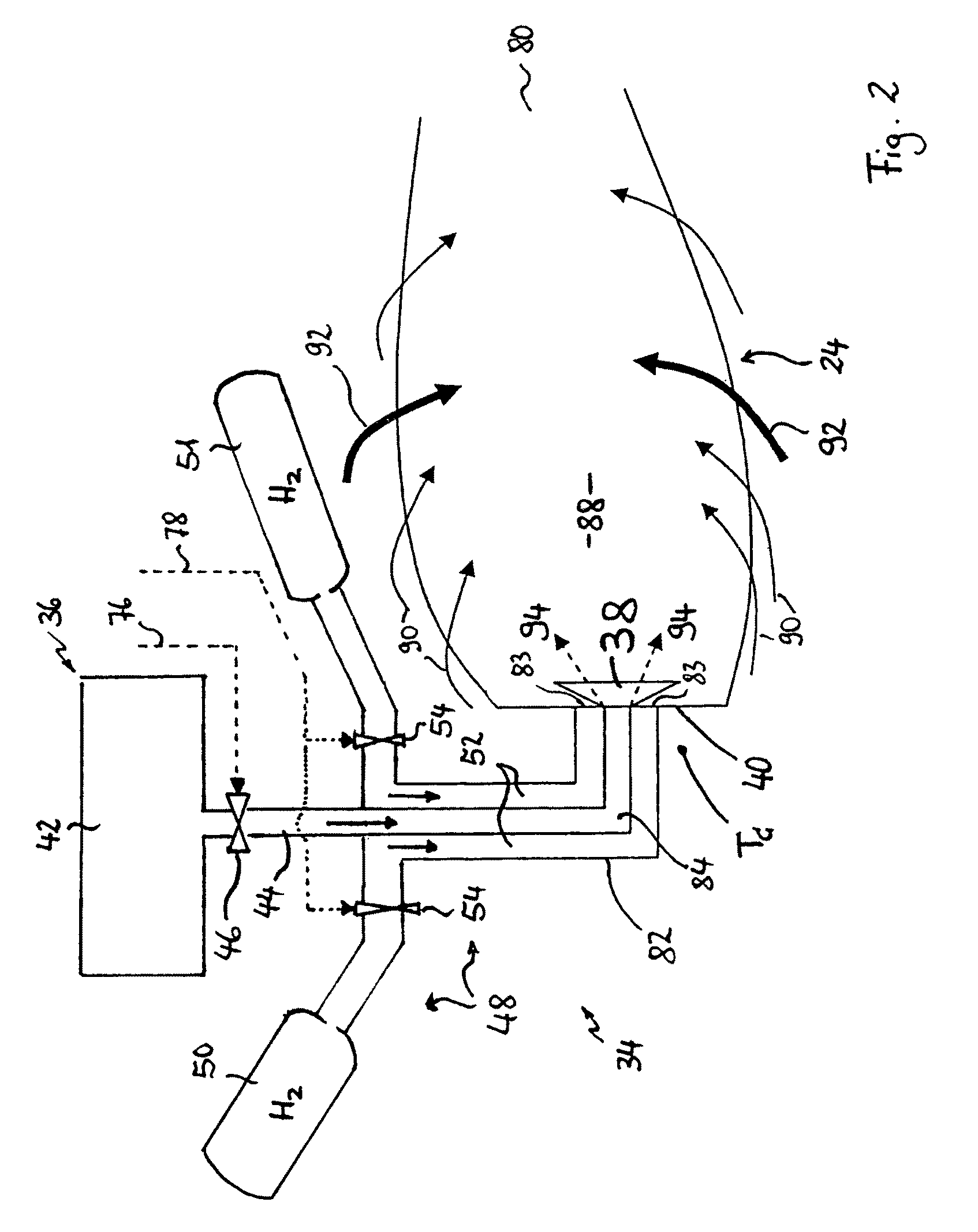
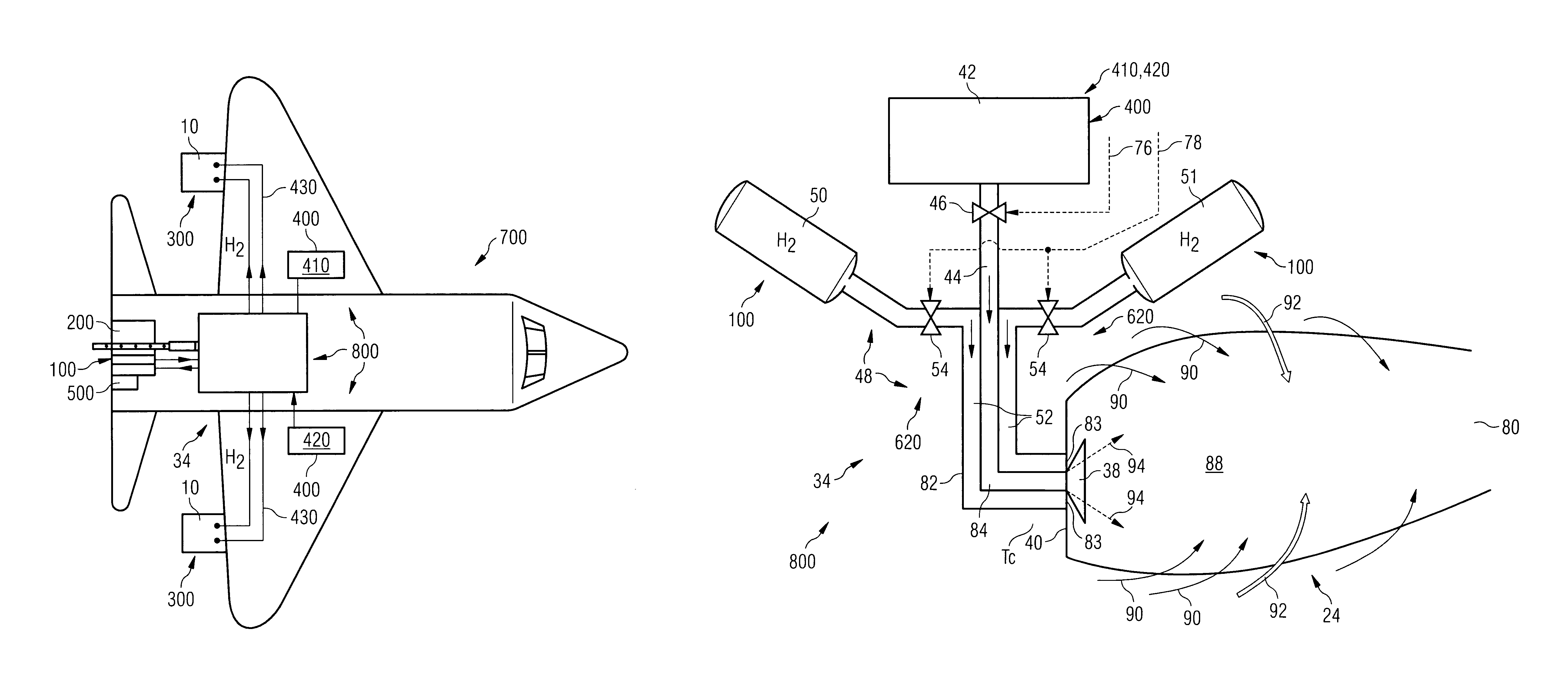
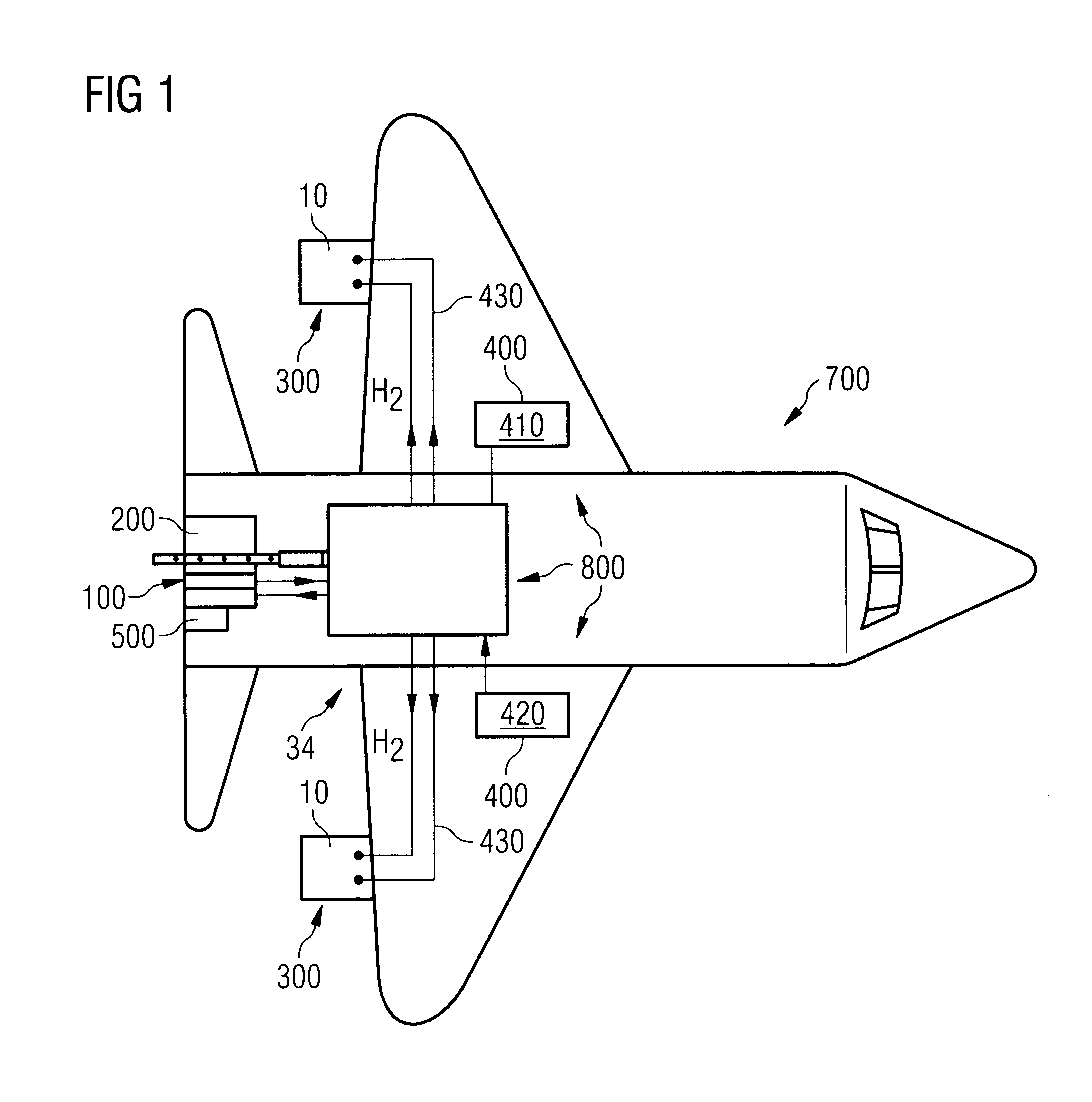
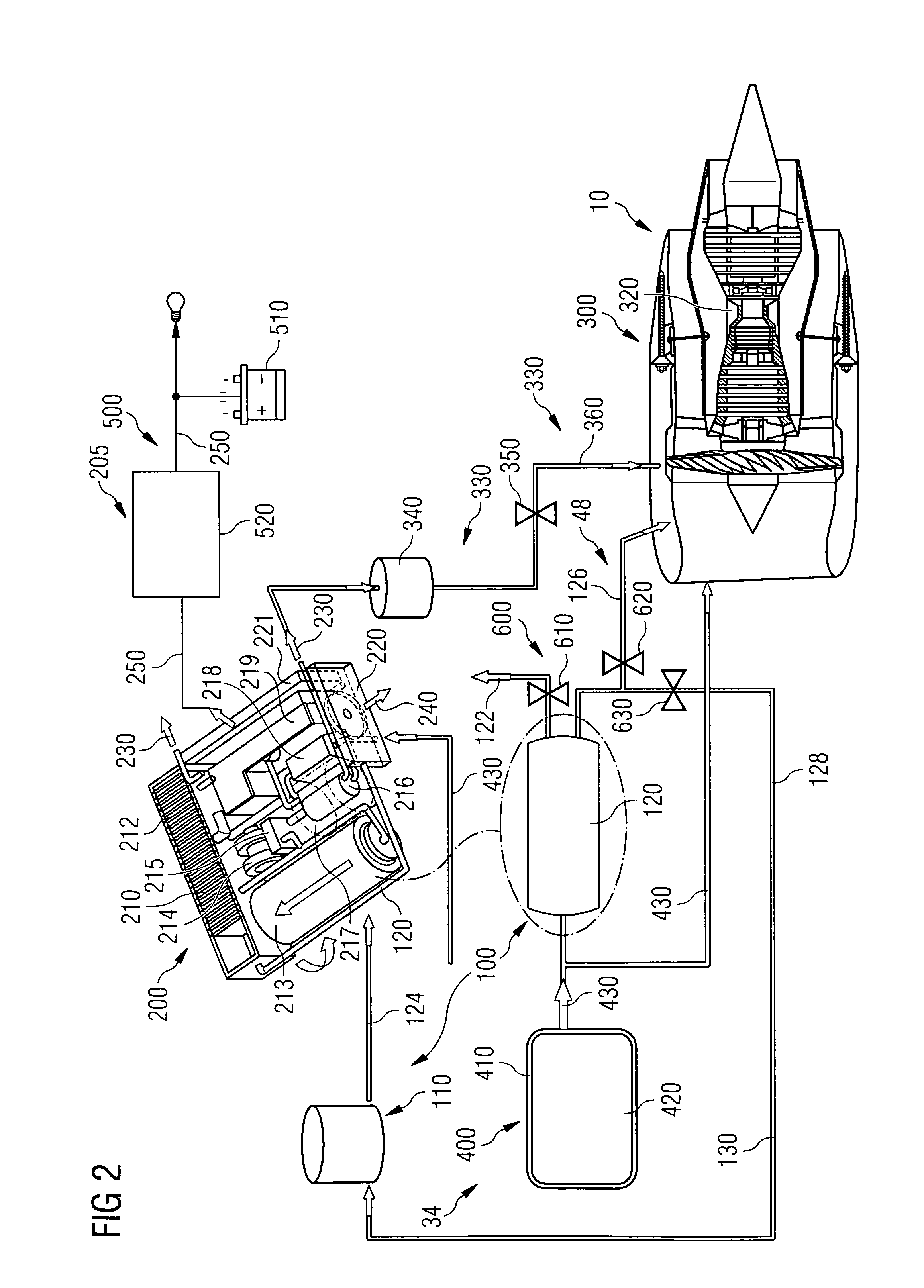
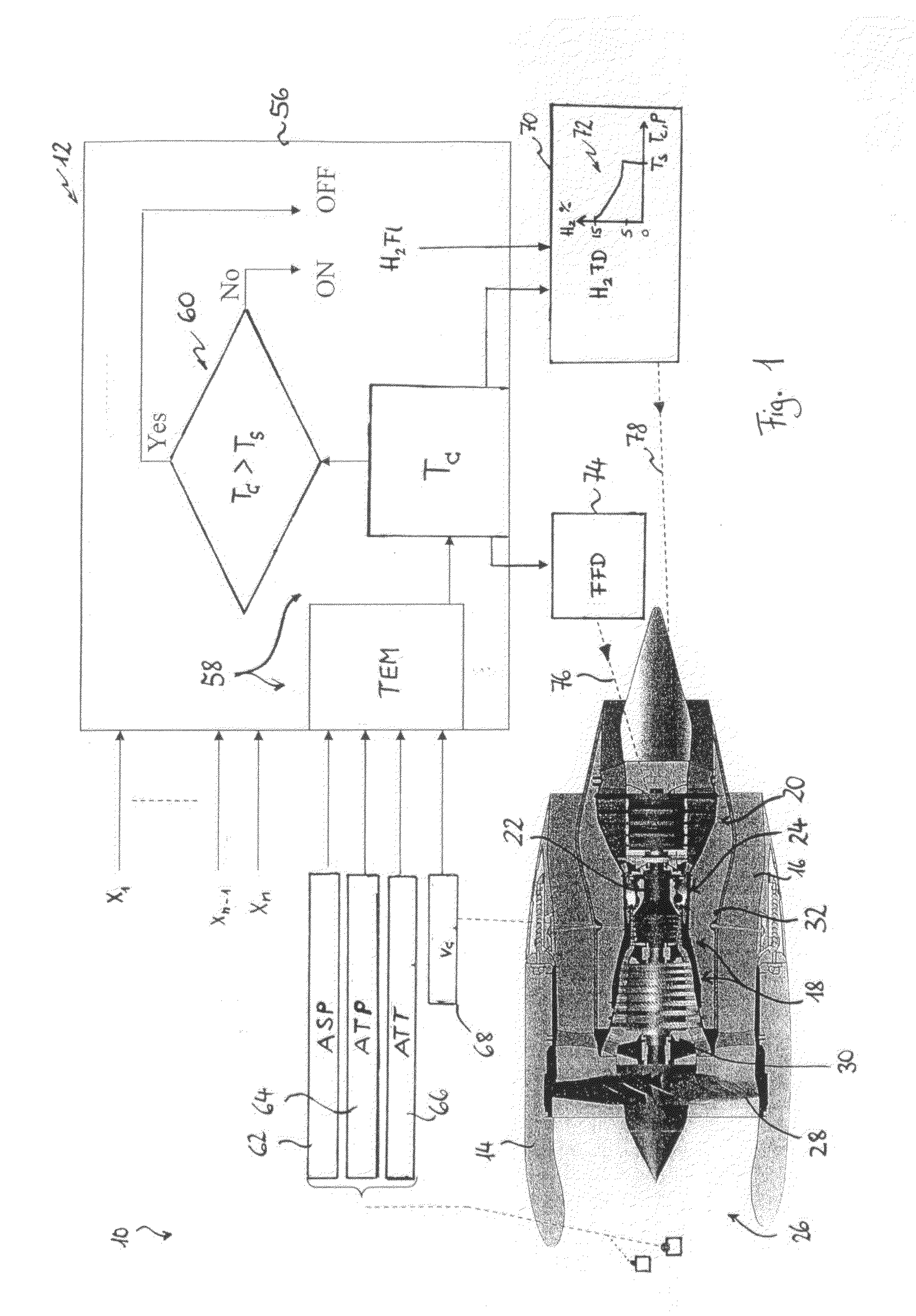
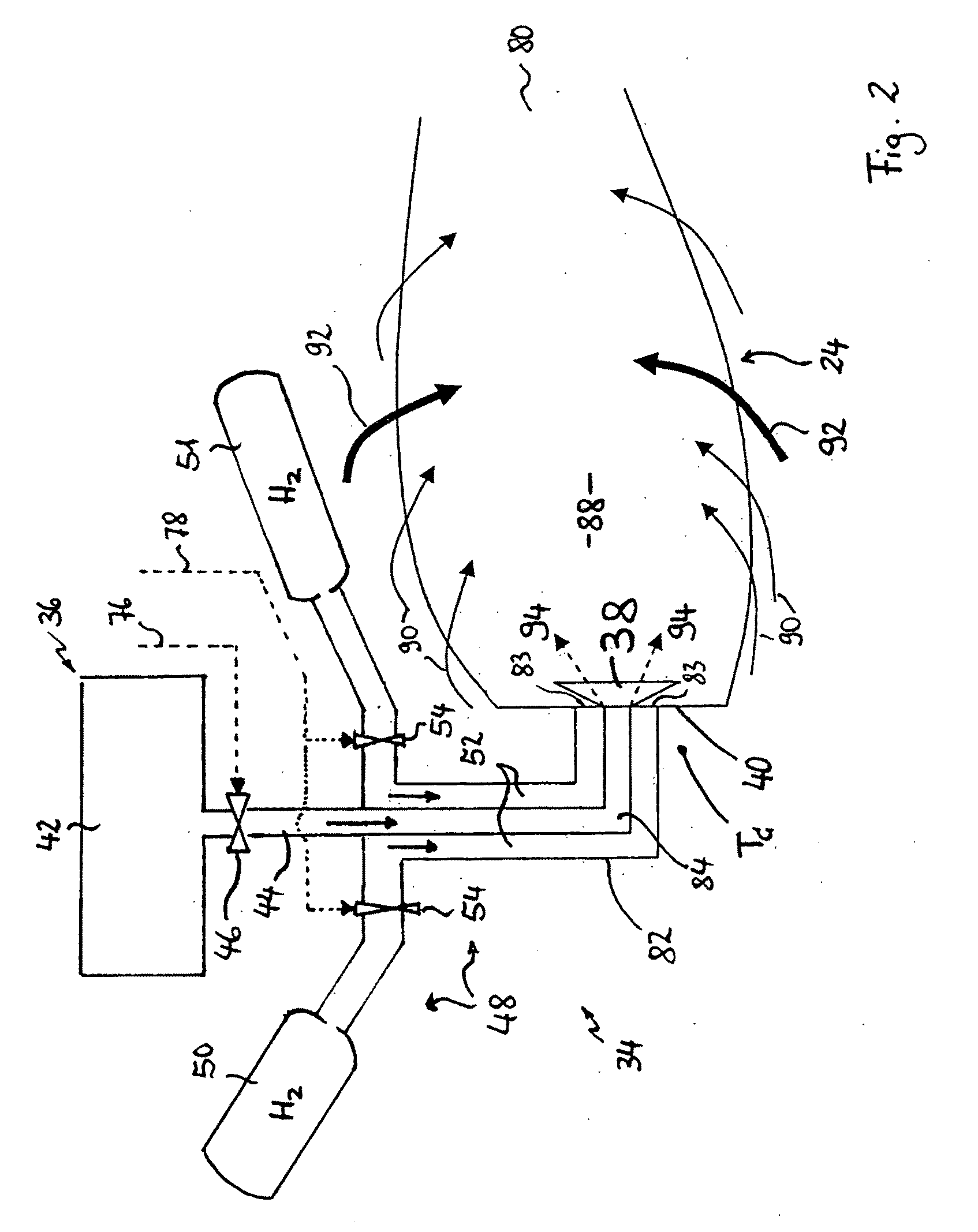
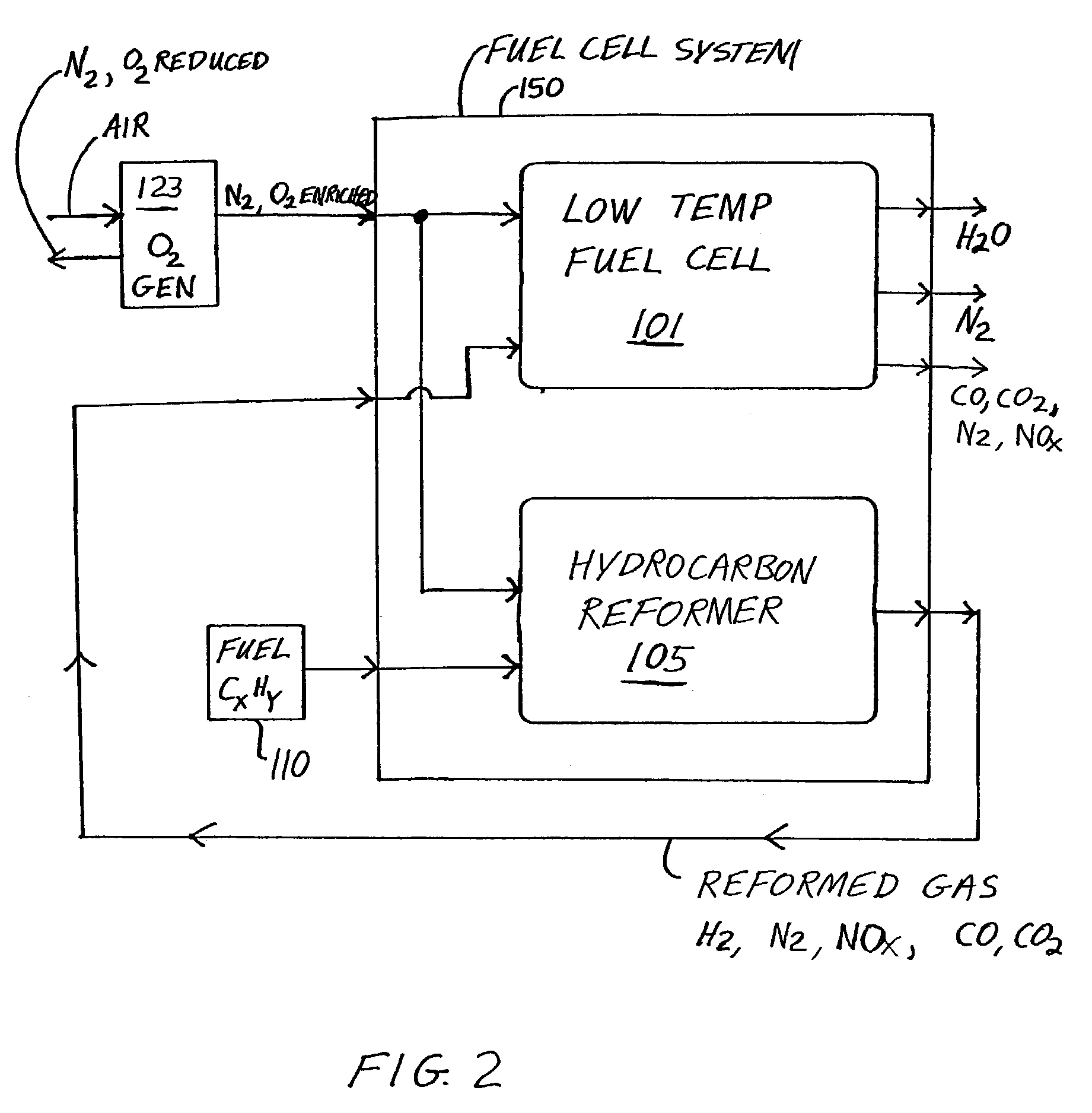
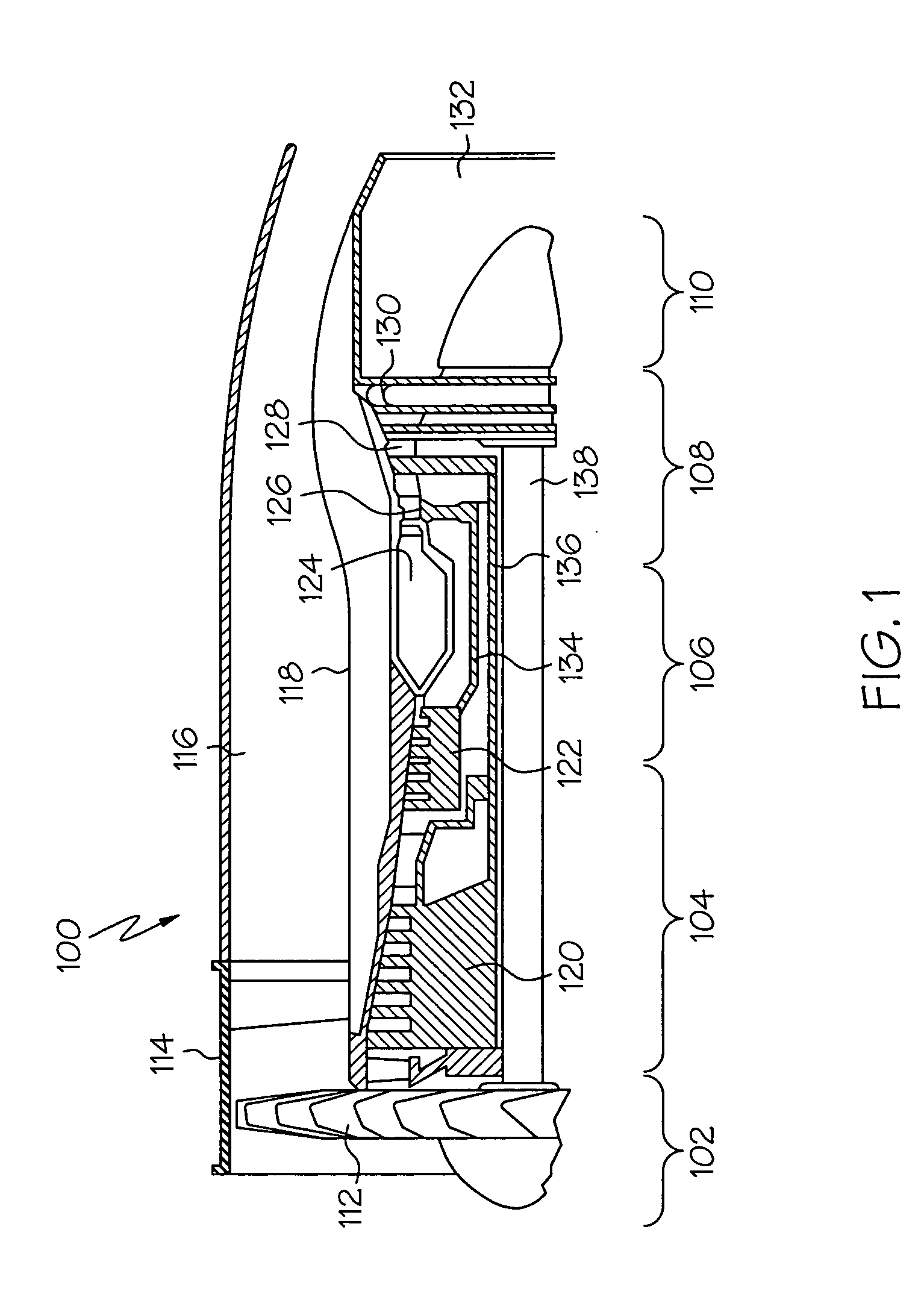
Method for Operating a Gas Turbine Engine, Power Supplying Device for Conducting such Method and Aircraft using such Method
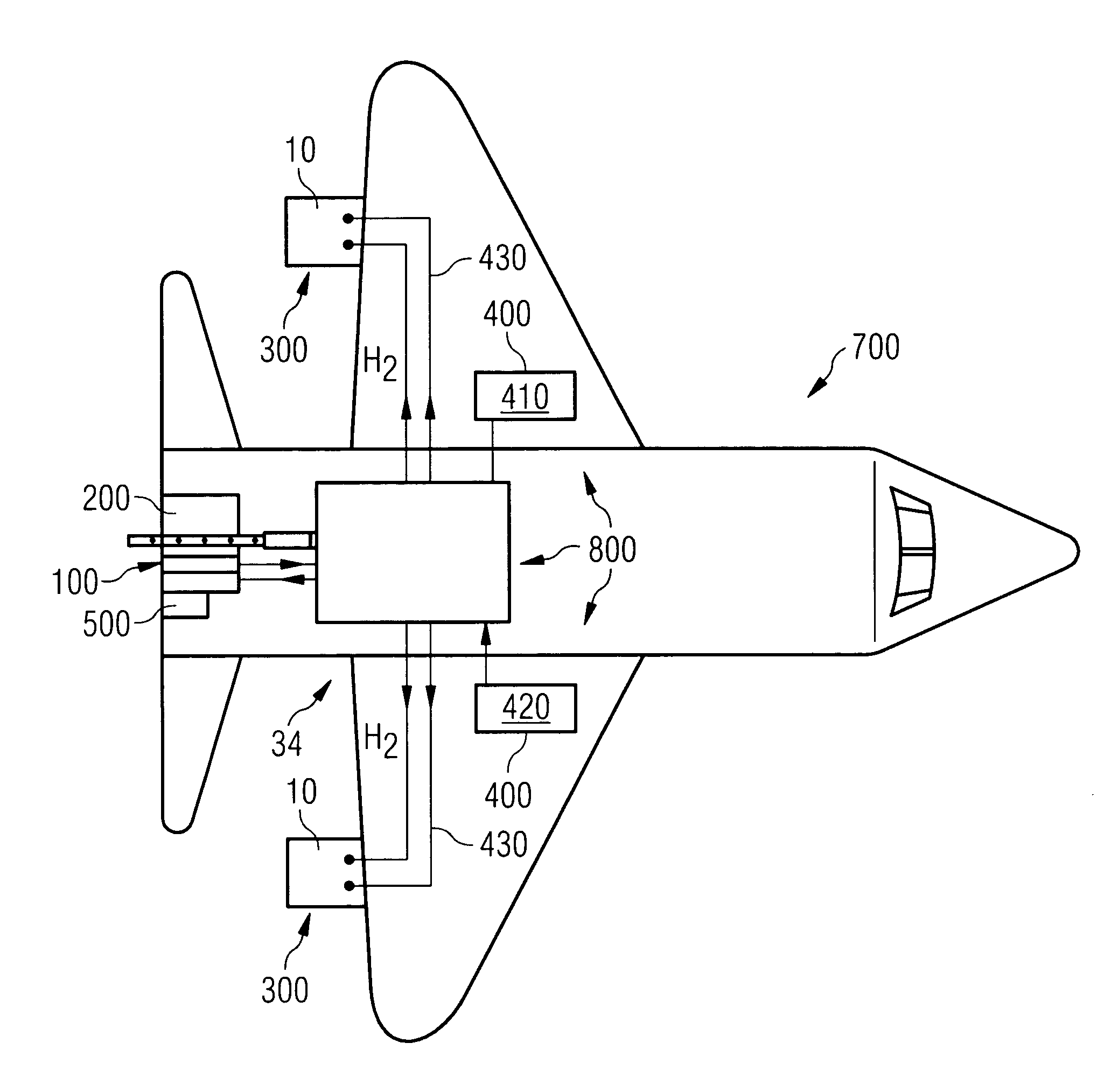
ActiveUS20100293959A1Emission reductionReduce hydrogen consumptionContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionAviationCombustion chamber
A power supply device or system for aeronautics, having a hydrocarbon supply for supplying an engine with hydrocarbon fuel and a hydrogen supply having a fuel reformer for producing hydrogen from hydrocarbon fuel from said hydrocarbon supply. The hydrogen supply is connected to a hydrogen-powered fuel cell for producing electric power and to a hydrogen injecting system for injection of hydrogen into a combustion chamber of the engine. Further, the invention relates to an aircraft having an engine that can be supplied by that power supplying device or system, and to a method for operating said engine.
Owner:AIRBUS SAS
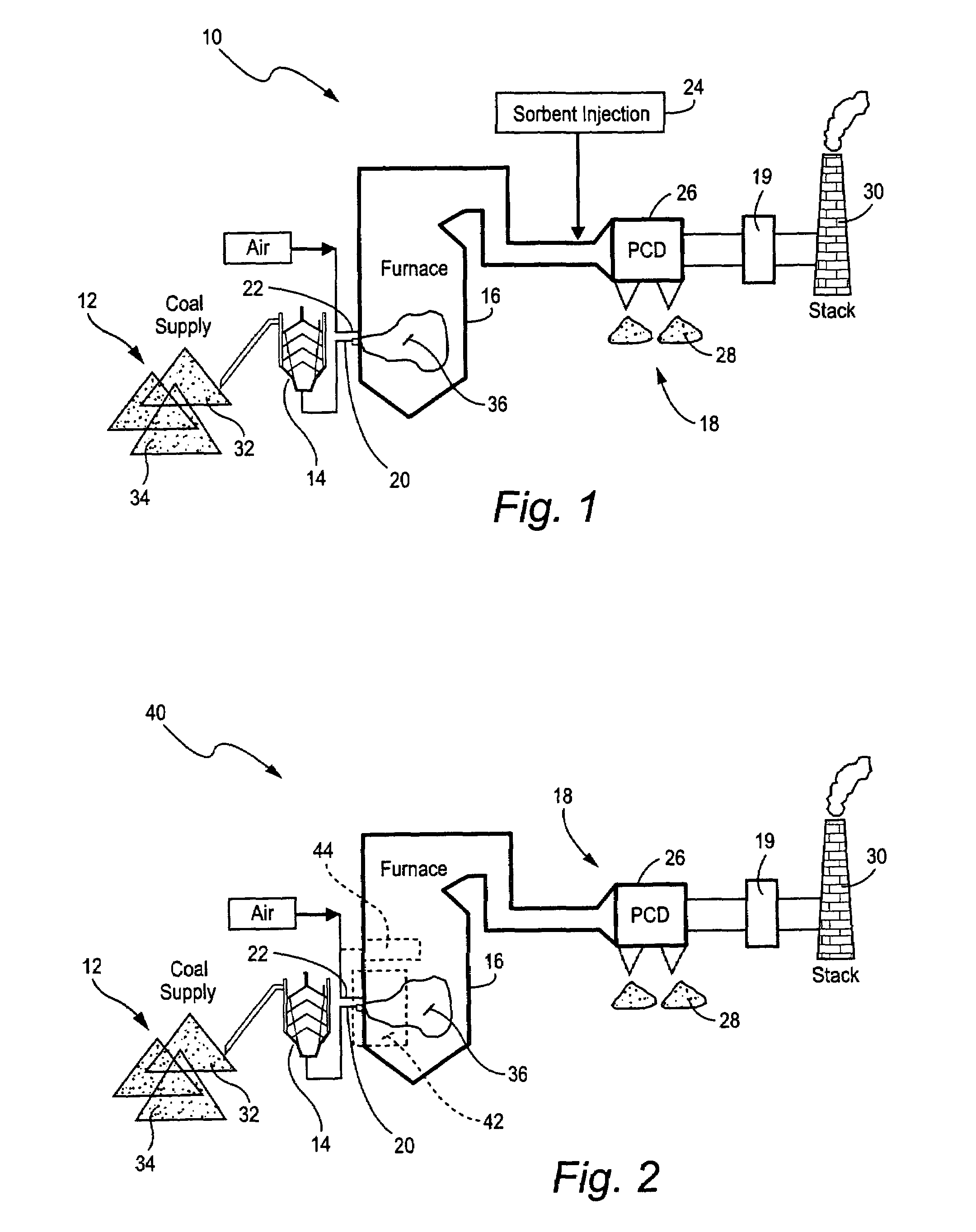
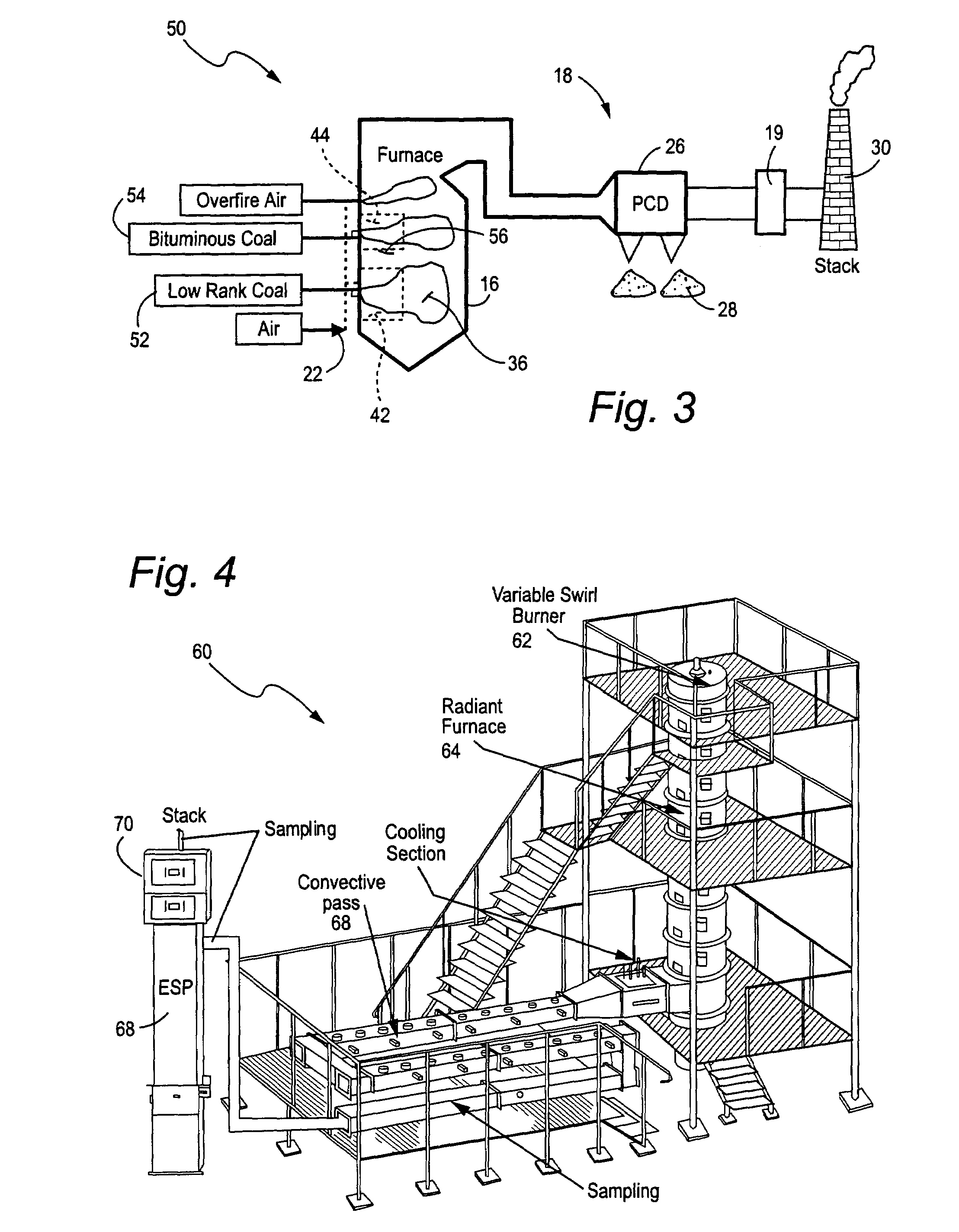
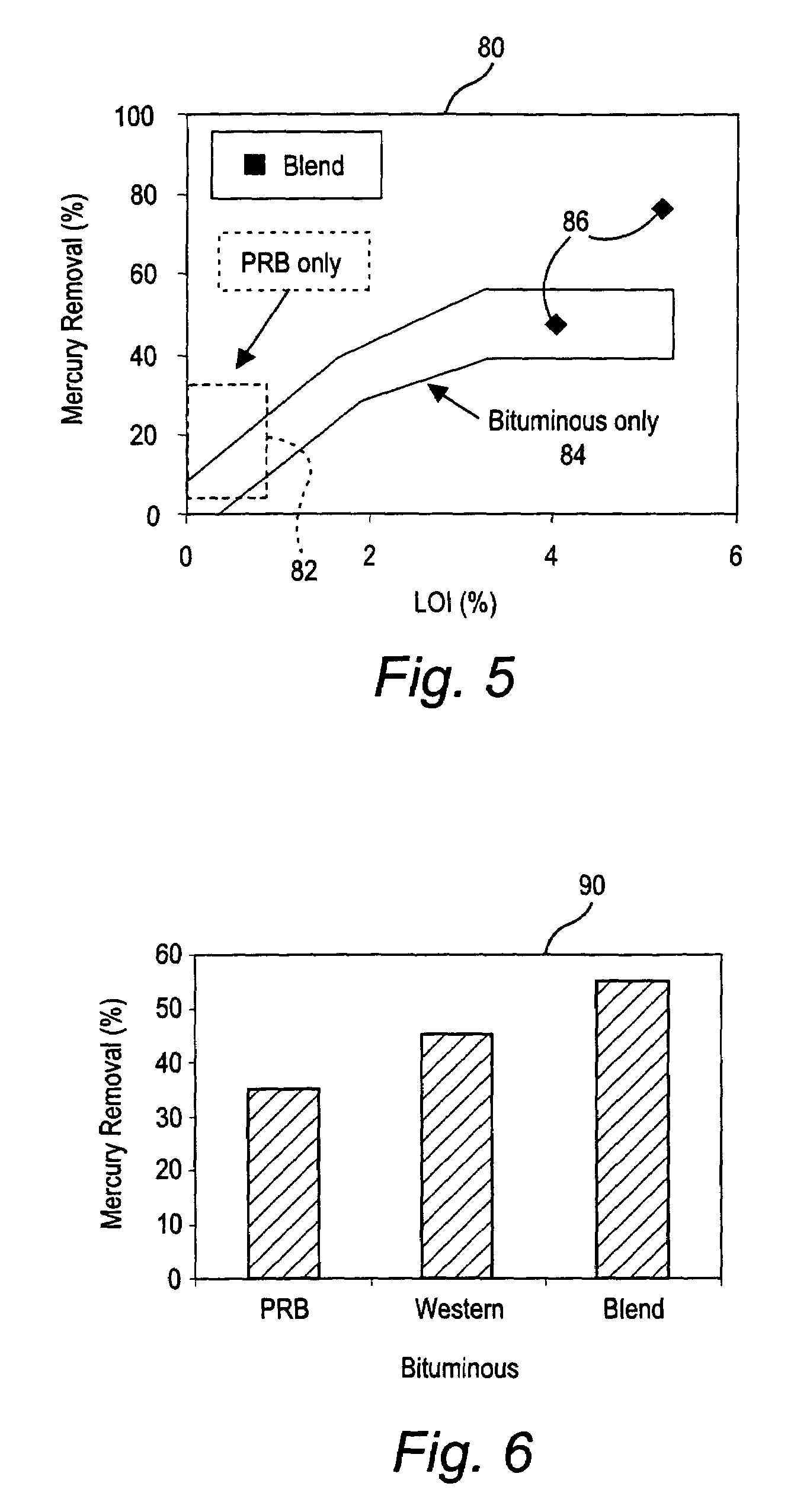
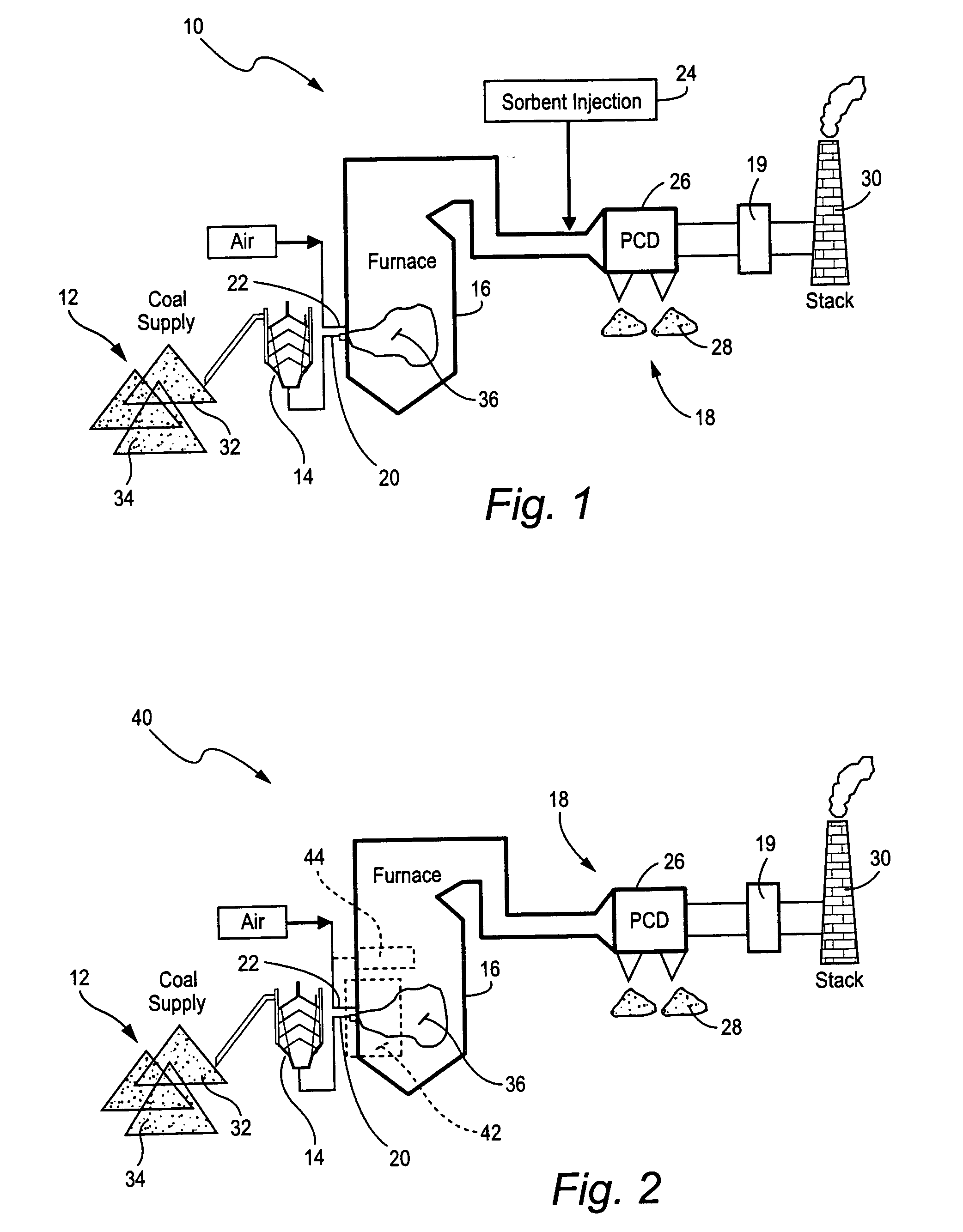
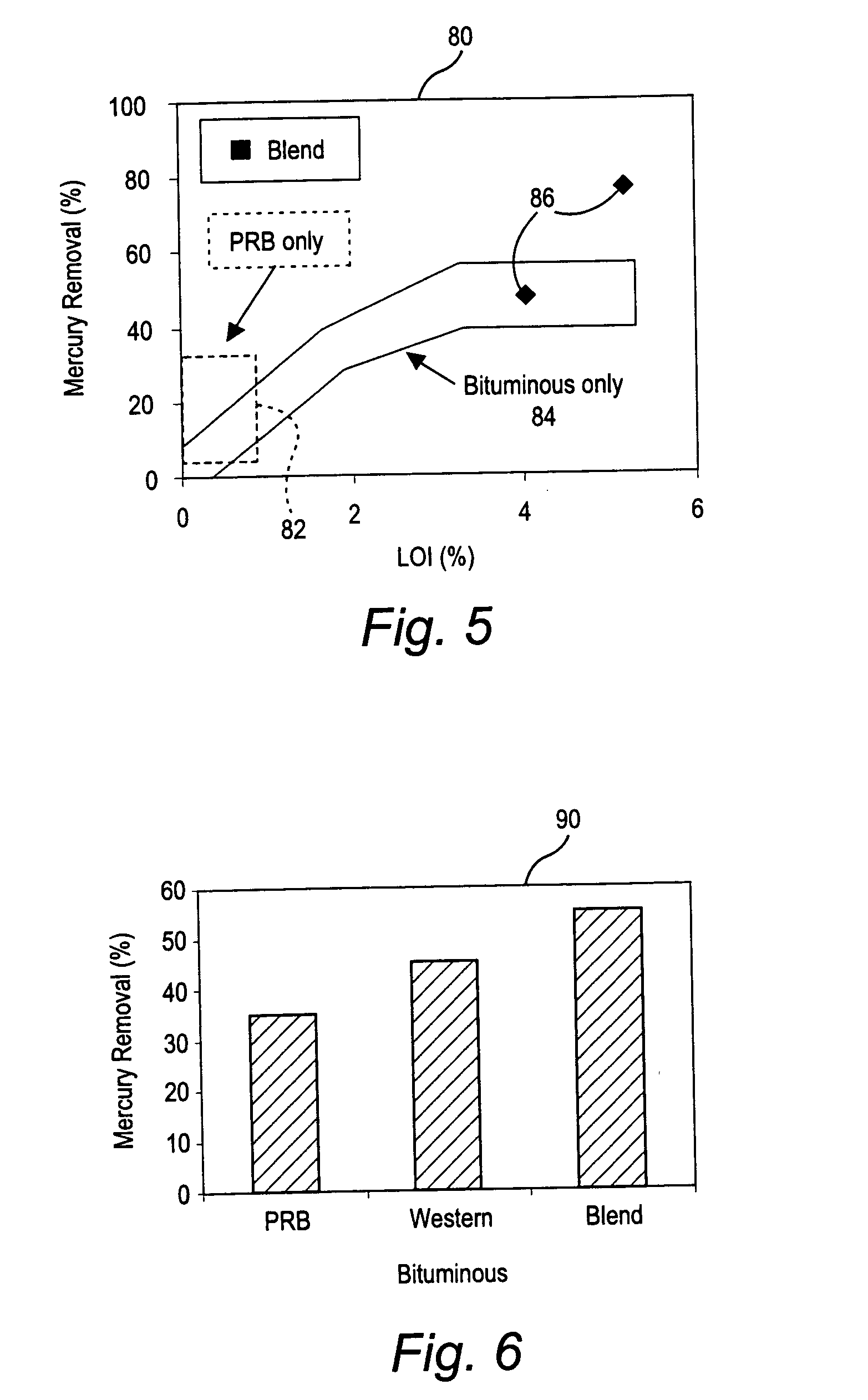
Mercury reduction system and method in combustion flue gas using coal blending
ActiveUS7381387B2Reduce gas emissionsGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentCombustion systemCombustion
A method to reduce mercury in gas emissions from the combustion of low rank coal in a combustion system including: combusting coal having a low chlorine content in the combustion system, wherein elemental mercury (Hg0) is released in the flue gas produced by the combustion of the low rank coal; releasing chlorine into the flue gas by combusting a coal having a high chlorine in the combustion system; reacting the elemental mercury and released chlorine in the flue gas to oxidize the mercury; adsorbing at least a portion of the oxidized mercury generated by the combustion of the coal with an adsorbent in the flue gas, and collecting the adsorbent with the oxidized mercury in a combustion waste treatment system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Bituminous binder for preparing low-temperature asphalt or coated materials
InactiveUS20120060722A1Demonstrated effectReduce manufacturing and processing and compacting temperatureIn situ pavingsOrganic dyesMaterials scienceFatty acid
The present disclosure relates to a bituminous binder including bitumen and at least two additives making it possible to reduce the manufacturing, processing and compacting temperatures of mixes and asphalts, the first additive being a Tall Oil derivative, alone or in a mixture, and the second additive being a monoester of a mixture of fatty acids. The disclosure also relates to low-temperature methods for the preparation of the mixes and asphalts obtained from the binder containing additives. The disclosure finally relates to the use of the binder containing additives in order to produce mixes and asphalts at lower temperatures, and the use of these mixes or asphalts, in particular in road applications, for sub-base courses, base courses, foundation courses, surface courses such as binder courses and / or wearing courses.
Owner:TOTAL RAFFINAGE MARKETING
Multilayer ceramic NOx gas sensor device
InactiveUS20070012566A1Improve performanceFaster sensor light off timeWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementMiniaturizationExhaust gas emissions
A mixed potential NOx sensor apparatus for measuring the total NOx concentration in a gas stream is disclosed. The NOx sensing apparatus comprises a multilayer ceramic structure with electrodes for sensing both oxygen and NOx gas concentrations and includes screen-printed metallized patterns that function to heat the ceramic sensing element to the proper temperature for optimum performance. This design may provide advantages over the existing technology by miniaturizing the sensing element to provide potentially faster sensor light off times and thereby reduce undesired exhaust gas emissions. By incorporating the heating source within the ceramic sensing structure, the time to reach the temperature of operation is shortened, and thermal gradients and stresses are minimized. These improvements may provide increased sensor performance, reliability, and lifetime.
Owner:EMISENSE TECH
Fuel supply system for an internal combustion engine
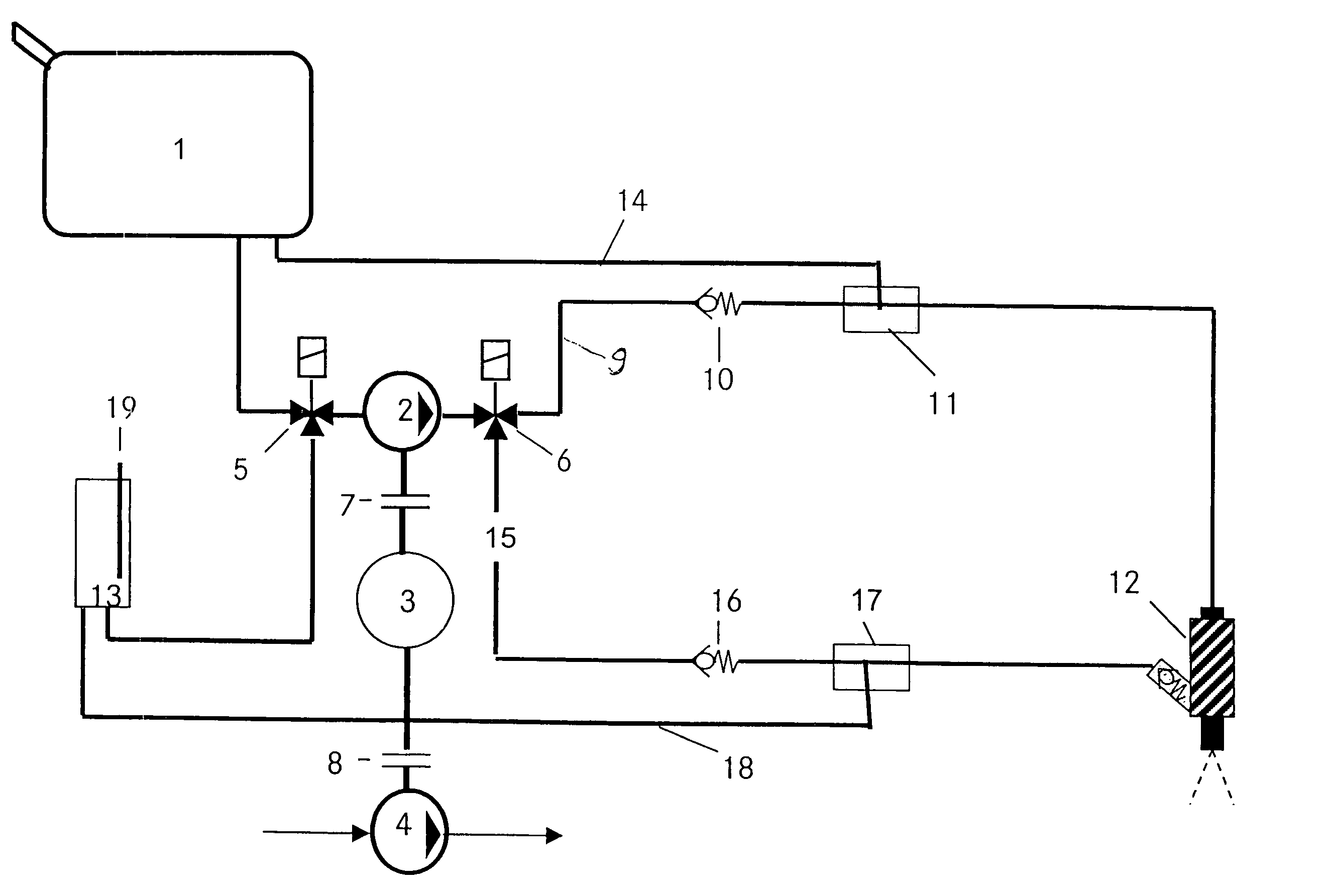
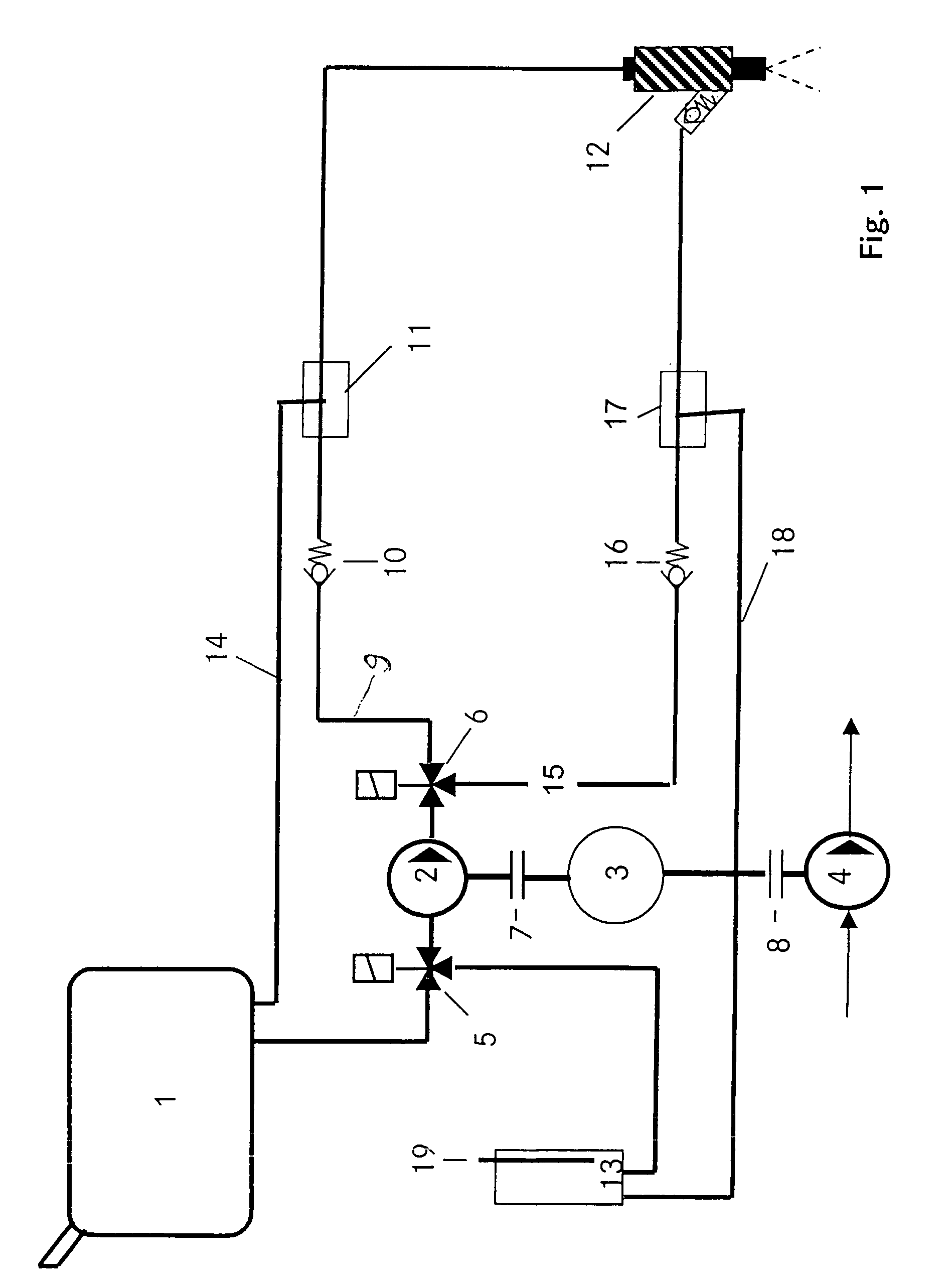
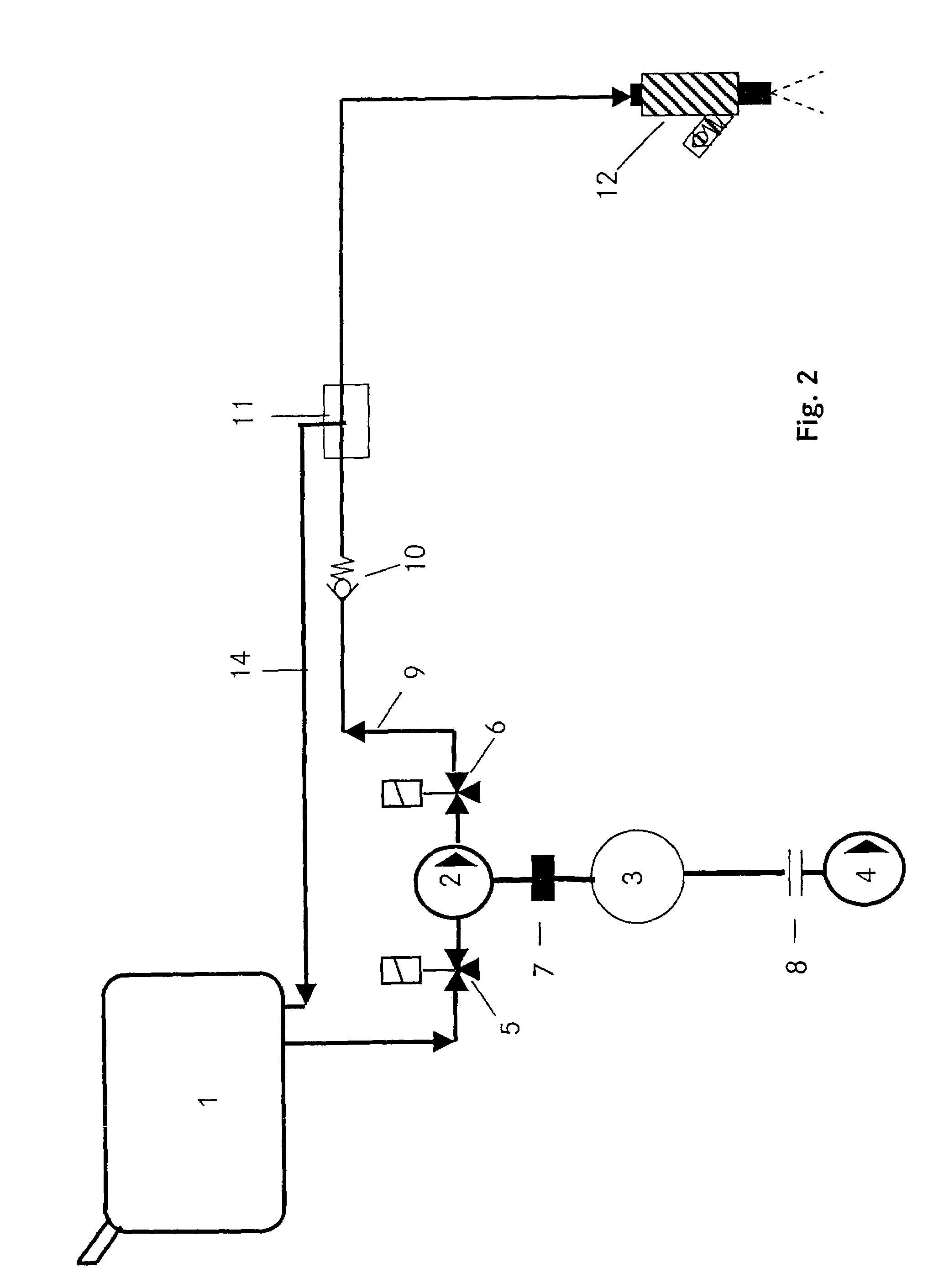
InactiveUS7028672B2Reduce gas emissionsReduce metal contentInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion-air/fuel-air treatmentEngineeringLiquid fuel
In a fuel supply system for an internal combustion engine having two separate storage containers for liquid fuels, both connected to a first controllable valve which is connected, via a connecting line including a fuel pump to an inlet of a second controllable valve having two outlets in communication by separate fuel lines with a fuel injection nozzle of the internal combustion engine, each of the two separate fuel lines includes a fuel pressure regulator, one being in communication with one and the other with the other of the two separate fuel storage containers for returning exess fuel to the fuel storage container from which fuel is being supplied to the fuel injection nozzle.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Gas turbine engine and method for reducing turbine engine combustor gaseous emission
ActiveUS8056344B2Reduce hydrogen consumptionSmall sizeAnalogue computers for vehiclesFuel supply regulationCombustorGaseous hydrogen
Owner:AIRBUS SAS
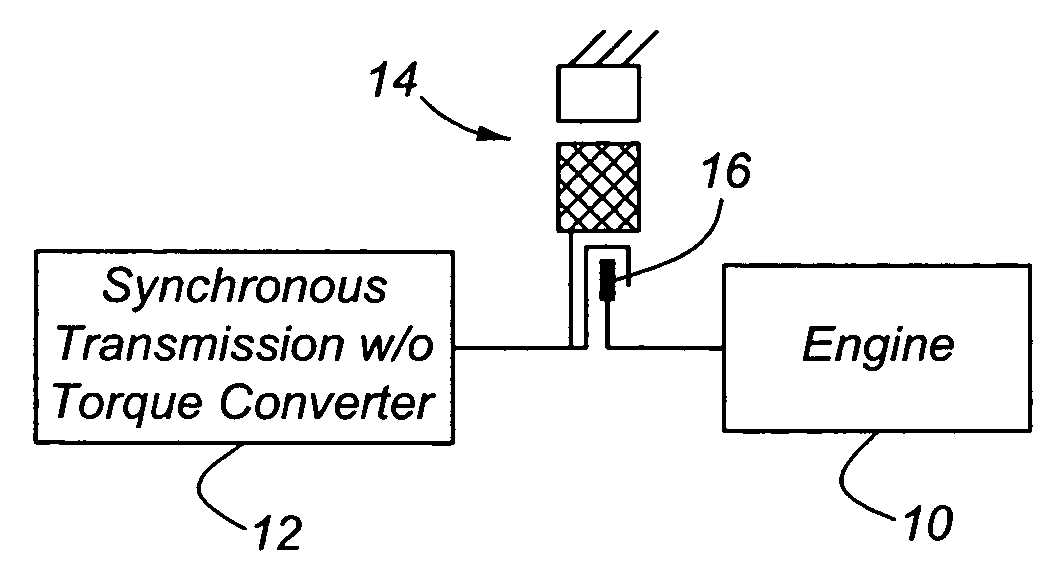
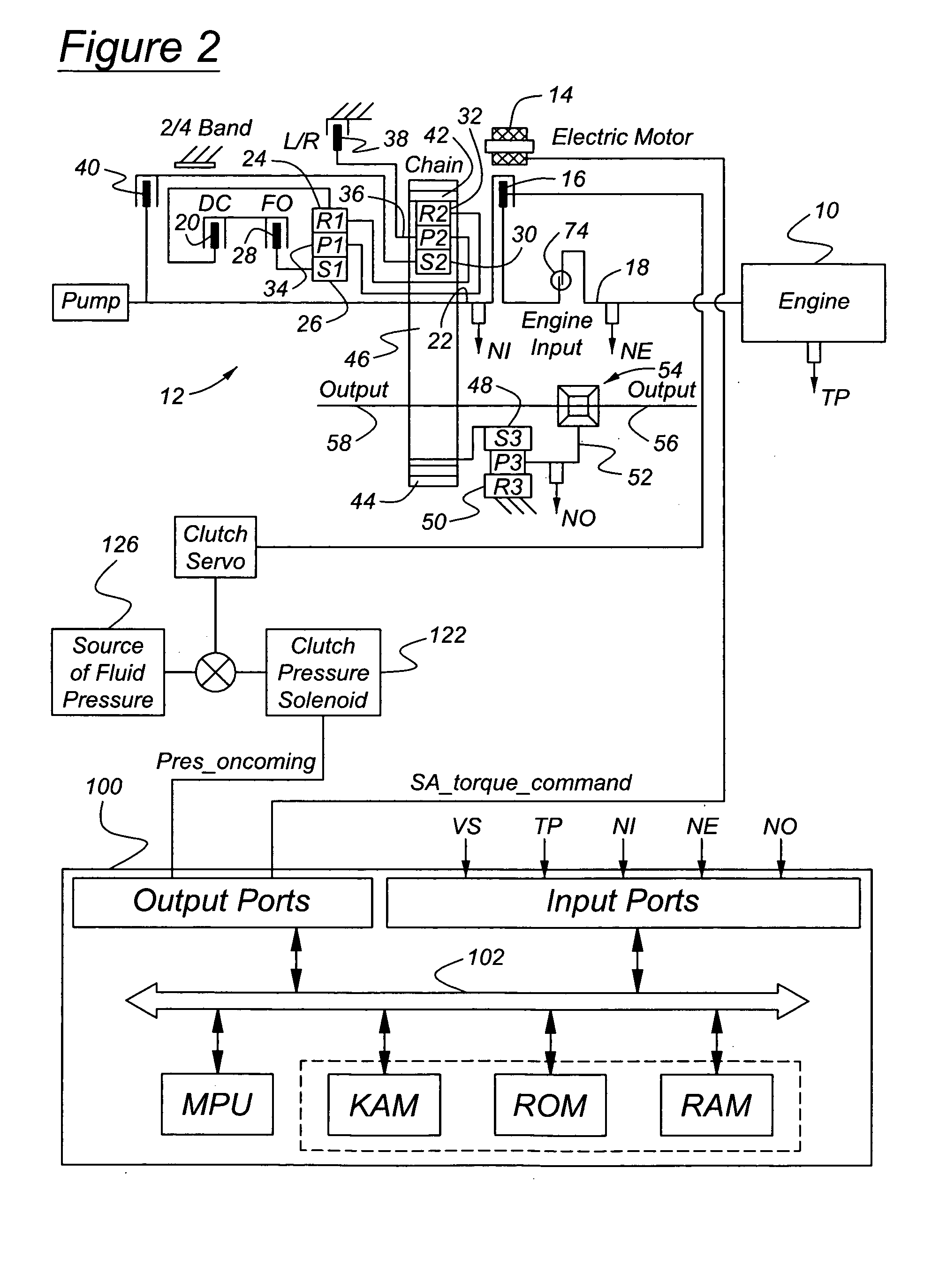
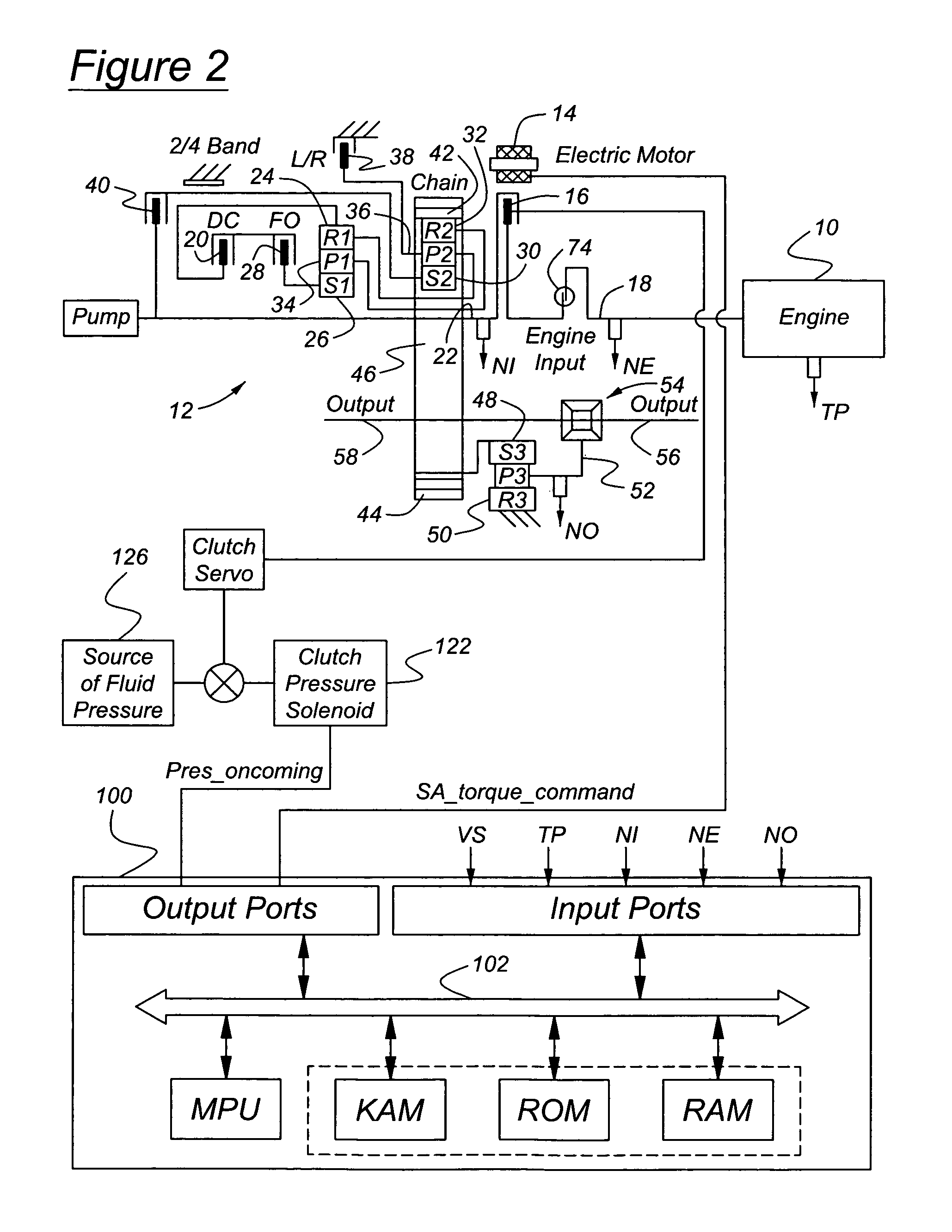
Launch control of hybrid electric vehicle having a torque converterless driveline
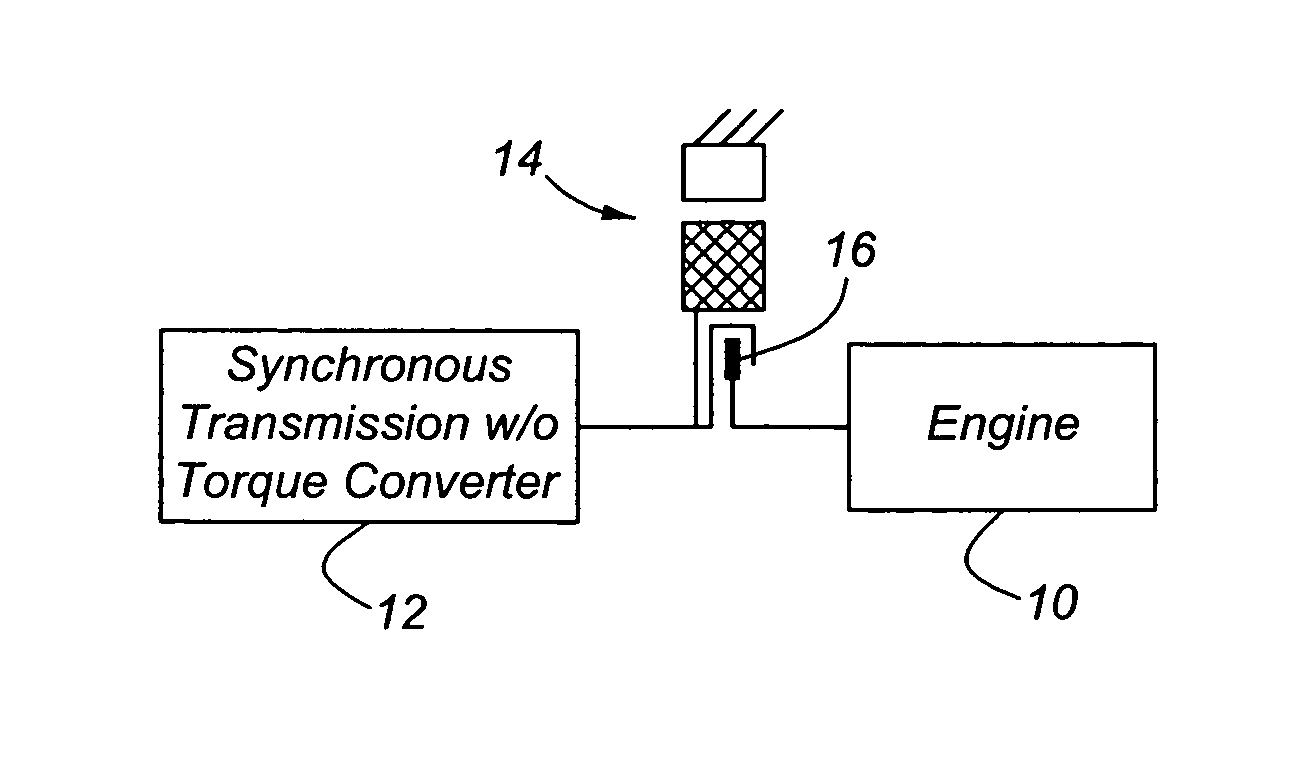
InactiveUS20050181907A1Quick restartTorque output can be optimizedElectric propulsion mountingElectric machinesSeparated stateElectric vehicle
A powertrain assembly for an automotive vehicle having an internal combustion engine, transmission, electric induction motor, a clutch for connecting and releasing the engine and transmission, and a controller for controlling the state of engagement and disengagement of the clutch and the torque produced by the motor during the launch. The engine increases torque produced by the induction motor during a vehicle launch condition, permitting the engine to be turned off when the vehicle is at rest. The torque multiplication that would normally be available from a hydrokinetic torque converter is replaced with auxiliary launch torque supplied by the induction motor.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Rapid catalyst warm-up control device for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20040250534A1Efficient mixingReduce gas emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEngineering
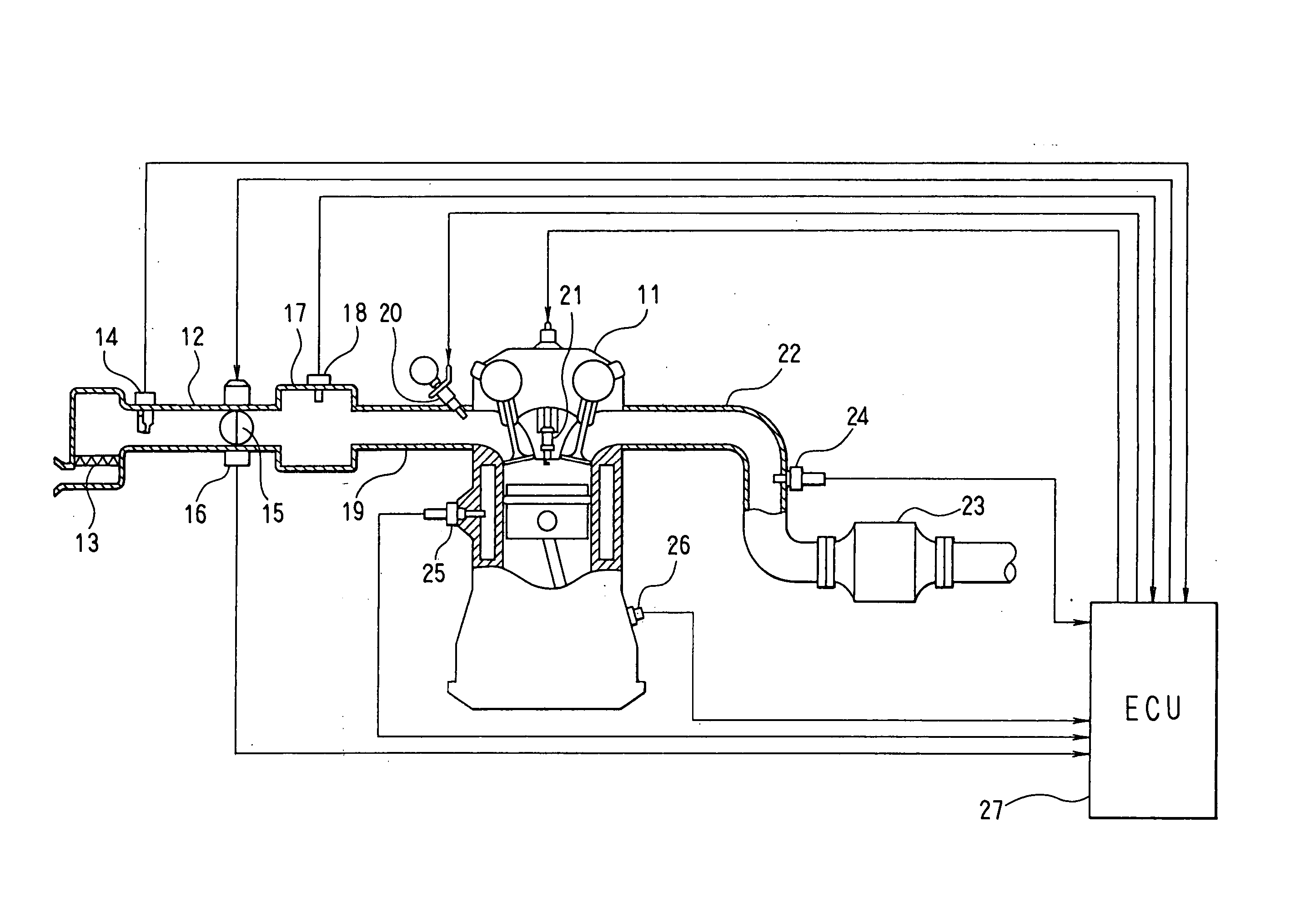
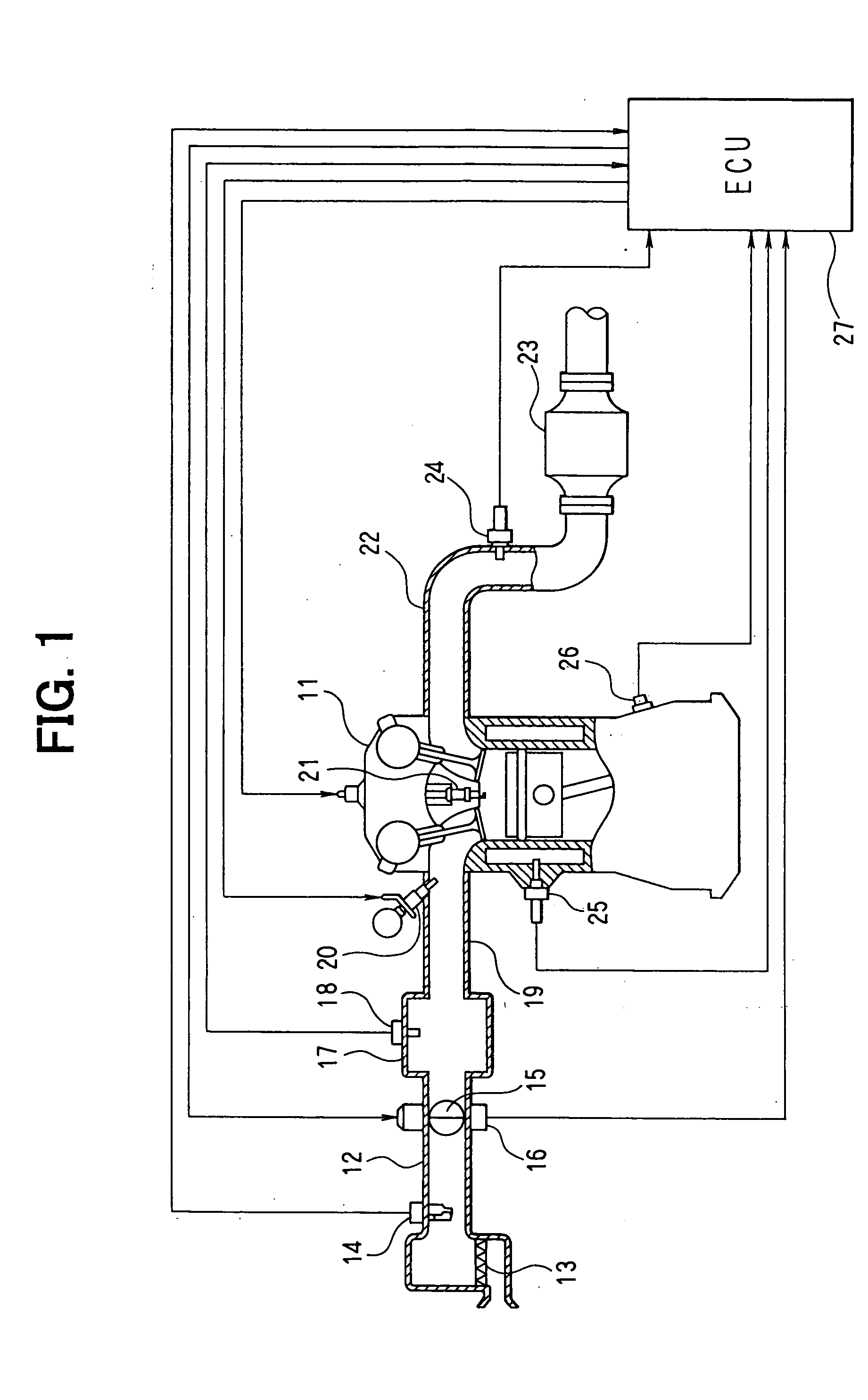
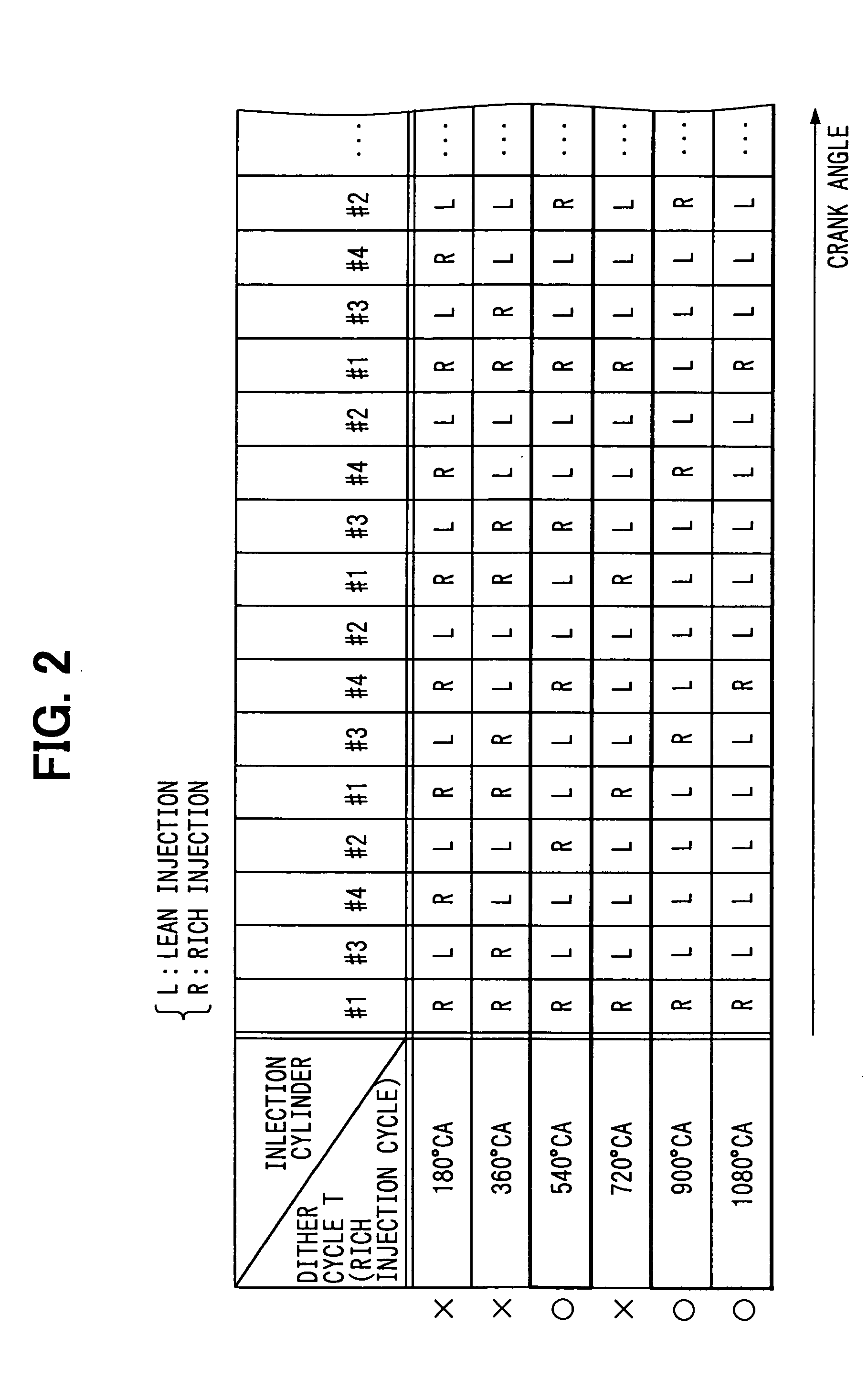
A rapid catalyst warm-up control device for an internal combustion engine performs irregular injection dither control during the rapid catalyst warm-up control after starting the engine. In the irregular injection dither control, injection modes are switched after every fuel injection to the cylinders (every 180° CA for a 4-cylinder engine) between a lean injection mode and a rich injection mode in such a pattern that rich injections will not occur consecutively for the same cylinder (dither cycle=540° CA, 900° CA, 1080° CA, or the like). In the lean injection mode, fuel is injected such that the air-fuel ratio is leaner than the stoichiometric ratio, and in the rich injection mode, air-fuel ratio is richer than the stoichiometric ratio. The rich gas emitted from the cylinders where the rich injection has been performed is thus allowed to flow through a different catalyst region every time instead of flowing only through the same region.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Selective Compound Engine
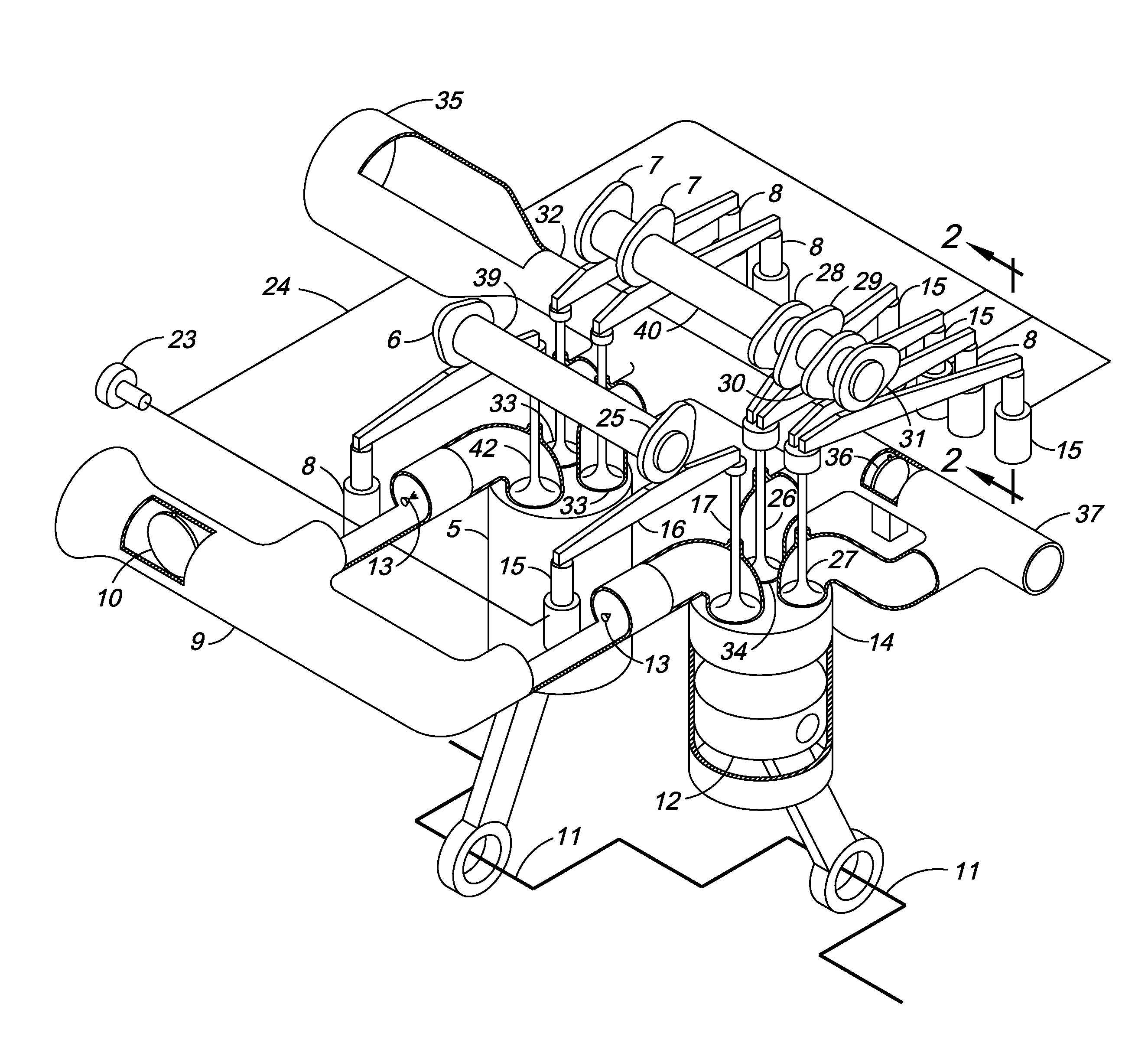
InactiveUS20090301086A1Improve fuel efficiencyReduce cylinder compression ratioCombustion enginesHot gas positive displacement engine plantsExhaust valveFuel efficiency
The fuel efficiency of an internal combustion reciprocating piston engine may be increased through selective secondary expansion of exhaust gas in the engine cylinders in order to recover exhaust gas energy which is otherwise wasted by cylinder blow-down at the end of the power stroke. Exhaust valve cam switching, intake valve deactivation, multiple exhaust valves, a specialized exhaust manifold arrangement and an exhaust gas diverter valve can be configured to enable a reciprocating engine to selectively operate in efficient eight stroke cycle compound mode when moderate engine power is demanded, then revert to conventional four stroke cycle non-compound mode operation when high engine power is demanded, without stopping the engine. For a road vehicle application, the benefit is substantially reduced highway cruising fuel consumption, while incurring minimal impact on engine weight, minimal impact on engine manufacturing cost, and no adverse impact on vehicle acceleration performance, hill climbing performance or trailer towing performance.
Owner:RALSTON MARK DIXON
Mercury reduction system and method in combustion flue gas using coal blending
ActiveUS20050036926A1Reduce mercury in gas emissionReduce gas emissionsGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentCombustion systemSorbent
A method to reduce mercury in gas emissions from the combustion of low rank coal in a combustion system, said method including: combusting coal having a low chlorine content in the combustion system, wherein elemental mercury (Hg0) is released in the flue gas produced by the combustion of the low rank coal; releasing chlorine into the flue gas by combusting a coal having a high chlorine in the combustion system; reacting the elemental mercury and released chlorine in the flue gas to oxidize the mercury; adsorbing at least a portion of the oxidized mercury generated by the combustion of the coal with an adsorbent in the flue gas, and collecting the adsorbent with the oxidized mercury in a combustion waste treatment system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for operating a gas turbine engine, power supplying device for conducting such method and aircraft using such method
ActiveUS9464573B2Reduce hydrogen consumptionSmall sizeContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionAviationCombustion chamber
A power supply device or system for aeronautics, having a hydrocarbon supply for supplying an engine with hydrocarbon fuel and a hydrogen supply having a fuel reformer for producing hydrogen from hydrocarbon fuel from said hydrocarbon supply. The hydrogen supply is connected to a hydrogen-powered fuel cell for producing electric power and to a hydrogen injecting system for injection of hydrogen into a combustion chamber of the engine. Further, the invention relates to an aircraft having an engine that can be supplied by that power supplying device or system, and to a method for operating said engine.
Owner:AIRBUS SAS
Emission control apparatus
InactiveUS7282185B2Reduce gas emissionsReduce noiseCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesNitrogen oxidesEngineering
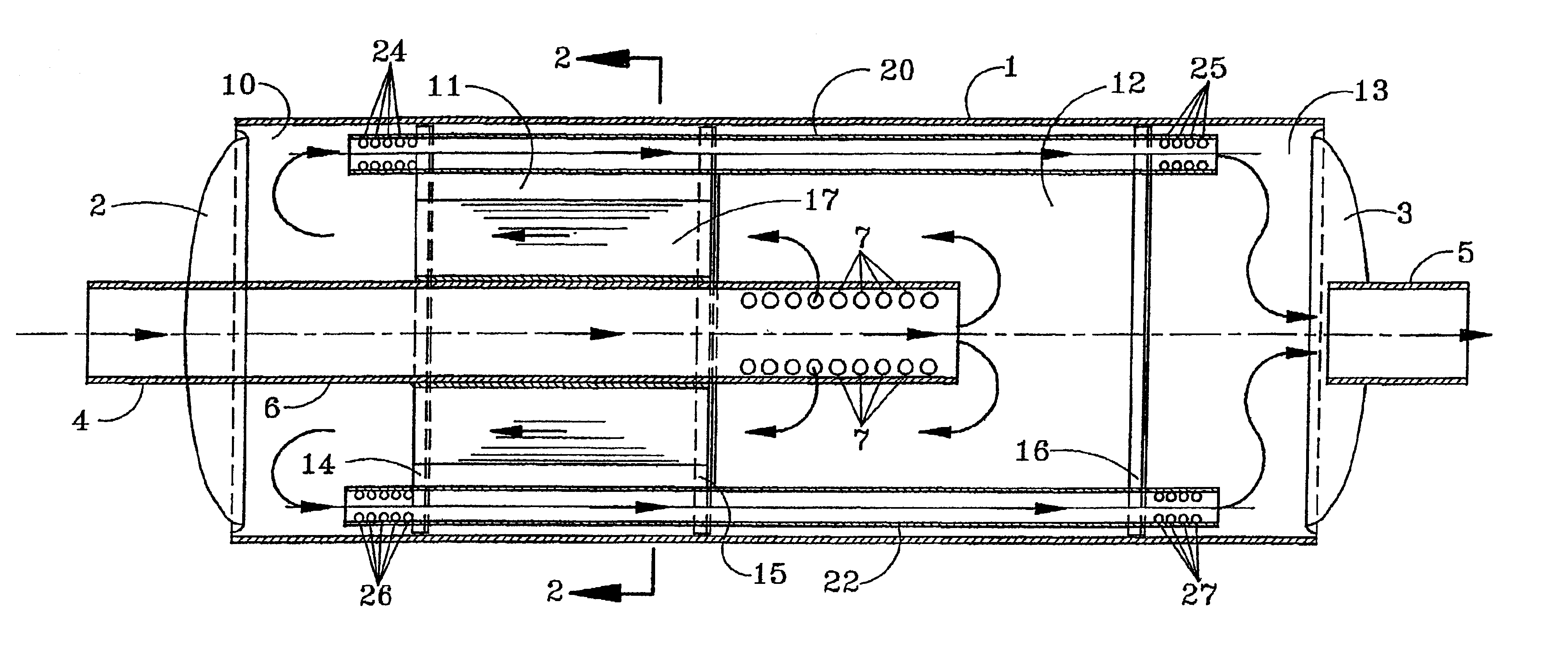
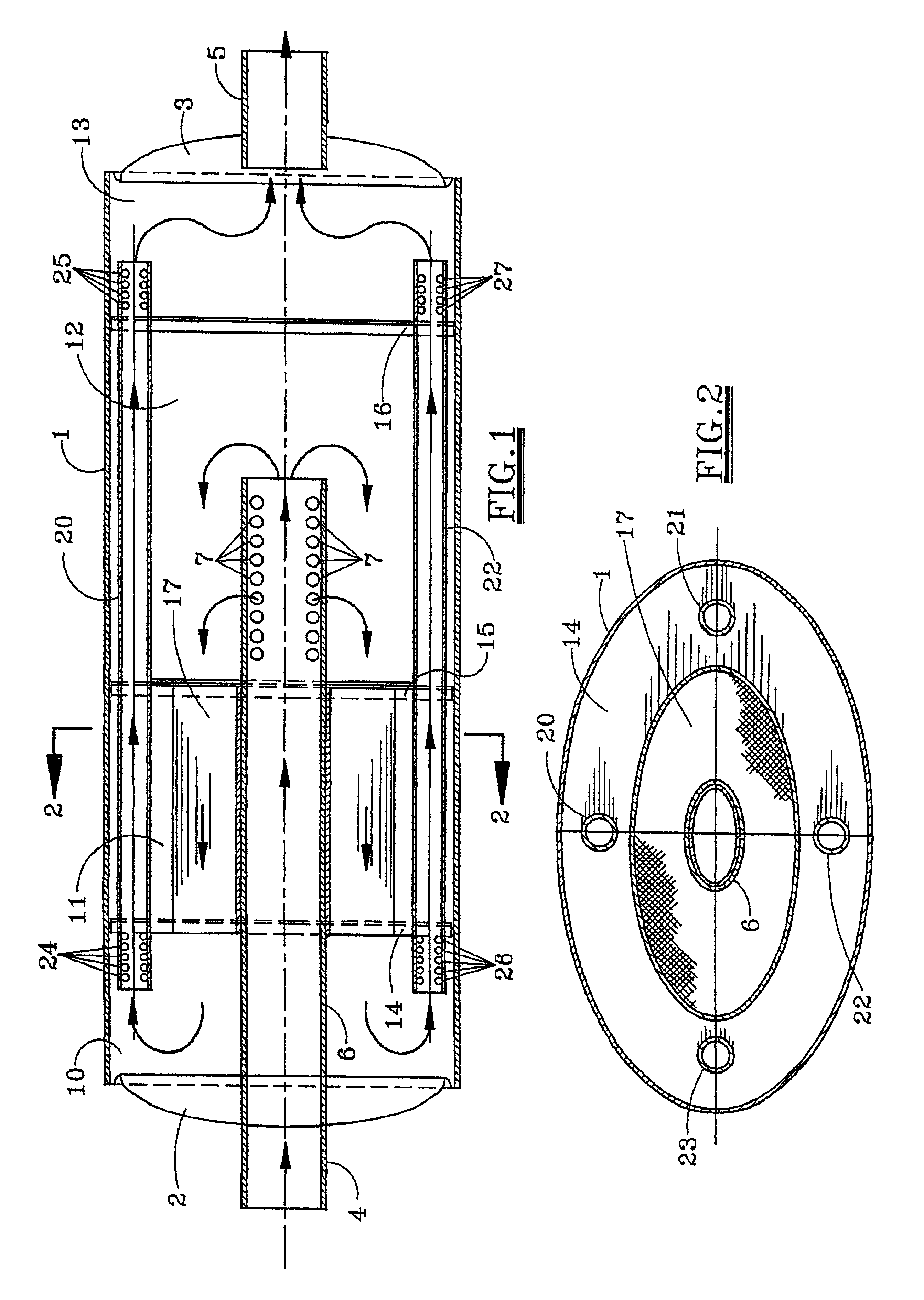
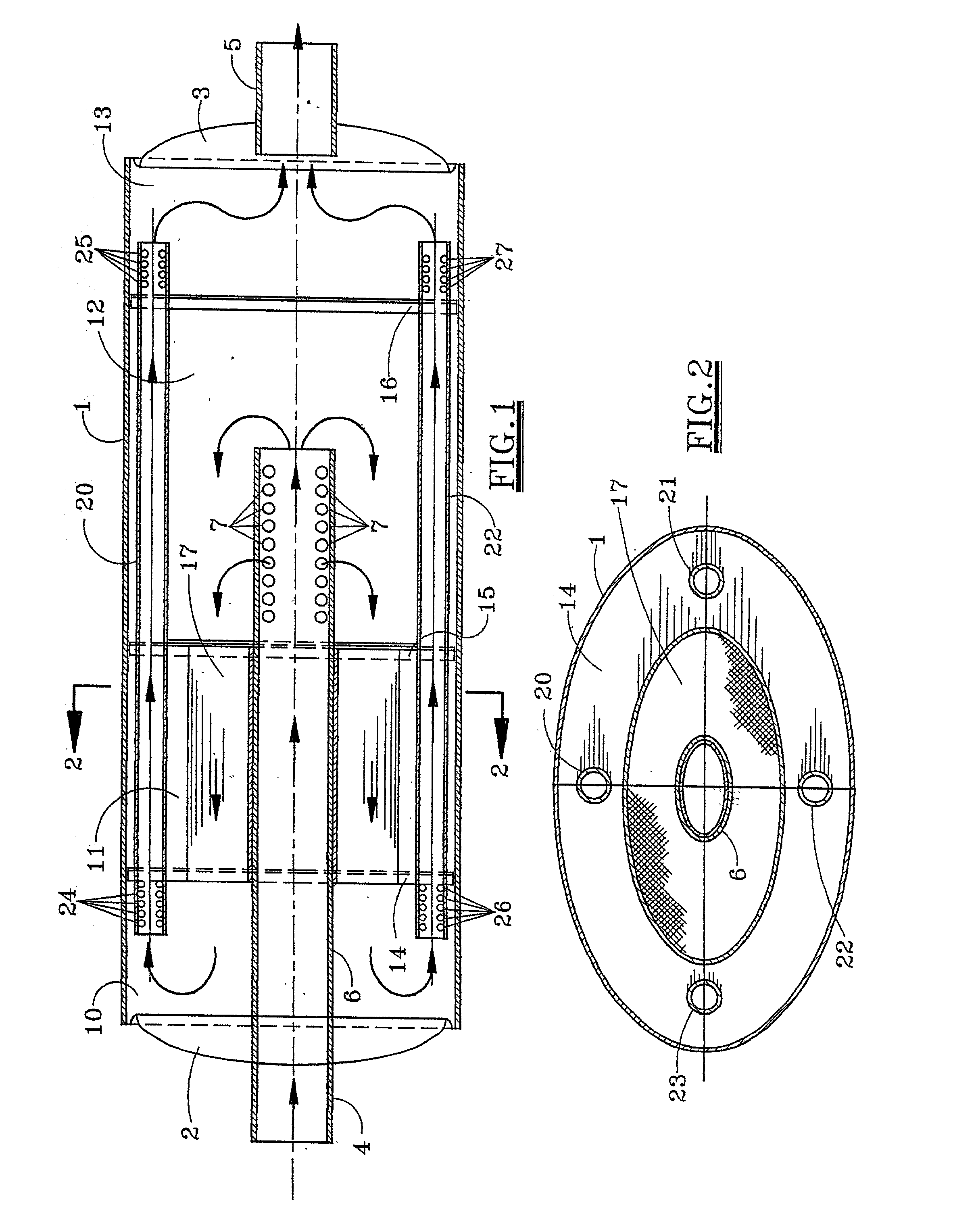
Apparatus for controlling emissions from an internal combustion engine including an enclosed housing one end of which is provided with an inlet and the other end an outlet. A coaxial tubular member extends from the inlet into the housing. A catalytic cell surrounds the tubular member and separates two chambers, a first surrounding the tubular member near the inlet and the other on the opposite side of the catalytic cell. Exhaust gases from the internal combustion engine flow through the tubular member, expanding into the other chamber, then through the catalytic cell for conversion of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and unburned hydrocarbons to less noxious components, expanding into the first chamber for eventual discharge through the outlet.
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
Emission control apparatus
InactiveUS20020106312A1Reduce gas emissionReduce noiseCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust gasNitrogen oxides
Owner:CLEAN AIR POWER
Method and apparatus for mixing fluids
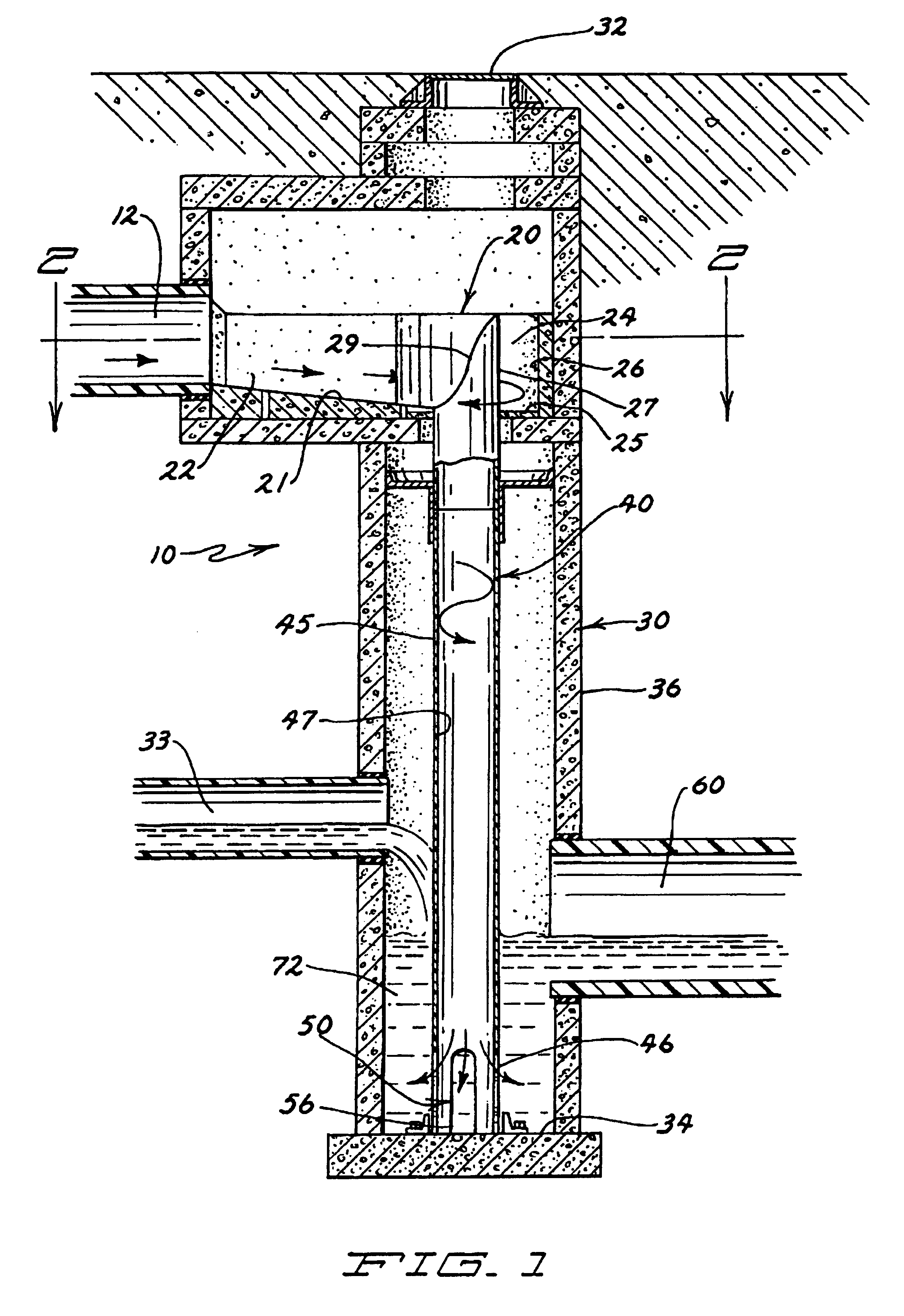
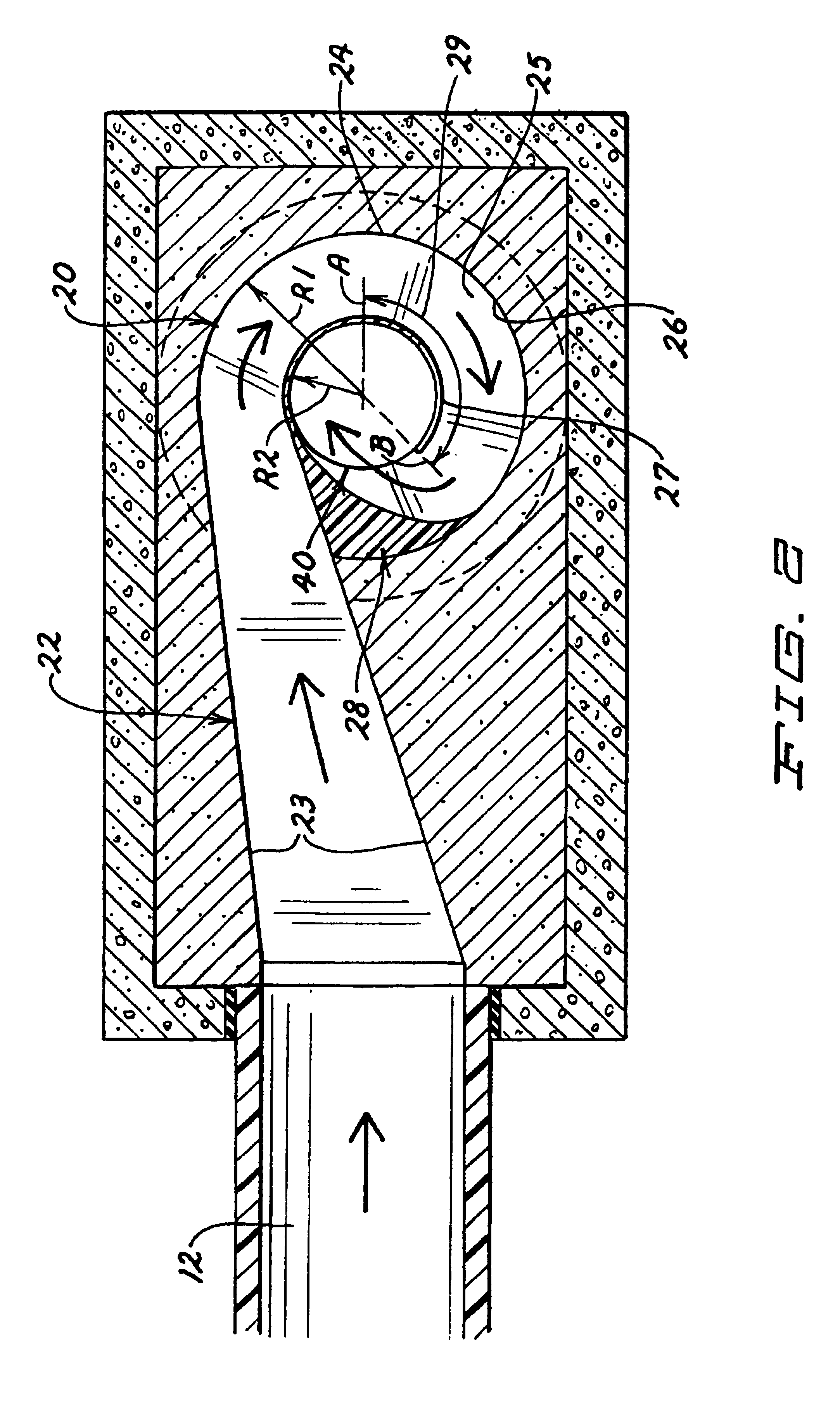
InactiveUSRE40407E1Reduce gas emissionsReduces odorous gas emissionReversed direction vortexFlow mixersEngineeringDrop structure
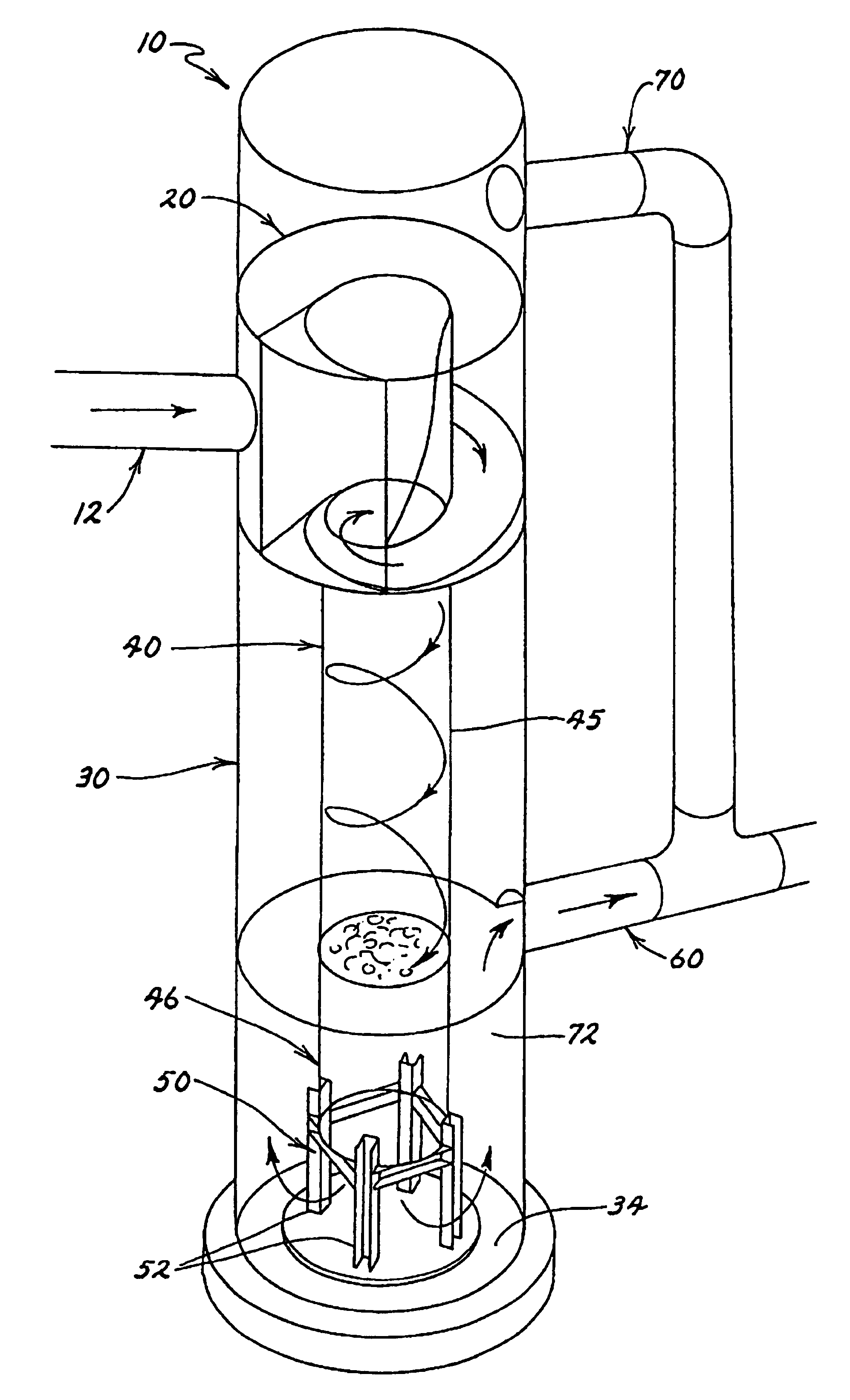
A method for entraining and mixing gas with liquids within a conduit or drop structure, comprising the channeling of one or more liquid flows into spiral flows of predetermined radius (radii), reducing the predetermined radius (radii) to increase the centrifugal forces acting upon the spiral flow(s) as the spiral flow(s) enter the conduit, and allowing gas access to the conduit to mix with and entrain within the spiral flow within the conduit or drop structure. The method can facilitate the mixing of gas with one or more fluid flows and / or reduce the release of gas emissions from the fluid(s) into the surrounding environment.
Owner:VORTEX FLOW
Launch control of hybrid electric vehicle having a torque converterless driveline
InactiveUS6974402B2Improve fuel economyReduce gas emissionsElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingSeparated stateElectric vehicle
A powertrain assembly for an automotive vehicle having an internal combustion engine, transmission, electric induction motor, a clutch for connecting and releasing the engine and transmission, and a controller for controlling the state of engagement and disengagement of the clutch and the torque produced by the motor during the launch. The engine increases torque produced by the induction motor during a vehicle launch condition, permitting the engine to be turned off when the vehicle is at rest. The torque multiplication that would normally be available from a hydrokinetic torque converter is replaced with auxiliary launch torque supplied by the induction motor.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
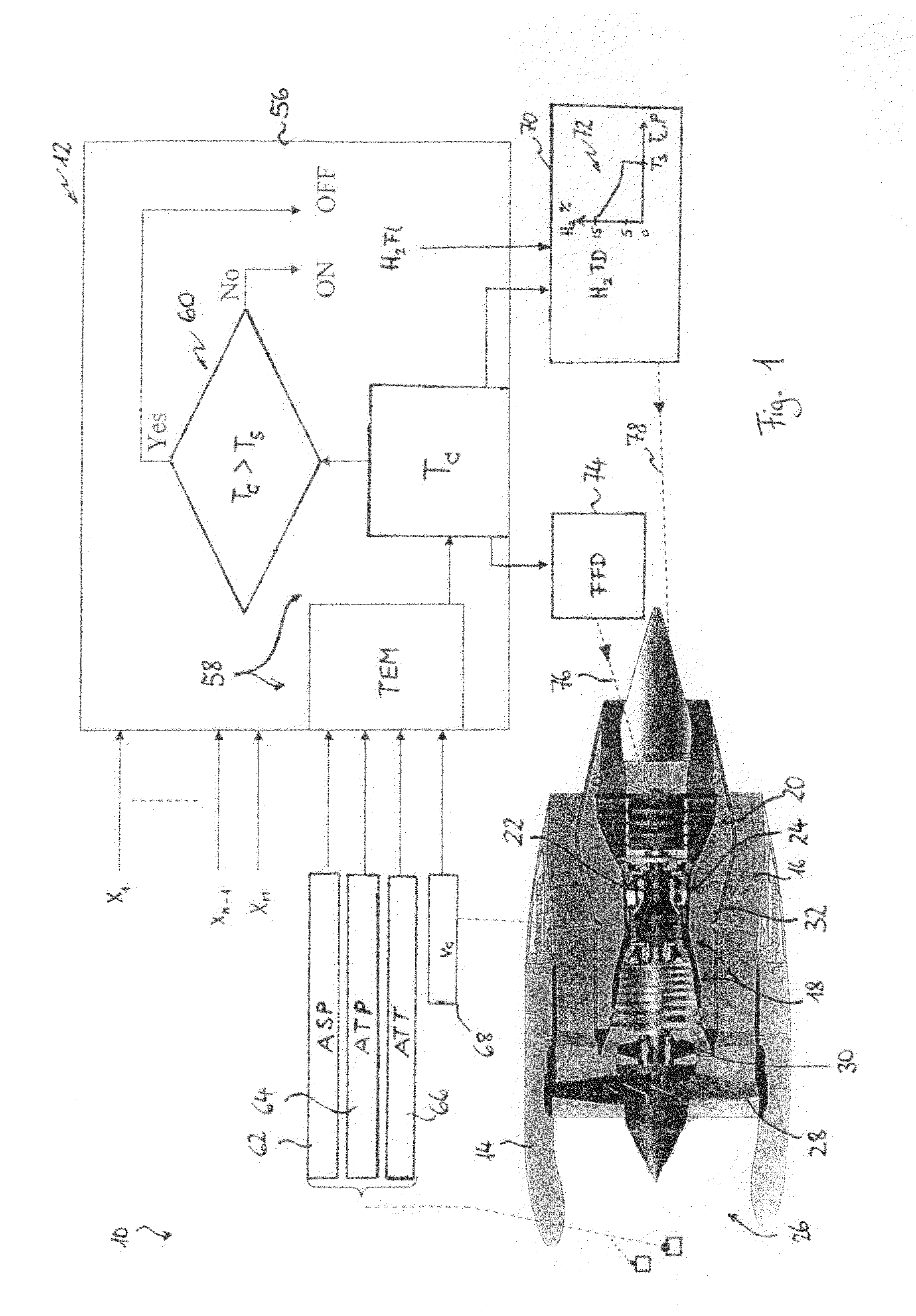
Gas Turbine Engine and Method for Reducing Turbine Engine Combustor Gaseous Emission
ActiveUS20090301096A1Emission reductionReduce hydrogen consumptionAnalogue computers for vehiclesFuel supply regulationAviationCombustor
The invention relates to turbine engines used in aeronautics, but also for industrial and marine turbine engines. To reduce turbine engine combustor gaseous emissions at given combustor sizes or to reduce combustor sizes at given combustor gaseous emissions, the invention proposes the injection of hydrogen into the combustor in response to a power output level. According to a preferred embodiment, gaseous hydrogen is always injected at low-power operations and switched off at mid-power and high-power operations.
Owner:AIRBUS SAS
Fuel cell system and method with increased efficiency and reduced exhaust emissions
InactiveUS7208239B2Improve efficiencyEfficient and effective usePower installationsFuel cells groupingAtmospheric airNitrogen gas
An apparatus includes a low temperature fuel cell, a high temperature fuel cell or a hydrocarbon reformer, a hydrocarbon fuel supply, an oxygen generator, and a molecular sieve. The oxygen generator separates air to provide oxygen enriched air to the fuel cells and the reformer. Hydrocarbon fuel is provided to the high temperature fuel cell or the reformer, and the exhaust gas thereof may be separated through the molecular sieve, to provide hydrogen enriched gas to the low temperature fuel cell, water, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. The low temperature fuel cell outputs nitrogen gas and high purity water. The emitted carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides are catalytically converted to nitrogen and carbon dioxide being returned to the atmosphere. The process and apparatus are very efficient, produce high purity water and electrical energy, and are environmentally friendly.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Adjustable fuel power booster component composition
InactiveUS20070204506A1Reduce gas emissionsBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsMethyl carbonateInternal combustion engine
An adjustable fuel power booster component composition having three components: (A) an ignition accelerator which is preferably normal propyl nitrate and / or diterbutyl peroxide; (B) propylene glycol monoalkyl ether and / or butylene glycol monoalkyl ether; and (C) methyl carbonate and / or ethyl carbonate and / or propyl carbonate and / or butyl carbonate, which may be used mixed in any proportion with methylal (dimethoxymethane) or ethylal (diethoxymethane). The adjustable fuel power booster component composition of the present invention can be used by itself or in mixture with gasoline, diesel or burning oils in combustion engines without the need for modification thereof. The adjustable fuel power booster component composition enables low energy content alcohol based fuels to substitute conventional fuels, such as gasoline or diesel, in conventional non-modified internal combustion engines, thereby generating lower amounts of toxic gas emission all the while proving more power.
Owner:BRENES MARIO ARAYA
Organic slurry storage basin cover
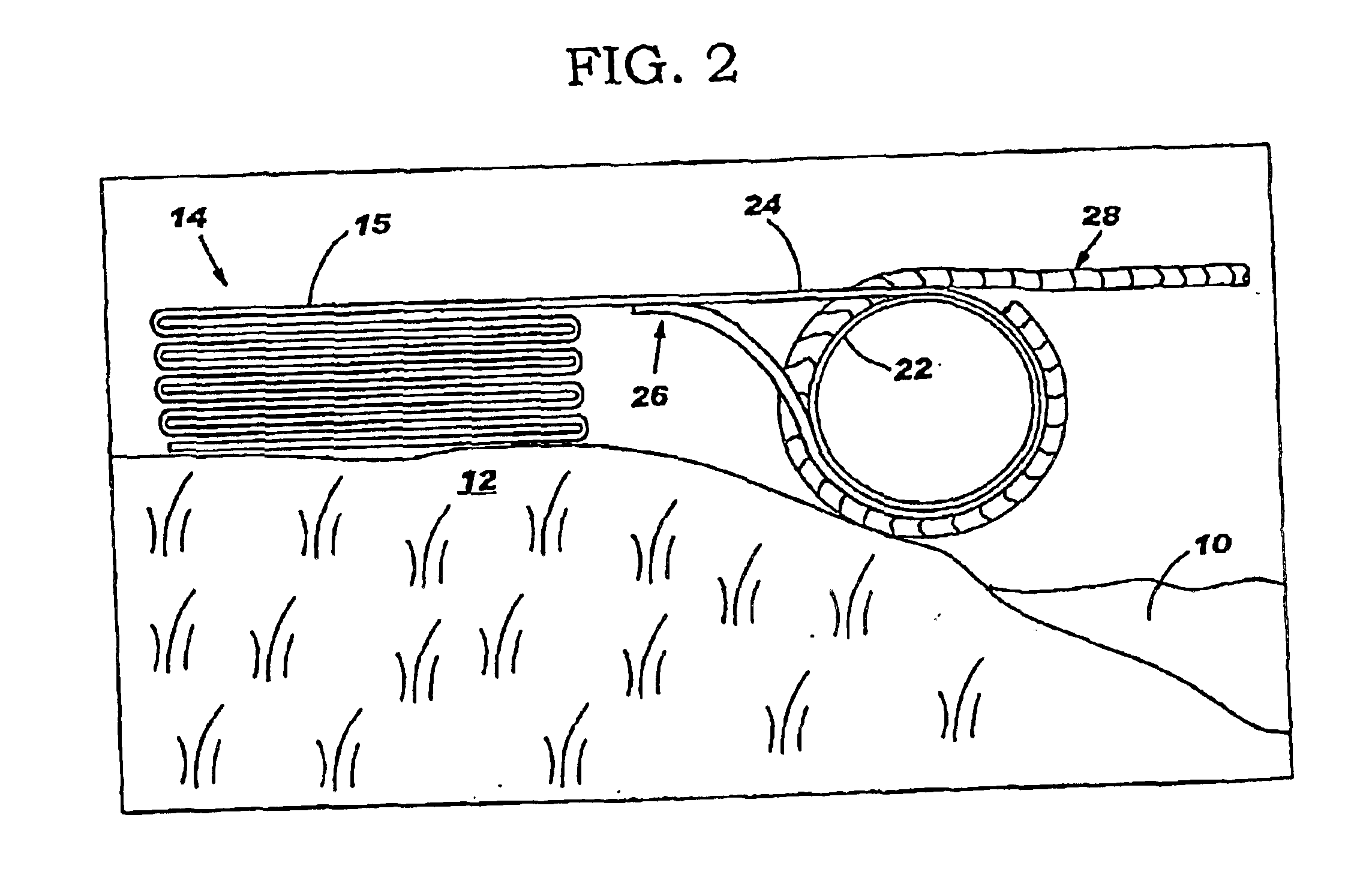
InactiveUS6851891B2Reduce malodorous gas emissionAvoid insufficient lengthLandfill technologiesSolid waste disposalGeotextileSurface plate
A cover assembly for an organic waste lagoon basin and a method of making and deploying such a cover assembly. A cover includes connected cover panels or sections. In one form of the invention the panels are comprised of a single layer of geotextile fabric. In another form of the invention the panels are comprised of interconnected strata including a sacrificial layer which faces the sun and protects the cover from ultraviolet light degradation; a foam layer that floats the cover; and a geotextile fabric layer. The geotextile fabric is porous and suppresses the release of malodorous gases from the lagoon basin. The cover can be constructed and deployed by laying out cover panels in fanfold fashion along a side of the basin; connecting adjacent edges of the panels; attaching flotation to the free edge of the top panel; and using deployment lines and a mandrel to move the cover across the filled basin.
Owner:BAUMGARTNER ENVIRONICS
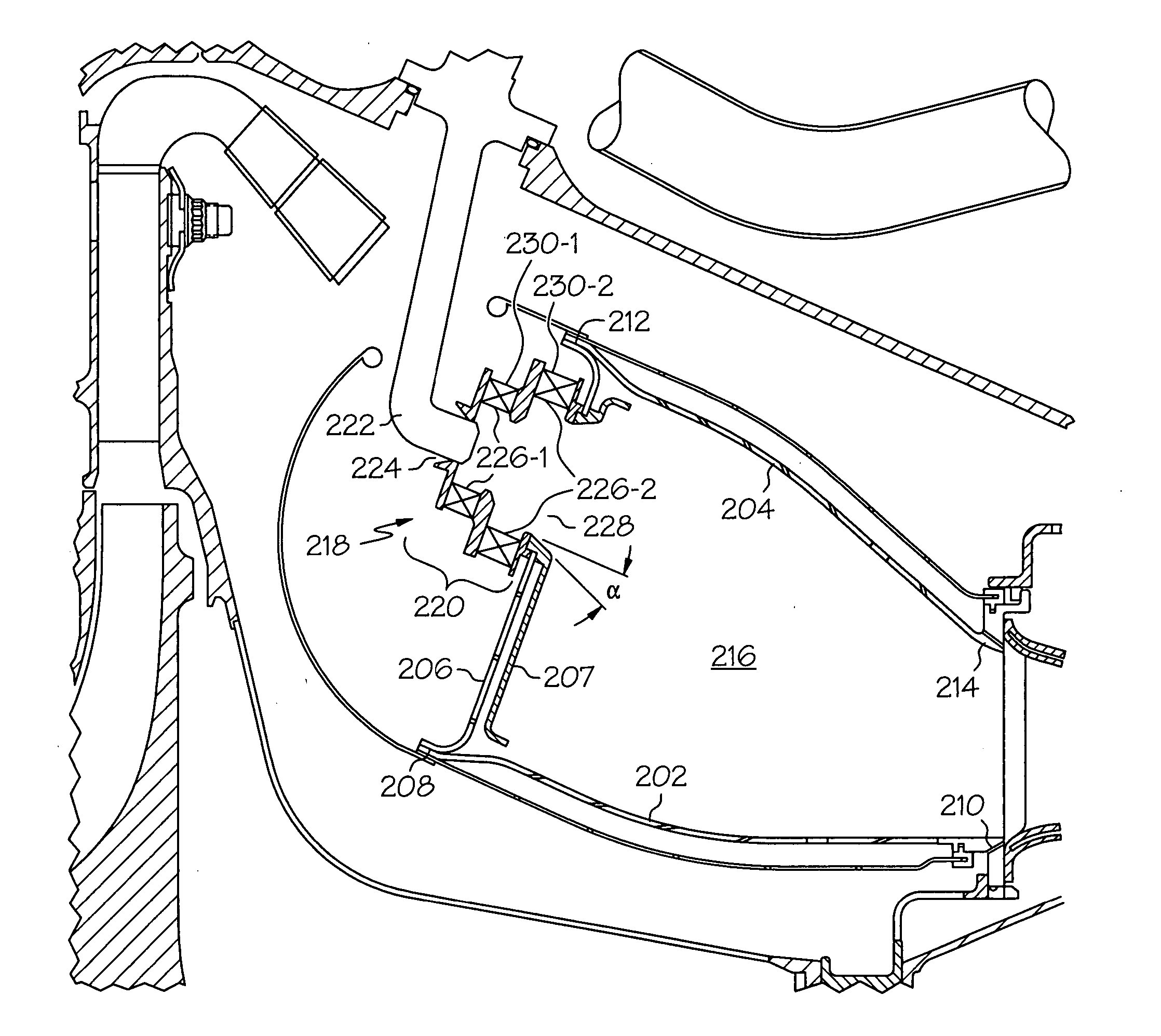
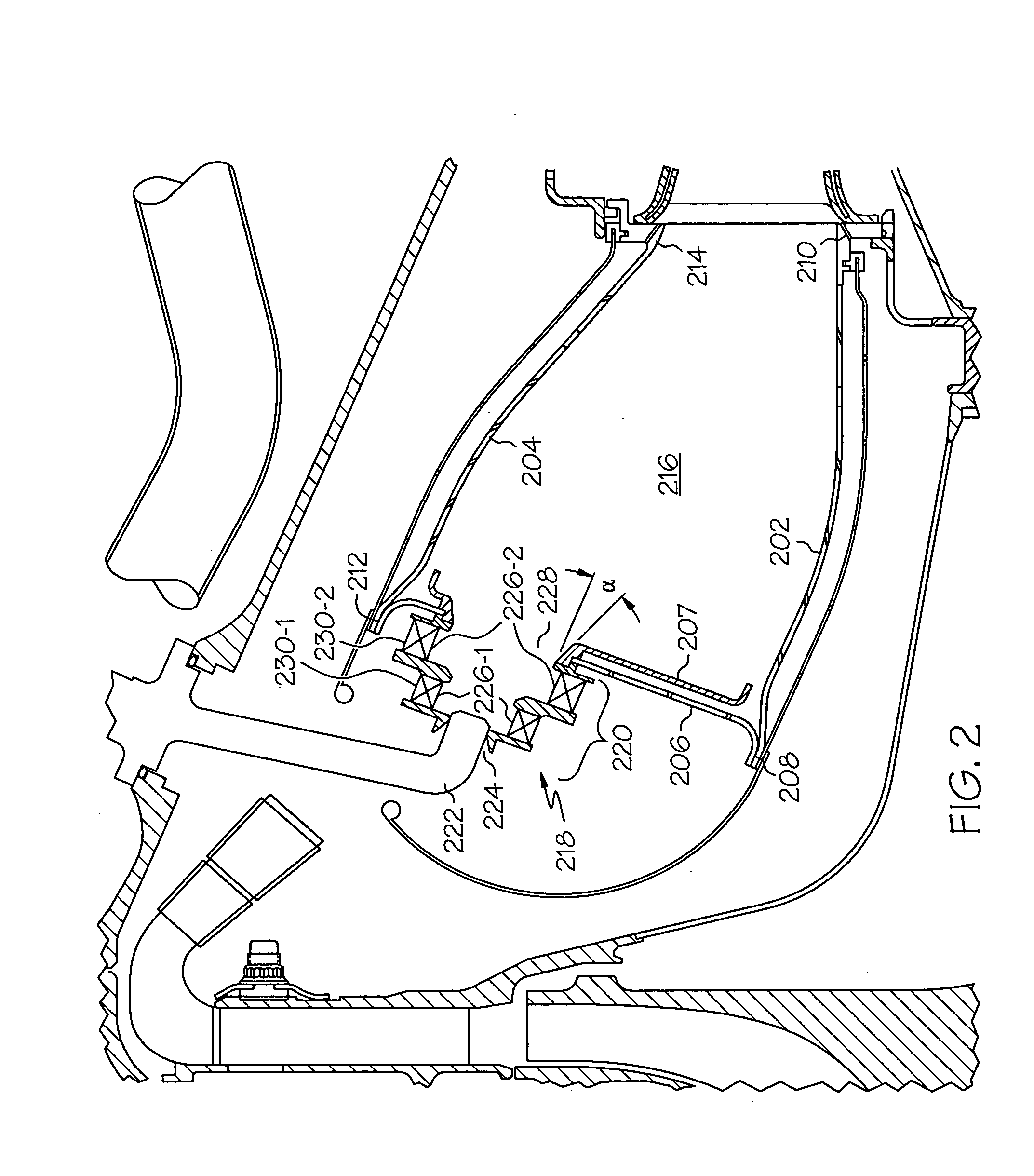
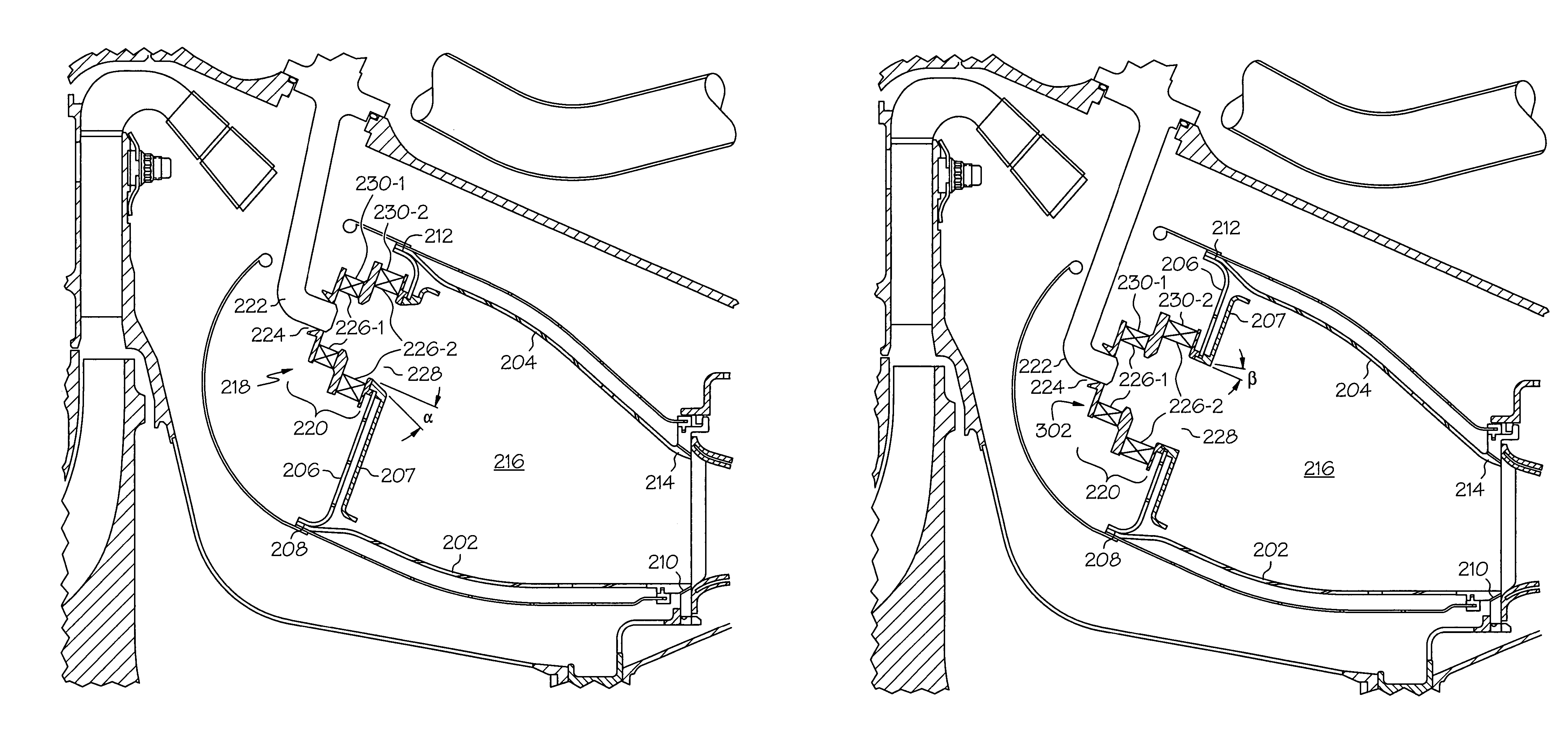
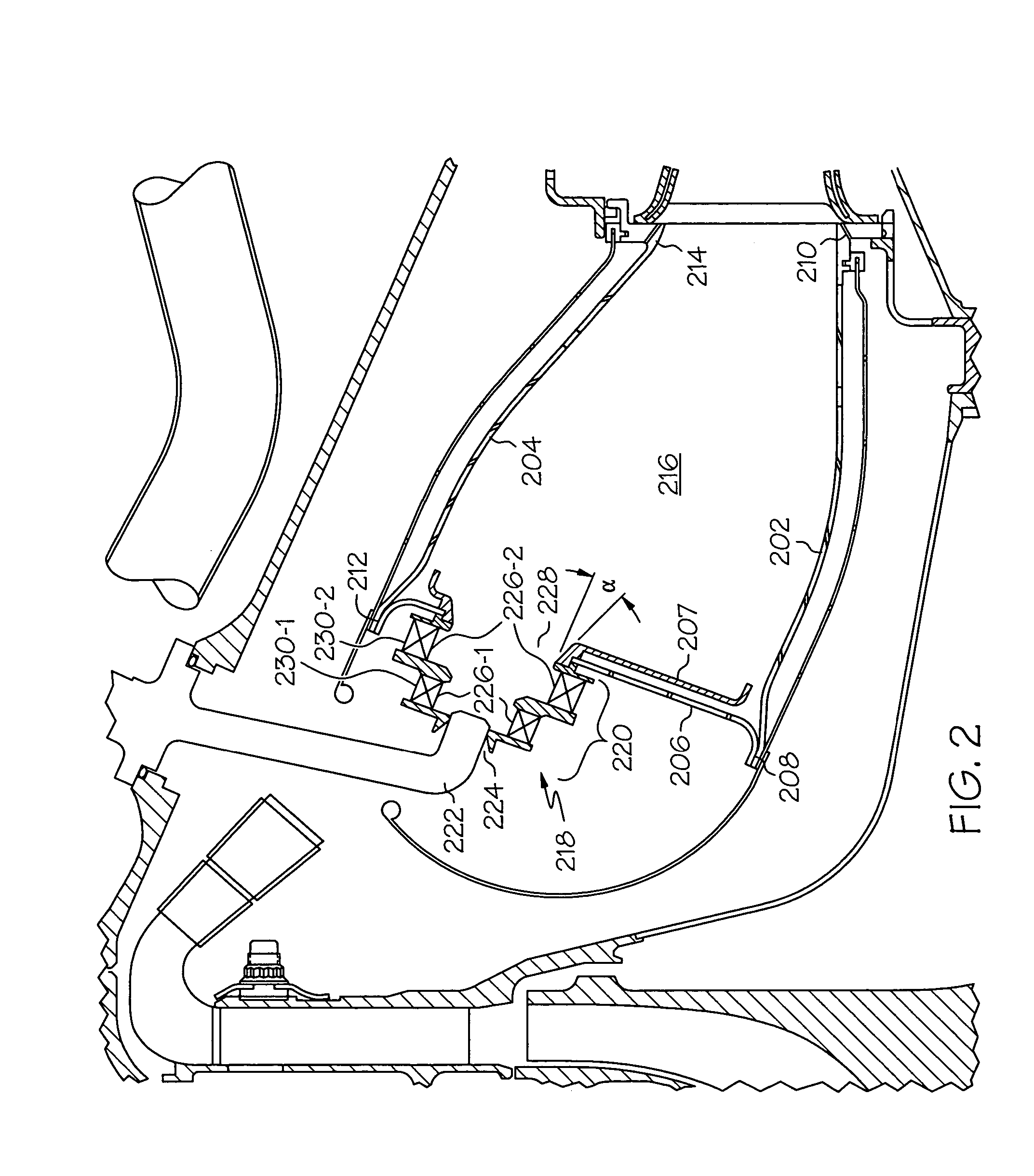
Reduced exhaust emissions gas turbine engine combustor
ActiveUS20050132716A1Reduce gas emissionsContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberCombustor
A gas turbine engine combustor includes a plurality of main fuel injector assemblies, and a plurality of pilot fuel injector assemblies, that are arranged and configured to reduce exhaust gas emissions during engine operation. The plurality of main fuel injector assemblies are arranged in a substantially circular pattern of a first radius, and each includes an outlet port having a first divergence angle. The plurality of pilot fuel injector assemblies are arranged in a substantially circular pattern of a second radius. Each pilot fuel injector assembly is disposed between at least two main fuel injector assemblies, and each includes an outlet port having a second divergence angle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Reduced exhaust emissions gas turbine engine combustor
ActiveUS7506511B2Reduce gas emissionsContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustorCombustion chamber
A gas turbine engine combustor includes a plurality of main fuel injector assemblies, and a plurality of pilot fuel injector assemblies, that are arranged and configured to reduce exhaust gas emissions during engine operation. The plurality of main fuel injector assemblies are arranged in a substantially circular pattern of a first radius, and each includes an outlet port having a first divergence angle. The plurality of pilot fuel injector assemblies are arranged in a substantially circular pattern of a second radius. Each pilot fuel injector assembly is disposed between at least two main fuel injector assemblies, and each includes an outlet port having a second divergence angle.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Controller of internal combustion engine
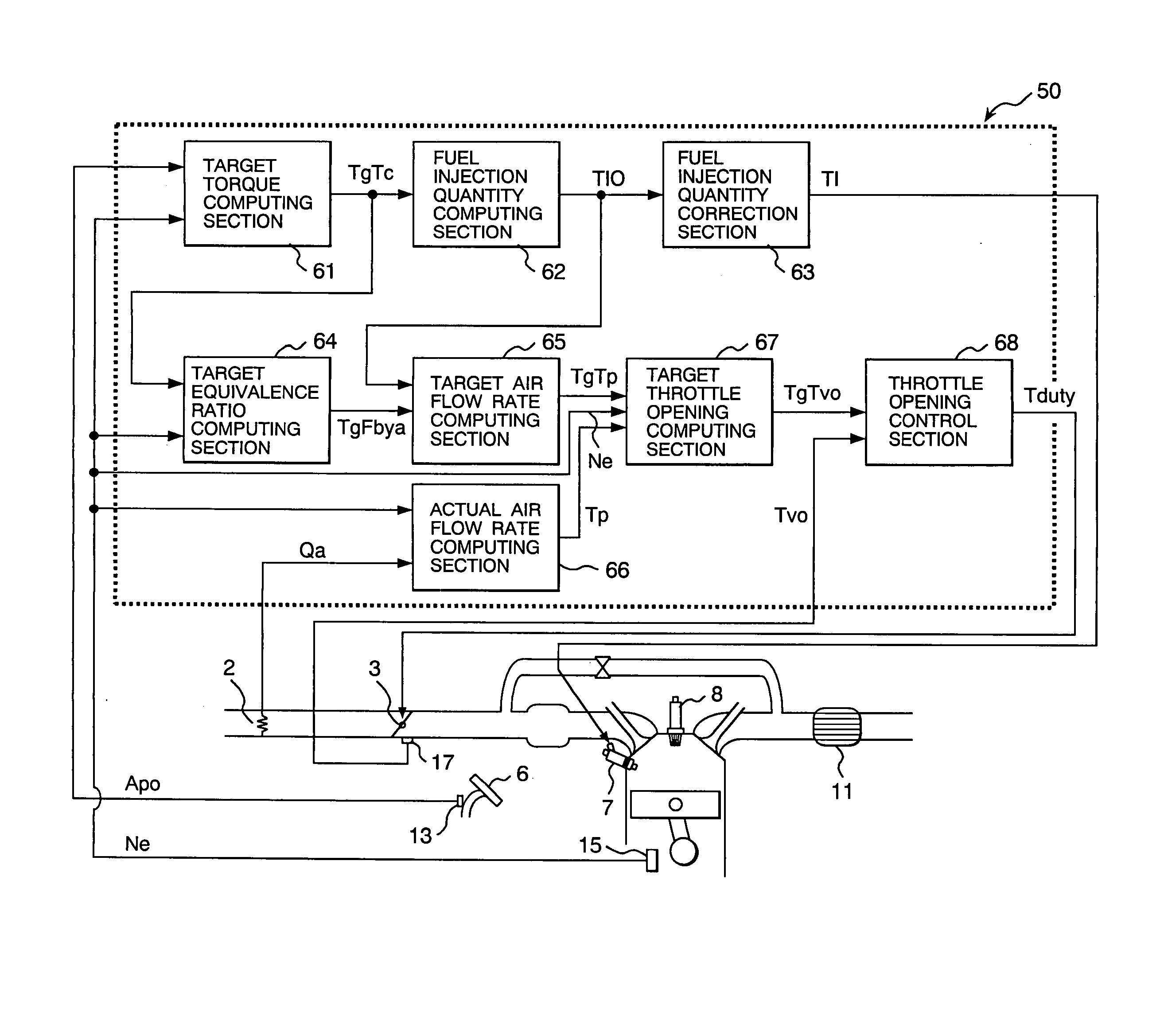
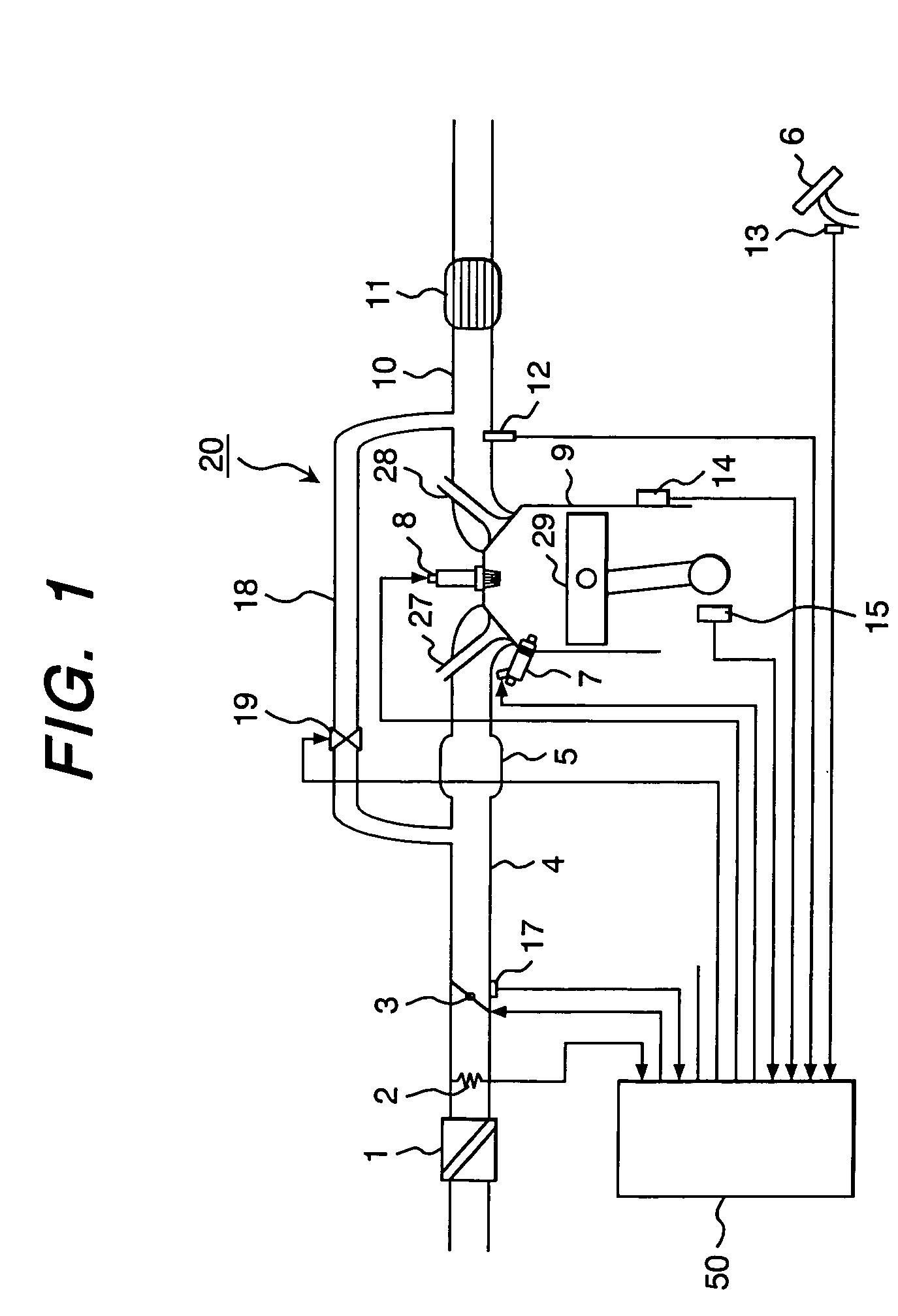
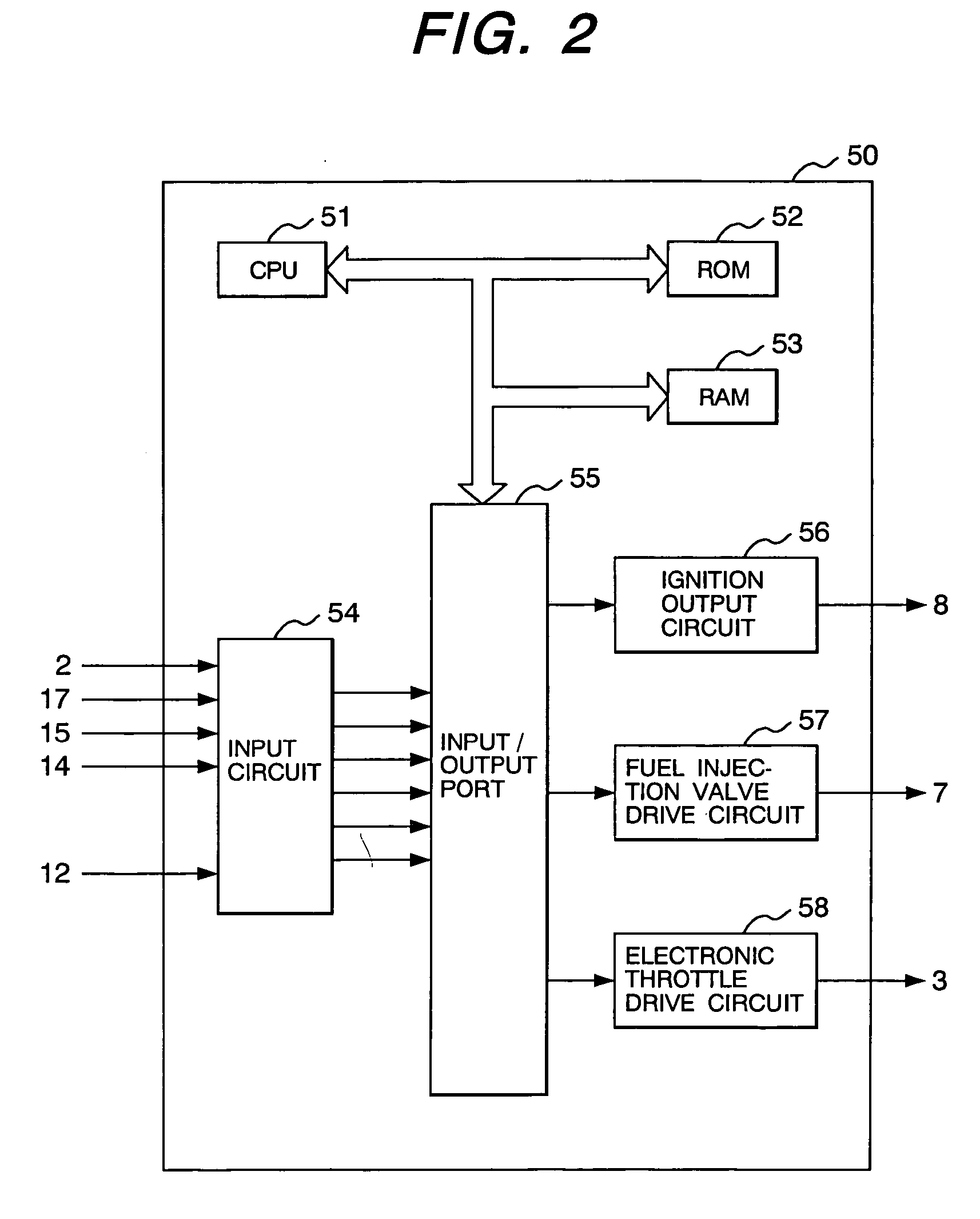
InactiveUS20050103309A1Limiting air flow rateFast convergenceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineFeedback control
Disclosed is an internal combustion engine controller, which is used with a fuel-based torque-on-demand control type, multi-cylinder, direct-injection internal combustion engine to provide an air flow rate control means that excels in response and convergence. This internal combustion engine controller comprises means for computing a target throttle opening from operating conditions. The means for computing a target throttle opening includes: a first computing means for determining a target throttle opening by exercising feedback control in accordance with operating conditions including an intake air flow rate; a second computing means for determining a target throttle opening by exercising feed-forward control in accordance with operating conditions; and a third computing means for determining a target throttle opening in accordance with a target throttle opening value determined by the first computing means and a target throttle opening value determined by the second computing means.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com