Patents
Literature
1643 results about "Heterogeneous catalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heterogeneous catalysis is the type of catalysis where the phase of the catalyst differs from the phase of the reactants or products. Contrasts with homogeneous catalysis where the reactants, products and catalyst exist in the same phase. Phase distinguishes between not only solid, liquid, and gas components, but also immiscible mixtures (e.g. oil and water), or anywhere an interface is present. Catalysts are useful because they increase the rate of a reaction without themselves being consumed and are therefore reusable.
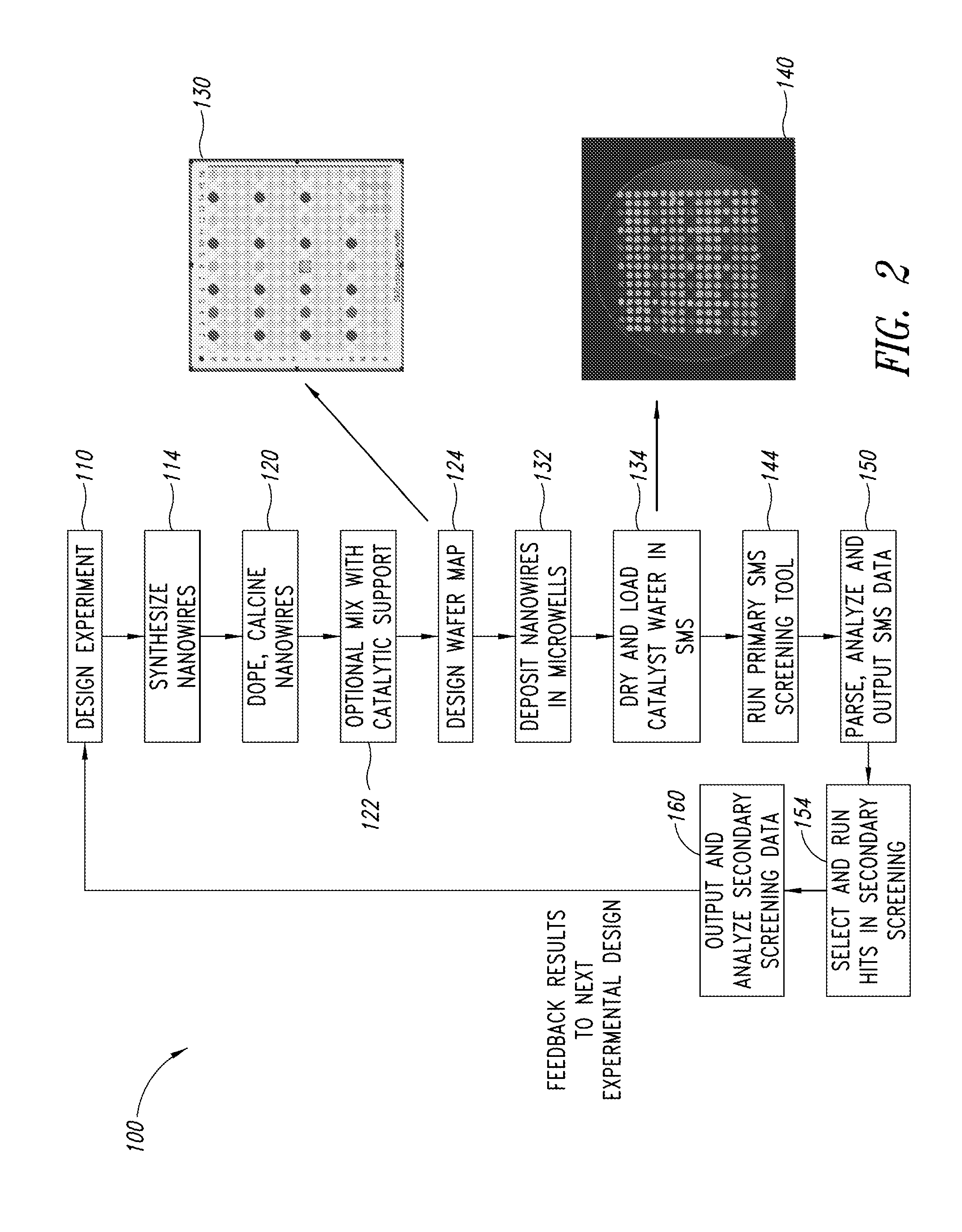
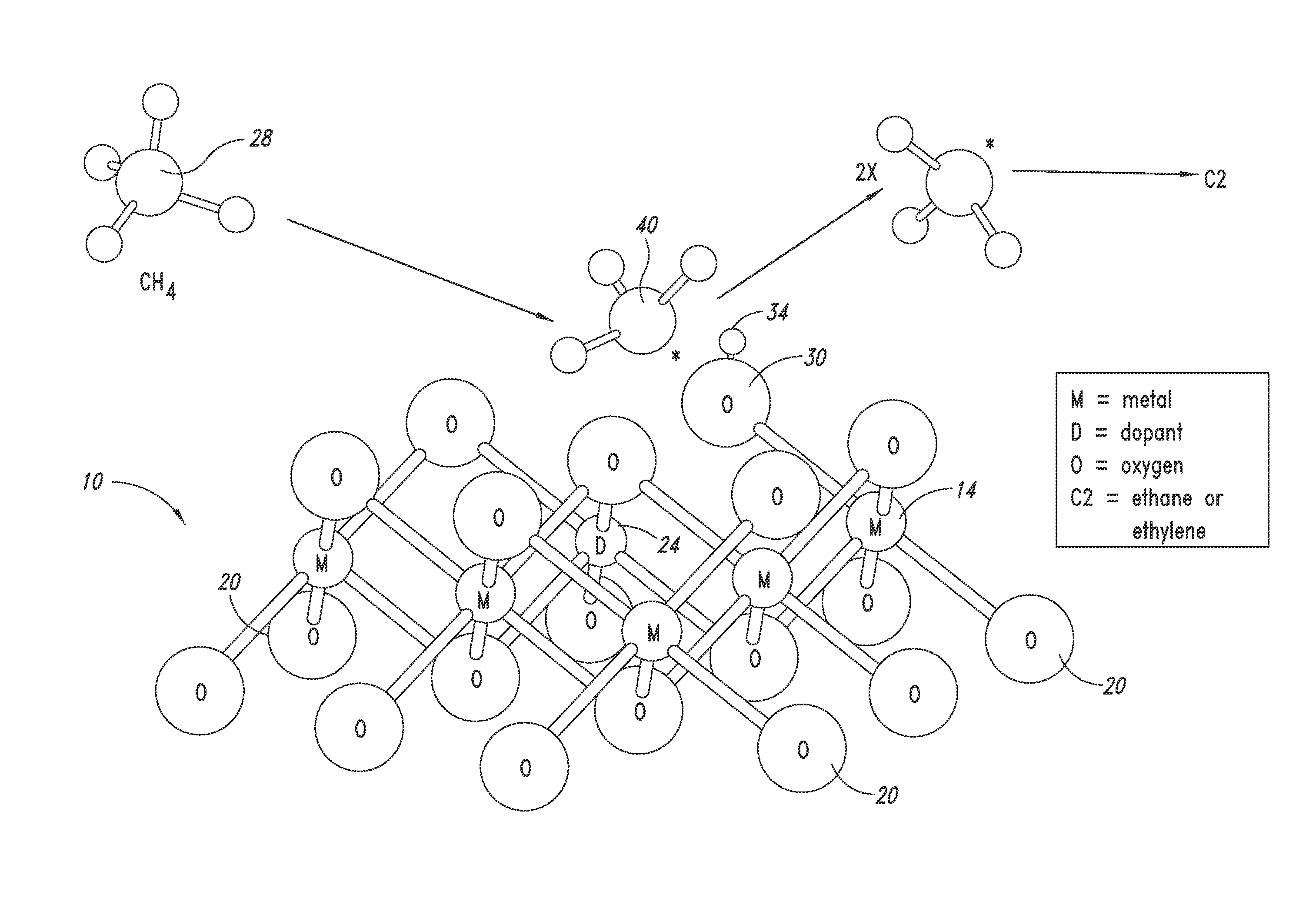
Nanowire catalysts
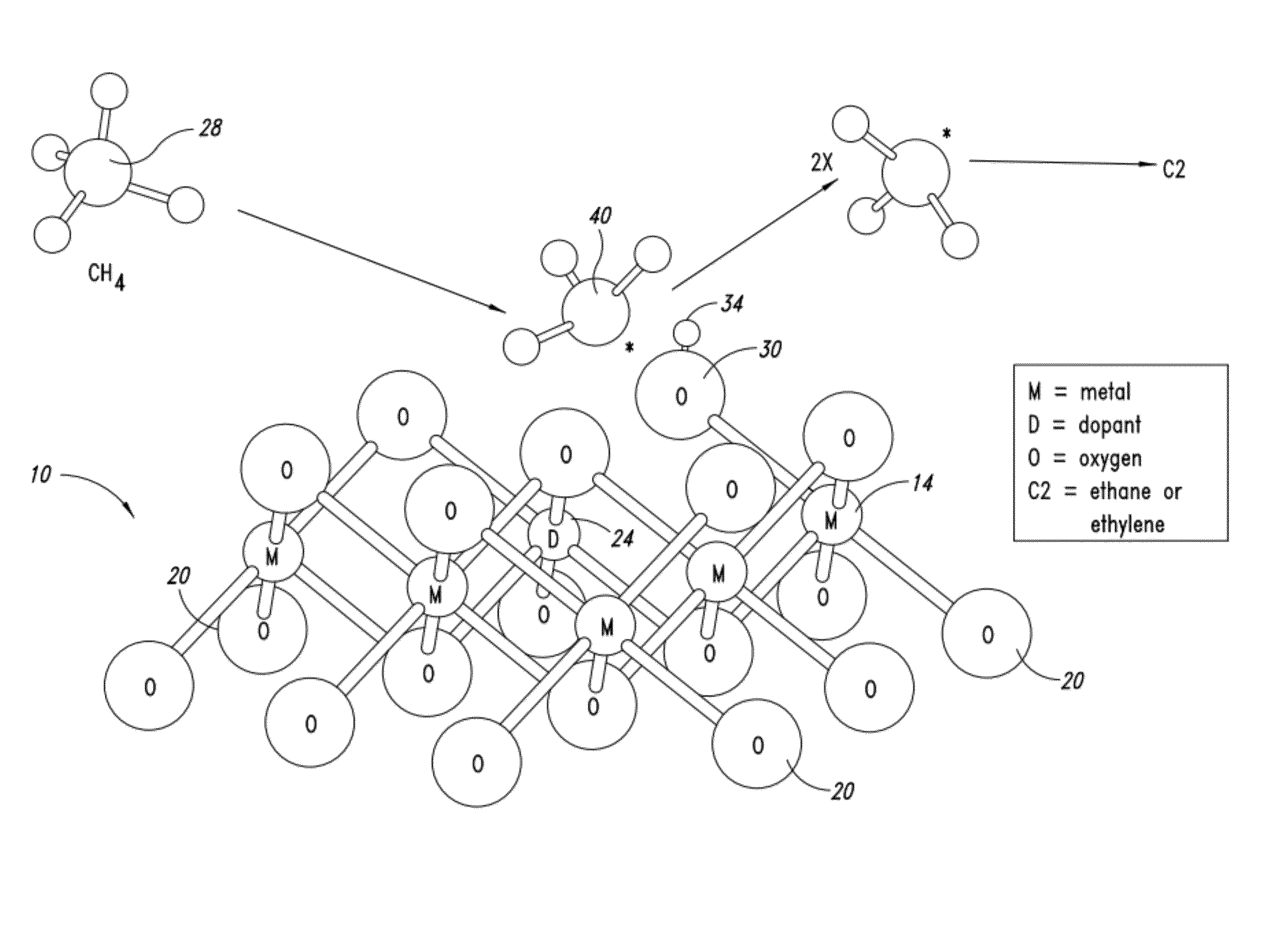
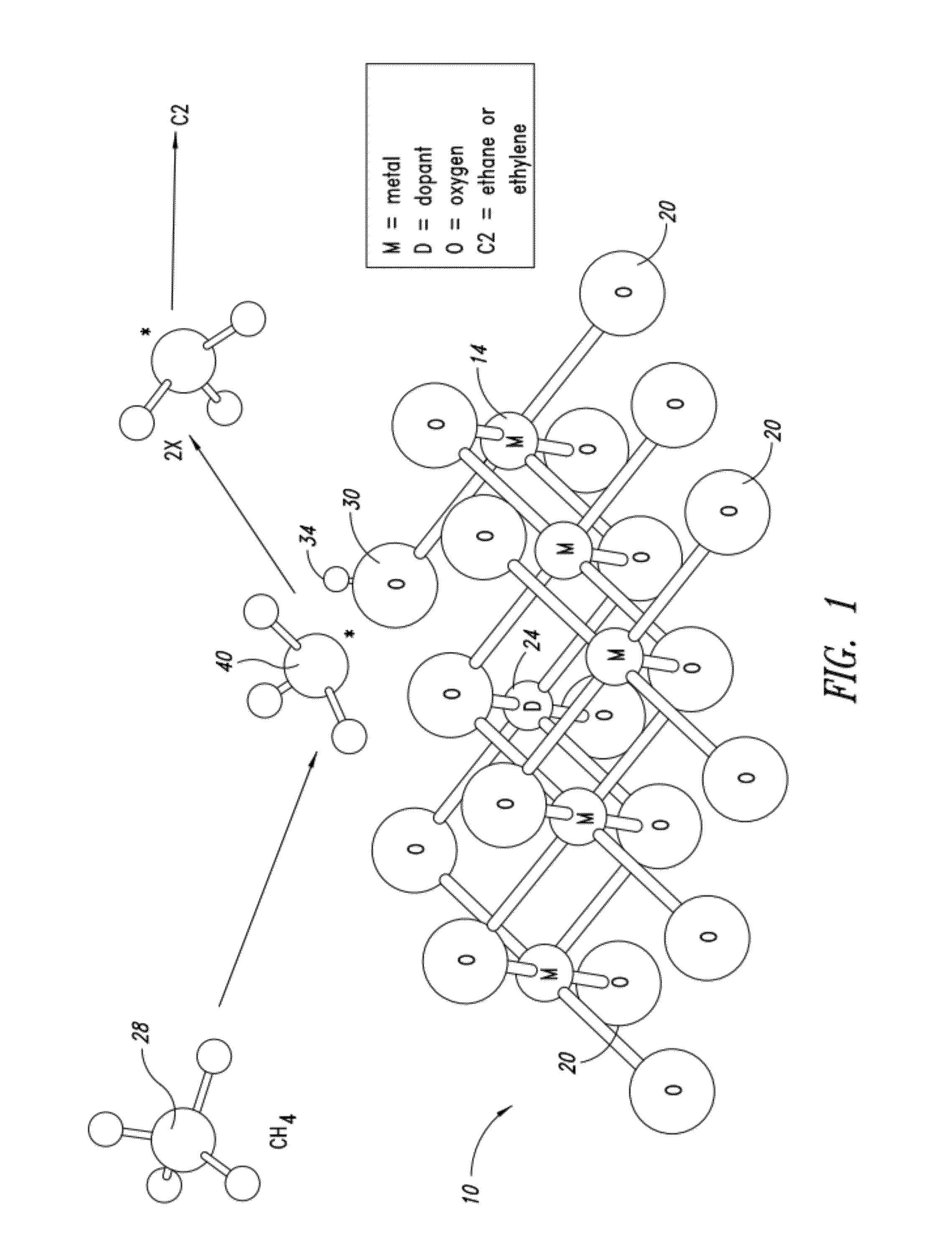
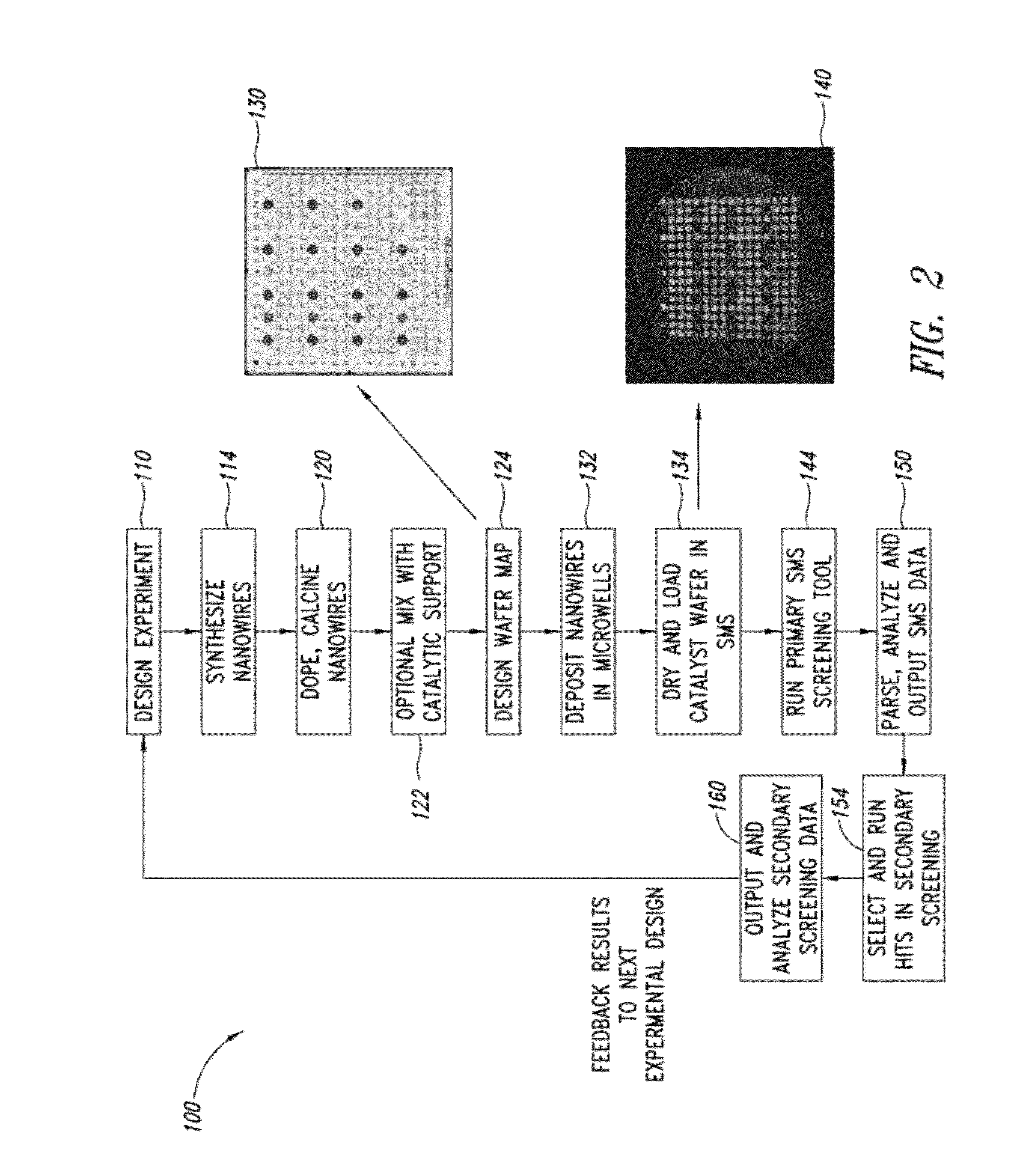
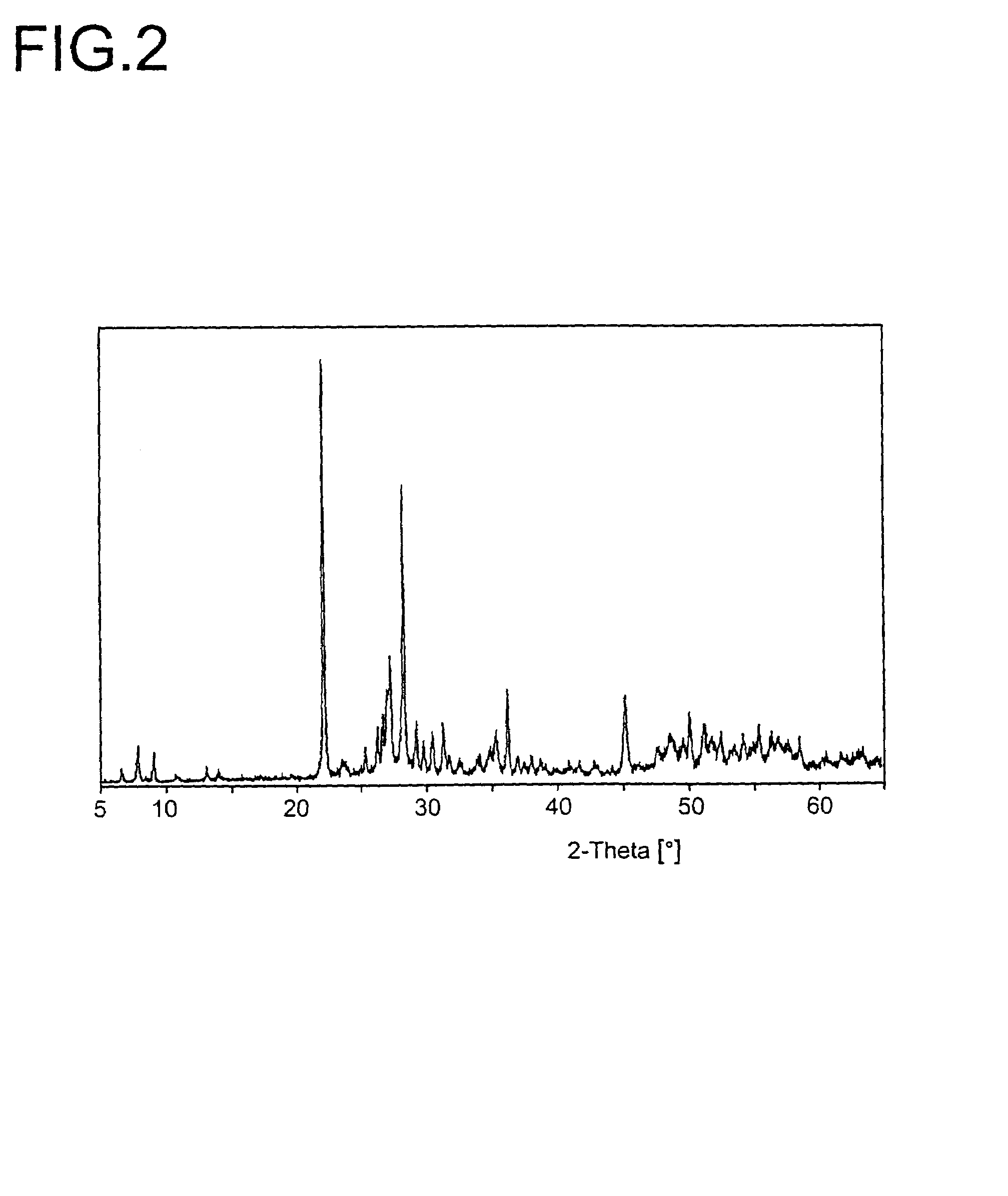
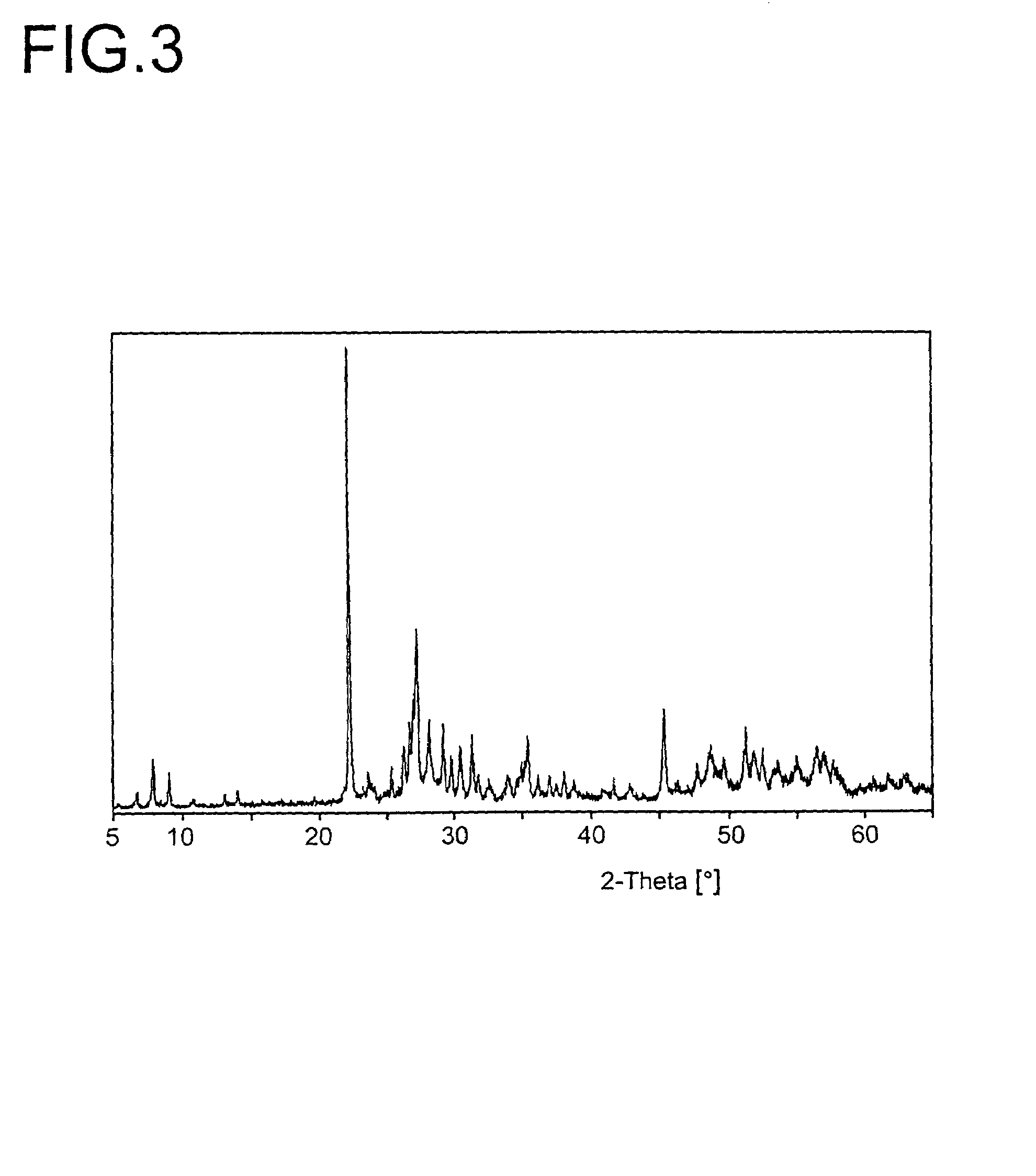
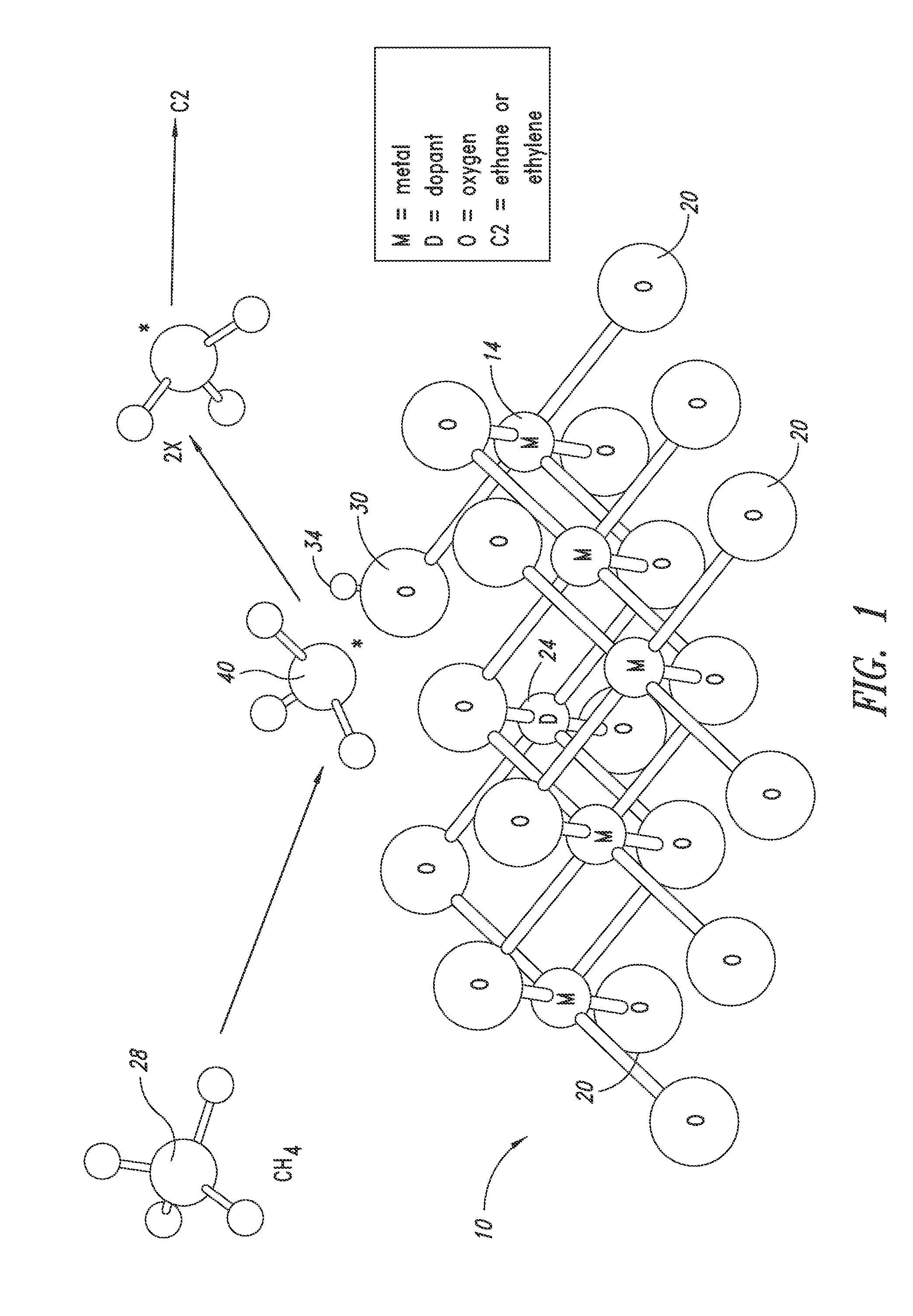
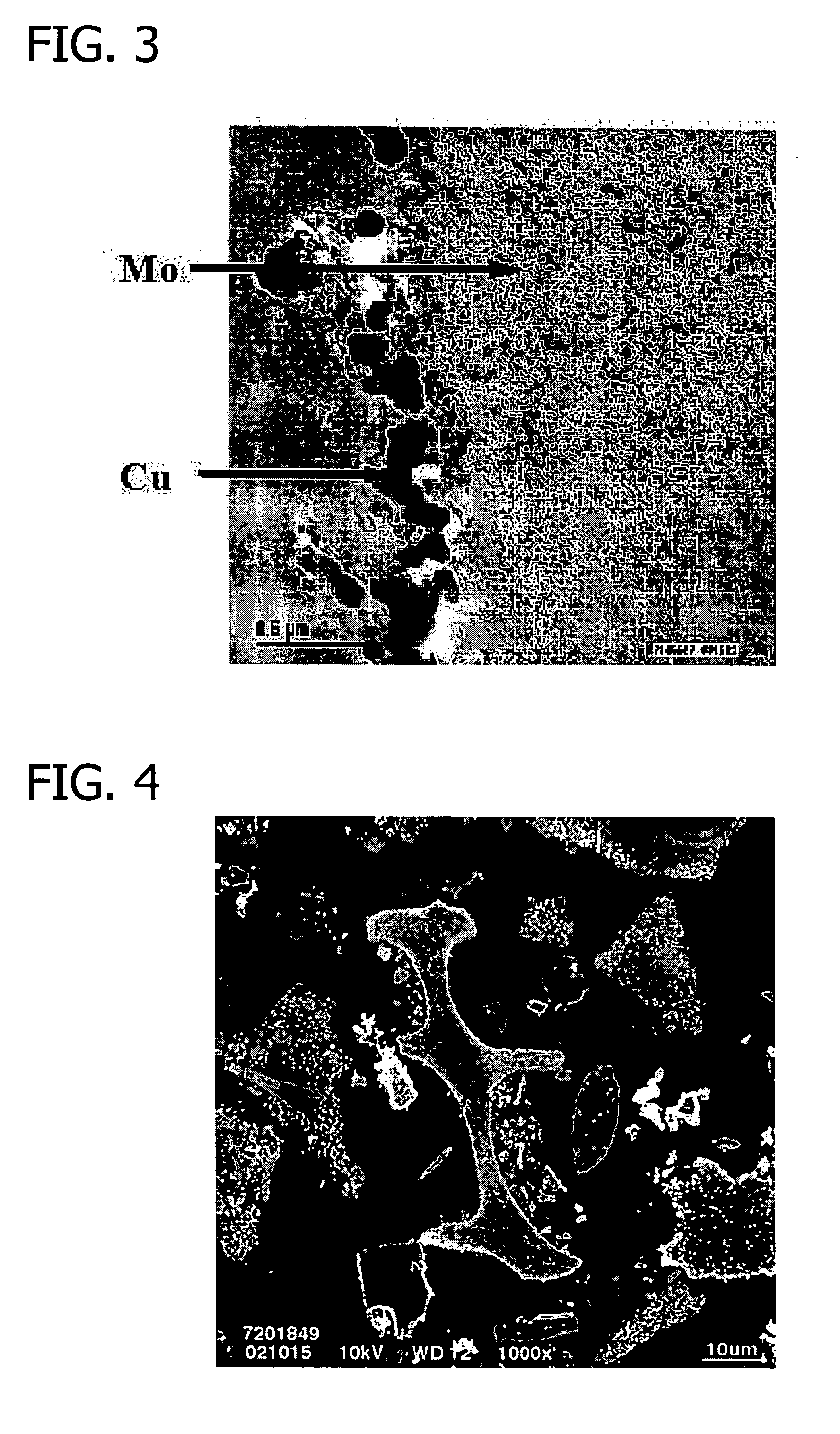
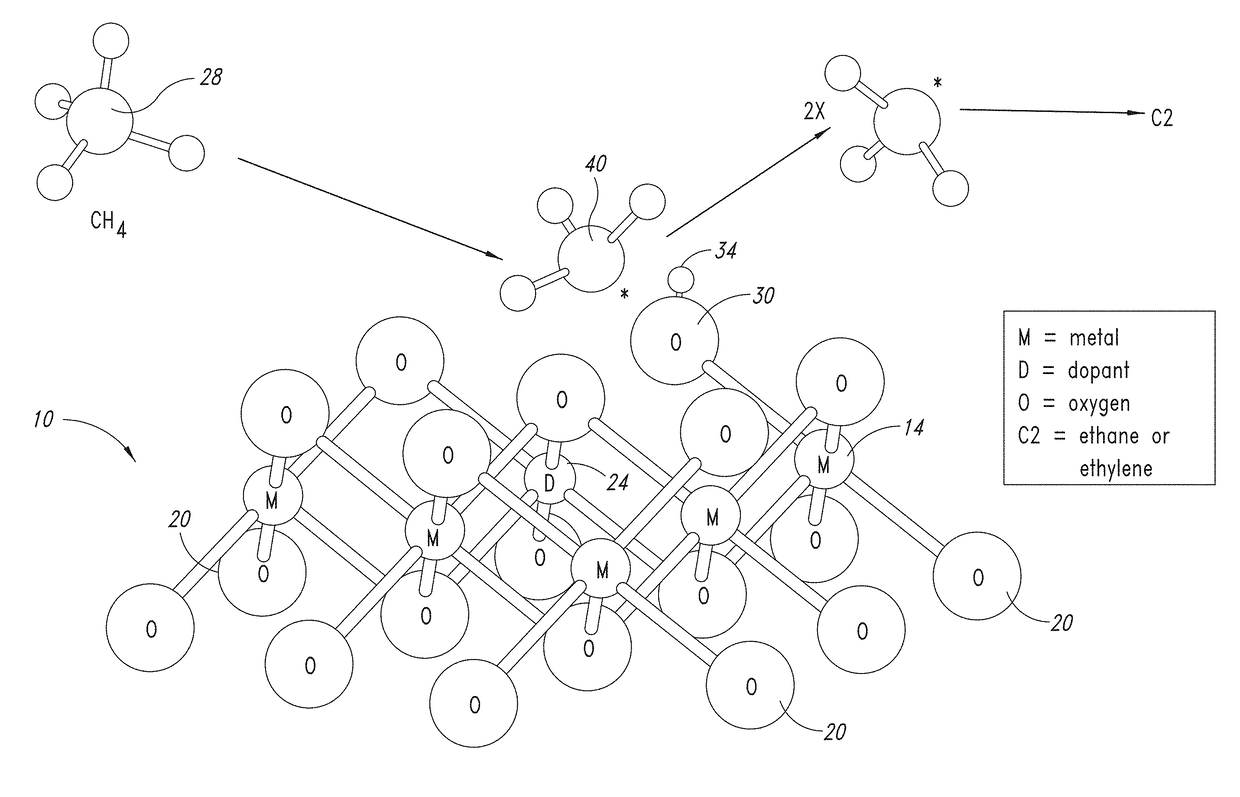
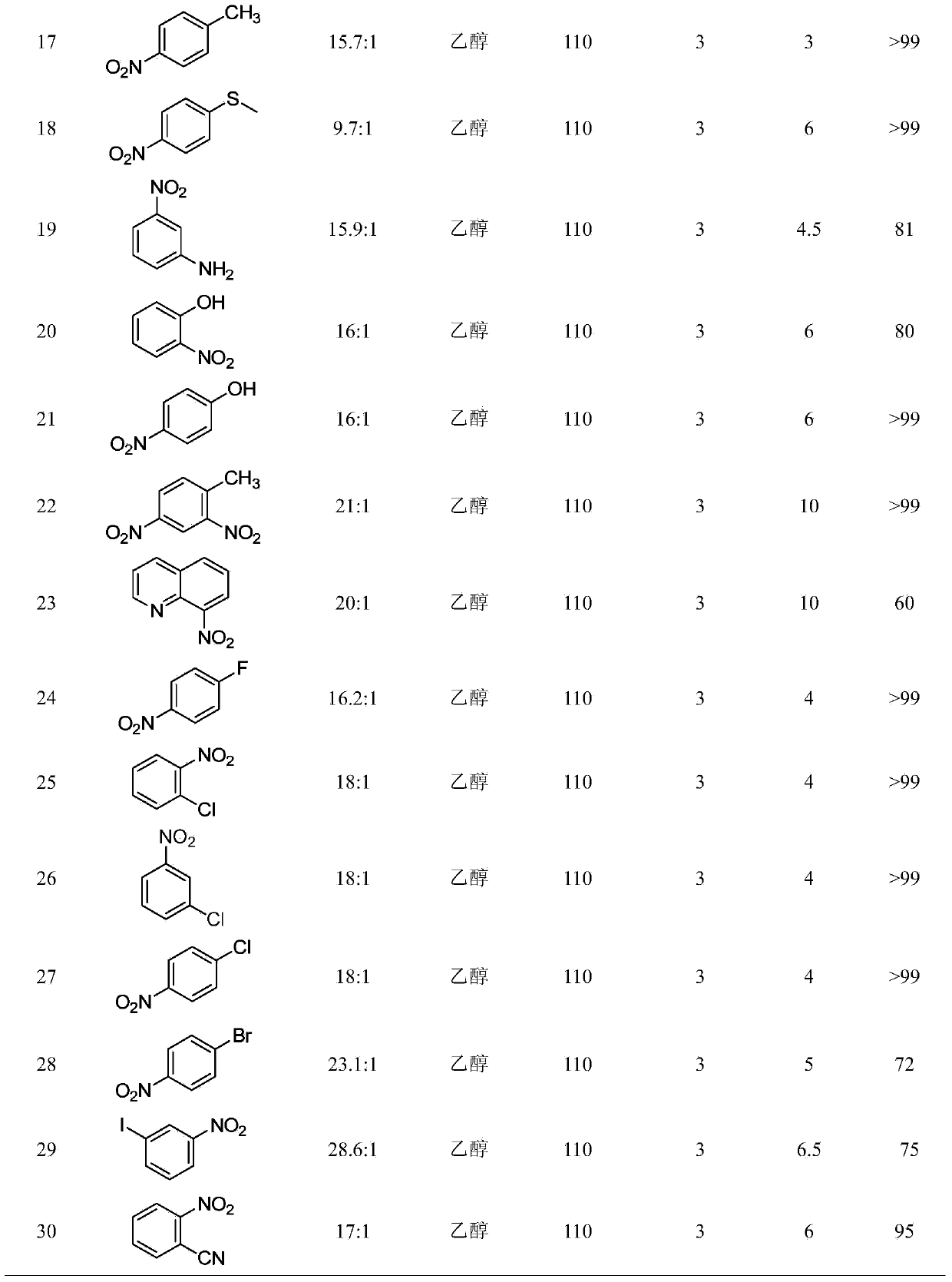
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Multimetal oxide materials
Owner:BASF SE
Nanowire catalysts and methods for their use and preparation
ActiveUS20130165728A1Material nanotechnologyManganese oxides/hydroxidesNanowireOxidative coupling of methane
Nanowires useful as heterogeneous catalysts are provided. The nanowire catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to C2 hydrocarbons. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH LLC
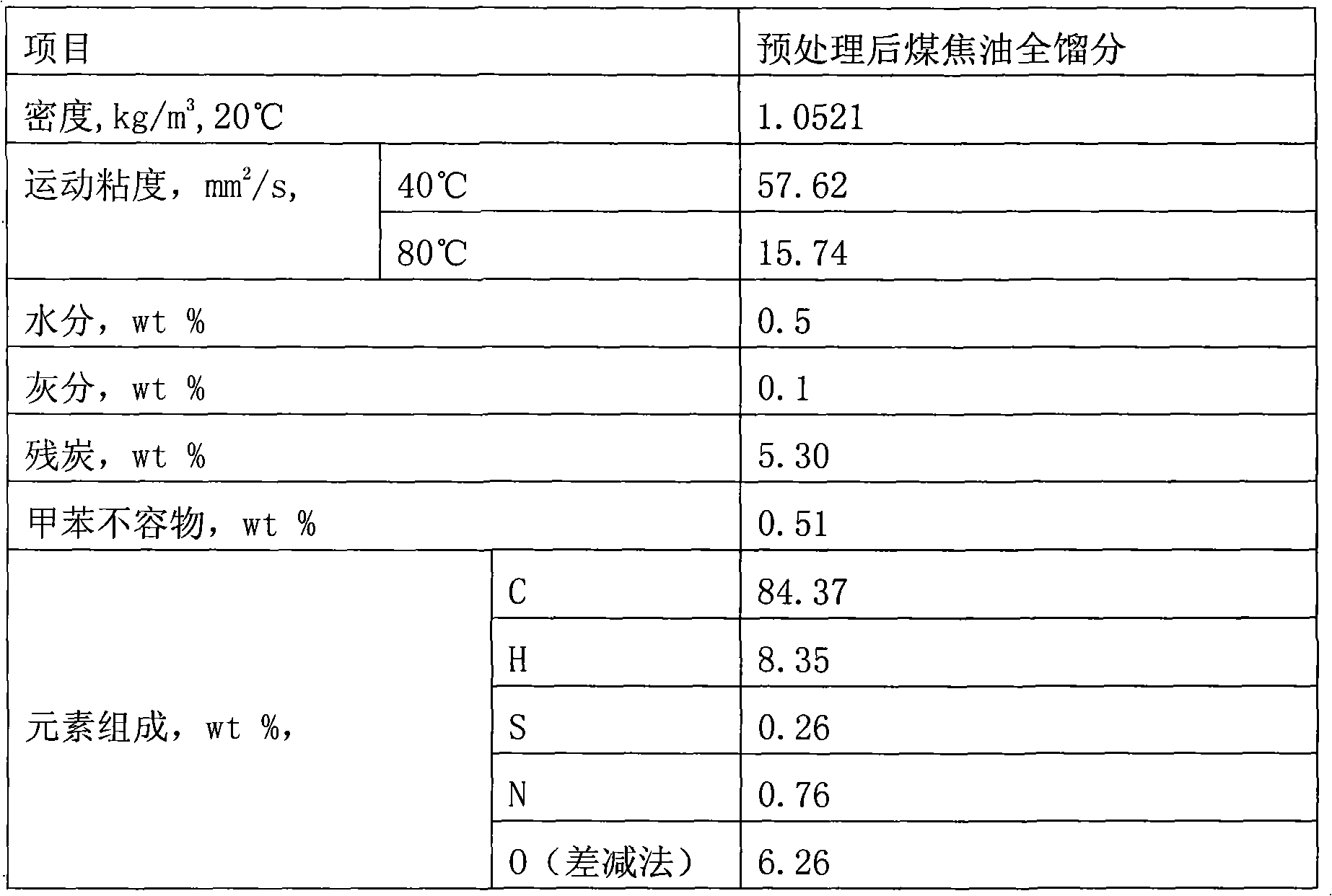
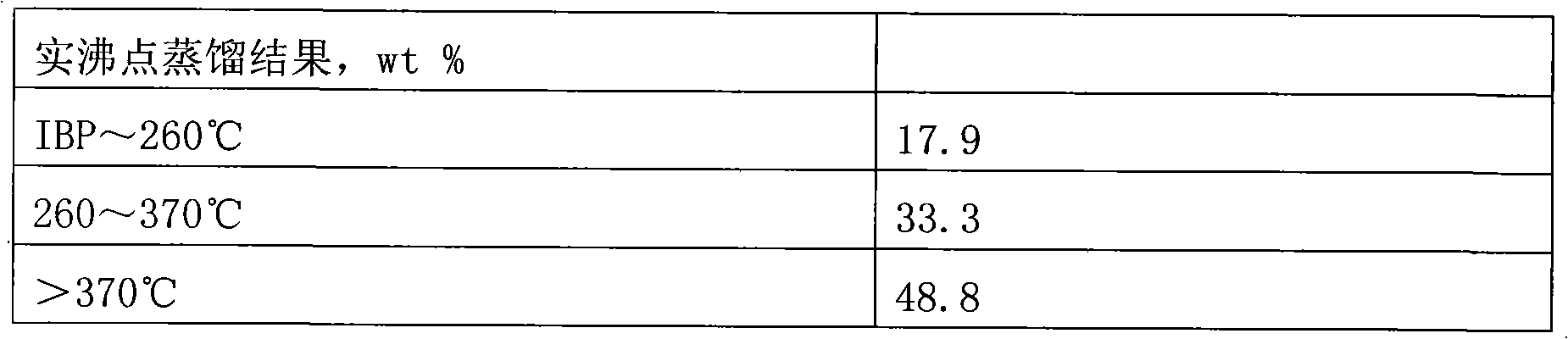
Hydrogenation method for coal tar suspension bed of heterogeneous catalyst
ActiveCN101885982ATo achieve the purpose of recyclingImprove utilization efficiencyTreatment with hydrotreatment processesFuel oilBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a hydrogenation method for a coal tar suspension bed of a heterogeneous catalyst. The method comprises processes of coal tar raw material pretreatment and distillatory separation, coal tar heavy fraction suspension bed hydrogenation cracking and conventional light fraction oil extraction, wherein the suspension bed hydrogenation reaction temperature is between 320 and 480DEG C, the reaction pressure is 8 to 19MPa, the volume air speed is 0.3 to 3.0h<-1>, the hydrogen oil volume ratio is 500 to 2,000, the catalyst is a powdery granular coal tar suspension bed hydrogenation catalyst of a single metal active ingredient containing molybdenum, nickel, cobalt, tungsten or iron or a composite multi-metal active ingredient, the adding amount of the catalyst is based on the ratio of the metal quantity of the active ingredient to the weight of the coal tar raw materials of 0.1: 100-4: 100, most of tail oil containing the catalyst after lightweight oil is separated froma hydrogenation reaction product is directly circulated to a hydrogenation bed reactor, a small part of tail oil is subjected to catalyst removal treatment and then circulated to the hydrogenation bed reactor to be subjected to further lightweight treatment, and the heavy oil is totally or furthest circulated. The method fulfills the purposes of maximum production of the lightweight oil in the coal tar and cyclic utilization of the catalyst, and greatly improves the utilization efficiency of the raw materials and the catalyst.
Owner:CCTEG CHINA COAL RES INST
Catalysts for petrochemical catalysis
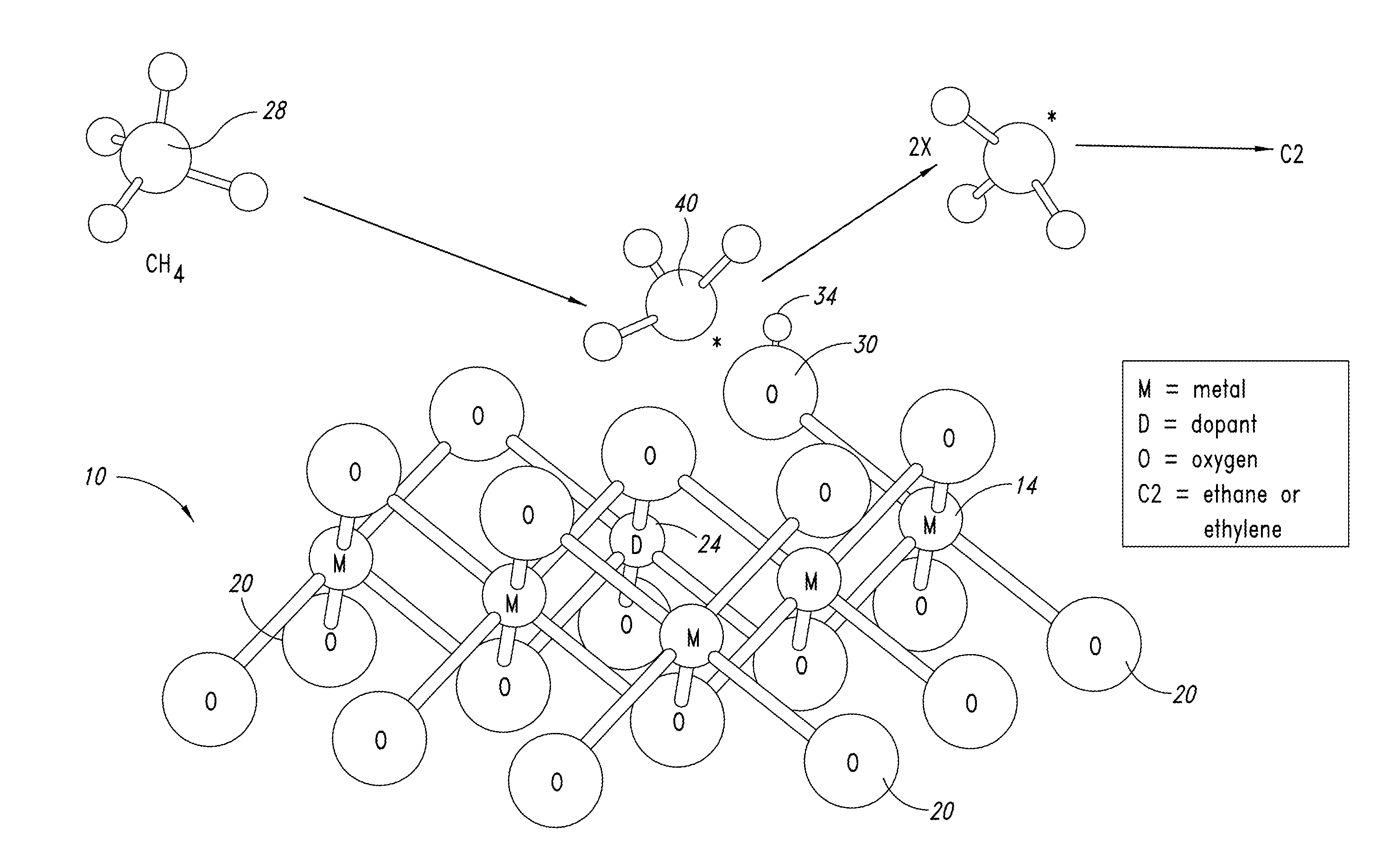
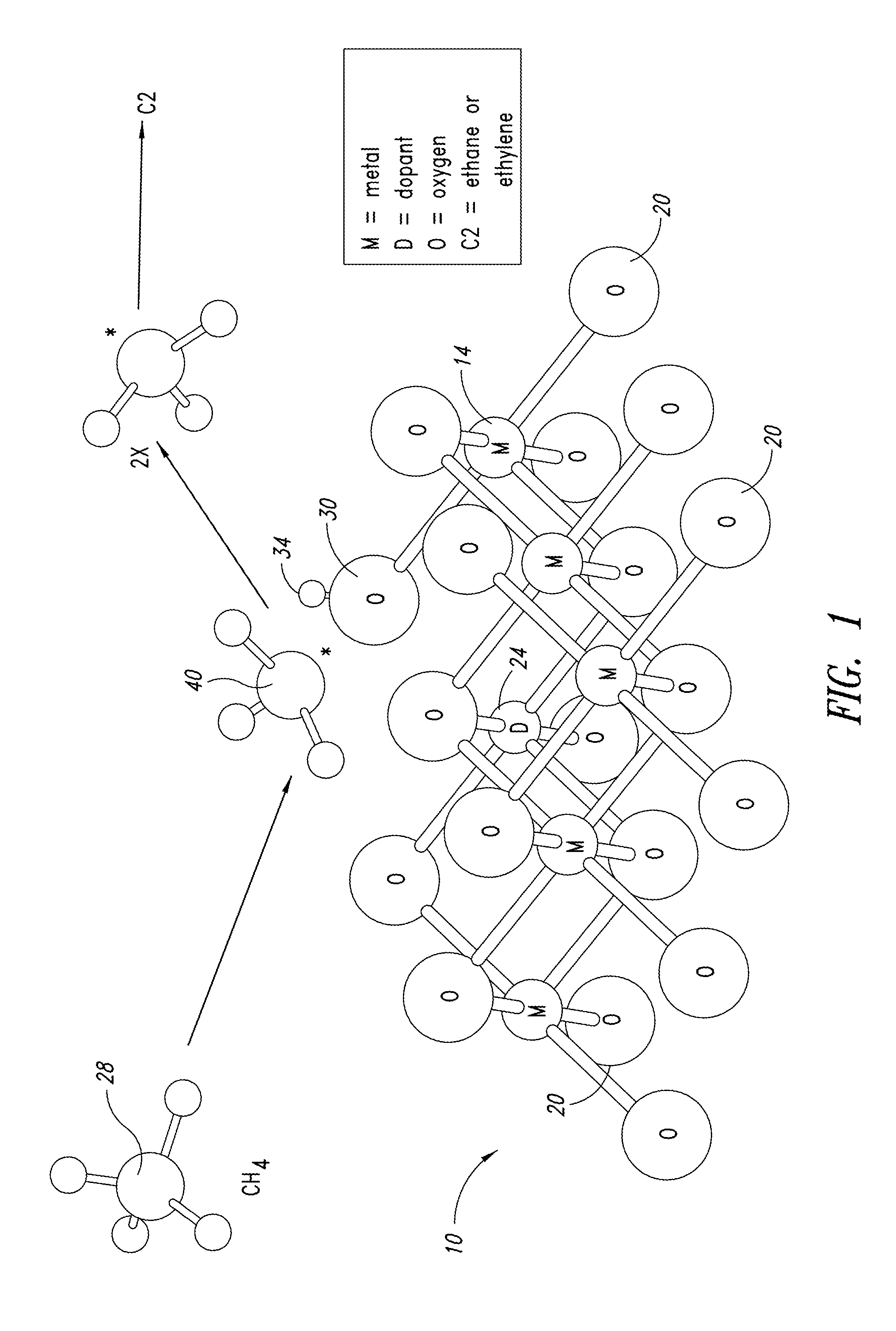
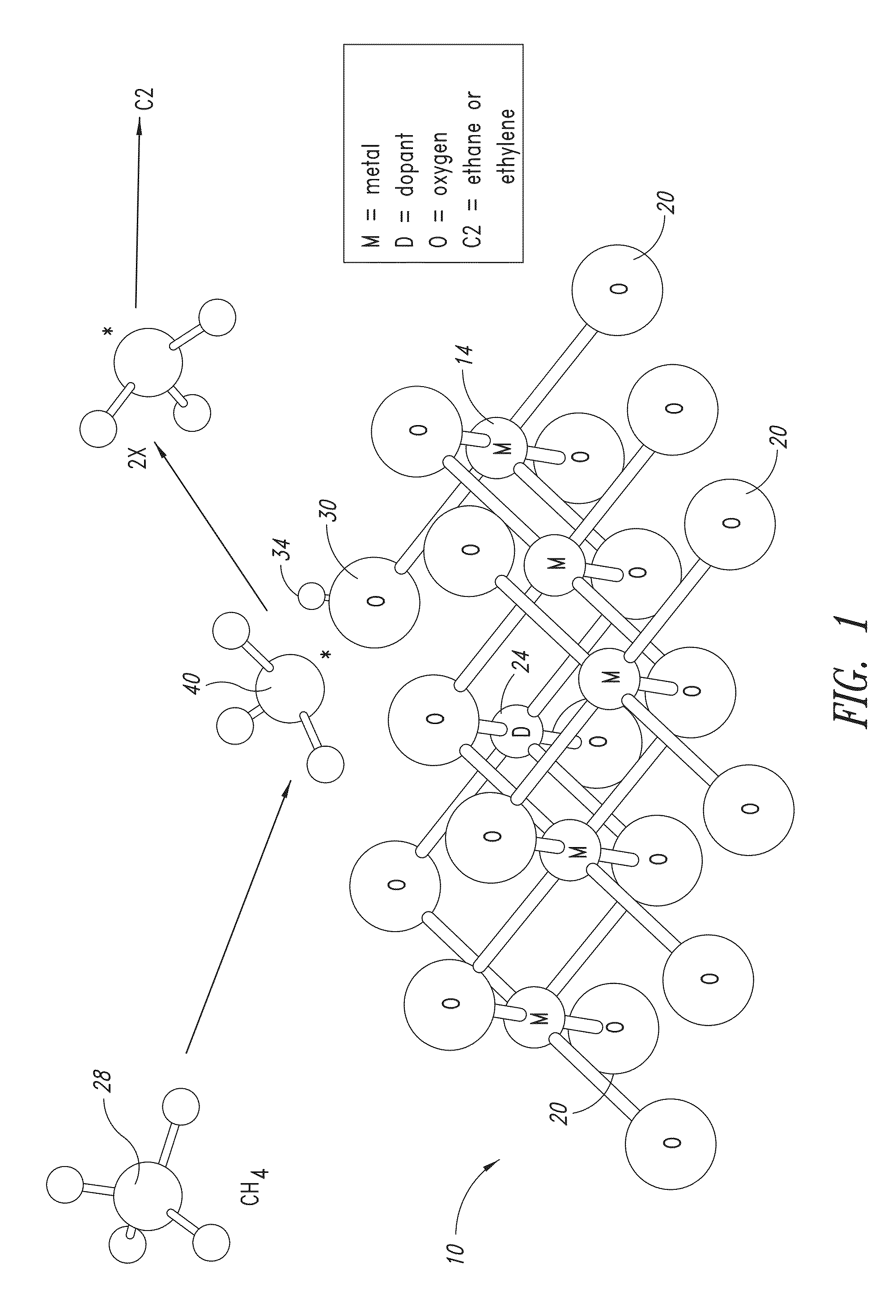
Metal oxide catalysts comprising various dopants are provided. The catalysts are useful as heterogenous catalysts in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to C2 hydrocarbons such as ethane and ethylene. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
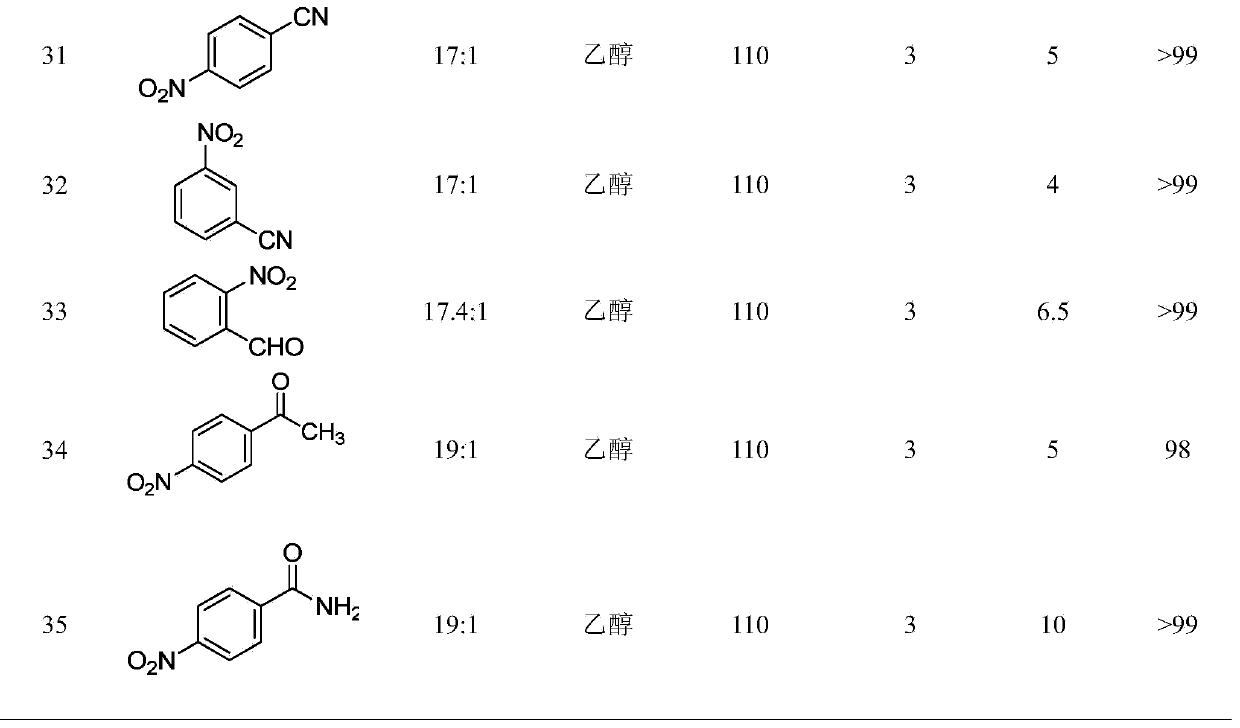
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Oxidation catalyst and process
InactiveUS20050176990A1Amino preparation from aminesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic oxidationNitrogen
This invention relates to the field of heterogeneous catalysis, and more particularly to catalysts including carbon supports having formed thereon compositions which comprise a transition metal in combination with nitrogen and / or carbon. The invention further relates to the fields of catalytic oxidation, including the preparation of secondary amines by the catalytic oxidation of tertiary amines.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Heterogeneous mass comprising foam absorbent core structure
InactiveUS20170119598A1Enhanced capillary actionImprove permeabilityAbsorbent padsBaby linensEngineeringVertical axis
An absorbent core structure comprising two or more layers wherein the upper layer is a heterogeneous mass layer comprising a longitudinal axis, a lateral axis, a vertical axis, one or more enrobeable elements, and one or more discrete open-cell foam pieces wherein the open-cell foam pieces.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Transition metal-containing catalysts and catalyst combinations including transition metal-containing catalysts and processes for their preparation and use as oxidation catalysts
ActiveUS20060229466A1Organic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCatalytic oxidationNitrogen
This invention relates to the field of heterogeneous catalysis, and more particularly to catalysts including carbon supports having compositions which comprise one or more transition metals in combination with nitrogen and / or carbon formed on or over the surface of the carbon support. The present invention also relates to catalyst combinations comprising catalysts including carbon supports having compositions which comprise one or more transition metals in combination with nitrogen and / or carbon formed on or over the surface of a carbon support and a secondary catalyst or, co-catalyst, including a secondary transition metal. The invention further relates to the field of catalytic oxidation reactions, including the preparation of secondary amines by the catalytic oxidation of tertiary amines.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Integral macroporous alumina and preparation method thereof
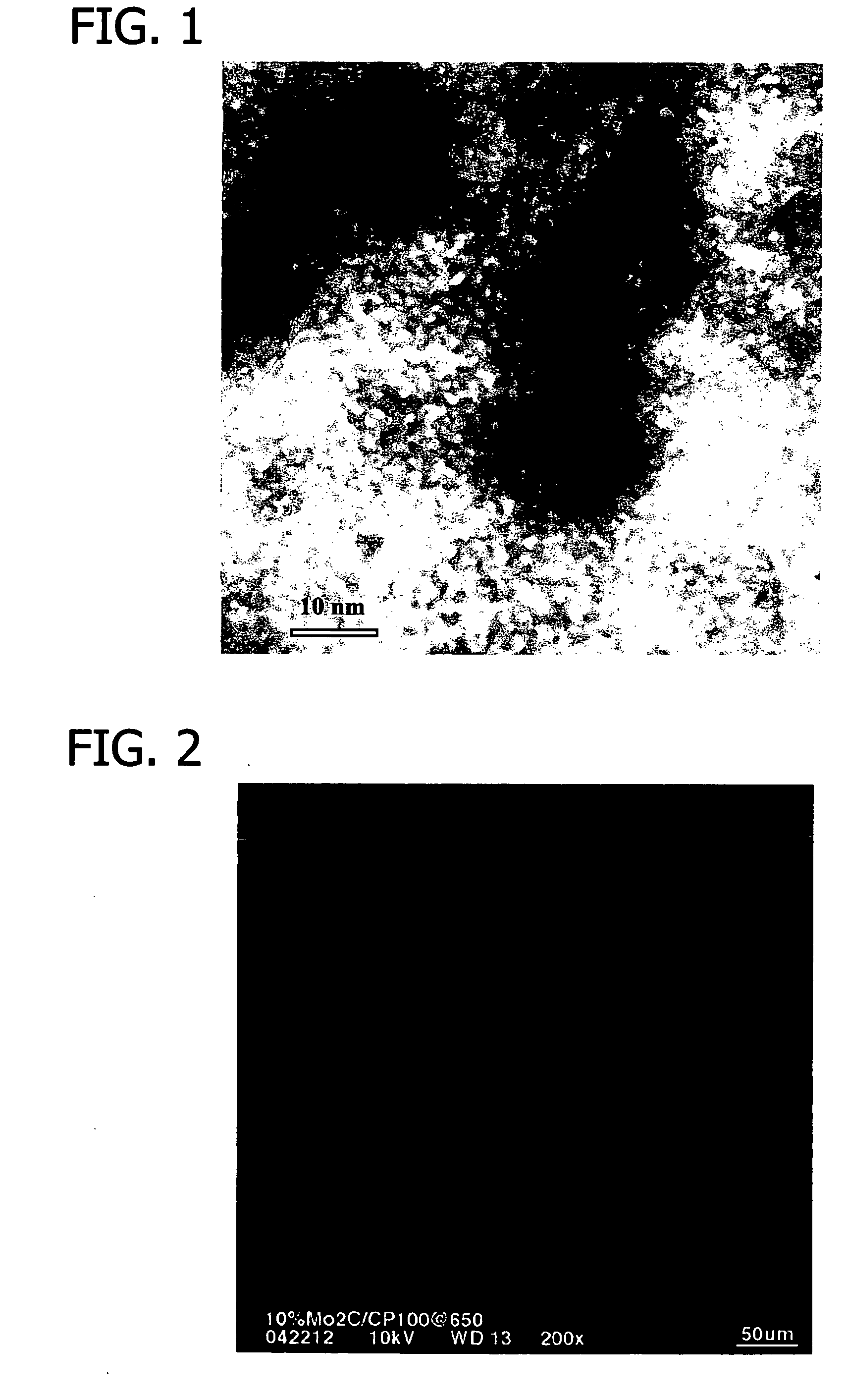
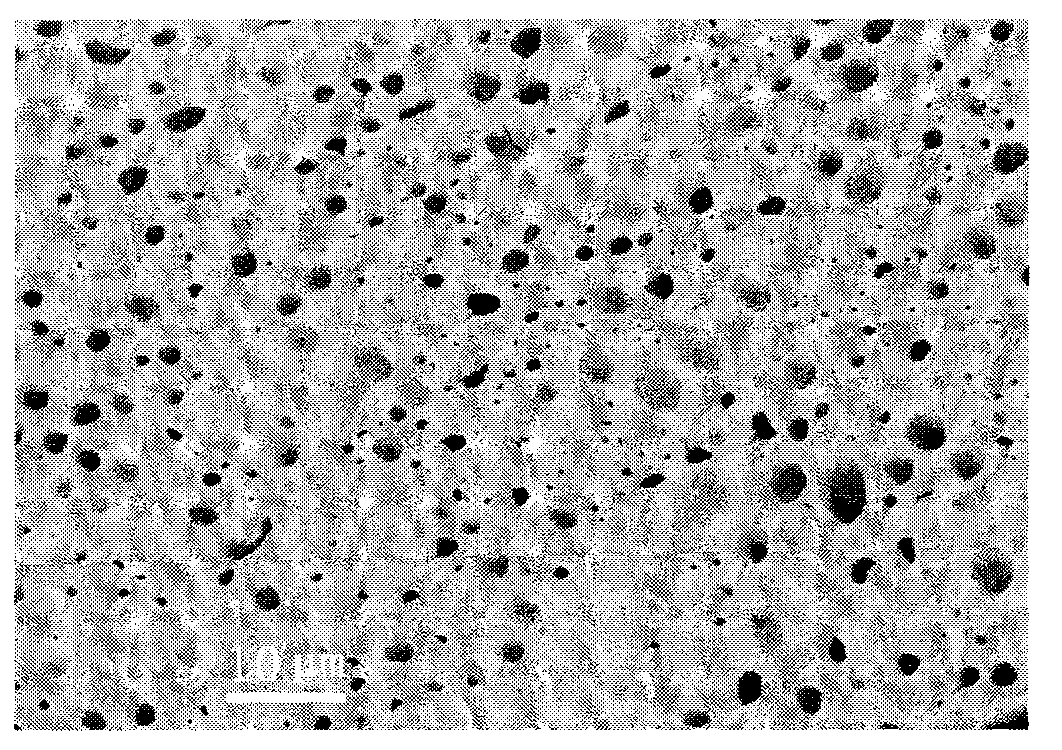
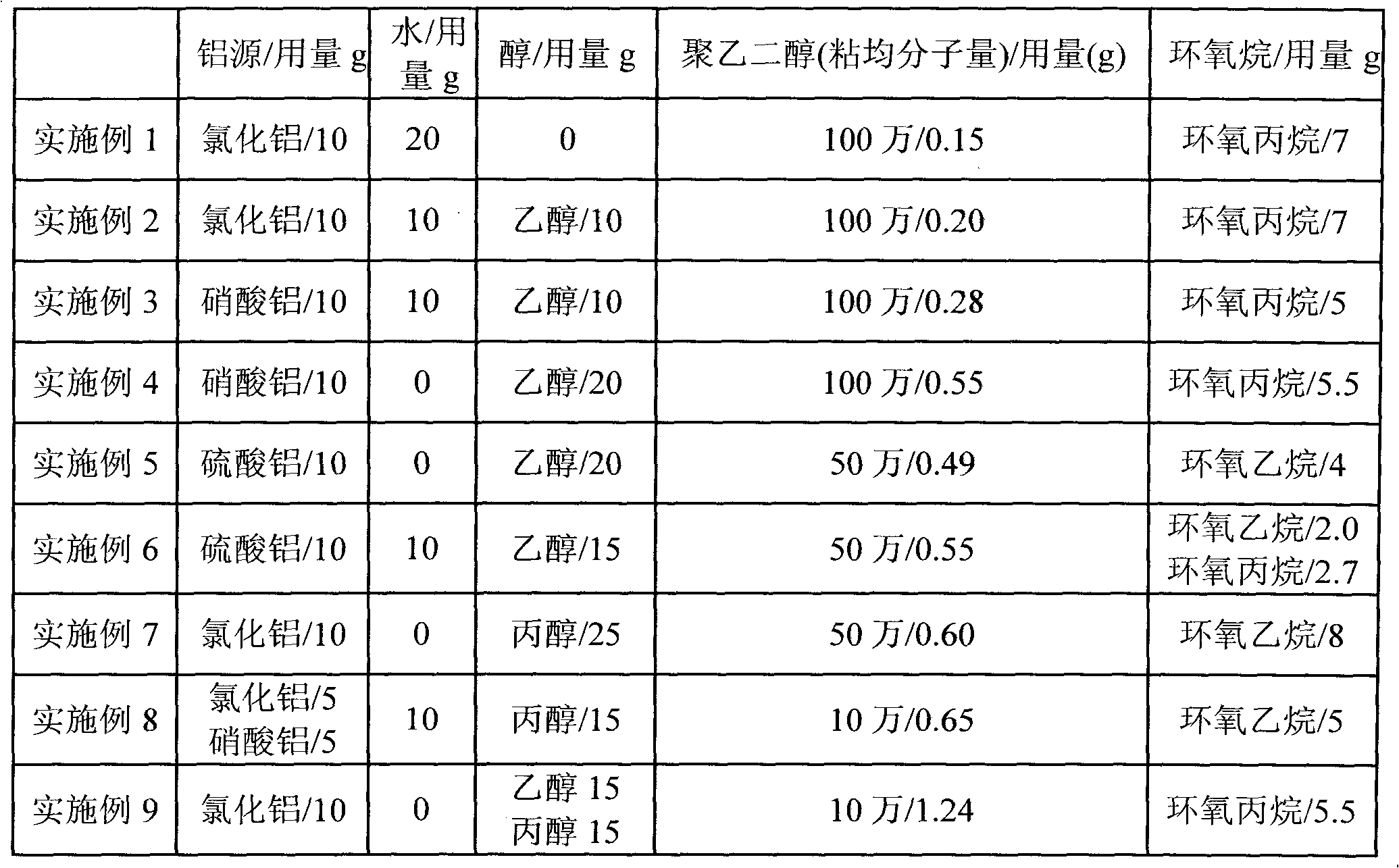
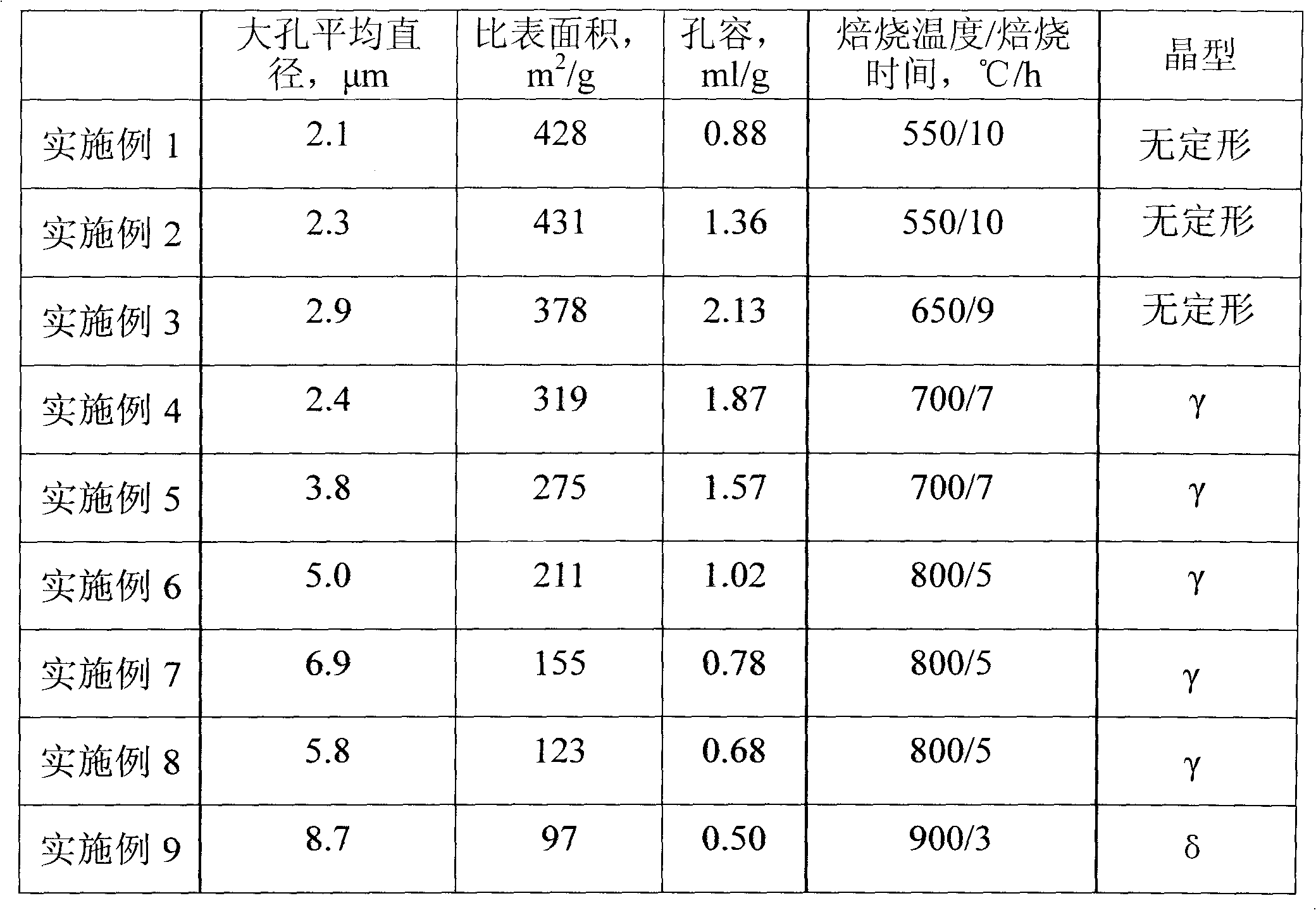
The invention discloses a method for preparing integral macroporous alumina. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing an aluminum source, polyethylene glycol and at least one of lower alcohol and water, adding low-carbon alkylene oxide into the mixture, ageing, soaking, drying and roasting to obtain the integral macroporous alumina. The preparation method is simple, feasible, and environment-friendly; and the obtained integral macroporous alumina has the controllable pore size of 0.05 to 10 mu m. The integral macroporous alumina can be applied to the fields such as macromolecular heterogeneous catalysis, adsorption and separation materials, chromatographic fillers, acoustic resistant and thermal resistant materials and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Metal complexes useful in metathesis and other reactions
InactiveUS20050043541A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic chemistry methodsFuranHigh activity
This invention provides metal complexes being useful as catalyst components in metathesis reactions and in reactions involving the transfer of an atom or group to an ethylenically or acetylenically unsaturated compound or another reactive substrate and, with respect to a sub-class thereof, for the polymerisation of α-olefins and optionally conjugated dienes, with high activity at moderate tempera-tures. It also provides methods for obtaining polymers with very narrow molecular weight distribution by means of a living reaction. It also provides methods for making said metal complexes and novel intermediates involved in such methods. It further provides derivatives of said metal complexes which are suitable for covalent bonding to a carrier, the product of such covalent bonding being useful as a supported catalyst for heterogeneous catalytic reactions. It also provides a direct one-step synthesis of pyrrole, furan and thiophene compounds from diallyl compounds.
Owner:RIMTEC CORP
Metal complexes useful in metathesis and other reactions
This invention provides metal complexes being useful as catalyst components in metathesis reactions and in reactions involving the transfer of an atom or group to an ethylenically or acetylenically unsaturated compound or another reactive substrate and, with respect to a sub-class thereof, for the polymerisation of α-olefins and optionally conjugated dienes, with high activity at moderate tempera-tures. It also provides methods for obtaining polymers with very narrow molecular weight distribution by means of a living reaction. It also provides methods for making said metal complexes and novel intermediates involved in such methods. It further provides derivatives of said metal complexes which are suitable for covalent bonding to a carrier, the product of such covalent bonding being useful as a supported catalyst for heterogeneous catalytic reactions. It also provides a direct one-step synthesis of pyrrole, furan and thiophene compounds from diallyl compounds.
Owner:RIMTEC CORP
Transition metal-containing catalysts and processes for their preparation and use as oxidation and dehydrogenation catalysts
ActiveUS20050176989A1Efficient oxidationMaterial nanotechnologyAmino preparation from aminesAlcoholDehydrogenation
This invention relates to the field of heterogeneous catalysis, and more particularly to catalysts including carbon supports having formed thereon compositions which comprise a transition metal in combination with nitrogen and / or carbon. The invention further relates to the fields of catalytic oxidation and dehydrogenation reactions, including the preparation of secondary amines by the catalytic oxidation of tertiary amines and the preparation of carboxylic acids by the catalytic dehydrogenation of alcohols.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Heterogeneous catalysts
ActiveUS20150314267A1High catalytic activityMolecular sieve catalystCatalystsDopantOxidative coupling of methane
Heterogeneous catalysts with optional dopants are provided. The catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to C2+ hydrocarbons. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Mixed-phase ceramic oxide three-way catalyst formulations and methods for preparing the catalysts
InactiveUS7641875B1Improve efficiencyLess timeOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsLanthanidePt element
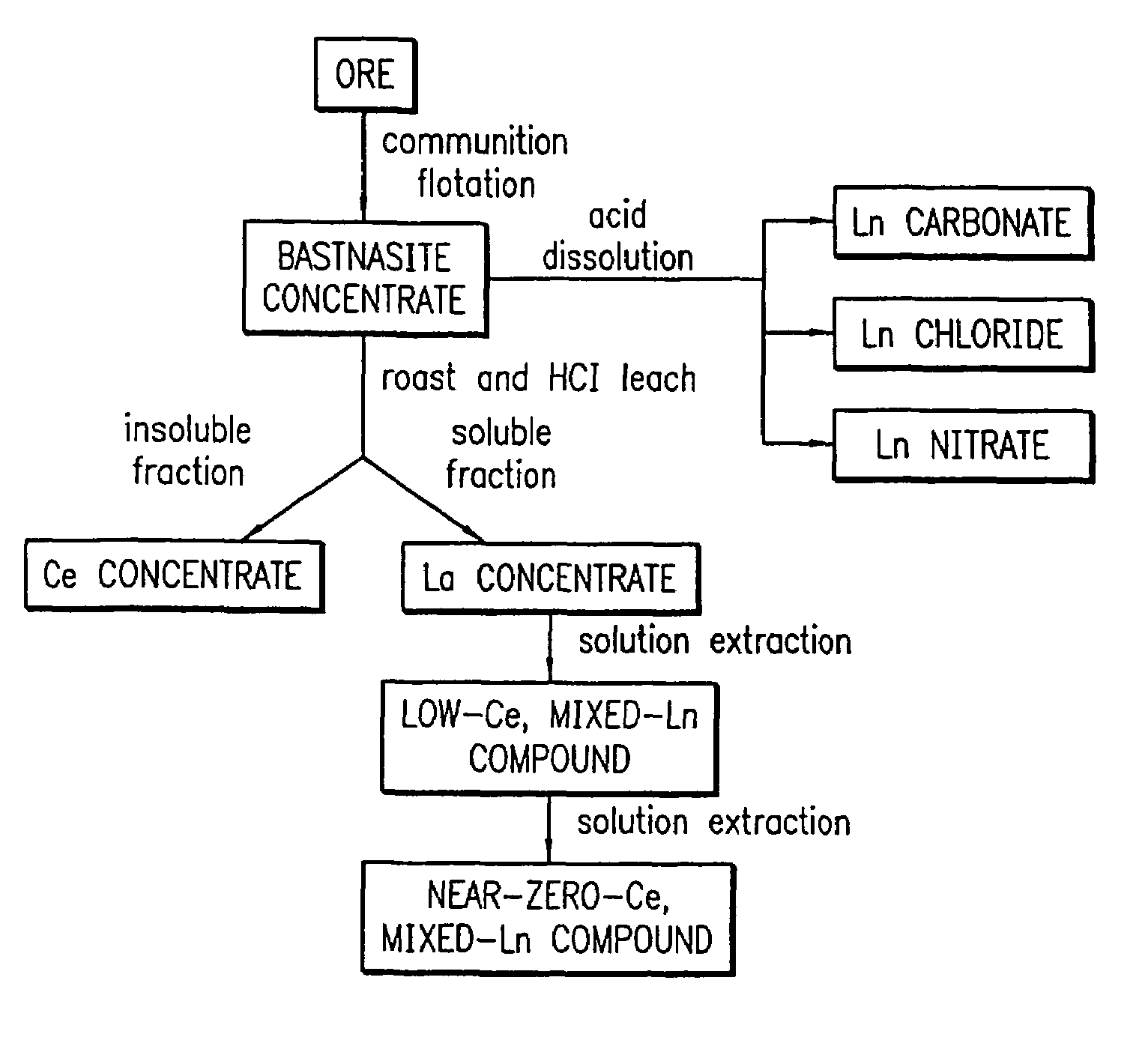
A multi-phase catalyst for the simultaneous conversion of oxides of nitrogen, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons is provided. A catalyst composition comprising the multi-phase catalyst and methods of making the catalyst composition are also provided. The multi-phase catalyst may be represented by the general formula of CeyLn1-xAx+sMOZ, wherein Ln is a mixture of elements originally in the form of single-phase mixed lanthanides collected from natural ores, a single lanthanide, or a mixture of lanthanides; A is an element selected from a group consisting of Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Li, Na, K, Cs, Rb, or any combination thereof; and M is an element selected from the group consisting of Fe, Mn, Cr, Ni, Co, Cu, V, Zr, Pt, Pd, Rh, Ru, Ag, Au, Al, Ga, Mo, W, Ti, or any combination thereof; x is a number defined by 0≦x<1.0; y is a number defined by 0≦y<10; s is a number defined by 0≦s<10; where s=0 only when y>0 and y=0 only when s>0. The multi-phase catalyst can have an overlayer of an oxide having the fluorite structure with a combination of platinum and / or rhodium.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope, electrochemical testing device and leveling system
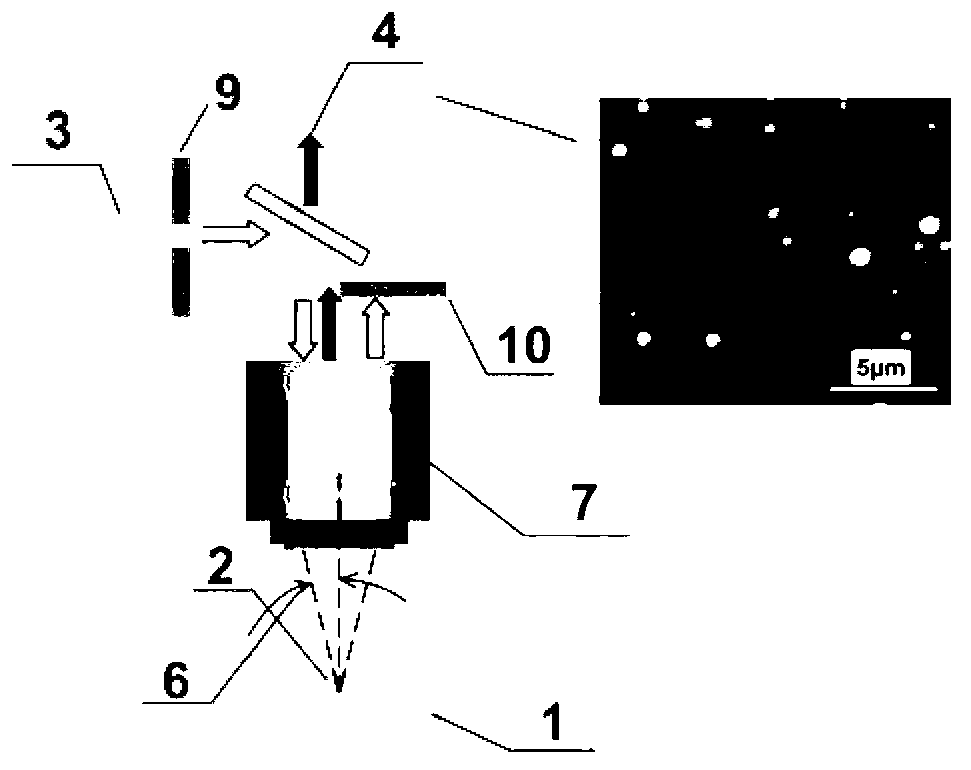
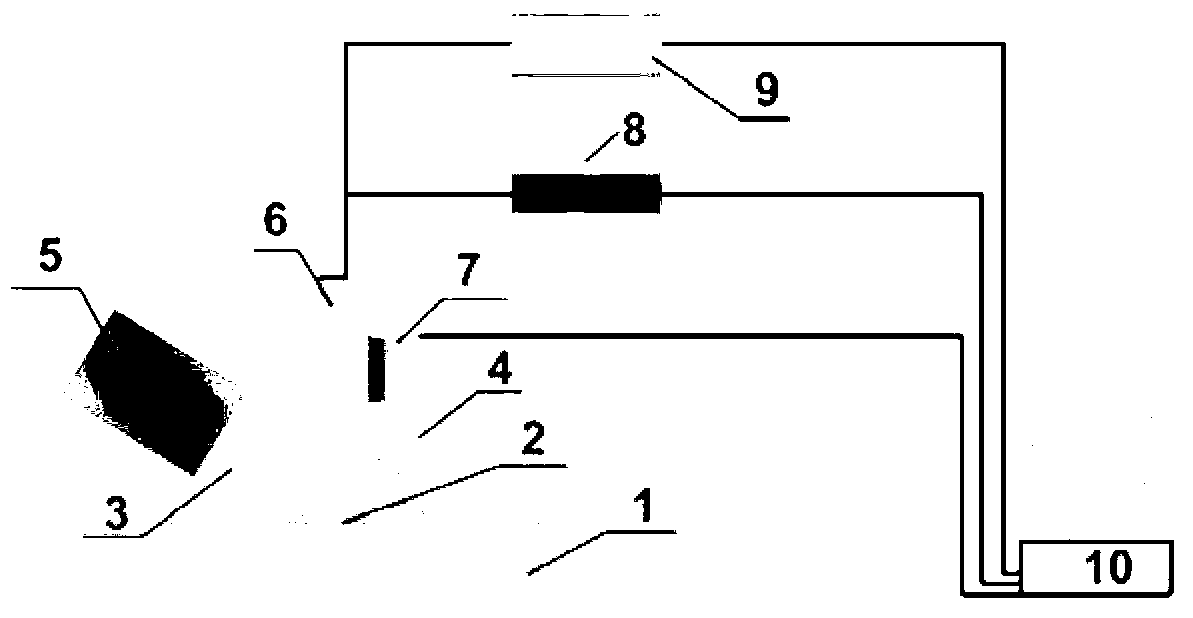
InactiveCN102798735AAchieve positioningAchieve levelingScanning probe microscopyDesorptionMetal particle
The invention provides a pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope, an electrochemical testing device and a leveling system. The pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope is characterized by using an optical fiber probe, wherein metal nanometer particles for decoration are arranged at the pinpoint of the optical fiber probe, incident lights are transmitted inside the optical fiber probe which is provided with the metal nanometer particles for decoration, and the distance between the pinpoint and a sample adopts a light intensity control mode; and the pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope is a localized surface plasmon resonance dark-field coupling device which utilizes the near-field coupling function of the nanometer metal particles at the pinpoint of the probe and a metal substrate material. The microscope can be used for researching basic surface and interface chemical problems such as a double-electric-layer structure of a substrate surface, adsorption / desorption behaviors and multi-phase catalysis. In addition, based on the LSPR (Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance) distance sensitiveness principle, the pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope can be applied to a three-probe horizontal sensor to perform self-adaptive leveling on a nanometer processing platform.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
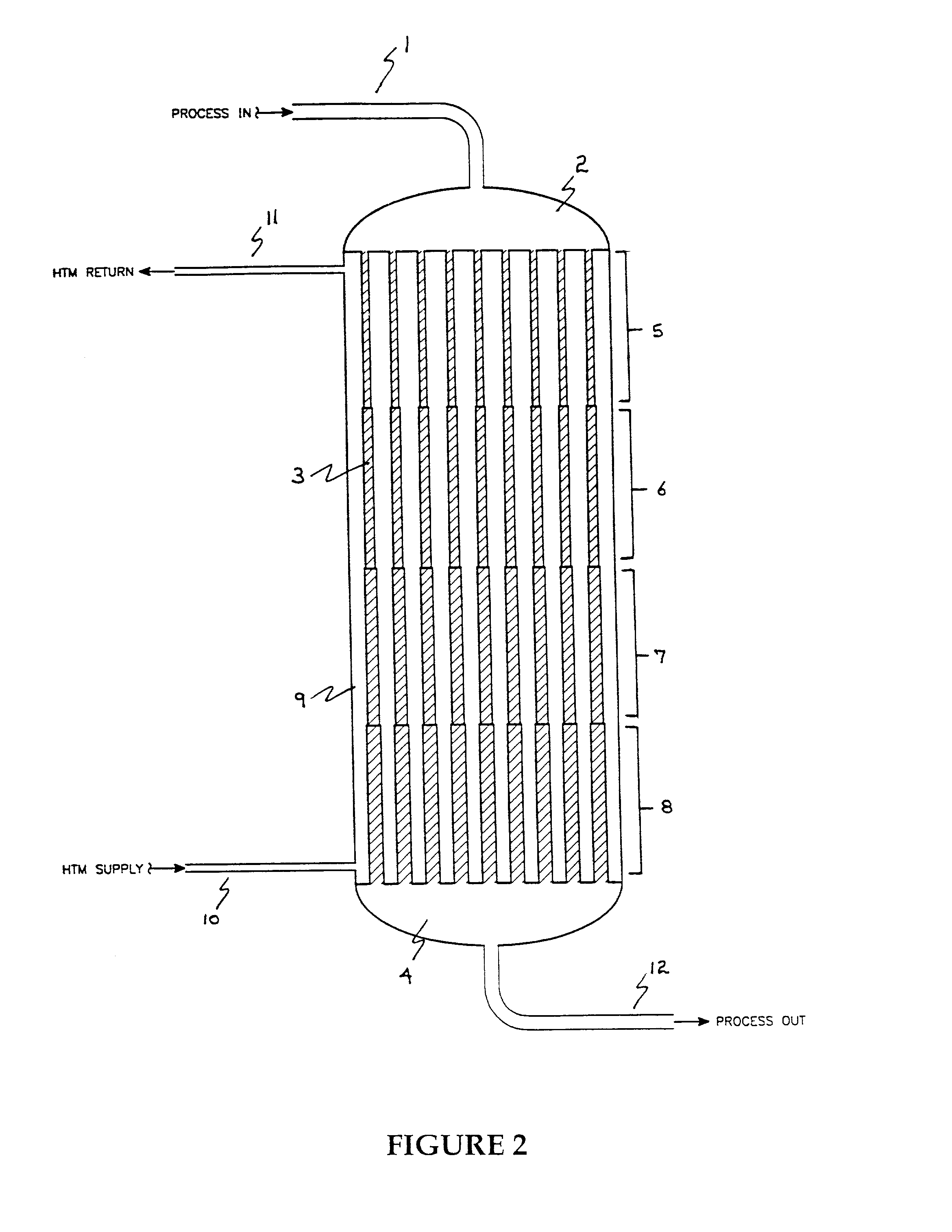
Flow reactors for chemical conversions with heterogeneous catalysts
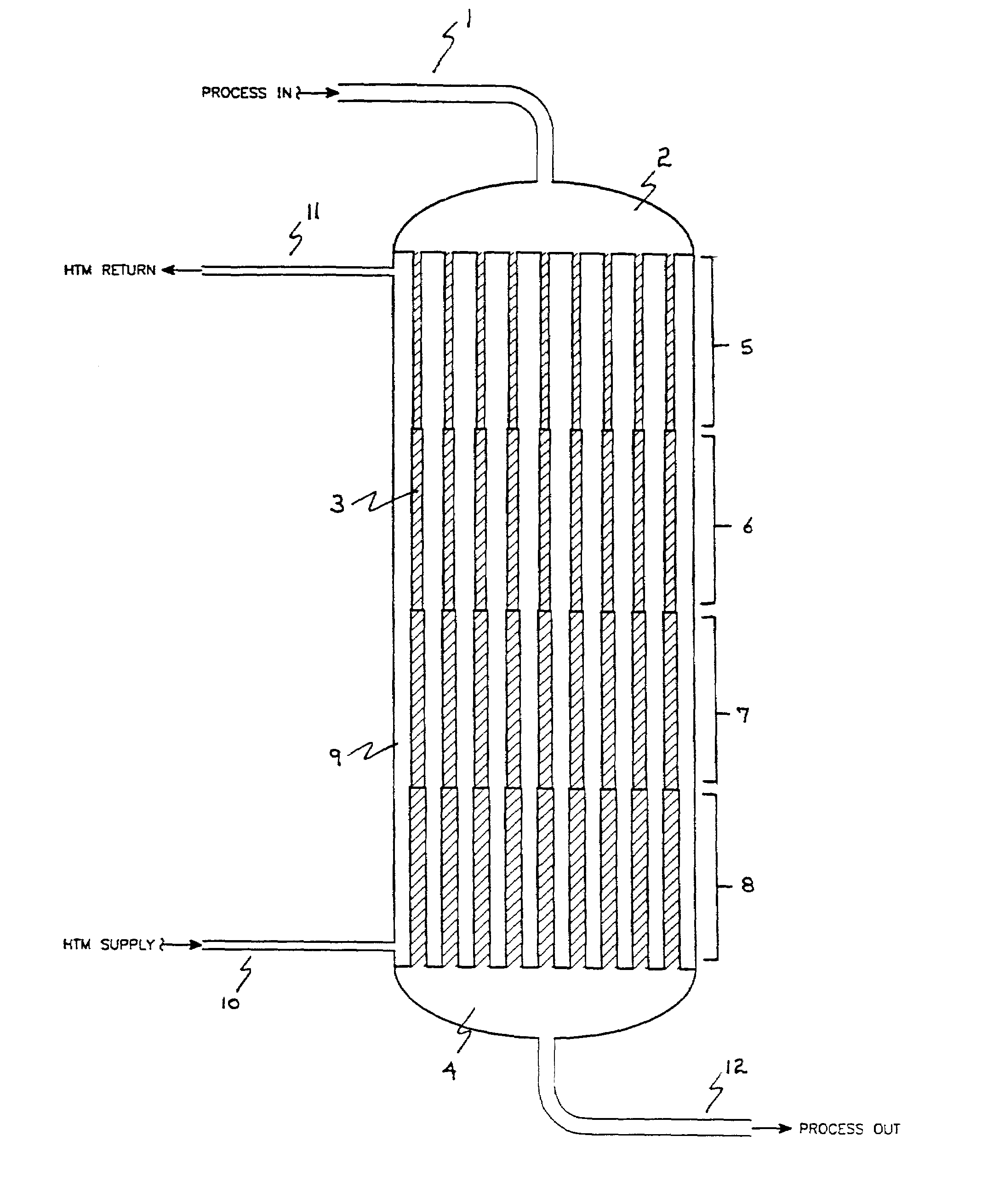
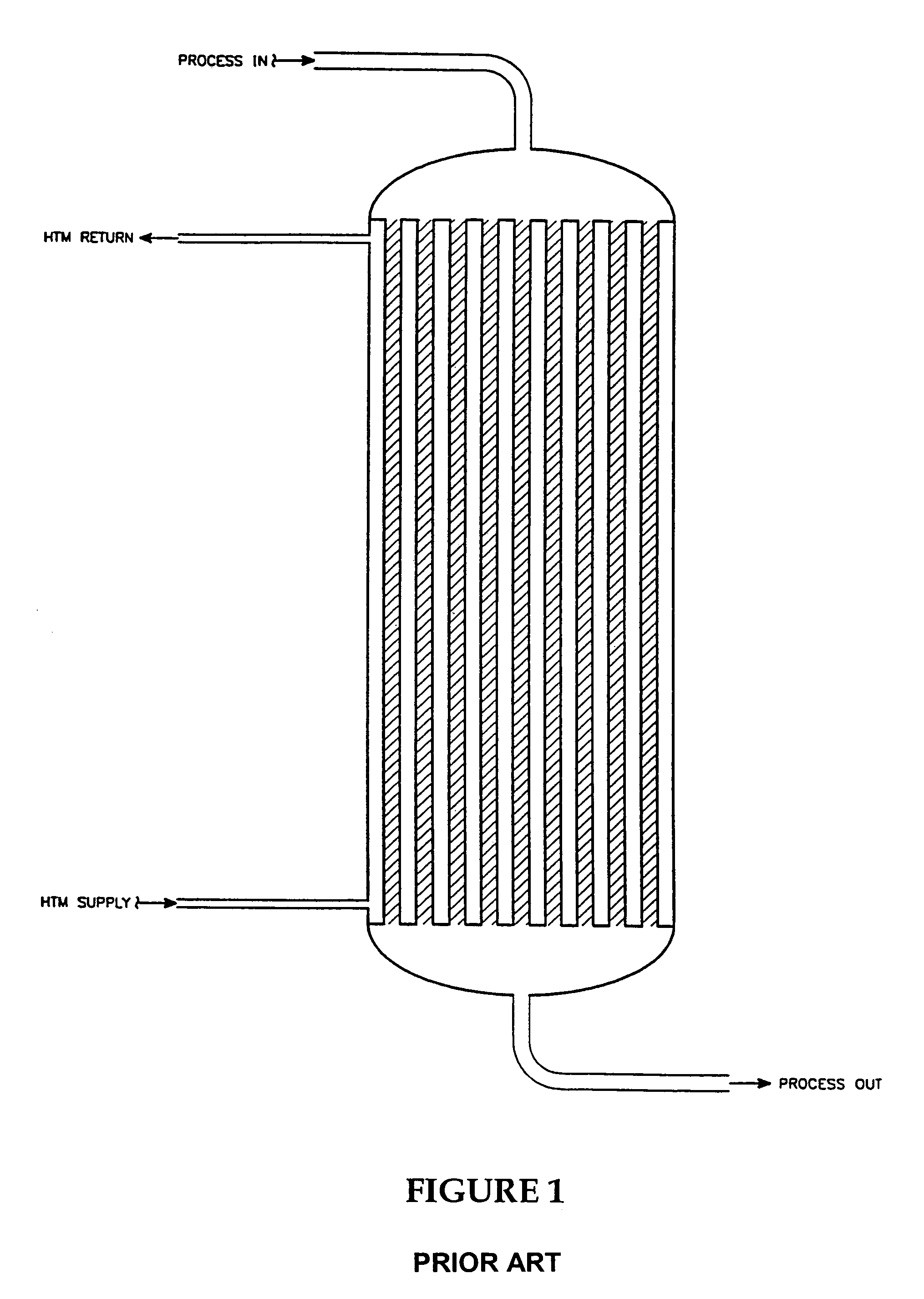
InactiveUS7316804B2High trafficPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationProcess systemsProcess engineering
Improved apparatus for use in process systems which include exothermic chemical conversions of organic compounds to value added products is disclosed, more particularly, flow reactors for exothermic chemical conversions using a fixed heterogeneous catalyst with means for control of the exotherm. Flow reactors of the invention comprise a plurality of walled conduits each having an outer surface disposed for contact with a heat-transfer medium, an inlet distribution manifold adapted for flow communication with a downstream manifold through channels formed by heterogeneous catalytic material disposed within each conduit during operation in a sequence of zones for catalyst having the same or different length along the longitudinal coordinate of the conduit and within each zone essentially uniform cross-section of the conduit measured in a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal coordinate thereby defining volume of the zone, and the sequence of zones comprising of at least two zones such that each downstream zone has a larger or smaller cross-section than the contiguous upstream zone. Another aspect of the invention includes processes which use such flow reactors, for example the continuous manufacture of maleic anhydride.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
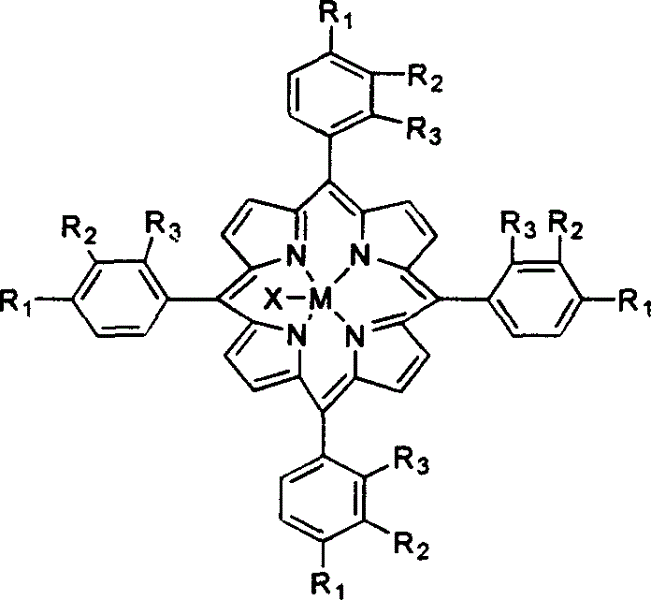
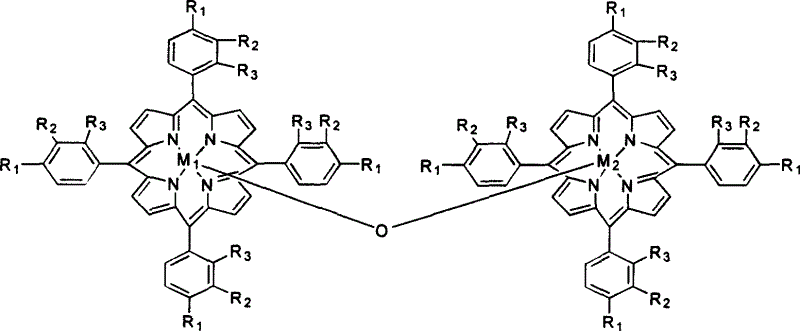
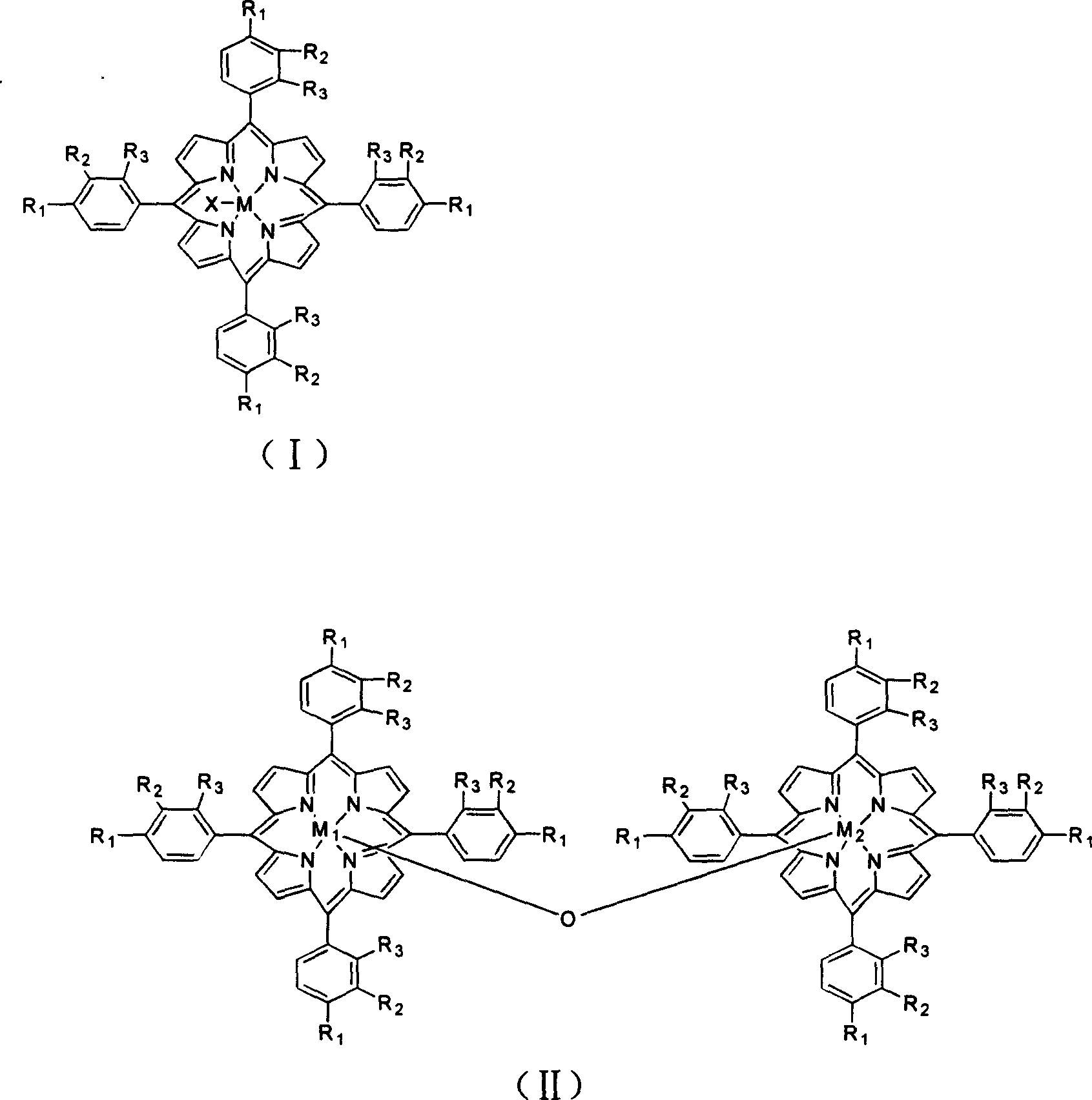
Method for atmospheric catalytic oxidation of cyclohexane by metalloporphyrin
InactiveCN1405131APreparation by oxidation reactionsOxygen compounds preparation by hydrocarbon oxidationCyclohexanoneReaction temperature
The invention relates to a new process in which under the catalytic action of metal porphyrin the cyclohexane can be selectively oxdated by air and made into cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone. Under the condition of 2-10 atm air, reaction temp. is 125-150 deg.C, it selects and uses micro-oxo double metal porphyrin and single metal porphyrin or their solid carrier as main catalyst, and uses transition metal salt or oxide as co-catalyst, the metal porphyrin can high-effectively and high-selectively catalyze oxidation of cyclohexane by using air in the biological concentratino as biological enzyme. The dose of metal porphyrin is small and said metal porphyrin can be repeatedly used, and said catalyst dose also is small, its catalystic effect is good, said catalyst can be used for making homogeneous catalysis, and after it is solid-carried, it also can be used for making heterogeneous catalysis.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for low-temperature atmosphere-pressure hydrothermal synthesis of stephanoporate metal-organic framework
InactiveCN101429209AFully contactedQuality improvementCadmium organic compoundsZinc organic compoundsMetal-organic frameworkChemistry
The invention discloses a method for hydrothermally synthesizing a porous metal-organic framework under low temperature and normal pressure, which comprises the following steps: 1) bivalent transition metal salt is put into proper amount of distilled water to be dissolved; 2) a multidentate organic ligand is put into proper amount of distilled water, and ammonia (30 percent, W / W) is added into the solution until the organic ligand is dissolved; 3) solutions obtained in step 1) and step 2) are mixed, and diluted by the distilled water; 4) the solution obtained in step 3) reacts for 4 to 24h at a temperature of between 80 and 100 DEG C, and is naturally cooled to room temperature at an environmental temperature to obtain an MOF crystal product; and 5) the MOF crystal product obtained in step 4) is filtered, MOF crystals are colleted and washed by the distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol respectively, and the product is obtained after the natural drying. By performing a hydrothermal reaction in an ammonia solution, the method has mild conditions needed by the synthesis, less energy consumption and time consumption, and does not need a voltage resistant reactor. Therefore, the method is simpler and has lower cost; and a porous crystal material obtained by the synthesis has potential application value in the fields of gas separation, gas storage and heterogeneous catalysis.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Process for producing fatty acid alkyl esters and glycerol of high-purity
InactiveUS20060014974A1Process economyFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationAlcoholGlycerol
In a process for producing fatty acid alkyl esters and glycerol comprising at least one reaction stage in which a charge comprising a vegetable and / or animal oil and an alcohol are brought into contact, in the presence of a heterogeneous catalyst, so as to obtain an effluent comprising at least alkyl esters, glycerol and alcohol, and at least one separation stage during which a separation is carried out of at least one portion of the effluent so as to separate an alcohol-rich effluent and an alkyl esters-rich effluent, at least one separation stage consists of a membrane separation using at least one alcohol-permeable membrane.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Gas agitated multiphase catalytic reactor with reduced backmixing
InactiveUS7022741B2Optimizing degree of backmixingImproved gas distributionOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationProduct gasEngineering
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for optimizing the degree of backmixing within a gas agitated multiphase reactor at a given gas linear velocity. The embodiments of the present invention involve novel configurations of the multiphase reactor internal structures. In general, the configurations comprise creating a dense area of internal structures in the central region and / or wall regions of the multiphase reactor.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Method of preparing adipic acid by air-oxidating hexacarbocyclic compound
InactiveCN1535947AReduce dosageHigh catalytic efficiencyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationCyclohexanoneCyclohexene
The present invention relates to a new process for preparing adipic acid by air oxidating cyclohexane, cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone and cyclohexene or mixture of cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone under the catalysis of metal porphyrin. Under the condition of 1-20 atm air and reaction temp. is 50-200 deg.C it can select and use mu-oxidized metal porphyrin and monometal porphyrin or their fixed carrier material as catalyst independently, also can select and use metal porphyrin or their fixed carrier material as main catalyst, and use transition metal salt or oxide as co-catalyst. The metal porphyrin like biological-enzyme can high-effectively and high-selectivity catalyze air under the biologicae concentration to directly oxidate the cyclohexane into adipic acid. Said invented dose of metal porphyrin is less, and its catalytic effect is good, it can make homogeneous catalysis, also can make heterogeneous catalysis after the carrier is fixed.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Advanced treatment method for fracturing flow-back fluid
ActiveCN102161536AHigh removal rateSimple processMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationLiquid wasteTreatment effect
The invention discloses an advanced treatment method for fracturing flow-back fluid, belongs to the field of water treatment of the development of oil and gas fields, and particularly relates to an advanced treatment method for the fracturing flow-back fluid generated during the operation of the oil and gas fields. The treatment method for the fracturing flow-back fluid, which has high effect and continuous treatment process, is provided to solve the problems that the treatment effect is lower, the continuous treatment cannot be performed, and the cost is higher existing in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-oxidizing waste liquor with the pH value of between 8 and 12, adding a coagulant and performing gel breaking treatment and adding a Fenton reagent and treating, and performing secondary coagulation and oxidization treatment. In the method, through homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis reactions, the treatment cost is reduced, and the removal rate of organic substances is also high; and chemical oxygen demand (COD) of effluent can meet the national sewage discharge standard.
Owner:四川绿源环保技术开发有限公司
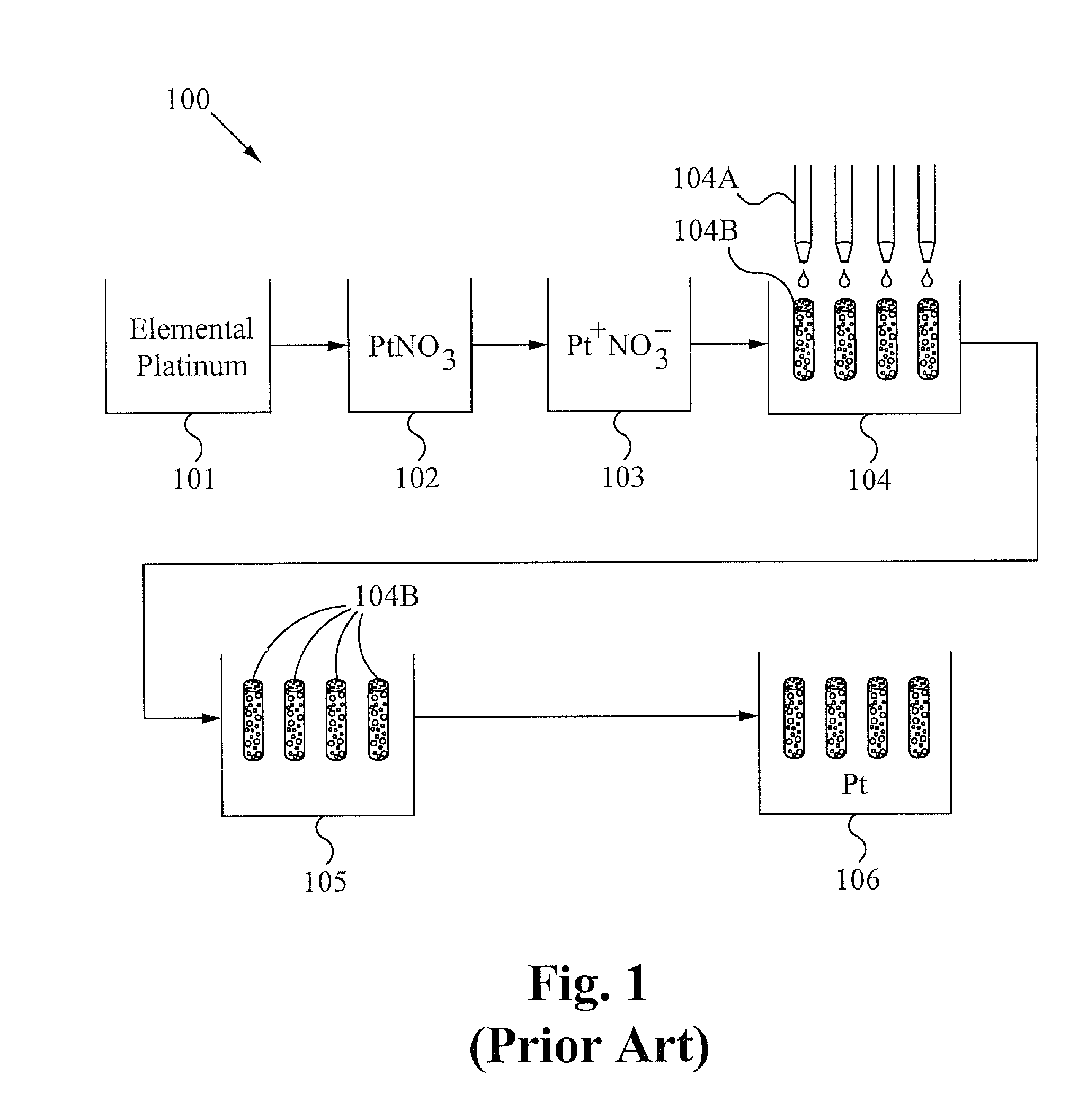
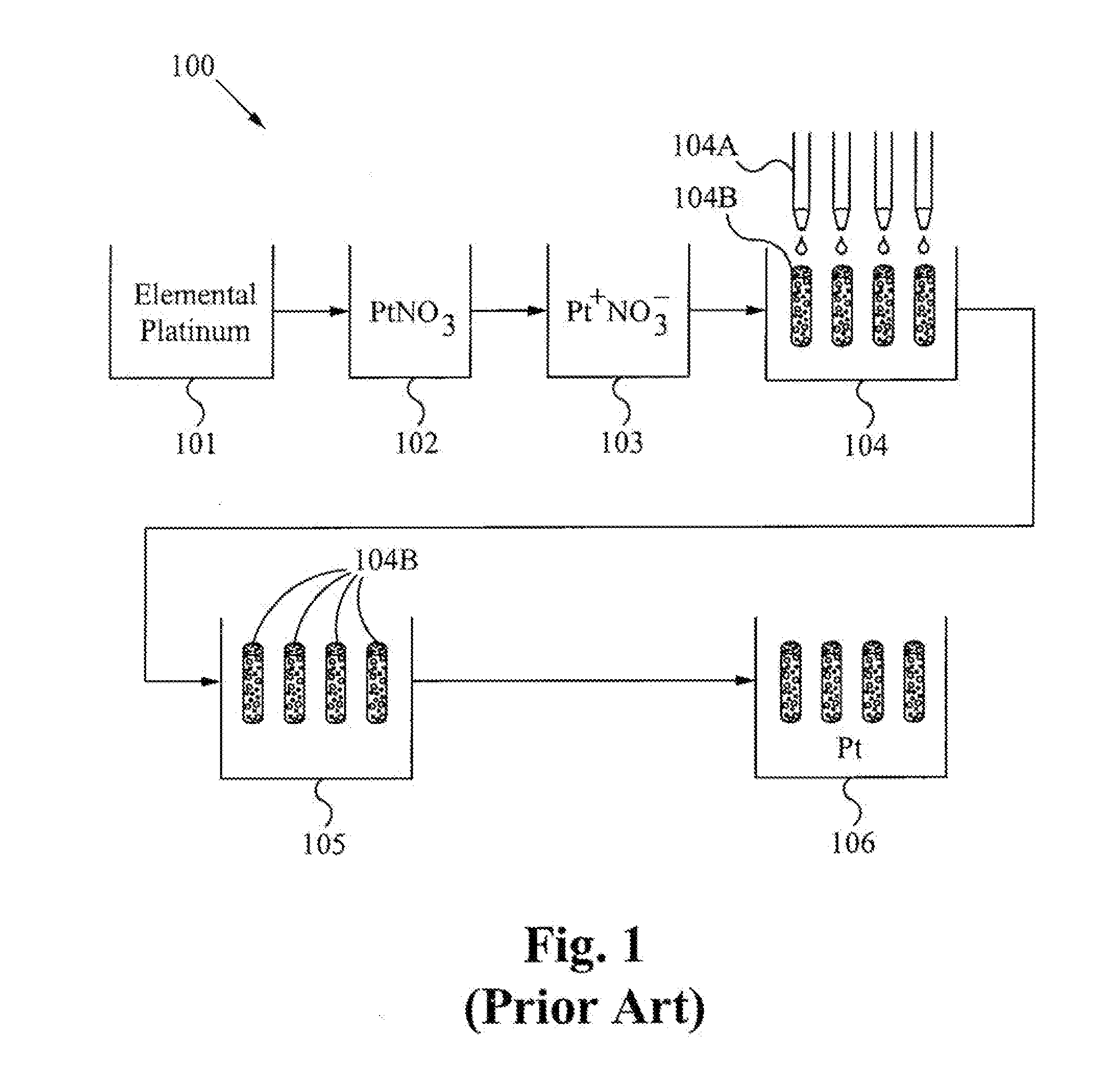
Method and system for forming plug and play metal catalysts
A metal catalyst is formed by vaporizing a quantity of metal and a quantity of carrier forming a vapor cloud. The vapor cloud is quenched forming precipitate nanoparticles comprising a portion of metal and a portion of carrier. The nanoparticles are impregnated onto supports. The supports are able to be used in existing heterogeneous catalysis systems. A system for forming metal catalysts comprises means for vaporizing a quantity of metals and a quantity of carrier, quenching the resulting vapor cloud and forming precipitate nanoparticles comprising a portion of metals and a portion of carrier. The system further comprises means for impregnating supports with the nanoparticles.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Heterogeneous catalysts for alkene hydroformylation reaction and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103521268AHigh activityImprove stabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide reactionFormylation reactionMetal catalyst
The invention discloses a supported metal catalyst under double modification of an anchoring ligand and an auxiliary and a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst comprises an active component, an auxiliary, a carrier and a ligand, wherein the active component is one or more of metals Rh, Ru and Co; the auxiliary is one or more of Al, K, Zn, Cu and Ag; the carrier is a molecular sieve SiO2, Al2O3, MCM-41 or SBA-15; the ligand is an N or P-containing organic ligand capable of acting with silicon hydroxyl. In the catalyst, the metal component and the auxiliary are directly fixed on the carrier, and then the anchoring ligand and the metal generate a coordination action to in-situ generate an active species; due to the double modification of the ligand and the auxiliary, the activity and stability of the catalyst are remarkably improved. The catalyst can be applied to alkene hydroformylation to prepare various organic aldehydes, has relatively high catalytic activity and excellent stability, and is easy to separate.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for forming plug and play metal catalysts
A metal catalyst is formed by vaporizing a quantity of metal and a quantity of carrier forming a vapor cloud. The vapor cloud is quenched forming precipitate nanoparticles comprising a portion of metal and a portion of carrier. The nanoparticles are impregnated onto supports. The supports are able to be used in existing heterogeneous catalysis systems. A system for forming metal catalysts comprises means for vaporizing a quantity of metals and a quantity of carrier, quenching the resulting vapor cloud and forming precipitate nanoparticles comprising a portion of metals and a portion of carrier. The system further comprises means for impregnating supports with the nanoparticles.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS +1
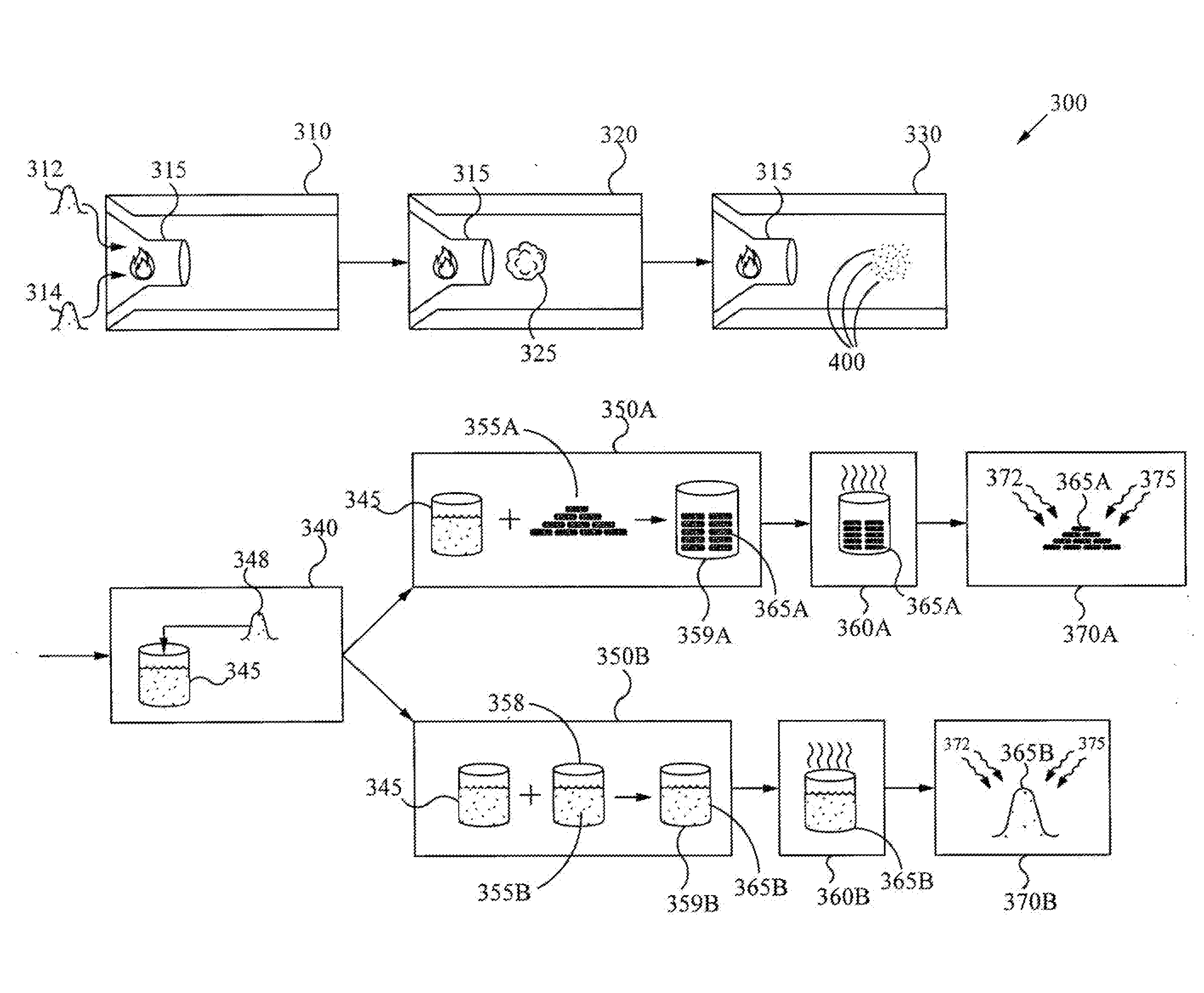
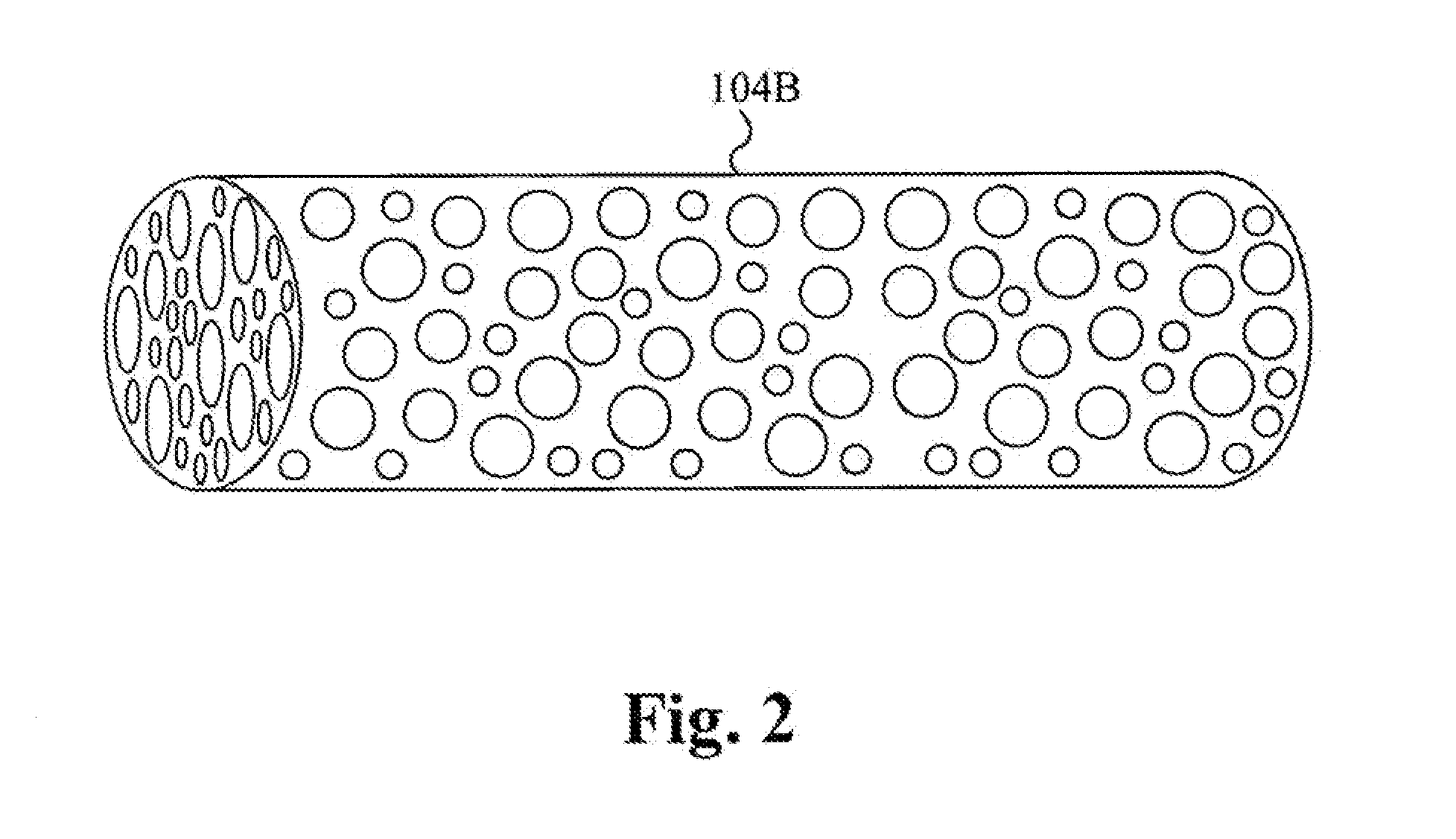
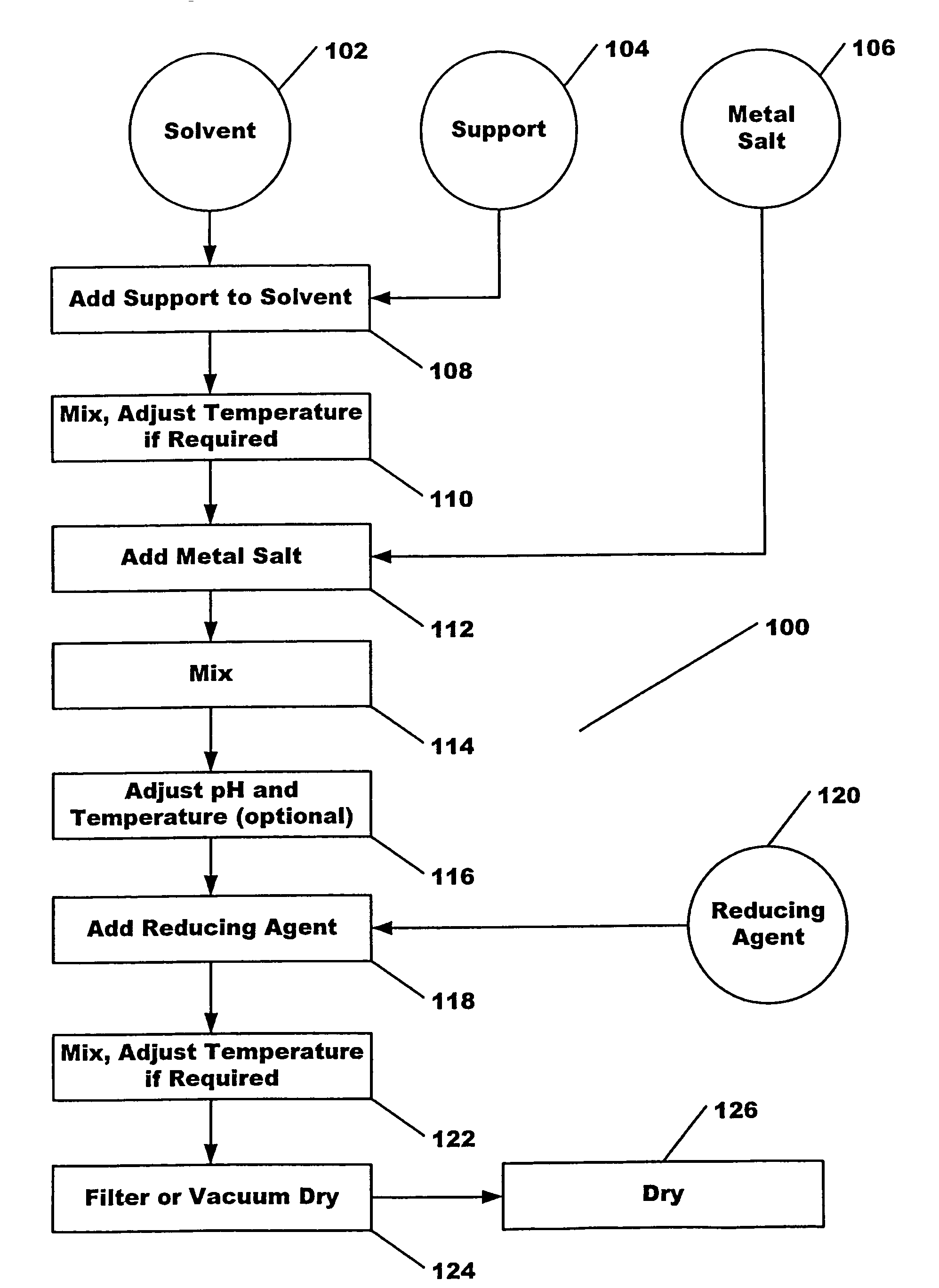
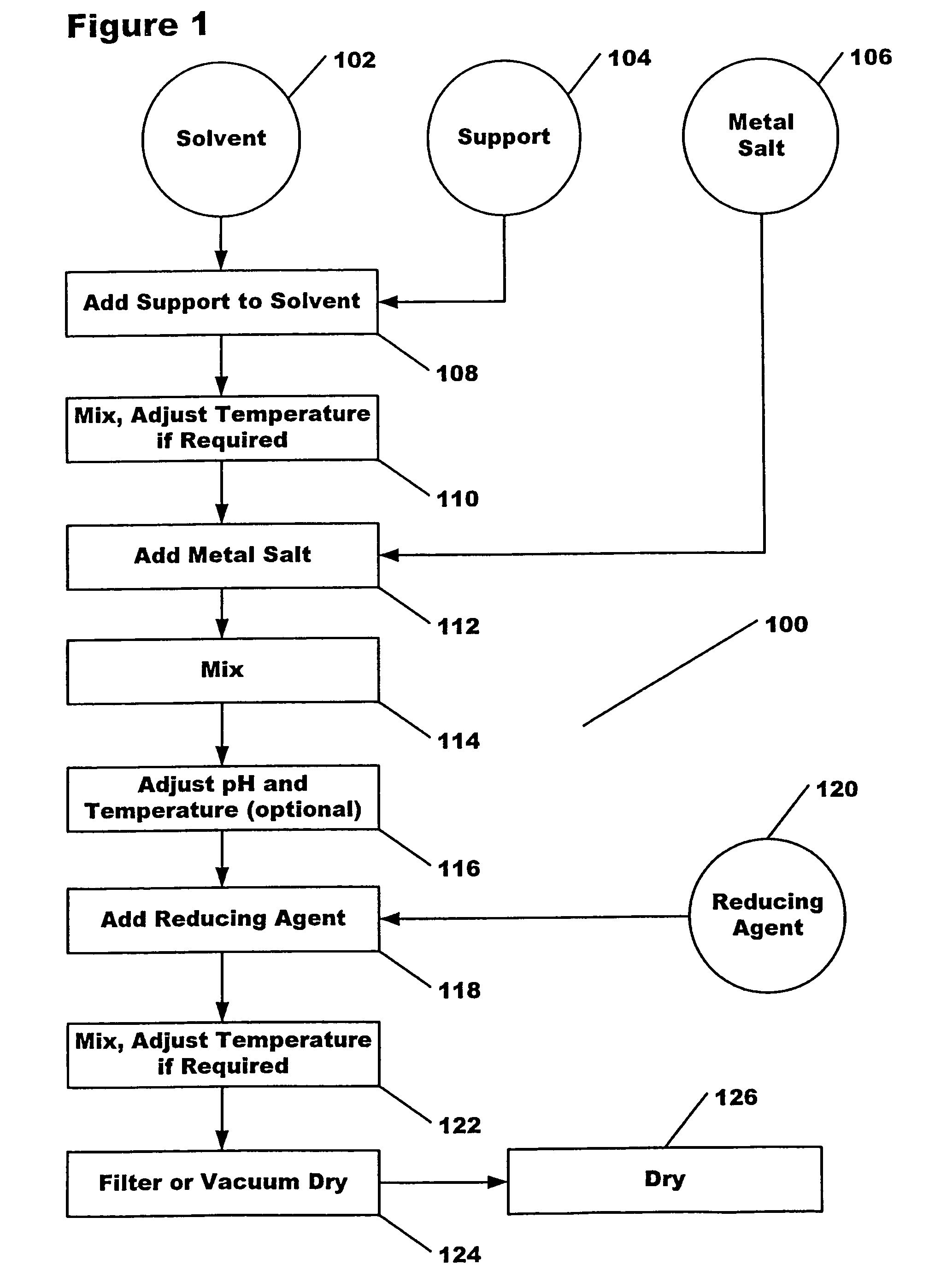
Method for producing heterogeneous catalysts containing metal nanoparticles
A method for producing highly dispersed catalysts is disclosed. The method includes contacting a support material with a solvent for a period of time, adding a metal salt to the solvent and support mixture, and then adding a reducing agent to the solution to reduce the metal salt to nanometer sized metal particles on the surface of the support. Excess solvent is used in the process, the volume of solvent being greater than two times the pore volume of the support.
Owner:DONGUANN INNOVATIVE NEW MATERIALS
Process for preparing epoxy cyclohexane by catalytic cyclooxidation of cyclohexene
A process for preparing epoxy cyclohexane by catalytic epoxidation of cyclohexene is disclosed. It is characterized by use of a phase-transfer catalyst which is insoluble in reaction medium but can become the active substance soluble in reactino medium under action of hydrogen peroxide. Said catalyst can be cyclically used. Its advantages are high selectivity (97%), easy recovery of catalyst, no by-product and low cost.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Heterogeneous catalysts
Heterogeneous catalysts with optional dopants are provided. The catalysts are useful in a variety of catalytic reactions, for example, the oxidative coupling of methane to C2+ hydrocarbons. Related methods for use and manufacture of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:SILURIA TECH INC
Heterogeneous catalyst for selective hydrogenation reaction of aryl nitro-compound and application of heterogeneous catalyst
ActiveCN104174421AEasy to prepareMild conditionsPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationNitro compoundAryl
The invention discloses a heterogeneous catalyst for selective hydrogenation reaction of an aryl nitro-compound. The heterogeneous catalyst consists of 10-90 weight percent of base metal particles and 10-90 weight percent of nitrogen-doped carbon nano tubes, wherein the nitrogen content in the nitrogen-doped carbon nano tubes is 0.01-20.0 weight percent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking a carbohydrate as a raw material, uniformly mixing the carbohydrate with an artificial template agent in the presence of base metal salts, preserving the temperature of 400-650 DEG C for 0.5-2 hours in an inert atmosphere, raising the temperature to 700-1200 DEG C, and calcining for 0.5-2 hours, thereby obtaining the heterogeneous catalyst. The heterogeneous catalyst containing base metals is generated in situ through a specific method, is stable to air and water heat, is applied to the selective hydrogenation reaction of the aryl nitro-compound and has excellent catalytic activity and selectivity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for conducting catalytic reaction in ultragravity field
ActiveCN1743064AEasy to prepareExtended regeneration cycleChemical/physical/physico-chemical moving reactorsEmulsionActive component
The present invention discloses a method for making catalytic reaction in supergravitational field. Said method includes the following steps: after the heterogeneous catalyst is formed into liquid phase, it can be used for making catalystic reaction, and said reaction is made in the supergravitational rotary bed reactor, in which the described liquid phase formation is characterized by that the active component of catalyst is dissolved in the liquid phase reaction material or solvent to form homogeneous mixture or dispersed in the liquid phase reaction material or solvent to form emulsion
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com