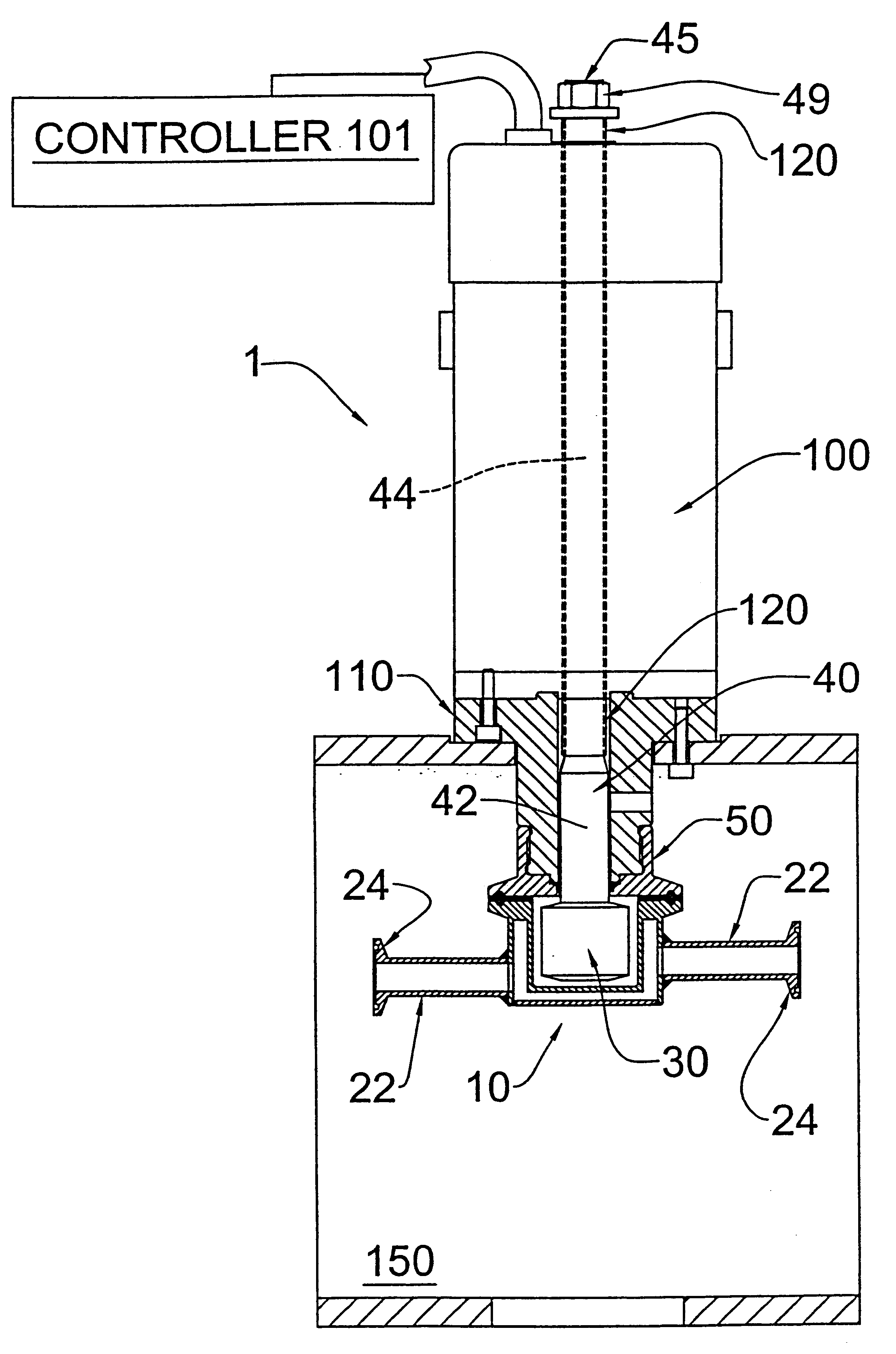
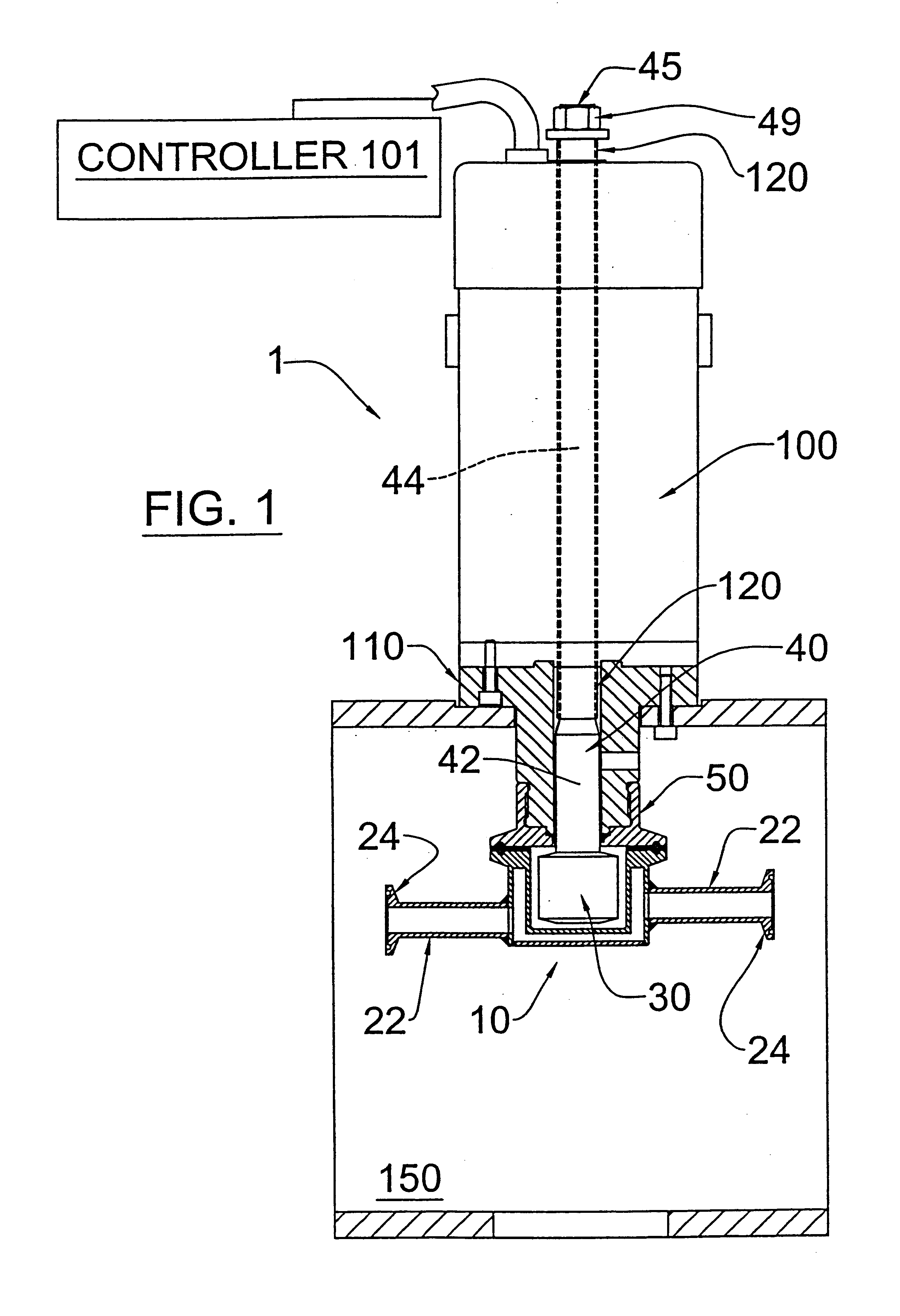
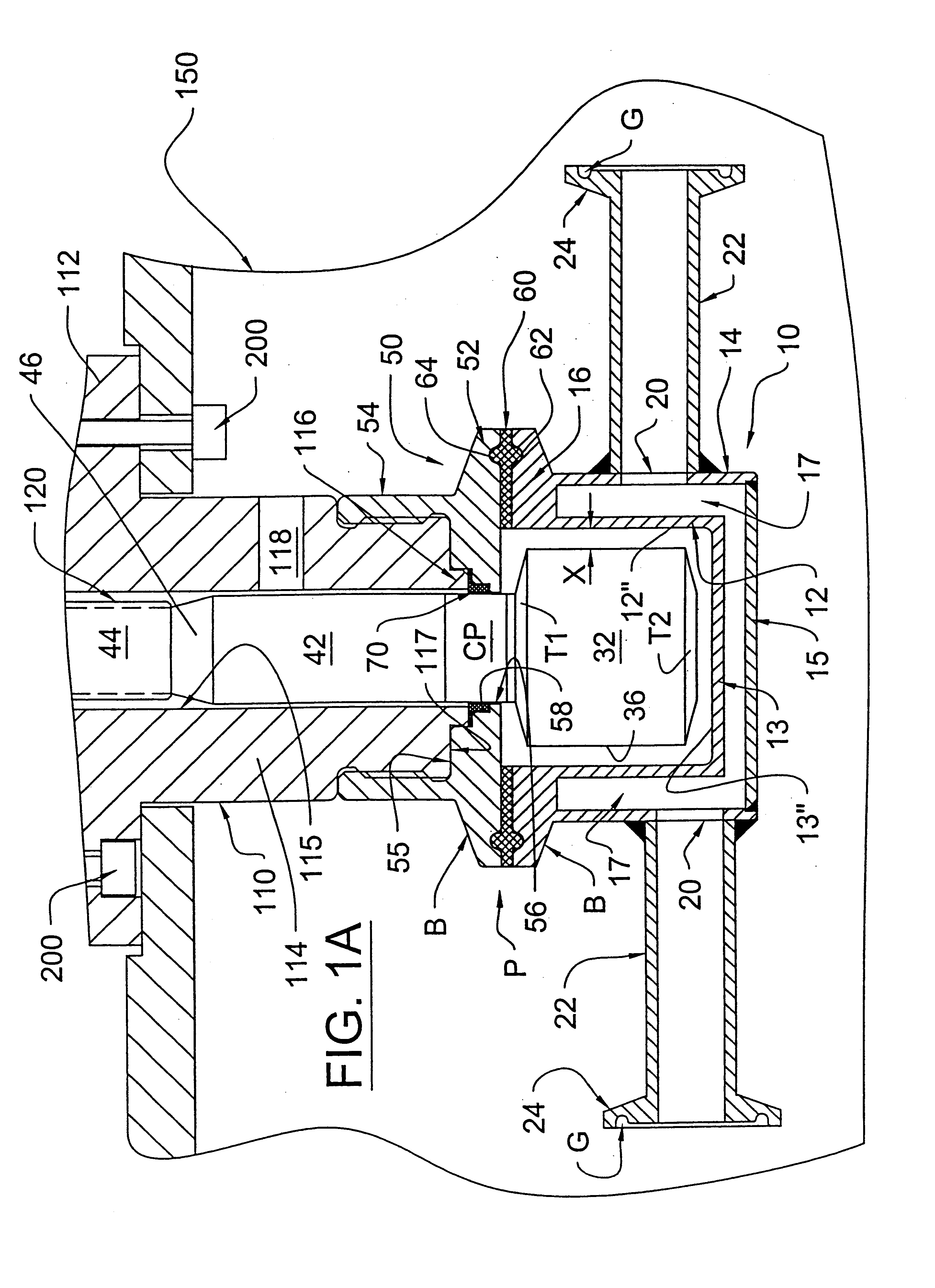
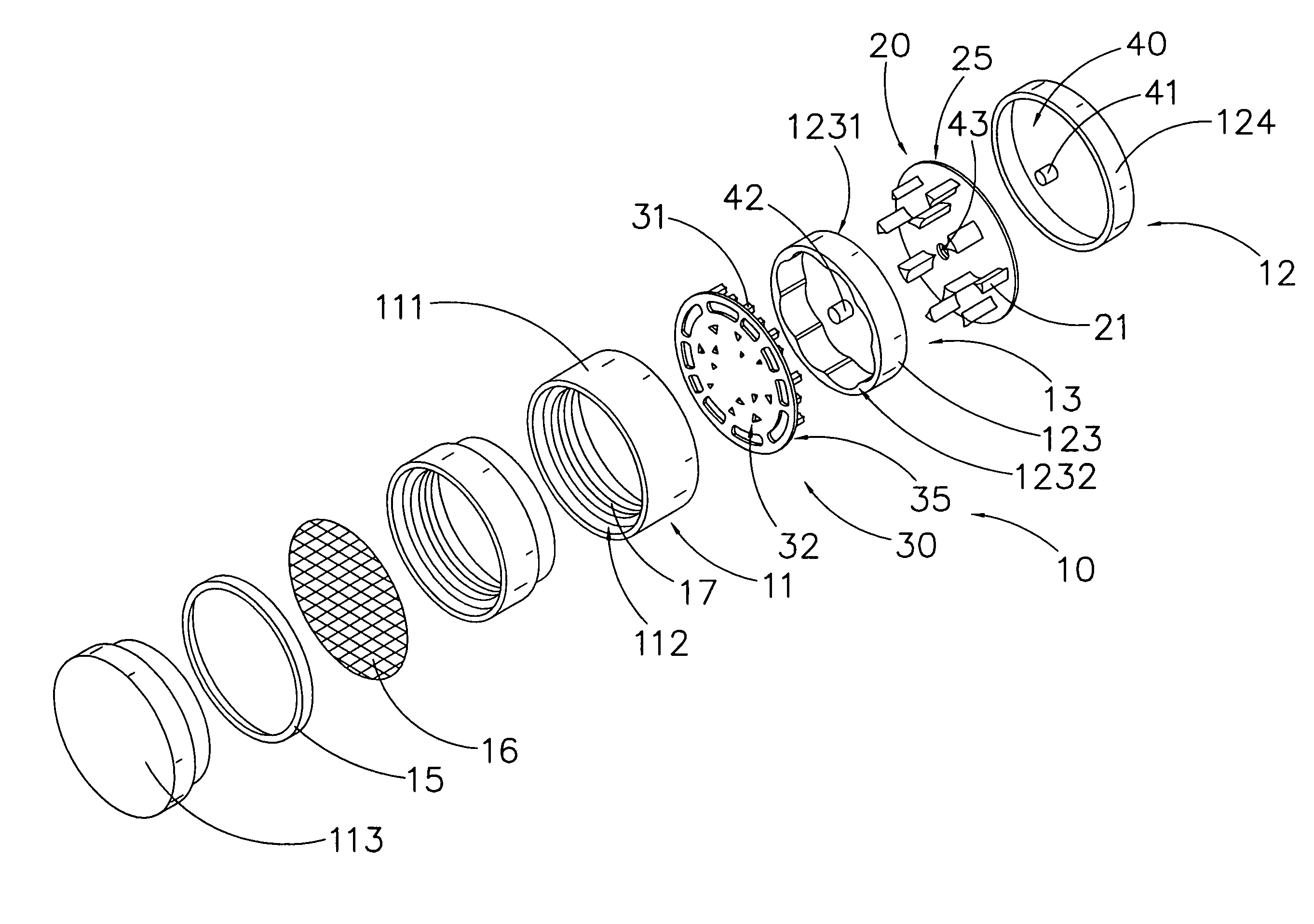
Patents
Literature
78753results about "Grain treatments" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
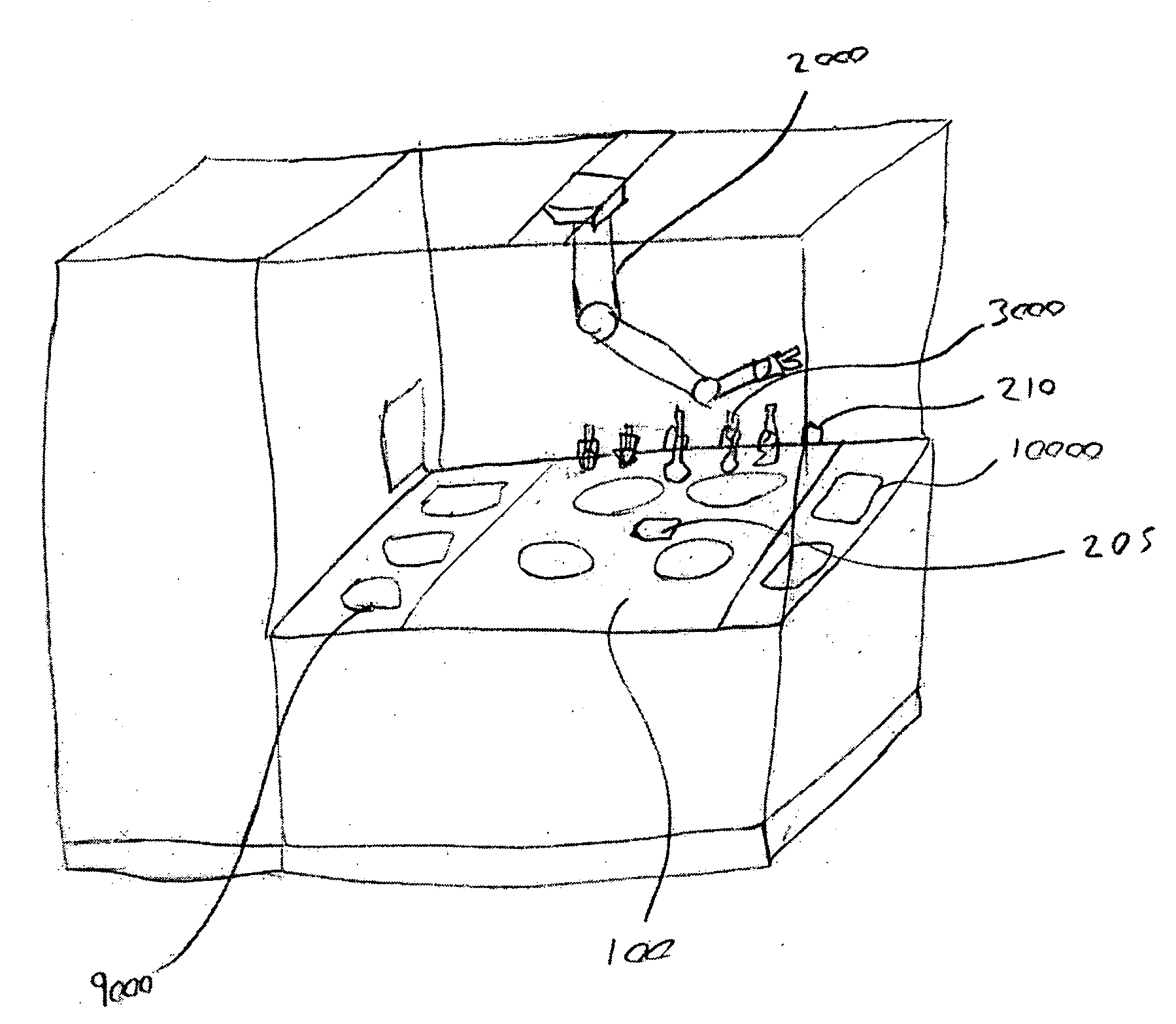
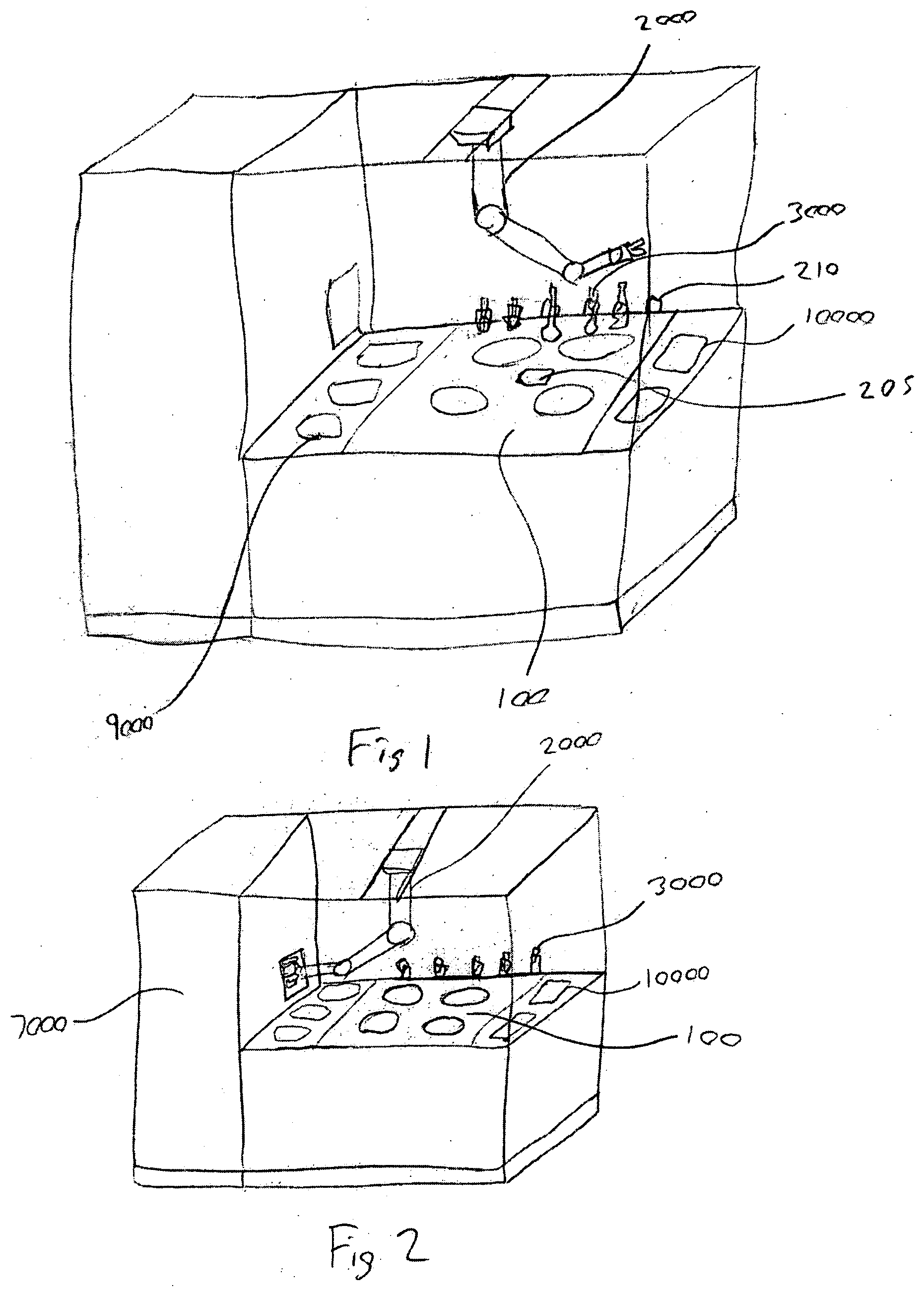
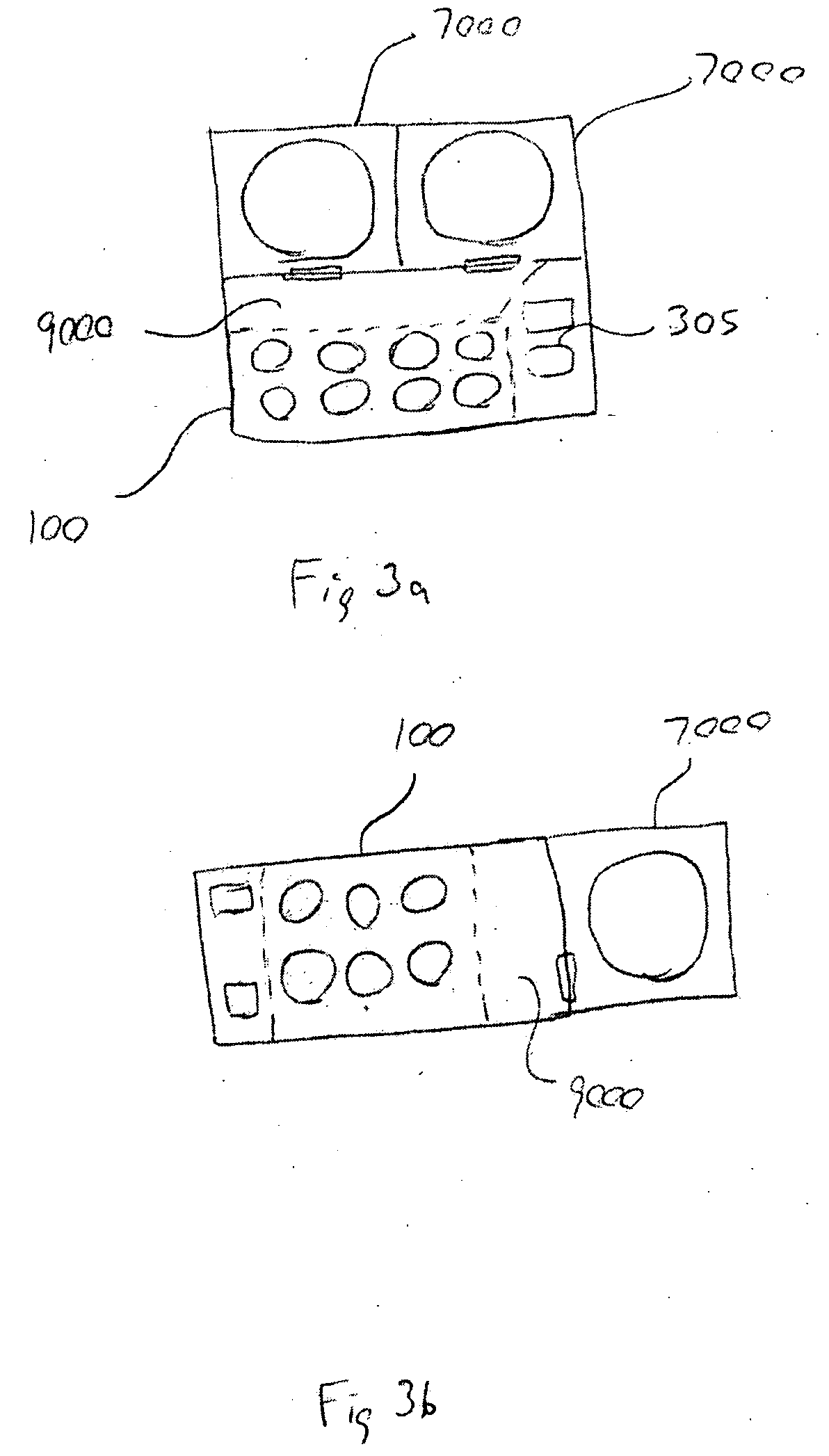
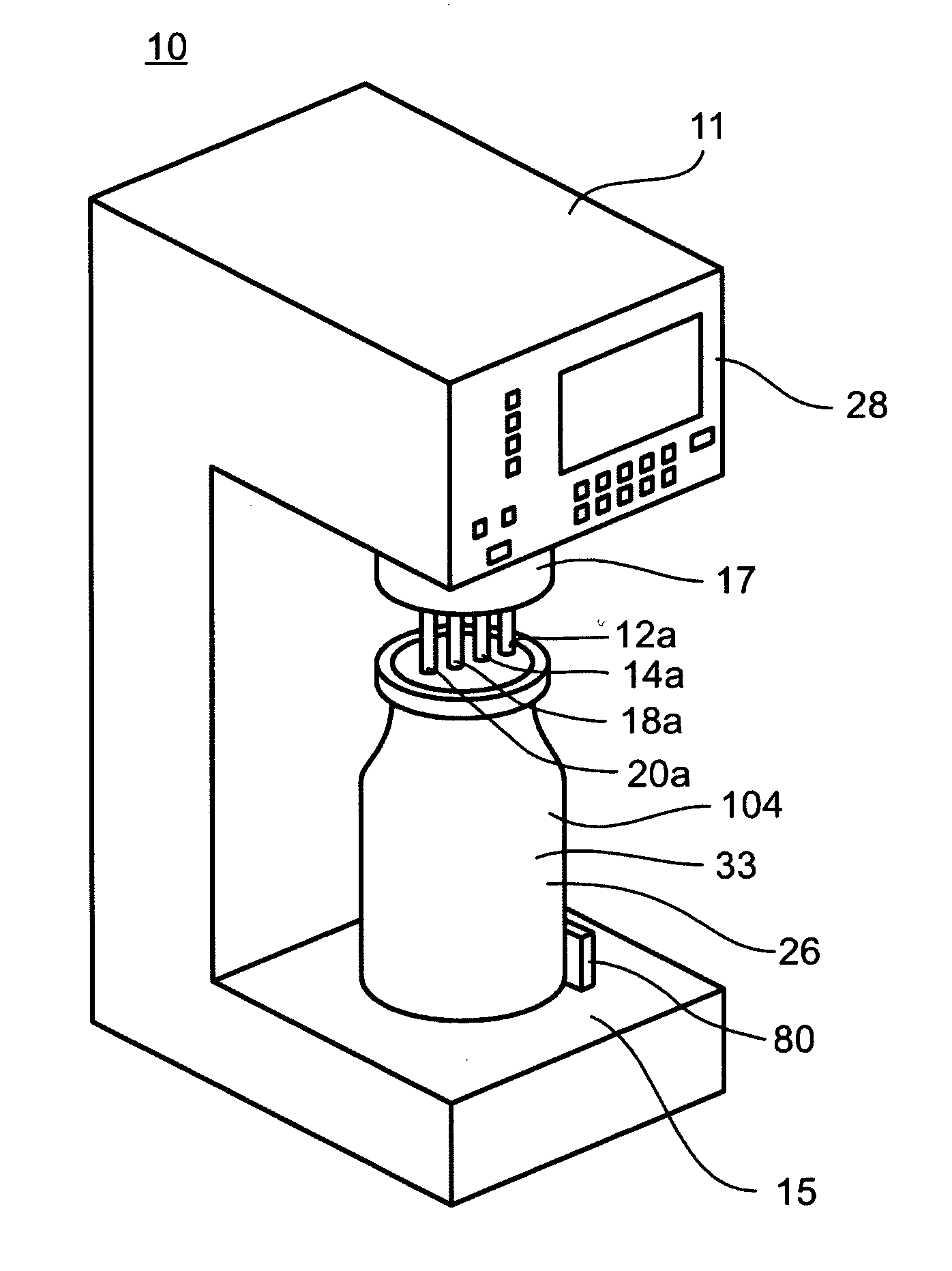
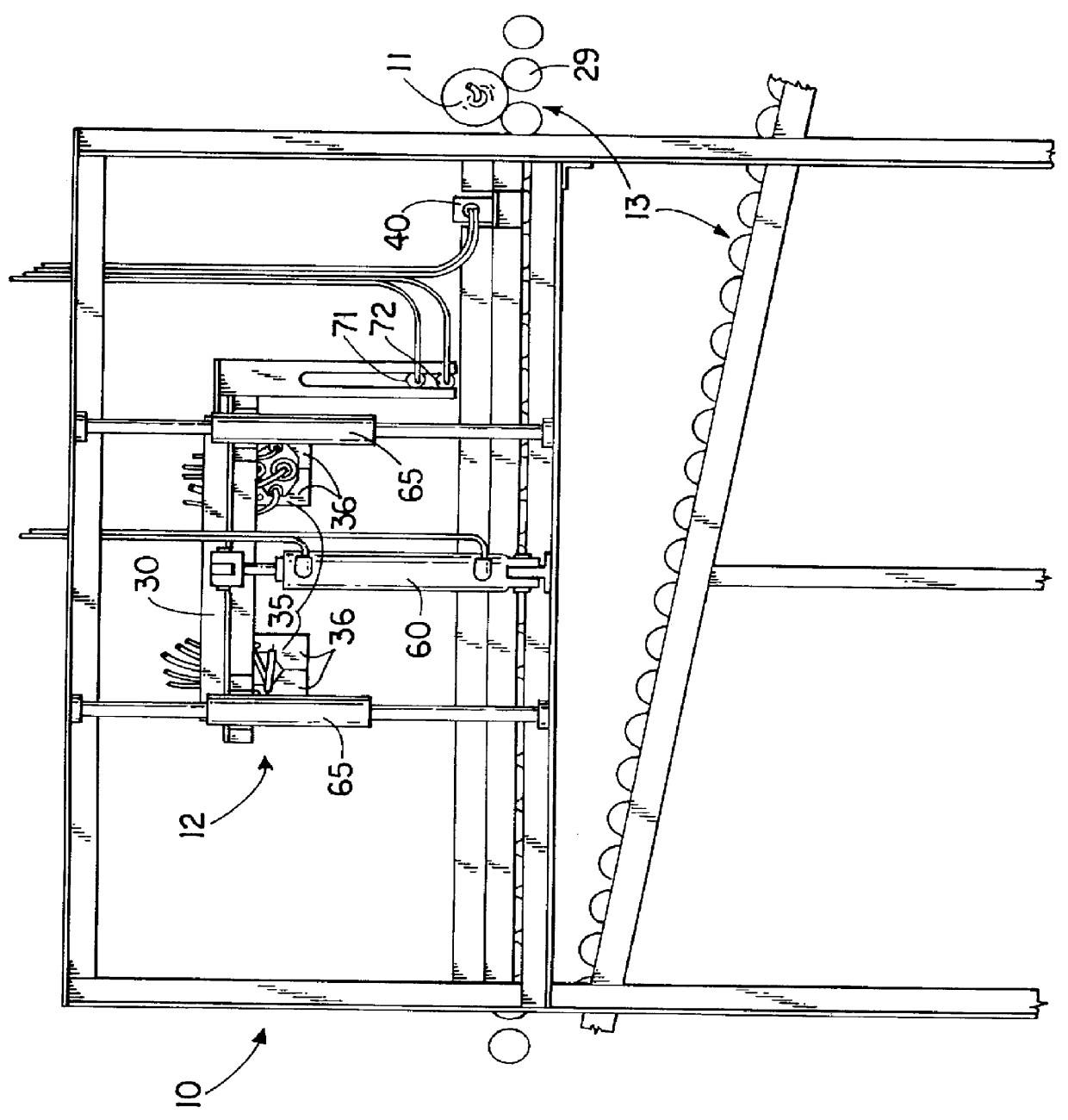
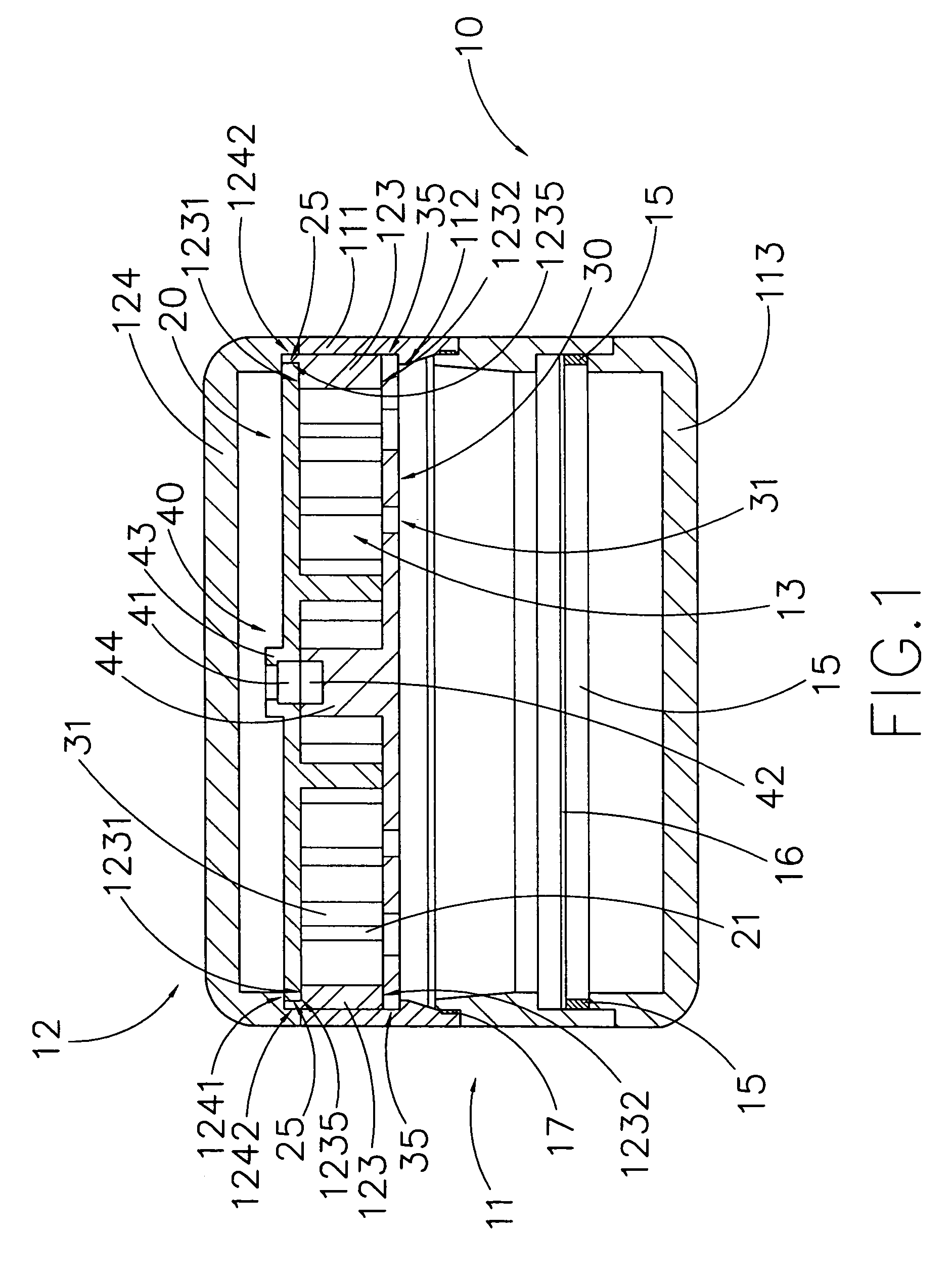
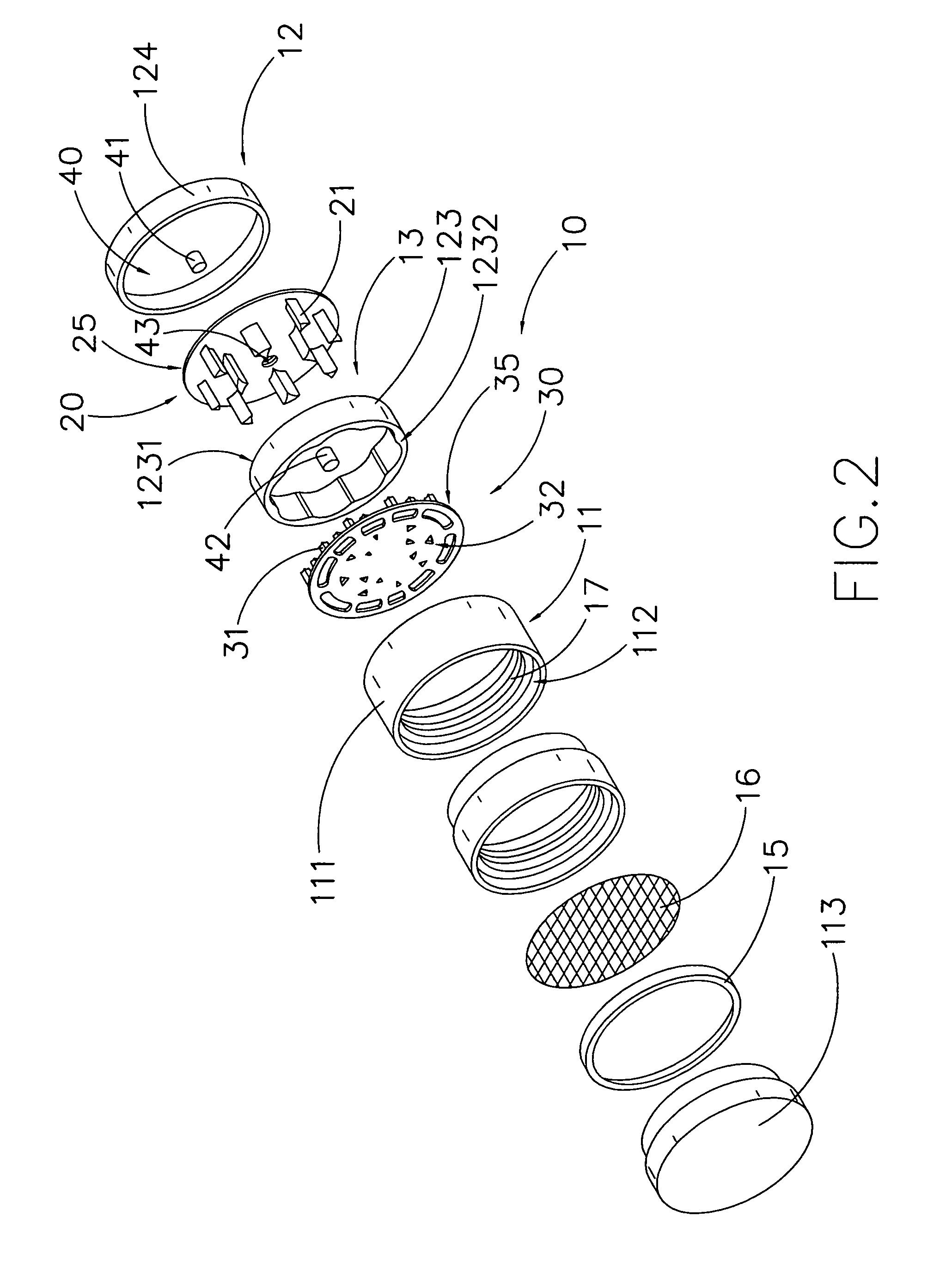
Food preparation system
InactiveUS20050193901A1Eliminate all packaging materialGood for foodFeeding apparatusRoasters/grillsAdditive ingredientControl system
An automated food preparation system is described. It allows precise, automated control of the food preparation process, and has the ability to perform an automated cleanup. It comprises at least one manipulator to process and move ingredients, a control system, an autonomously accessible ingredient storage system, and at least one cooking receptacle.
Owner:BUEHLER DAVID BENJAMIN
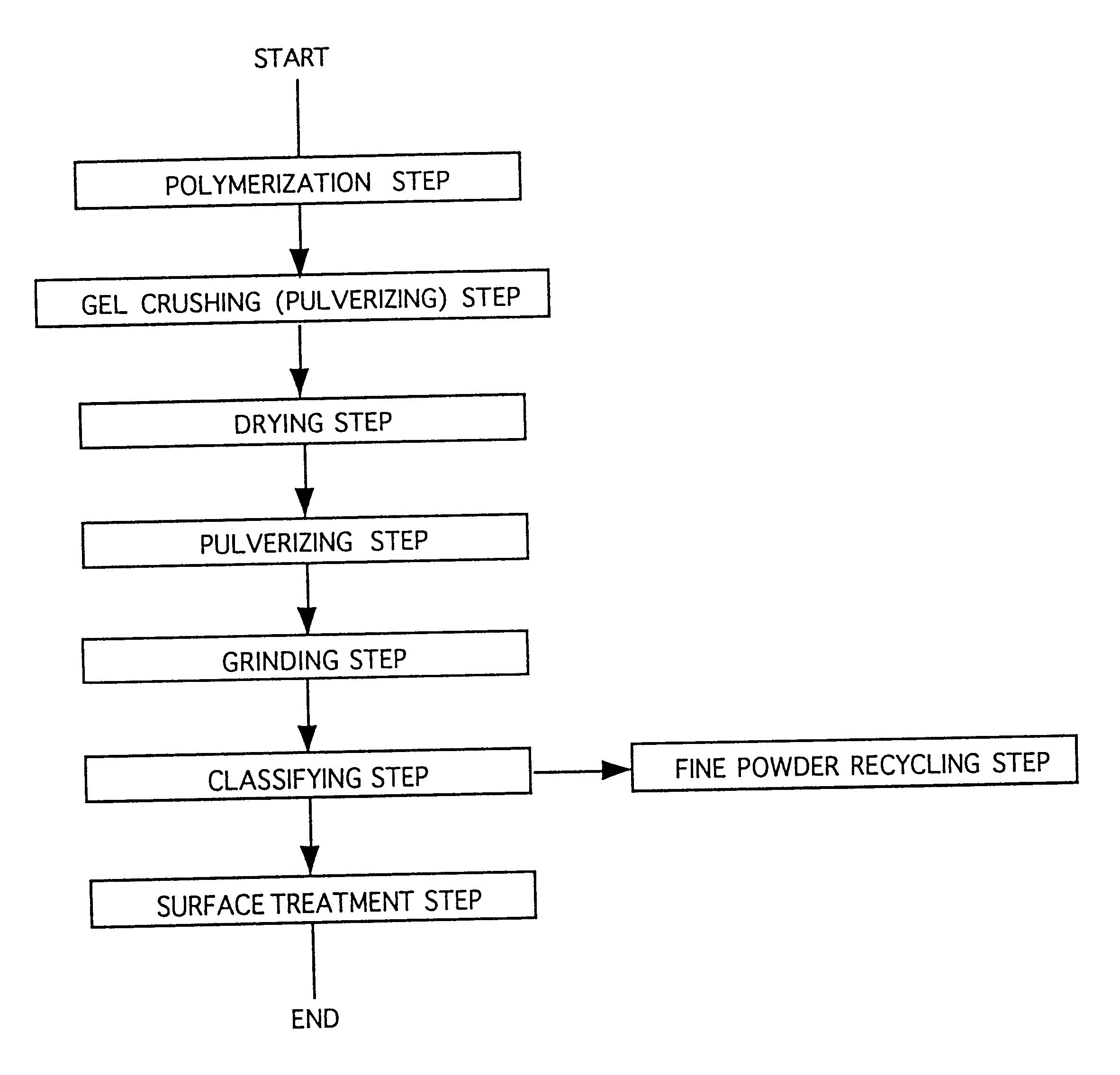
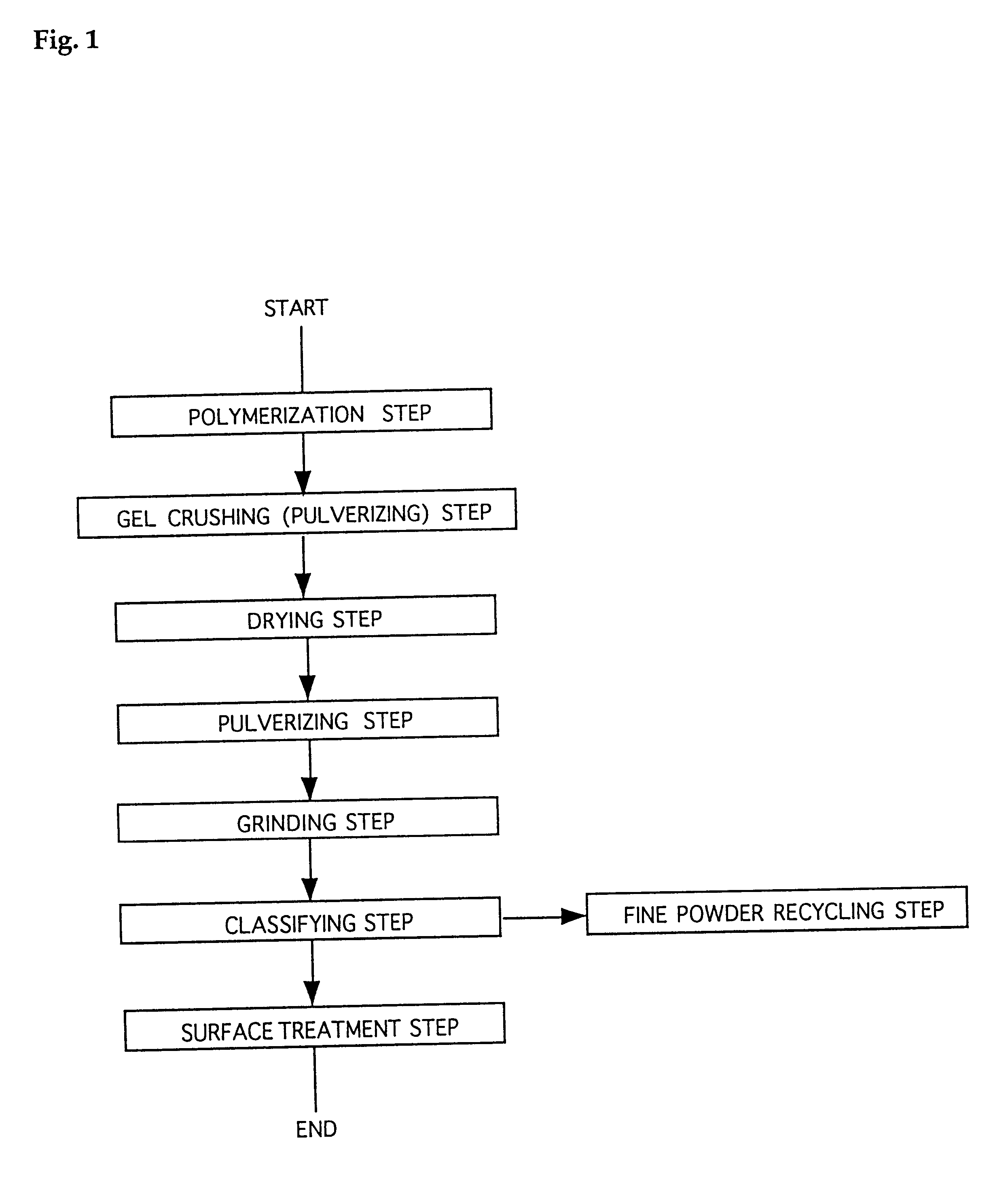
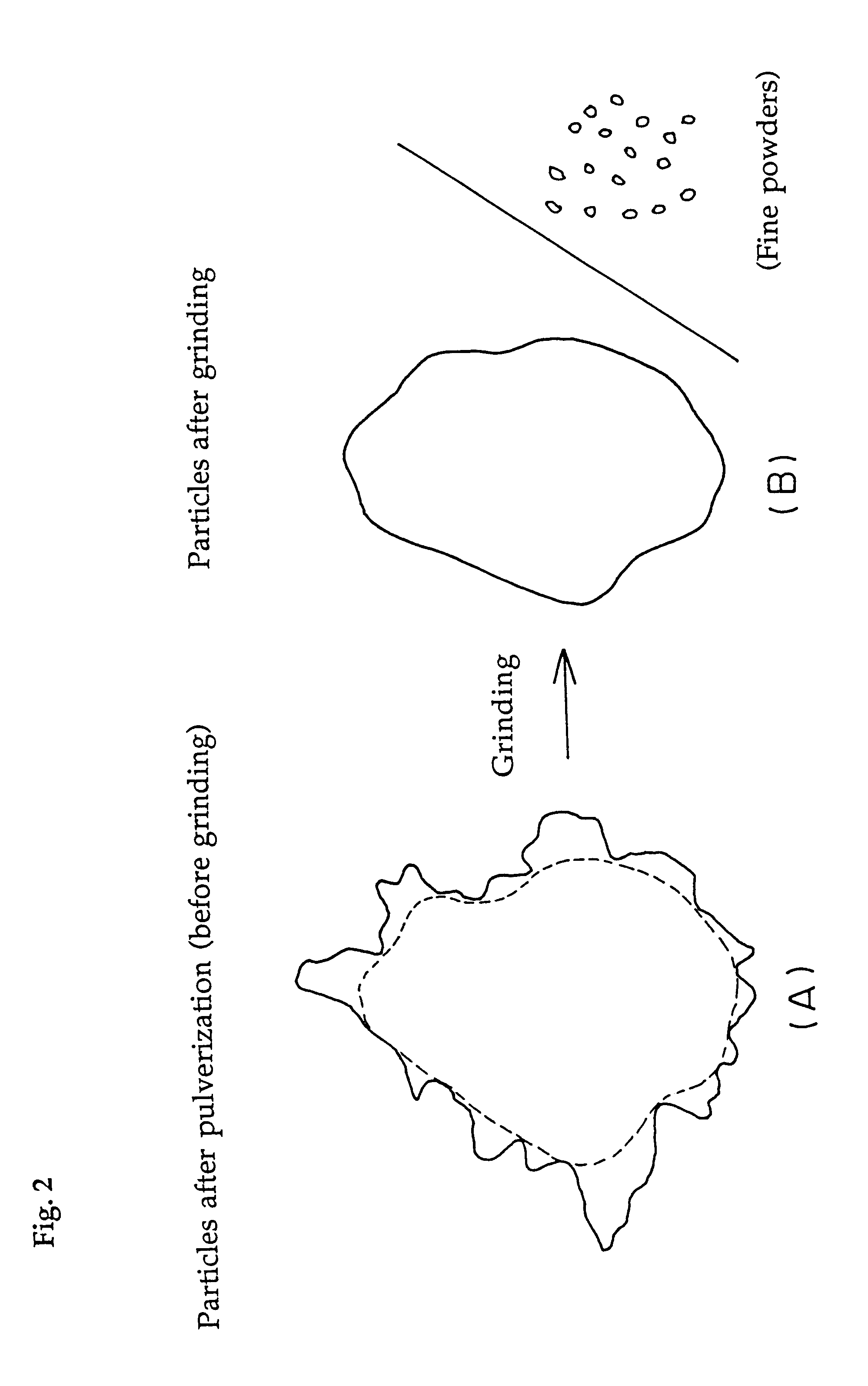
Water-absorbent resin powder and its production process and use
The present invention provides a water-absorbent resin powder and its production process and use, wherein the water-absorbent resin powder has high liquid permeability and high water absorbency. The production process for a water-absorbent resin powder, according to the present invention, comprises the step of obtaining water-absorbent crosslinked polymer particles by an aqueous solution polymerization step, and grinding the resultant crosslinked polymer particles until the bulk density thereof increases to not lower than 0.72 (g / ml). The water-absorbent resin powder is characterized by being arbitrarily pulverized and having a bulk density of not lower than 0.74 (g / ml) and a water absorption capacity of not lower than 20 (g / g) for 0.9 weight % physiological saline under a load of 0.7 psi (4.83 kPa). In addition, the absorbent structure comprises the above water-absorbent resin powder and a fibrous material. The absorbent article comprises an absorbent layer including the above absorbent structure.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Milled particles
InactiveUS6634576B2Increase incorporationOptimal for incorporationPowder deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsParticulatesPolymer science
A process for milling a solid substrate in the milling chamber of a dispersion or media mill in the presence of a two or more compositions of milling media bodies is disclosed wherein all milling media bodies contribute to the grinding of the solid substrate and wherein at least one composition of media bodies provides fragments of milling media bodies that are retained with the milled solid substrate particles in the form of a synergetic commixture produced in the milling process. More specifically, a process is disclosed for preparing a synergetic commixture comprising small particles of a solid substrate and small particulates of a first material of a desired size comprising the steps of (a) providing to the milling chamber of a media mill a contents comprising a pre-mix of a solid substrate, a fluid carrier, a plurality of milling bodies of a first material having a fracture toughness Kc1, and a plurality of milling bodies of a second material having a fracture toughness Kc2; (b) operating the media mill to grind the solid substrate and degrade at least a portion of the milling bodies of first material to produce a dispersion in the fluid carrier comprising a synergetic commixture of small particulates of the first material and small particles of the solid substrate having a desired size equal to or less than a size Sp; (c) separating the dispersion from any milling bodies and solid substrate particles having a size larger than Sp; and (d) optionally removing the fluid carrier from the dispersion to form a synergetic commixture free of fluid and comprising the particles and the small particulates, wherein KC2 is greater than KC1.
Owner:RTP PHARMA +1
Milled particles
InactiveUS20020047058A1Increase incorporationOptimal for incorporationPowder deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsParticulatesPolymer science
Owner:RTP PHARMA +1
Method for discriminating between used and unused gas generators for air bags during car scrapping process
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 01644 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 12, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 12, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 14, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 00144 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 3, 1997To provide a method for easily discriminating used and unused gas generators from among gas generators for air bags separated from used cars in a car scrapping process. A method for discriminating between used and unused gas generators according to the present invention is a method for discriminating used and unused gas generators from among gas generators for air bags separated from used cars in a car scrapping process, and this method comprises the steps of: a) crushing used cars mounted with gas generators each having on a surface thereof a material discoloring according to the surface temperatures in actuating the gas generator to separate the gas generators, and b) discriminating the gas generators in which surfaces are discolored and the gas generators in which surfaces are not discolored from among the separated gas generators.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD +1
Feeding formula appliance
A device for preparing a fluid food at a desired consumption temperature on demand, comprising two reservoirs of water, a container containing a formula, a data processor and a controller for dispensing water of the correct temperature from each of the reservoirs and the formula from the container into a vessel. Also provided are methods for preparing specialized foods at desired consumption temperatures on demand, and methods for marketing both foods and food-preparation devices.
Owner:BIDERMAN EYTAN
Methods for making pharmaceutical formulations comprising microparticles with improved dispersibility, suspendability or wettability
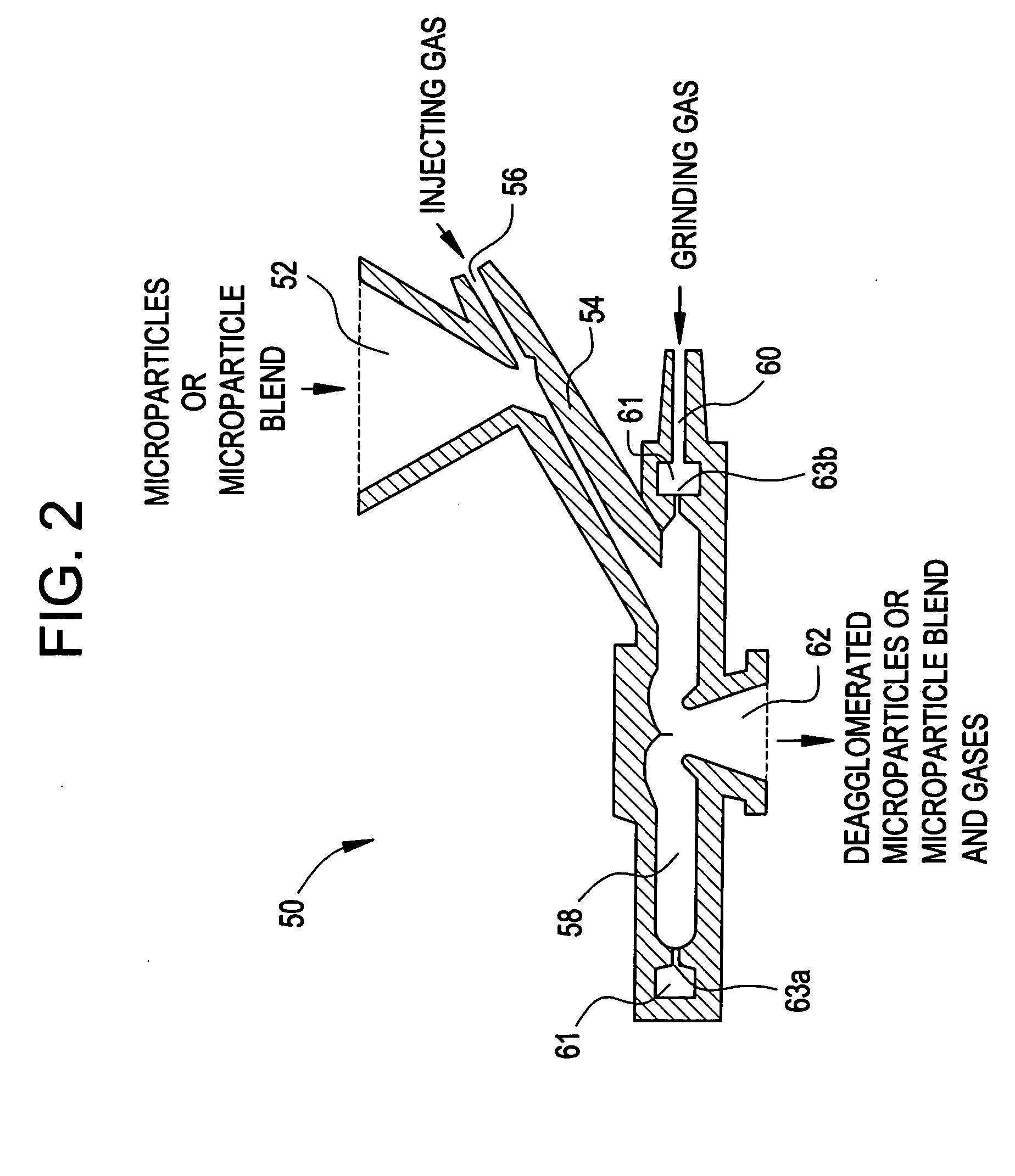
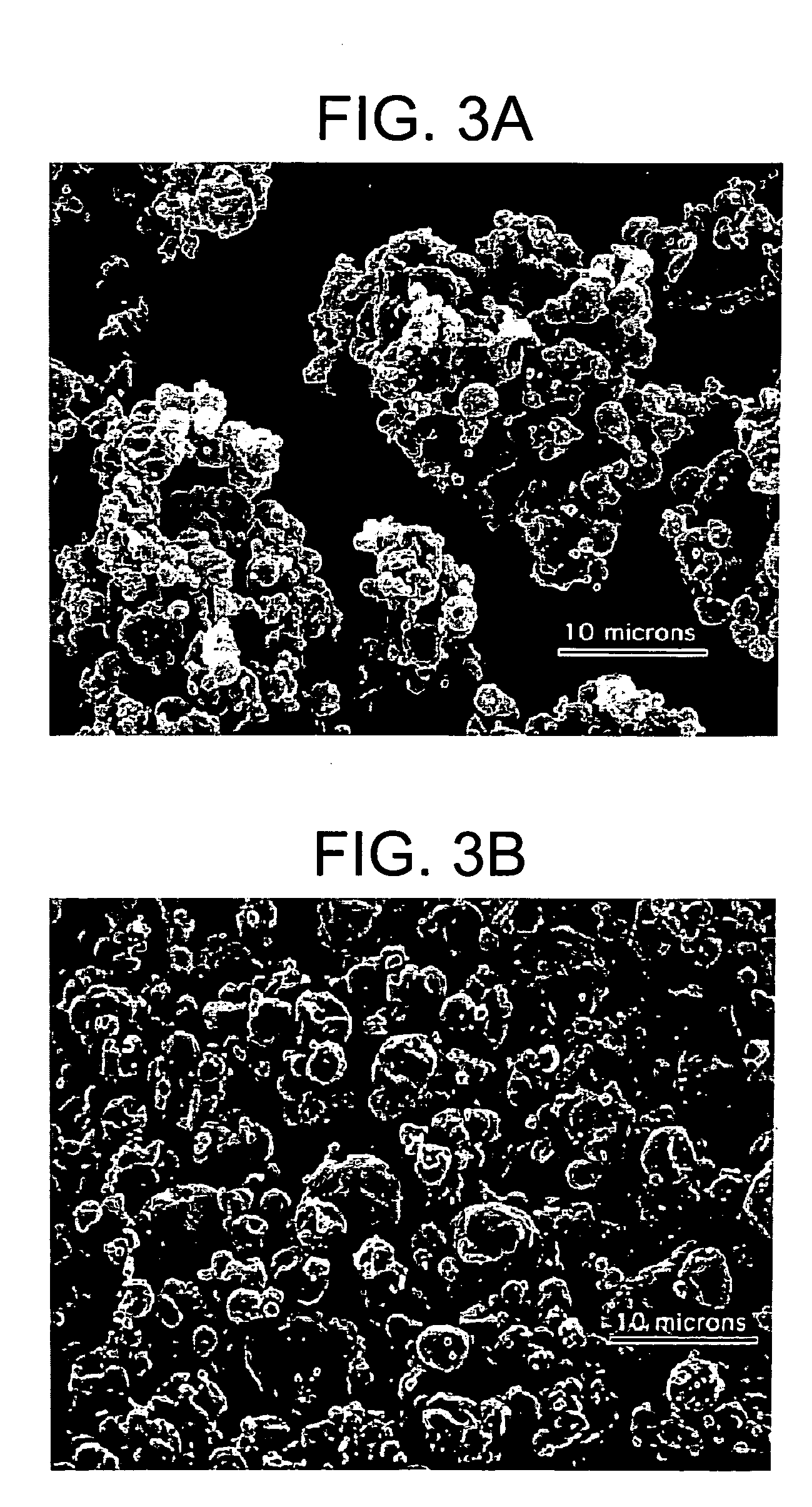
InactiveUS20050079138A1Good dispersibilityImproved suspendabilityPowder deliveryGranulation by liquid drop formationPowder mixtureMicroparticle
Methods are provided for making a dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation, comprising the steps of: (a) providing microparticles which comprise a pharmaceutical agent; (b) blending the microparticles with at least one excipient in the form of particles to form a powder blend; and (c) jet milling the powder blend to form a dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation having improved dispersibility, suspendability, or wettability as compared to the microparticles of step (a) or the powder blend of step (b). The method can further include dispersing the dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation in a liquid pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle to make an formulation suitable for injection. Alternatively, the method can further include processing the dry powder blend pharmaceutical formulation into a solid oral dosage form. In one embodiment, the microparticles of step (a) are formed by a solvent precipitation or crystallization process.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
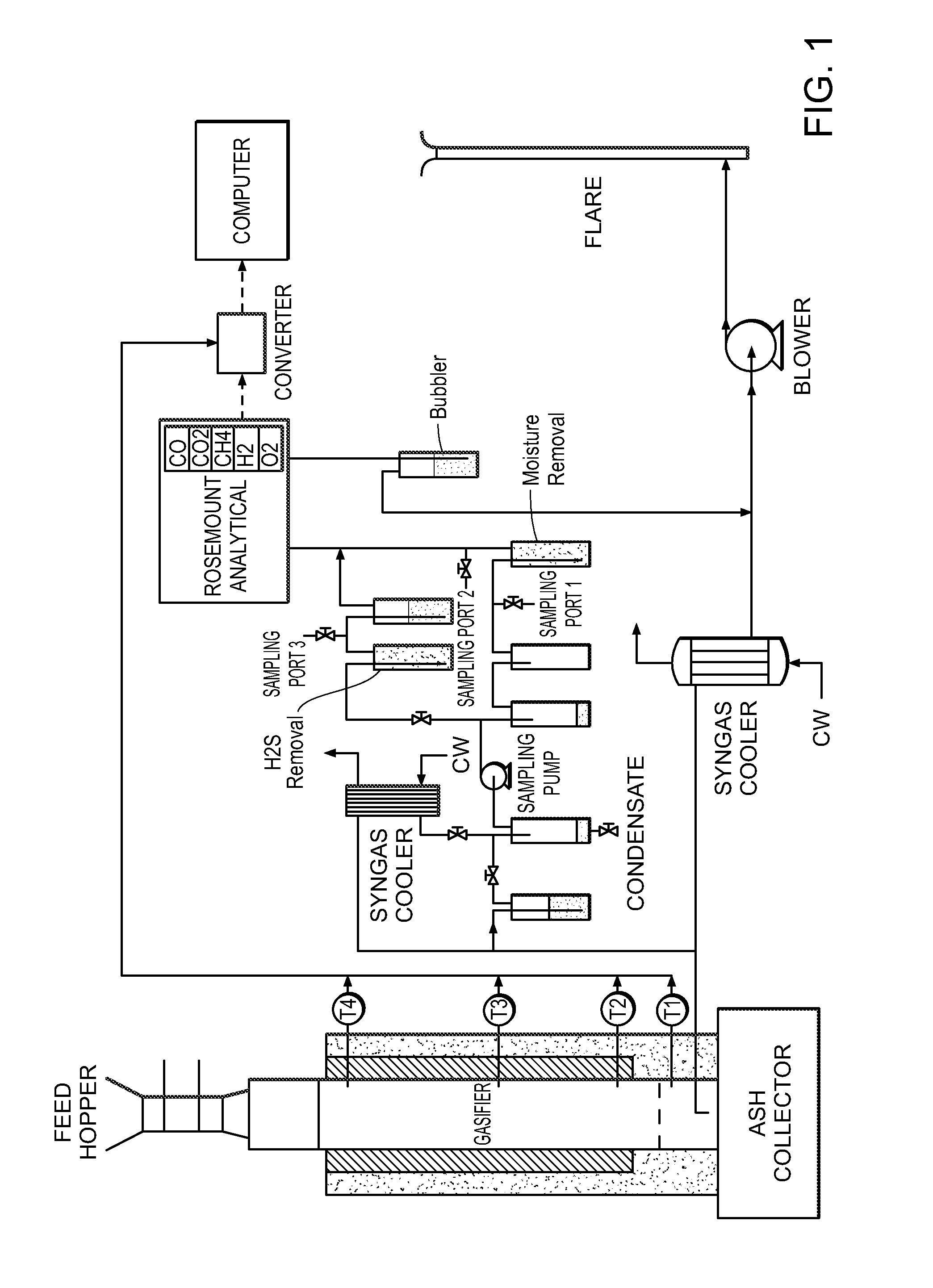
Coal Compositions for Catalytic Gasification
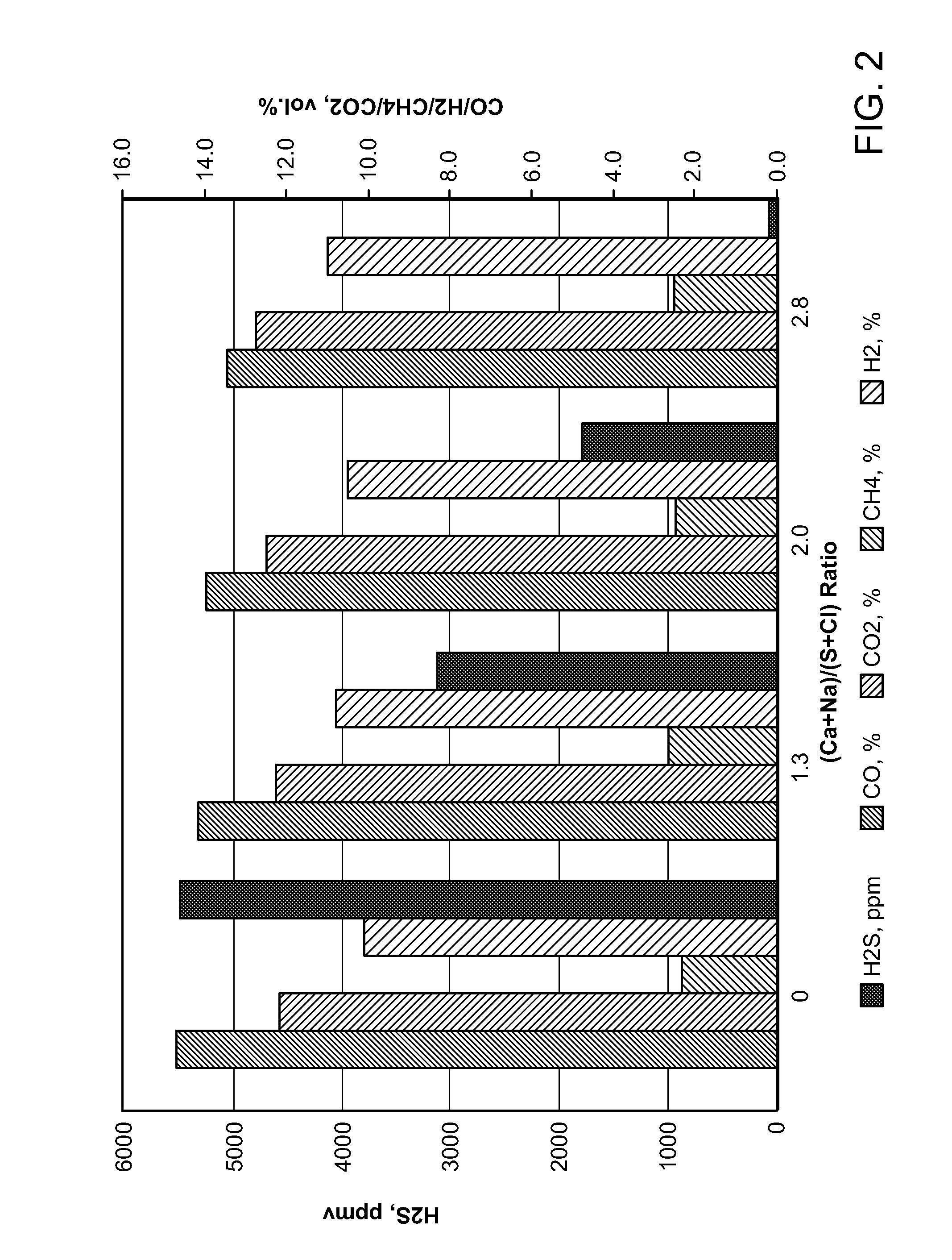
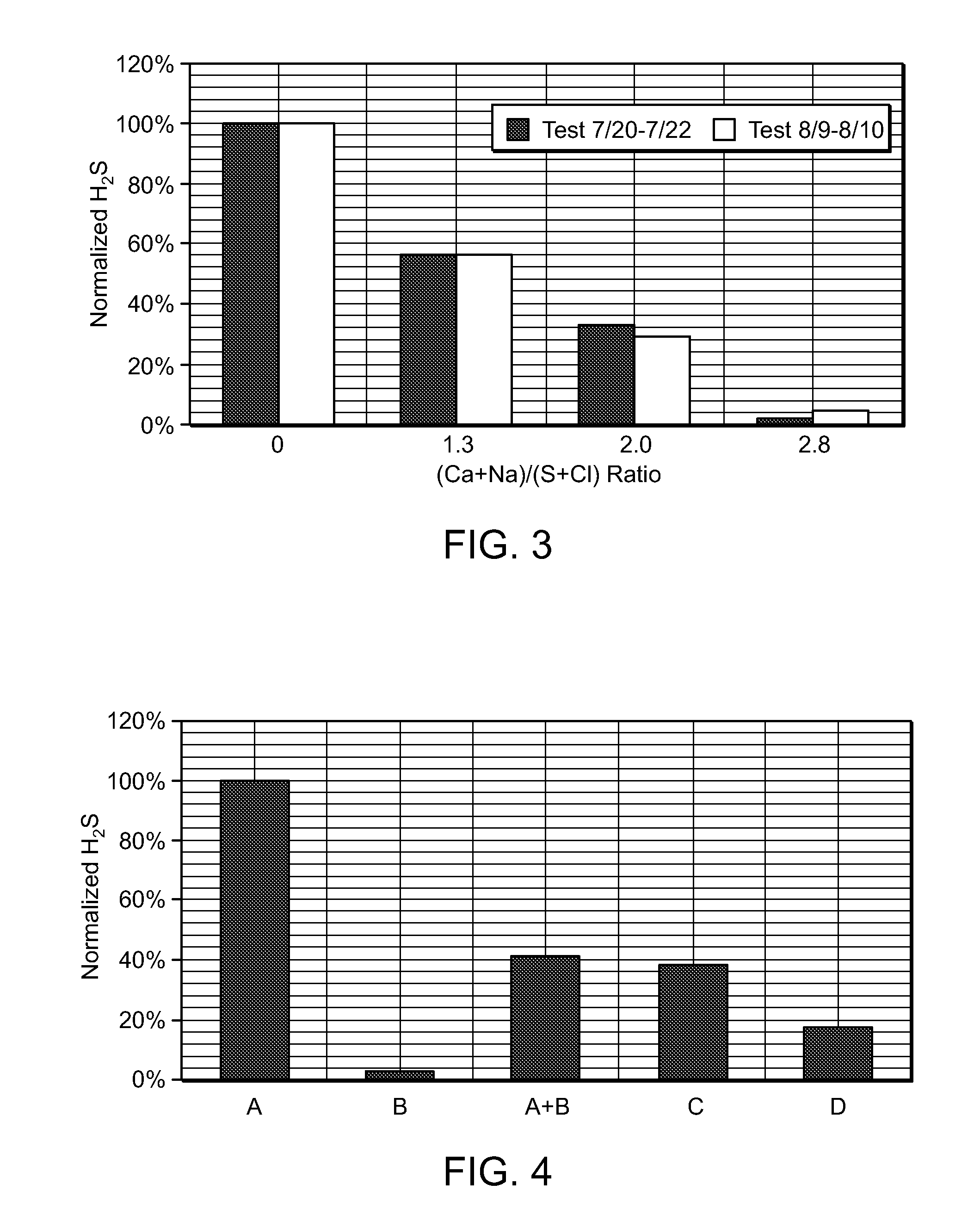
Particulate compositions are described comprising an intimate mixture of a coal and a gasification catalyst. The particulate compositions are gasified in the presence of steam to yield a plurality of gases including methane and at least one or more of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and other higher hydrocarbons. Processes are also provided for the preparation of the particulate compositions and converting the particulate composition into a plurality of gaseous products.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Methods and systems for mobile device messaging
ActiveUS20050164721A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSubstation equipmentWeb serviceMobile device
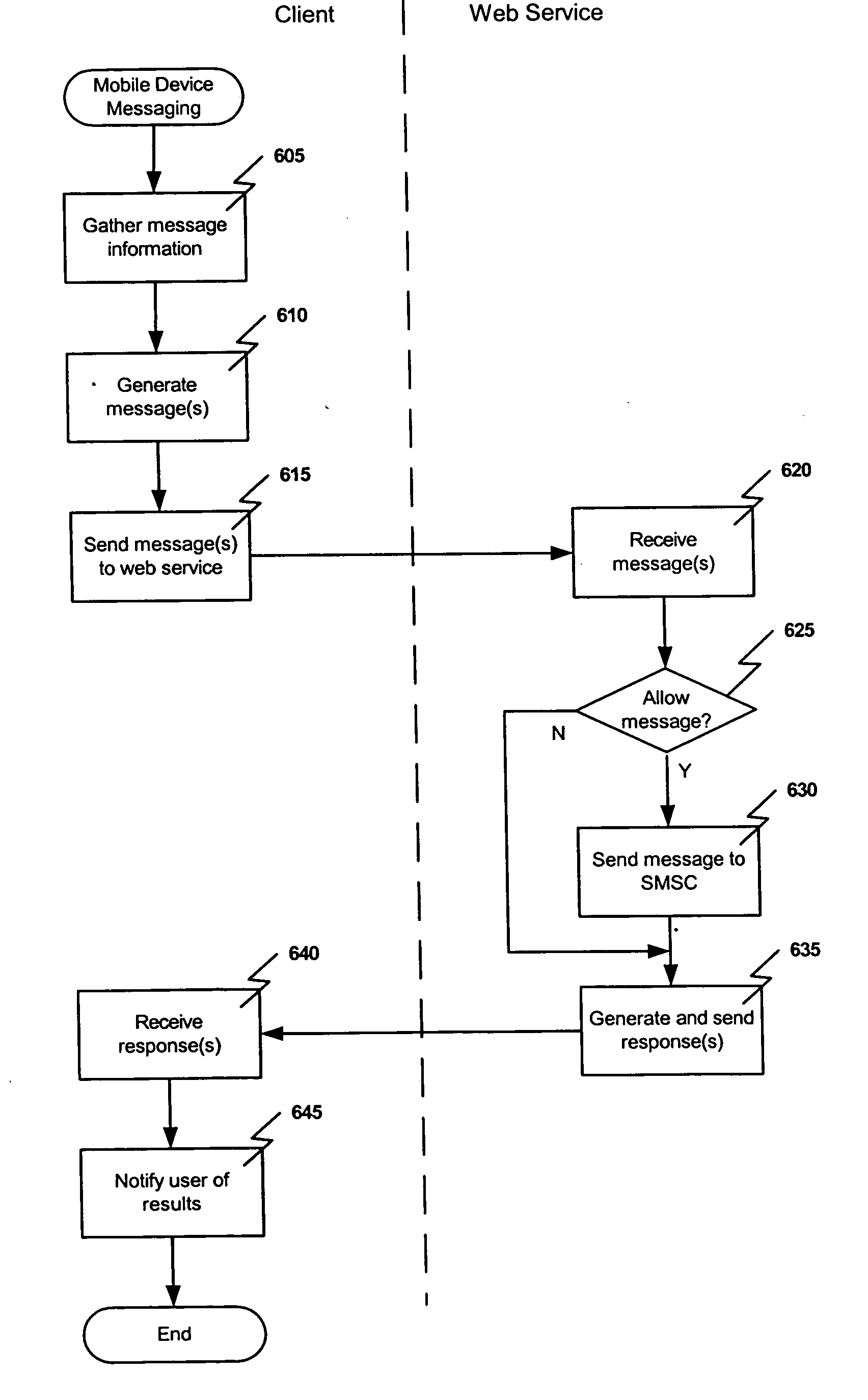
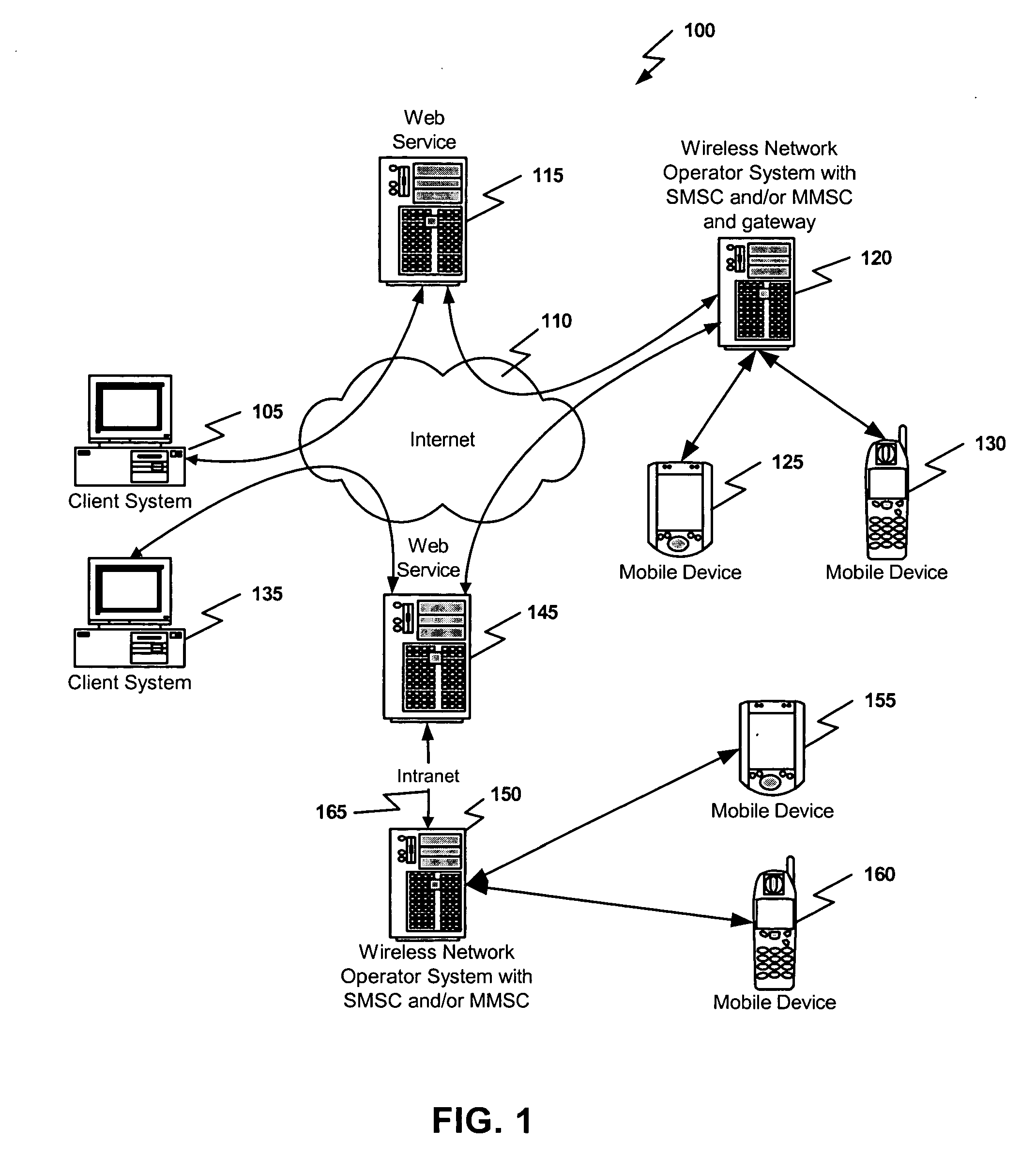
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods, systems, and computer-readable media for mobile device messaging. Mobile device messaging comprises collecting from an originating system information including content data to be sent to the mobile device. One or more short messages are generating for encapsulating the content data. The one or more short messages are formatted to be readable by a web service and the content data is formatted to be readable by the mobile device. The one or more short messages are sent to the web service for delivery to the mobile device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Coal Compositions for Catalytic Gasification
ActiveUS20090217590A1Drying solid materials with heatGaseous fuelsPtru catalystHydrocotyle bowlesioides
Particulate compositions are described comprising an intimate mixture of a coal and a gasification catalyst in the presence of steam to yield a plurality of gases including methane and at least one or more of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and other higher hydrocarbons are formed. Processes are also provided for the preparation of the particulate compositions and converting the particulate composition into a plurality of gaseous products.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
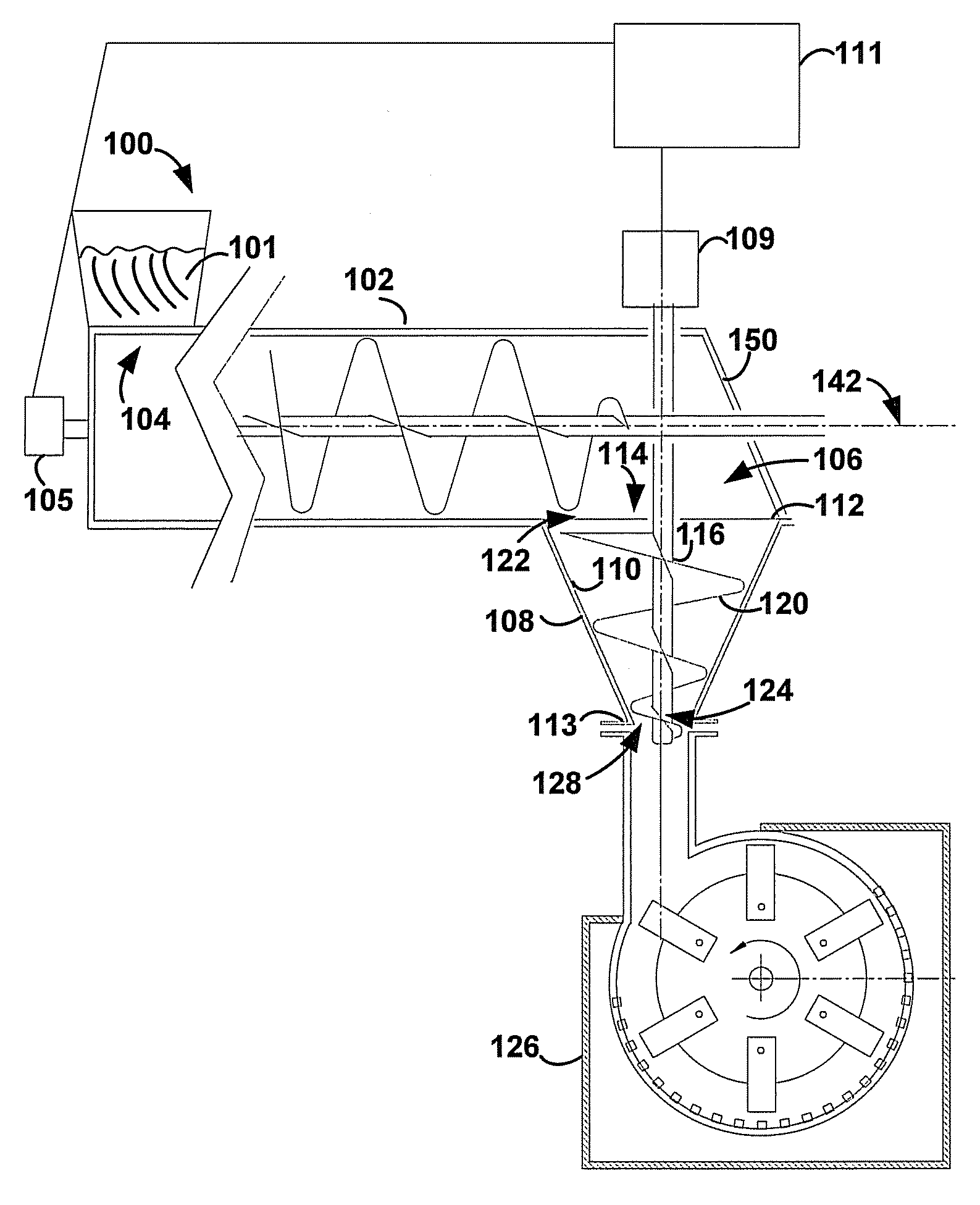
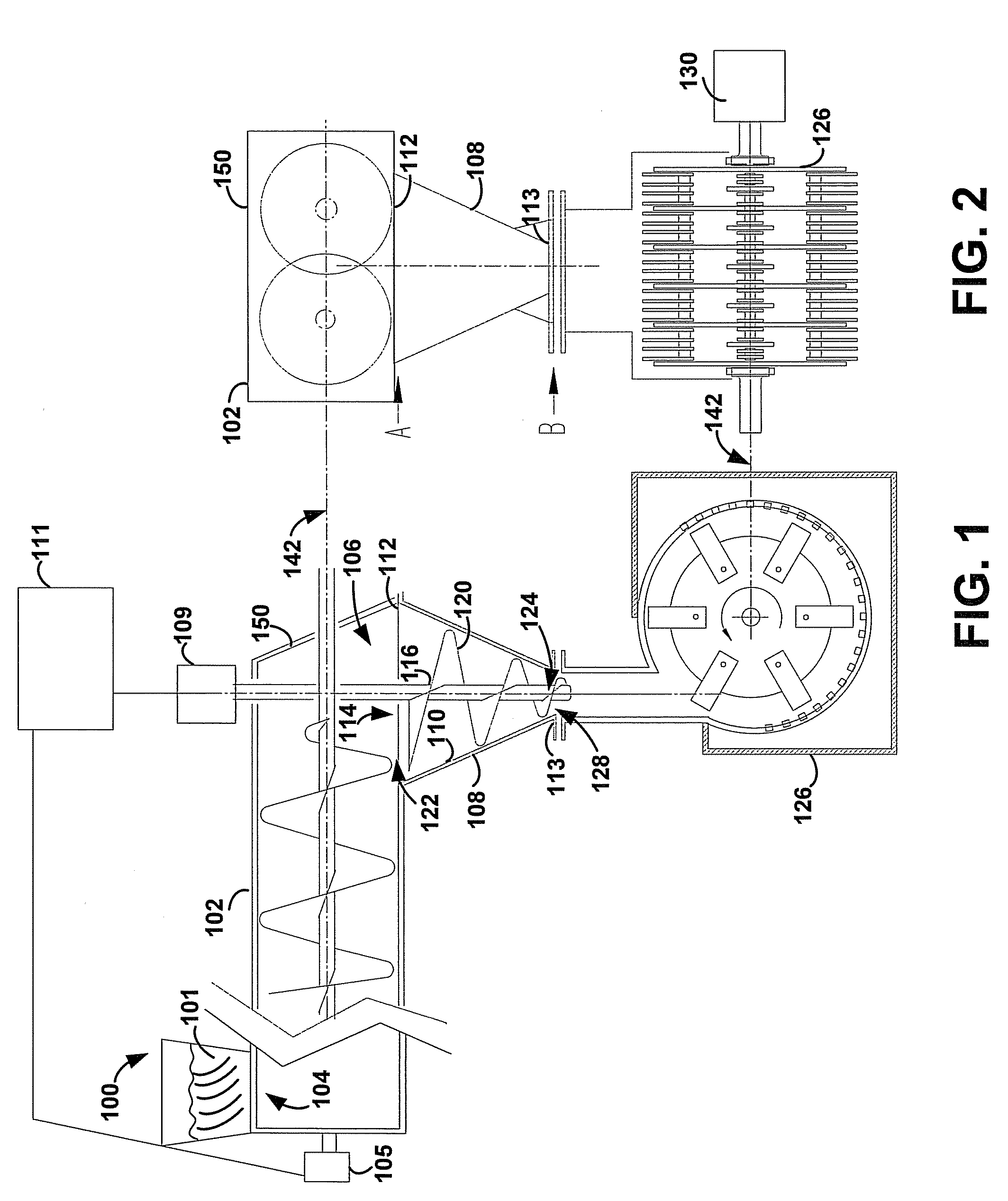
Compactor Feeder
A compactor feeder and methods for feeding relatively low-density biomass materials into a grinding device (such as a hammer mill) is described. The compactor feeder increases the density of the relatively low-density biomass materials in order to fill the grinding device with the biomass materials at a rate that is sufficient to substantially equal the design capacity of the grinding device.
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
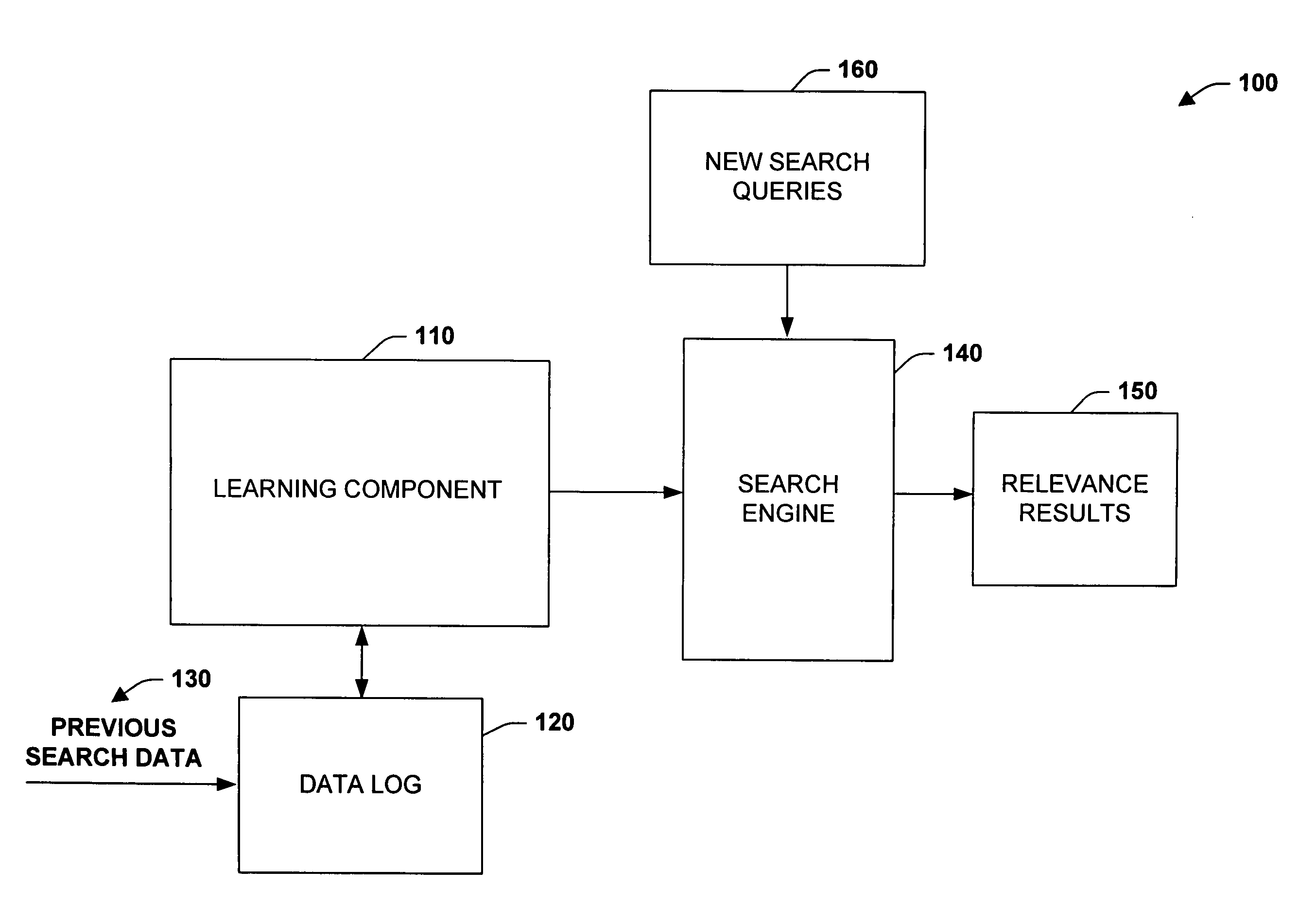
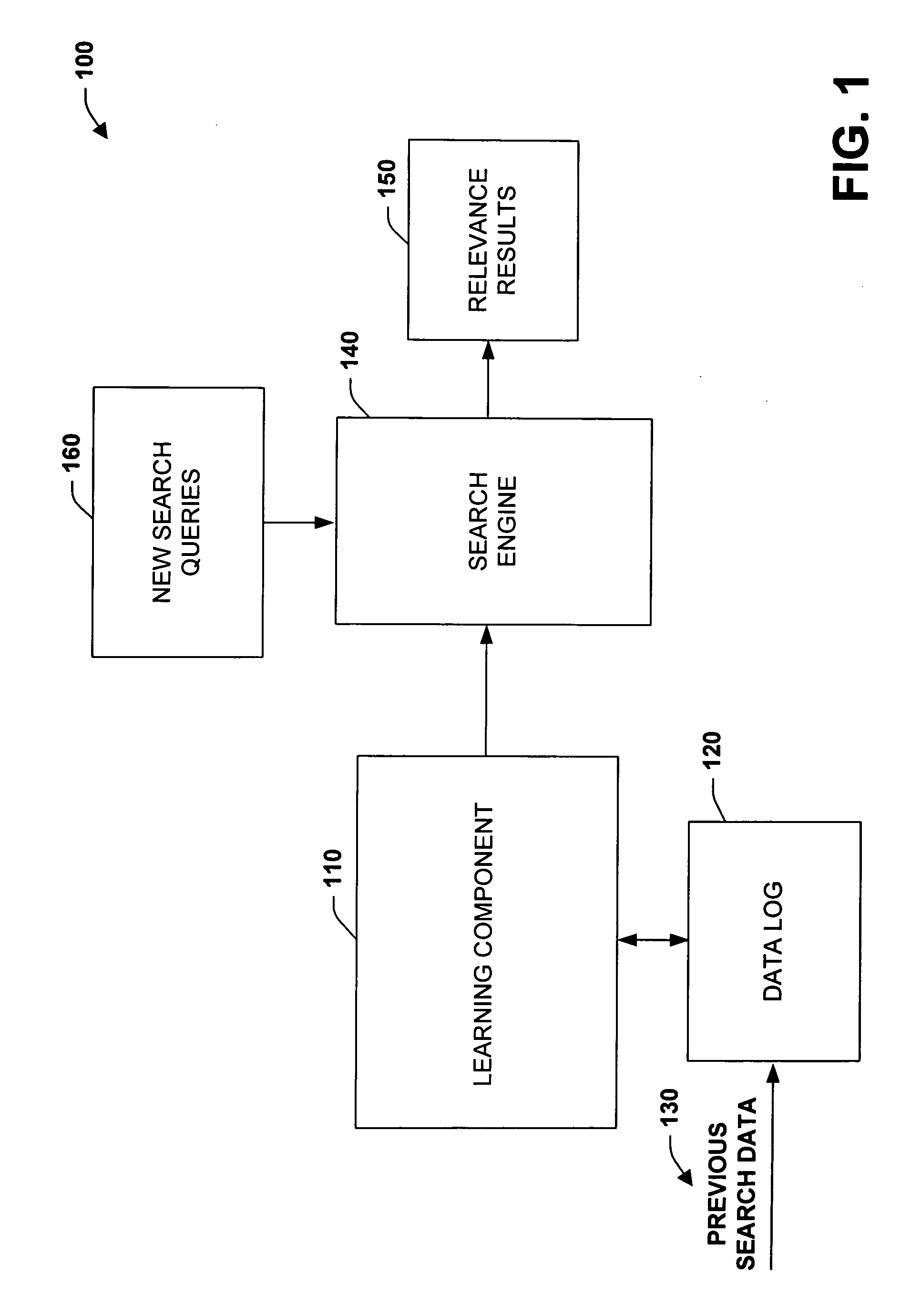
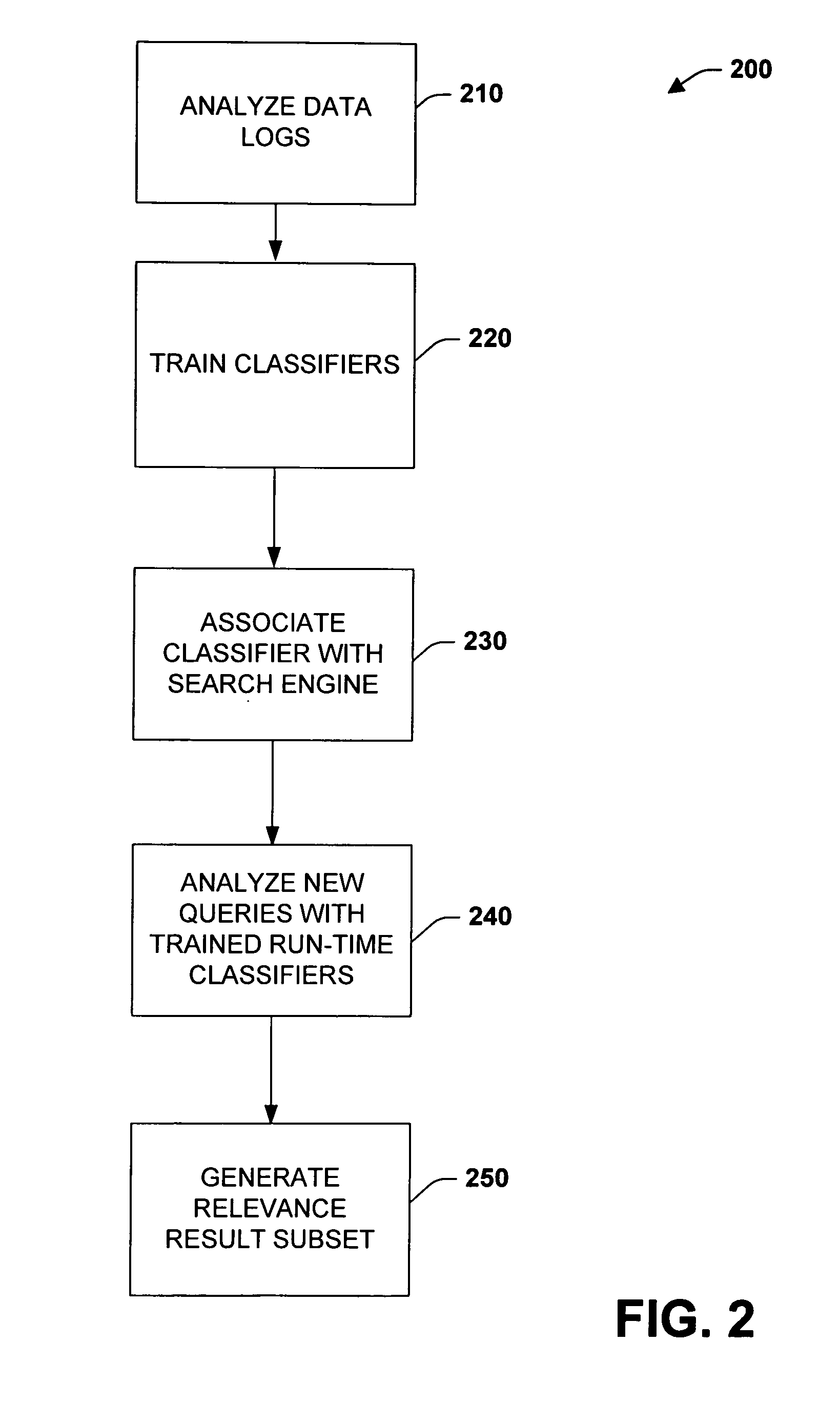
Data mining techniques for improving search engine relevance
InactiveUS20060224579A1Facilitate efficient searching and retrieval and analysisSimple processWeb data indexingSolid waste disposalLearning dataInformation retrieval
The subject invention relates to systems and methods that automatically learn data relevance from past search activities and apply such learning to facilitate future search activities. In one aspect, an automated information retrieval system is provided. The system includes a learning component that analyzes stored information retrieval data to determine relevance patterns from past user information search activities. A search component employs the learning component to determine a subset of current search results based at least in part on the relevance patterns, wherein numerous variables can be processed in accordance with the learning component to efficiently generate focused, prioritized, and relevant search results.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
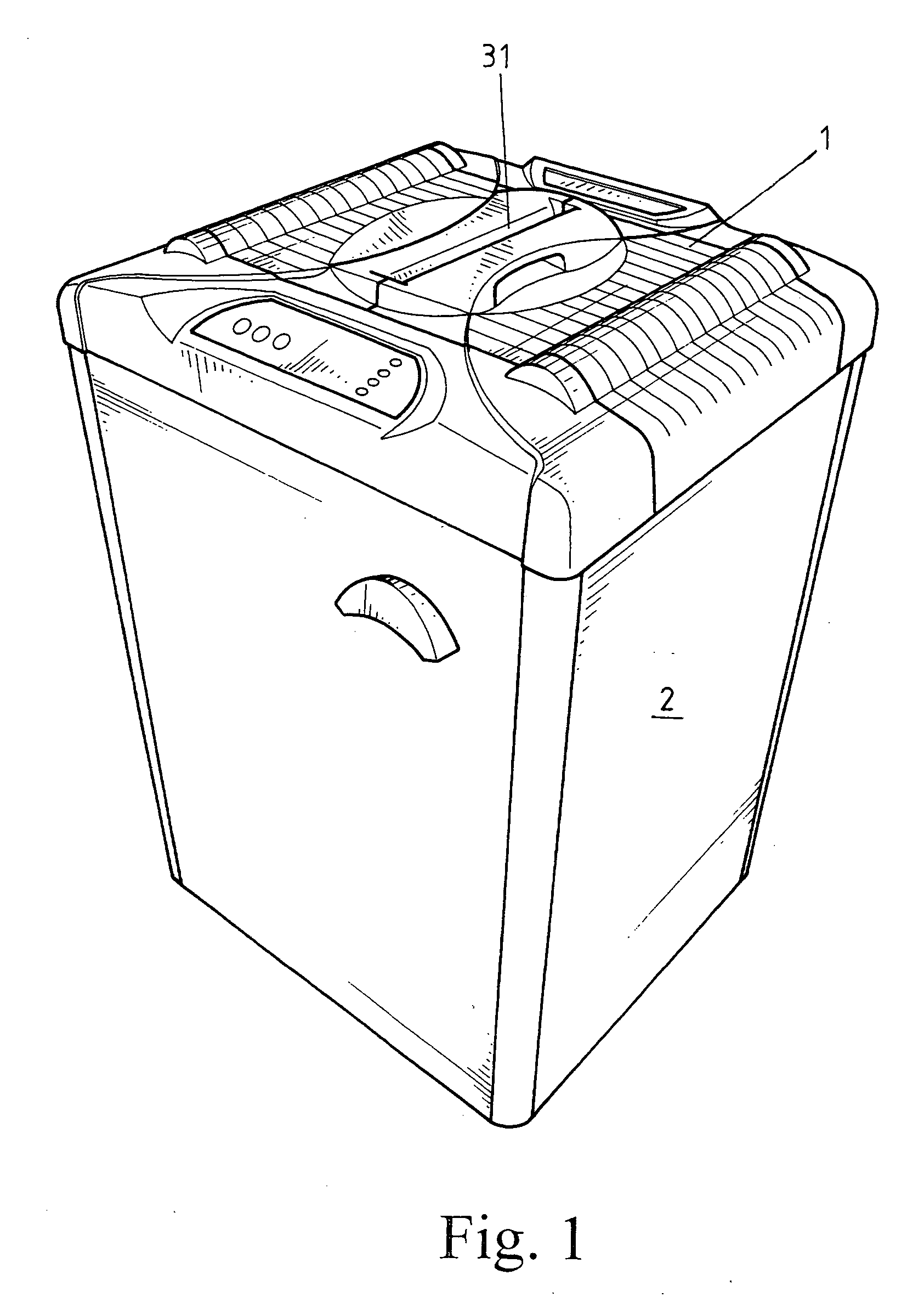
Dual-functional medium shredding machine structure
This invention is related to a dual-functional medium shredding machine structure, specifically designed for shredding or destroying paper printed with data to be destroyed, optical discs containing data to be destroyed, or expired credit cards. This invention mainly implements a pair of shredding roller blades with sharp teeth as shredding means, and is characterized by providing separate feeding inports, including a paper inport for feeding paper in an inclined orientation, and a disc inport for feeding discs in a vertical orientation, wherein the inports are each led to the same shredding roller blades such that, regardless of the type of substance being fed by the user, the paper or the discs can both be shredded by the shredding roller blades, and the shredded scraps are dispensed to separate collectors through an identical exit by means of an auto-revolving switch plate; and a touch switch at each of the inports such that, while feeding the paper or the discs, the touch switch activates the shredding roller blades to perform shredding task, and drives the switch plate so as to dispense shredded scraps of different substance into different collectors.
Owner:MICHILIN PROSPERITY
Process for the production of ultrafine powders of metal oxides
InactiveUS6503475B1Low costHigh yield rateAlkaline earth titanatesMaterial nanotechnologyDiluentBiological activation
A process for the production of ultrafine powders that includes subjecting a mixture of precursor metal compound and a non-reactant diluent phase to mechanical milling whereby the process of mechanical activation reduces the microstructure of the mixture to the form of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase. The process also includes heat treating the mixture of nano-sized grains of the metal compound uniformly dispersed in the diluent phase to convert the nano-sized grains of the metal compound into a metal oxide phase. The process further includes removing the diluent phase such that the nano-sized grains of the metal oxide phase are left behind in the form of an ultrafine powder.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD +1
System and method for milling materials
A system for milling at least one material, e.g., a drug, is described. The system includes a milling apparatus. In another embodiment of the invention, the system includes at least one milling medium. The milling apparatus includes a chamber having a rotary milling head located in it. The milling head is rotated within the chamber by a magnetic drive system.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Methods and systems for producing ethanol using raw starch and fractionation
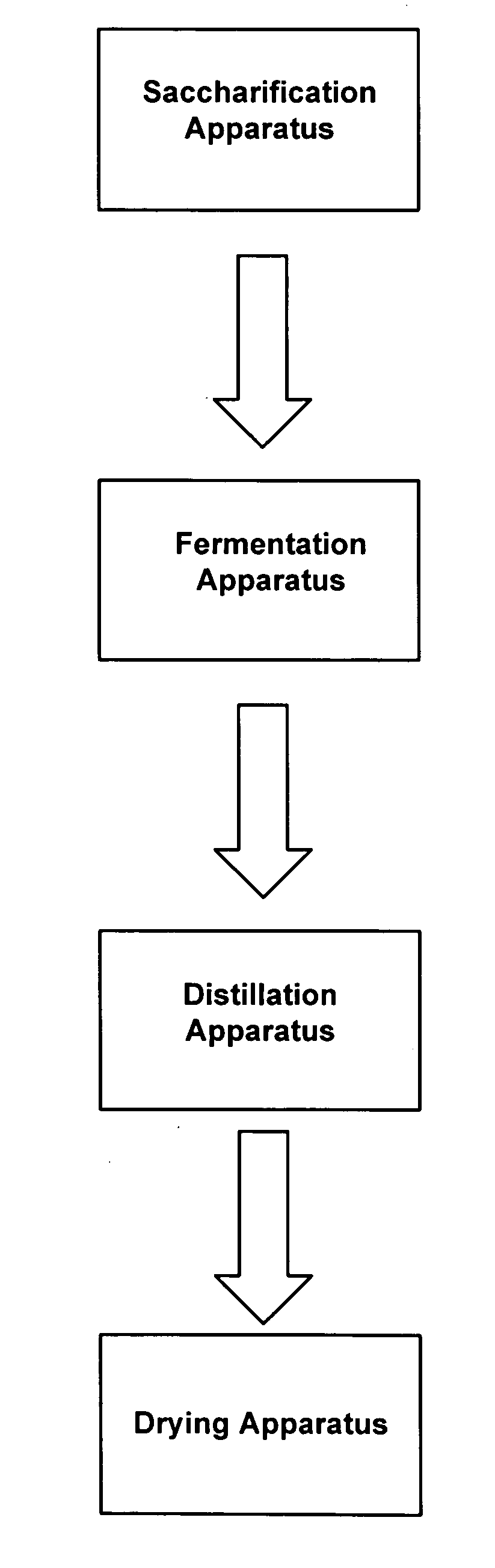
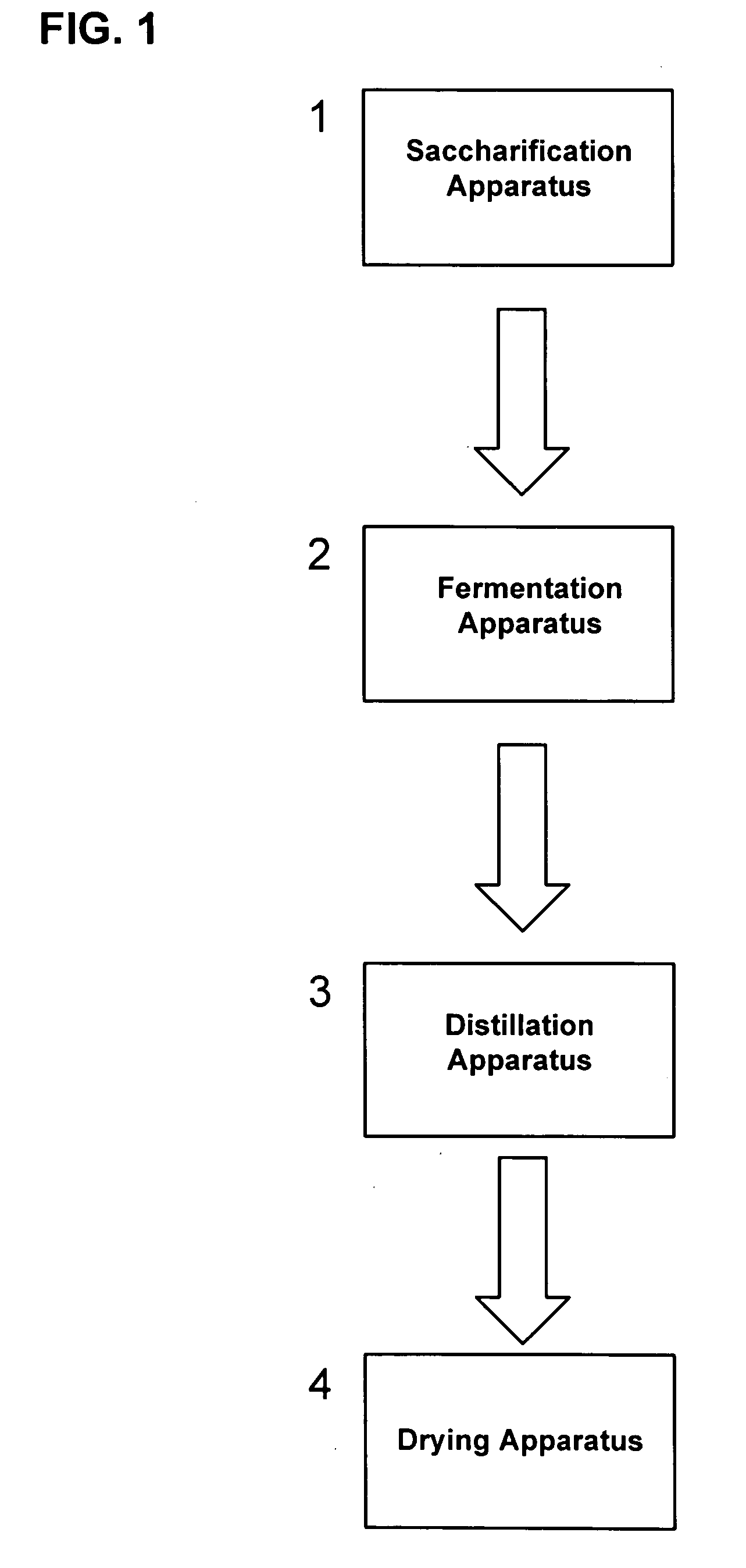
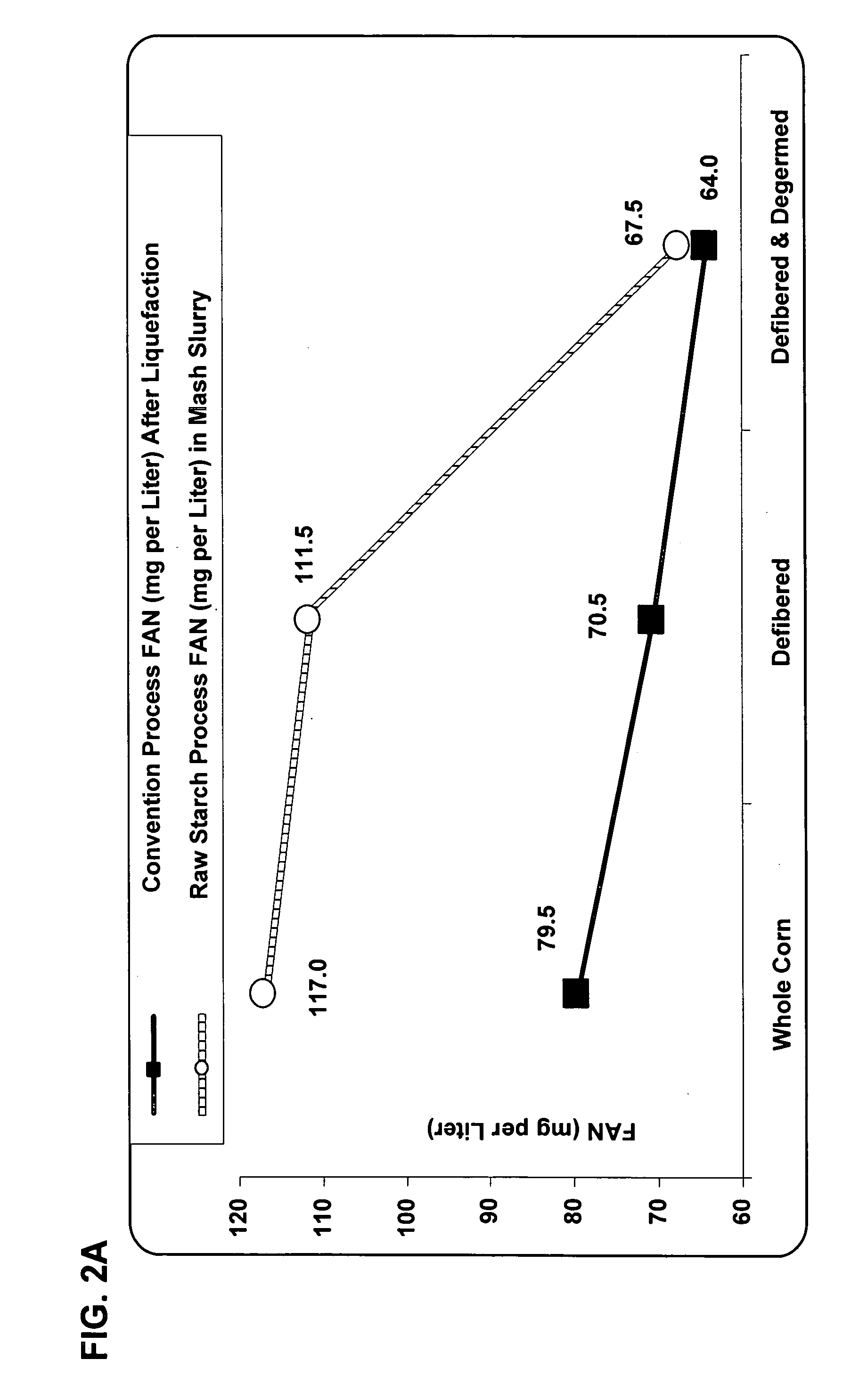
InactiveUS20070037267A1Improve the level ofImprove the immunityBiofuelsFermentationFluidized bed dryingHigh alcohol beer
The present invention relates to methods for producing high levels of alcohol during fermentation of plant material, and to the high alcohol beer produced. The method can include fractionating the plant material. The present invention also relates to methods for producing high protein distiller's dried grain from fermentation of plant material, and to the high protein distiller's dried grain produced. The method can include drying a co-product by ring drying, flash drying, or fluid bed drying. The present invention further relates to reduced stack emissions from drying distillation products from the production of ethanol.
Owner:BROIN & ASSOC
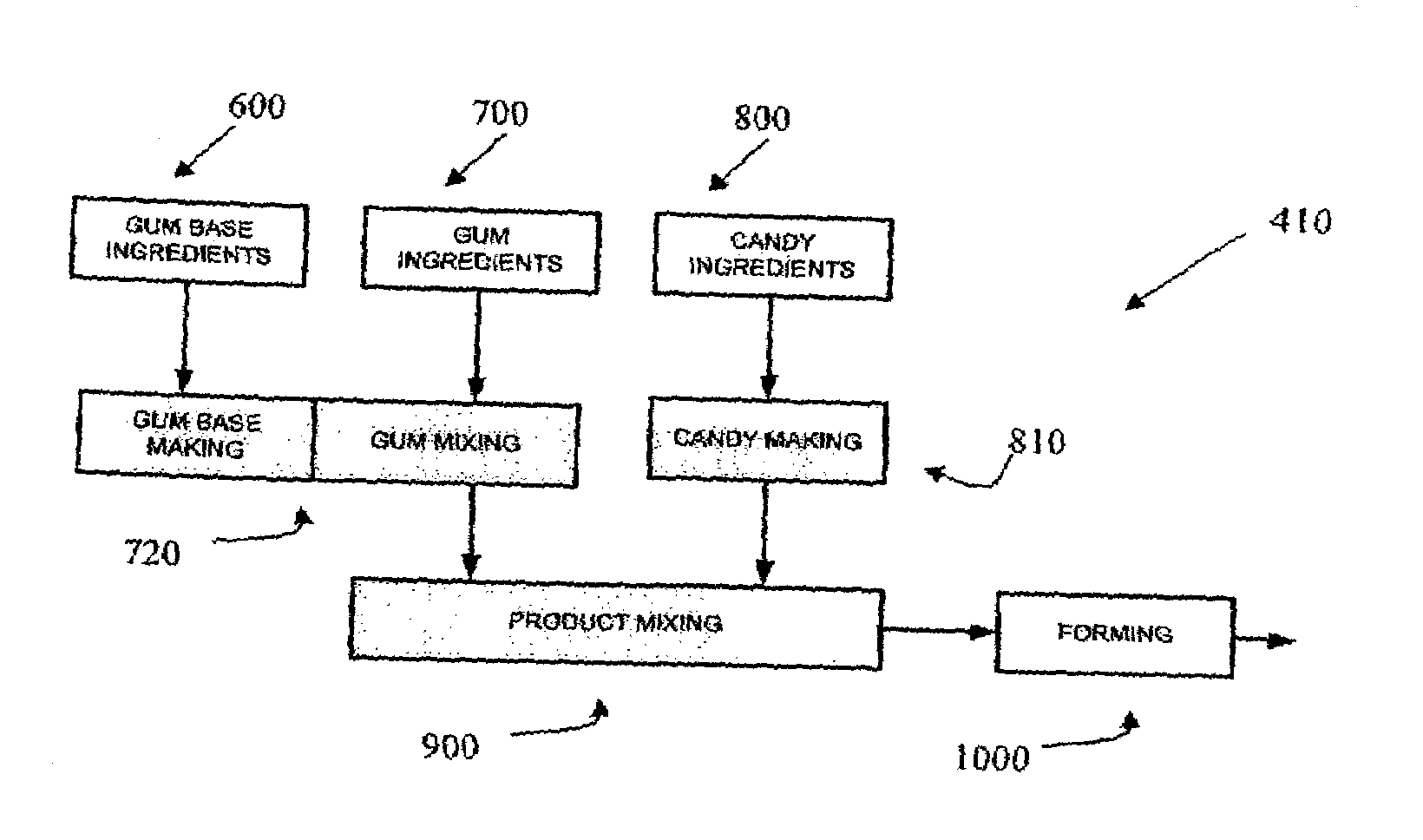
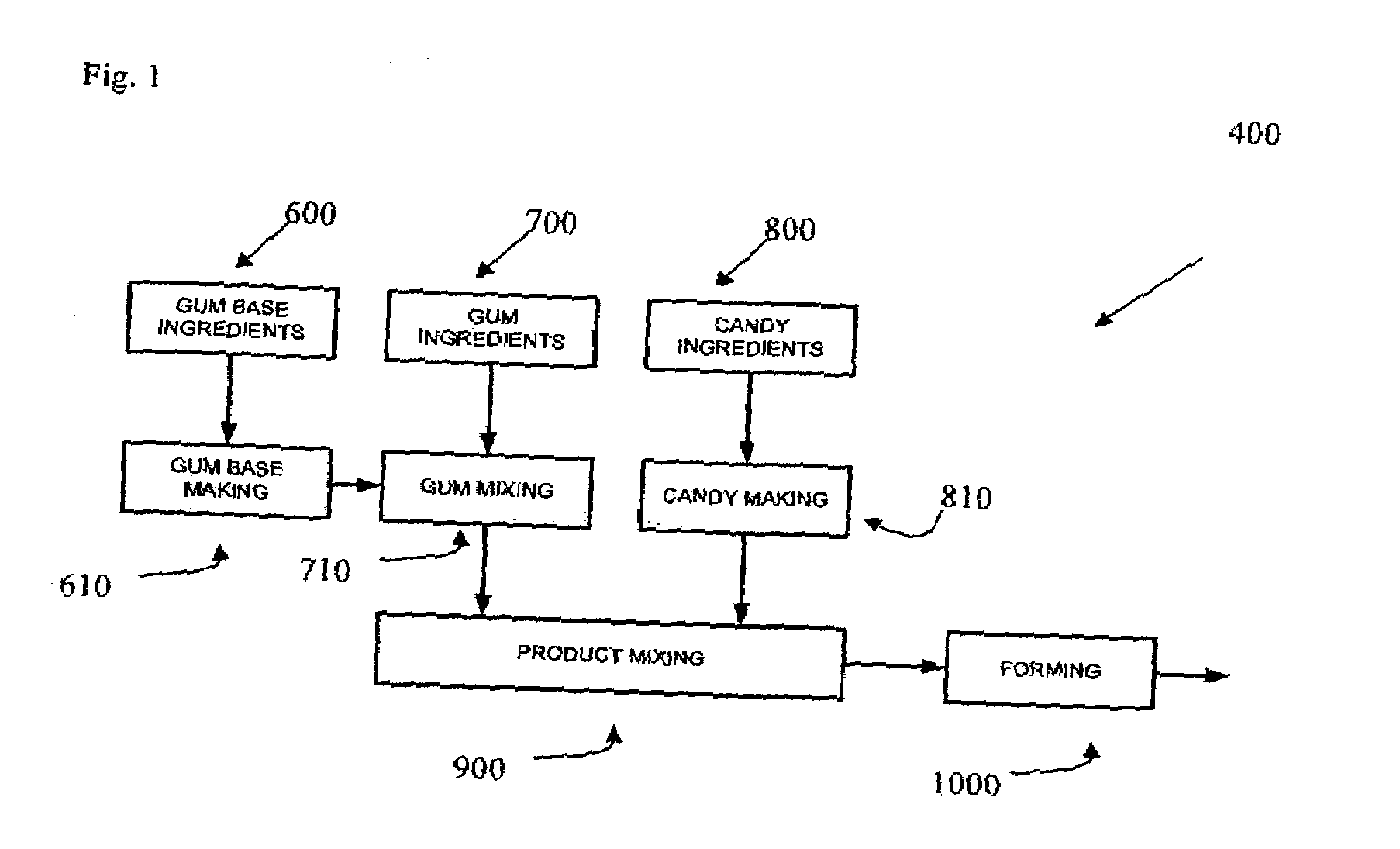
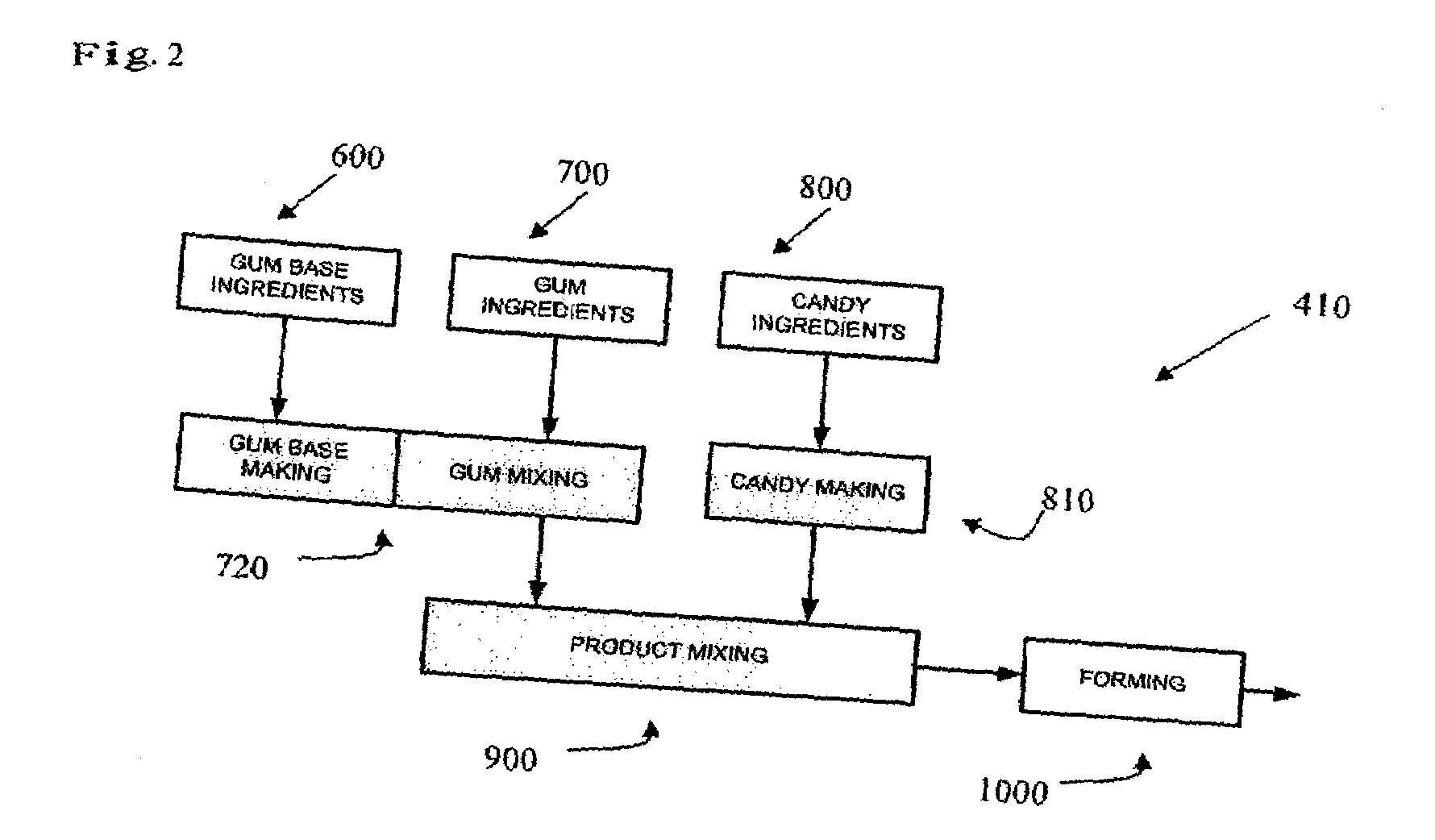
Confectionery compositions including an elastomeric component and a saccharide component
InactiveUS20080166449A1Center edible coresCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsElastomerChewing gum
The present invention relates to the confectionery compositions including a saccharide and a chewing gum base.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS
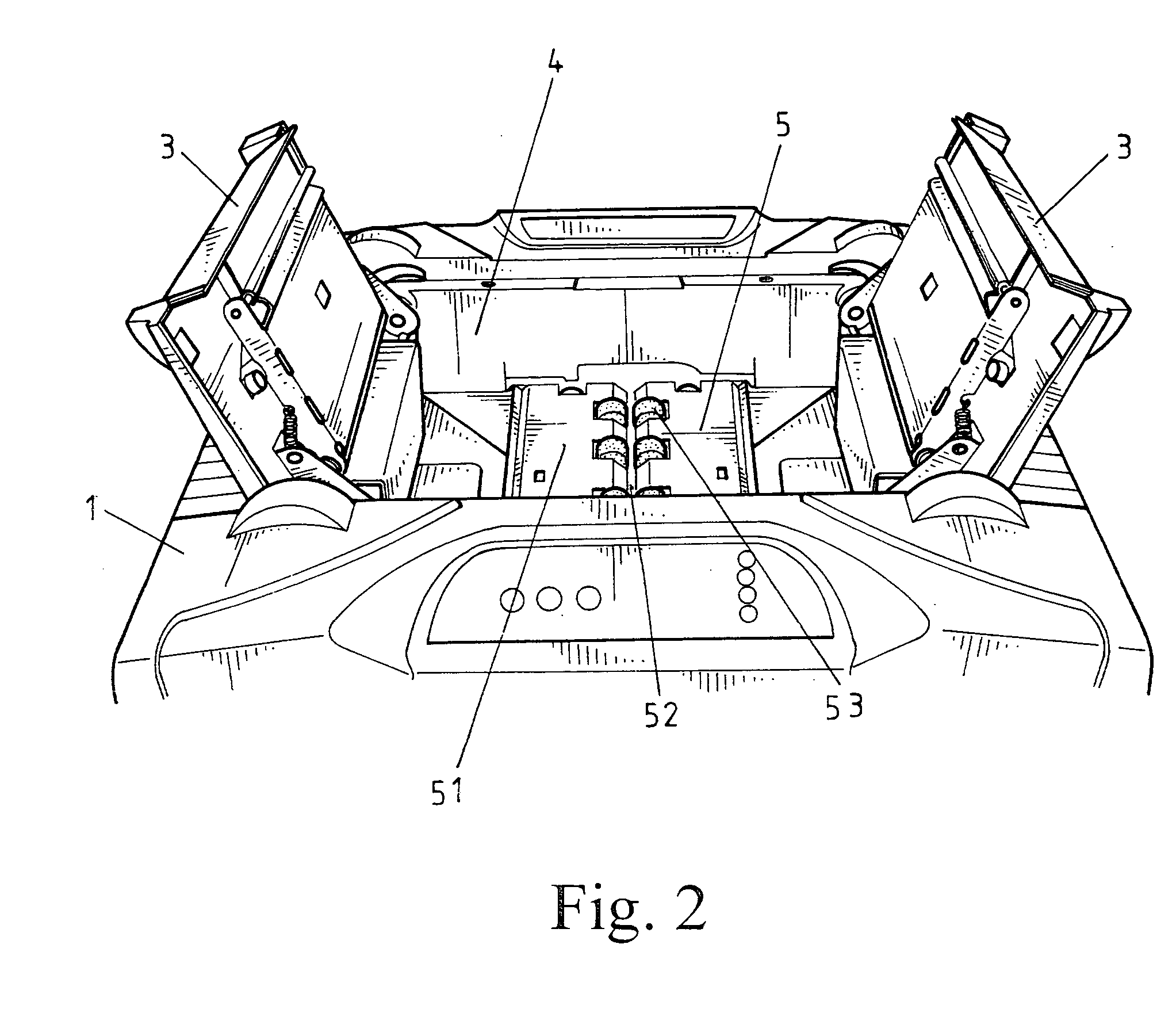
Auto-feed buit-in a paper shredder
InactiveUS20050274836A1Reduce spacingLow costCocoaGrain treatmentsPulp and paper industryPaper sheet
Disclosed is an auto-feed buit-in a paper shredder, including a pair of bisecting lids that are each provided at an inside thereof with a paper press, a paper receiving compartment, an auto-feed, and a paper shredding device located exactly below the auto-feed, wherein the auto-feed includes a paper tray, a paper inlet and two roller assemblies; the paper inlet and the paper shredding device located therebelow are aligned along an identical central axis; the two roller assemblies are provided at opposing sides of the paper inlet in parallel and project into the paper tray, whereby after placing a pile of paper into the paper receiving compartment to be supported by the paper tray, and closing the bisecting lids, the paper presses provided at the insides of the lids would apply a force against the pile of paper, such that a bottommost paper of the pile of paper would be folded in half by the two rollers rotating towards each other and then fed into the paper inlet to be subsequently shredded by the paper shredding device located below the paper inlet.
Owner:MICHILIN PROSPERITY
Method and apparatus for a UV light disinfection system
An ultraviolet (UV) light disinfection method and apparatus is provided that disinfects produce products such as fruits and vegetables by direct exposure to ultraviolet light. The disinfecting UV light eliminates pathogens, such as molds and bacteria from the surfaces that it illuminates. The produce product is disinfected over its entire surface. The produce product can be rotated on a conveyor, to illuminate all of the exterior surface of the produce product with a disinfecting UV light source. To better respond to produce products of varying height and size, the UV light disinfection apparatus can include an automatic actuator. The automatic actuator maintains the UV light source at a preselected level of separation between the produce product and the UV light source. The automatic actuator is responsive to a height sensor that detects the top height of the produce product.
Owner:E W BRANDT & SONS
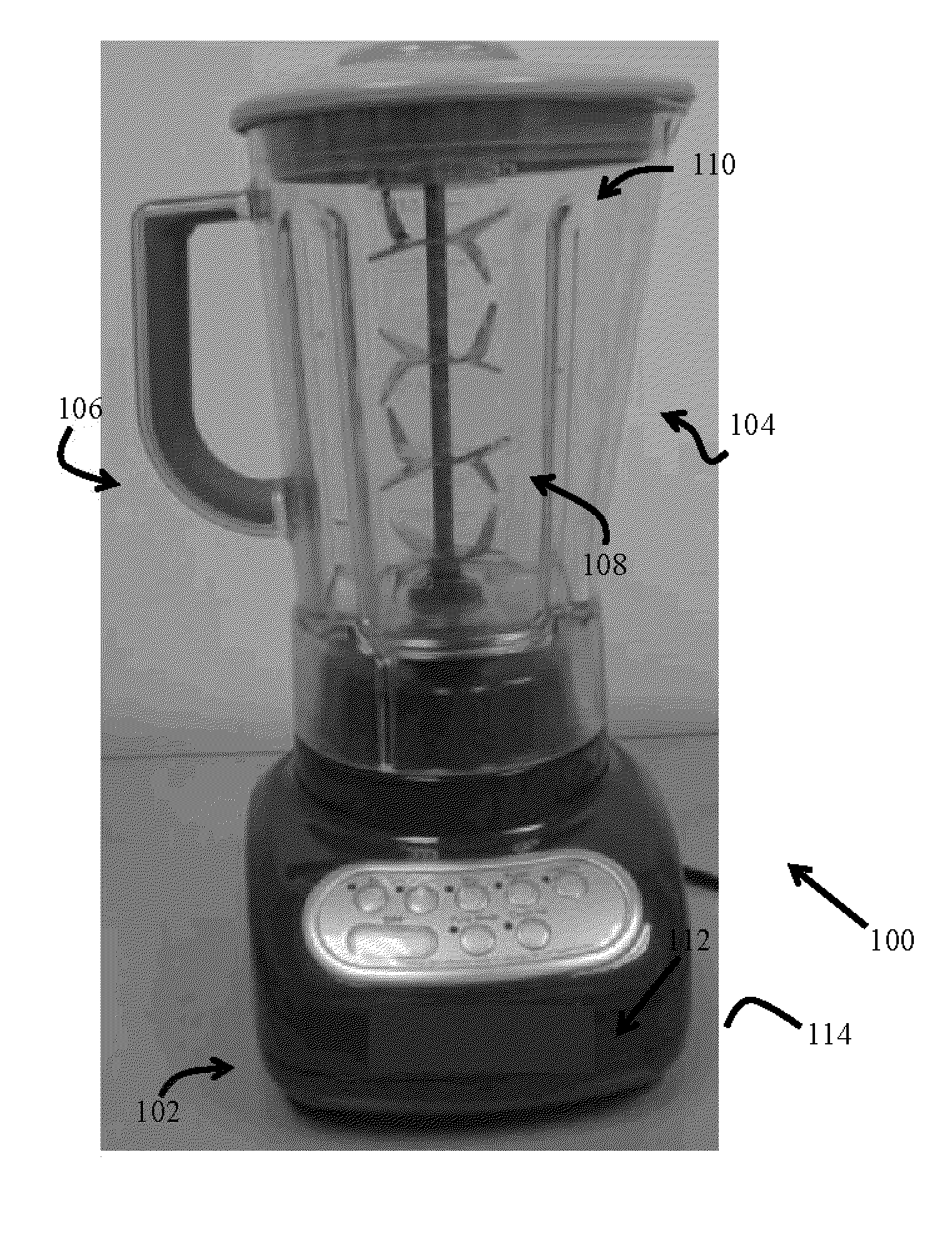
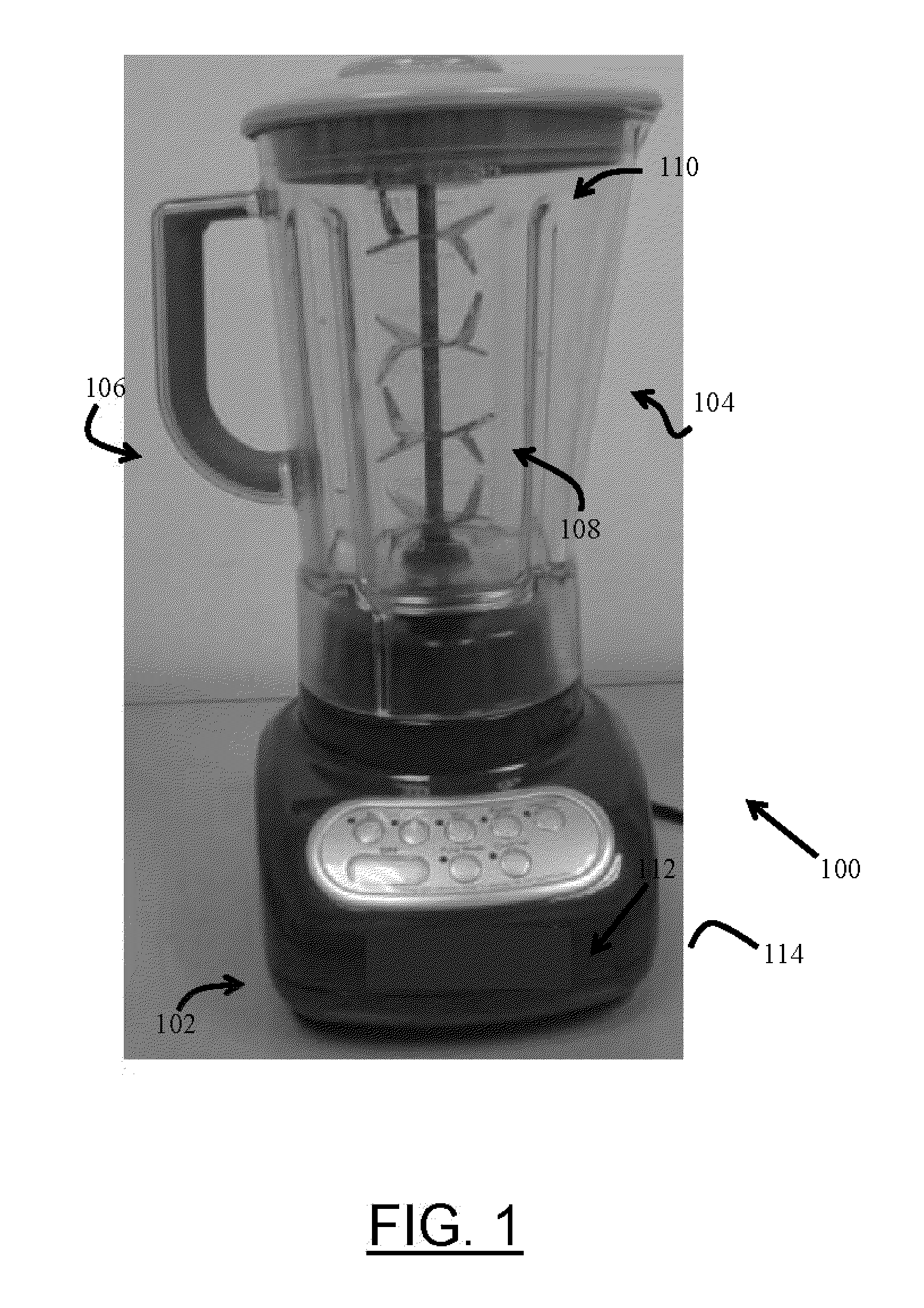
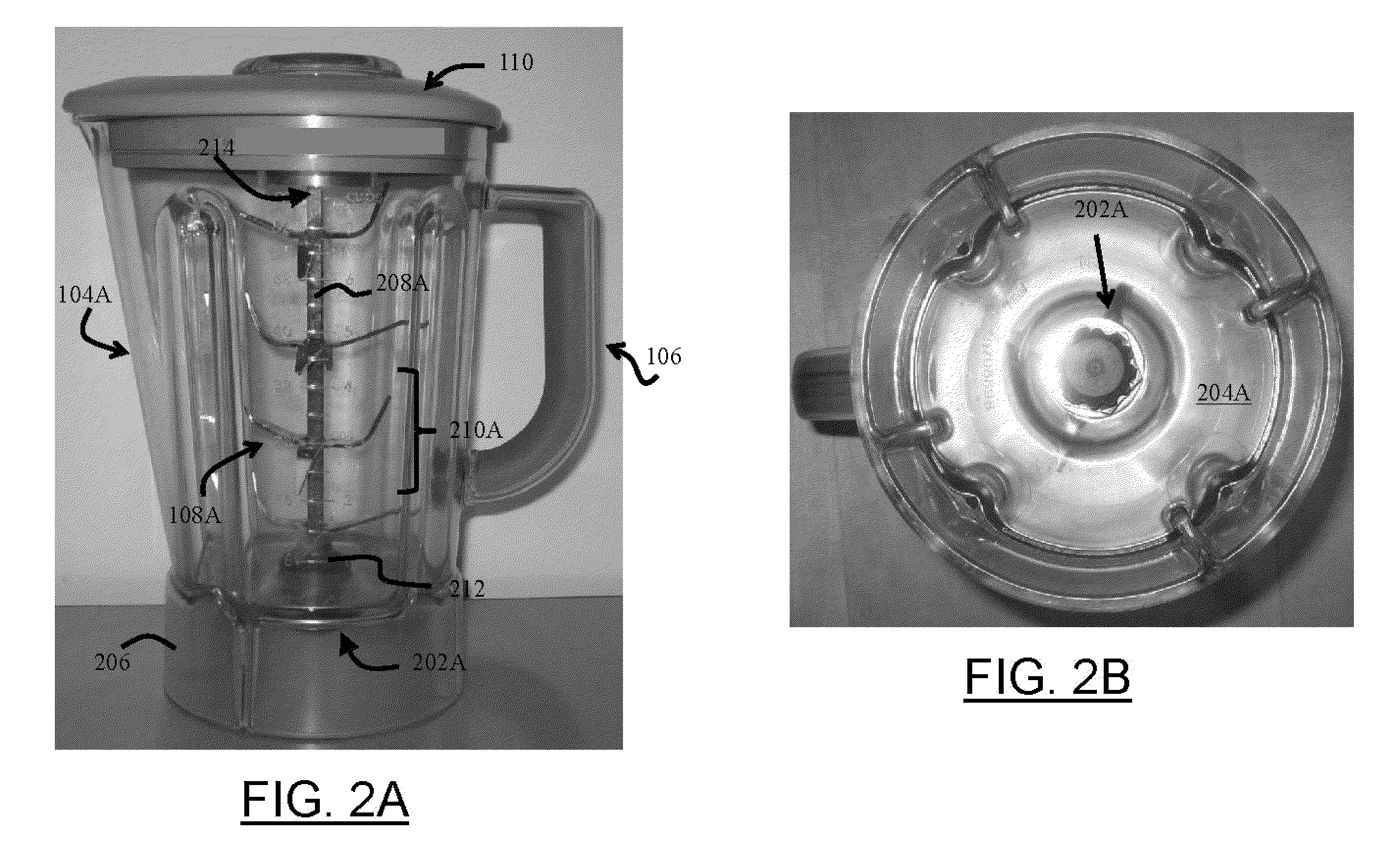
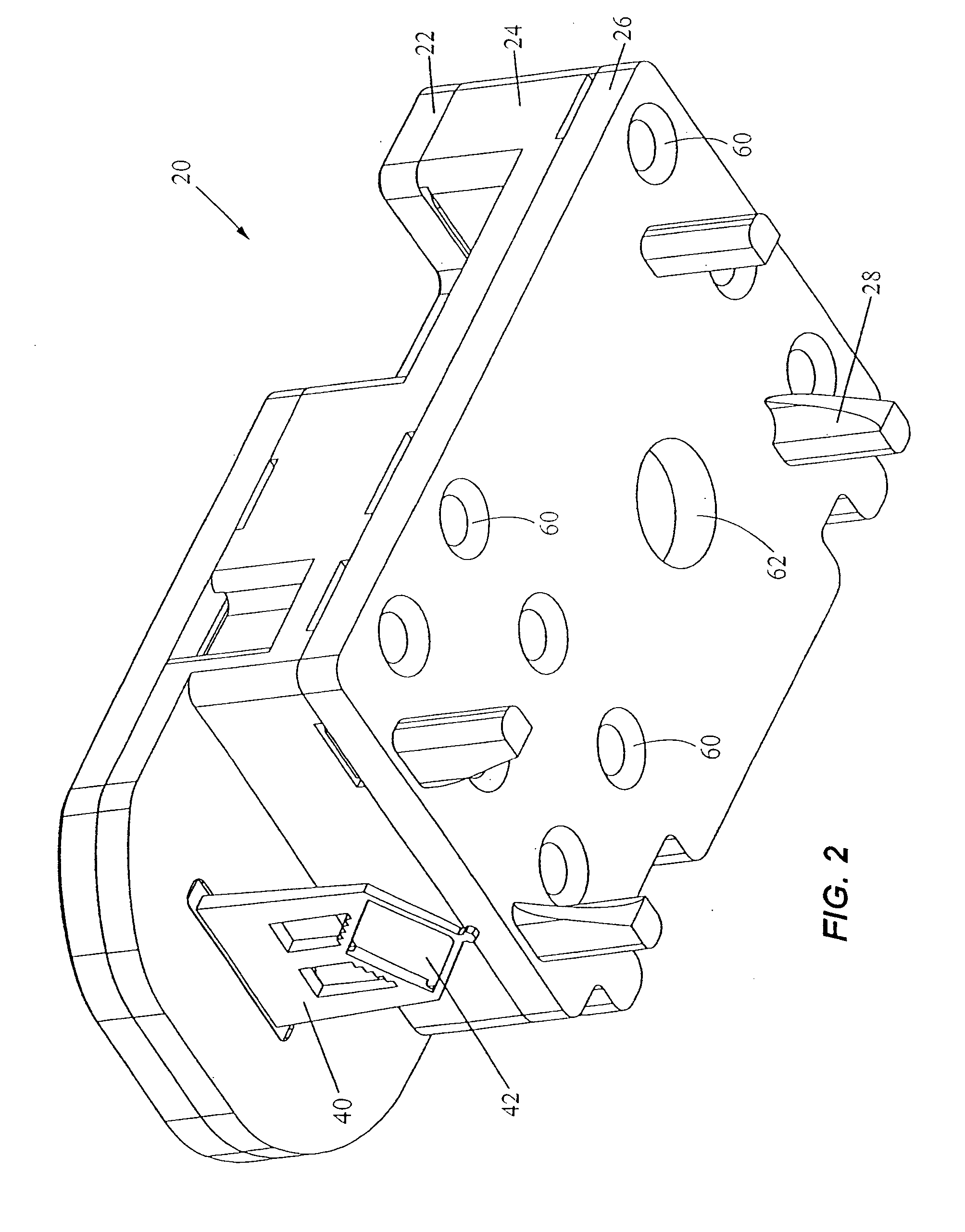
Blender and food processor device
Owner:CARRIERE MARK C
Lipid-Rich Microalgal Flour Food Compositions
InactiveUS20110256282A1Extended shelf lifeSimple compositionDough treatmentFrozen sweetsAlgaeBiology
Algal flour and algal biomass are disclosed. Food compositions comprising algal biomass or algal flour with a high lipid content are disclosed.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
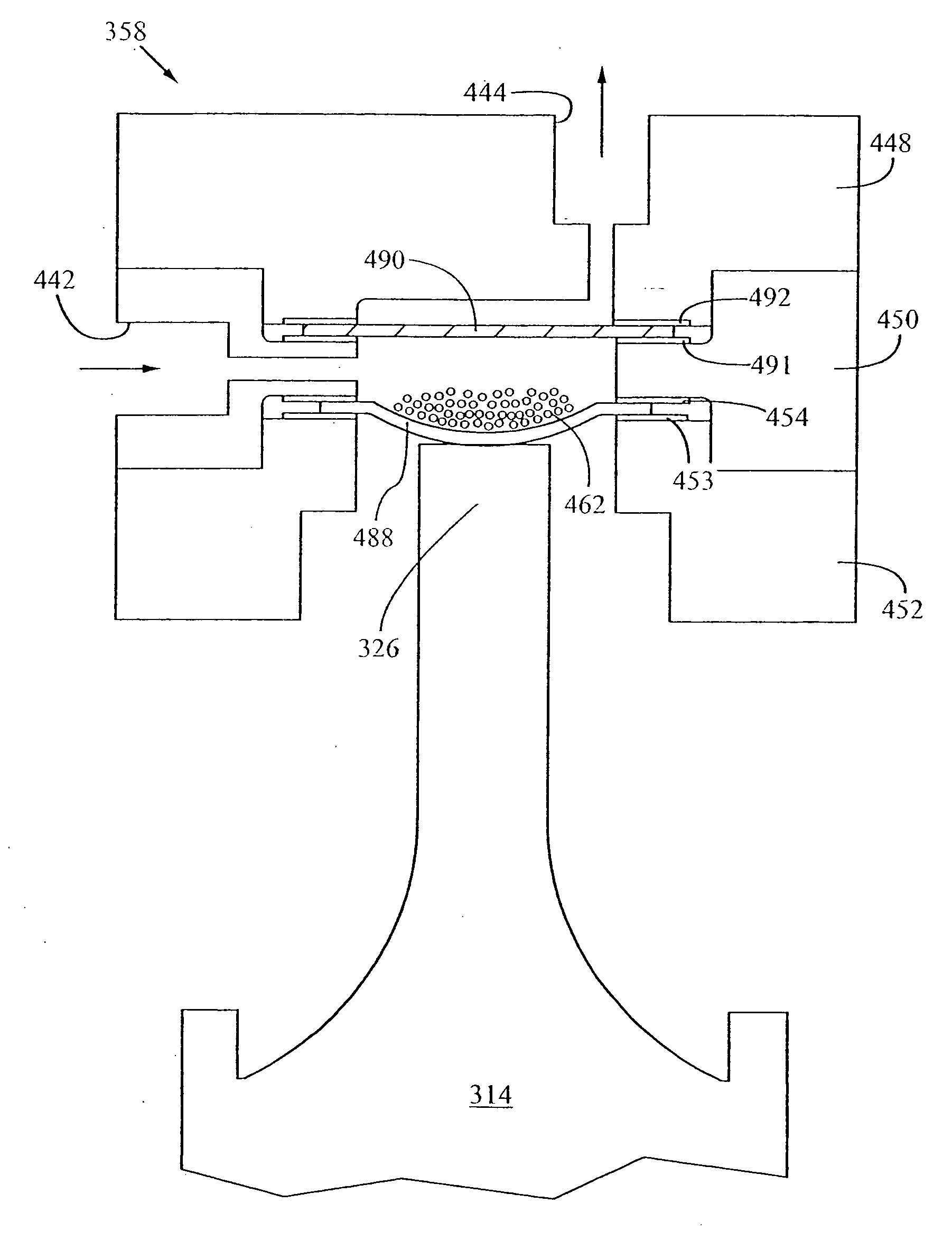
Small-scale mill and method thereof
A small-scale or micro media-mill and a method of milling materials or products, especially pharmaceutical products, use a dispersion containing attrition milling media and the product to be milled. The milling media can be polymeric, formed of polystyrene or cross-linked polystyrene, having a nominal diameter of no greater than 500 microns. Other sizes include 200 microns and 50 microns and a mixture of these sizes. The mill has a relatively small vessel having an opening, an agitator, a coupling and a motor. The agitator can have a rotor and a shaft extending therefrom. The rotor can be cylindrical or have other configurations, and can have tapered end surfaces. The coupling can close the vessel opening, or attaching the coupling to the motor can close the opening. The coupling has an opening through which the rotor shaft extends into the motor. A sealing mechanism, such as a mechanical or lip seals the shaft while permitting the rotor shaft to rotate. The vessel can contain one or more ports for circulating the dispersion, where milling can be made in batches or recirculated through the milling chamber. The media can be retained in the vessel or recirculated along with the process fluid. The rotor is dimensioned so that its outer periphery is spaced with a small gap from an inner surface of the vessel. The vessel also can have a way of cooling the dispersion.
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Leaves and seeds hand grinder
A grinder includes a grinder housing having a grinder actuator, a first grinding plate, a second grinding plate and a detachable coupling arrangement. The first grinding plate is detachably coupling with the grinder actuator, wherein the first grinding plate has a plurality of first grinding knifes downwardly and spacedly extended from a bottom side of the first grinding plate. The second grinding plate has a plurality of second grinding knifes upwardly and spacedly extended from the top side of the second grinding plate at a position that the first and second grinding knifes are spacedly disposed within a grinding compartment, such that when the grinder actuator is turned with respect to the grinder base to drive the first grinding plate to rotate, the first and second grinding knifes are correspondingly moved within the grinding compartment to provide a grinding action.
Owner:BAO FAN
Carbon Fibrous Conjunct and Composite Material Using Thereof
InactiveUS20080254296A1High strengthImprove abilitiesMaterial nanotechnologyNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFiberCarbon fibers
Carbon fibrous conjunct is provided by adding to carbon fibrous structures, which each comprises a three dimensional network of carbon fibers each having an outside diameter of 15-100 nm, wherein the carbon fibrous structure further comprises a granular part with which the carbon fibers are bound in the state that the carbon fibers extend outwardly from the granular part, a binder for binding the carbon fibrous structures. The fine carbon fibrous structures having such unique configuration and also bearing physical properties suitable for a filler for a composite material can be provided with a good handleability by this carbon fibrous conjunct. Composite material is prepared by adding to the matrix the carbon fibrous conjuncts, at an amount of 0.1 to 30% by weight based on the total weight of the composite material.
Owner:HODOGOYA CHEMICAL CO LTD
Apparatus and method for cell disruption
InactiveUS20060030038A1Quick destructionHighly consistent repeatable lysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusTransducerEngineering
An apparatus for disrupting cells or viruses comprises a container having a chamber for holding the cells or viruses. The container includes at least one flexible wall defining the chamber. The apparatus also includes a transducer for impacting an external surface of the flexible wall to generate pressure waves in the chamber. The apparatus also includes a pressure source for increasing the pressure in the chamber. The pressurization of the chamber ensures effective coupling between the transducer and the flexible wall. The apparatus may also include beads in the chamber for rupturing the cells or viruses.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
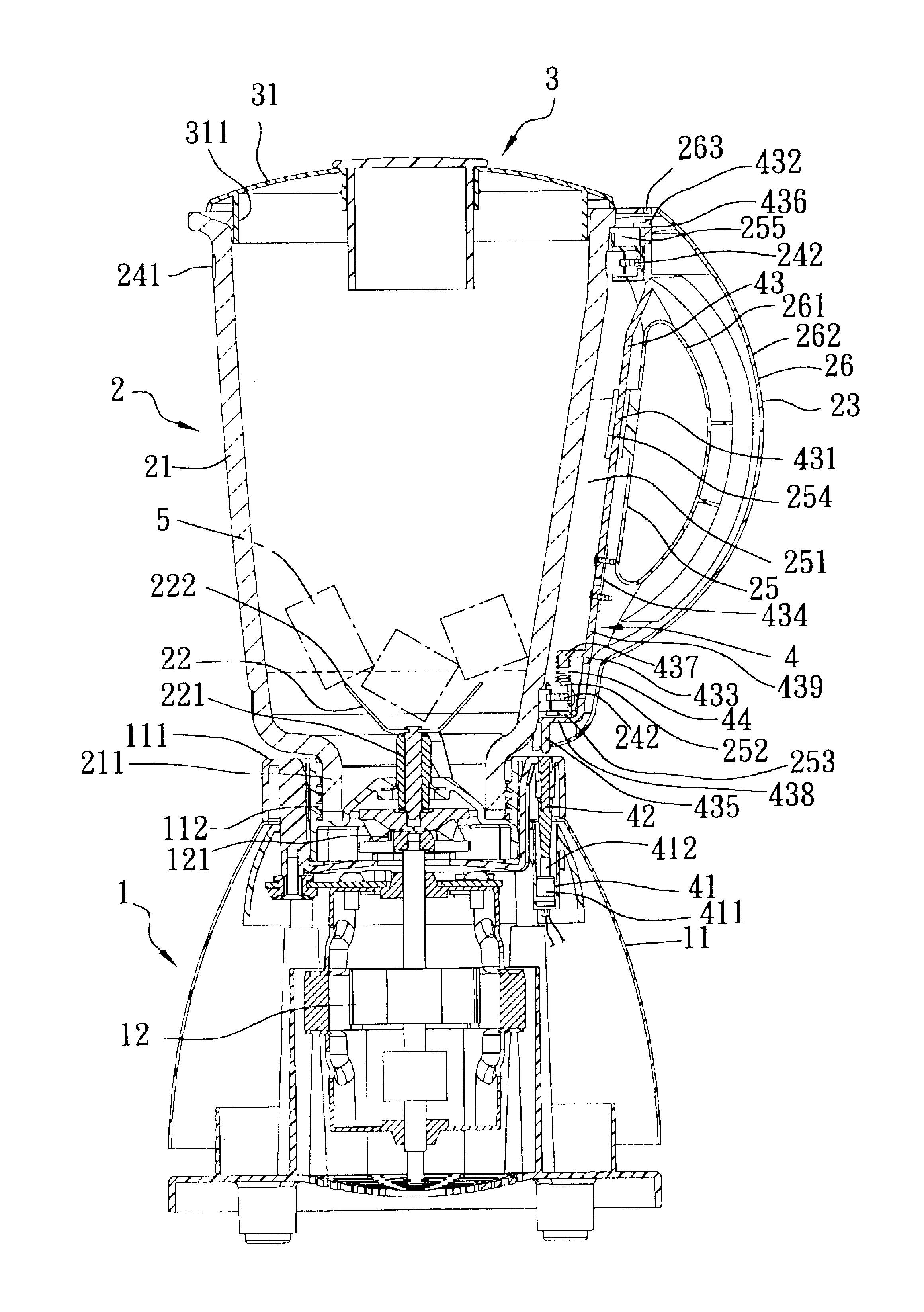
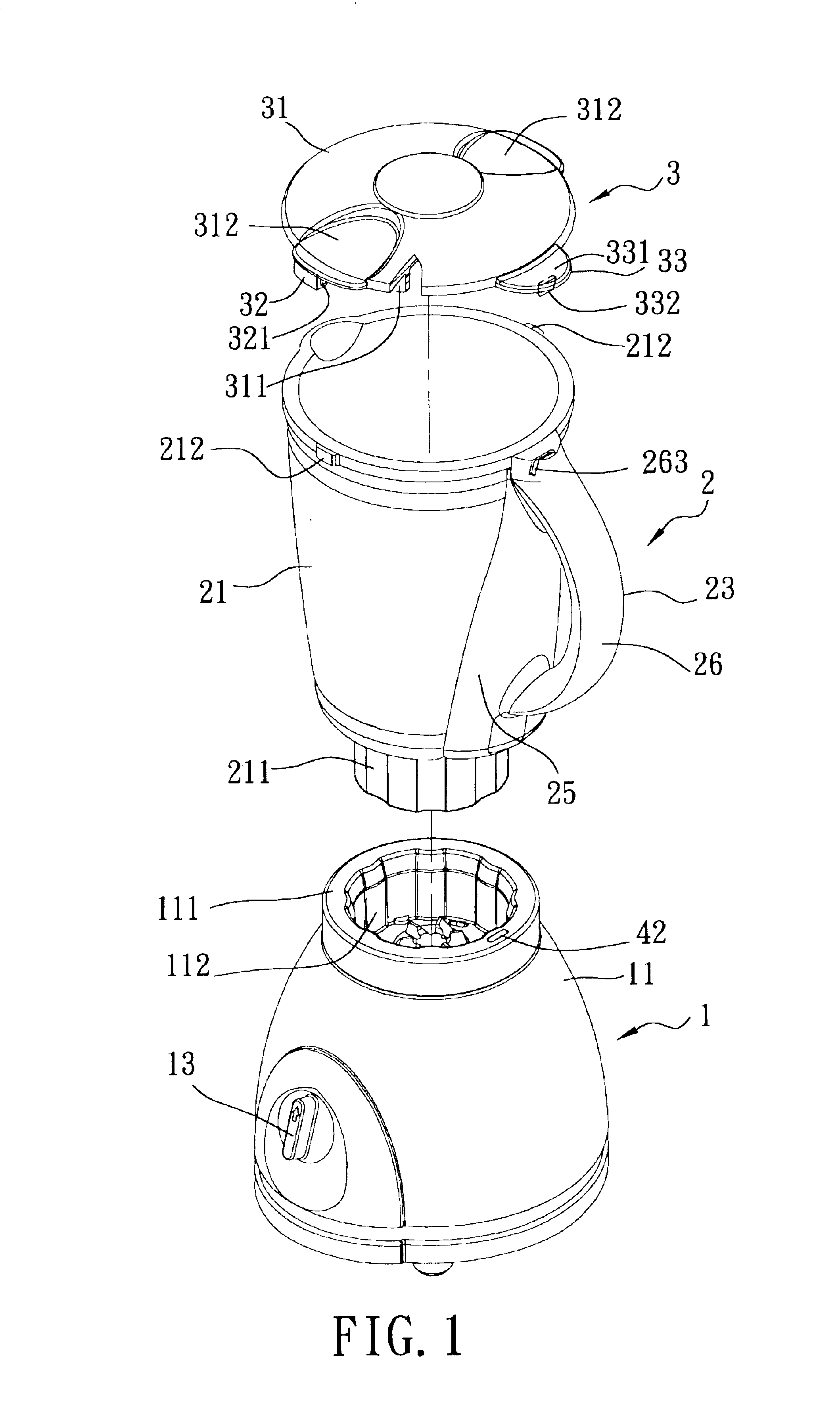
Blender having a top cover provided with a switch actuating block
A blender includes a motor base, a container, and a top cover. The motor base includes a motor unit having a blade driving section, and a contact switch unit connected electrically to the motor unit. The contact switch unit includes a press button that is depressible so as to permit activation of the motor unit. The container has a container bottom provided with a cutting blade unit that is coupled to the blade driving section so as to be driven rotatably by the motor unit. The container has a spring-loaded push rod unit mounted movably thereon. The push rod unit has a bottom rod section associated with the press button of the contact switch unit, and a top rod section depressible by a switch actuating block of the top cover so as to move the push rod unit against biasing action from a deactivating position to an activating position.
Owner:EUPA INT CORP
Sorbent containing engineered fuel feed stock
ActiveUS20110099890A1Less-harmful emissionEmission reductionSolid fuel pretreatmentBiofuelsPower stationCombustion
Disclosed are novel engineered fuel feed stocks, feed stocks produced by the described processes, methods of making the fuel feed stocks, methods of producing energy from the fuel feed stocks. Components derived from processed MSW waste streams can be used to make such feed stocks which are substantially free of glass, metals, grit and noncombustibles and contain a sorbent. These feed stocks are useful for a variety of purposes including as gasification and combustion fuels. In addition, one or more sorbents can be added to the feed stocks in order to reduce the amount of a variety of pollutants present in traditional fuel and feed stocks, including, but not limited, sulfur and chlorine. Further, these feed stocks with added sorbent can mitigate corrosion, improve fuel conversion, extend power generating plant lifetime, reduce ash slagging, and reduced operating temperature.
Owner:REPOWER IP LLC
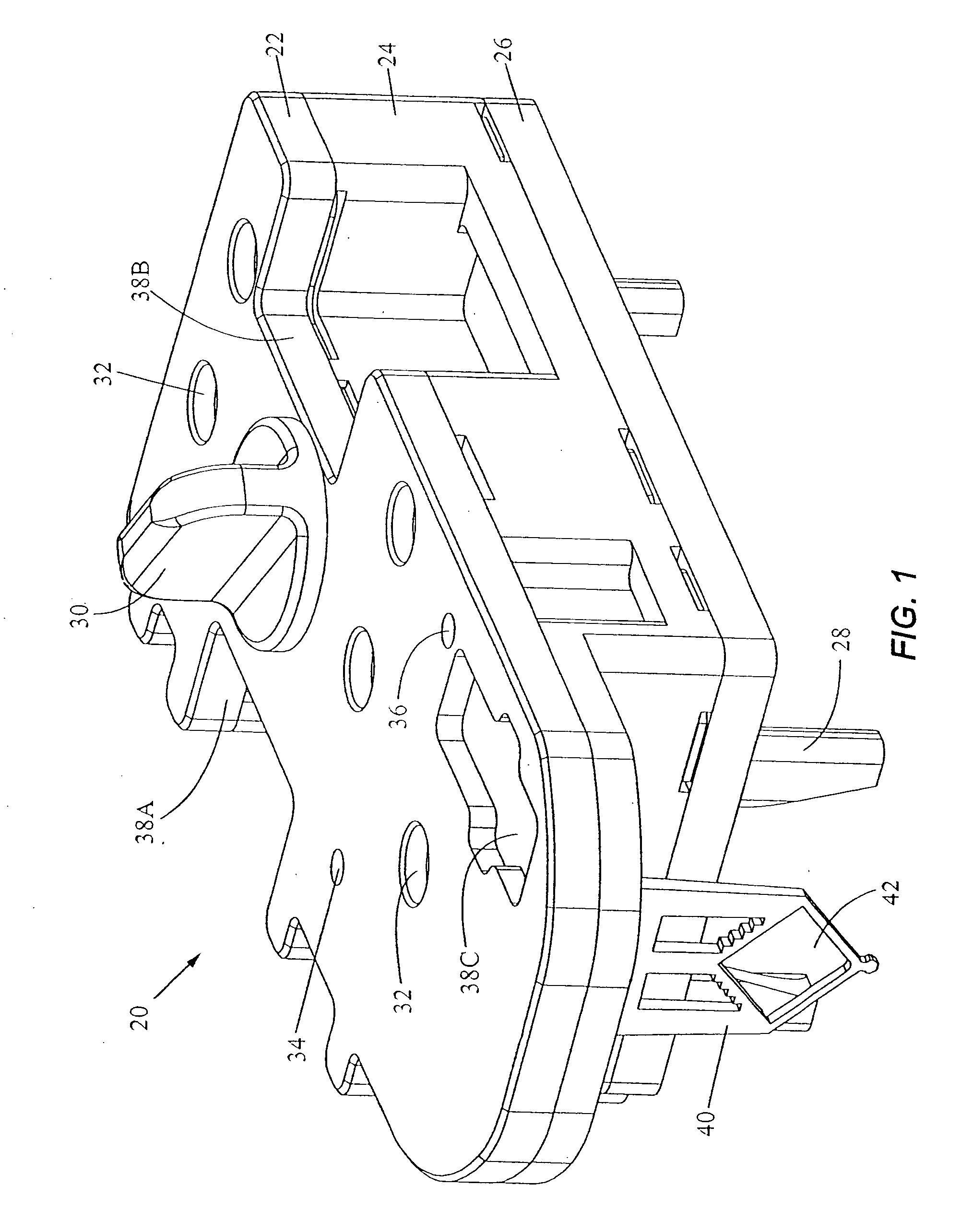
Feeding mechanism auto-adjusting to load for use in automatic high-security destruction of a mixed load, and other feeding systems
A inventive feeding mechanism continuously feeds and continuously subjects to shredding, cutting, recycling, sorting, or other processing, a load consisting of a mixture of different-thickness materials, such as a mixture of paper, compact disks (CDs), cassette tapes, videotapes, etc. The auto-adjusting feeding mechanism is useable in high-security destruction, food processing, recycling, sorting, processing, and other applications.
Owner:CASTRONOVO CHARLES A
Slotted hammermill hammer
An improved hammermill hammer is provided wherein the hammer body has an interlocking slot, to receive one of a pair of retaining rods, and a rod hole through which a second rod is interfitted to lock the hammer securely to the hammermill rotor.
Owner:DZ GRINDERS LLC
Method for producing a microparticle
InactiveUS6022564AQuality improvementEfficient productionBiocidePowder deliveryHydrogen atomCarboxylic acid
This invention provides a method for producing a microparticle which comprises pulverizing a solid preparation comprising a compound represented by the formula: wherein ring A is an optionally substituted benzene ring; R is a hydrogen atom or an optionally substituted hydrocarbon group; B is an optionally esterified or amidated carboxyl group; X is -CH(OH)- or -CO-; k is 0 or 1; and n is 0, 1 or 2 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a biodegradable polymer of alpha -hydroxycarboxylic acid in the presence of a pulverizing auxiliary, which can provide microparticles which are less adhesive and involve less aggregation and are thus excellent in drug entrapment ratio and control of drug-release in a desired particle size.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com