A method of using biomass fuel to strengthen the sintering of refractory iron ore
A biomass fuel and biomass technology, which is applied in the field of iron ore sintering, can solve the problems of poor air permeability of the sintering material layer, low utilization coefficient, and deterioration of fuel combustion in the sintering material layer, so as to achieve the strength of the drum without reducing, increasing the temperature, burn-promoting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
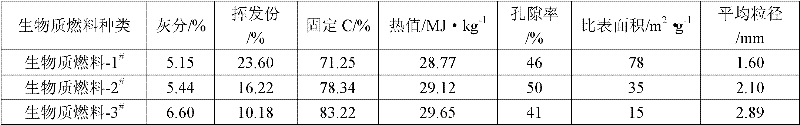
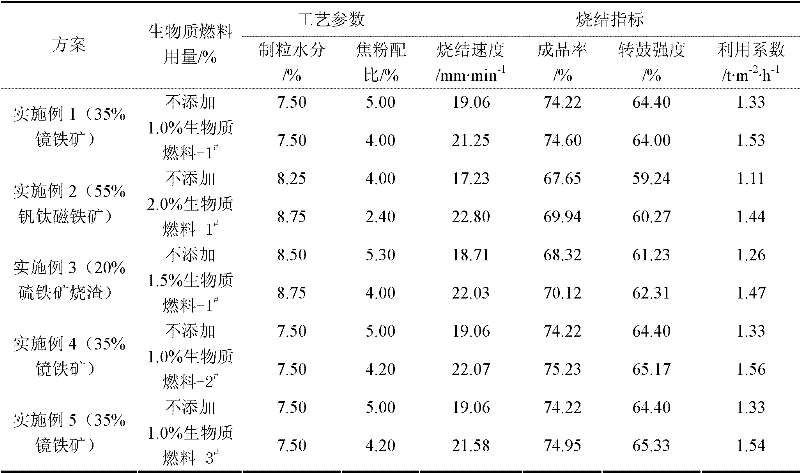
[0028] Example 1: Add 35% specularite in the sinter, and the chemical composition of the produced sinter is TFe57.63%, R2.00, SiO 2 4.83%, MgO2.00%. It can be seen from Table 3 that adding 1.0% biomass fuel-1 # Sintering, the sintering speed is 2.19mm / min faster than the sintering speed without adding biomass fuel, and the utilization factor is increased by 0.20t / (m 2 h), the strength of the drum is basically the same.
example 2
[0029] Example 2: Add 55% vanadium-titanium magnetite into the sinter, and the chemical composition of the produced sinter is TFe50.37%, R2.28, SiO 2 4.61%, MgO2.45%, TiO 2 7.72%. It can be seen from Table 3 that adding 2.0% biomass fuel-1 # Sintering, the sintering speed is 5.57mm / min faster than the sintering speed without adding biomass fuel, and the utilization factor is increased by 0.33t / (m 2 h), the strength of the drum is also slightly improved.
example 3
[0030] Example 3: Add 20% pyrite slag to the sinter, and the chemical composition of the produced sinter is TFe56.85%, R1.90, SiO 2 5.32%, MgO2.00%, TiO 2 7.72%. It can be seen from Table 3 that adding 1.5% biomass fuel-1 # Sintering, the sintering speed is 3.32mm / min faster than the sintering speed without adding biomass fuel, and the utilization factor is increased by 0.21t / (m 2 h), the strength of the drum is also slightly improved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com