Patents
Literature
706 results about "Screen method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
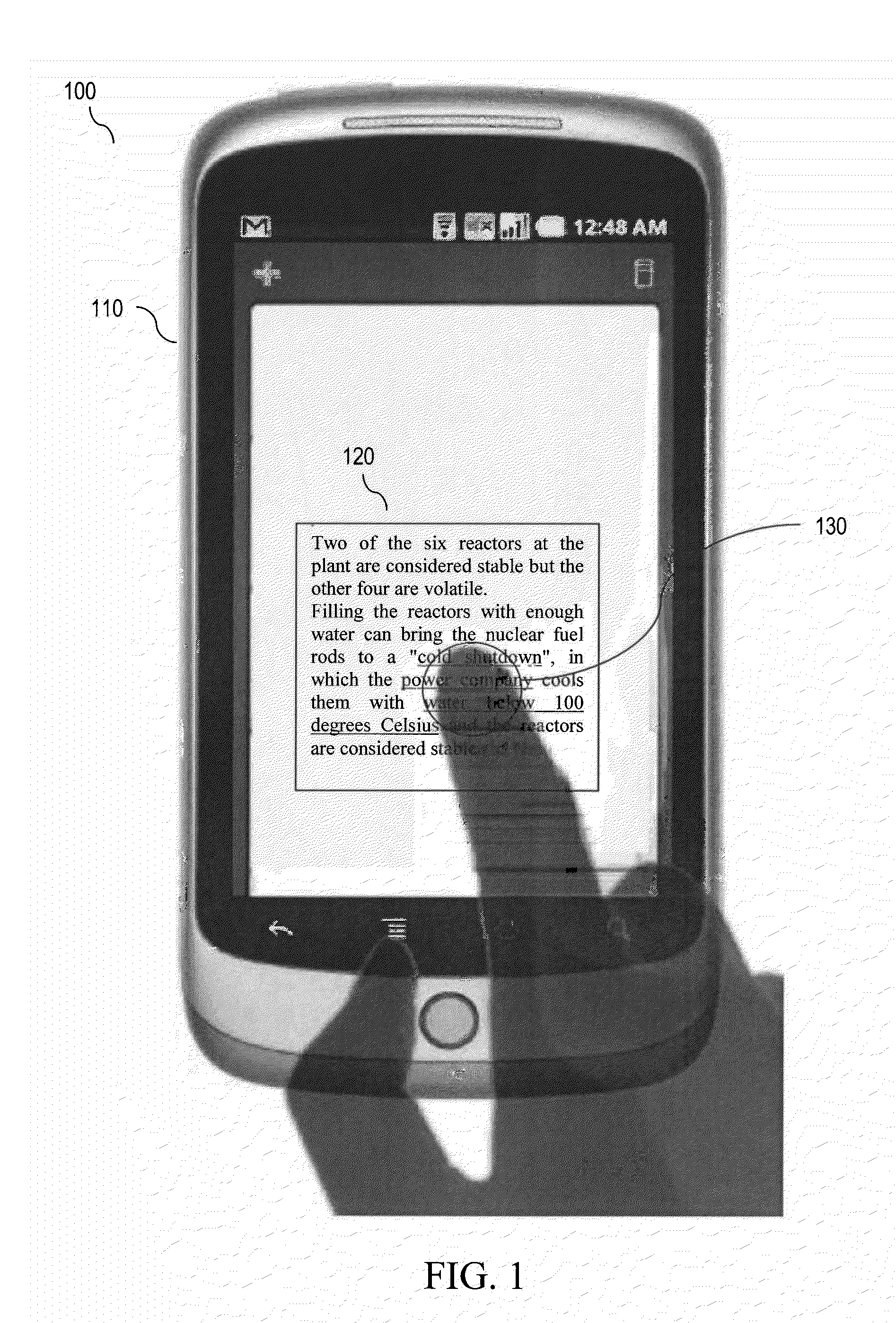
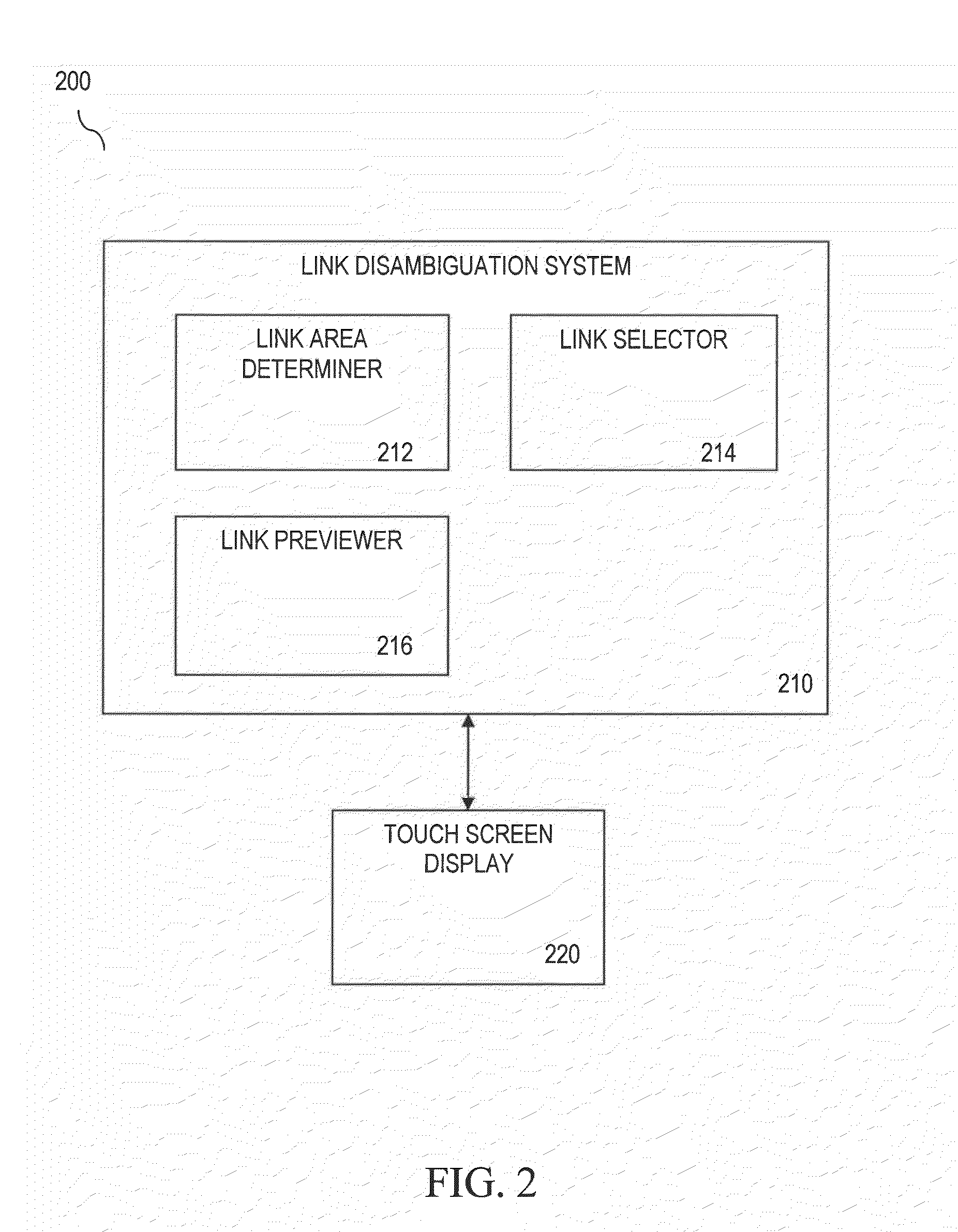
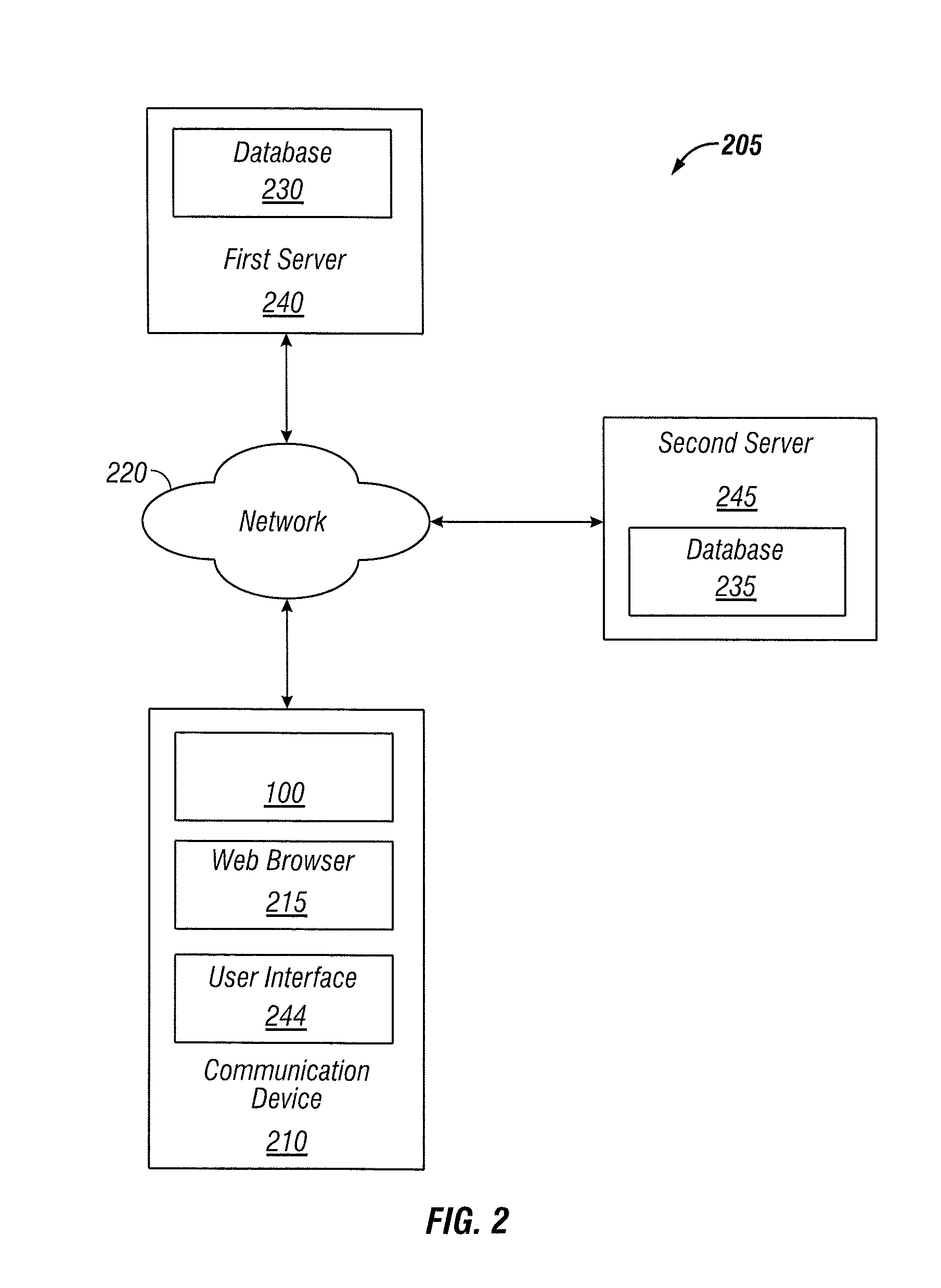
Link Disambiguation For Touch Screens
InactiveUS20130047100A1Special data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingTouchscreenScreen method
Methods, systems and computer program products for displaying links on a touch screen are disclosed. A link area of uncertainty at a touch point of a touch screen gesture may be determined. Two or more links may be determined at the link area. A predicted link of the two or more links may be selected. An enlarged display of the predicted link may be previewed. A system for displaying links on a touch screen may include a link area determiner, a link selector and a link previewer.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
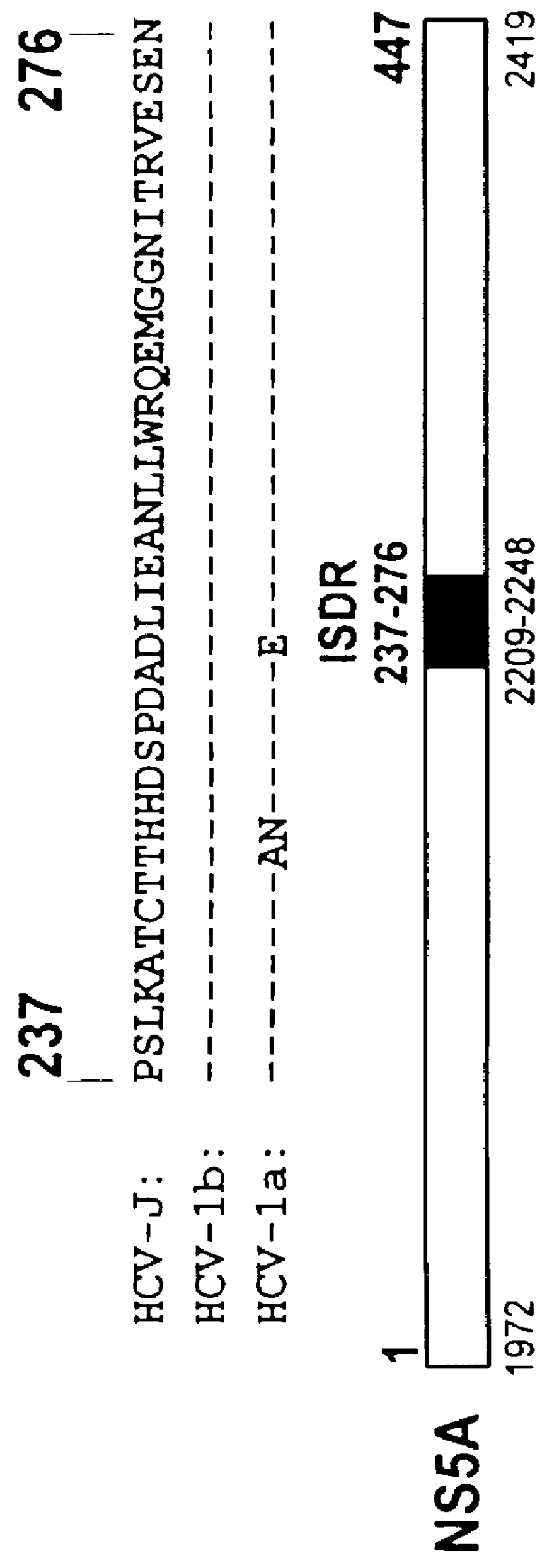
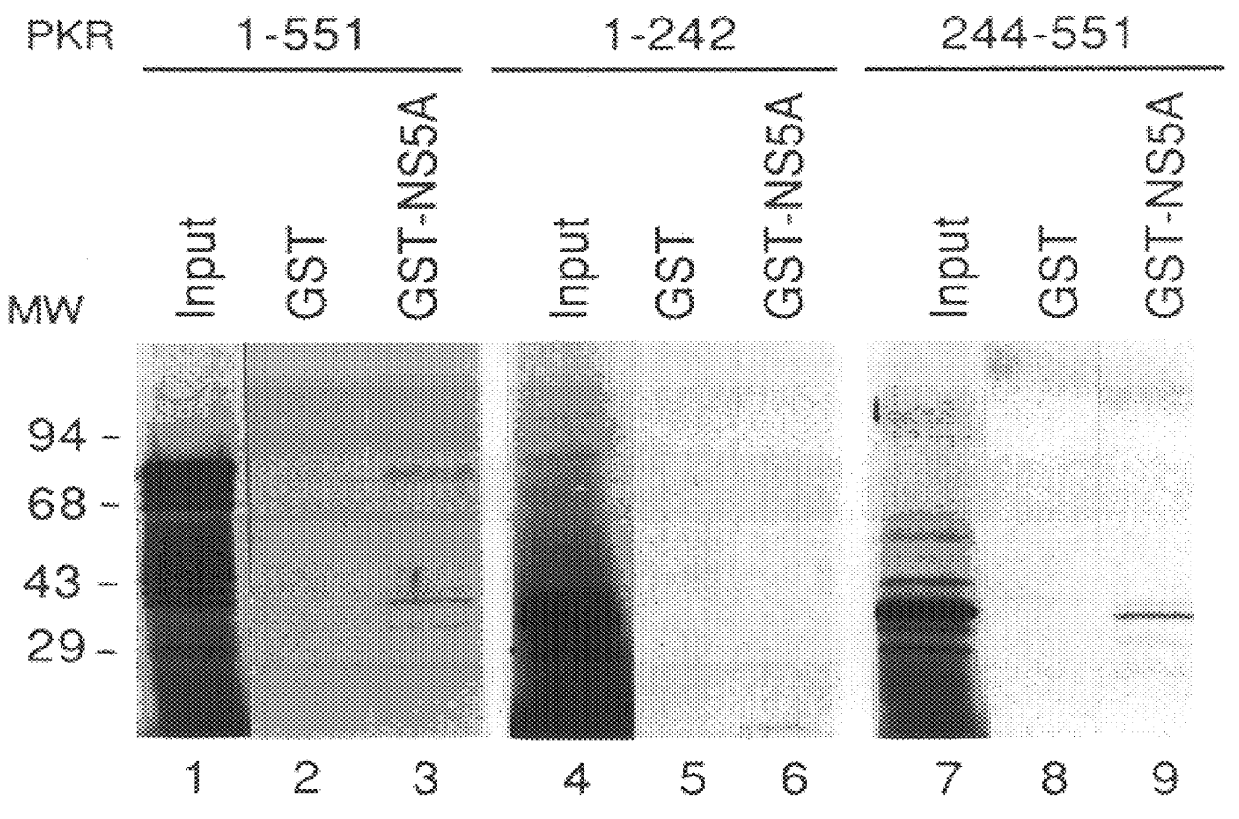
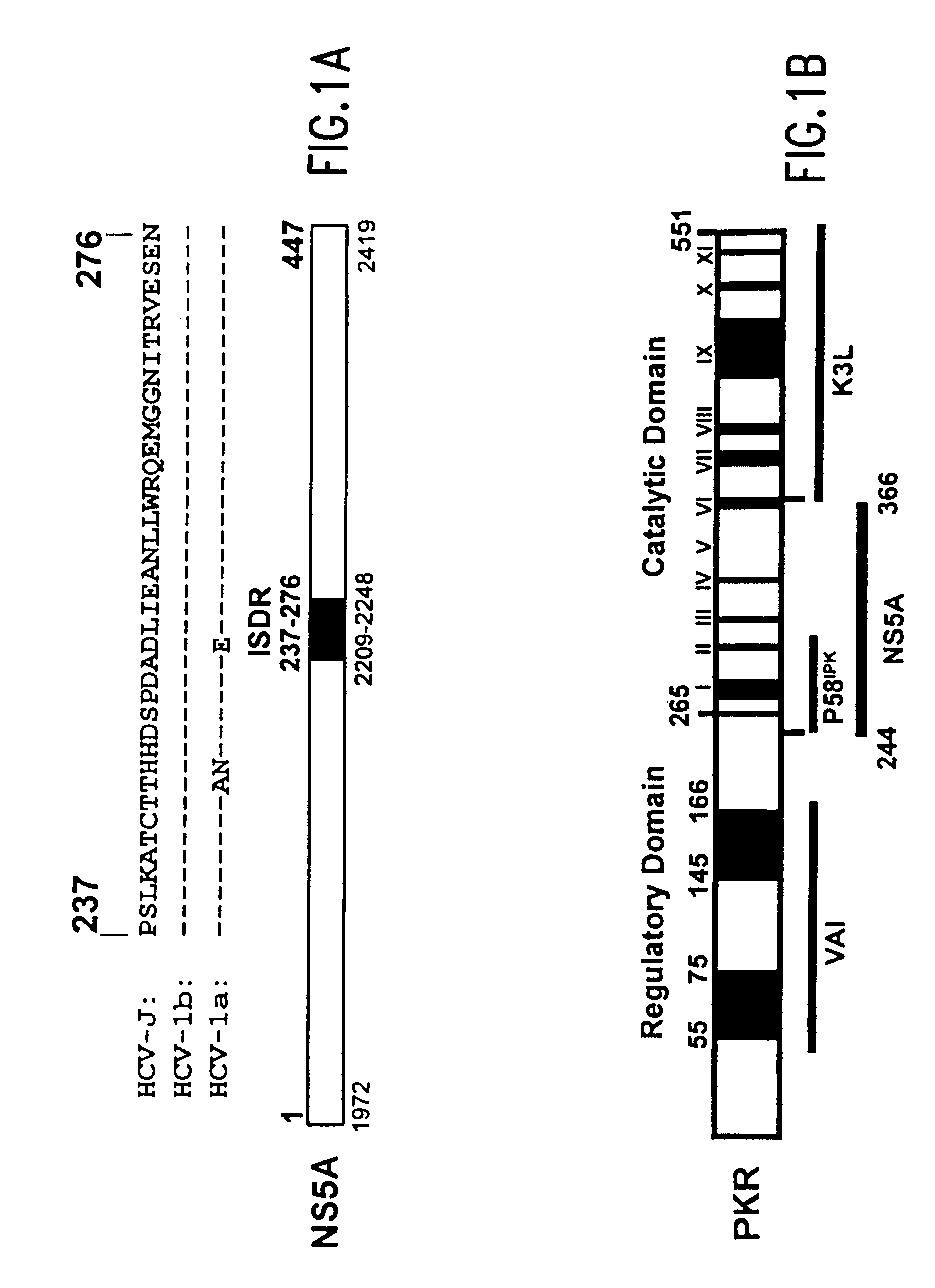
Screening methods to identify agents that selectively inhibit hepatitis C virus replication
InactiveUS6030785APrevent dimerizationBlock viral inhibitionFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseCellular defenseViral infection
The present invention relates to novel methods for identifying antiviral agents which selectively interfere with viral proteins that override the interferon(IFN)-induced cellular defense mechanisms against viral infection. In particular, the present invention relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between viral proteins containing an interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR) and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The present invention more particularly relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A protein (NS5A), which contains an ISDR, and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The interaction between the viral ISDR and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase results in the override of IFN-induced cellular defense mechanisms to combat viral infection. Therefore the agents identified using the assays of the invention may have utility as antiviral agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
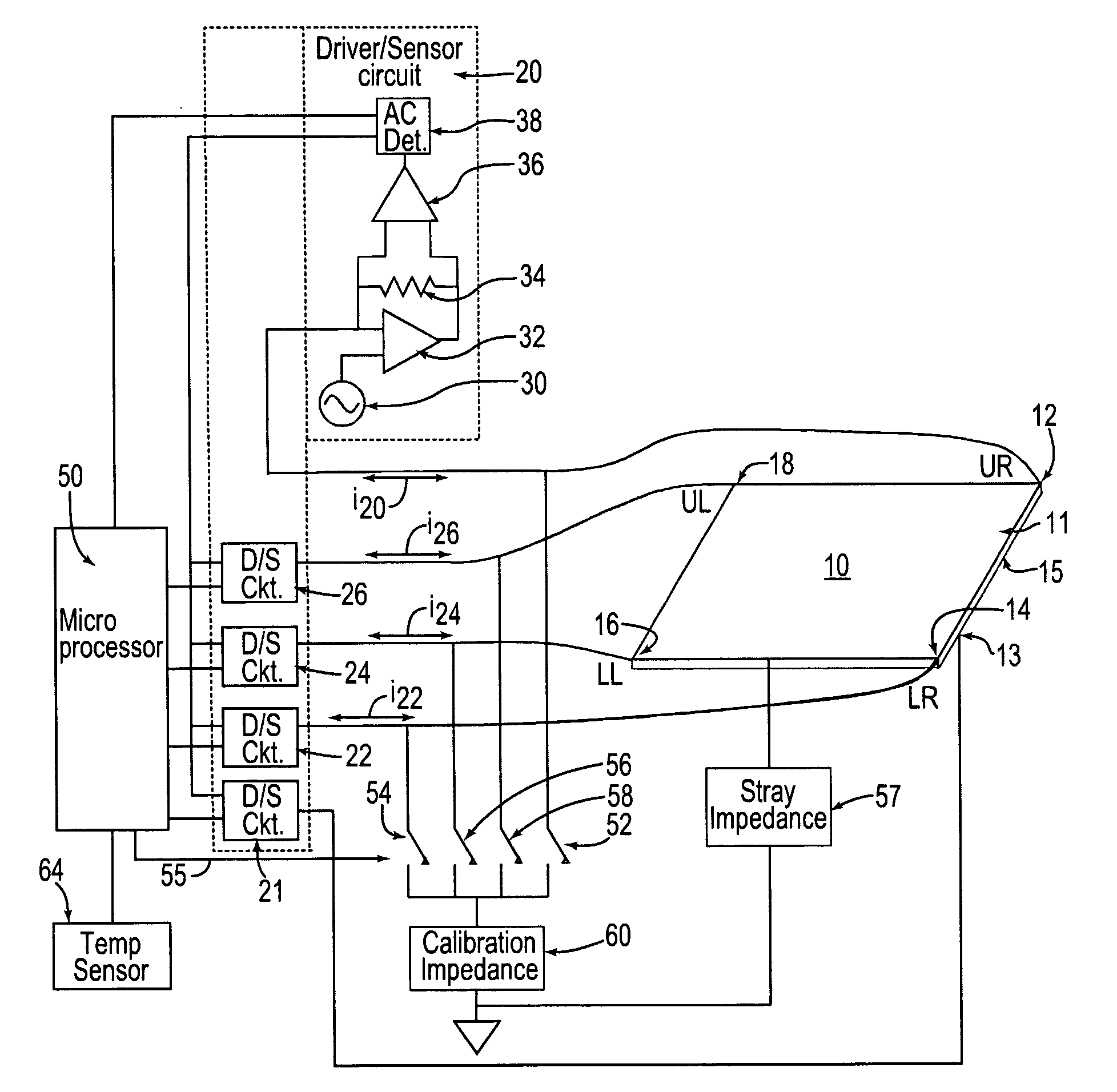
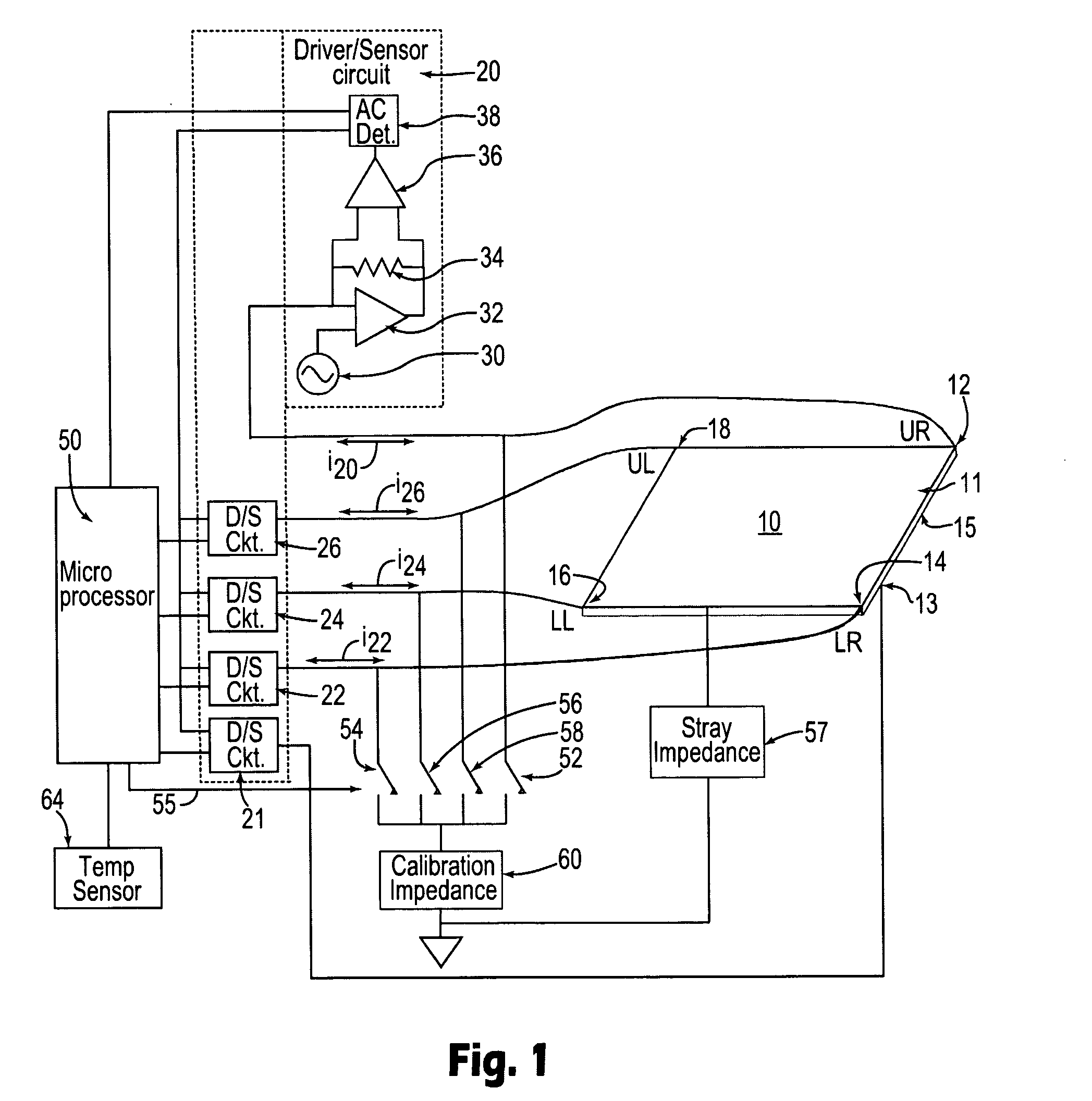
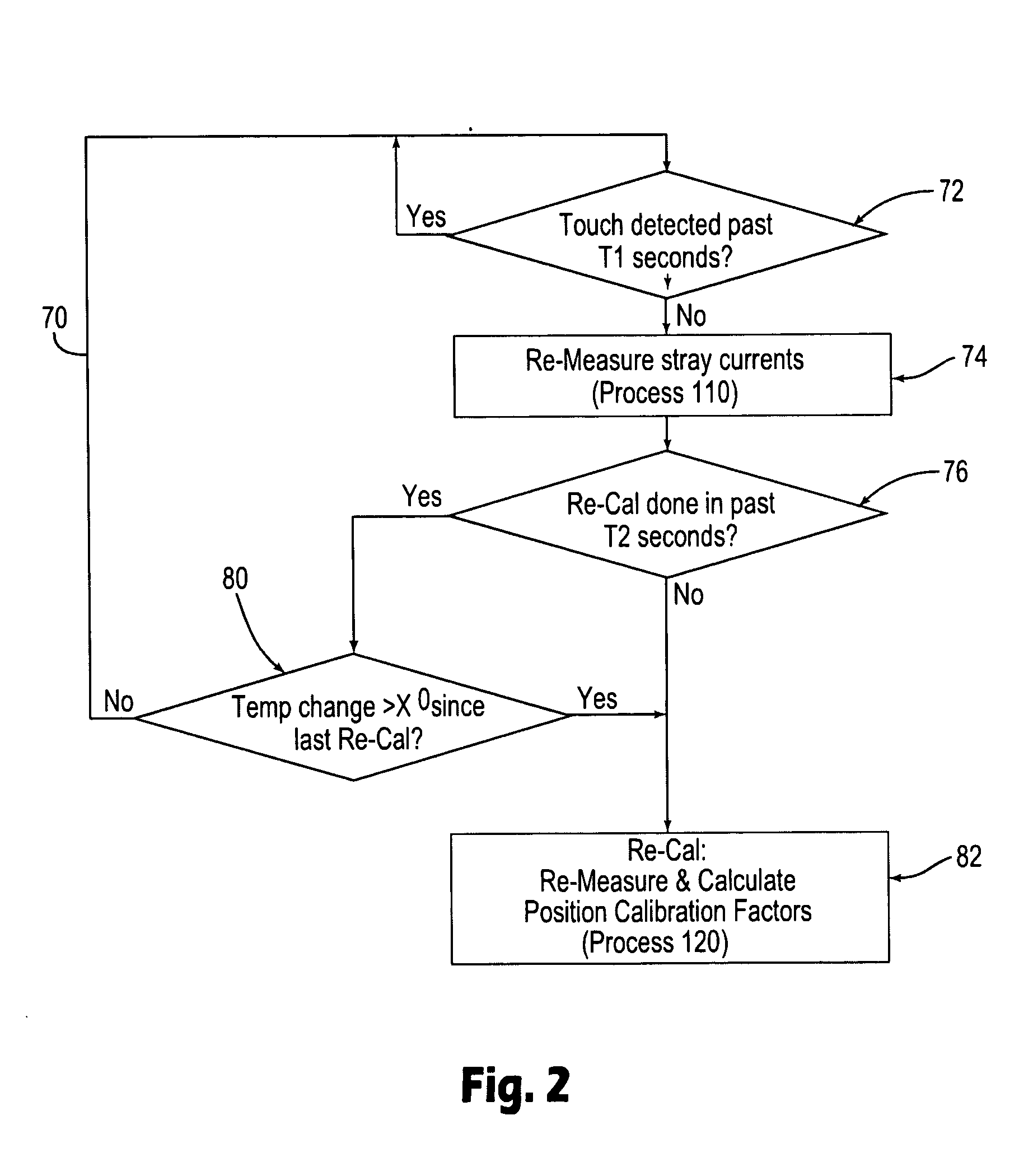
Method for simulating a touch on a touch screen
InactiveUS20060202969A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTouchscreenCalibration function
Methods are provided for simulating a touch on a touch screen by applying a first signal to a first surface of the touch screen, applying a second signal to a second, opposing surface of the touch screen sensor, and changing the first signal relative to the second signal. Such methods can be used to simulate a touch to the center of the touch screen, for example. The simulated touch can be used in some embodiments to perform diagnostics and / or calibrations functions.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
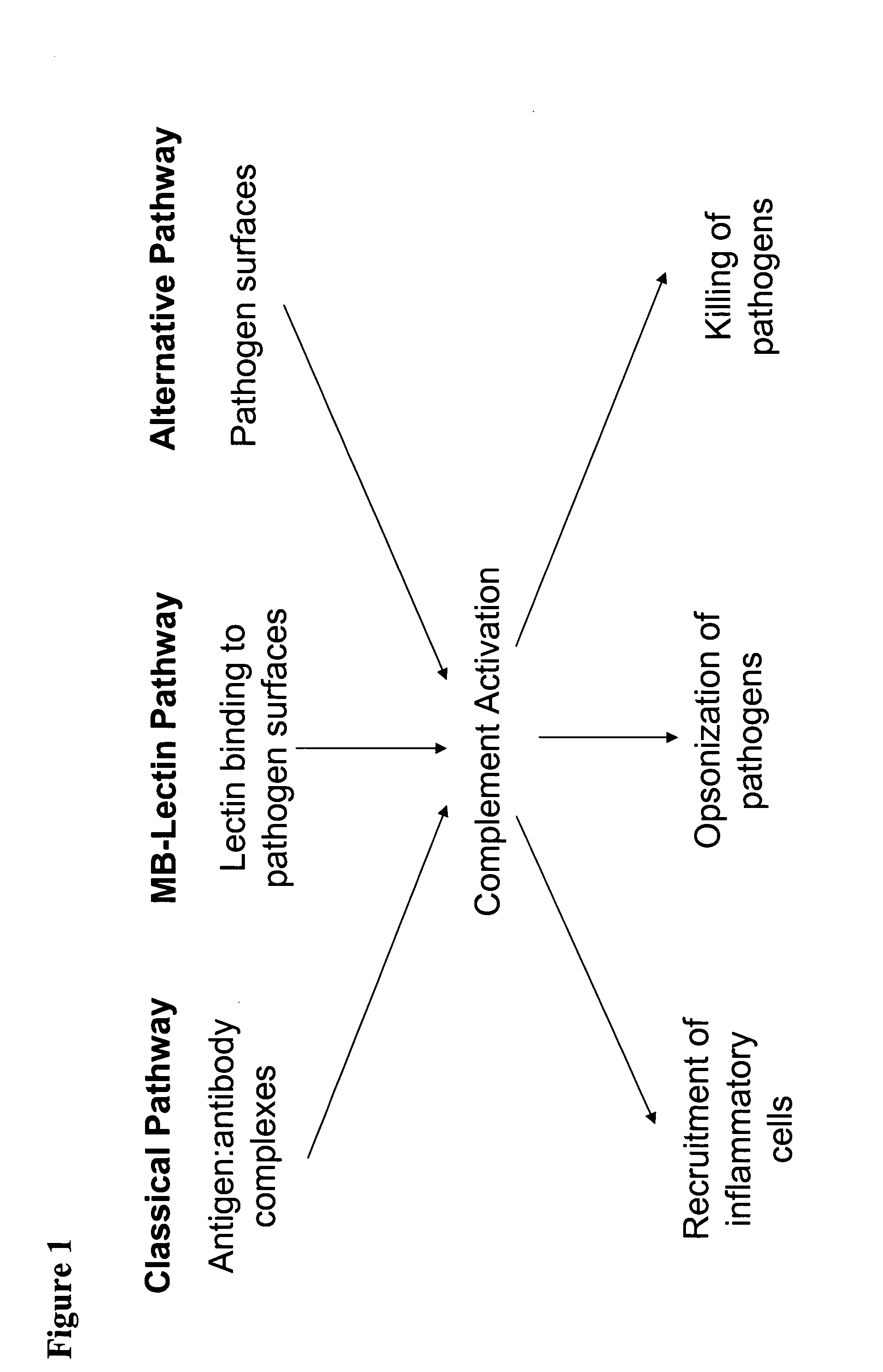
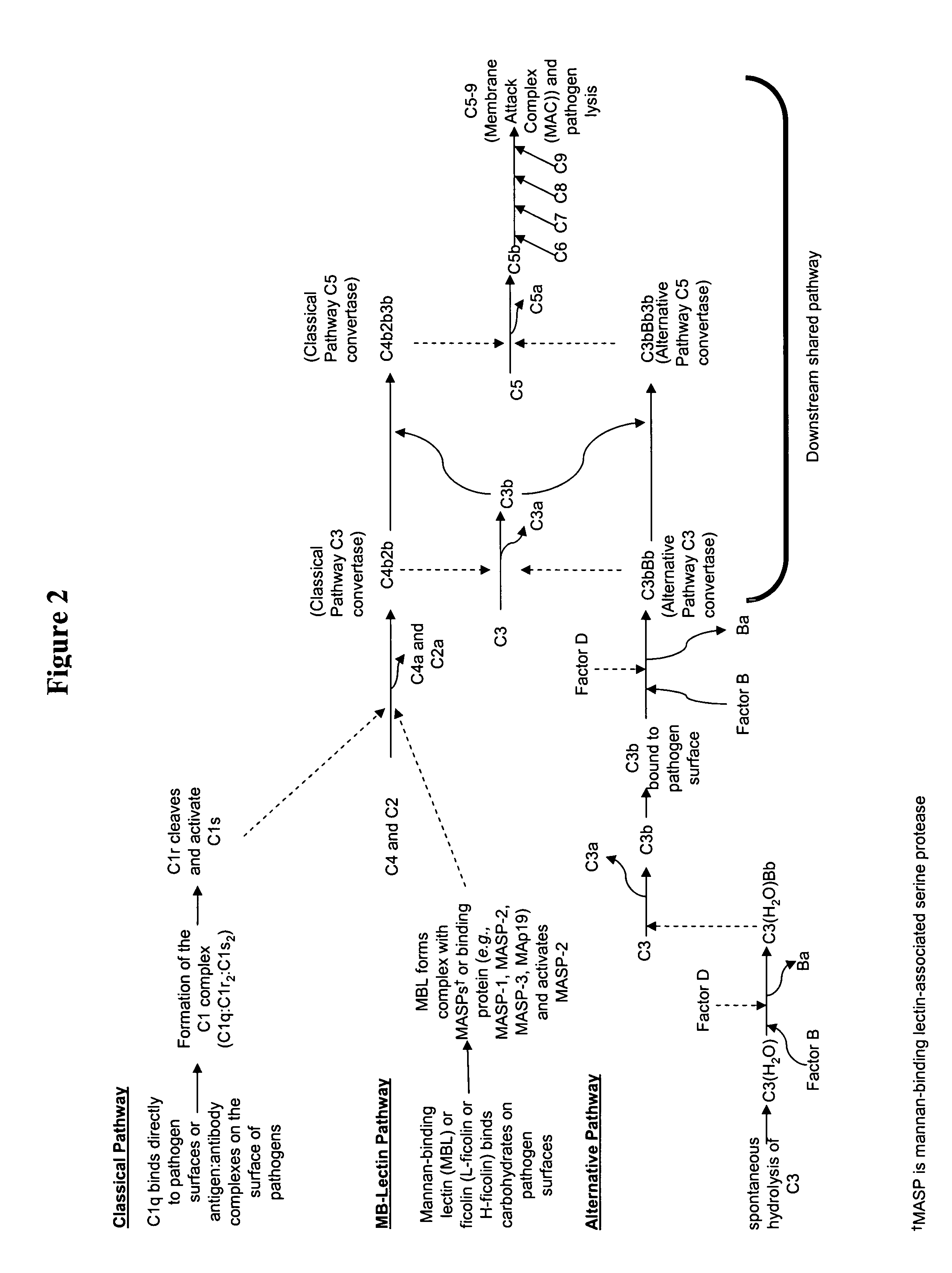
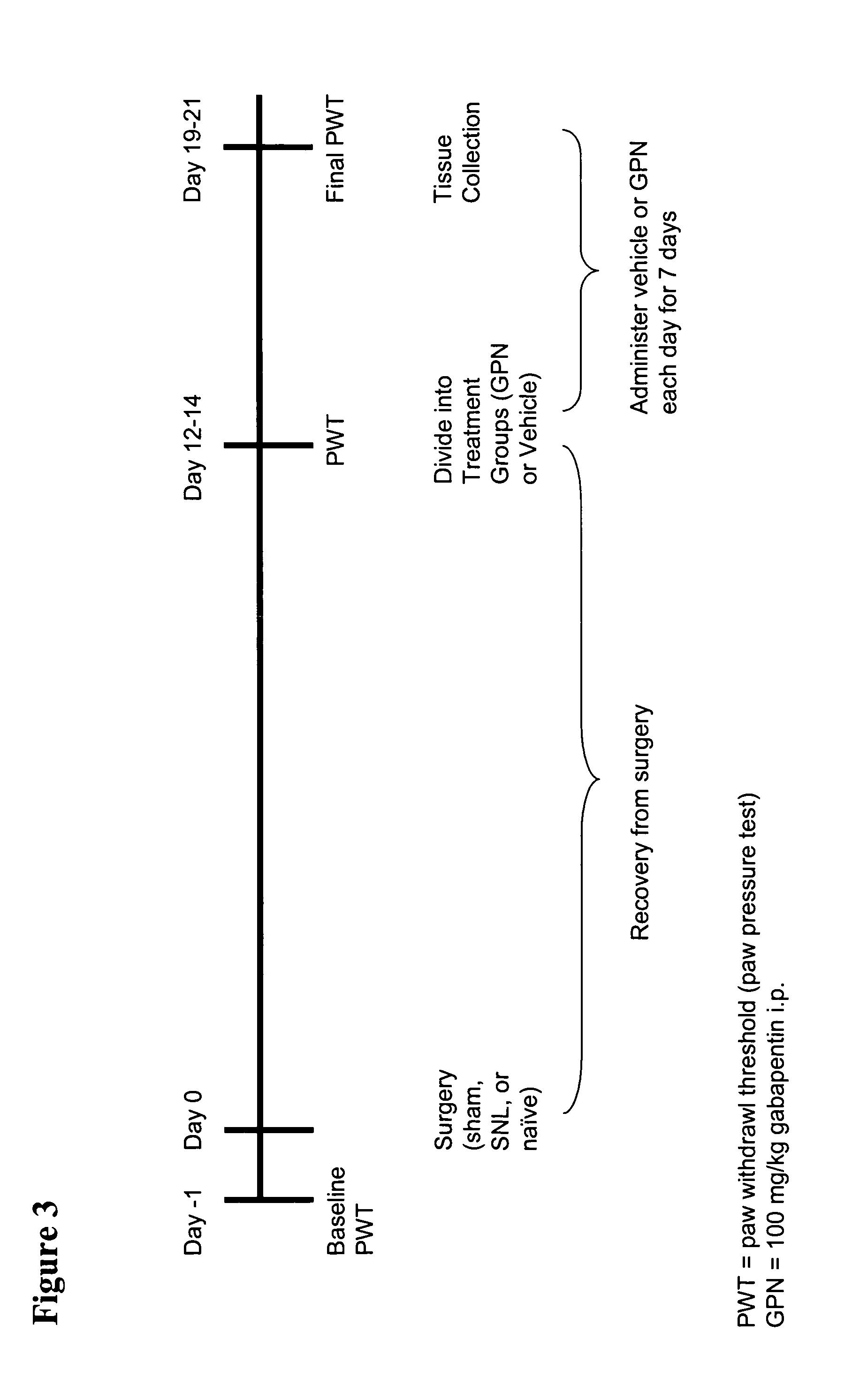
Modulation of complement to treat pain
InactiveUS20050222027A1High expressionIncreasing endogenous expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMedicineNeuropathic pain
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating pain, including neuropathic pain, by modulating the expression or activity of one or more components of the complement pathway. The present invention further provides screening methods to identify therapeutic agents for treating pain by screening for compounds capable of modulating the expression or activity of one or more components of the complement pathway.
Owner:EURO-CELTIQUE SA
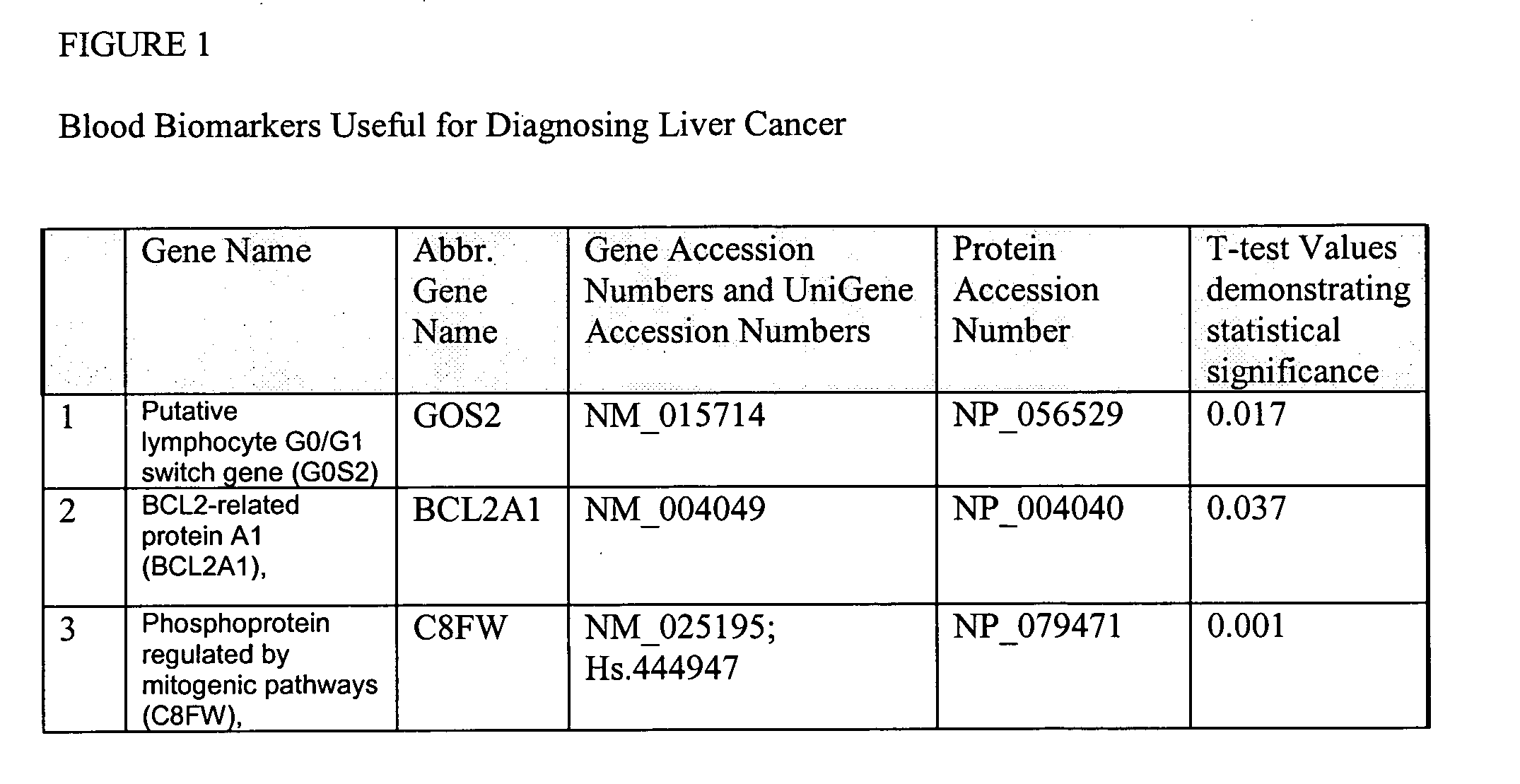
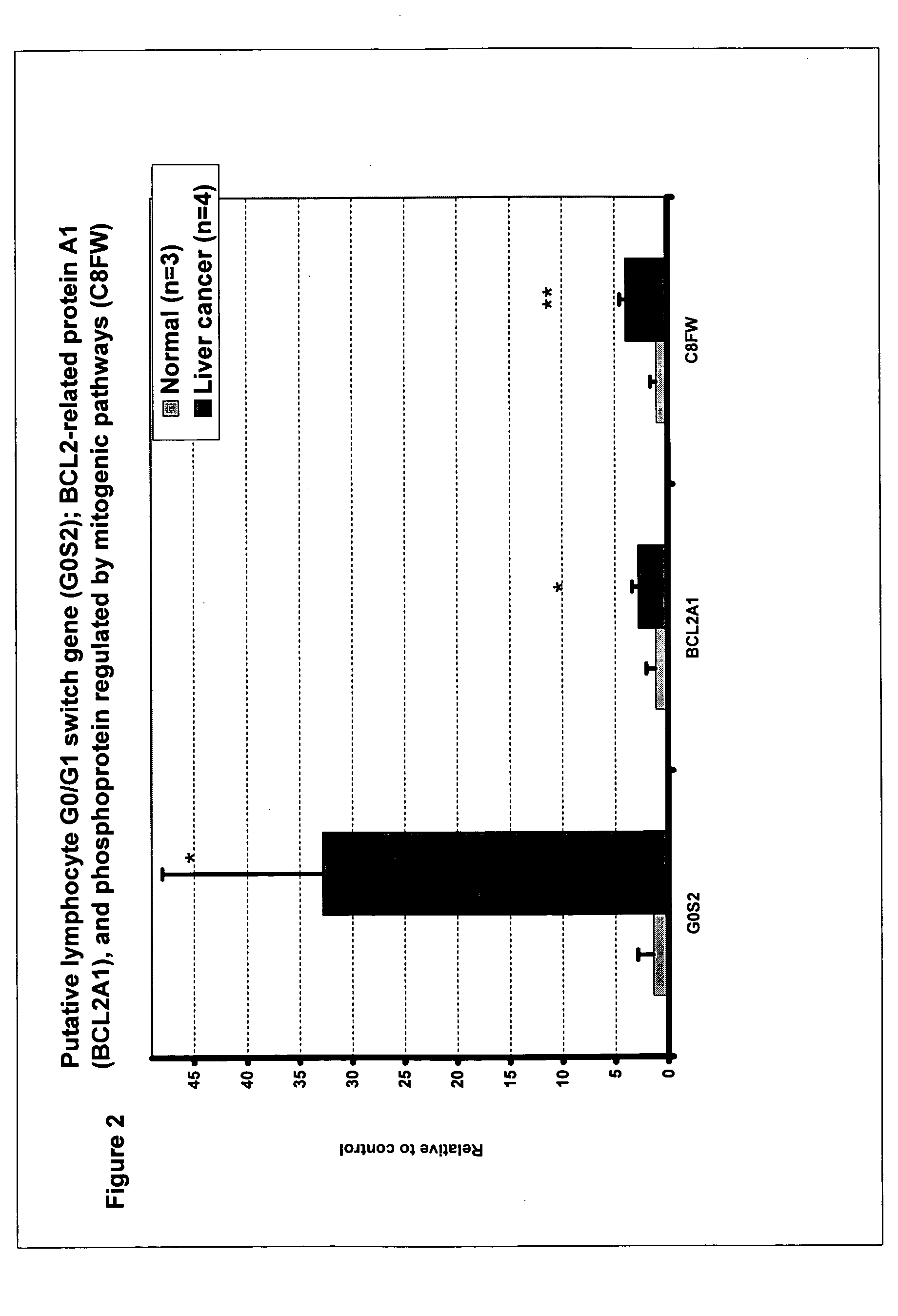
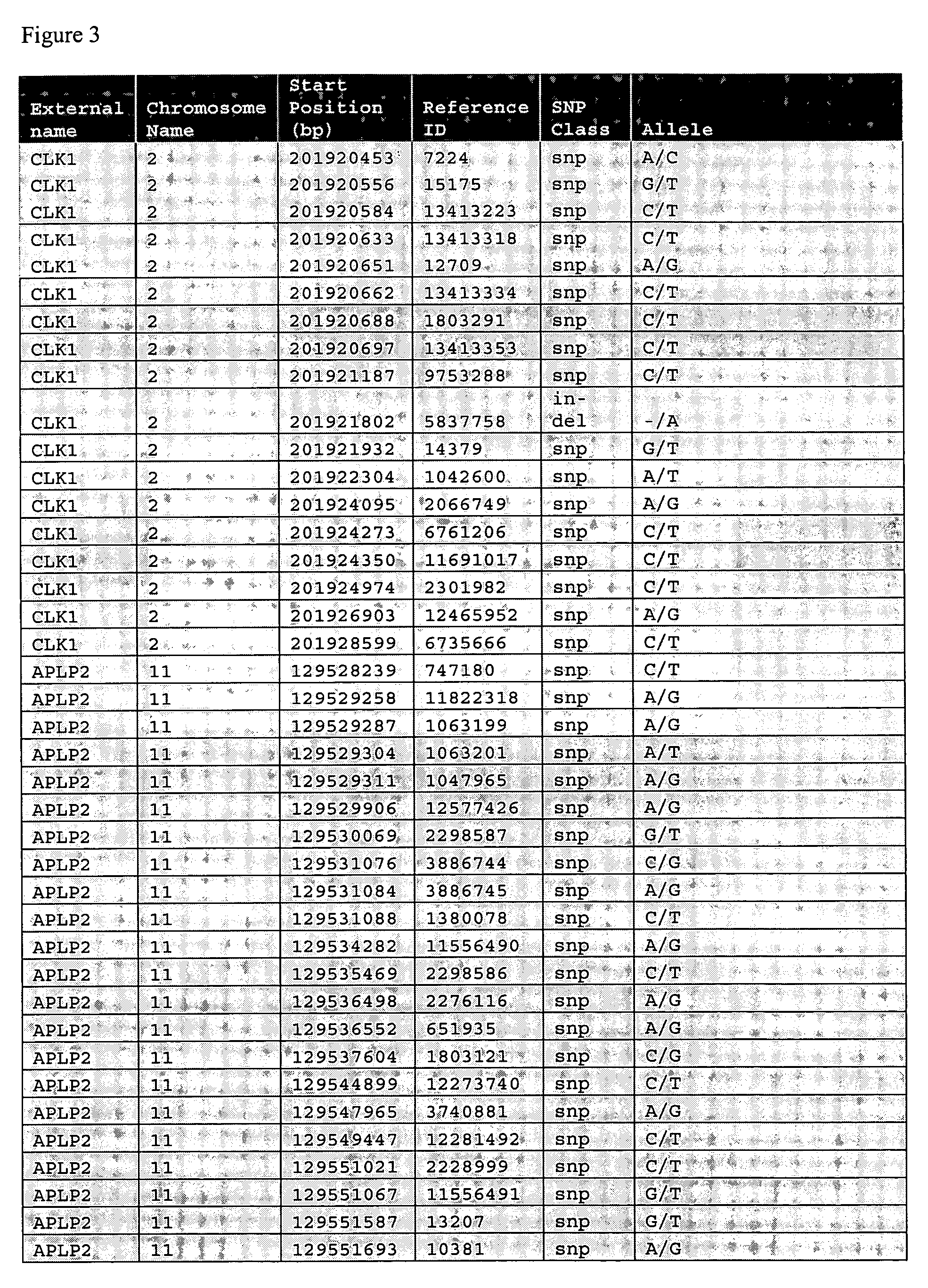
Liver cancer biomarkers
InactiveUS20050152908A1Small amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRegimenScreening method
The invention relates to the identification and selection of biomarkers which demonstrate particular advantage in identifying individuals having liver cancer. The invention further relates to useful combinations of biomarkers for diagnosing liver cancer. The invention further provides for the polynucleotides and polypeptides and kits thereof for use as a tool to diagnose disease and to monitor the efficacy of therapeutic regimens. The invention further provides a method of selecting biomarker combinations and the combinations thus identified for diagnosis of liver cancer. Also encompassed by the invention are screening methods to identify therapeutic targets for treating liver cancer, and identify single nucleotide point mutations related to liver cancer.
Owner:GENENEWS
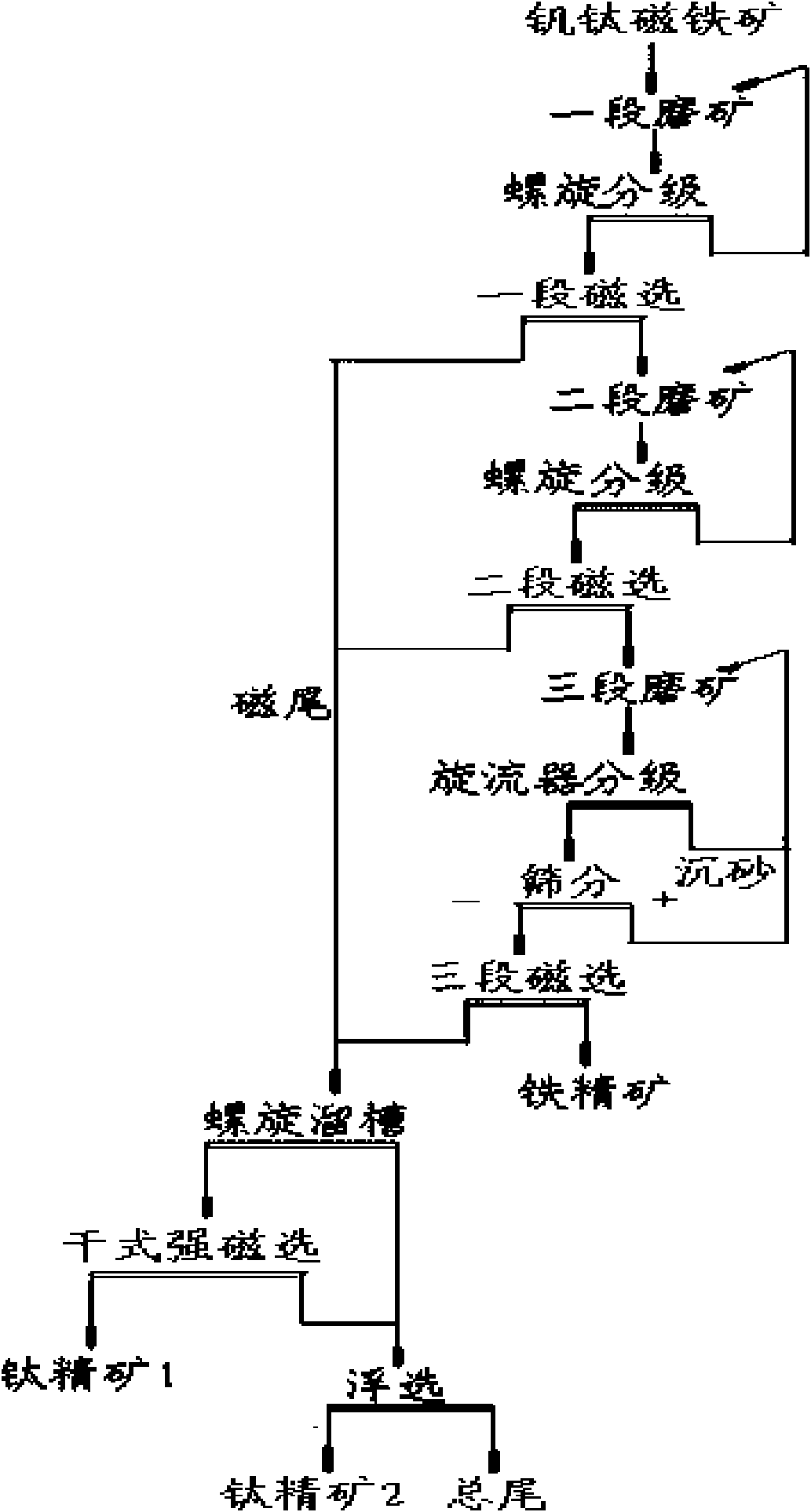
Vanadium titano-magnetite screen method
ActiveCN101564707AQuality improvementHigh recovery rateFlotationMagnetic separationMagnetiteMaterials science
The invention relates to a screen method for vanadium titano-magnetite with high quality, belonging to the ore screen field. The method adopts three stage-grinding and stage-concentration process for magnetic separation, wherein the field intensity of one-stage magnetic separation is 3000-4000 Gs; the field intensity of two-stage magnetic separation is 1800-2200 Gs; and the field intensity of three-stage magnetic separation is 1300-1700 Gs. The recovery rate of the screened iron ore concentrate and the titanium ore concentrate is high and the screened cost of the screened iron ore concentrate and the titanium ore concentrate is low, thus providing a new selection for the low grade vanadium titano-magnetite resource and having a broad application prospect.
Owner:四川安宁铁钛股份有限公司
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
This invention relates to methods of reducing the damaging effect of an injury to mammalian cells by treatment with compounds which reduce cell death or dysfunction, including cellular damage following episodes of tissue ischemia, trauma, epilepsy, and acute or chronic degeneration. The invention discloses methods of treating these disorders by administering inhibitors that disrupt protein-protein interactions involved in these disorders, screening methods to identify such inhibitors and specific compositions useful for treating these disorders.
Owner:NONO INC
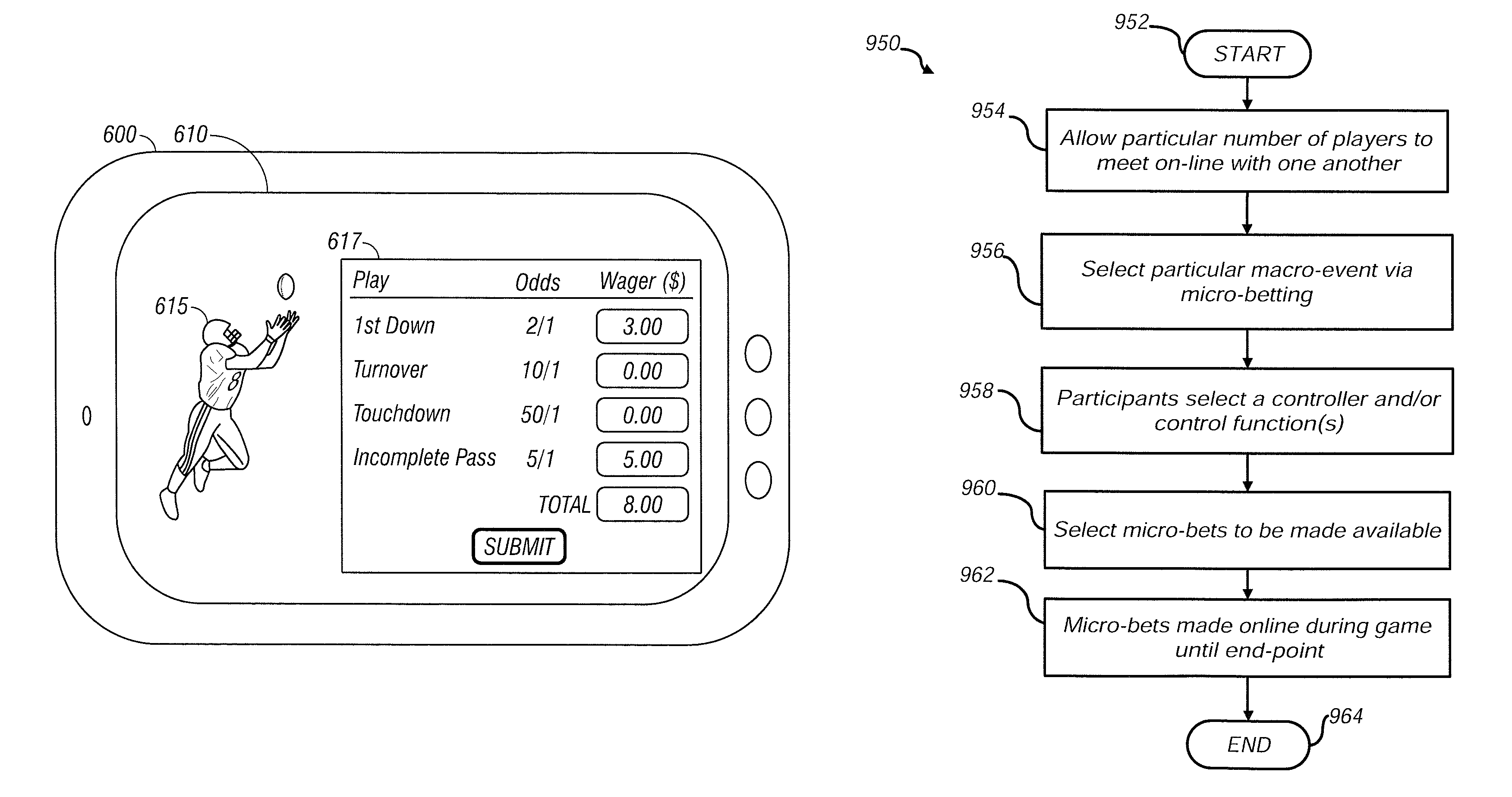
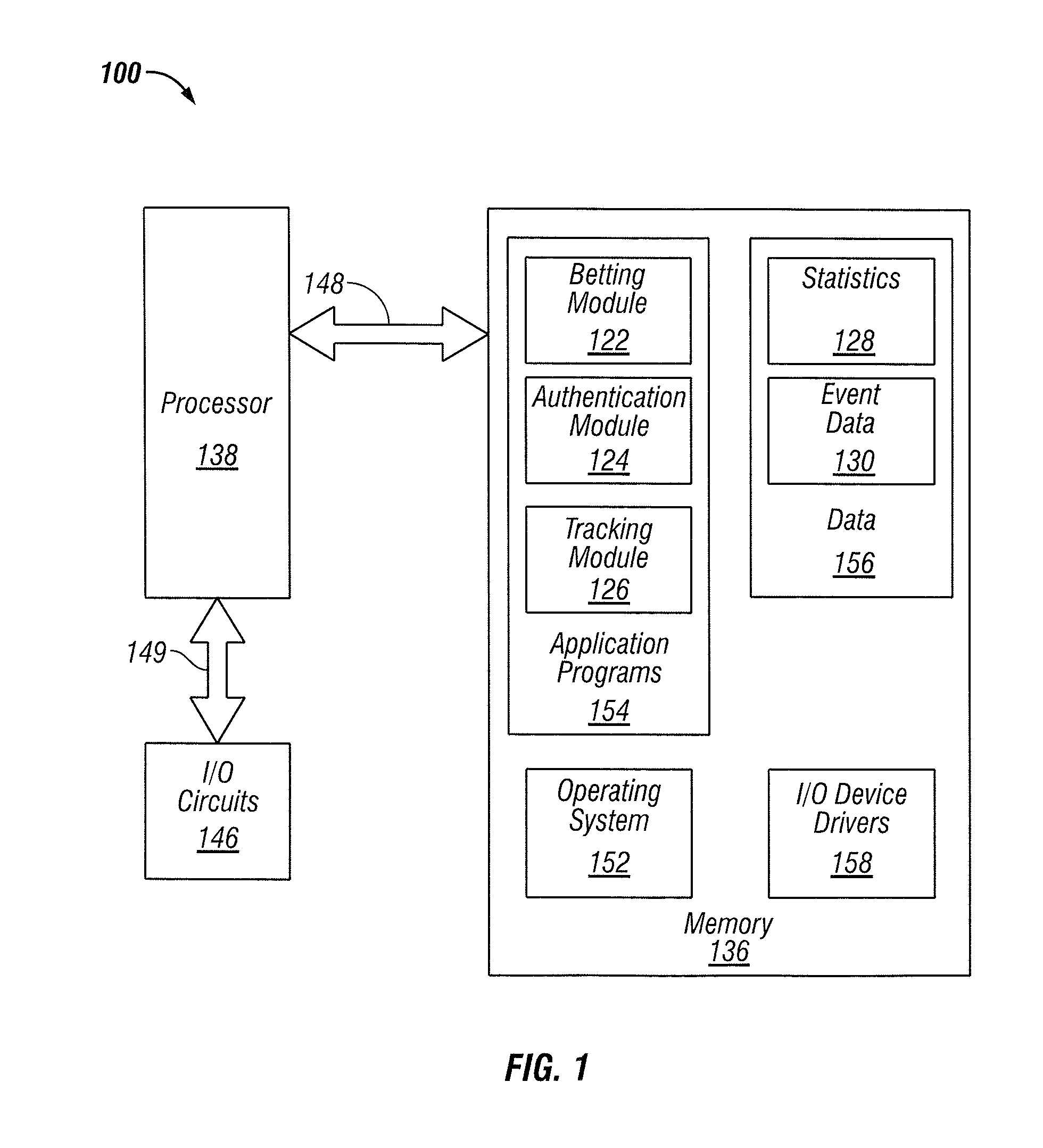
Systems and methods for enabling remote device users to wager on micro events of games in a data network accessible gaming environment
ActiveUS8632392B2Prevent cheatingApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesMicrobloggingComputer science
Owner:MICRO GAMING VENTURES
Self-discharge screening method for lithium ion phosphate battery
ActiveCN102117937ASolving the Difficult Problem of Self-Discharge ScreeningImprove consistencyFinal product manufactureElectrolyte accumulators manufacturePhosphateScreening method
The invention discloses a self-discharge screening method for a lithium ion phosphate battery, belongs to the technical field of lithium ion batteries, and aims to provide a method for effectively screening the lithium ion phosphate battery with high self-discharge rate by using shelving in a charging state. According to the technical key points, the method comprises the following steps of: adding laminar lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide or spinel lithium nickel manganese oxide which comprises 0.5 to 5 weight percent of lithium ion phosphate and has high voltage platform into a lithium ion phosphate-containing compound positive electrode; assembling the lithium ion phosphate battery by taking graphite as a negative electrode; fully charging the battery and then shelving the battery at an ambient temperature of between 20 and 45 DEG C; recording voltages before and after the shelf and shelf time; calculating the voltage difference before and after the shelf or a voltage variation value in unit time; and determining a critical value of the voltage difference of the batteries with the high self-discharge rate which are shelved in the same period or voltage variation in the unit time, and determining that the self-discharge rate of the battery of which the voltage difference or the voltage variation value in the unit time is greater than the critical value is high.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Methods for treating pain
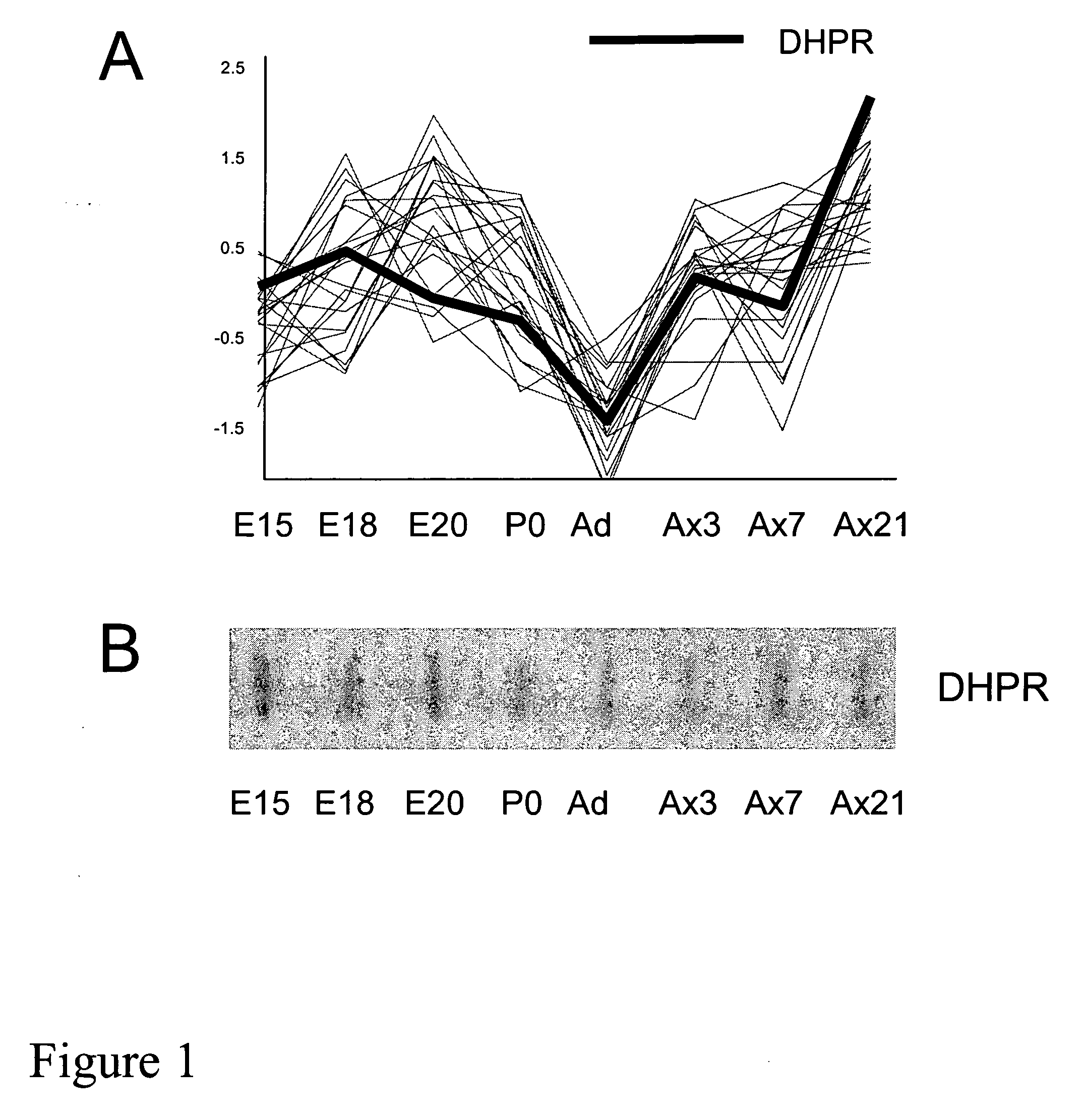
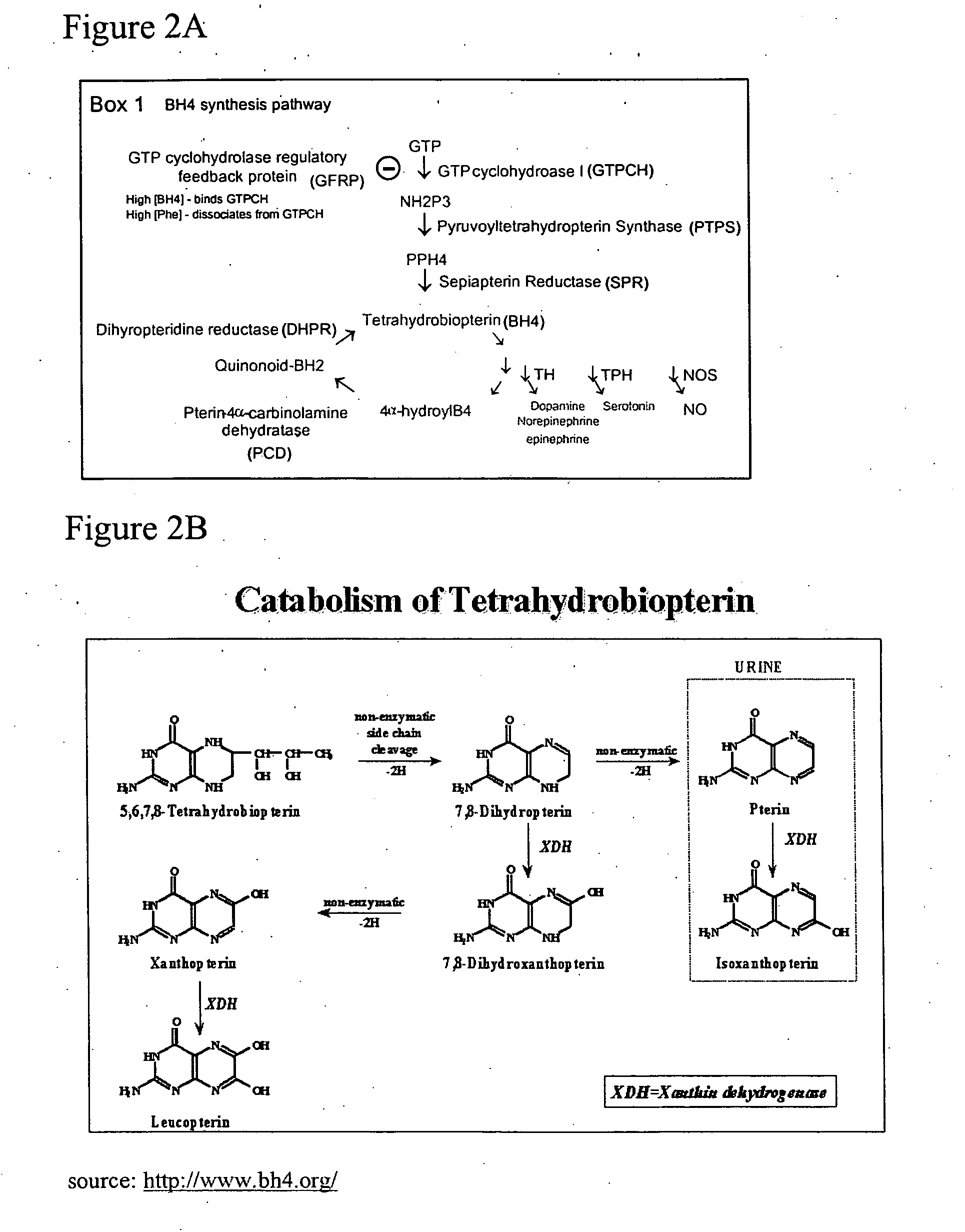
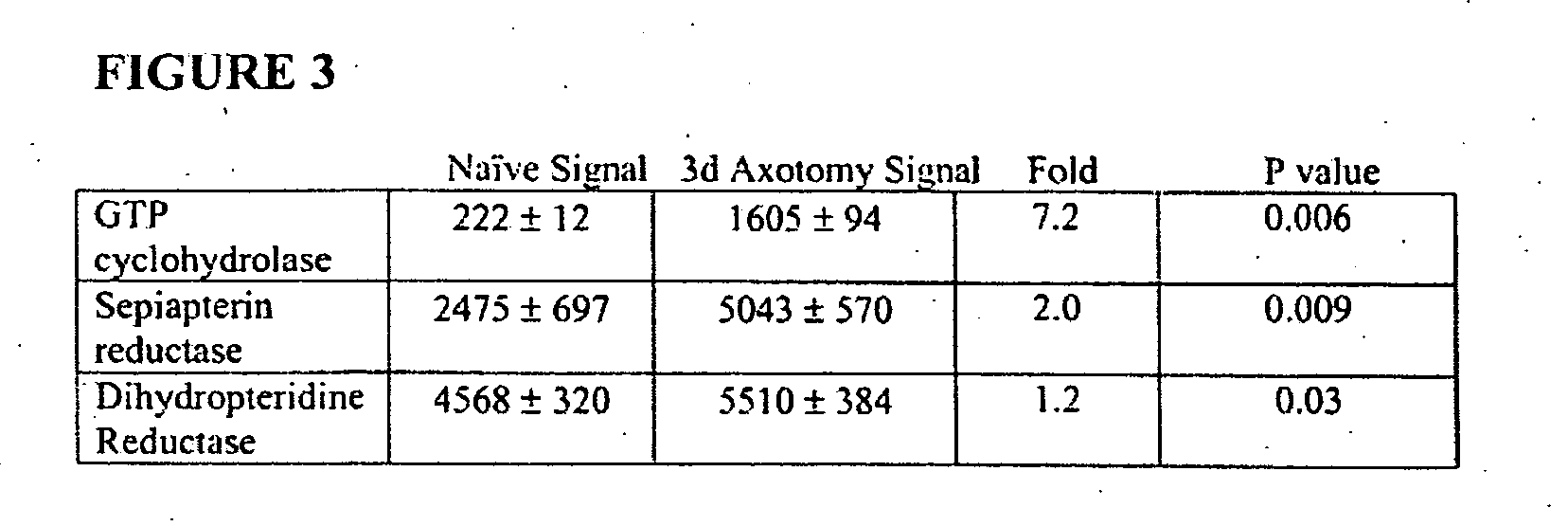
InactiveUS20050197341A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityBiocideNervous disorderGtp cyclohydrolaseMetabolite
The present invention features methods and compositions for preventing, reducing, or treating a traumatic, metabolic or toxic peripheral nerve lesion or pain including, for example, neuropathic pain, inflammatory and nociceptive pain by administering to a mammal in need thereof a compound that reduces the expression or activity of BH4. According to this invention, this reduction may be achieved by reducing the enzyme activity of any of the BH4 synthetic enzymes, such as GTP cyclohydrolase (GTPCH), sepiapterin reductase (SPR), or dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR); by antagonizing the cofactor function of BH4 on BH4-dependent enzymes; or by blocking BH4 binding to membrane bound receptors. The compounds of the invention may be administered alone or in combination with a second therapeutic agent. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing pain or a peripheral nerve lesion in a mammal by measuring the levels of BH4 or its metabolites in biological sample. Alternatively, pain or a peripheral nerve lesion may be diagnosed by measuring the levels or activity of any one of the BH4 synthetic enzymes in tissue samples of a mammal. Also disclosed are screening methods that make use of BH4 or BH4 synthetic enzymes, BH4-dependent enzymes, and BH4-binding receptors for the identification of novel therapeutics for the treatment, prevention, or reduction of pain.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
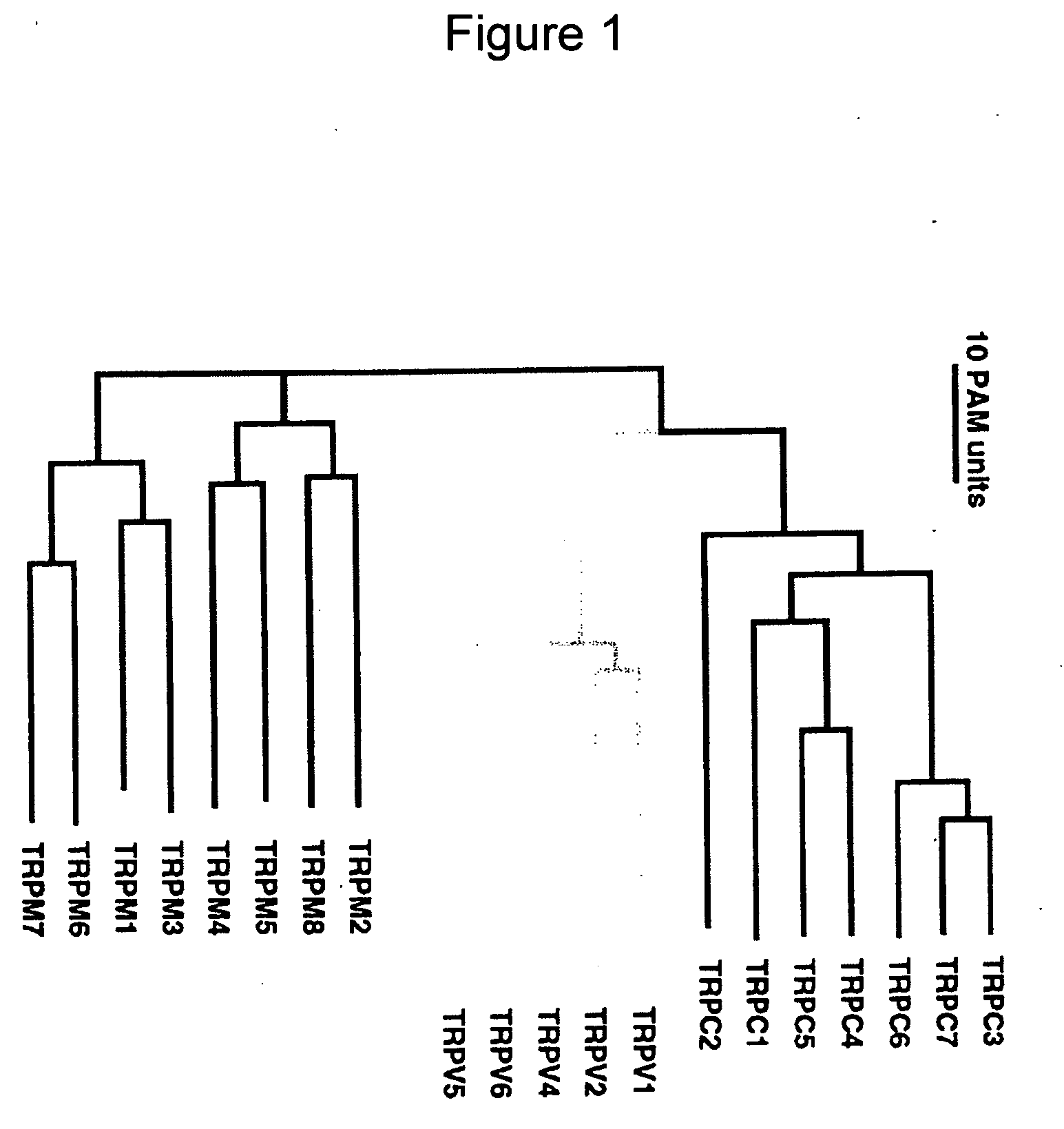
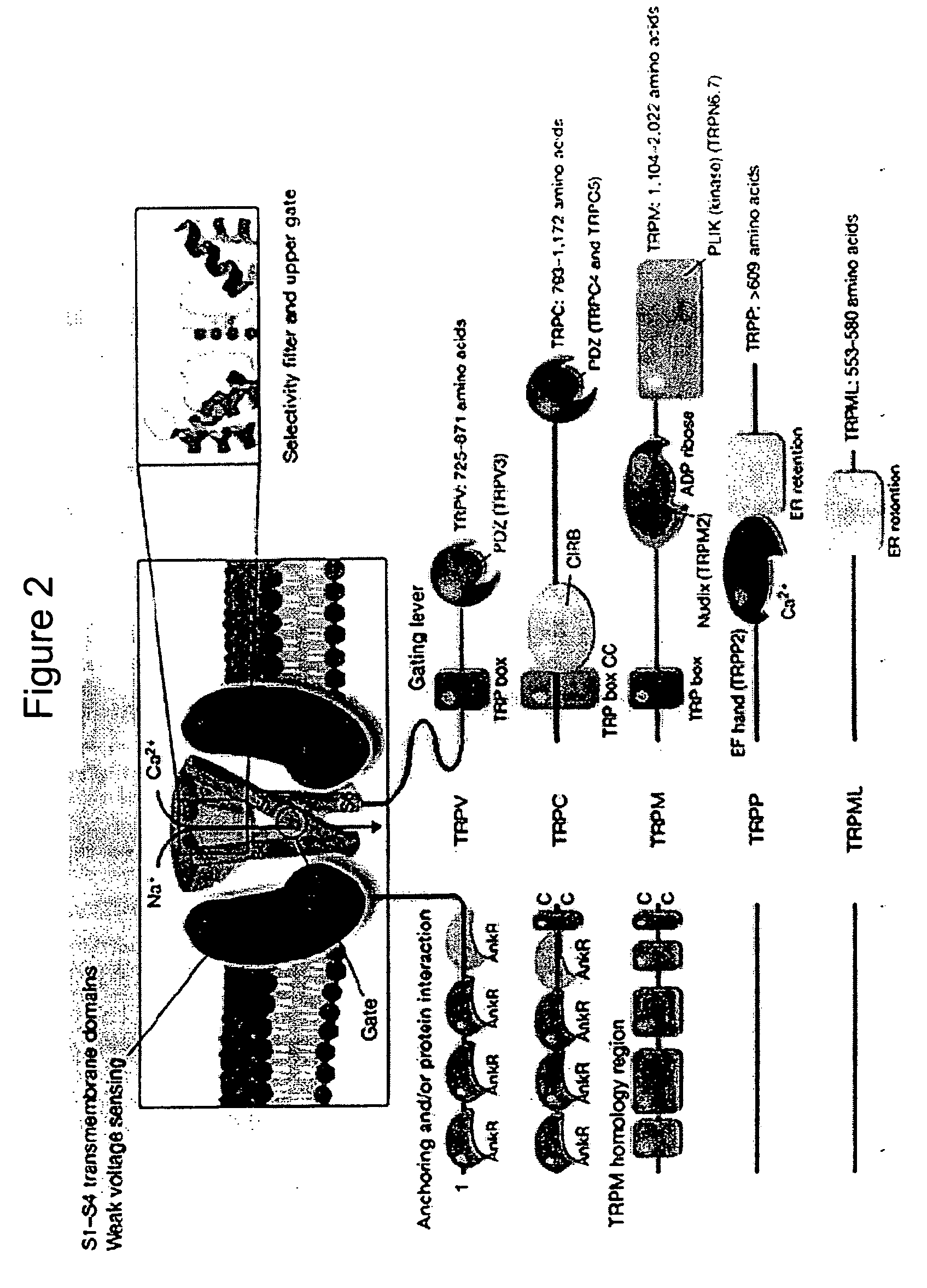
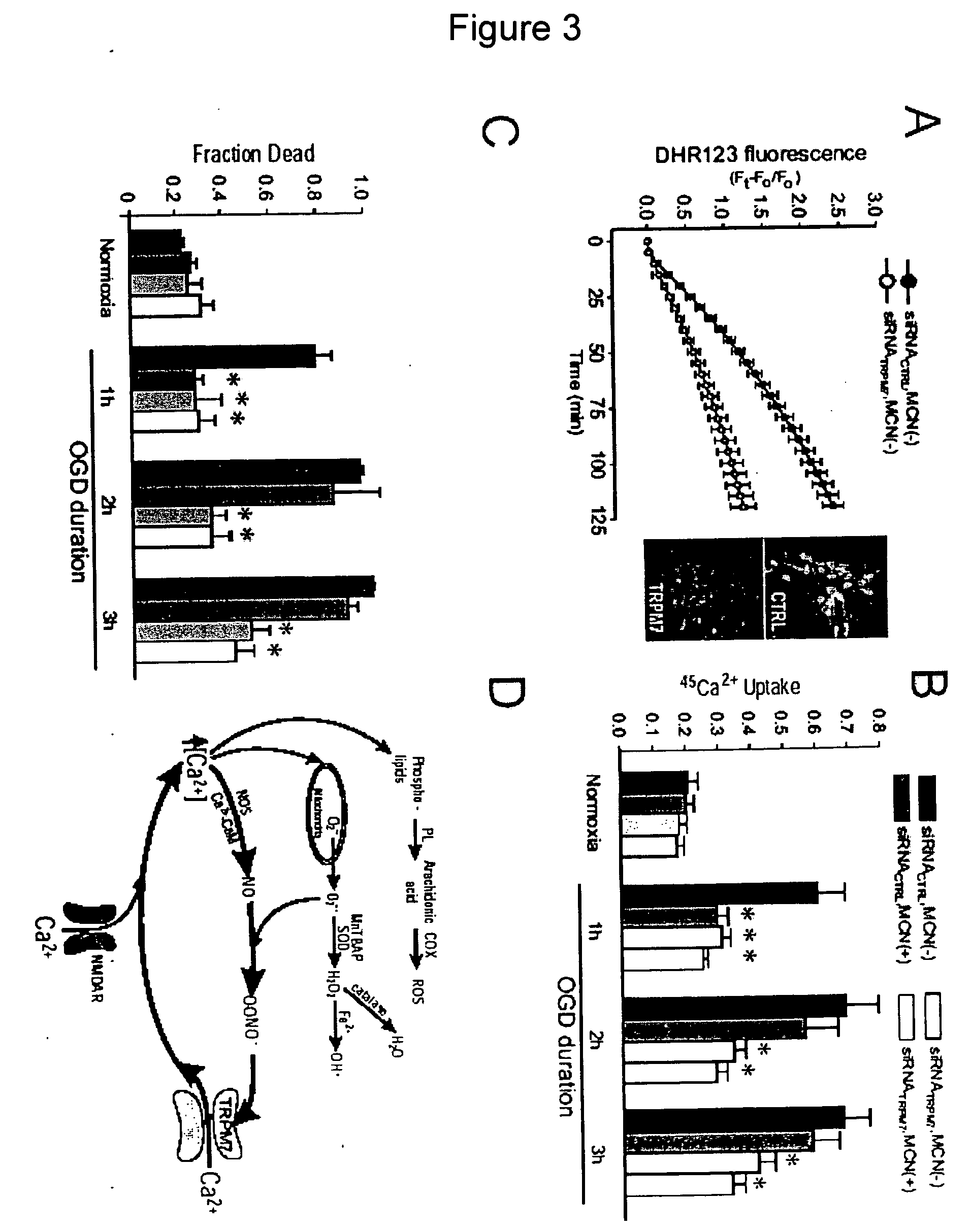
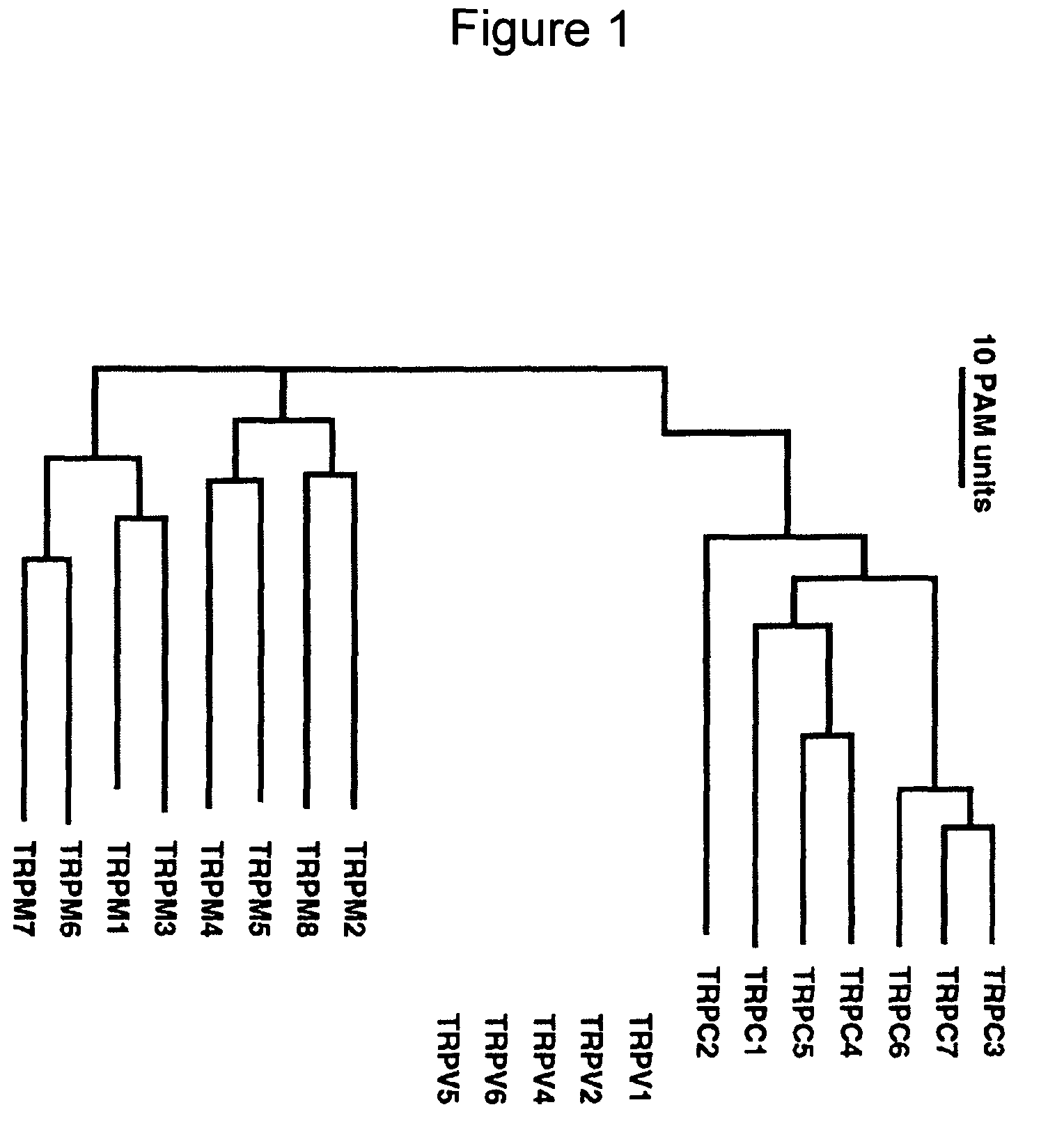
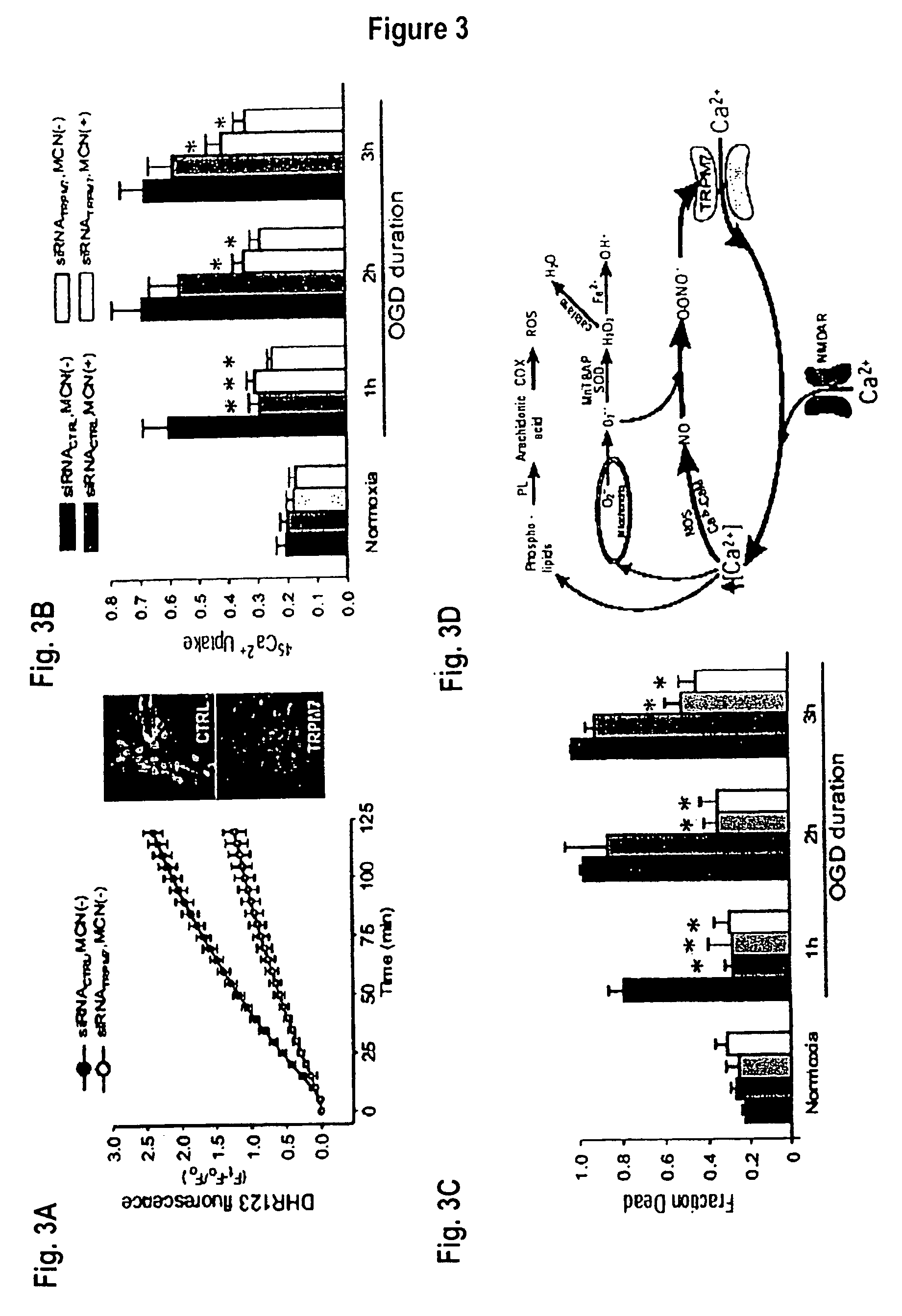
Method of determining inhibition of binding to TRPM7 protein
This invention relates to methods of reducing the damaging effect of an injury to mammalian cells by treatment with compounds which reduce cell death or dysfunction, including cellular damage following episodes of tissue ischemia, trauma, epilepsy, and acute or chronic degeneration. The invention discloses methods of treating these disorders by administering inhibitors that disrupt protein-protein interactions involved in these disorders, screening methods to identify such inhibitors and specific compositions useful for treating these disorders.
Owner:NONO INC
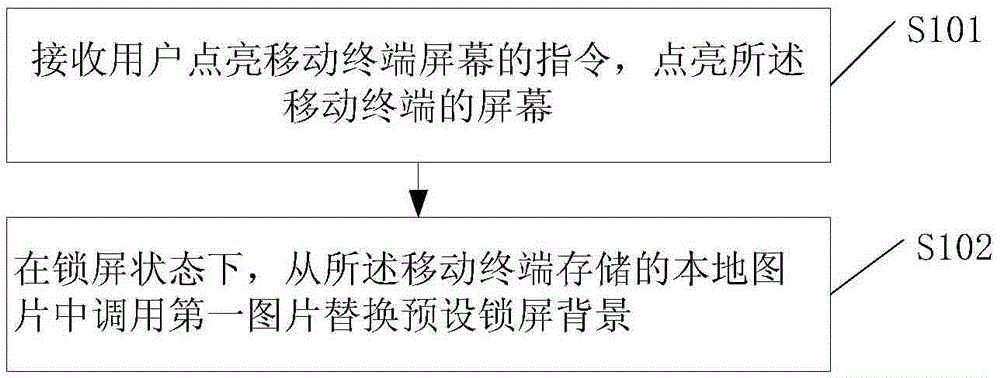
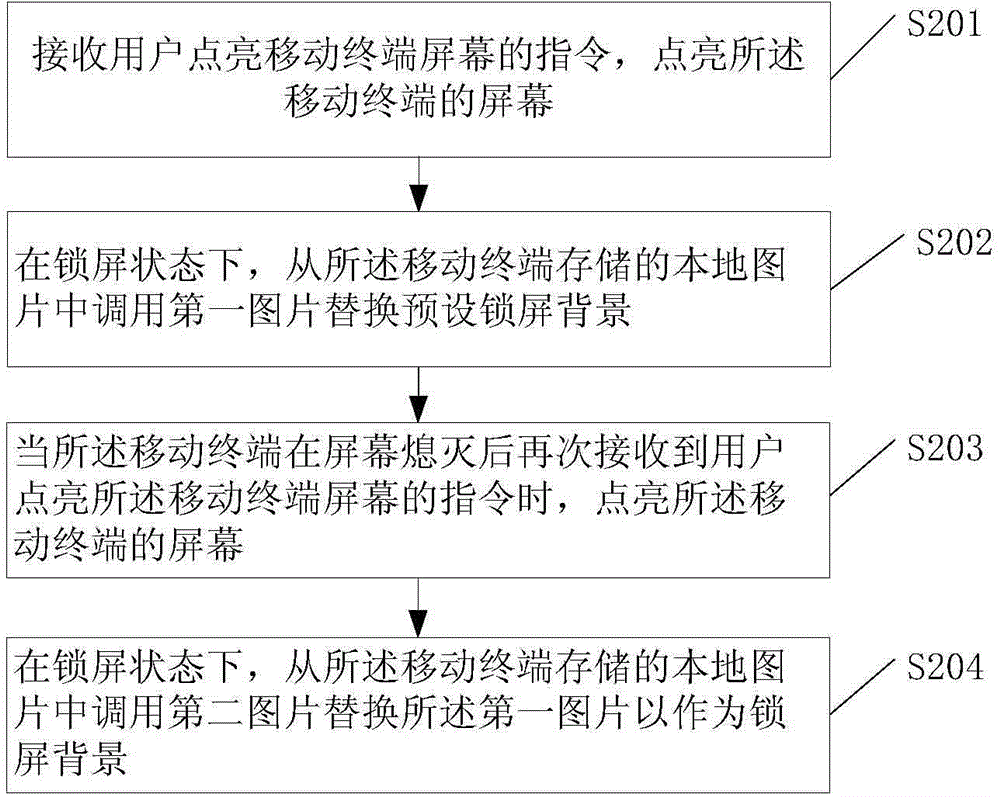
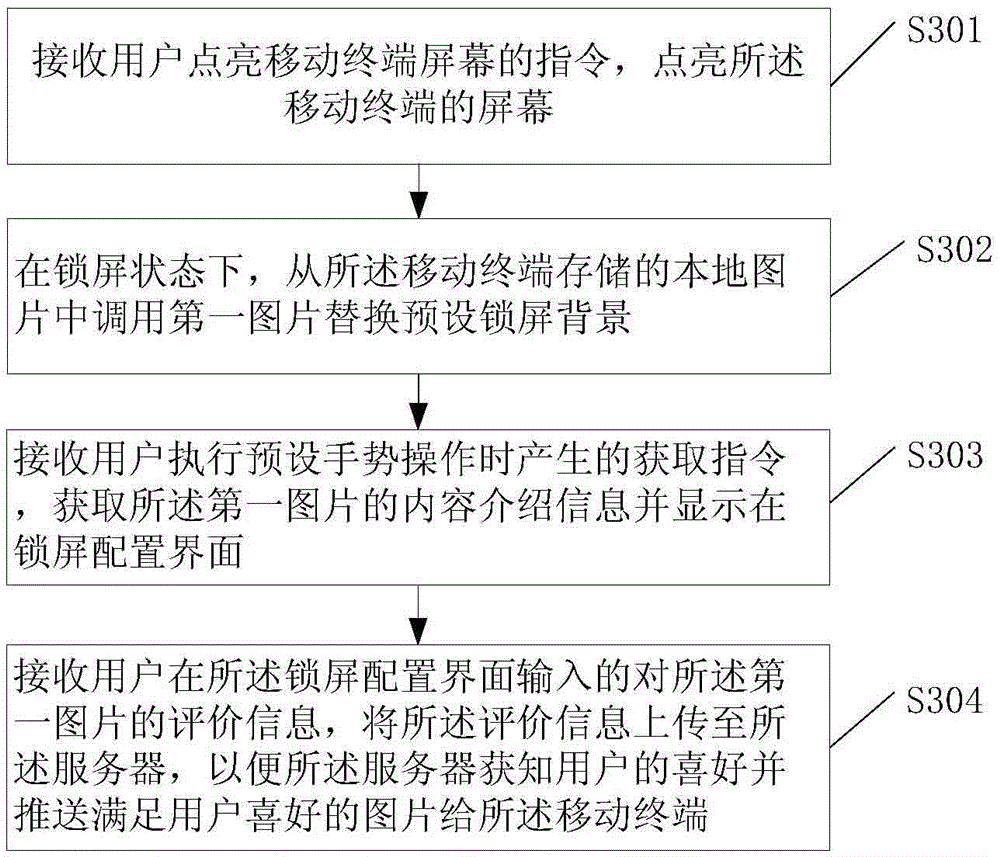
A lock screen method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN104885049AImprove freshnessIncrease variabilityUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionExecution for user interfacesComputer terminalLock screen
Disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention is a lock screen method. The method comprises: receiving an instruction that a user lights the screen of a mobile terminal, and lighting the screen of the mobile terminal; in a lock screen state, calling a first picture from local pictures stored in the mobile terminal to replace the predefined lock screen background, wherein the first picture is obtained by user downloading or photoing, or pushed by a server to the mobile terminal based on the preference of the user. A mobile terminal is also disclosed in the embodiment of the present invention. By the present invention, auto-switch of the lock screen backgrounds may be implemented in the lock screen state, and the user may see the new lock screen background immediately by lighting the screen, thus improving the variability and switch efficiency of the lock screen background , and increasing the freshness of the lock screen for the user.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
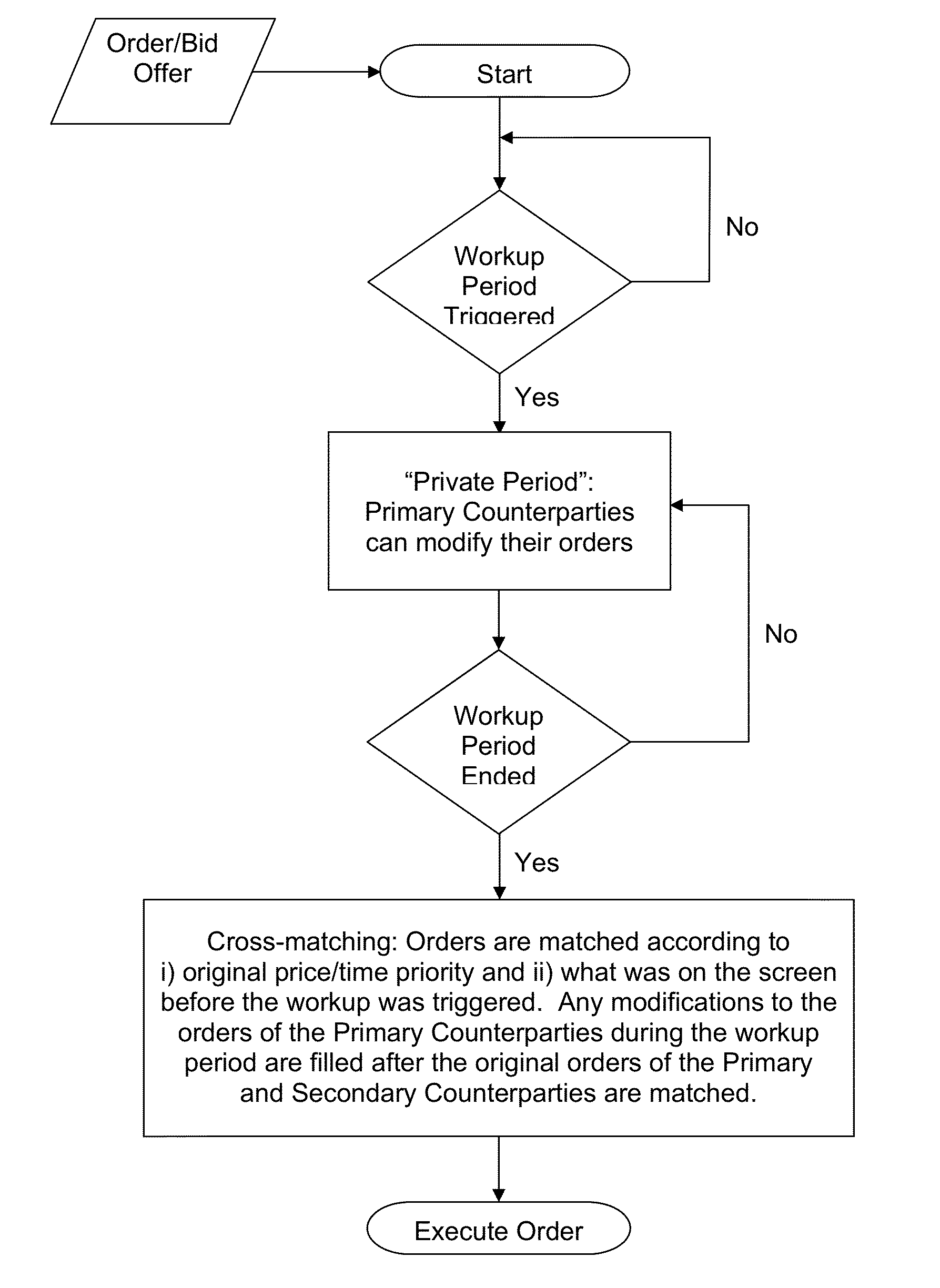
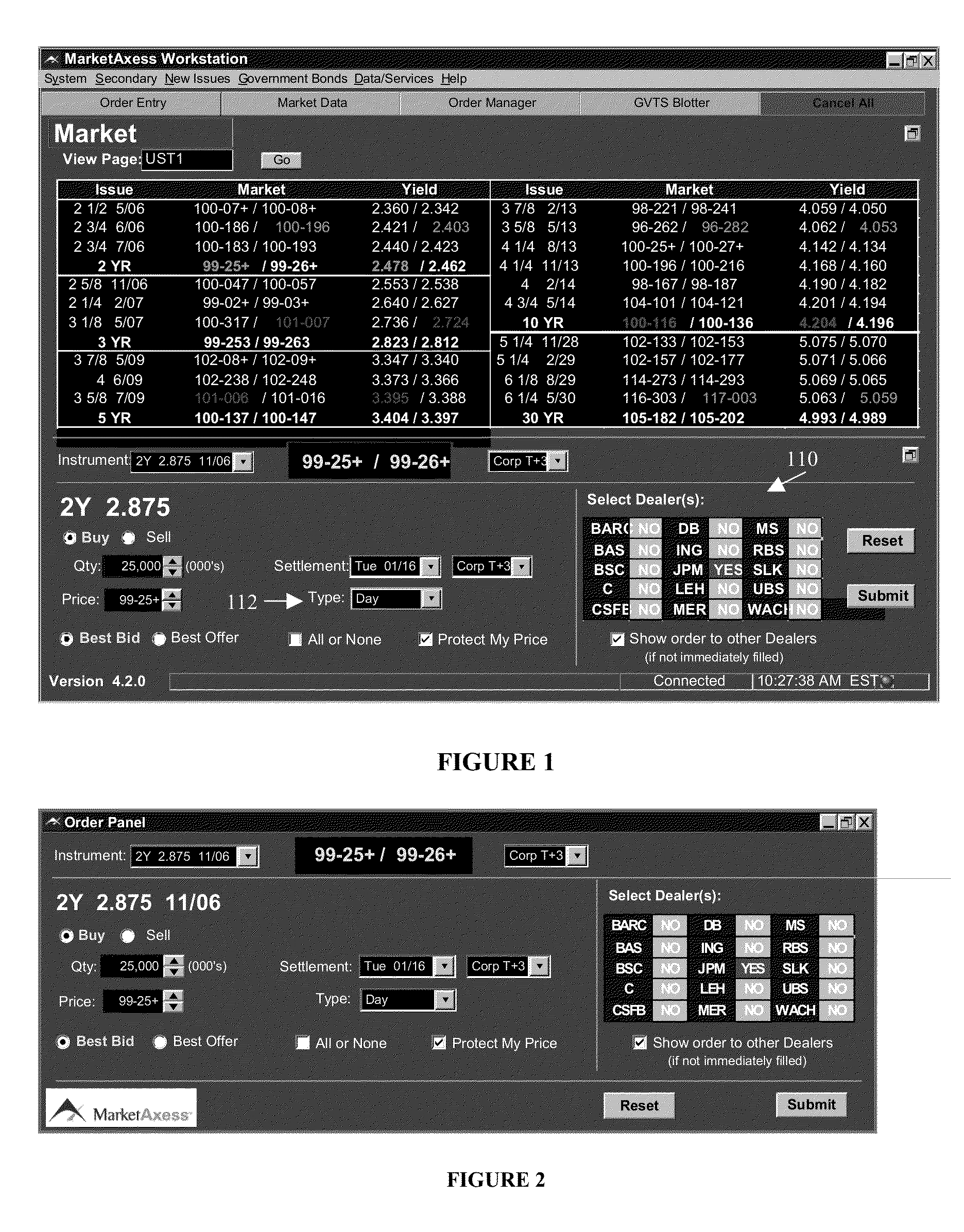
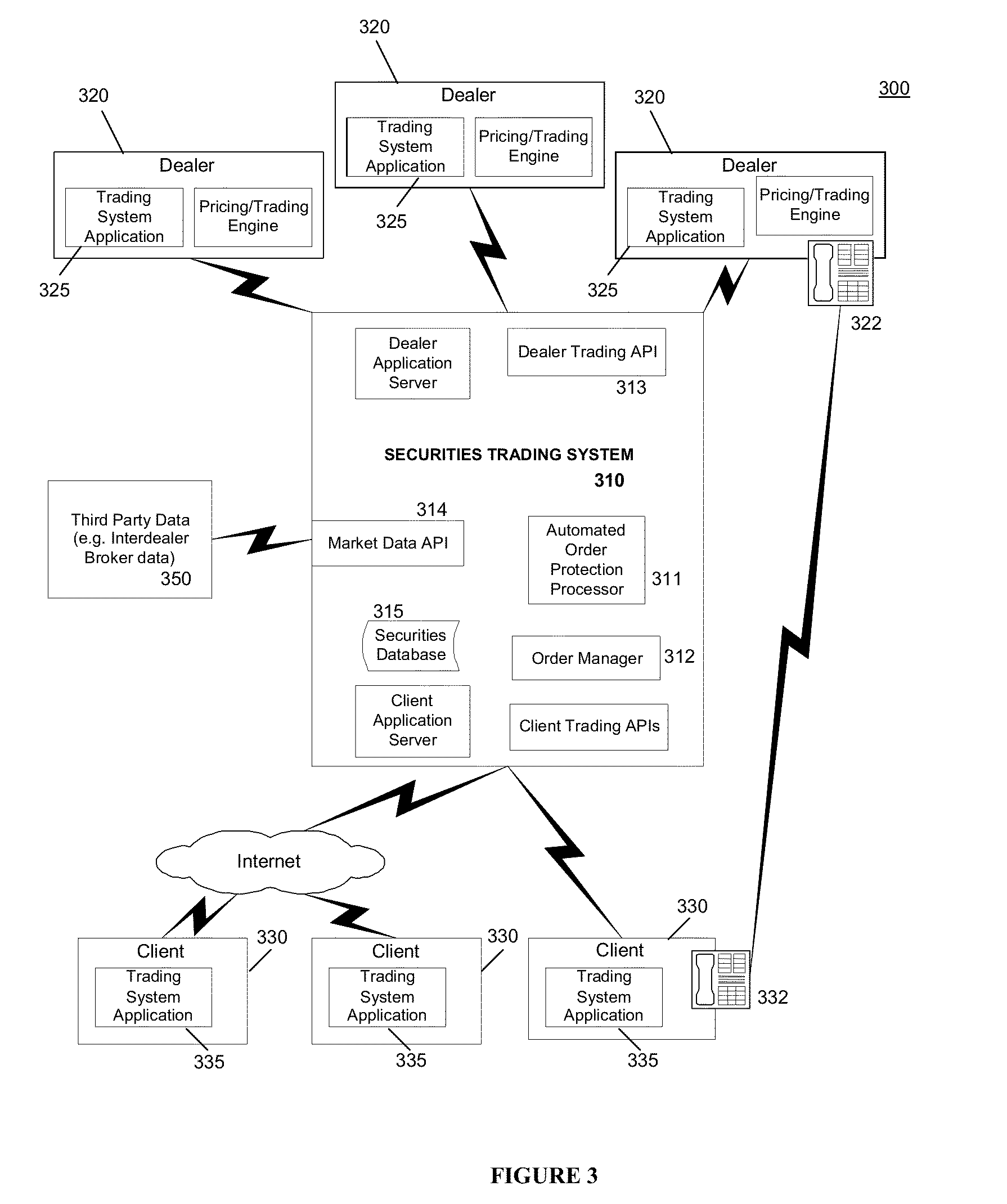
Methods and systems for computer-based trading enhanced with market and historical data displayed on live screen
Owner:MARKETAXESS HLDG
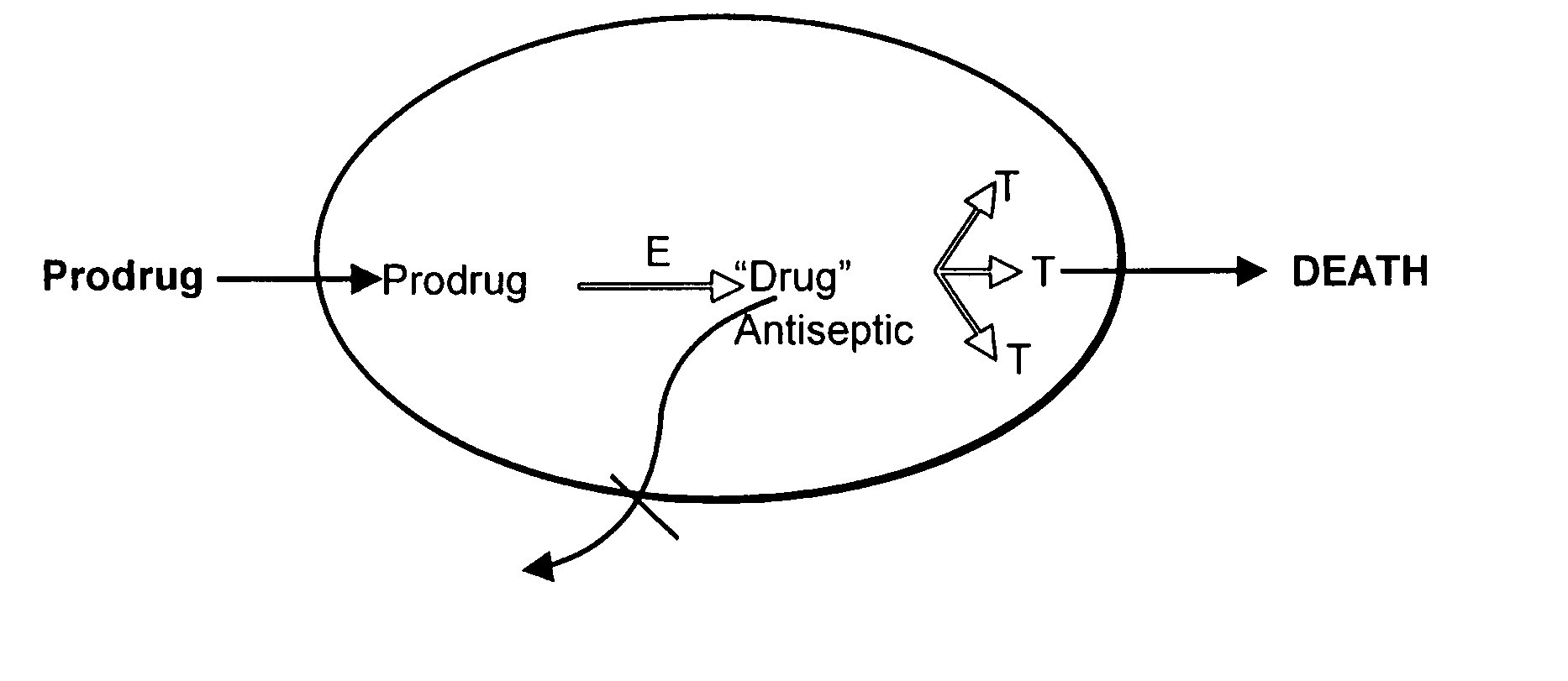
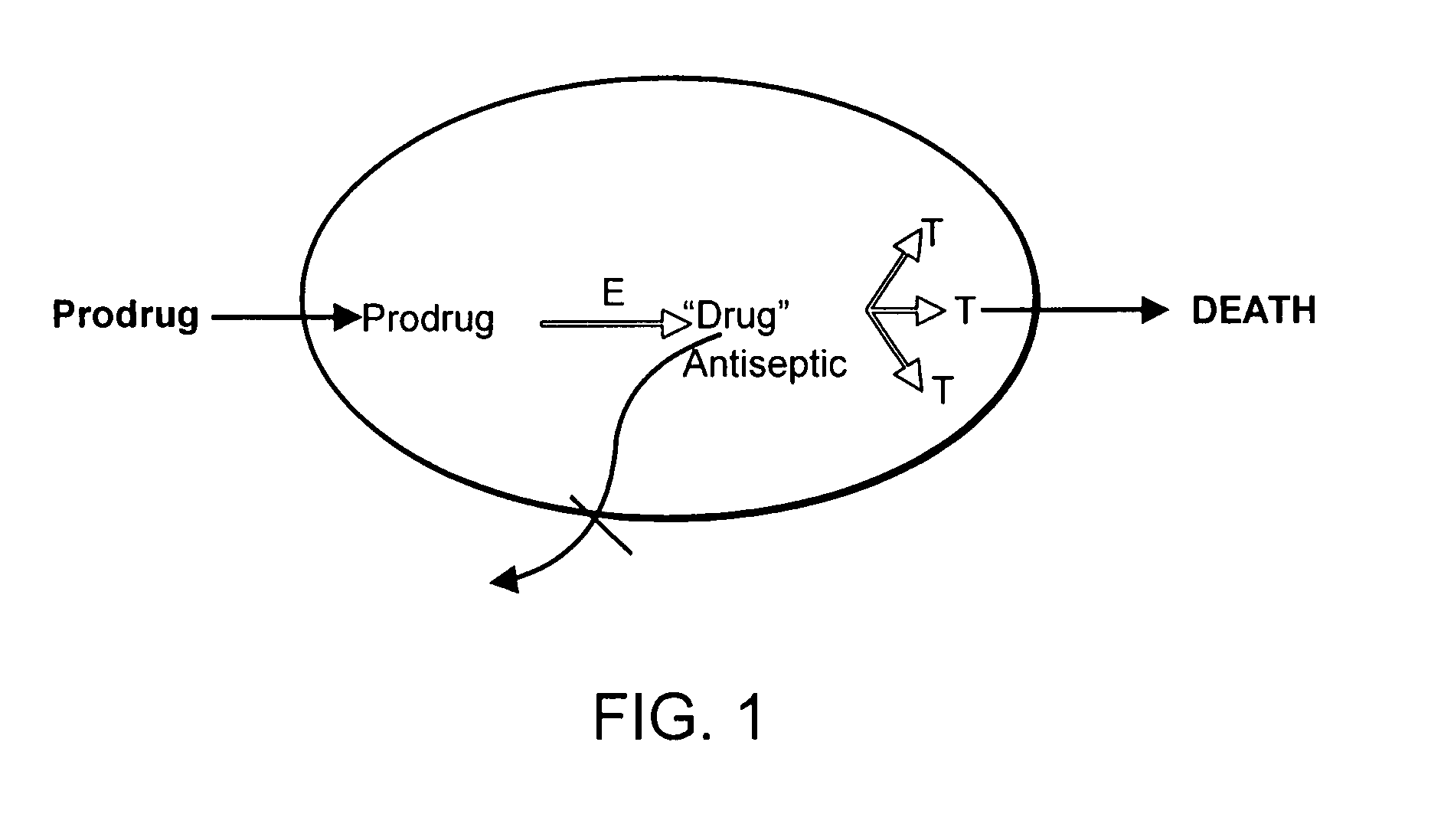
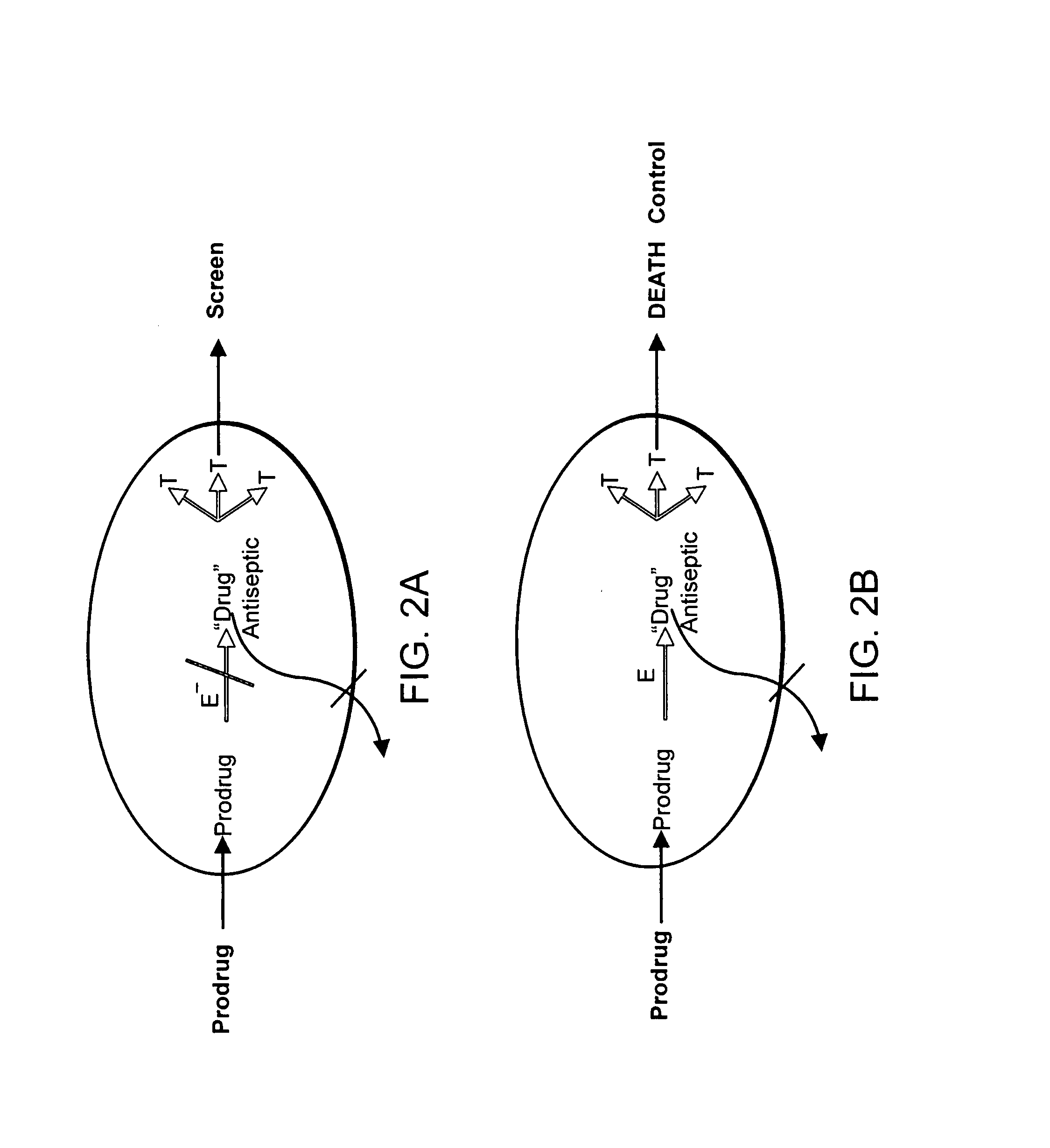
Prodrug antibiotic screens
InactiveUS20080027044A1High sensitivityFunction increaseBiocideOrganic chemistryMicroorganismDrug compound
Methods for identifying prodrug activity utilizing screens with microbial mutants, including null and conditional mutants, transiently gene-repressed microbes, and gene-overexpressing microbes, as well as pooled collections of these are provided. Effective prodrug antibiotics differentially kill or inhibit microbes overexpressing prodrug activating genes and allow non-expressing strains to grow and be readily identified. Methods for detecting prodrug antibiotic activity by detecting a lack of differential sensitivity of multidrug efflux mutant or deficient strains are also provided. Novel pharmaceutical compounds identified by the methods of the invention, pharmaceutical formulations, and methods for treating an infection comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of a Compound of the Invention are also provided.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Switching between icon and application window by dragging across multiple screens
InactiveCN102150120ADevices with multiple display unitsDevices with sensorGraphicsGraphical user interface
Methods, apparatuses, and computer-readable storage media for displaying an image at an electronic device are disclosed. In a particular embodiment, an electronic device is disclosed that includes a first panel having a first display surface to display a graphical user interface element associated with an application. The electronic device also includes a second panel having a second display surface. The first display surface is separated from the second display surface by a gap. A processor is configured to execute program code including a graphical user interface. The processor is configured to launch or close the application in response to user input causing a movement of the graphical user interface element in relation to the gap.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Screening methods to identify agents that selectively inhibit hepatitis C virus replication
InactiveUS6326151B1Prevent dimerizationBlock viral inhibitionFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseCellular defenseViral infection
The present invention relates to novel methods for identifying antiviral agents which selectively interfere with viral proteins that override the interferon(IFN)-induced cellular defense mechanisms against viral infection. In particular, the present invention relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between viral proteins containing an interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR) and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The present invention more particularly relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A protein (NS5A), which contains an ISDR, and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The interaction between the viral ISDR and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase results in the override of IFN-induced cellular defense mechanisms to combat viral infection. Therefore the agents identified using the assays of the invention may have utility as antiviral agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
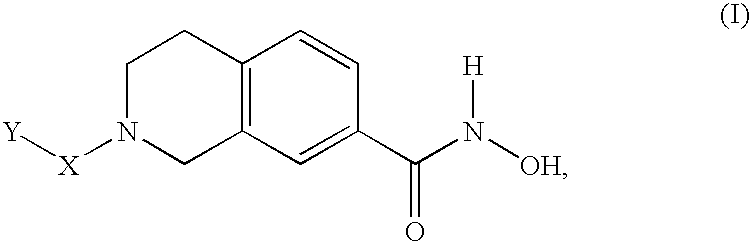
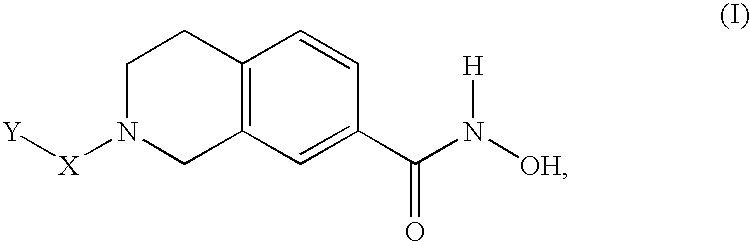
Compounds for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
The present invention relates to a class of small molecule hydroxamic acid compounds capable of inhibiting histone deacetylases (HDACs). The present invention also relates to methods of preparation of hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitor compounds of the invention, which are N-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydroxamic acid derivatives, and their incorporation into pharmaceutical compositions and methods of administration. The present invention also relates to N-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydroxamic acid derivatives, which may be prepared as a hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitor compound library that can be utilized in screening methods known in the art.
Owner:FORUM PHARMA
Cells screening method
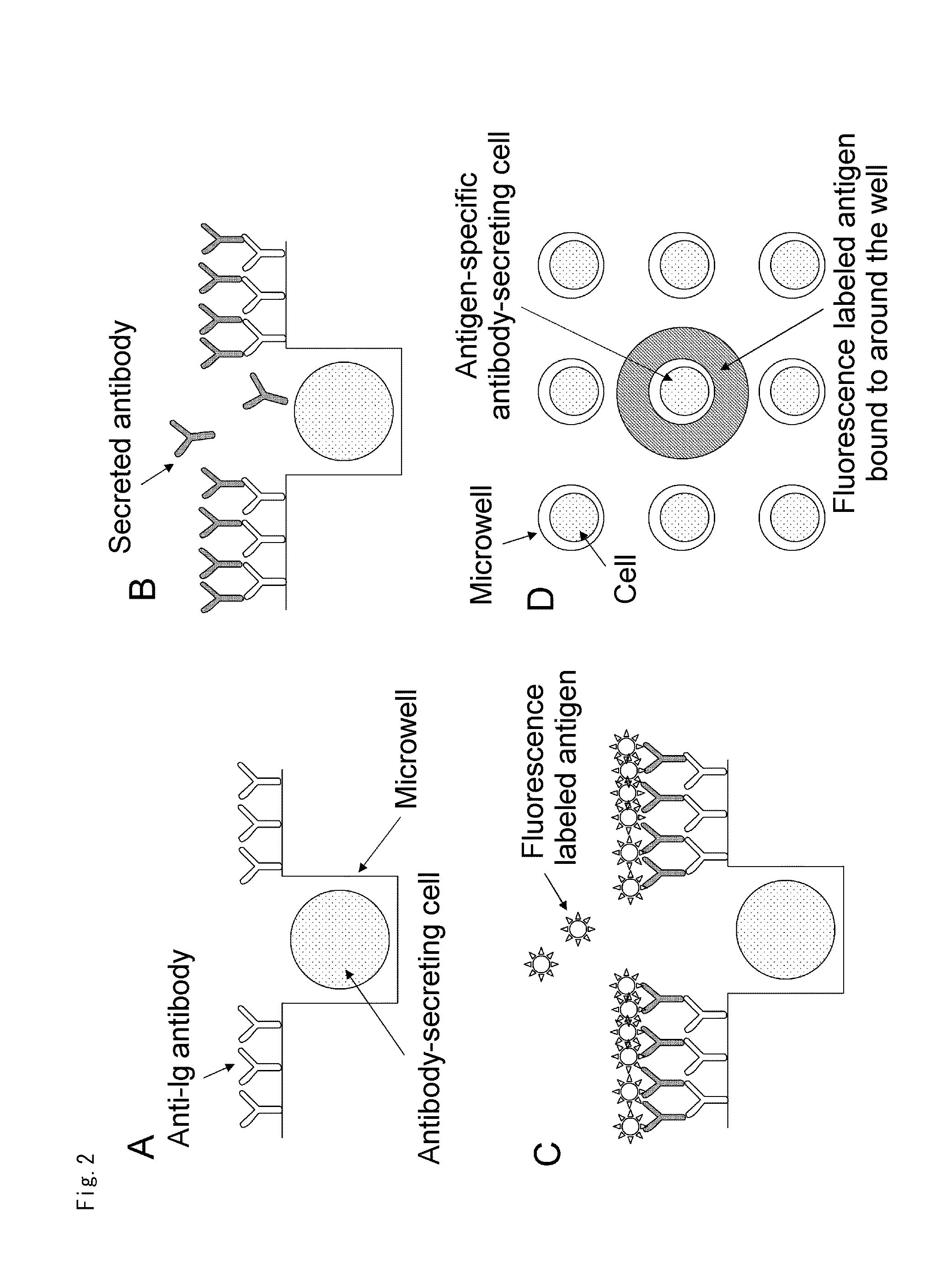
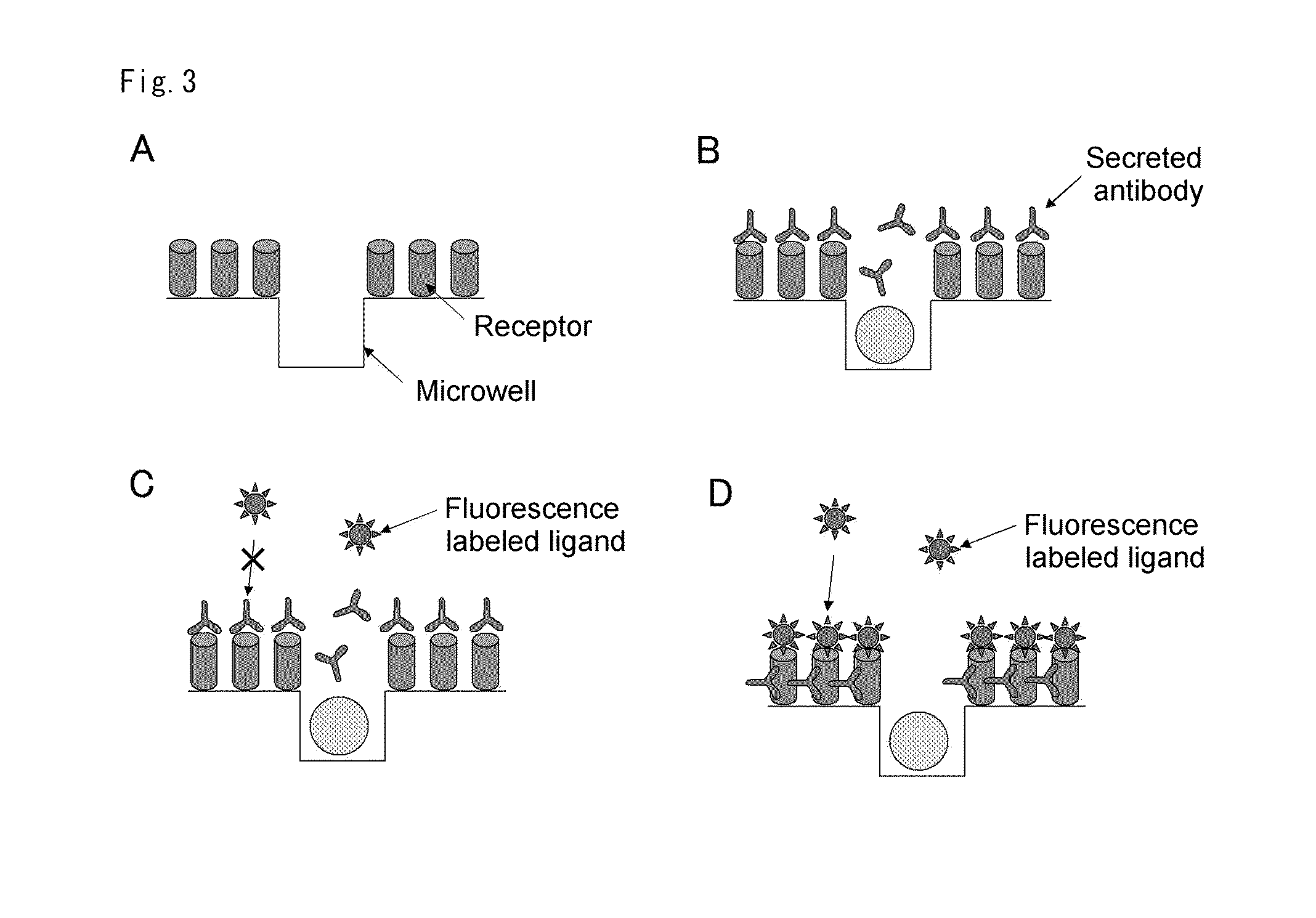
ActiveUS20110294678A1Simultaneous measurementLibrary screeningBiological material analysisAntigenDiffusion
Provided are a method and means permitting the simultaneous measurement of the reactive properties of more than 10,000 of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes being held on a chip and the separate determination of the states of individual cells. A microwell array comprises multiple wells and a coating layer on one of the principal surfaces of a base member, the wells being of a size permitting the entry of only a single cell into each well. A coating layer of a substance capable of binding to a substance produced by the cells contained in the wells is present on the principal surface around the wells. A method of screening for a target cell, comprises: causing specimen cells and a cell culture broth to be contained in the wells of the above microwell array; immersing the coating layer and the wells in the culture broth and culturing the cells in a state permitting the diffusion of substances in the culture broth from the wells into the coating layer; feeding a label substance binding specifically to a substance produced by a target cell present among the specimen cells onto the coating layer; and detecting the substance produced by the target cell that has bound to the substance in the coating layer by the label substance to specify the target cell.
Owner:TOYAMA PREFECTURE +1
Strain capable of degrading feather keratin efficiently and screening method thereof
ActiveCN102154144AEfficient degradationPromote sheddingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisScreening method
The invention relates to a strain capable of degrading feather keratin efficiently and a screening method thereof. According to result of the analysis and identification of the sequence of 16SrDNA and the result of the identification of a Biolog system, F4 is determined to be Bacillus licheniformis and is named Bacillus licheniformis F4. The Bacillus licheniformis F4 was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a collection number of CGMCC No.4229 on October 22th, 2010. The screening method comprises: primarily screening, separating, enriching, and secondarily screening to obtain the strain capable of degrading feather keratin efficiently. In the invention, the strain capable of degrading feather keratin efficiently is obtained by two steps of screenings under strict conditions, wherein primary screening conditions are a carbon source and a nitrogen source, and secondary screening conditions are complete degradation of feathers and measurement of enzymatic activity of keratin. The strain is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium containing complete feathers to perform fermentation culture for 60 hours, all barbules of the feathers are removed, the left feather stems and a major part of removed pinnules are degraded, and the feather removing and feather keratin degrading effects of the strain are obvious.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Imaging modalities for screening Alzheimer's disease therapeutics
InactiveUS20060117397A1Compounds screening/testingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsImaging modalitiesMedicine
Owner:WYETH
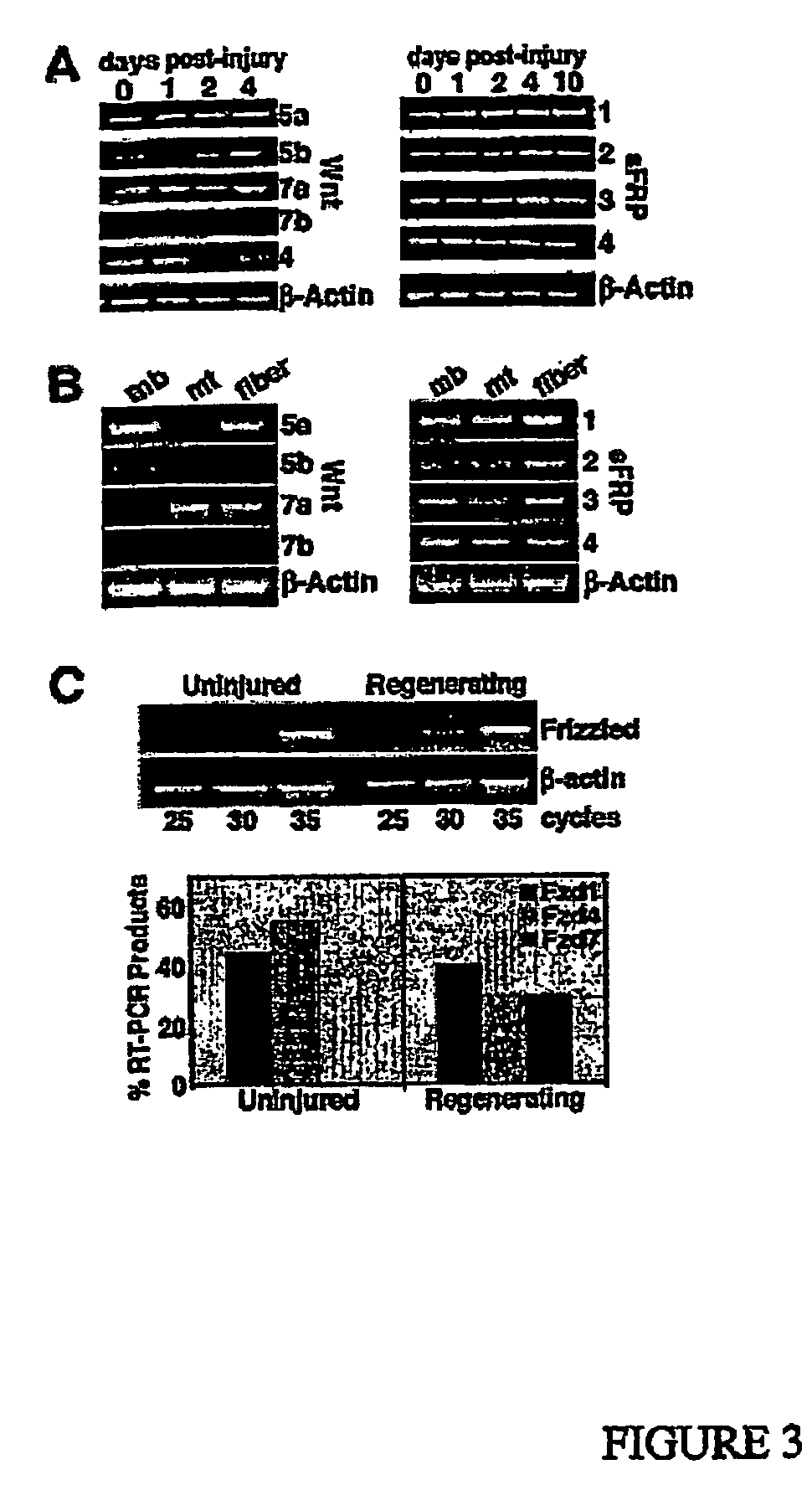
Growth and differentiation of adult muscle stem cells with activators or inhibitors of Wnt signaling
InactiveUS7541183B2Improve survivalIncrease the number ofPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderMuscle stem cellIn vivo
Compositions and methods for modulating proliferation and / or lineage commitment of stem cells by modulating the Wnt signalling pathways. Modulators of the Wnt signalling pathways and screening methods to identify modulators are also provided. The methods of the invention may be conducted in vitro or in vivo to induce or inhibit stem cell proliferation and / or lineage commitment, and are particularly useful for in vivo stimulation of proliferation and / or lineage commitment of resident stem cells in a tissue.
Owner:OTTAVA HEALTH RES INST (CA)
Compounds for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20060004041A1Potential limitationInhibit deacetylationBiocideOrganic chemistryHydroxamic acidNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention relates to a class of small molecule hydroxamic acid compounds capable of inhibiting histone deacetylases (HDACs). The present invention also relates to methods of preparation of hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitor compounds of the invention, which are N-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydroxamic acid derivatives, and their incorporation into pharmaceutical compositions and methods of administration. The present invention also relates to N-substituted-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydroxamic acid derivatives, which may be prepared as a hydroxamic acid HDAC inhibitor compound library that can be utilized in screening methods known in the art.
Owner:FORUM PHARMA
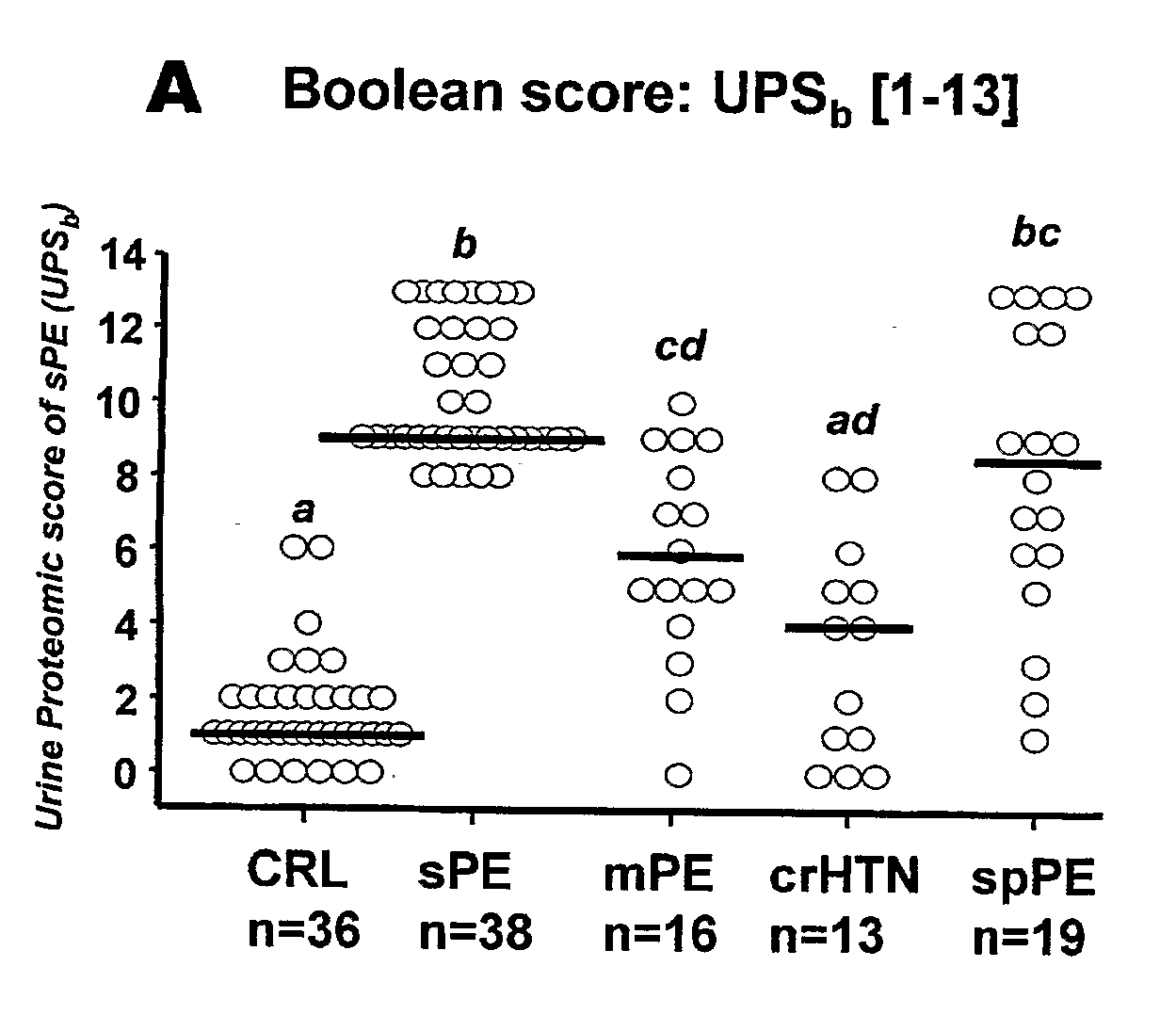
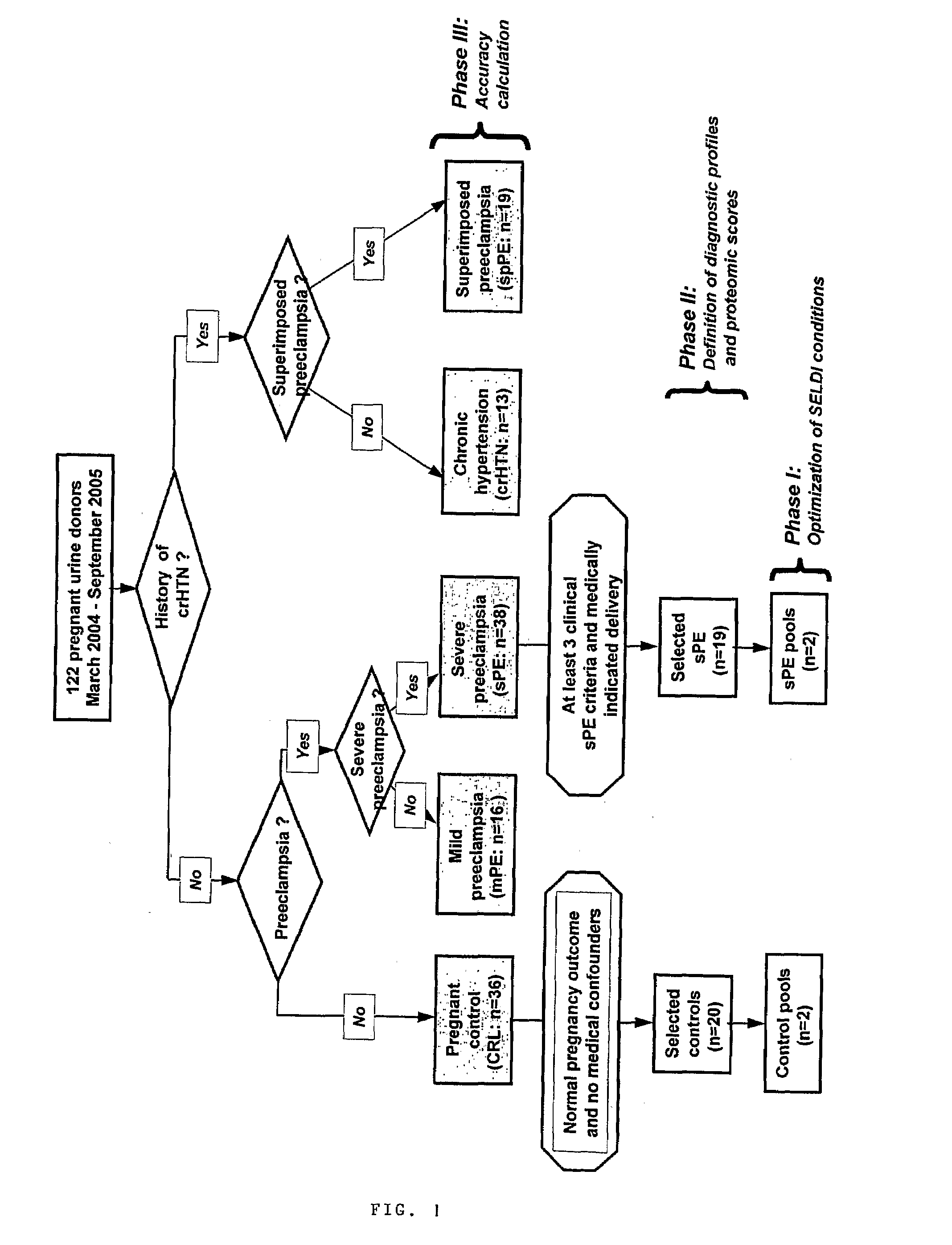
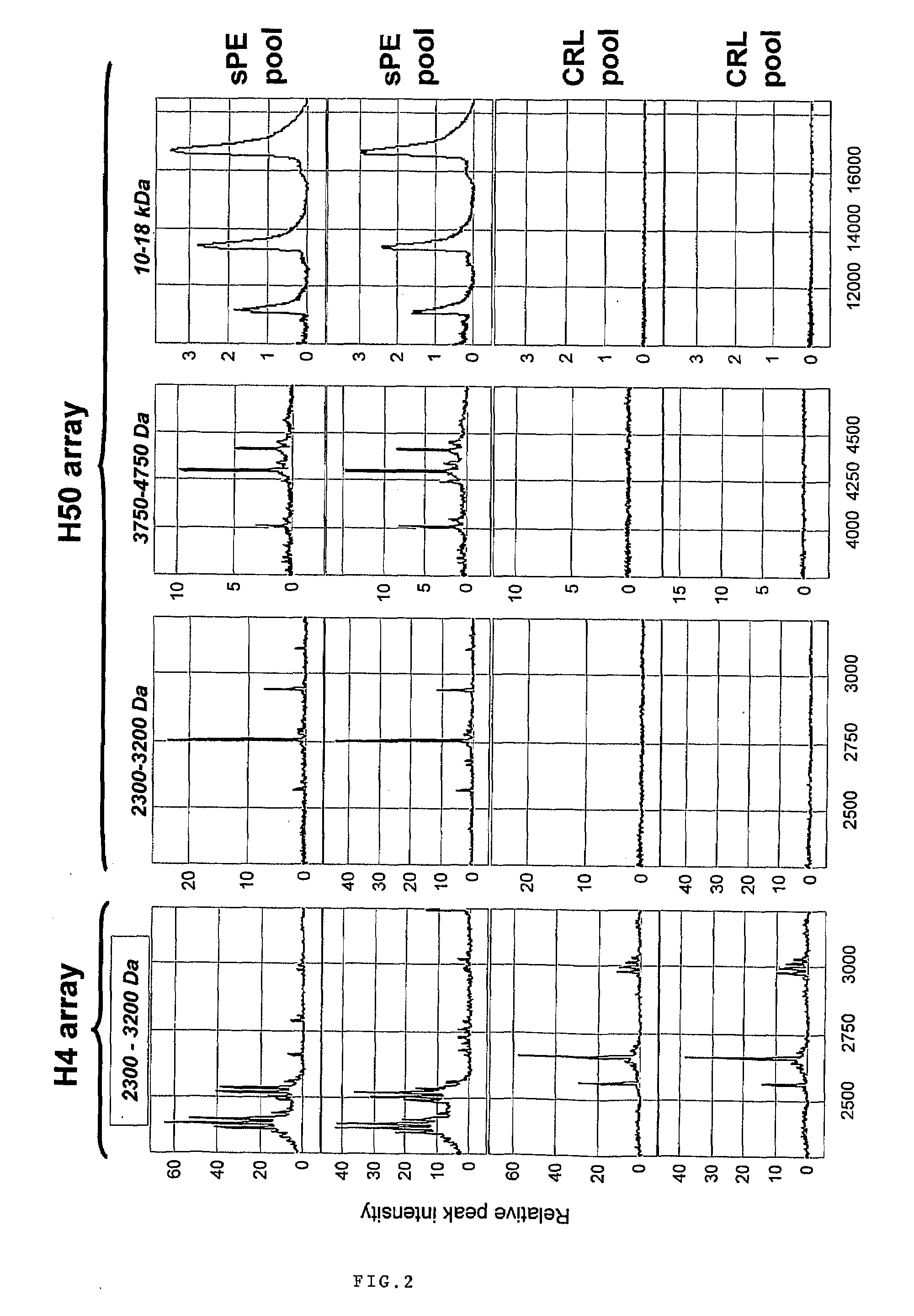
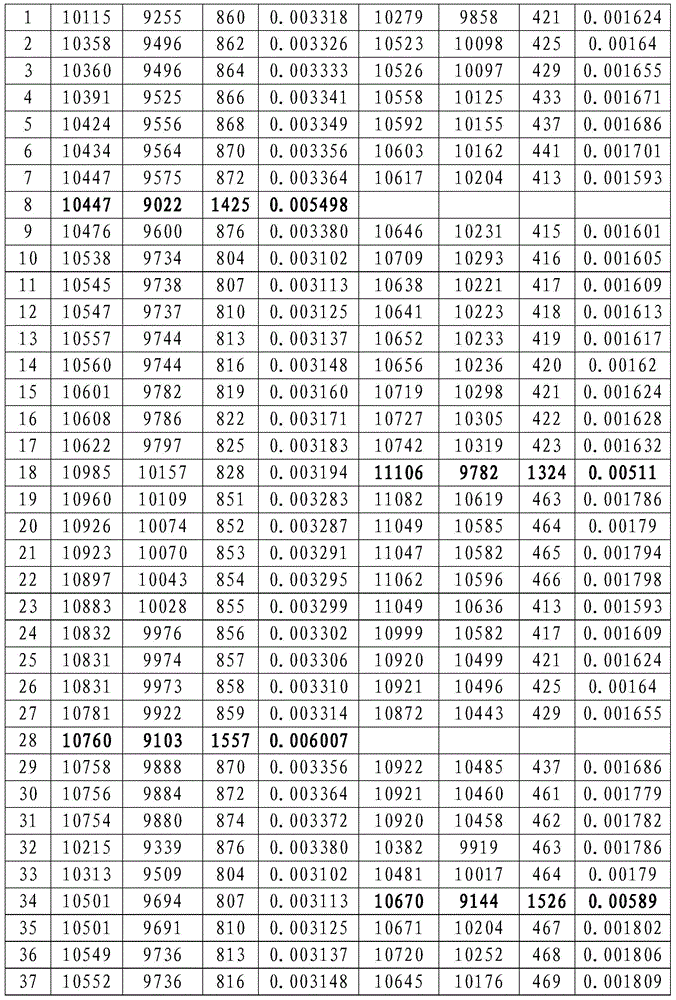
Urinary Proteomic Biomarker Patterns in Preeclampsia
The invention relates, in part, to methods of using proteomic biomarkers to diagnose preeclampsia. In some aspects the invention, in part, relates to the detection of serpina-1 polypeptide and / or albumin polypeptide in samples from pregnant subjects. Samples from subjects may be compared to control samples to diagnose preeclampsia and / or to determine the onset, progression, or regression of preeclampsia in a subject. The invention also relates, in part, to screening methods to identify agents that can be used to treat preeclampsia and to determine the efficacy of a preeclampsia treatment. The invention, in part, also includes kits that are useful to diagnose and assess preeclampsia in a subject.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Lithium battery self-discharge screening method
ActiveCN104090241AImprove the accuracy of judgmentSimple methodElectrical testingPower flowScreening method
A lithium battery self-discharge screening method includes the steps that lithium batteries are charged in advance, the total capacity C1 of the batteries is recorded, constant-temperature aging is carried out on the batteries, the aged batteries are discharged through constant current under the environment with normal temperature, the batteries are charged through the same constant current, the capacity C2 obtained after constant current discharging is carried out and the capacity C3 obtained after charging are recorded respectively, C1 minus C2 is the capacity difference delta1, and then K1 is calculated by dividing delta1 by T1; batteries of which K1 is within the qualified range are directly transferred to the next process; constant-temperature aging is carried out on the batteries which are transferred normally; the aged batteries are discharged through the constant current under the normal temperature and normal voltage, and the capacity C4 obtained after discharging is finished is recorded; C4 minus C3 is delta2, K2 is calculated by dividing delta2 by T2, and batteries of which K2 is within the qualified process range are batteries small in self discharge. Through changes of battery capacities within a certain period, lithium batteries high in self discharge are effectively selected out through two times of screening, the method is simple and easy to implement, and production and operation are convenient.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
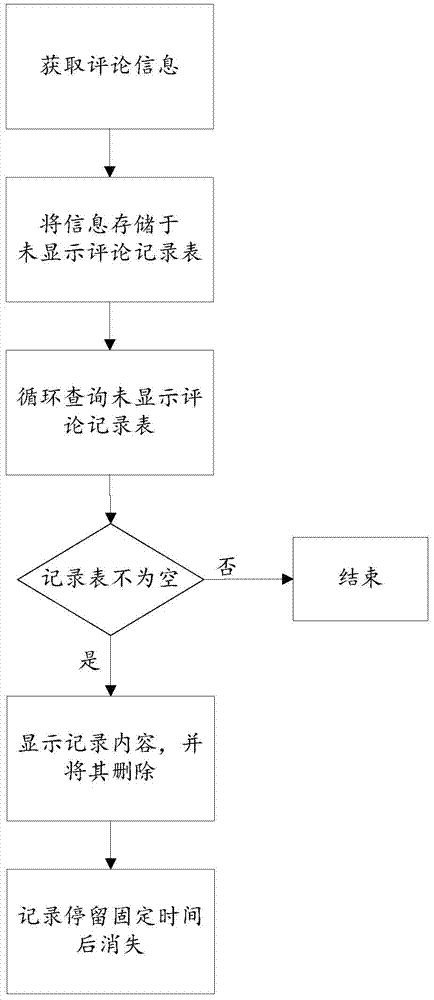
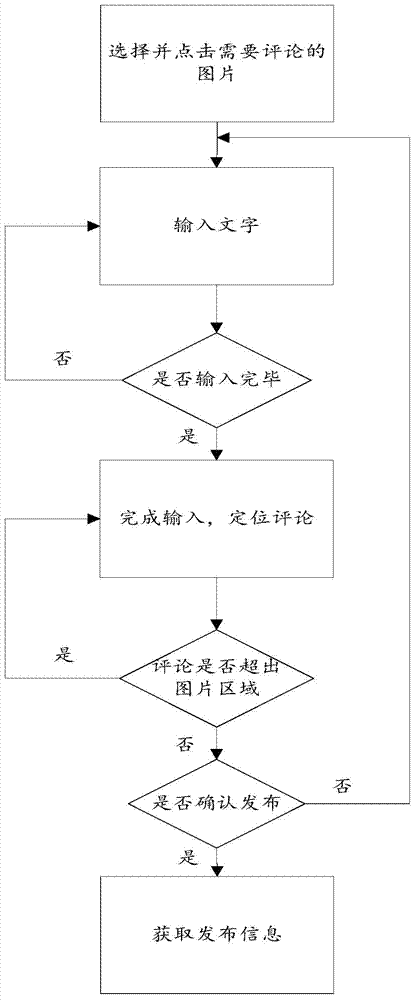
Image bullet screen method
InactiveCN104504063AEasy to identifyImprove interactivitySelective content distributionSpecial data processing applicationsScreen methodSoftware
The invention provides an image bullet screen method. The method is characterized in that the bullet screen can be performed for the image, and the commenting operation can be directly performed for the image; space coordinates are added to the comment record, and the display position of the comment in the image is controlled, so that the comment display and interaction mode is greatly improved; the user information is added to the bullet screen comment, thus the recognition degree of a comment author can be improved, and the software interaction is increased; the image bullet screen displaying method is that the ever-increasing comments are displayed everywhere, and the comments can automatically disappear after being displayed for a while; therefore, commenting with a sarcastic tone is achieved in the image, and the image and the user comments for the image can be displayed well.
Owner:北京橘子文化传媒有限公司
Terminal screen control method and terminal
InactiveCN102779502AReduce stepsReduce lossCathode-ray tube indicatorsConverting sensor output opticallyControl signalComputer terminal
The invention provides a terminal screen control method. The method comprises the following steps that after a terminal detects that the time that human eyes stare at a terminal screen exceeds a given time, a screen lightening control signal is generated; and the terminal lightens the terminal screen according to the screen lightening control signal. The invention also provides the terminal. The terminal screen control method provided by the invention has the advantages that operation of a user and wastage of the terminal are reduced, electric quantity can be saved to certain degree, and the incidence caused by mistaken pressing is reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Systems and methods for enabling remote device users to wager on micro events of games in a data network accessible gaming environment
ActiveUS20120046094A1Prevent cheatingApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesMicrobloggingComputer science
A method and system for micro-betting. A control function can be designated for managing a series of micro-bets with respect to one or more events. The control function can be configured to determine when said series of micro-bets are set and when no more micro-bets among said series of micro-bets can be placed with respect to said event(s). Additionally, a multiple display screen method and system for the placement of micro-bets includes one or more display screens for displaying a micro-betting GUI for placing and managing micro-bets with respect to one or more macro-events and / or micro-events thereof. At least one other display screen can be utilized to provide video of the macro-event and / or micro-event(s). Available micro-bets among said micro-bets can be randomized to prevent cheating
Owner:MICRO GAMING VENTURES
Sliding type screen-unblocking method
InactiveCN101311891AGood user interfaceImprove friendlinessTelephone set constructionsInput/output processes for data processingComputer terminalComputer science
The invention discloses a mobile communication terminal which is characterized in that the interface of the mobile communication terminal comprises a virtual function bond region which comprises a locking icon. The locking and unlocking function can be realized by dragging the locking icon. A sliding type unlocking screen method provided by the invention provides a good interface for users by the visual sliding operation, improves the interface operation method of the users and leads to the result that the users feel more humanization and friendliness of the interface.
Owner:TECHFAITH WIRELESS TECH BEIJING
A kind of digital photography equipment with touch screen and its zooming method
InactiveCN102281399ALive viewSave spaceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTime controlTouchscreen
A zooming method for a digital photography device with a touch screen, characterized in that: the touch screen provided by the digital photography device is used to input a zoom gesture, and the digital photography device is controlled in real time to perform a zoom operation according to the change of the zoom gesture. The zooming method of the digital photographic device with a touch screen of the present invention can control the digital photographic device to perform the zooming operation in real time according to the change of the zooming gesture, and can check the zooming effect in real time during the process of inputting the zooming gesture, which is convenient and intuitive. In addition, the use of the touch screen to input zoom gestures eliminates the need to add physical buttons on the digital photography equipment, saving equipment space.
Owner:GUANGDONG BUBUGAO ELECTRONICS IND
Screening method of colorectal cancer treatment prognosis biomarkers
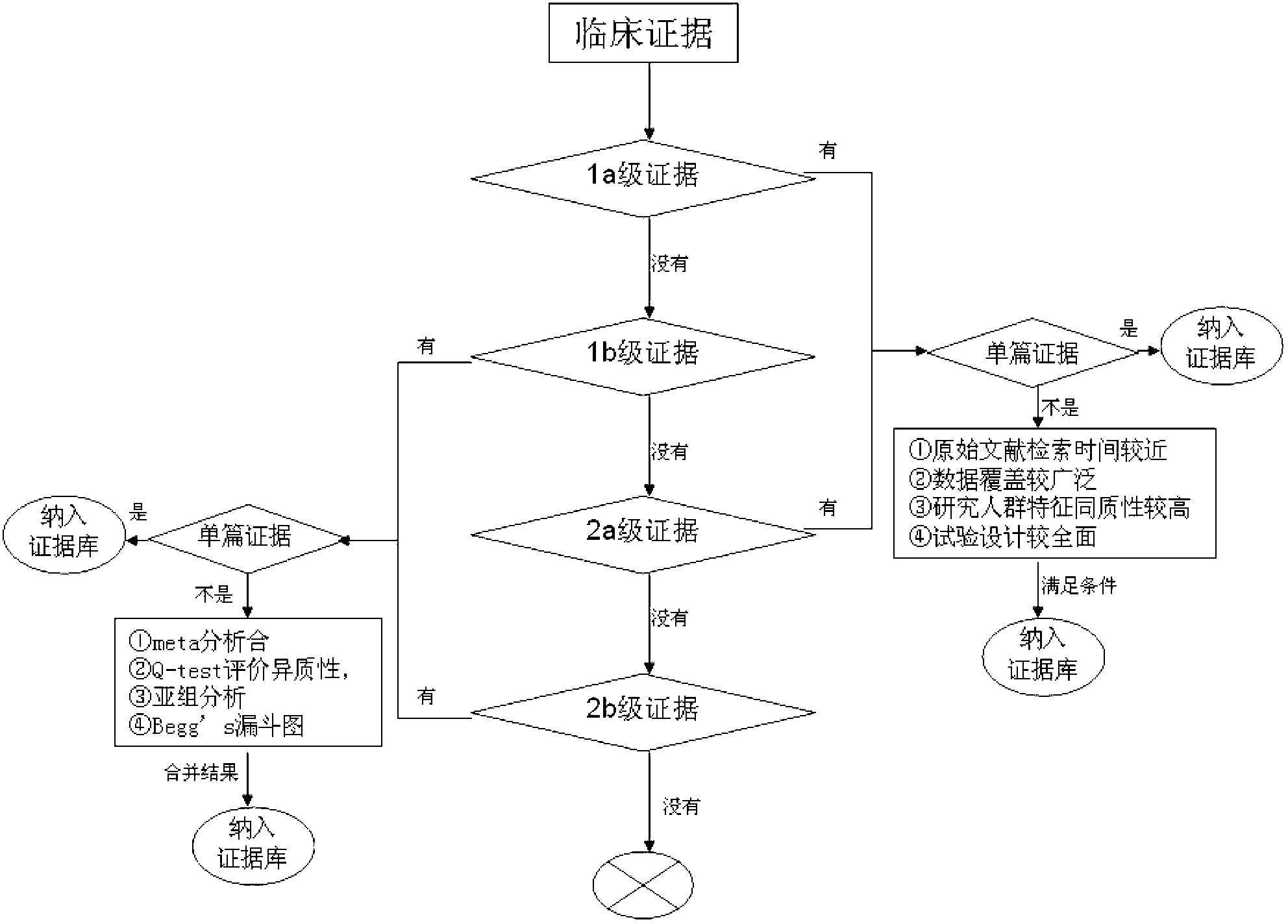
InactiveCN103324846AShorten screening timeReduce screening costsSpecial data processing applicationsDNA/RNA fragmentationKRASPrognosis biomarker
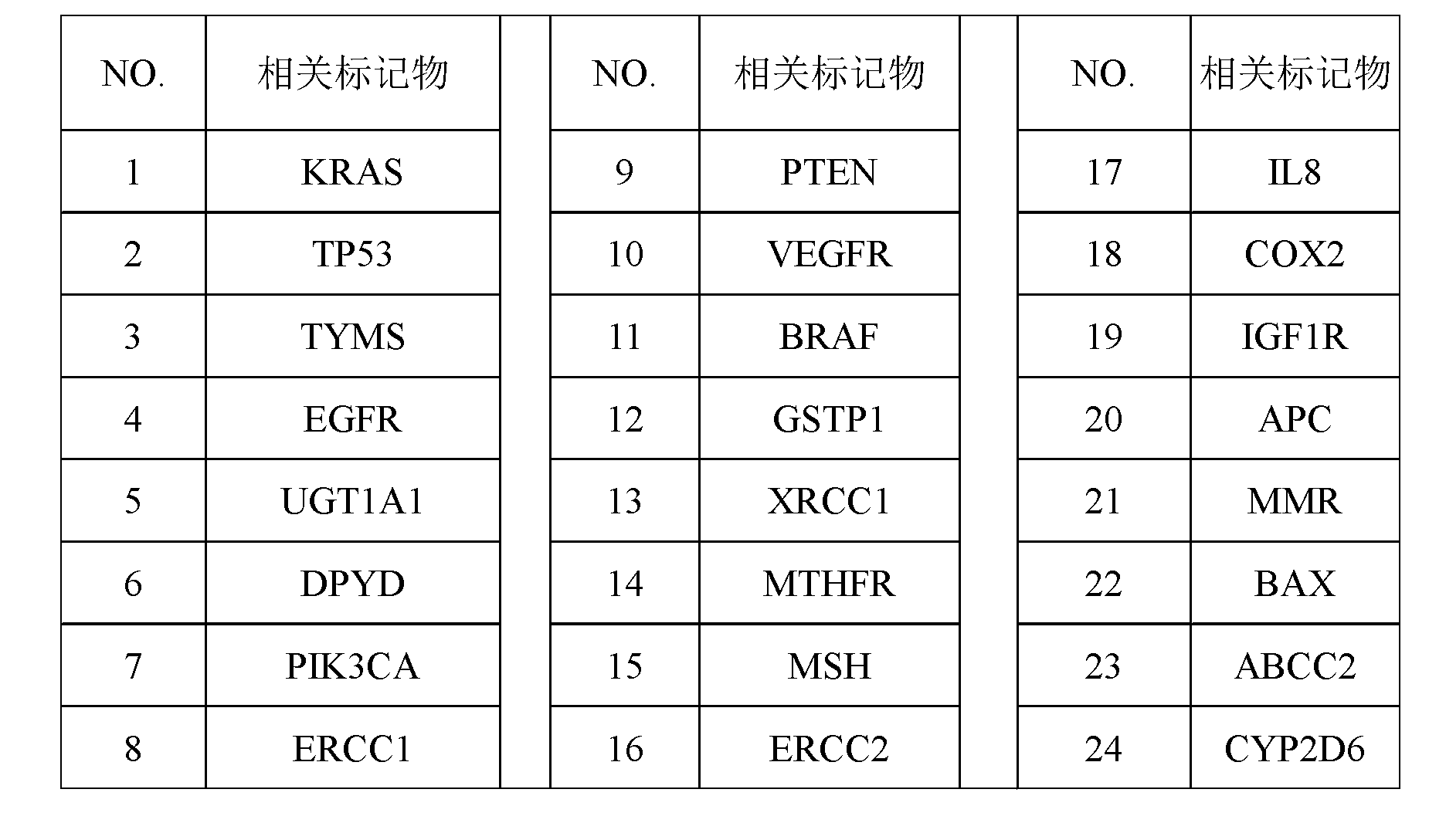
The invention discloses a screening method of colorectal cancer treatment prognosis biomarkers. The screening method includes the following steps of: (1) making a primary search strategy for screening the biomarkers; (2) making a literature adopting and exclusion criterion; (3) analyzing data and primarily screening the biomarkers; (4) making evident grades; (5) making a high quality evident evaluation criterion; (6) performing grading retrieval and quality evaluation on biomarker clinic evident; (7) performing data analyzing and statistics on the biomarker clinic evident; (8) screening the prognosis biomarkers. The invention further provides the colorectal cancer treatment prognosis biomarkers obtained through screening according to the screening method, and the prognosis biomarkers include KRAS, TYMS, TYMS, EGFR, UGT1A1*28, DPYD, PIK3CA, ERCC1, PTEN, VEGFR, BRAF, GST P1, XRCC1, MTHFR, MSI and the like.
Owner:浙江加州国际纳米技术研究院绍兴分院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com