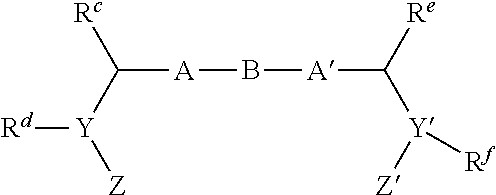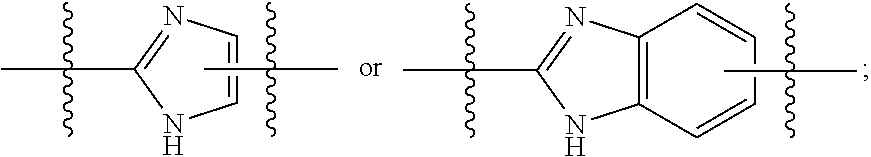Patents
Literature
146 results about "NS5A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
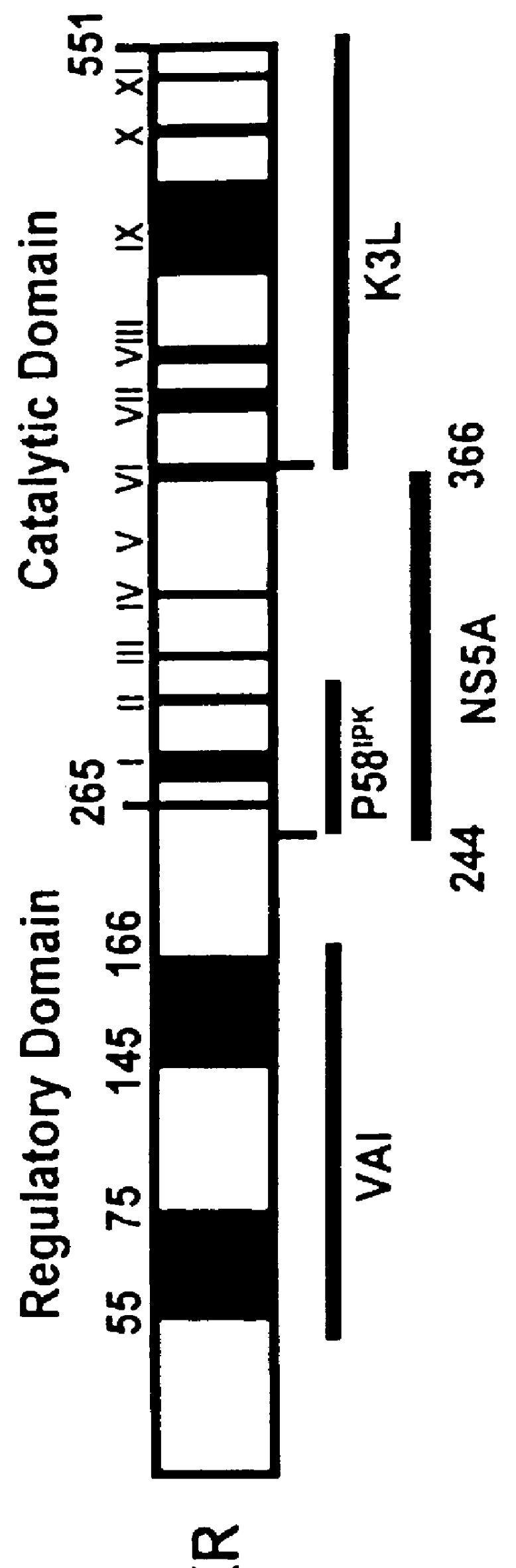
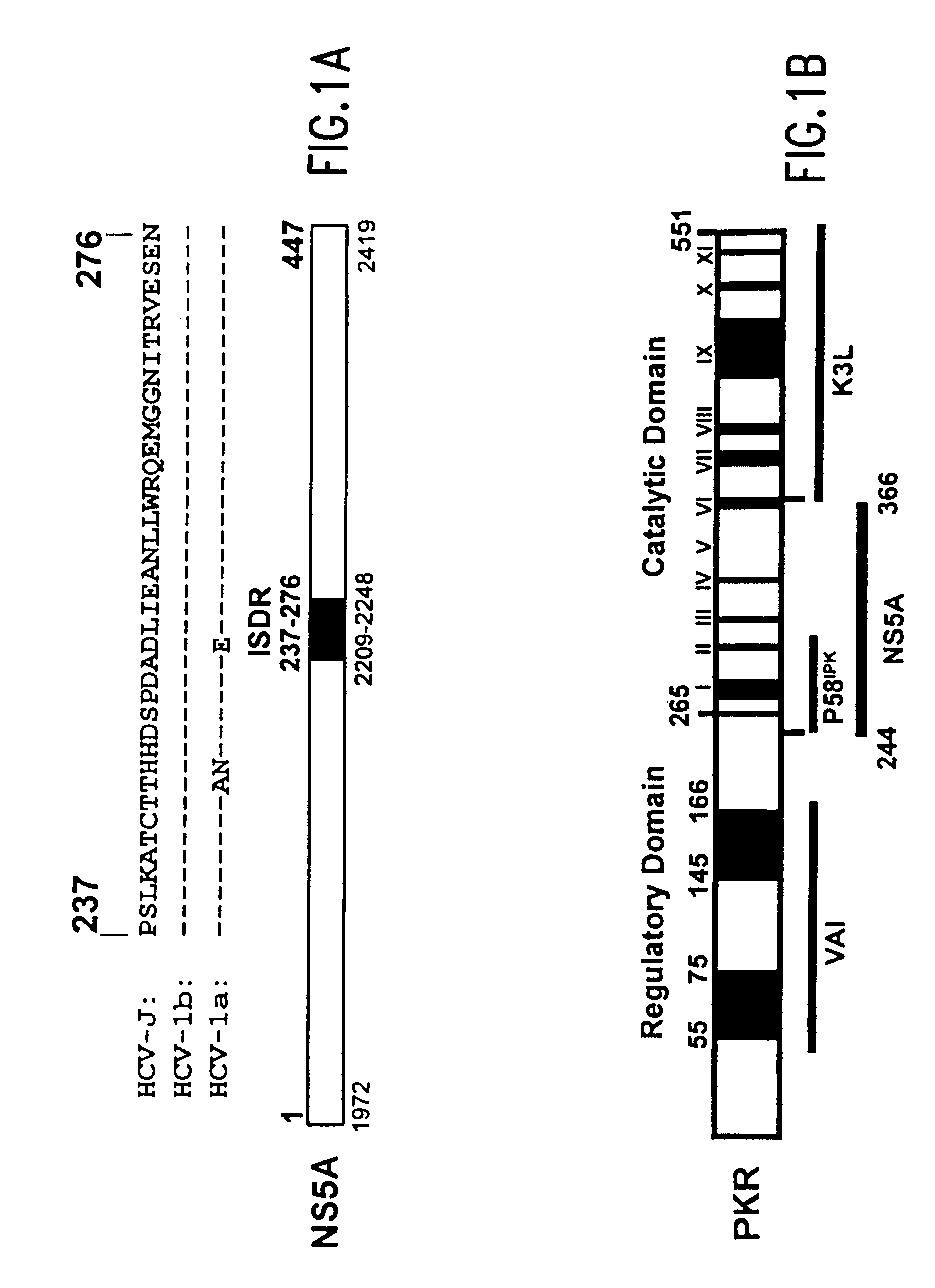
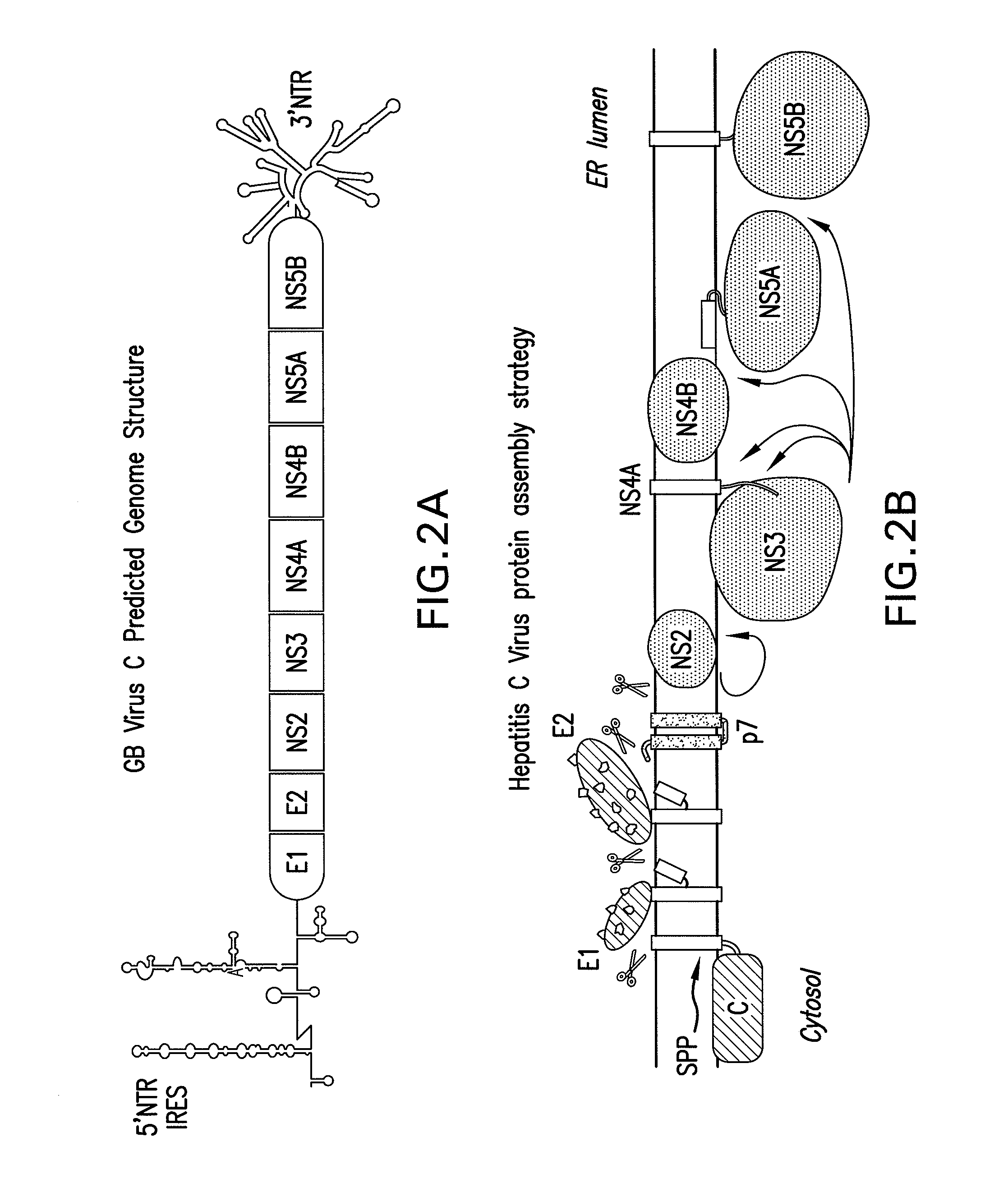
Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) is a zinc-binding and proline-rich hydrophilic phosphoprotein that plays a key role in Hepatitis C virus RNA replication. It appears to be a dimeric form without trans-membrane helices.
Inhibitors of HCV replication
ActiveUS20060276511A1Inhibit functioningEffective treatmentBiocideOrganic chemistryArrestinStereochemistry
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Screening methods to identify agents that selectively inhibit hepatitis C virus replication
InactiveUS6030785APrevent dimerizationBlock viral inhibitionFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseCellular defenseViral infection
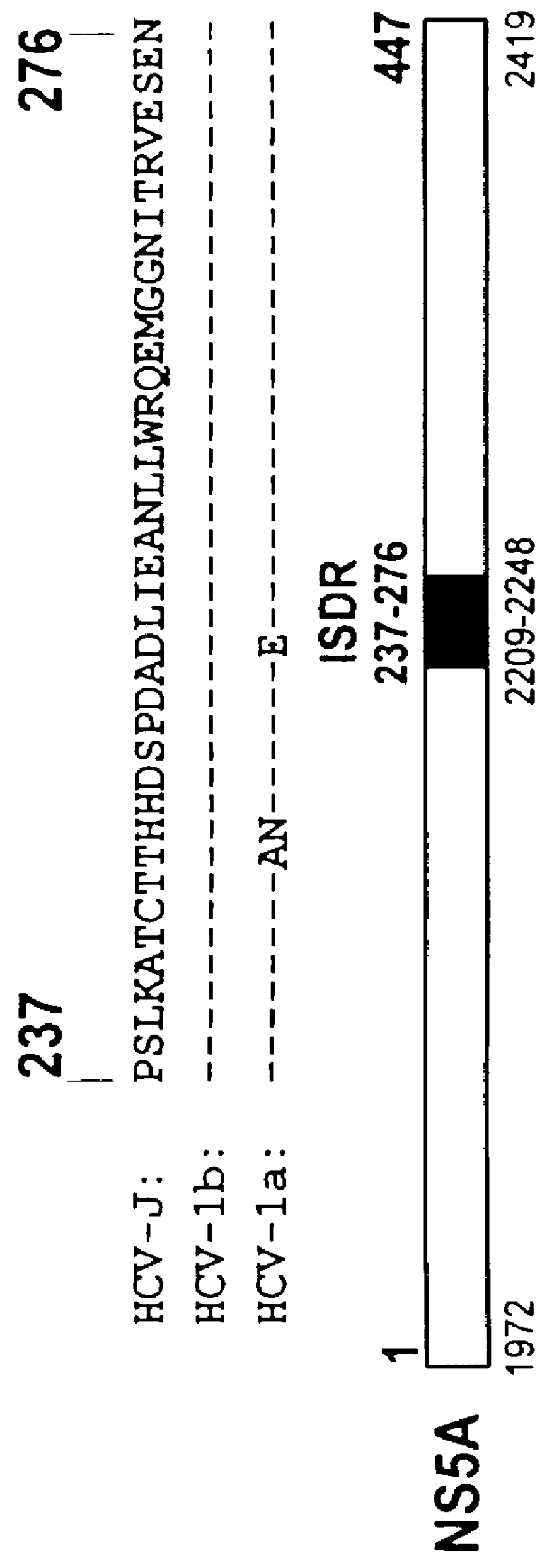
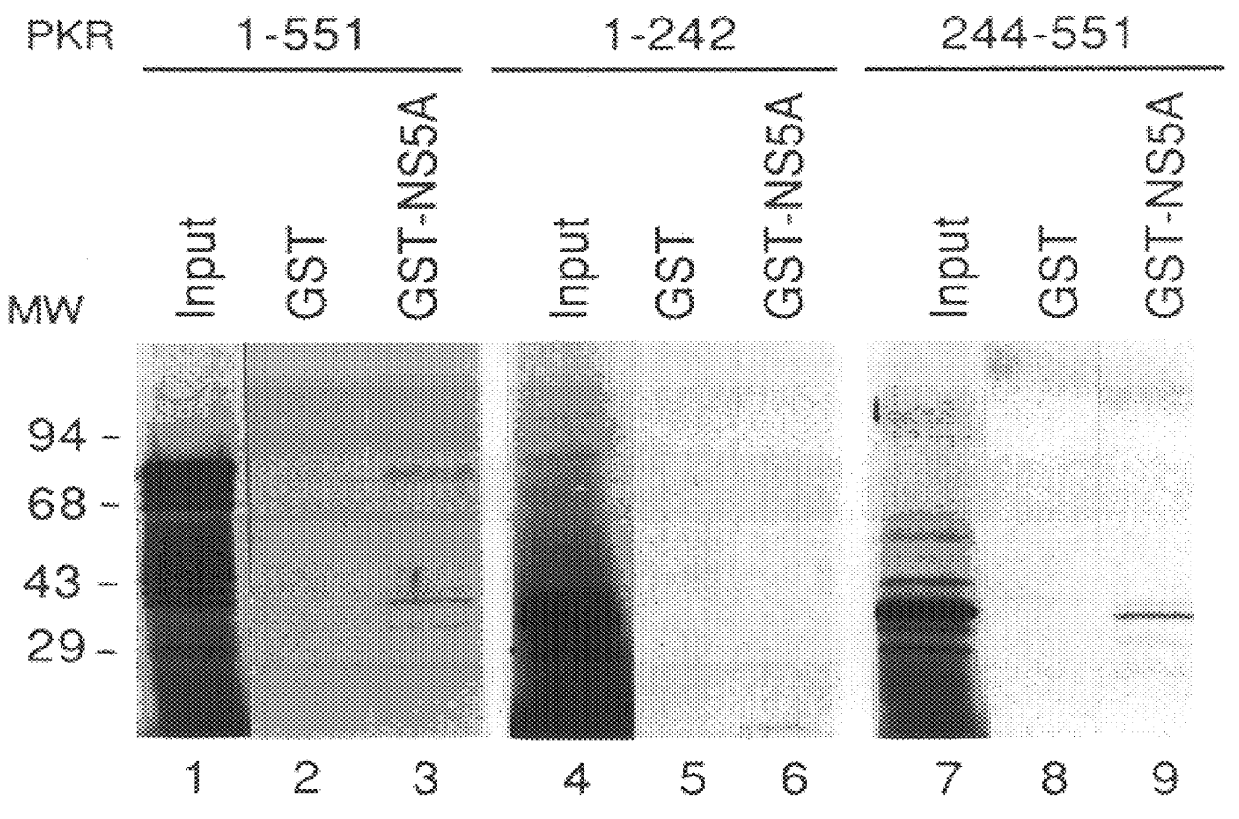
The present invention relates to novel methods for identifying antiviral agents which selectively interfere with viral proteins that override the interferon(IFN)-induced cellular defense mechanisms against viral infection. In particular, the present invention relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between viral proteins containing an interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR) and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The present invention more particularly relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A protein (NS5A), which contains an ISDR, and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The interaction between the viral ISDR and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase results in the override of IFN-induced cellular defense mechanisms to combat viral infection. Therefore the agents identified using the assays of the invention may have utility as antiviral agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Inhibitors of hepatitis c virus replication
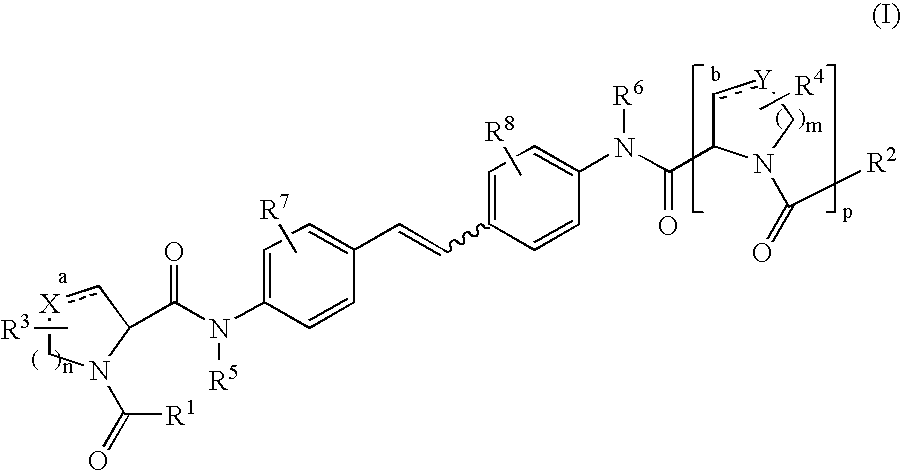
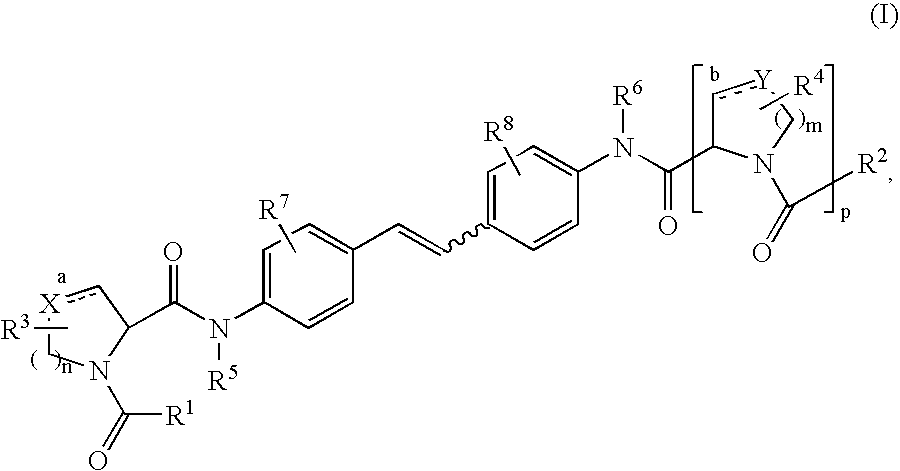
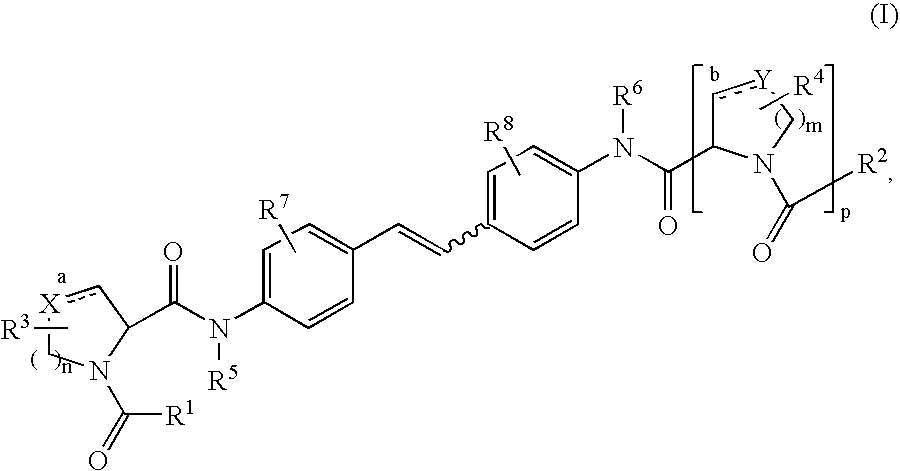
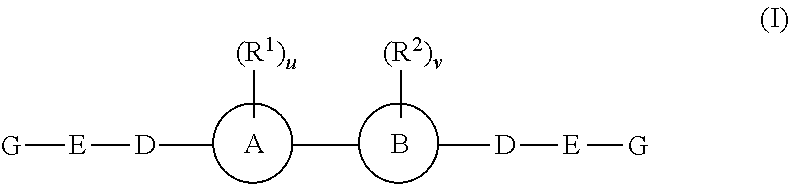
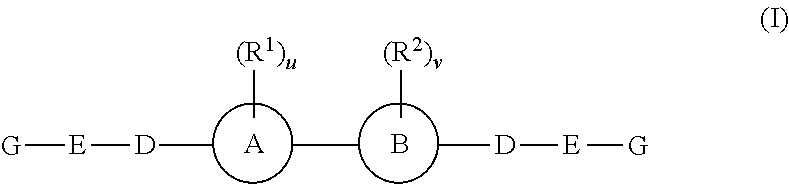
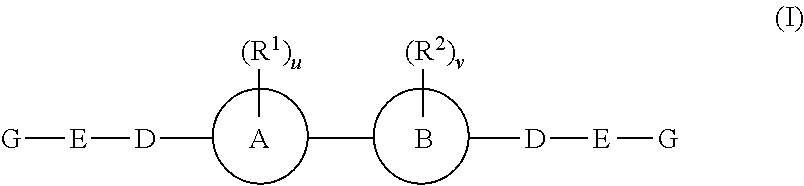
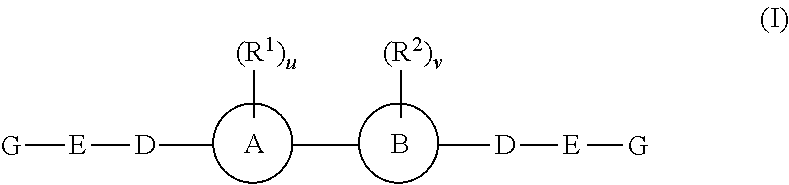
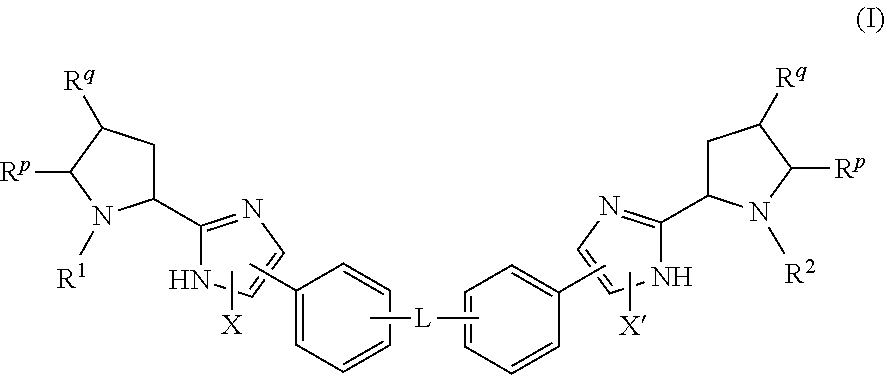
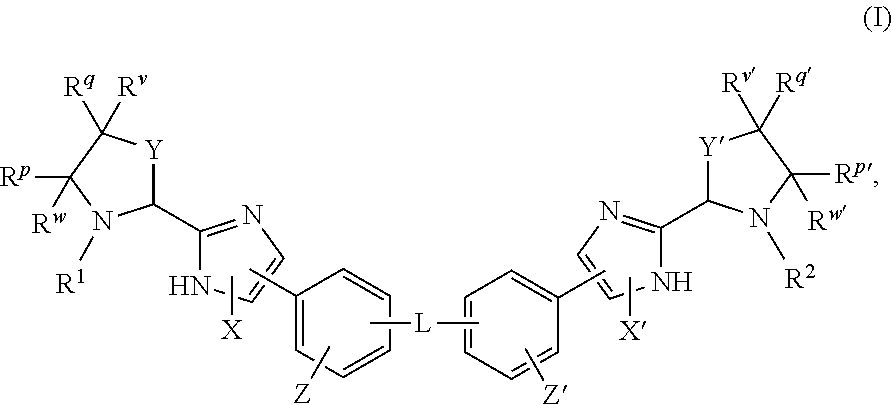
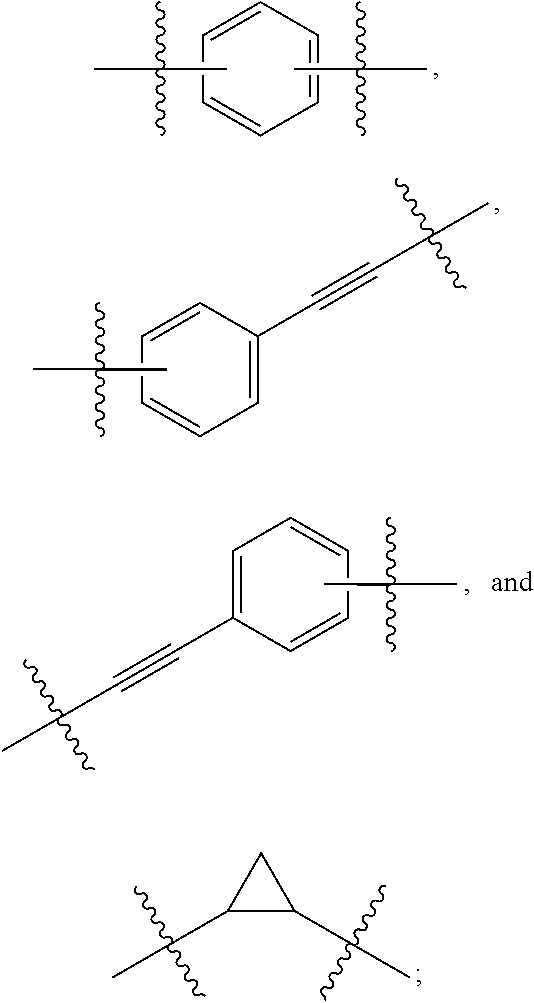
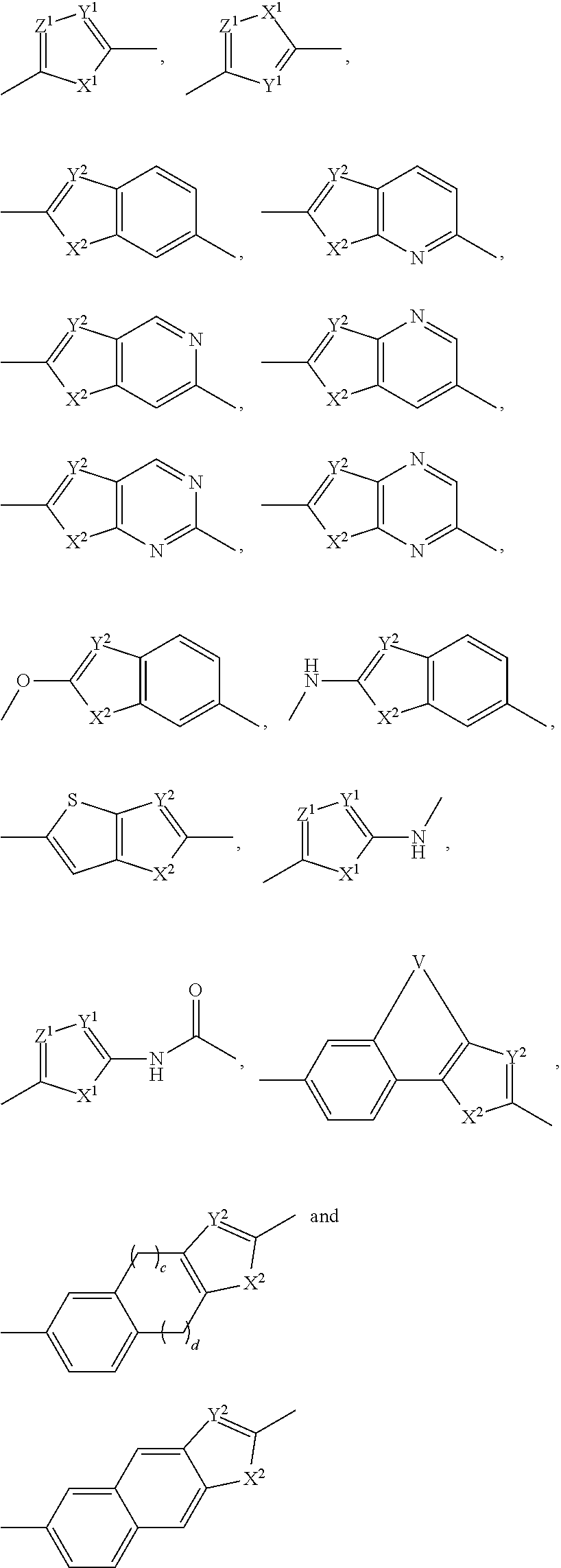
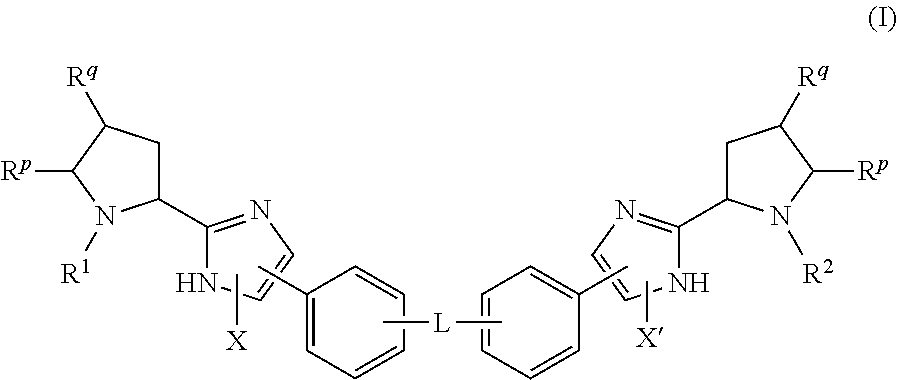
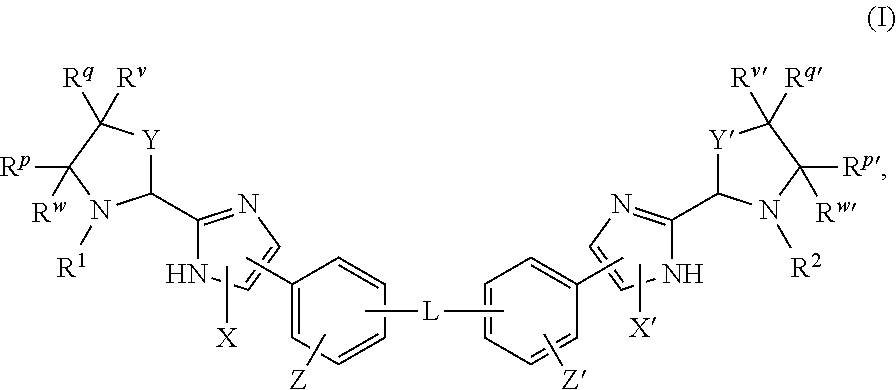
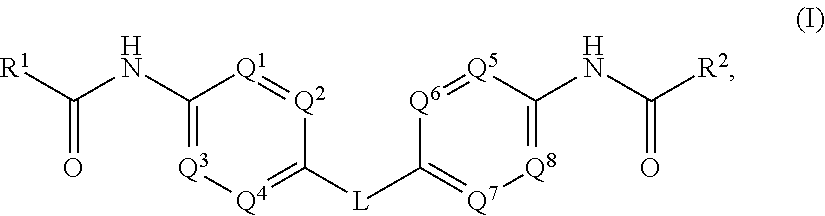
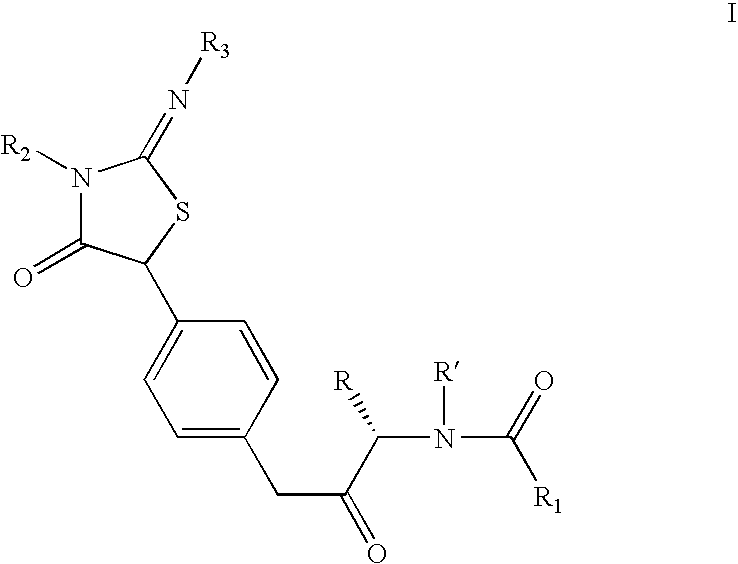
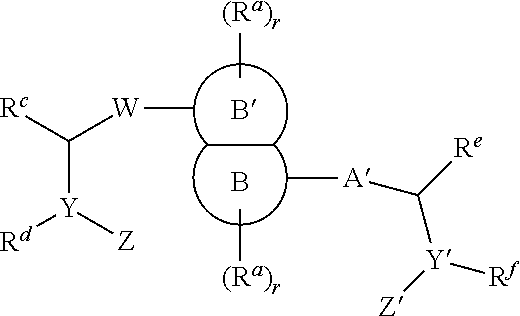
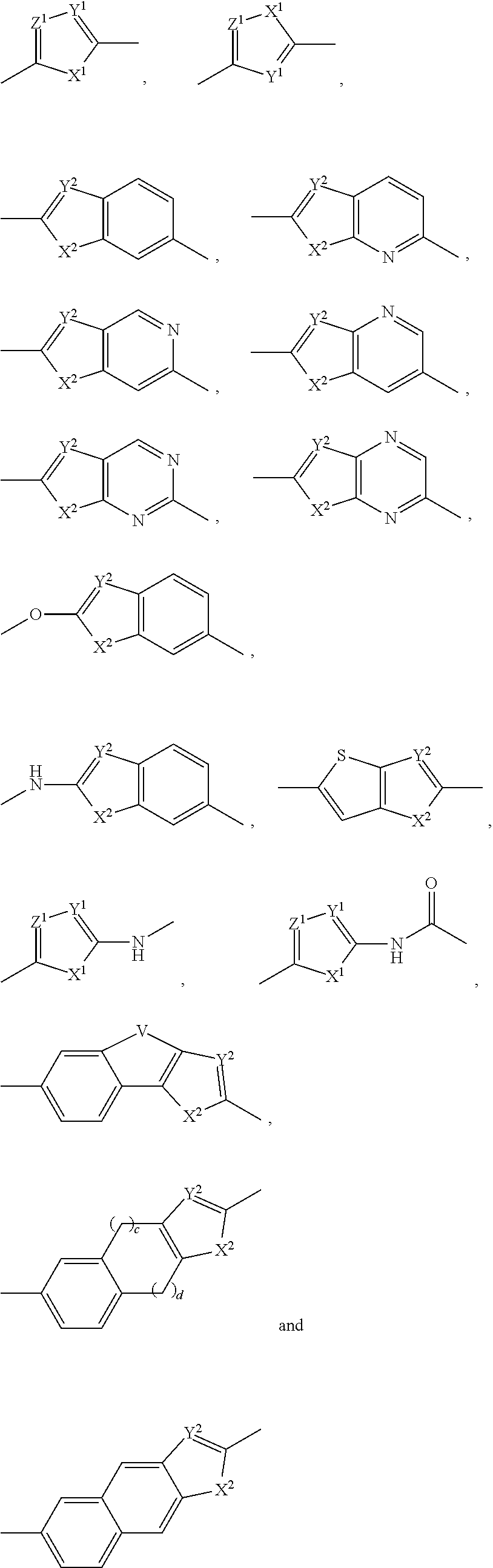
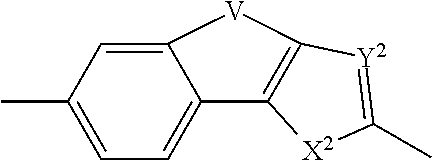
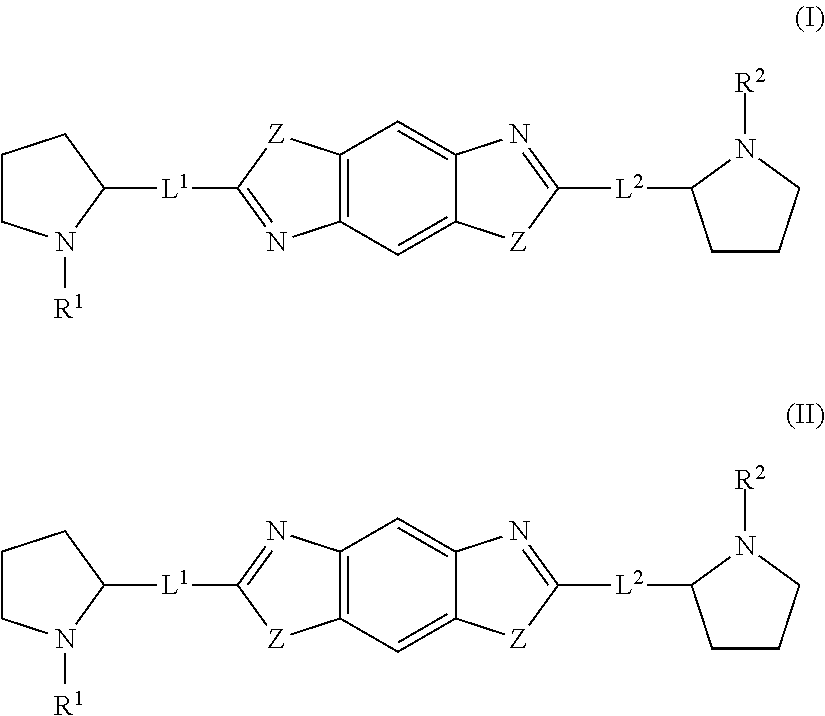
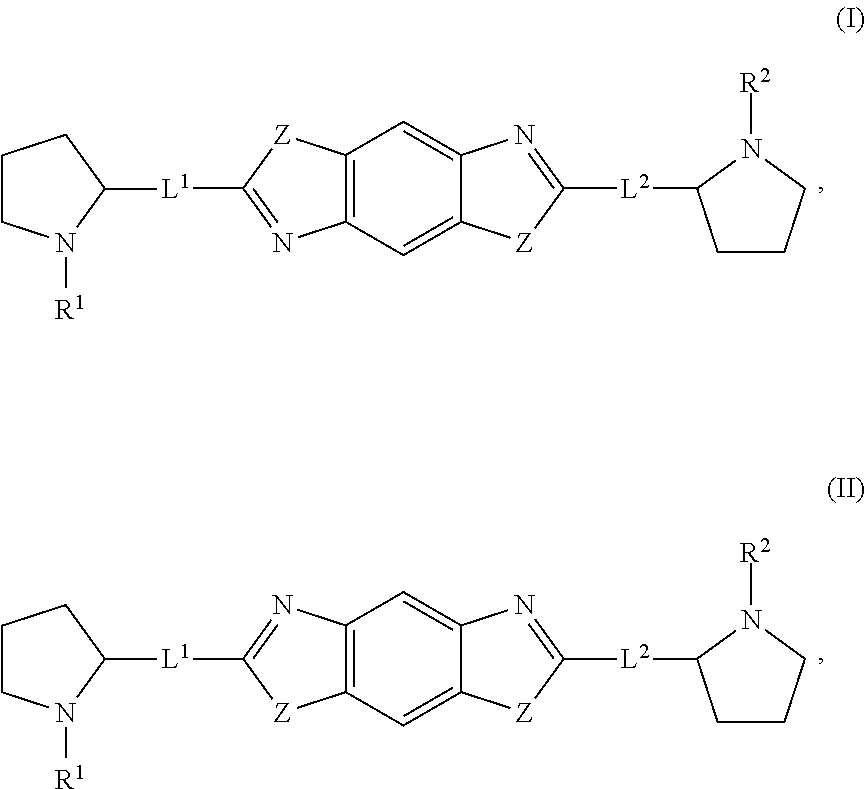
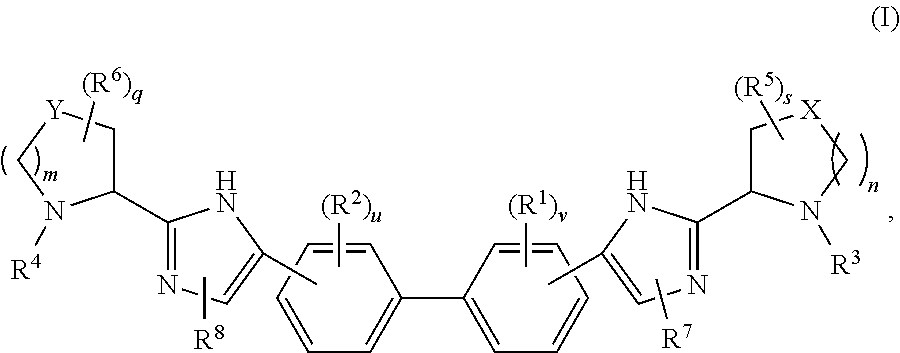
The present invention relates to compounds of formula (I) that are useful as hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors, the synthesis of such compounds, and the use of such compounds for inhibiting HCV NS5A activity, for treating or preventing HCV infections and for inhibiting HCV viral replication and / or viral production in a cell-based system.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication
ActiveUS8871759B2Organic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsHcv hepatitis c virusViral replication
The present invention relates to compounds of formula (I) that are useful as hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors, the synthesis of such compounds, and the use of such compounds for inhibiting HCV NS5A activity, for treating or preventing HCV infections and for inhibiting HCV viral replication and / or viral production in a cell-based system.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Hepatitis C Virus Inhibitors
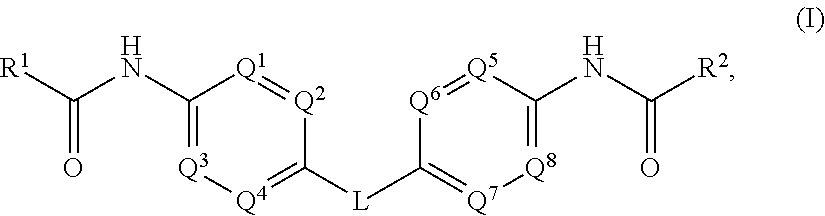
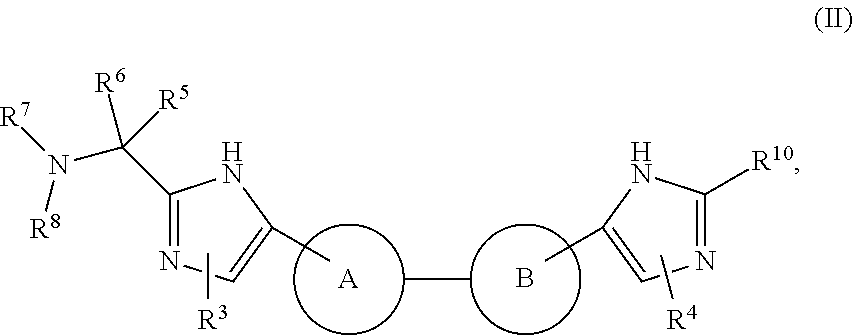
This disclosure concerns novel compounds of Formula (I) as defined in the specification and compositions comprising such novel compounds. These compounds are useful antiviral agents, especially in inhibiting the function of the NS5A protein encoded by Hepatitis C virus (HCV). Thus, the disclosure also concerns a method of treating HCV related diseases or conditions by use of these novel compounds or a composition comprising such novel compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Inhibitors of hcv ns5a
Owner:PRESIDIO PHARMA
Hepatitis C Virus Inhibitors
This disclosure concerns novel compounds of Formula (I) as defined in the specification and compositions comprising such novel compounds. These compounds are useful antiviral agents, especially in inhibiting the function of the NS5A protein encoded by Hepatitis C virus (HCV). Thus, the disclosure also concerns a method of treating HCV related diseases or conditions by use of these novel compounds or a composition comprising such novel compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Screening methods to identify agents that selectively inhibit hepatitis C virus replication
InactiveUS6326151B1Prevent dimerizationBlock viral inhibitionFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseCellular defenseViral infection
The present invention relates to novel methods for identifying antiviral agents which selectively interfere with viral proteins that override the interferon(IFN)-induced cellular defense mechanisms against viral infection. In particular, the present invention relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between viral proteins containing an interferon sensitivity determining region (ISDR) and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The present invention more particularly relates to screening assays that identify agents which selectively inhibit the interaction between hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A protein (NS5A), which contains an ISDR, and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase. The interaction between the viral ISDR and IFN-induced PKR protein kinase results in the override of IFN-induced cellular defense mechanisms to combat viral infection. Therefore the agents identified using the assays of the invention may have utility as antiviral agents.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Modified Human Hepatitis C Virus Genomic RNA That can be Autonomously Replicated
ActiveUS20090176200A1Easy to useSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideGenetics
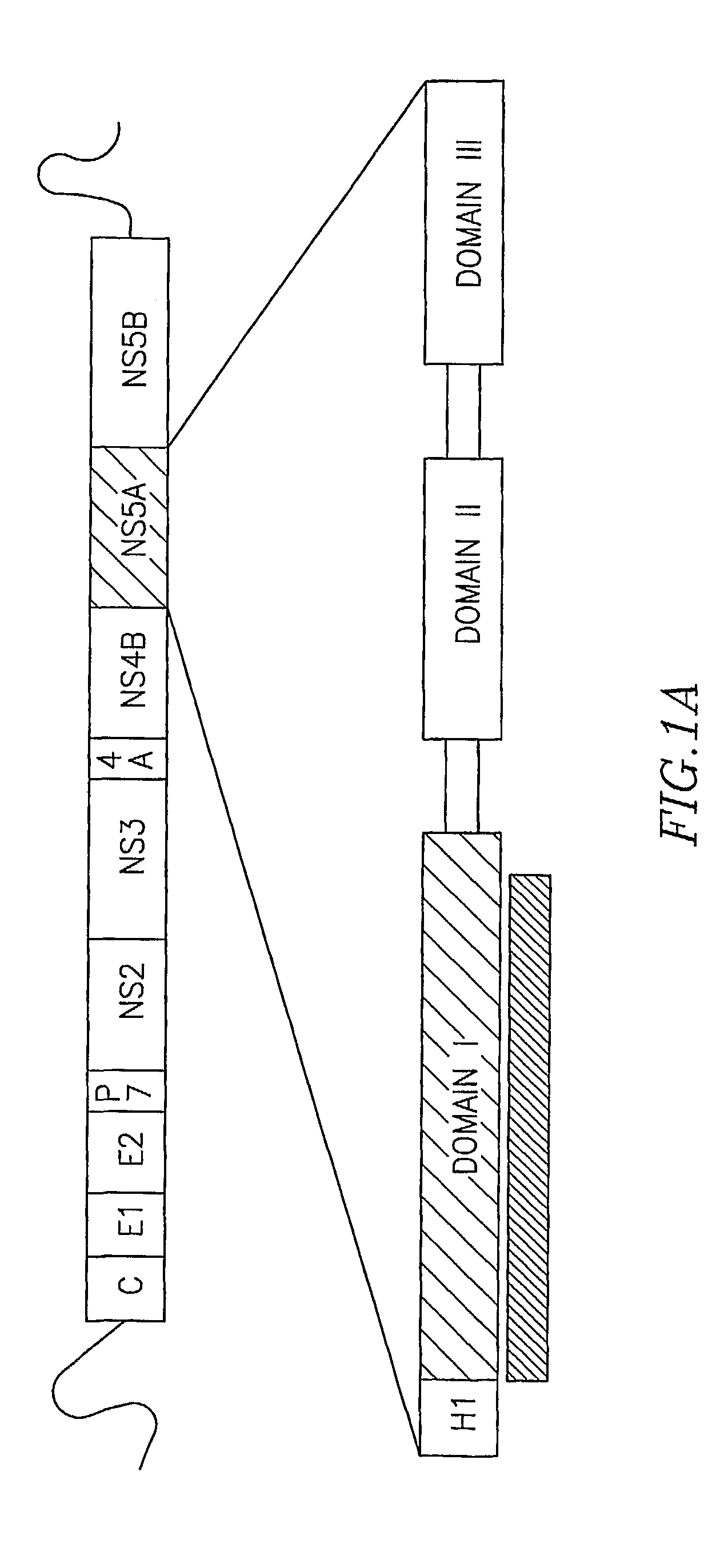
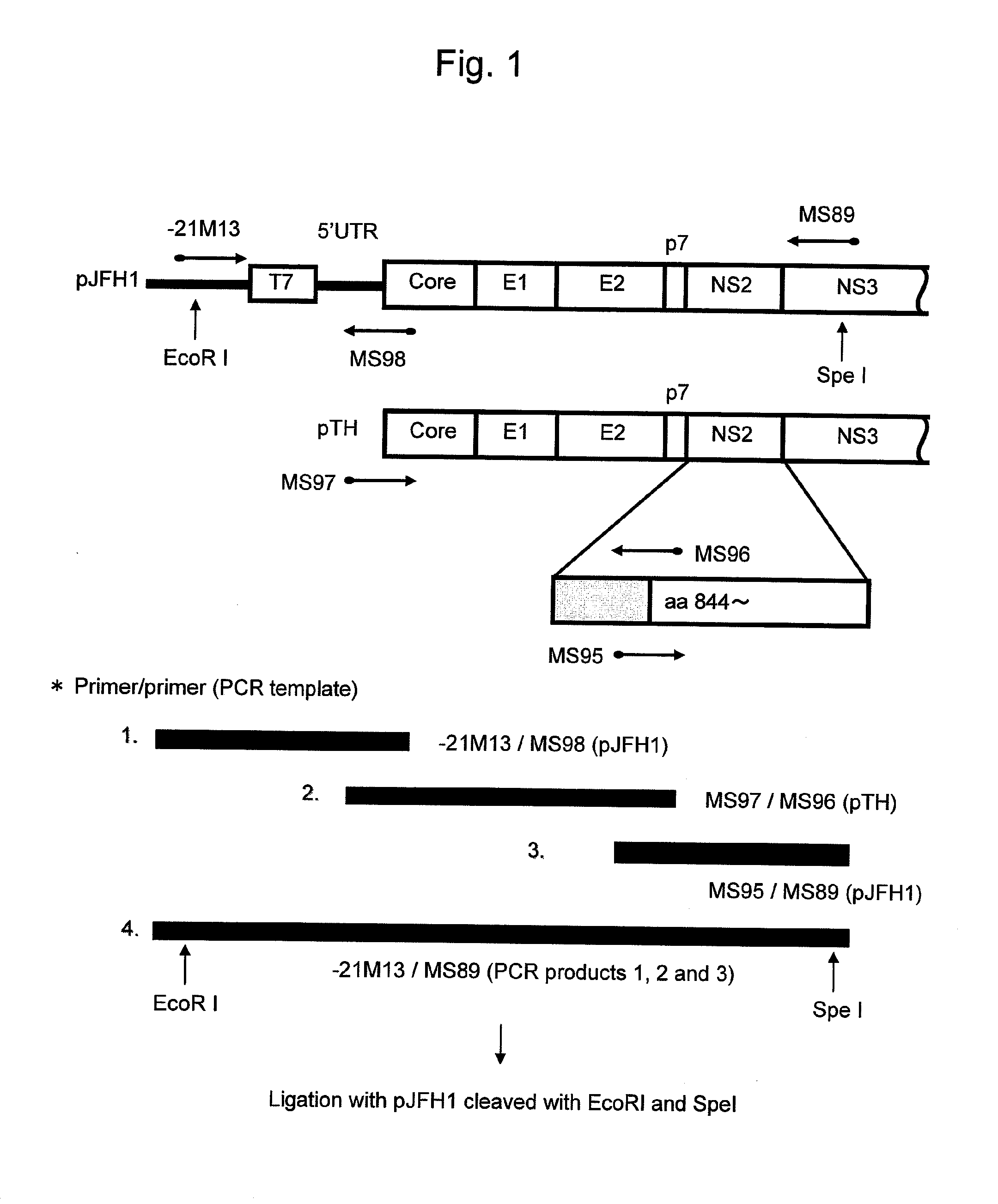
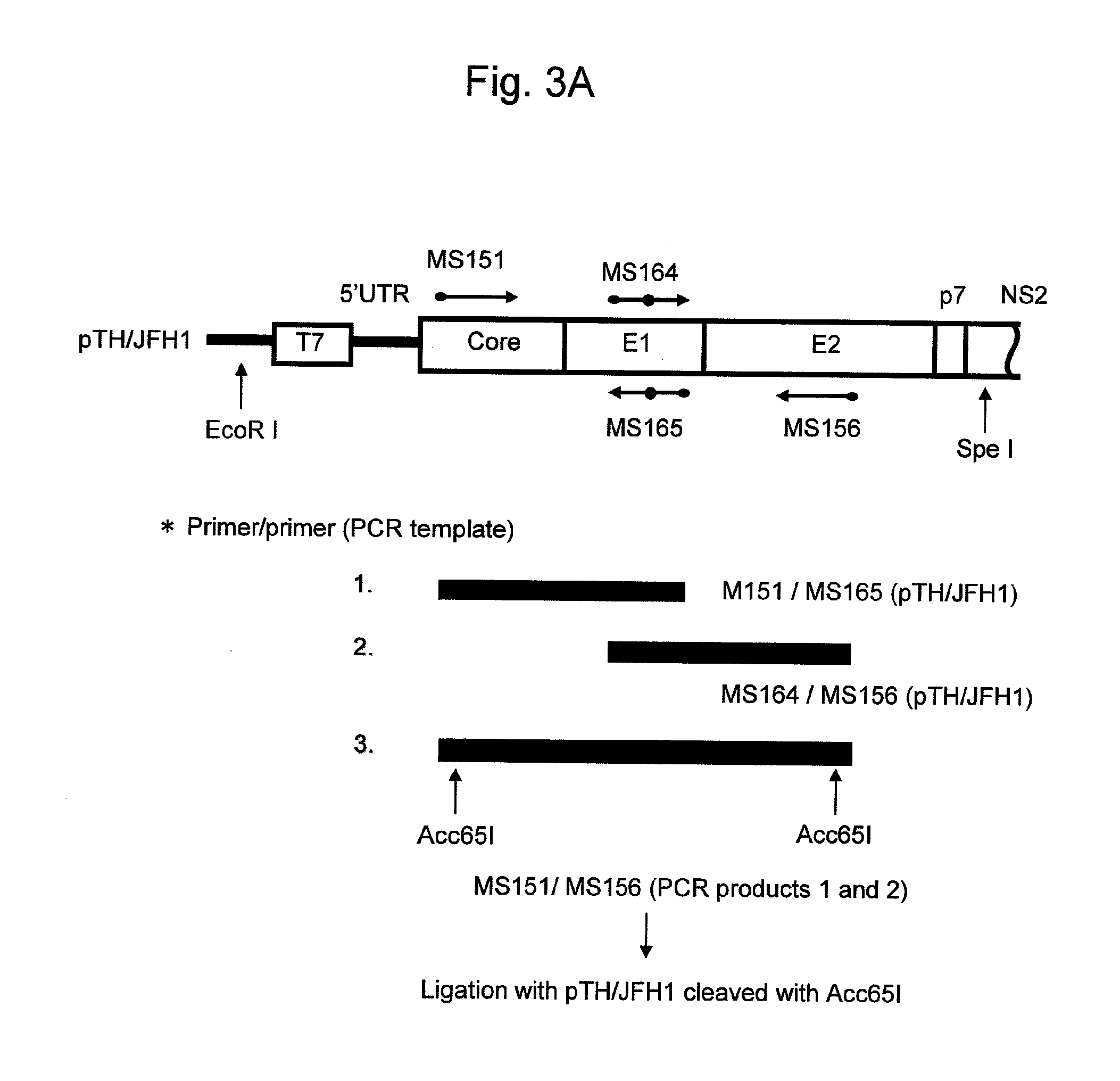
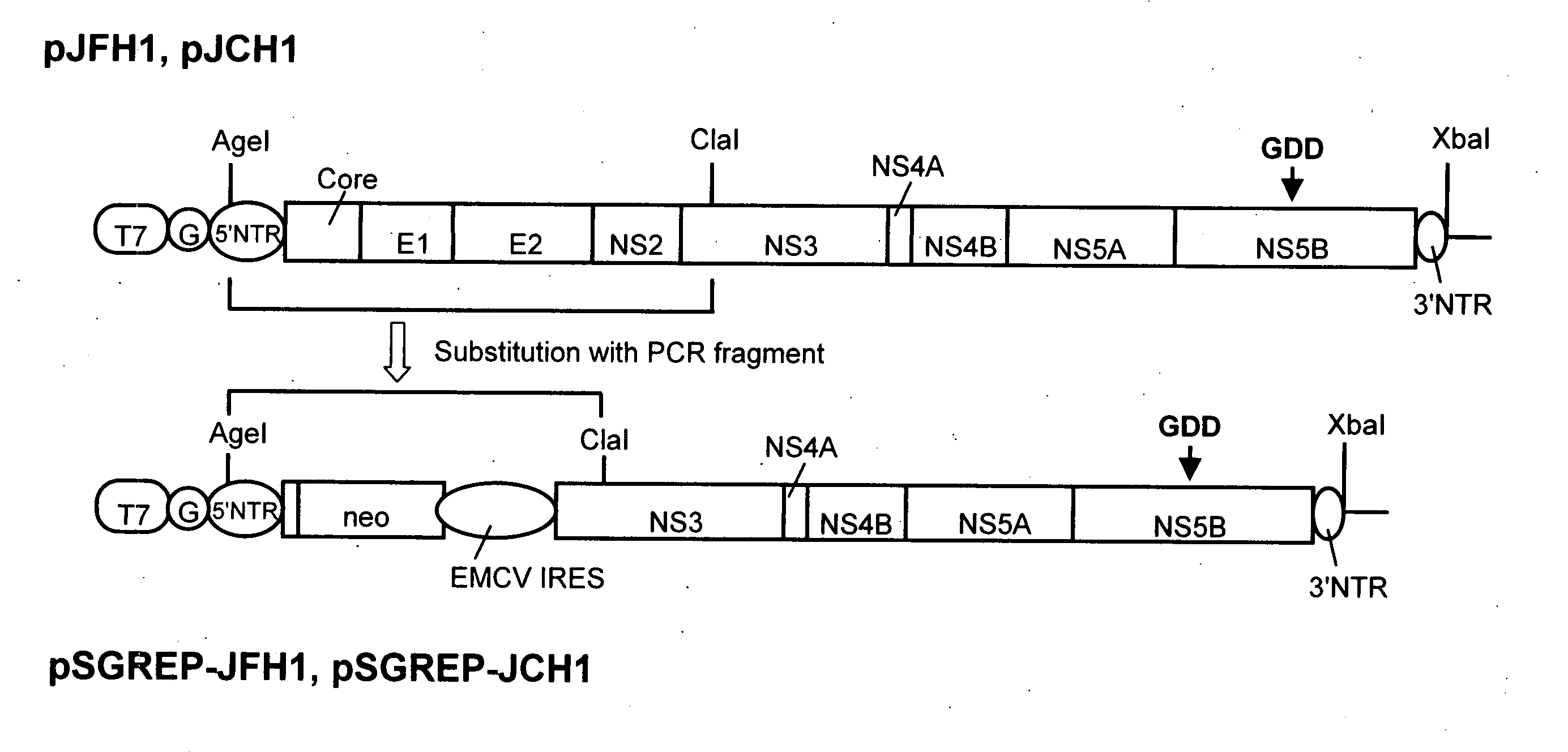
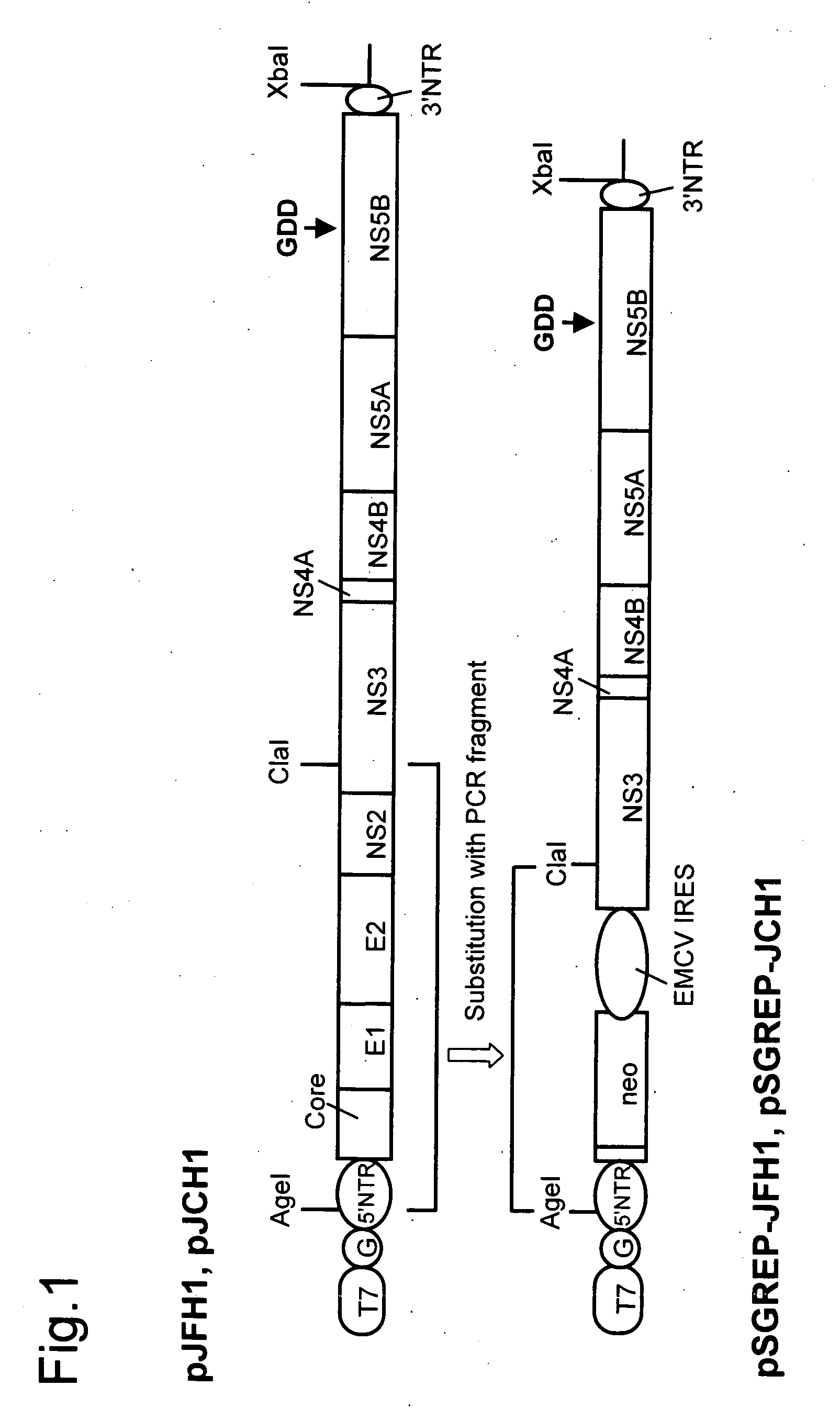
The present invention provides modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, comprising nucleotide sequences of genomic RNA portions of two or more types of hepatitis C viruses, which comprises a 5′ untranslated region, a core protein coding sequence, an E1 protein coding sequence, a p7 protein coding sequence, an E2 protein coding sequence, an NS2 protein coding sequence, an NS3 protein coding sequence, an NS4A protein coding sequence, an NS4B protein coding sequence, an NS5A protein coding sequence, an NS5B protein coding sequence, and a 3′ untranslated region, and which can be autonomously replicated. In particular, the present invention relates to modified hepatitis C virus genomic RNA, which can be autonomously replicated by substitution of the RNA sequence portion encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of hepatitis C virus genomic RNA with a partial RNA sequence encoding NS3, NS4, NS5A, and NS5B proteins of a JFH1 strain shown in SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Hepatitis C Virus Inhibitors
The present disclosure is generally directed to antiviral compounds, and more specifically directed to compounds which can inhibit the function of the NS5A protein encoded by Hepatitis C virus (HCV), compositions comprising such compounds, and methods for inhibiting the function of the NS5A protein.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
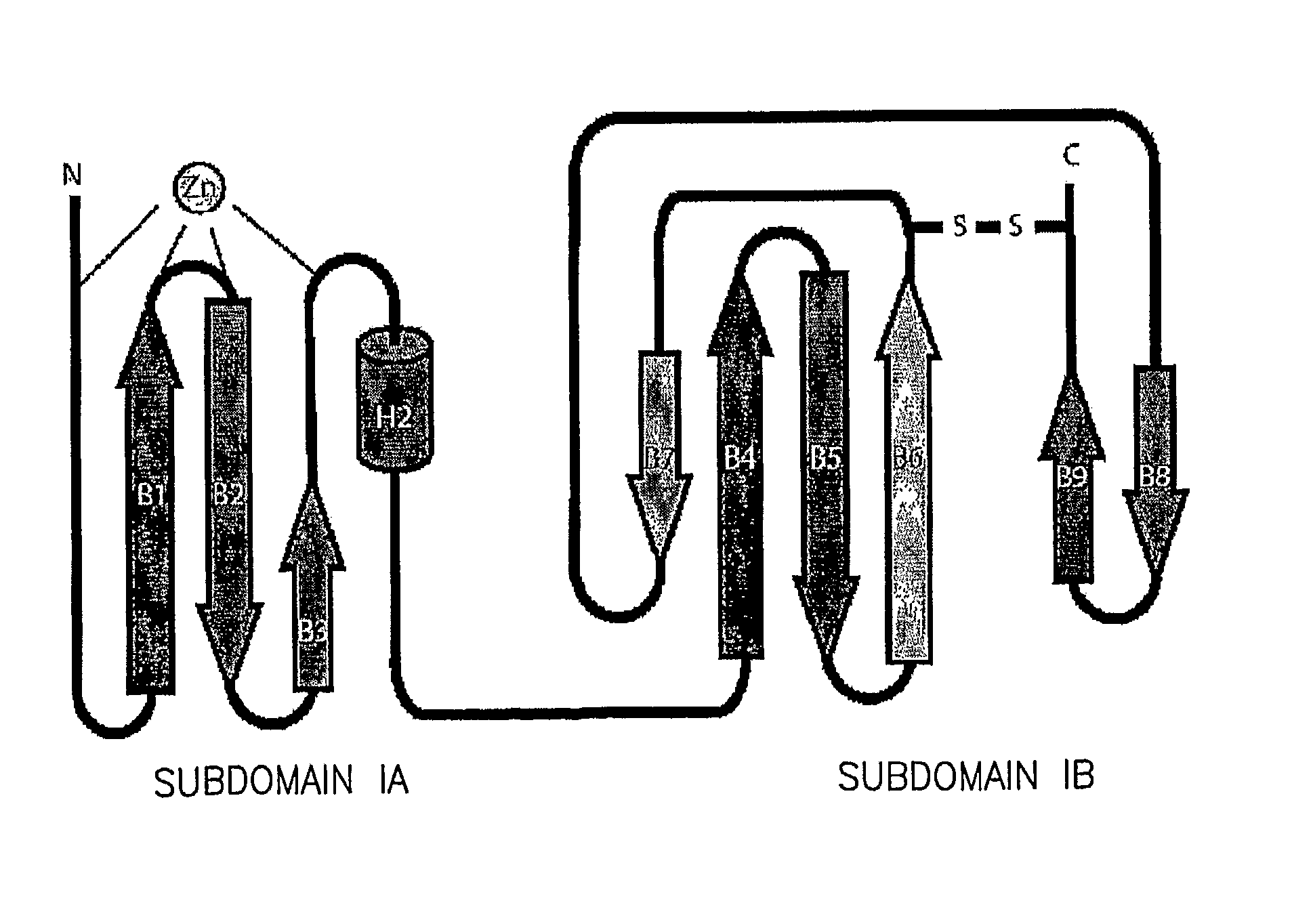
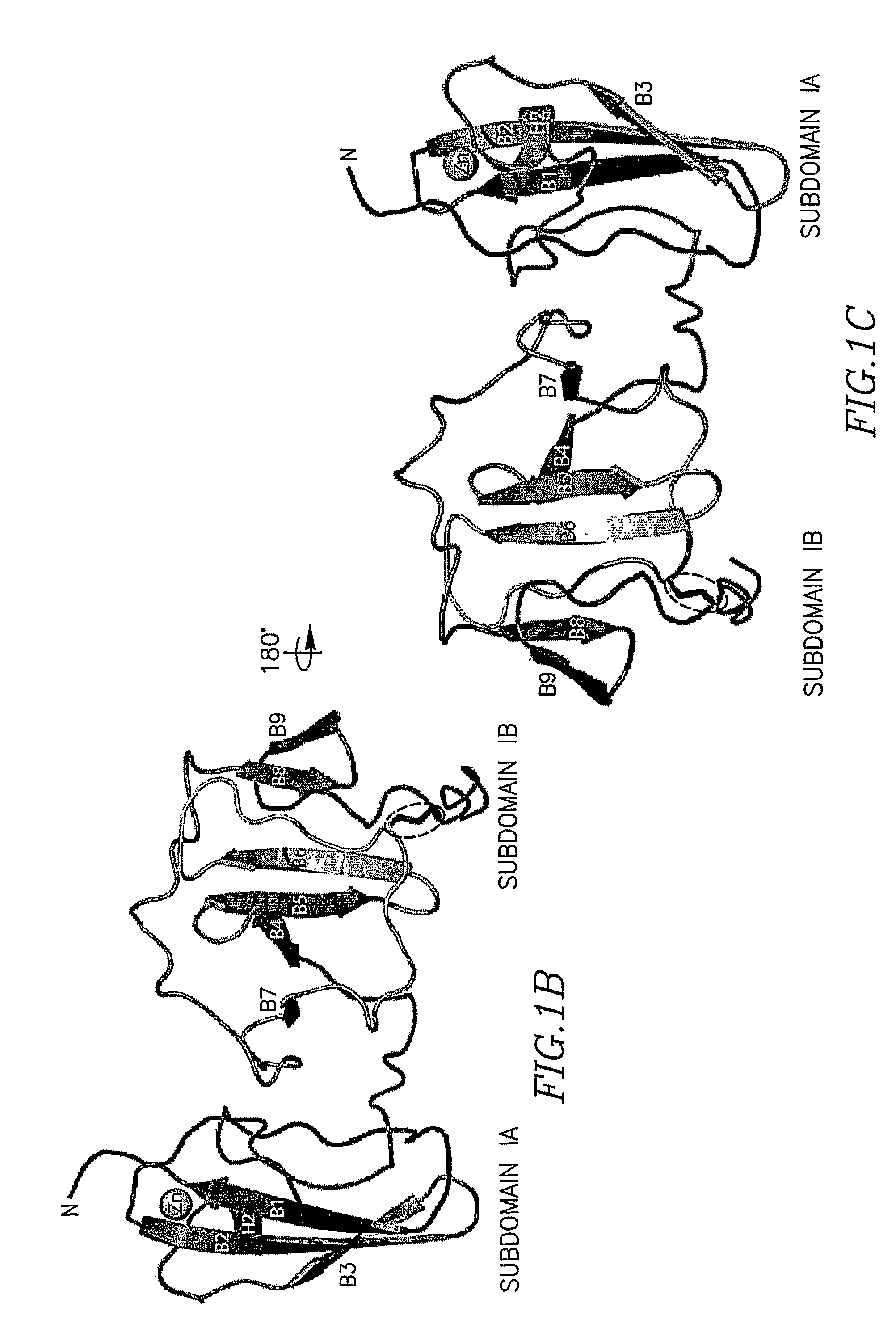
Structure of the hepatitis C NS5A protein
The present invention provides a crystallized N-terminal domain of an NS5A protein of hepatitis C virus, methods of producing the same and methods of use thereof. The present invention also relates to structural elements of the N-terminal domain of hepatitis C virus NS5A protein, and methods of inhibiting hepatitis C virus infection, replication and / or pathogenesis, by interacting with the same.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Inhibitors of hcv ns5a
Provided herein are compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and combination therapies for inhibition of hepatitis C.
Owner:PRESIDIO PHARMA
Antigenic epitopes and mosaic polypeptides of hepatitis C virus proteins
InactiveUS7052696B2Rapid and simple and reliable and sensitiveNot labor intensiveSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeImmunogenicity
Antigenic epitopes of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and mosaic HCV polypeptides useful as reagents in assays for the diagnosis or monitoring of HCV in a biological sample. The antigenic epitopes and mosaic polypeptides are also useful for the construction of immunogenic pharmaceutical compositions, such as vaccines. The mosaic polypeptides are artificial composite proteins constructed from diagnostically relevant antigenic regions derived from different HCV proteins. Preferably, the mosaic polypeptides contain antigenic epitopes from the core protein, NS3 protein, and NS4 protein. The preferred mosaic polypeptides optionally contain an additional antigenic epitope from either the NS4 protein or the NS5a protein or both.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Hepatitis C virus nucleic acid vaccine
ActiveUS9056090B2Reduce capacityReduce loadSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsMolecular biologyNucleic Acid Vaccines
The present invention features nucleic acid constructs that can be used as a HCV nucleic acid vaccine, vaccine component, or in the production of a HCV vaccine. Described constructs include those: (1) encoding for a chimeric HCV polypeptide containing a NS3-4A region based on a first HCV strain and an NS3-NS4A-NS4B-NS5A or an NS3-NS4A-NS4B-NS5A-NS5B region based on a second strain; and (2) a chimpanzee based adenovector encoding an HCV polypeptide.
Owner:MSD ITAL
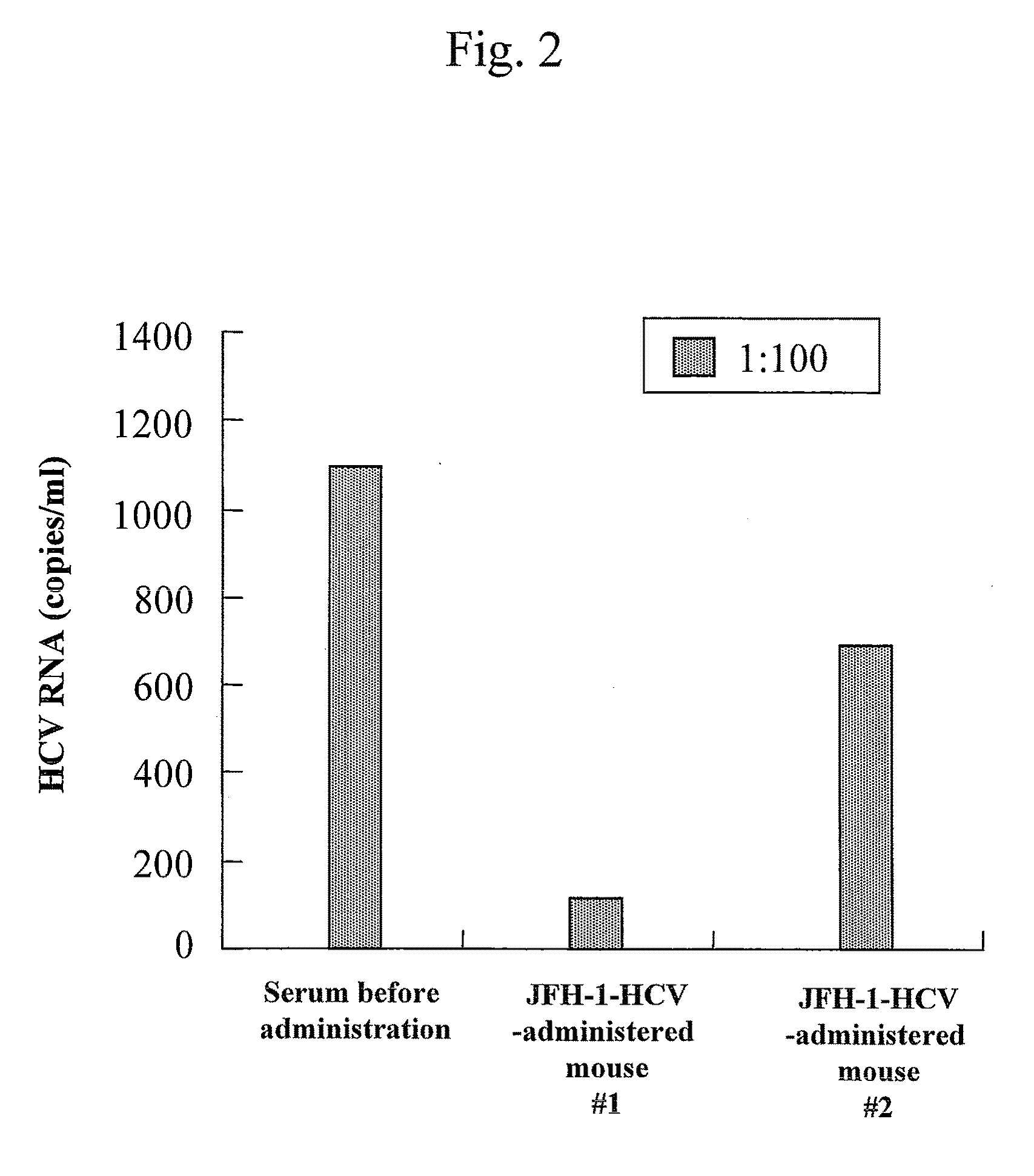
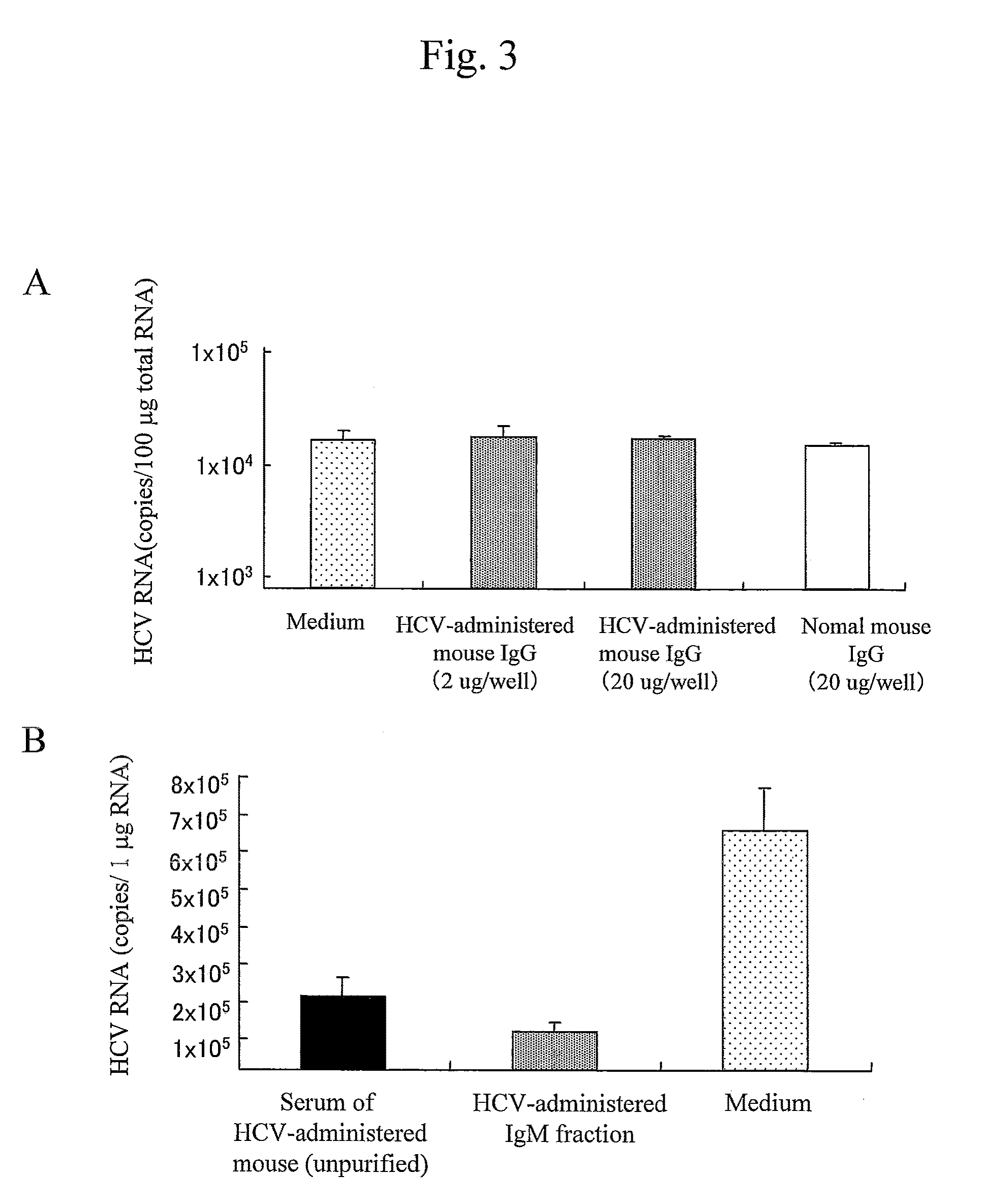
Antibody having inhibitory activity on infection with hepatitis c virus (HCV) and use thereof
The objection of the invention is to provide an antibody that inhibits infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV). To this end, this invention provides an antibody that recognizes the hepatitis C virus (HCV) particle obtained from the hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome comprising the following (i) and (ii) ligated to each other as an antigen and has an inhibitory activity on infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV): (i) (a) the 5′-untranslated region, the core protein-encoding sequence, the E1 protein-encoding sequence, the E2 protein-encoding sequence, and the p7 protein-encoding sequence of the JFH-1 strain of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) or (b) the 5′-untranslated region, the core protein-encoding sequence, the E1 protein-encoding sequence, the E2 protein-encoding sequence, and the p7 protein-encoding sequence of the J6CF strain the hepatitis C virus (HCV); and (ii) the NS2 protein-encoding sequence, the NS3 protein-encoding sequence, the NS4A protein-encoding sequence, the NS4B protein-encoding sequence, the NS5A protein-encoding sequence, the NS5B protein-encoding sequence, and the 3′-untranslated region of the JFH-1 strain.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
Hepatitis C virus inhibitors
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Hepatitis C virus vaccine
ActiveUS7598362B2Facilitates cleavageFacilitates ribosome bindingFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntigenRNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
Cell culture system of a hepatitis c genotype 3a and 2a chimera
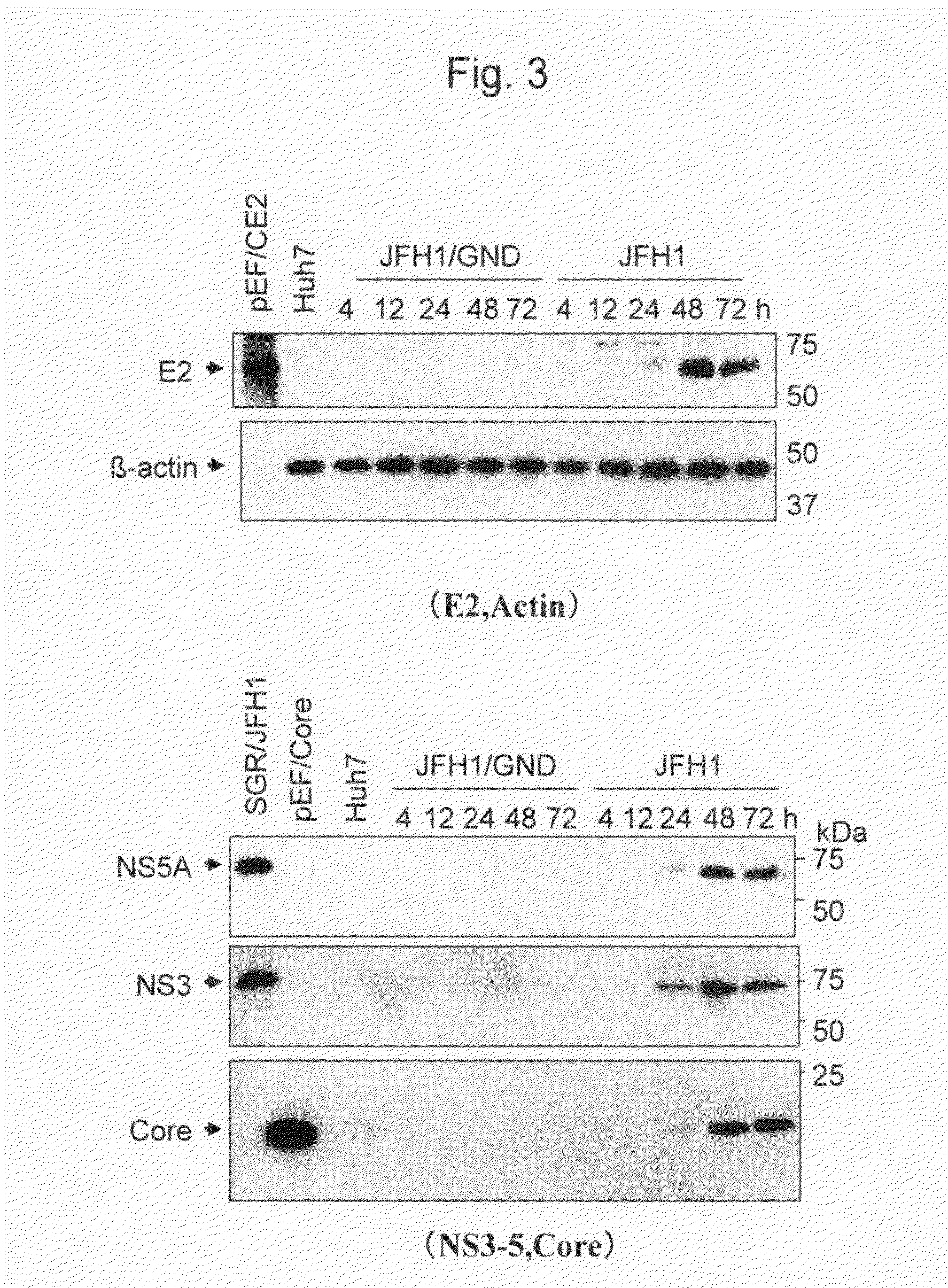
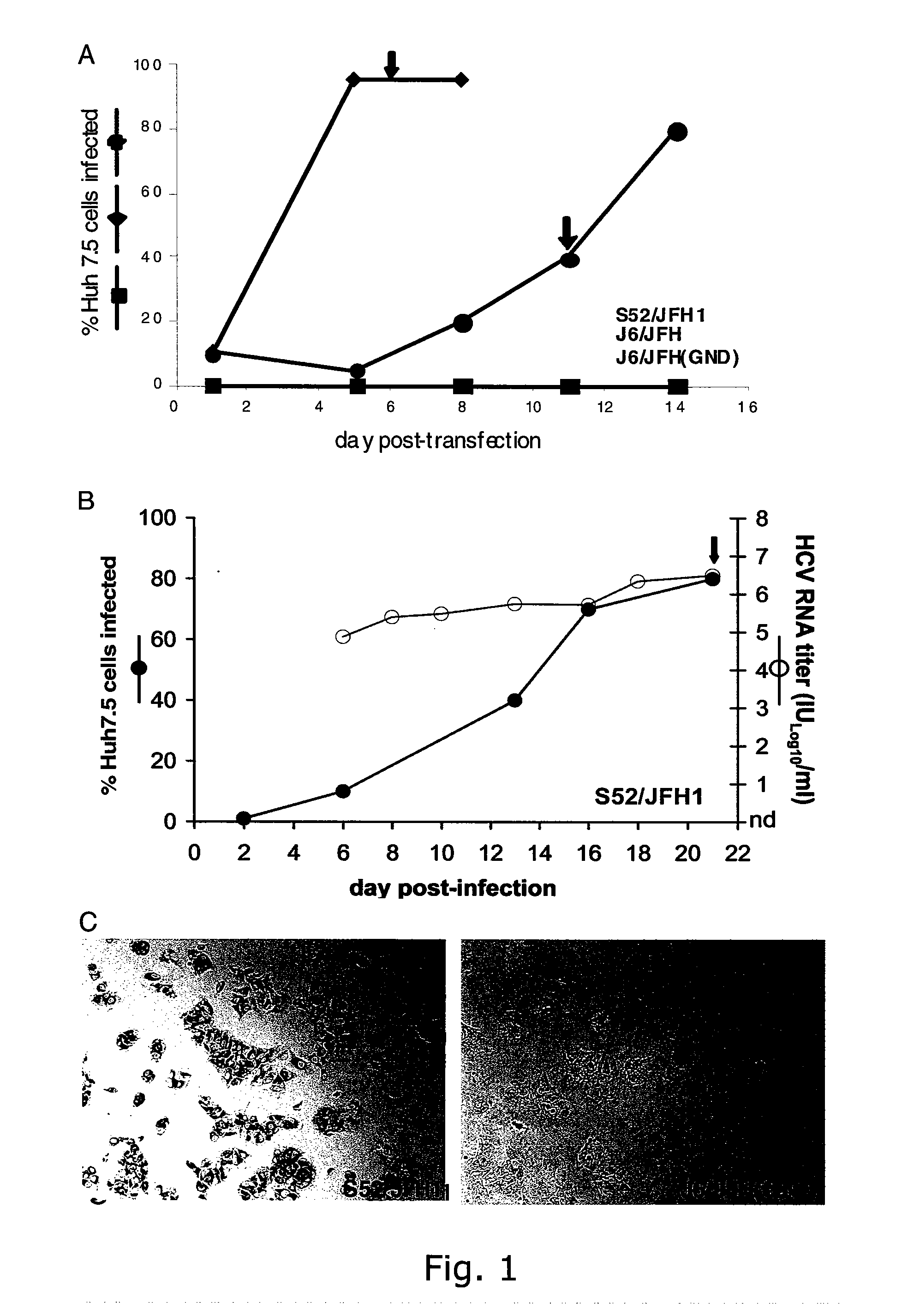
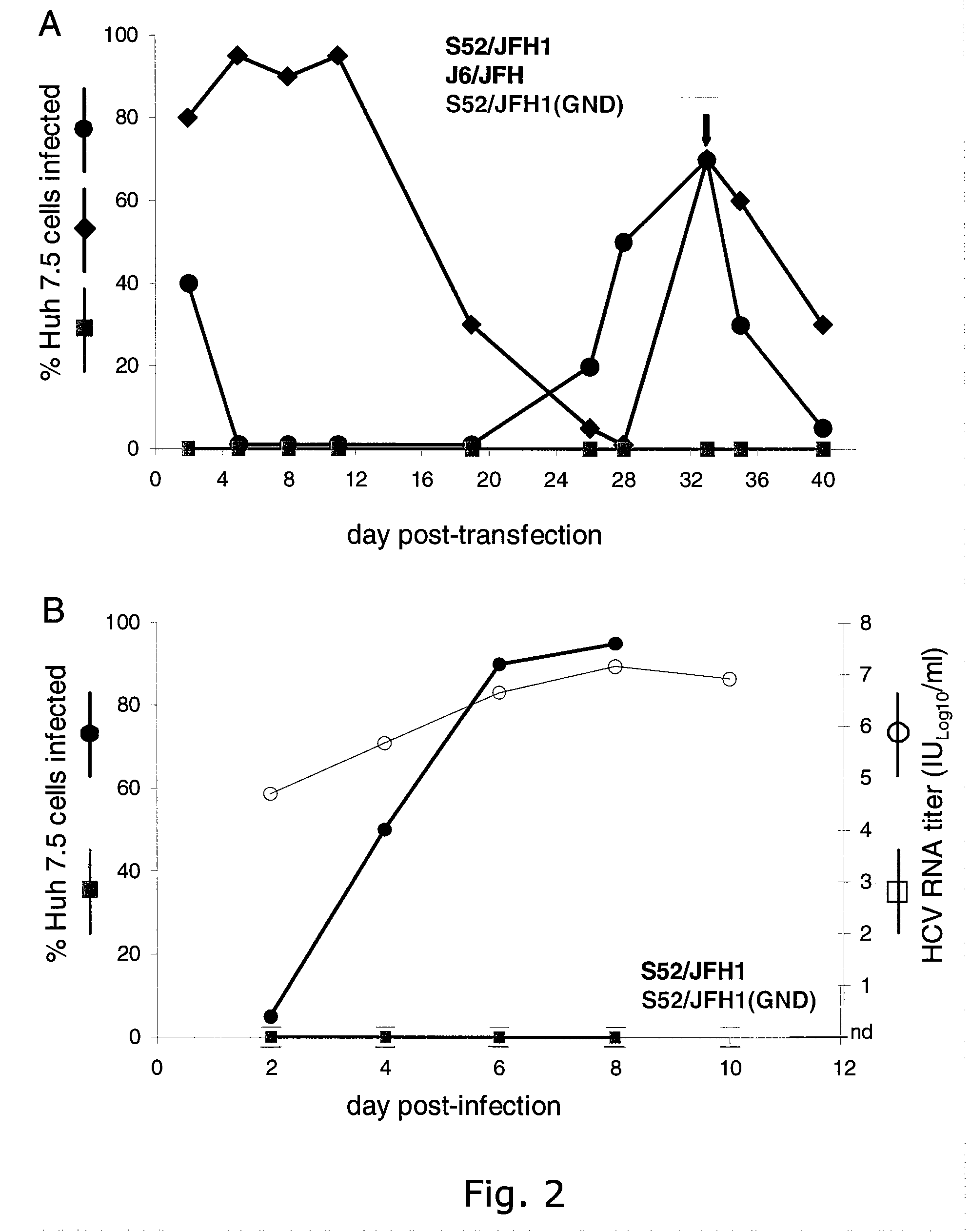
InactiveUS20100093841A1Efficient and sustainable growthDifferential efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenomic sequencingNS5A
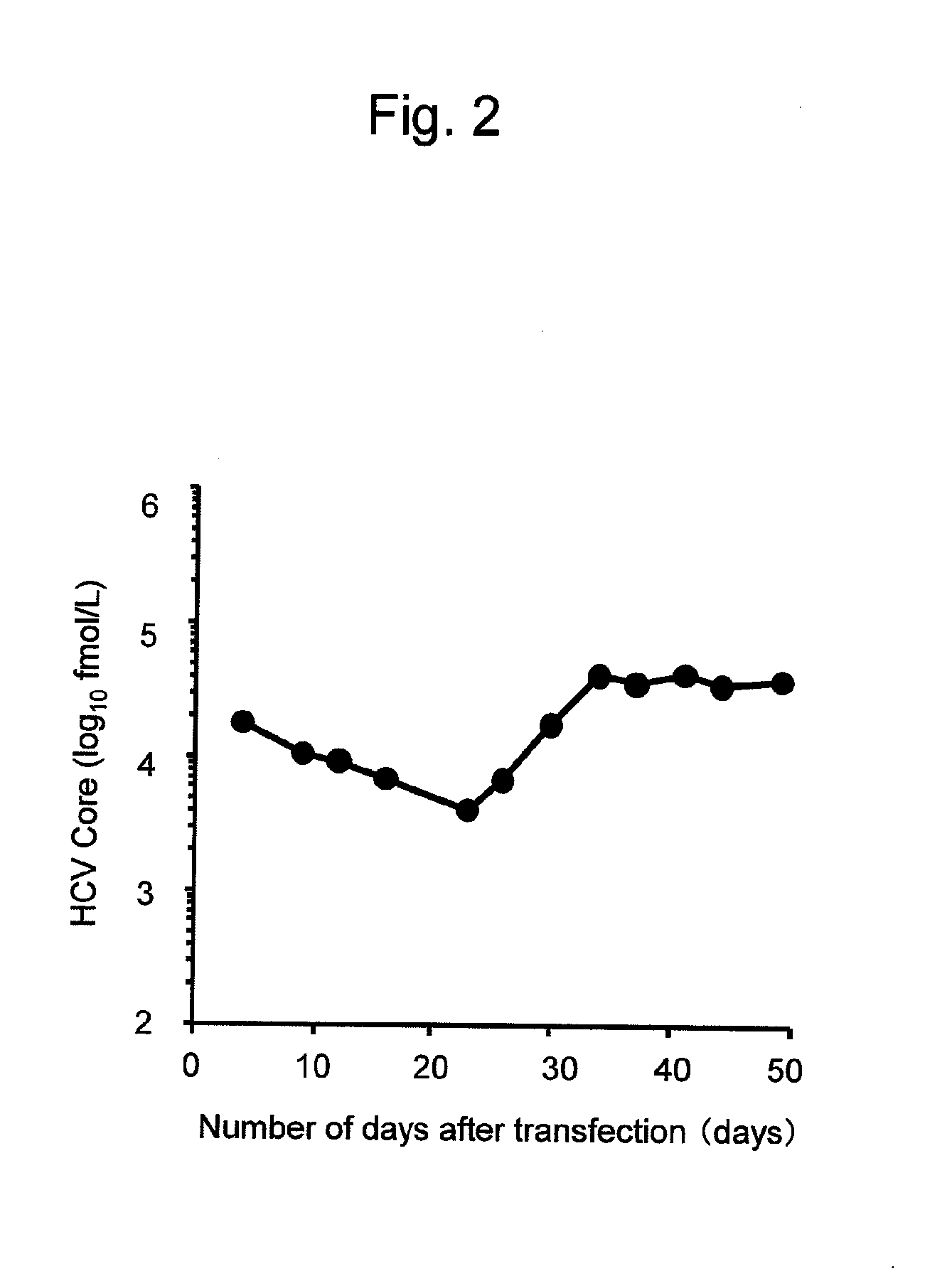
The present inventors have developed a culture system for genotype 3a, which has a high prevalence worldwide. Since intergenotypic recombinant genomes exploiting the replication characteristics of JFH1 will be a valuable tool for the genotype specific study of the replaced genes and related therapeutics, the present inventors constructed a genotype 3a / 2a (S52 / JFH1) recombinant containing the structural genes (Core, E1, E2), p7 and NS2 of strain S52 and characterized it in Huh7.5 cells. S52 / JFH1 and J6 / JFH viruses passaged in cell culture had comparable growth kinetics and yielded similar peak HCV RNA titers and infectivity titers. Direct genome sequencing of cell culture derived S52 / JFH1 viruses identified putative adaptive mutations in Core, E2, p7, NS3 and NS5A; clonal analysis revealed, that all genomes analyzed exhibited different combinations of these mutations. Finally, viruses resulting from transfection with RNA transcripts of five S52 / JFH1 recombinant containing these combinations of putative adaptive mutations performed as efficiently as J6 / JFH viruses in Huh7.5 15 cells and were all genetically stable after viral passage. In conclusion, the present inventors have developed a robust and genetically stable cell culture system for HCV genotype 3a.
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
Medicine and treatment method for treating hepatic fibrosis
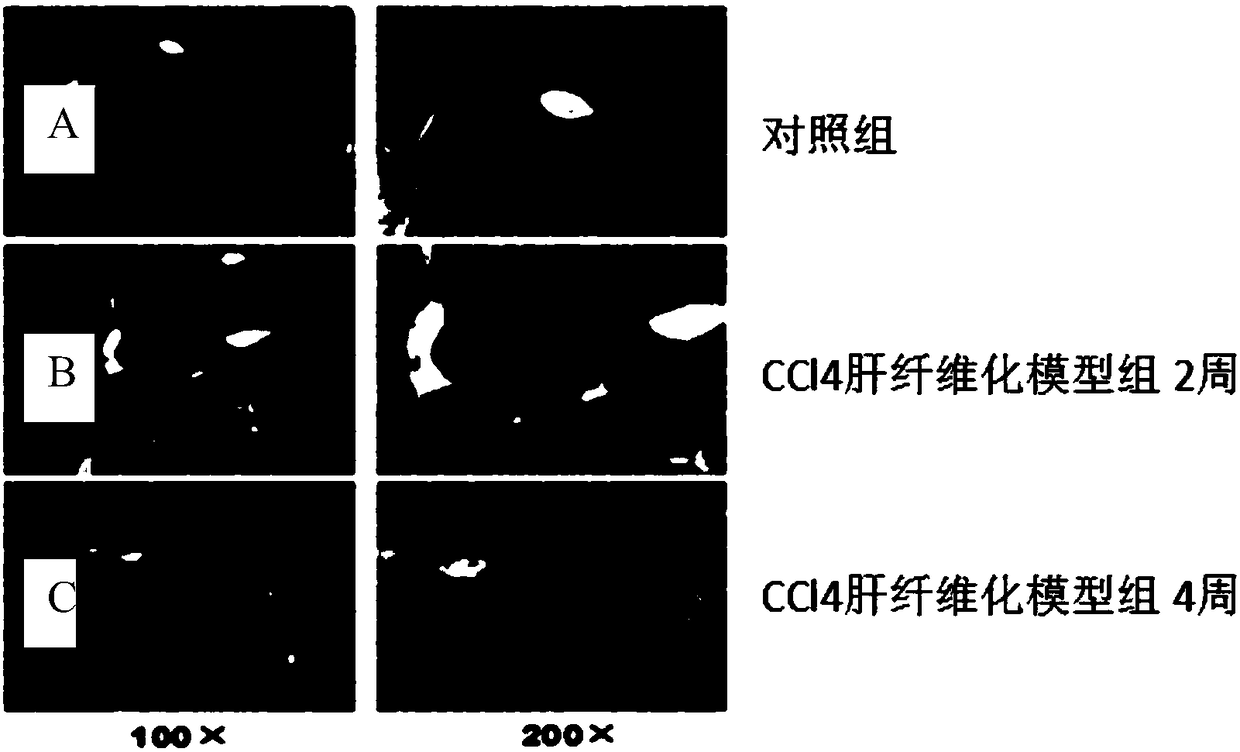
InactiveCN108686211AImprove expression levelPromote apoptosisCompounds screening/testingSsRNA viruses negative-senseCell-Extracellular MatrixPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a screening method for a medicine for targeting NS5ATP9 (HCV NS5A-transactivated protein 9) prevention or treatment of tissue fibrosis and tissue sclerosis, and the medicine obtained by screening using the method. NS5ATP9 significantly regulates the expression of extracellular matrix collagen and non-collagen glycoprotein and affects the occurrence and development of tissue fibrosis by regulating a TGFbeta1 / Smad3 signaling pathway; and the NS5ATP9 promotes the apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells, inhibits the proliferation of the hepatic stellate cells and regulates extracellular matrix deposition by regulating the phosphorylation level and the intracellular translocation condition of a Smad3 protein. TDF / TAF can effectively regulate the expression of NS5ATP9 gene,and is verified in CCl4-induced mouse liver fibrosis model, and the TDF / TAF achieves significant effects in the prevention or treatment of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice.
Owner:北京泛亚同泽生物医学研究院有限公司
NS5A nucleotide sequence variation as a marker for interferon response
InactiveUS20050260567A1Raise the possibilitySustained responseSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementInterferon therapyNucleotide variation
Methods and reagents for determining a nucleotide variation at position 937 of the HCV-1a NS5A gene useful in predicting an individual's response to interferon treatment are presented.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Nucleic acid comprising chimeric gene derived from hepatitis c virus
InactiveUS20110045020A1Improve productivityImprove abilitiesSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGeneProline
This invention provides infectious chimeric HCV particles that can be used for vaccines. This invention further provides a nucleic acid comprising a chimeric gene derived from the hepatitis C virus comprising regions each encoding Core protein, E1 protein, E2 protein and p7 protein derived from a hepatitis C virus strain other than JFH-1 strain; NS2 protein derived from JFH-1 strain or a hepatitis C virus strain other than JFH-1 strain, or a chimeric NS2 protein of NS2 protein derived from JFH-1 strain and NS2 protein derived from a hepatitis C virus strain other than JFH-1 strain; and NS3 protein, NS4A protein, NS4B protein, NS5A protein, and NS5B protein derived from JFH-1 strain in that order in 5′ to 3′ direction, wherein the 328th proline residue from the amino acid residue at N-terminus of the Core protein is substituted with an amino acid residue other than proline. This invention further provides chimeric HCV particles comprising such nucleic acid, and use of such HCV particles for vaccines.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI +2
Nucleic Acid Construct Containing a Nucleic Acid Derived From the Genome of Hepatitis C Virus (Hcv) of Genotype 2A, and a Cell Having Such Nucleic Acid Construct Introduced Therein
ActiveUS20080032323A1Improve replication efficiencyEasy to copySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesNS5AUntranslated region
The present invention relates to a replicon RNA comprising a nucleotide sequence at least containing the 5′ untranslated region, the nucleotide sequence encoding NS3 protein, NS4A protein, NS4B protein, NS5A protein and NS5B protein, and the 3′ untranslated region on the genomic RNA of hepatitis C virus of genotype 2a.
Owner:TOKYO METROPOLITAN INST OF MEDICAL SCI +2
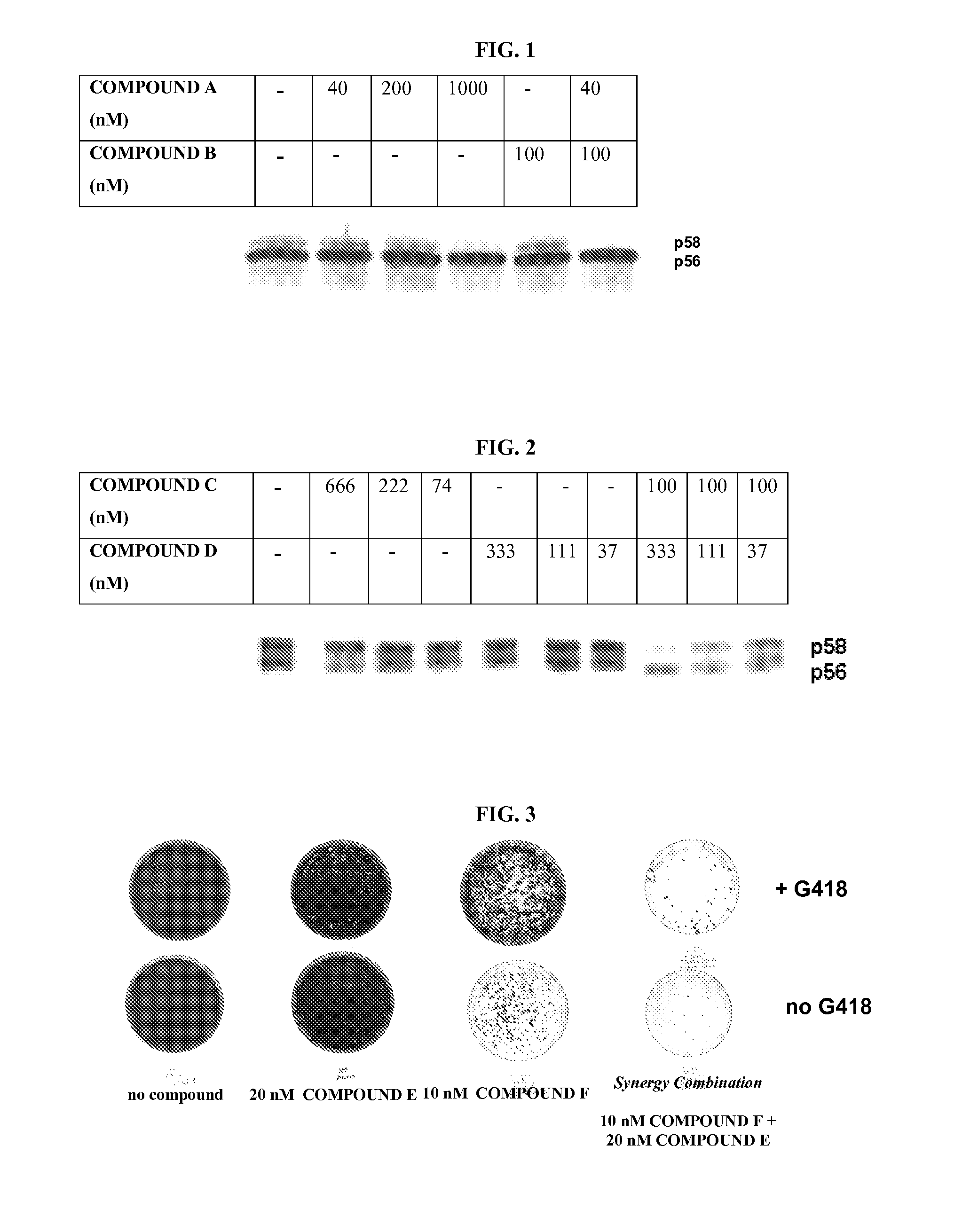
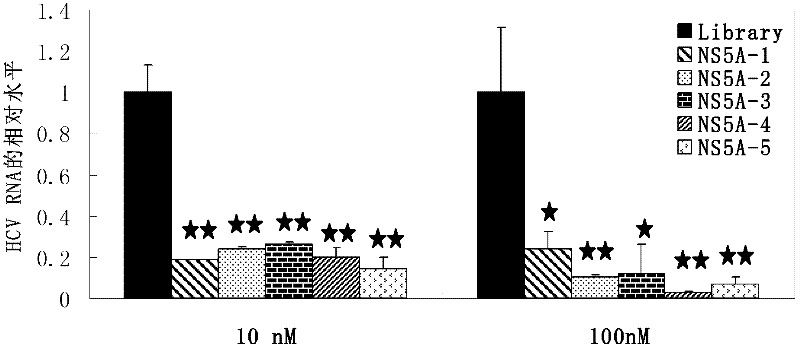
Methods to identify combinations of ns5a targeting compound that act synergistically to inhibit hepatitis c virus replication
InactiveUS20130157894A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningWild typeCombination therapy
The present invention is based on the surprising finding that pairs of HCV NS5A-targeting inhibitors can be identified which display similar resistance profiles yet, when combined, exhibit synergistic inhibition of wild type replicons and / or replicons carrying mutations conferring resistance to the HCV NS5A-targeting inhibitor. In addition, combinations of these molecules result in a higher genetic barrier to resistance, demonstrating their potential utility as novel combination therapies for treatment of HCV.
Owner:SUN JIN HUA +6
Aptamer capable of identifying hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein, derivatives thereof and screening method and use thereof
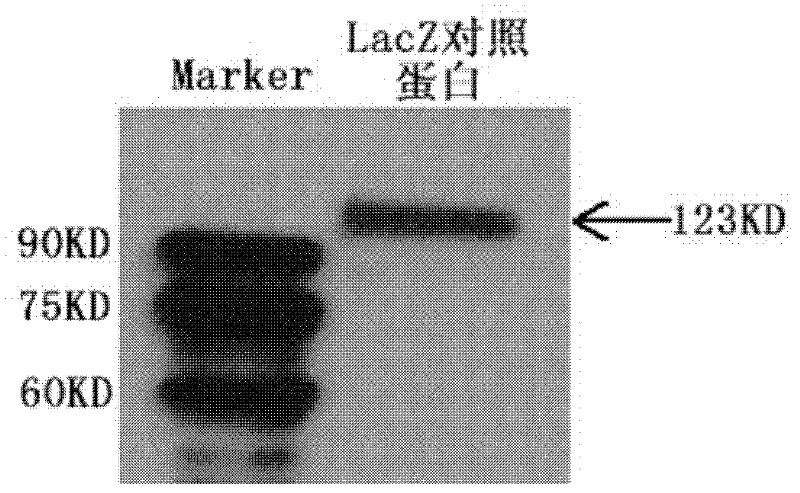
InactiveCN102229933ALow costEfficient preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideScreening method
The invention discloses an aptamer capable of identifying a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein, which is a DNA fragment represented by any of sequences from SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.5. The derivatives of the aptamer comprise nucleotide substituted RNA aptamers, skeleton-restructured derivatives, restructured peptide nucleic acid derivatives and radioactive molecule connected derivatives. The screening method of the aptamer comprises: preparing HCV NS5A protein with histidine marker, and preparing protein pET200 / D / LacZ; immobilizing the proteins, and designing a random nucleic acid library; and finally, screening the aptamer by pretreating the DNA library, performing reverse screening, screening and repeated screening and other steps, wherein the obtained aptamer has high competition power and optimized sequence length. The aptamer and the derivatives thereof can be used in the preparation of detection kit or diagnosis reagent for the HCV NS5A protein and can also be used in preparation of reagents for inhibiting replication of hepatitis C virus in liver cells.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
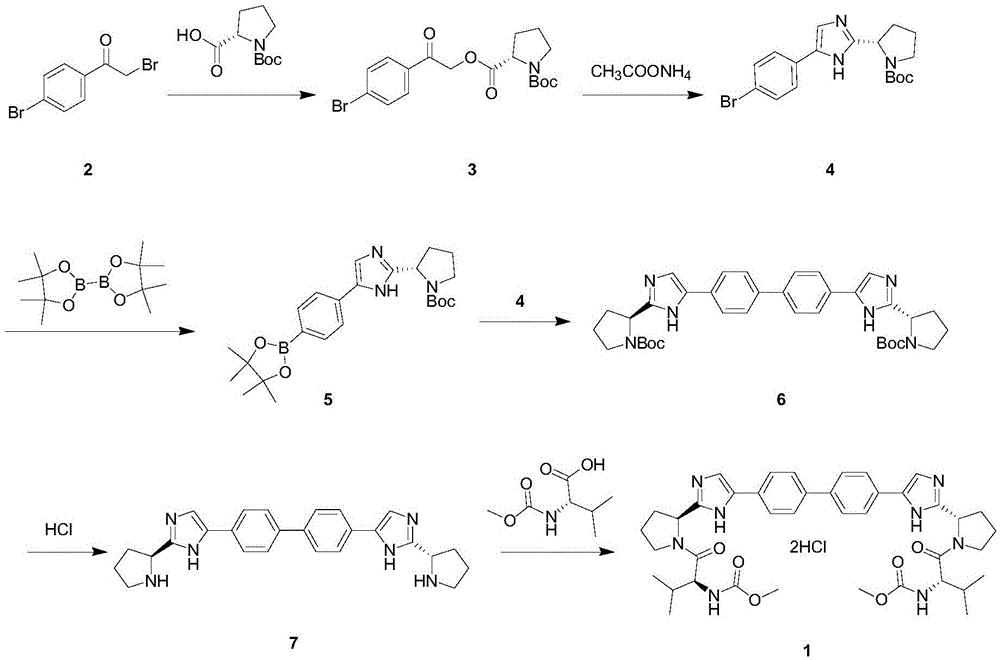
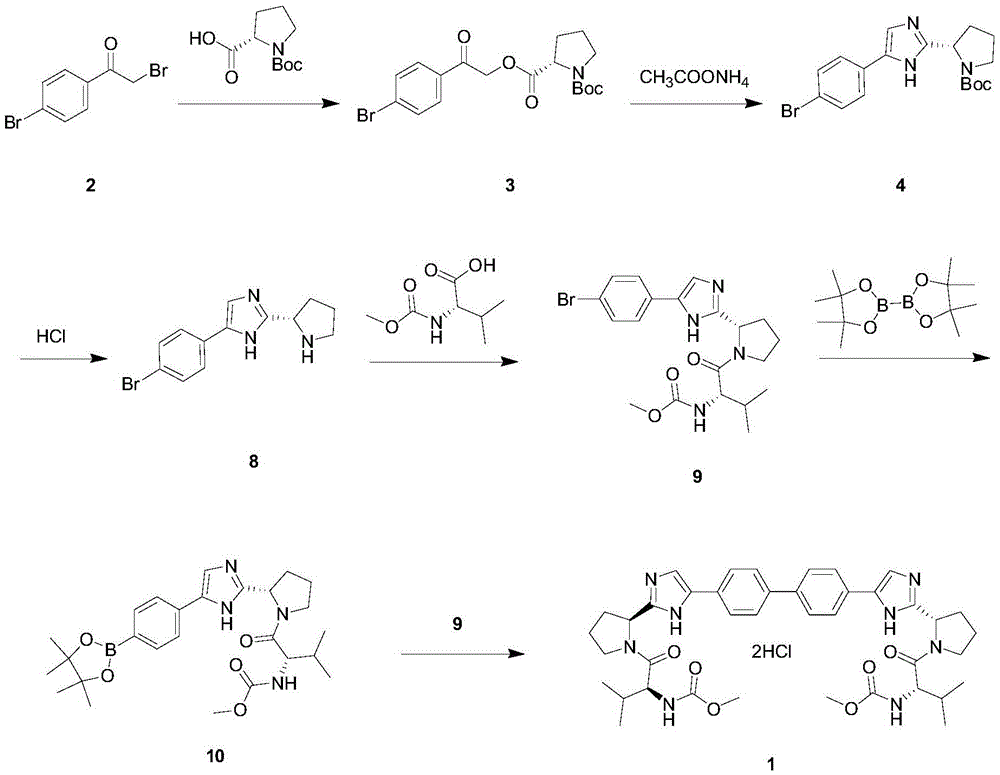
Novel method for synthesizing anti-hepatitis C virus novel medicine daclatasvir
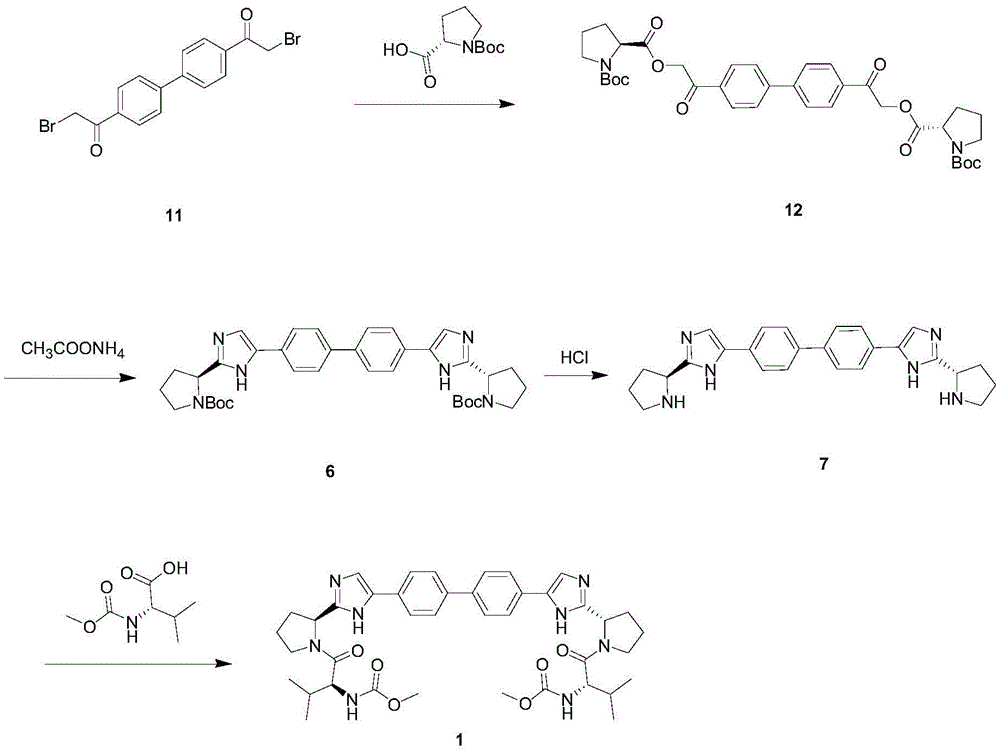
The invention provides a novel method for synthesizing anti-hepatitis C virus novel medicine daclatasvir. 4,4'-di(2-bromoacetyl) biphenyl serve as a raw material and first undergoes the condensation reaction with N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-valyl-L-proline to obtain 4,4'-di(N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-valyl-L-proline ester acetyl) biphenyl, and 4,4'-di(N-(methoxycarbonyl)-L-valyl-L-proline ester acetyl) biphenyl undergoes ring closing reaction with ammonium acetate to synthesize hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitor daclatasvir through two-step reaction. The novel method for synthesizing anti-hepatitis C virus novel medicine daclatasvir has the advantages that the reaction and separation and purification steps are fewer, the synthetic cycle is short and the production cost is low; and the method has wide prospect of large scale industrial application.
Owner:上海步越化工科技有限公司
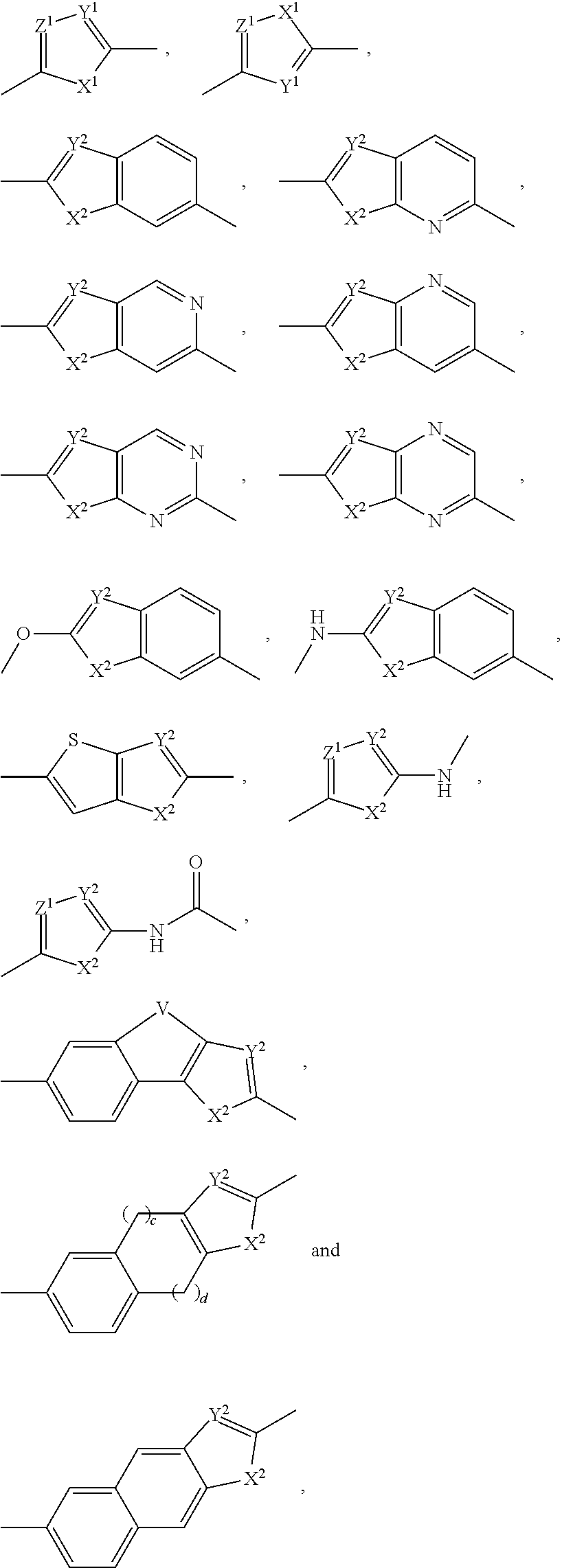
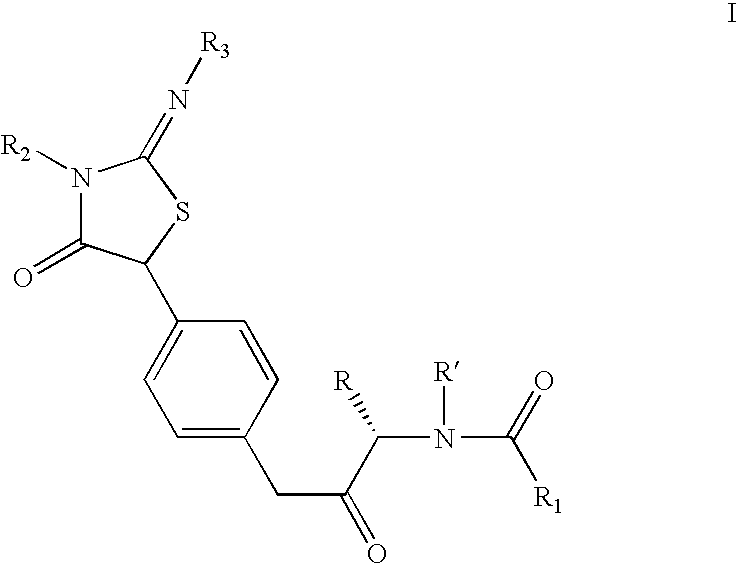
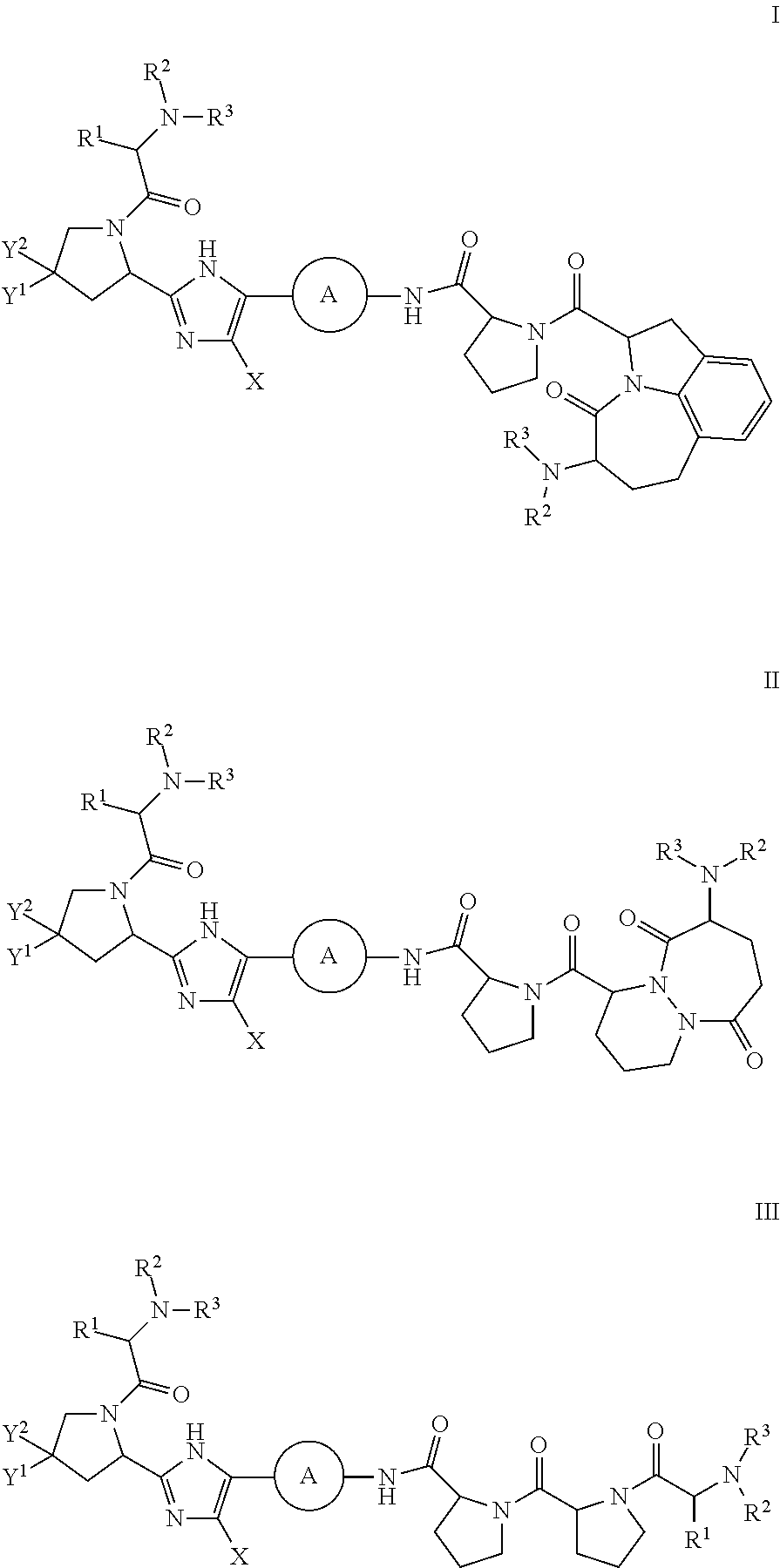
Pan-genomic inhibitors of NS5A protein encoded by HCV, pharmaceutical compositions, intermediates for inhibitor synthesis, and their synthesis and application methods
ActiveUS20170066746A1Organic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHalogenTert-Butyloxycarbonyl protecting group
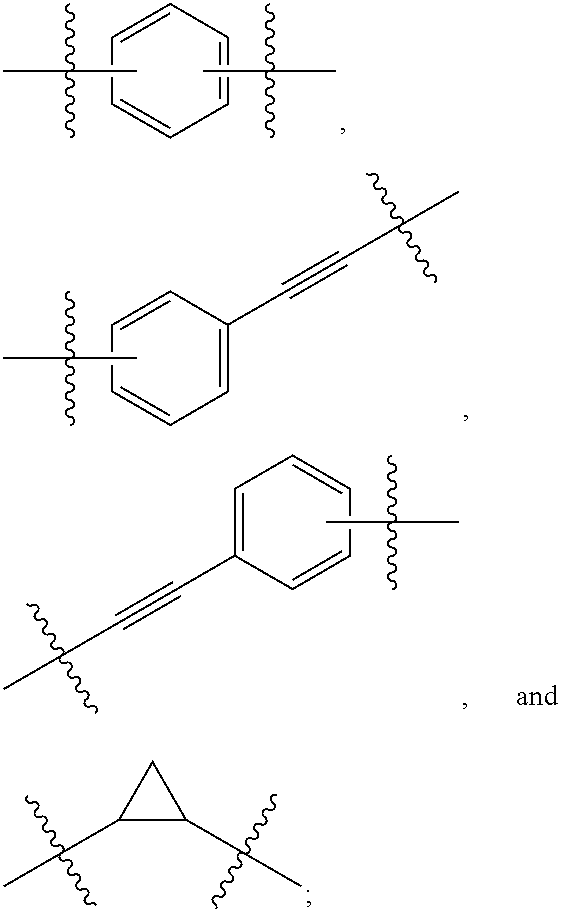
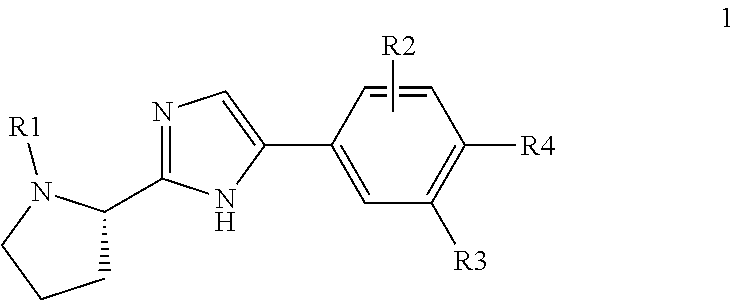
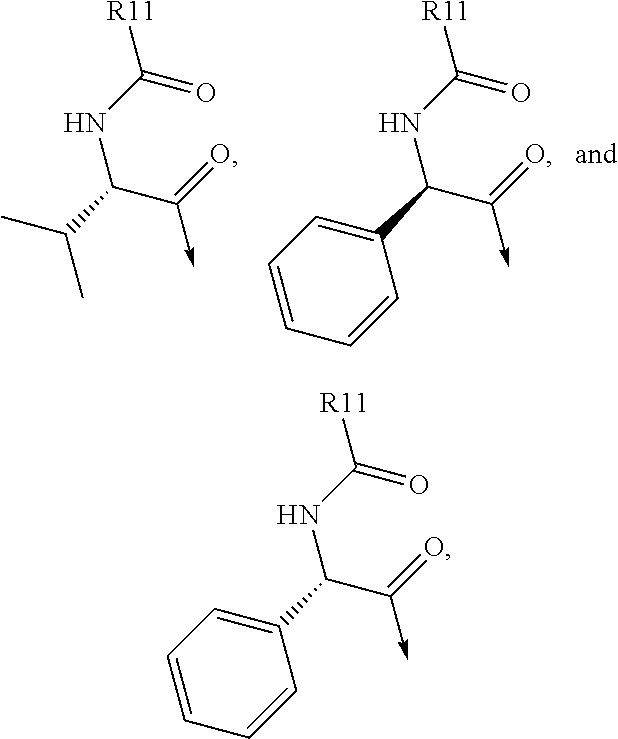
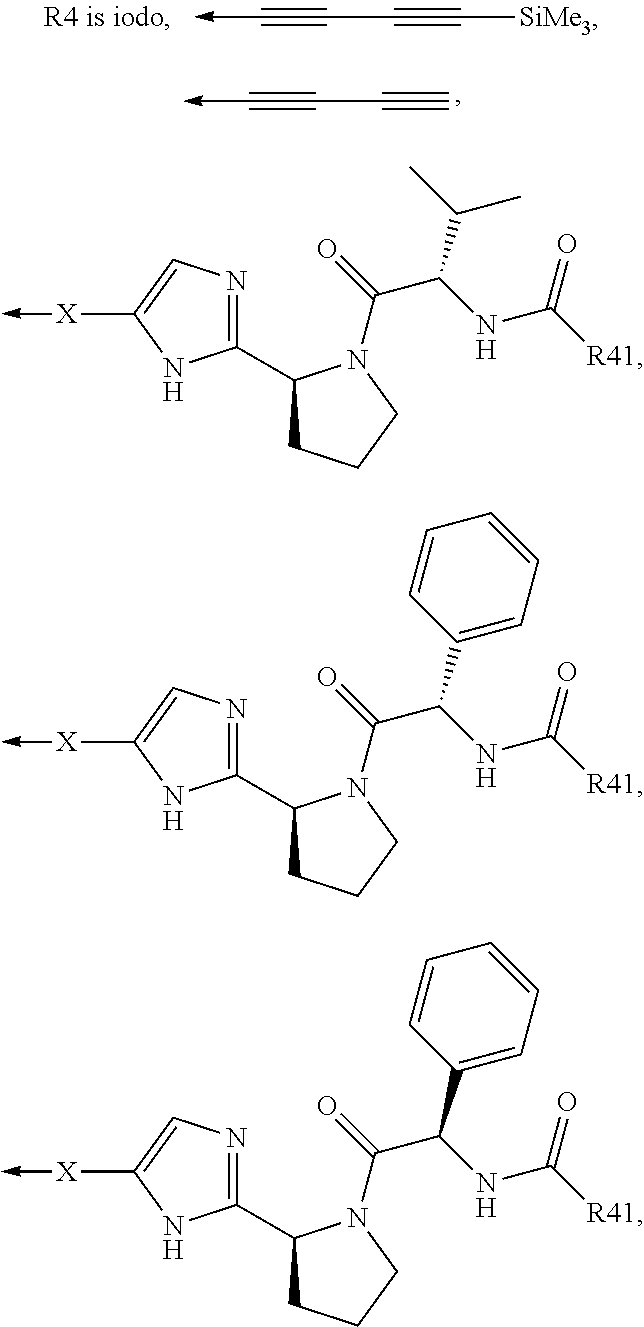
Compound represented by formula 1:or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a hydrate, a crystalline form, or a stereoisomer thereof, wherein:R1 is hydrogen, tert-butoxycarbonyl,where R11 is an optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl, an optionally substituted C3-C6 cycloalkyl, or an optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyloxy, and arrows (←) indicate the position of substituents attachment;R2 is hydrogen, halogen, or C1-C4alkyl;R3 is an optionally substituted aryl, an optionally substituted aryloxy, an optionally substituted arylsulfanyl, an optionally substituted arylamino, or an optionally substituted nitrogen hetaryl;where R41 is an optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl, an optionally substituted C3-C6 cycloalkyl, or an optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyloxy; X is buta-1,3-diynylene or 1,4-phenylene; arrows (←) indicate the position of substituents attachment.
Owner:IVACHTCHENKO ALEXANDRE VASILIEVICH +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com