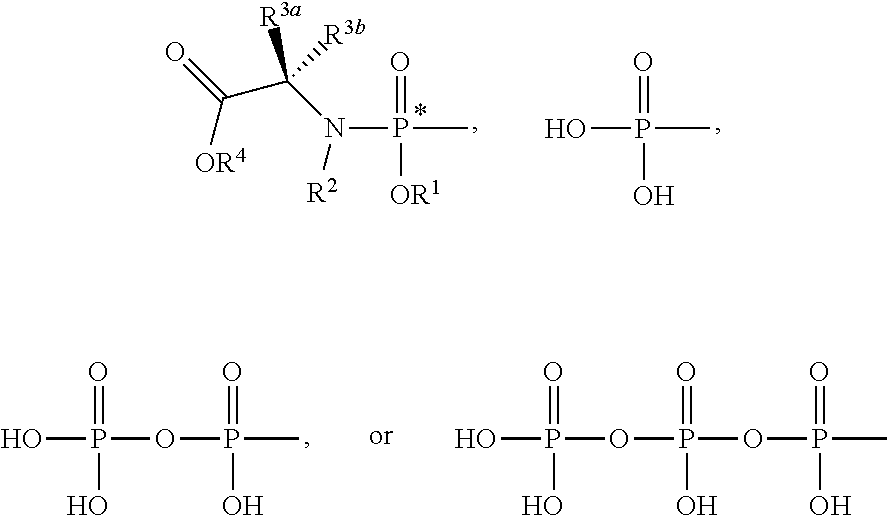
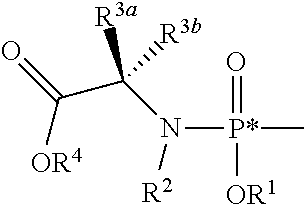
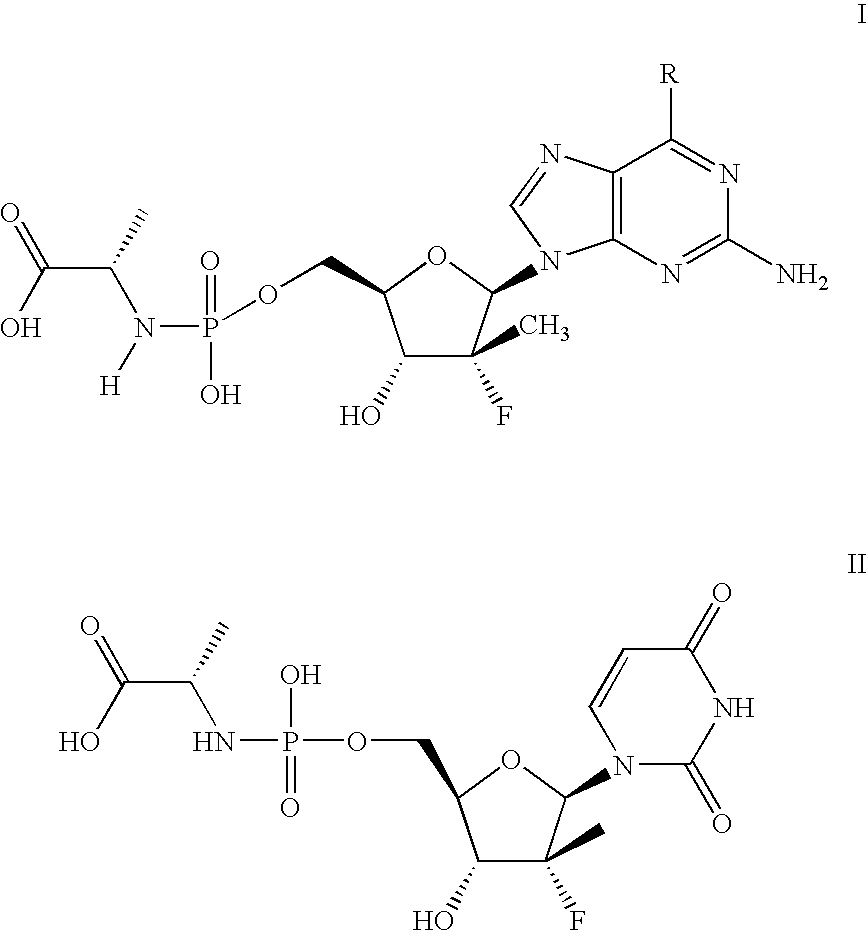
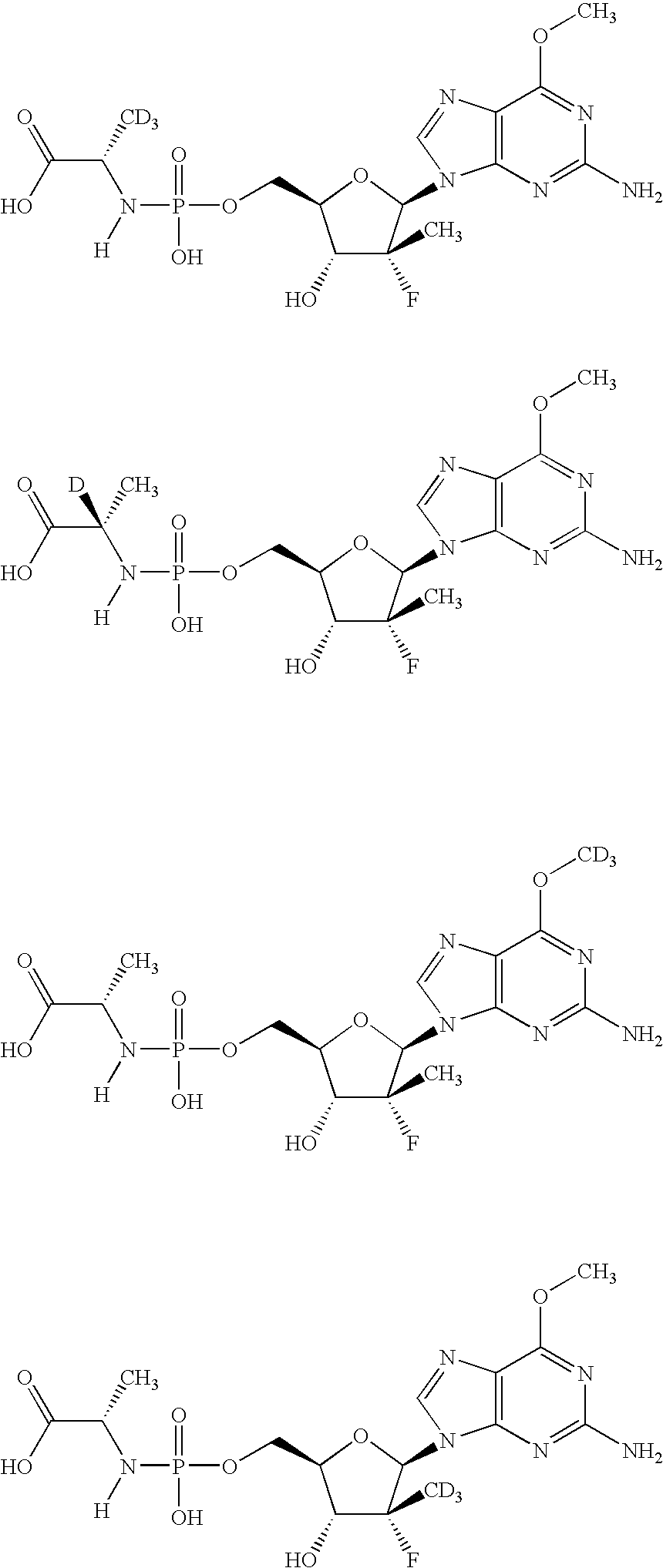
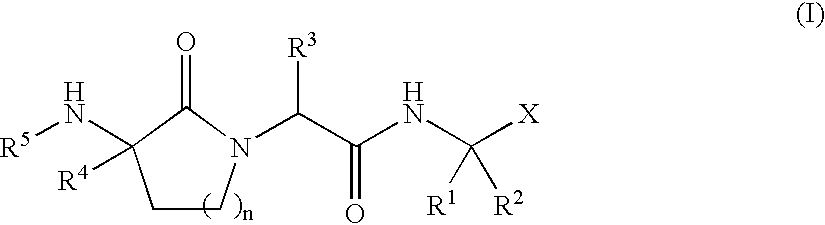
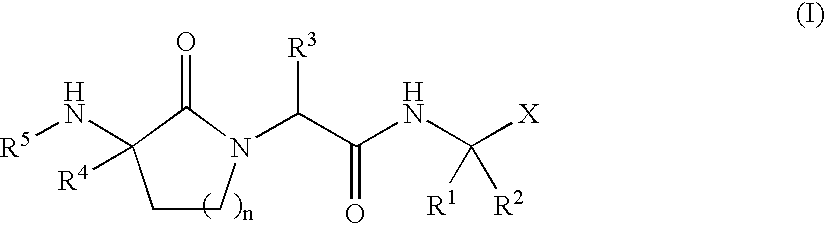
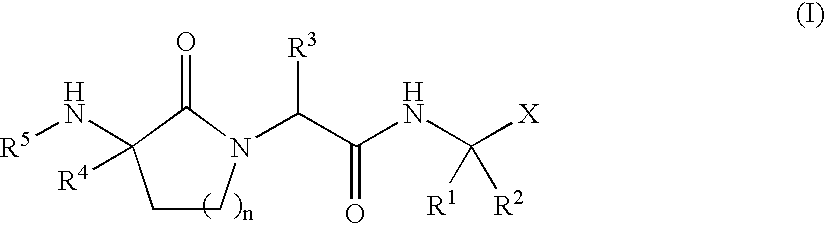
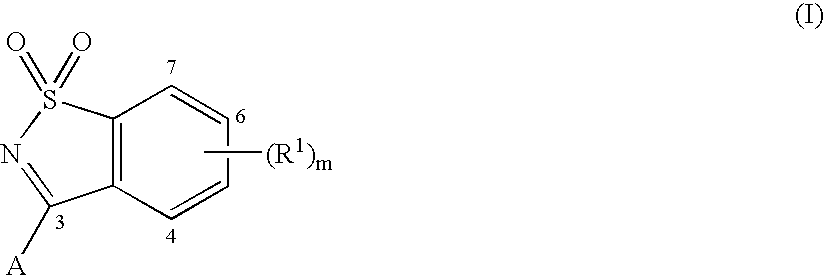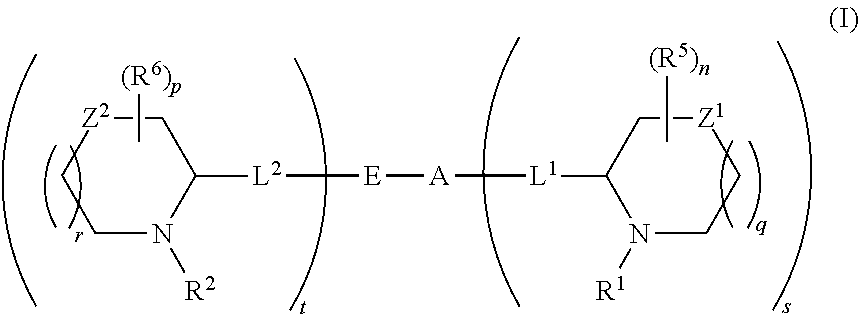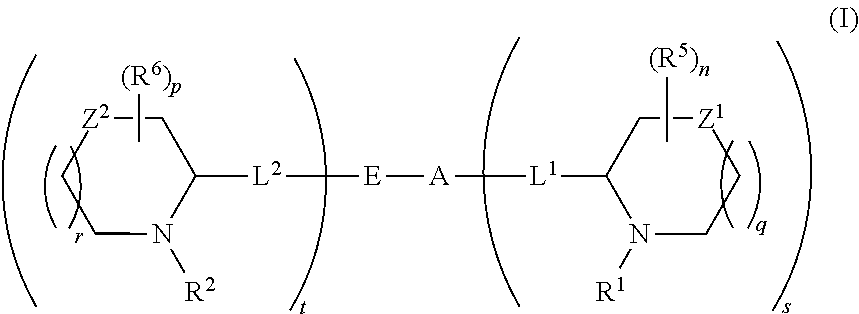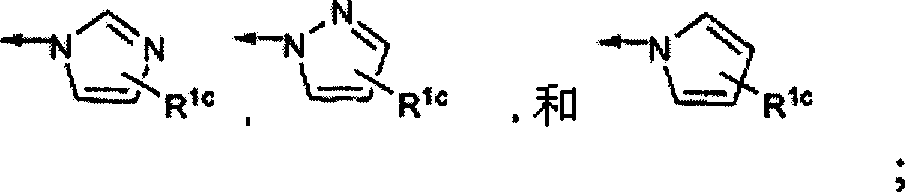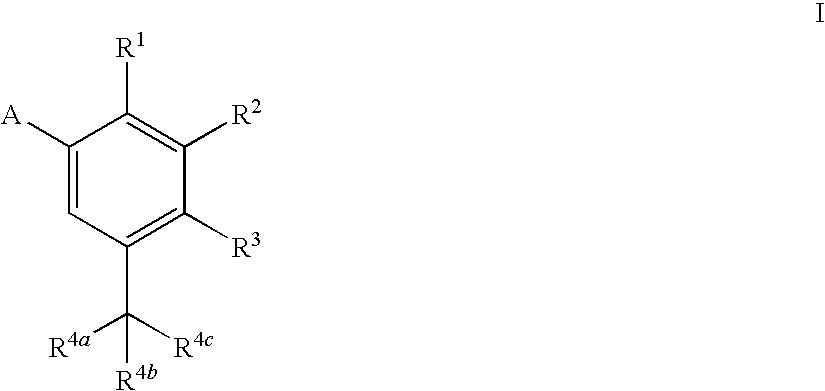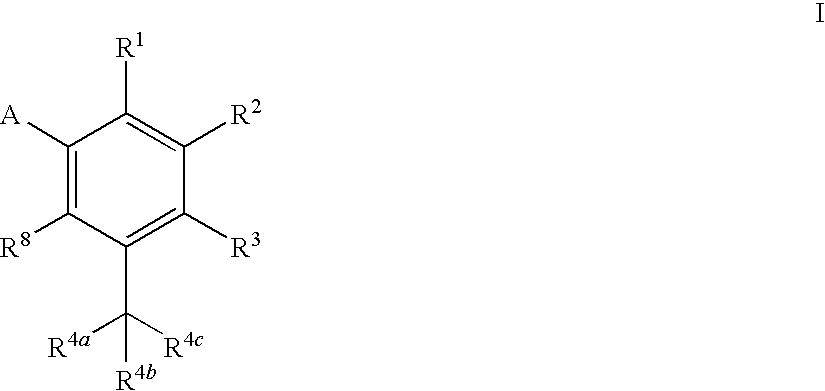Patents
Literature
355 results about "Hepatitis virus c" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
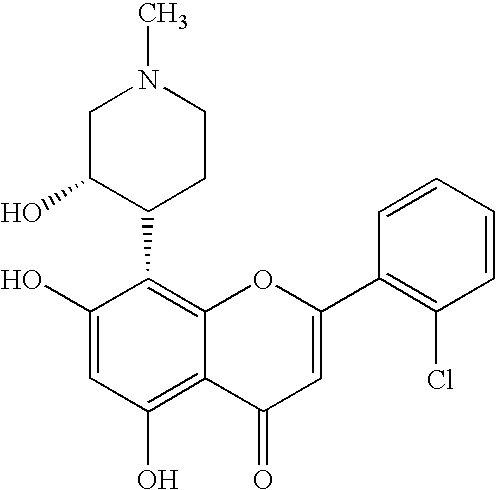
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae. Hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans.
Nucleoside derivatives for treating hepatitis C virus infection
Owner:GENELABS TECH INC
3′-or 2′-hydroxymethyl substituted nucleoside derivatives for treatment of hepatitis virus infections
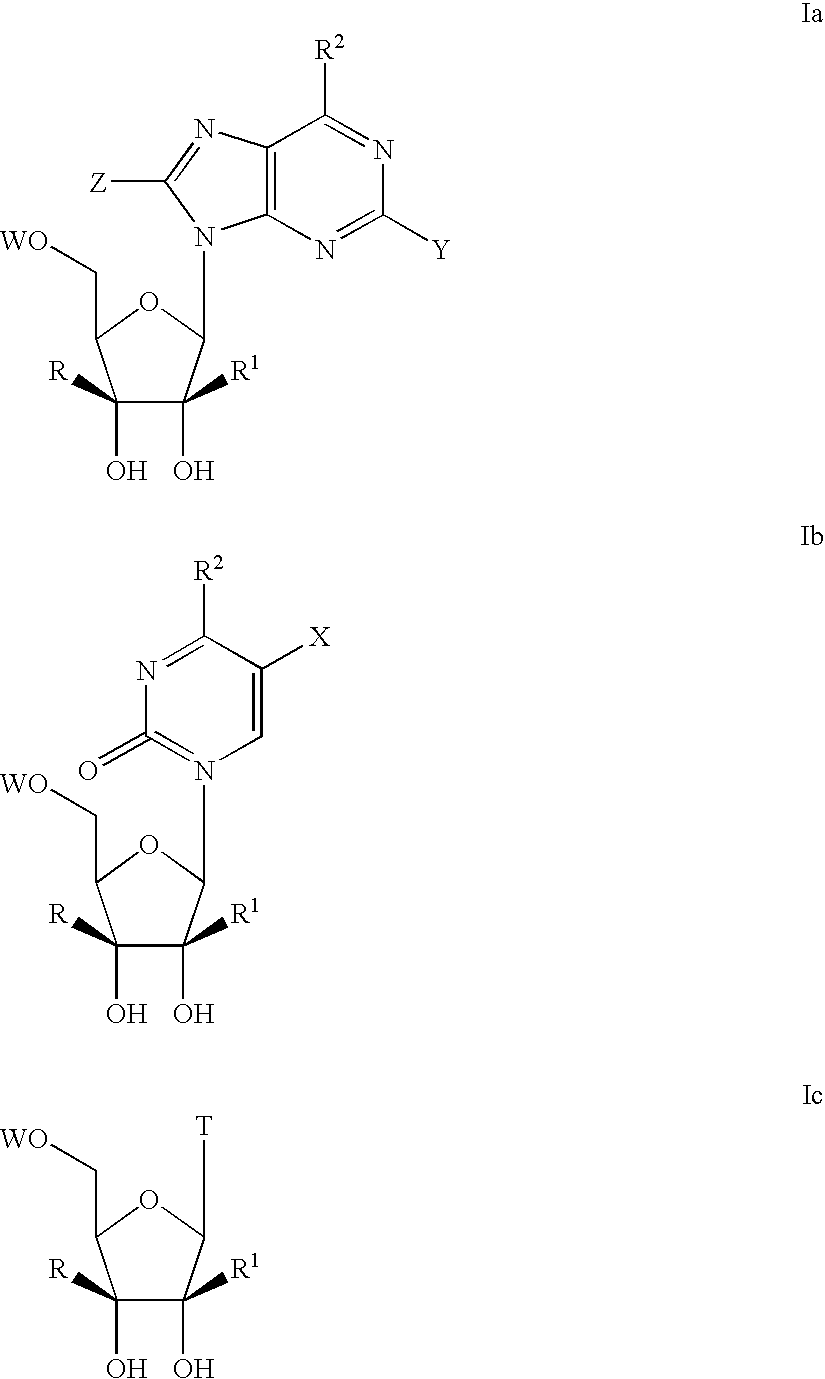
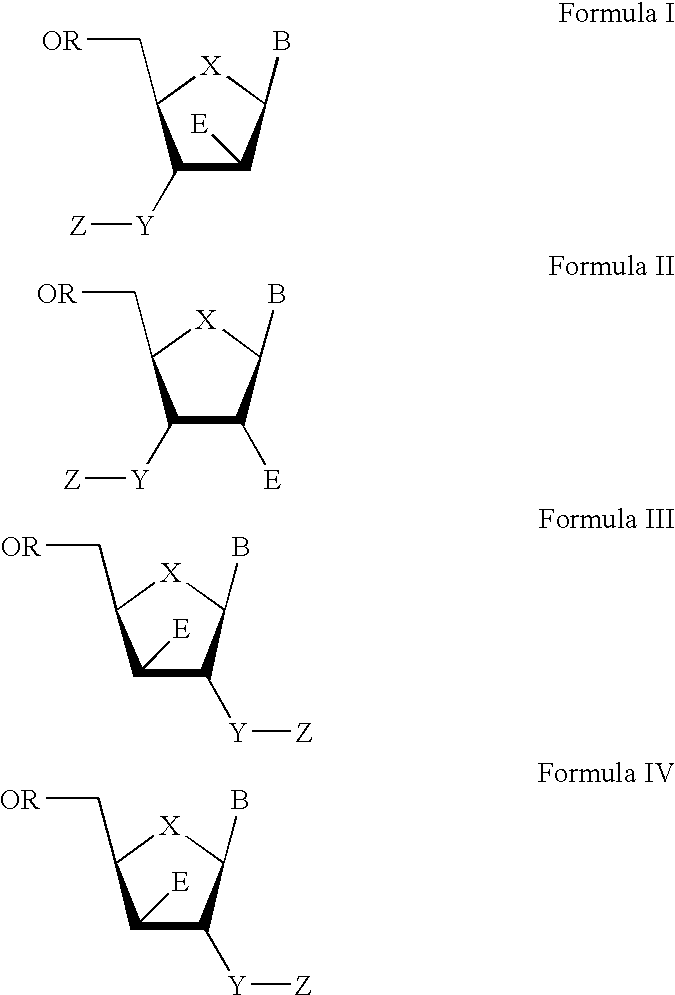
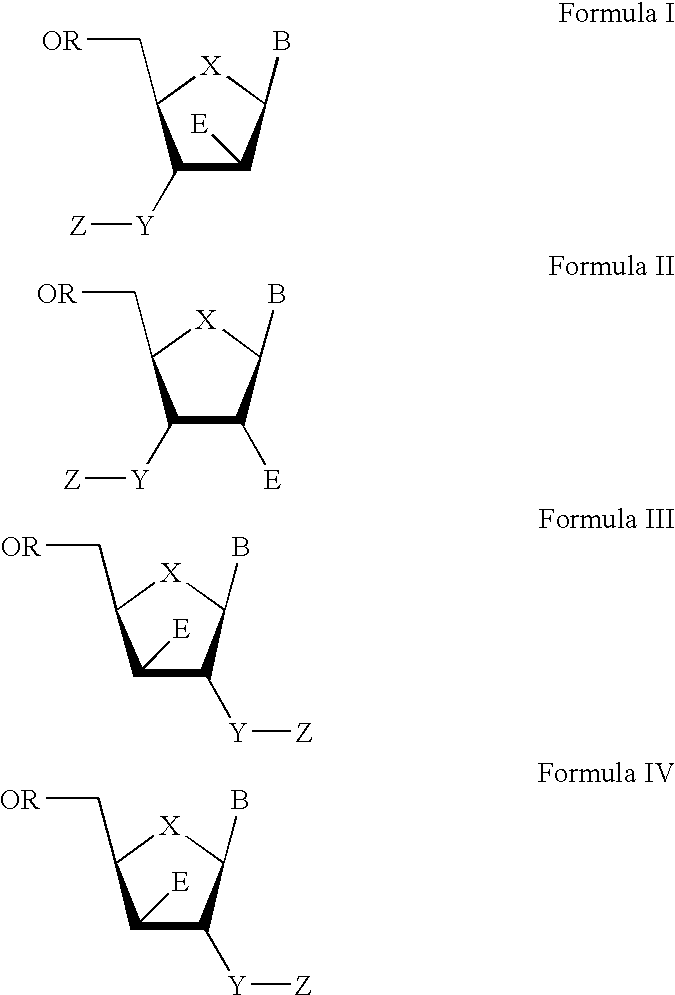
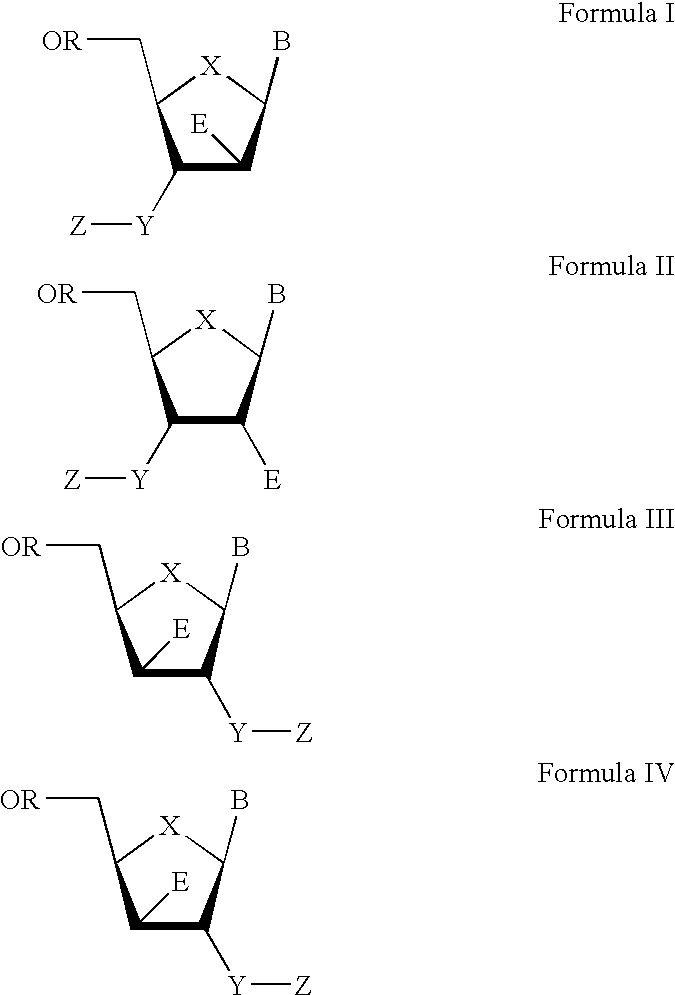
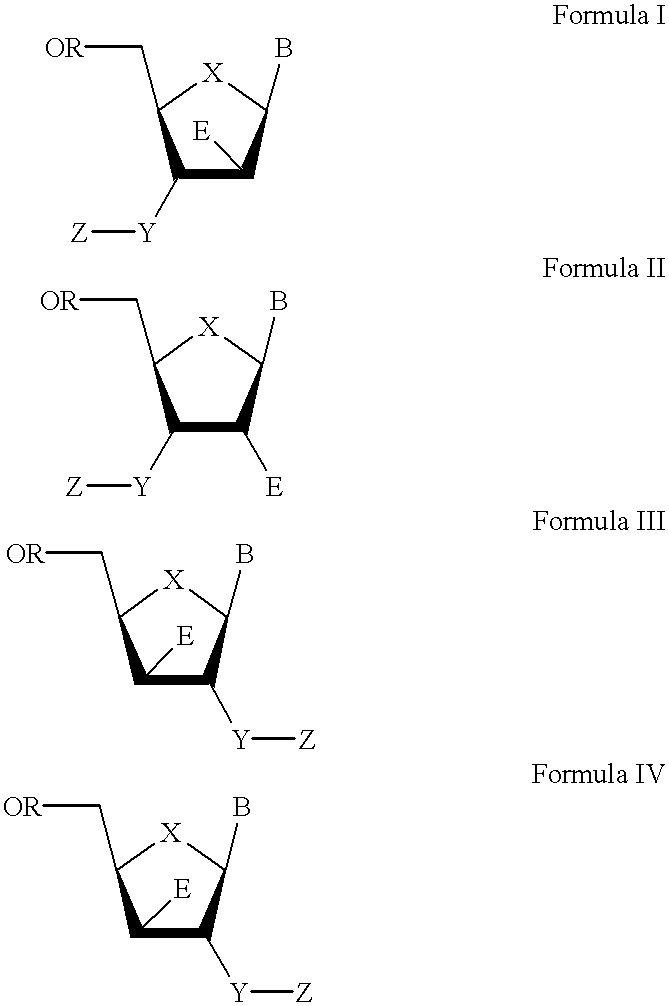
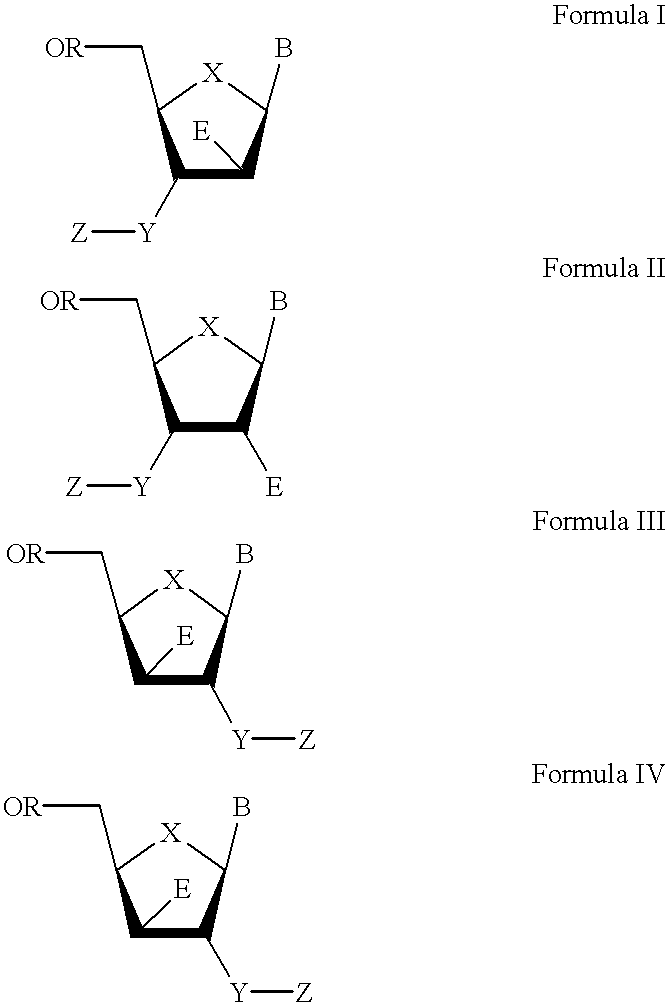
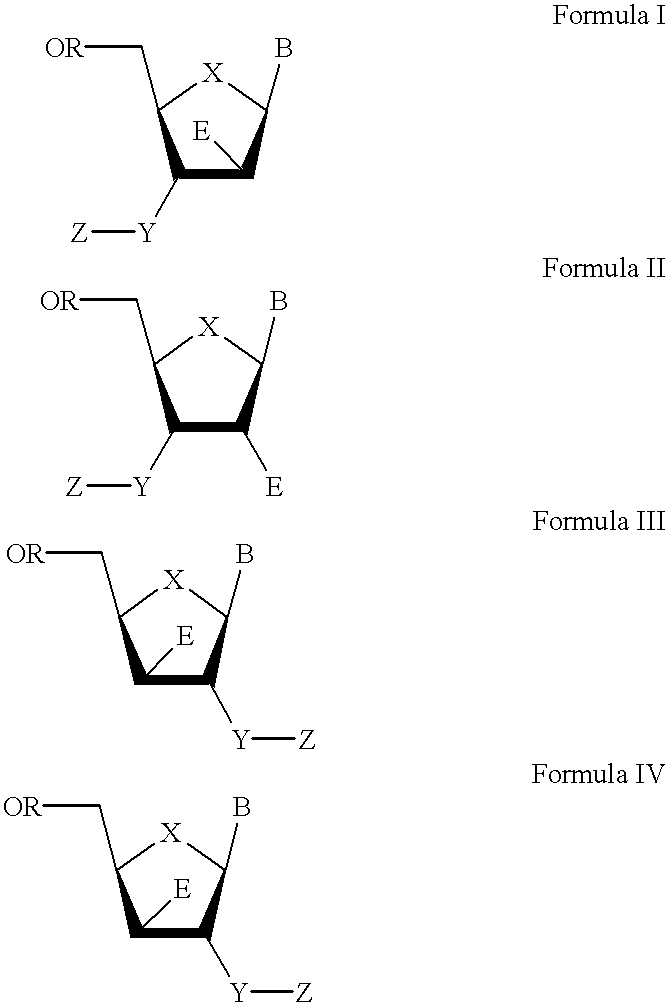
The present invention relates to a composition for and a method of treating hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, hepatitis D virus (HDV) infection or a proliferative disorder in a patient using an effective amount of a compound selected from the group consisting of formulas [I]–[IV] below and mixtures of two or more thereof:wherein the substituents are as defined herein. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds in combination with other HBV, HCV, or HDV agents is also disclosed.
Owner:PHARMASSET
Inhibitors of HCV replication
ActiveUS20060276511A1Inhibit functioningEffective treatmentBiocideOrganic chemistryArrestinStereochemistry
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
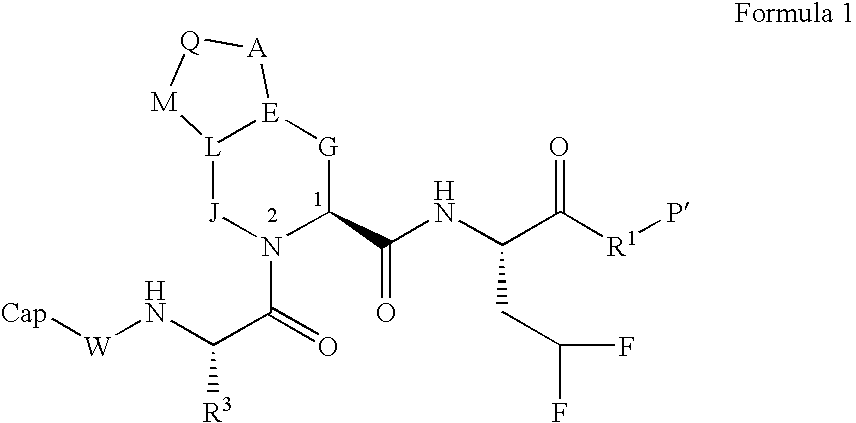
Macrocyclic NS3-serine protease inhibitors of hepatitis C virus comprising N-cyclic P2 moieties
The present invention discloses novel macrocyclic compounds which have HCV protease inhibitory activity as well as methods for preparing such compounds. In another embodiment, the invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions comprising such macrocycles as well as methods of using them to treat disorders associated with the HCV protease.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Pyrazolopyrimidines as protein kinase inhibitors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine compounds as inhibitors of protein and / or checkpoint kinases, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions including one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations including one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with the protein or checkpoint kinases using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also relates to the inhibition of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication. In particular, embodiments of the invention provide compounds and methods for inhibiting HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzymatic activity. The invention also provides compositions and methods for the prophylaxis and treatment of HCV infection.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Macrocyclic inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3-serine protease
InactiveUS20050119168A1HCV infectionImprove overall utilizationBiocideAntiviralsDiseaseStructural formula
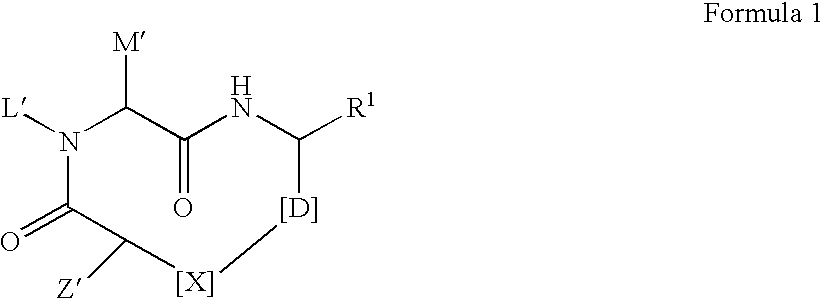
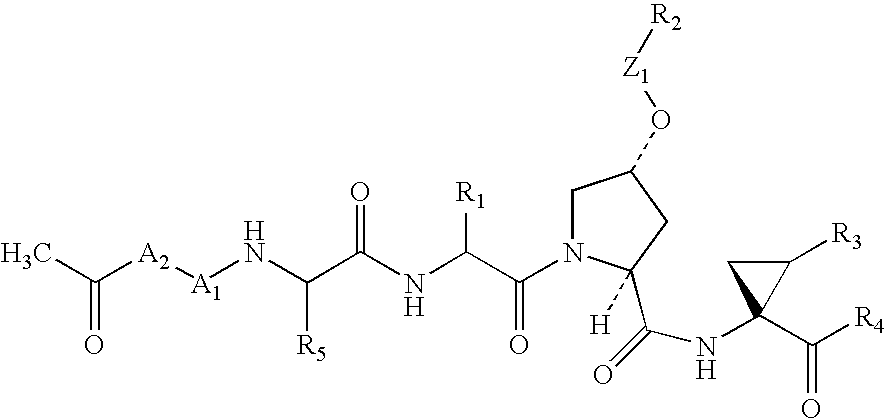
The present invention discloses novel compounds which have HCV protease inhibitory activity as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of using them to treat disorders associated with the HCV protease. The novel compounds typically include a 15-20 member macrocycle and have the general structure of structural Formula 1: wherein Z′, L′, M′, R1, X and D are defined herein.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Anti-Viral Compounds
ActiveUS20100168138A1Lower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHepacivirusAnti virals
Owner:ABBVIE INC
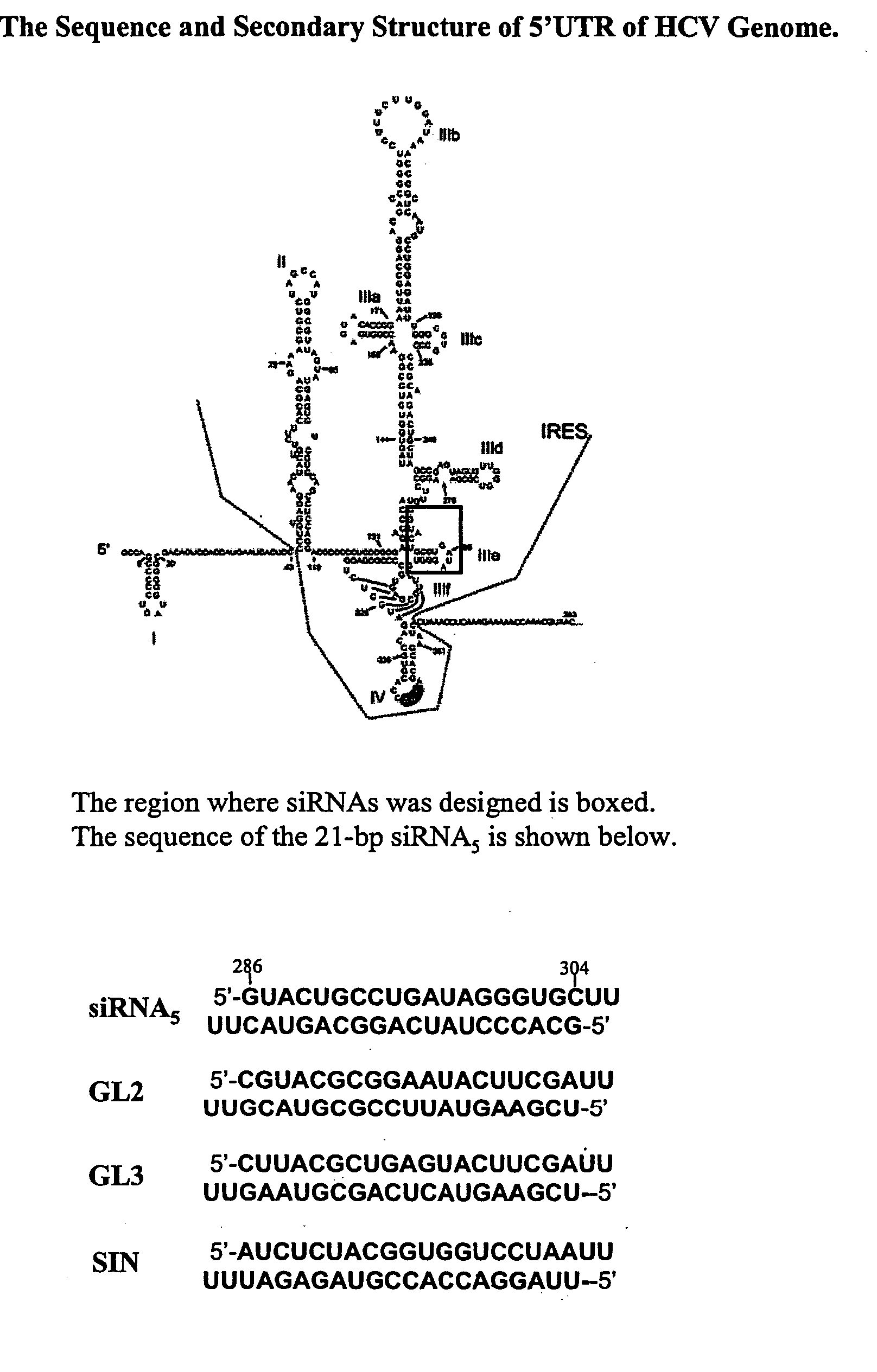
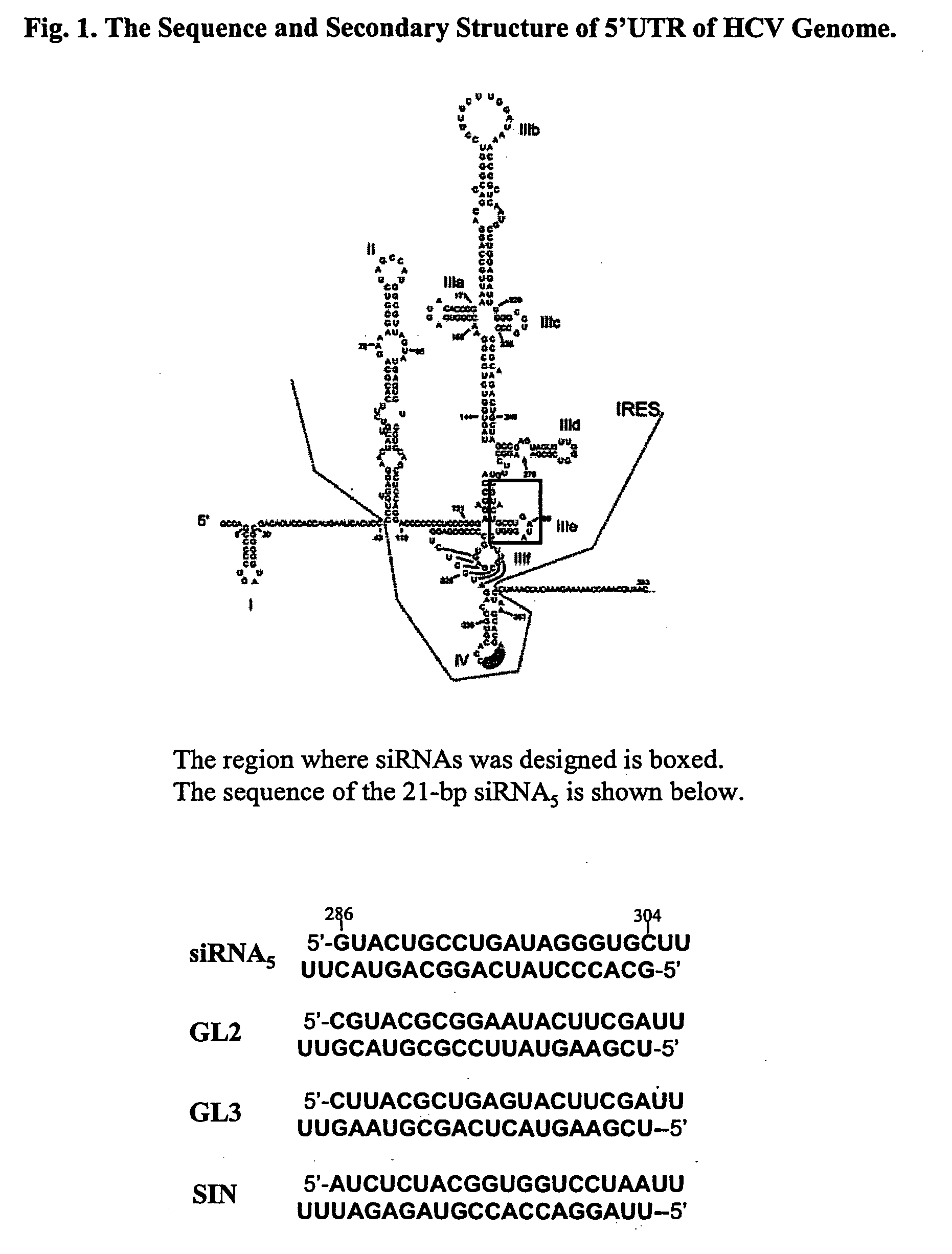
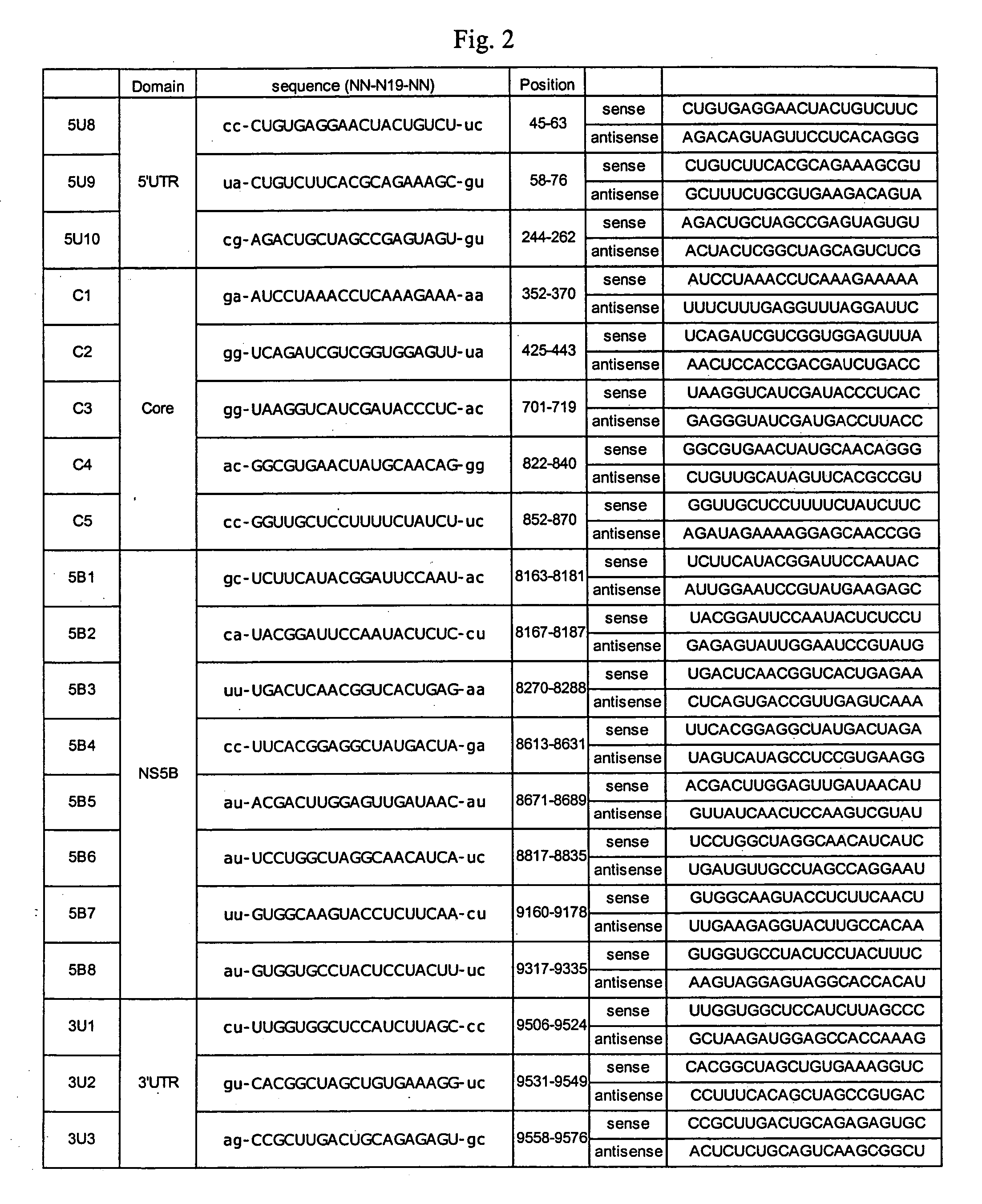
Modified small interfering RNA molecules and methods of use
InactiveUS20050058982A1Inhibit replicationInhibit viral replicationOrganic active ingredientsFungiNucleaseDicer
The present invention provides double-stranded RNA molecules that mediate RNA interference in target cells, preferably hepatic cells. The invention also provides double-stranded RNA molecules that are modified to be resistant to nuclease degradation, which inactivates a virus, and more specifically, hepatitis C virus (HCV). The invention also provides a method of using these modified RNA molecules to inactivate virus in mammalian cells and a method of making modified small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) using human Dicer.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Hepatitis C virus inhibitors
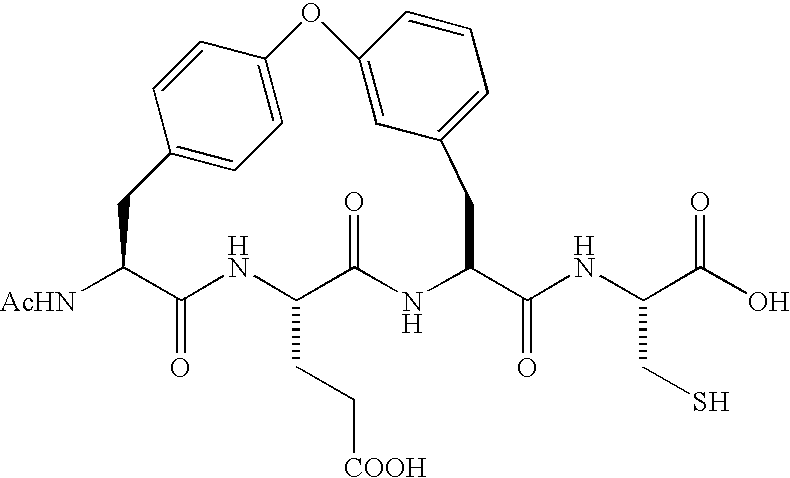
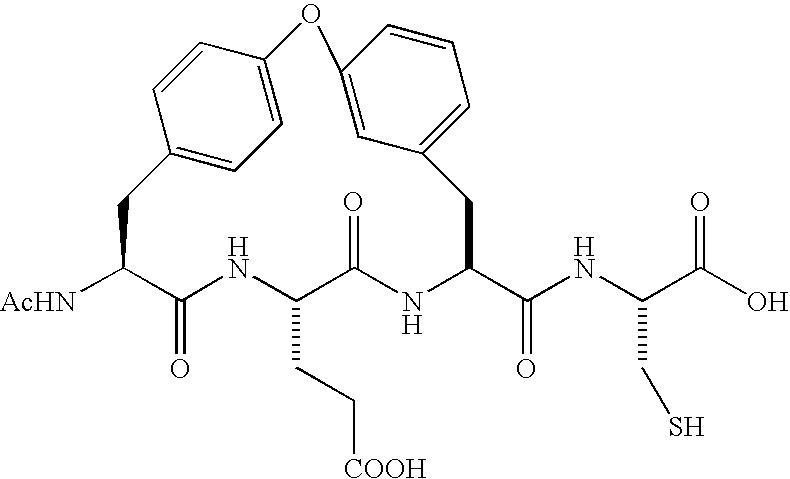
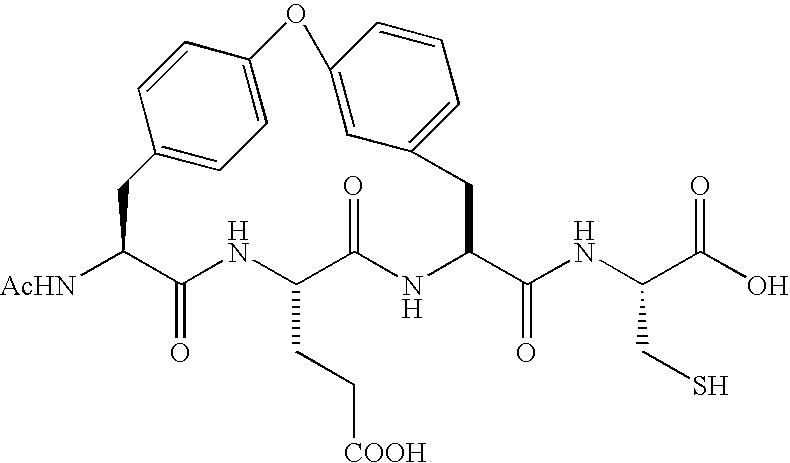
ActiveUS7132504B2Inhibit functioningEffective treatmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiochemistryVirus
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Nucleoside derivatives for treating hepatitis C virus infection
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
3'-or 2'-hydroxymethyl substituted nucleoside derivatives for treatment of hepatites virus infections
InactiveUS20020055483A1Good effectEasy to modifyBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseHepatitis B immunization
The present invention relates to a composition for and a method of treating hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, hepatitis D virus (HDV) infection or a proliferative disorder in a patient using an effective amount of a compound selected from the group consisting of formulas [I]- [IV] below and mixtures of two or more thereof: wherein the substituents are as defined herein. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds in combination with other HBV, HCV, or HDV agents is also disclosed.
Owner:PHARMASSET
Heterocyclic antiviral compounds
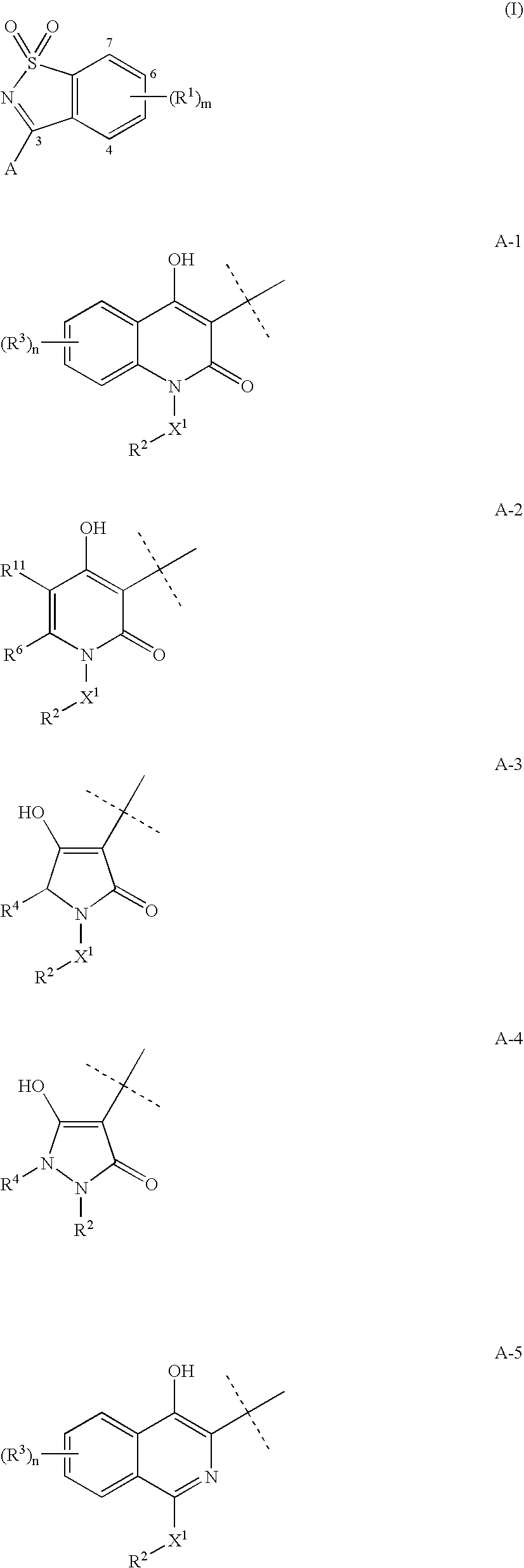
Compounds having the formula I wherein A, m and R1 are herein defined are Hepatitis C virus NS5b polymerase inhibitors. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for inhibiting hepatitis replication, processes for making the compounds and synthetic intermediates used in the process
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
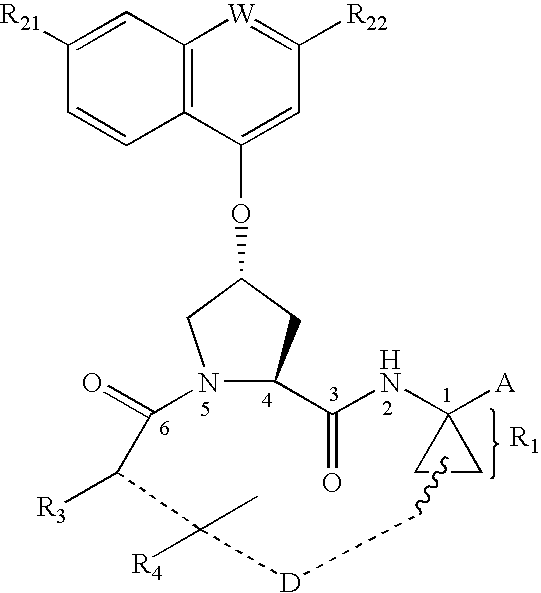
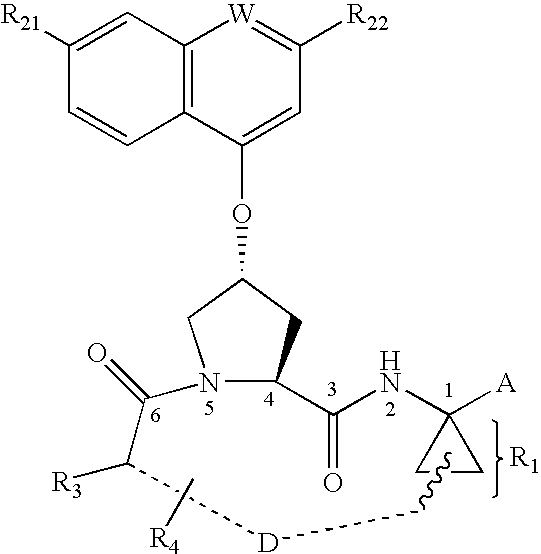
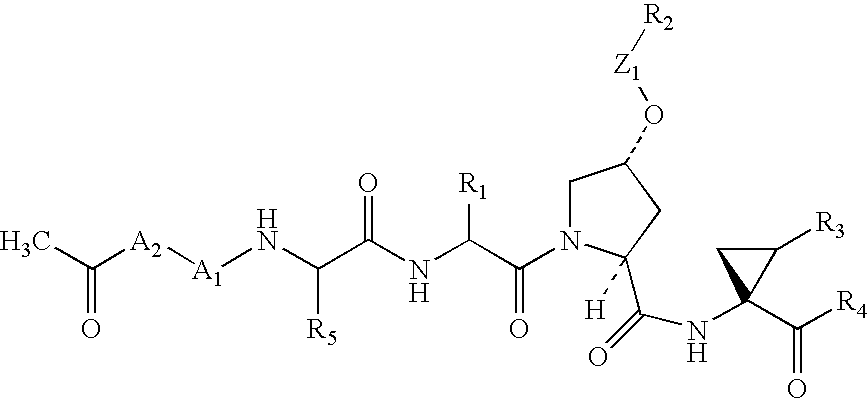
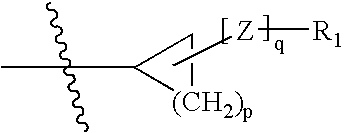
Process for preparing macrocyclic compounds
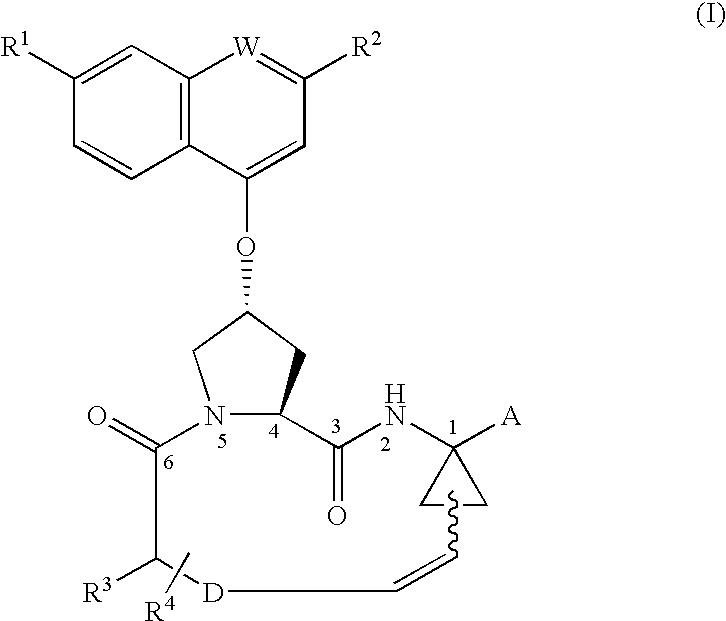
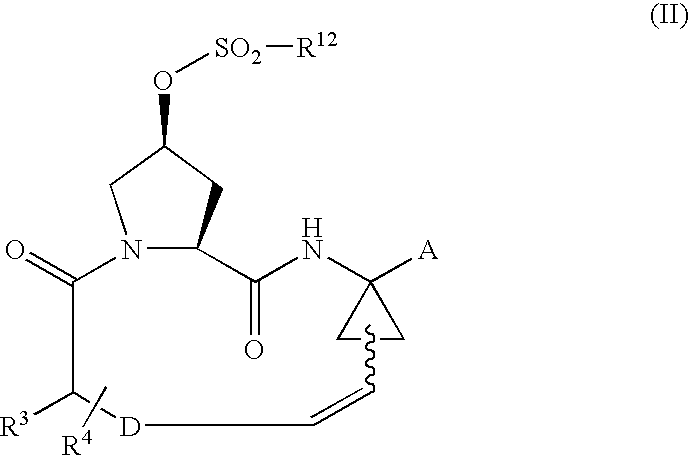
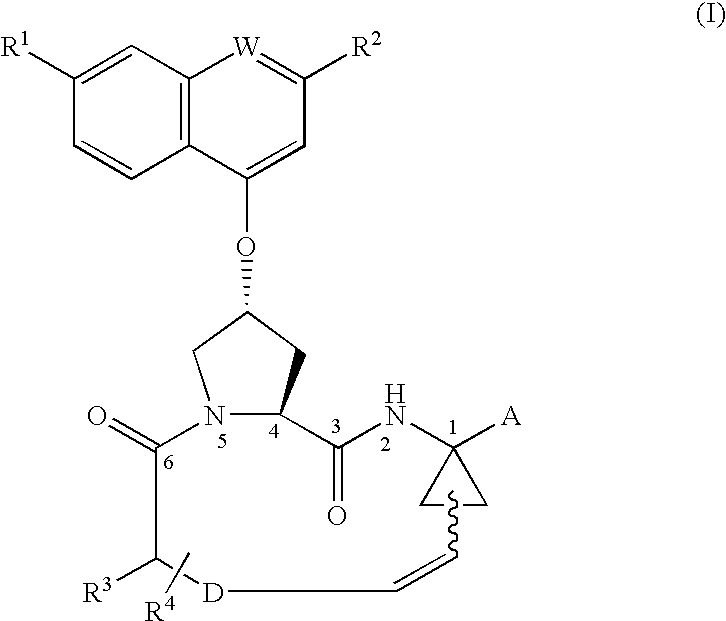
Disclosed is a process for preparing a macrocyclic compound of the formula (I): which is carried out using an intermediate of the formula (II): wherein W, R1 through R4, D, A and R12 are as defined herein. The compounds of formula (I) are potent active agents for the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Nucleoside phosphoramidates
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Nucleoside analogs
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Hepatitis C virus inhibitors
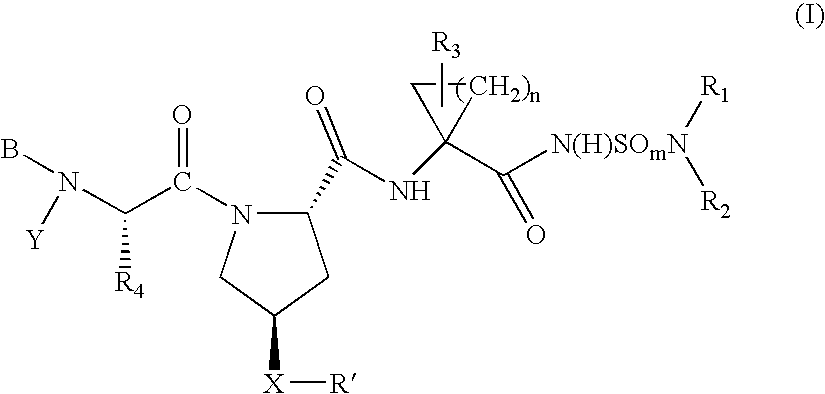
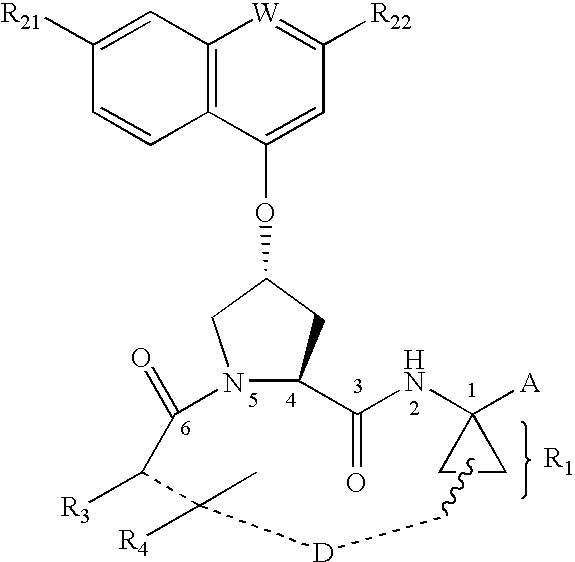
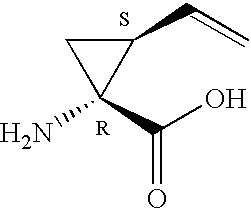
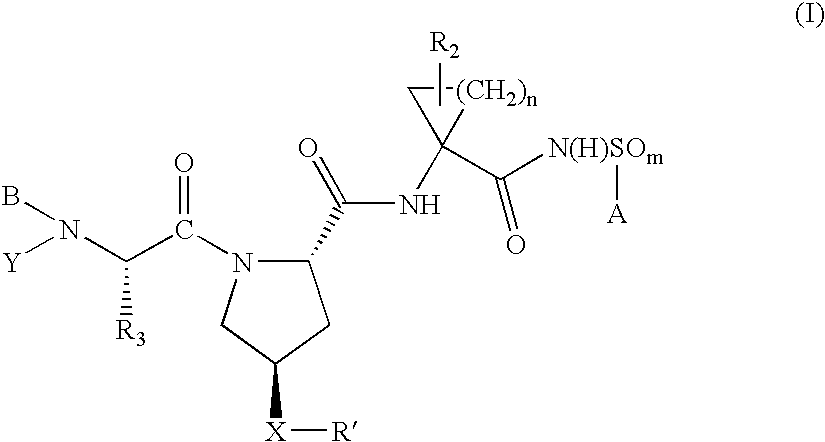
ActiveUS20050187165A1Inhibit functioningEffective treatmentBiocideDipeptide ingredientsStereochemistryHepatitis virus c
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Compounds as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 serine protease
The present invention discloses novel compounds which have HCV protease inhibitory activity as well as methods for preparing such compounds. In another embodiment, the invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds as well as methods of using them to treat disorders associated with the HCV protease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
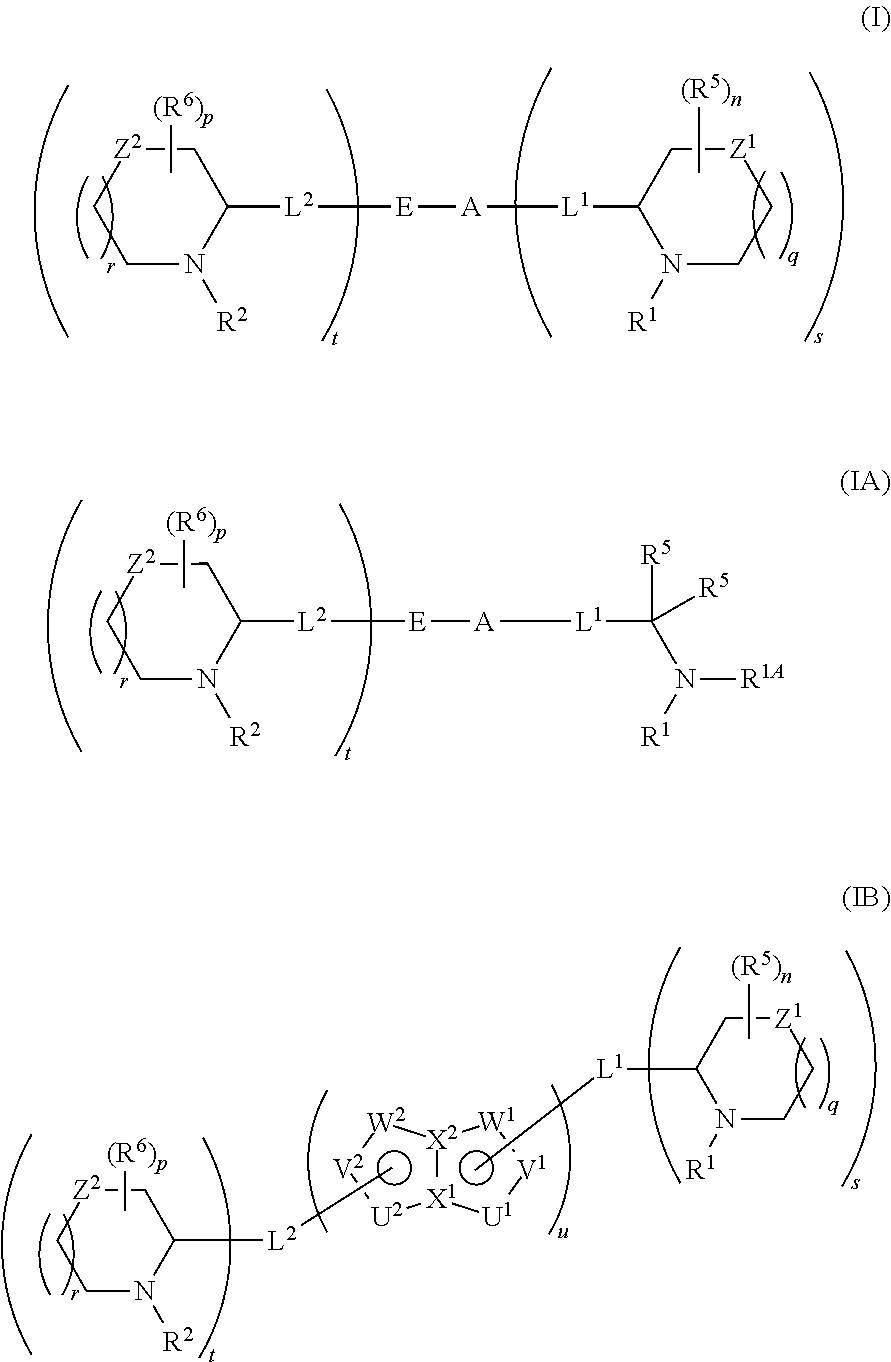
5,5-fused arylene or heteroarylene hepatitis C virus inhibitors
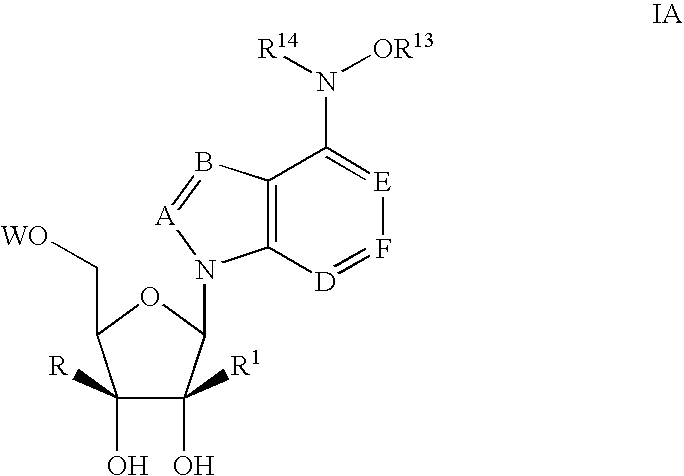
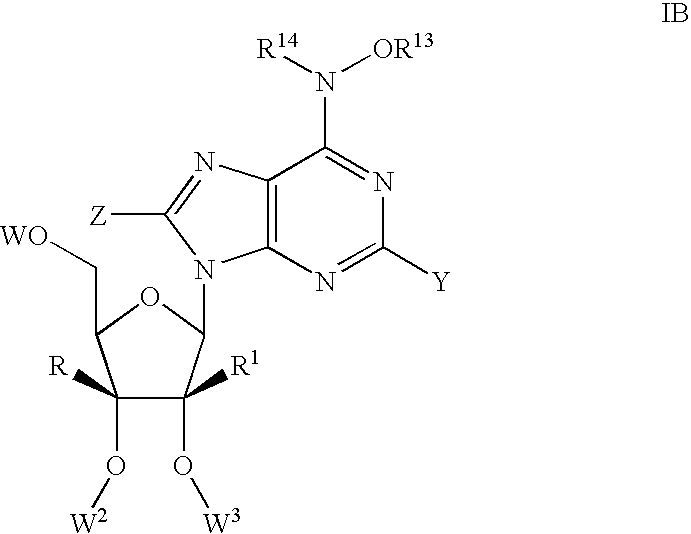
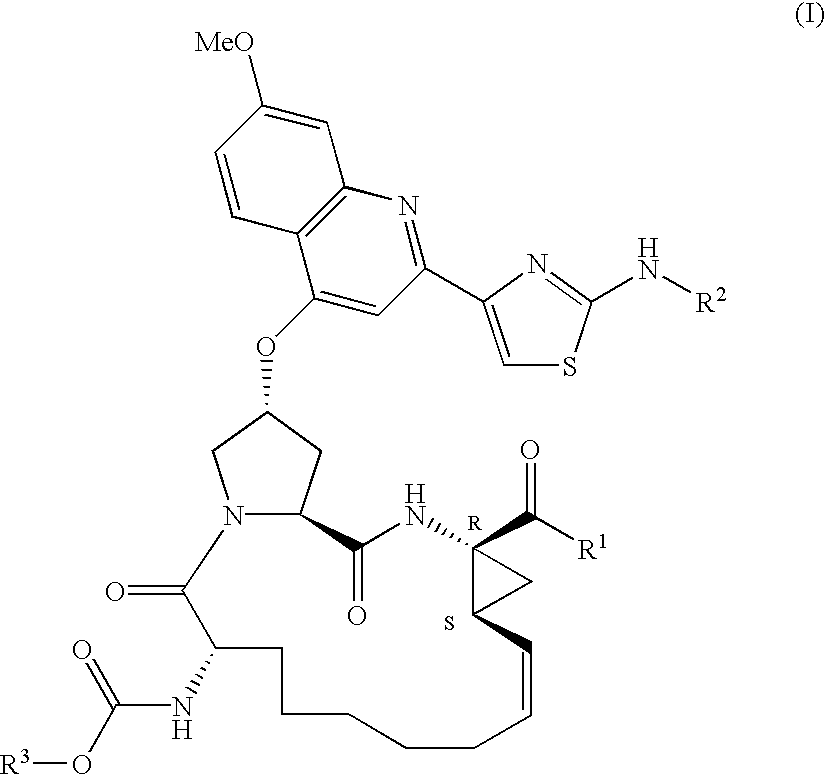
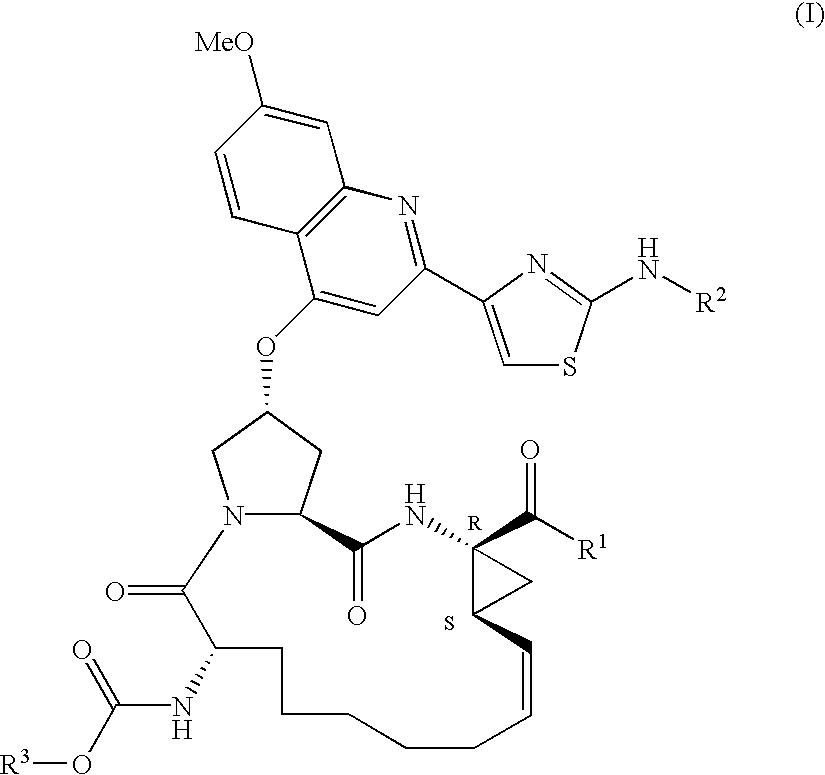
Provided herein are 5,5-fused heteroarylene hepatitis C virus inhibitor compounds, for example, of Formula I, IA, or IB, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and processes of preparation thereof. Also provided are methods of their use for the treatment of an HCV infection in a host in need thereof.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
Macrocyclic compounds as inhibitors of viral replication
The embodiments provide compounds of the general formulas I-XIX, as well as compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions, comprising a subject compound. The embodiments further provide treatment methods, including methods of treating flaviviral infection, including hepatitis C virus infection and methods of treating liver fibrosis, the methods generally involving administering to an individual in need thereof an effective amount of a subject compound or composition.
Owner:INTERMUNE INC
Heterocyclic antiviral compounds
Compounds having the formula I wherein A, R1, R2, R3, R4a, R4b, R4c, R5, R6, R7a, R7b, Ar1, Rc, Rd, Re, Rf, X, n and p are as defined herein are Hepatitis C virus NS5b polymerase inhibitors. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for treating an HCV infection and inhibiting HCV replication.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
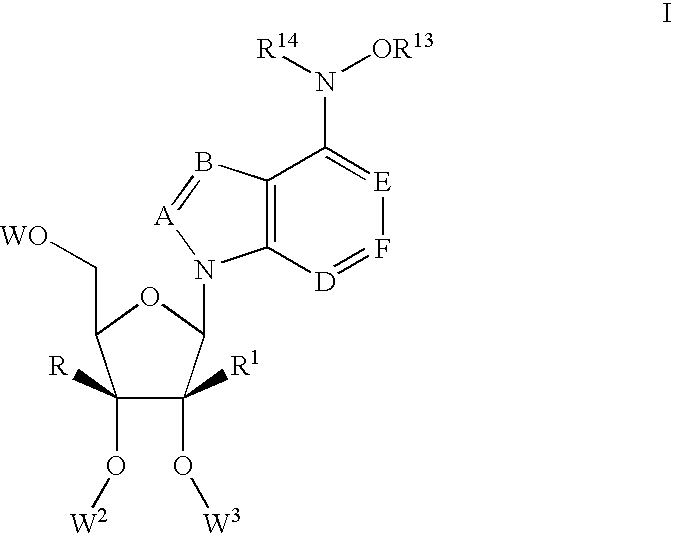
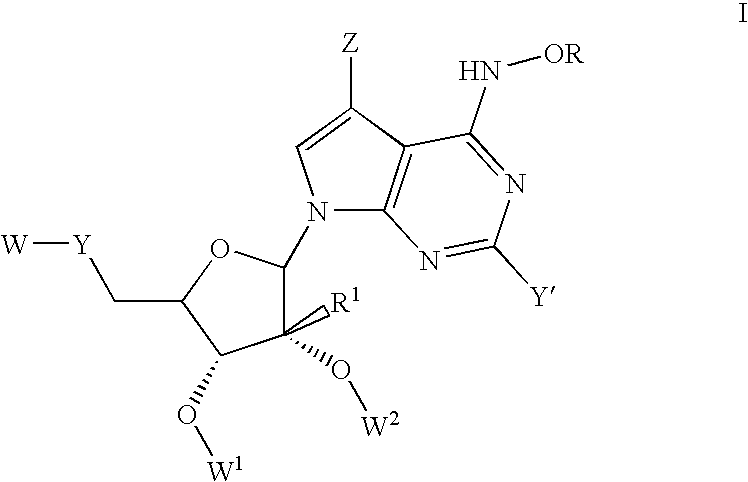
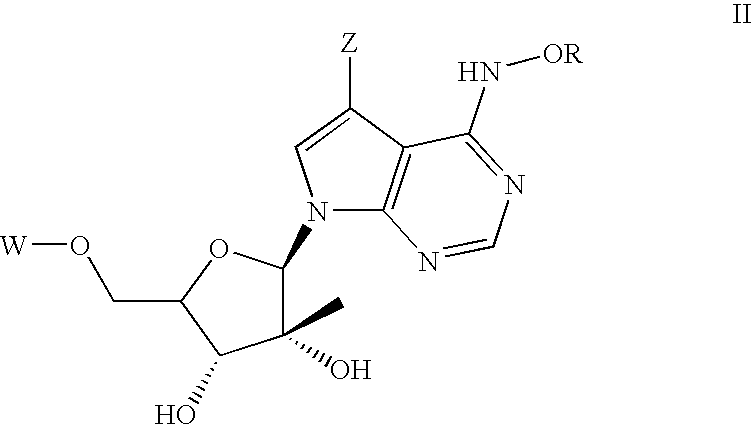
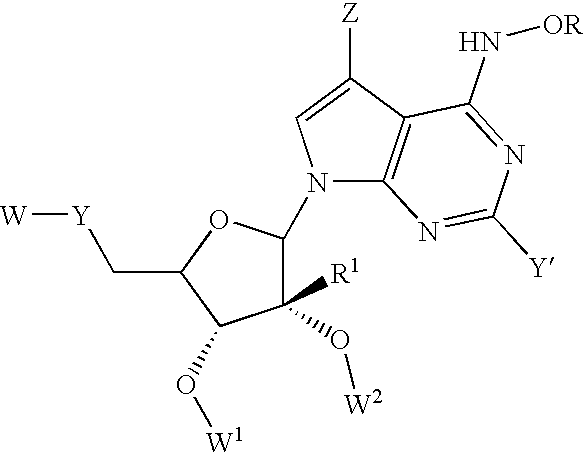
Nucleoside derivatives for treating hepatitis C virus infection
Disclosed are 6-hydroxyamino- or a 6-alkoxyamino-7-deazapurine-ribofuranose derivatives, salts, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of use thereof for treating viral infections caused by a flaviviridae family virus, such as hepatitis C virus.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
3,4-(cyclopentyl)-fused proline compounds as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 serine protease
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Macrocyclic peptides active against the hepatitis C virus
Compounds of formula I:wherein R1 is hydroxy or NHSO2R1A wherein R1A is (C1-8)alkyl, (C3-7)cycloalkyl or {(C1-6)alkyl-(C3-7)cycloalkyl}, which are all optionally substituted from 1 to 3 times with halo, cyano, nitro, O(C1-6)alkyl, amido, amino or phenyl, or R1A is C6 or C10 aryl which is optionally substituted from 1 to 3 times with halo, cyano, nitro, (C1-6)alkyl, O(C1-6)alkyl, amido, amino or phenyl; R2 is (C5-6)cycloalkyl and R3 is cyclopentyl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, useful as inhibitors of the HCV NS3 protease.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM CANADA LTD
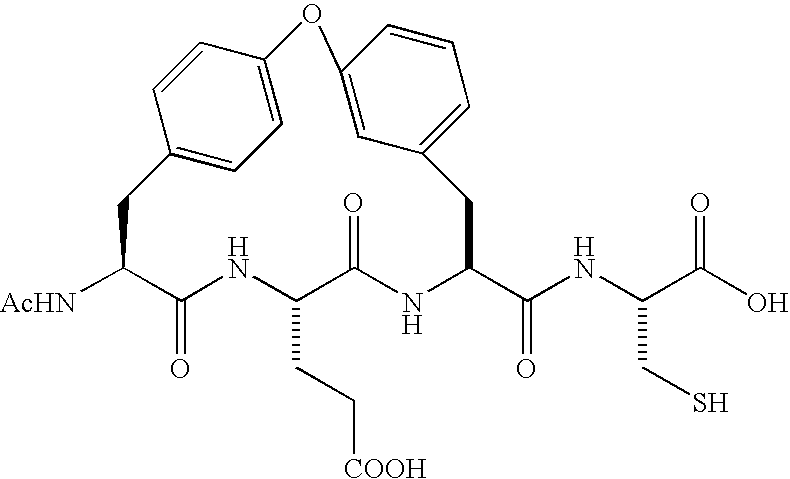
Novel peptidomimetic NS3-serine protease inhibitors of hepatitis C virus
InactiveUS20050085425A1Inhibit serine protease activityImprove overall utilizationBiocideTripeptide ingredientsSerine Protease InhibitorsPharmaceutical medicine
The present application discloses a compound, or enantiomers, stereoisomers, rotamers, tautomers, racemates or prodrug of said compound, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or solvates of said compound, or of said prodrug, said compound having the general structure shown in Formula 1: useful in the treatment or prevention or amelioration of one or more symptoms of hepatitis C.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
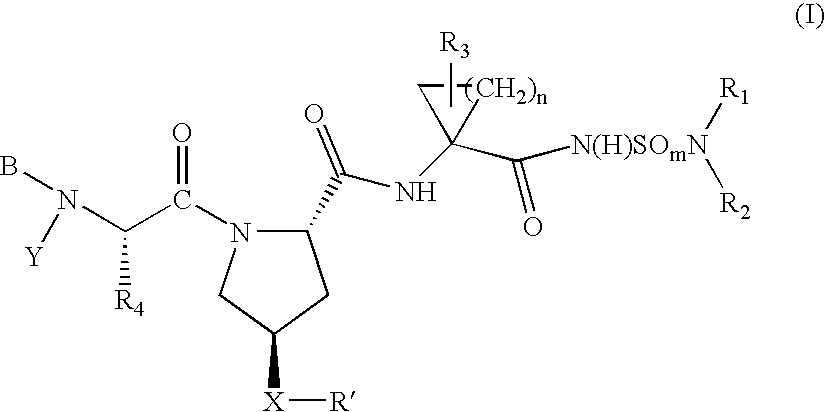
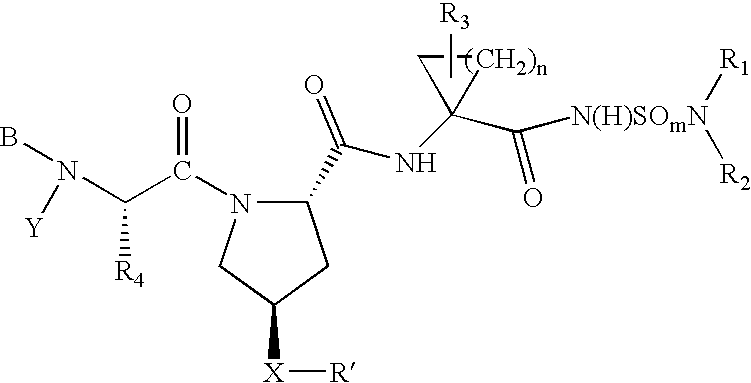
Lactam inhibitors of Hepatitis C virus NS3 protease
The present invention relates to lactams of Formula (I): or stereoisomeric forms, stereoisomeric mixtures, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof, which are useful as inhibitors of HCV NS3 protease, and to pharmaceutical compositions and diagnostic kits comprising the same, and methods of using the same for treating viral infection or as an assay standard or reagent.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Immunogenic Hepatitis C virus non-structural polypeptides
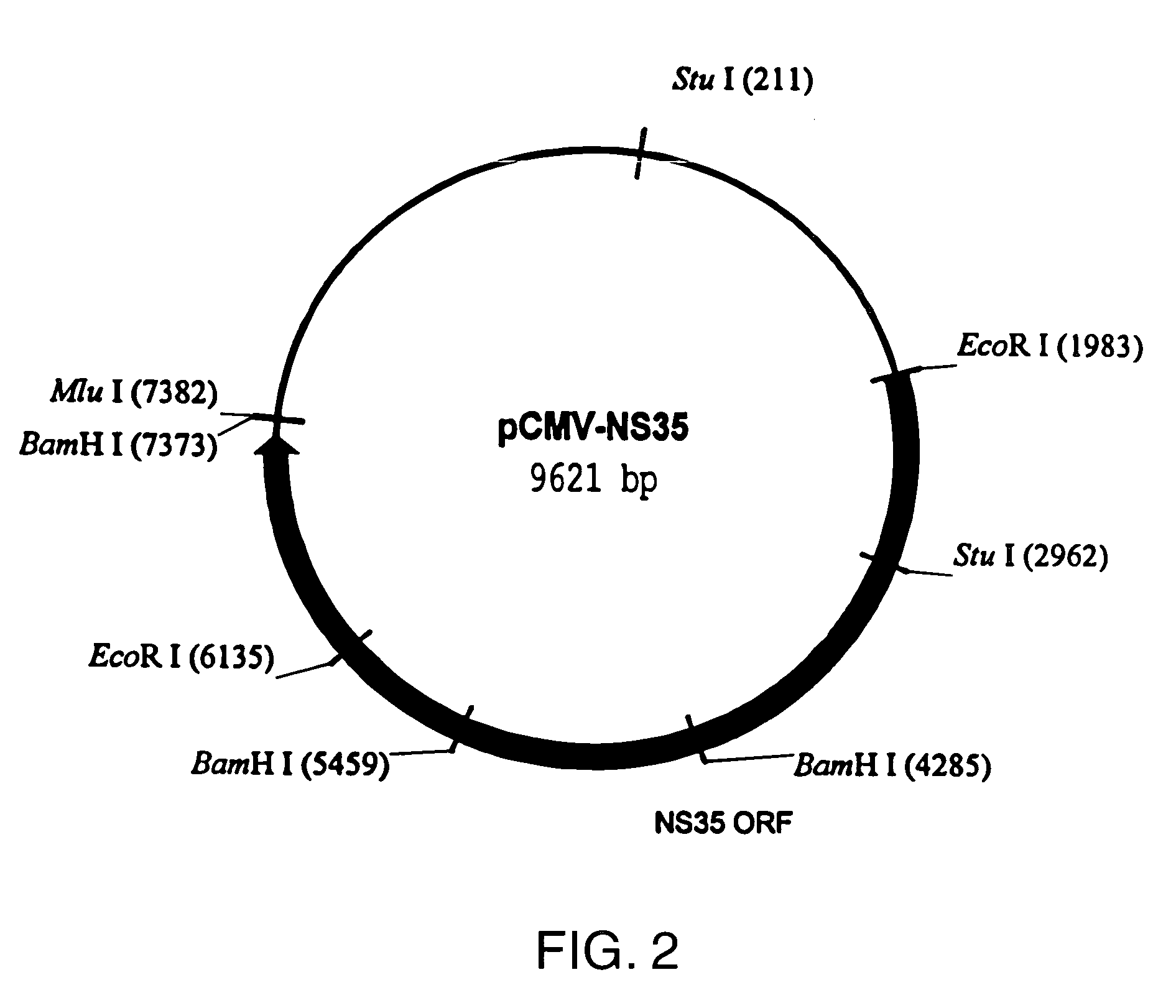
InactiveUS6986892B1Easy to produceSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsMutantPolynucleotide
Polypeptides comprising a mutant non-structural Hepatitis C virus useful in diagnostic and / or immunogenic compositions are disclosed, in which the mutant is an N-terminal mutation that functionally disrupt the catalytic domain of NS3. Polynucleotides encoding these polypeptides, host cells transformed with polynucleotides and methods of using the polypeptides and polynucleotides are also disclosed.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Direct detection of disease biomarkers in clinical specimens using cationic nanoparticle-based assays & versatile and green methods for synthesis of anisotropic silver nanostructures
InactiveUS20150017258A1Enhances thermalImprove electricityBiocideInorganic active ingredientsSilica nanoparticlesPurification methods
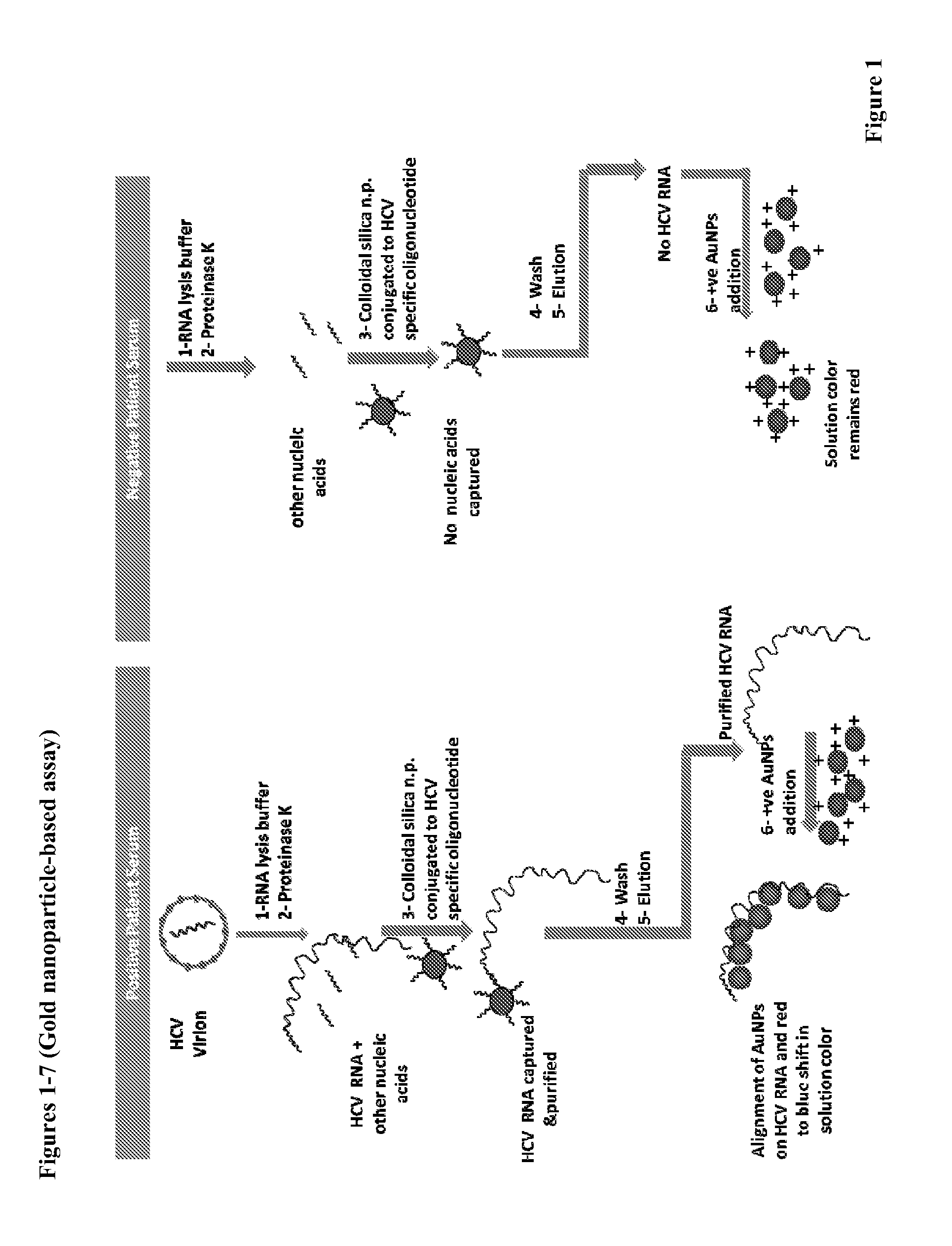
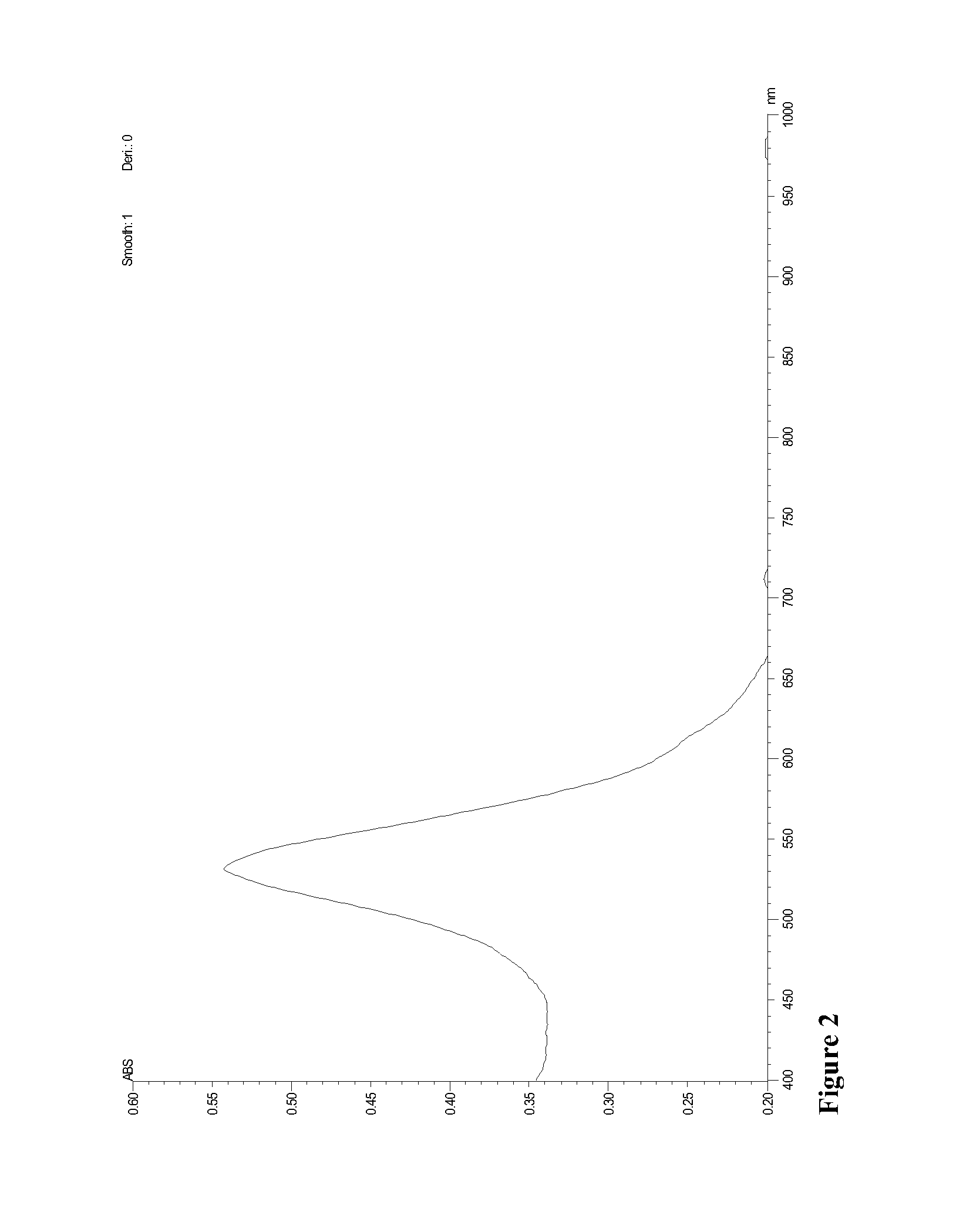
A gold nanoparticle-based assay for the detection of a target molecule, such as Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) RNA in serum samples, that uses positively charged gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) in solution based format. The assay has been tested on 74 serum clinical samples suspected of containing HCV RNA, with 48 and 38 positive and negative samples respectively. The developed assay has a specificity and sensitivity of 96.5% and 92.6% respectively. The results obtained were confirmed by Real-Time PCR, and a concordance of 100% for the negative samples and 89% for the positive samples has been obtained between the Real-Time PCR and the developed AuNPs based assay. Also, a purification method for the HCV RNA has been developed using HCV RNA specific probe conjugated to homemade silica nanoparticles. These silica nanoparticles have been synthesized by modified Stober method. This purification method enhanced the specificity of the developed AuNPs assay. The method can detect a target molecule, such as HCV RNA in serum, by employing modified silica nanoparticles to capture the target from a biological sample followed by detection of the captured target molecule using positively charged AuNPs. The assay is simple, cheap, sensitive and specific. Another aspect of the invention is anisotropic silver nanoparticles and methods of their use.
Owner:AMERICAN UNIV OF CAIRO AUC
Methods for treating HCV
ActiveUS9393256B2Fewer unwanted side-effectsReduce the potential for viral reboundBiocideDigestive systemRegimenHepatitis C virus
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
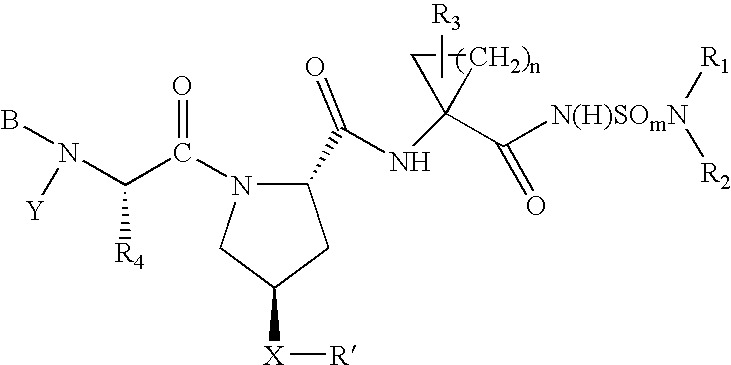
Hepatitis C virus inhibitors
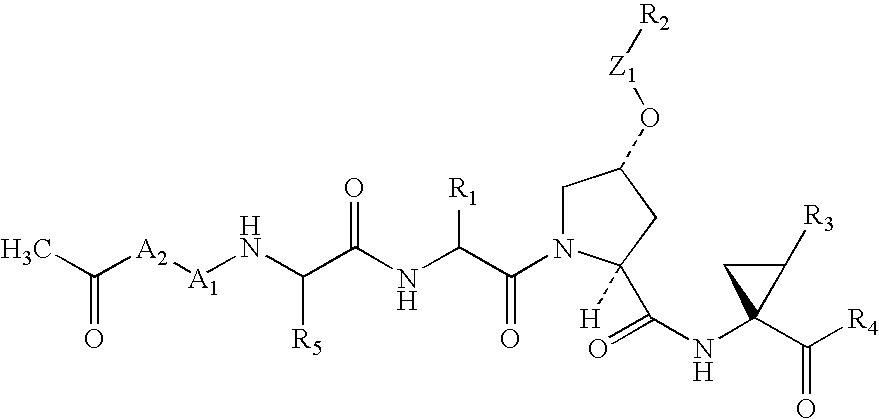
ActiveUS20050267040A1Inhibit functioningEffective treatmentBiocideDipeptide ingredientsHepatitis C virusChemistry
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
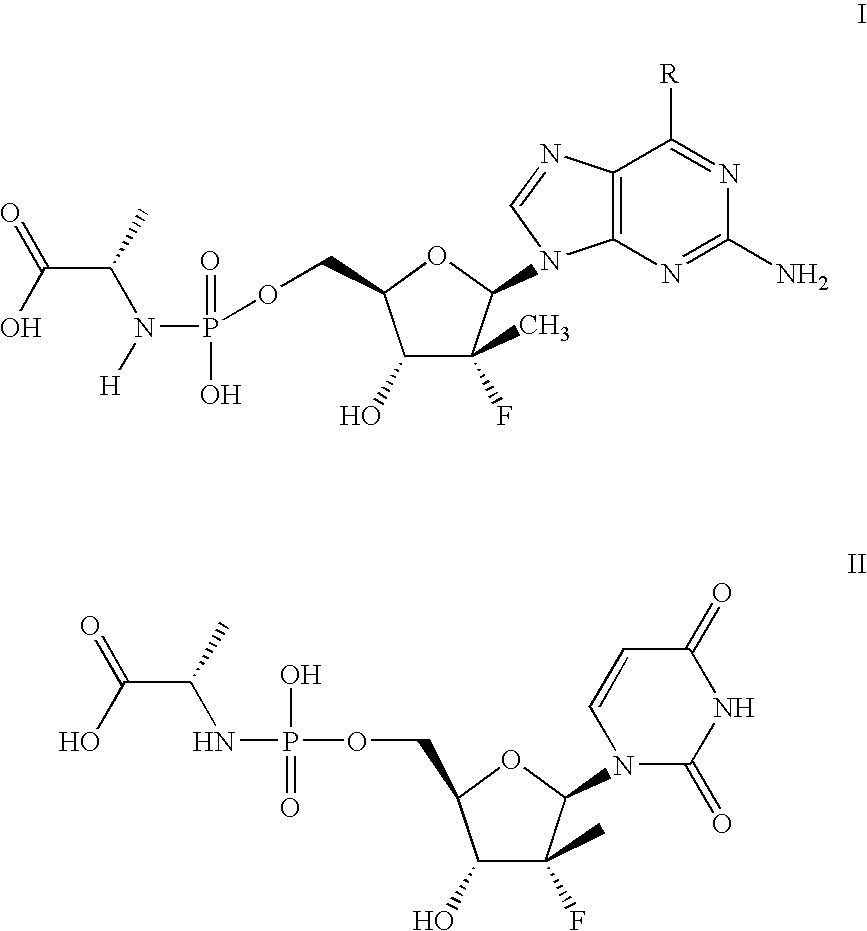
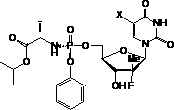
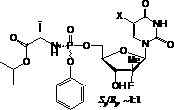
Nucleoside phosphamide prodrug as well as preparation method and application of nucleoside phosphamide prodrug
The invention relates to a nucleoside phosphamide prodrug as well as a preparation method and application of the nucleoside phosphamide prodrug. The nucleoside phosphamide prodrug is selected from any one of a compound I and a compound II, wherein in the formulas of the compound I and the compound II, X is selected from any one of F, Cl, Br and I. Compared with GS7977andGS7851, The compound I or II disclosed by the invention has more excellent resistance to hepatitis C virus, wherein the formulas I and II are respectively as shown in specifications.
Owner:ANHUI BIOCHEM UNITED PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com