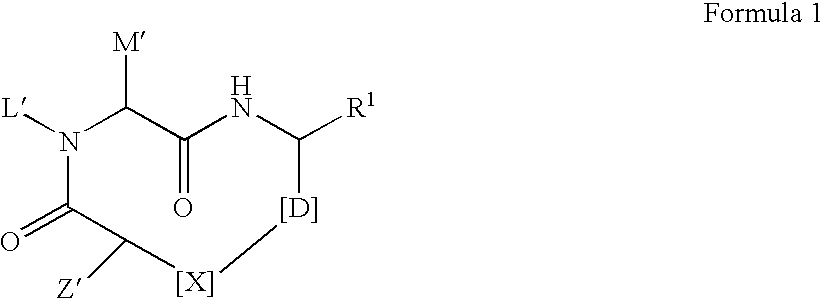
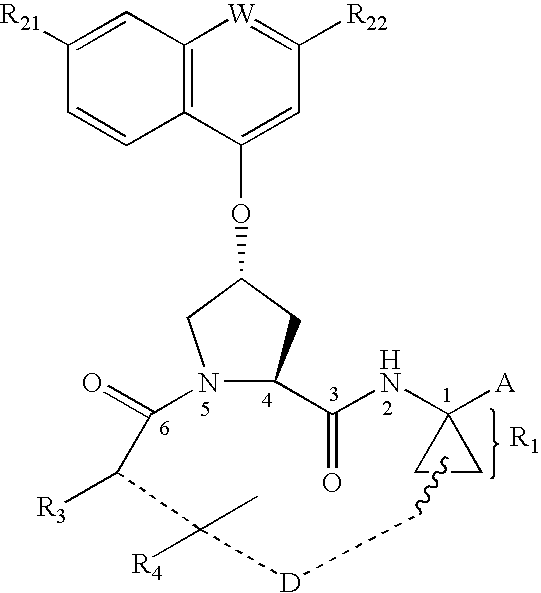
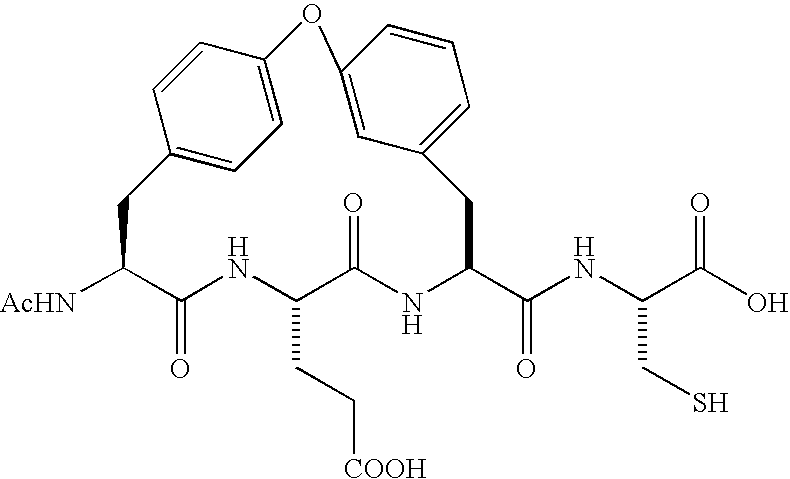
Macrocyclic inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3-serine protease
a hepatitis c virus and macrocyclic inhibitor technology, applied in the direction of cyclic peptide ingredients, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of low sustained response rate of therapies, frequent side effects, and poor treatment progress of patients with hcv infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
PREPARATIVE EXAMPLE 1
[0342]
[0343] The synthesis of 1b can be accomplished using the procedure of (1) Myers, A. G.; Gleason, J. L.; Yoon, T.; Kung, D. W.; J. Am. Chem. Soc 1997, 119, 656; (2) Myers, A. G.; Schnider, P.; Kwon, S.; Kung, D. W.; J. Org. Chem., 1999, 64, 3322.; or (3) Myers, A. G.; Gleason, J. L.; Org. Synth. 1998, 76, 57.
[0344] A solution of amine 1a (24 g, 120 mmol) in THF (300 mL) was treated with anhydrous LiCl (16.80 g, 400 mmol) over 0.5 h and stirred till the reaction mixture turns homogeneous. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0° C. and treated with a THF solution of LiHMDS (66.80 g, 400 mmol in 300 ml of THF) over 20 min. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0° C. for 0.5 h and treated with 6-bromohexene (19.44 g, 120 mmol) and stirred at rt. for 24 h. The reaction mixture was dissolved in aq. 1 M HCl and concentrated in vacuo to remove THF. The mostly aq. layer was further diluted with 3M aq HCl (300 mL) and extracted with ether (2×200 mL). The aqueous layer w...
example 2
PREPARATIVE EXAMPLE 2
[0365]
[0366] A solution of alcohol 1i (1.1 g, 2.25 mmol) in methanol (30 mL) was treated with Pd / C (10% w / w, 100 mg) and hydrogenated at 60 psi for 3 h. The reaction mixture was filtered through a plug of celite, concentrated in vacuo to yield 2a which was used in the next step without further purification.
[0367] Crude 2a from step A was oxidized using Dess-Martin reagent (1.14 g, 2.68 mmol) following the procedure similar to step H (preparative example 1) to yield 2b (760 mg) as a colorless foam.
[0368] MS (ESI), m / z, relative intensity 1005 [(2M+Na)+, 10], 530 [(M+K)+, 20], 514 [(M+Na)+, 90], 492 [(M+1)+, 30], 436 (40), 392 (100).
[0369] Compound 2b (200 mg, 0.41 mmol) from step B was converted to 2c (250 mg) using CH3COOH (60 mg) and methylisocyanoacetate (99 mg, 1 mmol) following the procedure similar to step I (preparative example 1) as a mixture of diastereomers.
[0370]1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz, mixture of diastereomers) 8.05, 7.93 (d, 1H), 6.60 (d, 1H, J=...
example 3
PREPARATIVE EXAMPLE 3
[0375]
[0376] A solution of 2 (40 mg, 0.0053 mmol) in HCOOH (2 mL) was stirred at rt. for 2 h and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was repeatedly dissolved in toluene and dried in vacuo to remove residual formic acid. The residue was dissolved in CH2Cl2 / DMF (1 mL each) and treated with tBuNCO (10 μL) and NMM (15 μL) at 0° C. and left in the refrigerator for 12 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo and purified by chromatography (SiO2, acetone / hexanes 1:2) to yield 3 (21 mg) as a colorless solid.
[0377] MS (ESI), m / z, relative intensity 774 [(M+Na)+, 50], 752 [(M+1)+, 70], 653 (90), 420 (30), 297 (30), 148 (100), 134 (40).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electric dipole moment | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com