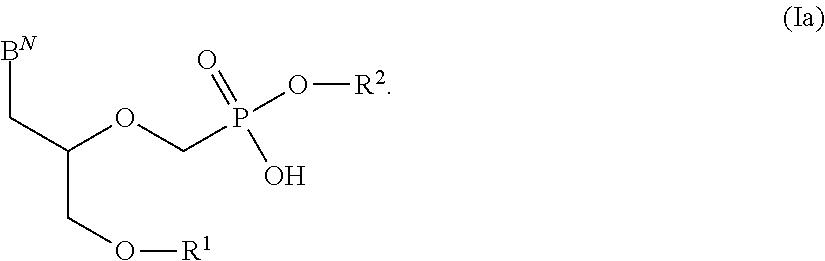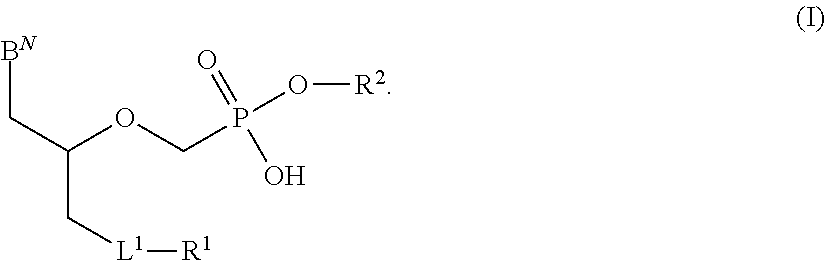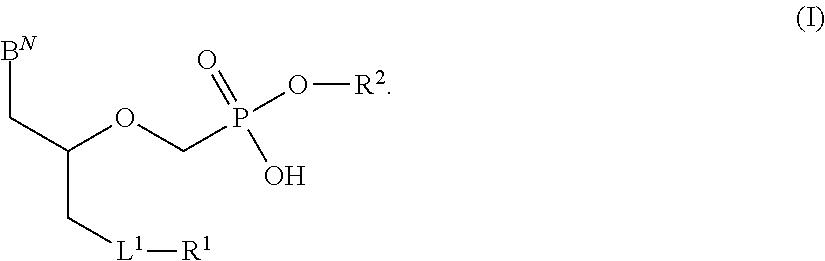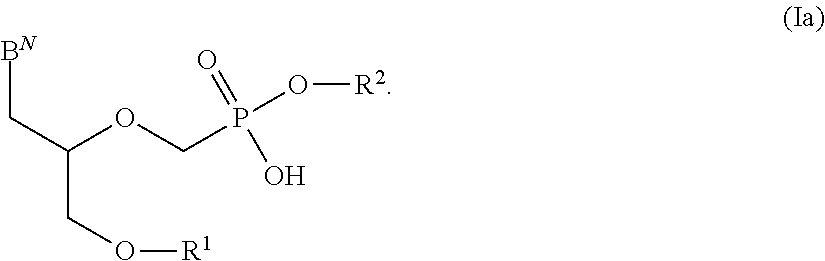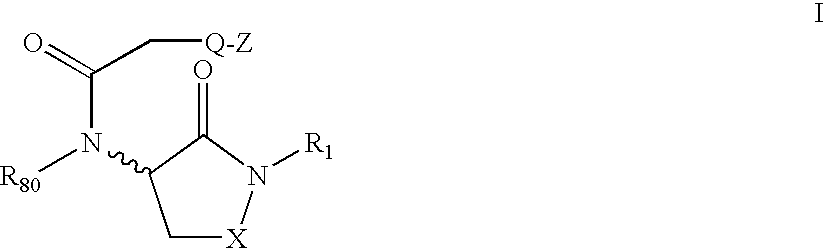Patents
Literature
56 results about "Hcv hepatitis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
HCV is an acronym for the Hepatitis C virus. To put it another way, HCV is the virus that causes Hep C. In turn, Hep C is a liver disease that leads cirrhosis, or a hardening, of the liver. There are seven different types of HCV. These are labeled genotypes 1 to 7. Genotype 1 is the most common form of Hep C,...
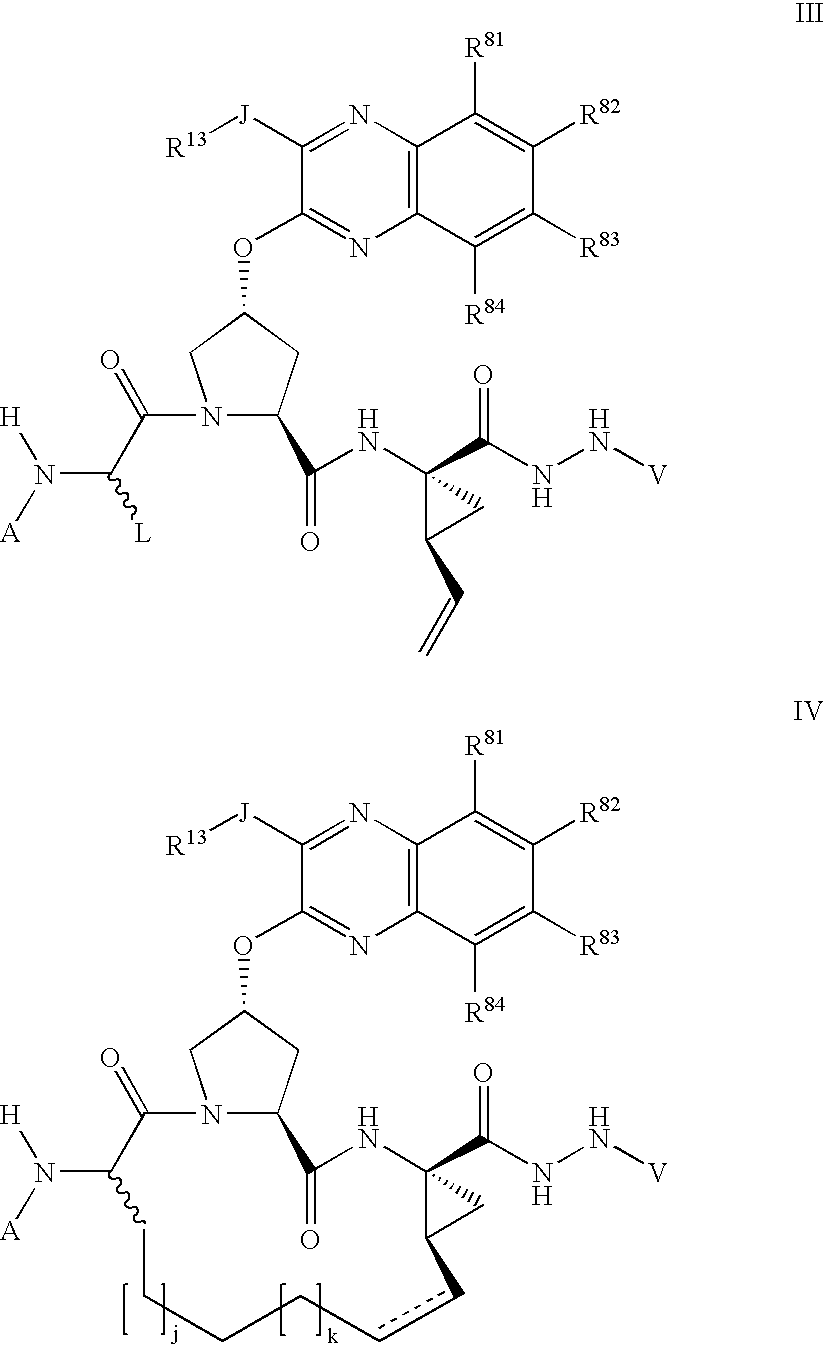
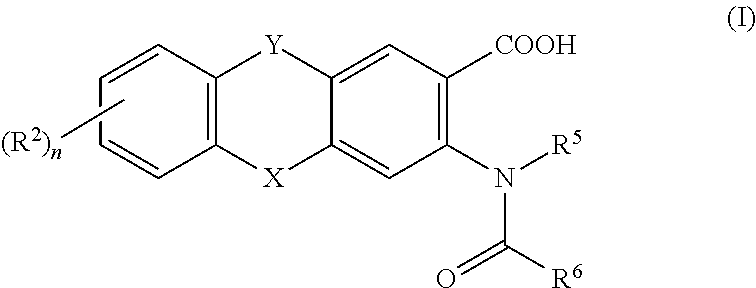
Macrocyclic inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3-serine protease
InactiveUS20050119168A1HCV infectionImprove overall utilizationBiocideAntiviralsDiseaseStructural formula
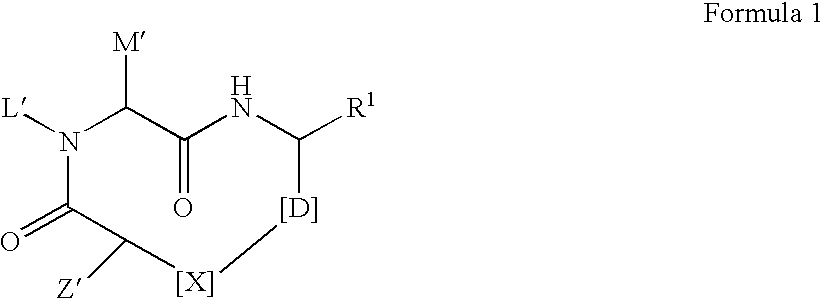
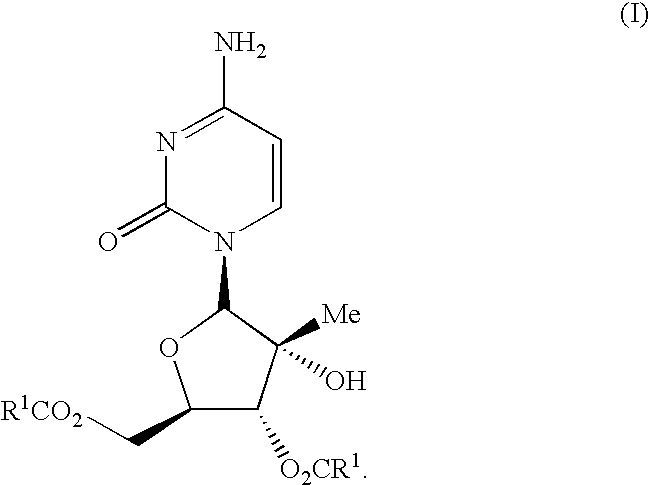
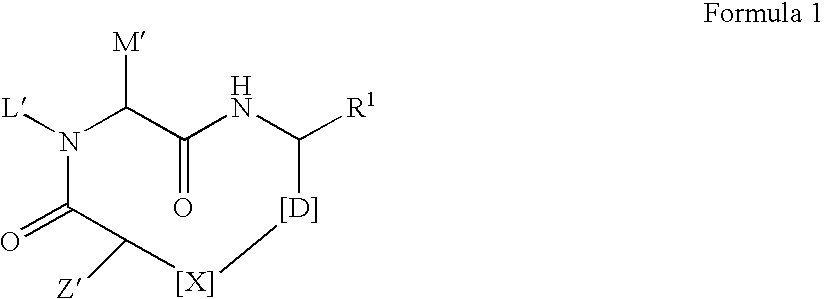
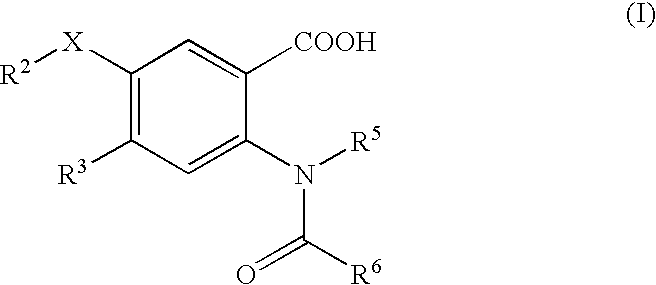
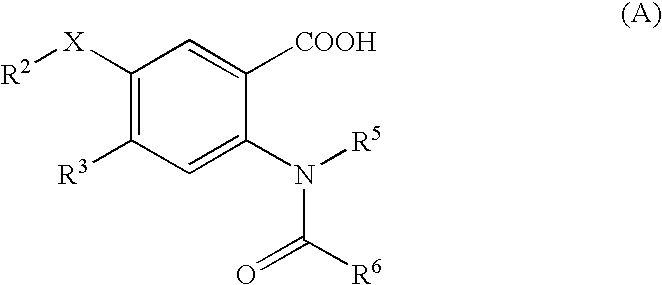
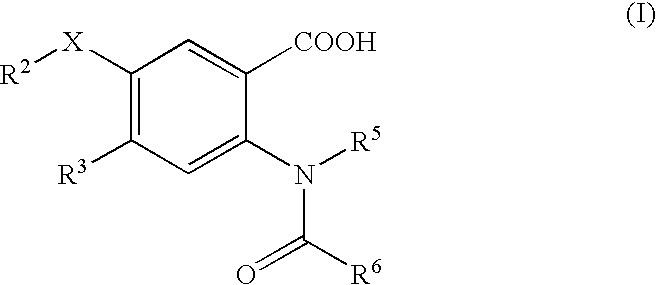
The present invention discloses novel compounds which have HCV protease inhibitory activity as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of using them to treat disorders associated with the HCV protease. The novel compounds typically include a 15-20 member macrocycle and have the general structure of structural Formula 1: wherein Z′, L′, M′, R1, X and D are defined herein.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease
The present invention discloses novel compounds which have HCV protease inhibitory activity as well as methods for preparing such compounds. In another embodiment, the invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds as well as methods of using them to treat disorders associated with the HCV protease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Hydrazide-containing hepatitis c serine protease inhibitors
The present invention relates to novel hydrazide-containing compounds of Formula I or Formula II, including pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, or prodrugs thereof which inhibit serine protease activity, particularly the activity of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3-NS4A protease. Consequently, the compounds of the present invention interfere with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus and are also useful as antiviral agents. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aforementioned compounds for administration to a subject suffering from HCV infection. The invention also relates to methods of treating an HCV infection in a subject by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compounds of the present invention.
Owner:ENANTA PHARM INC
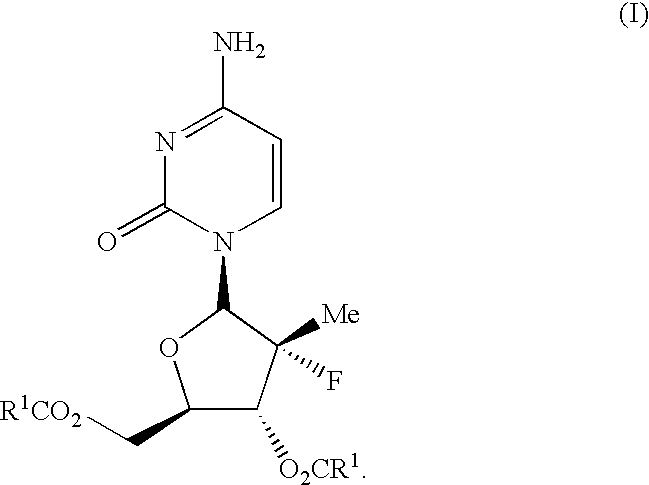
Antiviral nucleosides
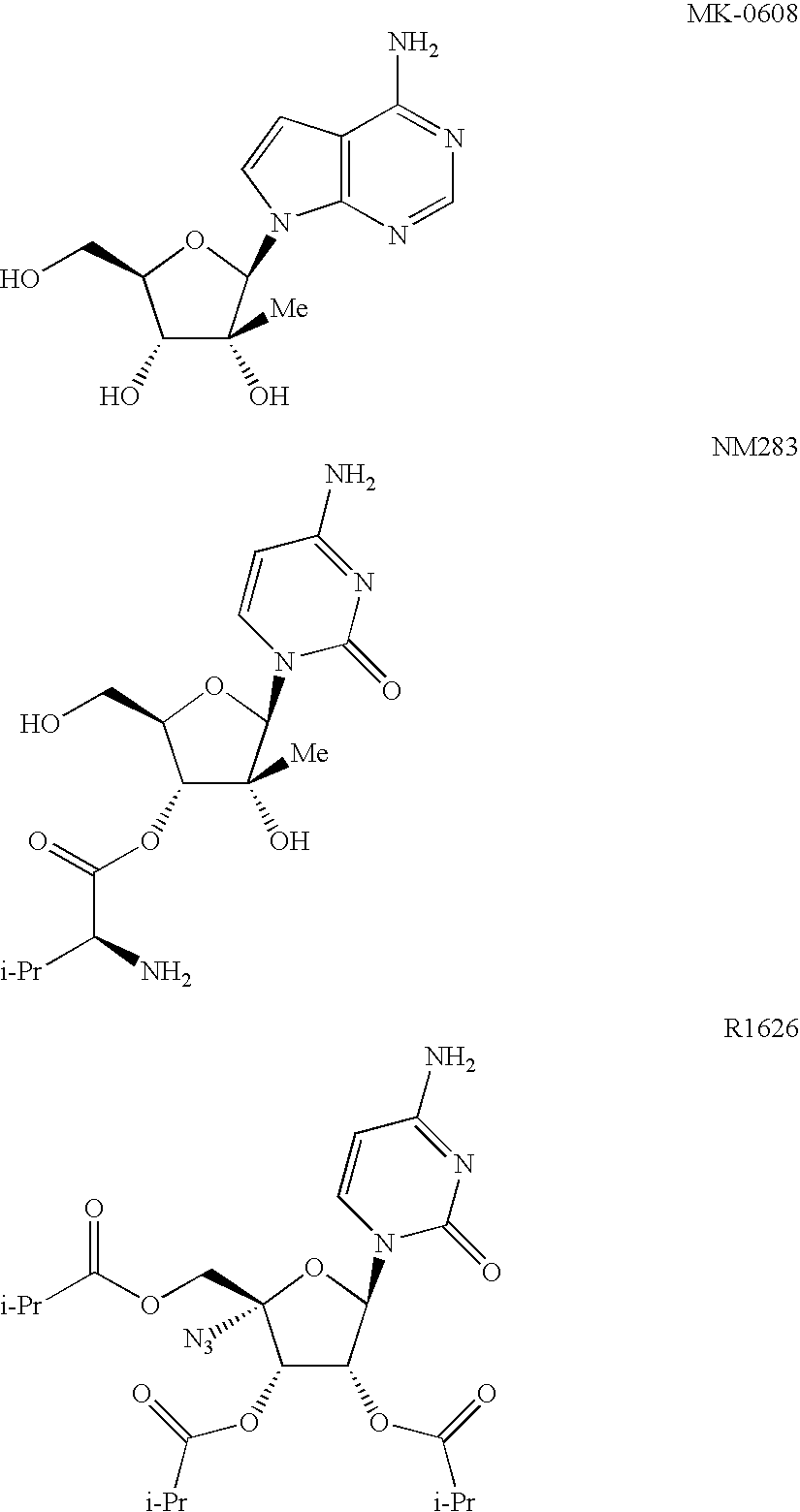
Compounds having the formula I wherein R1 is as herein defined are Hepatitis C virus NS5b polymerase inhibitors. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for inhibiting hepatitis replication, and processes for making the compounds of formula I
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC +1
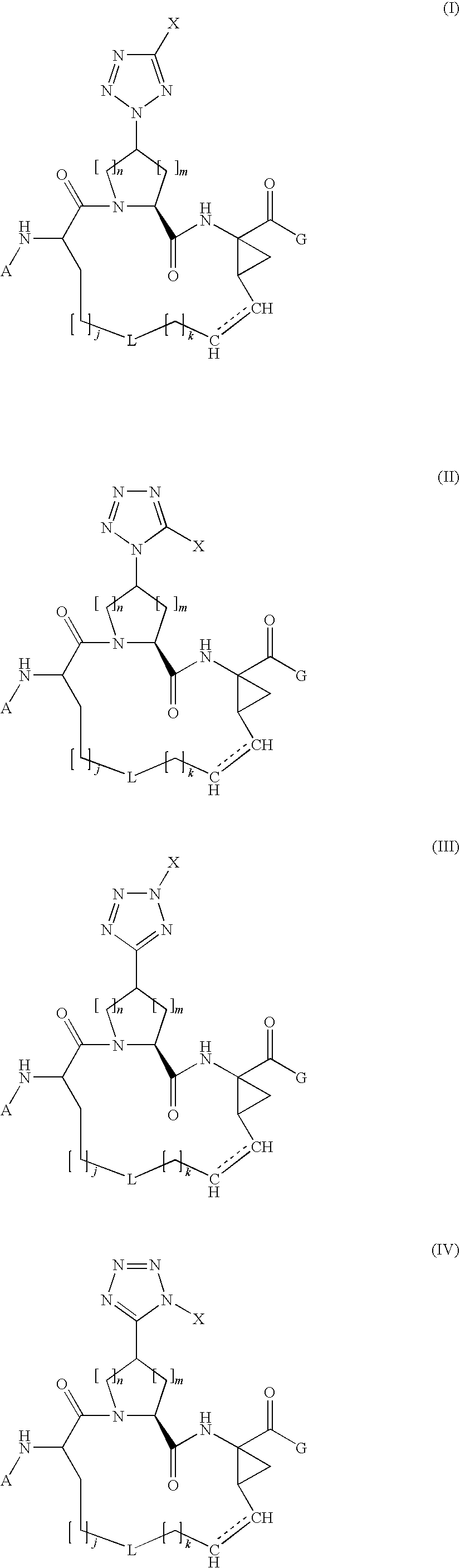
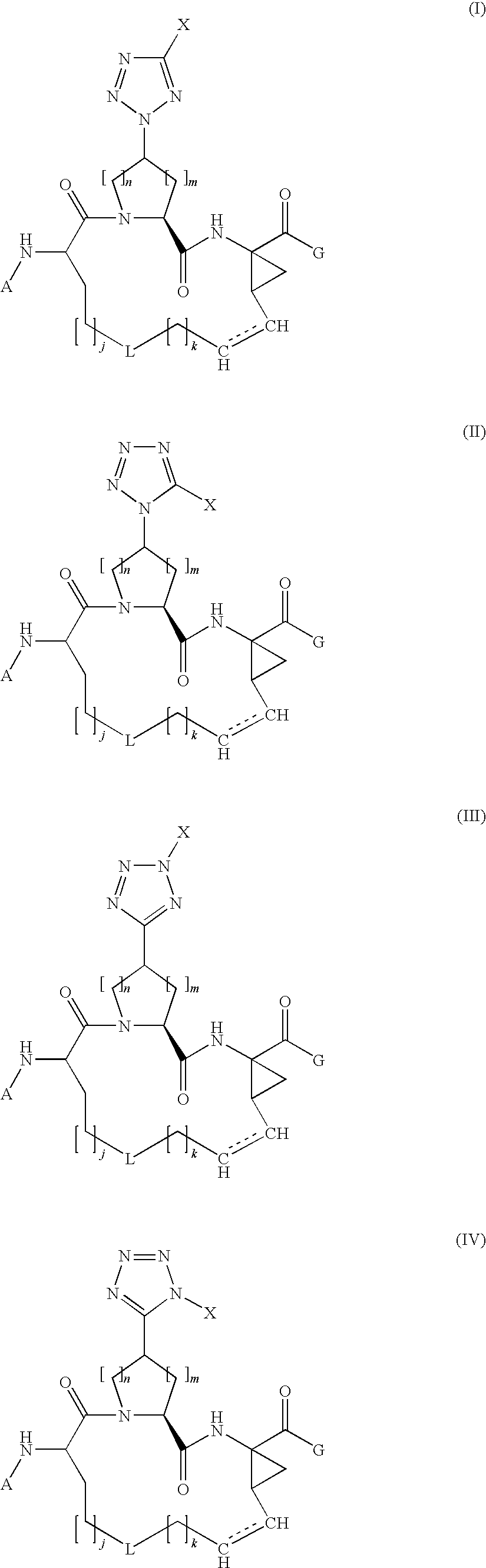
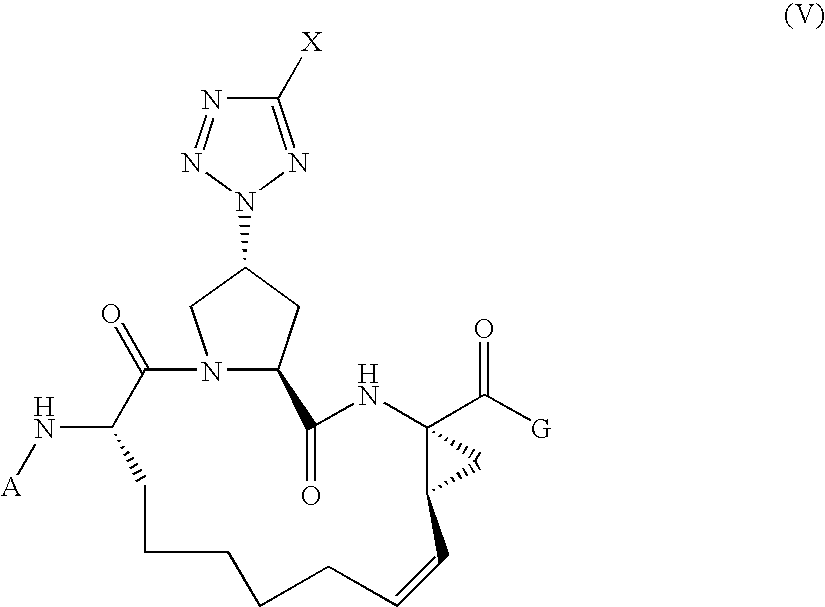
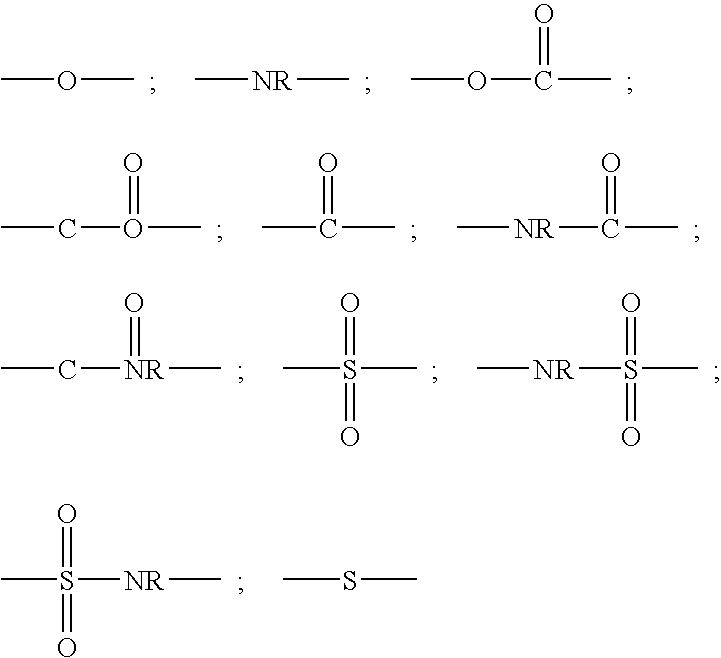
Tetrazolyl macrocyclic hepatitis c serine protease inhibitors
The present invention relates to compounds of Formula I, II, III or IV, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, or prodrugs thereof:which inhibit serine protease activity, particularly the activity of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3-NS4A protease. Consequently, the compounds of the present invention interfere with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus and are also useful as antiviral agents. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aforementioned compounds for administration to a subject suffering from HCV infection. The invention also relates to methods of treating an HCV infection in a subject by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of the present invention.
Owner:ENANTA PHARM INC
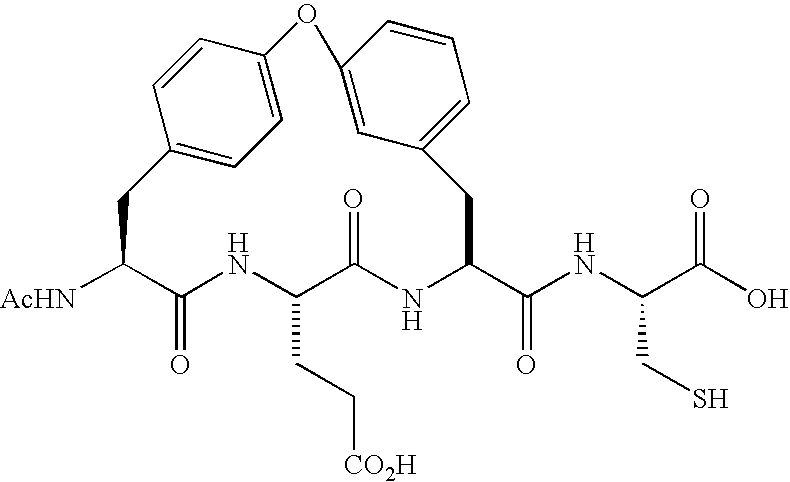
Peptide inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease
InactiveUS6867284B1Organic compound preparationTripeptide ingredientsProteinase activityHcv hepatitis
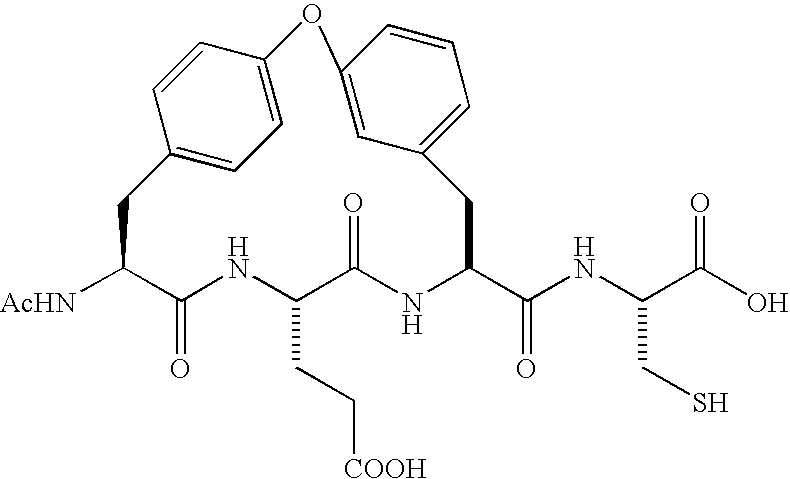
Fluorinated oligopeptides, especially those having 4,4-difluoro-2-amino butyric acid at the C terminus, may be effective inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease. Examples of hexapeptides of the invention, optimized for binding in the S1 specificity pocket of the enzyme, may display IC50s at the sub-micromolar level. Embodiments of tripeptides of the invention, having a keto-acid group at the C-terminus are, likewise, potent inhibitors of NS3 protease.
Owner:IST DI RICERCHE DI BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE P ANGELETTI
Phosphonates with reduced toxicity for treatment of viral infections
There are provided, inter alia, acyclic nucleoside phosphonate compounds having reduced toxicity and enhanced antiviral activity, and pharmaceutically accepted salts and solvates thereof. There are also provided methods of using the disclosed compounds for inhibiting viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting viral reverse transcriptase, inhibiting replication of virus, including hepatitis C virus or a human retrovirus, and treating a subject infected with a virus, including hepatitis C virus or a human retrovirus.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Acyclic, pyridazinone-derived hepatitis c serine protease inhibitors
InactiveUS20090035267A1Inhibit serine protease activityInhibitory activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPyridazinePharmaceutical medicine
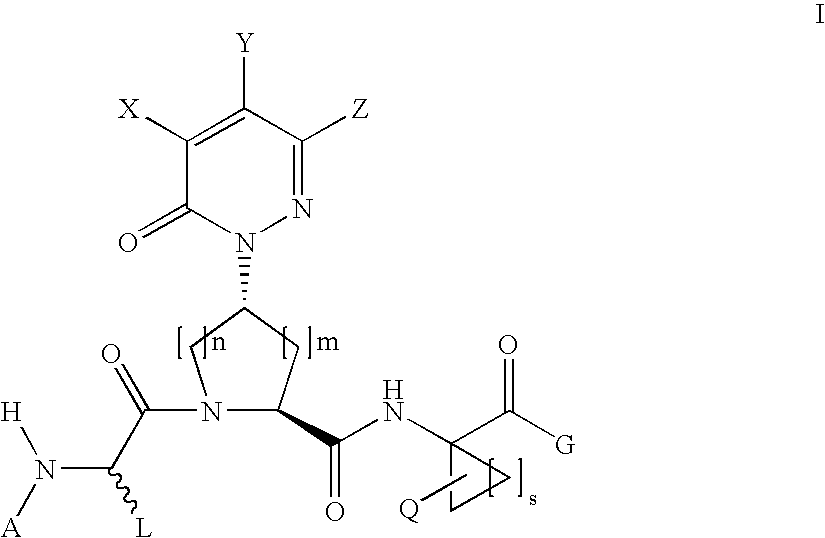
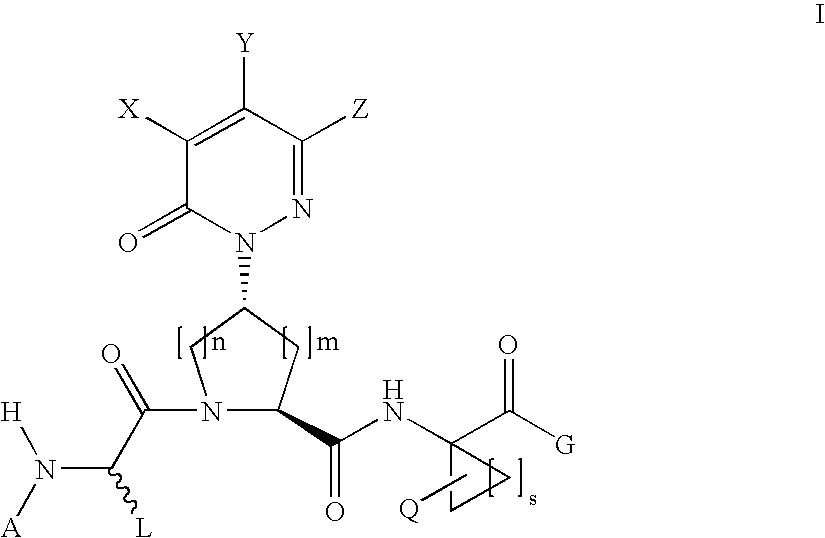
The present invention relates to compounds of Formula I, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, or prodrugs thereof, which can inhibit serine protease activity, particularly the activity of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3-NS4A protease. Consequently, the compounds of the present invention interfere with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus and are also useful as antiviral agents. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aforementioned compounds for administration to a subject suffering from HCV infection. The invention also relates to methods of treating an HCV infection in a subject by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of the present invention.
Owner:ENANTA PHARM INC
Antiviral nucleosides
Compounds having the formula I wherein R1 is as herein defined are Hepatitis C virus NS5b polymerase inhibitors. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for inhibiting hepatitis replication, processes for making the compounds and synthetic intermediates used in the process
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Hepatitis C virus-derived peptides capable of inducing cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses
InactiveUS7220420B2Strengthen and boostSubstantial homologySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsCtl epitopeChronic hepatitis
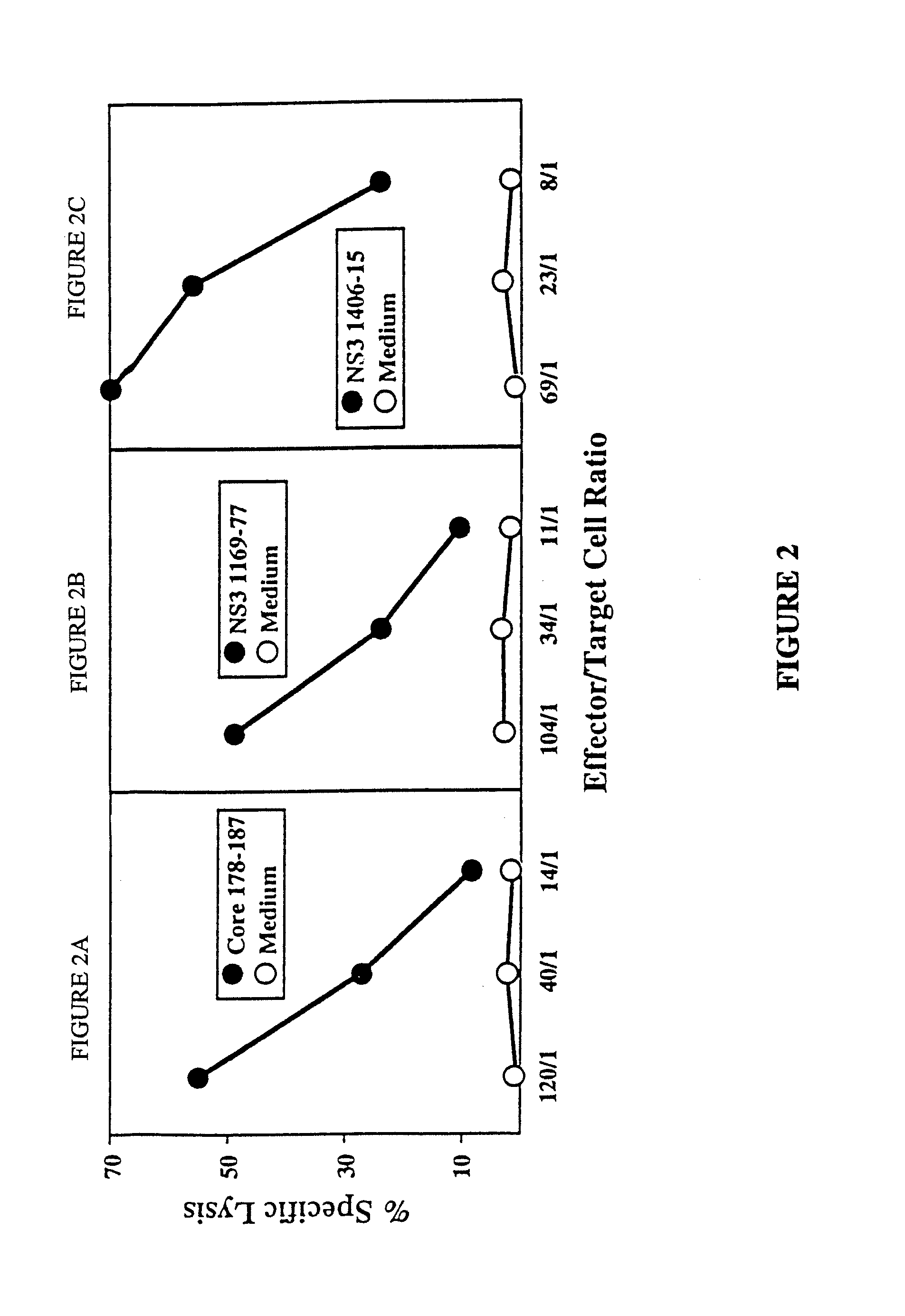
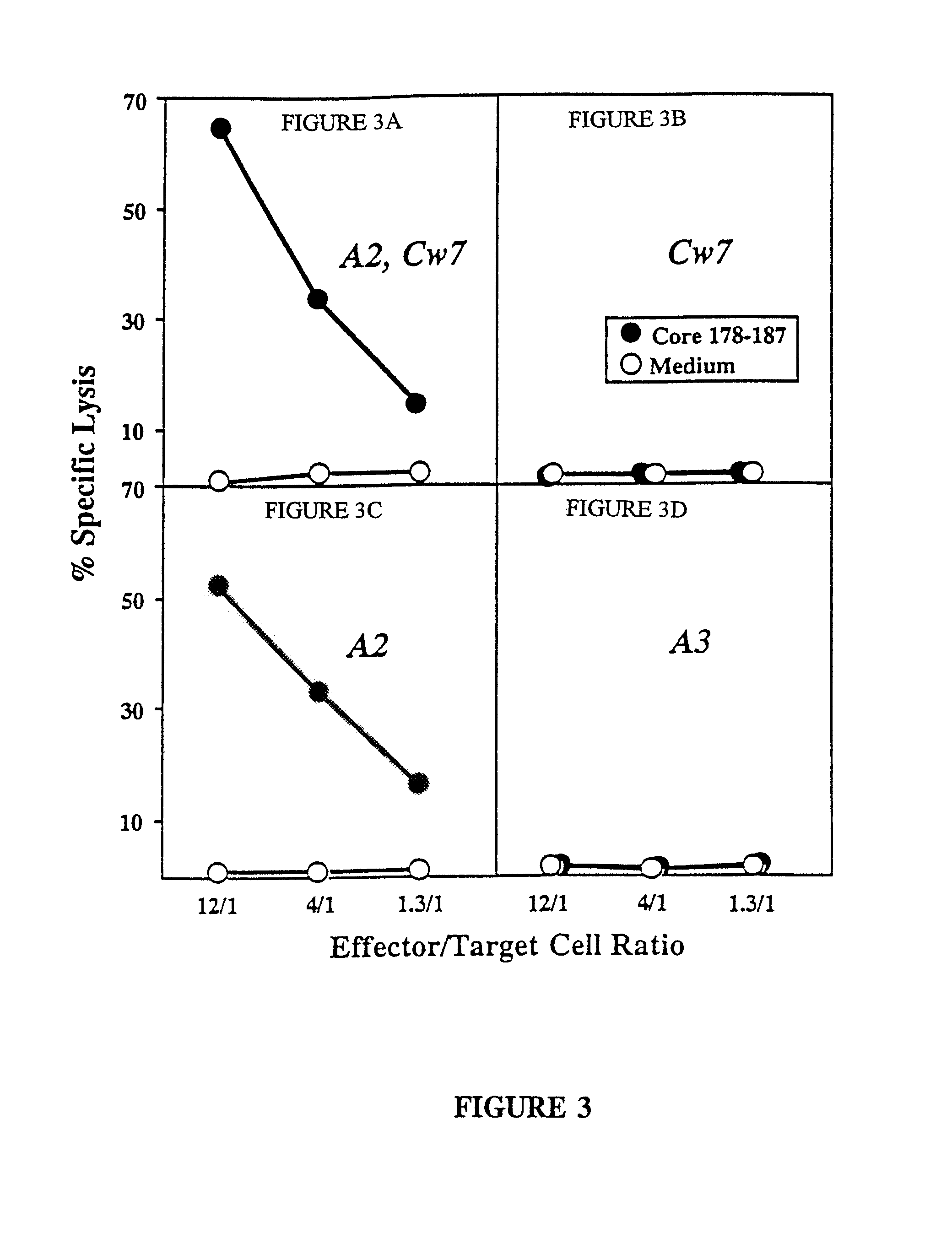
The present invention is directed to a molecule comprising a polypeptide having substantial homology with a CTL epitope selected from the group consisting of ADLMGYIPLV (Core131-140; SEQ ID NO:1), LLALLSCLTV (Core178-187; SEQ ID NO:2), QLRRHIDLLV (SEQ ID NO:55), LLCPAGHAV (NS31169-1177; SEQ ID NO:26), KLVALGINAV (NS31406-1415; SEQ ID NO:28), SLMAFTAAV (NS41789-1797; SEQ ID NO:34), LLFNILGGWV (NS41807-1816; SEQ ID NO:35), and ILDSFDPLV (NS52252-2260; SEQ ID NO:42). Such molecules are used for the treatment and prevention of acute or chronic HCV hepatitis; suitable pharmaceutical compositions and methods using such compositions are disclosed.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
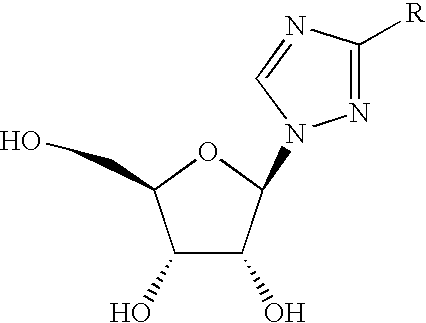
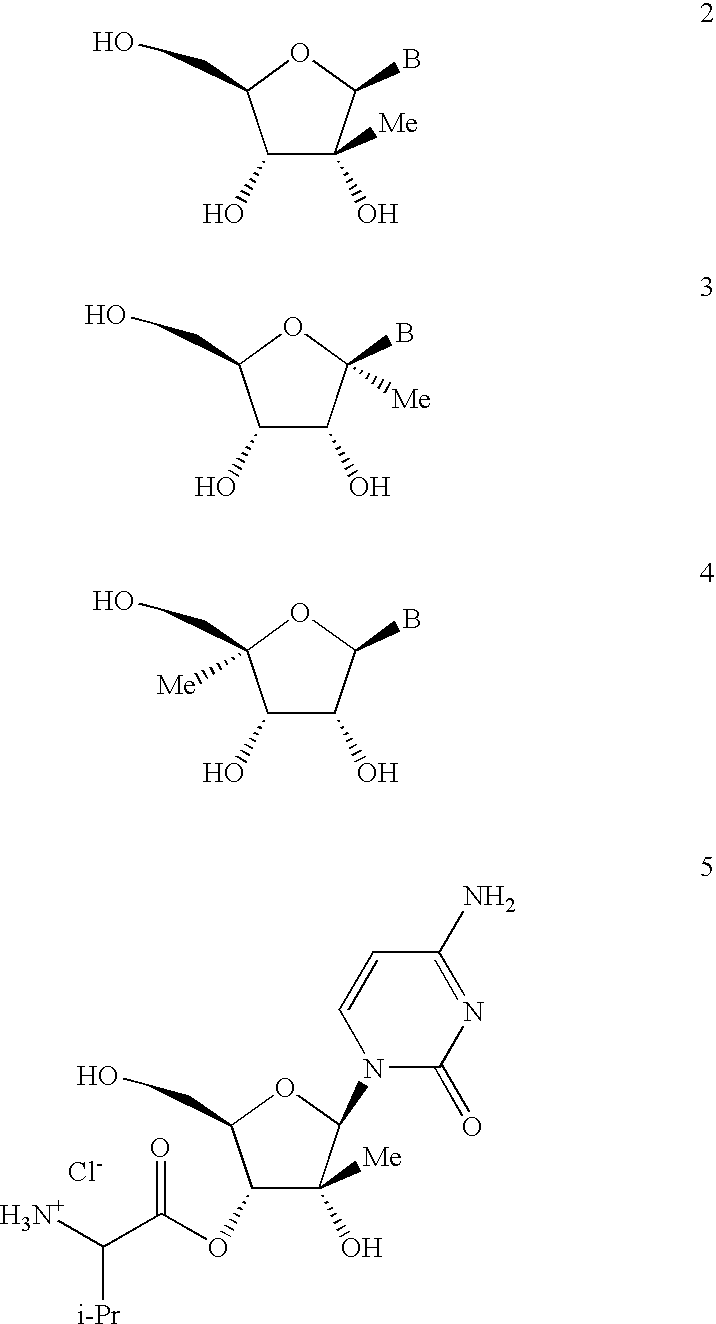
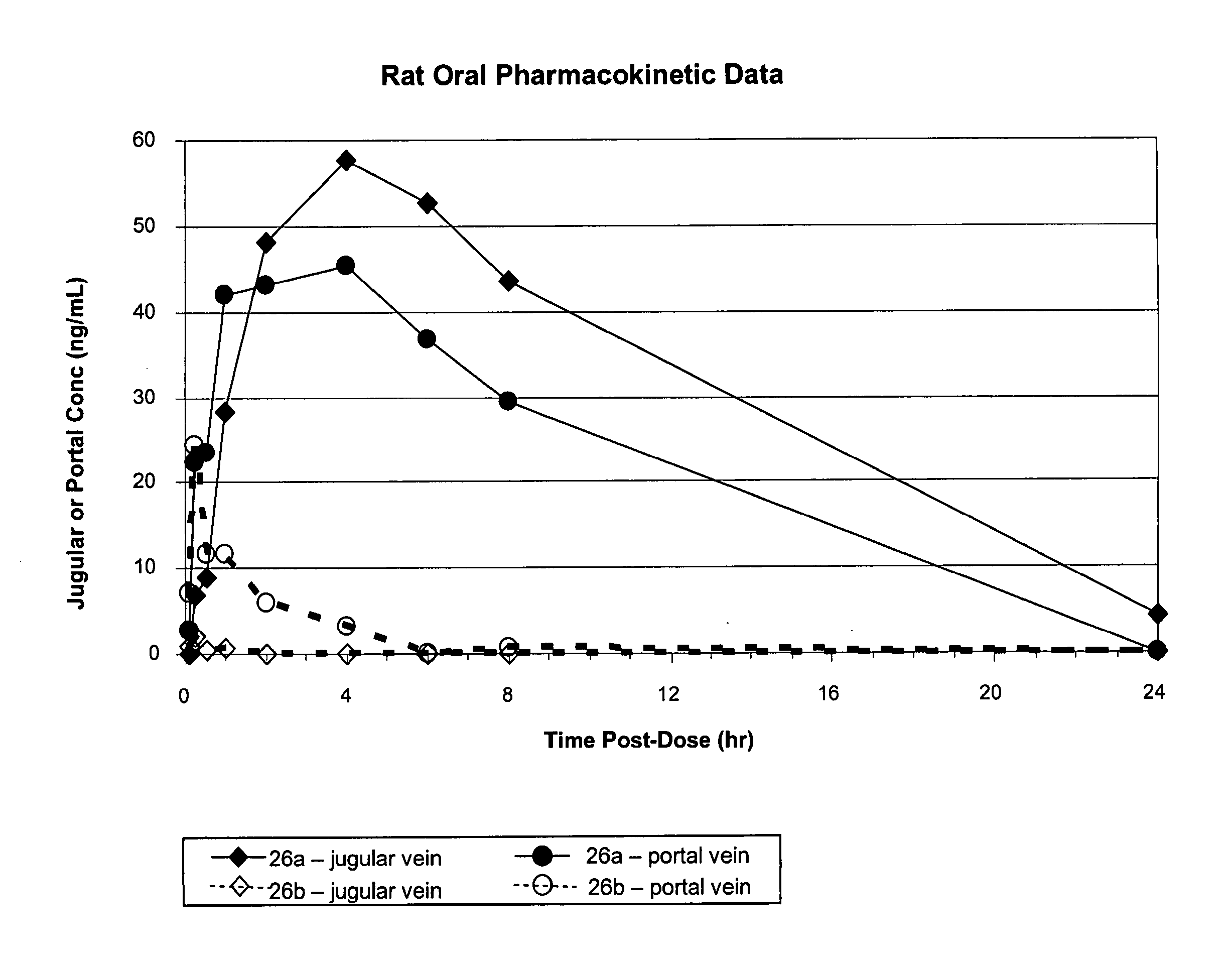
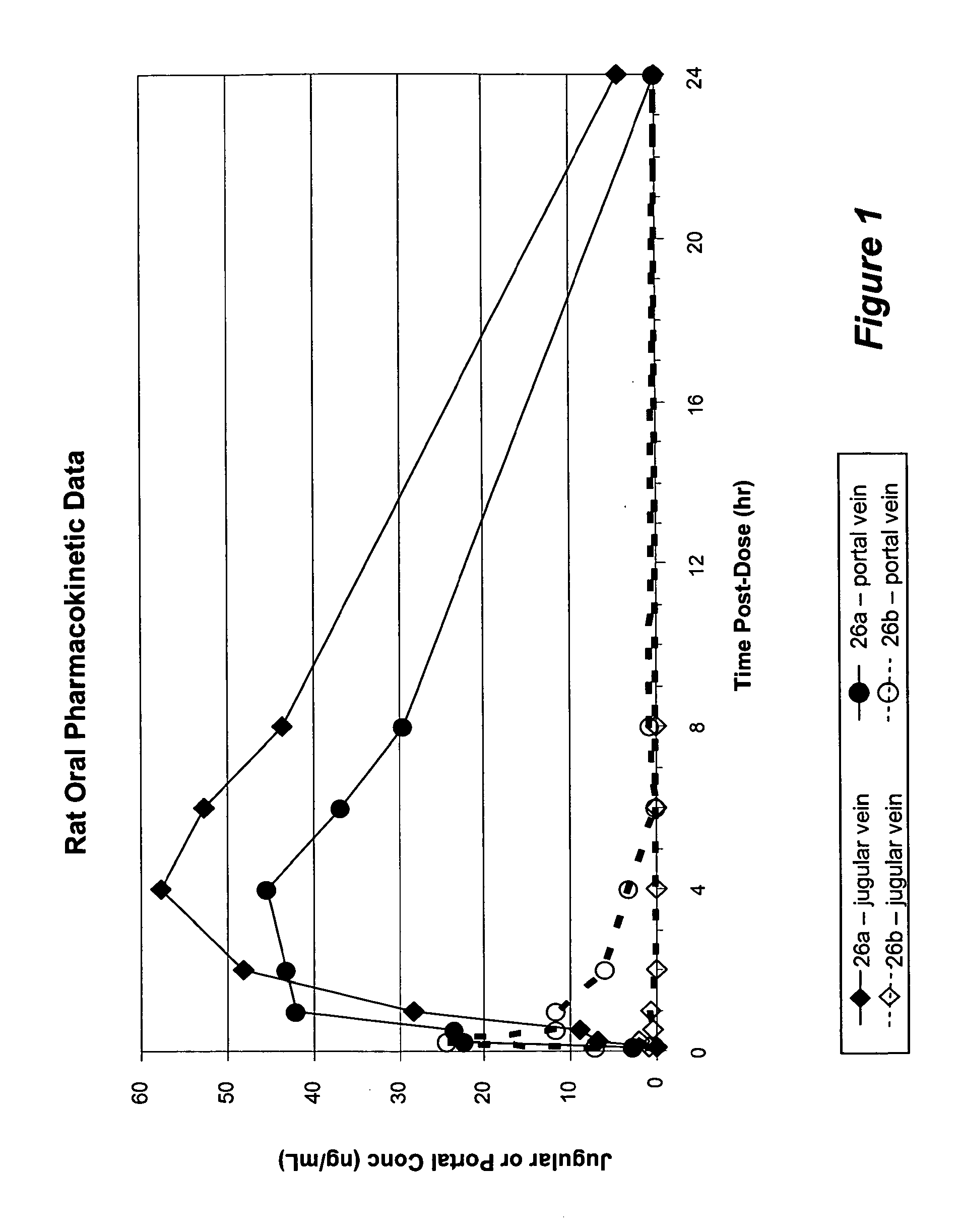
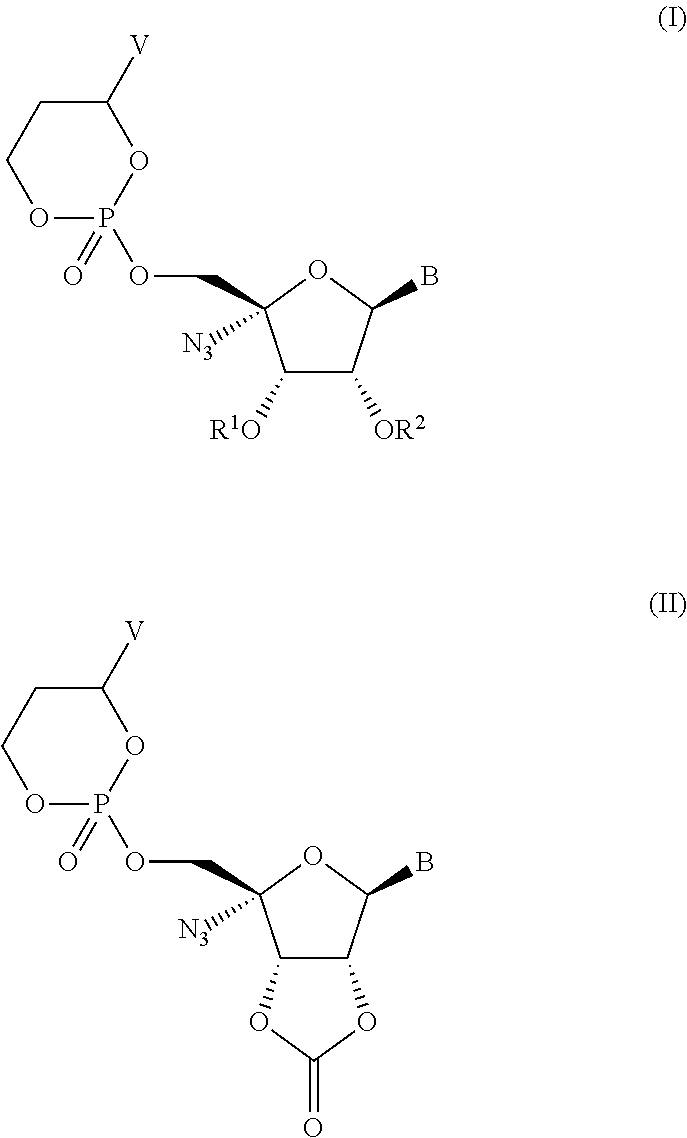
Nucleoside prodrugs and uses thereof
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
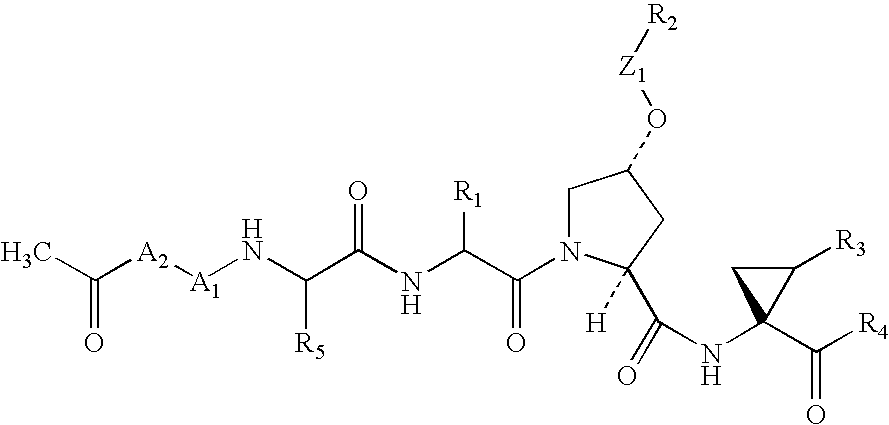
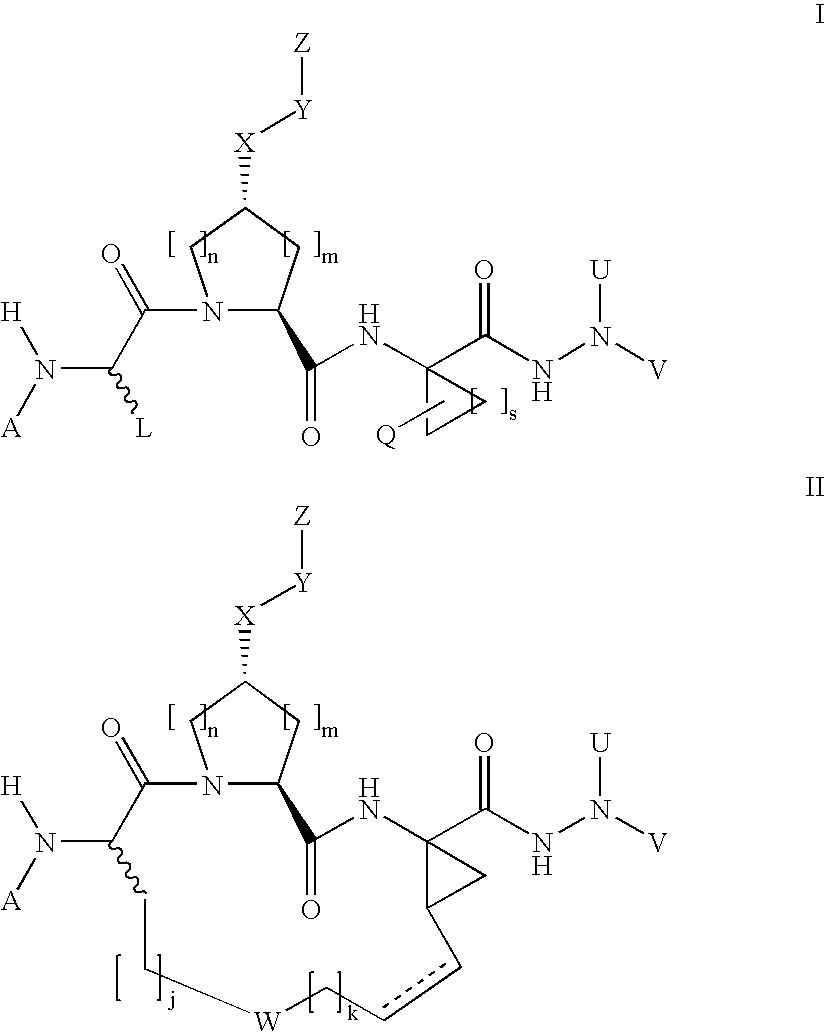
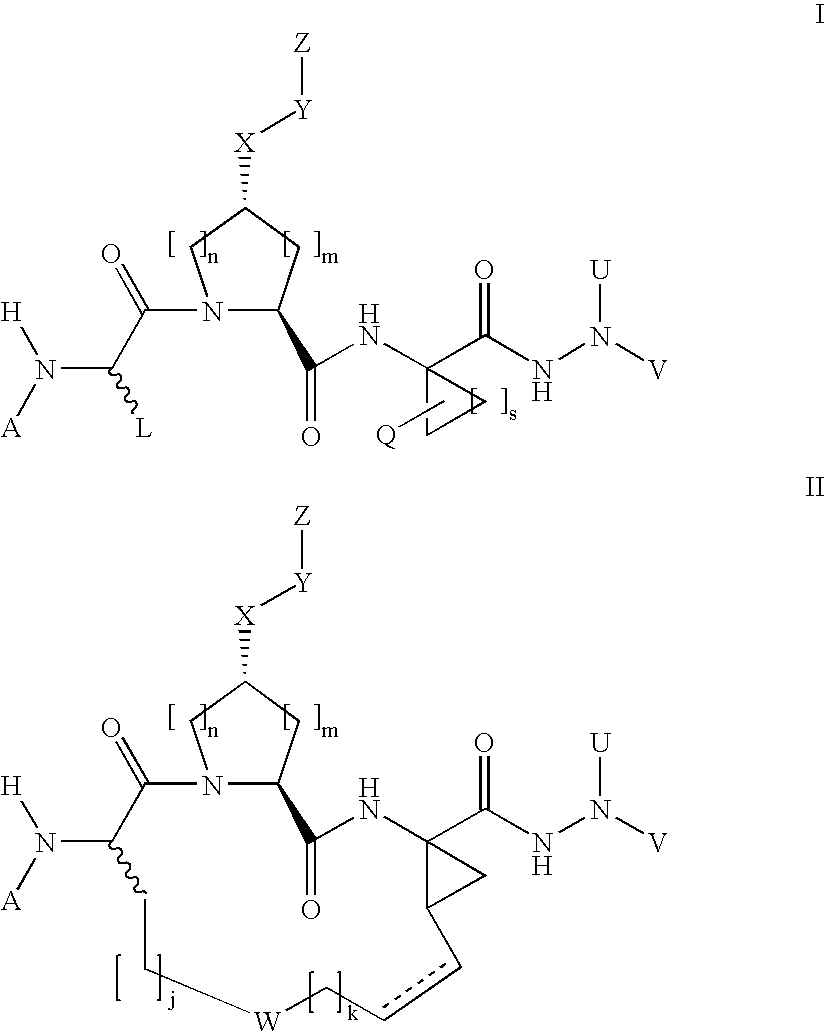
Hcv protease inhibitors
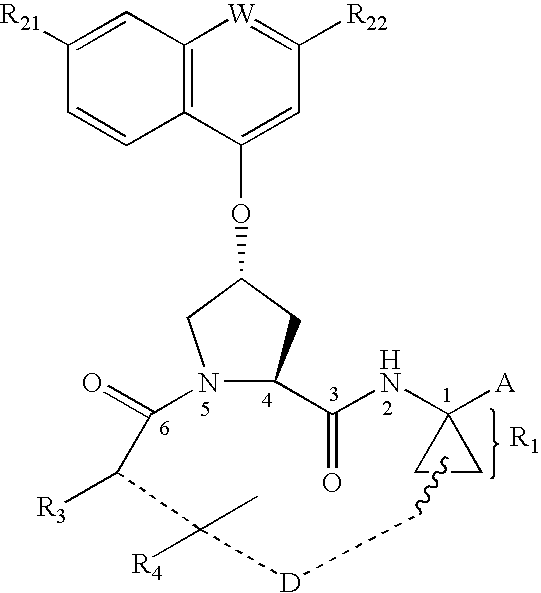
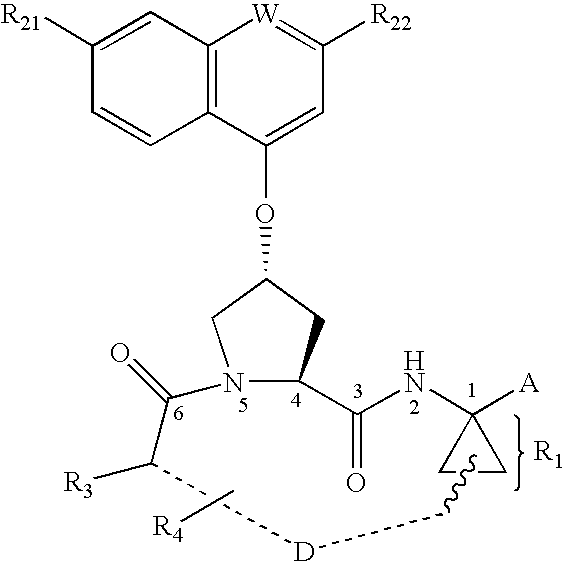
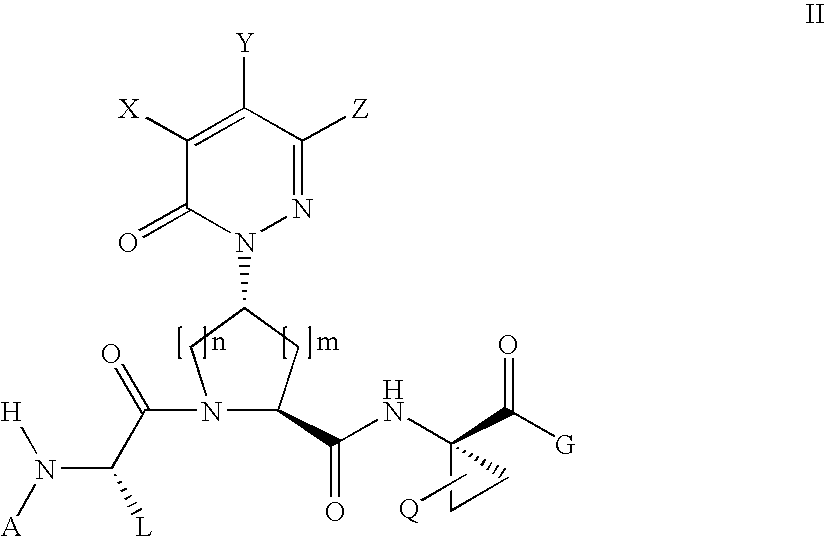
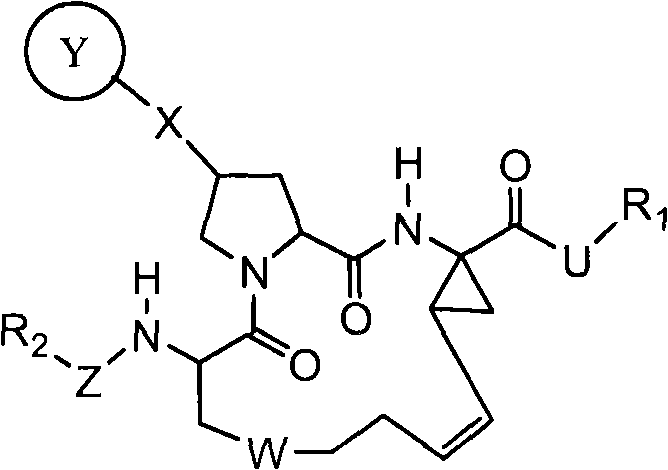
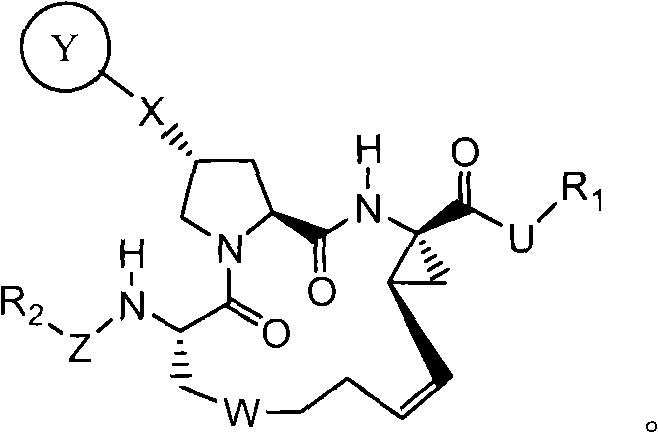
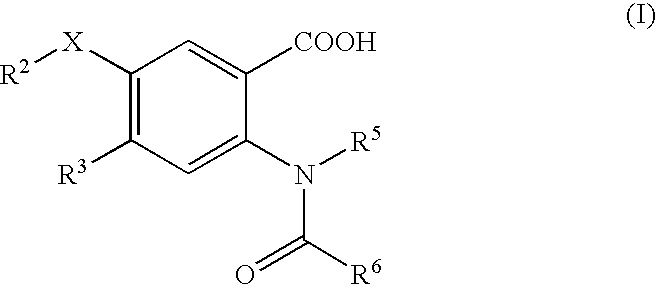
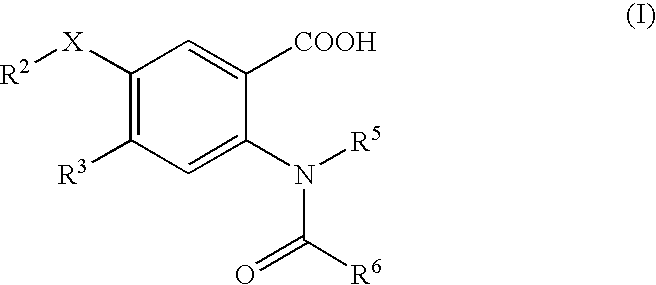
This invention relates to HCV protease inhibitors, in particular a macrocyclic compound shown in formula (I) or (II). Definition of each substituent R1, R2, U, W, X, Y and Z in formula (I) and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, U, W, X, T and Z in formula (II) is described in instruction. The compound can be used for treating HCV. The invention further discloses a medicine composition containing the macrocyclic compound and an application of the macrocyclic compound for treating HCV.
Owner:DONGGUAN HEC TAIGEN BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
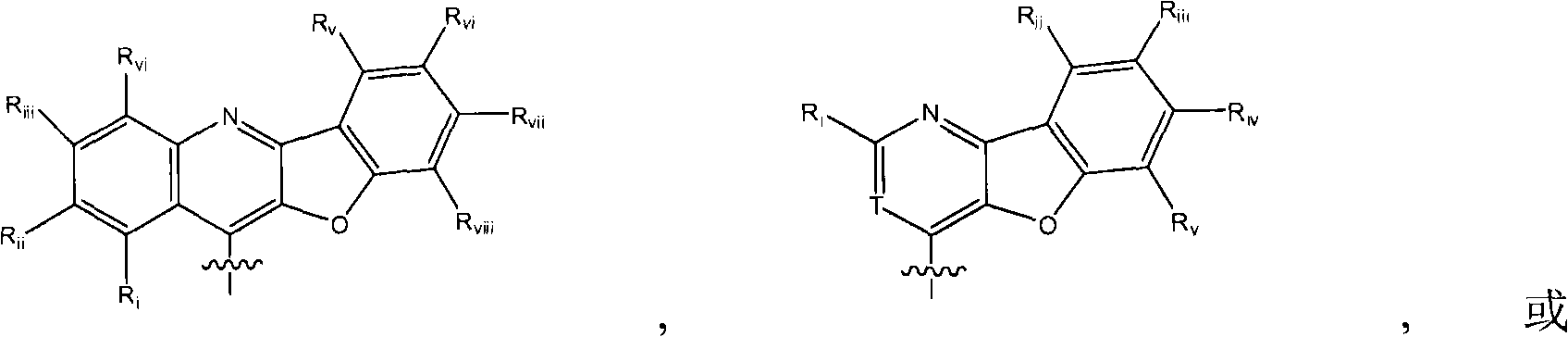
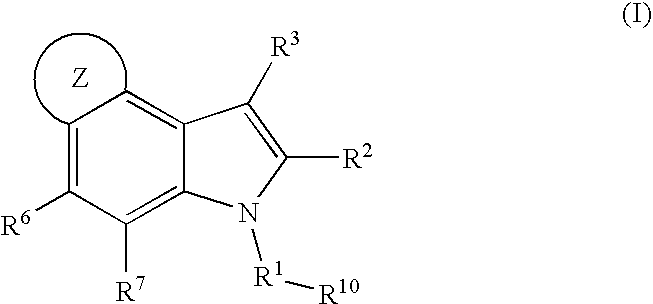
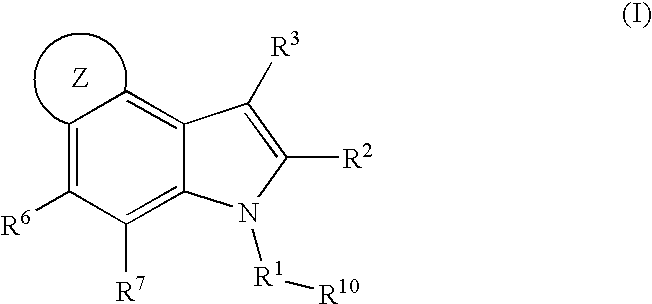
4, 5-ring annulated indole derivatives for treating or preventing of hcv and related viral infections
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Phosphonates with reduced toxicity for treatment of viral infections
There are provided, inter alia, acyclic nucleoside phosphonate compounds having reduced toxicity and enhanced antiviral activity, and pharmaceutically accepted salts and solvates thereof. There are also provided methods of using the disclosed compounds for inhibiting viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, inhibiting viral reverse transcriptase, inhibiting replication of virus, including hepatitis C virus or a human retrovirus, and treating a subject infected with a virus, including hepatitis C virus or a human retrovirus.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Macrocyclic inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3-serine protease
The present invention discloses novel compounds which have HCV protease inhibitory activity as well as pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of using them to treat disorders associated with the HCV protease. The novel compounds typically include a 15-20 member macrocycle and have the general structure of structural Formula 1:wherein Z′, L′, M′, R1, X and D are defined herein.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Viral polymerase inhibitors
ActiveUS20100190779A1Low to very low and even non-significant activityInhibit synthesisBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicinePolymerase L
Compounds of formula I:wherein X, R2, R3, R5 and R6 are defined herein, are useful as inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Hepatitis c virus NS3/4A protease, gene and method for detecting activity of inhibitor
ActiveCN105985970AAvoid cumbersomeLow costBacteriaHydrolasesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleotide
The invention discloses hepatitis c virus NS3 / 4A protease, a gene and a method for detecting activity of an inhibitor. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table or the encoded amino acid sequence of the gene is the nucleotide sequence of protein shown as SEQ ID No.2 in the sequence table. According to the method for detecting the activity of the inhibitor, the defects that when a common cell screening model is used for screening medicine, the process is complex, and cost is high are avoided, and the advantages of being clear in medicine acting mechanism, low in cost, high in efficiency, high in sensitiveness and capable of achieving high-throughput screening are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Viral polymerase inhibitors
ActiveUS7816348B2Inhibition of replicationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPolymerase LHcv hepatitis
Compounds of formula I:wherein X, R2, R3, R5 and R6 are defined herein, are useful as inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
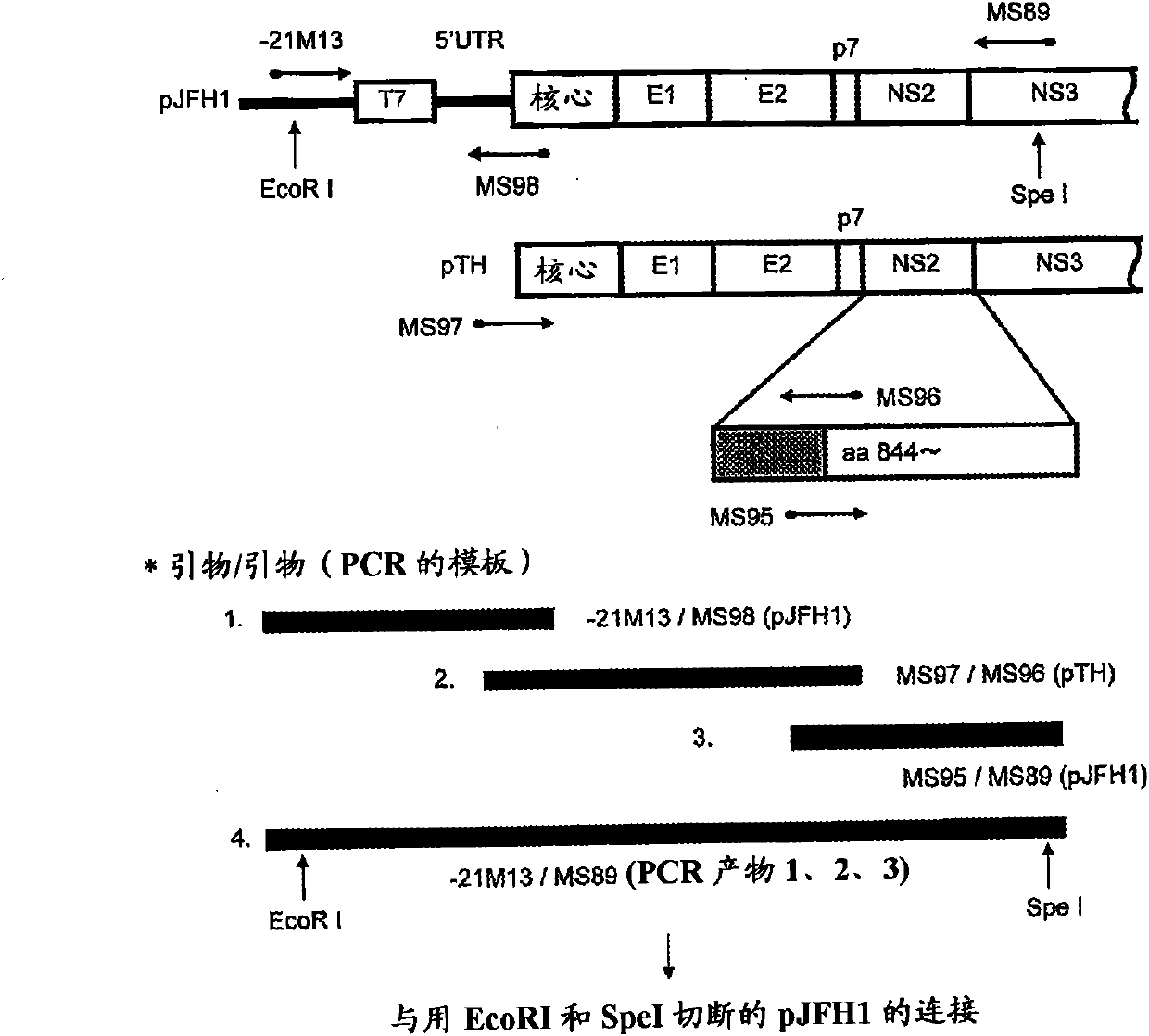
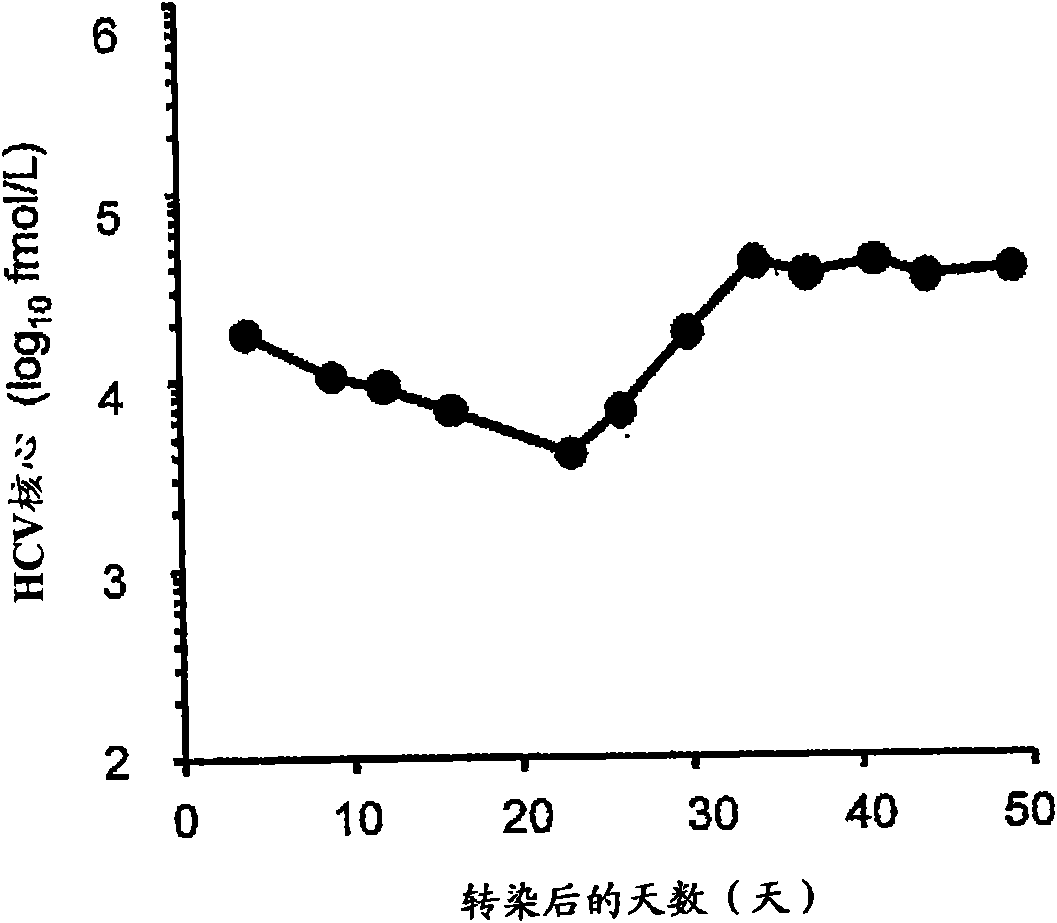
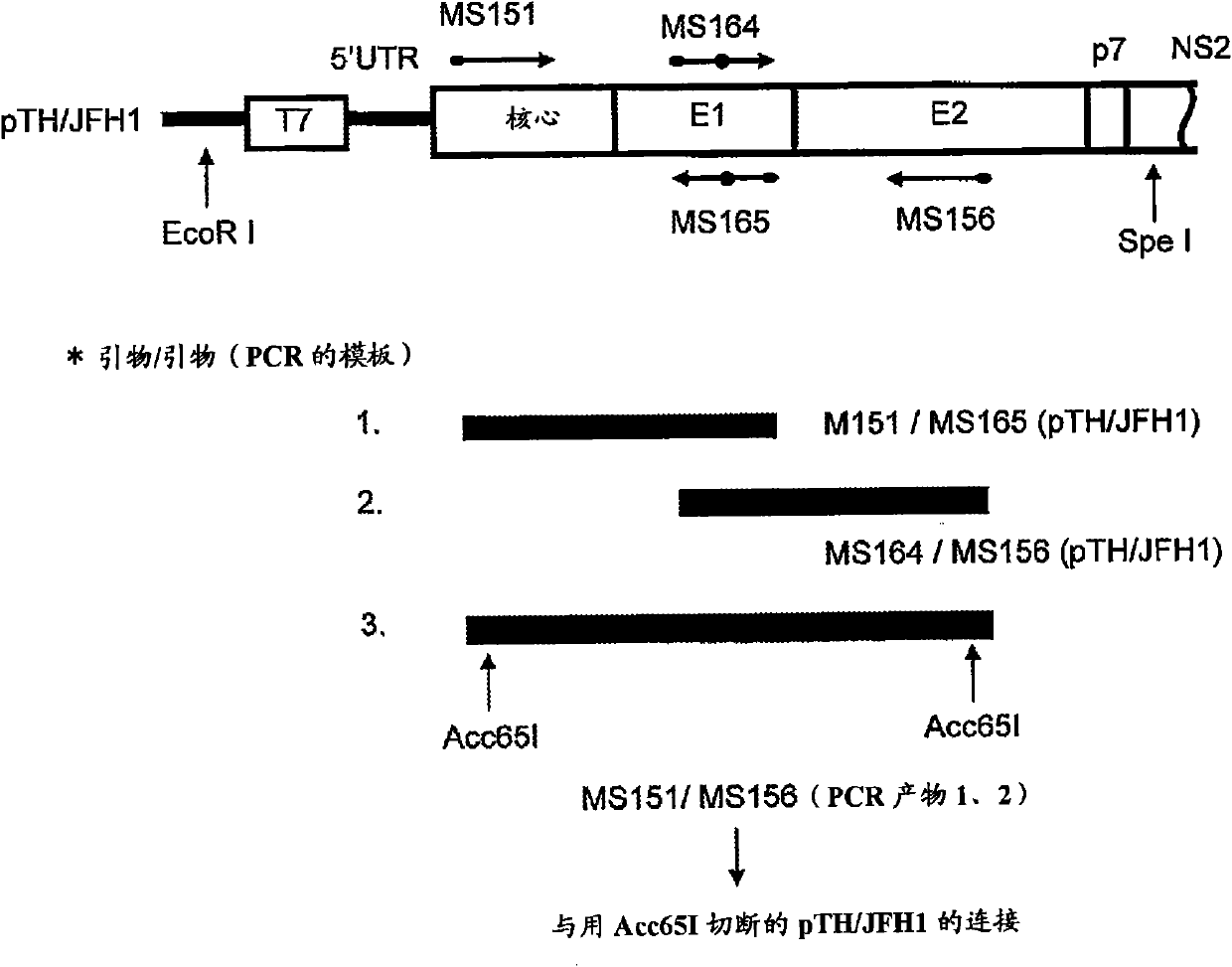
EFFICIENT CELL CULTURE SYSTEM FOR HEPATITIS C VIRUS GENOTYPE 7a
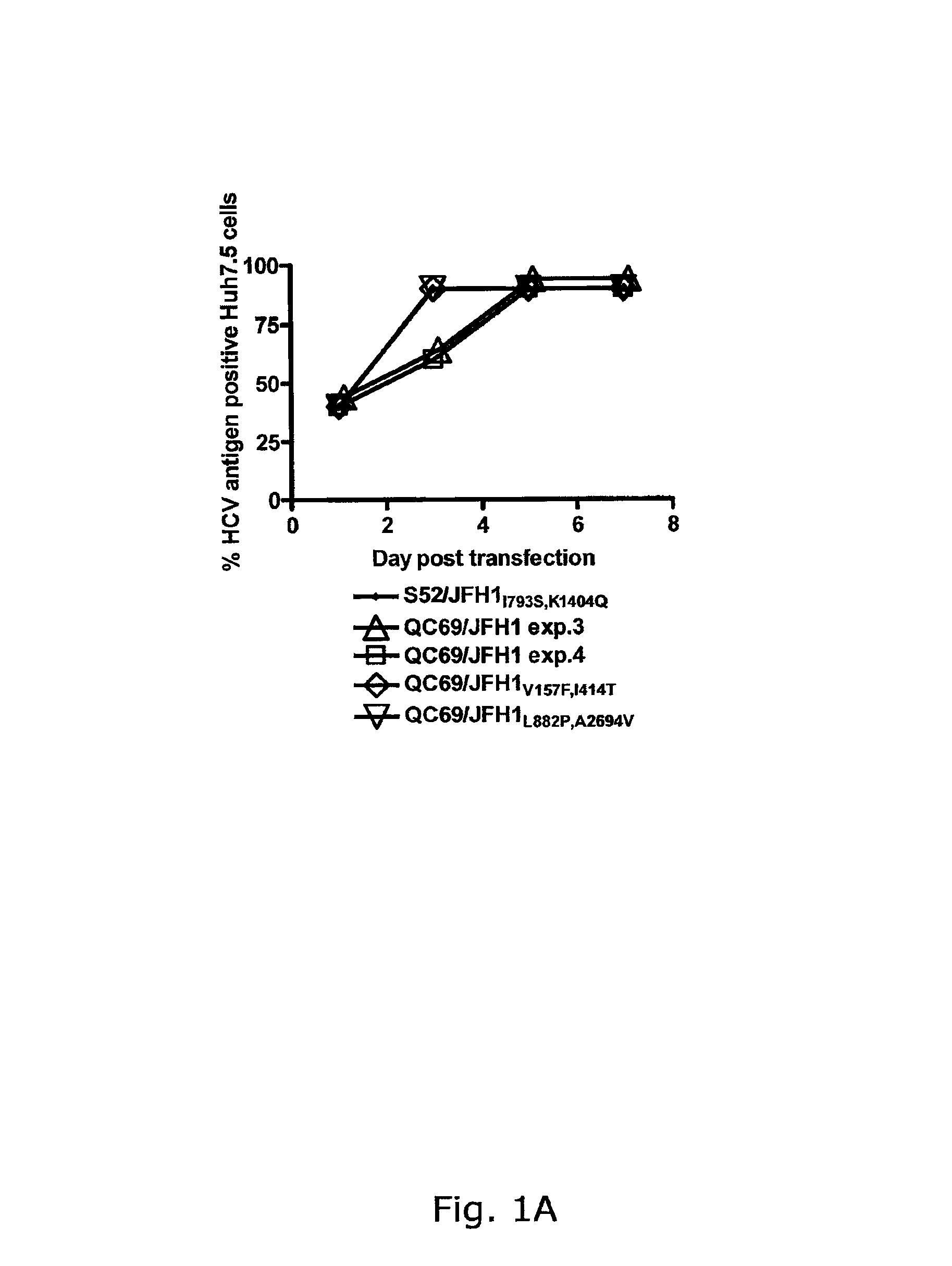
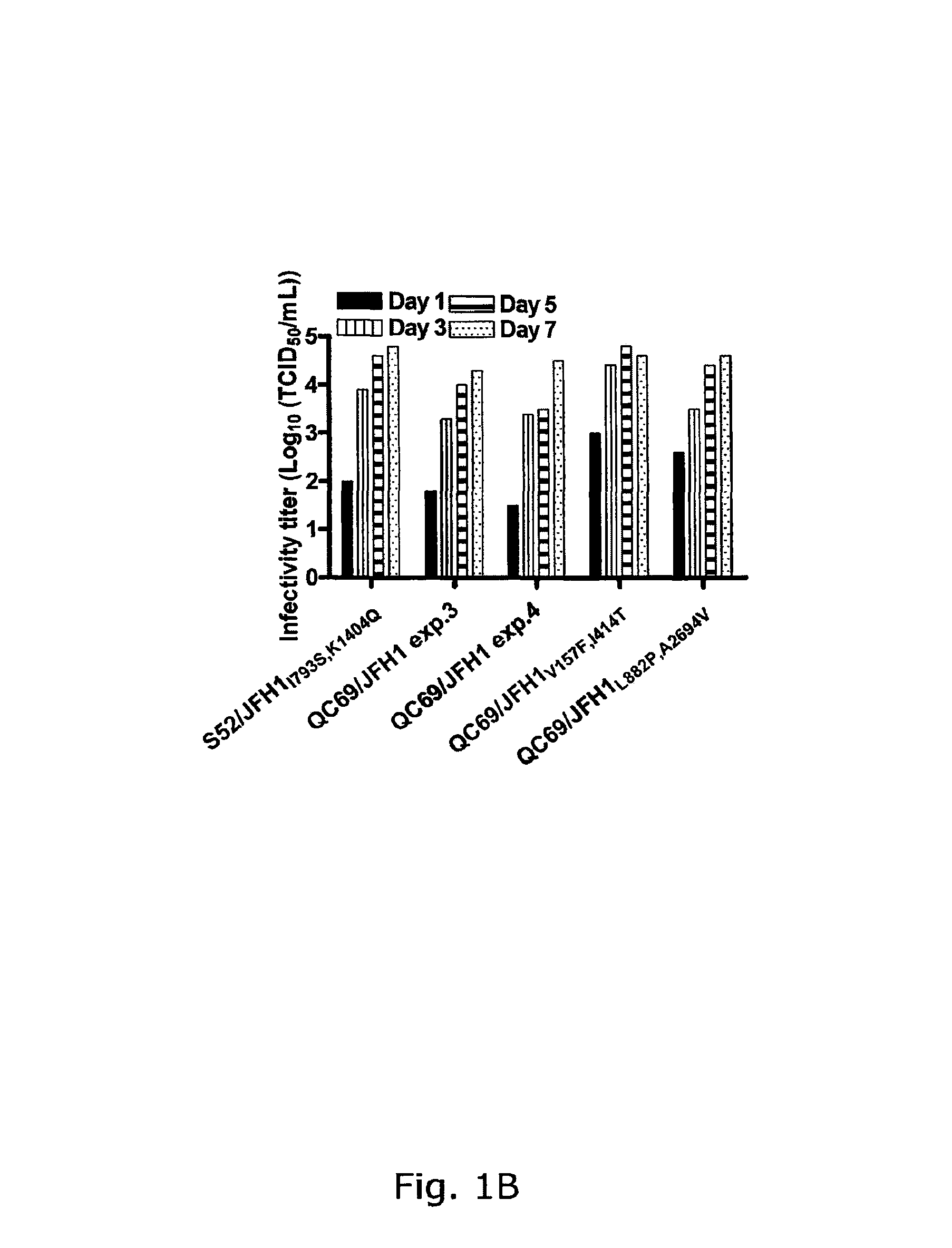
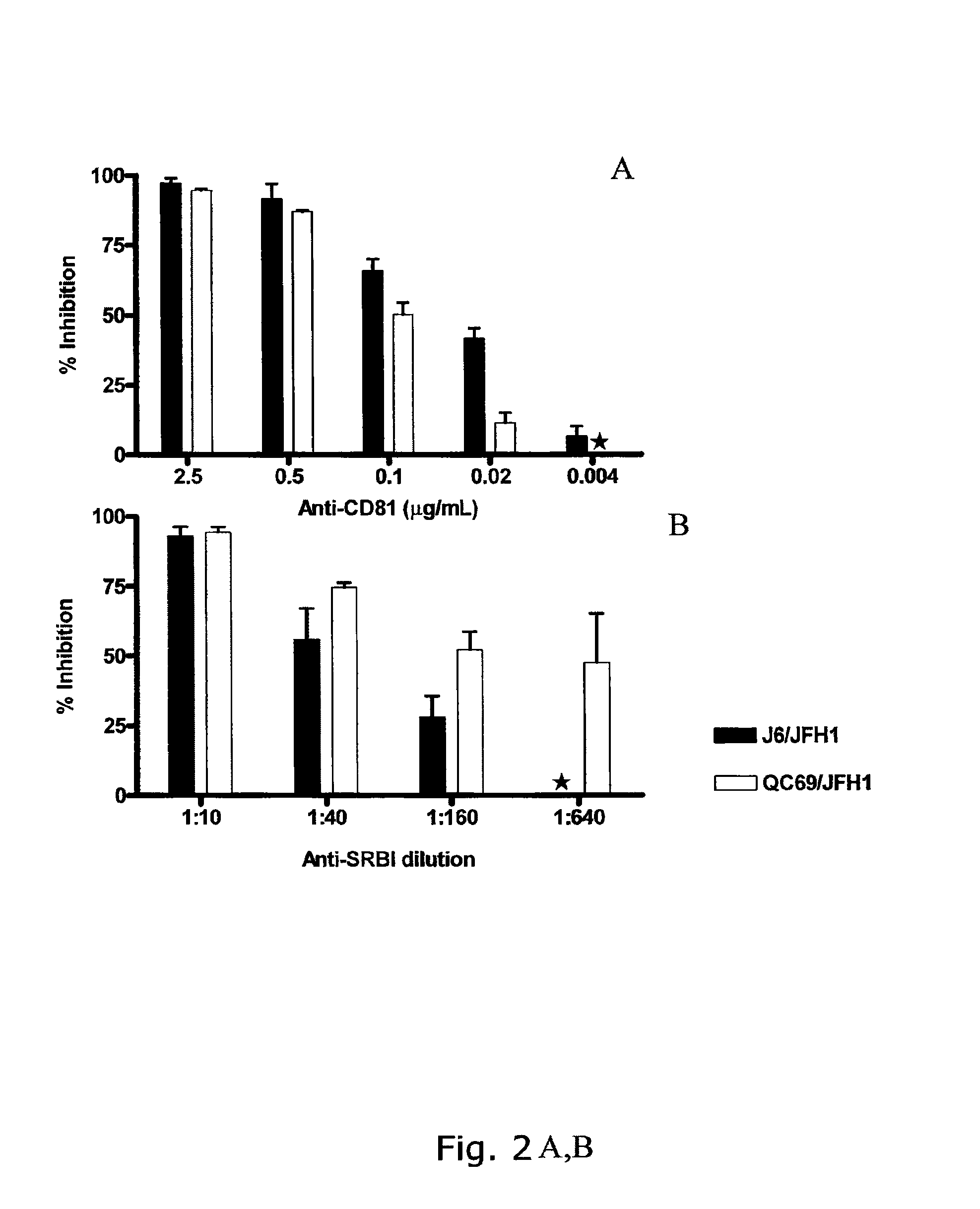
InactiveUS20110294195A1High infectivity titerEfficient growth processSsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaSequence analysisHepatitis C virus genotype
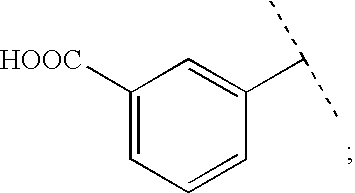
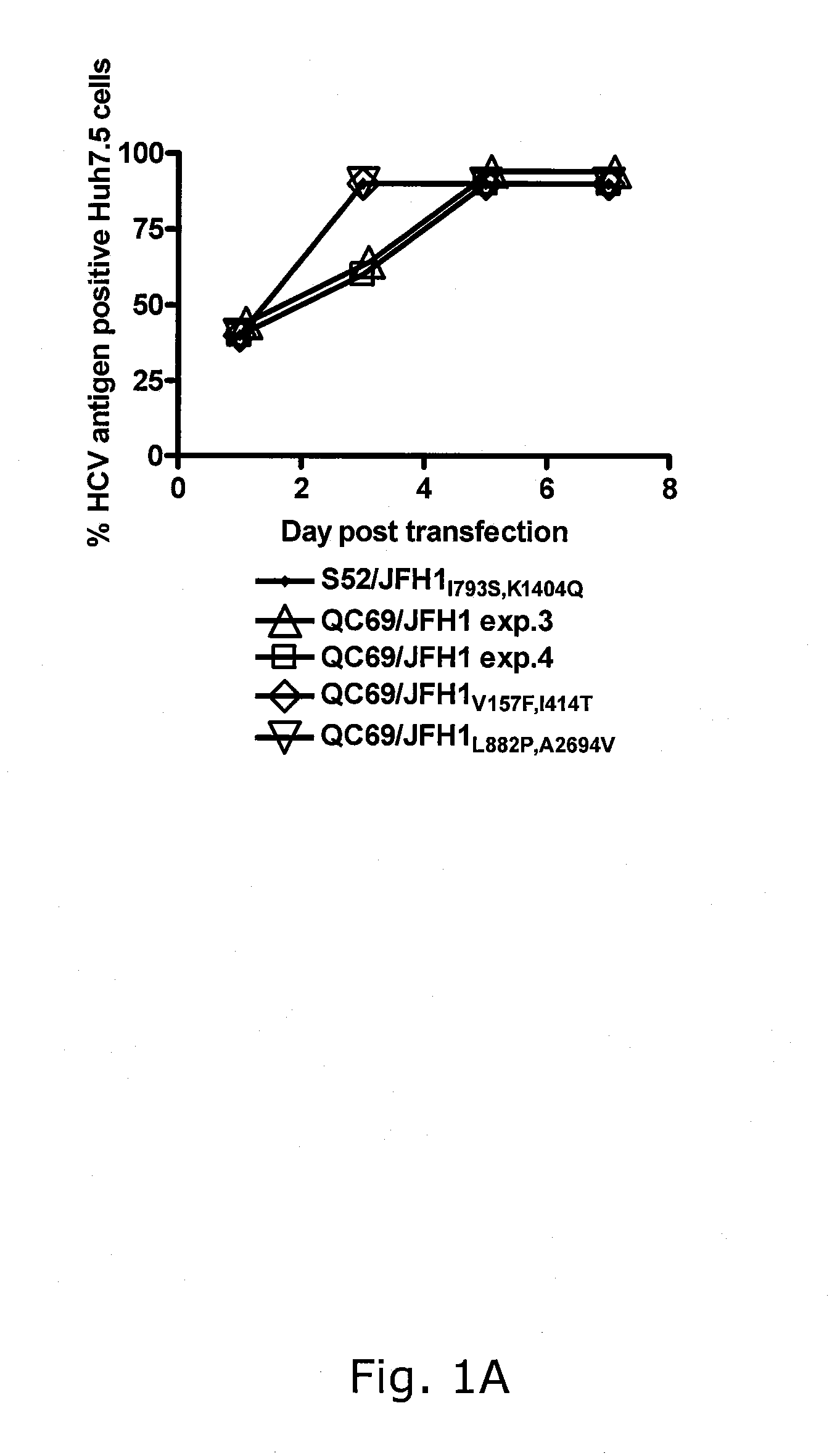
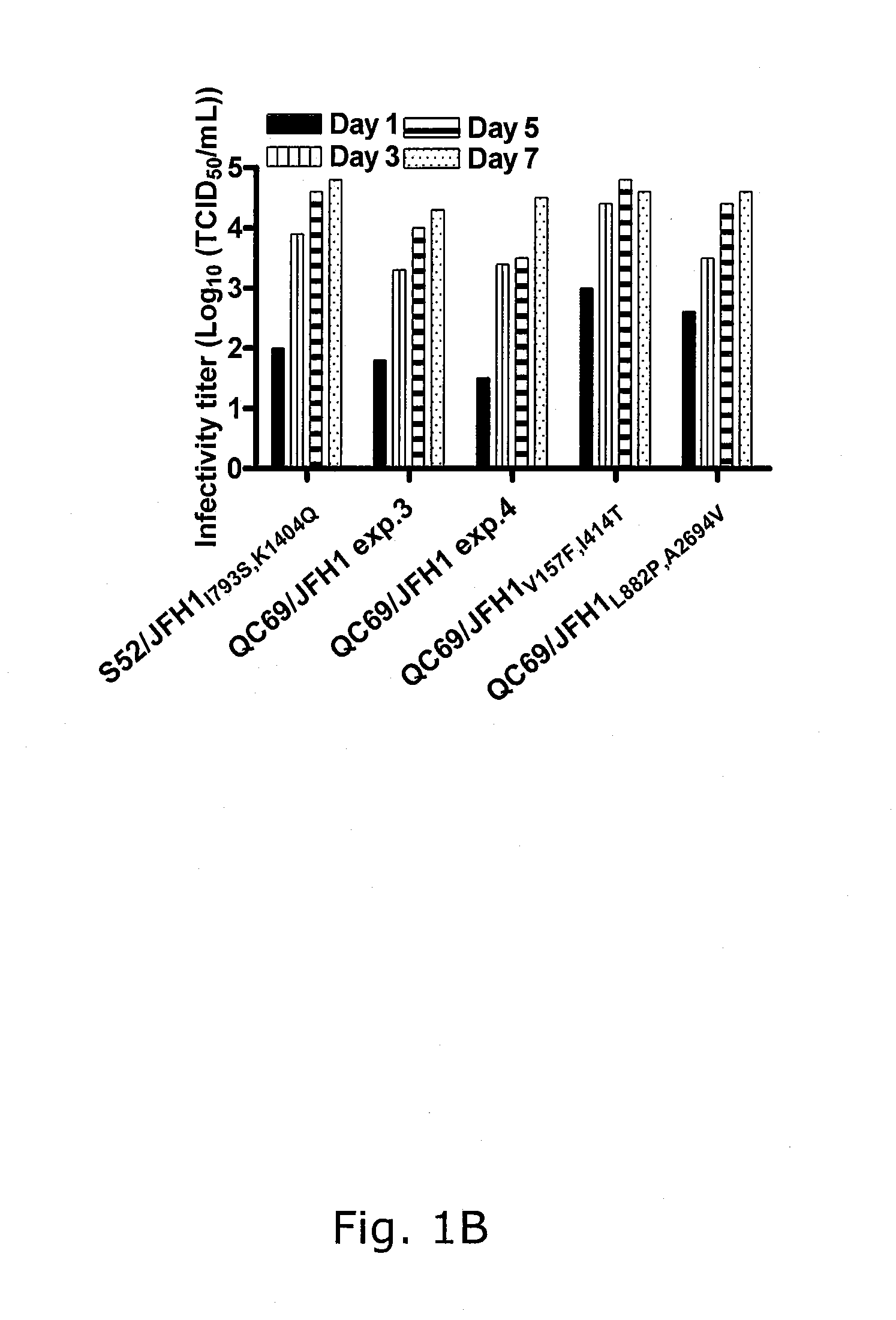
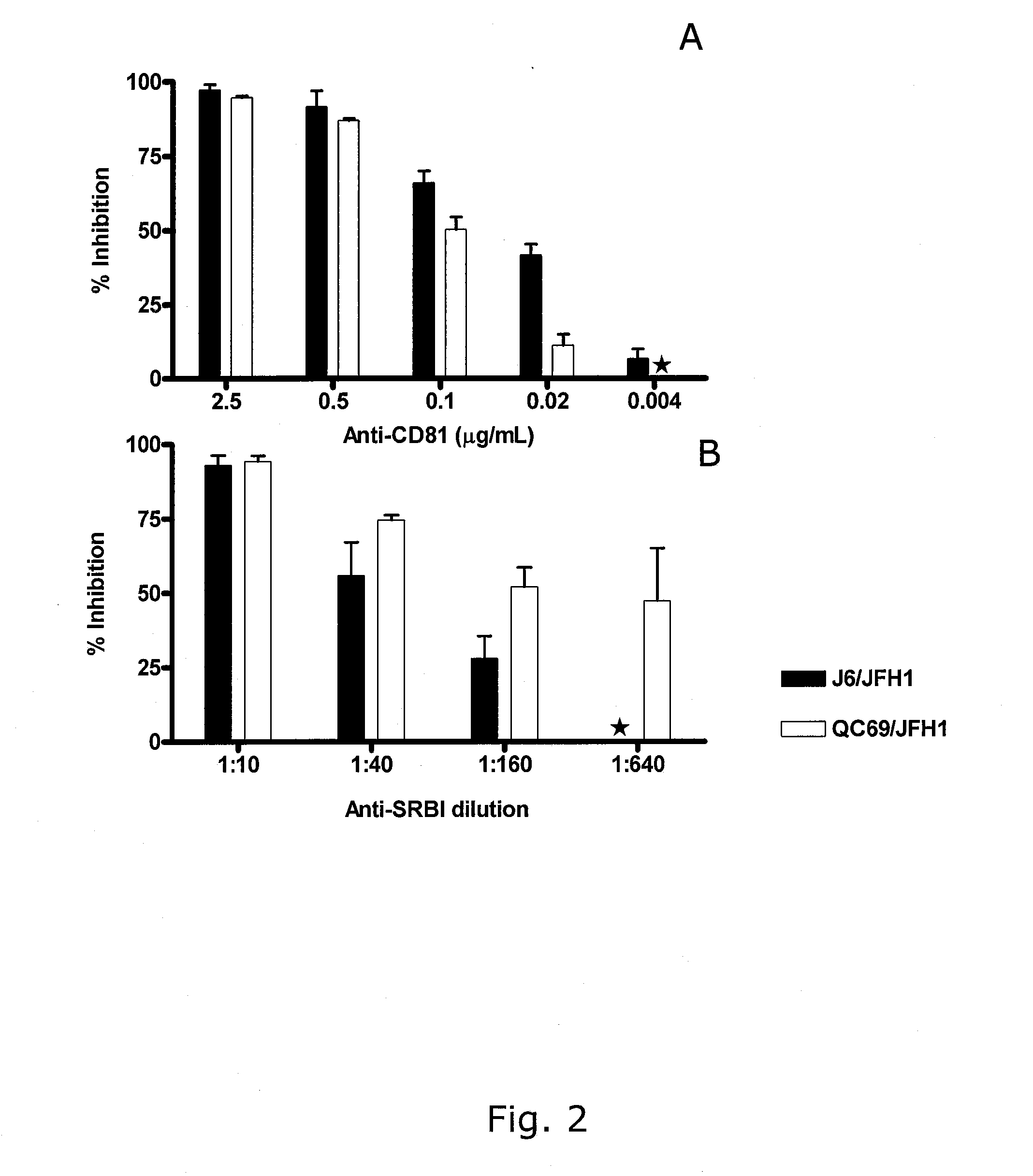
Genotype 7a has been identified recently, thus not much is known about the biology of this new, major HCV genotype. The present inventors developed hepatitis C virus 7a / 2a intergenotypic recombinants in which the JFH1 structural genes (Core, E1 and E2), p7 and the complete NS2 were replaced by the corresponding genes of the genotype 7a strain QC69 and characterized them in Huh7.5 cells. Sequence analysis of 7a / JFH1 recombinants recovered after viral passage in Huh7.5 cells following 4 independent transfection experiments revealed adaptive mutations in Core, E2, NS2, NS5A and NS5B. In reverse genetic studies the importance of these mutations for improved growth kinetics was shown. Adapted 7a / JFH1 viruses showed growth kinetics, infectivity and RNA titers comparable to a previously developed 3a / JFH1 reference virus. Conclusion: The developed 7a / JFH1 viruses provide a robust in vitro tool for research in HCV genotype 7, including vaccine studies and functional analyses.
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
Efficient cell culture system for hepatitis C virus genotype 7a
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
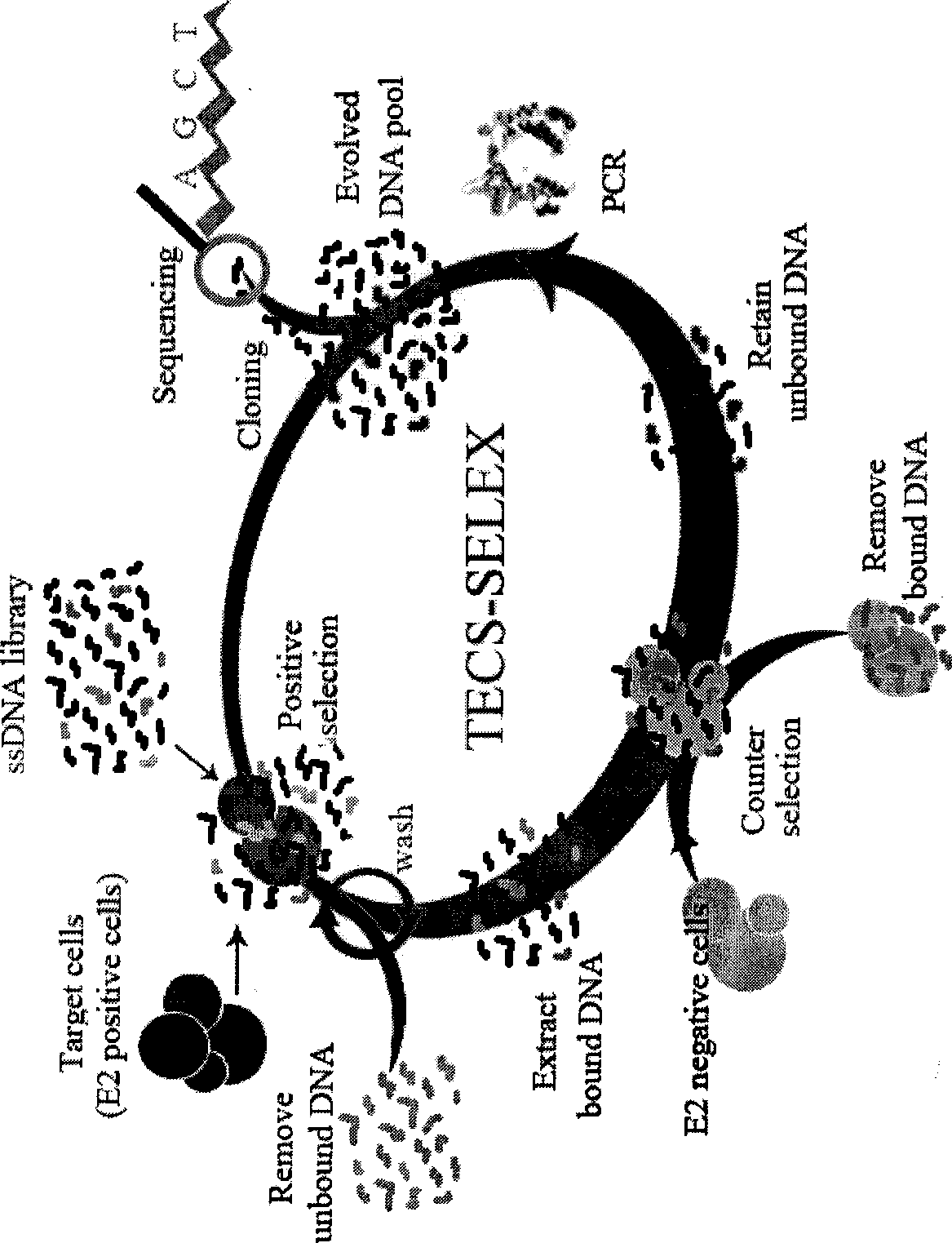
Small molecule nucleotide aptamer medicament for hepatitis C virus, preparation and use
InactiveCN101481685AReduce the binding forceLow cytotoxicityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSide effectNucleotide
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
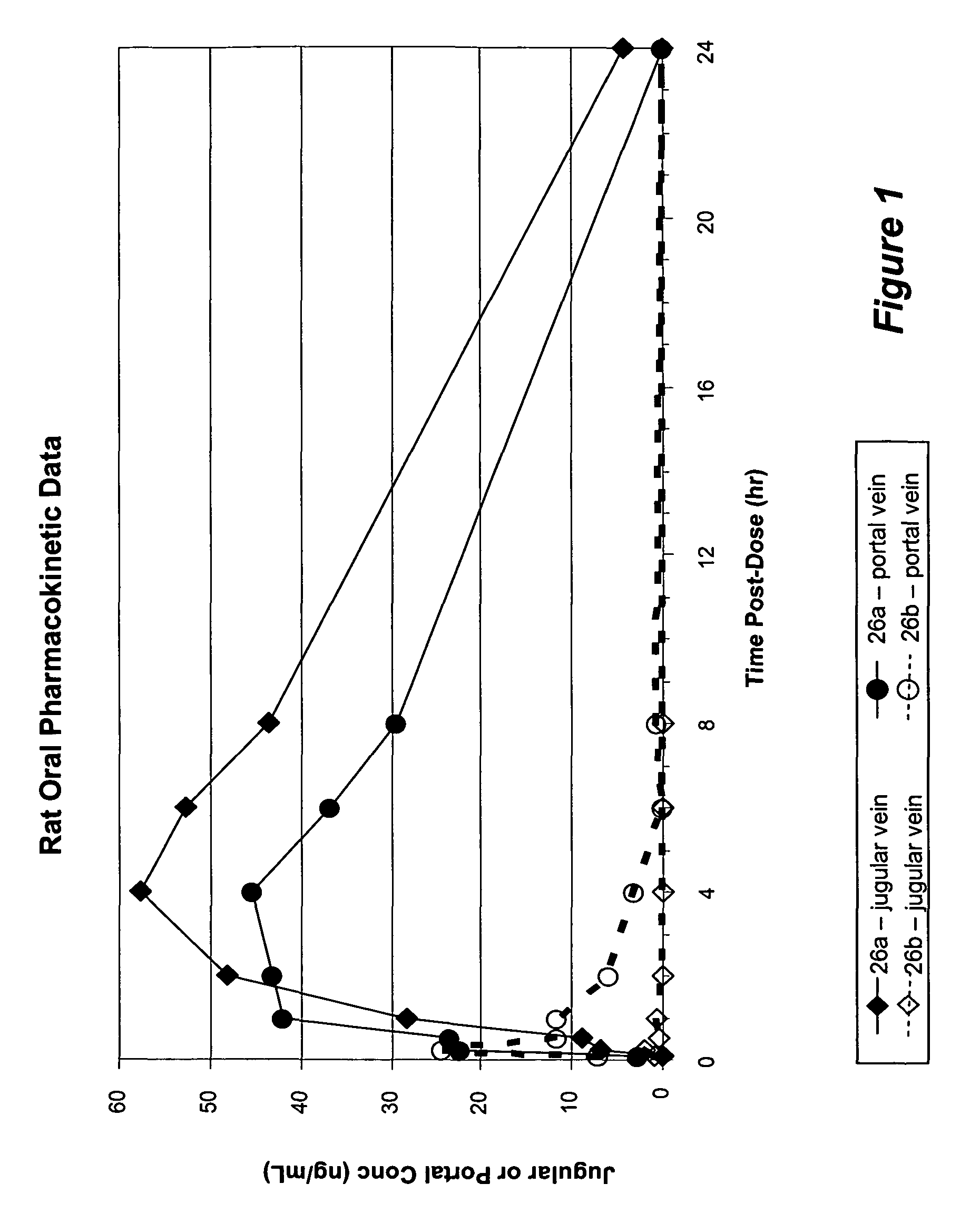
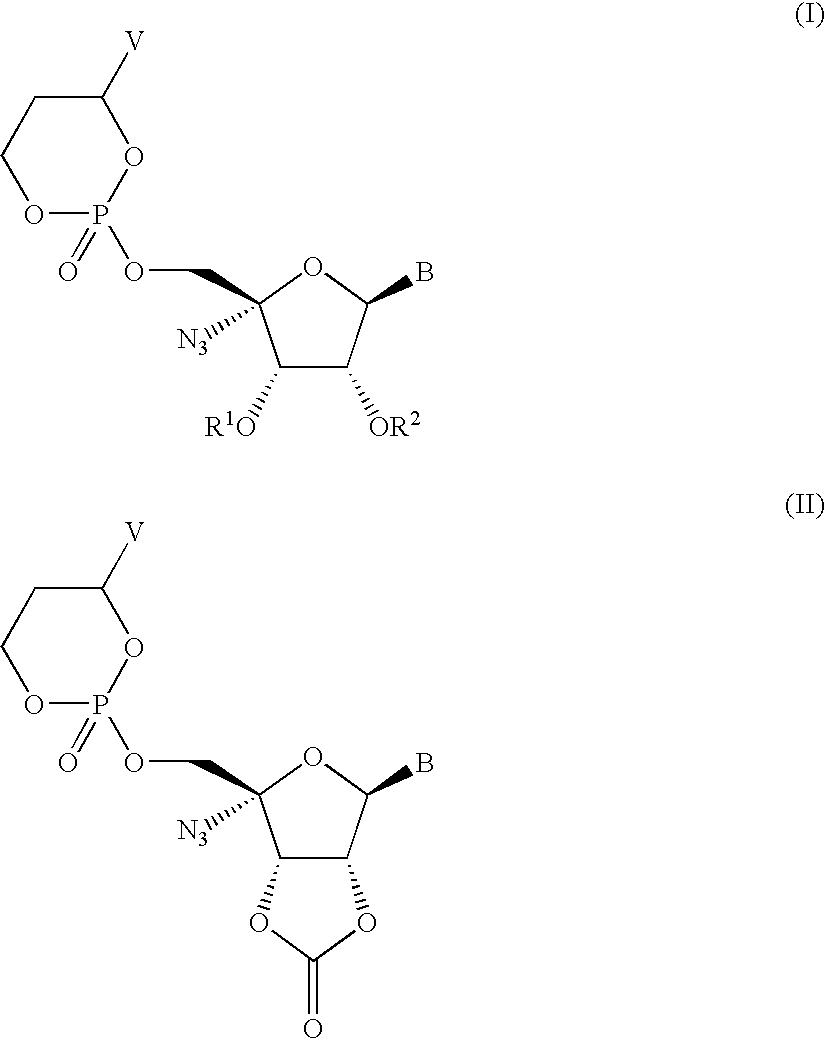
Nucleoside prodrugs and uses thereof
Compounds having the formula I or II, wherein R1, R2, B, and V are as defined herein, are Hepatitis C virus NS5b polymerase inhibitors. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for treating an HCV infection and inhibiting HCV replication.
Owner:METABASIS THERAPEUTICS INC
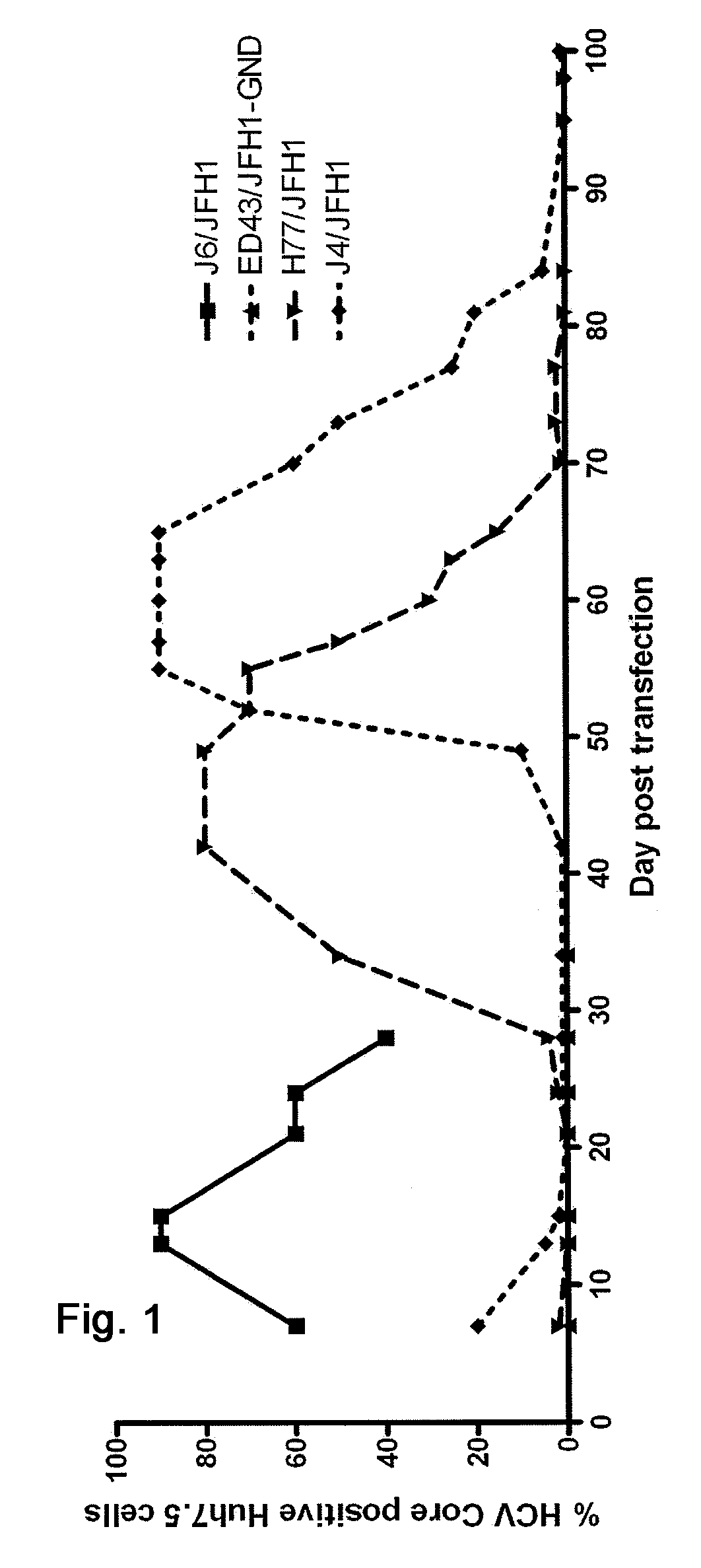
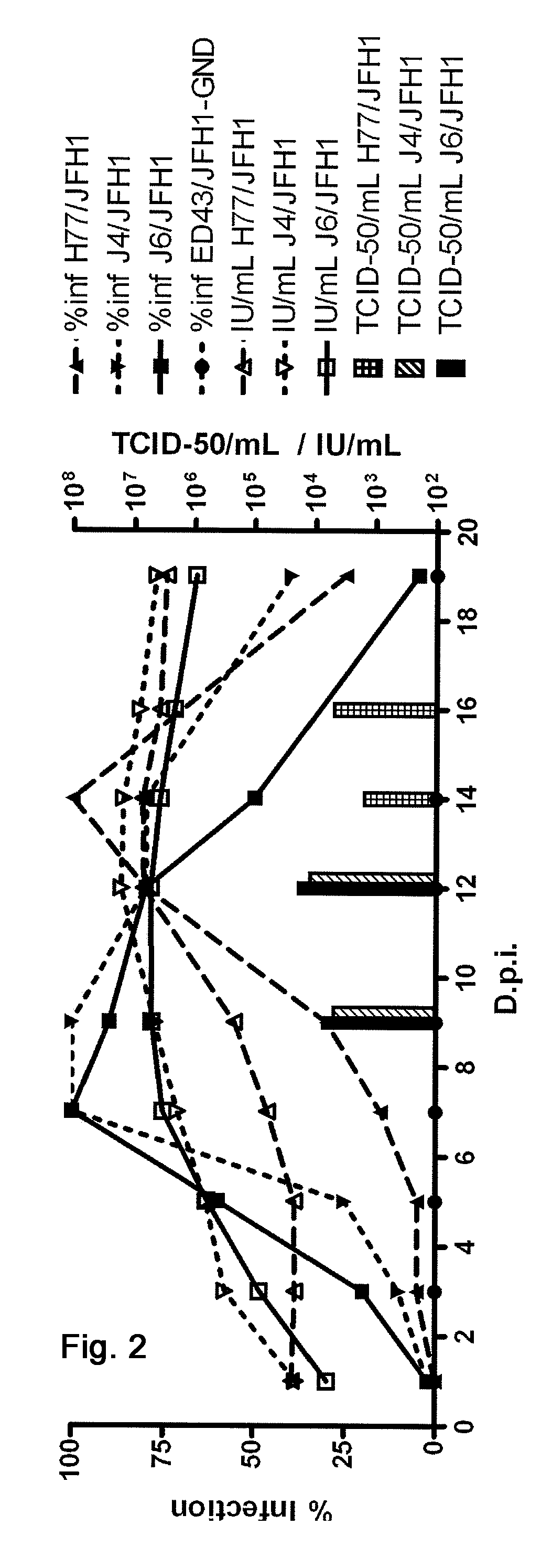
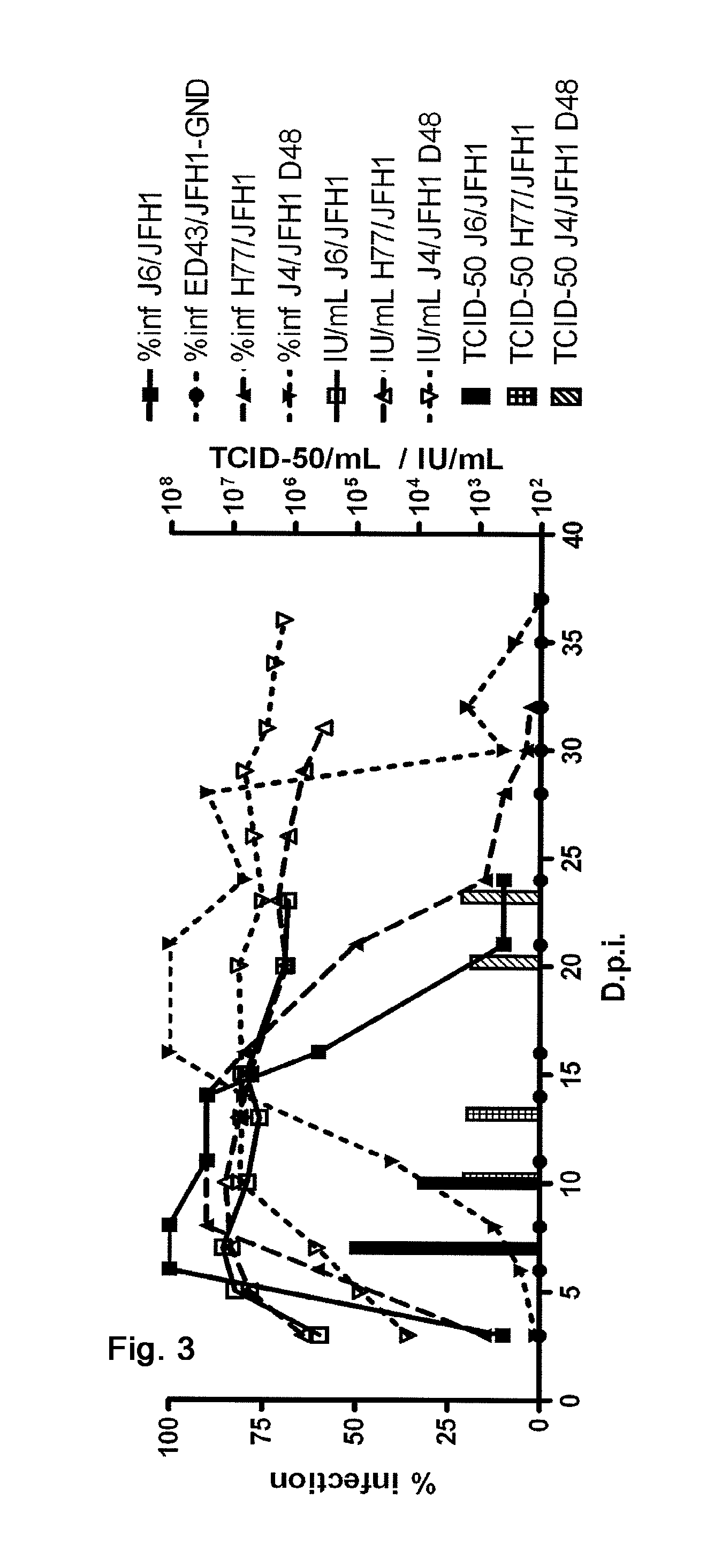
Efficient cell culture system for hepatitis C virus genotype 1A and 1B
The present inventors developed hepatitis C virus 1a / 2a and 1b / 2a intergenotypic recombinants in which the JFH1 structural genes (Core, E1 and E2), p7 and NS2 were replaced by the corresponding genes of the genotype Ia reference strain H77C or TN or the corresponding genes of the genotype Ib reference strain J4. Sequence analysis of recovered 1a / 2a and 1b / 2a recombinants from 2 serial passages and subsequent reverse genetic studies revealed adaptive mutations in e.g. p7, NS2 and / or NS3. In addition, the inventors demonstrate the possibility of using adaptive mutations identified for one HCV isolate in generating efficient cell culture systems for other isolates by transfer of mutations across isolates, subtypes or major genotypes. Furthermore neutralization studies showed that viruses of e.g. genotype 1 were efficiently neutralized by genotype Ia, 4a and 5a serum, an effect that could be utilized e.g. in vaccine development and immunological prophylaxis. The inventors in addition demonstrate the use of the developed systems for screening of antiviral substances in vitro and functional studies of the virus, e.g. identification of receptors required for HCV entry.
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
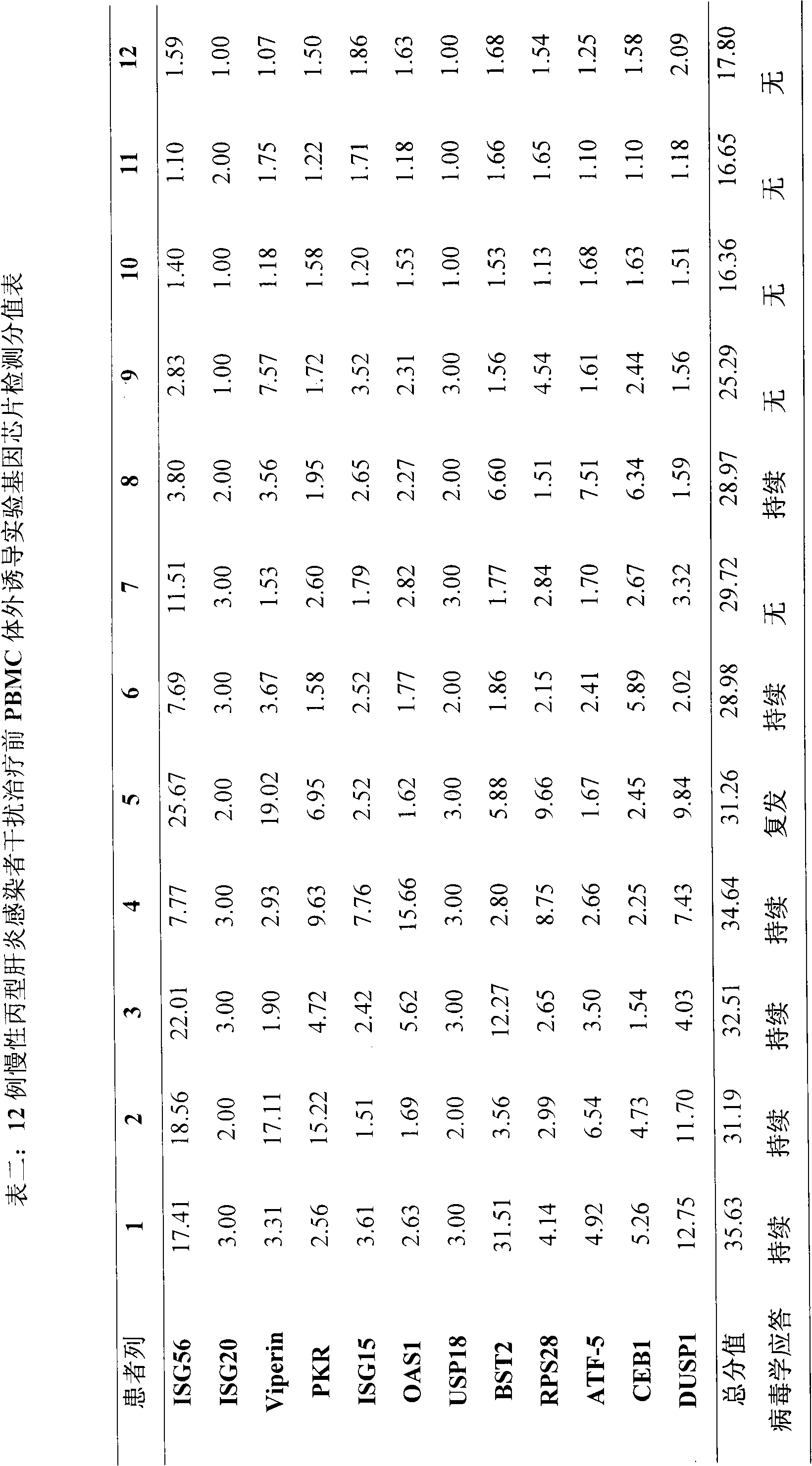
Gene chip for chronic hepatitis C outcome prediction in chronic hepatitis C interferon treatment
InactiveCN102485907ARelieve painLow cost of treatmentNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementChronic viral hepatitis CInterferon therapy
The invention relates to a gene chip for chronic hepatitis C outcome prediction in chronic hepatitis C interferon treatment. The gene chip comprises 12 gene fragments of ISG56, ISG20 and the like. Through the gene chip, in an early stage of chronic hepatitis C interferon treatment on patients or before the chronic hepatitis C interferon treatment on patients, interferon treatment long-term effects can be predicted. Therefore, the gene chip is conducive to optimization and selection of a chronic hepatitis C patient therapeutic schedule, reduces patient pain and treatment costs, and is convenient for detection and clinical application.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Viral polymerase inhibitors
InactiveUS20120101091A1Low to very low and even non-significant activityInhibit synthesisBiocideOrganic chemistryMedicinePolymerase L
The present application provides compounds of formula I wherein X, Y, R2, n, R5 and R6 are defined herein, useful as inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase The present application also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing said compounds, methods of using said compounds as pharmaceuticals alone or with other antiviral agent in the treatment of a hepatitis C viral infection in a mammal having or at risk of having the infection.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
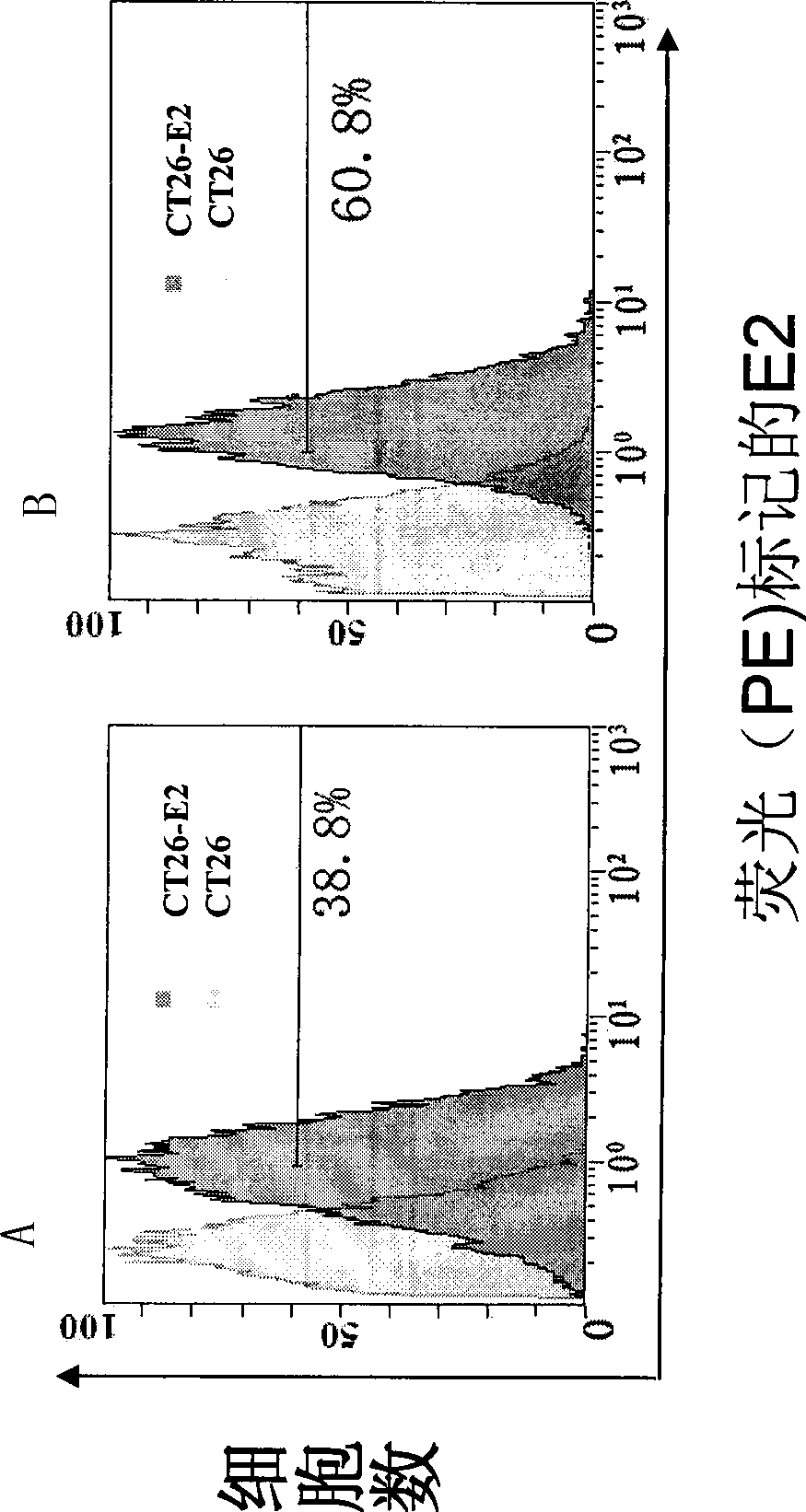
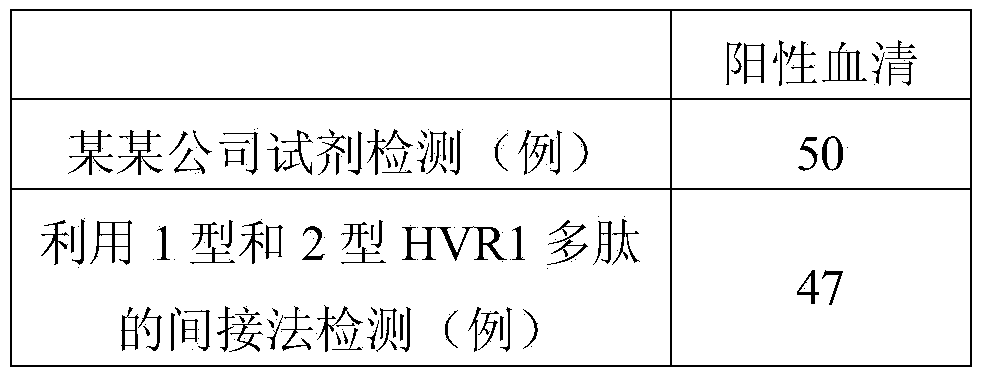
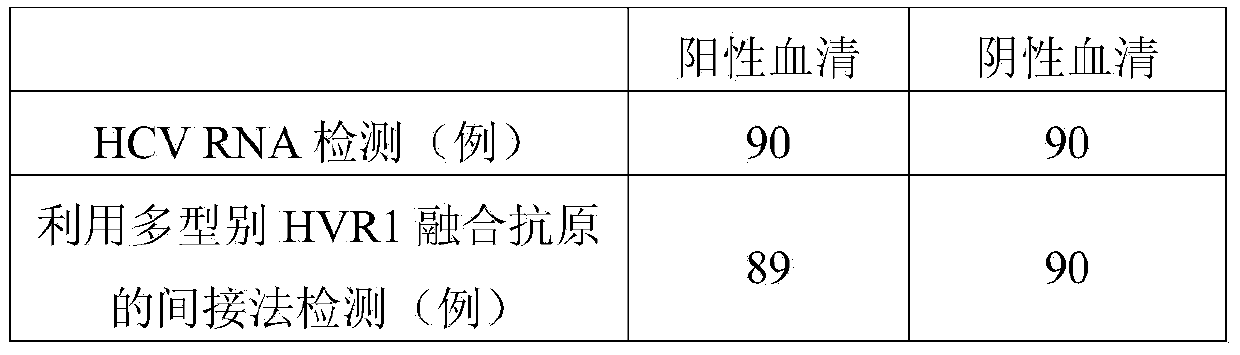
Hepatitis C virus HVR1 (Hypervariable Region 1) fusion antigen and application thereof
ActiveCN104193827AAvoid disadvantagesEliminate missed detectionBiological testingHybrid peptidesHcv hepatitisAntibody hypervariable region
The invention discloses a hepatitis C virus HVR1 (Hypervariable Region 1) fusion antigen. An amino acid sequence of the fusion antigen is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The invention also discloses application of the fusion antigen in preparation of a hepatitis C virus HVR1 antibody detection kit. The experiment proves that the cross reactivity of the fusion antigen is obviously improved compared with that of a single segment HVR1 antigen, and the detection coincidence rate of hepatitis C virus RNA positive patients is 99 percent. Because the HVR1 is a main neutralizing antigen epitope in the hepatitis C virus, the antigen can be used for achieving an aim of comprehensively detecting HCV infection for hepatitis C virus HVR1 antibody detection and effectively solving the problems such as outcome and prognosis of HCV diseases and prediction of interferon curative effect and has extremely great clinical application prospects.
Owner:山东莱博生物科技有限公司
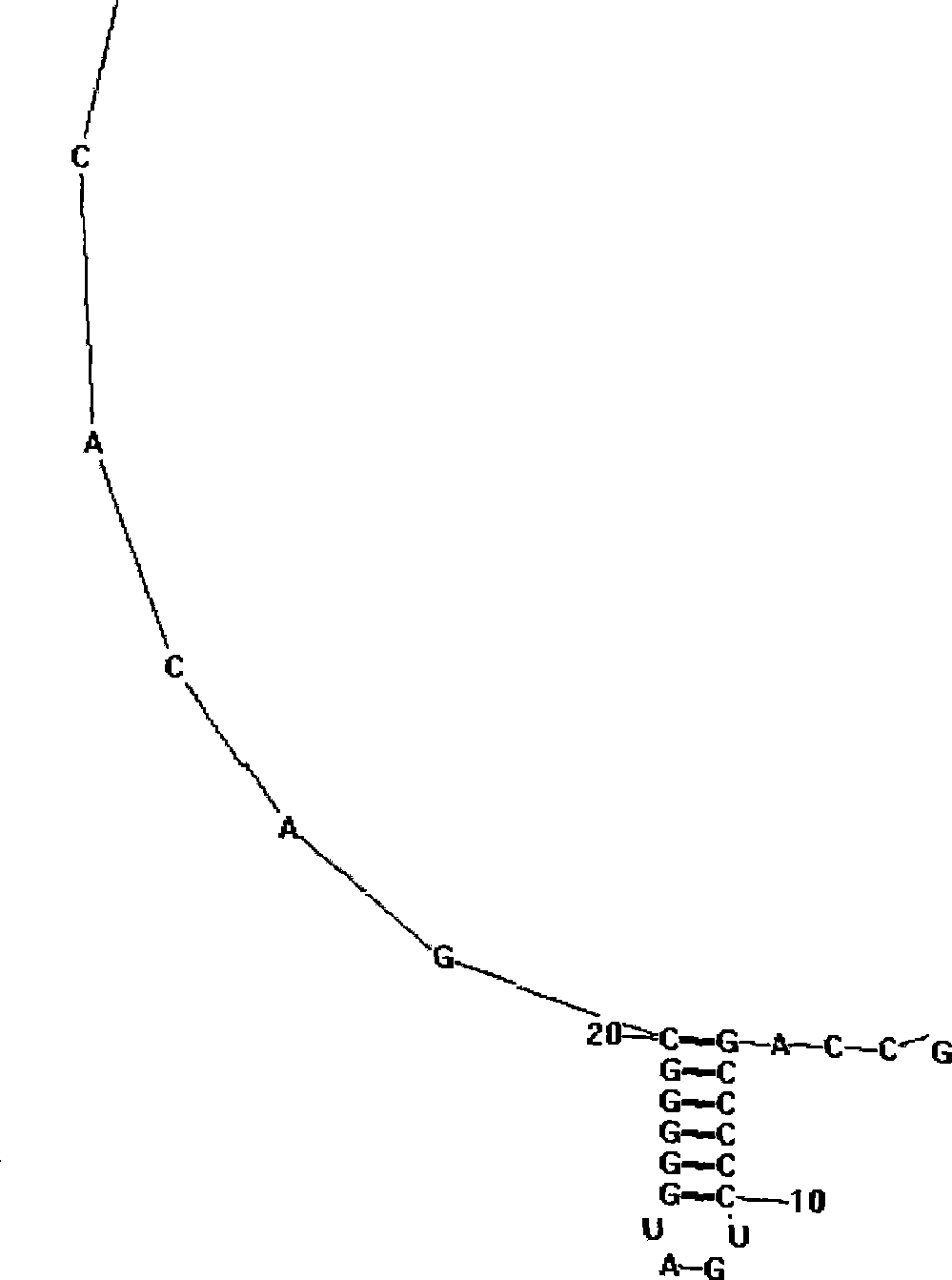
Method for constructing hepatitis C virus specific ribozyme M1GS-hcv/C20 and uses thereof
InactiveCN101250510AClearly targeted cleavage activityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesEscherichia coliSingle strand
The invention discloses a method for constructing hepatic c virus specific ribozyme MIGS-hcv / C20, which comprises: selecting a sequence between 21nt and 36nt of hepatitis c virus HCV genomere 5' UTR as a target site to design a guide sequence and obtaining through associating and constructing the guide sequence and escherichia coli ribozyme P covalently. The guide sequence is designed to be effectively combined with the hepatic c virus specific ribozyme successfully through selecting a single-stranded region sequence between the 21nt-36nt of the hepatitis c virus as a candidate target site, the ribozyme which is designed accordingly displays clear targeting cutting activity for a substrate, successful construction of the ribozyme provides experimental materials which are accurate and can be depended for subsequent experiments, and thereby the method lays a foundation for researching new anti-HCV medicine and an antisense gene therapy.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Lactam containing hcv inhibitors
Owner:BARSANTI PAUL +5
Nucleic acid containing chimeric gene derived from hepatitis type-C virus
InactiveCN102016026AImprove infection abilityImprove the production effectSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHcv hepatitisTGE VACCINE
Disclosed are: an infectious chimeric HCV particle which can be used as a vaccine; Core protein, E1 protein, E2 protein and p7 protein, all of which are derived from a hepatitis type-C virus strain other than JFH-1 strain; NS2 protein derived from hepatitis type-C virus JFH-1 strain or a hepatitis type-C virus strain other than JFH-1 strain, or a chimeric NS2 protein composed of NS2 protein derived from hepatitis type-C virus JFH-1 strain and NS2 protein derived from a hepatitis type-C virus strain other than JFH-1 strain; a nucleic acid containing a chimeric gene derived from a hepatitis type-C virus, which comprises domains respectively encoding NS3 protein, NS4A protein, NS4B protein, NS5A protein and NS5B protein all derived from JFH-1 strain in this order from the 5'-side toward the 3'-side, wherein a proline residue at position-328 from the amino acid residue located at the N-terminal of the Core protein is substituted by an amino acid residue other than a proline residue; a chimeric HCV particle containing the nucleic acid; and use of the HCV particle as a vaccine.
Owner:TORAY IND INC +1
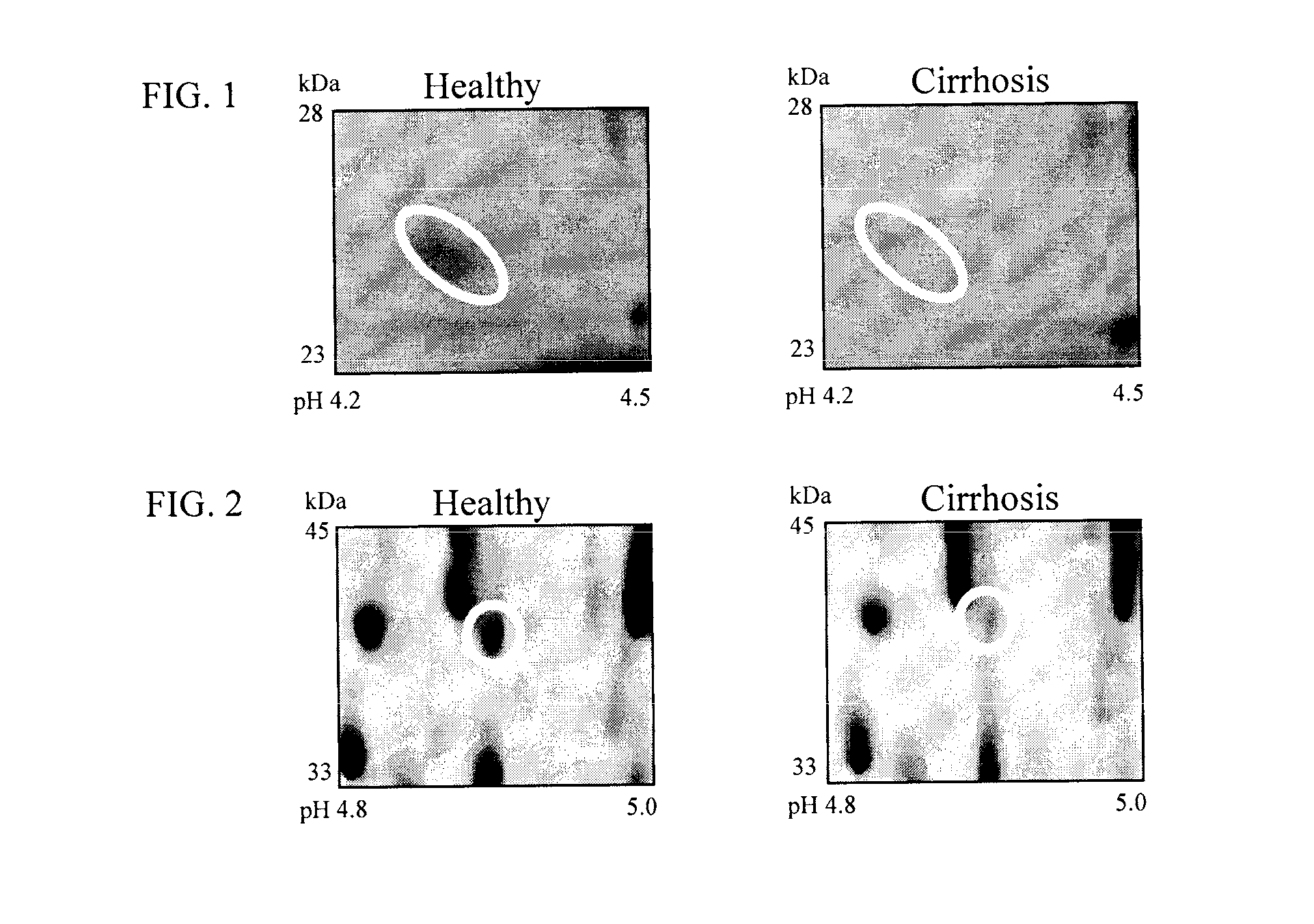
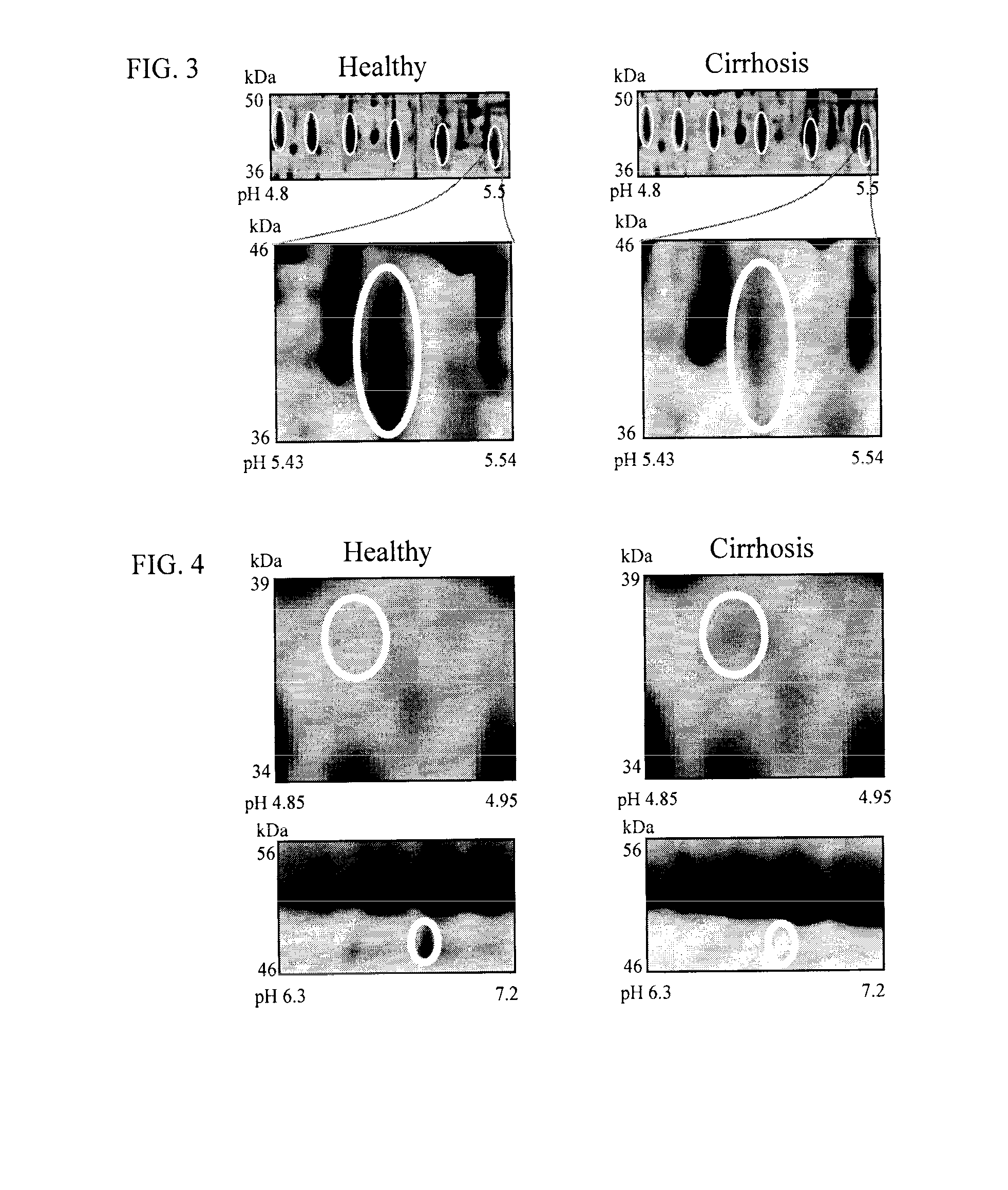
Clinical diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis using a novel panel of low abundant human plasma protein biomarkers
The inventors have proposed a novel panel of human plasma protein biomarkers for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Presently there is no reliable non-invasive way of assessing liver fibrosis. A 2D-PAGE based proteomics study was used to identify potential fibrosis biomarkers. Plasma from patients with hepatic cirrhosis induced by infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) were analysed. Several proteins associated with liver scarring and potentially also related to viral infection were identified. These proteins include 14-3-3 protein zeta / delta, adiponectin, afamin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein, apolipoprotein C-M, apolipoprotein E, C4b-binding protein beta chain, intact / cleaved complement C3dg, corticosteroid-binding globulin, fibrinogen gamma chain, beta haptoglobin at pH 5.46-5.49, haptoglobin-related protein, hemopexin, immunoglobulin J chain, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein, lipid transfer inhibitor protein, retinol-binding protein 4, serum paraoxonase / arylesterase 1, sex hormone-binding globulin and zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein.
Owner:THE CHANCELLOR MASTERS & SCHOLARS OF THE UNIV OF OXFORD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com