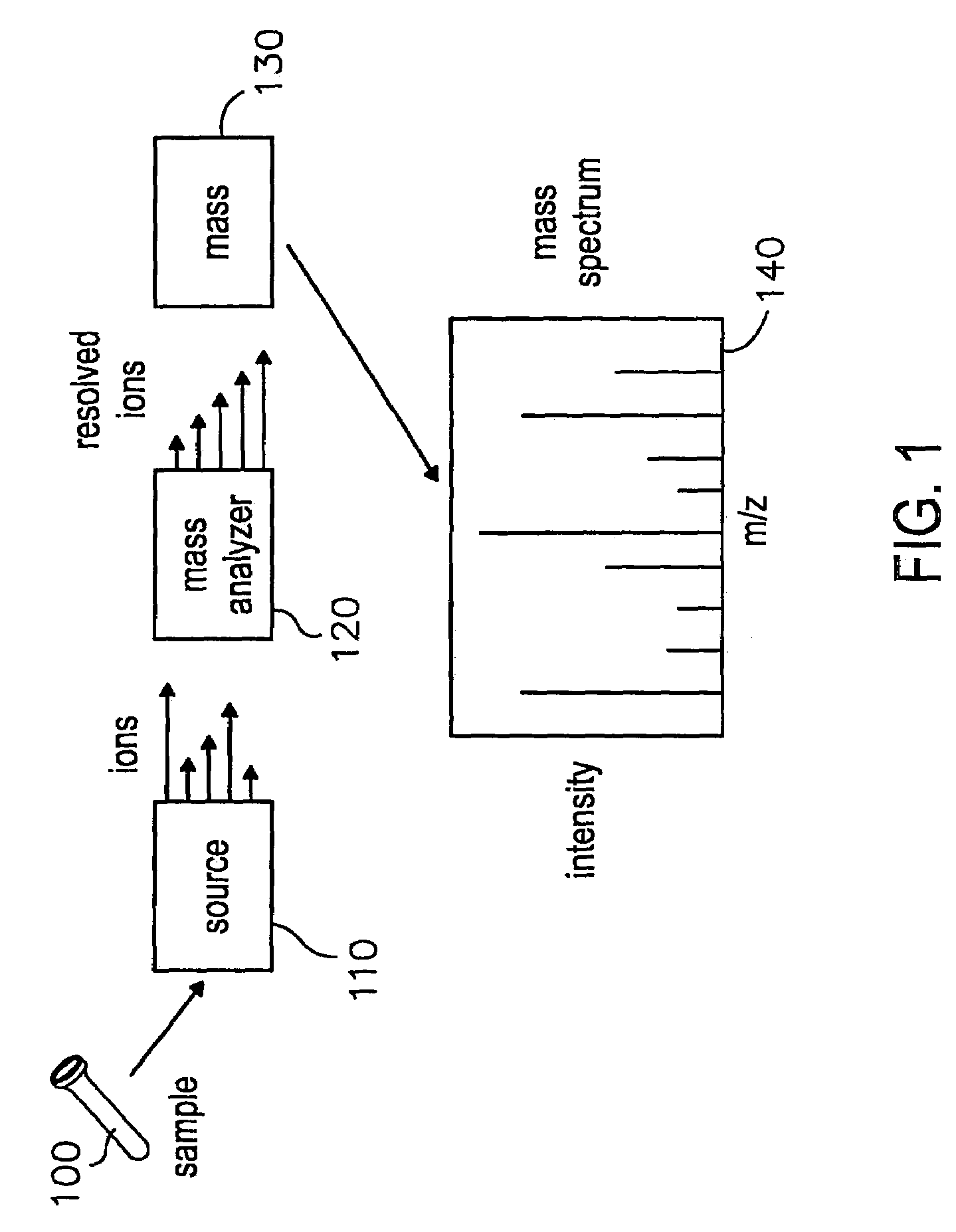
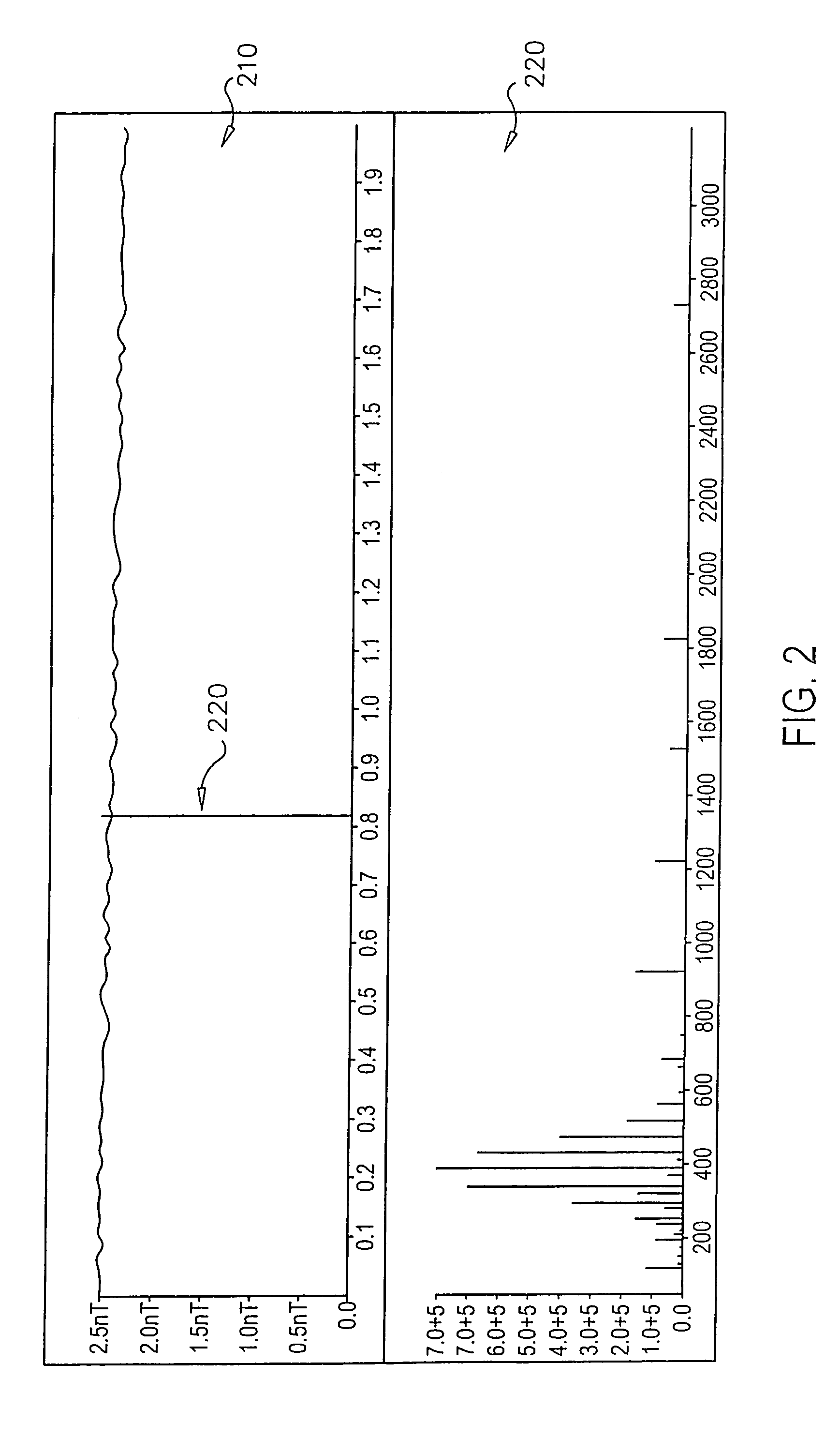
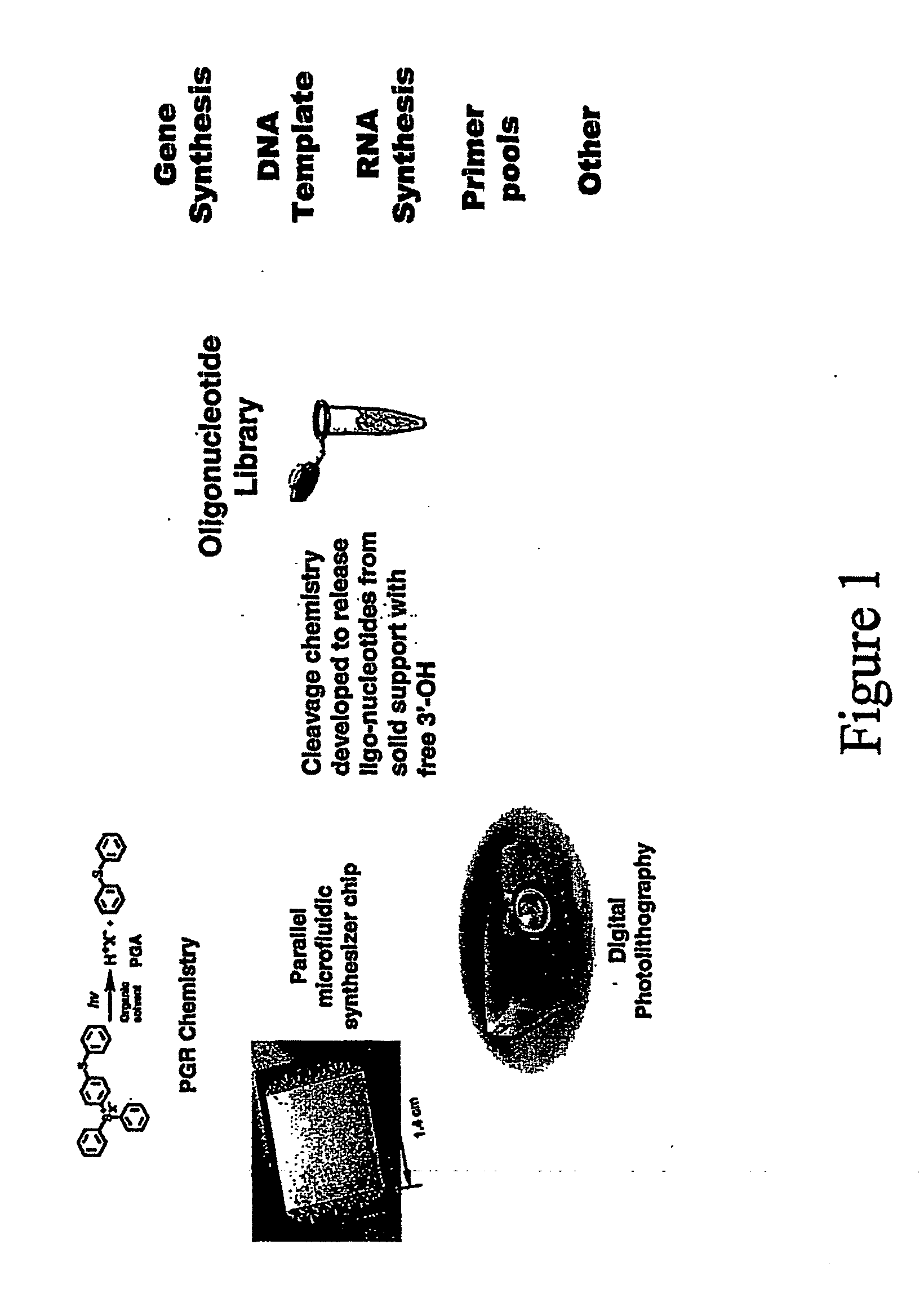
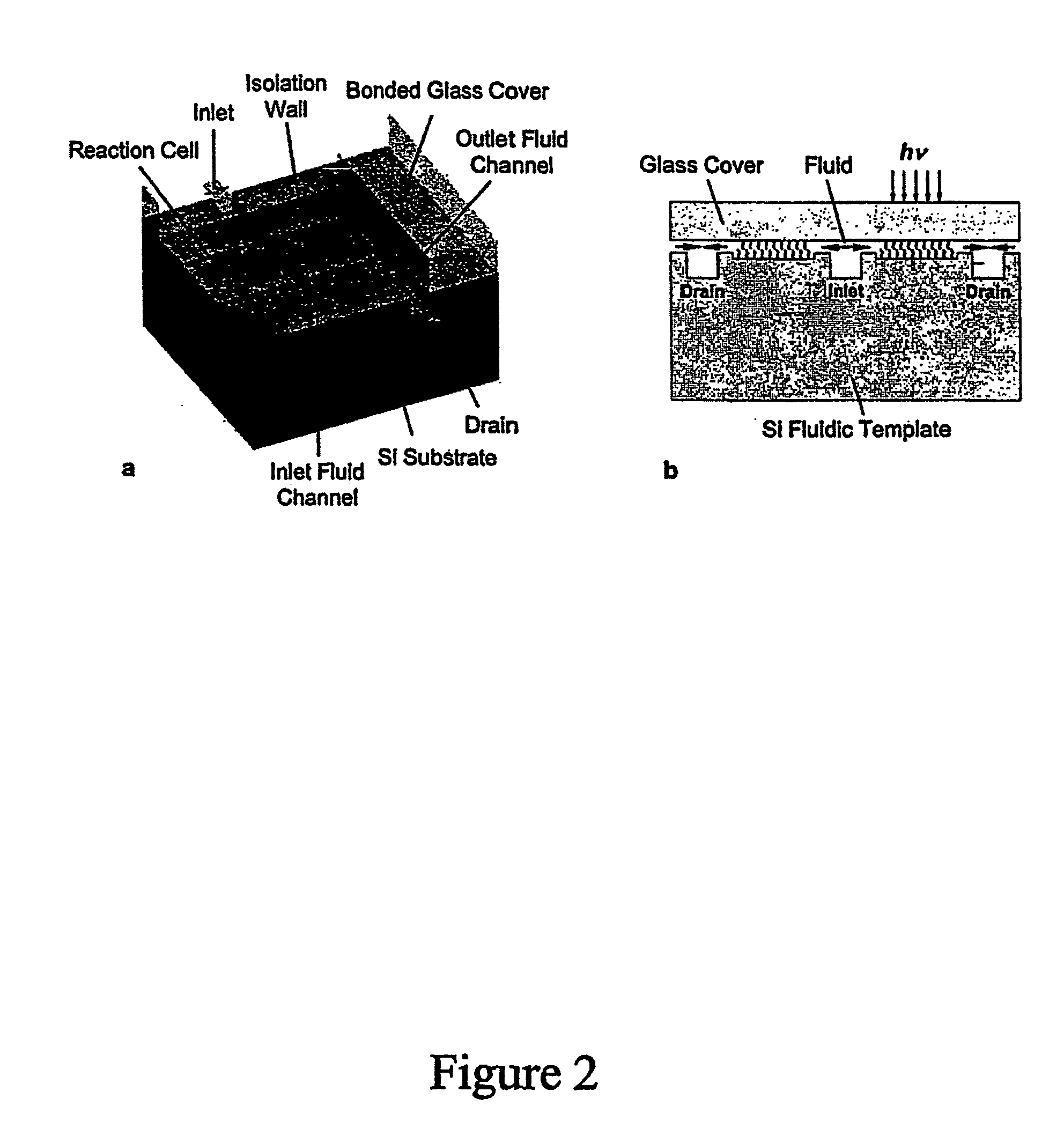
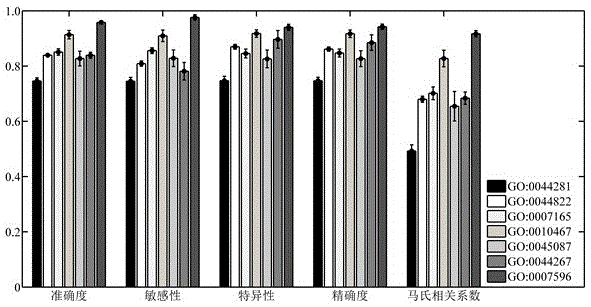
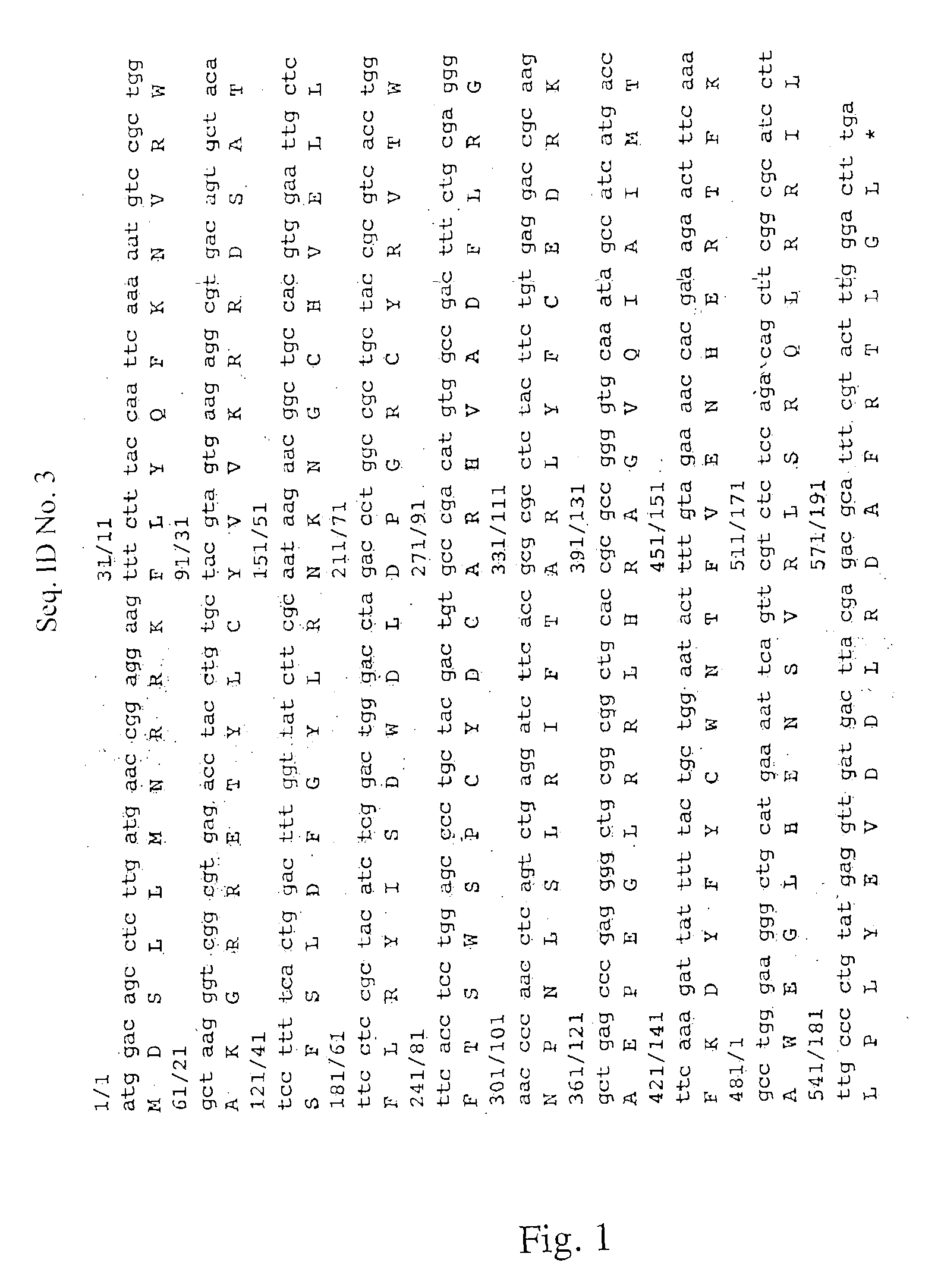
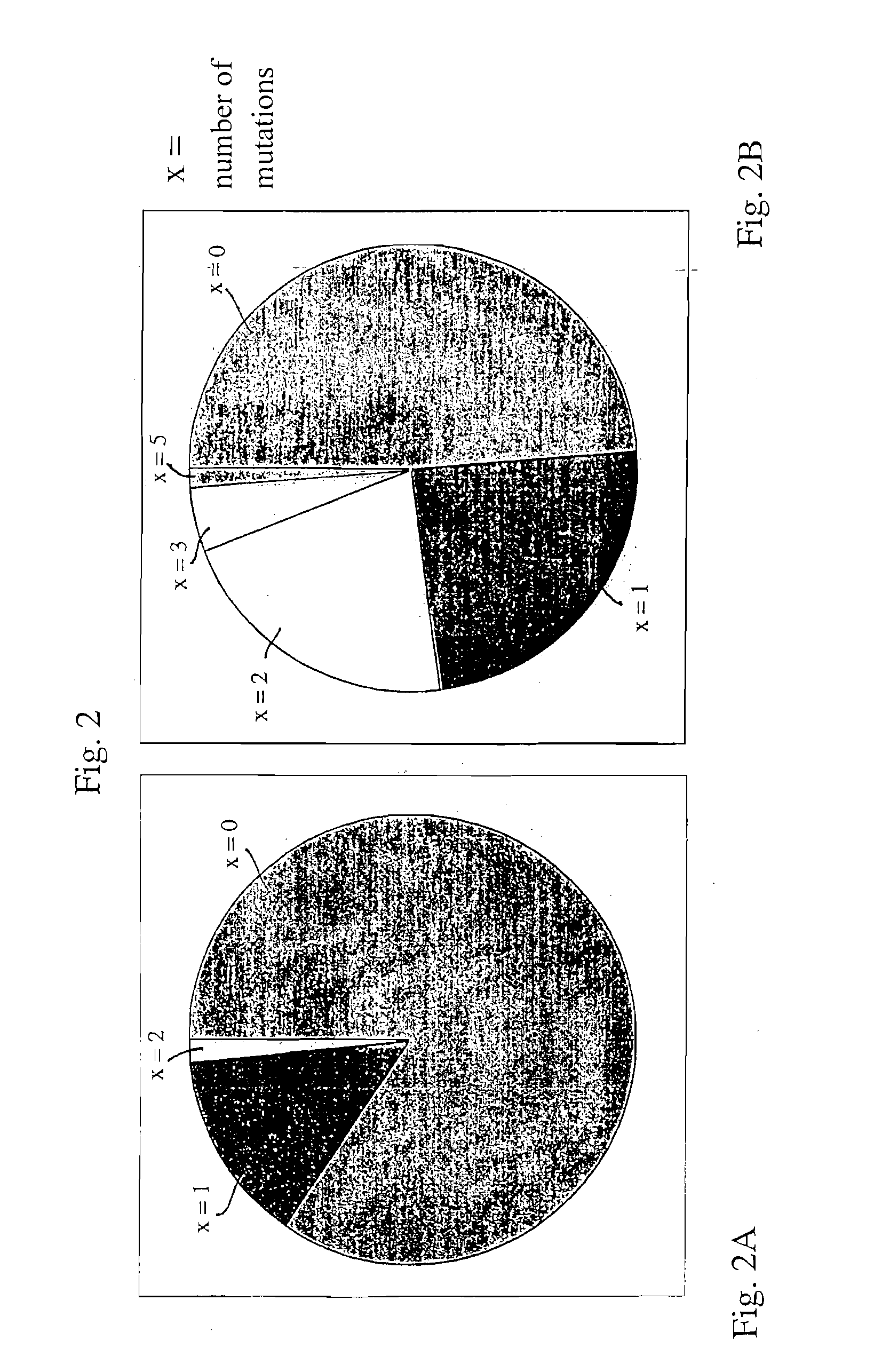
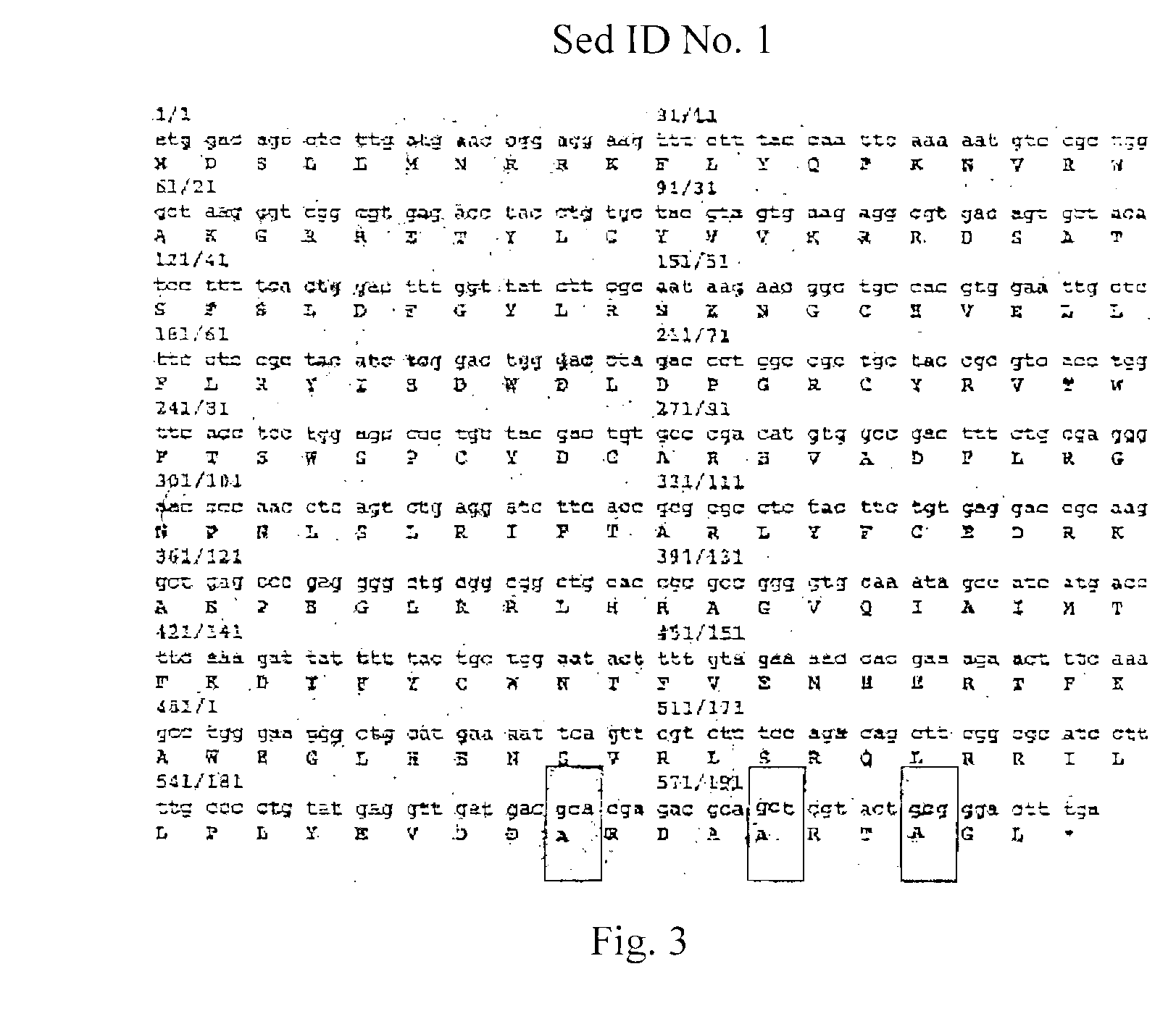
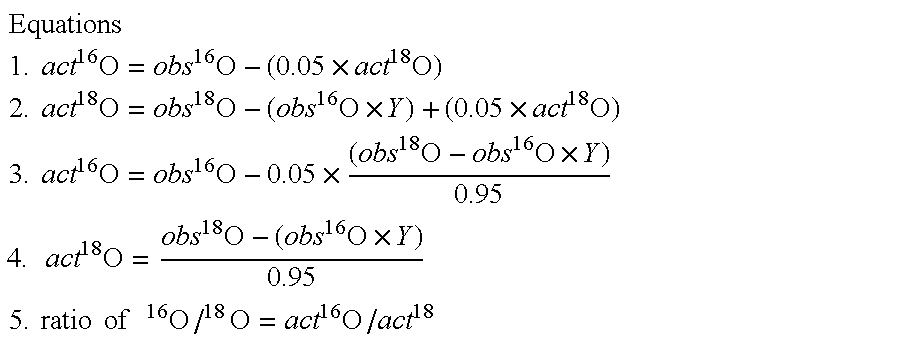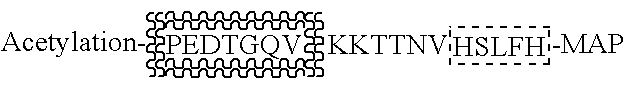Patents
Literature
623 results about "Proteomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
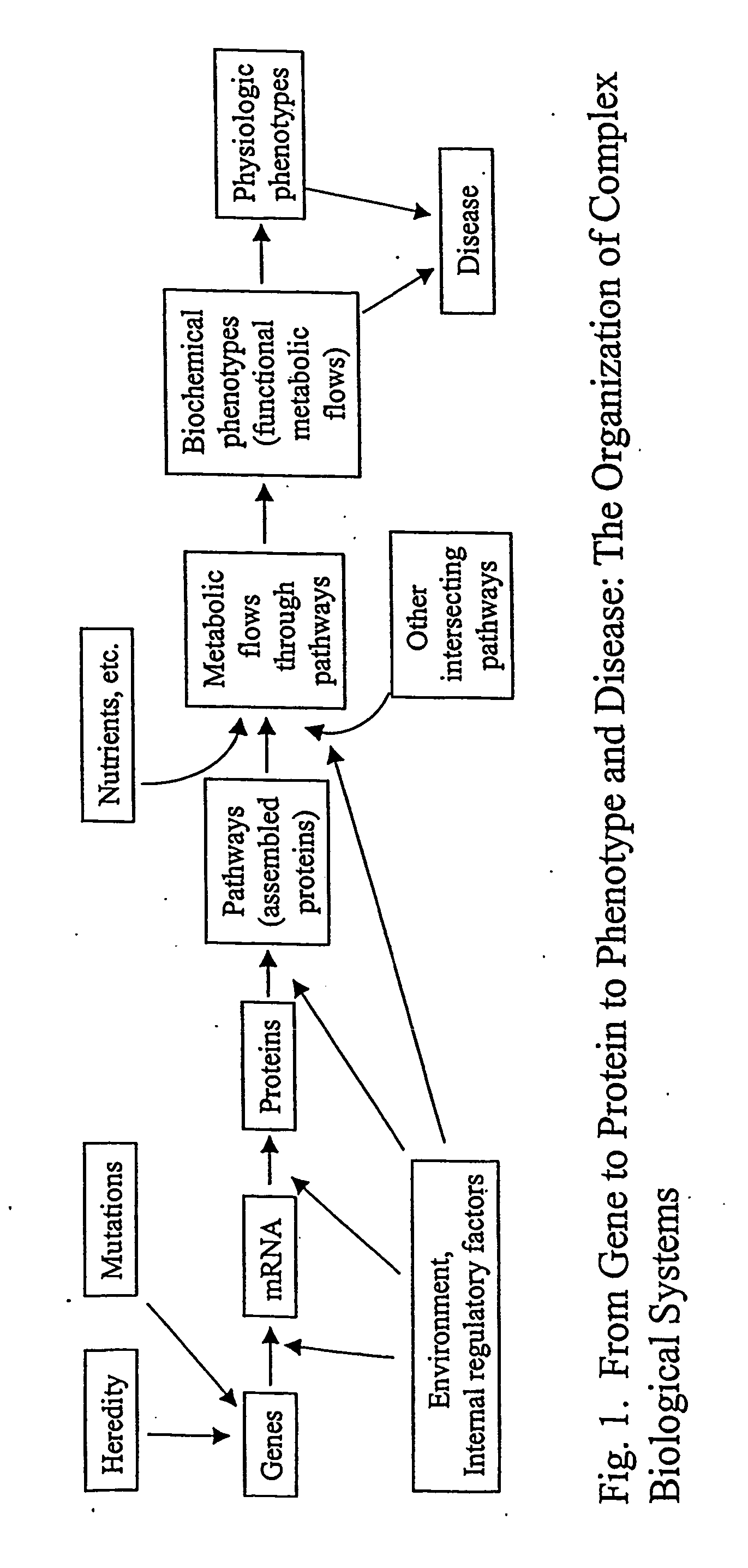
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions. The term proteomics was coined in 1997, in analogy to genomics, the study of the genome. The word proteome is a portmanteau of protein and genome, and was coined by Marc Wilkins in 1994 while he was a Ph.D. student at Macquarie University. Macquarie University also founded the first dedicated proteomics laboratory in 1995.
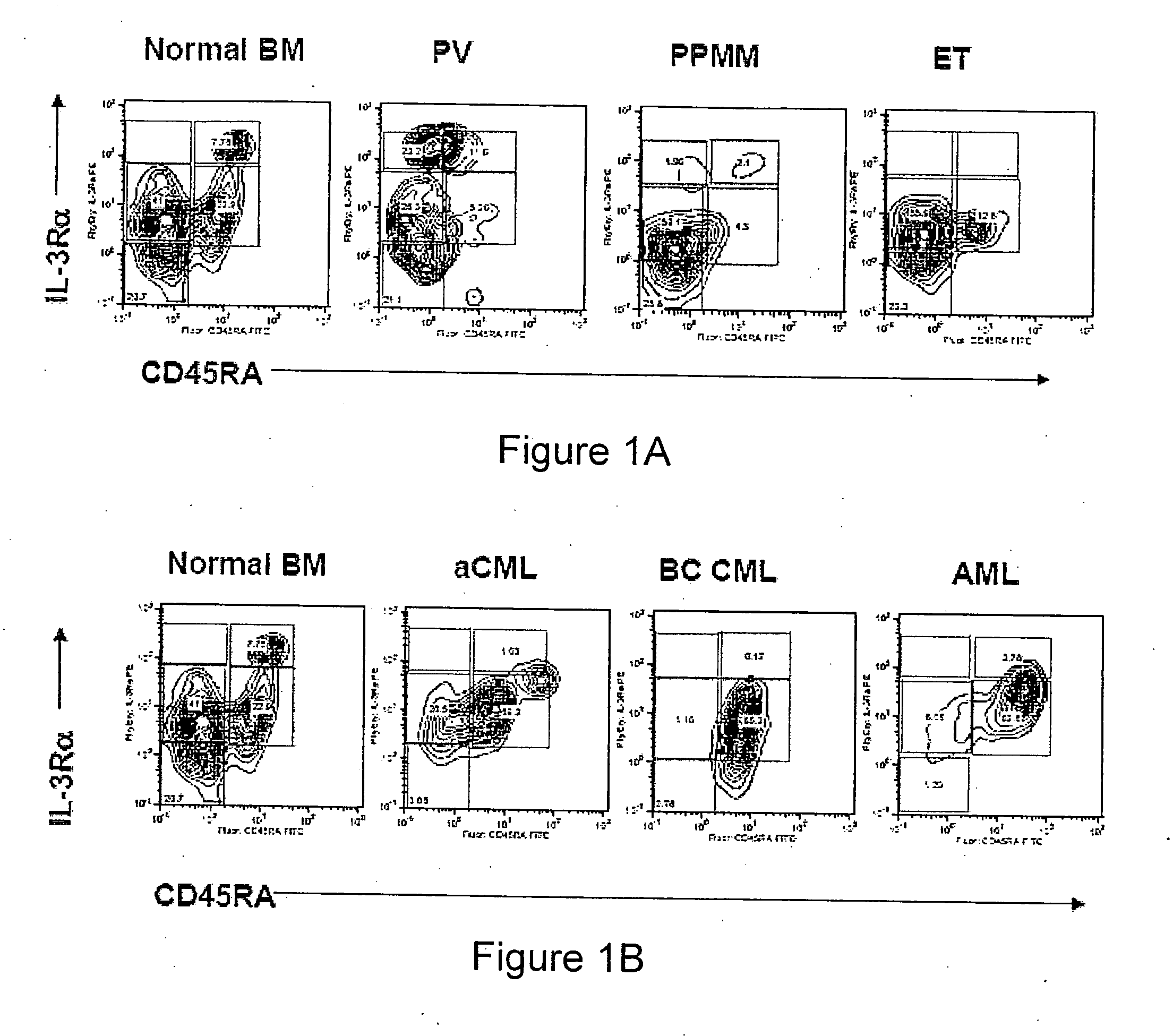
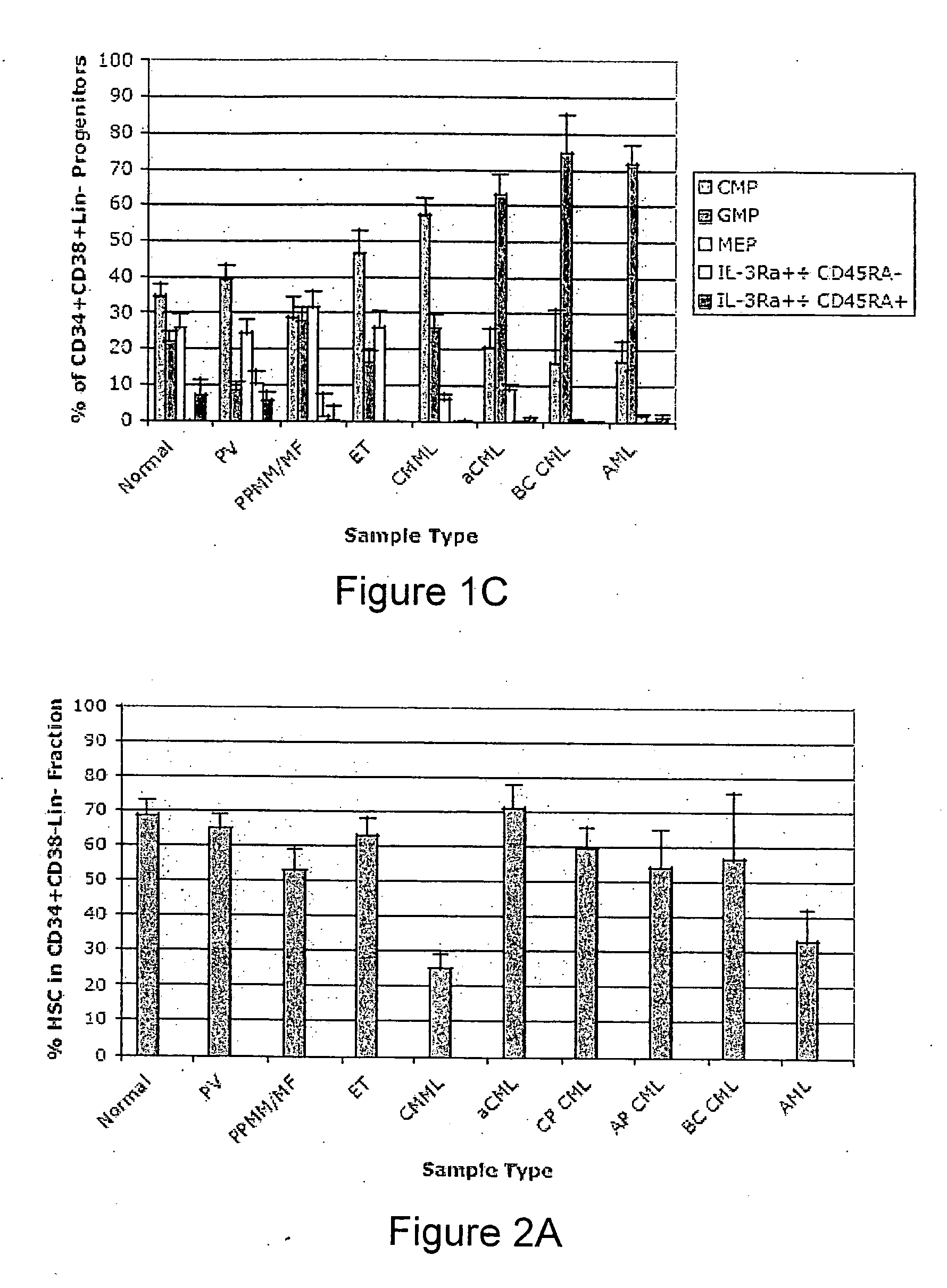
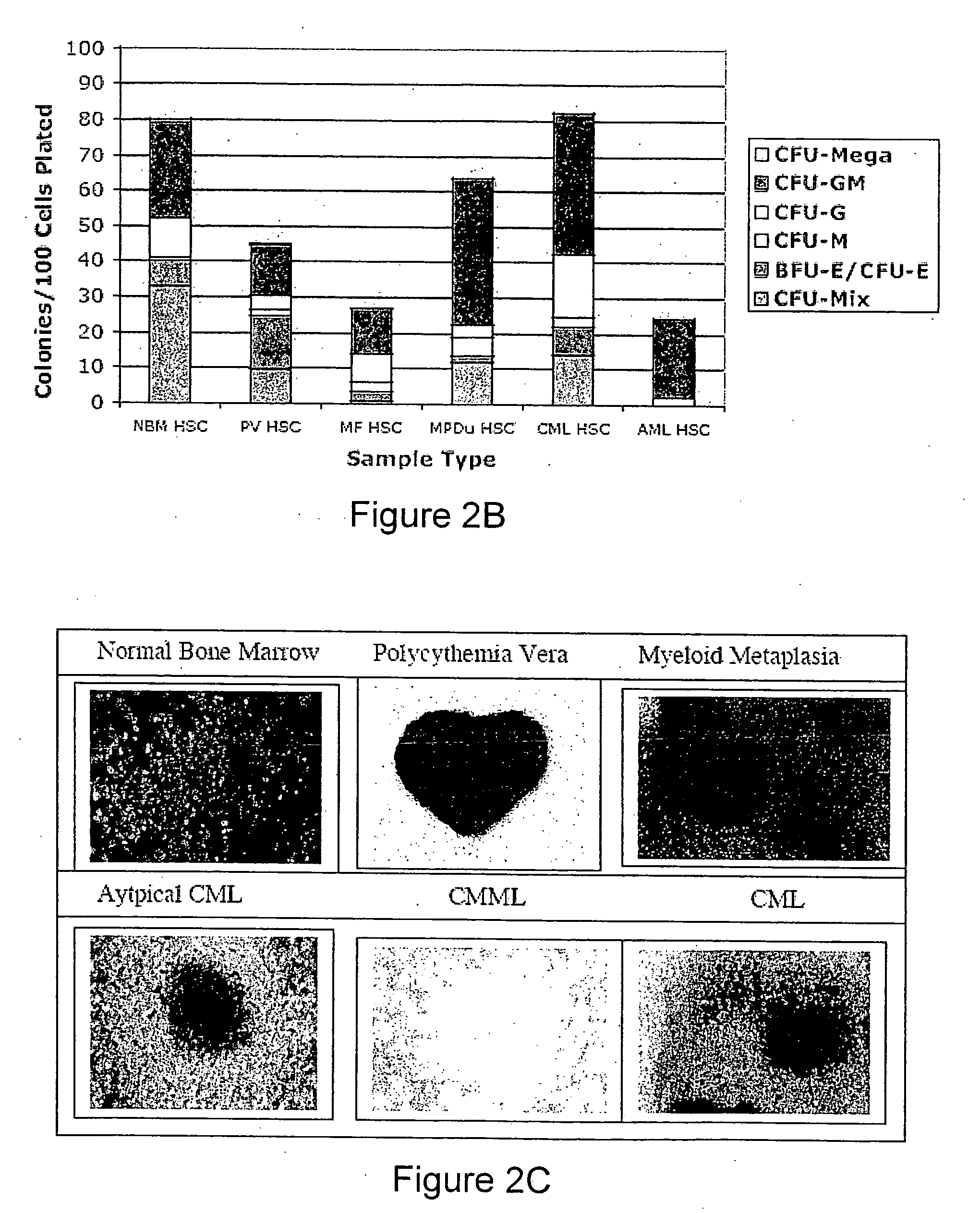
Methods for diagnosing and evaluating treatment of blood disorders
Methods, systems and kits are provided for the clinical staging of blood disorders including myelodysplastic syndrome, myeloproliferative diseases and leukemias by differential analysis of hematologic samples for the distribution of one or more hematopoietic stem or progenitor cell subsets. Additional functional, genetic, gene expression, proteomic or other molecular analyses of the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from the patients can also be employed in the staging methods of the invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Arrays of protein-capture agents and methods of use thereof
Owner:WAGNER PETER +3
System and methods for navigating and visualizing multi-dimensional biological data
InactiveUS20060036425A1Easy to identifyFacilitate correlation2D-image generationData visualisationData setEeg data
Methods systems and computer readable media for manipulating and displaying sparse data contained within very large datasets. Particular applications includes those to proteomics and metabolomics. Navigation of the large data sets from a global perspective may be practically implemented, so that a user is not confined to a narrow slice of data at a time, thus providing context of the whole dataset while viewing data within the dataset.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for performing peptide digestion on a microfluidic device
ActiveUS20060246533A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAlkyl transferContinuous flow
The invention provides methods and apparatuses that allow a protein sample to undergo reduction, alkylation, and digestion in a continuous flow process carried out within a microfluidic device. Methods and apparatuses in accordance with the invention can be employed as part of an automated proteomics analysis carried out in an integrated proteomics system.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
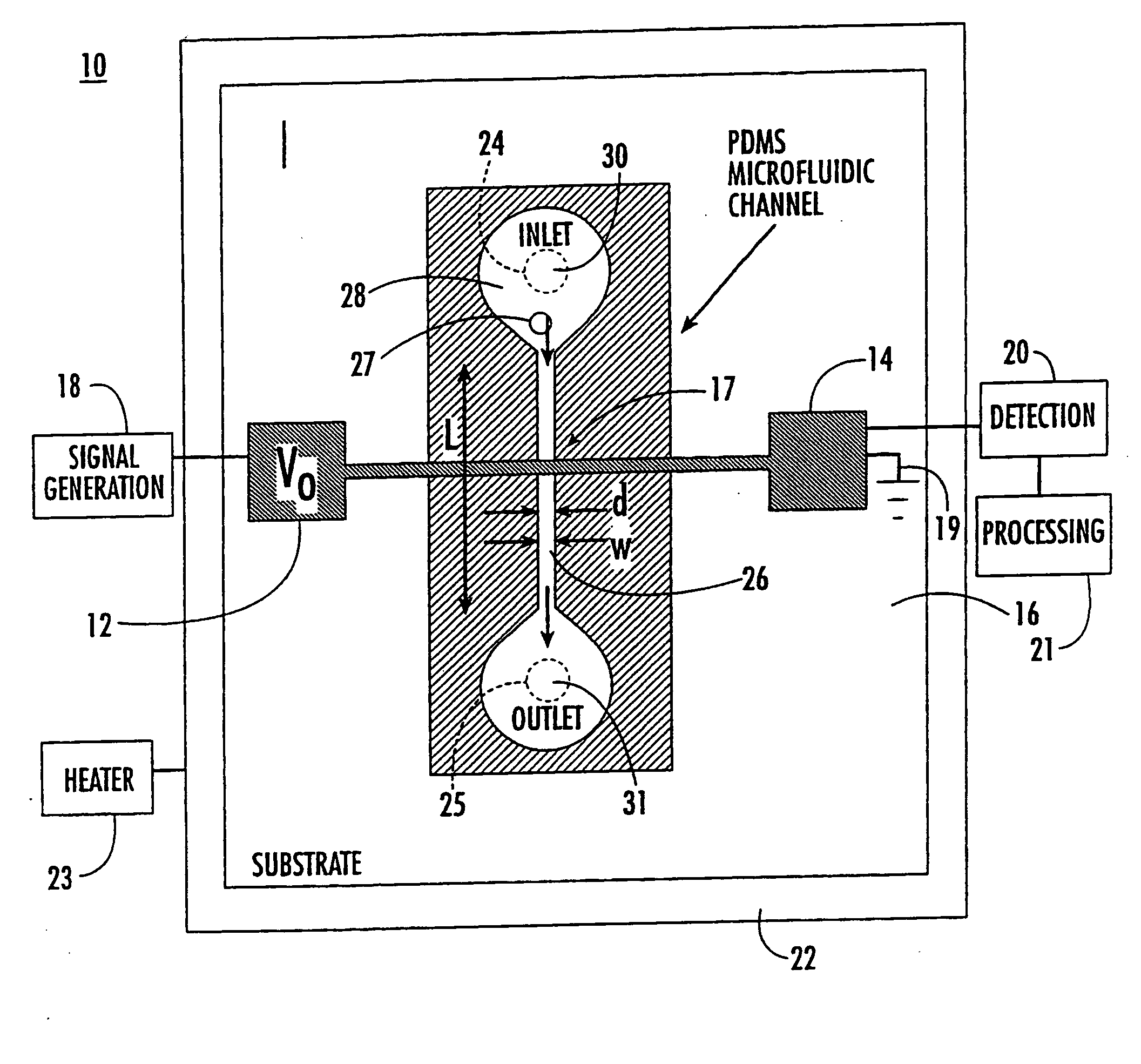
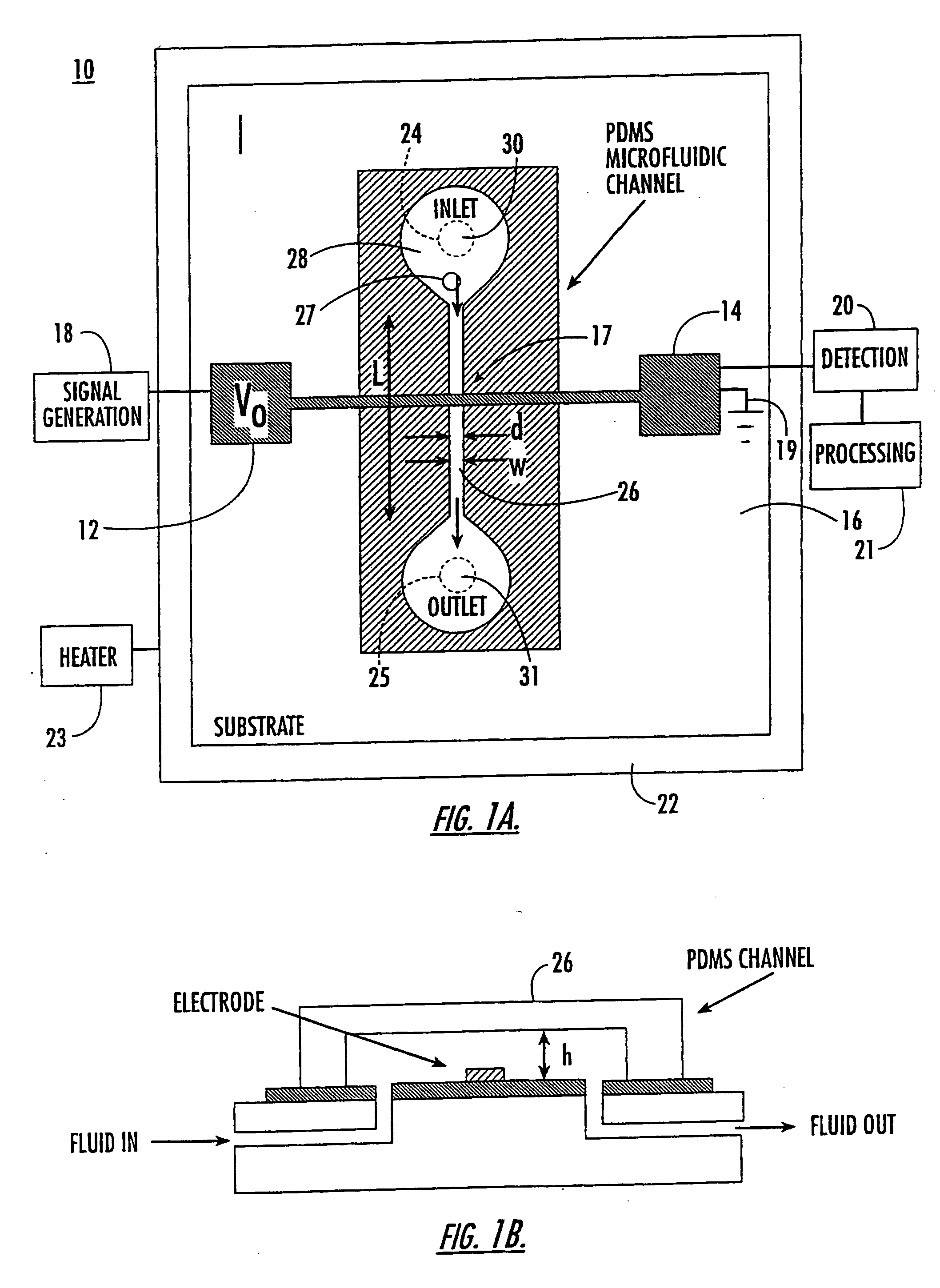
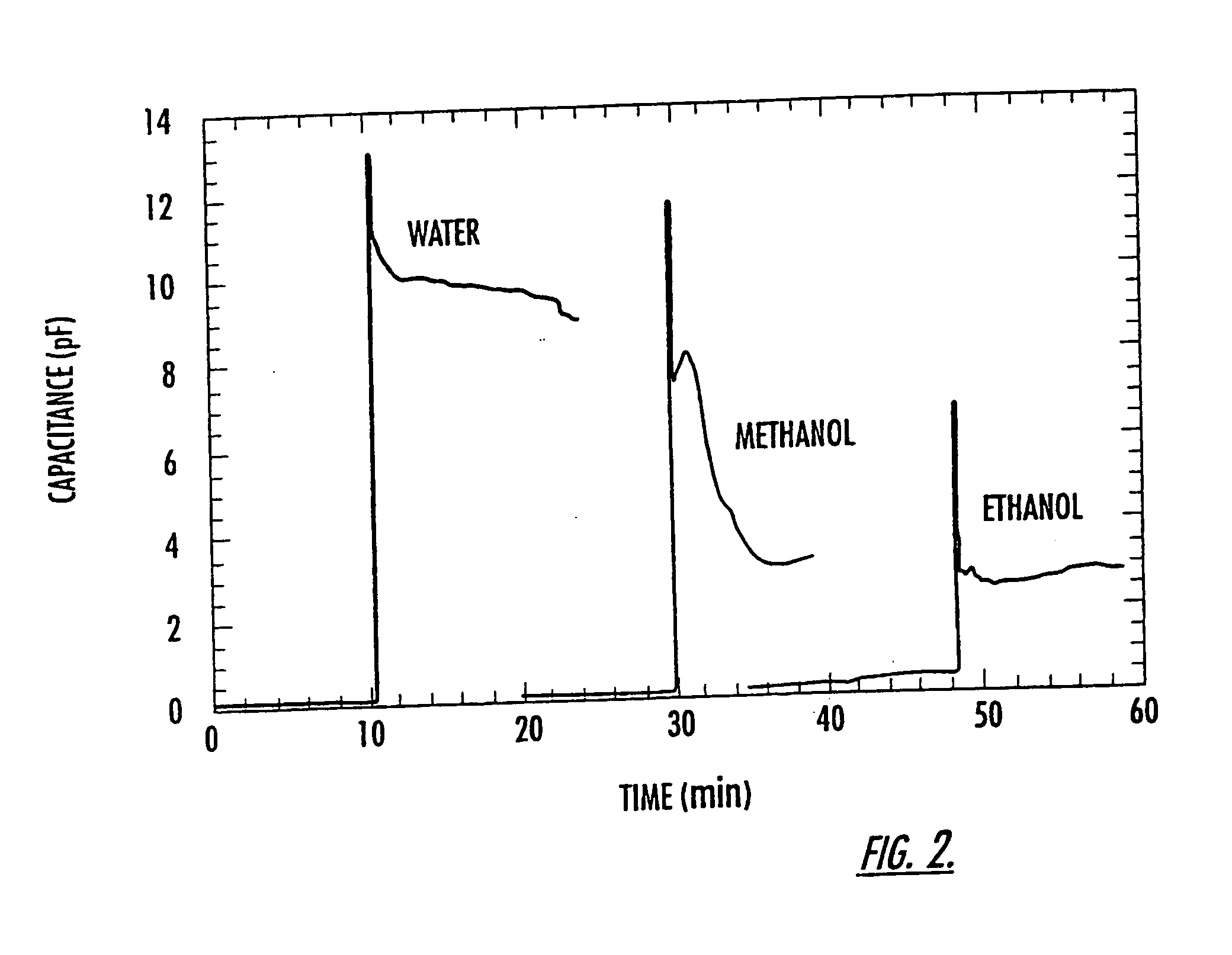
Microfluidic and nanofluidic electronic devices for detecting changes in capacitance of fluids and methods of using
InactiveUS20070238112A1Simpler and faster and less-expensiveMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceCell Cycle Kinetics
The present invention (also identified as “Capacitance cytometry”) relates to microfluidic and nanofluidic devices for detecting or measuring an electrical property of a fluid (liquid or aerosol), a single molecule, particle, or cell in fluid. In a particular embodiment, the devices detect or measure changes in capacitance of a fluid, molecule, particle or cell as it passes through the device. The invention relates to detection and measurement of single molecules, particularly biological molecules, and to methods of sequencing polynucleotide molecules (RNA or DNA) by detecting differentially labeled single nucleotides. Single molecule detection applications include DNA or RNA sequencing, detection of SNPs, protoemics, and particle sizing. The device can be used to determine cell DNA content, to analyze cell-cycle kinetics of cell populations, and to assay for abnormal changes in cell DNA content. Nano-microfluidic devices of this invention also have utility as detectors in molecular sorting systems and for detecting pathogens.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
System and methods for navigating and visualizing multi-dimensional biological data
InactiveUS7181373B2Facilitate identification and correlation and other useful relationshipImprove abilitiesData visualisation2D-image generationData setProteomics
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
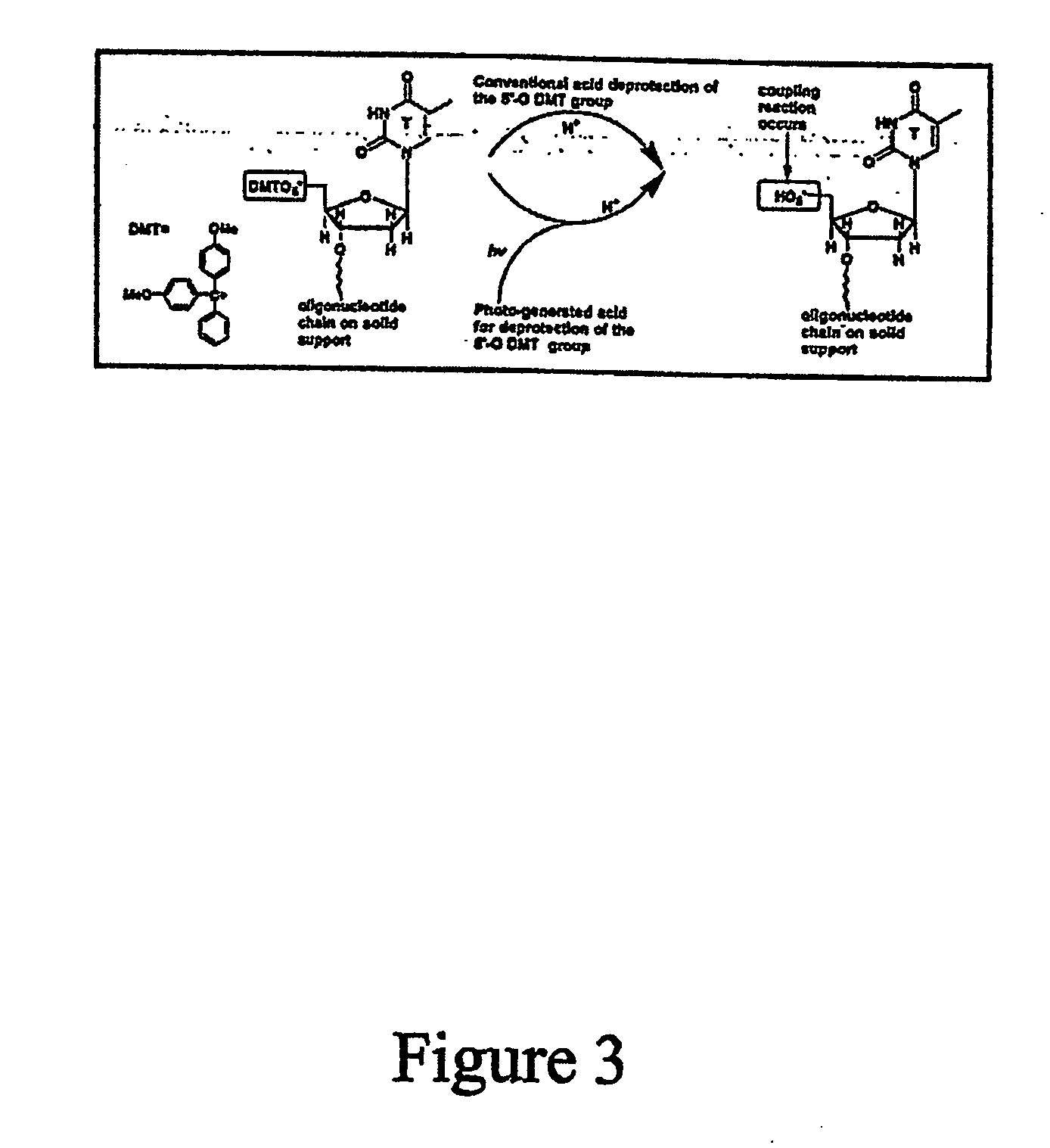
Array oligomer synthesis and use
InactiveUS20070059692A1Simple processShorten the timePeptide librariesSugar derivativesOligomerProteomics
The present disclosure provides efficient and reproducible methods for individually synthesizing oligomers in a parallel manner (e.g., oligonucleotides) on a solid support to produce pools of oligomers. Pools of oligonucleotides can be used for a variety of genomic and proteomic applications, including synthesis of genes or long DNA of any arbitrary sequence, PCR template amplification, and to generate primers for multiplexing PCR or transcription. Rapid availability of these oligonucleotide products will greatly accelerate the processes of de novo protein design, vaccine development, production of short RNA fragments, such as siRNA, oligonucleotide-based drug screening, and SNP sample preparation.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
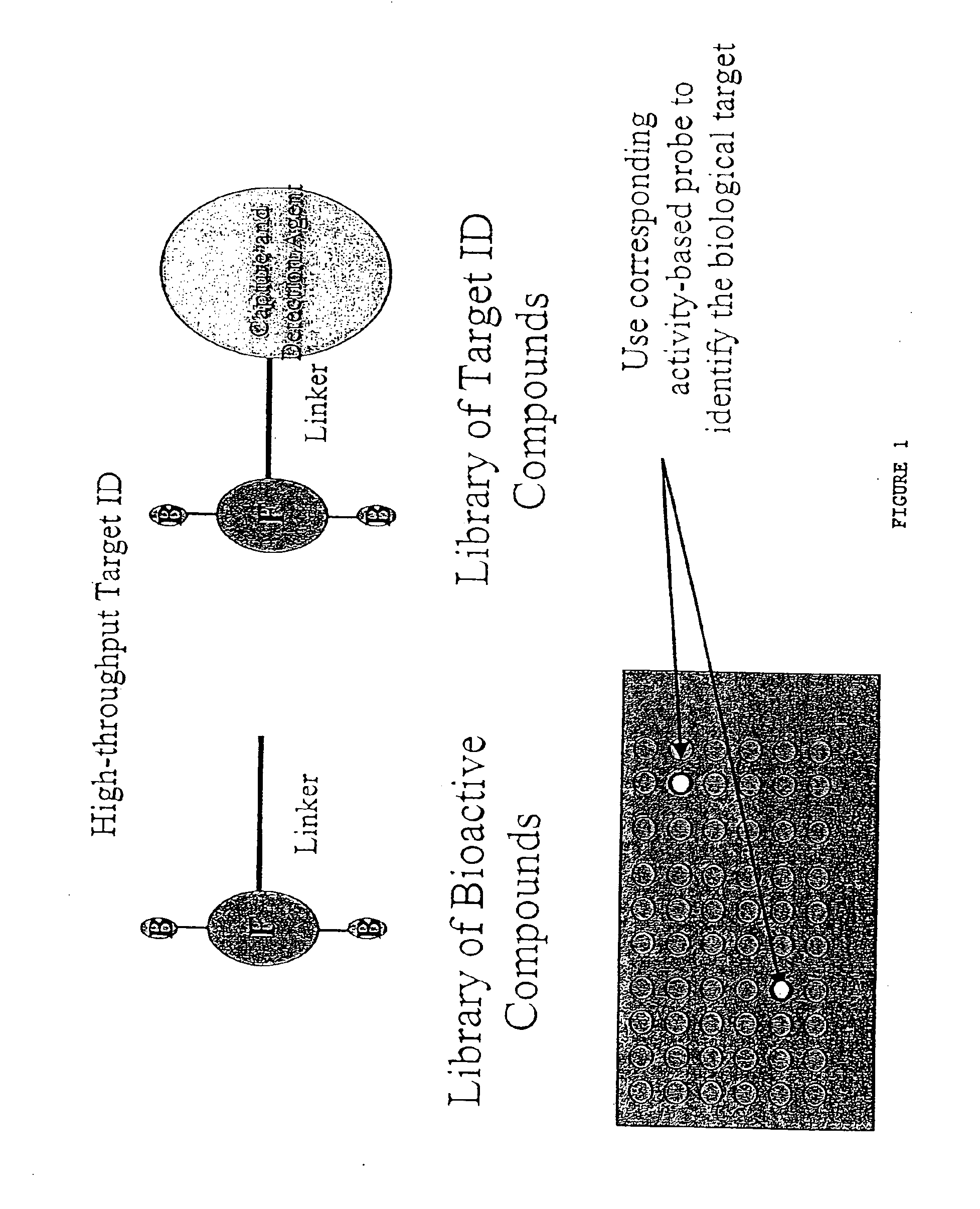
Proteomic analysis
InactiveUS6872574B2Reduce reactivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein targetBiological target
The present invention provides methods for analyzing proteomes, as cells or lysates. The analysis is based on the use of probes that have specificity to the active form of proteins, particularly enzymes and receptors. The probes can be identified in different ways. In accordance with the present invention, a method is provided for generating and screening compound libraries that are used for the identification of lead molecules, and for the parallel identification of their biological targets. By appending specific functionalities and / or groups to one or more binding moieties, the reactive functionalities gain binding affinity and specificity for particular proteins and classes of proteins. Such libraries of candidate compounds, referred to herein as activity-based probes, or ABPs, are used to screen for one or more desired biological activities or target proteins.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Systems and methods for automated proteomics research
InactiveUS20070184546A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWorkcellBiological body
A robotic laboratory automation workcell preferably includes instruments and equipment that are integrated by using conveyor or track elements and a robotic arm. The automation workcell is controlled by a centralized or main controller or processor using specialized control software to automate the proteomics research process. The automated workcell is capable of performing genetic laboratory experiments from start to finish by moving samples or microplates between the instruments for analysis. A goal of the automated workcell is to perform repetitive procedures in an effort to build and maximize the efficiency of a gene(s) of a targeted organism.
Owner:HUDSON CONTROL GROUP
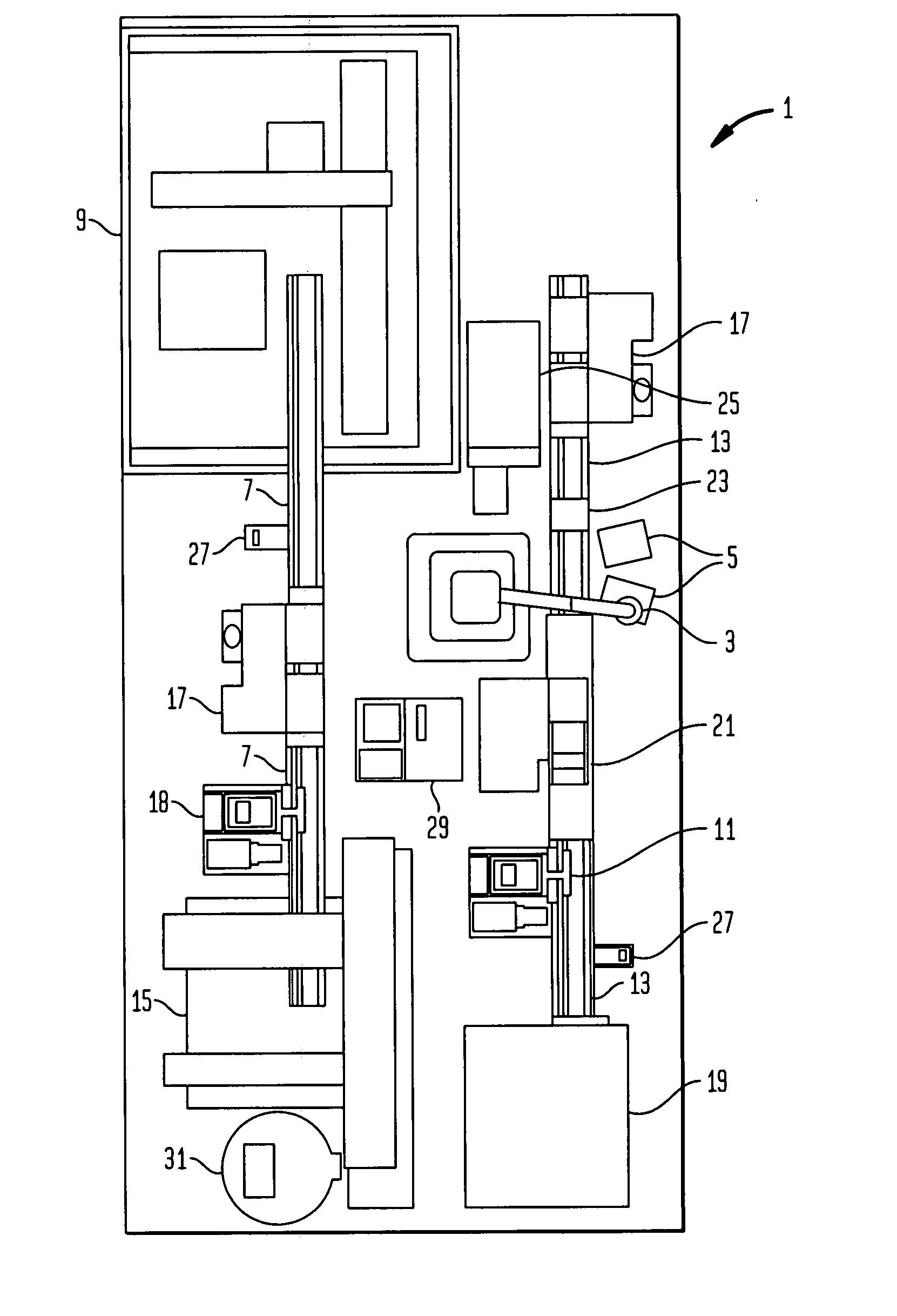
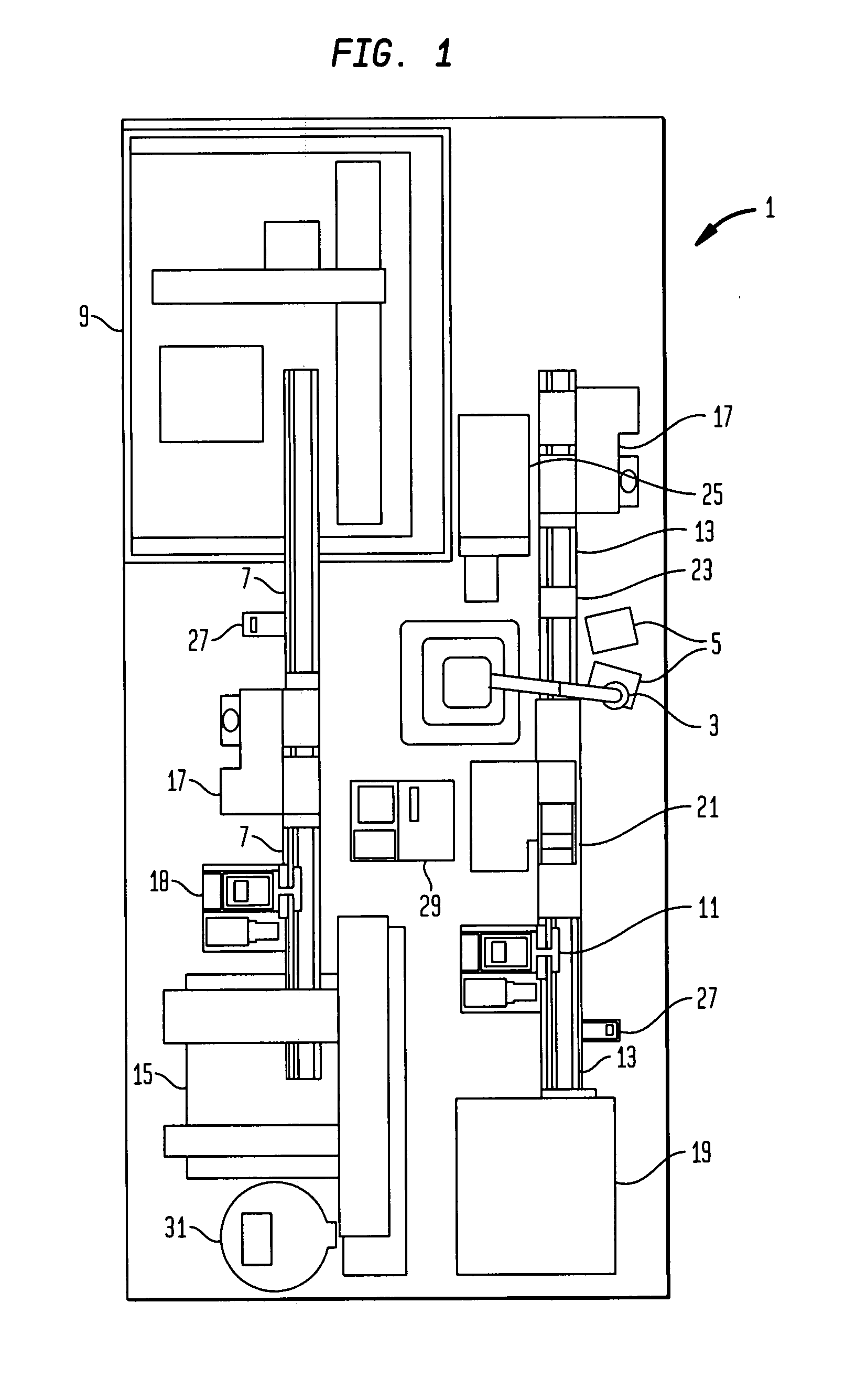
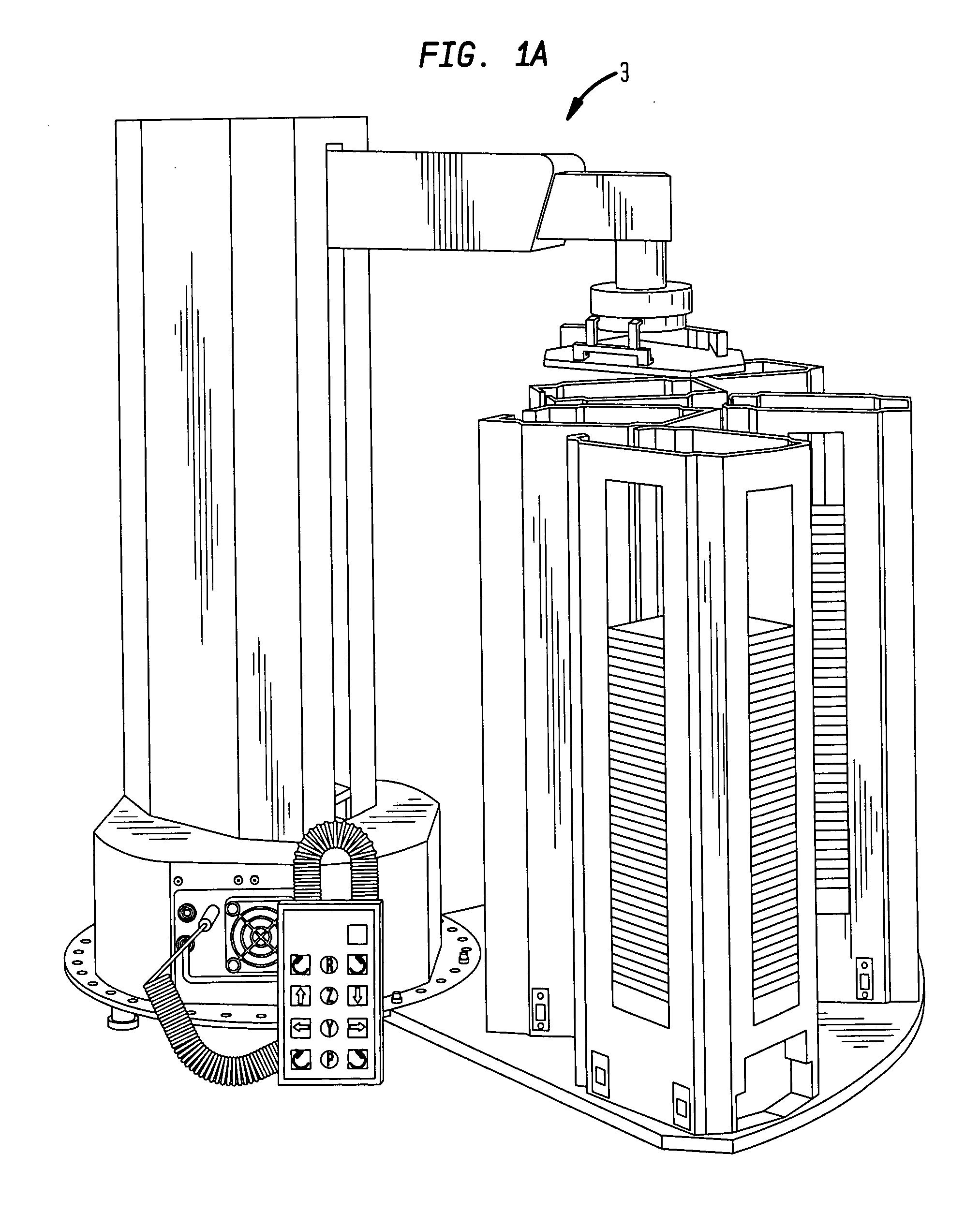
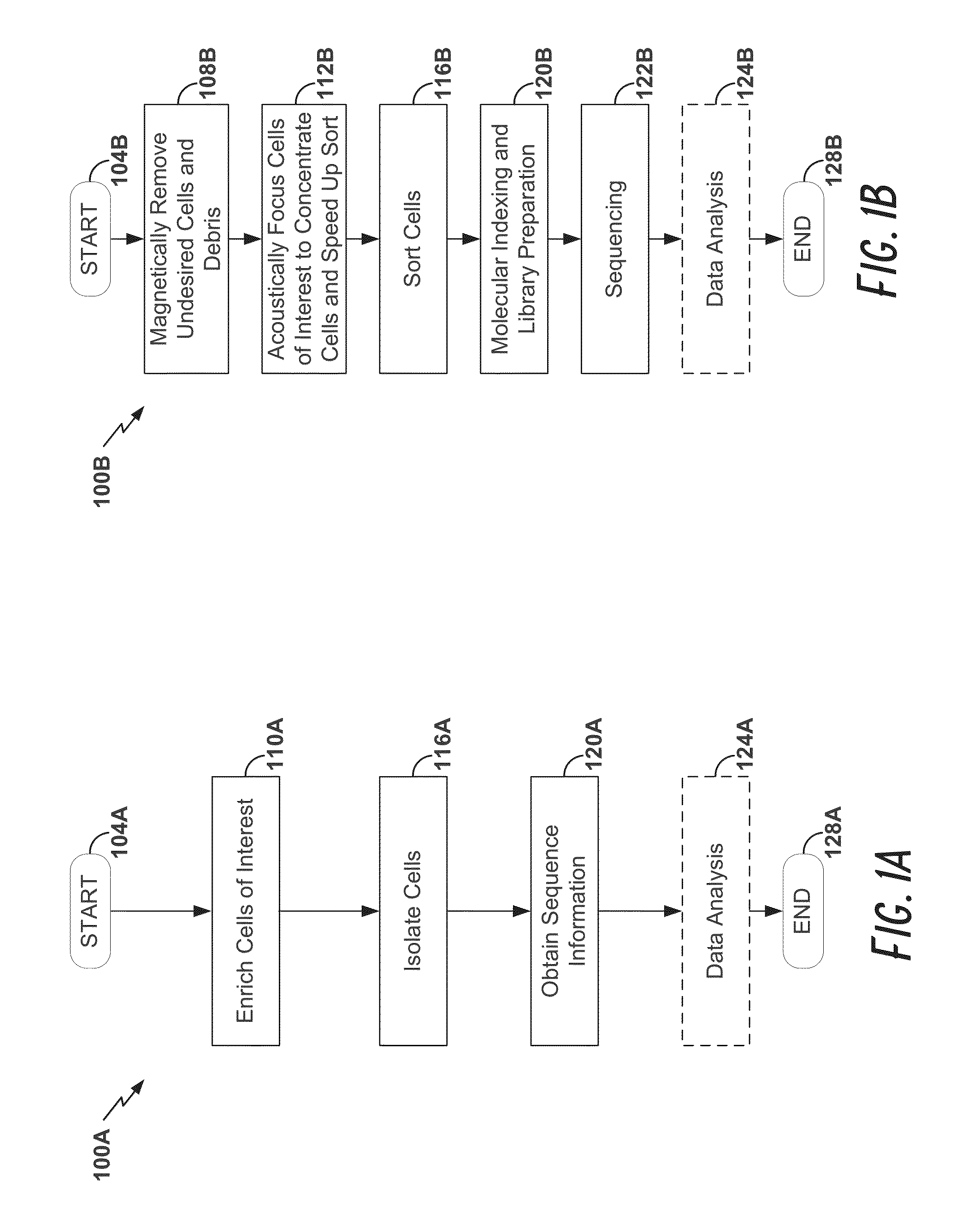
High-throughput single-cell analysis combining proteomic and genomic information
ActiveUS20160244828A1Predict susceptibilityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsPolynucleotide
Disclosed herein are methods for single-cell sequencing. In some examples, the methods include enriching a sample comprising a plurality of cells for cells of interest to produce an enriched cell sample; isolating one or more cells of interest in the enriched cell sample; and obtaining sequence information of one or more polynucleotides from each of the one or more isolated cells. Obtaining sequence information may include generating a molecularly indexed polynucleotide library from the one or more isolated cells. Enriching the sample may include focusing cells of interest in the sample using acoustic focusing.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
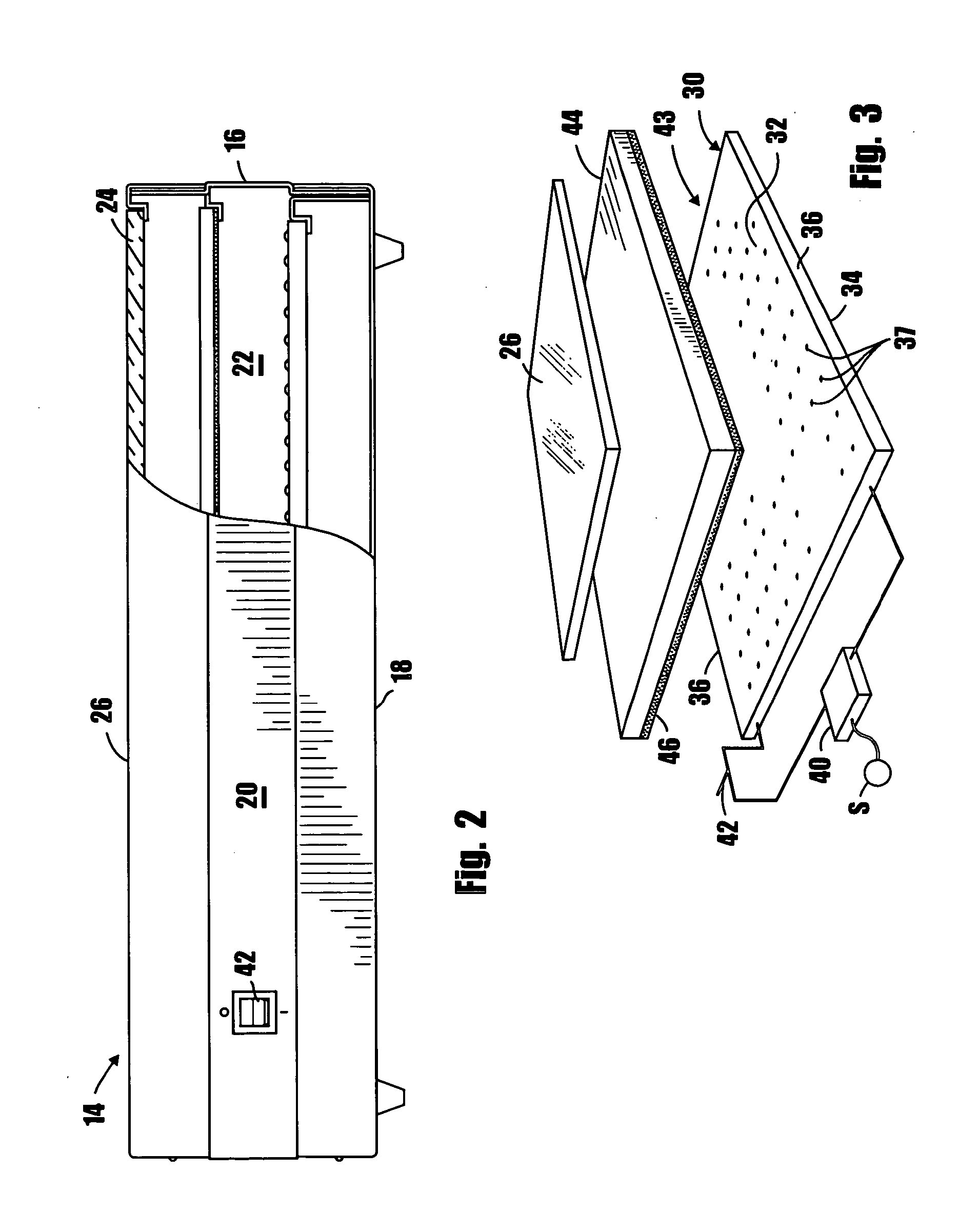
Transilluminator with ultraviolet light emitting diode array
InactiveUS20060237658A1UniformityImprove uniformityColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsFluorescencePhysics
A method and apparatus for genomic or proteomic research to visualize fluorescent labeled DNA, RNA or protein samples that have been separated for documentation and analysis. The apparatus includes a novel radiation source for uniformly irradiating the samples which comprises an array of UV LEDS. In one form of the invention the apparatus also includes a first conversion plate that is carried by the housing at a location intermediate the radiation source and the sample supporting platform for converting the radiation emitted from the source to radiation at a second wavelength.
Owner:WALUSZKO ALEX
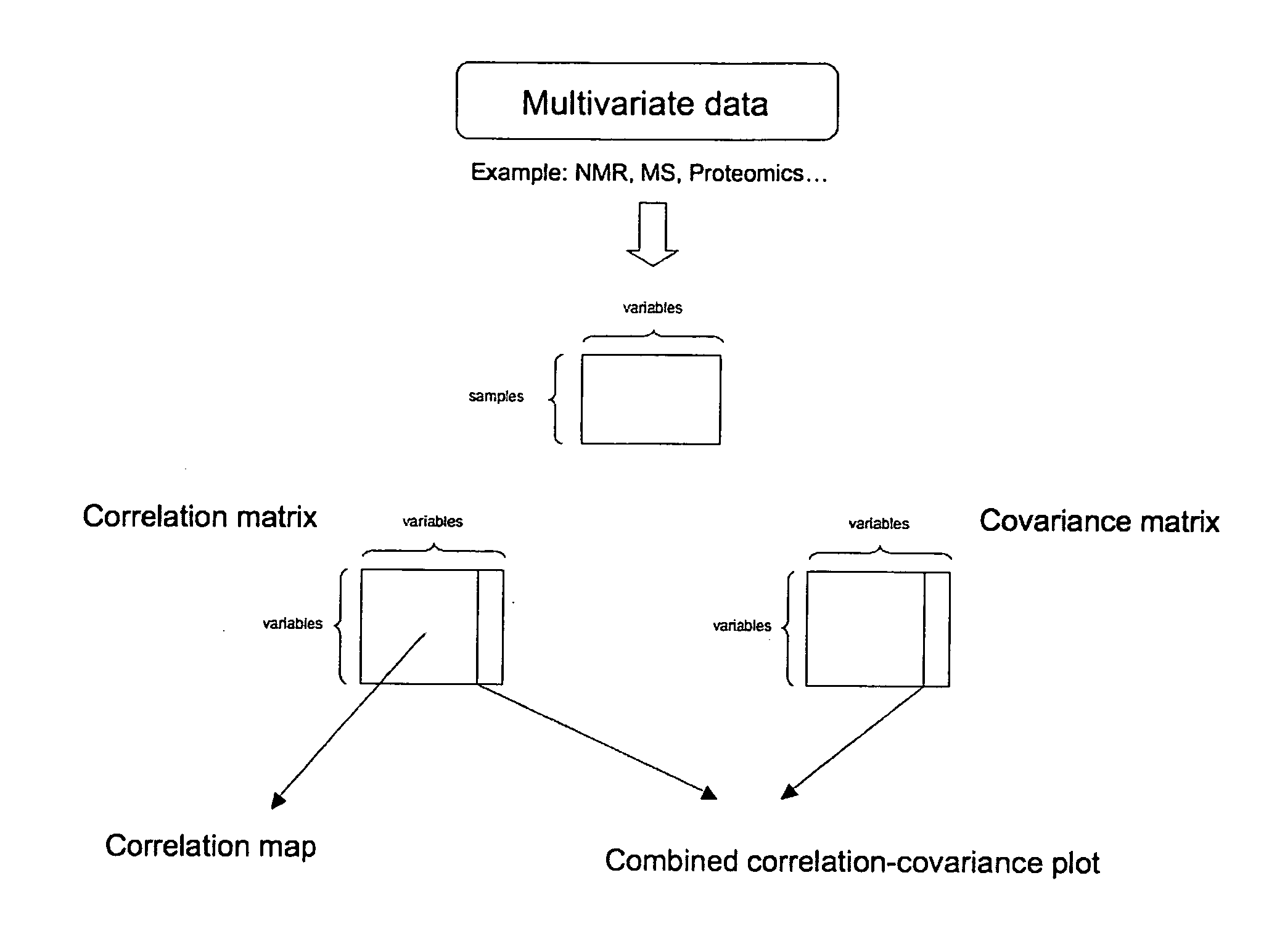
Method for the identification of molecules and biomarkers using chemical, biochemical and biological data
ActiveUS20070043518A1Molecular entity identificationProteomicsGenomicsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
This invention pertains generally to the field of multivariate statistics, and in particular to new methods for the analysis (e.g., chemometrics) of chemical, biochemical, and biological data, including, for example, spectral data, including but not limited to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral data. These methods are useful, for example, in metabonomics, proteomics, transcriptomics, genomics, etc., and form a part of other methods, for example, methods for the identification of chemical species, methods for the identification of biomarkers that are useful in methods of classification, diagnosis, prognosis, etc.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
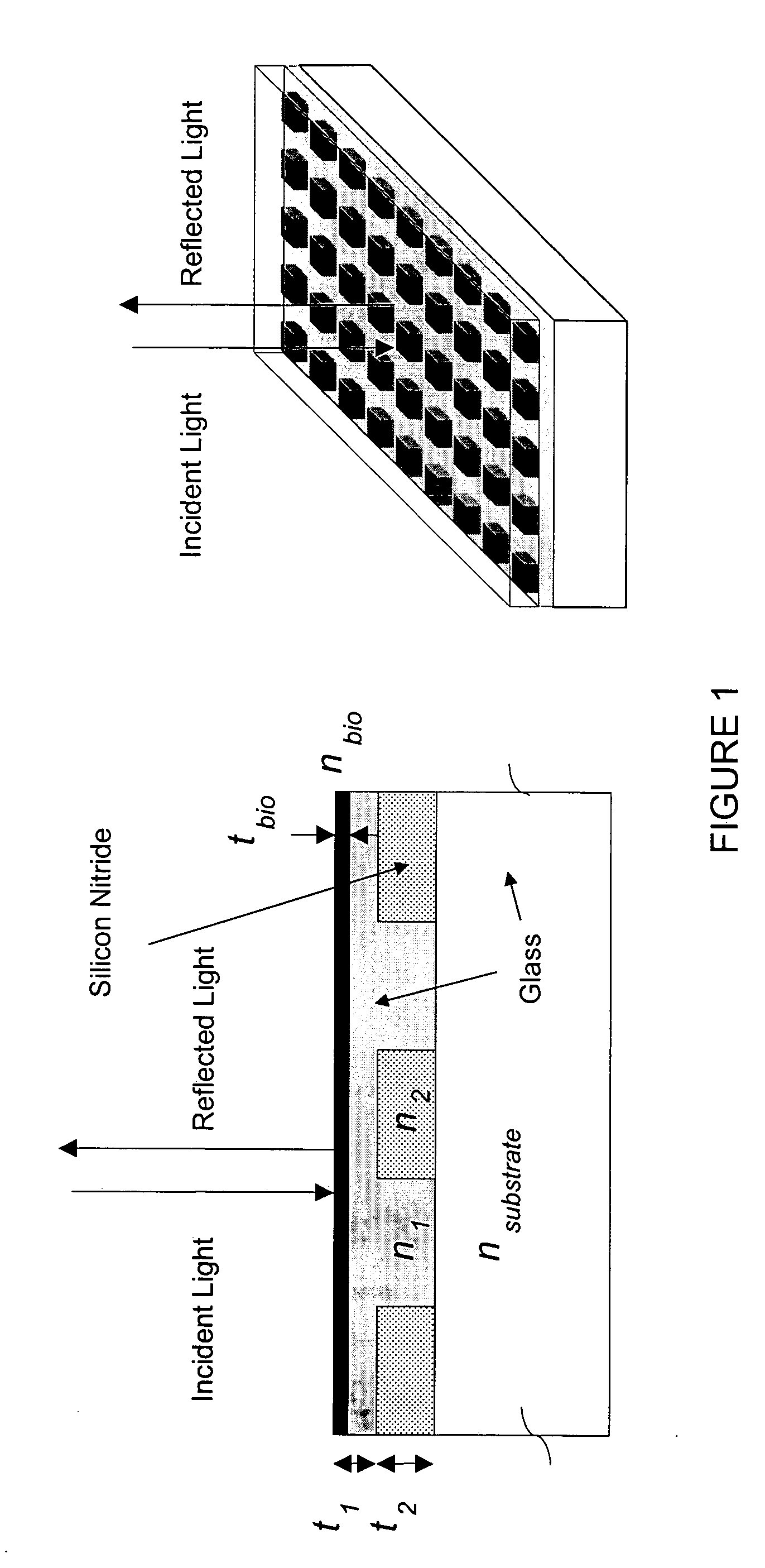
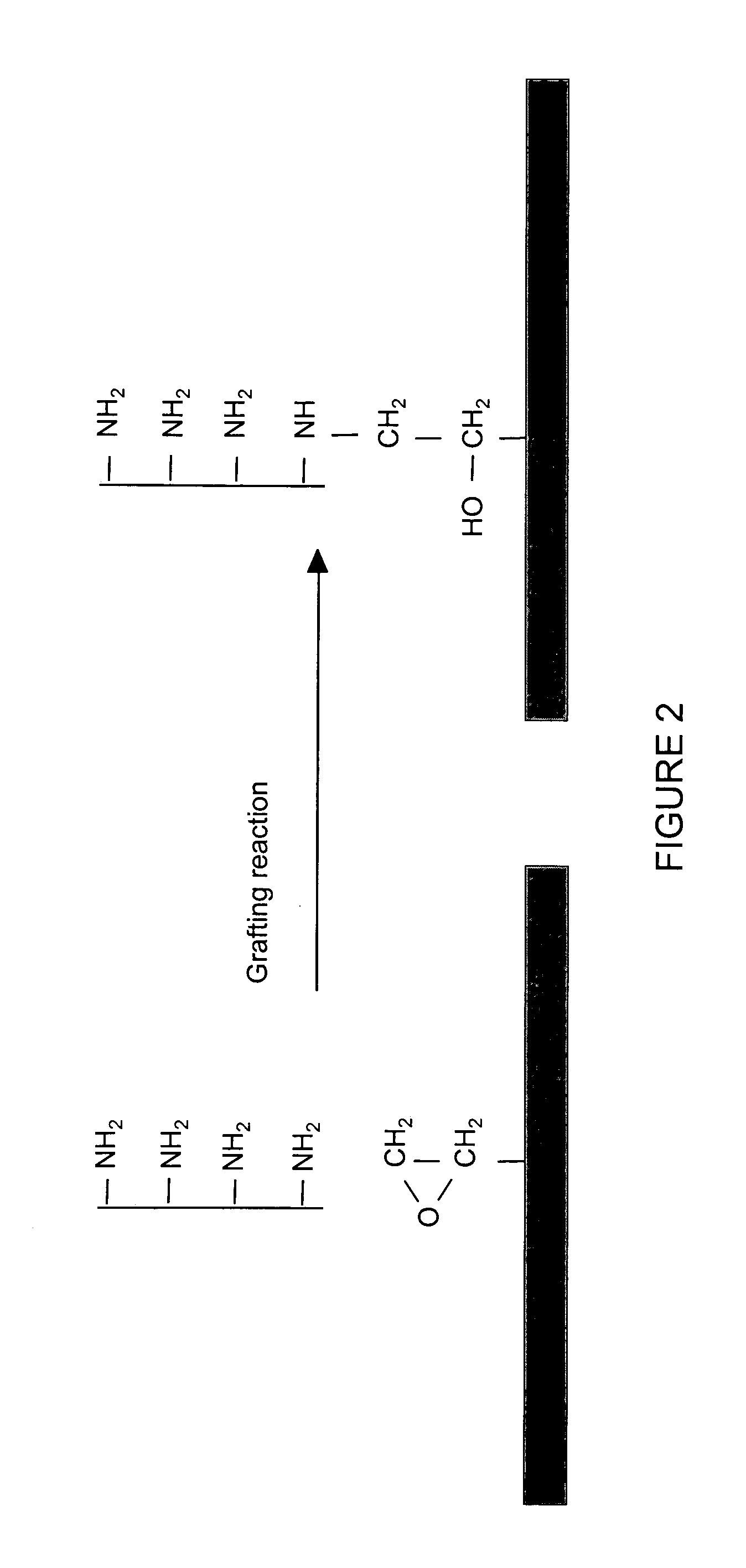
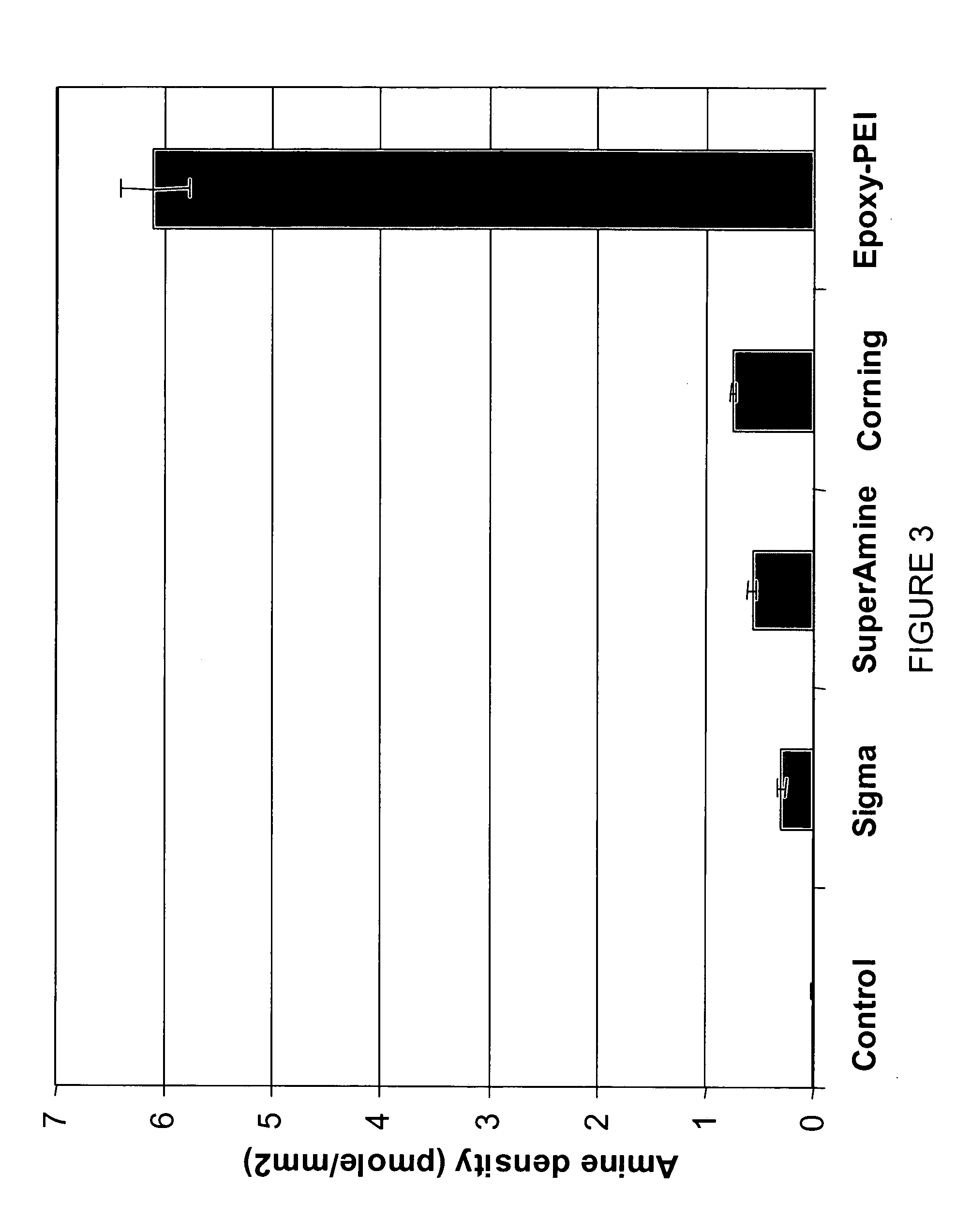
High-density amine-functionalized surface
InactiveUS20050214803A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDrug discoveryChemistry
A method for providing amine functional groups on a surface for binding proteins, peptides, DNAs, cells, small molecules, and other chemical or biological molecules that are of interests in the areas of proteomic, genomic, pharmaceutical, drug discovery, and diagnostic studies.
Owner:SRU BIOSYST
Proteomic analysis of biological fluids
ActiveUS7191068B2Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseFetal growth
The invention concerns the identification of proteomes of biological fluids and their use in determining the state of maternal / fetal conditions, including maternal conditions of fetal origin, chromosomal aneuploidies, and fetal diseases associated with fetal growth and maturation. In particular, the invention concerns the identification of the proteome of amniotic fluid (multiple proteins representing the composition of amniotic fluid) and the correlation of characteristic changes in the normal proteome with various pathologic maternal / fetal conditions, such as intra-amniotic infection, or chromosomal defects.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC +1
Method and kit for proteomic identification
InactiveUS20020012920A1Cost-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHuman cellProteomics
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES US SEC THE DEPT OF +1
Applications of laser-processed substrate for molecular diagnostics
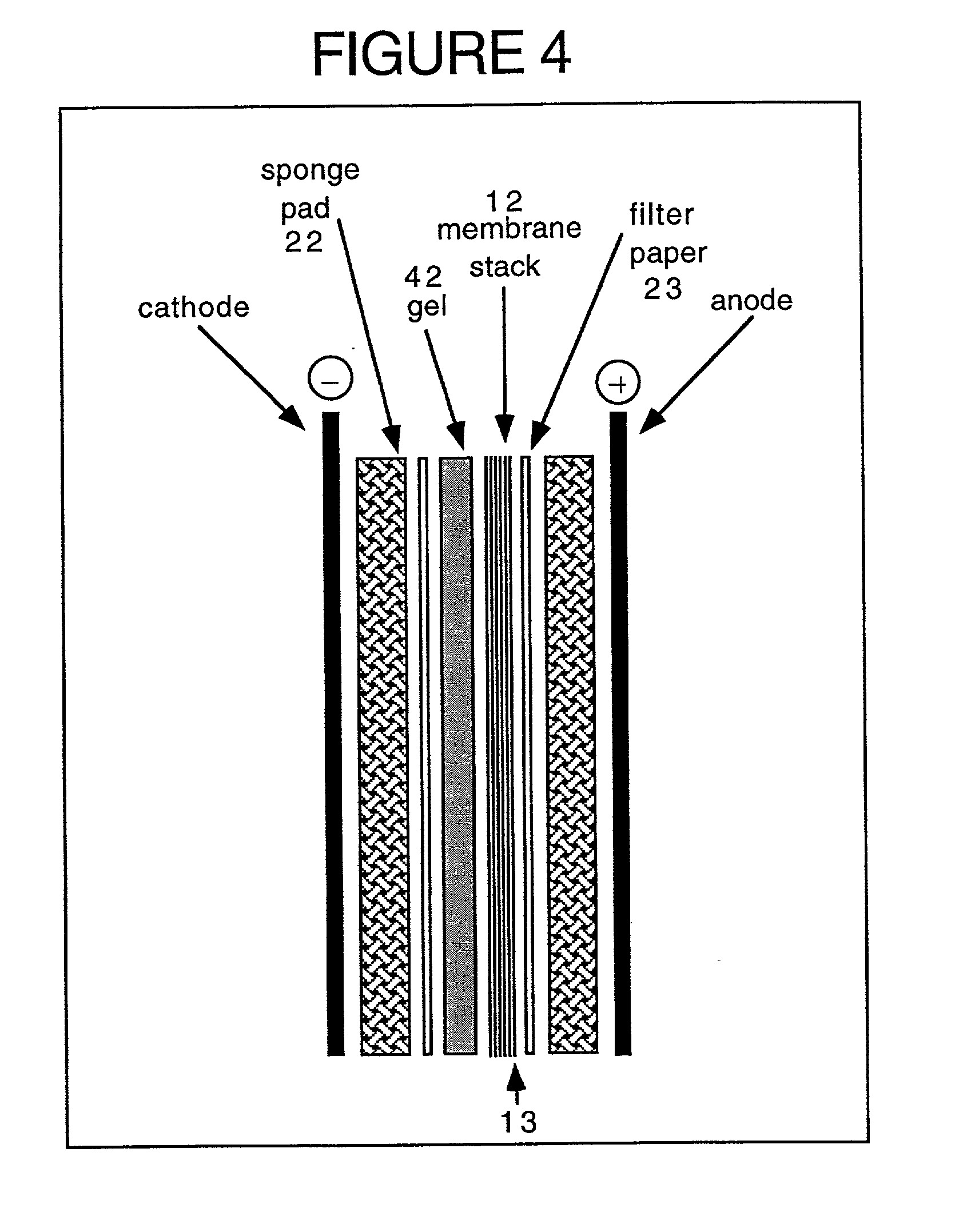
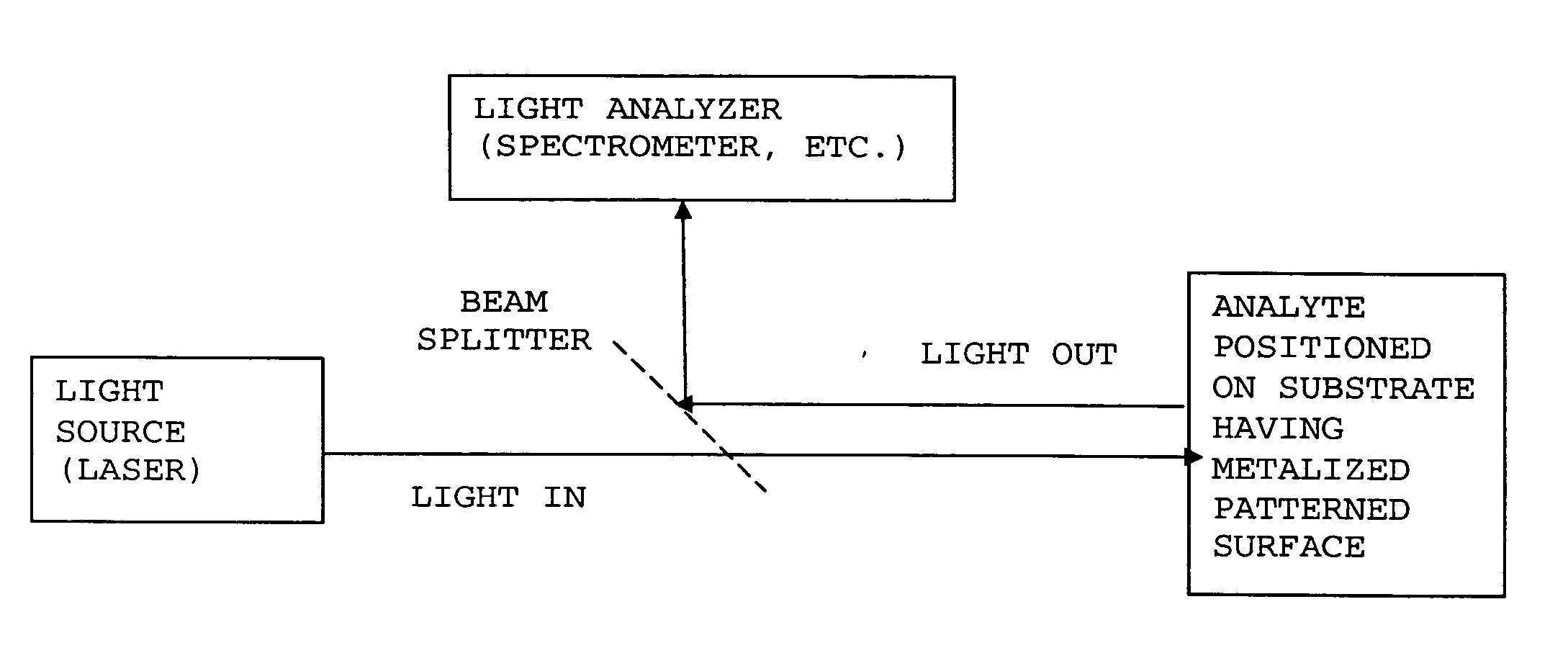
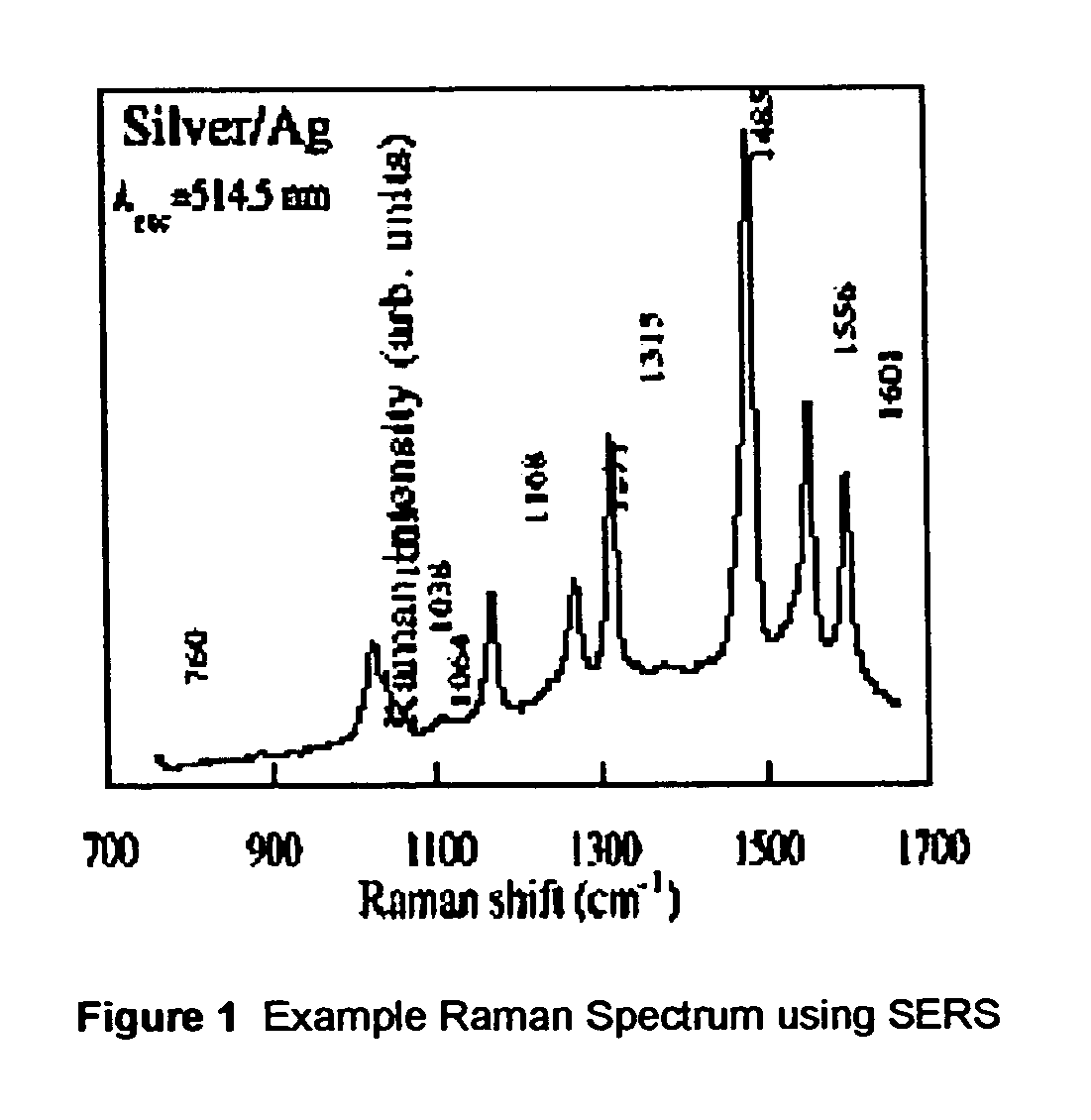
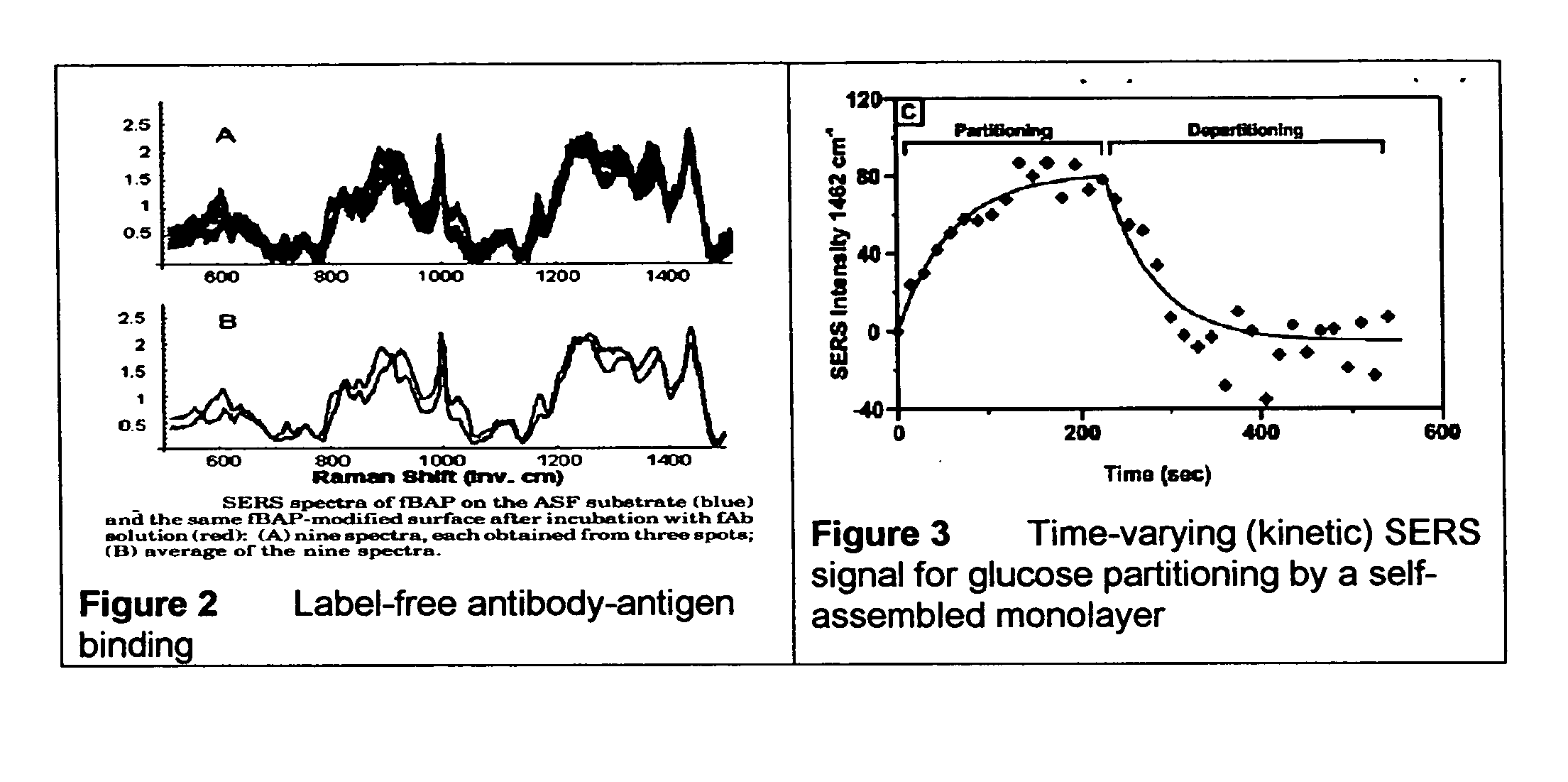
ActiveUS20070115469A1Facilitate SERS analysisMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryChemical reactionPhotonics
Surface enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) and related modalities offer greatly enhanced sensitivity and selectivity for detection of molecular species through the excitation of plasmon modes and their coupling to molecular vibrational modes. One of the chief obstacles to widespread application is the availability of suitable nanostructured materials that exhibit strong enhancement of Raman scattering, are inexpensive to fabricate, and are reproducible. I describe nanostructured surfaces for SERS and other photonic sensing that use semiconductor and metal surfaces fabricated using femtosecond laser processing. A noble metal film (e.g., silver or gold) is evaporated onto the resulting nanostructured surfaces for use as a substrate for SERS. These surfaces are inexpensive to produce and can have their statistical properties precisely tailored by varying the laser processing. Surfaces can be readily micropatterned and both stochastic and self-organized structures can be fabricated. This material has application to a variety of genomic, proteomic, and biosensing applications including label free applications including binding detection. Using this material, monolithic or arrayed substrates can be designed. Substrates for cell culture and microlabs incorporating microfluidics and electrochemical processing can be fabricated as well. Laser processing can be used to form channels in the substrate or a material sandwiched onto it in order to introduce reagents and drive chemical reactions. The substrate can be fabricated so application of an electric potential enables separation of materials by electrophoresis or electro-osmosis.
Owner:EBSTEIN STEVEN M
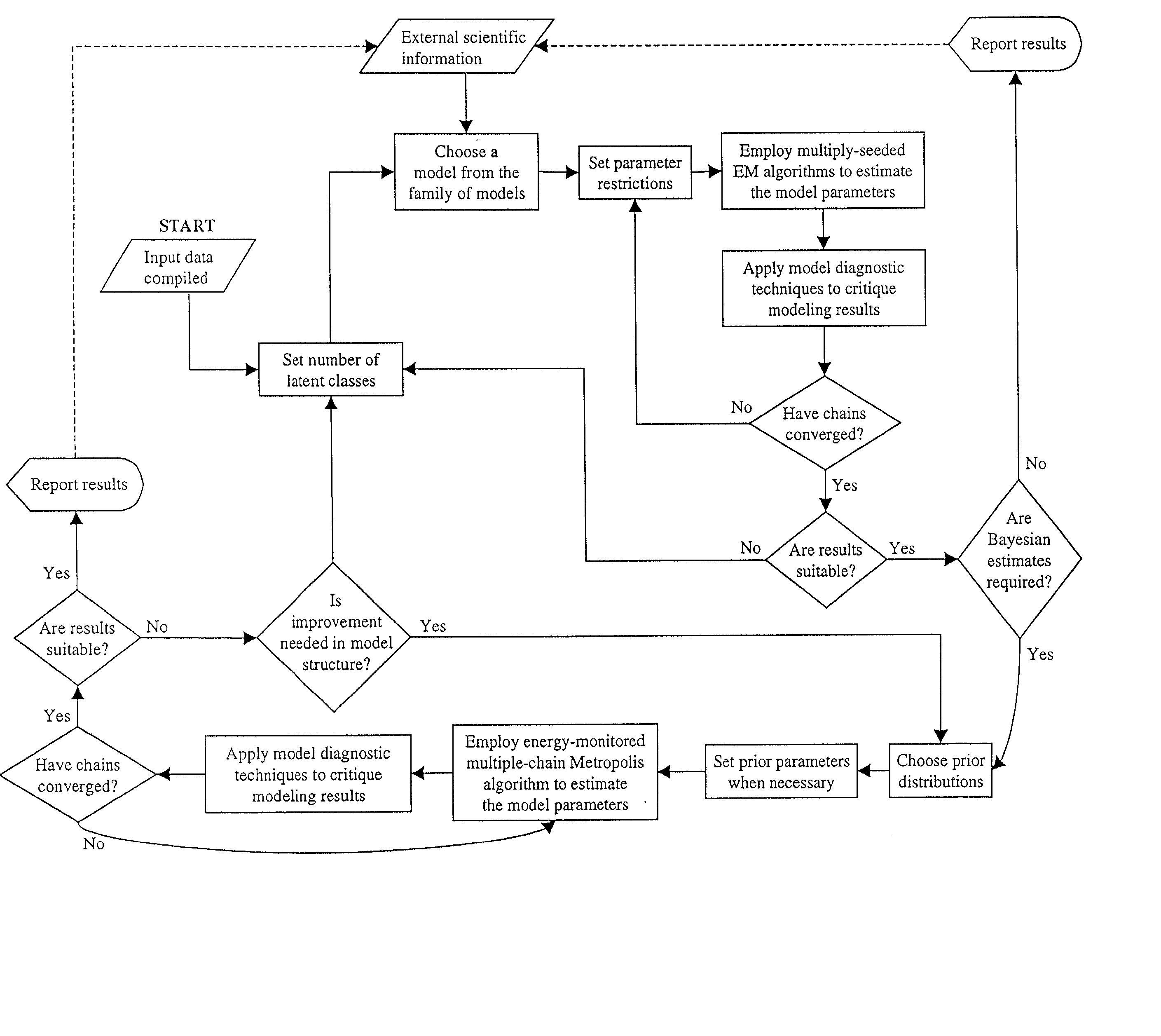
Methods for classifying objects and identifying latent classes
The present invention relates to certain computational methods for classifying a plurality of objects or for identifying one or more latent classes among a plurality of objects. The present invention presents methods that glean relationships across at least two distinct sets of objects, allowing one to identify latent classes of objects along one set of margins, observations about which objects provide insight into possible properties or characteristics of objects along another set of margins. More specifically, the present invention relates to a process for analyzing multivariate sets of data utilizing tools that combine, for example, aspects of fuzzy logic and statistics. The present invention finds a number of practical applications, including the sensible analysis of large amounts of information, such as those generated sequence analysis, gene expression and proteomics in the field of biology.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
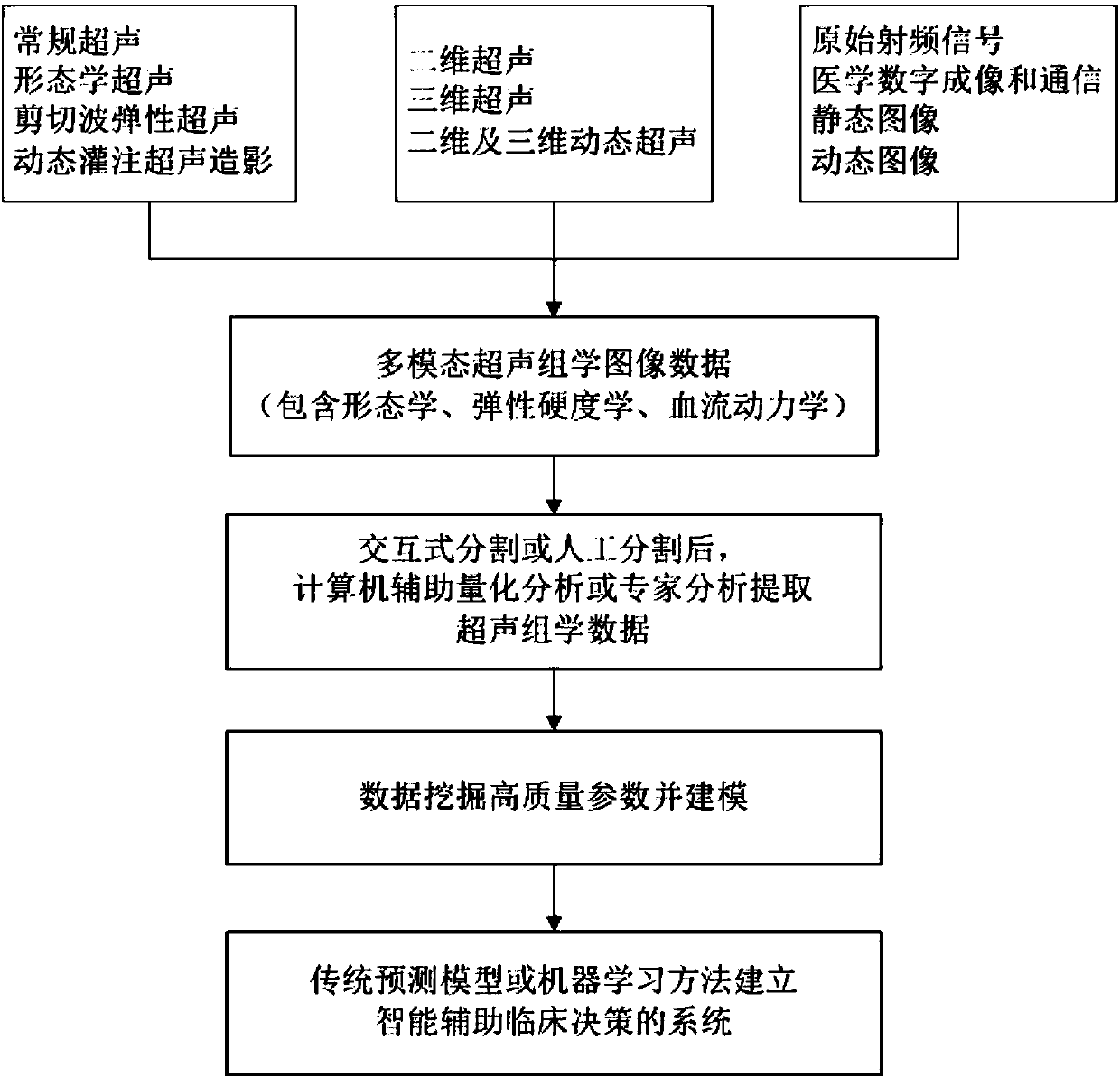
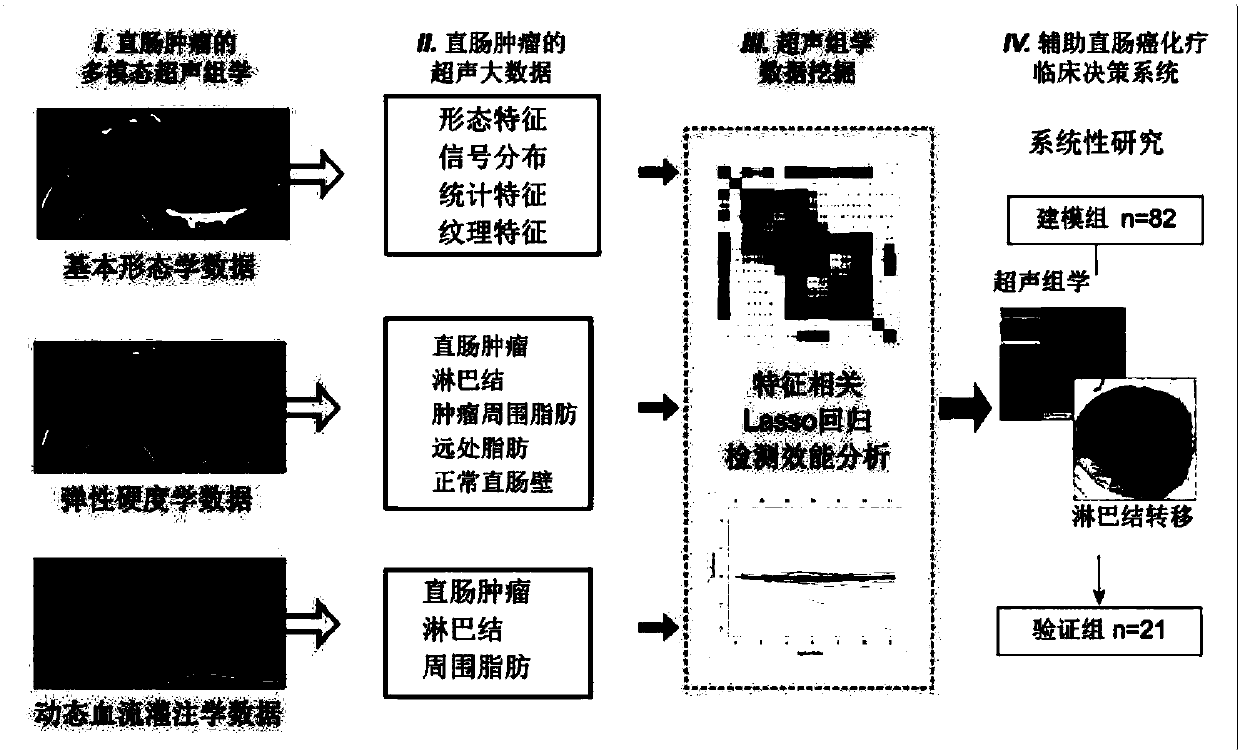
Intelligent decision-making assisting system based on multi-modal ultrasomics
InactiveCN107582097AGood segmentation resultComplete individualized precision medical adviceBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseGenomics
The invention discloses an intelligent decision-making assisting system based on multi-modal ULTRASOMICS. Firstly, ultrasonic data from different signal sources of an instrument is acquired, an interactive or manual dividing method is adopted to locate an interested area in an ultrasonic image, data of morphology, blood perfusion and hardness science of diseases is obtained, and a multi-modal ultrasonic characteristic database is constructed; through the combination of relevant clinical information, laboratory checking information and gene chip information, ultrasomics data is mined, a machinelearning method is utilized to construct different models, the recurrence rate and the survival rate are predicted, the curative effect and the radiotherapy and chemotherapy sensitivity are judged inthe early stage, and the correlation of ultrasomics, genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics and metabonomics is analyzed. As macroscopic ultrasomics, the intelligent decision-making assisting system provides a repeatable evaluation means for noninvasive individualized precise medicine.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
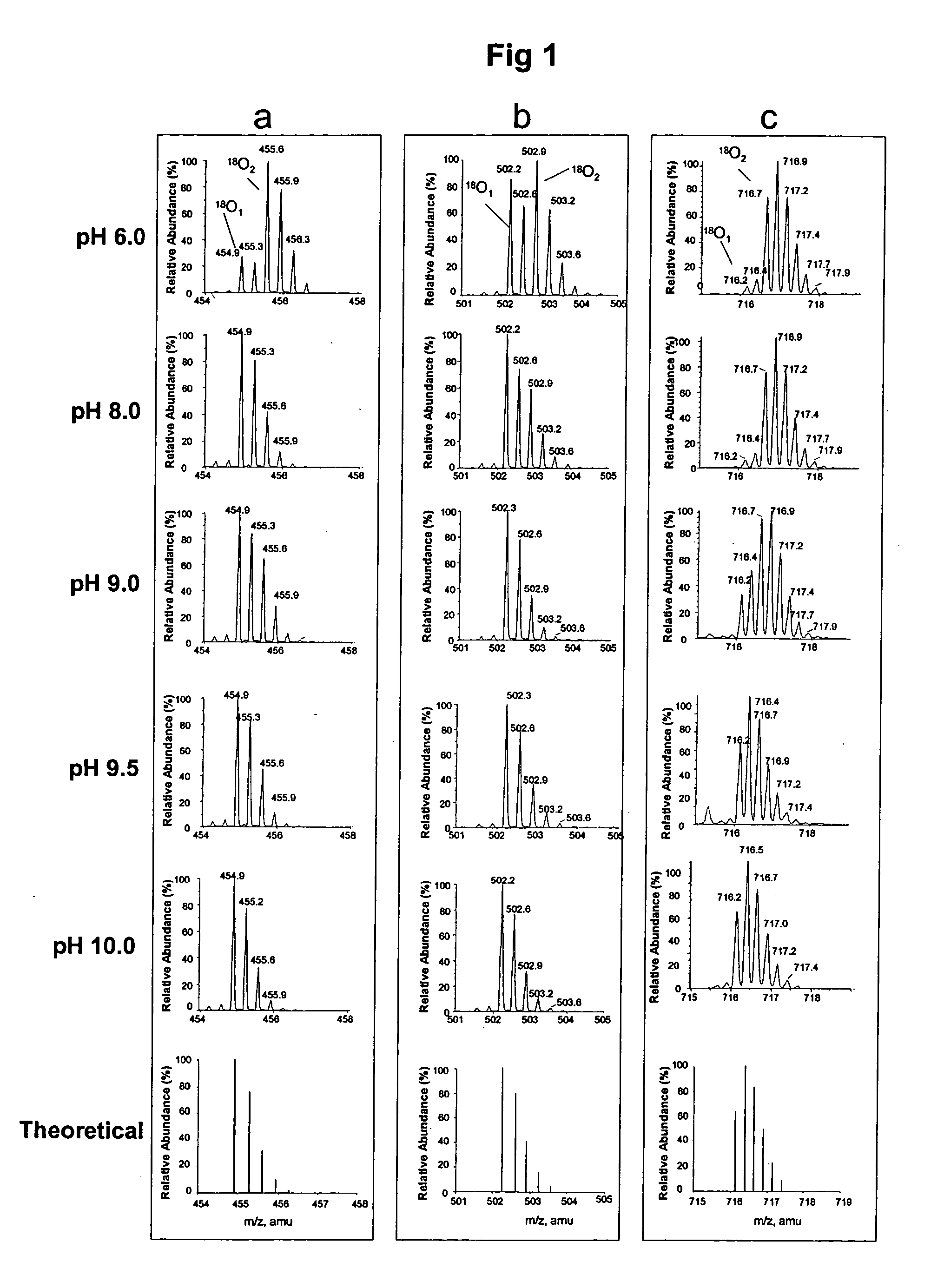
Method for single oxygen atom incorporation into digested peptides using peptidases
InactiveUS20060105415A1Highly accurate quantification methodAccurately quantify different protein populationsSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementIsotopic labelingProteomics
Optimized enzymatic conditions incorporate a single oxygen atom into digested peptides using a peptidase. The incorporation of a single oxygen atom is especially useful for proteolytic 18O labeling in comparative proteomics. The optimized proteolytic 18O labeling minimizes the generation of a mixture of isotopic isoforms of the peptides resulting from incorporation of either one or two 18O atoms. The outcome is accurate quantification of isotopically labeled peptides.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NORTH DAKOTA +1
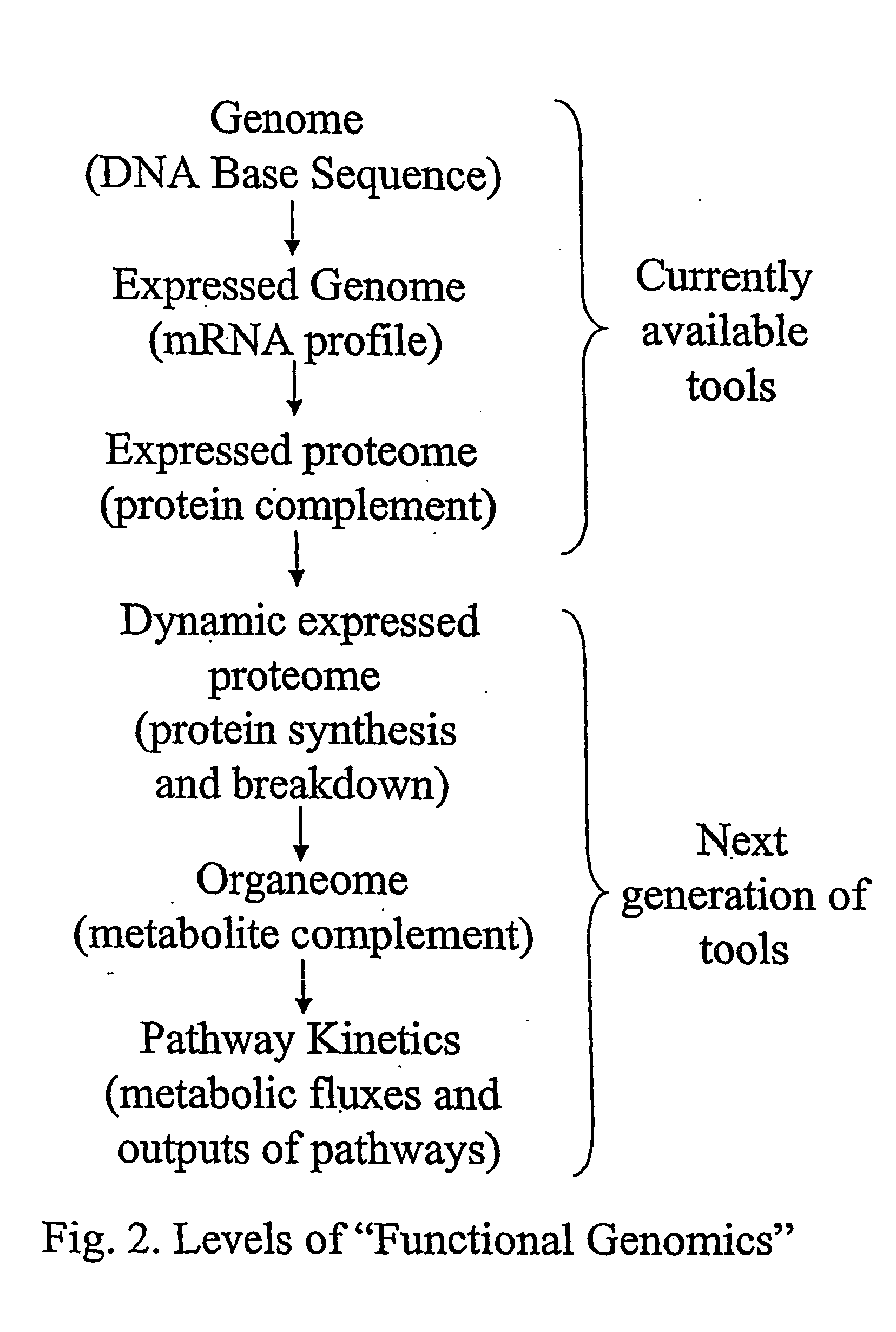
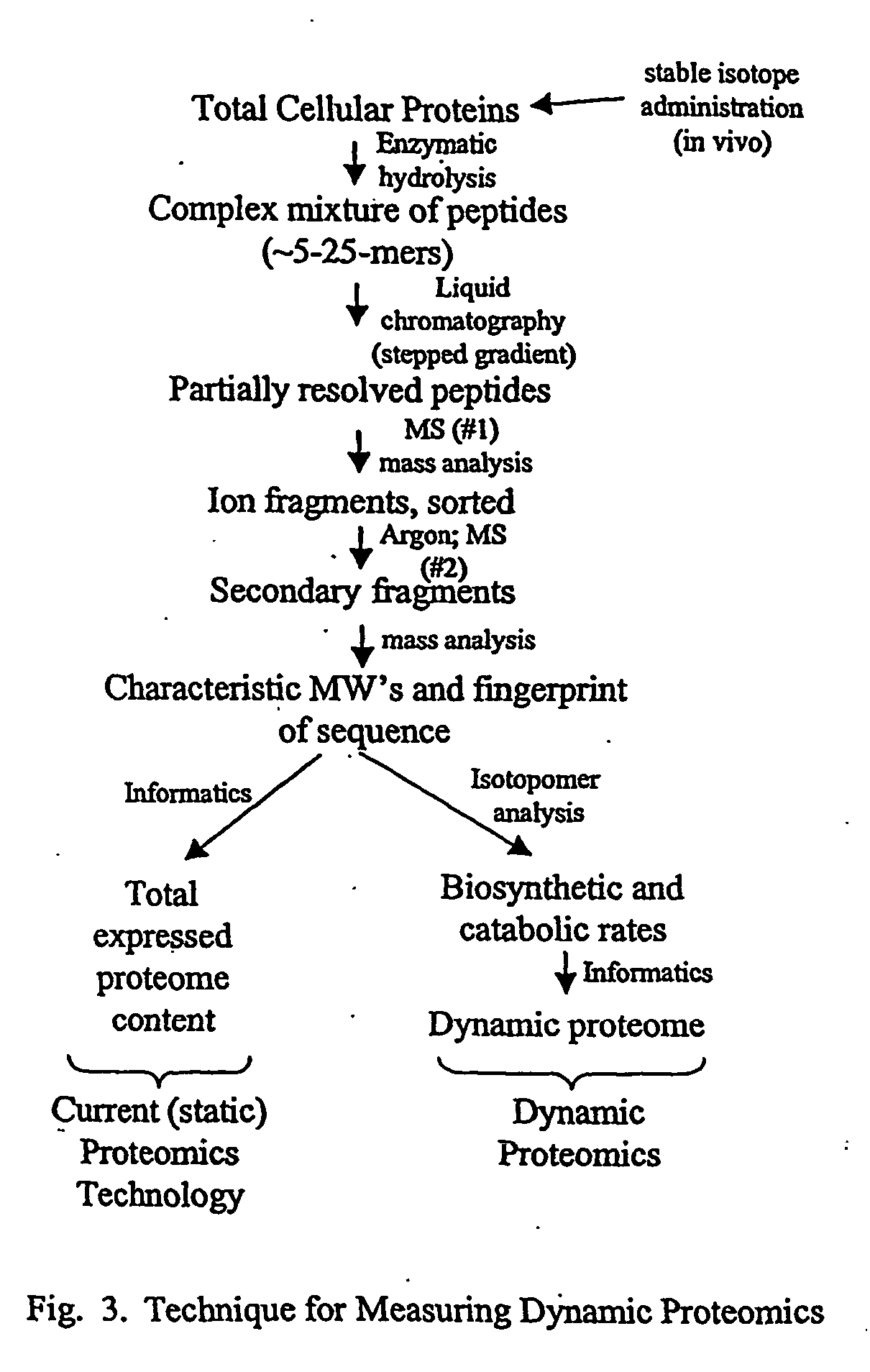
Method for automated, large-scale measurement of the molecular flux rates of the proteome or the organeome using mass spectrometry
Disclosed here is a method for measuring the kinetics (i.e., the molecular flux rates—synthesis and breakdown or removal rates) of a plurality of proteins or organic metabolites inn living systems. The methods may be accomplished in a high-throughput, large-scale automated manner, by using existing mass spectrometric profiling techniques and art well known in the fields of static proteomics and static organeomics, without the need for additional biochemical preparative steps or analytic / instrumental devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for reducing complexity of a sample using small epitope antibodies
InactiveUS20050131219A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsEpitopeProteomics
The present invention relates generally to methods for reducing the complexity of a sample. More specifically, the present invention relates to proteomics, the measurement of the protein levels in biological samples, and analysis of proteins in a sample using antibodies that recognize small epitopes.
Owner:TETHYS BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for assessing a sample by maldi mass spectrometry
The invention provides methods for preparing a sample for matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI). In general, the methods involve: binding analytes in a sample to capture agents that are bound to matrix that is present in a plurality of wells of a multi-well sample plate, washing any unbound analytes from the matrix, cleaving any bound analyte / capture agent complexes with a MALDI cleavage agent, and depositing the cleavage products on a multi-sample MALDI sample plate. Kits and other compositions are provided for performing the subject methods. The subject invention finds use in methods of simultaneously assessing the presence of several analytes in a single sample, and, as such, the invention finds use in a variety of different medical, research and proteomics applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
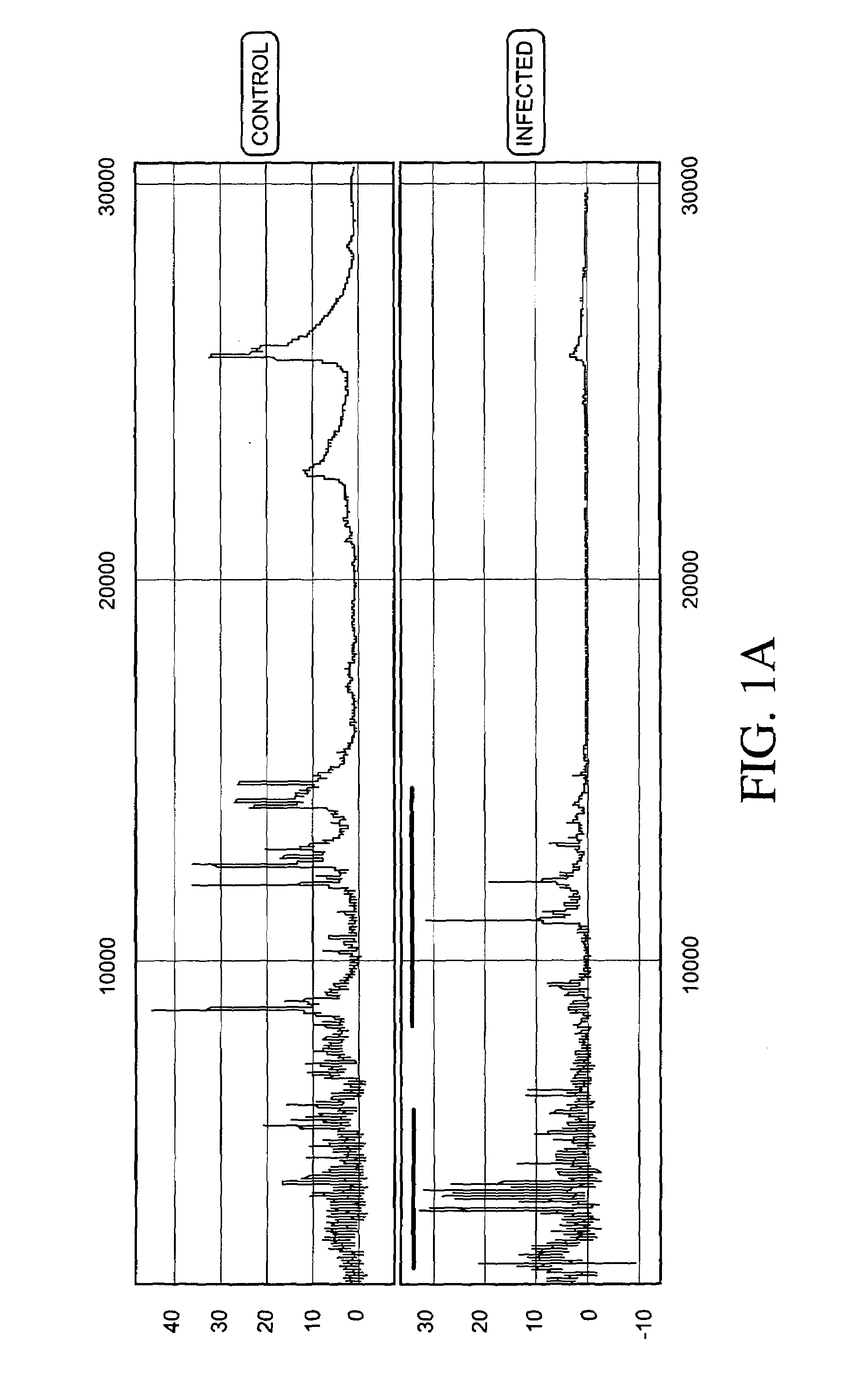
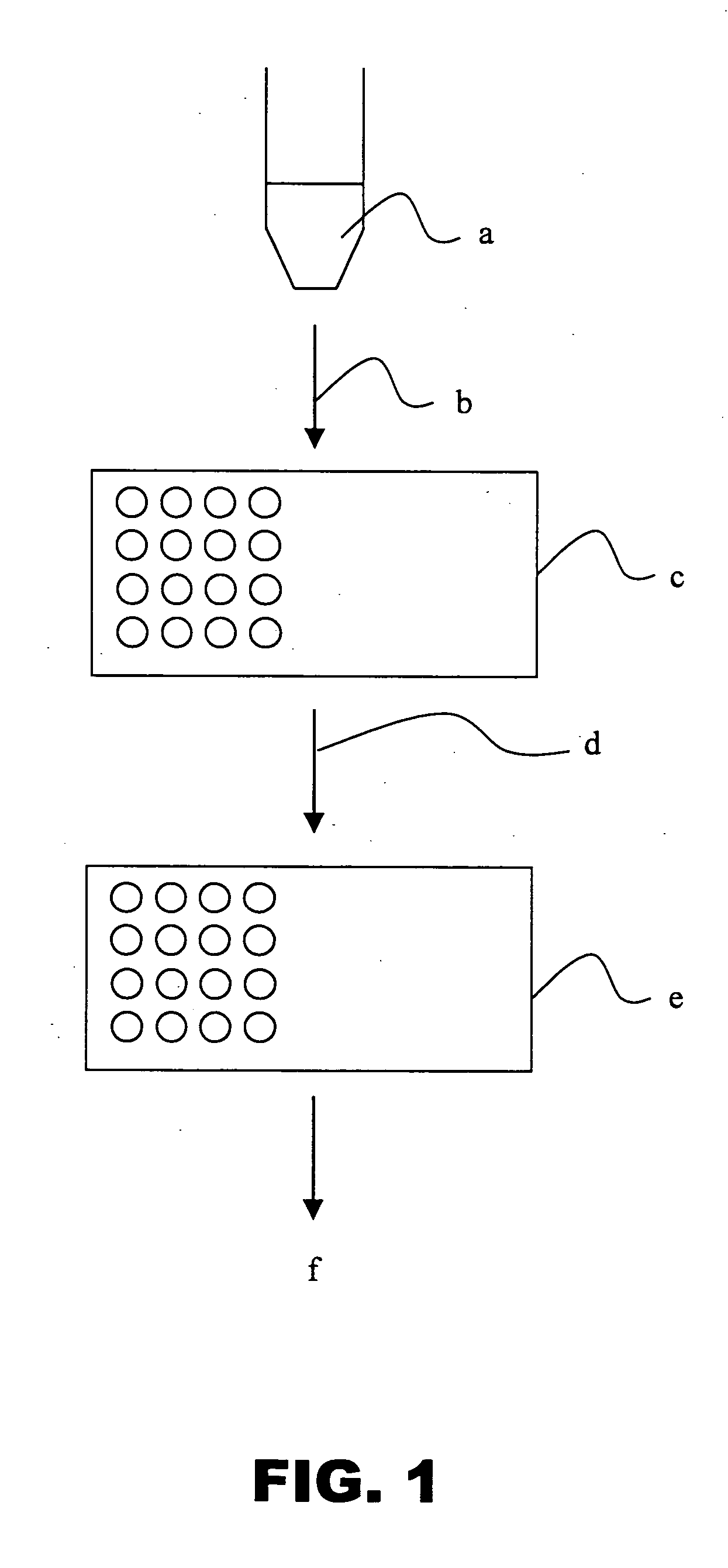
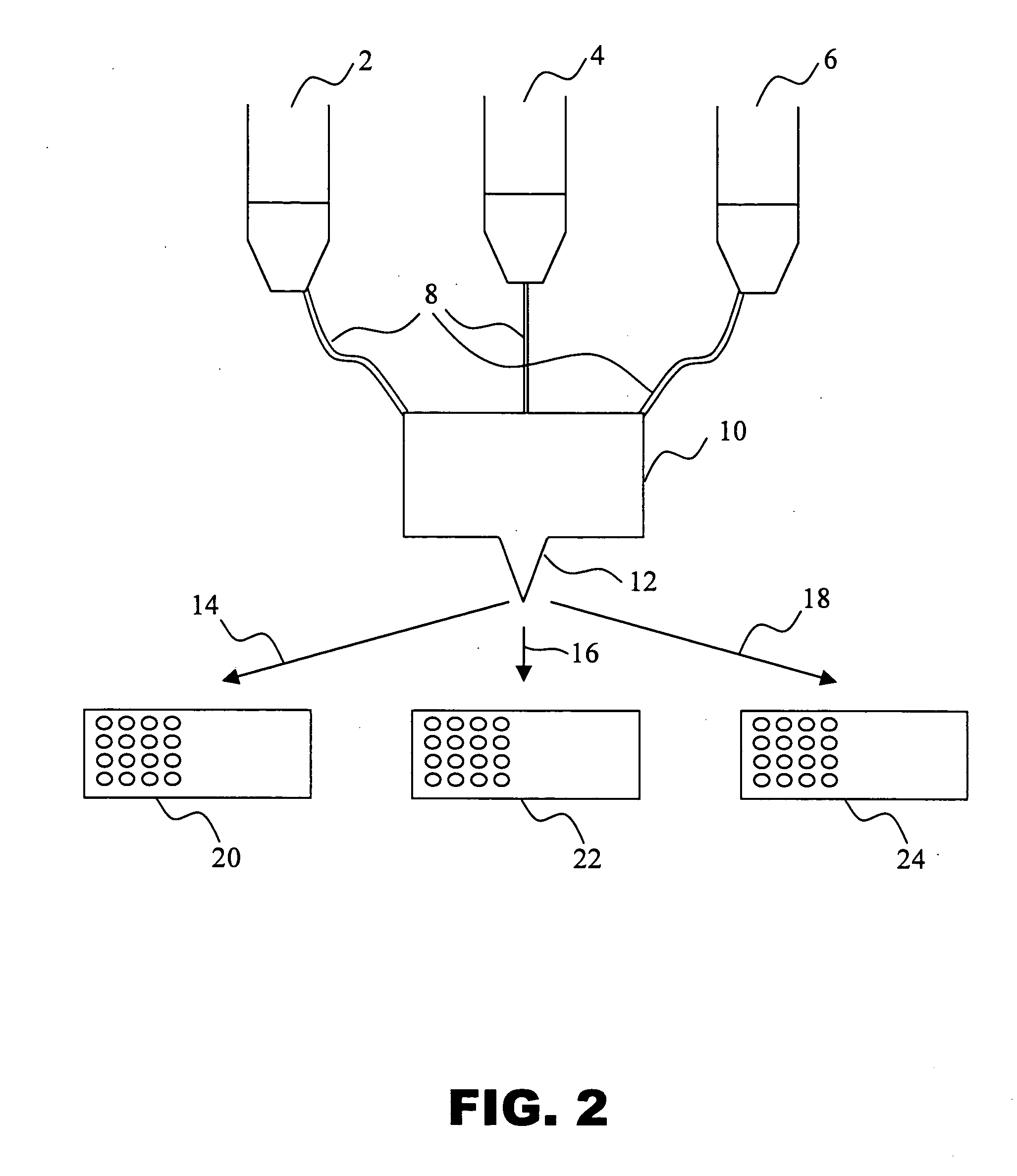
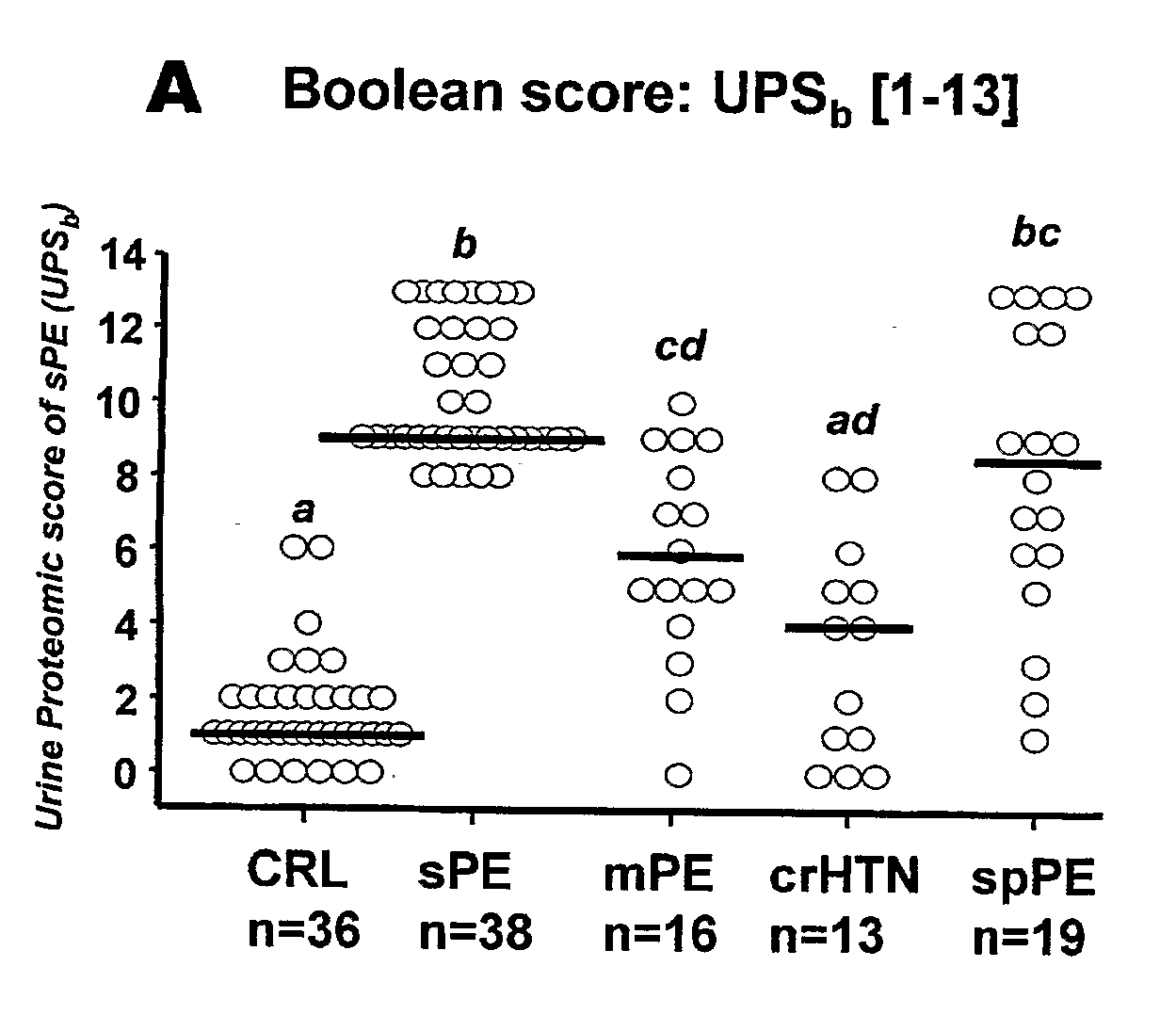
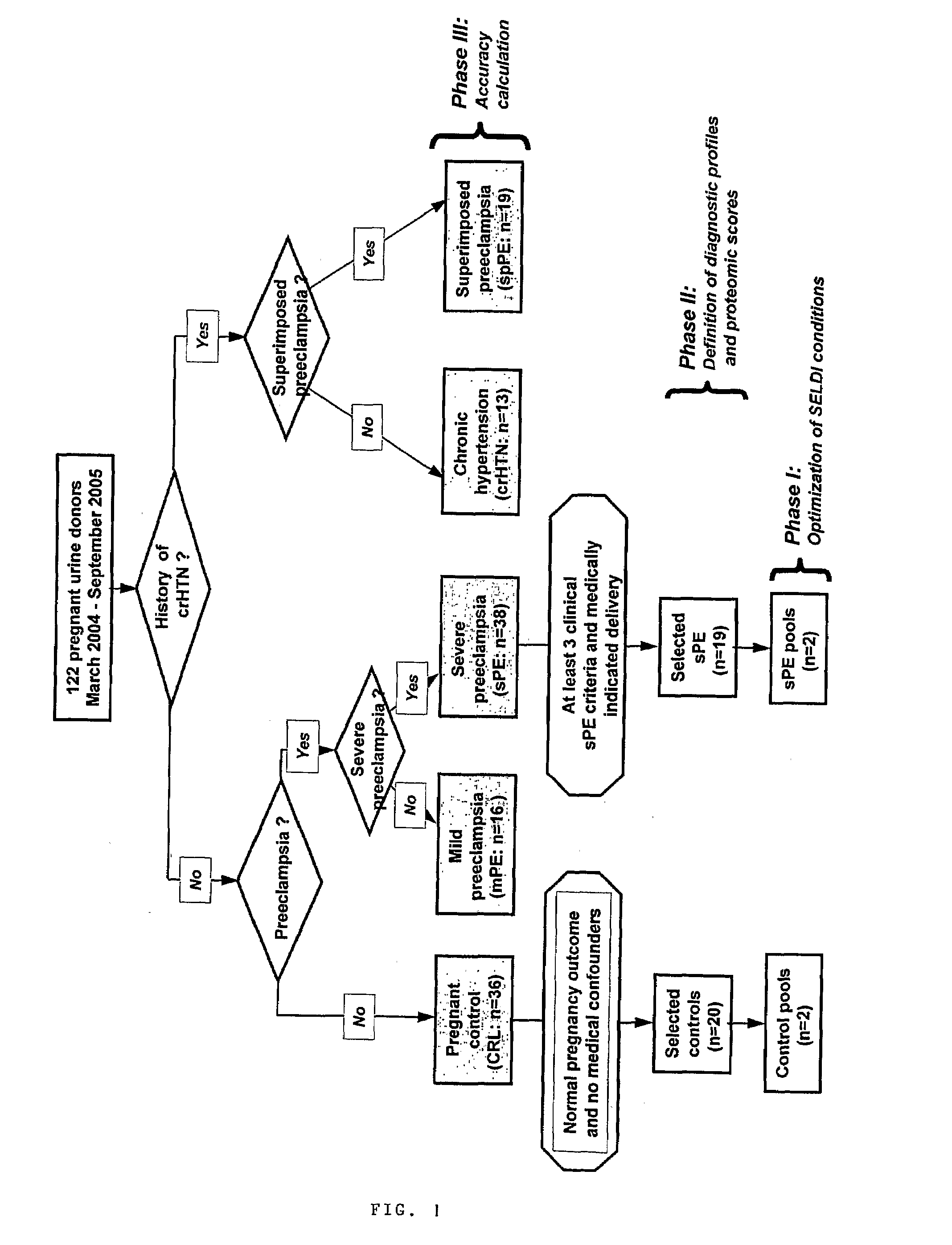
Urinary Proteomic Biomarker Patterns in Preeclampsia
The invention relates, in part, to methods of using proteomic biomarkers to diagnose preeclampsia. In some aspects the invention, in part, relates to the detection of serpina-1 polypeptide and / or albumin polypeptide in samples from pregnant subjects. Samples from subjects may be compared to control samples to diagnose preeclampsia and / or to determine the onset, progression, or regression of preeclampsia in a subject. The invention also relates, in part, to screening methods to identify agents that can be used to treat preeclampsia and to determine the efficacy of a preeclampsia treatment. The invention, in part, also includes kits that are useful to diagnose and assess preeclampsia in a subject.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Synthetic method and application of metal-organic framework composite nanomaterial
InactiveCN106512965AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesSynthesis methodsMetal-organic framework
The invention provides a synthetic method and application of a metal-organic framework (MOF) composite nanomaterial. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing ferriferrous oxide magnetic spheres which are synthesized through a traditional hydrothermal technology in a weakly alkaline solution of dopamine hydrochloride to carry out self-polymerization of dopamine on the surfaces of the magnetic spheres; and sequentially dispersing polydopamine coated magnetic spheres in a dimethylformamide solution of zirconium chloride and a dimethylformamide solution of 2-amino-terephthalic acid to obtain the MOF composite nanomaterial with the magnetic sphere surfaces coated with polydopamine and modified with an amino group and with zirconium as a center metal ion. The material has the advantages of large specific surface area, good hydrophilicity and suitable pore structure, can be applied to further researches of the proteomics, and can specifically enrich Which can specifically enrich phosphorylated peptide segments and glycopeptides; the synthetic method is simple and quick; and the synthesized material has good hydrophilicity and biocompatibility, and can be used for selectively enriching endogenous phosphorylation peptide segments and glycopeptide in complex biological samples.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
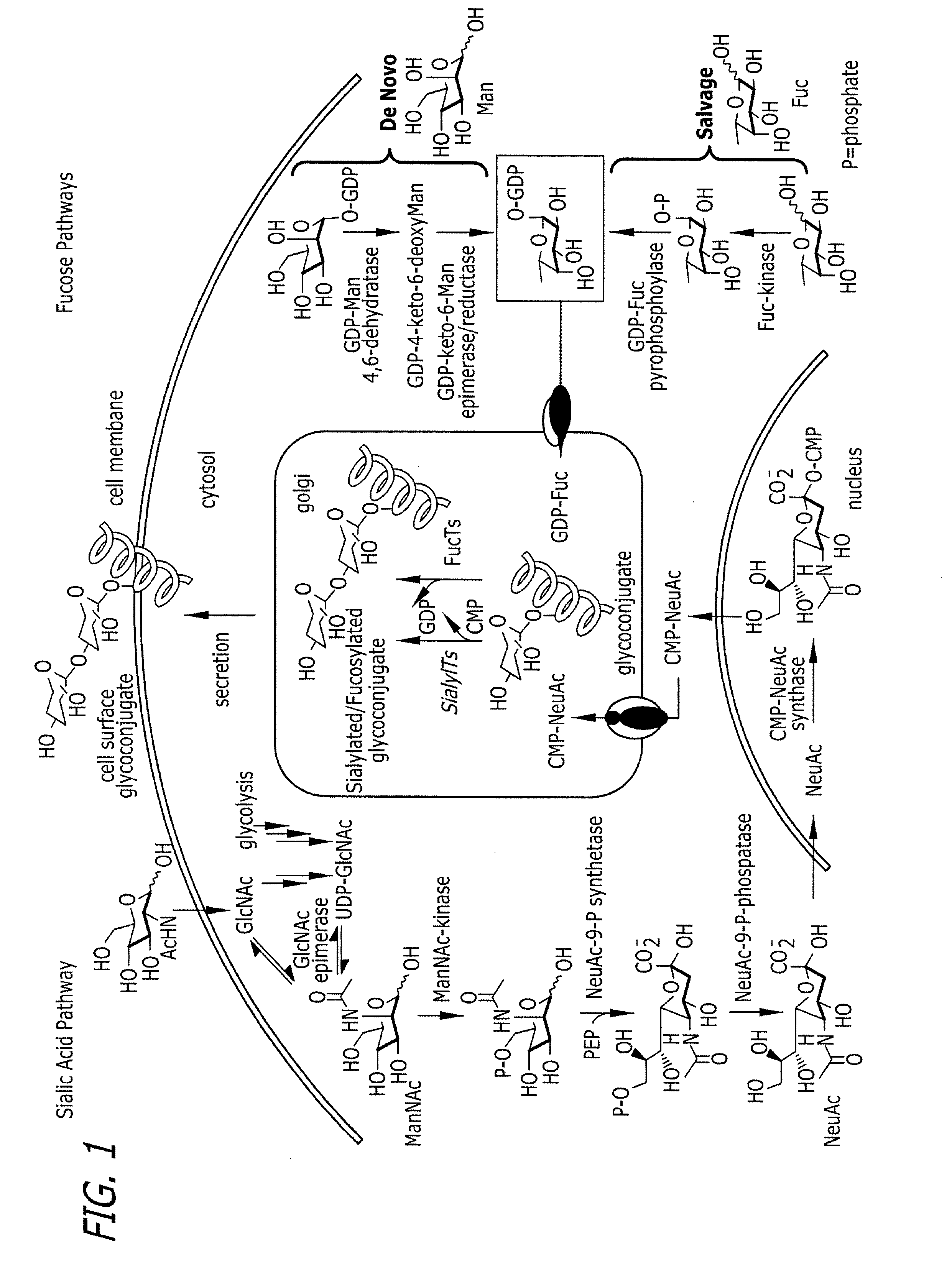
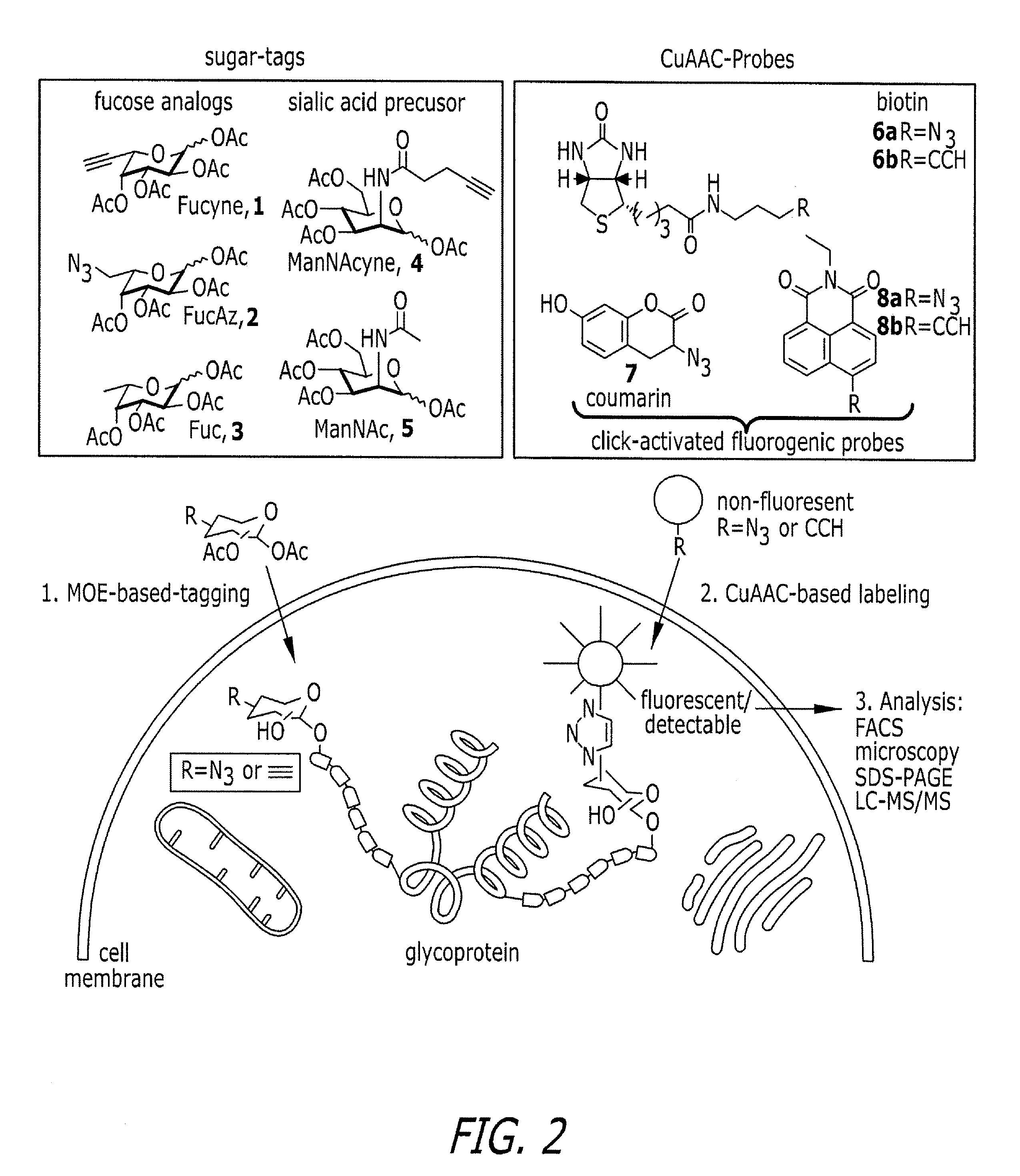
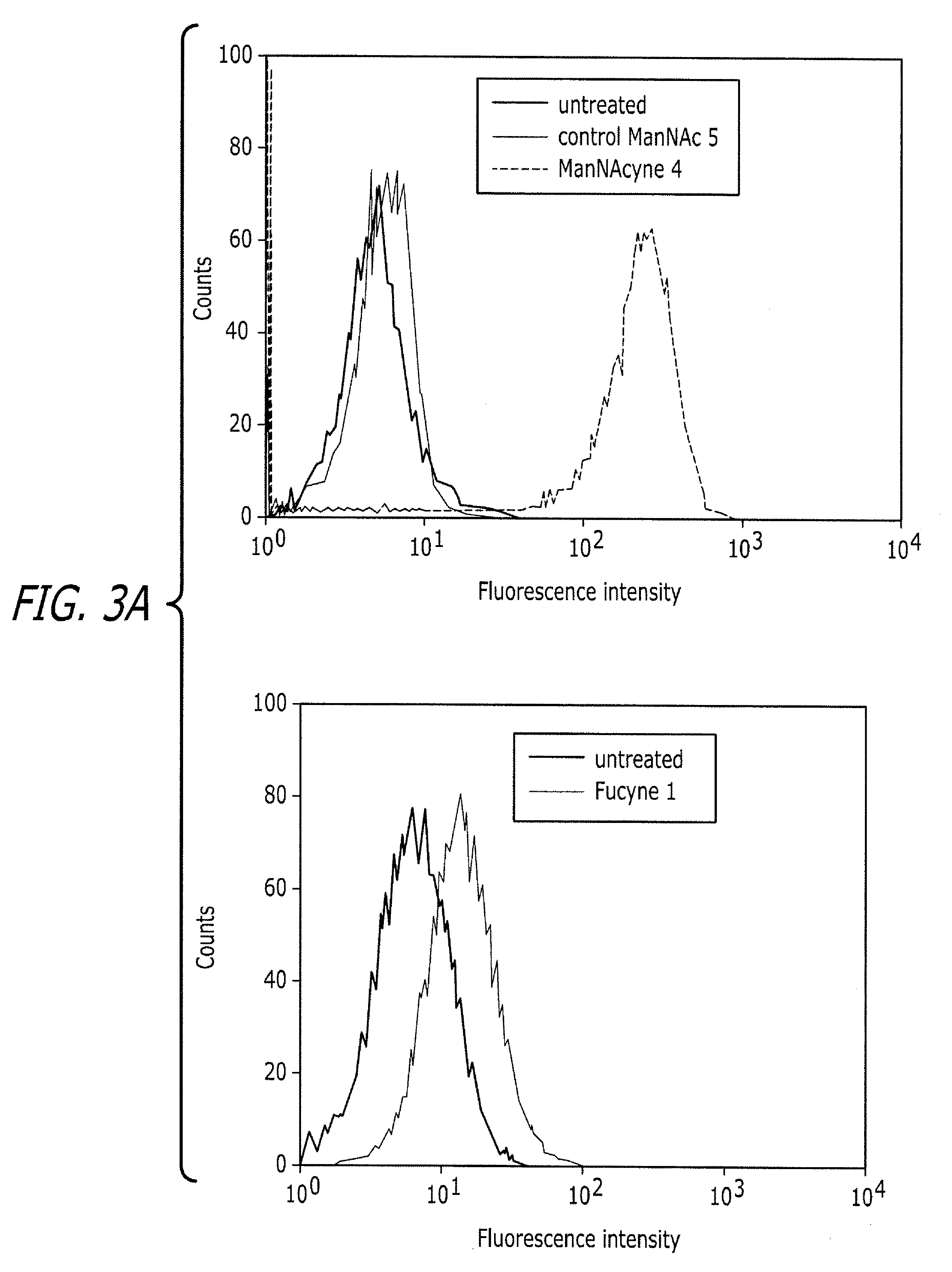
Tailored glycoproteomic methods for the sequencing, mapping and identification of cellular glycoproteins
ActiveUS7943330B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsSpectroscopyProteomics
The present disclosure relates to tailored glycoproteomic methods, and more particularly to methods for the sequencing, mapping and identification of cellular glycoproteins using saccharide-selective bioorthogonal probes. A method is disclosed for saccharide-selective glycoprotein identification (ID) and glycan mapping (GIDmap) that generates glycoproteins tailored with bioorthogonally tagged alkynyl saccharides that can be selectively isolated, allowing for glycoprotein ID and glycan mapping via mass spectromic proteomics, including liquid chromatography-tandmen mass spectroscopy (LC-MS2). LC-MS2 may be used to identify cellular glycans, and more specifically cancer-related glycoproteins.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
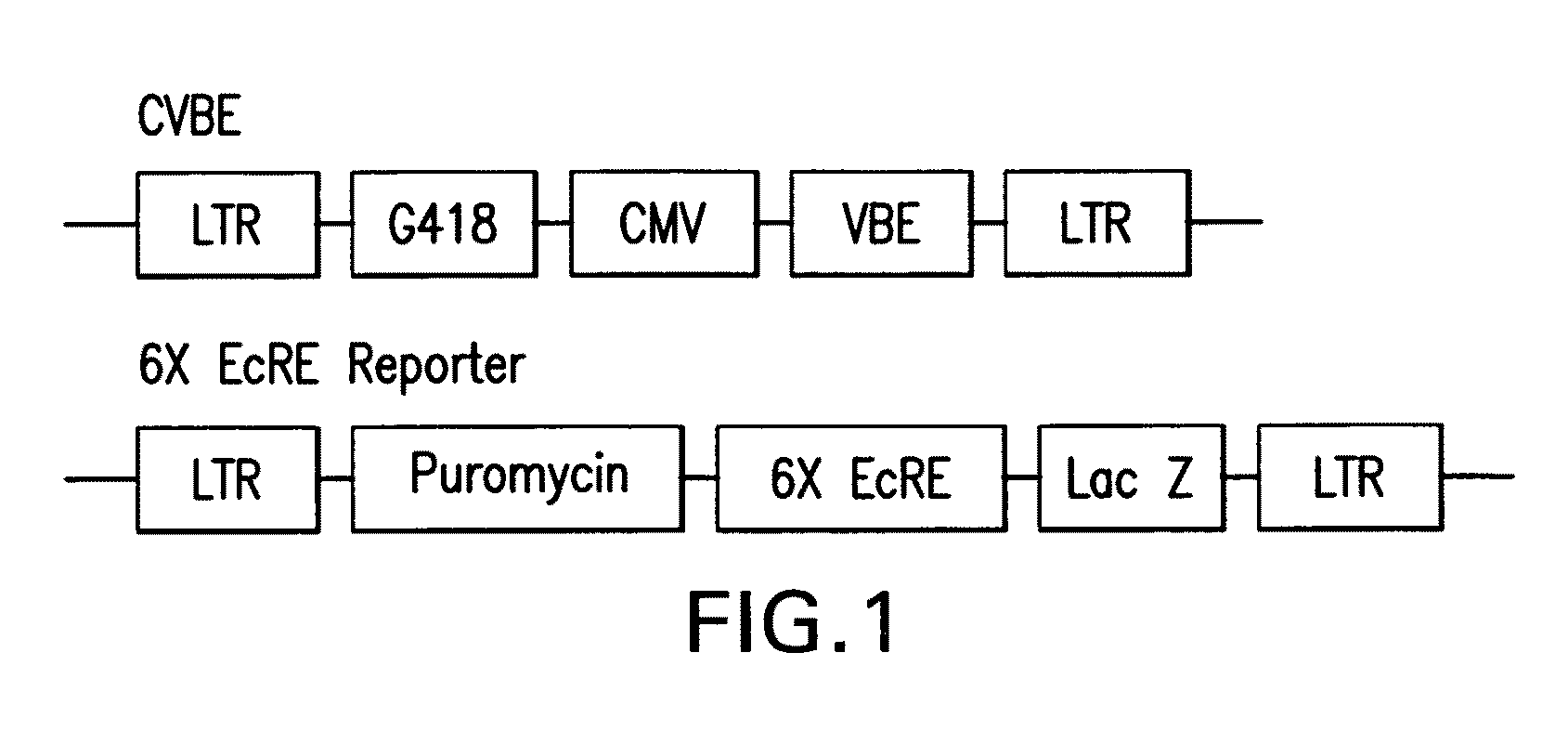
Chiral diacylhydrazine ligands for modulating the expression of exogenous genes via an ecdysone receptor complex
ActiveUS8076517B2Inhibit expressionUrea derivatives preparationOrganic active ingredientsGene expression levelOrganism
The present invention provides diacylhydrazine ligands and chiral diacylhydrazine ligands for use with ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression systems. Thus, the present invention is useful for applications such as gene therapy, large scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based screening assays, functional genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and regulation of traits in transgenic organisms, where control of gene expression levels is desirable. An advantage of the present invention is that it provides a means to regulate gene expression and to tailor expression levels to suit the user's requirements.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
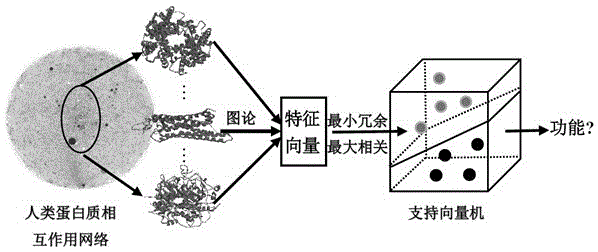
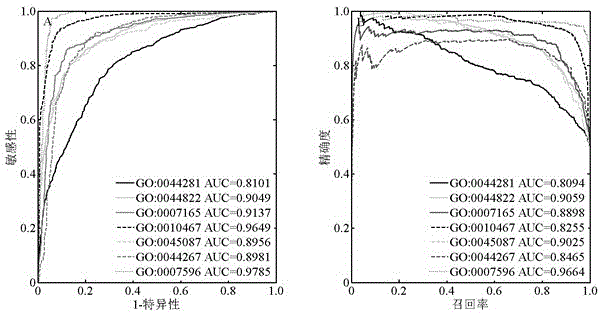
Method for identifying protein functions based on protein-protein interaction network and network topological structure features
InactiveCN105138866ARobustSignificant predictive advantageSpecial data processing applicationsNODALData set
The invention discloses a method for identifying protein functions based on a protein-protein interaction network and network topological structure features. Firstly, a node and side-weighted protein-protection interaction network is established, wherein the node represents protein while the edge represents the interaction; then the nodes and the sides in the network are weighted by protein first-grade structural description and protein-protein interaction trust scoring; protection functional annotation data is collected to establish a data set, and a new protein with overall and local information network topological structure features is provided based on a graph theory; and finally, the protein functions are predicated by choosing features through adopting a minimum-redundancy maximum-correlation method and by modeling through a support vector machine. The protein function predication method is greatly better than the prior art, and has robustness on sequence similarity and sampling; and meanwhile, information of three-dimensional structure and the like of protein is not required, so that the method is simple, rapid, accurate and efficient, and the method is expected to be applied in the research fields of proteomics and the like.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +2
Method for Accelerating Somatic Mutations and use Thereof in Proteomics
The invention relates to a method of accelerating the induction of somatic mutations in vitro. The inventive method comprises the expression of at least one cDNA expressing a modified version of the AID gene in the cells to be mutated, in culture conditions and a medium that are suited thereto, said modified version resulting from an AID gene in which the three hydrophobic amino acids, leu189, phe193 and leu196, have been replaced by means of alanine mutations in each case. The invention can be used to induce mutations in Burkitt's lymphoma BL2. The invention can also be used to induce mutations in the immunoglobulin genes of immortalised antibody-producing cells, such as mouse hybridoma cells, human hybridoma cells or human B-cell lines immortalised by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Owner:INST NECKER
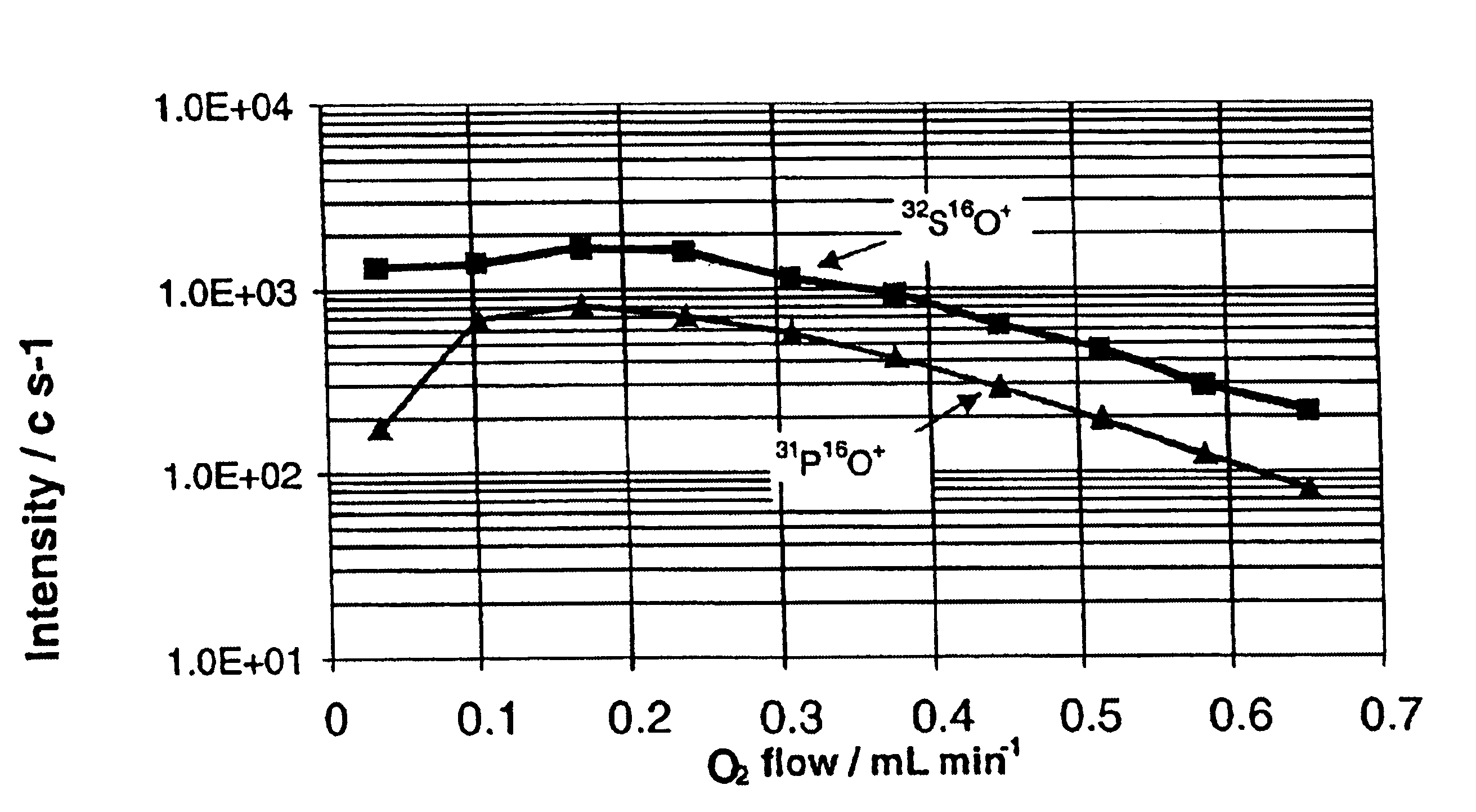
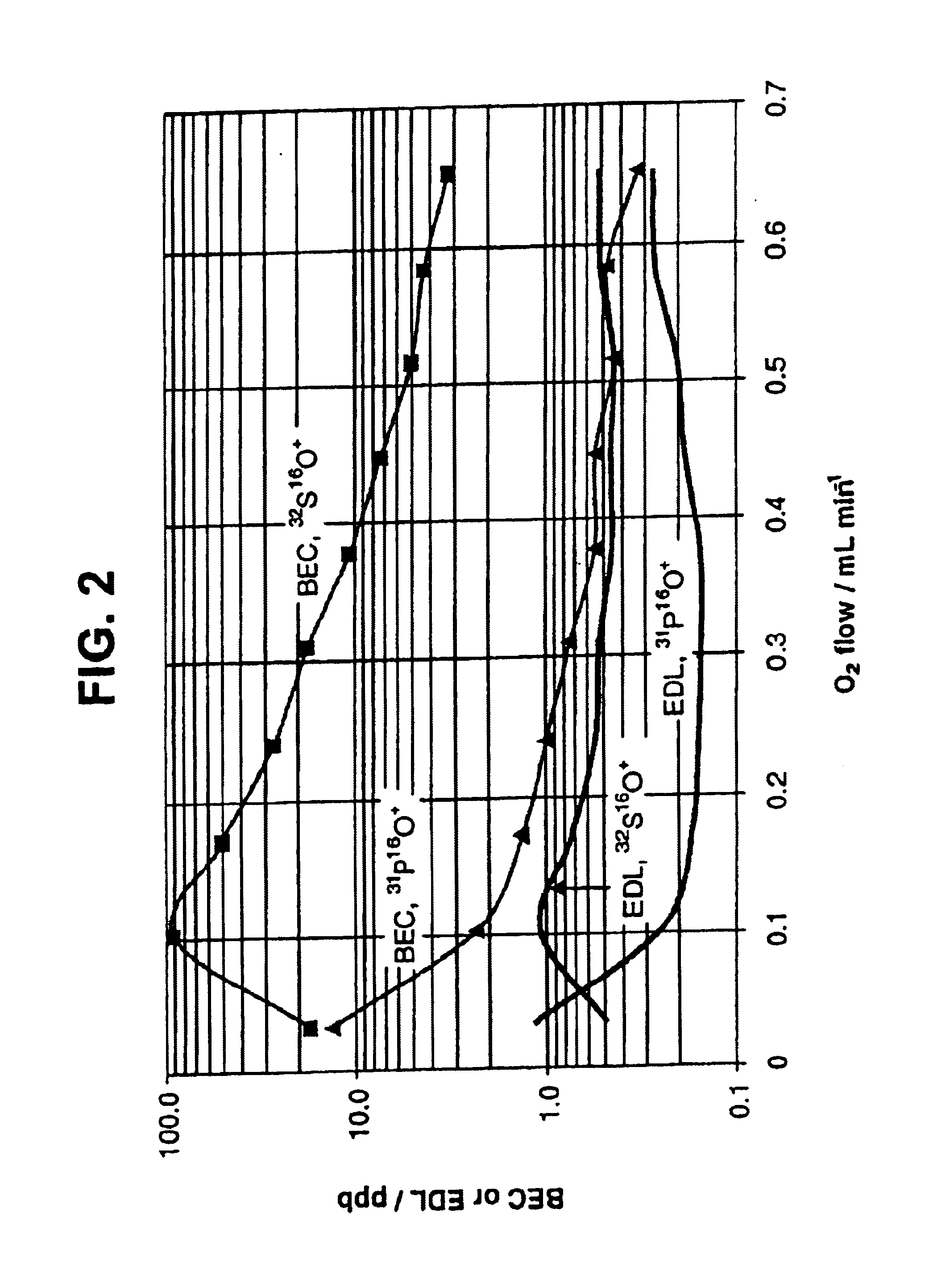
Method for phosphorus quantitation
InactiveUS6875618B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationComponent separationPhosphorylationInductively coupled plasma
A method of detecting and measuring phosphorus in samples is disclosed. The measurement of phosphorylation is made with an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS), coupled to a reactive collision cell. The reactive collision cell is employed to ensure interference-free detection of phosphorus ions, by the formation of product ions with a different mass to charge ratio. Accurate measurement of phosphorylation in samples is important in proteomics.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
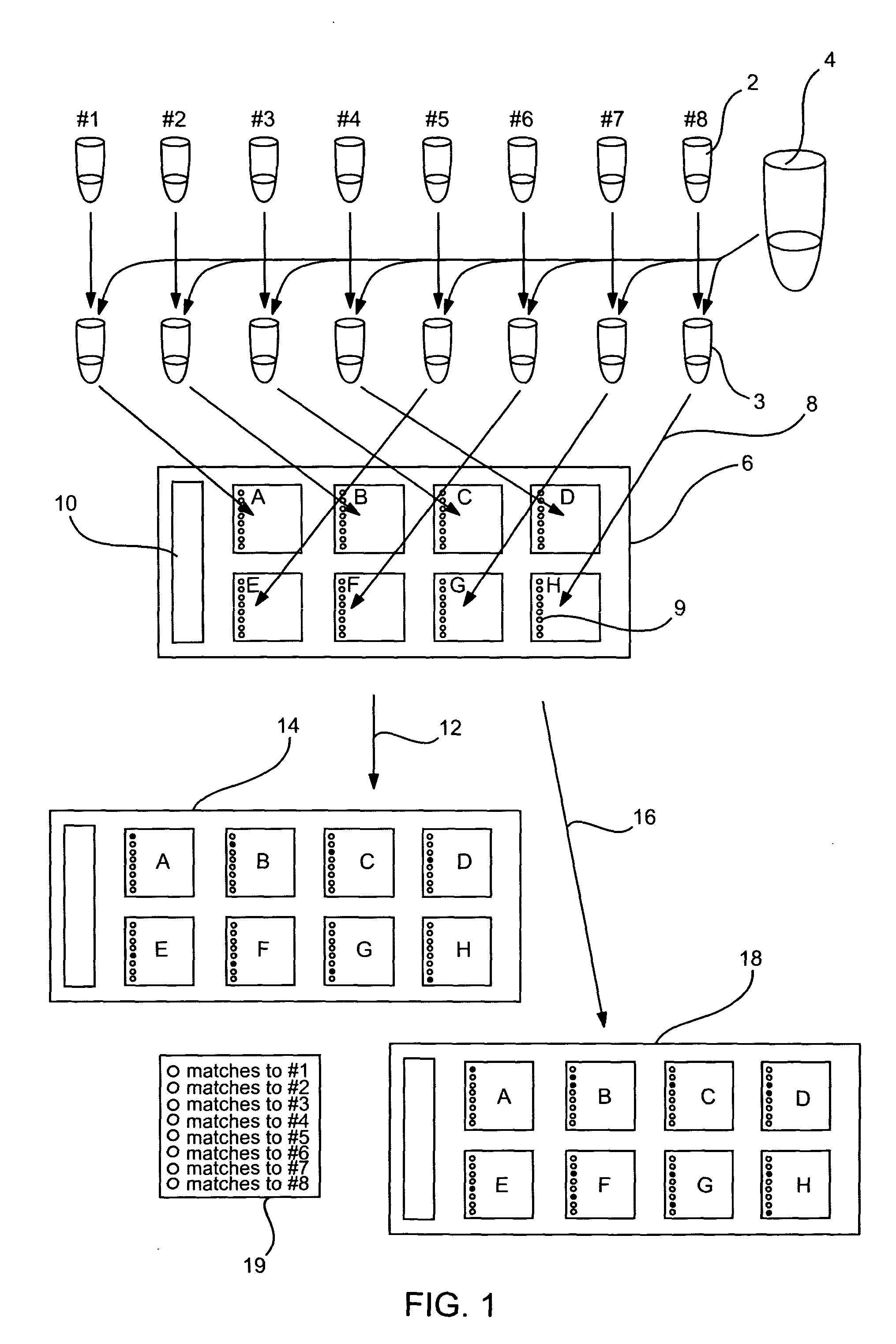
Methods to detect cross-contamination between samples contacted with a multi-array substrate
InactiveUS20050048505A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomicsMutation detection
Methods and compositions for detecting cross-contamination between samples contacted with different arrays of a multi-array substrate are provided. The methods involve contacting sample to arrays of a multi-array substrate that contains cross-contamination probes in each of its arrays, and evaluating the resultant sample contacted arrays for cross-contamination between the samples. In many embodiments, the arrays of the multi-array substrate contain a set of cross-contamination probes for a corresponding set of cross-contamination targets in the sample(s). Kits and systems are provided for performing the invention. The subject methods may be used in a variety of different applications, such as gene expression analysis, DNA sequencing, mutation detection, as well as other genomics and proteomics applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com