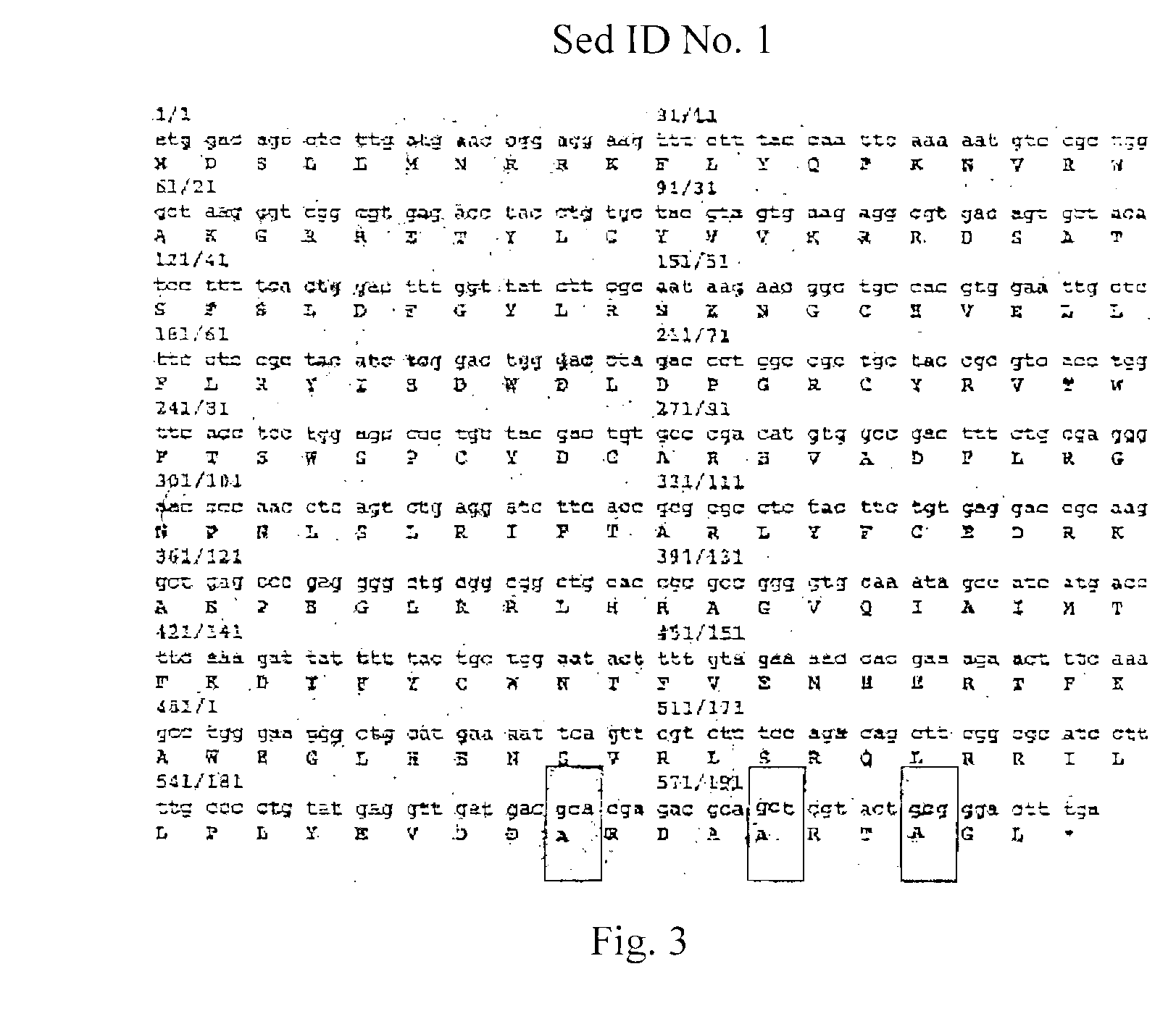
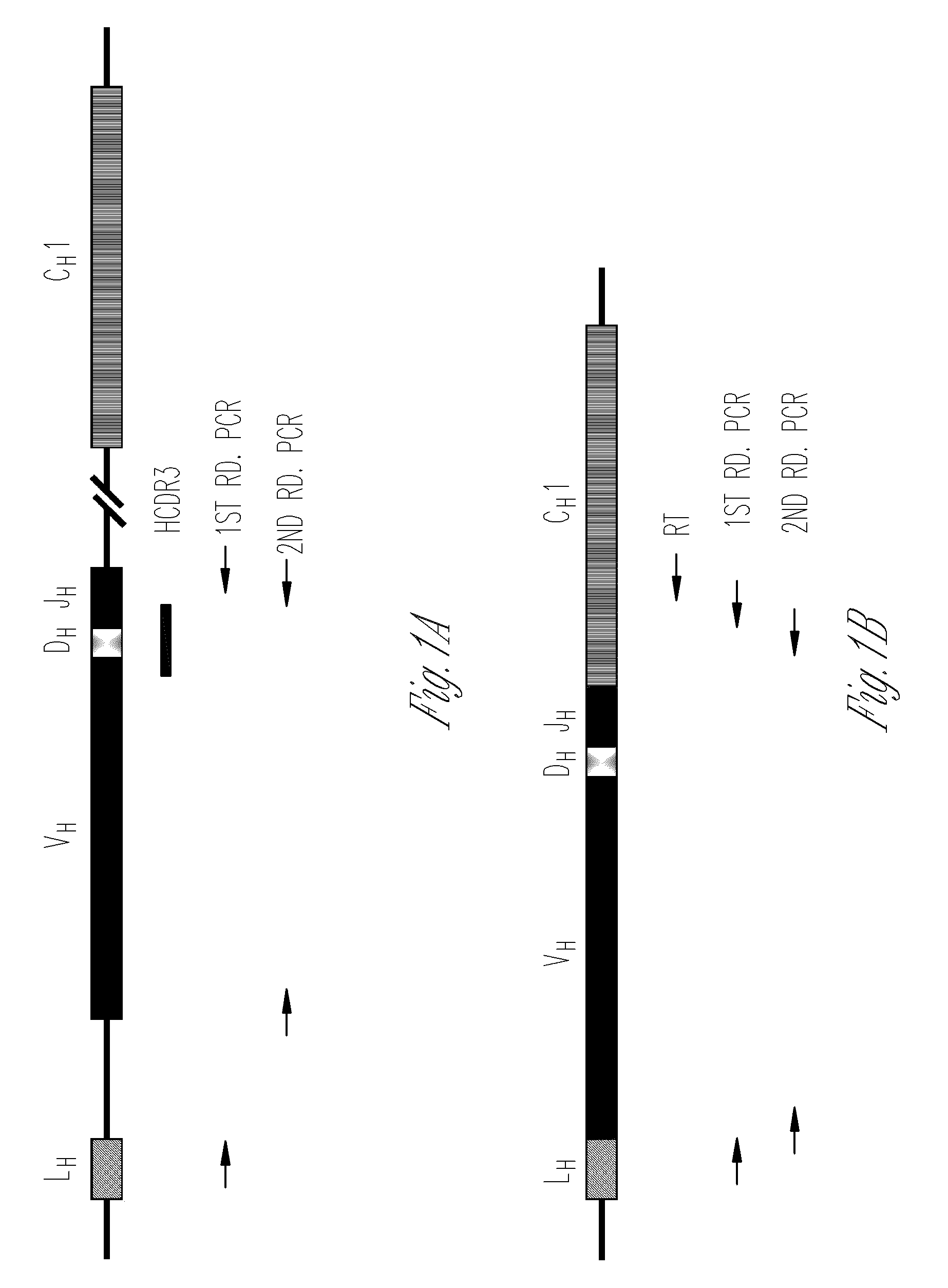
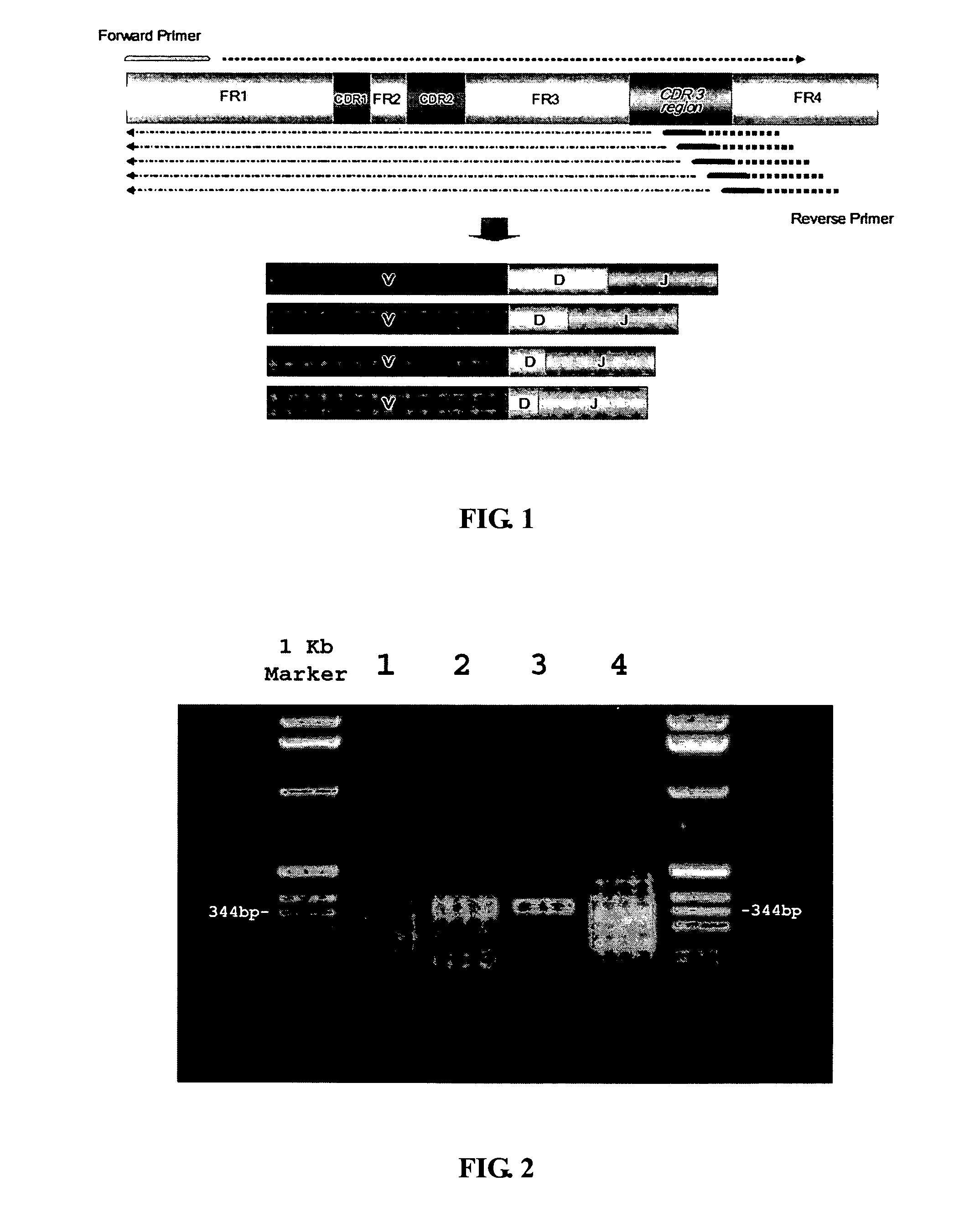
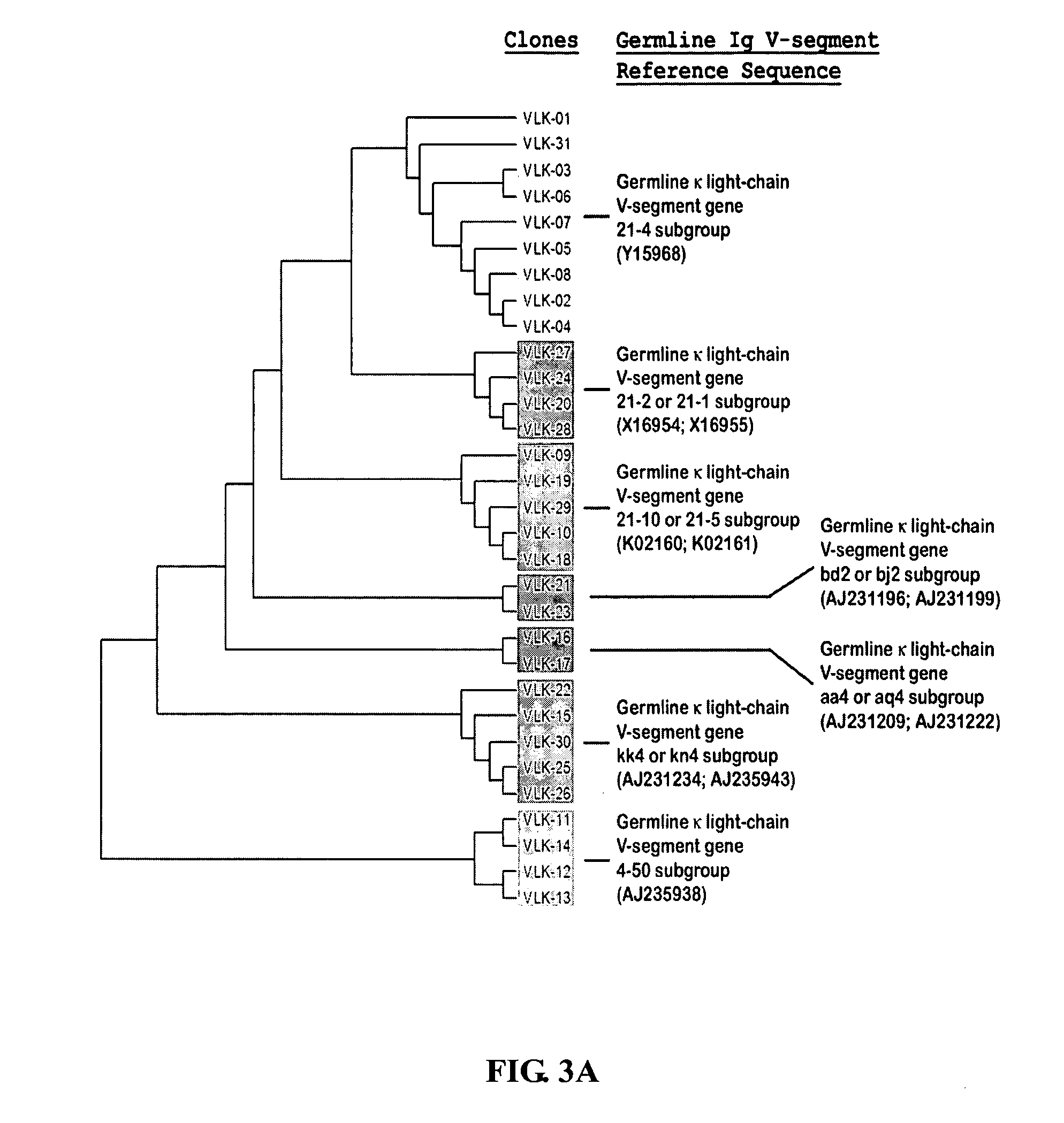
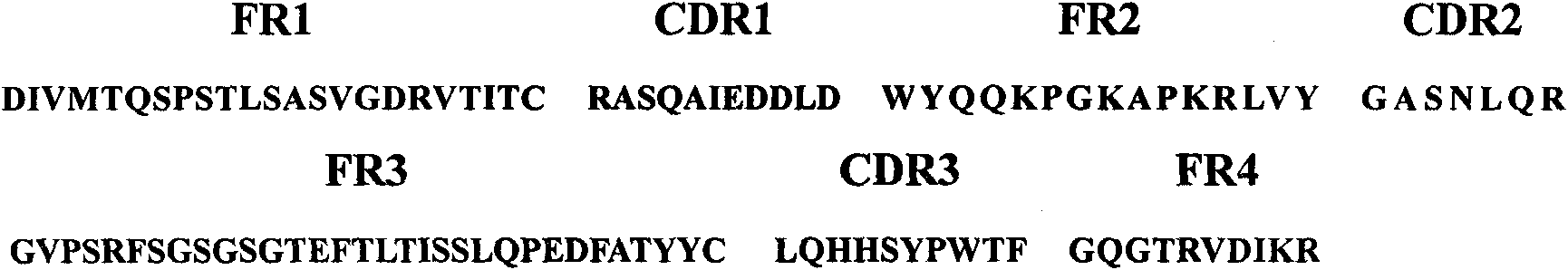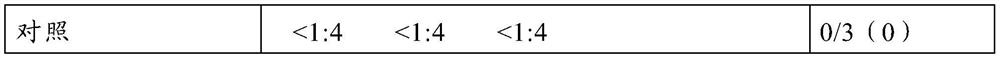Patents
Literature
34 results about "Immunoglobulin genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
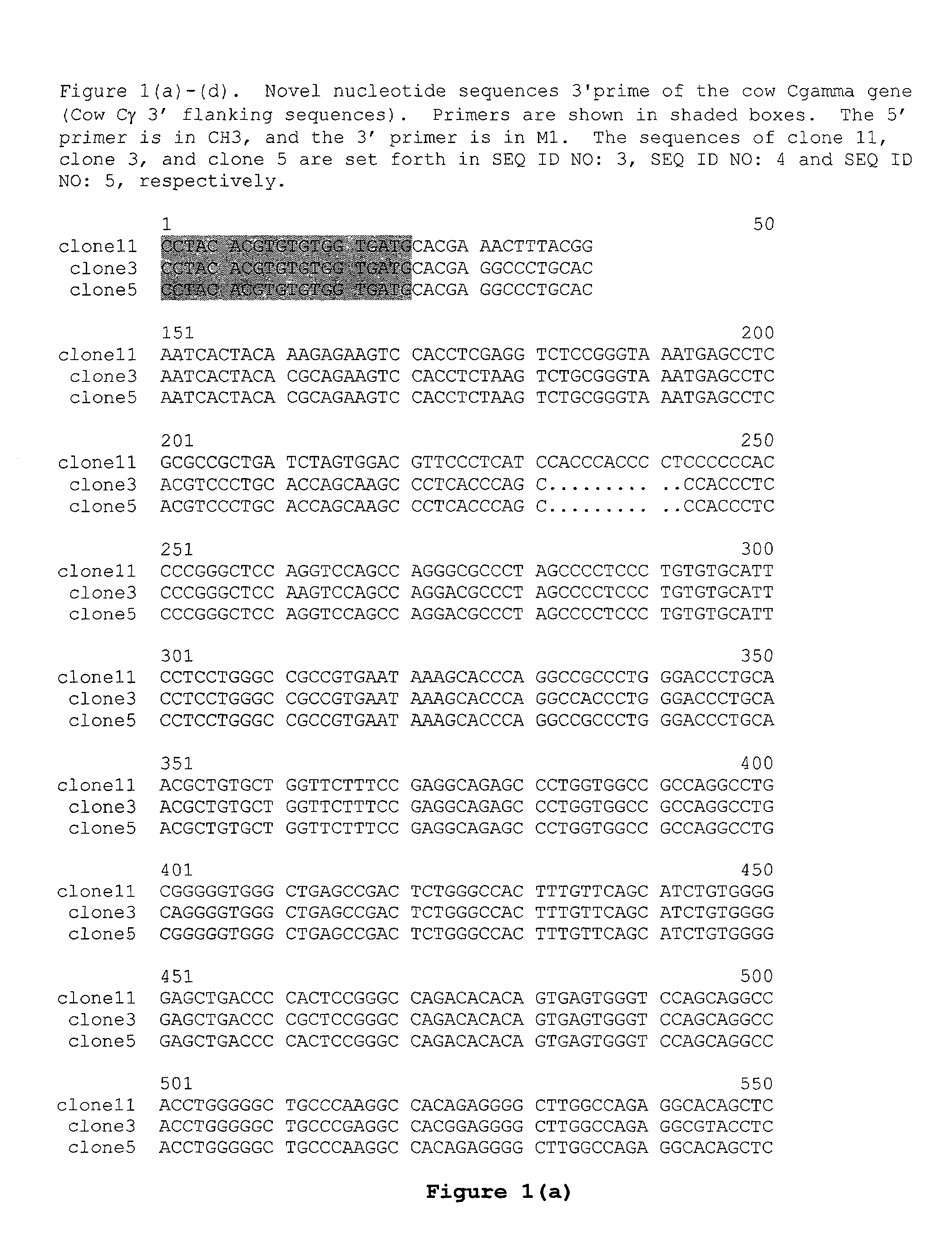
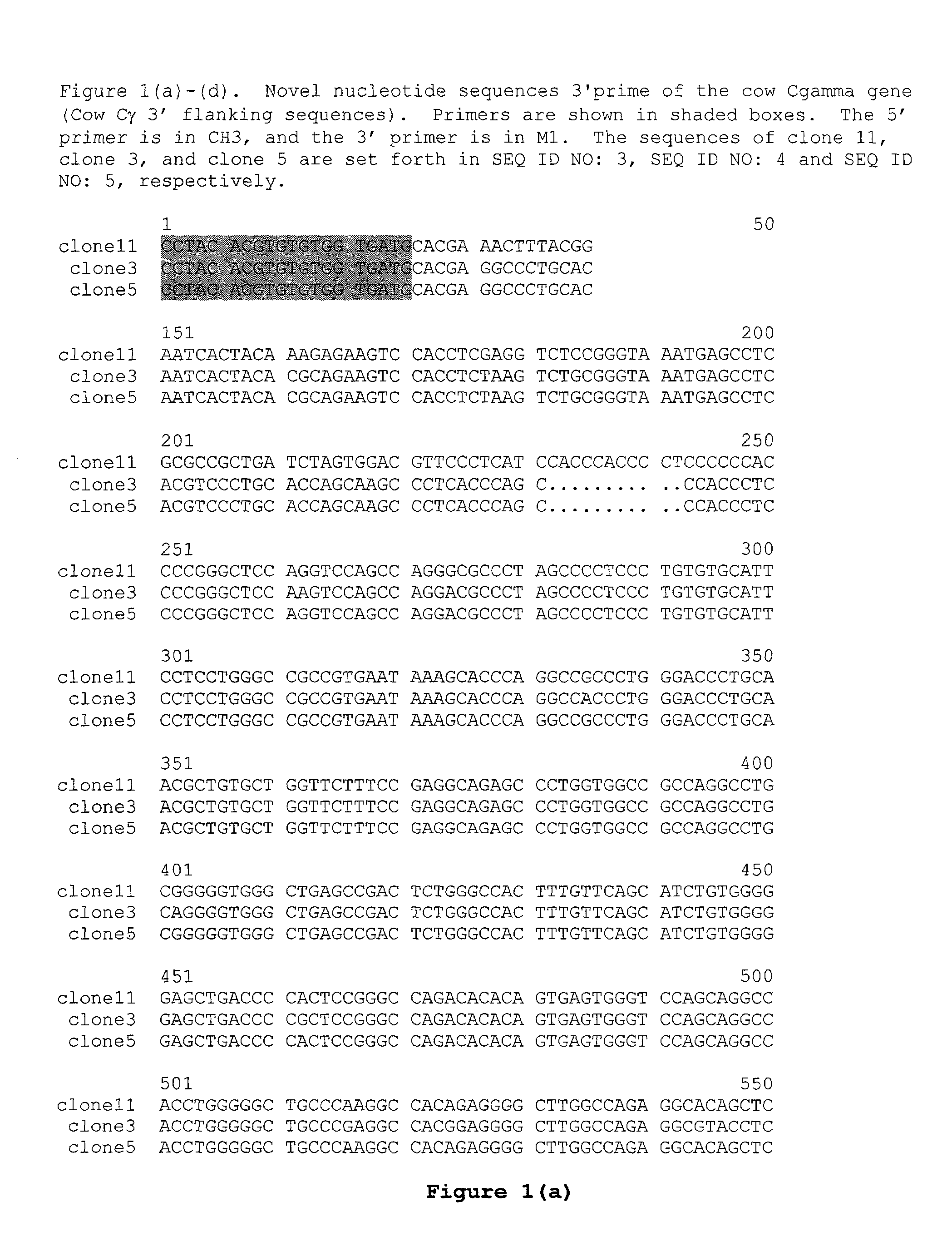
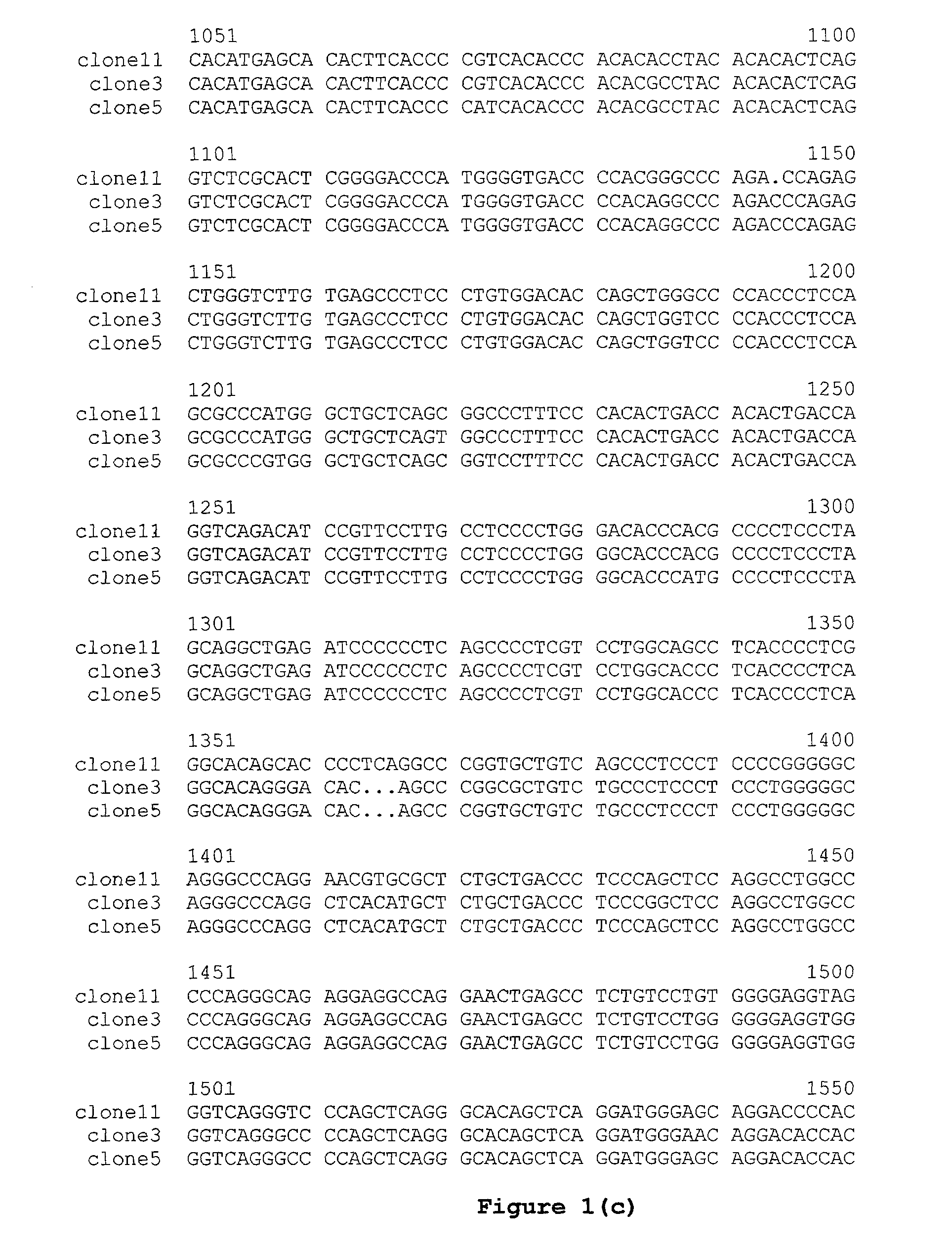
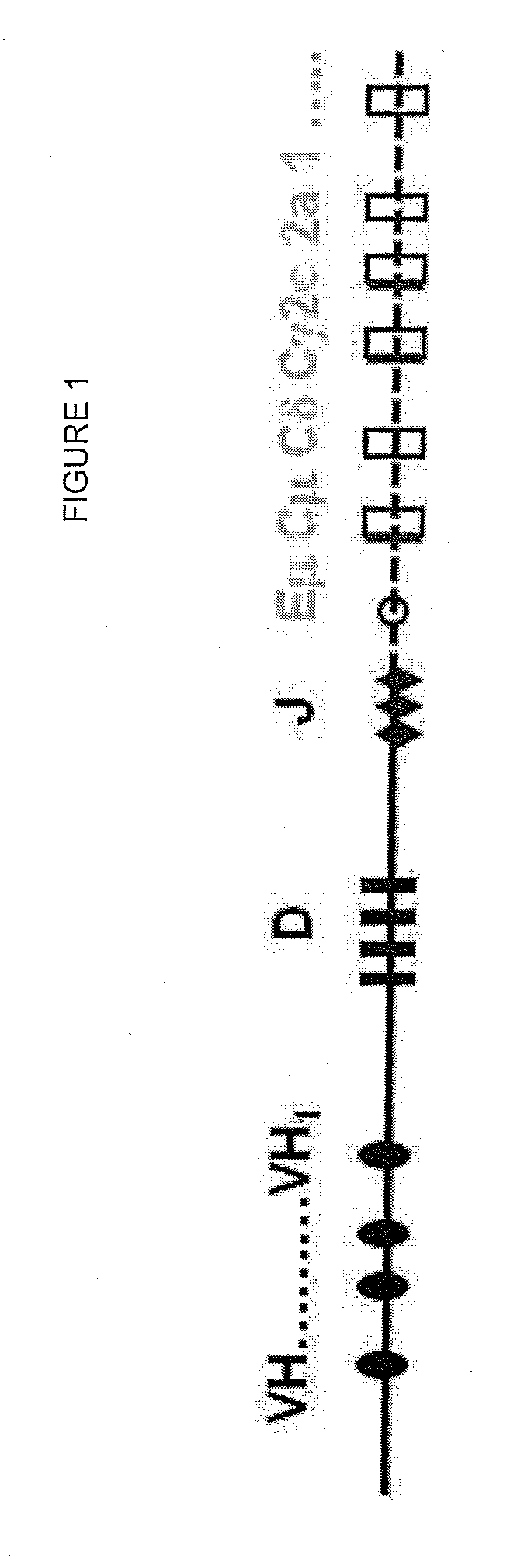
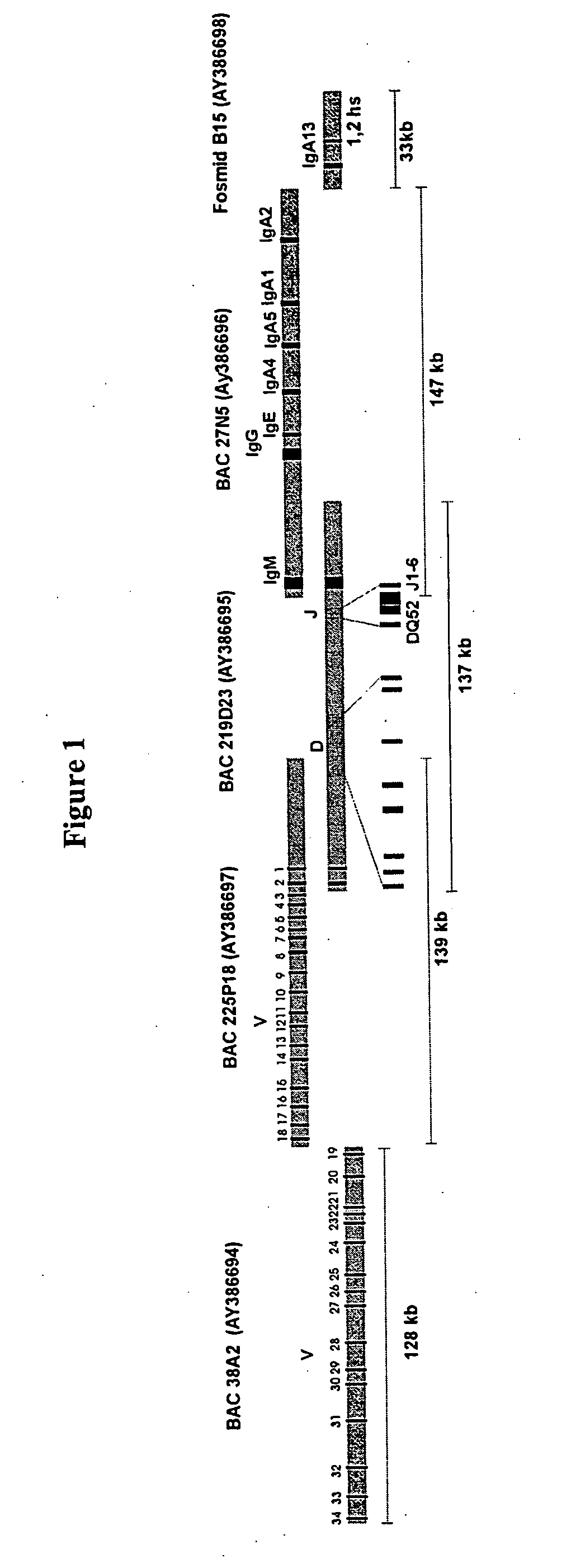
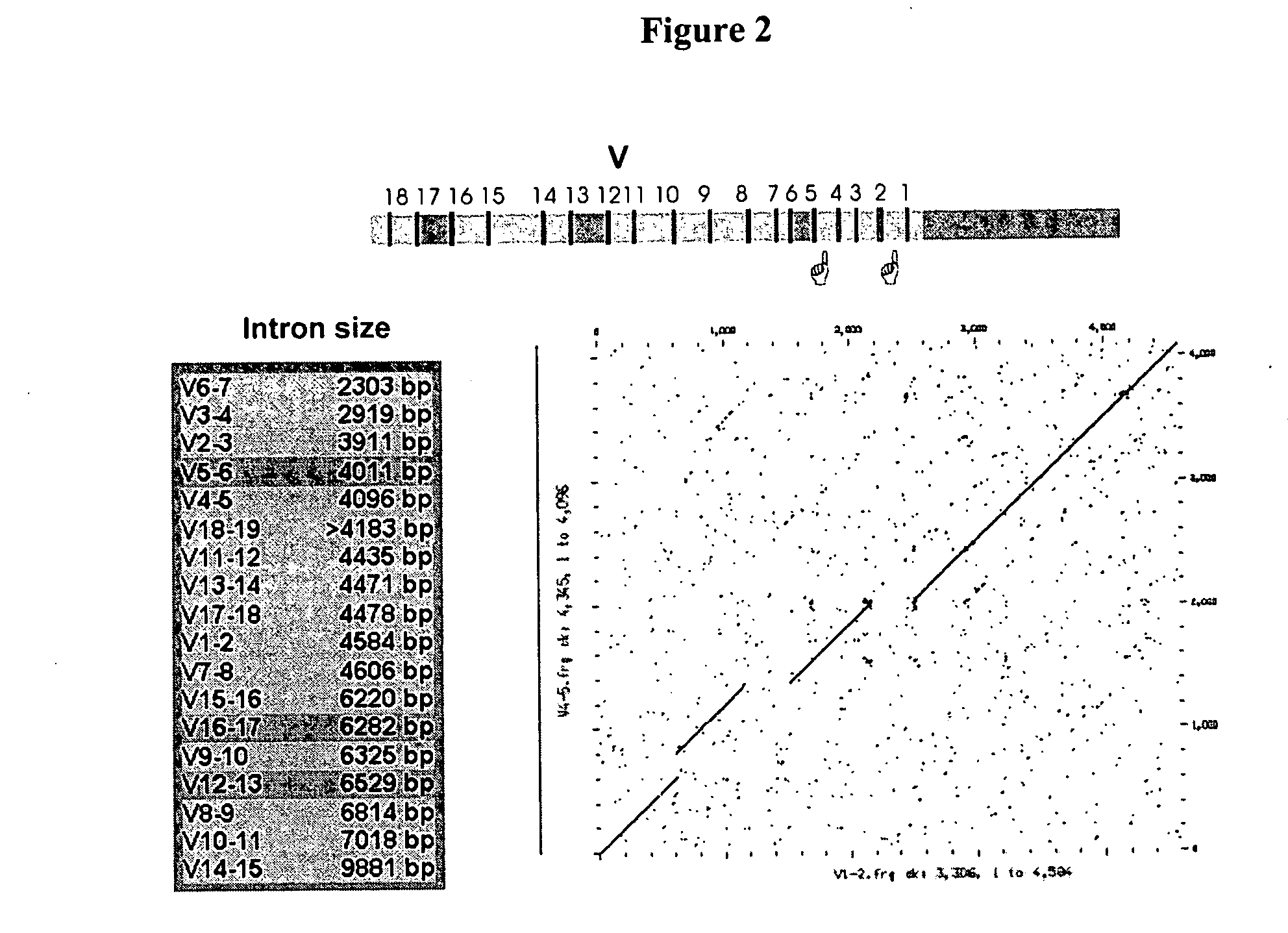
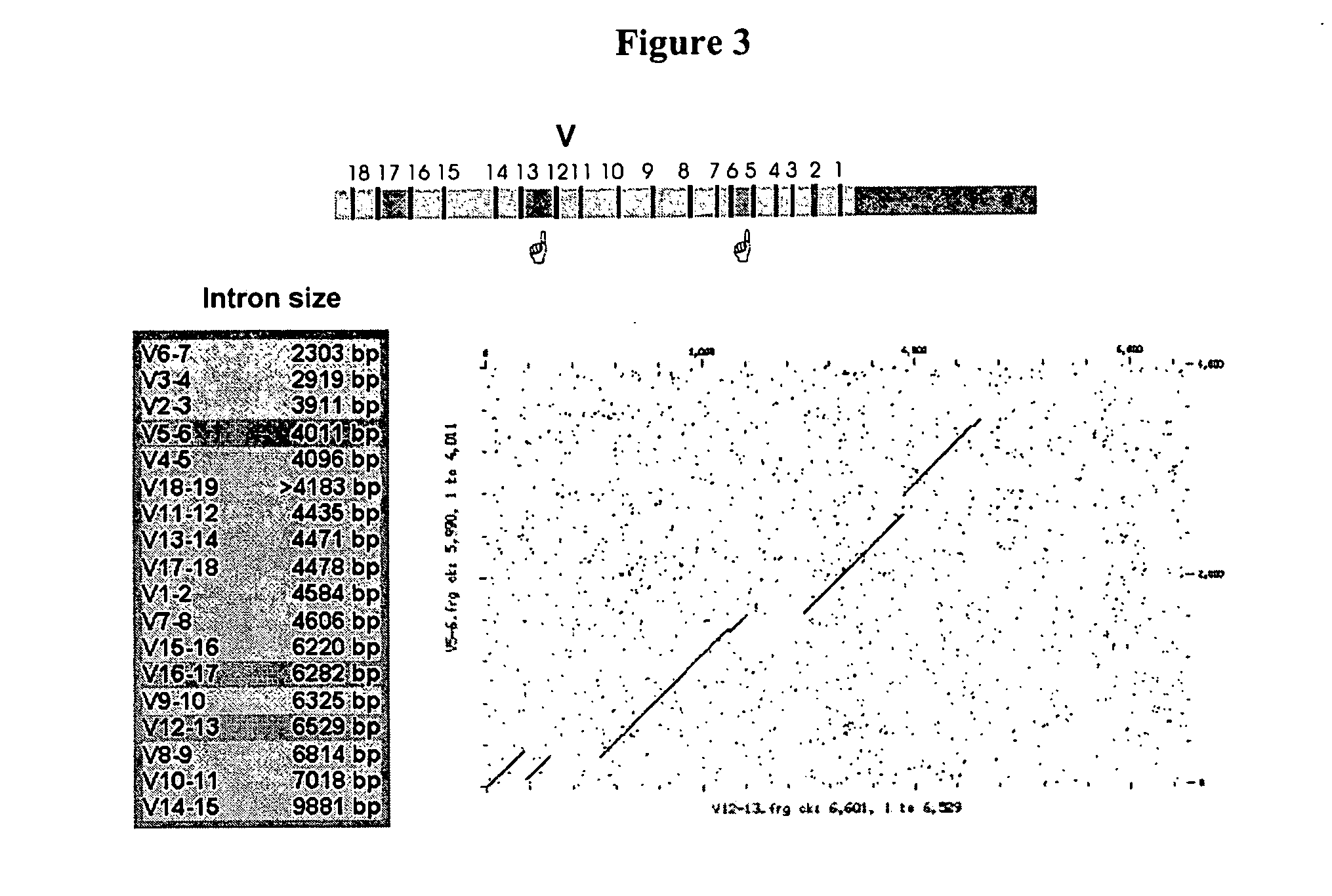
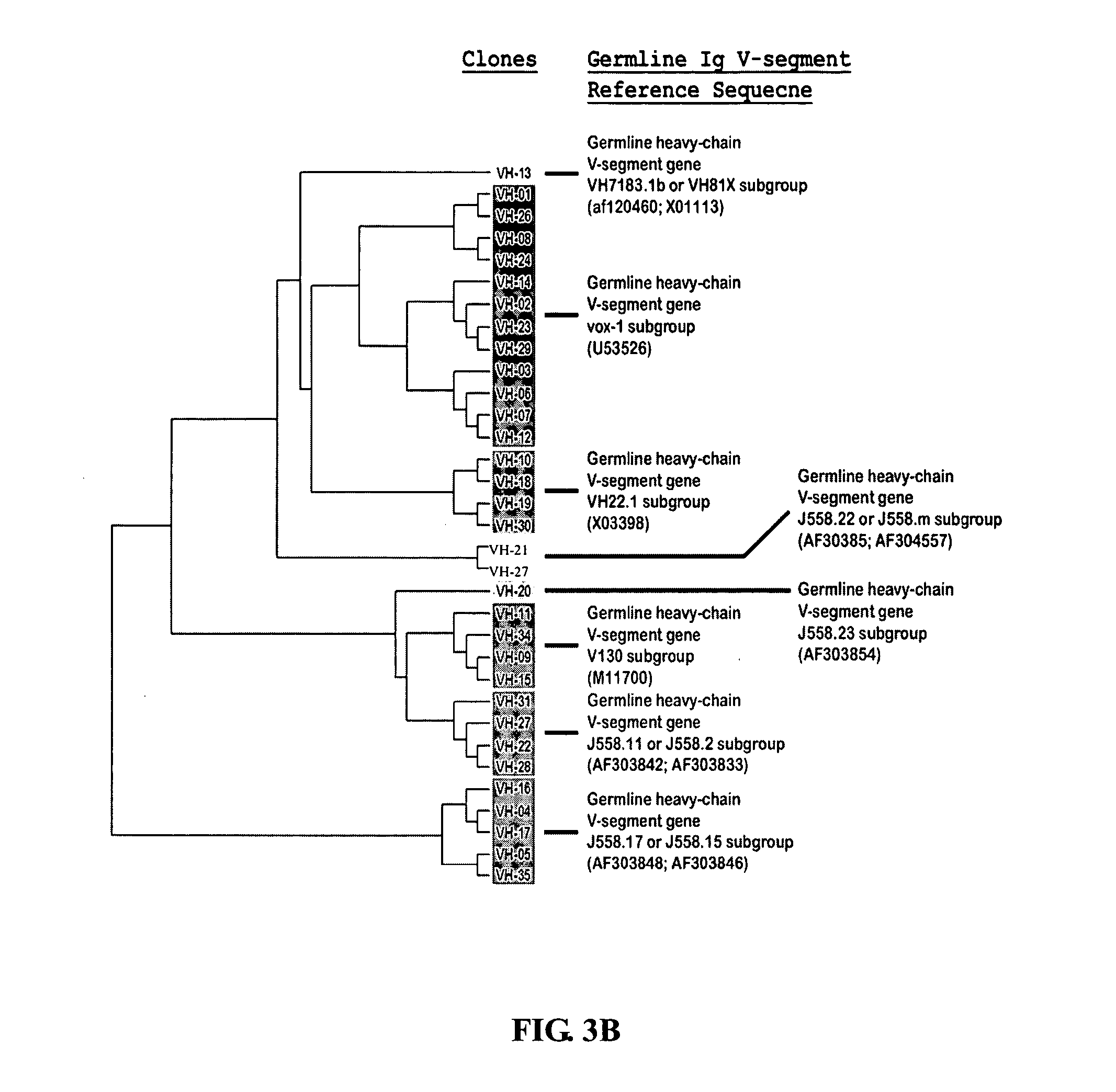
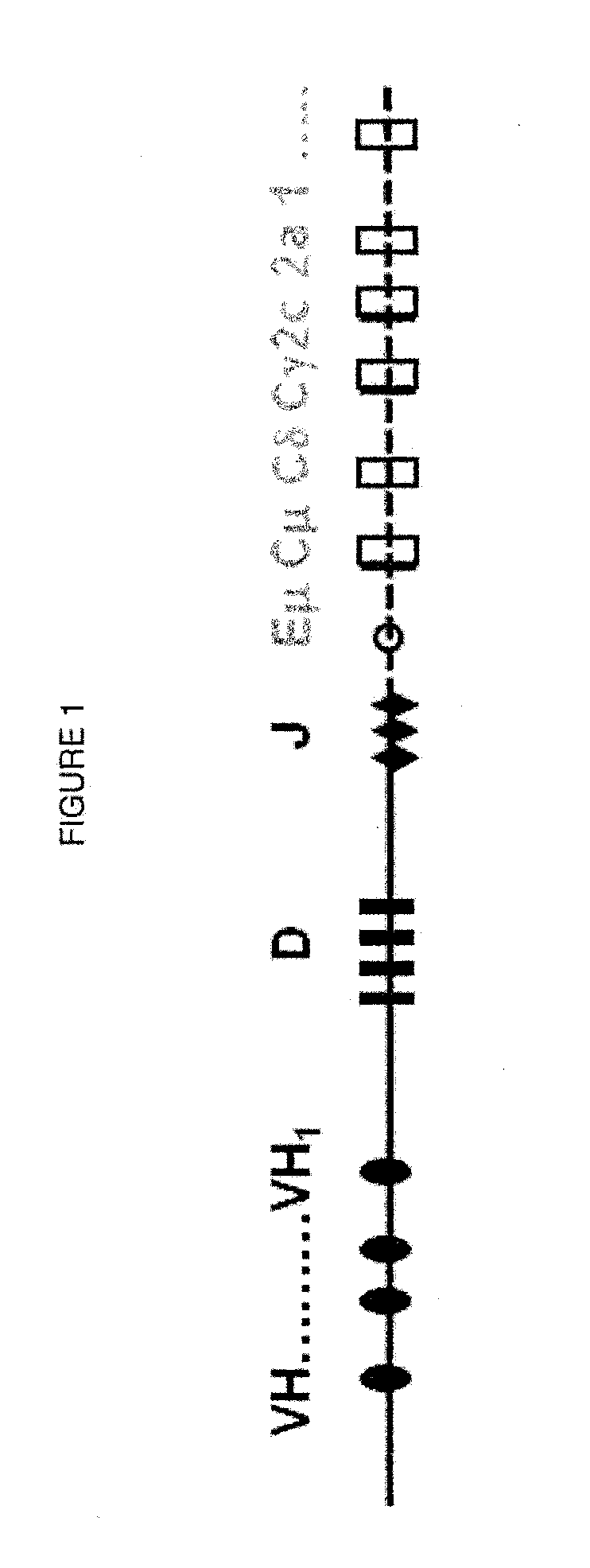
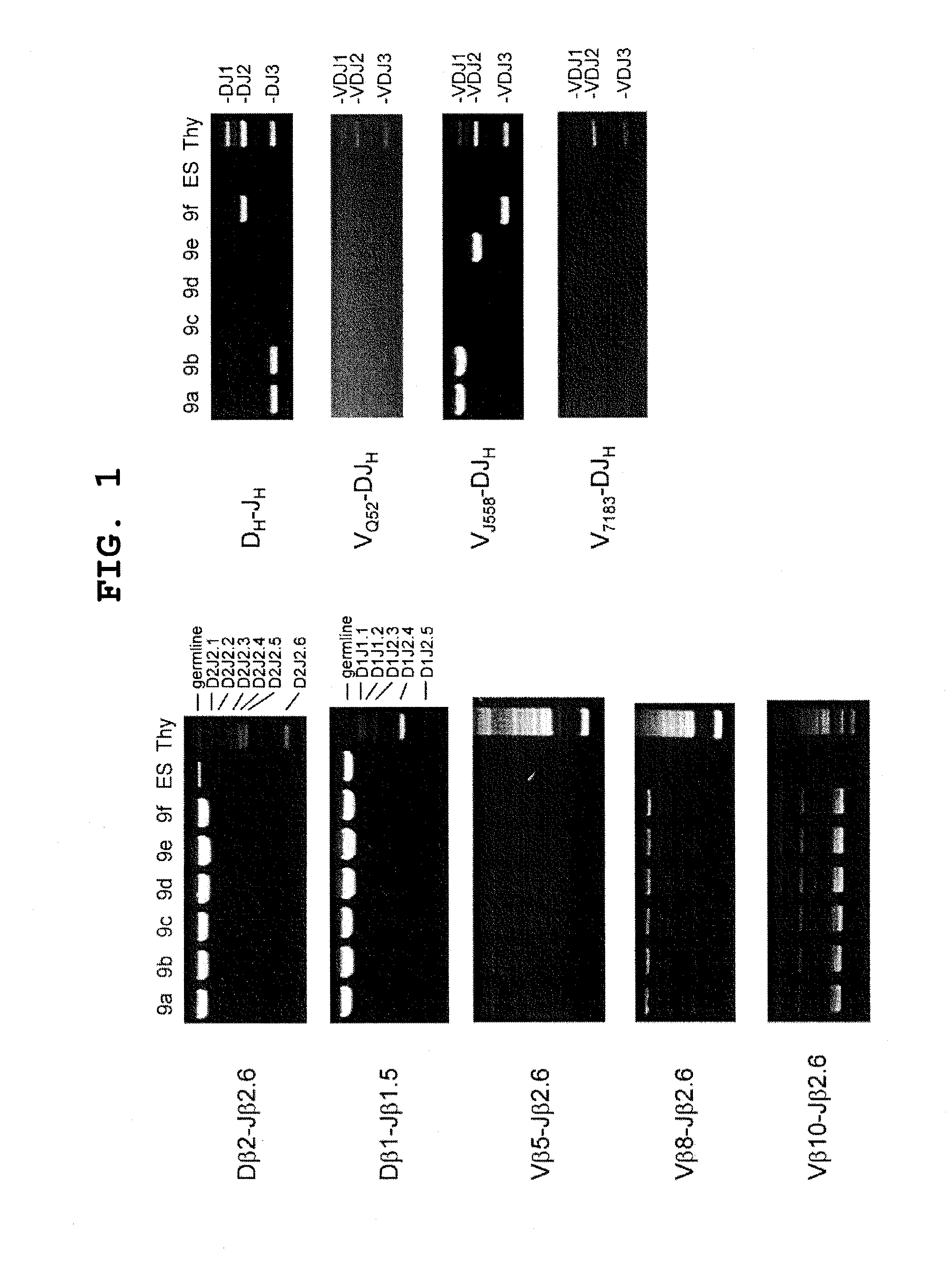
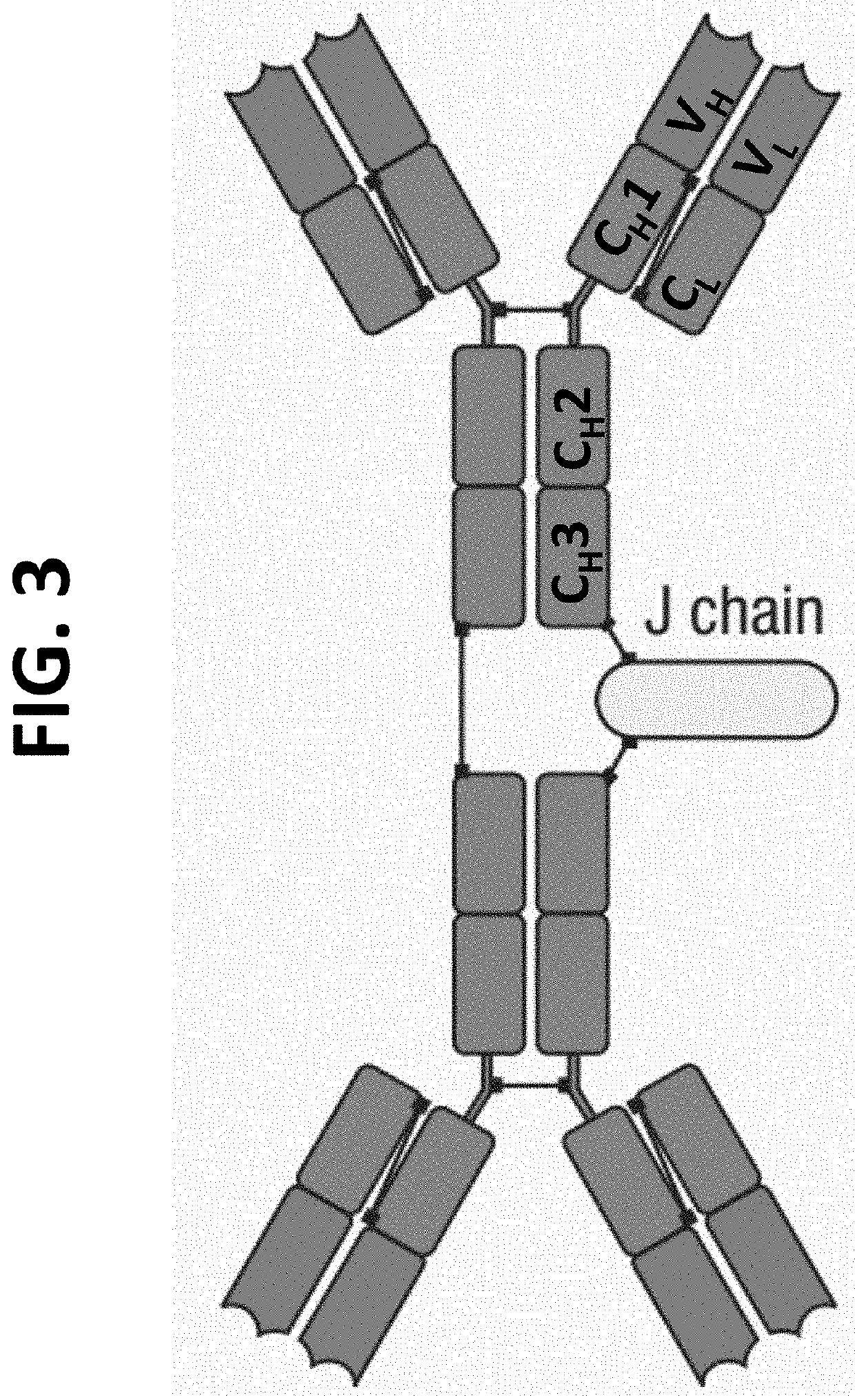
The multigene organization of immunoglobulin genes. From studies and predictions such as Dreyer and Bennett's, it shows that the light chains and heavy chains are encoded by separate multigene families on different chromosomes. They are referred to as gene segments and are separated by non-coding regions.
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS20030017534A1Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS7129084B2Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Compositions and methods for inhibiting endogenous immunoglobulin genes and producing transgenic human idiotype antibodies
ActiveUS20090098134A1Efficiently deletingHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsAlpha globulinTransgene
Owner:OMNIAB OPERATIONS INC
Humanized immunoglobulin loci
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Monitoring treatment-resistant clones in lymphoid and myeloid neoplasms by relative levels of evolved clonotypes
The invention is directed to a method of monitoring or detecting treatment-resistant clones in a patient being treated for a lymphoid or myeloid neoplasm from which patient-specific correlating clonotypes have been identified. In some embodiments, such method includes the steps of obtaining a sample from the patient comprising T-cells and / or B-cells; amplifying molecules of nucleic acid from the T-cells and / or B-cells of the sample, the molecules of nucleic acid comprising recombined DNA sequences from T-cell receptor genes or immunoglobulin genes; sequencing the amplified molecules of nucleic acid to form a clonotype profile; determining from the clonotype profile a level of each correlating clonotype and clonotypes clonally evolved therefrom; and correlating a presence of a treatment-resistant clone of the neoplasm with a change in relative levels of the correlating clonotypes and clonotypes clonally evolved therefrom. In part, the invention permits one to distinguish between cases where treatment is effective but insufficiently intense and cases where a cancer clone arises that is resistant to a current treatment approach.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Ig genes specific oligonucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090280489A1Minimal cross-reactivityLow degeneracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellImmunoglobulin Gene Rearrangement
The present invention provides oligonucleotides for detection of rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes for identifying clonality of cells, cancer cells, hypermutation in immunoglobulin gene, antibody isotype producing cell and / or assaying B cell repertoire in a sample. The oligonucleotides disclosed in the present invention are very specific to the immunoglobulin genes.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTUTUTE OF IMMUNOLOGY
Functionally assembled antigen-specific intact recombinant antibody and a method for production thereof
Functionally assembled antigen-specific intact recombinant monoclonal antibody produced by transformation of the methylotropic yeast, P. pastoris with mouse / human immunoglobulin genes encoding heavy and light chains. A method for production of the intact monoclonal antibodies, a recombinant yeast expression vector and the antibody-specific MRNA synthesis. A process for a large-scale production of the functionally assembled intact recombinant antibody.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Remedy for diseases associated with immunoglobulin gene translocation
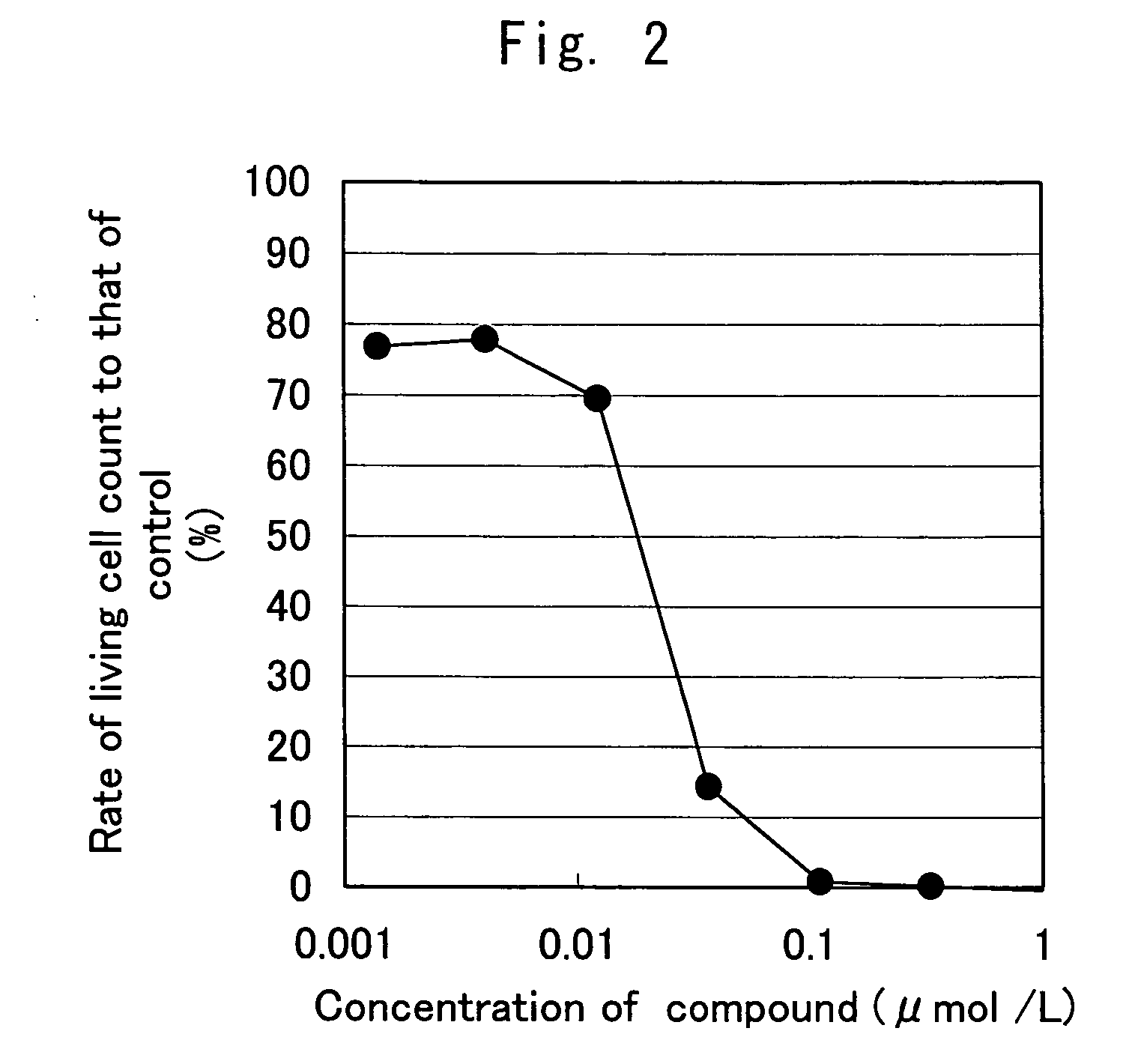
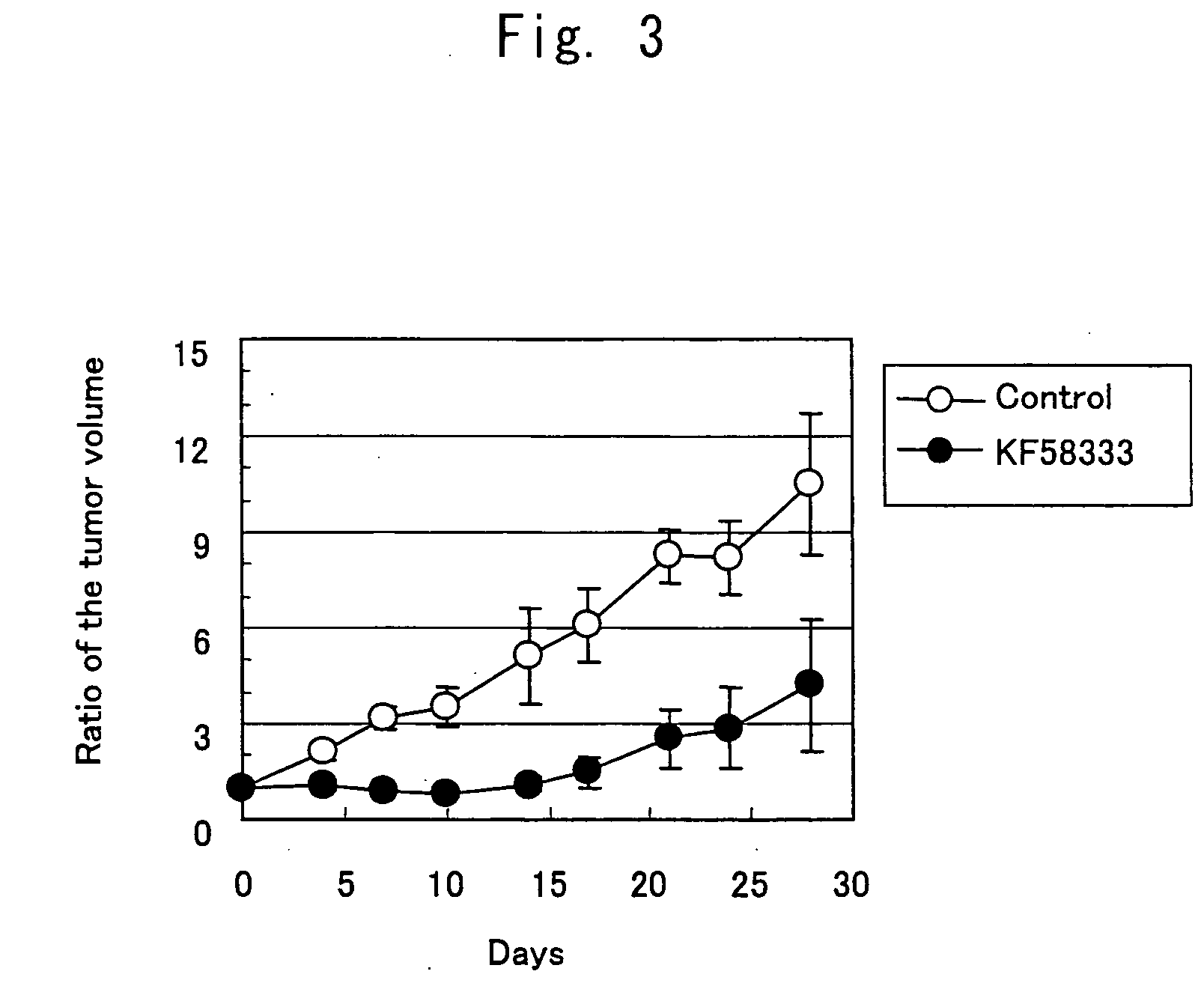
InactiveUS20070004674A1Easy to produceEasy to implementBiocideOrganic chemistryHSP90 Heat-Shock ProteinsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A medicament comprising a compound having an inhibitory action on Hsp90 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as an active ingredient is used as a therapeutic agent for diseases associated with immunoglobulin gene translocations. In diseases associated with immunoglobulin gene translocations, abnormal enhancement of the expression of a partner gene in immunoglobulin gene translocation participates in the development of the diseases and the progress of the symptoms. By administering the compound having an inhibitory action on Hsp90 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, degradation of protein encoded by the partner gene is promoted and the diseases can be treated.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Method for Accelerating Somatic Mutations and use Thereof in Proteomics
The invention relates to a method of accelerating the induction of somatic mutations in vitro. The inventive method comprises the expression of at least one cDNA expressing a modified version of the AID gene in the cells to be mutated, in culture conditions and a medium that are suited thereto, said modified version resulting from an AID gene in which the three hydrophobic amino acids, leu189, phe193 and leu196, have been replaced by means of alanine mutations in each case. The invention can be used to induce mutations in Burkitt's lymphoma BL2. The invention can also be used to induce mutations in the immunoglobulin genes of immortalised antibody-producing cells, such as mouse hybridoma cells, human hybridoma cells or human B-cell lines immortalised by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Owner:INST NECKER
Nested primer sets for amplifying mouse immunoglobulin variable gene segments
ActiveUS8143007B2Minimal cross-reactivityLow degeneracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellImmunoglobulin Gene Rearrangement
The present invention provides oligonucleotides for detection of rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes for identifying clonality of cells, cancer cells, hypermutation in immunoglobulin gene, antibody isotype producing cell and / or assaying B cell repertoire in a sample. The oligonucleotides disclosed in the present invention are very specific to the immunoglobulin genes.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTUTUTE OF IMMUNOLOGY
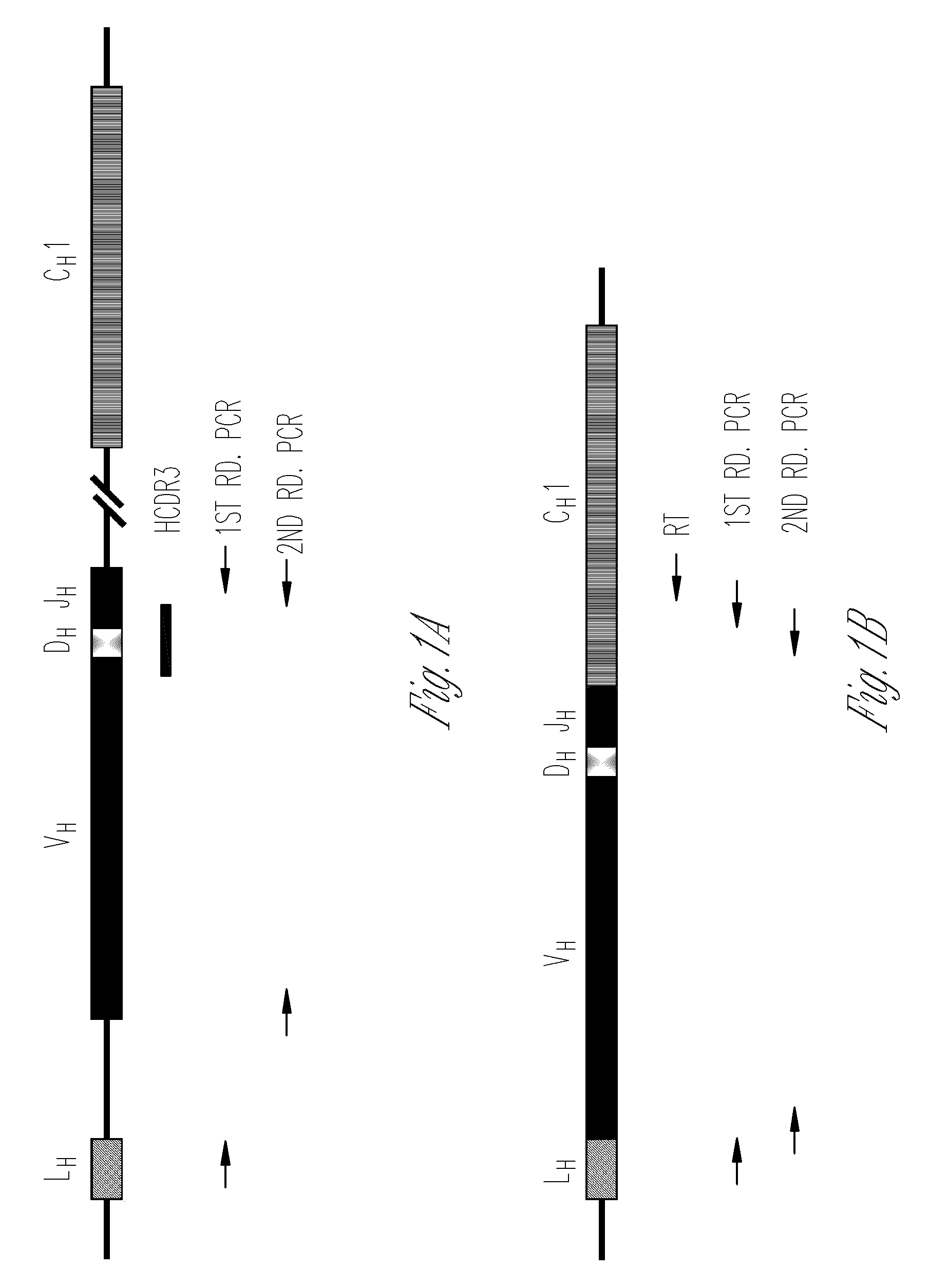
Frame-shifting PCR for germline immunoglobulin genes retrieval and antibody engineering
A method for preparing an antigen-specific antibody by constructing a library of phage-displayed single chain variable fragment of an antibody with a novel frame-shifting PCR is disclosed. Also disclosed is a method for preparing a clone for producing an antigen-specific antibody.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Monitoring mantle cell lymphoma clonotypes in peripheral blood after immunotransplant
InactiveUS20150299800A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDiseaseAutologous T-cells
The invention is directed to a method of monitoring a mantle cell lymphoma residual disease in an immunotransplant patient by post-treatment analysis of clonotype profiles from patient blood samples. In some embodiments, methods of the invention comprising steps of (a) treating a patient by immunotransplanting the patient with vaccine-primed autologous T cells; (b) obtaining a peripheral blood sample from the patient comprising B-cells and / or cell-free nucleic acids; (c) amplifying molecules of nucleic acid from the B-cells of the sample and / or cell-free nucleic acids in the sample, the molecules of nucleic acid comprising recombined DNA sequences from immunoglobulin genes; (d) sequencing the amplified molecules of nucleic acid to form a clonotype profile; and (e) determining from the clonotype profile a presence, absence and / or level of the one or more patient-specific clonotypes correlated with the mantle cell lymphoma, including phylogenic clonotypes thereof.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Compositions and Methods for Inhibiting Endogenous Immunoglobulin Genes and Producing Transgenic Human Idiotype Antibodies
Owner:OMNIAB INC
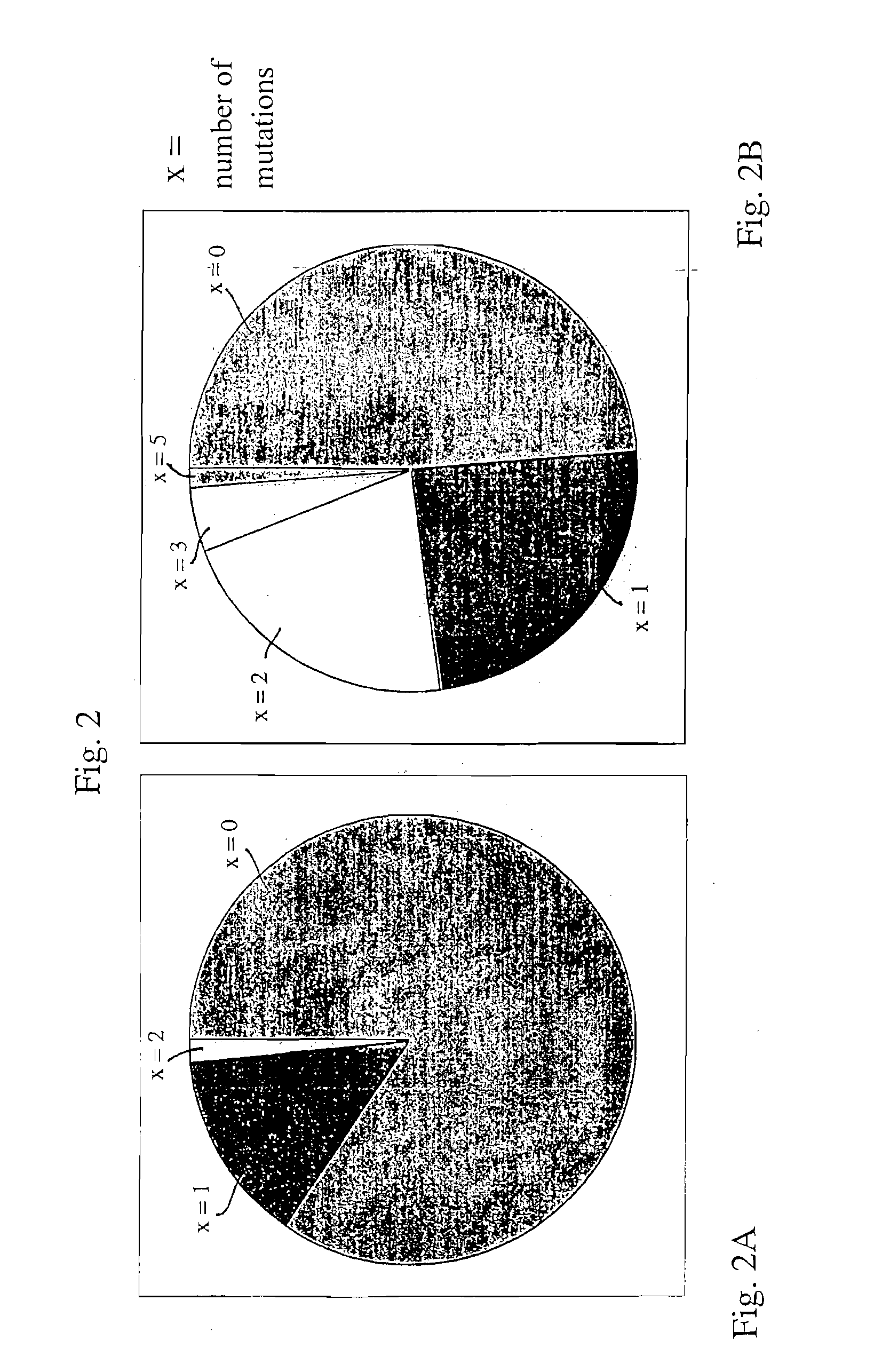
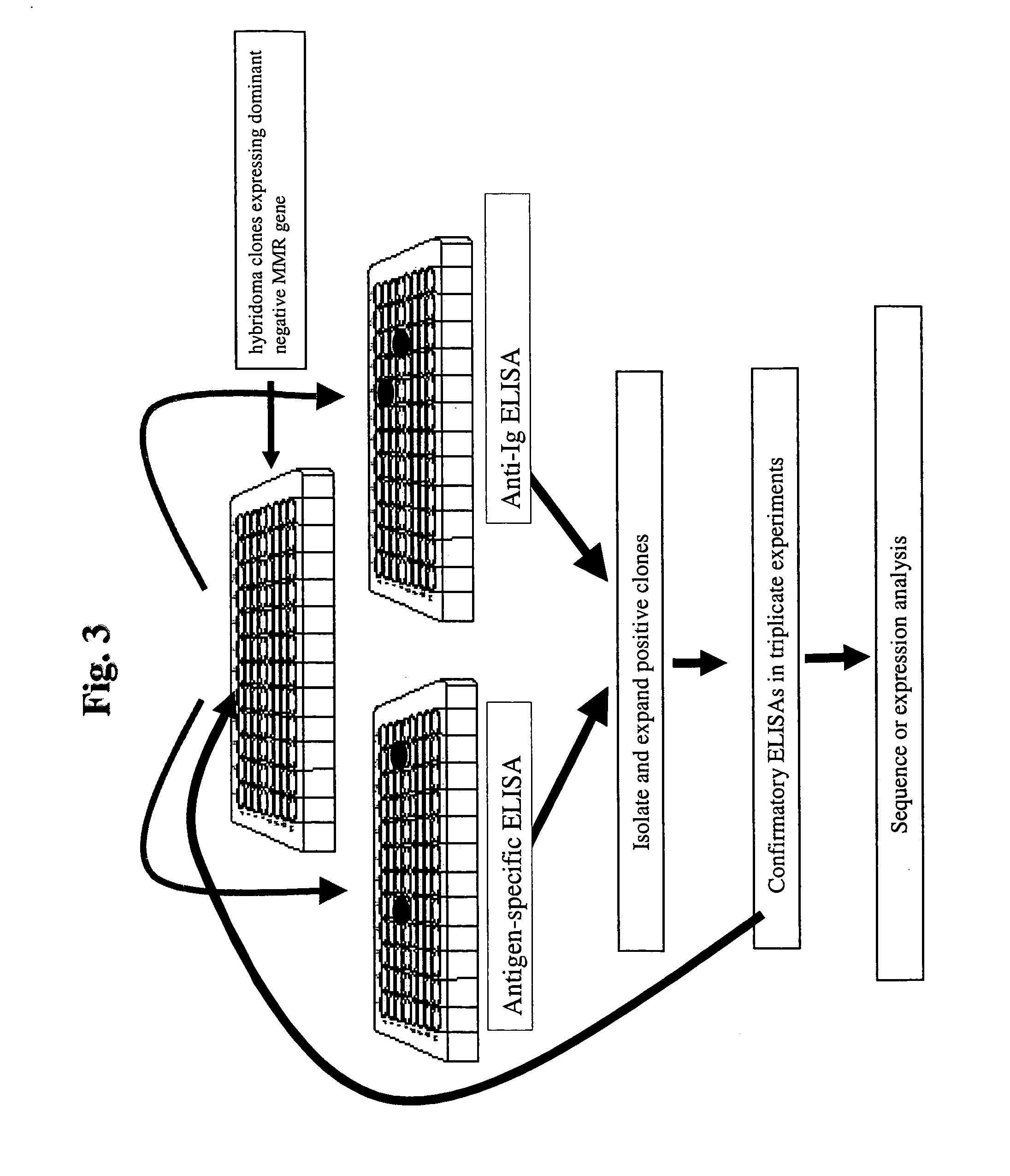
Antibodies and methods for generating genetically altered antibodies with high affinity
InactiveUS7235643B2Increase variabilityBetter pharmacokinetic profileAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGenetic diversityMonoclonal antibody
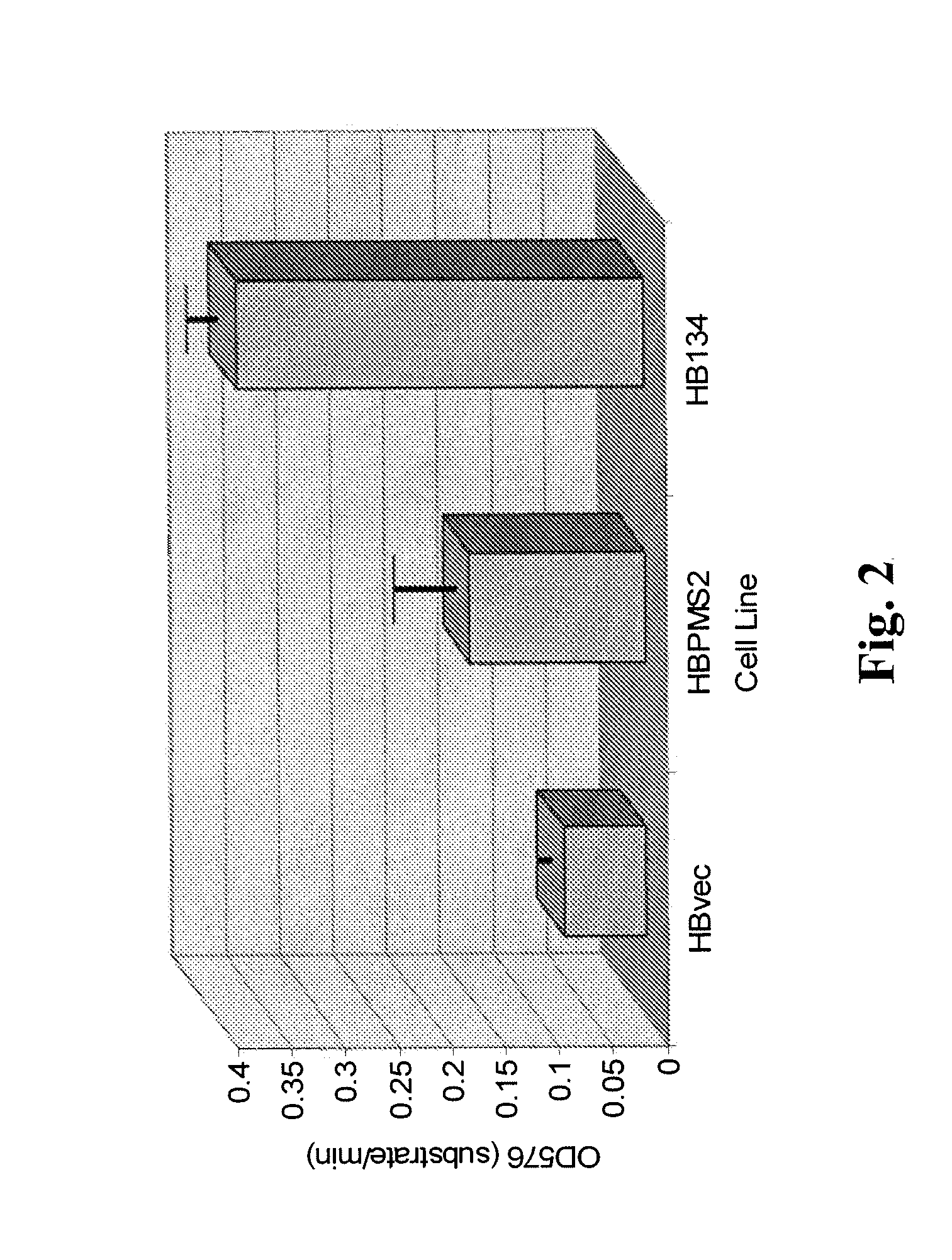
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. By introducing these genes into cells and transgenic animals, new cell lines and animal varieties with novel and useful properties can be prepared more efficiently than by relying on the natural rate of mutation. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production. The invention also provides methods for increasing the affinity of monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibodies with increased affinity.
Owner:EISAI INC
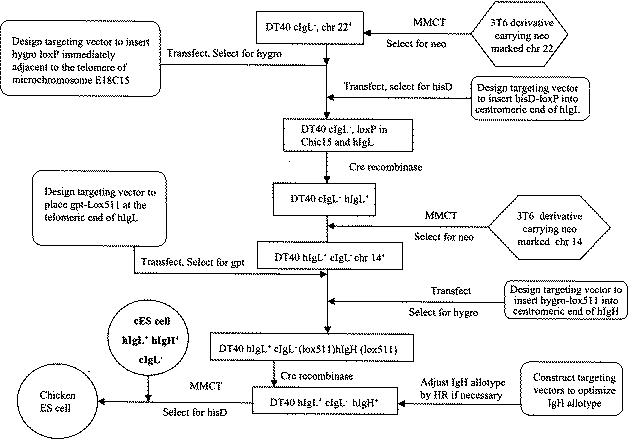
Targeting constructs for the functional disruption of avian immunoglobulin genes
InactiveUS20090083871A1Suppress gene expressionDisrupts productionNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsTargeted disruptionEmbryo
A transgenic chicken is disclosed having disrupted endogenous immunoglobulin production. In one embodiment, a targeting construct is stably integrated into the genome of the chicken by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells, and injection of the engineered embryonic stem cells into recipient embryos, thereby knocking out the endogenous immunoglobulin gene locus in resulting animals. The targeted disruption of the locus in embryonic stem cells is particularly useful in combination with the insertion of genetic elements encoding exogenous immunoglobulin molecules. After these chickens are cross-bred, a line of chickens is produced that has a reduction of endogenous immunoglobulin molecule production.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Functional Disruption Of Avian Immunoglobulin Genes
A transgenic chicken is disclosed having disrupted endogenous immunoglobulin production. In one embodiment, a targeting construct is stably integrated into the genome of the chicken by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells, and injection of the engineered embryonic stem cells into recipient embryos, thereby knocking out the endogenous immunoglobulin gene locus in resulting animals. The targeted disruption of the locus in embryonic stem cells is particularly useful in combination with the insertion of genetic elements encoding exogenous immunoglobulin molecules. After these chickens are cross-bred, a line of chickens is produced that has a reduction of endogenous immunoglobulin molecule production.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
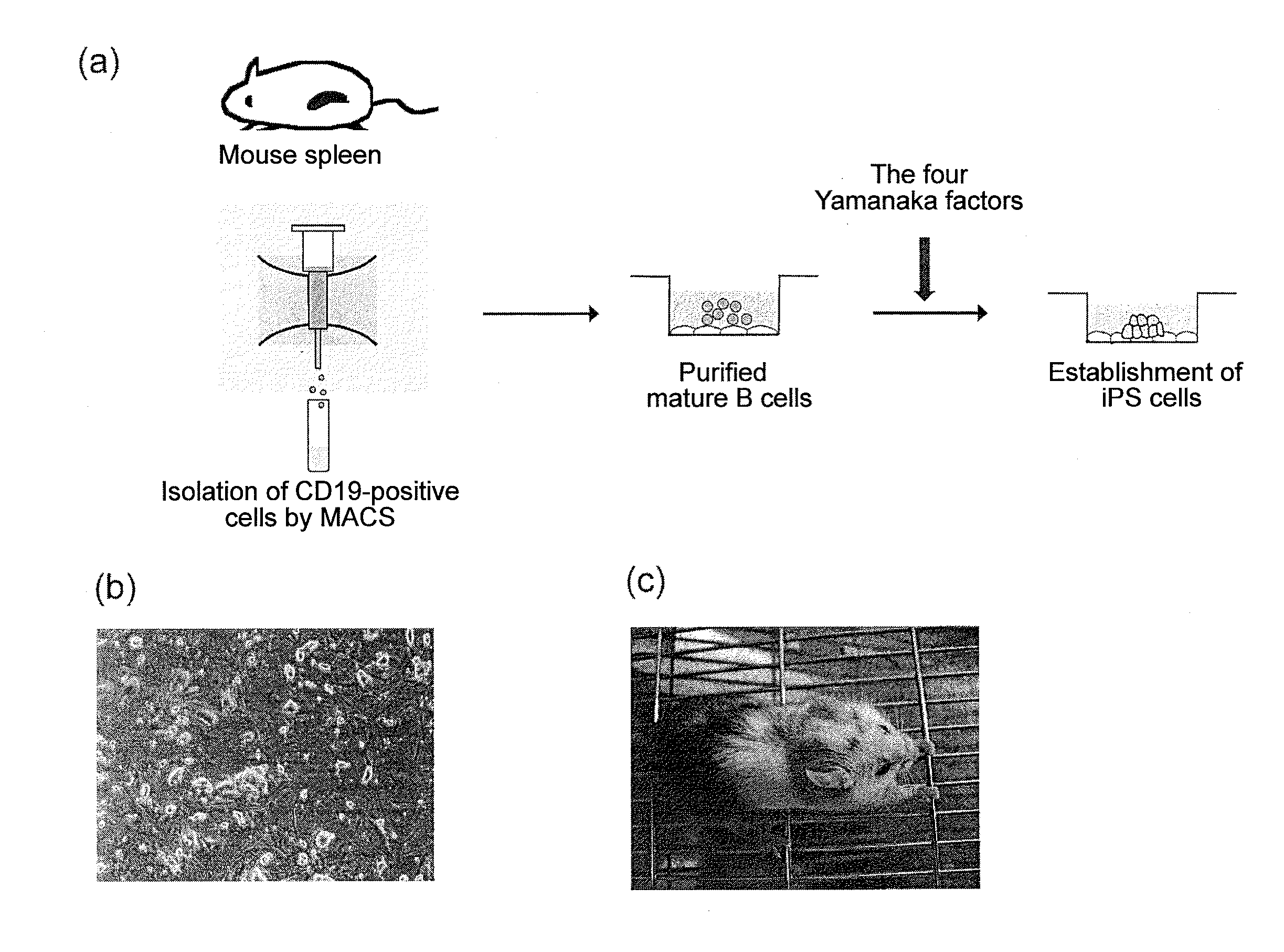
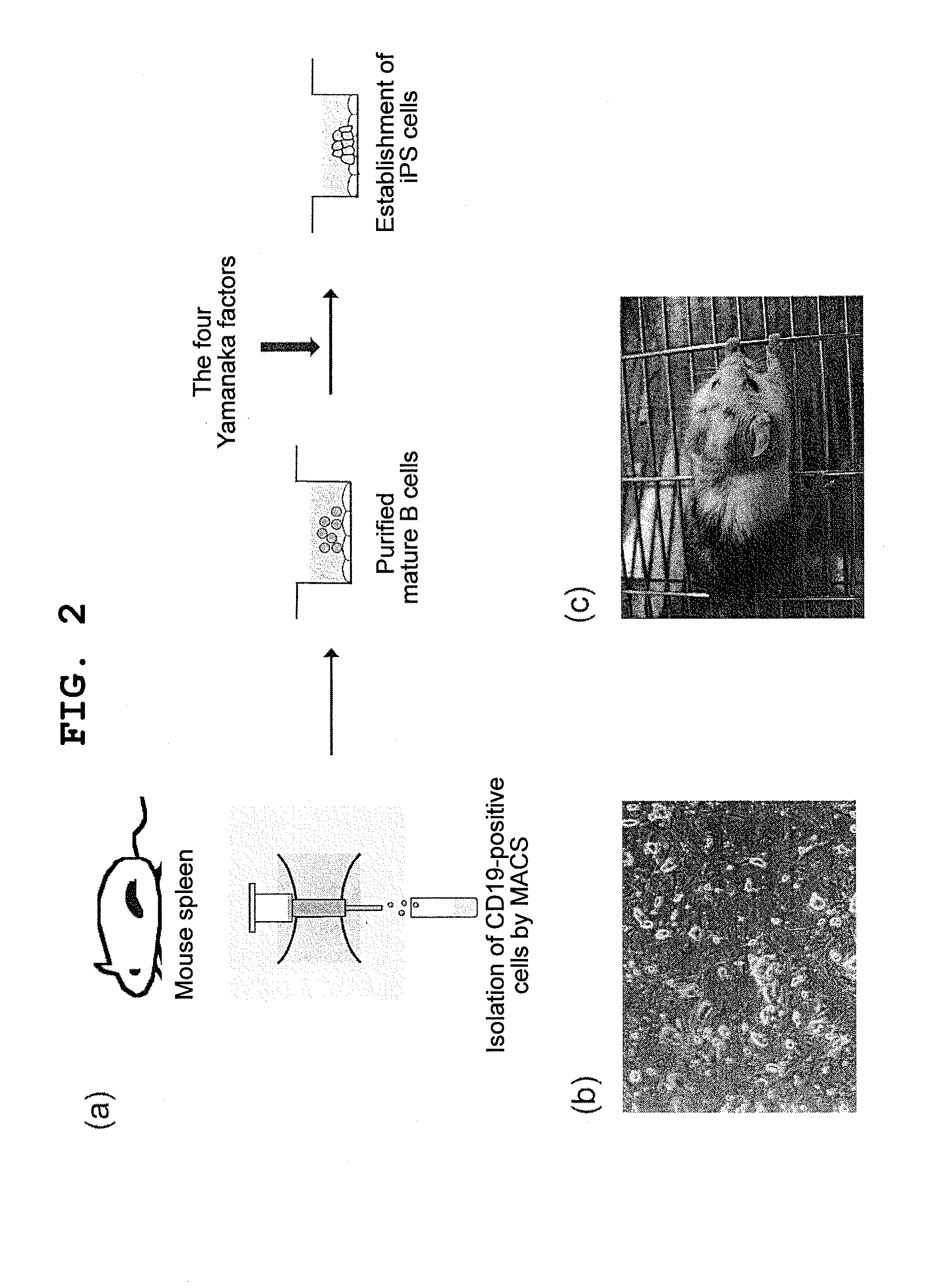
B cell-derived ips cells and application thereof
InactiveUS20110231944A1Low costLow cost productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsMonoclonal antibodyImmunodeficient Mouse
Provided are a B cell-derived iPS cell generated using a convenient technique, a technology for providing a human antibody at low cost using the iPS cell, an immunologically humanized mouse prepared using cells differentiated from the iPS cell, and the like. Also provided are a cloned cell obtained by contacting a B cell with nuclear reprogramming factors excluding C / EBPα and Pax5 expression inhibiting substances, particularly nucleic acids that encode Oct3 / 4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc, wherein the cloned cell has an immunoglobulin gene rearranged therein and possesses pluripotency and replication competence (B-iPS cell). Still also provided are a method of producing a monoclonal antibody against a specified antigen, comprising recovering an antibody from a culture of B cells obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell derived from a B cell immunized with the specified antigen, and a method of generating an immunologically humanized mouse, comprising transplanting to an immunodeficient mouse a human immunohematological system cell obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell.
Owner:RIKEN
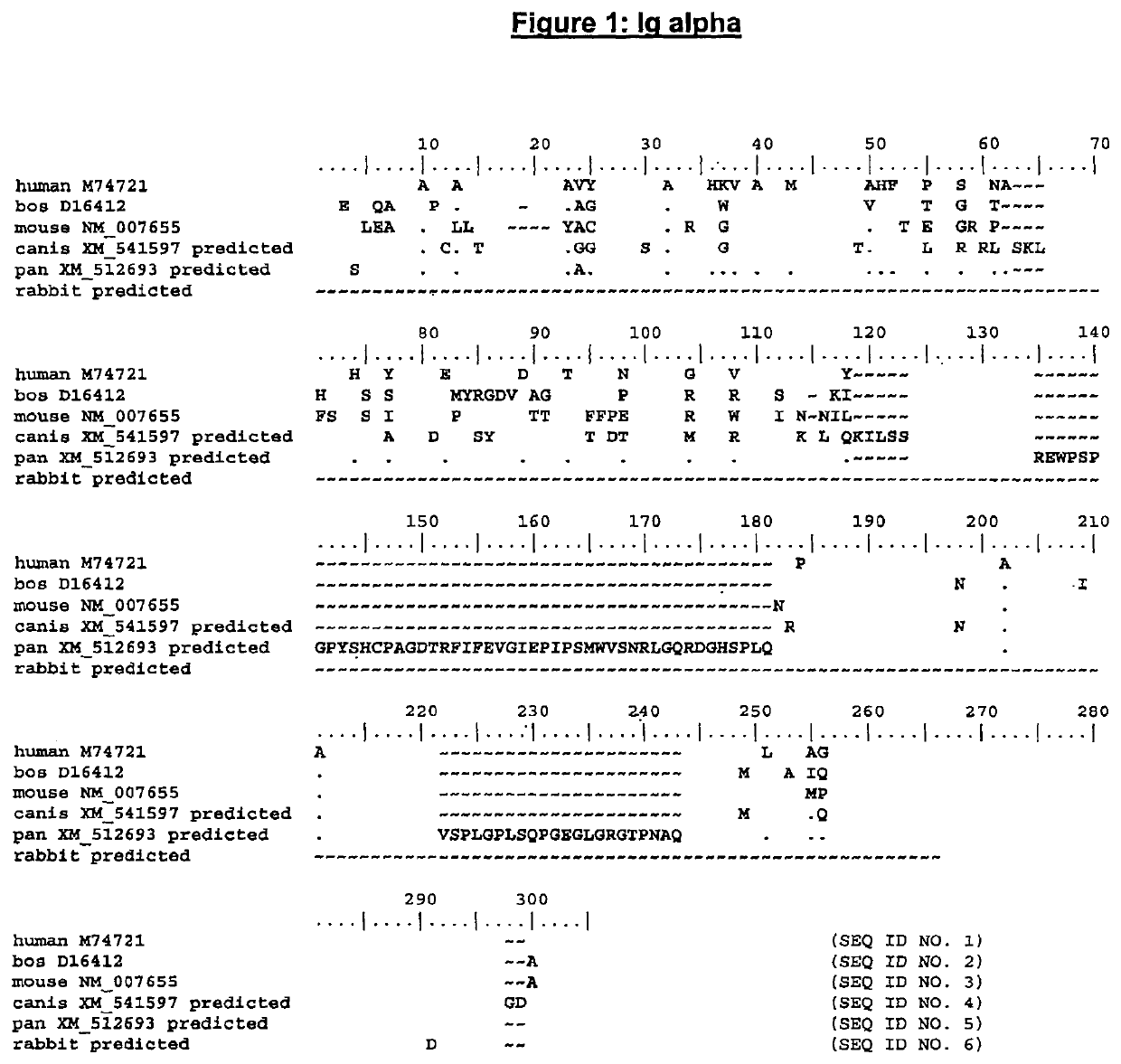
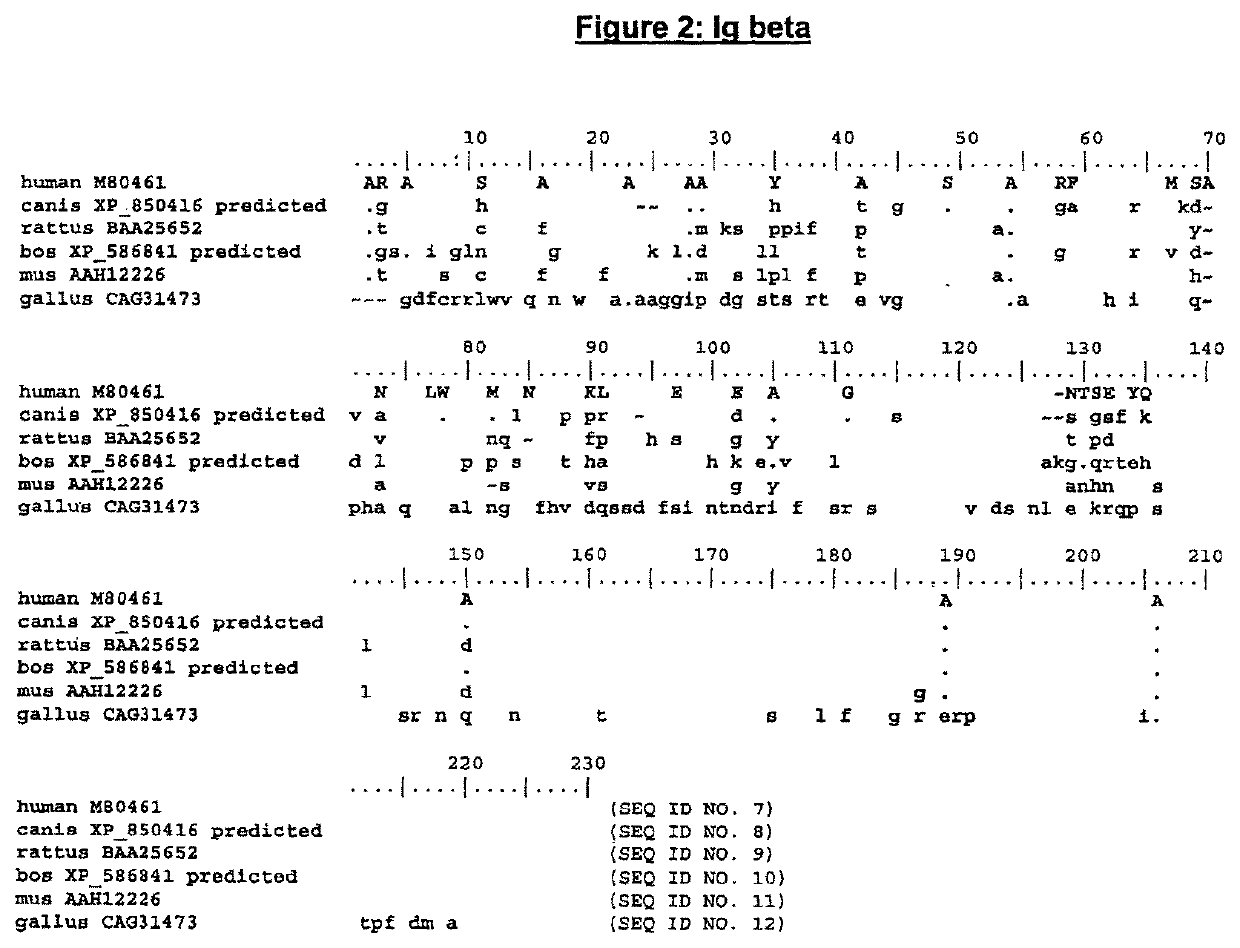
Enhanced expression of human or humanized immunoglobulin in non-human transgenic animals
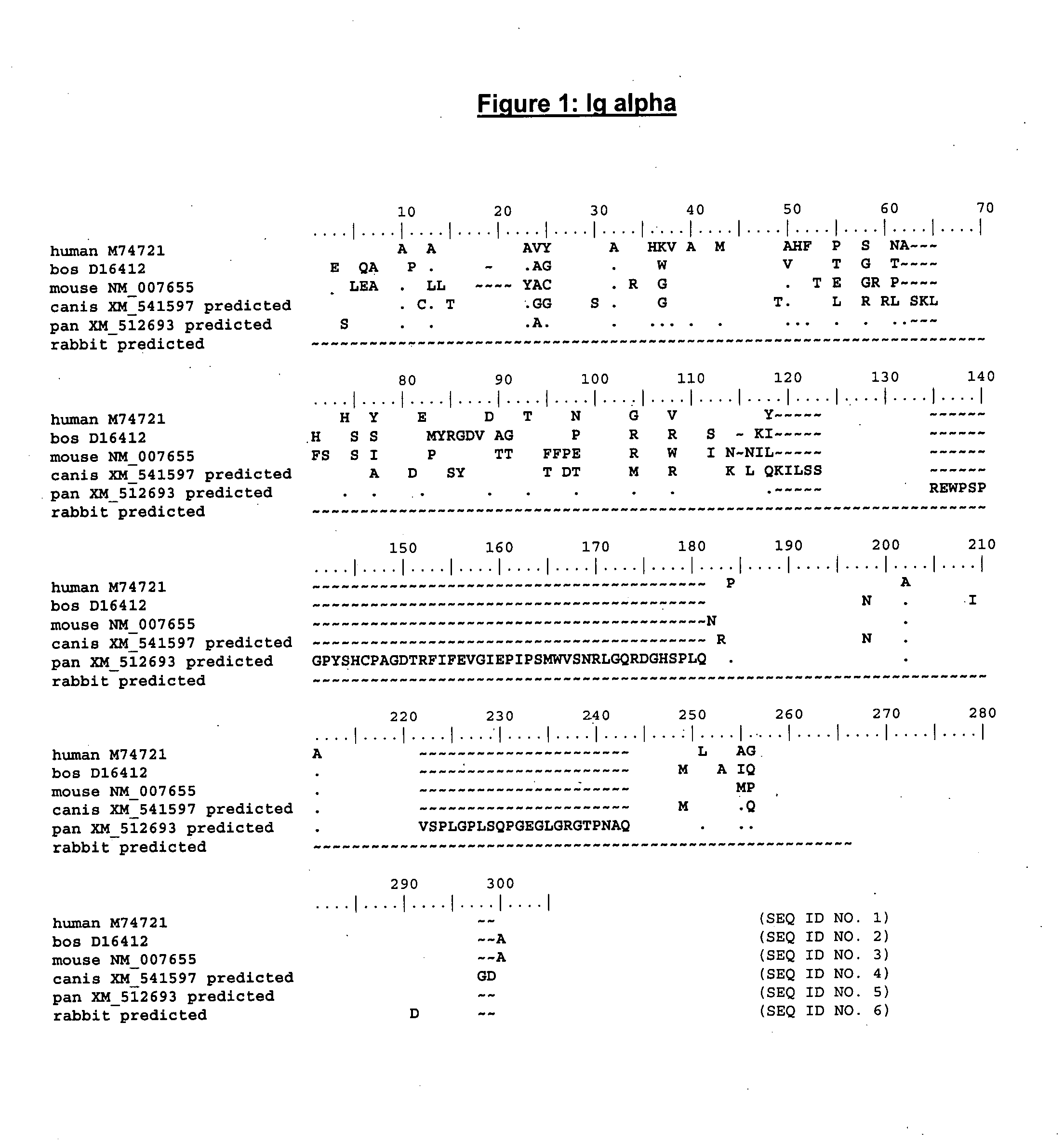
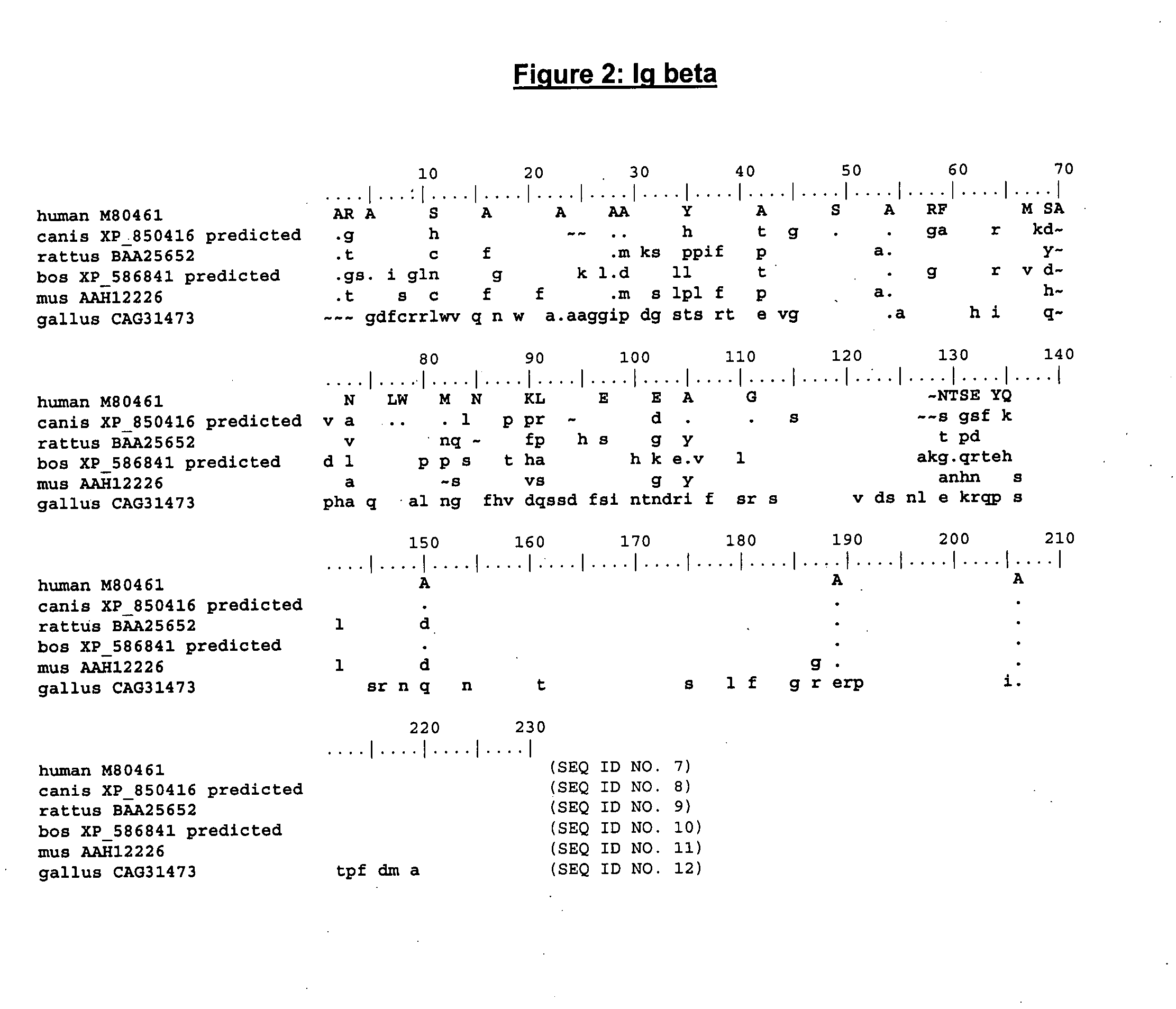
The present invention describes transgenic animals with human(ized) immunoglobulin loci and transgenes encoding human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ sequences. Of particular interest are animals with transgenic heavy and light chain immunoglobulin loci capable of producing a diversified human(ized) antibody repertoire that have their endogenous production of Ig and / or endogenous Igα and / or Igβ sequences suppressed. Simultaneous expression of human(ized) immunoglobulin and human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ results in normal B-cell development, affinity maturation and efficient expression of human(ized) antibodies.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Surface antigen 1 of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment and encoded gene thereof
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment, encoded gene and use thereof. According to the invention, the surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is filtered from a base through establishing a Toxoplasma gondii human immunoglobulin, ELISA, diluting the prothrombin time, sequencing analysis, etc. Through expression purifying and authenticating, the human antigen Fab fragment is authenticated to specifically identify the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii and have higher affinity with the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii, for being identified with the specificity of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite. The human antigen Fab fragment of the invention does not contain Fc segment and does not activate the alexin or cause the histopathological damages of human immune response, etc. when the function of restricting the invasion of Toxoplasma gondii to the host cell is exerted. The surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is safe and reliable when applied for the human body. The antigen medicine for treating toxoplasmosis or the antigen targeted medicine can be prepared.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
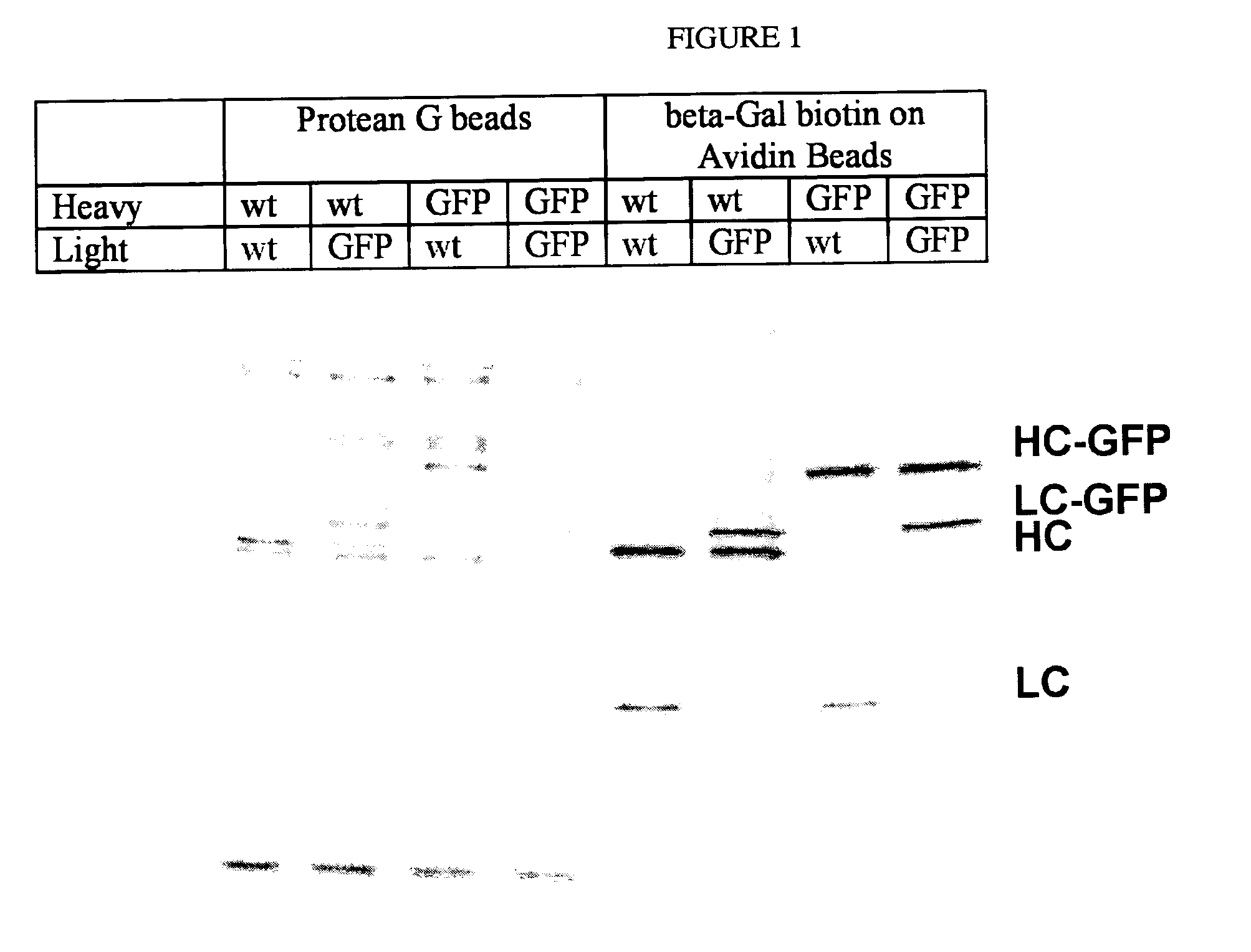
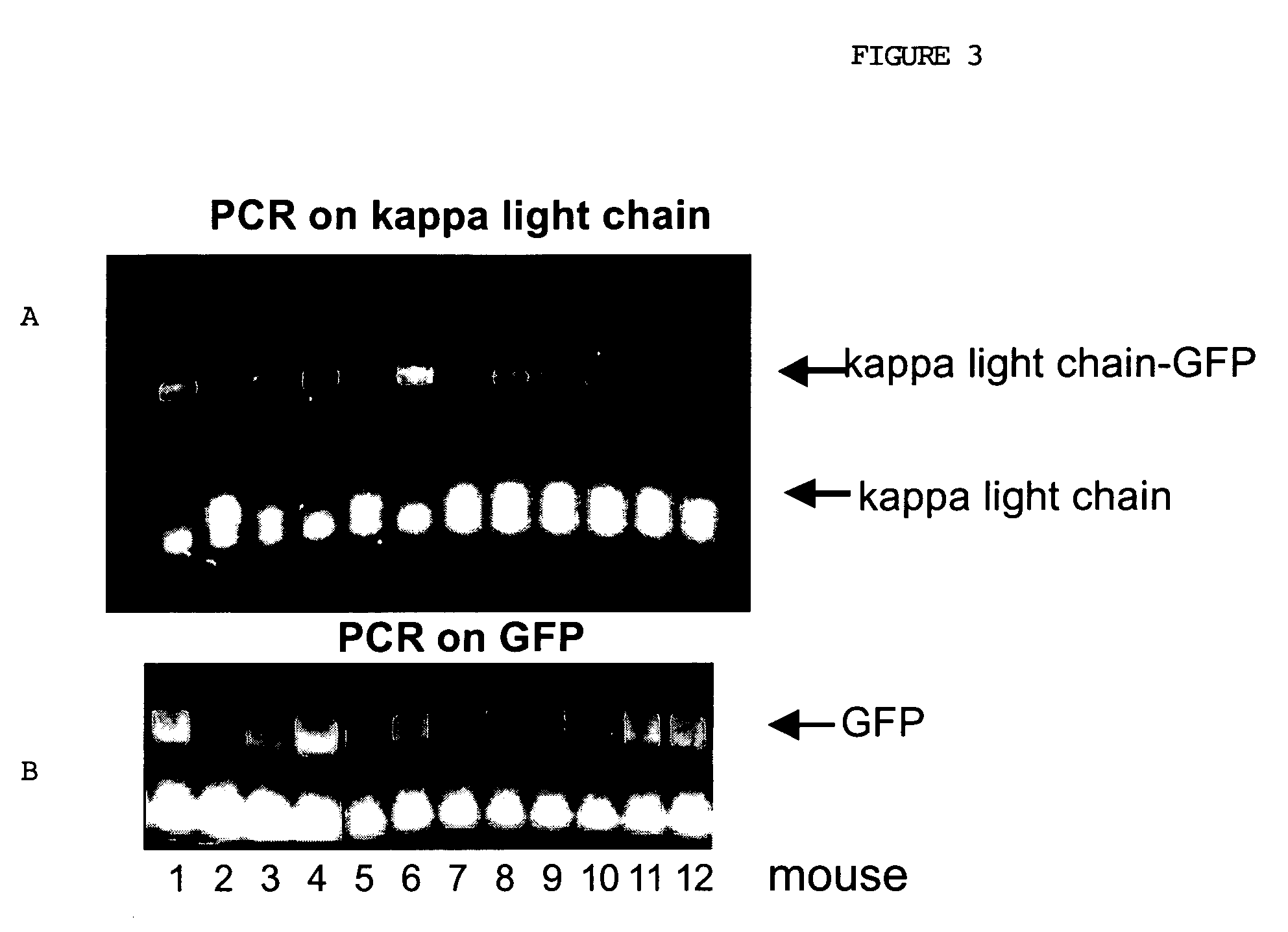
Animals, cells and methods for production of detectably-labeled antibodies
Genetically-modified mammals and immune cells are provided which are capable of producing or secreting detectably-labeled immunoglobulin molecules as a result of genetic modifications of at least one immunoglobulin gene in the genome thereof, such that a fusion polynucleotide encoding a detectable protein or peptide and an immunoglobulin component molecule is present.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Antibodies And Methods For Generating Genetically Altered Antibodies With High Affinity
InactiveUS20070244302A1Altering the hypermutability of an antibody-producing cellGenetic stabilityMutant preparationImmunoglobulinsGenetic diversityMonoclonal antibody
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. By introducing these genes into cells and transgenic animals, new cell lines and animal varieties with novel and useful properties can be prepared more efficiently than by relying on the natural rate of mutation. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production. The invention also provides methods for increasing the affinity of monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibodies with increased affinity.
Owner:EISAI INC
Episomal Expression of Potent Immunoglobulins Derived from Human Blood or Convalescent Plasma to Enable Short term Vaccination / Immunization to COVID, COVID-19 and Mutants and Other Pandemic and non-Pandemic Viruses designed from Rapid FDA approval.
PendingUS20220064265A1Preventing adverse health effectEliminate damageGenetic material ingredientsBiological material analysisVaccinationViral vector
The present invention provides methods, immunoglobulin compositions and vector constructs as a general approach to provide episomal based immune protection from the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19), its variants / mutants and other pandemic and even non-pandemic viruses. The immunoglobulin compositions include the heavy chain variable, diversity and joining (VDJ or Variable Heavy Region genes) segment immunoglobulin DNA and / or polypeptide sequence from humans identified to have developed high affinity immunoglobulins (ideally antibodies with nanomolar to picomolar dissociation constants to virus proteins with additional emphasis on cell surface proteins and further emphasis on the Spike protein as related to COVID-19) against the virus of interest and either to use the exact immunoglobulin composition identified from the donor or to combine that variable immunoglobulin region for both heavy and light chains with a non-divergent well-conserved amino acid sequence for the constant regions especially, Hinge region, Constant Heavy 2 (CH2) and Constant Heavy 3 (CH3) for the immunoglobulin heavy chain polypeptide with optional use of donor based Constant Heavy 1 (CH1) or non-divergent well conserved CH1 heavy chain constant region and optional use of hinge region peptides. The immunoglobulin light chain will use either entirely donor based amino acid sequence or donor based light chain variable and joining (VJ or Variable light region genes) segments immunoglobulin polypeptide sequence with a well-conserved non-divergent constant light (CL) chain region for immunoglobulin Kappa locus (κ) or immunoglobulin lambda locus (λ) light chain. The resulting antibodies can either be used as a monoclonal or polyclonal mix of (Immunoglobulin Class G subclass1) IgG1, IgG3 and other subclasses, IgA1 monomer and IgA2 monomer and dimeric IgA1 (dIgA1) immunoglobulins (as identified by the potency of associated memory B-cells) to be expressed via intramuscular administration, intravenous or proximal to lymph nodes. The immunoglobulins will be expressed in the vaccine / immunization recipient via an episome. The vector will be ideally delivered in a recombinant Adeno Associated Virus (rAAV) with preference for AAV serotype 8 (AAV8) containing a single-stranded Deoxyribonucleic acid (ssDNA) non-viral vector or lentivirus virion containing double stranded DNA as a non-viral vector. A single non-viral vector will code for the entire immunoglobulin and J-chain expression for dIgA1 where expression will occur with a single start codon and stop codon for the amino acid sequence and in some embodiments a second start codon for J chain expression. The specific DNA of the immune donor can be identified as follows: Cluster of Differentiation 27+ (CD27+) IgG+ and CD27+ IgA+ memory B cells or other CD memory B-cells will be isolated from serum using established methods. Each resulting isotype of memory B-cell will be subjected to a competitive binding assay using flow cytometry methods such as Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) to identify the memory B-cells with the greatest binding affinity to the COVID-19 antigens of interest. Isolated memory B-cells will have their DNA sequenced to identify the genetic sequence of their cell surface IgG+ or IgA+ receptor. That information and potentially other sources of immunoglobulin genetic information will be used to create vector construct coding for antibodies to be further evaluative for potency and safety and then to be incorporated into a vector construct for episomal immunoglobulin expression. Episomes will be designed to express IgG1, IgG3, IgA1, IgA2 and dIgA1 with potent binding to COVID antigens or antigens of other viruses. A central part of this patent application is the method used to identify the high affinity immunoglobulins expressed by those that were exposed to COVID or other virus of interest.
Owner:SWARTZ ROGER B
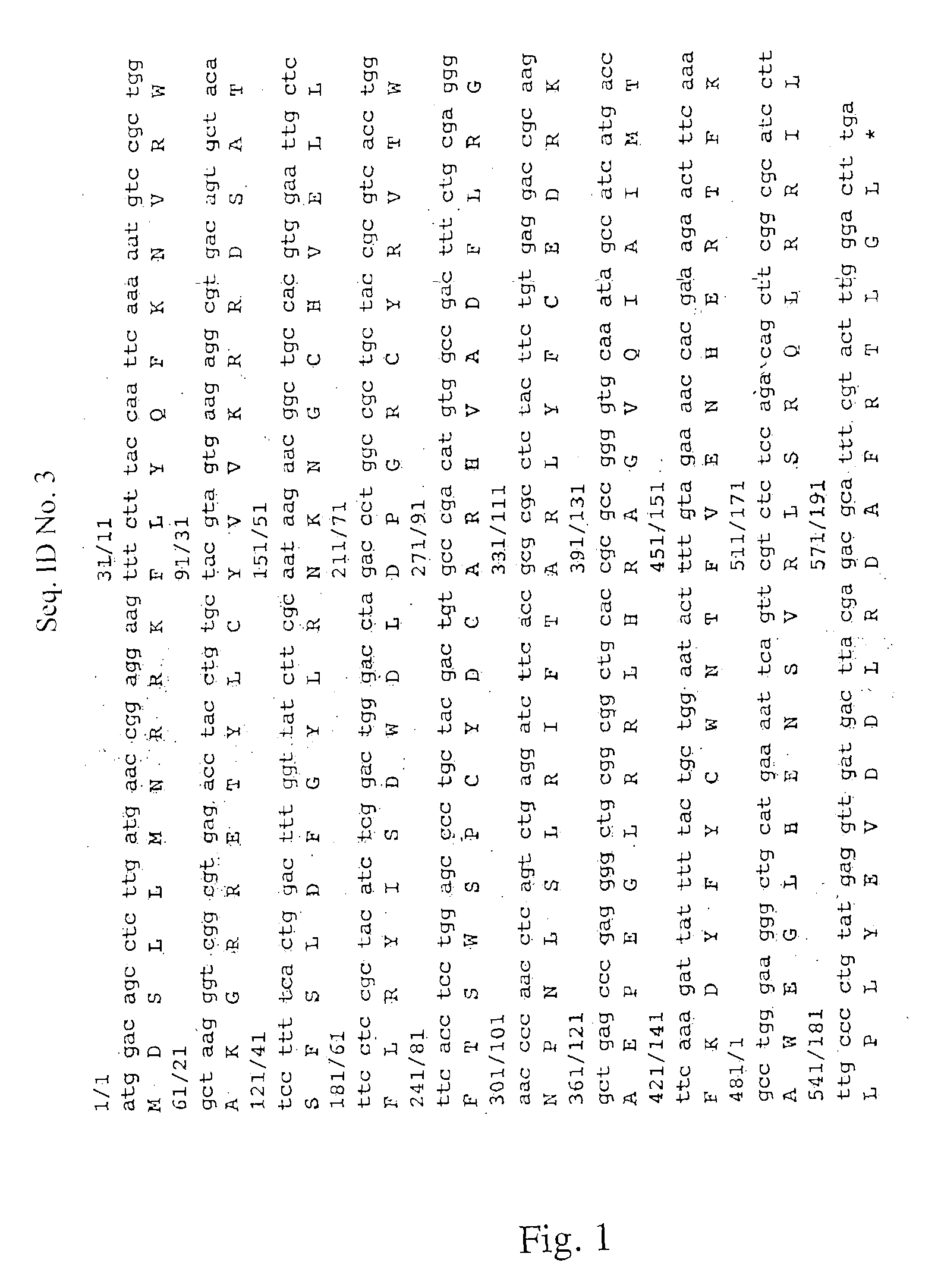
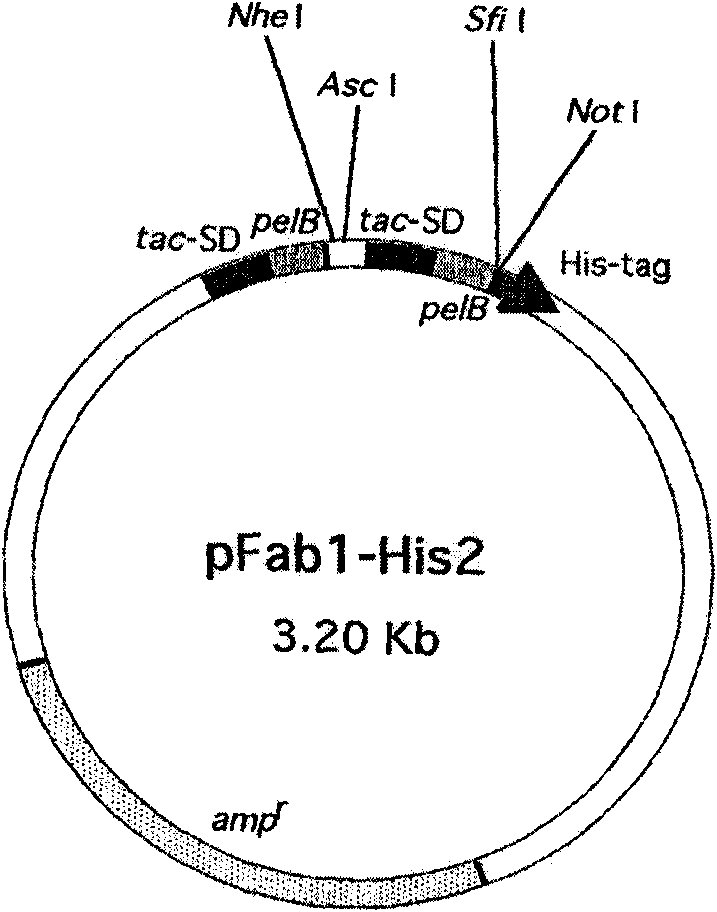
Carrier containing immunoglobulinlg gene, construction method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101509011AHigh molecular weightIncrease spatial structureBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The invention discloses a vector containing immunoglobulin gene, belonging to the field of molecular biology. The nucleotide sequence of the vector is shown in SEQID No.1. The invention also discloses a method for constructing the vector, and the vector can be used for remarkably prolonging the half life period of recombinant protein drug in vivo, thus prolonging the drug efficacy, reducing the times of medicine use of patients and lowering the cost.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Method for improving detection of b cell immunoglobulin gene recombination
InactiveCN103154015AIncrease the number of detectable recombinant moleculesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementB cellGenetic recombination
Disclosed is a method for generating primers to increase the yield of PCR products that represent the various genetic recombination events and antibodies that exist in a sample from a human or animal.
Owner:韩建
Enhanced expression of human or humanized immunoglobulin in non-human transgenic animals
The present invention describes transgenic animals with human(ized) immunoglobulin loci and transgenes encoding human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ sequences. Of particular interest are animals with transgenic heavy and light chain immunoglobulin loci capable of producing a diversified human(ized) antibody repertoire that have their endogenous production of Ig and / or endogenous Igα and / or Igβ sequences suppressed. Simultaneous expression of human(ized) immunoglobulin and human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ results in normal B-cell development, affinity maturation and efficient expression of human(ized) antibodies.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
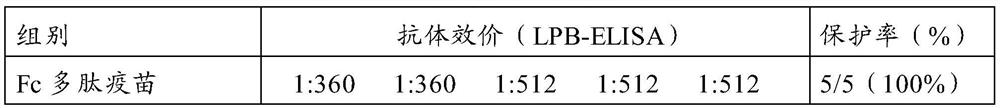
Porcine foot-and-mouth disease virus type a fc polypeptide vaccine and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108059685BEnsure natural formOptimizing expression conditionsSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsDiseaseFoot mouth disease virus
The invention discloses a swine foot-and-mouth disease virus type A Fc polypeptide vaccine and a preparation method and application thereof. The present invention takes the Fc of swine IgG as the skeleton, combined with the current situation of swine A-type foot-and-mouth disease epidemic and the prevention and control requirements in my country, and uses reverse vaccinology, bioinformatics and biochemical knots and other technologies to screen and design different topological types of swine foot-and-mouth disease A. The epitope antigen gene of the virus strain is used to display the antigenic epitope in the functional region of the immunoglobulin Fc gene, and a swine foot-and-mouth disease type A Fc polypeptide vaccine suitable for the epidemic situation and prevention and control needs of my country has been developed. And by screening the prokaryotic expression system and optimizing the expression conditions, the soluble expression of the fusion protein was realized, and the antigenic epitope was displayed to the greatest extent. Experiments have proved that the swine foot-and-mouth disease type A Fc polypeptide vaccine of the present invention has stronger immune efficacy, and can induce the body to produce higher protective antibodies after boosting immunization; the difference in antibody levels of immunized animals is small, and the immunized pigs are highly virulent. After attack, 100% get protection.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Animals, cells and methods for production of detectably-labeled antibodies
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Primer group for amplifying B lymphocyte immune repertoire and application of primer group
PendingCN112301099AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerMedicine
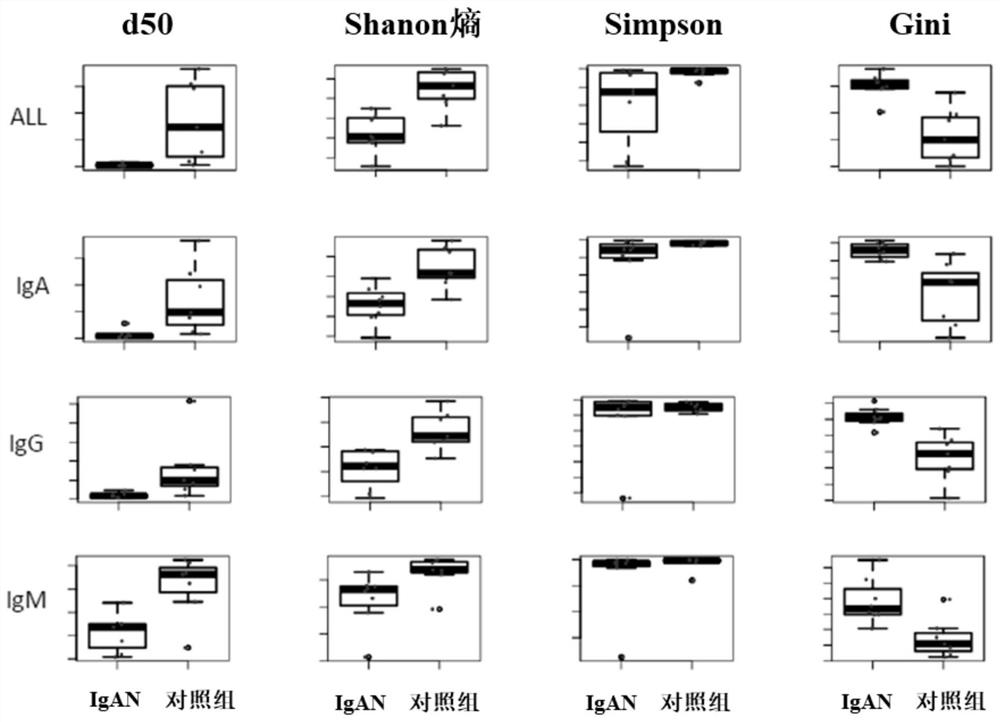
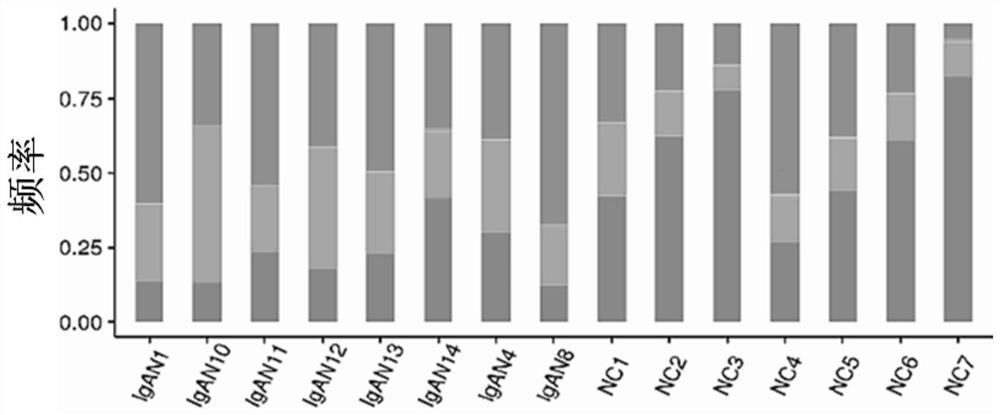
The invention provides a primer group for amplifying a B lymphocyte immune repertoire and an application of the primer group. The primer group comprises a group of forward primers and a group of reverse primers. The forward primers comprise a linker sequence 1, a bar code sequence 1 and a specific sequence aiming at an immunoglobulin variable region complementation determining region 3, which areconnected in sequence from a 5' end to a 3' end, wherein the specific sequence aiming at the immunoglobulin variable region complementary determining region 3 is shown as any one of SEQ ID NO. 1 to SEQ ID NO. 12; and the reverse primers sequentially comprise a linker sequence 2, a bar code sequence 2 and a specific sequence aiming at an immunoglobulin gene constant region from the 5' end to the 3'end. The primer group is used for amplifying B lymphocytes of an IgAN patient and a normal control group, library information is collected, and the length and diversity changes of CDR3 of the IgAN patient are analyzed through sequencing.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Nucleic acids for detecting B-cell malignancy
This document provides methods and materials related to detecting gene rearrangements (e.g., MYC gene rearrangements). For example, nucleic acid probe sets for detecting MYC-immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in mammals are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Nucleic acids for detecting b-cell malignancy
This document provides methods and materials related to detecting gene rearrangements (e.g., MYC gene rearrangements). For example, nucleic acid probe sets for detecting MYC-immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in mammals are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com