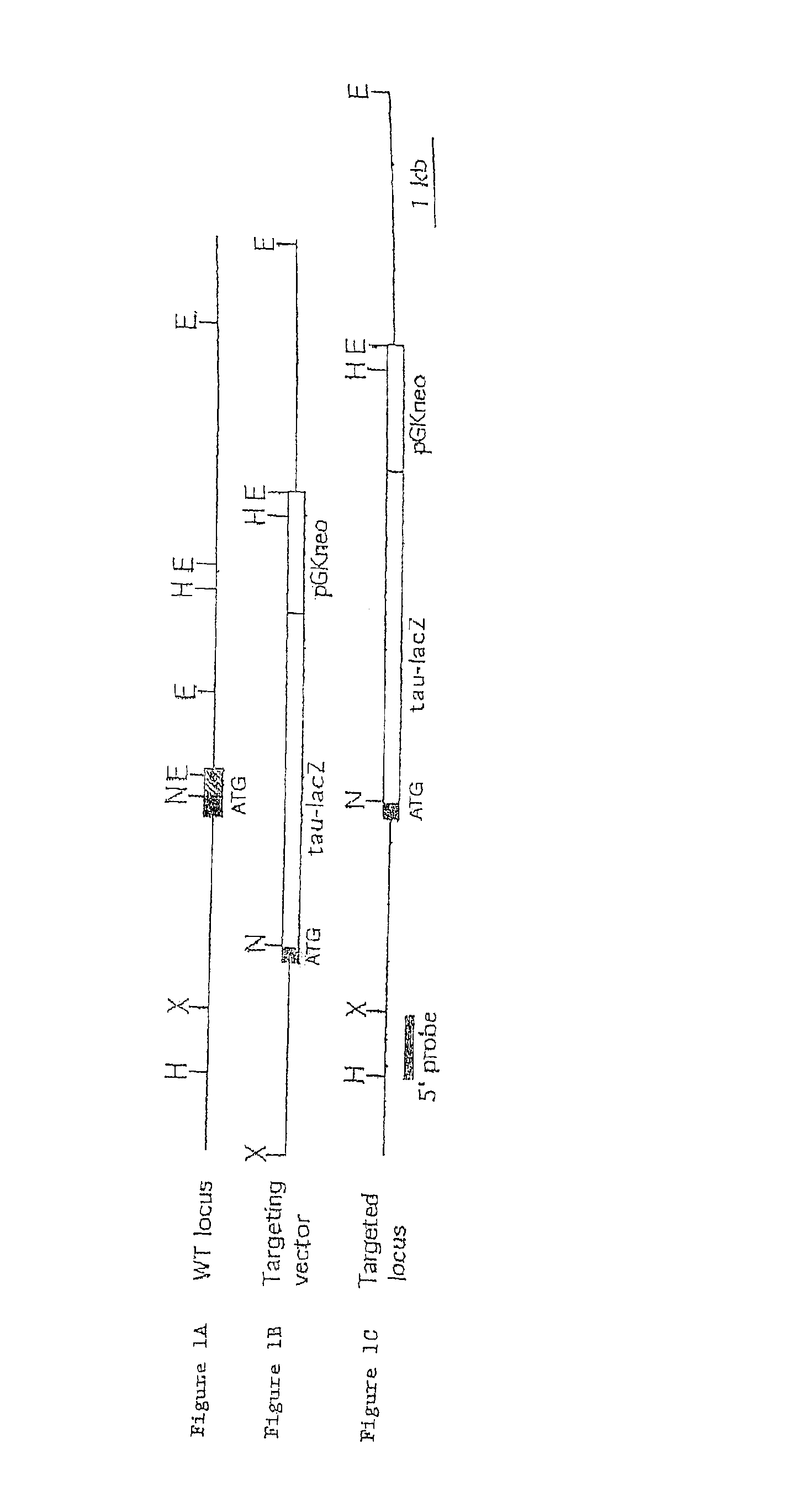
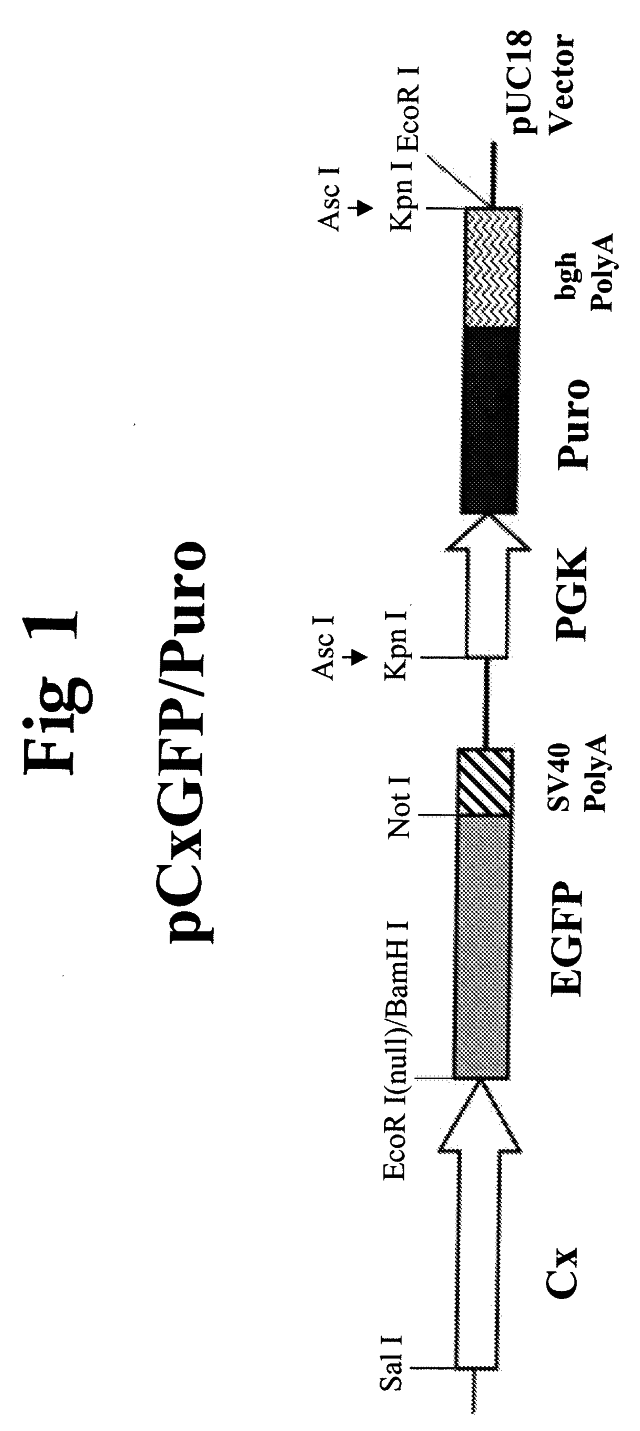
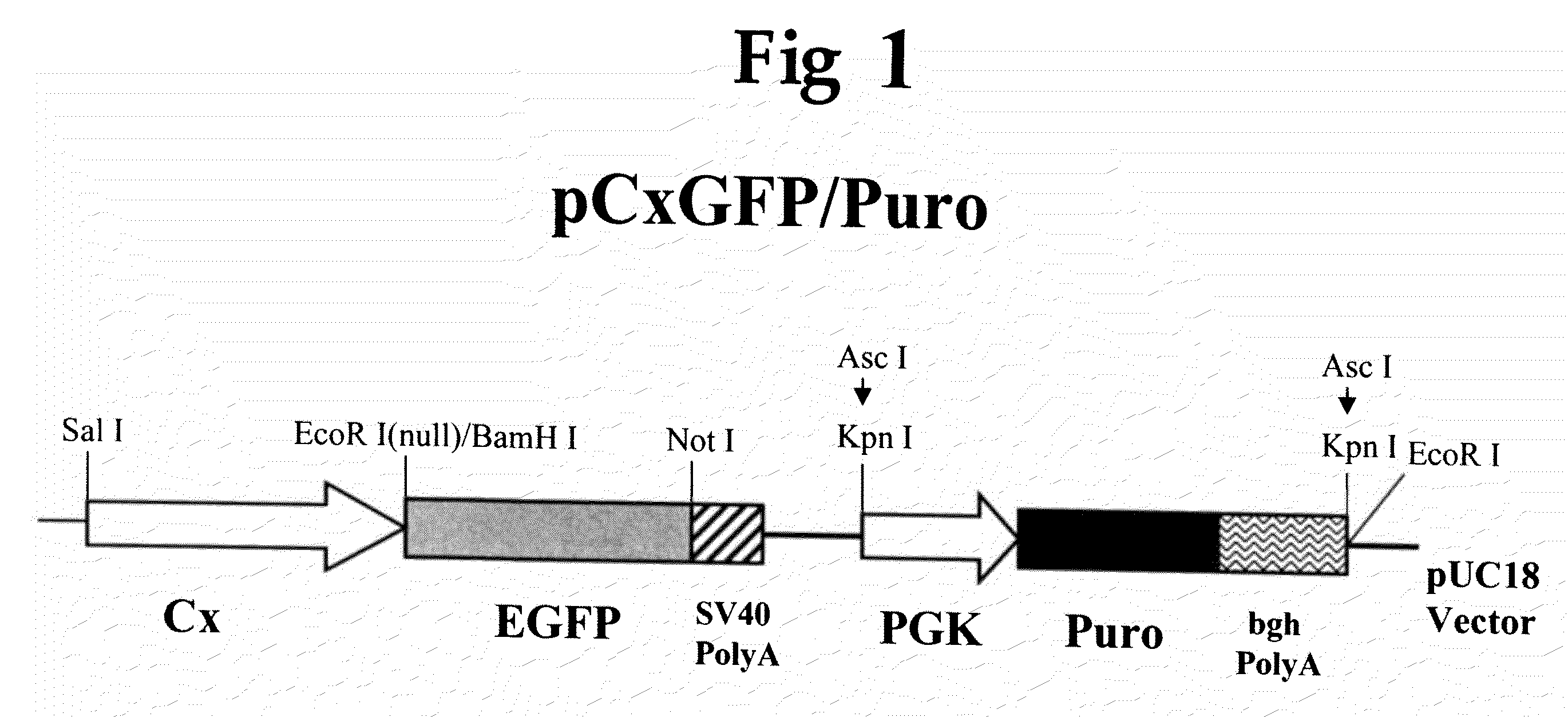
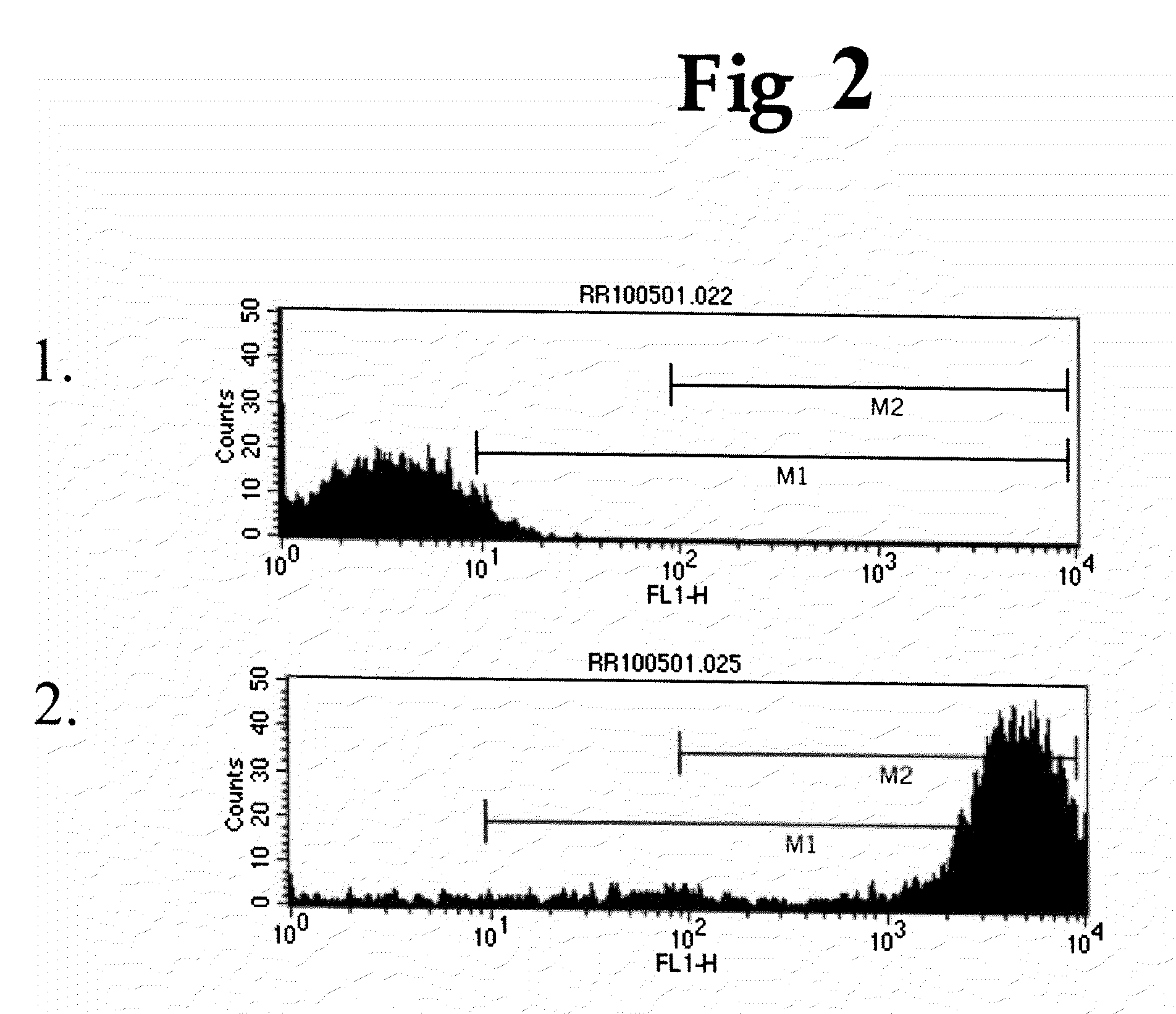
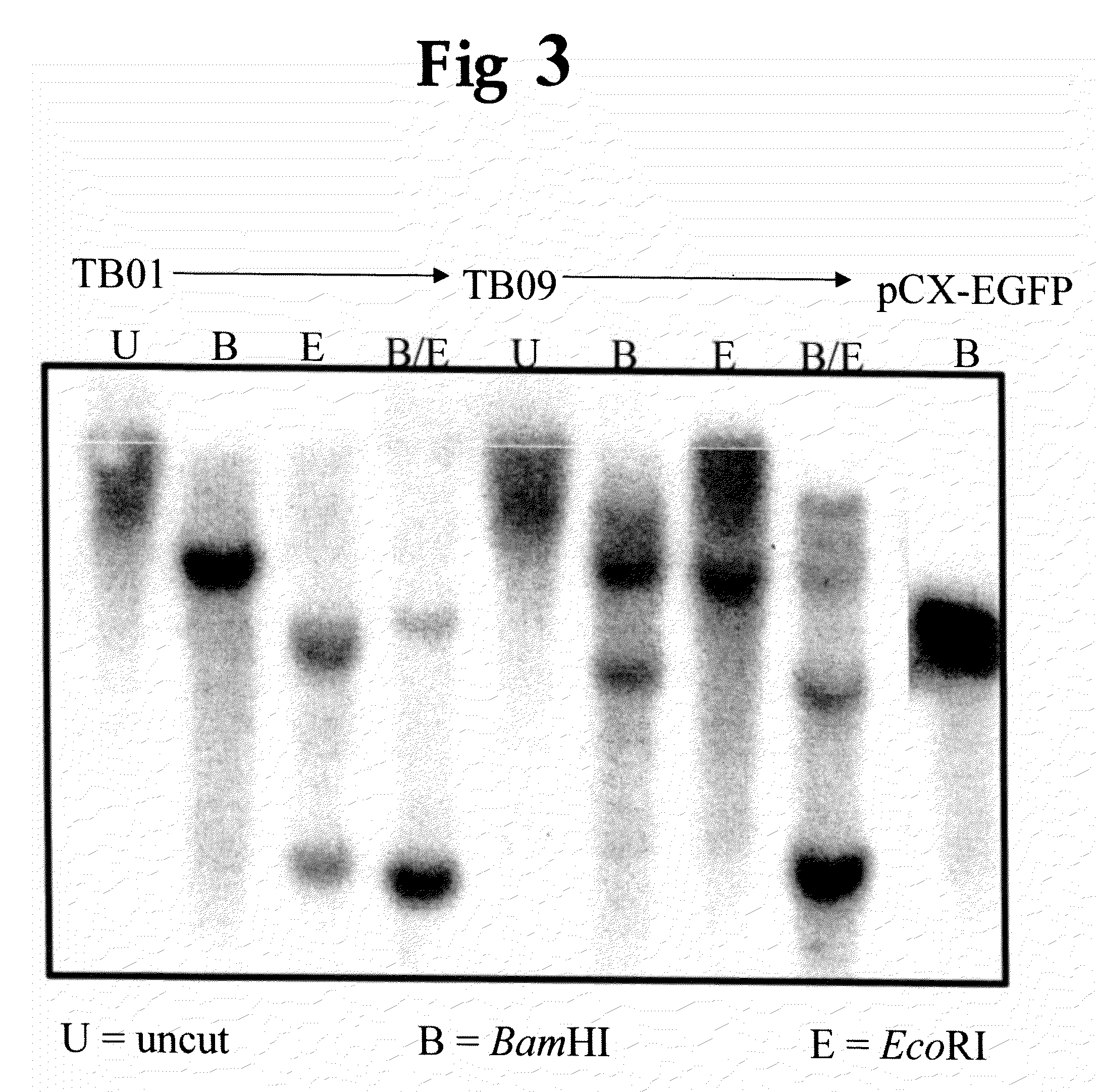
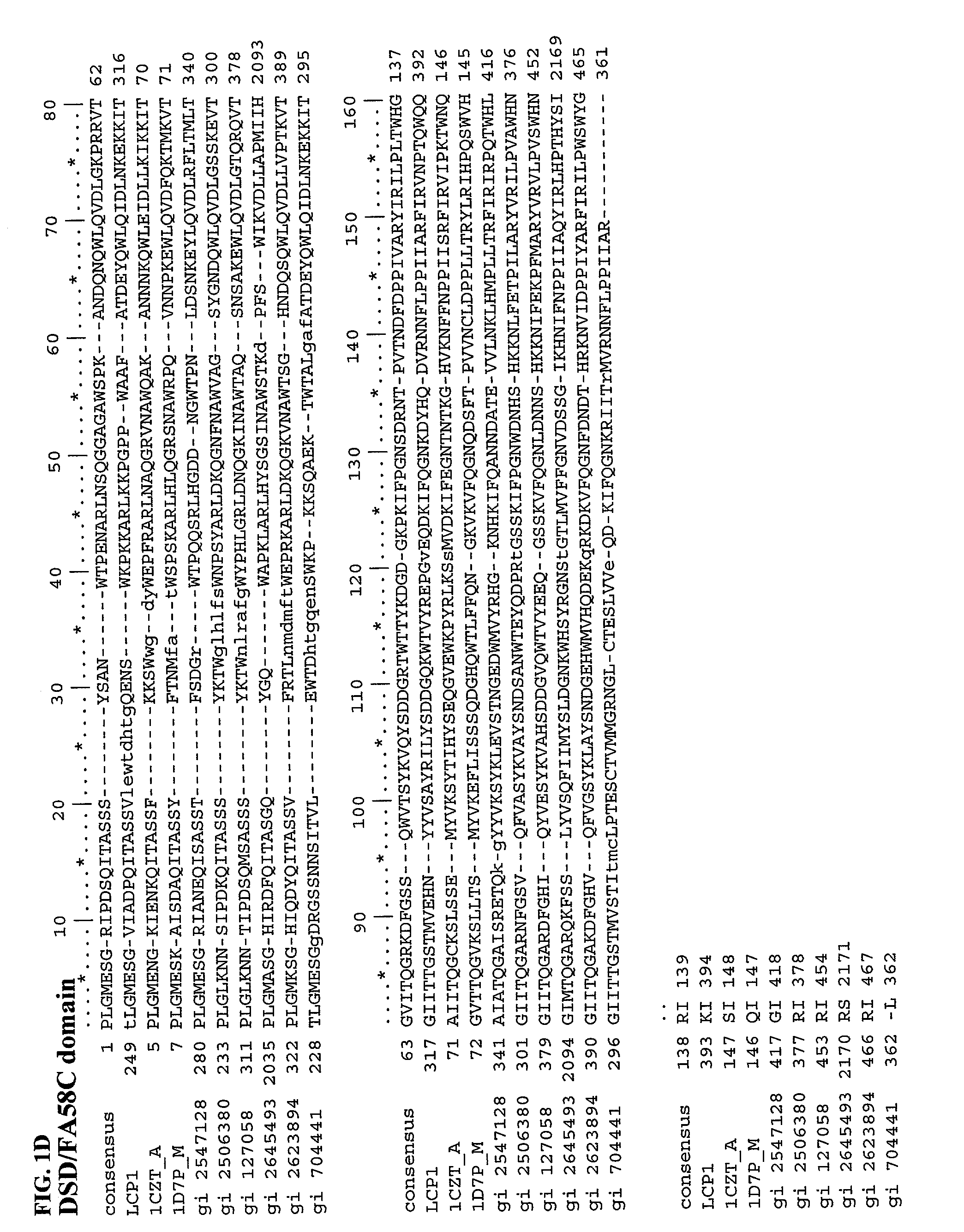
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Targeted disruption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blood Coagulation FVIII Analogues
InactiveUS20080227691A1High molecular weightFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsTargeted disruptionChemical groups
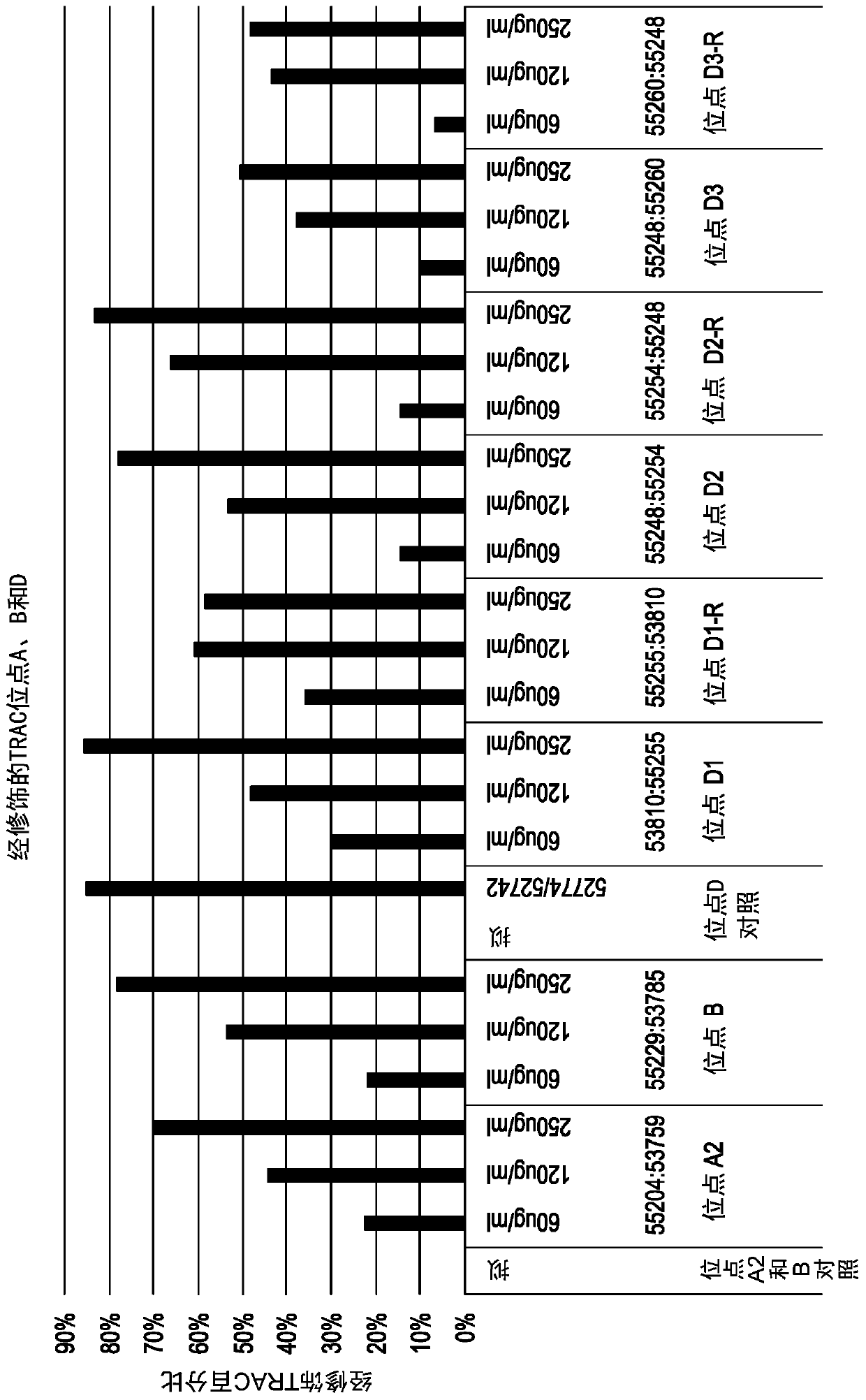
The invention is related to a FVIII analogue which has a circulation time in the blood stream before activation of at least about two times of that of native FVIII and a week after injection to a patient retains at least about 5% of the FVIII activity compared to the initial activity peak value reached after injection. The claimed FVIII analogues comprise a targeted disruption of one or more of the clearance sites in the FVIII molecule by introduction of at least one N-glycosylation site or by introduction of at least one Cys residue within or spatially close to the clearance site in the A2 domain or a combination thereof. The inserted cysteine residues may be further modified by conjugation with a chemical group increasing the molecular weight of the FVIII analogue.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Artery- and vein-specific proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS6887674B1Enhancing and inhibiting effectCompounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood vesselReceptor for activated C kinase 1
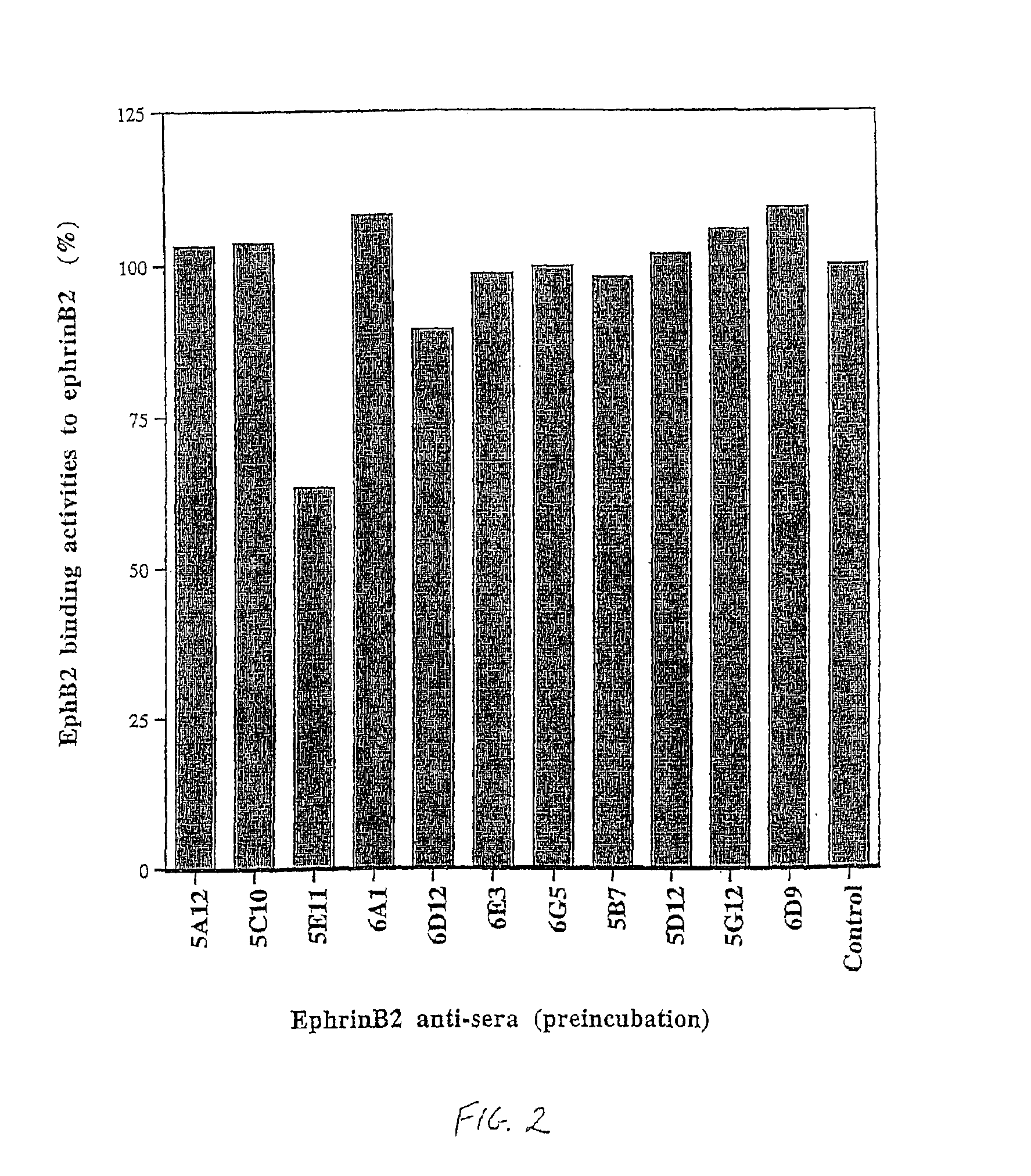
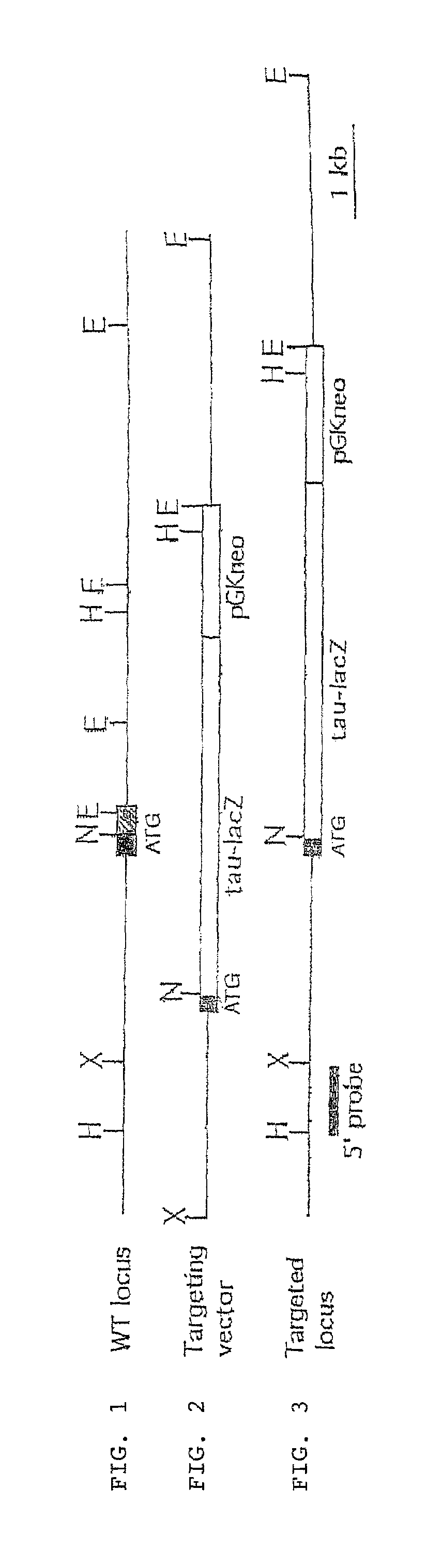
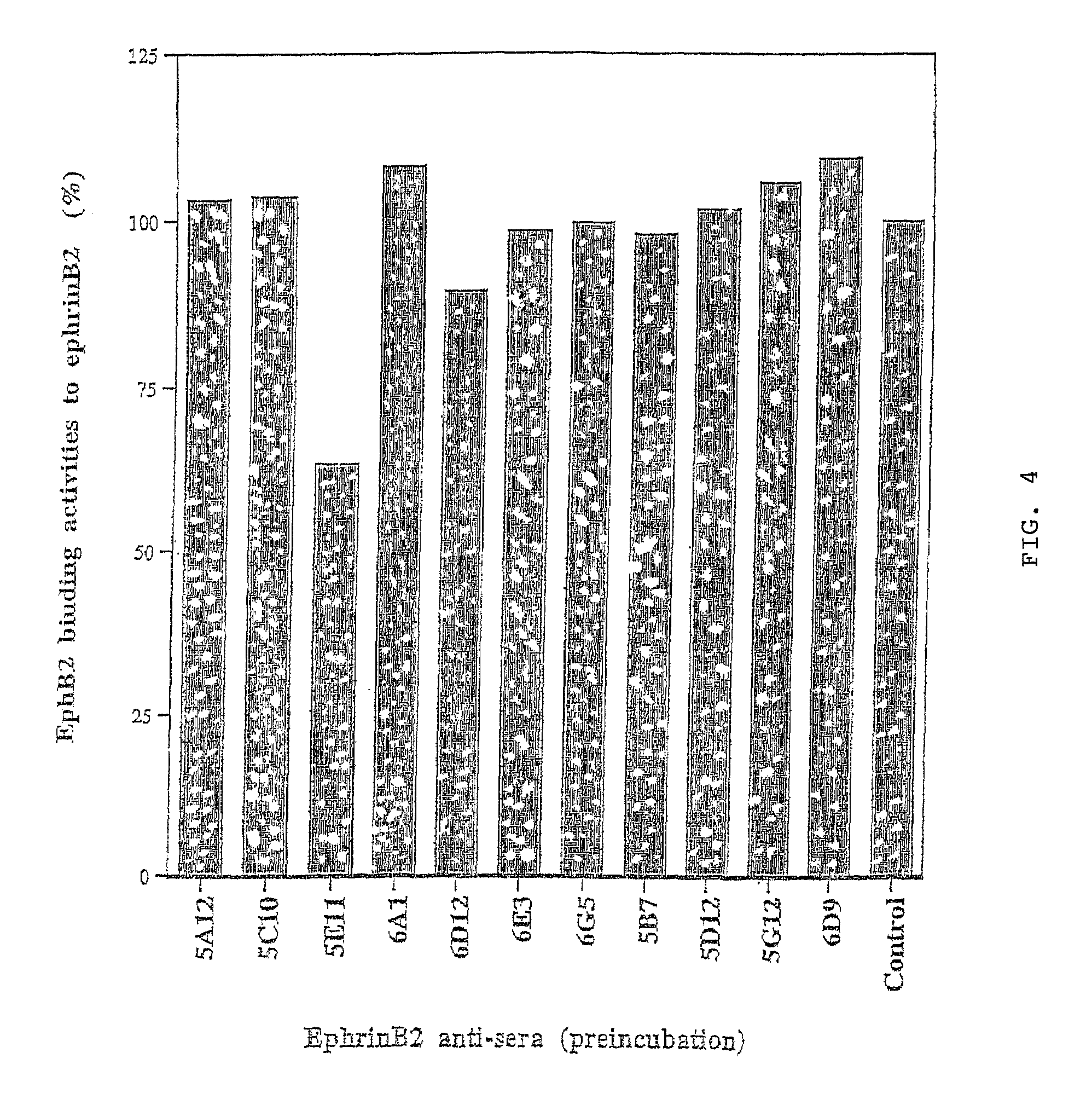
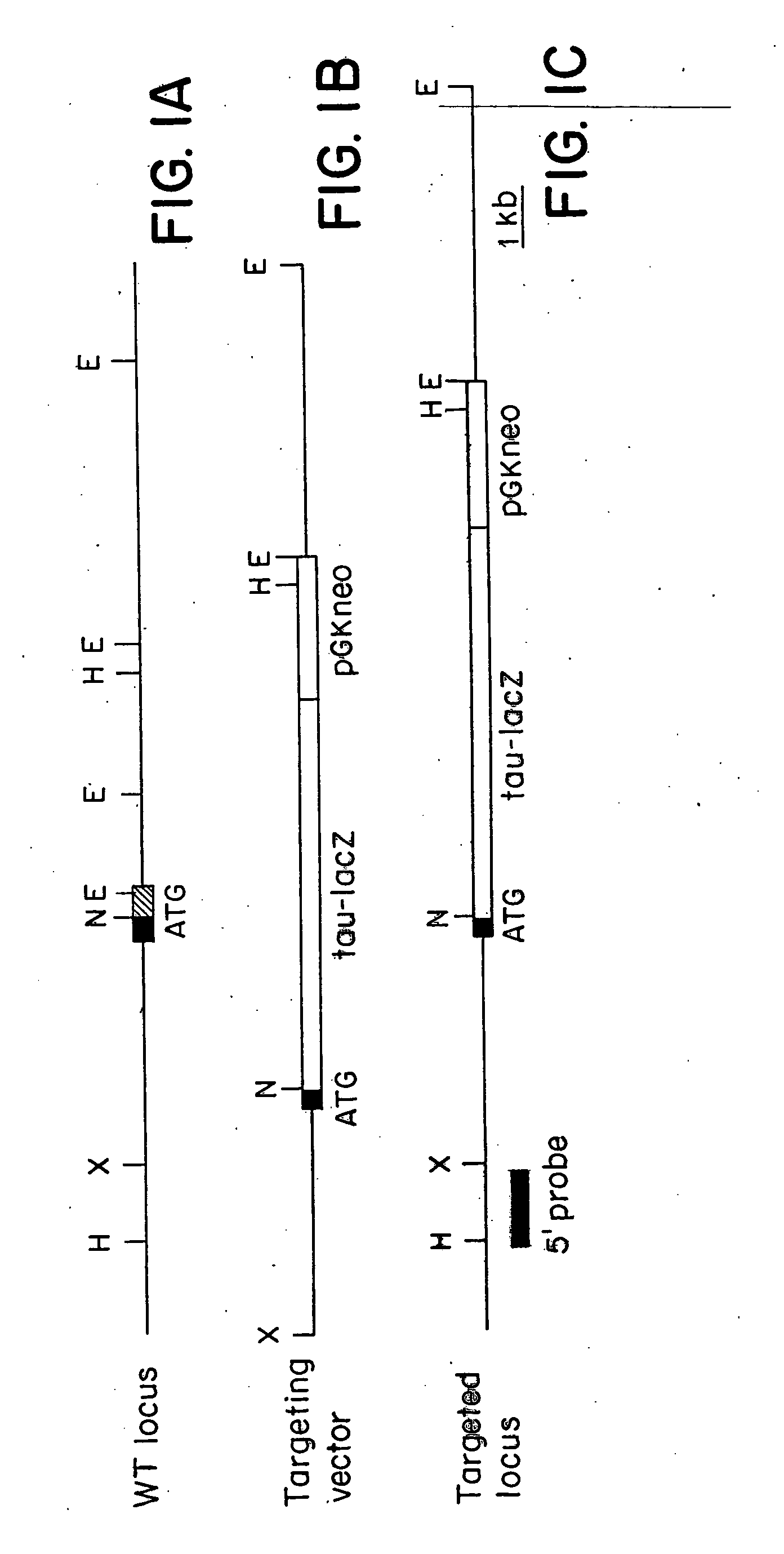
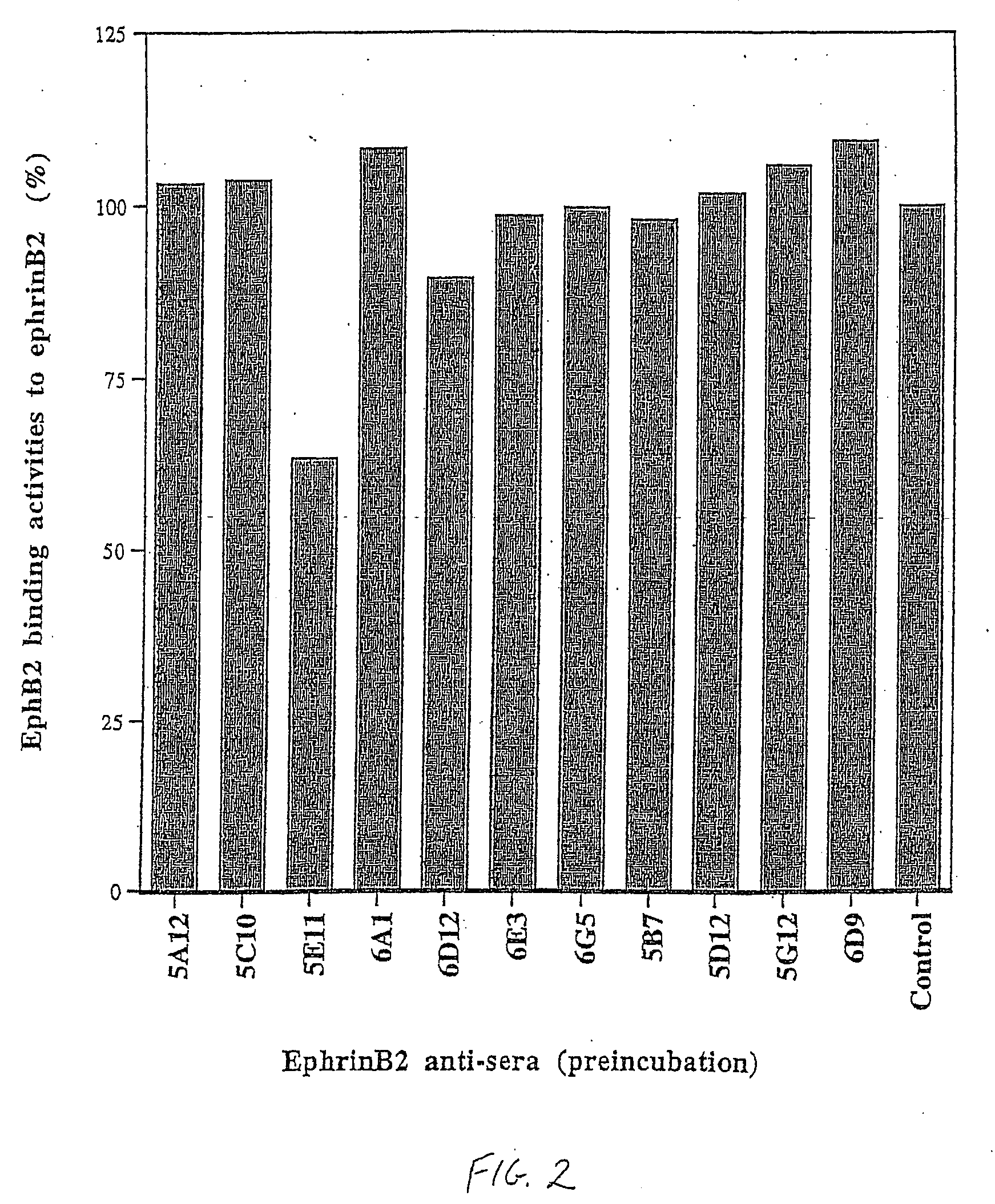
Arterial and venous endothelial cells are molecularly distinct from the earliest stages of angiogenesis. This distinction is revealed by expression on arterial cells of a transmembrane ligand, called EphrinB2 whose receptor EphB4 is expressed on venous cells. Targeted disruption of the EphrinB2 gene prevents the remodeling of veins from a capillary plexus into properly branched structures. Moreover, it also disrupts the remodeling of arteries, suggesting that reciprocal interactions between pre-specified arterial and venous endothelial cells are necessary for angiogenesis. This distinction can be used to advantage in methods to alter angiogenesis, methods to assess the effect of drugs on artery cells and vein cells, and methods to identify and isolate artery cells and vein cells, for example.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods of increasing proliferation of adult mammalian cardiomyocytes through p38 map kinase inhibition
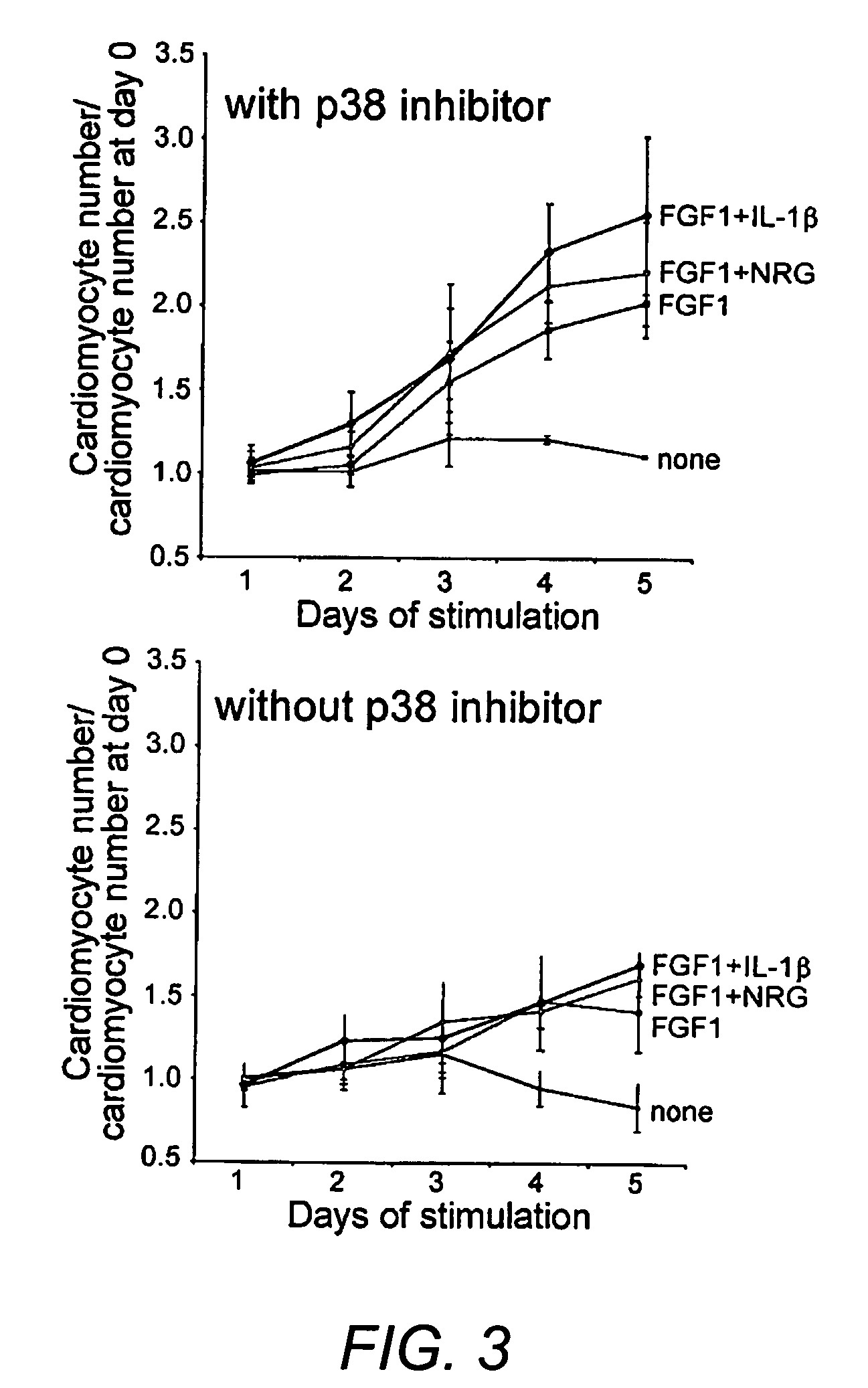
InactiveUS20060281791A1Increased proliferationSlow and reduce and prevent onsetBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTargeted disruptionTissue Grafting
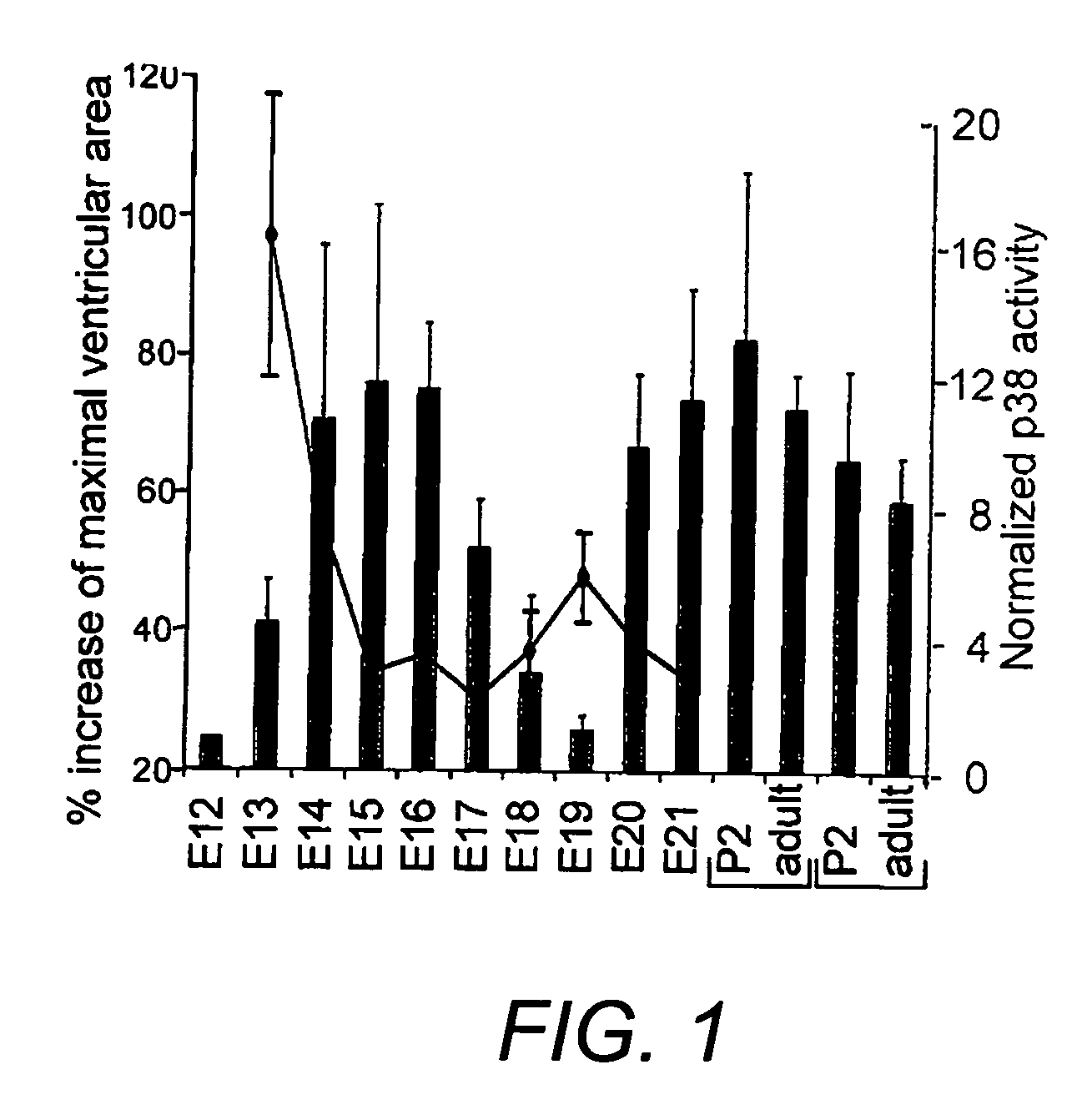
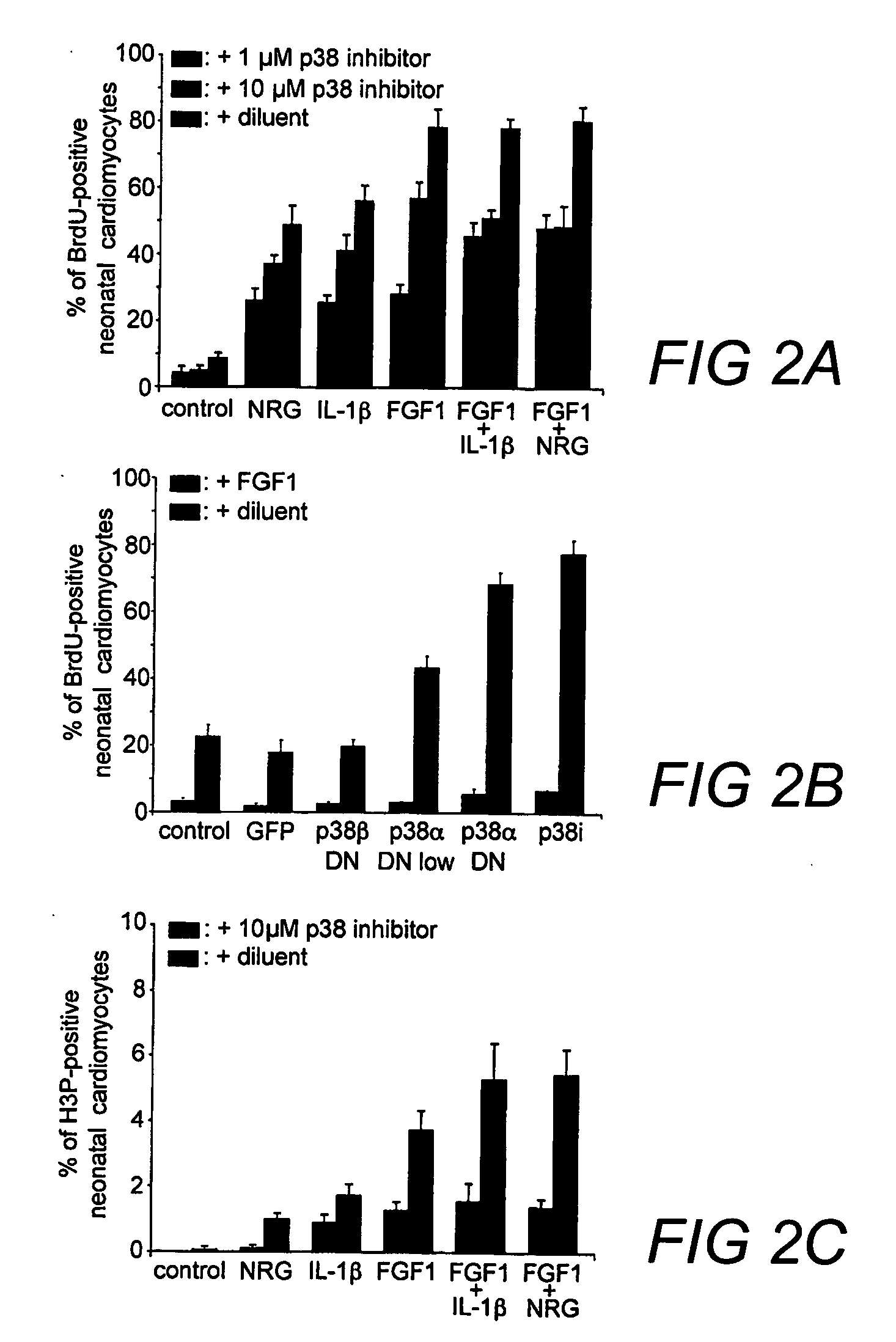
Compositions and methods for increasing proliferation and / or de-differentiation of postmitotic mammalian cardiomyocytes are disclosed to slow, reduce, or prevent the onset of cardiac damage. In addition, the methods and compositions of the invention can used to produce de-differentiated cardiomyocytes, which can then be used in tissue grafting, implantation or transplantation. The invention is based, in part, on the discovery that postmitotic mammalian cardiomyocytes can proliferate as a result of targeted disruption of p38 MAP kinase. p38 inhibition with optional growth factor stimulation can induce cytokinesis in adult cardiomyocytes.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Artery- and vein-specific proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS6916625B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsTargeted disruptionVenous endothelium
Arterial and venous endothelial cells are molecularly distinct from the earliest stages of angiogenesis. This distinction is revealed by expression on arterial cells of a transmembrane ligand, called EphrinB2 whose receptor EphB4 is expressed on venous cells. Targeted disruption of the EphrinB2 gene prevents the remodeling of veins from a capillary plexus into properly branched structures. Moreover, it also disrupts the remodeling of arteries, suggesting that reciprocal interactions between pre-specified arterial and venous endothelial cells are necessary for angiogenesis.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
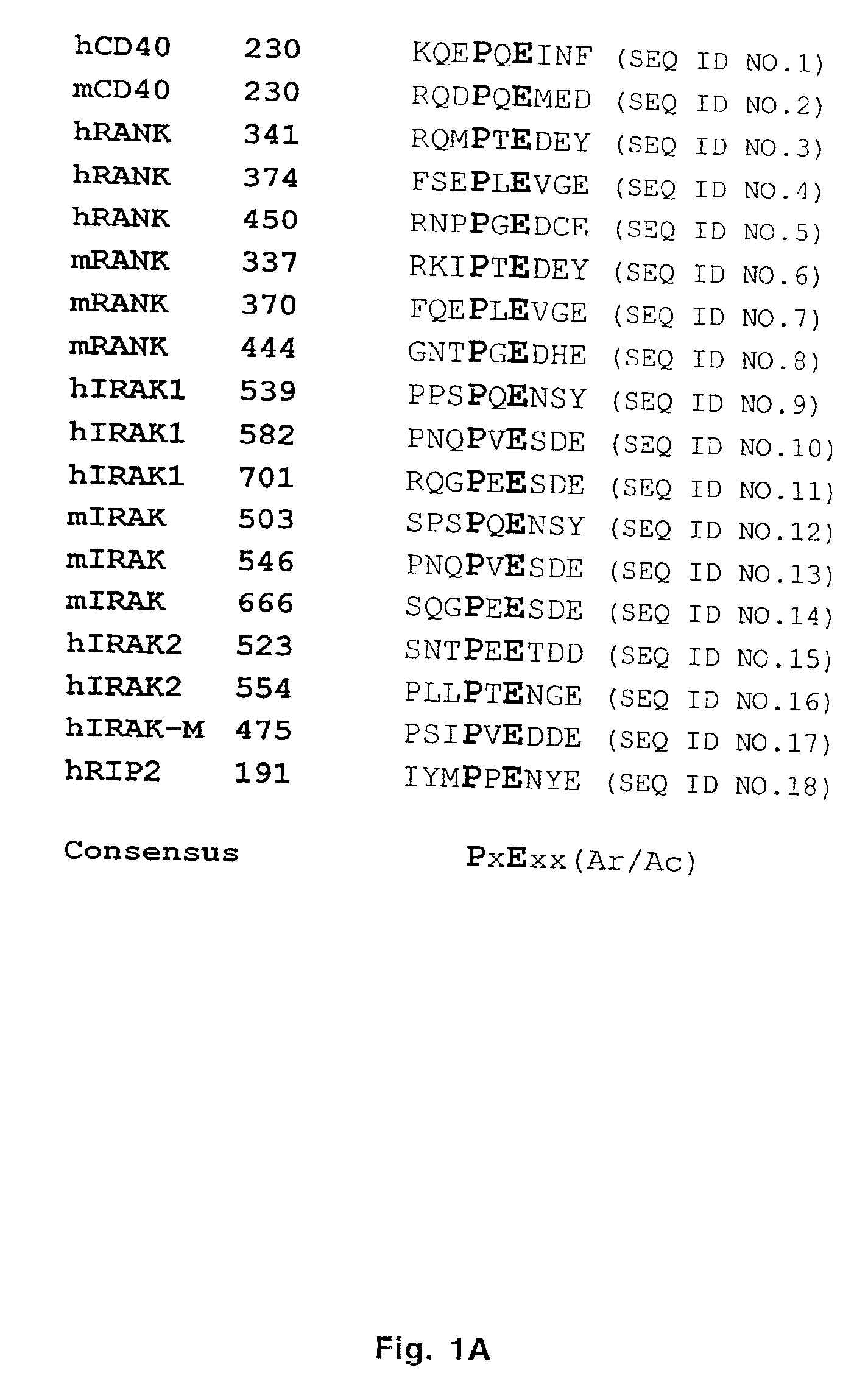
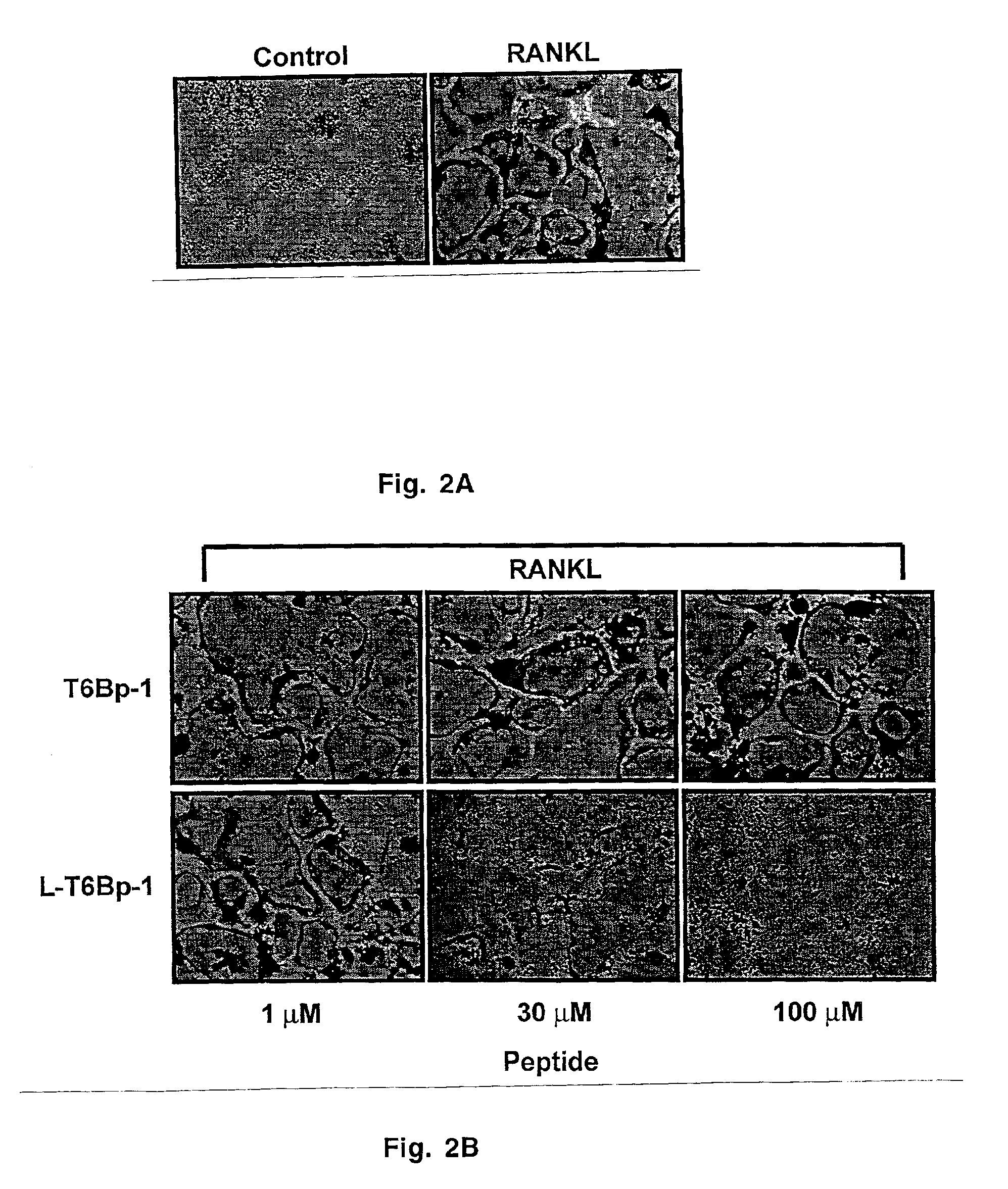
Inhibitors of receptor activator of NF-κB and uses thereof
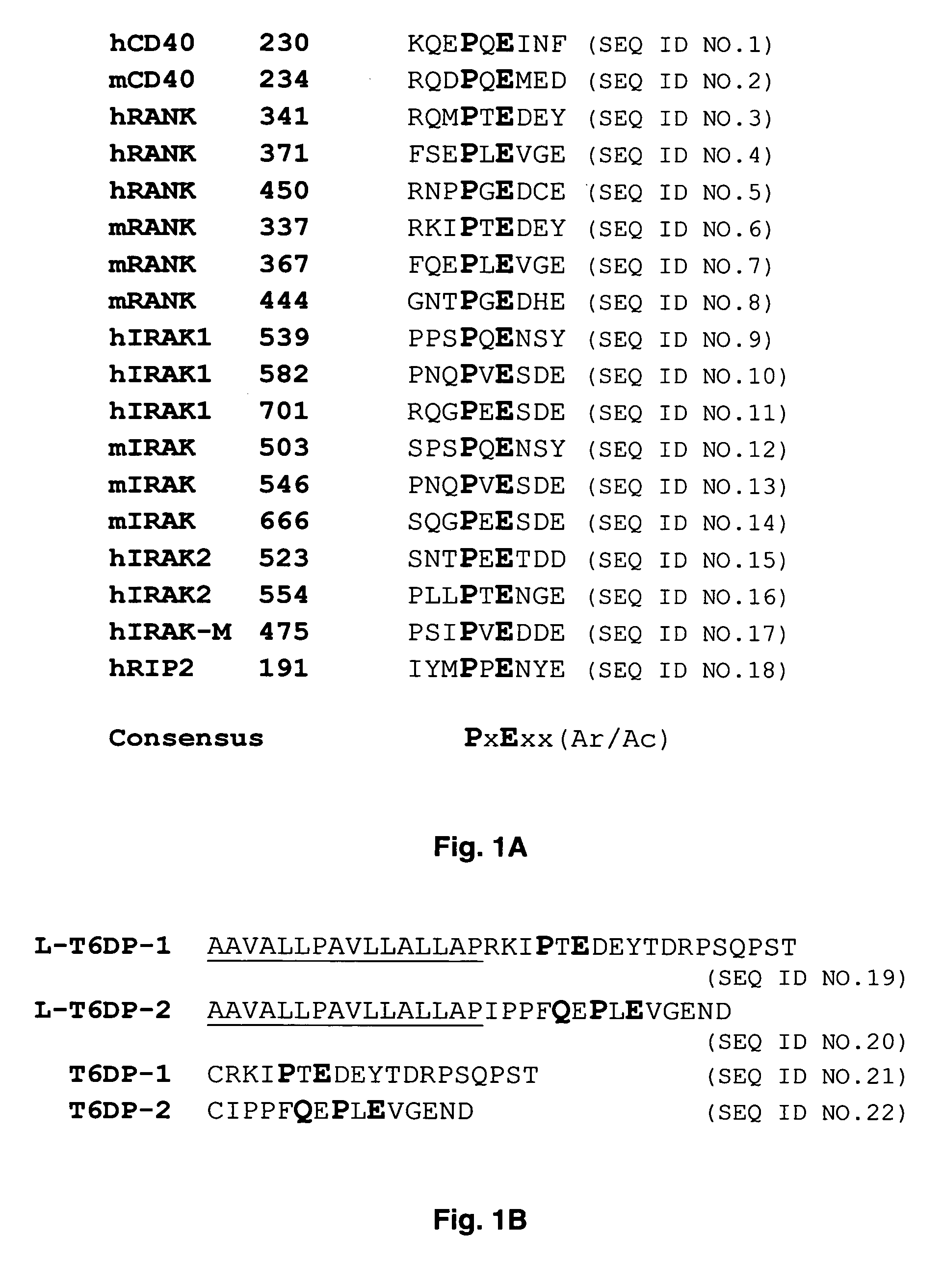
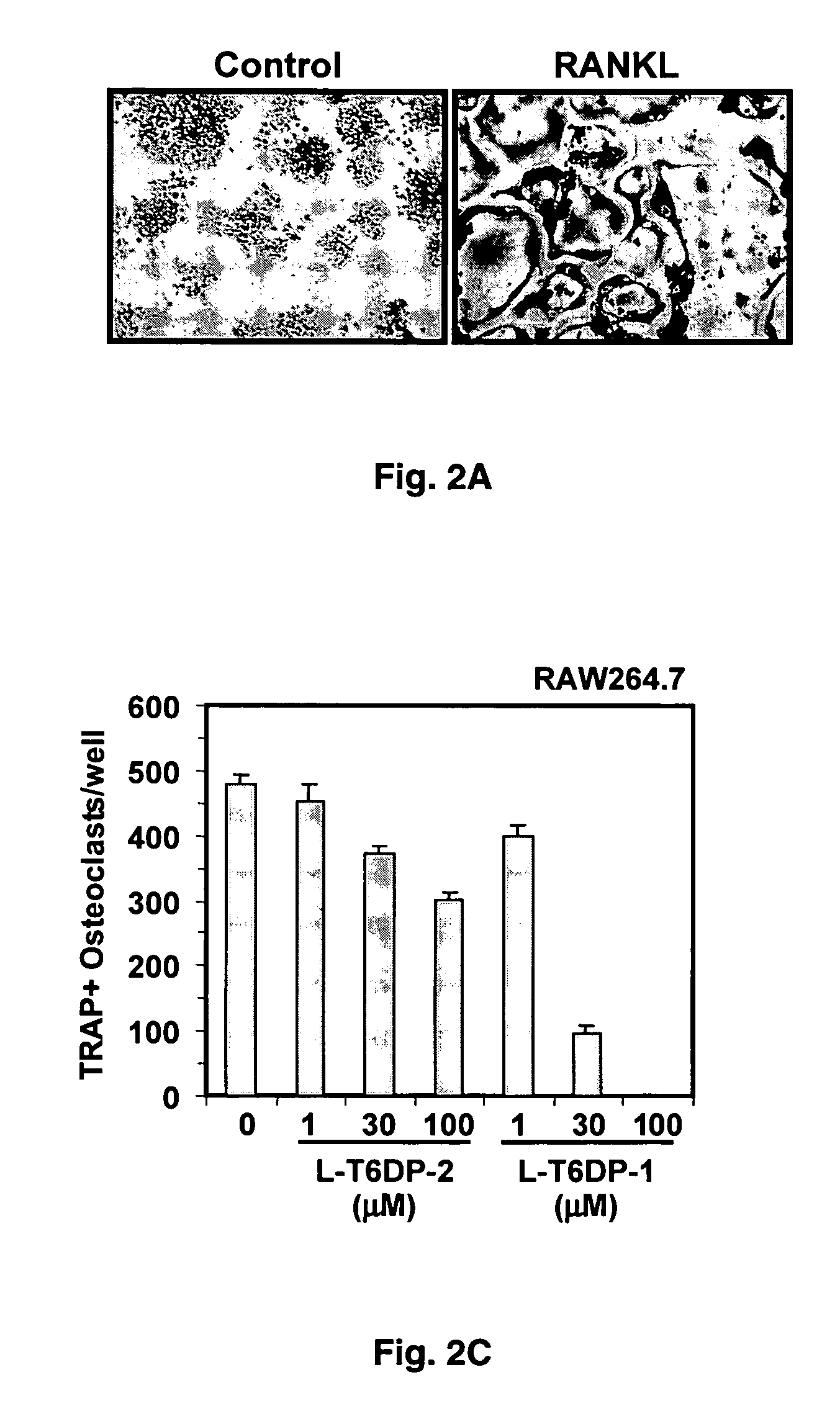
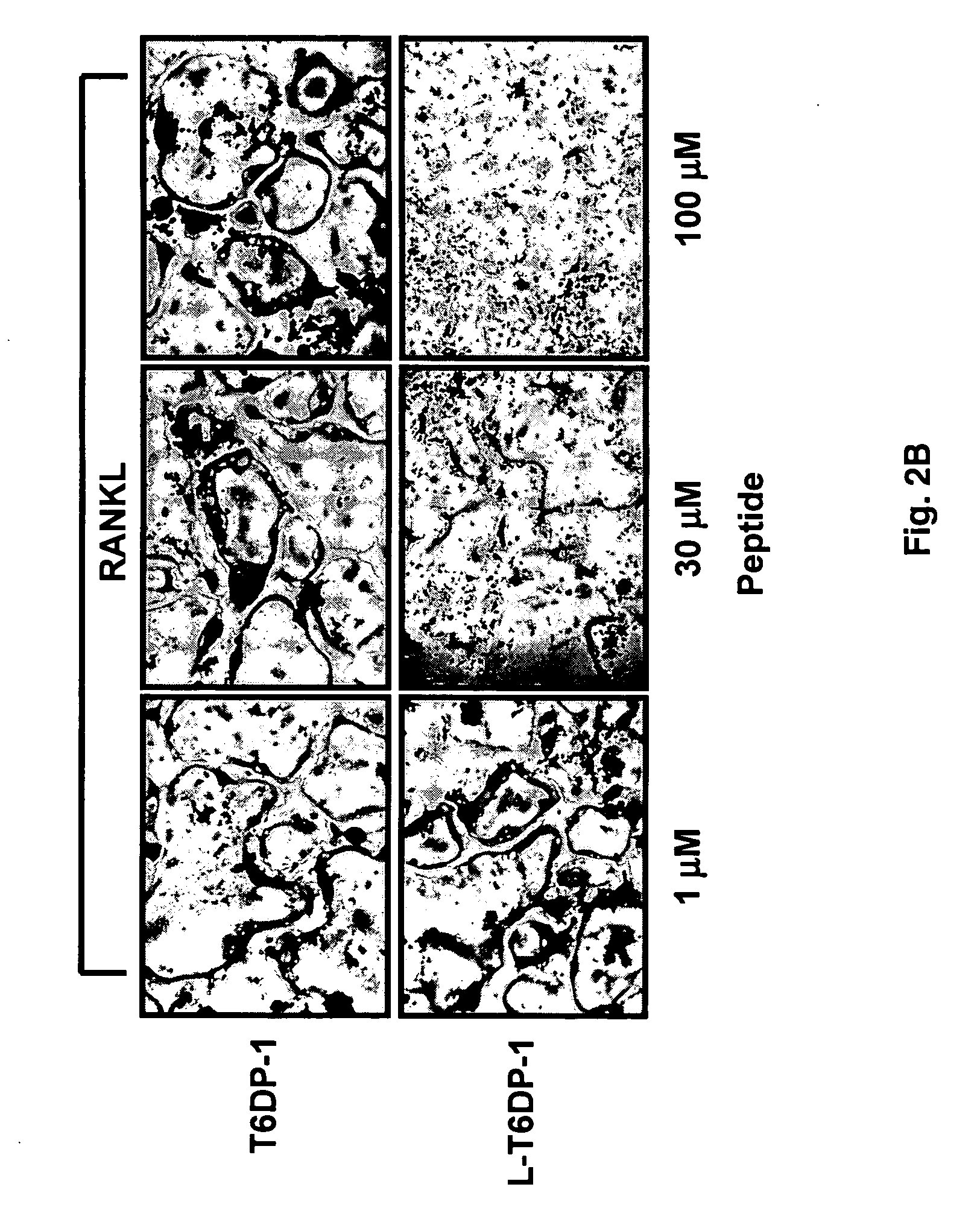
The present invention provides a RANK (receptor activator of NF-κB) inhibitor consisted of a TRAF-6 (TNF receptor-associated factor-6) binding domain attached to a leader sequence. The peptide inhibitor inhibits RANKL (RANK ligand)-mediated osteoclast differentiation, thus indicating that targeted disruption of interaction between RANK and TRAF6 may prove useful as a therapeutic for metabolic bone disorders, leukemia, arthritis, and metastatic cancer of the bone.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Artery smooth muscle- and vein smooth muscle-specific proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS7163808B2Enhancing and inhibiting effectCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsArterial smooth muscle cellsBlood vessel
Arterial and venous smooth muscle cells are molecularly distinct from the earliest stages of angiogenesis through to adulthood. This distinction is revealed by expression on arterial cells (e.g., arterial endothelial cells, arterial smooth muscle cells) of a transmembrane ligand, called EphrinB2 whose receptor EphB4 is expressed on venous cells. Targeted disruption of the EphrinB2 gene prevents the remodeling of veins from a capillary plexus into properly branched structures. Moreover, it also disrupts the remodeling of arteries, suggesting that reciprocal interactions between pre-specified arterial and venous cells are necessary for angiogenesis. Expression of EphrinB2 in arterial cells (e.g., arterial endothelial cells, arterial smooth muscle cells) can be used to advantage in methods for targeting agents and / or encoded polypeptides to arterial smooth muscle cells, altering angiogenesis, assessing the effect of agents on arterial smooth muscle cells, identifying arterial smooth muscle cells, isolating arterial smooth muscle cells and production of artificial vessels, for example.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Artery- and vein-specific proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS20050204412A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsTargeted disruptionVenous endothelium
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Targeting constructs for the functional disruption of avian immunoglobulin genes
InactiveUS20090083871A1Suppress gene expressionDisrupts productionNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsTargeted disruptionEmbryo
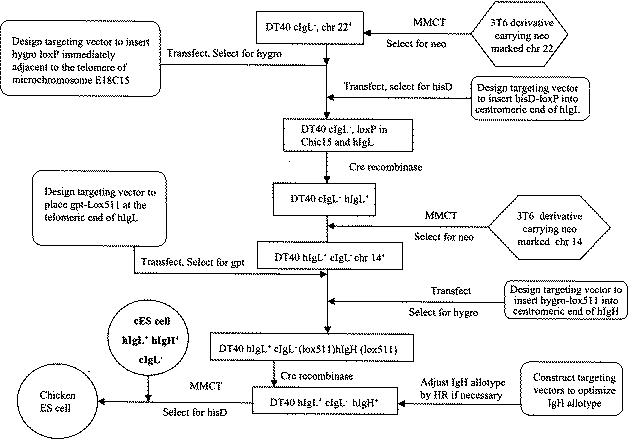
A transgenic chicken is disclosed having disrupted endogenous immunoglobulin production. In one embodiment, a targeting construct is stably integrated into the genome of the chicken by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells, and injection of the engineered embryonic stem cells into recipient embryos, thereby knocking out the endogenous immunoglobulin gene locus in resulting animals. The targeted disruption of the locus in embryonic stem cells is particularly useful in combination with the insertion of genetic elements encoding exogenous immunoglobulin molecules. After these chickens are cross-bred, a line of chickens is produced that has a reduction of endogenous immunoglobulin molecule production.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Inhibitors of receptor activator of NF-kappaB and uses thereof
The present invention provides a RANK (receptor activator of NF-kappaB) inhibitor consisted of a TRAF-6 (TNF receptor-associated factor-6) binding domain attached to a leader sequence. The decoy peptide inhibits RANKL (RANK ligand)-mediated osteoclast differentiation, thus indicating that targeted disruption of interaction between RANK and TRAF6 may prove useful as a therapeutic for metabolic bone disorders, leukemia, arthritis, and metastatic cancer of the bone.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
JNK3 modulators and methods of use
InactiveUS6943000B2Potential damageEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderTargeted disruptionExcitotoxicity
The c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) group of MAP kinases are activated by exposure of cells to environmental stress. The role of JNK in the brain was examined by targeted disruption of the gene that encodes the neuronal isoform JNK3. It was found that JNK3 is required for the normal response to seizure activity. Methods of screening for molecules and compounds that decrease JNK3 expression or activity are described. Such molecules or compounds are useful for treating disorders involving excitotoxicity such as seizure disorders, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington disease, Parkinson's disease, and ischaemia.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Functional Disruption Of Avian Immunoglobulin Genes
A transgenic chicken is disclosed having disrupted endogenous immunoglobulin production. In one embodiment, a targeting construct is stably integrated into the genome of the chicken by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells, and injection of the engineered embryonic stem cells into recipient embryos, thereby knocking out the endogenous immunoglobulin gene locus in resulting animals. The targeted disruption of the locus in embryonic stem cells is particularly useful in combination with the insertion of genetic elements encoding exogenous immunoglobulin molecules. After these chickens are cross-bred, a line of chickens is produced that has a reduction of endogenous immunoglobulin molecule production.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Human LCCL domain containing protein
InactiveUS20030032154A1Easy adhesionFacilitates denaturationTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical formulationProtein neddylation
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids that encode LCP, including two isoforms, and fragments thereof, vectors for propagating and expressing LCP nucleic acids, host cells comprising the nucleic acids and vectors of the present invention, proteins, protein fragments, and protein fusions of the novel LCP isoforms, and antibodies thereto. The invention further provides transgenic cells and non-human organisms comprising human LCP nucleic acids, and transgenic cells and non-human organisms with targeted disruption of the endogenous orthologue of the human LCP gene. The invention further provides pharmaceutical formulations of the nucleic acids, proteins, and antibodies of the present invention, and diagnostic, investigational, and therapeutic methods based on the LCP nucleic acids, proteins, and antibodies of the present invention.
Owner:AMERSHAM INT PLC
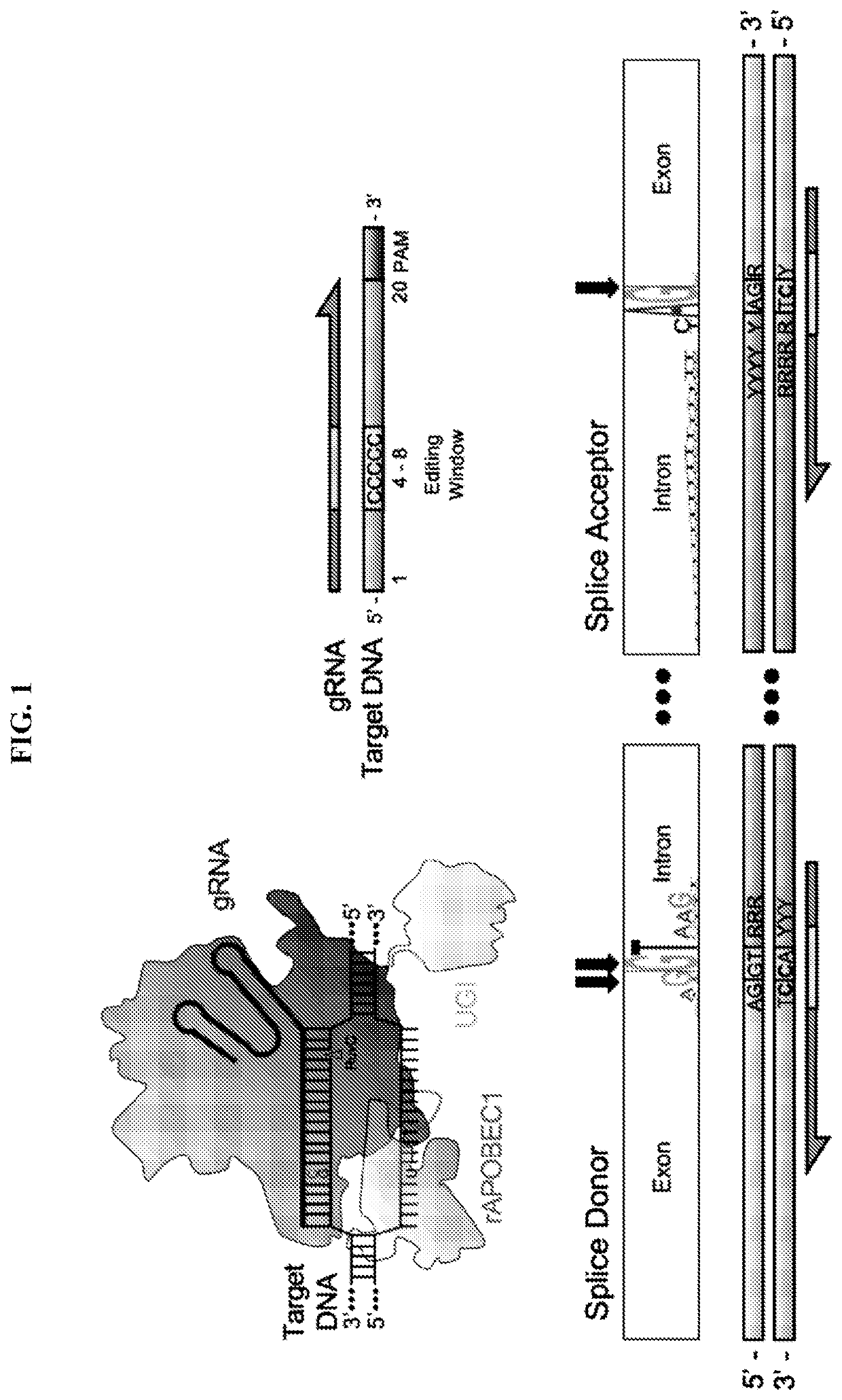
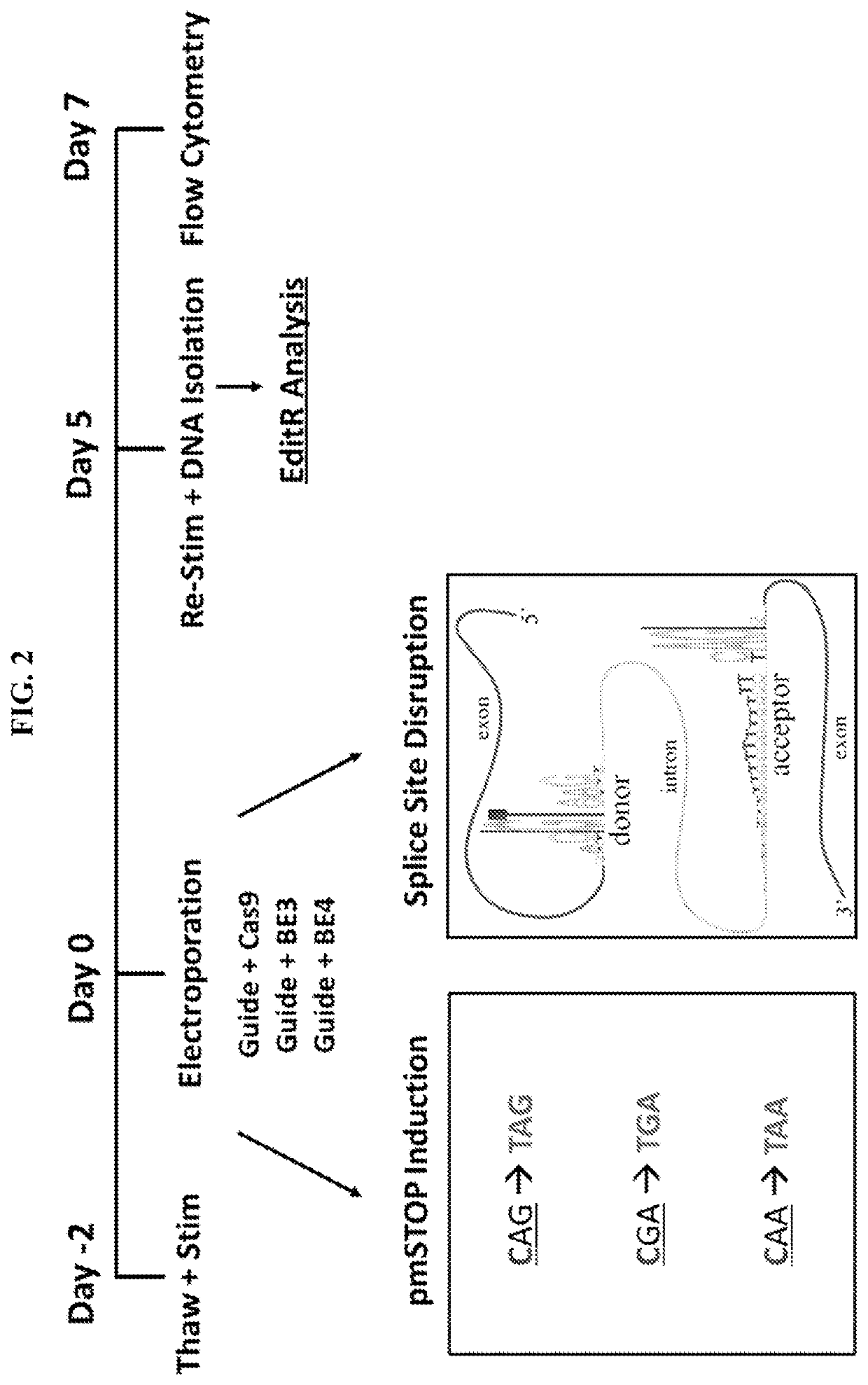
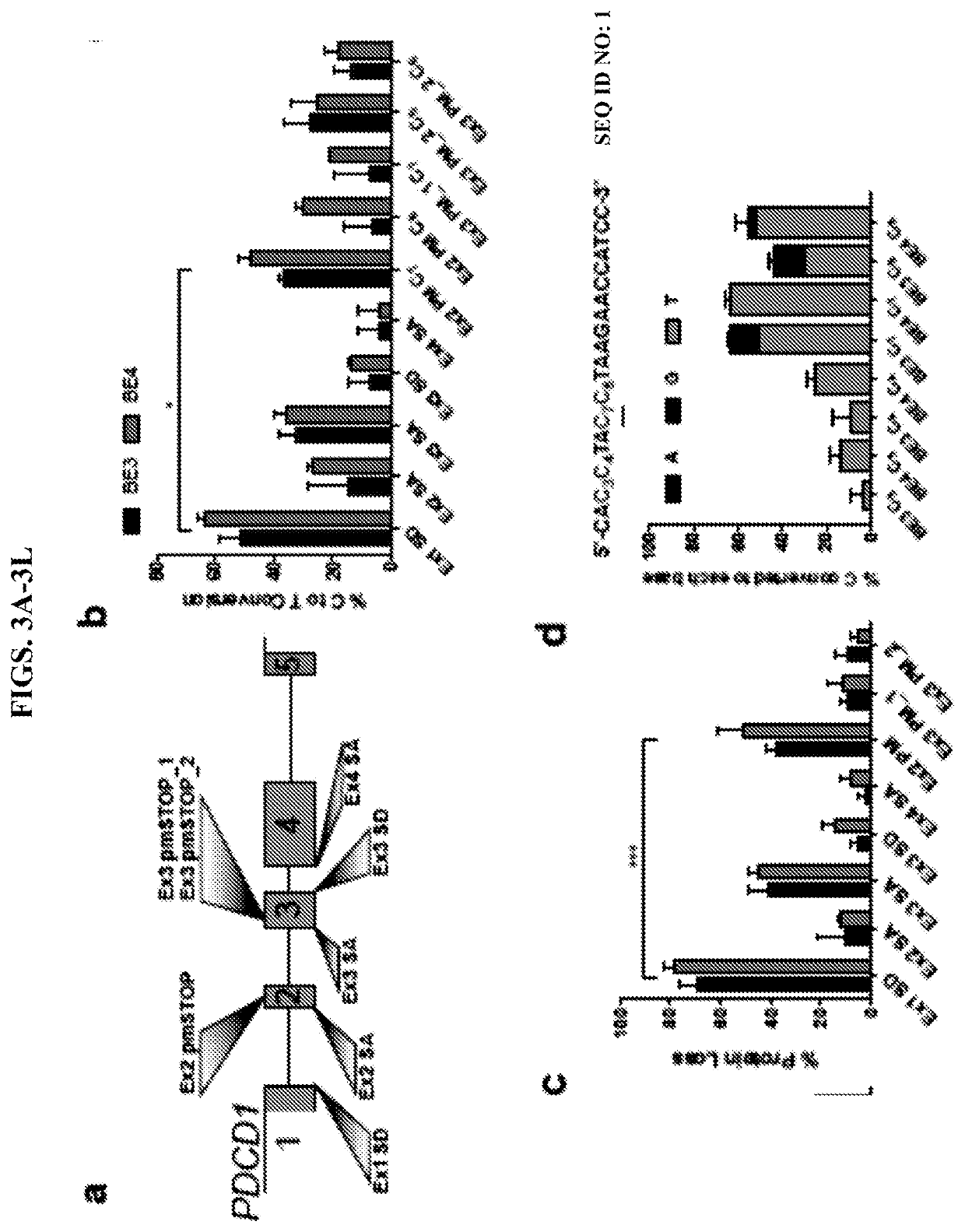
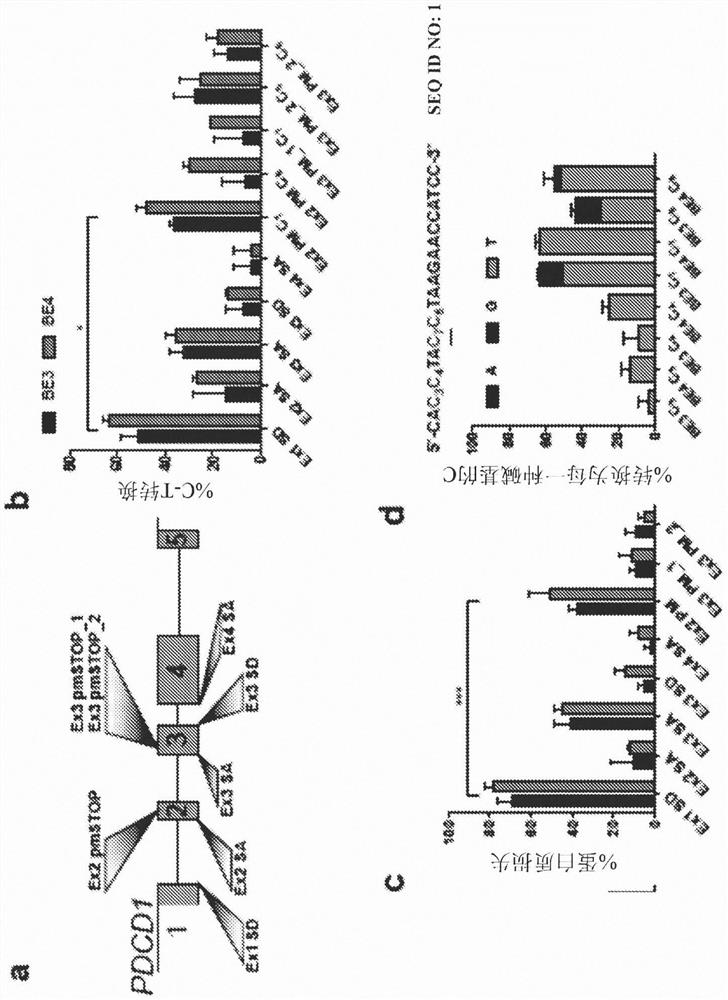
Lymphohematopoietic engineering using cas9 base editors
PendingUS20210040507A1Easily damagedGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNABase JEngineered genetic
Provided herein are methods and systems for targeted gene disruption (knock-out, missense mutation) and targeted gene knock-in in mammalian cells using base editors and guide RNAs (gRNAs) designed to target splice acceptor-splice donor sites. Also provided herein are universally acceptable genetically engineered cells comprising targeted disruptions in immunotherapy-related genes and comprising a CAR / TCR for therapeutic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
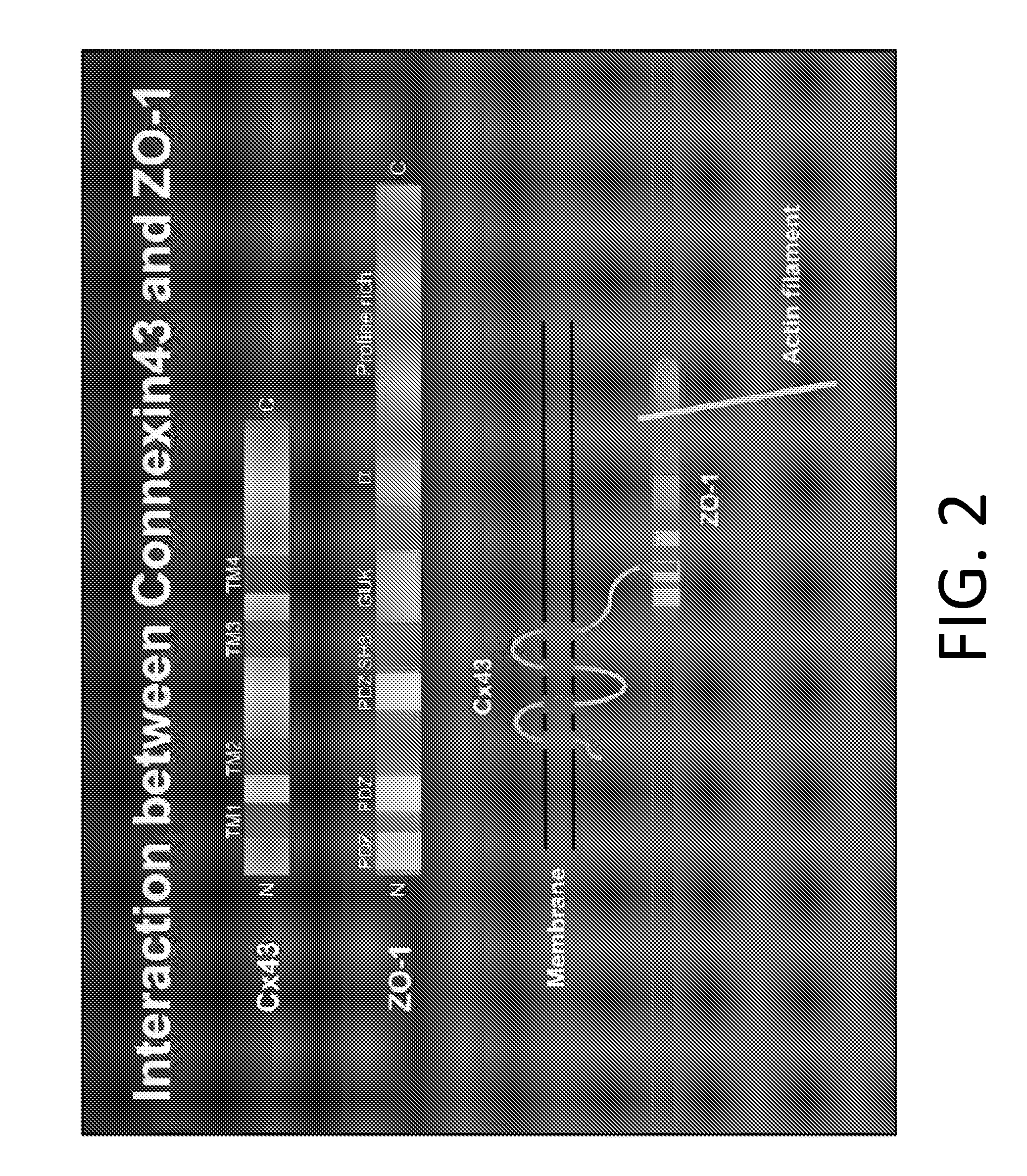
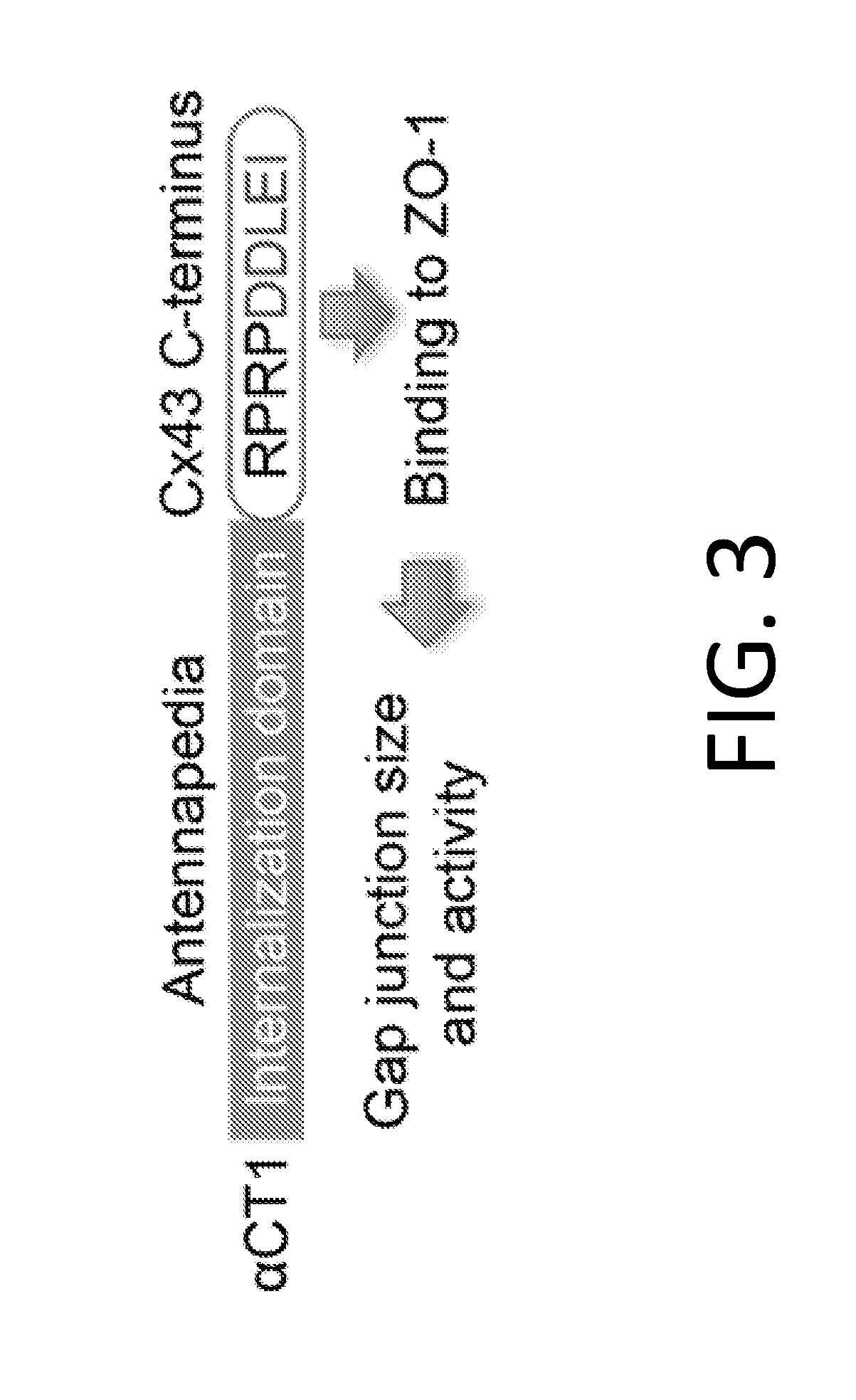
Methods of treating a cancer through targeted disruption of alpha connexin 43-zonula occludens-1 (zo-1) interaction
InactiveUS20160166637A1Organic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsTargeted disruptionTransmembrane domain
The present disclosure describes methods of treating a cancer based on the targeted disruption of alpha connexin 43-zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) interaction. The methods may include administering to a subject an effective amount of a composition comprising a peptide with a contiguous sequence of amino acids representing a portion of the carboxy terminus of an alpha connexin protein or conservative variant thereof, wherein said carboxy terminus includes the sequence up to the transmembrane domain, optionally in combination with administration of a chemotherapeutic agent. In embodiments, the cancer is glioma and the chemotherapeutic agent is temozolomide. The methods may also include administration of vectors encoding the peptide or host cells comprising the vectors. Also described are compositions for treating a cancer comprising one or more peptides, nucleic acids, vectors, and / or host cells, optionally in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent such as temozolomide.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
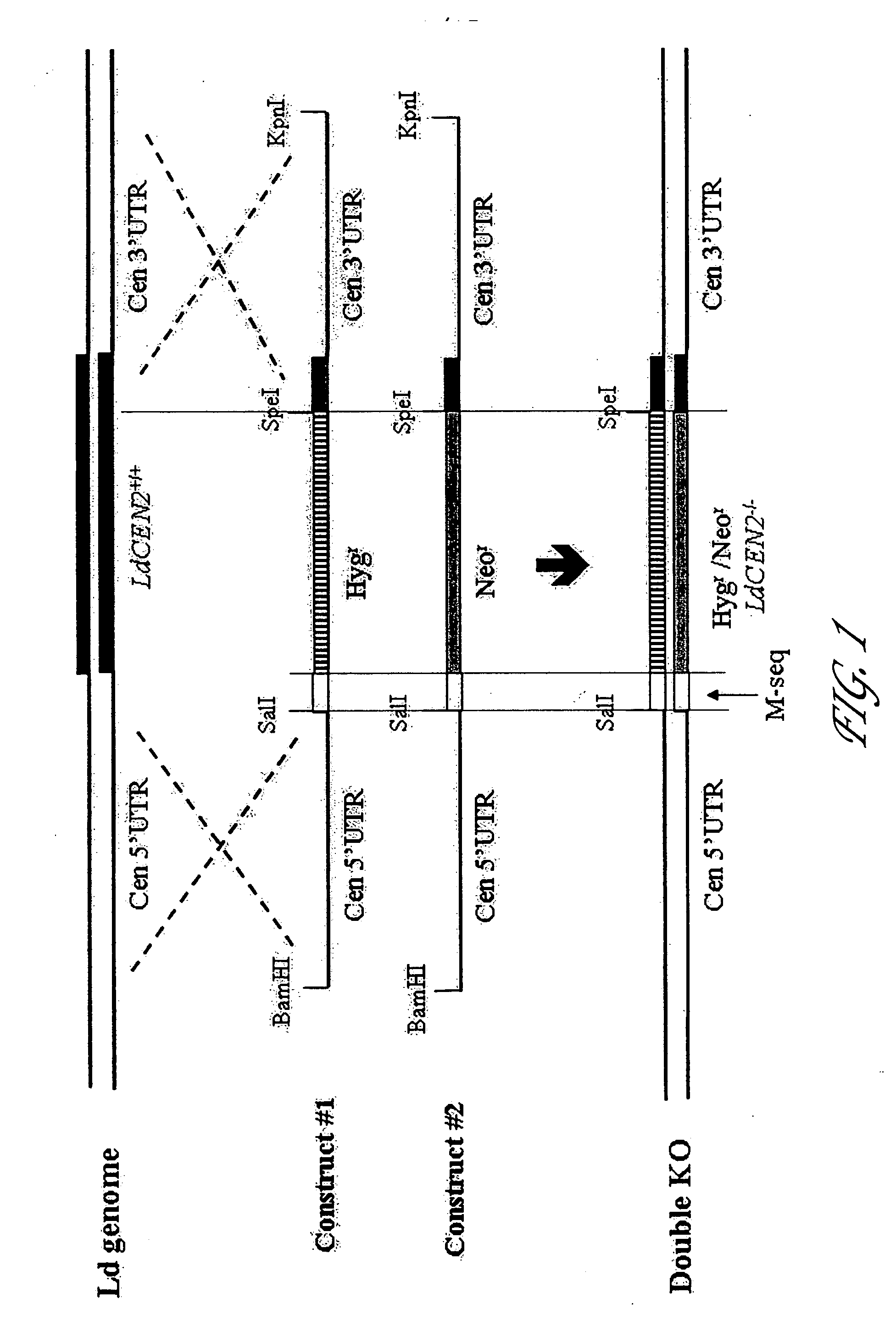
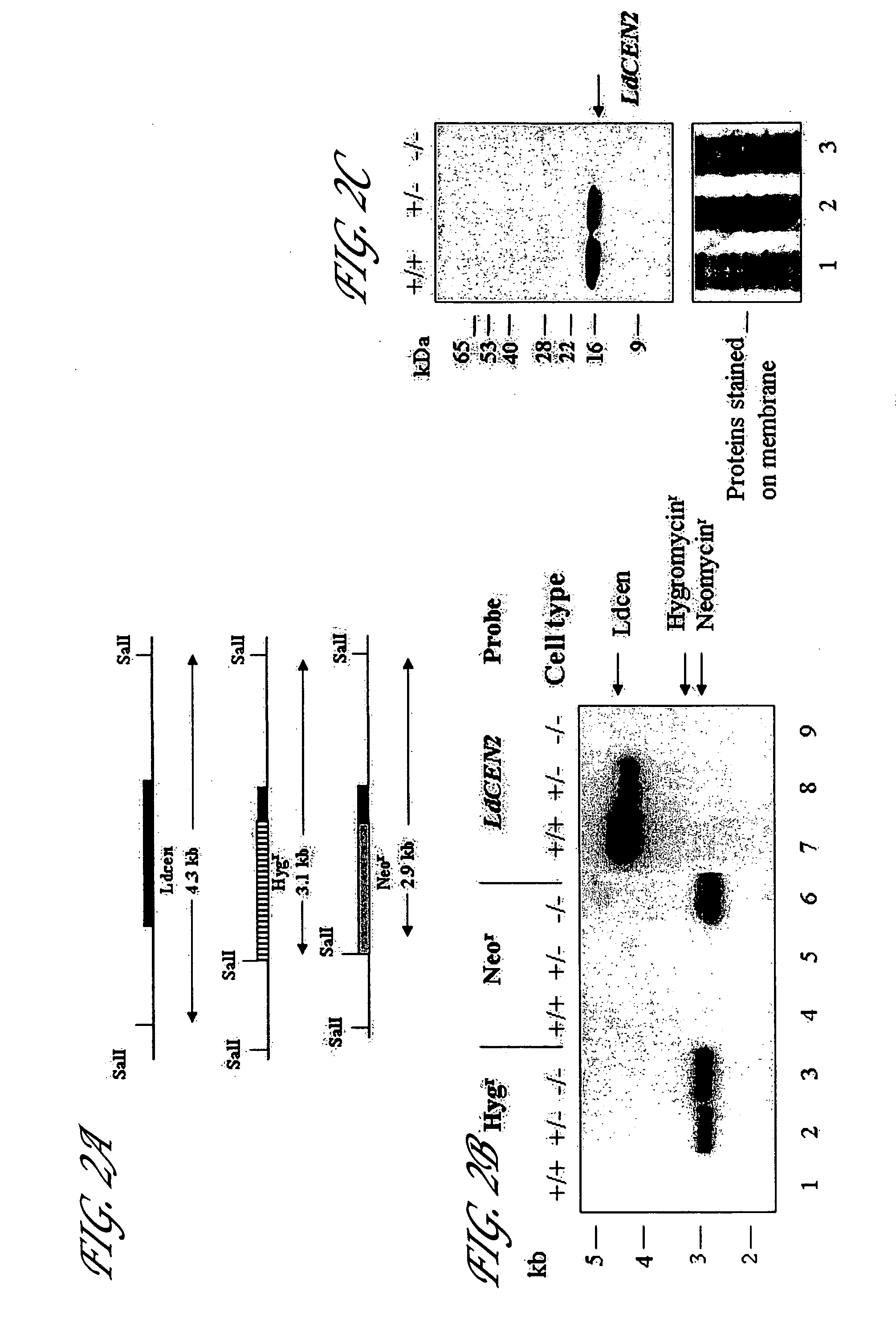
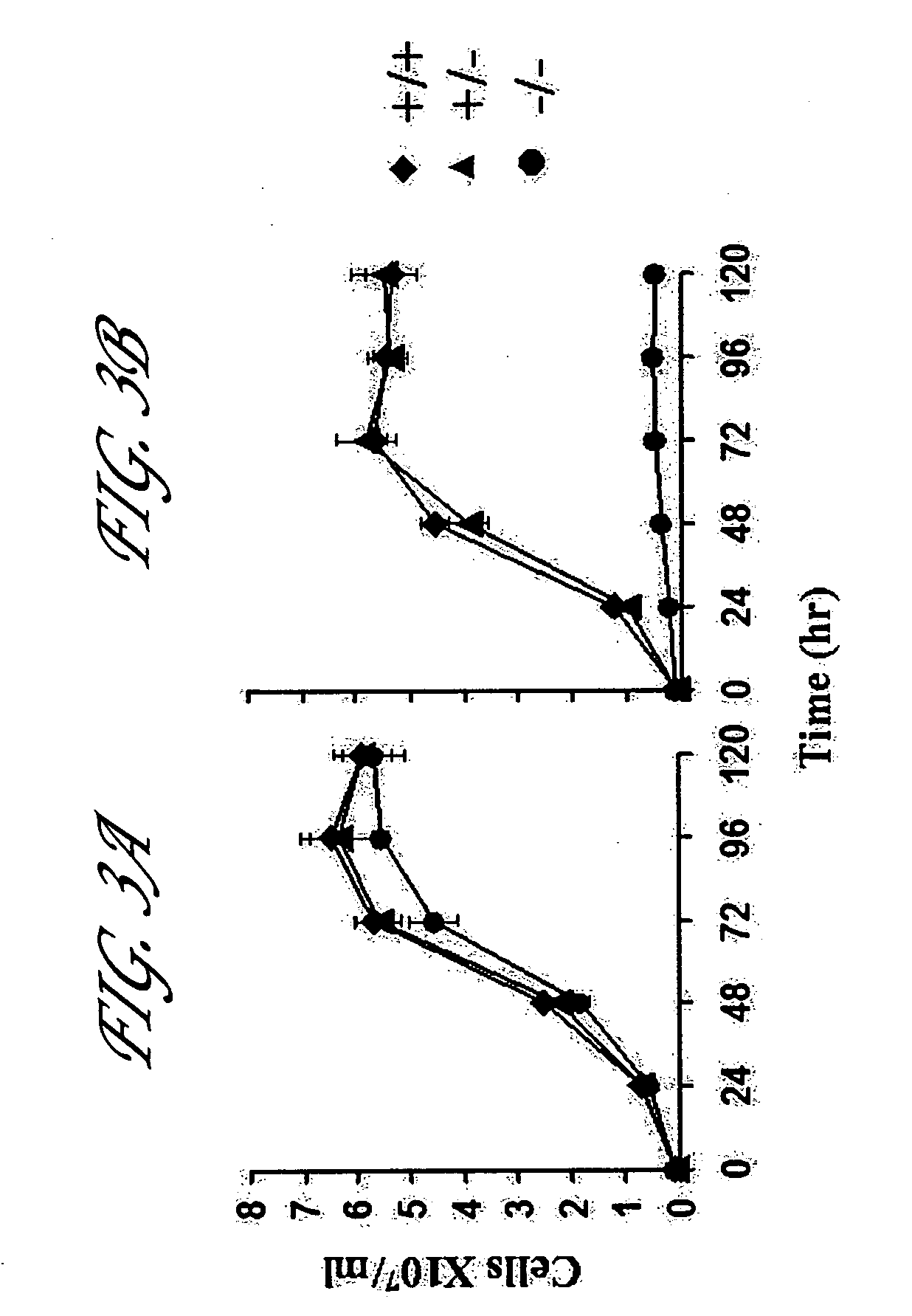
Live attenuated Leishmania vaccines
InactiveUS7887812B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsTargeted disruptionCentrin
Targeted disruption of the centrin gene leads to attenuation of growth in Leishmania. Preferred embodiments of the invention provide attenuated strains of Leishmania useful for the preparation of immunogenic preparations including vaccines against a disease caused by infection with a virulent Leishmania strain and as tools for the generation of immunological and diagnostic reagents. Other preferred embodiments provide related immunogenic compositions, methods of generating an immune response, methods for producing a vaccine, and methods of forming attenuated strains of Leishmania.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +1
Non human animal model for ulcerative colitis and its main complications
InactiveUS20140373186A1Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementTargeted disruptionHuman animal
The present invention relates to a non human model animal for ulcerative colitis and its main complications such as primary sclerosing cholangitis and colorectal cancer. More particularly, the present invention relates to a transgenic non human animal model for ulcerative colitis and its main complications such as primary sclerosing cholangitis, and colorectal cancer comprising a targeted disruption in the IL10 and NOX1 genes so that IL10 and NOX1 are not expressed in said animal.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
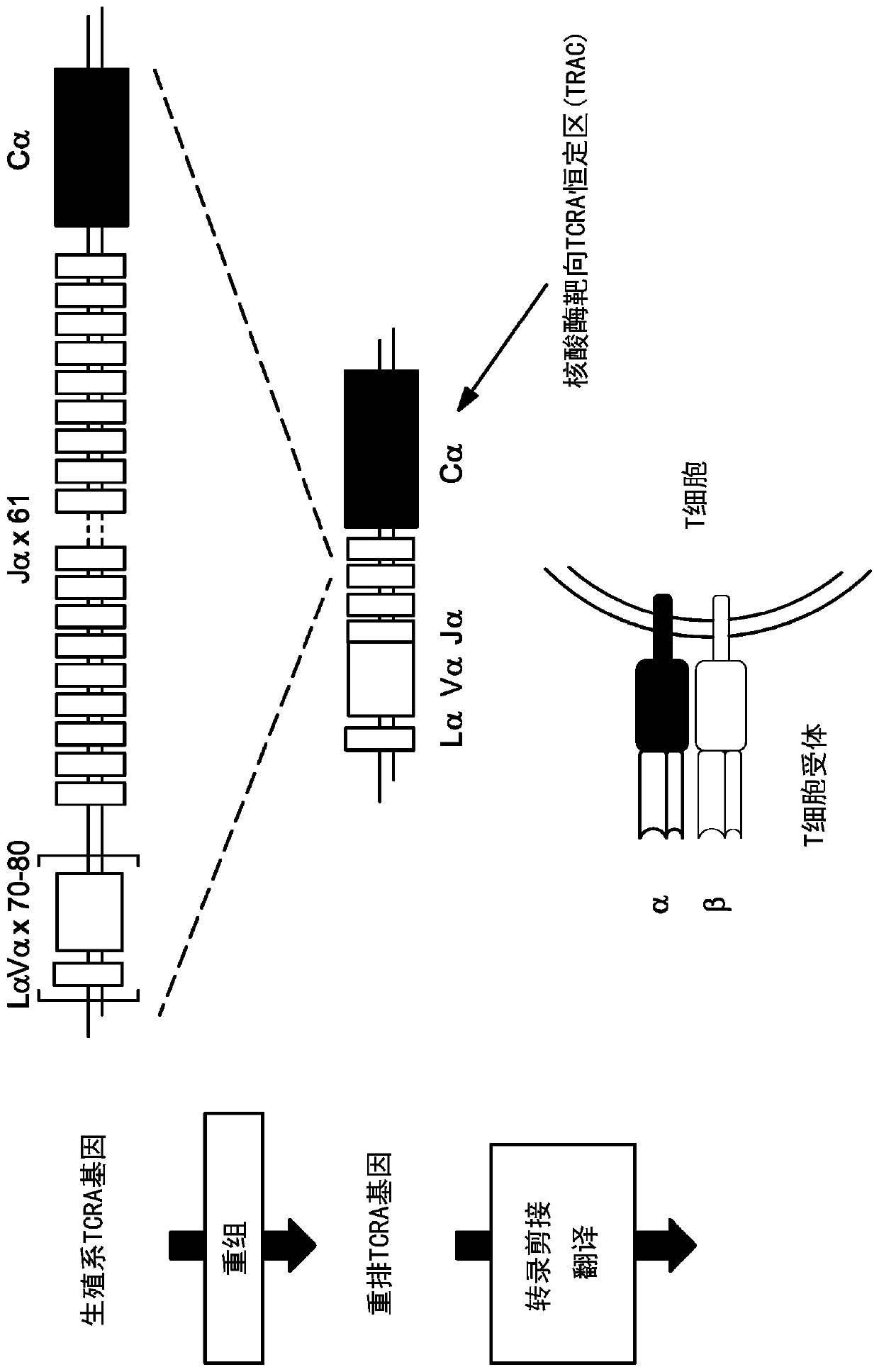
Targeted disruption of the t cell receptor
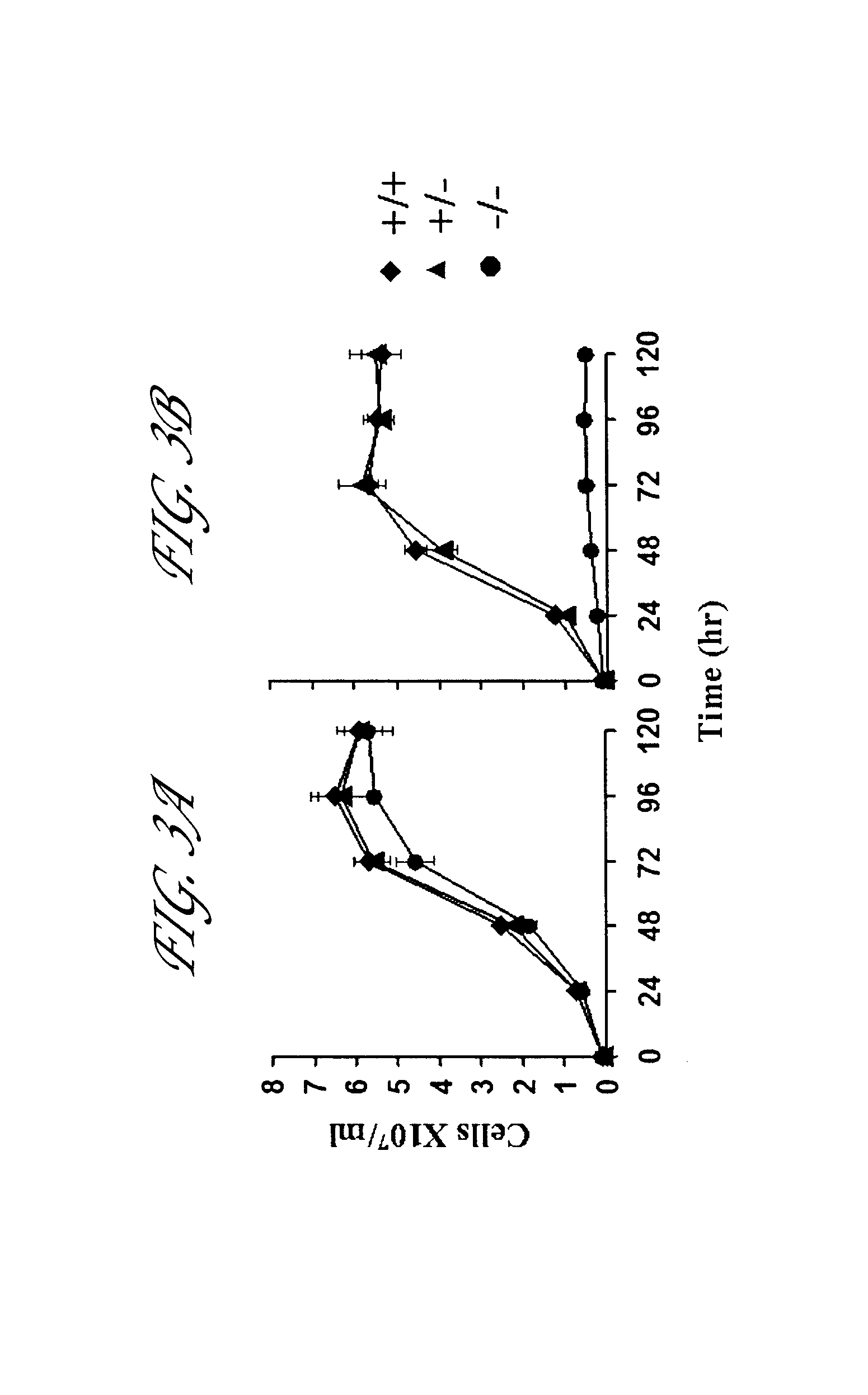
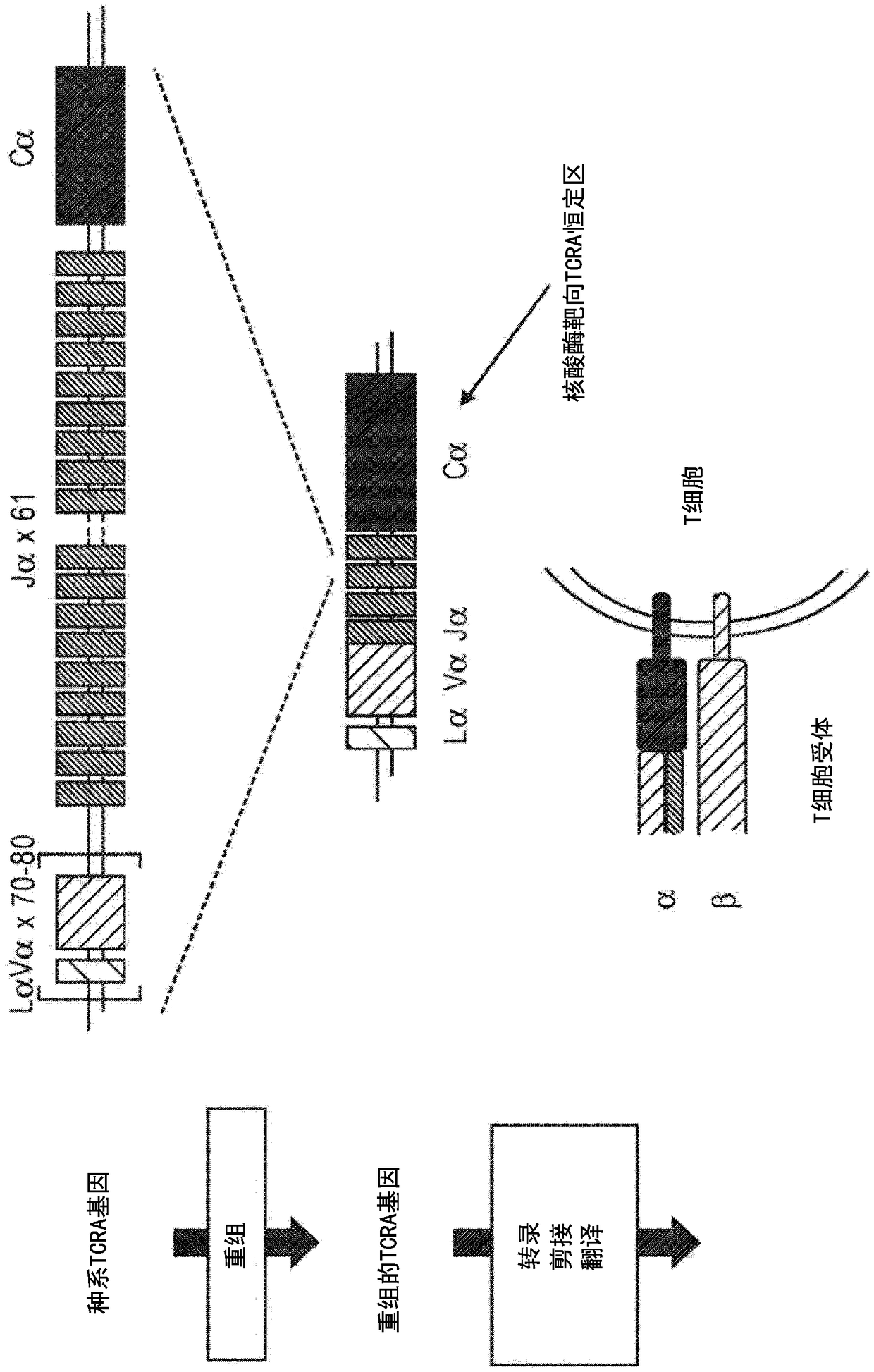
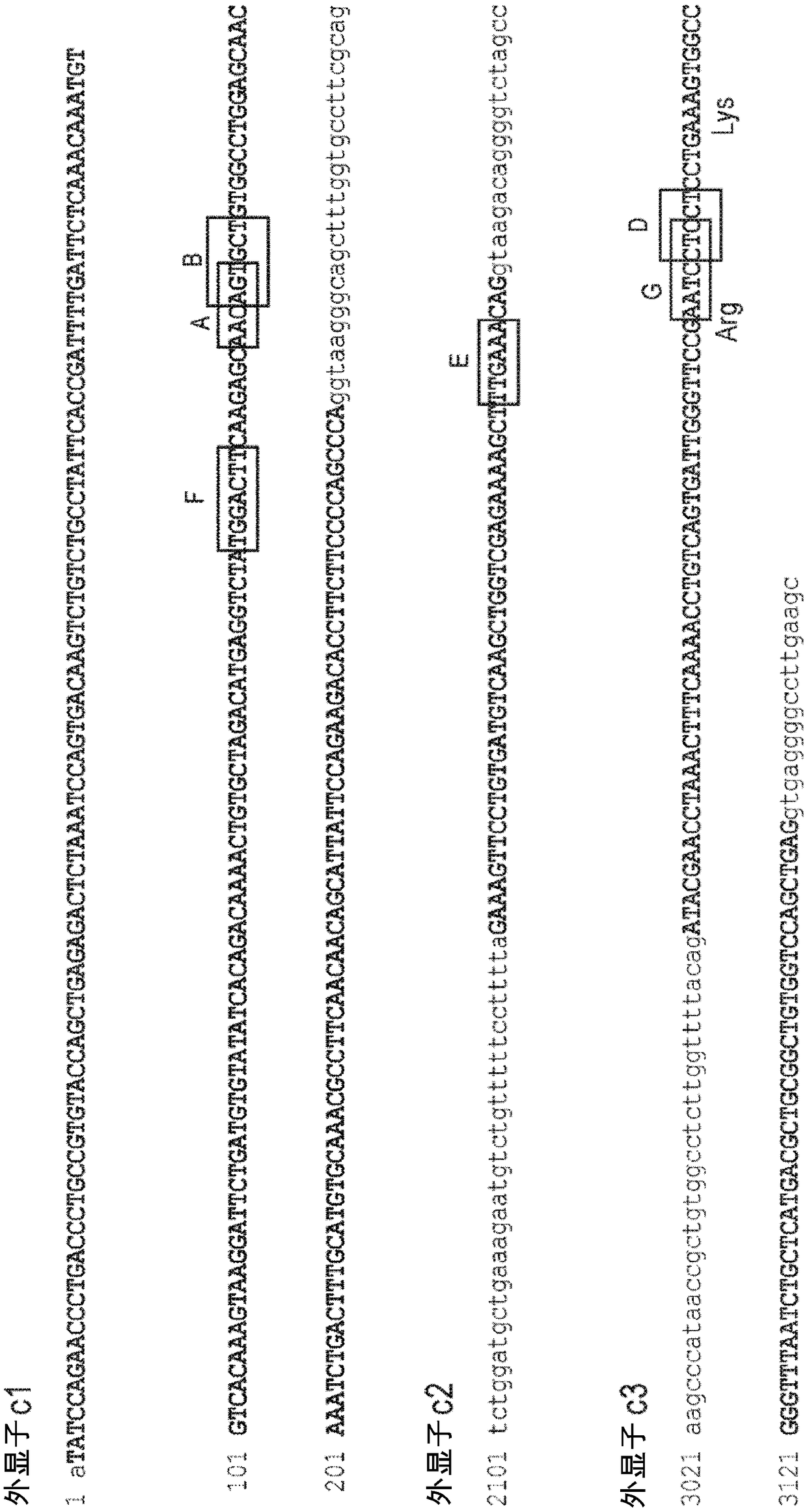
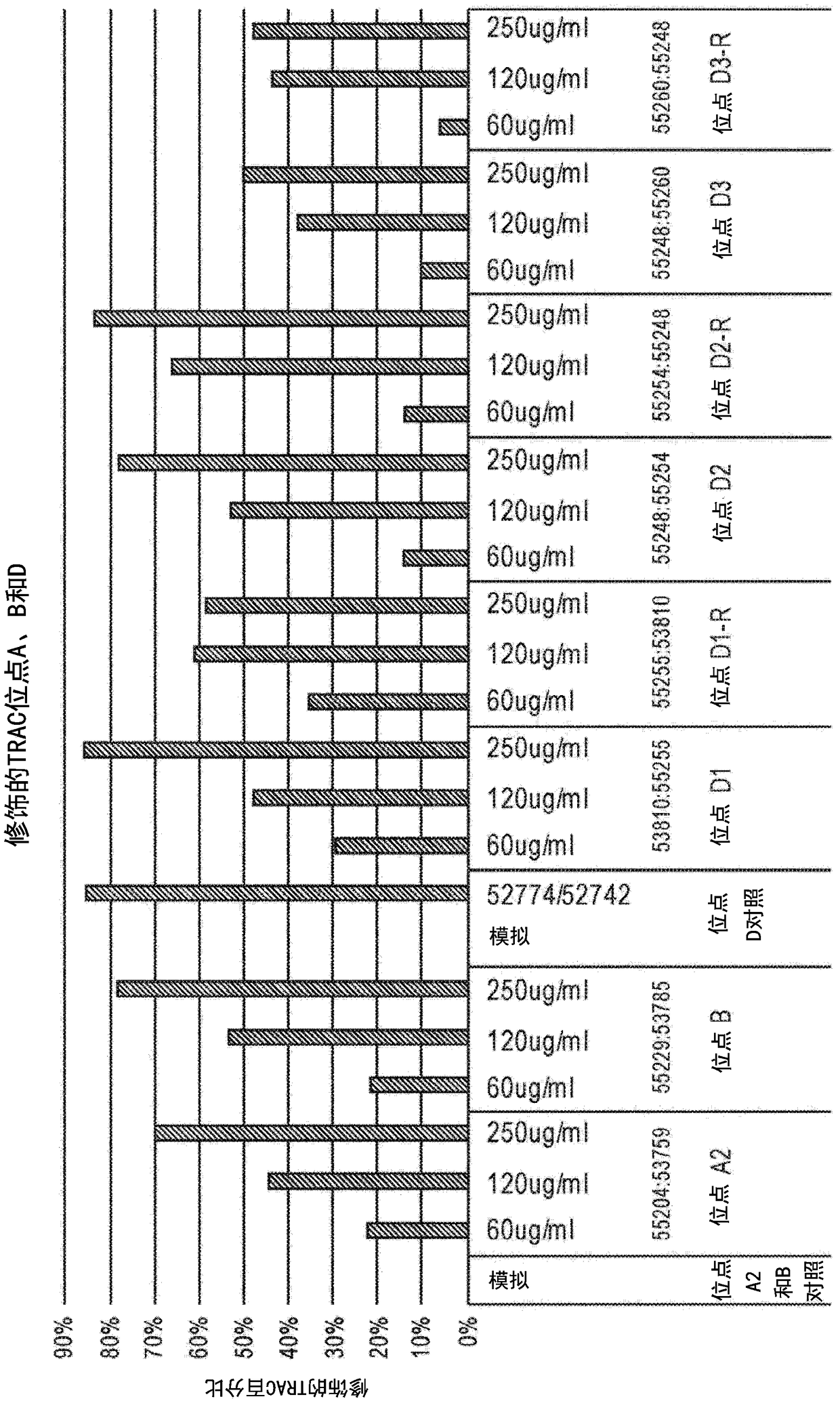
PendingCN108778297ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHydrolasesTargeted disruptionDNA-binding domain
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for inactivating TCR genes, using engineered nucleases comprising at least one DNA binding domain and a cleavage domain or cleavage half-domain in conditions able to preserve cell viability. Polynucleotides encoding nucleases, vectors comprising polynucleotides encoding nucleases and cells comprising polynucleotides encoding nucleases and / or cells comprising nucleases are also provided. Disclosed herein are also methods and compositions for expressing a functional exogenous TCR in the absence of endogenous TCR expression in T lymphocytes, includinglymphocytes with a central memory phenotype. Polynucleotides encoding exogenous TCR, vectors comprising polynucleotides encoding exogenous TCR and cells comprising polynucleotides encoding exogenousTCR and / or cells comprising exogenous TCR are also provided.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
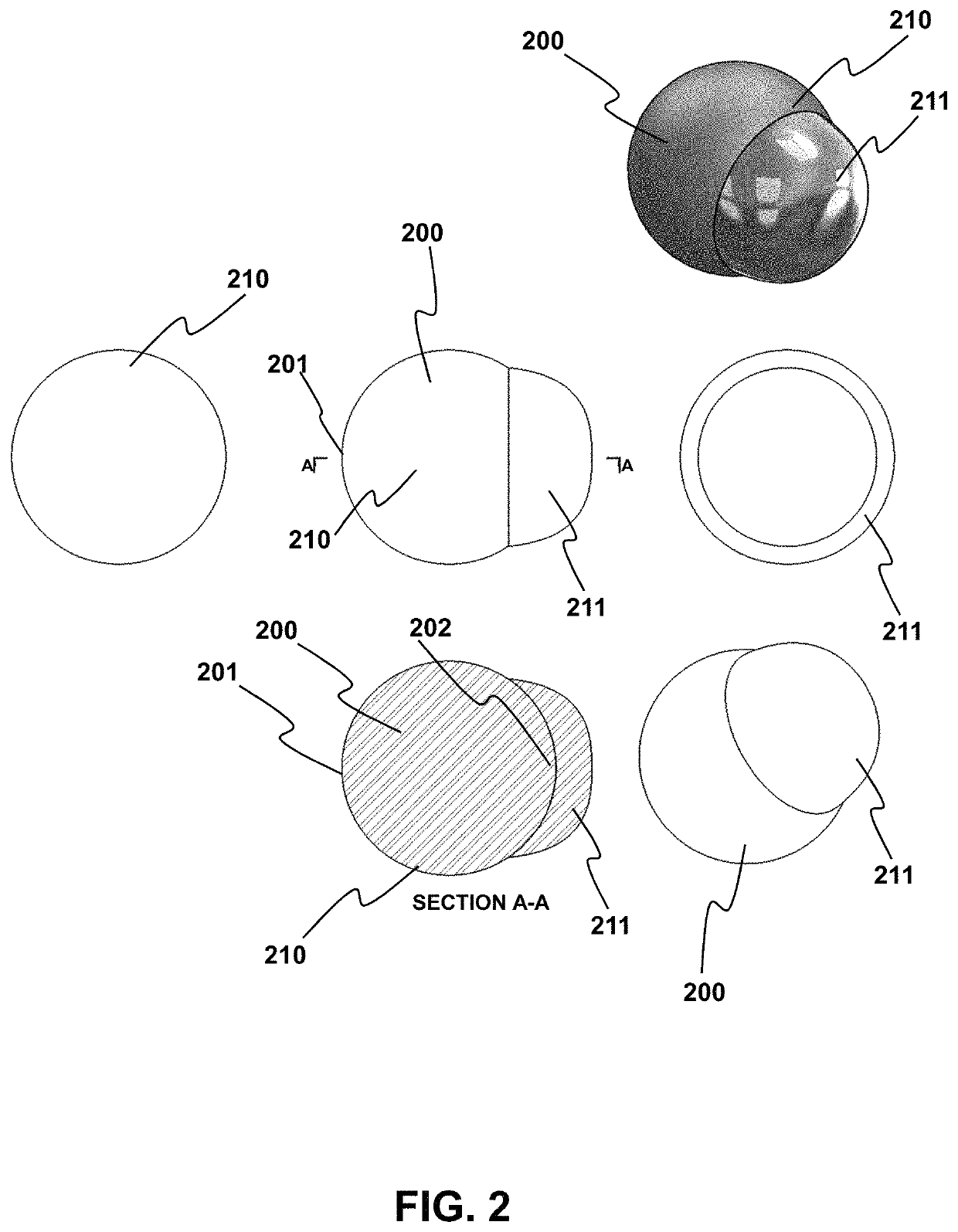
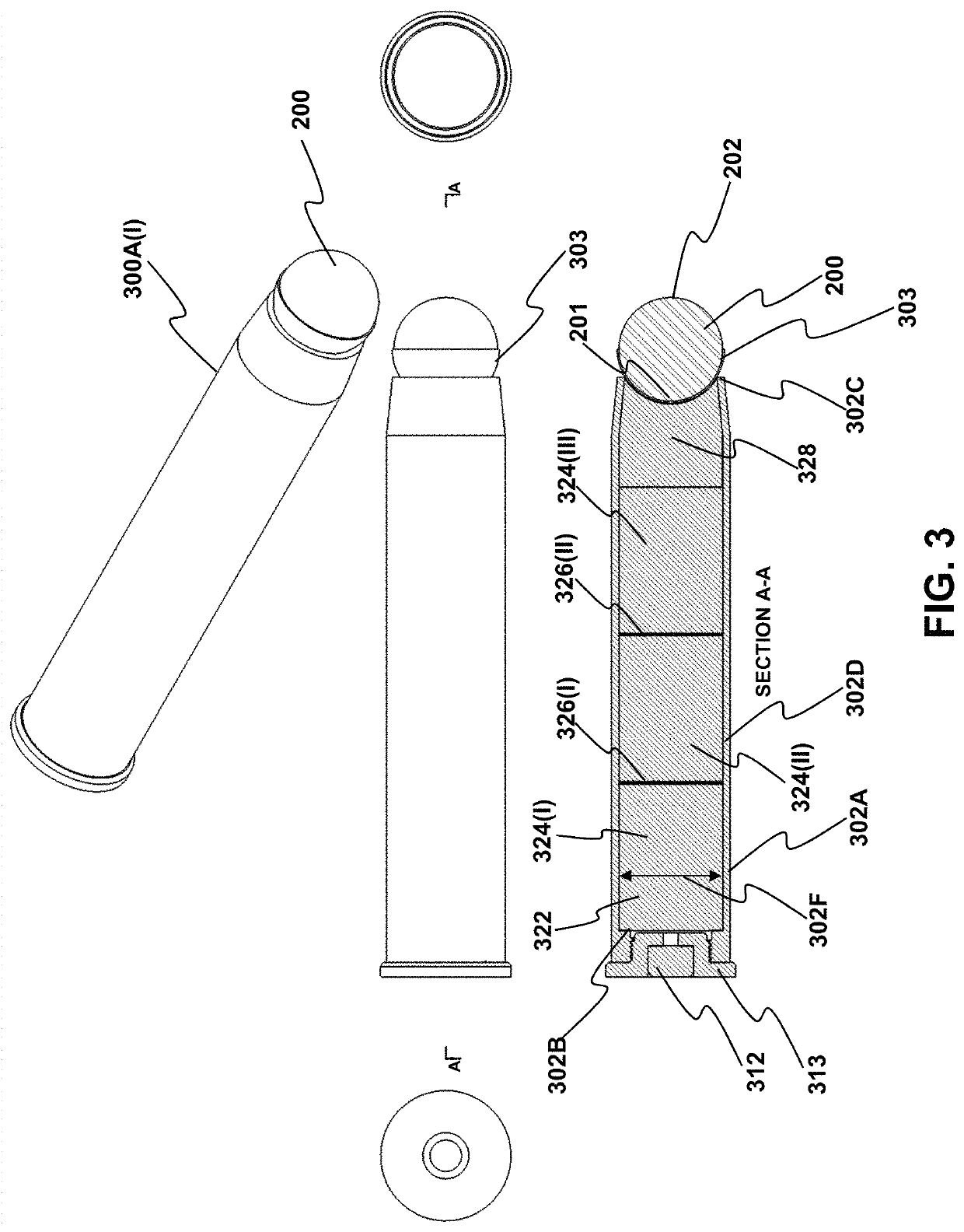
Rounded Projectiles for Target Disruption
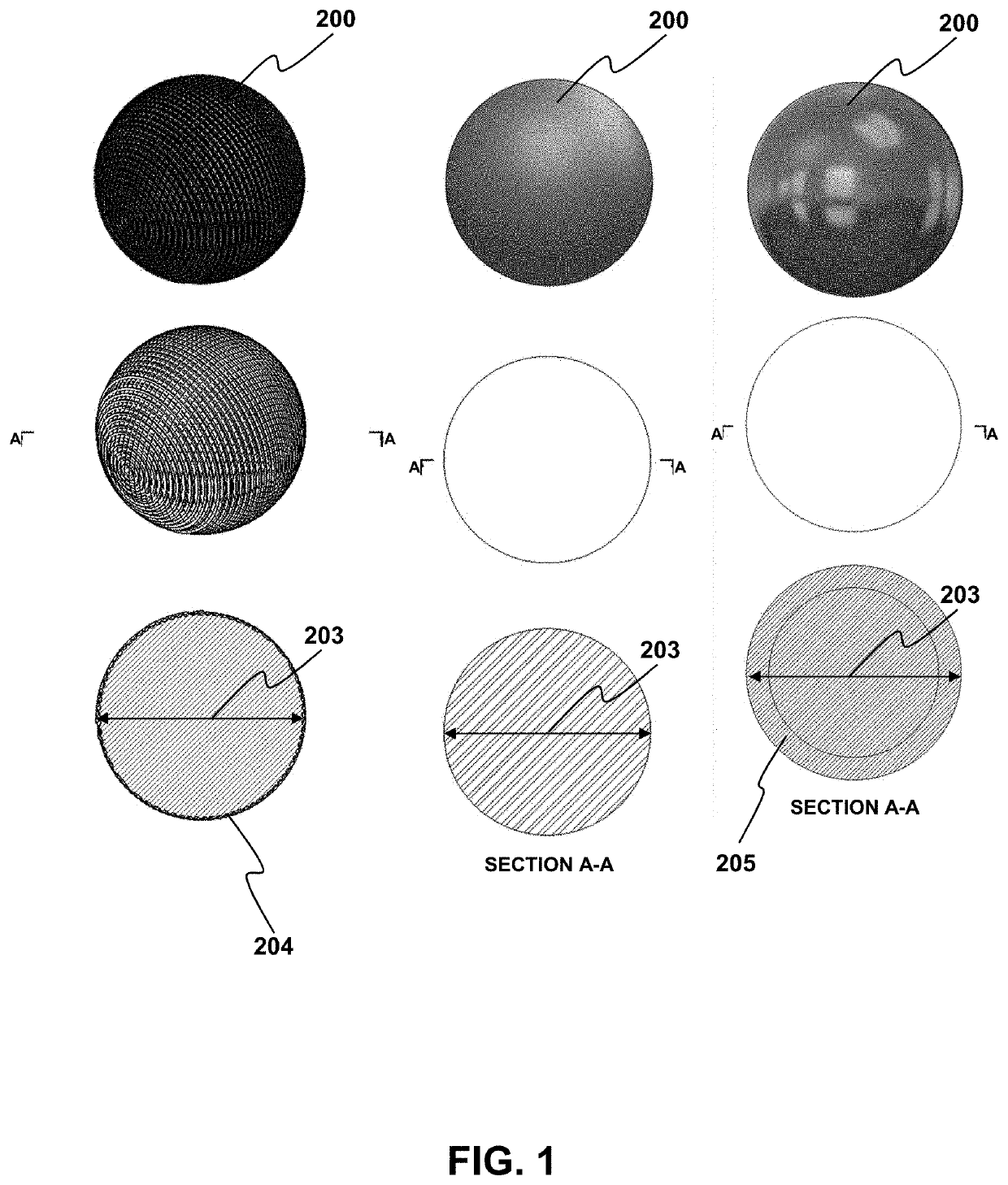
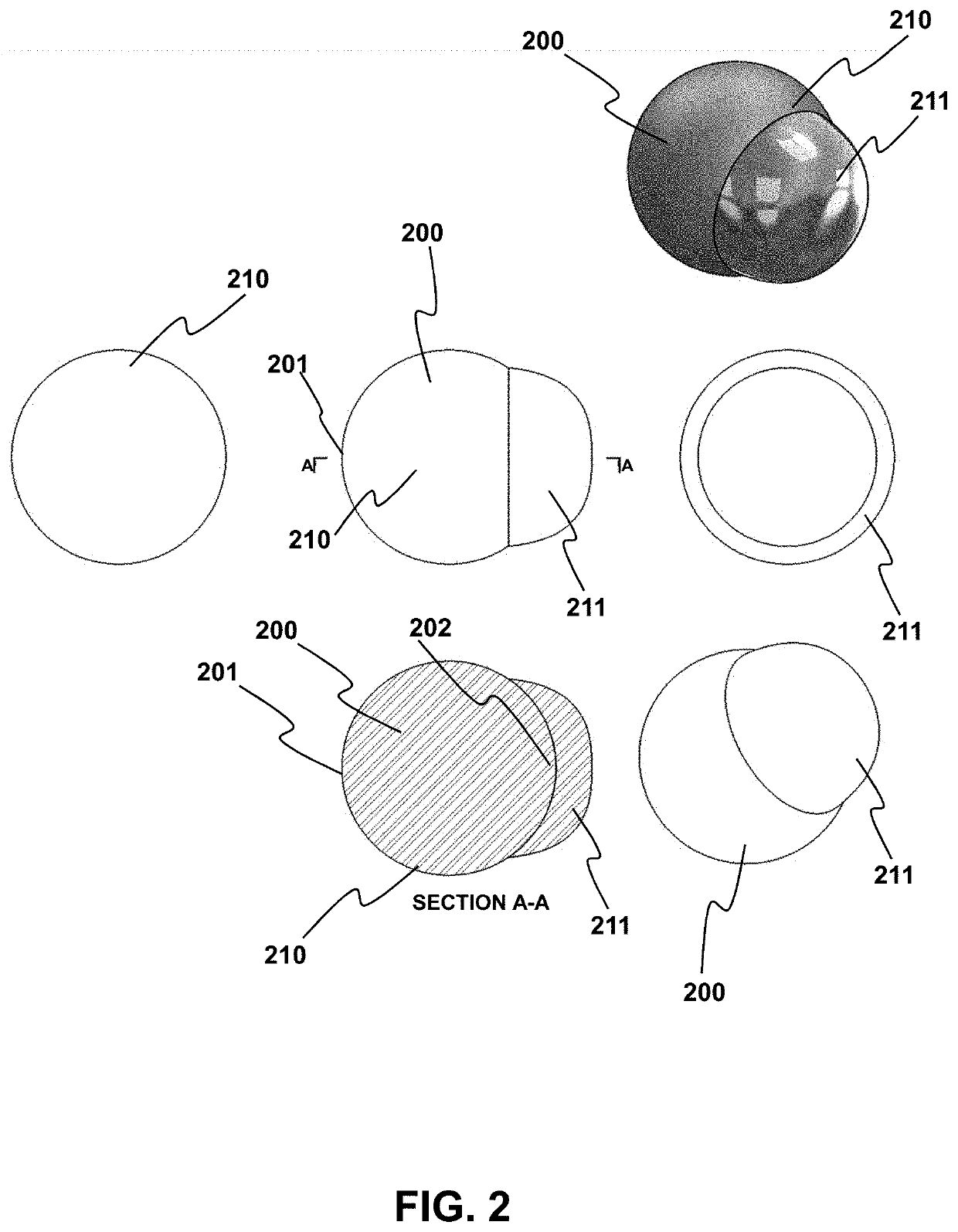
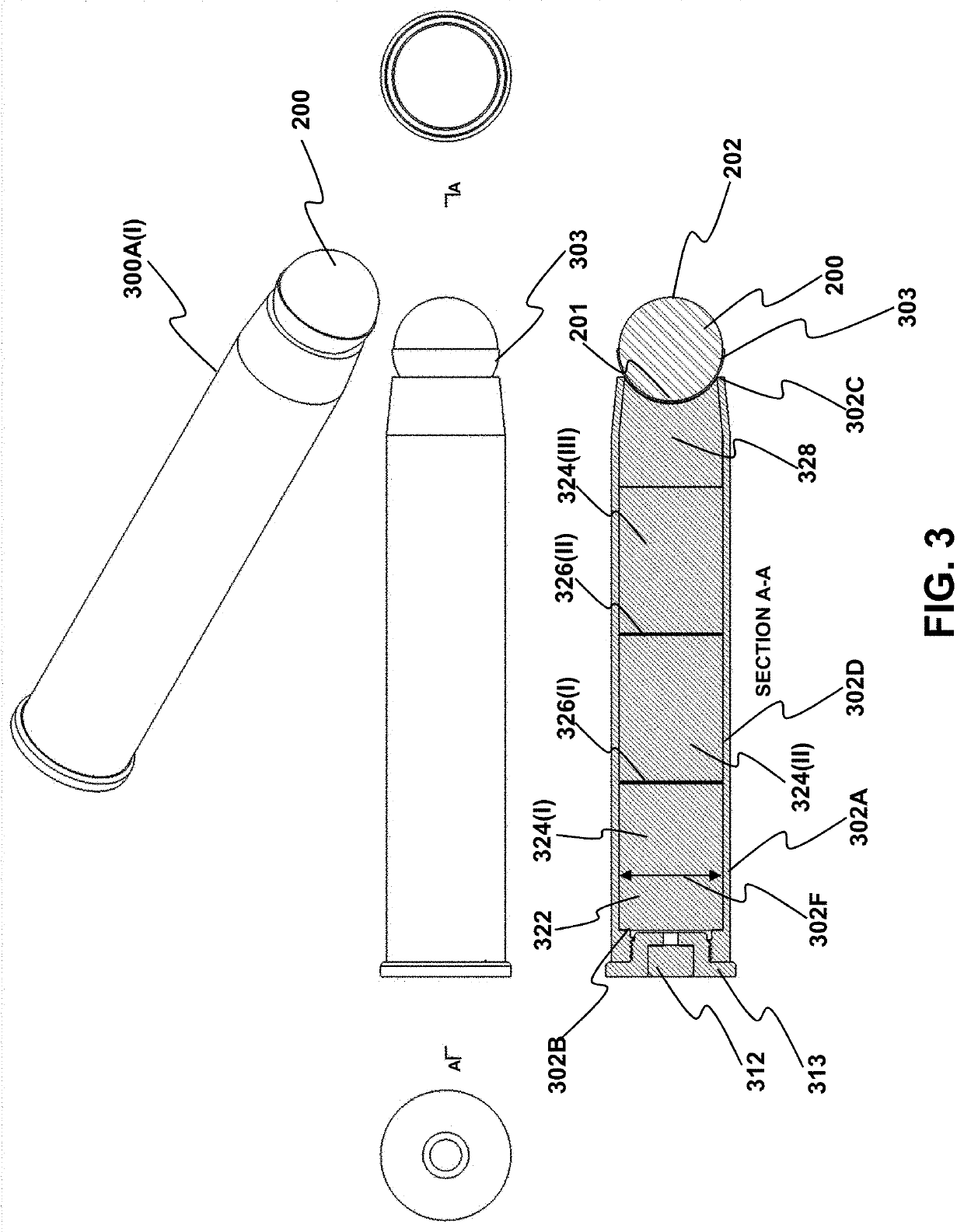
ActiveUS20210389107A1No reasonable riskLack of propulsionAmmunition projectilesBarrelsTrajectory of a projectileTargeted disruption
Provided are methods and related devices for disrupting an explosive device using a propellant driven disrupter (PDD) that propels a rounded projectile (RP) toward an explosive device. The RP travels along a linear trajectory and impacts the target, including a barrier portion of the explosive device. The impacting between the RP and barrier forms a composite projectile via a solid state weld between a portion of the barrier and the RP distal end, thereby minimizing or avoiding spall and fragment generation into the explosive device. The projectile traverses a penetration distance along the linear trajectory, or a defined-angle relative thereto, to disrupt the explosive device without unwanted explosive detonation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE FEDERAL BUREAU OF INVESTIGATION DEPT OF JUSTICE
Targeted gene disruption methods and immunogenic compositions
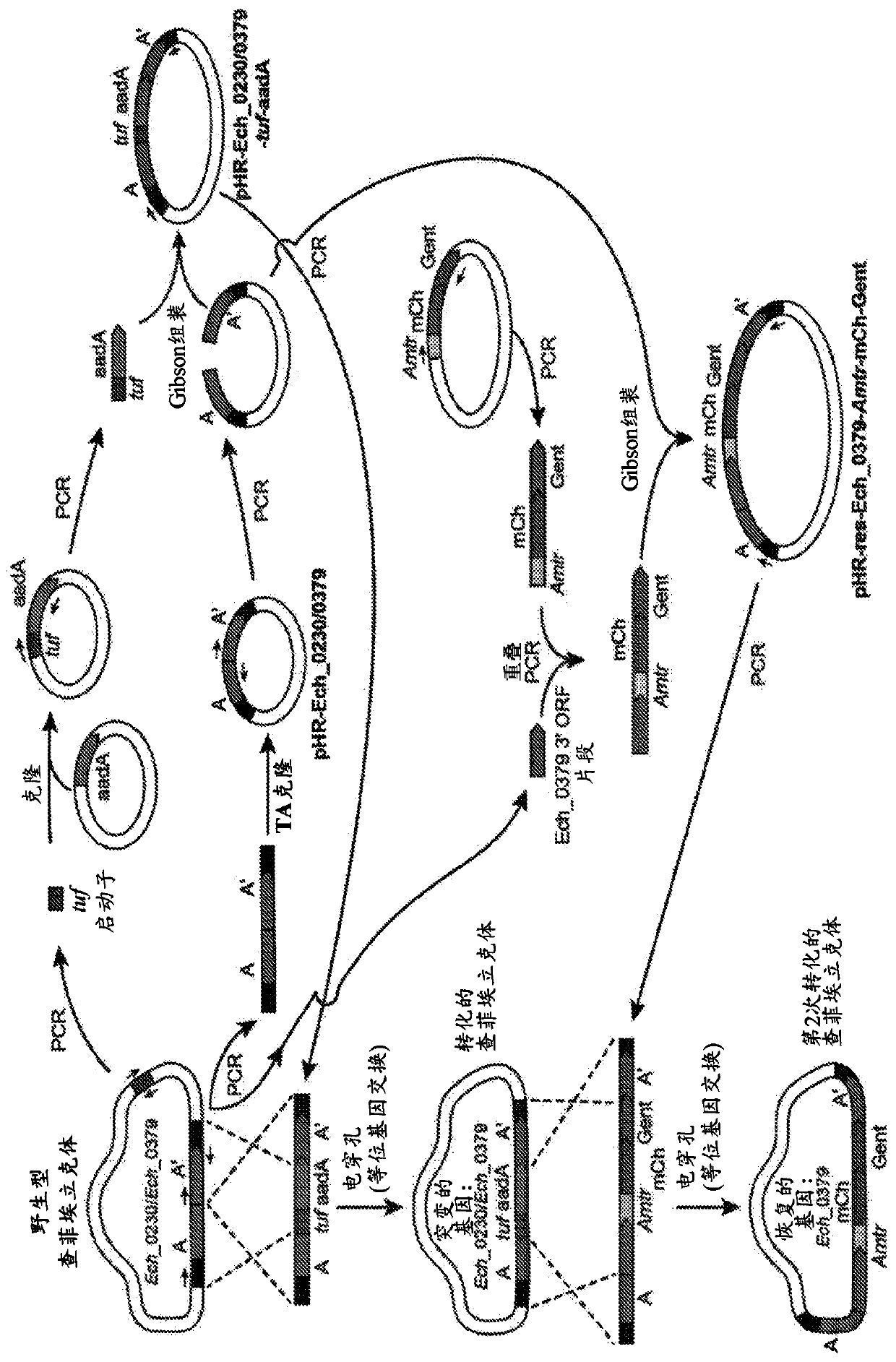
PendingCN110913877AReduce incidenceReduce severityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaRickettsiaAnaplasma phagocytophilum DNA
Targeted disruption of a specific gene and its subsequent restoration in obligate intracellular bacteria remains extremely challenging due to their absolute requirement for residence inside a host cell to replicate. Here, targeted allelic exchange mutations were created to inactivate two genes and then to restore one of the two genes of a rickettsial pathogen, Ehrlichia chaffeensis. These methodswere then also successfully utilized in Ehrlichia canis and Anaplasma phagocyophilum. The resultant mutated pathogens are useful in immunogenic compositions for reducing the incidence of or severity of infection with ricksettsial pathogens.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Artery-and vein-specific proteins and uses therefor
InactiveUS20060288434A1Compounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood vesselReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Saspase knockout animal
InactiveUS20100005534A1Reduce saggingReduce wrinklesEnzymesGenetic engineeringTargeted disruptionWrinkle skin
Knockout animals in which a gene encoding a SASPase has been deleted (hereinafter, referred to as SASPase KO animals) are provided. The SASPase KO animals deficient in expression of functional SASPase were produced by deleting a gene encoding a stratified epithelium-specific protease, SASPase, through targeted disruption. The SASPase KO animals showed a significant increase in wrinkles on the sides of the body and so on. The SASPase KO animals find utility as animal models of wrinkles.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
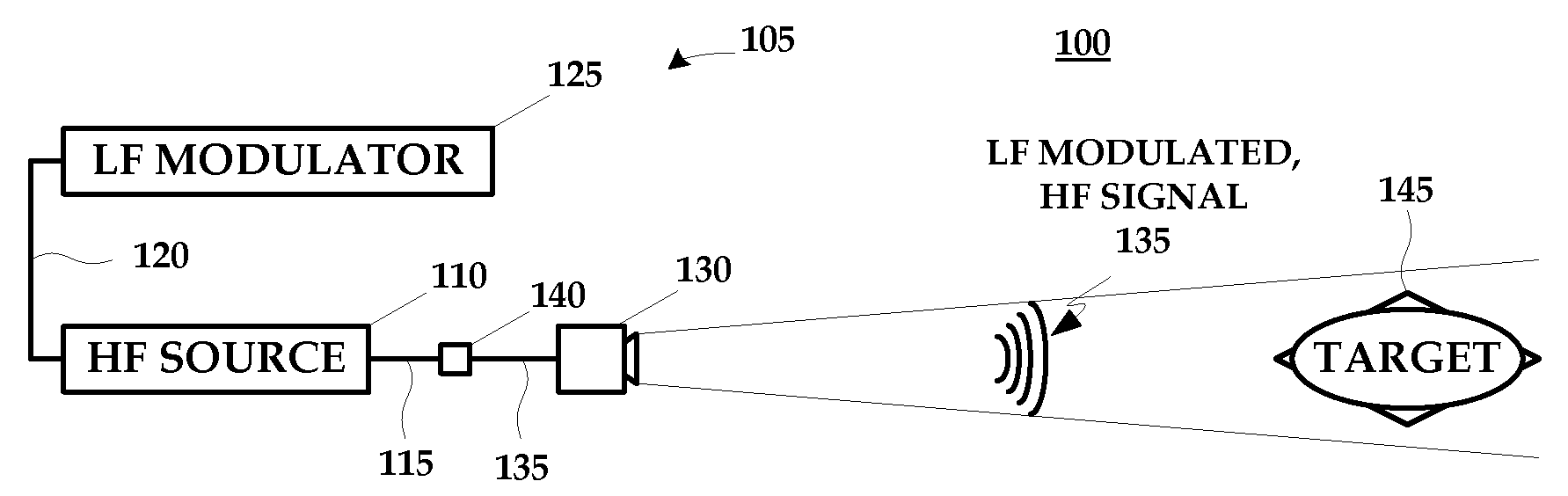
Hybrid band directed energy target disruption
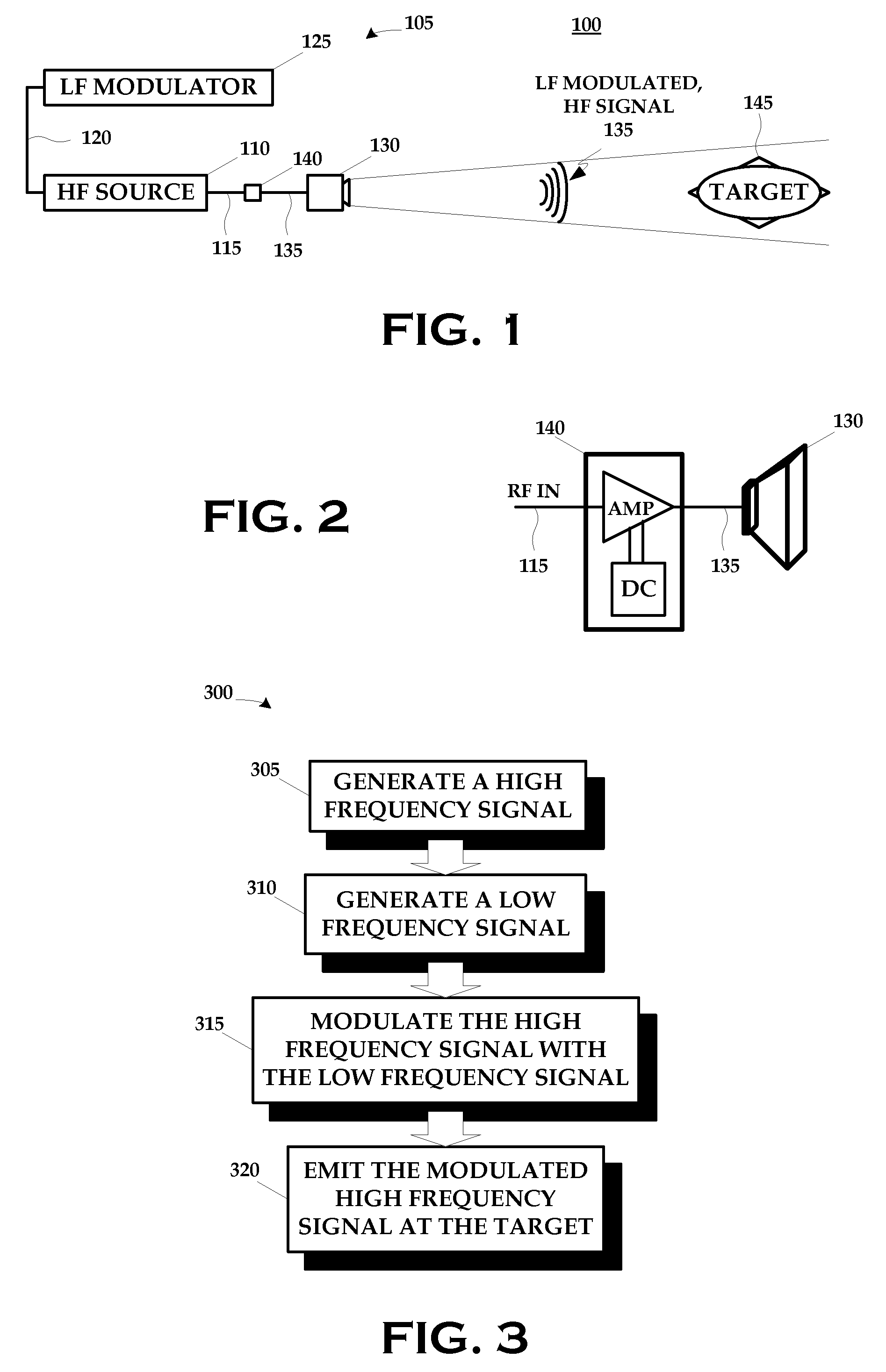
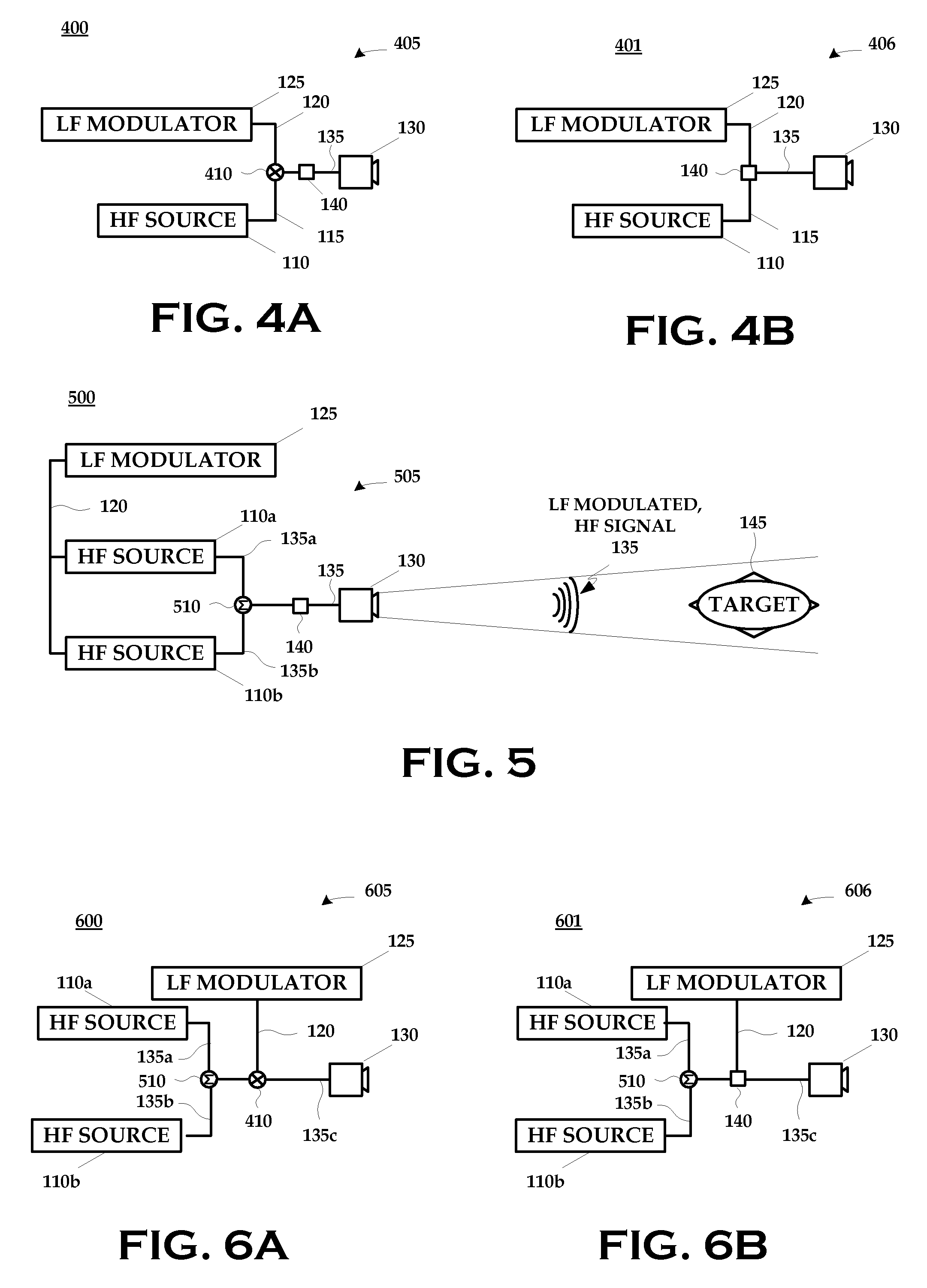
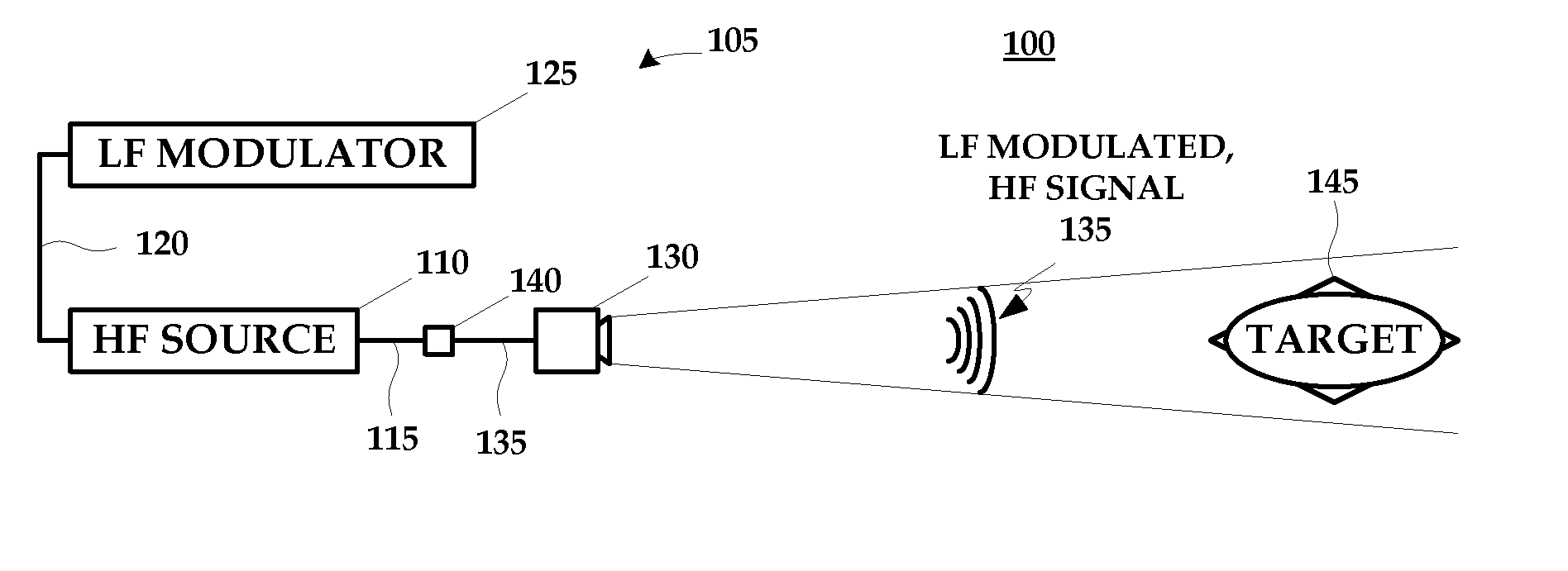
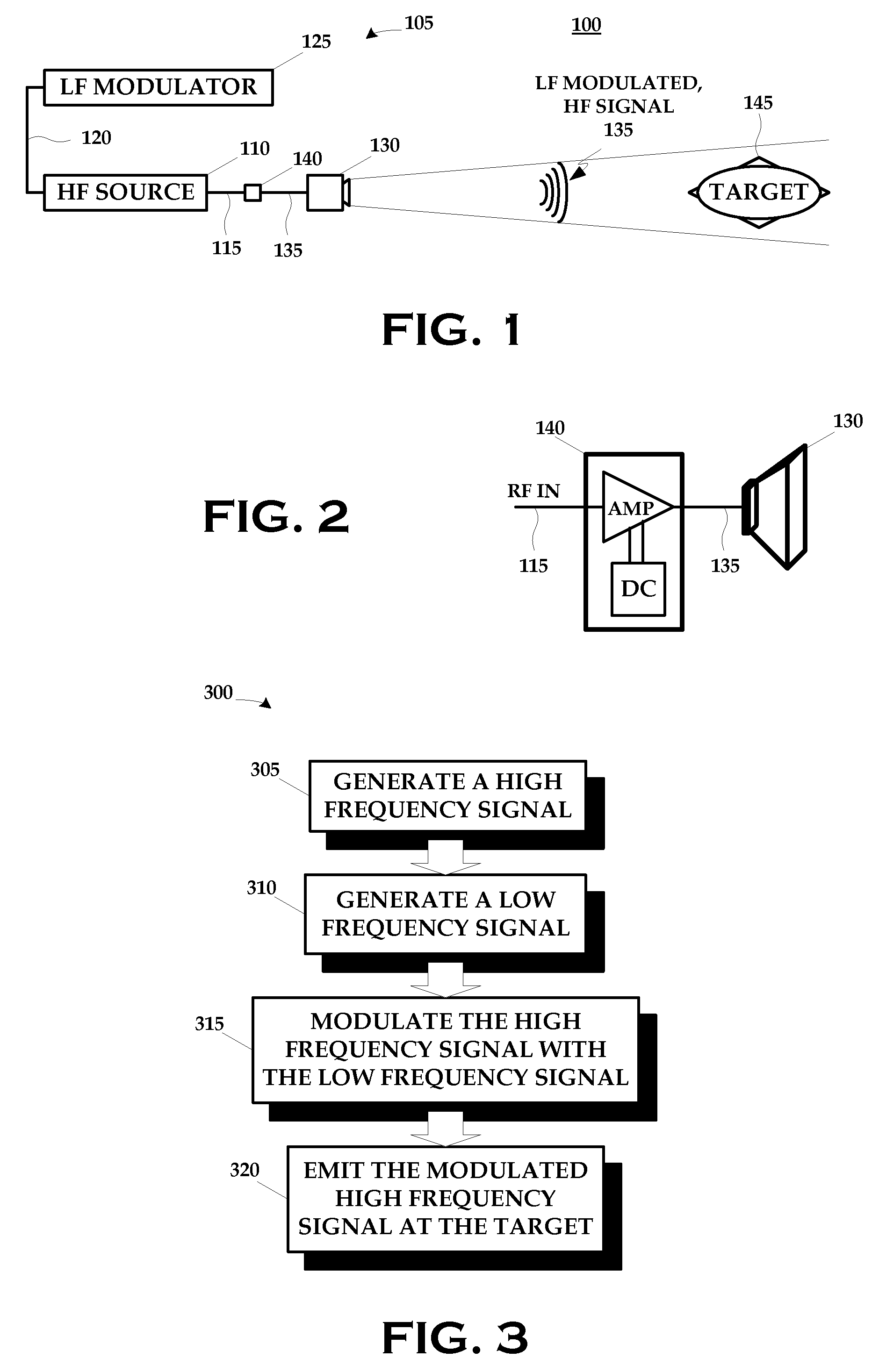
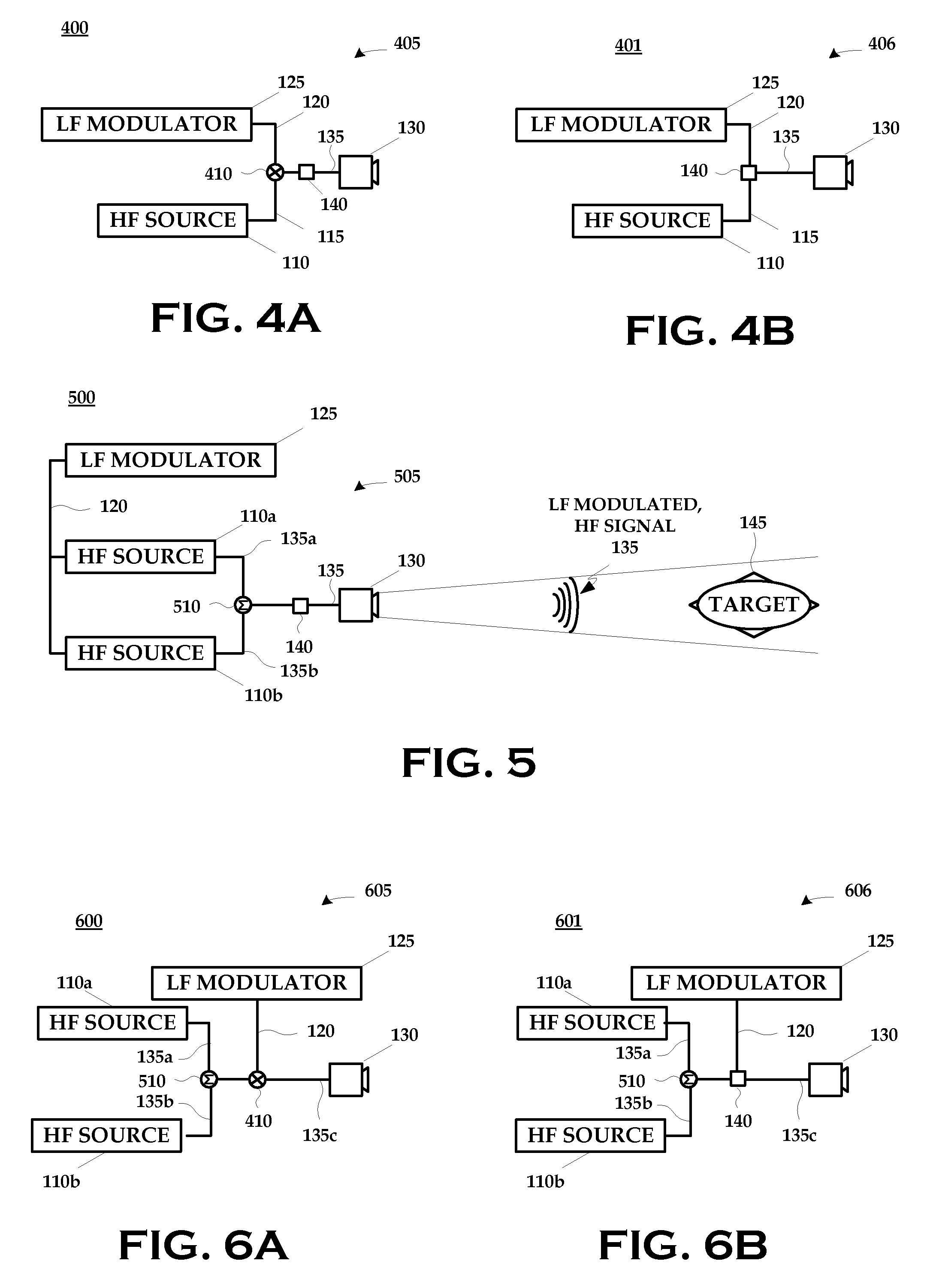
ActiveUS20080304549A1Disrupt operationFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTargeted disruptionLow frequency
A technique for disrupting the operation of a target containing nonlinear electronic devices generally includes generating a high frequency signal; generating a low frequency signal; modulating the high frequency signal with the low frequency signal; and emitting the modulated high frequency signal at the target.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Lymphohematopoietic engineering using cas9 base editors
PendingCN112292139AGenetically modified cellsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBase JMissense mutation
Provided herein are methods and systems for targeted gene disruption (knock-out, missense mutation) and targeted gene knock-in in mammalian cells using base editors and guide RNAs (gRNAs) designed totarget splice acceptor-splice donor sites. Also provided herein are universally acceptable genetically engineered cells comprising targeted disruptions in immunotherapy-related genes and comprising aCAR / TCR for therapeutic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Targeted disruption of t cell and/or HLA receptors
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for inactivating TCR and / or HLA genes, using engineered nucleases comprising at least one DNA binding domain and a cleavage domain or cleavage half-domainin conditions able to preserve cell viability. Polynucleotides encoding nucleases, vectors comprising polynucleotides encoding nucleases and cells comprising polynucleotides encoding nucleases and / orcells comprising nucleases are also provided.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Saspase knockout animal
InactiveUS7834238B2Reduce saggingReduce wrinklesEnzymesGenetic engineeringTargeted disruptionAnimal science
Knockout animals in which a gene encoding a SASPase has been deleted (hereinafter, referred to as SASPase KO animals) are provided. The SASPase KO animals deficient in expression of functional SASPase were produced by deleting a gene encoding a stratified epithelium-specific protease, SASPase, through targeted disruption. The SASPase KO animals showed a significant increase in wrinkles on the sides of the body and so on. The SASPase KO animals find utility as animal models of wrinkles.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Hybrid band directed energy target disruption
ActiveUS8600290B2Frequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTargeted disruptionEngineering
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Live attenuated Leishmania vaccines
InactiveUS20060240046A1Reduce the overall heightUseful in preparationBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsTargeted disruptionCentrin
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC +1
JNK3 modulators and methods of use
The c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) group of MAP kinases are activated by exposure of cells to environmental stress. The role of JNK in the brain was examined by targeted disruption of the gene that encodes the neuronal isoform JNK3. It was found that JNK3 is required for the normal response to seizure activity. Methods of screening for molecules and compounds that decrease JNK3 expression or activity are described. Such molecules or compounds are useful for treating disorders involving excitotoxicity such as seizure disorders, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington disease, Parkinson's disease, and ischaemia.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Rounded projectiles for target disruption
ActiveUS11421971B2No reasonable riskLack of propulsionAmmunition projectilesBarrelsTrajectory of a projectileTargeted disruption
Provided are methods and related devices for disrupting an explosive device using a propellant driven disrupter (PDD) that propels a rounded projectile (RP) toward an explosive device. The RP travels along a linear trajectory and impacts the target, including a barrier portion of the explosive device. The impacting between the RP and barrier forms a composite projectile via a solid state weld between a portion of the barrier and the RP distal end, thereby minimizing or avoiding spall and fragment generation into the explosive device. The projectile traverses a penetration distance along the linear trajectory, or a defined-angle relative thereto, to disrupt the explosive device without unwanted explosive detonation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE FEDERAL BUREAU OF INVESTIGATION DEPT OF JUSTICE
Non human animal model for ulcerative colitis and its main complications
InactiveUS9217156B2Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementTargeted disruptionColon rectal cancer
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com