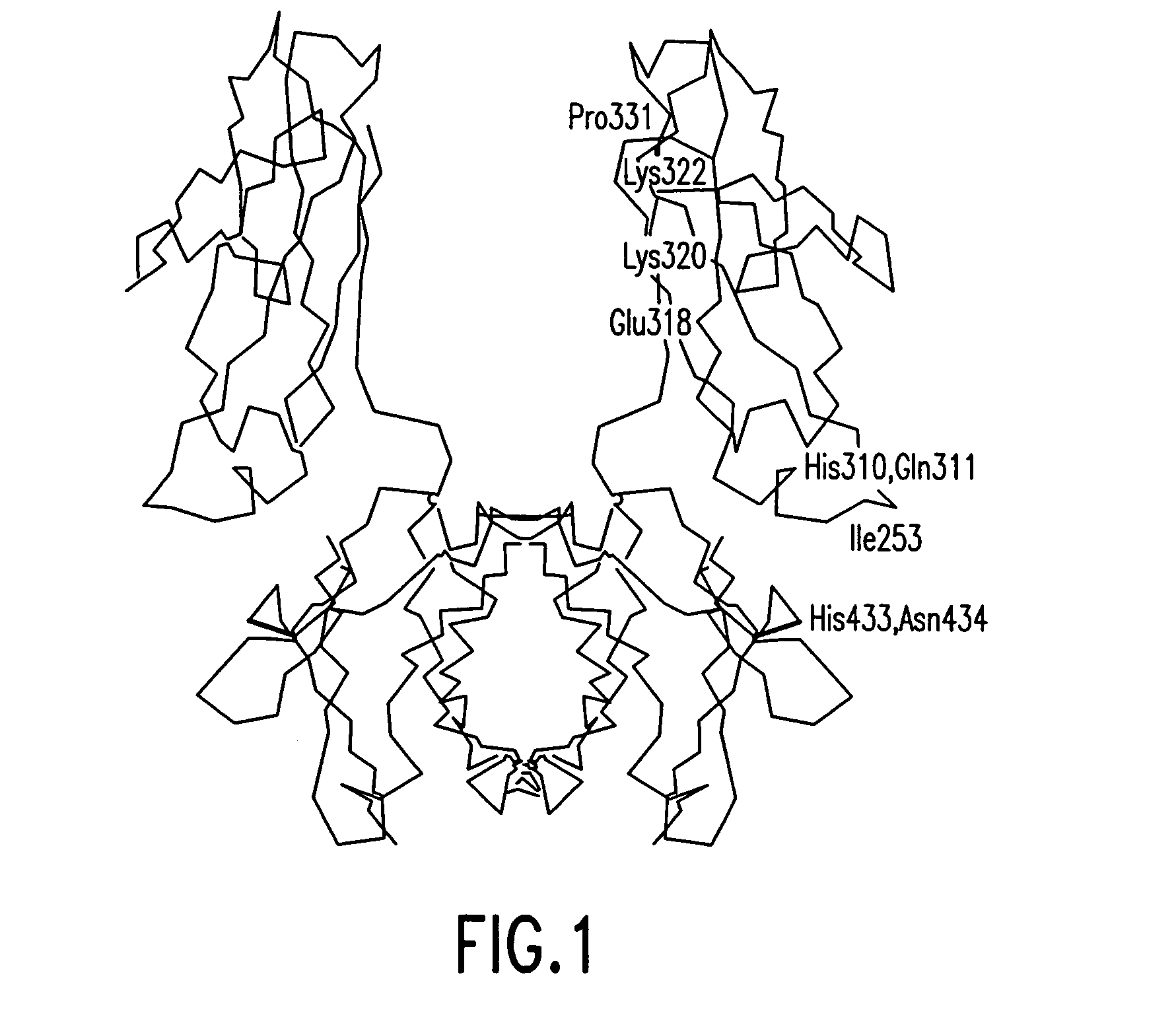
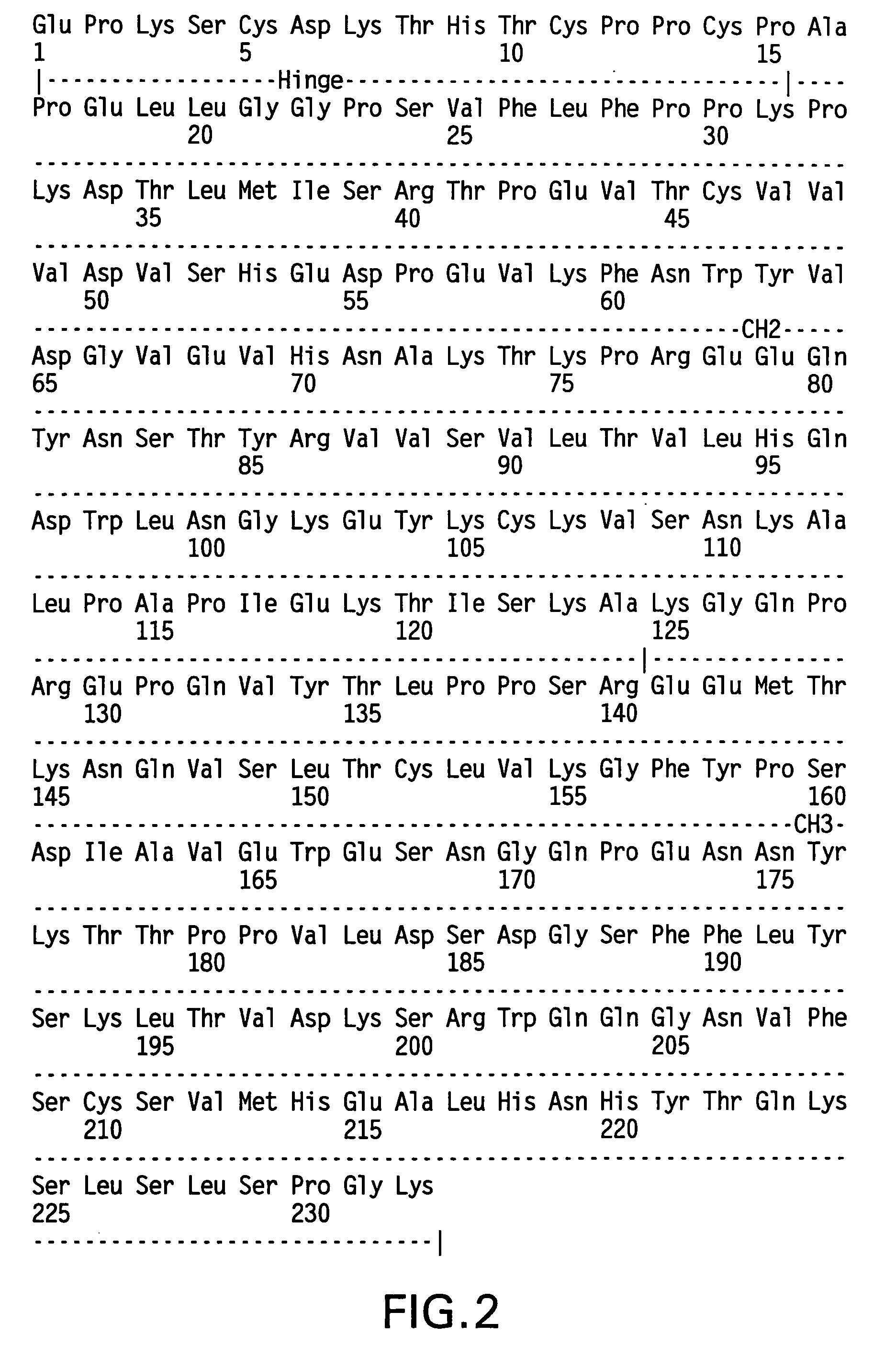
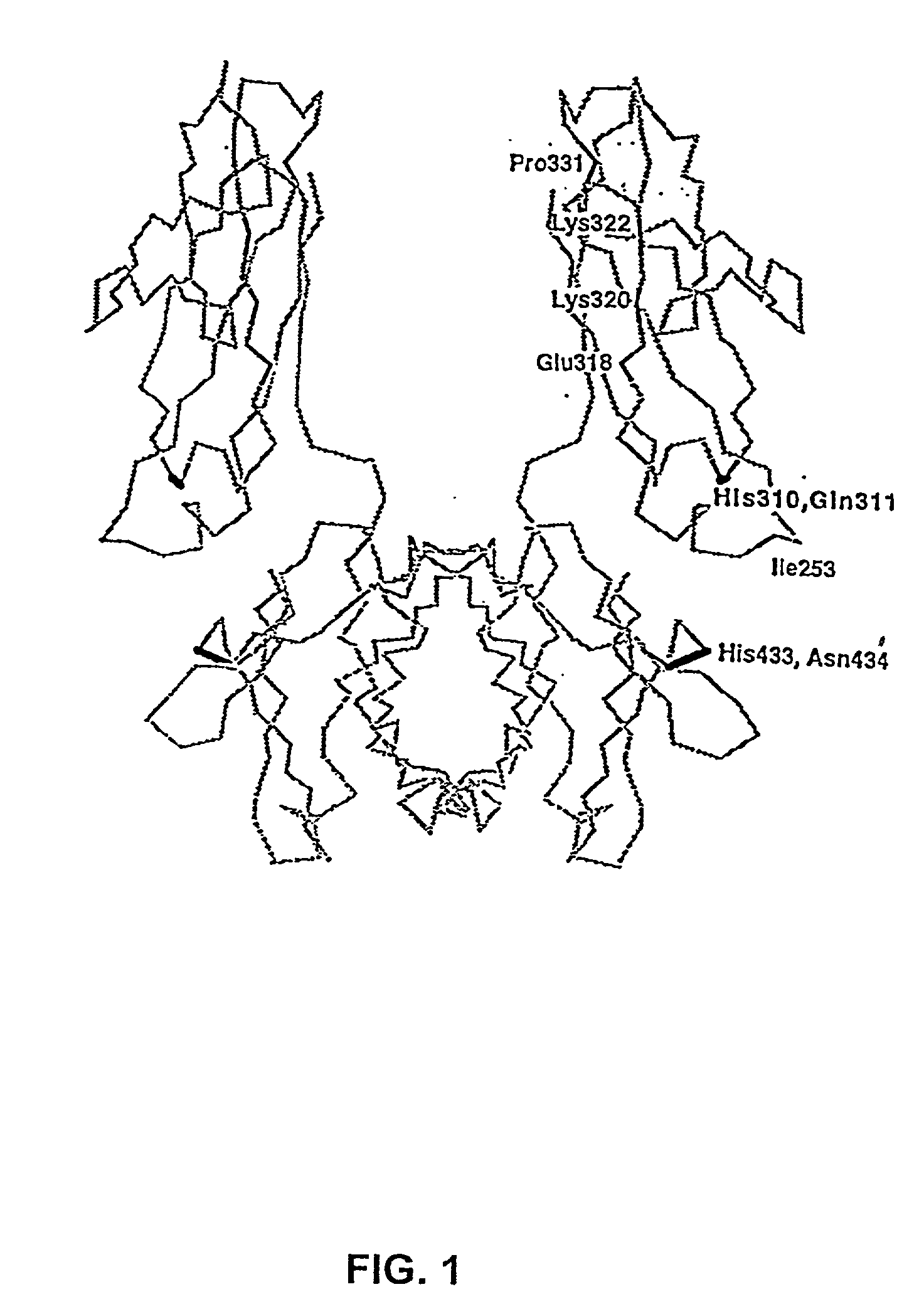
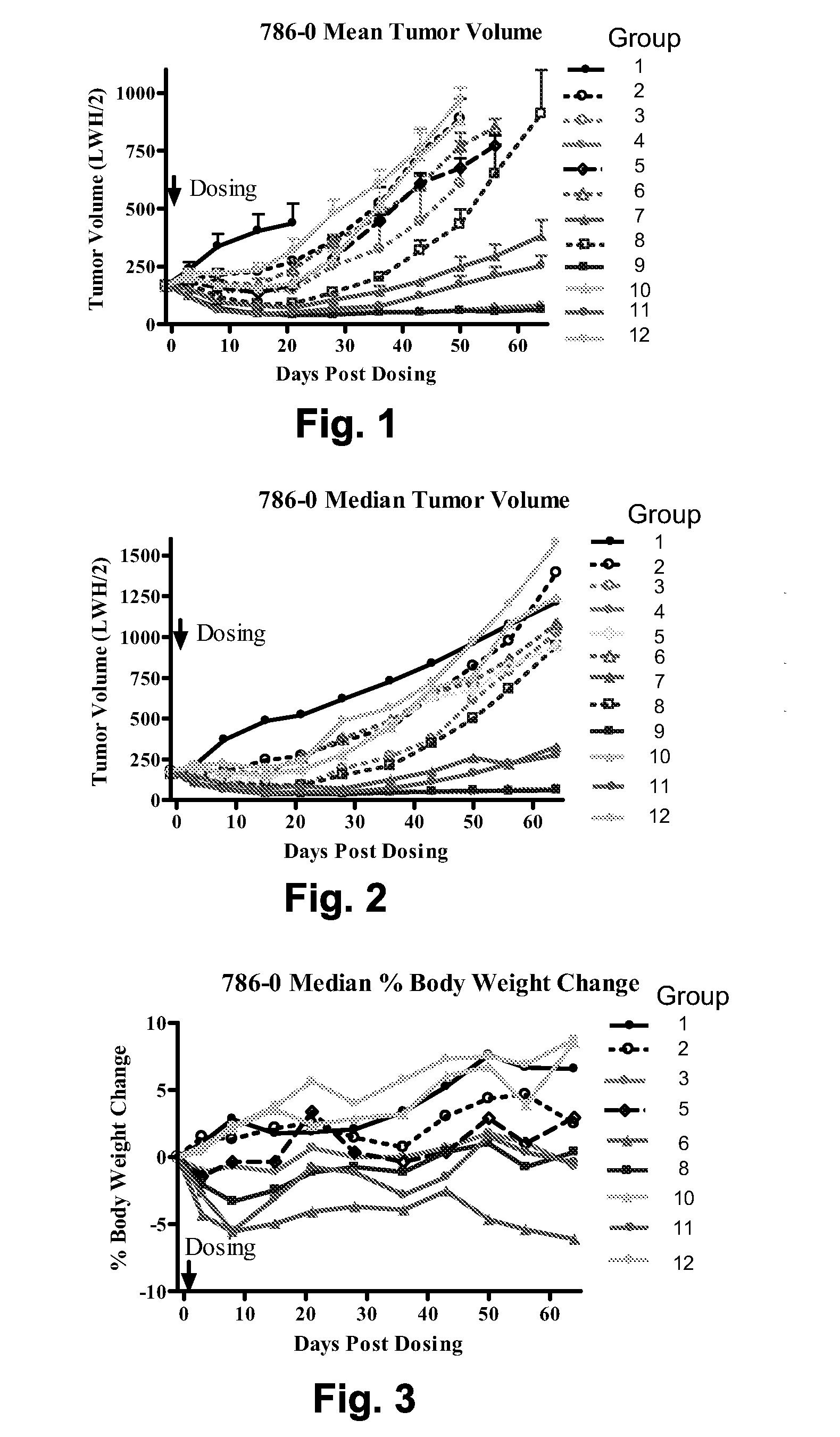
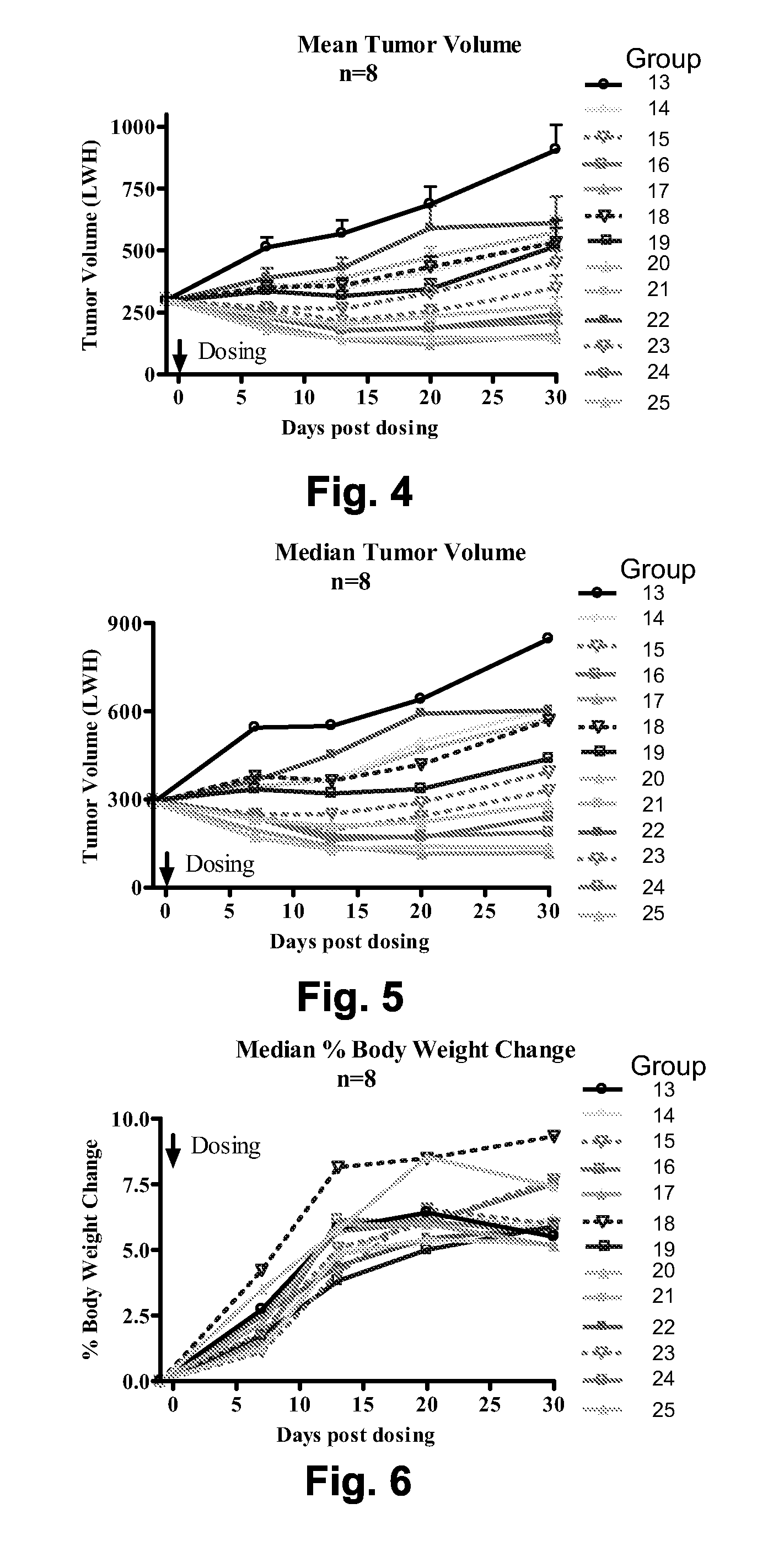
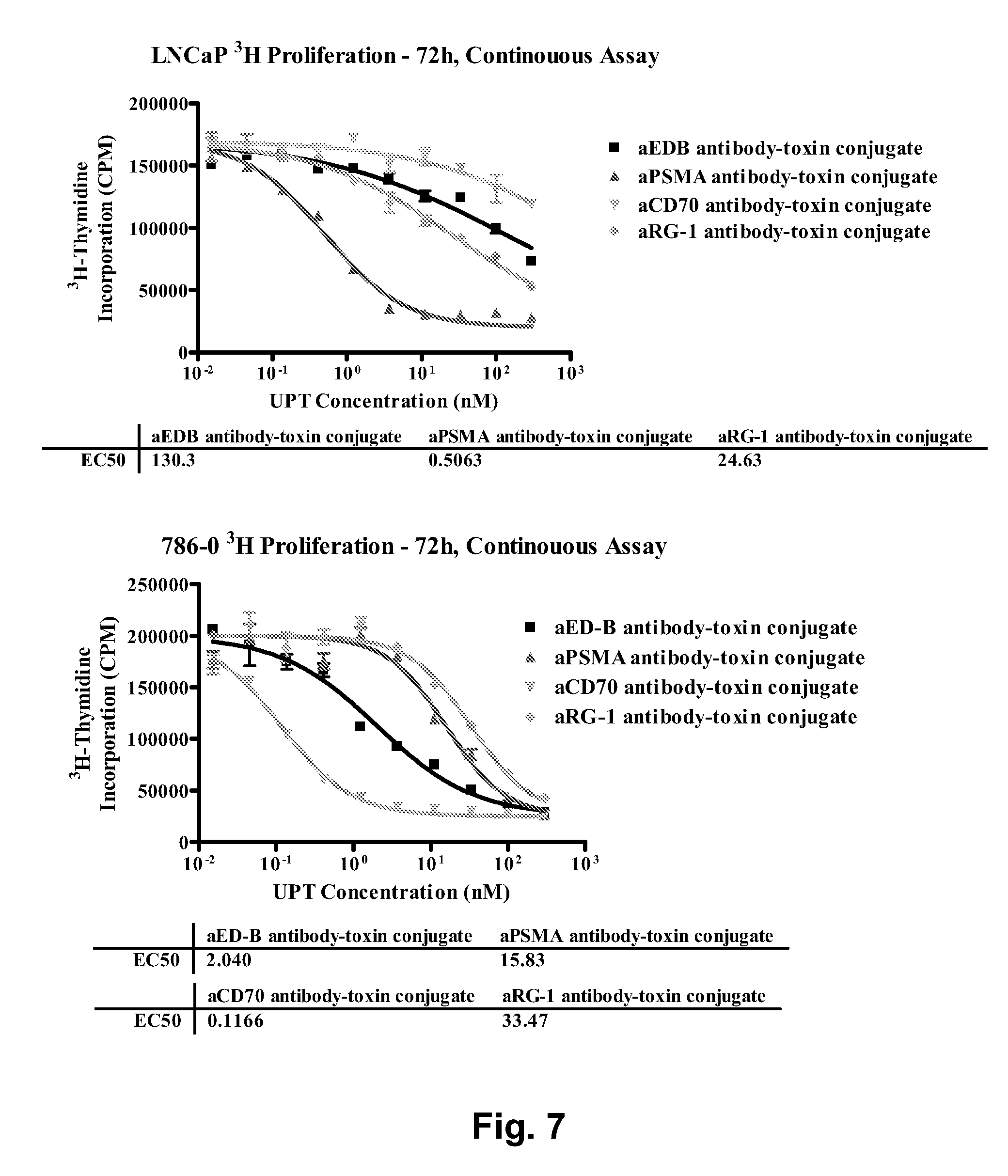
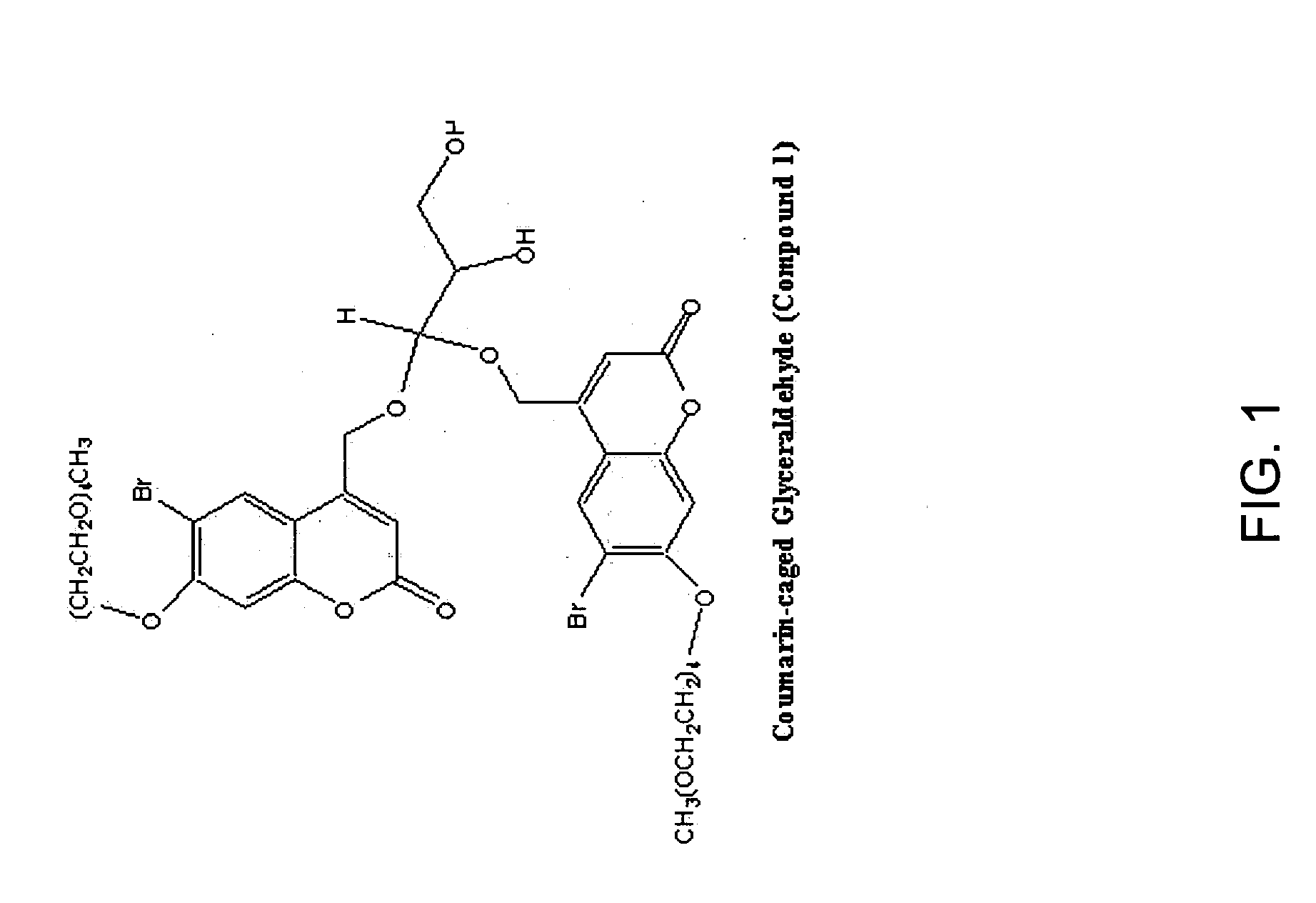
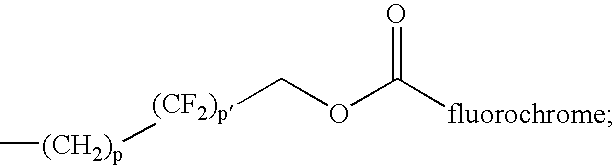
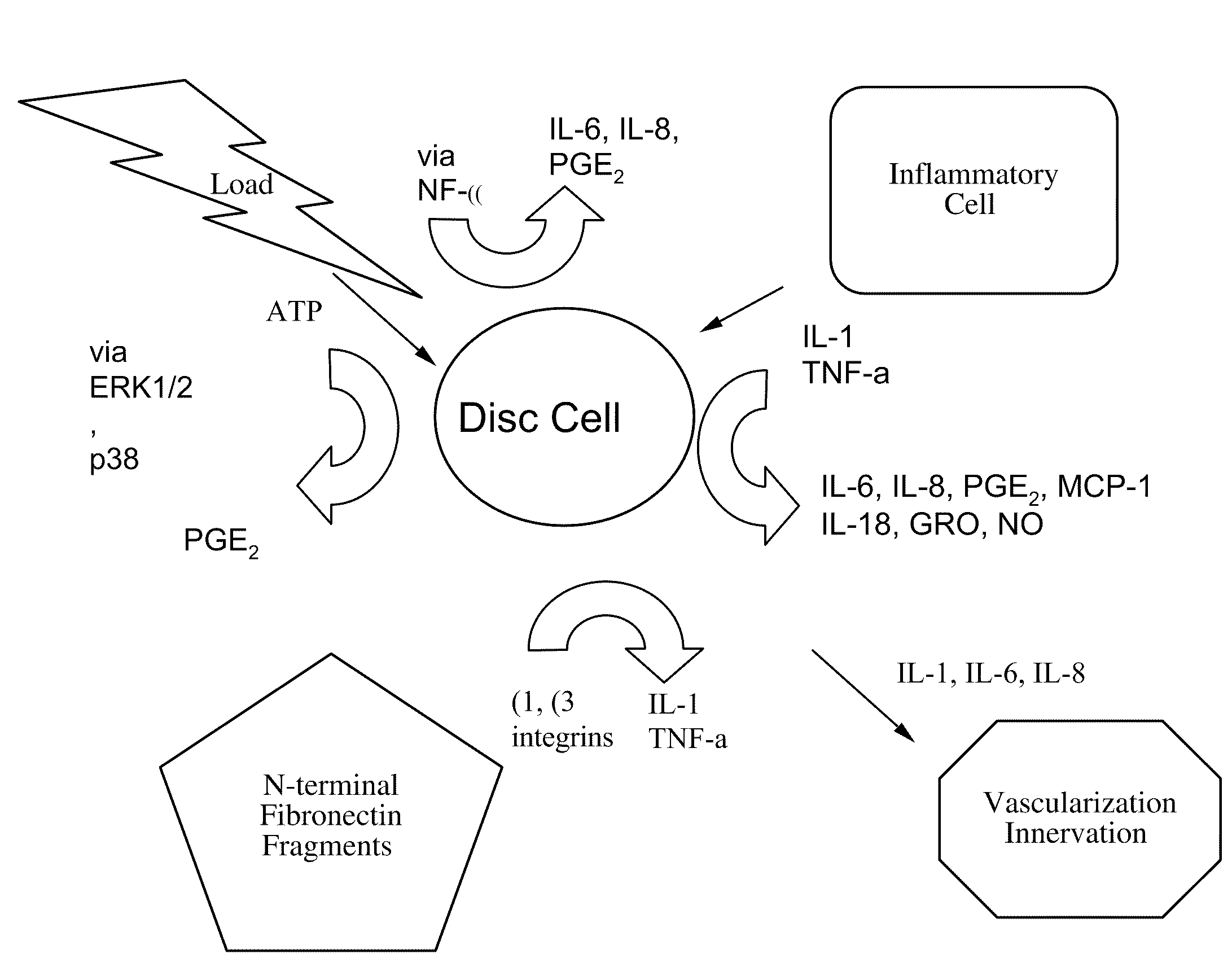
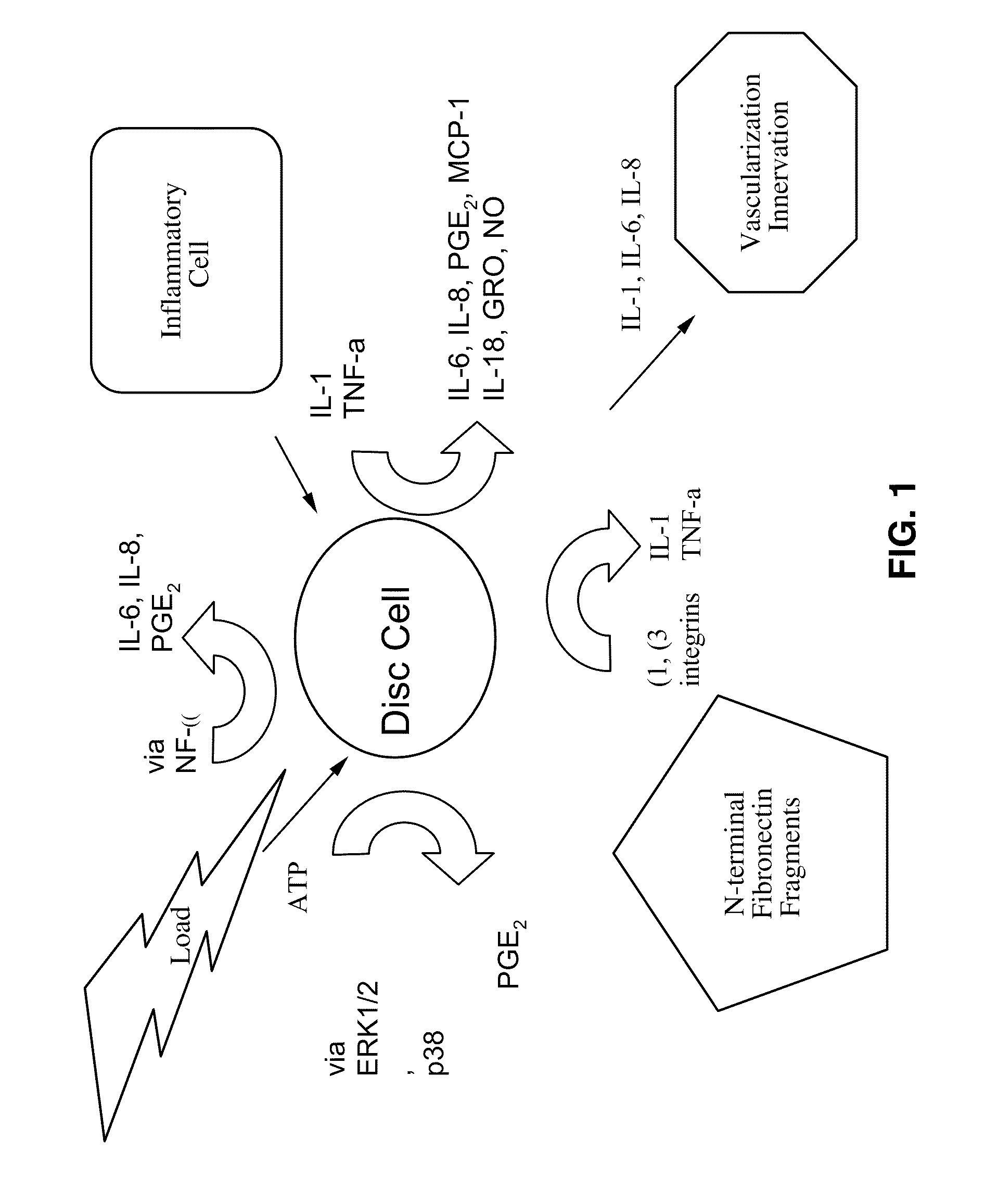
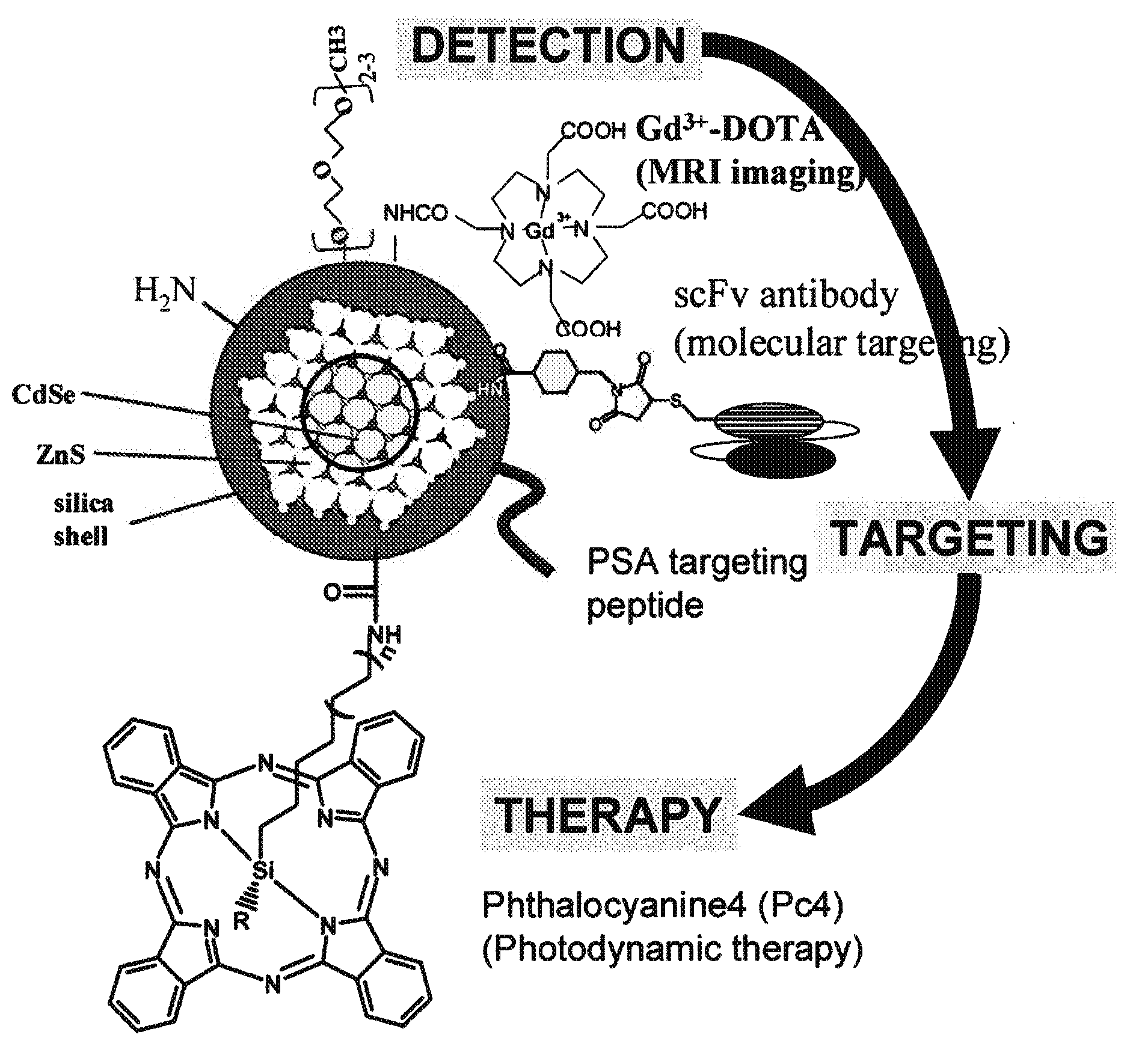
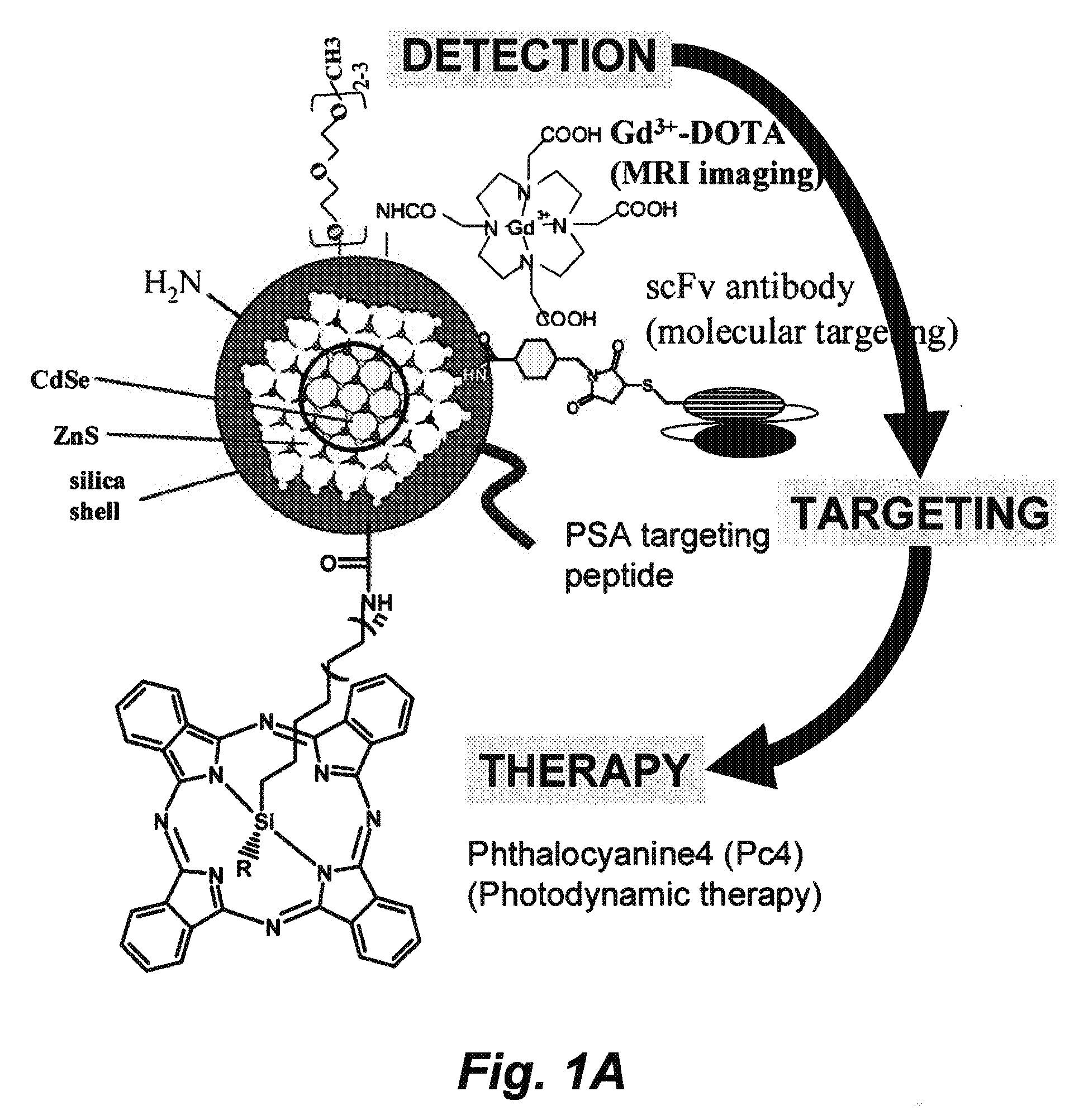
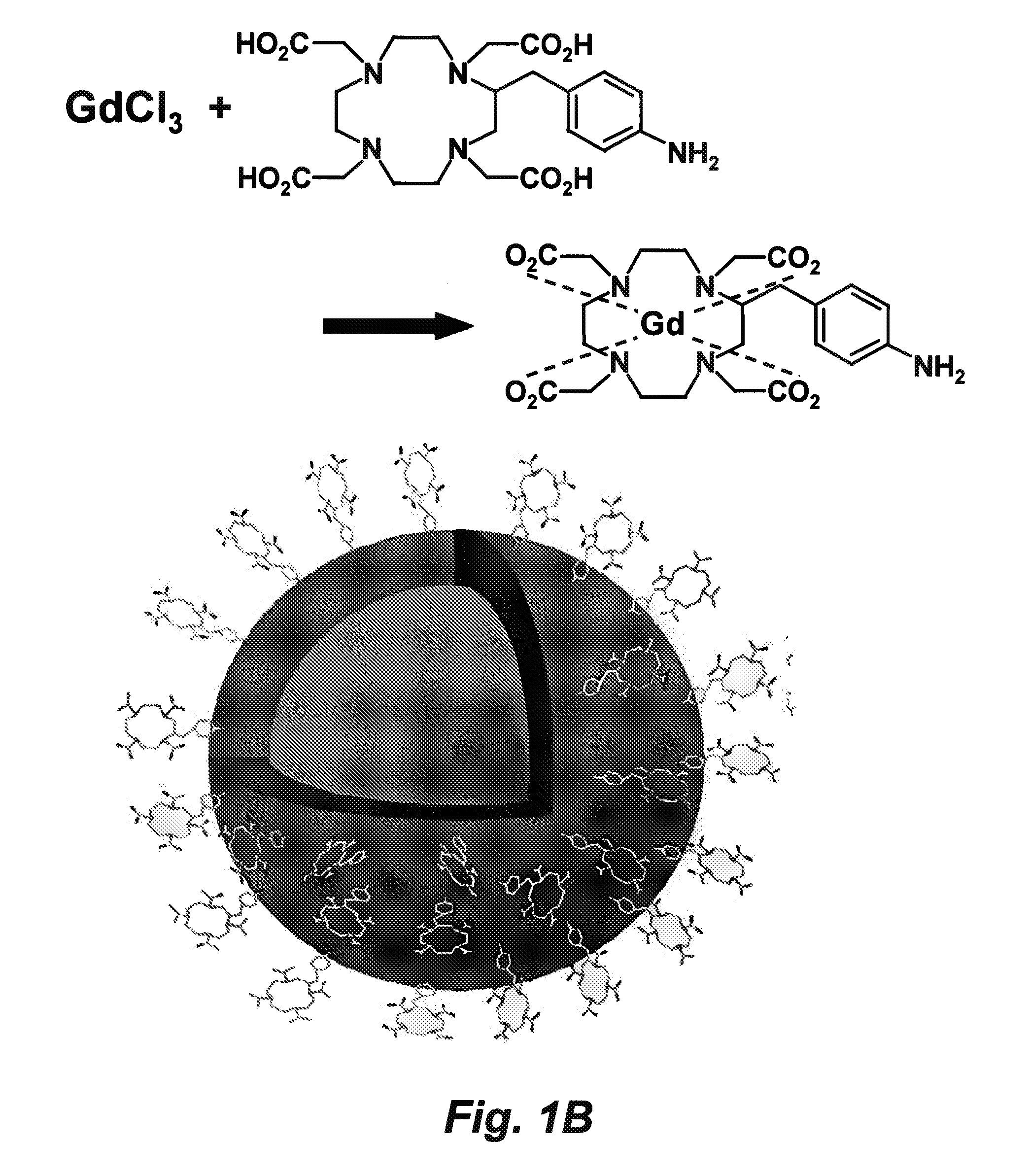
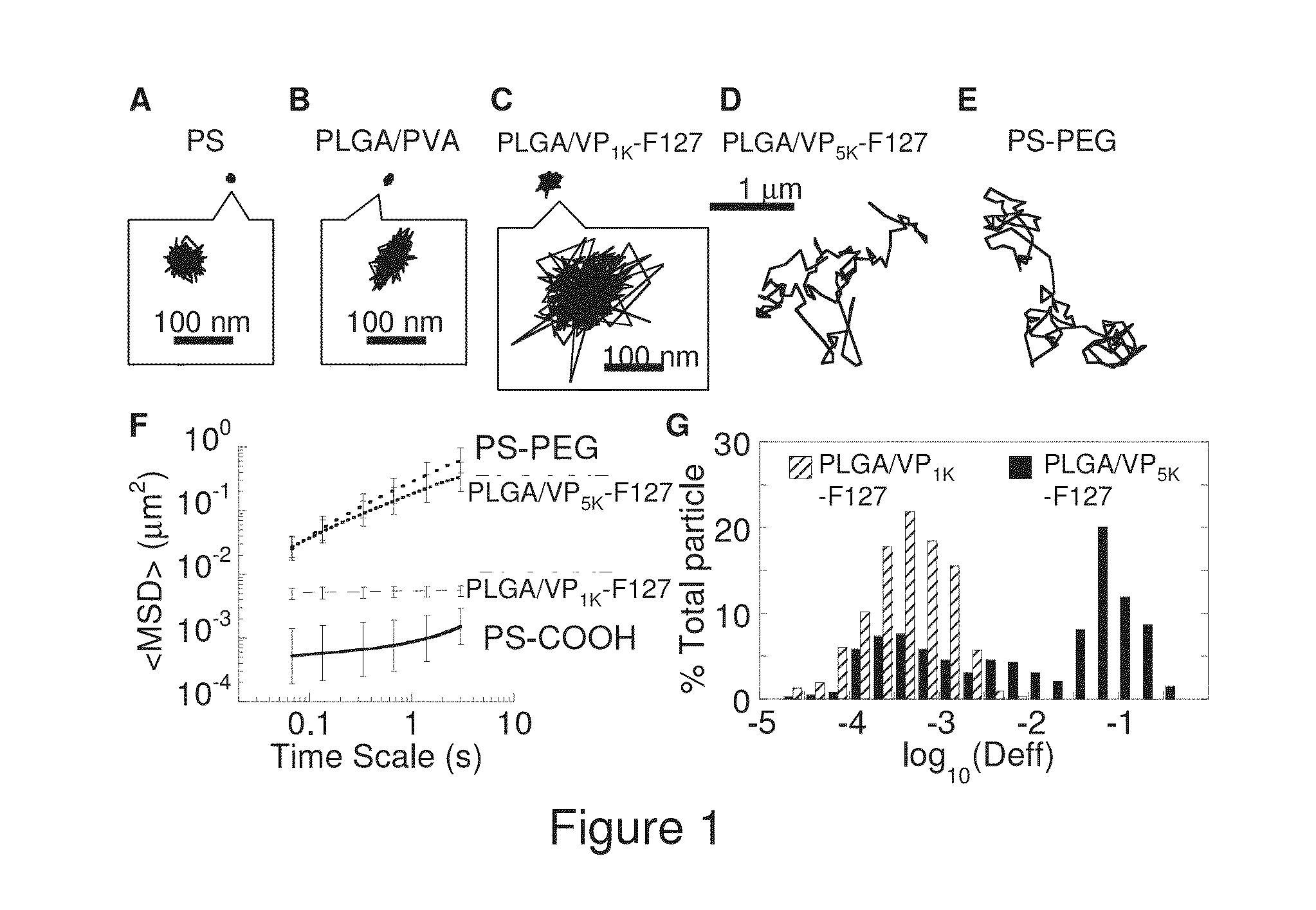
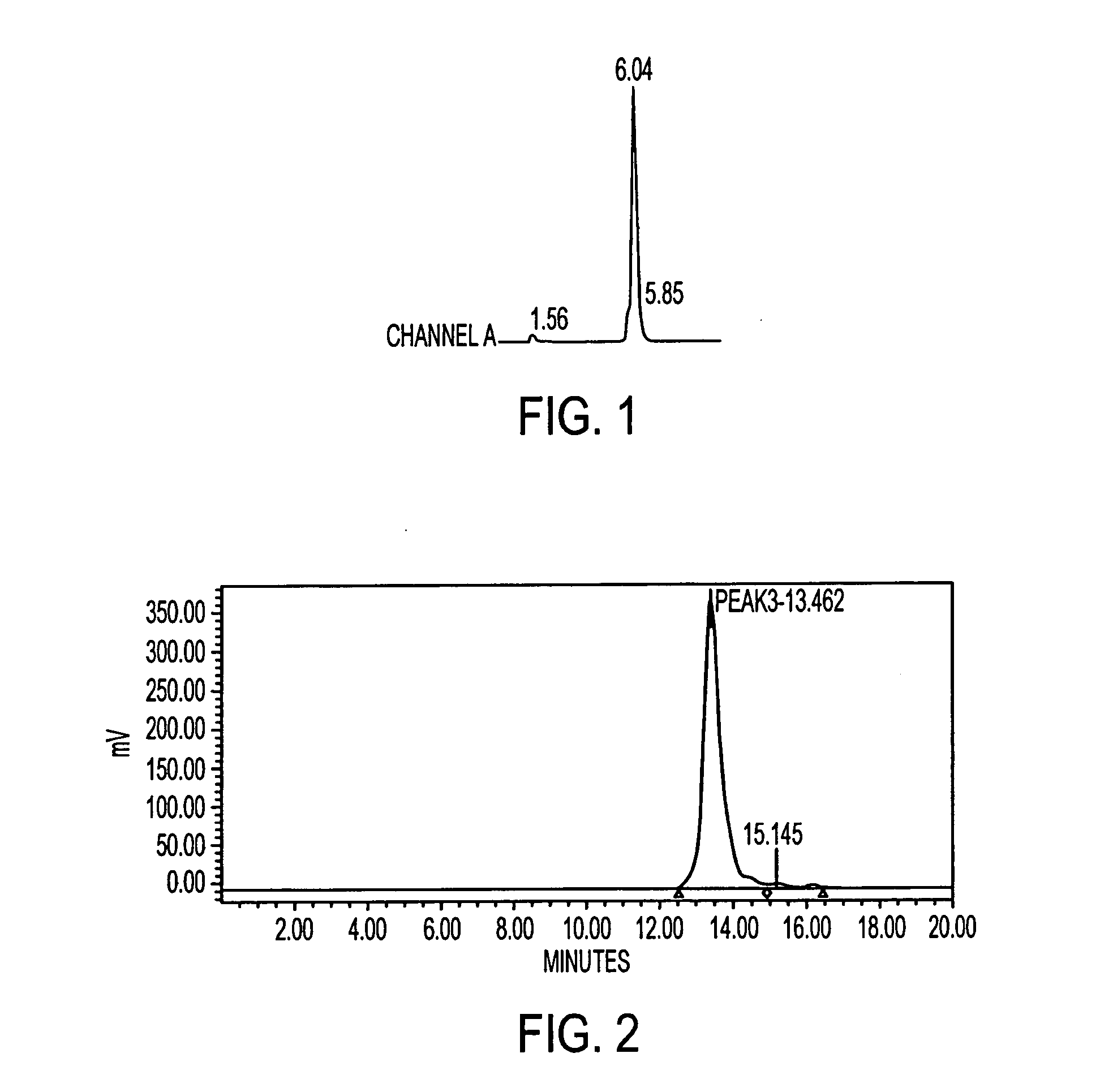
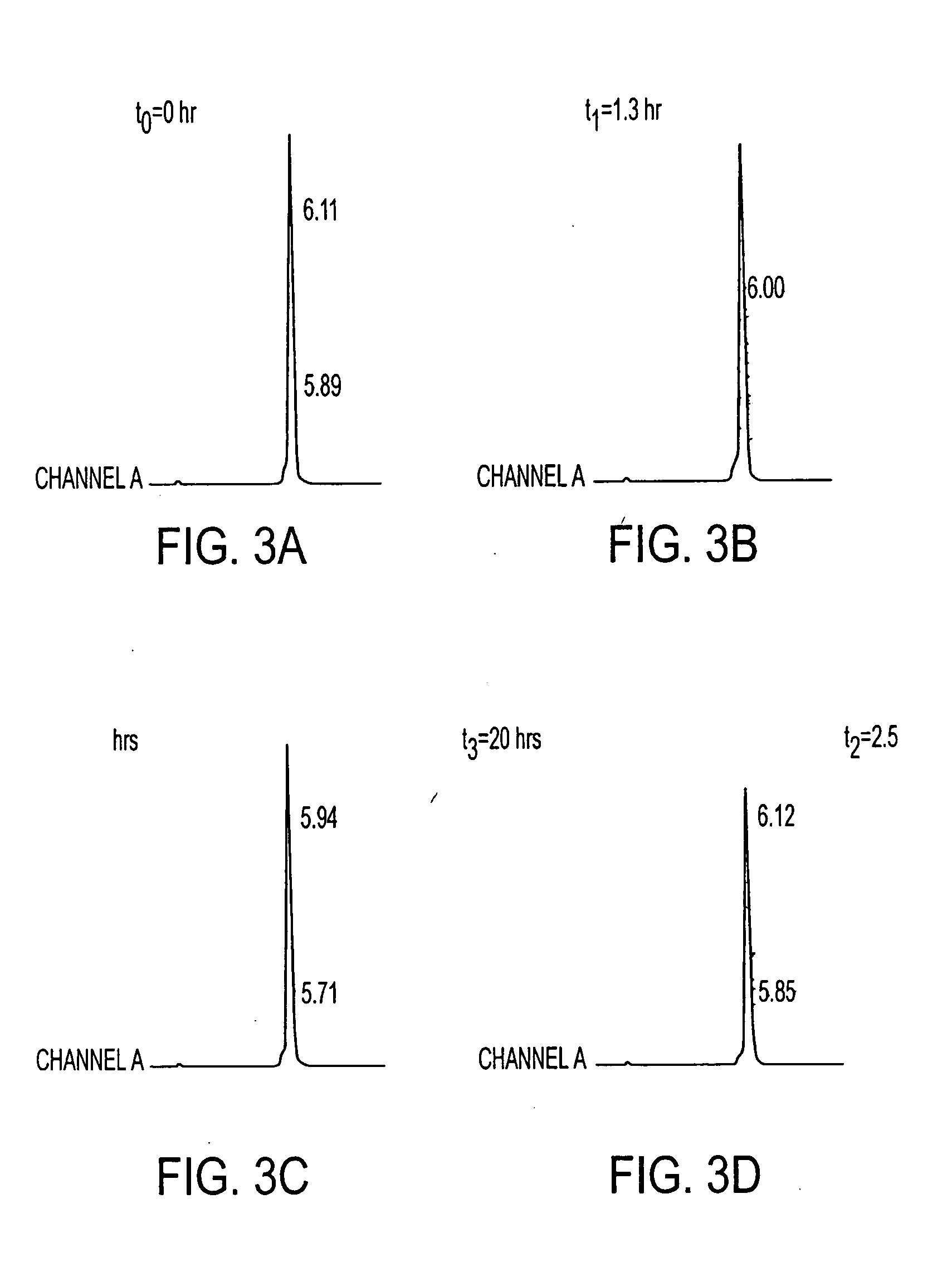
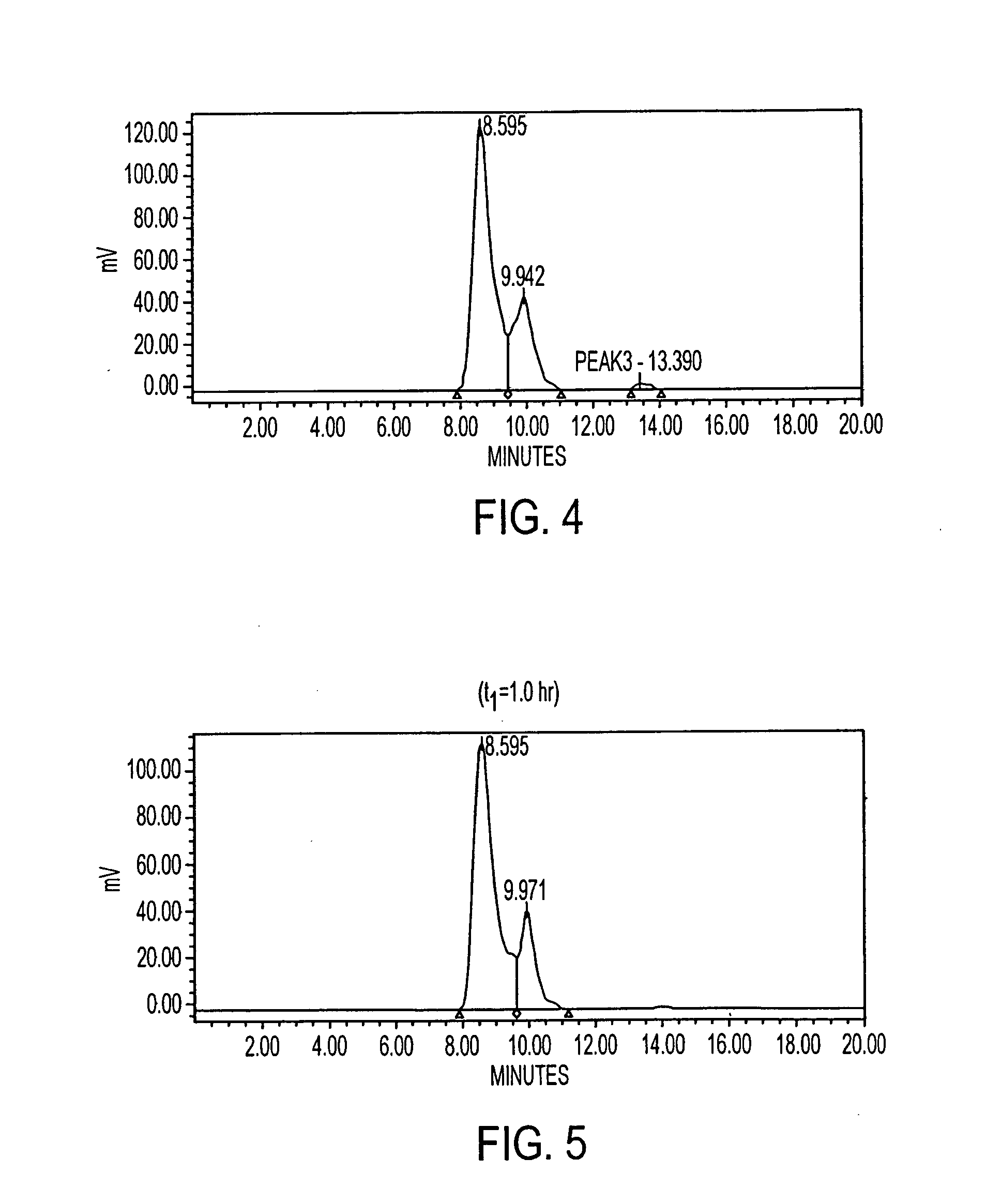
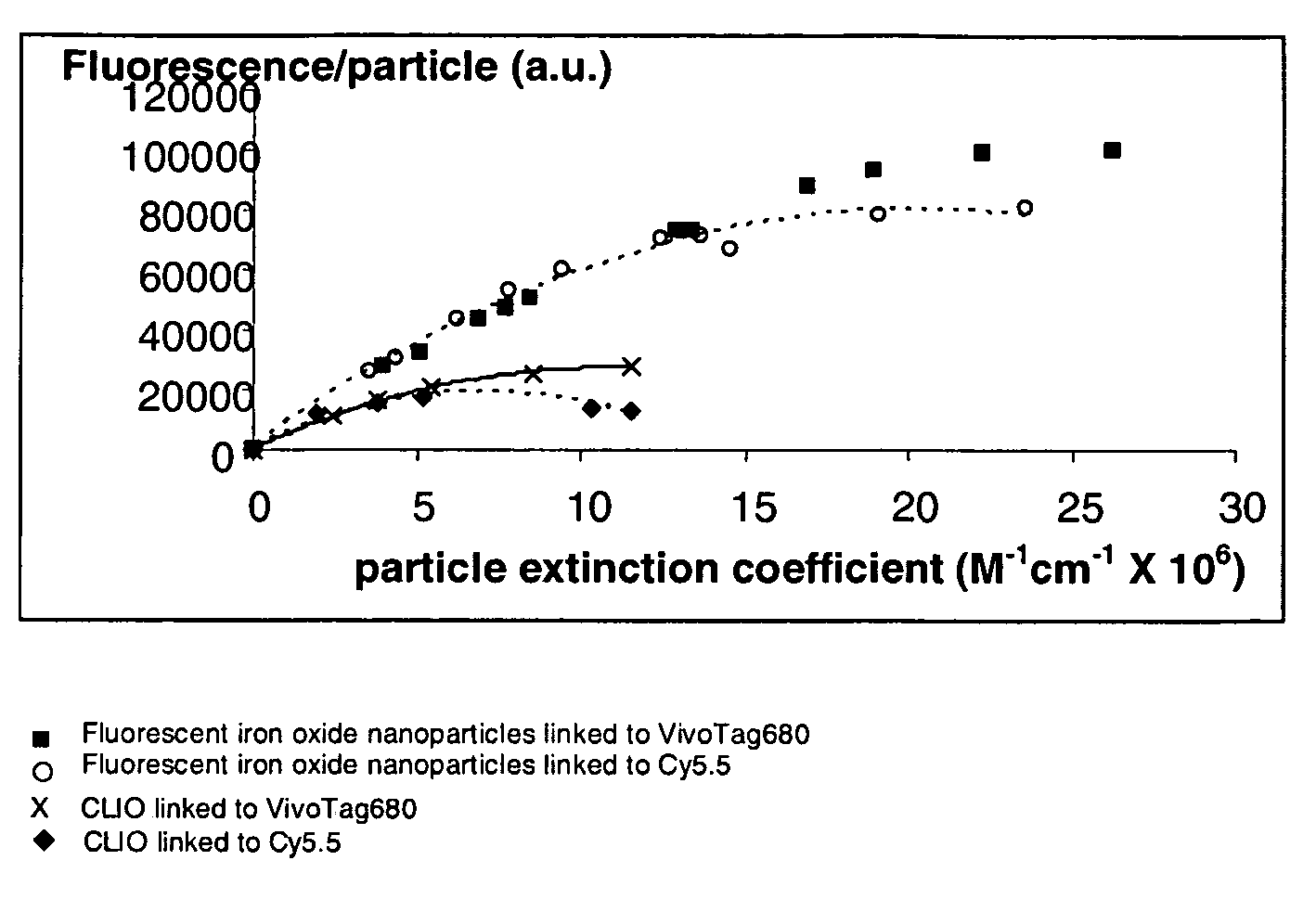
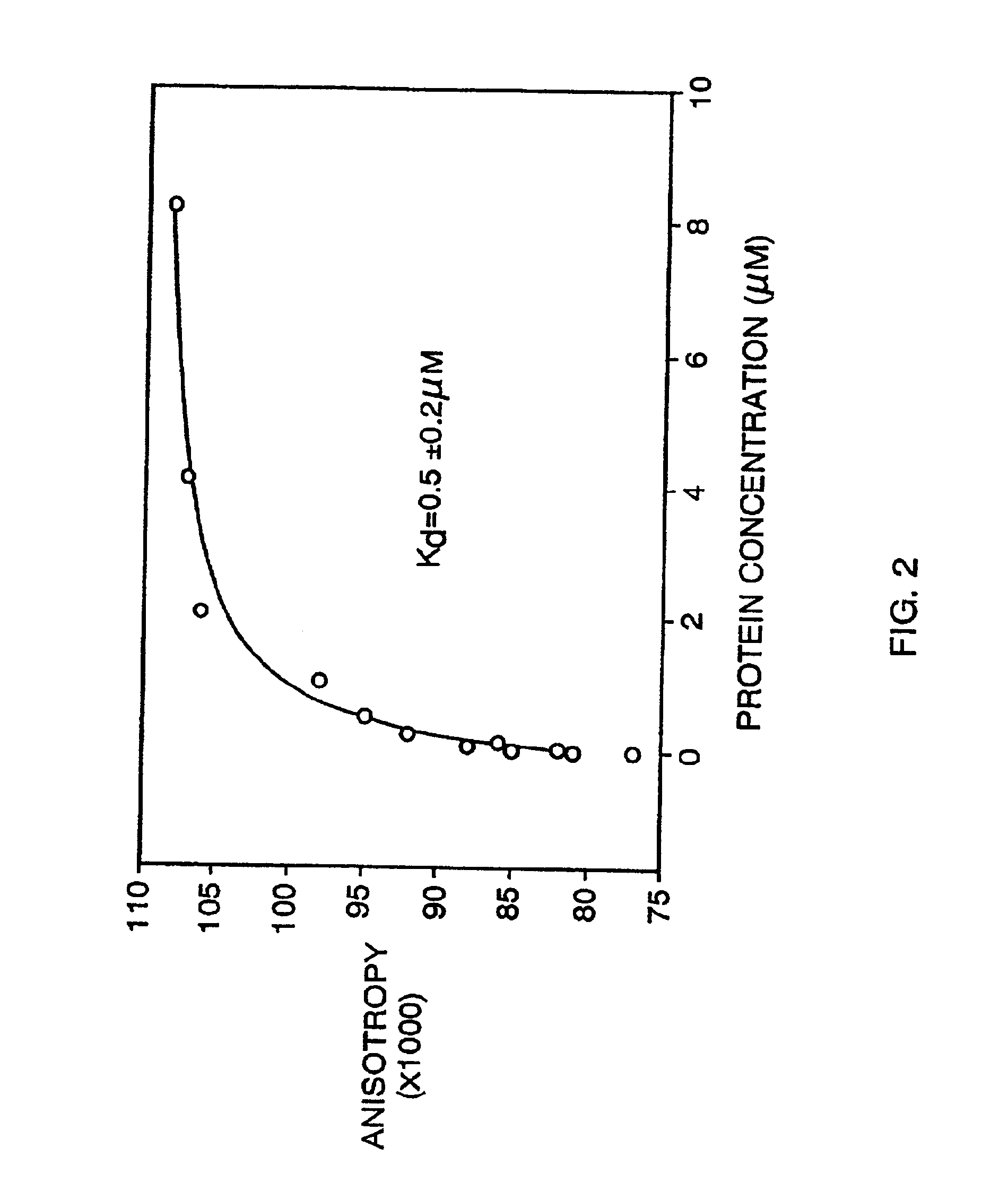
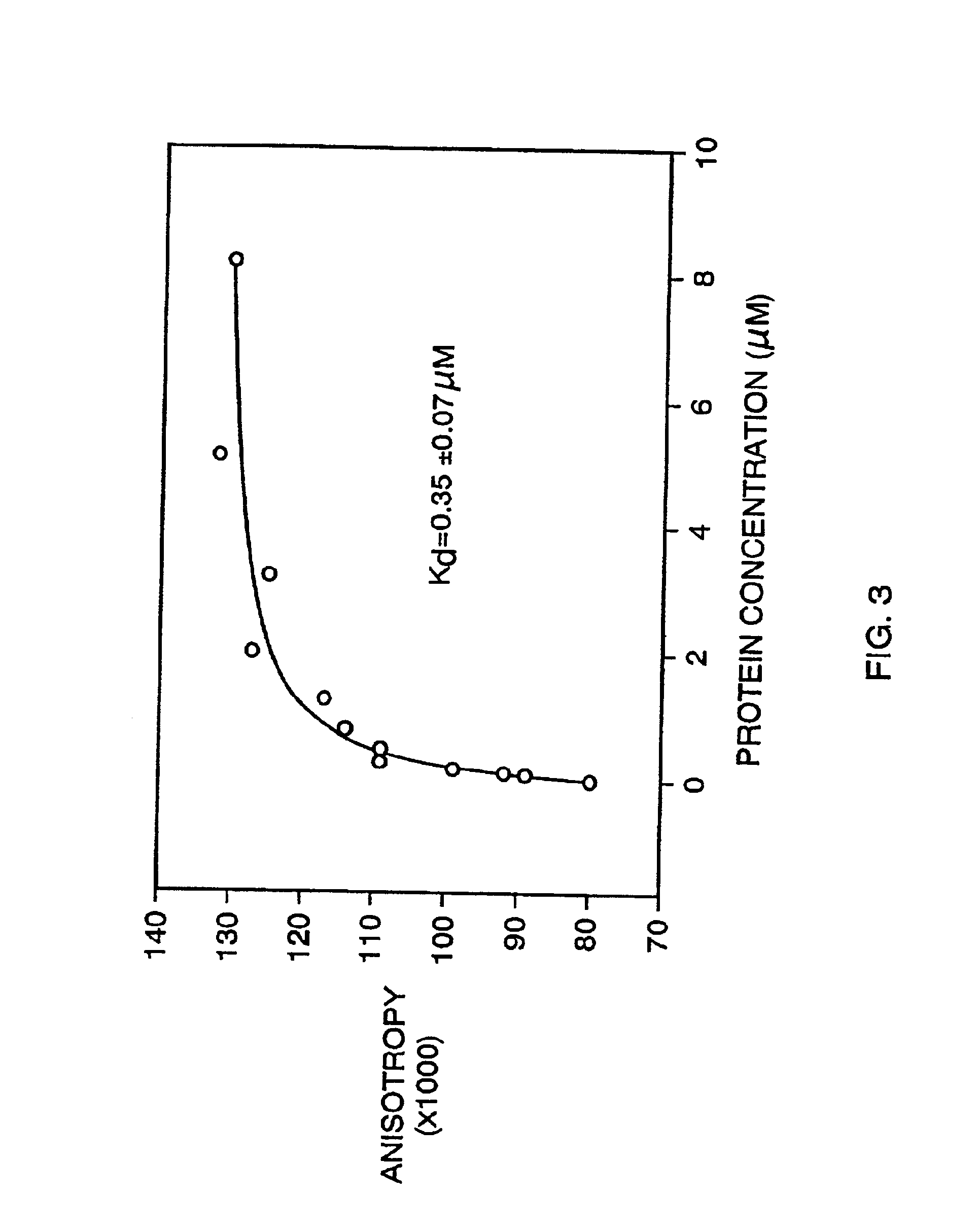
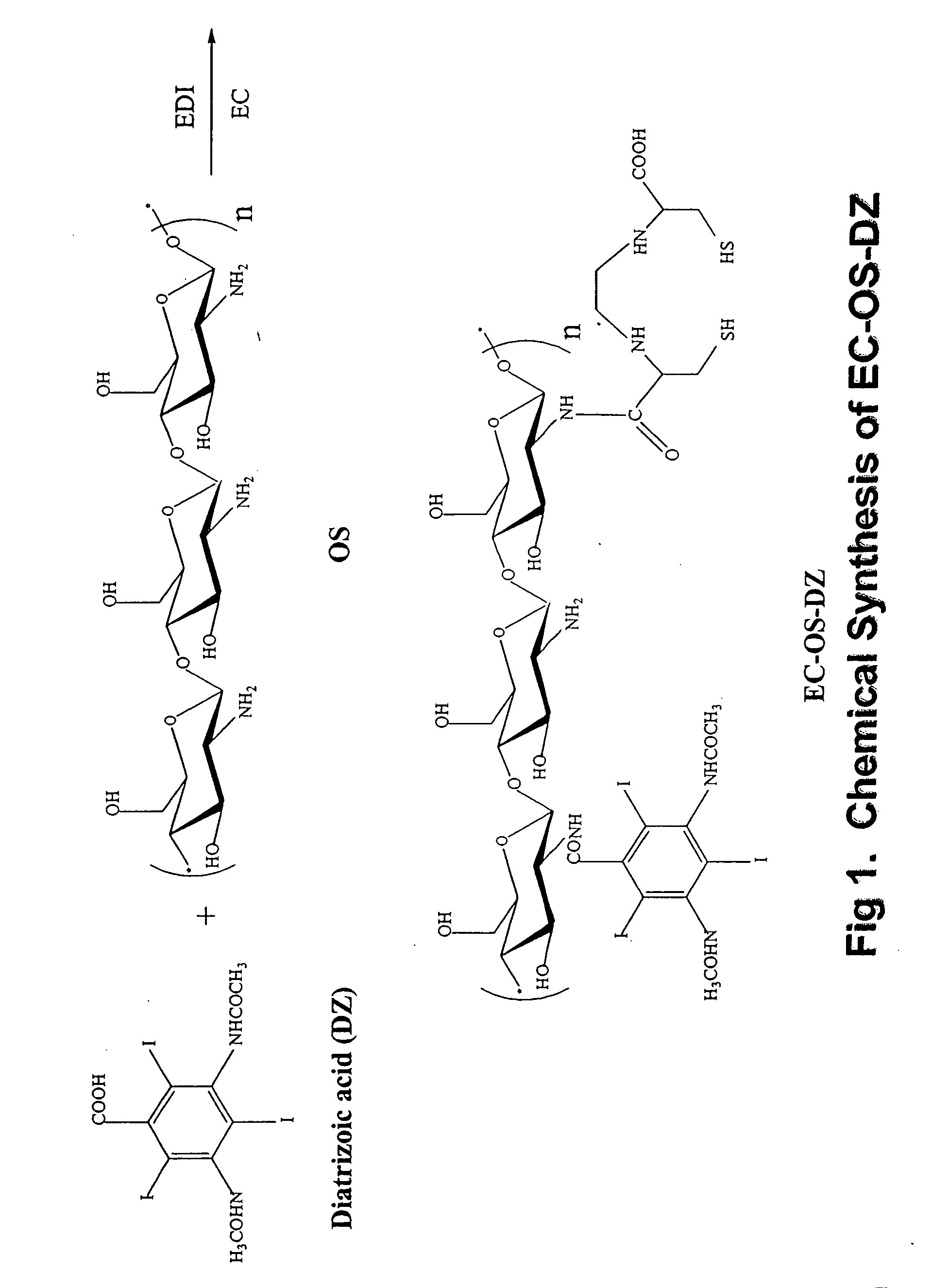
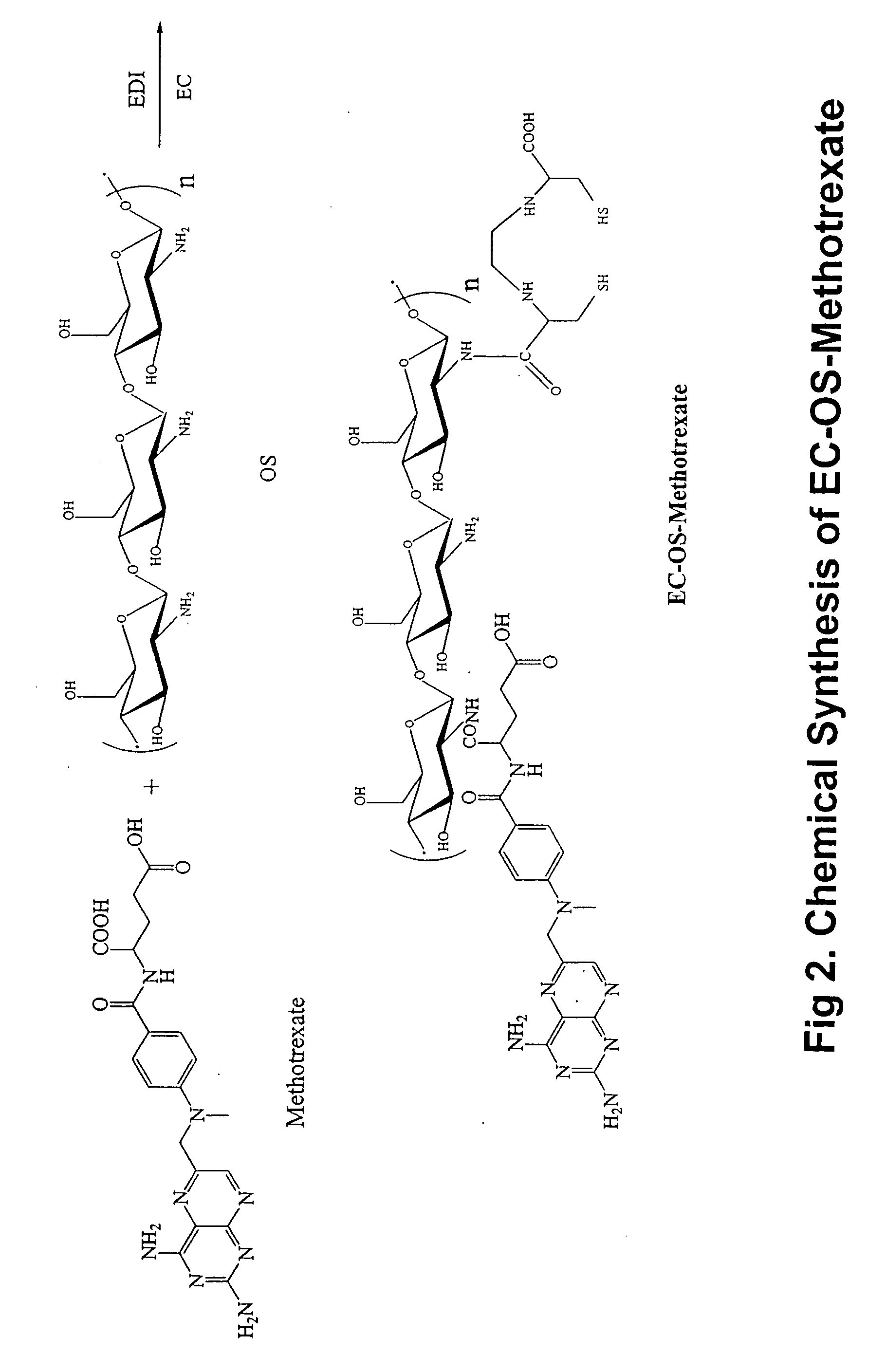
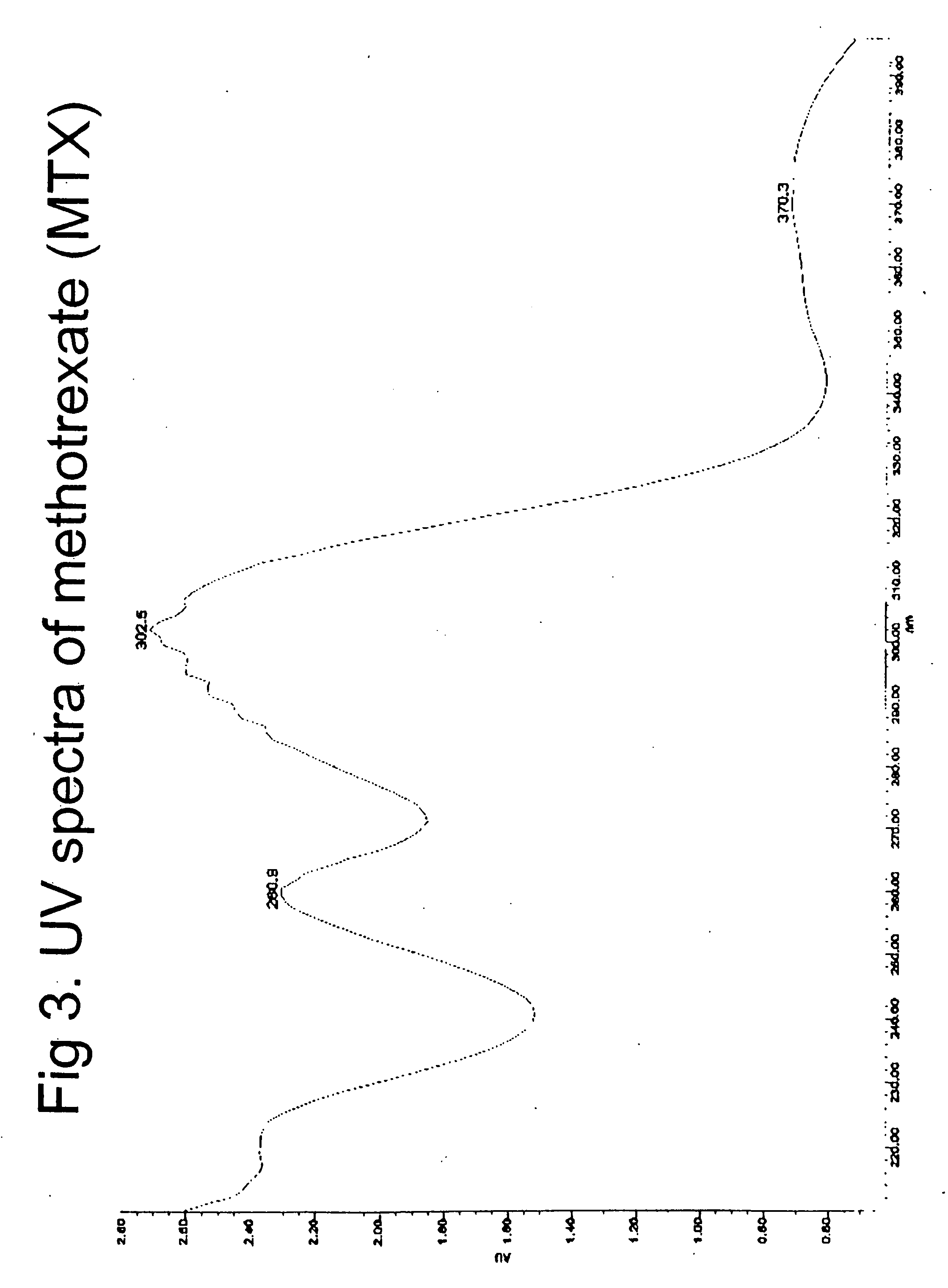
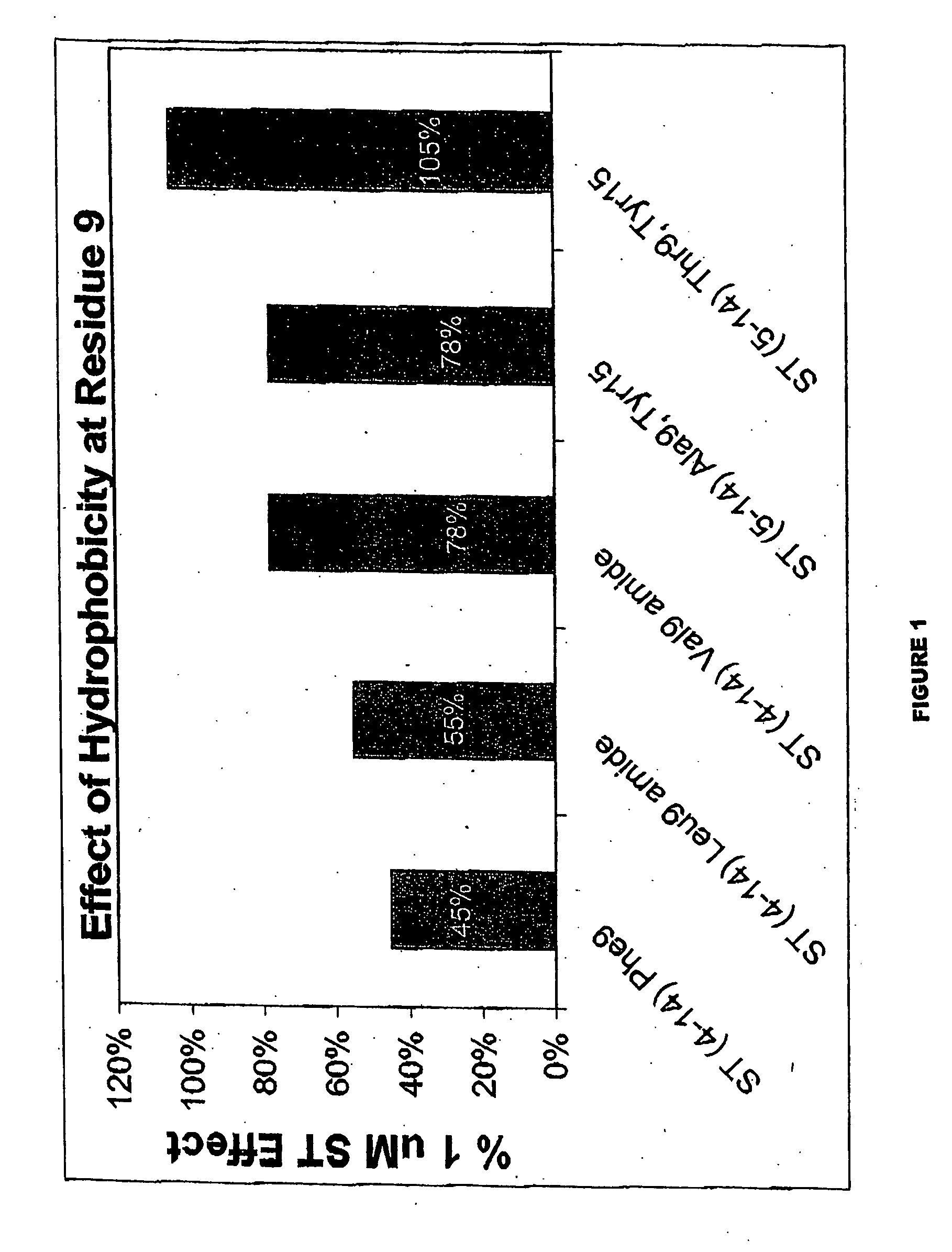
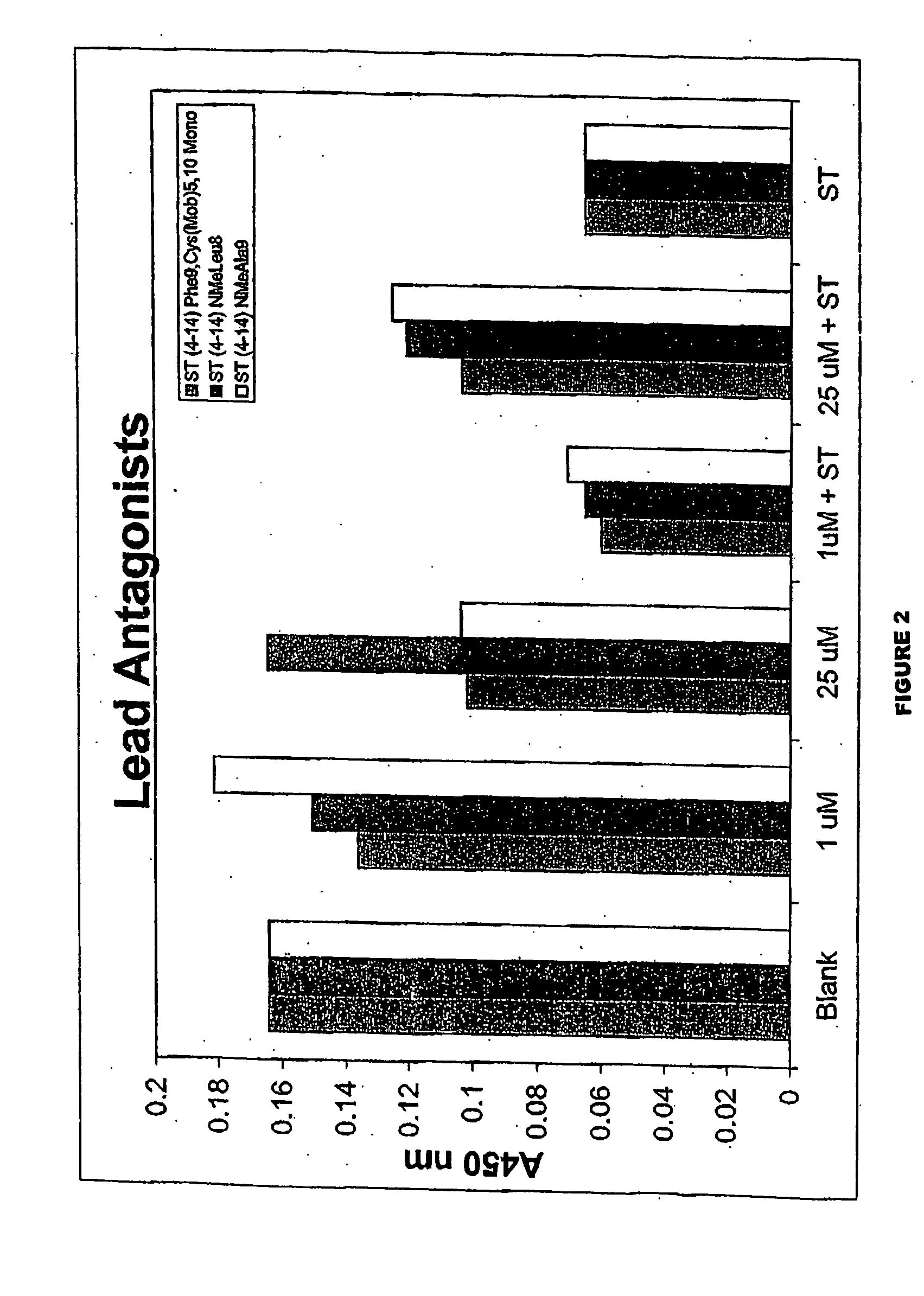
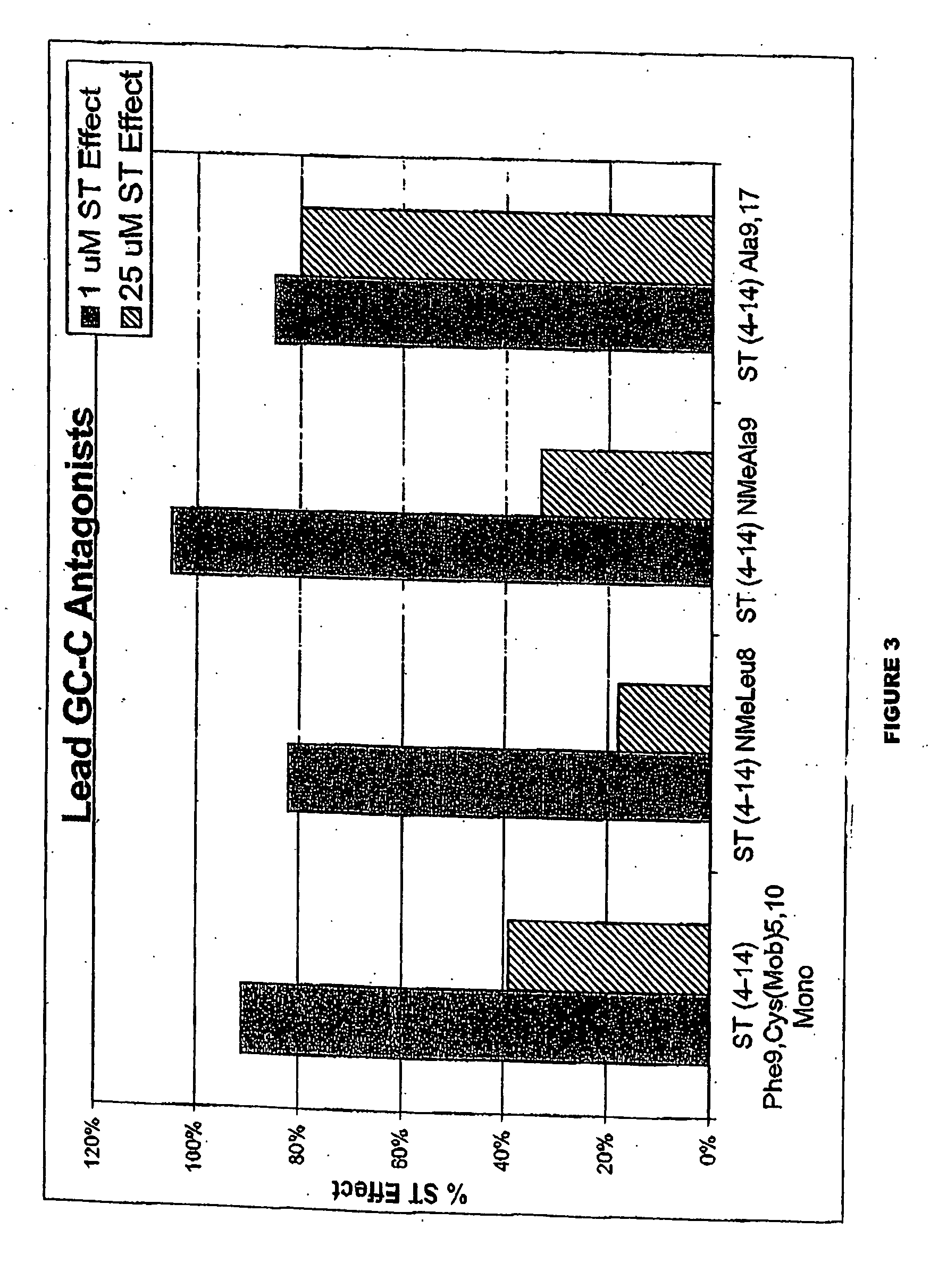
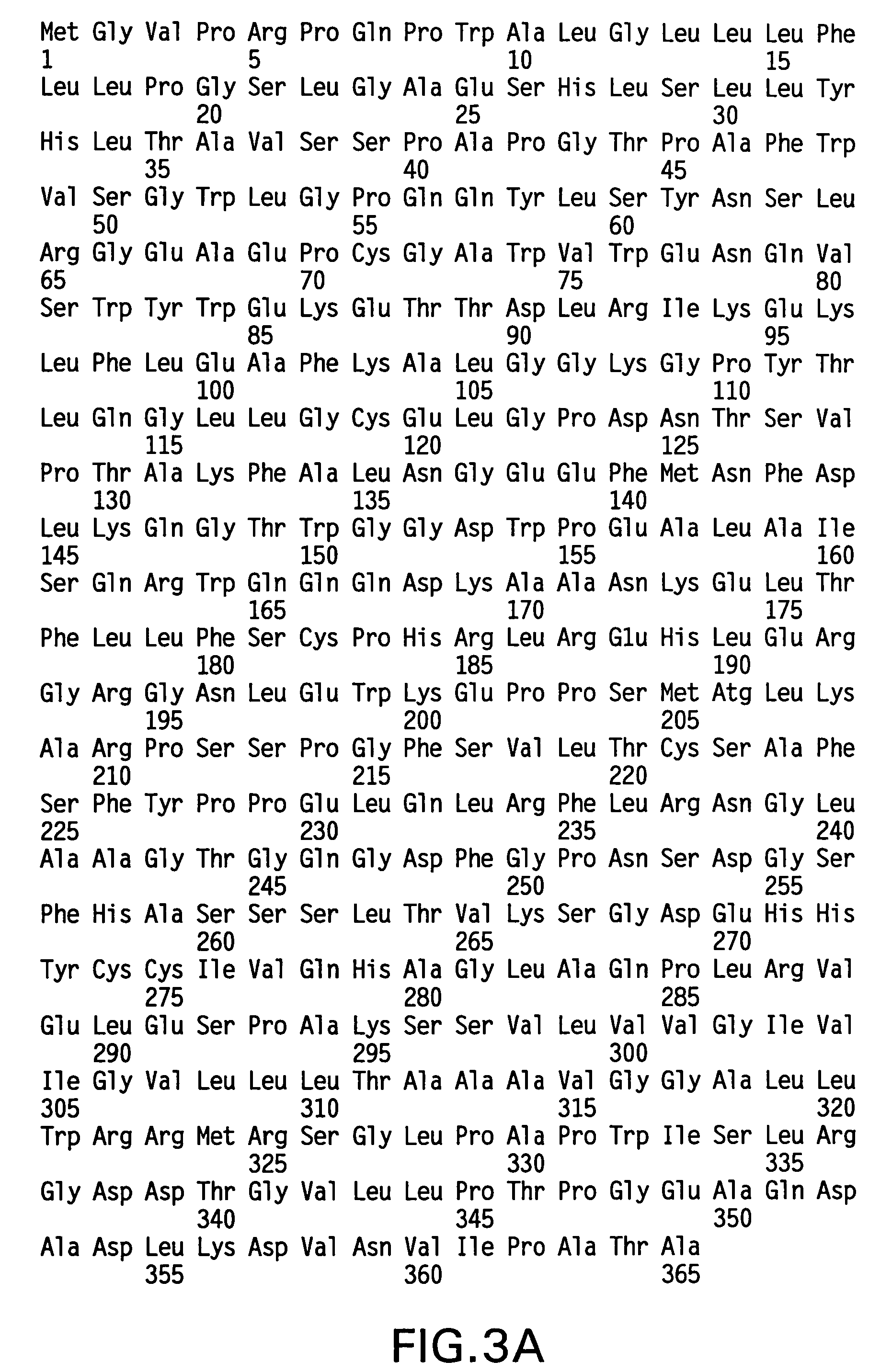Patents
Literature
1370results about "General/multifunctional contrast agents" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecules with extended half-lives, compositions and uses thereof
The present invention provides molecules, including IgGs, non-IgG immunoglobulin, proteins and non-protein agents, that have increased in vivo half-lives due to the presence of an IgG constant domain, or a portion thereof that binds the FcRn, having one or more amino acid modifications that increase the affinity of the constant domain or fragment for FcRn. Such proteins and molecules with increased half-lives have the advantage that smaller amounts and or less frequent dosing is required in the therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic use of such molecules.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Molecules with extended half-lives, compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20030190311A1High affinityExtended half-lifeCompounds screening/testingFungiIntravenous gammaglobulinIn vivo
The present invention provides molecules, including IgGs, non-IgG immunoglobulin, proteins and non-protein agents, that have increased in vivo half-lives due to the presence of an IgG constant domain, or a portion thereof that binds the FcRn, having one or more amino acid modifications that increase the affinity of the constant domain or fragment for FcRn. Such proteins and molecules with increased half-lives have the advantage that smaller amounts and or less frequent dosing is required in the therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic use of such molecules.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Compositions and methods relating to reduced mucoadhesion
InactiveUS20120121718A1Reduced mucoadhesionDiffusion fastOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryMedicineParticle composition
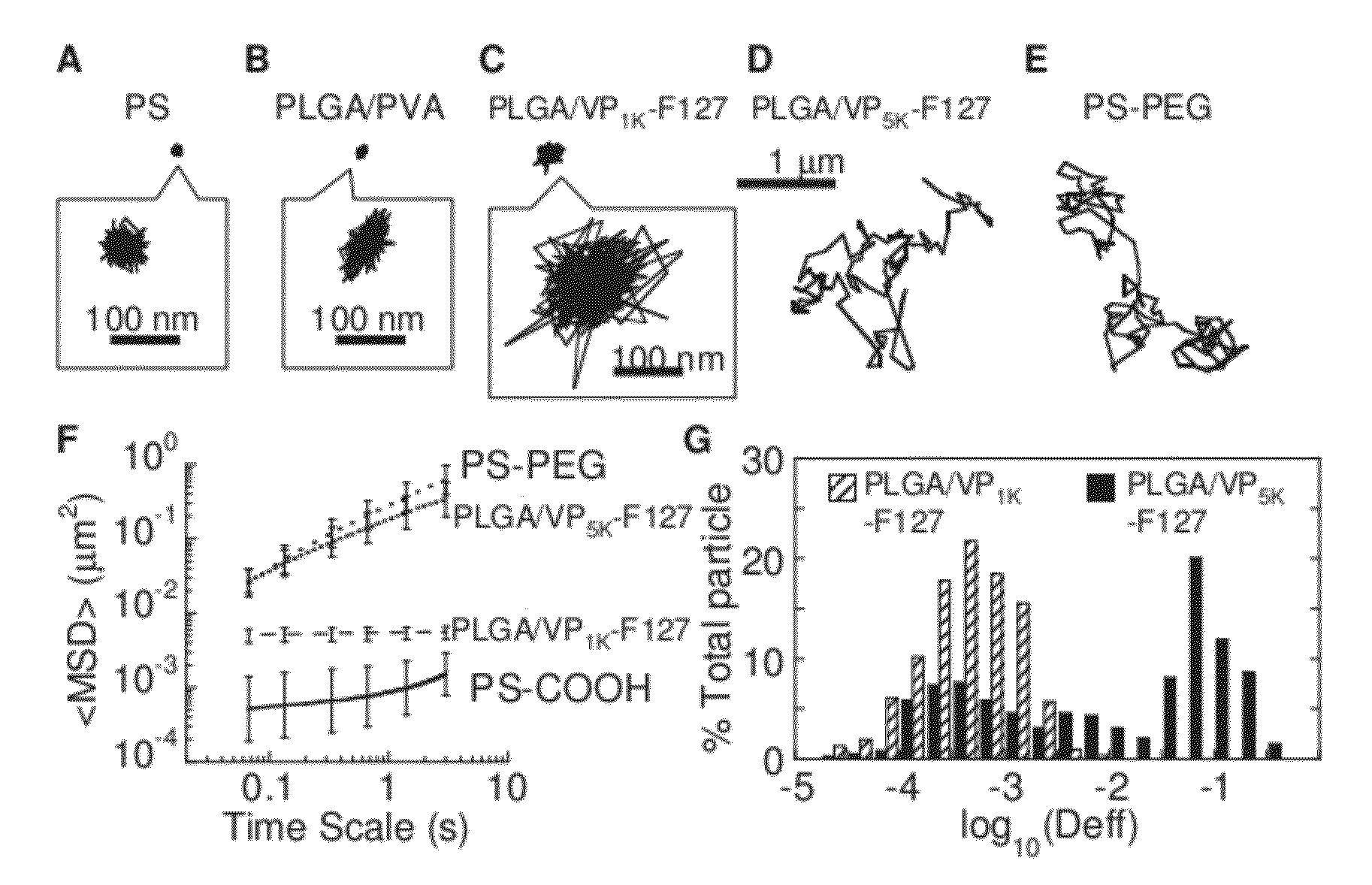
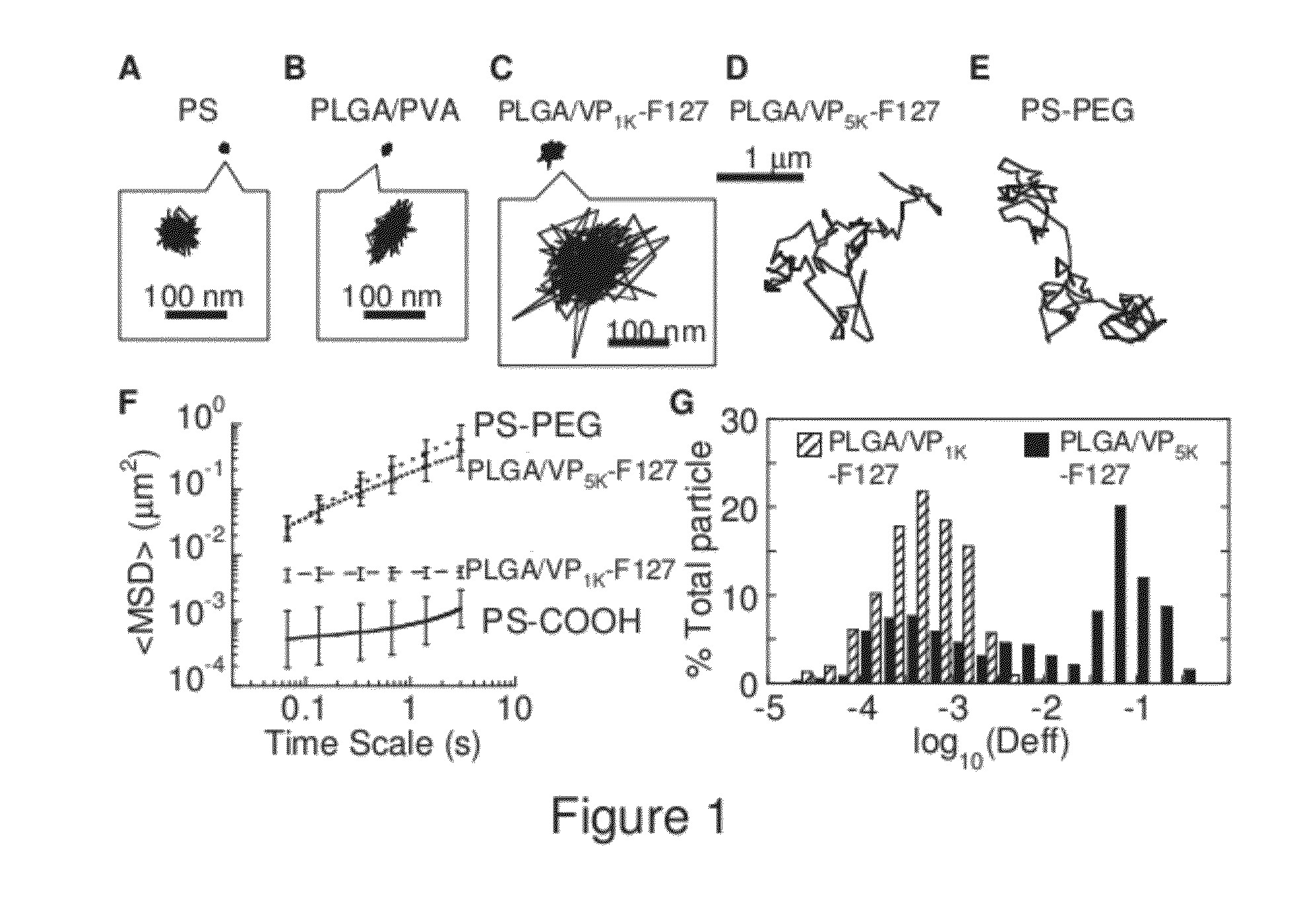
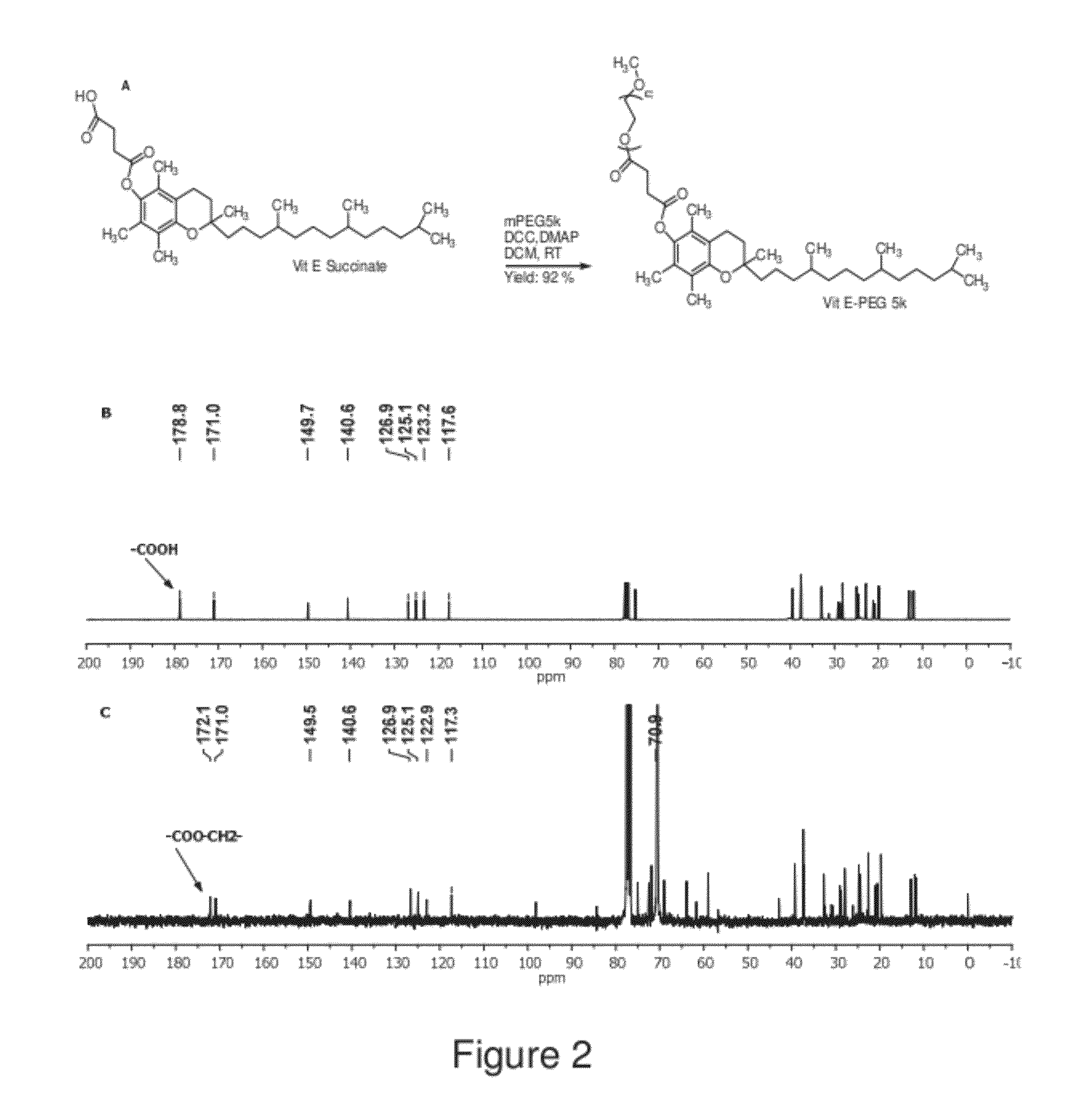
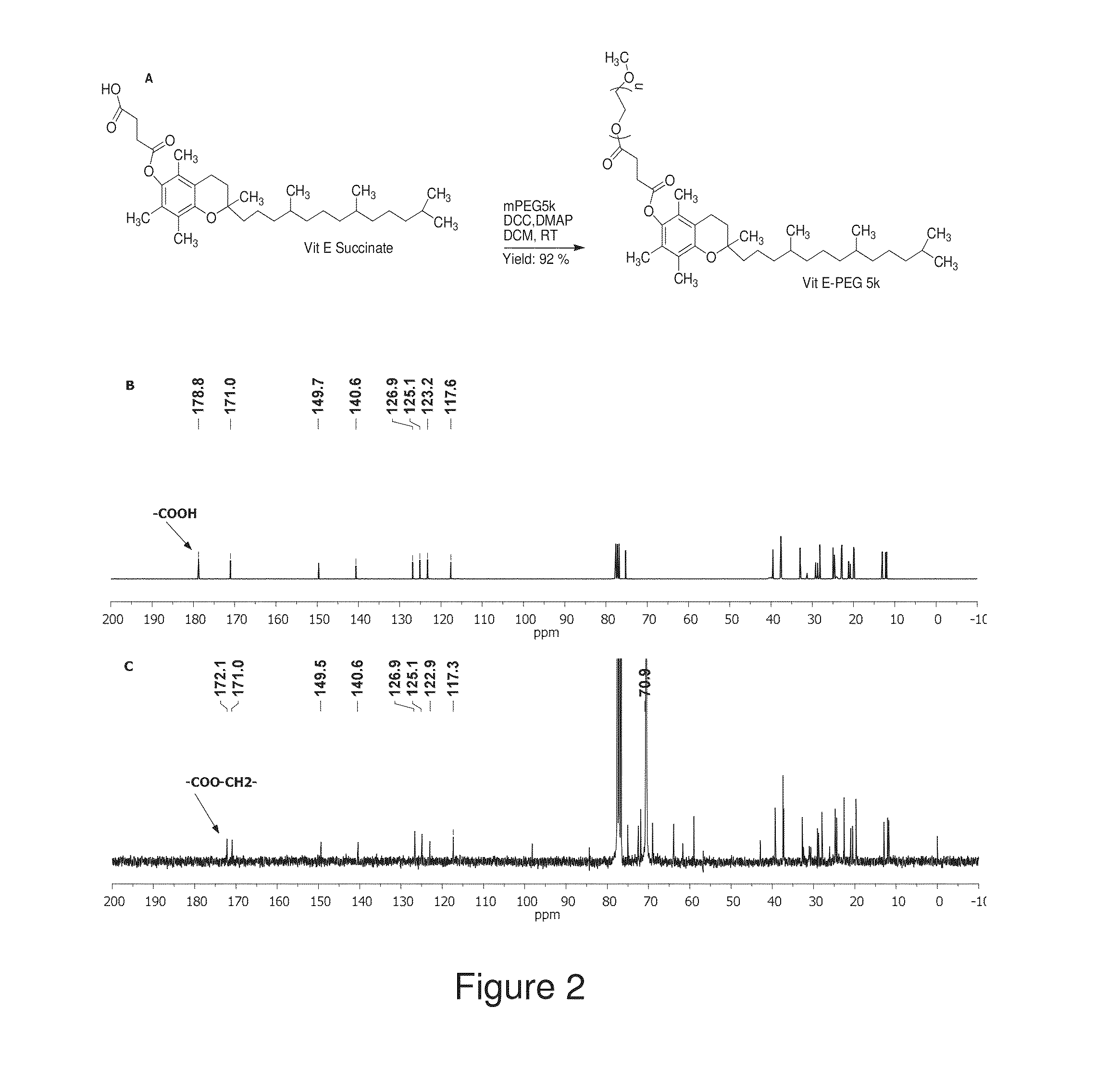
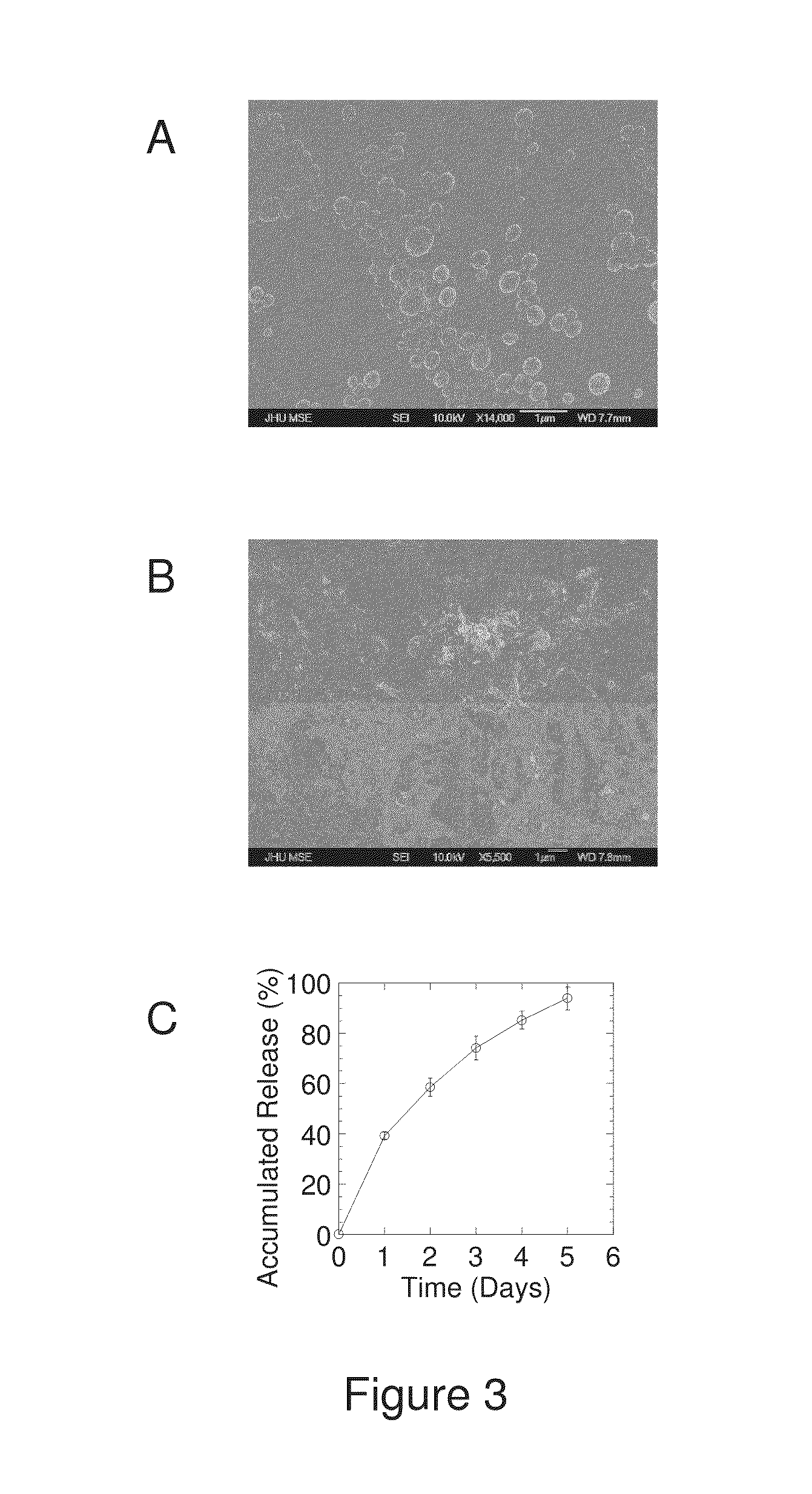
The present invention generally relates to reducing the mucoadhesive properties of a particle. In some embodiments, the particle is coated with and / or associated with a (poly(ethylene glycol))-(poly(propylene oxide))-(poly(ethylene glycol)) triblock copolymer. Methods for preparing inventive particles using a poly(ethylene glycol)-vitamin E conjugate as a surfactant are also provided. In some embodiments, methods are provided comprising administering to a subject a composition of particles of the present invention. Such particles with reduced mucoadhesive properties are useful in delivering agents to mucosal tissues such as oral, ophthalmic, gastrointestinal, nasal, respiratory, and genital mucosal tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
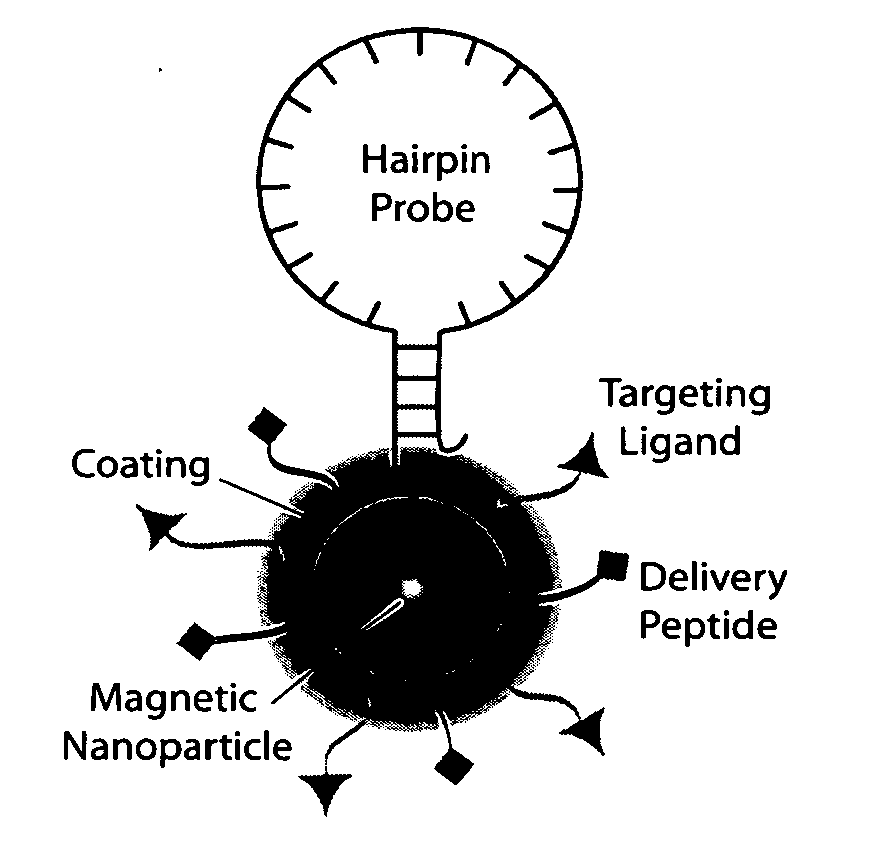
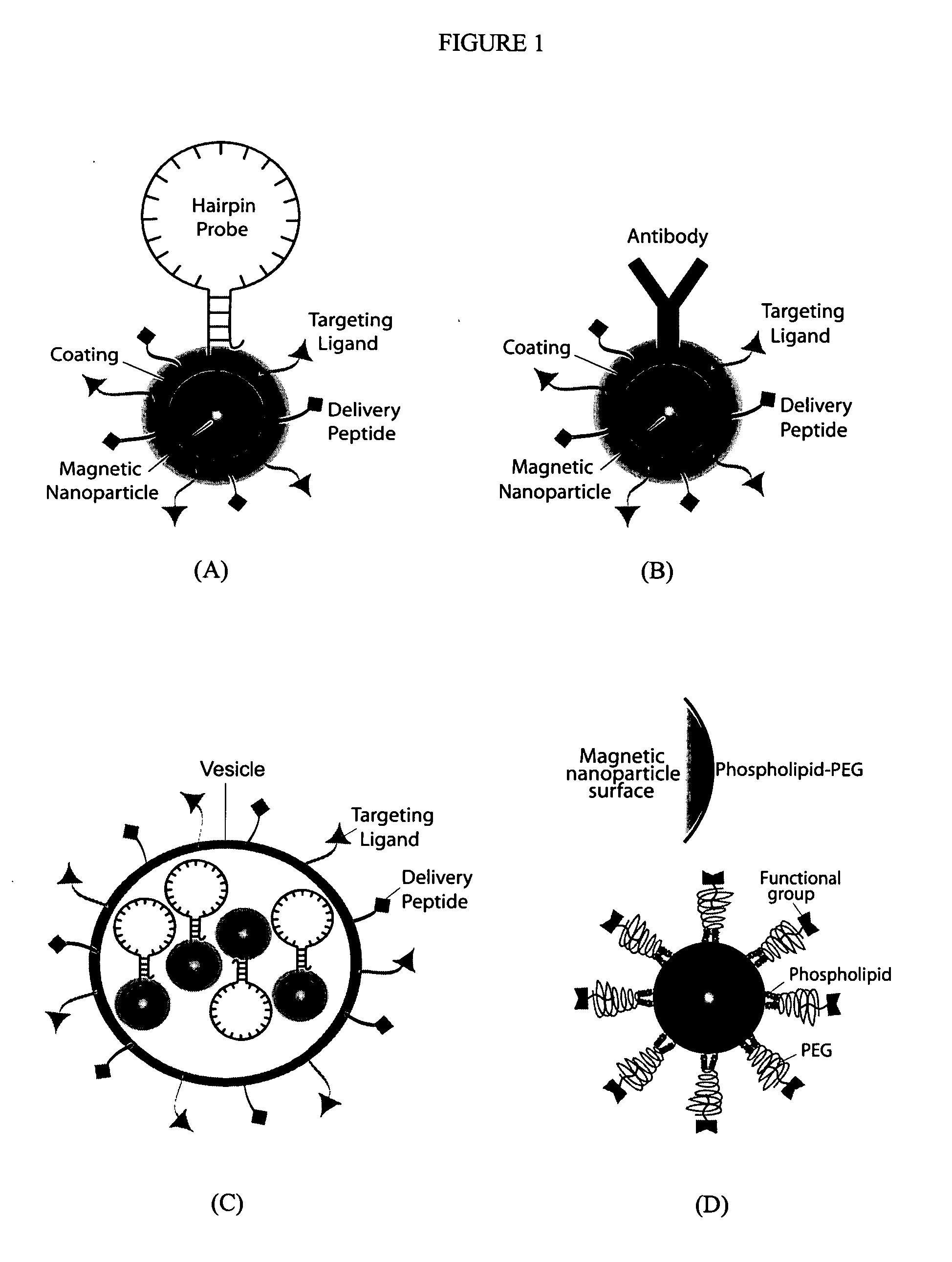
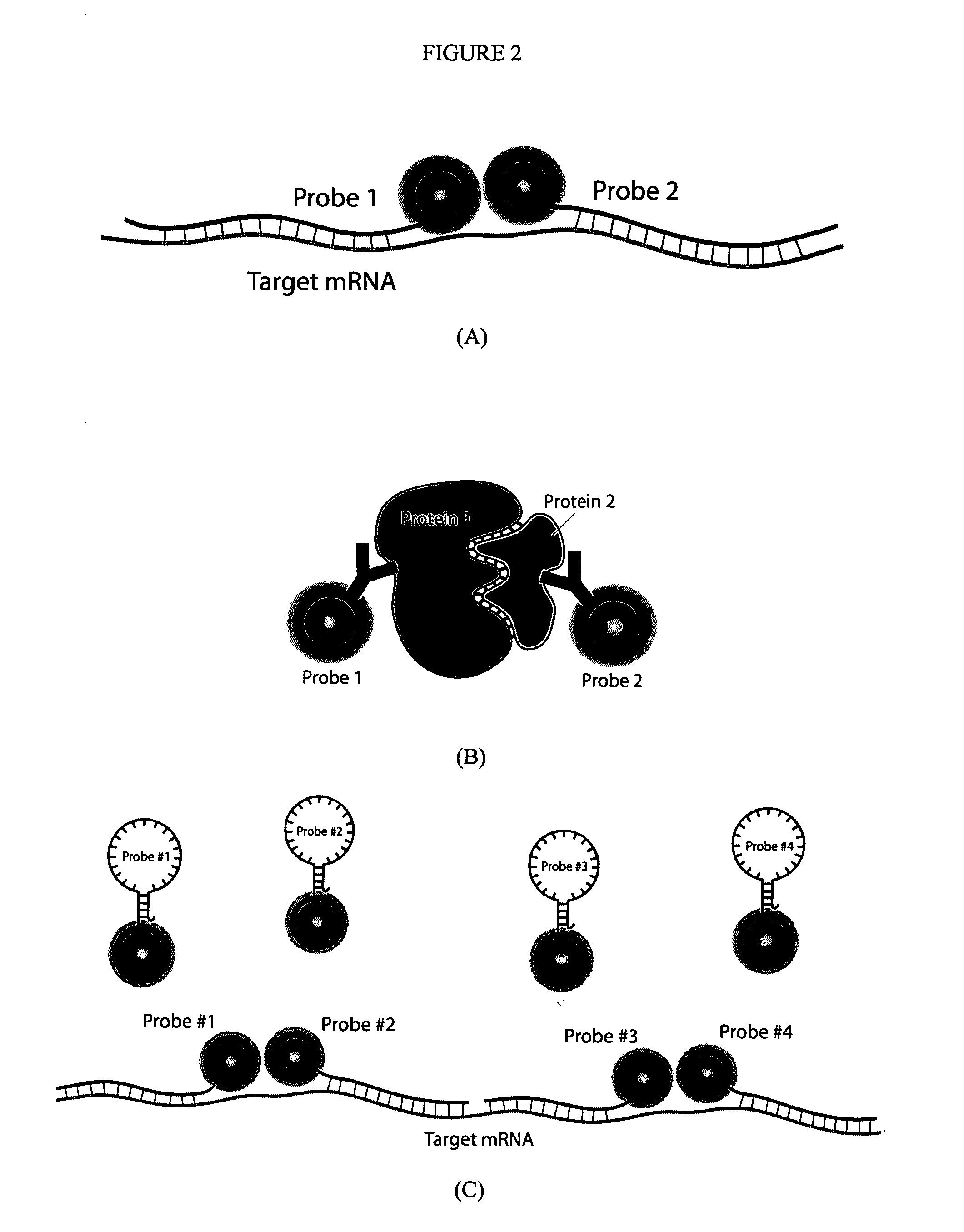
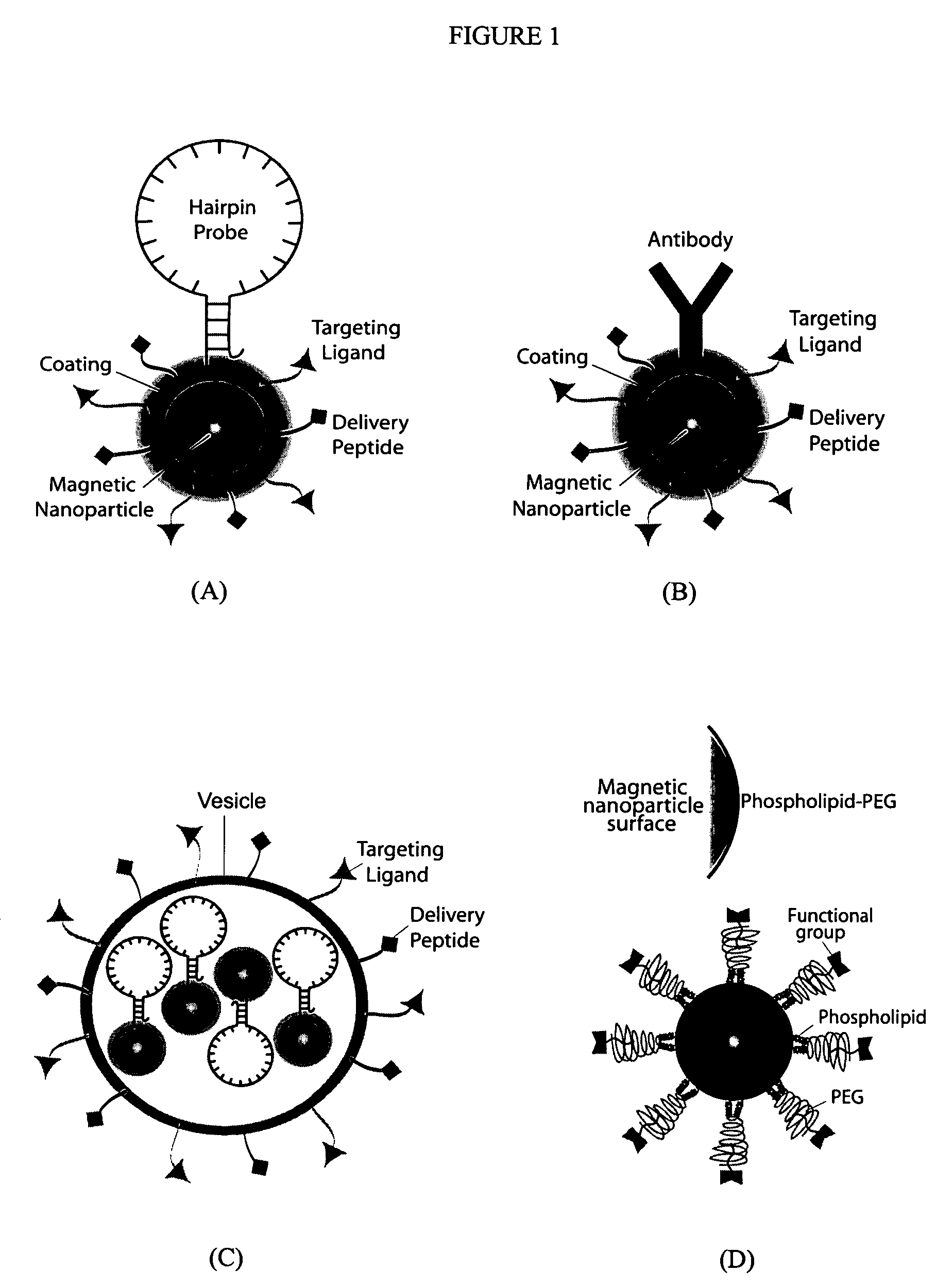
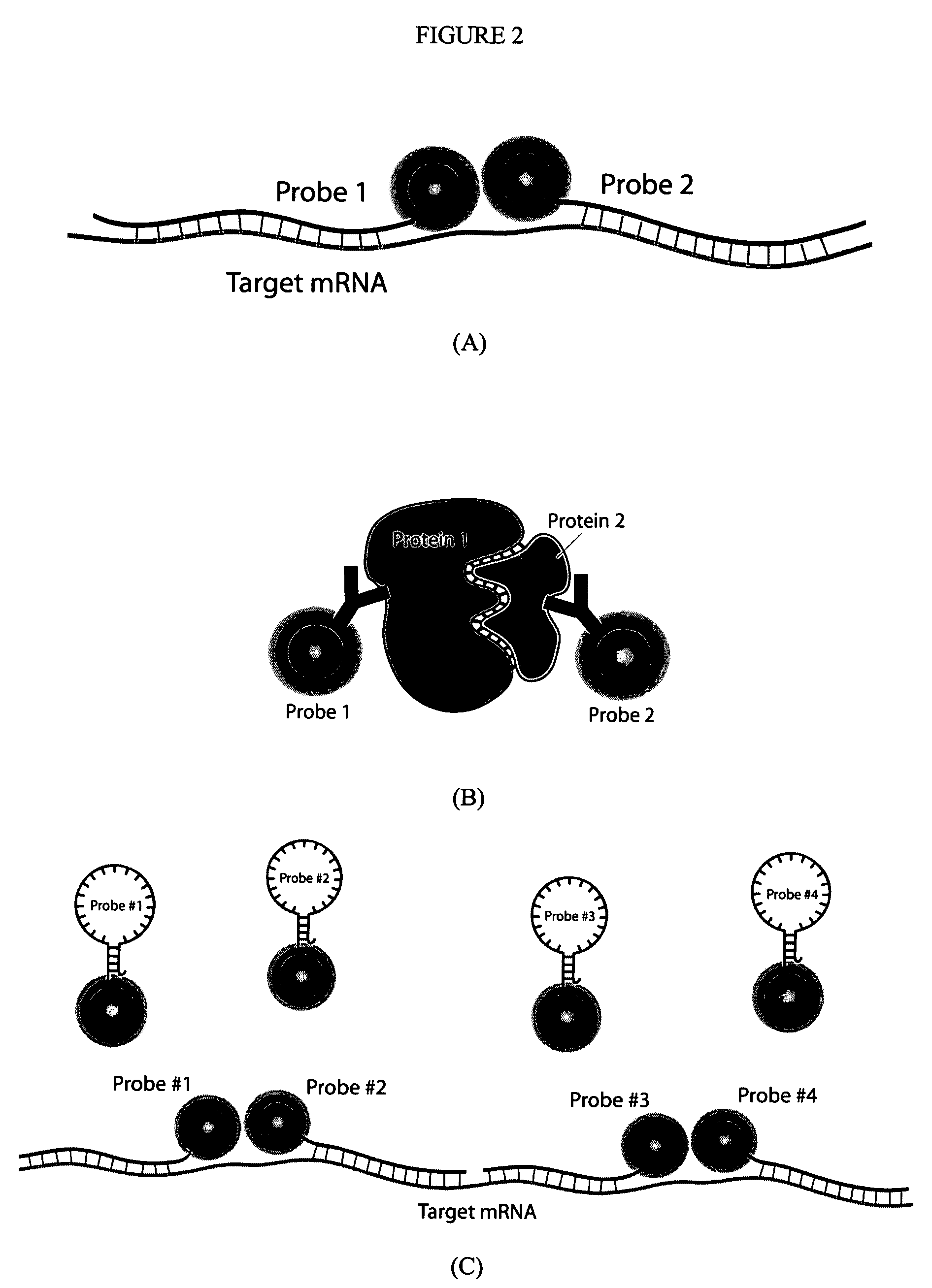
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for intracellular molecular imaging and monitoring
InactiveUS20050130167A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryFluorescenceBiocompatible coating
The present invention provides multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probe compositions for molecular imaging and monitoring, comprising a nucleic acid or polypeptide probe, a delivery ligand, and a magnetic nanoparticle having a biocompatible coating thereon. The probe compositions may further comprise a fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moiety. Also provided are compositions comprising two or more such multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging or monitoring. In particular, the nucleic acid or polypeptide probes bind to a target and generate an interaction observable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or optical imaging. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of nucleic acids, polypeptides, and interactions thereof in vivo.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Device and method for examining a body lumen
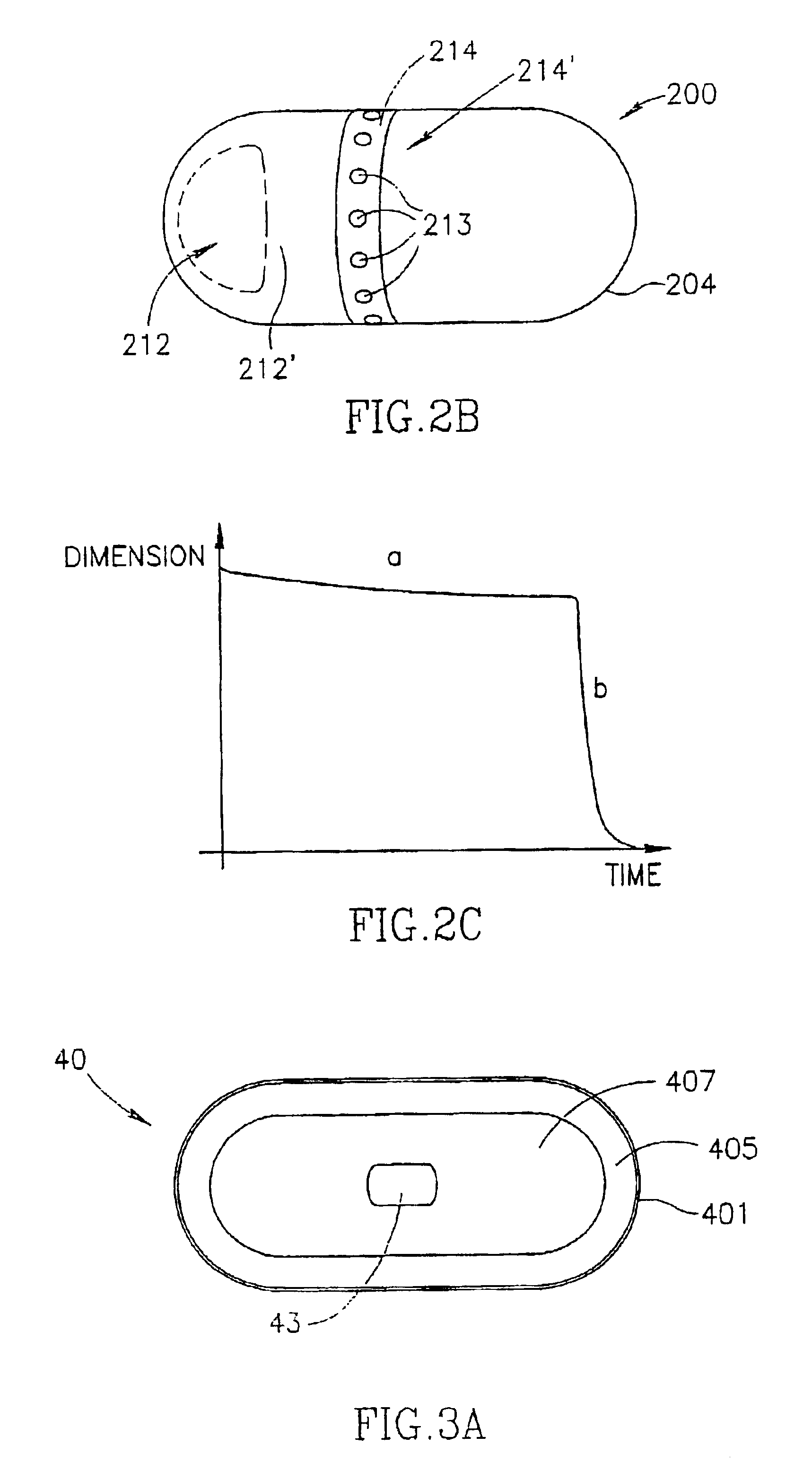
InactiveUS7083578B2Simple and safe processTesting motility in the GI tractGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsPerson identificationIn vivoBiomedical engineering
An in vivo examining device and method are described. The in vivo examining device has two operational phases; an initial phase in which the device is of initial dimensions and a final phase in which the device is of final dimensions. In the initial phase the device can pass freely through a normally configured body lumen whereas it may not be able to pass freely through an abnormally configured lumen. In the final phase the device can pass freely through a body lumen even if it is abnormally configured.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
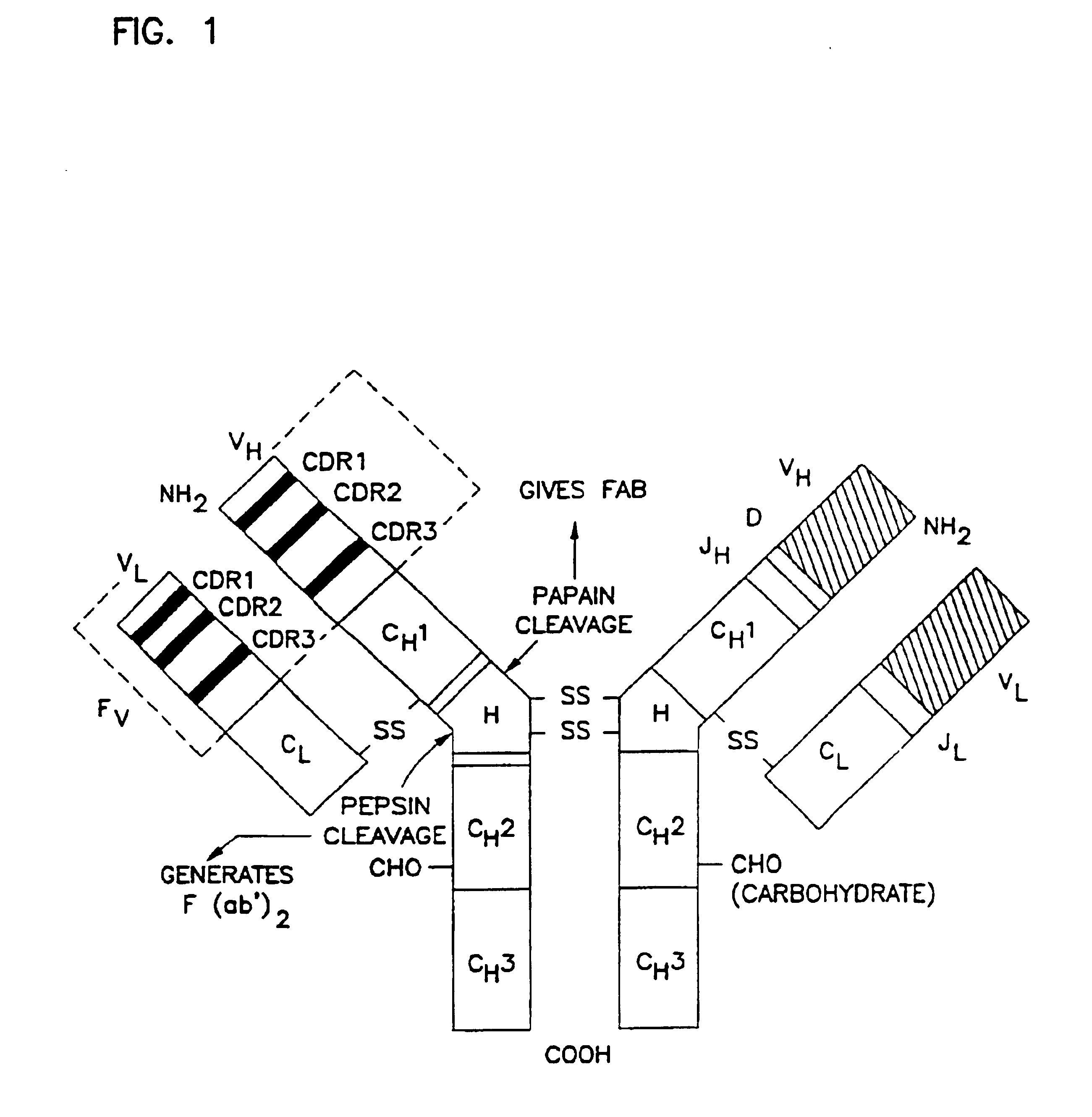
Variants of humanized anti carcinoma monoclonal antibody cc49
InactiveUS6818749B1Elicit adverse responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsComplementarity determining regionHeavy chain
The invention is directed towards mouse-human chimeric variants of CC49 monoclonal antibodies with minimal murine content. A first aspect of the invention provides CDR variants of humanized monoclonal antibody (HuCC49) in which less than all six (three heavy chain and three light chain) Complementarity Determining Regions (CDRs) of CC49 are present. A second aspect of the invention provides SDR variants of humanized monoclonal antibody (HuCC49) in which only Specificity Determining Regions (SDRs) of at least one CDR from CC49 are present. The invention is also directed towards biotechnological methods of making the variants and therapeutic methods of using the variants.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for intracellular molecular imaging and monitoring
InactiveUS7459145B2Efficient internalizationHigh sensitivityBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescenceBiocompatible coating
The present invention provides multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probe compositions for molecular imaging and monitoring, comprising a nucleic acid or polypeptide probe, a delivery ligand, and a magnetic nanoparticle having a biocompatible coating thereon. The probe compositions may further comprise a fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moiety. Also provided are compositions comprising two or more such multifunctional magnetic nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging or monitoring. In particular, the nucleic acid or polypeptide probes bind to a target and generate an interaction observable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or optical imaging. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific, and sensitive detection of nucleic acids, polypeptides, and interactions thereof in vivo.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Method and apparatus for monitoring and quantitatively evaluating tumor perfusion
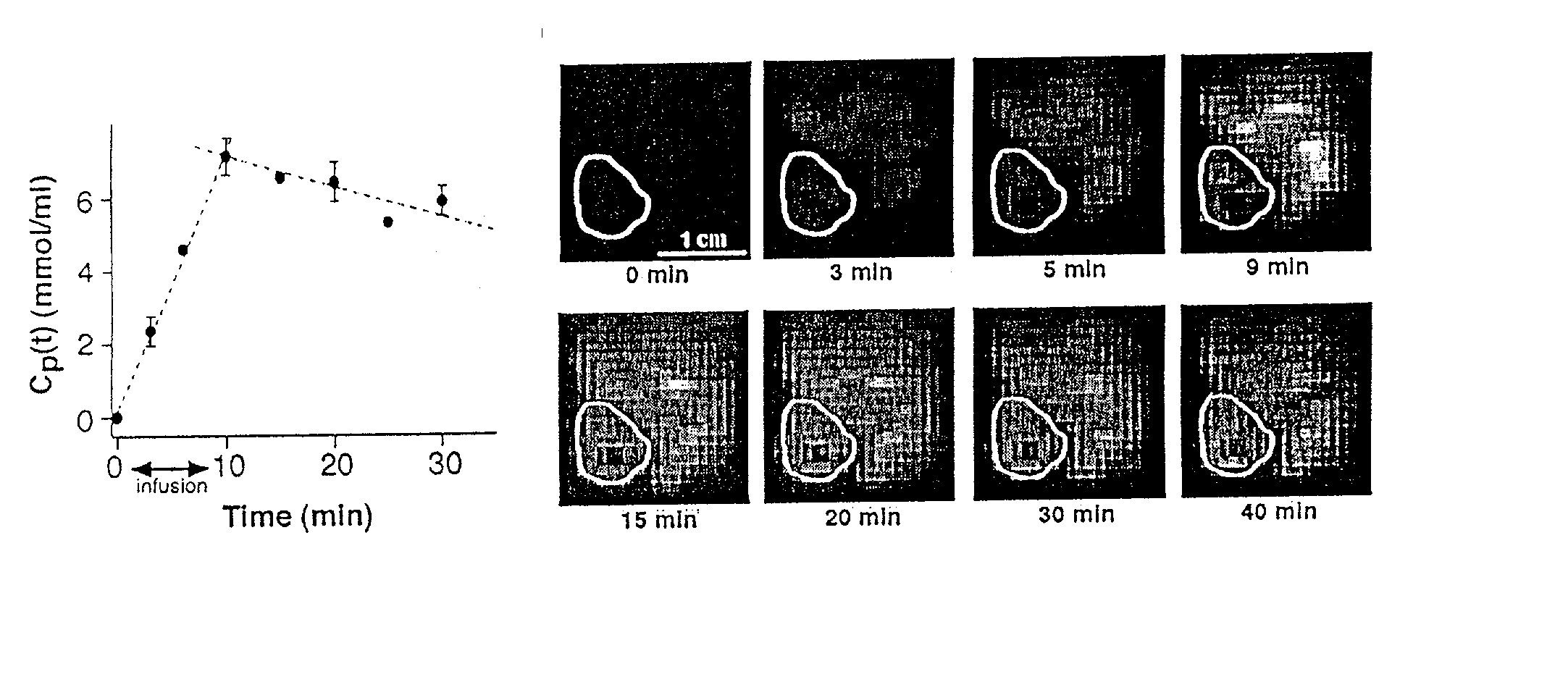
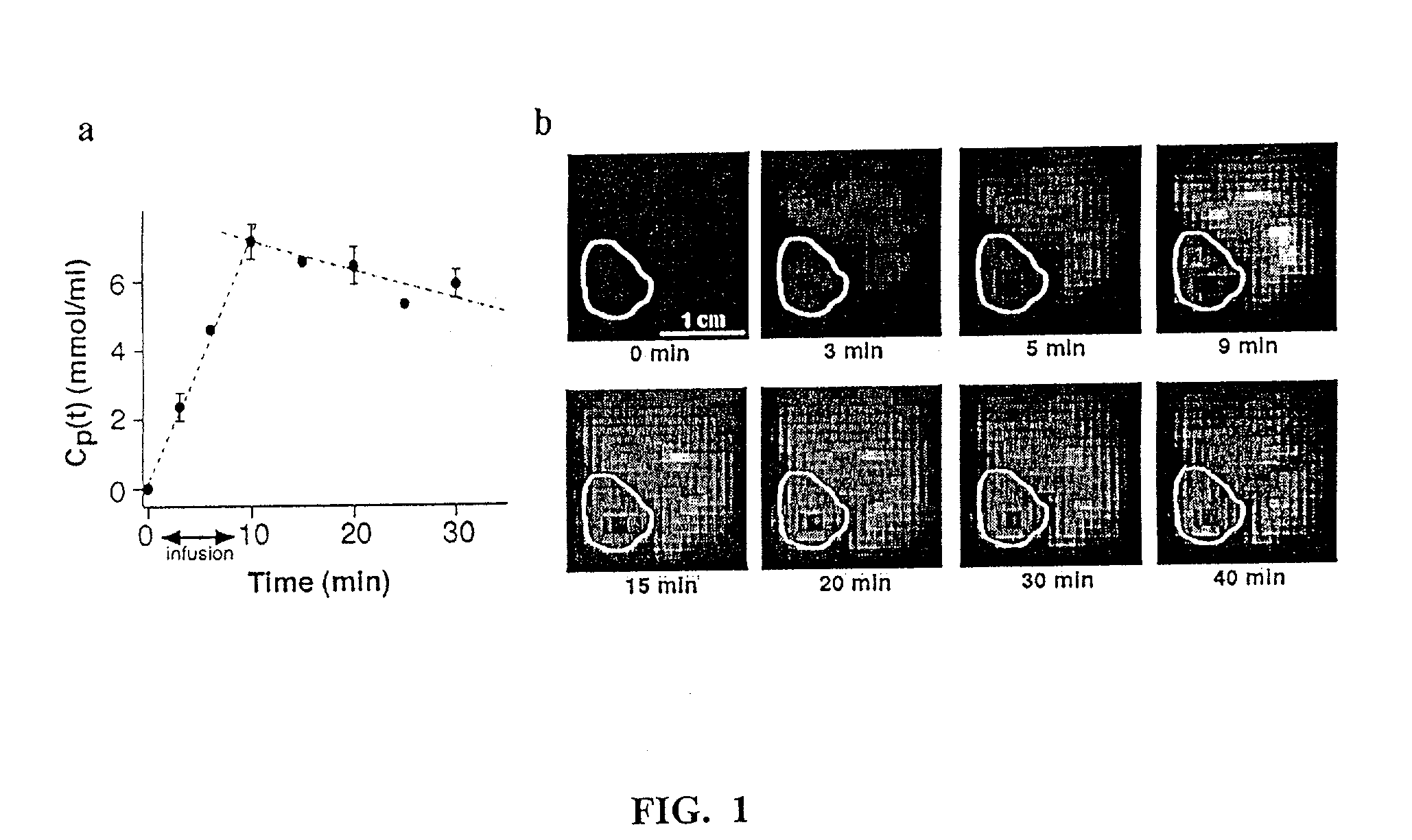
InactiveUS20030211036A1Deeper understandingNo adverse effect on general well-beingImage analysisIn-vivo radioactive preparationsVoxelResonance
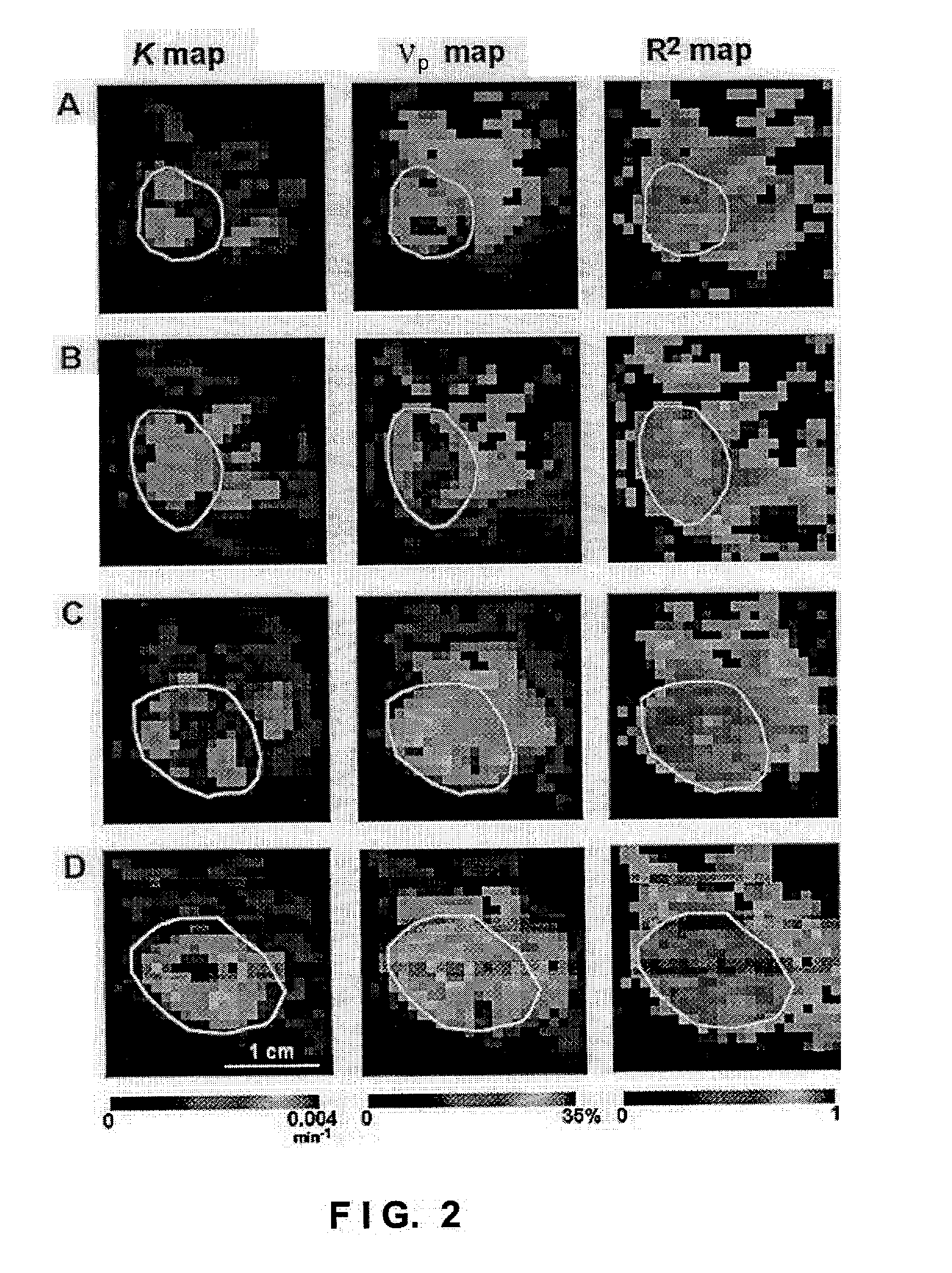
Method and apparatus for monitoring a patient having a tumor to determine perfusion tumor heterogeneity wherein a solution containing a tracer, preferably a <2>H-saline solution is infused into the patient's bloodstream at a predetermined slow rate to effect perfusion into the tumor. An MRI machine is adjusted to acquire a set of dynamic <2>H magnetic resonance images of the tumor. The <2>H-images are obtained before infusion, during infusion and post infusion. First, the obtained images are processed to quantitatively determine perfusion per voxel of the images. Next, maps of perfusion parameters are generated to indicate spatial distribution of tumor perfusion. The maps are displayed in color code and analyzed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD AT THE WEISZMANN INST OF SCI
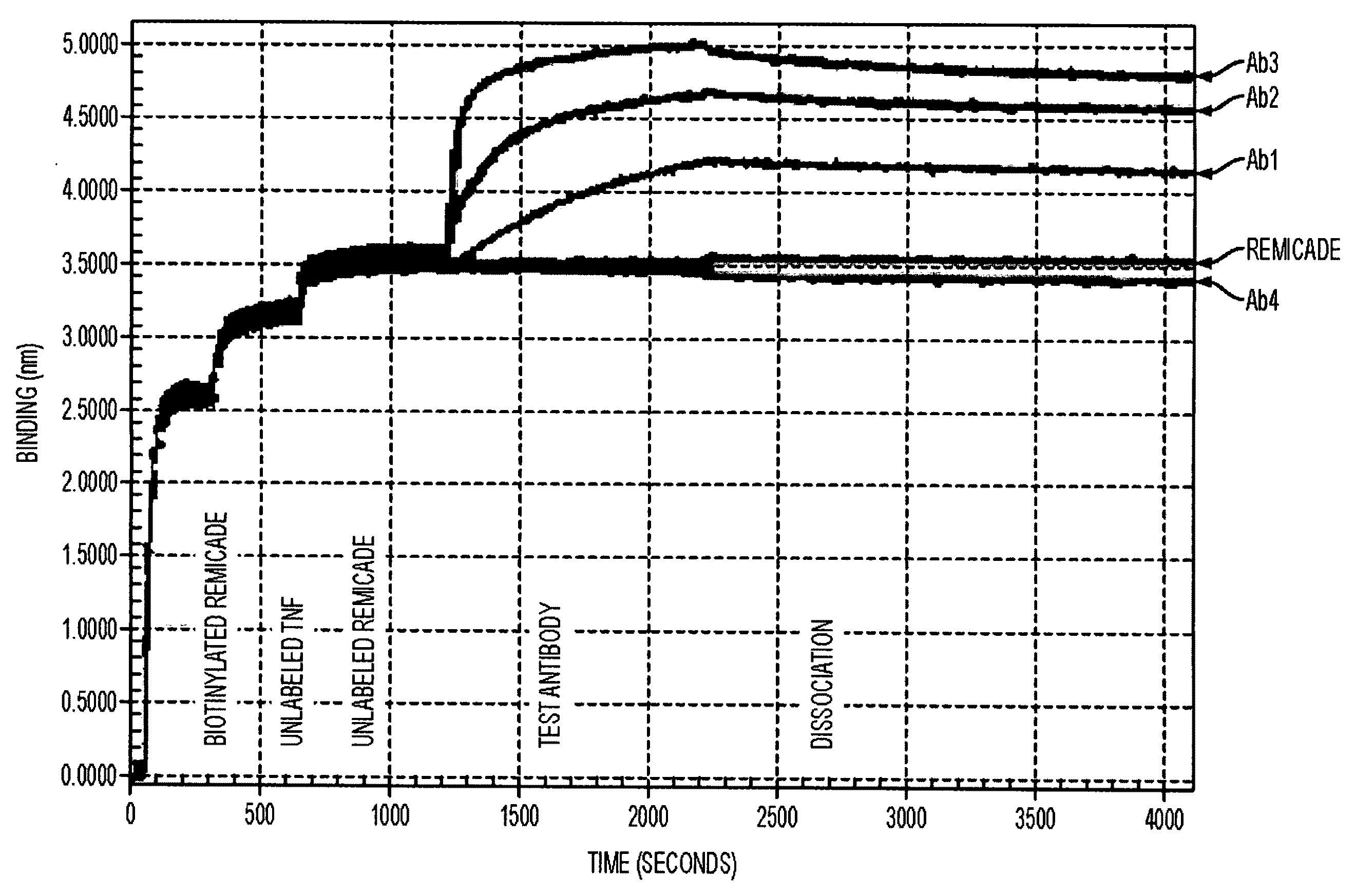
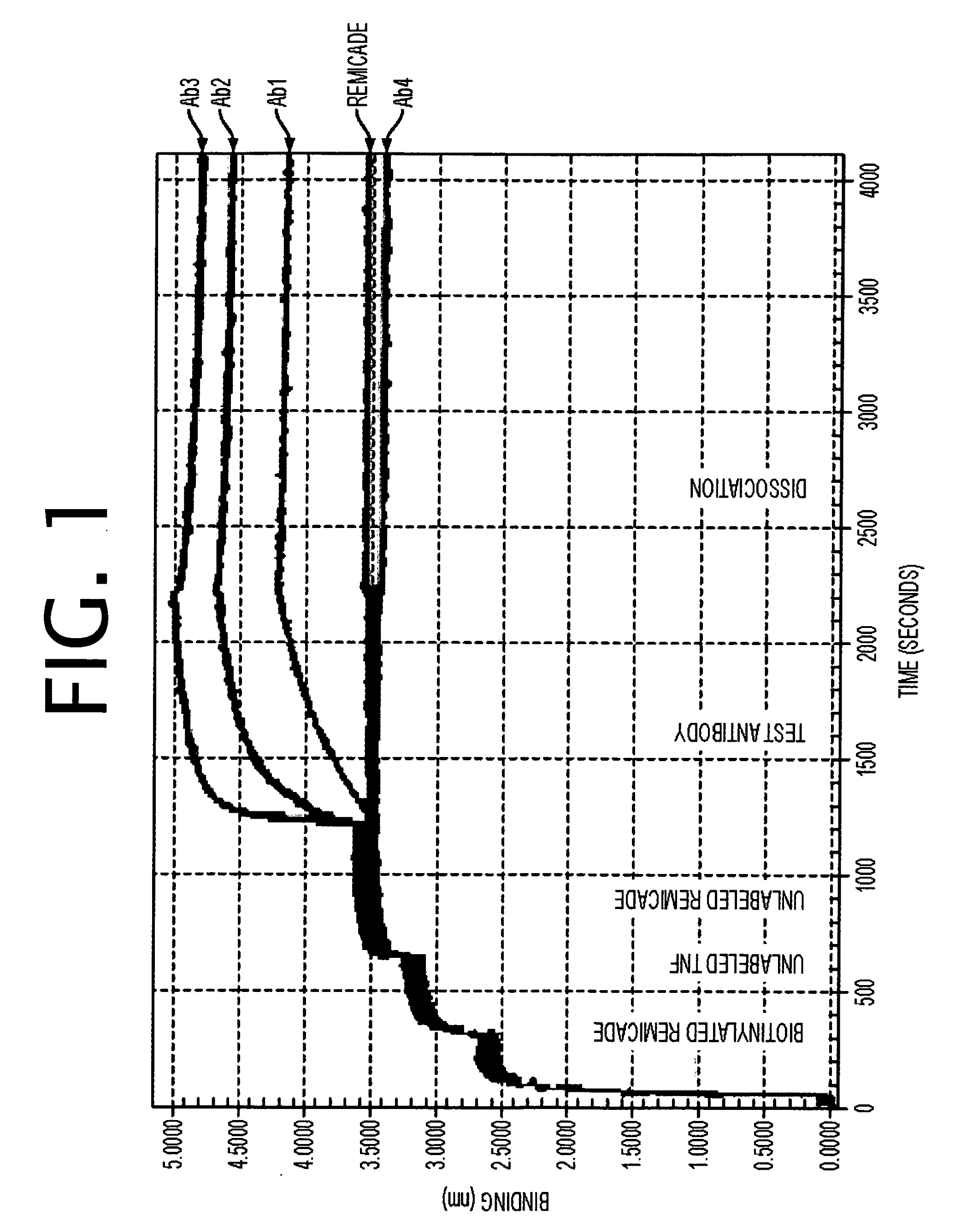
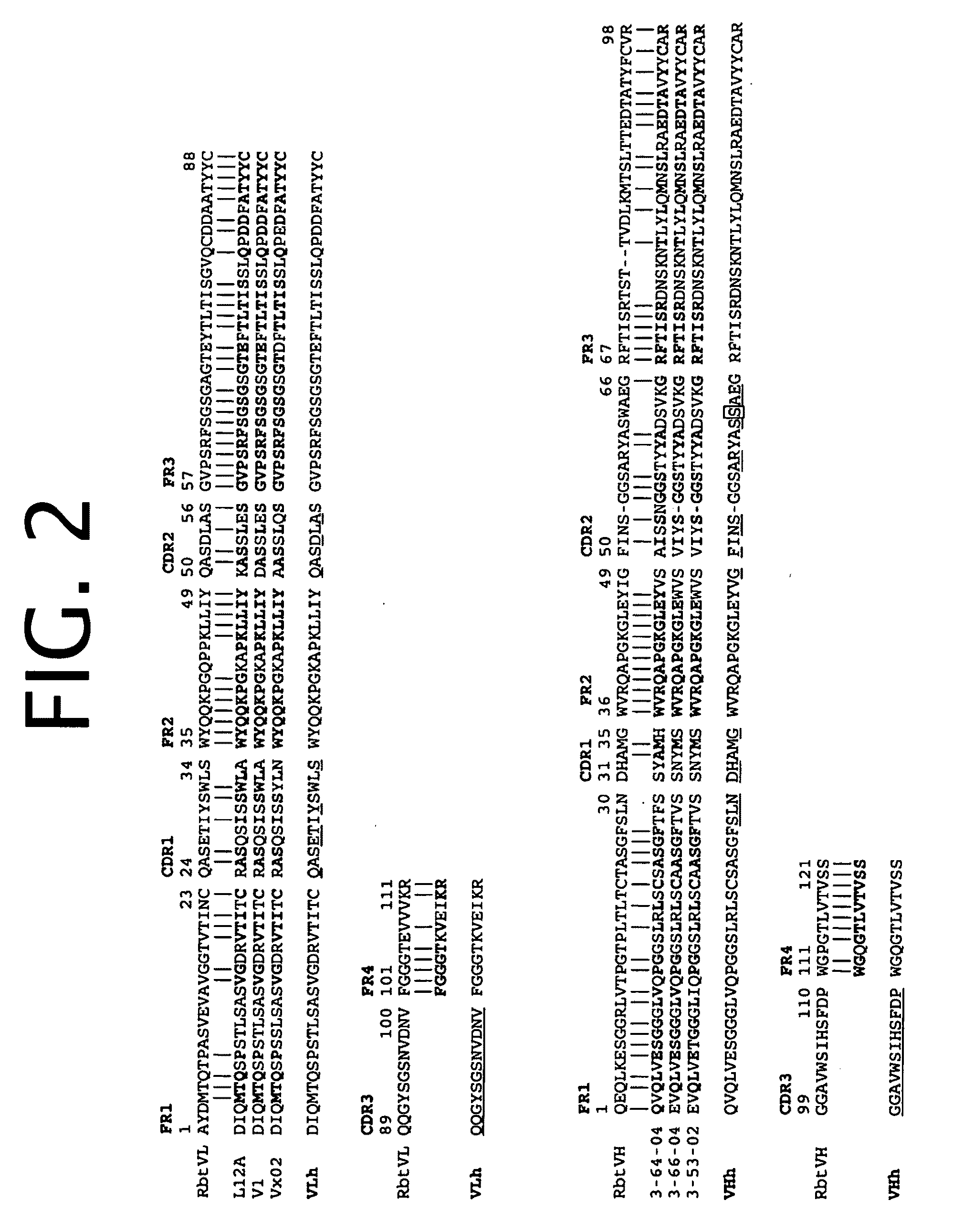
Antibodies to TNF alpha and use thereof
Owner:ALDERBIO HLDG LLC +1
Chemical linkers and cleavable substrates and conjugates thereof
ActiveUS20100145036A1Inhibit cell activityMaximum efficacySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical drugCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Treatment of myopia
InactiveUS20050271590A1Improve mechanical stabilityHigh modulusUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSenses disorderMedicineUltimate tensile strength
The present invention relates to altering the physical and / or chemical properties of at least part of at least one tissue in the eye. In a specific embodiment, it relates to the treatment and / or prevention of myopia. An activating energy source is utilized to photopolymerize or crosslink molecules in the sclera, thereby increasing the strength of the tissue. The individual is administered a crosslinking reagent or photopolymerizable molecule that becomes associated with the membrane, which is then precisely exposed to an energy source, such as light or ultrasound.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Amphiphilic polymers and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20060269479A1Effective amountOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryCrystallographyTherapeutic intent
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS LOWELL +1
Systems, compositions, and methods for local imaging and treatment of pain
ActiveUS20090030308A1Significant comprehensive benefitsImprove abilitiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsNervous disorderCytokineImaging Tool
Pain factors are labeled with targeted agents or markers delivered into the body. The labeled pain factors are imaged with appropriate imaging tools in a manner allowing selective identification and localization of areas of pain source or transmission. The labeled pain factors allow spatial differentiation in the imaging sufficient to specify the location of the pain so as to drive therapeutic decisions and techniques in order to treat the pain. Pain factors labeled and imaged in this manner may include one or more of nerve factors, blood vessel factors, cellular factors, and inflammation factors. Labeled markers may include for example radioactive materials (e.g. tritiated or iodinated molecules) or other materials such as metal (e.g. gold) nanoparticles. Intermediary binding materials may be used, such as for example bi-specific antibodies. Therapeutic components of the system and method include for example localized energy delivery or ablation treatments, or local drug or other chemical delivery. Locations containing pain factor selectively bound by targeted agents are selectively treated with directed energy into a region containing the targeted agent bound to the pain factor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multimodal imaging probes for in vivo targeted and non-targeted imaging and therapeutics
In certain embodiments this invention provides a nanoparticle-based technology platform for multimodal in vivo imaging and therapy. The nanoparticle-based probes detects diseased cells by MRI, PET or deep tissue Near Infrared (NIR) imaging, and are capable of detecting diseased cells with greater sensitivity than is possible with existing technologies. The probes also target molecules that localize to normal or diseased cells, and initiates apoptosis of diseased cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods relating to reduced mucoadhesion
InactiveUS20130236556A1Reduced mucoadhesionDiffusion fastBiocidePowder deliveryMedicineParticle composition
The present invention generally relates to reducing the mucoadhesive properties of a particle. In some embodiments, the particle is coated with and / or associated with a (poly(ethylene glycol))-(poly(propylene oxide))-(poly(ethylene glycol)) triblock copolymer. Methods for preparing inventive particles using a poly(ethylene glycol)-vitamin E conjugate as a surfactant are also provided. In some embodiments, methods are provided comprising administering to a subject a composition of particles of the present invention. Such particles with reduced mucoadhesive properties are useful in delivering agents to mucosal tissues such as oral, ophthalmic, gastrointestinal, nasal, respiratory, and genital mucosal tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Chemical linkers and cleavable substrates and conjugates thereof
ActiveUS8461117B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsTreatment useOrganic chemistry
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Method for treatment of uterine fibroid tumors
InactiveUS20060251581A1Improve delivery efficiencyMinimize adverse effectsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliverySemi solidViscosity
Various injectable or insertable uterine fibroid treatment formulations are provided, which comprise a uterine fibroid treatment agent in an amount effective to cause shrinkage or elimination of uterine fibroids. The injectable or insertable formulations are typically solids, semi-solids or high-viscosity fluids. Other aspects of the invention are directed to systems and methods for treatment of uterine fibroids.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Drug adherence monitoring system
InactiveUS20070224128A1Low costImprove efficacyCompounds screening/testingGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsDrug adherenceEnvironmental health
The present invention provides novel methods for monitoring subject adherence in taking prescribed drugs by detecting markers in exhaled breath after a subject takes the prescribed drug. In particular, the present invention provides novel methods for making additives that are combined with the drug(s). Upon biological breakdown of the drug / additive formulation in a subject's body, markers resulting directly from the biological breakdown of the additives are detected in exhaled breath using sensor technology. In certain embodiments of the invention, the drug adherence monitoring systems and methods include a reporting system capable of tracking subject compliance (either remotely or proximately) and of providing necessary alerts to the subject, caregiver, healthcare provider, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Multimodal silica-based nanoparticles
ActiveUS20140248210A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryCellular componentDisease
The present invention provides a fluorescent silica-based nanoparticle that allows for precise detection, characterization, monitoring and treatment of a disease such as cancer. The nanoparticle has a range of diameters including between about 0.1 nm and about 100 nm, between about 0.5 nm and about 50 nm, between about 1 nm and about 25 nm, between about 1 nm and about 15 nm, or between about 1 nm and about 8 nm. The nanoparticle has a fluorescent compound positioned within the nanoparticle, and has greater brightness and fluorescent quantum yield than the free fluorescent compound. The nanoparticle also exhibits high biostability and biocompatibility. To facilitate efficient urinary excretion of the nanoparticle, it may be coated with an organic polymer, such as poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The small size of the nanoparticle, the silica base and the organic polymer coating minimizes the toxicity of the nanoparticle when administered in vivo. In order to target a specific cell type, the nanoparticle may further be conjugated to a ligand, which is capable of binding to a cellular component associated with the specific cell type, such as a tumor marker. In one embodiment, a therapeutic agent may be attached to the nanoparticle. To permit the nanoparticle to be detectable by not only optical fluorescence imaging, but also other imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), computerized tomography (CT), bioluminescence imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), radionuclides / radiometals or paramagnetic ions may be conjugated to the nanoparticle.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
D-amino acid peptides
The present invention provides compounds of the formula X—R1-D-[Dpr, Orn or Lys](A)-R2(Z)-D-[Dpr, Orn or Lys](B)—R3(Y)—NR4R5; or R1(X)-D-[Dpr, Orn or Lys](A)-R2(Z)-D-[Dpr, Orn or Lys](B)—R3(Y)—NR4R5, in which X is a hard acid cation chelator, a soft acid cation chelator or Ac—, R1, R2 and R3 are independently selected from a covalent bond or one or more D-amino acids that can be the same or different, Y is a hard acid cation chelator, a soft acid cation chelator or absent, Z is a hard acid cation chelator, a soft acid cation chelator or absent, and A and B are haptens or hard acid cation chelators and can be the same or different, and R4 and R5 are independently selected from the group consisting of hard acid cation chelators, soft acid cation chelators, enzymes, therapeutic agents, diagnostic agents and H. The present invention also provides methods of using these compounds and kits containing the compounds.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
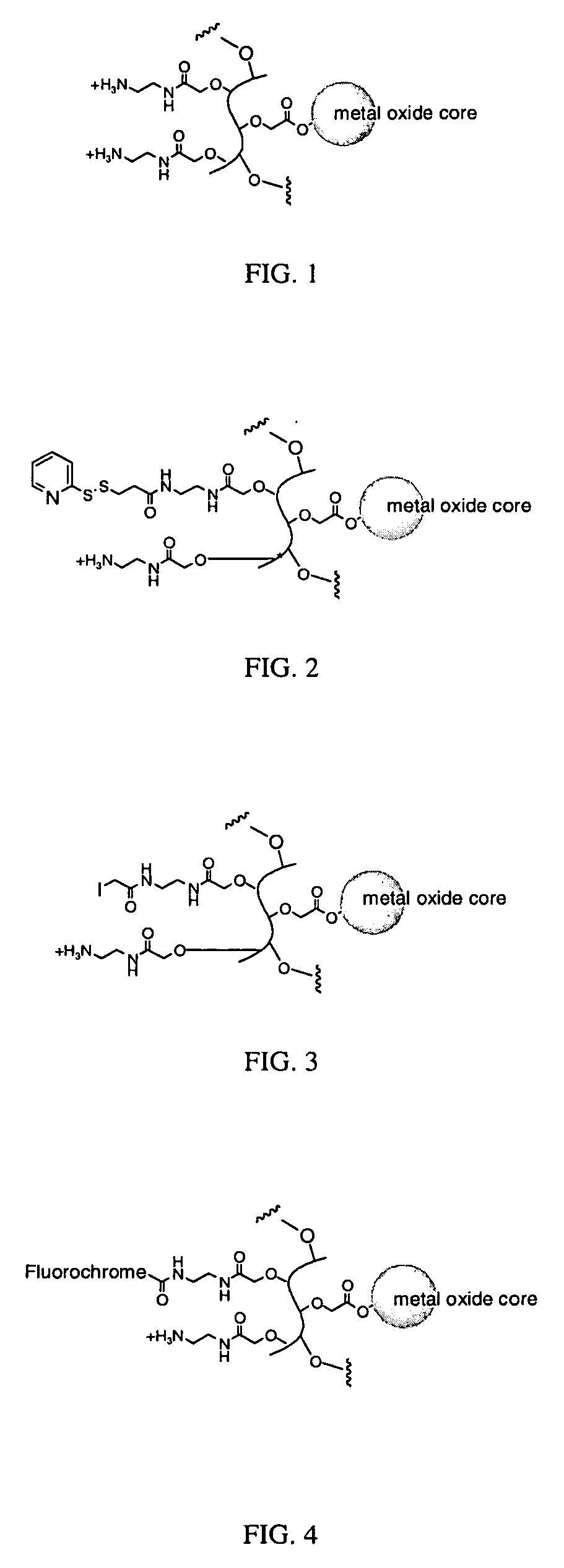
Biocompatible fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS20080226562A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryMetal oxide nanoparticlesChemical ligation
The invention relates to highly fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles to which biomolecules and other compounds can be chemically linked to form biocompatible, stable optical imaging agents for in vitro and in vivo applications. The fluorescent metal oxide nanoparticles may also be used for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), thus providing a multi modality imaging agent.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
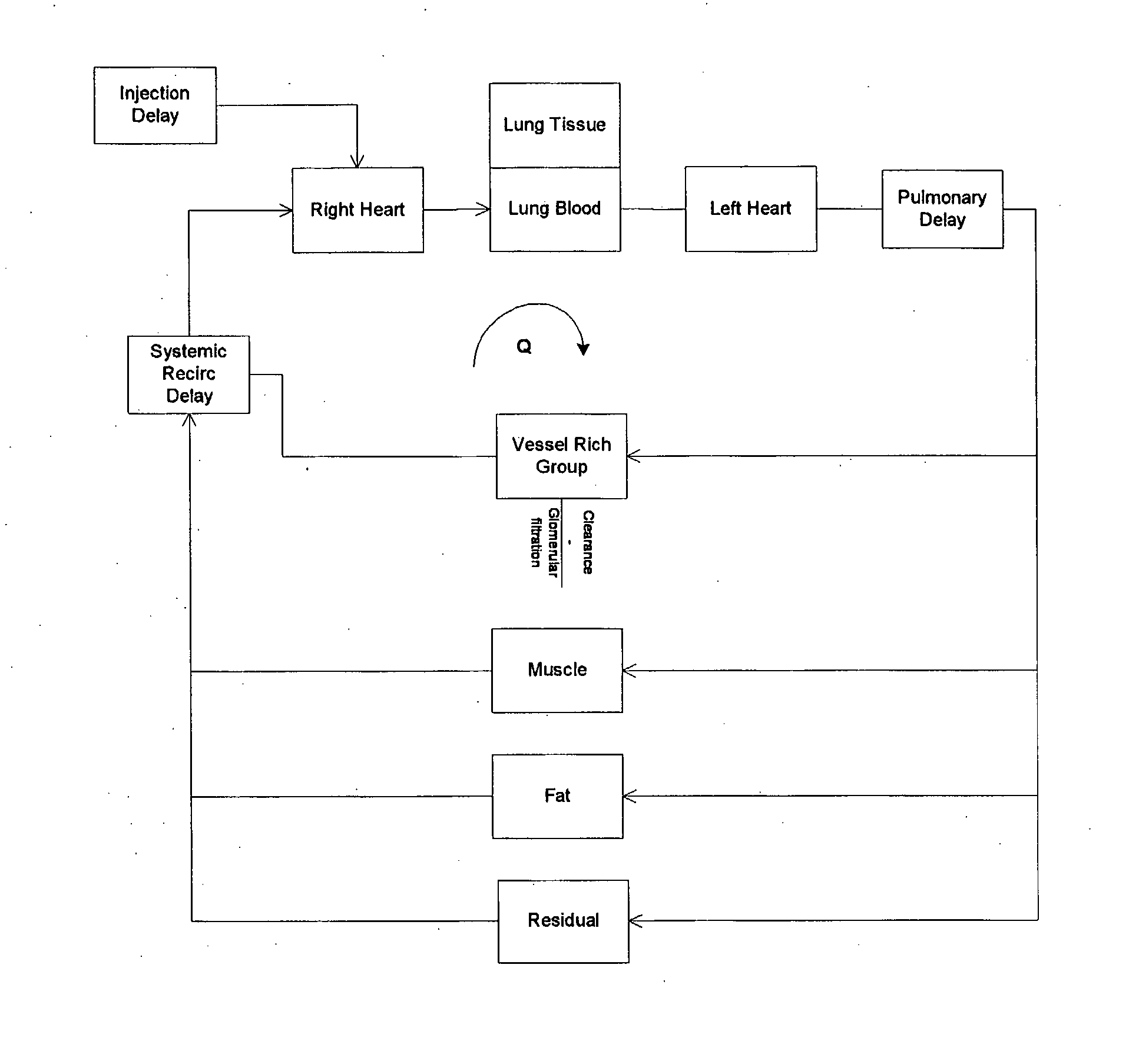
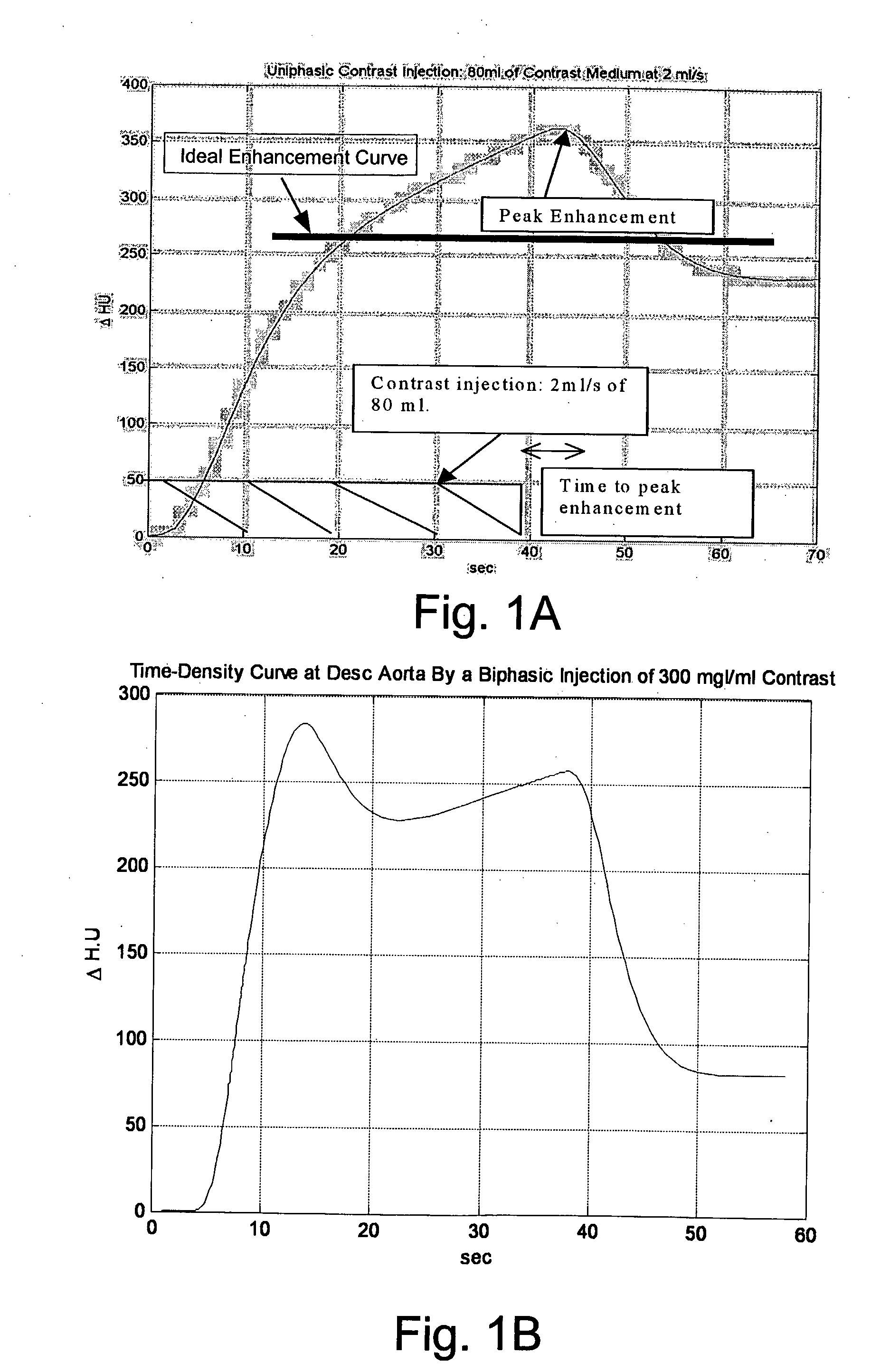
Modeling of Pharmaceutical Propagation
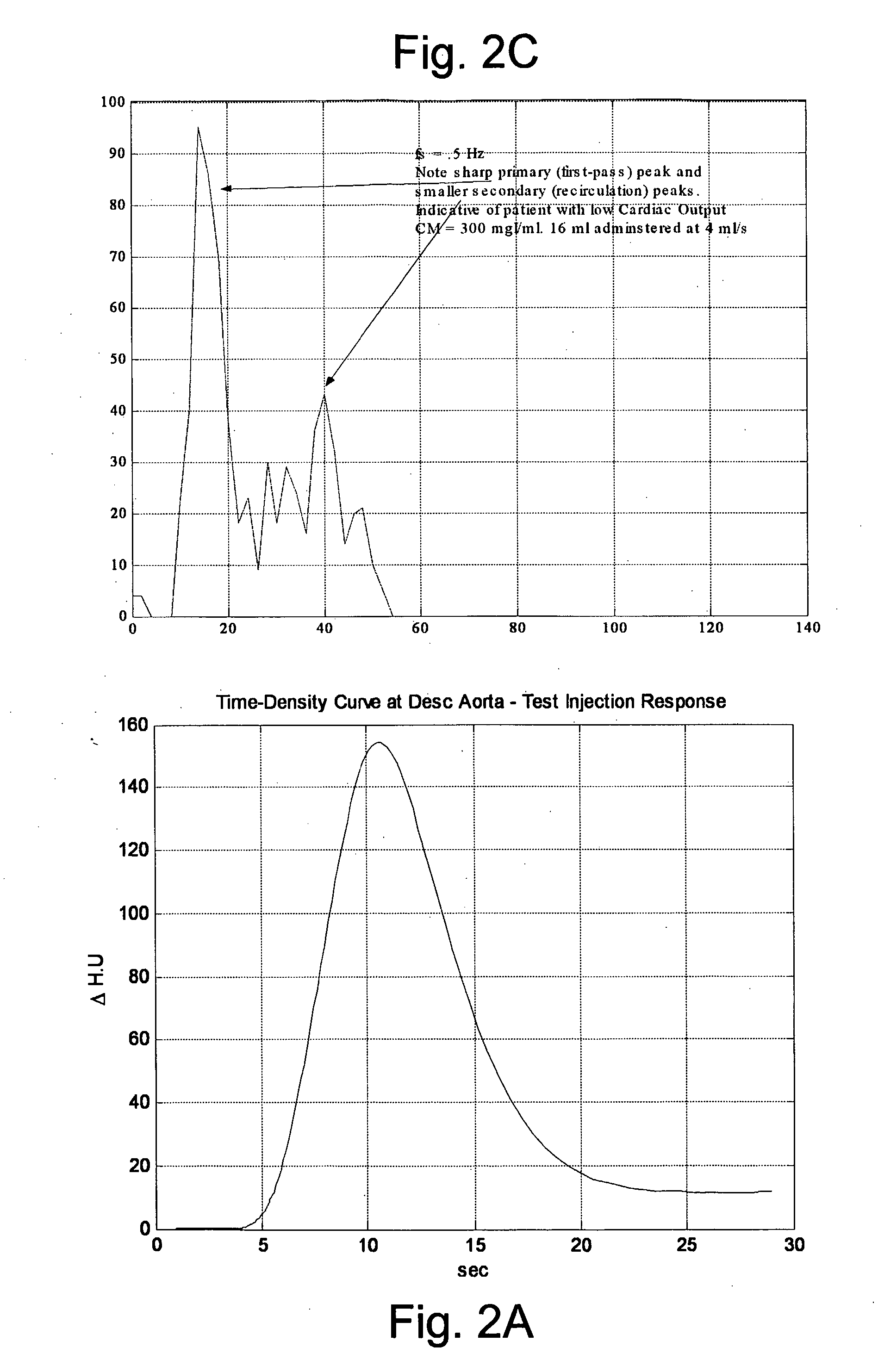
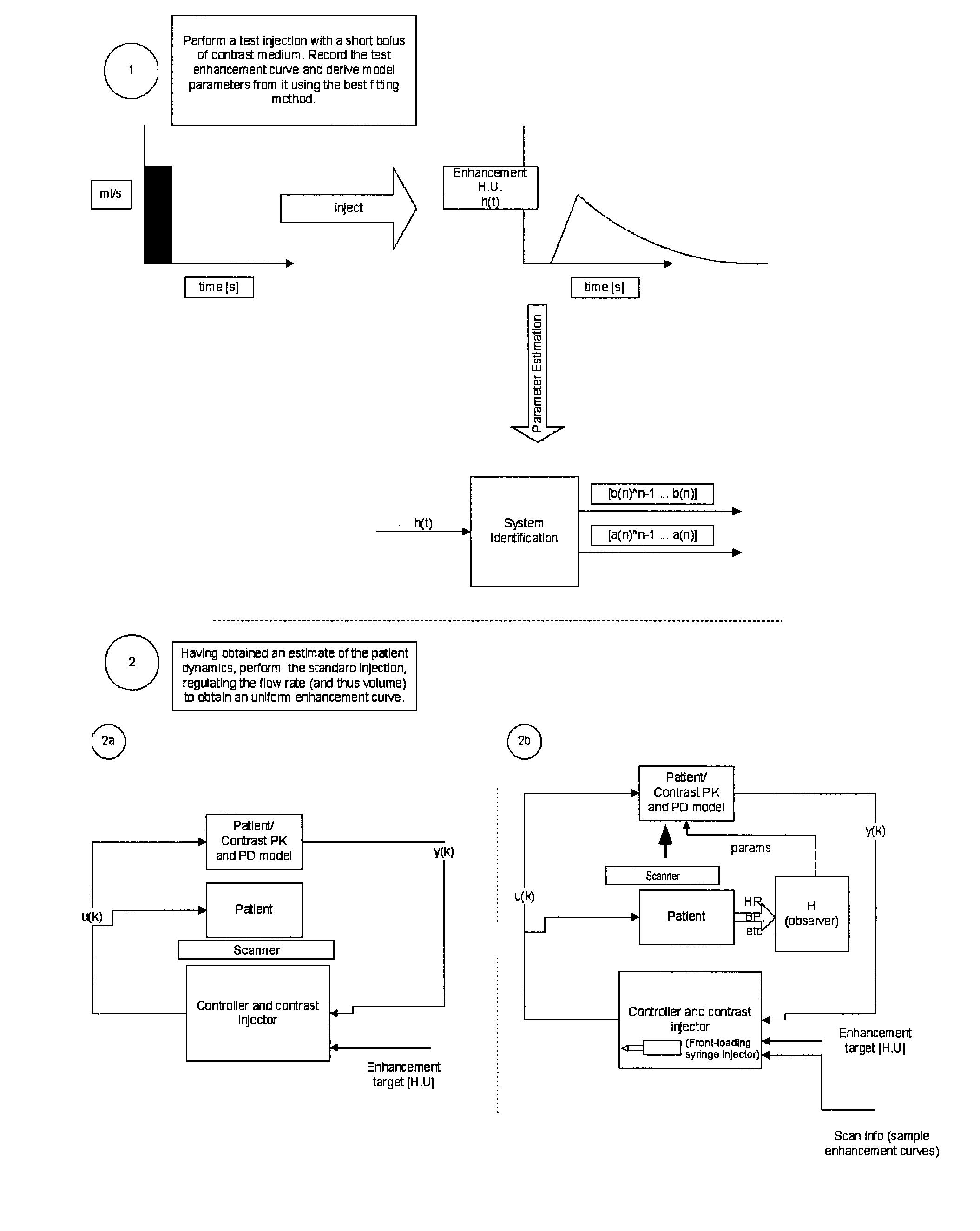
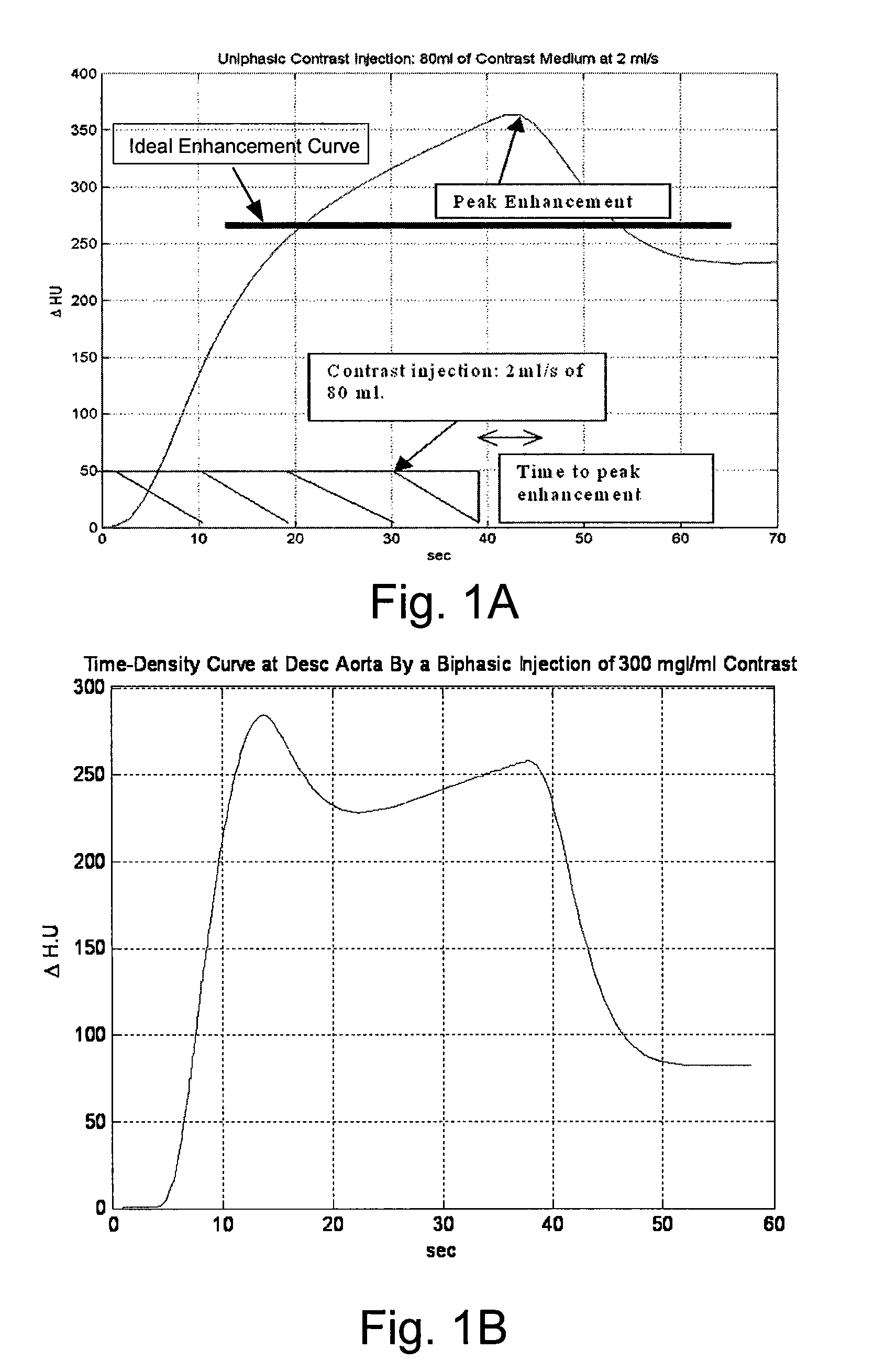
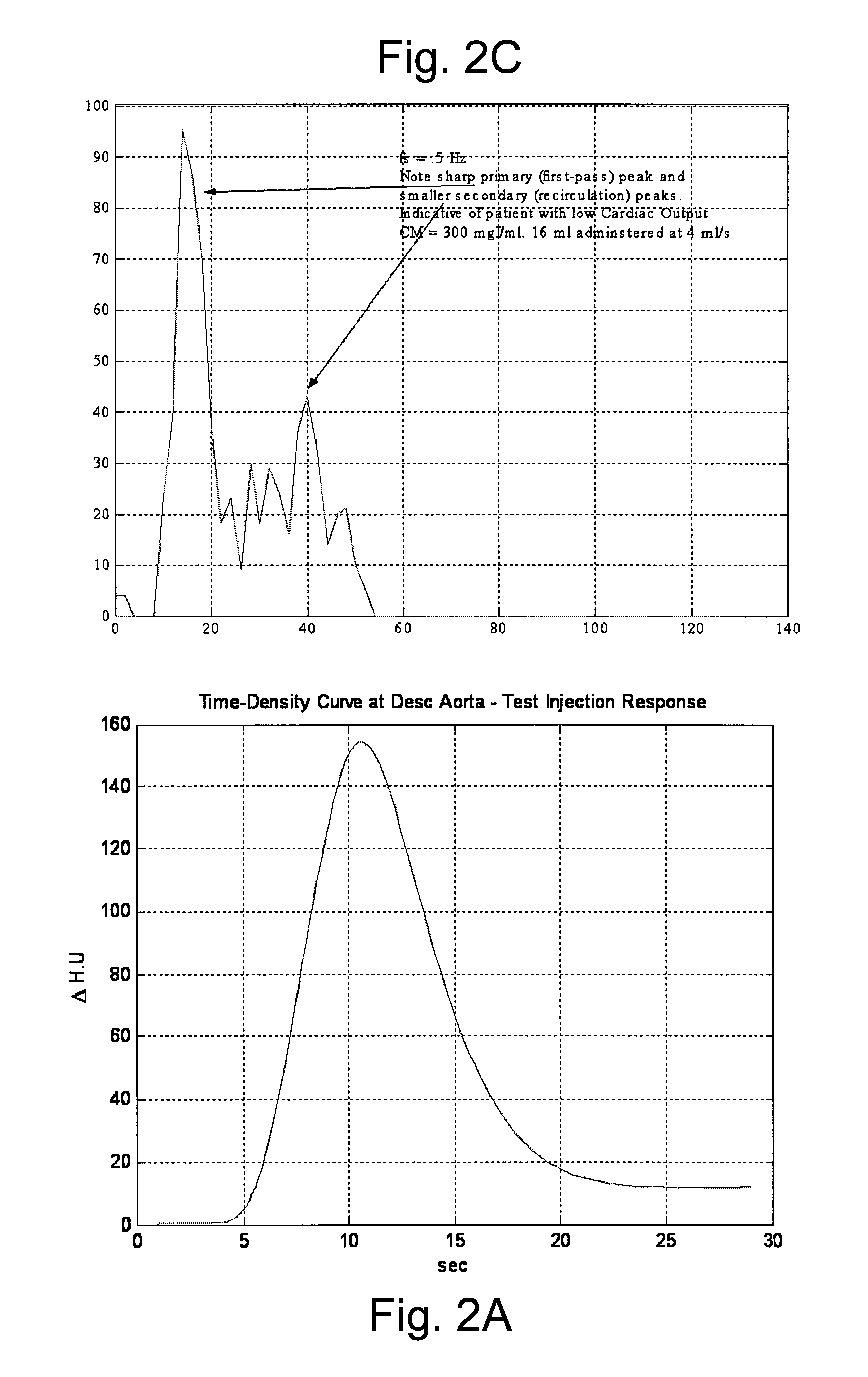
InactiveUS20080097197A1Overall light weightReduce contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsMathematical modelContrast medium
A method of modeling propagation of a pharmaceutical fluid in a patient, includes: collecting data corresponding to a time response curve resulting from injection of the fluid; and determining at least one mathematical model describing the data. The mathematical model can, for example, be a model which is not determined by a continuous or a discrete-time Fourier transform of the data. A method of controlling injection of a pharmaceutical fluid into a patient using an injector in a medical procedure, includes: collecting data corresponding to a patient response curve resulting from injection of the fluid; determining at least one mathematical model describing the data; and controlling the injector during the medical procedure to control injection of the fluid into the patient to create patient response at least in part on the basis of the mathematical model. A method of controlling injection of a contrast medium into a patient using an injector in a medical imaging procedure using an imaging scanner, includes: determining at least one mathematical model to predict a time enhancement response resulting from injection of the contrast medium; determining an injection protocol to approximate a predetermined time enhancement response in the patient by determining a constrained input solution to the mathematical model; and using the injection protocol to control the injector during the medical imaging procedure to control injection of the contrast medium into the patient to create an image of a region of interest.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Medical and Imaging Nanoclusters
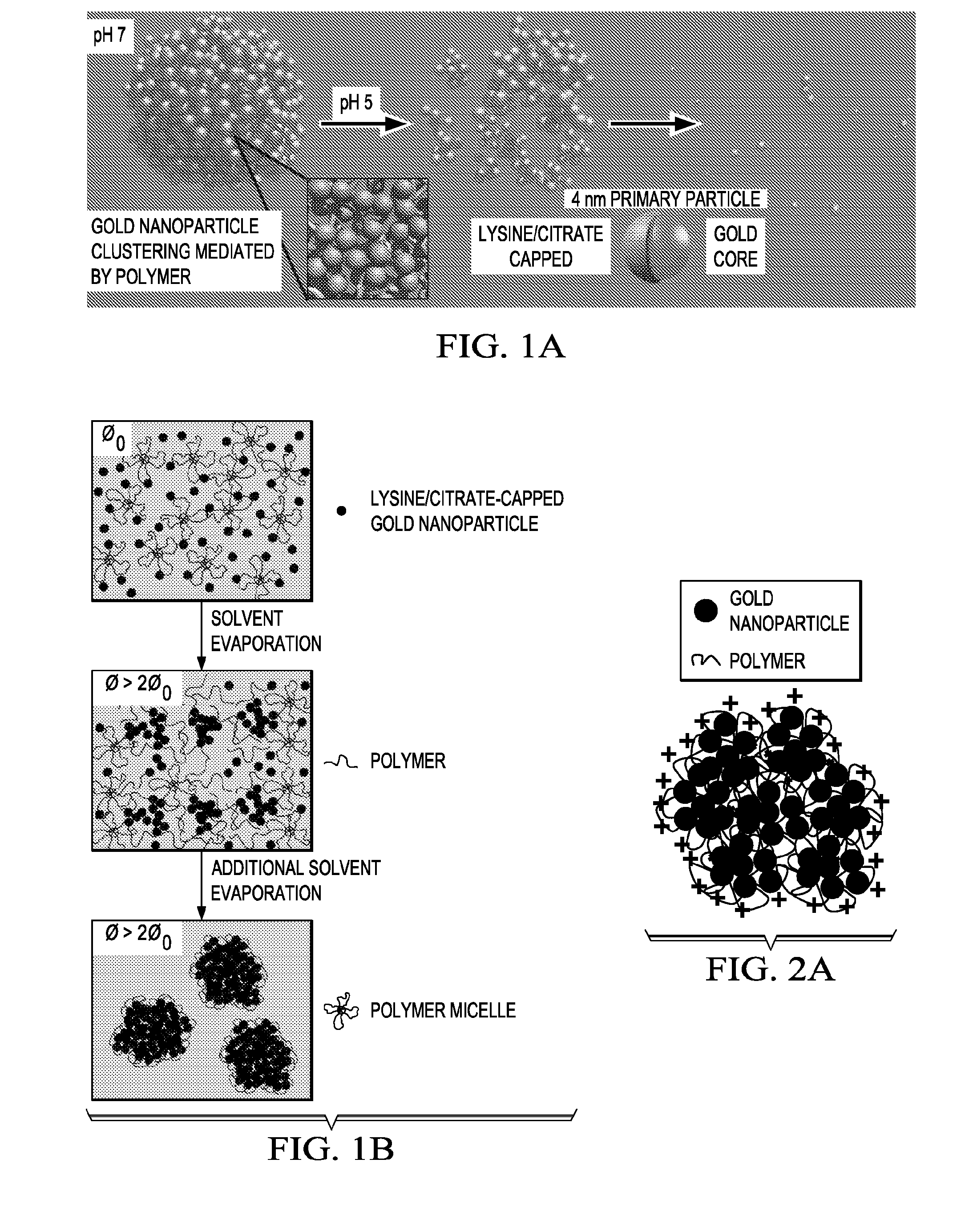
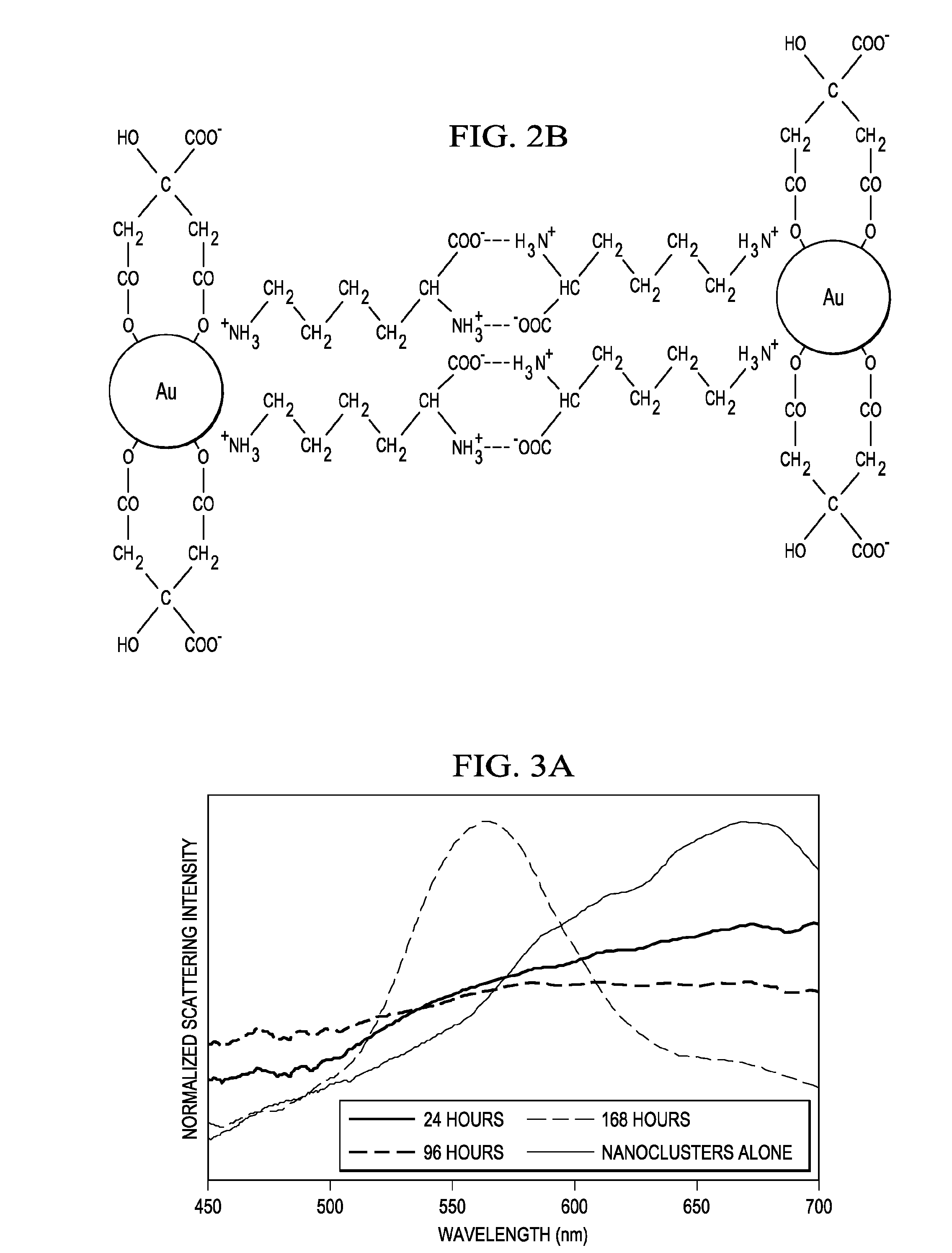
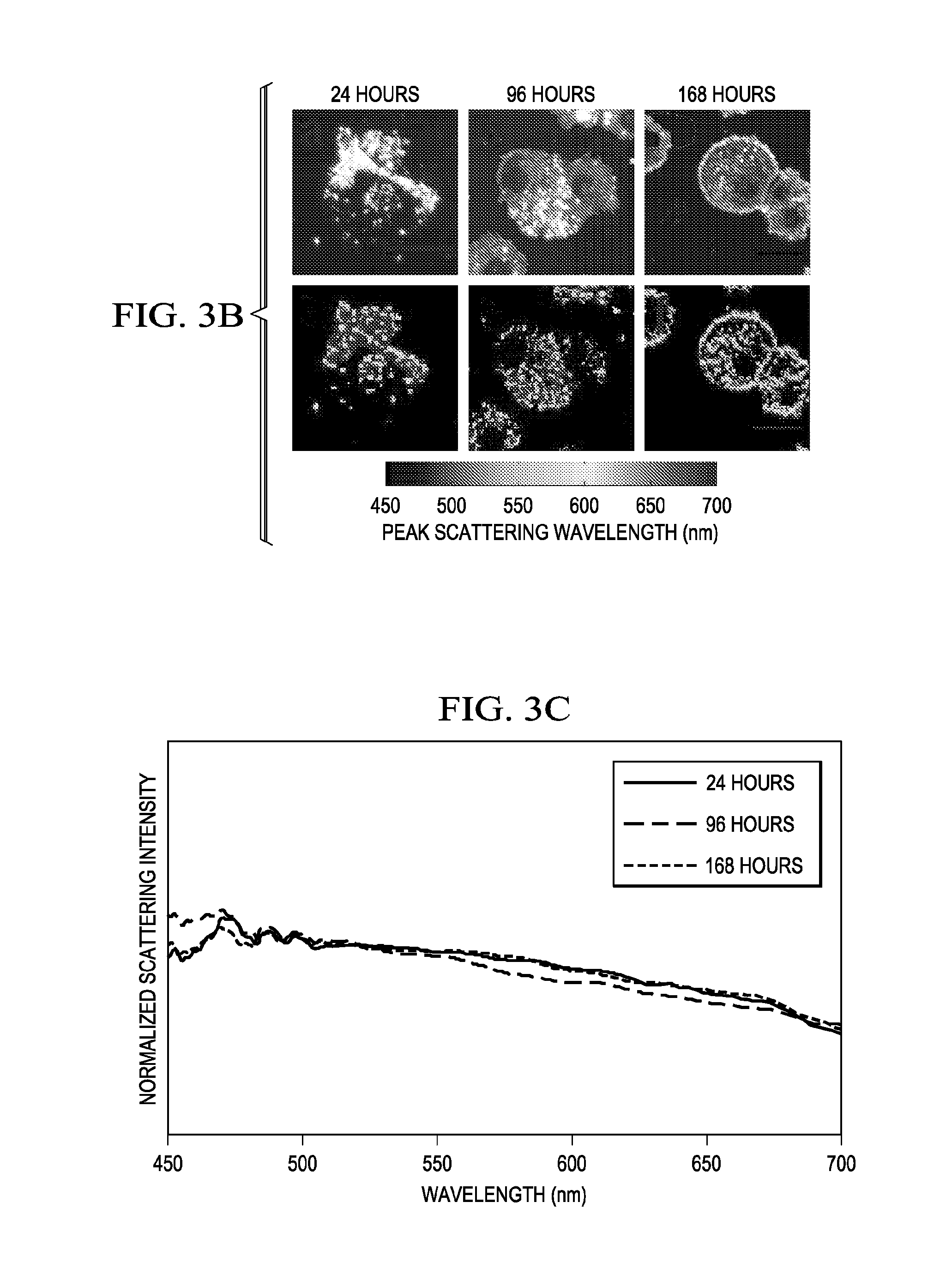
InactiveUS20130023714A1Promote cell deathFacilitated releaseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsOptical propertyNanoparticle
In one embodiment the present invention discloses a nanocluster or a nanorose composition comprising two or more closely spaced nanoparticles each comprising one or more metals, metal oxides, inorganic substances, or a combination thereof and one or more stabilizers. The stabilizers are in contact with the two or more closely spaced nanoparticles to form a nanocluster composition in which the inorganic weight percentage is greater than 50% and the average size is below 300 nm, and the nanocluster composition has magnetic properties, optical properties or a combination of both.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Targeted nanoclusters and methods of their use
InactiveUS20120269721A1High sensitivityGood effectIn-vivo radioactive preparationsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsNanoparticleNanometre
This invention provides targeted nanoclusters comprising multiple polyvalent nanoparticle core units or nanoscaffolds, each nanoparticle core unit attached to multiple targeting moieties and multiple detectable moieties. The nanoclusters find use in a broad range of analytical assays, diagnostic assays and as targeted therapeutics.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nanoparticular tumor targeting and therapy
InactiveUS20050008572A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryNoninvasive imagingTumor targeting
The present invention provides a series of biocompatible, nanoparticulate formulations that are designed to retain and deliver peptides such as anti-angiogenic factors over an extended time course. The nanoparticles can be targeted to a cell or tissue by targeting ligands crosslinked or conjugated to the corona of the nanoparticles. In addition to selective targeting, the nanoparticles also may perform noninvasive imaging using bioluminescence and / or magnetic resonance imaging via a contrast agent in the core of the nanoparticle. Also provided are methods of delivering to and, optionally, imaging of a cell or tissue. Furthermore, methods of producing the nanoparticles in batch or continous mode via simple mixing or micromixing.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy and detection of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory disease, infectious disease, pathologic angiogenesis and cancer
InactiveUS20060140936A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Methods and compositions for immunotherapy of inflammatory and immune-dysregulatory diseases, using multispecific antagonists that target at least two different markers are disclosed. The different targets include (i) proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system, (ii) coagulation factors, and (iii) targets specifically associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, wherein the targets included in group (iii) are neither a proinflammatory effector of the immune system nor a coagulation factor. When the multispecific antagonist reacts specifically with a target associated with an inflammatory or immune-dysregulatory disorder, with a pathologic angiogenesis or cancer, or with an infectious disease, it also binds specifically with at least one proinflammatory effector of the immune system or at least one coagulation factor. Thus, the multispecific antagonist contains at least one binding specificity related to the diseased cell or condition being treated and at least one specificity to a component of the immune system, such as a receptor or antigen of B cells, T cells, neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages, and dendritic cells, a modulator of coagulation, or a proinflammatory cytokine. The multispecific antagonists are used in the treatment of various diseases that are generated or exacerbated by, or otherwise involve, proinflammatory effectors of the innate immune system or coagulation factors. Such diseases more particularly include acute and chronic inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, giant cell arteritis, septicemia and septic shock, coagulopathies (including diffuse intravascular coagulation), neuropathies, graft versus host disease, infectious diseases, acute respiratory distress syndrome, granulomatous diseases, transplant rejection, asthma, cachexia, myocardial ischemia, and atherosclerosis. Other diseases also responsive to these therapies include cancers and conditions with pathological angiogenesis.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Fibrin binding moieties useful as imaging agents
InactiveUS6984373B2Easy to optimizeEffective treatmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCompound screeningMedicineImaging agent
The present invention provides binding moieties for fibrin which have a variety of uses wherever detecting, isolating or localizing fibrin, and particularly fibrin as opposed to fibrinogen, is advantageous. Particularly disclosed are synthetic, isolated polypeptides capable of binding fibrin and recognizing the form of polymerized fibrin found in thrombi. In addition, the polypeptides have a slow dissociation rate from fibrin, which improves their ability to form a contrast image at the site of a fibrin clot, making the disclosed binding moieties particularly useful as imaging agents for thrombi.
Owner:DYAX CORP
Conjugates for dual imaging and radiochemotherapy: composition, manufacturing, and applications
ActiveUS20060182687A1High resolutionNon toxicUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCosmetic preparationsDual imagingSynthesis methods
Compositions and methods for dual imaging and for dual chemotherapy and radiotherapy are disclosed. More particularly, the invention concerns compounds comprising the structure X1-Y-X2, wherein Y comprises two or more carbohydrate residues covalently attached to one another, X1 and X2 are diagnostic or therapeutic moieties covalently attached to Y, provided that when Y does not comprise a glucosamine residue, X1 and X2 are diagnostic moieties. The present invention also concerns methods of synthesis of these compounds, application of such compounds for dual imaging and treatment of hyperproliferative disease, and kits for preparing a radiolabeled therapeutic or diagnostic compound.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF TEXAS SYST THE
Compounds of the inventions of guanylyl cyclase C
InactiveUS20050287067A1Activity can be delayedControllable conversionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCyclaseMedicine
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Systems and methods of modeling pharmaceutical propagation in a patient
InactiveUS20070255135A1Reduce contrastIncrease doseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsTime responseMedicine
A method of delivering a contrast enhancing fluid to a patient using an injector system, includes determining at least one patient transfer function for the patient based upon data specific to the patient, the at least one patient transfer function providing a time enhancement output for a given input; determining a desired time enhancement output; using the at least one patient transfer function to determine an injection procedure input; and controlling the injector system at least in part on the basis of the determined injection procedure input. The injection procedure input can be determined considering at least one operational limitation or constraint of the injector system. A method of modeling propagation of a pharmaceutical fluid in a patient, includes: collecting data corresponding to a time response curve resulting from injection of the fluid; and determining at least one mathematical model describing the data. The mathematical model can, for example, be a model which is not determined by a continuous or a discrete-time Fourier deconvolution of the data. Further, the injection of fluid by the injector can be controlled at least in part on the basis of the mathematical model.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com