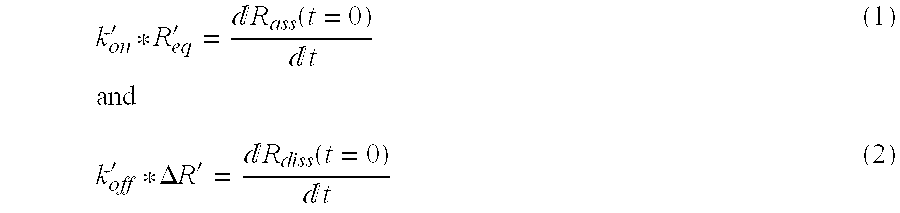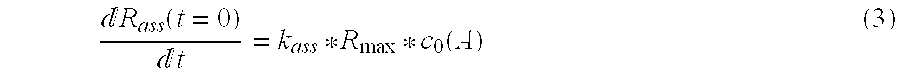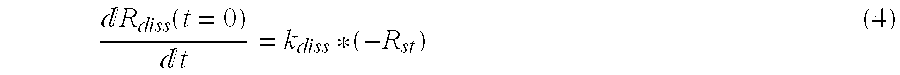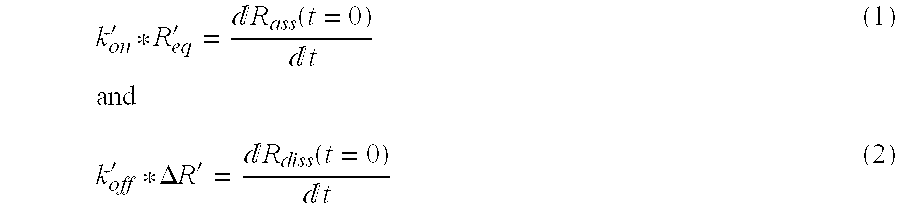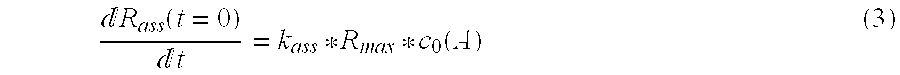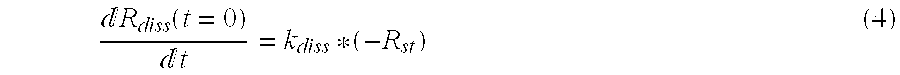Patents
Literature
64 results about "Dissociation rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The dissociation rate in chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology is the rate or speed at which a ligand dissociates from a protein, for instance, a receptor. It is an important factor in the binding affinity and intrinsic activity (efficacy) of a ligand at a receptor. The dissociation rate for a particular substrate can be applied to enzyme kinetics, including the Michaelis-Menten model. Substrate dissociation rate contributes to how large or small the enzyme velocity will be. In the Michaelis-Menten model, the enzyme binds to the substrate yielding an enzyme substrate complex, which can either go backwards by dissociating or go forward by forming a product. The dissociation rate constant is defined using Koff.
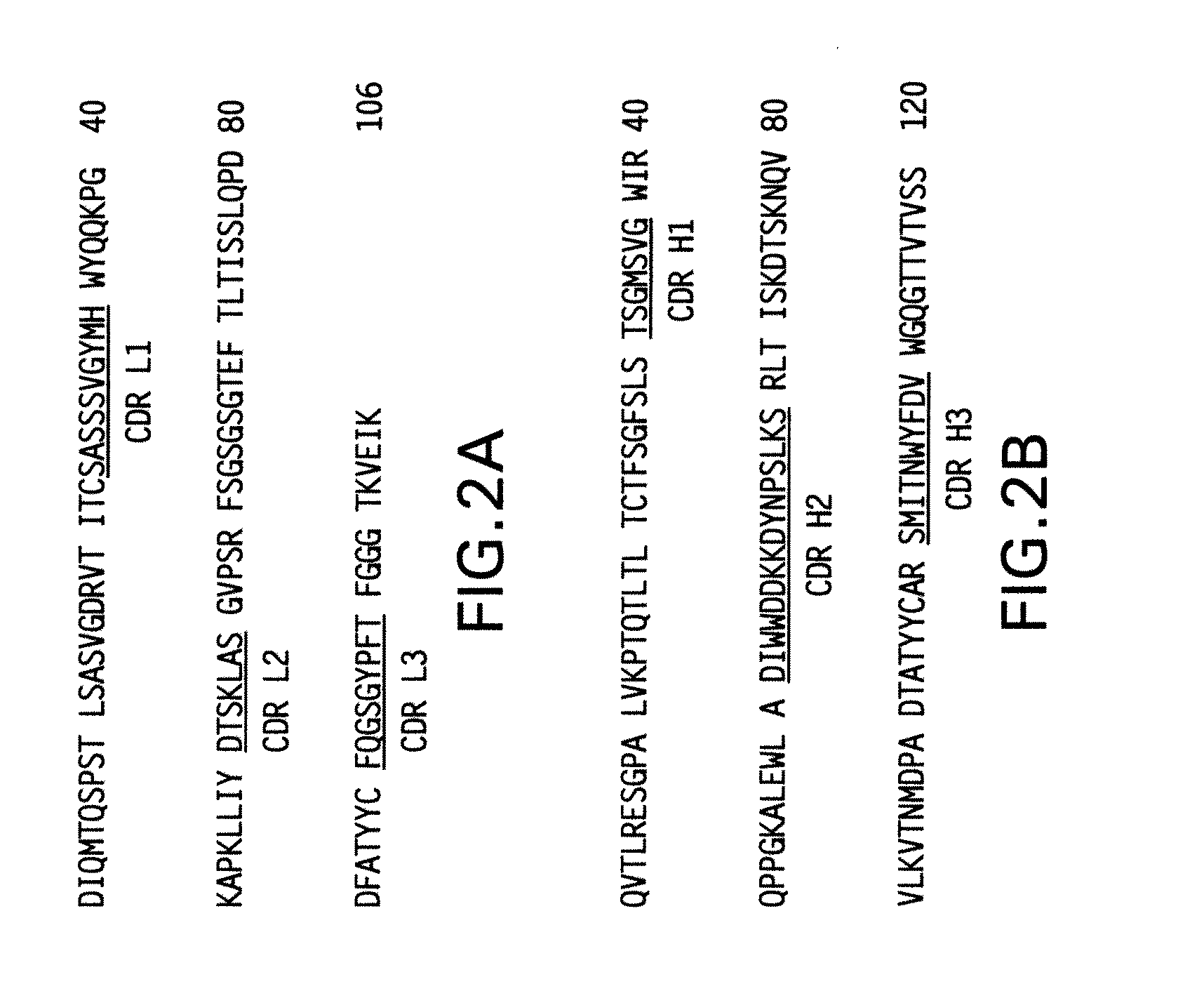
Methods of preventing and treating RSV infections and related conditions
InactiveUS20060115485A1High affinityEfficient reductionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderAntigenHalf-life
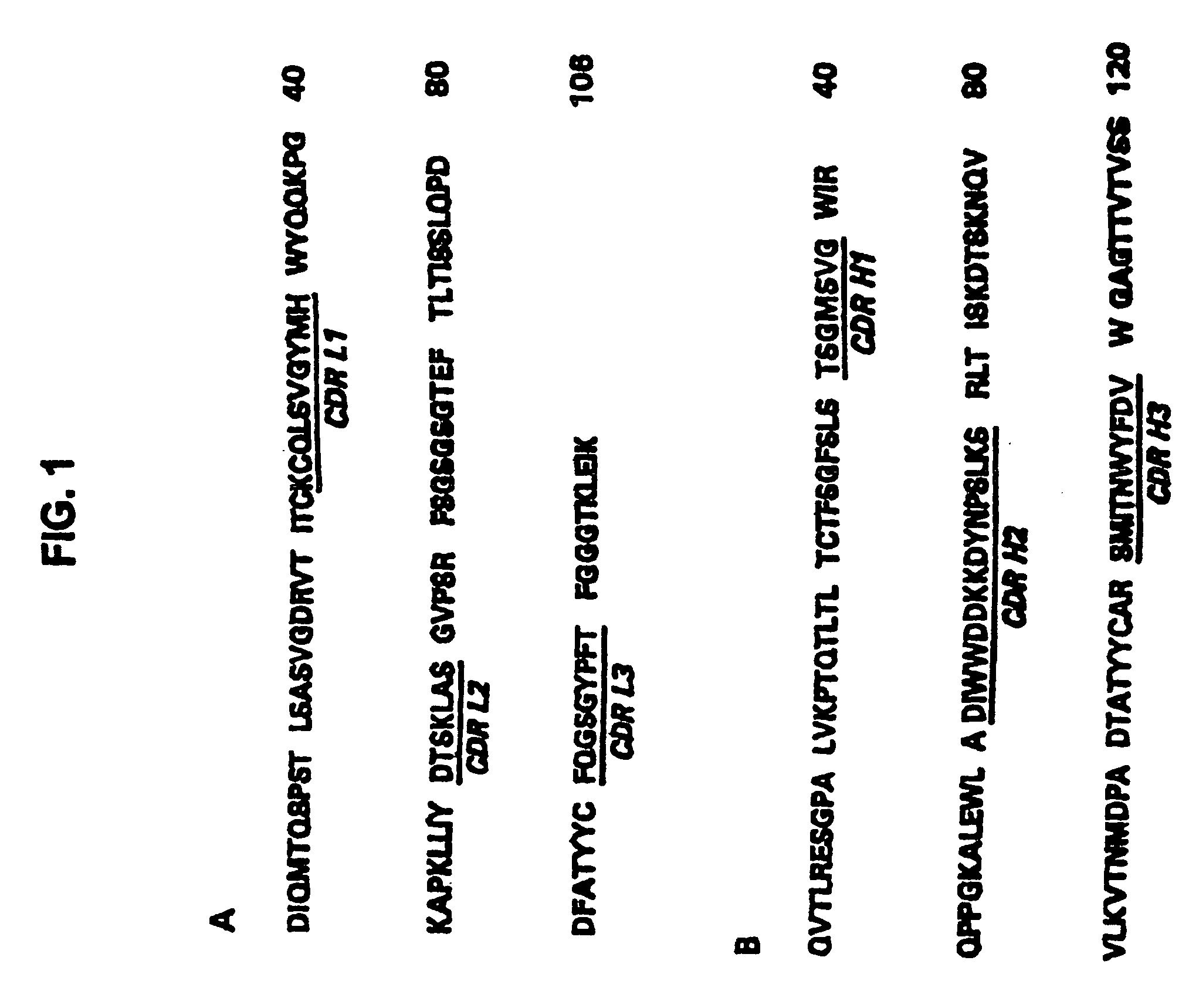
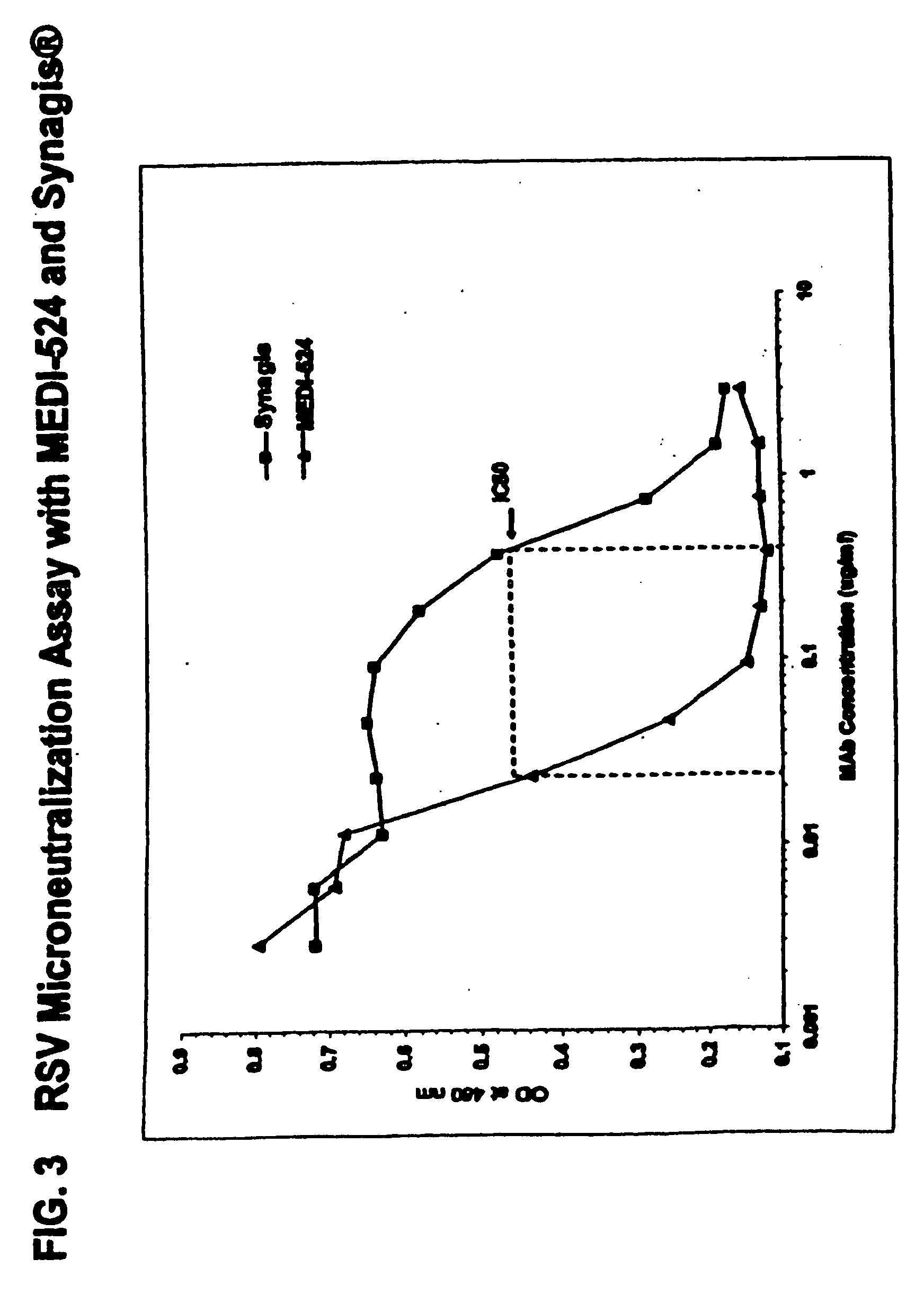
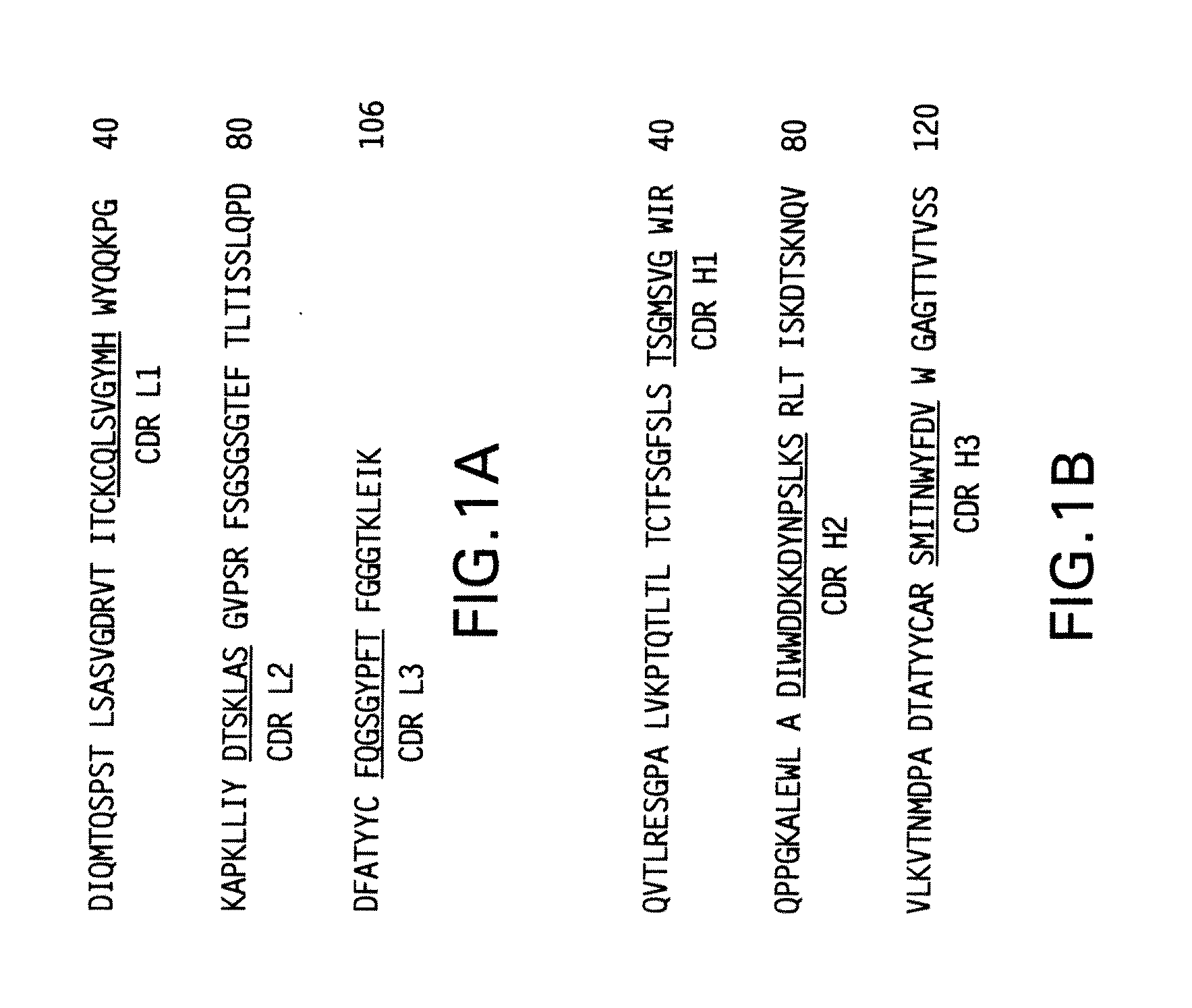
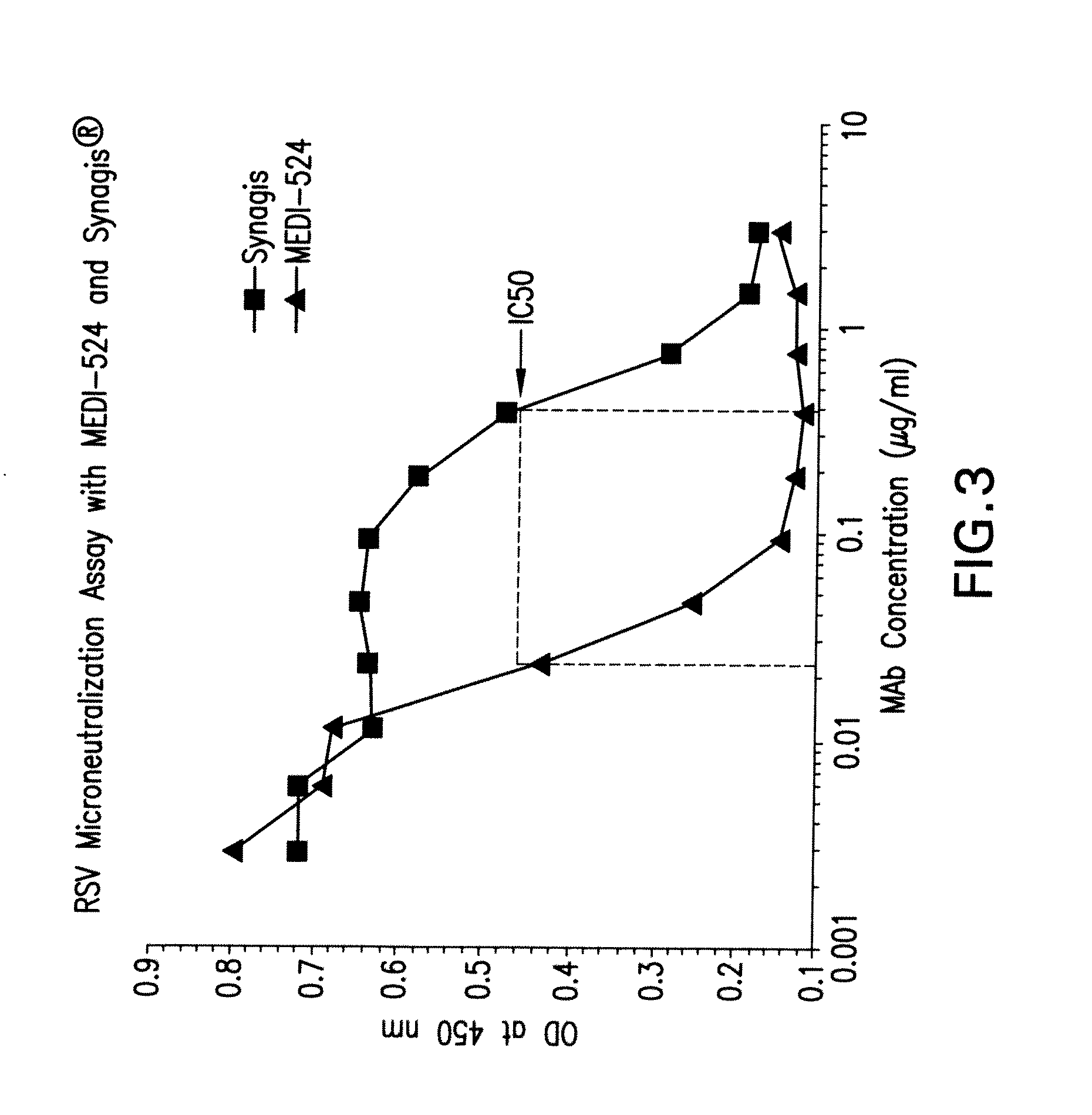
The present invention provides methods for preventing, managing, treating and / or ameliorating a Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) infection (e.g., acute RSV disease, or a RSV upper respiratory tract infection (URI) and / or lower respiratory tract infection (LRI)), otitis media (preferably, stemming from, caused by or associated with a RSV infection, such as a RSV URI and / or LRI), and / or a symptom or respiratory condition relating thereto (e.g., asthma, wheezing, and / or reactive airway disease (RAD)) in a subject, comprising administering to said human an effective amount of one or more antibodies that immunospecifically bind to one or more RSV antigens with a high affinity and / or high avidity. In some embodiments, one or more antibodies comprise a modified IgG constant domain, or FcRn-binding fragment thereof resulting in longer in vivo serum half-life. In particular embodiments the methods of the invention comprising administering to subject an effective amount of one or more modified antibodies that immunospecifically bind to one or more RSV antigens with an association rate (kon) of at least 2×105 M−1s−1 and a dissociation rate (koff) of less than 5×10−4 s−1.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
CD20 binding molecules
ActiveUS8153125B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD20Heavy chain
The present invention relates to CD20 binding molecules and nucleic acid sequences encoding CD20 binding molecules. In particular, the present invention relates to CD20 binding molecules with a high binding affinity, and a low dissociation rate, with regard to human CD20. Preferably, the CD20 binding molecules of the present invention comprise light and / or heavy chain variable regions with fully human frameworks (e.g. human germline frameworks).
Owner:APPLIED MOLECULAR EVOLUTION
Methods of preventing and treating rsv infections and related conditions
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
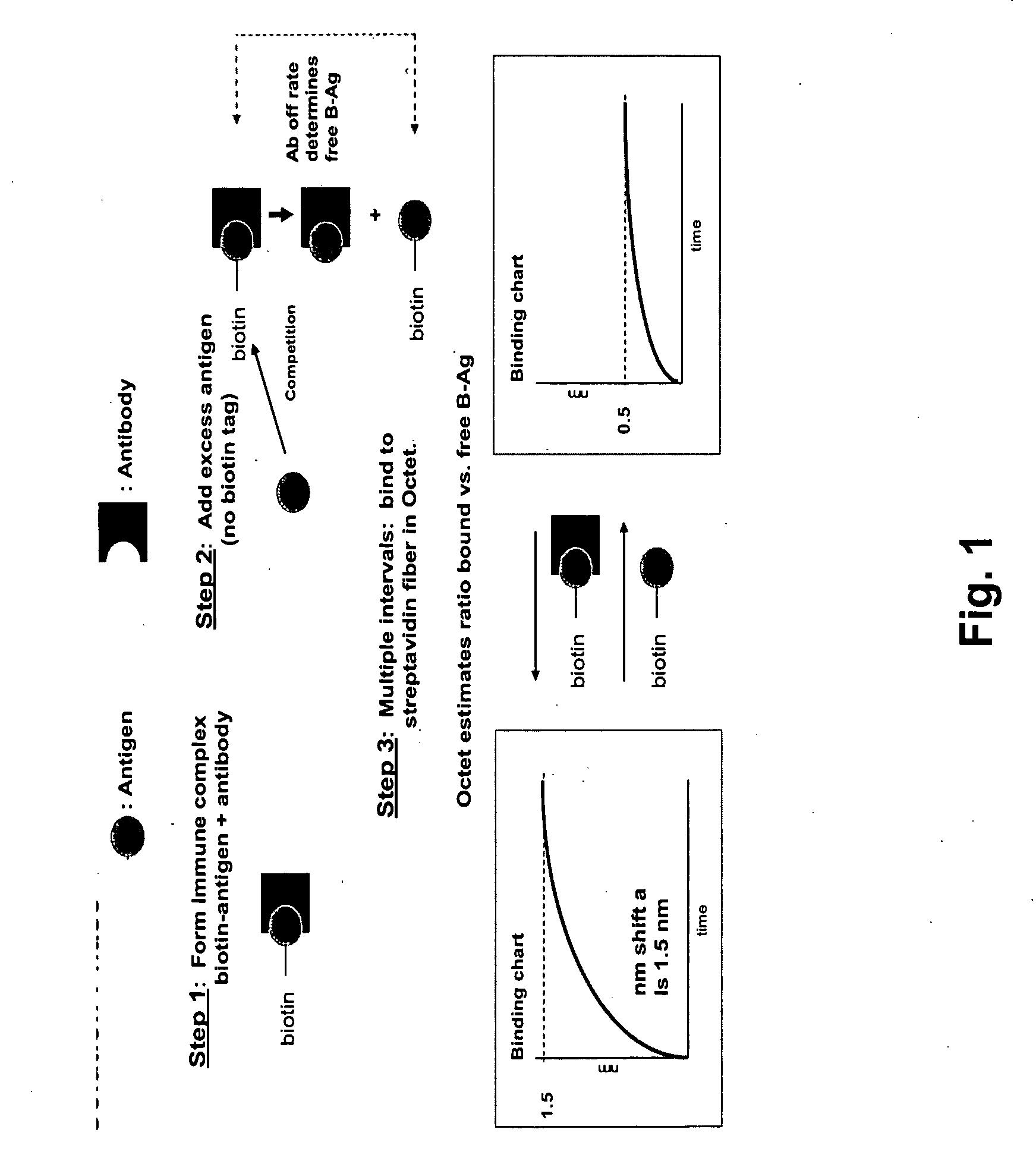
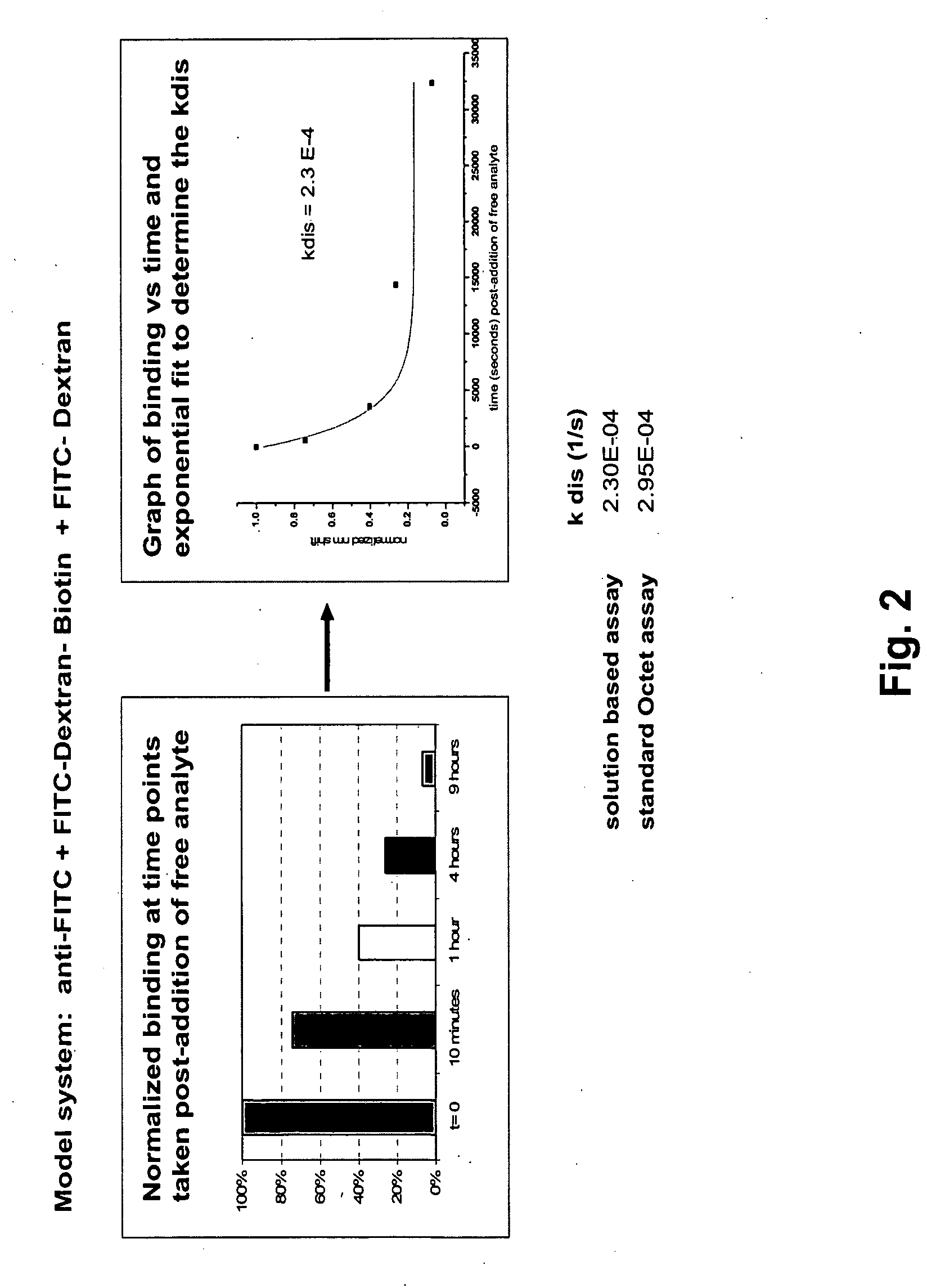
Methods for characterizing molecular interactions
InactiveUS20070161042A1Biological testingChemical methods analysisDissociation rate constantContinuous measurement
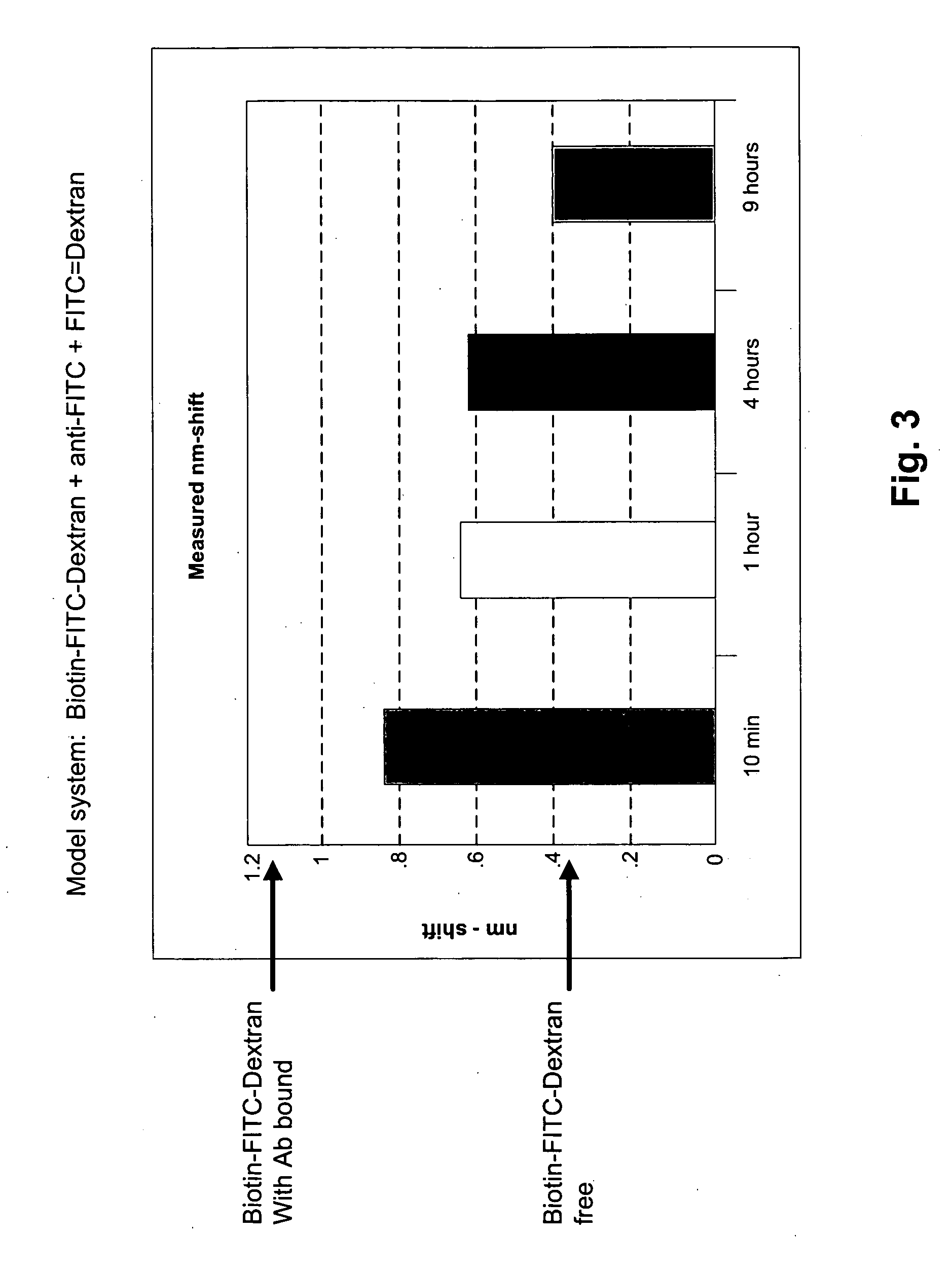
Methods are provided for measuring rate constants for high affinity molecular interactions using an assay format for determining dissociation rates in liquid phase. The invention uses a biosensor that at selected time intervals is contacted with a sample solution to estimate the ratio of bound vs. free ligand. Dissociation rate constants determined according to the methods of the invention more closely mimic in vivo binding constants and avoid diffusional barrier artifacts that accompany measurements performed using solid phase devices. The methods of the invention provide further advantage by not requiring continuous measurements be made on a biosensor instrument thus leaving it available to process other samples. The methods permit accurate determination of dissociation rates of reactions for which dissociation slowly occurs over intervals of hours to days or more.
Owner:PALL FORTEBIO
Analytical measuring and evaluation method for molecular interactions
InactiveUS20030143565A1Concentration of analyte can be raised and loweredImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAnalyteDissociation constant
The invention relates to an analytical measuring and evaluation method for determining the interaction parameters between an analyte and a ligand, preferably in a biosensor. According to the inventive method, the concentration of the analyte is gradually changed at defined intervals ti and the initial association or dissociation rates or association and dissociation constants are determined. The invention further relates to a device for carrying out the inventive method.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Polymerase variants
ActiveUS20180245147A1Easy to processIncrease read lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPolymerase LBiology
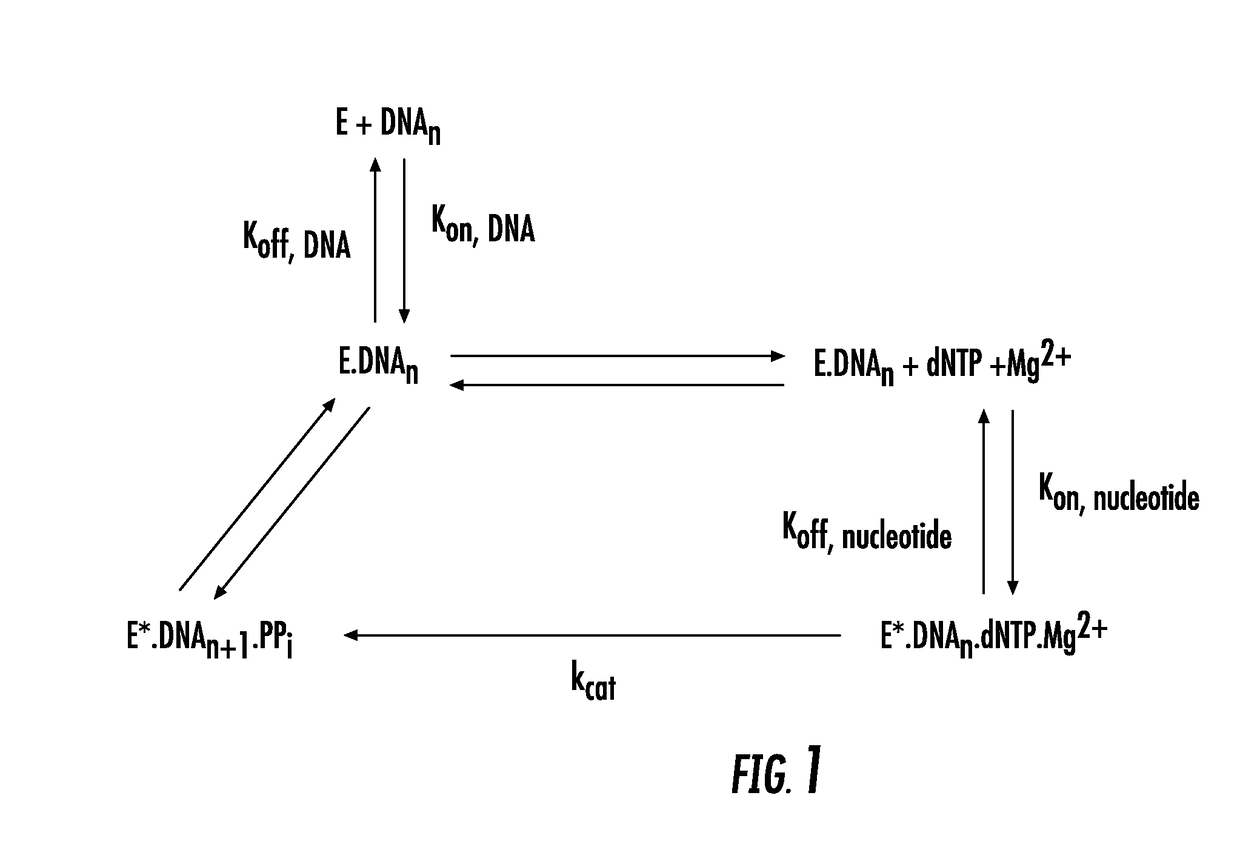
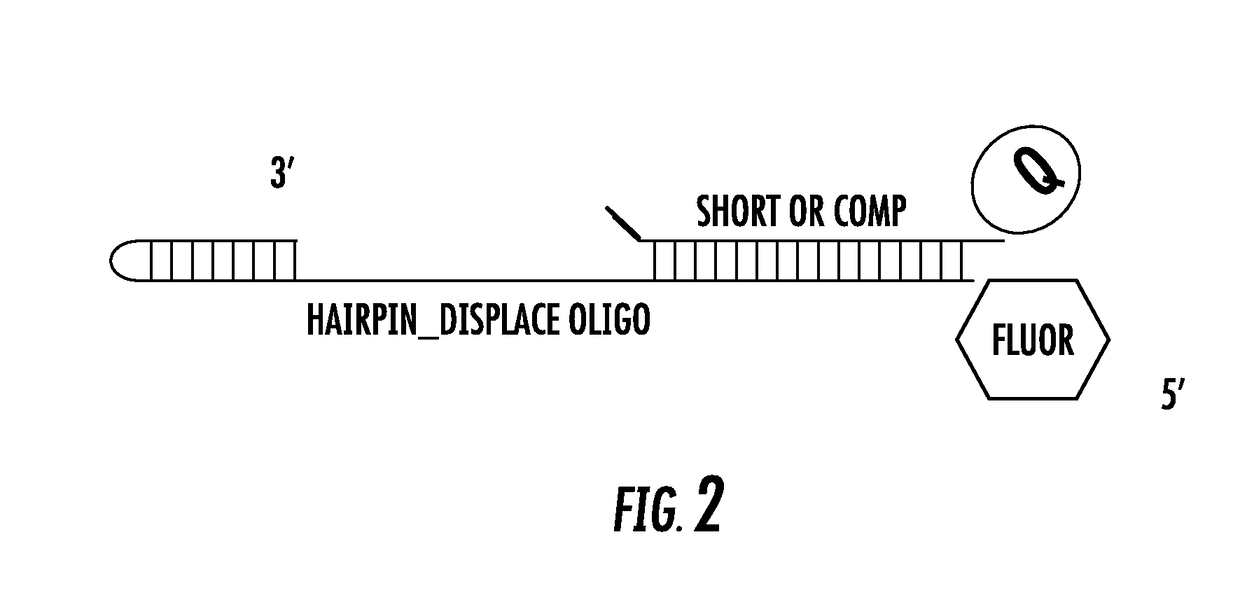
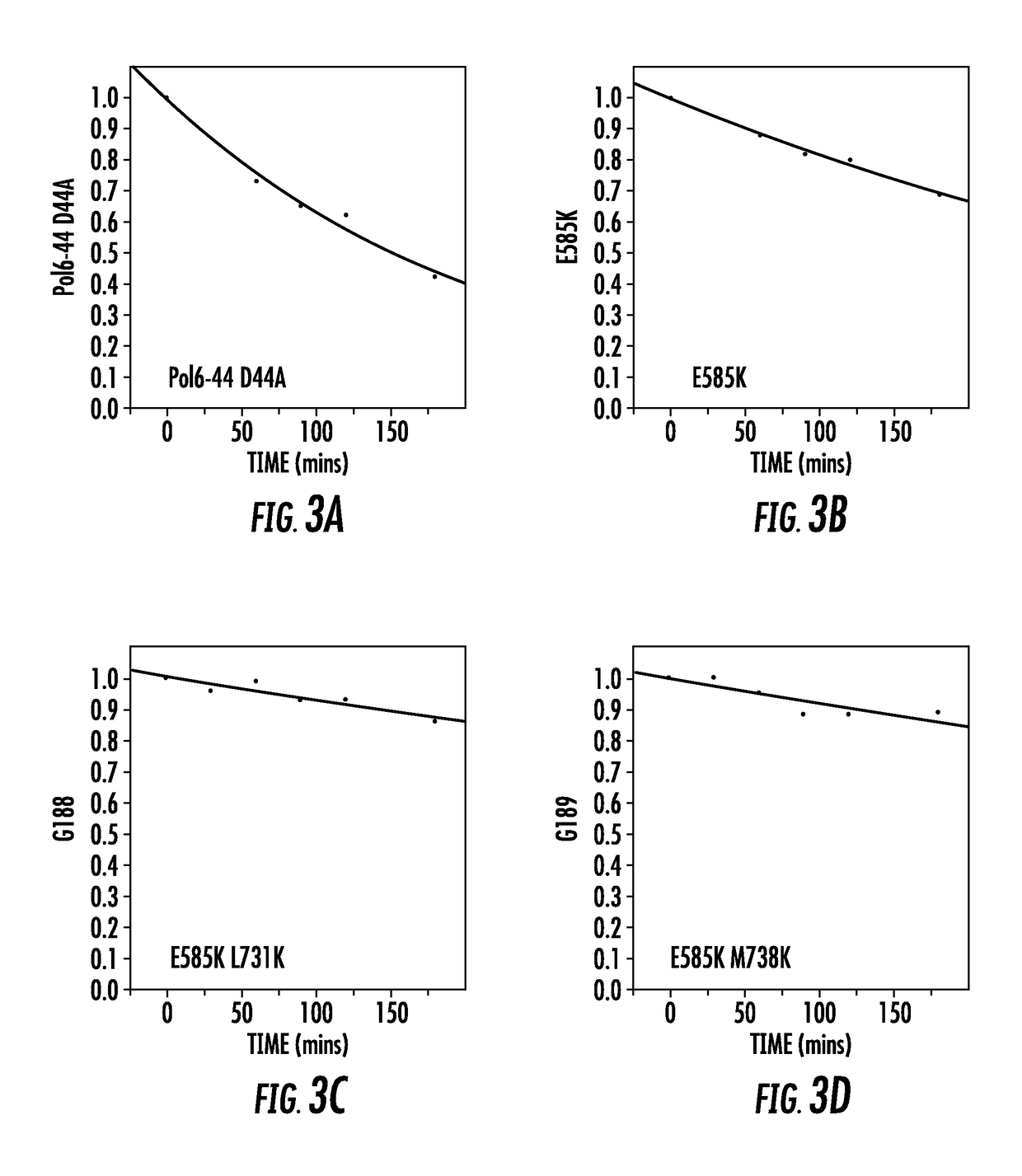
The present of disclosure provides variant Pol6 polymerase polypeptide, compositions comprising the Pol6 variant polypeptides, and methods for using the variant Pol6 polypeptides for determining the sequencing of nucleic acids, for example, by nanopore sequencing. The variant Pol6 polymerases possess decreased rates of dissociation of template from the polymerase-template complex, which result n increased processivity relative to the parental Pol6 polypeptides from which they are derived.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
Encoding/decoding method and device for orthogonal repeated accumulate codes
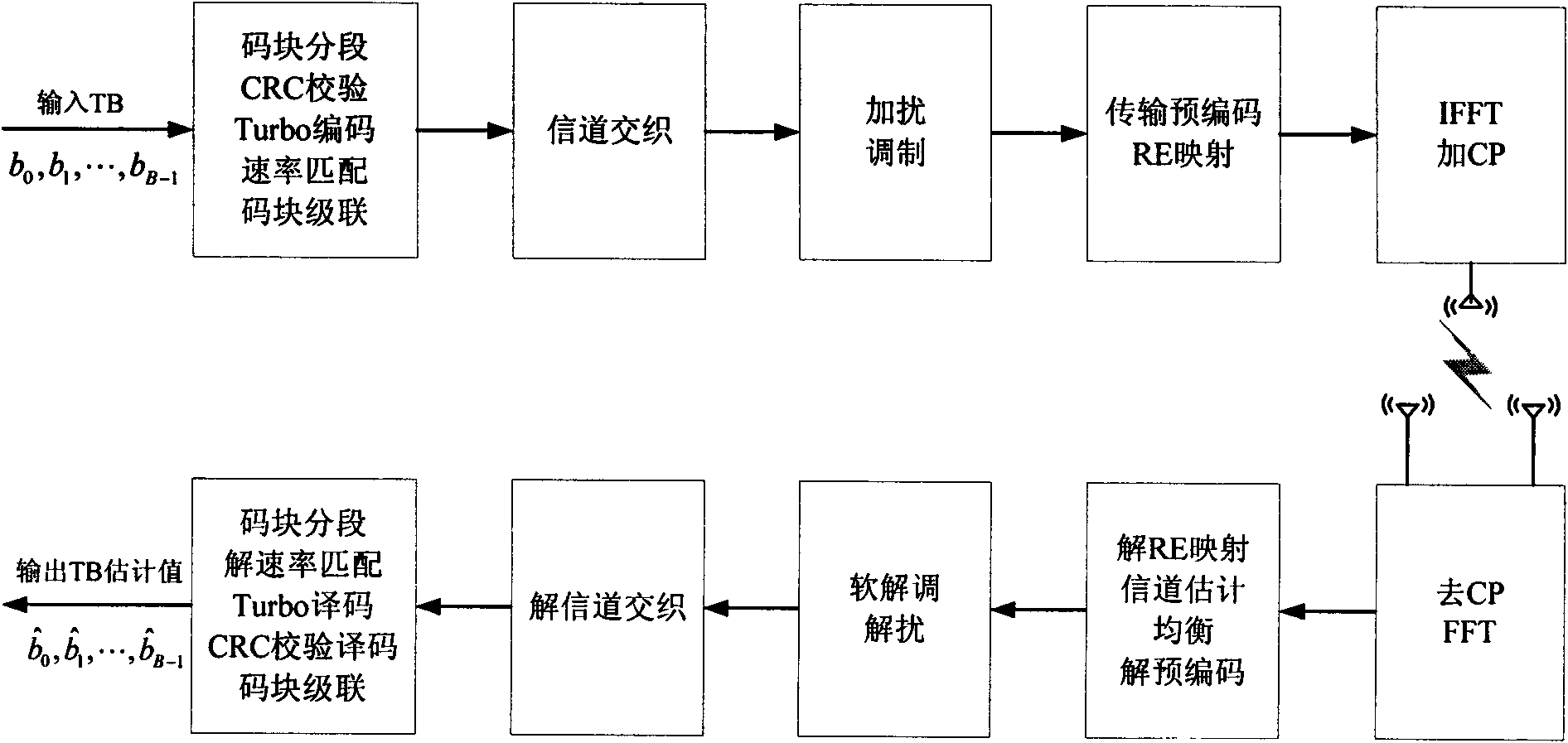
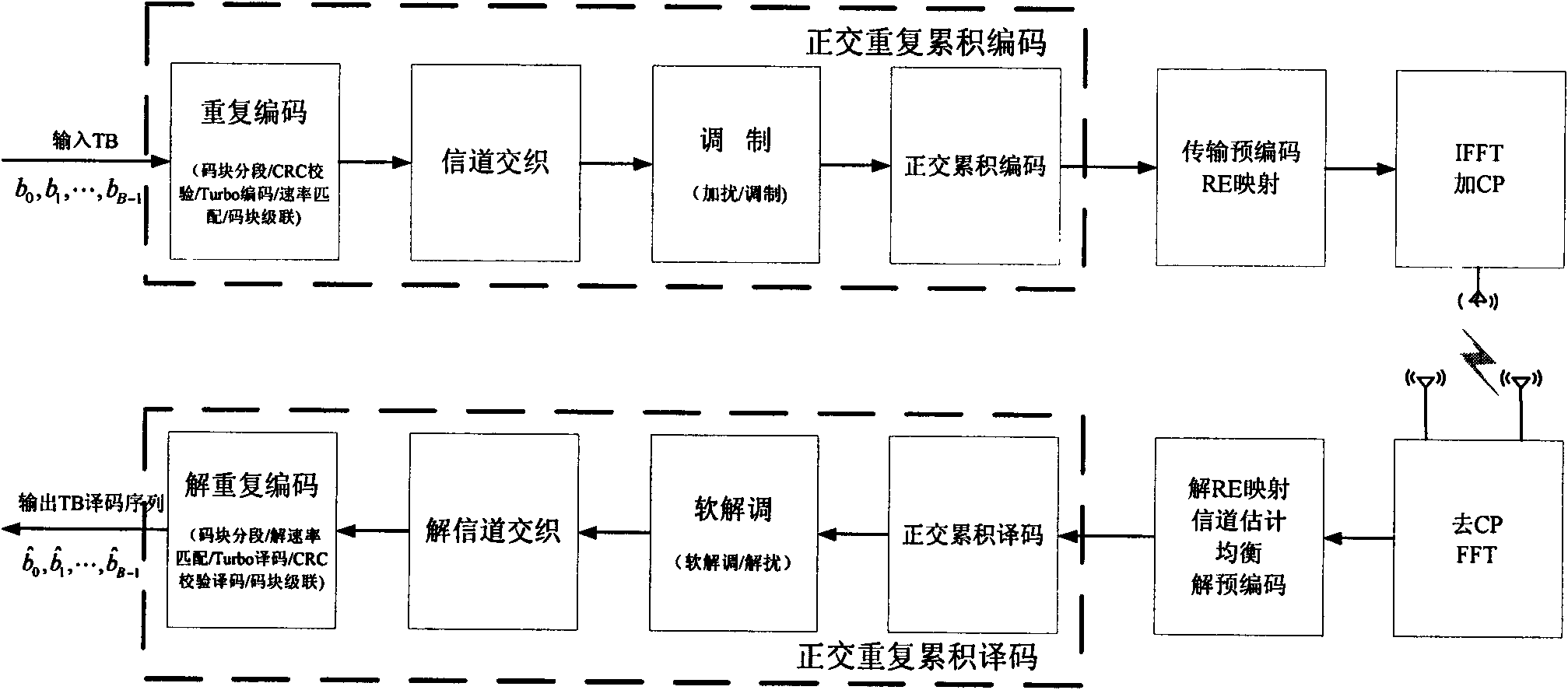
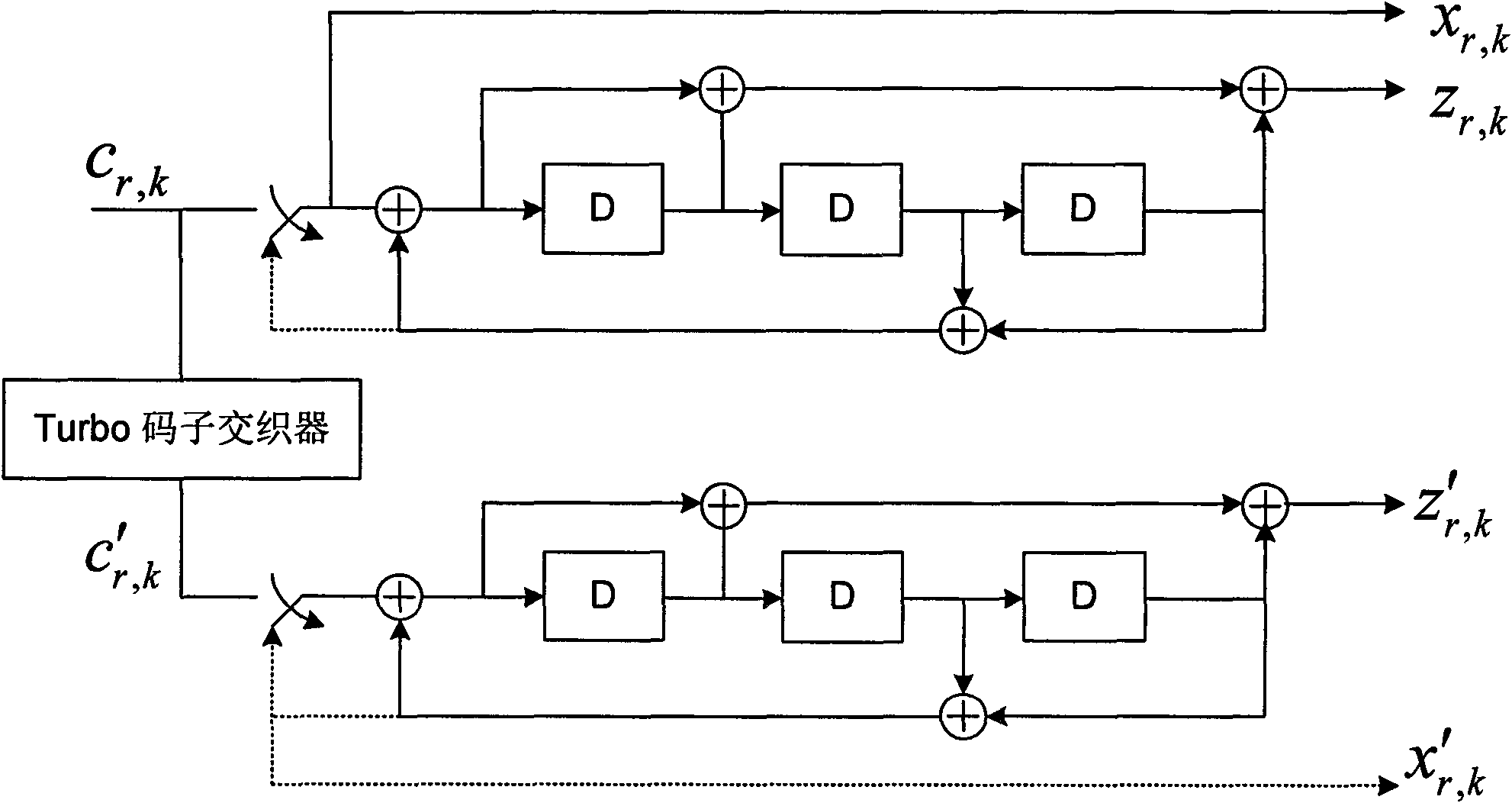
The invention discloses an encoding / decoding method and device for orthogonal repeated accumulate codes. In encoding, a repeatedly encoding submodule conducts code block segmentation, CRC (cyclic redundancy check), Turbo encoding and code block cascade to input TB bit information so as to obtain a repeated encoding bit sequence; the repeated encoding bit sequence is multiplexed with control information and then interleaved by a channel and processed by a modulation submodule for orthogonal accumulate encoding; further, the information is subjected to transmission precoding / RE mapping, and CP adding on IFFT, and then is transmitted; in decoding, the accumulative relationship of all codes in a receiving estimating sequence is relieved; then a modulation code estimating sequence is subjected to flexible modulation and channel de-interleaving in sequence, the processed information is sent to a repeated decoding submodule; and code block segmentation, dissociation rate matching, Turbo decoding, CRC decoding and code block cascade are conducted in sequence to complete decoding. The encoding / decoding method and device can effectively improve the system decoding performance in a serious multipath fading condition, and reduce the processing cost of the system and the processing time delay.
Owner:西安新邮通信设备有限公司
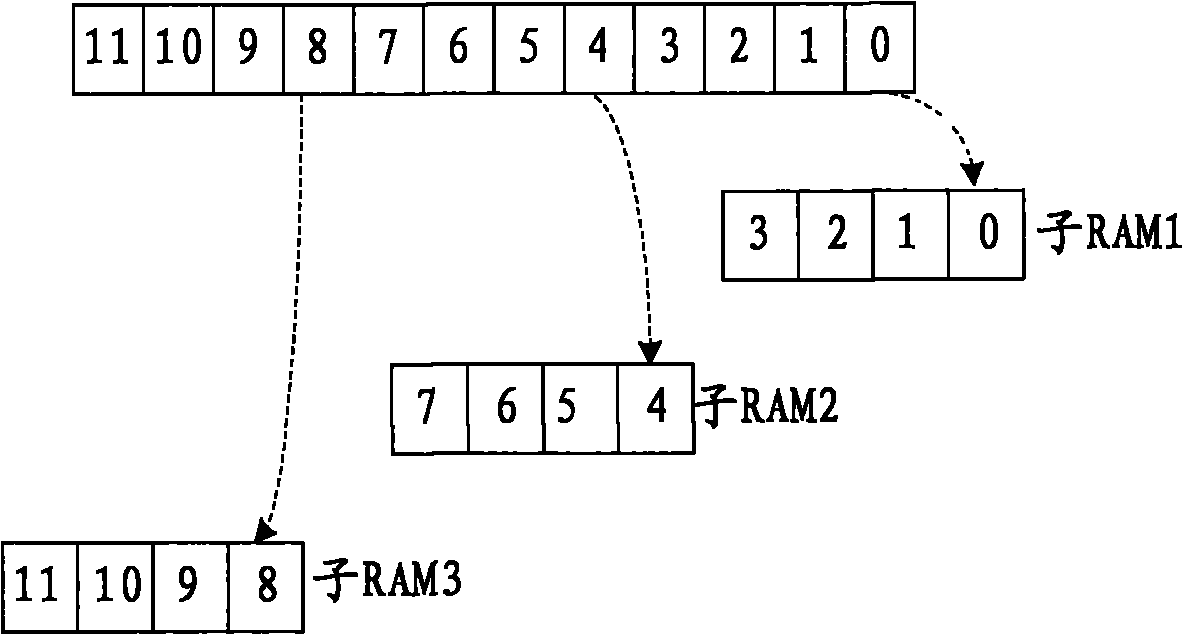
Dissociation rate matching method and device
ActiveCN101789846AShorten the timeImprove processing efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelRandom access memoryData needs
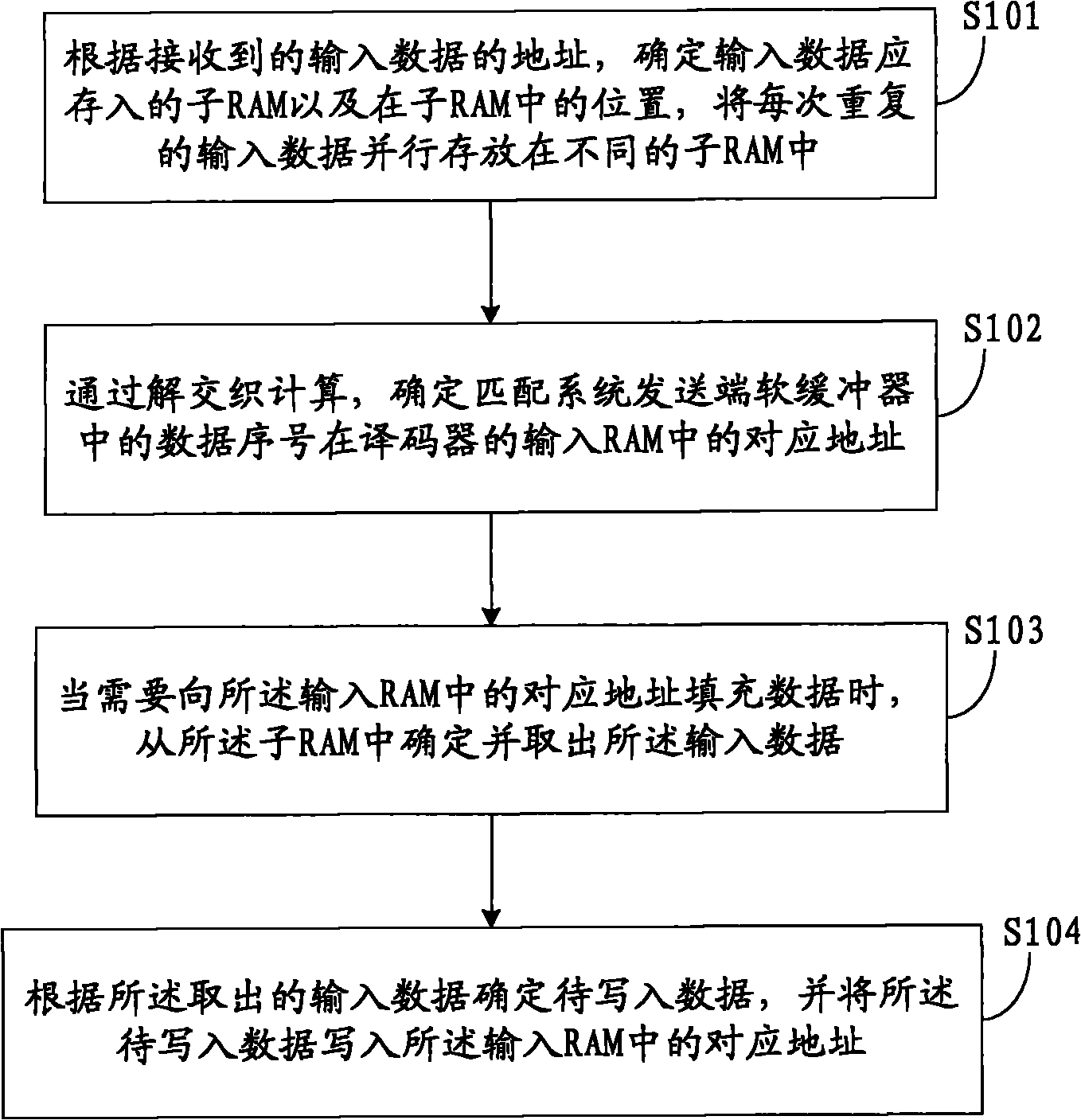
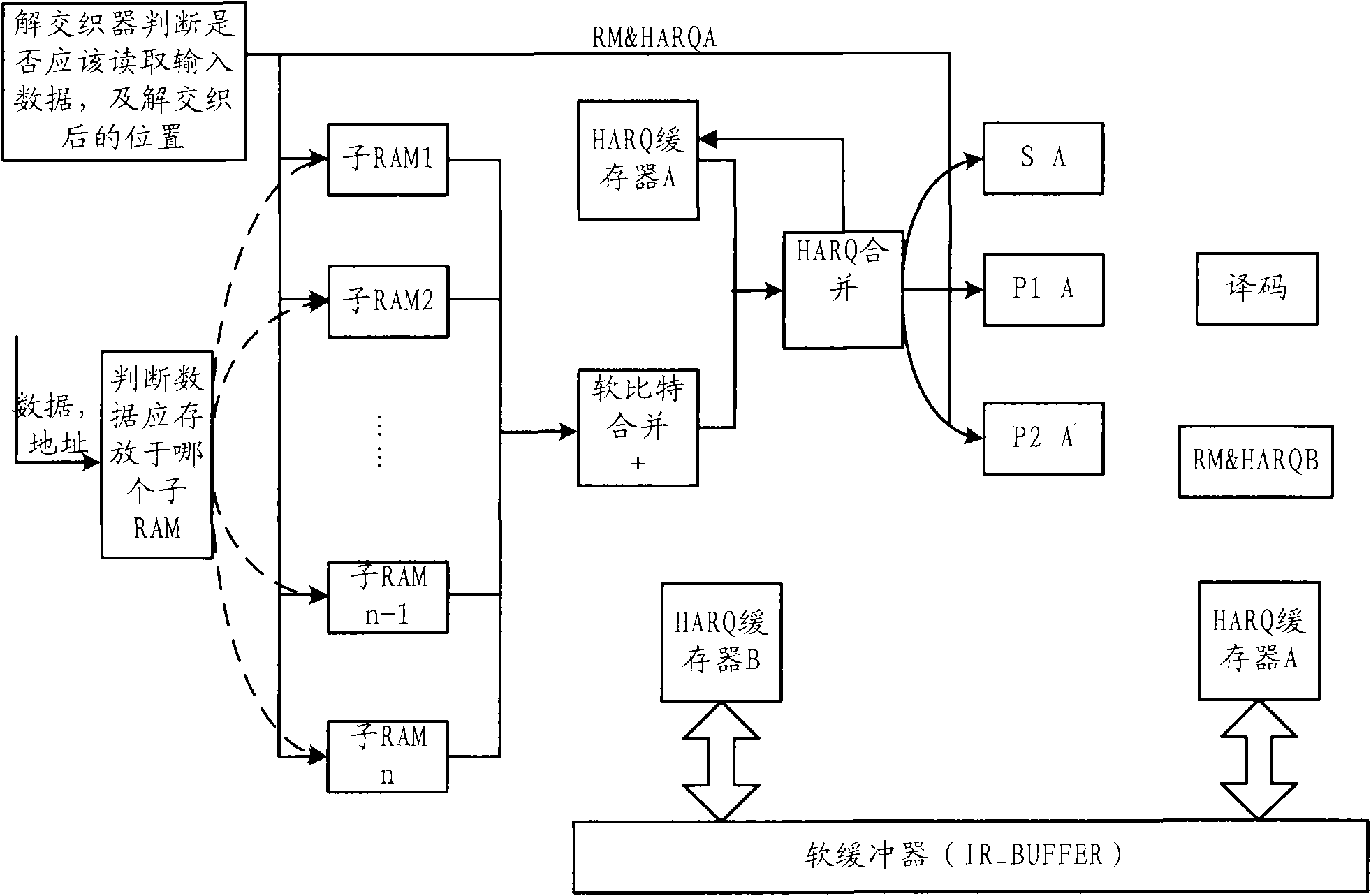
The invention discloses a dissociation rate matching method and a device, which are used for a dissociation rate matching system. The system comprises a plurality of sub-random access memories (sub-RAMs) for storing input data, wherein the number of the sub-RAMs is the same as the maximum number of repeated sending supported by a receiver of a matching system. The method comprises the following steps: determining the sub-RAM in which the input data needs to be stored and the position of the input data in the sub-RAM based on the address of the received input data, and storing the repetitive input data for each time in different sub-RAMs in parallel; determining the corresponding address of the data serial number in a soft buffer at the sending end of the matching system in the input RAM of a decoder by the deinterleaving calculation; determining and withdrawing the input data from the sub-RAM when the corresponding address in the input RAM needs to be filled with data; and determining the data to be written based on the withdrawn input data, and writing the data to be written in the corresponding address in the input RAM. By using the invention, the processing efficiency at the bit level can be improved.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
Avidin-like proteins from symbiotic bacteria
InactiveUS20100022401A1Small fluctuationStrong potentialPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningSymbiotic bacteriaBiotin-binding proteins
An isolated protein which is structurally and functionally similar to avidin but with improved properties, such as better affinity towards biotin conjugate, useful immunological properties or faster biotin dissociation rate, compared to avidin and streptavidin.
Owner:RICOH KK
Device and method for preparing single crystal diamonds by laser enhanced plasma CVD
ActiveCN108251892AHigh densityIncrease dissociation ratePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesMicrowaveSingle crystal
The invention discloses a device and method for preparing single crystal diamonds by laser enhanced plasma CVD. The device comprises plasma CVD equipment and laser equipment, wherein more than 1 set of laser equipment is respectively positioned on the outside of a cylindrical cavity of the plasma CVD equipment, laser emitted by the laser equipment can irradiate onto a substrate table positioned inthe cavity of the plasma CVD equipment; the substrate table is positioned in the middle of the cavity of the plasma CVD equipment, a cooling water circulation system is arranged at the lower part ofthe substrate table and comprises a cooling water inlet and a cooling water outlet; and a raw material gas inlet and an extraction opening are formed in the bottom of the cavity of the plasma CVD equipment. The method combines microwave energy (or electric energy) with laser energy and improves the energy of plasma and the gas dissociation rate in a diamond synthesizing process by using low-cost high-energy laser, thereby improving the synthetic rate of the diamonds and effectively solving the problem of high-speed mass preparation of diamonds.
Owner:湖北碳六科技有限公司
Quantitative ranking of transient ligand binding to target biomolecules
InactiveUS20050287527A1Improve applicabilityEfficient methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyRankingOrganism
There is provided a method of quantitatively ranking transient ligand binding to target biomolecules by means of NMR relaxation dispersion profiles. The present invention also relates to a method to identify ligand site obeying two-state and more complex binding behavior in a transient complex of a ligand with a target molecule, still with the use of NMR. There is also provided an efficient method to quantitate fast dissociation rates of ligands containing at least one magnetic nuclei by performing NMR relaxation dispersion experiments at different protein concentrations, enabling the evaluation of populations and exchange rates, and extending the practical applicability of the NMR relaxation dispersion experiments.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
TNF-α binding molecules
ActiveUS7101978B2High association rateLow dissociation rateImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiological material analysisHeavy chainNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to TNF-α binding molecules and nucleic acid sequences encoding TNF-α binding molecules. In particular, the present invention relates to TNF-α binding molecules with a high binding affinity, a high association rate, a low dissociation rate with regard to human TNF-α and that are capable of neutralizing TNF-α at low concentrations. Preferably, the TNF-α binding molecules of the present invention comprise light and / or heavy chain variable regions with fully human frameworks (e.g. human germline frameworks).
Owner:TRIMER BIOTECH LLC
Fluorescent compounds that bind to histone deacetylase
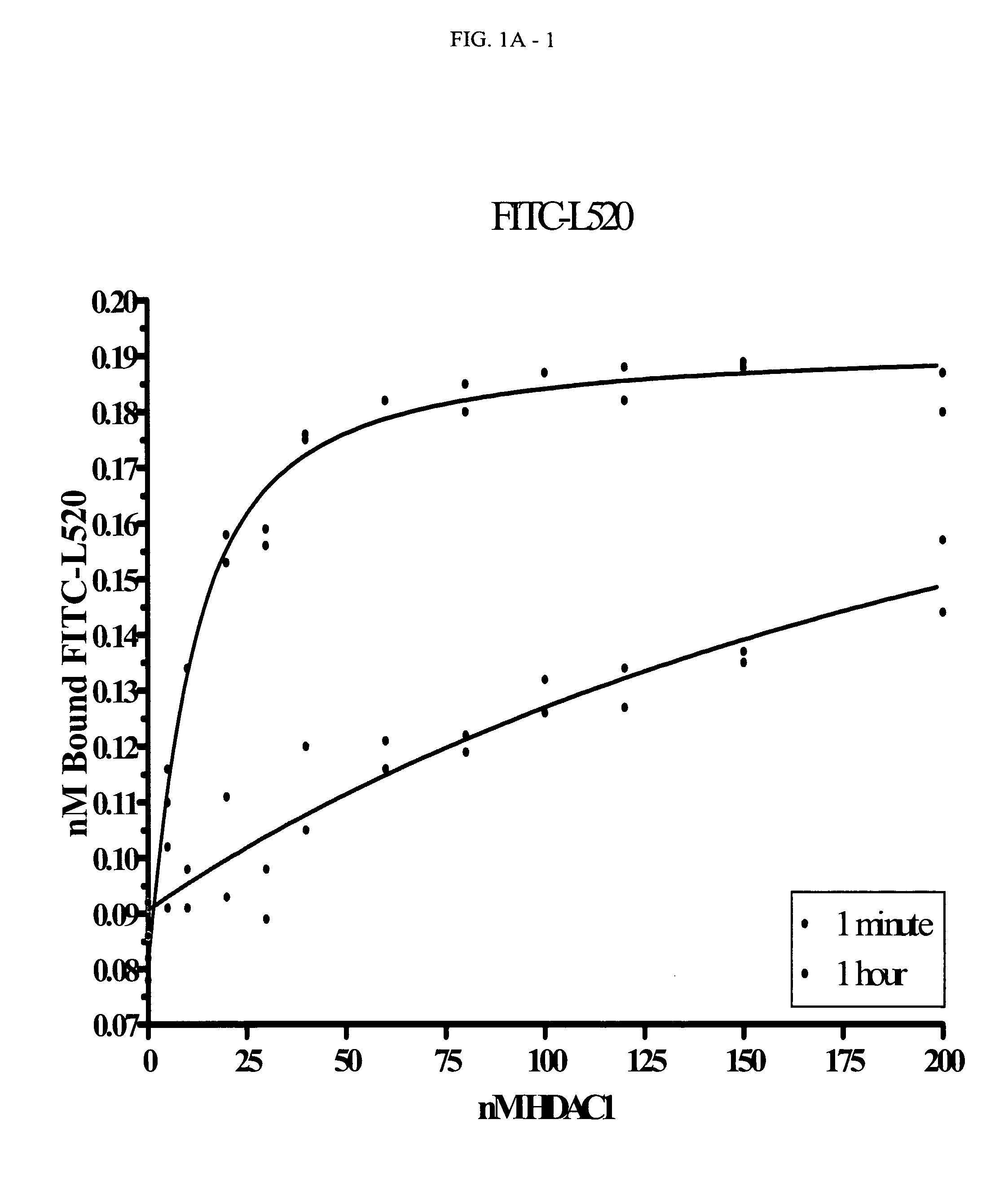
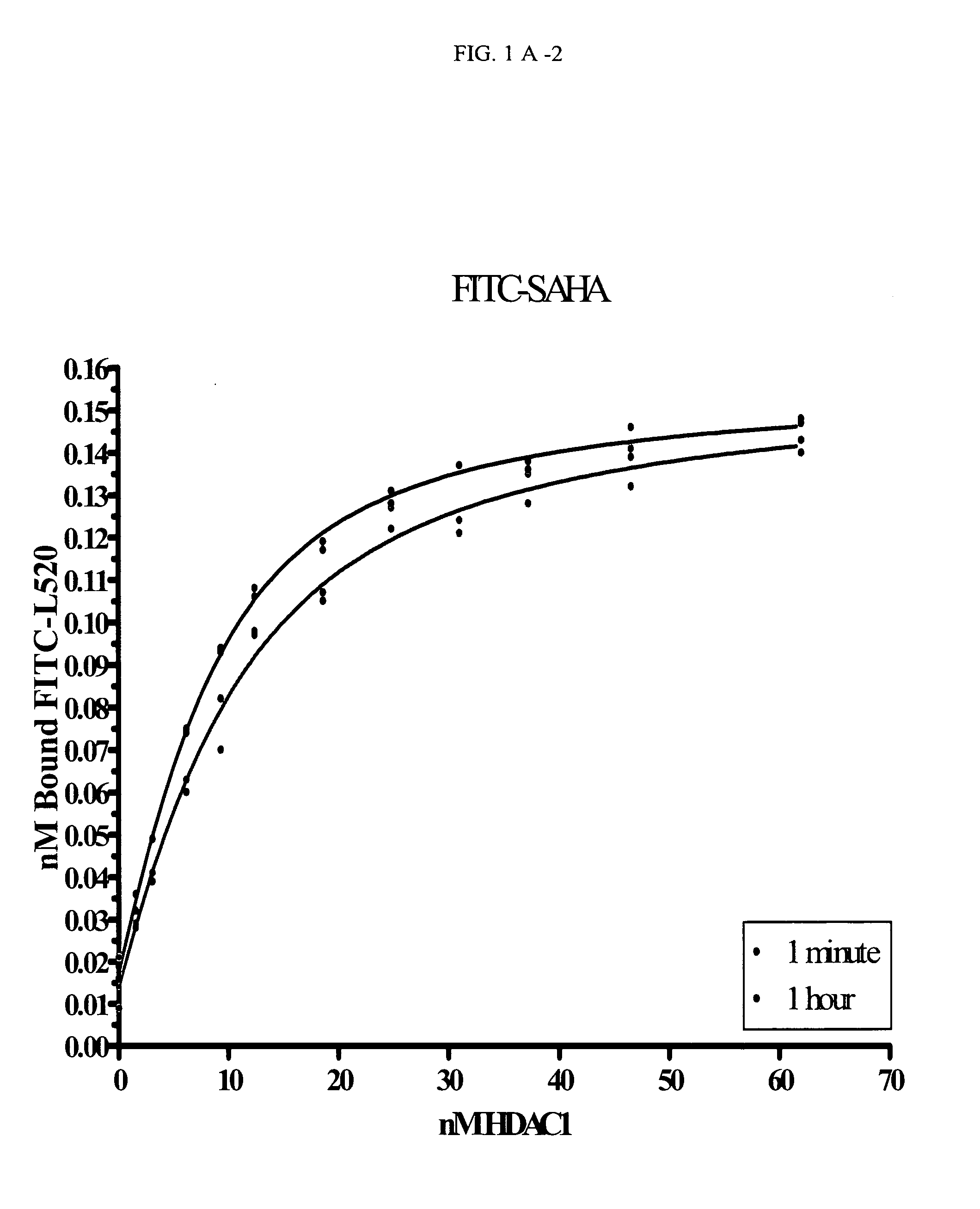
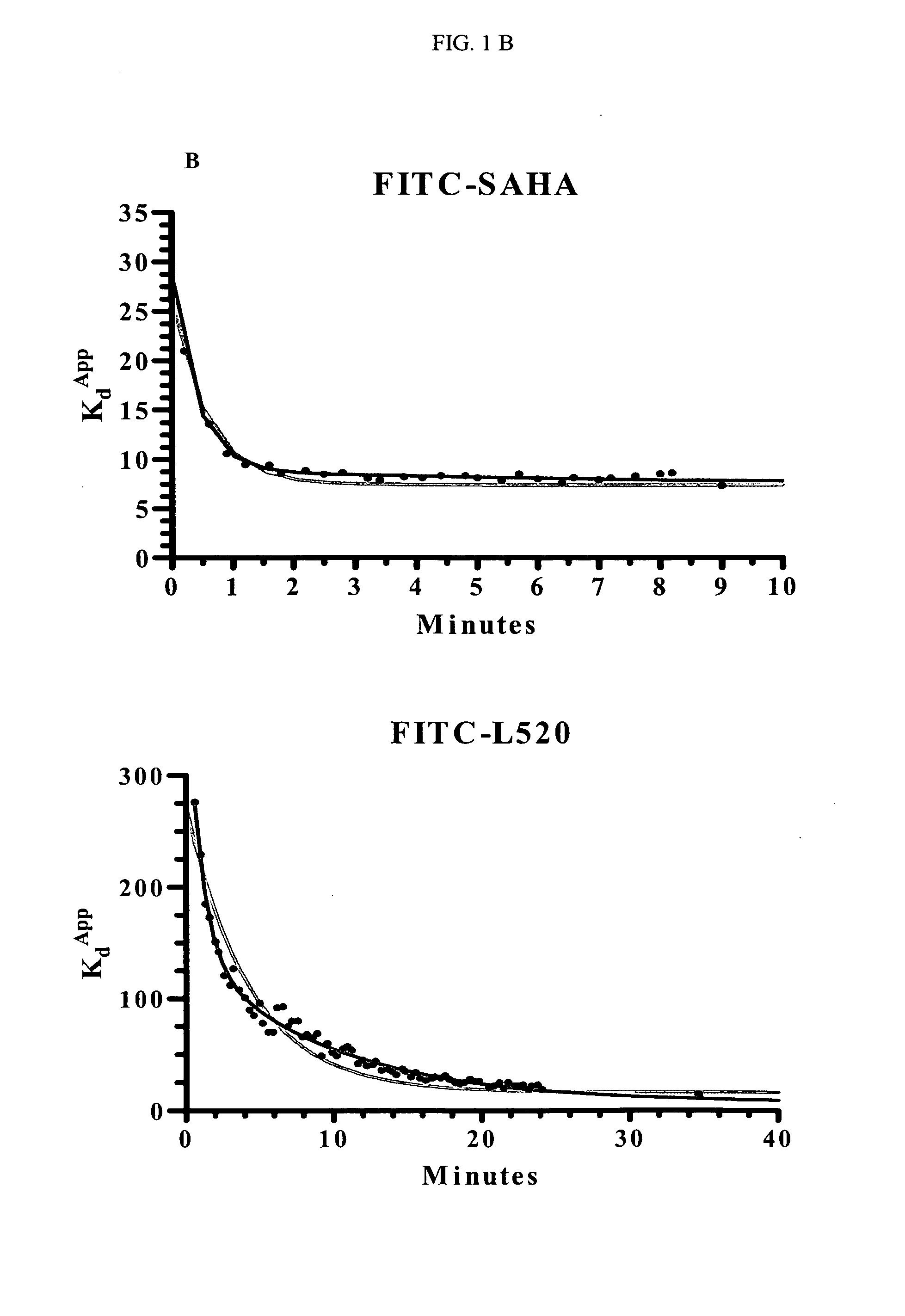
The present invention relates to a novel class of fluorescent compounds that bind to histone deacetylases. The fluorescent compounds can be used to determine binding association and dissociation rates of histone deacetylase inhibitors via fluorescence polarization.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Pretreatment method for recycling waste power lithium battery
InactiveCN108832216AReduce stickingThe production will notWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingPretreatment methodEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of battery recovery, in particular to a pretreatment method for recycling a waste power lithium battery. The method comprises the following steps of performing perforated discharge on a waste power lithium battery with completely released electrolyte; disassembling the completely-discharged waste power lithium battery, so that a battery shell and a battery inner core are obtained; performing low-temperature heat treatment on positive and negative electrode materials, and damaging the bonding effect of an adhesive PVDF; performing shearing type crushing on the positive and negative electrode materials which are already subjected to low-temperature heat treatment; and carrying out ultrasonic cleaning on an aluminum foil and a copper foil in the primary dissociation material, so as to obtain the aluminum foil and the copper foil which are completely dissociated from a lithium iron phosphate powder coating layer and a carbon powder coating layer, wherein the dissociation rate reaches 90%-95%. By adoption of the pretreatment method for recycling the waste power lithium battery, the dissociation rates of lithium battery positive and negative electrode copper foil and the carbon powder coating layer, and the aluminum foil and the lithium iron phosphate powder coating layer are improved, the time for recycling the waste power lithium batteries is shortened, and then the recovery efficiency of the waste power lithium batteries is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
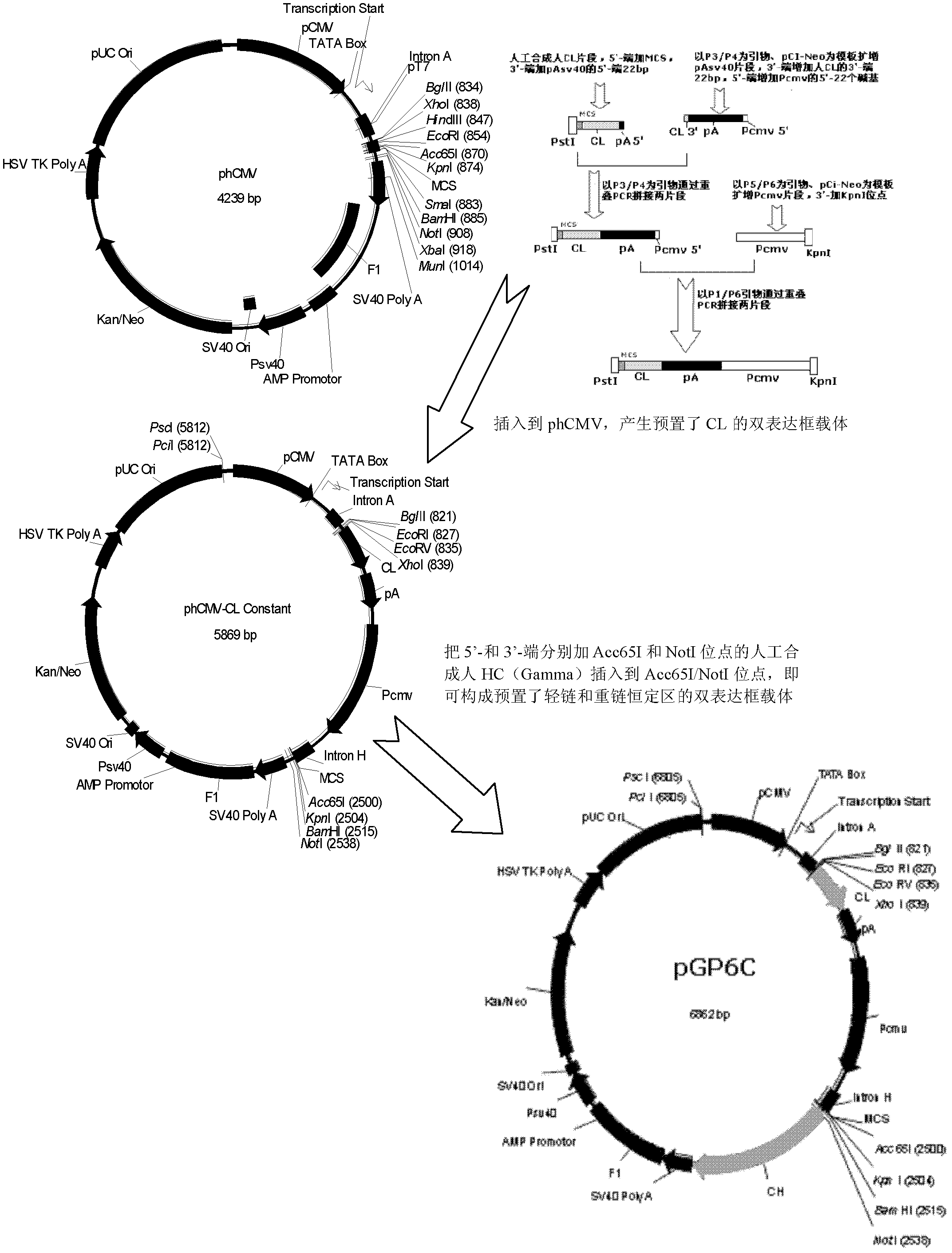
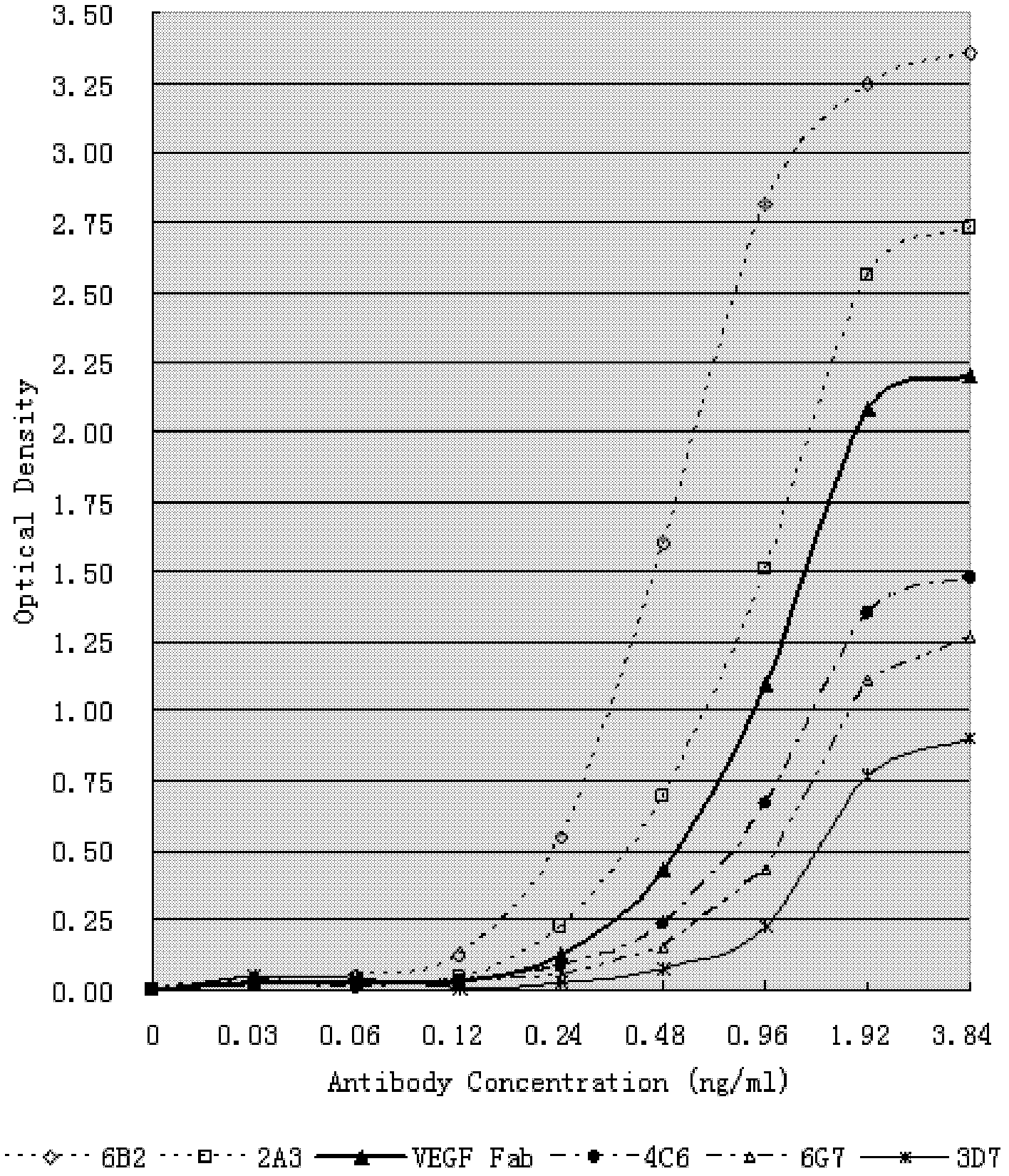
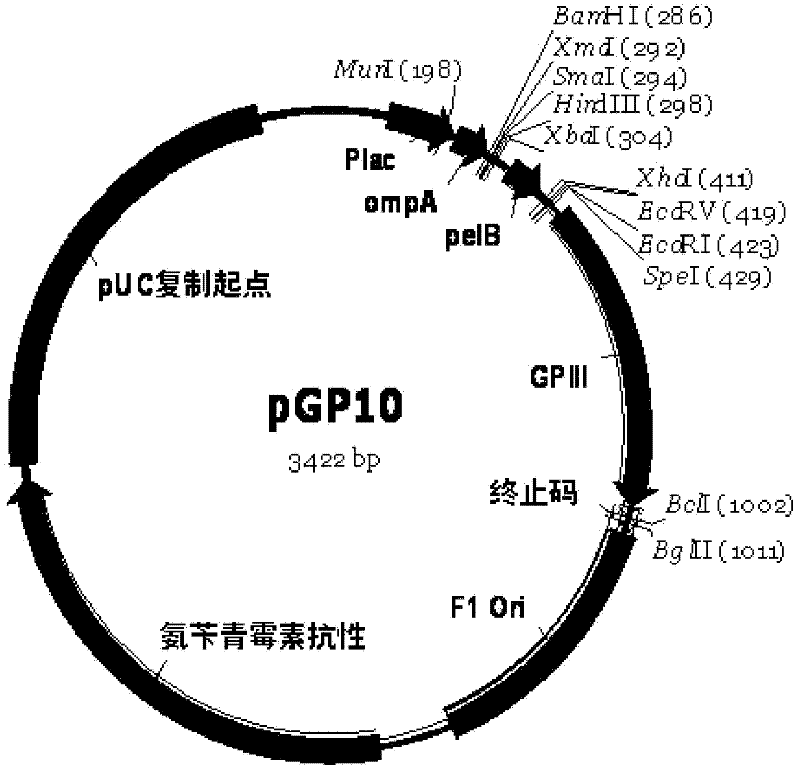
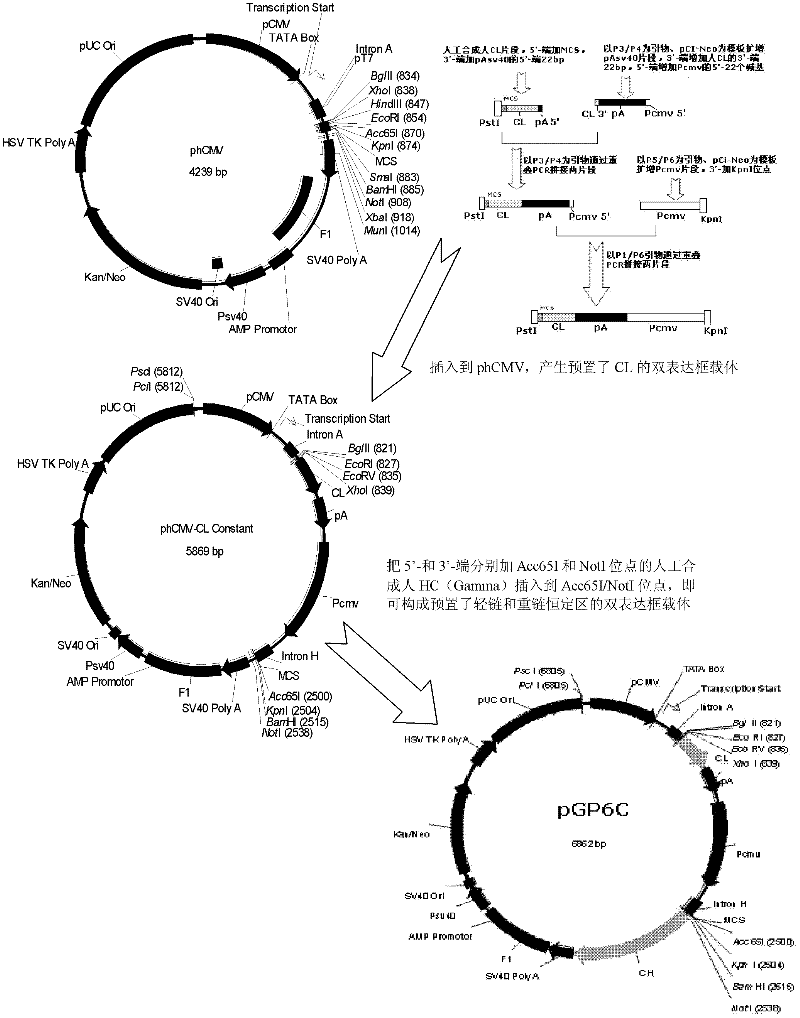
Human anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody molecule and application thereof
The invention relates to an anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody and a coding nucleic acid sequence thereof, and especially relates to an anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody having a high affinity and a low dissociation rate. The preferable anti-human VEGF monoclonal antibody comprises a human Fc region, a framework region, and a human light-chain and / or heavy-chain variable region obtained through molecular evolution. The invention also discloses medicinal compositions composed of the human antibody, an application of the human antibody in human disease treatment, and a method for using the human antibody in the treatment.
Owner:DANYANG ZHENGYUAN BIOTECH
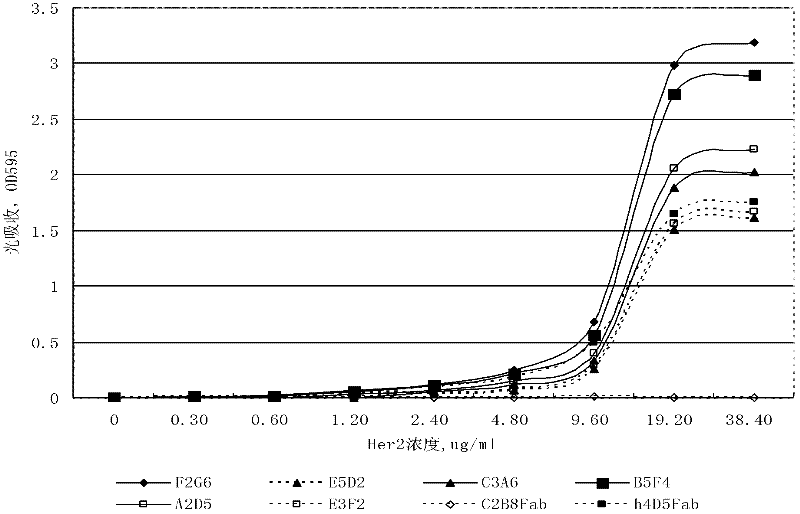
Fully humanized antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody
The invention relates to a fully humanized antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody, particularly an antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody having high affinity and low dissociation rate. The antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody preferred by the invention comprises a fully humanized Fc region, a framework region, and a CDR region of a fully humanized light chain and / or heavy chain, wherein the CDR region is obtained by molecular evolution. The invention also discloses an application of a medicine composition consisting of the antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody in treating human diseases and a method for using the antihuman HER2 monoclonal antibody in treatment.
Owner:广州誉嘉生物科技有限公司
Method for measuring reaction rate coefficient by surface plasmon resonance analysis
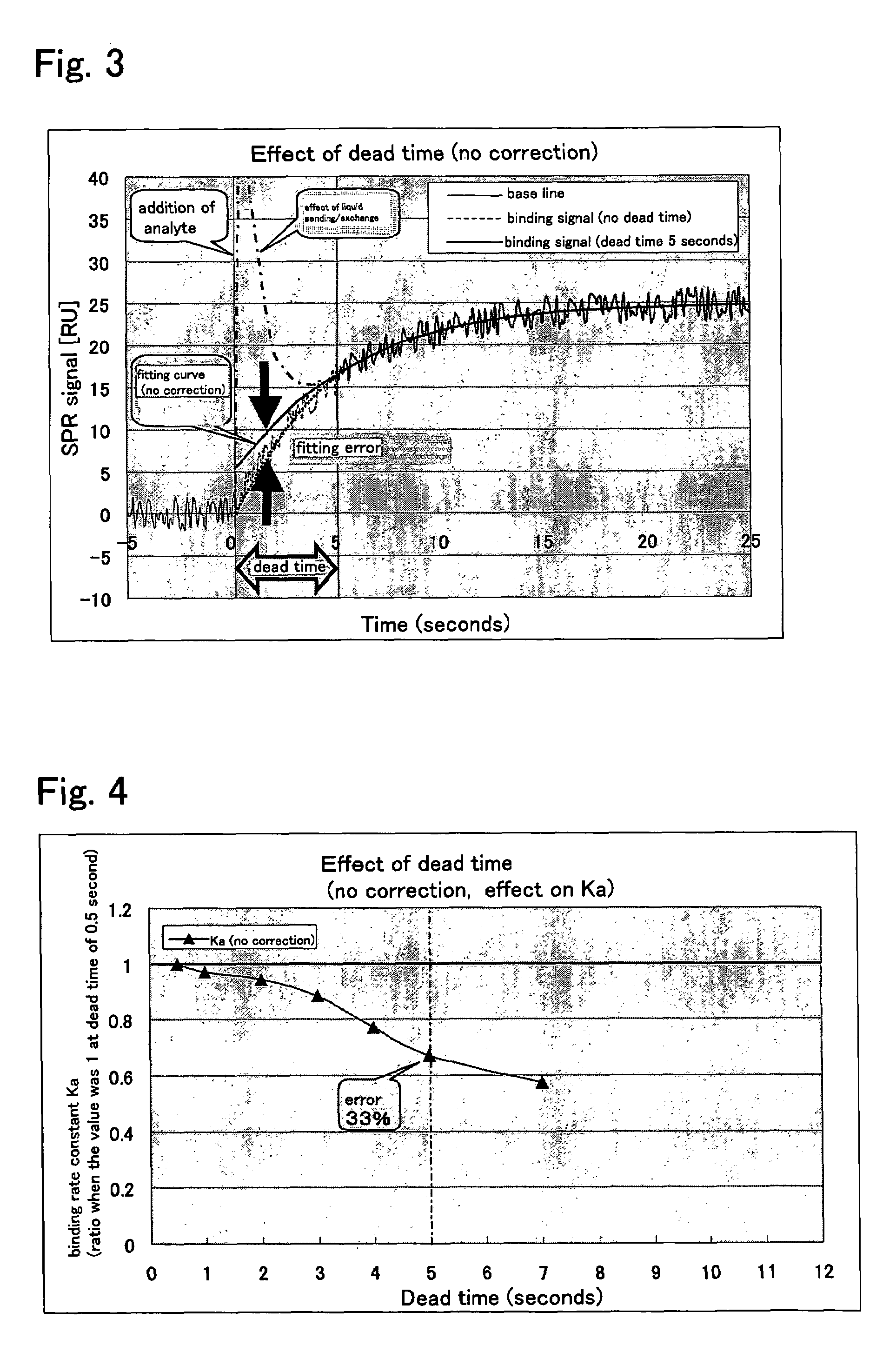
InactiveUS20060040326A1Improve detection accuracySimple equipmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMeasurement deviceReaction rate
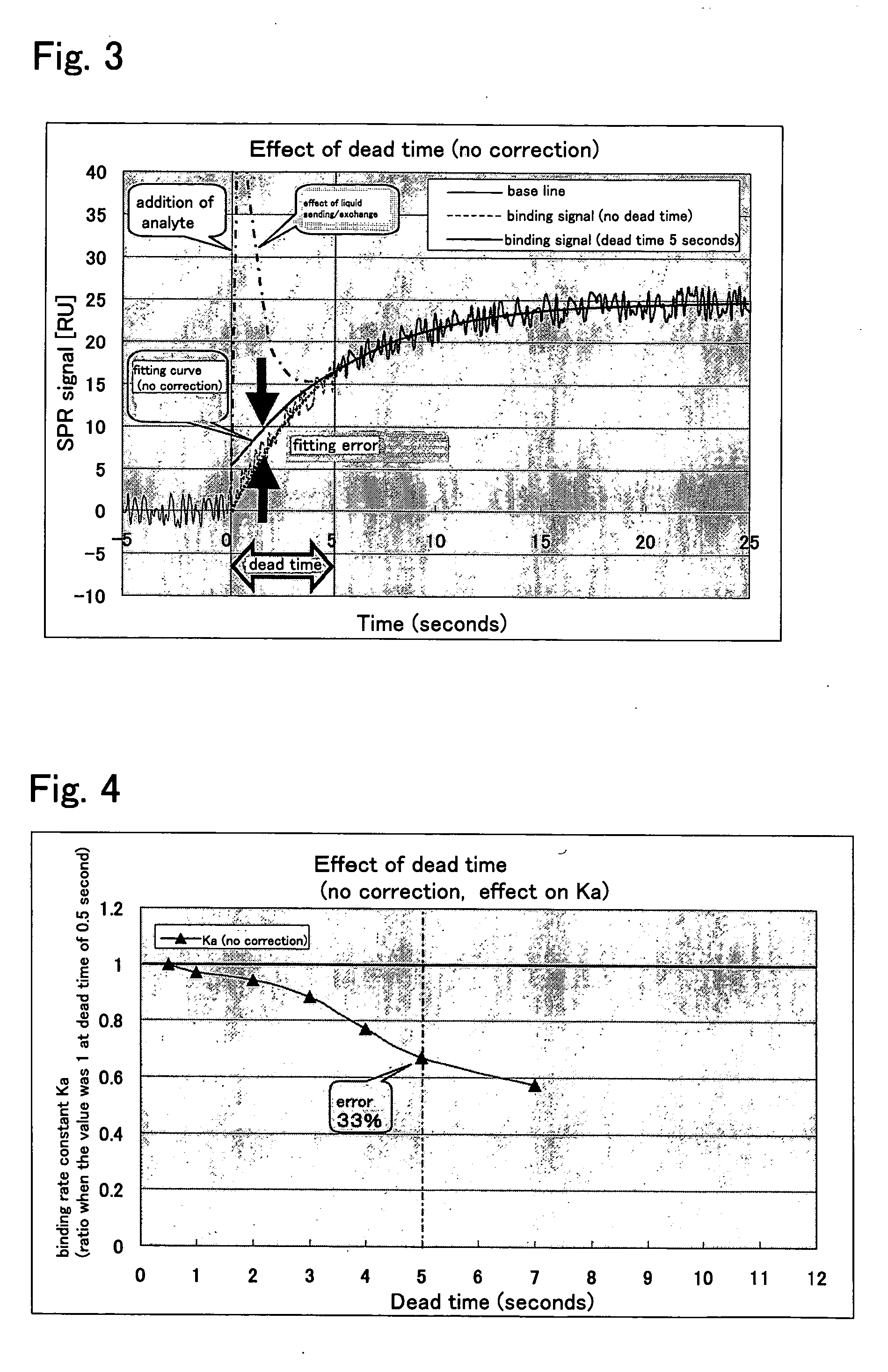
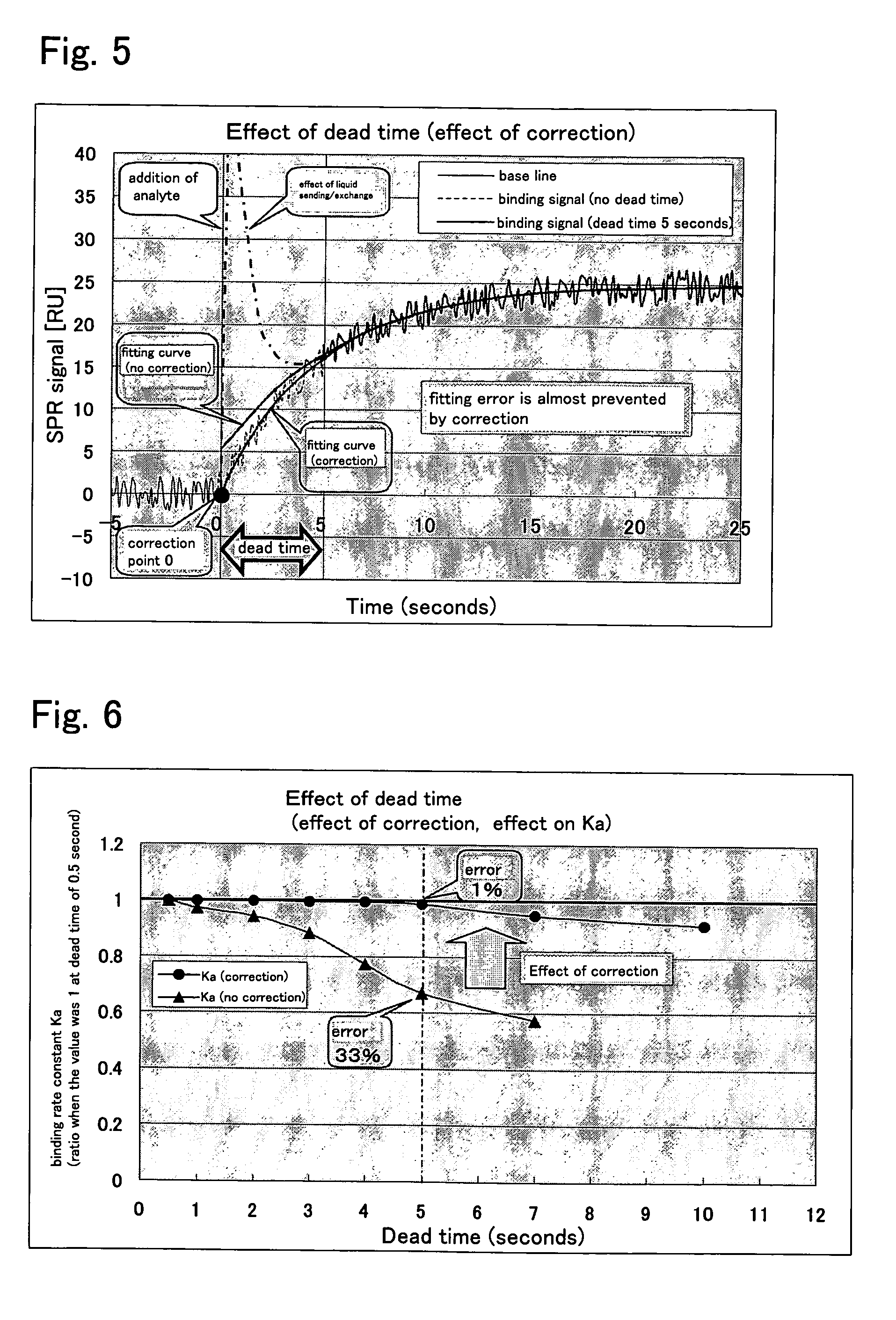
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for measuring a rate coefficient by surface plasmon resonance analysis with excellent accuracy, reliability, and cost performance that can improve the assay accuracy and simplify the apparatus. The present invention is provides a method for determining the adsorption rate coefficient (Ka) and the dissociation rate coefficient (Kd) of the reaction between an analyte molecule immobilized on a metal surface and a molecule that interacts with the analyte molecule by measuring changes in surface plasmon resonance signals using a surface plasmon resonance measurement device and performing fitting to a signal curve obtained by such measurement, wherein fitting is performed to the signals from which data obtained at the time of liquid exchange and data obtained at a given time point thereafter have been removed, and that an algorithm is adopted wherein the fitted curve passes through a point representing a baseline value obtained at the time of liquid exchange or immediately therebefore.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
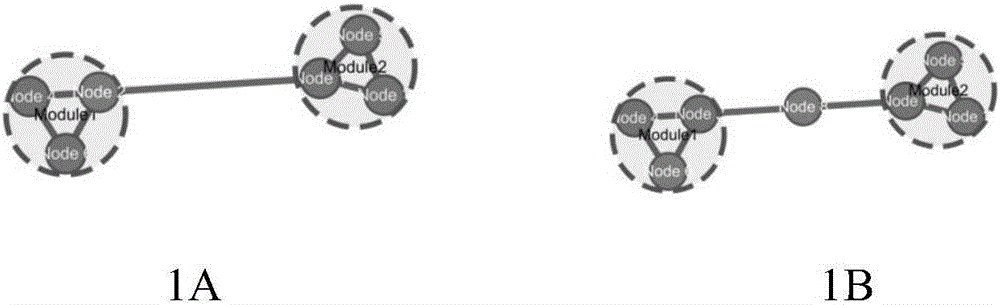
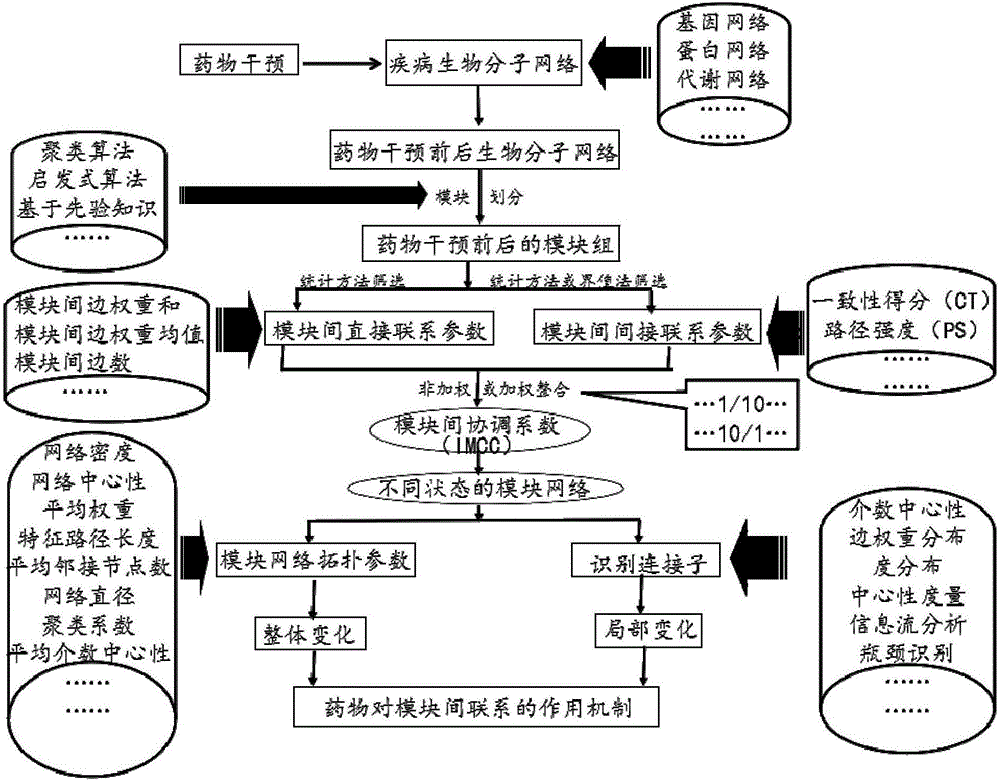
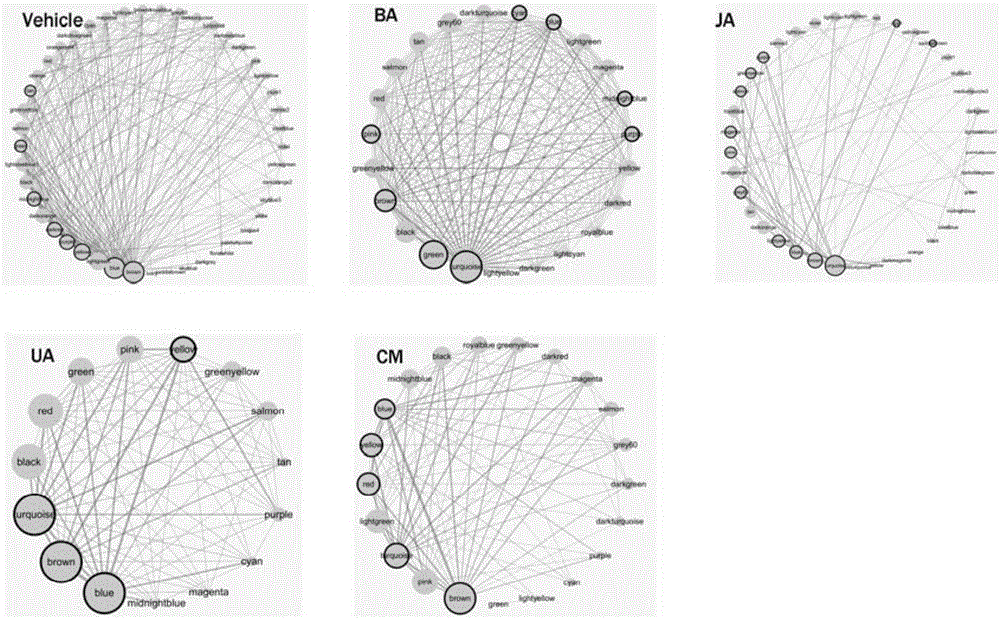
Method for evaluating influences of drugs on inter-module relations in biomolecule network
ActiveCN106709231AIntegratedMolecular designSpecial data processing applicationsRegulation of gene expressionComplex network
The invention provides a method for evaluating influences of drugs on inter-module relations in a biomolecule network, and the method targets complex networks of biomolecules, such as a protein-protein interaction network, a gene expression regulation network, a biological metabolism network, an epigenetic network, a phenotype network and a signal transduction network. The method mainly comprises the steps that module recognition is performed on the biomolecule network before and after drug intervention; inter-module direct relation parameters and inter-module indirect relation parameters are calculated, screened and integrated based on two groups of recognized modules to obtain inter-module coordination coefficients of two arbitrary modules in each group of modules; a module network is constructed based on the inter-module coordination coefficients; and module network topological parameters before drug intervention and module network topological parameters after drug intervention are compared, or module network connectors before and after drug intervention are recognized, and the dissociation rate of the connectors is calculated.
Owner:王忠 +1
Nitridation apparatus and process for cast iron piston ring
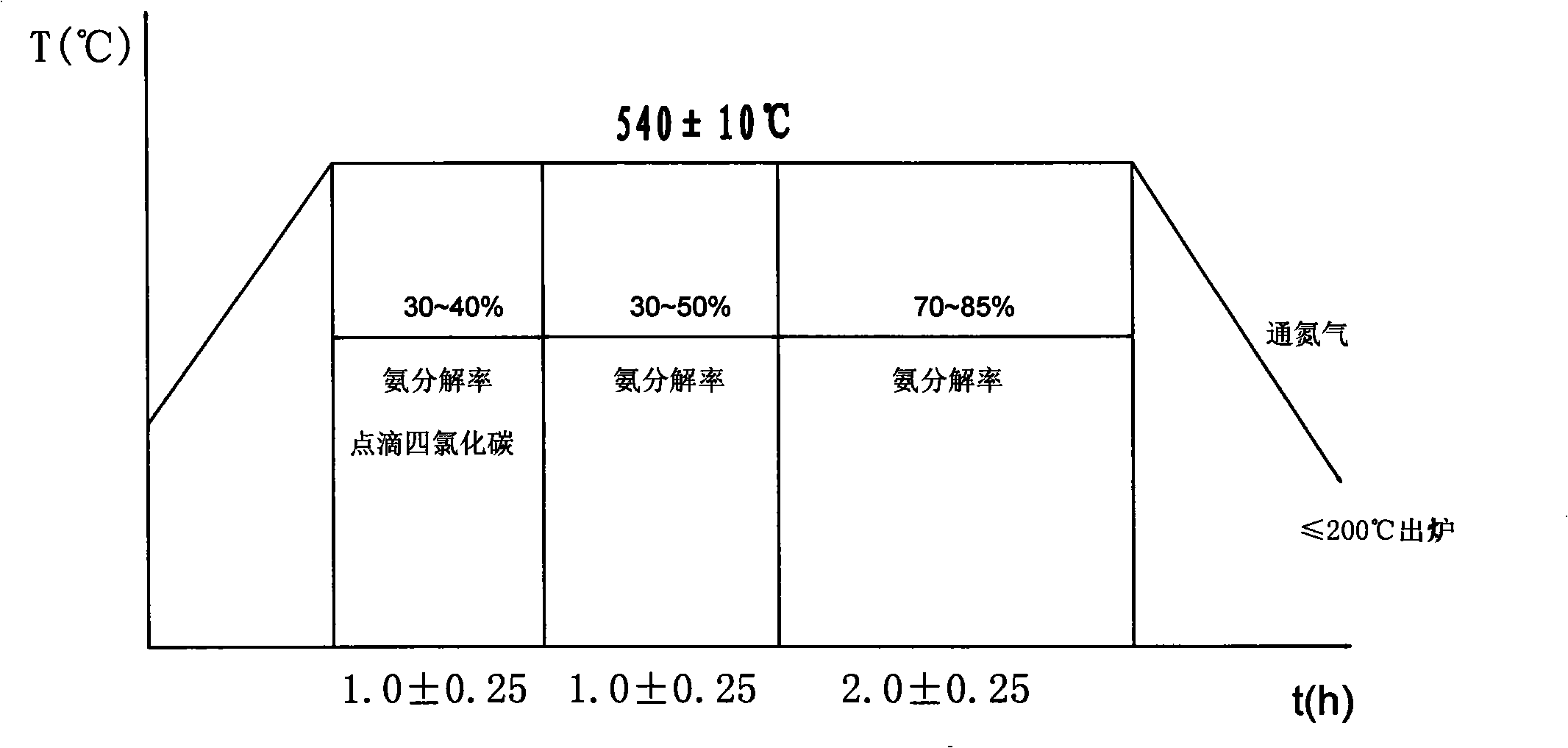
InactiveCN101403087AMeet needsReasonable structureSolid state diffusion coatingDissociation rateCast iron
The invention provides a nitriding device for a cast-iron piston ring and a nitriding process thereof, wherein the nitriding device comprises a nitriding furnace, and the nitriding furnace is provided with a nitrogen inlet pipe, an ammonia gas inlet pipe, a mixed gas outlet pipe, a carbon tetrachloride titration device and an indicating device for the pressure inside the furnace; the other end of the mixed gas outlet pipe is connected with a determinator for ammonia dissociation rate. The process comprises: the preparation before nitriding, the preparation period, the temperature-rise period and the temperature-fall period of the nitriding process. The device of the invention has the advantages of reasonable structure, reasonable process flow, simple operation, low production cost, reliable performance of the treated product and further has the advantages of completely meeting client requirements, being applicable to the nitriding of vehicle cast-iron piston rings, gas rings or oil rings, meeting market requirements and having pretty high economic benefit.
Owner:HUAMIN NANPING AUTOMOBILE FITTINGS GROUP
Analytical measuring and evaluation method for molecular interactions
InactiveUS7824924B2Concentration of analyte can be raised and loweredBiological testingDissociation rate constantAnalyte
The invention relates to an analytical measuring and evaluation method for determining the interaction parameters between an analyte and a ligand, preferably in a biosensor. According to the inventive method, the concentration of the analyte is gradually changed at defined intervals ti and the initial association or dissociation rates or association and dissociation rate constants are determined. The invention further relates to a device for carrying out the inventive method.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Method of improving t cell receptors
ActiveUS20090054257A1Immunoglobulin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementB-cell receptorBiology
Owner:IMMUNOCORE LTD +1
Human anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody molecule and application thereof
The invention relates to an anti-human monoclonal antibody and a coding nucleic acid sequence thereof, and especially relates to an anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody having a high affinity and a low dissociation rate. The preferable anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody comprises a human Fc region, a framework region, and a human light-chain and / or heavy-chain variable region obtained through molecular evolution. The invention also discloses medicinal compositions composed of the human antibody, an application of the human antibody in human disease treatment, and a method for using the human antibody in the treatment.
Owner:广州市流式生物科技有限公司
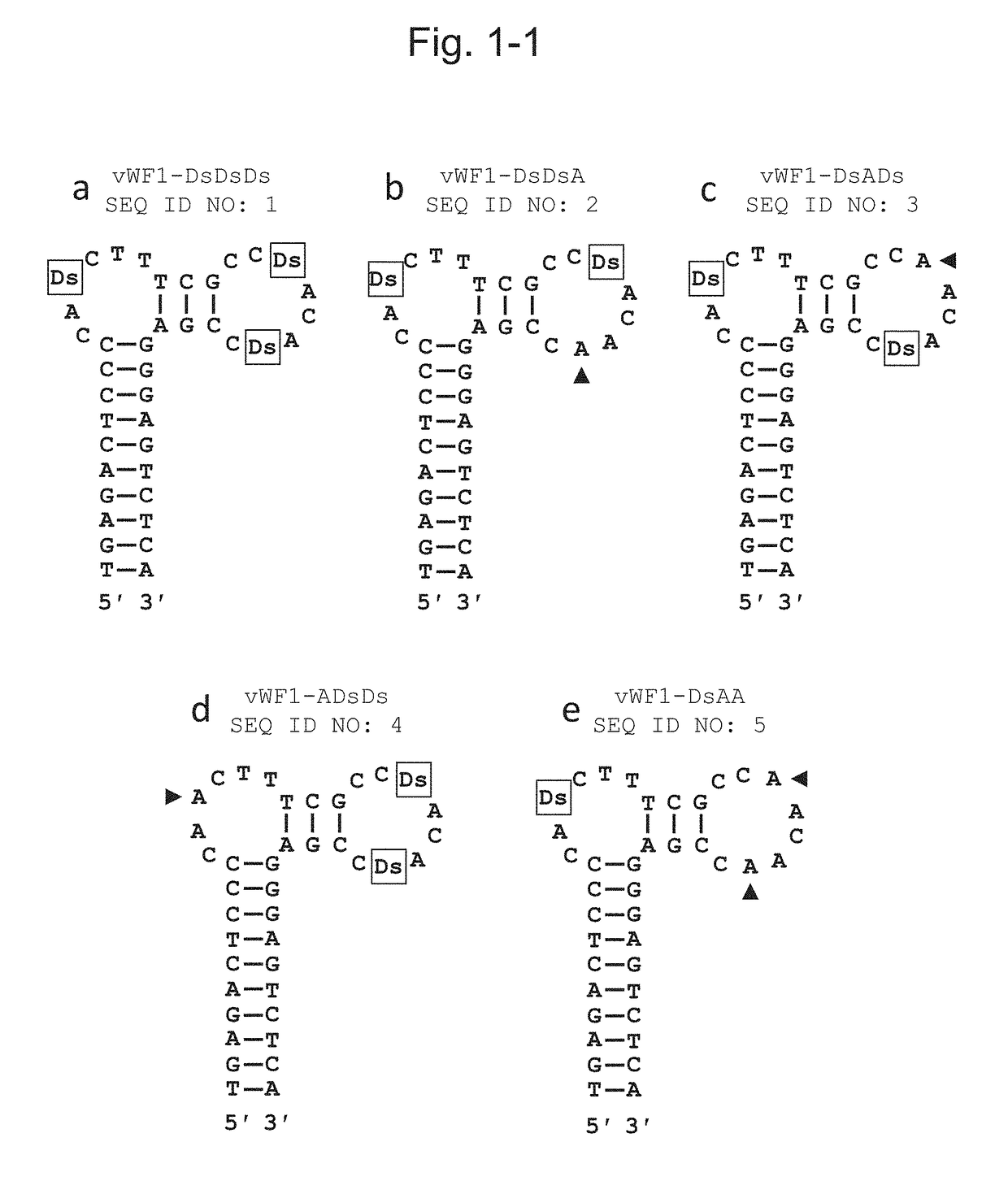
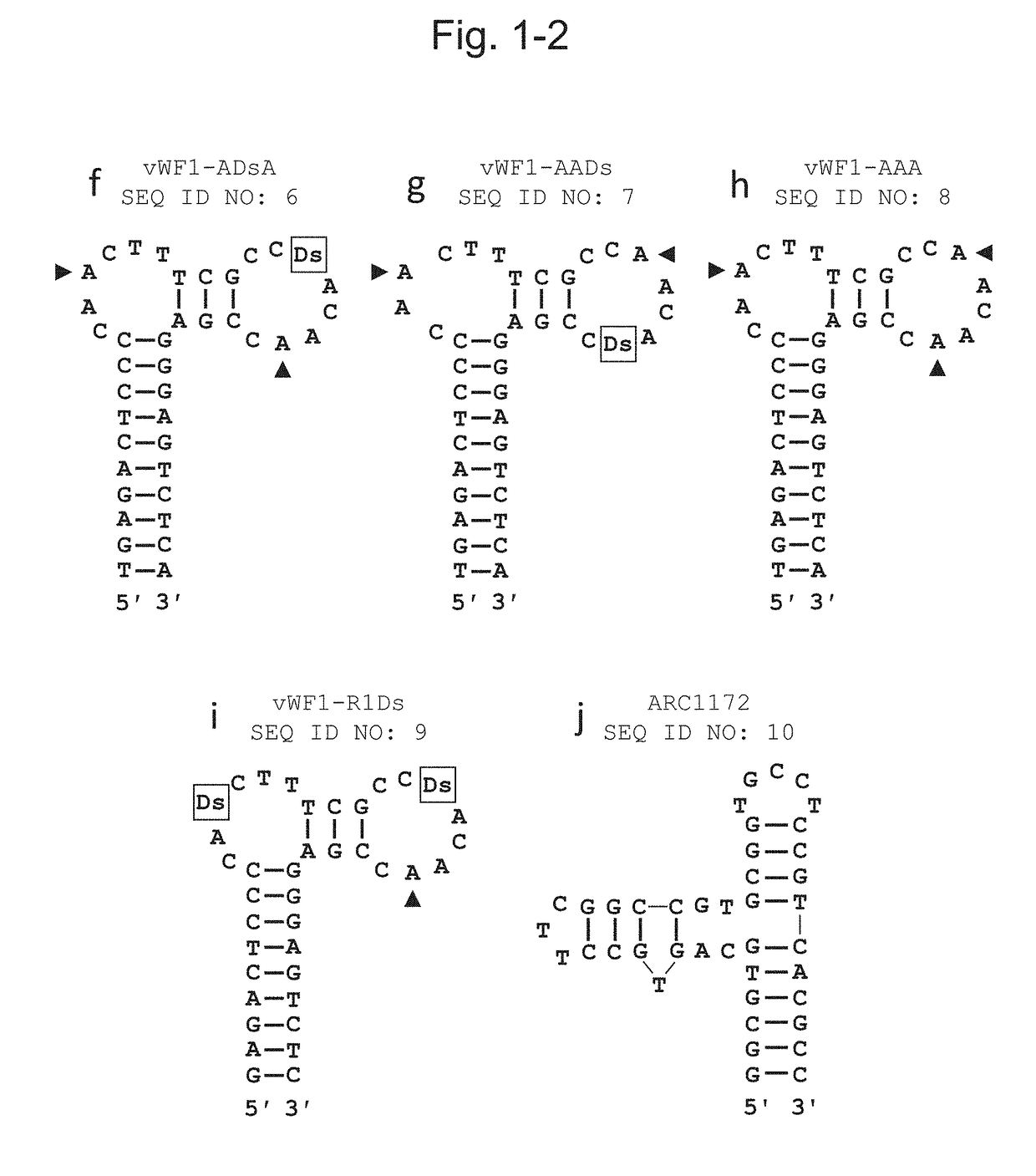
DNA APTAMER THAT BINDS TO vWF
ActiveUS20180305695A1Ability to bindIncrease ratingsOrganic active ingredientsFactor VIIDissociation rateBinding ability
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an aptamer for vWF, which is superior in a binding ability, a dissociation rate, and / or stability to the conventional nucleic acid aptamers. The present invention can solve the problem by a DNA aptamer which contains artificial nucleotides and binds to vWF.
Owner:TAGCYX BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
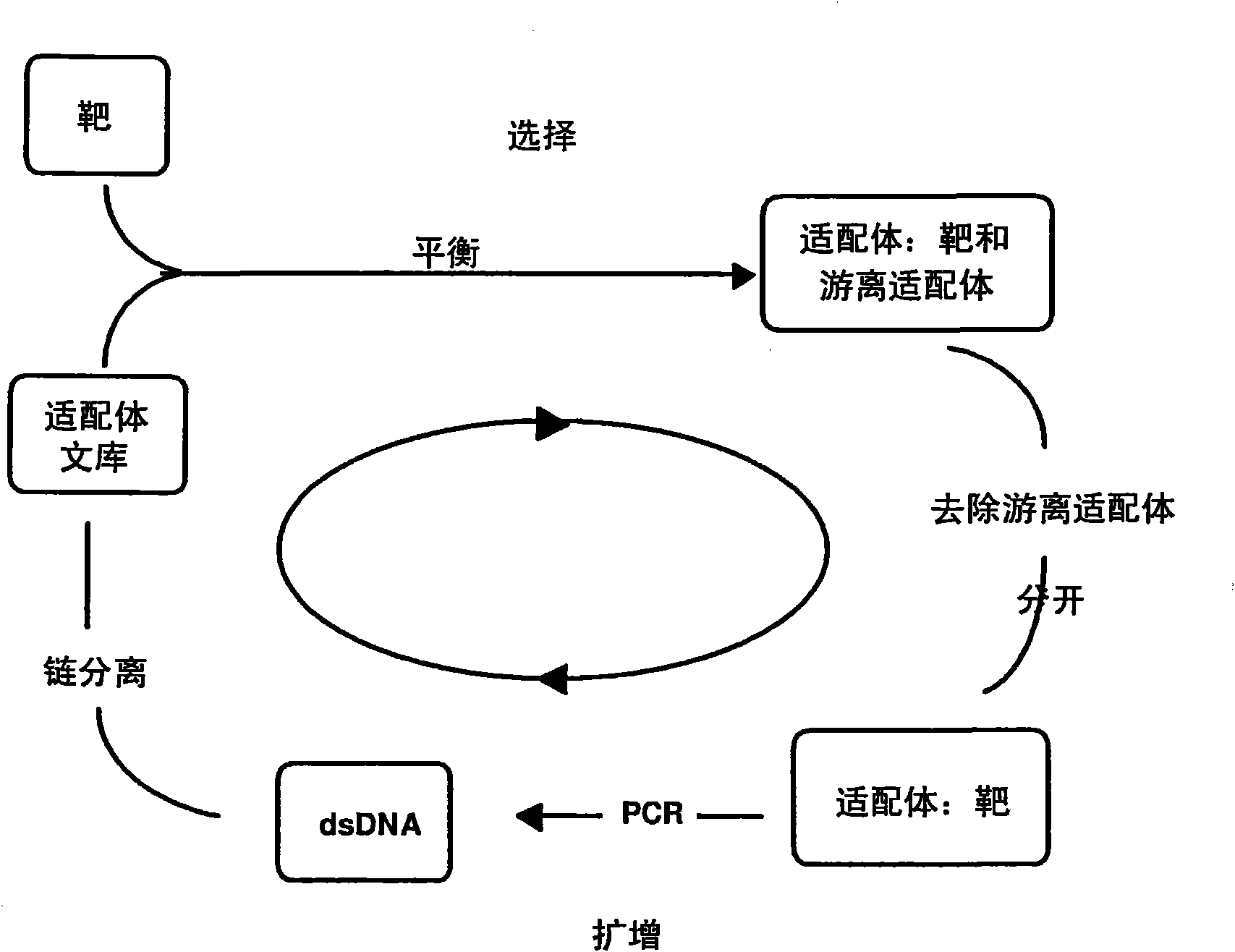
Method for generating aptamers with improved off-rates
ActiveCN101809167AImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processCross-linkDissociation rate constant
The present disclosure describes improved SELEX methods for producing aptamers that are capable of binding to target molecules and improved photoSELEX methods for producing photoreactive aptamers that are capable of both binding and covalently cross linking to target molecules. Specifically, the present disclosure describes methods for producing aptamers and photoaptamers having slower dissociation rate constants than are obtained using prior SELEX and photoSELEX methods. The disclosure further describes aptamers and photoaptamers having slower dissociation rate constants than those obtained using prior methods. In addition, the disclosure describes aptamer constructs that include a variety of functionalities, including a cleavable element, a detection element, and a capture or immobilization element.
Owner:SOMALOGIC OPERATING CO INC
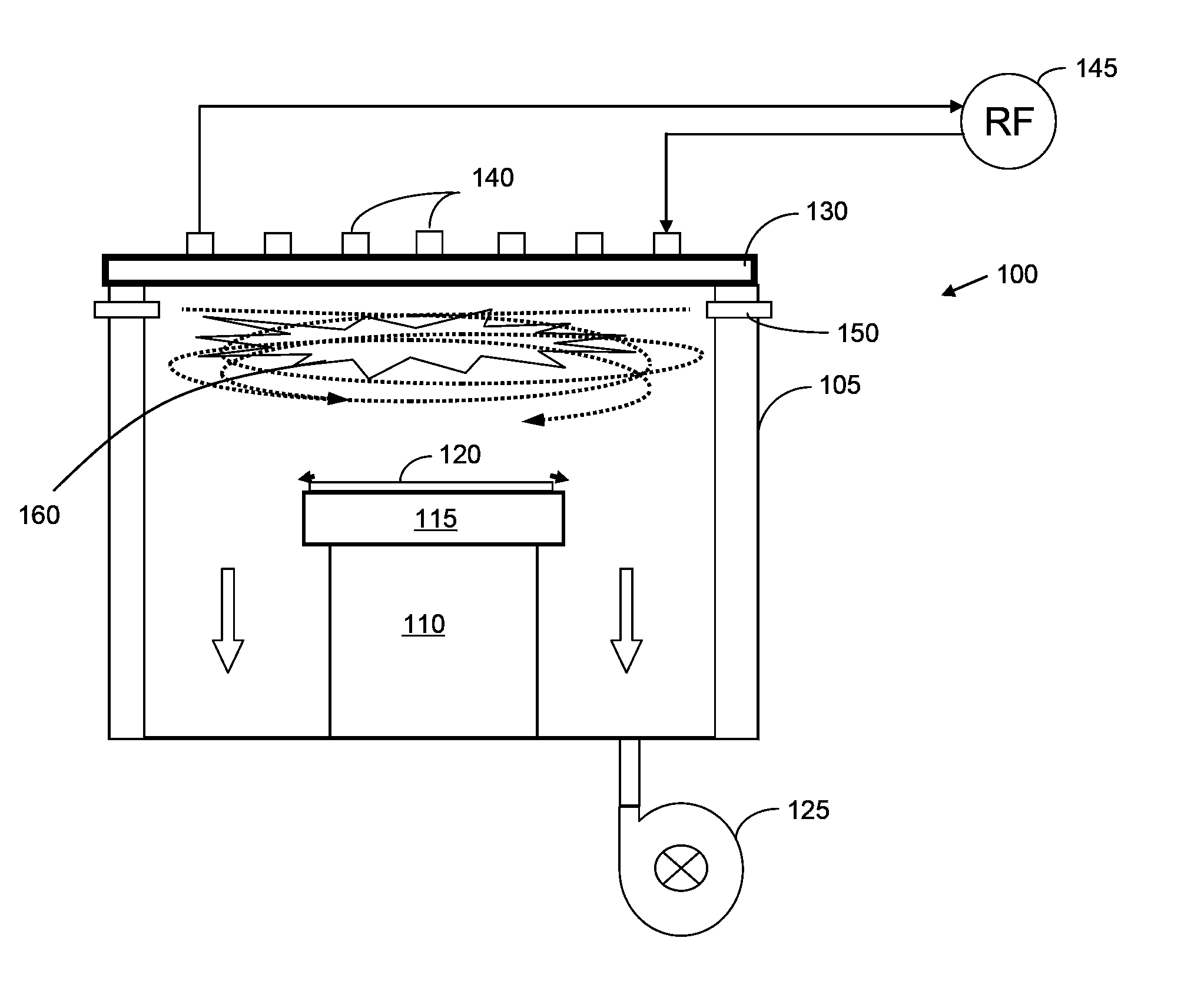
Plasma process chamber and gas injection apparatus for same
ActiveCN103915307ASlow the rate of sinkingSink rate slows downElectric discharge tubesWalking distanceEddy current
The invention discloses a plasma process chamber and a gas injection apparatus for the same. The inner wall of an annular gas injection pipeline is provided with a plurality of gas inlets, an acute angel is formed between a gas output direction and the direction directed towards the circle center of the annular gas injection pipeline by the gas inlet, and it is ensured that gas, after being injected into an reaction chamber, forms eddy current shaped distribution in a dissociation area, so that the gas sinking rate is delayed, the walk distance formed when the gas reaches a substrate is prolonged, and the gas is dissociated as much as possible in the dissociation area. Compared to a conventional gas inlet vertical to the inner wall of the annular gas injection pipeline, the advantages are as follows: the gas sinking rate is slowed, the gas dissociation rate is improved, the reaction gas utilization rate is improved, and at the same time, since the concentration of plasma in the reaction chamber rises, the etching rate is improved.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
Preparation method for monoclonal antibodies with functions of anti-tumor angiogenesis
InactiveCN103396493AIncrease salesStrong specificityLibrary screeningImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHumanized antibodyHigh affinity antibody
The invention discloses a preparation method for monoclonal antibodies with functions of anti-tumor angiogenesis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: expression and purification of cell receptor protein VEGFR2, preparation of completely humanized phage Fab antibody libraries, selection of antibodies with high affinity from the phage antibody libraries, immobilization of purified VEGFR2 on CM5 chips of Biacore, testing of association rates and dissociation rates of AVR2 antibodies with different concentrations and VEGFR2 respectively, selection of antibody libraries based on high affinity and high specificity of antibodies and antigens, cloning of antibody genes to expressing cells, construction of engineered cell lines with high expression level, and detection and evaluation of anti-angiogenesis. By utilizing the phage antibody library technology, the preparation method can produce humanized antibodies directly. In addition, the monoclonal antibodies are advantaged by strong drug specificity, minimal side effects and remarkable effects.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining binding kinetic rate constants using fiber optic particle plasmon resonance (FOPPR) sensor
ActiveUS20140051188A1Simple and concise computationScattering properties measurementsFiberKinetic rate
A method for obtaining the binding kinetic rate constants using fiber optic particle plasmon resonance (FOPPR) sensor, suitable for a test solution with two or more concentrations, which employs the following major steps: providing one FOPPR sensor instrument system, obtaining optical time-resolved signal intensities starting at the initial time to the steady state of the two or more regions, substituting the measured signal intensity values into the formula which is derived by using the pseudo-first order rate equation model. In addition, this method measures the temporal signal intensity evolution under static conditions as the samples are quickly loaded. As a result, unlike the conventional device where the sample is continuously infused, the method is able to measure the association and dissociation rate constants of which the upper bounds are not limited by the sample flow rate.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Bipolar membrane using zinc-metal organic framework material as middle interface layer and preparation method thereof
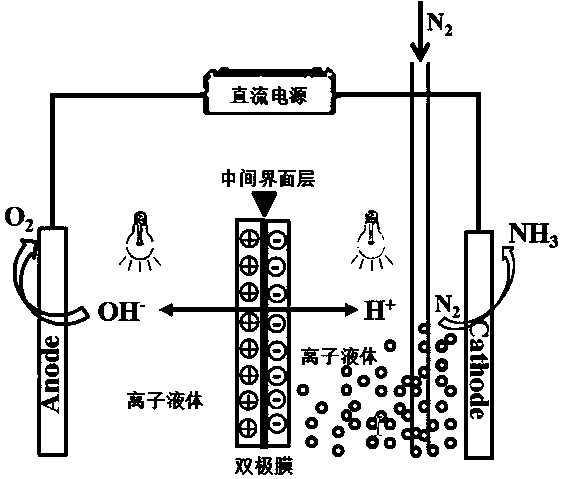
ActiveCN108866567ALower activation energyPromote water dissociation reactionCellsOrganic diaphragmsZinc metalMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to a bipolar membrane using a zinc-metal organic framework material as a middle interface layer and a preparation method thereof. The middle interface layer of the bipolar membrane is characterized in that the inner surfaces of a cation exchange membrane layer and an anion exchange membrane layer are crosslinked or coated with a zinc-metal organic framework material catalyst.The preparation method comprises the following steps of firstly, casting an anion exchange membrane to a clean glass plate by a gradual-layer casting method, and air-drying at room temperature, so asto obtain the anion exchange membrane; then, casting a middle interface layer membrane liquid to the surface of the anion exchange membrane by a chemical crosslinking or physical adsorption method, and drying, so as to form the middle interface layer; finally, casting the cation exchange membrane to the surface of the middle interface layer to form the cation exchange membrane layer, and drying,so as to obtain the bipolar membrane. The prepared bipolar membrane has the advantages that the water dissociation rate is high, the water dissociation voltage is low, the density of working current is high, the property is stable, the service life is long, and the like; the bipolar membrane is suitable for the sustained operation of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia.
Owner:TAIYUAN NORMAL UNIV
Wet-strength wastepaper recycling double-pH-value chemical and mechanical pulping method
ActiveCN105568726AReduce consumptionImprove chemical reaction efficiencyPretreatment with water/steamPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsChemical treatmentFiber
The invention discloses a wet-strength wastepaper recycling double-pH-value chemical and mechanical pulping method. The method includes a material preparation section, a steaming section, a first extrusion and impregnation chemical and mechanical treatment section, a second extrusion and impregnation chemical and mechanical treatment section, a latency and re-defibering section and a purification, screening and concentration section. Wet-strength wastepaper fiber dissociation re-pulping is achieved while original pulp strength is not reduced through the mechanical strong force effect and the chemical treatment effect. Furthermore, on the two extrusion and impregnation chemical and mechanical treatment sections connected in series, a wet strength agent in wastepaper is oxidized under the acid condition firstly, hydrolysis is further promoted under the alkaline condition, chemical bonding between molecules of the wet strength agent and between the wet strength agent and pulp fibers is more effectively damaged, and the fiber dissociation rate and the re-pulping yield are effectively increased. The problems that the wet-strength wastepaper recycling pulping dissociation rate is low and strength is greatly decreased are solved, and continuous, large-scale, low-water-consumption and low-energy-consumption pollution-free and environment-friendly pulping can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU JINWO MACHINERY
Method for measuring reaction rate coefficient by surface plasmon resonance analysis
InactiveUS7413911B2Improve accuracyLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMeasurement deviceReaction rate
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for measuring a rate coefficient by surface plasmon resonance analysis with excellent accuracy, reliability, and cost performance that can improve the assay accuracy and simplify the apparatus. The present invention is provides a method for determining the adsorption rate coefficient (Ka) and the dissociation rate coefficient (Kd) of the reaction between an analyte molecule immobilized on a metal surface and a molecule that interacts with the analyte molecule by measuring changes in surface plasmon resonance signals using a surface plasmon resonance measurement device and performing fitting to a signal curve obtained by such measurement, wherein fitting is performed to the signals from which data obtained at the time of liquid exchange and data obtained at a given time point thereafter have been removed, and that an algorithm is adopted wherein the fitted curve passes through a point representing a baseline value obtained at the time of liquid exchange or immediately therebefore.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com