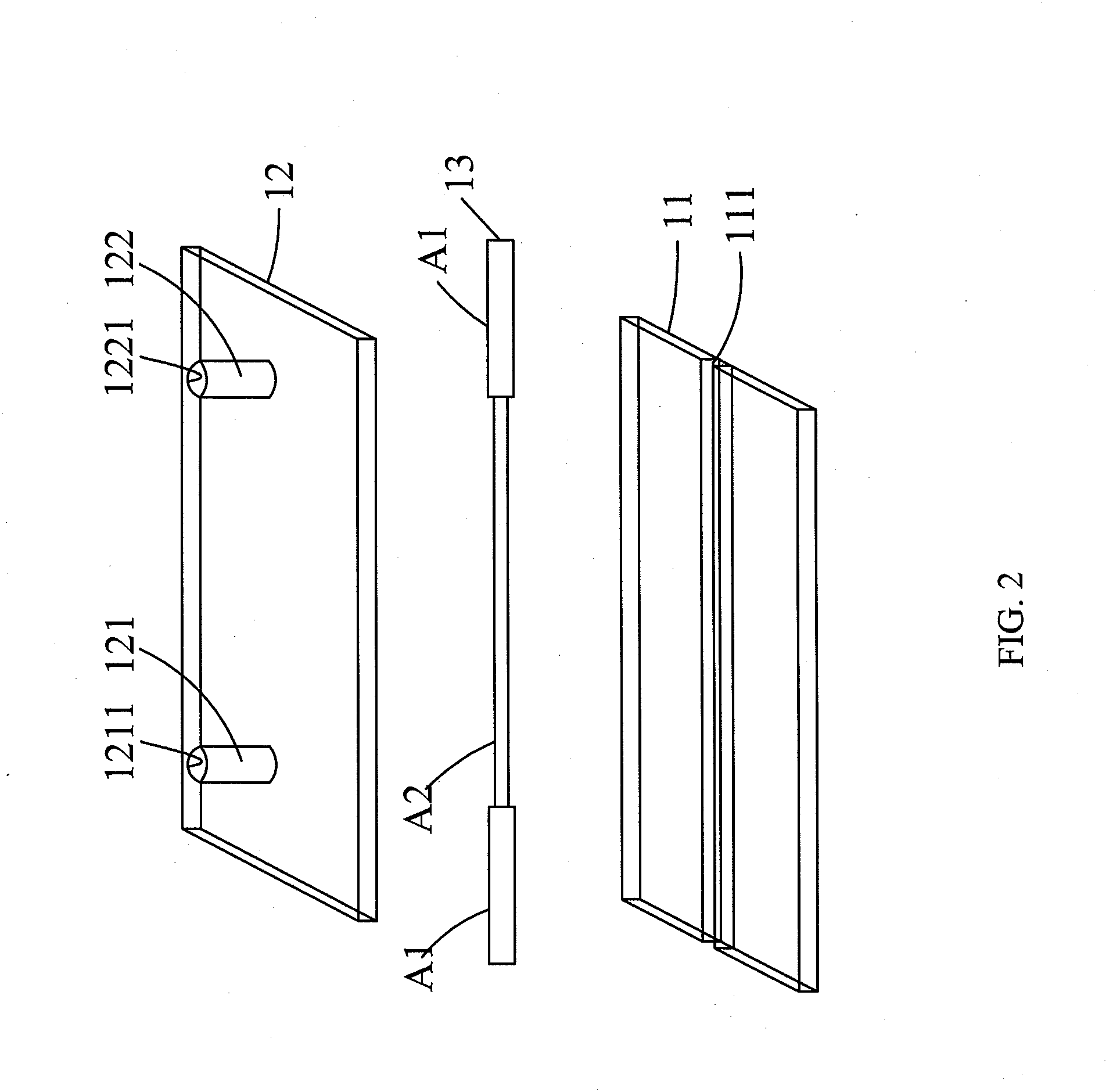
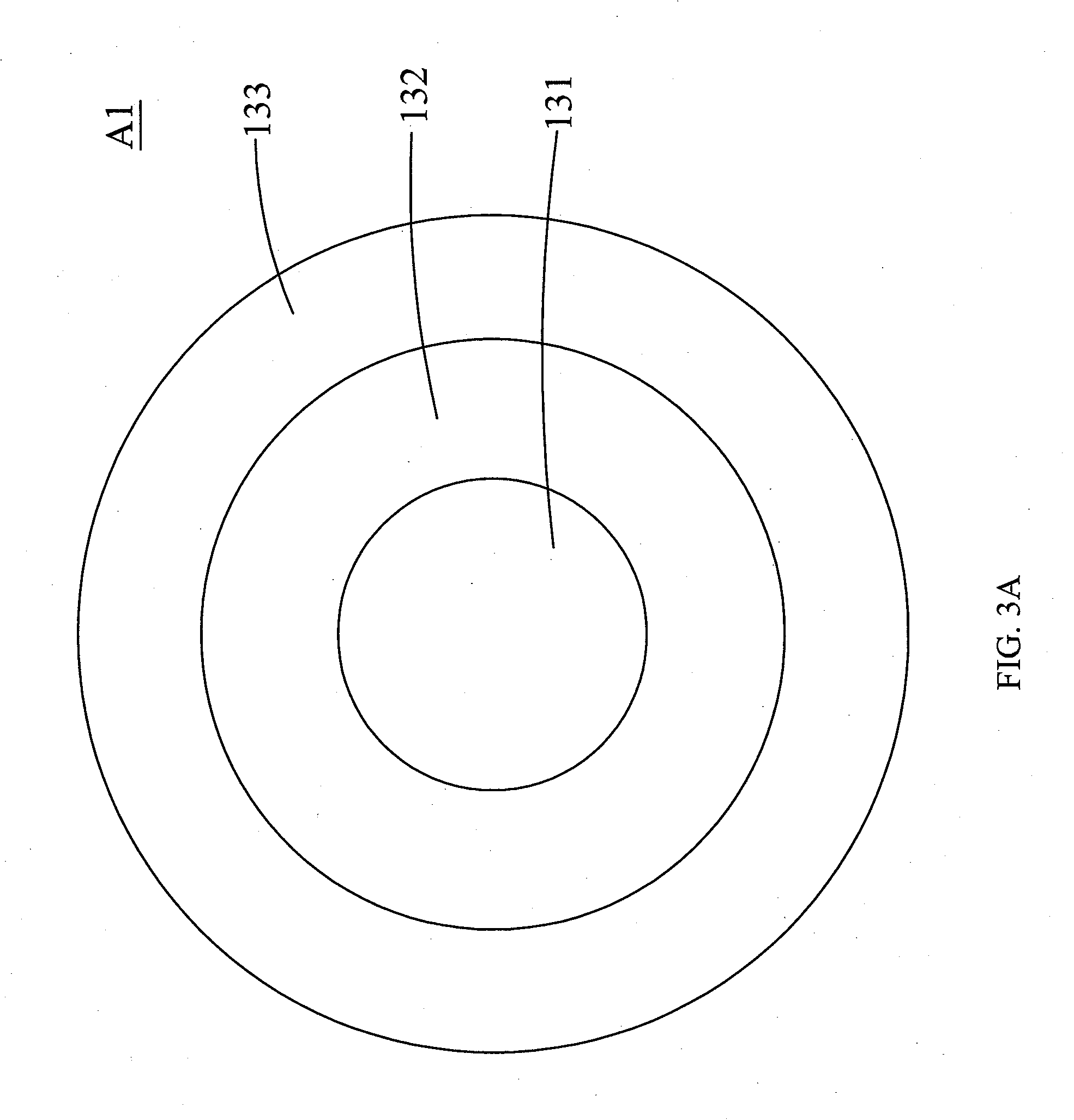
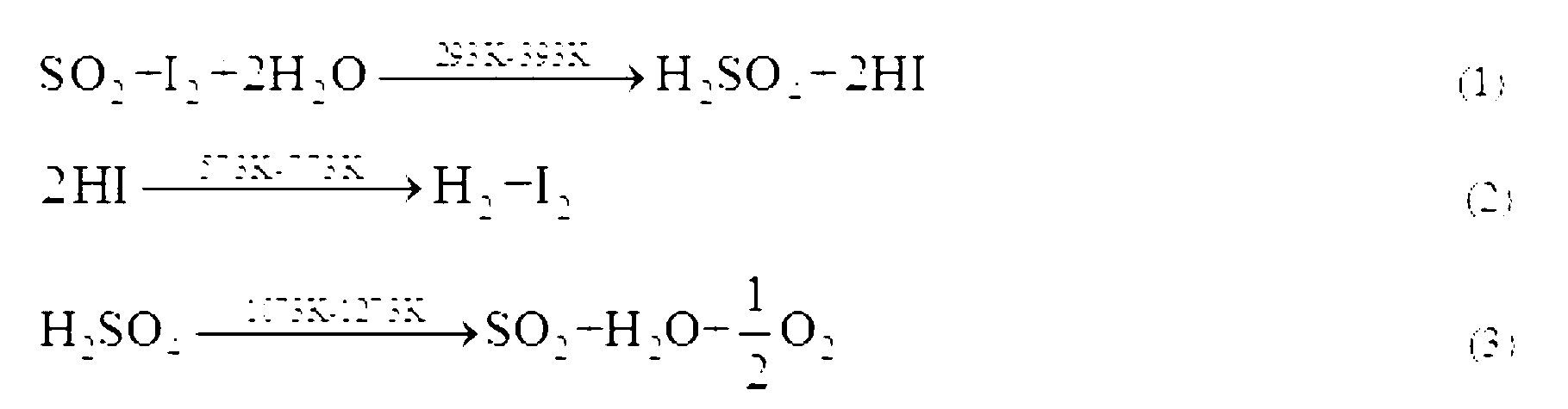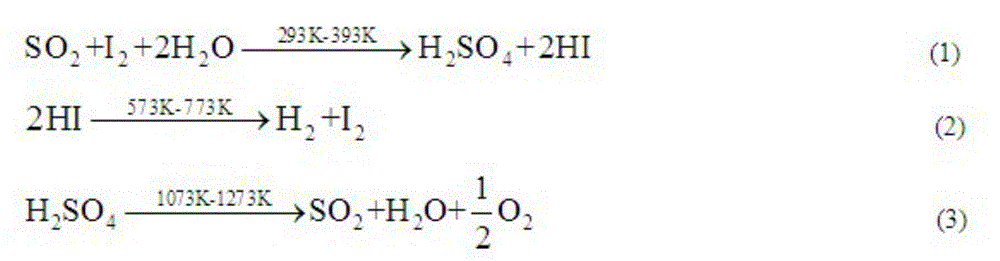Patents
Literature
33 results about "Kinetic rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mesoporous network electrode for electrochemical cell
InactiveUS20040131934A1Simplifies production of cellFull penetrationMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode manufacturing processesLithiumNanoparticle
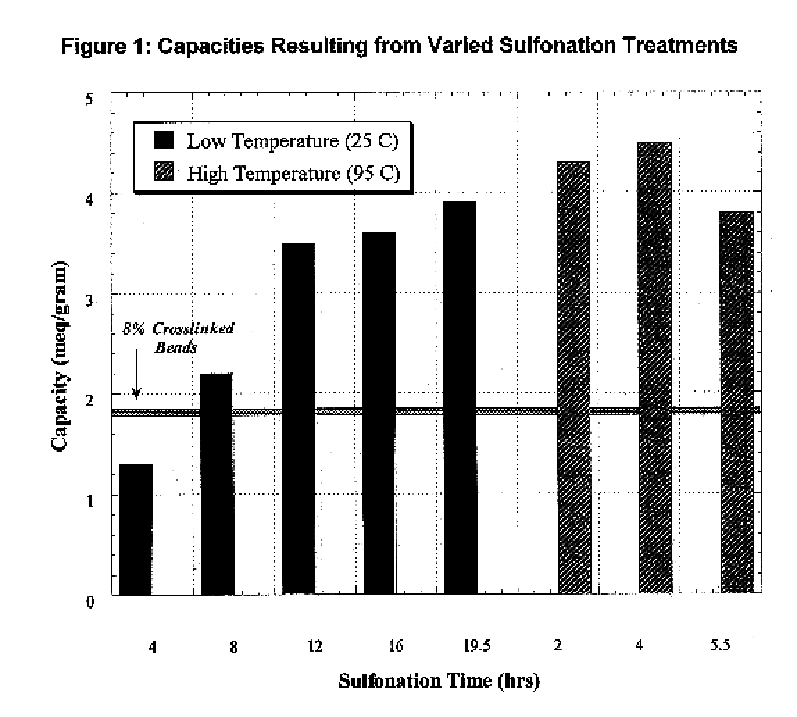
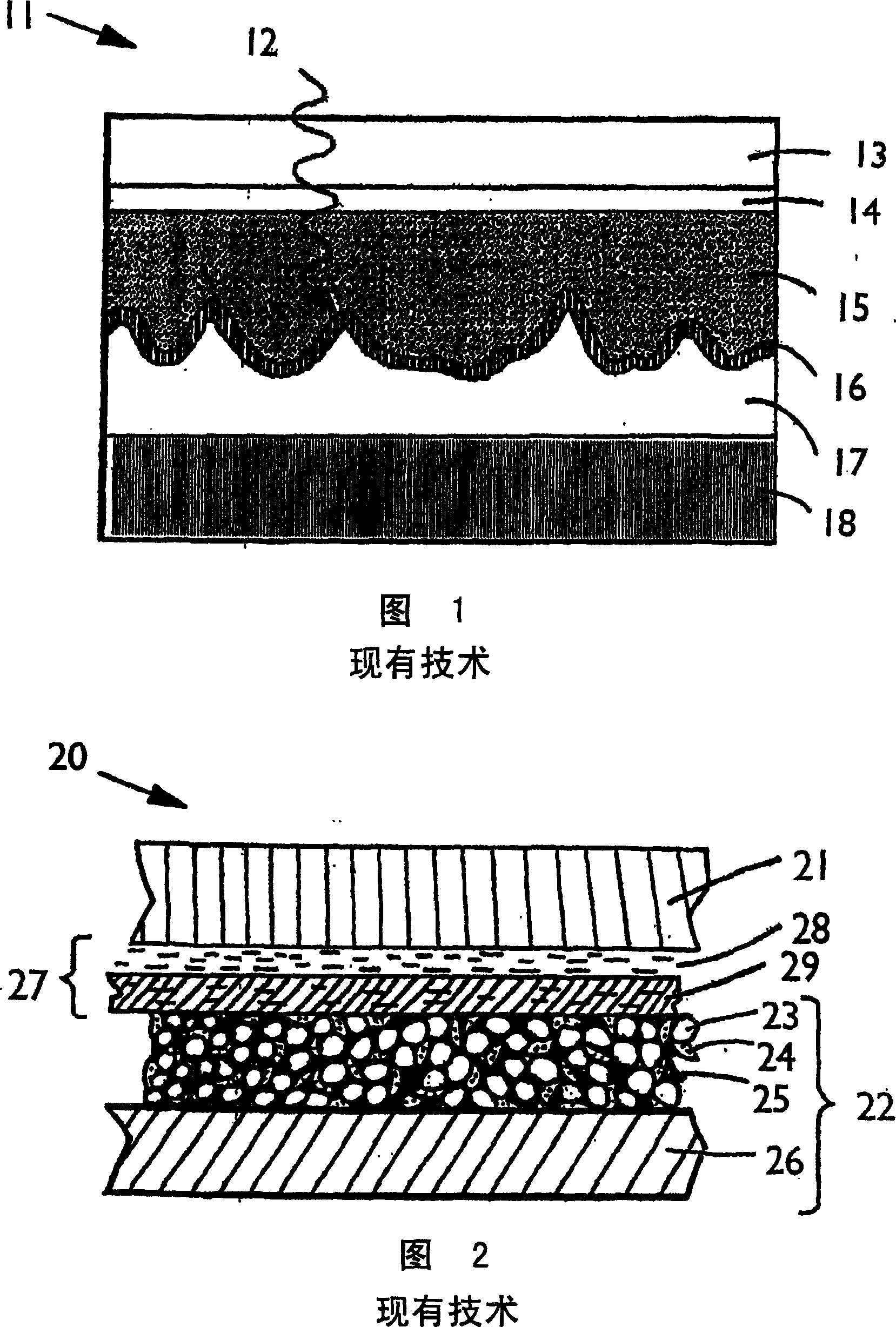
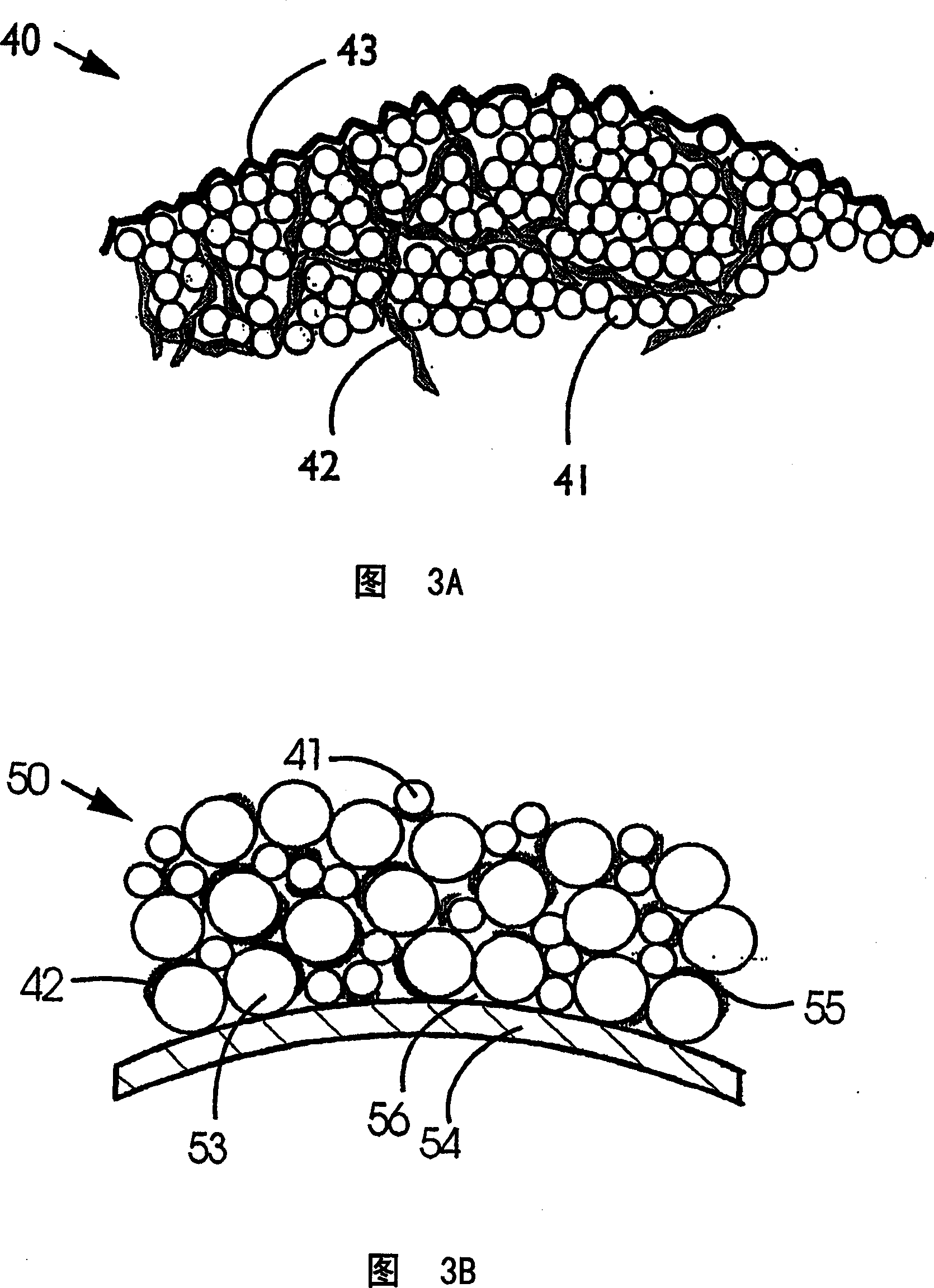
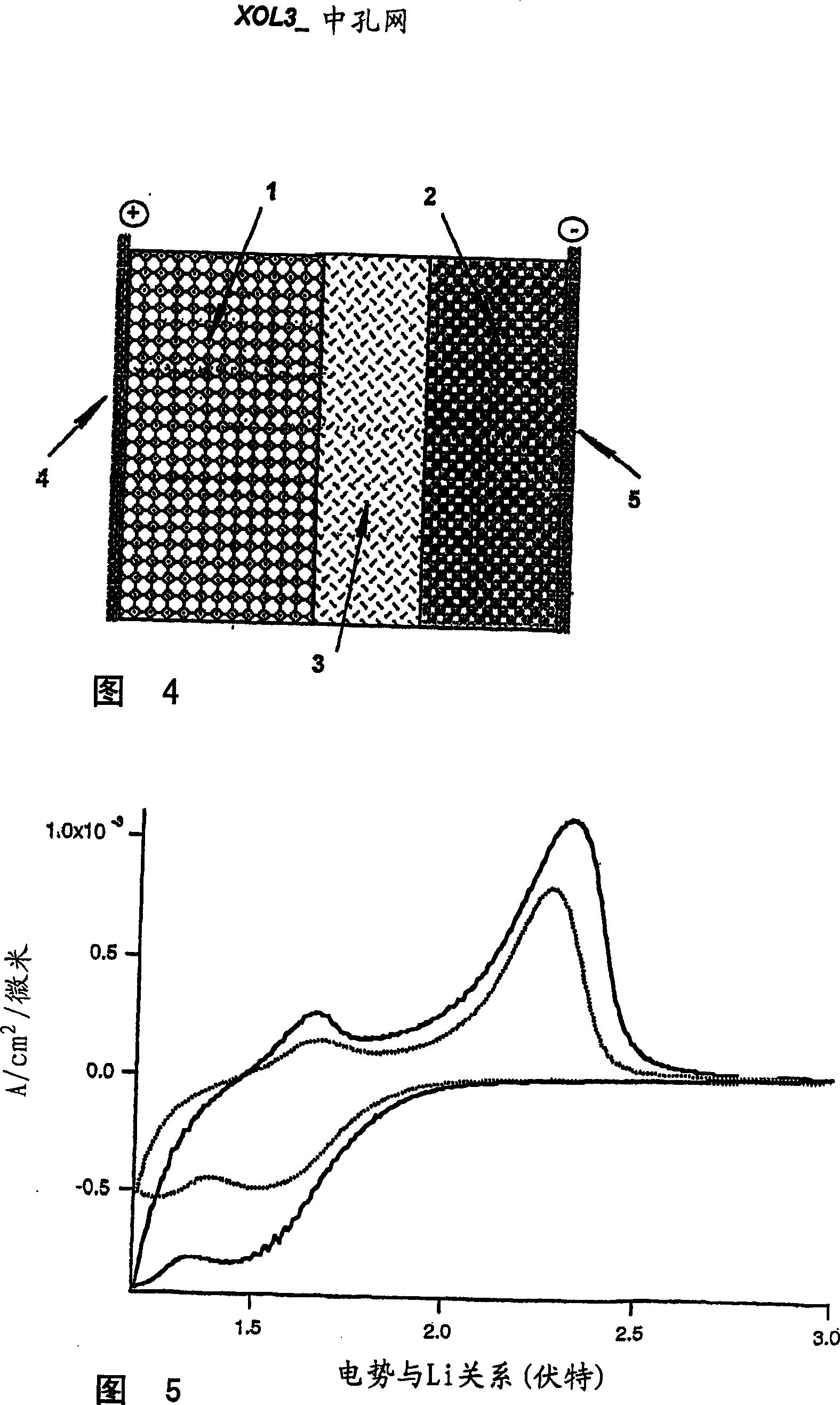
A high kinetics rate electrochemical cell in which at least one of the electrodes is composed of a mesostructural electroactive material comprising nanoparticles forming a three-dimensional framework structure of mesoporous texture having a bicontinuous junction of large specific surface area with the electrolyte. A low temperature method of preparation of the electrodes employs a high-speed deposition of the electrically active material in the form of a thin film. The application of said electrodes in high power lithium ion insertion batteries, photovoltaic cells, supercapacitors and fast electrochromic devices is disclosed.
Owner:FRANCOIS SUGNAUX
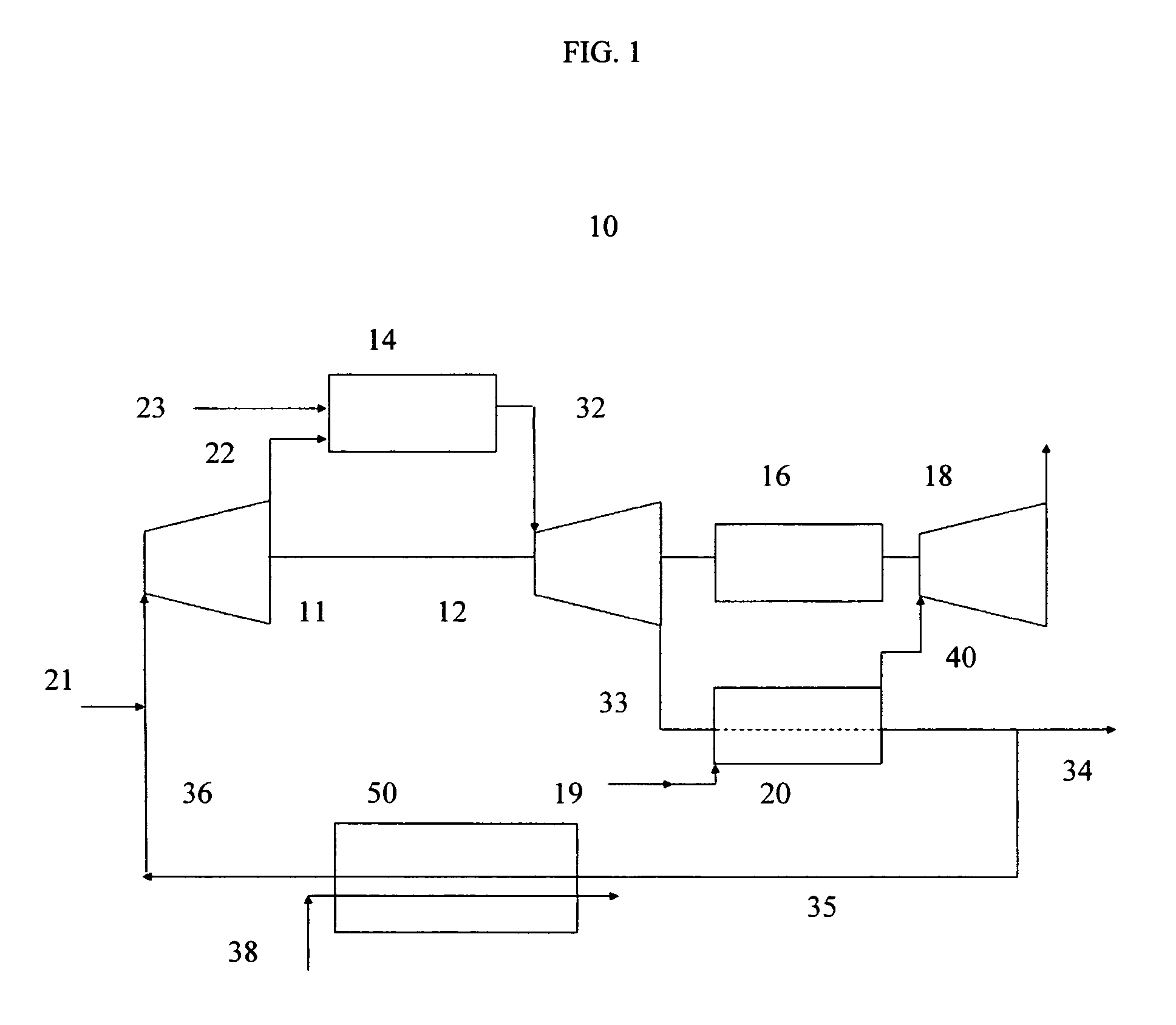
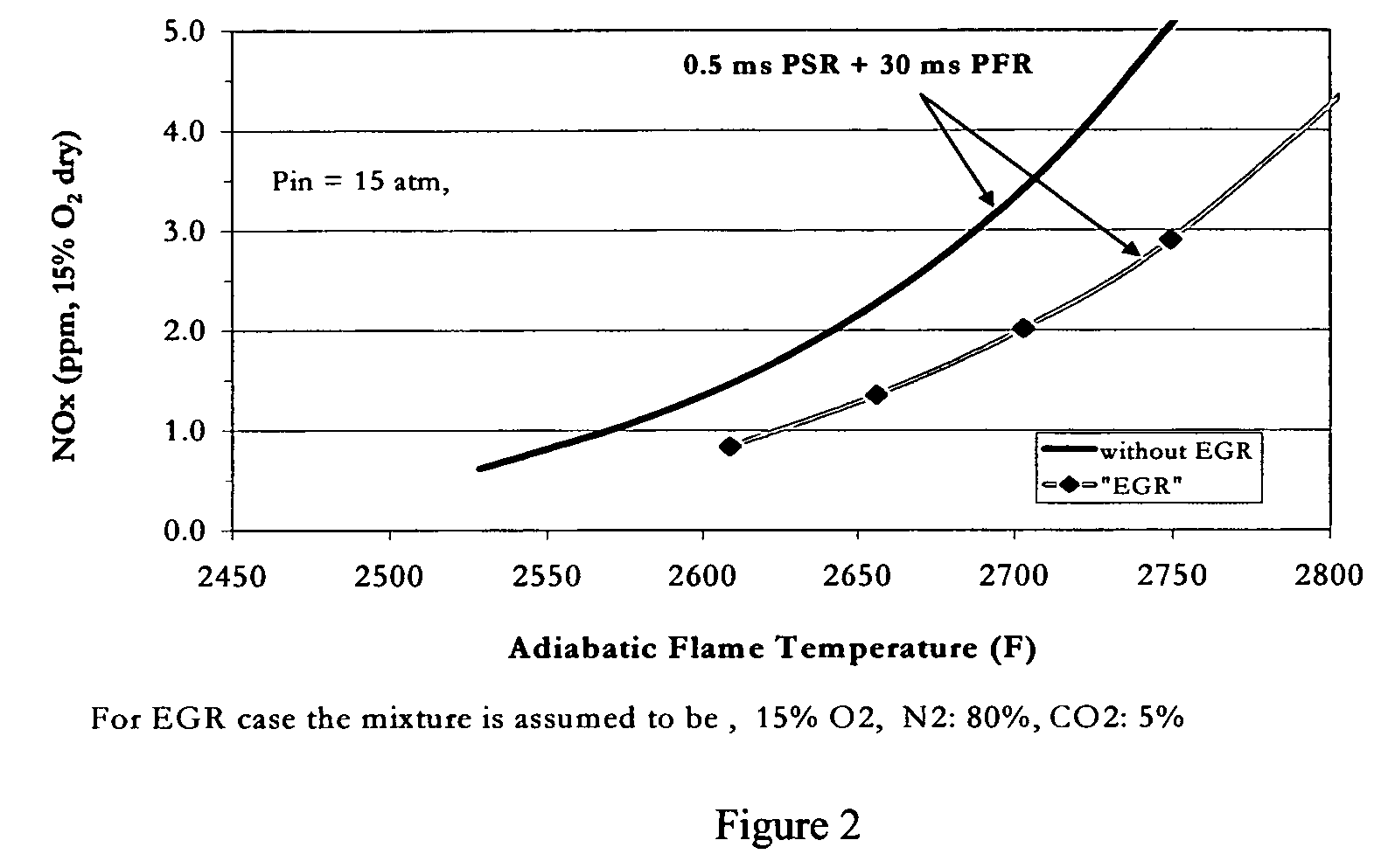
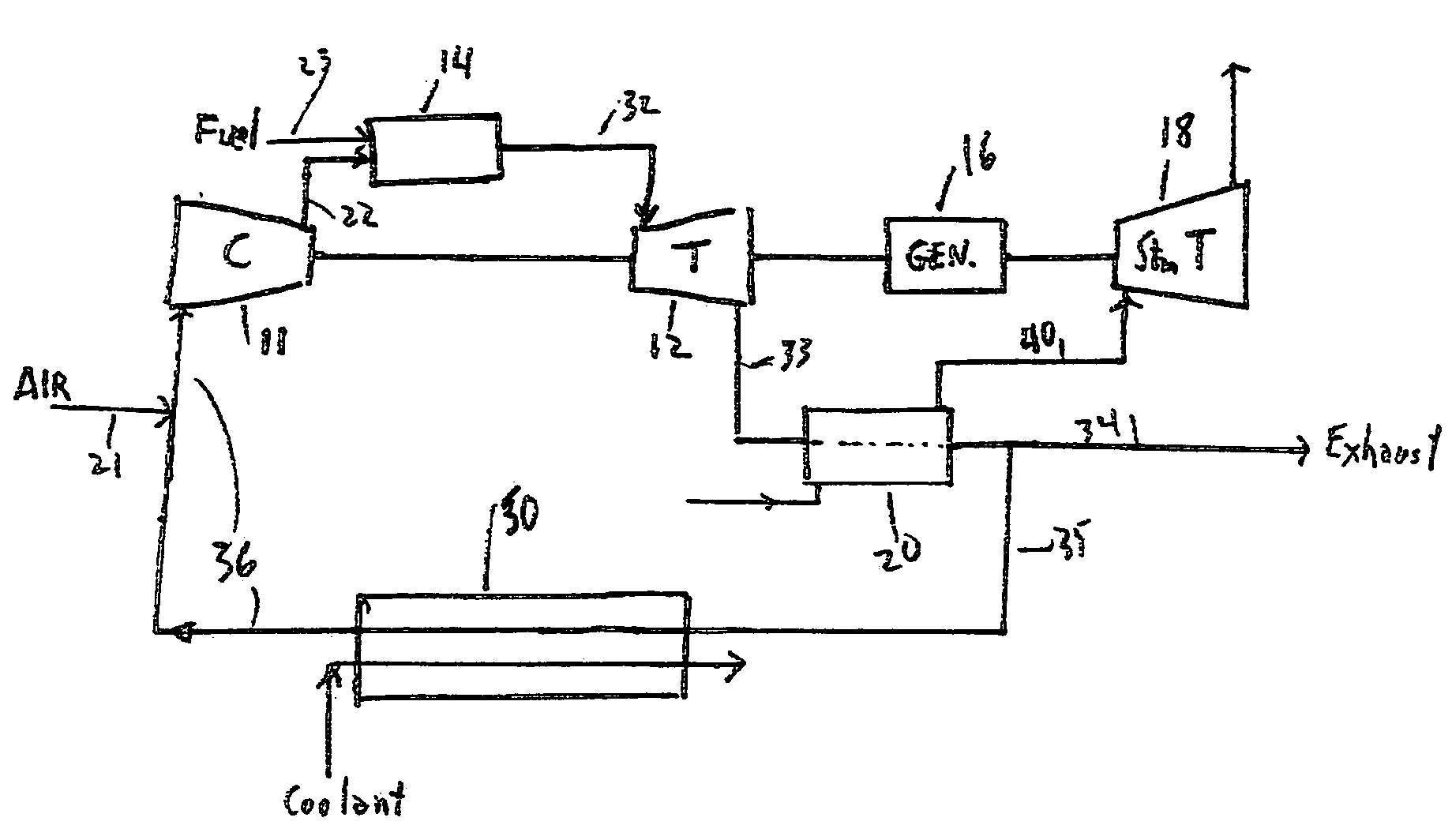
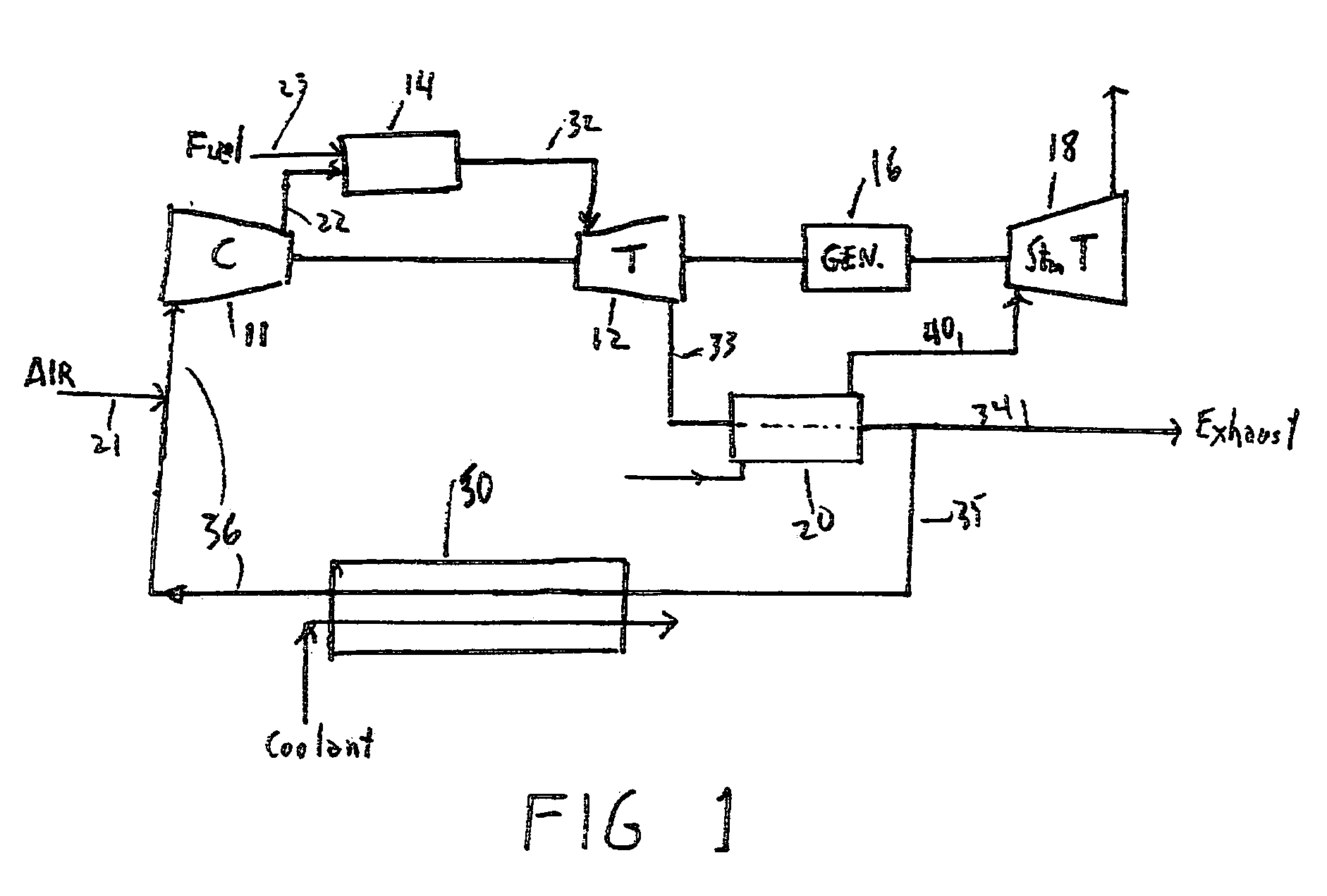
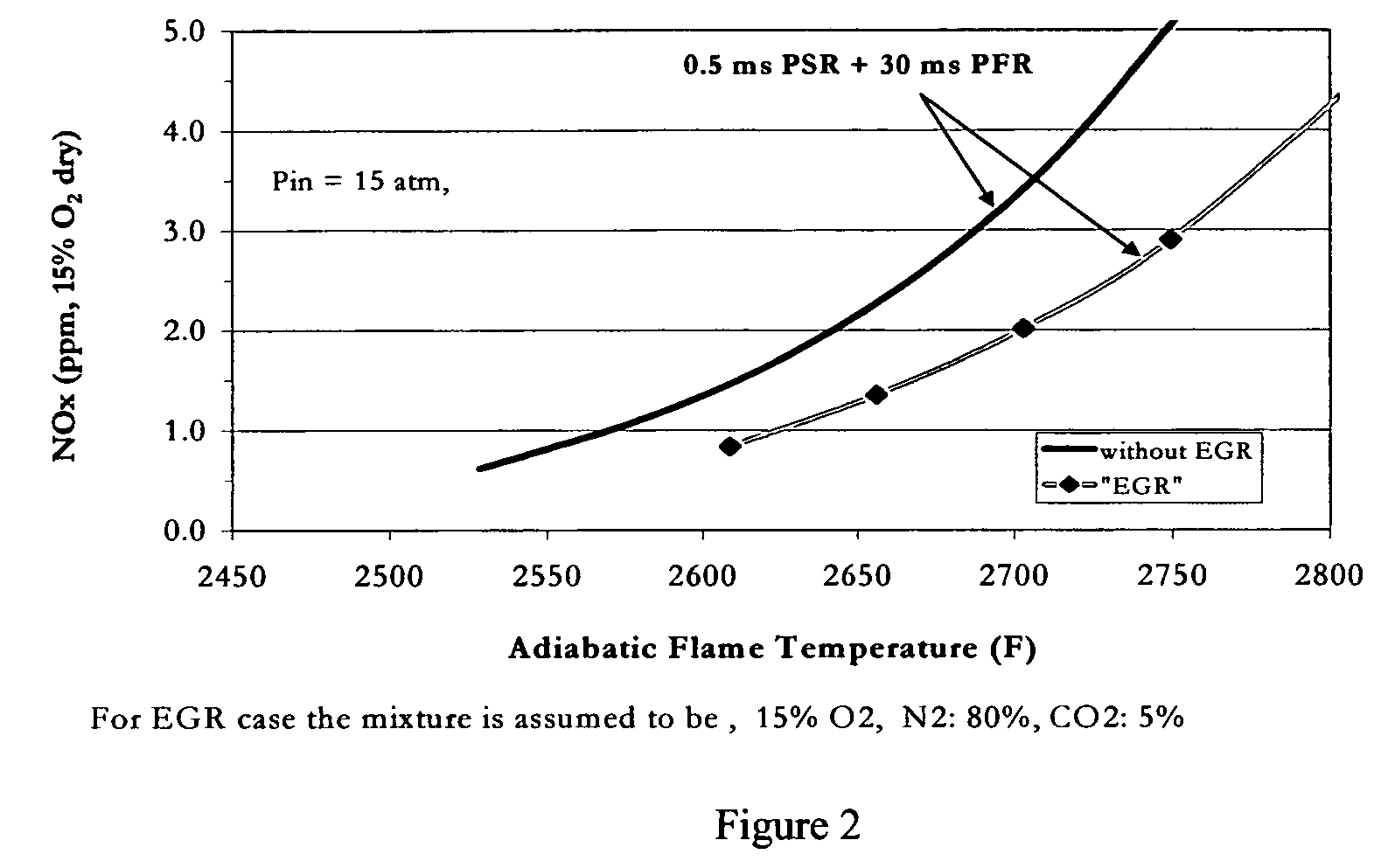
Method for obtaining ultra-low NOx emissions from gas turbines operating at high turbine inlet temperatures
ActiveUS7765810B2Improve combustion stabilityEasy to controlTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCombustion chamberEquivalence ratio
A method of lowered NOx combustion is taught wherein the kinetic rate of NOx formation is reduced for a given combustion temperature in a gas turbine combustor. A supply of fuel is provided along with a supply of ambient air in sufficient quantity to form a fuel / air mixture having an equivalence ratio greater than about 0.55 when mixed with the fuel. The fuel / air mixture is mixed with a supply of cooled combustion gases in sufficient quantity such that the oxygen content of the resulting air mixture is less than about 18 percent. The resulting air mixture is then passed into the combustor.
Owner:PRECISION COMBUSTION
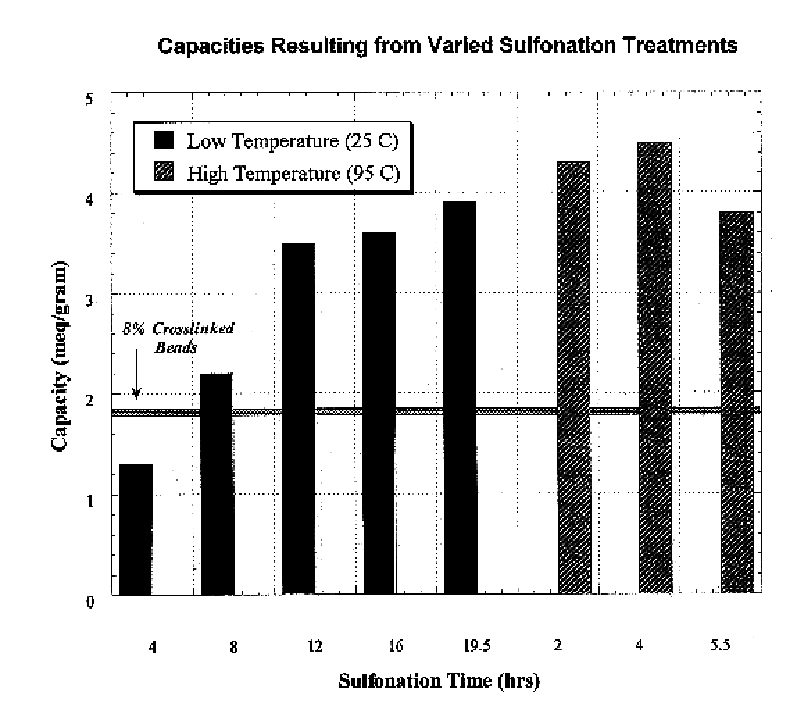
Polymeric ion exchange fibers
InactiveUS6706361B1Increase kinetic rateVarious kindsIon-exchange process apparatusFibreboardFiberIon exchange
Ion exchange resin composite fibers include a substrate fiber, and an ion exchange resin, on the substrate fiber. The ion exchange resin composite fibers exhibit greatly increased kinetic rates of reaction and regeneration.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Mesoporous network electrode for electrochemical cell
InactiveCN101009368ALow costSimple and convenient methodMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesLithiumNanoparticle
A high kinetics rate electrochemical cell in which at least one of the electrodes is composed of a mesostructural electroactive material comprising nanoparticles forming a three-dimensional framework structure of mesoporous texture having a bicontinuous junction of large specific surface area with the electrolyte. A low temperature method of preparation of the electrodes employs a high-speed deposition of the electrically active material in the form of a thin film. The application of said electrodes in high power lithium ion insertion batteries, photovoltaic cells, supercapacitors and fast electrochromic devices is disclosed.
Owner:XOLIOX SA
Method for promoting Bunsen reaction in thermochemical iodine-sulfur cycle for hydrogen manufacturing
ActiveCN103213945AOmit the concentration stepIncreased reaction kinetic rateHydrogen productionMass ratioDistillation
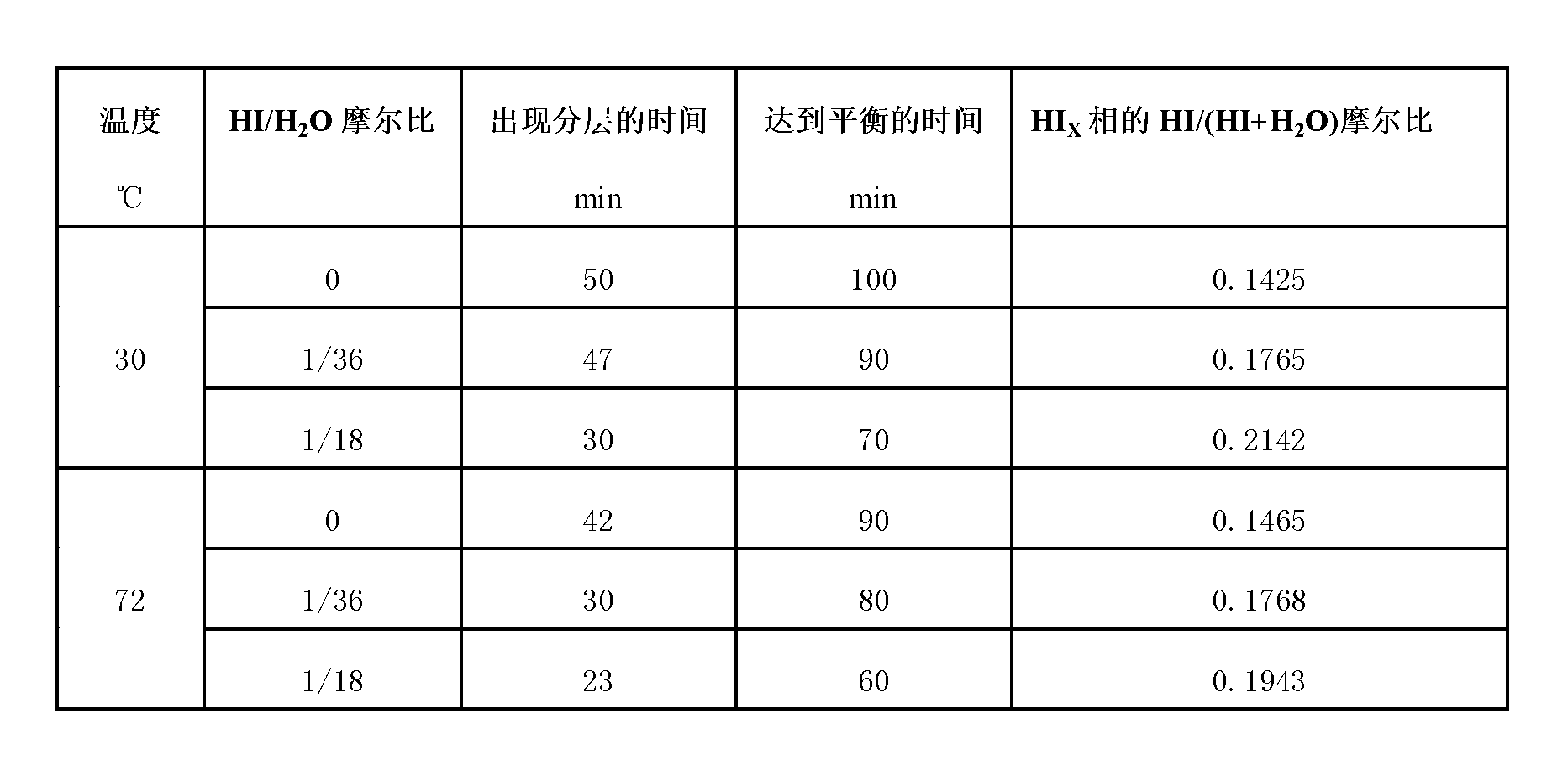
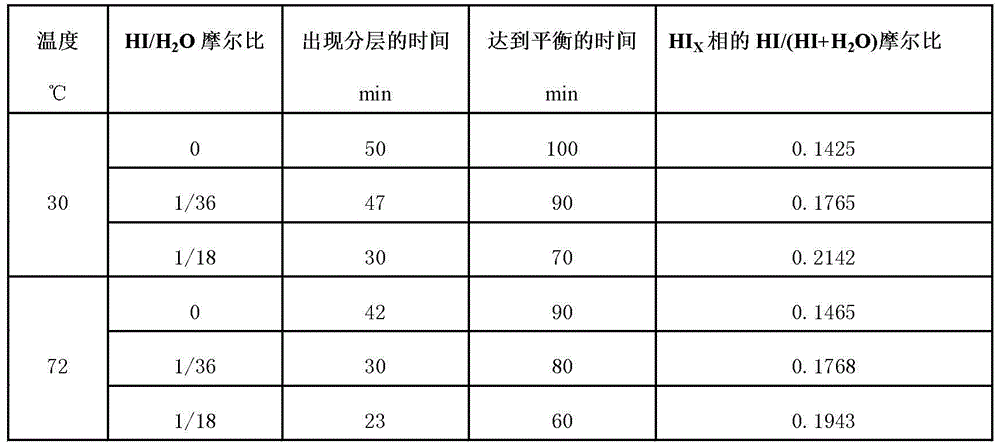
The invention relates to a technique of iodine cycles for hydrogen manufacturing, and aims to provide a method for promoting a Bunsen reaction in a thermochemical iodine-sulfur cycle for hydrogen manufacturing. The method comprises the following steps: adding I2 and H2O in a reactor, and heating a reaction solution to 30-72 DEG C; adding hydroiodic acid under the condition that the mass ratio of HI / H2O is 1 / 36-1 / 18: 1, and mixing the reaction solution at a uniform speed so as to ensure I2 is completely dissolved; feeding SO2 at a constant flow rate, and spontaneously carrying out the Bunsen reaction so as to obtain H2SO4 and HI; and in the presence of excessive iodine, carrying out the separation of liquid-liquid phases, so that the reaction achieves a liquid-liquid equilibrium state finally. According to the invention, the original gas-liquid-solid three-phase reaction is transferred into a gas-liquid reaction, and then the kinetic velocity of the Bunsen reaction is improved; and added HI has certain contribution to the improvement of the concentration of HI in a HIx phase in a thermodynamic equilibrium state, and HI achieves a super azeotropic concentration, so that the situation that pure HI steam is obtained through subsequent distillation is facilitated, and a HI concentration step can be cancelled, therefore, the method is extremely advantageous to the simplification of a whole SI circulation system and the improvement of the thermal efficiency of the system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Modeling method for residual oil catalytic cracking reaction mechanism model
InactiveCN1655165AImprove stabilityReduce initial value requirementsCatalytic crackingSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodDynamic equation
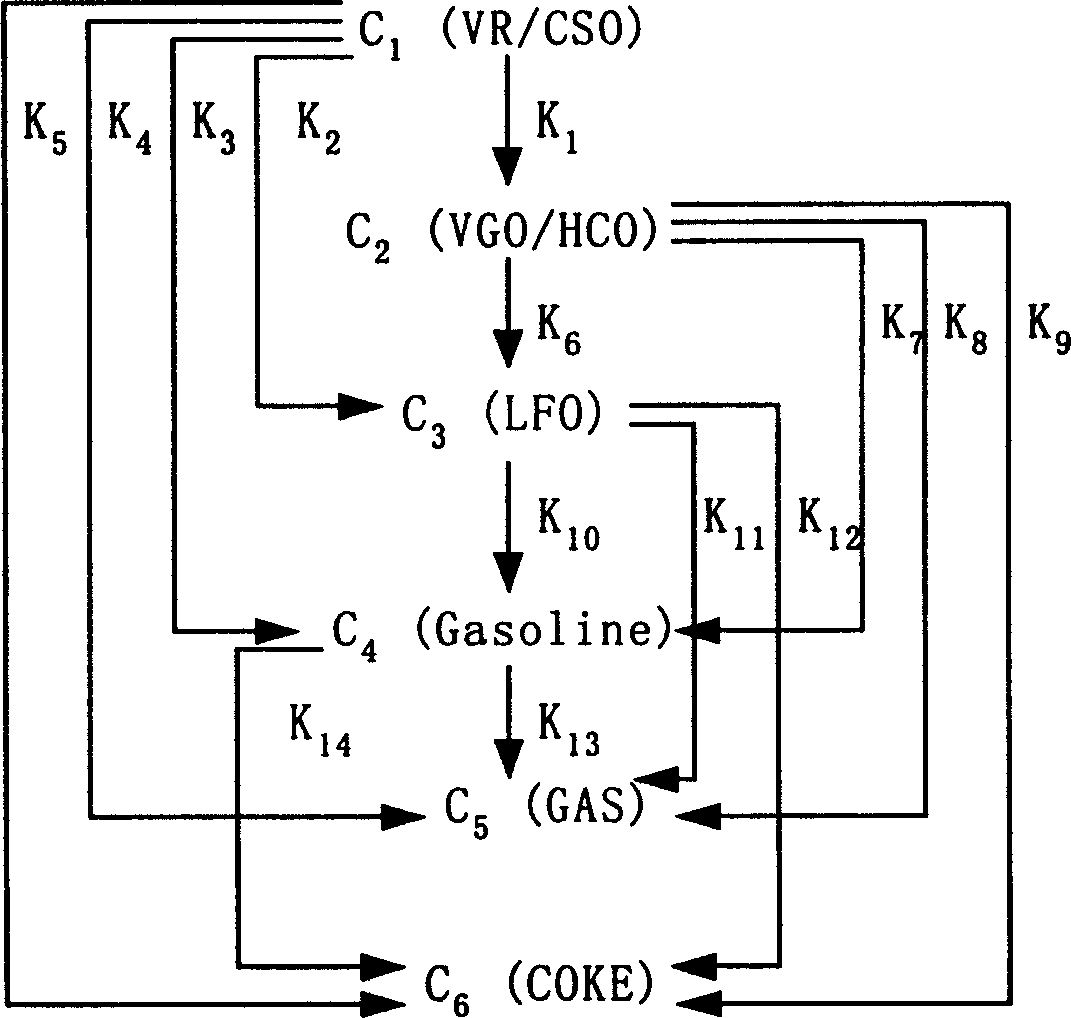
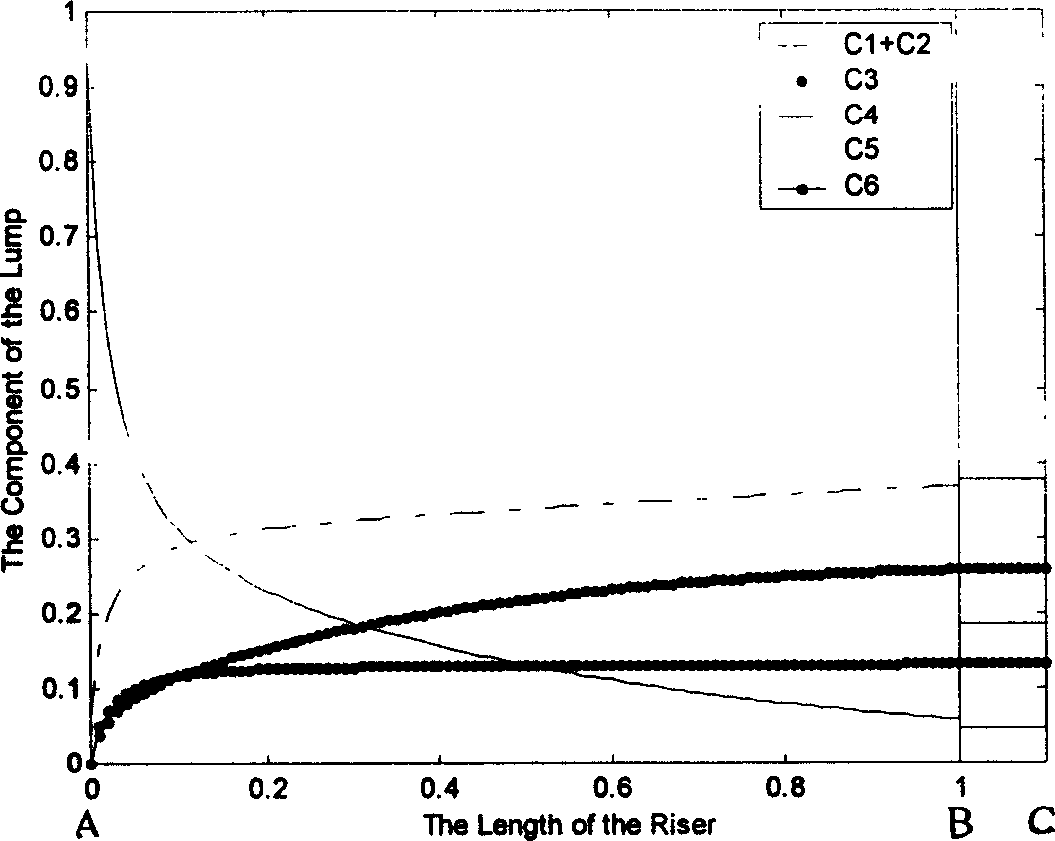
This invention discloses a model set up method for residual oil catalytic cracking reaction mechanism model, which divides the oil cut fraction into 6 lumps to set up serial and parallel reaction networks among 6 lumps and combines the character of the reactor with the experience dynamics equations among the lumps to set up a residual oil catalytic cracking reaction mechanism model. Besides, 6 device factors are set for calibrating the reacted dynamics rate constants among the lumps to increase the pretest accuracy of the model to product distribution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUPCON SOFTWARE +1
Methods for determining binding affinities
InactiveUS20050175999A1Microbiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsKinetic rateKinetic rate constant
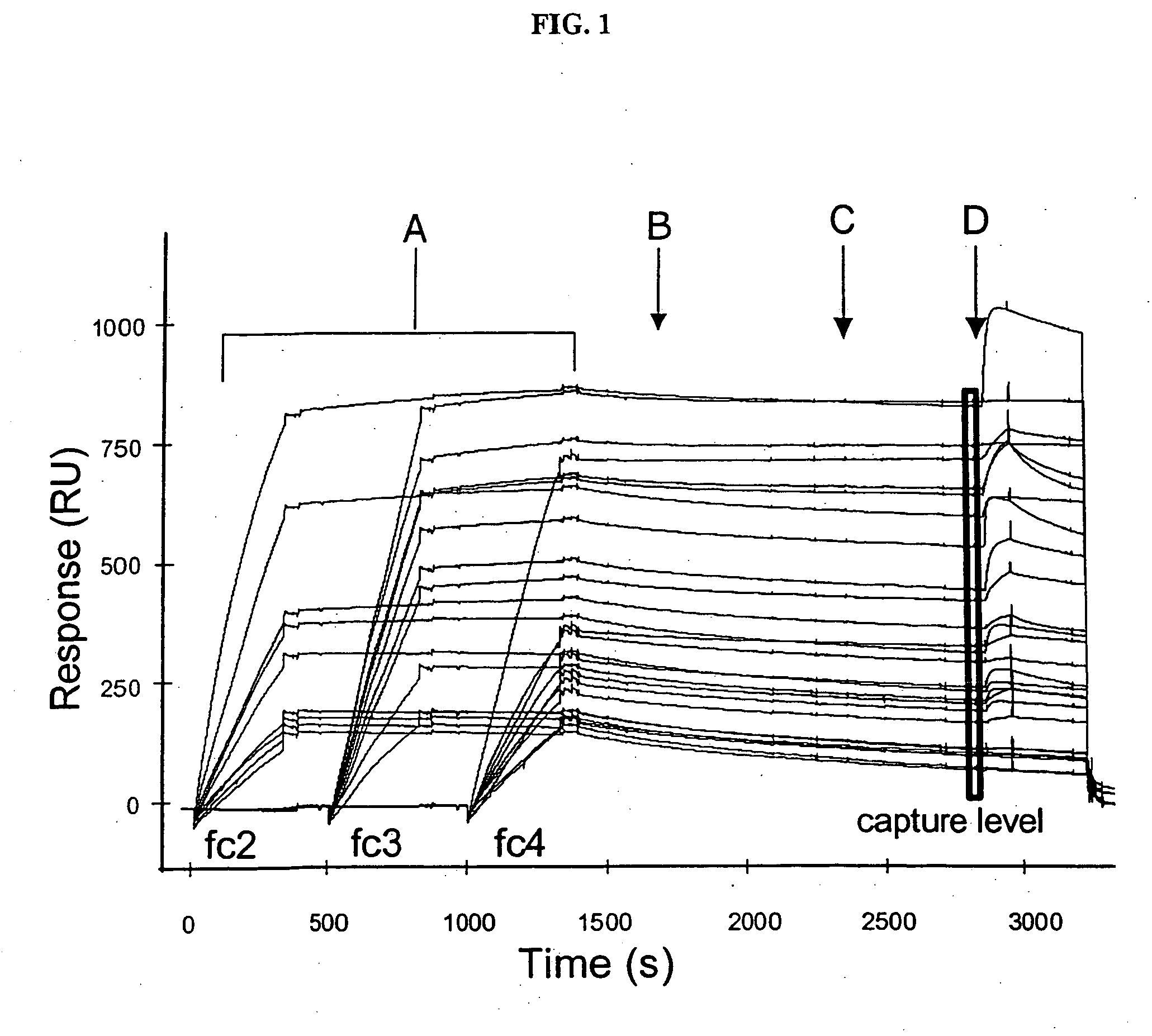
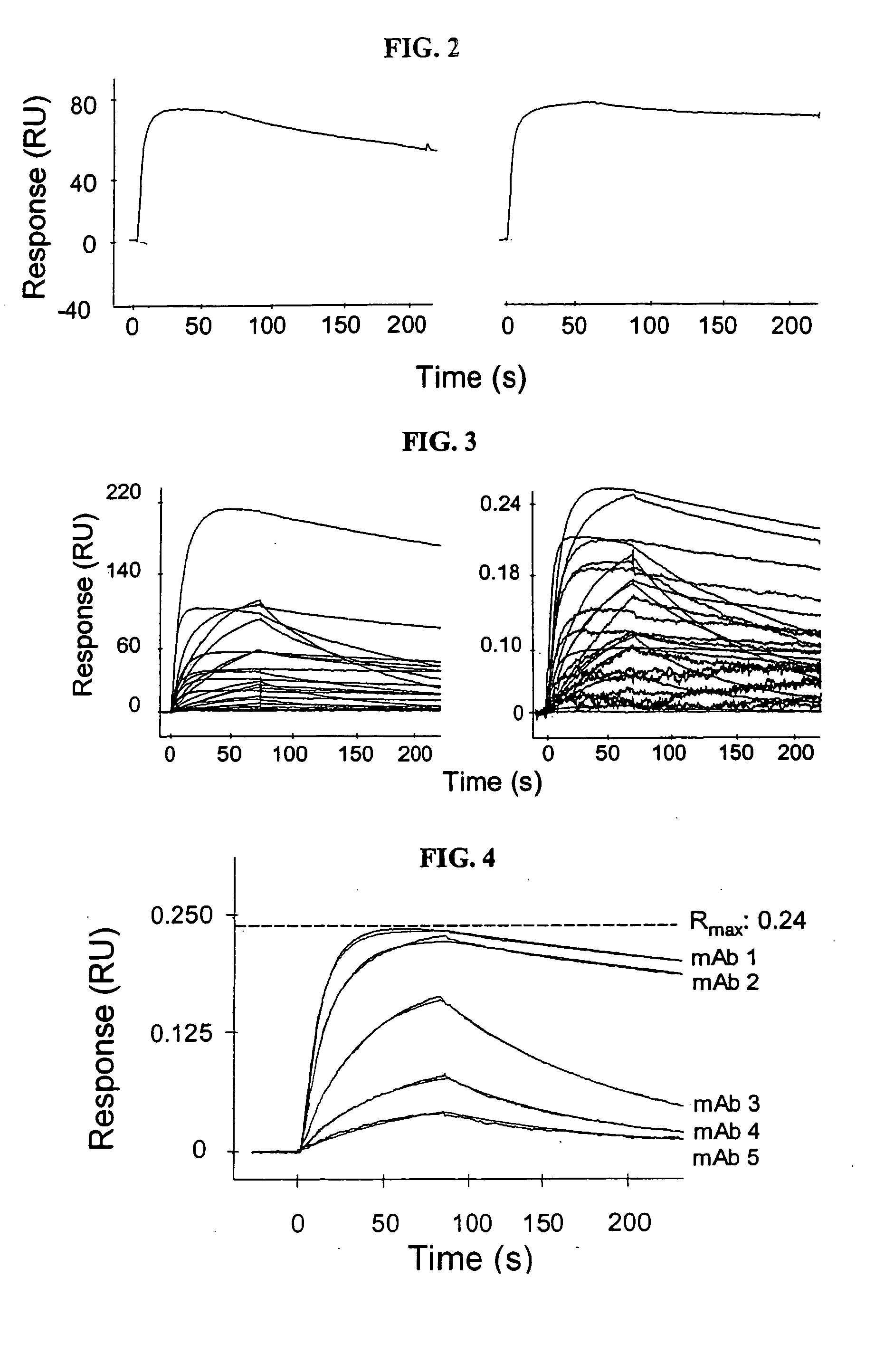
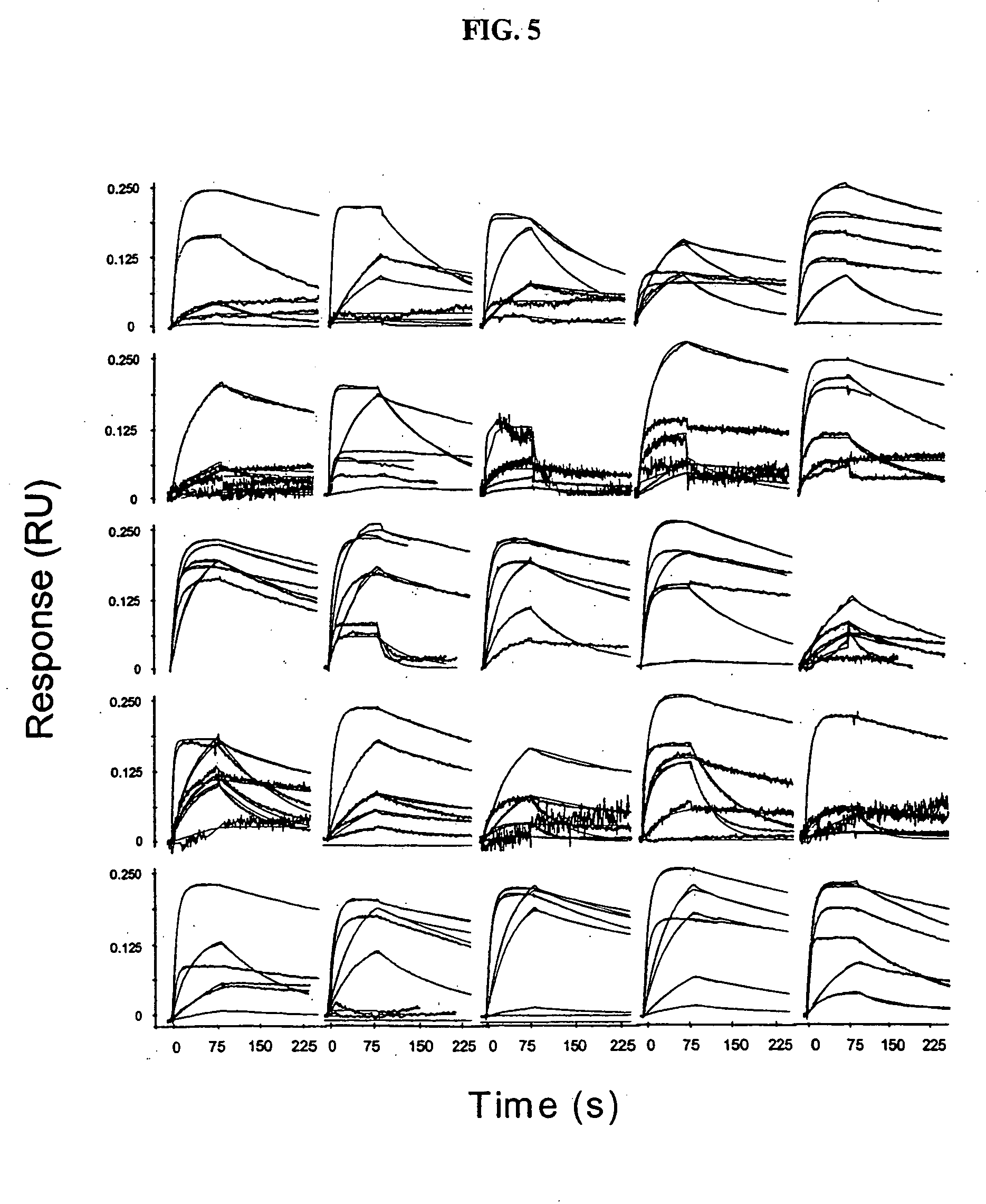
The present invention relates generally to methods for screening a plurality of ligands using a biosensor device. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for screening a plurality of antibodies from complex solutions using a surface plasmon resonance device. The methods of this invention provide kinetic and equilibrium information for such screening assays. The present invention also relates to systems for determining kinetic rate constants for such screening assays.
Owner:KLAKAMP SCOTT L +1
Method for analyzing dynamic transferred water quality based on fugacity theory
The invention disclose a method for analyzing dynamic transferred water quality based on a fugacity theory, relating to a water quality analysis method, and solving the problem of larger deviation between a simulated result and an actual condition caused by actually unobtainable required parameters and randomly non-modifiable inner parameters in a traditional water quality analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, confirming environment facies of a water area to be detected and acquiring geographic information parameters of the water area to be detected, environmental parameters of various environment and materialization parameters of a target pollutant; then computing fugacity capacity of each environmental facies, speed constant of reaction dynamics and transfer parameters among each environmental face; then establishing a system of differential equation by taking the fugacity of each environmental face as an unknown and solving the system of differential equation through a Runge-Kutta algorithm to obtain the fugacity of each environmental face; and calculating out pollutant concentration by the fugacity of each environmental facies and the fugacity capacity. The invention overcomes defects of the prior art, and can be applied to the field of analyzing transferring transformation of organic pollutants in the water area and distribution law of multi-medium environment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
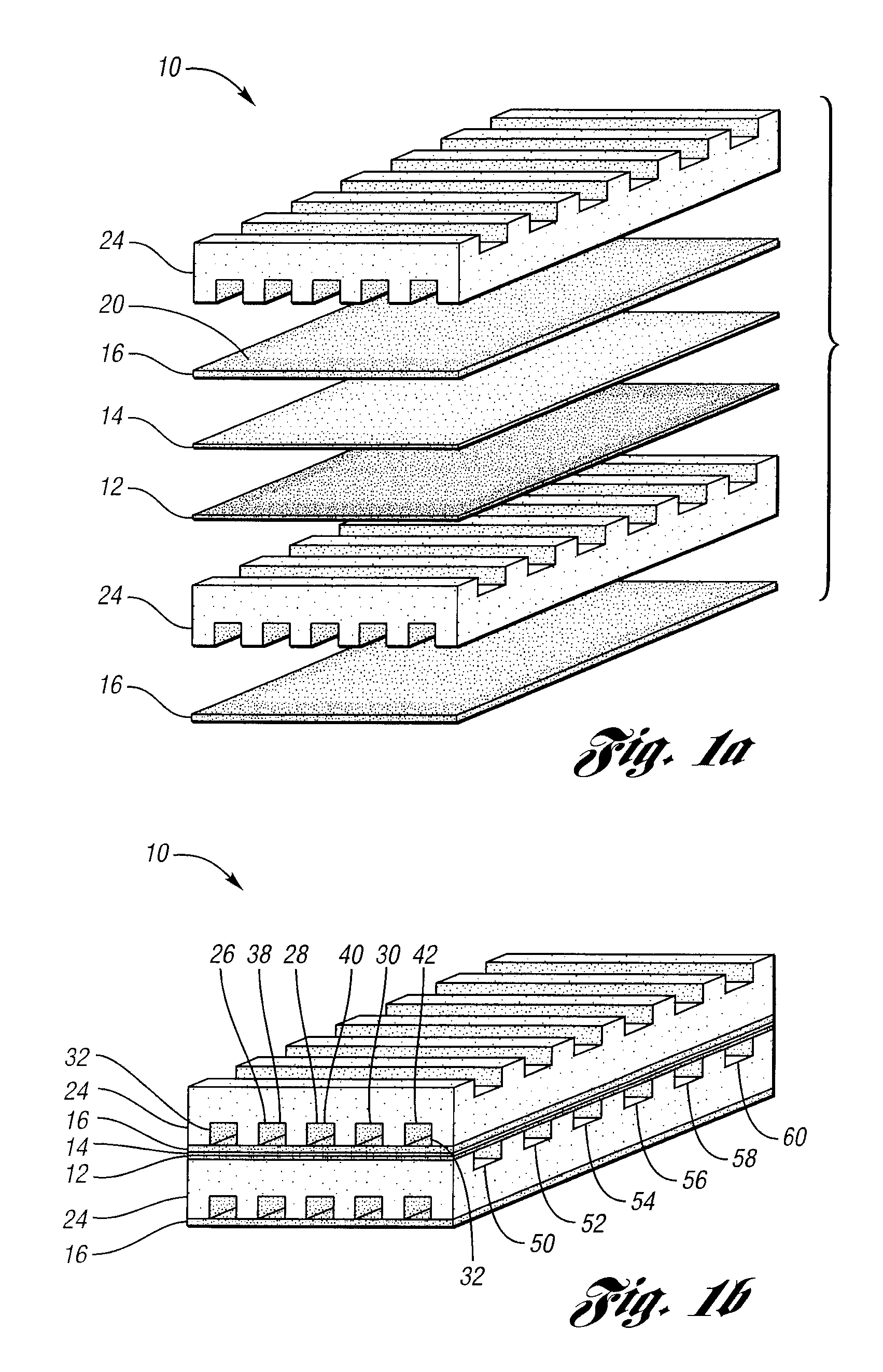
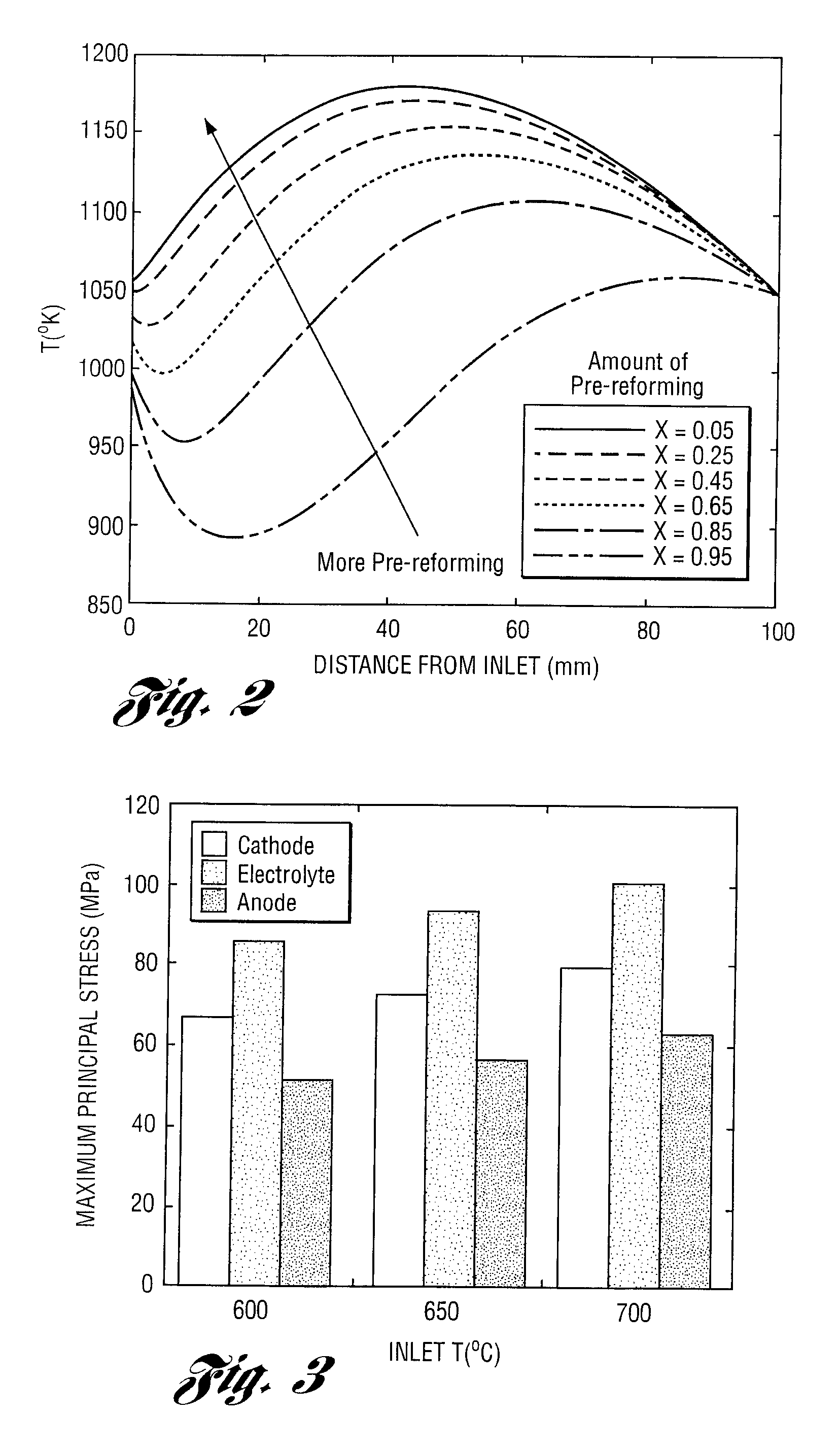
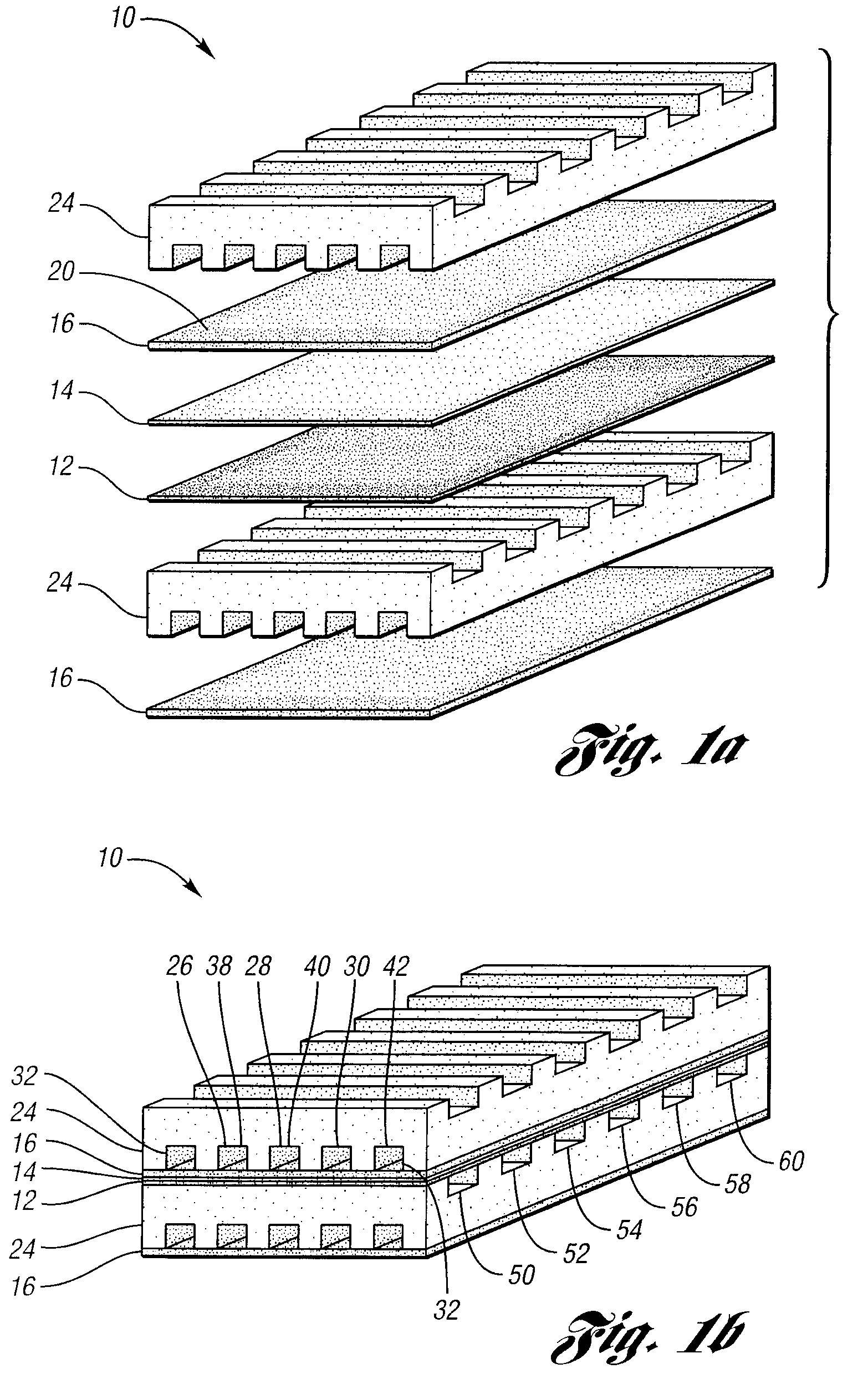
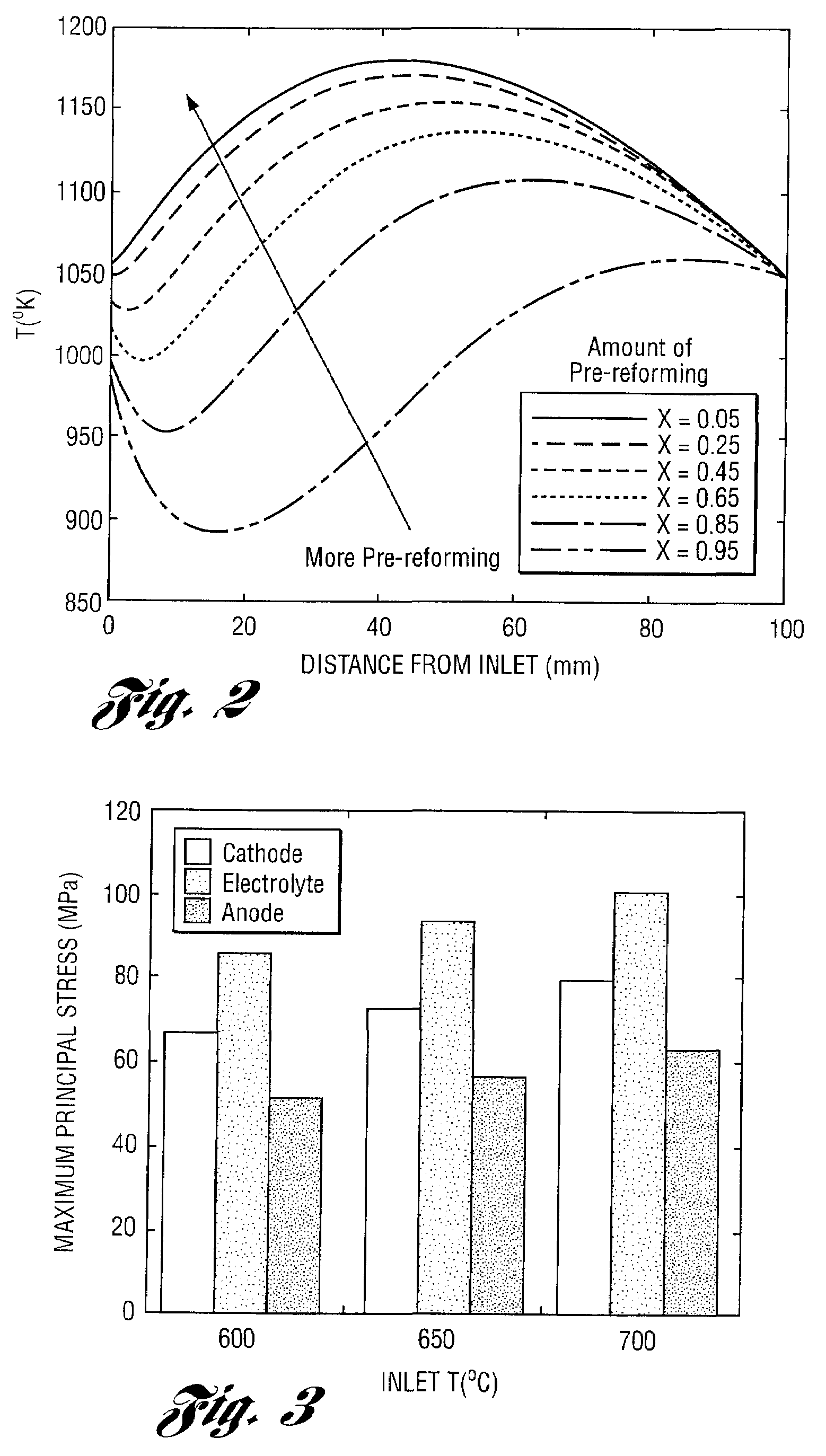
Apparatus and method for controlling kinetic rates for internal reforming of fuel in solid oxide fuel cells
ActiveUS20060014057A1Promote reformSlow reaction rateHydrogenActive material electrodesFuel cellsKinetic rate
The present invention provides a solid oxide fuel cell in which kinetic rates for internal reforming are controlled. The solid oxide fuel cell comprises a cathode, an electrolyte layer adjacent to the cathode, and an anode adjacent to the electrolyte layer. The anode used in the cell of the invention includes a support structure which defines at least a portion of an anode flow channel and a catalyst that promotes reforming. The anode flow channel has an anode flow channel entrance for the introduction of fuel to the solid oxide fuel cell and an anode flow channel exit for removing unreacted fuel and / or by-products. The catalyst is dispersed within or upon the support structure such that the rate of reforming increases at increasing distances from the anode flow channel entrance. The present invention also provides a method of controlling internal reforming kinetic rates in a solid oxide fuel cell.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
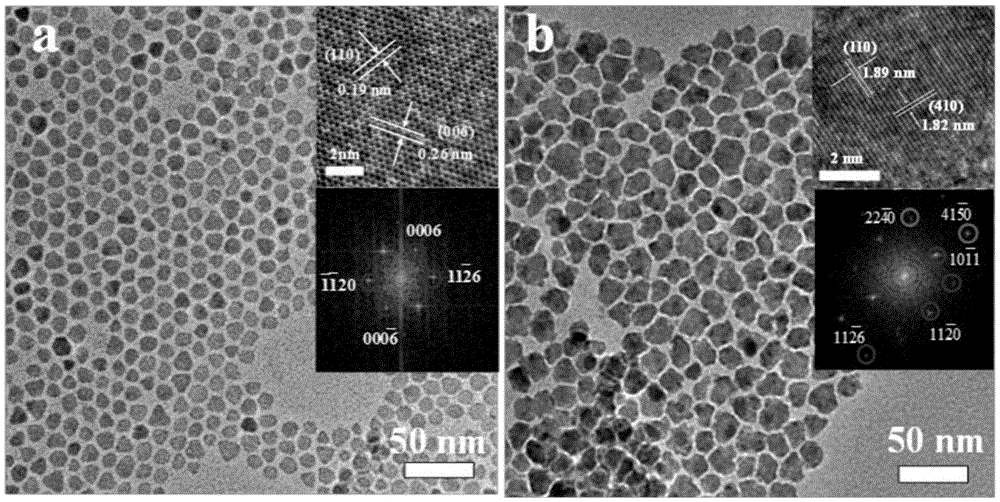
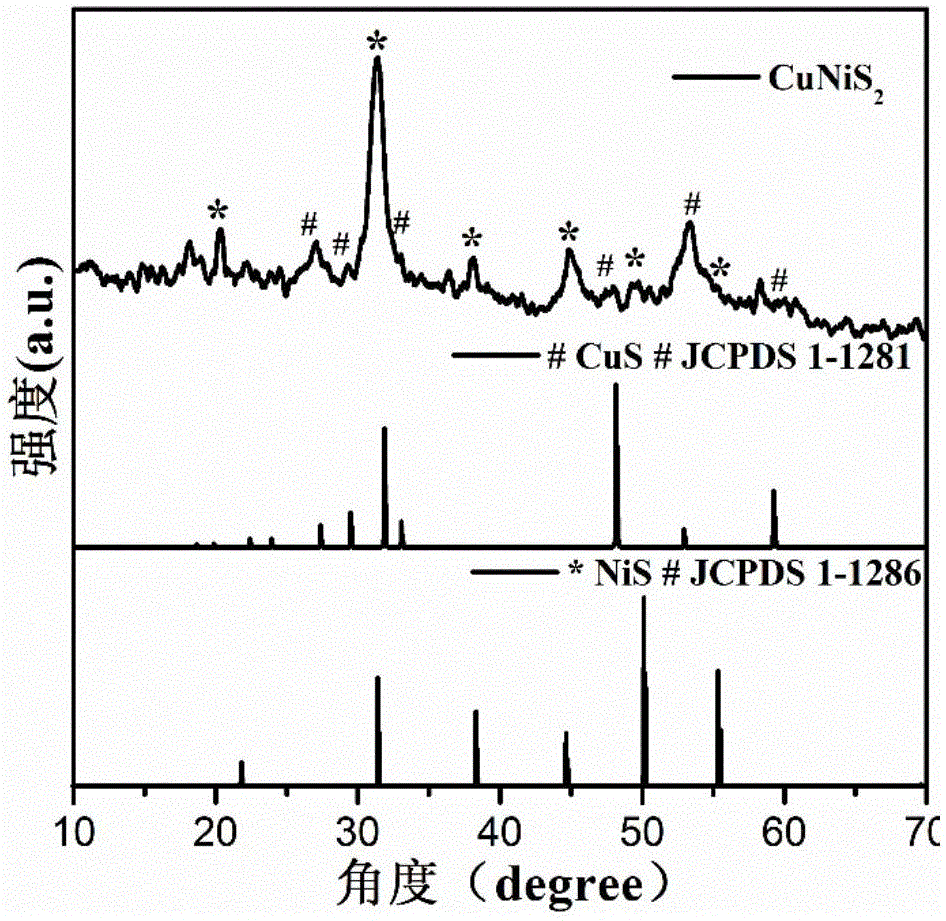
Non-noble metal oxygen evolution catalyst CuNiS2 with controllable shape
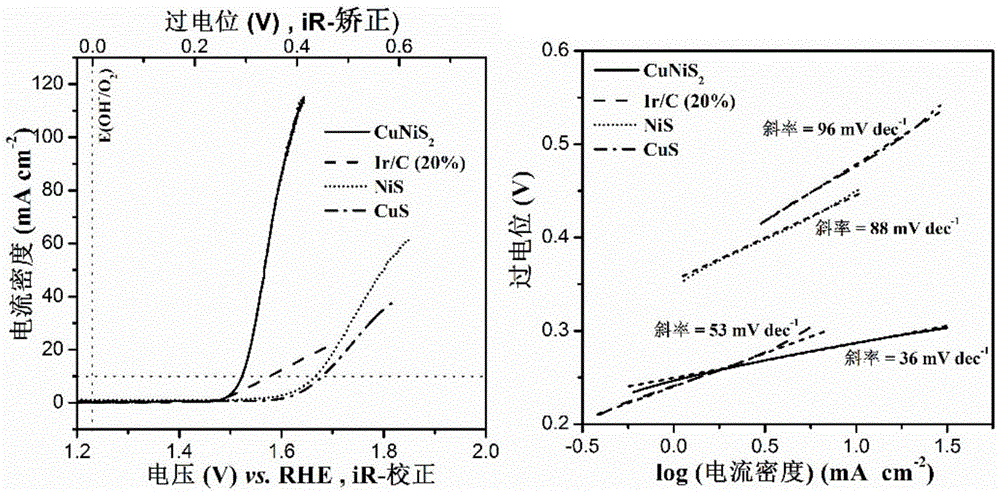
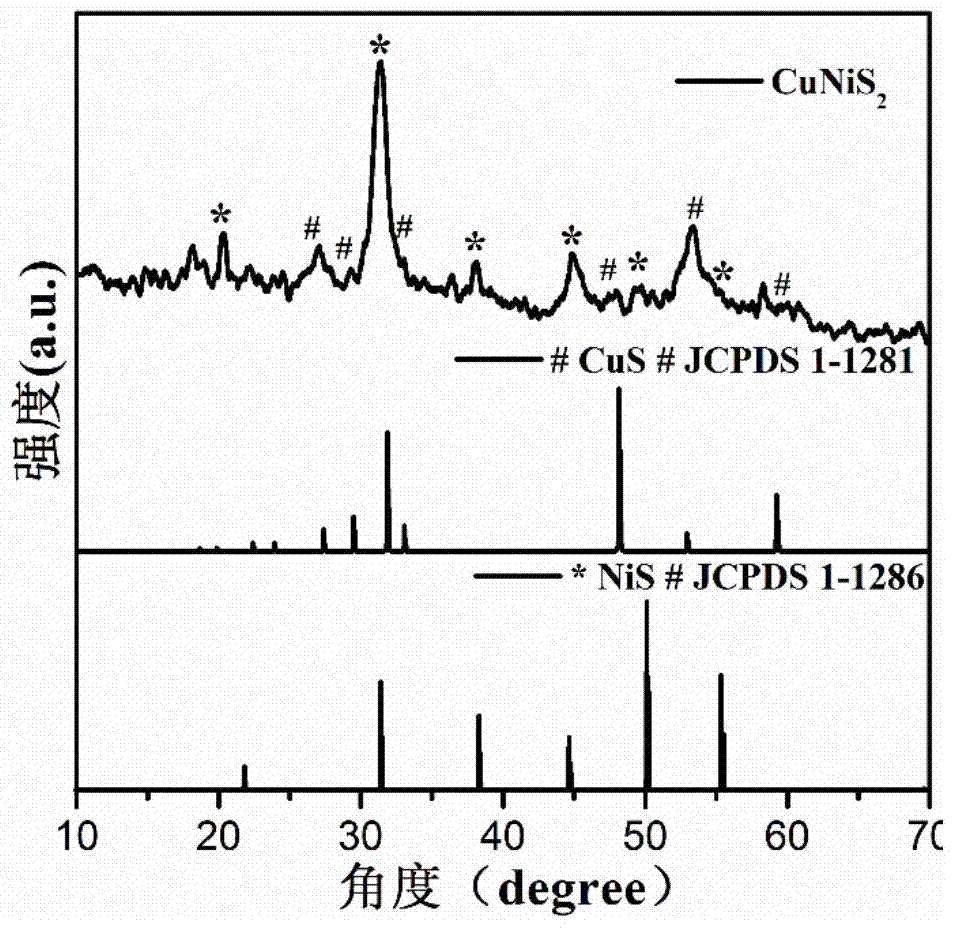
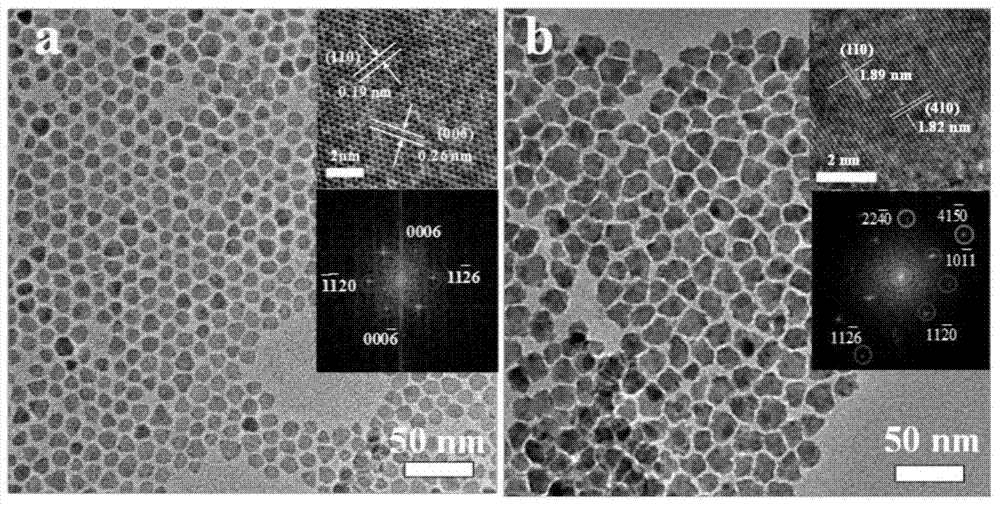
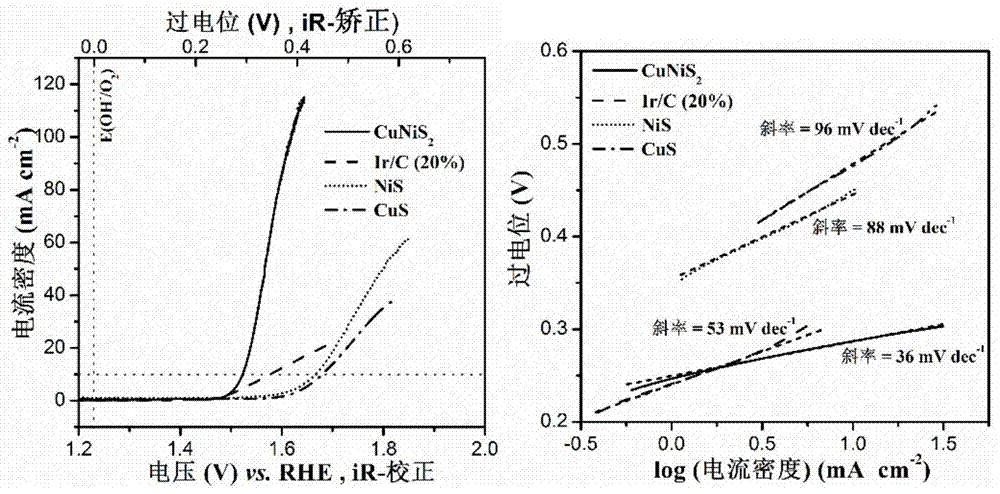
InactiveCN105148943AImprove stabilityIncrease the effective specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectronic transmissionKinetic rate
The invention discloses a non-noble metal oxygen evolution catalyst CuNiS2 with high activity, high stability and controllable shape, and discloses a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst is prepared by a method for high-temperature thermal injection, the operation is simple, and the aim of controllable synthesis of the shapes of nano particles is fulfilled. According to the preparation method, on the basis of a synthesized CuS nano hexagon, a nickel source is added into the system, so that a nano sheet CuNiS2 with an irregular edge structure is synthesized; therefore, the relative specific surface area of the catalyst system is enlarged; due to the special irregular edge structure, the oxygen evolution material has a large quantity of active sites, and metal nickel is extremely high in conductivity, so that the conductivity of the whole system is improved, the kinetic rate of electronic transmission is increased, and the activity of the material is enhanced.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
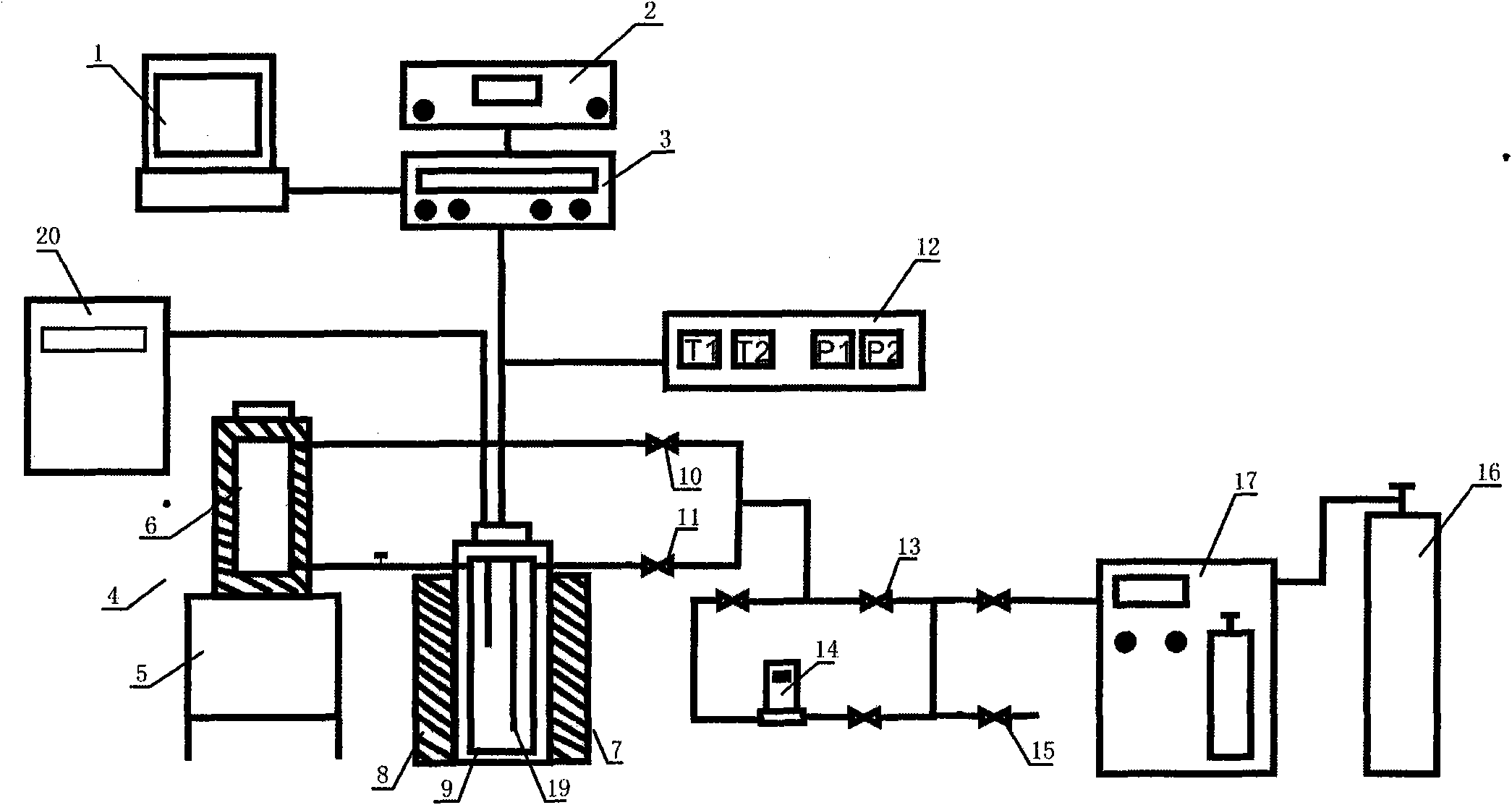
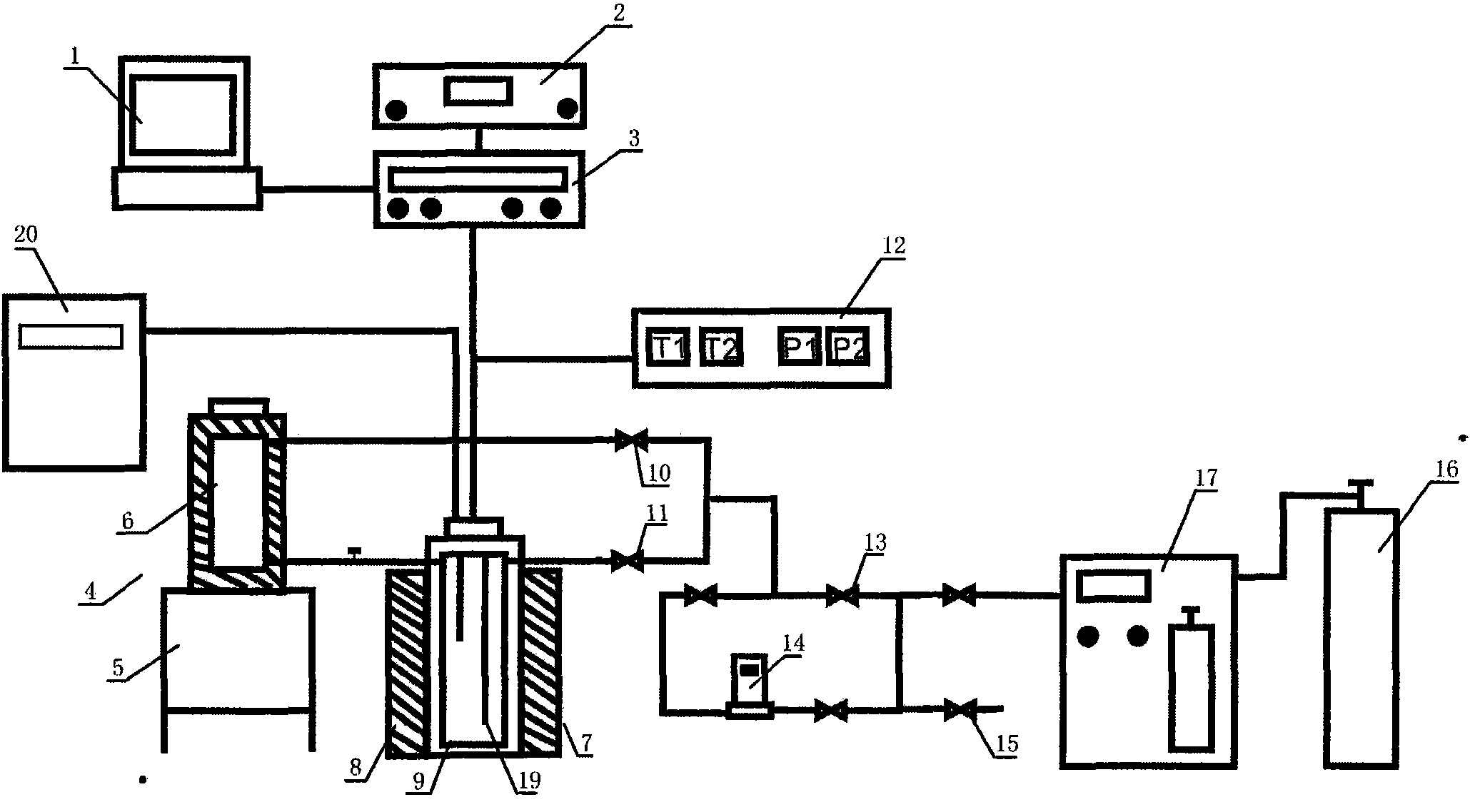
Hydrate formation kinetics simulation experiment device
InactiveCN102042998APrecise determination of kinetic rates of formationLow costMaterial resistanceMaterial electrochemical variablesKinetic rateData acquisition
The invention relates to a simulation experiment device, in particular to a hydrate formation kinetics simulation experiment device. The hydrate formation kinetics simulation experiment device comprises a pressure-stabilizing air supply unit, a saturation water preparation kettle, a hydrate reaction kettle, a constant temperature controller and a data acquisition processing unit, wherein the pressure-stabilizing air supply unit is respectively connected with the saturation water preparation kettle and the hydrate reaction kettle through a pipeline and a valve; the saturation water preparation kettle is connected with the hydrate reaction kettle through the pipeline; and the hydrate reaction kettle is respectively connected with the constant temperature controller and the data acquisition processing unit electrically. The hydrate formation kinetics simulation experiment device can accurately measure the kinetic rate of the formation of a hydrate, and is simple, low-cost and convenient to operate.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
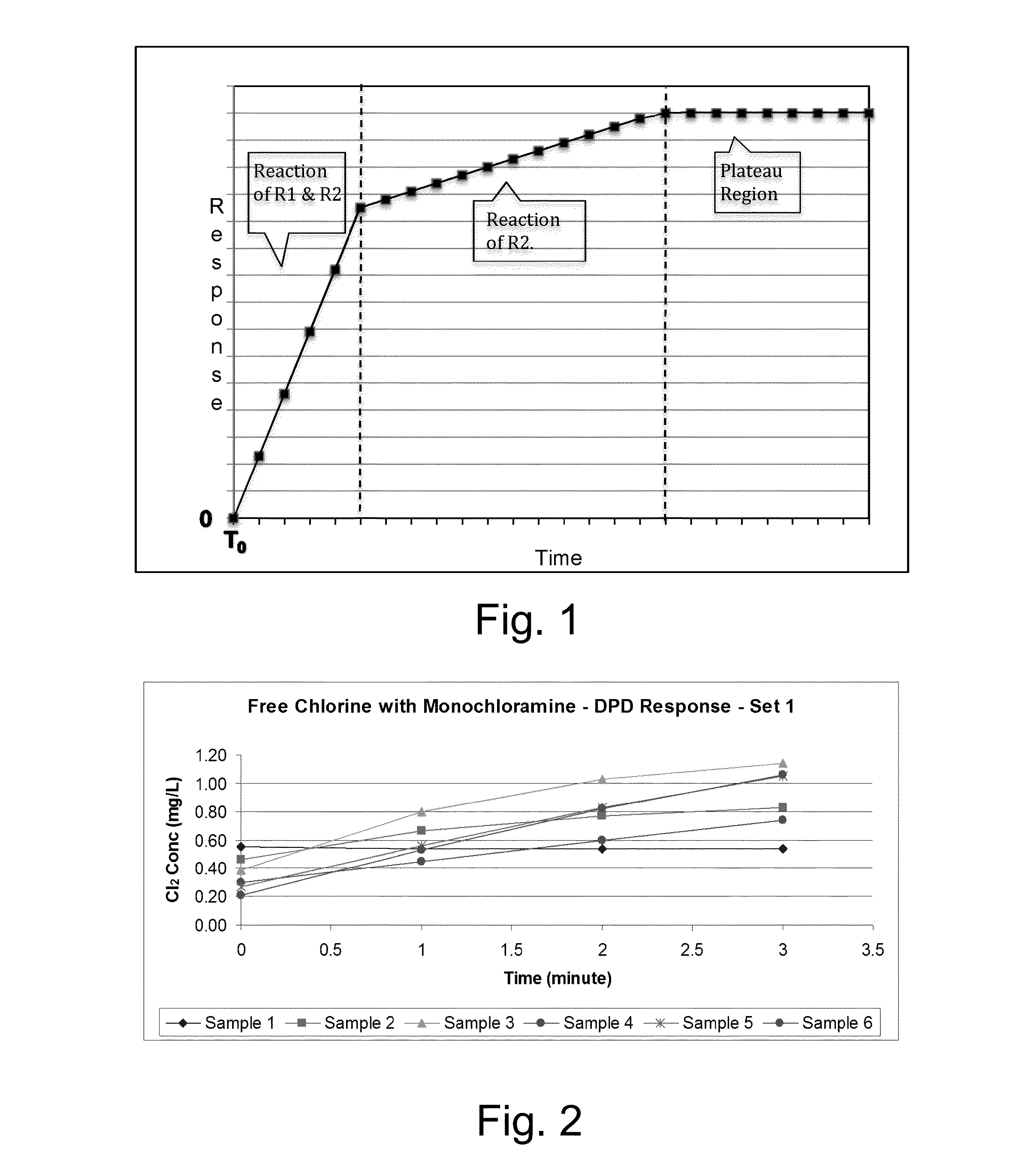
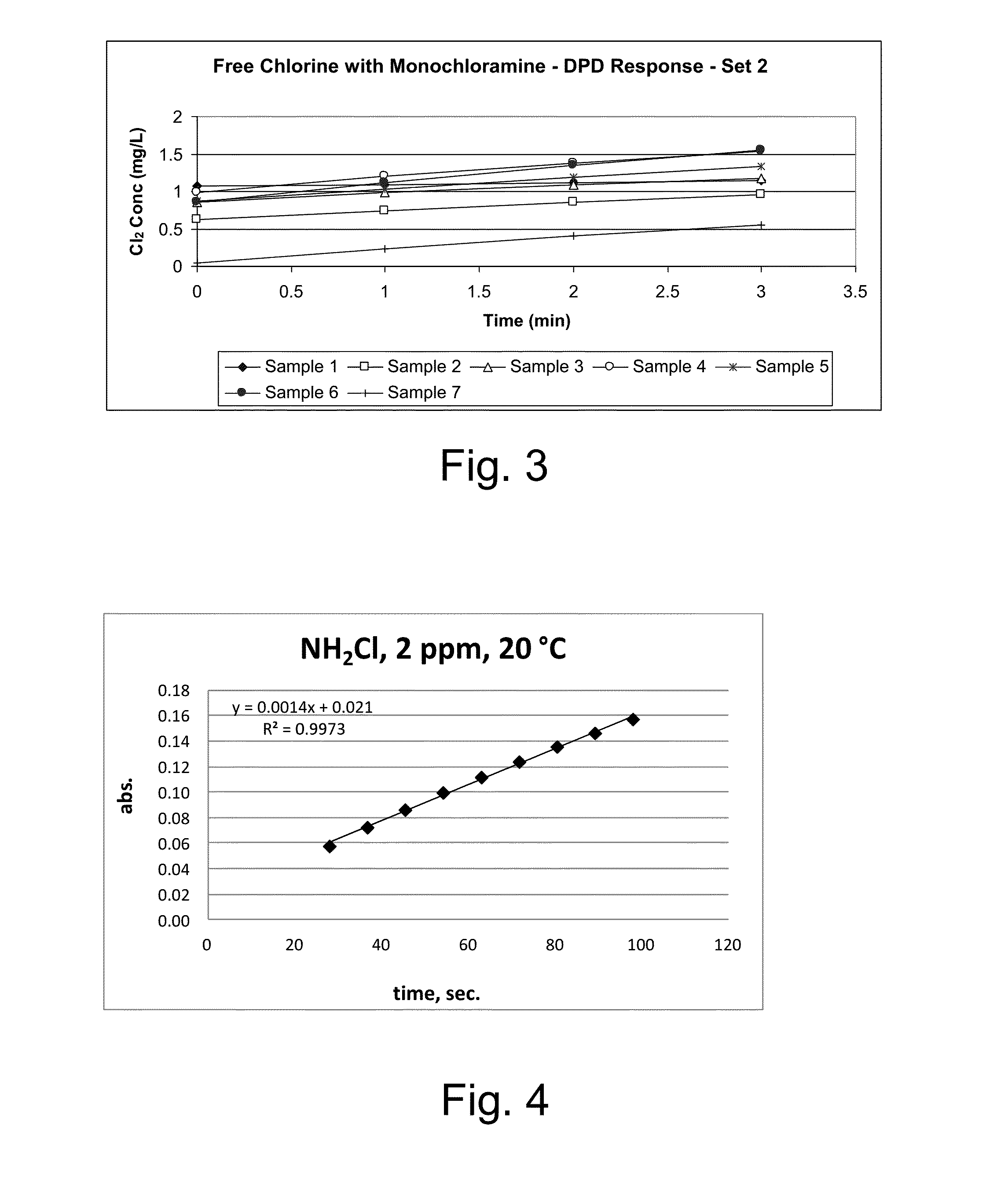
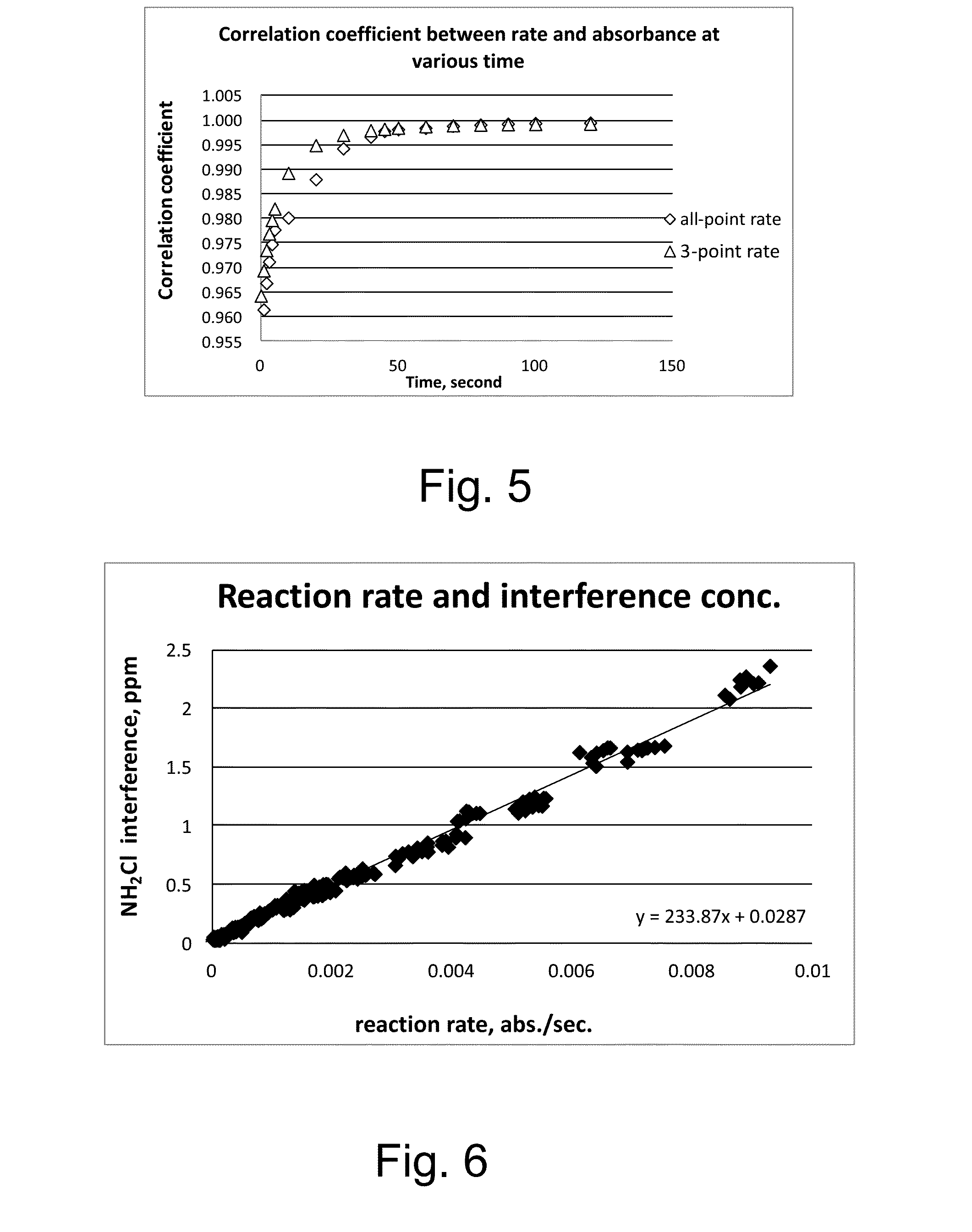
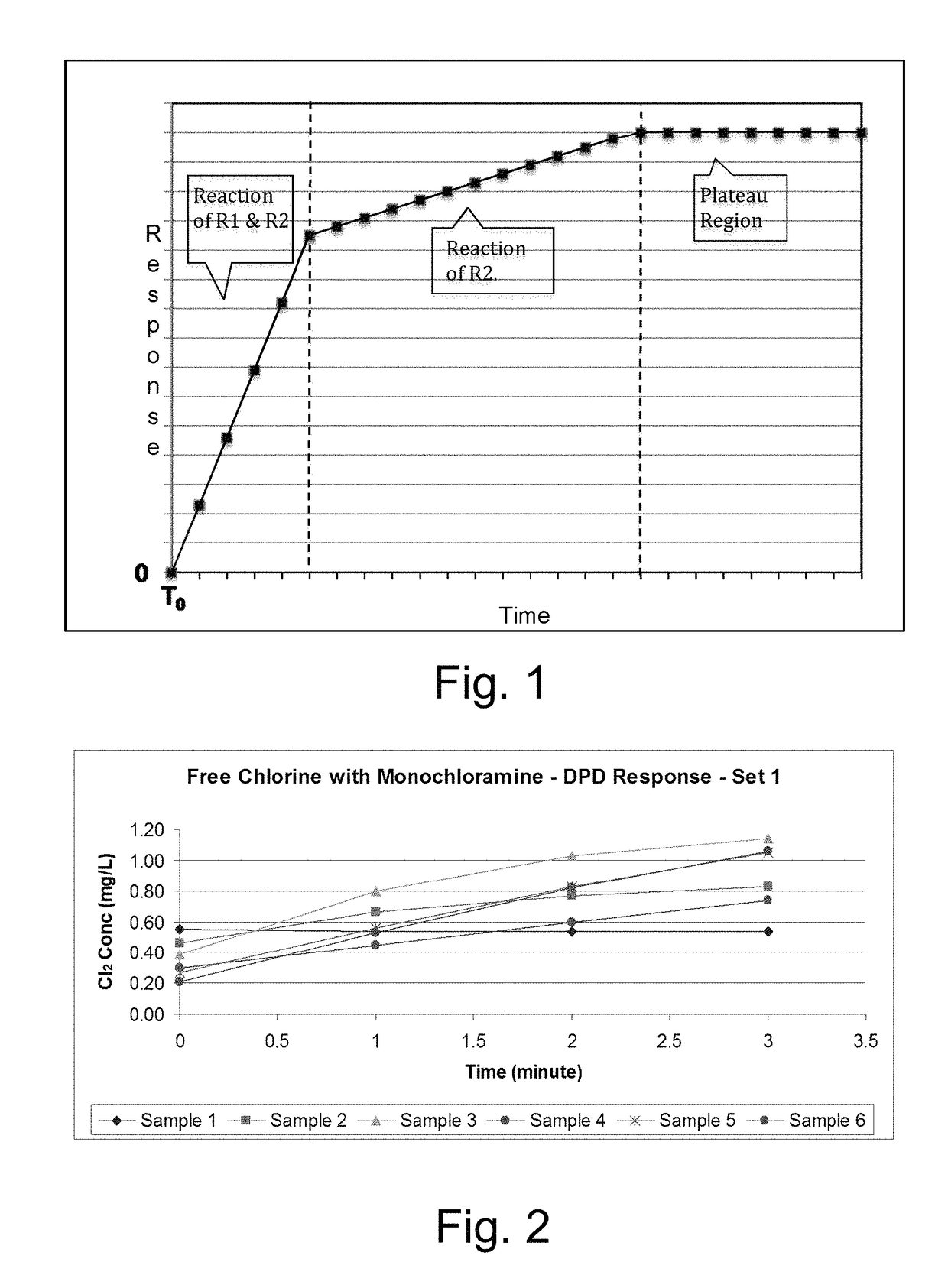
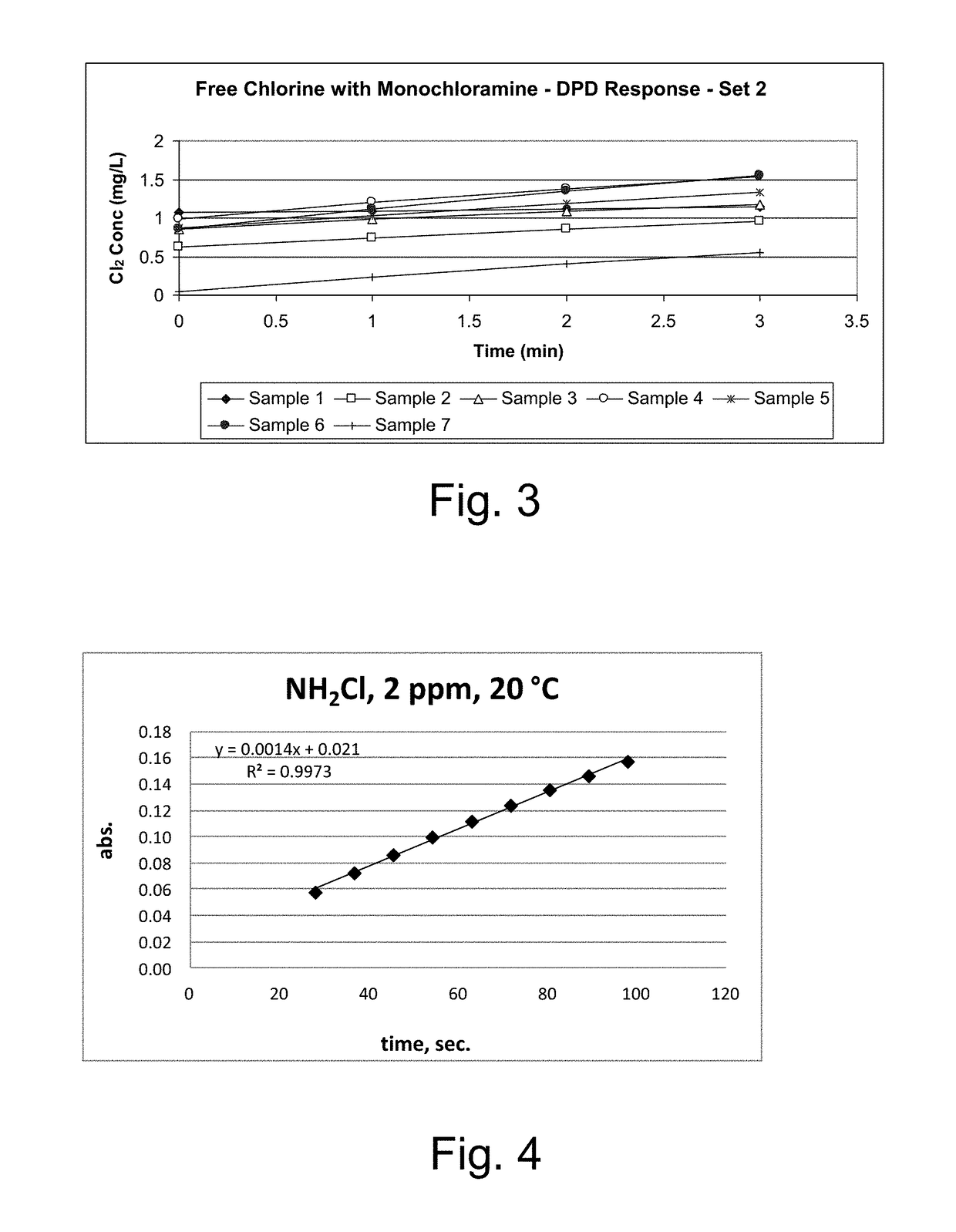
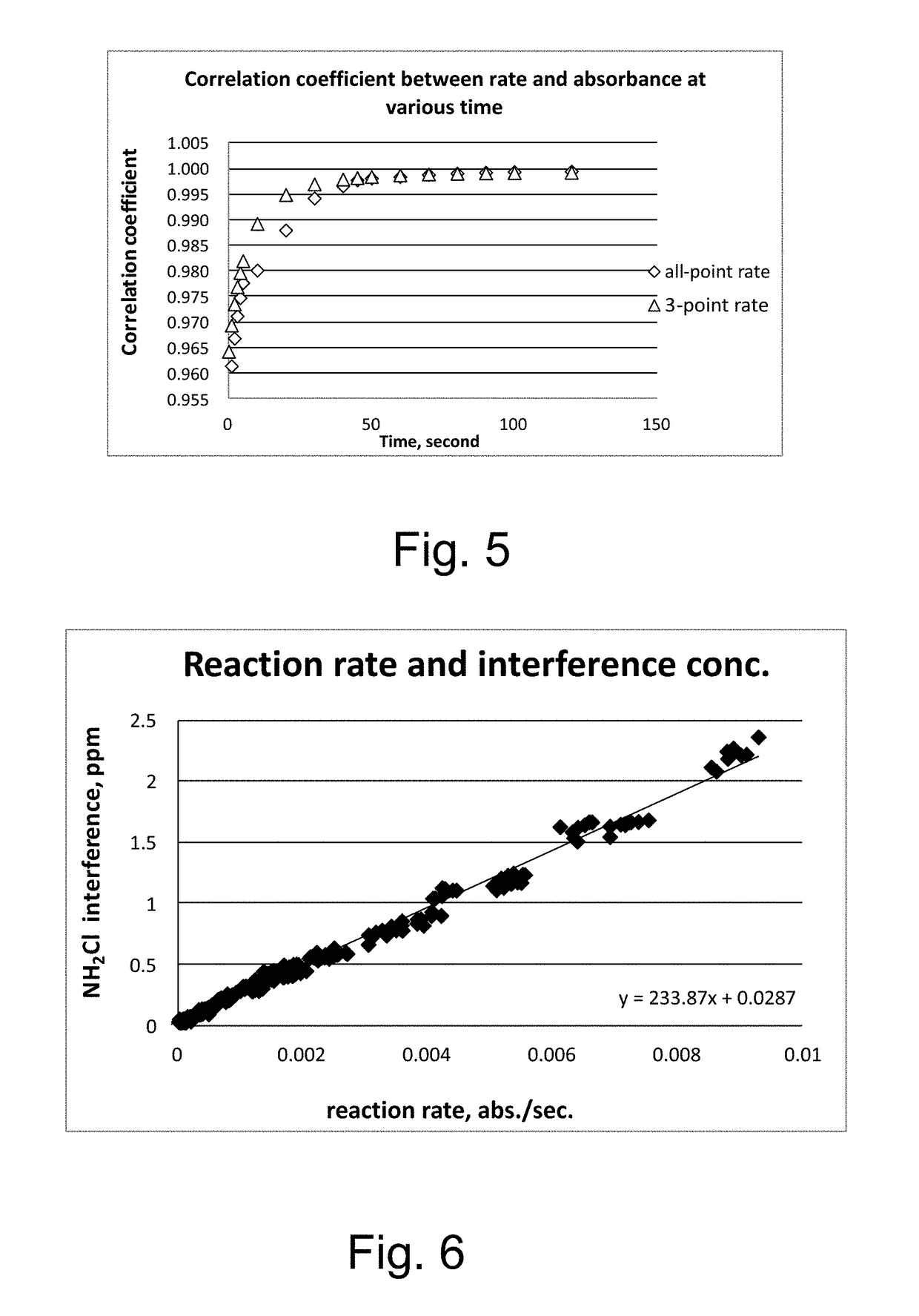
Kinetic chlorine measurement
ActiveUS20150285779A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by optical meansChloramine BKinetic rate
An aspect provides a method of determining a concentration of free chlorine in an aqueous sample, including adding a reagent to the sample, the reagent being reactive with the free chlorine at a first kinetic rate and reactive with at least one chloramine at a second kinetic rate, the first kinetic rate being different from the second kinetic rate; measuring an absorbance response over time resulting from reaction of the free chlorine and the at least one chloramine with the reagent over time; and determining the concentration of the free chlorine in the sample based on a determined rate of change of the absorbance response over time. Other aspects are described and claimed.
Owner:HACH CO
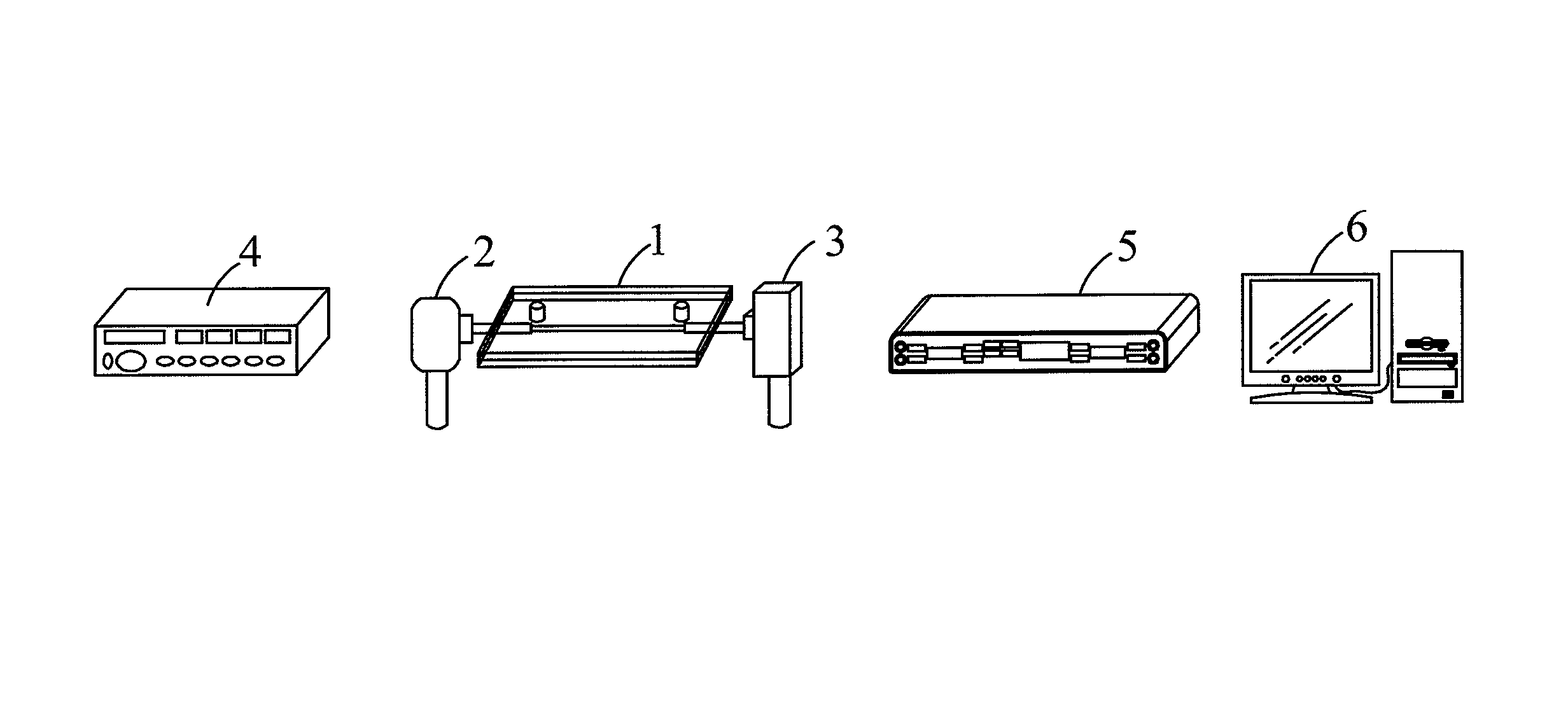
Method for obtaining binding kinetic rate constants using fiber optic particle plasmon resonance (FOPPR) sensor
ActiveUS20140051188A1Simple and concise computationScattering properties measurementsFiberKinetic rate
A method for obtaining the binding kinetic rate constants using fiber optic particle plasmon resonance (FOPPR) sensor, suitable for a test solution with two or more concentrations, which employs the following major steps: providing one FOPPR sensor instrument system, obtaining optical time-resolved signal intensities starting at the initial time to the steady state of the two or more regions, substituting the measured signal intensity values into the formula which is derived by using the pseudo-first order rate equation model. In addition, this method measures the temporal signal intensity evolution under static conditions as the samples are quickly loaded. As a result, unlike the conventional device where the sample is continuously infused, the method is able to measure the association and dissociation rate constants of which the upper bounds are not limited by the sample flow rate.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Normal-temperature ion exchange preparation method for silver tungstate photocatalyst
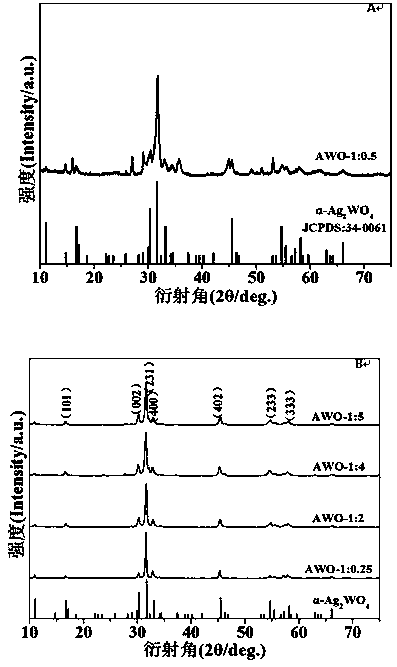
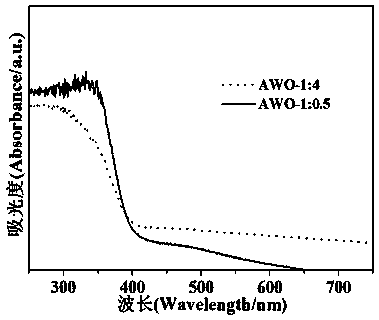
InactiveCN109012669AIncrease profitImprove separation efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsKinetic rateIon exchange
The invention discloses a normal-temperature ion exchange preparation method for an Ag2WO4 photocatalyst. According to the invention, AgNO3 is used as a salt source; the dual effects that Na2WO4 can provide both WO4<2-> ions and generate alkaline OH<-> thorugh hydrolysis are ingeniously utilized; and the crystal phase purity, morphology, microstructure and photocatalytic activity of an Ag2WO4 sample are changed by adjusting a raw material molar ratio of AgNO3 to Na2WO4. Results show that compared with a sample with a raw material ratio of an iso-stoichiometric ratio, the product with a AgNO3-to-Na2WO4 molar ratio in a range of 1: 0.25 to 1: 5 is obviously improved in the performance of photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants; the Ag2WO4 photocatalyst has optimal photocatalysis performance when a stoichiometric ratio of 1: 4; and the pseudo first-order kinetic speed constant k of the Ag2WO4 photocatalyst is 21.8 times higher than the pseudo first-order kinetic speed constant kof the sample with the raw material ratio of the iso-stoichiometric ratio. The results of mechanism analysis show that the light absorption range of the Ag2WO4 nanorod cluster is red-shifted, which indicates that the utilization of solar energy is increased; and at the same time, fluorescence intensity is decreased, which indicates that the separation efficiency of carriers is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Hydrated catalytic coating
InactiveUS20070245928A1Increase surface areaIncrease kinetic rateMaterial nanotechnologyCoatingsNano sizeUltraviolet lights
The hydrated catalytic coating is a coating that is applied to a substrate or target structure in the path of a broad spectrum ultraviolet light in the 100 nm to 300 nm range to decompose ozone. The coating is particularly useful in conjunction with germicidal UV lamps emitting UV radiation at 185 nm and 254 nm. The coating is a combination of a hydrophilic agent and the following metals: titanium dioxide (TiO2); silver (Ag); copper (Cu); nickel (Ni); and rhodium (Rh). At least three of the five metals are present as particles in the 50-100 nm range. The nanosize particles increase the surface area of the catalyst, improving the kinetic rate of reaction and the total reduction in ozone concentration. The particular mixture of catalytic metals and absorbed water also results in reaction products that have antimicrobial effect, including hydroxyl radicals and ions, superoxides, hydro peroxides and ozonide ions.
Owner:BENNERT JEFF E +3
Method for promoting bunsen reaction in thermochemical sulfur-iodide cycle hydrogen production
ActiveCN103213945BOmit the concentration stepIncreased reaction kinetic rateHydrogen productionDistillationKinetic rate
The invention relates to a technique of iodine cycles for hydrogen manufacturing, and aims to provide a method for promoting a Bunsen reaction in a thermochemical iodine-sulfur cycle for hydrogen manufacturing. The method comprises the following steps: adding I2 and H2O in a reactor, and heating a reaction solution to 30-72 DEG C; adding hydroiodic acid under the condition that the mass ratio of HI / H2O is 1 / 36-1 / 18: 1, and mixing the reaction solution at a uniform speed so as to ensure I2 is completely dissolved; feeding SO2 at a constant flow rate, and spontaneously carrying out the Bunsen reaction so as to obtain H2SO4 and HI; and in the presence of excessive iodine, carrying out the separation of liquid-liquid phases, so that the reaction achieves a liquid-liquid equilibrium state finally. According to the invention, the original gas-liquid-solid three-phase reaction is transferred into a gas-liquid reaction, and then the kinetic velocity of the Bunsen reaction is improved; and added HI has certain contribution to the improvement of the concentration of HI in a HIx phase in a thermodynamic equilibrium state, and HI achieves a super azeotropic concentration, so that the situation that pure HI steam is obtained through subsequent distillation is facilitated, and a HI concentration step can be cancelled, therefore, the method is extremely advantageous to the simplification of a whole SI circulation system and the improvement of the thermal efficiency of the system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Unbiased estimation method for reaction kinetics rate constant based on spectrum
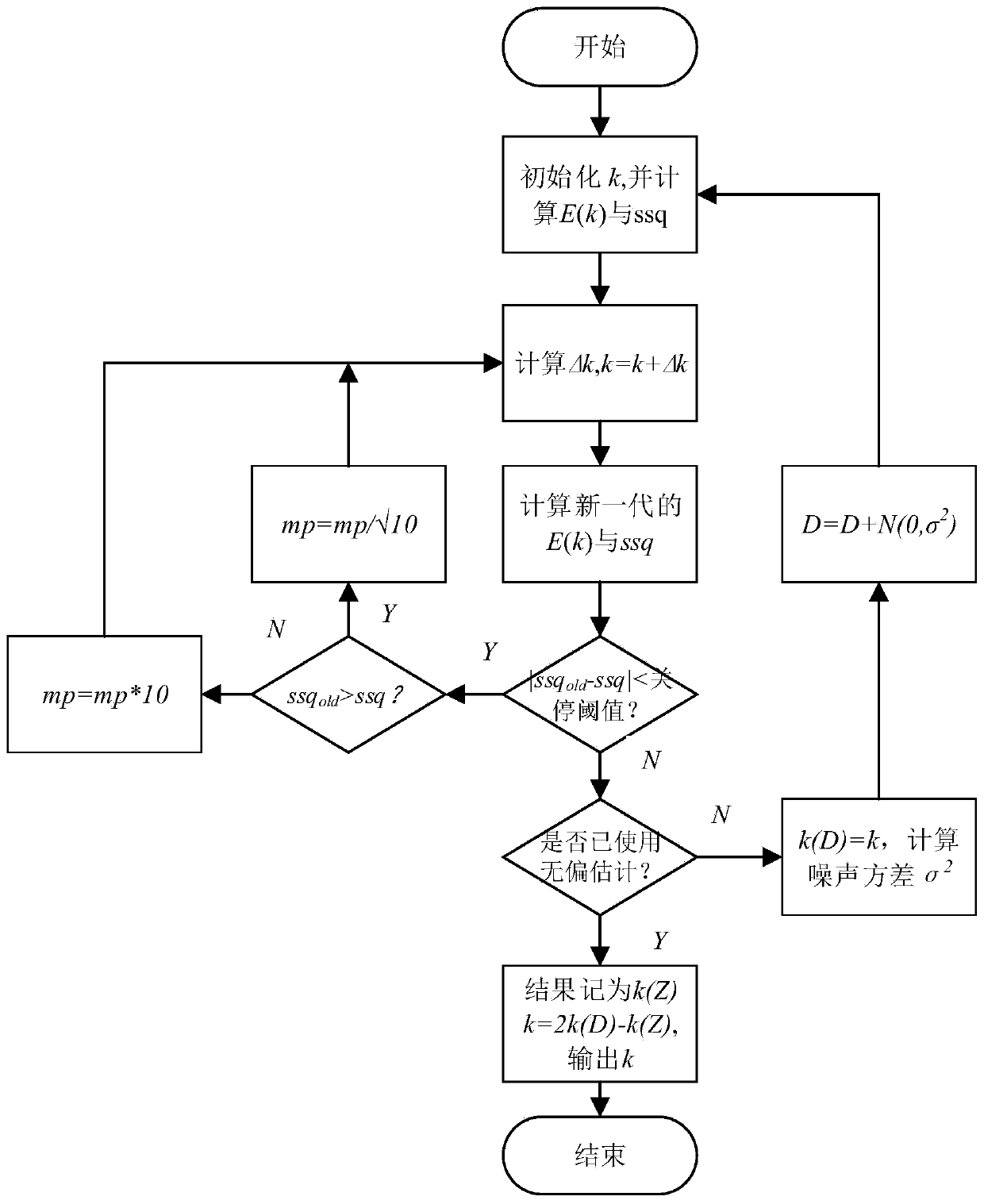
ActiveCN110514608AReaction kinetic rate constants are preciseColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical reaction kineticsKinetic rate
The invention provides an unbiased estimation method for a reaction kinetics rate constant based on the spectrum and belongs to the field of chemical reaction kinetics. The method comprises steps of firstly, constructing a spectral data structure, calculating a concentration distribution curve according to initial estimated values of initial concentrations of reactants and reaction kinetics rate constants, obtaining a spectral matrix, and comparing the spectral matrix with a measured spectral matrix to obtain an error matrix; adjusting an estimated value of the reaction kinetic rate constant according to the error matrix, recalculating the error matrix, and repeating iteration till the error reaches the minimum value; and lastly, estimating a noise variance by using the final error matrix,adding noise to the spectrum obtained by measurement, recalculating a reaction kinetics rate constant estimated value, and utilizing the unbiased estimation method to obtain the result which is closer to a real value. The unbiased estimation method is utilized, the method is independent of the pure spectrum and other information of reaction substances, the influence of noise is effectively reduced, and the obtained reaction kinetics rate constant is more accurate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for Estimating Binding Kinetic Rate Constants by Using Fiber Optics Particle Plasmon Resonance (FOPPR) Sensor
InactiveUS20130122608A1Quick testSimple and convenient and quick mannerScattering properties measurementsBiological testingFiberDecomposition
A method for estimating binding kinetic rate constants by using a fiber optic particle plasmon resonance (FOPPR) sensor mainly employs the steps of: providing a FOPPR sensor instrument system, obtaining optical signal intensities at an initial time and steady state signal intensities of first and second regions in an intensity versus time graph separately, substituting the measured signal intensity values into a formula derived by using a pseudo-first order rate equation model. According to this method, no fluorophore labeling is required. In addition, this method measures a temporal signal intensity evolution under static conditions as the samples are quickly loaded. As a result, unlike the conventional device where the sample is continuously infused, the method is able to measure binding and decomposition rate constants whose upper limit is not limited by a sample flow rate.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Method for Estimating Kinetic Rates
ActiveUS20120084017A1Chemical property predictionComputational theoretical chemistryKinetic rateEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for estimation of kinetic characteristics for the formation and dissociation of a complex using lateral flow. The present invention facilitates an easy to use method with high accuracy.
Owner:PHADIA AB
Apparatus and method for controlling kinetic rates for internal reforming of fuel in solid oxide fuel cells
ActiveUS7638226B2Promote reformSlow reaction rateHydrogenActive material electrodesFuel cellsKinetic rate
The present invention provides a solid oxide fuel cell in which kinetic rates for internal reforming are controlled. The solid oxide fuel cell comprises a cathode, an electrolyte layer adjacent to the cathode, and an anode adjacent to the electrolyte layer. The anode used in the cell of the invention includes a support structure which defines at least a portion of an anode flow channel and a catalyst that promotes reforming. The anode flow channel has an anode flow channel entrance for the introduction of fuel to the solid oxide fuel cell and an anode flow channel exit for removing unreacted fuel and / or by-products. The catalyst is dispersed within or upon the support structure such that the rate of reforming increases at increasing distances from the anode flow channel entrance. The present invention also provides a method of controlling internal reforming kinetic rates in a solid oxide fuel cell.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
Affinity chromatography-based method for measuring supramolecular interaction dissociation rate constant
The invention relates to an affinity chromatography-based method for measuring a dissociation rate constant, and especially aims at relatively extensive and relatively weak supramolecular interaction. The affinity chromatography-based method is a method for firstly fixing a host molecule and then measuring the host molecule, and comprises the following steps: under a certain temperature condition and at various flow rates, respectively acquiring chromatography flow curves of a first to-be-analyzed guest molecule and a second to-be-analyzed guest molecule on an affinity chromatography column which is bonded with a target host molecule, calculating retention time, half peak width and tower plate height by peak fitting, and calculating the dissociation rate constant. According to the method disclosed by the invention, special apparatus and equipment are not needed, and a normal chromatographic analysis method is adopted, so that the dynamic speed constant of the supramolecular weak interaction can be measured; meanwhile, the method can be combined with various detectors of ultraviolet rays, fluorescence, mass spectrum and the like to achieve unique advantages in detection of low-concentration drugs with poor water solubility as well as low-cost and quick measurement of supramolecular interaction dynamic parameters.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Asparaginase and treating diseases associated with asparagine dependence
Disclosed herein are polypeptides which exhibit asparaginase activity and little to no glutaminase activity. The polypeptides have sequences which correspond to W. succinogenes asparaginase, but have an amino acid residue other than proline at amino acid position 121. The polypeptides exhibit higher kinetic rates of asparaginase activity to glutaminase activity as compared to W. succinogenes asparaginase and Elspar®, an E. coli asparaginase.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
Method for obtaining ultra-low NOx emissions from gas turbines operating at high turbine inlet temperatures
ActiveUS20080098745A1Low oxygenSufficient oxygenTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionEquivalence ratioKinetic rate
A method of lowered NOx combustion is taught wherein the kinetic rate of NOx formation is reduced for a given combustion temperature in a gas turbine combustor. A supply of fuel is provided along with a supply of ambient air in sufficient quantity to form a fuel / air mixture having an equivalence ratio greater than about 0.55 when mixed with the fuel. The fuel / air mixture is mixed with a supply of cooled combustion gases in sufficient quantity such that the oxygen content of the resulting air mixture is less than about 18 percent. The resulting air mixture is then passed into the combustor.
Owner:PRECISION COMBUSTION
Method for obtaining binding kinetic rate constants using fiber optic particle plasmon resonance (FOPPR) sensor
ActiveUS9506861B2Simple and concise computationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorScattering properties measurementsFiberKinetic rate
A method for obtaining the binding kinetic rate constants using fiber optic particle plasmon resonance (FOPPR) sensor, suitable for a test solution with two or more concentrations, which employs the following major steps: providing one FOPPR sensor instrument system, obtaining optical time-resolved signal intensities starting at the initial time to the steady state of the two or more regions, substituting the measured signal intensity values into the formula which is derived by using the pseudo-first order rate equation model. In addition, this method measures the temporal signal intensity evolution under static conditions as the samples are quickly loaded. As a result, unlike the conventional device where the sample is continuously infused, the method is able to measure the association and dissociation rate constants of which the upper bounds are not limited by the sample flow rate.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Kinetic chlorine measurement
An aspect provides a method of determining a concentration of free chlorine in an aqueous sample, including adding a reagent to the sample, the reagent being reactive with the free chlorine at a first kinetic rate and reactive with at least one chloramine at a second kinetic rate, the first kinetic rate being different from the second kinetic rate; measuring an absorbance response over time resulting from reaction of the free chlorine and the at least one chloramine with the reagent over time; and determining the concentration of the free chlorine in the sample based on a determined rate of change of the absorbance response over time. Other aspects are described and claimed.
Owner:HACH CO
Novel Asparaginase and Treating Diseases Associated With Asparagine Dependence
Disclosed herein are polypeptides which exhibit asparaginase activity and little to no glutaminase activity. The polypeptides have sequences which correspond to W. succinogenes asparaginase, but have an amino acid residue other than proline at amino acid position 121. The polypeptides exhibit higher kinetic rates of asparaginase activity to glutaminase activity as compared to W. succinogenes asparaginase and Elspar®, an E. coli asparaginase.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
Quantitative methods for heterogeneous sample composition determination and biochemical characterization
InactiveUS20170220710A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelKinetic rate
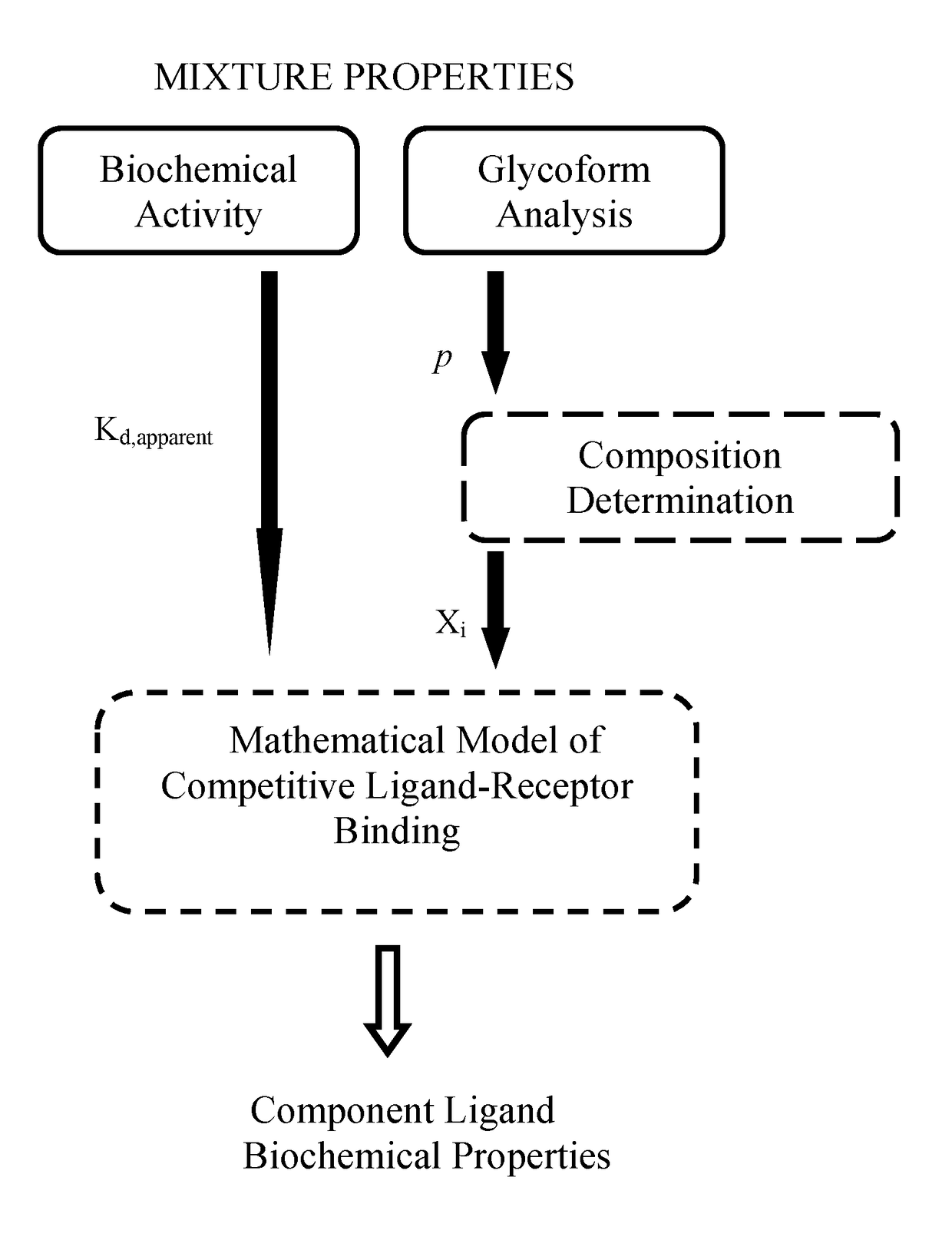
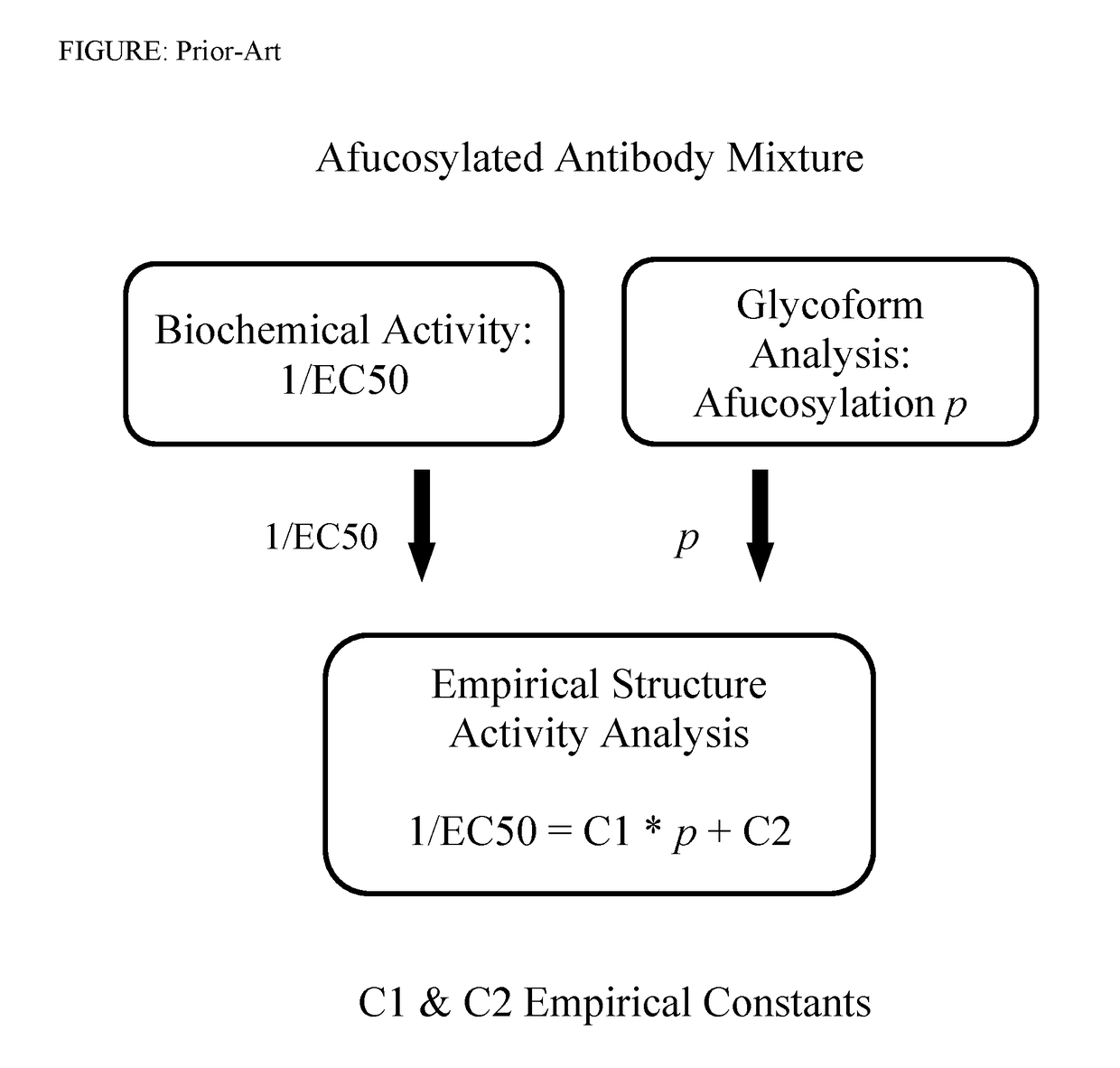
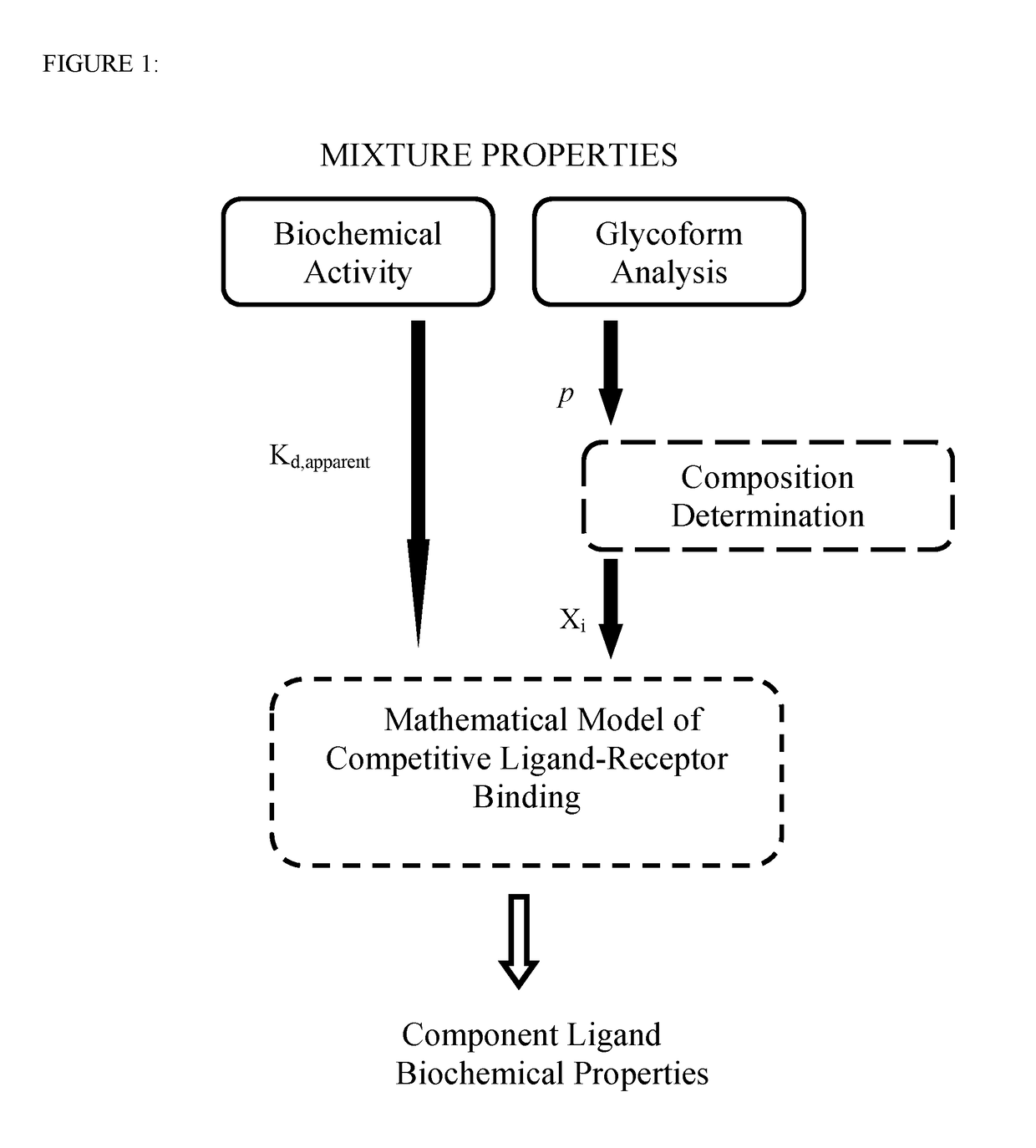
Methods involving the use of mathematical models of competitive ligand-receptor binding to characterize mixtures of ligands in terms of compositions and properties of the component ligands have been developed. The associated mathematical equations explicitly relate component ligand physical-chemical properties and mole fractions to measurable properties of the mixture including steady state binding activity, 1 / Kd,apparent or equivalently 1 / EC50, and kinetic rate constants kon,apparent and koff,apparent allowing; 1) component ligand physical property determination and 2) mixture property predictions. Additionally, mathematical equations accounting for combinatorial considerations associated with ligand assembly are used to compute ligand mole fractions. The utility of the methods developed is demonstrated using published experimental ligand-receptor binding data obtained from mixtures of afucosylated antibodies that bind FcγRIIIa (CD16a) to: 1) extract component ligand physical property information that has hitherto evaded researchers 2) predict experimental observations and 3) provide explanations for unresolved experimental observations.
Owner:CHUNG JOHN DAVID +1
A non-noble metal morphology-controllable oxygen evolution catalyst cunis 2
InactiveCN105148943BImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectronic transmissionKinetic rate
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method and system for determining dissociation rate constant based on affinity chromatography
The invention discloses a method and system for determining dissociation rate constant based on affinity chromatography, and belongs to the technical field of affinity chromatography. The method comprises the following steps: S1, taking a proper amount of meloxicam reference substances, adding methanol to prepare 0.25 mg / mL of a meloxicam stock solution, taking a proper amount of the meloxicam stock solution, and diluting with a mobile phase to obtain 2.5 mu g / mL of a meloxicam test substance solution for later use; S2, taking a proper amount of an acetaminophen reference substances, adding methanol to prepare 1.2 mg / mL of an acetaminophen stock solution, taking a proper amount of the acetaminophen stock solution, and diluting with a mobile phase to obtain 0.45 mu g / mL of an acetaminophentest substance solution for later use; and S3, taking a proper amount of uracil reference substances. The kinetic rate constant of supramolecular weak interaction can be measured by using a conventional chromatographic analysis method, and the method and system for determining the dissociation rate constant based on affinity chromatography have unique advantages in the aspects of detection of drugs with low concentration and poor water solubility and low-cost and rapid determination of supramolecular interaction kinetic parameters.
Owner:李雪明
Method for analyzing dynamic transferred water quality based on fugacity theory
The invention disclose a method for analyzing dynamic transferred water quality based on a fugacity theory, relating to a water quality analysis method, and solving the problem of larger deviation between a simulated result and an actual condition caused by actually unobtainable required parameters and randomly non-modifiable inner parameters in a traditional water quality analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, confirming environment facies of a water area to be detected and acquiring geographic information parameters of the water area to be detected, environmental parameters of various environment and materialization parameters of a target pollutant; then computing fugacity capacity of each environmental facies, speed constant of reaction dynamics and transfer parameters among each environmental face; then establishing a system of differential equation by taking the fugacity of each environmental face as an unknown and solving the system of differential equation through a Runge-Kutta algorithm to obtain the fugacity of each environmental face; and calculating out pollutant concentration by the fugacity of each environmental facies and the fugacity capacity. The invention overcomes defects of the prior art, and can be applied to the field of analyzing transferring transformation of organic pollutants in the water area and distribution law of multi-medium environment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com