Method for analyzing dynamic transferred water quality based on fugacity theory
A technology of dynamic migration and water quality analysis, applied in the direction of testing water, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of deviation of simulation results and inability to obtain internal parameters, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0012] Specific implementation mode one: the dynamic migration water quality analysis method based on the fugacity principle of the present embodiment, its process is as follows:
[0013] 1. Determine the various environmental phases of the water area to be tested, measure and obtain the geographic information parameters of the water area to be measured, and the environmental parameters of each environmental phase in each environmental phase; determine the target pollutants, and obtain the physical parameters of the target pollutants and chemical parameters;
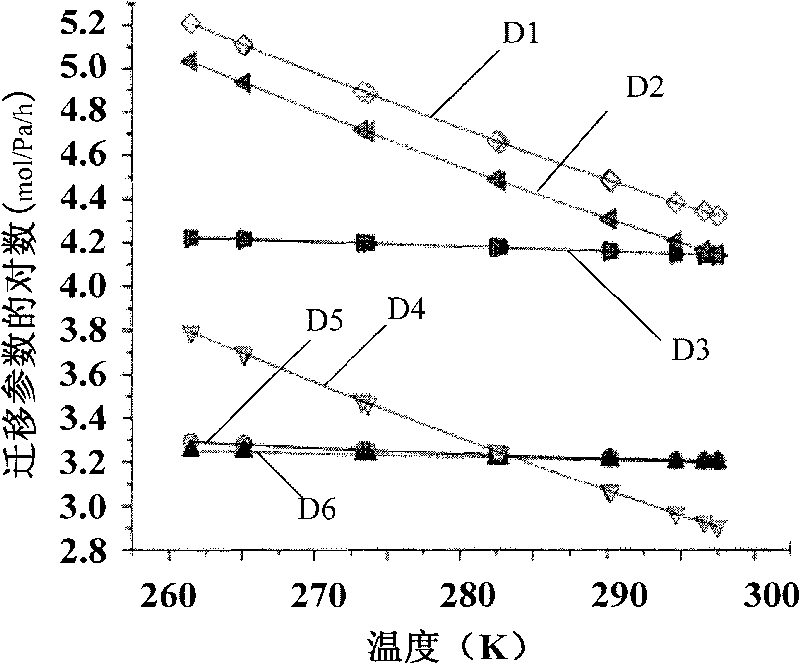
[0014] 2. Calculate and obtain the fugacity capacity of each environmental phase according to all parameters obtained in step 1; then calculate and obtain the reaction kinetics of each environmental phase by the fugacity capacity of each environmental phase obtained and all parameters obtained in step 1 The rate constants are used to obtain the migration parameters between the various environmental phases;
[0015] 3. U...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0059] Specific implementation mode two: this implementation mode is a specific embodiment for realizing specific implementation mode one:
[0060] In this example, the water area to be tested is the water area from Sancha River to Tongjiang River, the main stream of Songhua River. Assuming that a water pollution emergency occurs in Sancha River, it is determined that its environmental phases include air phase, water phase, soil phase and sediment phase. Environmental phase, measure and obtain the geographic information parameters of the river section and the environmental parameters of the above four environmental phases. The target pollutant is determined to be 2,4-DCP, and the physical and chemical parameters of the target pollutant are obtained, wherein the concentration of the pollutant entering the water body is 10.0 mg / L, and it migrates downward with the water flow.
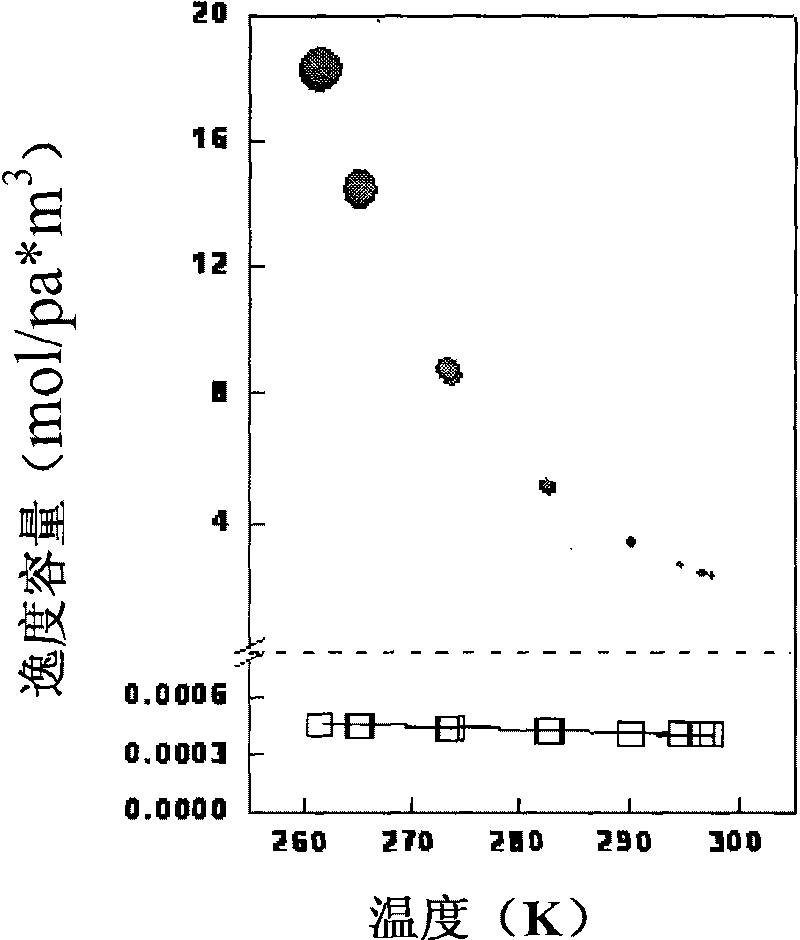
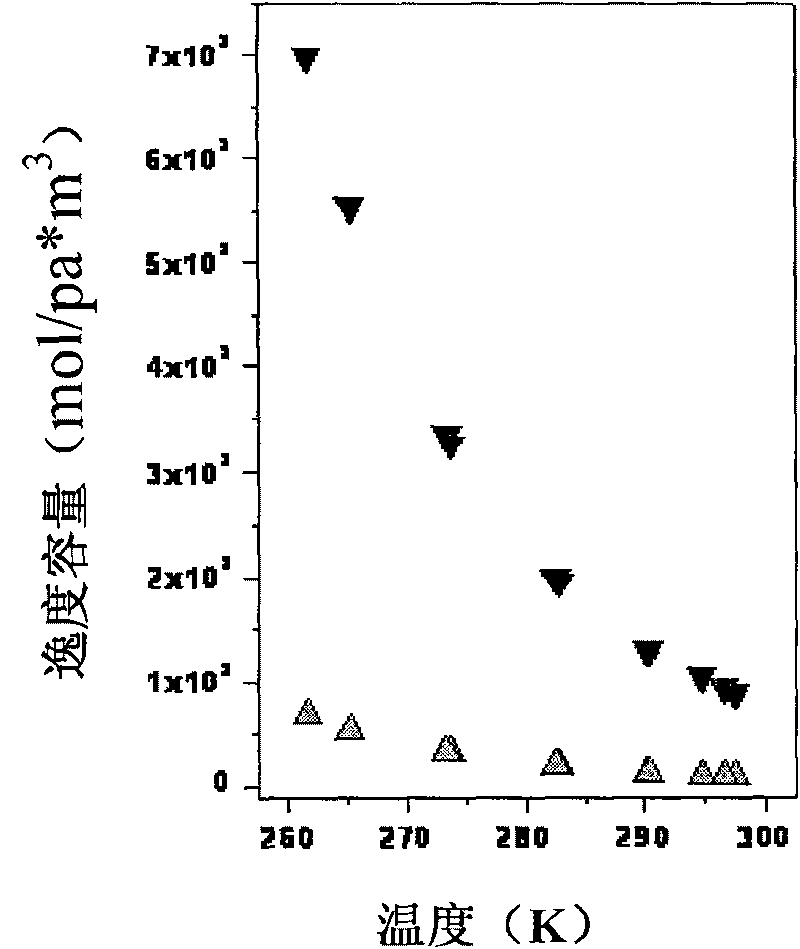
[0061] Calculate the fugacity capacities of the four environmental phases, and calculate and obtain th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com