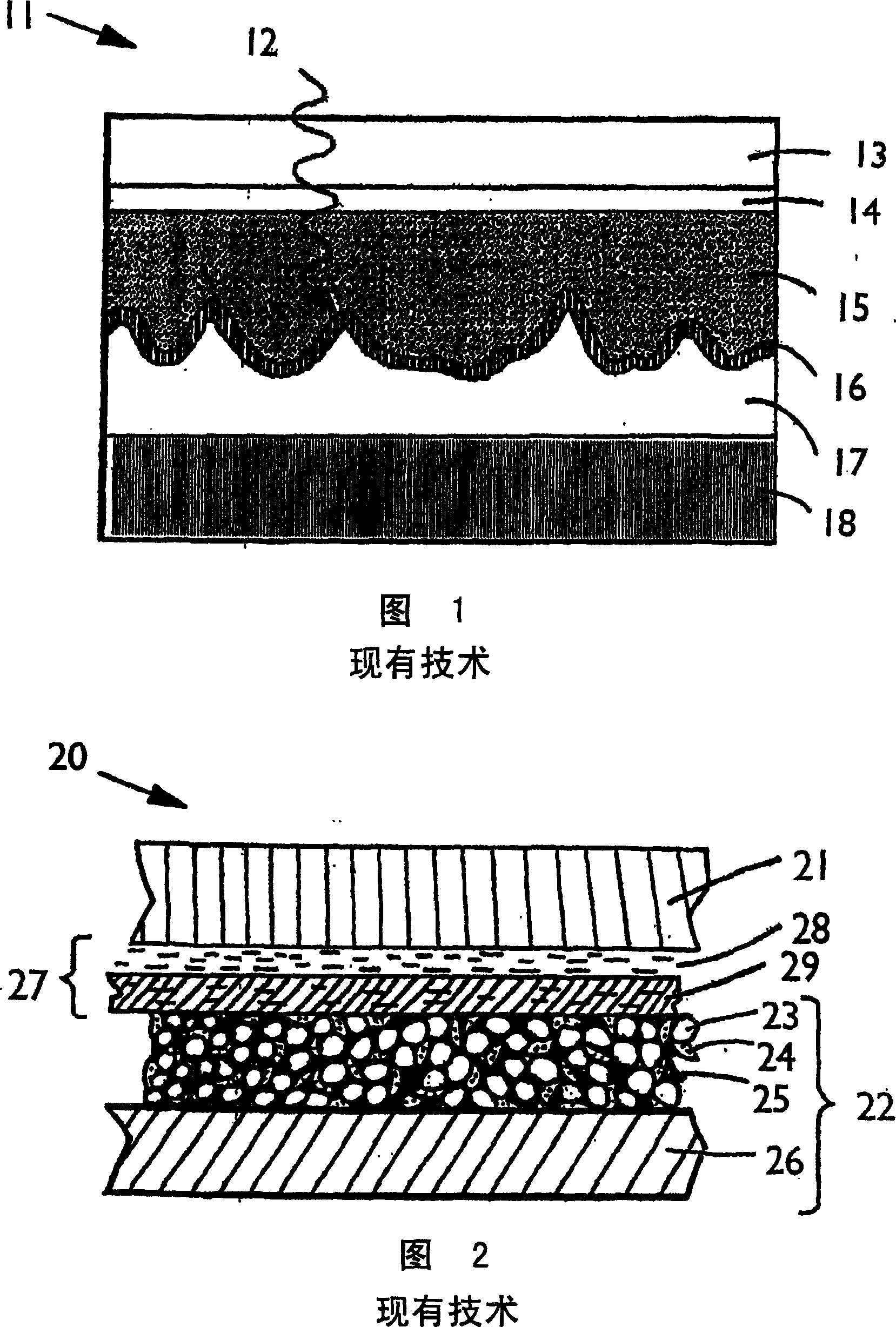
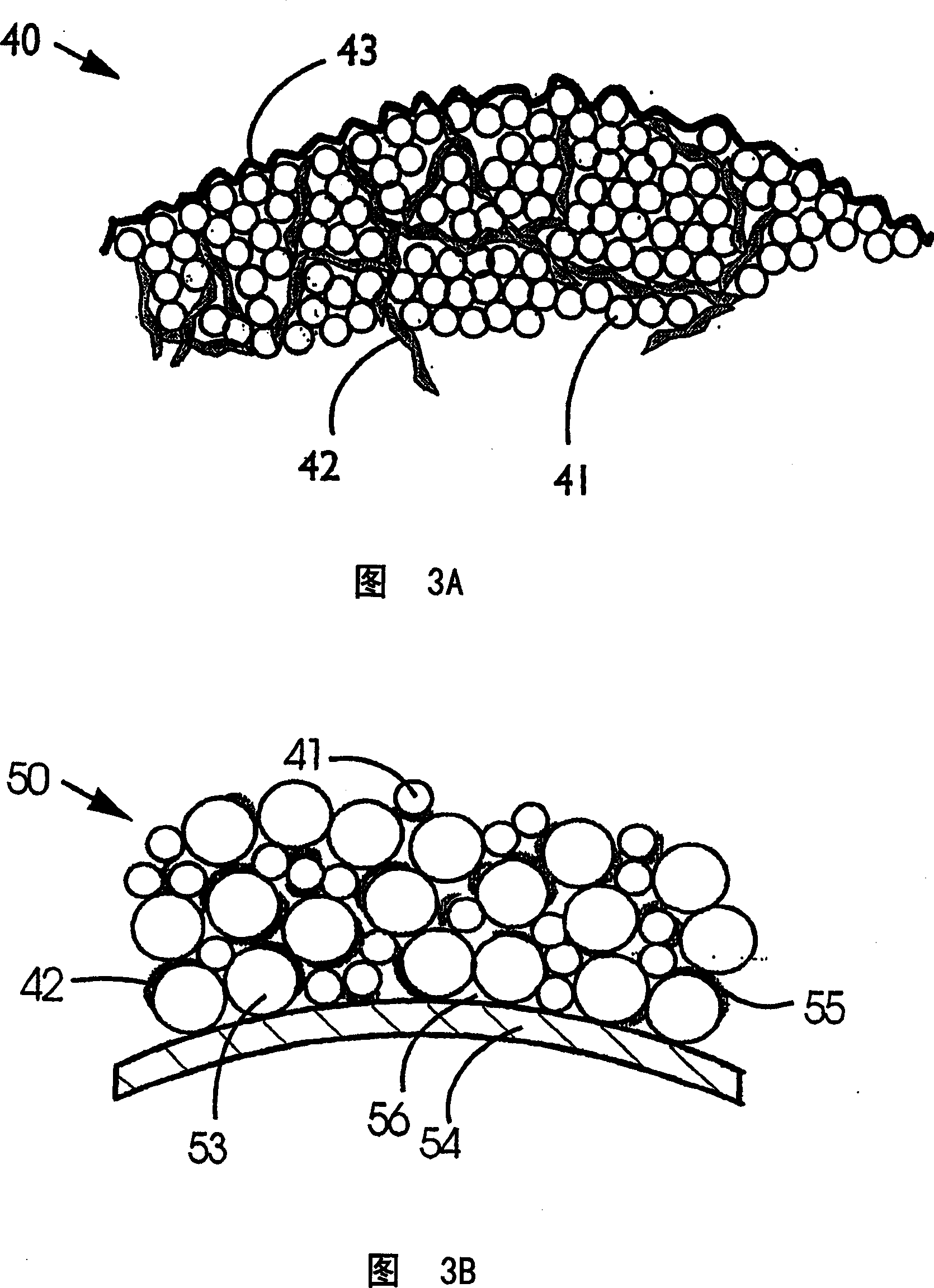
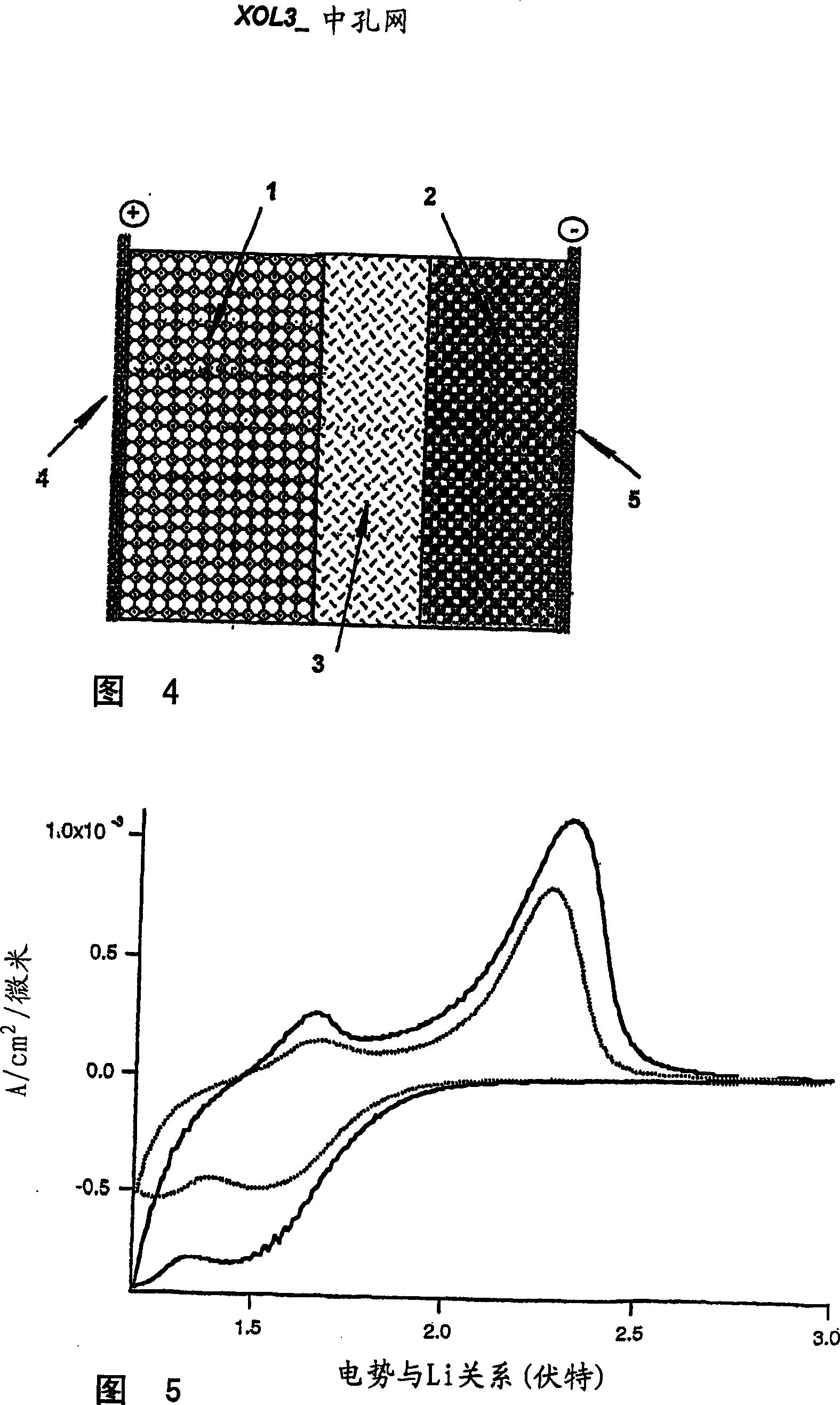
Mesoporous network electrode for electrochemical cell
An electrochemical and electrode technology, applied in the field of electrochemical cells, can solve problems such as limiting application fields
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0077] During the casting mix preparation step, the nanoparticles are mixed with a volatile carrier that does not dissolve the linking polymer or dye. Examples of such carriers are water, dibutyl phthalate, dioctyl phthalate, and acetates, ethylene carbonate, octene carbonate, tributyl phosphate, decalinone, diethylene glycol Such mixing of methyl ether and low molecular weight polymer is necessary to obtain a composition with the desired rheological properties. Finally, the composition is cooled or heated to form a coatable material. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that certain adjustments to the viscosity and rheological properties of the solution may be necessary to suit the particular technique employed, which can be achieved by varying the molecular weight and / or concentration of the carrier. adjustment.
[0078] In the casting step, the discrete particles can be cast on a suitable substrate (such as a metal or transparent conductive oxide electrode) by any atta...
example 1
[0095] Example 1 Preparation of aqueous titanium dioxide dispersion
[0096] 24.5 g of nanocrystalline TiO were purchased from FranKfurt am Main, Germany; Degussa-Huls AG; 2 (P-25, mainly anatase), dispersed it in 170 g of deionized water at 40°C, and then placed the mixture under ultrasonic waves for several minutes. Next, the pH of the dispersion was adjusted to 4.5 by adding an aliquot of 1% by weight KOH in water. Repeat the sonication and add more water to reach a final weight of 200g. Thus, the prepared dispersion contained 12.5% by weight of TiO 2 .
example 2
[0097] Example 2 Preparation of pastes for use as coating solutions
[0098] 65.04 g of the dispersion prepared as described in Example 1 were mixed with 7.2 g of deionized water at a temperature of 40°C. A 7.5% by weight aqueous solution of polyethylene glycol (average molecular weight 100,000, purchased from Frank Chemical Industries, Bachs, Switzerland) was added, and then the total weight of the solution was brought up to 80 g by adding water. Finally the solution was homogenized by sonication.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com