Patents
Literature
322 results about "Chloramine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chloramines refer to derivatives of ammonia and organic amines wherein one or more N-H bonds have been replaced by N-Cl bonds. Two classes of compounds are considered, inorganic chloramines and organic chloramines.
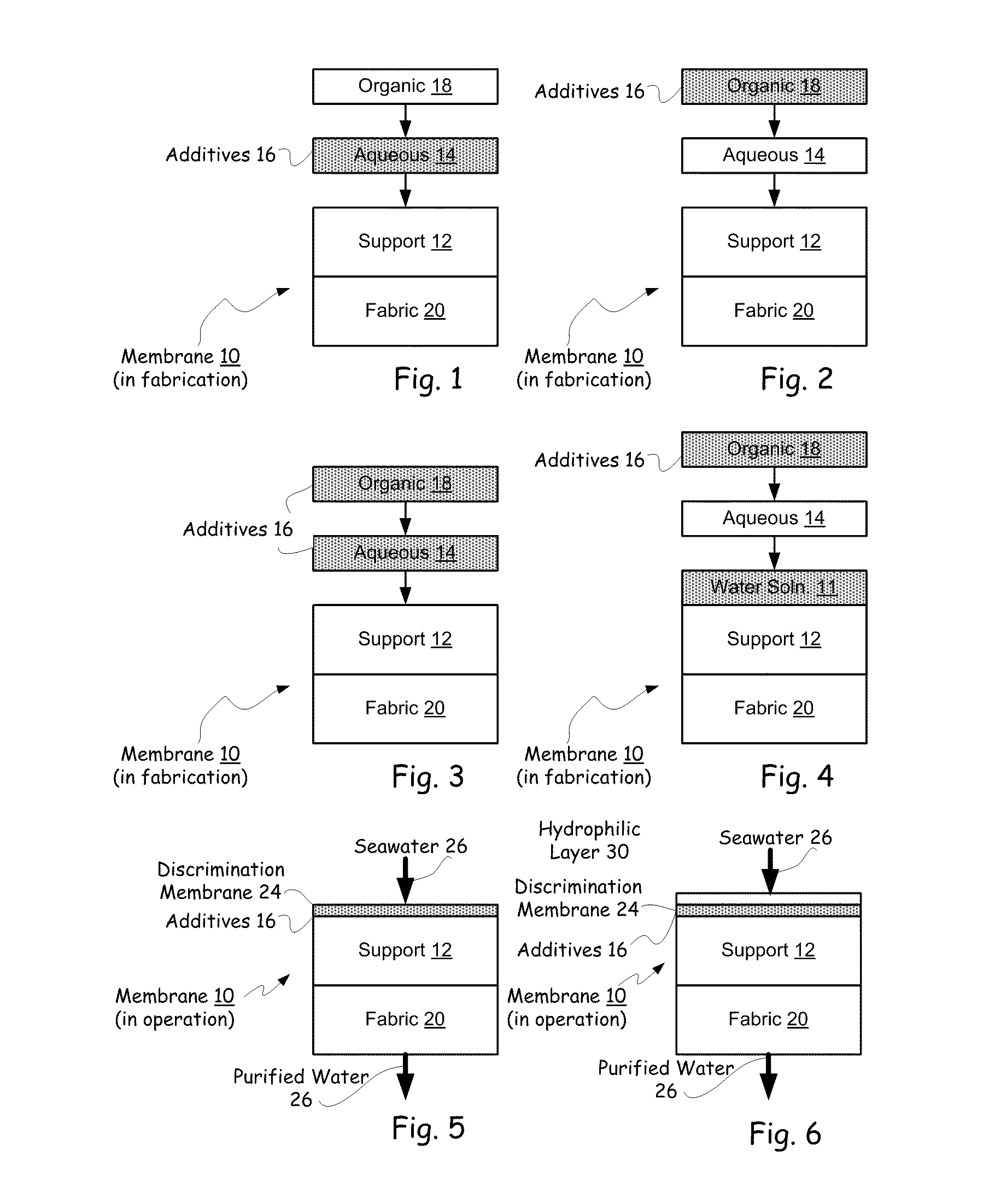
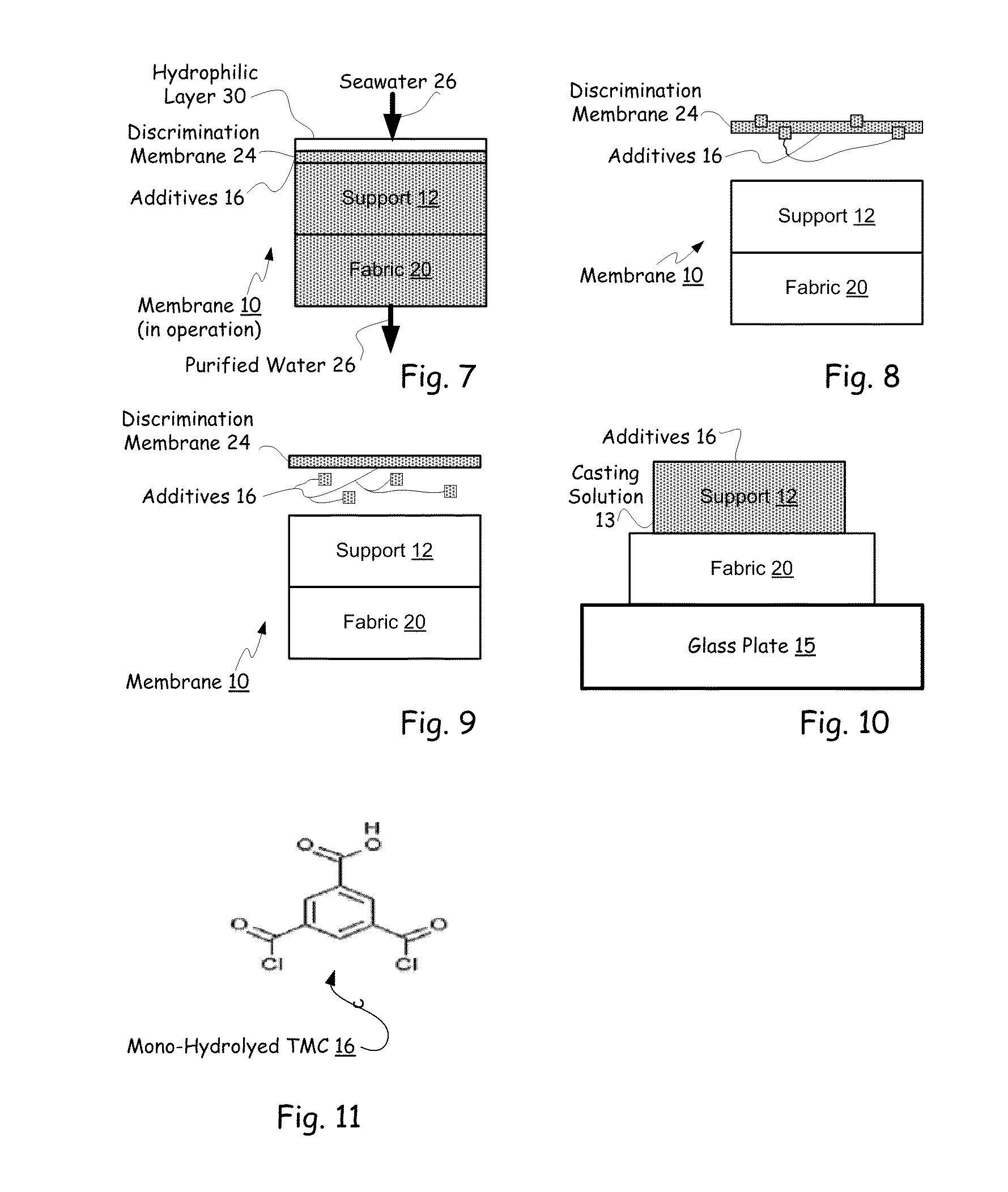
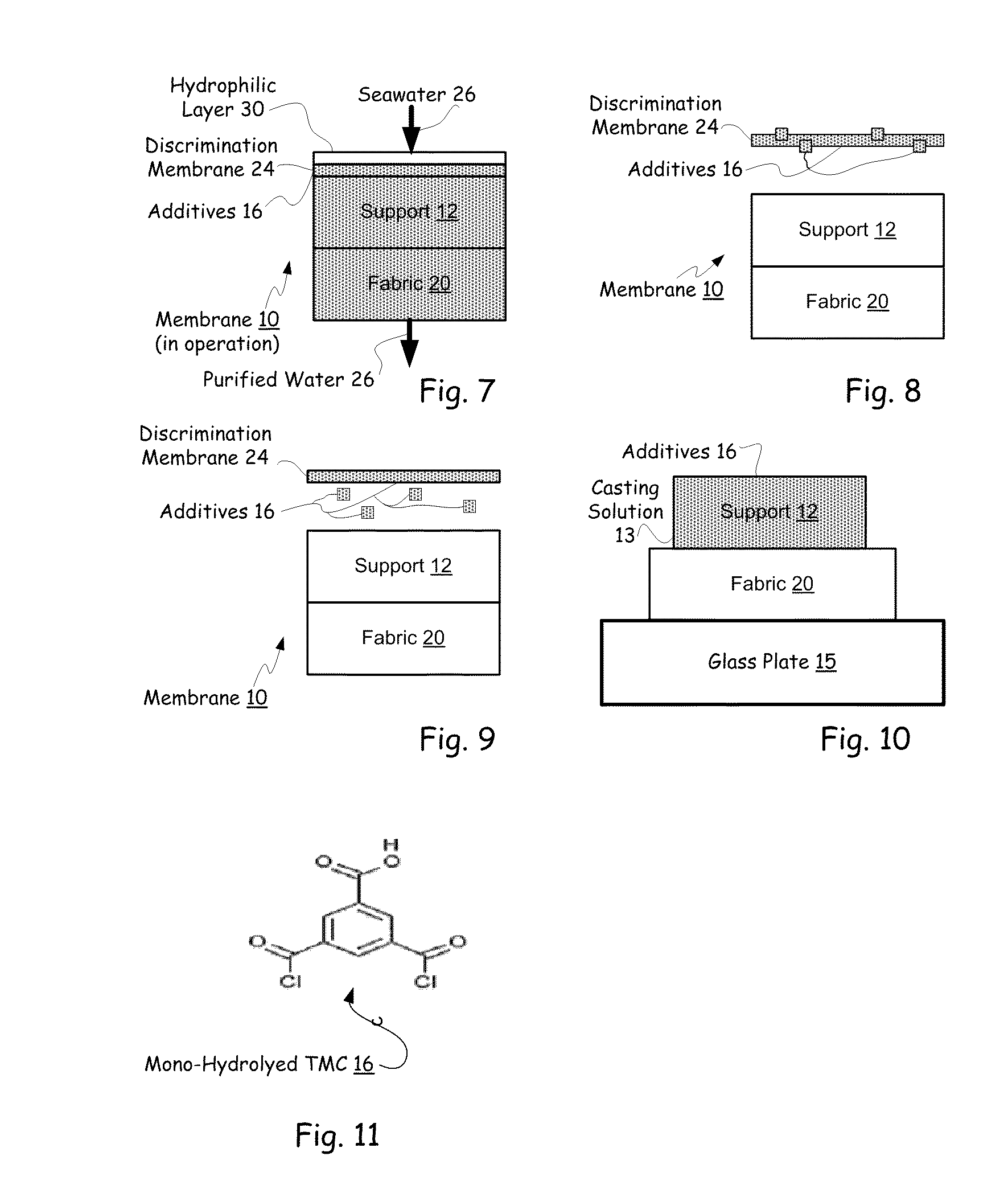
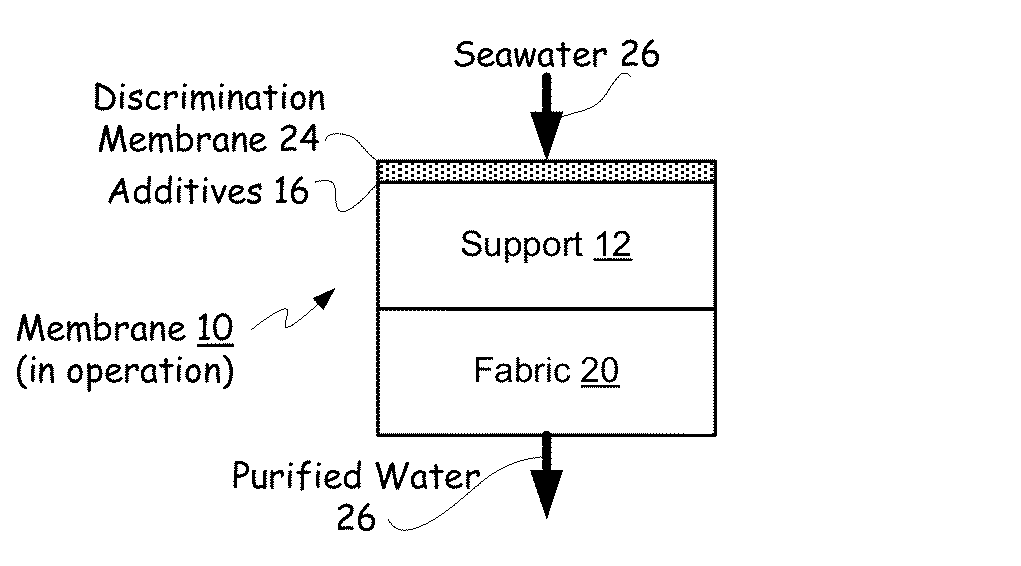
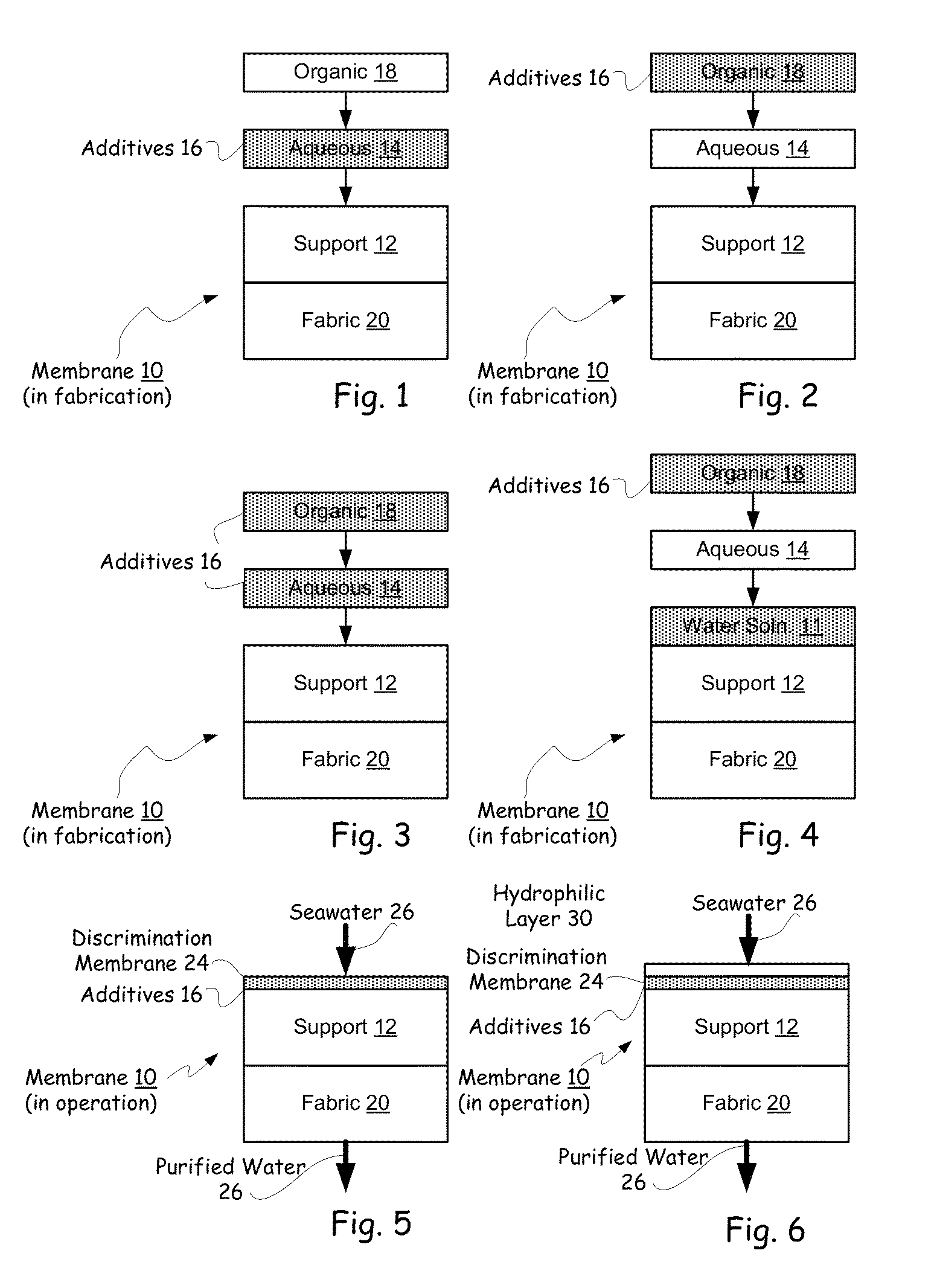
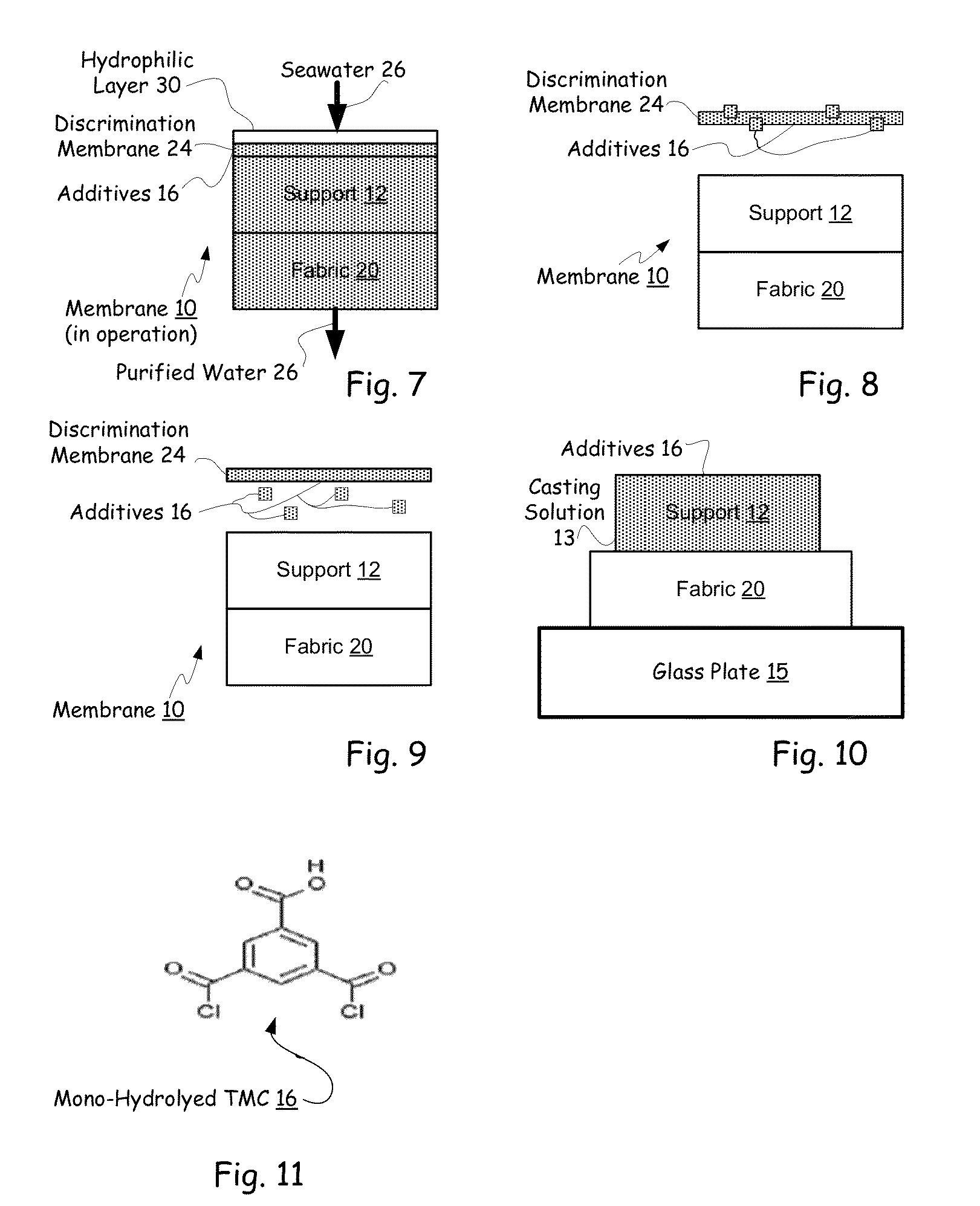
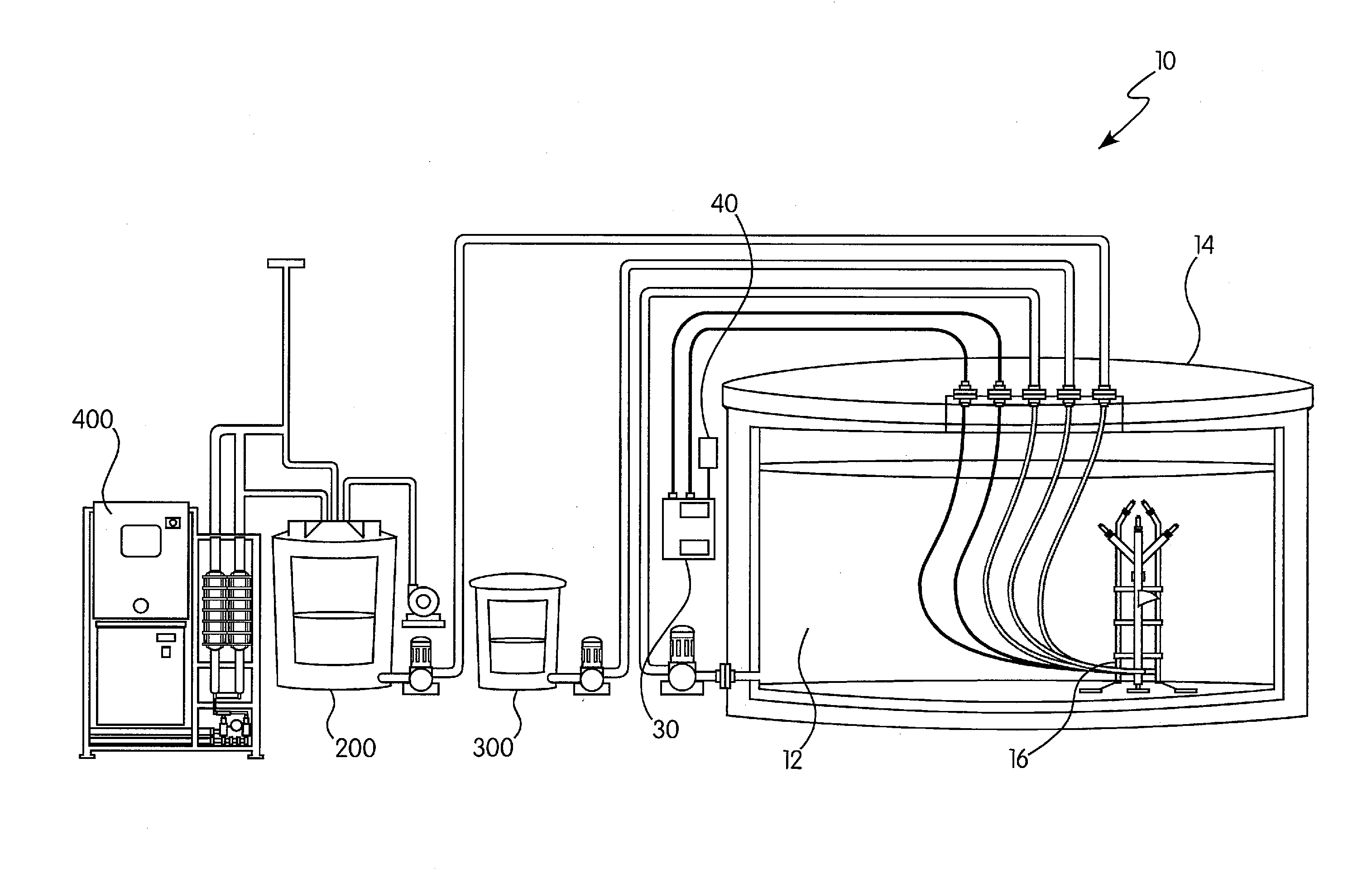
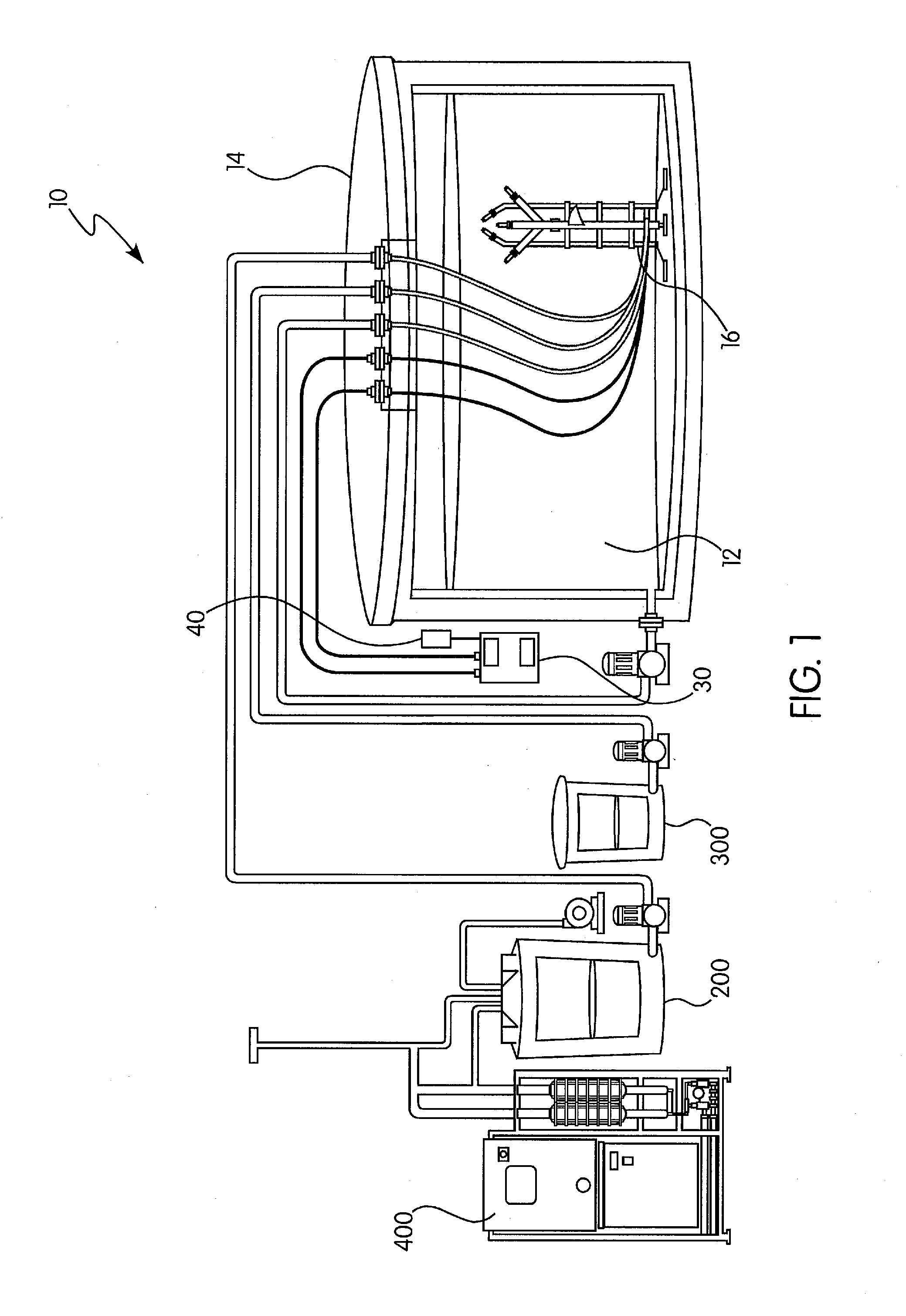
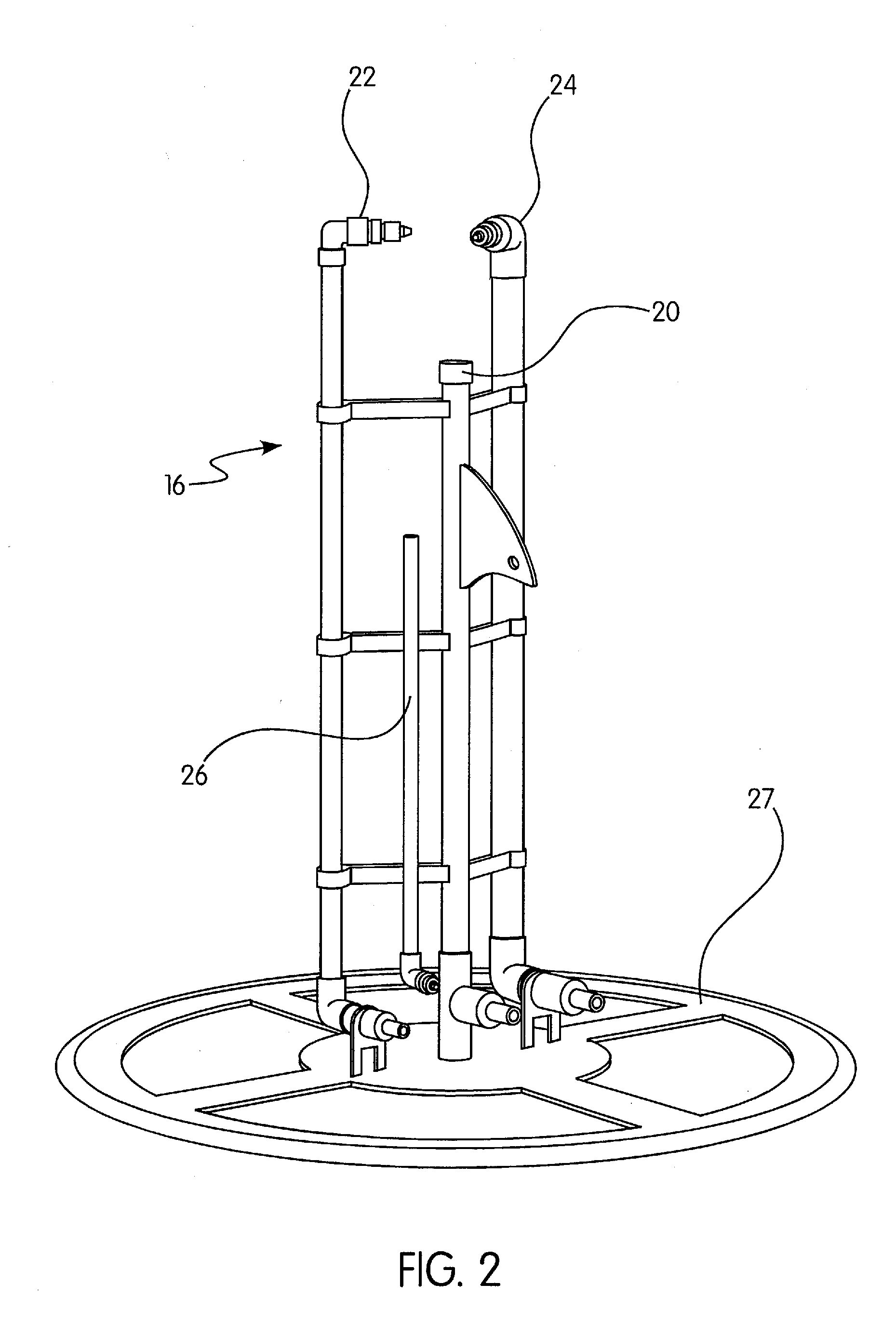
Hybrid tfc ro membranes with nitrogen additives
ActiveUS20110005997A1Increase fluxIncreased rejectionMembranesPretreated surfacesChloramine BAlkaline earth metal
Owner:NANOH2O
Treatment of swimming pool water
InactiveUS6146539AEasy to controlReduction of unpleasant chloraminesSeparation devicesSedimentation separationAlgal growthPhosphate
Methods and compositions are disclosed for treating swimming pool waters in order to remove one or more nutrients necessary for algal growth and to accelerate the breakdown of objectionable chloramines within chlorinated pool waters. The target nutrients of preference are those containing phosphorus or nitrogen. Phosphorus nutrients are preferably removed by ion-exchange with finely divided lanthanum carbonate, or by direct precipitation in the pool with liquid lanthanum chloride. Nitrogen nutrients (including, in particular, chloramines) may be removed (possibly with the aid of catalysts and in separate reactors). The same reagents used to scavenge phosphates are useful in this regard, the nitrogen being released from the pool water as a nitrogenous gas. To allow the fine lanthanum carbonates to be conveniently handled in the pool environment, they may be linked to larger carrier particles, such as those of diatomaceous earth, or they may be embedded within porous beads formed from polymers or gels. In this form the reagent can be either added to, retained within and backwashed from pool filters, or added directly to pools (with or without a flocculating agent) and sucked to waste after settling. A variety of formulations for these purposes is disclosed.
Owner:NATURAL CHEM
Hybrid TFC RO membranes with nitrogen additives
ActiveUS8567612B2Inhibits biofilm formationMembranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisChloramine BAlkaline earth metal
RO membranes using chlorinated water as a feed stream maybe protected from damage by the chlorine with a protective layer including reactive nitrogen which forms chloromines on the surface of the membrane that reduce chlorine penetration. This protective layer also provides substantial anti-fouling capabilities, whether used with a chlorinated or unchlorinated feed stream because the chloramines are anti-bacterial. Although chlorine is lost in use, the anti-fouling layer or coating can be recharged with additional chlorine without damaging the discrimination layer. The anti-fouling layer or coating may be advantageously used with Thin film composite, TFC, membranes for use in forward and reverse osmosis may include nanoparticles, monohydrolyzed and / or di-hydrolyzed TMC, and / or alkaline earth alkaline metal complexes or other additives.
Owner:NANOH2O
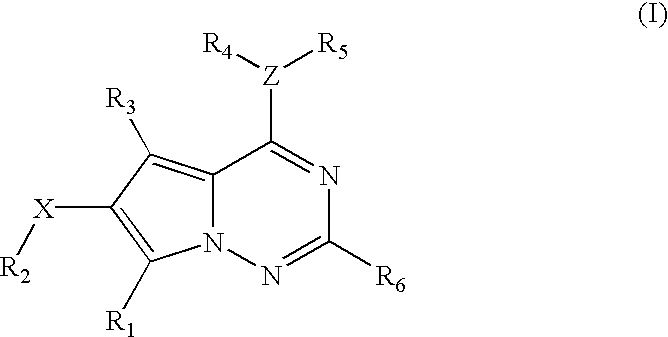
Methods for the preparation of pyrrolotriazine compounds useful as kinase inhibitors
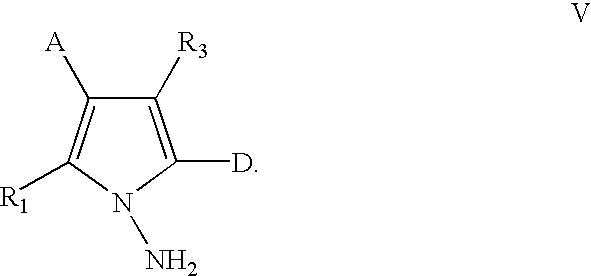
Methods of preparing kinase inhibiting pharmaceutical compounds having the formula (I): or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein R1 through R6 and Z are as described in the specification. The methods according to the invention utilize an amination process, in which a pyrrole is reacted with a haloamine, preferably chloramine. This step is followed by cyclization to form the pyrrolotriazine core.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Pathogen reduction using chloramines
InactiveUS20050211643A1Good effectEasy to receiveWaste water treatment from animal processingWater/sewage treatment by substance additionMicroorganismChloramine B
A method and apparatus for implementing pathogen reduction within a poultry processing or food processing plant that uses water that has been treated with chloramines at an advantageous dosage before being introduced to the production process at processing steps. The water treated with chloramines may be from a fresh water source or reclaimed water from the processing plant. The reintroduction of the treated reclaimed water advantageously causes a dramatic reduction in the levels of microorganisms associated with poultry processing, while substantially conserving water use.
Owner:ZENTOX CORP
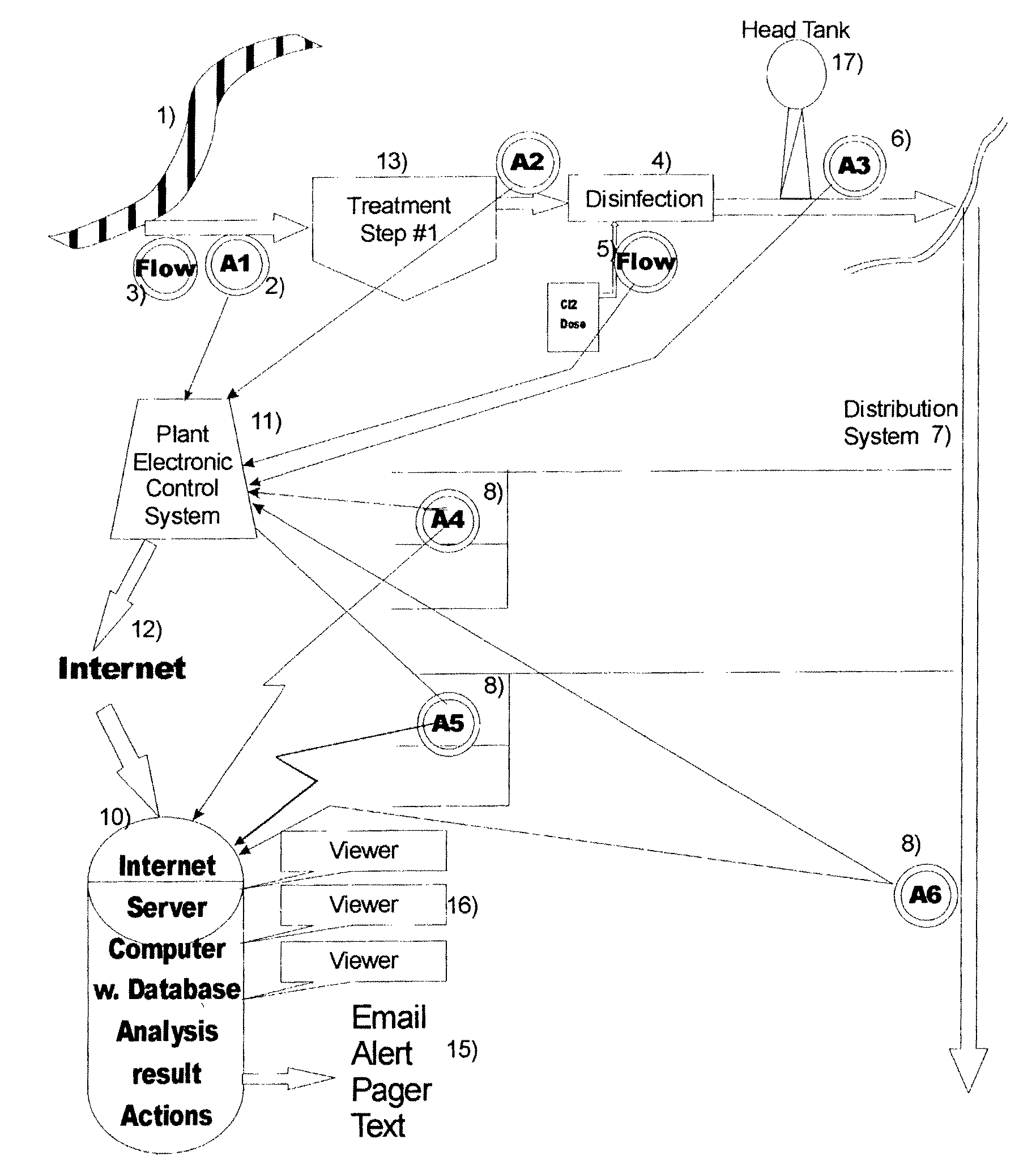
Anti-terrorism water quality monitoring system
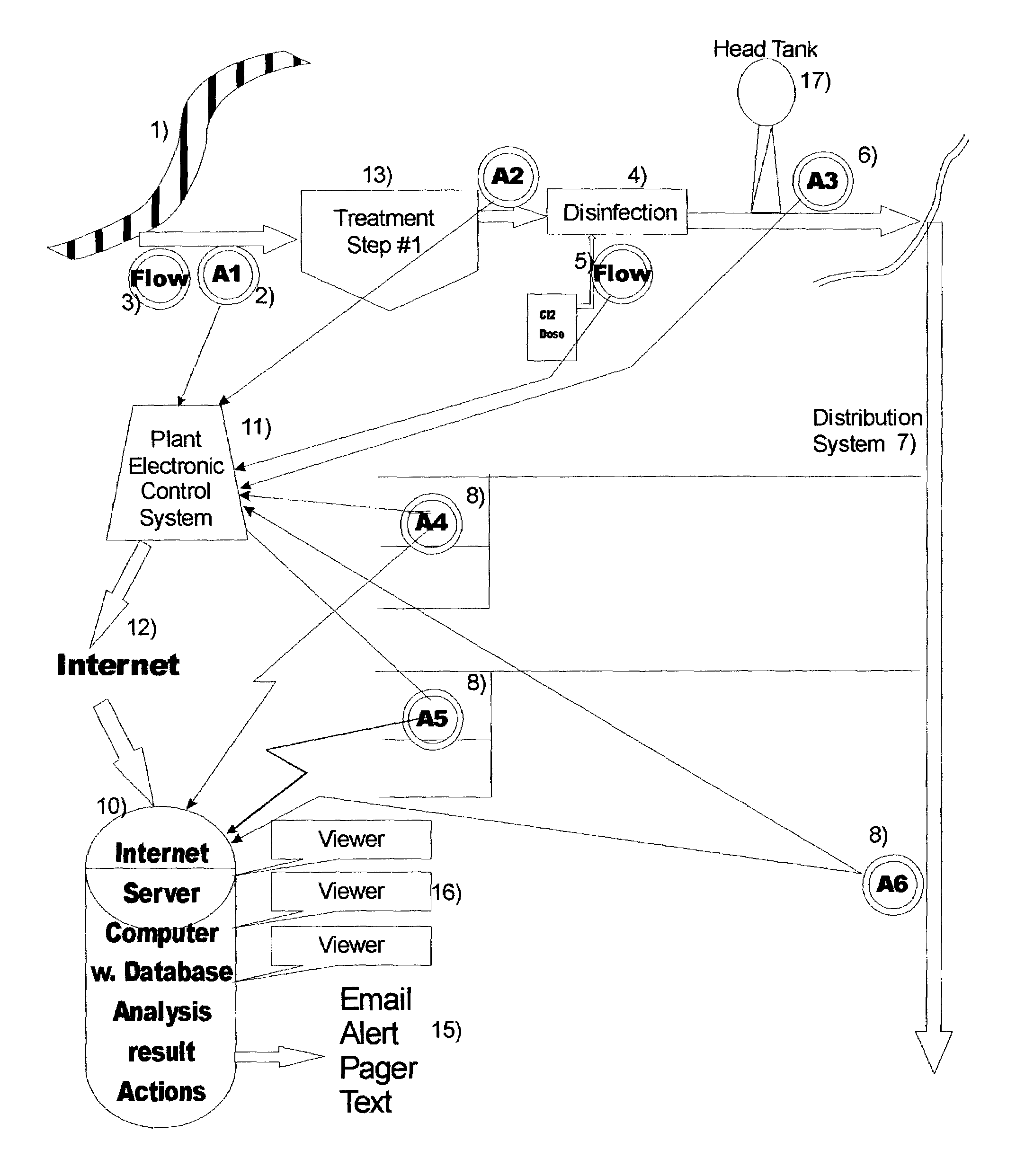
InactiveUS7454295B2Prevent hackingRule out the possibilityGeneral water supply conservation2D-image generationChloramine BChlorine dioxide
An Anti-Terrorism water quality monitoring system for continuously monitoring a potable water treatment system and related potable water distribution network that provides potable water to a municipality, city, housing development or other potable water consumer. The system includes the collection of data from the water distribution system and from the water treatment facility and from advanced separation processes which are integrated into analytical instruments. The data collected are stored in a remote database on a remote server computer or bank of computers and accessible by Homeland Security or its designated agency. Preferred parameters of monitoring include the turbidity and disinfectant such as chlorine, hypochlorous acid, sodium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite, ozone, chlorine dioxide, chloramines, hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid.
Owner:HACH CO
Methods for the on-site production of chloramine and uses thereof
A method of producing stable disinfectant for use as a biocidal composition. The method comprises: A) providing reagents, B) asynchronously feeding the at least two of the reagents into a wide space, and C) allowing all the reagents to conic into contact and mix with each other. The reagents comprise: a) an amine source of disinfectant in concentrated form, b) an oxidizing halogen compound in concentrated form, and c) a diluent. The use of asynchronous feeding and a wide space results in a dynamic biocide regimen. This regimen results in a changing environment that infestations have difficulty adapting to. This method also imparts superior results due to the avoidance of channeling effects which would otherwise weaken the effects of the biocide.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Activated carbon and use therefor
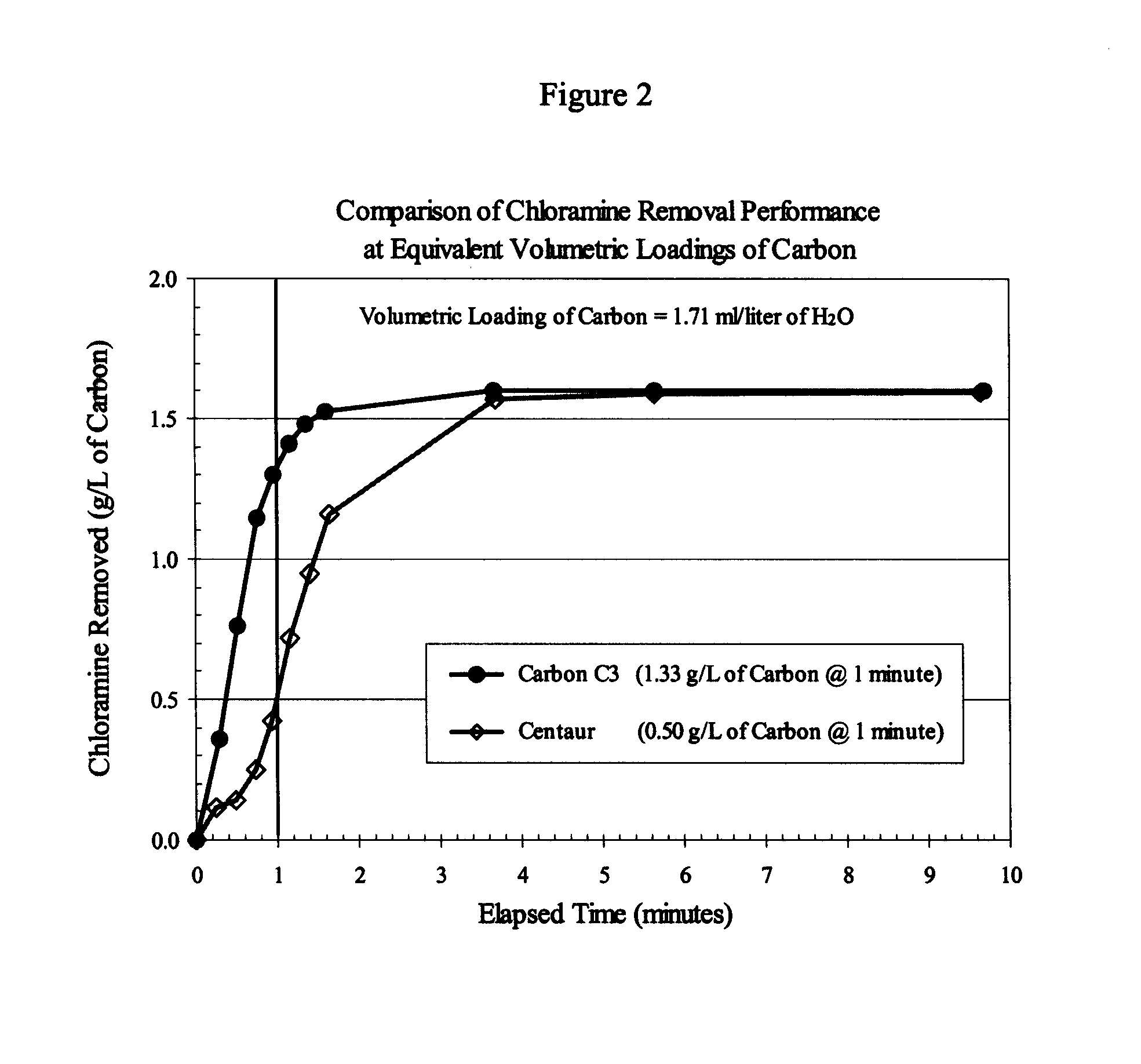
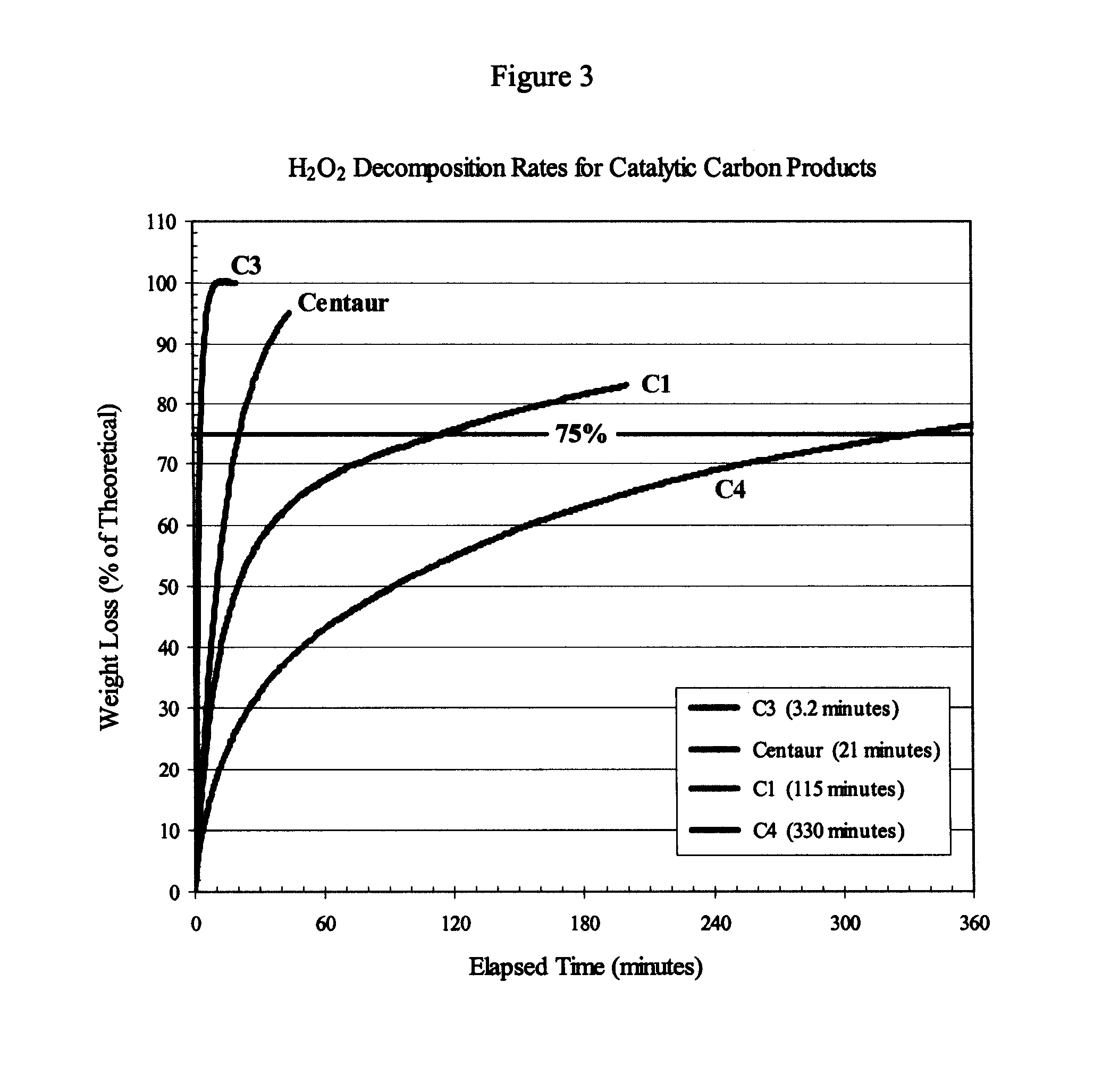
ActiveUS20130023405A1High catalytic activityEfficient decompositionPhysical/chemical process catalystsCarbon compoundsChloramine BActivated carbon
An activated carbon having a high catalytic activity as an oxidation catalyst or a decomposition catalyst, and use therefor are provided.The activated carbon has (a) an oxygen content in a range from 1.40 to 4.30% by mass, (b) a nitrogen content in a range from 0.90 to 2.30% by mass, (c) a sulfur content in a range from 0.50 to 1.20% by mass, and (d) a hydrogen content in a range from 0.40 to 0.65% by mass. The activated carbon may have at least one characteristic of (e) an amount of an acidic surface functional group of 0.10 to 0.36 meq / g, (f) an amount of a basic surface functional group of 0.50 to 1.30 meq / g, and (g) a benzene adsorption capacity of 25 to 50%. The activated carbon catalyzes an oxidation reaction of N-(phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid with a peroxide (e.g., hydrogen peroxide) and achieves an efficient production of N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine even after repetitive use. The activated carbon also efficiently decomposes a chloramine.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Dental Appliance Cleansing Composition
ActiveUS20090042756A1Effective compositionEasy to cleanInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideChloramine BAlkaline earth metal
A novel and safe composition has been discovered that is effective for cleaning dental appliances (e.g. removable braces, retainers, dentures, etc.). This composition bleaches, disinfects, and deodorizes the appliance, while removing plaque that has accumulated on the appliance during wear. The composition comprises a chloramine bleaching agent that liberates hypochlorous acid upon contact with water, a surfactant, a water-soluble carboxylic acid and an alkaline base to produce effervescence and regulate pH, a sequestering agent for alkaline earth metal ions, a drying agent, and an indicator dye that signifies the end of the cleansing process. In a preferred method of using this invention, the premixed components are added to water, and the dental appliance is submerged in the resulting effervescent solution until a color change indicates that cleaning is complete. This invention provides a safe, effective, and convenient method for cleansing and disinfecting dental appliances.
Owner:LMA SOLUTIONS
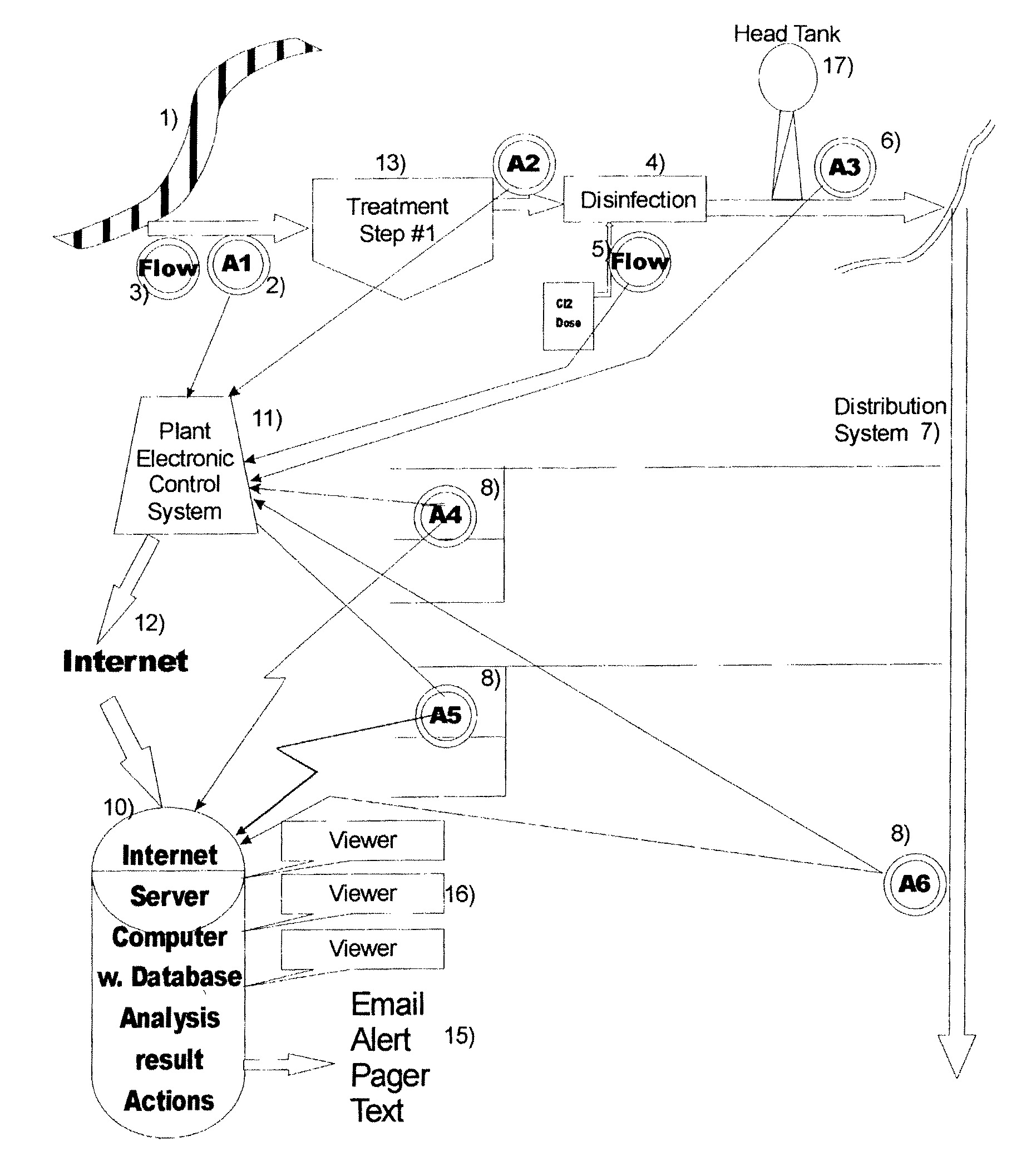
Anti-terrorism water quality monitoring system
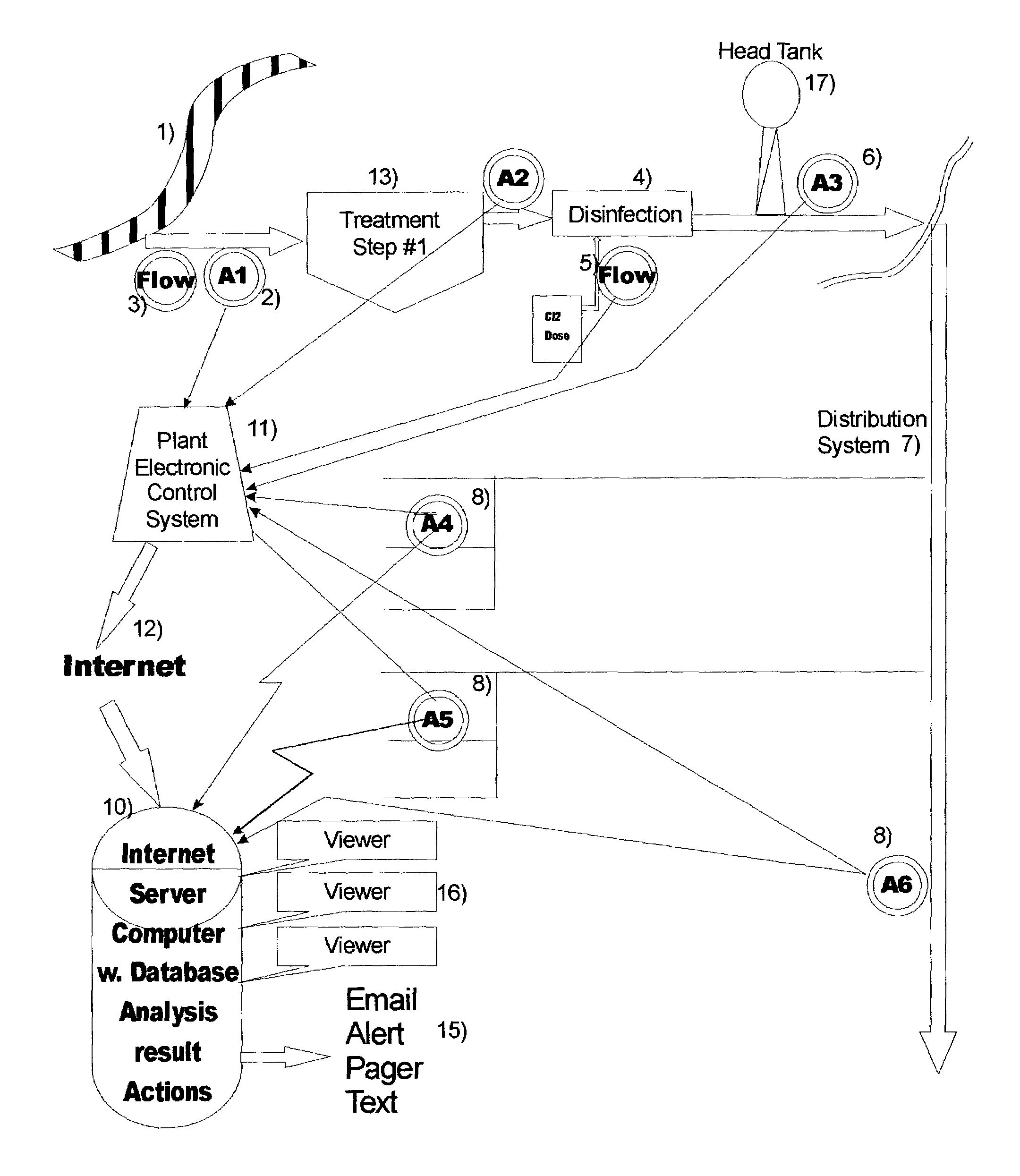
InactiveUS7698073B2Rule out the possibilityGeneral water supply conservationUltrafiltrationChloramine BChlorine dioxide
An Anti-Terrorism water quality monitoring system for continuously monitoring a potable water treatment system and related potable water distribution network that provides potable water to a municipality, city, housing development or other potable water consumer. The system includes the collection of data from the water distribution system and from the water treatment facility and from advanced separation processes which are integrated into analytical instruments. The data collected are stored in a remote database on a remote server computer or bank of computers and accessible by Homeland Security or its designated agency. Preferred parameters of monitoring include the turbidity and disinfectant such as chlorine, hypochlorous acid, sodium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite, ozone, chlorine dioxide, chloramines, hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid.
Owner:HACH CO
Integrated membrane system for distributed water treatment
InactiveUS20130032533A1Easy to operateLess-effectiveTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesChloramine BPh control
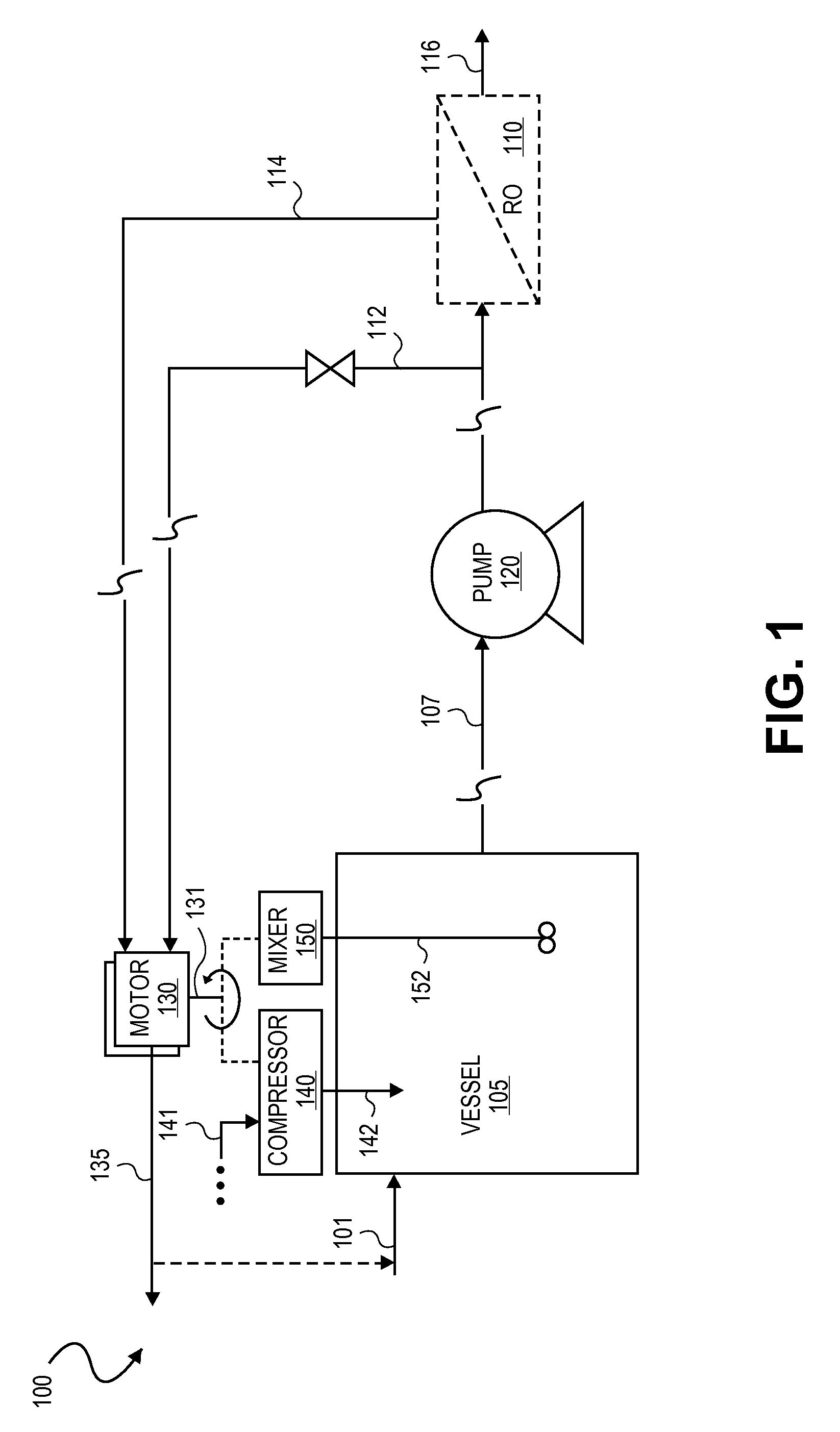
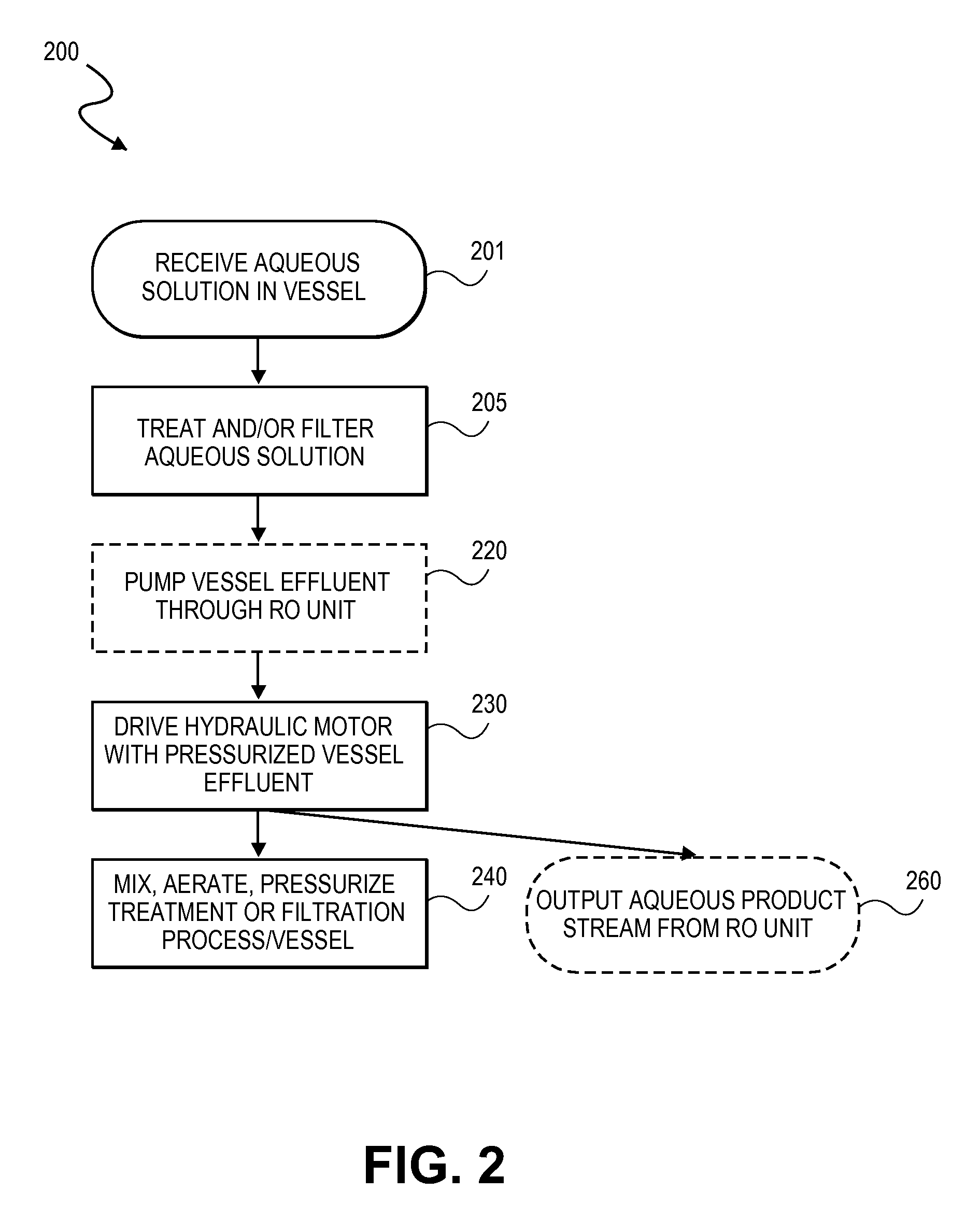
Integrated membrane treatment systems for treatment of an aqueous solution. In embodiments, components, such as an MBR, are integrated with means to recover energy from the system, for example from an RO concentrate, to operate the other components. In embodiments including biological treatment, RO is integrated with other components, such as an MBR with the ROs ability to remove inorganic nitrogen enabling biological treatment to be performed with only partial nitrification and the MBR operated without active pH control. In embodiments, RO is integrated with a chlorine generator to convert chlorides present in the RO concentrate for an in-situ source of oxidizing biocides for disinfection purposes. Chloramines may be generated in-situ from residual ammonia and chlorides in the RO reject. In embodiments, carrier media is employed in a membrane tank to enhance removal of residual organics by the MBR and to also improve effectiveness of membrane scouring.
Owner:ENVEERA
Method for removing nitrogenous disinfection byproducts in water on basis of persulfate/light combination
InactiveCN102381740ARemove completelyInhibit killWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processChloramine BPersulfate
The invention discloses a method for removing nitrogenous disinfection byproducts in water on the basis of persulfate / light combination, and relates to a method for removing nitrogenous disinfection byproducts in water. The method for removing nitrogenous disinfection byproducts in water on the basis of persulfate / light combination comprises the following steps of: dosing persulfate in water including nitrogenous disinfection byproducts and then carrying out light irradiation. In the invention, persulfate or related composite chemicals are dosed in water and ultraviolet irradiation is utilized, so that abundant radicals are generated to attack the nitrogenous disinfection byproducts so as to realize denitrification and dehalogenation. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the effect is clear, the use is sage and no toxic byproduct is generated. By using the method, various nitrogenous disinfection byproducts such as acetonitrile, halogenated nitromethane, nitrosamine compounds, halogenated cyanogens, halogenated acetamide, halogenated pyrrole and organic chloramines can be thoroughly removed; and moreover, the method can be used for synchronously removing other organic matters and restraining and killing the microorganisms in the water.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of retaining antimicrobial properties on a halamine-treated textile substrate while simultaneously reducing deleterious odor and skin irritation effects
This invention relates to antimicrobial fabrics which are treated with a specific durable and regenerable halamine / chlorine system and methods of removing residual active chlorine from the target textile surface without reducing the antimicrobial activity of the textile. Such methods comprise contacting an amine-treated fabric first with a halogen-based bleach (or other halogenated liquid) to produce halamines at the fabric surface, and subsequently washing the resultant halogenated fabric with a reducing agent which removes the residual, unbonded halogen (such as chlorine) from the fabric surface but does not, surprisingly, remove the halamine halogen. The remaining halamine halogen thus provides the desired antimicrobial activity. As a result, a method of substantially reducing fabric discoloration, odor, and potential skin irritation due to the presence of amounts of residual unbonded halogen (such as chlorine) on the target fabric surface is provided which simultaneously permits sufficient amounts of halamine halogen (such as chloramine chlorine) to remain on the target fabric for optimum microbiocidal propoerties. A fabric treated in accordance with this method is also provided.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Isomerization reaction
The invention discloses a highly selective novel reaction with an important application value in organic phosphorus synthesis methodology. The reaction can be applied in important pesticide commodities of acephate, glyphosate, glufosinate-ammonium, chloramine phosphorus, profenofos, and the like. With the reaction, innovative technical synthetic routes can be designed. With the reaction, standards of clean production technologies can be satisfied, and the production cost is greatly reduced compared to existing technical routes.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Disinfectant used in breeding industry
InactiveCN104054750AInexpensive componentsLow costBiocideDisinfectantsChloramine BSodium bicarbonate
The invention discloses a disinfectant used in the breeding industry. The disinfectant comprises the components in percent by volume: 20-30mL of a sodium hydroxide solution with the mass percent of 30-45 percent, 3-7mL of peroxyacetic acid, 5-9mL of chloramine, 12-17mL of a sodium bicarbonate solution with the mass percent of 20-45 percent, 4-12mL of absolute ethyl alcohol and 12-19mL of a saponated cresol solution. All components are stirred for a certain time at a normal temperature and a normal pressure, and sub-packaged and plastic-packaged to obtain the disinfectant. By adopting the mode, according to the disinfectant used in the breeding industry, disclosed by the invention, the components adopted by the disinfectant are low in price, so that the total cost of the disinfectant is reduced, the disinfection effect is good, a good medication effect can be achieved by only consuming less disinfectant, the medication efficiency is high, toxic and hazardous effects on bred livestock and fishes are avoided, and no toxin accumulation is caused.
Owner:TAICANG ROODEE BIOTECH RES INST
Assay for detecting inhibitors of the enzyme myeloperoxidase
The invention is an assay for detecting inhibitors of the enzyme myeloperoxdase The assay method comprises reacting myeloperoxdase with hydrogen peroxide and a chloride source to generate hypochlorous acid in the presence of a potential inhibitor of said myeloperoxidase; reacting any formed hypochlorous acid with an amine to form the corresponding chloramino; optionally removing any unreacted hydrogen peroxide; reacting any for-med chloramine with a detector compound in the presence of iodide to form oxidized detector compound; determining the amount of formed oxidized detector compound by measuring the absorbents or fluorescence at a suitable wavelength; and identifying as inhibitors of myeloperoxidase those compounds which cause the amount of formed oxidized detector compound to be decreased The assay is useful in diagnostic tests for myeloperoxidase activity.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Bleach and vinegar detersive system
InactiveUS6998379B1Easy to cleanInhibition releaseDetergent bleaching agentsNon-surface-active detergent solventsChloramine BFlavor
A detersive system containing surfactants, vinegar, bleach and alternatively emollients, foaming agents, perfumes, and builders has been developed. Due to the addition of both bleach and vinegar, the detersive system shows synergistic activity with regards to necessary areas and objects of cleanliness that can be found in restaurants and eating establishments. In addition to the synergistic activity, the formulation does not release harmful chloramine gas that is usually present when vinegars and bleach are mixed.
Owner:COSTAGLIOLA ANIELLO
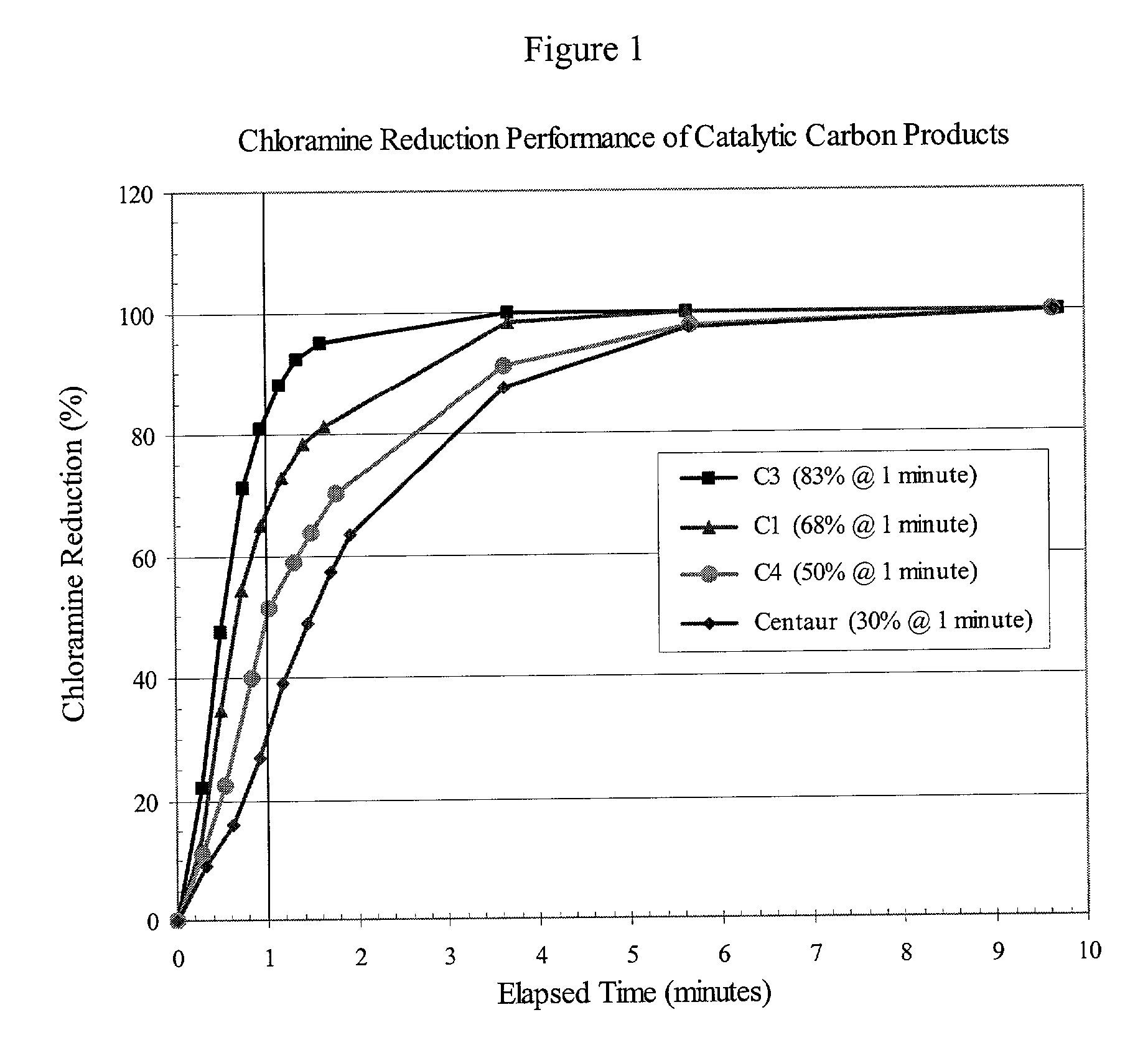
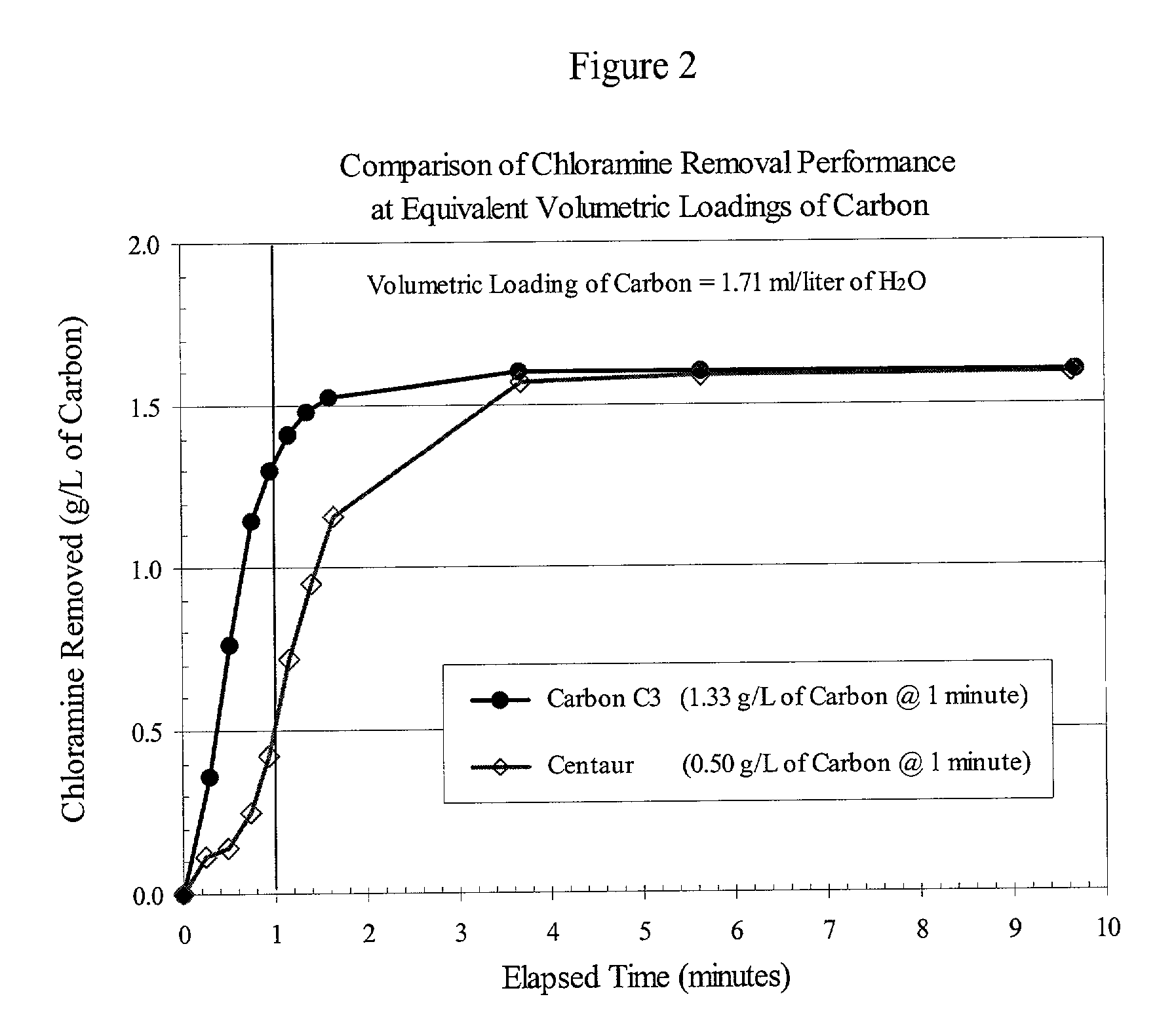
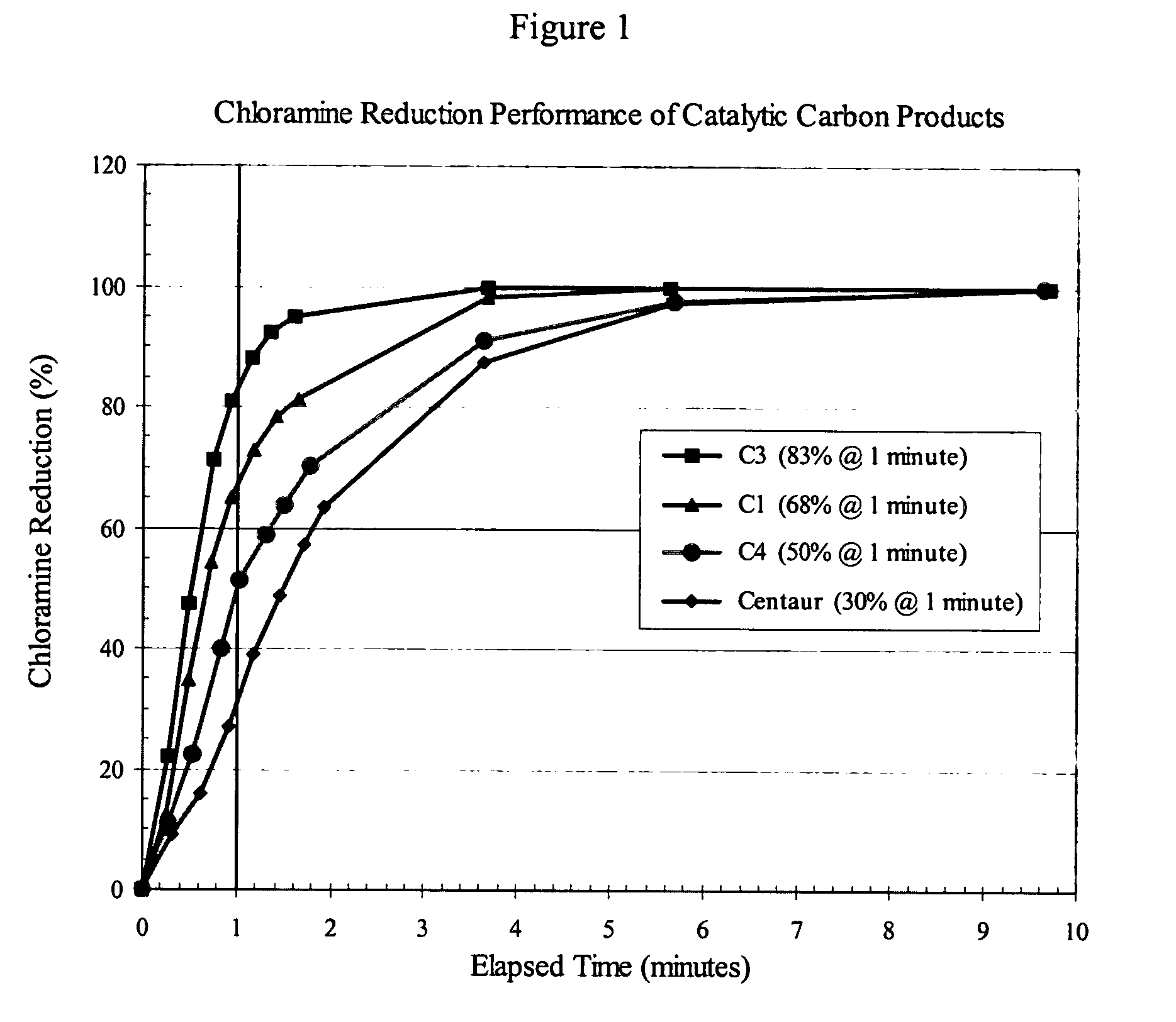
Method for removal of chloramines from drinking water
InactiveUS20030209498A1Convenient amountEfficient removalCarbon compoundsOther chemical processesSolid carbonActivated carbon
This application discloses a method for enhanced removal of chloramines from a fluid media by contacting said media with a catalytic activated carbon. The catalytic activated carbons used in the present invention may be prepared from carbon materials that have been contacted or otherwise exposed to nitrogen-containing compounds at temperatures above 700° C., and preferably are in the form of a solid carbon block.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Production of gaseous chloramine
InactiveUS7070751B2Prevent scalingSimple streamlined designCombination devicesExhaust apparatusChloramine BGas phase
The present invention provides a reactor for the gas-phase reaction of commercially available gases in the presence of an inert carrier gas to form product gas. The reactor has a streamlined, compact configuration and at least one solids collection and removal system downstream of the reactor, where solids are efficiently removed from the product gas stream, leaving high purity product gas. The removal system allows for a simple reactor design, which is easy to clean and operates continuously over longer periods of time.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
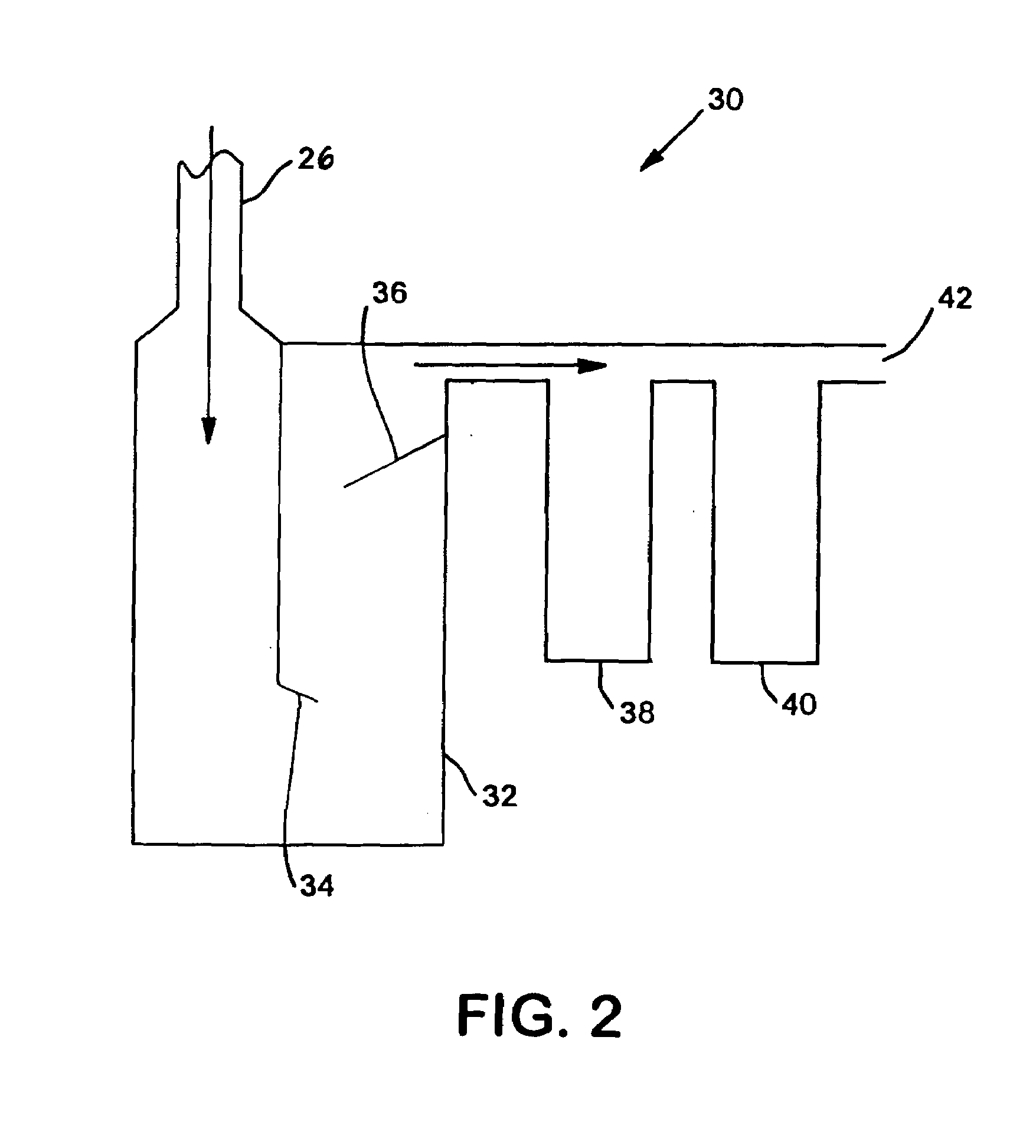
Methods Of Preserving Starch In Pulp And Controlling Calcium Precipitation And/Or Scaling
ActiveUS20130319627A1Improve the level ofHigh strengthBiocideNatural cellulose pulp/paperChloramine BChloramine
Methods to preserve starch present in pulp are provided and also methods to control calcium precipitation and / or scaling in digesters or BOD systems. The methods can be performed as part of a papermaking process. Process water containing pulp can be treated with a chloramine. Process water containing pulp with native starch can receive a double treatment with at least one biocide, such as chloramine, and at least one oxidant, such as sodium hypochlorite. The treatment can be performed in any suitable manner. The treatment can be performed at one or more stages or locations in a papermaking system. A target residual chloramine value or range can be achieved by the treatment. Packaging sheets / boards and other paper products manufactured using the methods provided exhibit superior strength and other desirable characteristics.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Catalytic activated carbon for removal of chloramines from water
This application discloses a method for enhanced removal of chloramines from a chloramines-containing fluid media by contacting said media with a catalytic activated carbon characterized by having present in the graphene structure of the carbon from 0.01 to 10 wt % of aromatic nitrogen species. The catalytic activated carbons used in the present invention may be prepared from carbon materials that have been contacted or otherwise exposed to ammonia, with or without simultaneous exposure to an oxygen-containing vapor or gas at temperatures above 700° C. and, preferably, are in the form of a solid carbon block.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Haloperoxidase treatment to control algae
A method for killing, preventing, or inhibiting the growth of algae in an aqueous system is provided by providing a haloperoxidase, and hydrogen peroxide or a peroxide source to a chlorinated water system under conditions in which the haloperoxidase, peroxide from the hydrogen peroxide or peroxide source, and chloride ions or chloroamines in the chlorinated water system interact to provide an antialgal agent.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
Method for disinfecting filtered water from water plant with cooperation between medium-pressure ultraviolet catalyzing peroxymonosulfate and chloramine
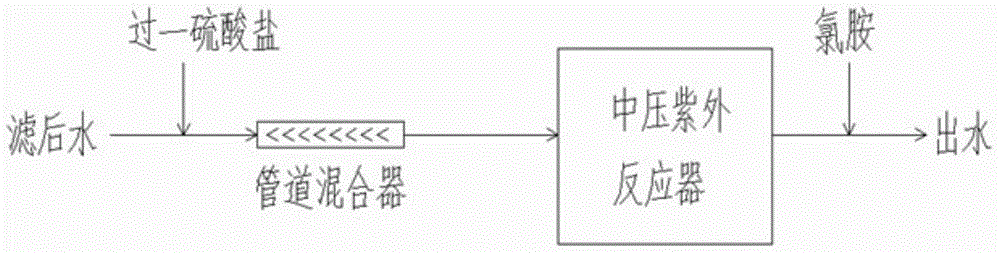
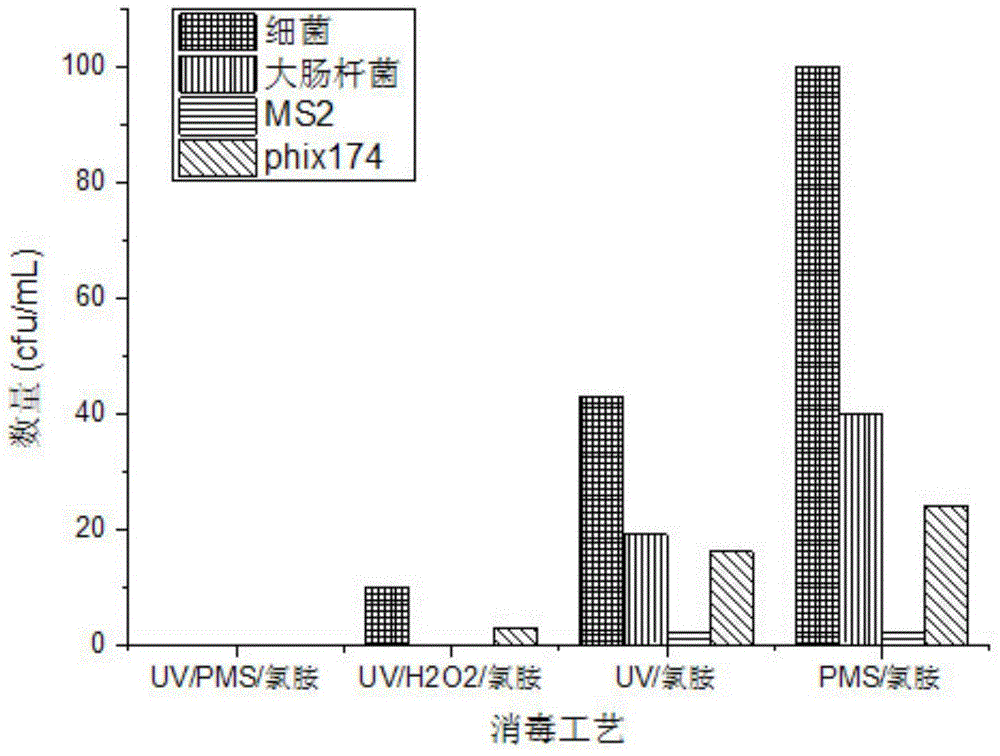
InactiveCN104150562ASmall doseImprove water qualityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processChloramine BUv disinfection
The invention discloses a method for disinfecting filtered water from a water plant with cooperation between medium-pressure ultraviolet catalyzing peroxymonosulfate and chloramines. The method includes following steps: adding peroxymonosulfate to outlet water from a water plant filtering tank to obtain a mixed solution with a concentration being 0.2-0.4 mmol / L through a tubular mixer; performing disinfection to the mixed solution in a medium-pressure ultraviolet disinfecting reactor, wherein an addition dosage of the medium-pressure ultraviolet is 10-20 mj / cm<2> and a disinfection time in the reactor is 5-10 min; and adding 0.3-0.4 mg / L chloramines to an end of the ultraviolet disinfecting reactor to complete the disinfection with cooperation between medium-pressure ultraviolet catalyzing peroxymonosulfate and chloramines. By means of the method, a cooperative effect of medium-pressure ultraviolet, peroxymonosulfate and chloramines fully works so that bacteria and microorganisms can be controlled in high efficiency and a reagent addition dosage and disinfection by-product can be reduced. Sustainability of disinfection and sterilization of water in a following water supply network can be ensured and drinking water safety can be ensured.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Shower filter apparatus
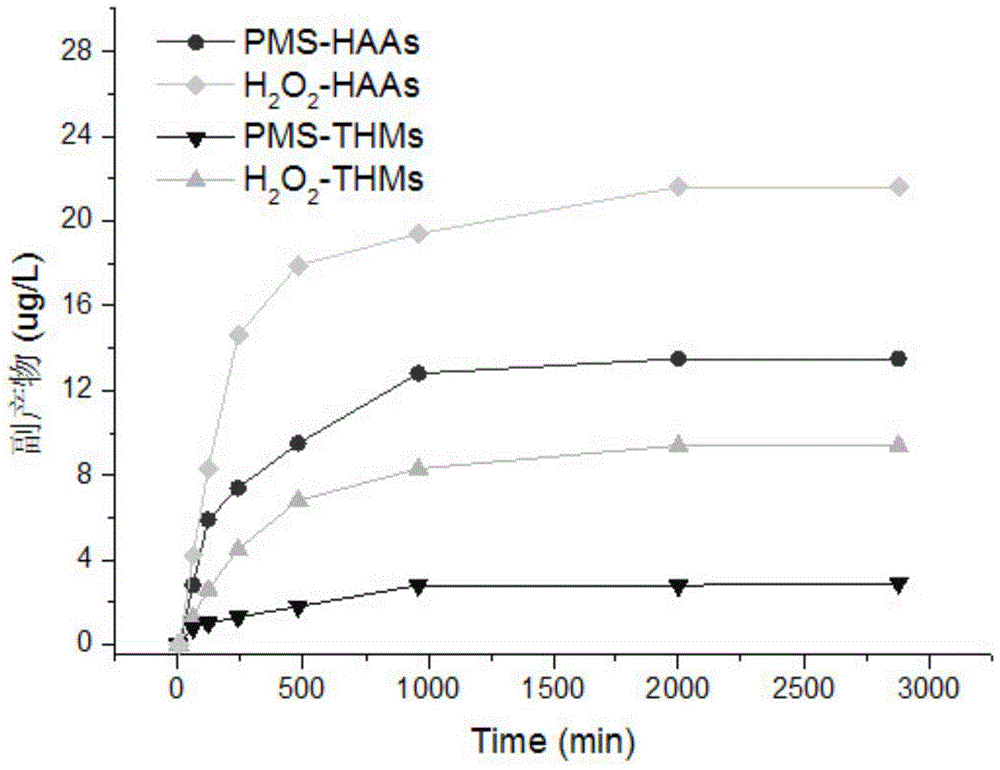
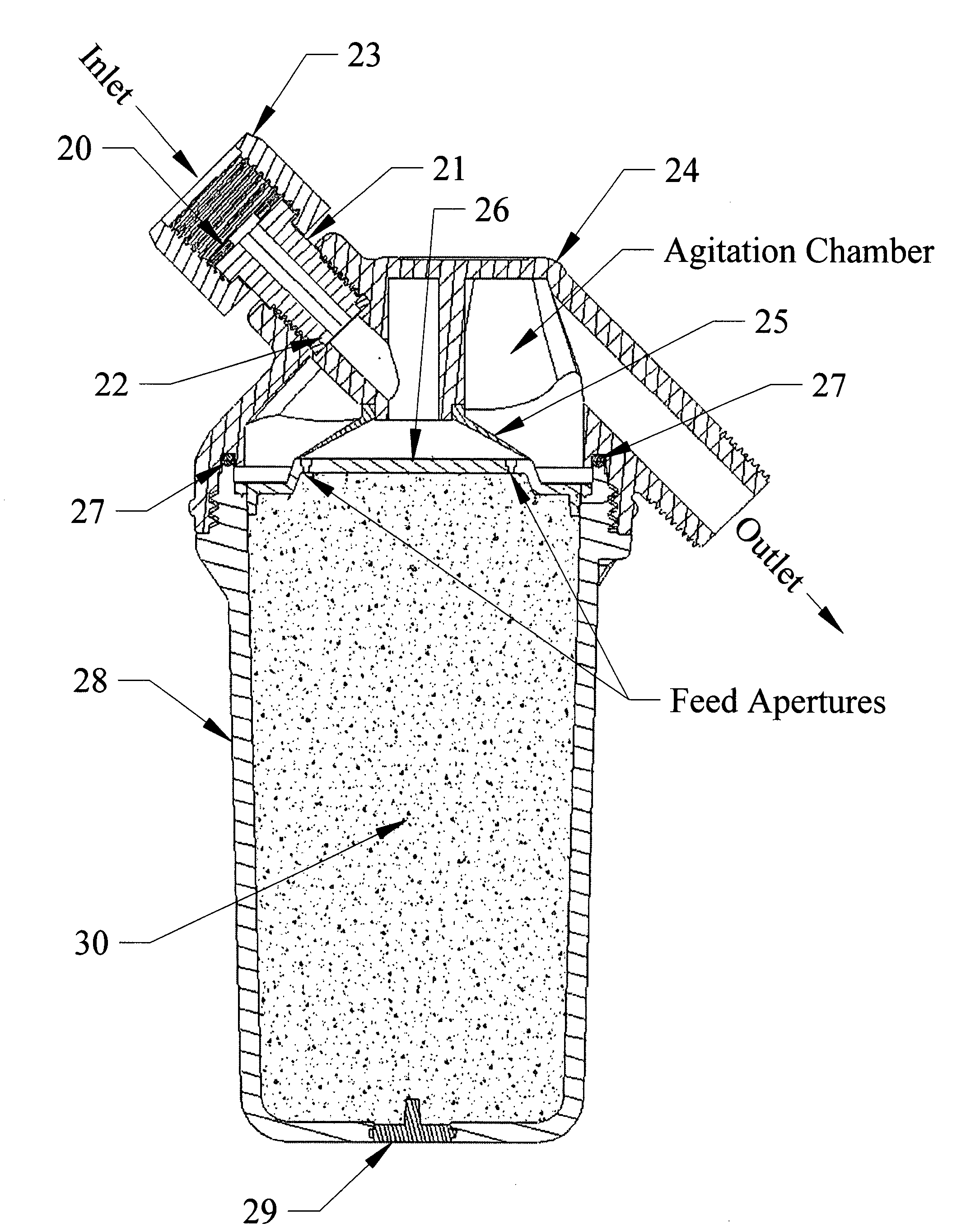
InactiveUS20080011656A1Extended service lifeEnhance stirringSpecific water treatment objectivesTreatment involving filtrationWater useChloramine B
A shower filter apparatus to neutralize chlorine and chloramines from water using water soluble vitamin c in the forms of ascorbic acid and sodium ascorbate, vitamin e in the form of tocopheryl acetate to prevent the oxidation of vitamin c, a cylindrical threaded replaceable sealed cartridge system with carefully sized media feed apertures to control delivery of said vitamin solution, a gasketed flow control device that creates a positive water tight seal over the media feed apertures when the device is not in use, a transparent observation window within the media cartridge.
Owner:LACY JARVIS MARCELLUS +2
Chemical Injection and Control System and Method for Controlling Chloramines
ActiveUS20160362318A1Water treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsChloramine BAutomatic control
Owner:UGSI SOLUTIONS INC
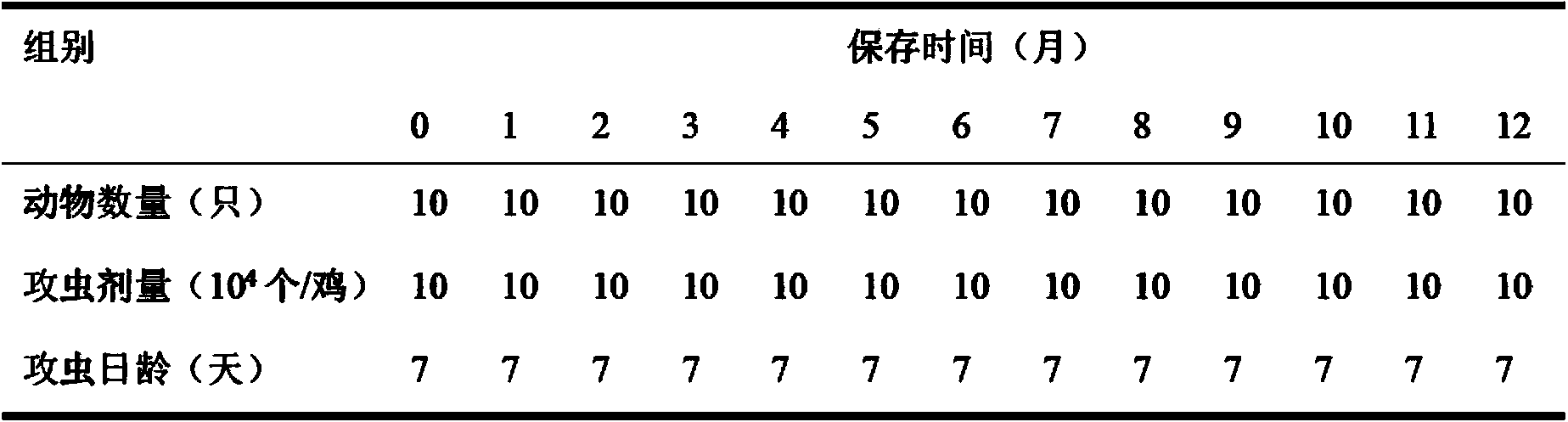
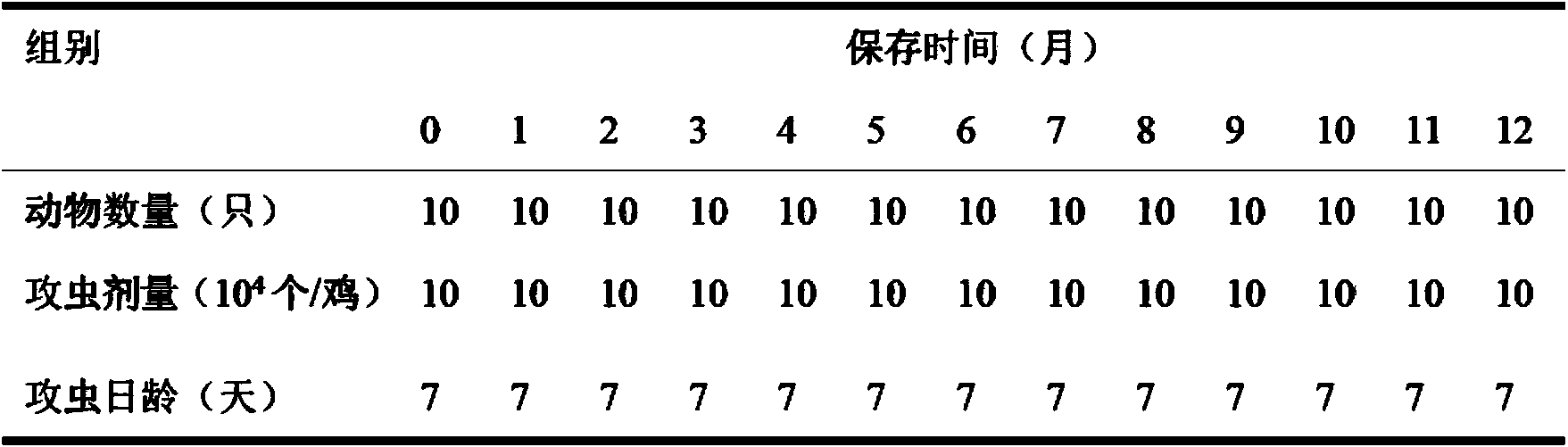
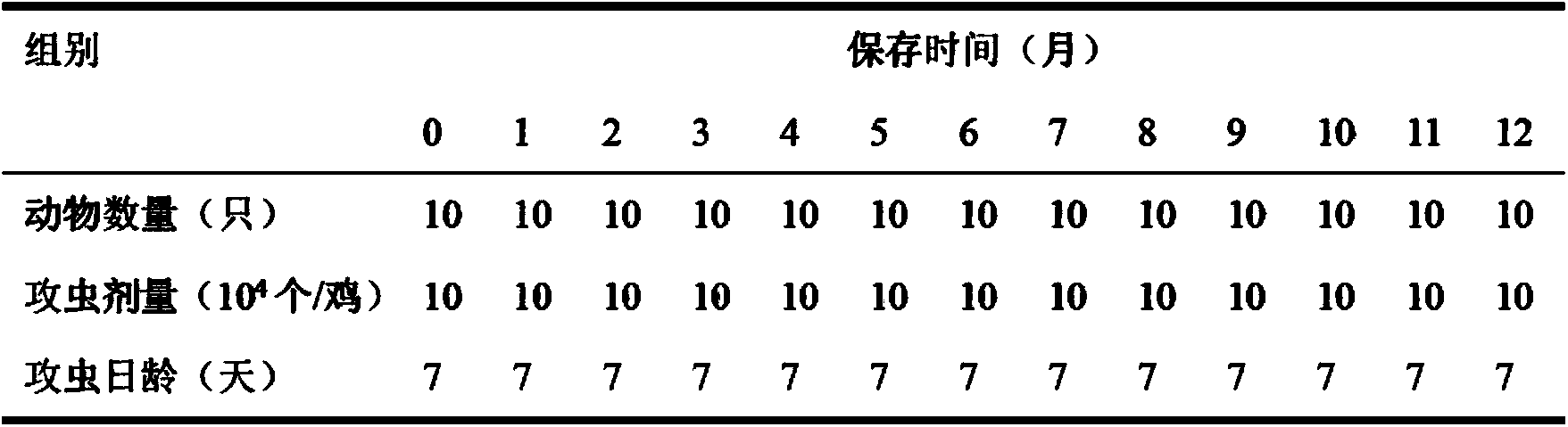
Application of chloramine B solution in chicken coccidiosis oocyst culture and preservation
InactiveCN103710265AHigh sporulation rateVigorousProtozoaMicroorganism based processesChloramine BEimeria maxima
The invention discloses an application of a chloramine B solution in chicken coccidiosis oocyst culture and preservation. According to the invention, study finds out that the sporulation rate of the chicken coccidiosis oocysts can be effectively improved with the chloramine B aqueous solution as a chicken coccidiosis oocyst culture solution. The oocysts of the chicken eimeria tenella, eimeria acevulina, eimeria maxima and eimeria necatrix are not affected in activity if being preserved within 6 months; if being preserved within 8 months, the yield of the oocysts is reduced within 25%; the pathogenicity is not obviously affected. Therefore, the chloramine B aqueous solution can be used as the culture and preservation solution for the chicken coccidiosis oocysts in stead of potassium dichromate.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HEALTH GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of catalyst for synthesizing diphenyl carbonate
ActiveCN106179515AIncrease production capacityReduced catalytic efficiencyOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChloramine BChloramine
The invention discloses a preparation method of a catalyst for synthesizing diphenyl carbonate, and belongs to the technical field of catalyst synthesis. The catalyst is obtained by modifying a transition metal oxide by poly-electrolyte until the transition metal oxide is positively or negatively charged, and wrapping a layer of metal organic framework (MOFs) on the outer surface of the transition metal oxide by an electrostatic layer-by-layer self-assembling method, namely the oxide is used as a core, and the MOFs is used as a shell; the catalyst is MalphaObeta@MOFs fort short (M is one of transition metal elements, and alpha and beta are valences). The catalyst is enabled to react with ammonia chloride with a certain concentration to convert the core MalphaObeta into corresponding chloramine salt M(NH3)nClbeta (n is the number of ammonia molecules and is equal to 1 to 8); after ammonia is removed by low-temperature roasting, the catalyst MClbeta@MOFs is obtained. The catalyst can be used in a system for generating diphenyl carbonate by transesterification between urea or carbamic acid ester and phenol; new coordination adsorption is performed on the catalyst and ammonia generated by the reaction system to push the reaction to move rightwards; the yield of a diphenyl carbonate product is up to 90 percent or above; after the catalyst is used for 5 times, the catalysis effect is still good.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
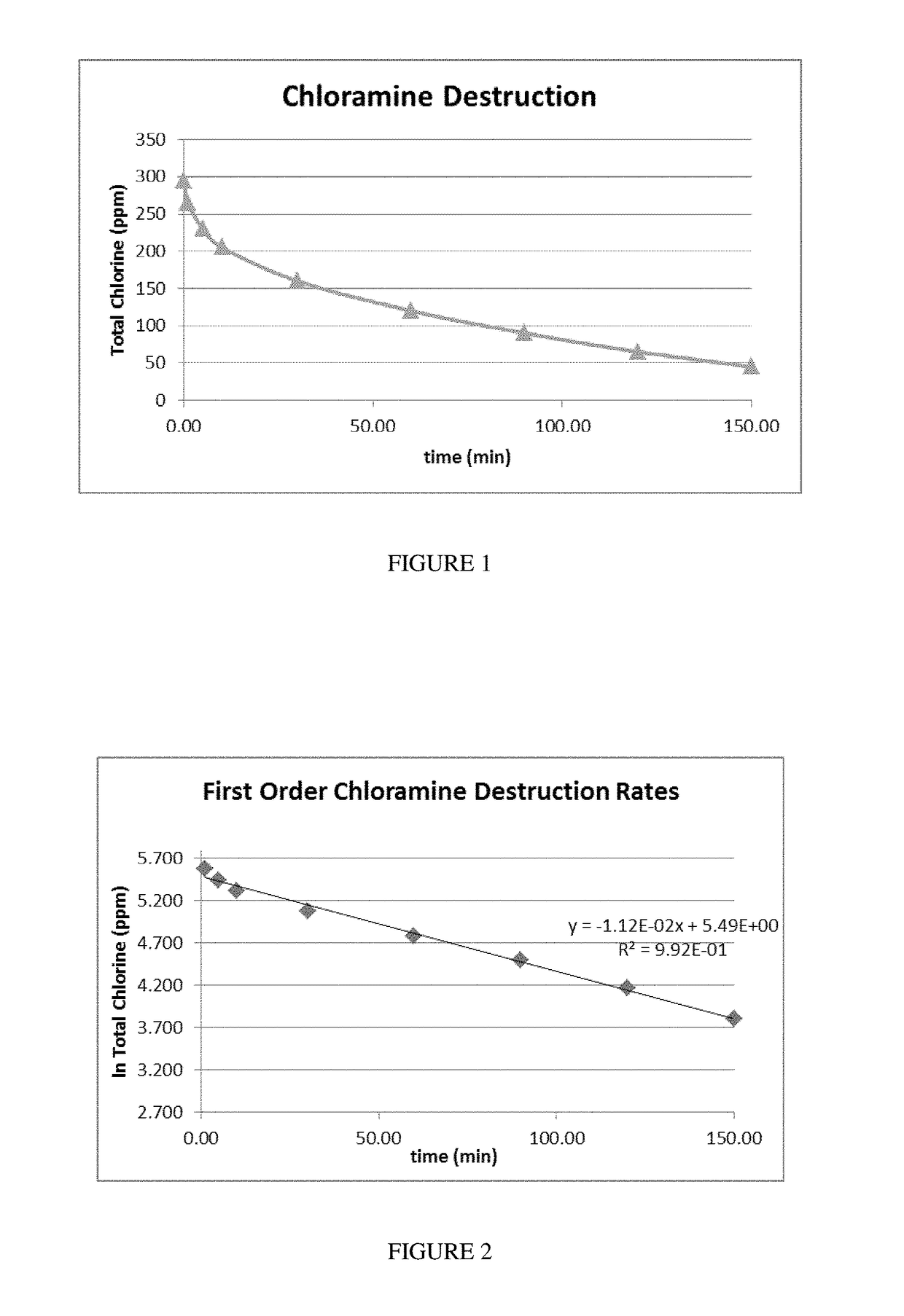
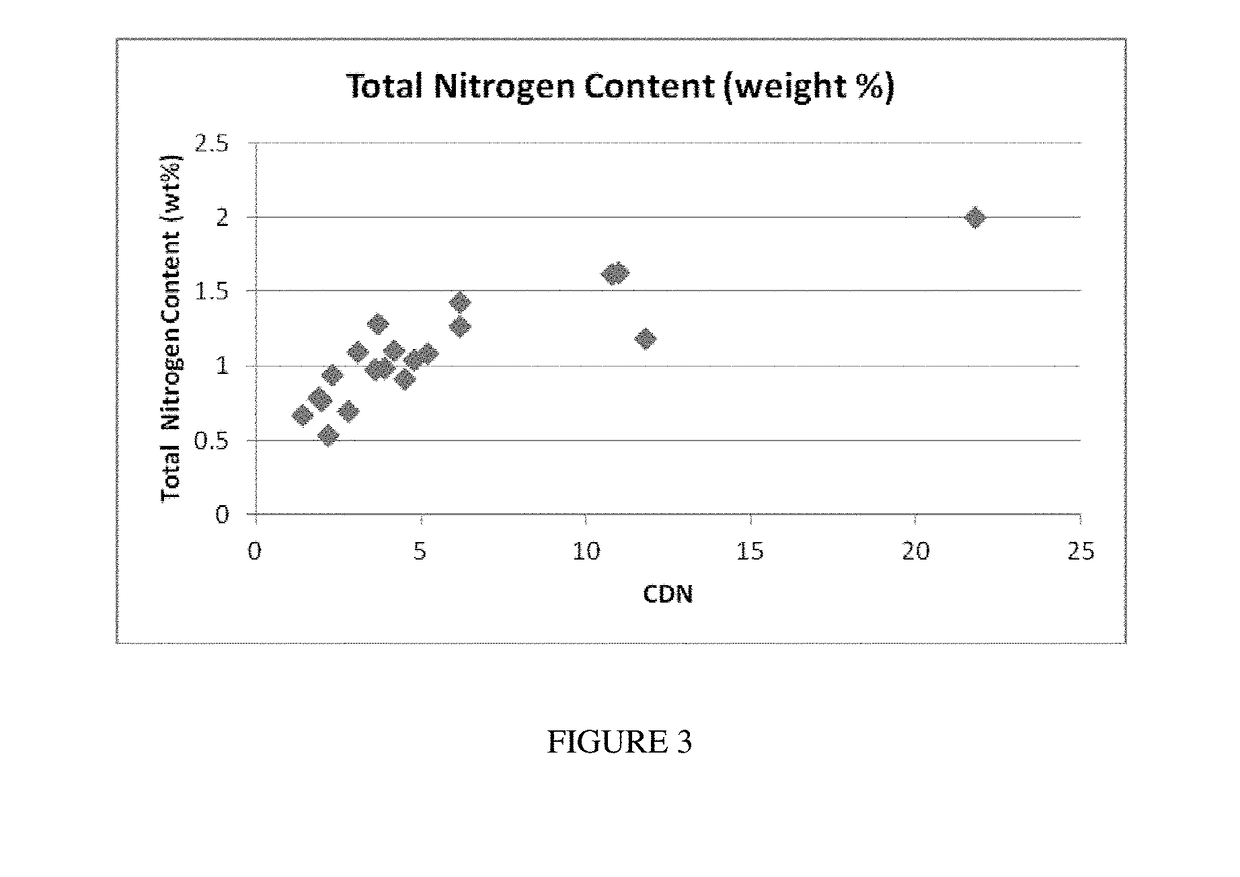
Chloramine and chlorine removal material and methods for making the same
ActiveUS20180229217A1Reduce concentrationOther chemical processesSpecific water treatment objectivesChloramine BSorbent
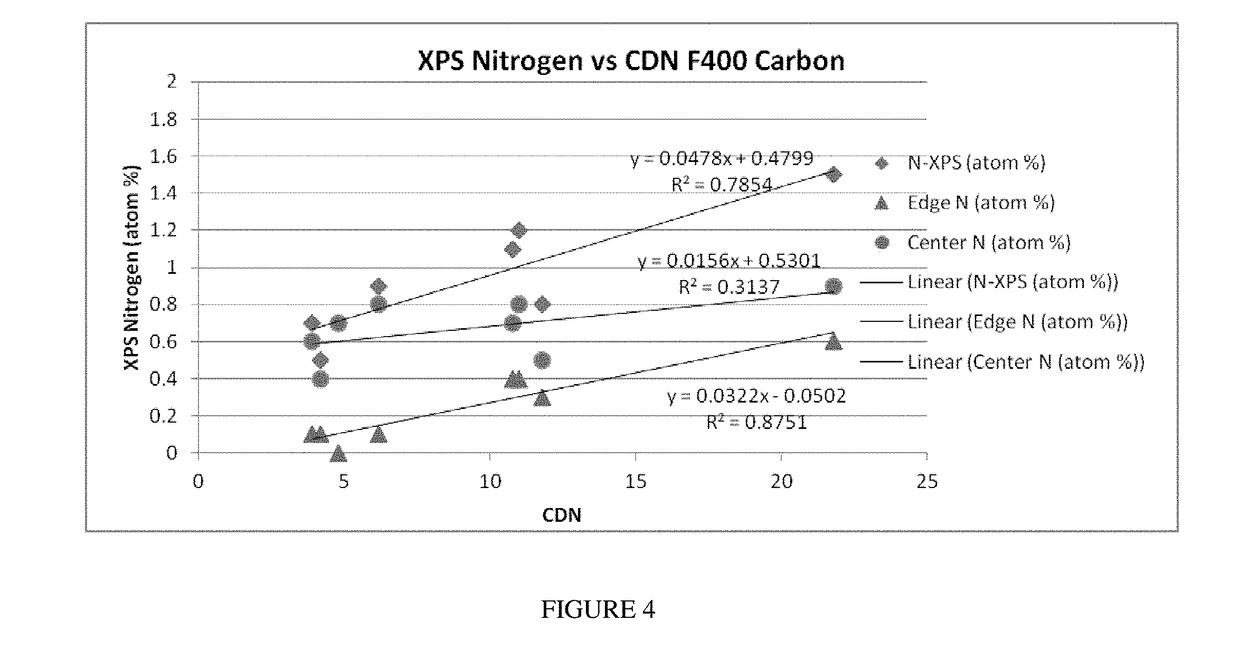
Sorbent materials are described that have enhanced performance in removing chlorine and chloramine, among other toxic compounds. The sorbent materials are formed by a process which includes steps of oxidation, adding a nitrogen-containing compound, and calcining the sorbent. The processes of forming the sorbent materials are also disclosed. The sorbent materials have excellent performance as measured by a chloramine and / or chlorine destruction number, and the sorbents retain a high nitrogen edge concentration. The sorbent materials may also be incorporated into devices such as filter assemblies.
Owner:CALGON CARBON
Pathogen reduction using chloramines
InactiveUS7387736B2Good effectEasy to receiveWaste water treatment from animal processingWater/sewage treatment by substance additionWater useChloramine B
A method and apparatus for implementing pathogen reduction within a poultry processing or food processing plant that uses water that has been treated with chloramines at an advantageous dosagebefore being introduced to the production process at processing steps. The water treated with chloramines may be from a fresh water source or reclaimed water from the processing plant. The reintroduction of the treated reclaimed water advantageously causes a dramatic reduction in the levels of microorganisms associated with poultry processing, while substantially conserving water use.
Owner:ZENTOX CORP
Method for determining and correcting cyanide
InactiveCN102564982AReduce riskReduce storageColor/spectral properties measurementsChloramine BChloramine
The invention discloses a method for determining and correcting cyanide. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) putting 10 milliliters of distillate in a colorimetric tube which has a volume of 25 milliliters and is provided with a plug; 2) adding 5 milliliters of phosphate buffer solution into the tube, mixing uniformly, quickly adding 0.2 milliliter of chloramine solution, immediately inserting the plug, mixing uniformly and placing for 3 to 5 minutes; 3) adding 5 milliliters of isonicotinic acid-pyrazolone mixed solution into the tube, uniformly mixing, adding water to dilute until mixture reaches a marked line, shaking uniformly, and placing in an aqueous solution at the temperature of between 25 and 35 DEG C for 40 minutes; and 4) determining absorbance by using a cuvette with height of 1cm, and using reagent blank as reference at the wave length of 638nm, and finding out the corresponding cyanide content from the standard curve. By using an intermediate medium, the cost of purchasing, storing and managing toxic and dangerous chemicals is reduced, and potential unsafe factors of the toxic and dangerous chemicals in using operation can be reduced.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com