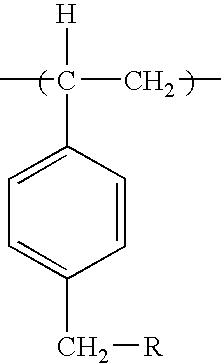
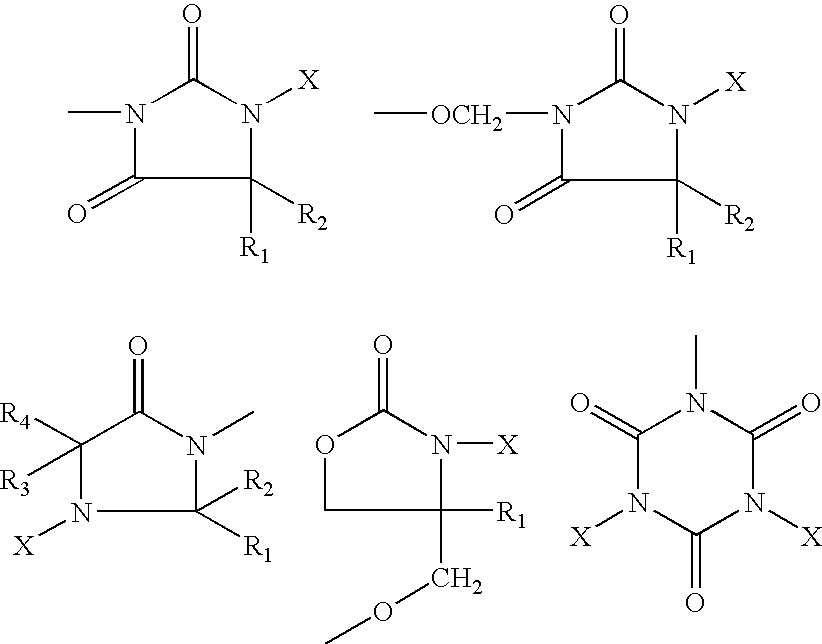
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Porous beads" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
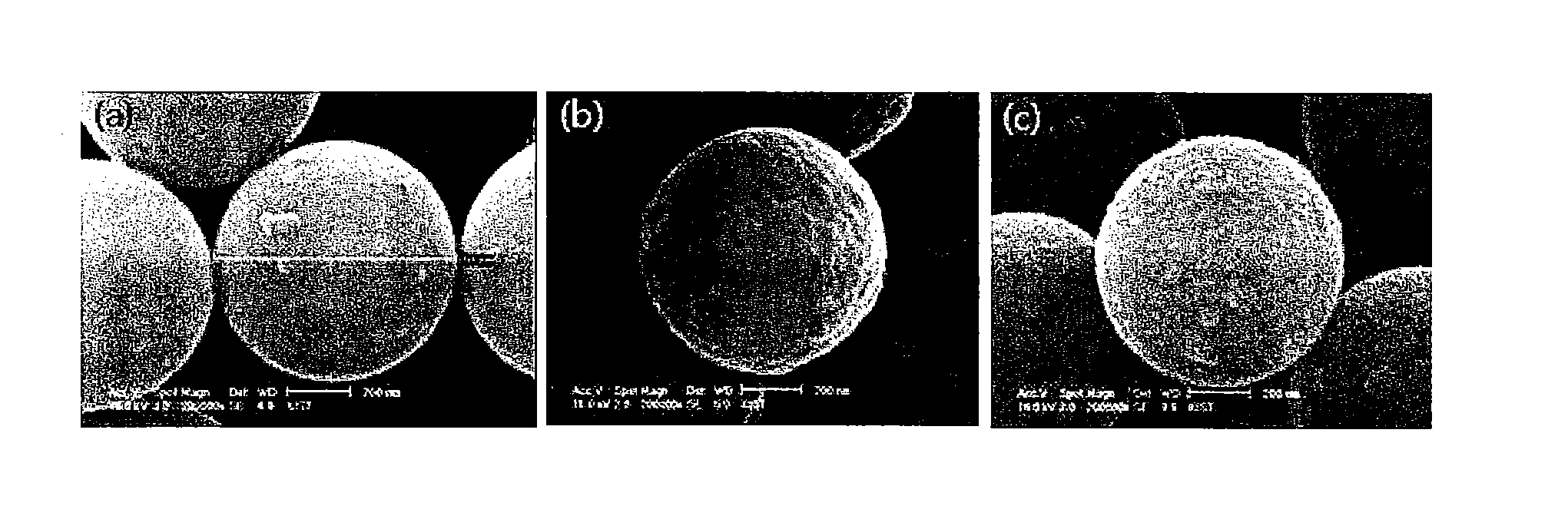
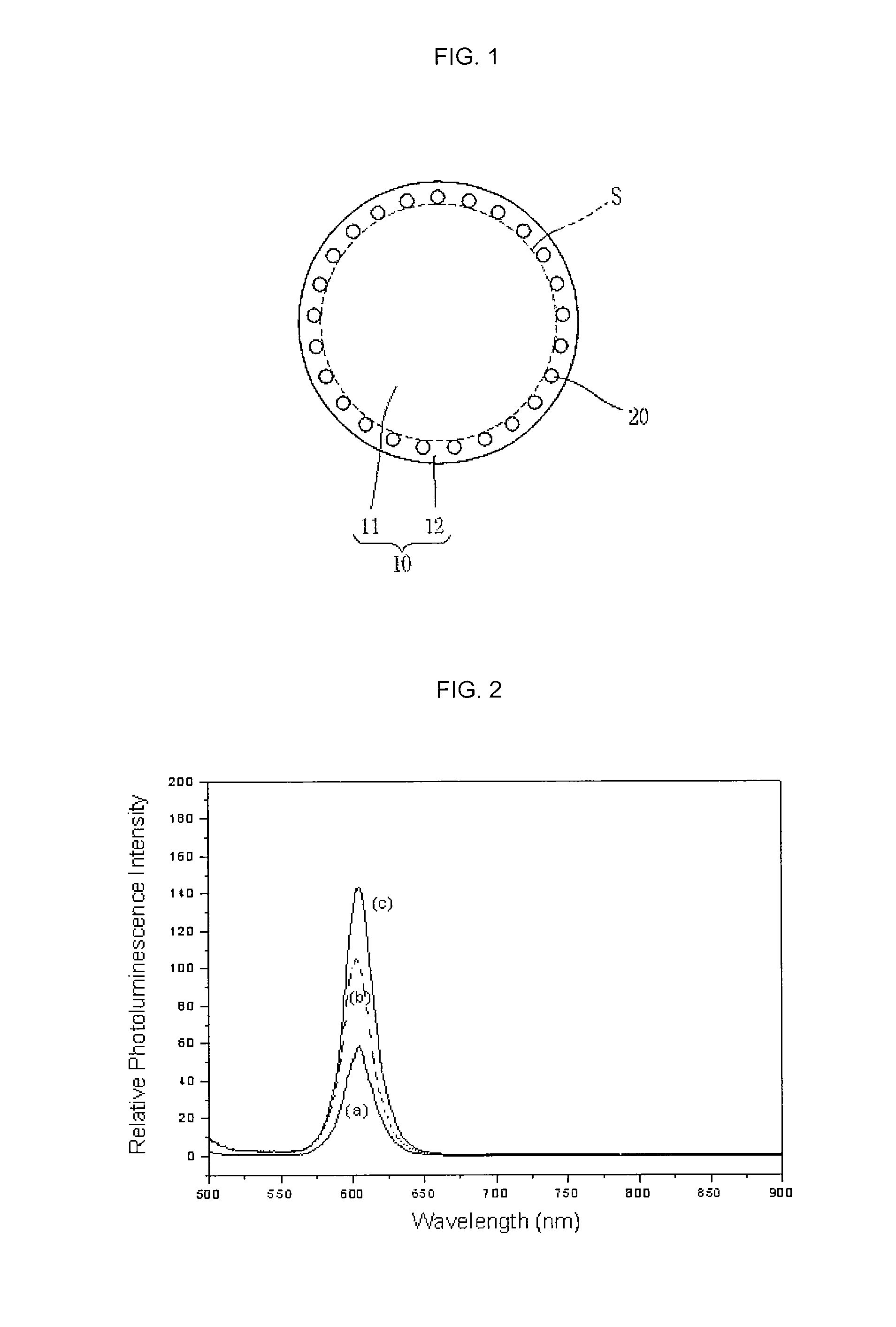
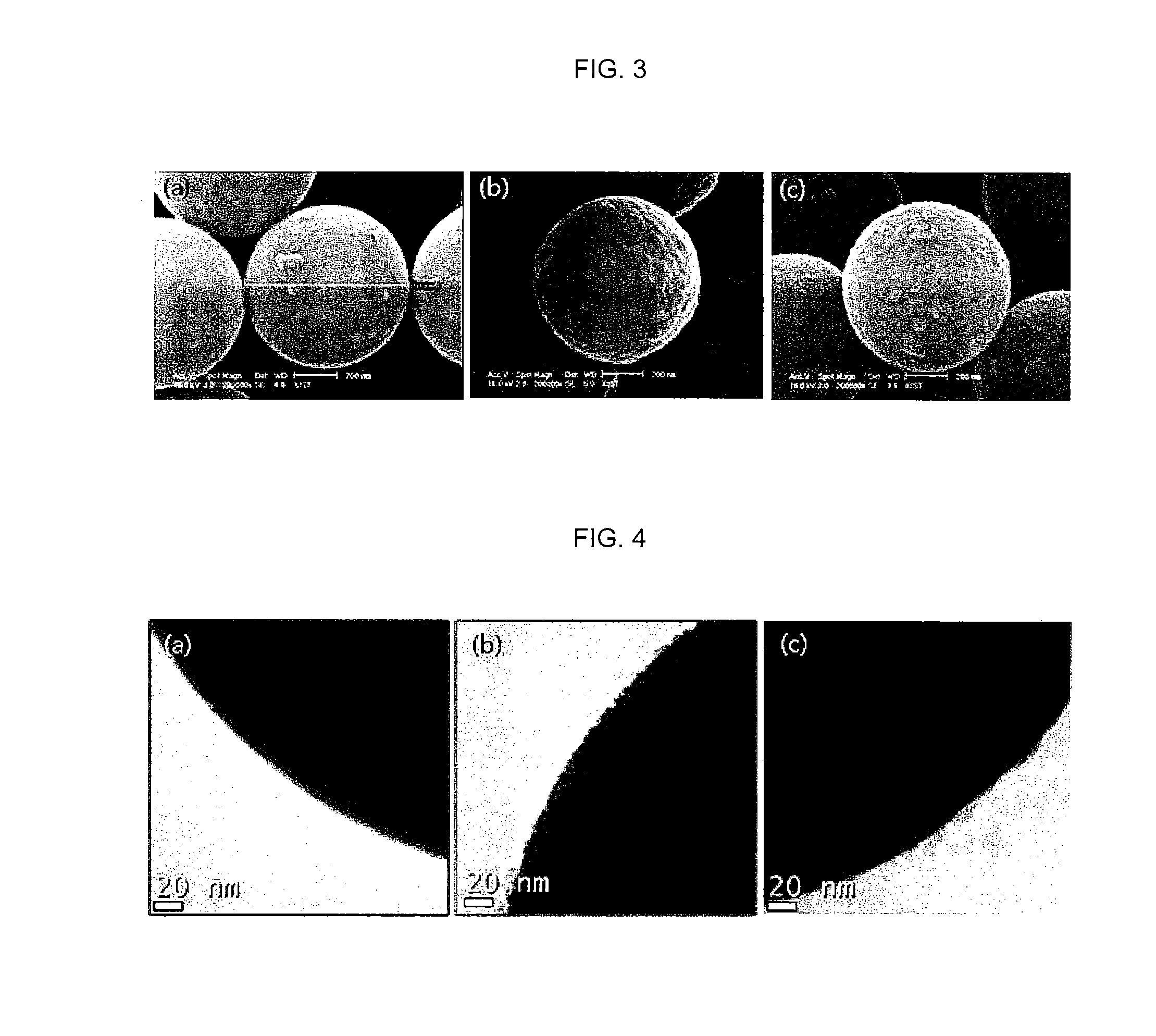
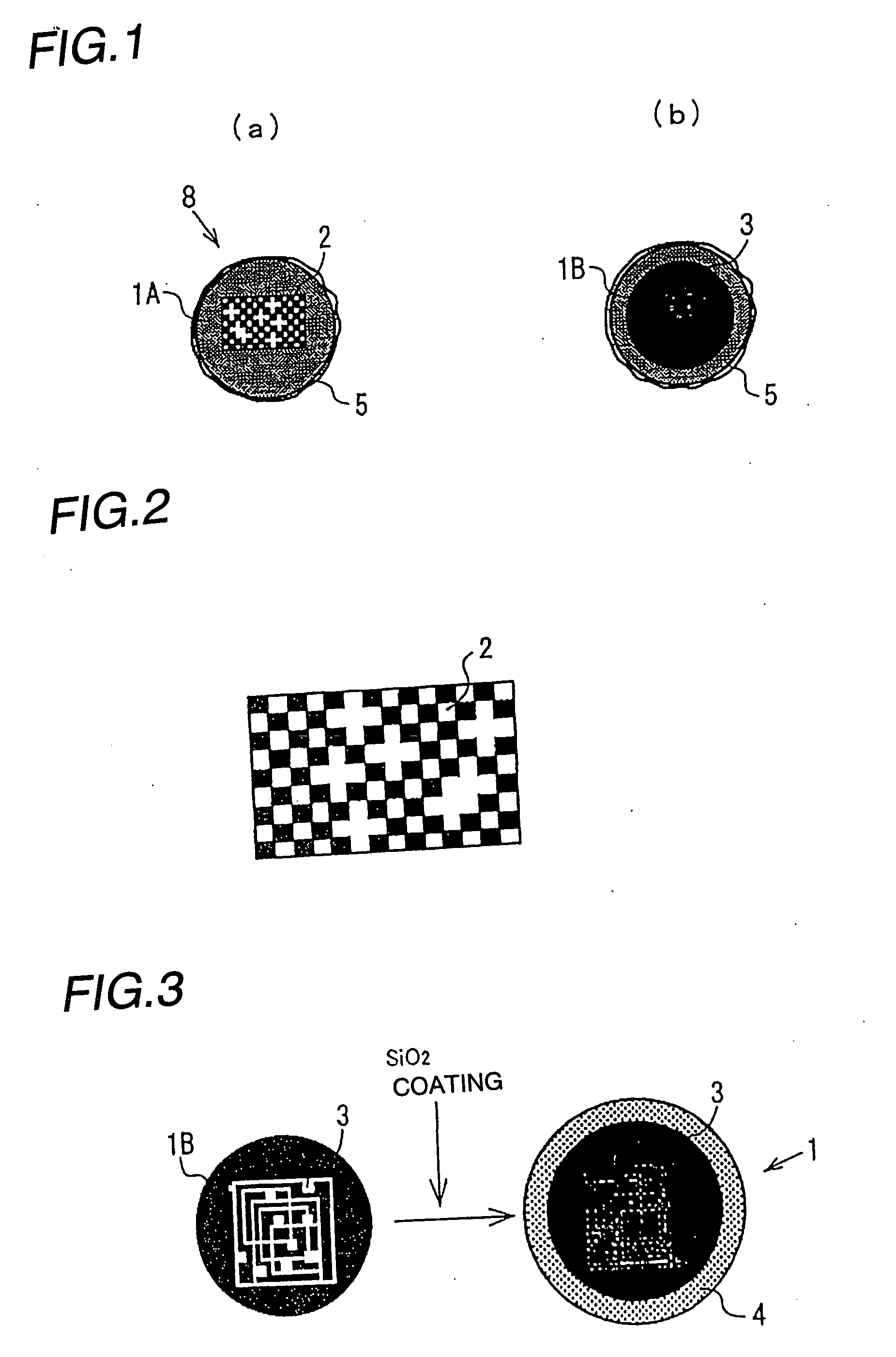
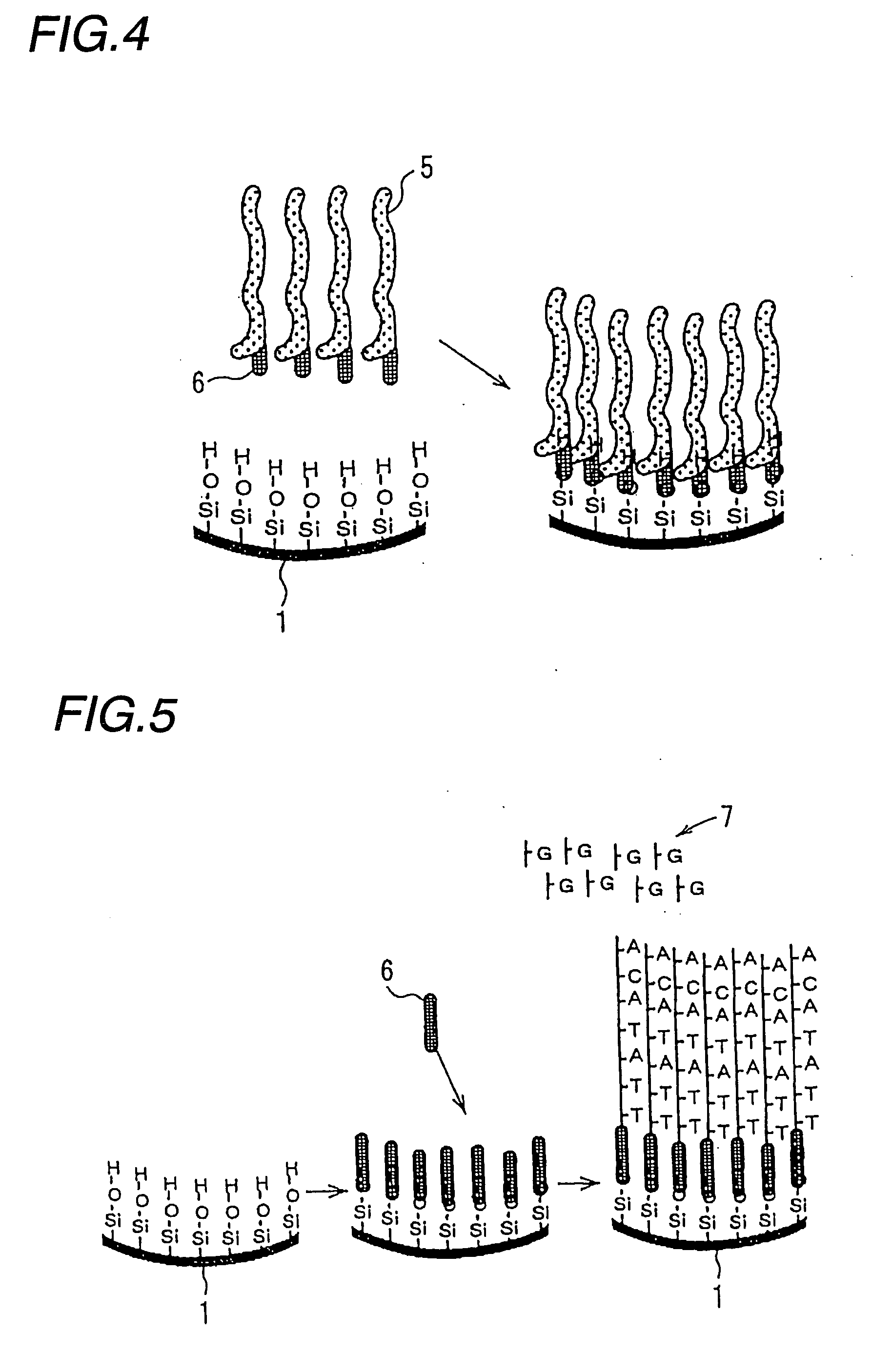
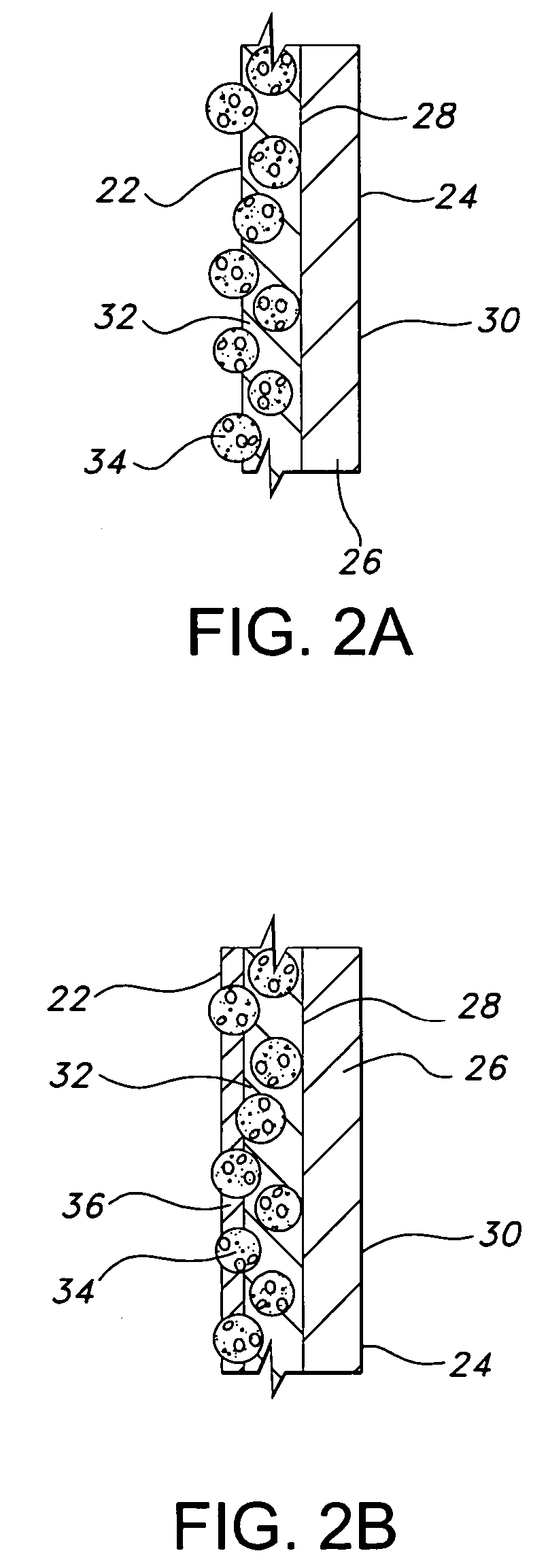
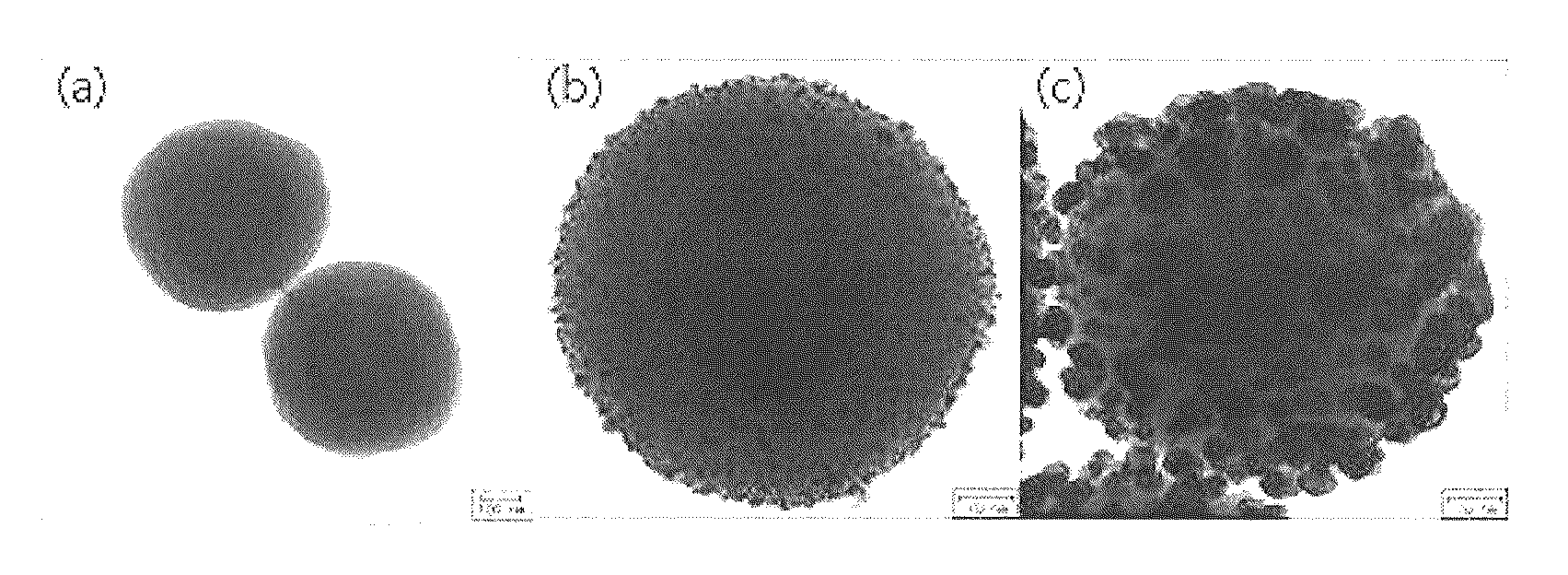
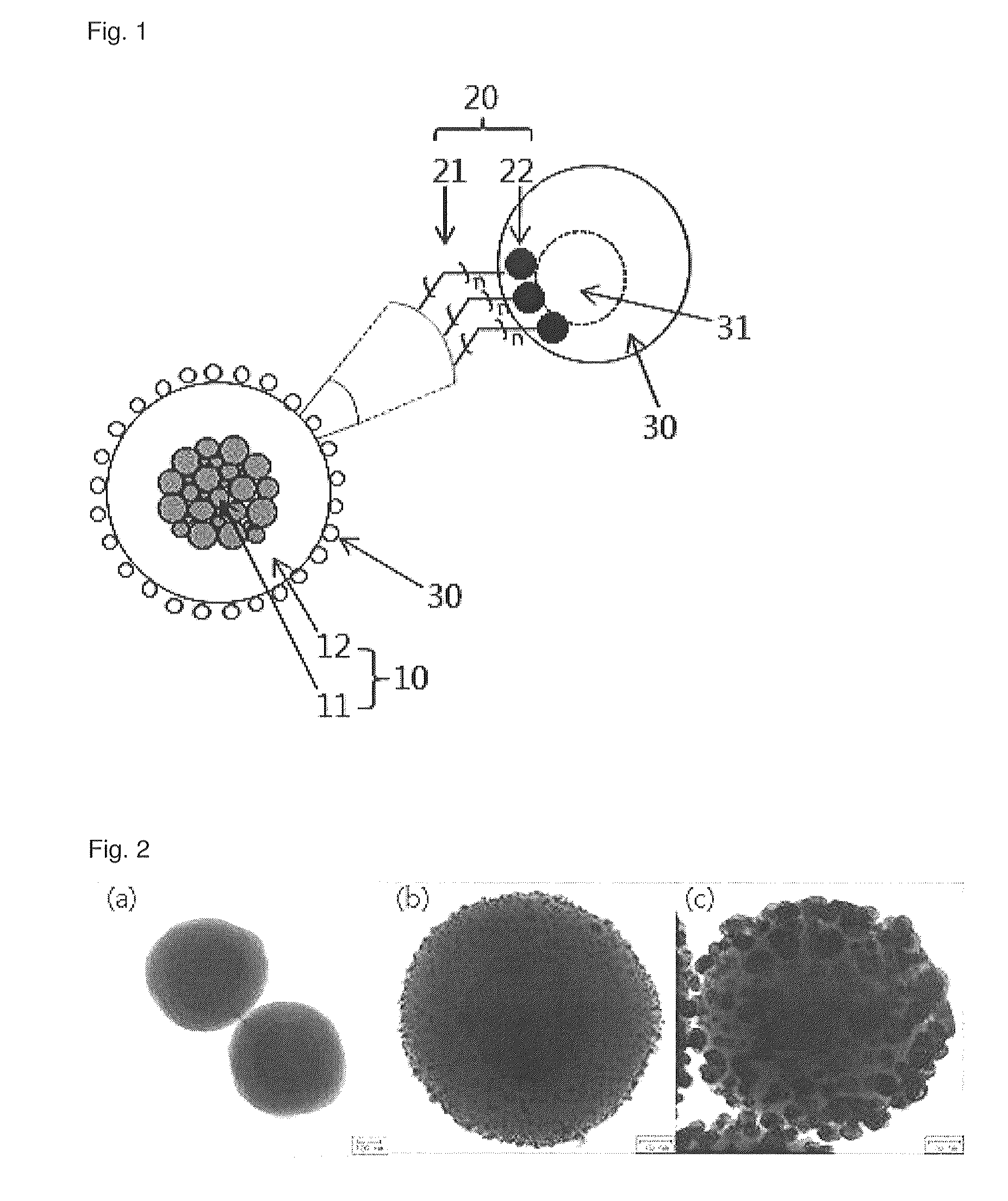
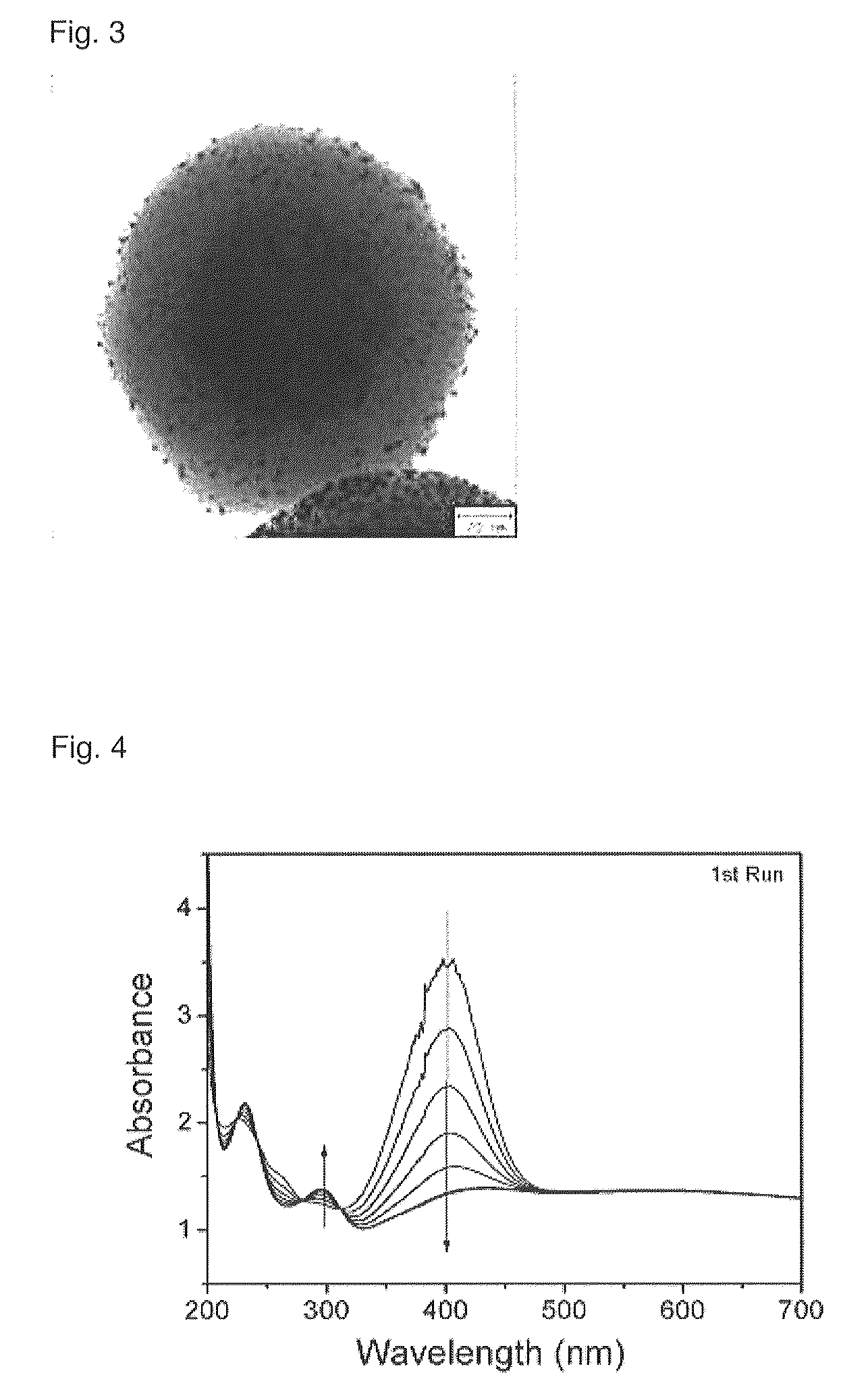
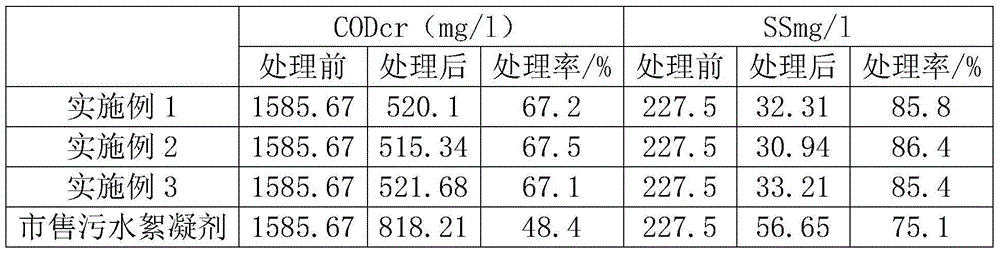
Nanoparticle-doped porous bead and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20100224831A1Improved photo-stabilityIncreased durabilityBleaching apparatusElectrostatic spraying apparatusMetal oxide nanoparticlesPhotoluminescence
Disclosed are a nanoparticle-doped porous bead with a highly enhanced photoluminescence without wavelength shift and improved durability, and a fabrication method thereof, the nanoparticle-doped porous bead comprising porous beads, and nanoparticles radially bonded onto homocentric spheres of the porous beads by an electrostatic attractive force, the homocentric sphere located inside the porous bead near a surface thereof, wherein the nanoparticles are photoluminescent nanoparticles or mixed nanoparticles of photoluminescent nanoparticles and another nanoparticles, wherein the another nanoparticle is one or more than two mixed, selected from a group consisting of magnetic nanoparticle, metallic nanoparticle and metal oxide nanoparticle.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Treatment of swimming pool water
InactiveUS6146539AEasy to controlReduction of unpleasant chloraminesSeparation devicesSedimentation separationAlgal growthPhosphate
Methods and compositions are disclosed for treating swimming pool waters in order to remove one or more nutrients necessary for algal growth and to accelerate the breakdown of objectionable chloramines within chlorinated pool waters. The target nutrients of preference are those containing phosphorus or nitrogen. Phosphorus nutrients are preferably removed by ion-exchange with finely divided lanthanum carbonate, or by direct precipitation in the pool with liquid lanthanum chloride. Nitrogen nutrients (including, in particular, chloramines) may be removed (possibly with the aid of catalysts and in separate reactors). The same reagents used to scavenge phosphates are useful in this regard, the nitrogen being released from the pool water as a nitrogenous gas. To allow the fine lanthanum carbonates to be conveniently handled in the pool environment, they may be linked to larger carrier particles, such as those of diatomaceous earth, or they may be embedded within porous beads formed from polymers or gels. In this form the reagent can be either added to, retained within and backwashed from pool filters, or added directly to pools (with or without a flocculating agent) and sucked to waste after settling. A variety of formulations for these purposes is disclosed.
Owner:NATURAL CHEM
Probe Beads for affirnity reaction and detection system
InactiveUS20050003556A1Stable to deteriorationStable to falling-offBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityGraphics
The present invention discloses affinity reaction probe beads having a structure comprising probe molecules immobilized on porous bead carriers provided with one or more individual identification signals among individual identification signals including optical signals such as digital signals using optical graphics, for example, bar codes or dot matrix bar codes, and color signals based on color information; and radio or electronic signals which issue individual information, such as IC tags, or tuning circuits or oscillation circuits for radio waves or electricity, a method for producing the affinity reaction probe beads, and an analyte detection system using the affinity reaction probe beads. By using the affinity reaction probe beads, the invention provides a reaction detection system which can be utilized for various physiological function diagnoses such as a diagnosis of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs).
Owner:EBARA CORP
Composite,fabrication and recovery methods thereof, catalyst, antibiosis or antiviral compounds
InactiveCN102728385AUniform and stable combinationEasy to recycleBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyAntibiosisRecovery method
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Polymers Selective for Nitro-Containing Compounds and Methods of Using the Same
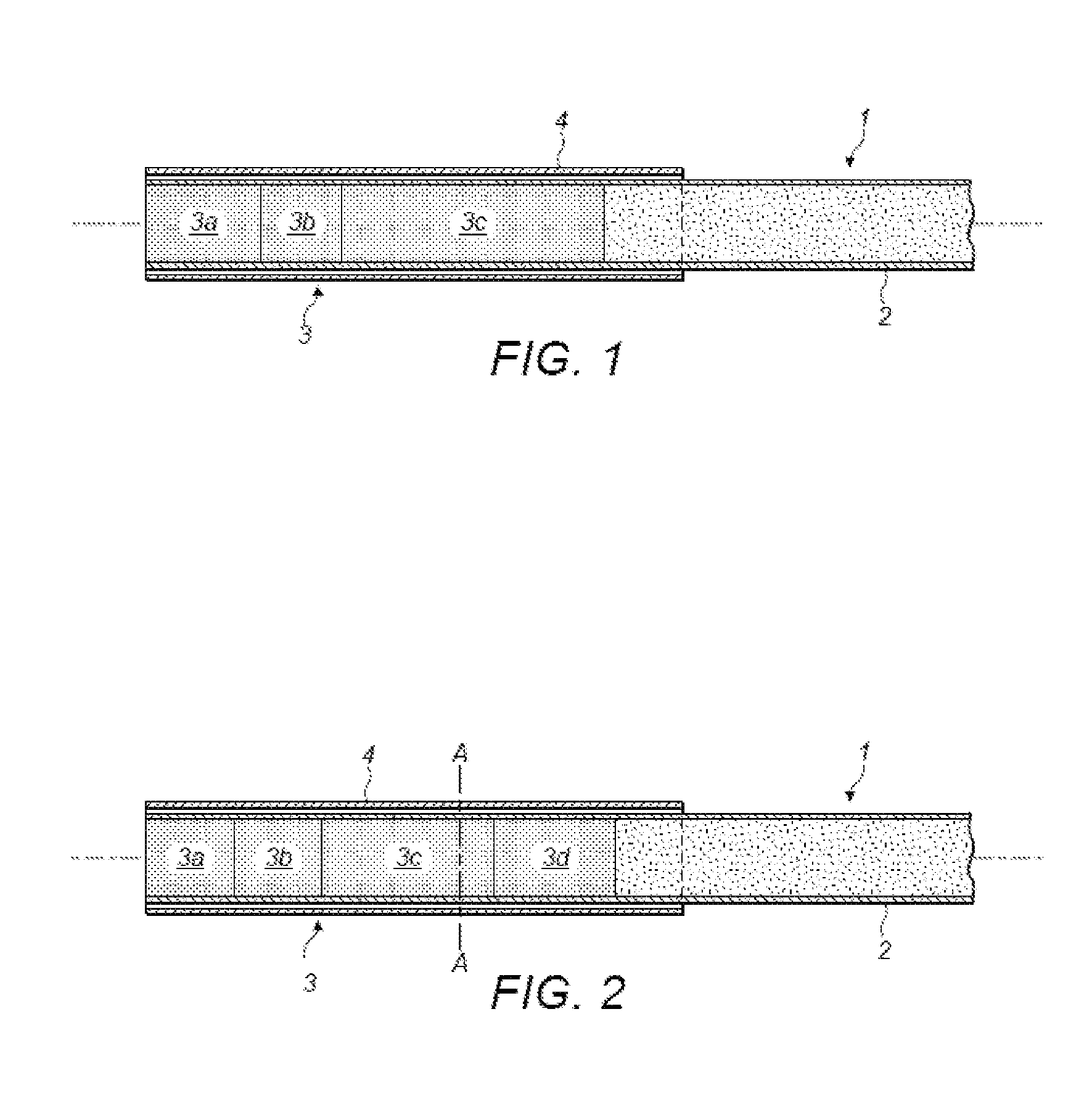
Porous beads are provided of a polymer of a non-acidic monomer and a cross-linker having polar functionality, one of which is hydrophilic, the other of which is hydrophobic, further comprising residues of polyvinyl alcohol. The beads may be molecularly imprinted or non-molecularly imprinted. The use of such beads in the removal of nitroso-containing compounds from material containing them is also disclosed. Also disclosed is a non-molecularly imprinted polymer which is selectively adsorbent for at least one tobacco specific nitrosamine in the presence of nicotine, said polymer being a polymerization product of a non-acidic monomer and a cross-linker having polar functionality, one of which is hydrophilic, the other of which is hydrophobic.
Owner:BRITISH AMERICAN TOBACCO (INVESTMENTS) LTD
Method of producing hierarchical porous beads
ActiveUS20050077221A1Quality improvementEasy to transportIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationEmulsionPorous beads
The present invention is a method of producing porous beads, which comprises the steps of providing a first liquid phase comprising a bead matrix material and essentially edgy templating particle(s), said particle(s) being treated with a surface modifying agent; providing a second liquid phase which is immiscible with the first liquid phase; contacting the first phase and the second phase under conditions resulting in an emulsion of droplets comprised of the first liquid phase dispersed in the continuous second liquid phase; transforming the droplets to mesoporous beads by solidification of the liquid; and removing the templating particle(s) from the beads without causing any essential change of the surrounding bead, whereby hierarchical networks of pores are provided in the beads.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
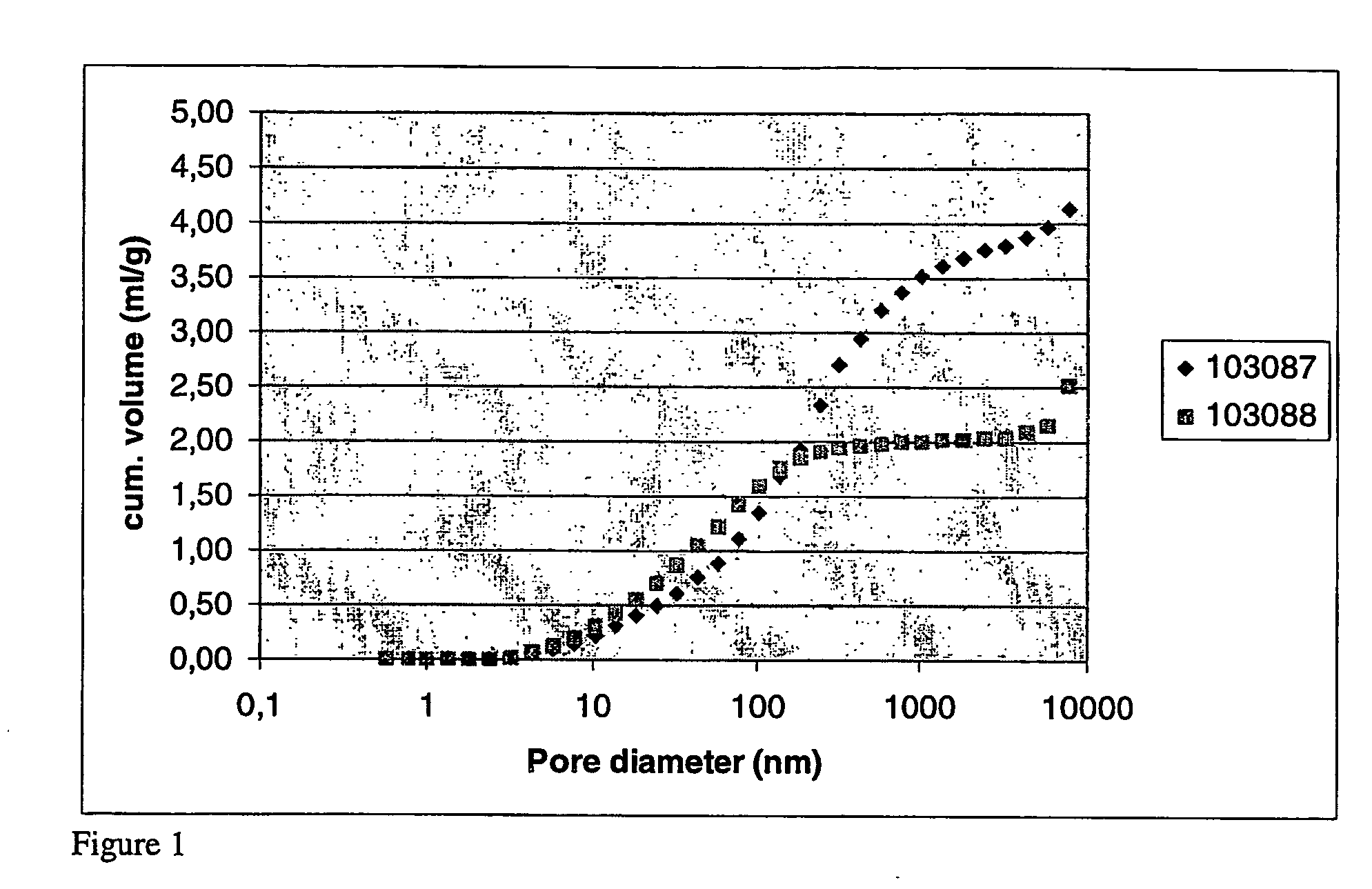
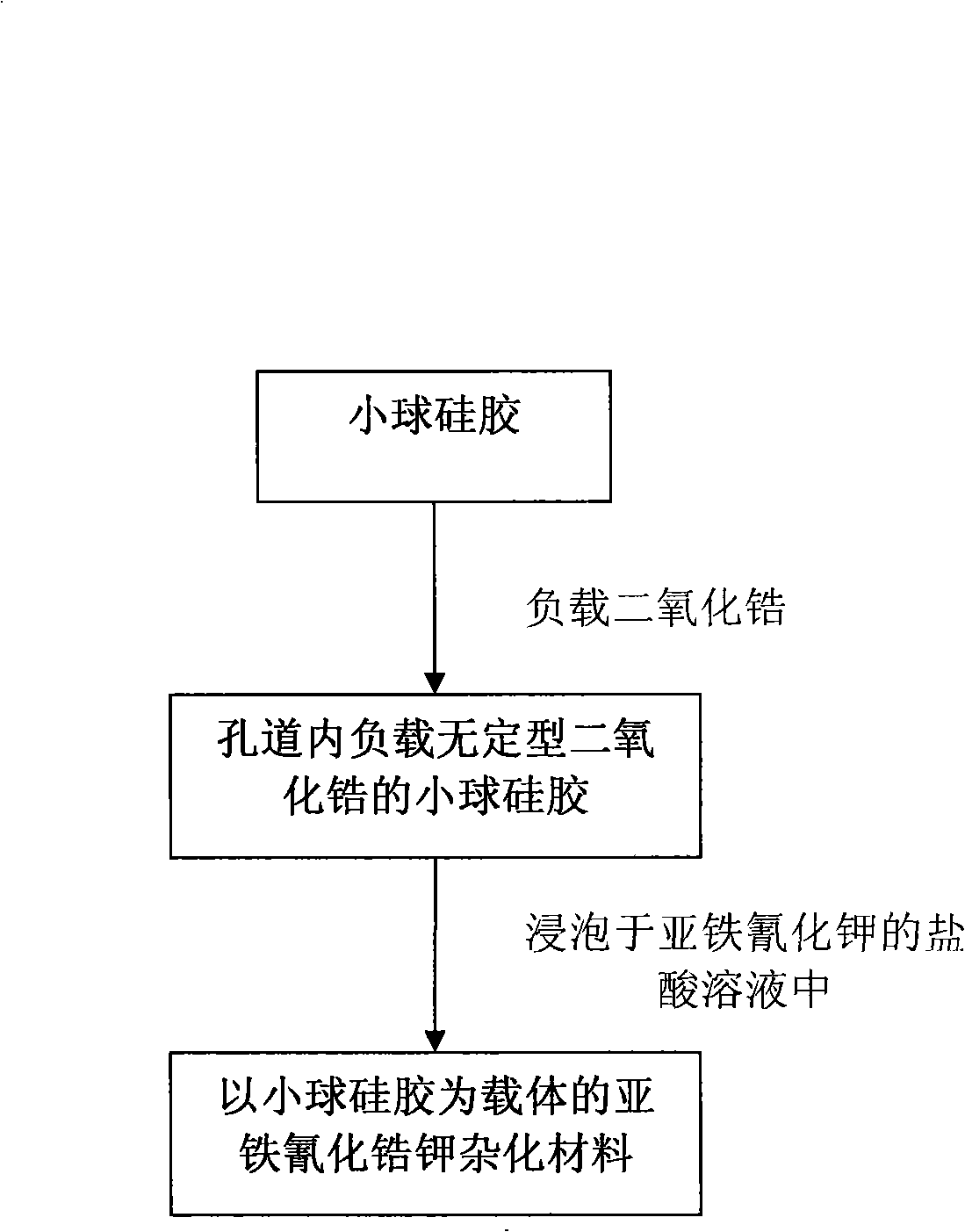
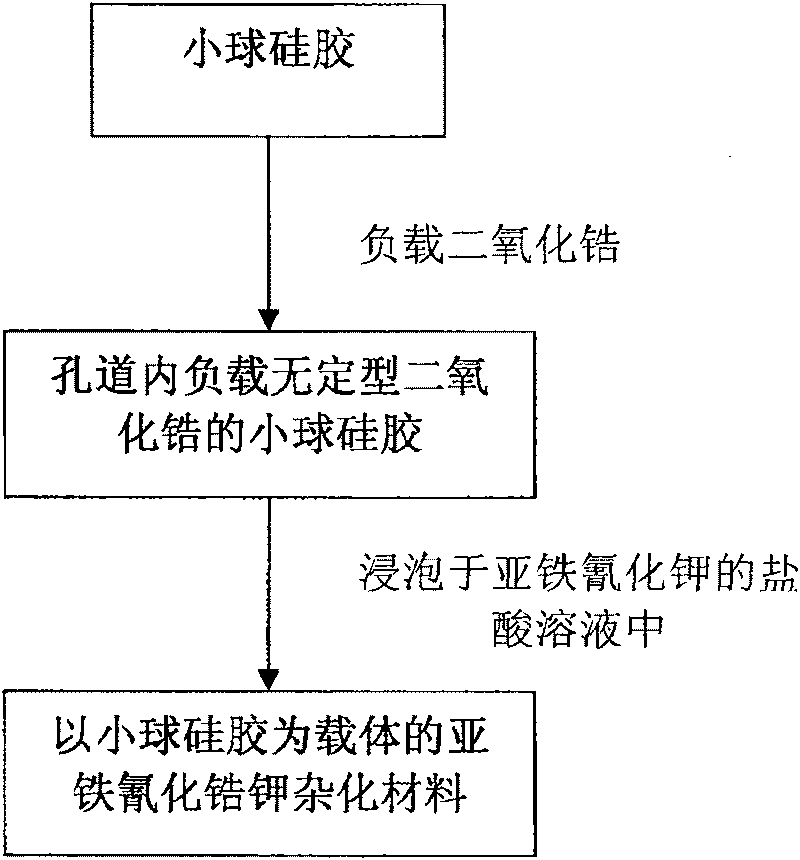
Preparation of potassium zirconium hexacyanoferrate using pellet silica-gel as carrier
ActiveCN101279249AThe load is easy to controlGood sphericityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPotassiumZirconium oxychloride
A preparation method for ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium taking bead silica gel as carrier relates to the preparation method for ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium with high specific surface and taking the bead silica gel as the carrier. In the method, fashioned porous bead silica gel react with the solution of zirconium oxychloride under the condition of heating and refluxing, acquired bead silica gel loaded with amorphous zirconium dioxide is dried and then dipped in the hydrochloric acid solution of yellow potassium ferrocyanide for reaction under stirring for 12-24 hours, thus the hybrid material of ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium with high specific surface and taking bead silica gel as the carrier is obtained. The load of ferrocyanide of the material can be adjusted and the material has strong adsorption capability for nuclide ion, high specific surface, good particle degree of sphericity, and being uneasy to break, which avoids the problem of oversized bed water resistance caused by using ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium particles separately; besides, owing to the existence of Zr-O-Si covalent bond, nano ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium particles can closely combine with the bead silica-gel, thus being uneasy to run away in the process of waste water treatment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
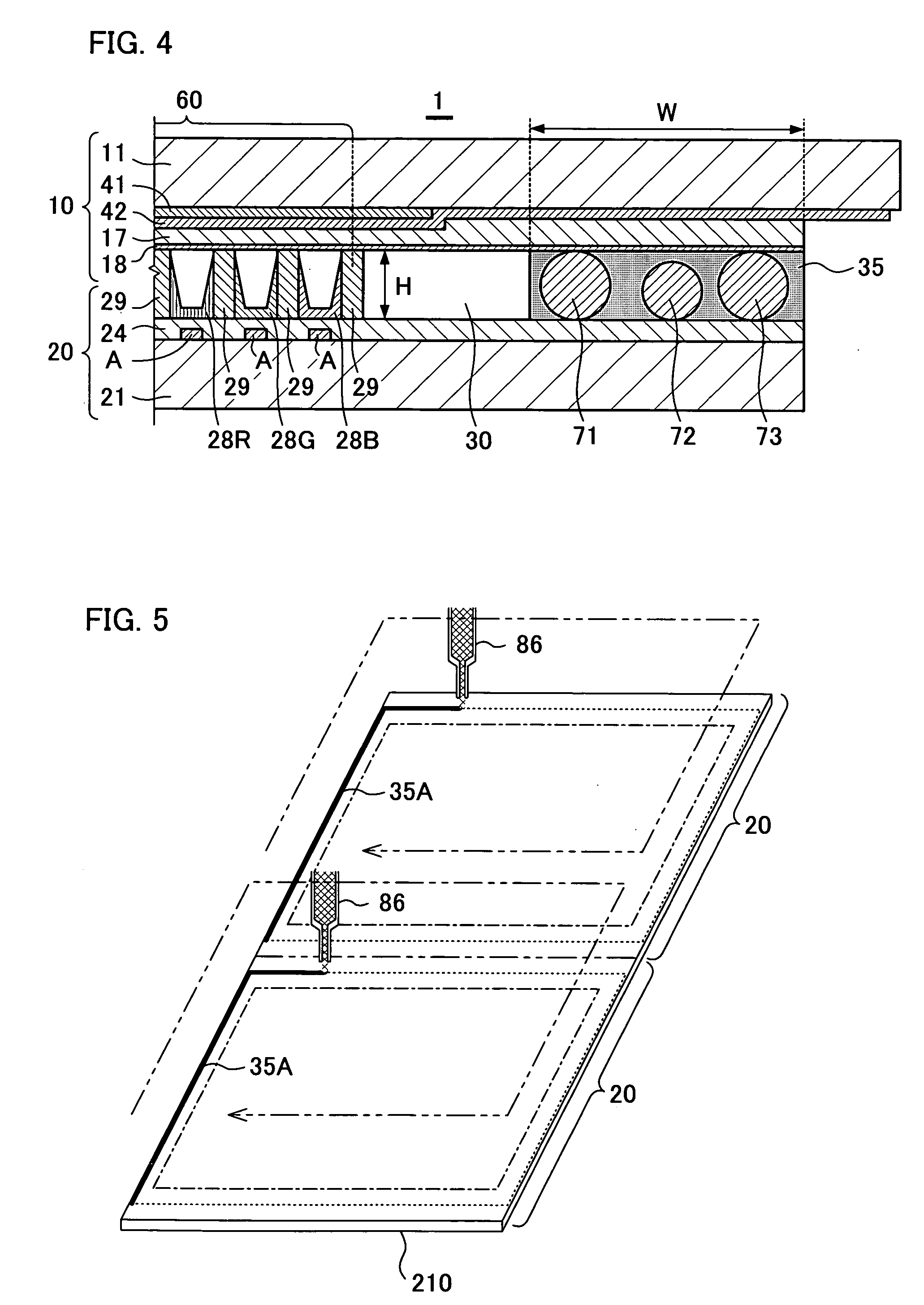
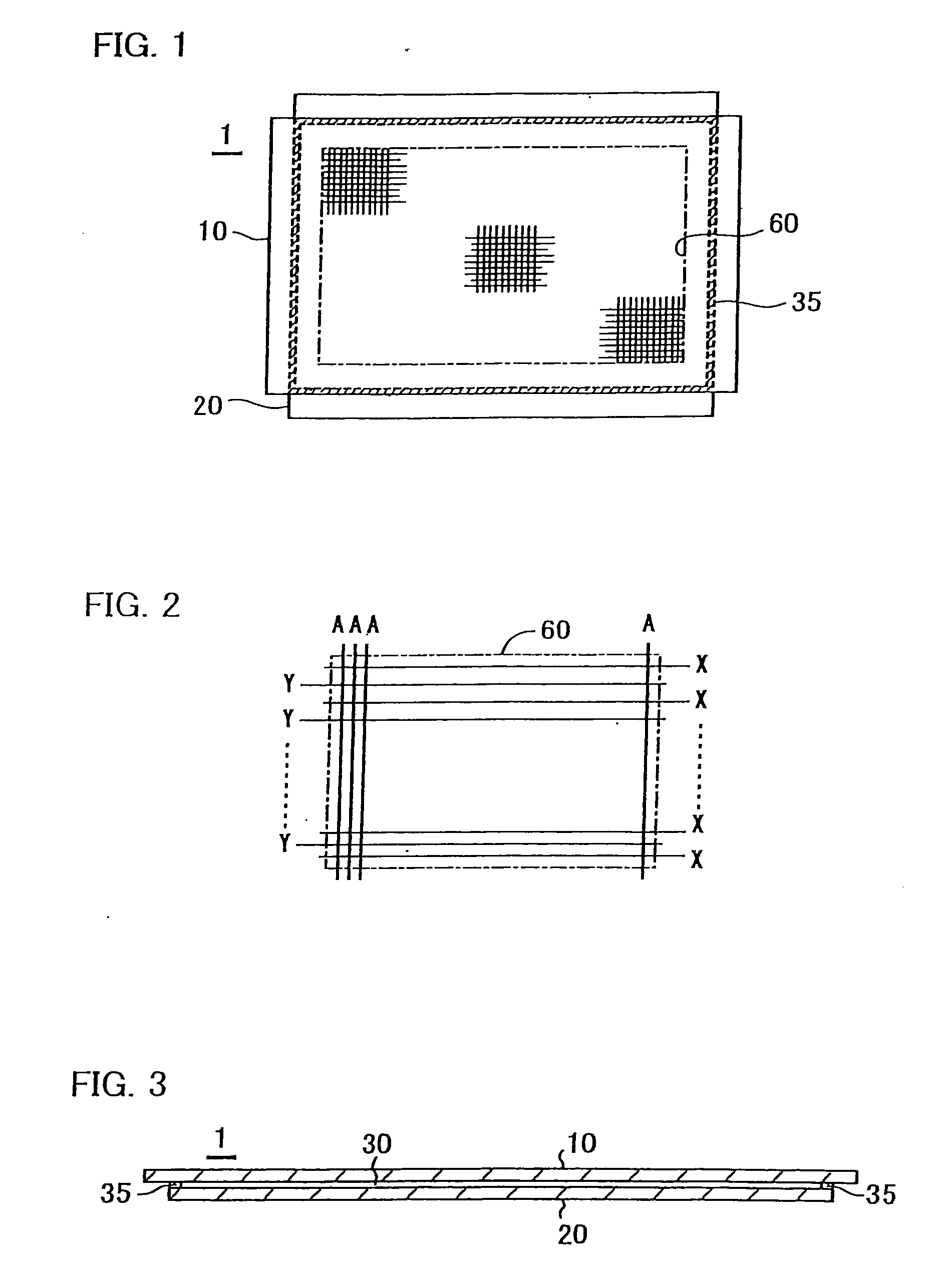
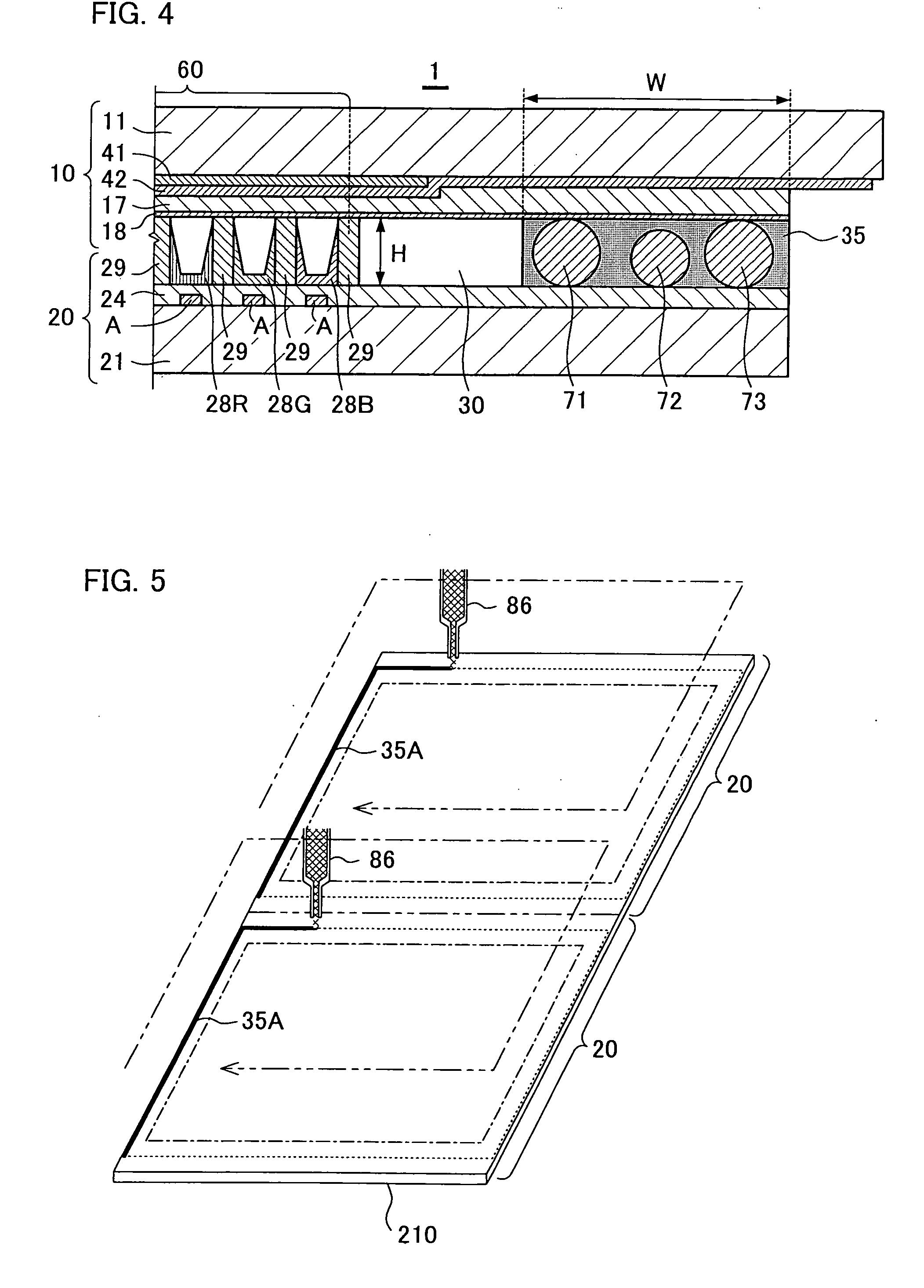
Plasma display panel
InactiveUS20060001373A1Avoid noiseUniform thicknessSustain/scan electrodesGas discharge connecting/feedingEngineeringPlasma display
A plasma display panel includes a front substrate and a rear substrate that are opposed to each other with a discharge gas space between them, and a sealing material for sealing the front substrate and the rear substrate at their peripheral portions. The sealing material contains an appropriate quantity of spacers so that a thickness of the plasma display panel is uniform along the entire perimeter of the sealing portion between the front substrate and the rear substrate. The sealing material contains non-porous beads as the spacers, preferably at a ratio within the range of 0.05-2.0 wt %.
Owner:FUJITSU HITACHI PLASMA DISPLAY LTD
Biocidal particles of methylated polystyrene
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
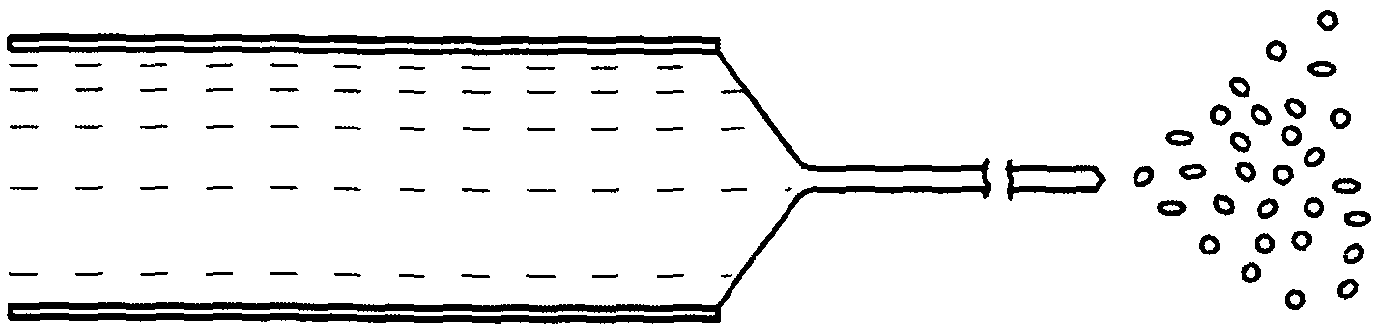
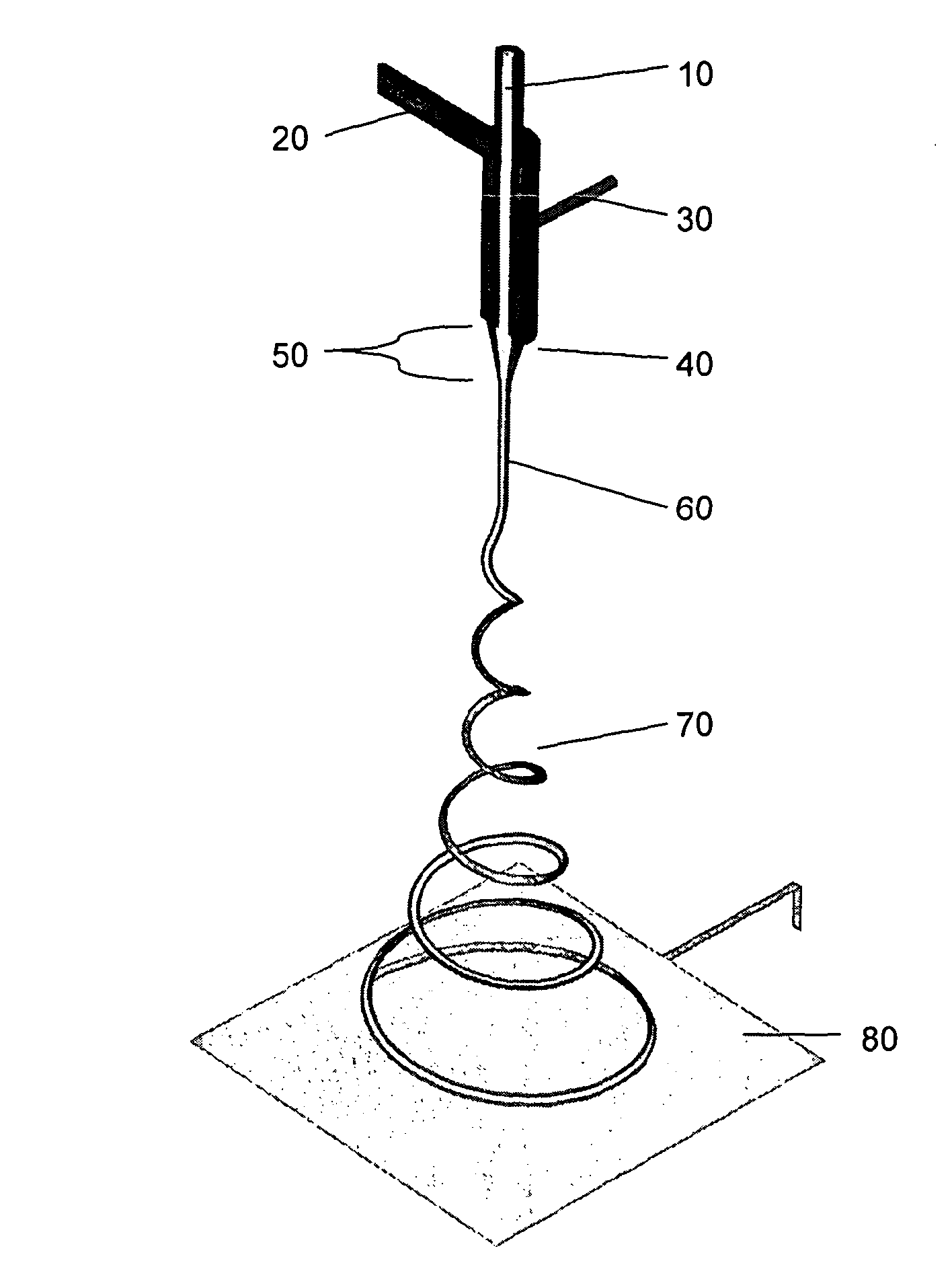
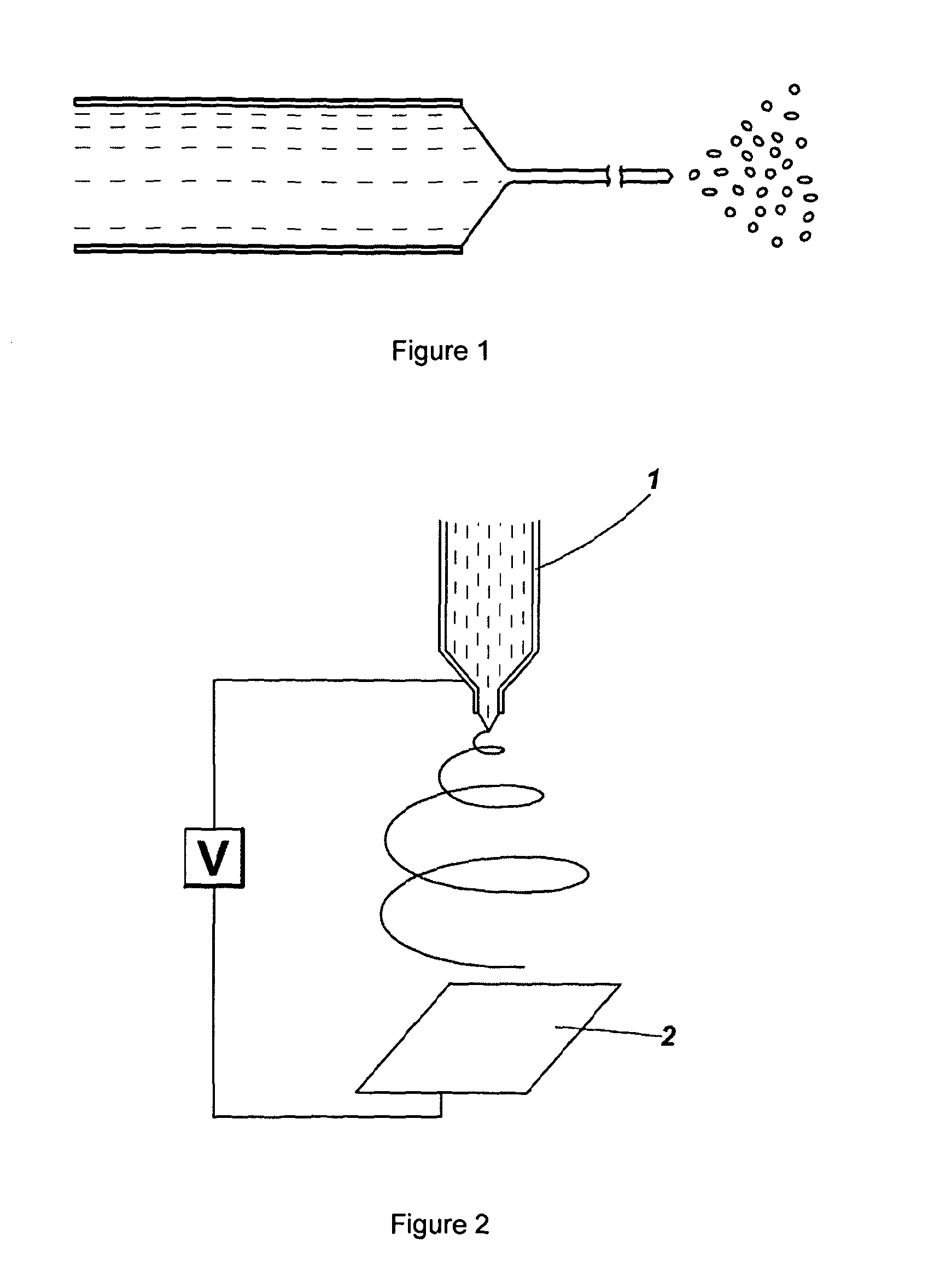
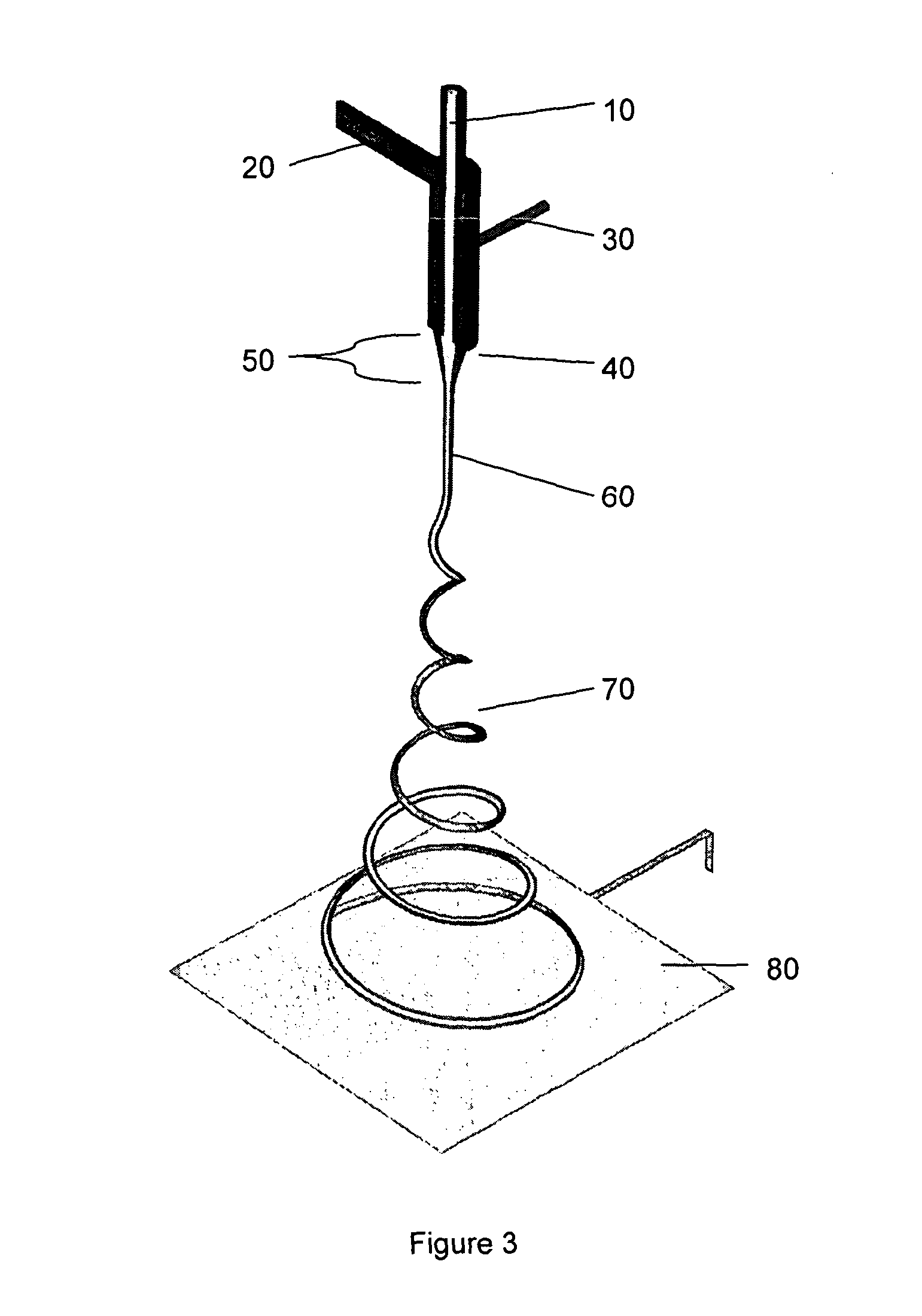
Method of electrospinning fibres
A method of electrospinning fibres is disclosed. The fibres have an inner core surrounded by a porous outer shell. The method comprises co-electrospinning first and second liquids as core and shell respectively, the second liquid surrounding the first liquid in a jet issuing from a Taylor cone, wherein the first and second liquids are miscible or semi-miscible with each other, such that pore generation is driven in the shell of the fibre. The liquids may be solutions or melts. The electrical conductivity, viscosity, miscibility and other parameters of the liquids determine the structure of the produced fibres. As well as producing fibres having a porous shell there are described methods of co-electrospraying porous beads as well as core- shell vesicles having a porous shell. The methods may be used to produce hydrogen storage fibres, vesicles and beads.; The methods may also be used for producing controlled drug- delivery fibres, vesicles and beads.
Owner:科学技术设备委员会
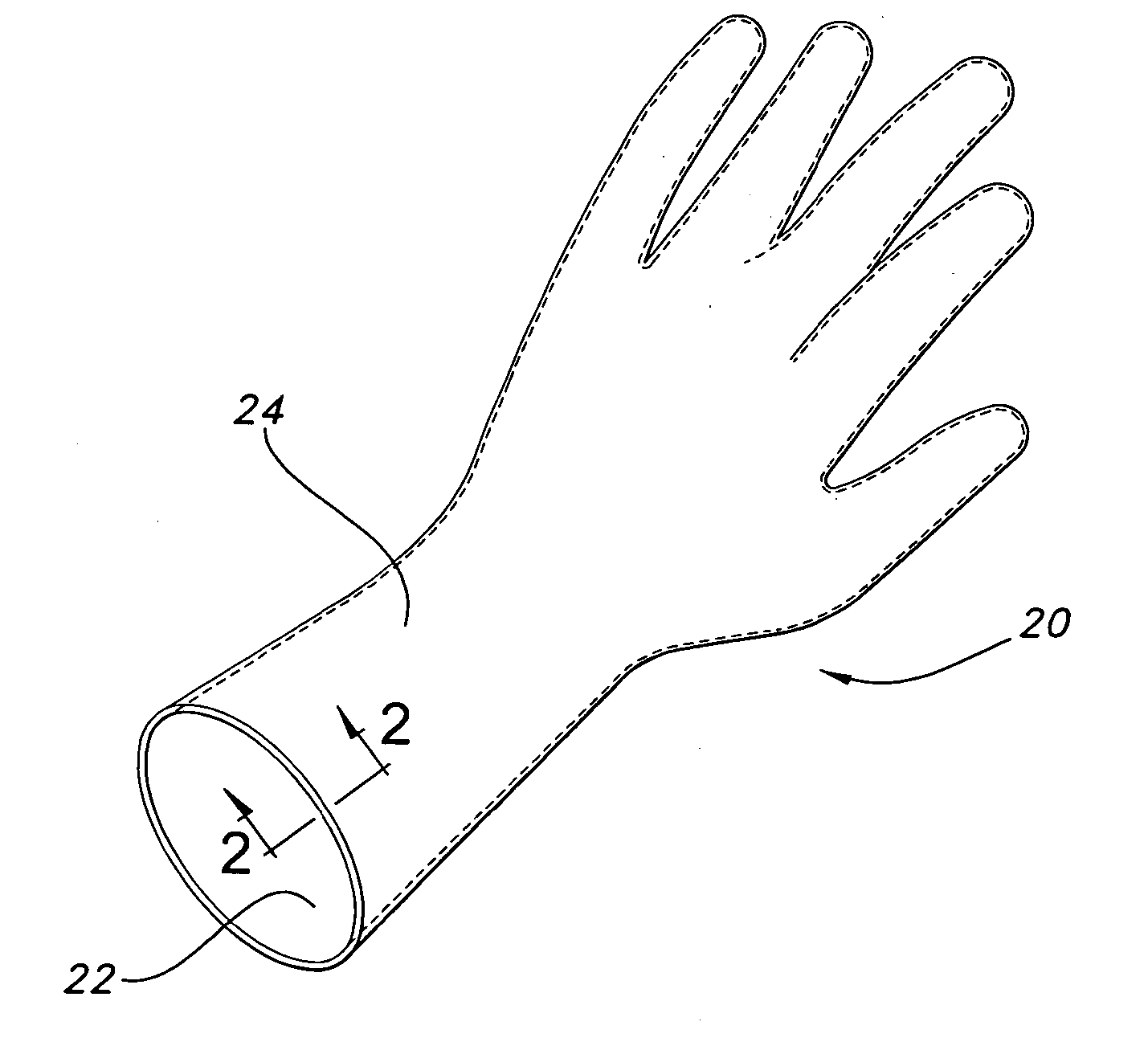
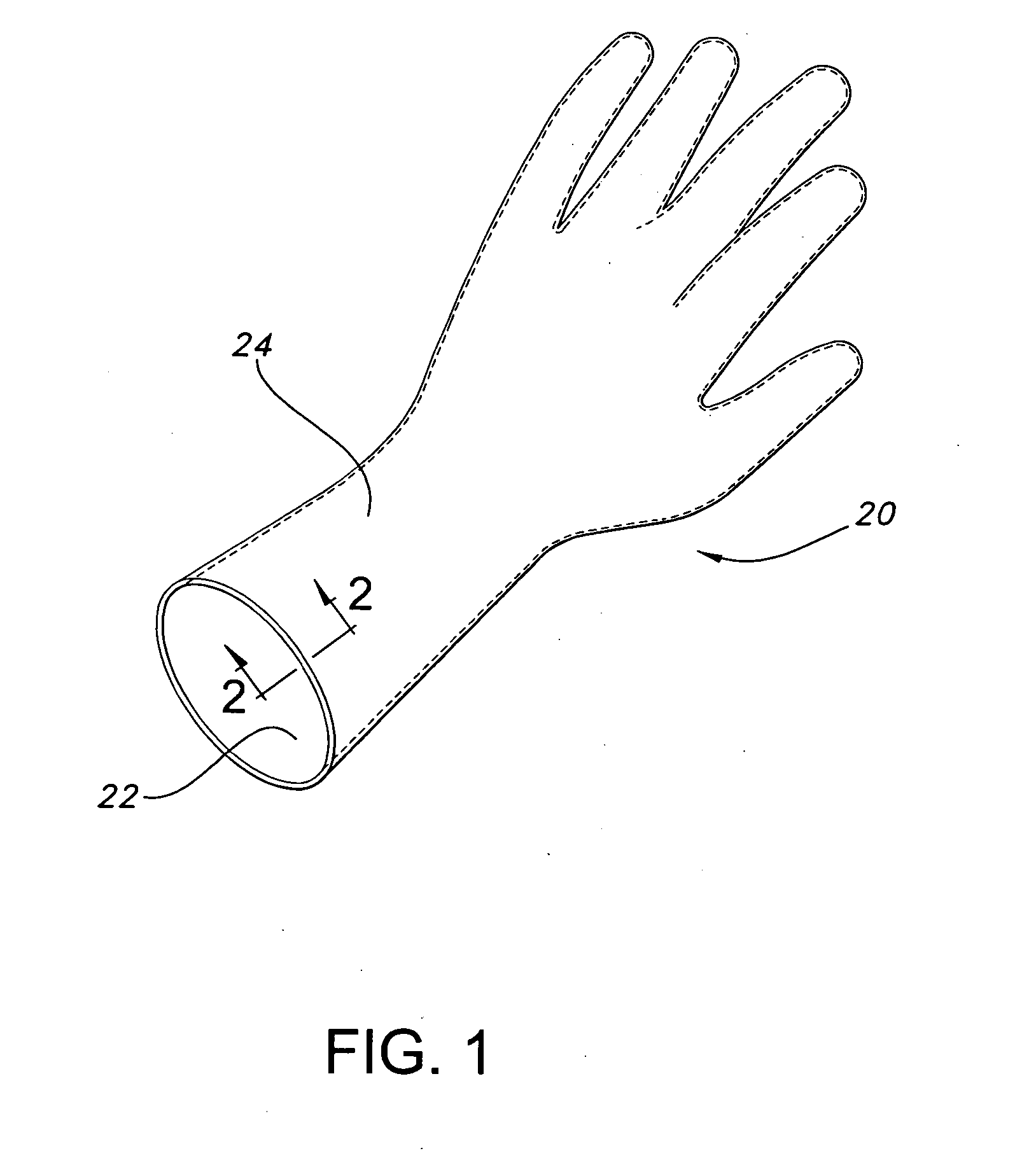
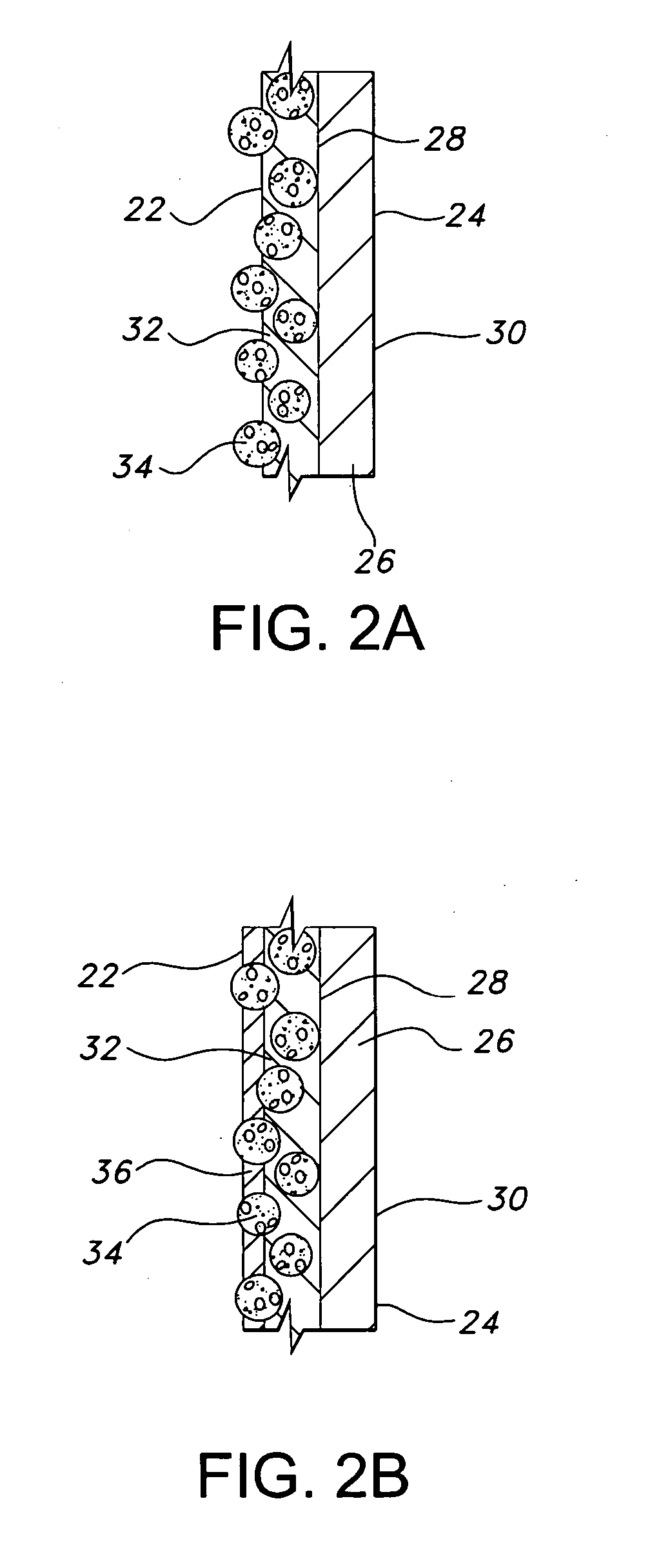
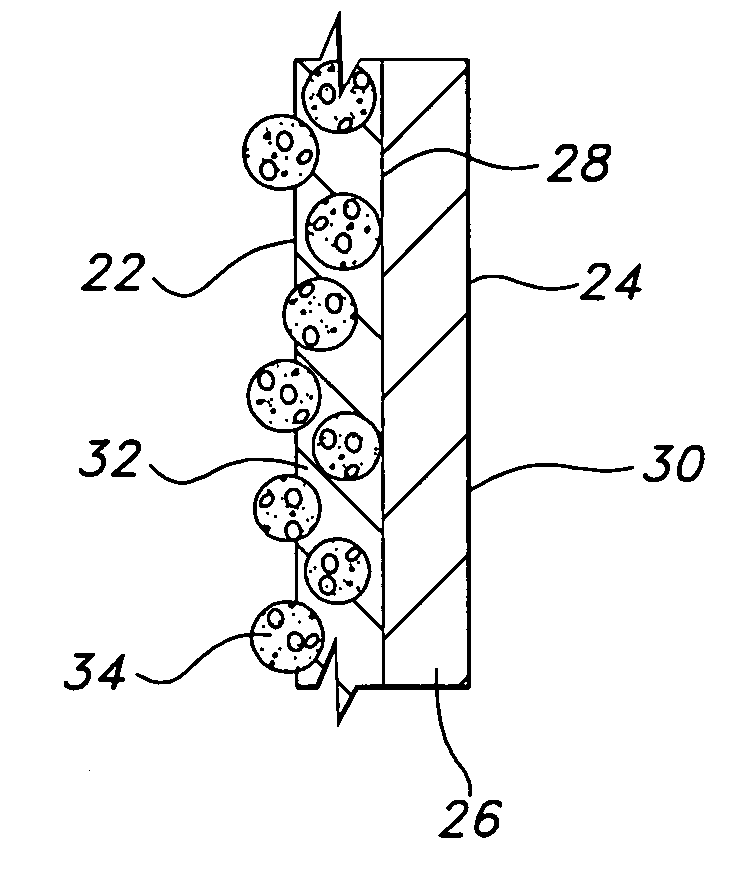
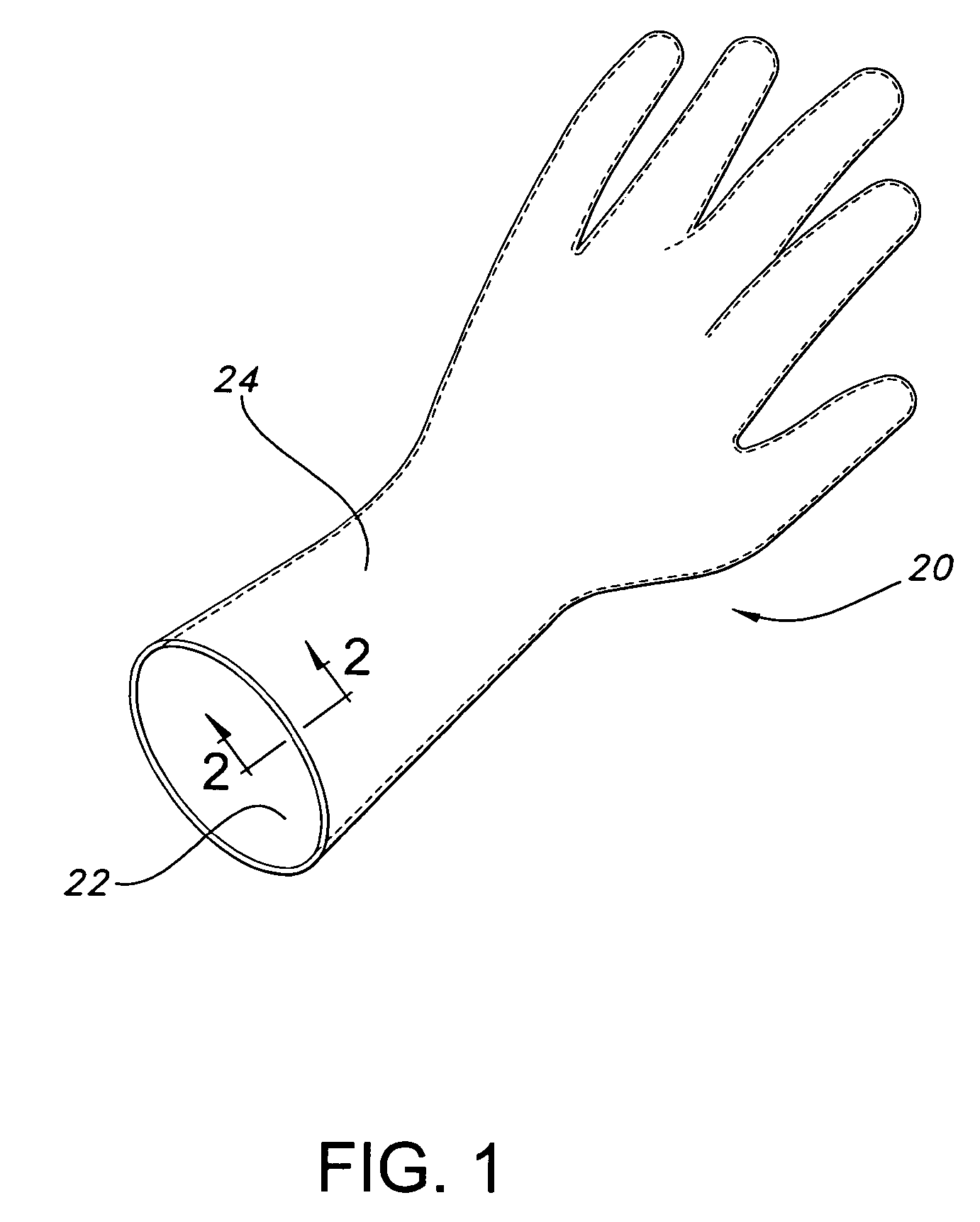
Glove with medicated porous beads
An elastomeric article includes a substrate body formed from an elastomeric material, and a plurality of porous beads capable of containing a treatment within the pores of the beads and dispensing the treatment to an end user.
Owner:O&M HALYARD INC
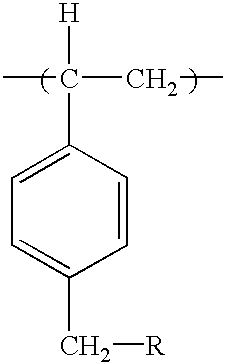
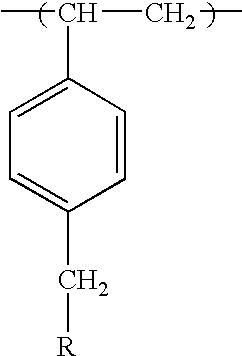
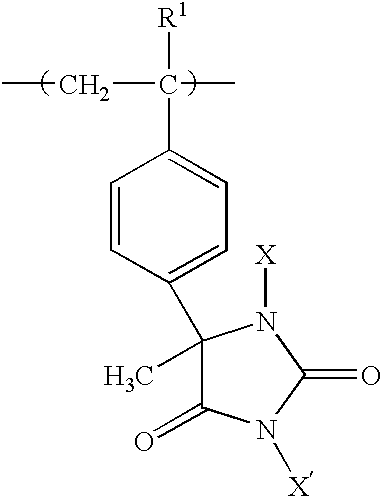
Biocidal polystyrene hydantoin particles
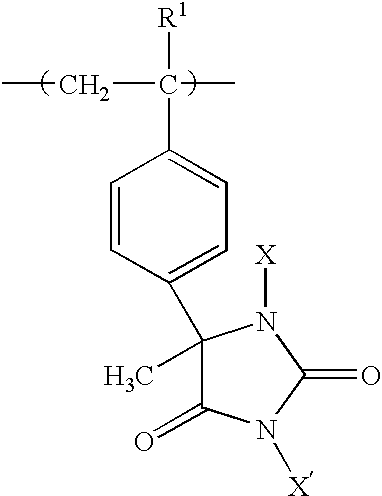
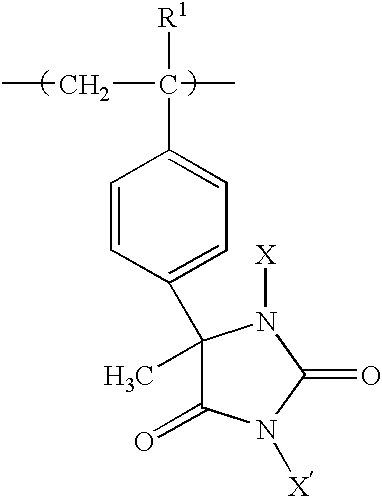
InactiveUS6852312B2Prevent and minimizePrevents and minimizes noxious odorBiocidePowder deliveryProtonationPolystyrene bead
Method for preparing biocidal halogenated polystyrene hydantoins. The biocidal polymers poly-1,3-dichloro-5-methyl-5-(4′-vinylphenyl)hydantoin, poly-1,3-dibromo-5-methyl-5-(4′-vinylphenyl)hydantoin, and their monohalogenated alkali metal salts and protonated derivatives have been prepared as porous beads by use of highly crosslinked polystyrene beads as starting materials. The porous beads will be useful in water and air disinfection applications when employed in cartridge filters and carafes (for water), as well as for controlling noxious odor when mixed with absorbent materials in items such as disposable diapers, incontinence pads, bandages, sanitary napkins, pantiliners, mattress covers, shoe inserts, sponges, animal litter, carpets, fabrics, and air filters or the like.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Method of electrospinning fibres
InactiveUS20130214457A1Improve conductivityGood miscibilityLiquid surface applicatorsReactant parameters controlFiberEngineering
A method of electrospinning fibres is disclosed. The fibres have an inner core surrounded by a porous outer shell. The method comprises co-electrospinning first and second liquids as core and shell respectively, the second liquid surrounding the first liquid in a jet issuing from a Taylor cone, wherein the first and second liquids are miscible or semi-miscible with each other, such that pore generation is driven in the shell of the fibre. The liquids may be solutions or melts. The electrical conductivity, viscosity, miscibility and other parameters of the liquids determine the structure of the produced fibres. As well as producing fibres having a porous shell there are described methods of co-electrospraying porous beads as well as core-shell vesicles having a porous shell. The methods may be used to produce hydrogen storage fibres, vesicles and beads. The methods may also be used for producing controlled drug-delivery fibres, vesicles and beads.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Biocidal particles of methylated polystyrene
InactiveUS20100029797A1Few stepsLess chlorine outgassingBiocidePeptide preparation methodsPolystyrene beadLitter
Methylated polystyrene having pendant N-halamine and N-halamine precursor groups. Biocidal particles have been prepared by reacting highly crosslinked methylated polystyrene beads as starting materials with various N-halamine precursor compounds. The resulting polymer beads are halogenated with chlorine or bromine. The porous beads will be useful in disinfection applications as well as for sanitization and controlling noxious odor when mixed with absorbent materials in items such as disposable diapers, infant swimwear, incontinence pads, bandages, sanitary napkins, pantiliners, mattress covers, shoe inserts, sponges, animal litter, carpets, and fabrics.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Glove with medicated porous beads
An elastomeric article includes a substrate body formed from an elastomeric material, and a plurality of porous beads capable of containing a treatment within the pores of the beads and dispensing the treatment to an end user.
Owner:O&M HALYARD INC
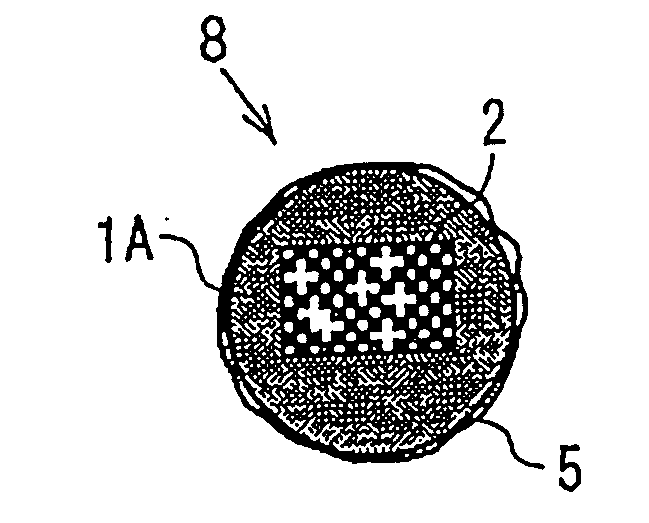
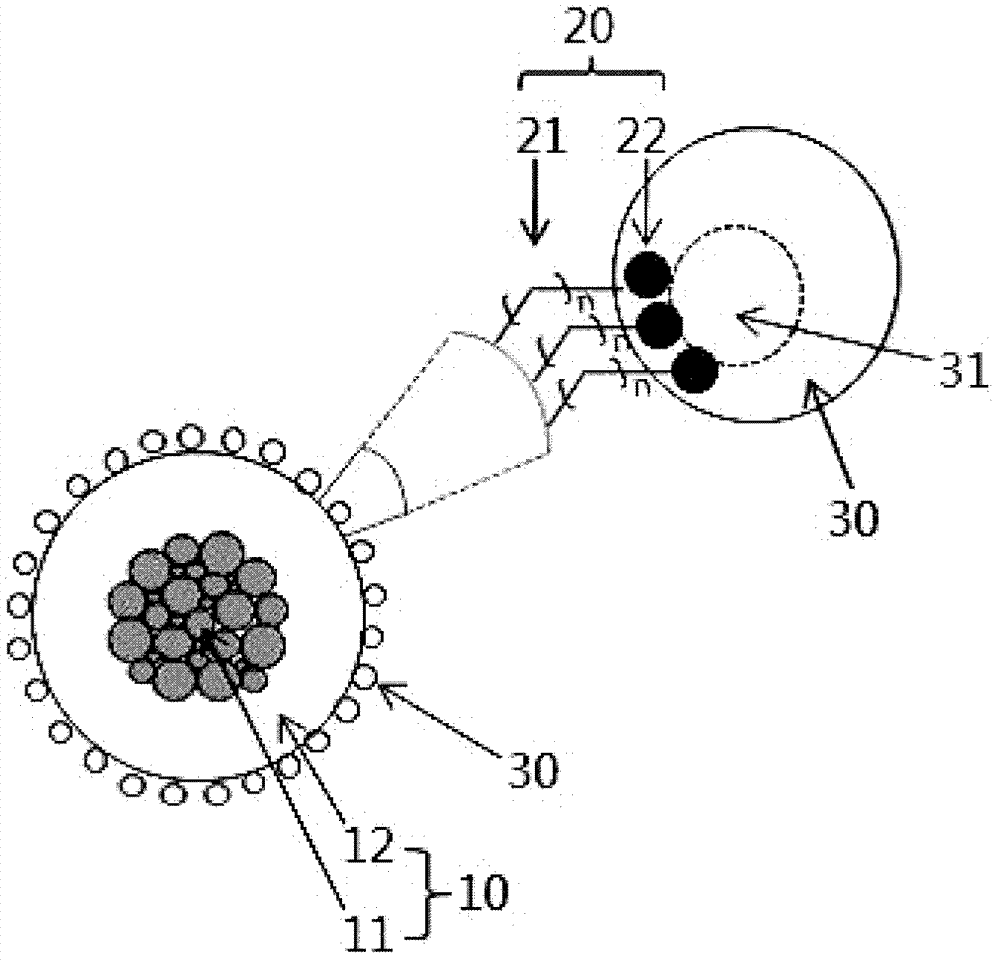
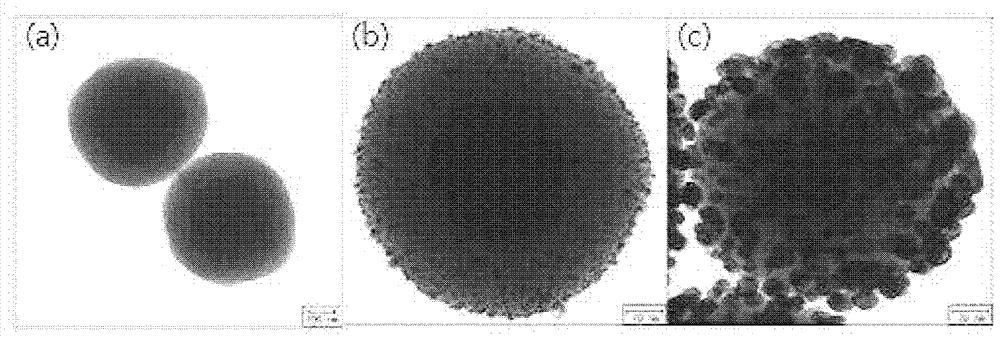
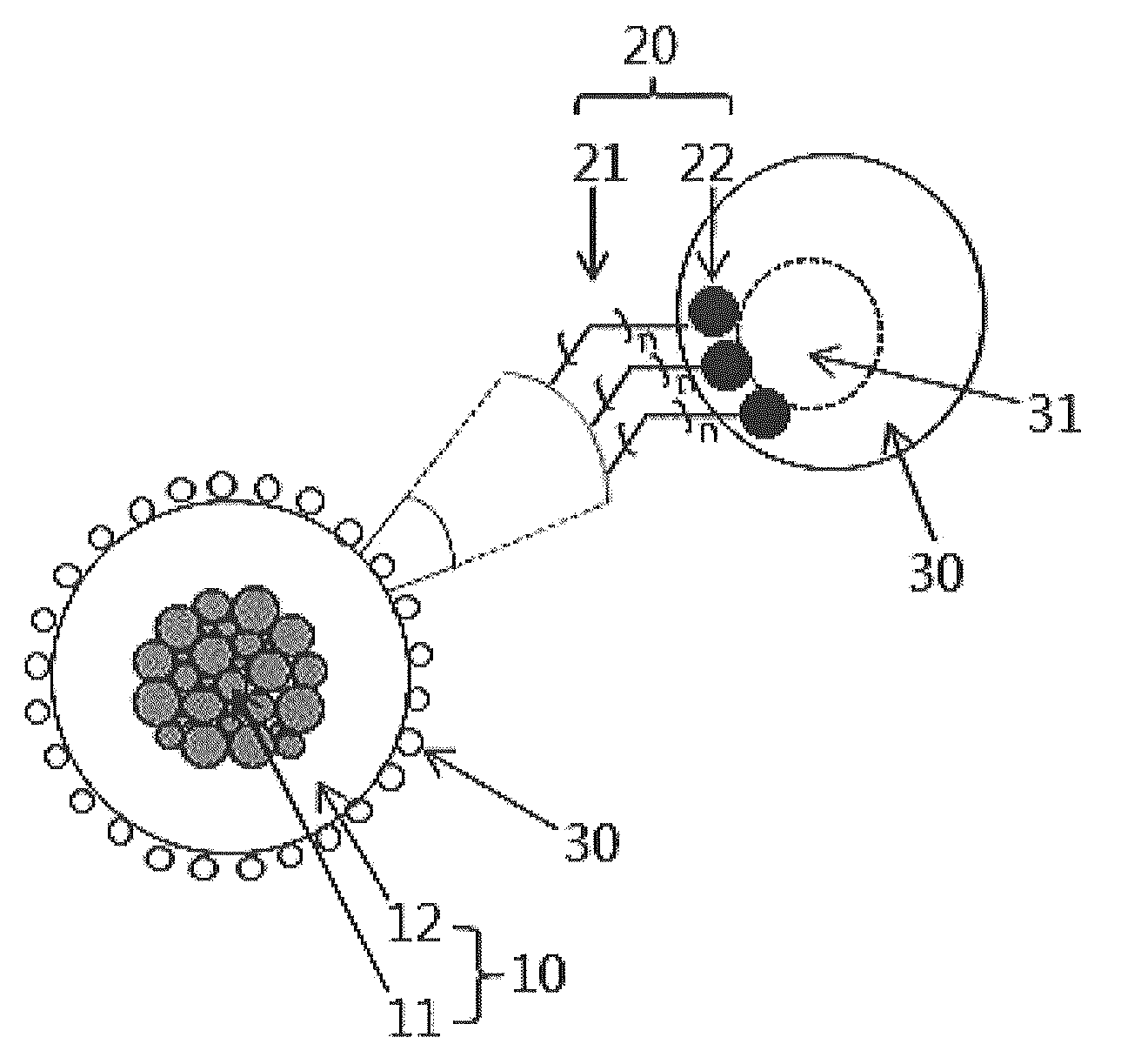
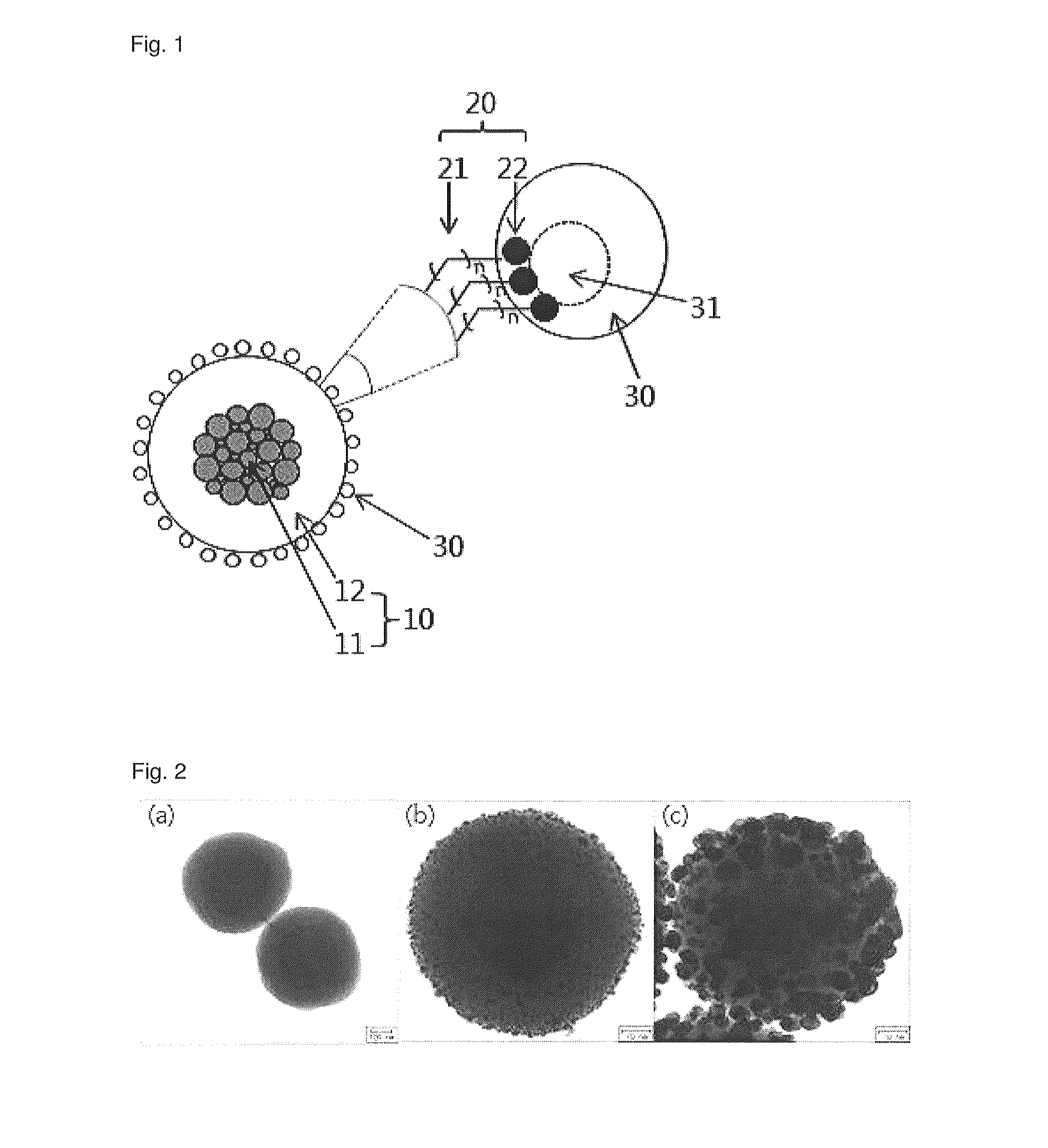
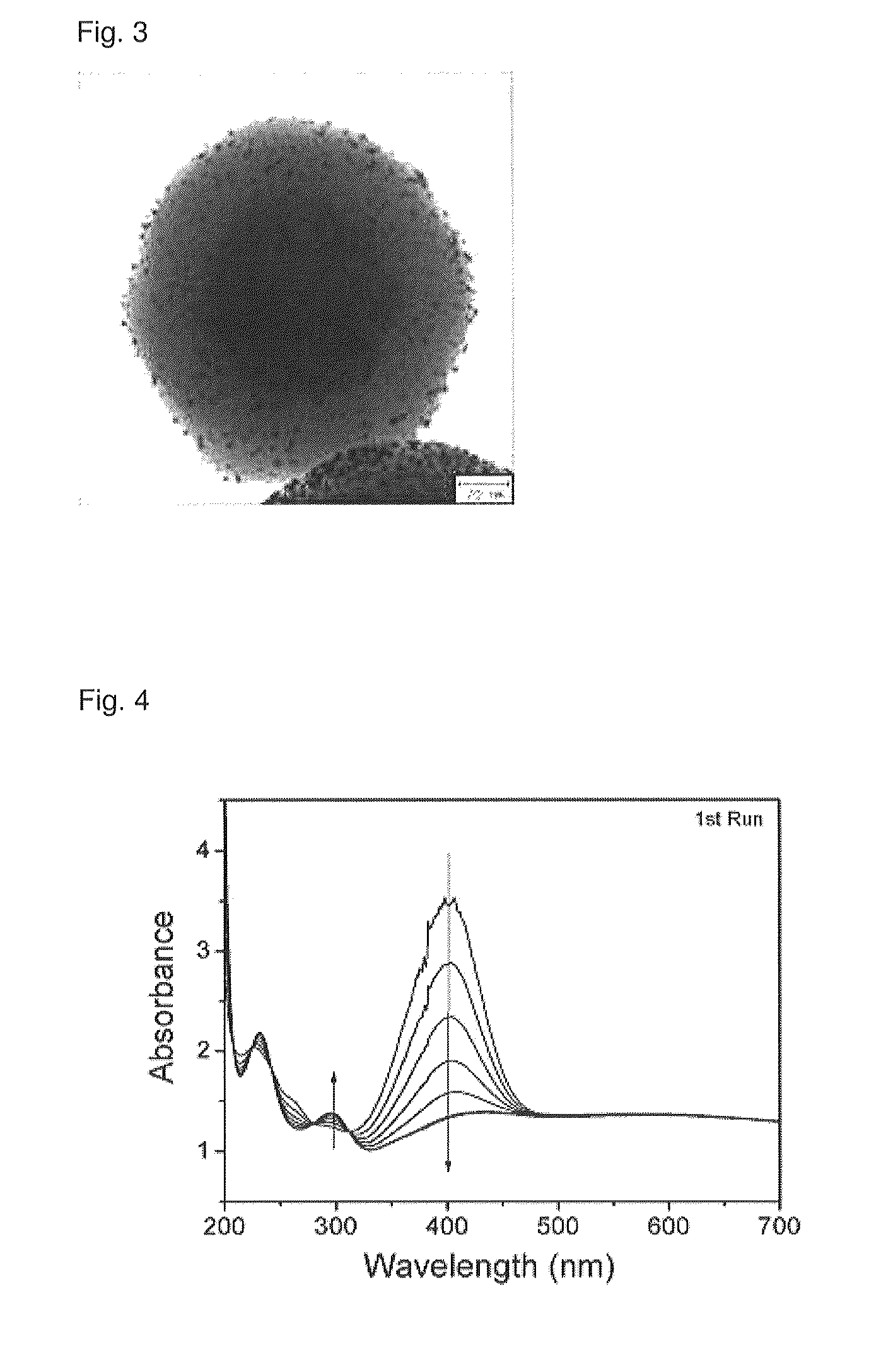
Recyclable porous bead - satellite nanoparticle composite and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20120263777A1Improve recovery performanceEasy to useCosmetic preparationsMaterial nanotechnologyNanoparticleCore shell
An environment-friendly porous bead-satellite nanoparticles composite which has excellent recovery and repeated usage performance and can be used as a catalyst, an antiviral agent, or an antimicrobial, and a fabrication method thereof are provided. The porous bead-satellite nanoparticles composite includes a porous bead, a molecule having a first end coupled to the surface of the porous bead and including a functional group at a second end, and satellite nanoparticles coupled to the functional group, wherein the porous bead may have a core-shell structure including a cluster core of nanoparticles and a porous bead shell covering the cluster core.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Automatic electric cooker production line and process
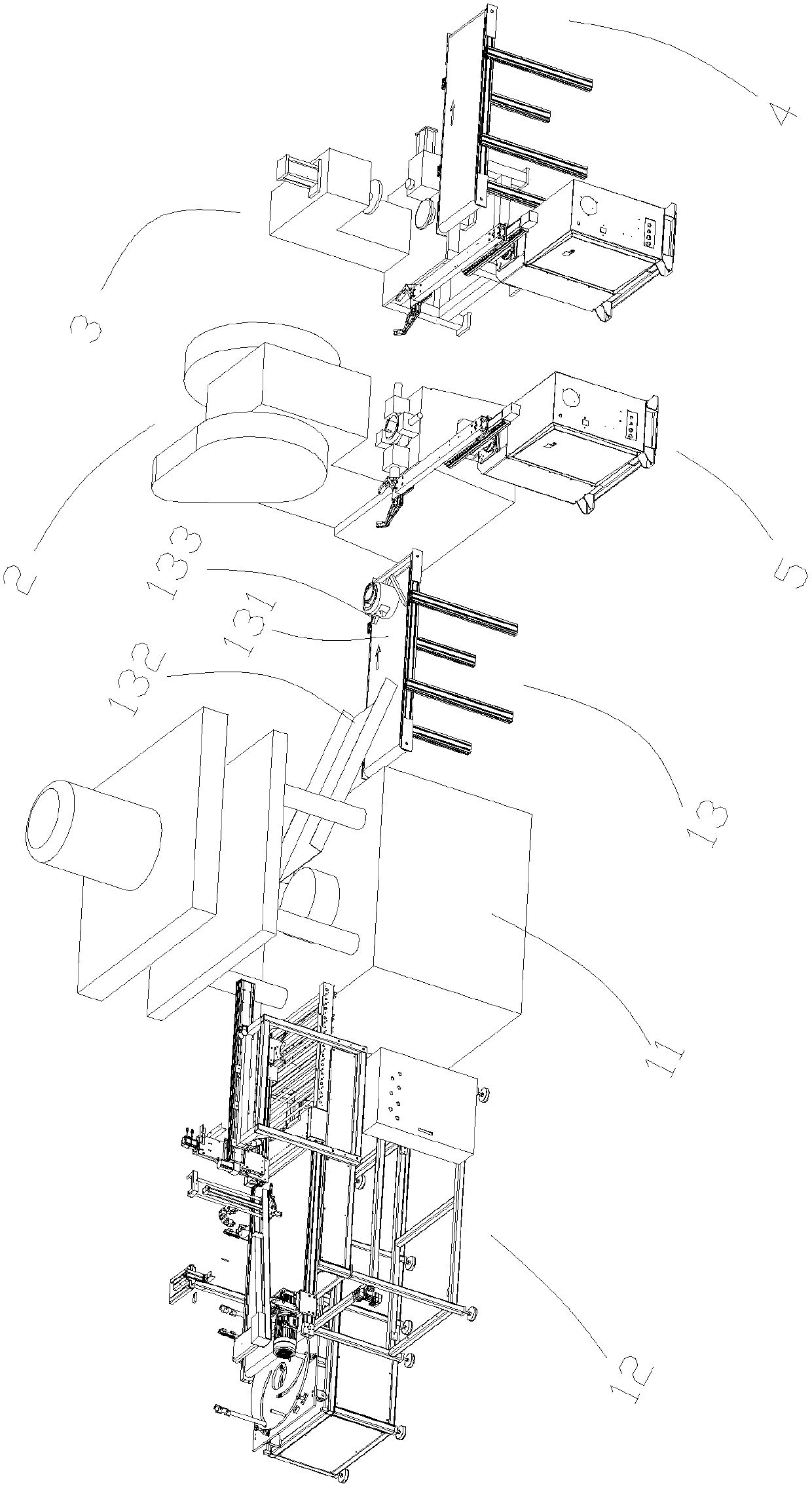
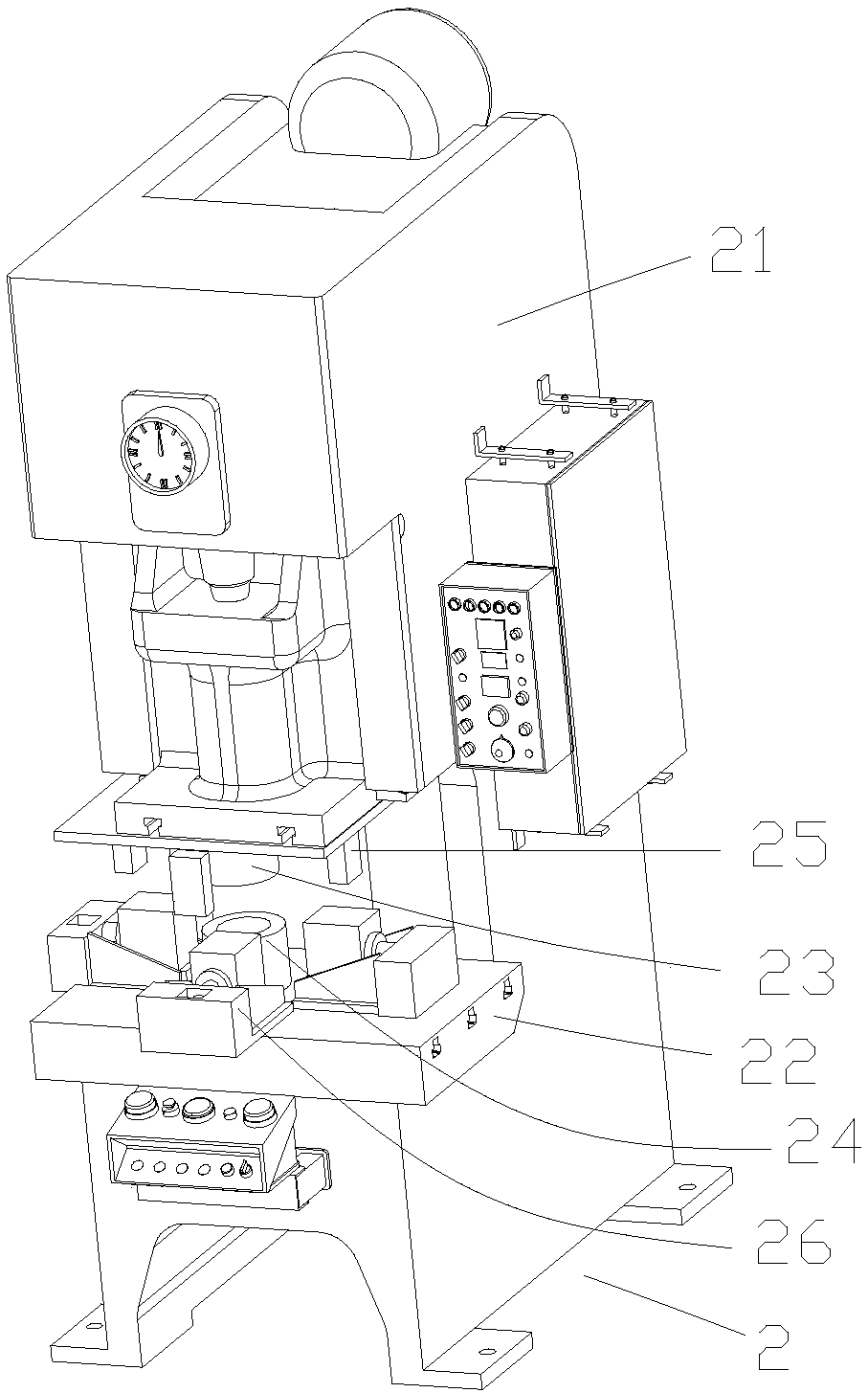
PendingCN107755565AImprove automationEasy to bookMetal-working feeding devicesPositioning devicesProduction linePunch press
The invention provides an automatic electric cooker production line. The automatic electric cooker production line comprises a material stretching unit set, a multi-hole punching machine, an edge rolling punching machine and a finished product recycling device, wherein the multi-hole punching machine, the edge rolling punching machine and the finished product recycling device are arranged behind the material stretching unit set and are sequentially arranged side by side; the material stretching unit set comprises a stretching device, an oil smearing machine arranged at the front end of the stretching device and a positioning device arranged at the rear end of the stretching device; and a transferring manipulator is arranged in the interval between the material stretching unit set and the multi-hole punching machine, and a transferring manipulator is arranged in the interval between the multi-hole punching machine and the edge rolling punching machine. Meanwhile, the invention providesan automatic electric cooker production process. The process includes the steps that materials in stacks are divided by the oil smearing machine into single piece materials, oil smearing is performedon the single piece materials, and the materials are transferred to the stretching device; the stretching device performs stretching on the materials, and the device is transferred to the multi-hole punching machine; the multi-hole punching machine performs bottom hole punching and side hole punching on the materials, and the materials are transferred to the edge rolling punching machine; and theedge rolling punching machine performs edge rolling on the materials, the materials are transferred to the finished product recycling device, and material machining is completed.
Owner:广州启盈机电设备有限公司
Recyclable porous bead--satellite nanoparticle composite and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS8815272B2Promote recoveryImprove reuseMaterial nanotechnologyWood layered productsNanoparticleCore shell
An environment-friendly porous bead-satellite nanoparticles composite which has excellent recovery and repeated usage performance and can be used as a catalyst, an antiviral agent, or an antimicrobial, and a fabrication method thereof are provided. The porous bead-satellite nanoparticles composite includes a porous bead, a molecule having a first end coupled to the surface of the porous bead and including a functional group at a second end, and satellite nanoparticles coupled to the functional group, wherein the porous bead may have a core-shell structure including a cluster core of nanoparticles and a porous bead shell covering the cluster core.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
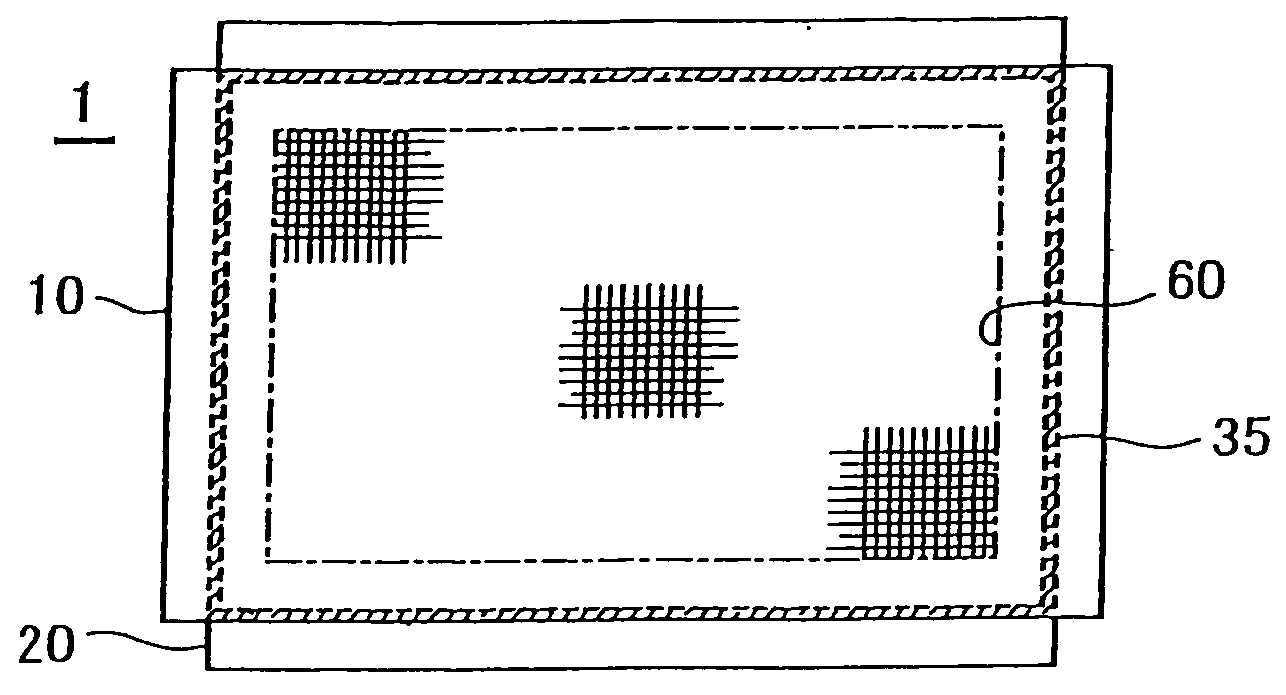
Papermaking sewage flocculant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104944544APromote flocculationHigh yieldWaste water treatment from plant processingWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationStock solutionChelation
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment, particularly a papermaking sewage flocculant and a preparation method thereof. The flocculant is composed of the following components in parts by mass: 10-20 parts of modified chitosan, 5-15 parts of polyferric magnesium silicate, 5-8 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 1-10 parts of ferrate, 2-8 parts of raw gypsum, 12-15 parts of zeolite, 12-20 parts of activated carbon and 100-150 parts of distilled water. The chitosan used in the papermaking sewage treatment flocculant has porous beads which have chelation actions on heavy metals so as to quickly flocculate and naturally precipitate suspended substances in the sewage, thereby enhancing the yield of the stock solution.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG SHANMU NEW MATERIAL TECH DEV
Preparation method of light-weight high-strength calcium hexaluminate fire resistant material
ActiveCN108558418AHigh porosityAperture size controllableCeramicwareCompression moldingSpray Granulation
The invention provides a preparation method of a light-weight high-strength calcium hexaluminate fire resistant material. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that (1) 38-60%of calcarea carbonica raw material and 40-62% of aluminium hydroxide are mixed by weight and mixed with, by weight, 80-120% of water, 0.02-0.05% of dispersing agent and 1-4% of binding agent, and ball-milling is carried out for 3-5 hours to obtain a mixed slurry; (2) spray granulation is carried out on the mixed slurry to obtain spherical fine particles; (3) the spherical fine particles are calcined at 1000-1200 DEG C to obtain light-weight porous beads; (4) 15-30% of light-weight porous beads and 70-85% of aluminium oxide raw material are mixed by weight and mixed with 2-6% of binding agent by weight, after stirring is uniform, compression molding is carried out under 10-30 MPa, and calcination is carried out for 6-8 hours at 1600-1700 DEG C to obtain the light-weight high-strength calcium hexaluminate fire resistant material.
Owner:遵义润辉实业有限公司
Method for producing slow-release fertilizer
InactiveCN105837323AIncrease available timeIncrease profitPotassium fertilisersLayered/coated fertilisersVacuum pumpingStone dust
The present invention provides a method for producing a slow-release fertilizer. The method is as below: placing stone powder extruded porous beads in a vacuumized vacuum container, sucking out the gas in the stone powder porous extruded beads, stopping vacuum pumping, injecting a fertilizer to the vacuum container, mixing the stone powder extruded porous beads with the fertilizer evenly, gradually reducing the degree of vacuum to atmospheric pressure, adsorbing the fertilizer as much as possible to into the pores of the stone powder extruded porous beads , thus preparing a primary product of the slow-release fertilizer. The production method of the slow-release fertilizer provided by the invention prolongs the available time of fertilizer in soil, increases the utilization rate of fertilizer, and reduce fertilizer pollution.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN CHENGMING AGRI TECH DEV CO LTD
Plasma display panel
InactiveUS20080305706A1Avoid noiseUniform thicknessSustain/scan electrodesGas discharge connecting/feedingOptoelectronicsPlasma display
A method for manufacturing a plasma display panel is provided. The method includes making a front substrate and a rear substrate individually and applying a low melting point glass paste including non-porous bead onto a portion of the front substrate or the rear substrate so that the applied low melting point glass paste forms a frame-like shape having a height greater than that of the structural member. The method includes assembling the front substrate and the rear substrate in a face-to-face relation with each other and burning the applied low melting point glass paste while vacuuming a discharge gas space between the front substrate and the rear substrate so as to seal the front substrate and the rear substrate.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Production and use of porous bead polymers in 3D printing using the binder jetting method
The present invention relates to the technical field of 3D printing, especially in the form of the binder jetting method, in which particulate material in a powder bed is bonded by means of a printed adhesive to form a three-dimensional object. The particulate materials may be inorganic materials, for example sand or a metal powder, or particulate polymeric materials, for example polymethacrylates or polyamides. For this purpose, polymethacrylates may take the form, for example, of suspension polymers, called bead polymers.The present invention relates to the use of porous particles in the binder jetting process, in particular of porous suspension polymers. These powders for 3-D printing differ from the prior art in that the porosity results in a faster and better absorption of the printed binder by the powder particles. A great advantage of this procedure is additionally that a product with less warpage is formed and that the end product has a better surface appearance.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
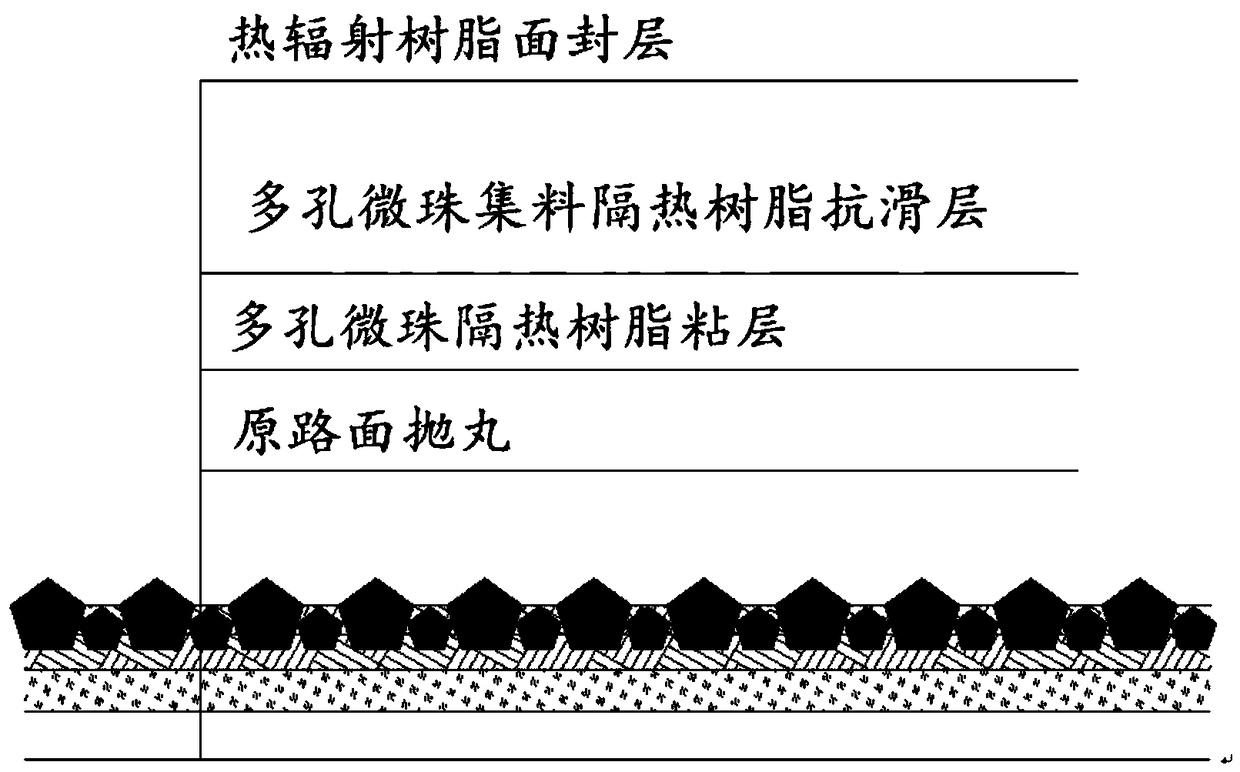
Multilayer composite thermal insulation covering and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109370462ABlock deliverySimple structureIn situ pavingsFilm/foil adhesivesBridge engineeringThermal insulation
The invention discloses a multilayer composite thermal insulation covering and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the field of civil engineering materials, and aims to provide a functional composite paving technology with the advantages of being obvious in thermal insulating and cooling effects and capable of improving the sliding resistance and abrasion resistance of the pavement. Accordingto key points of the technical scheme, the multilayer composite thermal insulation covering contains a porous bead insulating resin bonding layer, a porous aggregate insulating resin non-slip layer and a thermal radiation resin face seal layer arranged in sequence from bottom to top. On the basis of ensuring pavement performances of the pavement, such as sliding resistance, abrasion resistance and the like, the internal temperature of the pavement and paving can be reduced to 10-15 DEG C, the 'cool' pavement is realized, the rut resistance and slip resistance of the pavement in an extreme high temperature season are improved, the service life of the road is prolonged, and the overall service quality of the road is improved. The multilayer composite thermal insulation covering disclosed bythe invention can be applied to the field of road and bridge engineering such as steel bridge deck pavement, asphalt pavement and cement concrete pavement.
Owner:JIANGSU SINOROAD ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD +1
Antibacterial polycarbonate plastic
InactiveCN111732825AIncrease the areaImprove stabilityAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPolycarbonate plasticPolymer science
The invention provides an antibacterial polycarbonate plastic. The antibacterial polycarbonate plastic contains 0.2-5wt% of a plastic antibacterial agent, and the plastic antibacterial agent takes porous beads formed by pore-forming of beads formed after cross-linking reaction of a polystyrene-butadiene copolymer and chloromethyl styrene as a carrier, and takes loaded nano zinc oxide and nano titanium dioxide as active components. The polycarbonate plastic prepared by the invention has a long-acting antibacterial function.
Owner:智科通用技术研究(广州)有限公司
Two-dimensional plane structure or three-dimensional stereochemical structure composed of porous beads
The invention provides a two-dimensional plane structure or three-dimensional stereochemical structure composed of porous beads. The two-dimensional plane structure or three-dimensional stereochemical structure is formed by combining the porous beads and connecting piece or is formed by combining the porous beads and one-hole beads through connecting pieces. Each porous bead is provided with two or more bead holes. The porous beads achieve connection through the bead holes and the connecting pieces. By the adoption of the two-dimensional plane structure or three-dimensional stereochemical structure composed of the porous beads, various inconveniences caused when original one-hole beads are used for making the two-dimensional plane structure or three-dimensional stereochemical structure are eliminated, the operation is simple, and the applied porous beads can be detached or replaced. The two-dimensional plane structure or three-dimensional stereochemical structure composed of the porous beads has wide application prospects on the aspects of making clothes, furniture, toys, lamps, packaging materials, building materials and the like.
Owner:景少尉
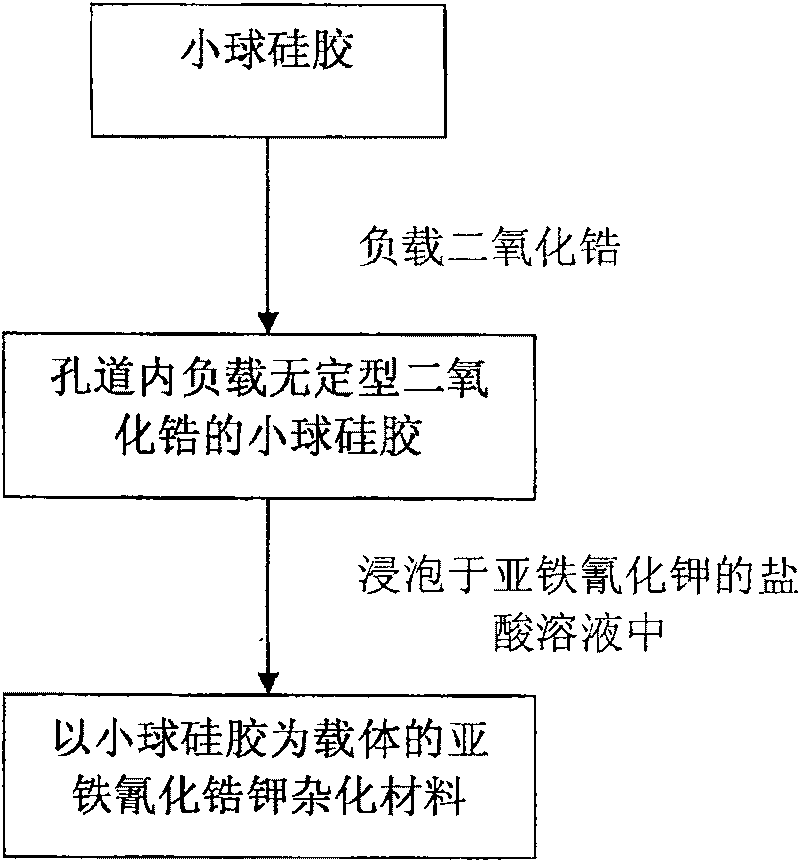
Preparation of potassium zirconium hexacyanoferrate using pellet silica-gel as carrier
ActiveCN101279249BHigh strengthImprove acid resistanceOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPotassiumZirconium oxychloride
A preparation method for ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium taking bead silica gel as carrier relates to the preparation method for ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium with high specific surface and taking the bead silica gel as the carrier. In the method, fashioned porous bead silica gel react with the solution of zirconium oxychloride under the condition of heating and refluxing, acquired bead silica gel loaded with amorphous zirconium dioxide is dried and then dipped in the hydrochloric acid solution of yellow potassium ferrocyanide for reaction under stirring for 12-24 hours, thus the hybrid materialof ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium with high specific surface and taking bead silica gel as the carrier is obtained. The load of ferrocyanide of the material can be adjusted and the material has strongadsorption capability for nuclide ion, high specific surface, good particle degree of sphericity, and being uneasy to break, which avoids the problem of oversized bed water resistance caused by usingferrocyanide zirconium Kalium particles separately; besides, owing to the existence of Zr-O-Si covalent bond, nano ferrocyanide zirconium Kalium particles can closely combine with the bead silica-gel, thus being uneasy to run away in the process of waste water treatment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
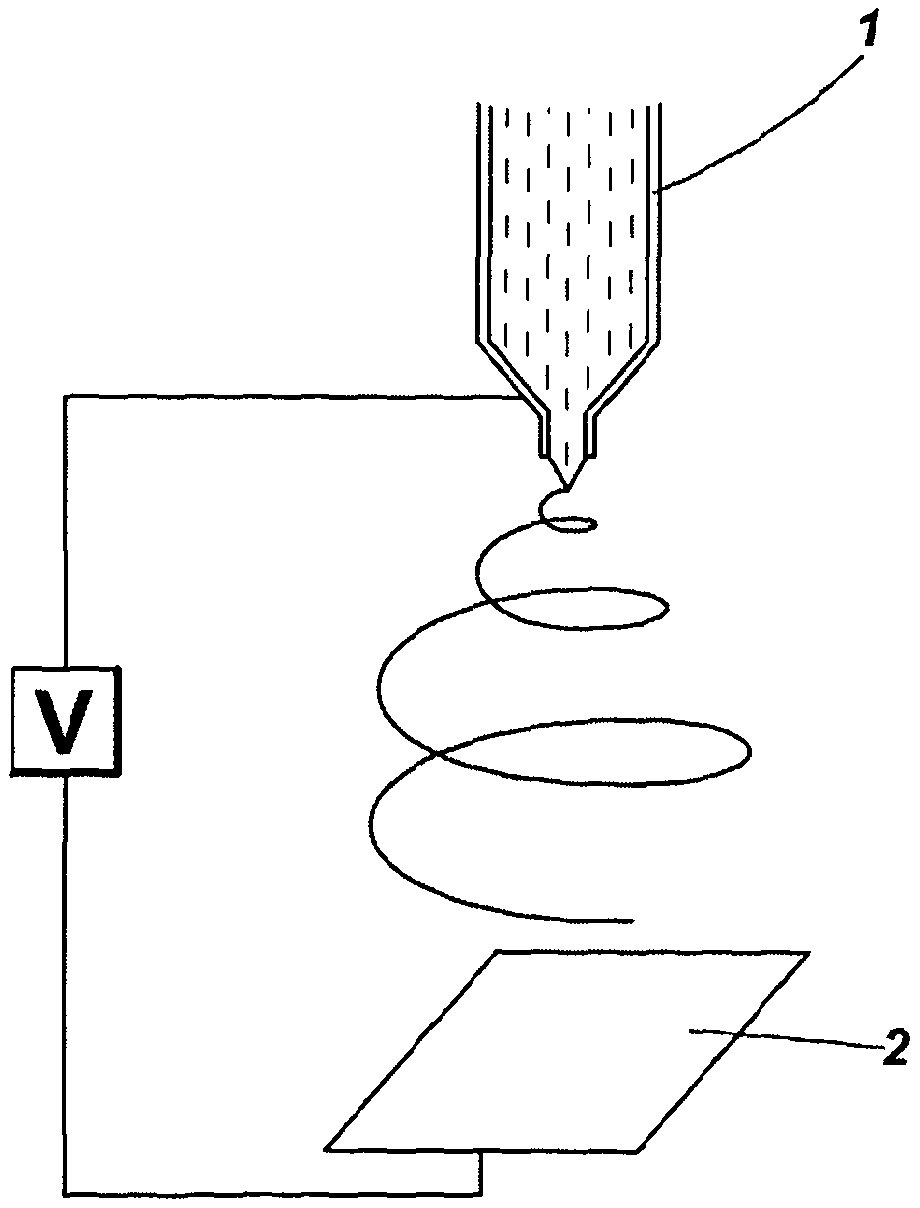
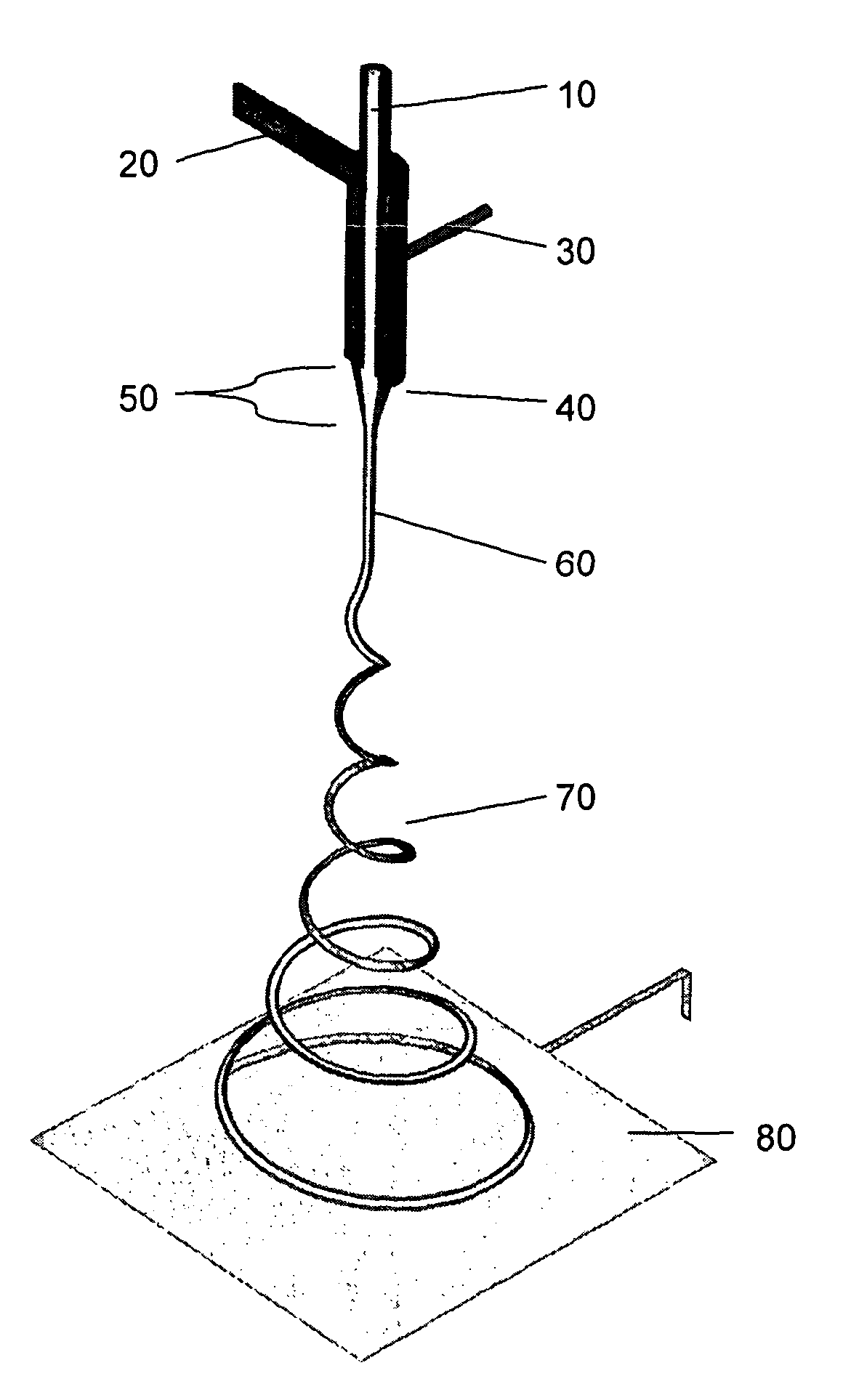
Method of preparing polymer porous beads based on liquid drop settling and freezing technology
The invention discloses a method of preparing polymer porous beads from polymer organic liquids through liquid drop settling and freezing. The method comprises the following steps: injecting polymer organic liquids with different concentrations into settling and freezing liquid at a certain temperature by virtue of an injecting device, and enabling liquid drops to freeze and crystallize from top to bottom to form polymer porous beads; collecting the polymer porous beads at the bottom, and freeze-drying after eluting the polymer porous beads by virtue of a de-eluting agent, wherein the velocity of the liquid drops of the injected liquid can be regulated by virtue of an injecting pump, and the temperature of the settling and freezing liquid is controlled by virtue of an external low-temperature circulating slot. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to implement, green and environmentally friendly and capable of obtaining the polymer porous beads with diameters of 1.50-2.95 millimeters.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing hydrogel bead for detection of hydrofluoric acid and kit comprising the same
ActiveUS20160146739A1Easy to carryChange colorAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHydrofluoric acidChange color
The present invention relates to a hydrogel bead for detecting hydrofluoric acid and a kit comprising the same, and more particularly, to a hydrogel bead capable of detecting hydrofluoric acid using an organometallic ligand compound that reversibly changes color depending on the concentration of hydrofluoric acid when coming into contact with hydrofluoric acid, and to a kit for detecting hydrofluoric acid comprising the same. In an embodiment, a method for preparing a hydrogel bead for detecting hydrofluoric acid comprises the steps of: mixing an organic compound, which contains an aromatic functional group having at least one hydroxyl group bonded thereto, with a solution of a metal-ligand compound that bonds with the organic compound, thereby preparing a mixed solution; dropping the mixed solution onto a gelling agent; and adding coagulating agent to the mixture resulting from the dropping step to form a porous bead.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Process for producing porous cellulose beads using alkali aqueous solution, carrier for ligand immobilization, and adsorbent
ActiveUS20160244483A1High compressive strengthReduced strengthOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationCelluloseSorbent
A process for producing porous cellulose beads of the present invention is characterized by comprising the steps ofa) mixing an alkali aqueous solution and cellulose to prepare cellulose micro dispersion at low temperature,b) adding water to the cellulose micro dispersion to prepare cellulose slurry, andd) bringing the cellulose slurry into contact with coagulation solvent.A carrier for ligand immobilization of the present invention is characterized by being by shrinking polysaccharide porous beads not less than 10% by a shrinkage rate defined by the following formula, and crosslinking the polysaccharide porous beads:Shrinkage rate (%)=(1−V2 / V1)×100(wherein, V1 indicates the gel volume of polysaccharide porous beads before shrinkage, and V2 indicates the gel volume of polysaccharide porous beads after shrinkage).
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com