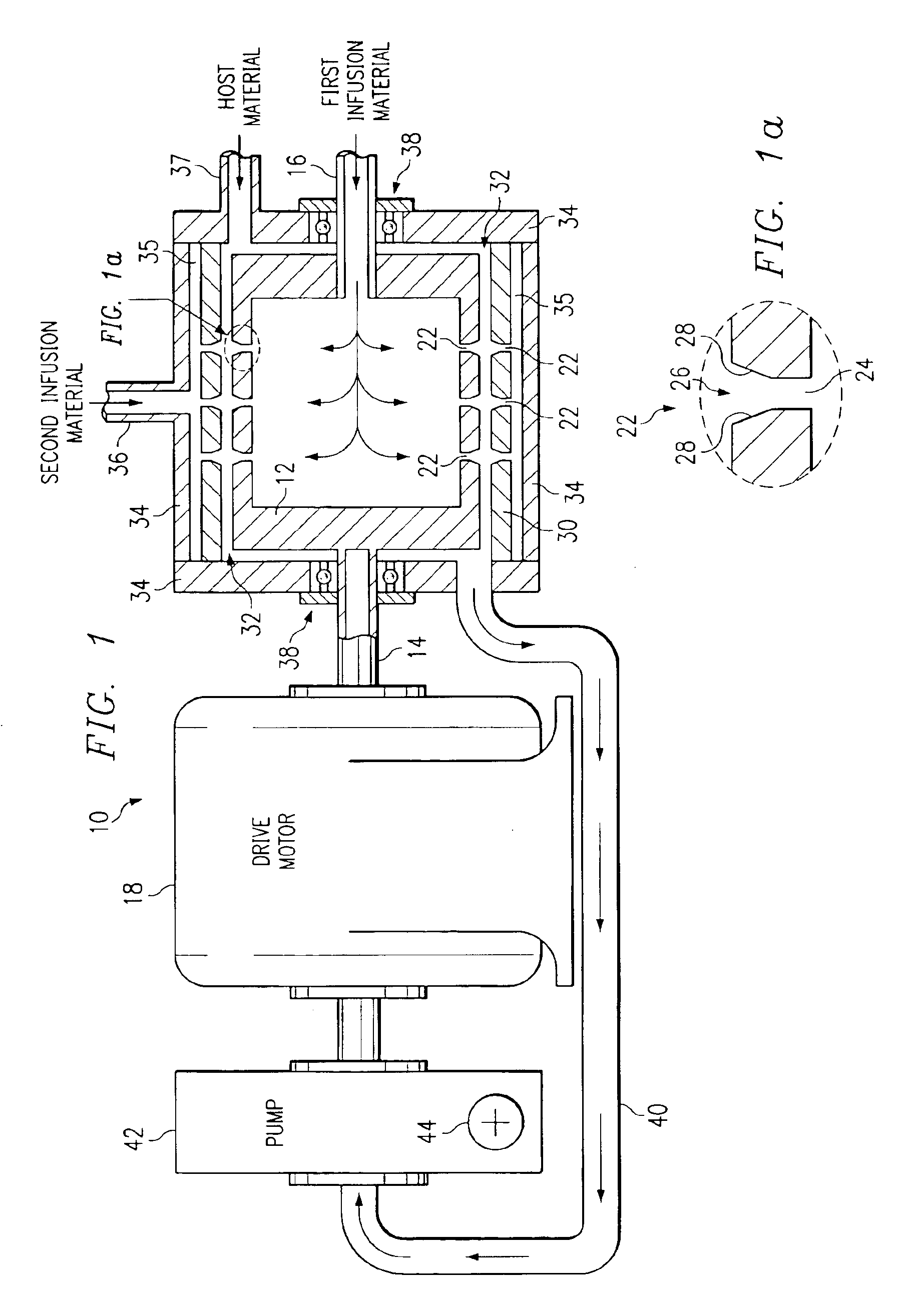
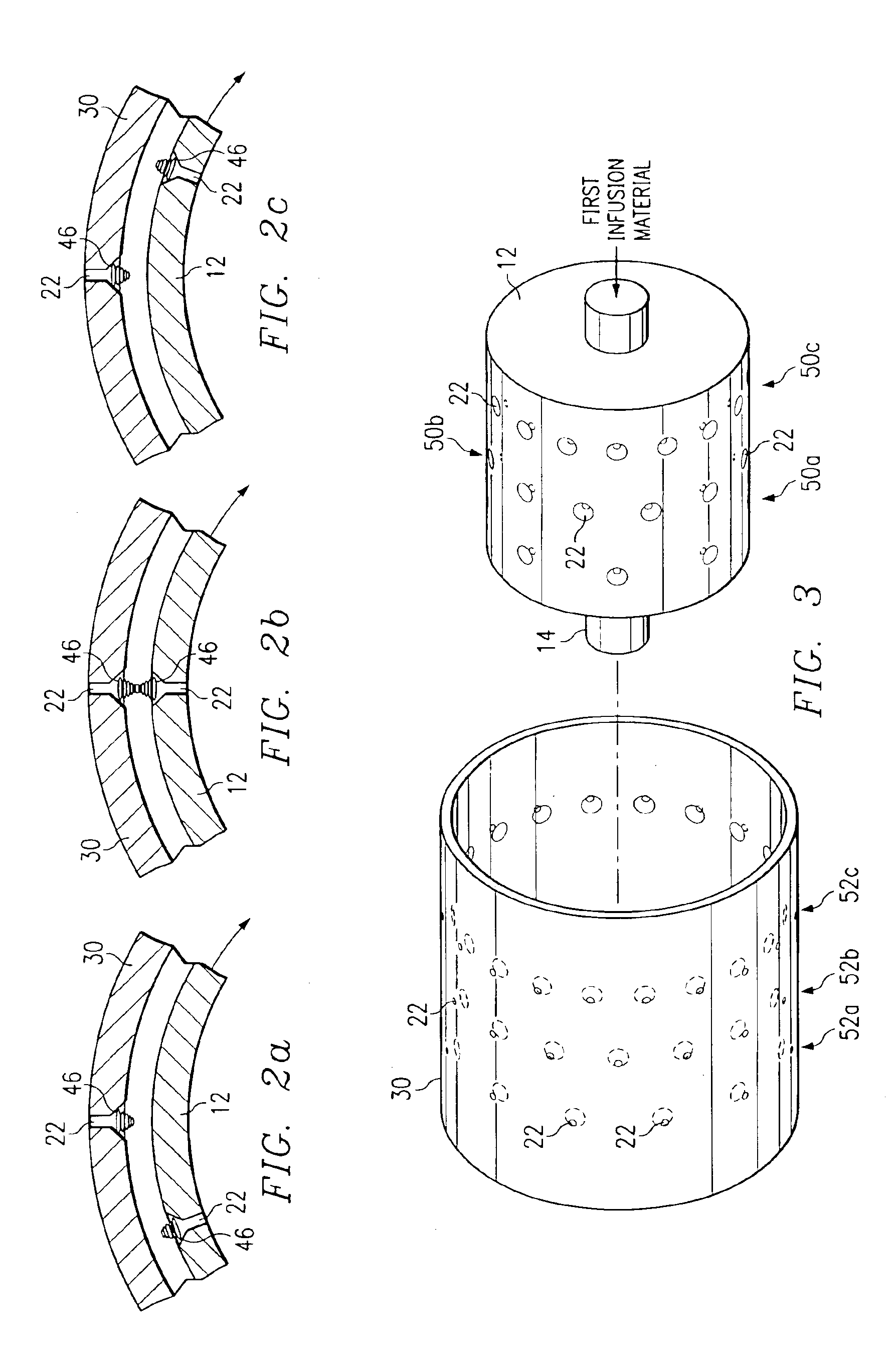
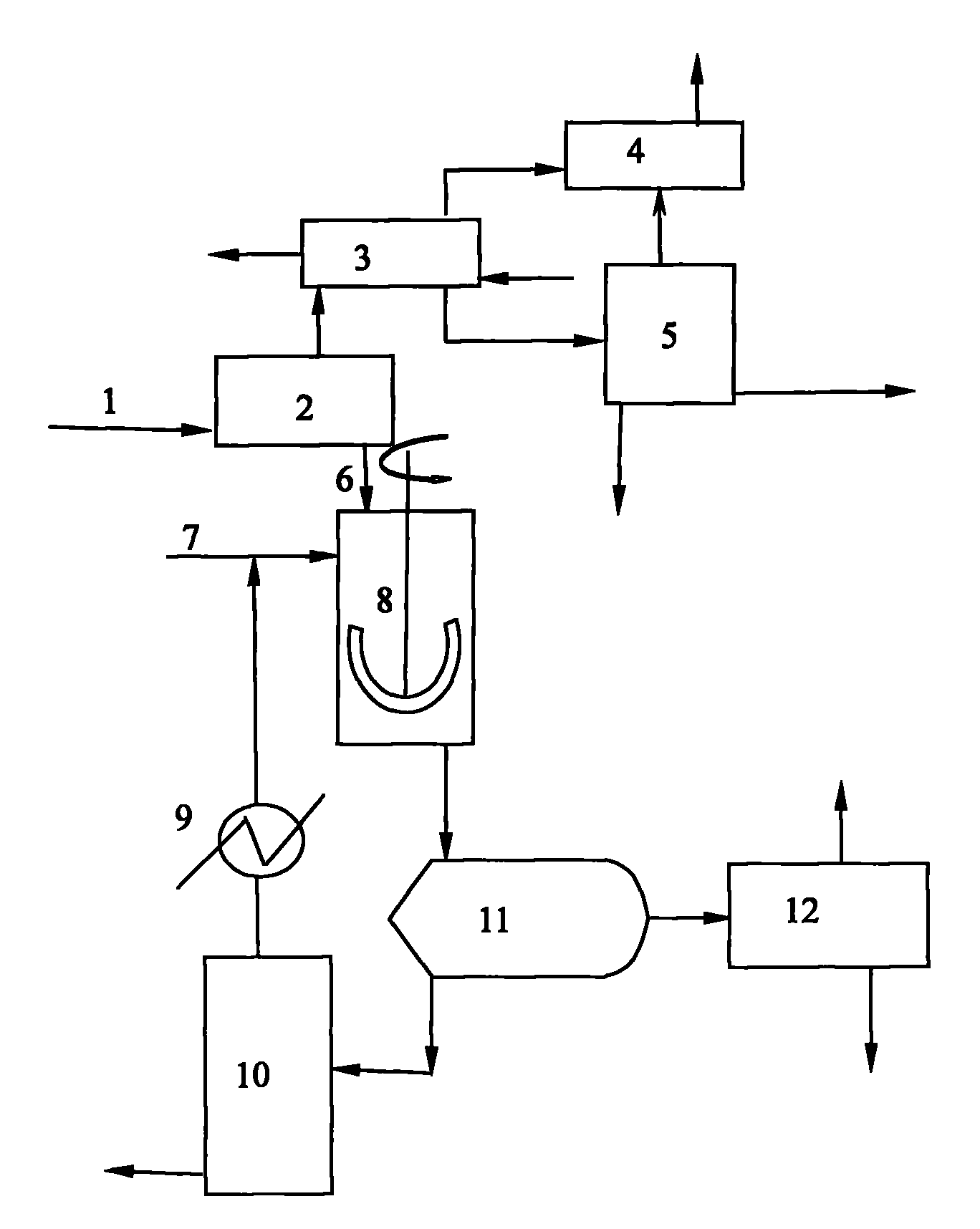
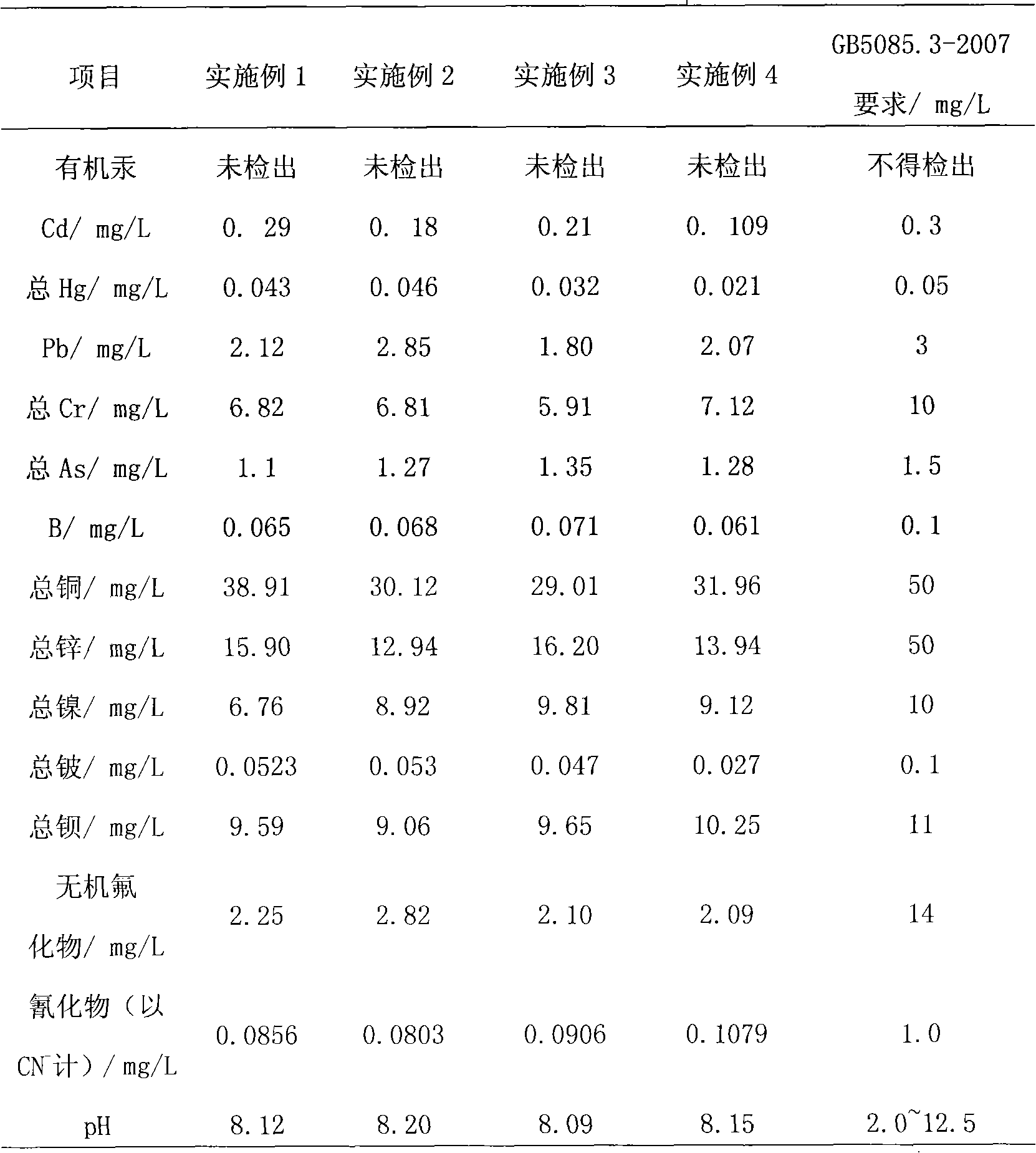
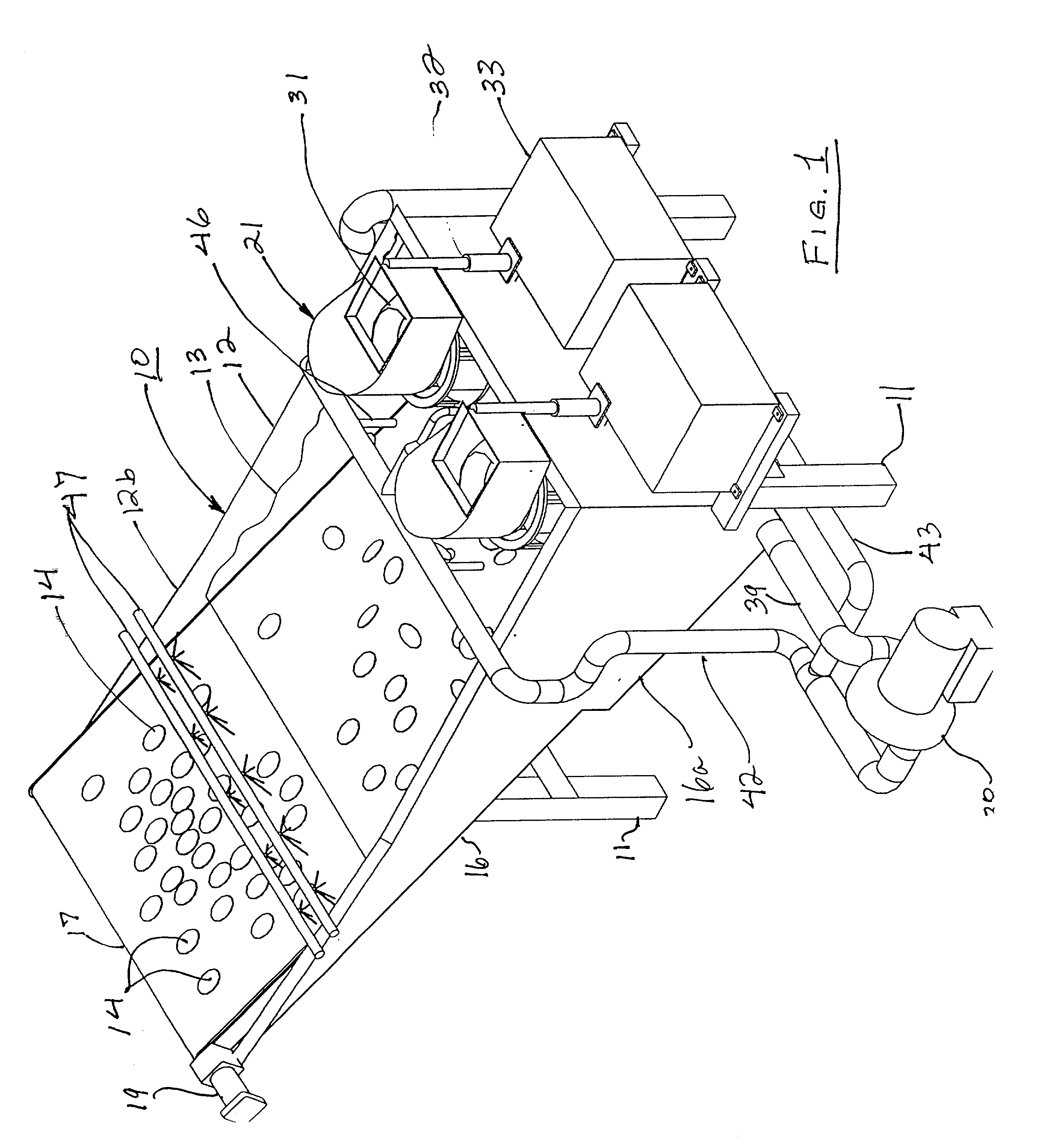
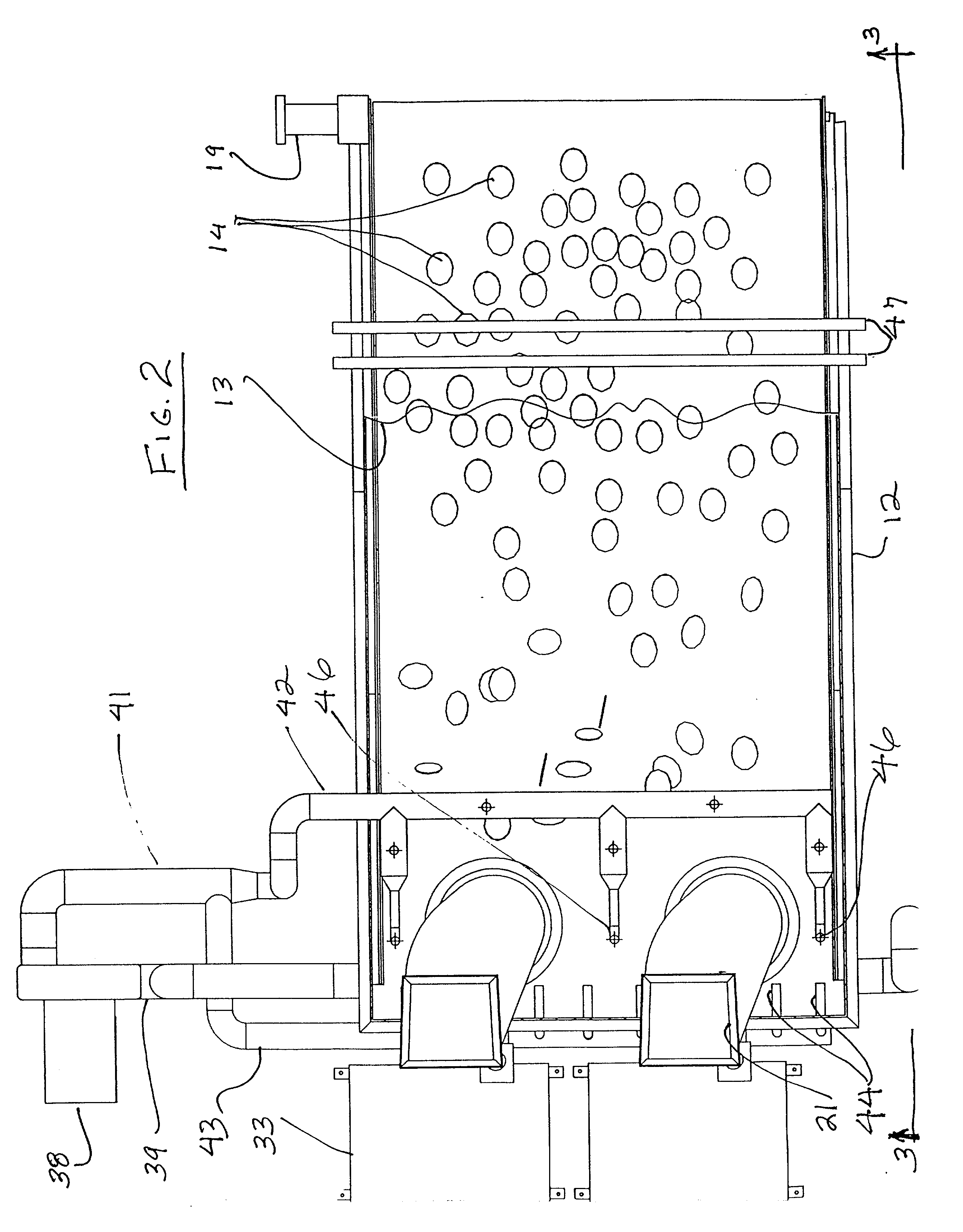
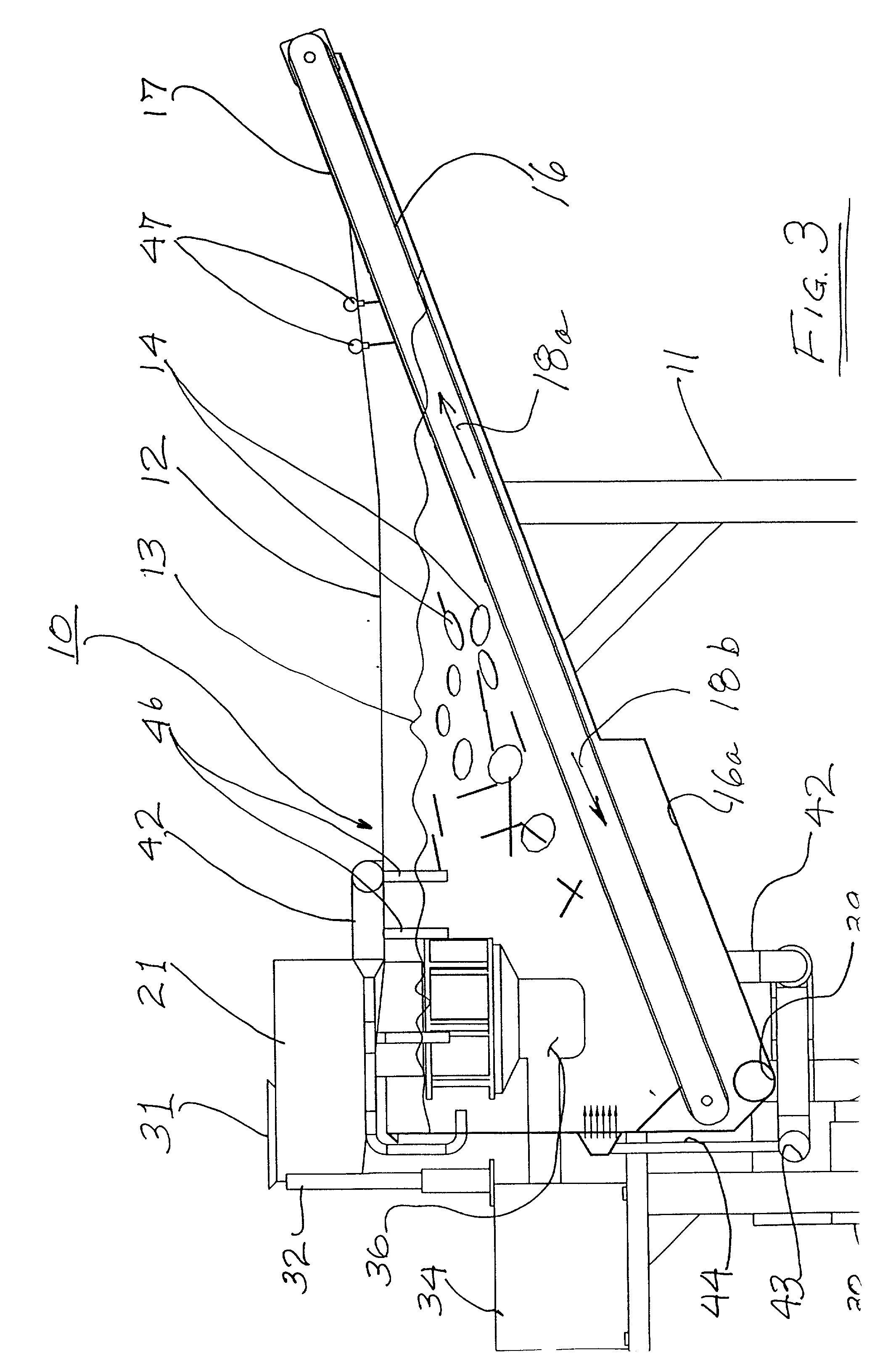
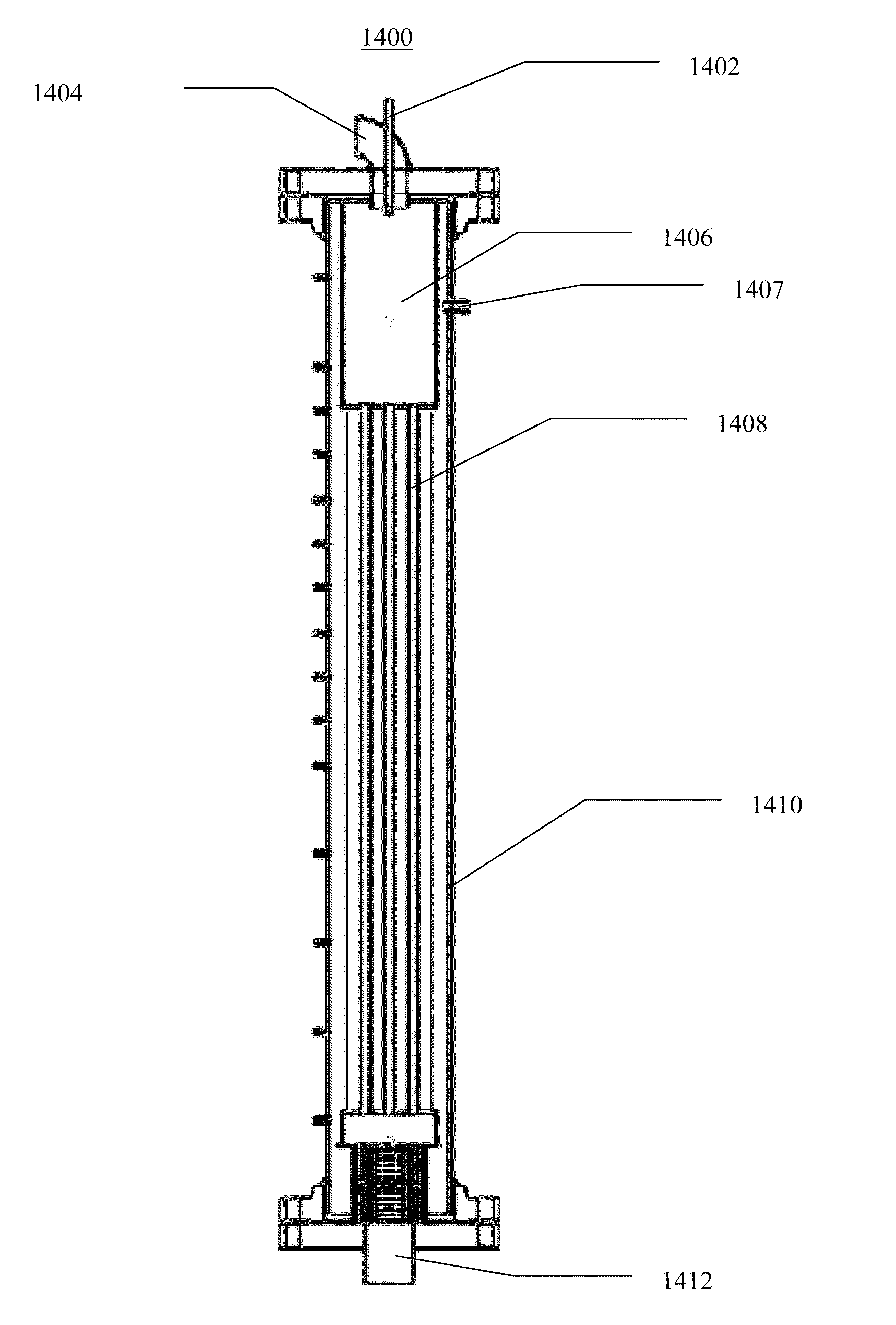
Patents
Literature
2561 results about "Reclaimed water" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reclaimed or recycled water (also called wastewater reuse or water reclamation) is the process of converting wastewater into water that can be reused for other purposes. Reuse may include irrigation of gardens and agricultural fields or replenishing surface water and groundwater (i.e., groundwater recharge). Reused water may also be directed toward fulfilling certain needs in residences (e.g. toilet flushing), businesses, and industry, and could even be treated to reach drinking water standards. This last option is called either "direct potable reuse" or "indirect potable" reuse, depending on the approach used. Colloquially, the term "toilet to tap" also refers to potable reuse.
Method for producing feed additive from livestock and poultry breeding wastewater and purifying breeding wastewater to reclaimed water
InactiveCN102161550AReduce water consumptionAchieving zero emissionsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryAnimal feeding stuffUltrafiltrationSlurry
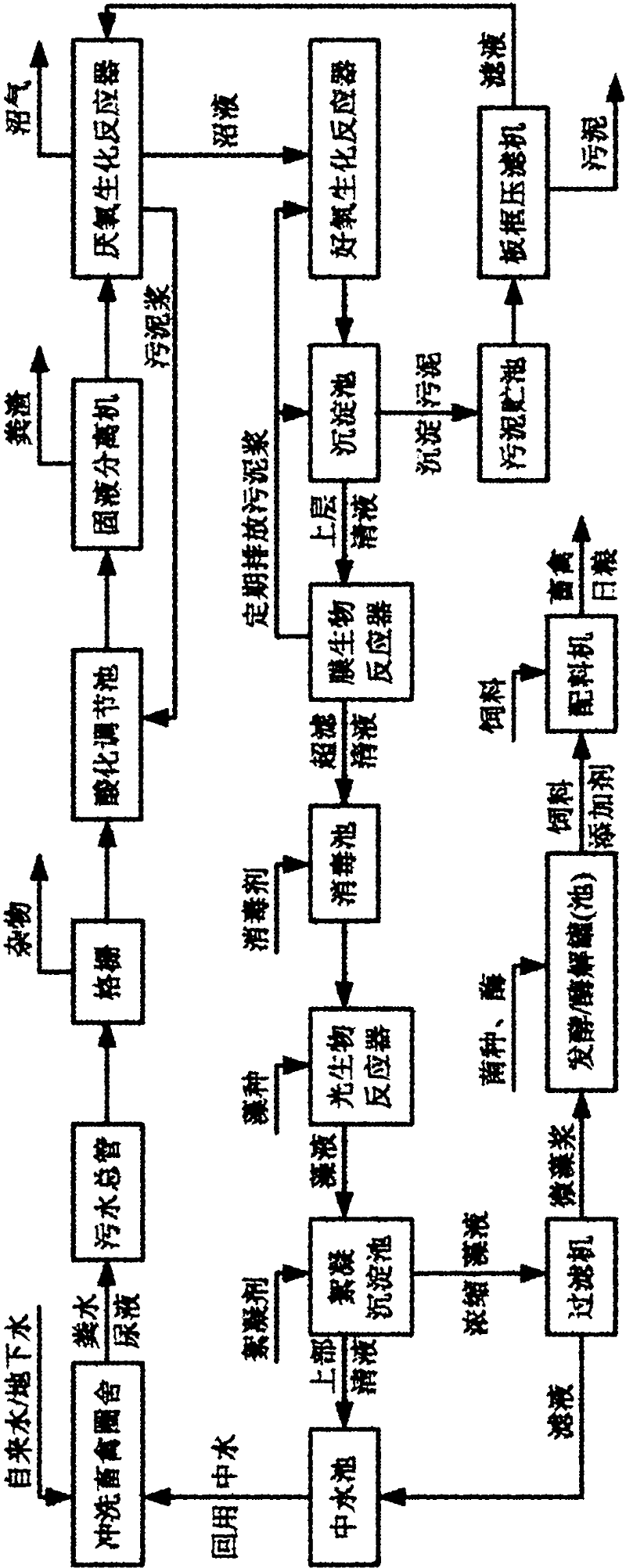
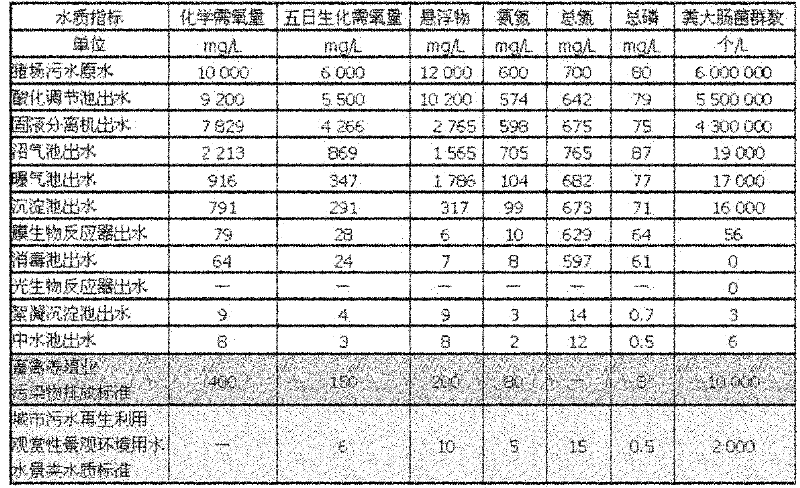
The invention relates to the fields of environmental technology and the breeding and processing of microalgae, in particular to a method for producing feed additive from livestock and poultry breeding wastewater and purifying breeding wastewater to reclaimed water. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that: wastewater enters an acidification adjusting tank through a grille, and the acidified wastewater enters an anaerobic biochemical reactor for treatment and then enters an aerobic biochemical reactor; after the aerobic biochemical treatment, the obtained biogas slurry enters a settling tank for settling, the supernatant enters a membrane bioreactor for further aerobic treatment and is filtered by an ultrafiltration membrane, the generated ultrafiltration clear liquid is sterilized and neutralized and then enters a photobioreactor, algae are added into the photobioreactor to perform microalgae cultivation, and the algae liquid is discharged from the photobioreactor and then enters a flocculation and settling tank; and after flocculation and settling, the supernatant is used for water recycling, the concentrated algae liquid at the bottom enters a filter, and the separated microalgae slurry enters a fermentation / enzymolysis pot (tank) to perform fermentation / enzymolysis to be used as the feed additive. The invention has the advantages of high economic adaptability, zero discharge and the like.
Owner:蔡志武 +1
Composite thermotropic phase separation film-making method
The invention relates to a composite thermotropic phase isolated membrane preparation method which is characterized in that used composite diluent is the mixture of water-soluble good solvent and water-soluble additive of polymers. The membrane forming separation is a composite process which mainly takes the thermotropic membrane phase separation as the dominant role and non-solvent induced phaseseparation as the subsidiary role. The membrane prepared through the method has the advantages of high abruption strength, high abruption elongation and high water flux. The method is applicable to the preparation of membranes which are made of a plurality of polymers, including polyvinylidene fluoride, polysulfone, polyether sulfone, polyvinyl chloride and polyacrylonitrile. The performances of the membranes are improved greatly. Thus, the membranes can be widely applied to the fields of drinking water advanced treatment, pretreatment before reverse permeation, membrane bioreactor wastewatertreatment, reclaimed water reuse, etc.
Owner:湖南坎普尔环保技术有限公司
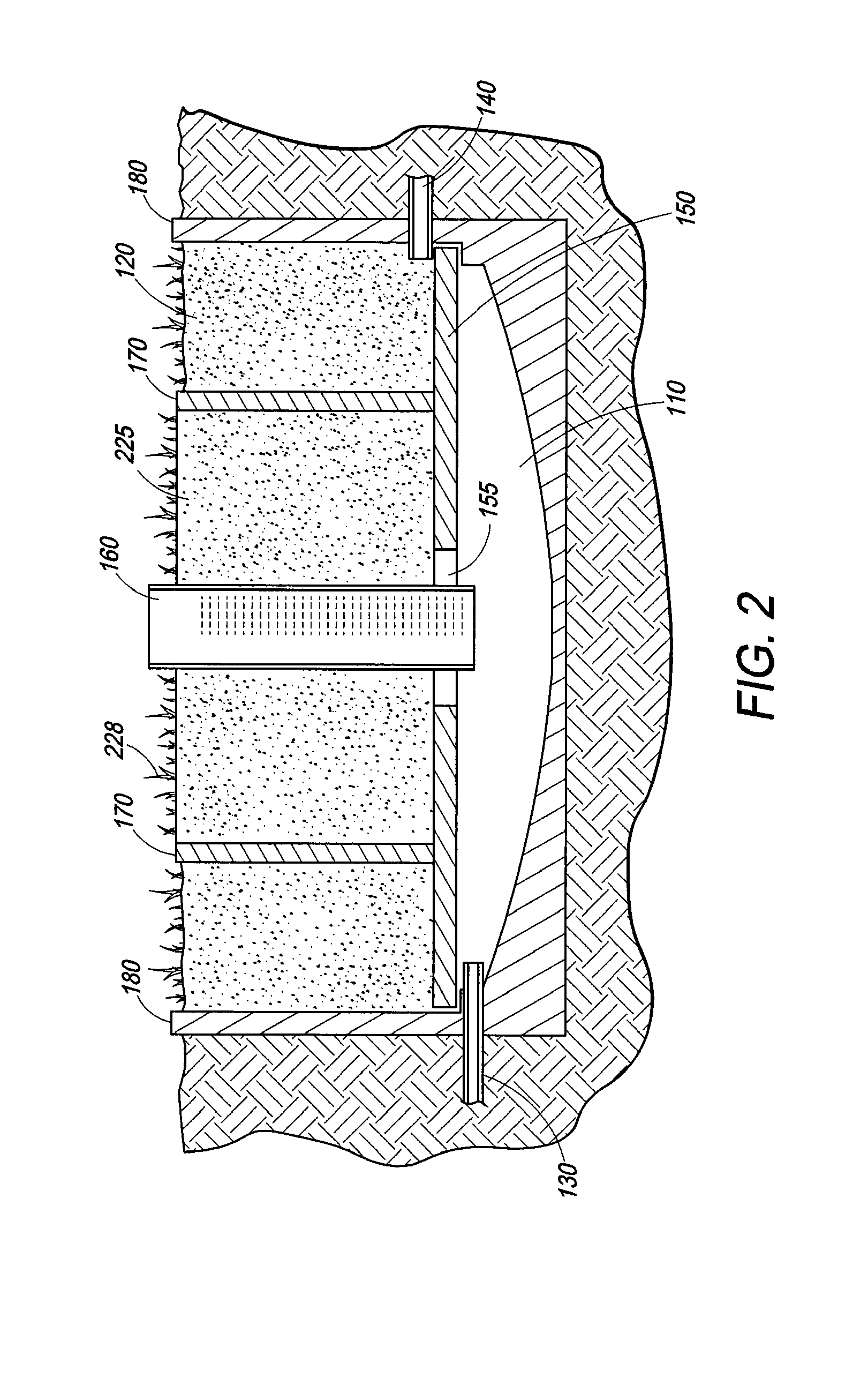
Wetland water treatment system
ActiveUS20080142438A1Easy maintenanceEasy constructionWater cleaningCentrifugal force sediment separationParticulatesWater treatment system
A self-contained wetlands treatment system to remove pollutants from water and treat stormwater runoff or other grey water. This is system and method wherein the water is passed through a wetland filtering and treatment system. This invention removes solids, metals (dissolved / particulate), nutrients (dissolved / particulate), oils, and bacterial contaminants from the water. The system and system housing can be fabricated, built, and assembled in a broad range of sizes and materials to accommodate and treat a broad range of influent flow rates.
Owner:MODULAR WETLAND SYST
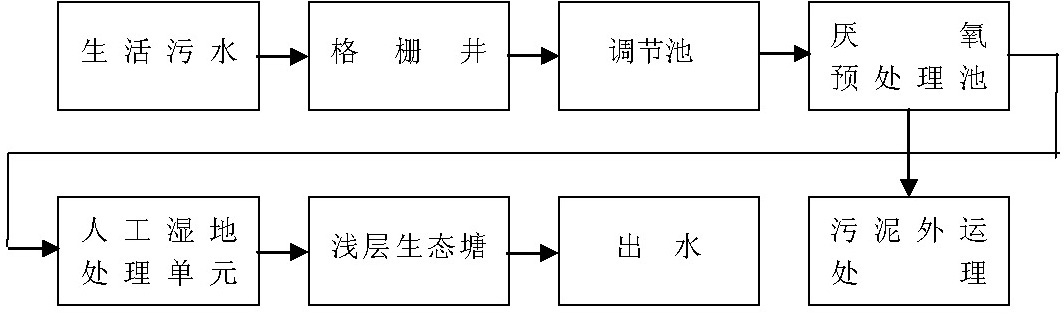
Ecological greenbelt treatment process and system for treating rural domestic sewage
ActiveCN101948214AEasy to handleLess investmentTreatment using aerobic processesWaste based fuelConstructed wetlandReclaimed water
The invention relates to an ecological greenbelt treatment process for treating rural domestic sewage, which mainly comprises the steps of: (1) anaerobic pretreatment: performing anaerobic hydrolysis pretreatment to domestic sewage; (2) artificial wetland treatment: performing artificial wetland treatment to pretreated domestic sewage; and (3) shallow ecological pond aerobic biotreatment: further performing shallow ecological pond aerobic biotreatment to outlet water treated by the artificial wetland, degrading and converting organic matters and nutrients entering the pond, and recycling purified sewage as a regenerated water resource. The invention adopts an ecological greenbelt treatment system comprising the anaerobic pretreatment, the artificial wetland and the shallow ecological pond to treat the rural domestic sewage, and has the characteristics of good treatment effect, recycling on site, low investment, low system operating cost, simple maintenance, obvious ecological benefit and the like.
Owner:浙江博世华环保科技有限公司
Airless engine with gas and water recycling
InactiveUS7958872B1Low costEliminate the problemNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesLiquid waterTurbocharger
An internal-combustion engine receives no air from outside atmosphere. Instead, combustion gas expelled from the engine is cooled and recycled back into the engine. That gas contains no nitrogen and consists mostly of carbon dioxide and water vapor. Oxygen and fuel are added to the recycled gas, and the resulting mixture is used to perform an internal-combustion cycle. Cooling that gas condenses its water vapor, and liquid water is separated from the gas. That water is used for injection into the recycled gas at a later time. A small amount of the expelled combustion gas is discharged into outside environment, and the rest is recycled. Water too is recycled back into the engine, and whatever is lost to outside environment is replaced by reclaiming water produced in combustion. No additional supply of water is needed. Since no nitrogen is present, no nitrogen oxides are produced. The amount of other harmful exhaust emissions is greatly reduced too, since most of them are recycled back into the engine. Water evaporation in the cylinders greatly improves fuel economy. The engine is inherently supercharged with combustion-gas pressure, and no turbocharger is needed. Since the combustion gas is heavier than air, the engine can be substantially smaller than a conventional engine of equal power. A smaller engine has less friction.
Owner:SCHECHTER MICHAEL MOSES
Active carbon fiber organic gas recovery method and system using nitrogen as desorption medium
InactiveCN101288820AReduce water contentAchieving zero emissionsDispersed particle separationCombustible gas purificationSolubilityFiber
The invention relates to a method for recovering active carbon fibre organic waste gas by taking nitrogen as desorption medium, belonging to the field of environmental protection. The method for recovering active carbon fibre organic waste gas by taking nitrogen as desorption medium takes the active carbon fibre as a fixed bed adsorber of the adsorbent, adopts thermal nitrogen desorption and can recover and reuse the organic waste gas and nitrogen at the same time. The method of the invention adopts the thermal nitrogen adsorption, generates no secondary contaminant, realizes that the exhaust reaches the standard of the environmental protection, leads the adsorption layer to keep dry at the same time, improves the utilization ratio of the active carbon fibre and prolongs the service life of the active carbon fibre. As vapour is not used for desorption, the equipment has no corrosion problem, thus greatly reducing the manufacture cost of the equipment. The method of the invention has extremely good recovery effects on solvent with large water solubility and easy hydrolysis performance and organic waste gas with high boiling point, has low water content in the recovered products, high quality of the solvent and reduces the running cost.
Owner:中节能天辰(北京)环保科技有限公司
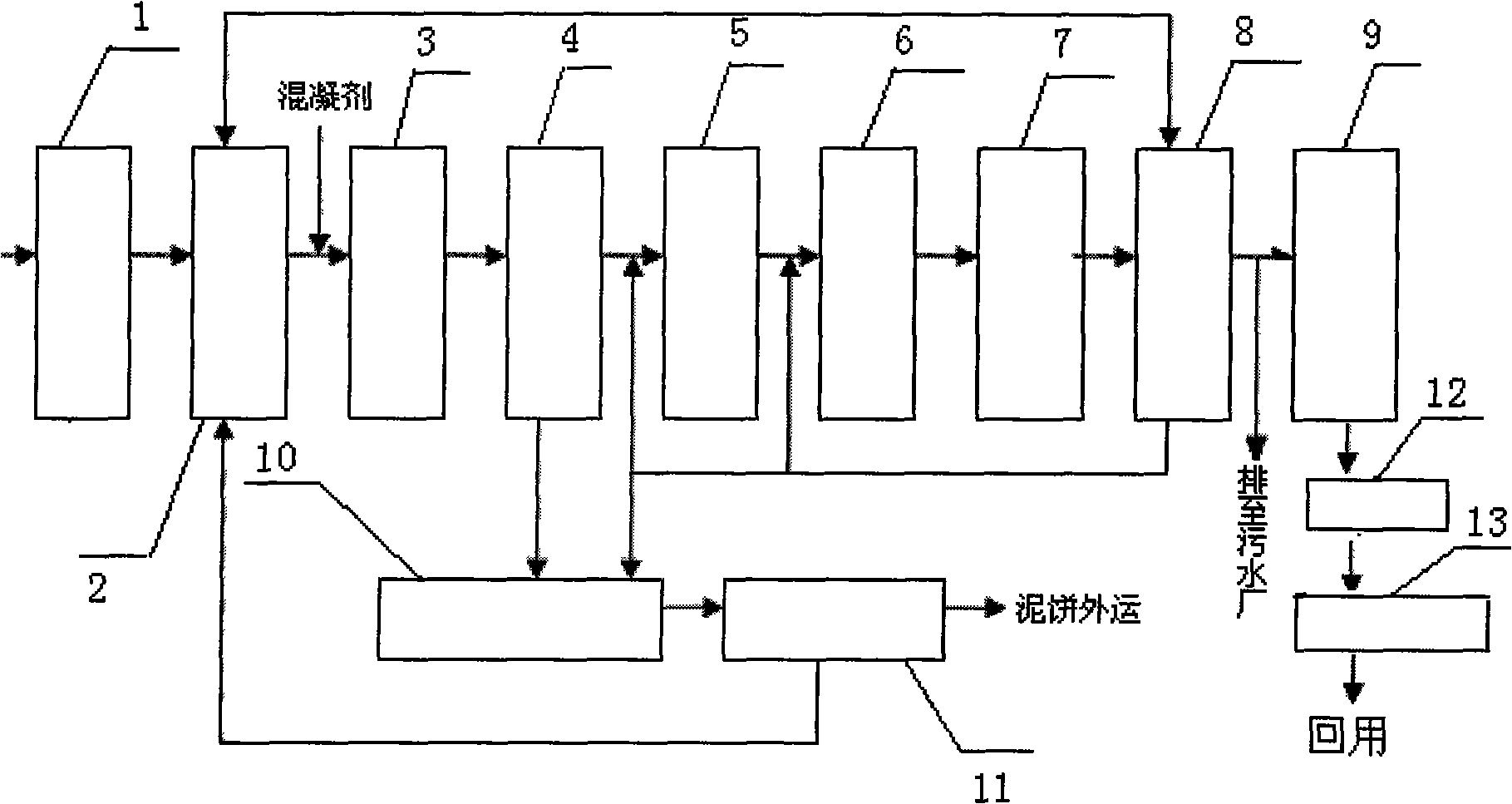
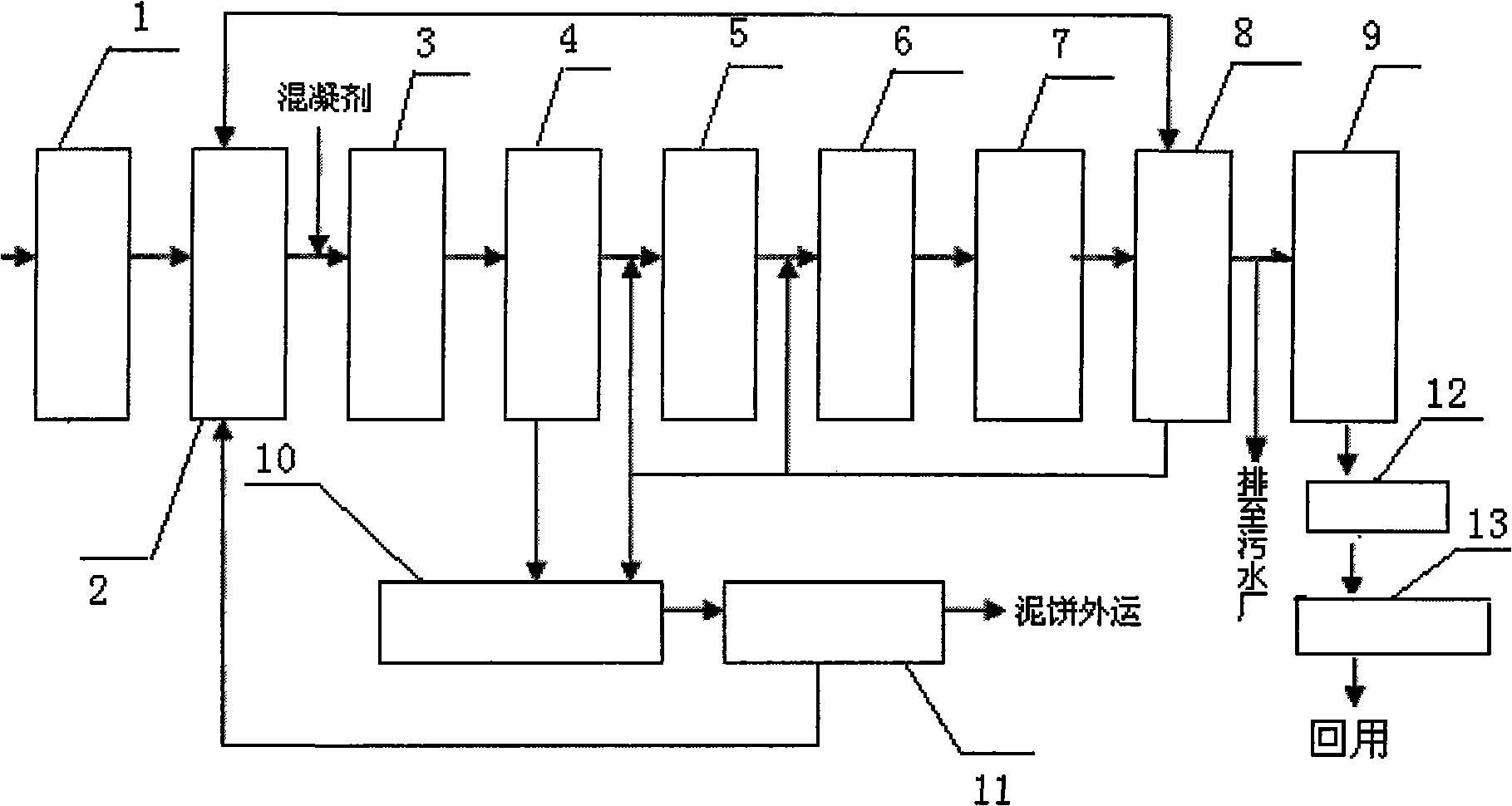
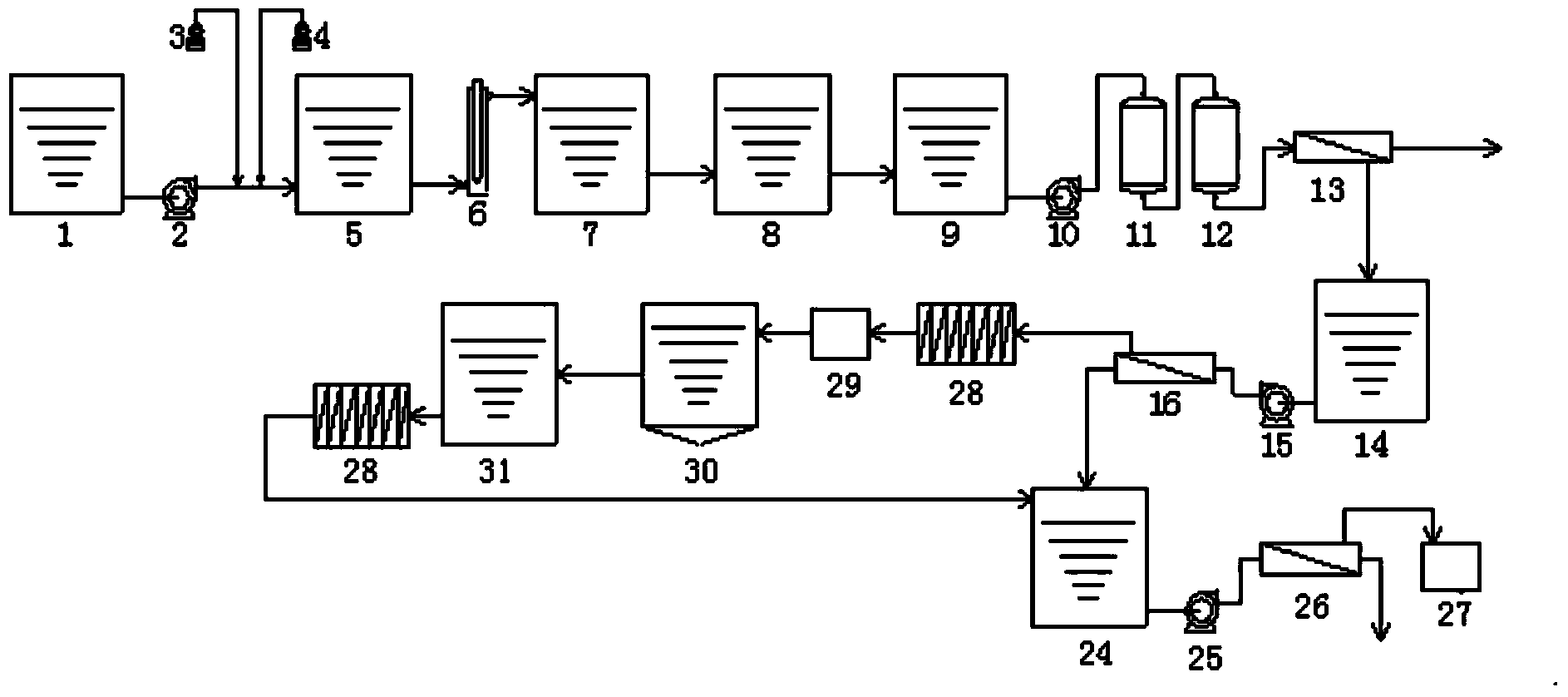
Advanced dyeing wastewater treatment and reclaimed water reuse system and method thereof
InactiveCN101525202ASimple processLow running costSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesBiological activated carbonReclaimed water
The invention relates to an advanced dyeing wastewater treatment and reclaimed water reuse system and a method thereof. The system consists of a regulating tank (2), a coagulation tank (3), a preliminary sedimentation tank (4), an acidification hydrolysis tank (5), a deep well (6), a deaeration tank (7), a secondary sedimentation tank (8), a biological activated carbon tank (9), a sludge concentration tank (10), a sludge dewatering tank (11), a filter tank (12) and an ozone oxidation tank (13). The method comprises the following steps: wastewater is sent to the regulating tank, the coagulation tank and the preliminary sedimentation tank, then sludge is returned to the coagulation tank, excess sludge is discharged to the sludge concentration tank, clarified water flows to the acidification hydrolysis tank, is sent to a deep well aeration tank and then sent to the secondary sedimentation tank; and the obtained clarified water is discharged after meeting the standard, or flows to the biological activated carbon tank and is treated for production. The system and the method have the advantages of simple process, low operating cost, high stability and reliability, convenient operation, and realization of automation control. Most of the wastewater discharged is reused in production after the treated wastewater meets the standard, thus reducing emission of pollutants, being capable of eliminating environmental pollution resulting from the wastewater and protecting environment.
Owner:常州市东霞房地产代理有限公司 +2
Aeroponic plant growing system
An aeroponic plant growing system includes a water reservoir and growing chambers for growing plants in an aeroponic environment. A pump, a water distribution manifold, and water lines are used to provide water and nutrients from the water reservoir to sprayers in the growing chambers where the water and nutrients are sprayed on the roots of plants growing therein. The water distribution manifold and water lines preferably are provided as closed loop systems, such that water is provided to all sprayers despite a blockage in the manifold or a water line. Non-absorbed water and nutrients are returned to the water reservoir from the growing chambers on water return lines via a filter that includes multiple types of filter media, including filter media that support the colonization of organisms that support plant growth.
Owner:WALHOVD ZACK ALLEN
Pathogen reduction using chloramines
InactiveUS20050211643A1Good effectEasy to receiveWaste water treatment from animal processingWater/sewage treatment by substance additionMicroorganismChloramine B
A method and apparatus for implementing pathogen reduction within a poultry processing or food processing plant that uses water that has been treated with chloramines at an advantageous dosage before being introduced to the production process at processing steps. The water treated with chloramines may be from a fresh water source or reclaimed water from the processing plant. The reintroduction of the treated reclaimed water advantageously causes a dramatic reduction in the levels of microorganisms associated with poultry processing, while substantially conserving water use.
Owner:ZENTOX CORP
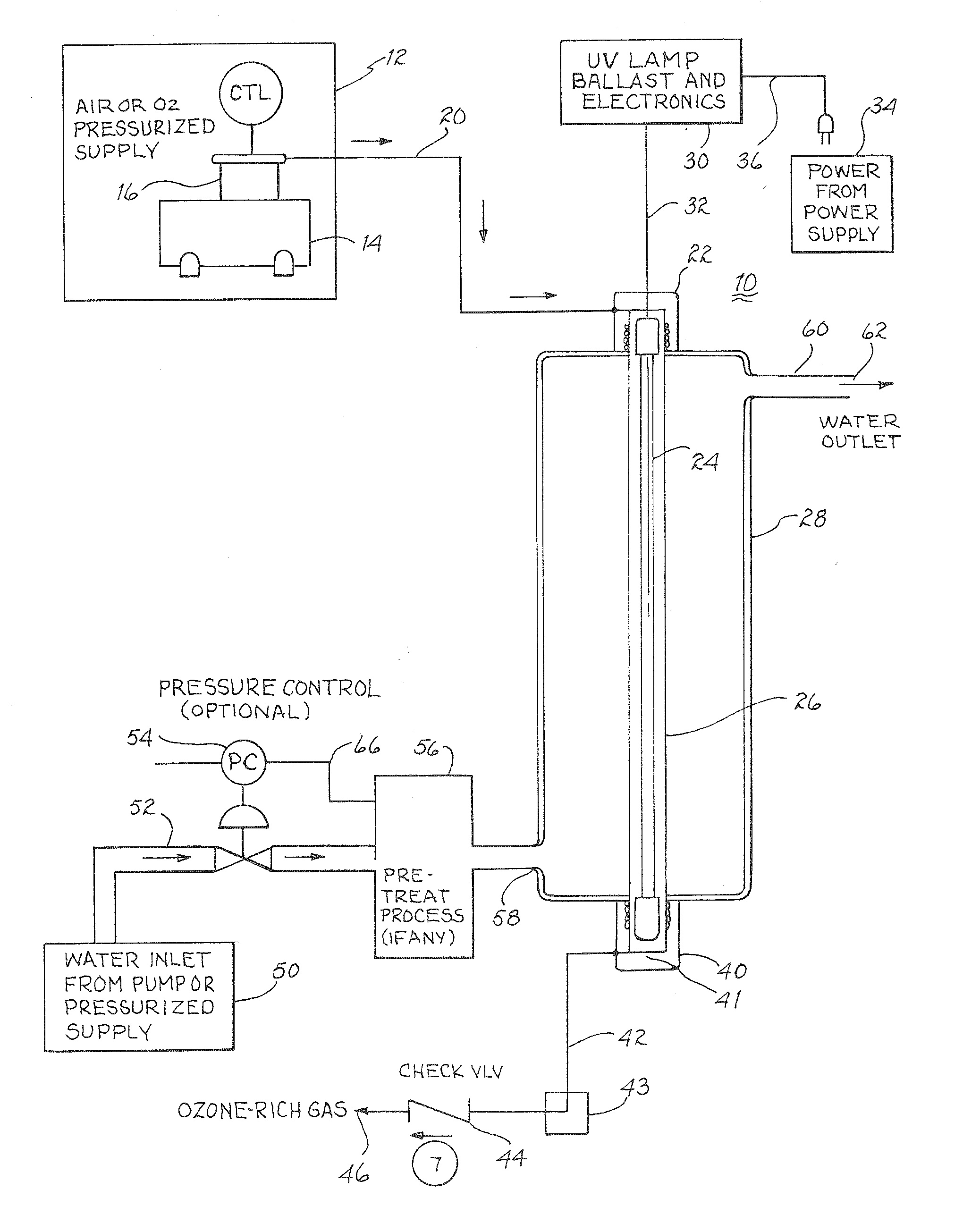
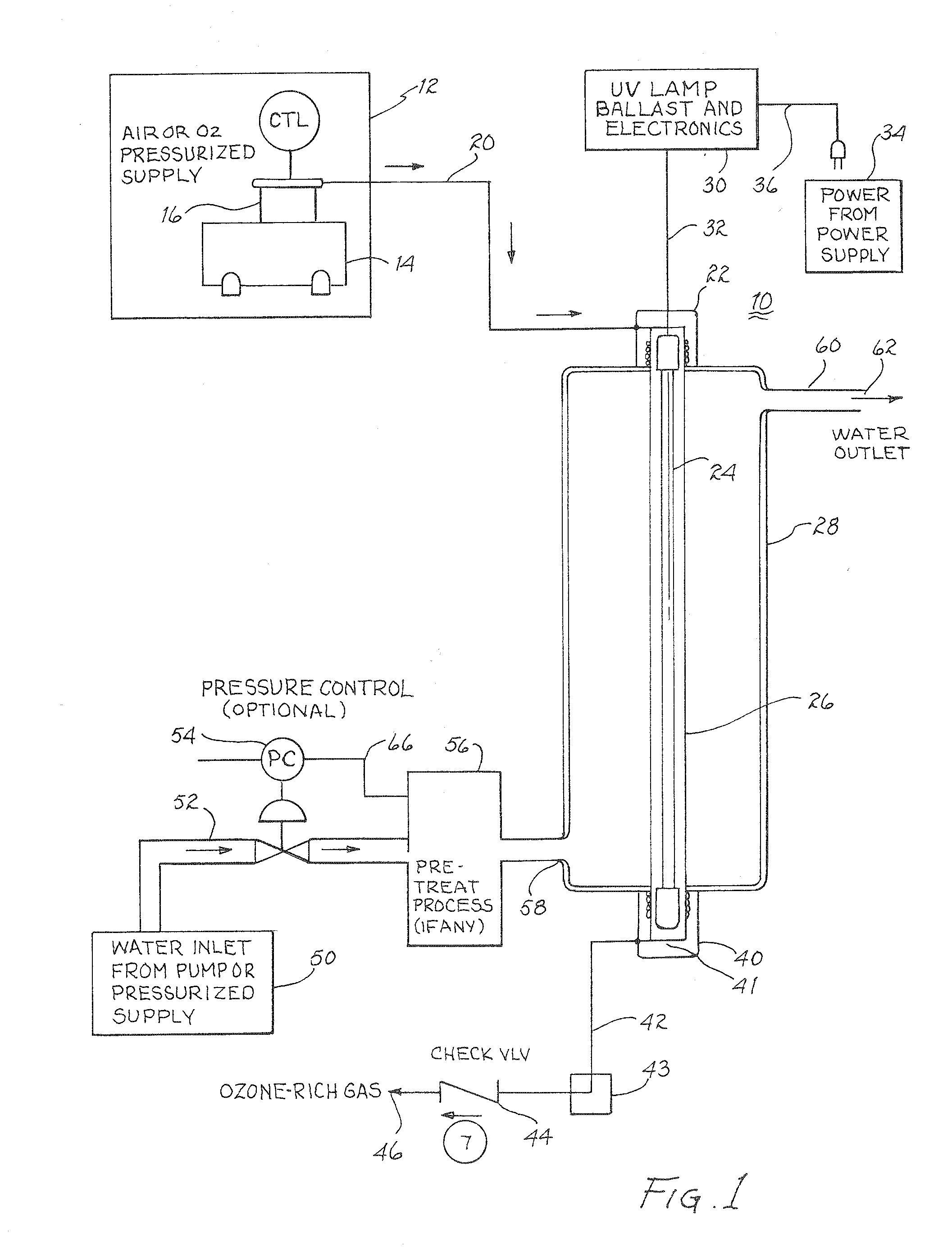
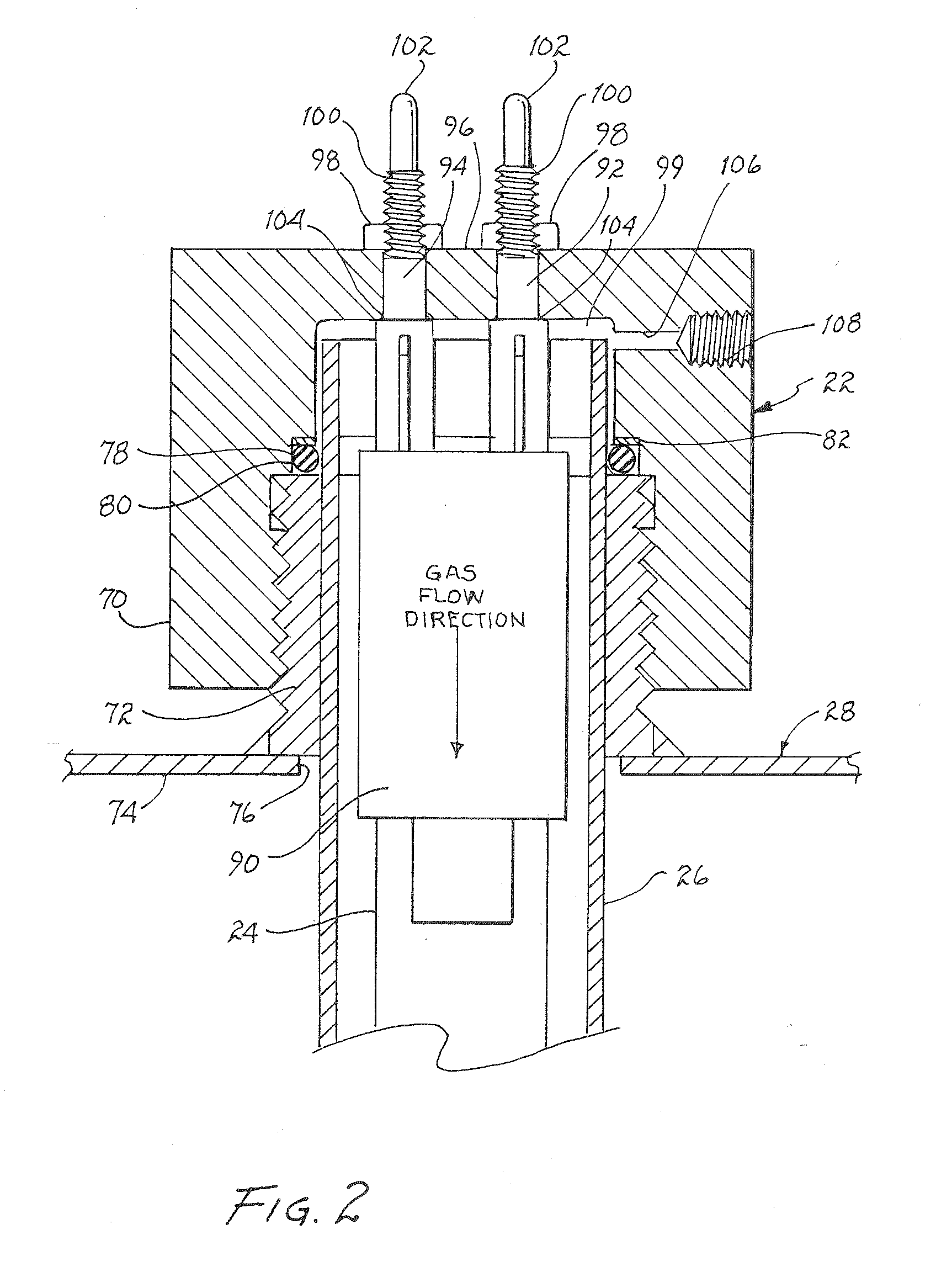
Pressurized uv/o3 water purification system
InactiveUS20080008632A1High ozone concentrationImprove concentrationWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsHigh concentrationDifferential pressure
An oxygen containing gas is injected at a pressure in the range of about two (2) to about five (5) atmospheres or more into an ultraviolet transmissive sleeve surrounding an ultraviolet lamp to produce a high concentration of ozone. Simultaneously, the ultraviolet lamp irradiates water to be purified disposed in a container surrounding the sleeve. The ozone enriched gas is entrained into the water flowing into the container resulting in an oxidative reaction with any organic matter present and coming into contact with the ozone. Alternatively, the ozone may be entrained in water in a second container downstream of the container wherein the water has been irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. In a further variant, the ozone may be entrained in water in a container upstream of the container wherein the water has been irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. In a yet further variant, the ozone may be entrained in one or more containers upstream and prior to irradiation of the water with ultraviolet radiation in the downstream most container. The ozone may be extracted from the ozonated water prior to discharge if the oxidative effect of the ozone is not desired for the intended end use. To enhance ozone production a predetermined pressure is maintained within the sleeve. To prevent damage to sleeve in the event of a drop in pressure of the water surrounding the sleeve, a further differential pressure regulator may be used to relieve the pressure within the sleeve by discharging ozonated gas from within the sleeve. By use of specifically configured end caps for the sleeve, certain existing water purification systems may be converted to embody the present invention.
Owner:ZUCO WATER LLC
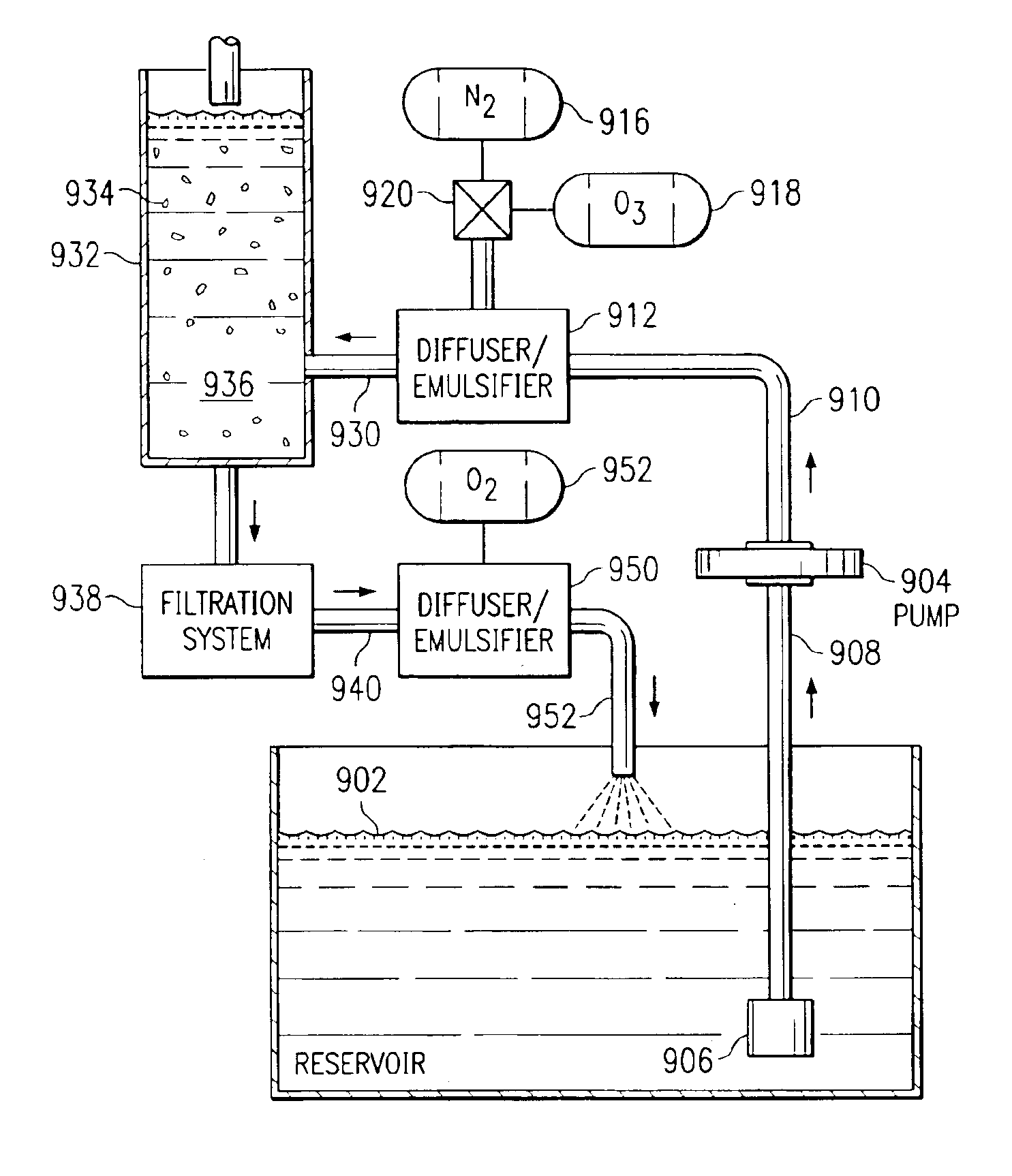
Diffuser/emulsifier for aquaculture applications
InactiveUS6974546B2Liquid separation auxillary apparatusLiquid degasificationReclaimed waterProduct gas
A method of treatment of water in an aquatic environment. Water is first pumped from a reservoir to a first mixing station. An inert gas is introduced into the pumped water at the first mixing station to provide inert gas saturated water, which inert gas saturated water will displace undesired gasses in the water in the reservoir. The inert gas saturated water is then pumped to a sparging column such that the inert gas and undesired gasses will be released from the inert gas saturated water to provide depleted water. The depleted water is then pumped to a second mixing station, wherein oxygen is introduced into the depleted water to provide oxygen enriched water. The oxygen enriched water is then returned to reservoir.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Process for treating oily sludge
ActiveCN101823824AEasy extractionImprove extraction abilitySludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningLiquid carbonaceous fuelsTemperature controlTreatment effect
The invention relates to a process for treating oily sludge and is particularly applicable to the oily sludge generated in the wastewater treatment process of an oil refinery. The process has the following steps of: after performing anhydration treatment on centrifugally dehydrated oily sludge in rotary-type anhydration treatment equipment under certain negative pressure and temperature control to destroy a water, oil and solid stabilizing system of the oily sludge, evaporating part of oil and water in the oily sludge, and performing solvent extraction treatment on coke generated after the anhydration. Solid residue obtained after treatment reaches the solid emission standard; the wastewater generated in the process can reach standard after biochemical treatment and is discharged; the extracted oil can be used as fuel or used for refining; and an extractant can be regenerated and recycled. The process has main characteristics of high sludge anhydrating and extracting speed, high efficiency, good effect, mild operating condition, little energy consumption, good sludge treatment effect and simple equipment operation and maintenance.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for producing high-quality sodium fluoride from fluorine-containing wastewater as raw material
ActiveCN106830012ARecovery rateRecycling rate due toAlkali metal fluoridesAlkali metal halide purificationNuclear chemistryPrecipitation
The invention discloses a method for producing high-quality sodium fluoride from fluorine-containing wastewater as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps: directly adding excessive sodium carbonate into the fluorine-containing wastewater to completely crystallize and separate fluorine in the solution in a mode of sodium fluoride, or firstly, adding amino into the fluorine-containing wastewater so as to obtain an ammonium fluoride solution, or firstly, precipitating and enriching the fluorine in the fluorine-containing wastewater, secondly, converting a precipitated and enriched product into an ammonium fluoride solution by using an ammonium salt solution, adding excessive sodium carbonate into the ammonium fluoride solution to completely crystal and separate the fluorine in the mode of sodium fluoride, and filtering so as to obtain sodium fluoride filter cakes and a post fluorine precipitation liquid; and washing the sodium fluoride filter cakes by using the ammonium fluoride solution, drying so as to obtain a high-quality sodium fluoride product of which the purity is up to 99.25% or greater, crystallizing the post fluorine precipitation liquid to recycle sodium carbonate in the post fluorine precipitation liquid, further desalting a sodium carbonate crystallization mother liquid, and recycling reclaimed water. The method has the advantages of being simple and convenient to operate, high in fluorine recycling rate, low in production cost, good in sodium fluoride product quality, free of fluorine-containing waste and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Thermal management system and method for vehicle electrochemical engine
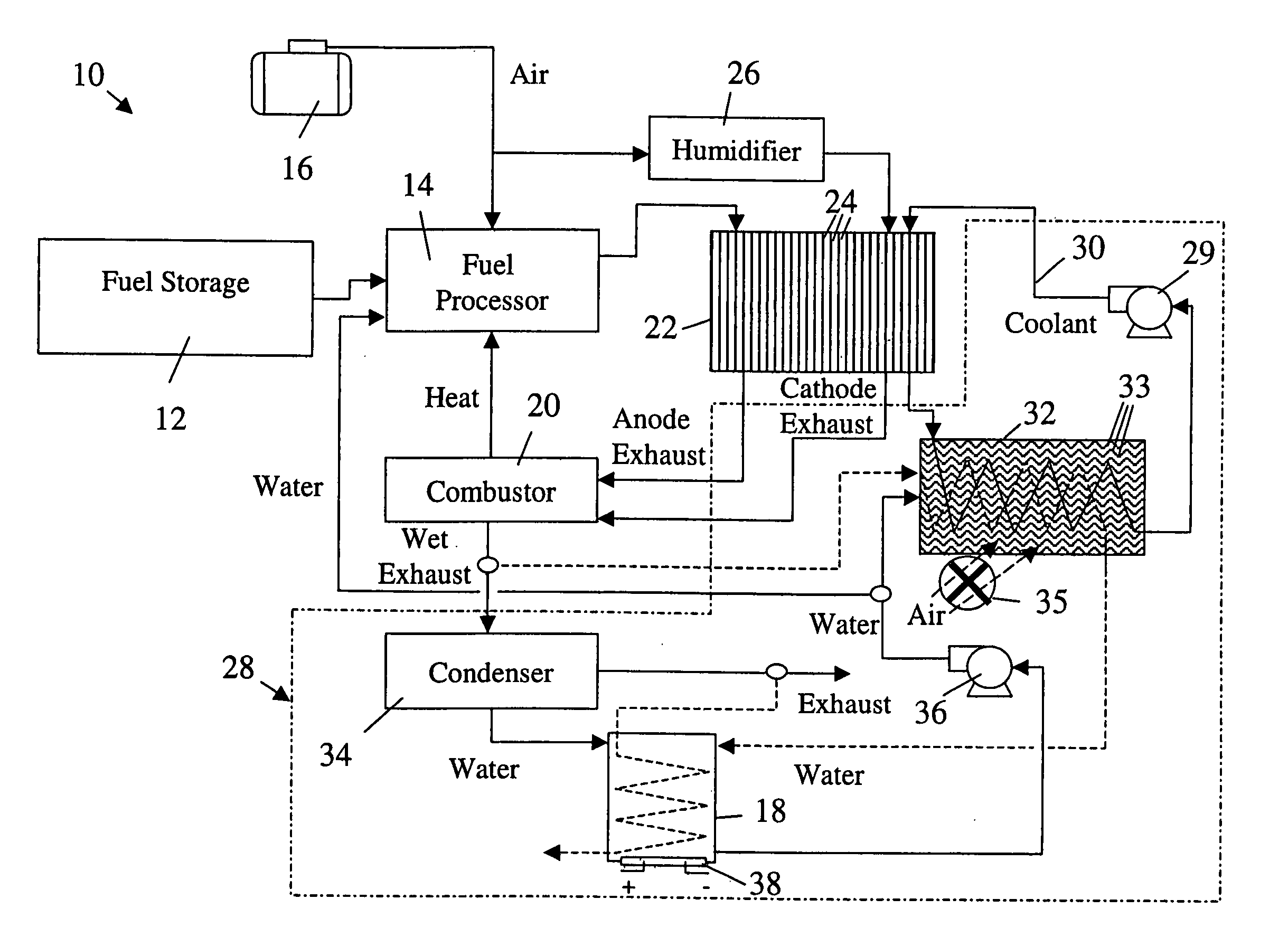
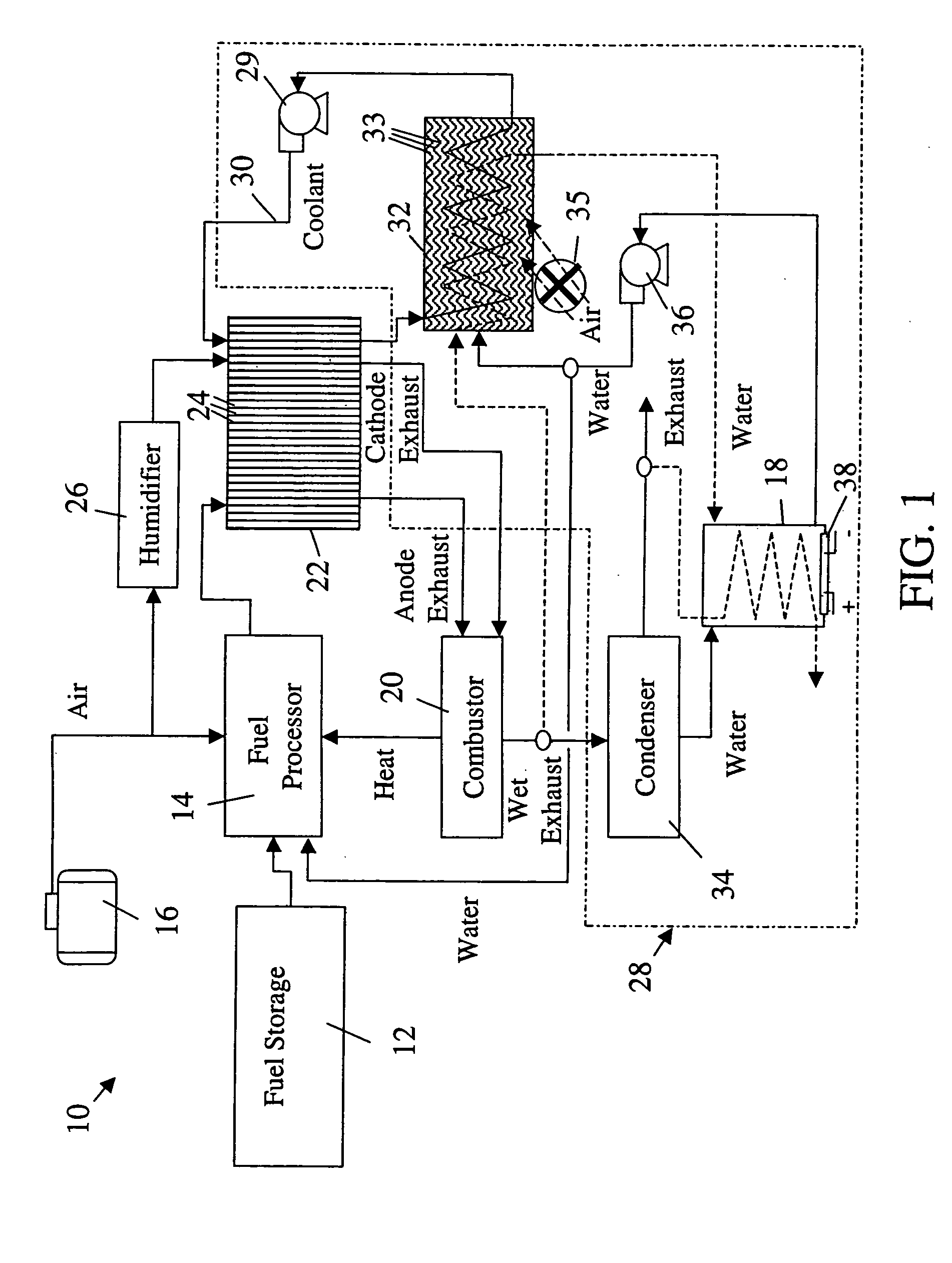
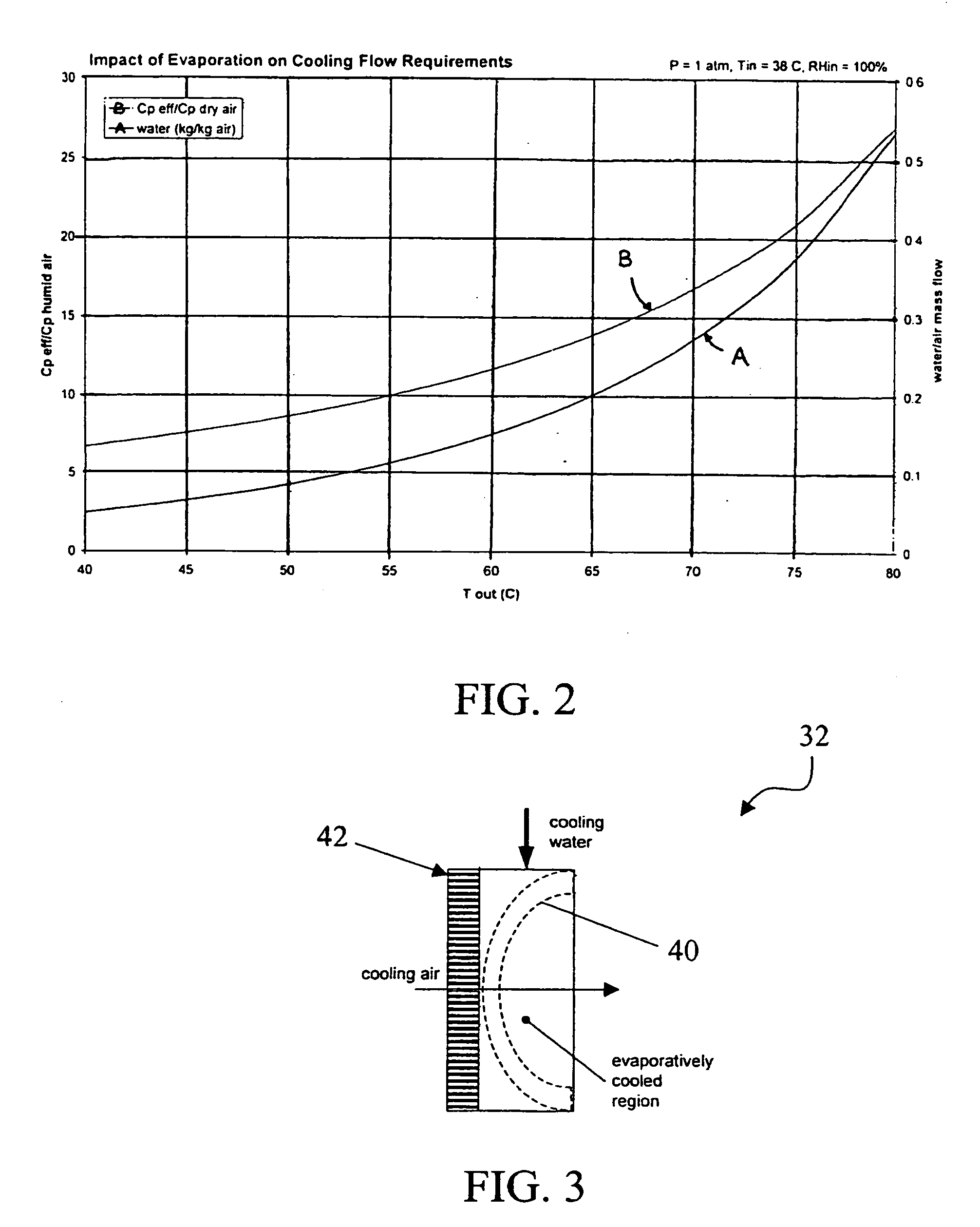
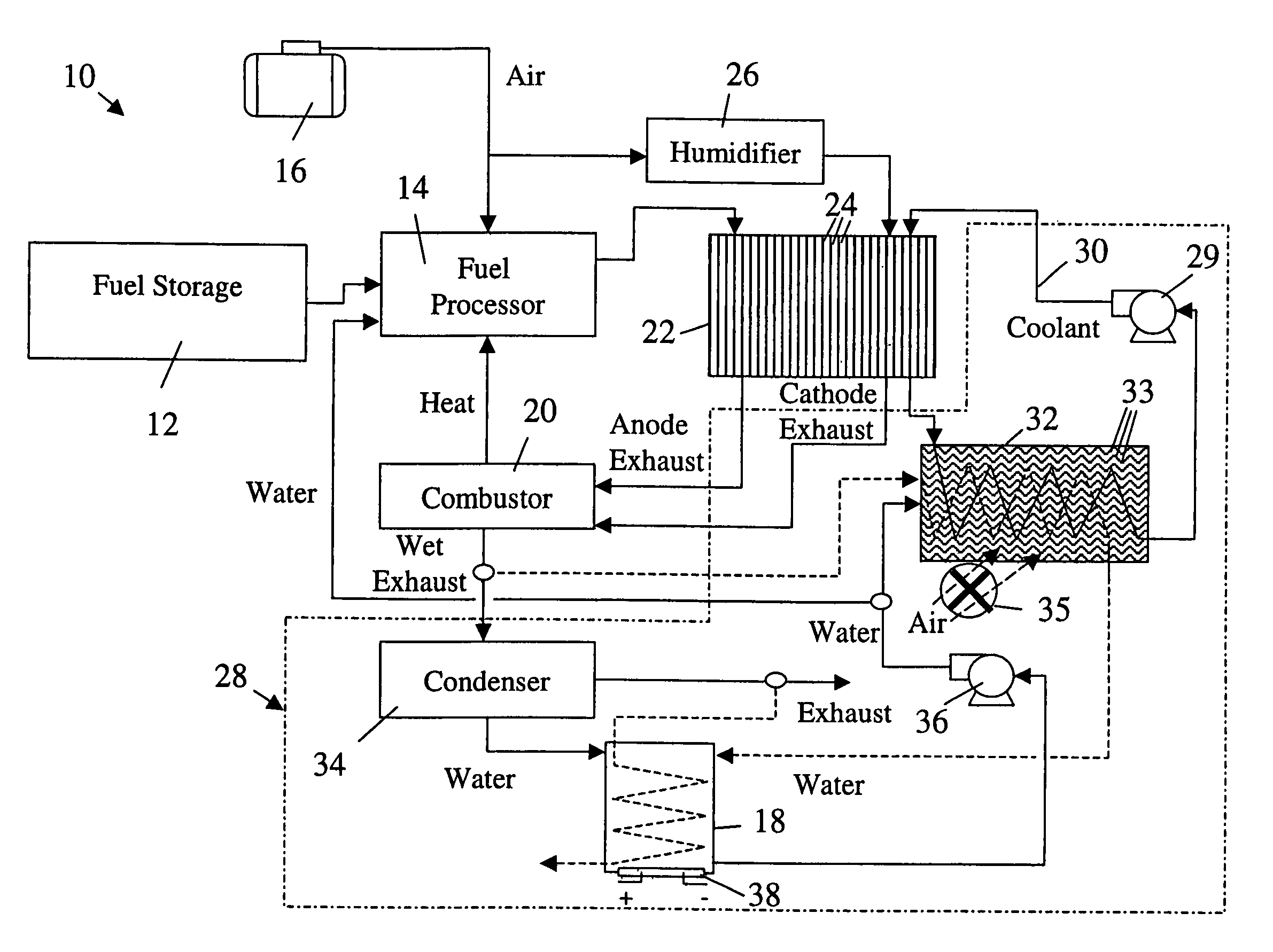
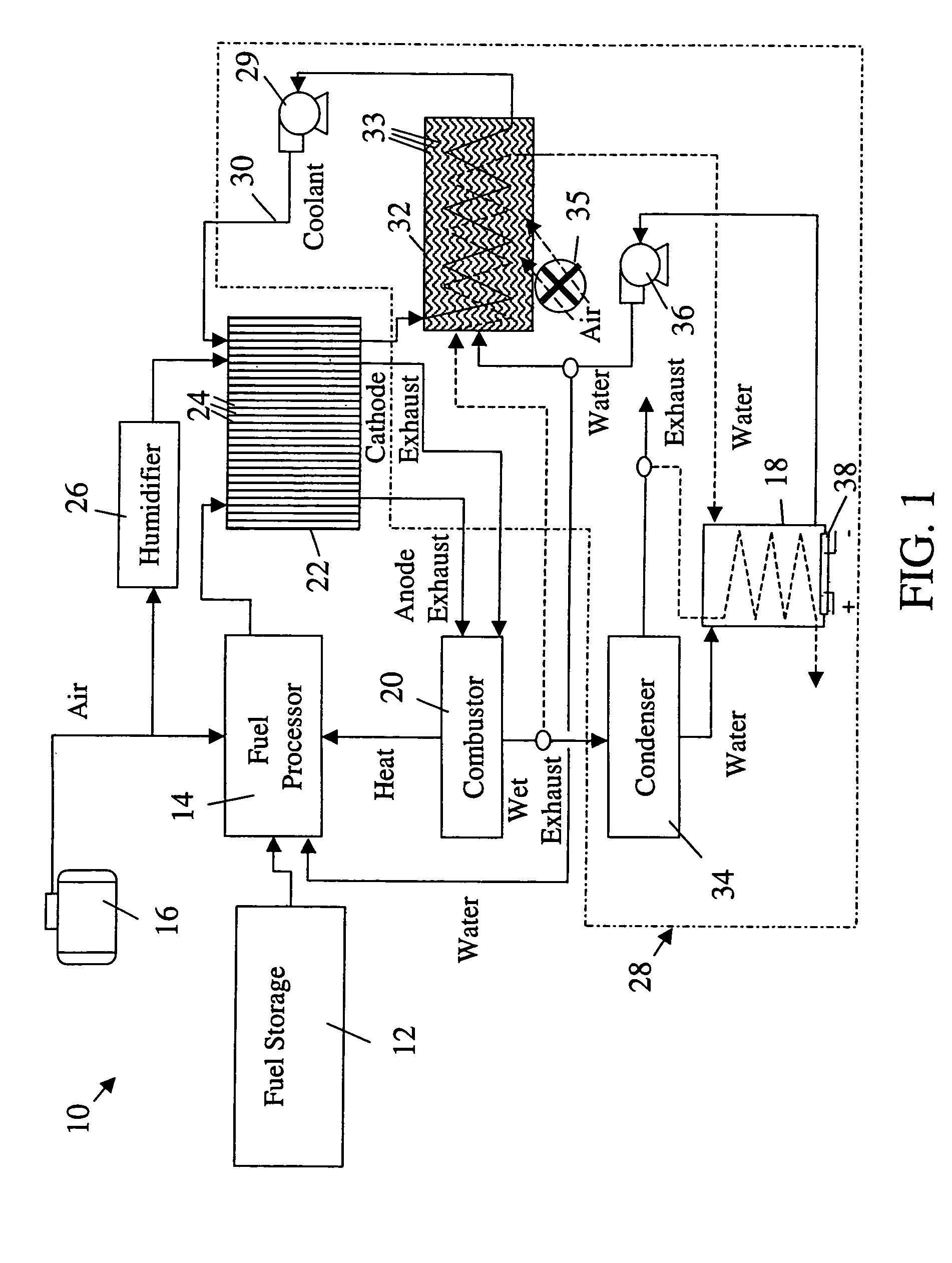
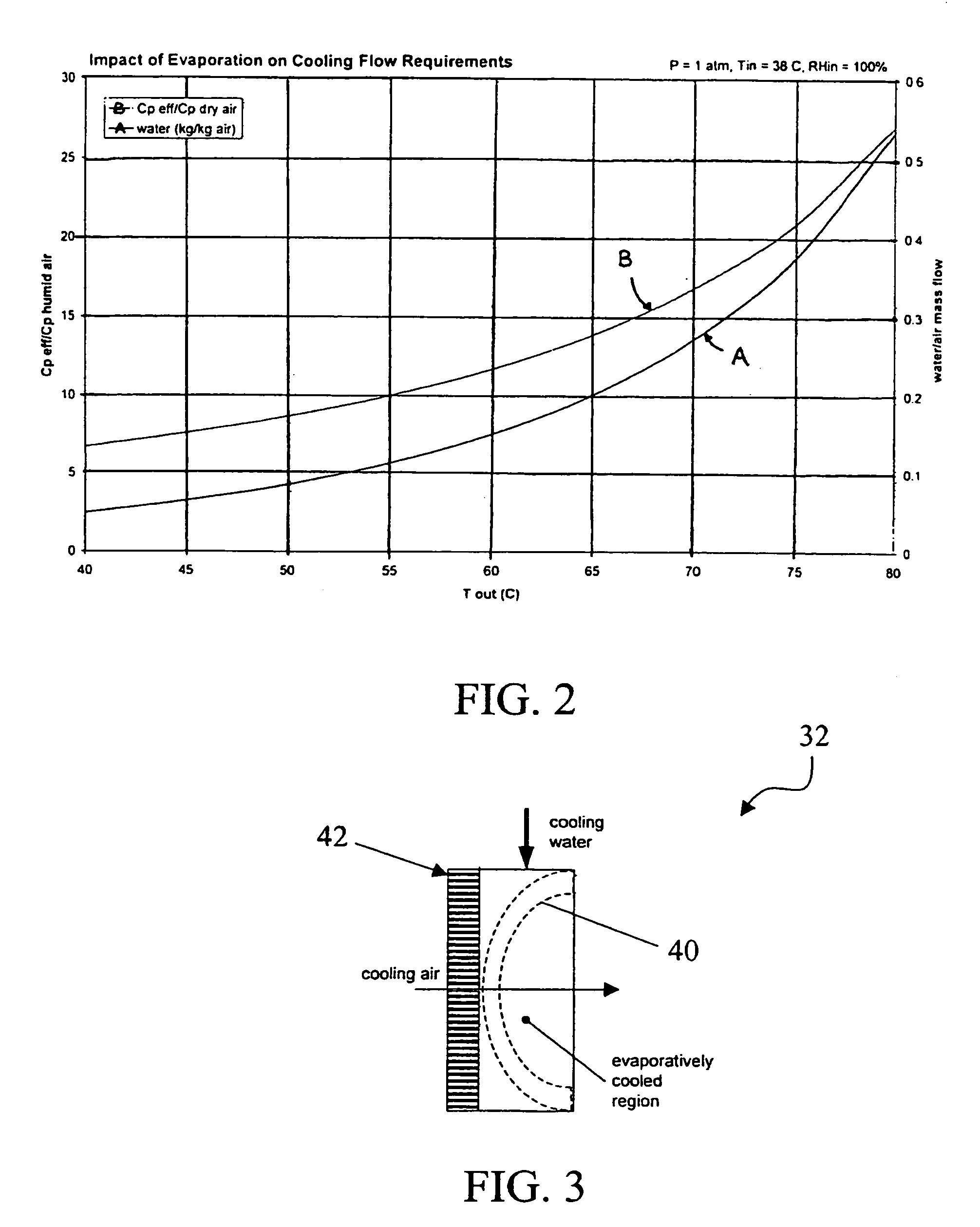
ActiveUS20050199192A1Easy to packReduce rateCoolant flow controlElectric machinesReclaimed waterFuel tank
A thermal management system of an electrochemical engine comprises a radiator provided with a wicking mechanism, a coolant pump fluidly connected to the radiator, a water tank, and a water pump. The water tank is located in the void spaces around fuel storage tanks, and may be filled directly or with reclaimed water from a vapor by-product of the electrochemical engine. The water pump is operable to supply water from the water tank to the wicking mechanism during peak power and / or hot day conditions. Moisture in the vapor by-product may be condensed with the excess cooling capacity of the radiator under less severe cooling conditions. Under freezing conditions, exhaust or coolant from the electrochemical engine may be used to unfreeze water in the tank and wicking mechanism supply lines.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and device for zero-emission treatment of high-hardness waste water containing sulfate
ActiveCN104291511AIncrease the concentration factorSave investmentWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeMultistage water/sewage treatmentSulfate radicalsIon exchange
The invention belongs to the field of waste water treatment and reclaimed water reuse, in particular to a method and a device for the zero-emission treatment of high-hardness waste water containing sulfate. The method for the zero-emission treatment of high-hardness waste water containing sulfate comprises the following steps: 1) sequentially substituting calcium and magnesium ions in waste water into sodium ions by a double-alkali process and an ion exchange process and simultaneously removing most alkalinity so as to promote sulfate radicals and chlorine ions to be the main components of rest anions in water and promote sodium ions to be the main component of cations; 2) concentrating waste water obtained in step 1) through reverse osmosis and reclaiming produced water; 3) separating and concentrating concentrated water treated by reverse osmosis in step 2) through nanofiltration so as to obtain nanofiltered concentrated water of which the main component is sodium sulfate and nanofiltered produced water of which the main component is sodium chloride; 4) after concentrating the produced water nanofiltered in step 3) through reverse osmosis or positive osmosis, evaporating and concentrating; 5) removing sulfate radicals from the concentrated water nanofiltered in step 3). The concentrating times of waste water is increased as much as possible, and the evaporating quantity of waste water is reduced.
Owner:山东泰禾环保科技股份有限公司
Nano crystallite composite filter material and supplement of manufacture method thereof
The invention extends the connotation range required to be protected on the basis of a previously issued patent ZL200710025045.4, i.e., a nanometer microcrystalline composite filter material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of a water disposal technique material. According to weight percentage, the nanometer microcrystalline composite filter material comprises 3-95 percent of attapulgite clay, 5-80 percent of sepiolite clay, 2-25 percent of kaolinite clay, 2-97 percent of tubular halloysite, 5-75 percent of diatomite, 5-75 percent of natural zeolite (clinoptilolite, mordenite and the like), 0-25 percent of pillared montmorillonite, 0-50 percent of expanded vermiculite, 0-5 percent of expanded perlite and 0-50 percent of active carbon or bamboo carbon powders. All raw materials which are powder shapes are mixed according to proportion and stirred to granulate by adding an inorganic adhesive, then sintered and activated at the temperature of 900-500 DEG C (inert gas is required for sintering and activating the filter material added with active carbon). The nanometer microcrystalline composite filter material has smooth shape, rough surface and uniform particle size, with the diameter of 1-10mm, and is used for biological filter tanks and high-class adsorption filter materials in deep purification systems of drinking water and reclaimed water sewage disposal systems.
Owner:傅成义
Wetland water treatment system
ActiveUS7674378B2Easy maintenanceEasy constructionWater cleaningCentrifugal force sediment separationParticulatesWater treatment system
A self-contained wetlands treatment system to remove pollutants from water and treat stormwater runoff or other grey water. This is system and method wherein the water is passed through a wetland filtering and treatment system. This invention removes solids, metals (dissolved / particulate), nutrients (dissolved / particulate), oils, and bacterial contaminants from the water. The system and system housing can be fabricated, built, and assembled in a broad range of sizes and materials to accommodate and treat a broad range of influent flow rates.
Owner:MODULAR WETLAND SYST
Simultaneous slicing and washing of vegetables
InactiveUS20010026824A1Process time savingSaving in equipment expenseMilk preservationDough treatmentVegetable matterReclaimed water
Simultaneous slicing and washing of relatively firm raw vegetable or fruit products is accomplished in a vat of water into which a slicer apparatus is positioned such that the slices are formed and discharge directly into the water An inclined takeout conveyor serves to receive the slices and remove them from the water. A circulating water current and fluid jets urge the slices to disperse onto the conveyor. A spray of water or air blast removes residual vegetable matter from the slice surfaces before leaving the takeout conveyor for further processing. Slicing and washing a vegetable in a flume volute where the slices are dispersed onto a takeout conveyor is disclosed where the water medium is collected in a tub and recycled back to flow in the flume to a level that covers the slicer's operative parts. The apparatus may be used for simultaneous slicing and cooling of raw vegetables where hot cooling oil is maintained in the system and recycled for reheating.
Owner:HEAT & CONTROL
Compact natural gas steam reformer with linear countercurrent heat exchanger
InactiveUS20110014088A1Cheap productionEconomic recoveryExhaust apparatusElement comparisonSteam reformingCombustion chamber
The present invention is natural gas steam reforming apparatus for generating an output gas mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The apparatus is made from two enclosures. A first enclosure contains a source of water, superheated steam, and channels, located within a lower portion of the first enclosure, which contain a water-gas-shift catalyst for converting CO into CO2 and H2. The heat from hot gas flowing through the channels is released into the first enclosure to boil the water to generate the superheated steam. A second enclosure, contained within an upper portion of the first enclosure, includes a steam inlet for receiving the superheated steam from the first enclosure; a combustion chamber; and a reformation chamber. The combustion chamber is used for combusting a portion of the natural gas to generate additional steam, heat, and a hot gas mixture of CO2, CO, and H2. The reformation chamber is used for steam reforming a remaining portion of the natural gas to generate additional hot gas mixture of CO2, CO, and H2. The hot gas mixture is directed through the channels installed in the first enclosure in which the water-gas-shift catalyst converts residual CO into additional CO2 and additional H2, to produce an output gas mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen. In the present invention, the first and second enclosures function as a top-to-bottom linear countercurrent heat exchanger. In one embodiment of the present invention, an external third enclosure containing a combustion chamber and a boiler for combusting natural gas with ambient air may be used to boil additional water into superheated steam which is then fed into the first enclosure.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
Method and equipment for treating sludge in normal state
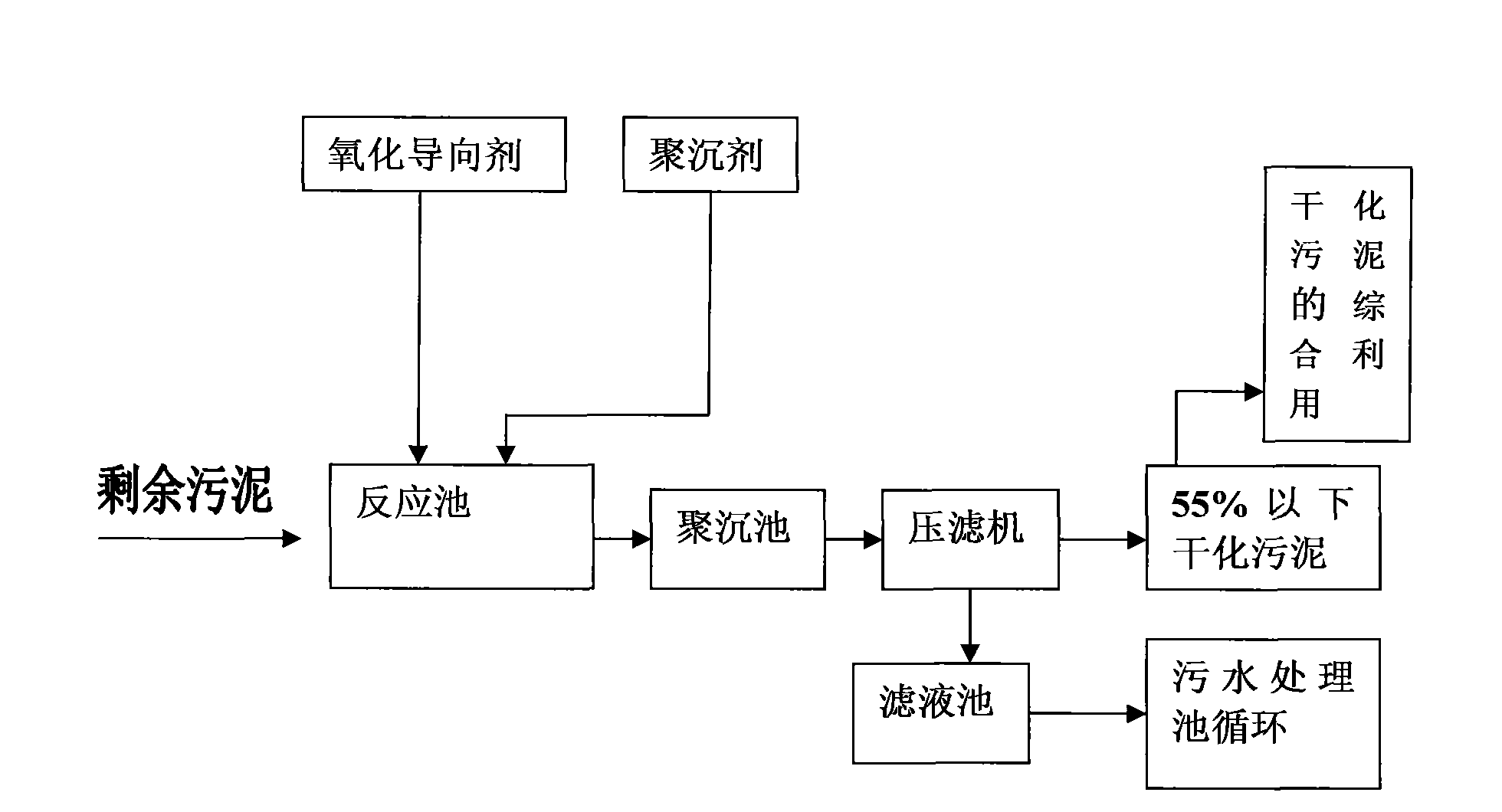
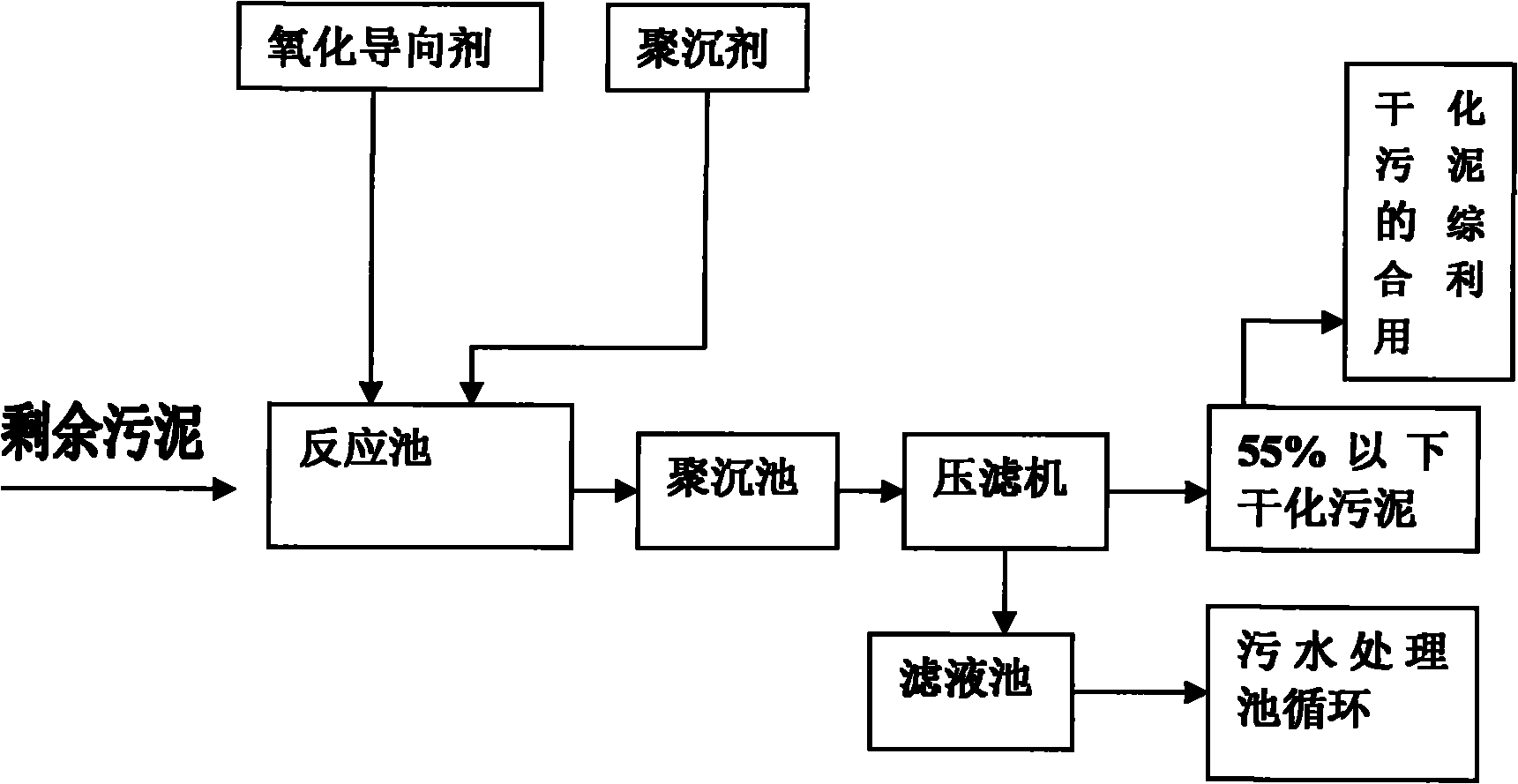
InactiveCN102145974ALow bacterial indexStable structureSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSludge treatment by oxidationFiltrationReclaimed water
The invention relates to a method for treating sludge in municipal sewage, in particular to a method for separating water from sludge in the watery sludge. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding an oxidation directing agent and a regulator into the sludge, stirring the sludge and filling ozone into the sludge; and (2) after stirring to perform a reaction, adding a coagulant agent, and finally carrying out pressing filtration on the sludge to obtain the sludge with the moisture content of below 55 percent. By the method overcomes the technical bottleneck that in a normal temperature sludge treatment process, water adsorbed by the sludge containing organic matter cannot be removed, and achieves the aims that the cost is low, the effect is good and the processed sludge reaches the national standard.
Owner:HUNAN XIANGNIU SLUDGE ADVANCED TREATMENT
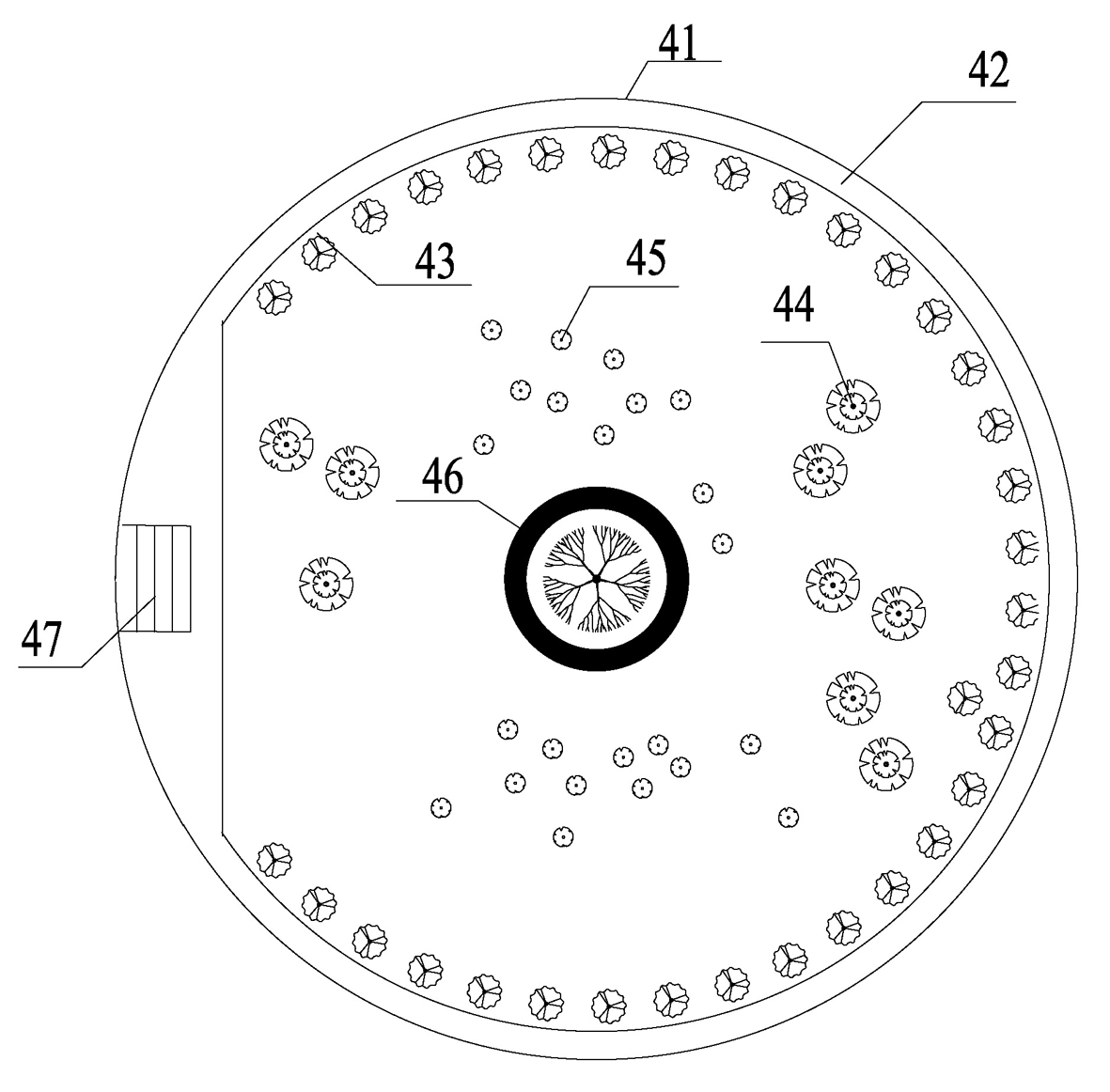
Reclaimed water treatment system combining upflow aerating biological filter with horizontal underflow artificial wetland
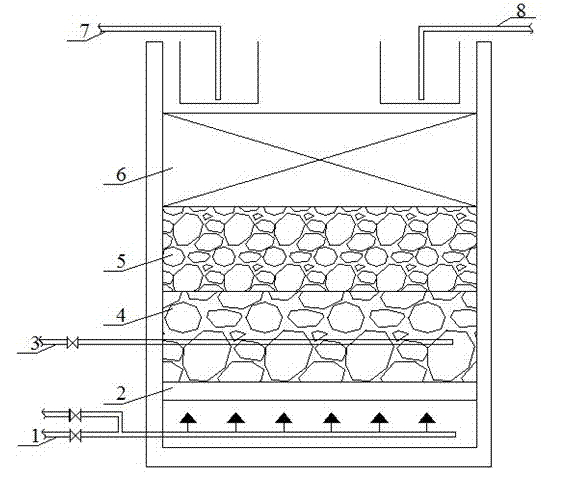
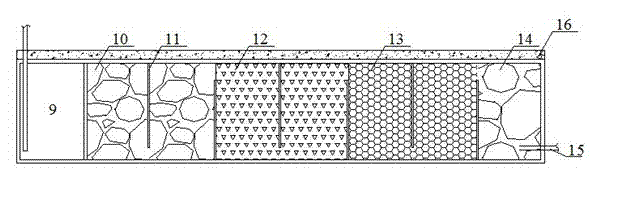
InactiveCN103043865AShort hydraulic retention timeHigh volume loadMultistage water/sewage treatmentSites treatmentConstructed wetland
The invention discloses a reclaimed water treatment system combining an upflow aerating biological filter with horizontal underflow artificial wetland. The system consists of the upflow aerating biological filter and the horizontal underflow artificial wetland; the upflow aerating biological filter comprises a water inlet guide tube positioned at the bottom of the filter; a filter plate, a supporting layer, an A section filler area, a B section filler area and a water outlet area are sequentially arranged above the water inlet guide pipe; a communicating water pipe is mounted on the water outlet area, and communicated with a regulating tank of the horizontal underflow artificial wetland; an aerator pipe is led out of the supporting layer; the regulating tank and a matrix area parallel to the regulating tank are arranged at the lower layer of the horizontal underflow artificial wetland; the matrix area sequentially comprises a macadam area, a steel slag area, a zeolite area and a water outlet gravel area from left to right; the water outlet gravel area is equipped with a water outlet pipe; and a soil covering layer and aquatic plants are arranged at the upper layer of the horizontal underflow artificial wetland. With the adoption of the system, on-site treatment and utilization of sewage are achieved; the sewage treatment process flow is simplified; and operation and management costs are lowered.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
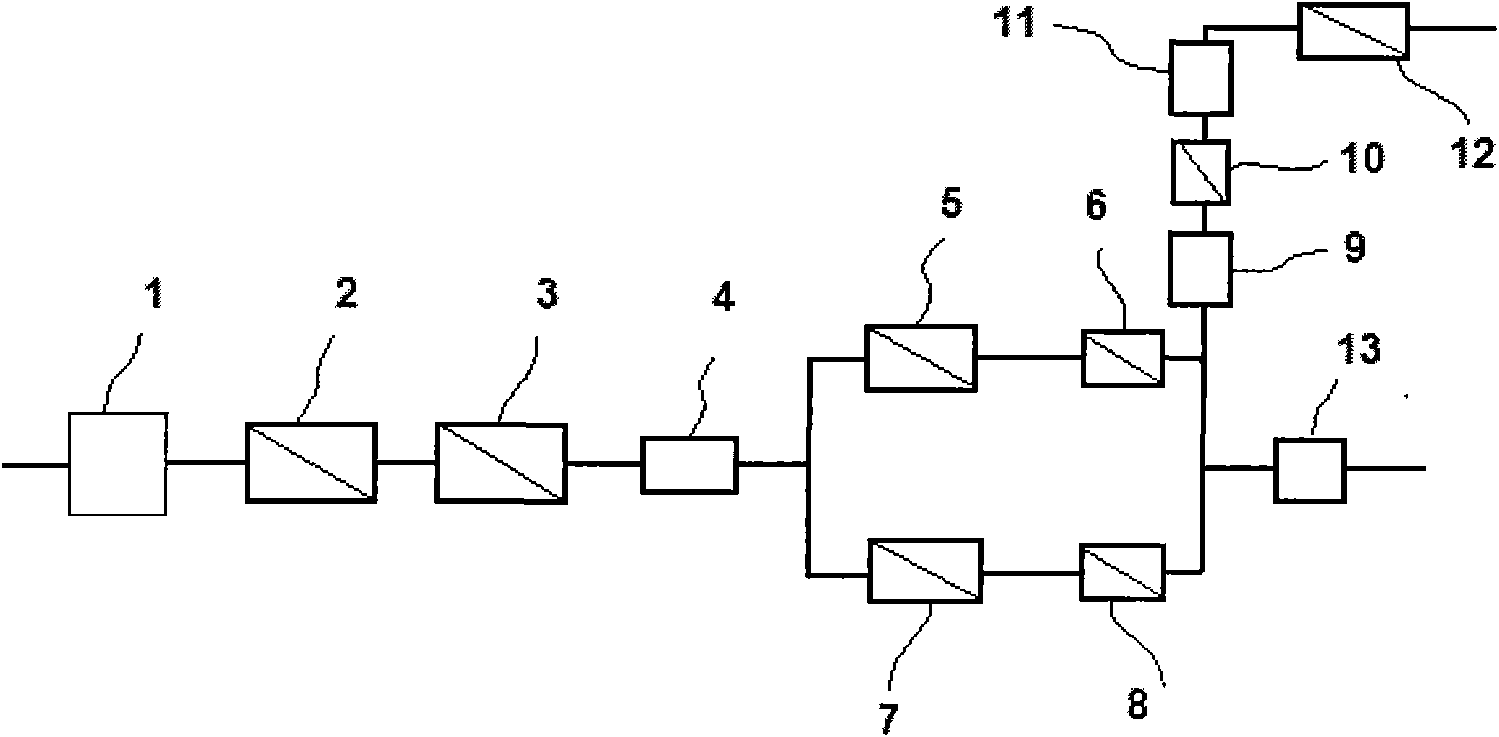
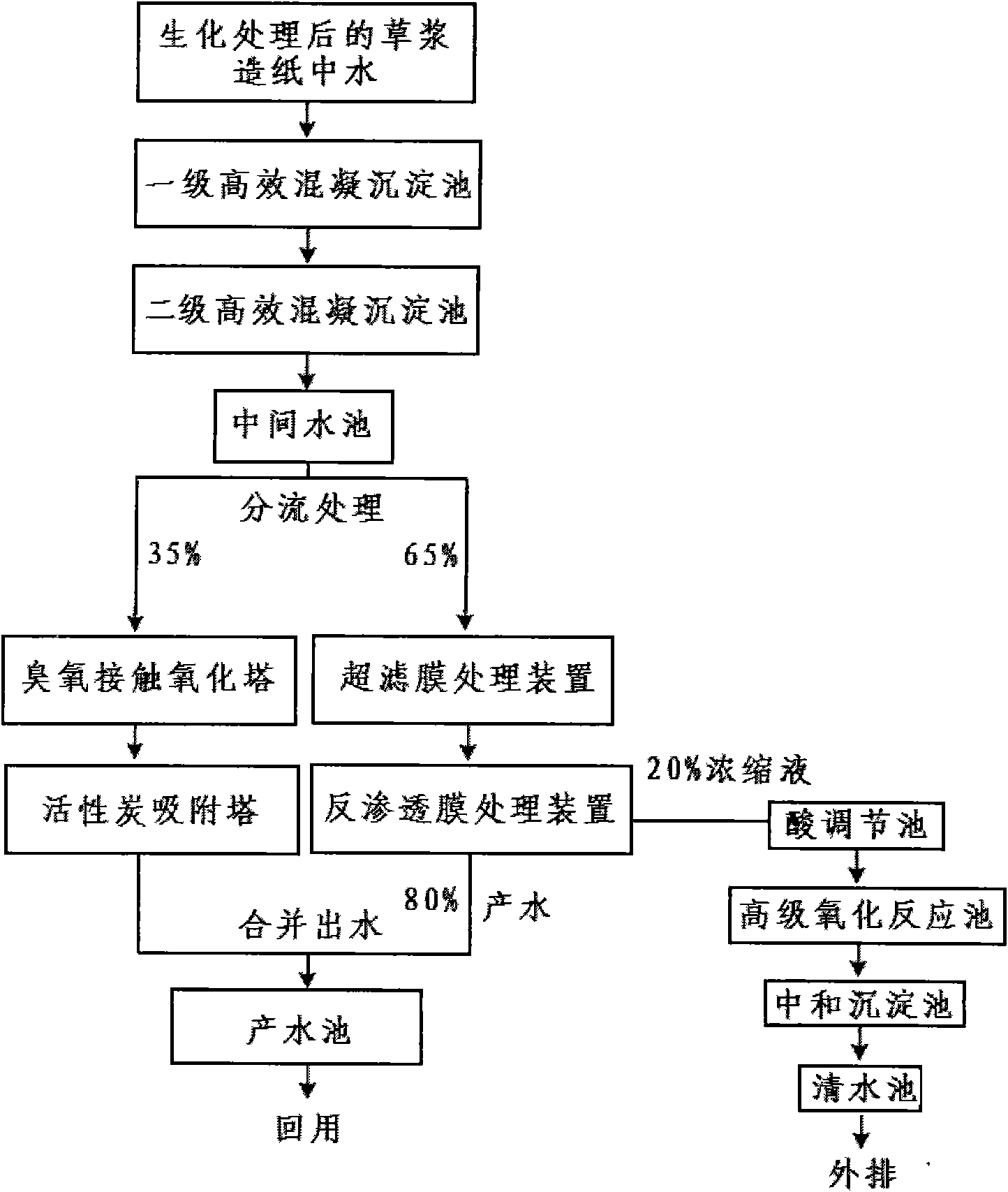
System and method for treating water recycled from straw pulp papermaking wastewater
InactiveCN101781049AReduce foulingReduce pollutionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from plant processingChemical treatmentUltrafiltration
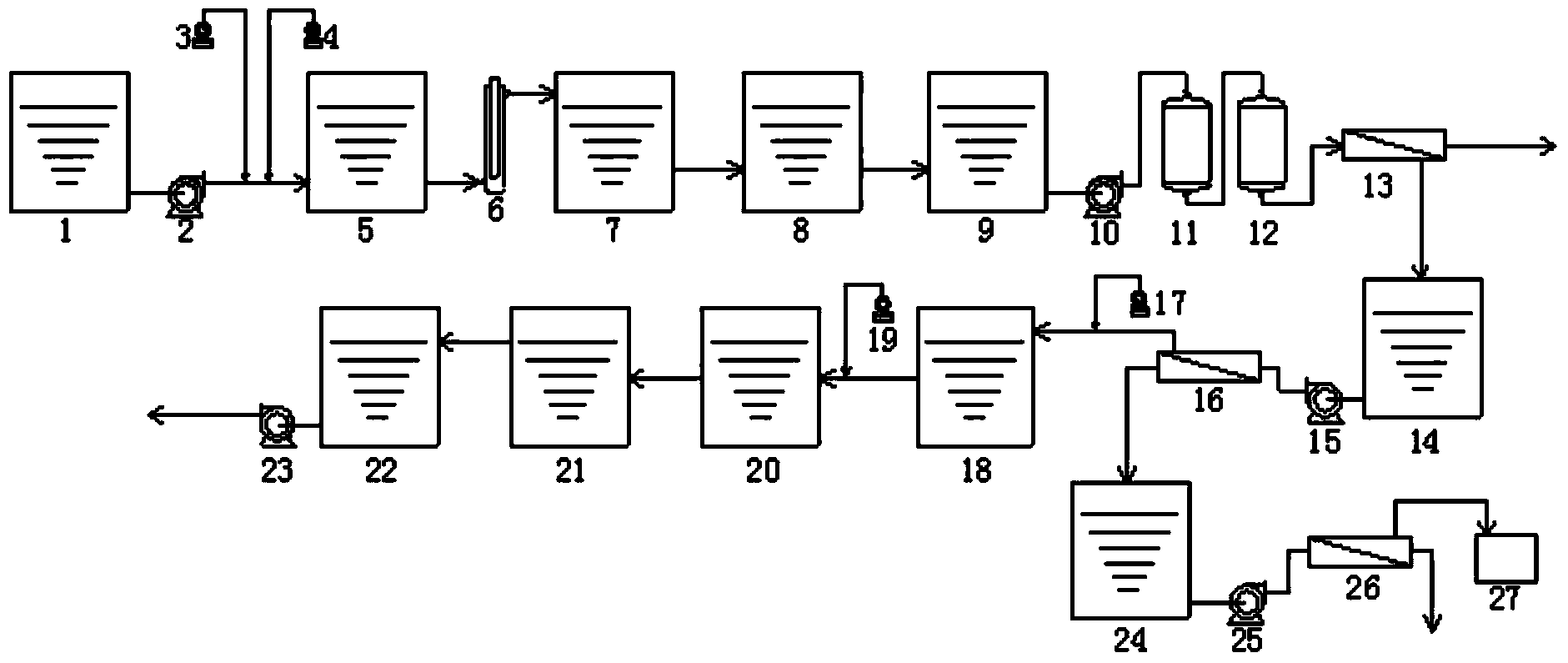
The invention discloses a system and a method for treating water recycled from straw pulp papermaking wastewater. The system is formed by sequentially or respectively connecting a regulating tank, a primary efficient coagulative precipitation tank, a secondary efficient coagulative precipitation tank, a middle water tank, an ultrafiltration membrane treatment device, a reverse osmosis membrane treatment device, an ozone contact oxidation tower, an active carbon adsorption tower, an acid regulating tank, a higher oxidization reaction tank, a neutralizing precipitation tank and a water-producing tank. The system organically combines the coagulative precipitation treatment, the higher oxidization treatment, the ozone catalysis oxidation treatment and the treatment of an ultrafiltration membrane and a nanofiltration membrane, treats the water recycled from the straw pulp papermaking wastewater by using a physical and chemical treatment technology and a shunting treatment and combined effluent treatment process and mode, can ensure that the large scale recycled water of the straw pulp papermaking industry reaches the requirement of reuse water after treated and does not affect a papermaking process and a paper product on the premise of ensuring the low operating cost, and the treated reverse osmosis concentrated water reaches the emission standard of the industry.
Owner:BEIJING SOUND ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
Integrated technology for deep purification treatment for printing and dyeing waste water
InactiveCN101633541AReduce ozoneEnough time to stayTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFiltrationBiological filter
The invention discloses integrated technology for reclaiming lightly-polluted printing and dyeing waste water or printing and dyeing waste water achieving a certain discharge standard through deep purification treatment for production. A related process of the technology mainly comprises an adjusting tank, a pressure moving bed bio-film reactor, a ceramsite and activated carbon biological filter, an air floating system, a laminated filter and an ultra-filtration and reverse osmosis system. The technology is characterized in that the technology improves the prior biochemical technology, and carries out process integration by combining technology such as ozone oxidation, air flotation, membrane separation and the like. The regeneration of the printing and dyeing waste water can be realized by adopting the treatment technology, and the regenerated water quantity can reach 70 to 80 percent; and the technology not only can effectively solve the pollution problem of the printing and dyeing industry and protect the environment, but also can provide theoretical and technical support for realizing closed-loop circulation of the printing and dyeing waste water and popularizing clean production in the printing and dyeing industry.
Owner:ZHEJIANG STONE ENVIRONMENTAL ENG CO LTD +2
Method and apparatus for parallel desalting
InactiveUS20040245177A1Reduce water hardnessPercent reusableLiquid separation auxillary apparatusGeneral water supply conservationPotable waterDesalination
Parallel desalting (PDS) includes a hybrid membrane softening (MS) system for de-mineralizing water for residential and commercial use. Parallel desalting produces "soft" water without the use of salt, or any other liquid chemical reagent normally used to carry out pH adjustment in industrial membrane and precipitation processes. The PDS process balances the operation of a RO (potable water) membrane unit with the operation of a tubular MF (wastewater) membrane unit, thereby providing a highly efficient and regenerative water treatment technology: (1) The optimum operation for the PDS system transforms roughly 90 percent of a potable, slightly brackish water supply into <50 mg / L TDS water with <1-grain (10-15 mg / L as calcium carbonate)-water hardness; and (2) The operation of the PDS system produces, in salinity terms, in a 100 percent reusable effluent for downstream recycling. Virtual prototype results suggest that with Colorado River Aqueduct source water (570-620 mg / L TDS and 16-grain water hardness), parallel desalting can produce an effluent with a TDS 40-70 mg / L lower than the originating supply (excluding TDS contributed directly by the particular type of use of the soft water).
Owner:PERRION
Advanced purification treatment system for high concentrated organic wastewater
InactiveCN101468859AReduce pollutant contentReduce loadWater/sewage treatment by irradiationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHigh concentrationParticulates
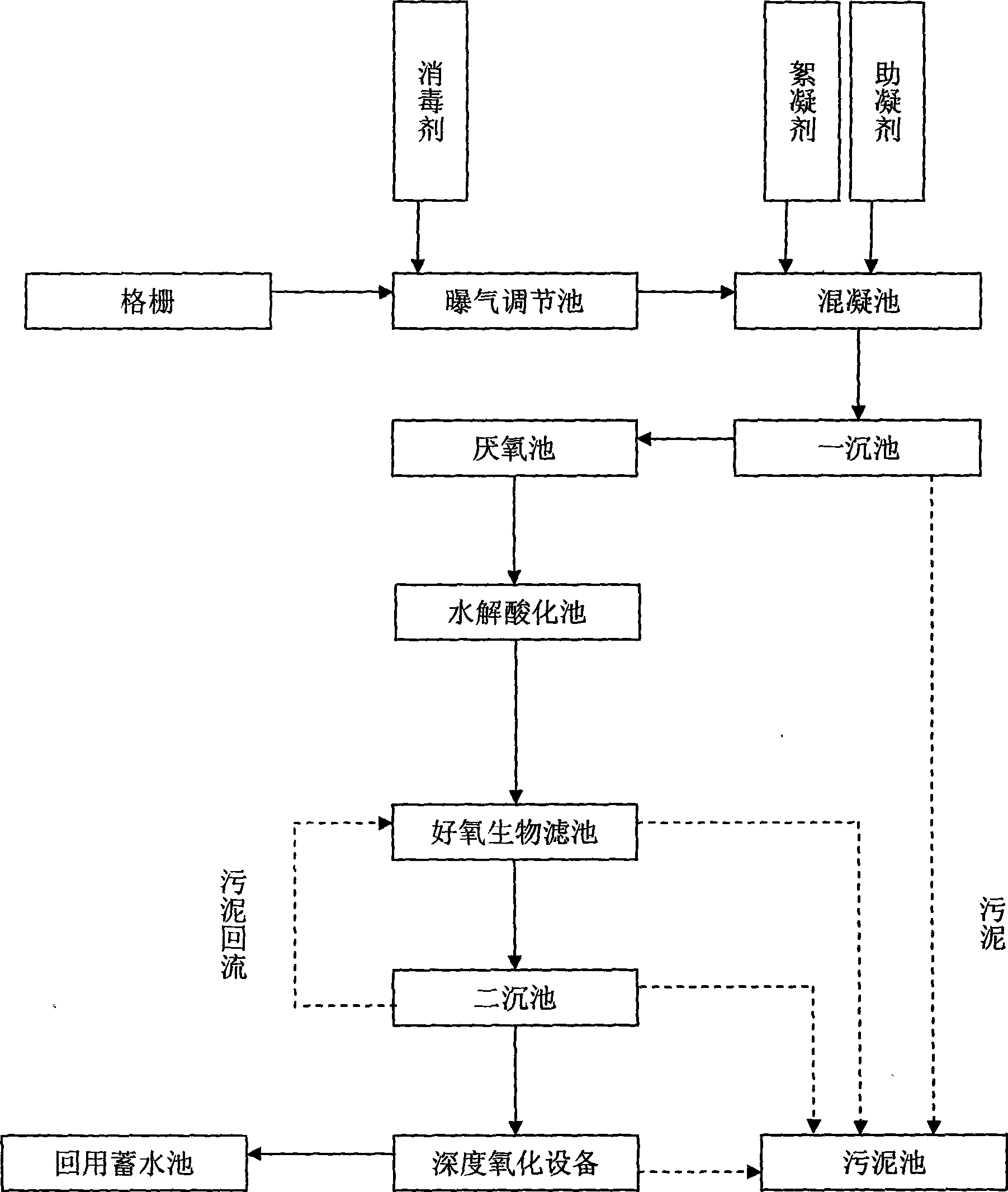
The invention relates to a deep purification treatment system for high-concentration organic wastewater. The system comprises a grid, an aeration adjustment pool, a coagulation pool, a primary precipitation pool, an anaerobic pool, a hydrolysis acidification pool, an aerobic biofilter, a secondary precipitation pool, deep oxidation equipment, a sludge pool and a recycling water storage pool; through coagulation and primary precipitation, partial organic pollutants and suspended particulate matters in wastewater are removed; through anaerobic, anoxic and aerobic multistage mutual function, firstly, large-molecule organic matters are degraded to small-molecule organic matters; the small-molecule organic matters are decomposed to inorganic oxide and water through aerobic microorganism; the residual organic molecules in the water which are different to have biological decomposition under usual condition are subjected to further oxidation treatment through the deep oxidation equipment; the deep oxidation equipment preferentially selects a photocatalytic oxidation purifier with ozone input; through the oxidation function of ozone under catalysis of an photocatalyst, outlet water formed finally has high purification degree and no biological pollution and can be used as recycled water; and the deep purification treatment system is suitable for treating various wastewater with high concentration and organic pollution.
Owner:BEIJING JINAOHUARONG TECH
Kitchen garbage disposal method
ActiveCN107824601AImprove processing efficiencyFull recoveryBio-organic fraction processingSolid waste disposalLitterReclaimed water
The invention relates to a kitchen garbage disposal method. The kitchen garbage disposal method adopts a kitchen garbage disposal device which comprises a crushing chamber, a disinfection chamber, a fermentation chamber, a separation chamber, a drying chamber, a sewage treatment cavity, a compression chamber and an organic fertilizer storage box. Through such steps as crushing, disinfection, fermentation, solid-liquid separation, sewage treatment, drying, compression and storage, solids of kitchen garbage form an organic fertilizer, liquid is processed to obtain reclaimed water, produced gas forms marsh gas, and therefore, full recycling and reusing of kitchen garbage are truly realized.
Owner:广东人峰实业有限公司
Treatment method of stainless steel pickling waste water
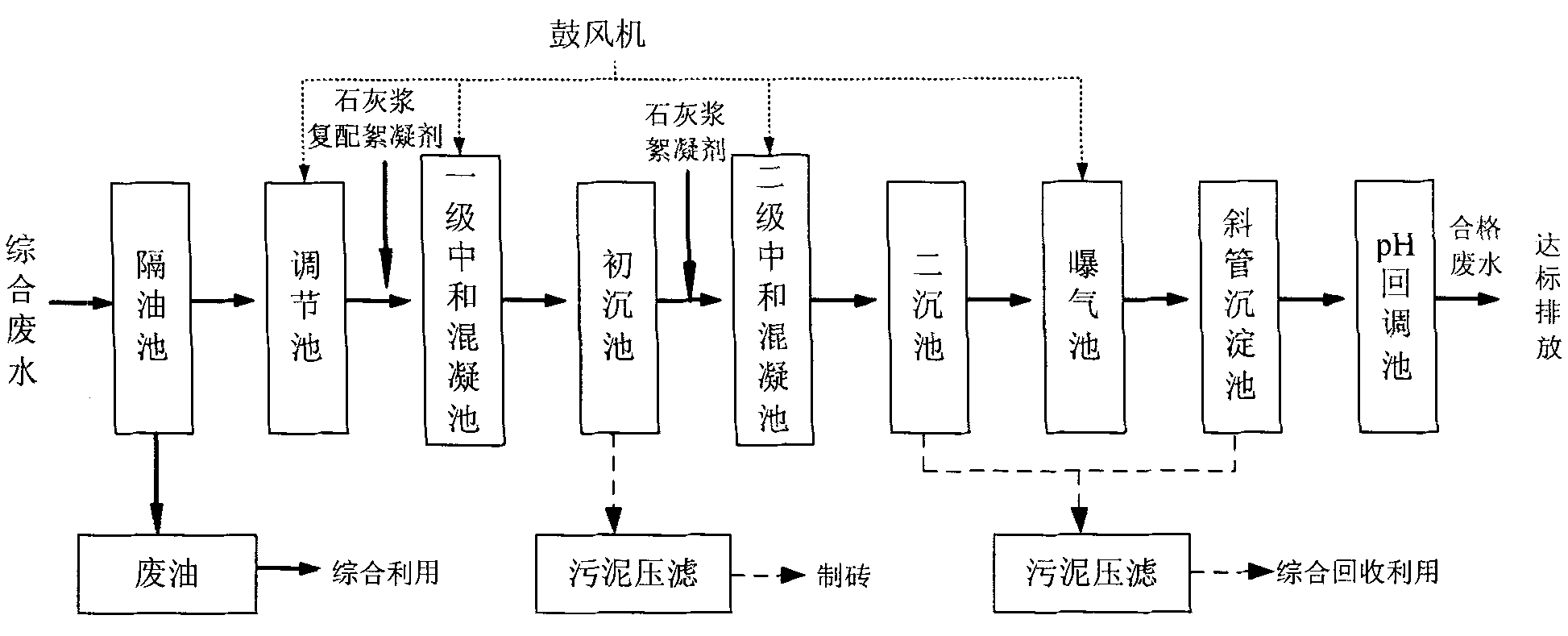
ActiveCN101875518AReduce processing costsAchieve reuseMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationFlocculationChemical treatment
The invention discloses a chemical treatment method, in particular to a method for treating waste water in an environment-friendly mode. The method comprises the steps of oil removal regulation, first-level neutralization / flocculation, first-level sedimentation, aeration oxidation, second-level neutralization / flocculation, second-level sedimentation, aeration oxidation and inclined tube sedimentation. In a first-level neutralization and flocculation pool, lime milk and formulation flocculant are added, and the pH value of the waste water is regulated, wherein the formulation flocculant consists of cationic flocculant and nonionic flocculant. The invention can greatly reduce the treating cost of the waste water and realize recycle of water without adding equipment investment and has the advantages of convenient operation, good effect and the like. The invention can be widely applied to enterprises with chemical engineering pollution.
Owner:陈宇青
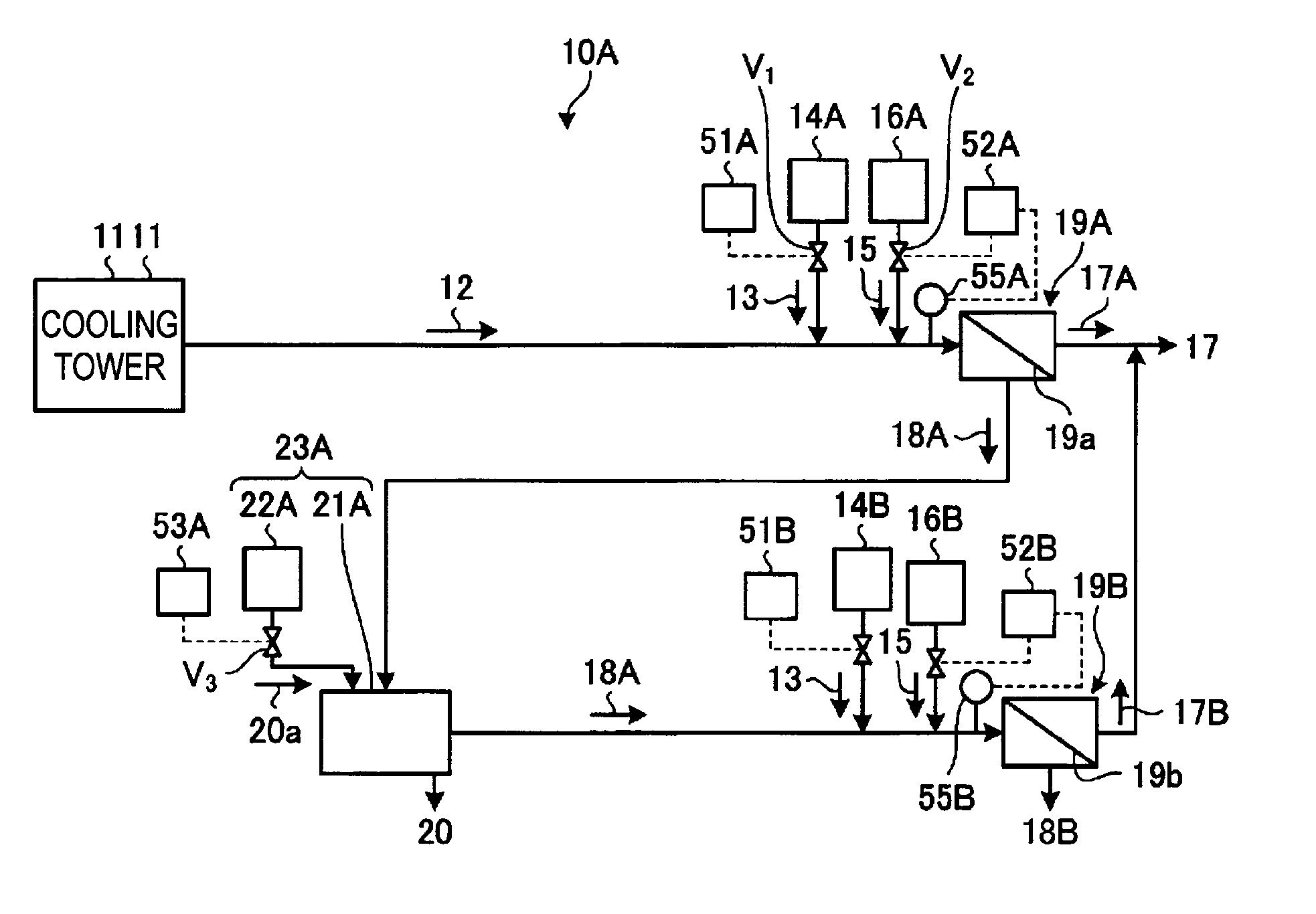
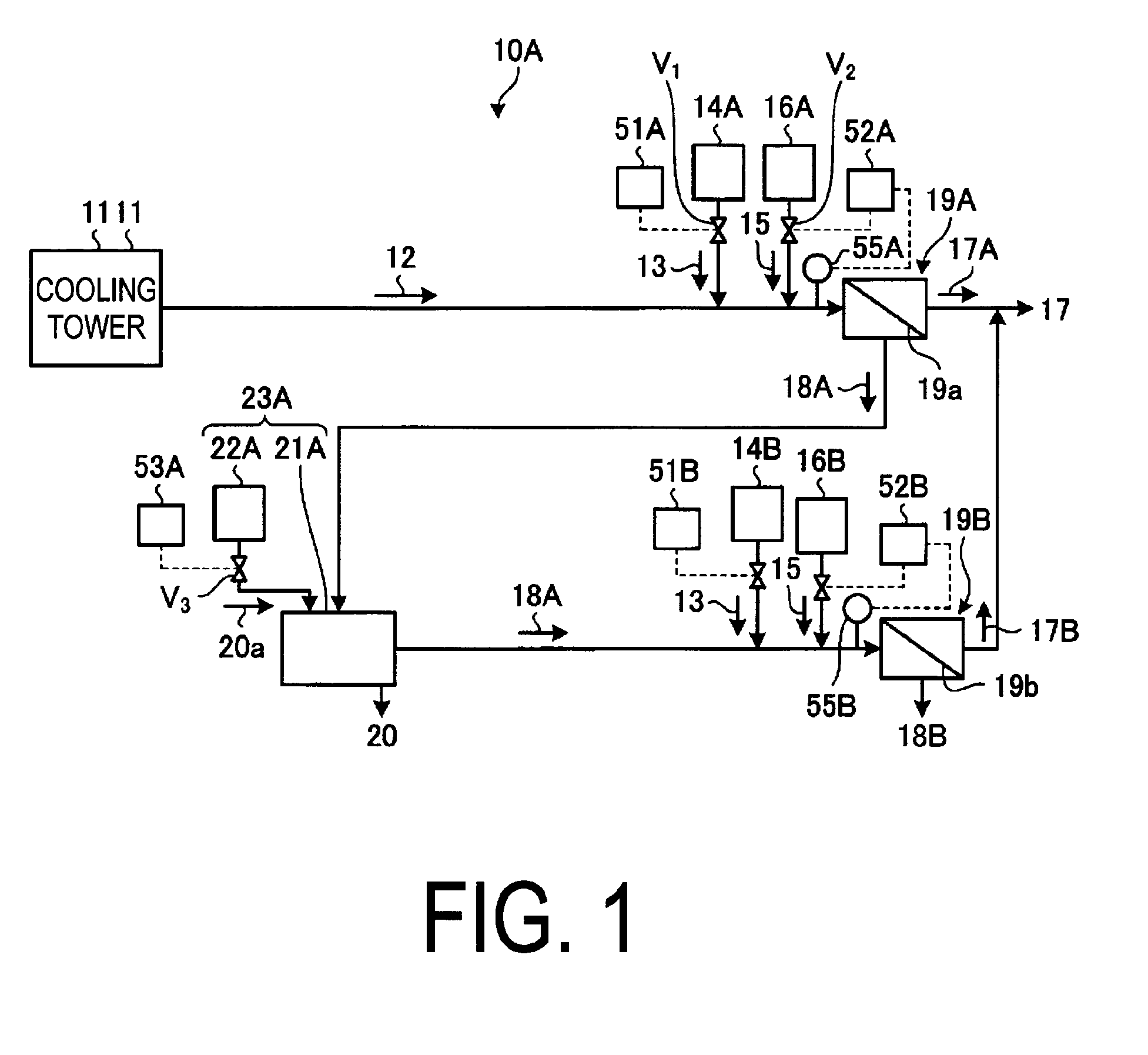
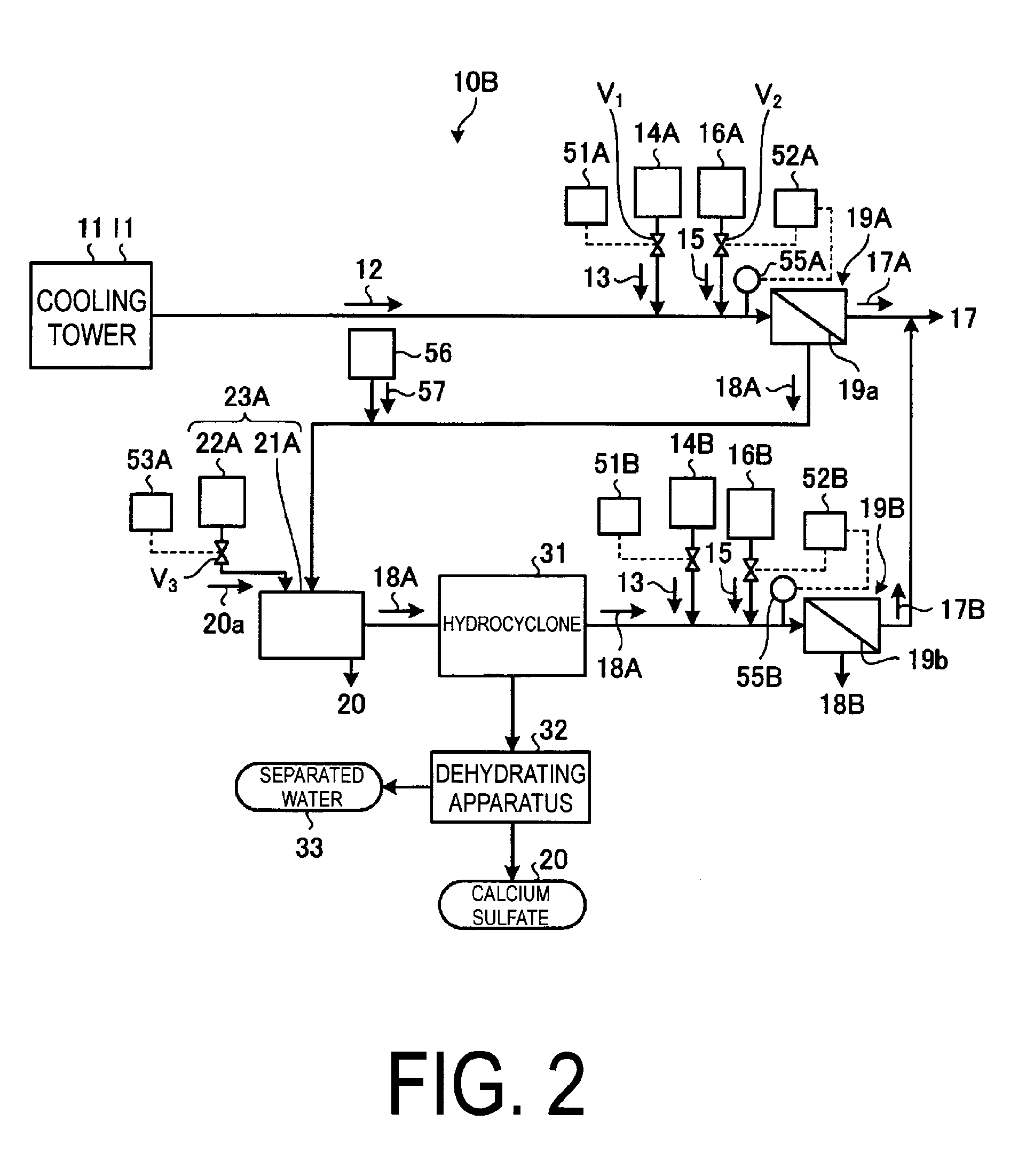
Water treatment system, water treatment method, cooling facility and power generating facility
InactiveUS20160115061A1Liquid degasificationGeneral water supply conservationWater treatment systemCooling tower
A water treatment system provided with: a first scale inhibitor-supplying unit which supplies a scale inhibitor to a blowdown water, the blowdown water being water to be treated that is generated in a cooling tower and contains at least a salt and silica; a first pH-adjusting unit which adjusts the pH of the blowdown water, to which the scale inhibitor has been supplied using a pH adjusting agent; a first desalinating apparatus which is provided downstream of the first pH-adjusting unit, removes the salt in the blowdown water, and separates the water into a first reclaimed water and a first concentrated water; and a first crystallizing unit which is provided downstream of the first desalinating apparatus and has a first crystallizing tank for calcium sulfate from the first concentrated water and a first seed crystal-supplying unit for supplying calcium sulfate seed crystals of calcium sulfate to the first crystallizing tank.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENG LTD
Thermal management system and method for vehicle electrochemical engine
ActiveUS7036466B2Easy to packReduce rateCoolant flow controlElectric machinesReclaimed waterThermal management system
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Reclaimed water processing device of washing machine, water processing method and washing machine
ActiveCN103361938AReduce water consumptionRealize circular water savingOther washing machinesWashing machine with receptaclesWater filterReclaimed water
The invention relates to a reclaimed water processing device of a washing machine, a reclaimed water processing method and the washing machine. The washing machine comprises an outer barrel, an inner barrel and a drive device. A water inlet and a water outlet are formed in the outer cylinder. A water inlet pipe is connected with the water inlet. A draining pipe is connected with the water outlet. The washing machine further comprises a water filter pipe, a filter unit and a water return pipe. The water filter pipe is connected with the draining pipe through a first three-way valve. The water return pipe is connected with the water inlet pipe through a second three-way valve. An inlet of the filter unit is connected with the water filter pipe, an outlet thereof is connected with the water return pipe. At least one water pump is disposed on a water circulation loop formed by the draining pipe, the water filter pipe, the filter element, the water return pipe and the water inlet pipe. Reclaimed water generated during operation of the washing machine flows into the filter unit through the water filter pipe, is filtered by the filter unit, and flows back to the inner barrel of the washing machine to take part in subsequent working procedures, and accordingly water user amount in the whole washing process is reduced, and water recycling is achieved.
Owner:XEROS LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com