Method and device for zero-emission treatment of high-hardness waste water containing sulfate
A sulfate and zero-emission technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high operating costs and large investment, achieve investment and operation savings, and reduce the amount of residual wastewater , The effect of increasing the amount of recycled water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 (adopt milk of lime to remove sulfate group)
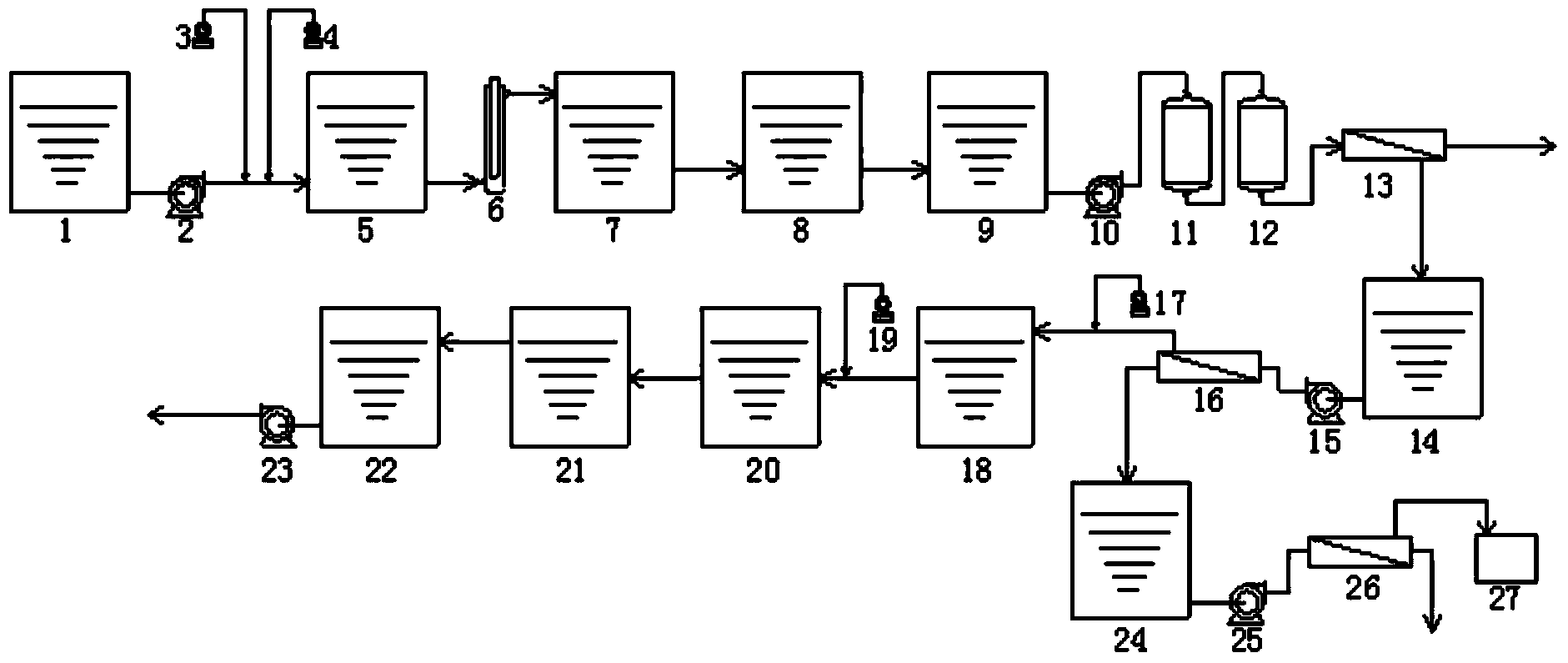
[0029] like figure 1 As shown, at first the concentration of 500ppm sulfuric acid radical wastewater flows into the raw water pool 1, transported by the raw water pump 2, and sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate are added with the first alkali adding pump 3 and the second alkali adding pump 4 to reach the first reaction pool After 5, stir and react for 10-30 minutes to form calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide precipitates. After electrocoagulation 6, large flocs are formed and reach the first sedimentation tank 7 for precipitation. The supernatant enters the filter tank 8 for filtration to further remove the suspended The filtered clean water enters the first clean water tank 9, is pressurized by the first booster pump 10, enters the sand filter 11 for filtration, and then passes through the ion exchanger 12 to further remove calcium and magnesium ions in the water, and the treated clean water enters the...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2 (adopt freezing method to remove sulfate radical)
[0031] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the method for removing sulfate radicals is different, and other steps are identical.
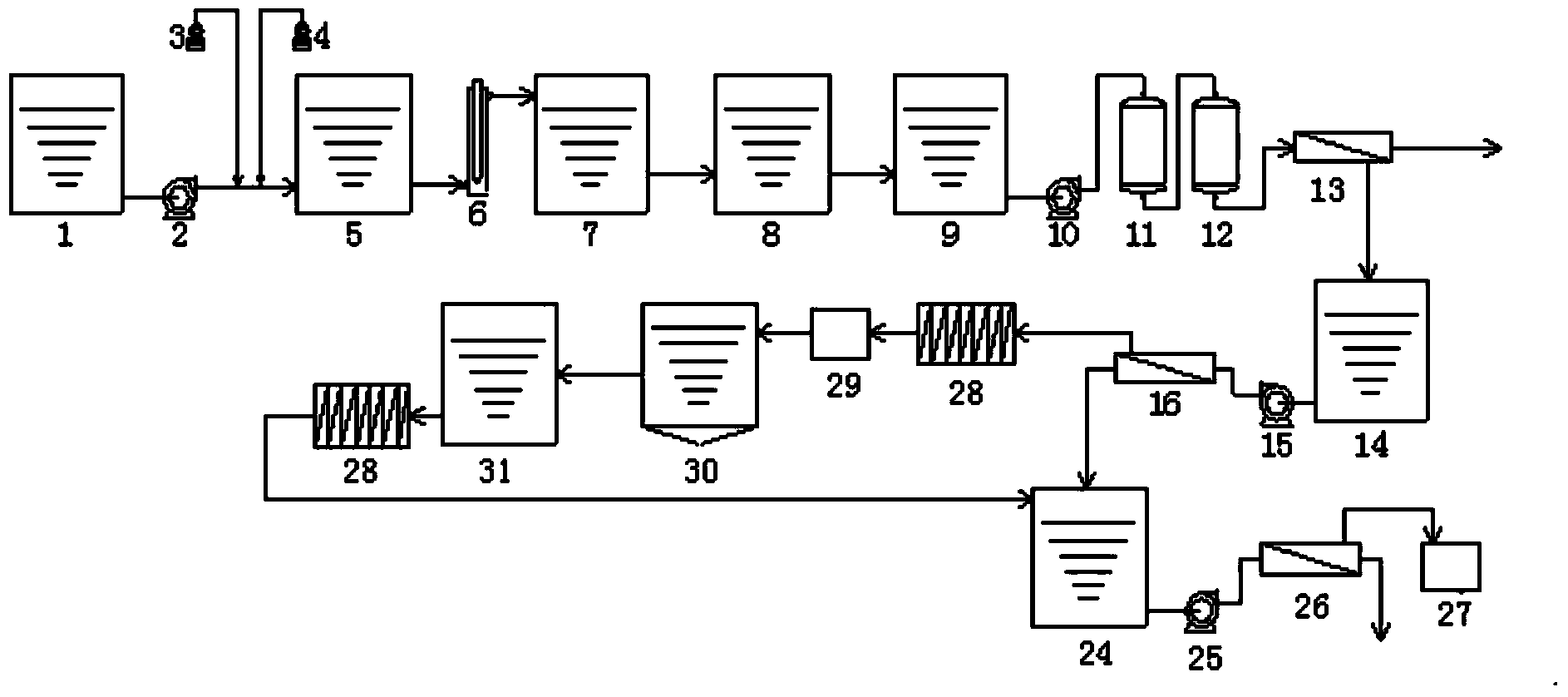
[0032] like figure 2 Shown, the step that present embodiment removes sulfate group is as follows:
[0033] The nanofiltration concentrated water mainly contains sodium sulfate, and the concentration can reach more than 50,000 ppm. The high-concentration sodium sulfate solution is initially cooled by the heat exchanger 28 and then cooled by the refrigeration device 29. After cooling, it enters the crystallization tank 30, crystallizes to form Glauber's salt, and the mother liquor after crystallization enters clear water The tank 31 enters the nanofiltration water tank 24 after being heated by the heat exchanger 28, mixes with the nanofiltration product water, and enters the membrane concentration device 26 to concentrate after being pressurized by t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com