Method and device for processing radioactive strontium-contained waste water
A radioactive wastewater and radioactive technology, applied in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering and other directions, can solve the problems of high power consumption, increased requirements for radiation protection of mechanical equipment, high cost, and achieve increased concentration multiples, significant environmental benefits, and broad application prospects. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
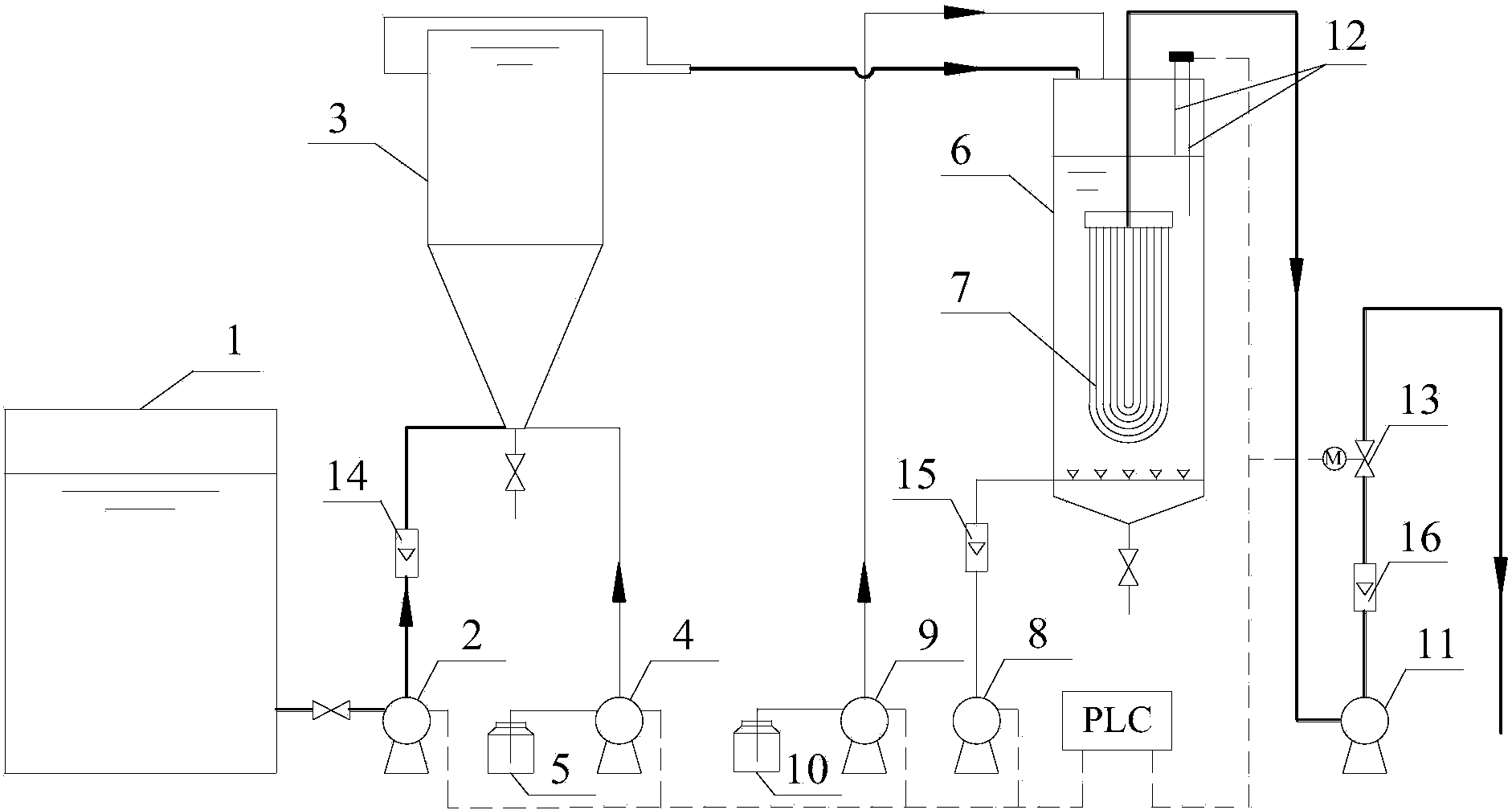
[0025] Embodiment 1: The flow rate of the device is 16.6 L / h, and the total residence time is 90 minutes, wherein the residence time of the hydrocyclone reactor is 45 minutes, and the hydraulic residence time of the membrane separator is 45 minutes. The simulated radioactive strontium-containing wastewater with a strontium concentration of 5 mg / L at the device is used. At the start of the experiment, 300mg / L of calcium carbonate seeds prepared in advance were added to the hydrocyclone reactor; in the experiment, the dosage of sodium carbonate was 1000mg / L, and the dosage of ferric chloride was 3.0mg / L (based on Fe 3+ meter), the mass concentration of strontium in the effluent was stable at 5 μg / L. The process has a concentration factor of 3150 and a decontamination factor of 1000.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: The flow rate of the device is 12.5 L / h, and the total residence time is 120 minutes, wherein the residence time of the hydrocyclone reactor is 60 minutes, and the hydraulic residence time of the membrane separator is 60 minutes. The device is used to treat simulated radioactive strontium-containing wastewater with a strontium concentration of 10mg / L. At the start of the experiment, 800mg / L of calcium carbonate seeds prepared in advance were added to the hydrocyclone reactor; 3+ meter), the mass concentration of strontium in the effluent was stable at 7 μg / L. The process has a concentration factor of 3400 and a decontamination factor of 1400.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Embodiment 3: The flow rate of the device is 15 L / h, and the total residence time is 100 minutes, wherein the residence time of the hydrocyclone reactor is 50 minutes, and the hydraulic residence time of the membrane separator is 50 minutes. The device is used to treat simulated radioactive strontium-containing wastewater with a strontium concentration of 8mg / L. At the start of the experiment, 500 mg / L of calcium carbonate seeds prepared in advance were added to the hydrocyclone reactor; in the experiment, the dosage of sodium carbonate was 1000 mg / L, and the dosage of ferric chloride was 3.0 mg / L (based on Fe 3+ meter), the mass concentration of strontium in the effluent was stable at 6 μg / L. The process has a concentration factor of 3200 and a decontamination factor of 1300.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com