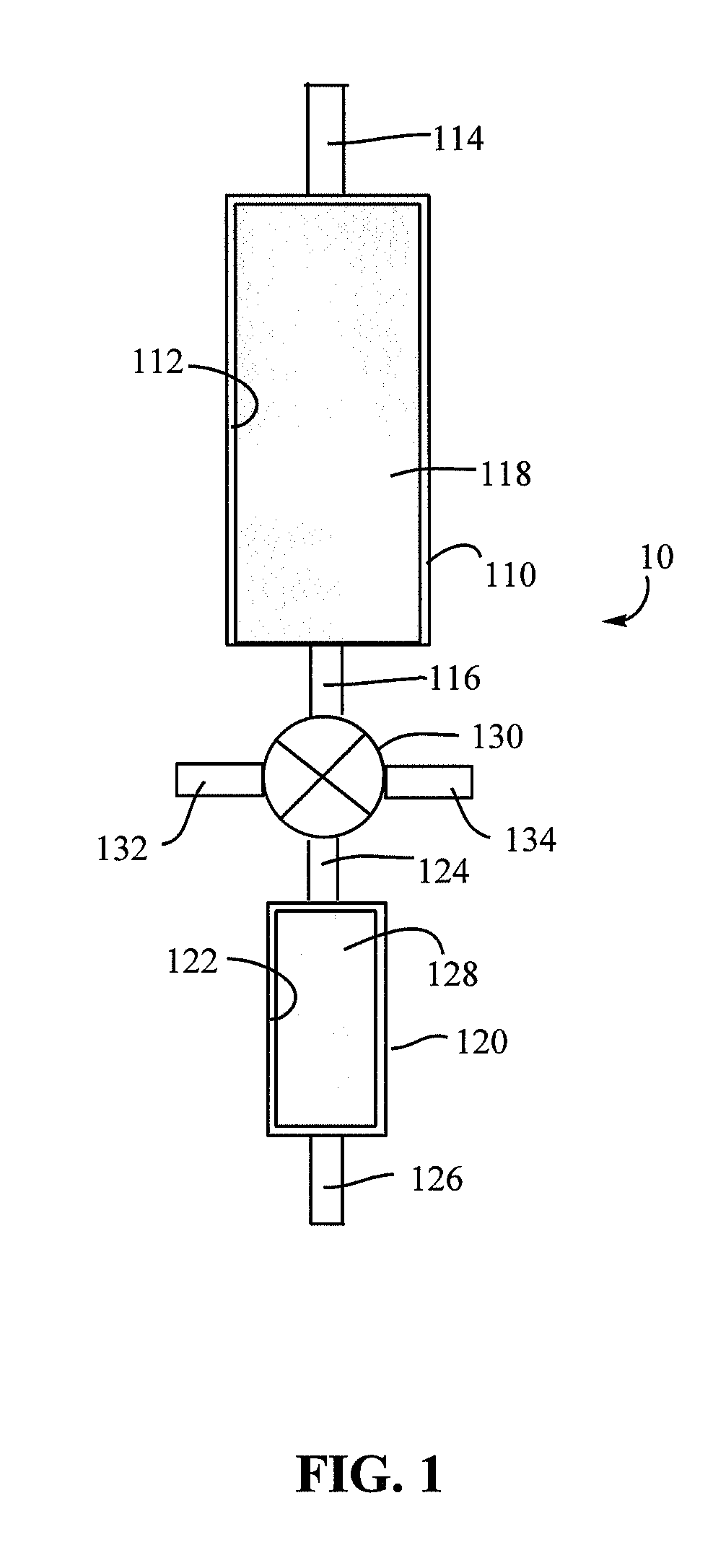
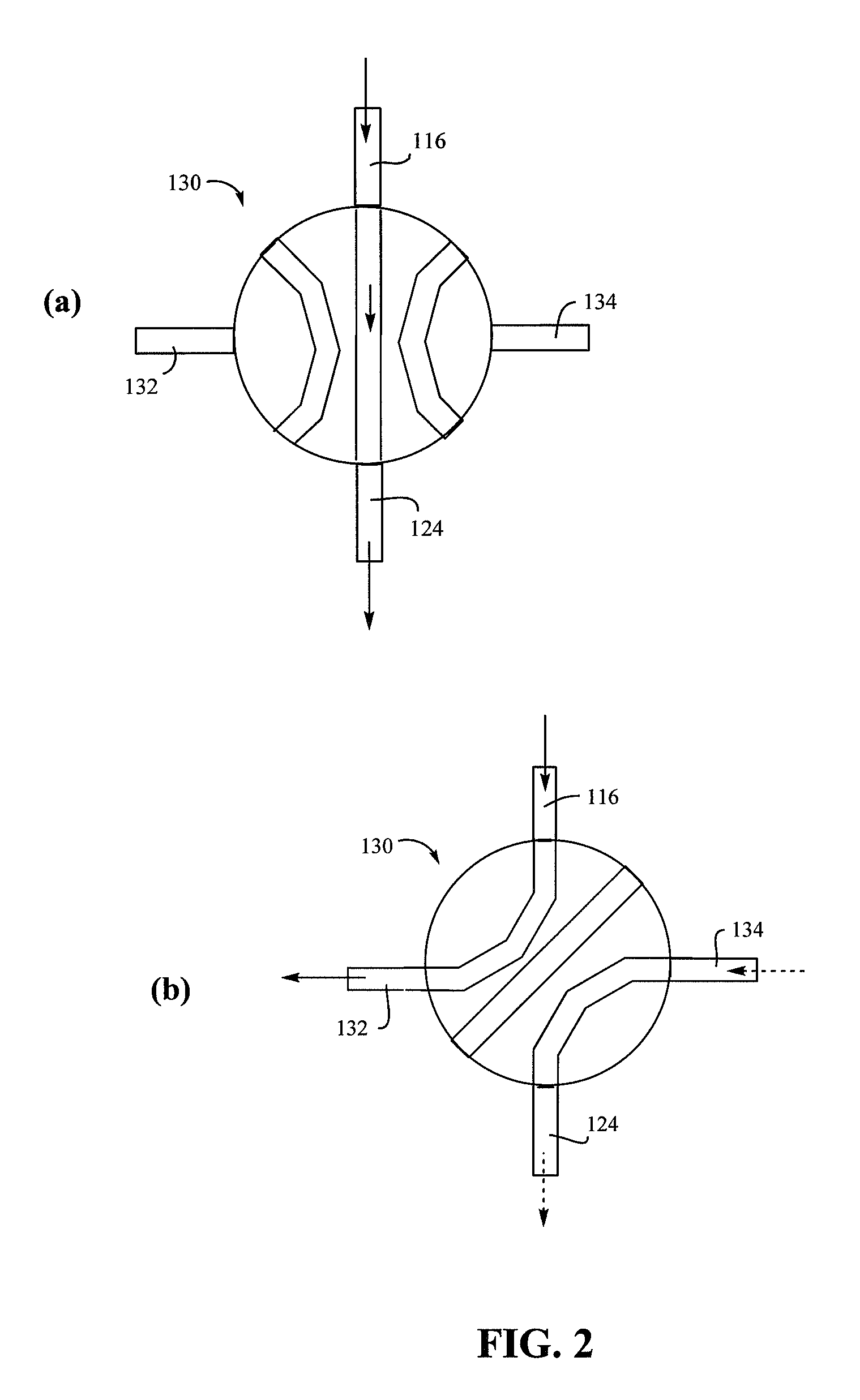
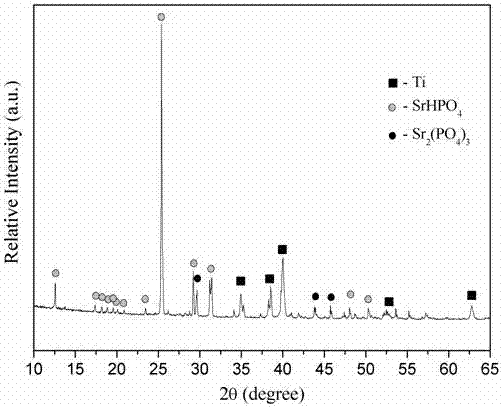
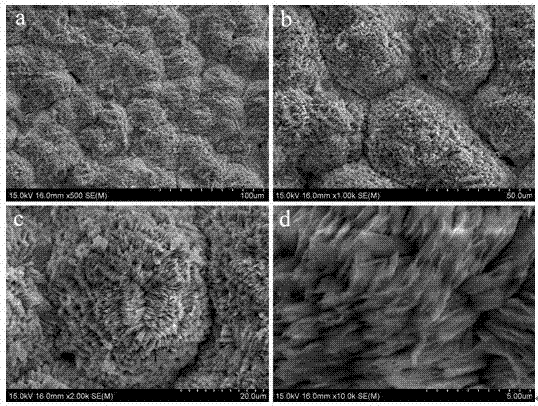
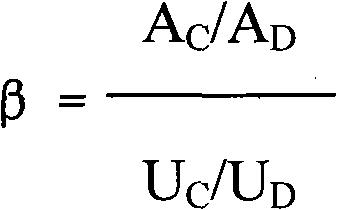Patents
Literature
258 results about "Strontium ions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Strontium nitride is an ionic compound formed by strontium and nitrogen. Strontium ion has a charge of 2+, while nitrogen ion has a charge of 3-. So 3 strontium ions and 2 nitride ions are needed to balance them. , Knows how to make miracles seem mundane.
Strontium fortified calcium nano-and microparticle compositions and methods of making and using thereof
InactiveUS20080317807A1Good biocompatibilityPrevent looseningHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseasePhosphate
Compositions containing strontium fortified calcium nanoparticles and / or microparticles, and methods of making and using thereof are described herein. The strontium fortified calcium compounds contain calcium ions, calcium atoms, strontium ions, strontium atoms, and combinations thereof and one or more anions. Exemplary anions include, but are not limited to, citrate, phosphate, carbonate, and combinations thereof. The particles can be formulated for enteral or parenteral administration by incorporating the particles into a pharmaceutically carrier. The compositions can further contain one or more active agents useful for bone diseases or disorders, such as vitamin D, growth factors, and combinations thereof. The compositions can be used to treat or prevent one or more bone diseases or disorders of the bone, such as osteoporosis. Alternatively, the particles can be coated onto a substrate, such as the surface of an implant. The coatings can be used to improved biocompatibility of the implant, prevent loosening of the implant, reducing leaching of metal ions from metallic implants, and reduce corrosion. The coatings can be applied to the substrate using a variety of techniques well known in the art. In one embodiment, the coating is applied using electrophoretic deposition. The use of nano- and / or microparticles that provide high surface area helps to improve interfacial strength between the coating and the implant, which allows for the use of lower sintering temperatures. Lowering sintering temperatures minimizes or prevents thermal decomposition of the coating material and / or degradation of the implant material.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Strontium containing hydroxyapatite biologically active film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1927410ANo side effectsHigh bonding strengthProsthesisElectrolytic agentPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention relates to the means of active biological film, especially the titanium radicel porous nanometer Strontium hydroxyapatite active biological film and the Process for the manufacture. The differential arc oxidation technology is used in the method, the film is generated in the surface of titanium and titanium alloy, a electrolyte solution with phosphate radical ion, calcium ion and Strontium ion is supplied; the titanium and titanium alloy is the anode and the rustless steel or the titanium is the cathode, the direct current power supply or the direct current impulsing power source is applied to differential arc oxygenize the titanium and titanium alloy; the oxidate time is 3-60min; the temperature of electrolyte is not above 50DEG C. There is no interface between the porous hydroxyapatite containing Strontium film produced by the invention and the basal body, the modulus of elasticity is approximate with the sclerotin, the porous hydroxyapatite containing Strontium film produced by the invention which has perfect bioactivity can be the alternate material of several parts with heavy load, such as femur, hip joint and teeth root.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods for preserving fresh produce
Methods of preserving fresh produce with a produce preservative which extends the shelf life of fresh produce, particularly cut fresh produce, and preserves the texture, flavor, appearance, crispness, and color of the fresh produce, particularly the exposed surface of the fresh produce, are provided. The method comprises: providing a solution of produce preservative comprising: water; a preservative cation which is selected from the group consisting of a strontium ion, lithium ion, barium ion, aluminum ion, copper ion, ammonium ion, iron ion, manganese ion, potassium ion, or mixtures thereof; and ascorbate ions, or erythorbate ions; wherein the ascorbate ions or erythorbate ions and the preservative cation are present in an ion ratio of preferably from 0.2:1 to 8:1, more preferably 0.75:1 to 8:1, even more preferably from 1:1 to 4:1, yet more preferably 1.5:1 to 3:1; most preferably 1.1:1 to 2.5:1; and, applying said produce preservative to the produce. The invention also relates to fresh produce preserved with the produce preservatives.
Owner:MANTROSE HAEUSER
Strontium-substituted apatite coating
The invention provides a method of preparing an implantable article with a bioactive strontium-substituted ceramic apatite coating. The method involves incubating a biocompatible substrate surface that is not coated with a calcium-containing compound with a composition comprising (i) strontium ions, (ii) calcium ions, (iii) phosphate ions, and (iv) a liquid carrier.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Layered perovskite structural ceramic and preparation method thereof
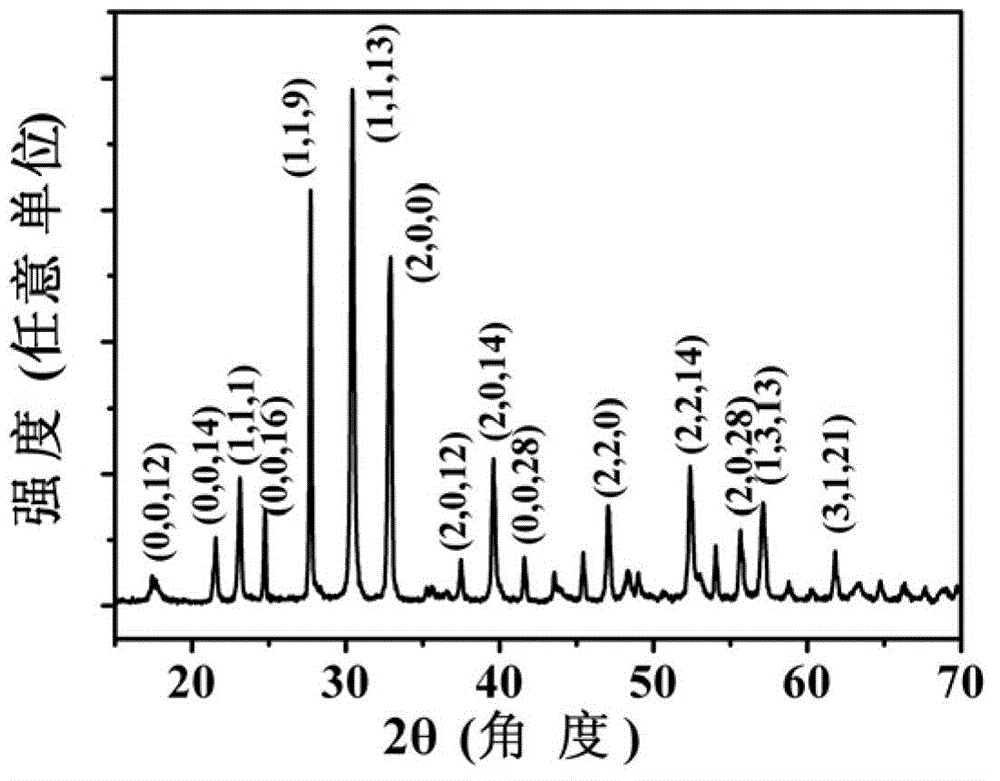
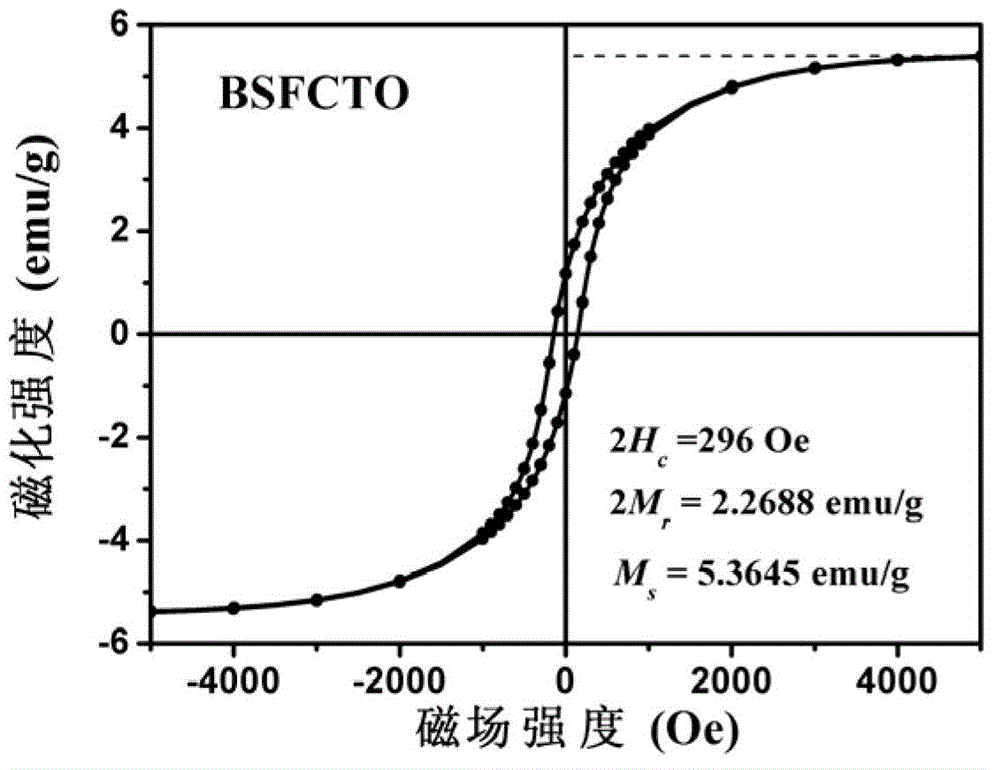
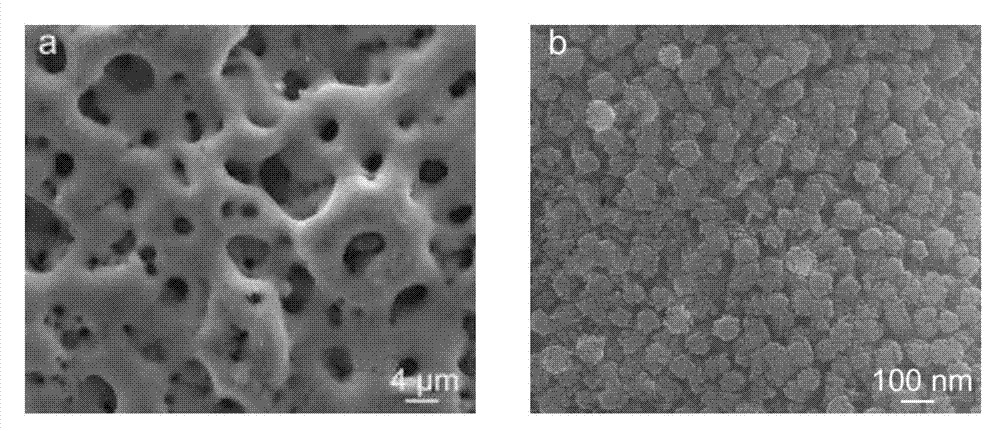
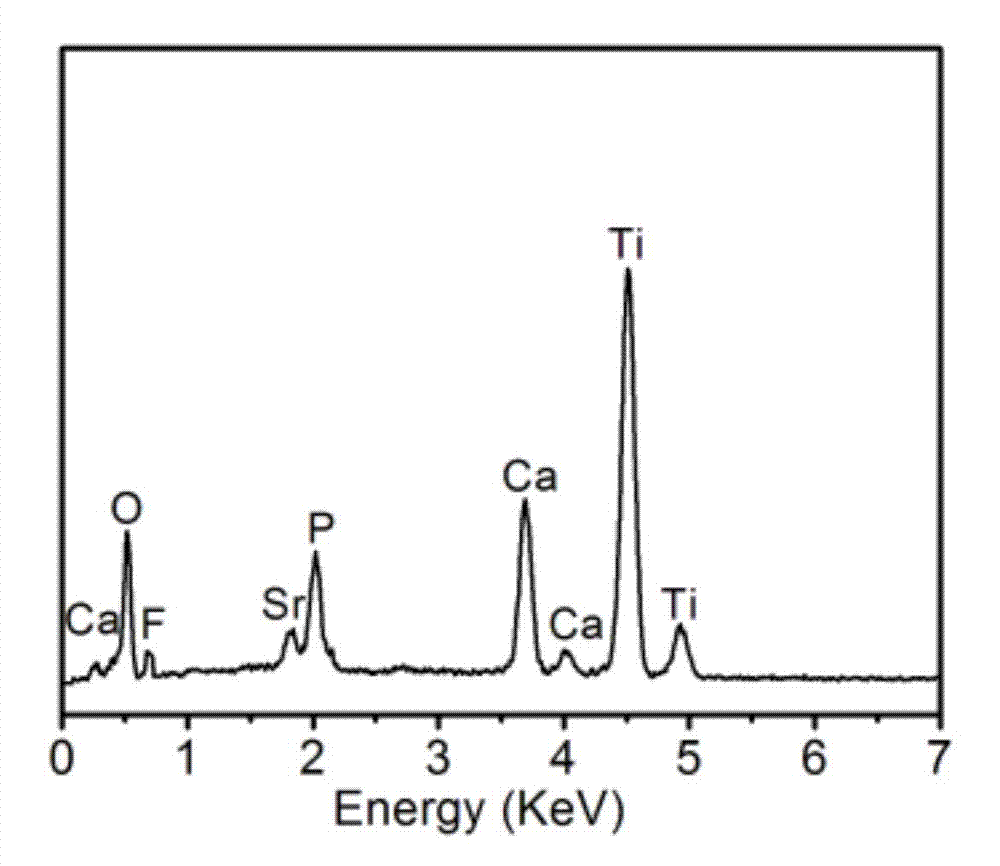
The invention provides layered perovskite structural ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes mixing well titanate compounds, bismuth compounds, strontium compounds, iron compounds, cobalt compounds and complexing agent in solvent, heating, drying and combusting to obtain powder, and presintering to obtain powder; performing the powder, and performing hot-pressing sintering to obtain the structural ceramic in in a formula (I). Compared with ceramics prepared in the prior art by solid phase sintering process, the structural ceramic in the formula (I) is prepared by solution process and hot pressing sintering. The preparation method has the advantages that less volatile low-valence strontium ions are introduced, increased leakage current due to volatilization of the strontium ions is improved, and ferroelectric properties are improved; the raw materials are evenly spread by the solution process, the power is even in component and has high reactivity, and Fe-Co ions are coupled fully; and the materials processed by hot pressing sintering are high in density and orientation, and the layered perovskite structural material can be obtained, namely Bi(n+1-x)SrxF3(n-3) / 2Co(n-3) / 2Ti3O3(n+1) (I).
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Titanium dioxide/strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104726921AEase of mass productionSimple and fast operationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisSolubilityPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention provides a titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing an electrolyte containing calcium ions, strontium ions, fluorine ions and phosphate anions; and then by taking titanium or a titanium alloy as an anode and stainless steel as a cathode, directly preparing the titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating on the surface of a titanium or titanium alloy substrate by virtue of a micro-arc oxidation technology. The coating consists of an inner layer combined on the surface of the substrate and a surface layer combined on the surface of the inner layer, wherein the inner layer is a titanium dioxide layer in a form of a nano crystal and the surface layer is a nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer. No non-continuous interfaces are available between the coating and the substrate and the coating has high combining strength and structural stable performance; the coating is relatively small in solubility in a simulated body fluid, so that the coating is effectively implanted and used; and the nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer in the surface layer can remarkably promote the osteogenic function of the cells to form new bones and inhibit bacterial adhesion and growth.
Owner:宝鸡卡斯特医疗科技有限公司
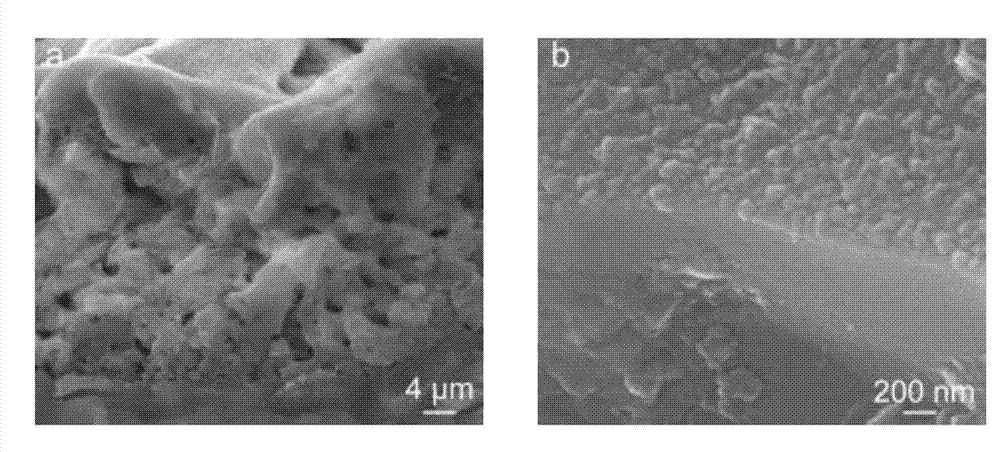
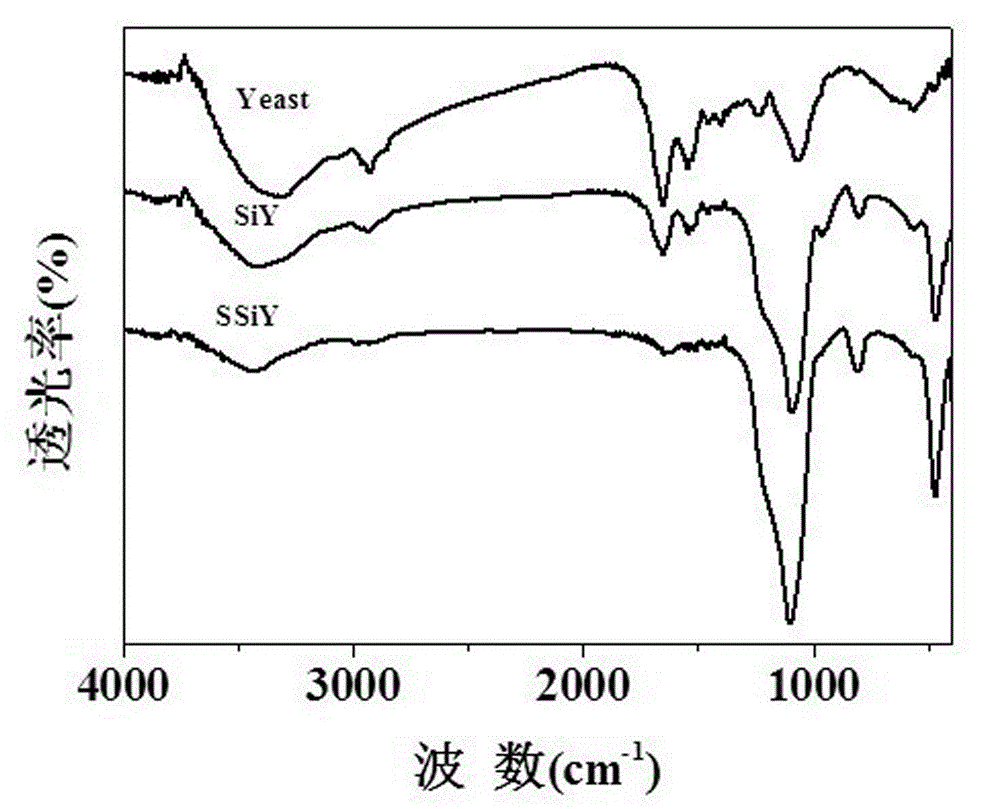
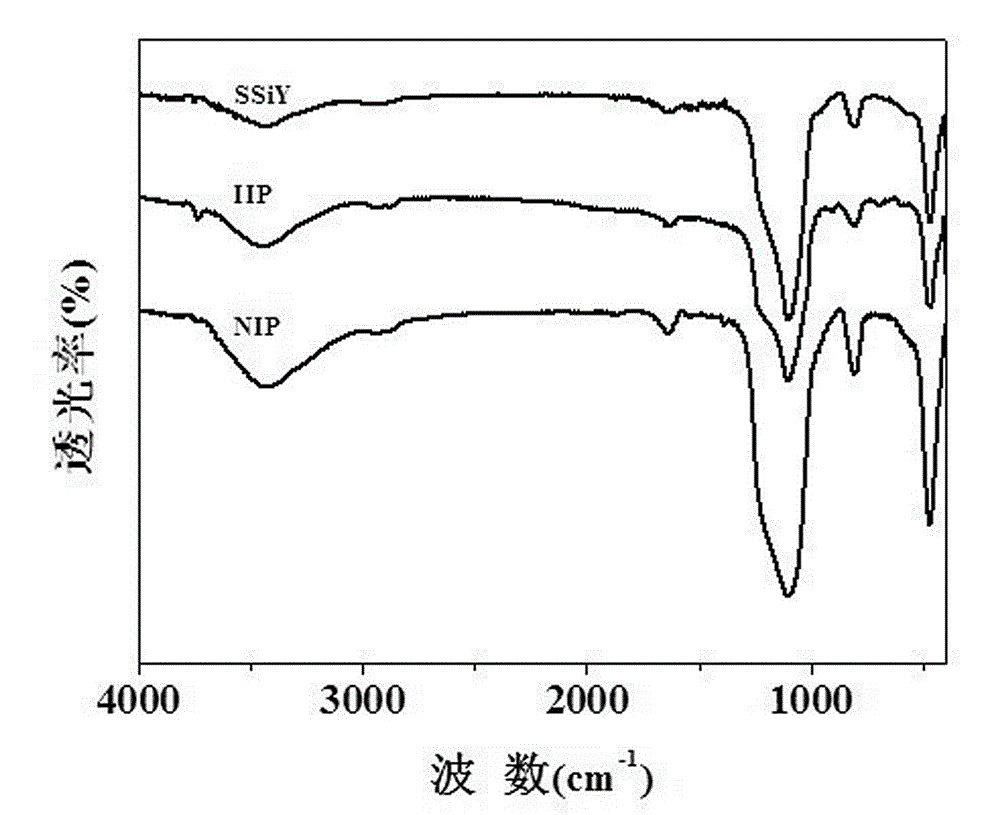
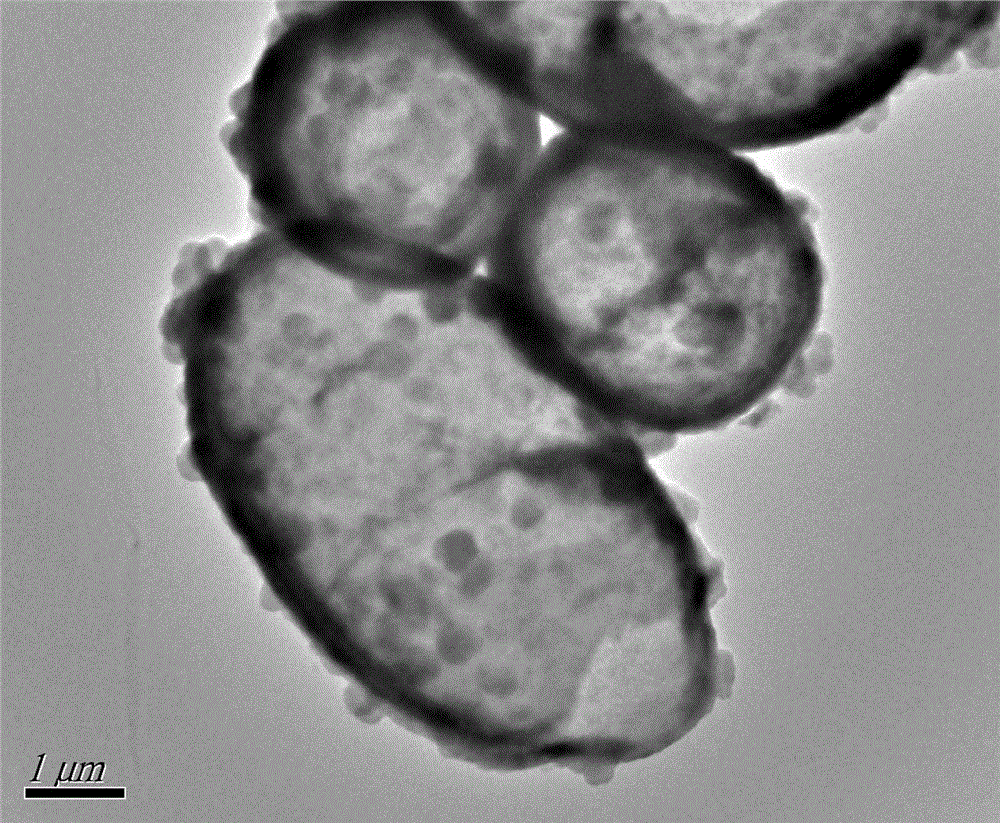
Preparation method of surface print adsorbent of yeast template hollow silica-based material for adsorbing and separating strontium ions and application thereof
InactiveCN103055823AImprove thermal stabilityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionFunctional monomerMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental material preparation and relates to a preparation method of surface print adsorbent of yeast template hollow silica-based material for adsorbing and separating strontium ions and application thereof. The technical scheme of preparation includes coating a yeast template surface with nanosilica particles to obtain yeast / silicon compound, removing yeast template to prepare yeast template hollow silica-based material through calcinations, using yeast template hollow silica-based material as a host material, divalent strontium ions as template ions, chitosan as functional monomer and gamma-(2,3glycidoxyprop) trimethoxypropylsilane as cross-linking agent and performing ionic imprinting polymeric modification by using suspension polymerization. The prepared adsorbent has the advantages of good mechanical property and heat stability, higher adsorption capacity and adsorption dynamics performance, low cost and large specific surface area and avoids the defects such as halfway elution and irregular microballoon shape due to too deep embedding of some template molecules to achieve the purpose of quickly, selectively and effectively adsorbing and separating divalent strontium ions.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation process of strontium nano calcium phosphate containing biological active bone cement
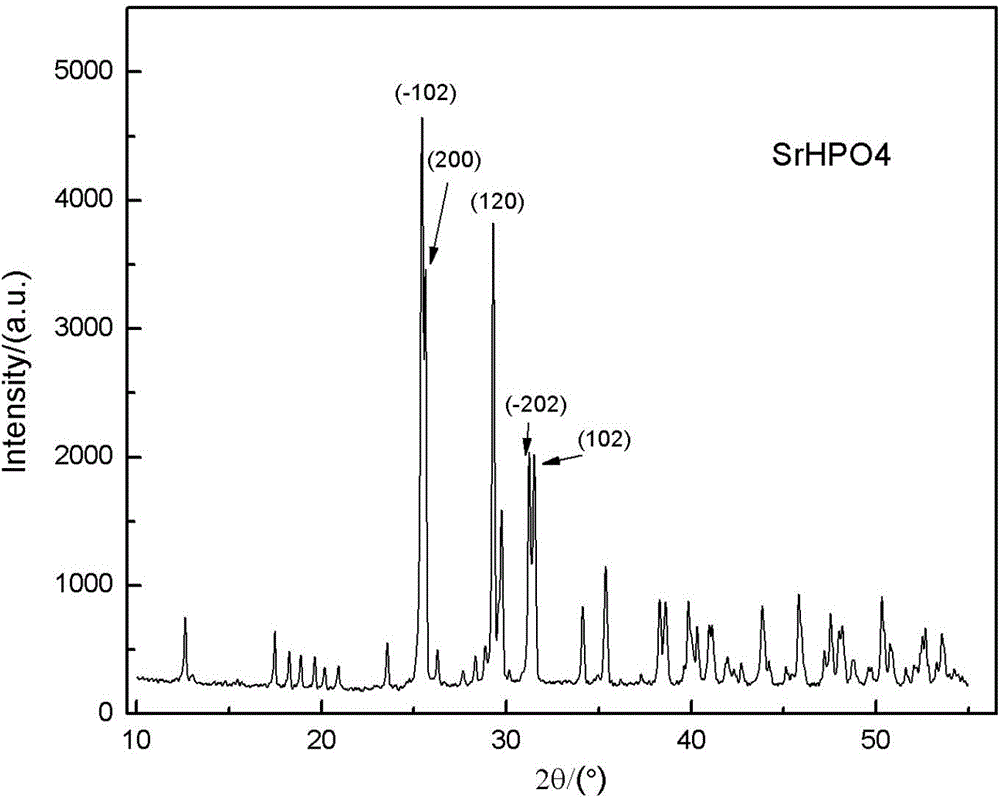
InactiveCN1559888AHas the effect of slow-release strontium ionsPromote degradationBone implantPhosphorus compoundsBone cementCytotoxicity testing
The invention discloses a preparing technique of special pharmacological strontium sustained-release and no-toxicity strontium-containing nano calcium phosphate bioactive cement. It adopts the cement solid phase: the mixed powder of Ca4(PO4)2O, CaHPO4 and SrHPO4 distributed at a certain particle size and prepared in a certain mole ratio and the liquid phase: H3PO4 solution at 0.5-1 mol / l, where the solid-liquid ratio is 1.5-3.0. On physiological conditions, and the final condensate product is strontium-containing acalcerosis hydroxyl phosphorite with a microscopic daisy-petal or bent-stick shaped nano crystal structure. This cement not only has higher mechanical and operable properties, but also sustainedly releases strontium ions with special pharmacological functions, and the result of preliminary cell toxicity test shows it has no toxicity. It has wider application prospect than traditional calcium phosphate cement.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Bone tissue implant comprising strontium ions
ActiveUS20100174382A1Increase productionImproved rate of bone formationDental implantsElectrolytic inorganic material coatingBone tissueBone mass
The present invention is based on that local administration of strontium ions in bone tissue has been found to improve the bone formation and bone mass upon implantation of a bone tissue implant in said bone tissue.In particular, the invention relates to a bone tissue implant having an implant surface covered by an oxide layer comprising strontium ions and a method for the manufacture thereof.A blasting powder comprising strontium ions, a method for locally increasing bone formation, and the use of strontium ions or a salt thereof for manufacturing a pharmaceutical composition for locally increasing bone formation are also provided by the present invention.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
Anti-skid and antibacterial ceramic tile and preparation process thereof
The invention relates to an anti-skid and antibacterial ceramic tile and a preparation process thereof and belongs to the technical field of architectural ceramics. The anti-skid and antibacterial ceramic tile consists of a blank material grain layer, a decorating glaze material layer and a functional glaze material layer, wherein the functional glaze material layer contains nanometer composite high temperature-resistant antibacterial particles, a skid-stopping glaze and glaze material oil paste; the nanometer composite high temperature-resistant antibacterial particles are prepared by ball-milling and drying strontium-containing ions, laminar clay and an aqueous solution of rare earths ions. The preparation method of the anti-skid and antibacterial ceramic tile comprises the following steps of sequentially applying the decorating glaze material and the functional glaze material onto the surface of a ceramic tile green, and drying and firing the ceramic tile green to obtain the anti-skid and antibacterial ceramic tile. Due to the fact that the laminar clay absorbs strontium ions and the rare earths ions to the parts among clay crystal layers, an antibacterial effect activated by the rare earths ions is achieved; meanwhile due to the fact that the decorating glaze material layer and the functional glaze material layer are matched, a decorating effect of the ceramic tile is achieved, and the ceramic tile is endowed with anti-skid and anti-contamination, antibacterial, negative ion-generating, and far infrared health-care functions.
Owner:ZIBO GOLD LION KING TECH CERAMICS CO LTD
Method of fabricating implant with improved surface properties and implant fabricated by the same method
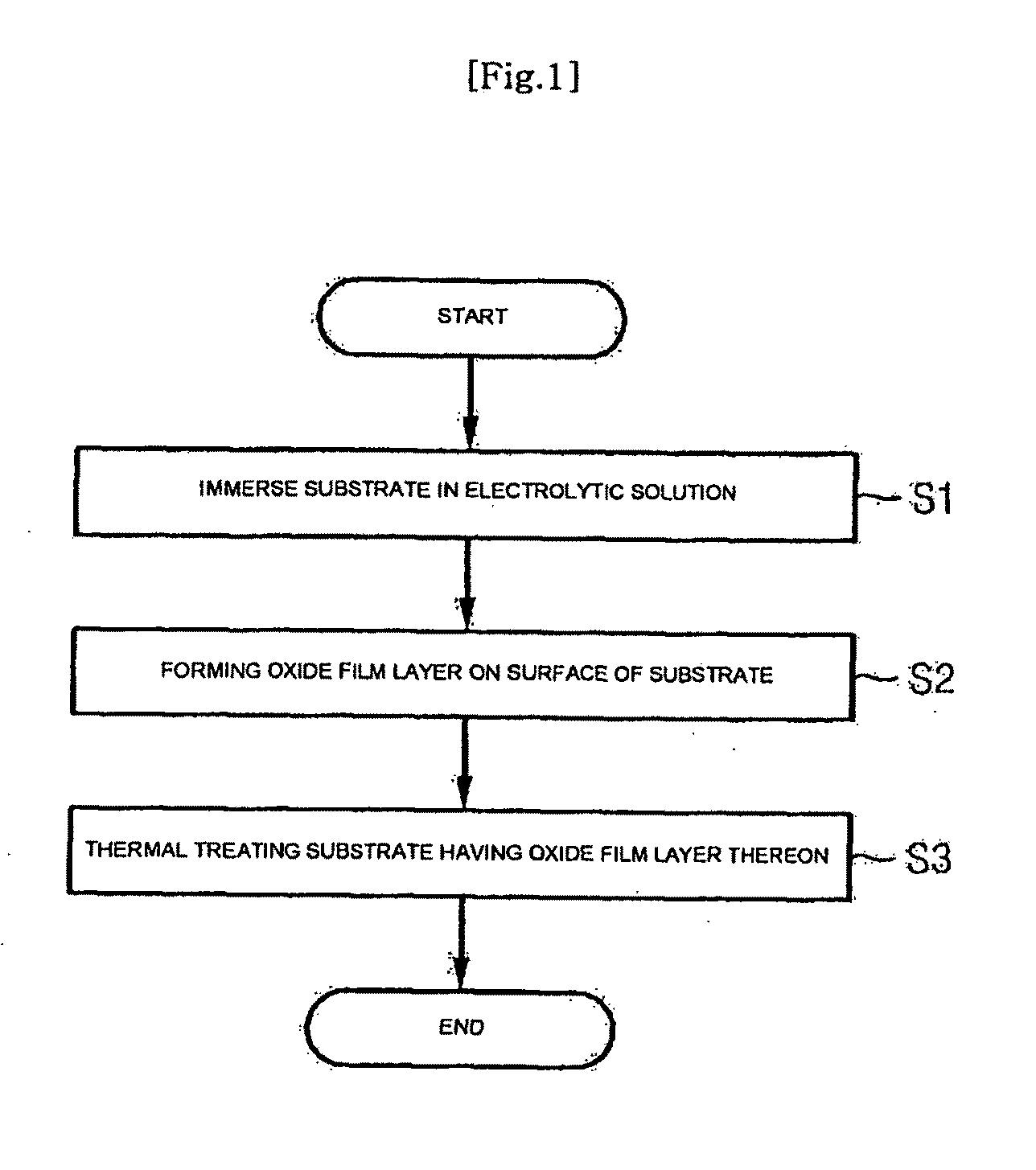
ActiveUS20100136506A1Well formedGood biocompatibilityDental implantsPretreated surfacesTime conditionPhosphate
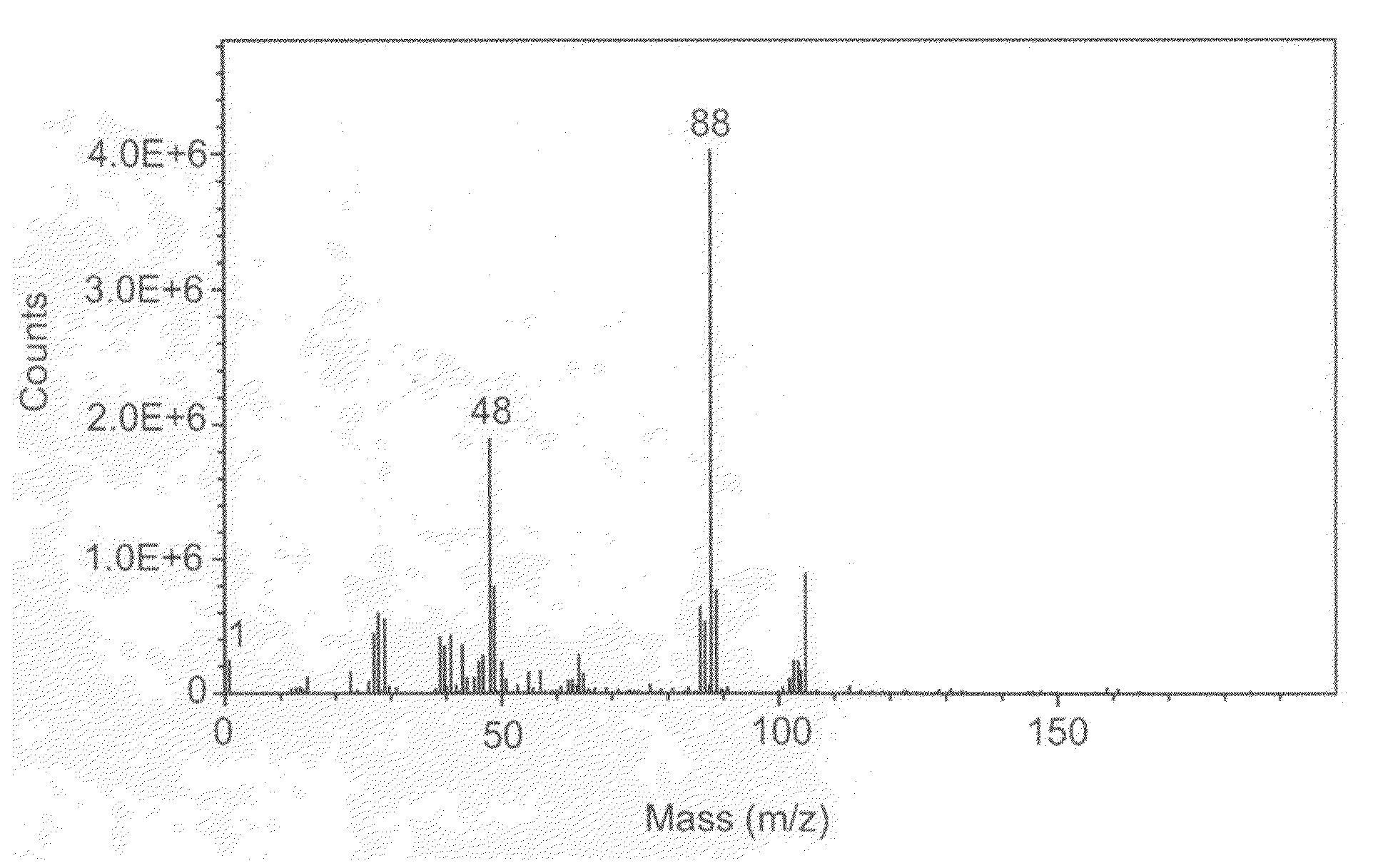
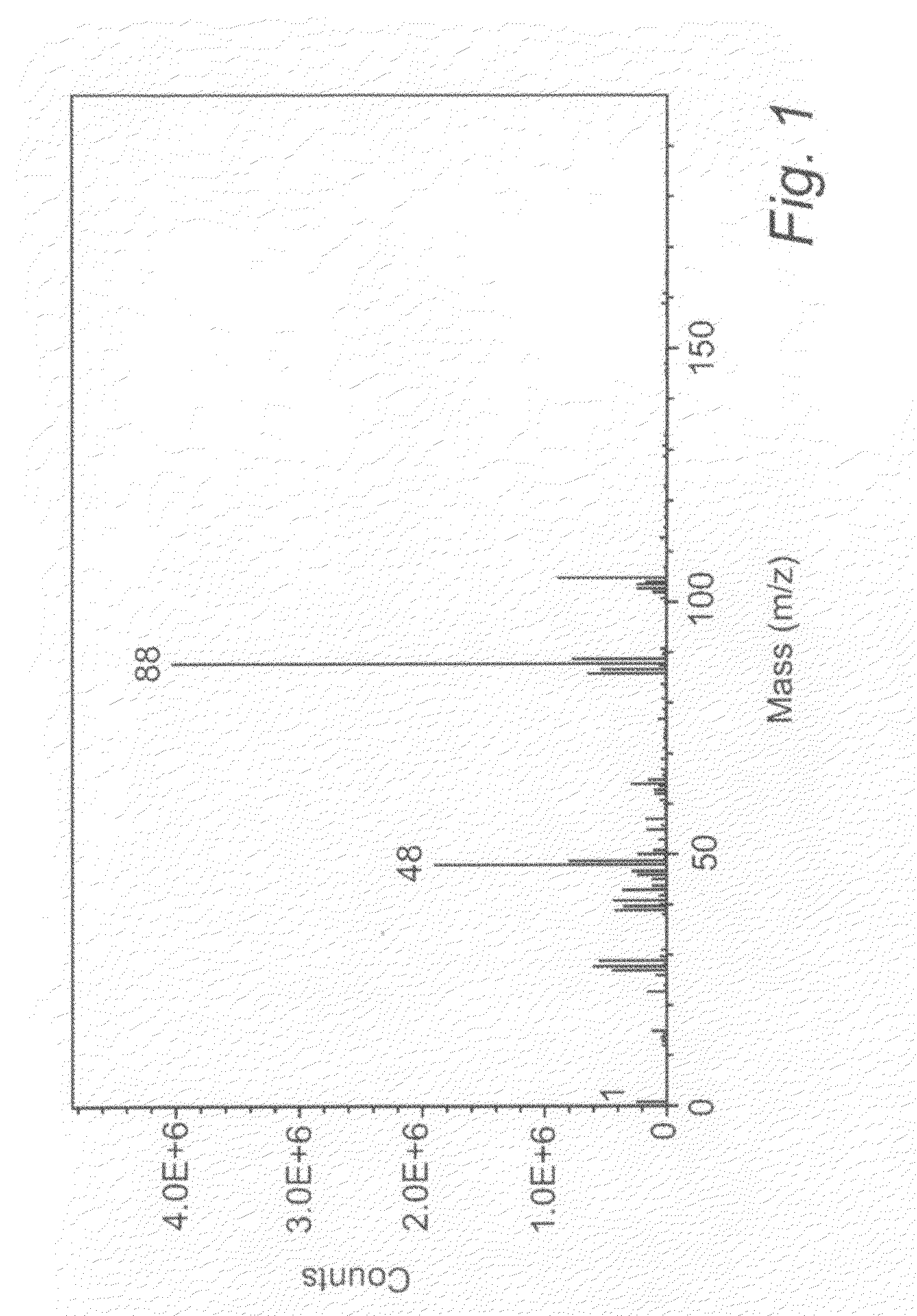
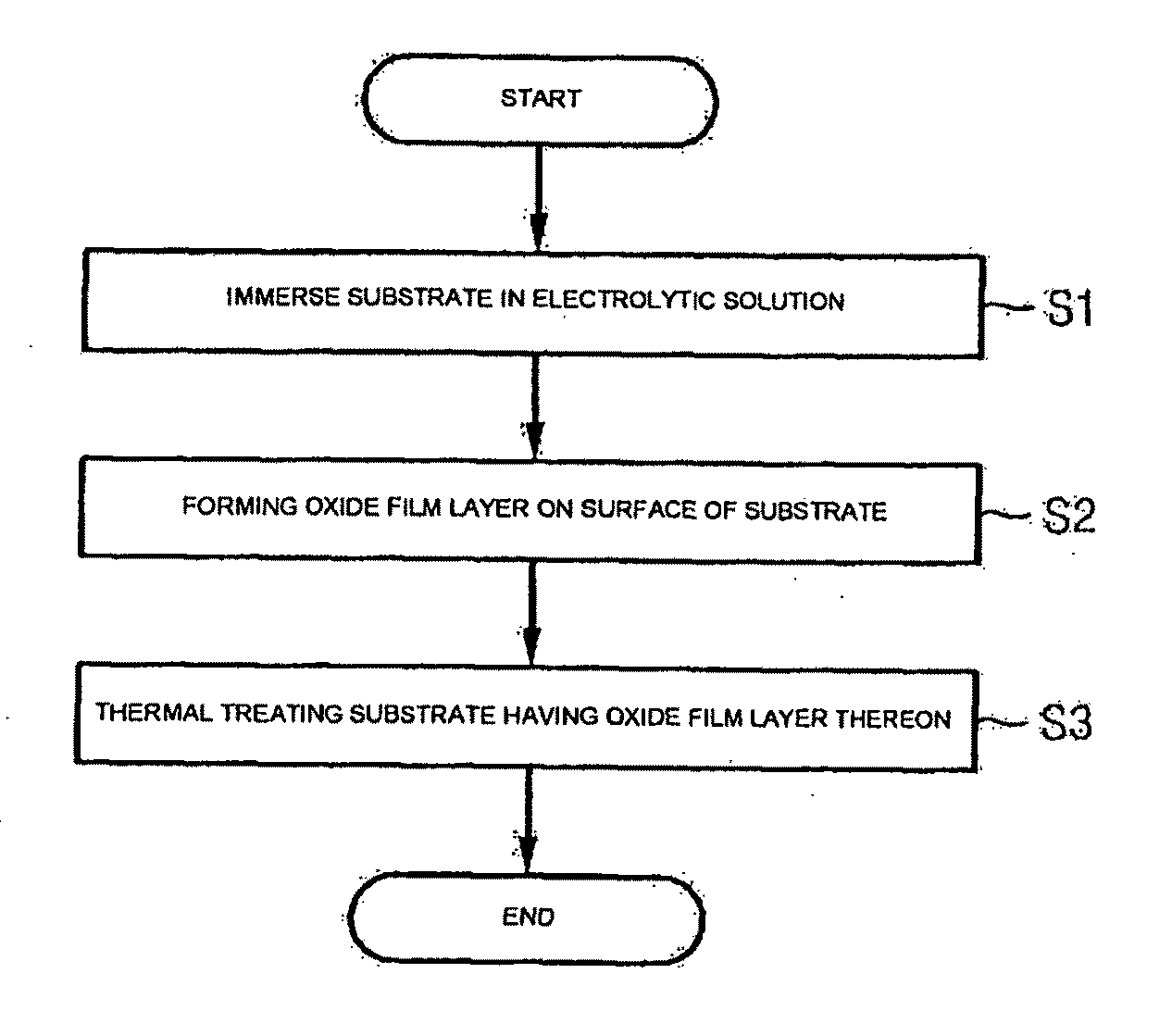
A method of fabricating an implant with improved surface properties and an implant fabricated using the same are provided. The method includes immersing a substrate that has titanium or titanium alloy in electrolytic solution including at least one of the group consisting of phosphate or fluoride ion and strontium ion, and forming an oxide film layer with a surface structure having a fine roughness of a micro scale by making at least one of phosphate or fluoride ion and strontium ion react to the titanium or the titanium alloy of the substrate on a surface of the immersed substrate using hydrothermal reaction associated with temperature, pressure and time conditions.
Owner:OSTEOPHIL
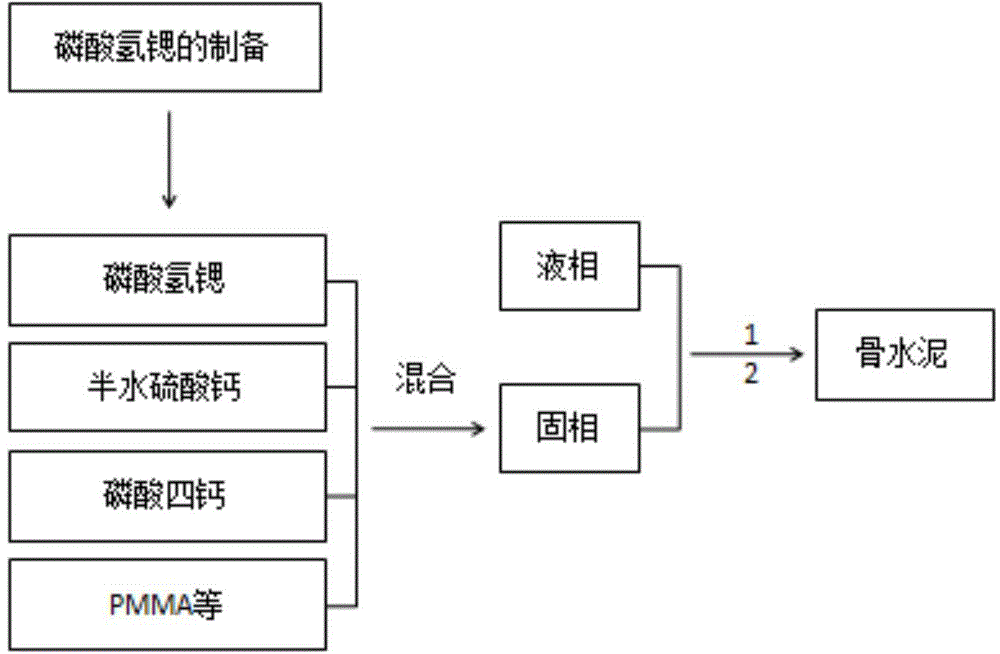
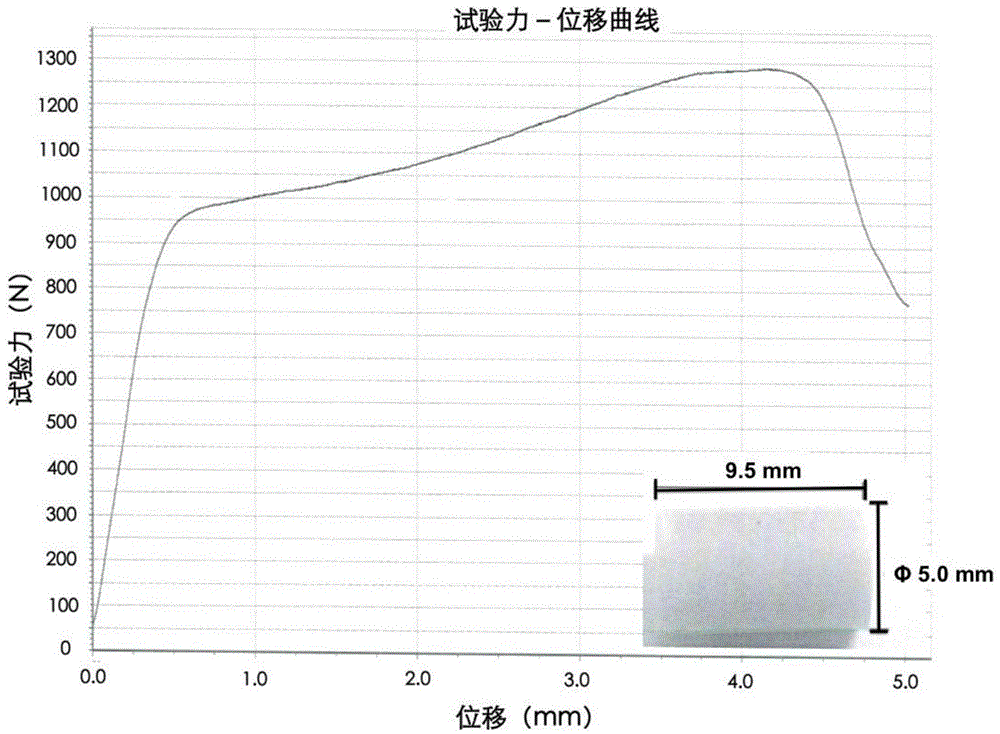
Injectable bone cement containing strontium and preparation method of bone cement
The invention relates to injectable bone cement containing strontium and a preparation method of the injectable bone cement. The injectable bone cement comprises solid phase and liquid phrase, wherein the solid phrase comprises polymethylmethacrylate, calcium sulfate hemihydrate, tetracalcium phosphate, strontium hydrogenphosphate, barium sulfate and benzoyl peroxide; the liquid phrase comprises a methyl methacrylate monomer, N,N dimethyl paratoluidine and hydroquinone; the preparation method of the injectable bone cement comprises the following steps: mixing solids and liquids at a mass ratio of 2 to 1; stirring uniformly by using a bone cement mixing and stirring system; using an injecting system to inject the bone cement; in the injectable bone cement containing the strontium, the calcium sulfate hemihydrate, the tetracalcium phosphate and the strontium hydrogenphosphate are distributed uniformly; after the injectable bone cement is implanted into a body, calcium ions and strontium ions are degraded and released gradually in the body to form a honeycomb structure and guide cells to ingrow, so that joint connection is formed so as to prevent looseness; the compressive strength of the prepared injectable bone cement containning the strontium are higher than 50 MPa. The injectable bone cement containing the strontium can be used in fracture fixation caused by osteoporosis and the like and bone defect filling.
Owner:山东明德生物医学工程有限公司
Calcium phosphate-based compound self-setting bone repair material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104056305AProlong pharmacological therapeutic efficacyLow costProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingBrushite
The invention discloses a calcium phosphate-based compound self-setting bone repair material and a preparation method thereof. A novel calcium phosphate-based compound self-setting bone repair material is prepared by combining brushite bone cement which is quick to set and degrade and has bioactivity and osteoconduction with hydroxyapatite cement which is good in mechanical property and biocompatibility supplemented by a structure enhancing and a doping and modifying technology, wherein the initial setting time of the bone repair material is 3-10 minutes, the final setting time is 12-20 minutes, the compressive strength after solidification is 21.2-40.0MPa, and the degradation rate within 14 days can reach 18.2%, so that the bone repair material is suitable for repairing bone defects in non-loading parts of human bodies. Compared with the prior art, the material and the preparation method provided by the invention have the advantages that the cost is low, the product quality is stable, the mechanics combination property is excellent, the biodegradability, osteoconduction and X ray resistance are good, the material of the invention can slowly release strontium ions, thus prolonging pharmacologic treating efficacy of the strontium ions to the implanting position, and being applicable to the industrialized mass production.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Preparation method of hybrid membrane for removing strontium ions in radioactive wastewater
ActiveCN106328235AEliminate hazardsStrong adsorption and removal capacityRadioactive decontaminationCross-linkEpoxy
The invention discloses a preparation method of a hybrid membrane for removing strontium ions in radioactive wastewater. The preparation method comprises the following steps that a chitosan-epoxy chloropropane cross-linking product and a metal titanium precursor are prepared and then added into a polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution to obtain a membrane coating solution; a support body is coated with the membrane coating solution until a membrane is obtained, and the membrane is separated from the support body and dried to obtain the hybrid membrane without the support body, or the membrane and the support body are not separated and dried to obtain the hybrid membrane with the support body; or the membrane coating solution is dissolved with solvent firstly, then the support body is coated with the membrane coating solution until the membrane is obtained, and the membrane is separated from the support body to obtain the hybrid membrane without the support body, or the membrane and the support body are not separated to obtain the hybrid membrane with the support body. The hybrid membrane prepared through the method is good in temperature resistance and high in adsorption efficiency, has the high adsorption capacity on strontium ions in water and not only can be used for adsorption removal of the strontium ions in the radioactive wastewater but also can be used for adsorption separation of strontium ions in nonradioactive wastewater.
Owner:太湖县市场监督检验所(太湖县功能膜检测研究院)
Methods for preserving fresh produce
InactiveUS20050084602A1Extended shelf lifePreserve textureMilk preservationDough treatmentAluminum IonFood flavor
Methods of preserving fresh produce with a produce preservative which extends the shelf life of fresh produce, particularly cut fresh produce, and preserves the texture, flavor, appearance, crispness, and color of the fresh produce, particularly the exposed surface of the fresh produce, are provided. The method comprises: providing a solution of produce preservative comprising: water; a preservative cation which is selected from the group consisting of a strontium ion, lithium ion, barium ion, aluminum ion, copper ion, ammonium ion, iron ion, manganese ion, potassium ion, or mixtures thereof; and ascorbate ions, or erythorbate ions; wherein the ascorbate ions or erythorbate ions and the preservative cation are present in an ion ratio of preferably from 0.2:1 to 8:1, more preferably 0.75:1 to 8:1, even more preferably from 1:1 to 4:1, yet more preferably 1.5:1 to 3:1; most preferably 1.1:1 to 2.5:1; and, applying said produce preservative to the produce. The invention also relates to fresh produce preserved with the produce preservatives.
Owner:MANTROSE HAEUSER
Method and device for processing radioactive strontium-contained waste water
InactiveCN103714874AImprove decontamination factorIncrease the concentration factorRadioactive decontaminationFiberParticulates
The invention relates to a method and device for processing radioactive strontium-contained waste water. Chemical reactions are achieved between the radioactive strontium-contained waste water in a hydrocyclone and calcium carbonate seed crystals through hydrocycolone stirring and between the radioactive strontium-contained waste water in the hydrocyclone and sodium carbonate through hydrocycolone stirring, and therefore strontium carbonate is deposited on the surfaces of the calcium carbonate seed crystals and forms large-grain-size tight crystal particulate matter, and the large-grain-size tight crystal particulate matter rapidly sedimentates at the bottom of the hydrocyclone so that a part of radioactive strontium ions can be removed; small-grain-size strontium carbonate and small-grain-size seed crystals enter a membrane separator along with the supernatant to react with ferric chloride, the radioactive strontium ions are further removed after the particulate matter is separated through a hollow fibrous membrane, and therefore the radioactivity of discharged water is greatly lowered. The particulate matter formed through the method is large in grain size, compact in structure and good in sedimentation performance, the defects that the chemical precipitation method is low in decontamination factor and large in mud production amount are effectively overcome, the disadvantage that the membrane is seriously contaminated in the membrane separation process is also eliminated, and the method for processing the radioactive strontium-contained waste water is economical and practical.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Adsorbent for adsorbing and separating m-xylene and preparation method of same
ActiveCN102167652AHigh m-xylene selectivityOther chemical processesAdsorption purification/separationHigh absorptionAromatic hydrocarbon
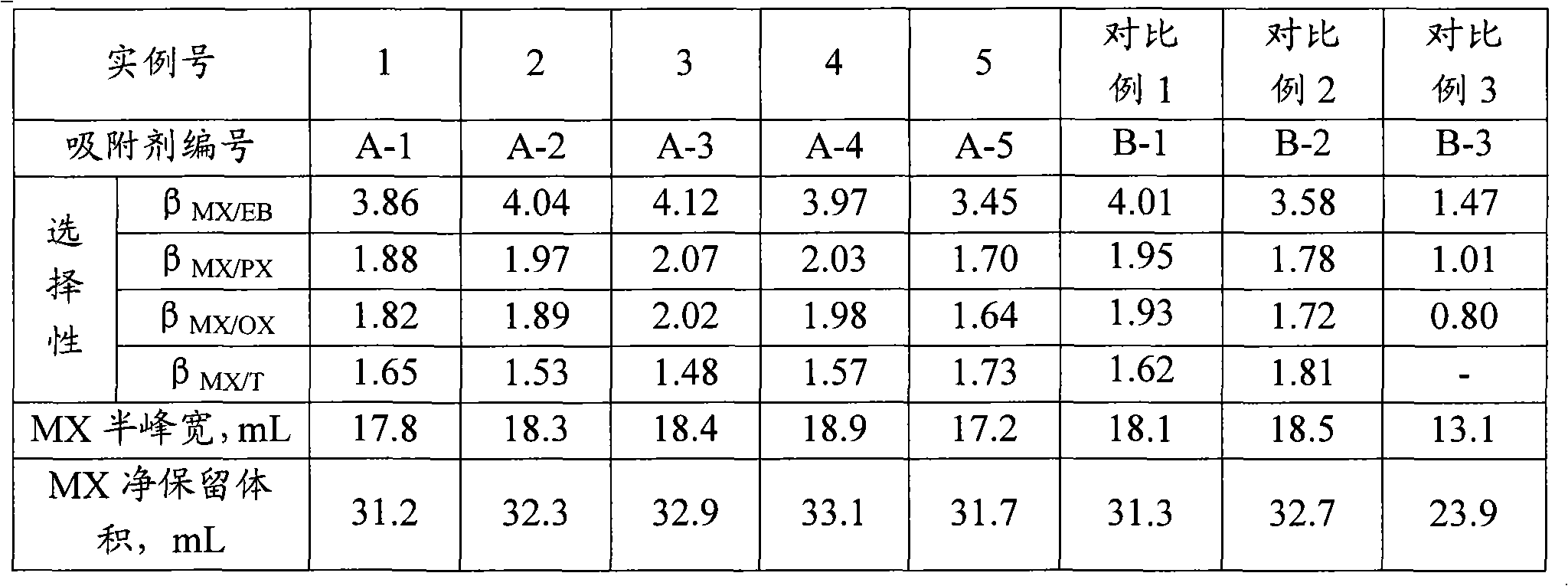
An adsorbent for adsorbing and separating m-xylene comprises 90-98 wt% of Y zeolite and 2-10 wt% of binder, wherein an exchangeable cation site of the Y zeolite is jointly occupied by a sodion and a strontium ion. With relatively high absorption capacity and absorption selectivity for m-xylene, the absorbent is used for adsorbing and separating m-xylene from C8 aromatic hydrocarbon.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Anode material suitable for aqueous metal ion battery and preparation method for same
ActiveCN106229498AApplicable preparation processStable output voltageMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureAluminum IonSodium-ion battery
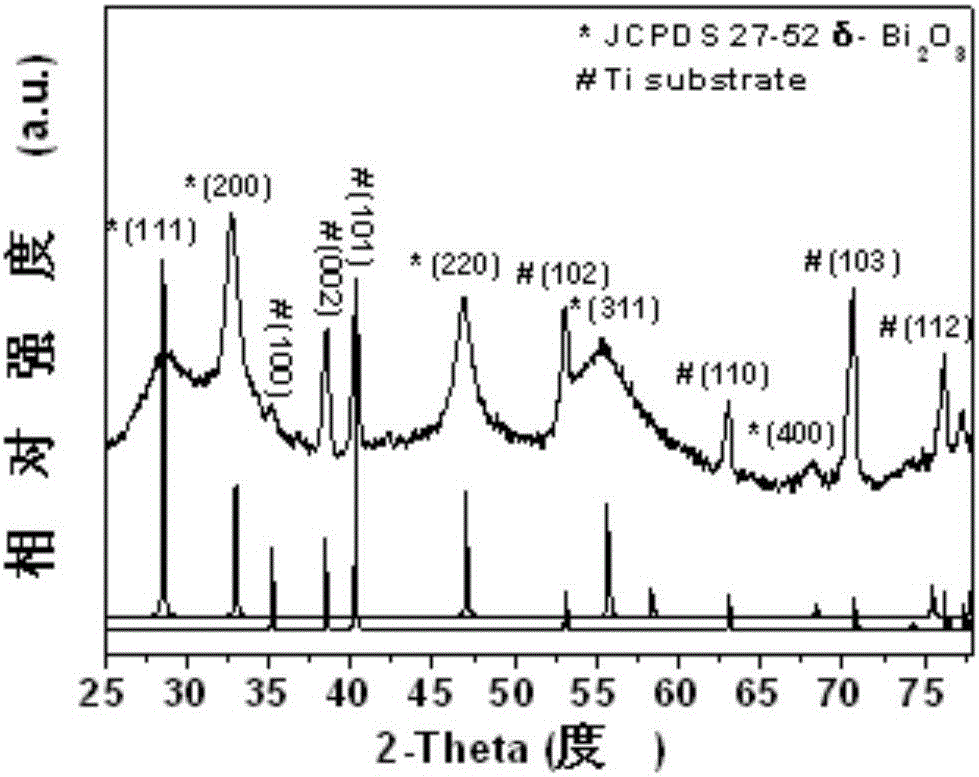
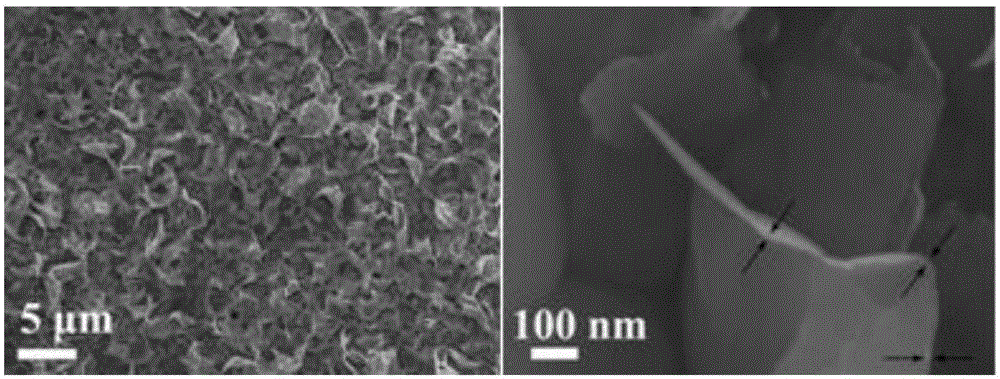
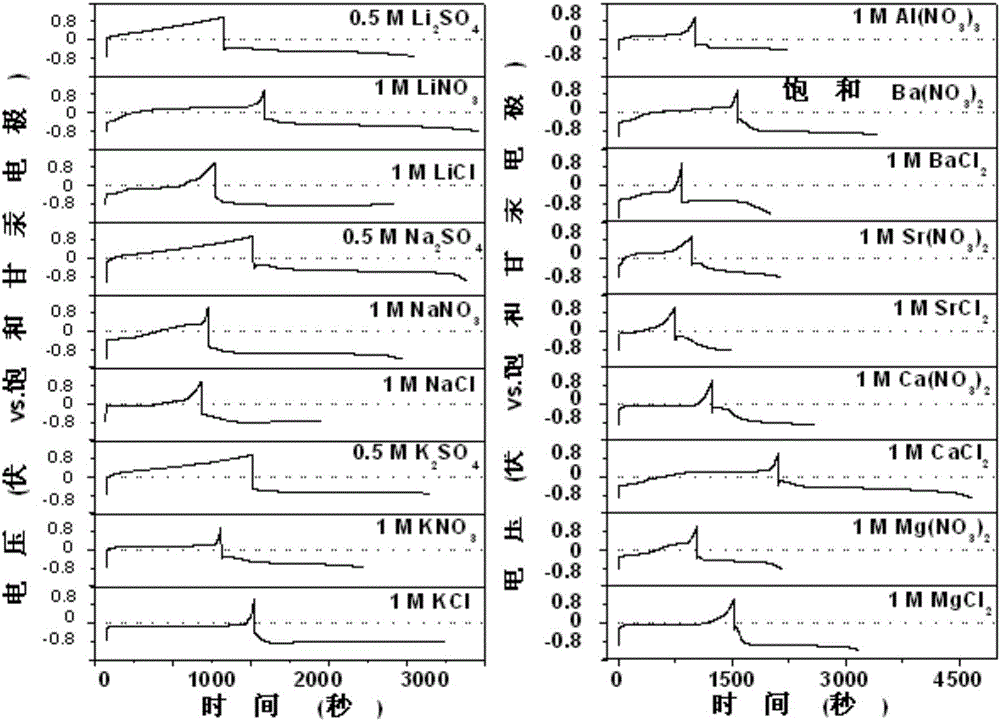
The invention relates to an anode material being suitable for an aqueous metal ion battery and a preparation method for the same. The anode material contains bismuth oxide and is a nano bismuth oxide array thin film, which is formed by oriented growth of bismuth oxide nano sheets on a metal substrate. The bismuth oxide nano sheets are vertically, uniformly and densely distributed on the metal substrate in an array structure, or that bismuth oxide powder is uniformly mixed with a conductive additive and a binder to form a film on the metal substrate. The anode material is suitable for many types of aqueous batteries, including aqueous lithium ion batteries, aqueous sodium ion batteries, aqueous potassium ion batteries, aqueous magnesium ion batteries, aqueous calcium ion batteries, aqueous strontium ion batteries, aqueous barium ion batteries, aqueous aluminum ion batteries, etc. The aqueous metal ion battery based on the anode material has high capacity, good charging / discharging platform, and high electrochemical reversibility.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method of preparing TiSrO3 coating on surface of titanium implant
ActiveCN104032291AImprove bindingLarge specific surface areaMetallic material coating processesHeat treatedMaterials science
The invention discloses a method of preparing TiSrO3 coating on the surface of a titanium implant. The method comprises the following steps: after carrying out sand blasting and double acid treatment on a pure titanium implant, putting the titanium implant in a hydrothermal solution containing strontium ions for hydrothermal treatment and surface modification; and forming a nanoscale protruding structure with multiple holes on the surface of the implant, wherein the protruding layer on the surface is a strontium titanate crystal structure and an anatase crystal structure and has the effects of promoting osteoblast and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. Meanwhile, the coating has good wettability and has a wide application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for extraction of strontium from urine
InactiveUS20130017613A1Simple mixingSimple filter operationTransuranic element compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationQuantitative determinationIon-exchange resin
The present invention provides an apparatus and rapid methods for extracting strontium ions from urine to provide a concentrated and purified strontium-90 extract suitable for scintillation measurements. The methods remove organic compounds, pigments, and alkali metal ions that can interfere with quantitative determination of strontium-90 in urine. A method of the invention comprises acidifying urine and removing organic pigments therefrom, loading a known quantity of so-treated urine onto a diphosphonic acid-based ion-exchange resin; flowing aqueous methanesulfonic acid through the diphosphonic acid-based ion-exchange resin to elute alkali metal ions therefrom; eluting strontium ions off of the diphosphonic acid-based resin and on to a strontium extraction chromatographic resin with a concentrated aqueous nitric acid solution; subsequently flowing water or a dilute acid stripping solution through the strontium extraction resin to strip the strontium from the strontium extraction resin; and collecting the strontium-containing stripping solution eluting from the strontium extraction resin.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Composition for lessening malodors during hair treatment and hair removal and method of use
InactiveUS20060034874A1Safe and effectiveSimple and inexpensive methodCosmetic preparationsHair removalMedicineCompound (substance)
The use of strontium ions to reduce malodors associated with various chemical hair removal and hair treatment procedures is disclosed. Typical formulations include alkali metal thioglycolate depilatories containing from 0.2% to 2% strontium chloride.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
Preparation method of strontium-containing phosphate bioactivity conversion coating on titanium surface
InactiveCN107338425ASimple preparation processNo pollution in the processLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingProsthesisPhosphate ionTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a preparation method of a strontium-containing phosphate bioactivity conversion coating on a titanium surface. According to the method, the strontium-containing phosphate bioactivity conversion coating with micron and nanoscale crystal structures grows on titanium and titanium alloy surfaces in situ directly by means of a phosphate chemical conversion technology. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a chemical conversion basic liquid containing phosphate ions, strontium ions and an accelerant; successively performing pickling, washing and surface activating on the surface of a titanium matrix; and immersing the treated titanium matrix in the chemical conversion basic liquid for chemical conversion treatment, wherein the conversion temperature is 55-75 DEG C and the conversion time is 20-50min. The strontium-containing phosphate bioactivity conversion coating on the titanium surface prepared by the method is in a porous multilayered micron and nanoscale crystal structure shape. The coating is primarily composed of strontium monophosphate strontium phosphate phases. The coating can effectively accelerate deposition of a hydroxyapatite phase in immersion in an in vitro simulation fluid.
Owner:SUZHOU RES INST SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method of hybrid membrane adsorbent for removing strontium ions in radioactive wastewater
InactiveCN104043348AStrong adsorption and separation abilityEliminate hazardsSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesPolyvinyl alcoholSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a hybrid membrane adsorbent for removing strontium ions in radioactive wastewater. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of adding a silane coupling agent with the mass being 0.01-0.3 time of the mass of PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) into a polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution with the mass percentage concentration being 0.1-10% at the temperature of 0-150 DEG C in inert atmosphere or air, carrying out sol-gel reaction for 1-48h, standing and defoaming a sol-gel product, coating the product to obtain a membrane, and drying for 2-72h under the conditions that the temperature is 0-200 DEG C and the relative humidity is 50-90% so as to obtain the hybrid membrane adsorbent for removing strontium ions in radioactive wastewater. According to the method, adsorption of metal ions and membrane separation of residual liquid left after adsorption can be implemented synchronously, and the operation process is simple and convenient; the prepared hybrid membrane adsorbent is good in membrane forming property, and has good adsorbing effect on low-concentration strontium ions, and can be used for adsorbing and removing low-concentration strontium ions in radioactive wastewater.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
Bioactive shell-core multiplelayer microstructure nanometer powder and its preparation method
InactiveCN1803205AControl release speedThe release rate is easy to controlProsthesisNano sizeHydrolysis
The invention discloses a multilayer microstructure nanometer powder body of biological active shell-core, which is characterized by the following: adapting silicon gel as inner core and porous calcium phosphate as outer shell; allocating spherical particle of multilayer microelement zinc or and strontium ion between shell and core; letting ammonia catalyze hydrolysis of ethyl silicate and polycondense into silicon gel nanometer ball in the absolute ethyl alcohol; mixing the zinc or strontium ion solution with the suspending solution of silicon gel nanometer ball; attaching the zinc or strontium ion to the silicon gel nanometer ball and micropore domain; packing the silicon gel layer and zinc or strontium ion; depositing the porous calcium phosphate on the silicon gel nanometer ball surface; filtering; drying; adjusting the releasing speed of inner core active material through changing the microstructure of outer shell; diminishing the explosive releasing behavior of active silicon, strontium and zinc during short period.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
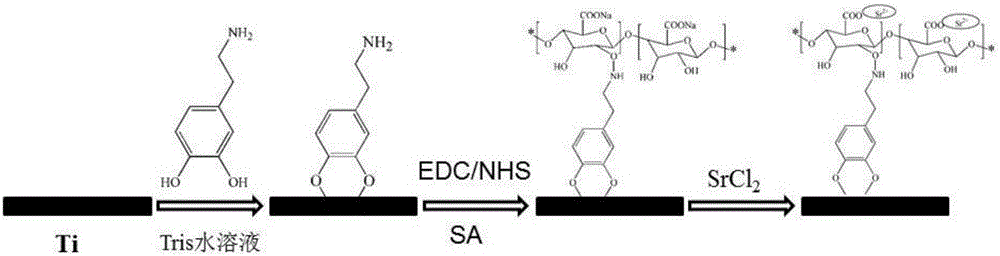
Preparation method of strontium chelated sodium alginate coating on titanium surface
ActiveCN106011834AImprove the problem of poor combinationImprove bindingMetallic material coating processesTissue regenerationBiocompatibility TestingChelation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a strontium chelated sodium alginate coating on a titanium surface. The preparation method comprises the steps that a trihydroxymethyl aminomethane water solution of dopamine is firstly utilized for treating the titanium surface, sodium alginate is grafted to the surface of the above material by means of an amide reaction of dopamine amidogen and sodium alginate carboxyl, then the obtained material is put into a strontium chloride solution, and chelation of strontium is achieved. A catechol functional group in the dopamine adheres to the titanium surface in a non-covalent manner, and then the coating is constructed on the surface of a substrate. The method is easy to operate, and bonding with a matrix is good. Sodium alginate biocompatibility is good, strontium alginate gel formed after a large quantity of carboxyl existing in molecules and strontium ions react has good chelation performance on the strontium, the strontium chelated sodium alginate coating on the titanium surface is prepared, and long-acting bone inductivity is given to transplant materials by means of slow release and degradation of the strontium. The adopted sodium alginate is good in biocompatibility and has good chelation performance with the strontium, slow release of the strontium is achieved, and quite high promotional value is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
Composite adsorption material for removing strontium ions from natural water and preparation method for adsorption material
InactiveCN102872837AHigh porosityEasy to operateOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeKaolinitePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a composite adsorption material for removing strontium ions from natural water and a preparation method for the adsorption material, and belongs to the field of material preparation. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: crushing and grinding kaolinite, putting powder into NaOH to prepare gel, crystallizing, washing buy using soft water, and drying to prepare 4A zeolite; performing oxidation reflux on Sb2O3 to prepare colloidal polyantimonic acid, drying, soaking in nitric acid, washing until the solution is neutral, and drying; and putting the prepared 4A zeolite and polyantimonic acid into a triethylamine solution, mixing, uniformly stirring, putting into a stainless steel reaction kettle with a polyethylene tetraether lining, crystallizing, performing filtering separation, washing until the solution is neutral, and drying to obtain the adsorption material which has a good adsorption effect and can selectively adsorb the strontium ions. The preparation method is innovative, novel and unique, and the prepared material has the good adsorption effect on the strontium ions in the water.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Process for preparing submicron grade barium strontium phthalate powder by packing method
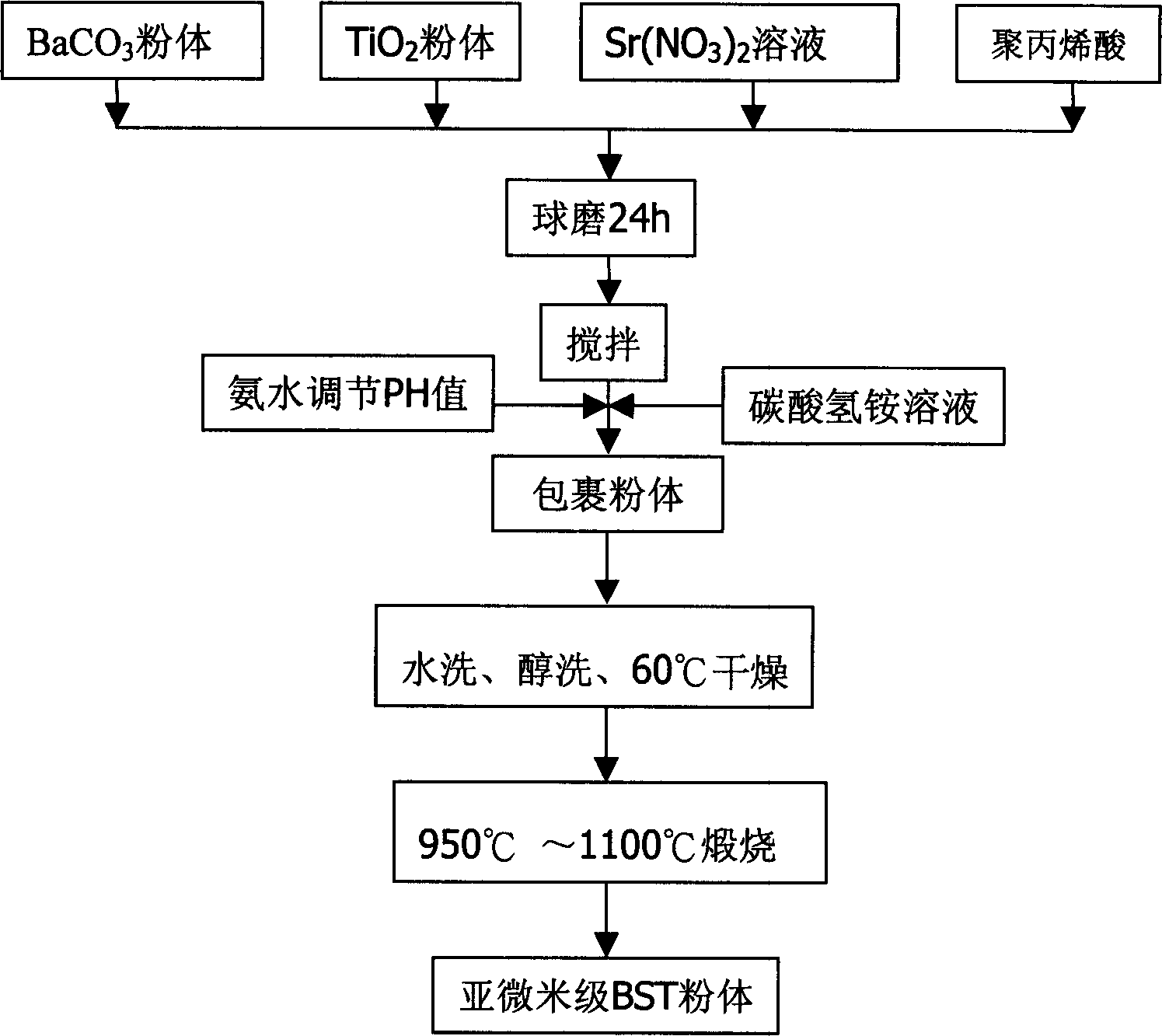
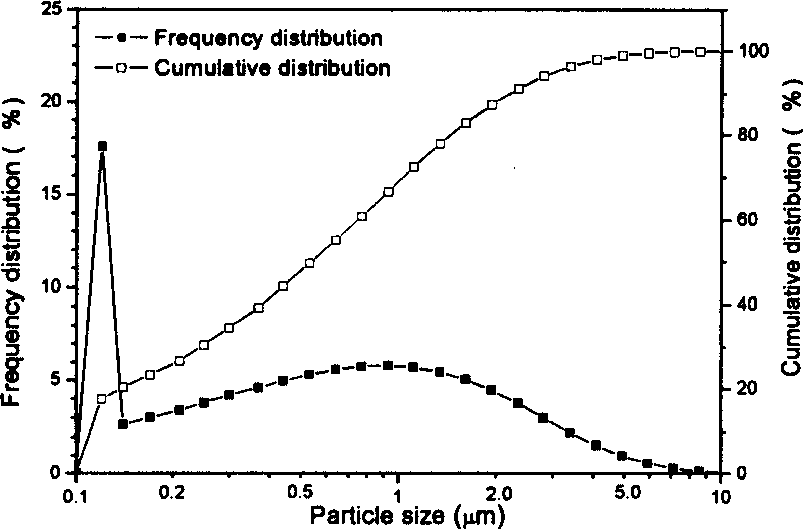
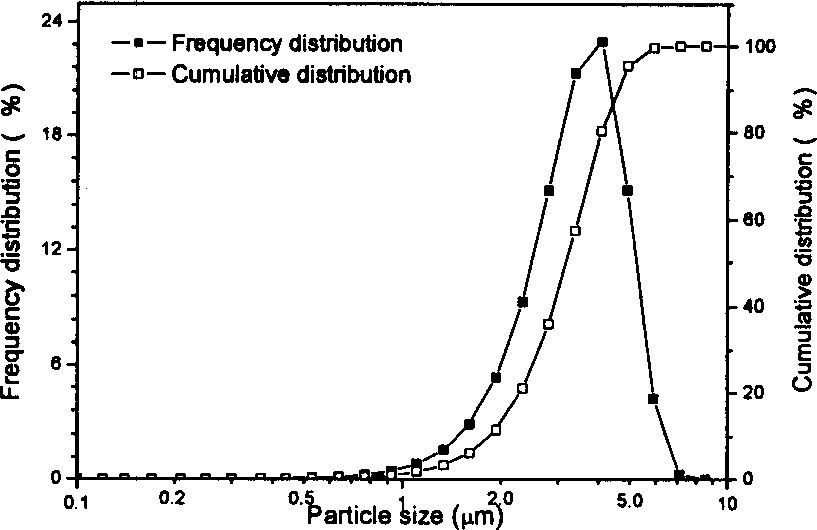
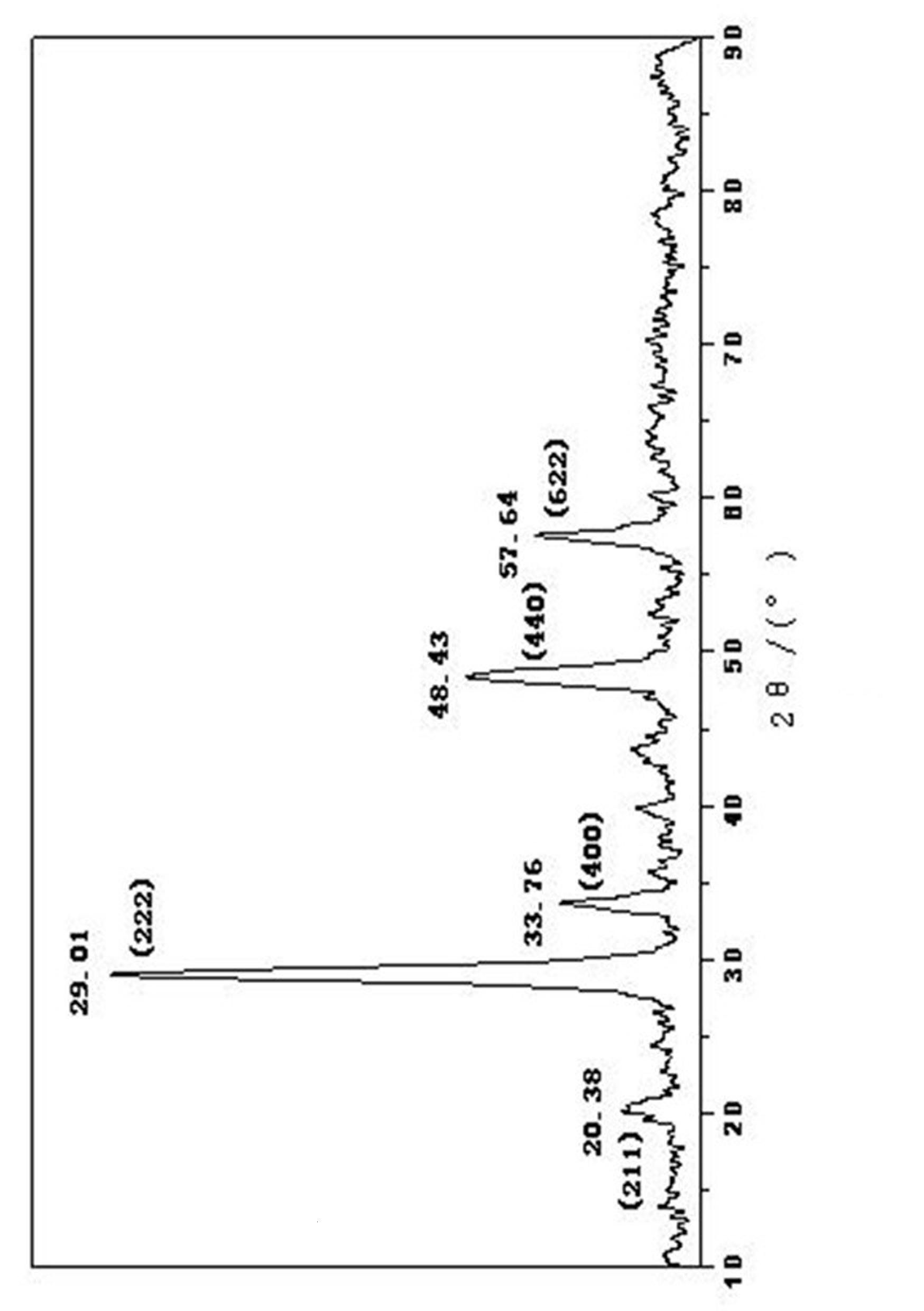
InactiveCN1792814ASimple processSmall granularityCalcium/strontium/barium compoundsTitanium compoundsBarium strontium titanateBarium carbonate
A process for preparing submicron-class barium strontium titanate (BST) powder by wrapping method includes such steps as mixing barium carbonate powder, TiO2 powder and strontium nitrate solution, adding polyacrylic acid, wet ball grinding, adding excessive ammonium bicarbonate solution while stirring, using ammonia water to regulate pH=7-10 for depositing the strontium carbonate on the surface of barium carbonate and TiO2 particles, filtering, washing, drying and calcining.
Owner:JIANGSU SOUTH PORCELAIN INSULATOR CO LTD
Method for preparing yttrium oxide substrate nano-oxide fluorescent powder
InactiveCN101928563AGood dispersionLow firing temperatureLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceLight emission
The invention relates to a method for preparing rare earth ion-doped yttrium oxide nano fluorescent powder by taking polyamidoamine (PAMAM) as a template. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving dysprosium oxide, yttrium nitrate and strontium nitrate in concentrated hydrochloric acid, heating and dissolving the mixture and adding deionized water into the dissolved product to obtain mixed solution of rare earth ions; dissolving the PAMAM in the deionized water to obtain aqueous solution of the PAMAM; dissolving ammonium oxalate in the deionized water to obtain solution of the ammonium oxalate; slowly adding the mixed solution of the rare earth ions into the aqueous solution of the PAMAM dropwise for reaction; adding the solution of the ammonium oxalate dropwise; centrifuging a precipitate and alternatively washing the precipitate with the deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol to obtain gel; and putting the gel into a drying oven for drying and baking to obtain nano-scale dysprosium and strontium-codoped yttrium oxide (Y2O3:Dy3<+>:Sr2<+>) fluorescent powder. The method has the advantages of nano-scale particle size of a material, high dispersivity, capability of enhancing the fluorescence emission intensity of dysprosium ions, adjusting the (yellow / blue) Y / B value of characteristic fluorescence of the dysprosium ions and presenting approximate white-light emission by using the strontium ions, low baking temperature, simple preparation process, low raw material price and low cost.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
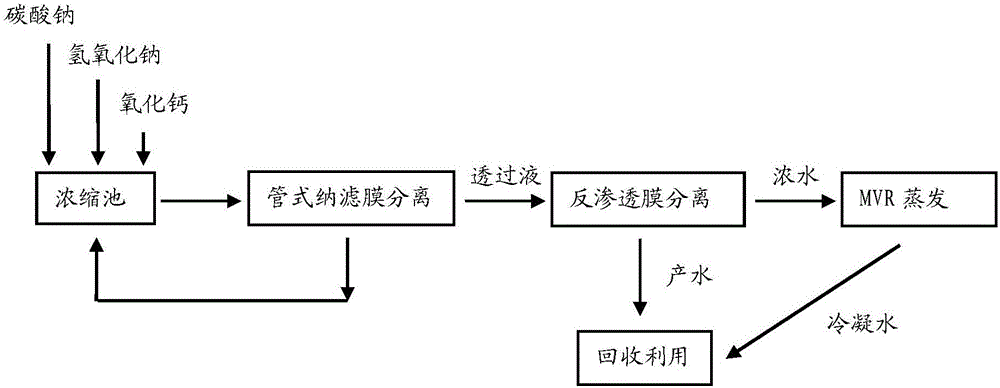
Treatment process of shale gas exploitation waste water based on membrane technology
InactiveCN106746033AOmission of processingBiochemical steps omittedWaste water treatment from quariesWater contaminantsIon contentWater based
The invention discloses a treatment process of shale gas exploitation waste water based on a membrane technology. The shale gas exploitation waste water is collected into a concentrated tank, the pH (Potential Of Hydrogen) value of the shale gas exploitation waste water ranges from 7 to 9, the oxygen consumption is less than or equal to 435ppm, the iron ion content is less than or equal to 6.2ppm, the potassium ion content is less than or equal to 152ppm, the sodium ion content is less than or equal to 8330ppm, the strontium ion content is less than or equal to 79ppm, the zinc ion content is less than or equal to 0.1ppm, the chloride is less than or equal to 13300ppm, and the ammonia-nitrogen content is less than or equal to 33.3ppm; the treatment process comprises sequentially carrying out concentrated treatment, tubular nanofiltration membrane separation and reverse osmosis membrane separation, finally carrying out secondary steam mechanical compression and evaporation on concentrated water, and recovering a crystal substance. According to the treatment process provided by the invention, the steps of preprocessing and biochemical engineering of a traditional process are skipped, the production cost is reduced, and the true zero-pollution emission is realized with lower cost.
Owner:苏州华辰净化股份有限公司
Preparation method for polylactic acid nanofiber scaffold functionally modified by two-dimensional nanometer black phosphorus
ActiveCN110917395AImprove hydrophilicityImprove adhesionEnergy modified materialsSkeletal disorderFiberMicrosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method for a polylactic acid nanofiber scaffold functionally modified by two-dimensional nanometer black phosphorus, and aim to provide a preparation method for amultifunctional modified polylactic acid scaffold. The preparation method is characterized in that a black phosphorus nanosheet is taken as a medicine carrier to load an anti-inflammatory medicine, i.e., ibuprofen, a natural high polymer material, i.e., sodium alginate, is taken as a coating material, and through a crosslinking function of strontium ions, a medicine-carrying microsphere is obtained; an electrostatic interaction is used for evenly doping a sodium alginate medicine-carrying microsphere into a modified polylactic acid basis material which is subjected to ammonolysis and modification by branched polyethyleneimine and is rich in an active amino group; and through freezing phase separation, the modified polylactic acid scaffold with a reticular nanometer fiber structure is obtained. The preparation method has the characteristics that the prepared modified polylactic acid nanofiber scaffold embedded with the medicine-carrying microsphere is a multifunctional system with thefunctions of performing photothermal therapy, accelerating bone growth, resisting bacteria, diminishing inflammation and intelligently releasing medicines, and the polylactic acid nanofiber scaffold is an ideal bone repairing material.
Owner:福建渤海传芳企业发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com