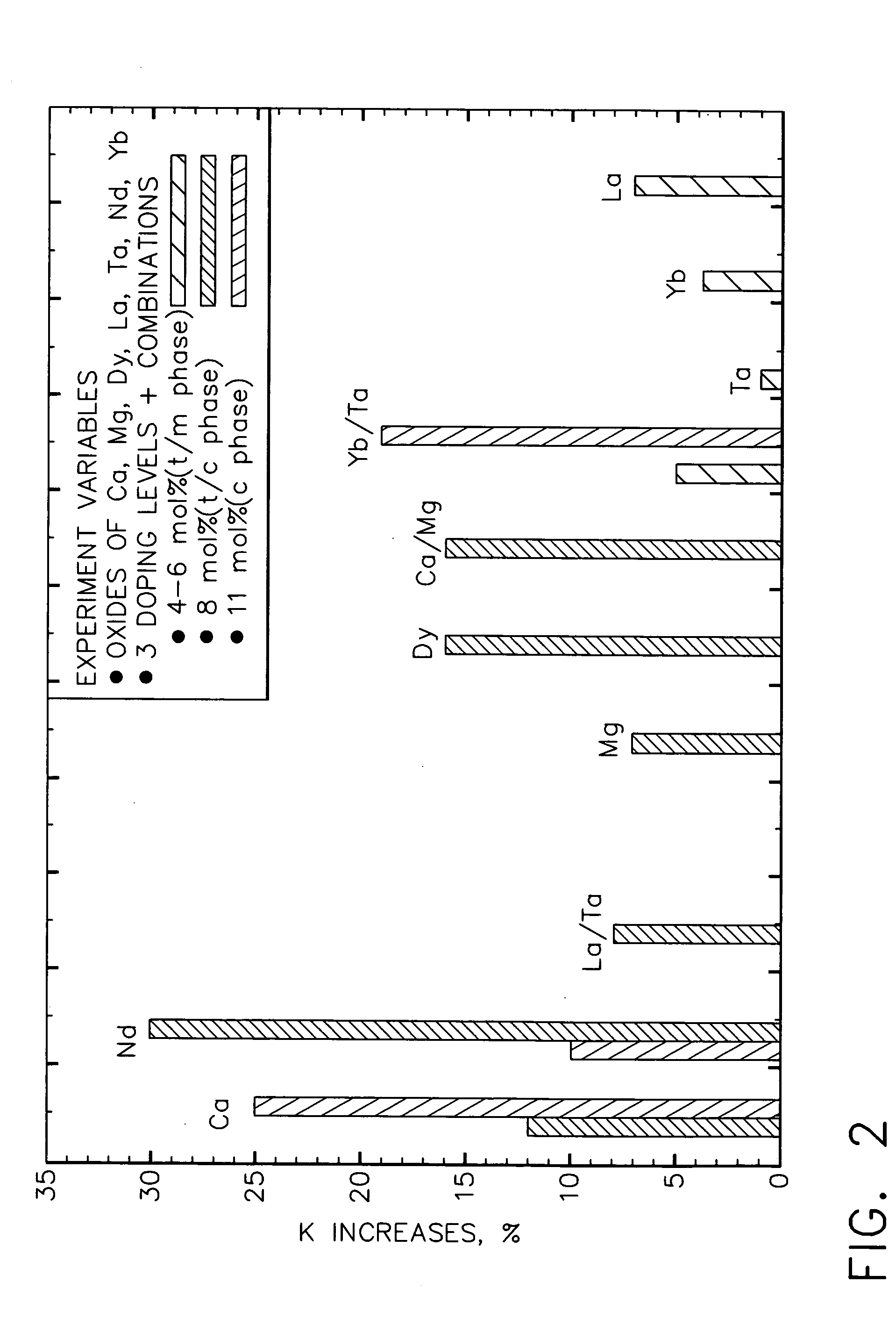
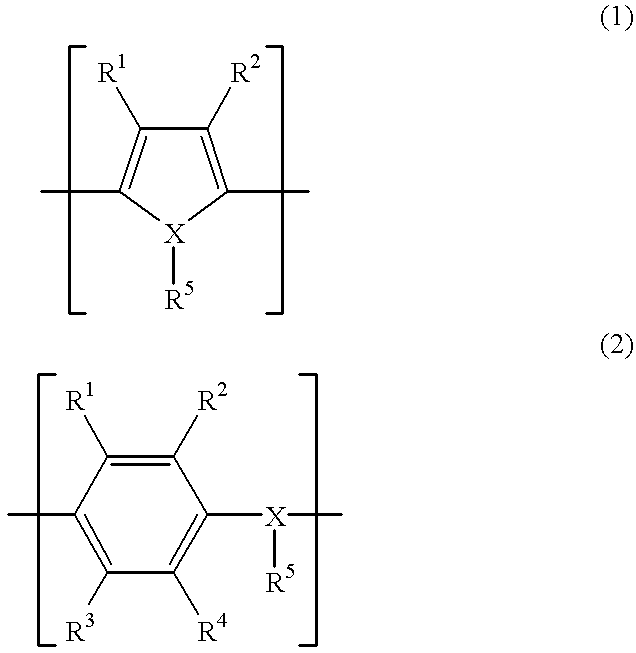
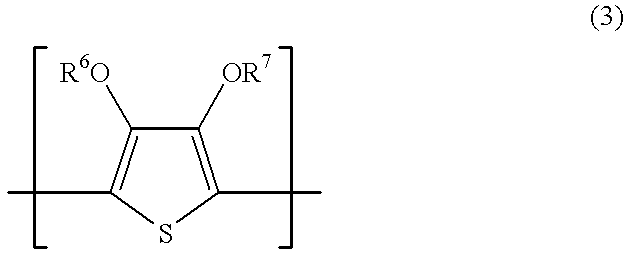
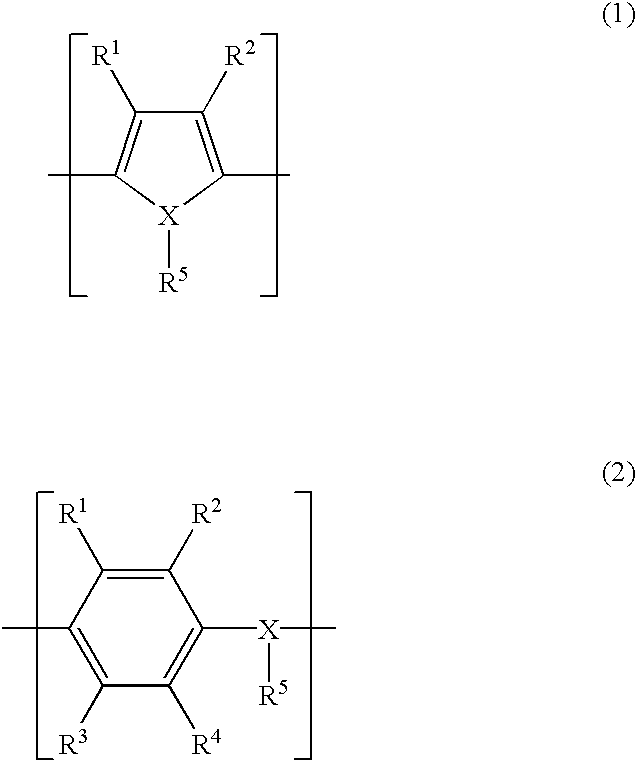
Patents
Literature
1577 results about "Dysprosium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dysprosium is a chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare earth element with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime. Naturally occurring dysprosium is composed of seven isotopes, the most abundant of which is ¹⁶⁴Dy.
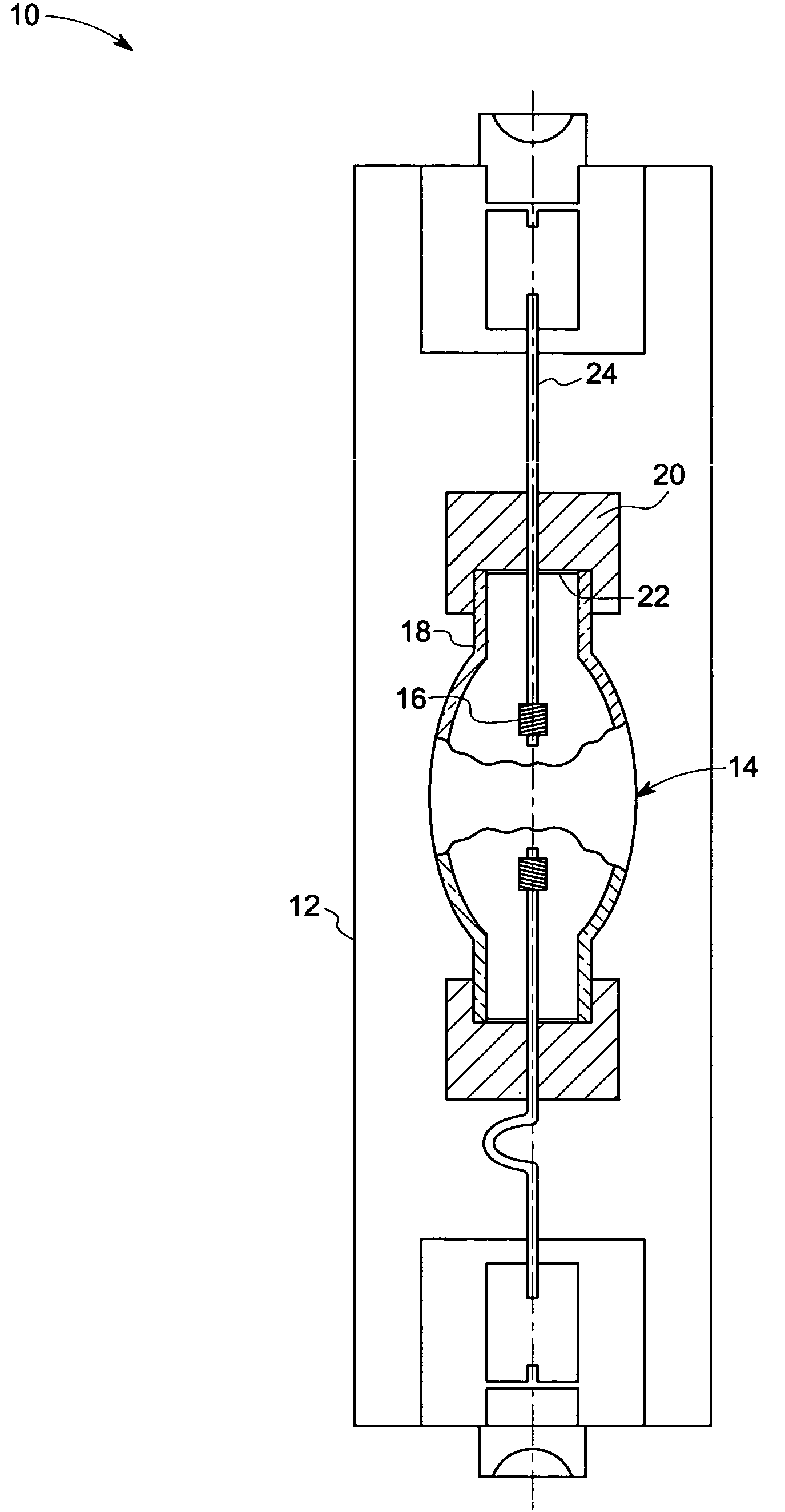
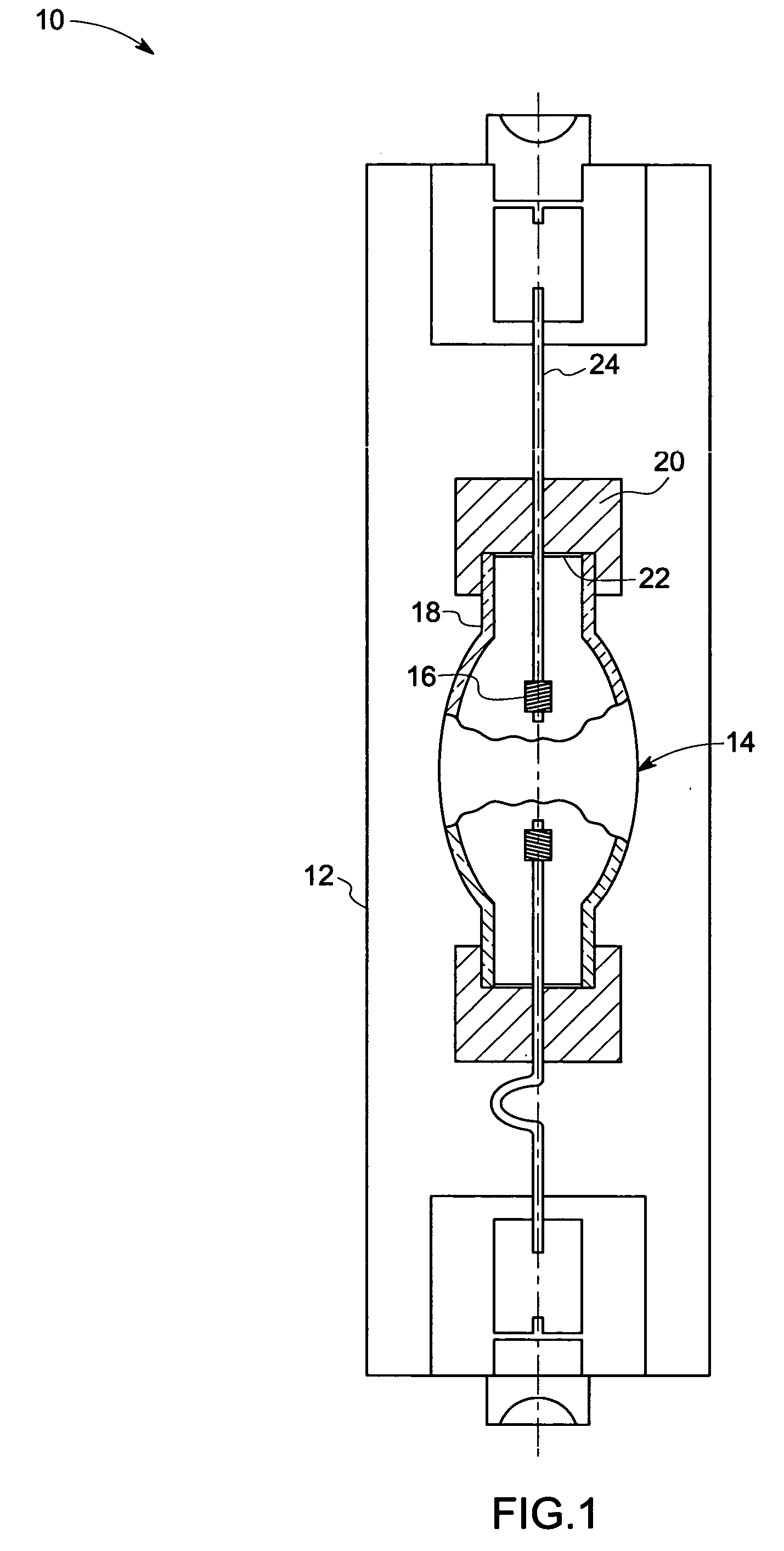
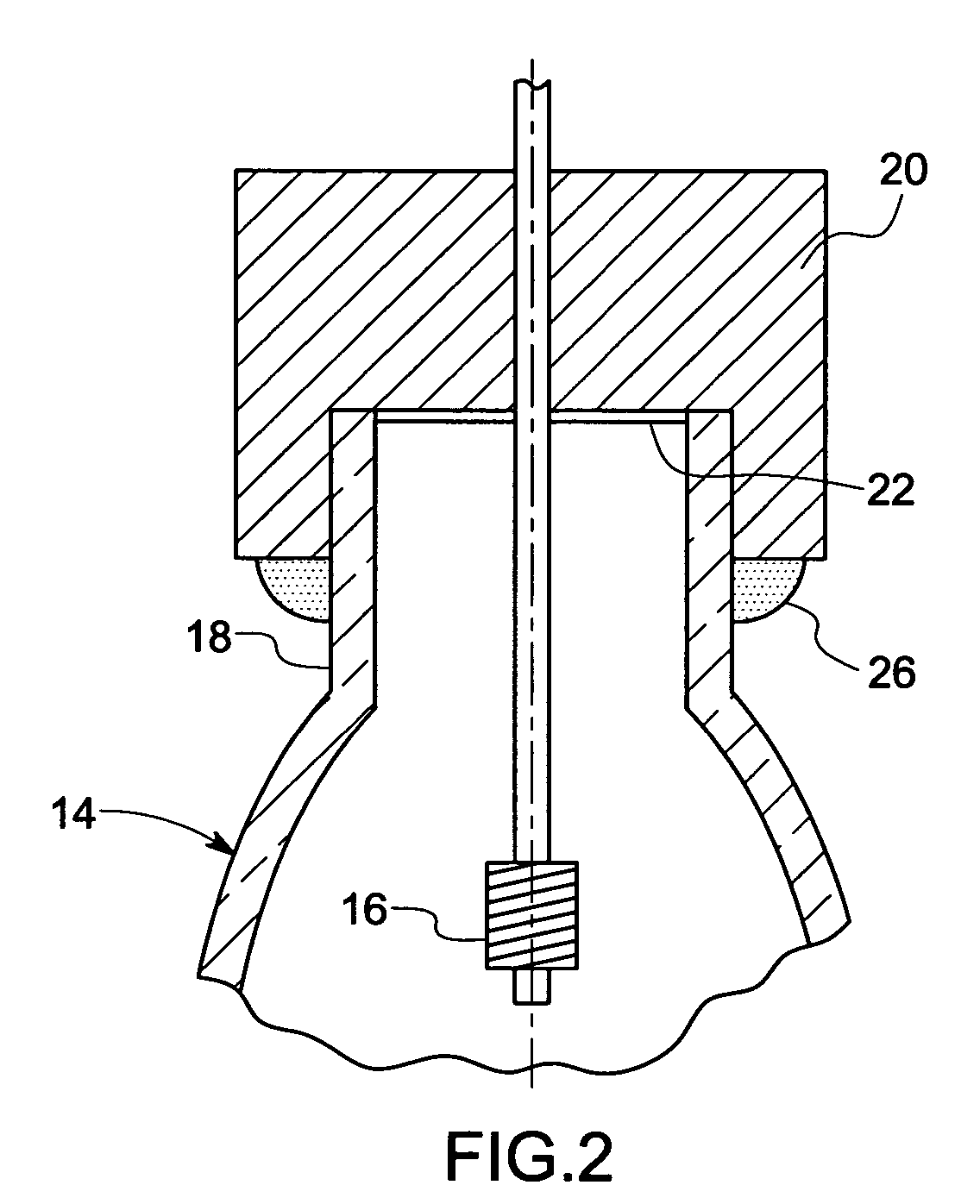
Single phosphor for creating white light with high luminosity and high CRI in a UV LED device
InactiveUS6853131B2Avoids and reduces problemGas-filled discharge tubesDischarge tube luminescnet screensX-rayUltraviolet
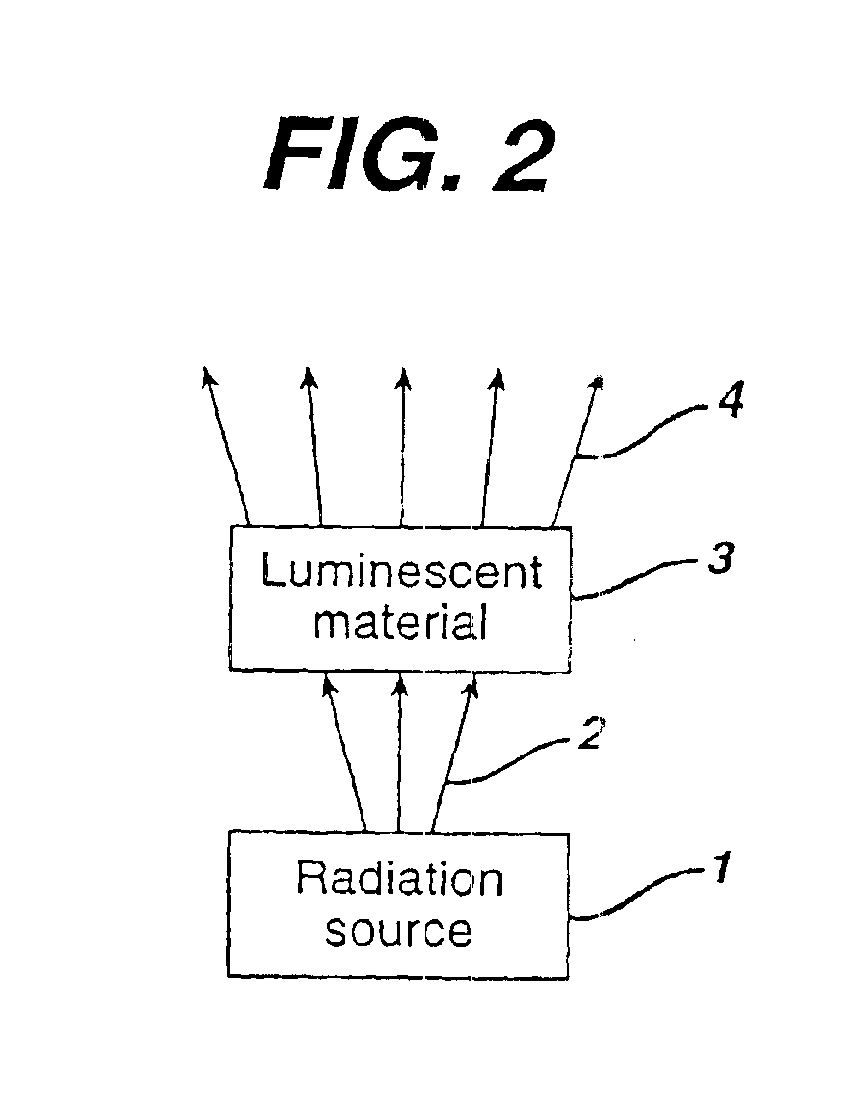
There is provided a white light illumination system. The illumination system includes a radiation source which emits either ultra-violet (UV) or x-ray radiation. The illumination system also includes a luminescent material which absorbs the UV or x-ray radiation and emits the white light. The luminescent material has composition A2−2xNa1+xExD2V3O12. A may be calcium, barium, strontium, or combinations of these three elements. E may be europium, dysprosium, samarium, thulium, or erbium, or combinations thereof. D may be magnesium or zinc, or combinations thereof. The value of x ranges from 0.01 to 0.3, inclusive.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Polymer nanocomposite implants with enhanced transparency and mechanical properties for administration within humans or animals
Polymer nanocomposite implants with nanofillers and additives are described. The nanofillers described can be any composition with the preferred composition being those composing barium, bismuth, cerium, dysprosium, europium, gadolinium, hafnium, indium, lanthanum, neodymium, niobium, praseodymium, strontium, tantalum, tin, tungsten, ytterbium, yttrium, zinc, and zirconium. The additives can be of any composition with the preferred form being inorganic nanopowders comprising aluminum, calcium, gallium, iron, lithium, magnesium, silicon, sodium, strontium, titanium. Such nanocomposites are particularly useful as materials for biological use in applications such as drug delivery, biomed devices, bone or dental implants.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Layered thermal barrier coatings containing lanthanide series oxides for improved resistance to CMAS degradation
InactiveUS20070160859A1Avoid damageElimination of expensiveBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesReaction layerCerium
A coating applied as a two layer system. The outer layer is an oxide of a group IV metal selected from the group consisting of zirconium oxide, hafnium oxide and combinations thereof, which are doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide. These metal oxides doped with a lanthanum series addition comprises a high weight percentage of the outer coating. As used herein, lanthanum series means an element selected from the group consisting of lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), lutetium (Lu) and combinations thereof, and lanthanum series oxides are oxides of these elements. When the zirconium oxide is doped with an effective amount of a lanthanum series oxide, a dense reaction layer is formed at the interface of the outer layer of TBC and the CMAS. This dense reaction layer prevents CMAS infiltration below it. The second layer, or inner layer underlying the outer layer, comprises a layer of partially stabilized zirconium oxide.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High performance lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a high performance lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate and a preparation method of the material. The lithium manganate is a doped lithium manganate LiMn2-yXy04 which is doped with one kind or a plurality of other metal elements X, wherein X element is at least one kind selected form the group of aluminium, lithium, fluorine, silver, copper, chromium, zinc, titanium, bismuth, germanium, gallium, zirconium, stannum, silicon, cobalt, nickel, vanadium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and rare earth elements lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium, and y is larger than 0 but less than or equal to 0.11. The lithium ion battery anode material lithium manganate provided in the invention has extraordinary charge and discharge cycle performance both in the environments of normal temperature and high temperature. According to the invention, the preparation method of the material is a solid phase method, the operation is simple and controllable and the cost is low so that it is easy to realize large-scale productions.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
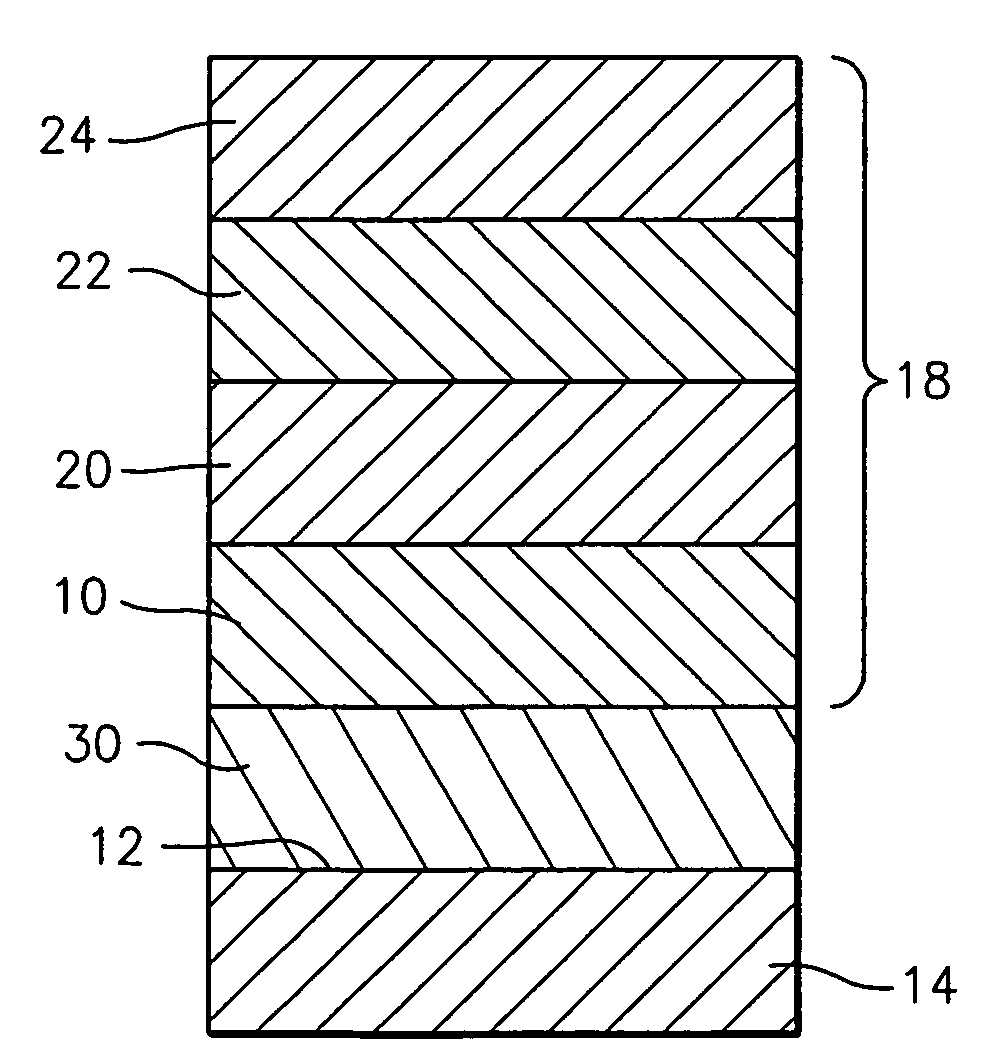
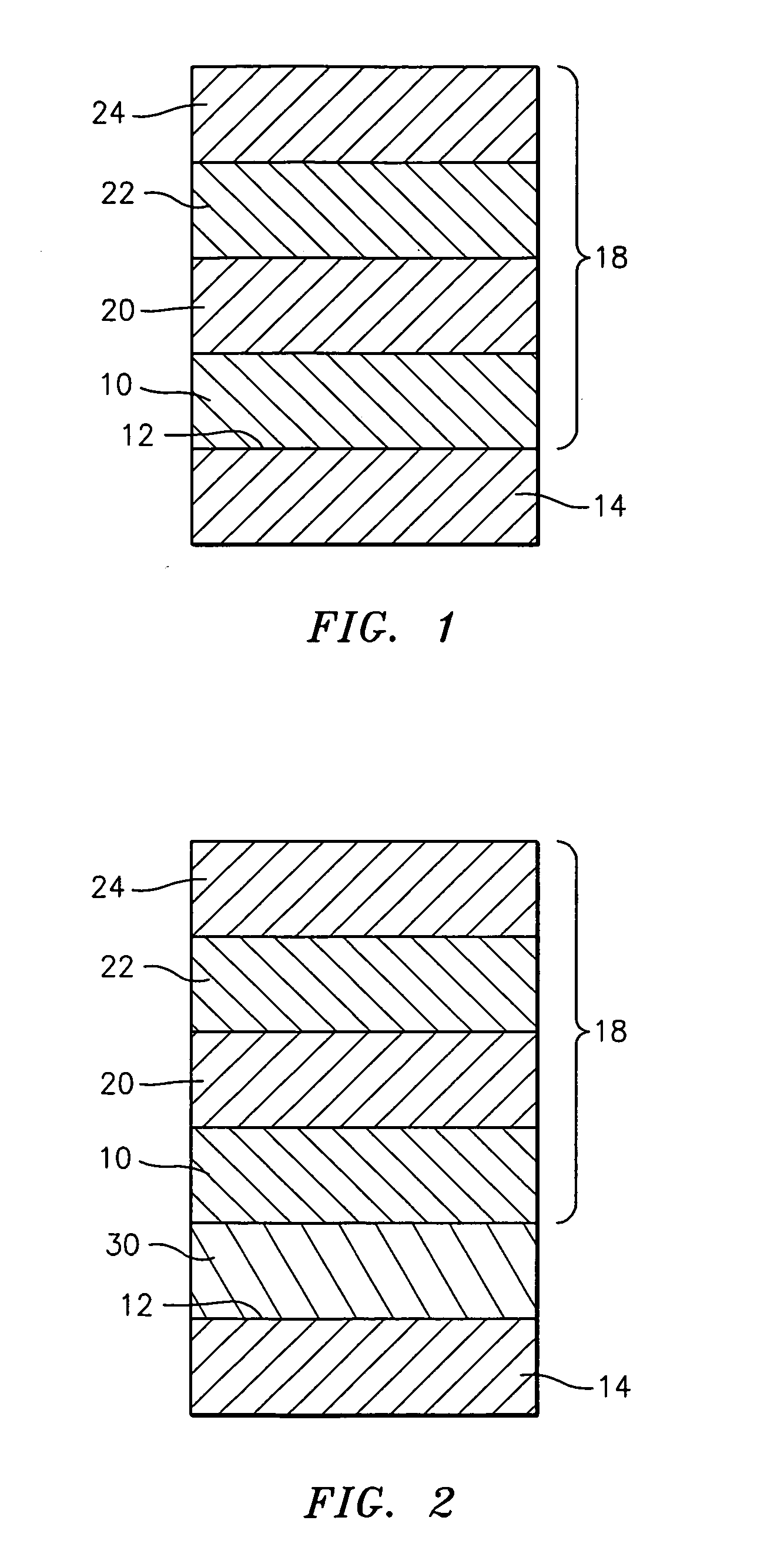
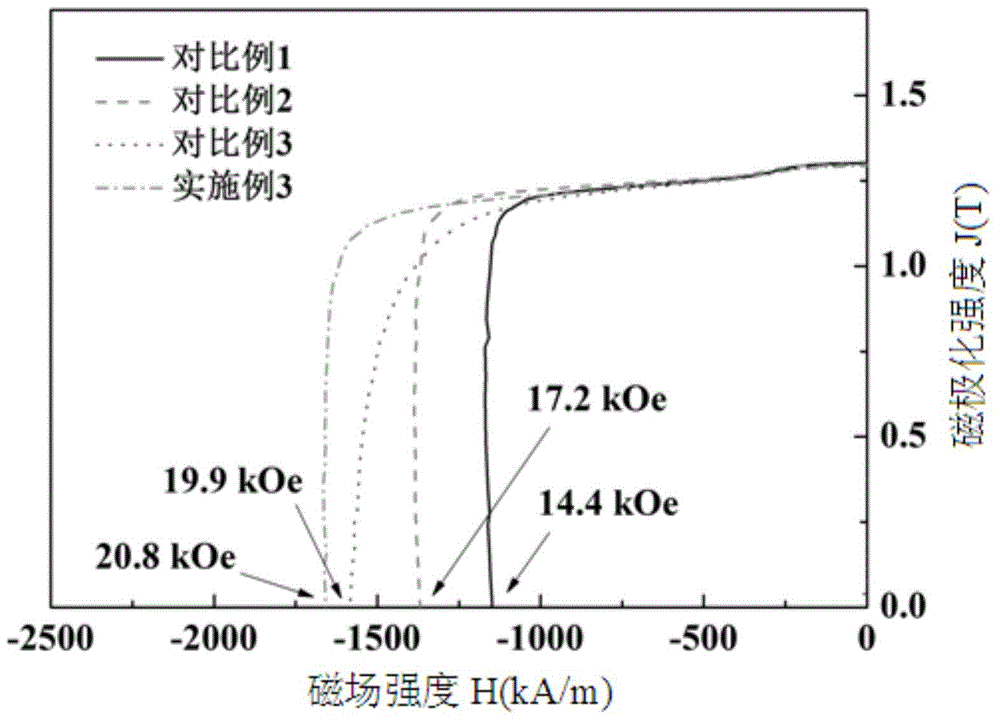
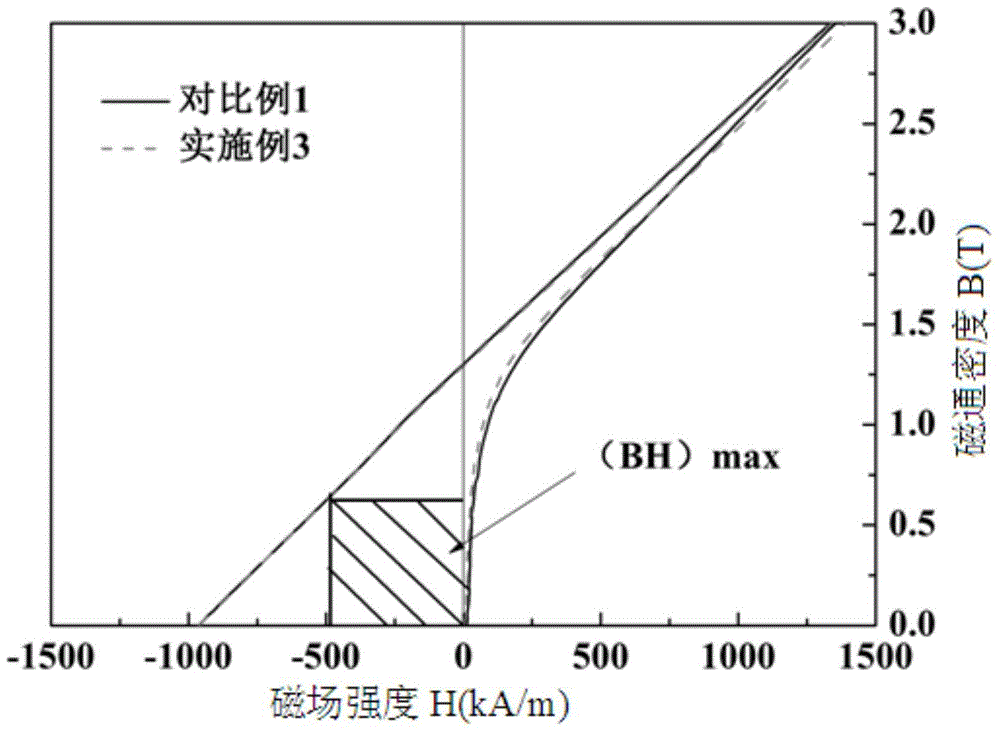
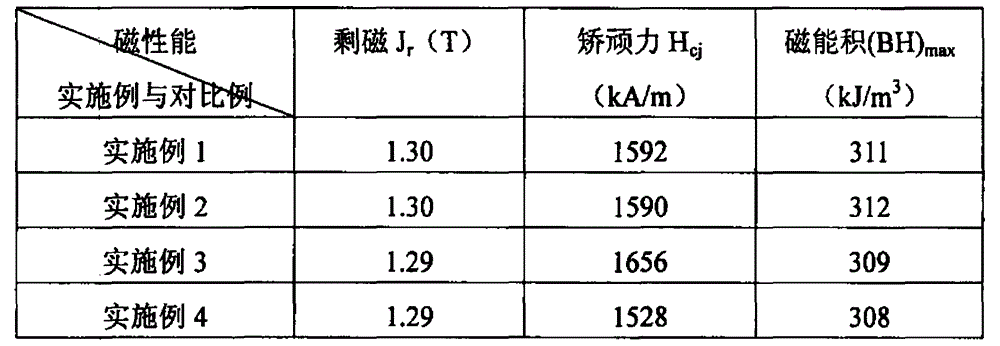
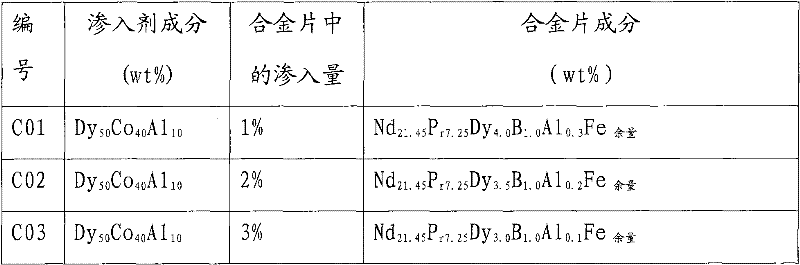
A preparation method of high-performance sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content
The invention discloses a method for preparing sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium (Dy) content and high performance; the method comprises the following steps of: sputtering and plating the Dy element on the surface of jet mill powder by using the powder plate technology based on magnetron sputtering on the basis of preparing NdFeB powder, and then sufficiently dispersing the Dy element to micron-sized NdFeB crystal particles by dispersing the Dy element at high temperature in the sintering and tempering process, thereby achieving the effect of improving magnetic performance of the sintered NdFeB. Compared with the introduction of the Dy element in the proportioning process of the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages: the low dysprosium content and high performance is limited in the nano-size by adopting the physical gas-phase deposition, the consumption quantity of the Dy element during the production process is controlled effectively and the preparationof sintered NdFeB with low dysprosium content and high performance is realized. Compared with the sintered NdFeB of the same components prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, both the intrinsic coercivity and the maximum magnetic energy product of the sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnetic material obtained according to the invention are improved obviously; compared with the sintered NdFeB with the same performance prepared by the traditional casting and powder metallurgy process, the dosage of the dysprosium element is reduced remarkably. The method can be widely applicable to producing and manufacturing sintered NdFeB with high performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
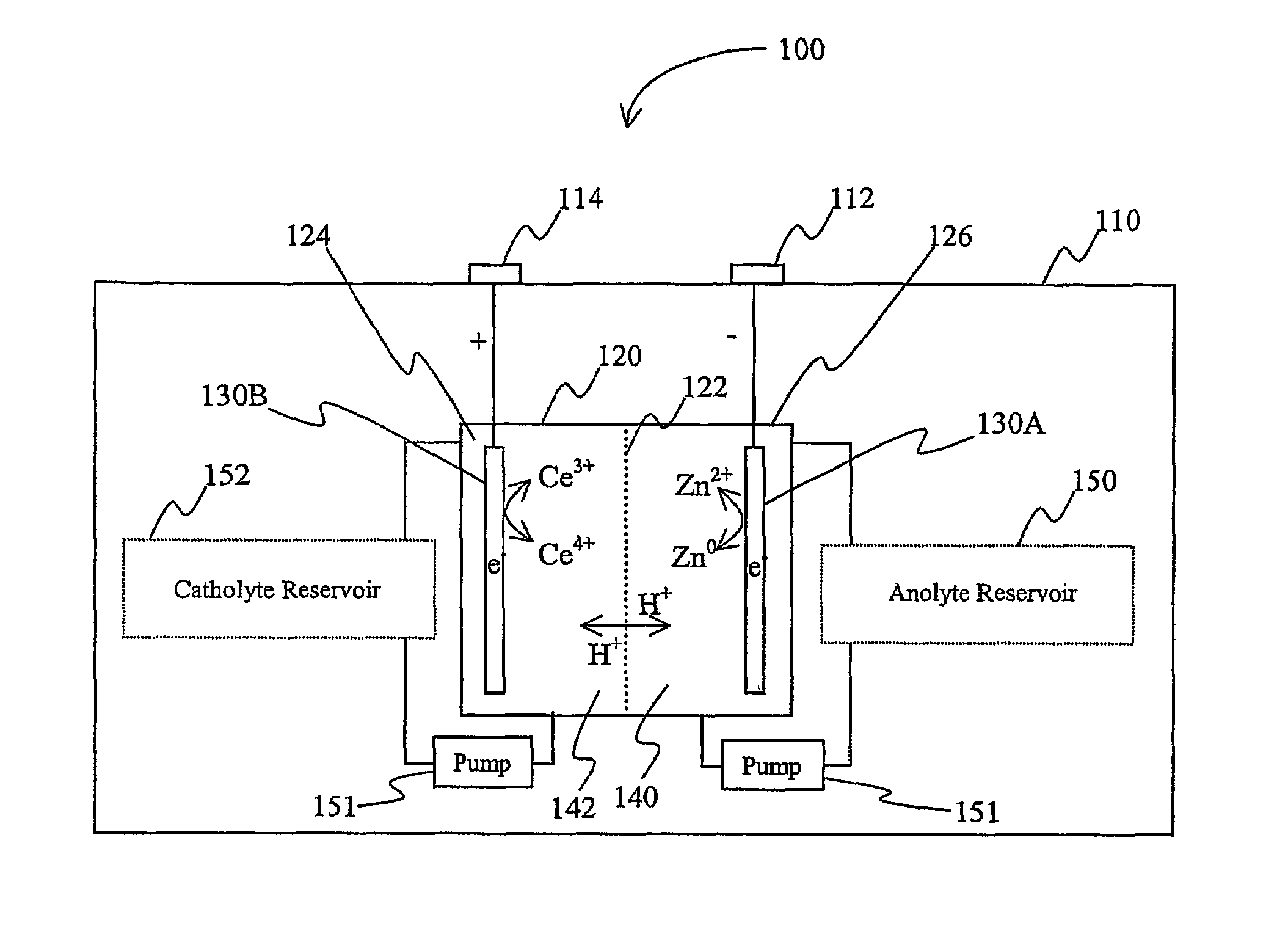
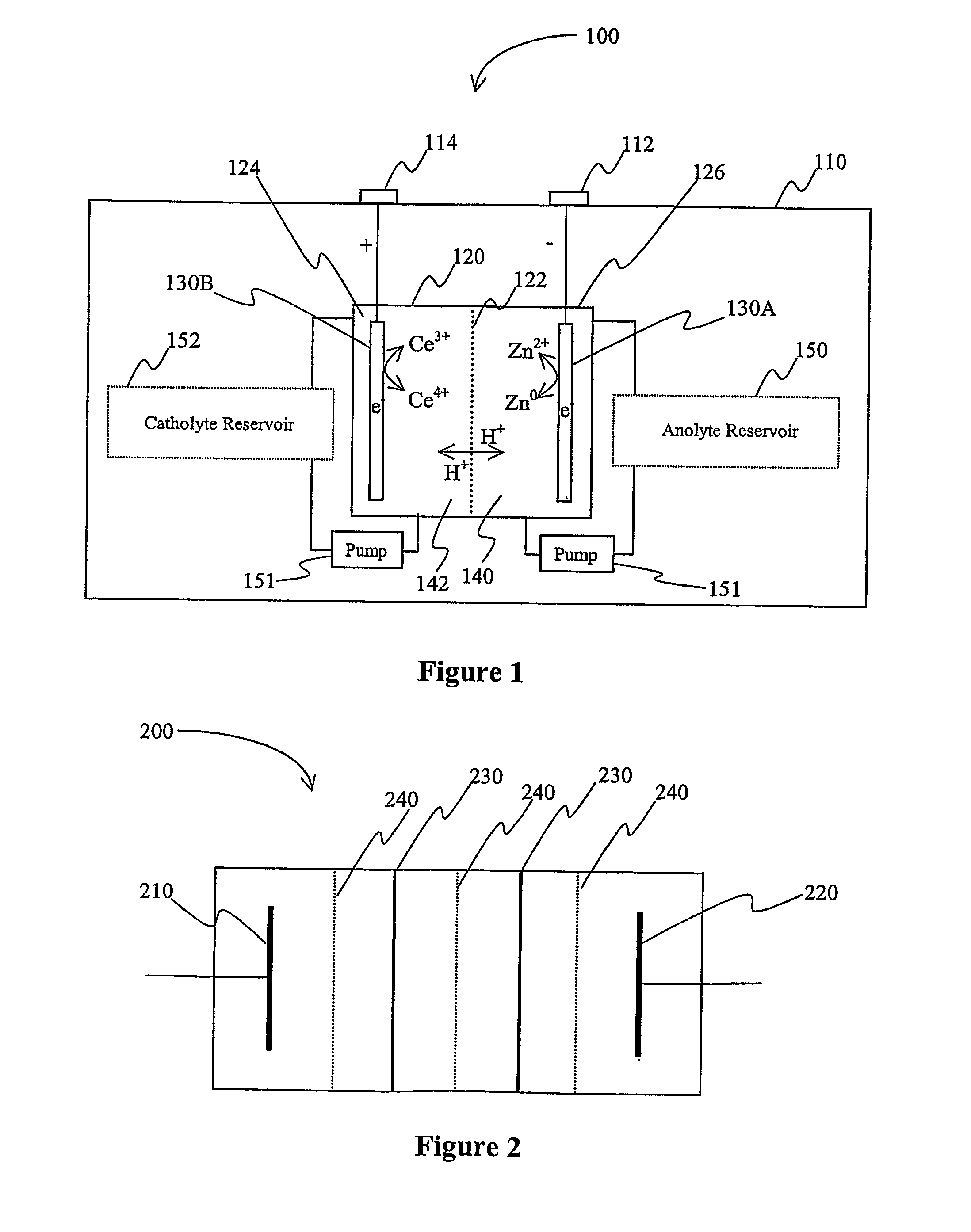
Lanthanide batteries
InactiveUS7252905B2Wide capacity rangeLarge capacityAlkaline accumulatorsSolid electrolyte cellsLanthanideCerium
A battery (100) comprises an electrolyte in which a lanthanide and zinc form a redox pair. Preferred electrolytes are acid electrolytes, and most preferably comprise methane sulfonic acid, and it is further contemplated that suitable electrolytes may include at least two lanthanides. Contemplated lanthanides include cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, terbium, and dysprosium, and further contemplate lanthanides are samarium, europium, thulium and ytterbium.
Owner:PLURION LTD
Method for preparing heavy rare earth hydride nano-particle doped sintered NdFeB permanent magnet
ActiveCN101521069AImprove coercive forceNot easily oxidizedInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a heavy rare earth hydride nano-particle doped sintered NdFeB permanent magnet, which belongs to the technical field of magnetic materials. The prior preparation method improves the coercive force and the temperature stability of magnets by adding heavy rare earth elements, namely terbium or dysprosium into master alloy, but the method can cause the residual magnetism of the magnets, the reduction of magnetic energy product and the increase of manufacturing cost. The method adopts heavy rare earth terbium hydride and dysprosium hydride nano-powder doping technology to prepare the sintered NdFeB permanent magnet with high coercive force and excellent magnetic property. The method comprises the following steps: preparing NdFeB powder by a rapidly solidified flake process and a hydrogen decrepitation process; preparing the terbium hydride or the dysprosium hydride nano-powder by physical vapor deposition technology; mixing the two powders, and performing magnetic field orientation and press forming; and performing dehydrogenation treatment, sintering and heat treatment on a green compact at different temperatures, and obtaining the sintered magnet. The coercive force of the magnet prepared by the method is higher than that of the prior sintered magnet with the same ingredients; and compared with the sintered magnet with the equivalent coercive force, the proportion of the terbium and dysprosium needed by the magnet prepared by the method is remarkably reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Ceramic bonding composition, method of making, and article of manufacture incorporating the same
A ceramic bonding composition comprises a first oxide and at least a second oxide having a formula of Me2O3; wherein the first oxide is selected from the group consisting of aluminum oxide, scandium oxide, and combinations thereof; Me is selected from the group consisting of yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, and combinations thereof. The ceramic bonding composition can further comprise silica. An article of manufacture comprising at least two members attached together with the ceramic bonding composition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rare earth permanent magnet produced by applying abundant rare earth cerium (Ce) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103123839AReduce production and sales balancePromote the balance of production and salesInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementCost Controls
The invention discloses a rare earth permanent magnet produced by applying abundant rare earth cerium (Ce) and a preparation method of the rare earth permanent magnet produced by applying abundant rare earth Ce. Based on a double-alloy process, main phase alloy formula uses Ce to partly replace neodymium (Nd), an optimized composition design enables a main alloy to form Ce2Fe14B phase and Nd2Fe14B phase to a greatest extent, and therefore high intrinsic magnetic property is guaranteed. A brand new crystal boundary phase is prepared by a crystal boundary reconstitution technology, and high integral magnetic property and corrosion resistant property are guaranteed, and meanwhile a nanometer powder crystal modification method is supplemented, a micro organization structure of a magnet is optimized, crystal boundary distribution is improved, and the magnetic property and the corrosion resistant property are further improved. By applying abundant rare earth cerium, cost is effectively reduced, and meanwhile balance between production and marketing is promoted. Praseodymium (Pr), Nd, and the like are chosen to form a hard magnetic shell layer of a main phase boundary in a composition design of crystal phase auxiliary alloy at the same time, compared high price heavy rare earth elements of dysprosium (Dy) and terbium (Tb) with the elements, and cost control can be further achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Rare earth aluminum alloy, and method and device for preparing same
The invention discloses a rare earth aluminum alloy, and a method and a device for preparing the same. The alloy contains at least one rare earth metal of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, lutetium, scandium and yttrium, the content of raw earth is 5 to 98 weight percent, and the balance is aluminum and inevitable impurities. The device for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy is characterized in that: a) graphite serves as an electrolysis bath, a graphite plate is an anode, a tungsten bar is a cathode and a molybdenum crucible serves as a rare earth aluminum alloy receiver; b) the diameter of the tungsten bar is 30 to 55 mm; and c) the anode of the graphite consists of a plurality of graphite plates. The rare earth aluminum alloy, and the method and the device for preparing the same have the advantages that: the alloy has uniform components, little segregation and low impurity content; technology for preparing the rare earth aluminum alloy through fusion electrolysis can maximally replace a process for preparing single medium-heavy metal through metallothermic reduction, greatly reduce energy consumption and the emission of fluorine-containing tail gas and solid waste residue, improve current efficiency and metal yield and reduce the consumption of auxiliary materials and the energy consumption; and the rare earth aluminum alloys with different rare earth contents can be obtained by controlling different electrolytic temperatures and different cathode current densities.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
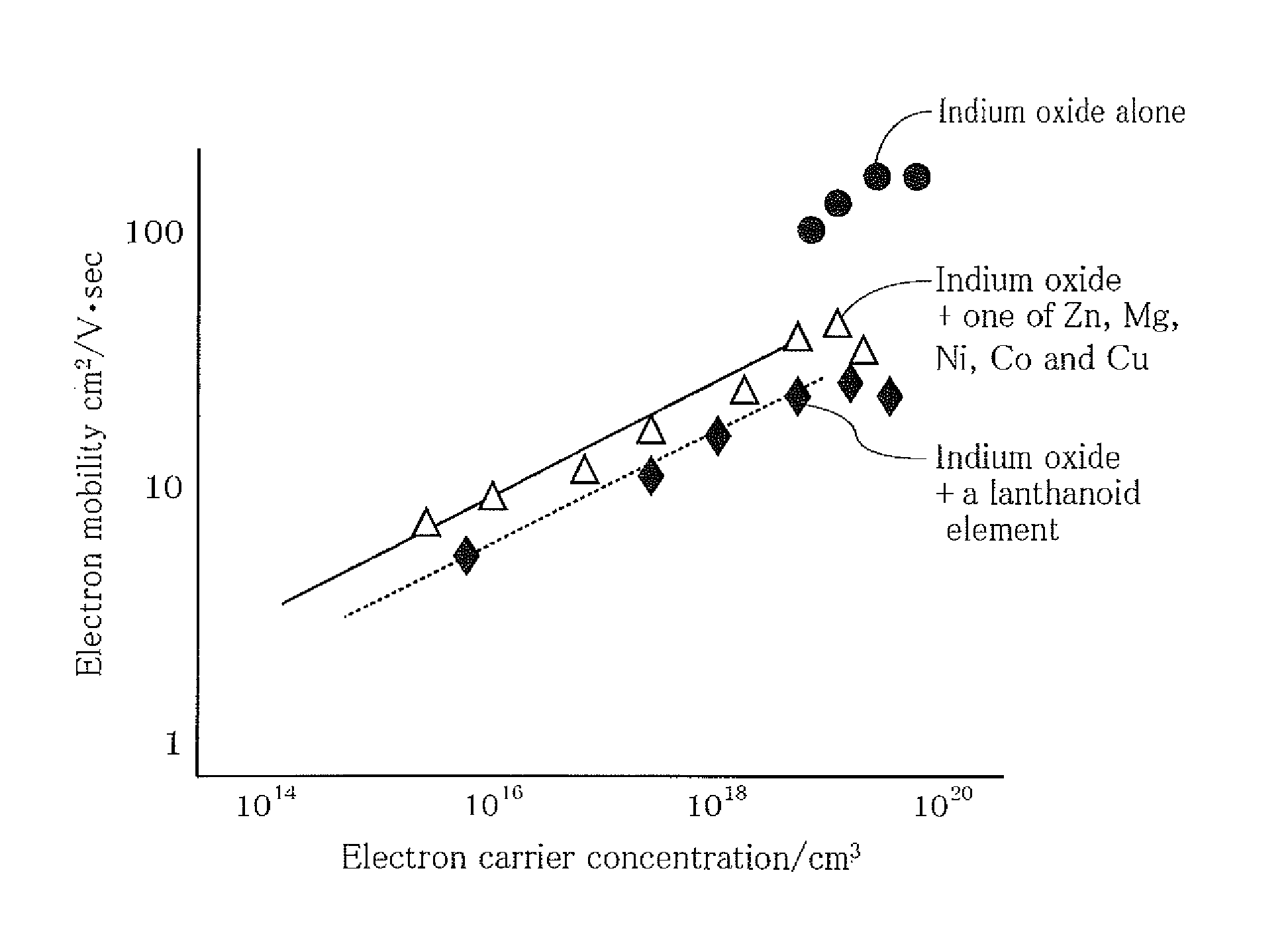
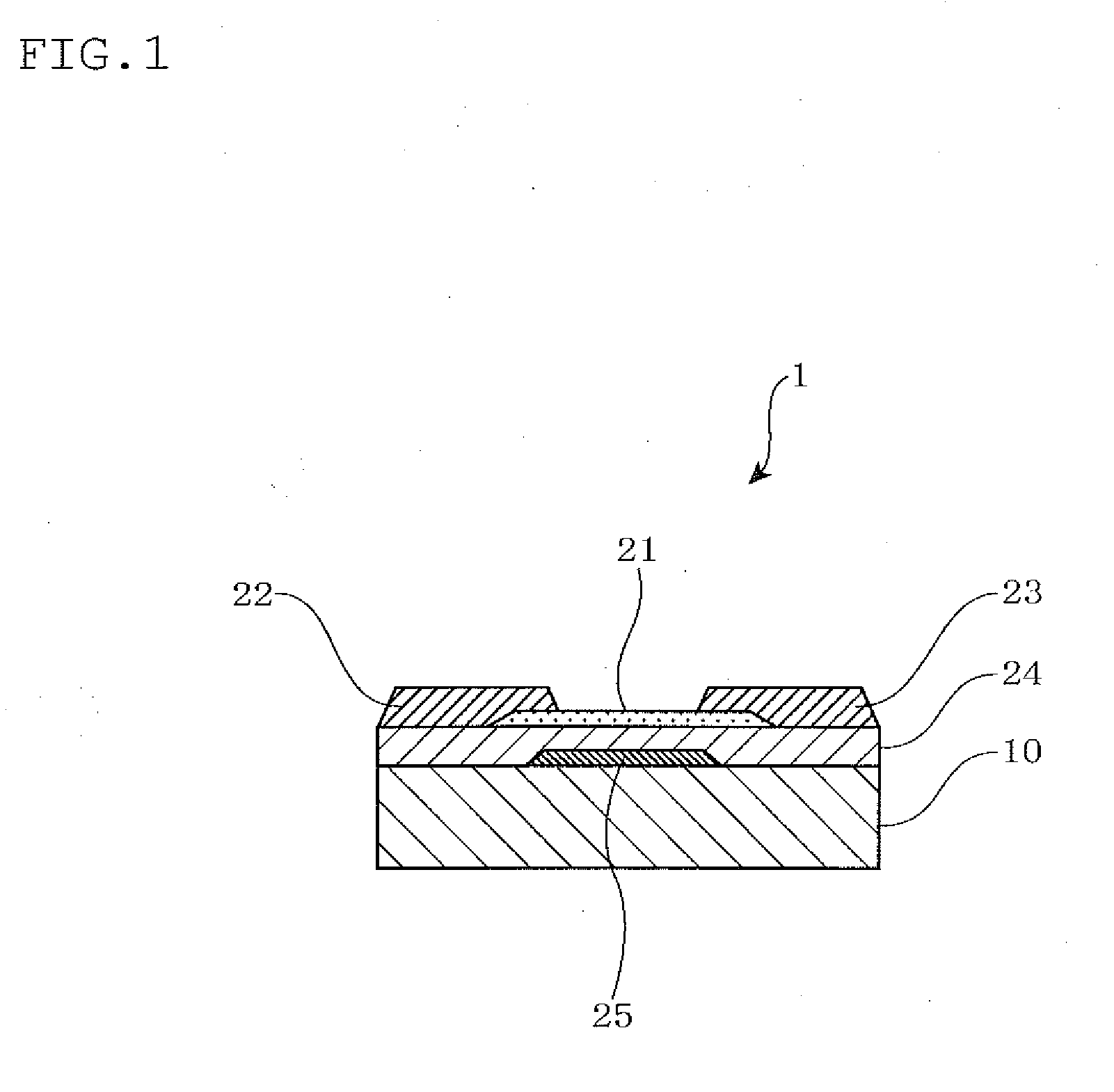
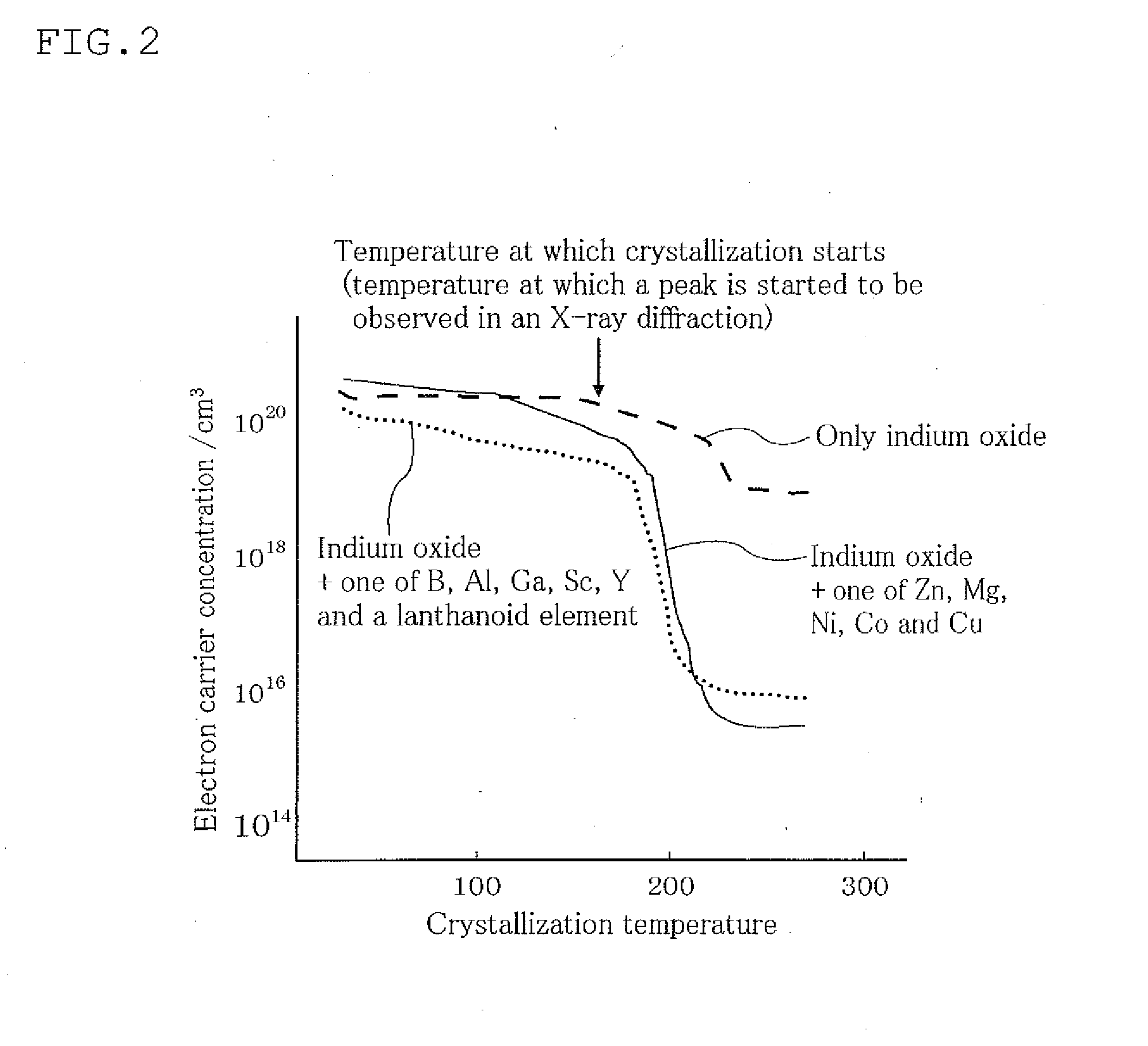
Sputtering target, oxide semiconductor film and semiconductor device
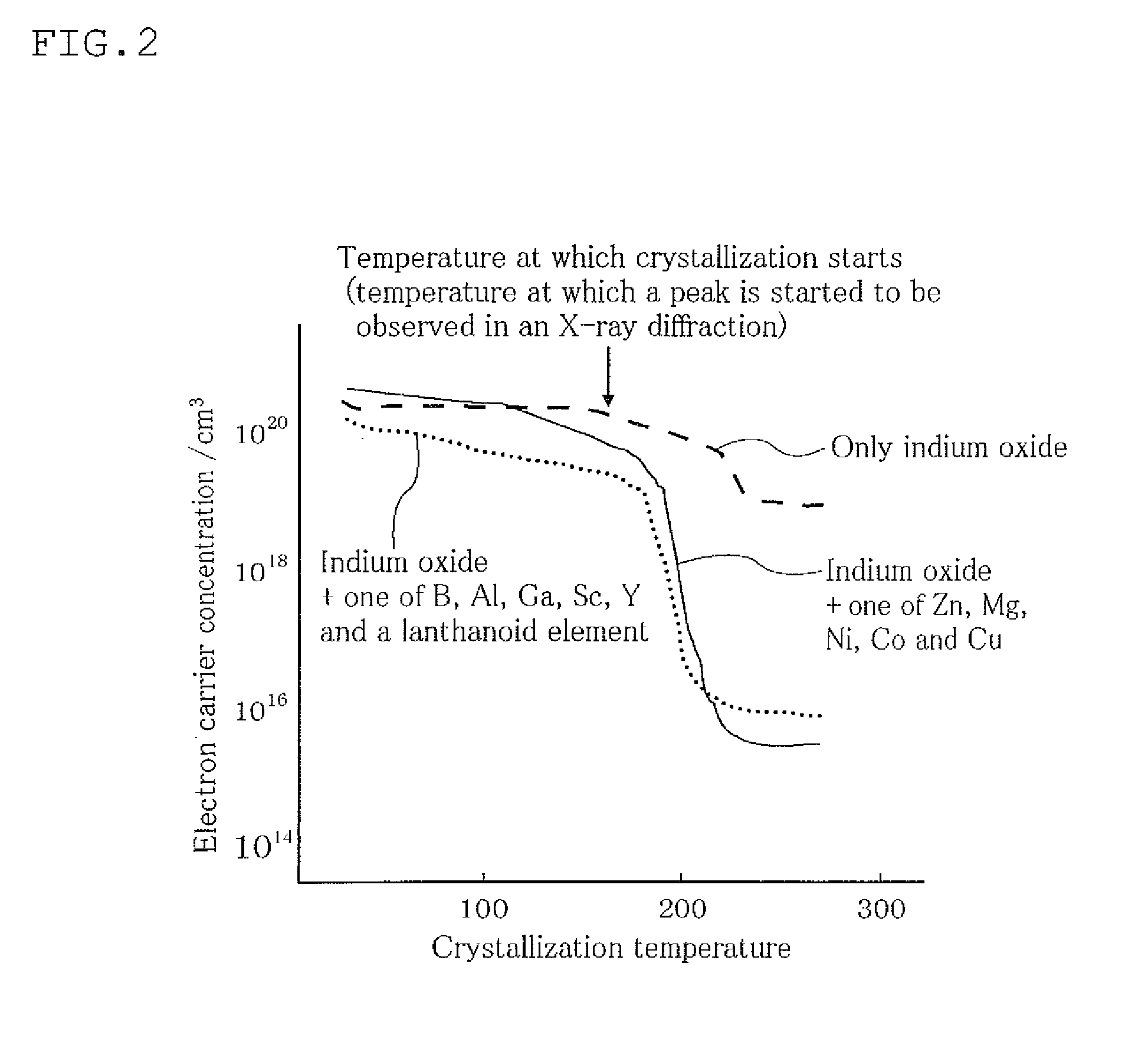
A sputtering target including an oxide sintered body, the oxide sintered body containing indium (In) and at least one element selected from gadolinium (Gd), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er) and ytterbium (Yb), and the oxide sintered body substantially being of a bixbyite structure.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Methods for making barrier coatings comprising taggants and components having the same
Methods for making barrier coatings including a taggant involving providing a barrier coating, and adding from about 0.01 mol % to about 30 mol % of a taggant to the barrier coating wherein the taggant comprises a rare earth element selected from lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, ytterbium, and lutetium, salts thereof, silicates thereof, oxides thereof, zirconates thereof, hafnates thereof, titanates thereof, tantalates thereof, cerates thereof, aluminates thereof, aluminosilicates thereof, phophates thereof, niobates thereof, borates thereof, and combinations thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
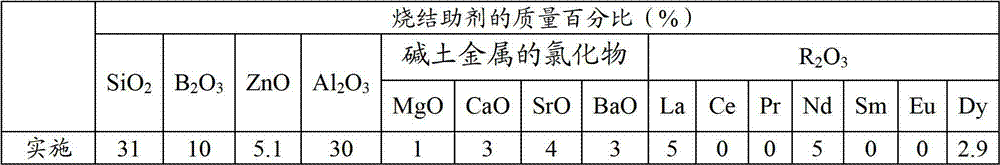
Method, sintering aid and materials for preparation of low-temperature cofired medium ceramic and application
A sintering aid for a low-temperature cofired medium ceramic material is composed of, by weight, 31%-45% of silicon dioxide, 1%-10% of boron oxide, 5.1%-10% of zinc oxide, 18%-30% of aluminum oxide, 11%-24% of alkaline earth metallic oxide and 5%-15% of oxide with the general formula of R2O3, wherein R refers to at least one of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium and dysprosium, and the alkaline earth metallic oxide refers to one of magnesium oxide, calcium oxide, barium oxide and strontium oxide. Adding the sintering aid into the low-temperature cofired medium ceramic material enables the prepared low-temperature cofired medium ceramic to have excellent thermal mechanical performance and dielectric performance. In addition, the invention provides the low-temperature cofired medium ceramic material and application thereof and a method for preparing the low-temperature cofired medium ceramic.
Owner:GUANGDONG FENGHUA ADVANCED TECH HLDG
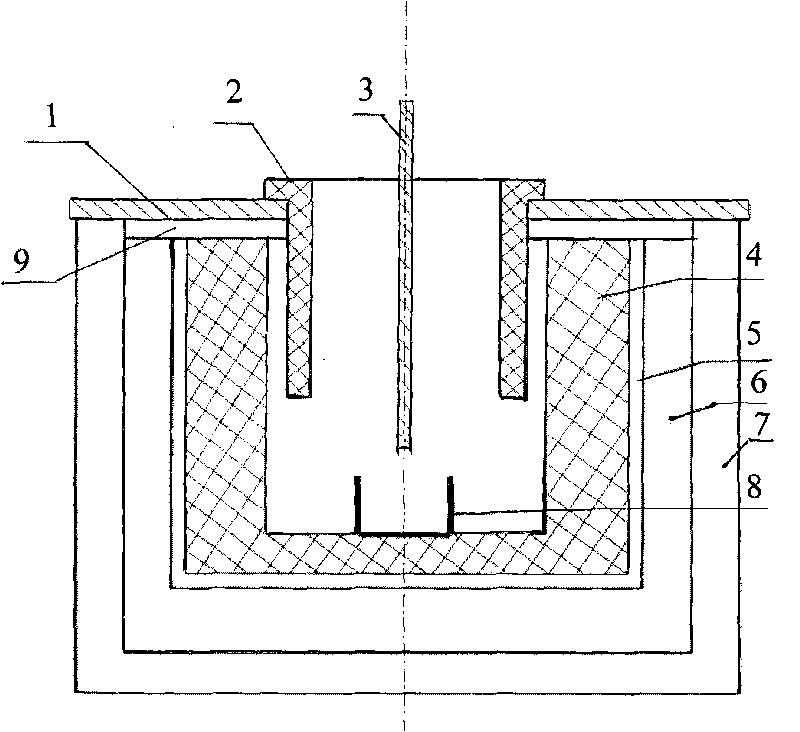
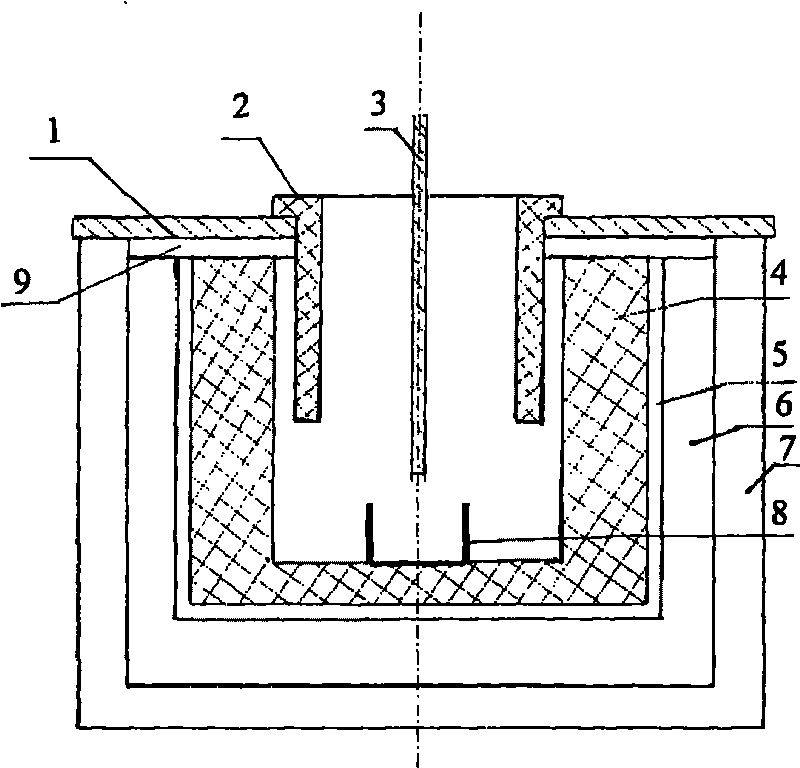
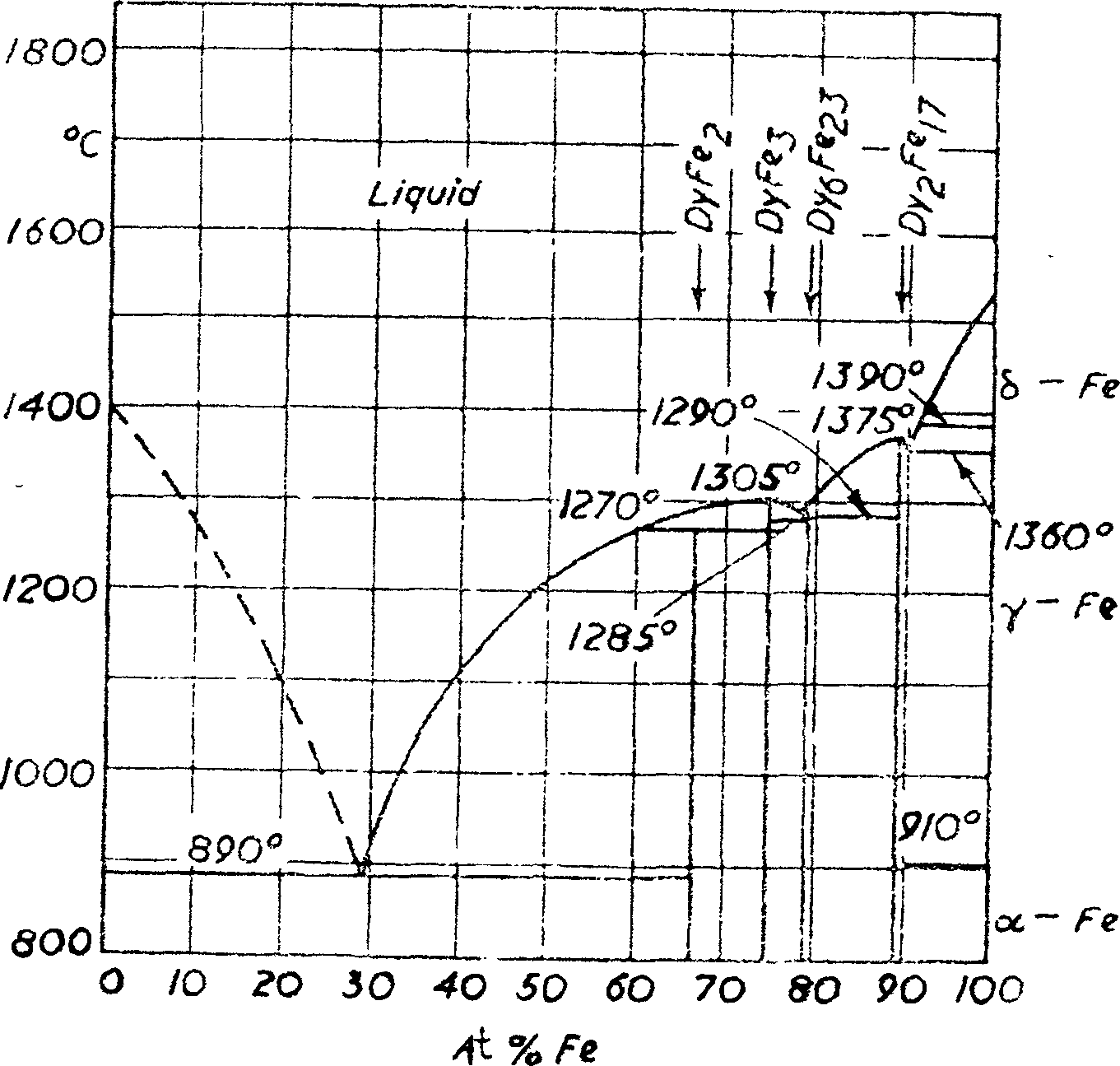
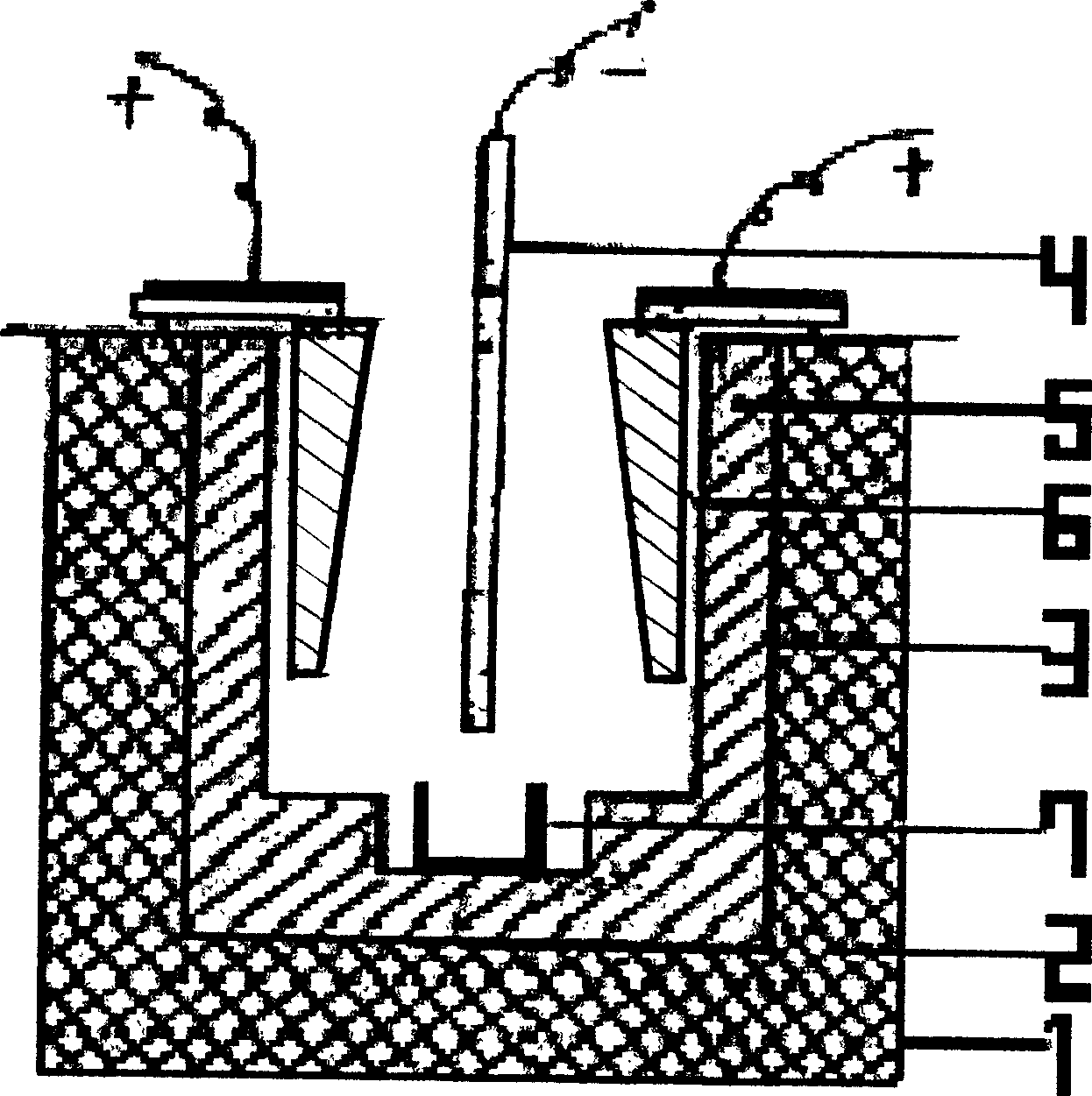
Process and apparatus for producing Dy-Fe alloy by molten salt electrolysis method
The invention relates the dysprosium-iron alloy technology with fused salt electrolysis process and device, belonging to rare-earth products preparing field. The method comprises the following steps: at high temperature, dysprosium oxide melting at fluoride, dysprosium oxide beginning ionizing; at the condition of 95V / M direct current field, separating out Dy3+ on the surface of iron cathode, deacidizing Dy3+ to Dy, and alloying Dy and Fe to form Dy-Fe. O2- is oxygenated to O2 on the surface of graphite cathode, and it reacts with carbite to form CO2. The melting point of dysprosium-iron (20úÑFe) is 1046Deg.C, and the melting point of Dy is 1407Deg.C, so the electrolyzation is carried out at 1050Deg.C. The invention has the advantages of low investment, low cost, simple technology, continuous production and low impurity content.
Owner:包头市稀土应用技术研究所
CMAS resistant thermal barrier coating
ActiveUS20070172703A1Reduce componentsReduces sand related distressMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesIndiumCerium
A turbine engine component is provided which has a substrate and a thermal barrier coating applied over the substrate. The thermal barrier coating comprises alternating layers of yttria-stabilized zirconia and a molten silicate resistant material. The molten silicate resistant outer layer may be formed from at least one oxide of a material selected from the group consisting of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, scandium, indium, zirconium, hafnium, and titanium or may be formed from a gadolinia-stabilized zirconia. If desired, a metallic bond coat may be present between the substrate and the thermal barrier coating system. A method for forming the thermal barrier coating system of the present invention is described.
Owner:RTX CORP
NdFeB magnet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104064346AReduce usageImprove intrinsic coercive forceInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsHolmiumGranularity
The invention relates to an NdFeB magnet and belongs to the technical field of rare earth magnetic materials. The NdFeB magnet is prepared by sintering a mixture of main phase alloy powder with the granularity of 2-5 <Mu>m, heavy rare earth alloy powder with the granularity of 1-2 <Mu>m and superfine powder with the granularity of 0.1-1.5 <Mu>m, which are mixed at the mass percents of 85-99.8, 0.1-10 and 0.1-5 respectively, the heavy rare earth alloy is one or more of dysprosium hydride and dysprosium-ferrum hydride compound, a holmium hydride and holmium-ferrum hydride compound and terbium hydride and terbium-ferrum hydride compound. The invention further provides a preparation method of the NdFeB magnet. According to the invention, 10-40 percent of heavy rare earth is saved, and the intrinsic coercive field of the NdFeB magnet is increased greatly without reducing the effect of residual magnetism.
Owner:宁波同创强磁材料有限公司
Rare earth element permanent magnet material
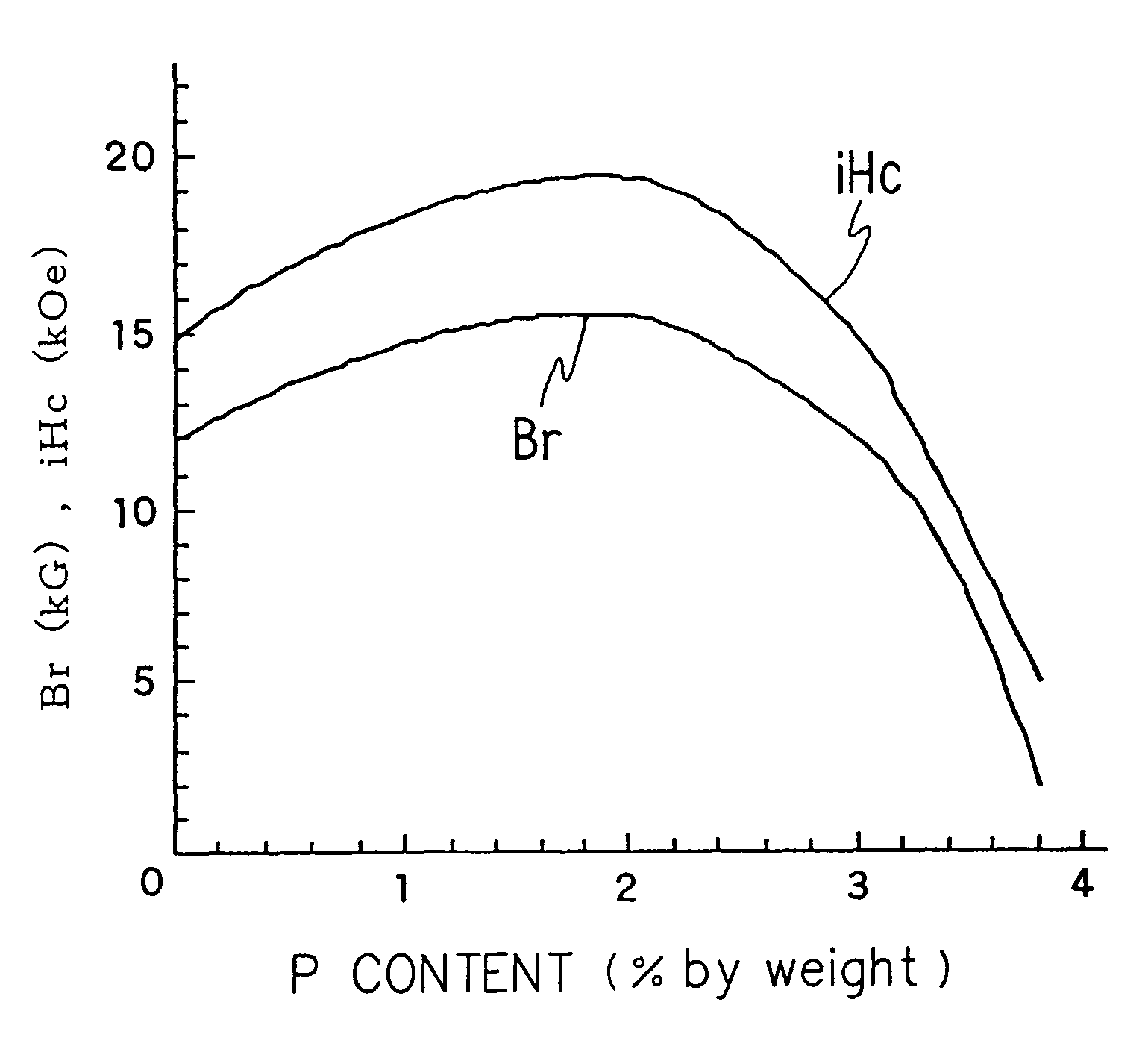
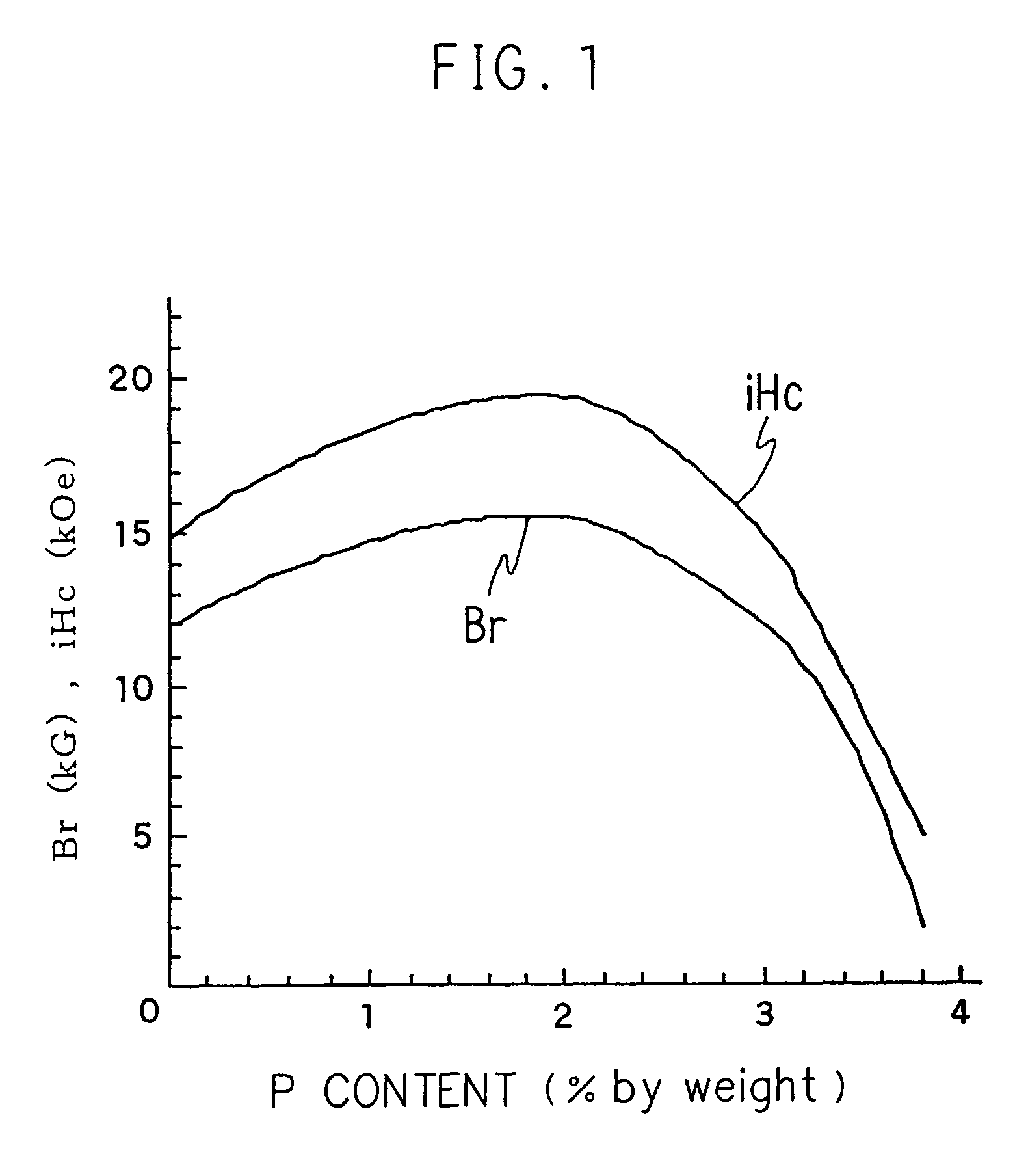
A material for a rare earth permanent magnet having a high magnetic coercive force and a high residual magnetic flux density. 28 to 35% by weight of at least one rare earth element selected from the group consisting of neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium, terbium, and holmium, 0.9 to 1.3% by weight of boron, 0.25 to 3% by weight of phosphorus, iron, and inevitable impurities. It can further comprise 0.1 to 3.6% by weight of cobalt and 0.02 to 0.25% by weight of copper.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Grain boundary diffusion method for improving properties of sintered NdFeB magnets
ActiveCN104388951AIncreased diffusion kinetic energyLow melting pointInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementDiffusion methods
The invention relates to a grain boundary diffusion method for improving properties of sintered NdFeB magnets. The grain boundary diffusion method comprises the following steps of stacking sintered NdFeB magnets and diffusion alloy sheets together and placing in a hot-pressing furnace; vacuumizing the hot-pressing furnace until the vacuum degree reaches a set value, heating the hot-pressing furnace, and when the temperature of the hot-pressing furnace reaches a set value, beginning to exert a pressure and maintaining the pressure and putting the diffused sample into a high-vacuum furnace for annealing, wherein the diffusion alloy sheets are low-melting-point eutectic diffusion alloys and are represented by R-TM, R is one or more of Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr or Nd and TM is one or more of Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn. Compared with the prior art, the sintered NdFeB magnets modified by the pressure diffusion method, which is provided by the invention, have the advantages of large diffusion depth of a diffusion agent, uniform distribution of grain boundary phases, high coercivity and the like, especially, low-melting-point diffusion alloys designed by the invention are free of expensive heavy rare earth element dysprosium and thus the cost of the raw materials is relatively low, the diffusion temperature is low and the energy consumption in the diffusion process is small.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Sputtering target, oxide semiconductor film and semiconductor device
A sputtering target including an oxide sintered body, the oxide sintered body containing indium (In) and at least one element selected from gadolinium (Gd), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er) and ytterbium (Yb), and the oxide sintered body substantially being of a bixbyite structure.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
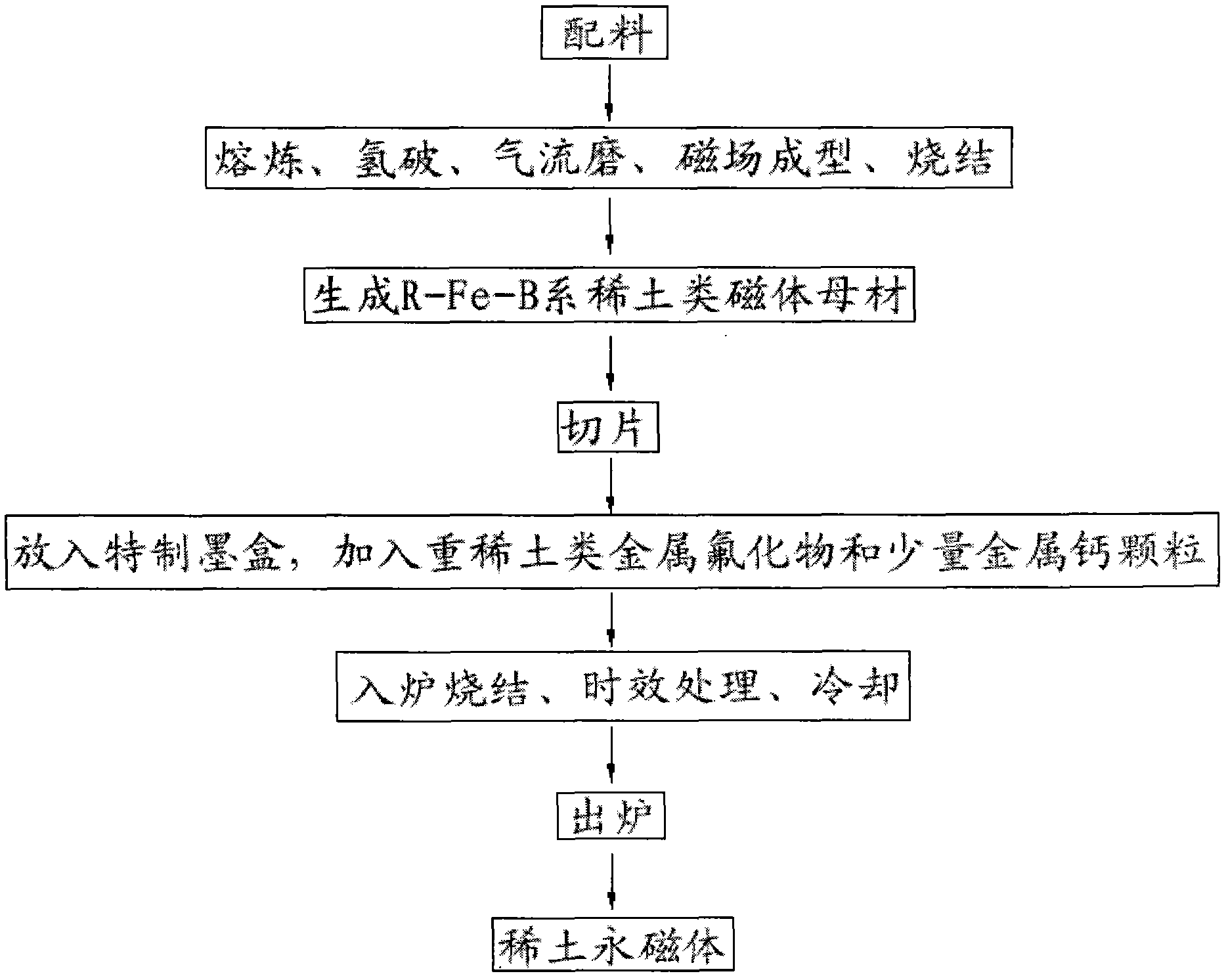
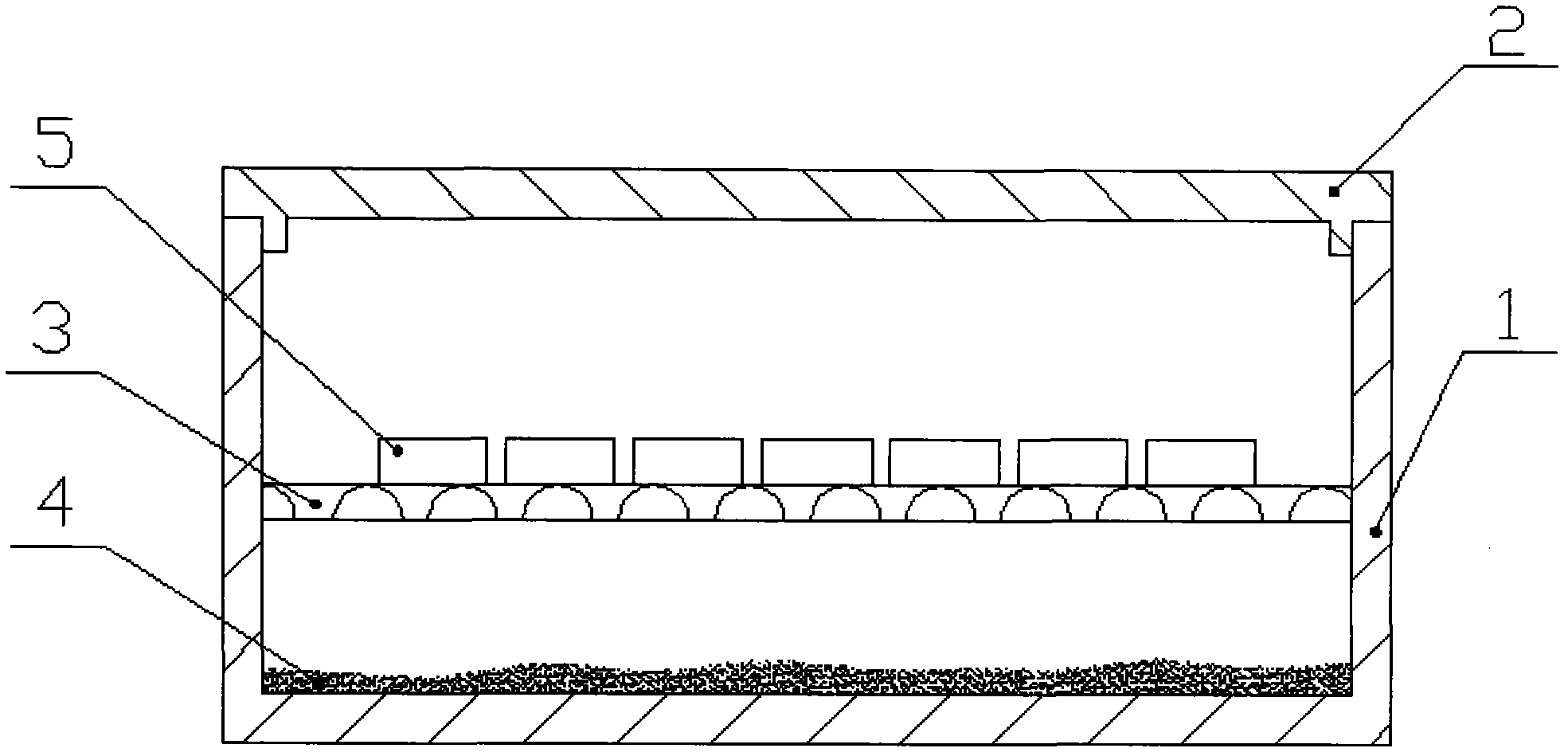
Method for preparing rare-earth permanent magnets by infiltration process and graphite box utilized in method
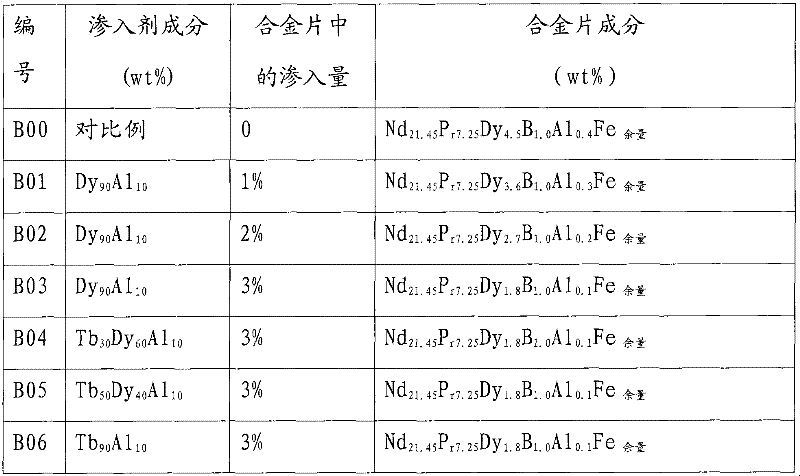
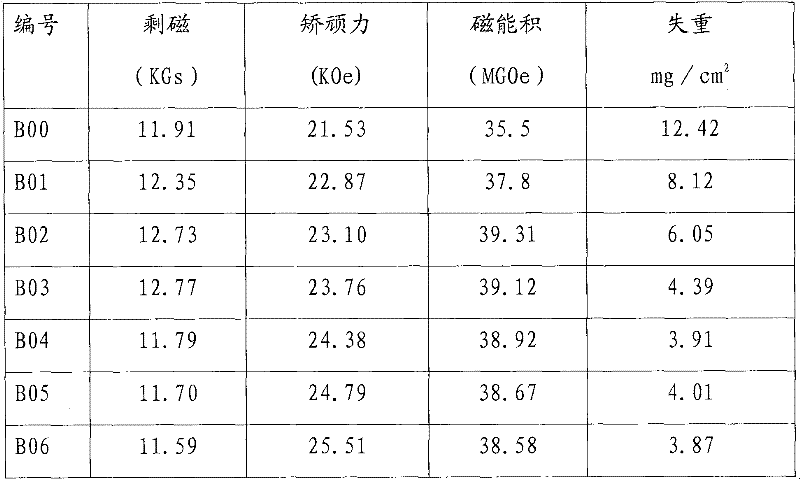
InactiveCN102568806AReduce manufacturing costReduce usagePermanent magnetsSolid state diffusion coatingRare earthMaterials science
Disclosed are a method for preparing rare-earth permanent magnets by the infiltration process and a graphite box utilized in the method. The method includes: preparing base materials of R (rare earth)-Fe (ferrum)-B (boron) rear earth magnets by prepared raw materials which are subjected to smelting, hydrogen decrepitation, magnetic field forming, sintering and the like; cutting the base material into slices with the thickness ranging from 2mm to 10mm; placing the slices into a specially-made graphite box and placing heavy rare earth type metal fluoride and a few of metal calcium particles into the bottom of the graphite box; sintering the graphite box in a sintering furnace, inflating air into the sintering furnace to cool the temperature to be lower than 60 DEG C, finally ageing magnets, then inflating Ar gas into the sintering furnace to cool the temperature to be lower than 60 DEG C after ageing, and finally obtaining the rare-earth permanent magnets. Elements including Dy (dysprosium), Tb (terbium), Ho (holmium) and the like are infiltrated into the crystal boundary of the R-Fe-B to prepare high-coercivity rare-earth permanent magnets by means of infiltration process, usage of heavy rare earth metal can be greatly reduced, and production cost of magnets can be effectively reduced. Additionally, the method for preparing rare-earth permanent magnets by the infiltration process is simple in operation and suitable for batch production.
Owner:BAOTOU TIANHE MAGNETICS TECH CO LTD
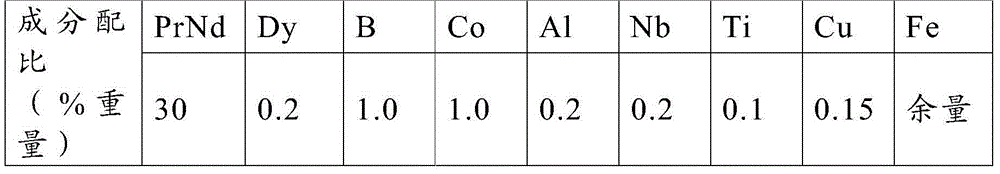
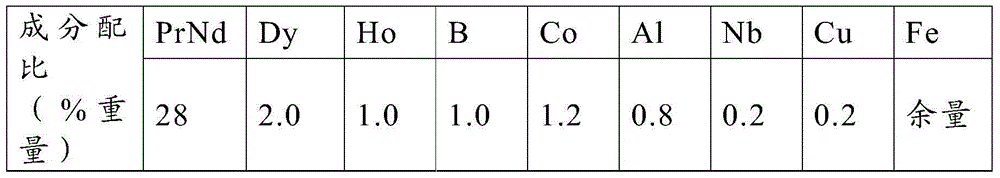
Neodymium iron boron permanent magnet for motor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101409121AReduce manufacturing costLow costInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsNiobiumMaterials science
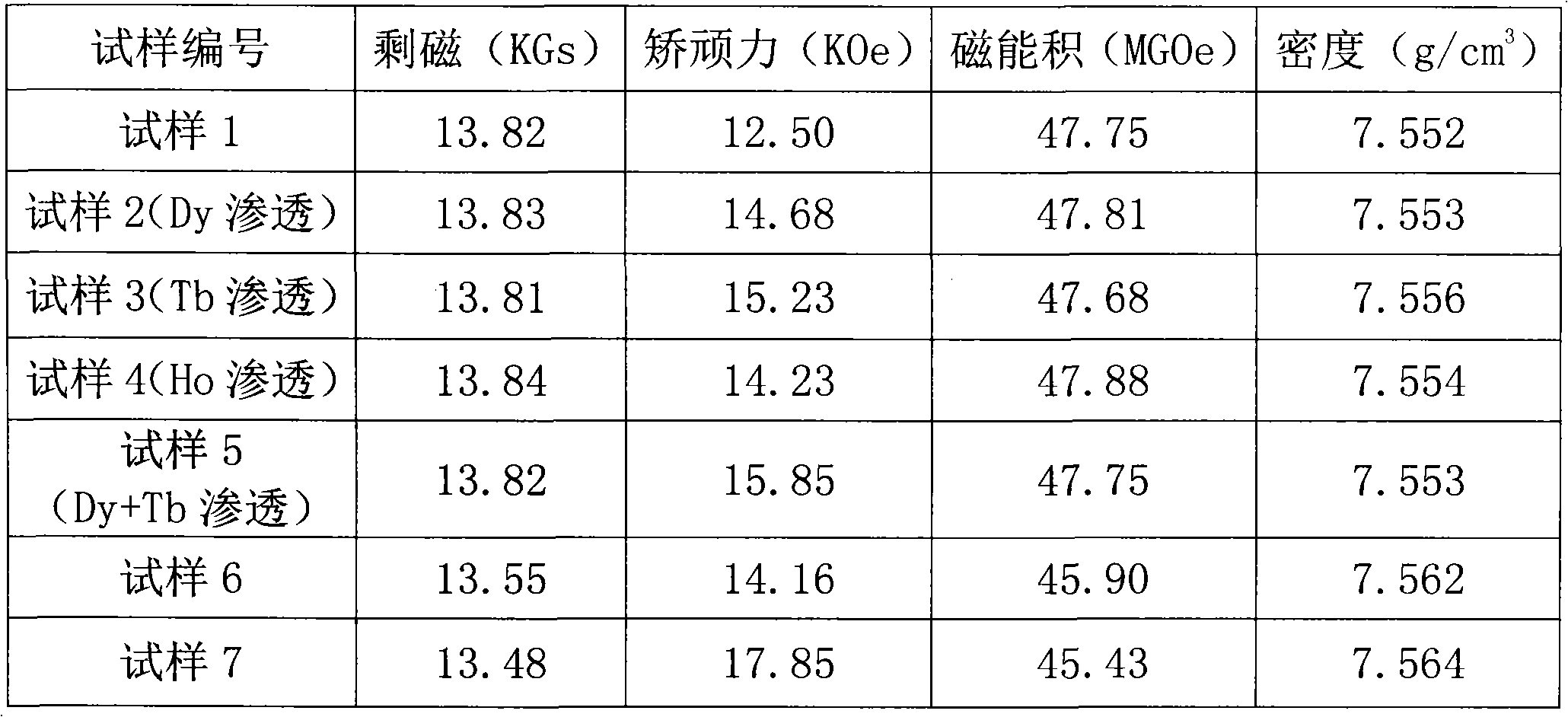
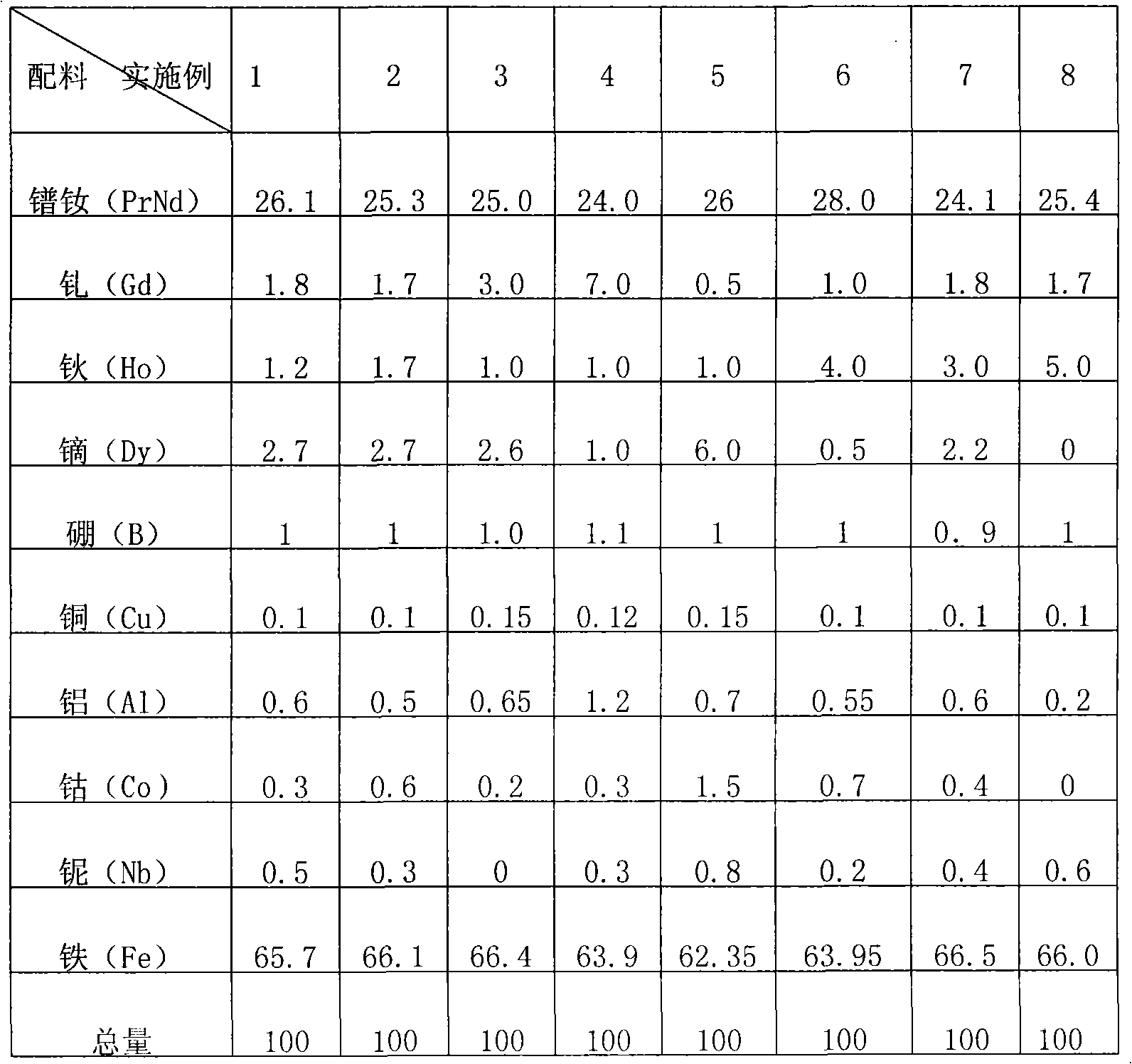
The invention discloses an NdFeB permanent magnet used for NdFe motors and a manufacture method thereof. The magnet comprises the following components by weight: 24-28 percent of PrNd, 0.5-7 percent of Gd, 1-5 percent of Ho, 0-6 percent of Dy, 0.9-1.1 percent of B, 0.1-0.15 percent of Cu, 0.2-1.2 percent of Al, 62.35-66.5 percent of Fe, 0.2-1.5 percent of Co and 0.2-0.8 percent of Nb. The magnet is manufactured through the procedures of mixing, melting, milling, forming, sintering and grinding processing. Through the use of cheap gadolinium and holmium instead of expensive praseodymium, neodymium, dysprosium and terbium for the production of high-performance NdFeB permanent magnet, the invention can greatly reduce production cost and the product has high magnetic property and strong market competitiveness.
Owner:SINOSTEEL ANHUI TIANYUAN TECH
High-performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron (Nd-Fe-B) rare-earth permanent magnet material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102347126AReduce dosageProtect scarce resourcesTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRare-earth elementCobalt
The invention discloses a high-performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron (Nd-Fe-B) rare-earth permanent magnet material and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: firstly, casting R-iron-boron-aluminum (R-Fe-B-Al) into a rapidly solidified alloy plate (R represents one and / or several of rare-earth elements containing Nd) by adopting a vacuum rapid solidifying process, then, coating a metal penetrant comprising the component Ra-Al or Ra-Al-X [the Ra represents dysprosium (Dy) and / or terbium (Tb), and the X represents one or several of cobalt, copper, gallium and zirconium (Co, Cu, Ga and Zr) elements] to the surface of the alloy plate, and heating to enable the metal penetrant to penetrate into the crystal boundary of the rapidly solidified alloy plate. A replacement reaction happens between the Ra in the penetrant entering the crystal boundary of the rapidly solidified alloy plate and the Nd and / or praseodymium (Pr) in the main phase of the alloy plate to form an Rh2(Fe, Al)14B phase with high content of the Dy and / or the Tb (the Rh represents that the content of the Dy and / or the Tb is higher than that of the Dy and / or the Tb in the R), and the positions of part of Fe atoms are replaced by Al atoms to encircle the double-main phase structure of an R2Fe14B phase. The high-performance sintered neodymium-iron-boron (Nd-Fe-B) rare-earth permanent magnet material disclosed by the invention is capable of effectively improving a coercive force and obviously reducing the use level of rare earth, and simultaneously, is also capable of improving the corrosion resistance of a magnet.
Owner:SHENYANG GENERAL MAGNETIC
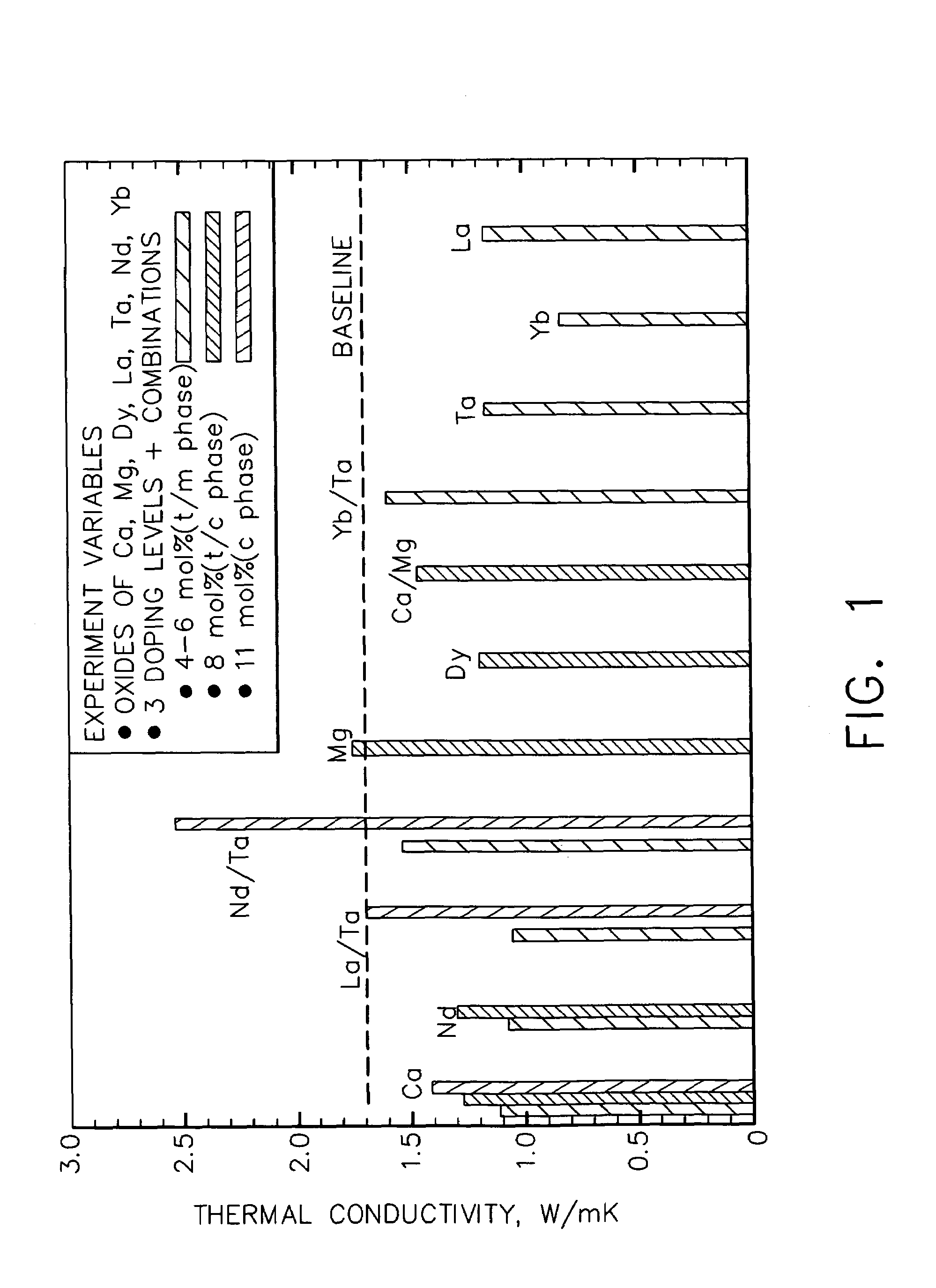
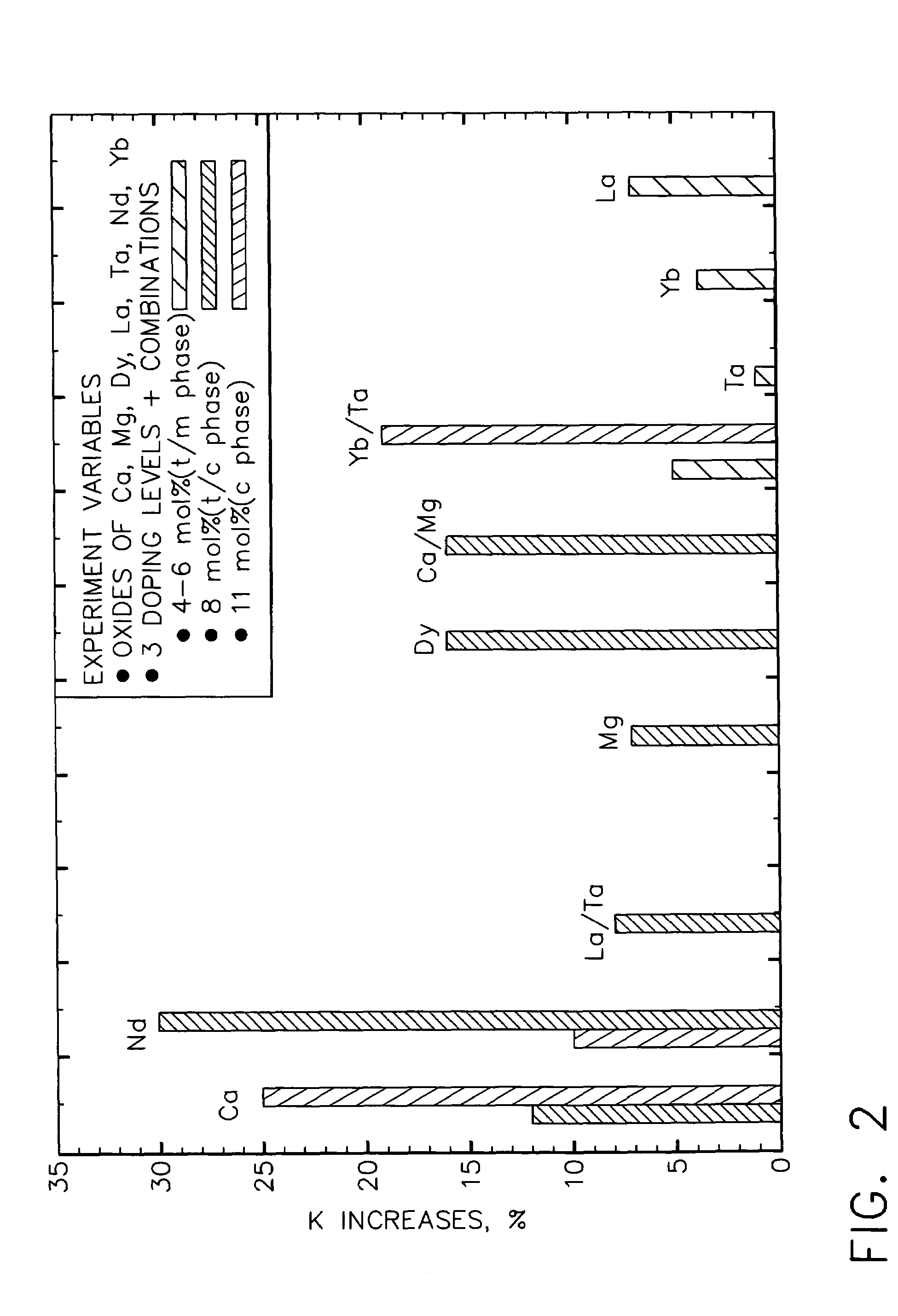
Ceramic compositions useful for thermal barrier coatings having reduced thermal conductivity
InactiveUS6960395B2Reduced and minimized tendency to sinterReduce conductivityMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingCeriumEngineering
Ceramic compositions comprising at least about 91 mole % zirconia and up to about 9 mole % of a stabilizer component comprising a first metal oxide having selected from the group consisting of yttria, calcia, ceria, scandia, magnesia, india and mixtures thereof. This stabilizer component further comprises a second metal oxide of a trivalent metal atom selected from the group consisting of lanthana, gadolinia, neodymia, samaria, dysprosium, and mixtures thereof and a third metal oxide of a trivalent metal atom selected from the group consisting of erbia, ytterbia and mixtures thereof. These ceramic compositions are useful in preparing thermal barrier coatings having reduced thermal conductivity for the metal substrate of articles that operate at, or are exposed to, high temperatures.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nanoparticles of rare earth oxides
ActiveUS20070104629A1Increase volumeLow cost productionMaterial nanotechnologyLanthanum oxide/hydroxidesCeriumScandium
Rare earth compositions comprising nanoparticles, methods of making nanoparticles, and methods of using nanoparticles are described. The compositions of the nanomaterials discussed may include scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), lanthanum(La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium(Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb), and lutetium (Lu). The nanoparticles can be used to make organometallics, nitrates, and hydroxides. The nanoparticles can be used in a variety of applications, such as pigments, catalysts, polishing agents, coatings, electroceramics, catalysts, optics, phosphors, and detectors.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Coating Method and Apparatus, a Permanent Magnet, and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080257716A1Improve productivityLow costCellsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh rateRare earth
A film is formed at a high rate on the surface of an iron-boron-rare-earth-metal magnet having a given shape, while effectively using dysprosium or terbium as a film-forming material. Thus, productivity is improved and a permanent magnet can be produced at low cost. A permanent magnet is produced through a film formation step in which a film of dysprosium is formed on the surface of an iron-boron-rare-earth-metal magnet of a given shape and a diffusion step in which the magnet coated is subjected to a heat treatment at a given temperature to cause the dysprosium deposited on the surface to diffuse into the grain boundary phase of the magnet. The film formation step comprises: a first step in which a treating chamber where this film formation is performed is heated to vaporize dysprosium which has been disposed in this treating chamber and thereby form a dysprosium vapor atmosphere having a given vapor pressure in the treating chamber; and a second step in which a magnet kept at a temperature lower than the internal temperature of the treating chamber is introduced into this treating chamber and the dysprosium is selectively deposited on the magnet surface based on a temperature difference between the treating chamber and the magnet until the magnet temperature reaches a given value.
Owner:ULVAC INC
Wetting resistant materials and articles made therewith
Ceramic materials with relatively high resistance to wetting by various liquids, such as water, are presented, along with articles made with these materials. The oxide materials described herein as a class typically contain one or more of ytterbia (Yb2O3) and europia (Eu2O3). The oxides may further contain other additives, such as oxides of gadolinium (Gd), samarium (Sm), dysprosium (Dy), or terbium (Tb). In certain embodiments the oxide, in addition to the ytterbia and / or europia, further comprises lanthanum (La), praseodymium (Pr), or neodymium (Nd).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Catalyst carrier, catalyst and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20100331172A1Improve heat resistanceHigh catalytic ability without increasing the specific surface areaCatalyst carriersCell electrodesIndiumCerium
The present invention provides a catalyst carrier having excellent durability and capable of attaining high catalytic ability without increasing the specific surface area thereof, and a catalyst obtainable by using the catalyst carrier. The catalyst carrier of the present invention comprises a metal oxycarbonitride, preferably the metal contained in the metal oxycarbonitride comprises at least one selected from the group consisting of niobium, tin, indium, platinum, tantalum, zirconium, copper, iron, tungsten, chromium, molybdenum, hafnium, titanium, vanadium, cobalt, manganese, cerium, mercury, plutonium, gold, silver, iridium, palladium, yttrium, ruthenium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, and nickel. Moreover, the catalyst of the present invention comprises the catalyst carrier and a catalyst metal supported on the catalyst carrier.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Autombobile windshield glass possessing infrared reflection performance and its preparation method
InactiveCN1555989AImprove transmittanceWith thermal insulation performanceWindowsWindscreensIndiumSilicon oxide
An anti-fogging insulating windshield with high infrared reflectivity (more than 70%) features that a semiconductor oxide film, which may be the indium oxide film doped by tin oxide or the zinc oxide film doped by at least one of aluminium oxide, silicon oxide, boron oxide, dysprosium oxide and gallium oxide, is arranged between PVB film and the internal or external surface of glass. Its preparing processis also disclosed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ceramic compositions useful for thermal barrier coatings having reduced thermal conductivity
InactiveUS20050142392A1Reduced and minimized tendency to sinterReduce conductivityMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingDysprosiumThermal barrier coating
Ceramic compositions comprising at least about 91 mole % zirconia and up to about 9 mole % of a stabilizer component comprising a first metal oxide having selected from the group consisting of yttria, calcia, ceria, scandia, magnesia, india and mixtures thereof. This stabilizer component further comprises a second metal oxide of a trivalent metal atom selected from the group consisting of lanthana, gadolinia, neodymia, samaria, dysprosium, and mixtures thereof and a third metal oxide of a trivalent metal atom selected from the group consisting of erbia, ytterbia and mixtures thereof. These ceramic compositions are useful in preparing thermal barrier coatings having reduced thermal conductivity for the metal substrate of articles that operate at, or are exposed to, high temperatures.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Niobium powder, sintered body thereof, and capacitor using the same
InactiveUS20020064476A1Improve heat resistanceLarge capacitance per unit weightTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusIndiumCerium
A niobium powder comprising at least one element selected from the group consisting of chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, boron, aluminum, gallium, indium, thallium, cerium, neodymium, titanium, rhenium, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, zinc, silicon, germanium, tin, phosphorus, arsenic, bismuth, rubidium, cesium, magnesium, strontium, barium, scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, praseodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, hafnium, vanadium, osmium, iridium, platinum, gold, cadmium, mercury, lead, selenium and tellurium; a sintered body of the niobium powder; and a capacitor comprising a sintered body as one electrode, a dielectric material formed on the surface of the sintered body, and counter electrode provided on the dielectric material.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com