Patents
Literature
259 results about "Plutonium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It reacts with carbon, halogens, nitrogen, silicon, and hydrogen. When exposed to moist air, it forms oxides and hydrides that can expand the sample up to 70% in volume, which in turn flake off as a powder that is pyrophoric. It is radioactive and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of plutonium dangerous.
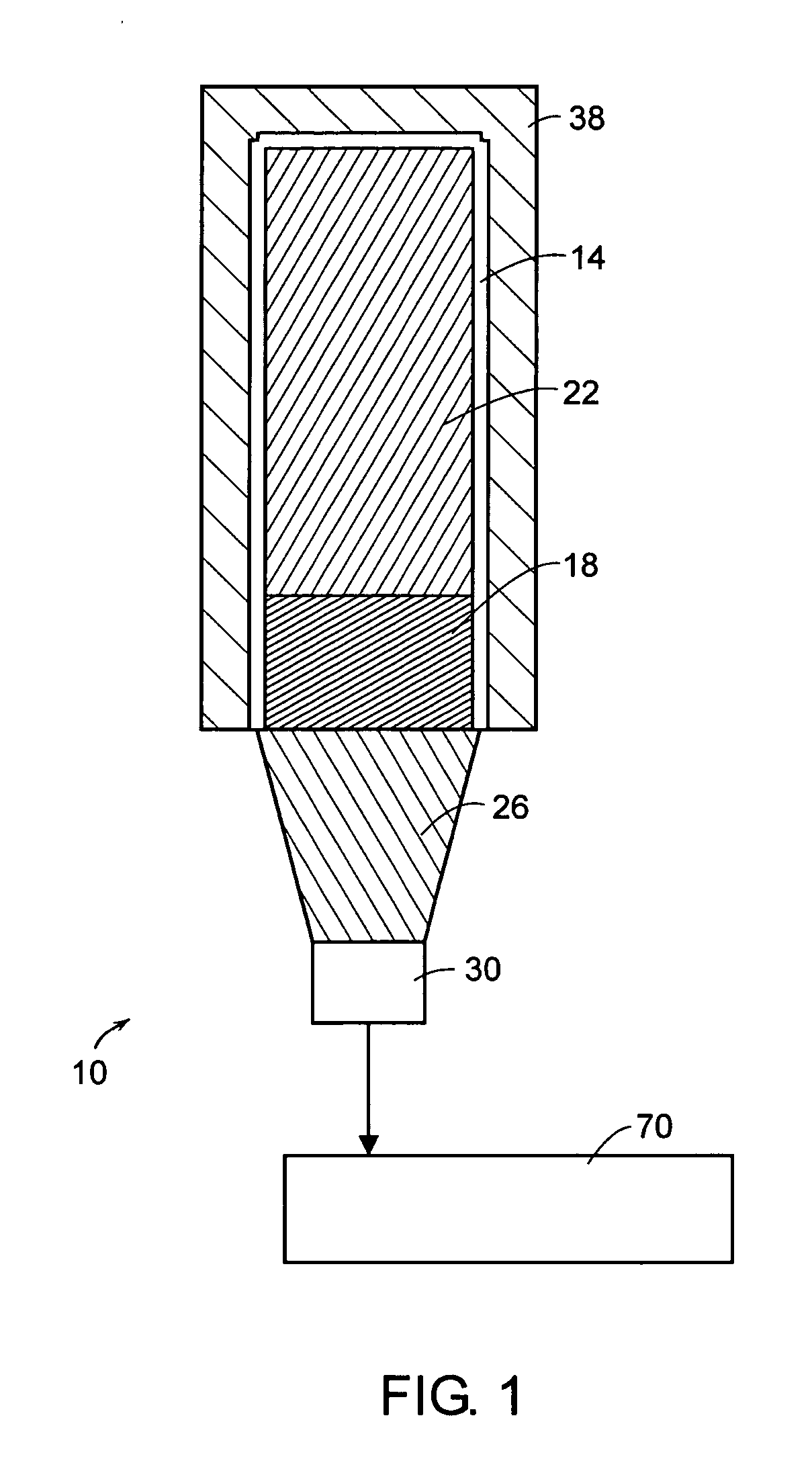
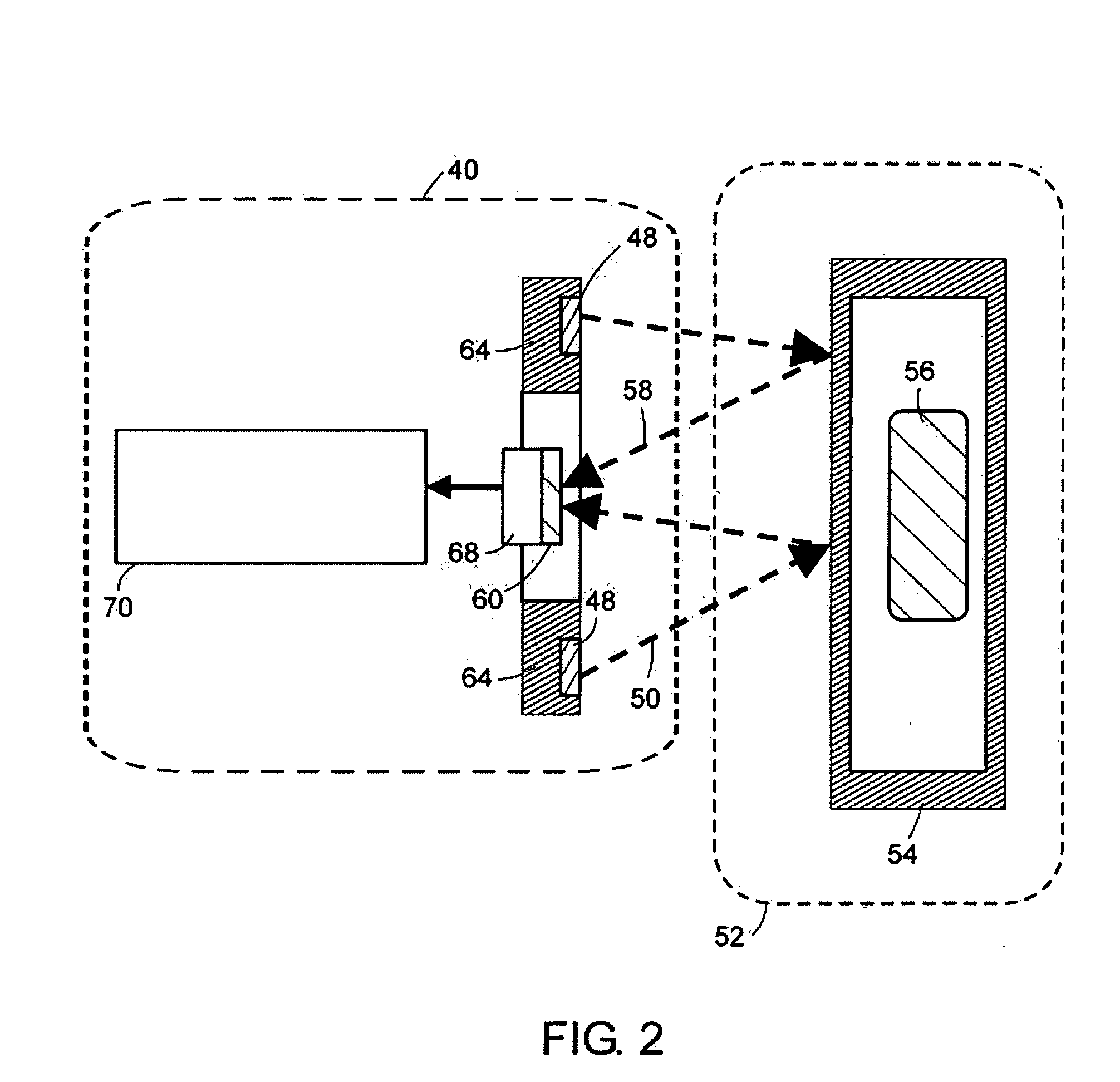
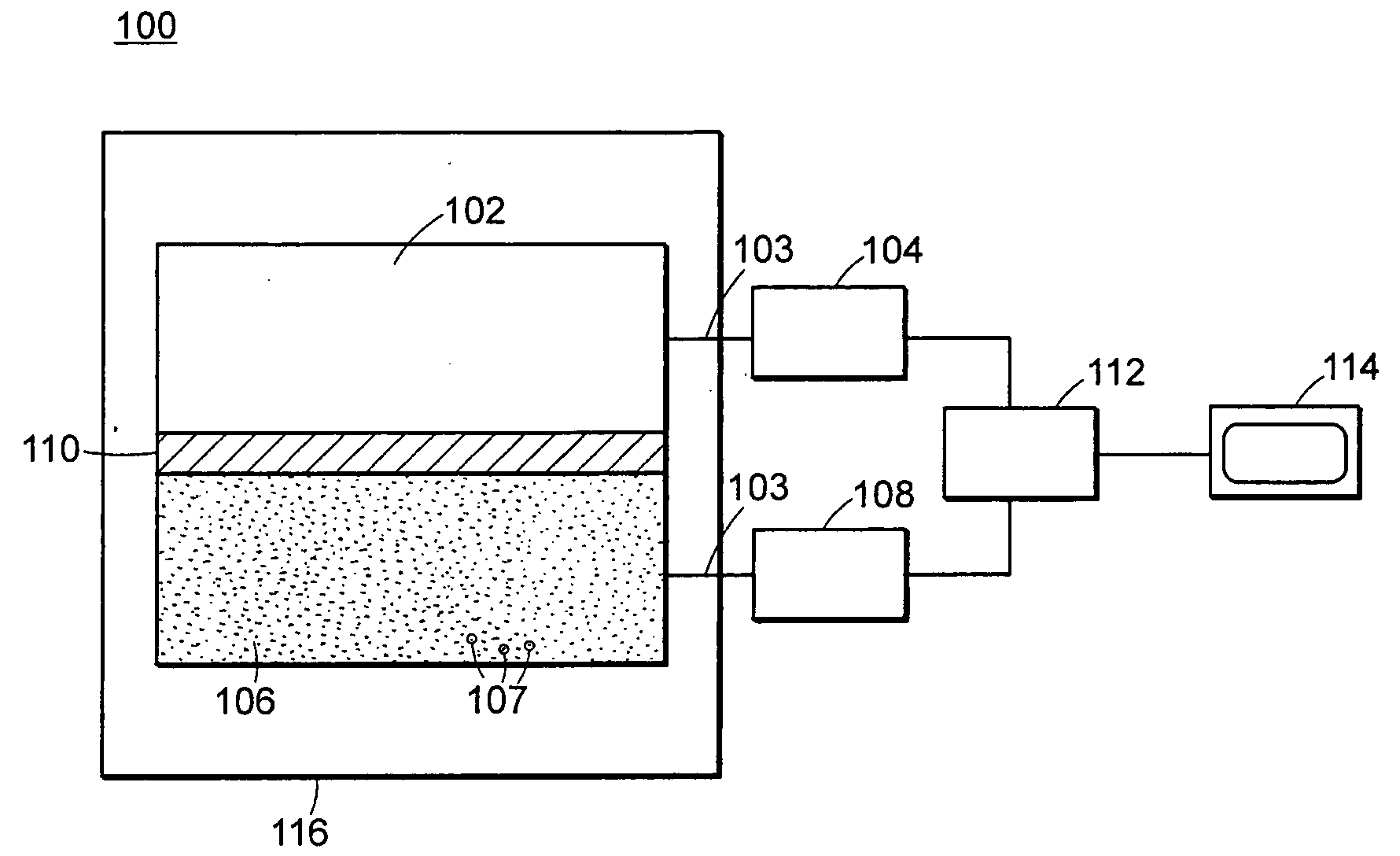
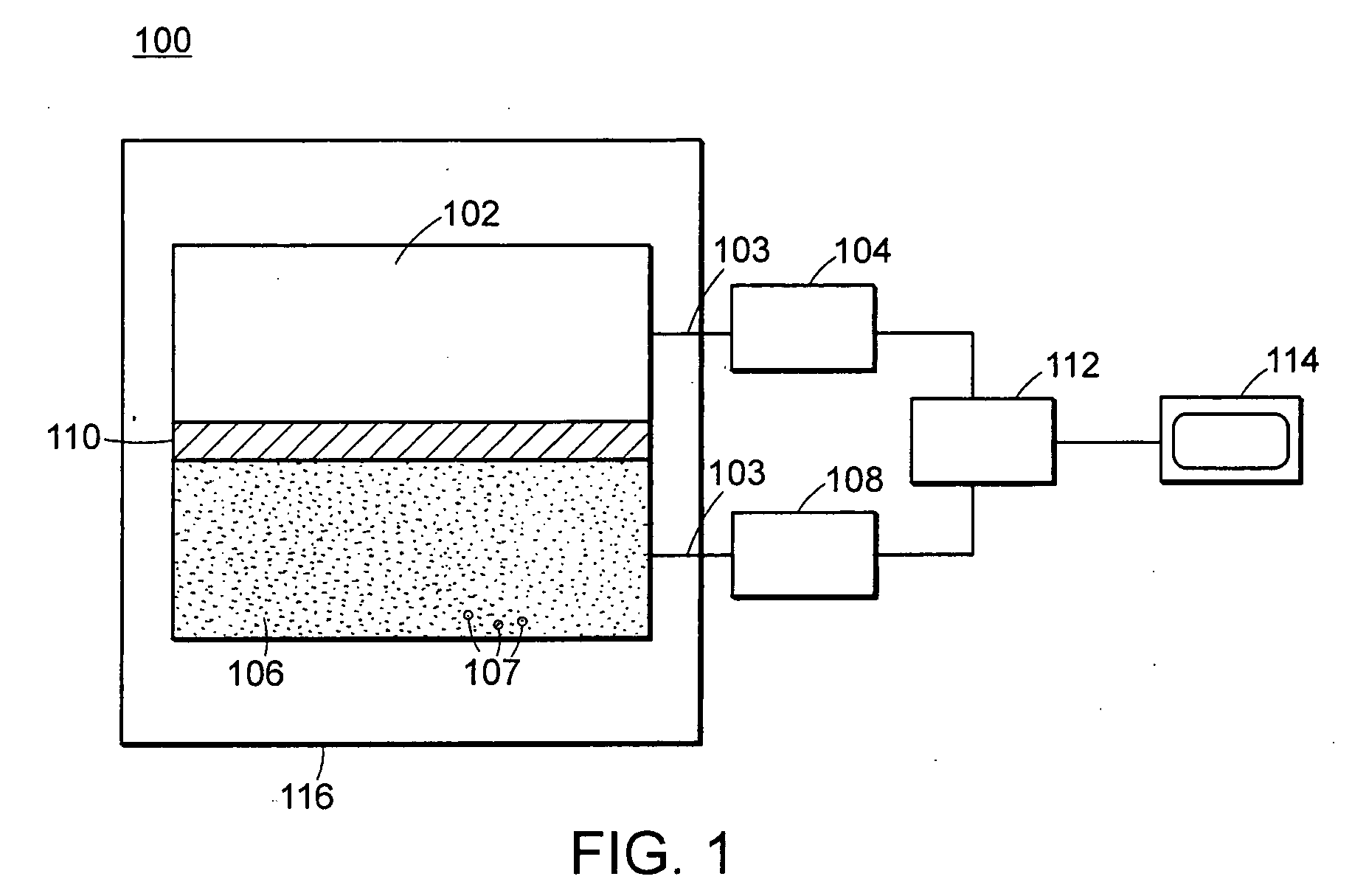
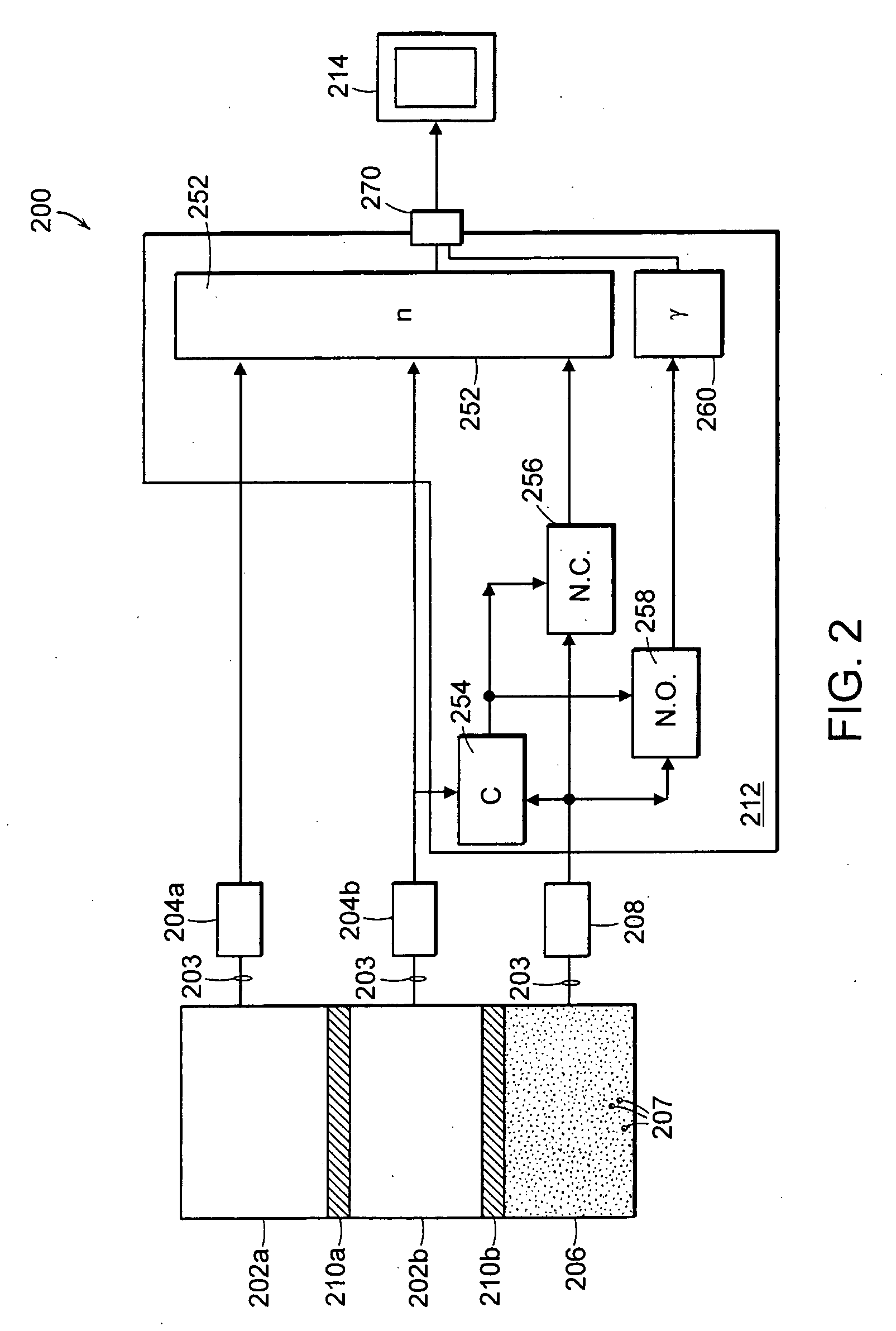
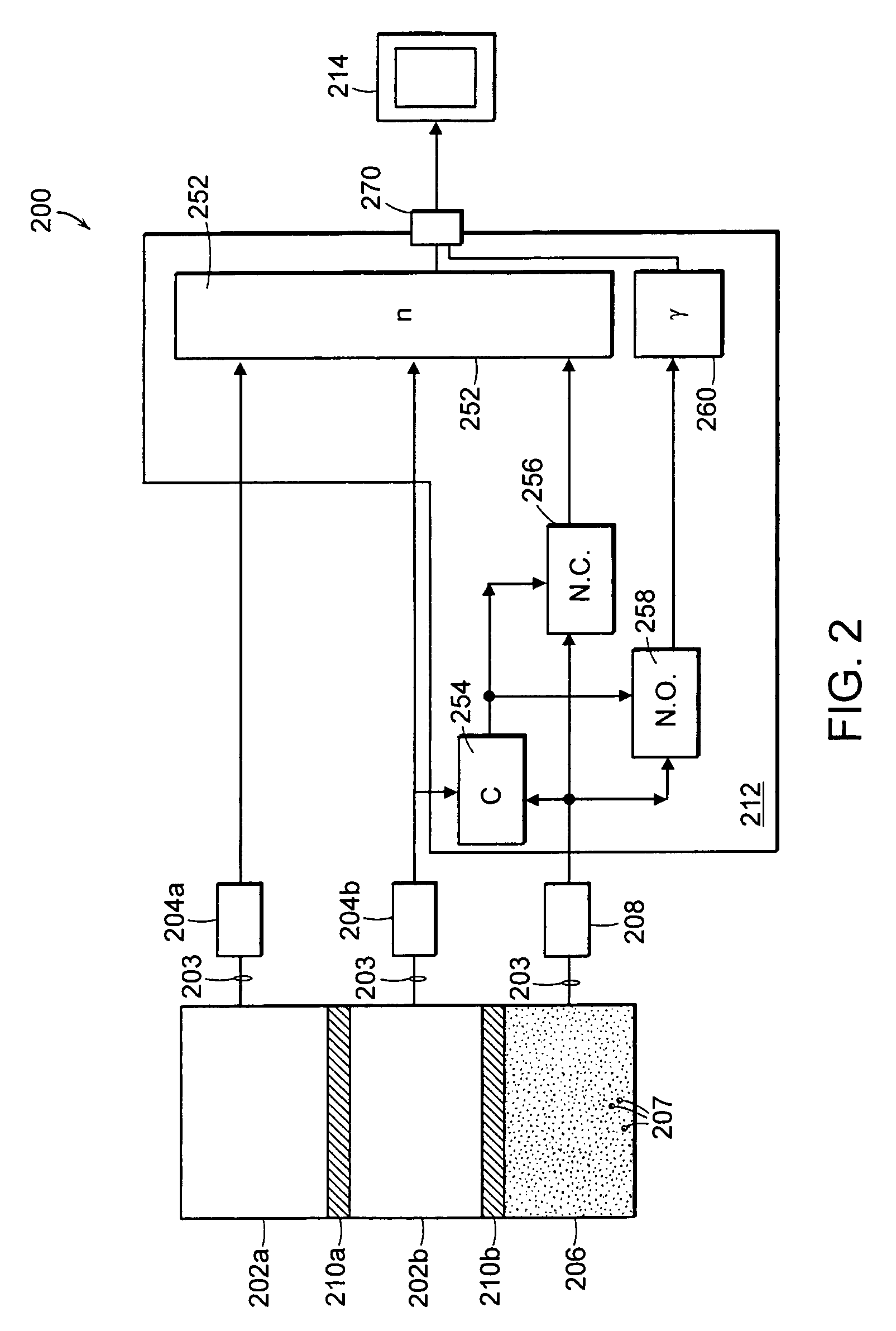
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
InactiveUS20050023479A1Light weightMore selectiveX-ray spectral distribution measurementMeasurement with scintillation detectorsNeutron emissionX-ray
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like; and / or an X-ray analyzer that facilitates detection of materials that can shield radioactive sources, e.g., lead, and the like.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
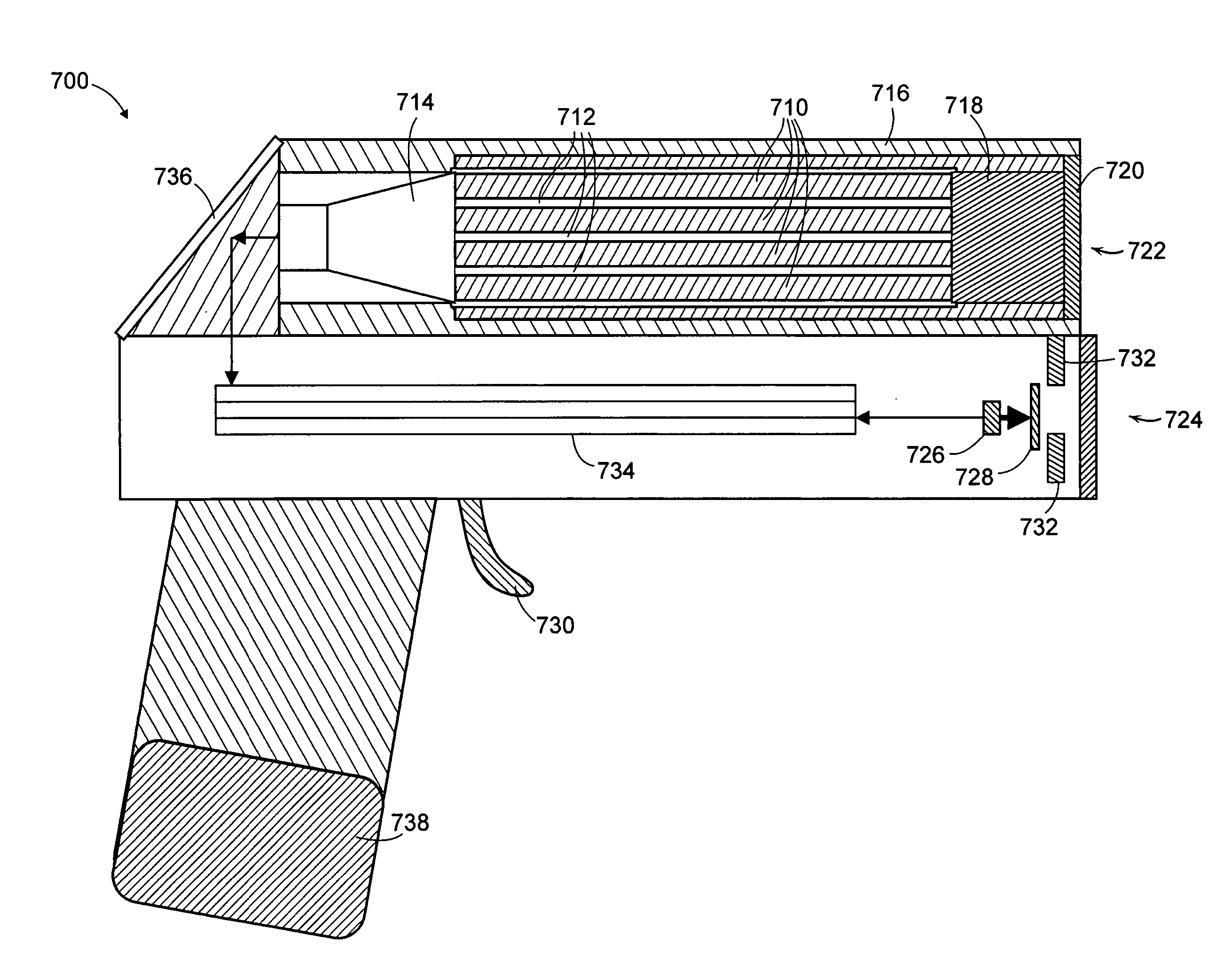
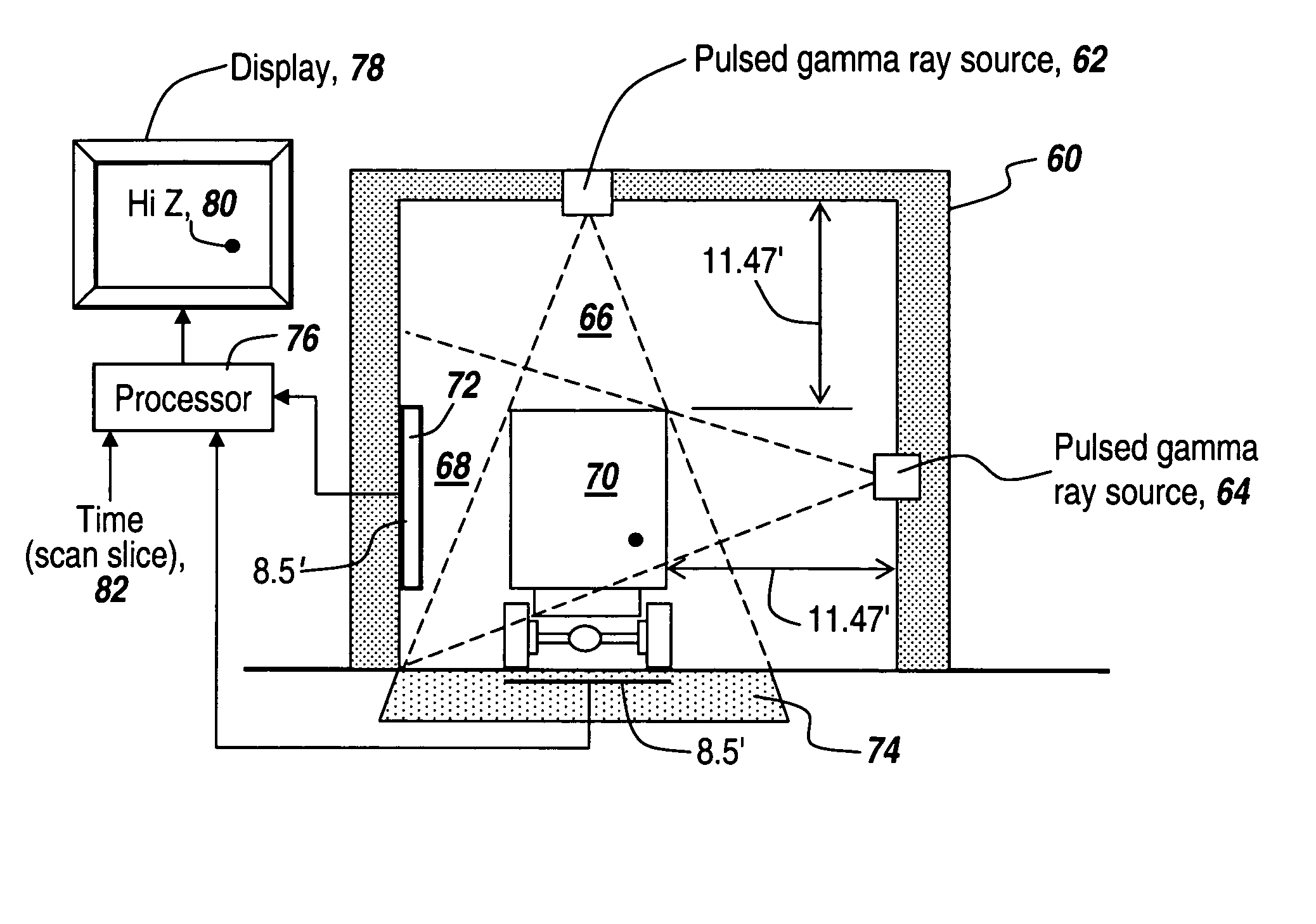
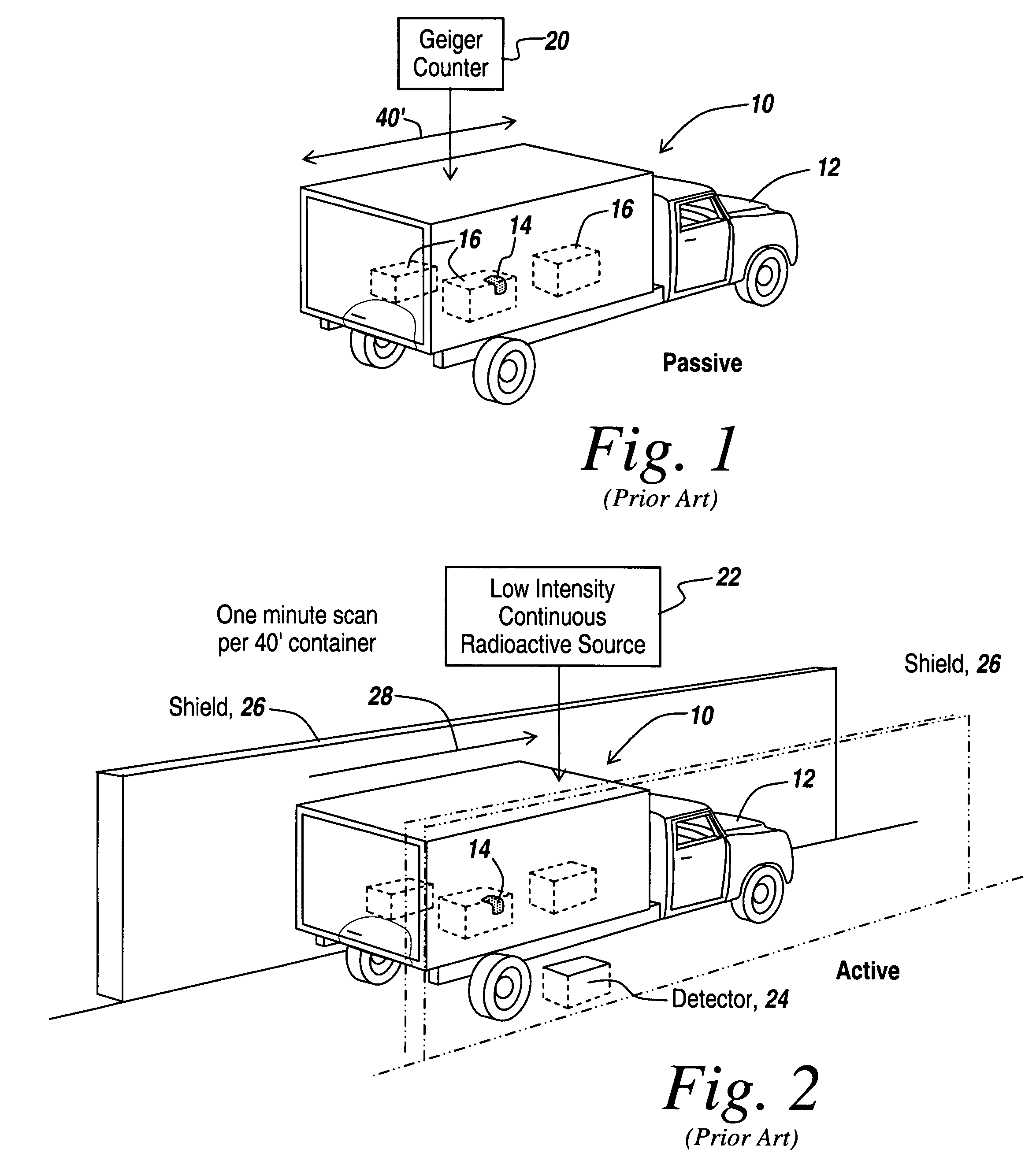
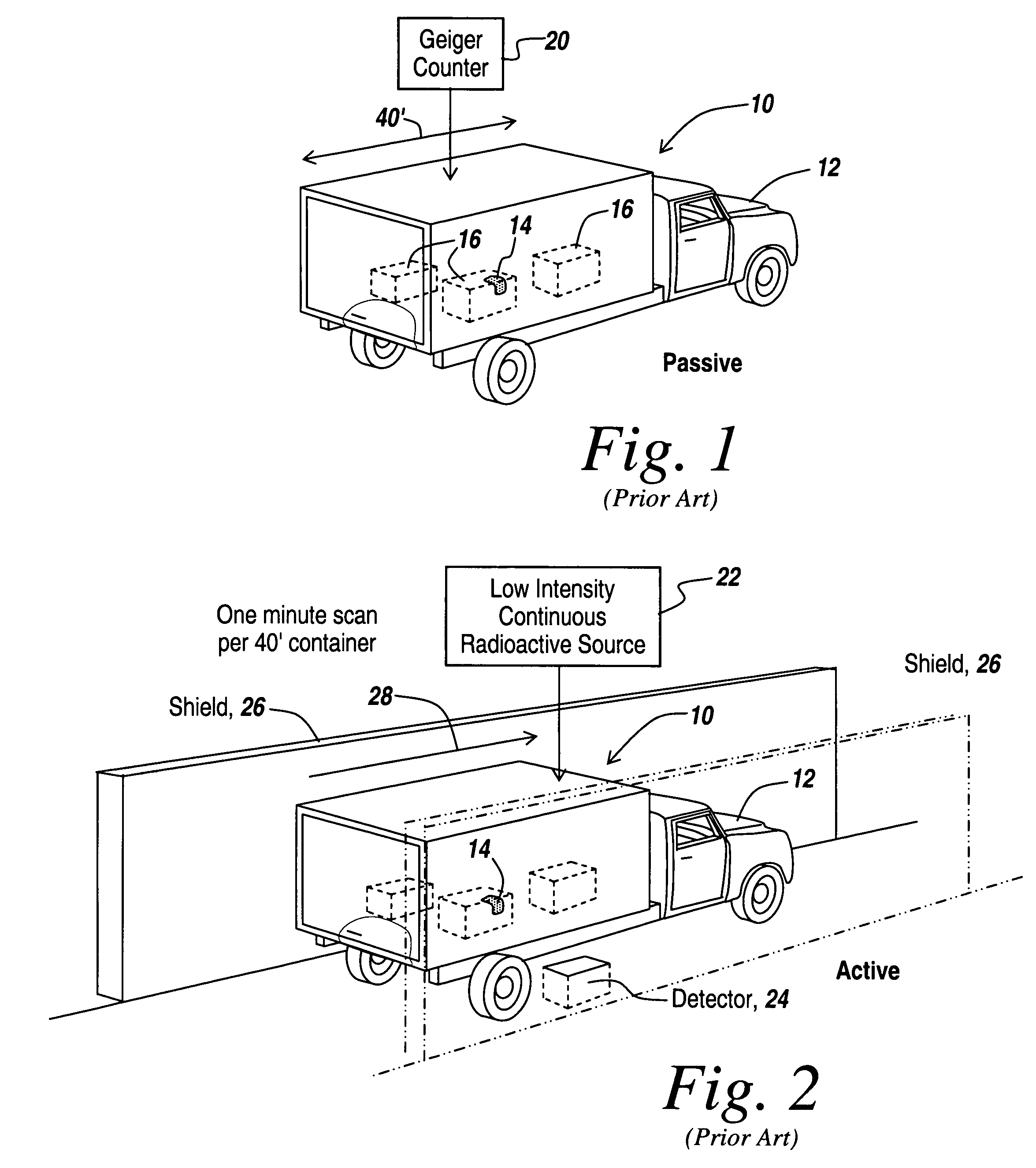
Method and apparatus for the safe and rapid detection of nuclear devices within containers
ActiveUS7379530B2Faster scan timeAccurate detectionX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationDisplay deviceHigh intensity
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS20070272874A1Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like. The apparatus comprises a first light guide, optically coupled to a first optical detector; a second light guide, optically coupled to a second optical detector a sheet of neutron scintillator, opaque for incoming optical photons, said sheet of neutron scintillator sandwiched between the first and the second light guides. The second light guide comprises a gamma ray scintillator material.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS7525101B2Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Nuclear Assisted Hydrocarbon Production Method
InactiveUS20100105975A1Reduced availabilityMinimized in sizeFluid removalShieldingHydrogenFormation fluid
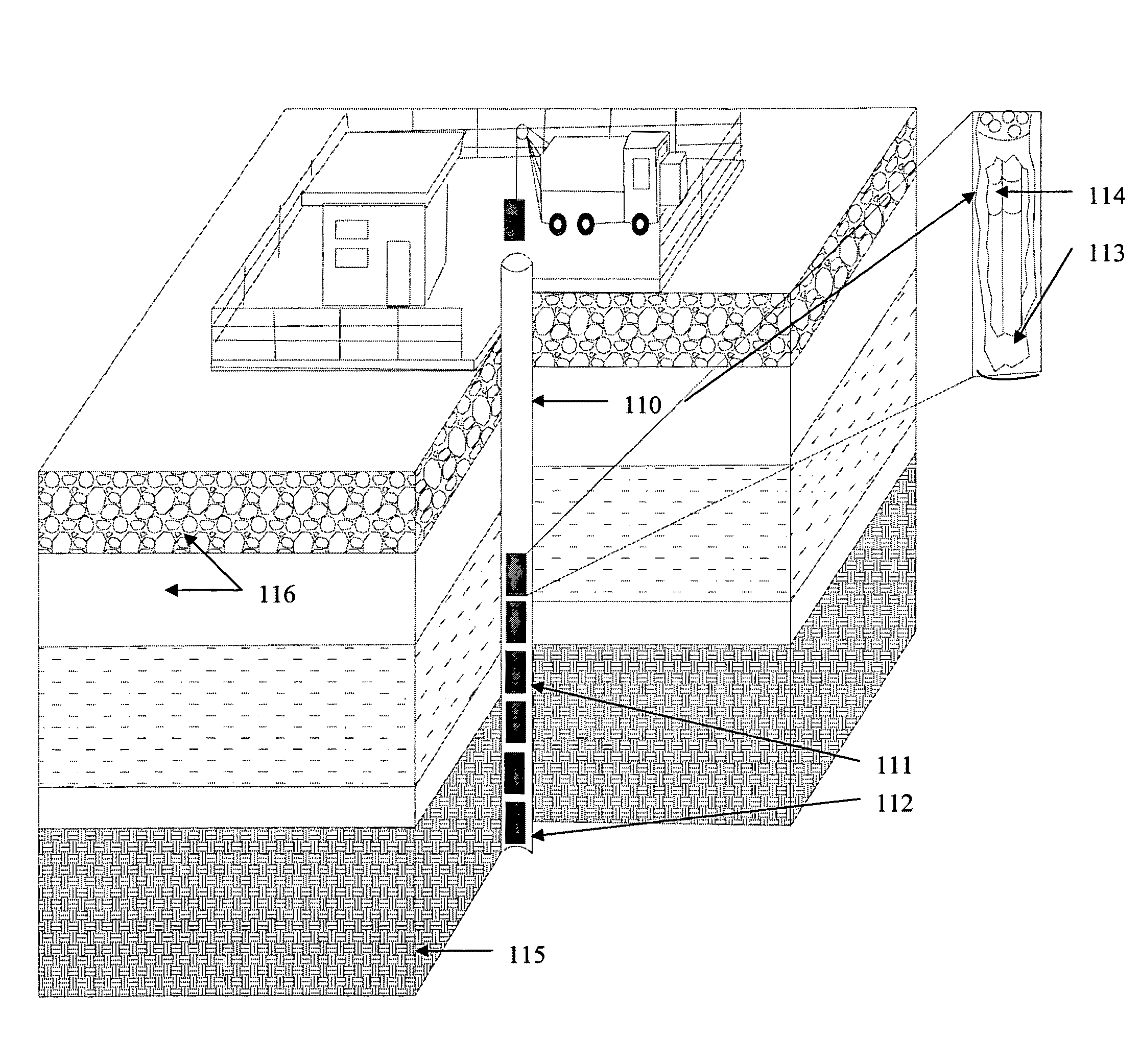
A method is disclosed for the temporary or permanent storage of nuclear waste materials comprising the placing of waste materials into one or more repositories or boreholes constructed into an unconventional oil formation. The thermal flux of the waste materials fracture the formation, alters the chemical and / or physical properties of hydrocarbon material within the subterranean formation to allow removal of the altered material. A mixture of hydrocarbons, hydrogen, and / or other formation fluids are produced from the formation. The radioactivity of high-level radioactive waste affords proliferation resistance to plutonium placed in the periphery of the repository or the deepest portion of a borehole.
Owner:BAIRD JAMES RUSSELL
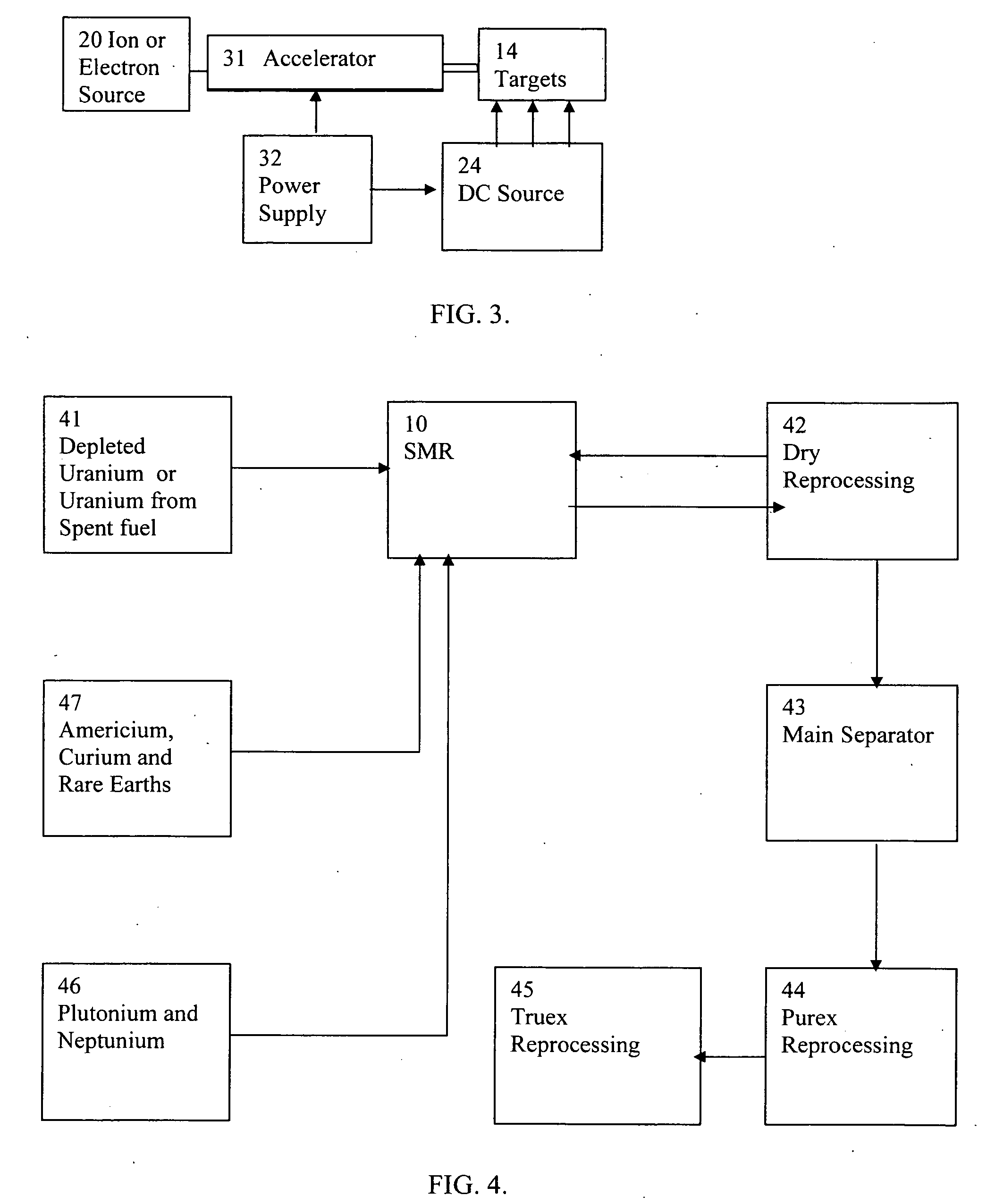
High flux sub-critical reactor for nuclear waste transmulation
InactiveUS20080232533A1Improve distributionImprove economyConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationHigh fluxPu element
A process to safely convert about 95% of the nuclear waste into a usable fuel source is disclosed. The process, involving a sub-critical power reactor and a proliferation-resistant fuel cycle, consumes depleted uranium or thorium fuel with fissionable fuel, including reactor or weapons-grade plutonium. The reactor is comprised of coaxial neutron and energy-amplifying regions separated by moderating and thermal neutron absorbing layers. Control of the water or gas-cooled reactor is provided by plutonium-helium loops with a variable volume flow rate and an external source of neutrons that quickly reacts to any fluctuations of the reactor parameters. A second embodiment of the invention is a compact sub-critical propulsion reactor utilizing fission electric cell and thermo-acoustic technology for electrical power generation.
Owner:BLANOVSKY ANATOLY
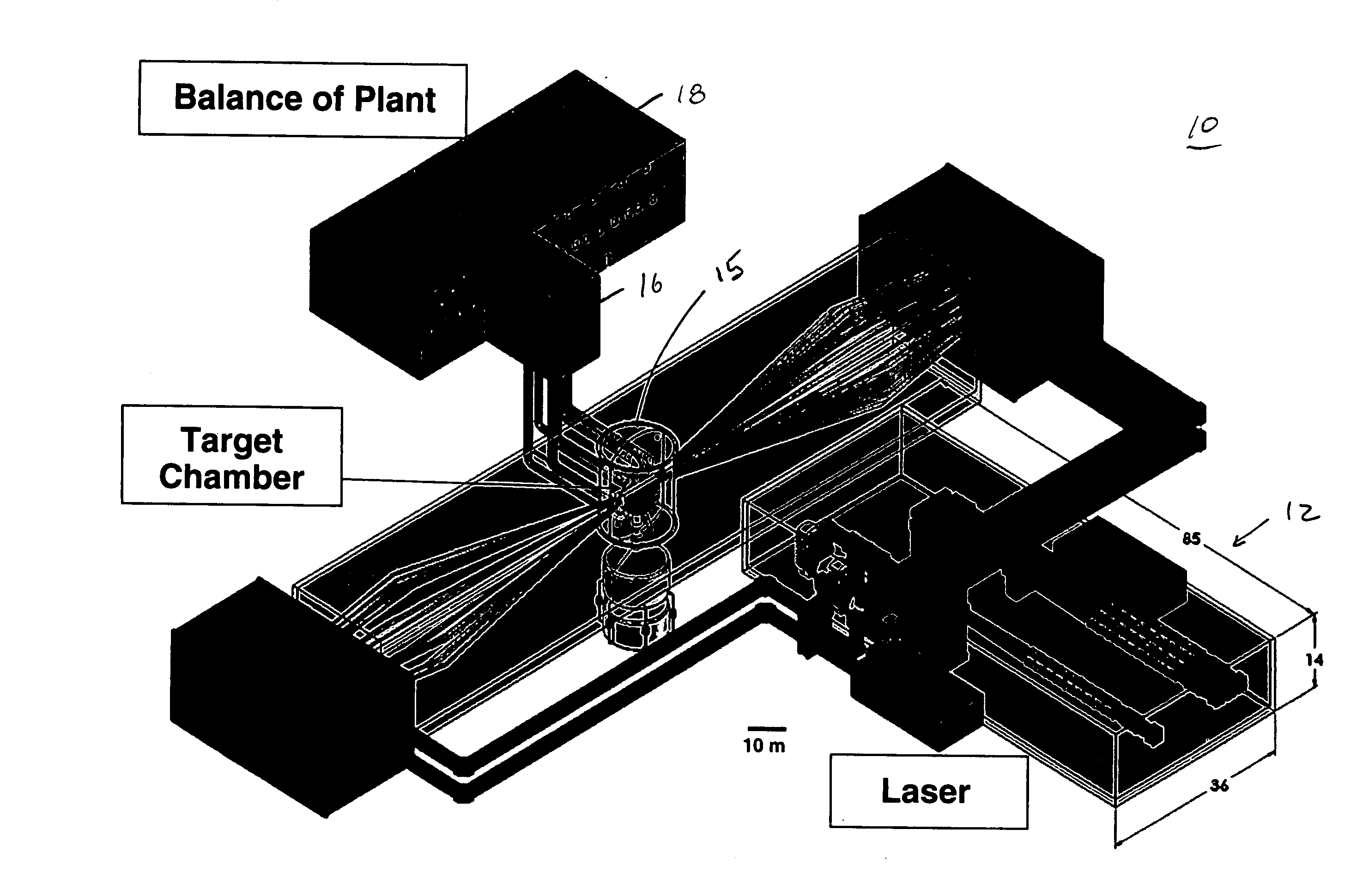
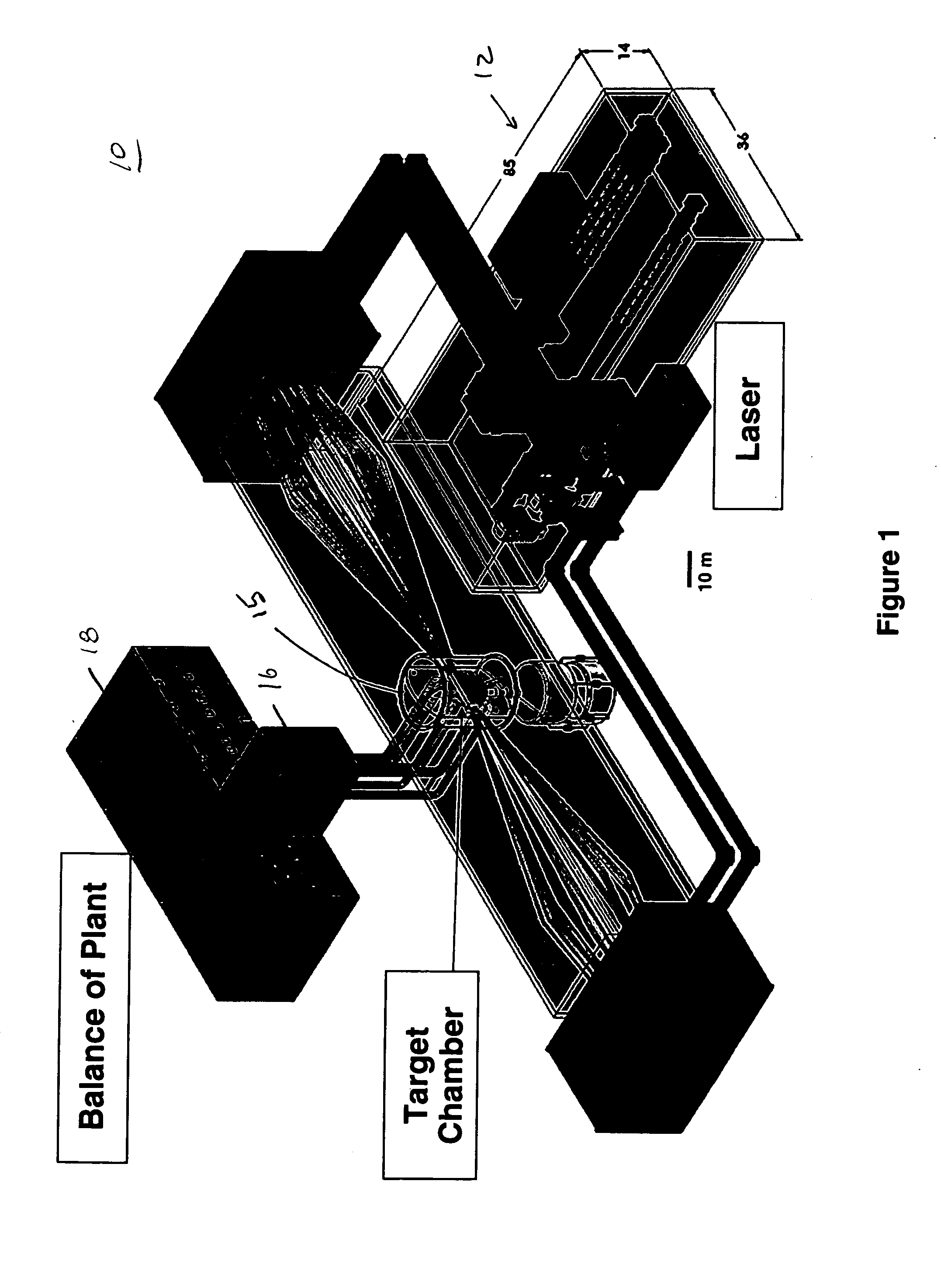
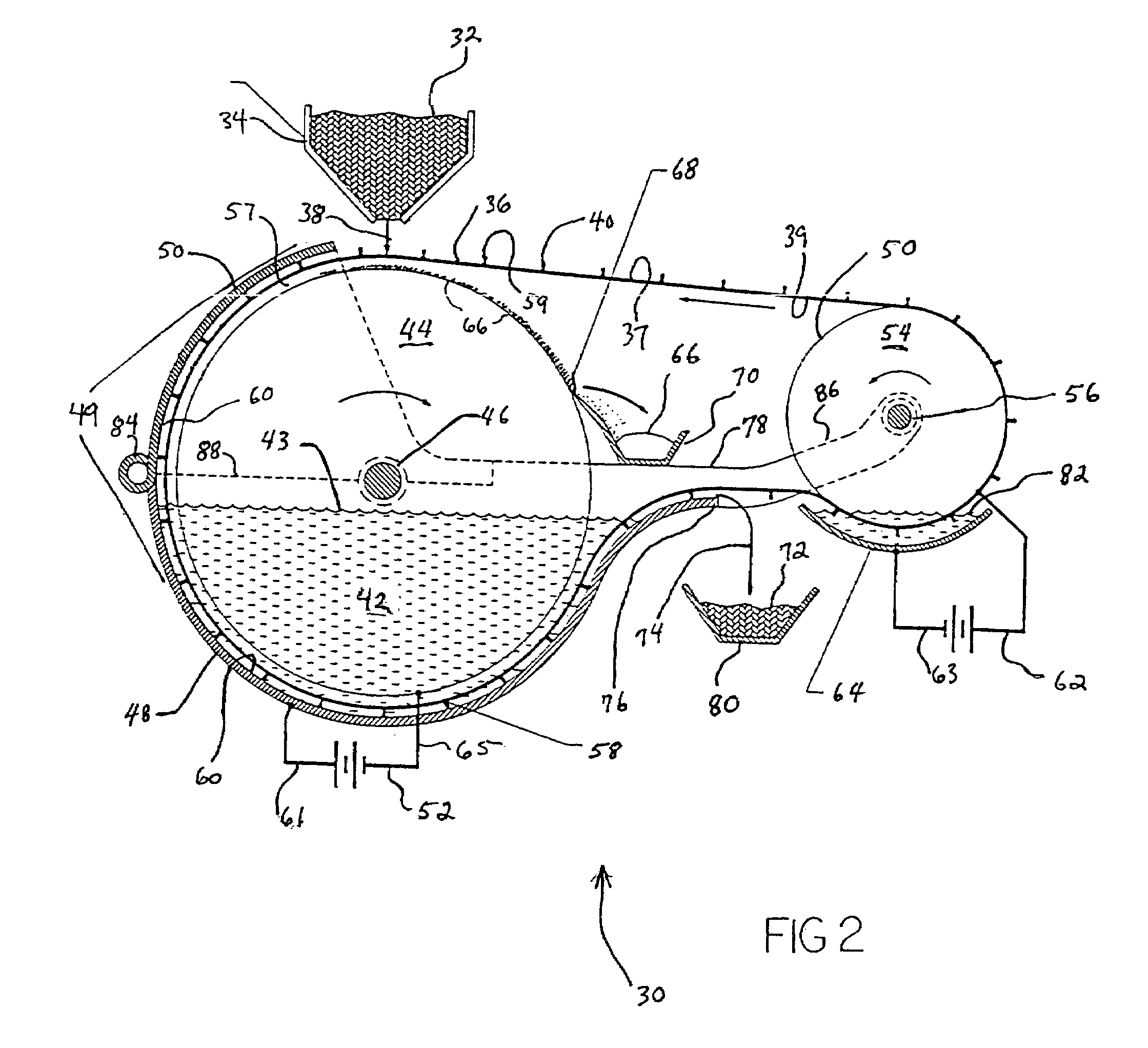
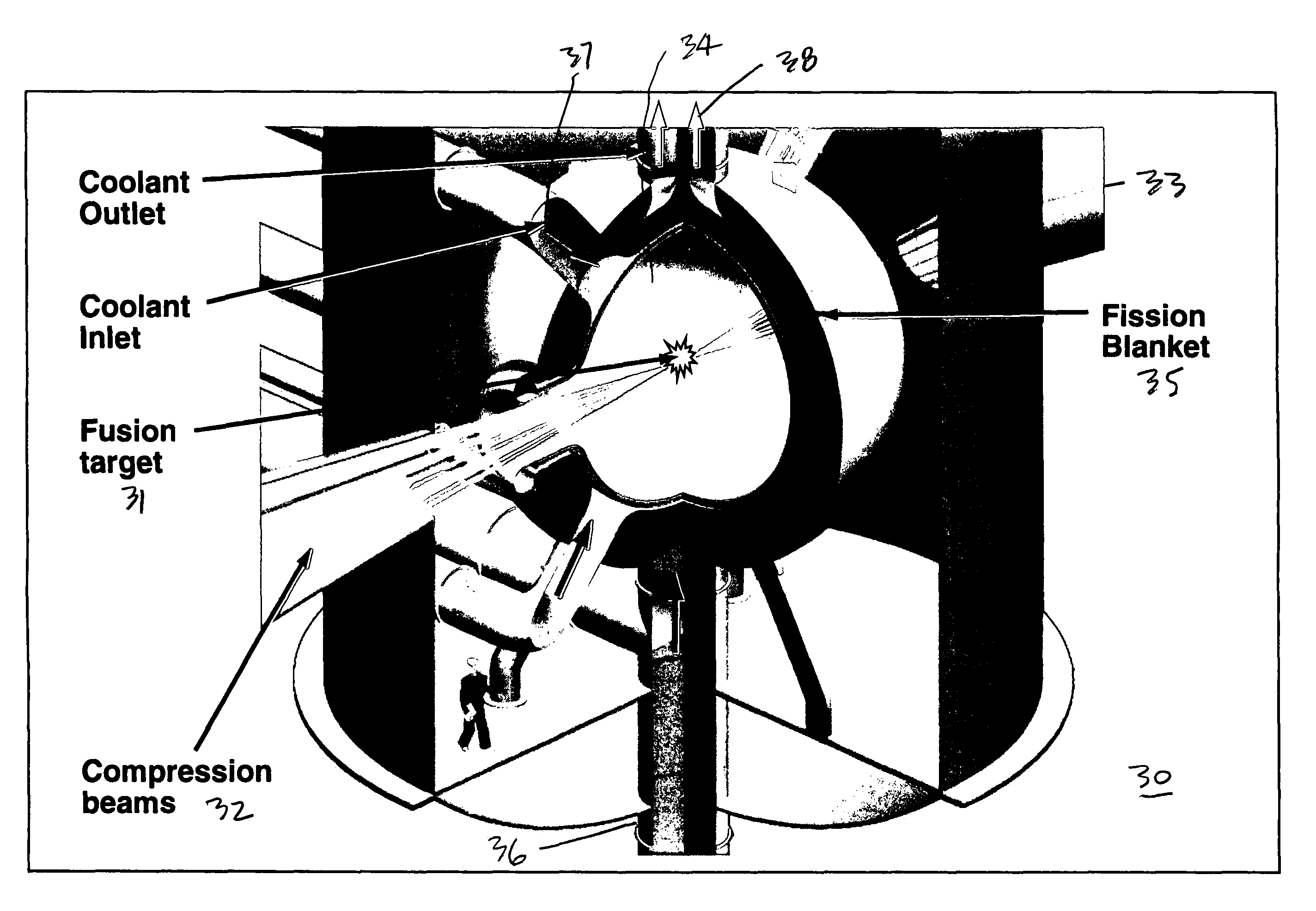
Control of a Laser Inertial Confinement Fusion-Fission Power Plant
ActiveUS20110286563A1Extended service lifeReduce spreadNuclear energy generationWaste based fuelFusion fissionEngineering
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
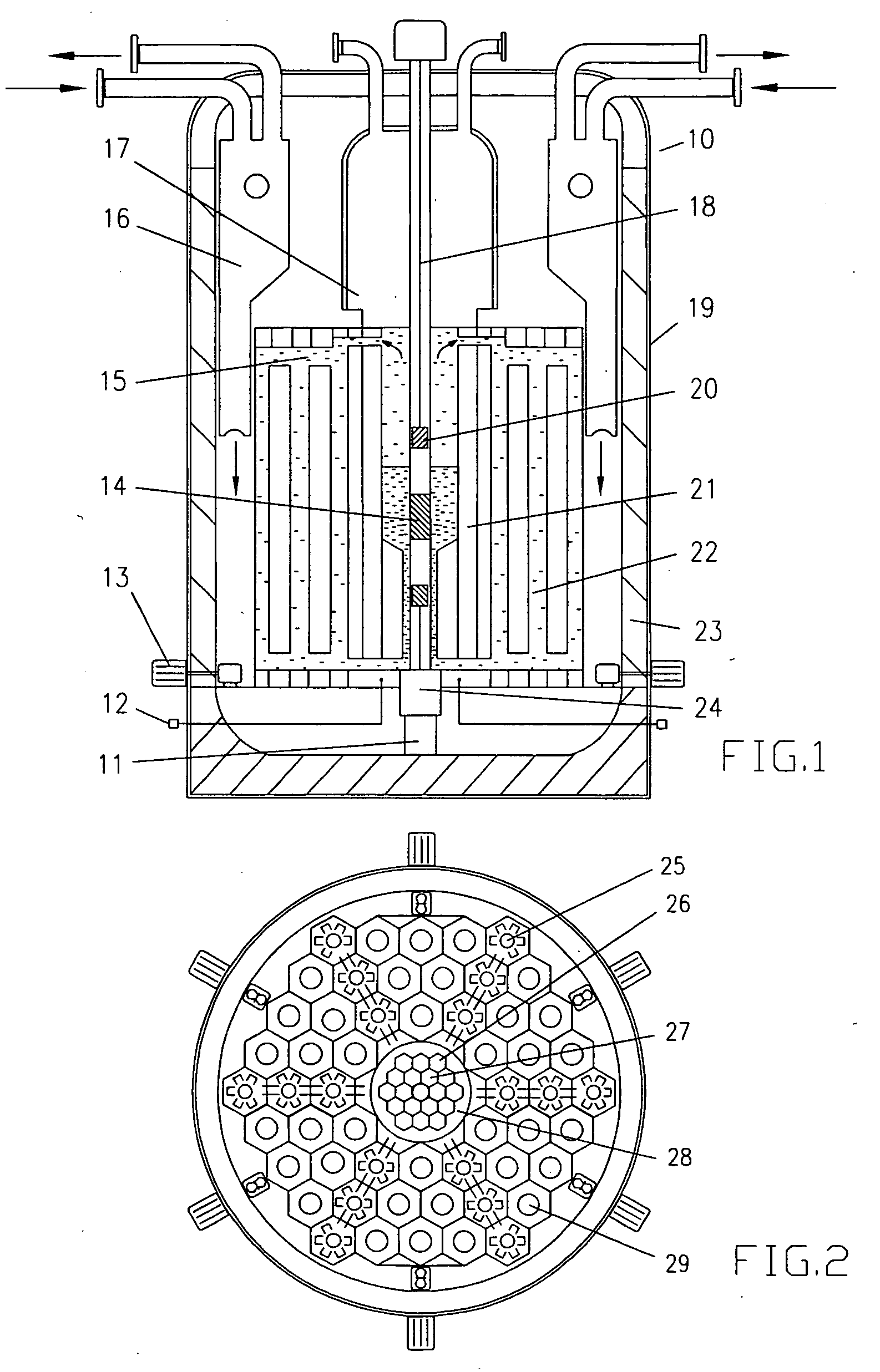
Sustainable Modular Transmutation Reactor
InactiveUS20150098544A1Improve distributionImprove economyIntegral reactorsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsFission fusionDelayed neutron
A light water reactor to safely convert depleted uranium into a fuel source that could be used as a sustainable source of energy for centuries. The reactor is a type of breed-burn reactor uniquely combined with a proliferation-resistant fuel cycle with no uranium enrichment and no plutonium isolation. It is comprised of a compact factory-produced fast region and a thermal region that produces about 95% of the core power and contains the passageways for transports of delayed-neutron emitters to the fast region, where they can provide additional neutrons (source-based mode) or all the necessary excitation without an external neutron source (self-regulating mode). A second embodiment of the invention is a small unit driven by a neutron source with beam recycling for propulsion, electrical power or radioisotope production. It could also serve as a demonstration facility for the transmutation reactor with fission-fusion fuel.
Owner:BLANOVSKY ANATOLY
Method and apparatus for the safe and rapid detection of nuclear devices within containers
ActiveUS20070237294A1Faster scan timeAccurate detectionX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationHigh intensityGamma ray
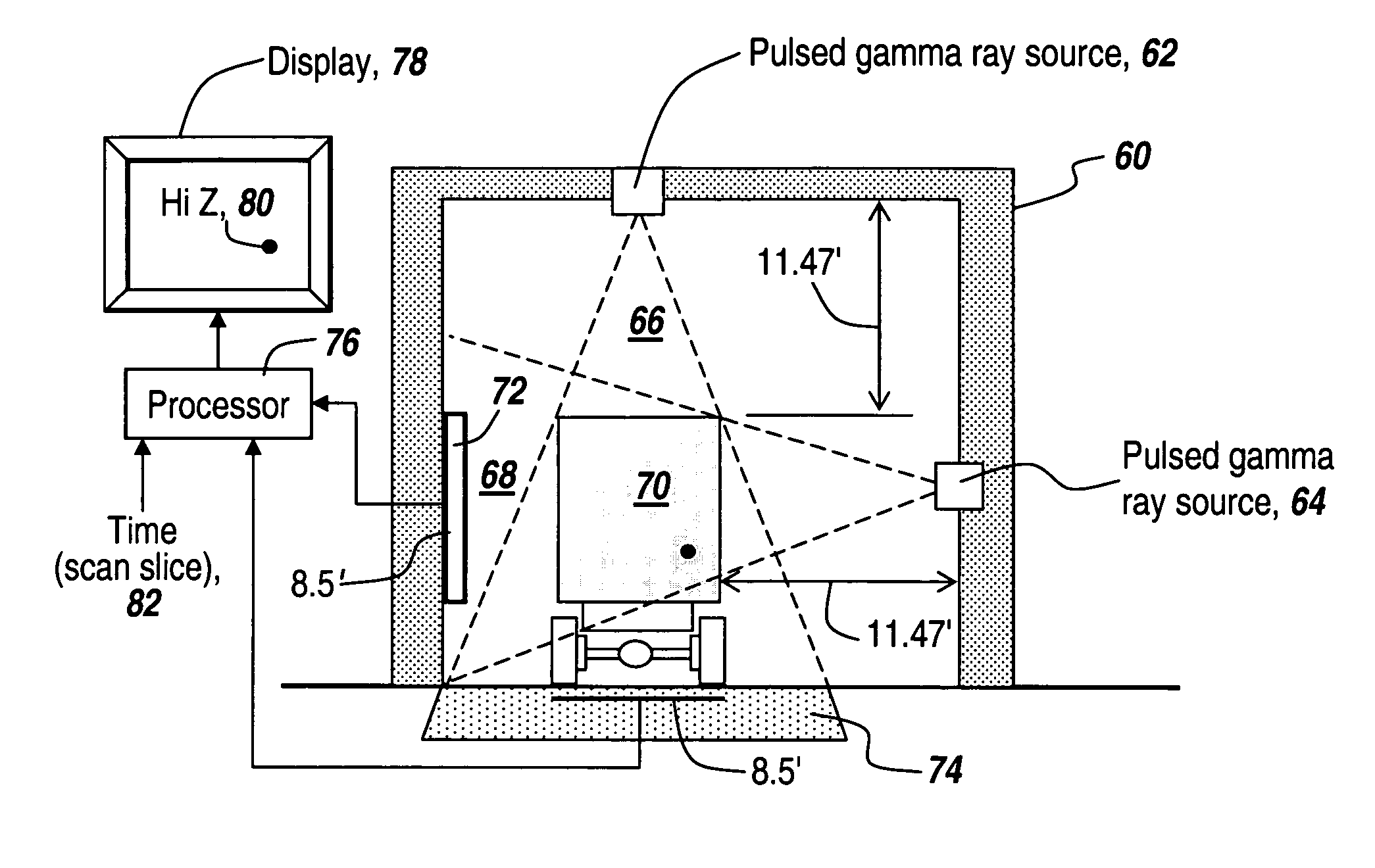
A safe, reliable and rapid system for the detection of nuclear materials within containers includes the use of pulsed high-intensity gamma rays that can penetrate a container and its contents and can be detected outside the container to provide a display in which high-Z material, including lead, uranium, plutonium and other nuclear substances that absorb gamma rays are detected as black regions on the display. In one embodiment, orthogonal pulsed gamma ray beams illuminate the container from two different directions to provide three-dimensional slices from which the existence and location of nuclear threat materials can be ascertained in as little as four seconds for a 40-foot container.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Catalyst carrier, catalyst and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20100331172A1Improve heat resistanceHigh catalytic ability without increasing the specific surface areaCatalyst carriersCell electrodesIndiumCerium
The present invention provides a catalyst carrier having excellent durability and capable of attaining high catalytic ability without increasing the specific surface area thereof, and a catalyst obtainable by using the catalyst carrier. The catalyst carrier of the present invention comprises a metal oxycarbonitride, preferably the metal contained in the metal oxycarbonitride comprises at least one selected from the group consisting of niobium, tin, indium, platinum, tantalum, zirconium, copper, iron, tungsten, chromium, molybdenum, hafnium, titanium, vanadium, cobalt, manganese, cerium, mercury, plutonium, gold, silver, iridium, palladium, yttrium, ruthenium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, lutetium, and nickel. Moreover, the catalyst of the present invention comprises the catalyst carrier and a catalyst metal supported on the catalyst carrier.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Method and device for measuring the relative proportions of plutonium and uranium in a body
InactiveUS6452992B1Change timeConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentDelayed neutronNeutron
The invention relates a device for measuring the relative proportions of uranium and plutonium in a radioactive package (16), having:a source of photons (10) for irradiating the package,at least one delayed neutron detector (18) able to deliver counting signals for neutrons emitted by the package,means (22, 30) of acquiring counting signals, able to establish a decrease over time in the neutrons emitted, characteristic of the radioactive package,calculation means (32) for comparing the decay characteristic of the radioactive package with the respective characteristic decays of uranium and plutonium and for establishing relative proportions of uranium and plutonium in the package.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
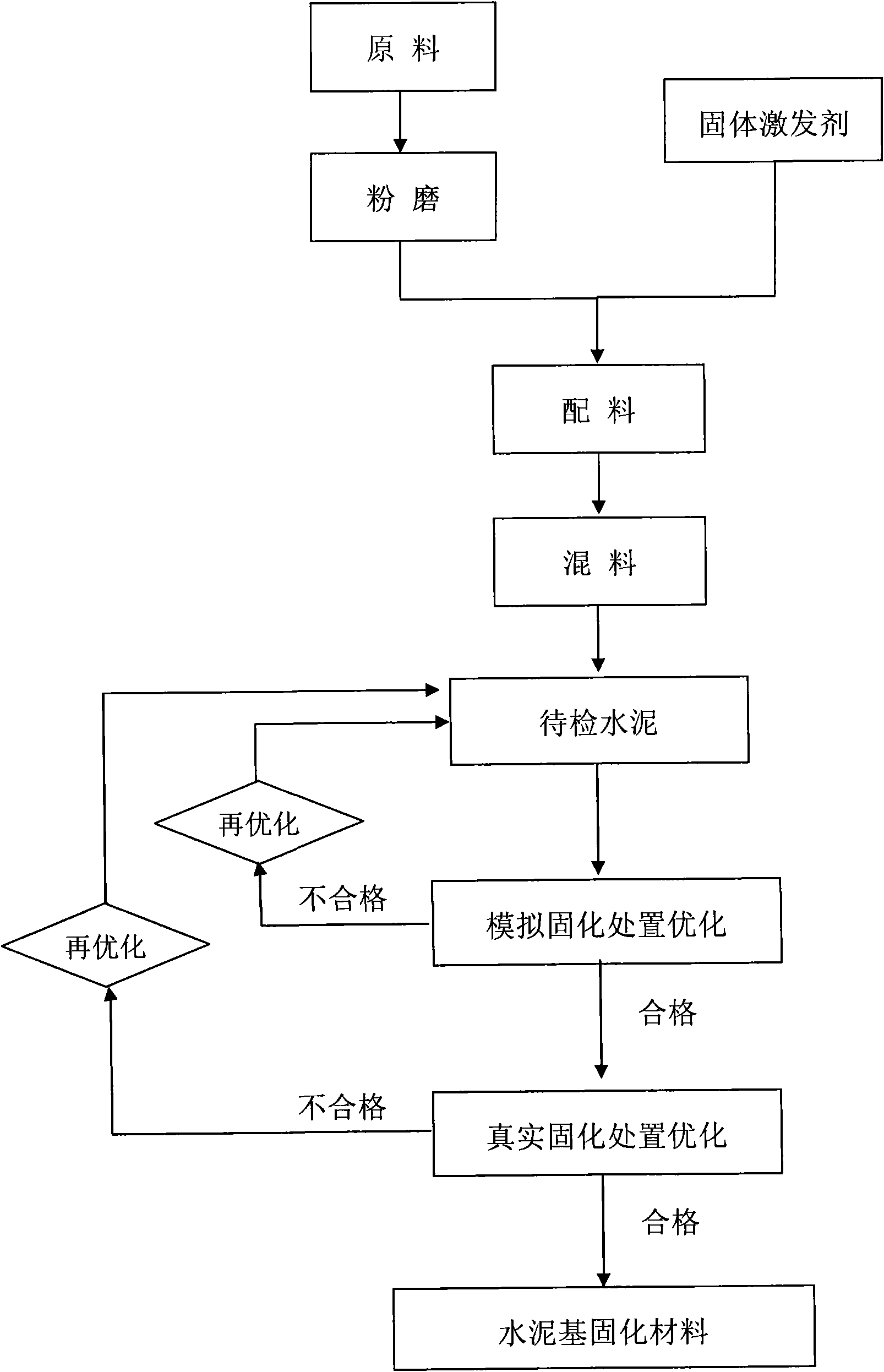
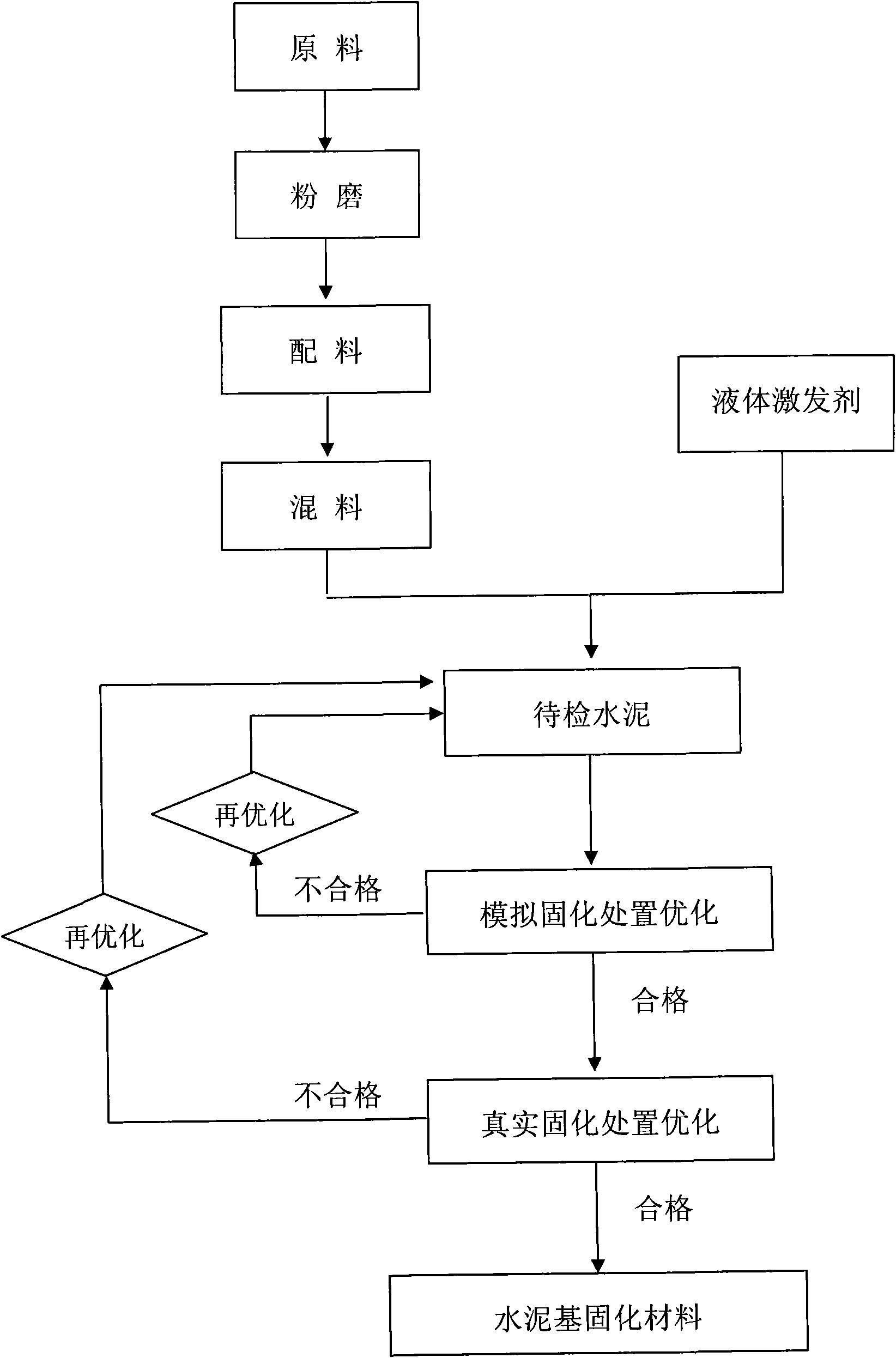
A cement-based solidified material for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash and a method for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash
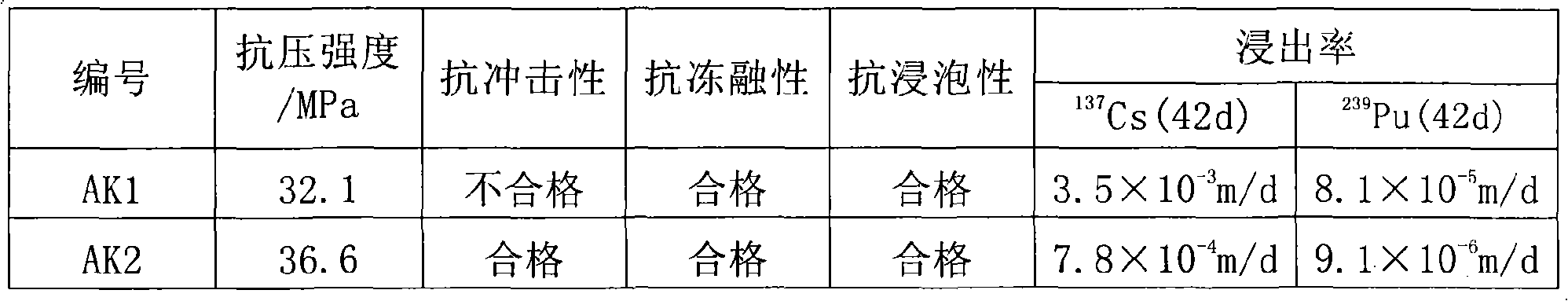
The invention discloses a cement-based solidified material for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash and a method for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash. The solidified material, using the slag, fly ash, zeolite, metakaolin, cement clinker as the material to be excited, is obtained through the even mixture with activator after grinding. The liquid activator or combined solid activator can be used as the activator. Mix the material to be excited and activator together, according to the package content of 30-40%, mix with the incineration ash, stir, and maintain to solidification in light of the solidification operation. The cement-based solidified material of the invention can prepare the nuclear waste solidified body with the incineration ash package content greater than 30%, stable mechanical performance, and low leaching rate of radionuclide ion. Especially when solidifying the plutonium-containing waste, the 42-day Pu leaching rate is 10 cm / d. The invention will play an important role in the middle and low radioactive incineration ash processing with good application prospect.
Owner:浙江合力海科新材料股份有限公司
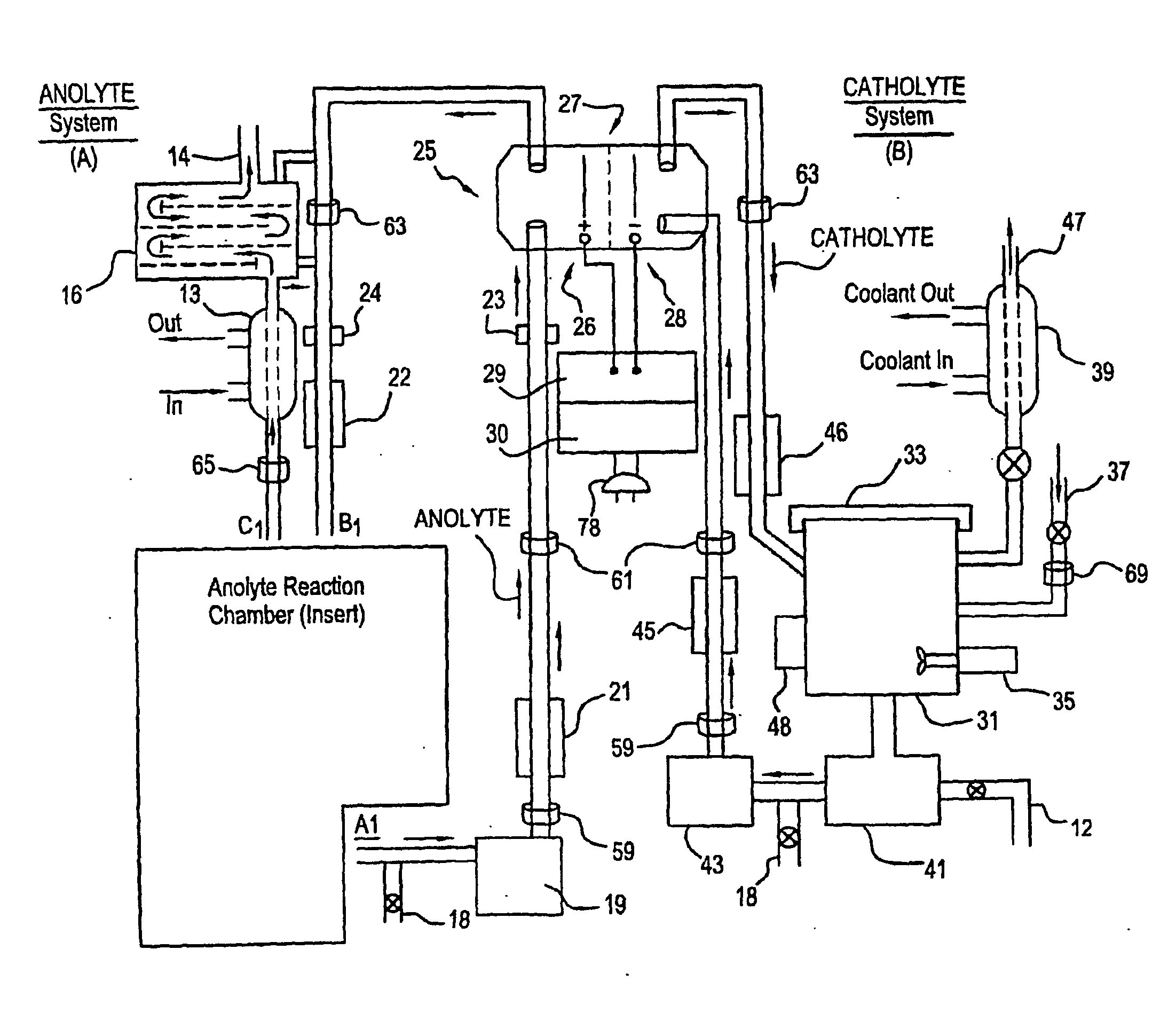
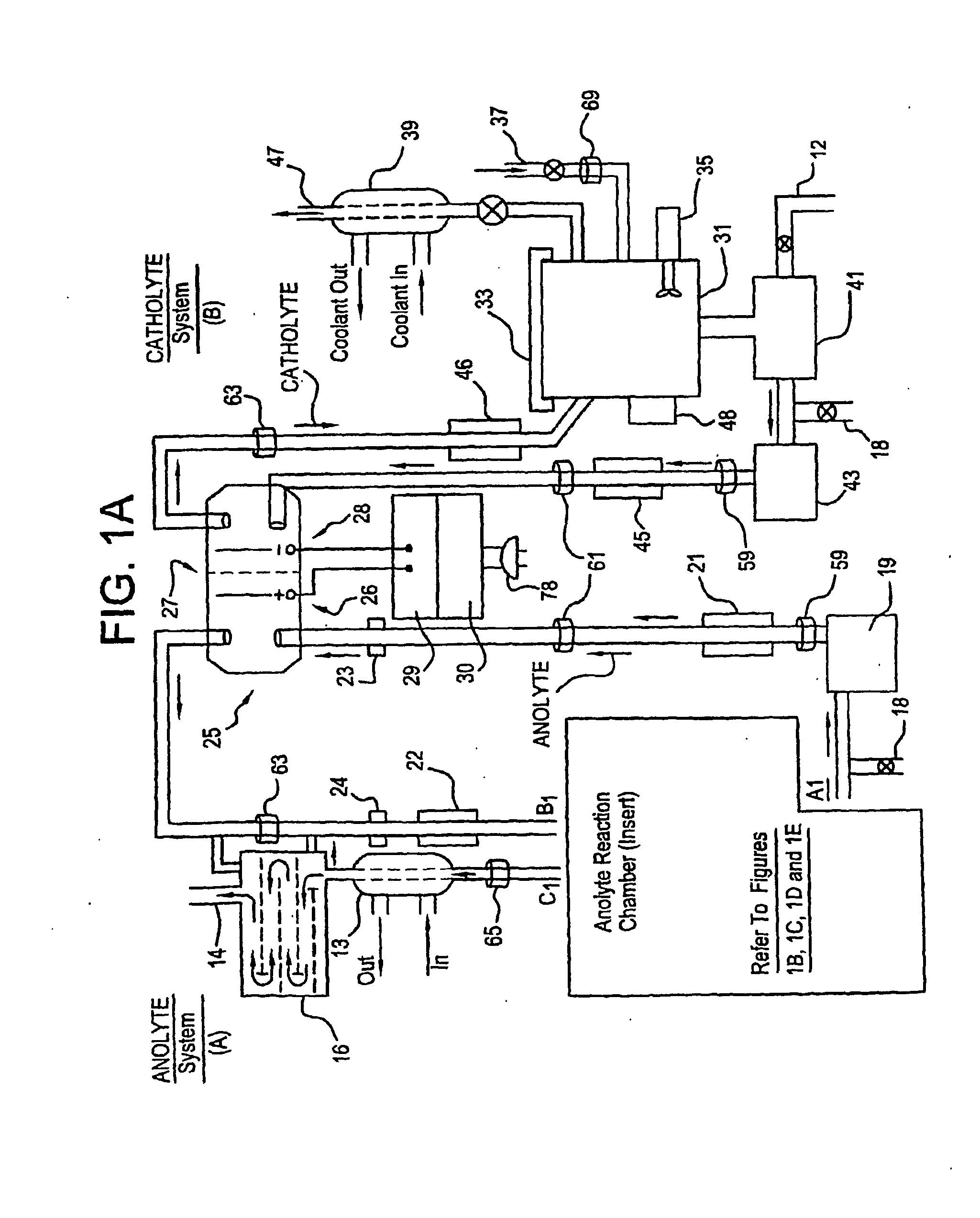
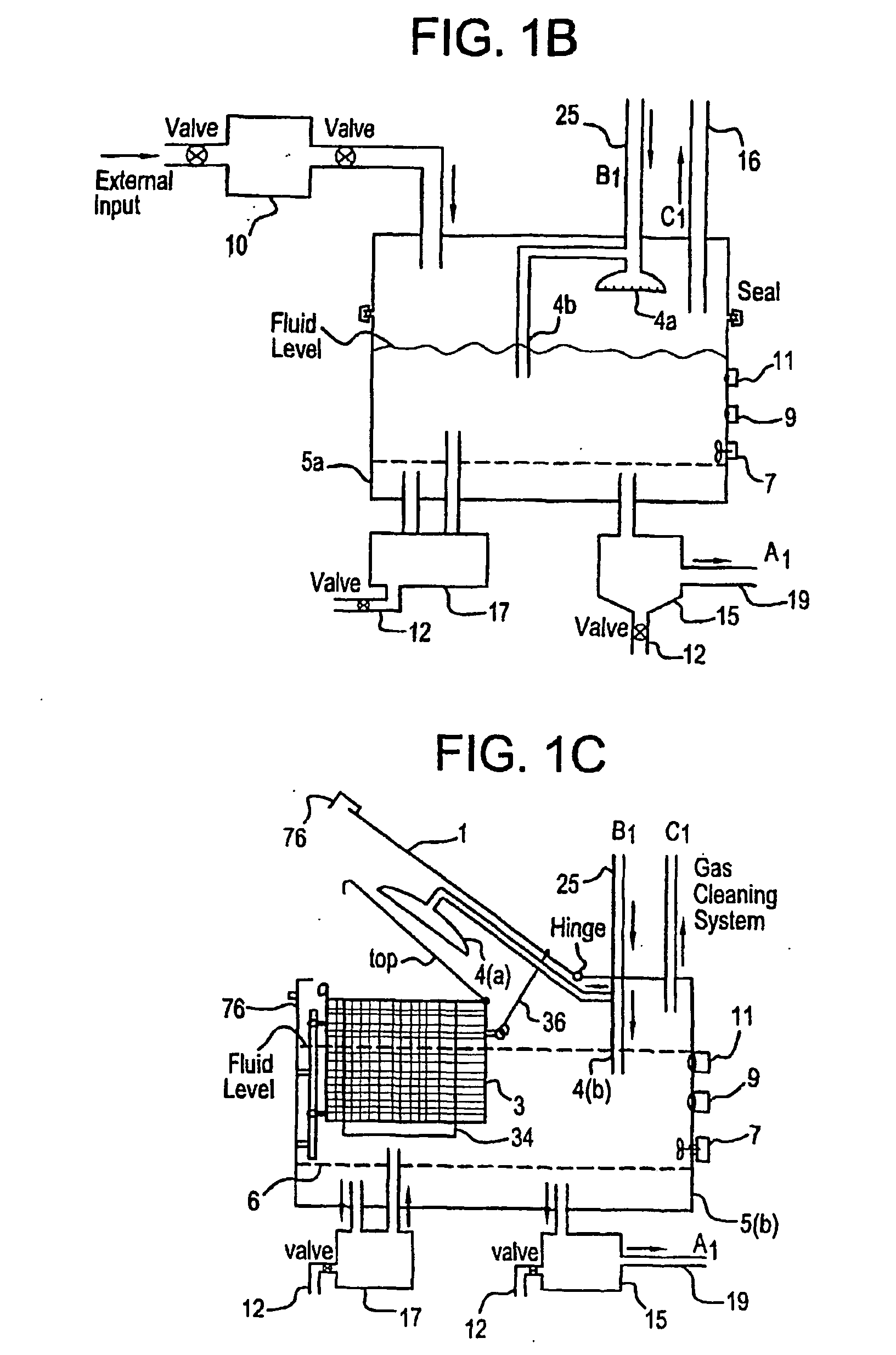
Mediated electrochemical oxidation used for the destruction of organics contaminated with radioactive materials, dissoulution of atransuranics, and the decontamination of equipment contaminated with mixed waste
InactiveUS20060016689A1Improve efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsRadioactive agentLow-level waste
A mixed waste mediated electrochemical oxidation process (MEO) process and apparatus for the dissolution of transuranic elements, and / or compounds thereof in transuranic waste, low level waste (LLW), low level mixed waste, special case waste, and greater than class C LLWS, and also the destruction of the non-fluorocarbon organic component in the waste. The MEO process and apparatus operates in three different modes: dissolution, destruction, and decontamination. In the first mode, dissolution, the process runs until the transuranics such as a mixed oxide or carbide, and / or mixture of oxides or carbides of uranium and plutonium are totally dissolved into solution. The second mode, destruction, the process is operated such that the mixed waste materials are reduced to CO2, water and small amounts of inorganic salts. The third mode, decontamination, involves contaminated equipment. In the decontamination mode the MEO process destroys the mixed wastes that have contaminated the equipment.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
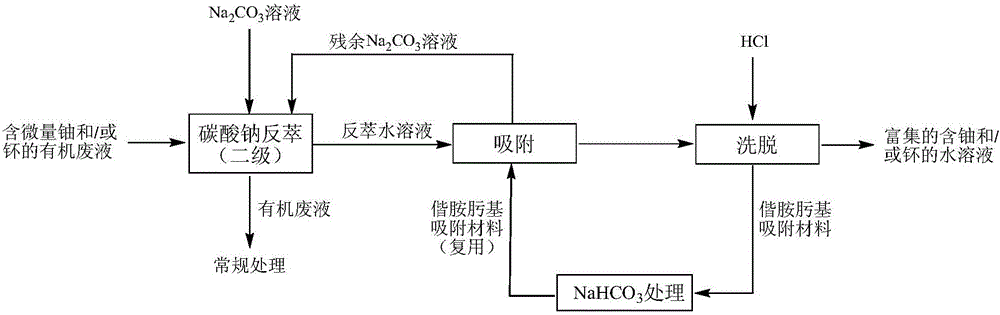
Recovery method for trace of uranium and/or plutonium in radioactive organic liquid waste
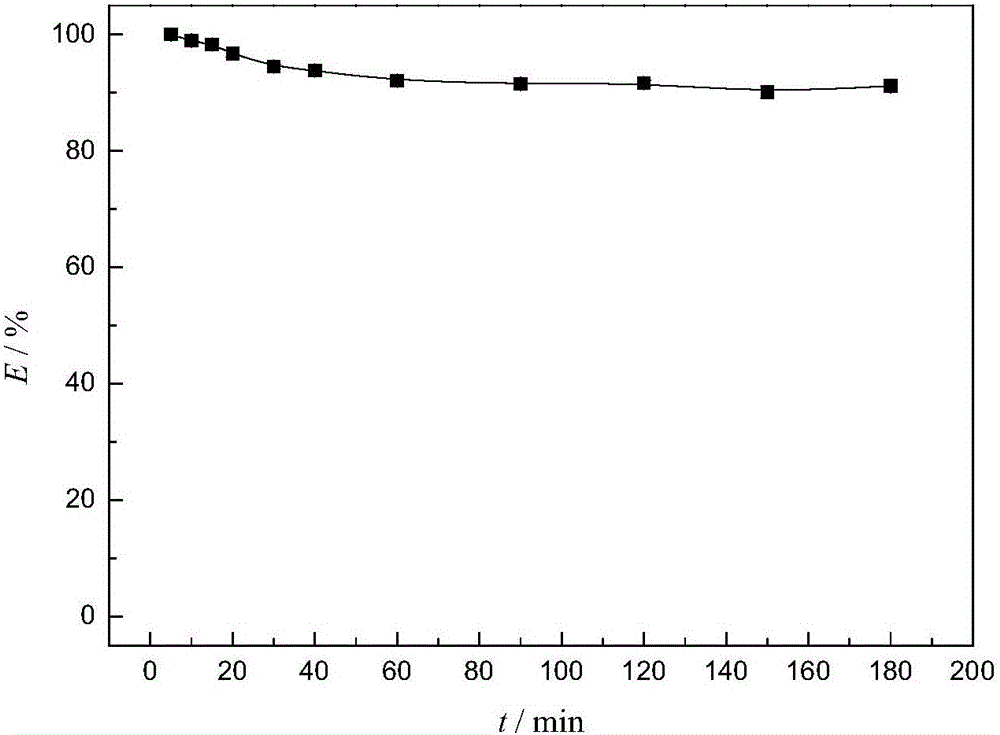
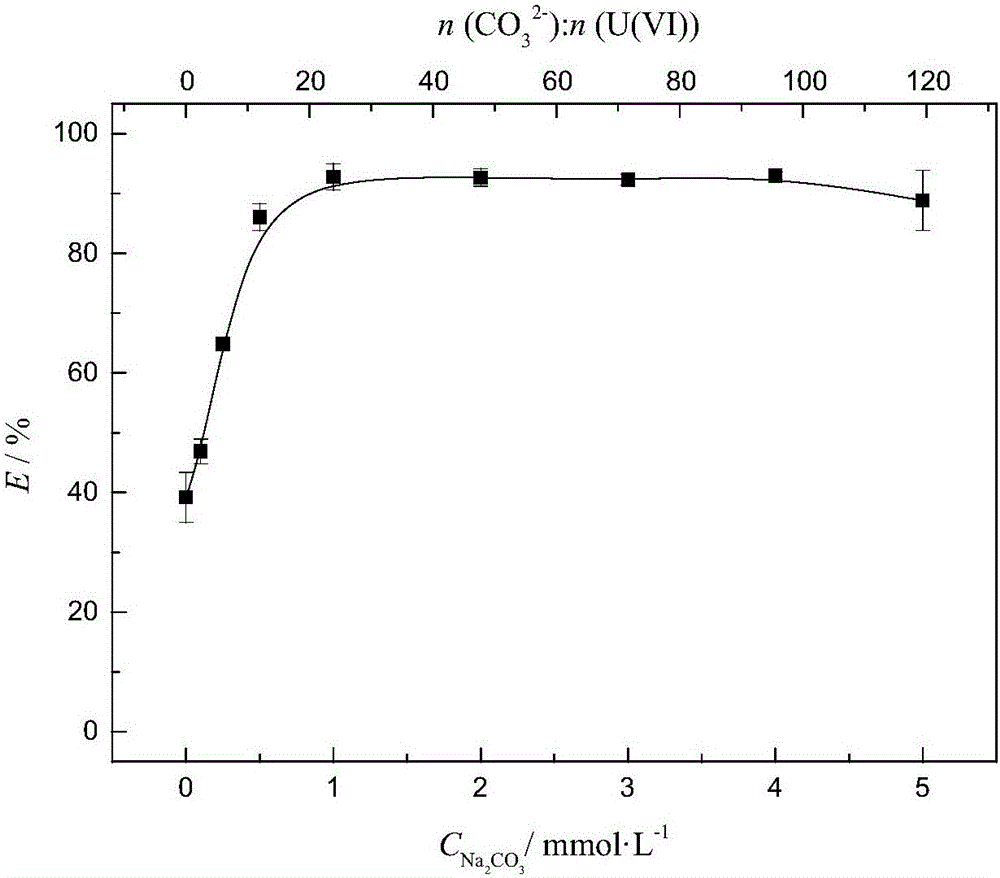
The prevent invention discloses a method for recovering a trace of uranium and / or plutonium from radioactive organic liquid waste. The method comprises: firstly, performing stripping on radioactive organic liquid waste with a carbonate solution; then performing oscillation adsorption, column chromatography or membrane filtration on a stripped aqueous phase by using a solid functional adsorption material; recycling a treated liquid again as a stripping solution; using acid to perform elution on the solid functional adsorption material that adsorbs the uranium and / or plutonium, to obtain a rich aqueous solution containing the uranium and / or plutonium; recycling the adsorption material after the elution by using an aqueous bicarbonate solution for soaking or washing. The method combines stripping of carbonate and recycling of a low concentration of uranium and / or plutonium from a (weak) alkaline aqueous solution, and achieves recycling of the functional adsorption material and the stripping solution, thereby reducing the amount of waste as much as possible.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Continuous process electrorefiner
A new device is provided for the electrorefining of uranium in spent metallic nuclear fuels by the separation of unreacted zirconium, noble metal fission products, transuranic elements, and uranium from spent fuel rods. The process comprises an electrorefiner cell. The cell includes a drum-shaped cathode horizontally immersed about half-way into an electrolyte salt bath. A conveyor belt comprising segmented perforated metal plates transports spent fuel into the salt bath. The anode comprises the conveyor belt, the containment vessel, and the spent fuel. Uranium and transuranic elements such as plutonium (Pu) are oxidized at the anode, and, subsequently, the uranium is reduced to uranium metal at the cathode. A mechanical cutter above the surface of the salt bath removes the deposited uranium metal from the cathode.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Control of a laser inertial confinement fusion-fission power plant
ActiveUS9171646B2Extended service lifeNuclear energy generationWaste based fuelFusion fissionEngineering
A laser inertial-confinement fusion-fission energy power plant is described. The fusion-fission hybrid system uses inertial confinement fusion to produce neutrons from a fusion reaction of deuterium and tritium. The fusion neutrons drive a sub-critical blanket of fissile or fertile fuel. A coolant circulated through the fuel extracts heat from the fuel that is used to generate electricity. The inertial confinement fusion reaction can be implemented using central hot spot or fast ignition fusion, and direct or indirect drive. The fusion neutrons result in ultra-deep burn-up of the fuel in the fission blanket, thus enabling the burning of nuclear waste. Fuels include depleted uranium, natural uranium, enriched uranium, spent nuclear fuel, thorium, and weapons grade plutonium. LIFE engines can meet worldwide electricity needs in a safe and sustainable manner, while drastically shrinking the highly undesirable stockpiles of depleted uranium, spent nuclear fuel and excess weapons materials.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Combinations of liquid filtration media and methods for enhanced filtration of selected water contaminants
InactiveUS20130022686A1Solve Porosity InsufficiencyAvoid bleedingBiocideInorganic active ingredientsFiltrationManganese
By sequentially aligning various filtration media and delivery systems, enhanced synergistic reduction of water contaminants is obtained compared to the prior art or separate use of the individual media / filters. Specific filtration media are formulated with proper proportioning and sequencing to enhance the ability to reduce metals that cause staining, odors and bad taste such as iron, copper and manganese. Also disclosed is the reduction of potentially hazardous metal radionuclides metals such as uranium, iodine, cesium, plutonium and radium. Also disclosed is improved removal of heavy metals such as arsenic, lead, chromium, and mercury as well as organic compounds such as halogenated carcinogenic compounds. The present devices and methods remove specific bacteria and their toxins from water to reduce the risk of dermatitis. Thus, the present invention enhances our ability to achieving cleaner and safer water for drinking, swimming, washing, bathing and cooking.
Owner:HYDROPURE TECH
High-temperature supercritical nuclear reactor
InactiveCN102568624AImprove economyTake advantage ofNuclear energy generationCooling arrangementFast-neutron reactorMaterials science
The invention relates to a high-temperature supercritical nuclear reactor. A spherical solid is used as a coolant of the nuclear reactor, which is different from common nuclear reactors that adopt light water, heavy water, gas and liquid sodium. The spherical solid coolant can be graphite spheres coated with silicon carbide, stainless steel spheres, graphite spheres coated with stainless steel and the like. The spherical solid has the characteristic of good rolling ability, so that the spherical solid can roll to a steam generator under the action of gravity after heating in the reactor, and the purpose of transferring heat from the reactor to the steam generator is achieved. The reactor is applicable to both thermal neutron reactor and fast neutron reactor, and natural uranium, low-enriched uranium, plutonium and thorium can be used as nuclear fuel. The temperature of high-temperature steam / water outputted by the steam generator can reach 900 DEG C, the same parameters to a thermal power station can be reached, the requirement of supercritical even ultra-supercritical can be satisfied, and the high-temperature supercritical nuclear reactor has high safety and reliability.
Owner:李正蔚
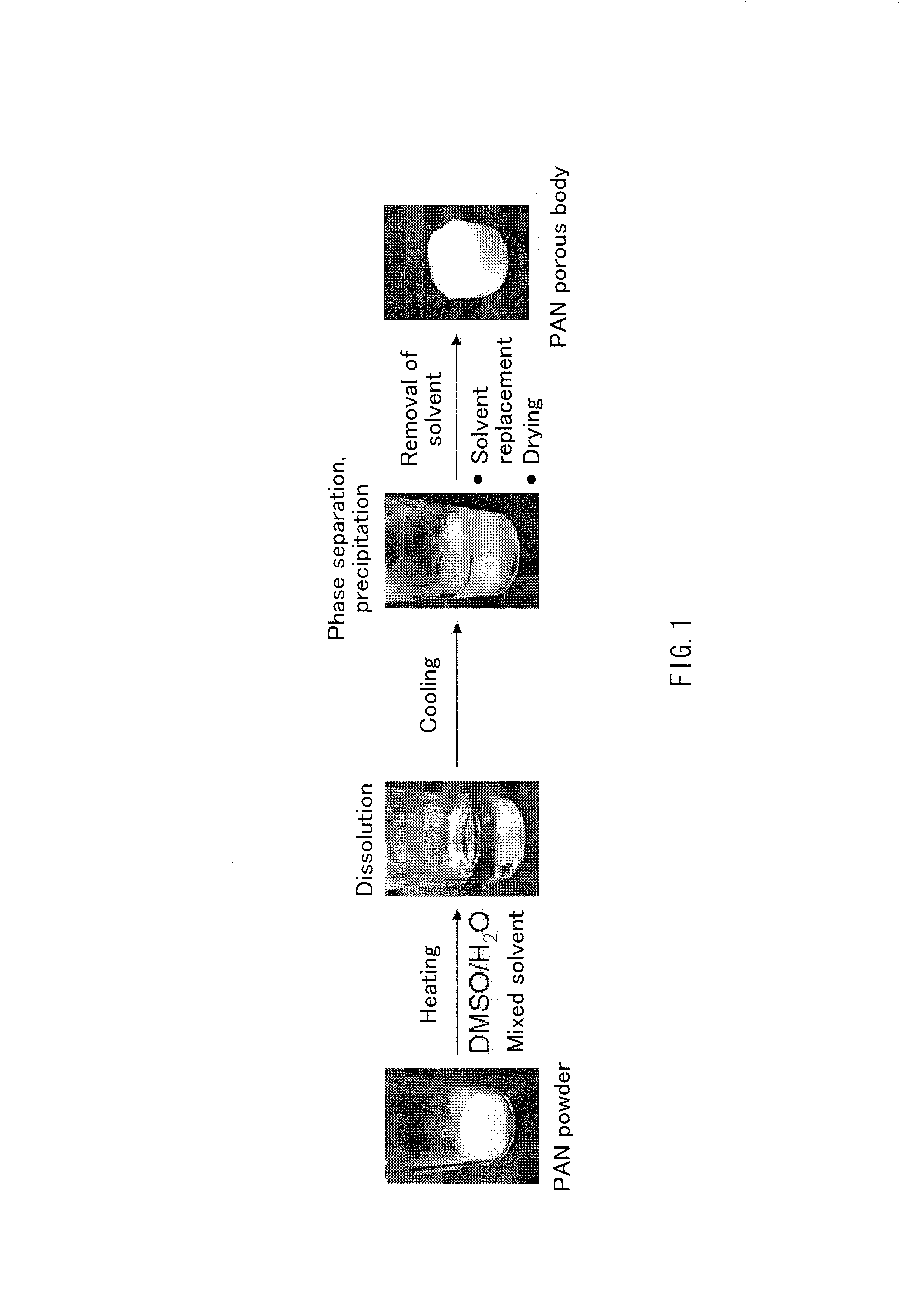
Amidoxime-modified polyacrylonitrile porous body
InactiveUS20130168322A1High metal adsorption capabilityCertain thicknessComponent separationOther chemical processesHydroxylamineIndium
An amidoxime-modified PAN porous body obtained by reacting with hydroxylamine a polyacrylonitrile porous body that is monolithic, has a thickness of 1 mm or more and contains polyacrylonitrile (PAN) as the main component to convert a nitrile group of the polyacrylonitrile porous body into an amidoxime group. This porous body is a porous body for adsorbing a metal ion, for example, an ion of metal such as copper, iron, nickel, vanadium, indium, gallium, silver, mercury, lead, uranium, plutonium, cesium, barium, lanthanum, thallium and strontium.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
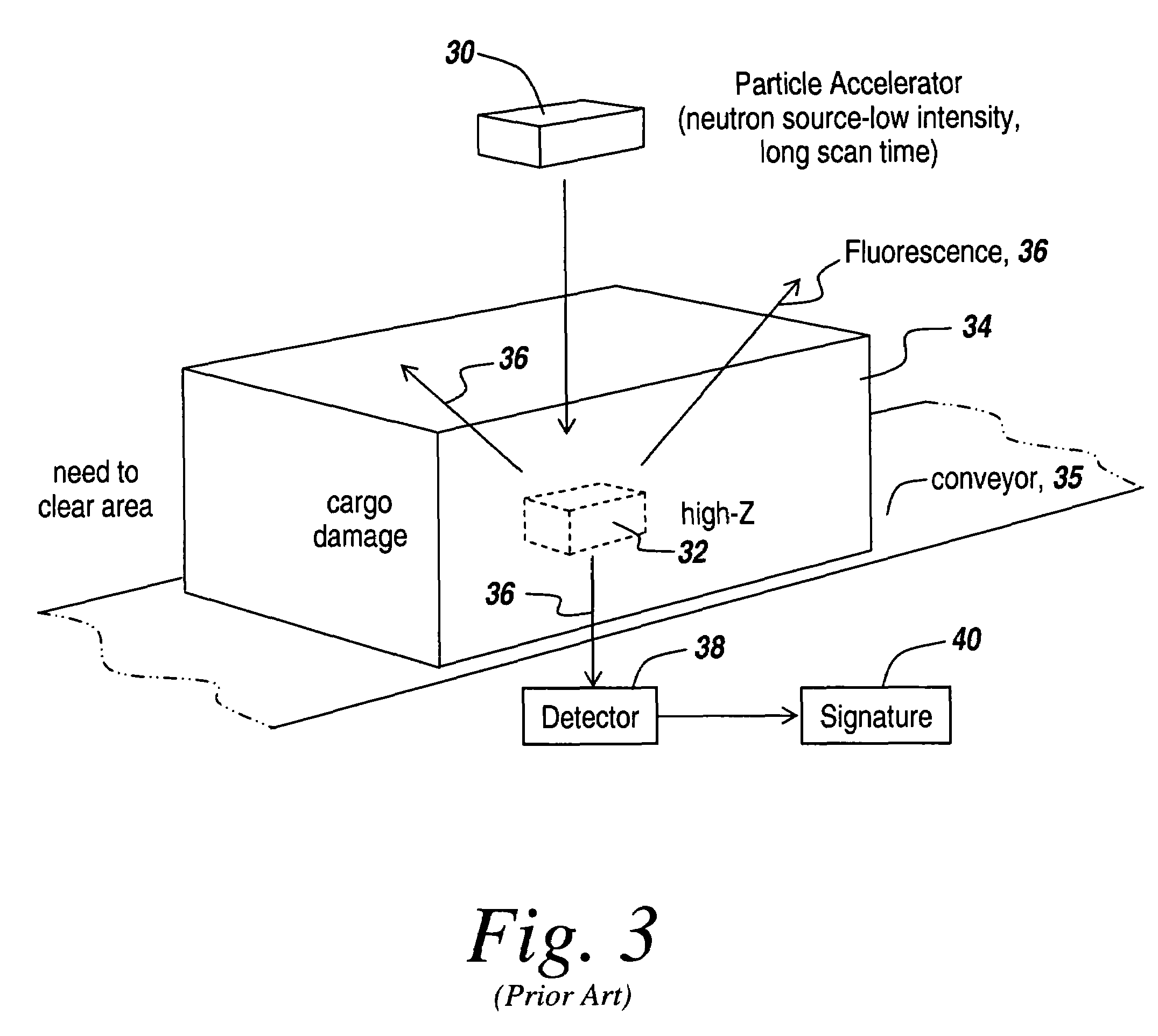
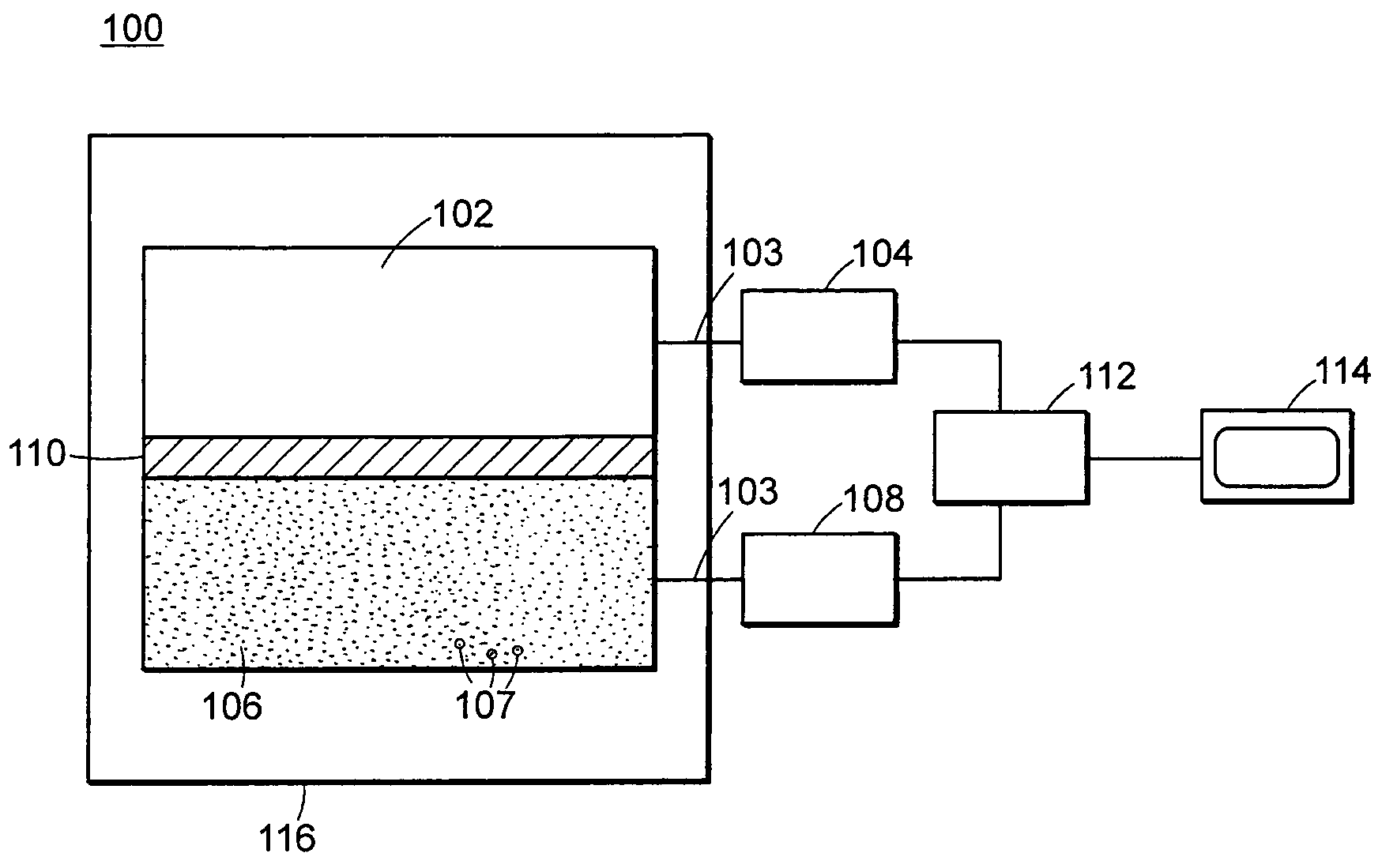
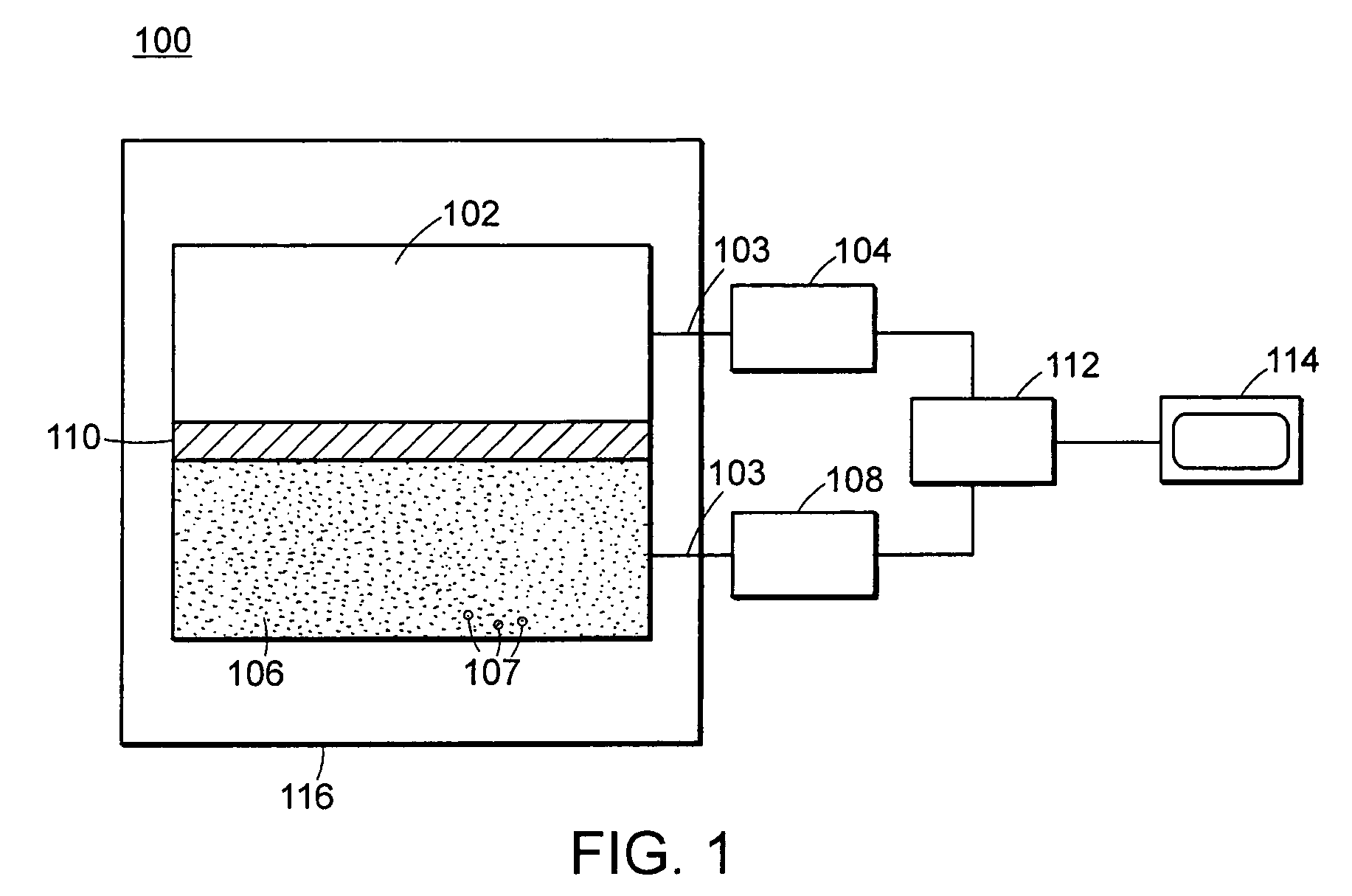
Apparatus and method for detection of fissionable materials
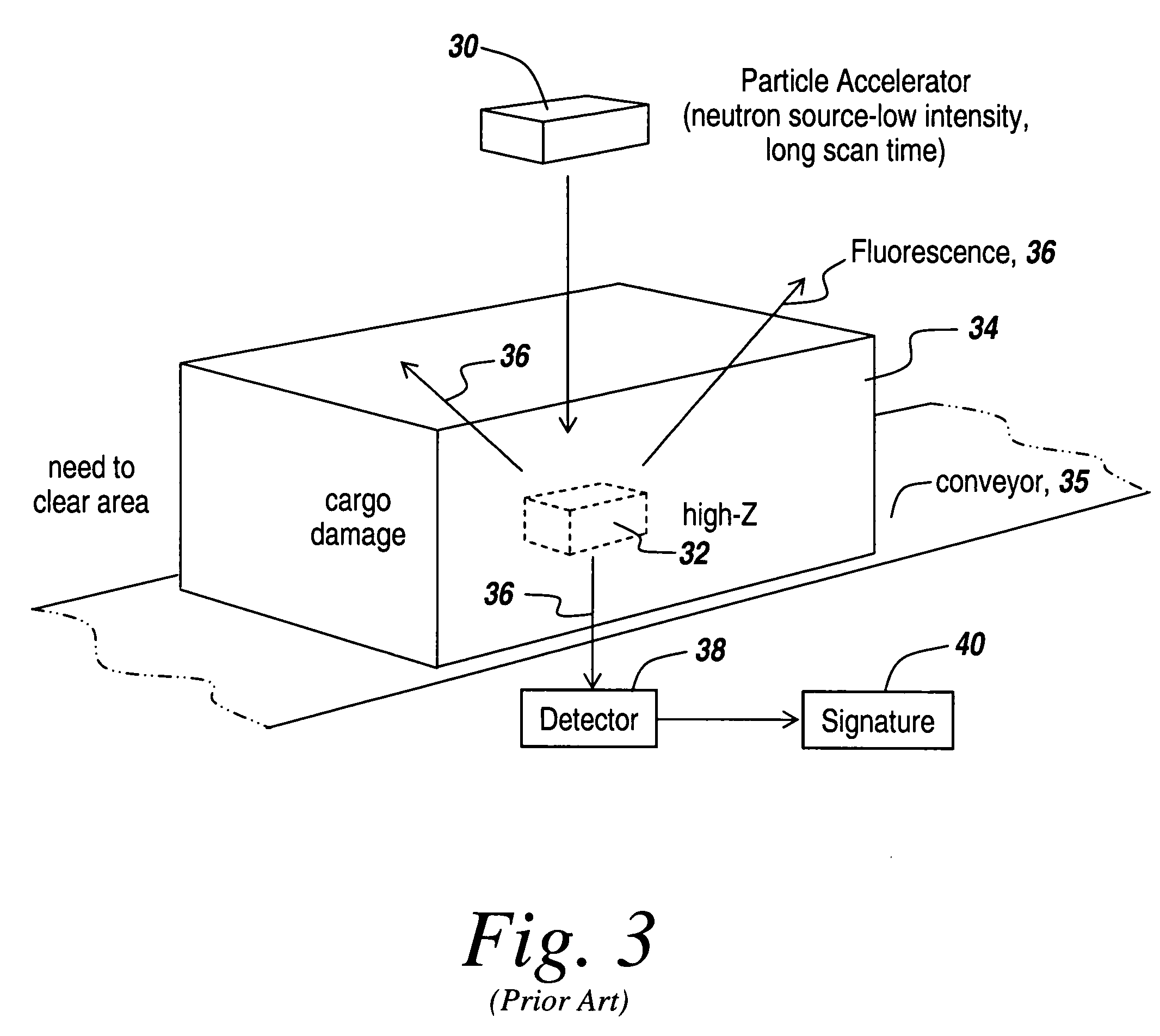
An apparatus and method for the detection of fissionable materials (e.g. uranium and plutonium) in cargo, vehicles, soil, waste, etc. utilizing a penetrating photon beam causing emission of neutrons from such materials. The neutrons are detected by selected detectors able to function throughout an appropriate test and emission period. Suitable detectors are of the super-heated droplet type. The photon energy, beam intensity and direction, number of beams, emission period and detector arrangement are chosen to give the desired sensitivity for the fissionable elements of concern.
Owner:BUBBLE TECH INDS
Nano polishing solution for chemically mechanical polishing of vanadium oxide and application thereof
ActiveCN102127372AEasy to corrodeEasy to polluteBiocideOther chemical processesOrganic basePolyethylene glycol
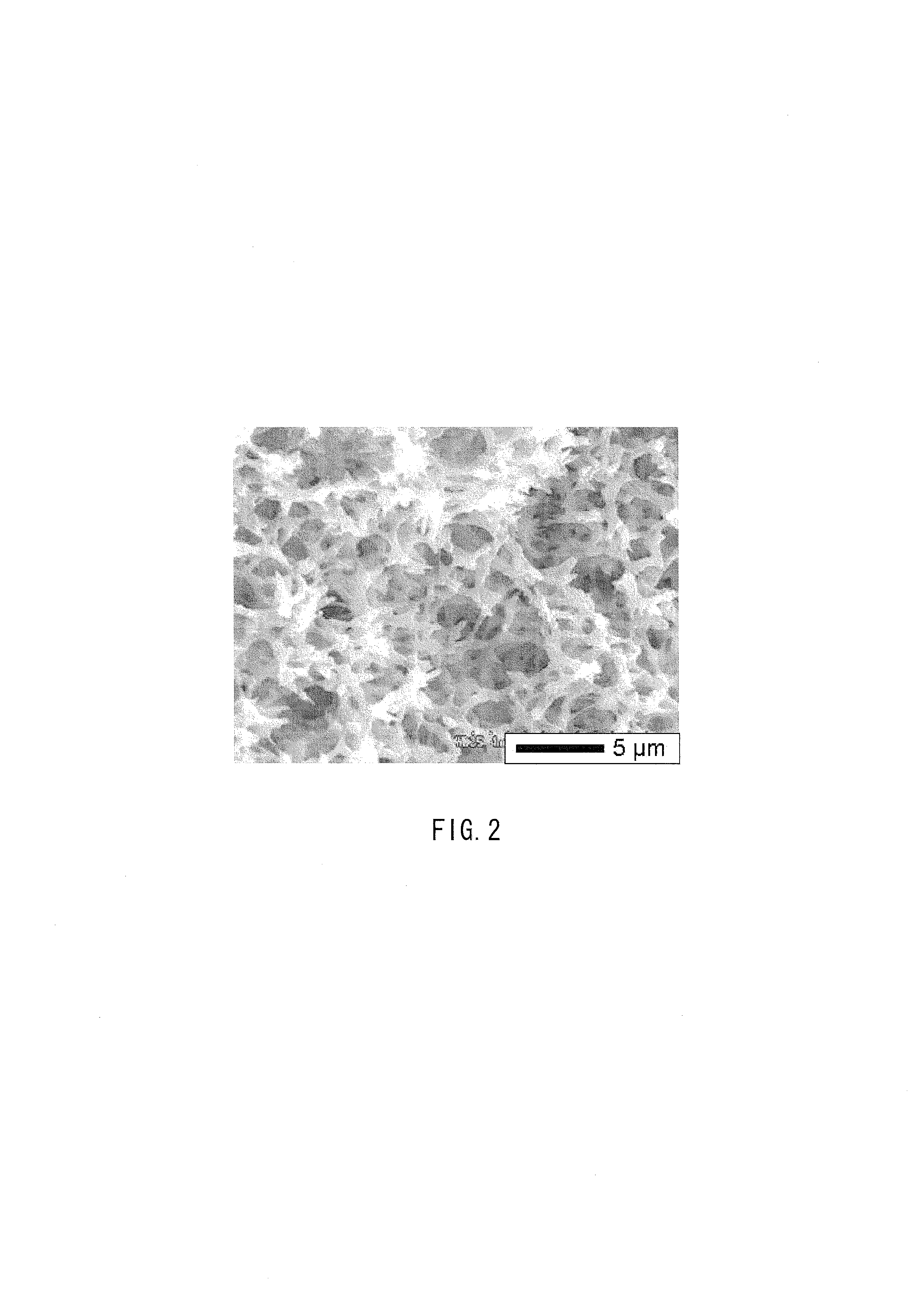
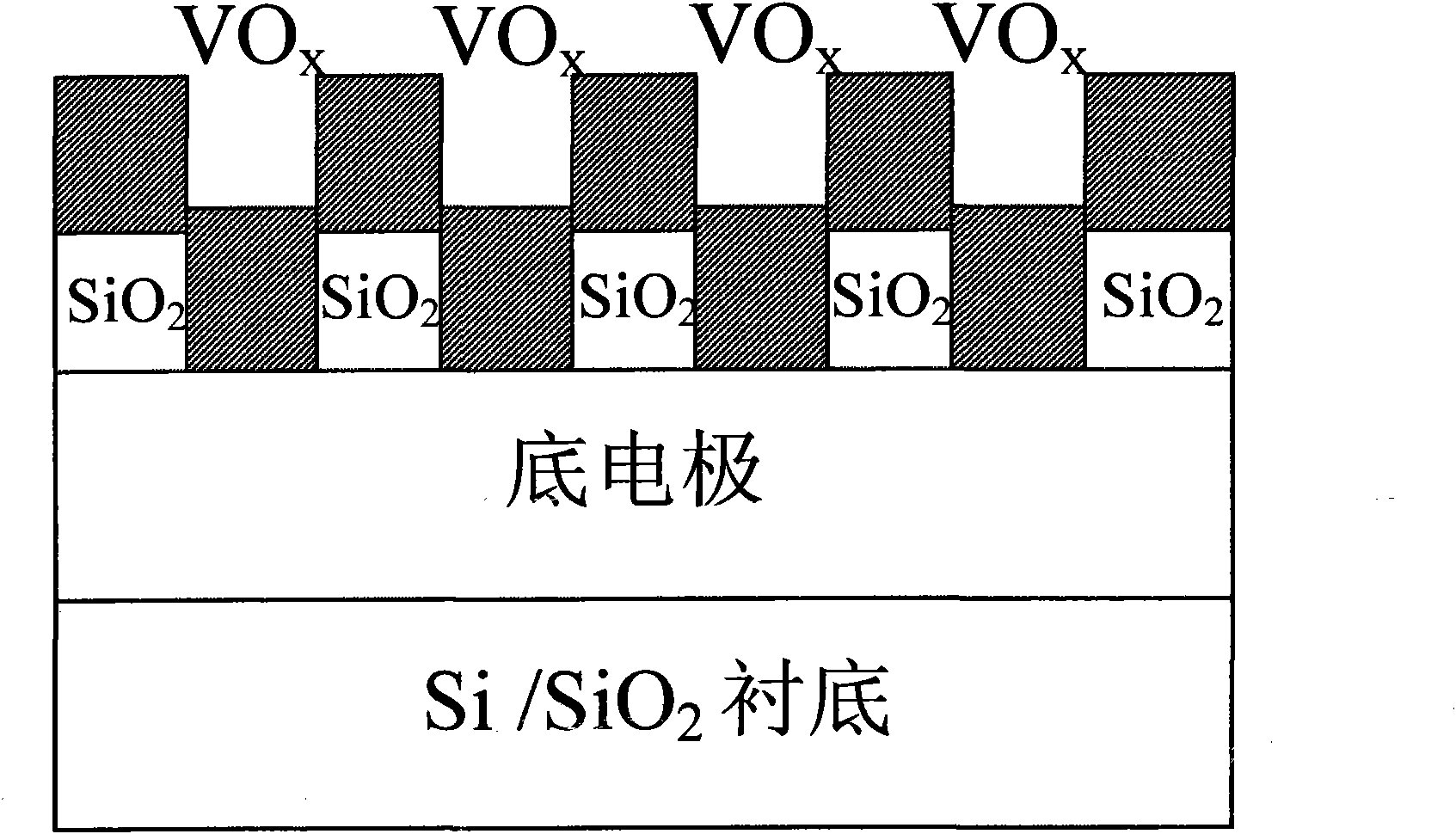
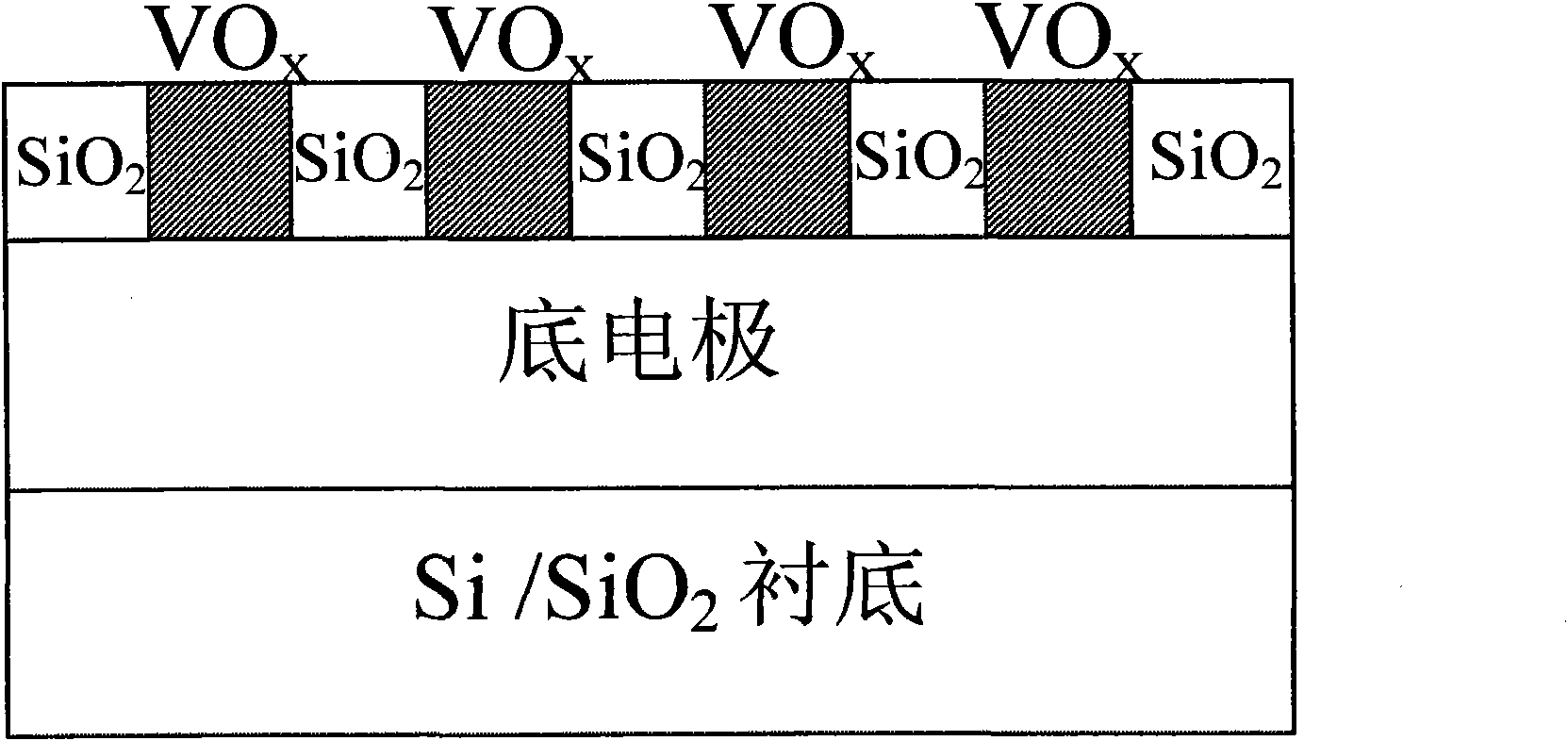
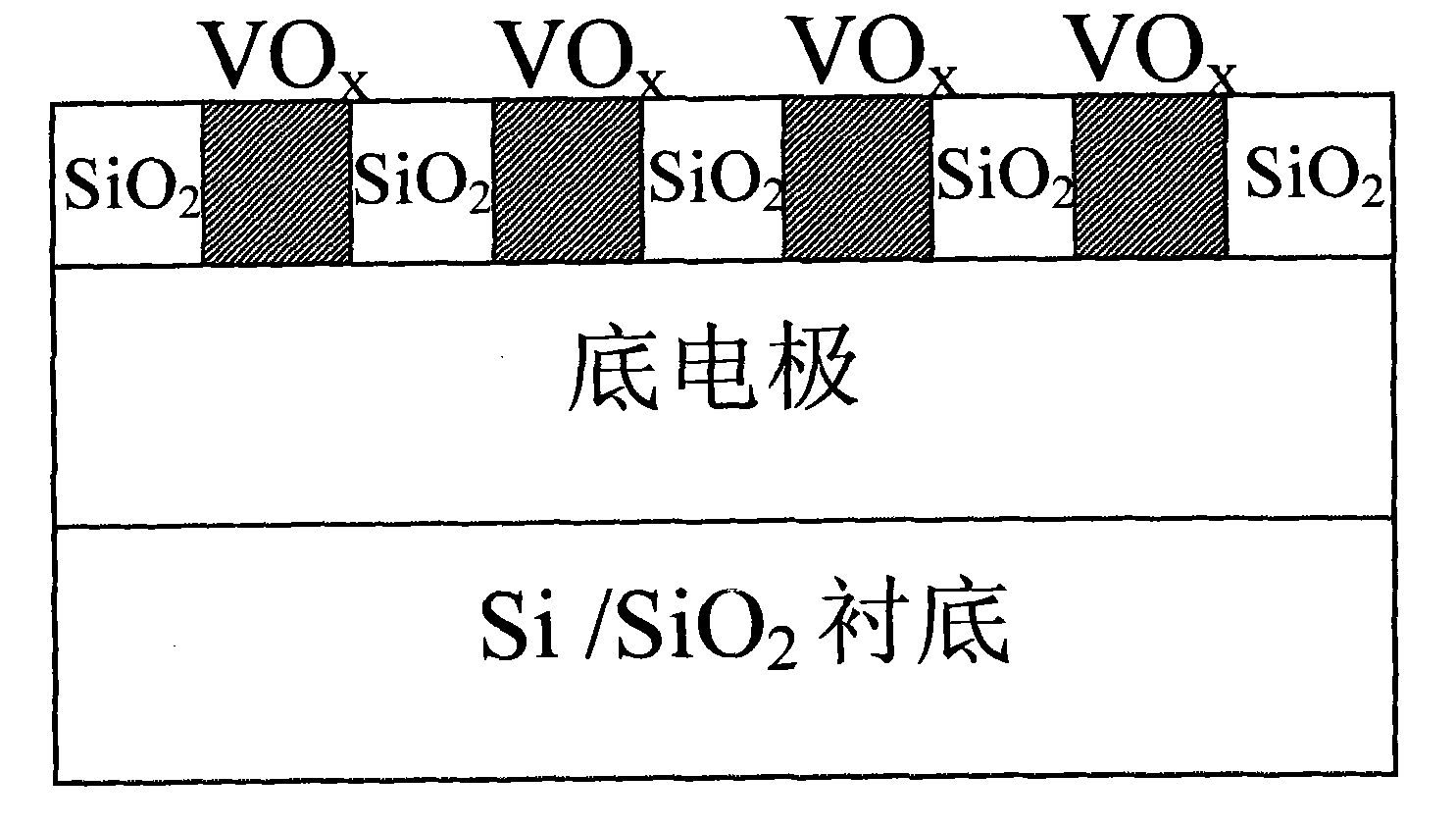
The invention relates to nano polishing solution for chemically mechanical polishing of vanadium oxide, which consists of a nano-abrasive, a pH regulator, a surfactant, a defoaming agent, a bactericide, a cleaning aid and a solvent, wherein the nano-abrasive is zirconium oxide, titanium oxide, plutonium oxide or silica; the pH regulator comprises inorganic base of KOH and organic base of tetramethylammonium, tetraethyl ammonium hydroxide or hydroxy amine; the surfactant is silicane polyethylene glycol ether, polyethylene glycol ether or 2-(2-dodecyloxyethoxy)ethanol; the defoaming agent is poly(dimethylsilane); the bactericide is isomerous thiazolidinone; the cleaning aid is isopropanol; and the solvent is deionized water. The invention has the advantages that: the polishing rate is stably controllable, the damage is low, the cleaning is simple, equipment is not corroded, the environment is not polluted, and the storage time is long; and a vanadium oxide film material is subjected to the chemically mechanical polishing by the nano polishing solution for preparing a resistive random access memory, and the method is simple and practicable, and is completely compatible with an integrated circuit process.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
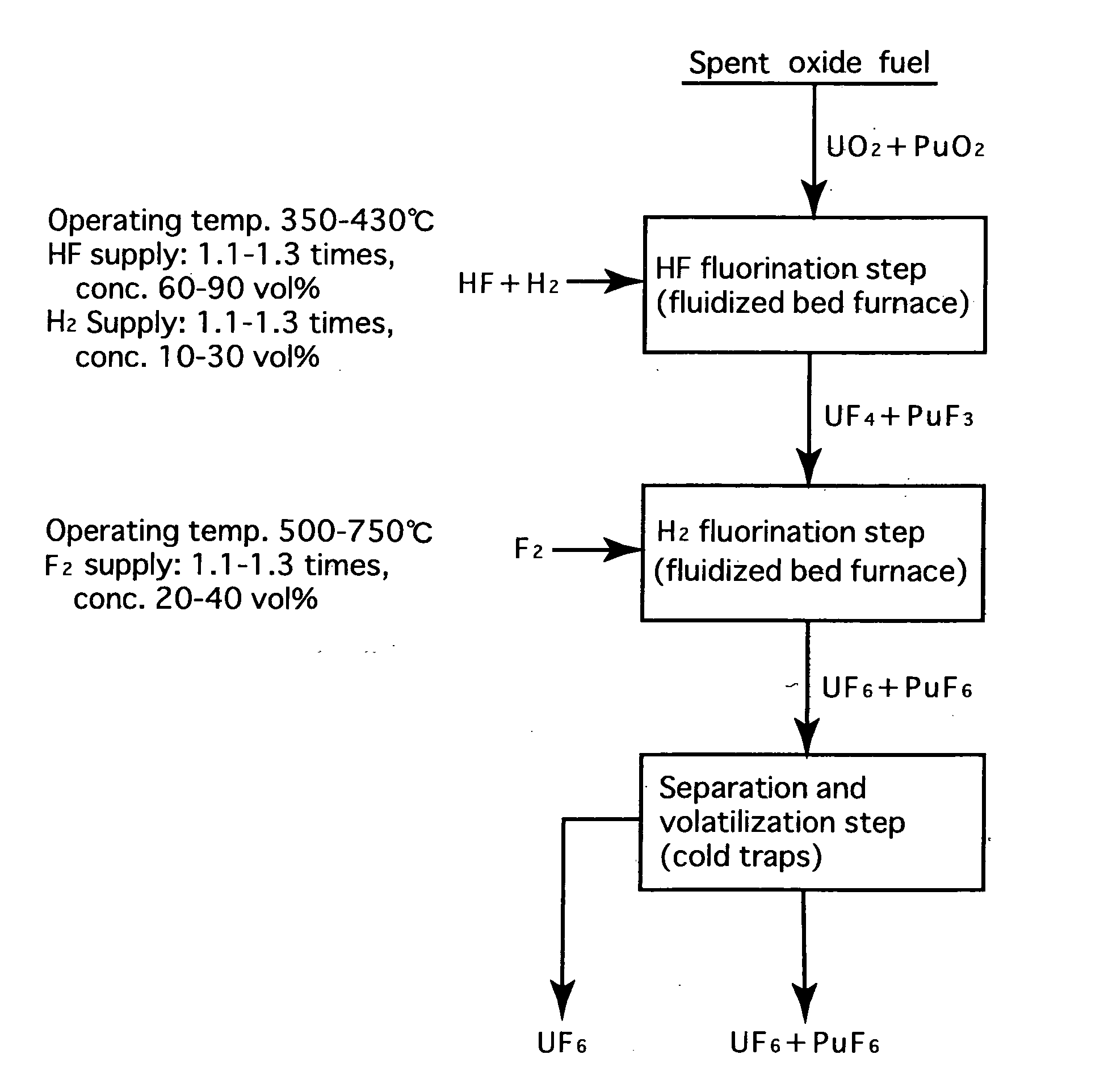
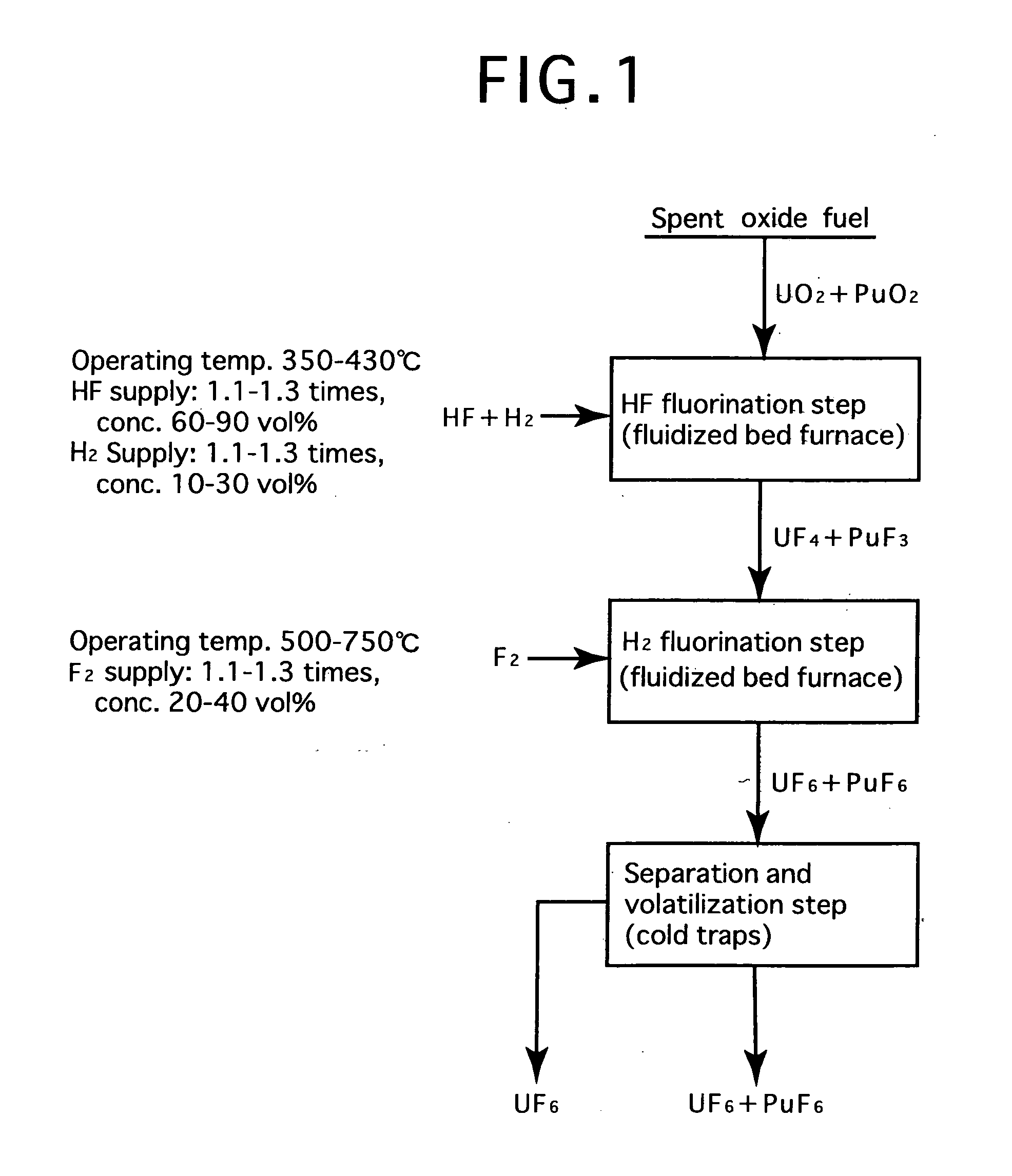
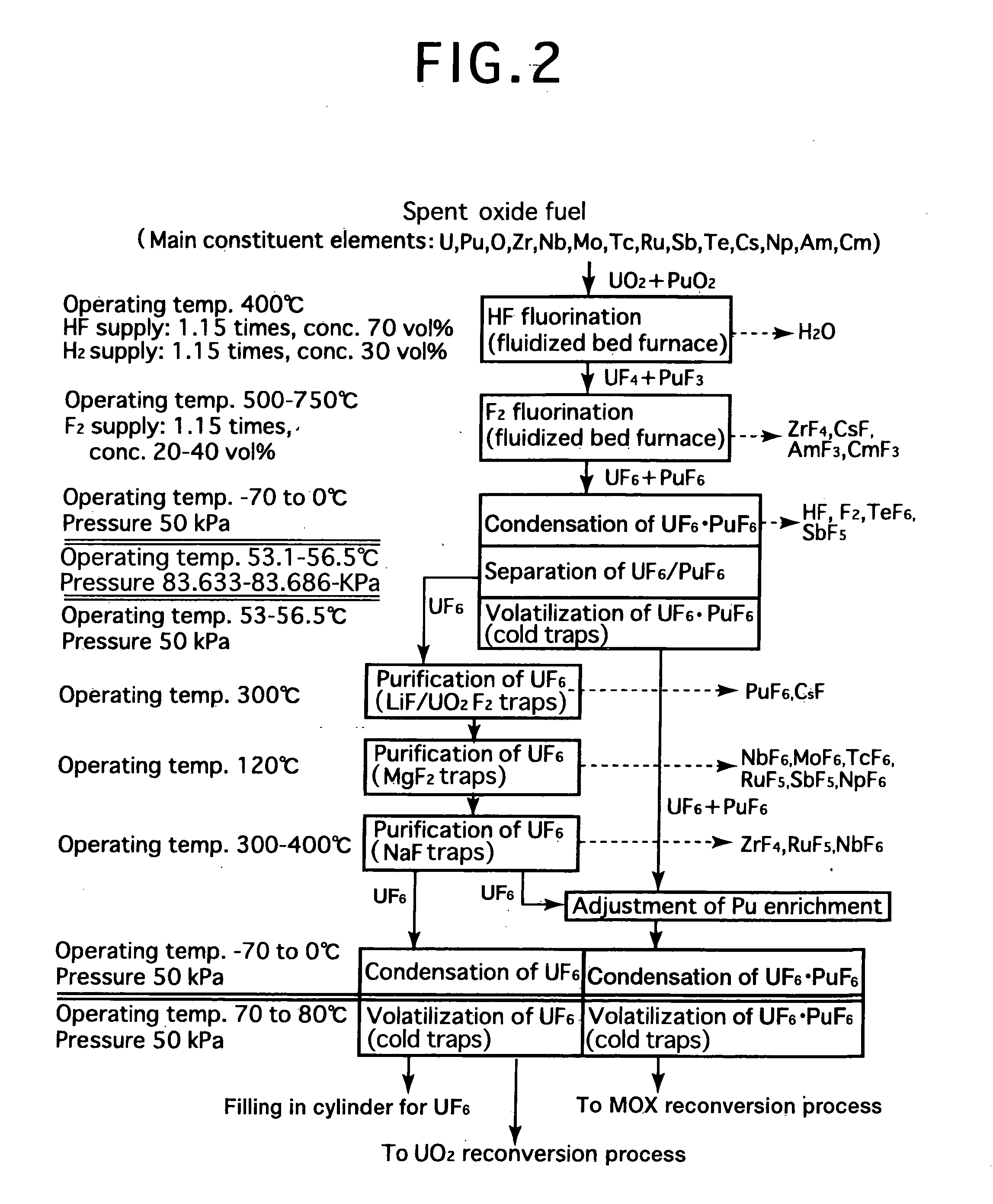
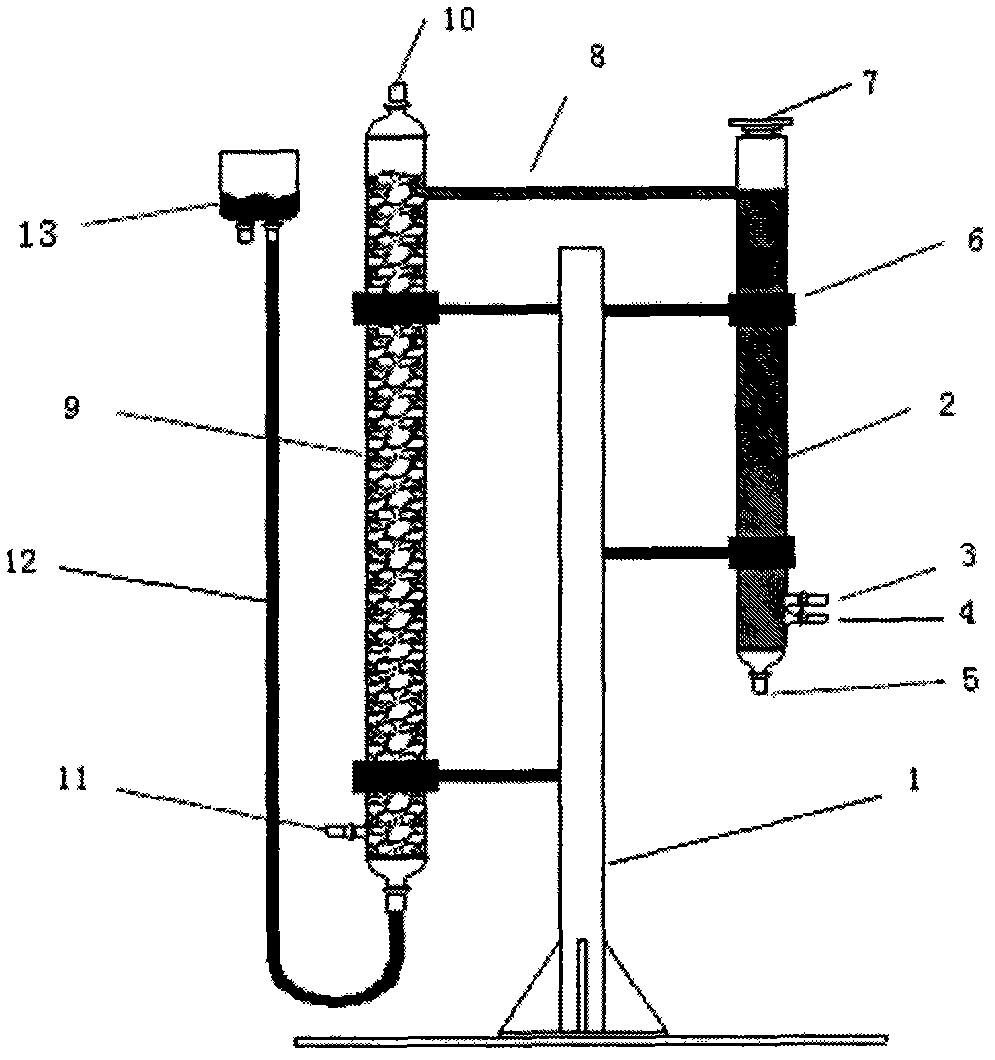
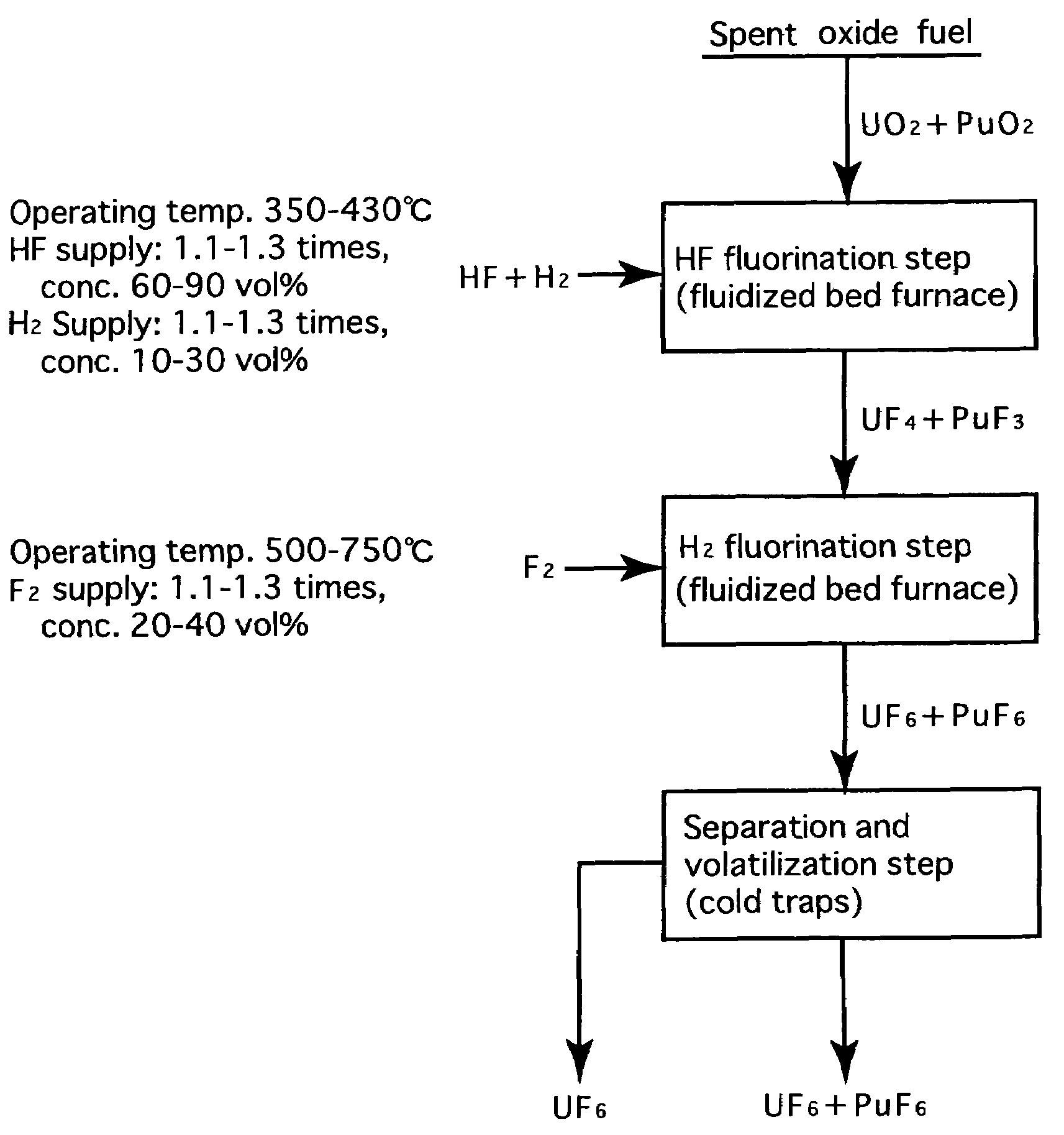
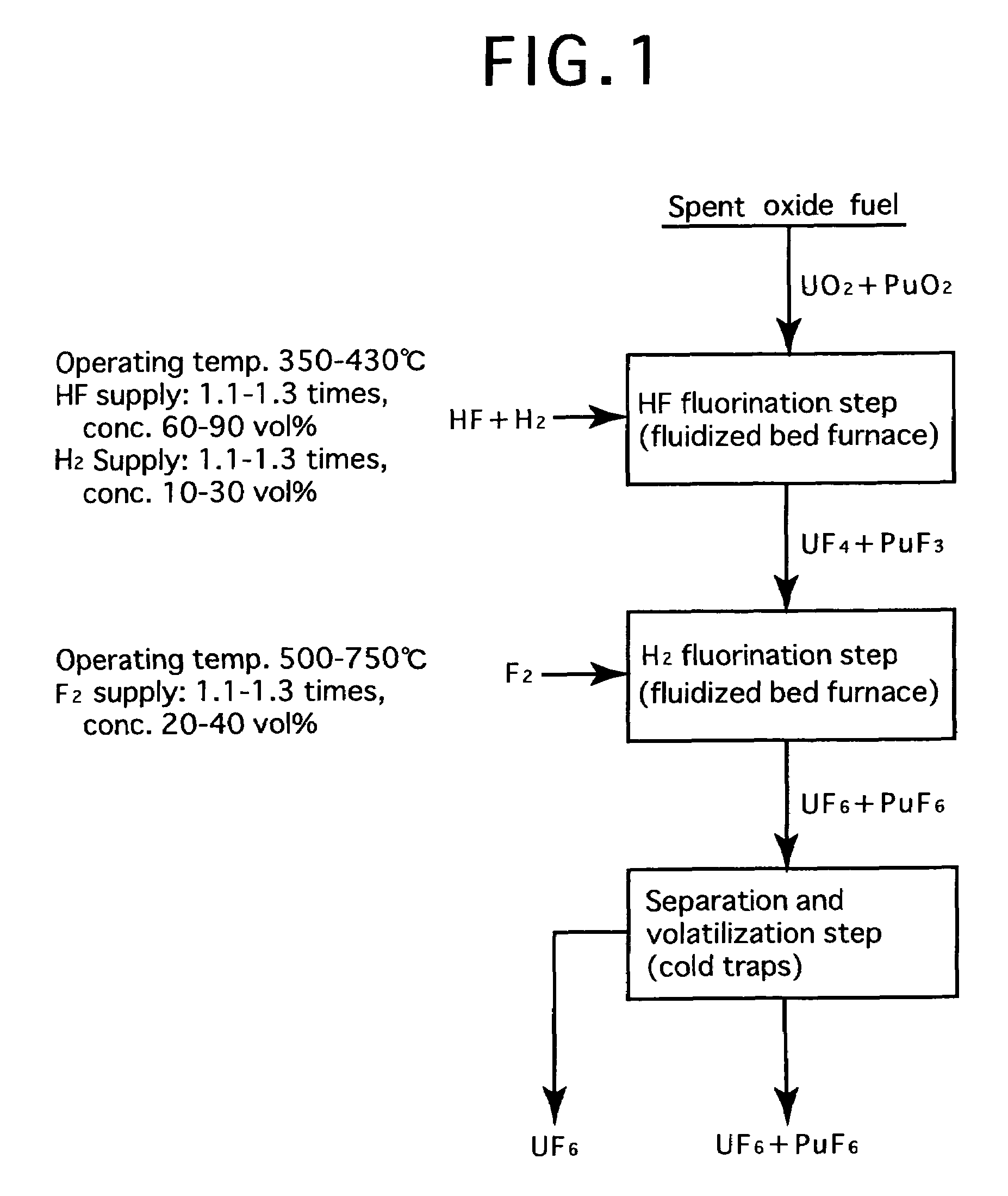
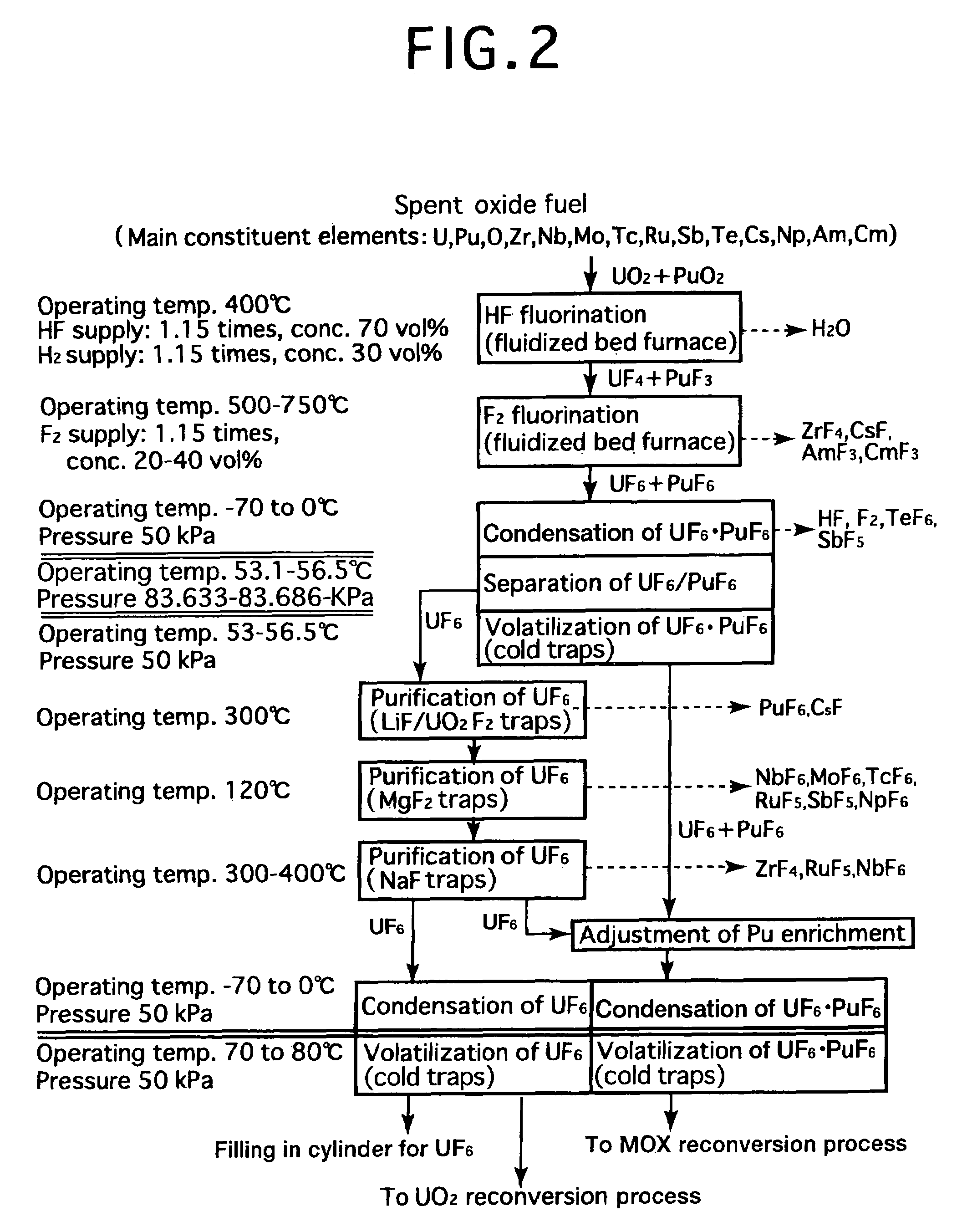
Reprocessing method by fluoride volatility process using fractional distillation
InactiveUS20060057042A1Increase ratingsRaise the ratioPlutonium compoundsUranium fluoridesHydrogen fluorideHydrogen
Fluorine or a fluorine compound is subjected to a reaction with a spent oxide fuel to produce fluorides of uranium and plutonium, and recovering the fluorides using a difference in volatility behavior. The method includes steps of: subjecting a mixture of UO2 and PuO2 with hydrogen fluoride mixed with hydrogen to HF-fluorinate uranium and plutonium into UF4 and PuF3; subjecting UF4 and PuF3 with a fluorine gas to F2-fluorinate uranium and plutonium into UF6 and PuF6; and fractionating UF6 and PuF6 using a difference in phase change of obtained UF6and PuF6, removing a part of UF6, and volatilizing the remaining UF6 and PuF6 at the same time. By such a reprocessing method, PuF4 hard to undergo a reaction is prevented from being formed as an intermediate fluoride, the material of a reactor is hard to be corroded, and a consumption of expensive fluorine gas is reduced.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
Portable/mobile fissible material detector and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20100301196A1Reduce total powerSmall sizeLaser detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDelayed neutronPu element
A portable and / or mobile detector for highly enriched uranium (HEU) and weapon grade plutonium (WGPu) is disclosed the detects HEU and / or WGPu based on neutron induced fission of a portion of the HEU and / or WGPu and detecting delayed neutron and / or γ-rays emission from delayed neutron emitters formed from the induced fission reactions.
Owner:CHU WEI KAN +1
Device for oxidized adjusting plutonium valence by N2O4
ActiveCN102412002AImprove contact effectNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsNitric oxideNitrogen oxide
The invention discloses a device for oxidized adjusting plutonium valence by N2O4, comprising a Pu (III) oxidized column and a nitrous acid eliminating column, wherein the Pu (III) oxidized column and the nitrous acid eliminating column are connected via a material fluid transporting pipe. The device provided by the invention increases the utilization rate of the N2O4, reduces the escaped nitric oxide and realizes the continuous operation of the plutonium valence adjusting process and the remaining nitrous acid eliminating process.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Reprocessing method by fluoride volatility process using fractional distillation
InactiveUS7323153B2Reduce consumptionNot easy to corrodePlutonium compoundsUranium fluoridesHydrogen fluorideFluoride volatility
Fluorine or a fluorine compound is subjected to a reaction with a spent oxide fuel to produce fluorides of uranium and plutonium, and recovering the fluorides using a difference in volatility behavior. The method includes steps of: subjecting a mixture of UO2 and PuO2 with hydrogen fluoride mixed with hydrogen to HF-fluorinate uranium and plutonium into UF4 and PuF3; subjecting UF4 and PuF3 with a fluorine gas to F2-fluorinate uranium and plutonium into UF6 and PuF6; and fractionating UF6 and PuF6 using a difference in phase change of obtained UF6 and PuF6, removing a part of UF6, and volatilizing the remaining UF6 and PuF6 at the same time. By such a reprocessing method, PuF4 hard to undergo a reaction is prevented from being formed as an intermediate fluoride, the material of a reactor is hard to be corroded, and a consumption of expensive fluorine gas is reduced.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
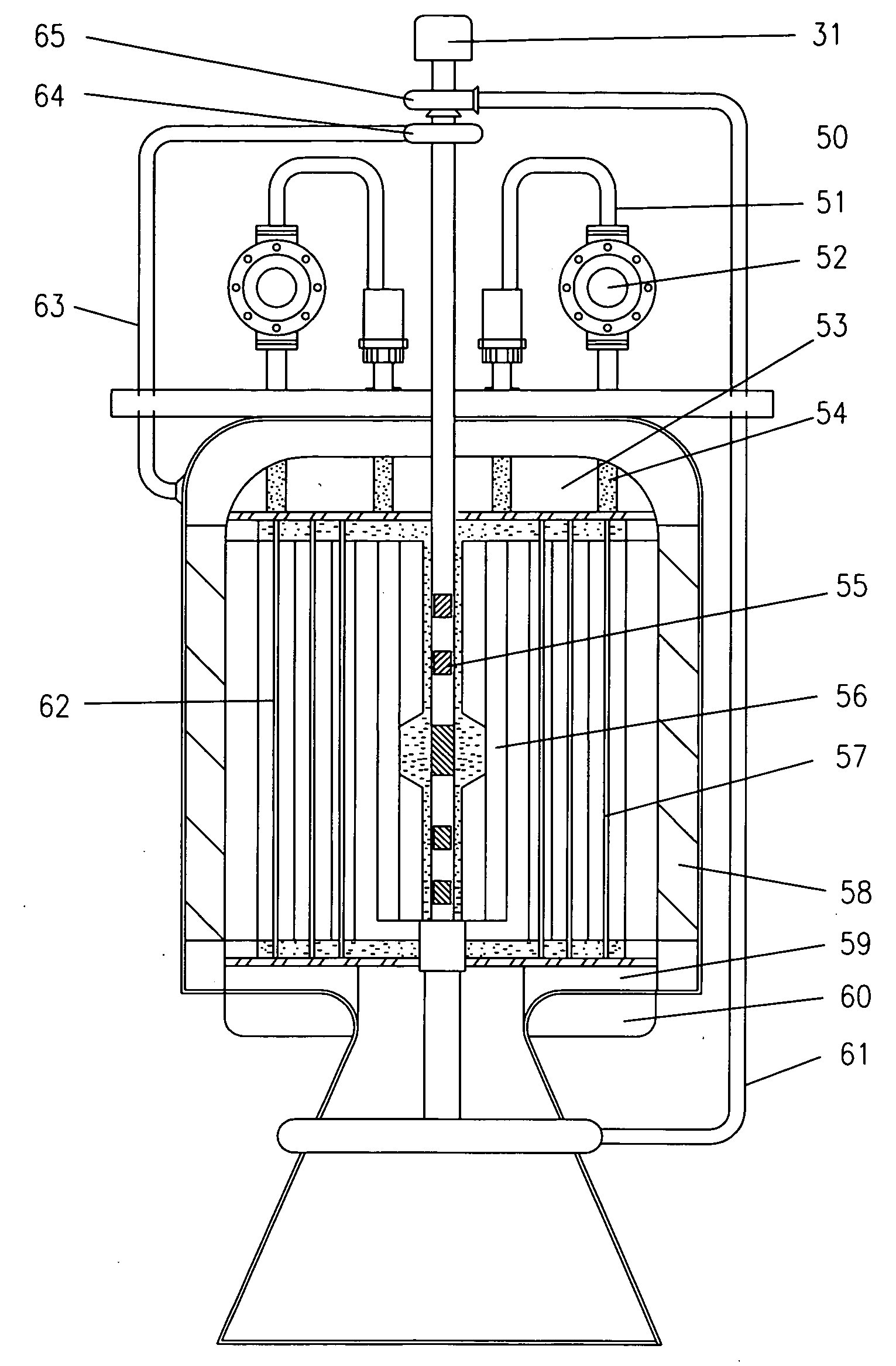
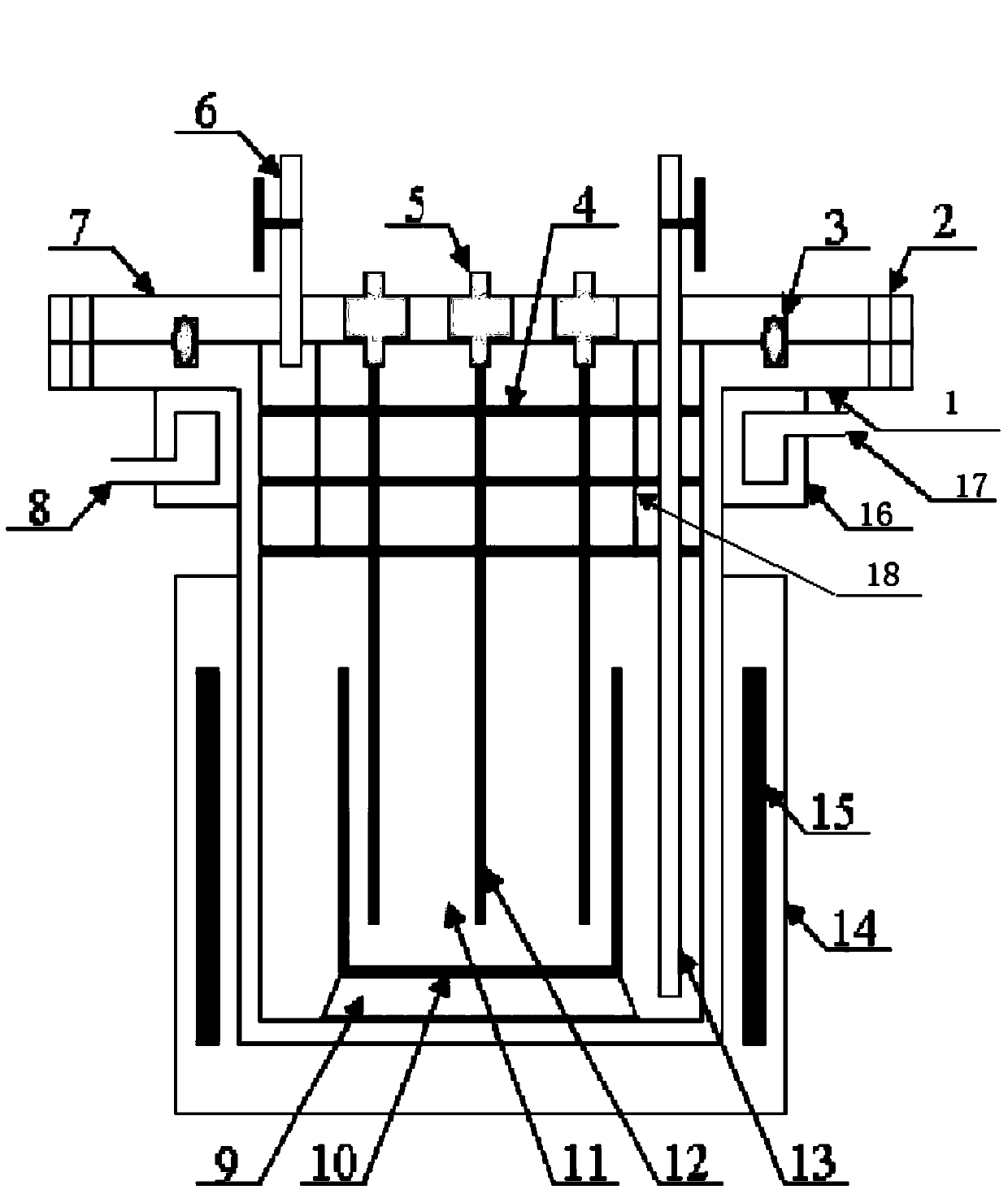
Sealed high-temperature electrochemical measuring device
The embodiment of the invention provides a sealed high-temperature electrochemical measuring device which comprises a sealing device, a heating device, an electrode body and a gas inlet and outlet, wherein the sealing device comprises an upper flange and a lower flange; both the upper flange and the lower flange are made of high-temperature alloys; the lower flange is tank-shaped; the upper flange is cover-shaped and is positioned at the opening of the lower flange; the upper flange and the lower flange are sealed through a metal graphite sealing ring and a bolt; the heating device is positioned on the outer side of the lower part of the lower flange and wraps the lower part of the lower flange; the electrode body and the upper flange are integrally designed; the electrode body extends into molten salt contained in a crucible in the tank body of the lower flange, and is used for outputting electrochemical signals from the sealed high-temperature electrochemical measuring device; the gas inlet and outlets are integrated on the upper flange in a sealed manner and are used for feeding and discharging inert gases. According to the embodiment of the invention, the device has the functions of high-temperature heating, high-temperature sealing, inert atmosphere protection, electrochemical signal output under sealing condition, and the like, and the accuracy in fused salt electrochemical measurement on uranium, plutonium and bothridium elements is improved.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
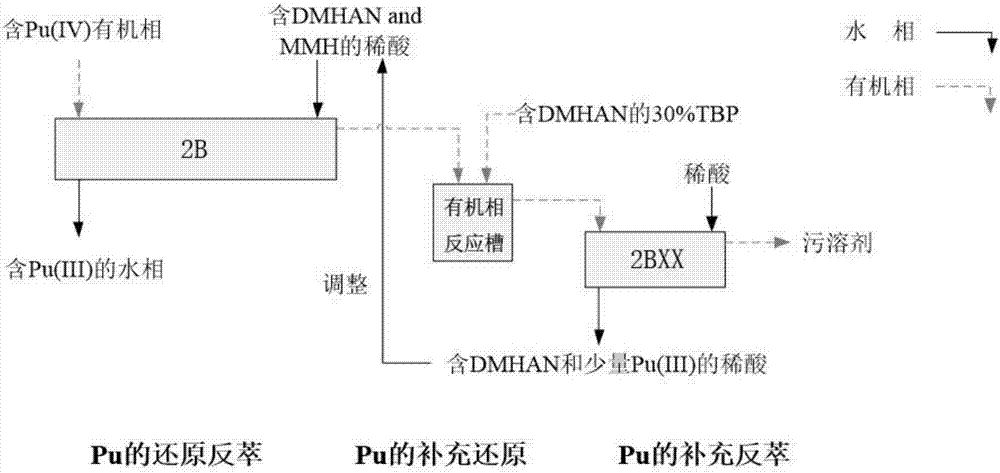
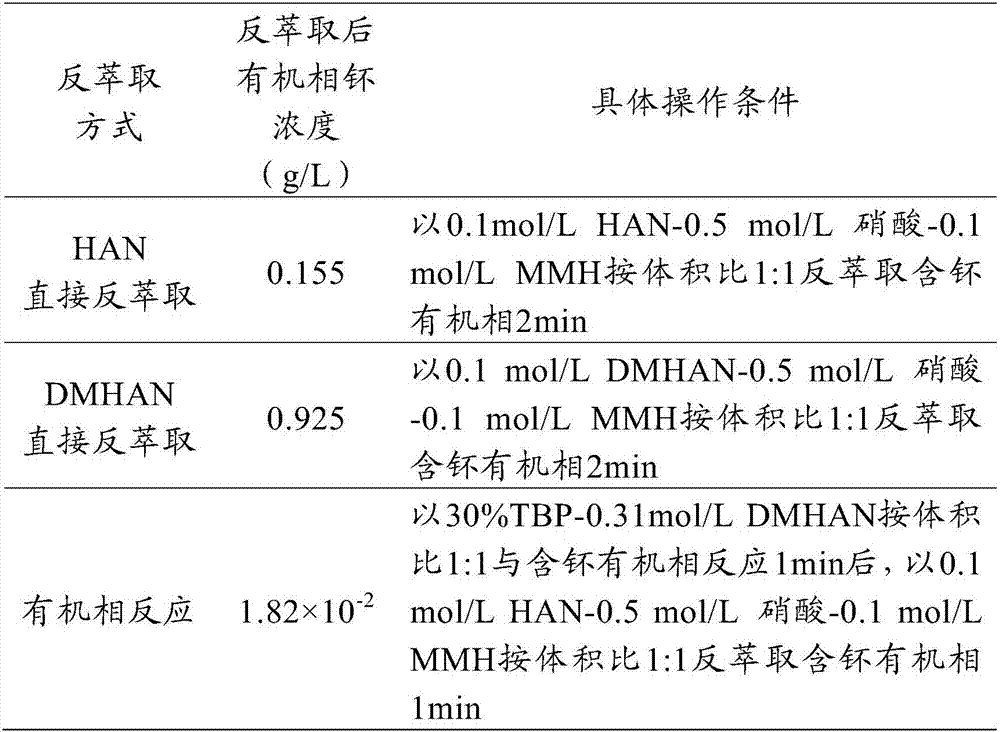
Method for recovering plutonium from radioactive spent fuel
ActiveCN106893878AAvoiding the Problems of Reductive ExtractionImproving the efficiency of recycling plutoniumPlutonium compoundsNuclear energy generationOrganic solventPhosphoric acid tributyl ester
The invention belongs to the technical field of treatment of nuclear materials and relates to a method for recovering plutonium from a radioactive spent fuel. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: performing extraction: extracting tetravalent plutonium in an aqueous solution of the radioactive spent fuel with an organic solvent containing tributyl phosphate; performing reduction on plutonium with a reducing agent: adding an organic solvent containing dimethylhydroxylamine in an organic phase to reduce the tetravalent plutonium into trivalent plutonium; and performing back extraction: adding a dilute acid aqueous solution in the organic phase to perform back extraction on the plutonium into a water phase, and performing recovering. Through adoption of the method for recovering the plutonium from the radioactive spent fuel, disclosed by the invention, the efficiency of recovering the plutonium from the radioactive spent fuel can be obviously improved compared with HAN back extraction, and the problem caused by reduction and extraction with U (IV) can be solved at the same time.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Radioactive wastewater treatment technology and synthesis of treatment agent of radioactive wastewater
The invention discloses a radioactive wastewater treatment technology and the synthesis of a treatment agent of radioactive wastewater. A modified product Y3-8103 is used for chemically reacting with radioactive wastewater, all heavy metal elements and all radioactive elements, namely cesium137, uranium 235, thorium, plutonium, thallium, protium, deuterium, tritium, radon, Sr-90 and radium, listed in the periodic table of elements and wastewater generated by all artificial nuclides. Alpha radioactive rays, beta radioactive rays, gamma radioactive rays and neutron radioactive rays are attenuated in a nationally specified mode. The radioactive wastewater treatment technology and the synthesis of the treatment agent of the radioactive wastewater can also be used for treating radioactive seawater or waste residues generated by wastewater treatment and can be used for treating heavy metal wastewater discharged by a lead-acid battery enterprise and an electronic plant and mine nucleus waste residues. The treatment cost of the radioactive wastewater is different along with different radioactive element concentration contents or different waste residue radioactive element concentration contents and different atomic weights in the wastewater, and the treatment cost of the wastewater and the waste residues ranges from RMB 90 yuan / m<3> to RMB 680 yuan / m<3>, radioactive energy with the alpha, beta and gamma radioactive ray radiant quantity smaller than or equal to 0.01Bq / 1-1.10Bq / 1 can be discharged to the ambient environment by the wastewater and the waste residues, the emission limit standard allowed by the international is reached, and secondary pollution is avoided. The radioactive wastewater treatment technology and the synthesis of the treatment agent of the radioactive wastewater are suitable for treating wastewater and waste residues of a nuclear power plant and treating wastewater and waste residues in mining with the radioactive elements, and are also suitable for treating wastewater containing heavy metal, namely lead, cadmium, mercury, arsenic, chromium, nickel, copper and manganese.
Owner:叶绍朋
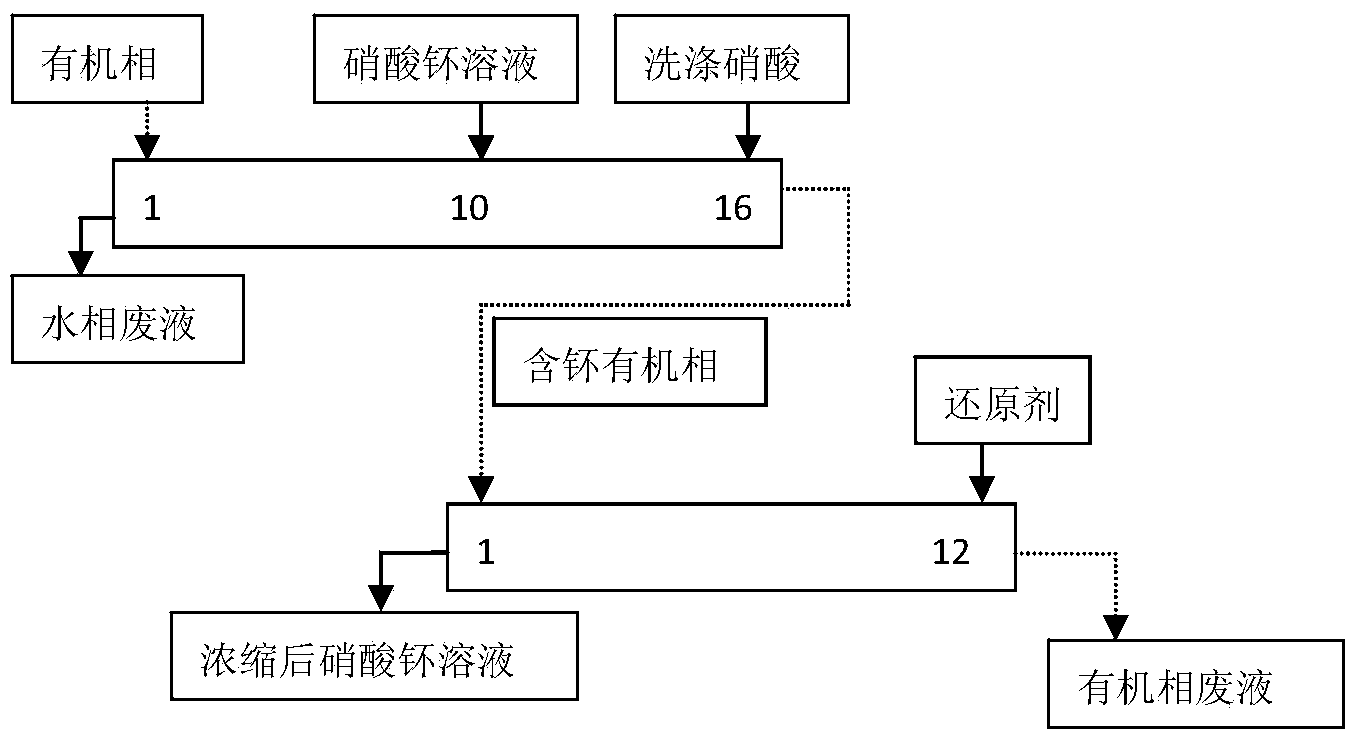
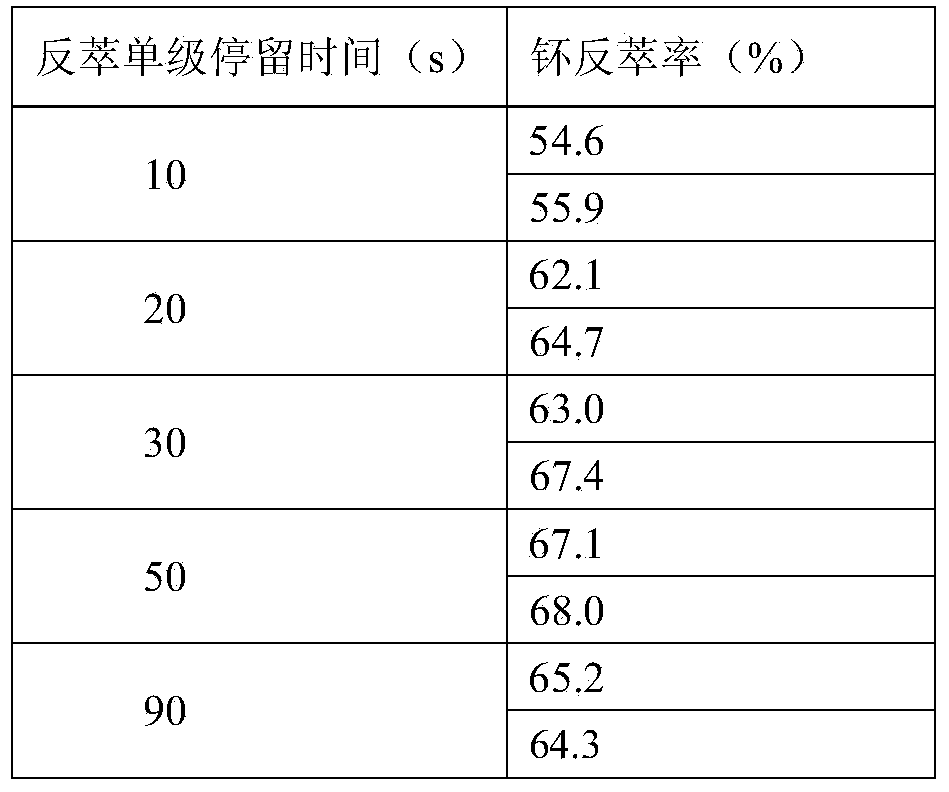
Plutonium purification and concentration method
ActiveCN104004928AHigh yieldIncrease the concentration factorProcess efficiency improvementFuel reprocessingAfter treatment
The invention belongs to the technical field of fuel-short after-treatment and discloses a plutonium purification and concentration method. The method comprises the following steps: extracting tetravalent plutonium in a nitric acid solution into a 30% TBP (tributyl phosphate)-kerosene solution with relatively small volume for purification and concentration in a centrifugal extractor, reducing tetravalent plutonium into trivalent plutonium by using a dimethylhydroxylamine-containing nitric acid solution with relatively small volume, performing back extraction on trivalent plutonium, and further purifying and concentrating plutonium in a water phase. In the whole concentration process, a plutonium replenishment and extraction link is removed. The method is simple in step, short in time and small in solvent radiation effect; the plutonium back-extraction yield reaches up to 99.98% while the plutonium concentration is increased by more than 10 times.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Radiation attenuation elastomeric material, a multilayer glove for protection against ionizing radiations and their uses
ActiveUS20120217423A1Remarkable flexibilityRemarkable propertyOther chemical processesShieldingElastomerPlastic materials
The invention relates to a radiation attenuation elastomeric material of the type comprising an elastomer in which a powder of metal oxides is dispersed, and which is characterized in that the powder of metal oxides comprises from 70 to 90% by mass of bismuth trioxide, from 5 to 15% by mass of tungsten trioxide and from 5 to 15% of lanthanum trioxide.It also relates to the use of this elastomeric material for making individual protective articles against ionizing radiations.It further relates to a multilayer protective glove against ionizing radiations, at least one layer of which is formed by said elastomeric material, as well as to the use of this glove for protection against ionizing radiations emitted by powders of nuclear fuels, notably with plutonium.Fields of application: the nuclear industry for handling powders of nuclear fuels but also medical imaging, interventional radiology, nuclear medicine, processing of plastic materials, inspection and control of manufactured parts, etc.
Owner:PIERCAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com