Patents
Literature
87 results about "Neutron emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neutron emission is a mode of radioactive decay in which one or more neutrons are ejected from a nucleus. It occurs in the most neutron-rich/proton-deficient nucleides, and also from excited states of other nucleides as in photoneutron emission and beta-delayed neutron emission. As only a neutron is lost by this process the number of protons remains unchanged, and an atom does not become an atom of a different element, but a different isotope of the same element.
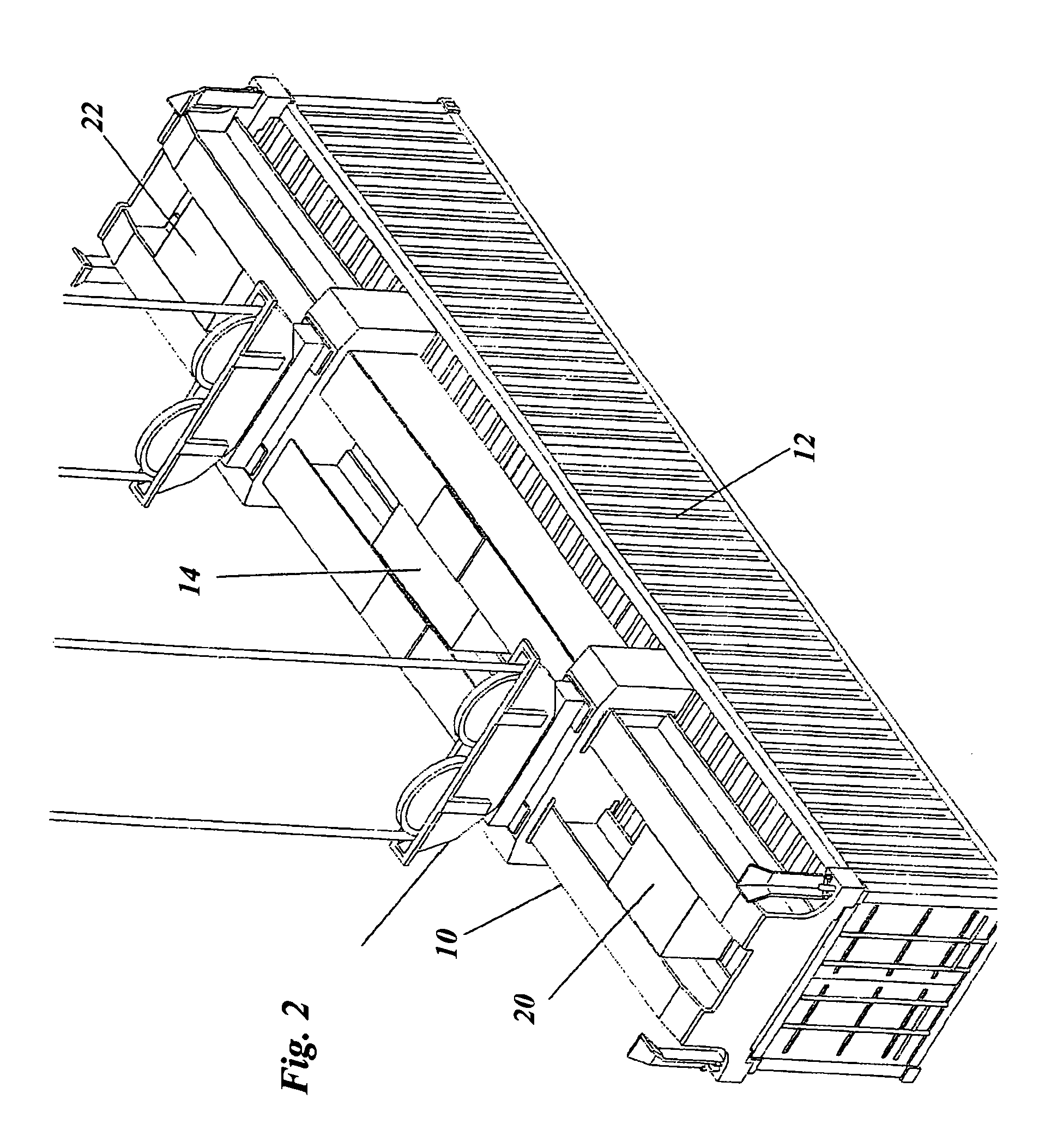
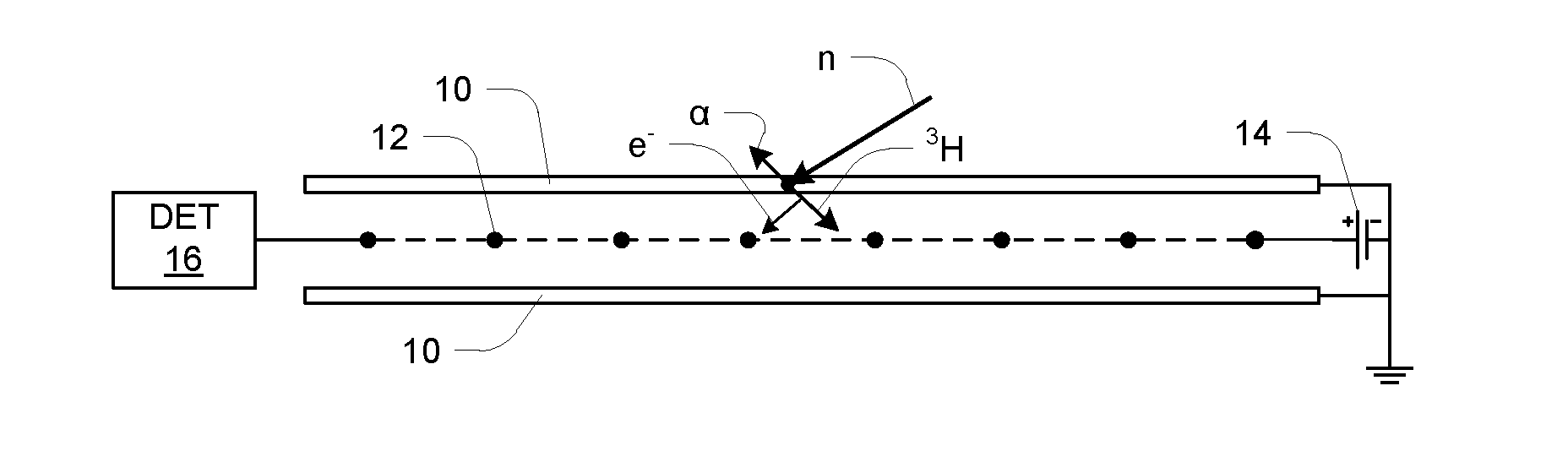
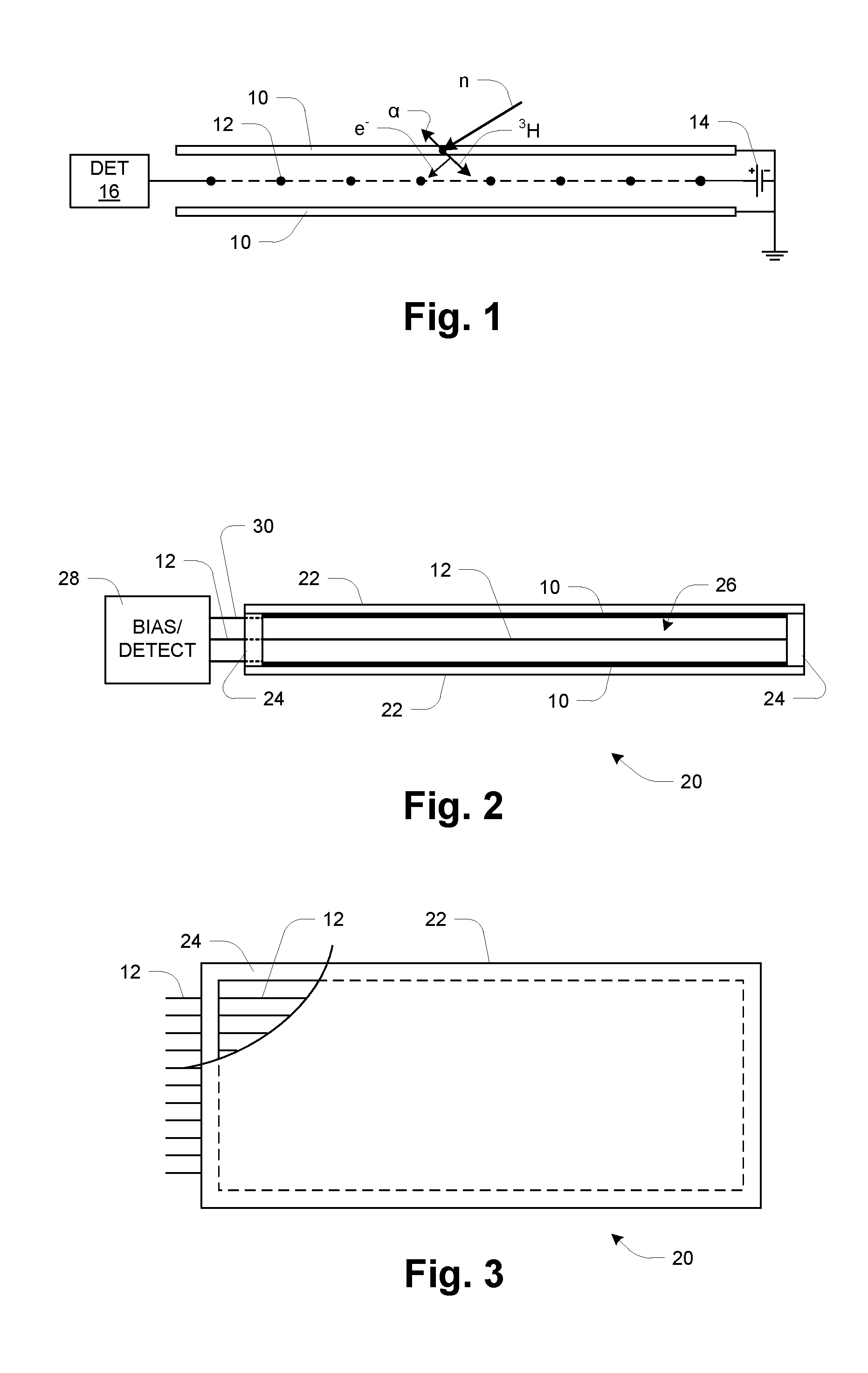
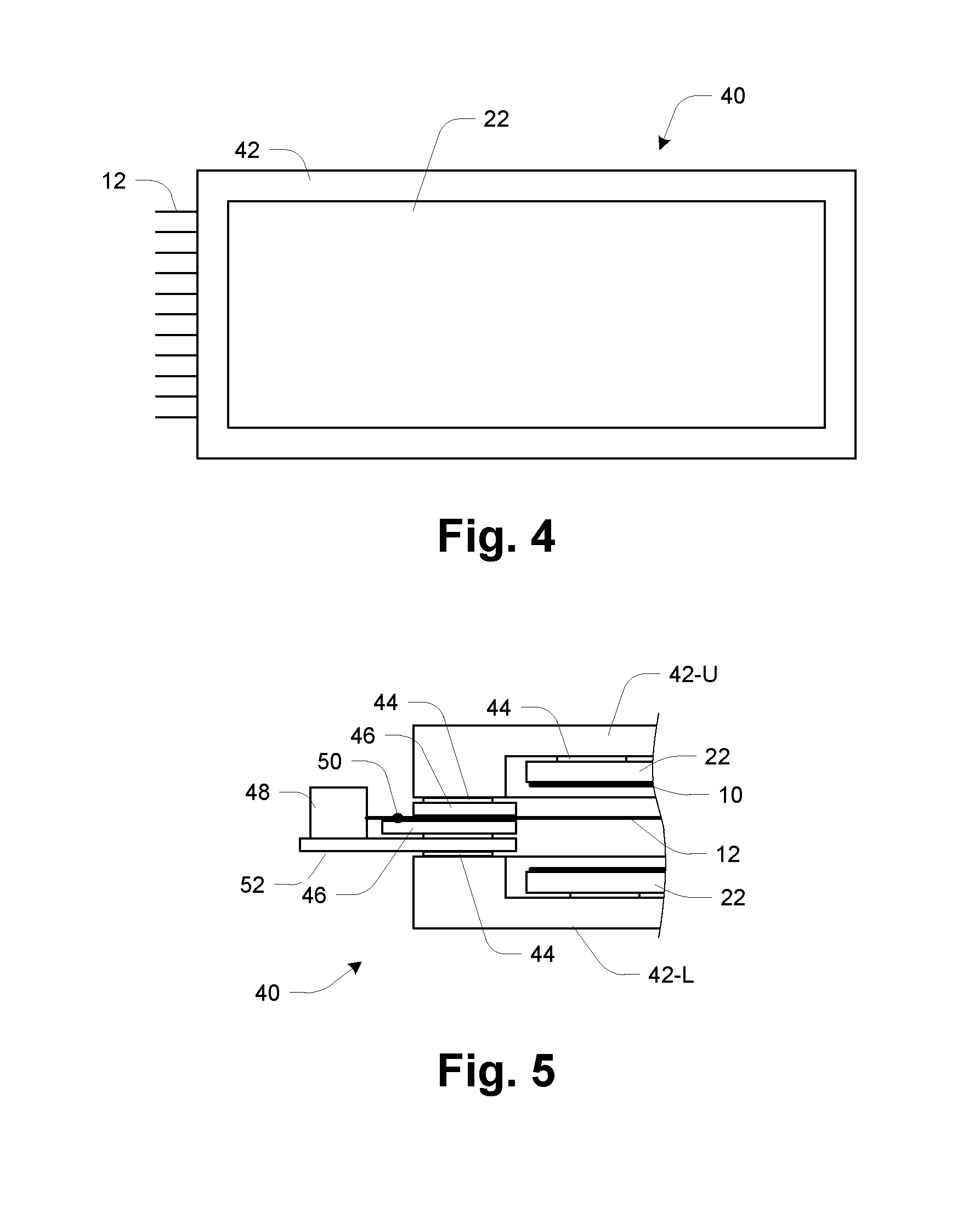
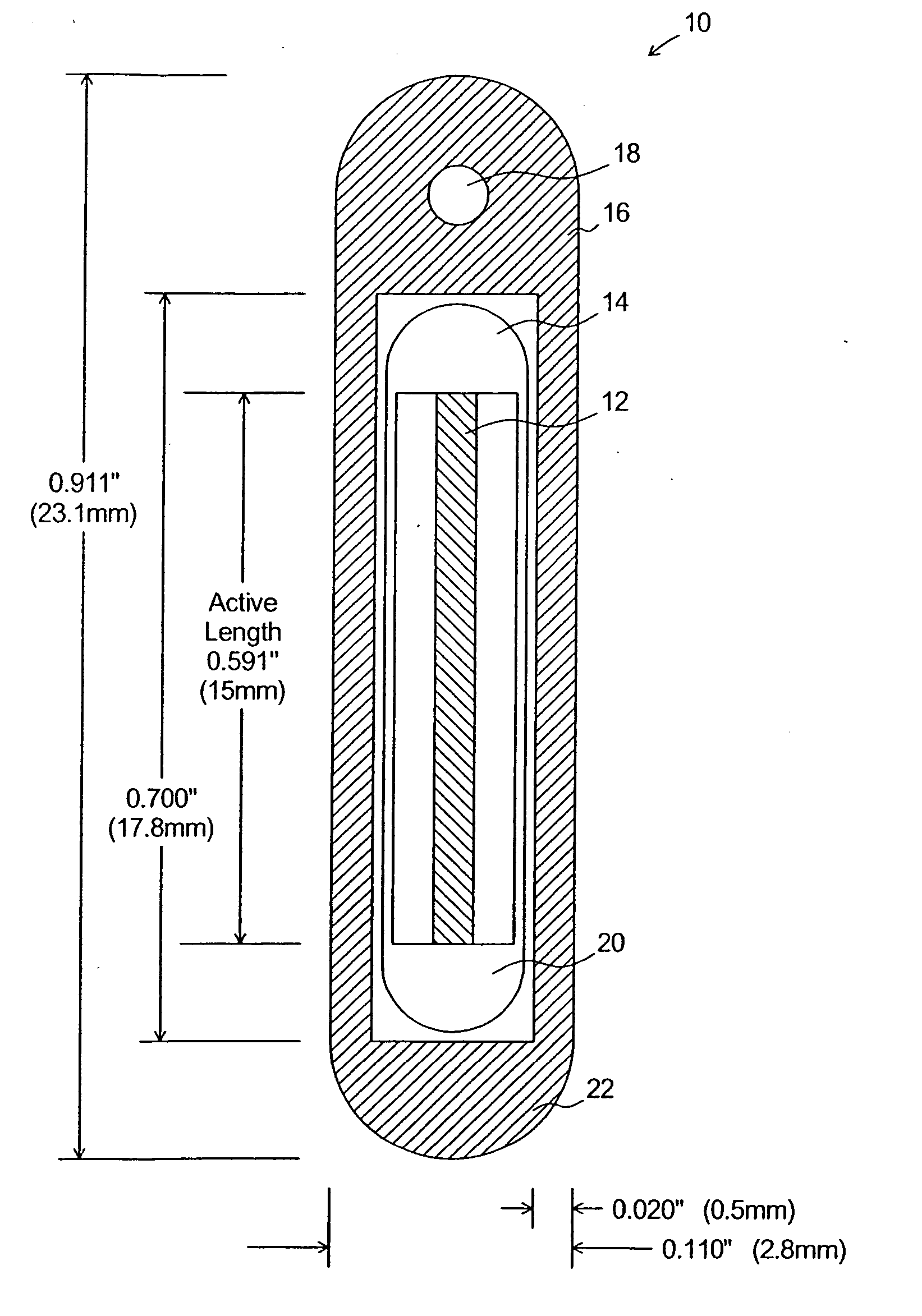
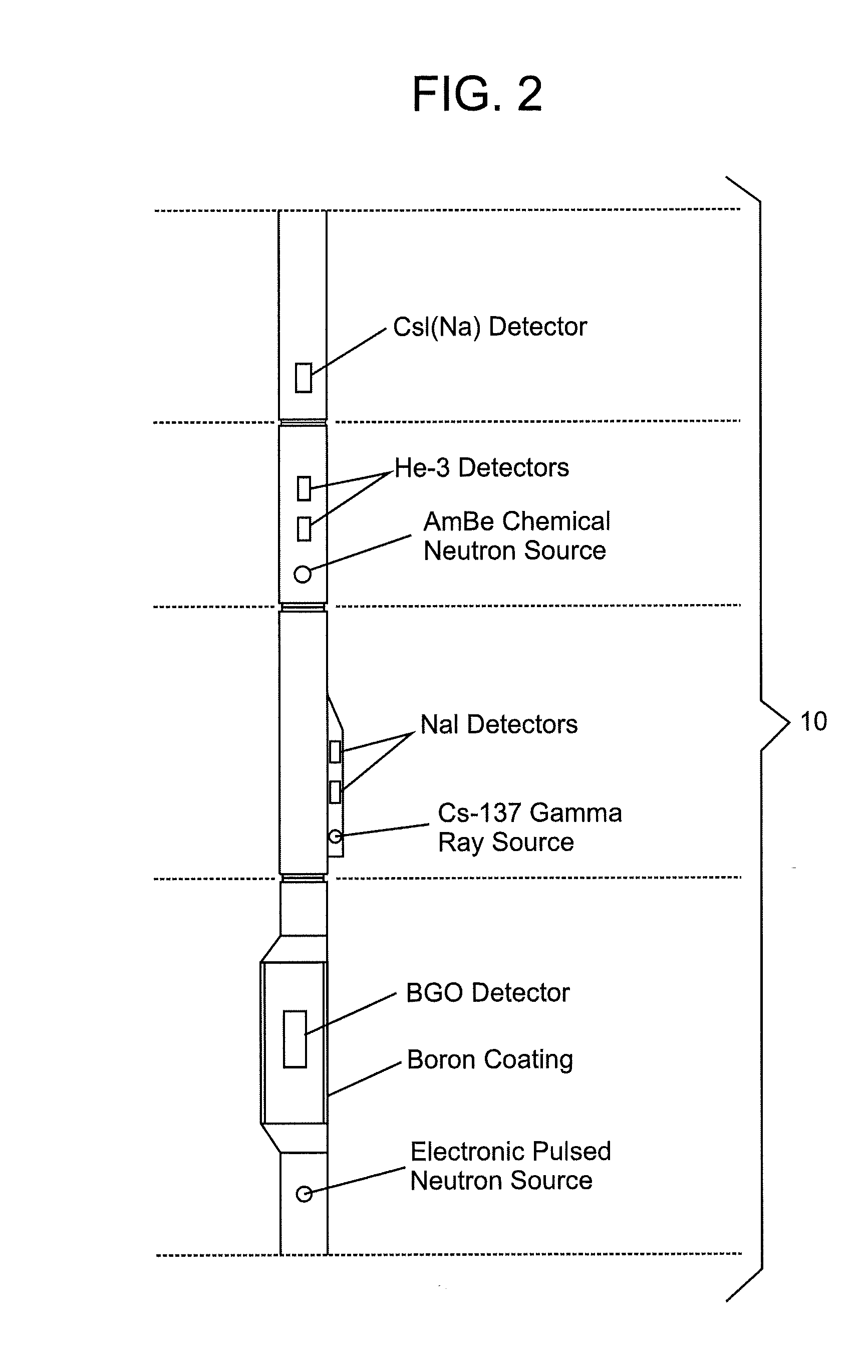
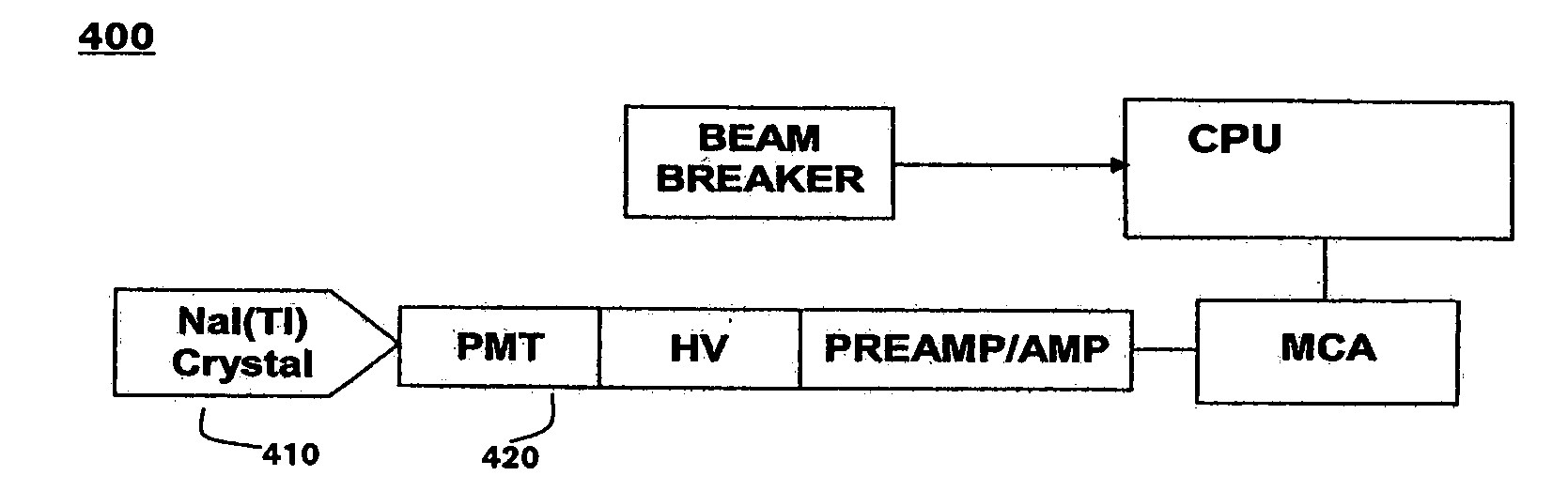
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
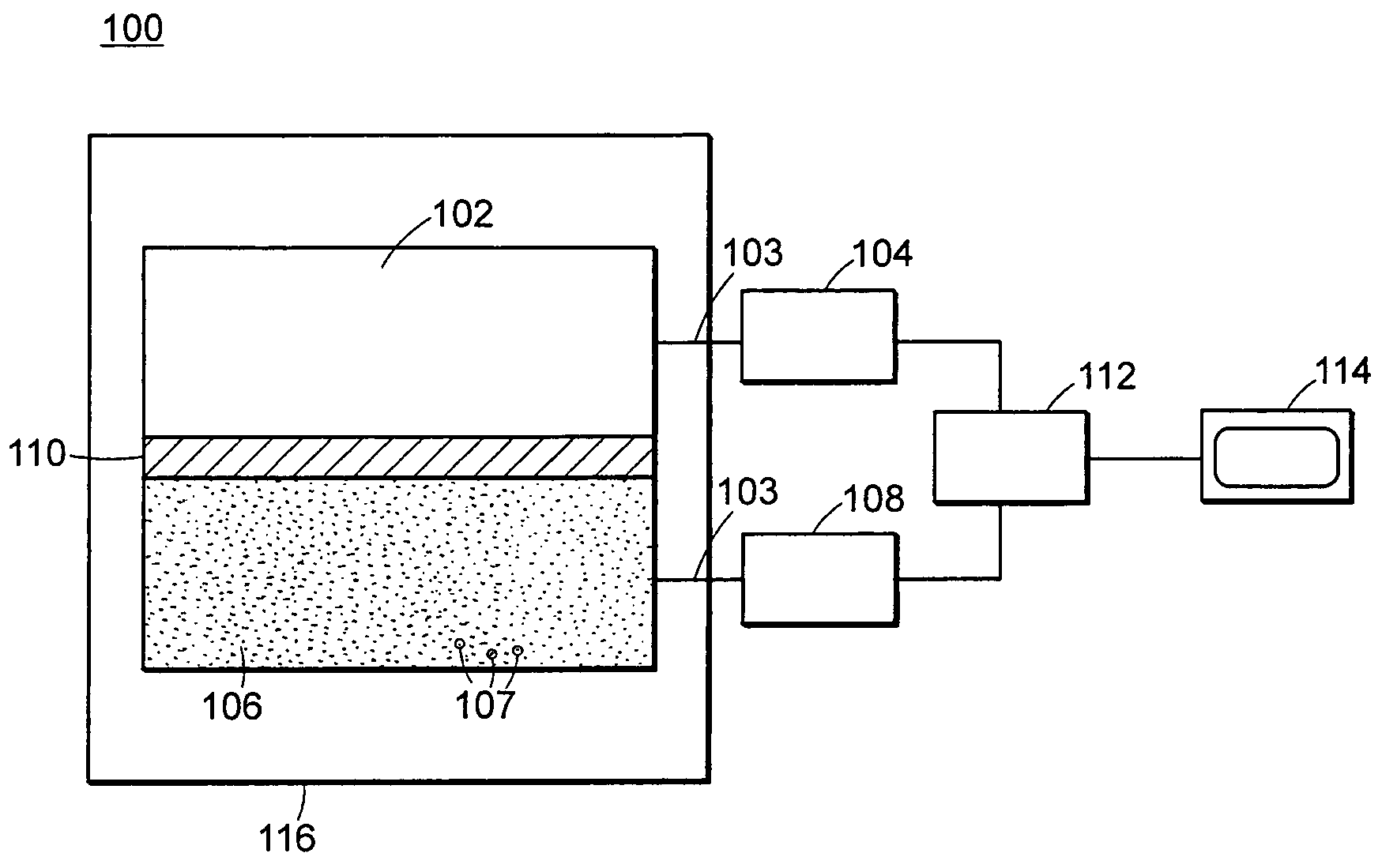
InactiveUS20050023479A1Light weightMore selectiveX-ray spectral distribution measurementMeasurement with scintillation detectorsNeutron emissionX-ray
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like; and / or an X-ray analyzer that facilitates detection of materials that can shield radioactive sources, e.g., lead, and the like.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Gas-target neutron generation and applications
InactiveUS6922455B2Improve performanceMaximize productionNuclear energy generationX-ray tube electrodesHigh resistanceNeutron emission
Described herein are integrated systems for generating neutrons to perform a variety of tasks including: on-line analysis of bulk material and industrial process control (as shown in FIG. 1), security interrogation (as shown in FIG. 2), soil and environmental analysis, and medical diagnostic treatment. These systems are based on novel gas-target neutron generation which embodies the beneficial characteristics of replenishable fusible gas targets for very long lifetime, stability and continuous operation, combined with the advantageous features common to conventional accelerator neutron tubes including: on / off operation, hermetically sealed operation, and safe storage and transport. Innovative electron management techniques provide gas-target neutron production efficiencies that are comparable or surpass existing sources. The high-pressure high-resistance gaseous discharge is presented as a favorable gas-target neutron generator embodiment, combining ion source regions, accelerator regions, gas-target regions and electron management components within a single simple cost-effective device that is adaptable to various geometric configurations that provide specific neutron emission profiles for greater analysis capacity.
Owner:STARFIRE INDS MANAGEMENT
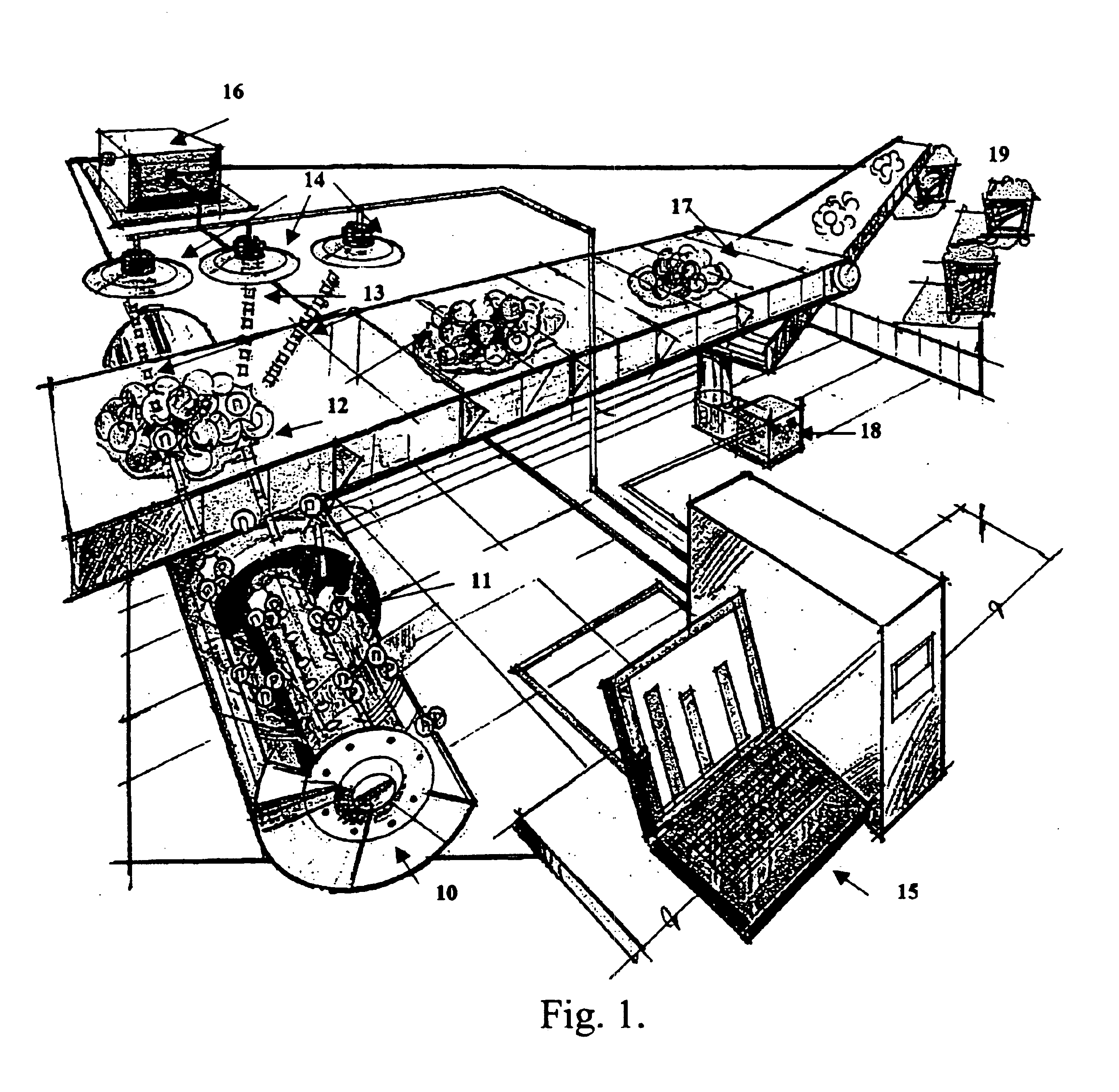
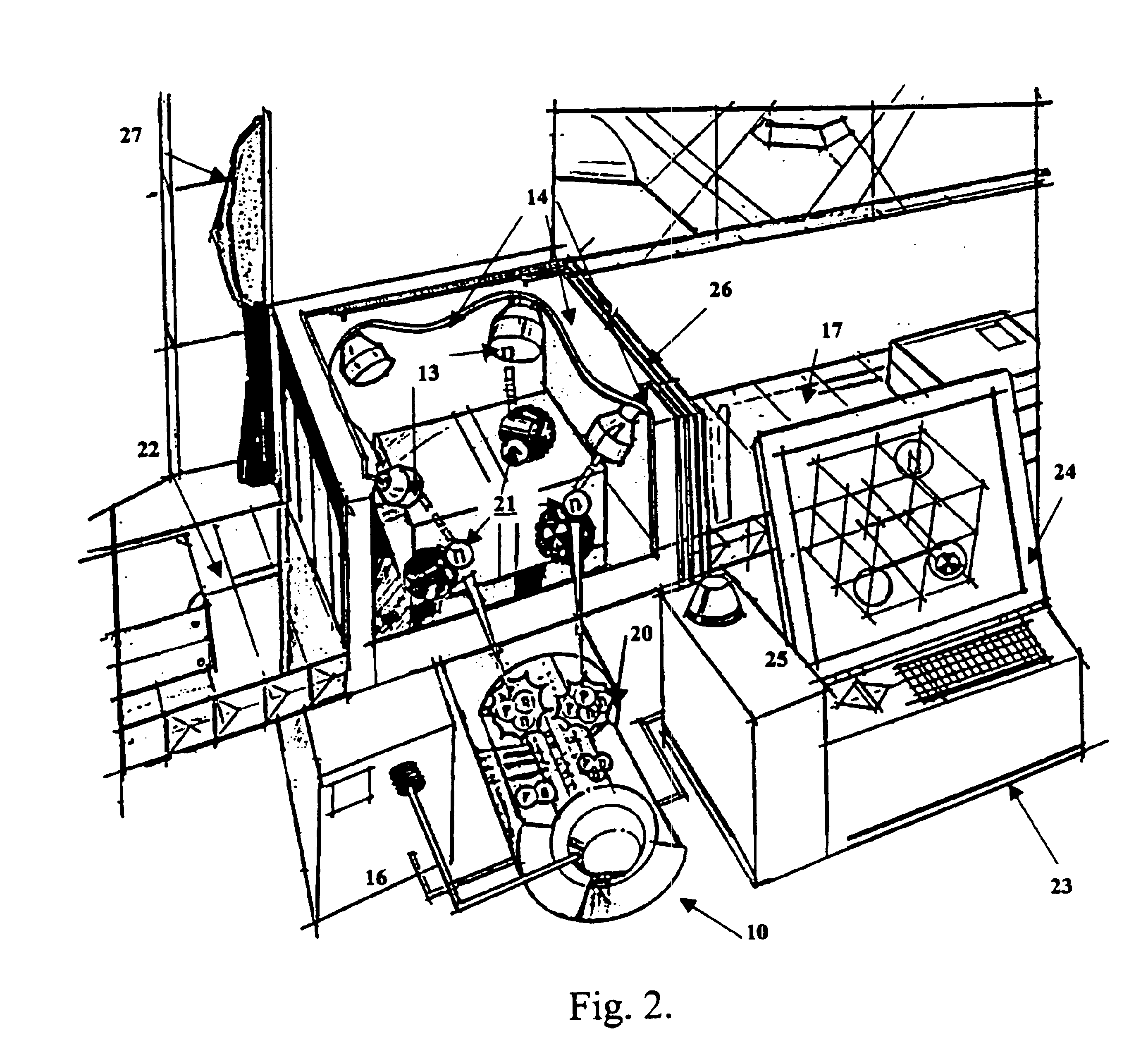
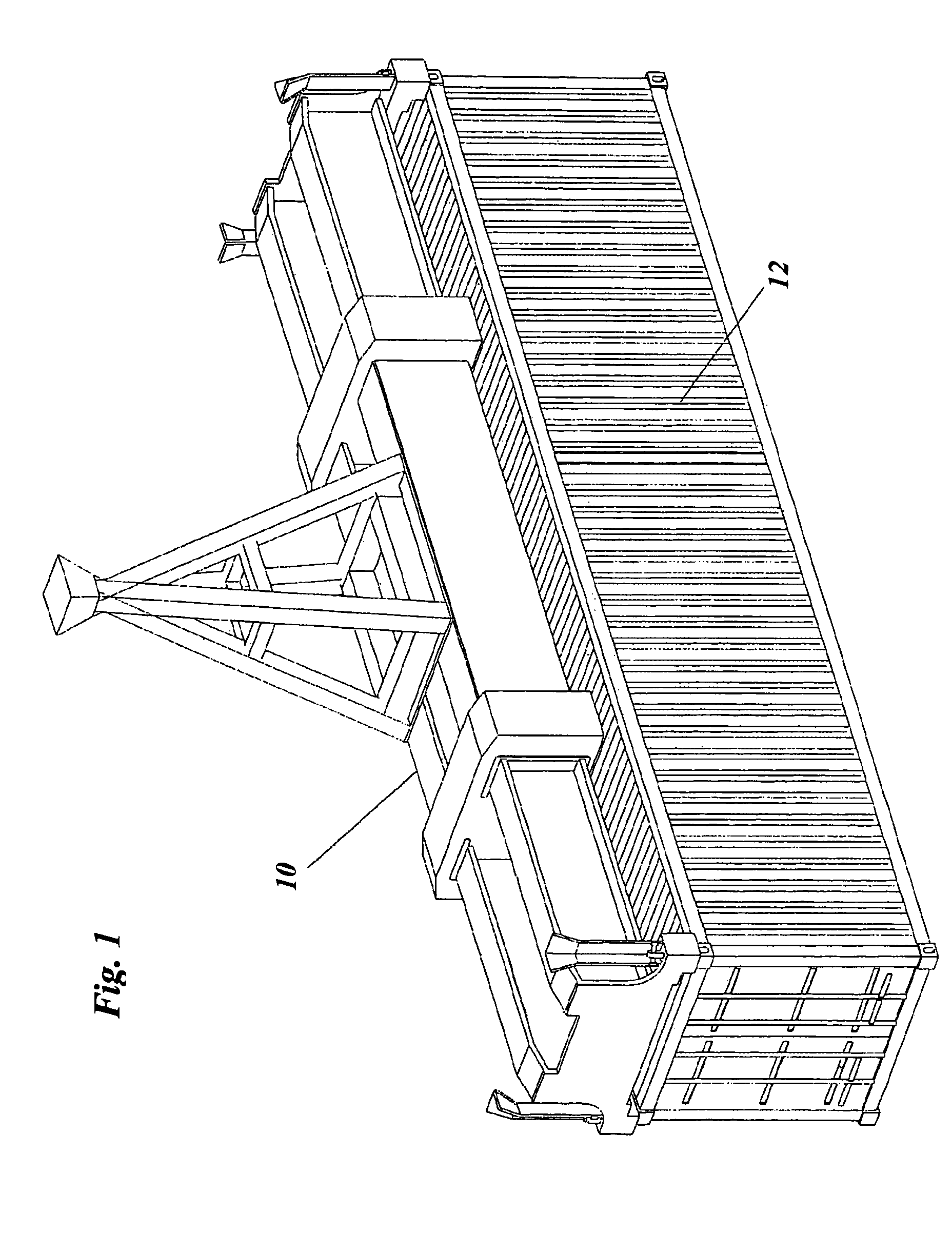
Inverse ratio of gamma-ray and neutron emissions in the detection of radiation shielding of containers
InactiveUS7116235B2Reduce instabilityTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionGamma ray
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
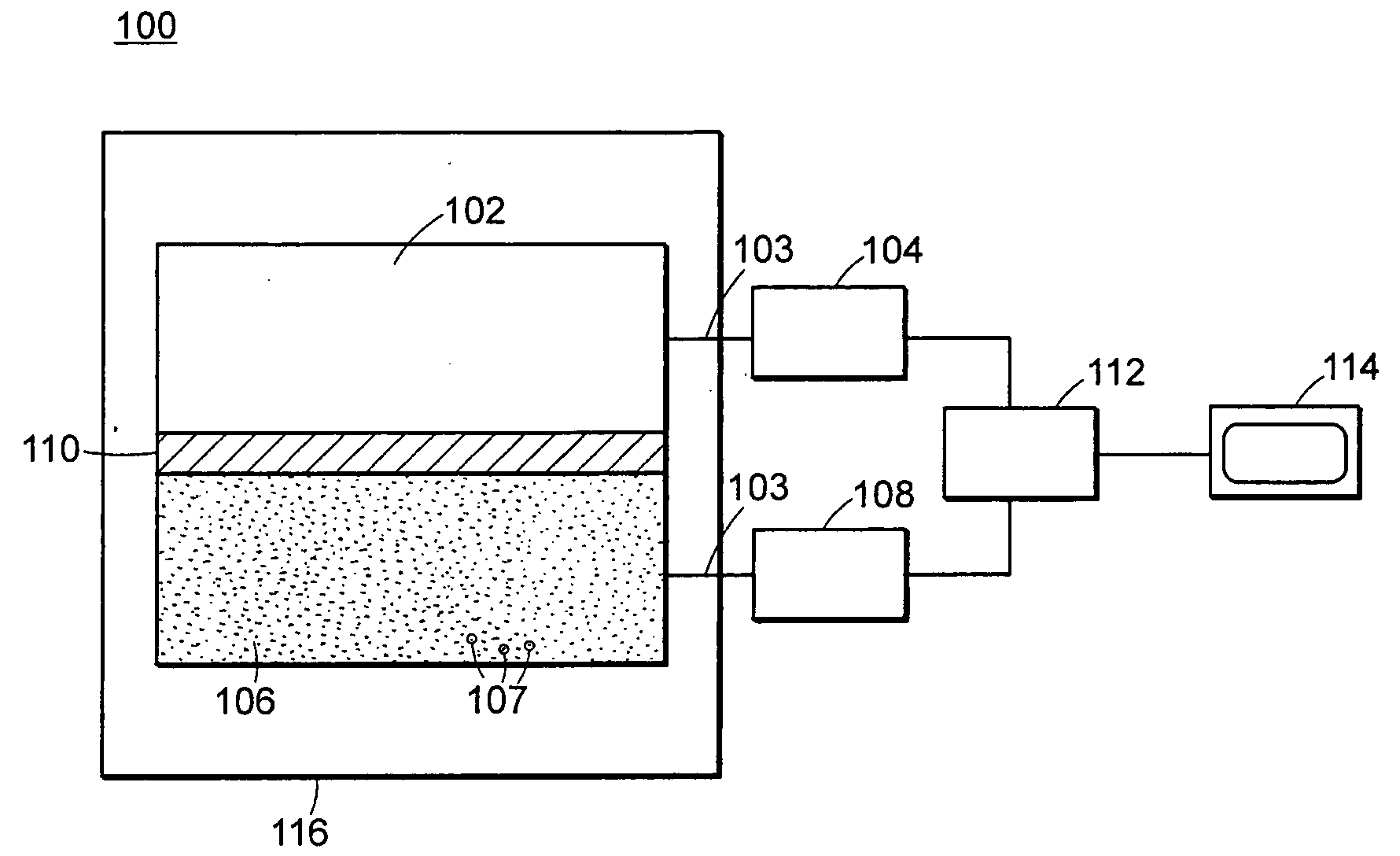
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
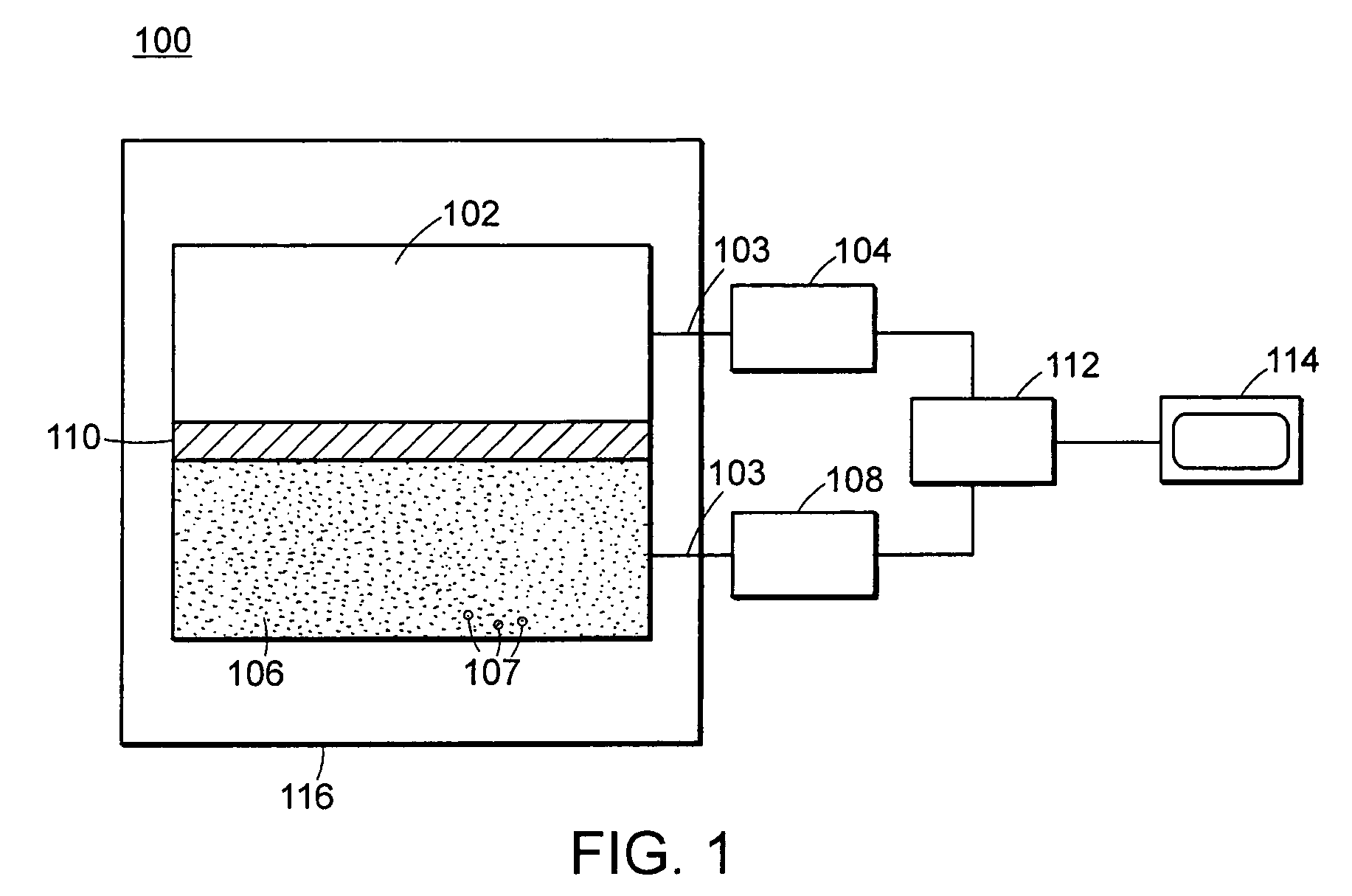
ActiveUS20070272874A1Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like. The apparatus comprises a first light guide, optically coupled to a first optical detector; a second light guide, optically coupled to a second optical detector a sheet of neutron scintillator, opaque for incoming optical photons, said sheet of neutron scintillator sandwiched between the first and the second light guides. The second light guide comprises a gamma ray scintillator material.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
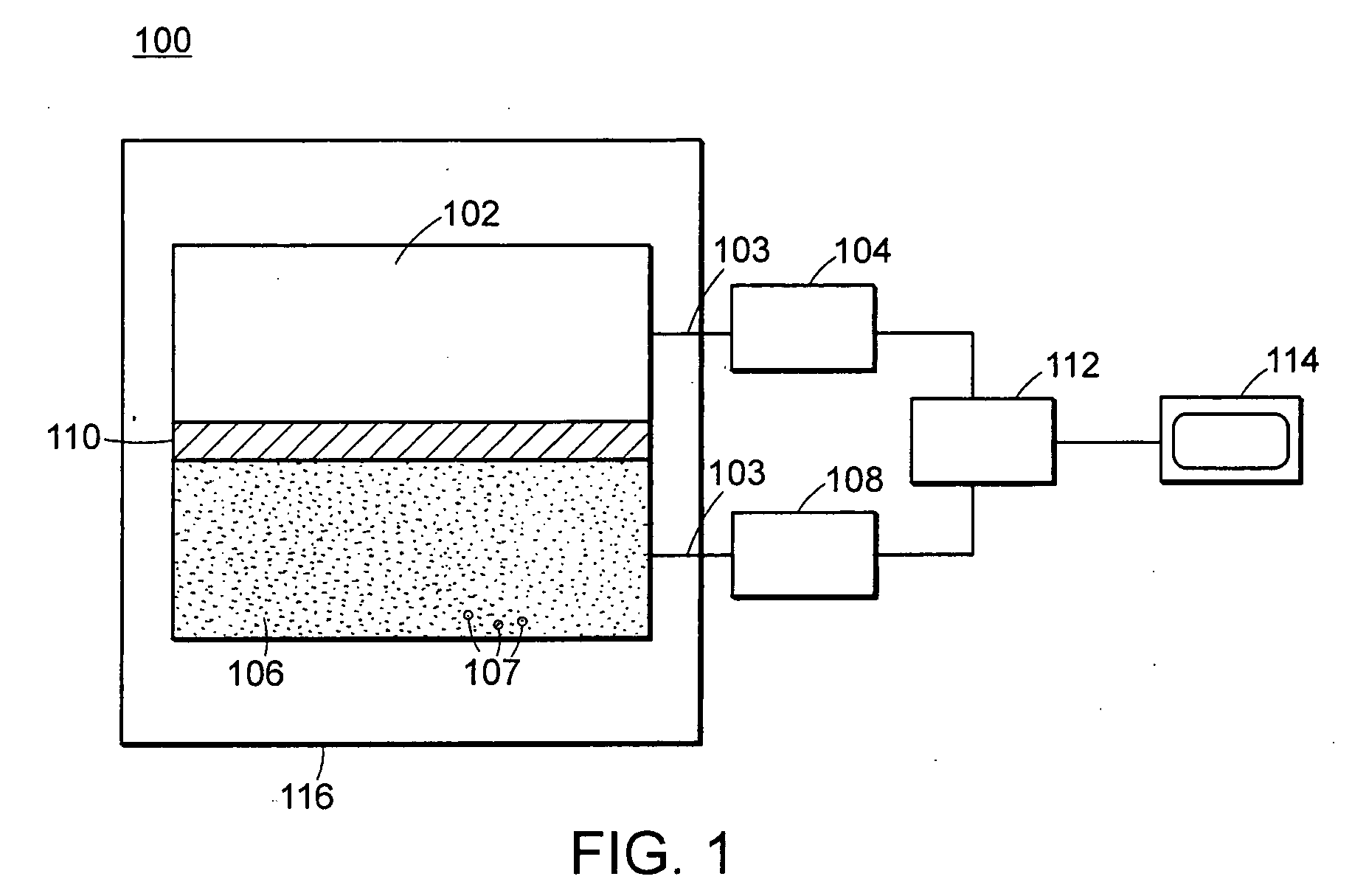
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS7525101B2Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Inverse ratio of gamma-ray and neutron emissions in the detection of radiation shielding of containers
InactiveUS20050275545A1Reduce instabilityTrolley cranesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionGamma ray
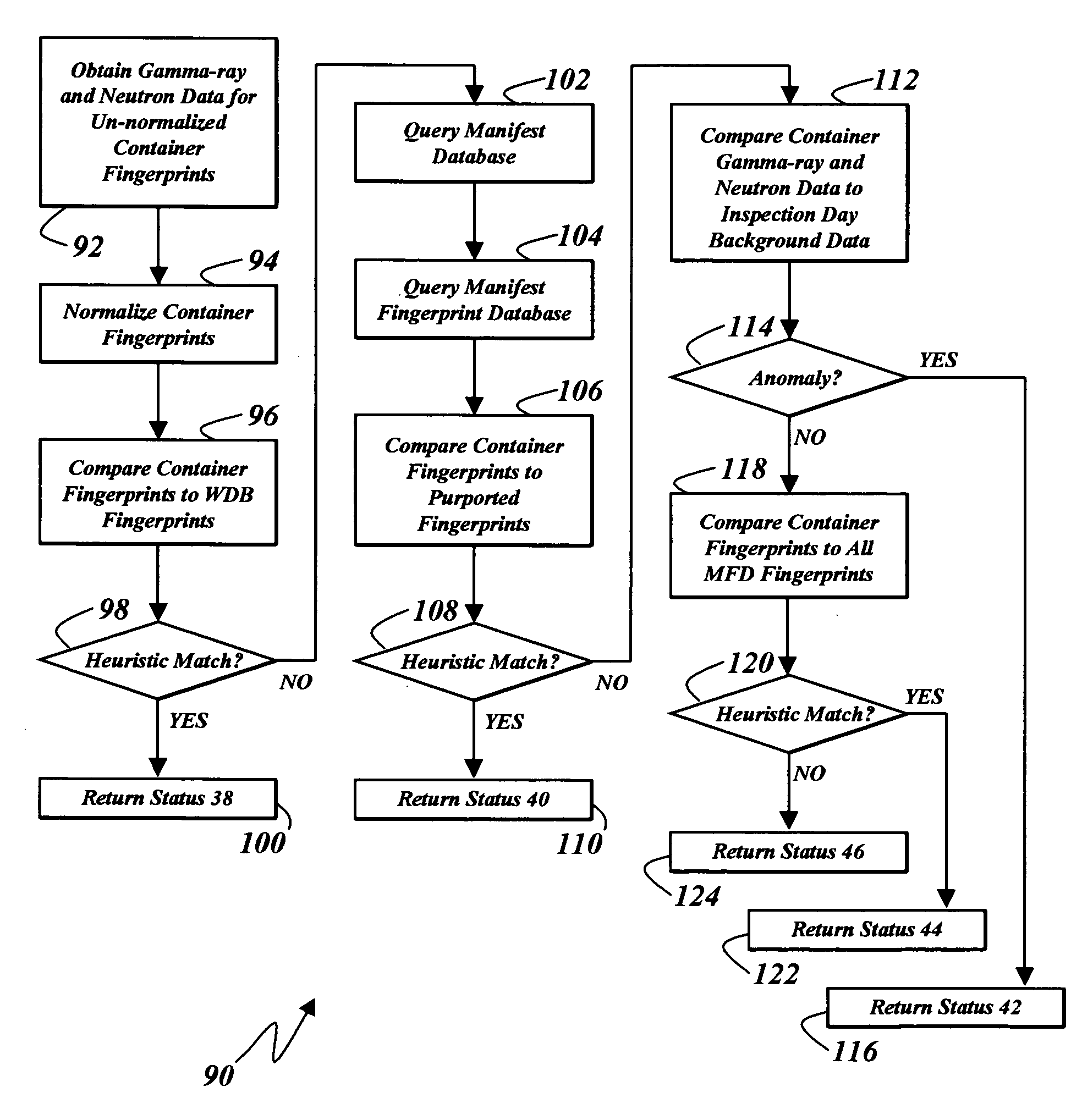
The presence of radiation shielding material concealing illegitimate content in a container is detected by obtaining each of measured gamma-ray data and measured neutron data from the container, and comparing the measured gamma-ray and neutron data to expected gamma-ray and neutron data. An anomaly between the measured data and the expected data is an indicum of the presence of such material shielding such illegitimate content.
Owner:VERITAINER ASSET HLDG LLC
Neutron source detection camera
InactiveUS20060017000A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionImaging equipment
A neutron imaging apparatus for obtaining an image of the general shape of a neutron emitting source and a bearing of the source relative to the apparatus, the apparatus comprising a chamber comprising a gas with a high probability of interacting with low energy neutrons, releasing collision products that maintain the neutron momentum, and generating ionization particles. The chamber comprises an electrode for providing an electronic signal indicative of the impact location of ionization particles on the electrode and a field to drift the ionization particles to the electrode. A readout indicates the location and time of impact of each ionization particle on the electrode; a memory stores a plurality of the electronic signals; and a computer receives and analyzes the signals and impact times and indicates the location of the source of neutrons by using back projection algorithms to calculate three-dimensional vectors indicative of the neutron path directions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
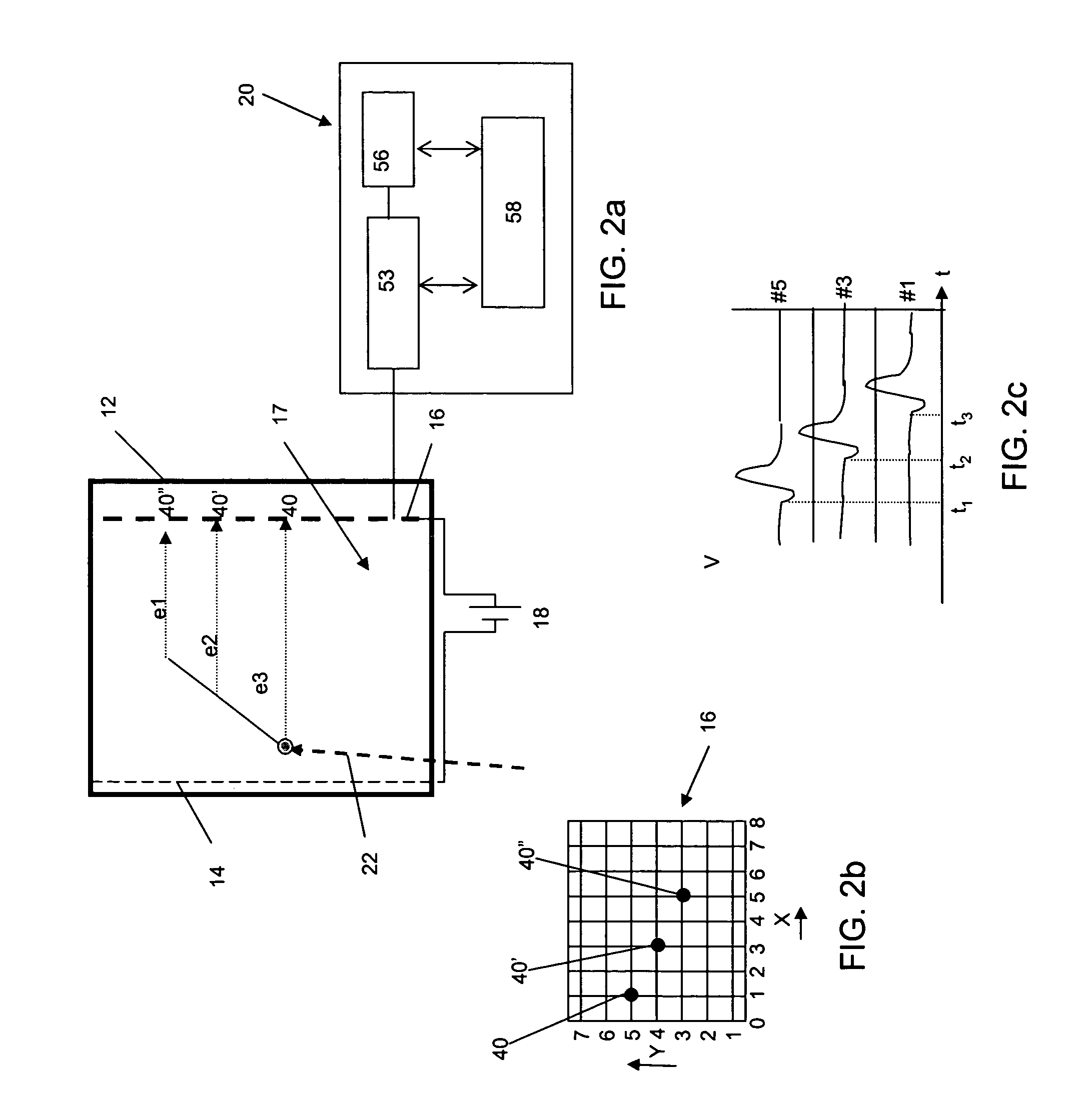
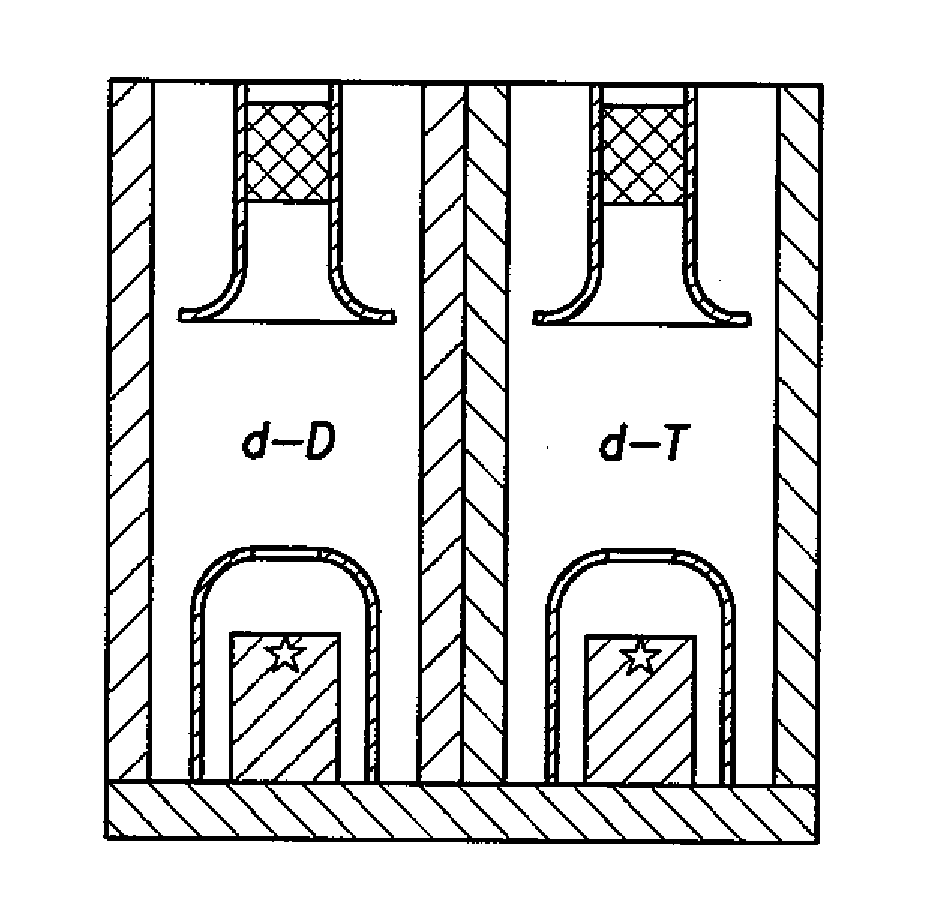
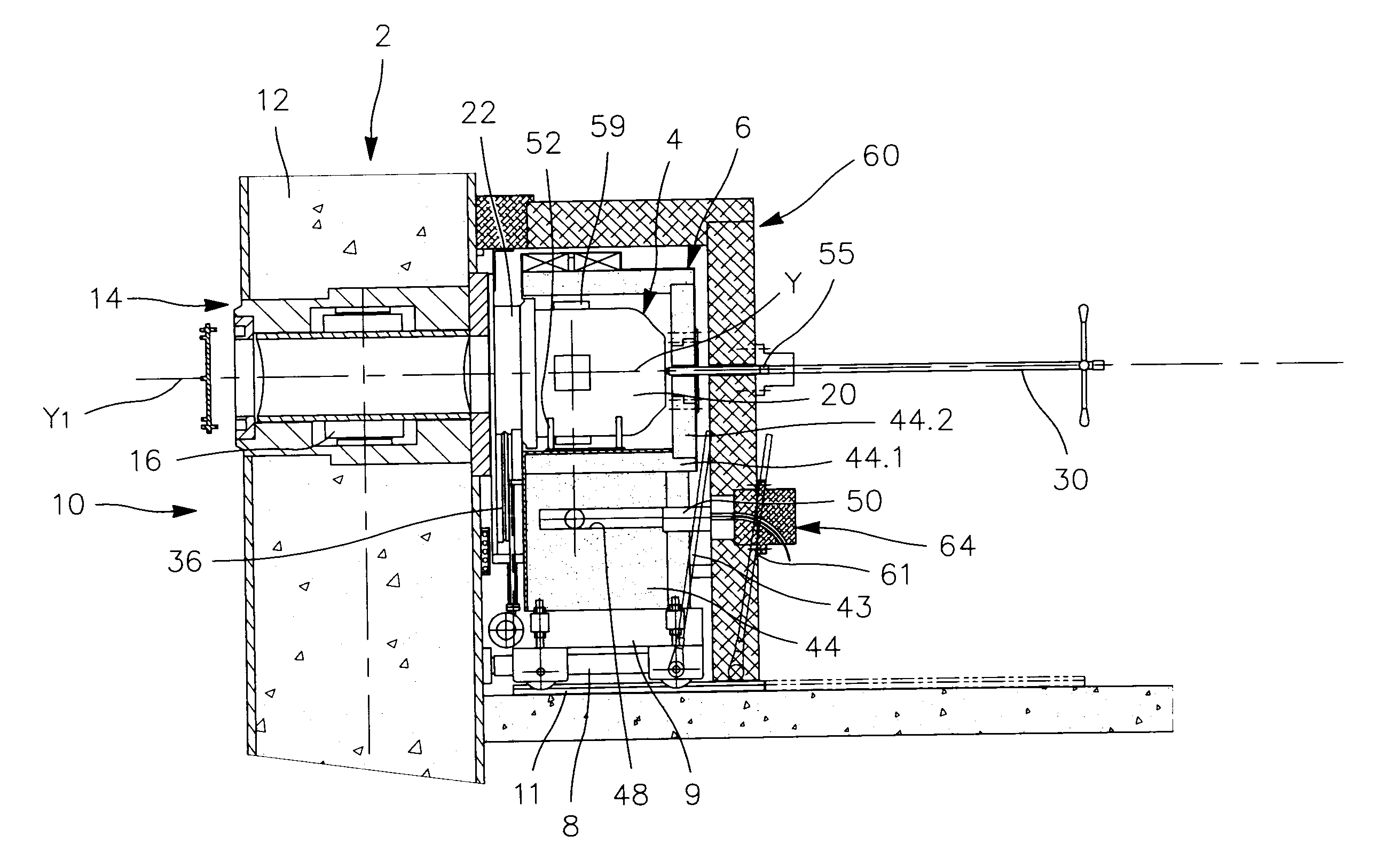
Downhole Tools Having Combined D-D and D-T Neutron Generators
A nuclear tool includes a tool housing; a d-D neutron generator disposed in the tool housing; a d-T neutron generator disposed in the tool housing; and, optionally, a control circuit for controlling pulsing of the d-D neutron generator and the d-T neutron generator. A method for well-logging using a nuclear tool includes disposing the nuclear tool in a wellbore penetrating a formation; pulsing a d-D neutron generator to emit neutrons at a first energy level into the formation; pulsing a d-T neutron generator to emit neutrons at a second energy level into the formation; and measuring signals returning from the formation.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Portable System for Analyzing and Determining Elemental Composition of Rock Samples
InactiveUS20120046867A1No impediment to efficiencyLow costElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElemental compositionNeutron emission
A portable system for elemental analysis includes one or more neutron emitters, a chamber for containing a test sample, at least one gamma ray detector electrically connected to a data acquisition system, and software or firmware executing on the data acquisition system from a non-transitory physical medium, the software or firmware providing a first function for producing one or more gamma ray spectrums, a second function for applying correction factors to the one or more gamma ray spectrums, and a third function for analyzing the corrected gamma ray spectrum or spectrums to determine a deconvolved elemental composition of the test sample.
Owner:HELIOCENTRIC TECH
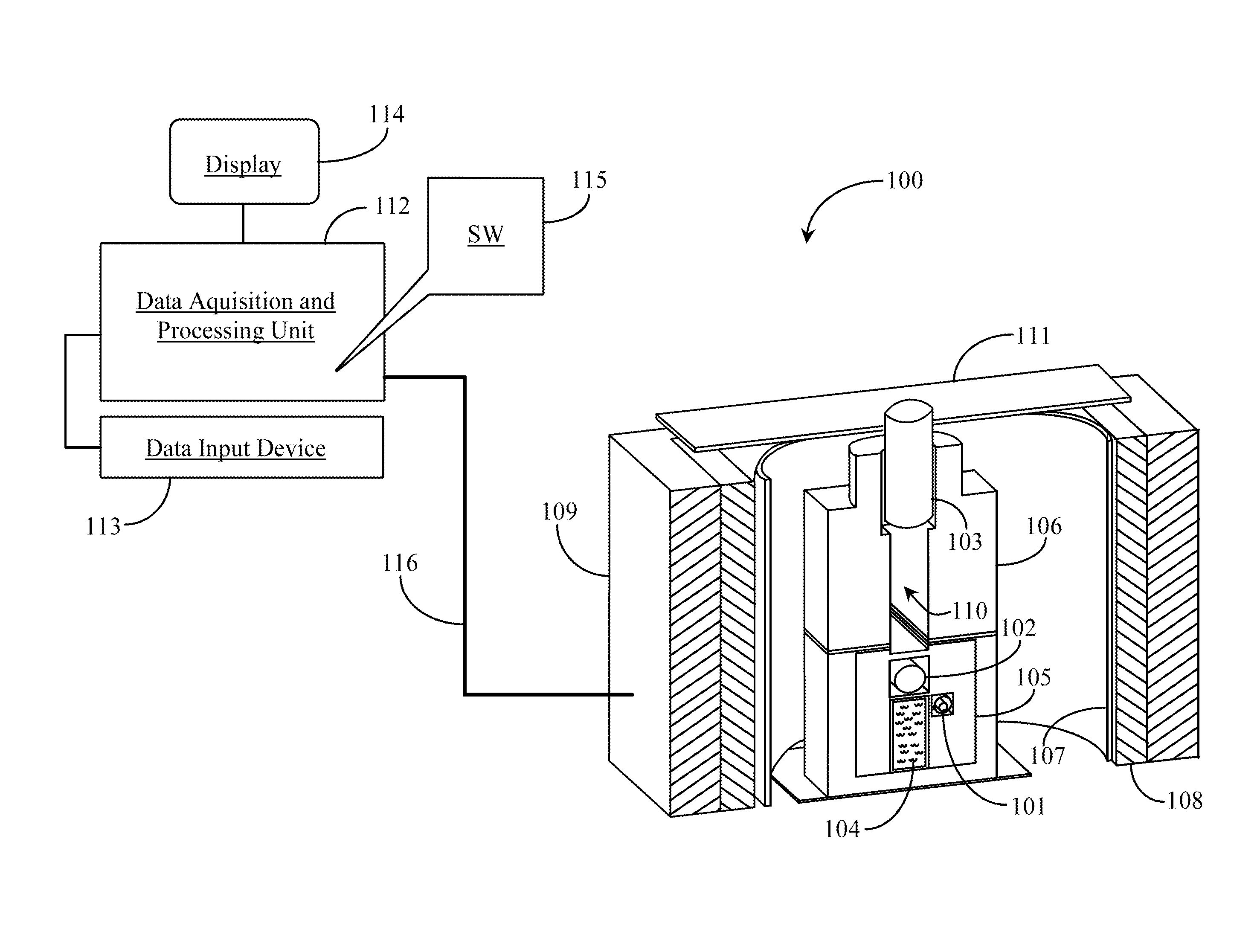
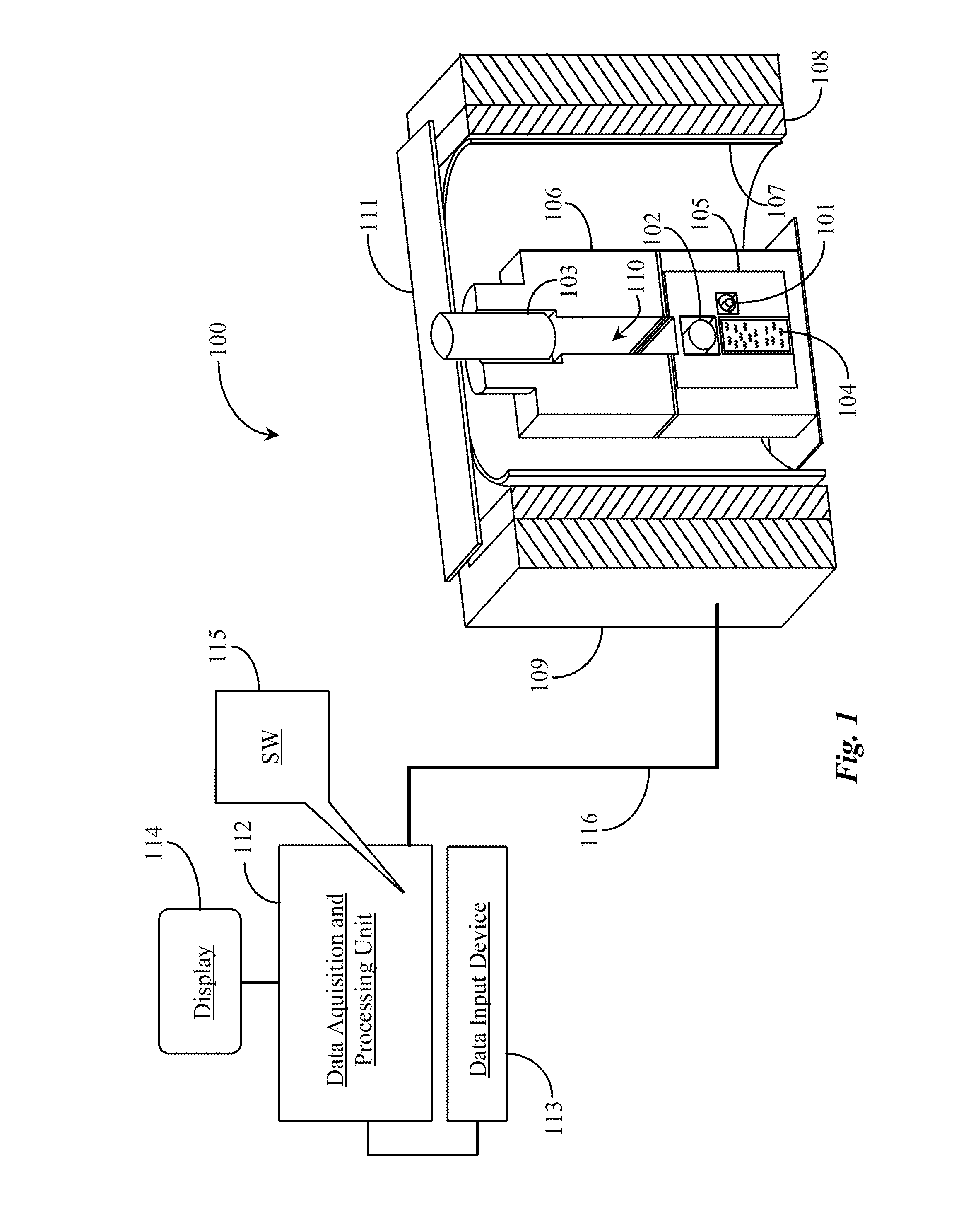
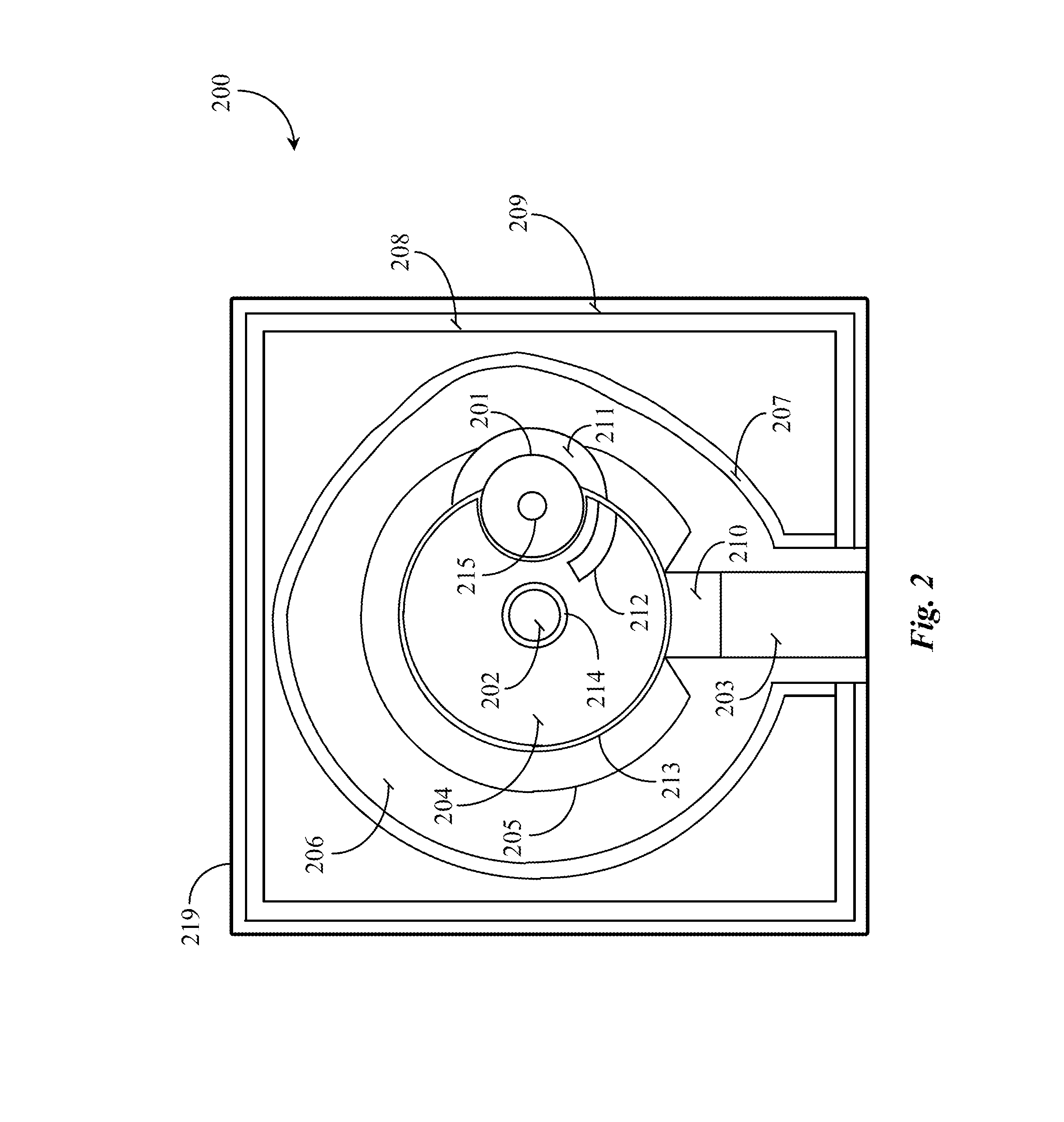
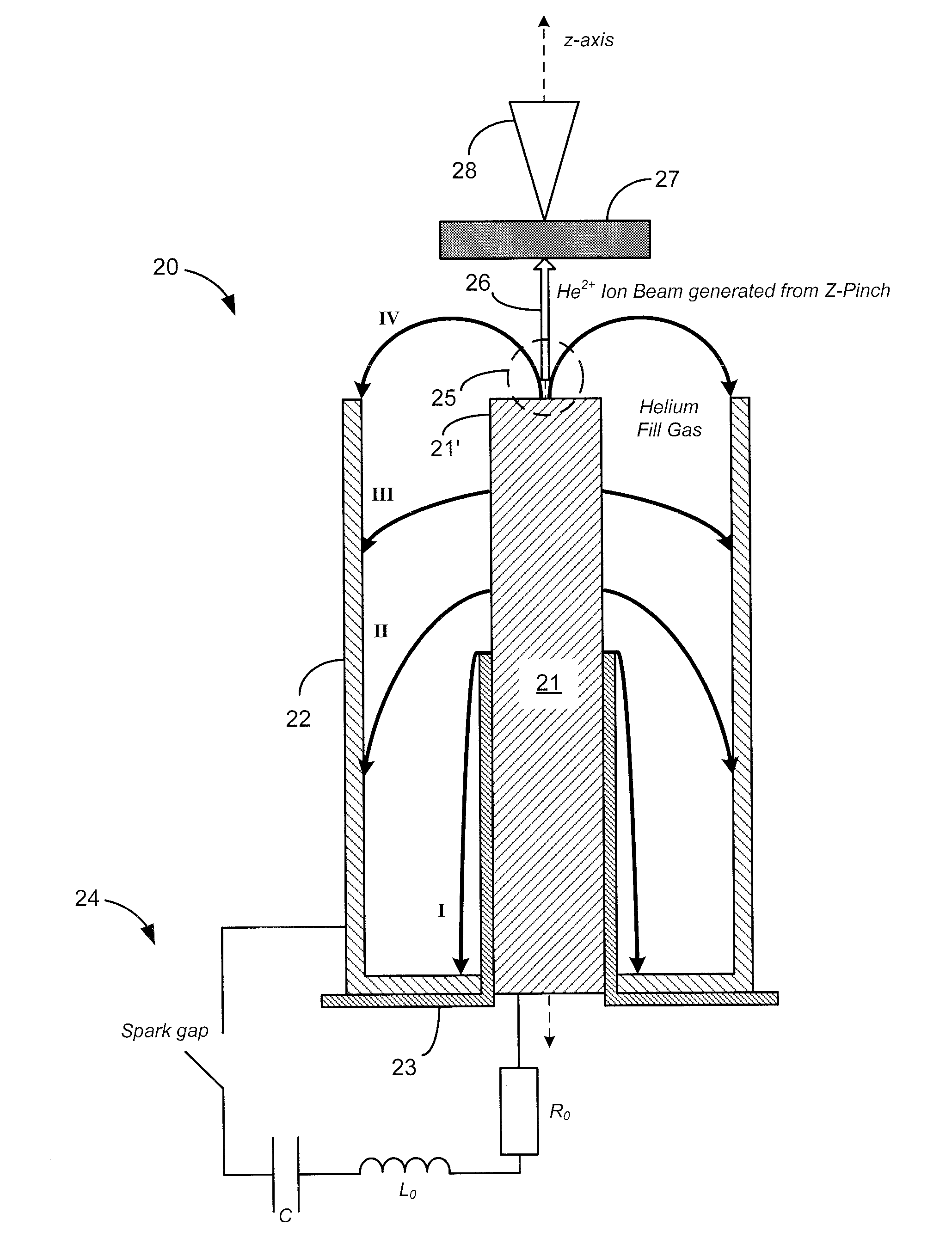
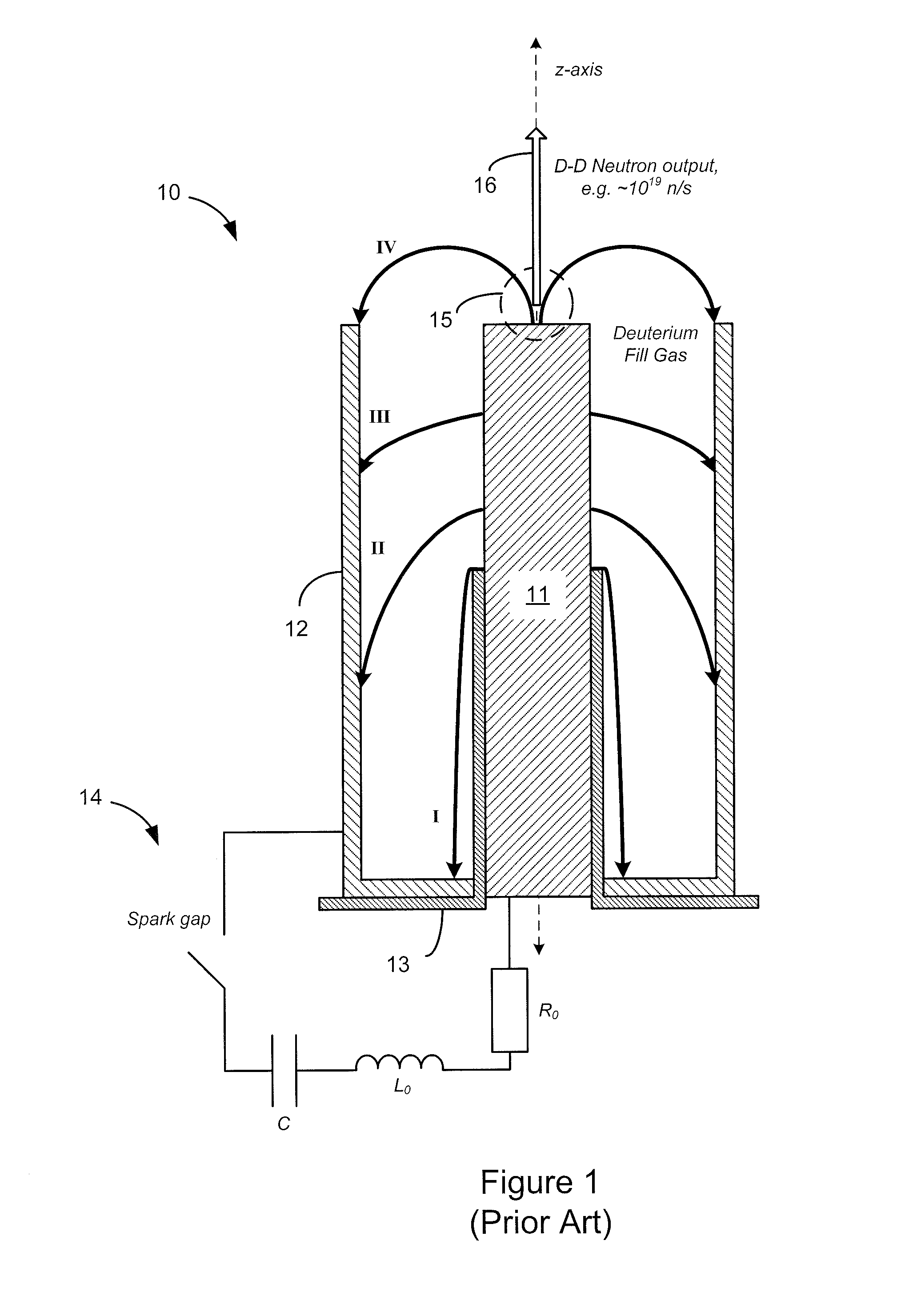
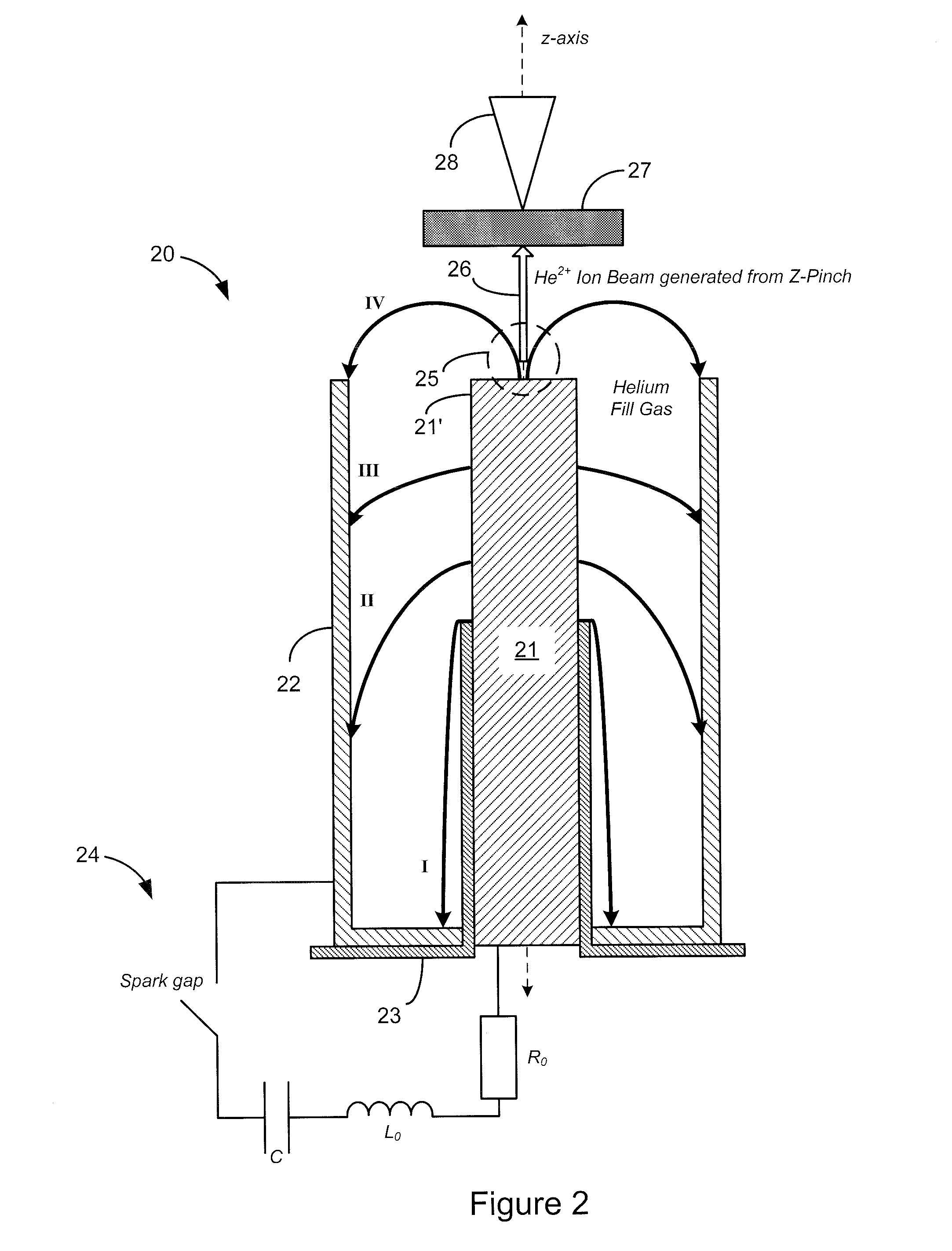
Dense plasma focus (DPF) accelerated non radio isotopic radiological source
ActiveUS20100215136A1High strengthEasy to adaptNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsNeutron emissionIon beam
A non-radio-isotopic radiological source using a dense plasma focus (DPF) to produce an intense z-pinch plasma from a gas, such as helium, and which accelerates charged particles, such as generated from the gas or injected from an external source, into a target positioned along an acceleration axis and of a type known to emit ionizing radiation when impinged by the type of accelerated charged particles. In a preferred embodiment, helium gas is used to produce a DPF-accelerated He2+ ion beam to a beryllium target, to produce neutron emission having a similar energy spectra as a radio-isotopic AmBe neutron source. Furthermore, multiple DPFs may be stacked to provide staged acceleration of charged particles for enhancing energy, tenability, and control of the source.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
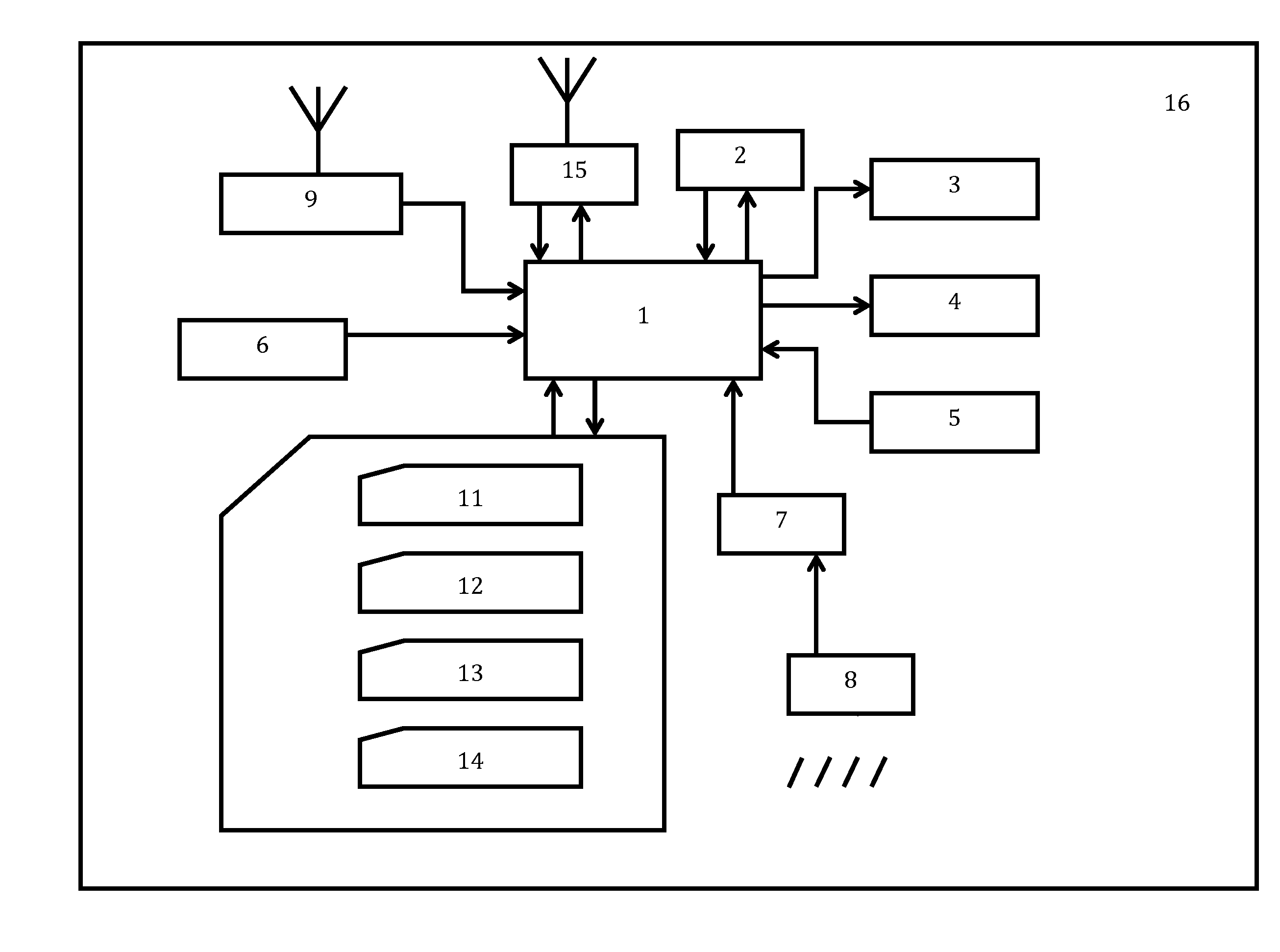
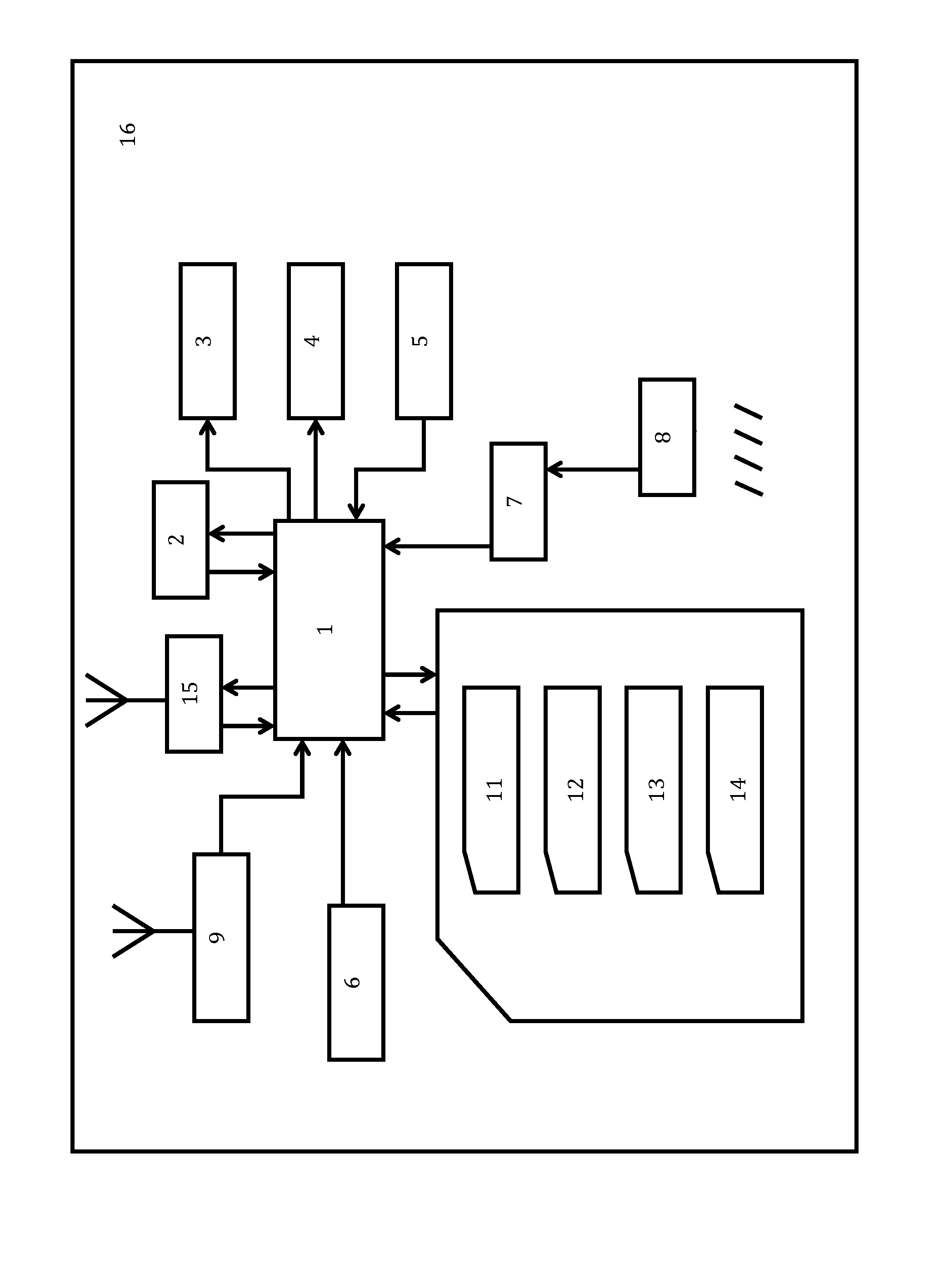
Mobile radio unit with a dosimeter-radiometer
InactiveUS20120329517A1Increase rangeGuarantee efficiencyDevices with GPS signal receiverRadiation measurementNeutron emissionTransceiver
The mobile radio unit (phone, smartphone) comprises body 16 with an incorporated processor 1. The processor 1 is connected with memory 2, display 3, audible alarm aids 4, keyboard 5, power unit 6, navigator 9, and transceiver 15. The radio unit is equipped with radiation detector 8, electronic amplifier 7 and interface 10 connected to the processor 1. The detector 8 provides measuring alpha-, beta-, gamma- and neutron emissions and solar radiation levels. The processor 1 is provided with software, which ensures both communication functions and control, warning of exposure levels, measuring background radiation, building diagrams illustrating state of human organs. The keyboard 5 comprises keys for dosimeter and / or radiometer mode control. The detector 8, the interface 10 and the amplifier 7 can be placed in the mobile unit body 16 or in separate detachable unit. Thus, there was constructed an efficient mobile unit, which ensures an extended functionality.
Owner:ELIN VLADIMIR ALEKSANDROVICH
Absolute elemental concentrations from nuclear spectroscopy
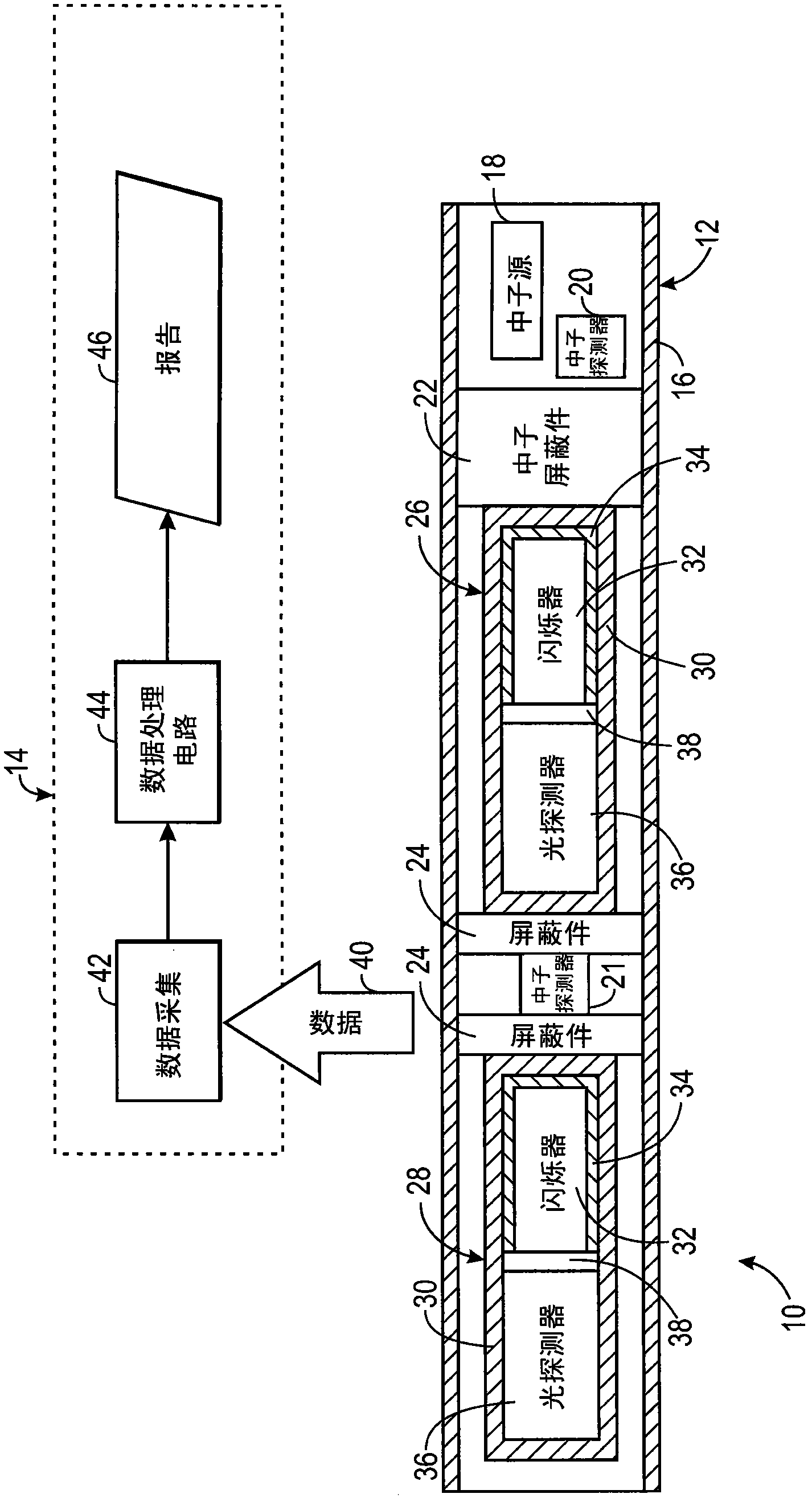
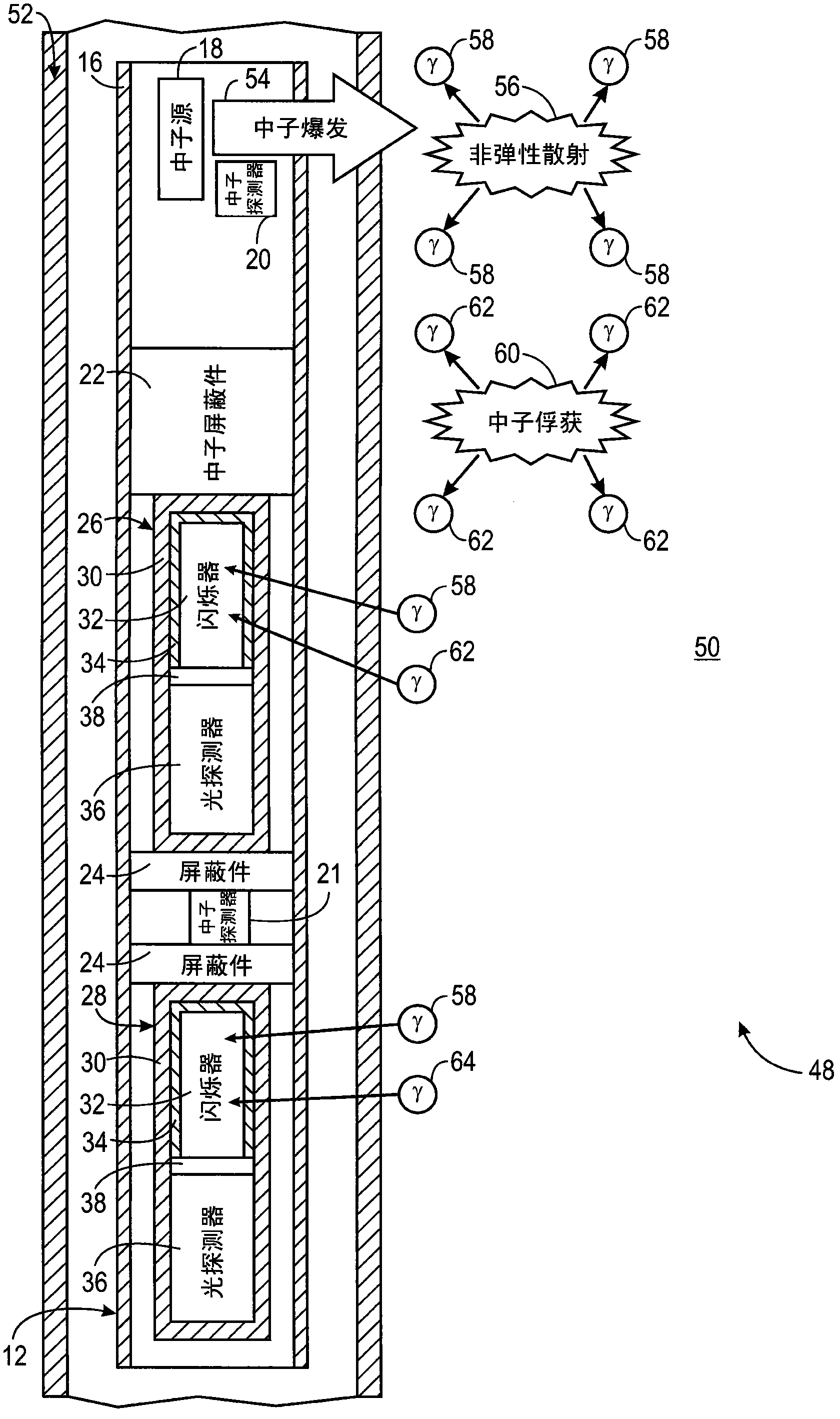
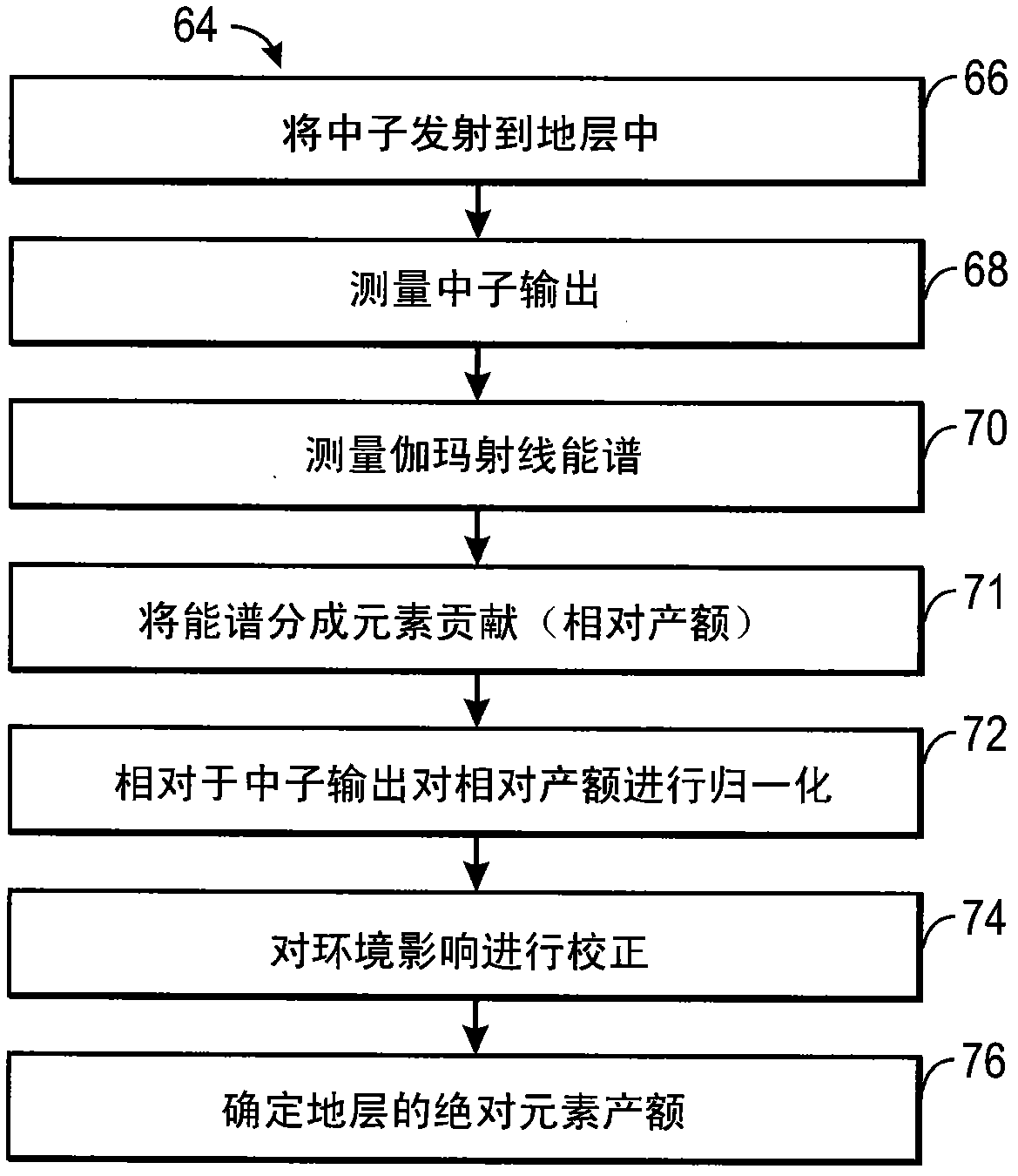
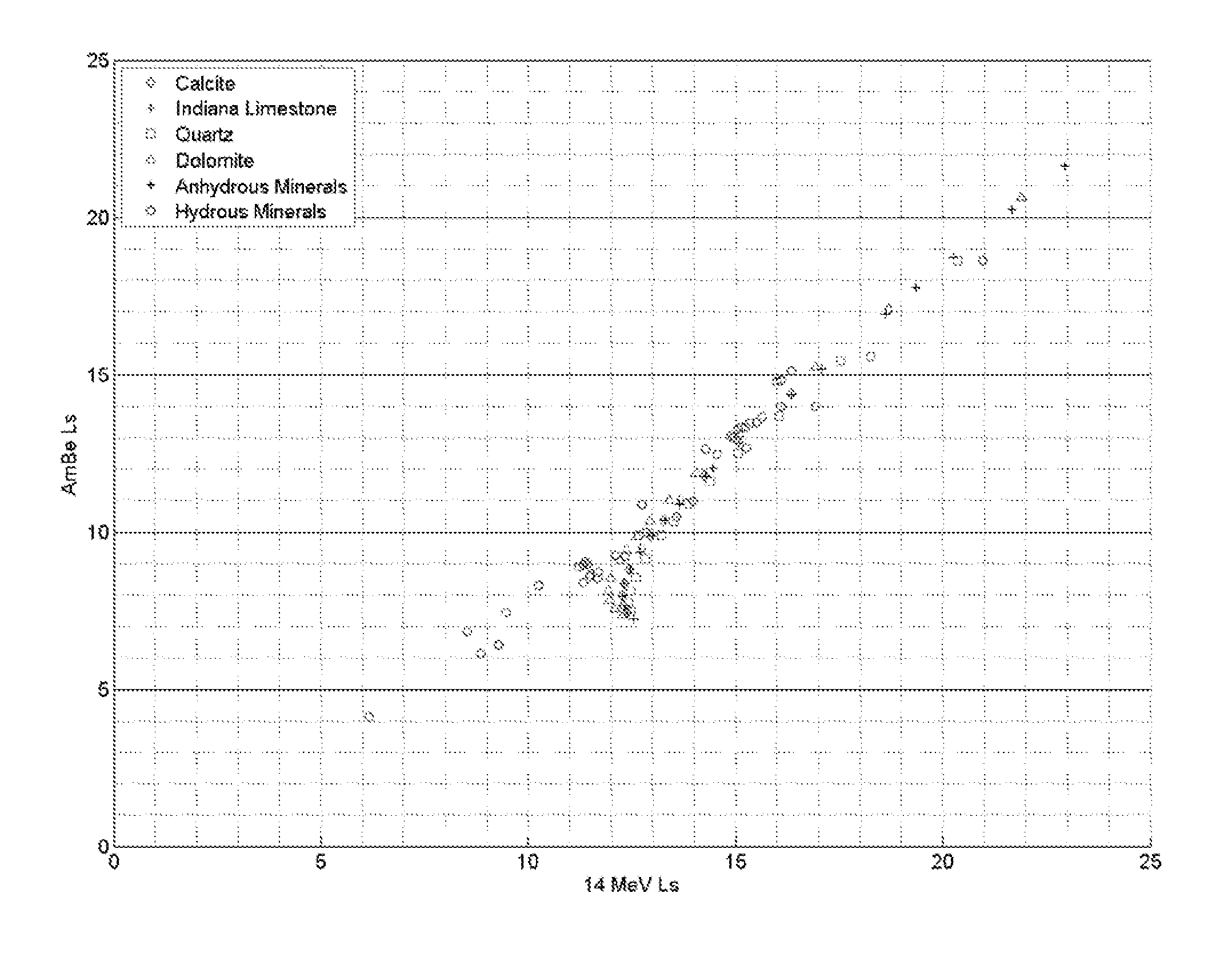
ActiveCN102084271AX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNuclear radiation detectionInelastic scatteringCounting rate
The present invention discloses a system and method for estimating absolute elemental concentrations of a subterranean formation from neutron-induced gamma-ray spectroscopy. In one example, a system (10) for estimating an absolute yield of an element in a subterranean formation may include a downhole tool (12) and data processing circuitry (14). The downhole tool may include a neutron source (18) to emit neutrons into the formation, a neutron monitor (20) to detect a count rate of the emitted neutrons, and a gamma-ray detector (26,28) to obtain gamma-ray spectra deriving at least in part from inelastic gamma- rays produced by inelastic scattering events and neutron capture gamma-rays produced by neutron capture events. The data processing circuitry may be configured to determine a relative elemental yield from the gamma-ray spectra and to determine an absolute elemental yield based at least in part on a normalization of the relative elemental yield to the count rate of the emitted neutrons.
Owner:PRAD RES & DEV LTD
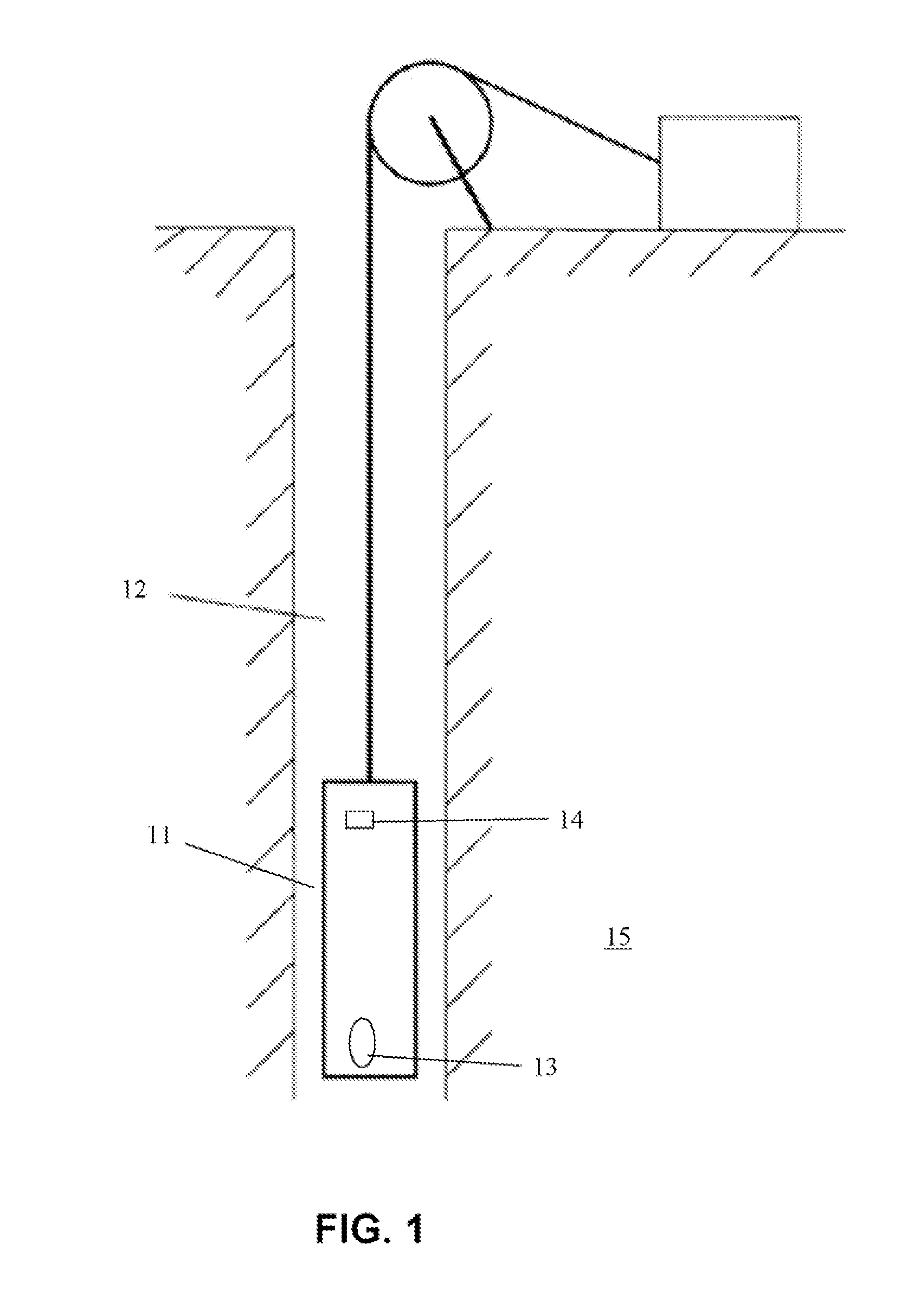
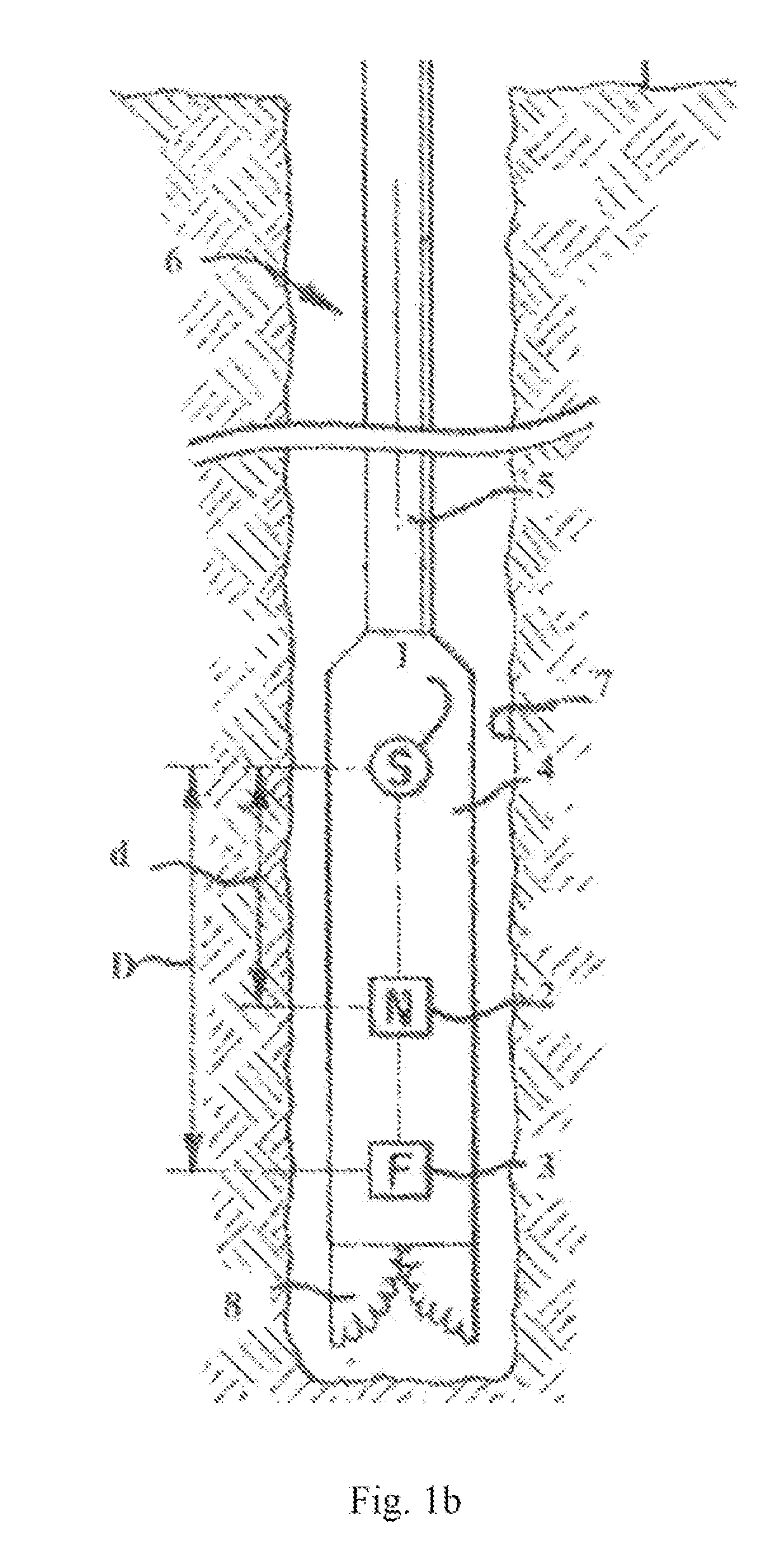
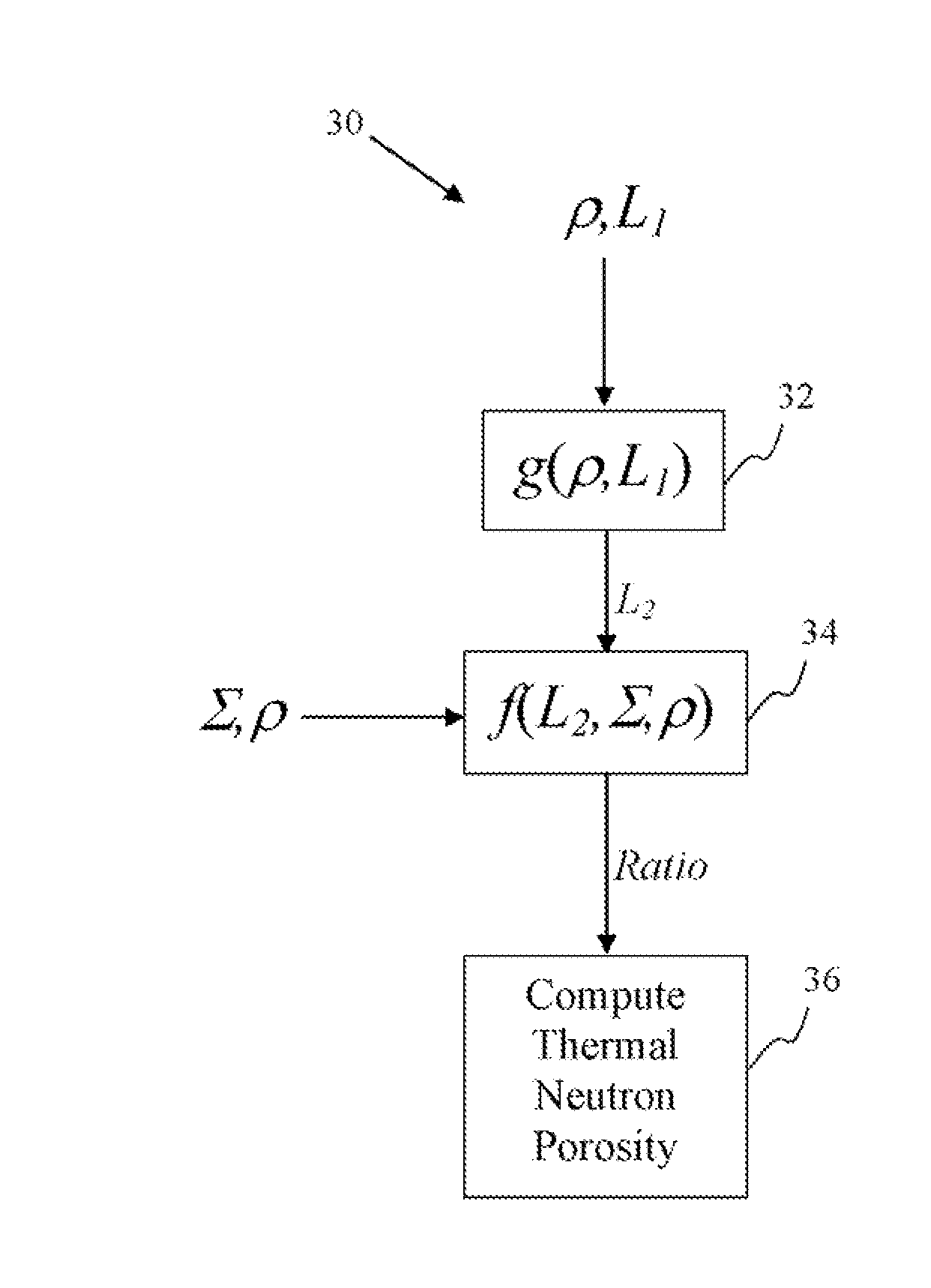
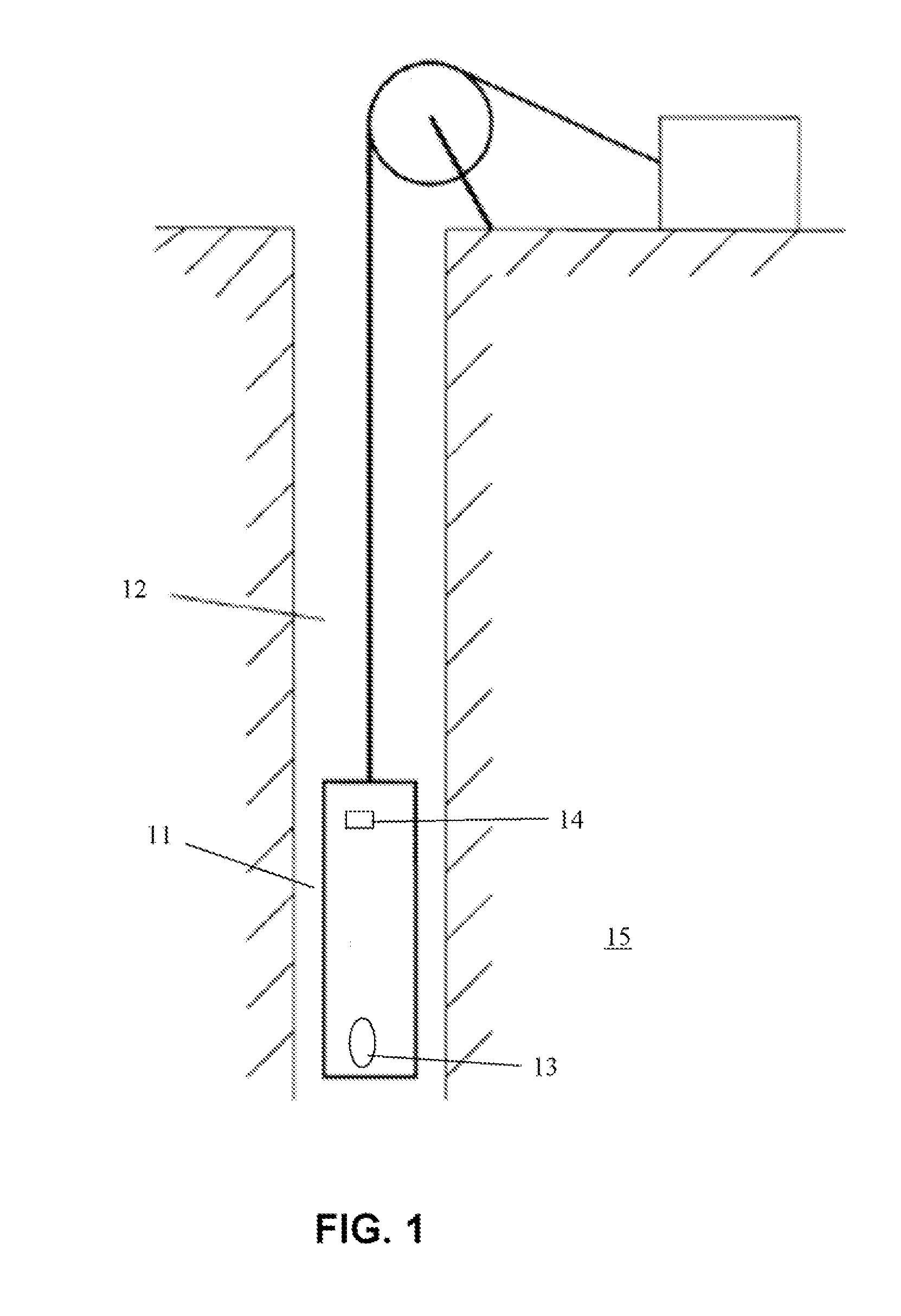
Thermal neutron porosity from neutron slowing-down length, formation thermal neutron capture cross section, and bulk density
A method for determining at least one formation property calculated from neutron measurements acquired with a downhole tool includes emitting neutrons from a source in the tool into the formation, detecting neutrons with at least one detector in the downhole tool, calculating a first slowing-down length (L1) based on the detected neutrons, and deriving a second slowing-down length (L2) based on the first slowing-down length (L1). Further steps include deriving a correlation function for relating slowing-down lengths from a first tool to slowing-down lengths associated with a different source, wherein the correlation function depends on formation properties such as bulk density; and applying the correlation function to the slowing-down length of the first tool to derive the slowing-down length of the second tool. A method for determining a thermal neutron formation porosity based on a slowing-down length from epithermal neutron measurements from an electronic neutron source includes converting the slowing-down length into a computed neutron slowing-down length from thermal neutron measurements from a chemical neutron source, wherein the converting uses a correlation function that depends on formation bulk density; deriving a thermal neutron countrate ratio based on the computed neutron slowing-down length, wherein the deriving uses a function that depends on the formation bulk density and formation sigma; and computing the thermal neutron formation porosity from the thermal neutron countrate ratio.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Thermal Neutron Porosity from Neutron Slowing-Down Length, Formation Thermal Neutron Capture Cross Section, and Bulk Density
A method for determining at least one formation property calculated from neutron measurements acquired with a downhole tool includes emitting neutrons from a source in the tool into the formation, detecting neutrons with at least one detector in the downhole tool, calculating a first slowing-down length (L1) based on the detected neutrons, and deriving a second slowing-down length (L2) based on the first slowing-down length (L1). Further steps include deriving a correlation function for relating slowing-down lengths from a first tool to slowing-down lengths associated with a different source, wherein the correlation function depends on formation properties such as bulk density; and applying the correlation function to the slowing-down length of the first tool to derive the slowing-down length of the second tool. A method for determining a thermal neutron formation porosity based on a slowing-down length from epithermal neutron measurements from an electronic neutron source includes converting the slowing-down length into a computed neutron slowing-down length from thermal neutron measurements from a chemical neutron source, wherein the converting uses a correlation function that depends on formation bulk density; deriving a thermal neutron countrate ratio based on the computed neutron slowing-down length, wherein the deriving uses a function that depends on the formation bulk density and formation sigma; and computing the thermal neutron formation porosity from the thermal neutron countrate ratio.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
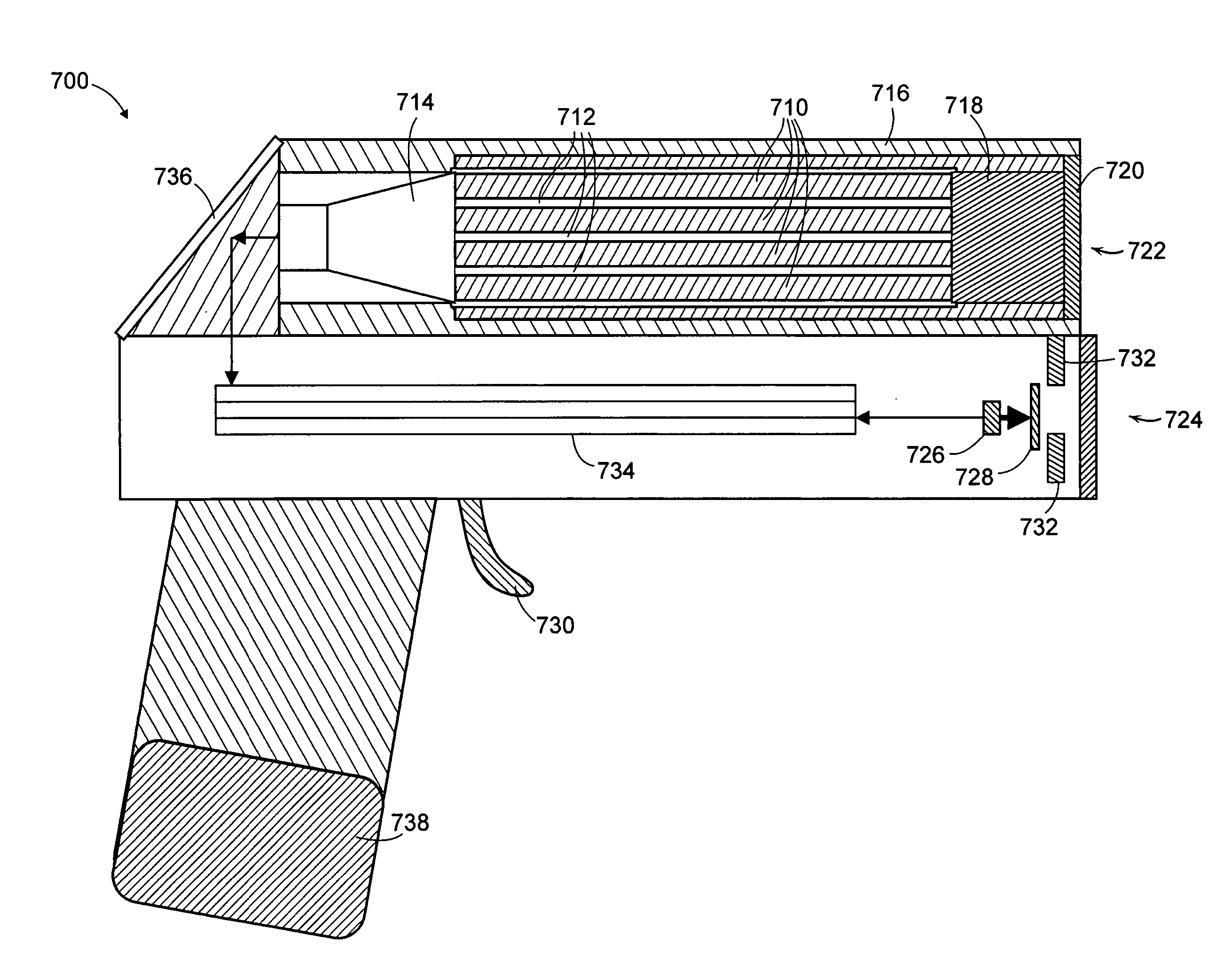
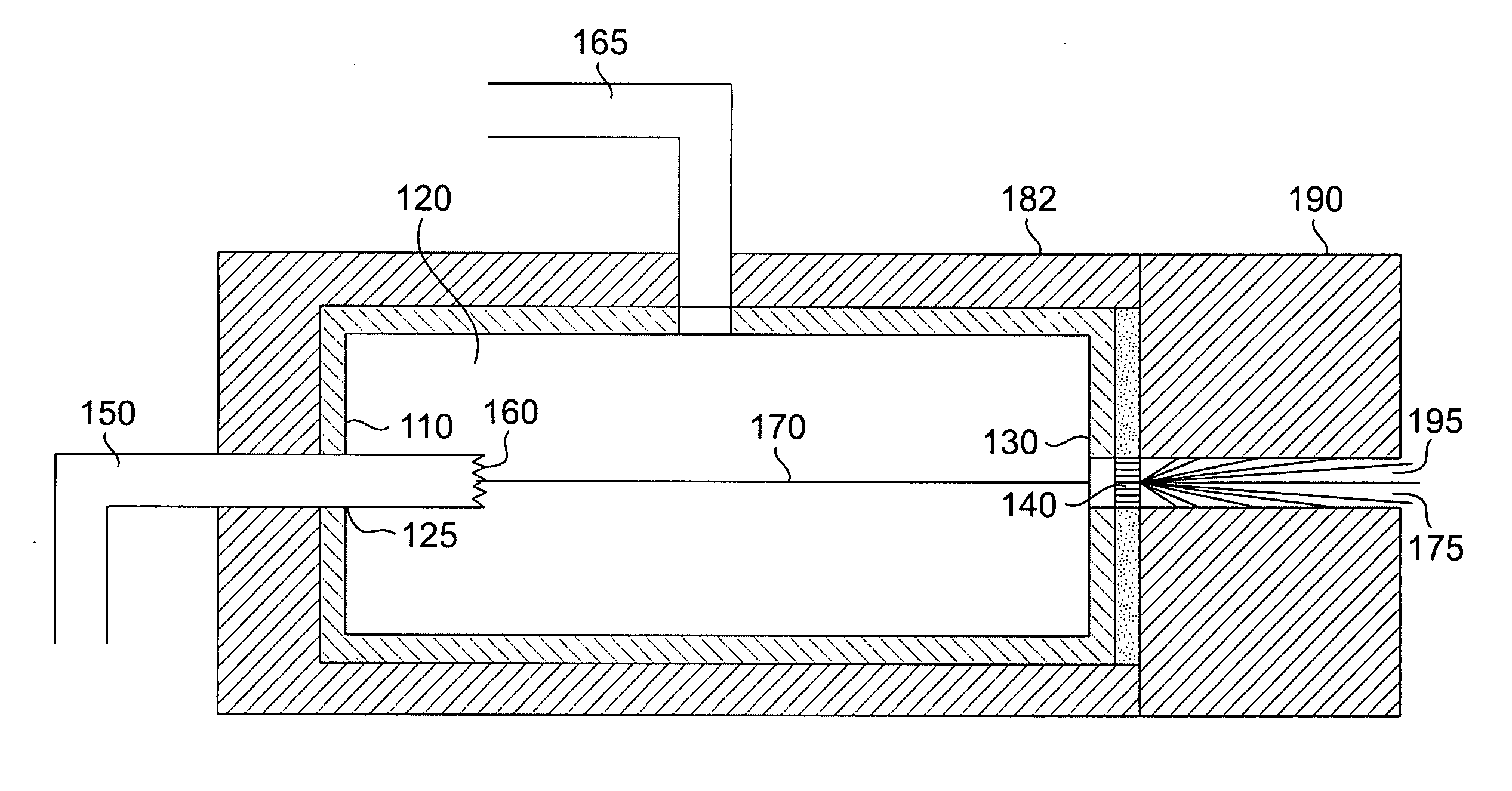
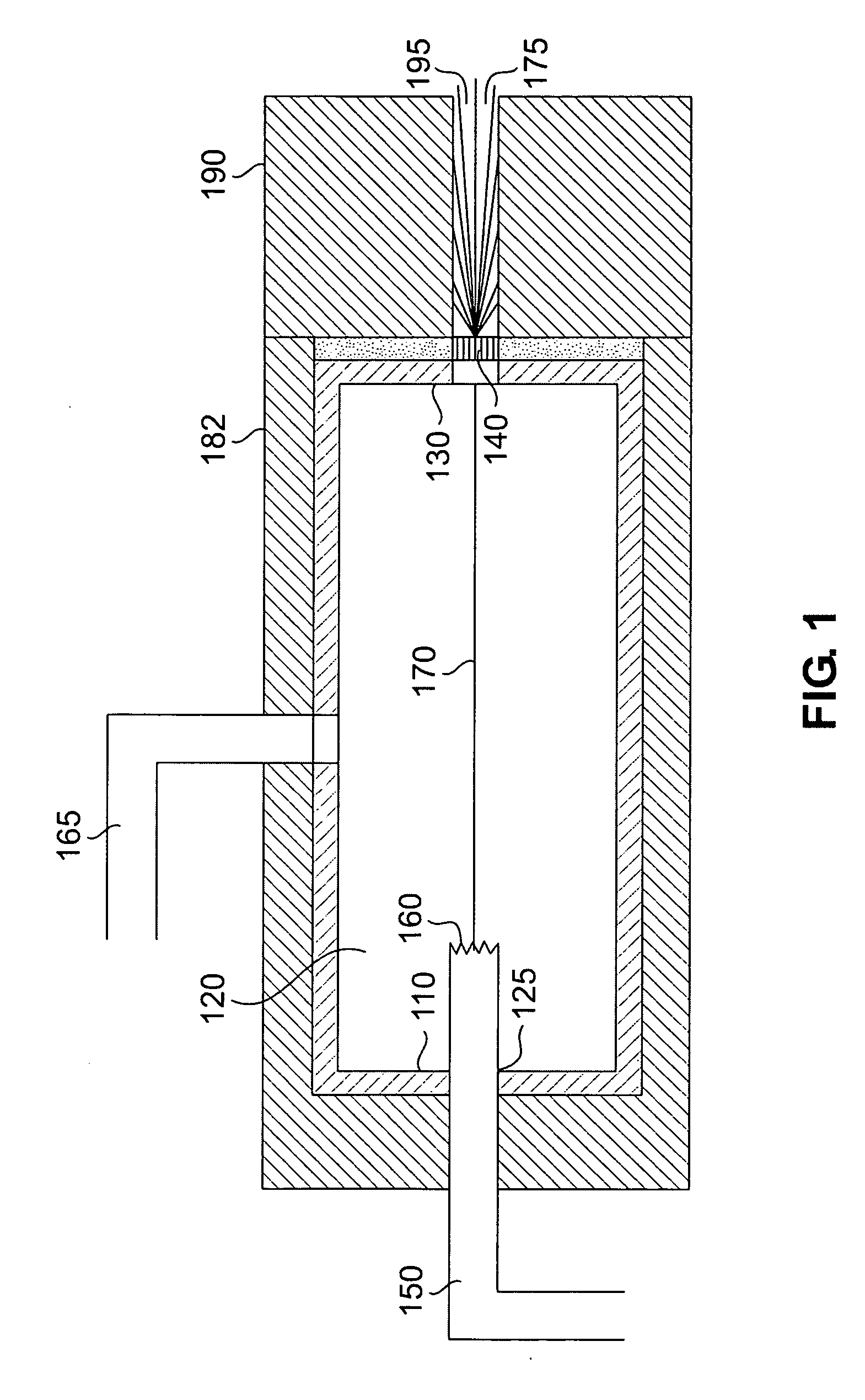
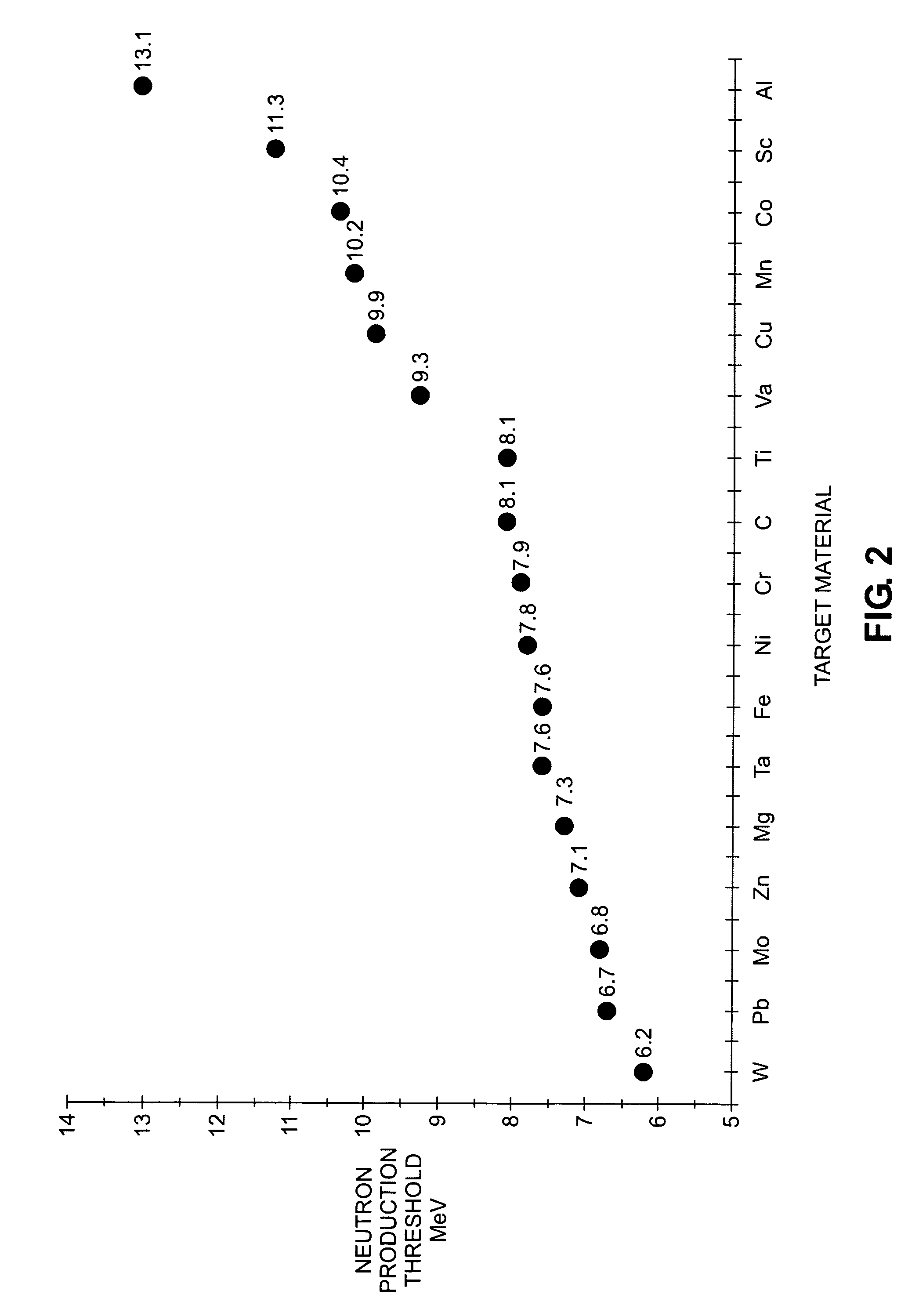
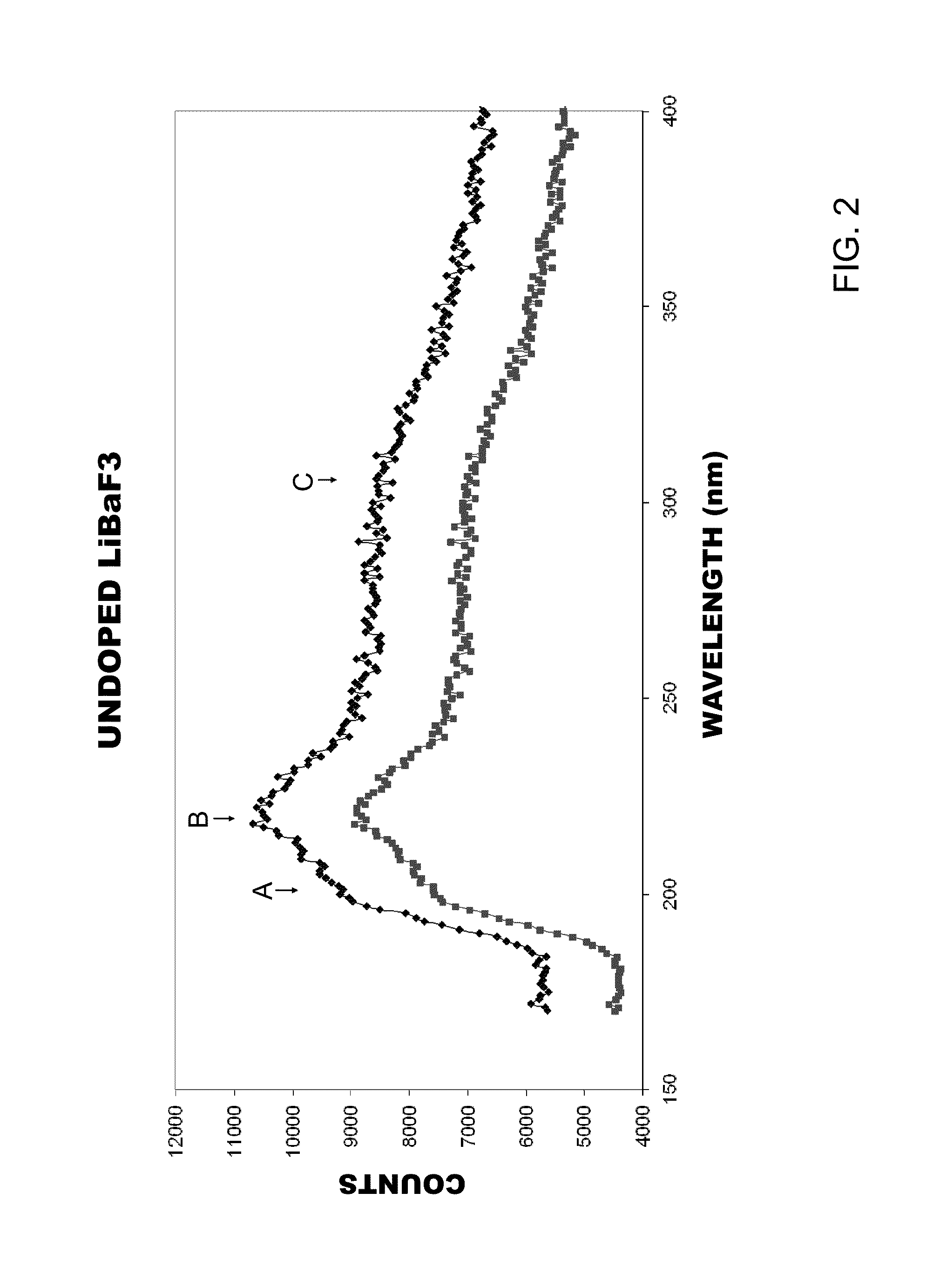
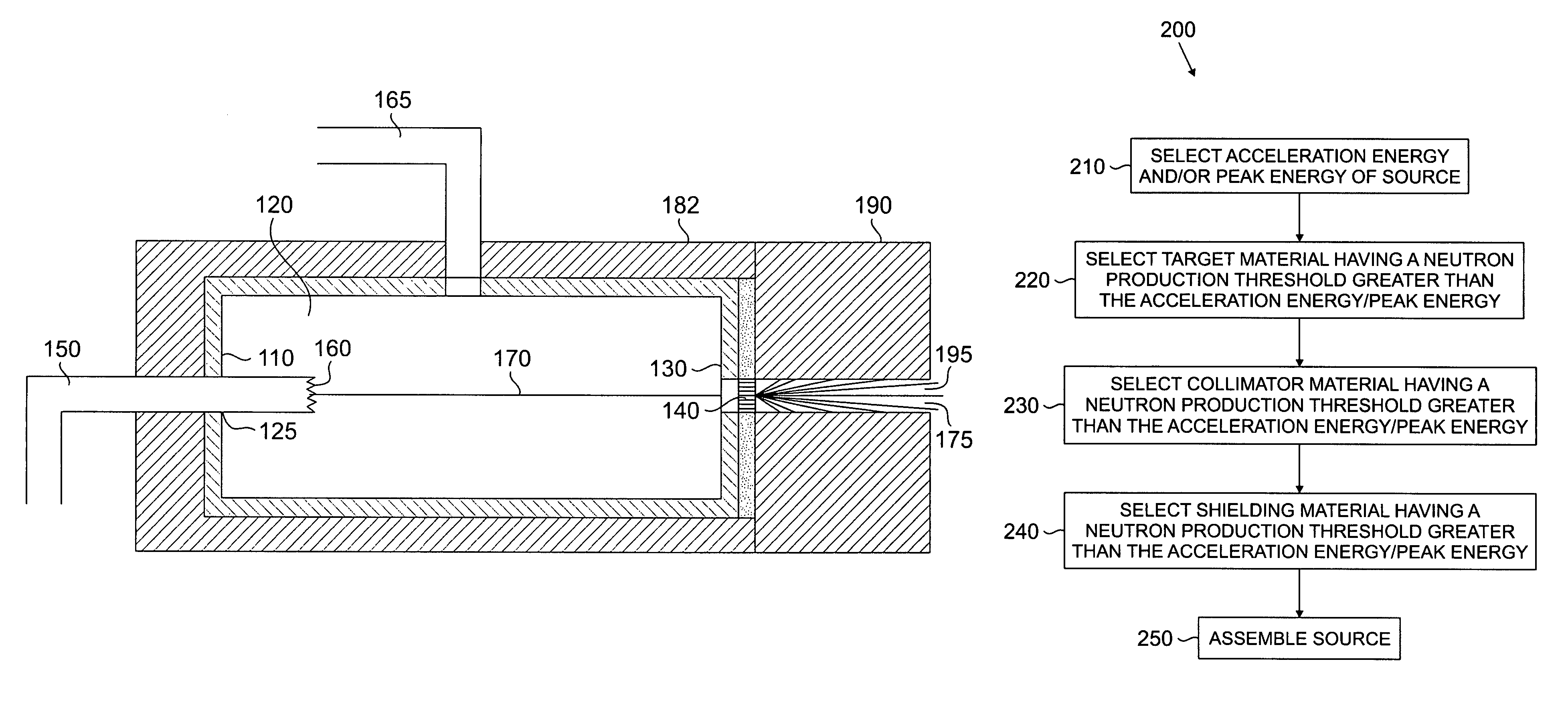
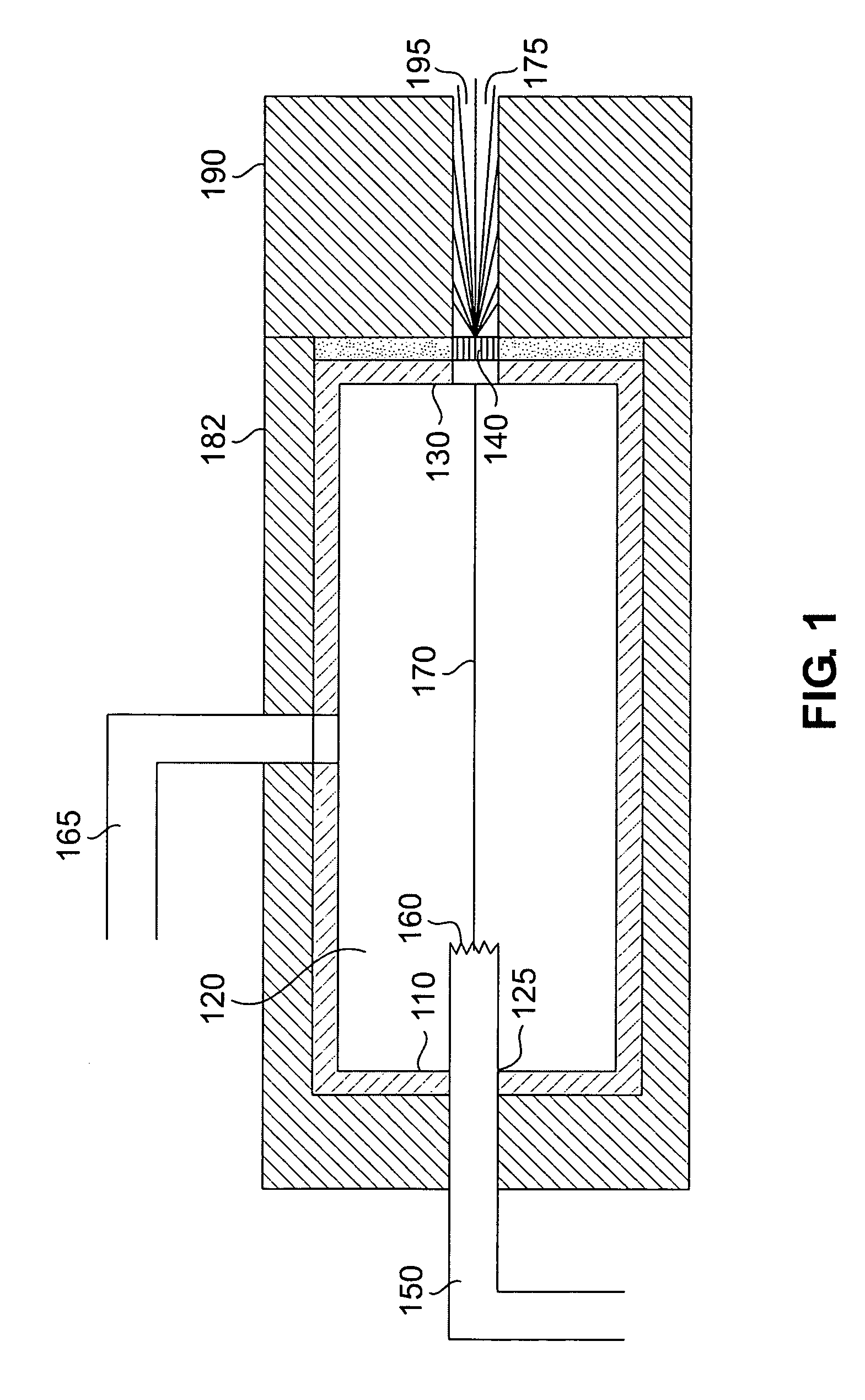
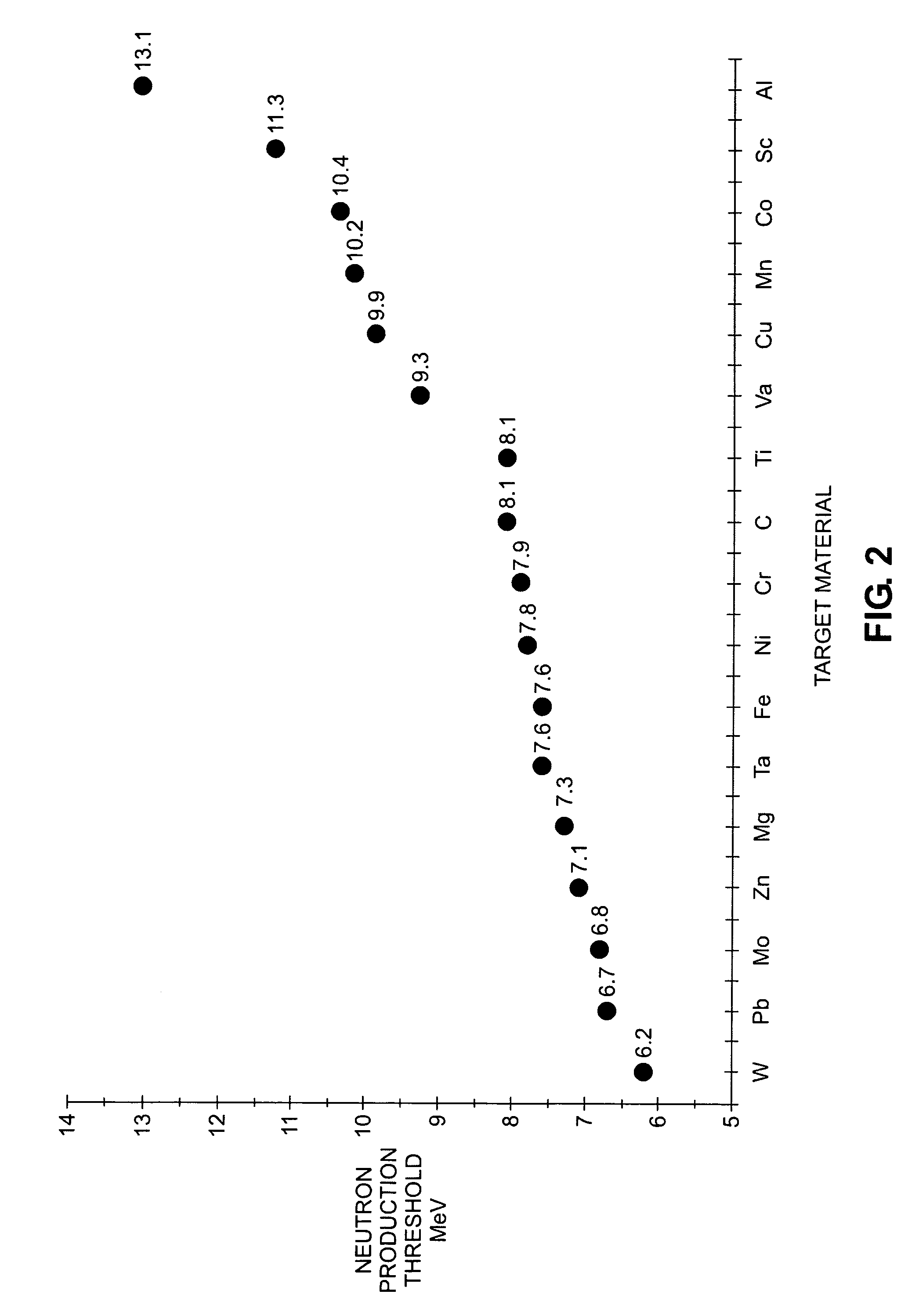
X-ray radiation sources with low neutron emissions for radiation scanning
In one example, a radiation source comprises a housing and an acceleration chamber within the housing, with a peak acceleration energy greater than the lowest neutron production threshold of tantalum. A source of charged particles is supported by the housing to emit charged particles into the acceleration chamber. A target is supported by the housing downstream of the acceleration chamber. The target consists essentially of at least one isotope having a neutron production threshold greater than the peak acceleration energy. No neutrons are therefore generated. The source may also comprise a collimator, target shielding, and / or housing shielding comprising at least one isotope having a neutron production threshold greater than the peak acceleration energy, reducing or eliminating neutron generation as compared to the prior art, as well. Systems comprising the source, methods of operation of the source, and methods of manufacture of the source are also disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
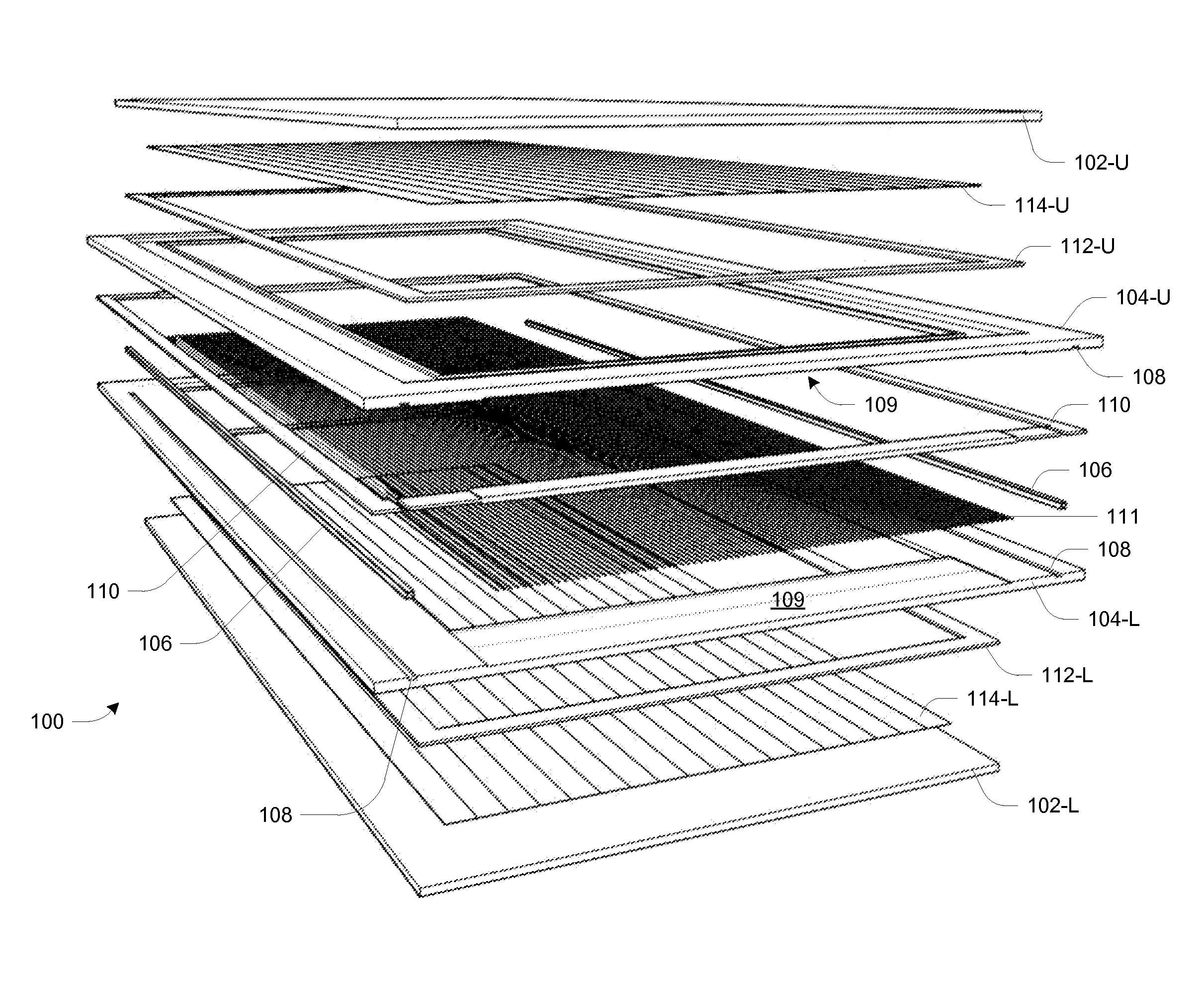
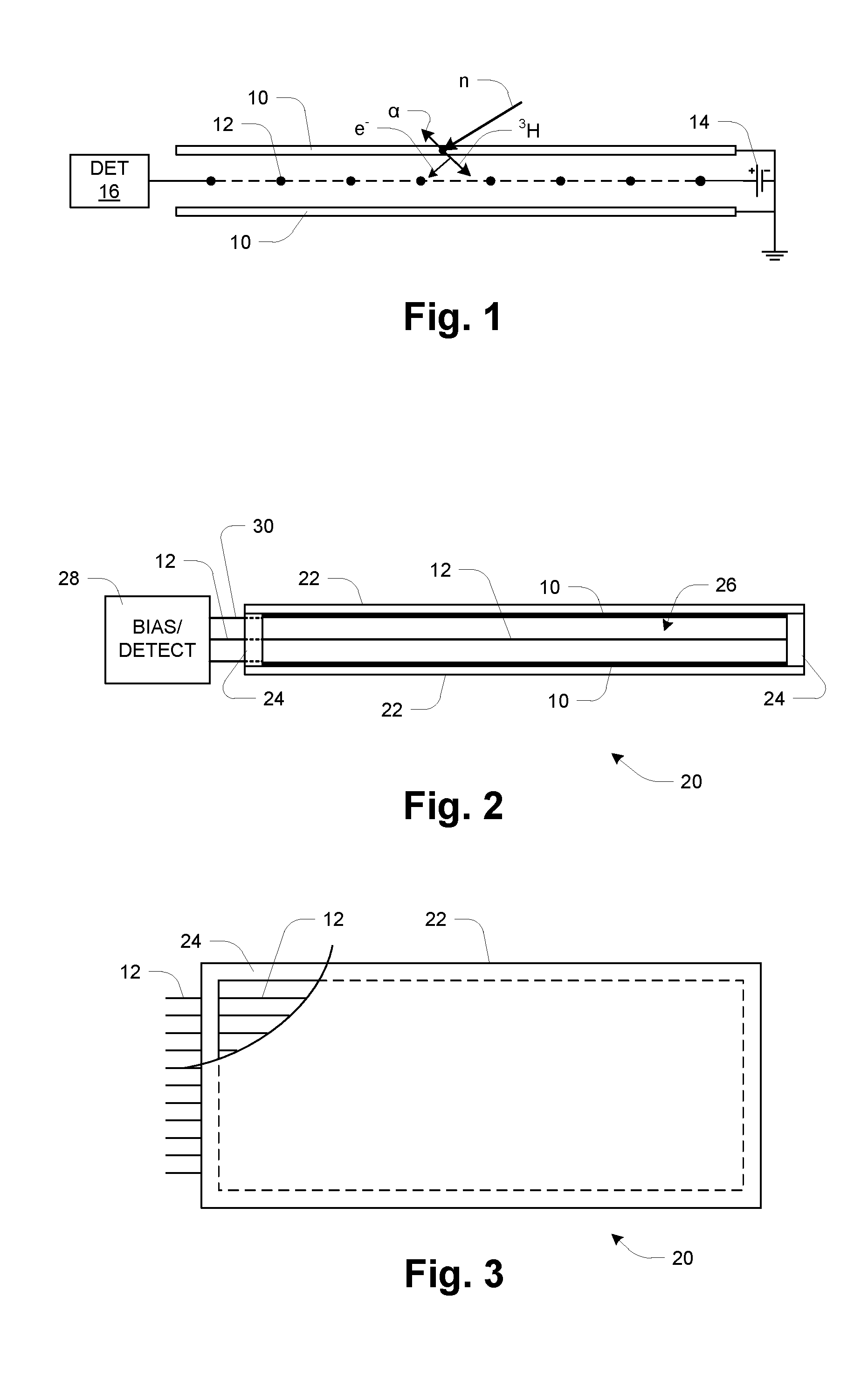
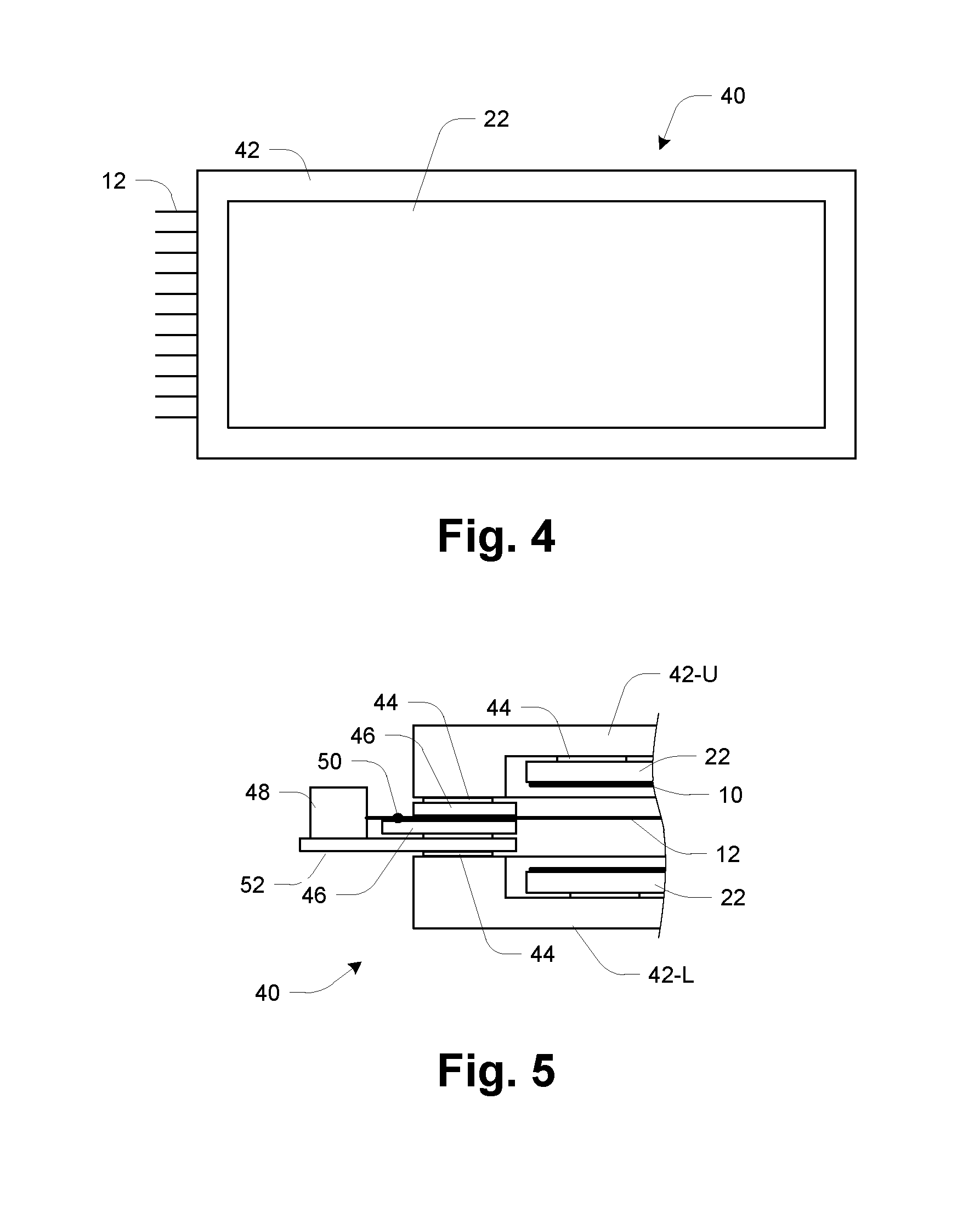
Glass-panel lithium-6 neutron detector
InactiveUS20140077091A1Leverage cost and design and durability and performanceMost efficientElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionElectron multiplication
A thermal neutron detector includes a planar detector housing having two glass panels spaced apart by a gas-tight seal defining a detection chamber including an inert detection gas and lithium foils adhered to inner surfaces of the glass panel(s). The lithium foils emit alpha particles and tritons in response to incident thermal neutrons, and the inert detection gas is ionized by the particles to generate drift electrons. A planar array of detection wires is spaced apart from the lithium foils and extends outside the detection chamber. Electronic bias applies a field voltage between the wires and the lithium foils to establish a drift electric field in the detection chamber effective to attract the drift electrons to the wires and provide a large electric field near the anode wires to cause electron multiplication near the wire resulting in large numbers of electrons and positive ions for each initial electron. Detection circuitry detects electric signals in wires generated by the drift of positive ions away from the wires and interpret the electrical signals as incidence of thermal neutrons on the detector.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
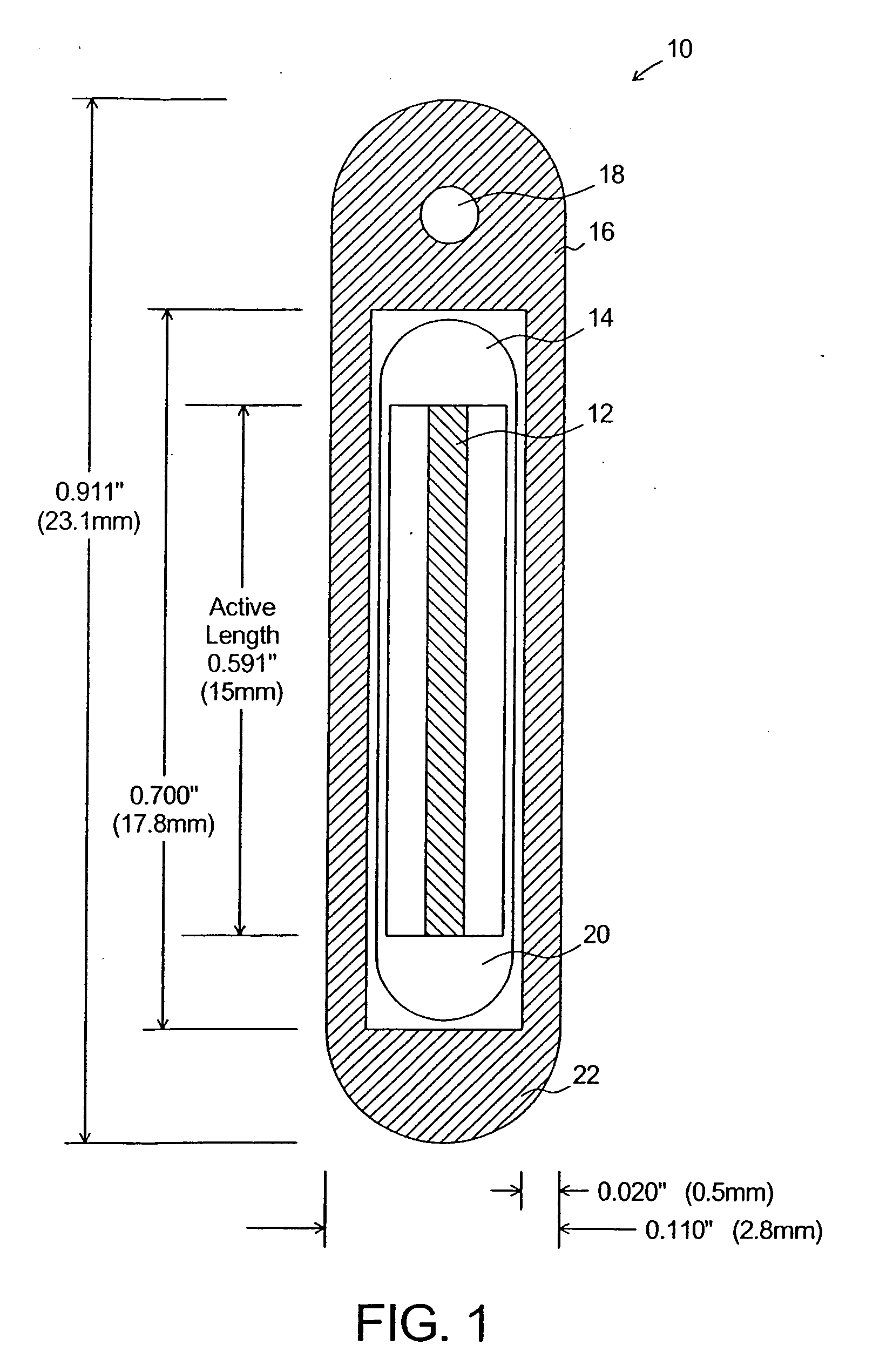
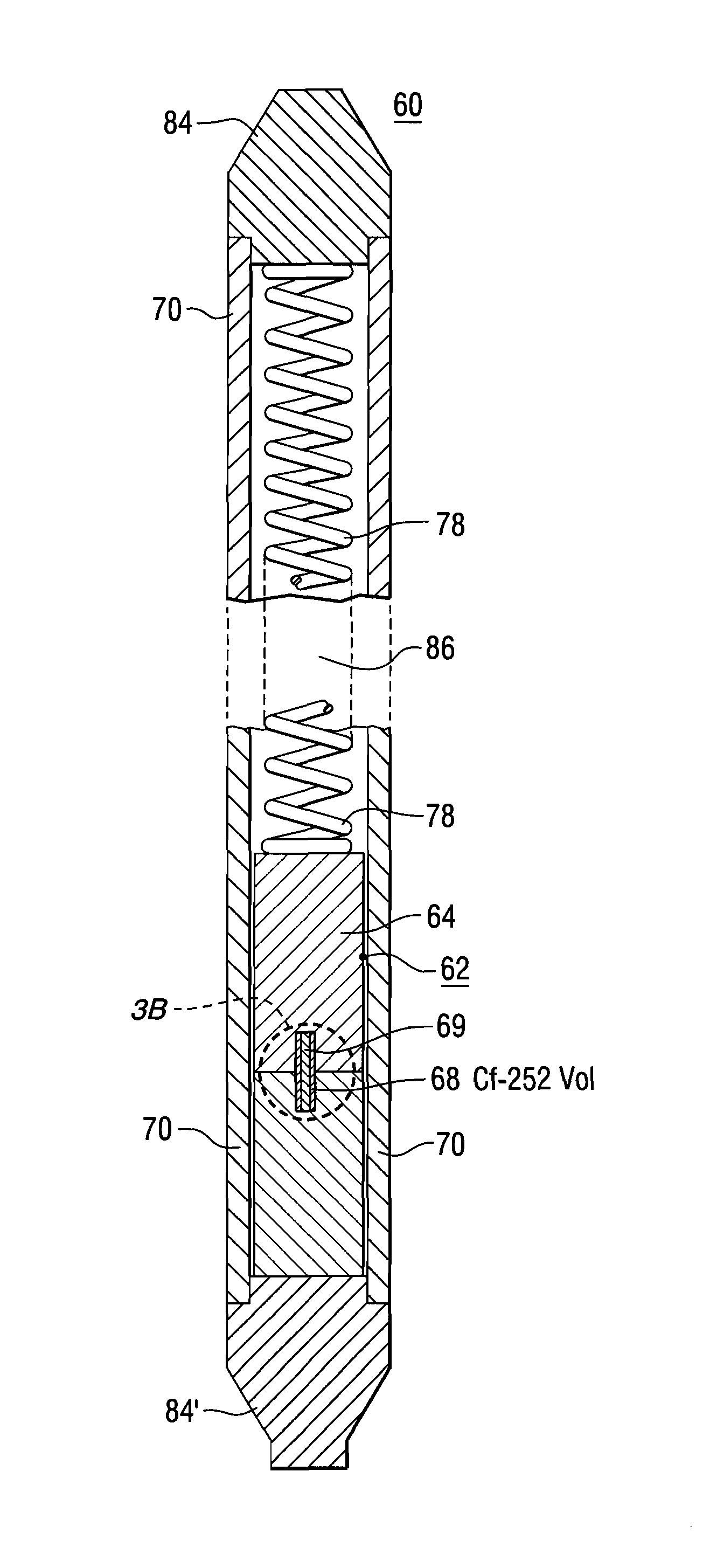
Dosimetry for californium-252 (252Cf) neutron-emitting brachytherapy sources and encapsulation, storage, and clinical delivery thereof
The present invention discloses a methodology for the characterization and determination of mixed-field dosimetry for 252Cf Applicator Tube (AT)-type medical sources, utilizing ionization chambers, GM counters, and Monte Carlo methods. Unlike the previous methodologies, the present invention discloses a specification of dose to muscle, rather than dose to water, for clinical dosimetry of 252Cf medical sources. A dosimetry protocol, similar to that utilized for ICRU-45, with parameters determined specifically for 252Cf brachytherapy is disclosed. Neutron isodose distributions and data necessary for clinical implementation of 252Cf AT sources are also disclosed herein. Additionally, novel methods for the encapsulation, storage, and delivery / implantation of 252Cf radionuclide sources are disclosed.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND MEDICAL CENT HOSPITALS
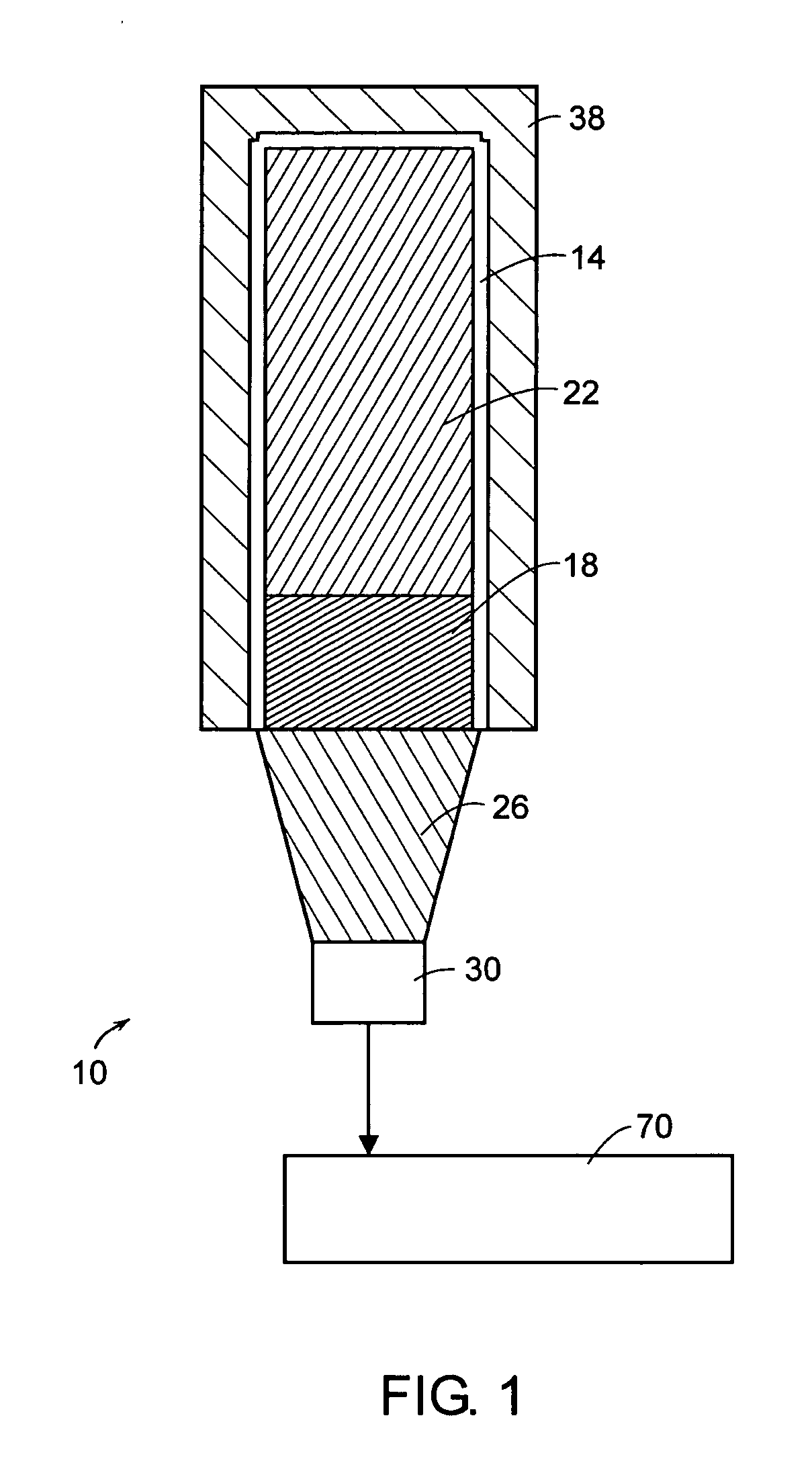
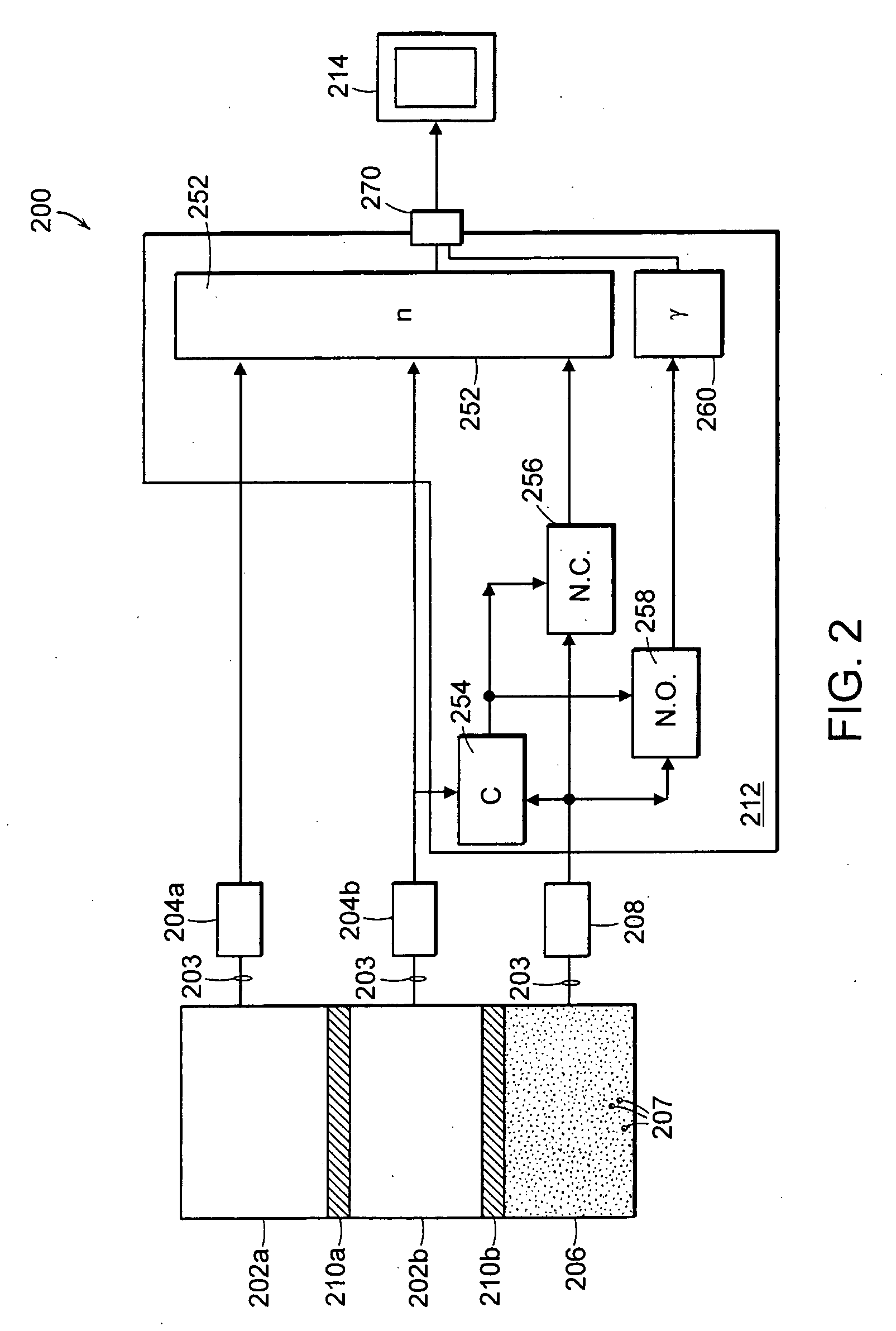
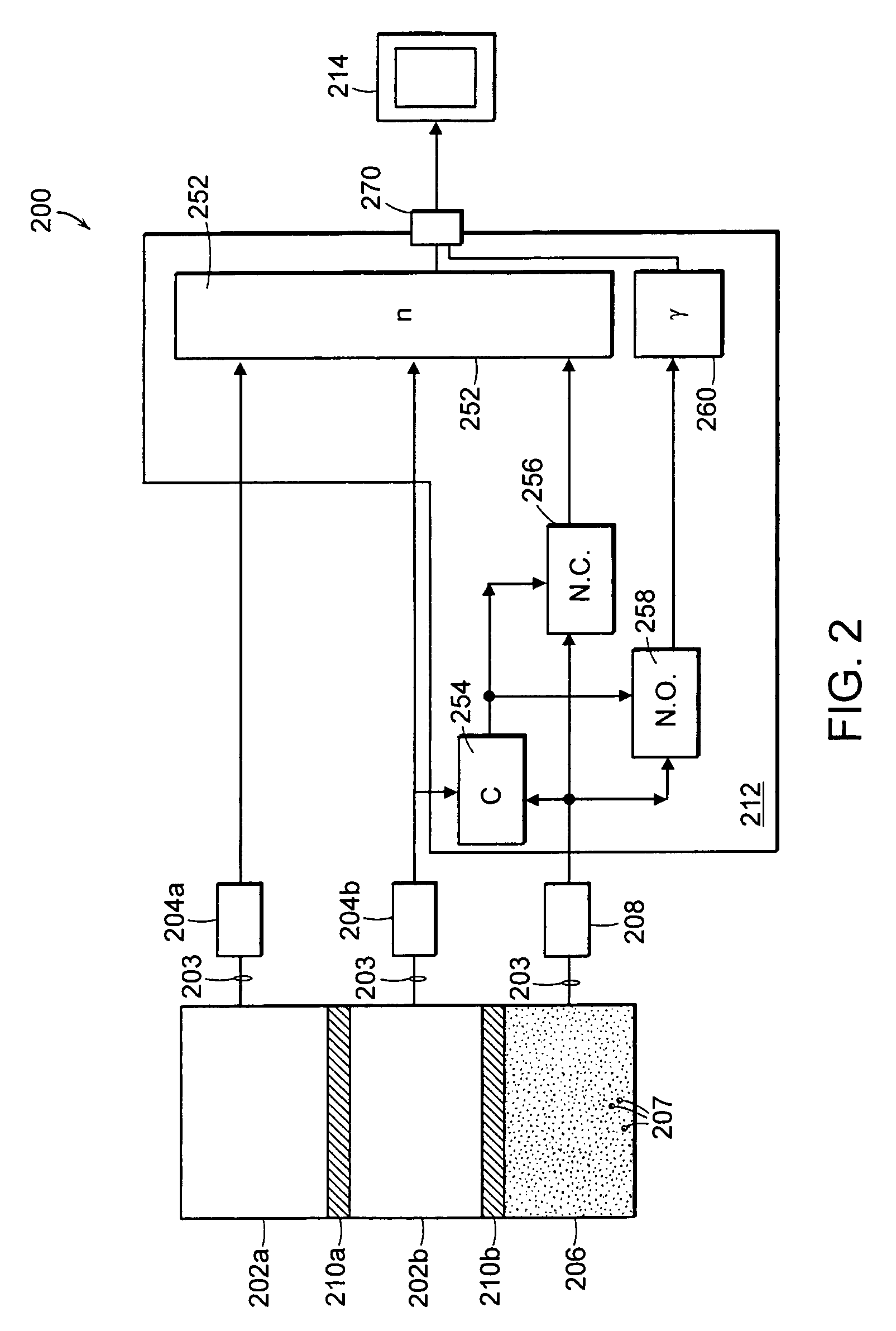
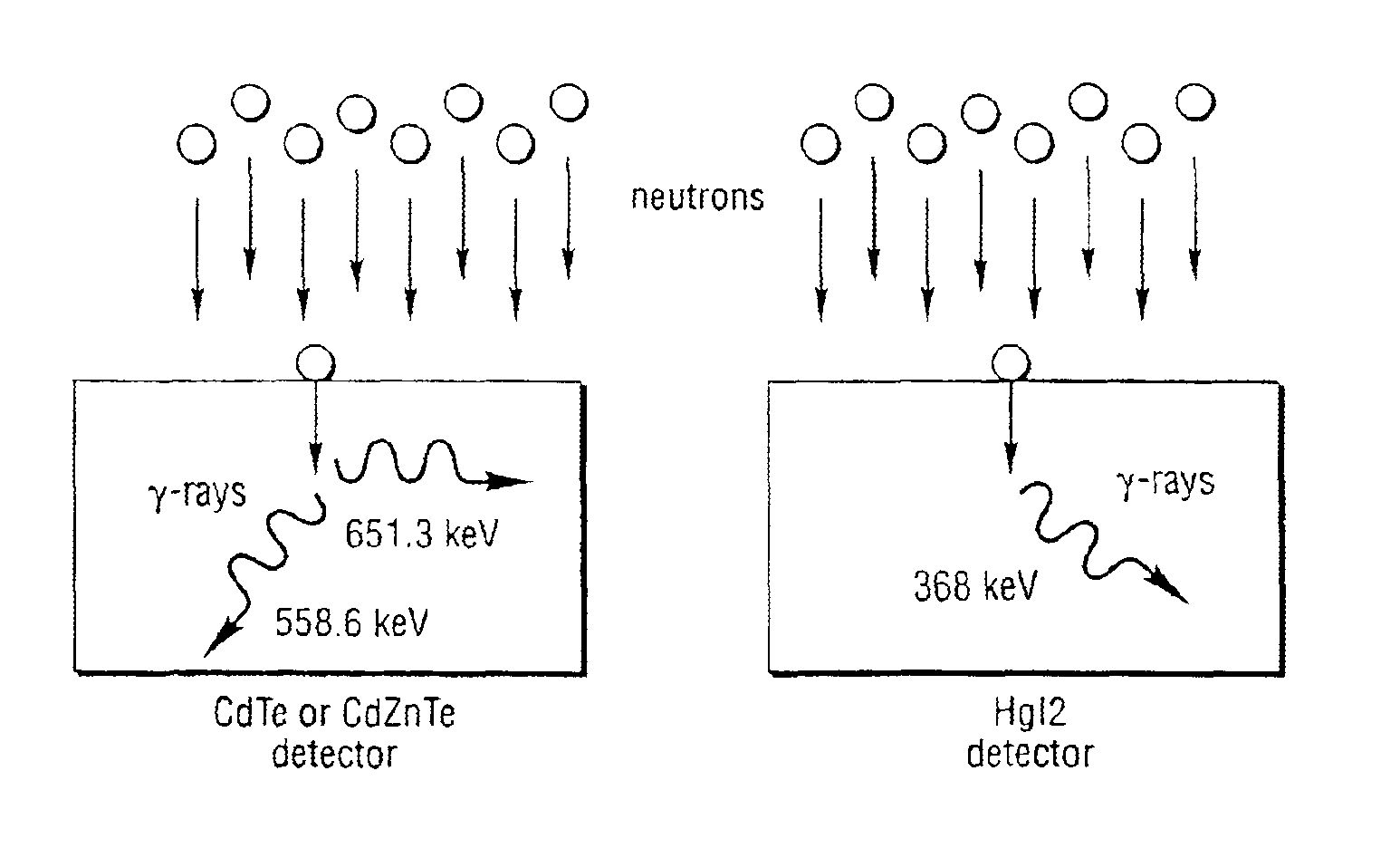
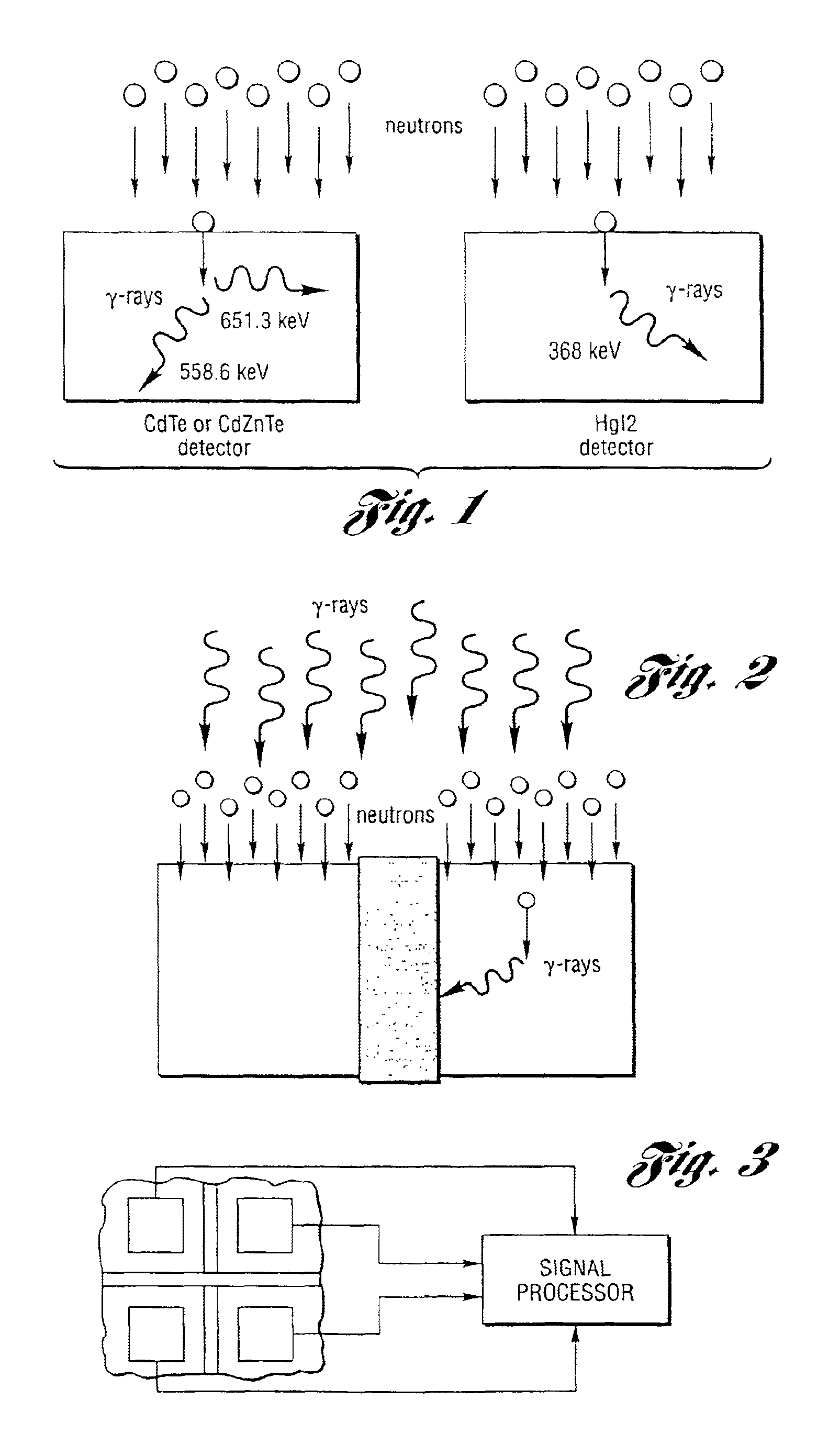
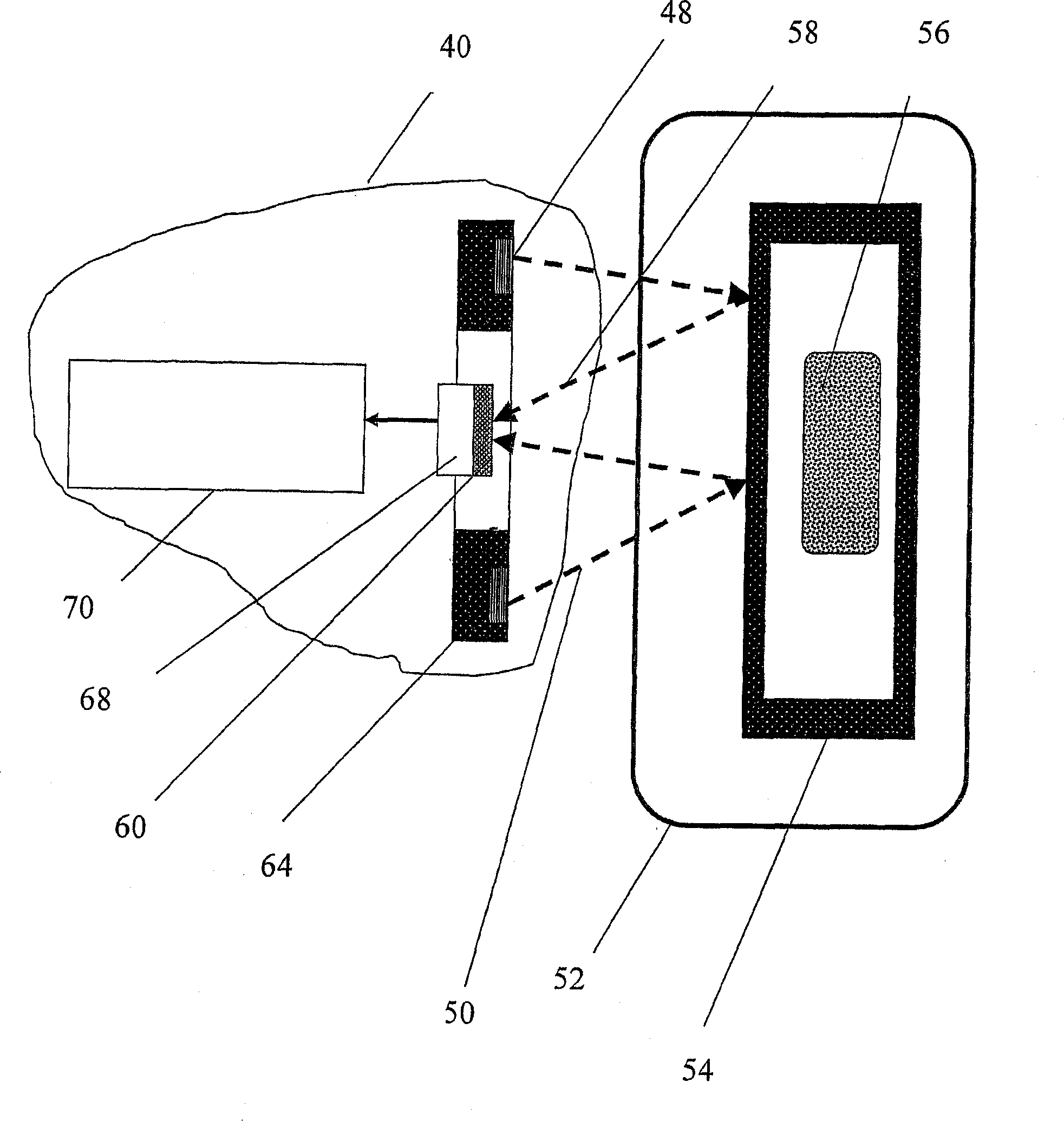
Method and system for measuring neutron emissions and ionizing radiation, solid state detector for use therein, and imaging system and array of such detectors for use therein
InactiveUS6921903B2Measurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesGamma ray spectrometerSolid state detector
A method and system for measuring neutron emissions and ionizing radiation, such as gamma emissions, solid state detector for use therein, and imaging system and array of such detectors for use therein are provided using Cd- and / or Hg-containing semiconductors or B-based, Li-based or Gd-based semiconductors. The resulting systems and detectors used therein may be not only compact and portable, but also capable of operating at room temperature. The detectors may also be operable as gamma ray spectrometers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Neutron source detection camera
InactiveUS7049603B2Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionMomentum
A neutron imaging method for obtaining an image of the general shape of a neutron emitting source and a bearing of the source relative to an apparatus comprising a chamber comprising a gas with a high probability of interacting with low energy neutrons, releasing collision products that maintain the neutron momentum, and generating ionization particles. The chamber comprises an electrode for providing an electronic signal indicative of the impact location of ionization particles on the electrode and a field to drift the ionization particles to the electrode. A readout indicates the location and time of impact of each ionization particle on the electrode; a memory stores a plurality of the electronic signals; and a computer receives and analyzes the signals and impact times and indicates the location of the source of neutrons by using back projection algorithms to calculate three-dimensional vectors indicative of the neutron path directions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Primary neutron source multiplier assembly
ActiveUS20120087454A1Reduce weightQuality improvementConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
InactiveCN1816757AReduce weightReduce temperature sensitivityMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNeutron emissionX-ray
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like; and / or an X-ray analyzer that facilitates detection of materials that can shield radioactiv sources, e.g., lead, and the like.
Owner:HERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Inelastic background correction for a pulsed-neutron instrument
ActiveUS20090242746A1Measurement by spectrometryMaterial analysis using neutronsNeutron emissionNeutron
A method for correcting data collected with a neutron emitting instrument, includes: obtaining characterization data for the instrument, the characterization data including inelastic background data of the instrument; and correcting the collected data according to the characterization data. A computer program product and an instrument are provided.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
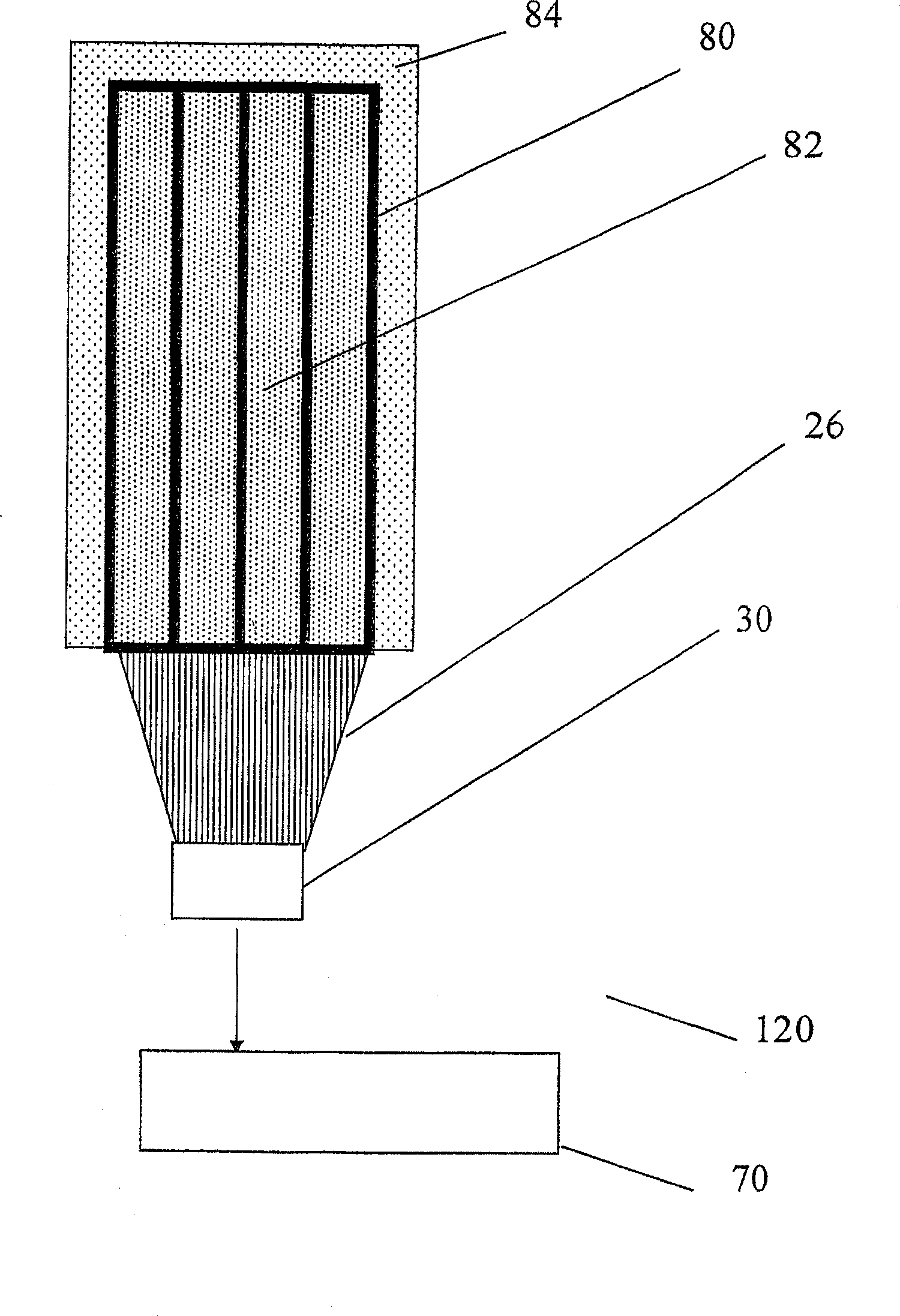
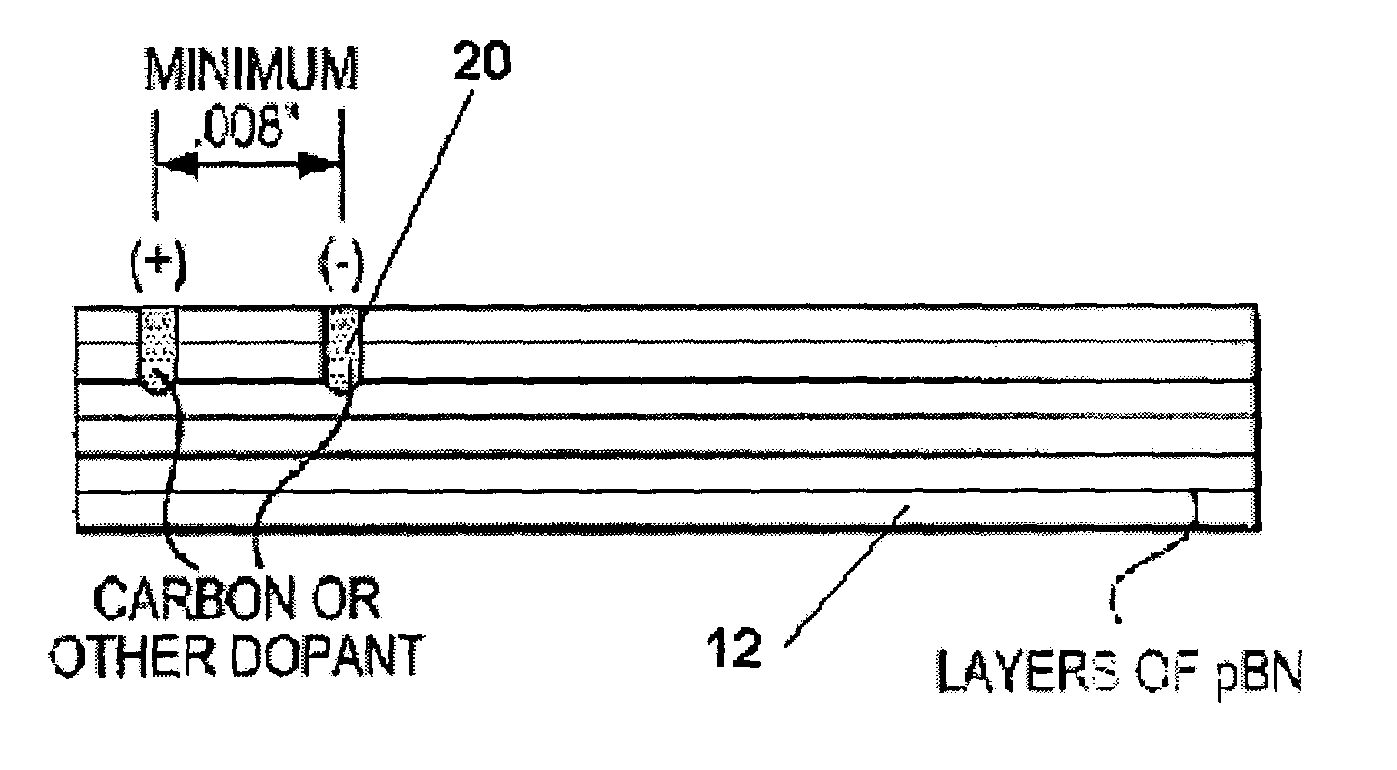
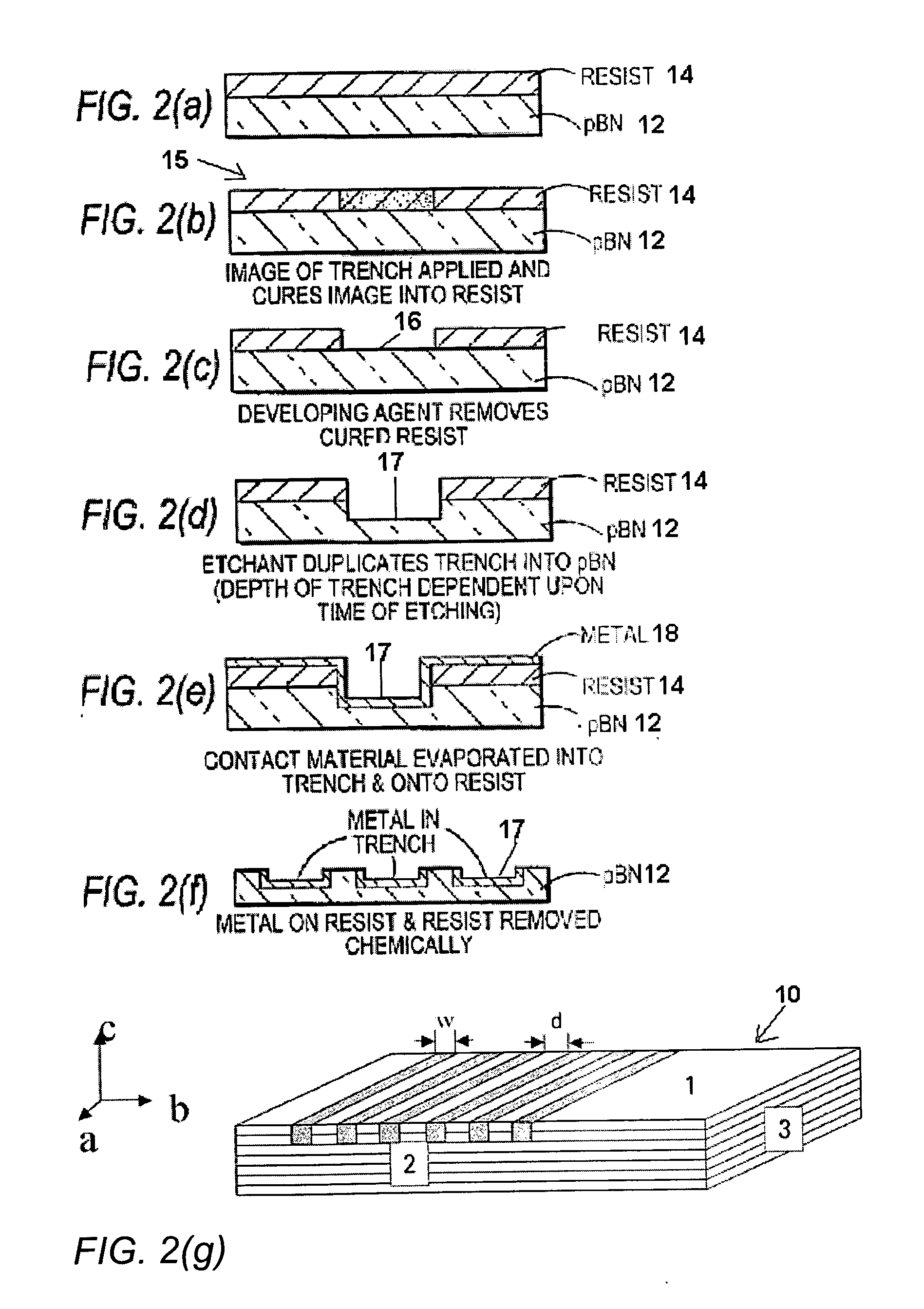
Neutron detector employing doped pyrolytic boron nitride and method of making thereof
InactiveUS7034307B2Measurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDopantNeutron emission
A system for measuring a thermal neutron emission from a neutron source is provided. The system employs a detector utilizing a plurality of doped pBN layers, wherein the doped pBN layers are doped with at least one dopant across an a-b plane of the layers for an electrical resistivity of 1014 ohm-cm or less.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Glass-panel lithium-6 neutron detector
InactiveUS9018594B2Leverage cost and design and durability and performanceMost efficientElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansLithiumNeutron emission
A thermal neutron detector includes a planar detector housing having two glass panels spaced apart by a gas-tight seal defining a detection chamber. Lithium foils adhered to inner surfaces of the glass panel emit alpha particles and tritons in response to incident thermal neutrons, and an inert detection gas is ionized to generate drift electrons. A planar array of detection wires is spaced from the lithium foils and extends outside the detection chamber. Electronic bias applies a field voltage between the wires and the lithium foils to establish a drift electric field to attract the drift electrons to the wires and provide a large electric field to cause electron multiplication. Detection circuitry detects electric signals in the wires generated by the drift of positive ions away from the wires and interprets the electrical signals as incidence of thermal neutrons on the detector.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Device for measuring physical quantities of nuclear materials and method of employing such a device
InactiveUS20110155920A1Improve measurement efficiencyAccurate measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansPortable shielded containersNeutron emissionComputer module
A movable device for measuring physical quantities of nuclear materials contained in a shielded cell, which device can be brought up against the shielded cell and can be retracted therefrom, the device configured to carry out the measurement in the position in which it is against the shielded cell. The device includes a carriage, a support member placed on the carriage, and a shielded container placed on the support member. The shielded container includes a transfer container configured to store the nuclear material to be measured, and an opening configured to be aligned with an opening in one wall of the shielded cell. The support member is made of graphite and includes a housing accommodating a neutron emission module, a casing covering the shielded container, the casing being made of graphite, and a neutron measurement mechanism fastened to the casing.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
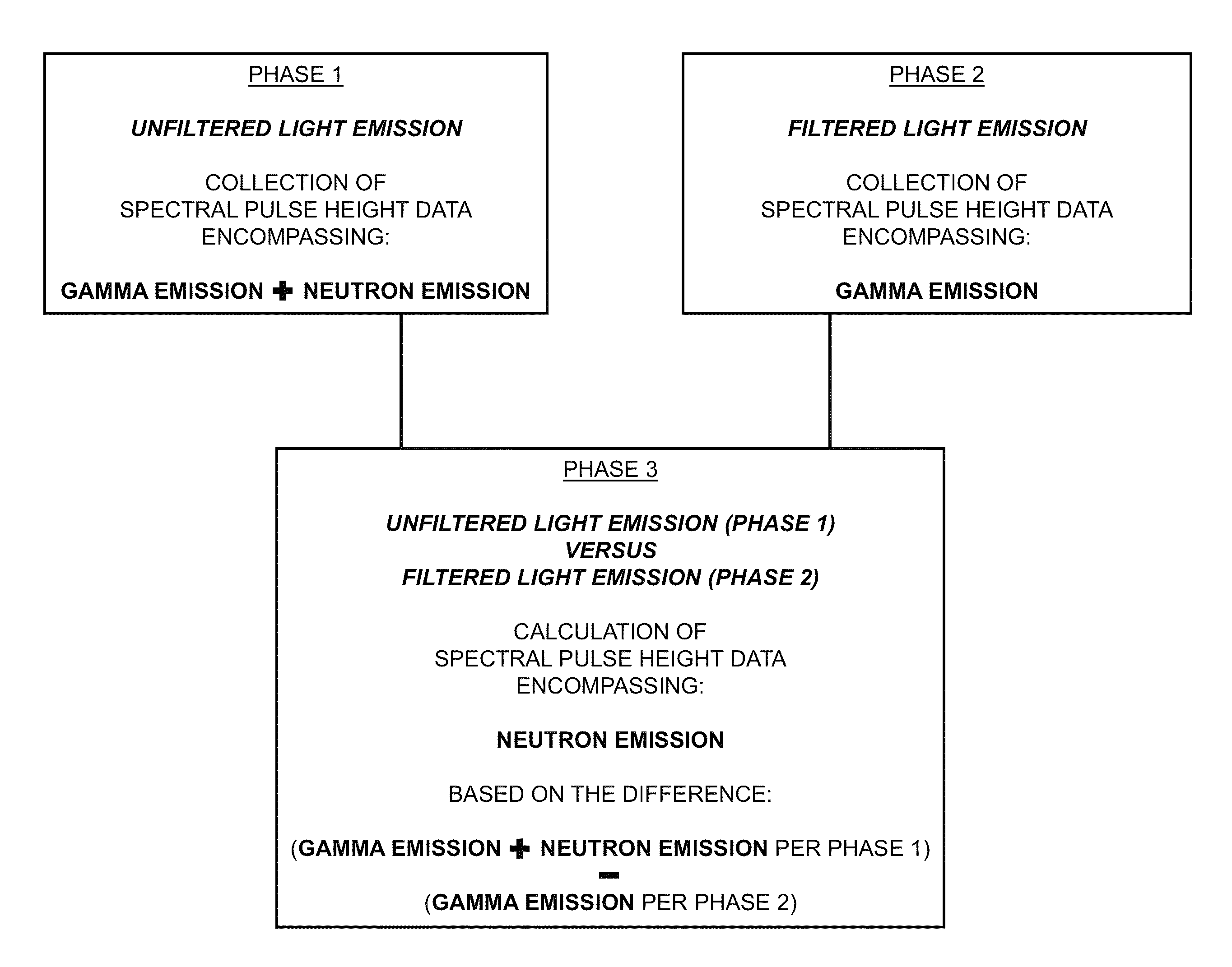
Spectrally resolved pulse height analysis for neutron-gamma discrimination
InactiveUS9029784B1Less complicatedEasy to analyzeMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionPulse height
Typical practice of the present invention performs measurement and processing of two forms of light emissions—viz., unfiltered and filtered—of a core-valence luminescent (CVL) scintillator impinged by ionizing radiation emanating from a radioactive source. When unfiltered, the CVL scintillator light emission is inclusive of gamma emissions and neutron emissions. When filtered by a filtering apparatus that transmits CVL light only, the CVL scintillator light emission is inclusive of gamma emissions but is exclusive of neutron emissions. Algorithmic comparison between the two sets of empirical data provides discriminative information regarding gamma emissions versus neutron emissions. Essentially, the difference is taken between the unfiltered pulse height spectra data and the filtered pulse height data. The set of pulse height spectral data thus computed via subtraction is indicative of the portion of the CVL scintillator light emissions that is inclusive of neutron emissions but is exclusive of gamma emissions.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
X-ray radiation sources with low neutron emissions for radiation scanning
InactiveUS7436932B2X-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube with very high currentNeutron emissionIsotopic composition
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Radionuclide detector and software for controlling same
InactiveUS20050205799A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsElectricityNeutron emission
A detector for detecting the presence of suspect radionuclides in a target is disclosed. The detector includes a first detection channel for a first detecting neutron emissions in the target and for providing a first output in accordance with the first detecting, a second detection channel for a second detecting x-ray emissions in the target and for providing a second output in accordance with the second detecting, a third detection channel for a third detecting and an identifying of gamma emissions in the target and for providing a third output in accordance with the third detecting and identifying, a signal manipulation electrically coupled to each of the first, second, and third detection channels, the signal manipulation for receiving the first, second and third outputs and for processing those outputs, and at least one processor electrically coupled to the signal manipulation. The processor determines if the suspect radionuclide is present in the target and provides an alert when the suspect radionuclide is present in the target.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Primary neutron source part for starting nuclear reactor
InactiveCN102243900AImprove securitySimple structureNuclear energy generationNeutron sourcesNuclear reactor coreEmissivity
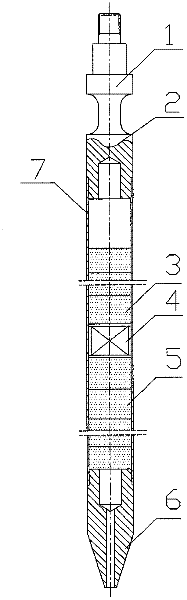
The invention discloses a primary neutron source part for starting a nuclear reactor. The primary neutron source part comprises a cladding tube, a neutron source, cushion blocks, an upper end plug and a lower end plug, wherein the neutron source is arranged in the cladding tube; two ends of the cladding tube are respectively sealed by the upper end plug and the lower end plug; the neutron source is a Cf-252 neutron source of which neutron emission rate is 1.0*10<8> to 1.0*10<10> n / s; and a compression cushion block and a supporting cushion block are arranged on two sides of the neutron source. The primary neutron source part for starting the nuclear reactor provided by the invention is simple in structure, safe, reliable and easy to process.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Multi-source spacing measurement device and method for neutron porosity during drilling
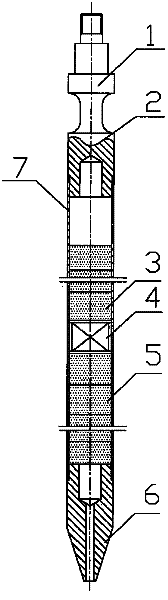
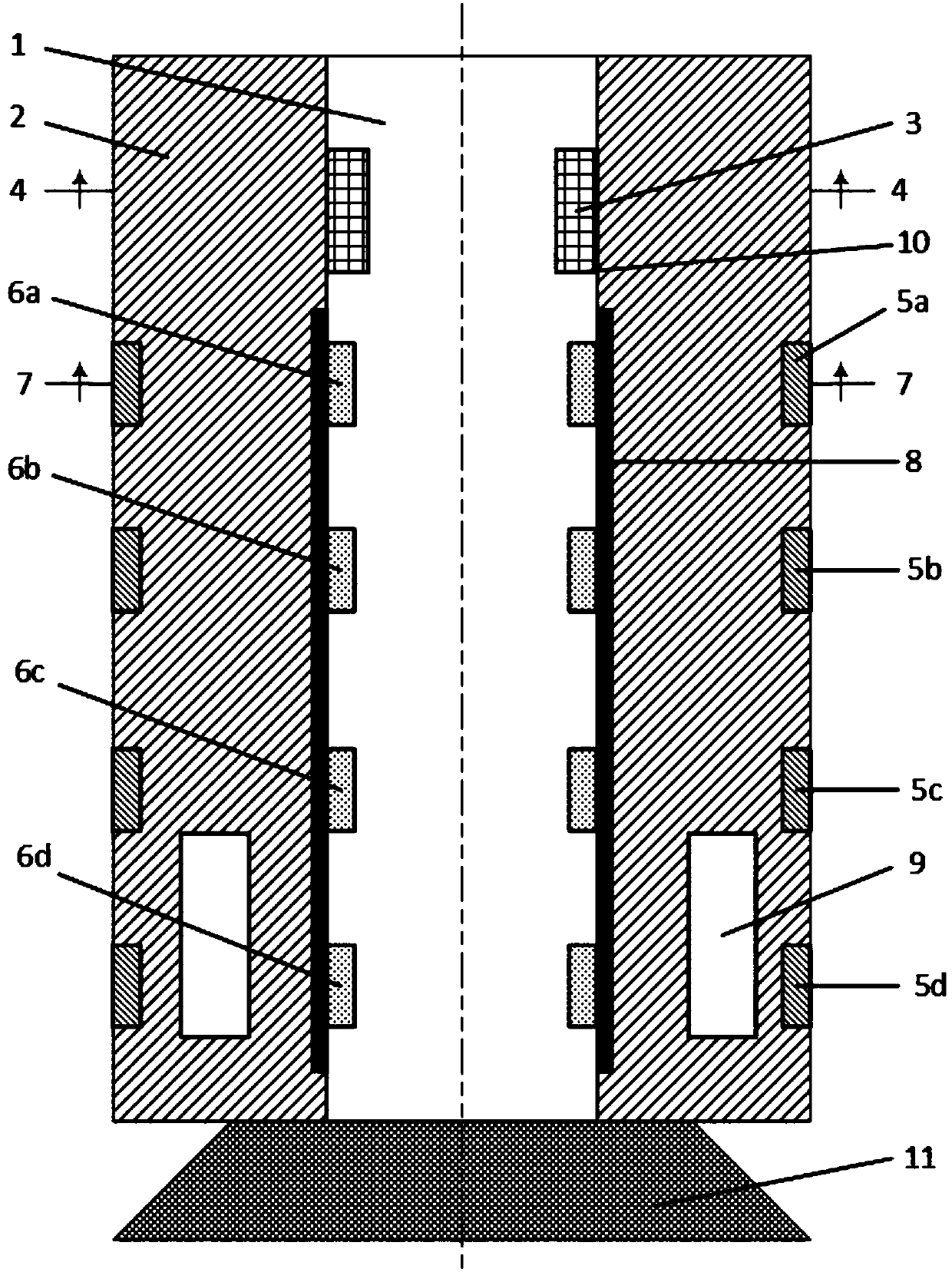
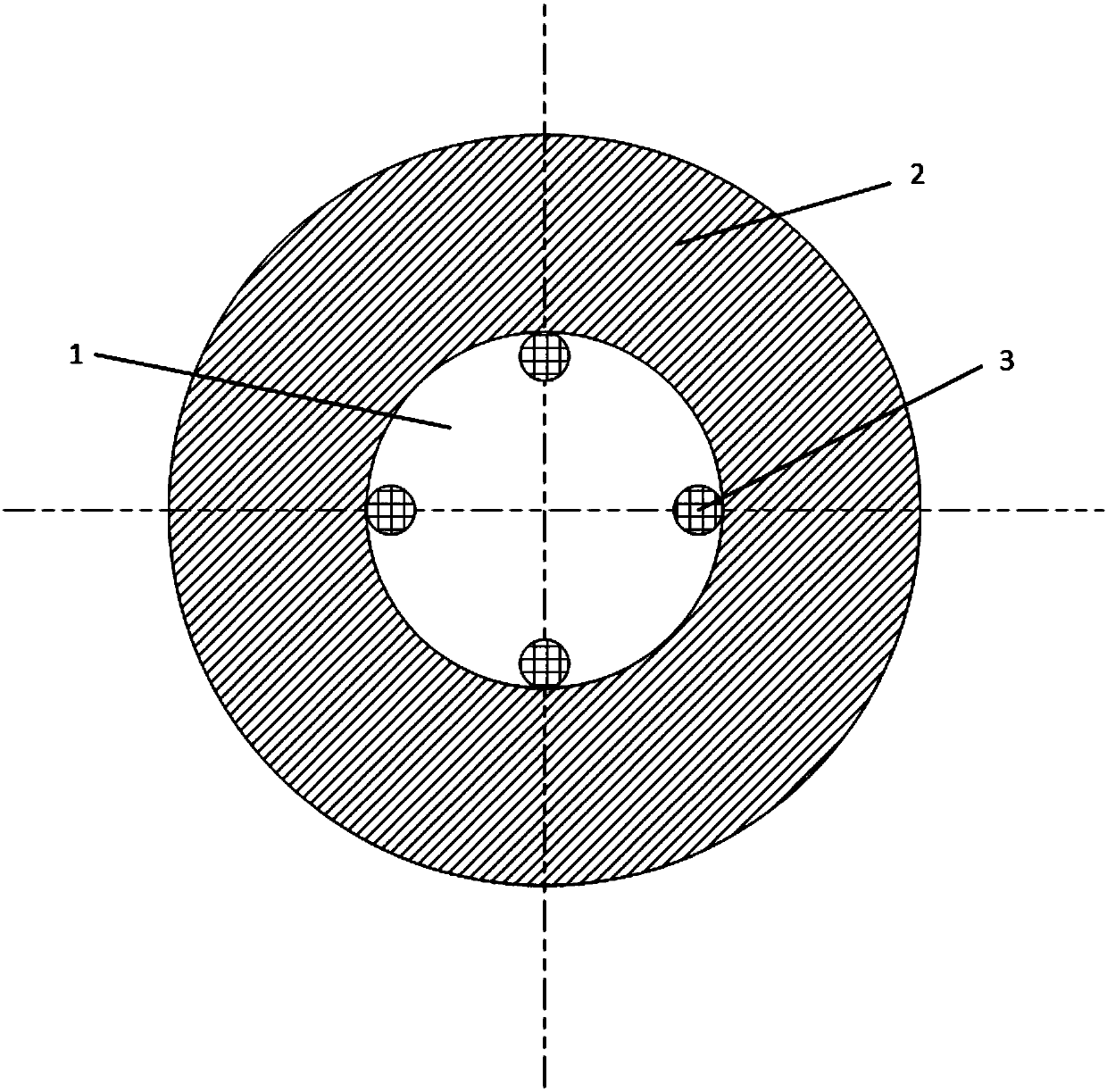
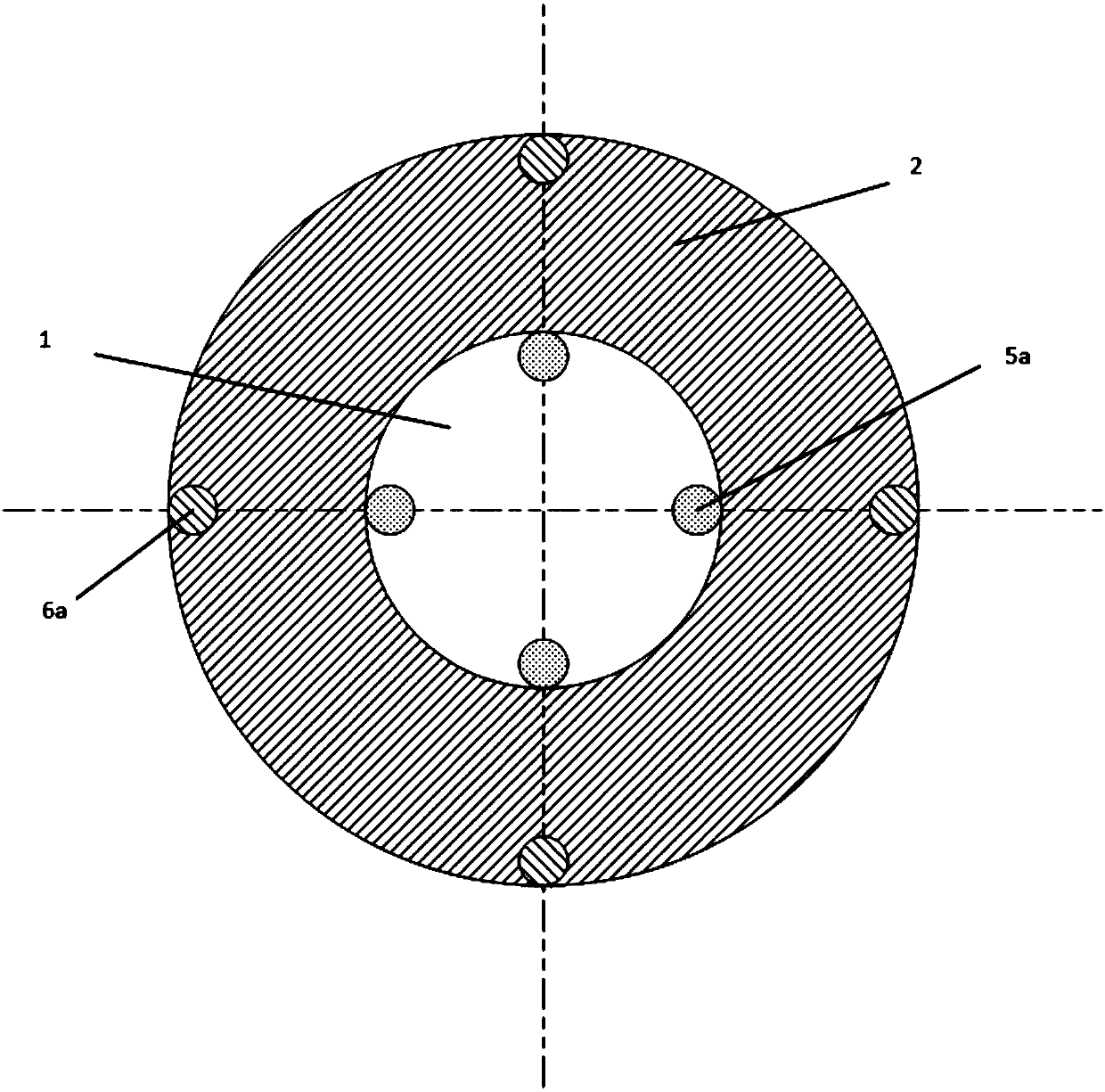
ActiveCN107829728AGuaranteed accuracyCorrection and Compensation EffectsSurveyMeasurement deviceNeutron emission
The invention discloses a multi-source spacing measurement device and method for neutron porosity during drilling. The measurement device includes a non-magnetic drill collar, a neutron emission unit,a fast neutron monitoring unit, a hot neutron detecting unit and a control unit; the neutron emission unit contains multiple accelerator neutron sources, the fast neutron monitoring unit includes multiple fast neutron monitor groups, the hot neutron detecting unit includes multiple hot neutron detector groups, and the control unit is connected to the neutron emission unit, the fast neutron monitoring unit and the hot neutron detecting unit separately. The multi-source spacing measurement device and method for the neutron porosity during drilling overcome the defects in the prior art, ensure the flexibility and data accuracy of detecting instruments under a complex geologic condition, effectively reduce the influences of well hole parameters, vibration, impact and random fluctuation of measurement data on the measurement result, solve problems in prior art, remove limitations in the prior art, and achieve accurate acquirement of stratum porosity parameters.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com