Patents
Literature
223 results about "Electron multiplication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
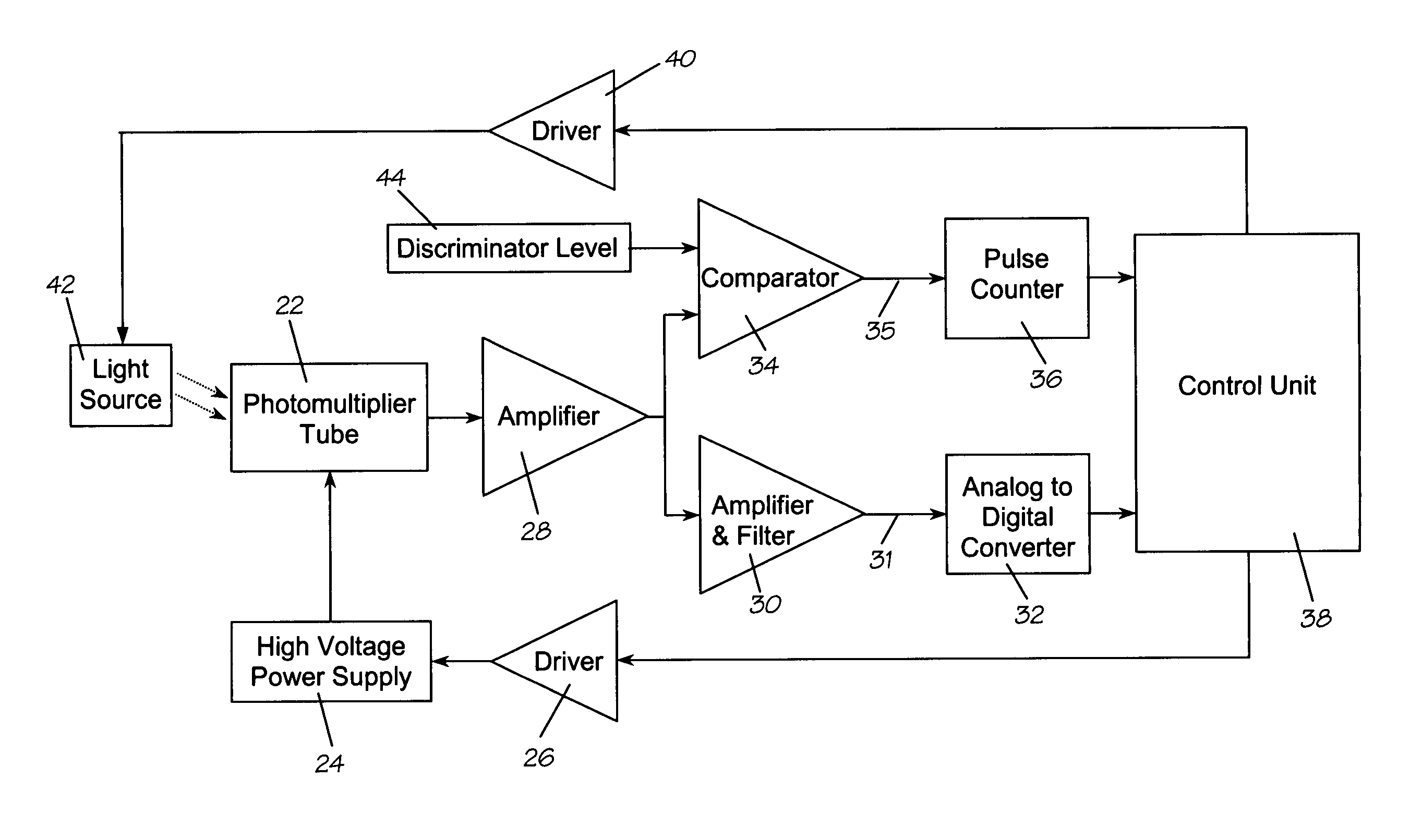
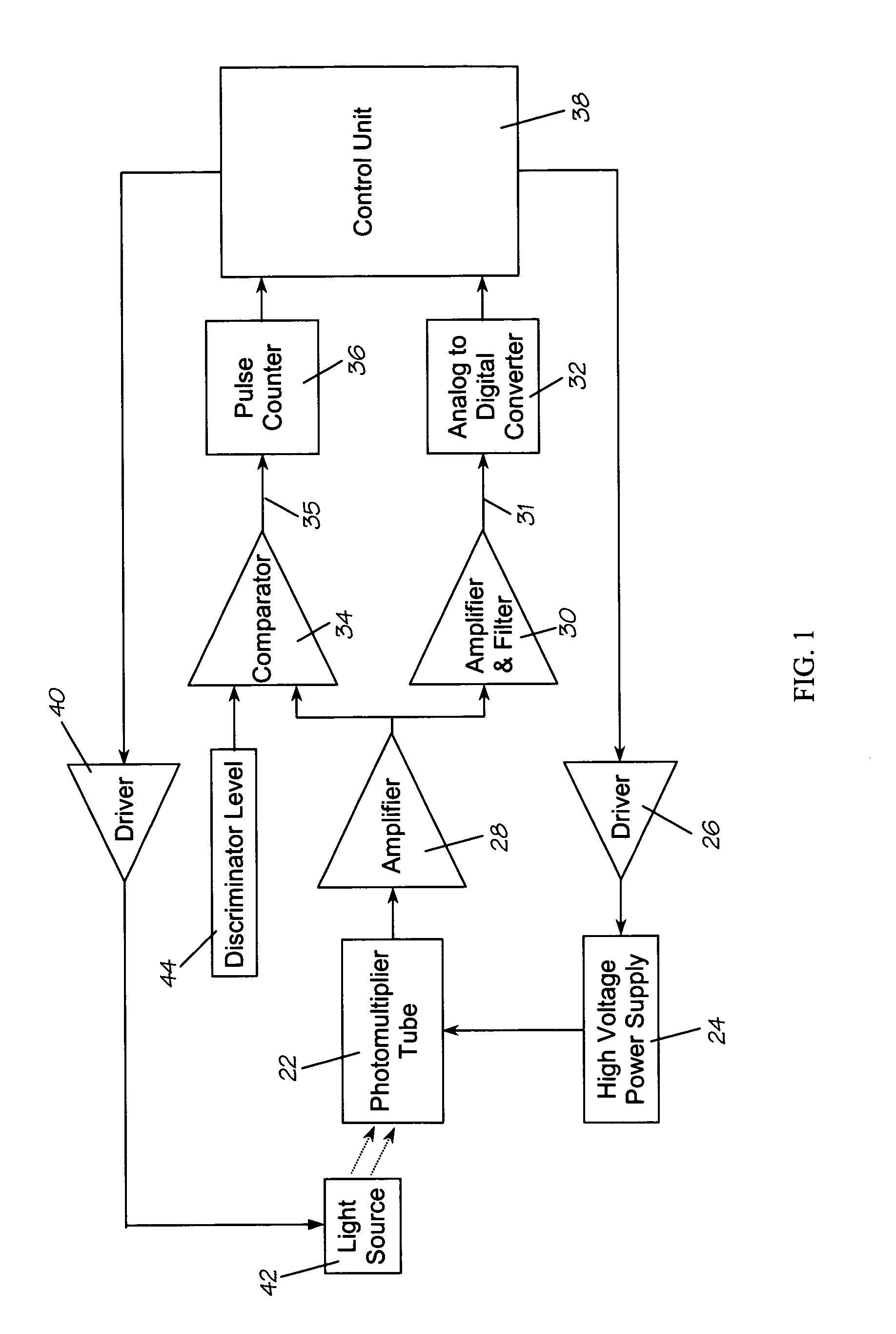
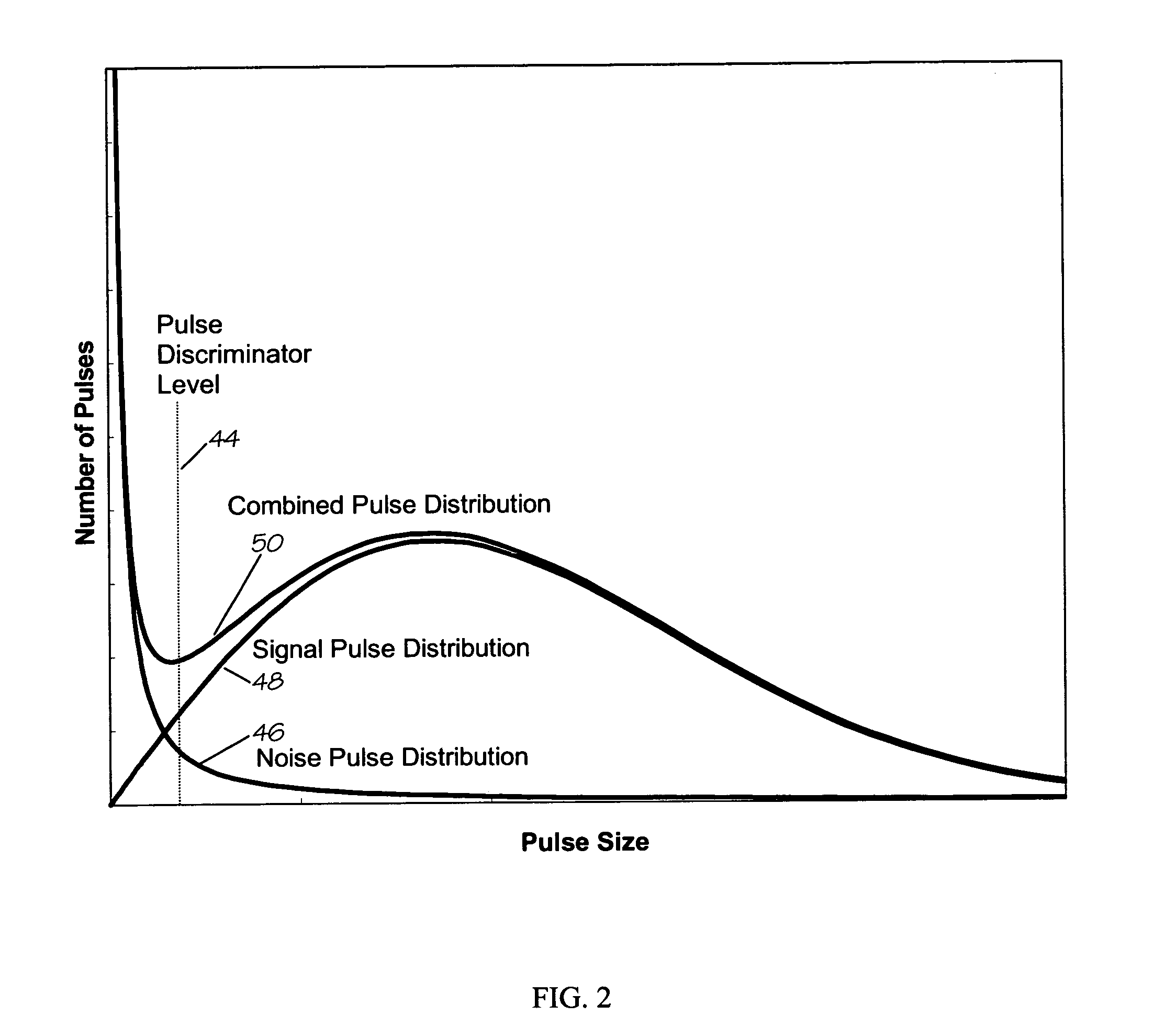
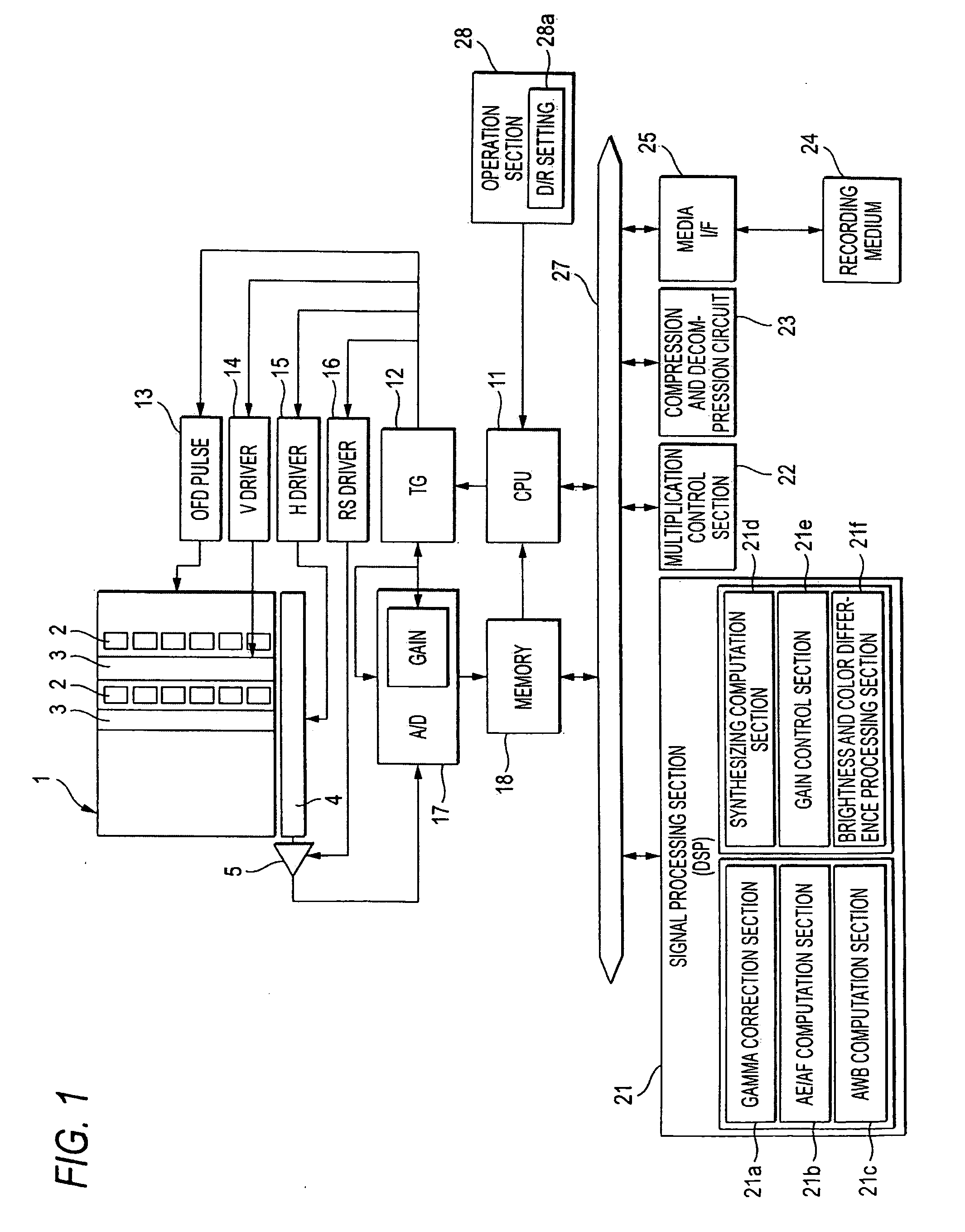
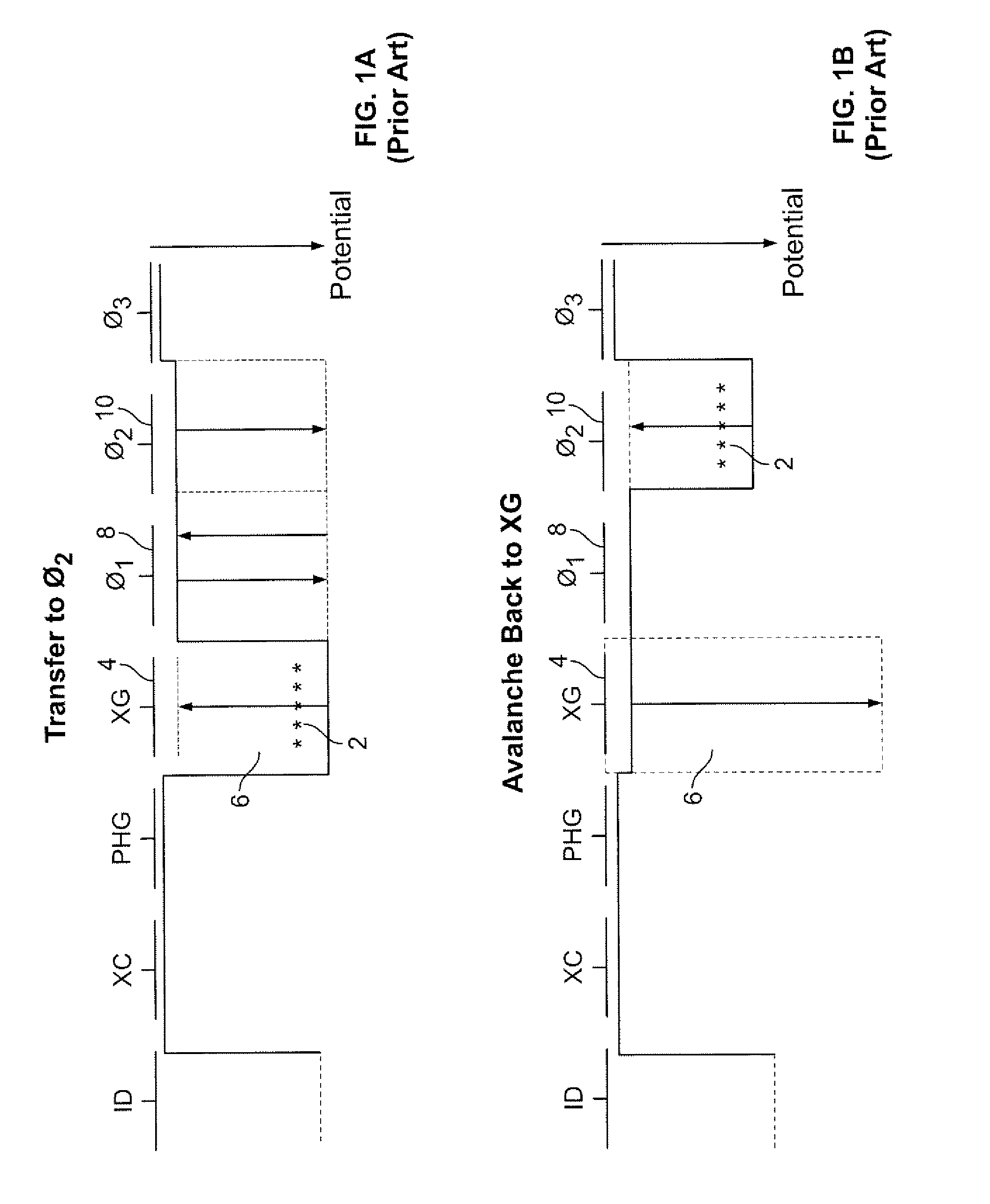
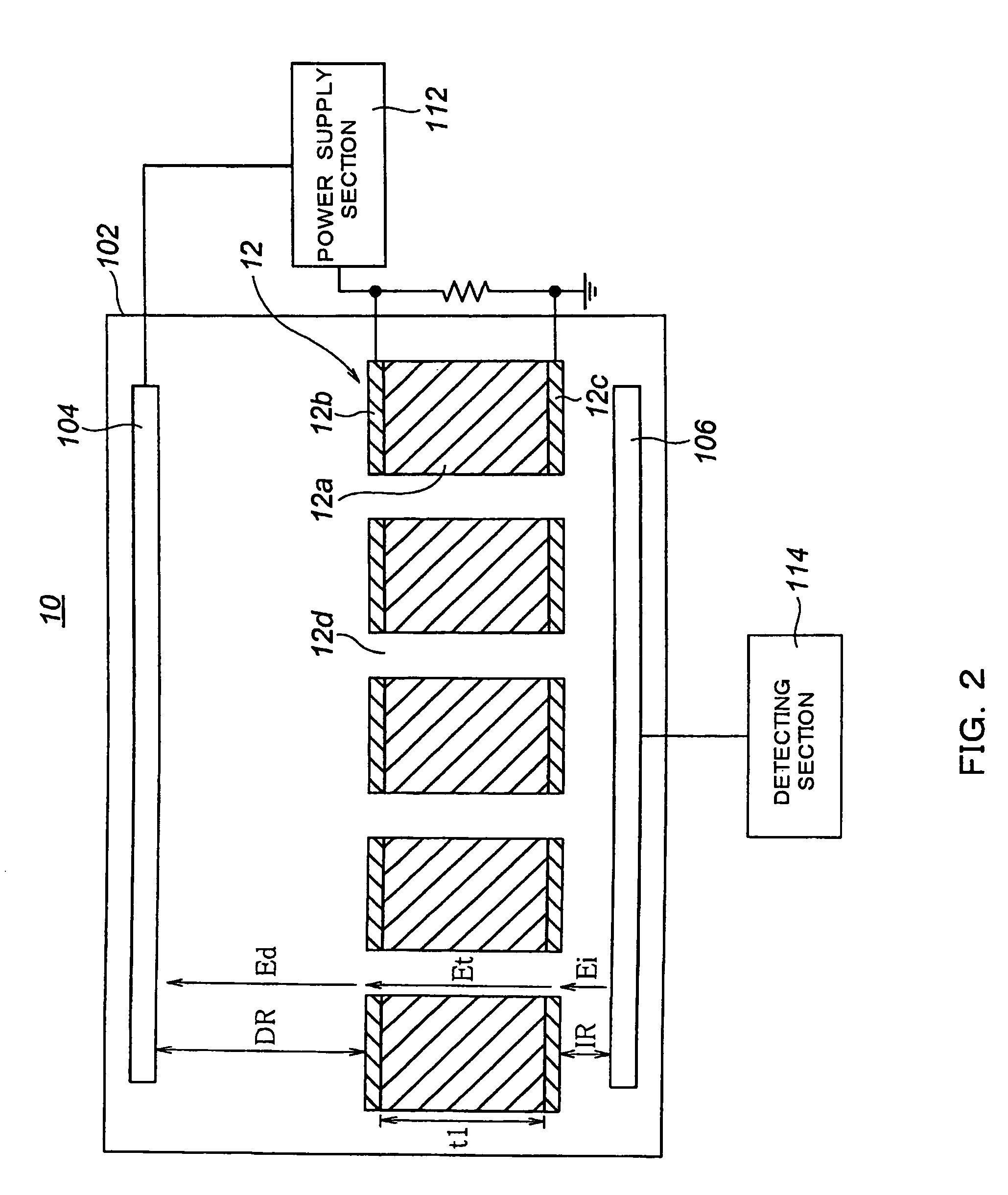
Photomultiplier tube gain stabilization for radiation dosimetry system
InactiveUS7157681B1Low costSmall sizePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimetry radiationDosimeter
Methods and means for measuring and adjusting the gain of a photomultiplier tube (PMT), or other photo-detector with electron multiplication gain, for the purpose of achieving accurate light measurement, such as in a luminescent radiation dosimeter reader. With a PMT illuminated by a light emitting diode or other light source, the PMT output signal is measured in two modes, signal integration and photon pulse counting. The measured PMT gain is calculated as the ratio of the integrated signal to the photon pulse count. The PMT high voltage may be adjusted to cause the measured PMT gain to correspond to an established calibration gain value, or the data from the PMT may be adjusted to compensate the deviation of the measured PMT gain from the calibration gain value. The light source may be a controllable light source that can be adjusted to provide a specific photon count rate output as measured by the PMT. This invention provides for maintaining light measurement calibration without requiring temperature stabilization or a fixed light source.
Owner:TETZLAFF WOLFGANG
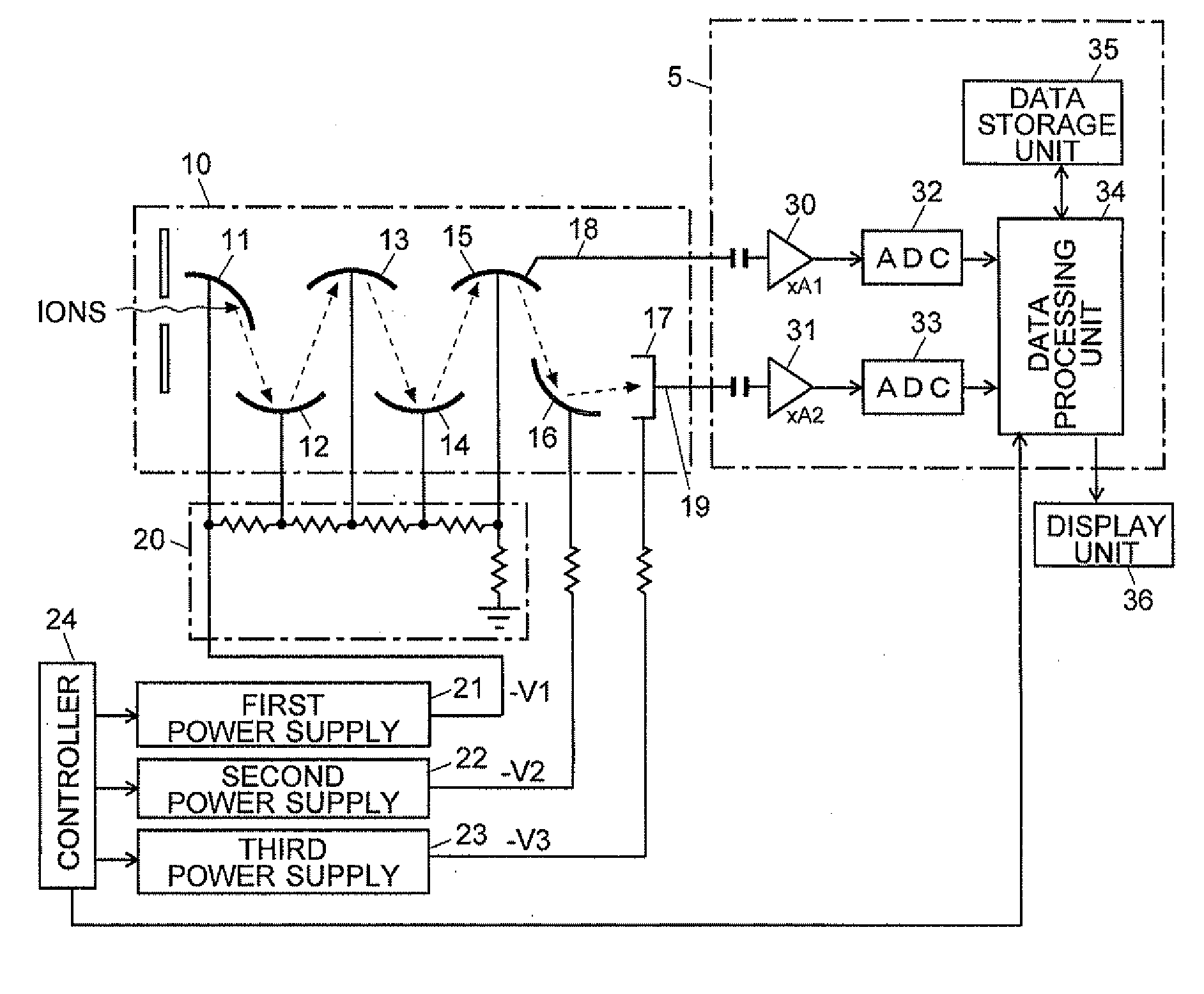
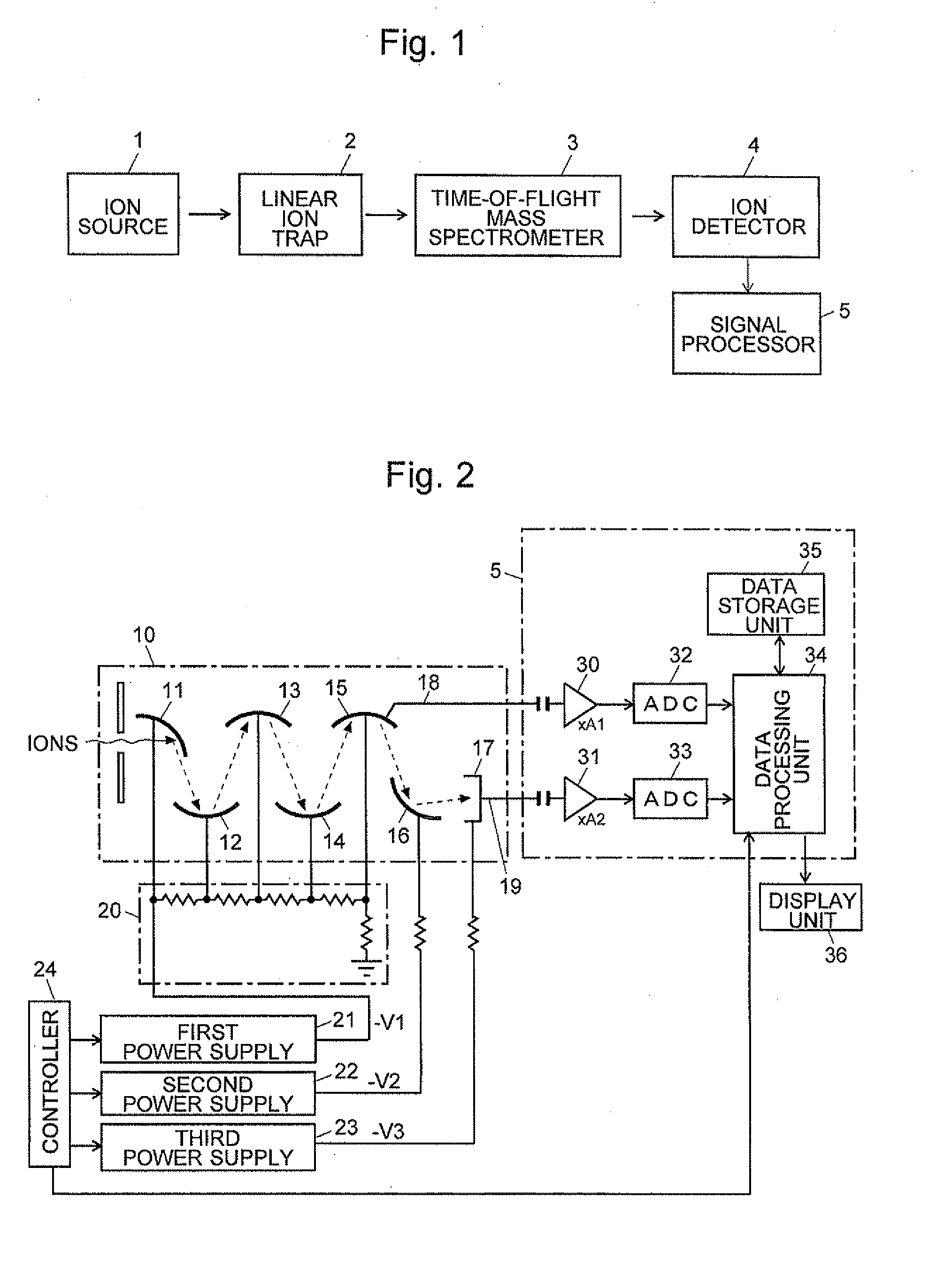
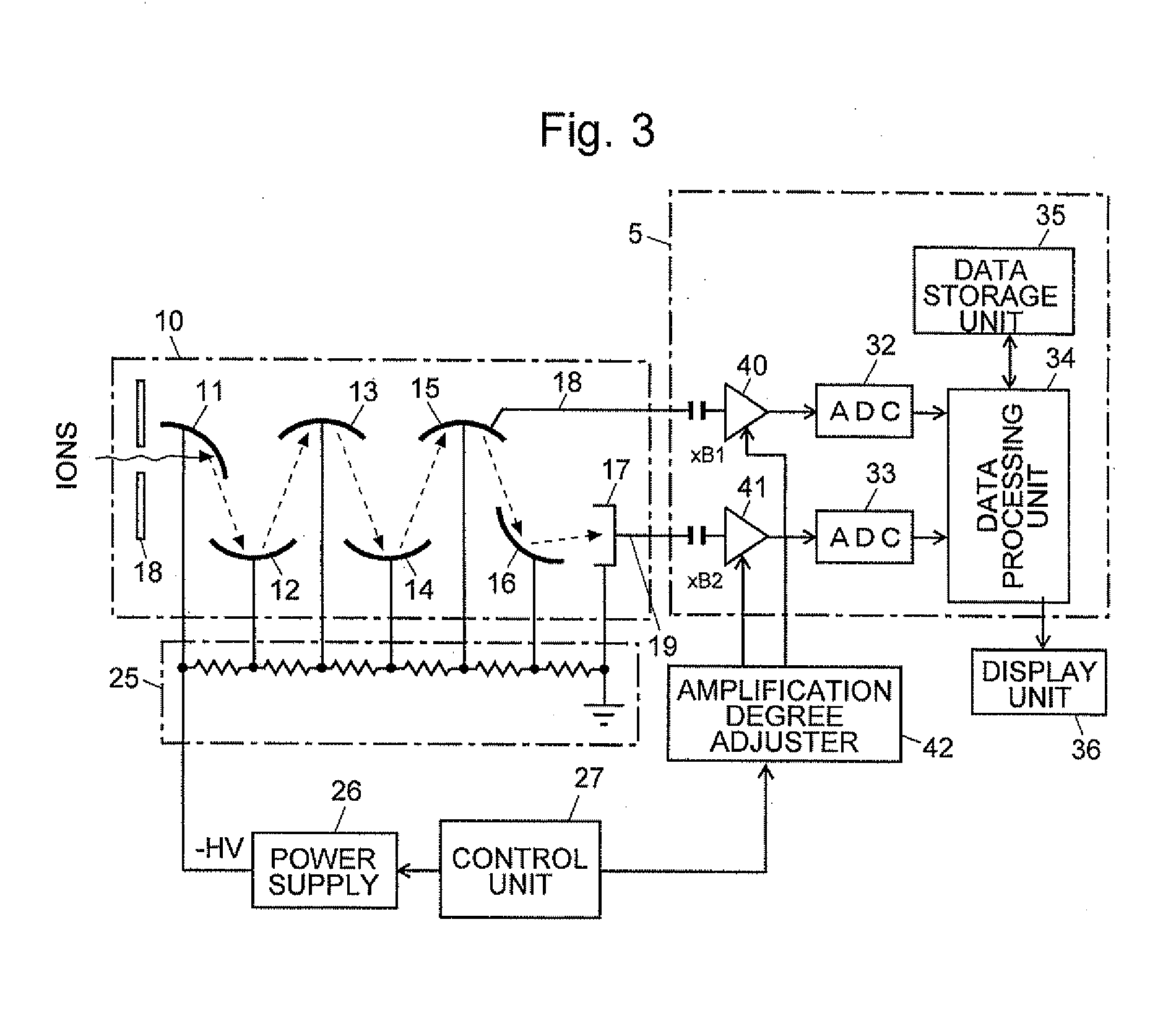
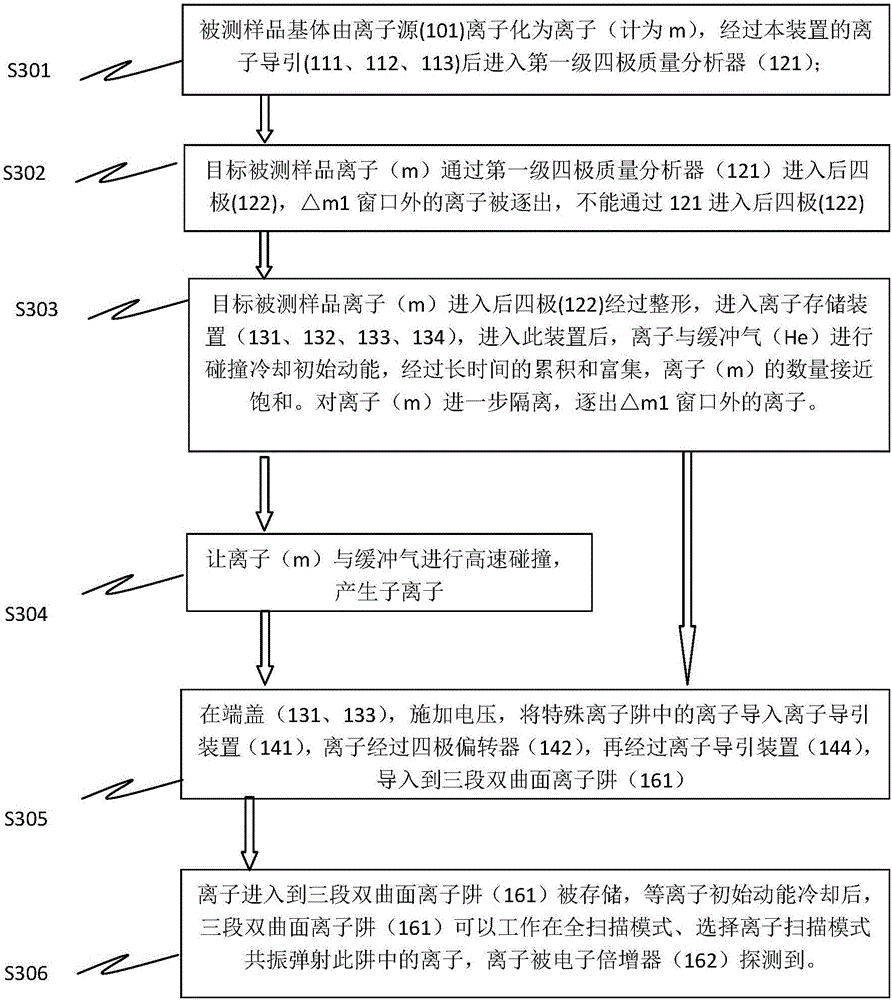
Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20120175514A1Improve dynamic rangeMultiplication factor can be restoredThermometer detailsTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron multiplicationHigh probability
In an ion detector, power supplies (21 through 23) generating independently controllable voltages are provided to respectively apply voltages to first to fifth dynodes (11 through 15), a final dynode (16), and an anode (17) in a secondary electron multiplier (10). Furthermore, the signal from the anode (17) is extracted, and the signal from the fifth dynode (15), which has a low electron multiplication rate, is extracted. These two signals are concurrently converted into digital values, taken in by a data processing unit (34), and stored in a data storage unit (35). When a mass spectrum is created in the data processing unit (34), the two detected data for the same time are read out and the presence or absence of signal saturation or waveform deformation is determined from the values of one of the detection data. If there is a high probability of signal saturation, the detection data based on the signals in the intermediate stages are selected, and the level of the selected data is corrected. The application of independent voltages to the secondary electron multiplier (10) makes the signal saturation less likely to occur. Even if saturation temporarily occurs, an unsaturated signal can be reflected in the mass spectrum.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
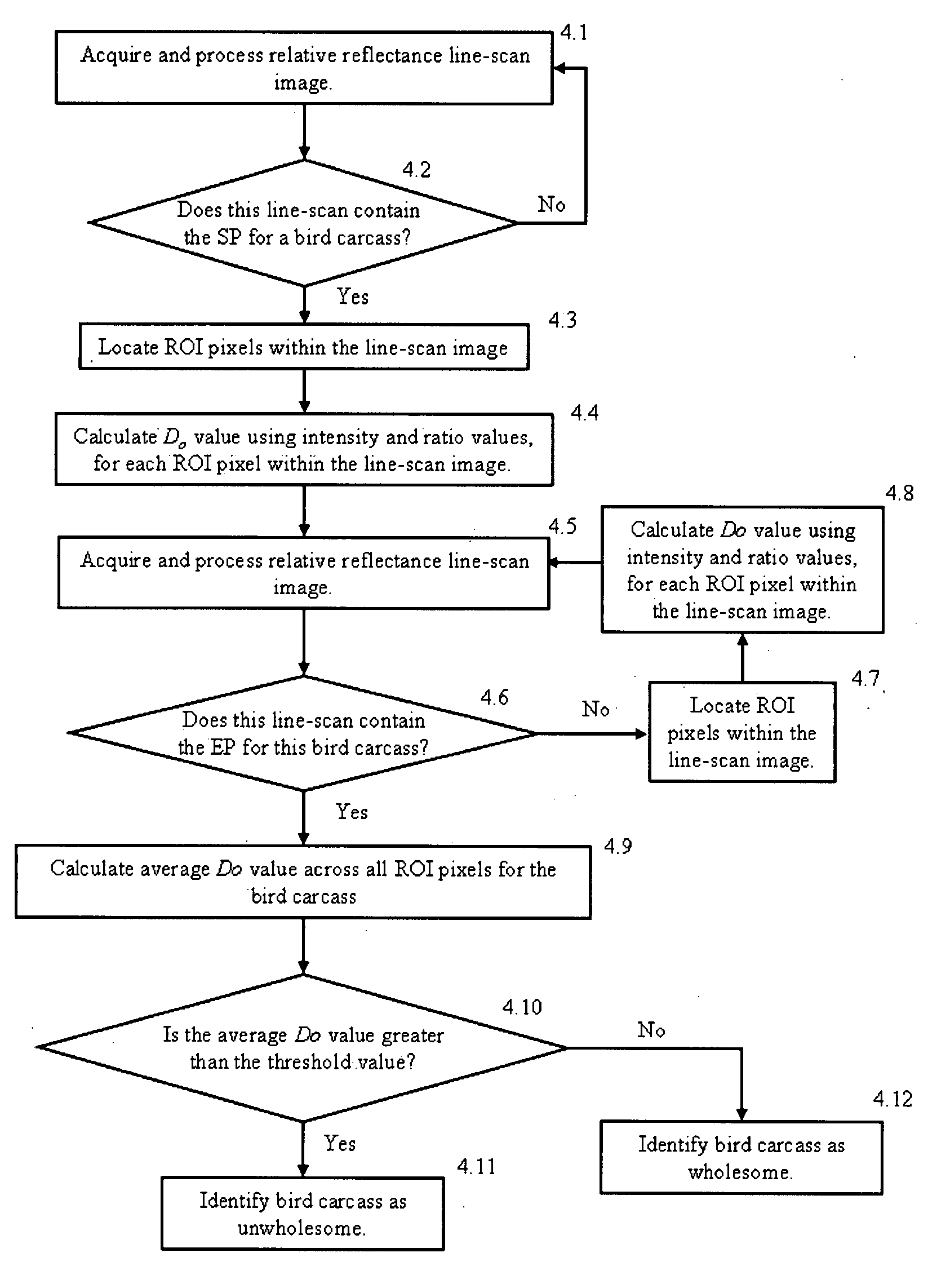
Method and system for wholesomeness inspection of freshly slaughtered chickens on a processing line
ActiveUS20090087033A1Quick and accurate identificationImage analysisCarcasses classification/gradingImaging algorithmSpectrograph
An imaging system containing an electron-multiplying charge-coupled device detector and line-scan spectrograph is used for identifying wholesome and unwholesome freshly slaughtered chicken carcasses on high-speed commercial chicken processing lines. Multispectral imaging algorithms allow for real-time online identification of wholesome and unwholesome chicken carcasses.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Method for inspecting pattern defect and device for realizing the same
InactiveUS20060163503A1Sensitive highHigh detection sensitivityTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementForeign matterElectron multiplication
When using a CCD sensor as a photo-detector in a device for inspecting foreign matters and defects, it has a problem of causing electric noise while converting the signal charge, produced inside by photoelectric conversion, into voltage and reading it. Therefore, the weak detected signal obtained by detecting reflected and scattered light from small foreign matters and defects is buried in the electric noise, which has been an obstacle in detecting small foreign matters and defects. In order to solve the above problem, according to the present invention, an electron multiplying CCD sensor is used as a photo-detector. The electron multiplying CCD sensor is capable of enlarging signals brought about by inputted light relatively to the electric noise by multiplying the electrons produced through photoelectric conversion and reading them. Accordingly, compared to a conventional CCD sensor, it can detect weaker light and, therefore, smaller foreign matters and defects.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
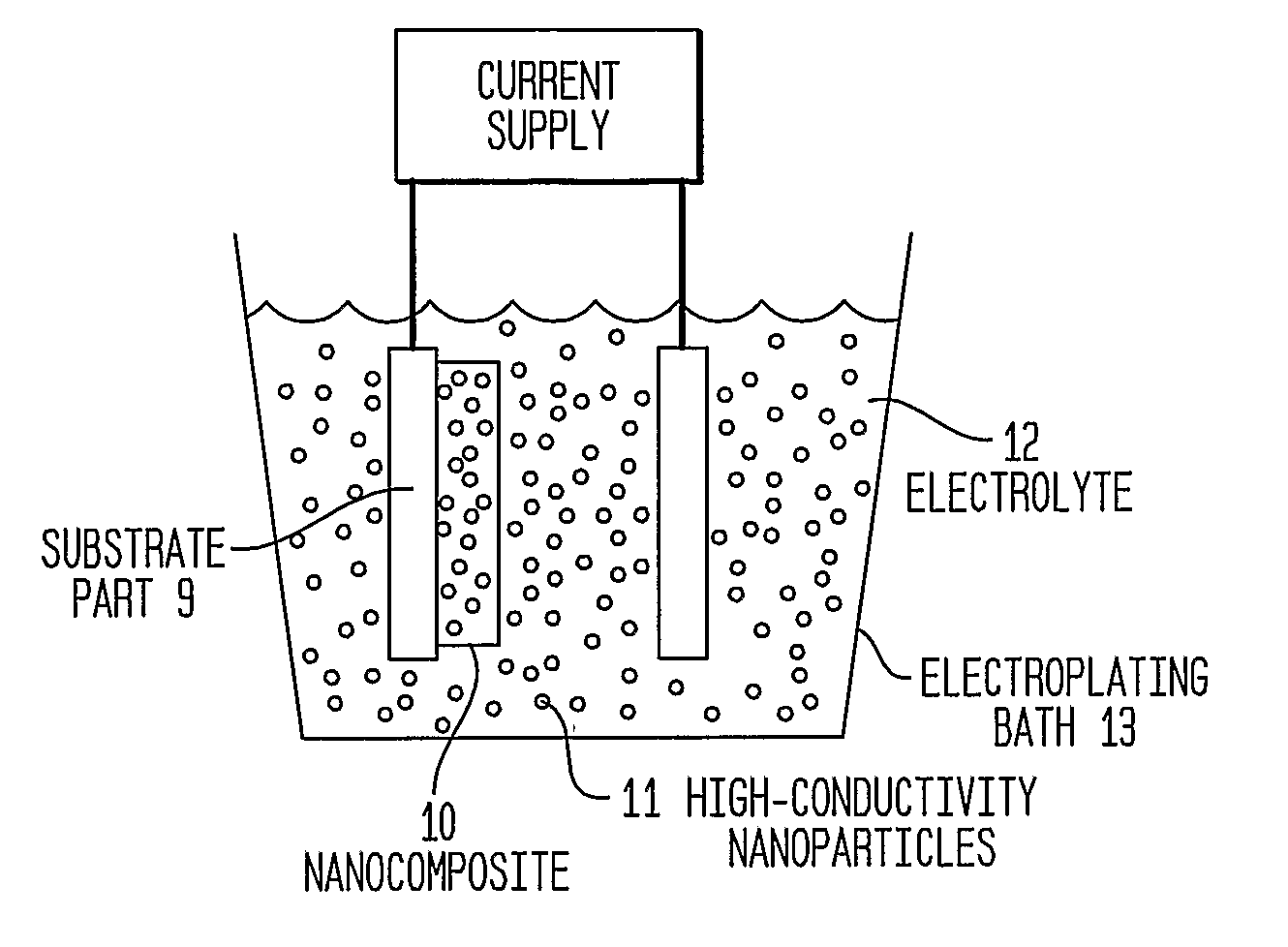
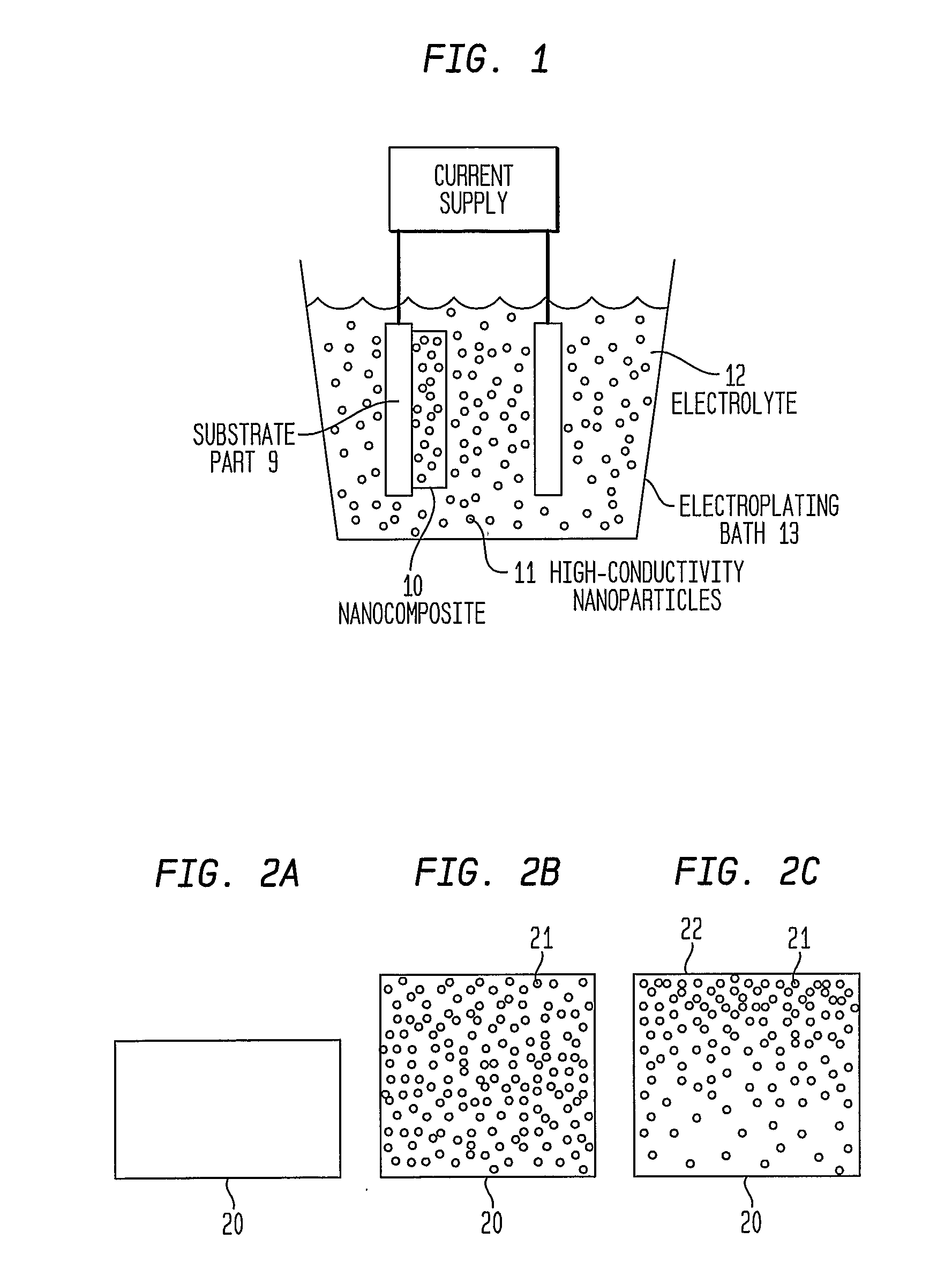
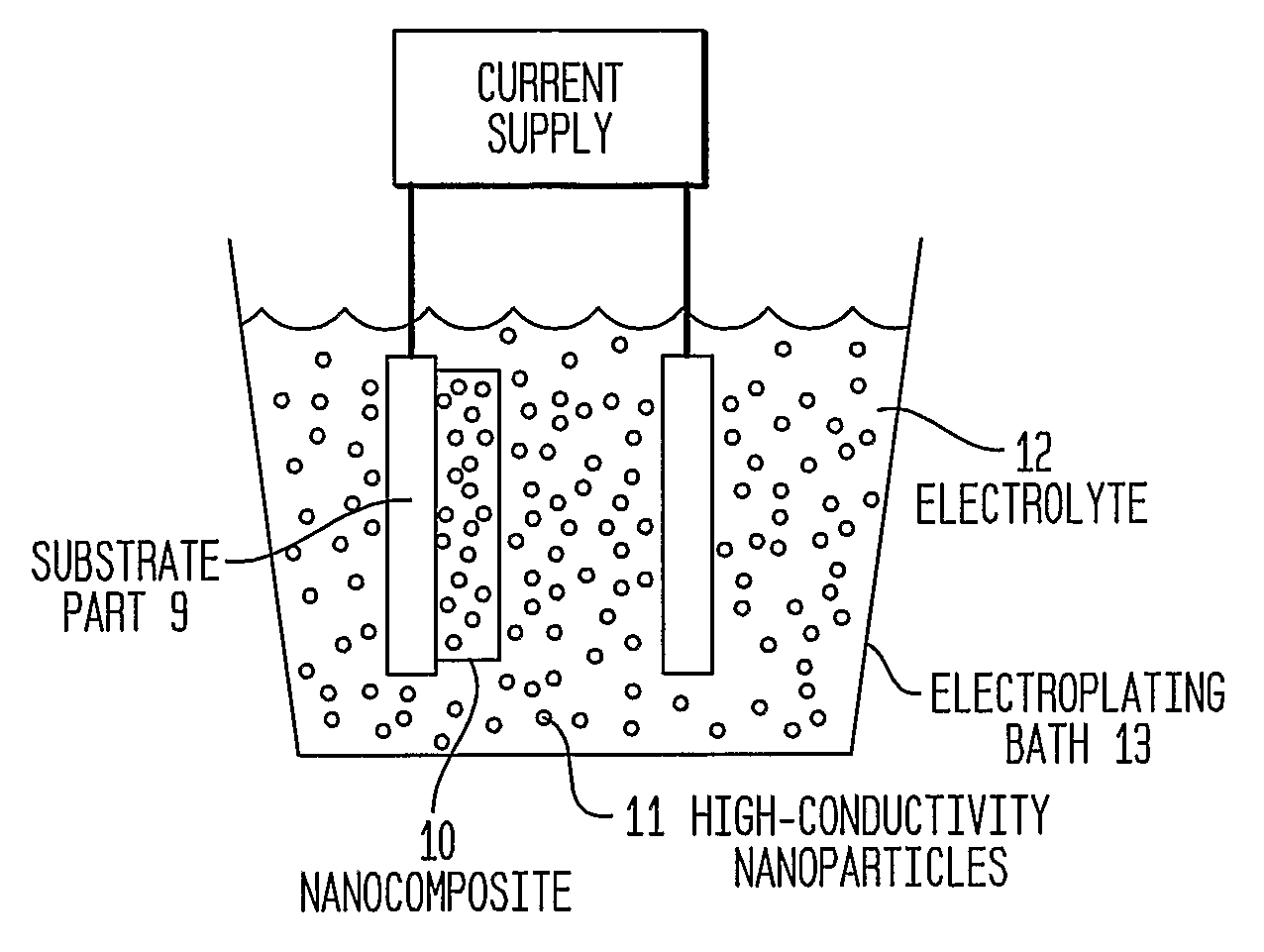
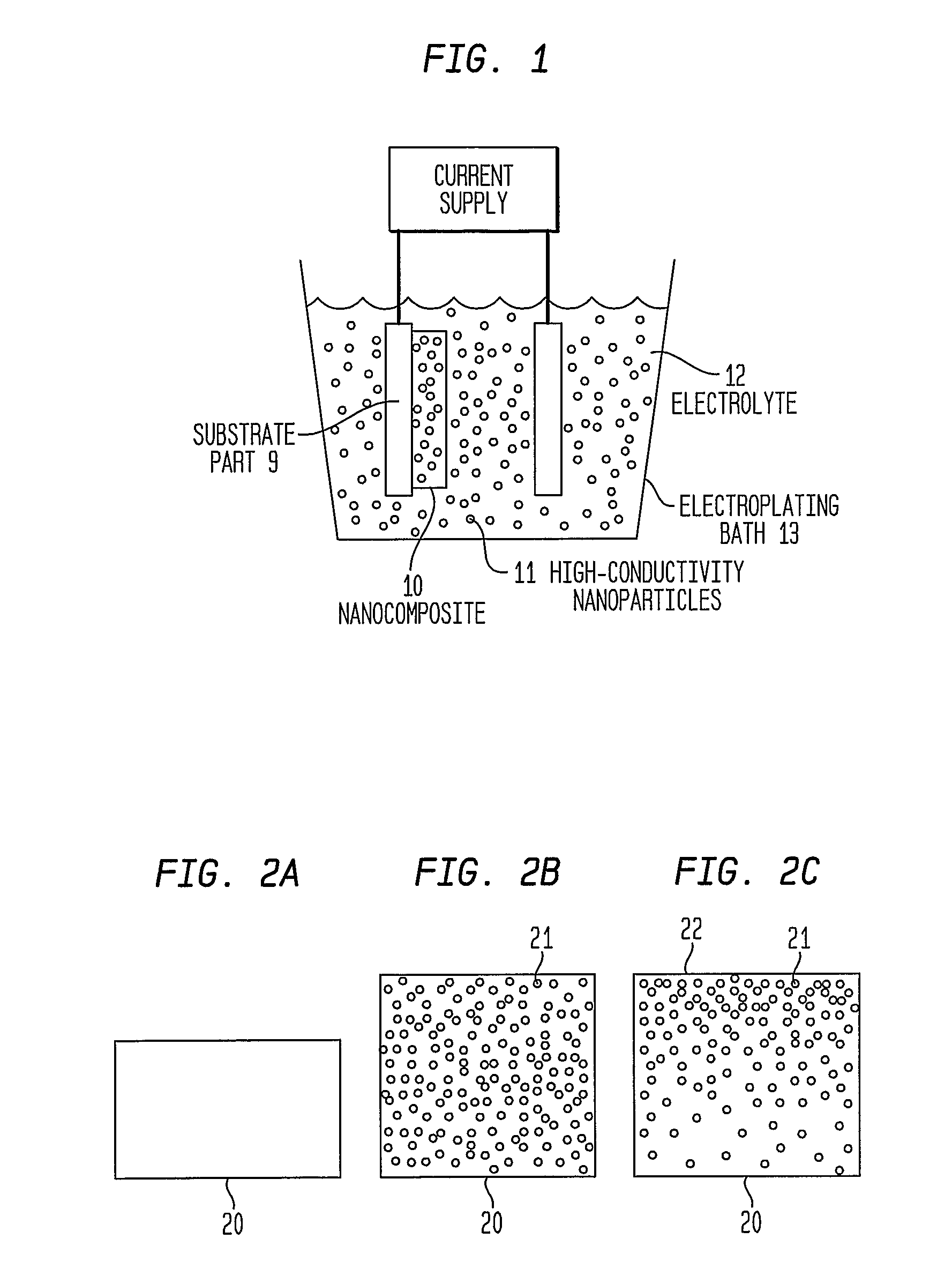
Articles Comprising High-Electrical-Conductivity Nanocomposite Material and Method for Fabricating Same
InactiveUS20080044685A1Minimize field enhancementImprove thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsManufacturing technologyElectron multiplication
This invention discloses novel nanocomposite material structures which are strong, highly conductive, and fatigue-resistant. It also discloses novel fabrication techniques to obtain such structures. The new nanocomposite materials comprise a high-conductivity base metal, such as copper, incorporating high-conductivity dispersoid particles that simultaneously minimize field enhancements, maintain good thermal conductivity, and enhance mechanical strength. The use of metal nanoparticles with electrical conductivity comparable to that of the base automatically removes the regions of higher RF field and enhanced current density. Additionally, conductive nanoparticles will reduce the surface's sensitivity to arc or sputtering damage. If the surface is sputtered away to uncover the nanoparticles, their properties will not be dramatically different from the base surface. Most importantly, the secondary electron emission coefficients of all materials in the nanocomposite are small and close to unity, whereas the previously used insulating particles can produce significant and undesirable electron multiplication.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
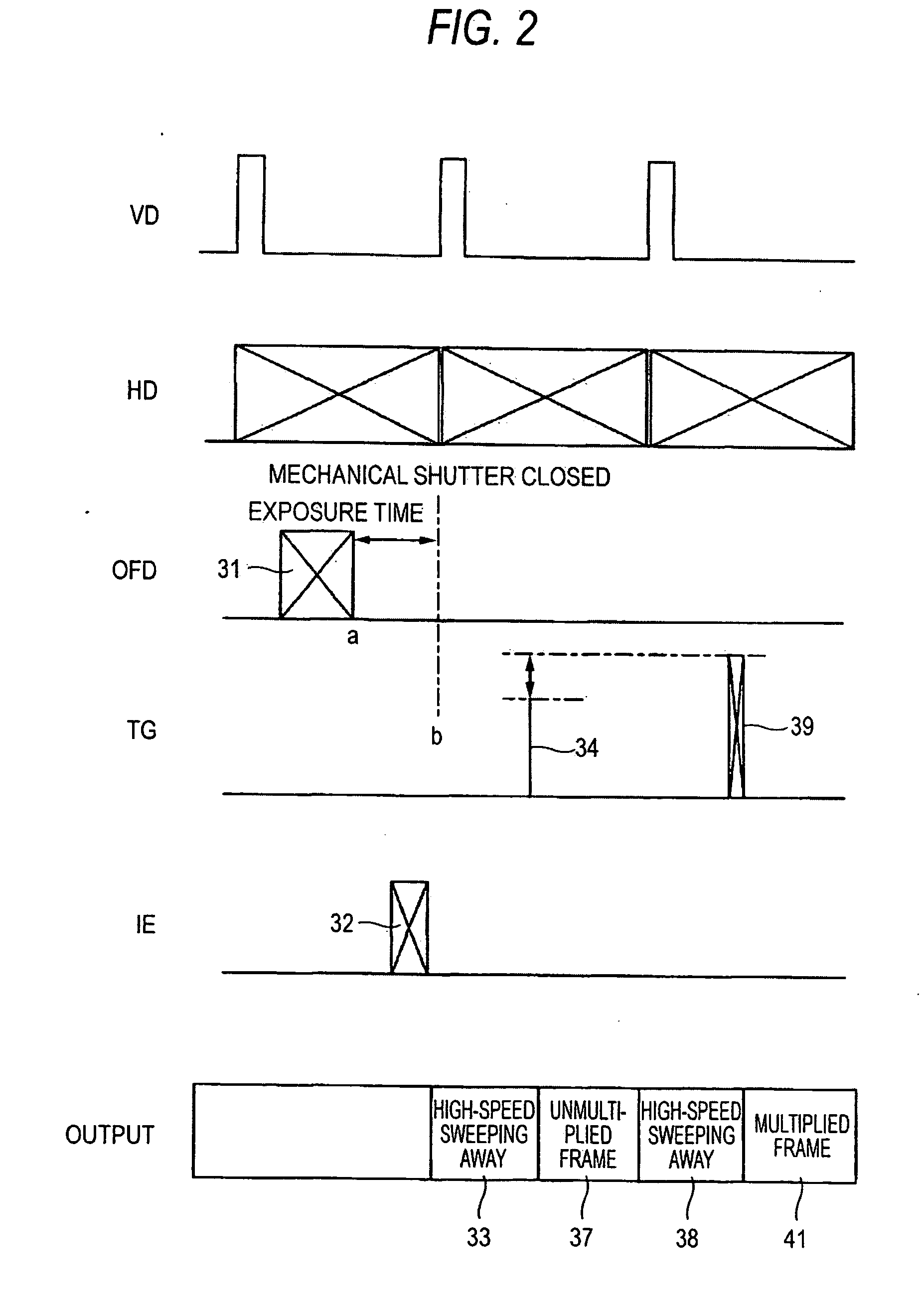
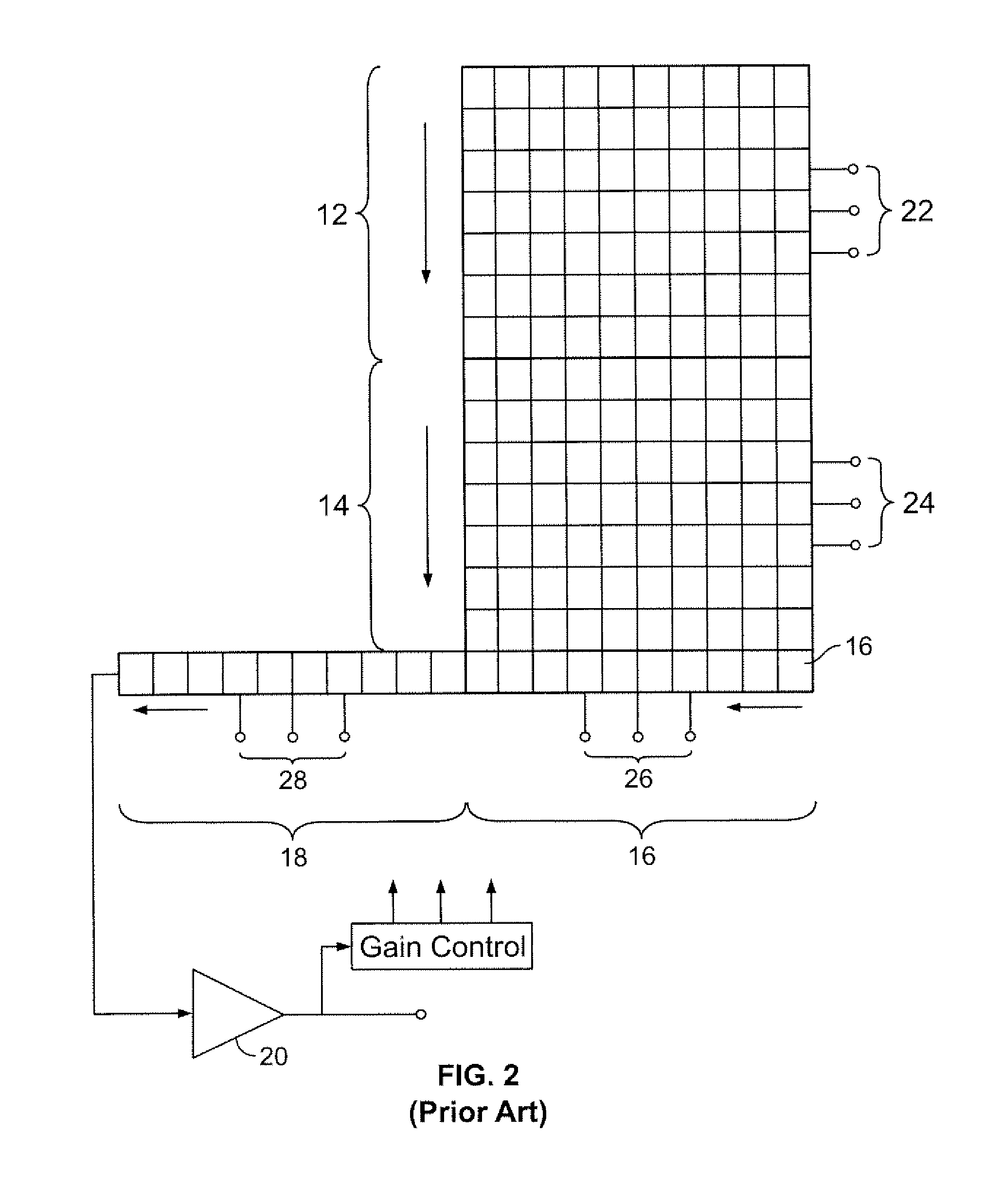
Method and device for driving solid-state imaging device, imaging apparatus, and image synthesizing method
InactiveUS20080239129A1Wide dynamic rangeAmount of signal becomes smallTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectron multiplicationImage signal
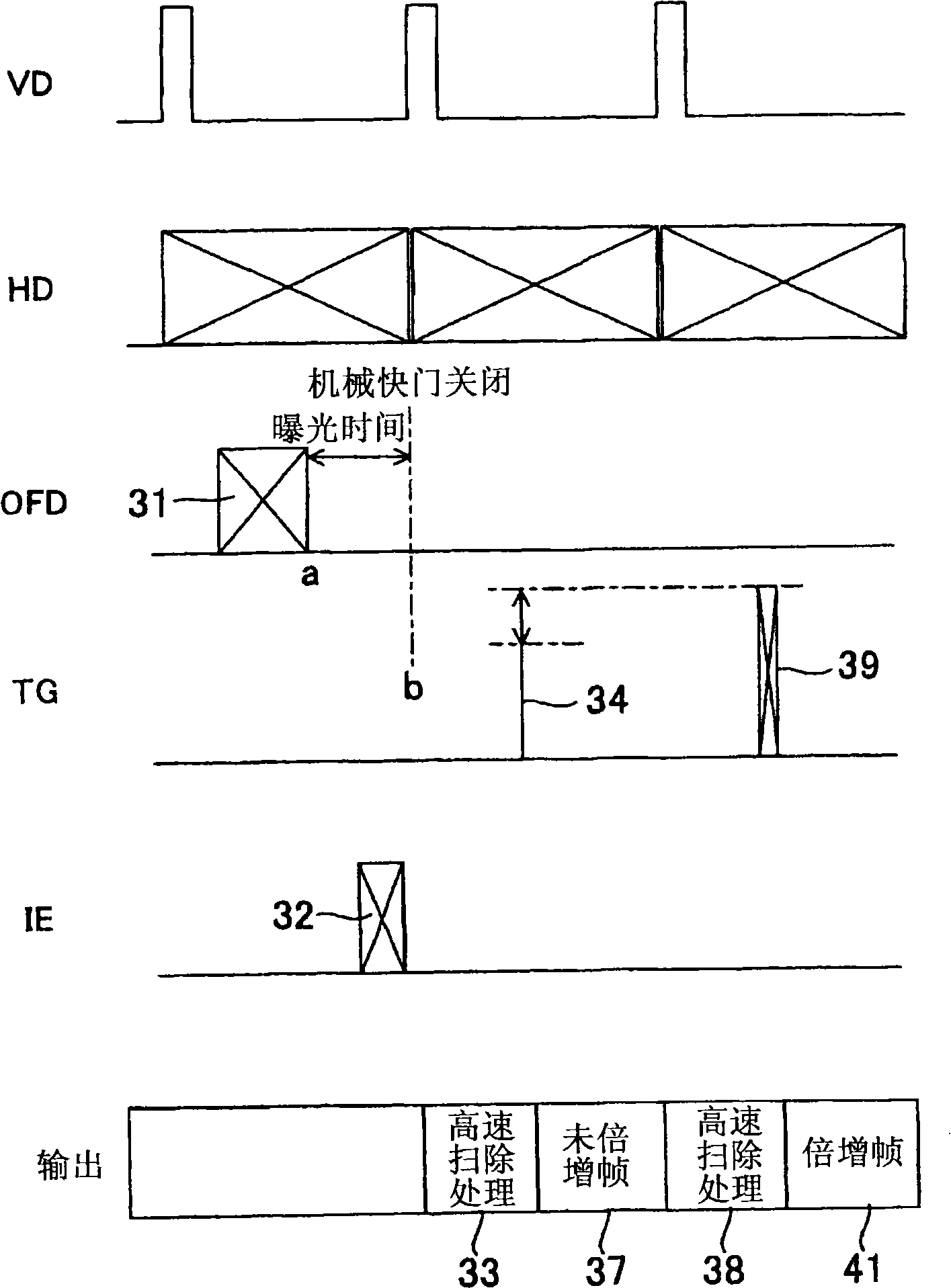
A method for driving a solid-state imaging device including a plurality of pixels arranged in a two-dimensional array, each of the plurality of pixels accumulating a signal charge according to an amount of incident light, is provided. The method includes: performing electron multiplication of a first signal charge at a first multiplication factor to output a first image signal; and performing electron multiplication of a second signal charge at a second multiplication factor to output a second image signal, at least the first and second image signals being image signals of the same scene of a subject and being successively output.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
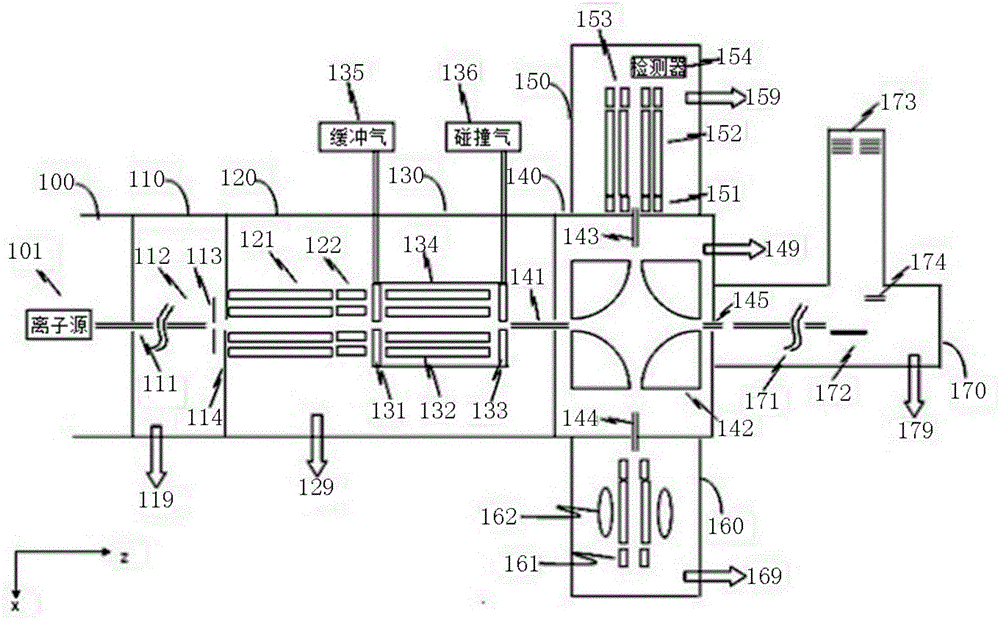
Novel series-parallel connection mass spectrum device system as well as parameter adjustment method and using method thereof
ActiveCN106169411AEasy to getReduce lossesStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGuidance systemMass analyzer
The invention provides a novel series-parallel connection mass spectrum device system. The system comprises mass spectrum necessary basic subsystems, such as a set of quadrupole mass filter system, a special quadrupole rod / linear ion trap mass analyzer system, an ion guidance system, a quadrupole deflector, a hyperbolic quadrupole rod mass analyzer and ion counter system, a low air pressure linear ion trap mass spectrometer and electron multiplier system, a flight time mass spectrum system, a multi-path gas flow control system, a vacuum gauge, a multi-section differential motion vacuum system and the like. Furthermore, the invention provides a method for operating above systems to perform quantitative analysis in a triplet quadrupole rod mode, qualitative analysis in a quadrupole filtering medium combined high / low air pressure ion trap mode, and quick / high-mass precision analysis in a quadrupole filtering combined flight time mass spectrum mode on ultra-trace materials in a complex matrix, a method for utilizing an effective combination of three different mass analyzers to achieve optimal ion optical parameter adjustment and a method for performing high-precision qualitative and quantitative analysis on the ultra-trace materials.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Electron multiplication CMOS imager
InactiveUS20090086055A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectron multiplicationImpact ionization
A pixel for an imager is disclosed that includes at least one electron multiplication (EM) gain stage configured in a loop and electrically coupled to a charge collection region and a charge readout region, the charge collection region being configured to generate a charge packet, the EM gain stage being configured to amplify the charge packet by impact ionization and to circulate the charge packet a predetermined number of times in one direction around the loop, the charge readout region being configured to receive the amplified charge packet and convert the amplified charge to a measurable signal. The at least one EM gain stage, the charge collection region, and the charge readout region can be formed monolithically in an integrated circuit. The pixel can be manufactured using a CMOS process. The pixel can further include a second EM gain stage formed in the integrated circuit to increase the amount of amplification around the loop.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
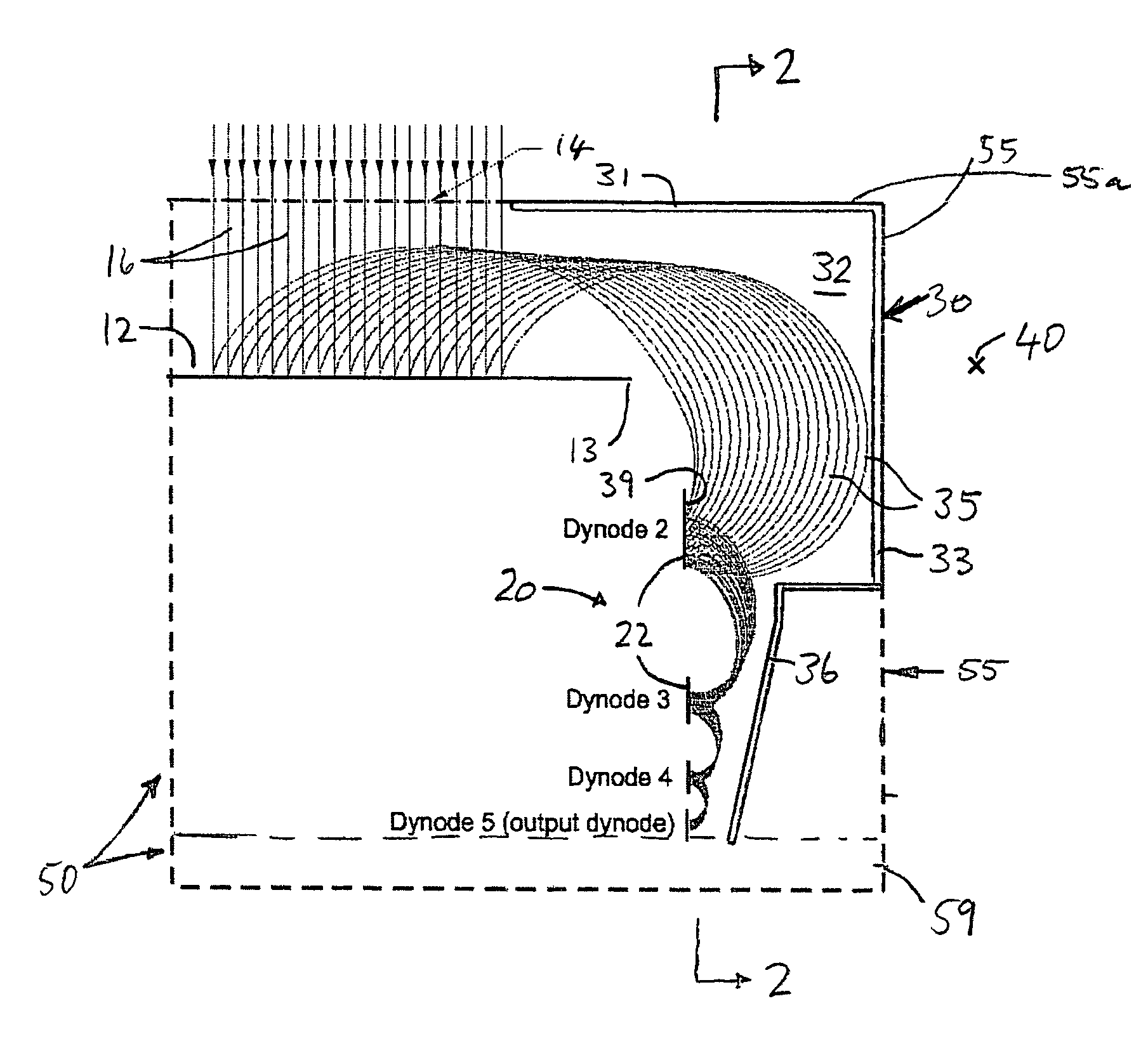
Particle detection by electron multiplication
ActiveUS6982428B2Great magnification and focussing capabilityVacuum tubesMagnetronsElectron multiplicationElectron trajectory
Electron focussing apparatus includes a cathode plate defining an impact surface on which particles impact, which surface has a finite probability of generating at least one electron for each impacting particle having predetermined characteristics. The apparatus also has an electron receiving element, and respective means for generating electrostatic and magnetic fields in a space extending from the impact surface to the electron receiving element. The means for generating the electrostatic and magnetic fields are configured whereby the E / B2 ratio adjacent the electron receiving element is smaller than adjacent the impact surface, whereby to decrease the radius of curvature of the electron trajectories adjacent the electron receiving element relative to adjacent the impact surface and to thereby focus the electron trajectories in at least one dimension. In another aspect the electron receiving element is positioned and the means for generating the electrostatic and magnetic fields are configured to cause the electrons to deflect on average through greater than 180° before impacting the electron receiving element, whereby to focus, in at least one dimension, multiple electrons generated from any given area of the impact surface to a smaller area at the electron receiving element.
Owner:ETP ION DETECT PTY LTD
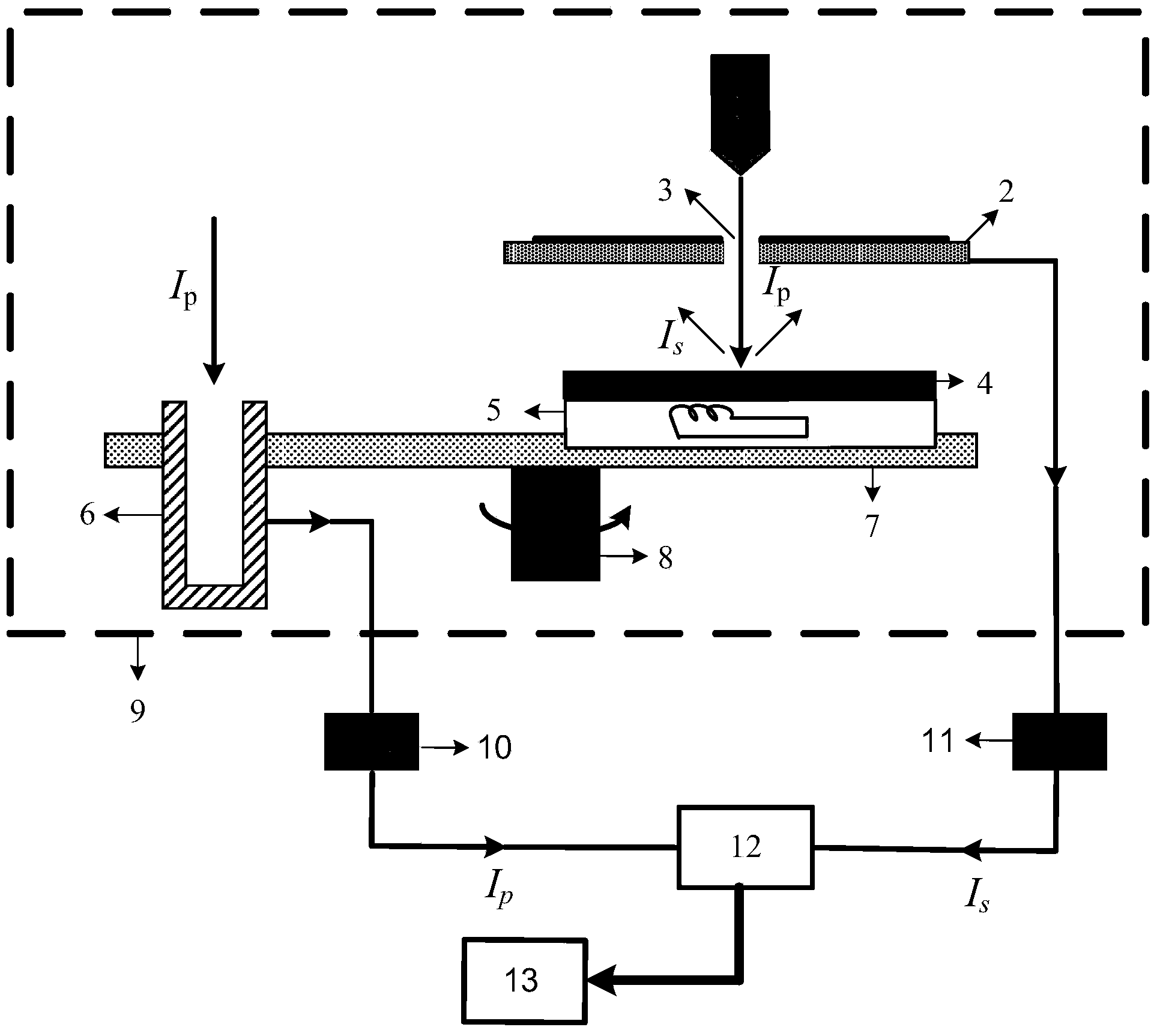
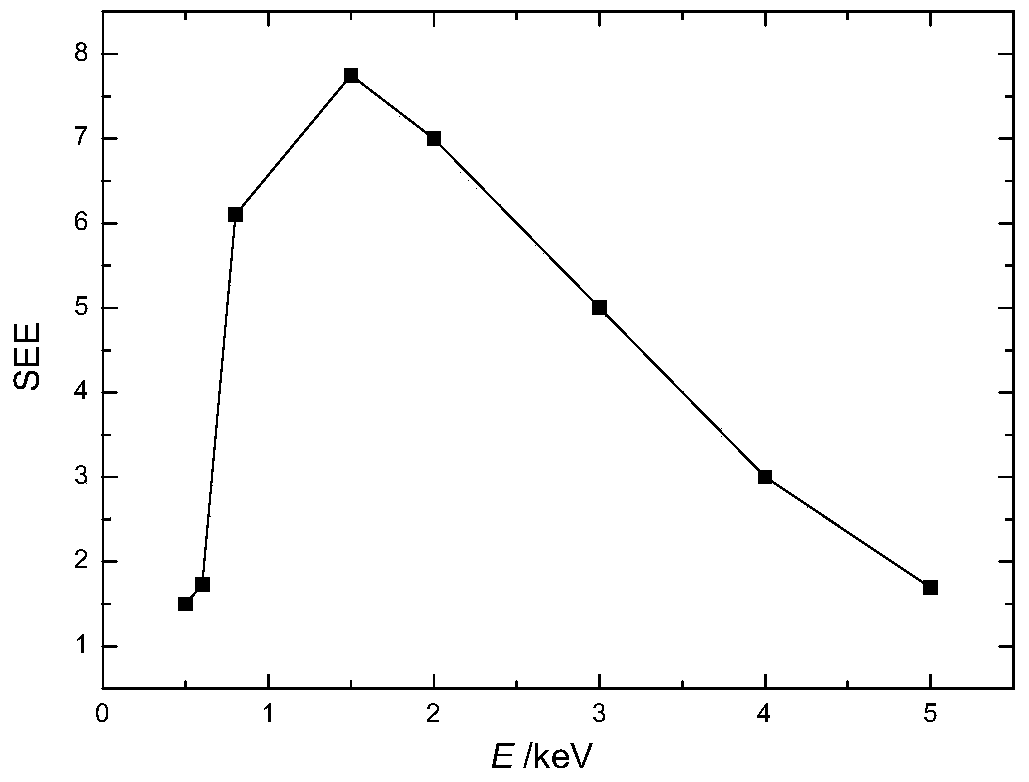
Panel type collection device and method for measuring secondary electron emission coefficient
ActiveCN103776858AEfficient collectionIntuitive and convenient adjustmentMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionTemperature controlMeasurement device
The invention discloses a panel type collection device and method for measuring a secondary electron emission coefficient. A measuring device mainly comprises a rotary platform, a sample table, a heating device, a Faraday cylinder, a current amplifier and a collection electrode, wherein the inner wall of the Faraday cylinder is plated with a layer of carbon, the Faraday cylinder is connected with a bias voltage device and the current amplifier and is used for measuring a primary incidence current; the collection electrode is in a panel structure, the upper surface of the collection electrode is coated with a layer of fluorescent powder so as to conveniently adjust and focus electron beam faculae, and the lower surface of the collection electrode is plated with a layer of carbon so as to inhibit electron multiplication phenomenon in a collection process; the collection electrode is connected with a bias voltage device and the current amplifier and is used for measuring secondary electron stream emitted by the surface of a material. By utilizing a rotary device, multiple samples can be simultaneously measured, so that the measuring time is saved; by utilizing the heating device and a temperature control device, the temperature of a sample can be accurately controlled in a range of 30-300 DEG C, and the heating device and a temperature control device are used for researching the influence of the temperature on the secondary electron emission coefficient; by providing the novel electron collection device for measuring the secondary electron emission coefficient, the measurement of the secondary electron emission coefficients under different temperatures is realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
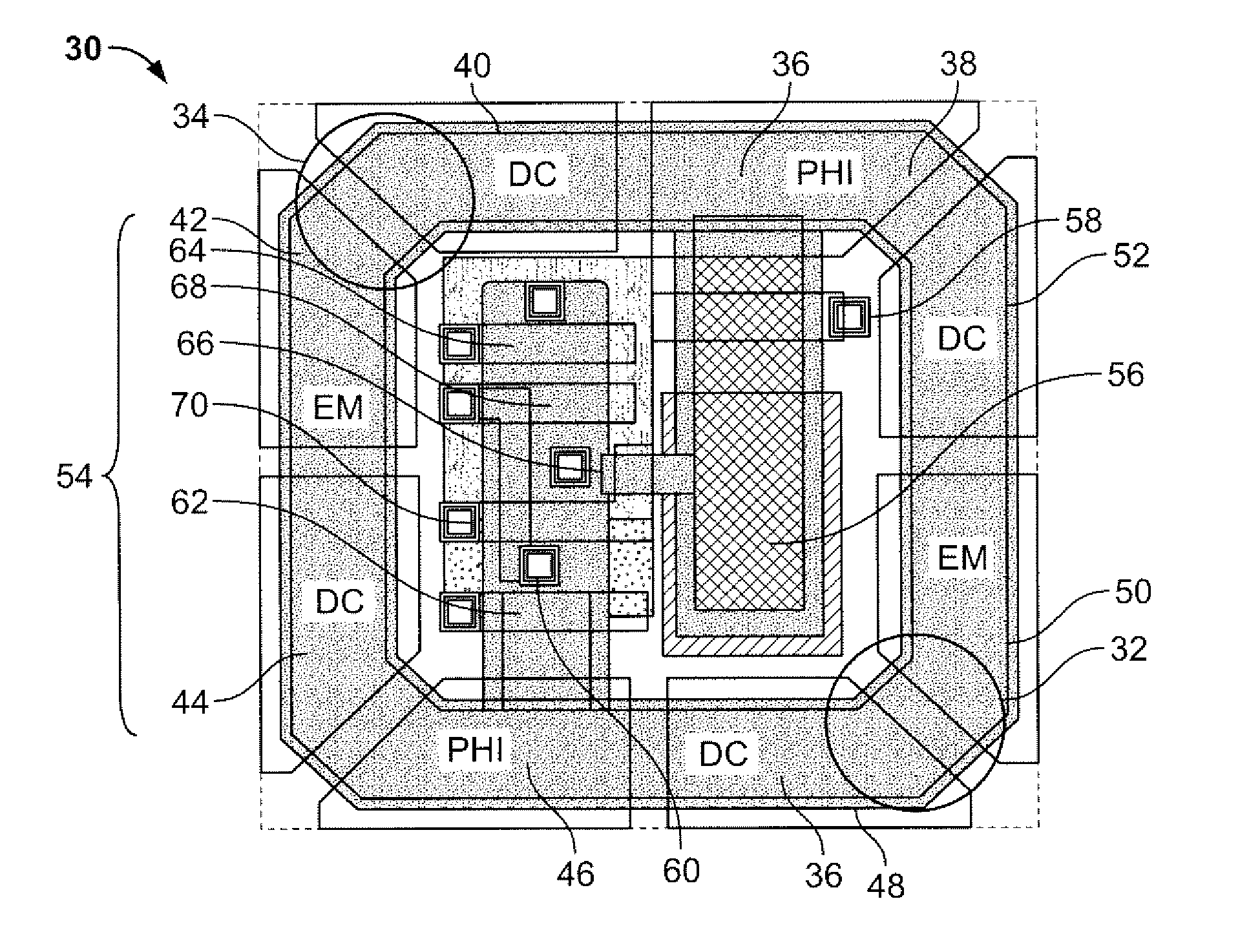
Image sensor with very high dynamics
InactiveCN102695000ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectron multiplicationElectron transfer
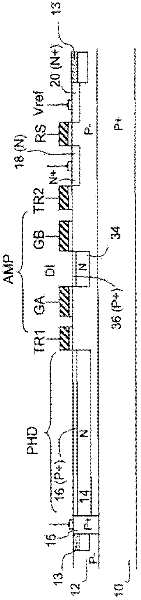
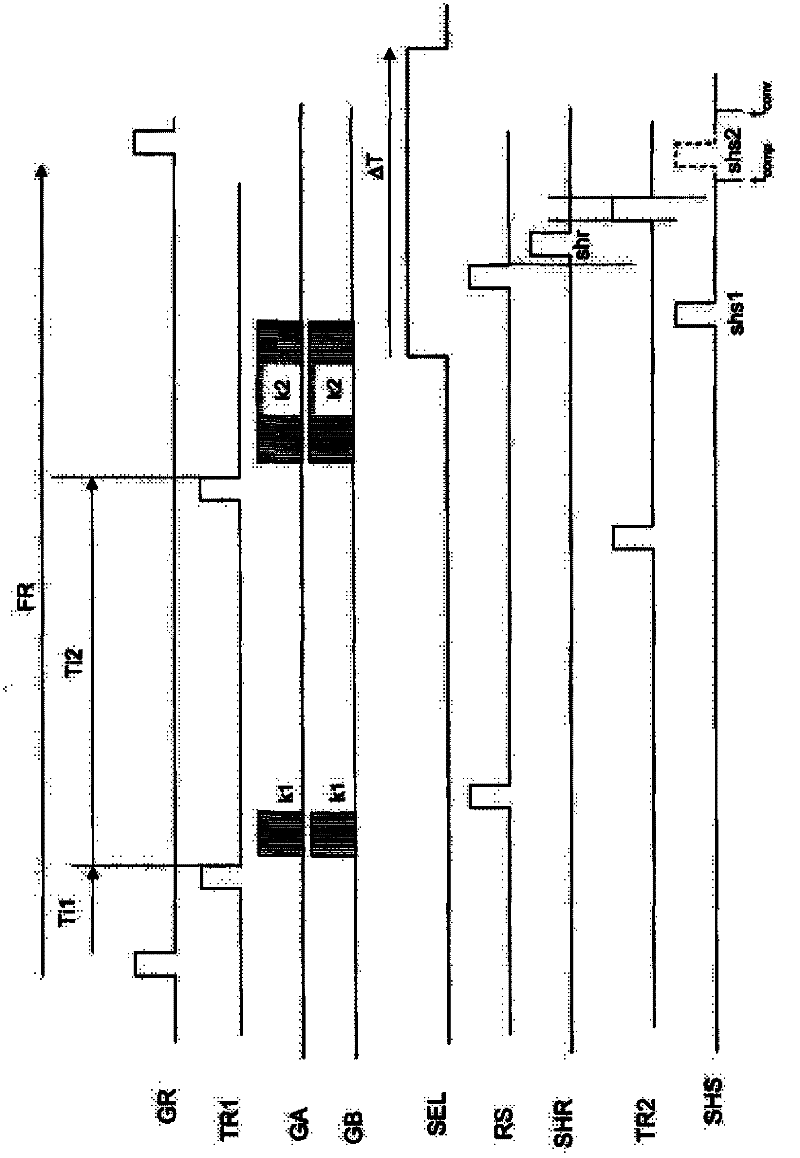
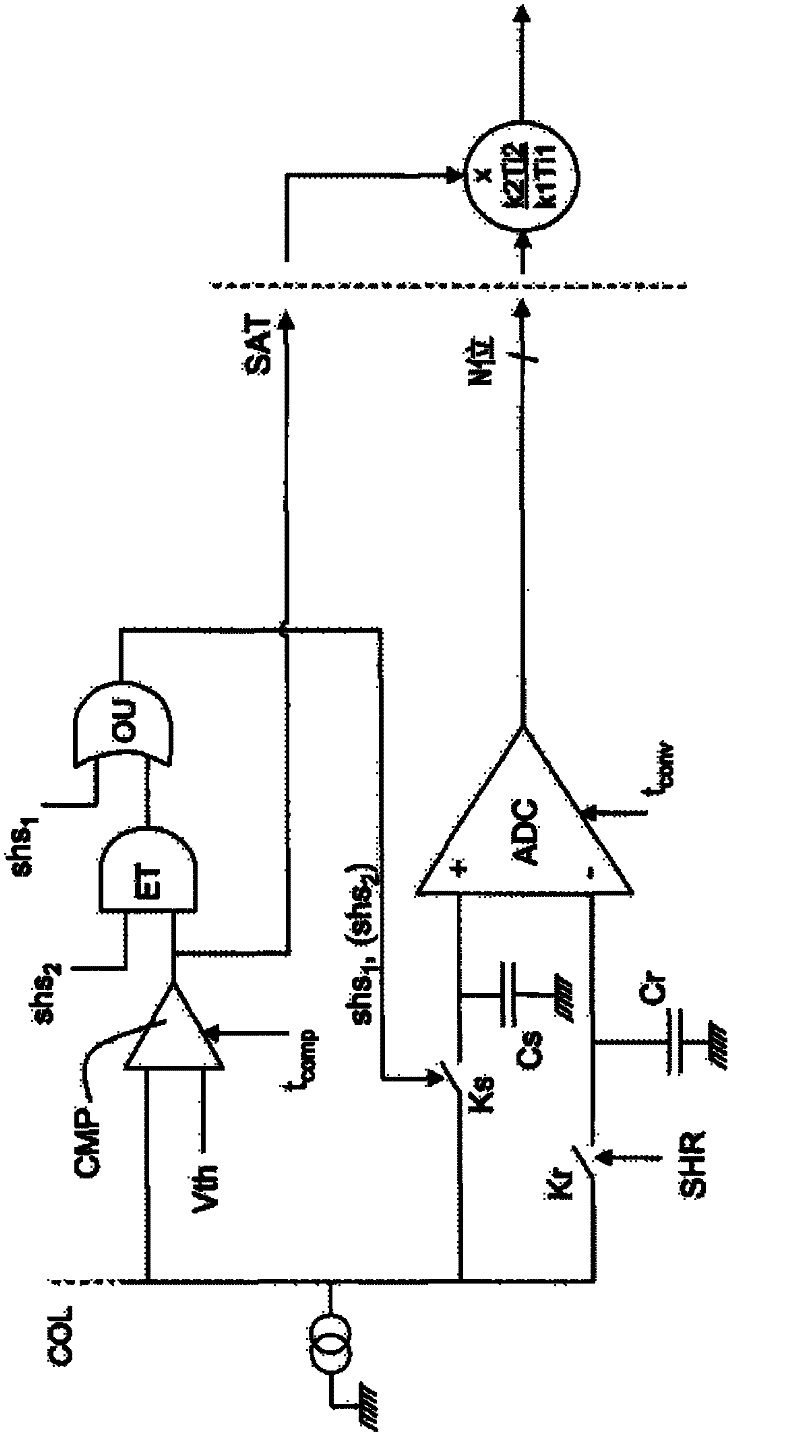
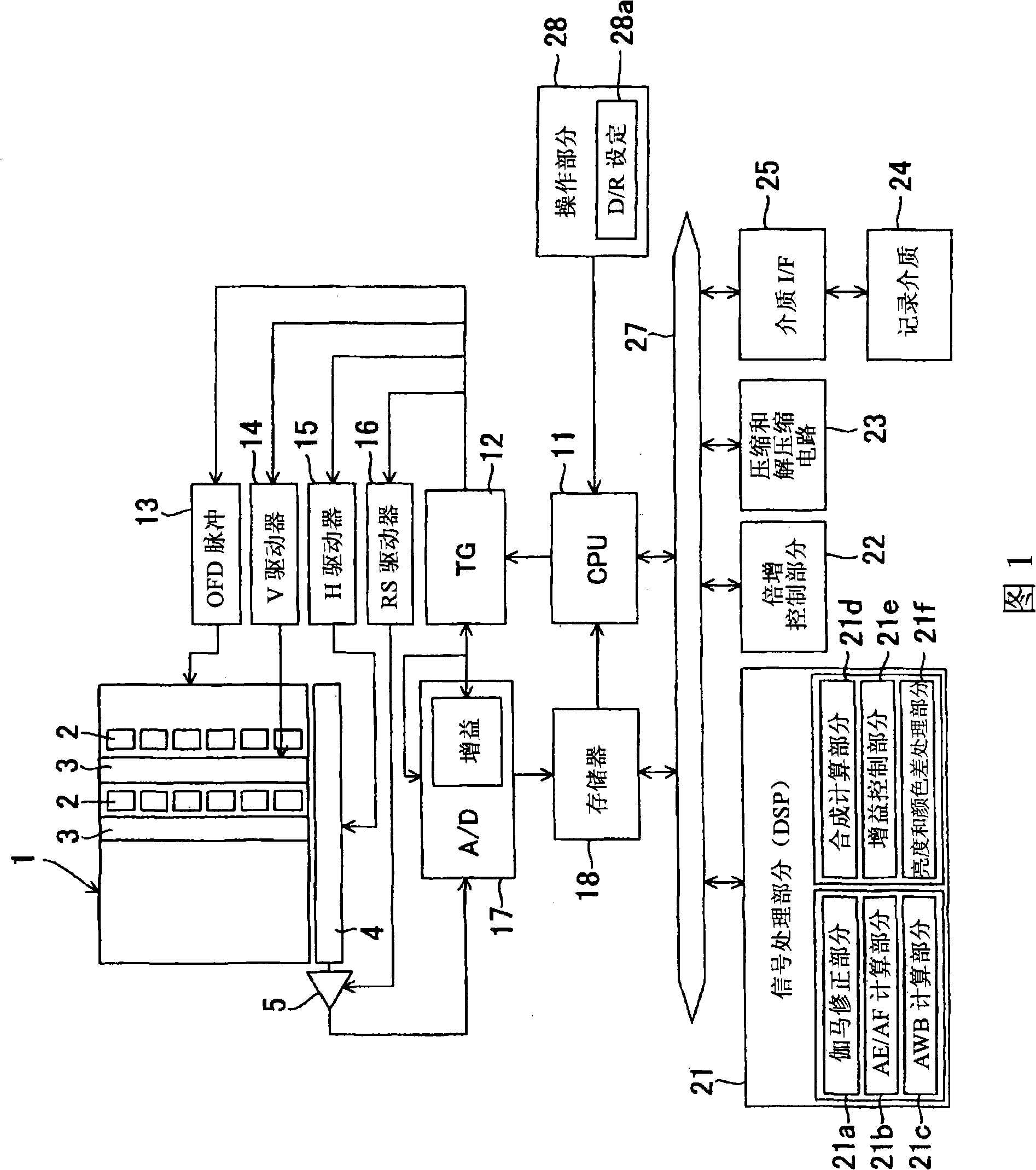
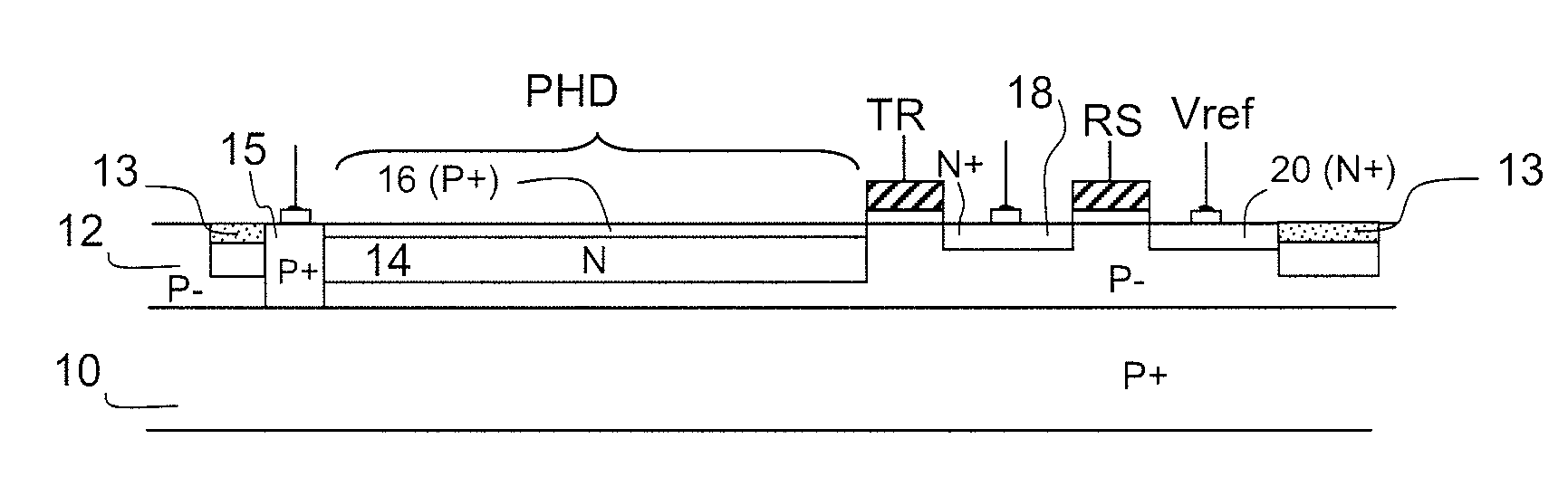
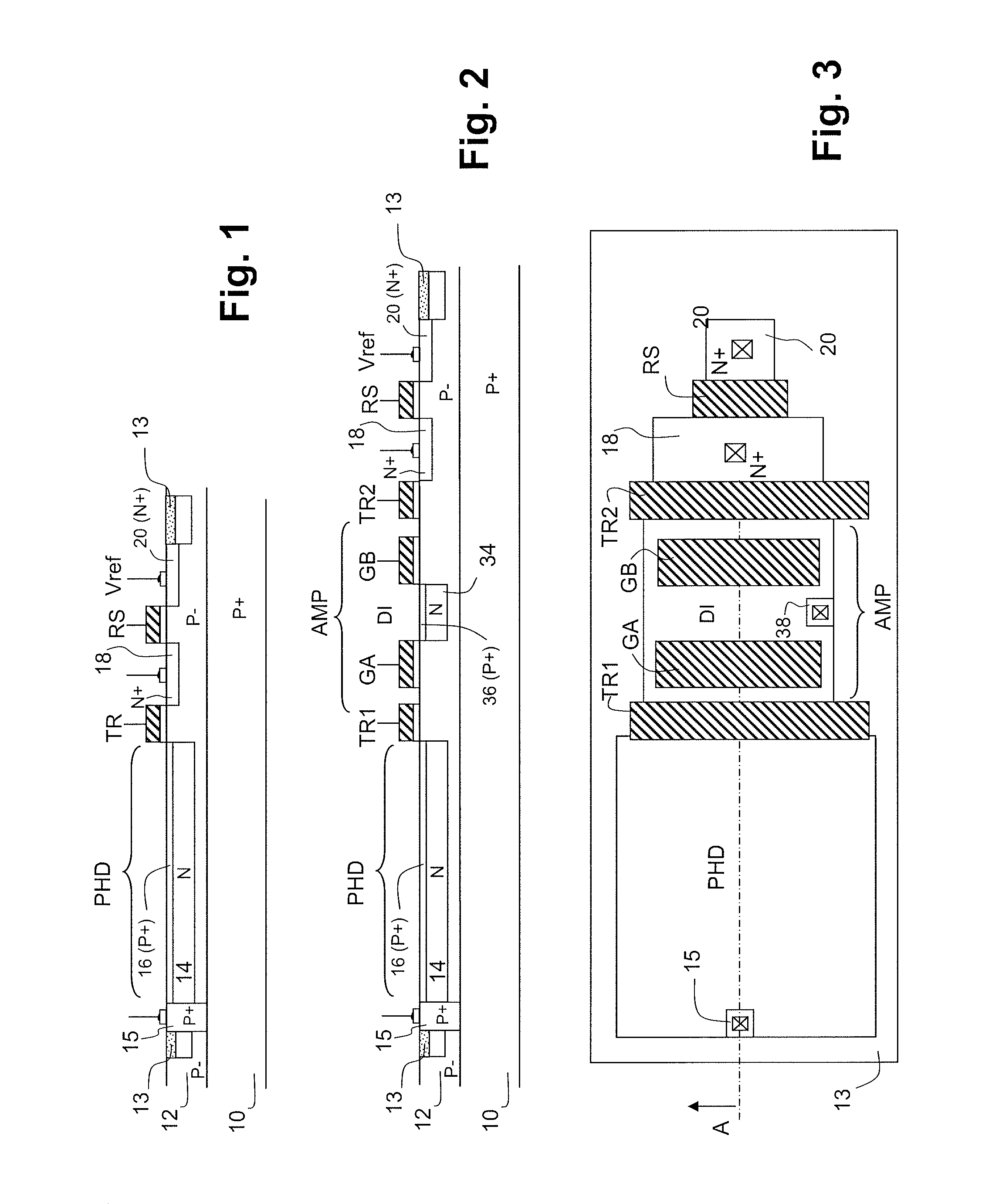
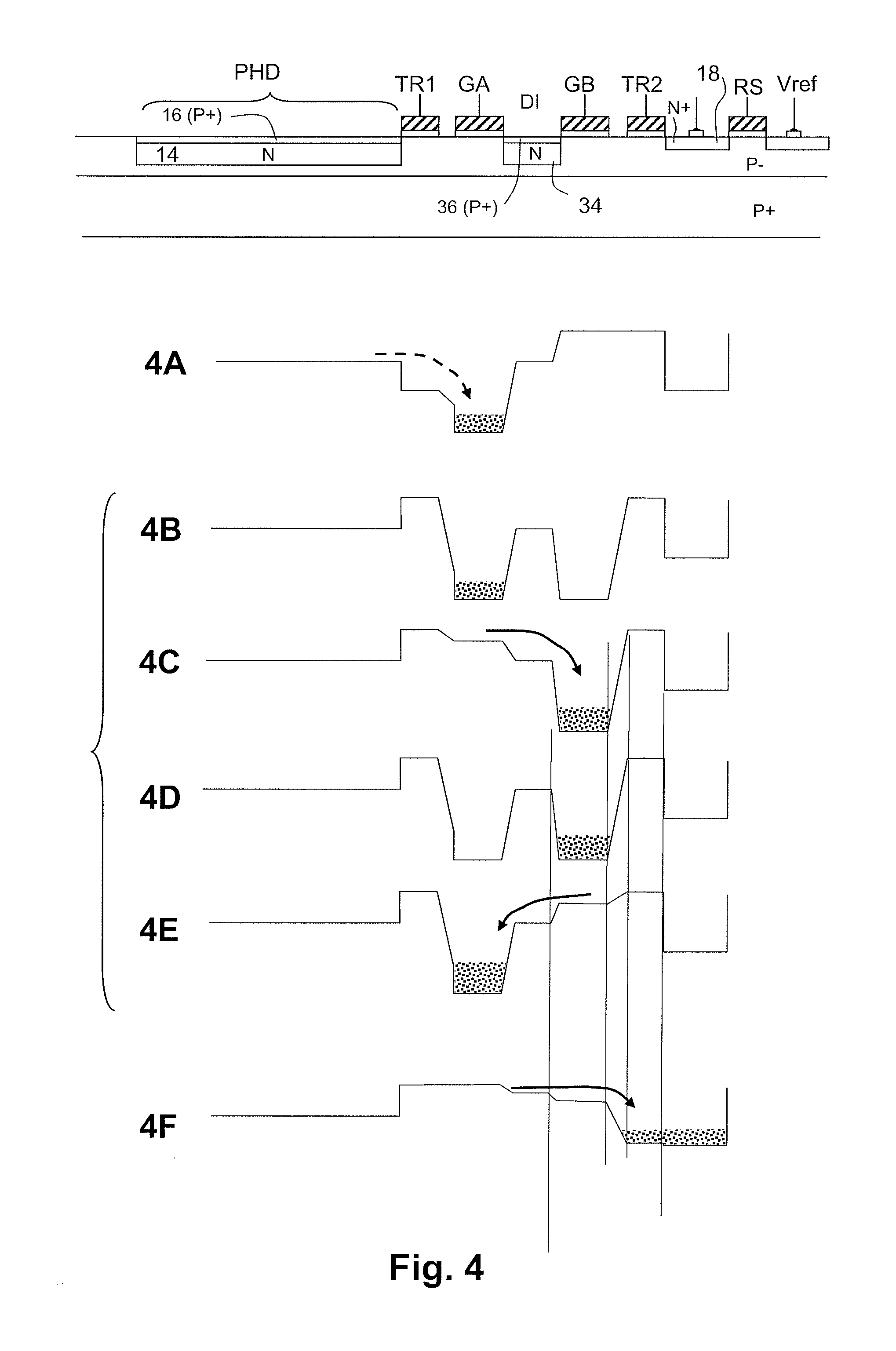
The invention relates to an image sensor with active pixels. The image sensor includes active pixels for gathering images at very high and very low luminance level. Each pixel includes at least one photodiode (PHD), a charge storage node (18), an electron multiplication amplification structure (AMP), a unit for transferring electrons from the photodiode to the structure (TR1), a unit for transferring electrons from the amplification structure to the storage node after multiplication (TR2), a transistor for reinitializing the potential of the storage node (RS). The pixels are read by a reading circuit which samples the potential of the charge storage node after reinitialization and after transfer of the electrons into the storage node and which provides a corresponding illumination measurement. The sensor furthermore includes a unit for carrying out the integration of charge in two different durations in the course of one and the same frame, and for giving the amplification structure multiplication factors different to the charge integrated in the course of these durations.
Owner:TELIDAS ETUVE SEMICON CO LTD
Imaging methods and apparatus having extended dynamic range
ActiveUS7378634B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectron multiplicationDynamic range
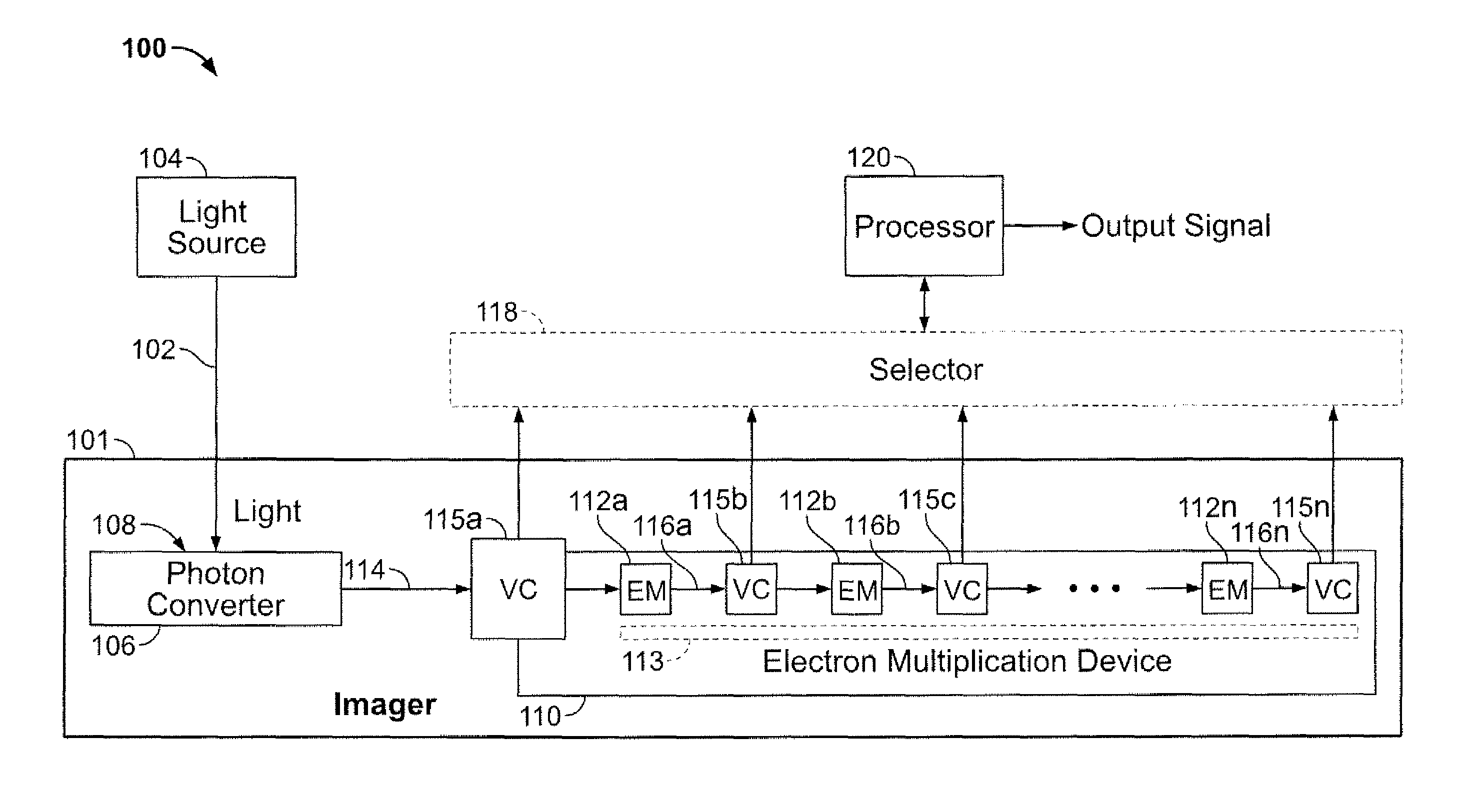
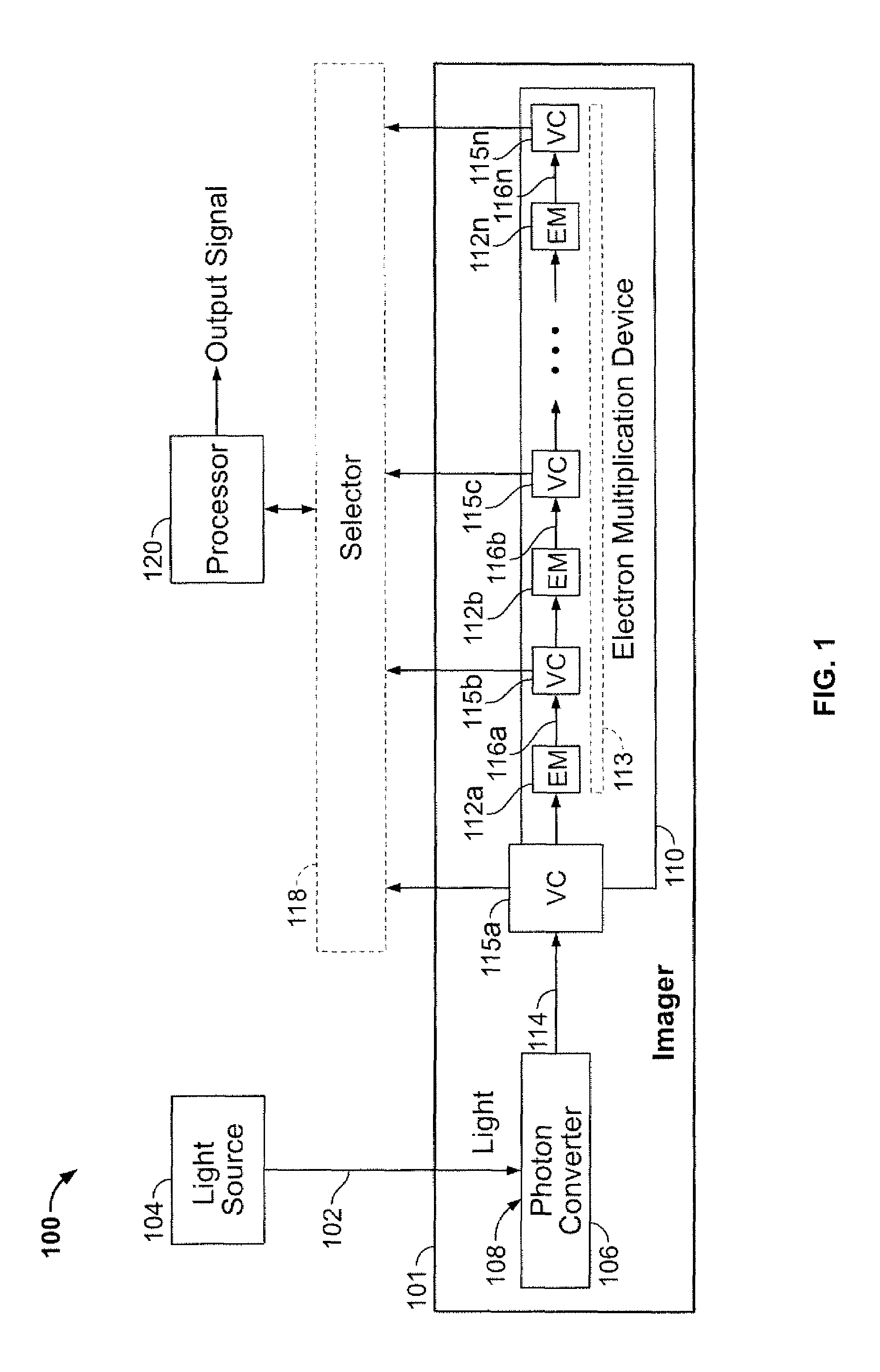
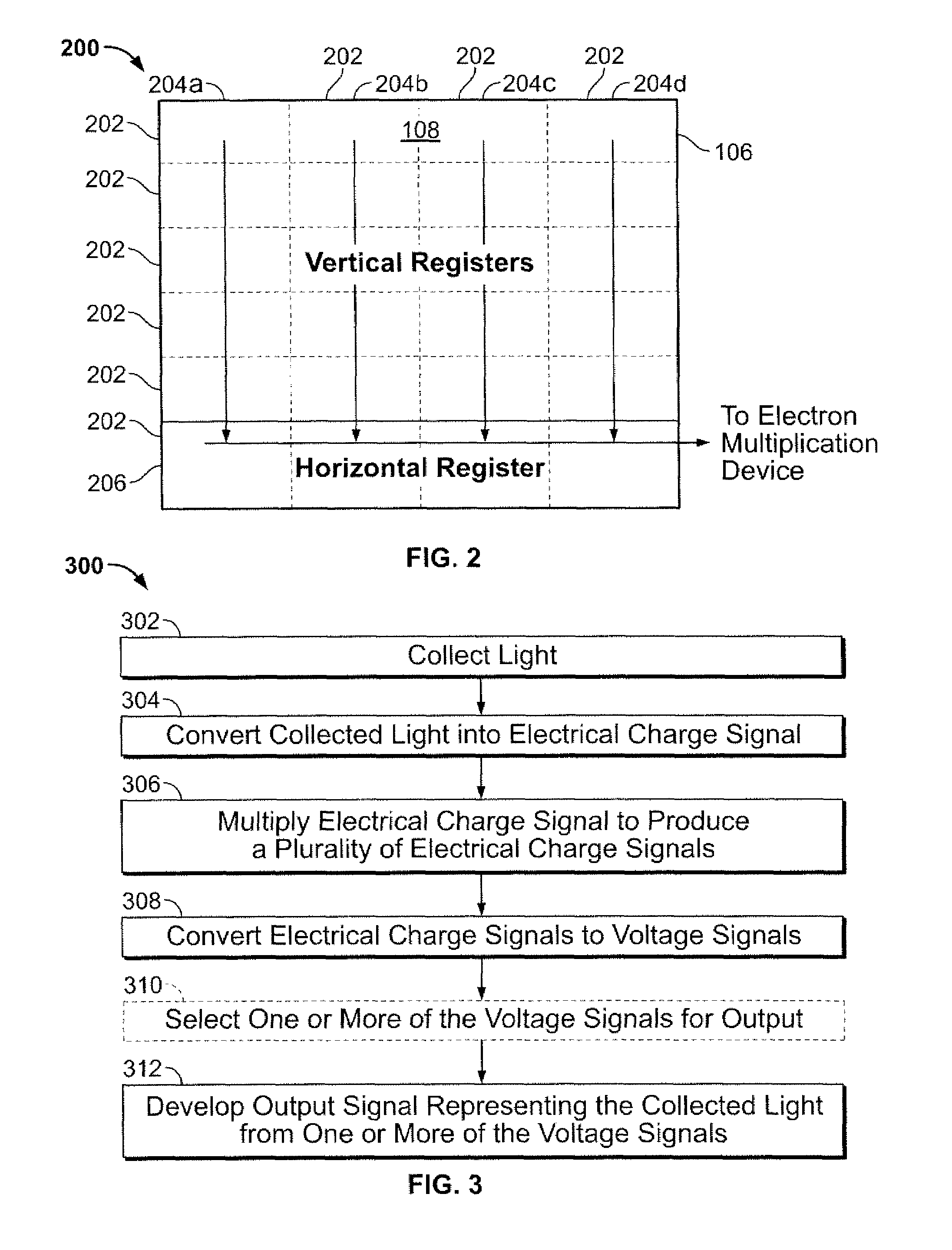
Methods and apparatus for imaging light are disclosed. Light is imaged by collecting light, converting the collected light into a electrical charge signal, multiplying the electrical charge signal to produce multiple electrical charge signals with associated levels of gain, converting the electrical charge signals to voltage signals, and developing an output signal from one or more of the voltage signals that represents the collected light. The electrical charge signal may be multiplied using an electron multiplication device associated with multiple taps to produce the electrical charge signal with different levels of gain.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
System for realizing signal driving of EMCCD (Electron Multiplication Charge Couple Device) by high-voltage operational amplifier
InactiveCN102447849AImprove stabilityReduce Op Amp Power ConsumptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLow-pass filterElectron multiplication
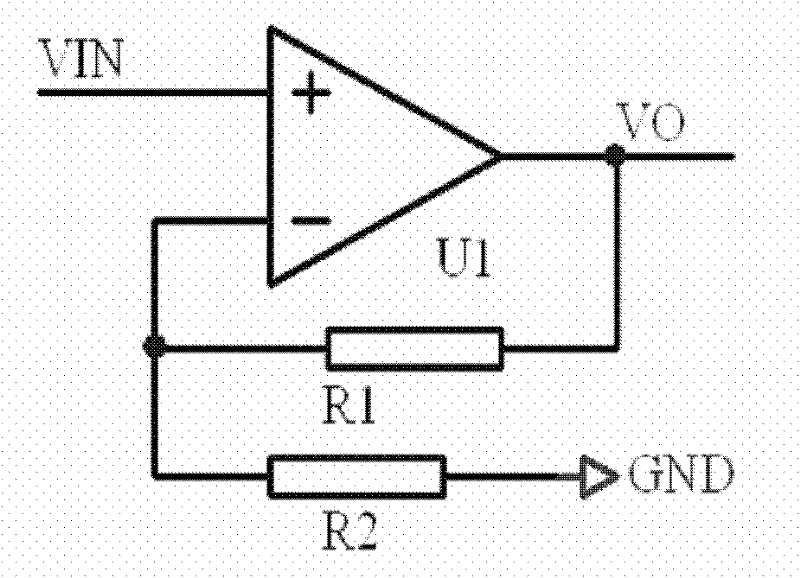
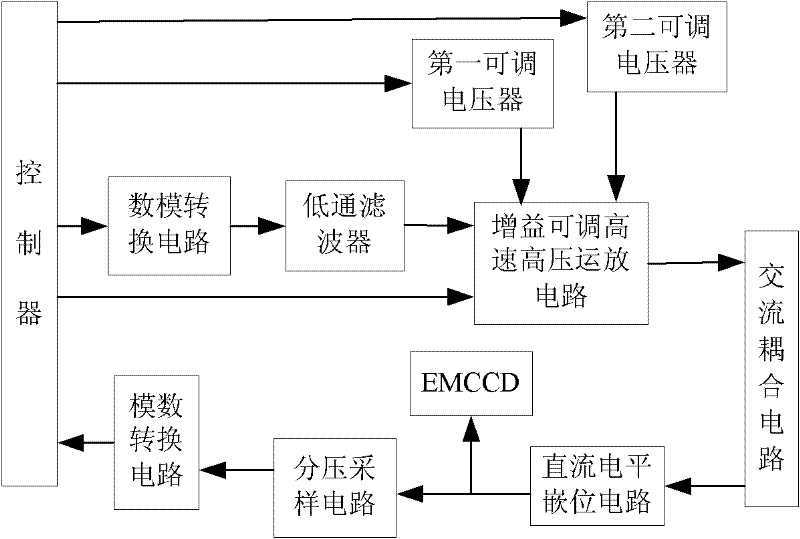
The invention provides a system for realizing signal driving of an EMCCD (Electron Multiplication Charge Couple Device) by a high-voltage operational amplifier, relating to a driving technology of a CCD (Charge Couple Device), and solving the problems which are difficult to realize by the existing driving method. In the invention, a high-speed and high-voltage driving signal is obtained by a gain-adjustable high-speed and high-voltage operational amplifying circuit and can be applied when the working frequency is high and the multiplier voltage is high; by directly adopting digital signal control, the circuit stability is high; by adopting a DC (Direct Current)-DC power supply for supplying power, the voltage of the power supply changes according to the amplitude change of an output signal, and the power consumption of the operational amplifier can be lowered when the amplitude of the output signal is lower; and a low-pass filter converts an amplitude-adjustable square wave generated by a digital-to-analog converter into a sine wave, and the sine wave is amplified by the high-speed and high-voltage operational amplifier so as to generate a high-speed and high-voltage driving signal. The amplitude of the output signal is changed through two paths of digital control signals so as to realize the digital control on the output signal, thereby ensuring that final high and low level values are in the allowable working range of the device.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
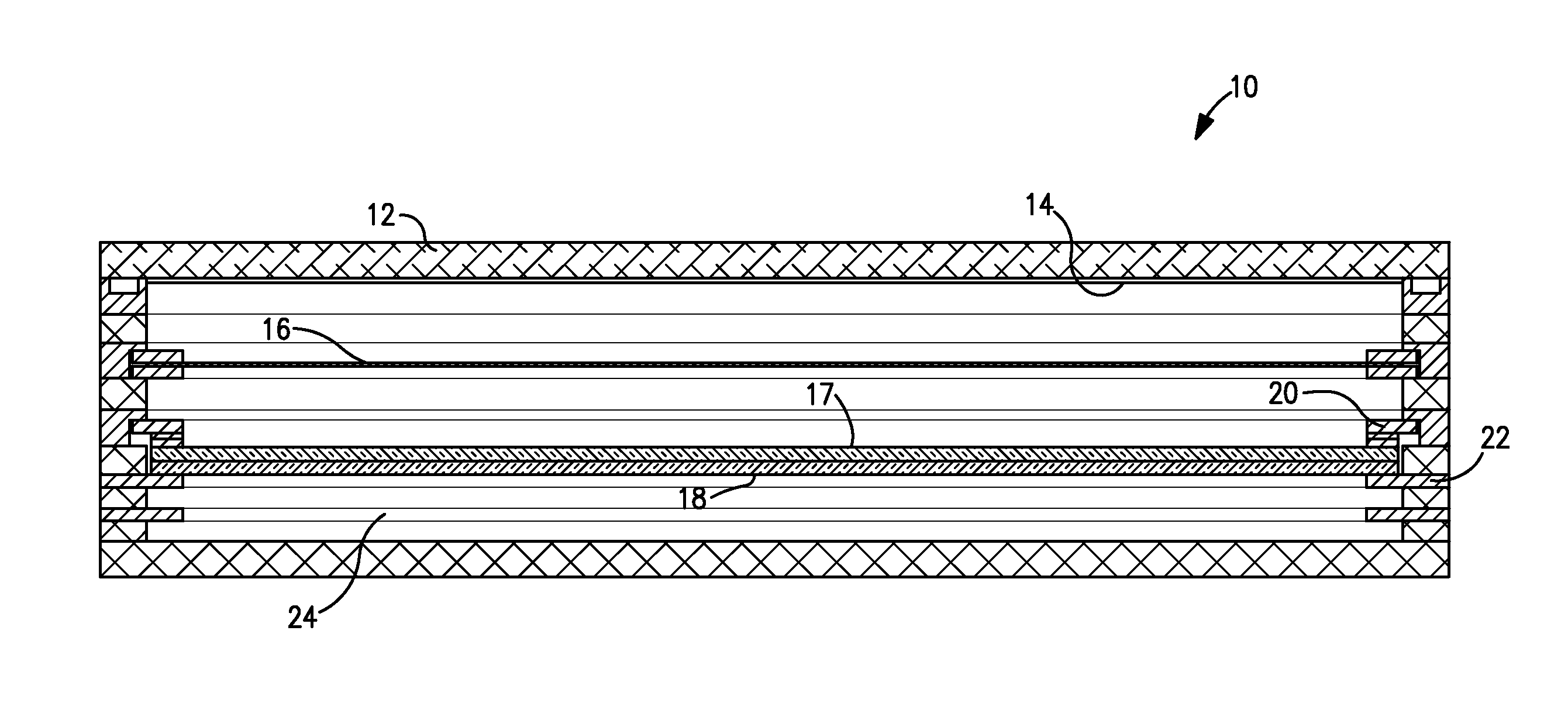
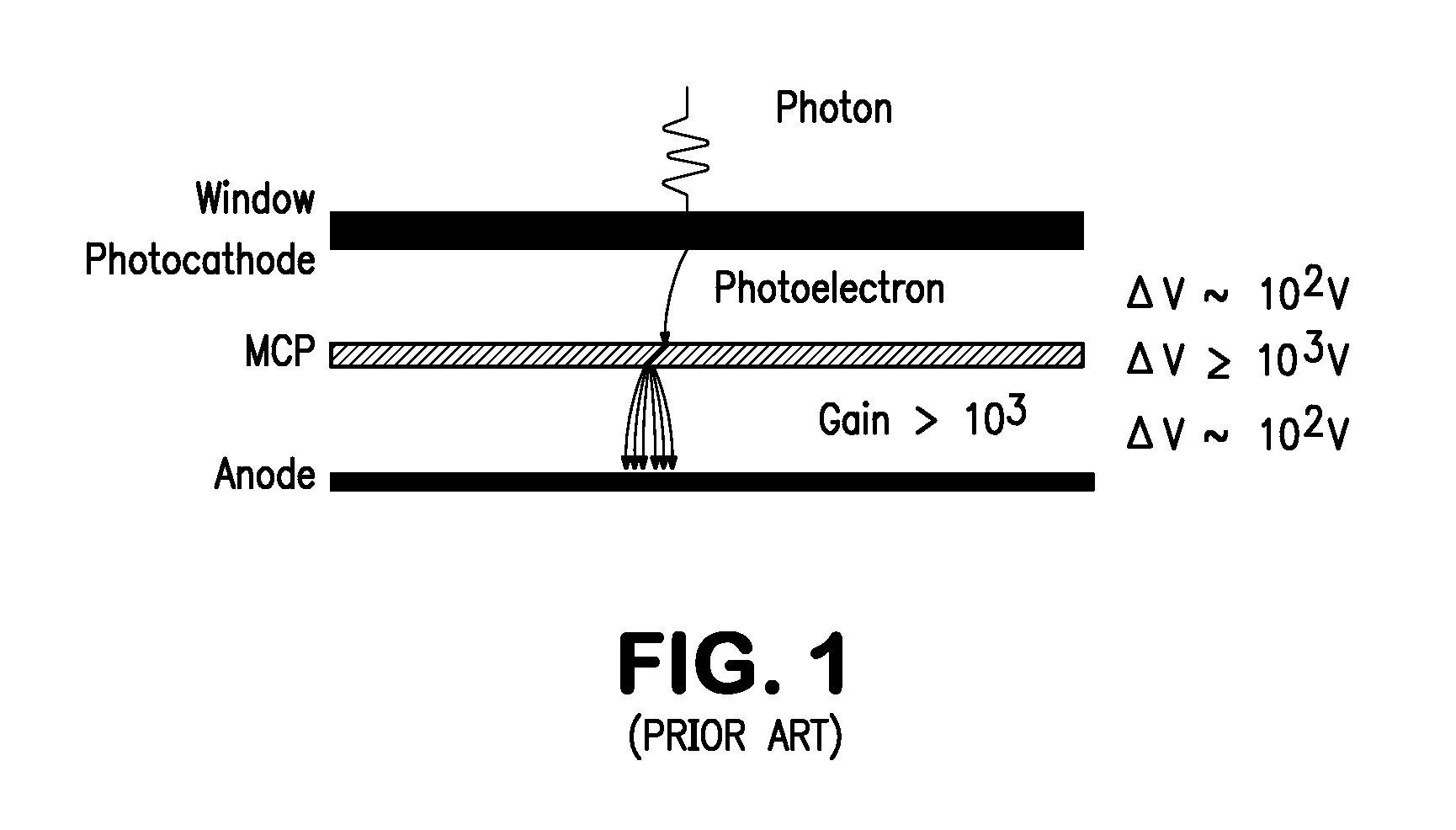
Microstructure photomultiplier assembly
InactiveUS20110133055A1Promote efficient transferPromote accelerationMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhotocathodeElectron multiplication
The subject invention provides for a novel photomultiplier assembly, termed the Microstructure Photomultiplier Assembly (MPA), which enables the effective conversion of light signals (received at the front of the assembly) into readily-detectable electrical signals. The MPA comprises a photocathode (which converts light into electrons and which is located in front of or on the front surface of the assembly), followed by an electron-multiplying plate, or series of plates, each made from an insulating substrate which does not emit sufficient contaminants to poison the photocathode. Each plate is coated on the front and rear faces with a conductive layer. In addition, the front face of each plate is further coated with a layer of secondary electron-emissive material which, when struck by an incoming electron, can produce secondary electrons. Each plate is perforated with channels (with non-conducting walls) and the number and geometry of these channels is designed to promote the efficient transfer and acceleration of electrons through the channel, under an applied voltage differential across the plate(s). The number of plates placed in series is determined by the desired degree of electron multiplication. At the exit of the last plate, an anode is located to collect the electrons and generate an electrical signal that can be read by conventional electronics. The anode can be a simple anode or can be a position-sensitive anode. The spacing between the photocathode, the electron-multiplying plates, and the anode is selected to promote the efficient transfer and acceleration of electrons across the assembly, as well as to promote the efficient production of secondary electrons. The photocathode, electron-multiplying plate(s) and anode are all contained within a vacuum enclosure.
Owner:BUBBLE TECH INDS
Solid state back-illuminated photon sensor
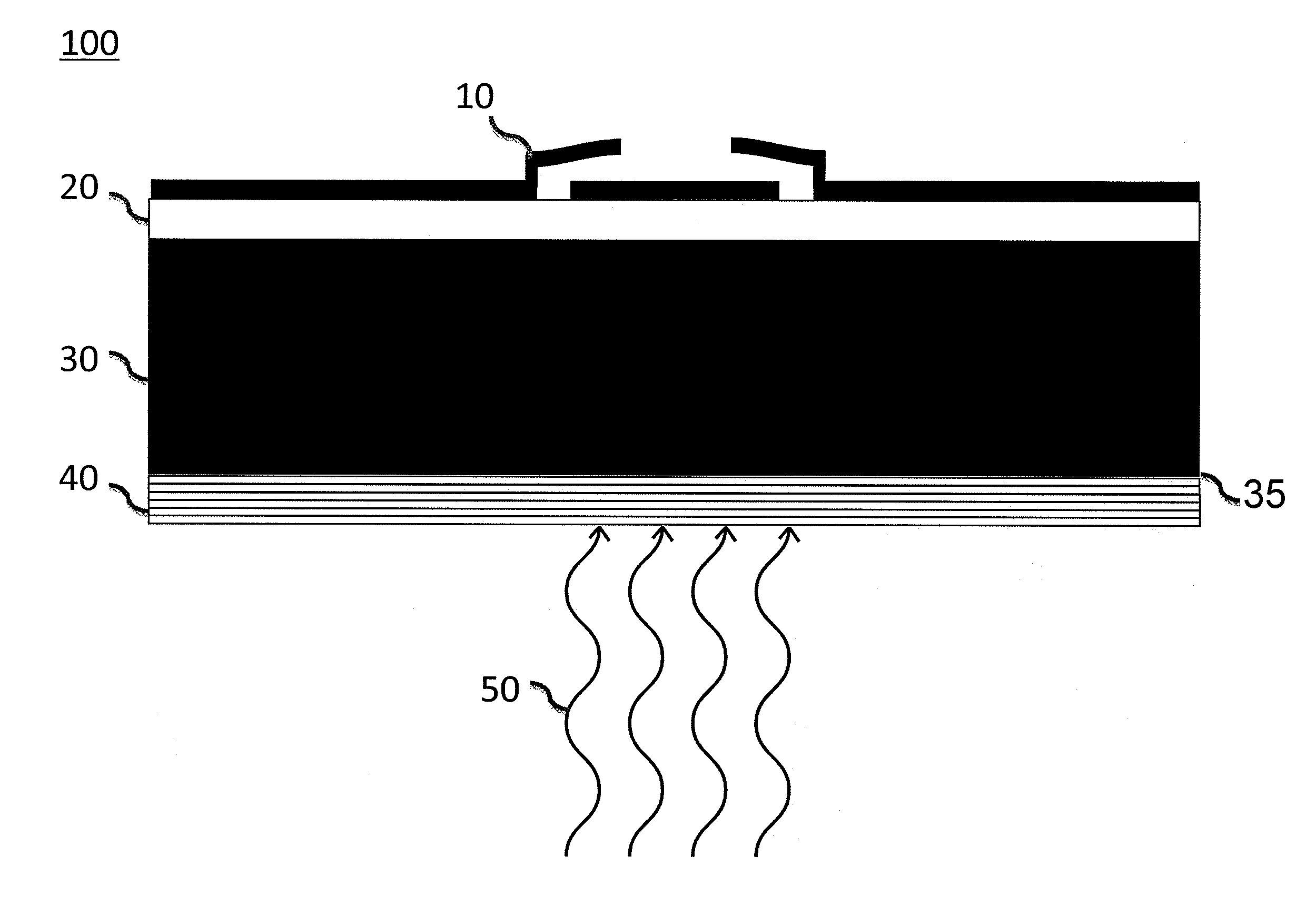
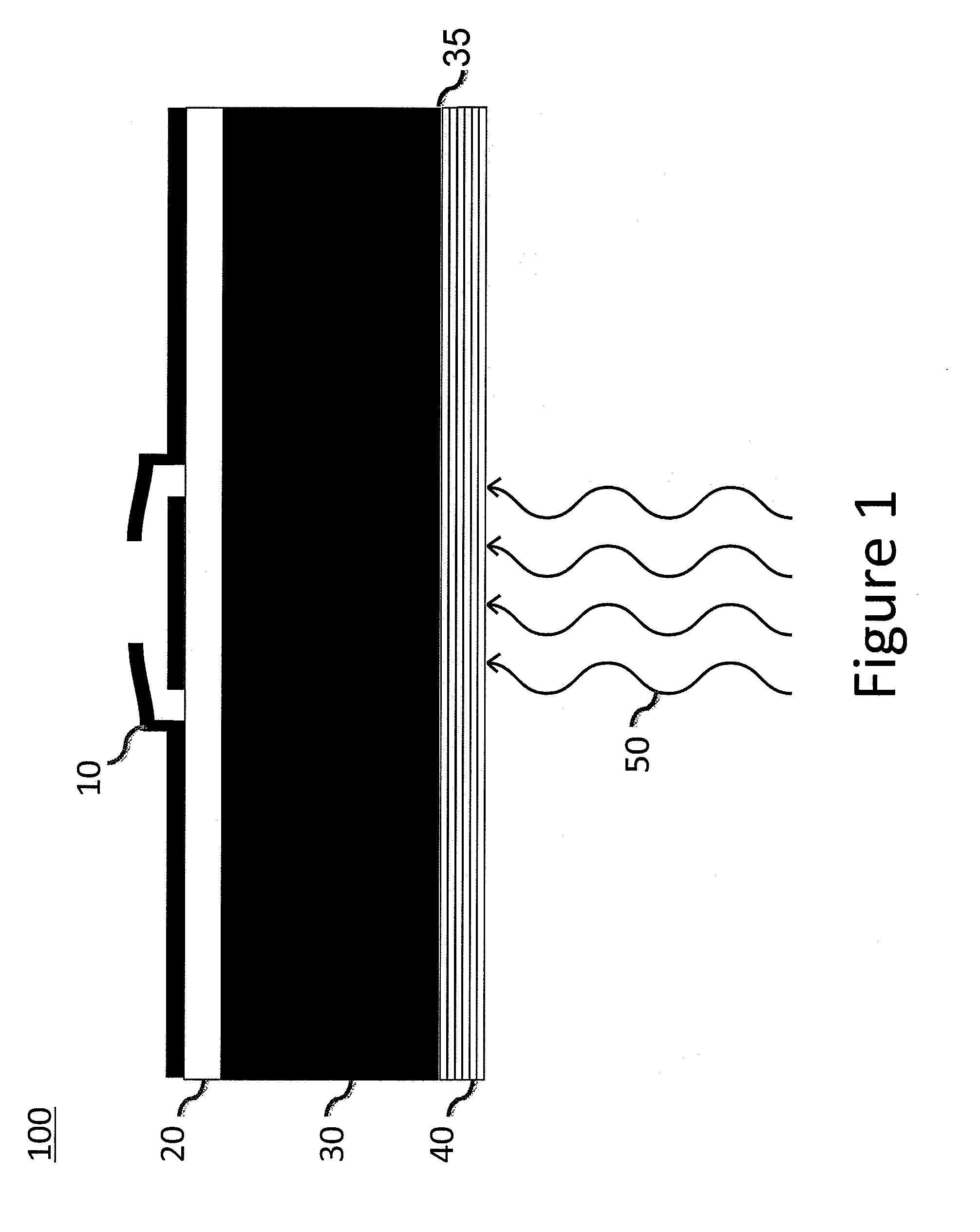
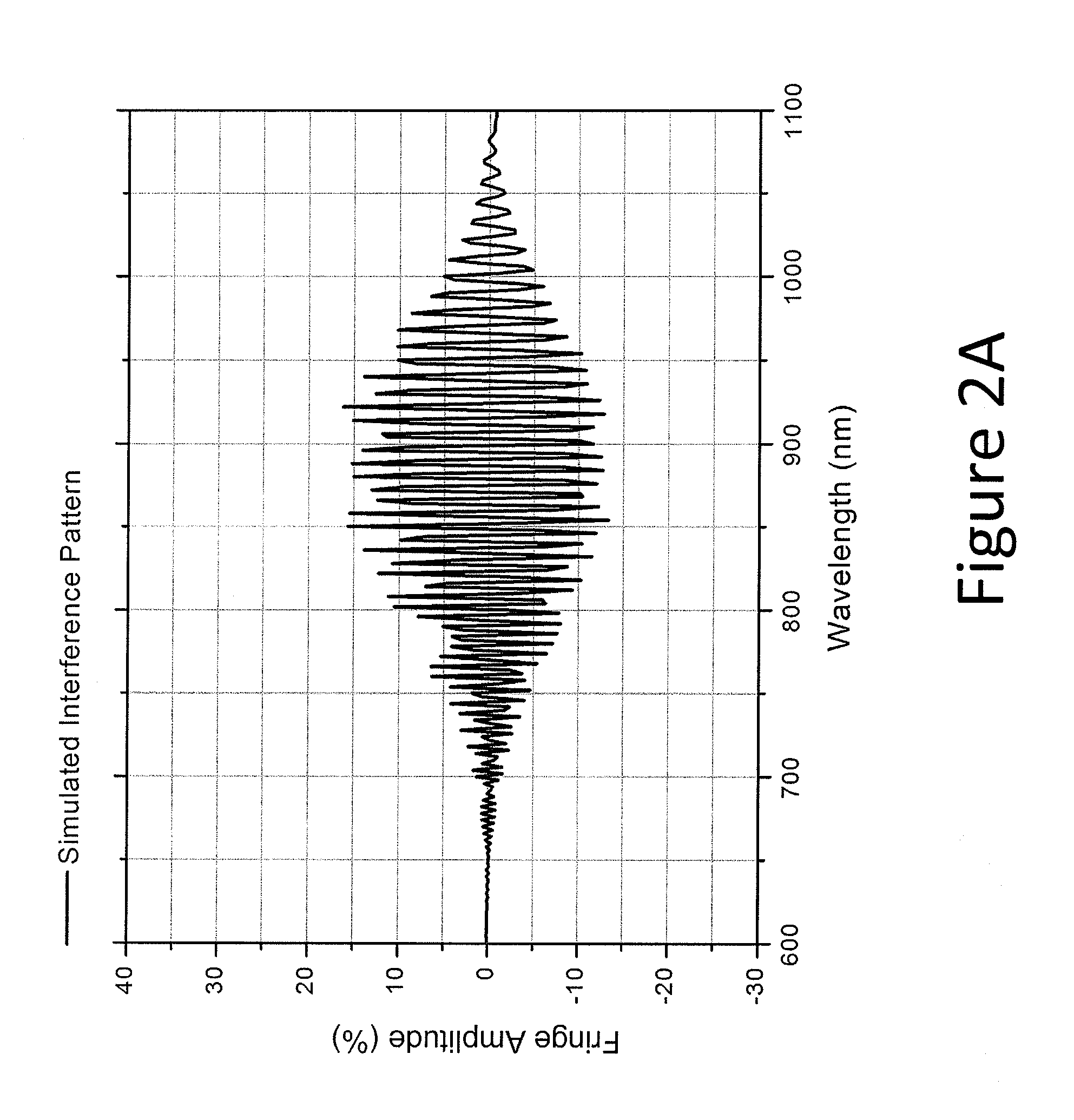
ActiveUS20110175185A1Minimizing etaloning spanning the NIRImprove quantum efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron multiplicationPhotonic sensor
A backside-illuminated image sensor is disclosed having improved quantum efficiency (QE) in the near infrared wavelengths (NIR: 750-1100 nm) with minimal optical interference fringes produced by multiple reflected rays within the photosensitive Si region of the sensor, which may be a charge-coupled device, a complementary metal oxide sensor or an electron-multiplication sensor. The invention comprises a fringe suppression layer applied to the backside surface of the photosensitive Si region of a detector (Si substrate) whereby the fringe suppression layer functions in concert with the Si substrate to reduce the occurrence of interference fringes in the NIR while maintaining a high QE over a broad range of wavelengths (300-1100 nm). The combination of a fringe suppression layer applied to a Si substrate provides a new class of back illuminated solid state detectors for imaging.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING US INC
Four-dimensional electronic shadow imaging device
InactiveCN102683146AImprove time resolutionQuality improvementElectric discharge tubesElectromagentic field characteristicsElectron multiplicationFemto second laser
The invention discloses a four-dimensional electronic shadow imaging device, comprising a Femtosecond laser light source, a laser frequency tripling device, a Femtosecond electron gun and an electronic attitude control system, an ultrahigh vacuum cavity, an electron multiplication system, an imaging acquisition system, a vacuum pump system, a sample operating system, an optical path regulation system, a shutter and a time synchronization system. The four-dimensional electronic shadow imaging device has the advantages of shingle-shot imaging, high time resolution, high sensitivity to electromagnetic field information, high signal-to-noise ratio and on the like, and can perform time and space four-dimensional shadow imaging for the plasma forming process, the photovoltaic process or other ultrafast processes in which the transient electromagnetic field participates observably. The four-dimensional electronic shadow imaging device can record the four-dimensional time-spatial revolution information of the transient electromagnetic field within a time scale from hundreds of picoseconds to nanosecond by an ultrahigh time resolution superior to one picosecond.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Space microwave component low pressure discharge value simulation method
ActiveCN102567780AShorten the design cycleReduce development costsBiological modelsThermodynamicsMicrowave
The invention relates to a space microwave component low discharge value simulation method, which includes steps as follows: establishing a low pressure discharge numerical model of a space microwave component, performing accurate numerical analysis aiming at the motion process of discharged particles during low pressure discharge as well as the total discharged particle number, and obtaining the low pressure discharge threshold value of the space microwave component. According to the invention, the second electron multiplication effect on a metal surface of a space microwave component is taken into consideration, and the discharge threshold value of an intersected stage under a low pressure environment and between the discharge under a vacuum environment and the discharge under a high pressure environment can be analyzed. Meanwhile, all collision types dominating an air space in the microwave component are taken into consideration and the accuracy of the low pressure discharge numerical simulation method in the space microwave component is ensured. Through the method, repeated tests for obtaining the low pressure discharge threshold value of the space microwave component are avoided, the design period is shortened, the preparation cost is reduced, and the method is extremely suitable for analyzing the numerical part of the low pressure discharge in the space microwave component.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Imaging device, method of driving imaging device, and method of manufacturing imaging device
InactiveUS20080303112A1Improve reliabilityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectron multiplicationCrystal structure
An imaging device is provided and includes: a photoelectric conversion layer that has a silicon crystal structure and generates signal charges upon incidence of light; a multiplication and accumulation layer that multiplies the signal charges by a phenomenon of avalanche electron multiplication; and a wiring substrate that reads the signal charges from the multiplication and accumulation layer and transmits the read signal charges. The photoelectric conversion layer includes: a first conductive impurity layer containing first impurities in an impurity concentration; an electron acceleration layer containing the first impurities in a lower impurity concentration than the first conductive impurity layer; and a second conductive impurity layer to which a voltage is applied, the second conductive impurity layer containing second impurities and disposed on a side opposite a light incidence side of the electron acceleration layer, and an insulating layer is disposed between the electron acceleration layer and the multiplication and accumulation layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
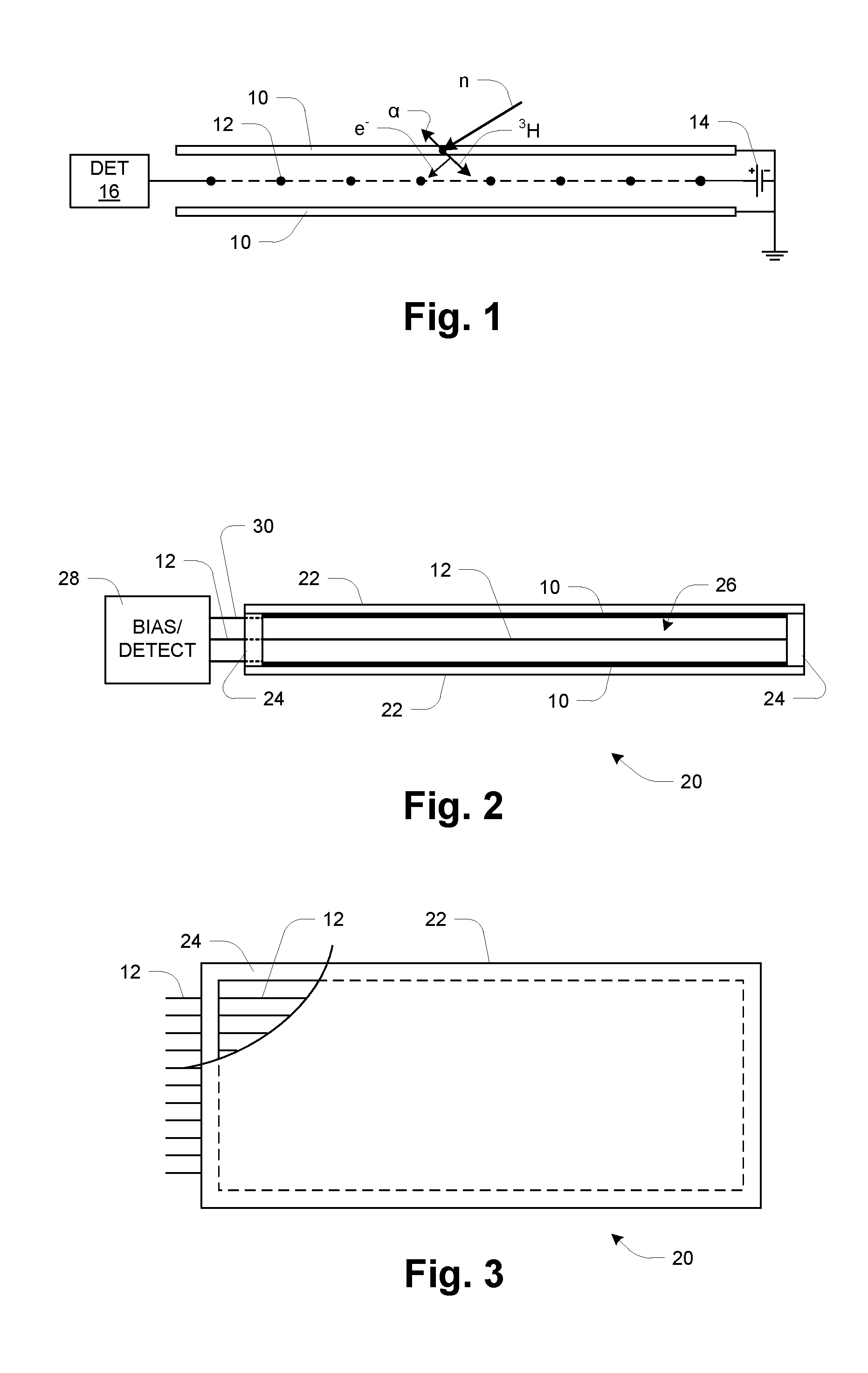
Glass-panel lithium-6 neutron detector
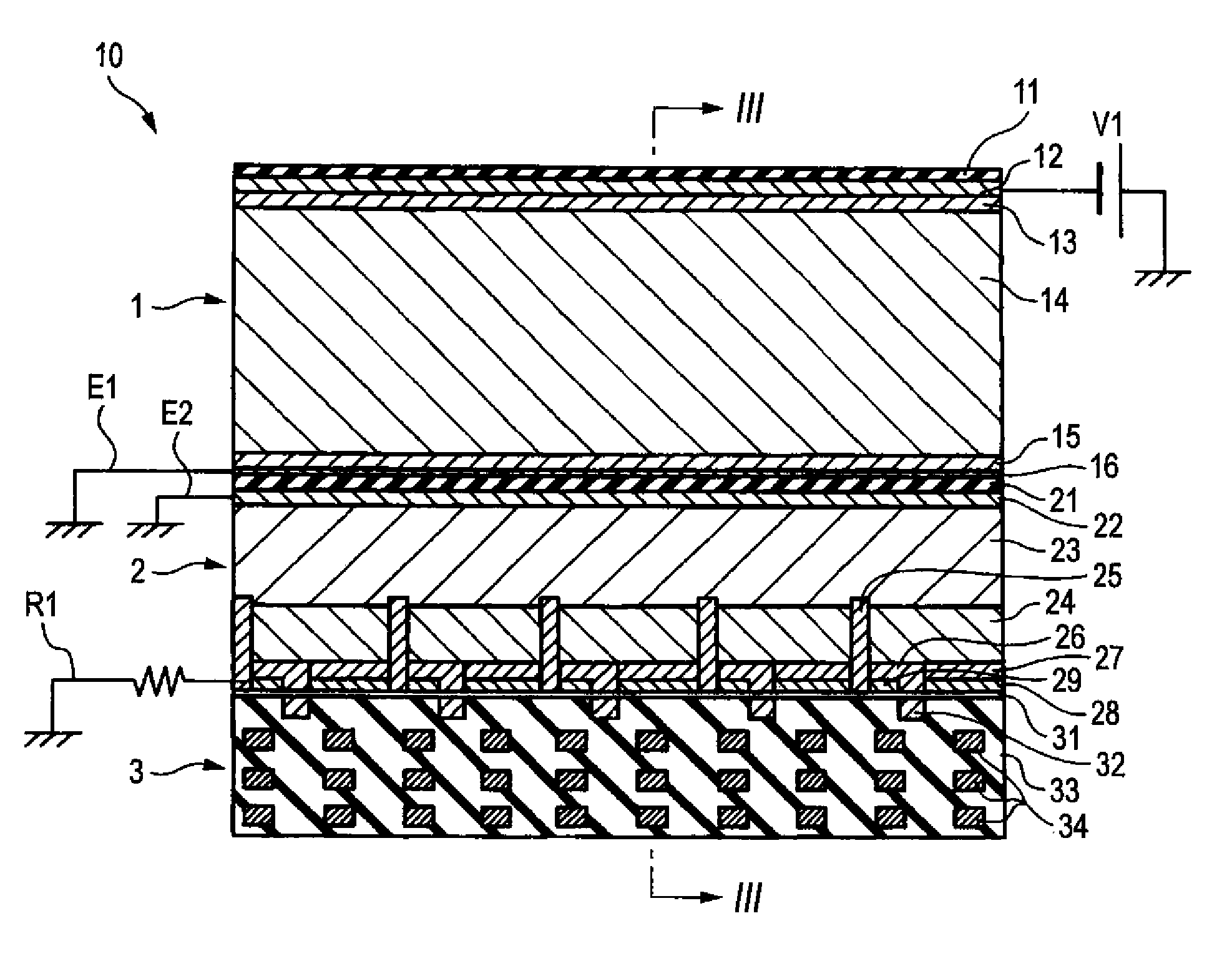
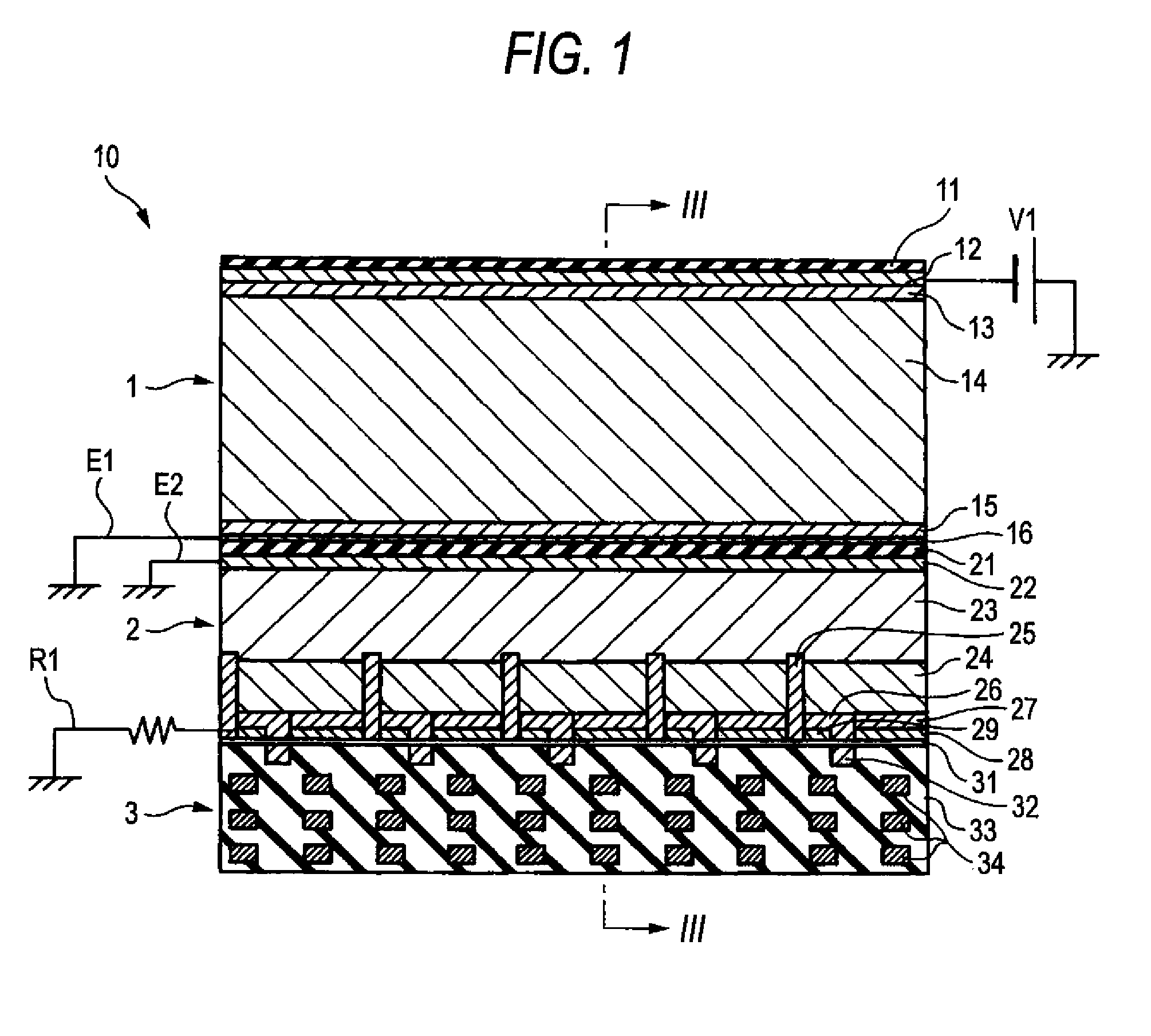
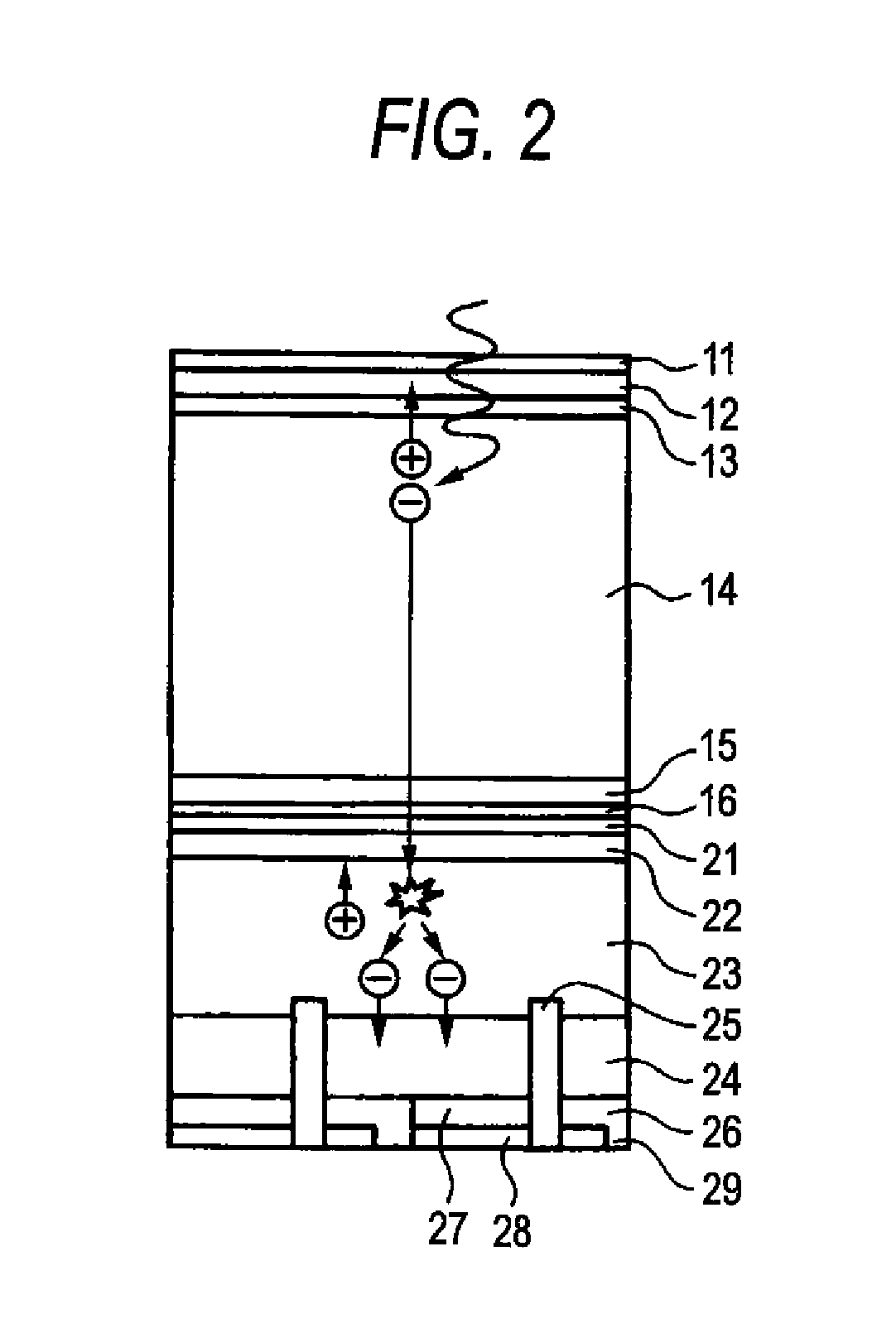
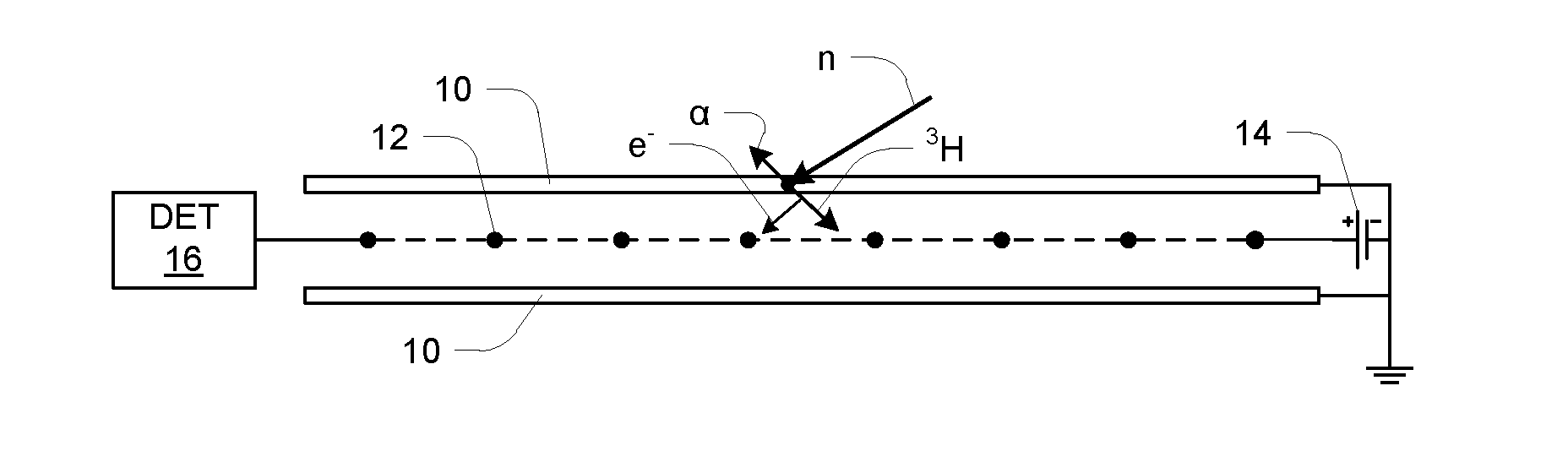
InactiveUS20140077091A1Leverage cost and design and durability and performanceMost efficientElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionElectron multiplication
A thermal neutron detector includes a planar detector housing having two glass panels spaced apart by a gas-tight seal defining a detection chamber including an inert detection gas and lithium foils adhered to inner surfaces of the glass panel(s). The lithium foils emit alpha particles and tritons in response to incident thermal neutrons, and the inert detection gas is ionized by the particles to generate drift electrons. A planar array of detection wires is spaced apart from the lithium foils and extends outside the detection chamber. Electronic bias applies a field voltage between the wires and the lithium foils to establish a drift electric field in the detection chamber effective to attract the drift electrons to the wires and provide a large electric field near the anode wires to cause electron multiplication near the wire resulting in large numbers of electrons and positive ions for each initial electron. Detection circuitry detects electric signals in wires generated by the drift of positive ions away from the wires and interpret the electrical signals as incidence of thermal neutrons on the detector.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
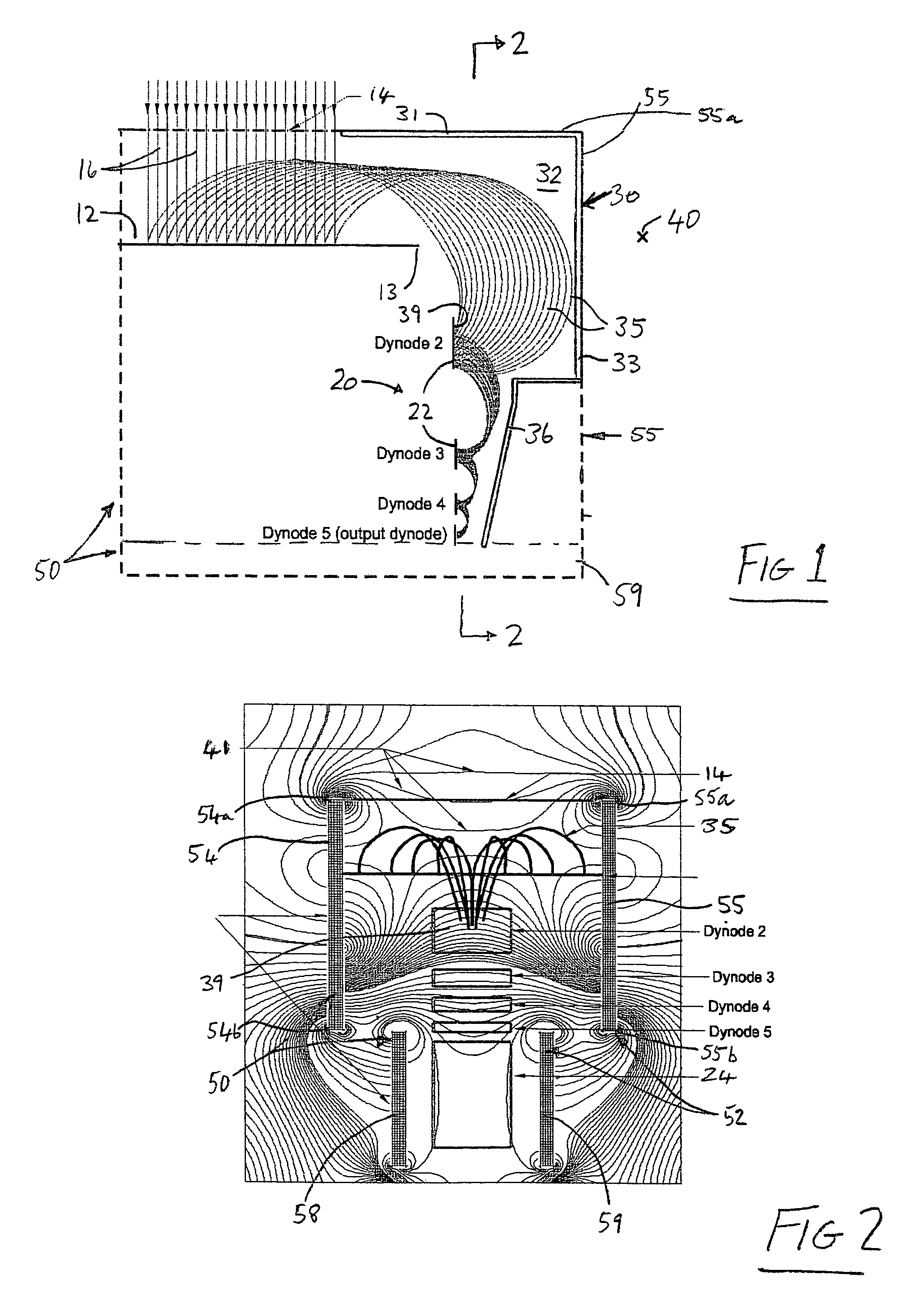
Particle detection by electron multiplication
InactiveUS20060231769A1Increase the sensitive areaSmall sizeThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron multiplicationElectron multiplier
An electron multiplier detector includes cathode structure defining a plurality of spaced co-planar impact surface segments on which particles impact. These surface segments each have a finite probability of generating at least one electron for each impacting particle having predetermined characteristics. The detector further includes respective sets of electron multiplication dynode segments associated with the impact surface segments, the sets being arranged as substantially parallel arrays extending behind the impact surface segments, and respective means for generating electrostatic and magnetic fields in a space extending from the impact surface segments past the dynode segments, whereby respective streams of electrons cascade and multiply successively along the arrays of dynode segments. Collector structure is provided to receive and detect the streams of electrons downstream of the last dynode segments in the arrays.
Owner:ETP ION DETECT PTY LTD
High-collecting-efficiency micro-channel plate, micro-channel plate type photomultiplier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106298427AImprove reflectivityFlat reflective surfaceMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureGlass ballElectron multiplication
The invention discloses a high-collecting-efficiency micro-channel plate, a micro-channel plate type photomultiplier and a preparation method thereof. The photomultiplier has a structure which can realize high gain, high collecting efficiency, good single photoelectron spectrum, and collecting efficiency uniformity. The photomultiplier disclosed by the invention comprises a glass ball shell, an electronic focusing barrel, a photocathode and a micro-channel plate electron multiplication system. A metal electrode surface of a first micro-channel plate in an electron incident direction of an electron multiplier of the micro-channel plate type photomultiplier disclosed by the invention and the inner wall surface of a channel are both covered with a thin film with a high secondary electron emission coefficient, so that effective multiplication of electrons can be realized and the high collecting efficiency and the collecting efficiency uniformity of the photomultiplier can be improved.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
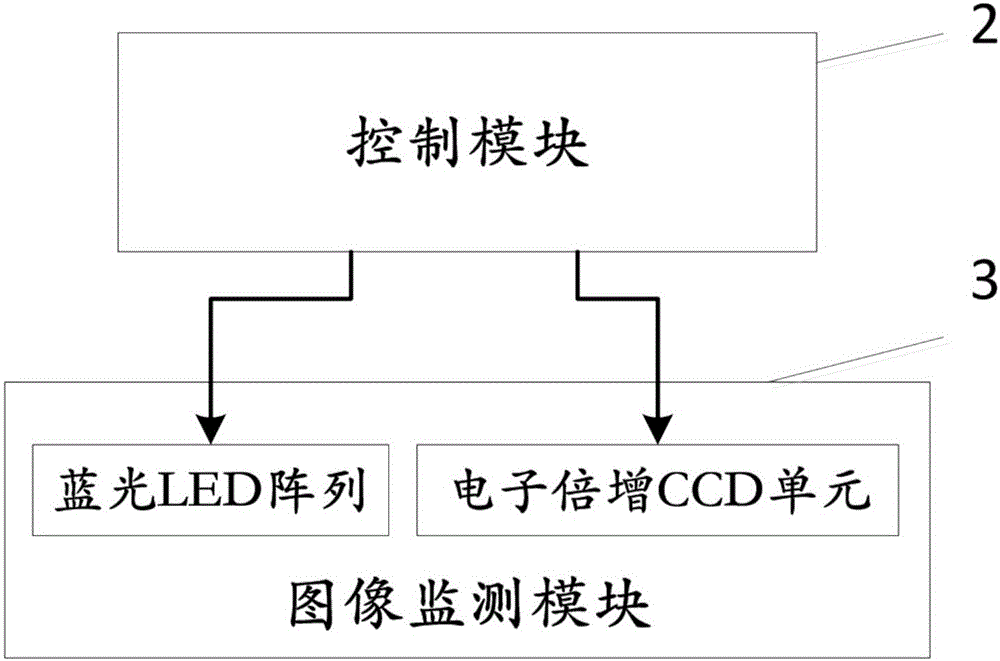
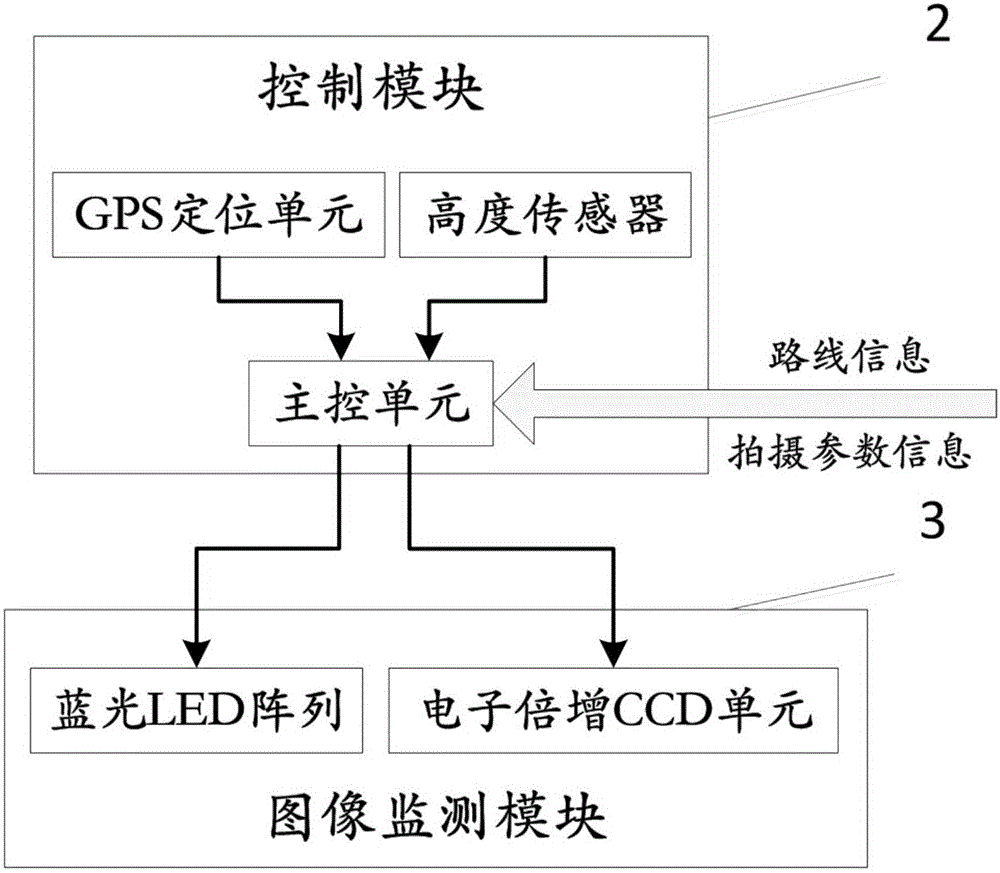
Plant growth condition monitoring device and method based on unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN105759838AReduce volumeReduce weightClosed circuit television systemsPosition/course control in three dimensionsUltrasound attenuationGrowth plant
The invention discloses a plant growth condition monitoring device and method based on an unmanned aerial vehicle. A blue LED array is adopted in an image monitoring module to replace a laser to serve as a fluorescence excitation light source, so that the size and weight of the excitation light source are greatly reduced, and the plant growth condition monitoring device is suitable for being used in the low-load unmanned aerial vehicle; besides, an electron multiplication CCD unit is adopted to collect fluorescence dynamic images of plants at night, and thus both fluorescence two-dimensional distribution information of a whole shooting area and comprehensive fluorescence dynamic attenuation information can be obtained. According to the plant growth condition monitoring device and method, the unmanned aerial vehicle flies along a path planned in advance and hovers at a designated shooting site, meanwhile, the fluorescence dynamic images are shot, and the unmanned aerial vehicle returns automatically after flying along the path planned in advance. Leaf dark adaptation is not needed, and thus measurement time is shortened; besides, in-situ measurement of plants is achieved, and thus the physiological growing state of plants can be reflected more accurately.
Owner:元谋县常荣农业发展有限公司
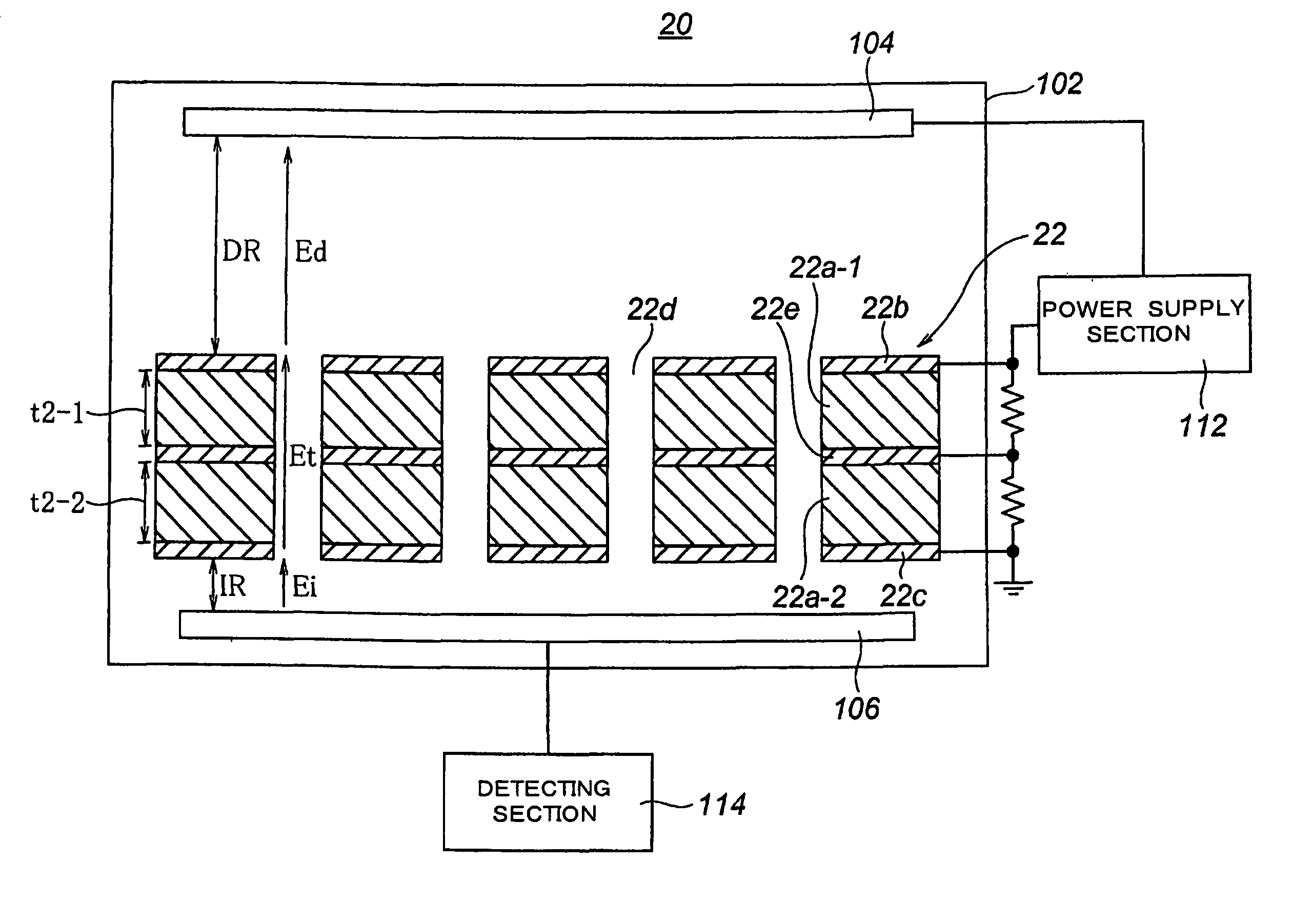
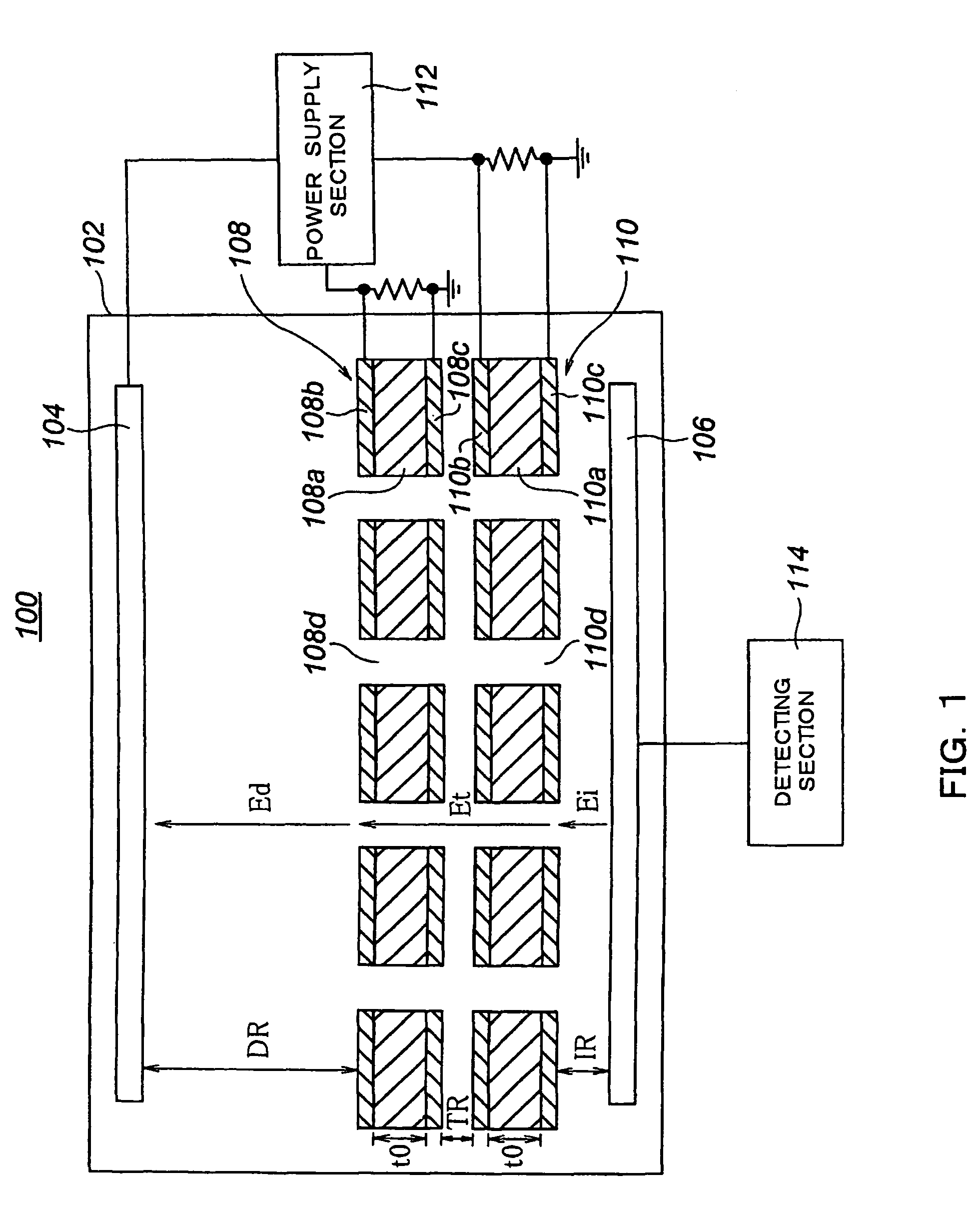
Gas electron multiplier and manufacturing method for gas electron multiplication foil used for same as well as radiation detector using gas electron multiplier
ActiveUS7994483B2Reduce transmissionGood effectElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsInsulation layerImage resolution
To attain objects to reduce the spread of electrons as compared with a conventional one without degrading the multiplication factor of electrons; to provide a large electron multiplication factor; and to improve positional resolution, there is provided a gas electron multiplier using interaction between radiation and gas through photoelectric effects including: a chamber filled with gas and a single gas electron multiplication foil arranged in the chamber wherein the gas electron multiplication foil is made of a plate-like multilayer body composed by having a plate-like insulation layer made of a macromolecular polymer material having a thickness of around 100 μm to 300 μm and flat metal layers overlaid on both surfaces of the insulation layer, and the plate-like multilayer body is provided with a through-hole structure.
Owner:RIKEN +2
Full metal sealed EMCCD camera refrigeration dewar
InactiveCN103456757AReduce leak rateGuaranteed vacuumDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusElectron multiplicationEngineering
A full metal sealed EMCCD(Electron Multiplication Charge Coupled Device) camera refrigeration dewar comprises a thermoelectric cooler(TEC), a cold finger, a CCD socket, an EMCCD, a window, an outer shell, a copper seal ring and a base. A full metal sealed vacuum cavity is formed by the window, the outer shell and the base, the window and the outer shell are welded through anode welding, the outer shell and the base are sealed through knife edge flanges, the TEC, the cold finger, the EMCCD and the like are placed in the vacuum cavity, and the TEC serves as a cold source of a system. The interior of the vacuum cavity is vacuated, heat exchange between the EMCCD and the external environment is reduced to the minimum though the vacuum environment in the cavity, and thus the refrigeration effect is guaranteed. The system is suitable for the field of EMCCD camera refrigeration.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
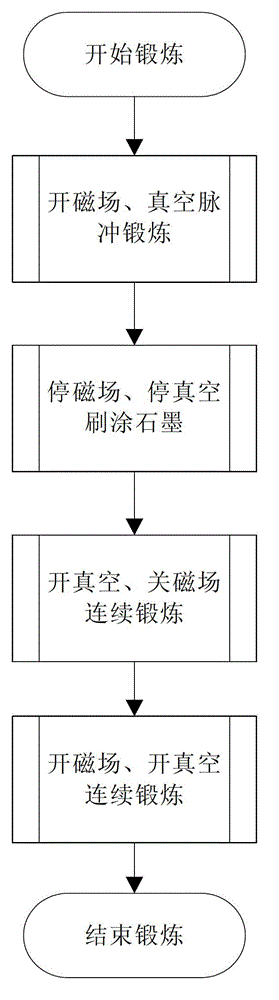
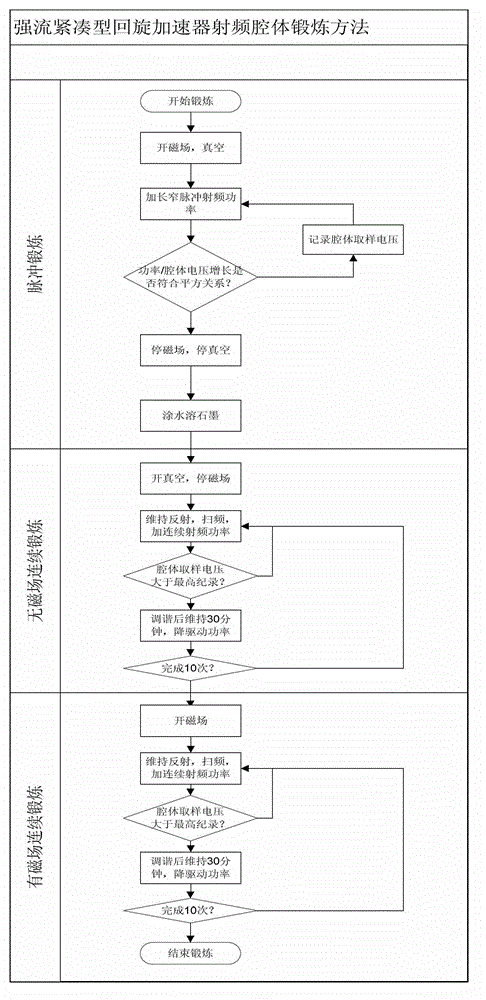
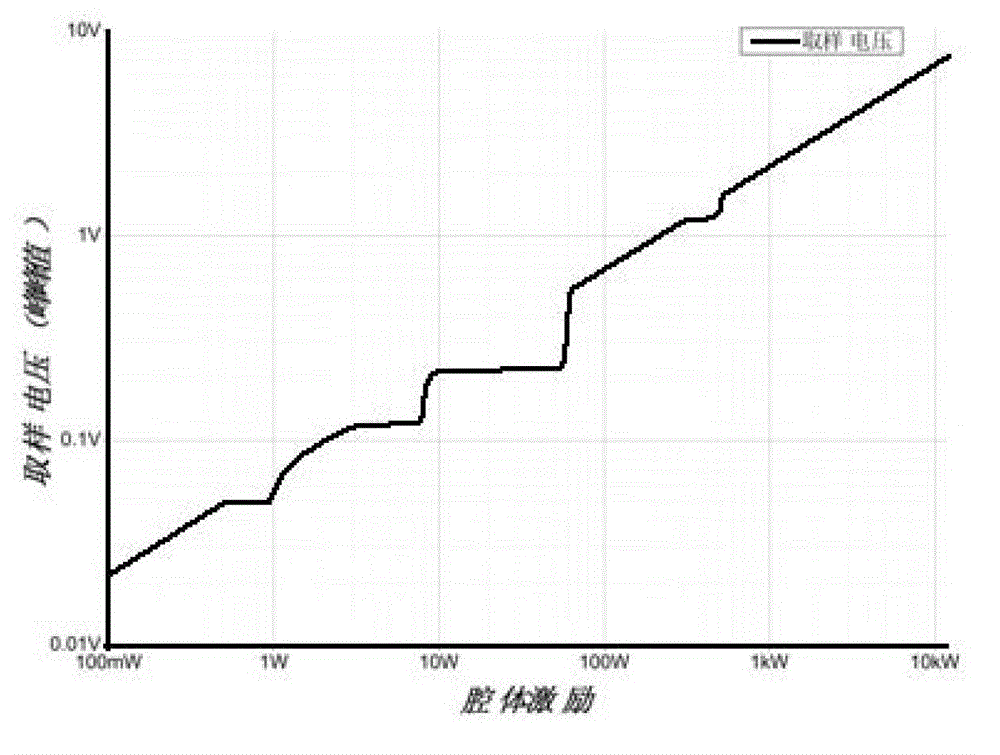
Cavity exercising method of high-current compact type editcyclotron
ActiveCN102869185AOut of breathMultiple electron multiplication effect overcomesMagnetic resonance acceleratorsElectron multiplicationMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a radio-frequency cavity exercising method of a high-current compact type editcyclotron. The method is mainly characterized in that a cavity is primarily exercised through long-cycle narrow pulses, and the range of a multi-electron multiplication effect generated voltage is judged; according to color changes of the surface of a radio-frequency cavity, a magnetic pole face or a panel of the editcyclotron in the process, a graphite material is brushed at corresponding positions so as to reduce the secondary electron emission coefficient of the region; afterwards, by means of closing a magnetic field of the editcyclotron, all multi-electron effect regions are exercised from low to high in sequence by using a continuous power increase method, when all the multi-electron effect regions are passed, power feed is tuned and maintained for a period of time to accelerate gas outlet on a surface, then, push power is reduced at fixed time interval, and all the multi-electron effect regions are exercised from high to low; and after the processes are repeated ten times, the power supply of the magnetic field is switched on, and the exercise of the radio-frequency cavity can be completed rapidly by using the same method.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Electrostatic Suppression of Ion Feedback in a Microchannel Plate Photomultiplier
A photomultiplier tube having an ion suppression electrode positioned between a photocathode and an electron multiplying device in the photomultiplier tube is disclosed. The ion suppression electrode includes a grid that is configured to provide sufficient rigidity to avoid deformation during operation of the photomultiplier tube. The photomultiplier tube also includes a source of electric potential connected to the electron multiplying device and to the ion suppression electrode to provide a first voltage to the second electrode and a second voltage to the suppression grid electrode wherein the second voltage has a magnitude equal to or greater than the magnitude of the first voltage. A method of making the photomultiplier and a method of using it are also disclosed.
Owner:PHOTONIS DEFENSE INC
Articles comprising high-electrical-conductivity nanocomposite material and method for fabricating same
InactiveUS7959830B2Avoid damageReduce sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsManufacturing technologyElectron multiplication
This invention discloses novel nanocomposite material structures which are strong, highly conductive, and fatigue-resistant. It also discloses novel fabrication techniques to obtain such structures. The new nanocomposite materials comprise a high-conductivity base metal, such as copper, incorporating high-conductivity dispersoid particles that simultaneously minimize field enhancements, maintain good thermal conductivity, and enhance mechanical strength. The use of metal nanoparticles with electrical conductivity comparable to that of the base automatically removes the regions of higher RF field and enhanced current density. Additionally, conductive nanoparticles will reduce the surface's sensitivity to arc or sputtering damage. If the surface is sputtered away to uncover the nanoparticles, their properties will not be dramatically different from the base surface. Most importantly, the secondary electron emission coefficients of all materials in the nanocomposite are small and close to unity, whereas the previously used insulating particles can produce significant and undesirable electron multiplication.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and device for driving solid-state imaging device, imaging apparatus, and image synthesizing method
InactiveCN101277374ATelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer hardwareElectron multiplication
A method for driving a solid-state imaging device including a plurality of pixels arranged in a two-dimensional array, each of the plurality of pixels accumulating a signal charge according to an amount of incident light, is provided. The method includes: performing electron multiplication of a first signal charge at a first multiplication factor to output a first image signal; and performing electron multiplication of a second signal charge at a second multiplication factor to output a second image signal, at least the first and second image signals being image signals of the same scene of a subject and being successively output.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Silicon microchannel production method
InactiveCN1736852AGood doubling effectImprove emission efficiencyDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingTetramethylammonium hydroxideElectron multiplication
The invention relates to a method for preparation of a micro channel in the process of preparing Micro Electro-Me-chanical Systems elements, belonging to the technical field of Micro Electro-Me-chanical Systems. The resistance silicon from n (100) can form a hole of about 1 micrometer in special condition in solution of a concentration of 40% of HF: C2H5OH=1: 1, with this layer as template to be corroded out a reverse pyramid depression by KOH or tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide or the similar solution, and with the cellular silicon corrosion technique, the micro channel is corroded. The micro channel sheet for night-vision device can be prepared by oxygenizing the micro channel structure. With the method, the minimum micro-channel diameter and the center distance of channel have a great improvement, the electron multiplication effect also is perfect, the treatment temperature of the micro channel plate can achieve to 1200Deg. C, and the secondary electron emission efficiency is highly improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Electron-multiplication image sensor
InactiveUS9040890B2Large dynamic rangeLow lightTransistorTelevision system detailsElectron multiplicationEngineering
This description relates to active-pixel image sensors. Each pixel includes, at the surface of a semiconductor active layer, a photodiode region, a charge storage node and a transfer structure for transferring charges from the photodiode to the storage node after a charge integration time for charges generated by the light in the photodiode. The transfer structure includes a first transfer gate adjacent to the photodiode, a second transfer gate adjacent to the storage node, and an electron-multiplication amplifying structure located between the first and second transfer gates. The amplifying structure includes two separate accelerating gates and an intermediate diode region at a fixed surface potential, located between the two accelerating gates. A succession of alternating high and low potentials is applied to the accelerating gates while the charges are in transit in the transfer structure, before they are transferred to the storage node.
Owner:TELEDYNE E2V SEMICON SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com