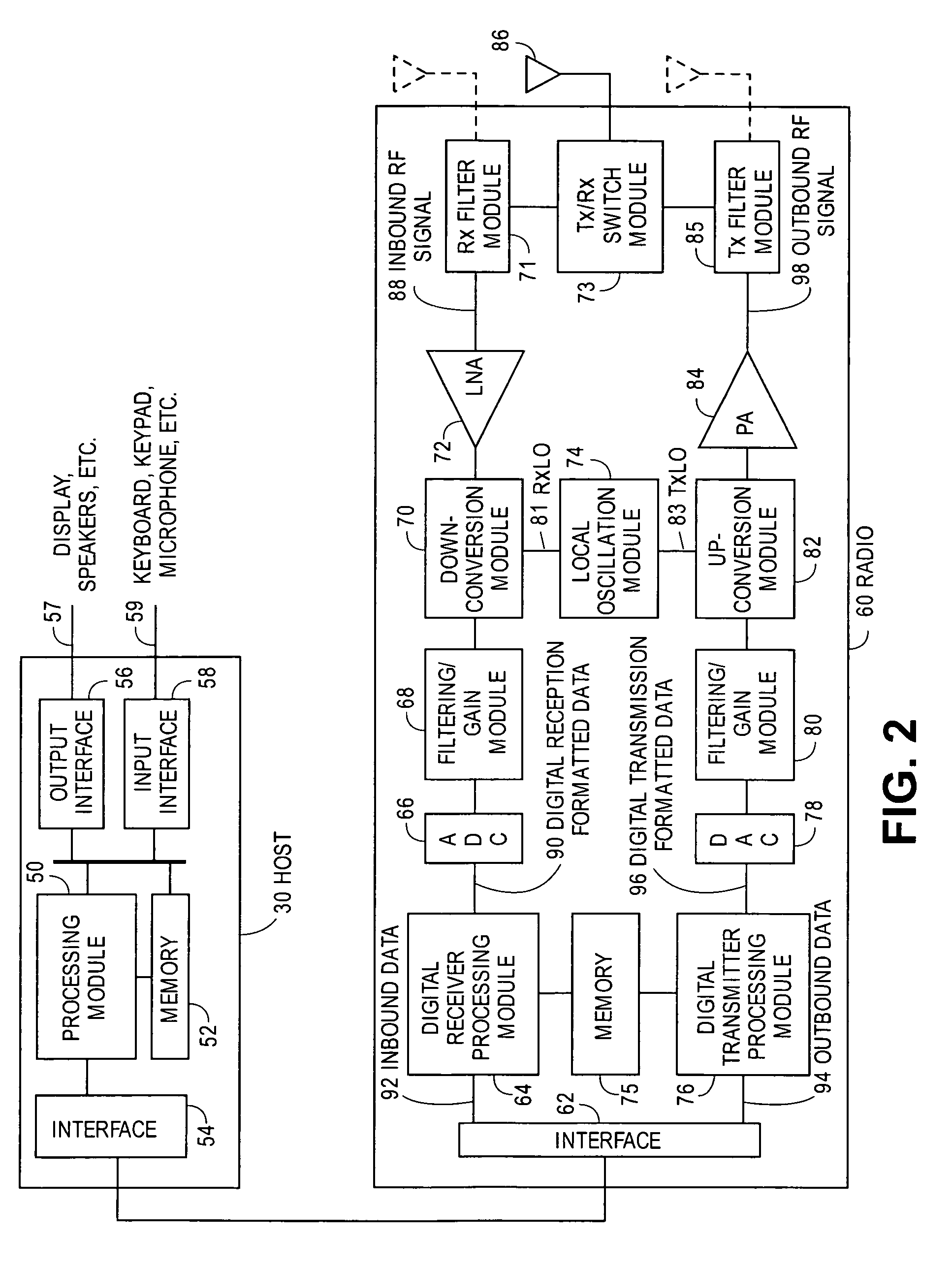
Patents
Literature
570 results about "Gain stage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
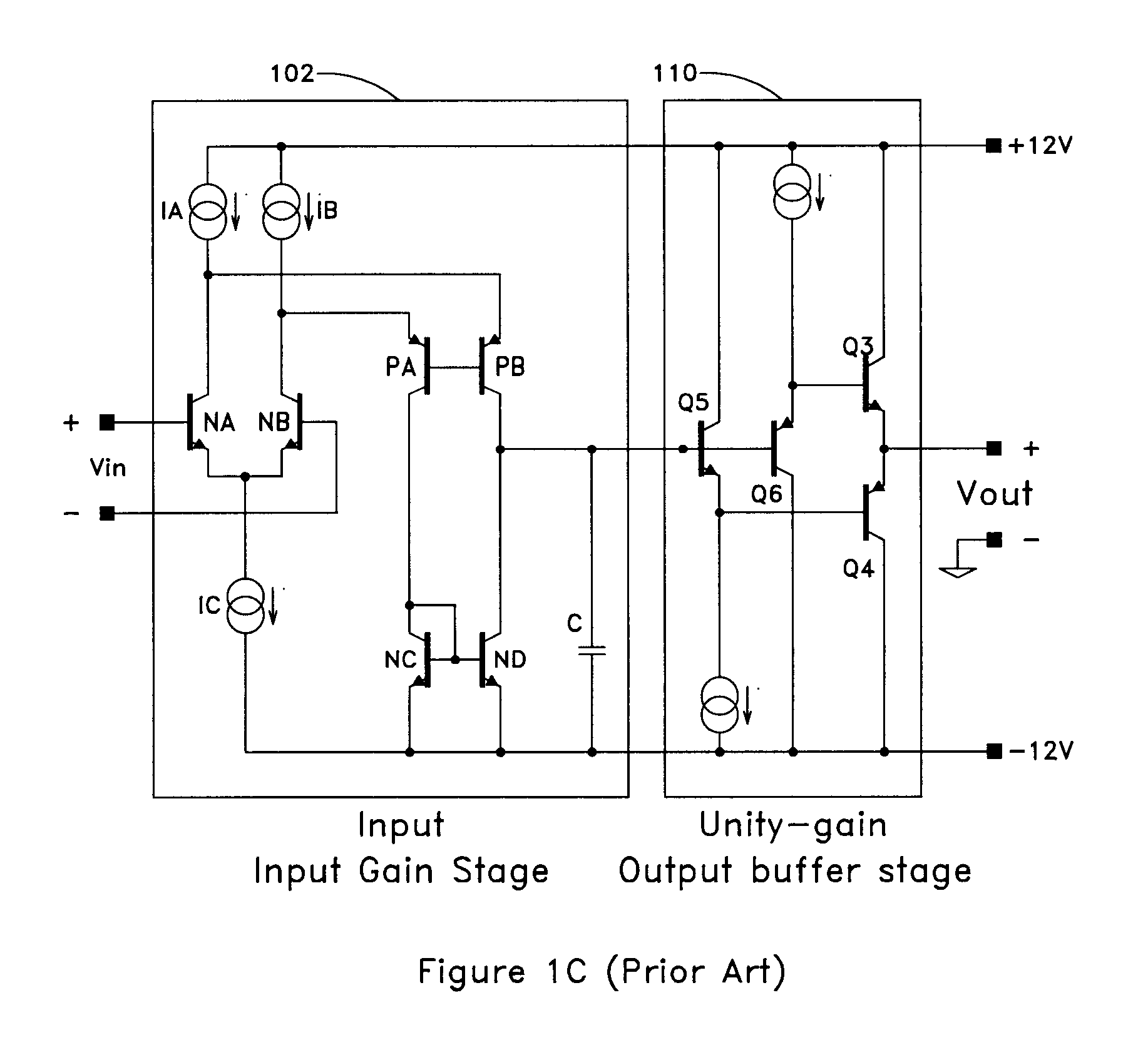
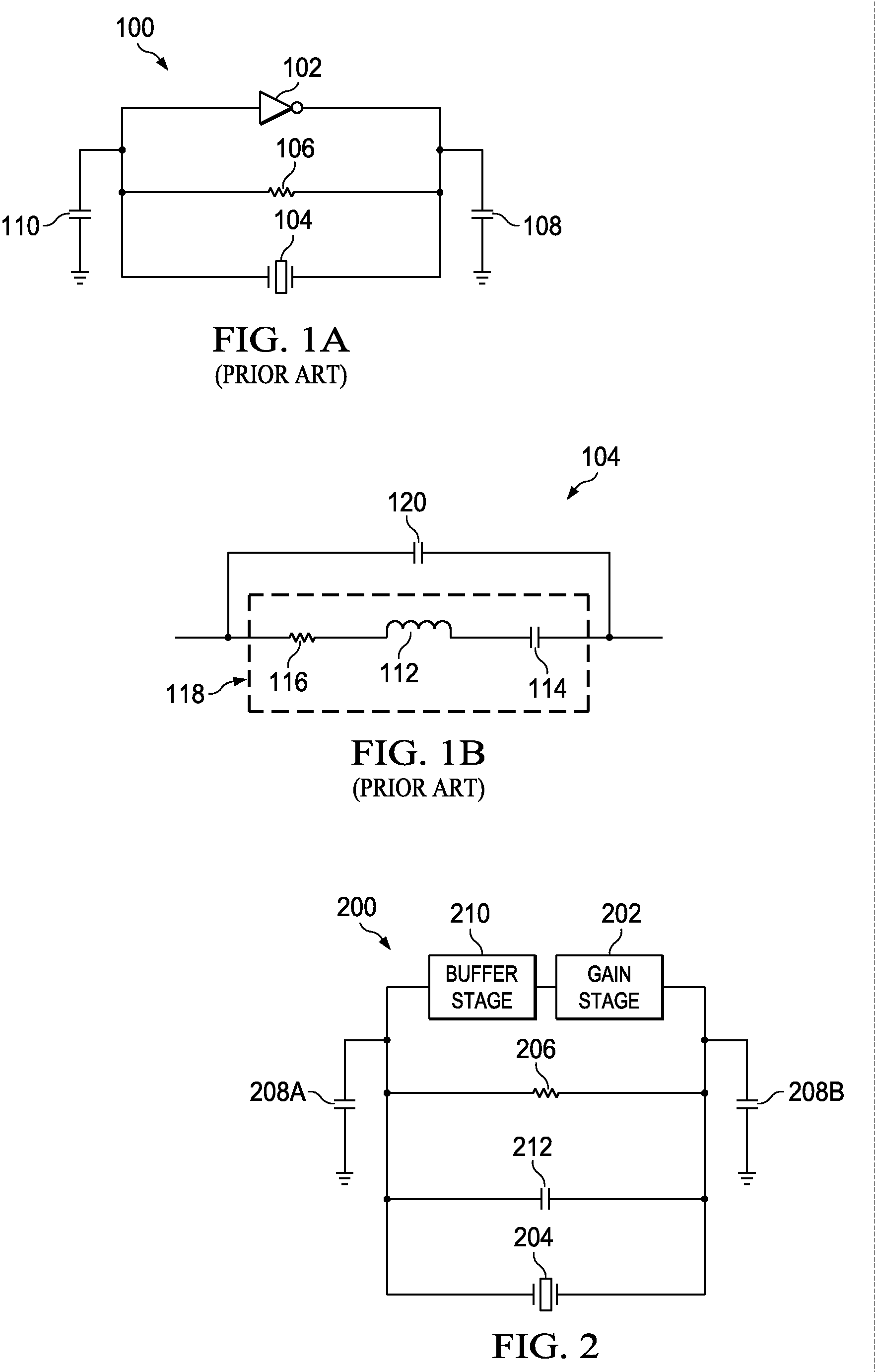
In audio engineering, a gain stage is a point during an audio signal flow that the engineer can make adjustments to the level, such as a fader on a mixing console or in a DAW. Gain staging is the process of managing the relative levels in each step of an audio signal flow to prevent introduction of noise and distortion. Ideal gain staging occurs when each component in an audio signal flow is receiving and transmitting signal in the optimum region of its dynamic range.
Radio frequency power amplifier and method using a controlled supply
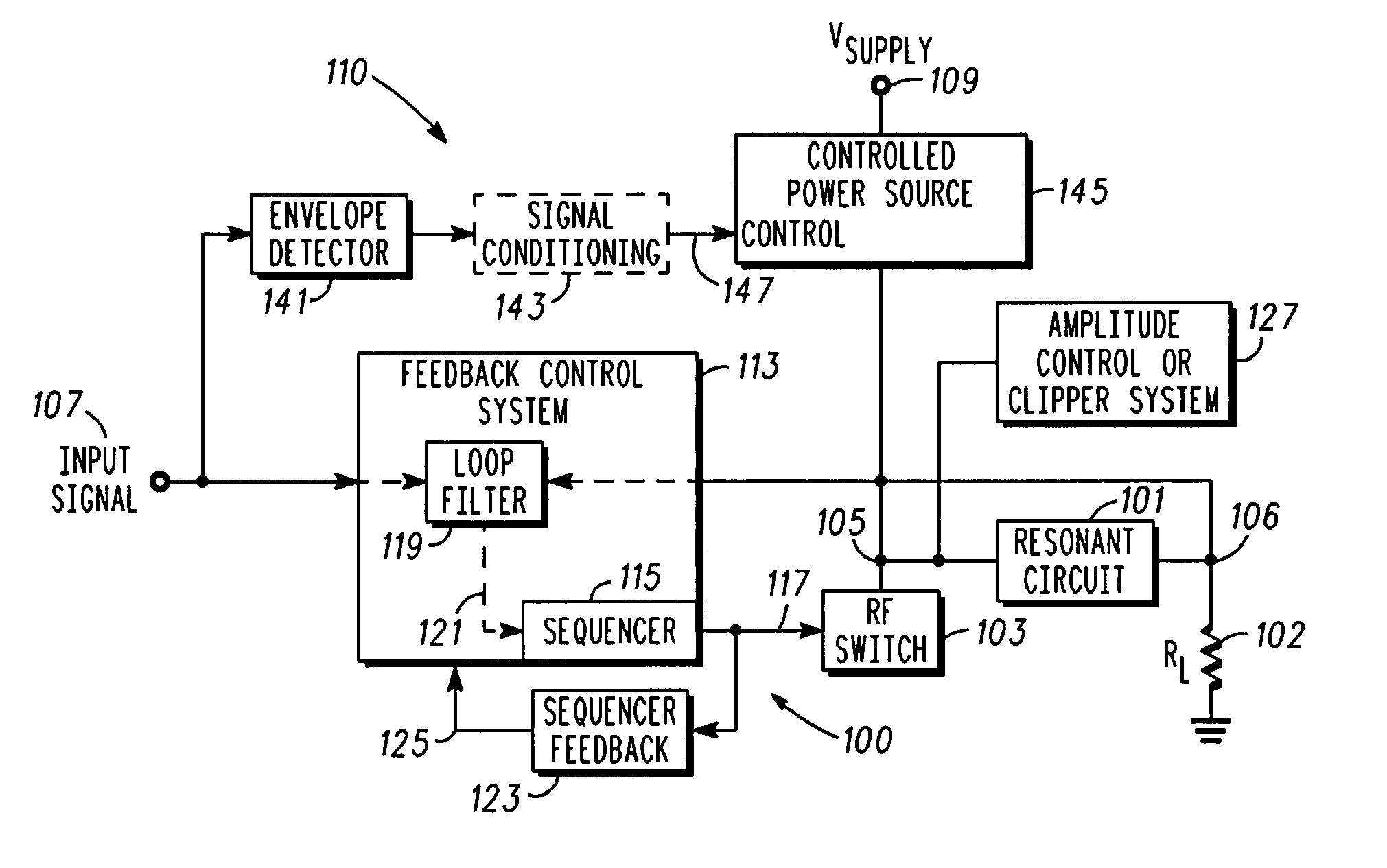
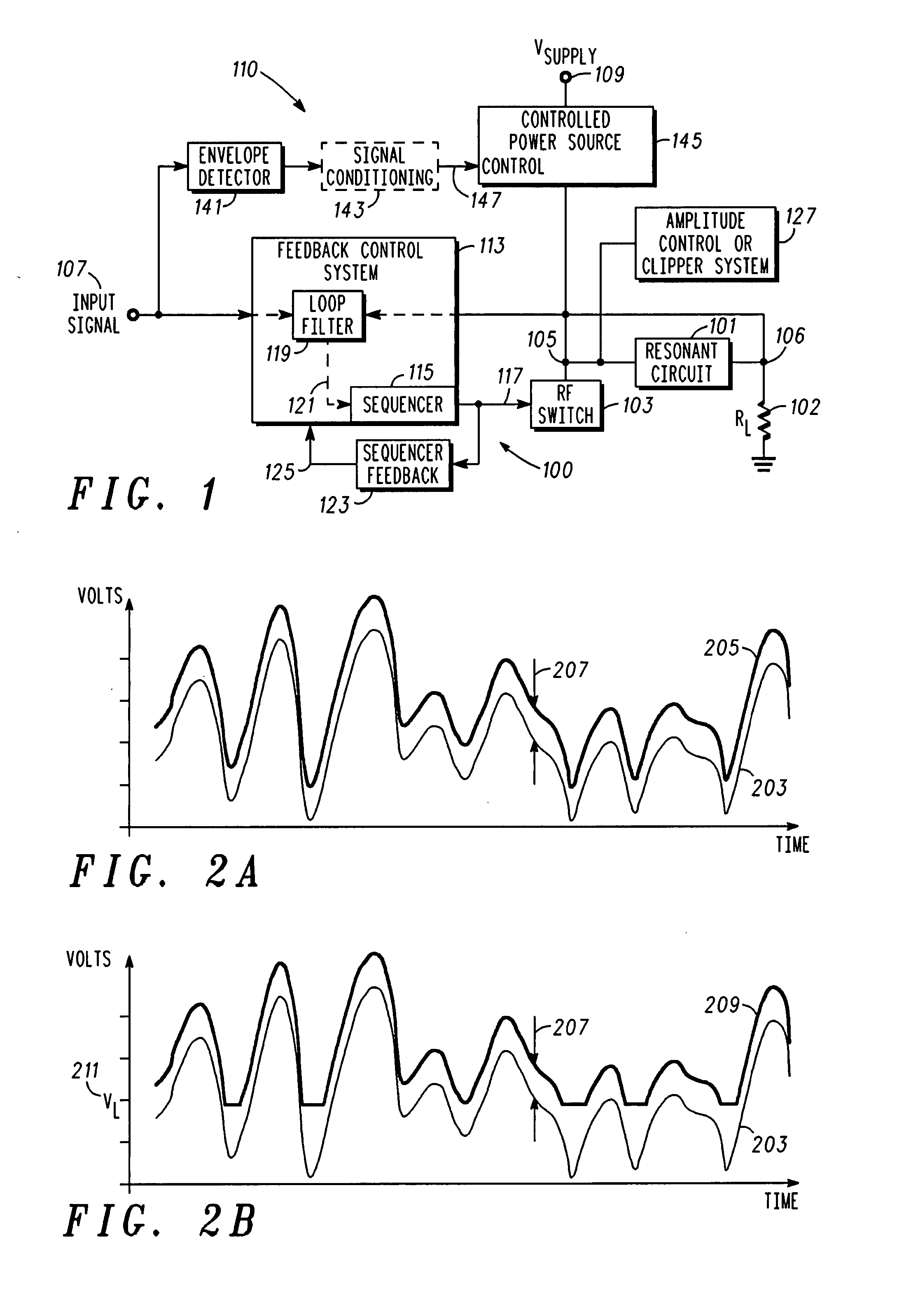
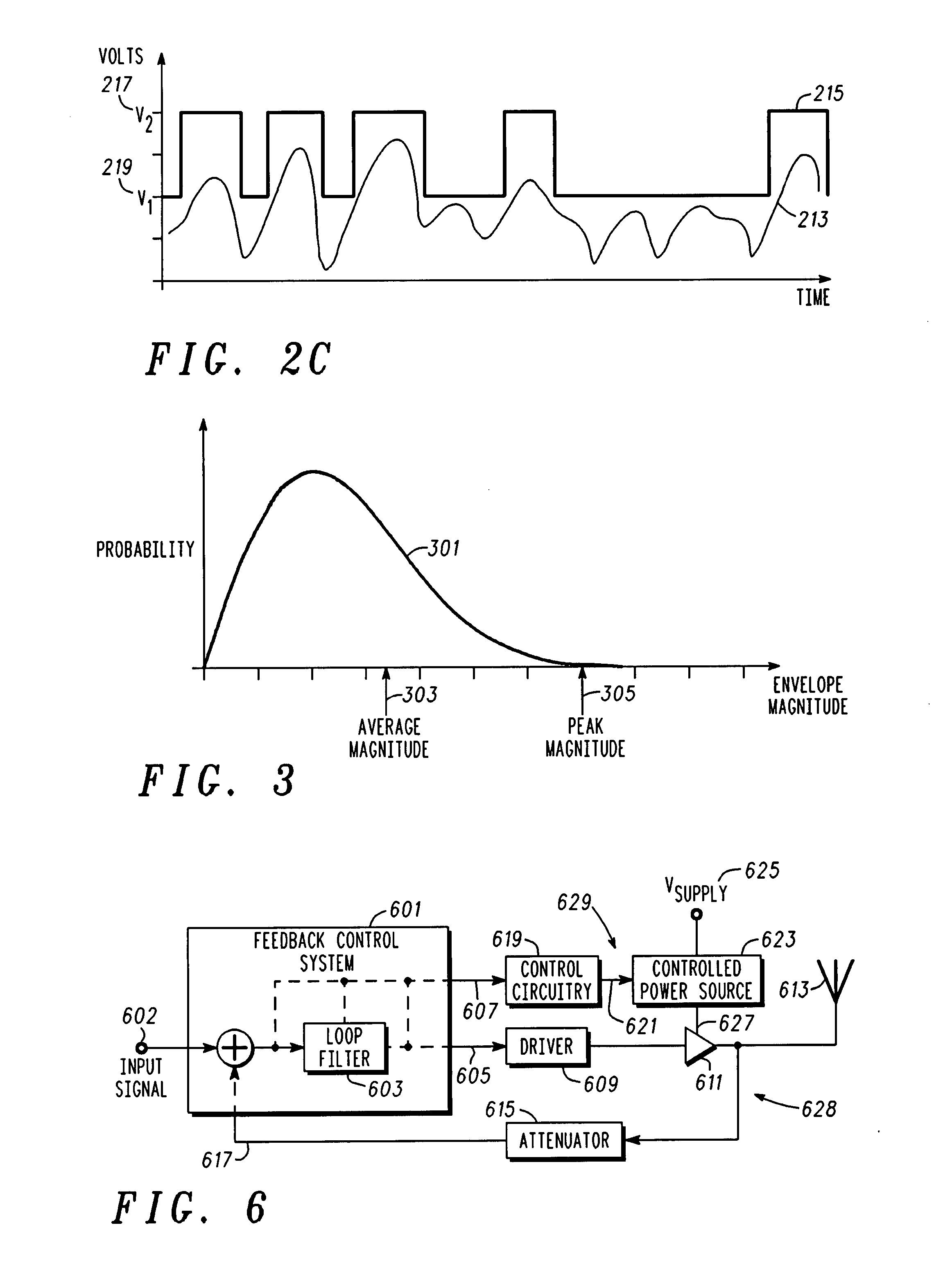
A radio frequency power amplifier includes a feedback control system coupled to an input signal and a first feedback signal and configured to provide an output; a controlled supply configured to provide power that is controlled in accordance with a signal; and a radio frequency gain stage powered from the controlled supply, driven by the output from the feedback control system, and configured to provide an output signal at the radio frequency to a resonant load, where the first feedback signal corresponds to the output signal. Some embodiments include a sequencer in the feedback control system and others utilize an additional feedback loop to control the power provided by the controlled supply.
Owner:PWRF
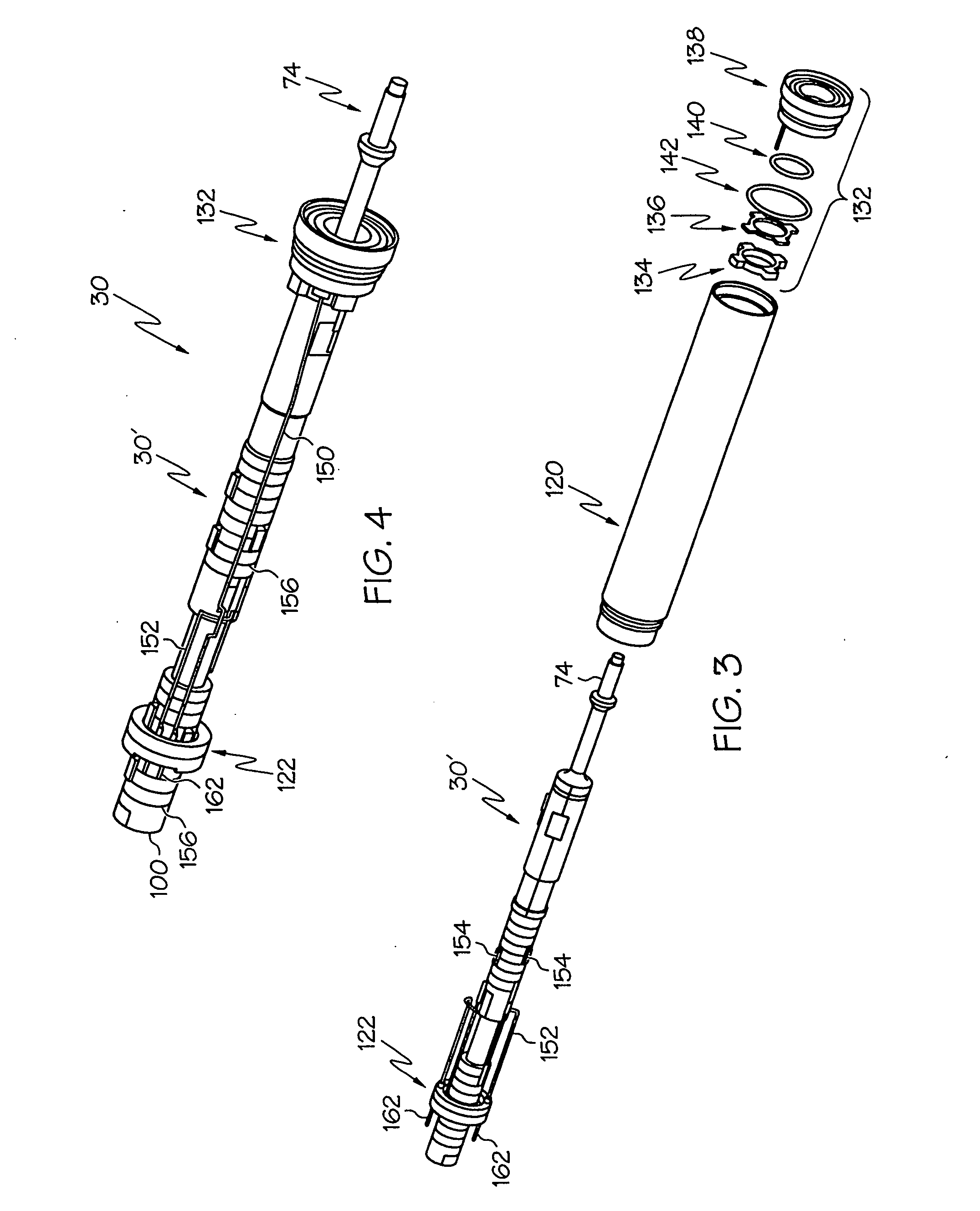
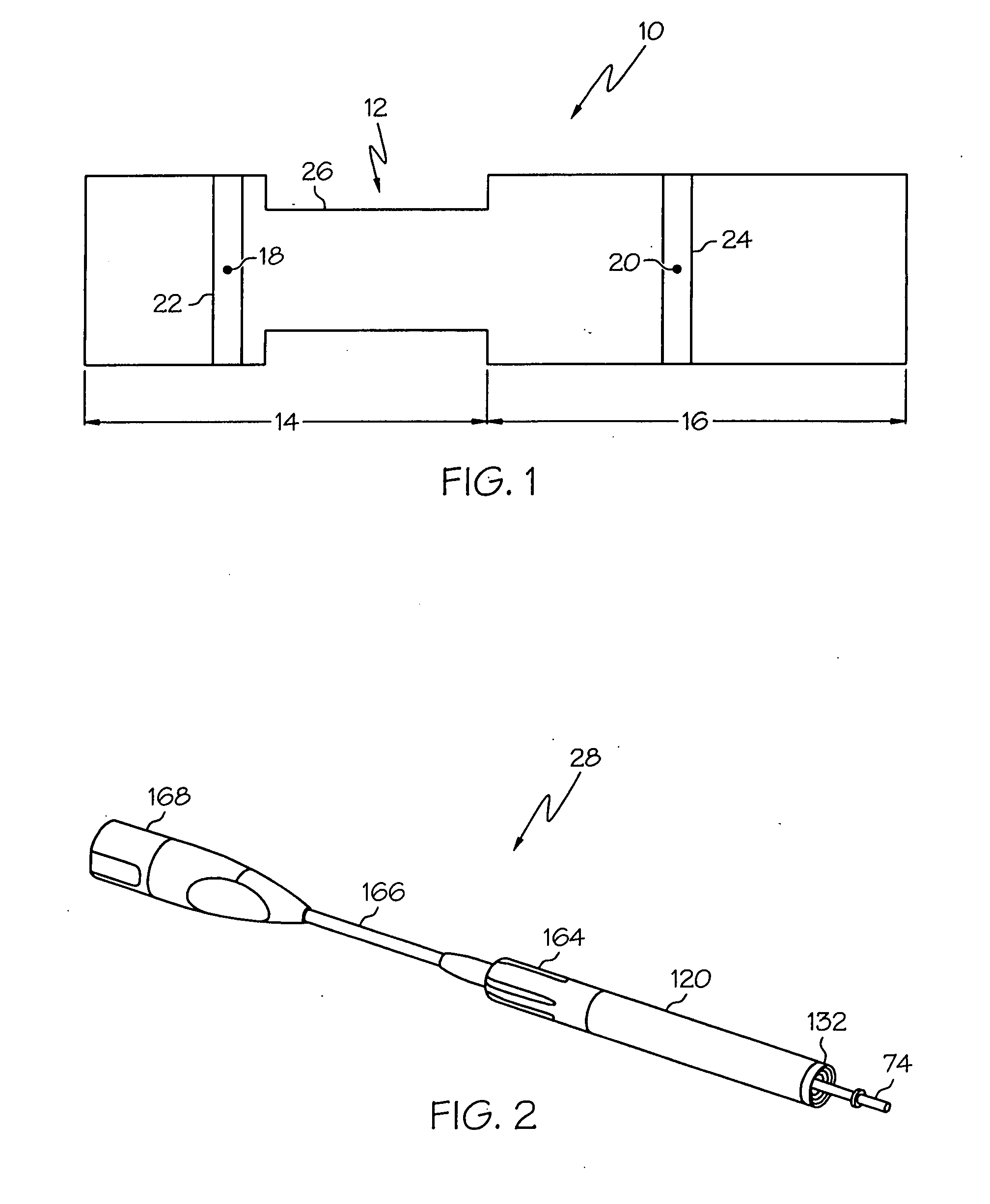
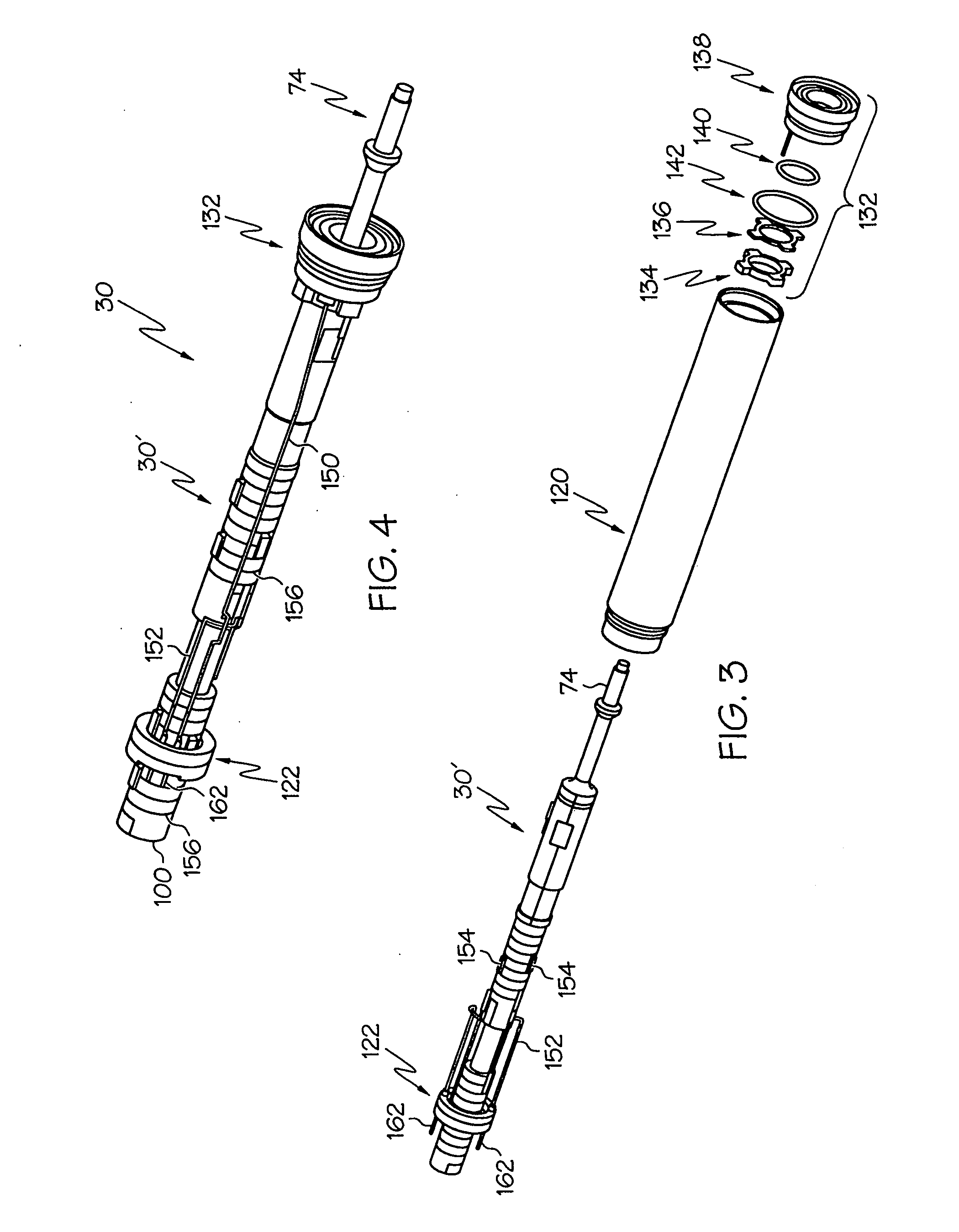
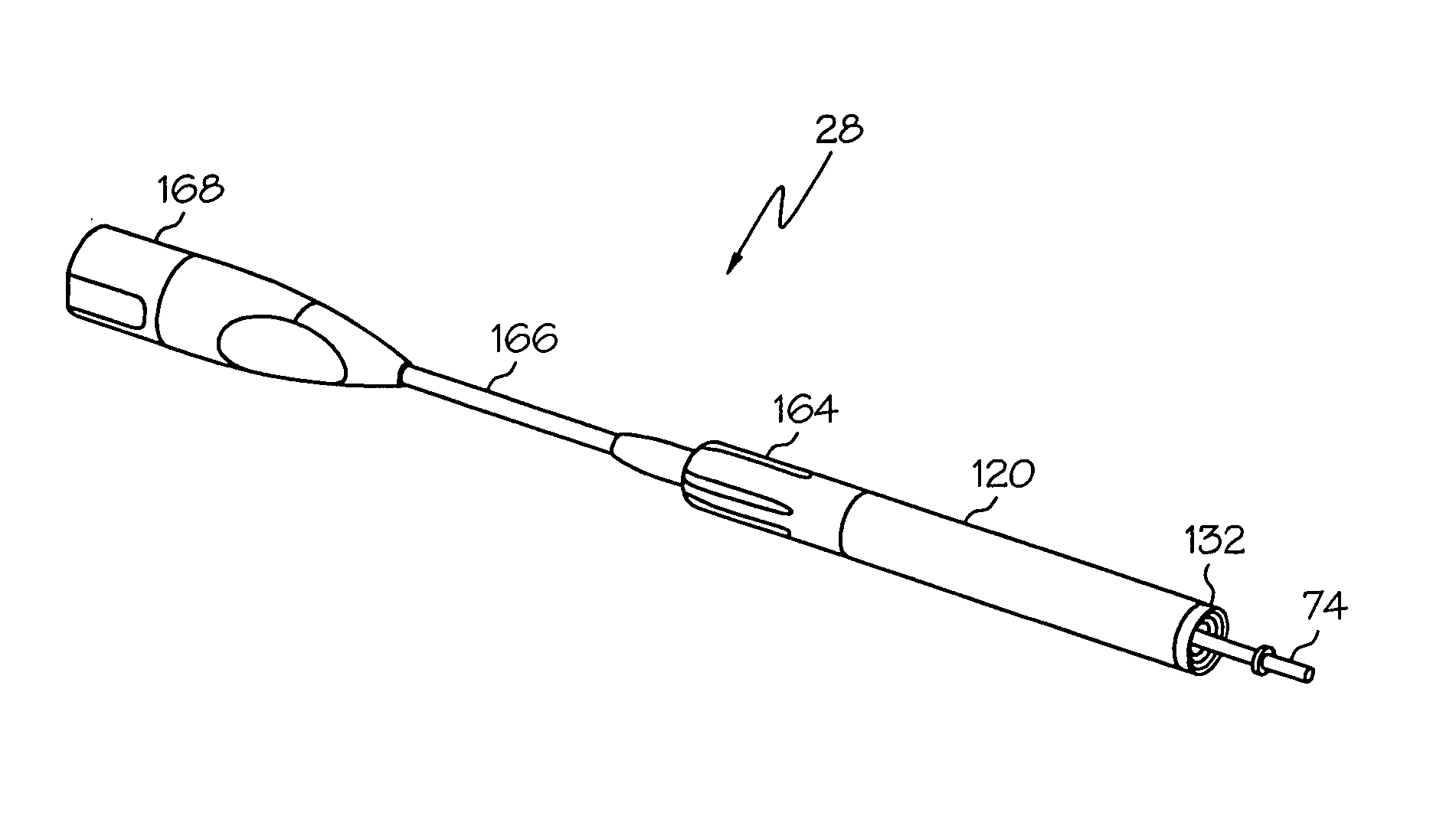
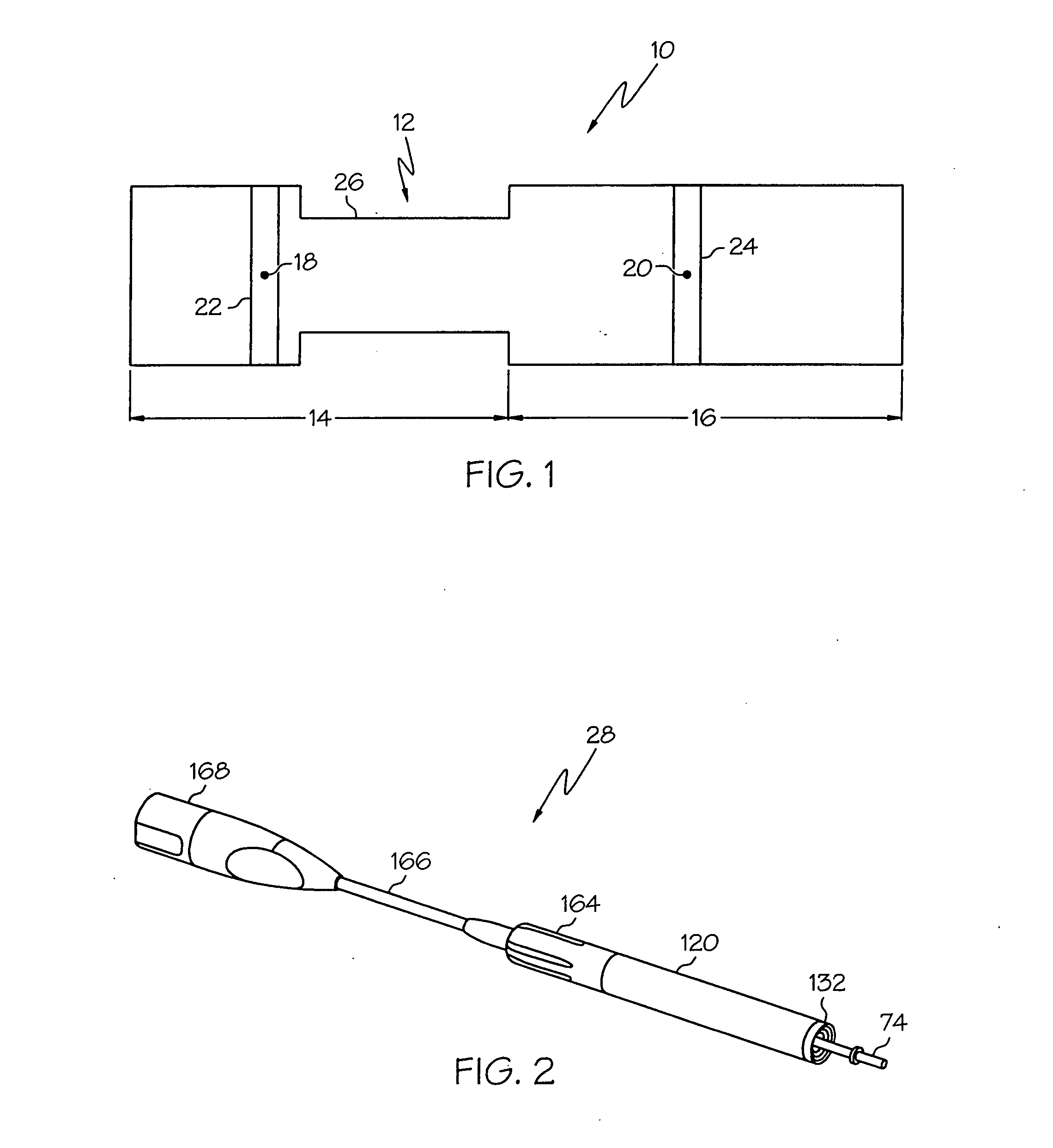
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
InactiveUS20070232926A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
InactiveUS20070232928A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
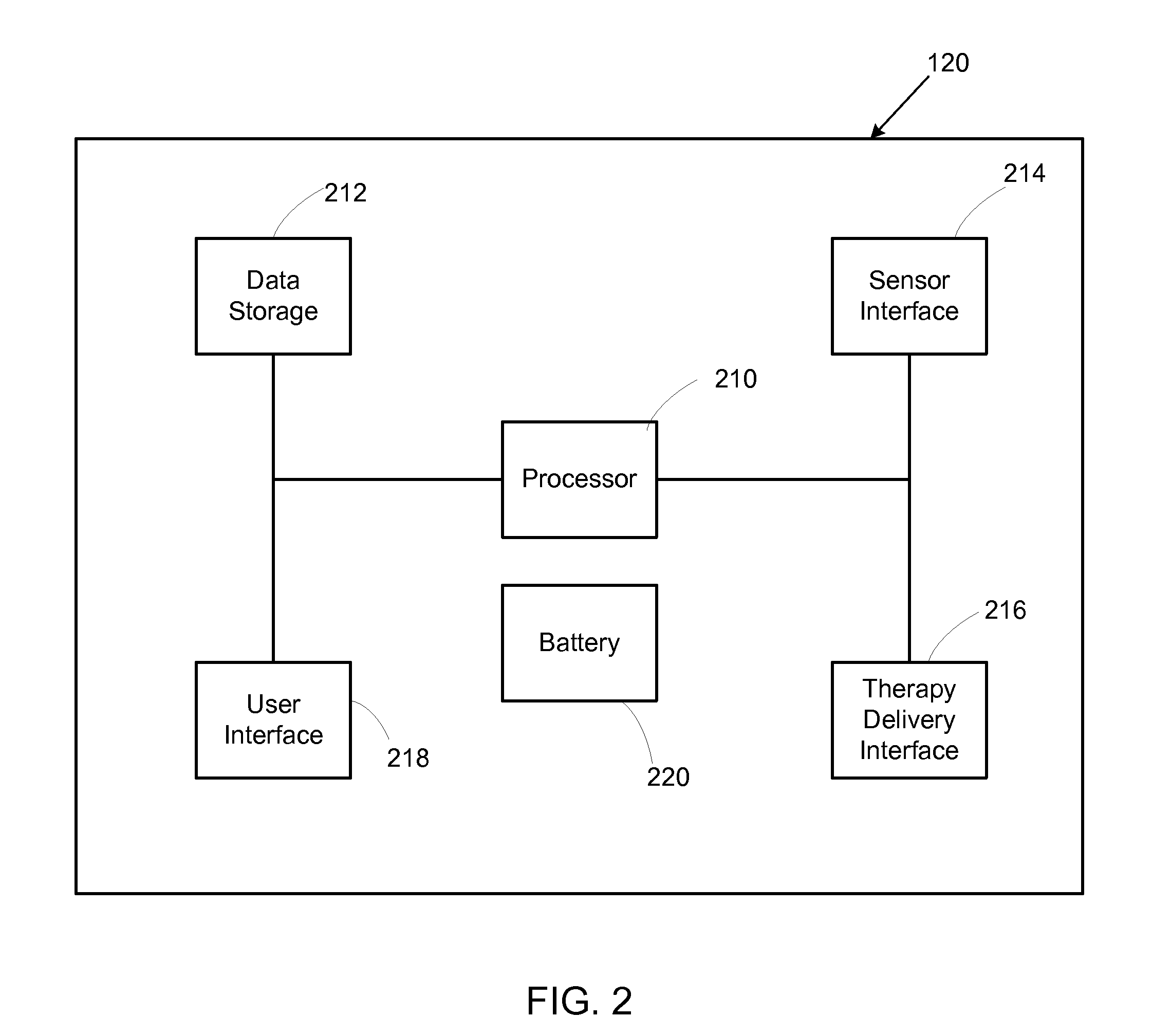
Method of detecting signal clipping in a wearable ambulatory medical device
A wearable medical device and method of detecting clipping of ECG signals is disclosed. In one embodiment, the wearable medical device comprises a plurality of ECG sensing electrodes configured to sense an ECG of a patient and an ECG acquisition circuit electrically coupled to a pair of the plurality of ECG sensing electrodes and configured to provide an amplified and conditioned analog ECG signal, a programmable attenuation / gain stage electrically coupled between a first gain stage and a second gain stage, an ADC electrically coupled to the ECG acquisition circuit to receive and digitize the amplified and conditioned analog ECG signal and provide a digitized ECG signal, and a signal conditioning and control unit electrically coupled to the ECG acquisition circuit and the ADC to receive and monitor the digitized ECG signal and to detect clipping of the amplified and conditioned analog ECG signal based upon the digitized ECG signal.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
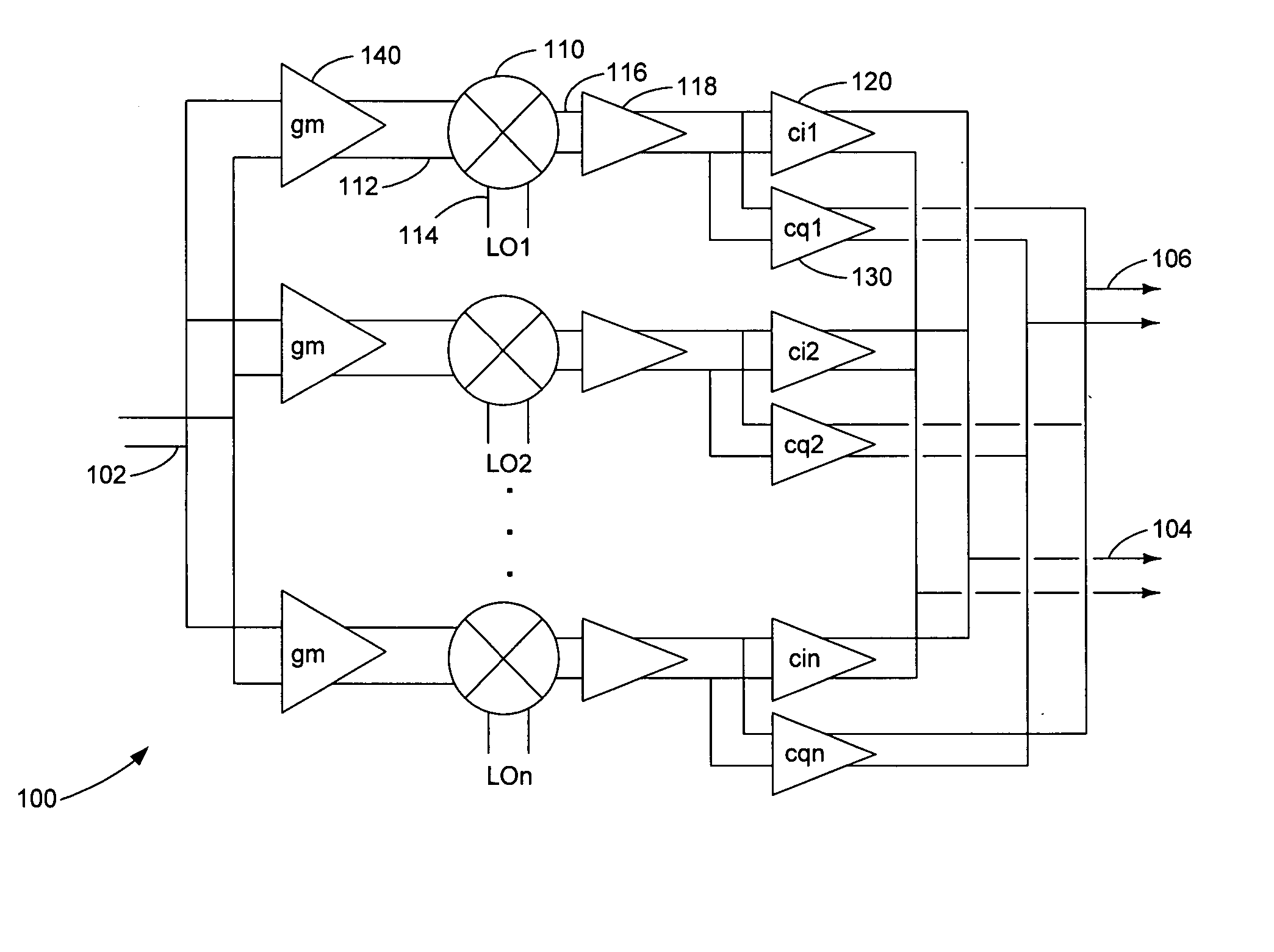
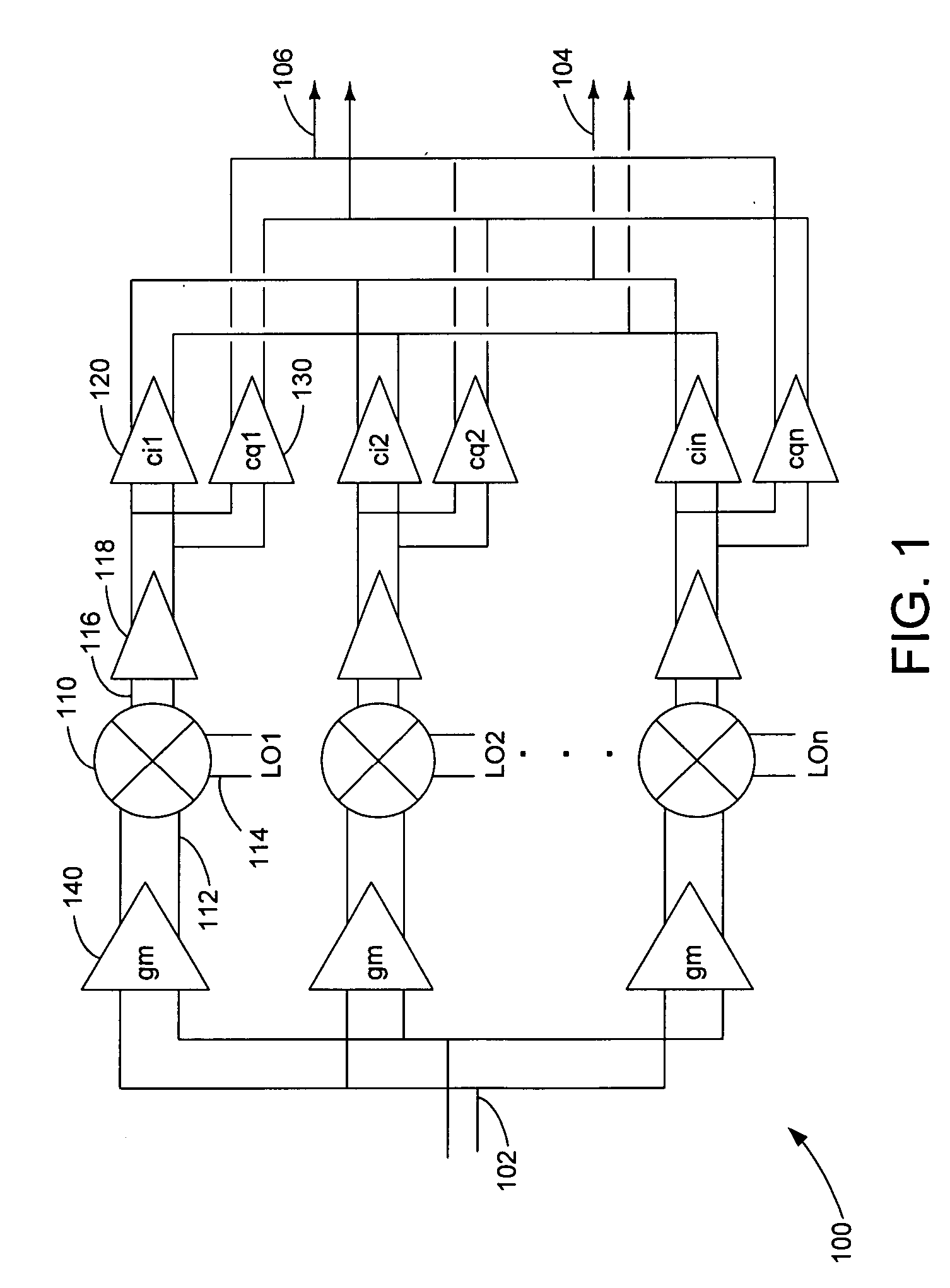
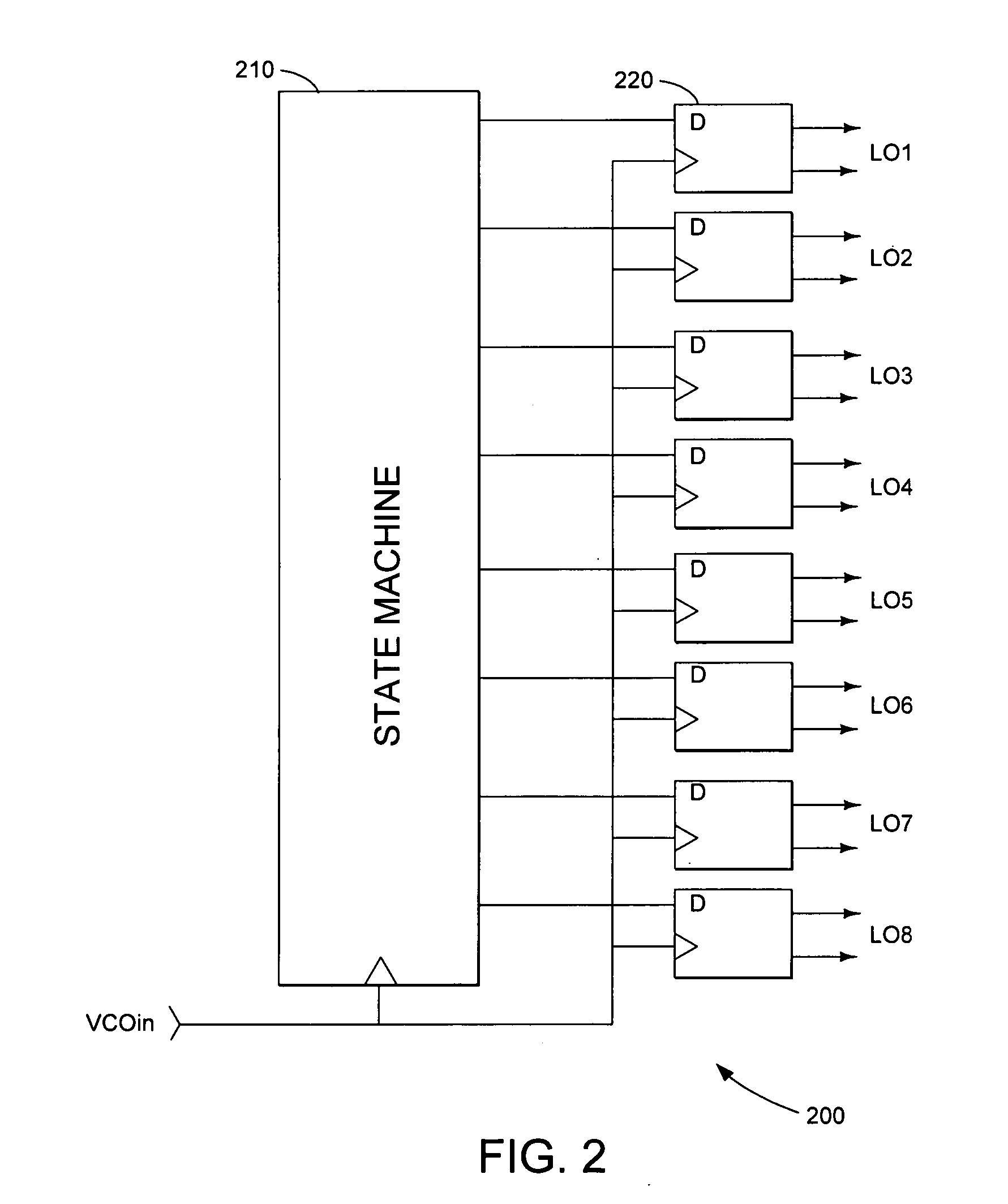
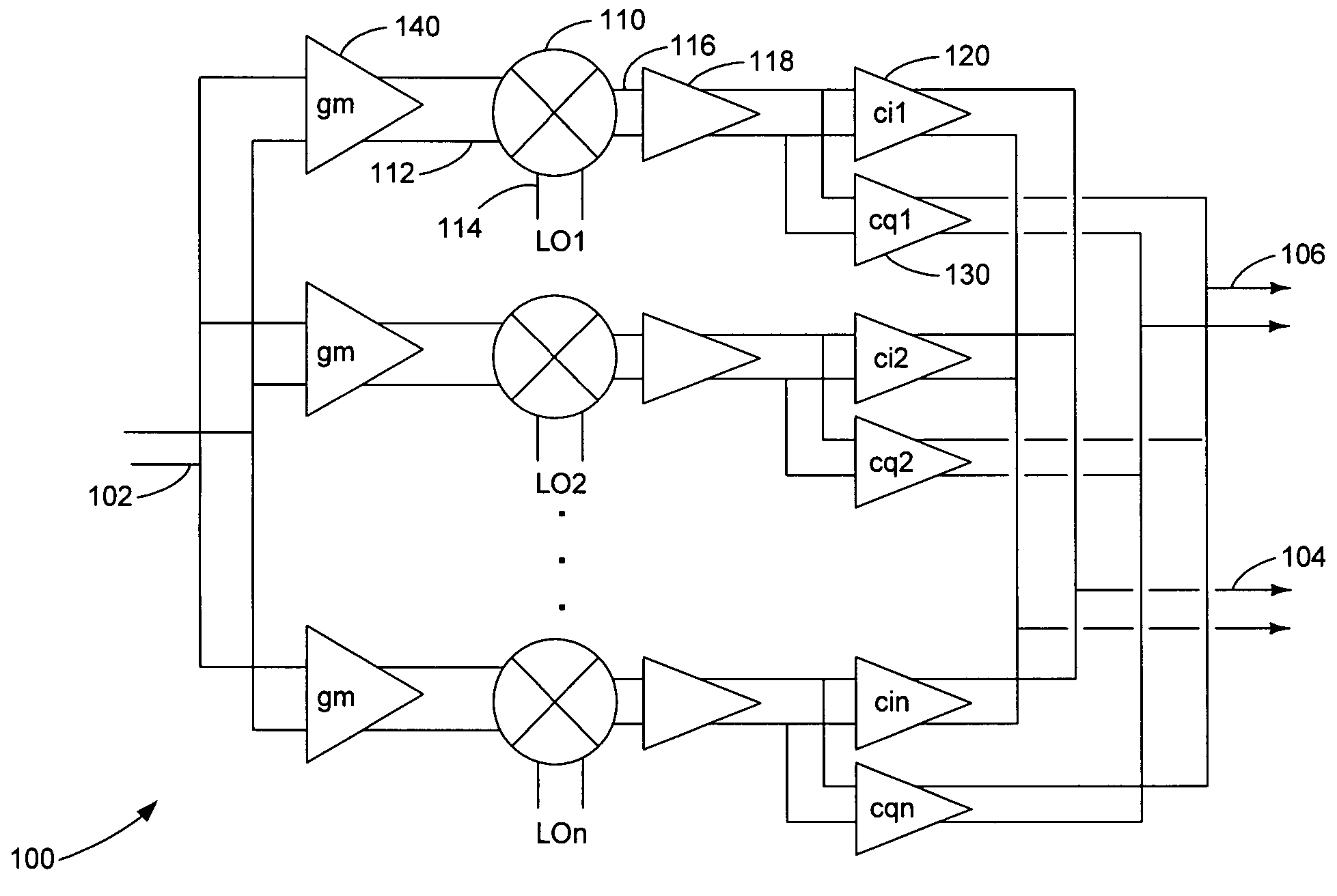
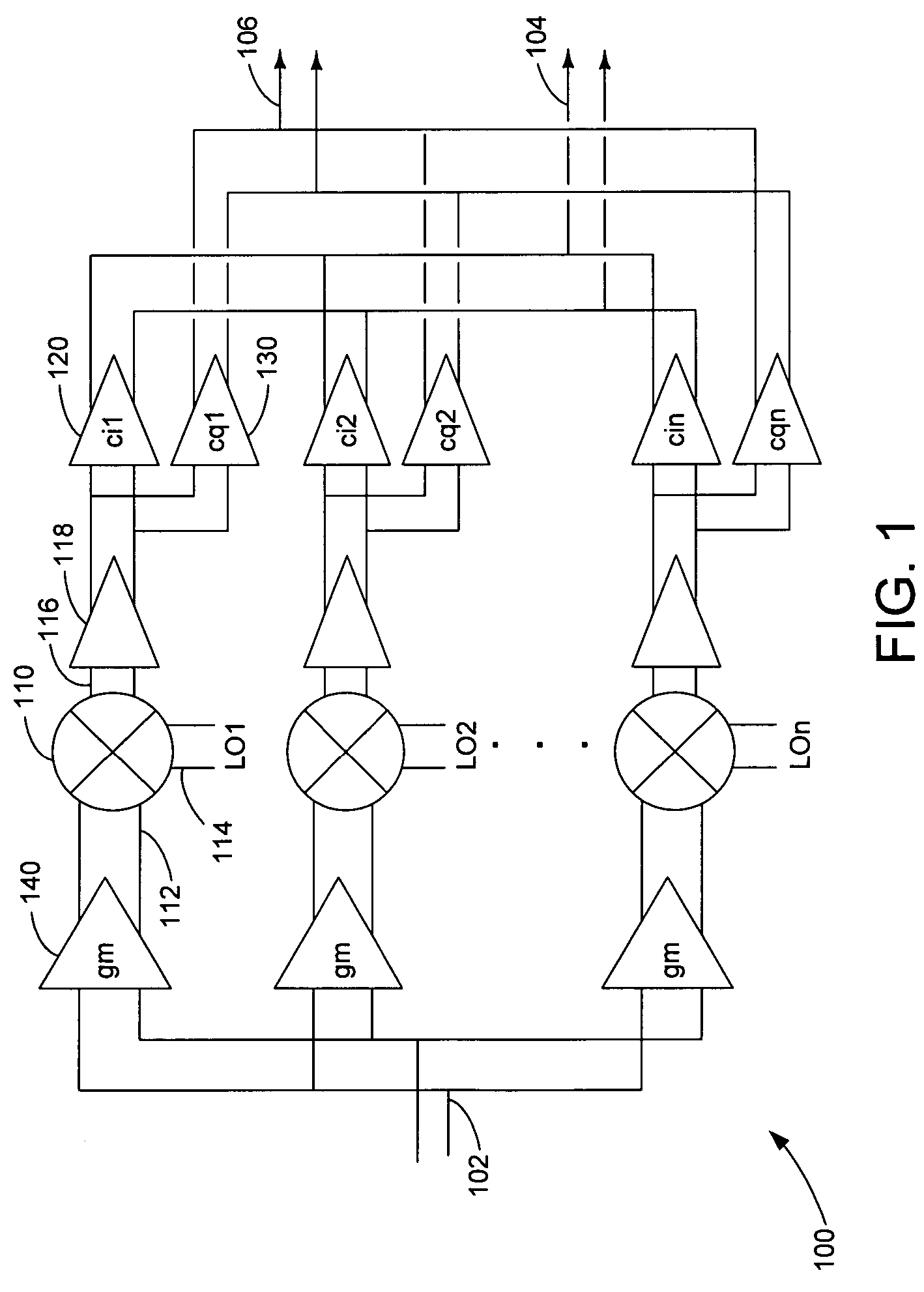
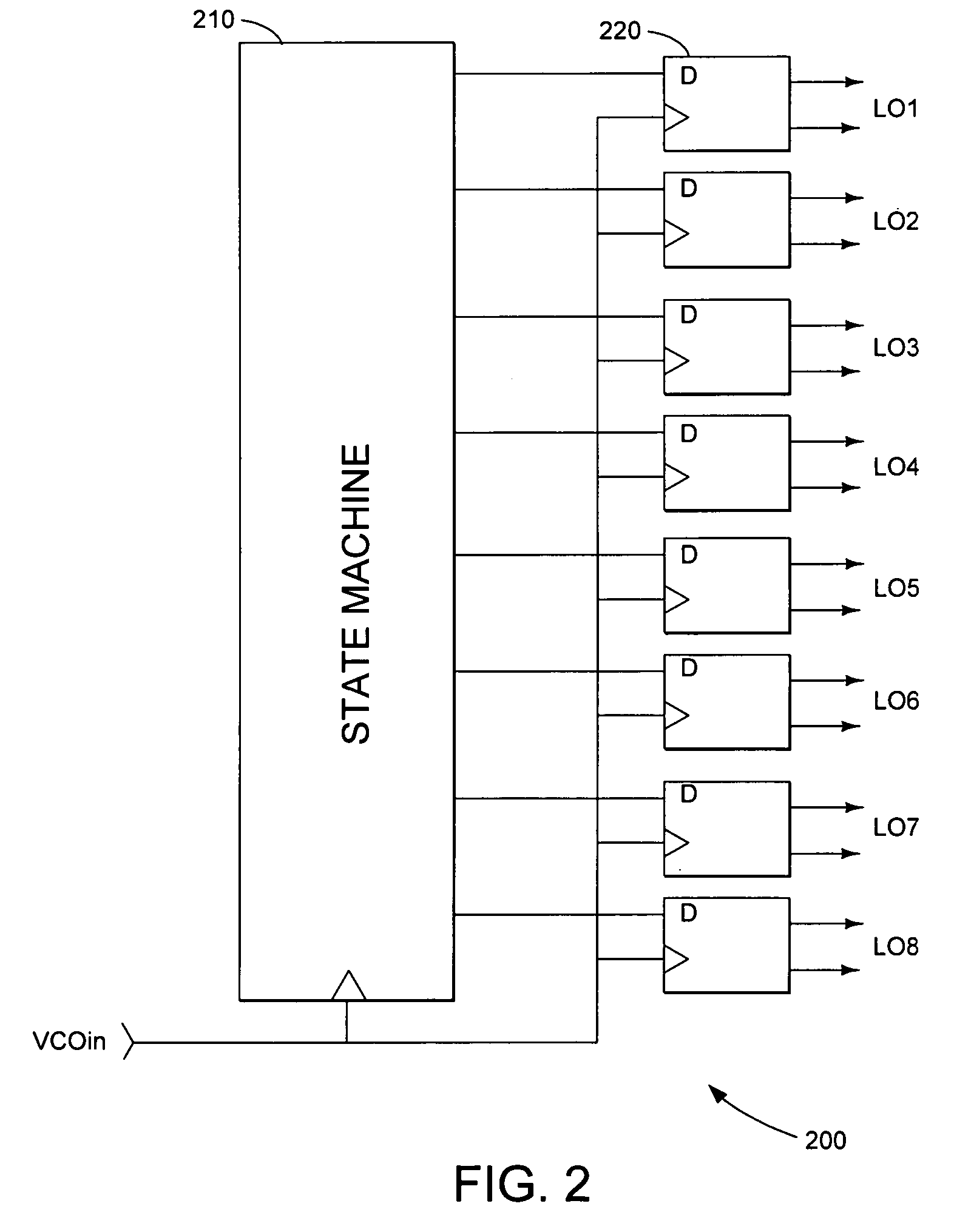
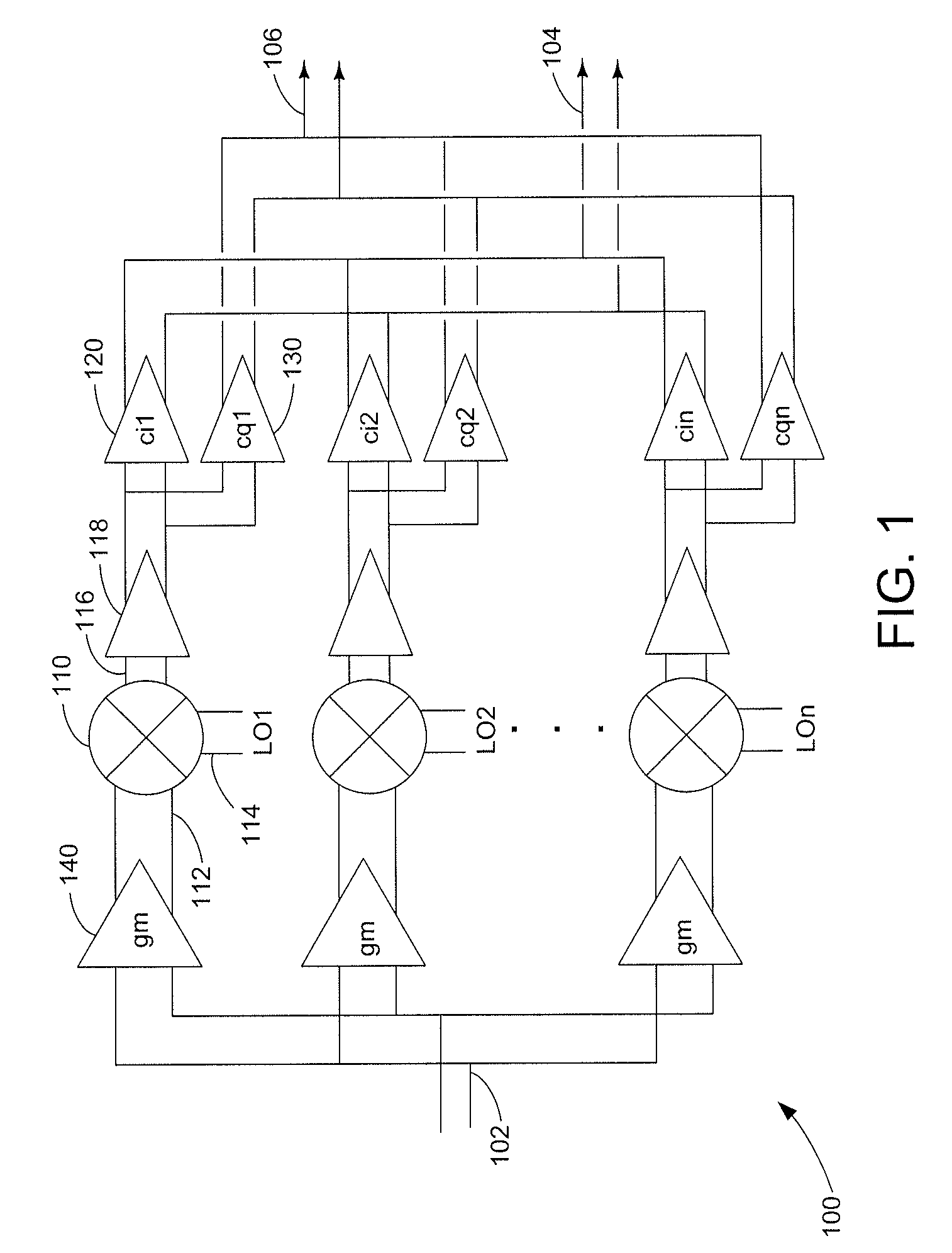
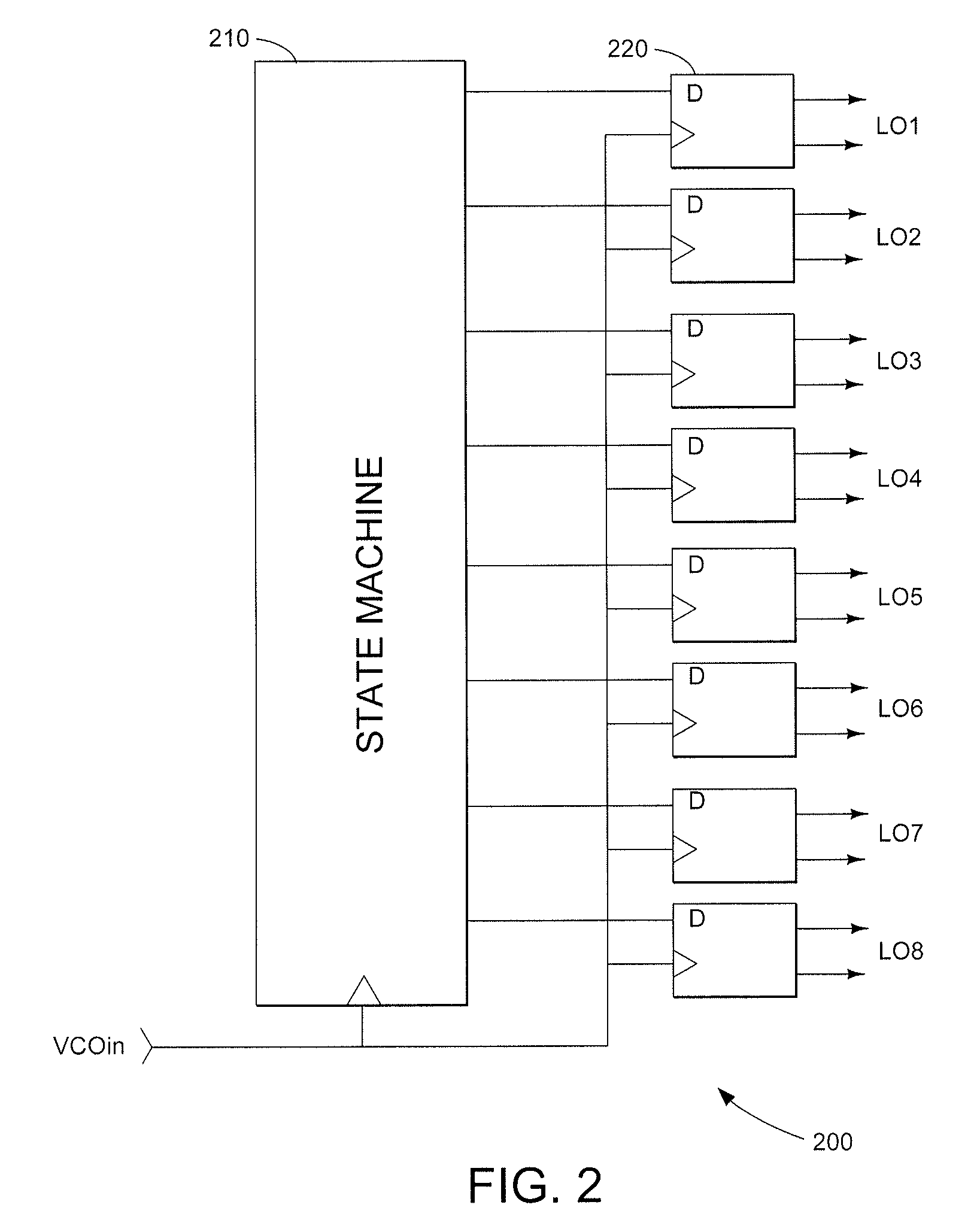
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
ActiveUS20050239430A1Enhanced inhibitory effectLess harmonic suppressionModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
ActiveUS20070106158A1Increase displacementLarge amplitudeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
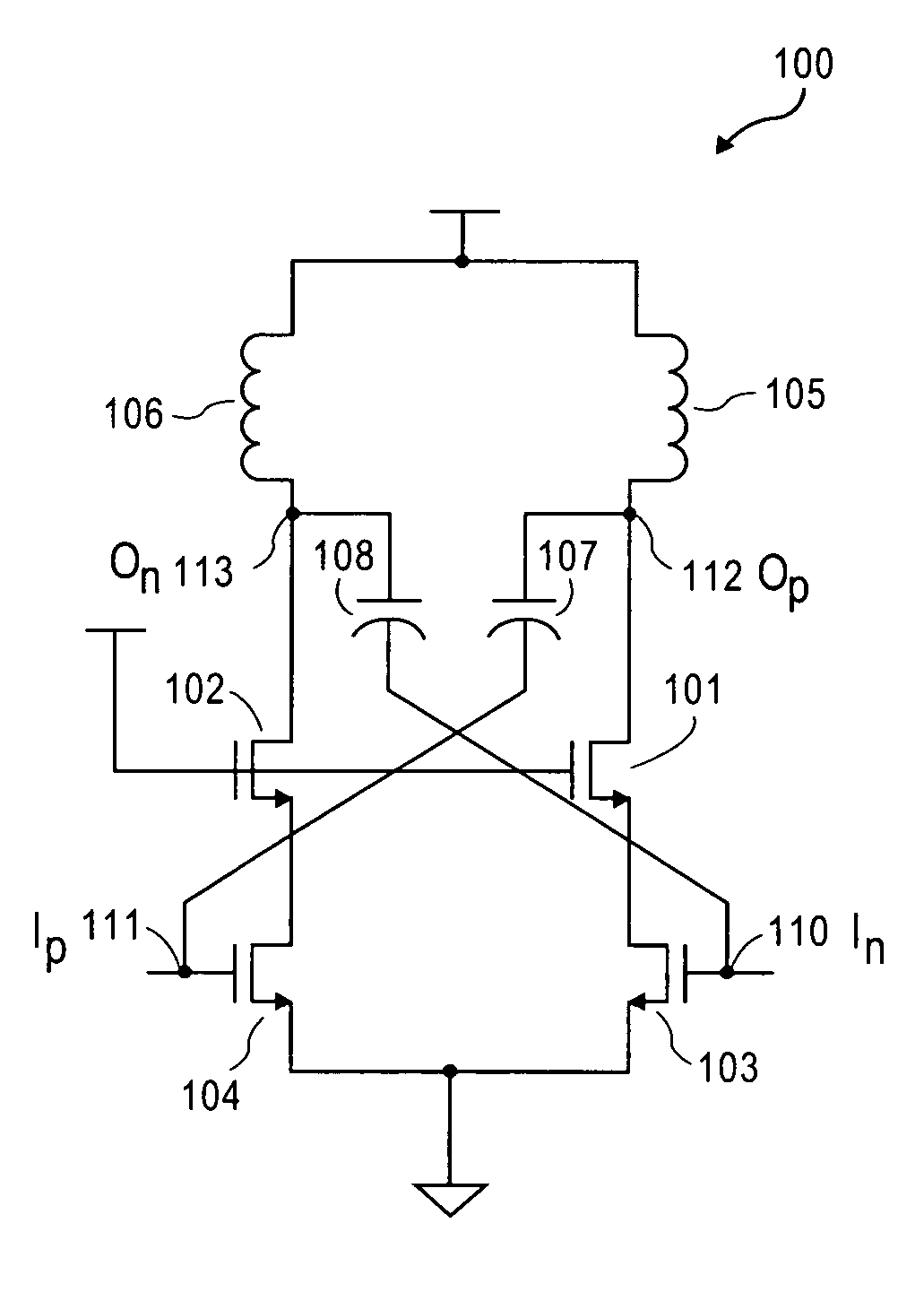
Gain boosting RF gain stage with cross-coupled capacitors
ActiveUS7697915B2Tighter current flow controlHigh gainHigh frequency amplifiersRadio transmissionCapacitanceGain stage
A RF differential gain stage has cross-coupled capacitors between input and output nodes of the amplifier stage to boost gain. The gain boost allows cancellation of the series resistance of an inductive load of the amplifier stage.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
ActiveUS7519348B2Reduce leakageEnhanced inhibitory effectModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Switched-capacitor circuit with scaled reference voltage
ActiveUS7009549B1Improve precisionImprove stabilityElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
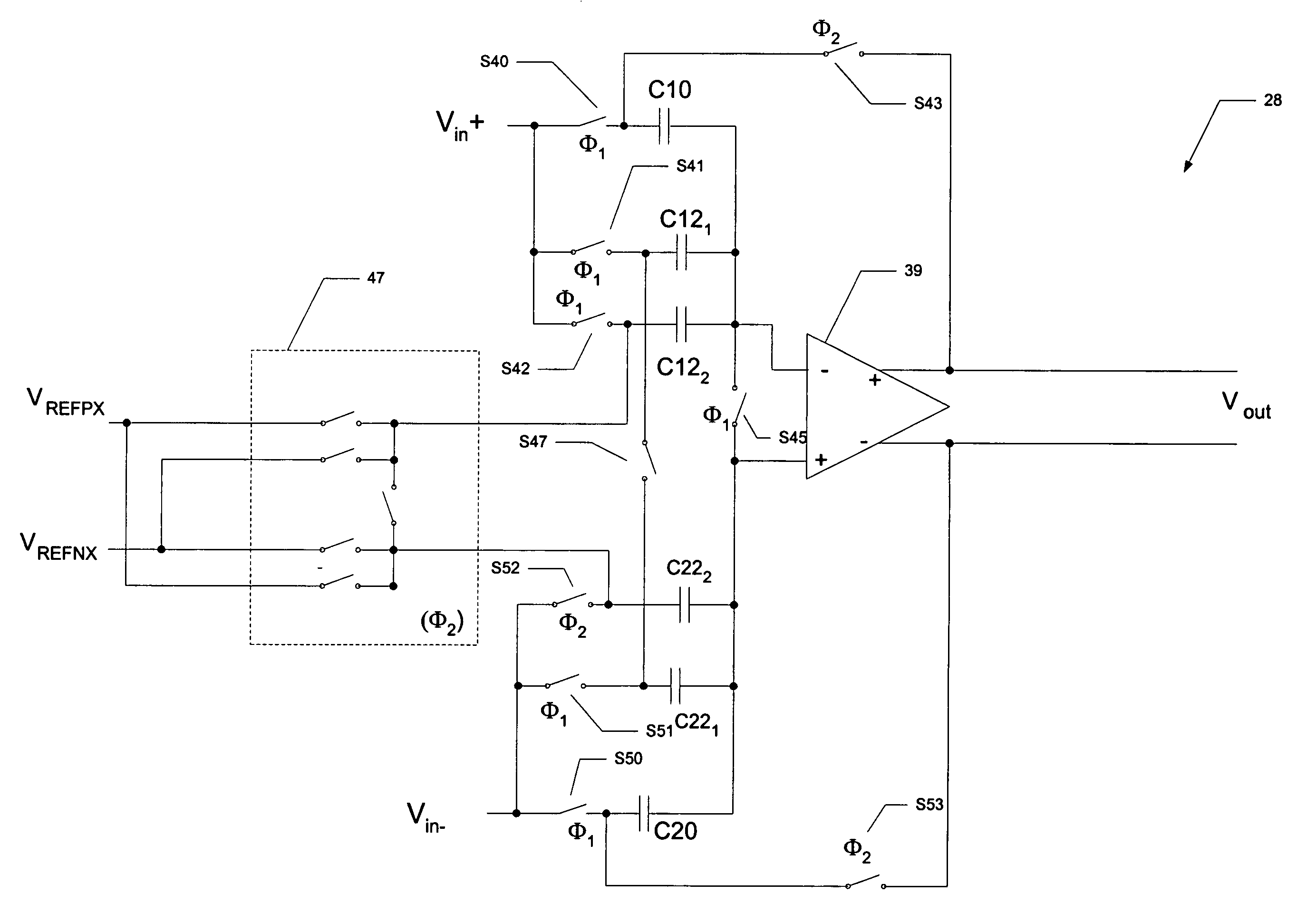
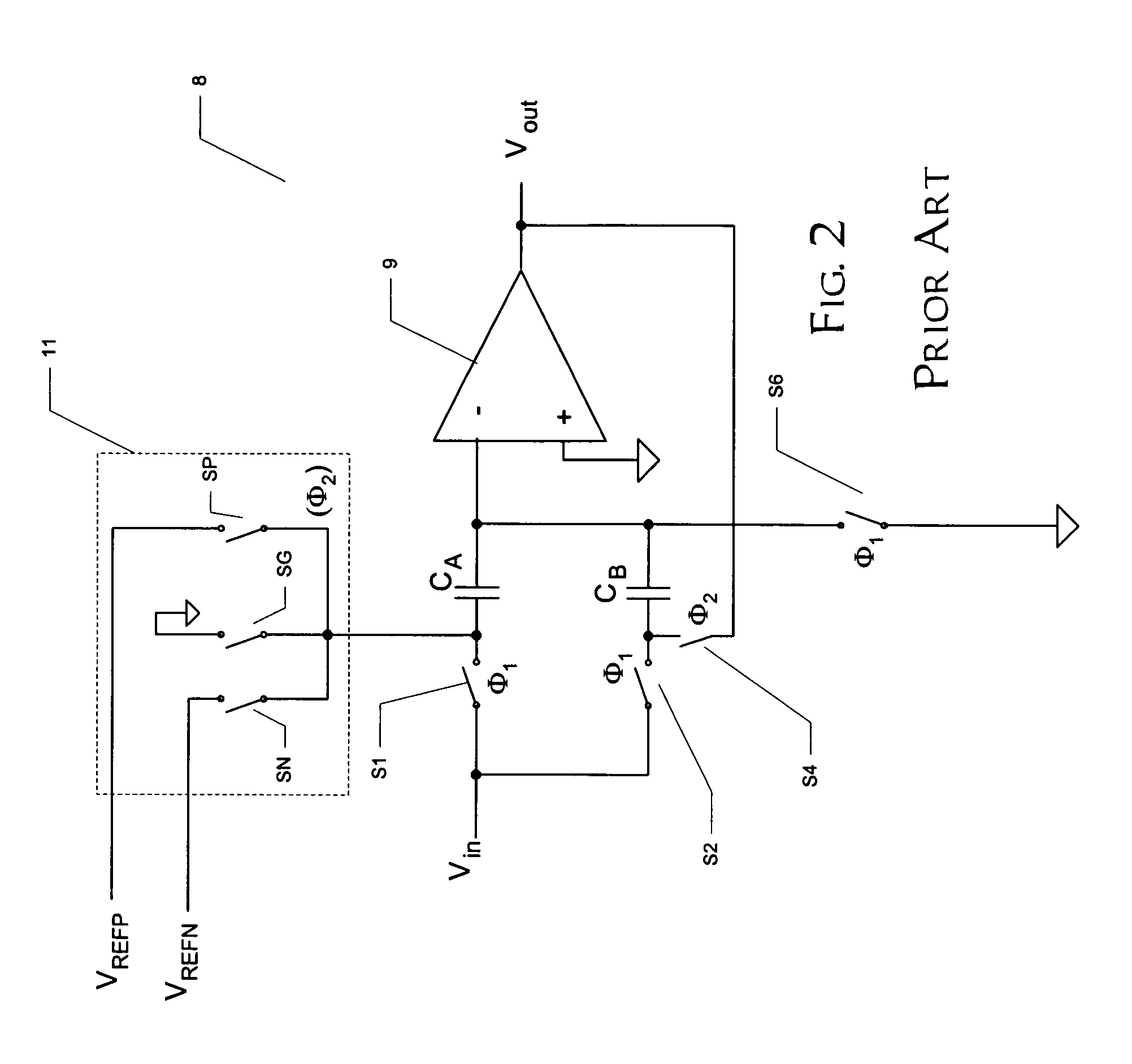
A pipelined analog-to-digital converter (ADC) (30) with improved precision is disclosed. The pipelined ADC (30) includes a sequence of stages (20), each of which includes a sample-and-hold circuit (22), an analog-to-digital converter (23), and the functions of a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) (25), an adder (24), and a gain stage (27) at which a residue signal (RES) is generated for application to the next stage (20) in the sequence. A multiplying DAC (28) performs the functions of the DAC (25), adder (24), and gain stage (27) in the stage (20), and is based on an operational amplifier (29). Sample capacitors (C10, C20) and reference capacitors (C122, C222) receive the analog input from the sample-and-hold circuit (22) in a sample phase; parallel capacitors (C121, C221) are provided to maintain constant circuit gain. Extended reference voltages (VREFPX, VREFNX) at levels that exceed the output range (V0+, V0−) of the operational amplifier (29) are applied to the reference capacitors, in response to the digital output of the analog-to-digital converter (23) in its stage (20). The reference capacitors (C12, C22) are scaled according to the extent to which the extended reference voltages (VREFPX, VREFNX) exceed the op amp output levels (V0+, V0−). The effects of noise on the reference voltages (VREFPX, VREFNX) on the residue signal (RES) are thus greatly reduced.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
ActiveUS20070232920A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
ActiveUS20070232927A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
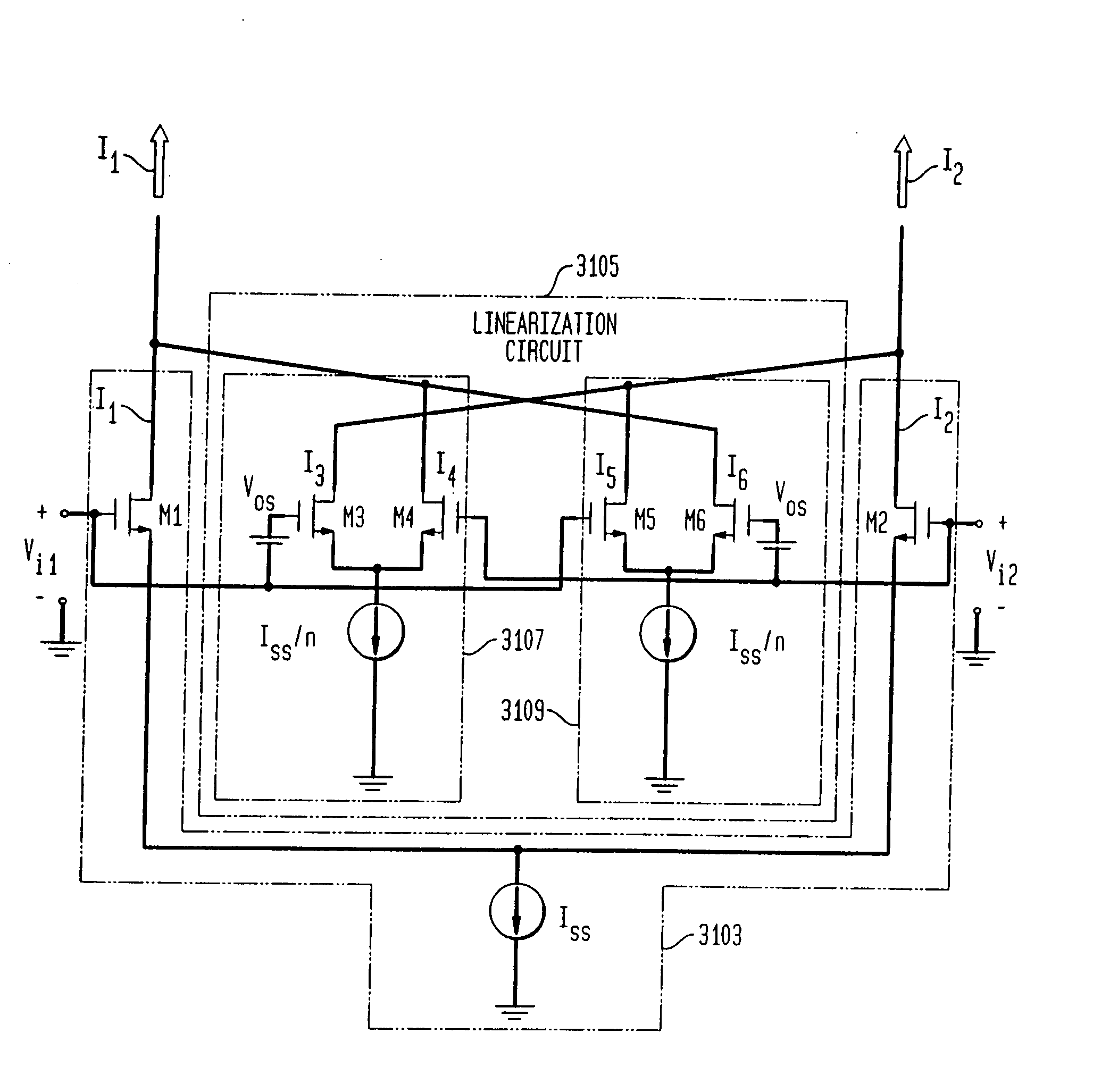
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS20080036536A1Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShunt DeviceFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers provide image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. Active filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters incorporate a gain stage that provides improved dynamic range through the use of cross coupled auxiliary differential pair CMOS amplifiers to cancel distortion in a main linearized differential pair amplifier. Frequency planning provides additional image rejection. Local oscillator signal generation methods on chip reduce distortion. A PLL generates needed out of band LO signals. Direct synthesis generates in band LO signals. PLL VCOs are centered automatically. A differential crystal oscillator provides a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission throughout the receiver is used. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure. Shunts utilize a gate boosting at each pin to discharge ESD build up. An IF VGA utilizes distortion cancellation achieved with cross coupled differential pair amplifiers having their Vds dynamically modified in conjunction with current steering of the differential pairs sources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low noise mixer circuit with improved gain
InactiveUS6947720B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio transmissionLow noiseGain stage
A mixer circuit of the present invention includes a gain stage configured to receive a first signal and a modulated bias current, and in accordance therewith, produce an output signal, the gain stage generating a first current and receiving the modulated bias current from a bias circuit on a common node. The bias circuit includes an input configured to receive a second signal, and in accordance therewith, generate the modulated bias current. The mixer circuit also includes a current shunt circuit for generating a second current. The first current, the second current, and the modulated bias current are coupled to the common node. In one embodiment, the first signal is approximately a square wave, and the frequency of the first signal is one-third the frequency of the second signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Harmonic suppression mixer and tuner
InactiveUS20090143031A1Enhanced inhibitory effectAvoid interferenceModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmissionLow noiseHarmonic mitigation
A harmonic suppression mixer for down converting an RF signal to a complex I and Q baseband signal that uses a plurality of switching mixers each with a gain stage to produce a sinusoidal weighted sum of the mixer outputs. Odd harmonics output by each switching mixer is suppressed in the composite signal. A low skew local oscillator (LO) clock generator creates multiple LO phases and drives the mixers. The mixer can be used in low noise direct conversion RF tuners. The mixer is configurable by programming gain stage coefficient values to achieve a variable number of effective mixers used in combination. At low tuning frequencies, all available mixers are programmed with unique coefficients and driven by different LO clock phases to achieve maximum harmonic suppression. At high tuning frequencies, some mixers are paralleled and duplicate coefficients are programmed or mixers are disabled to reduce the number of effective mixers.
Owner:SHAH PETER
Method of detecting signal clipping in a wearable ambulatory medical device
A wearable medical device and method of detecting clipping of ECG signals is disclosed. In one embodiment, the wearable medical device comprises a plurality of ECG sensing electrodes configured to sense an ECG of a patient and an ECG acquisition circuit electrically coupled to a pair of the plurality of ECG sensing electrodes and configured to provide an amplified and conditioned analog ECG signal, a programmable attenuation / gain stage electrically coupled between a first gain stage and a second gain stage, an ADC electrically coupled to the ECG acquisition circuit to receive and digitize the amplified and conditioned analog ECG signal and provide a digitized ECG signal, and a signal conditioning and control unit electrically coupled to the ECG acquisition circuit and the ADC to receive and monitor the digitized ECG signal and to detect clipping of the amplified and conditioned analog ECG signal based upon the digitized ECG signal.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
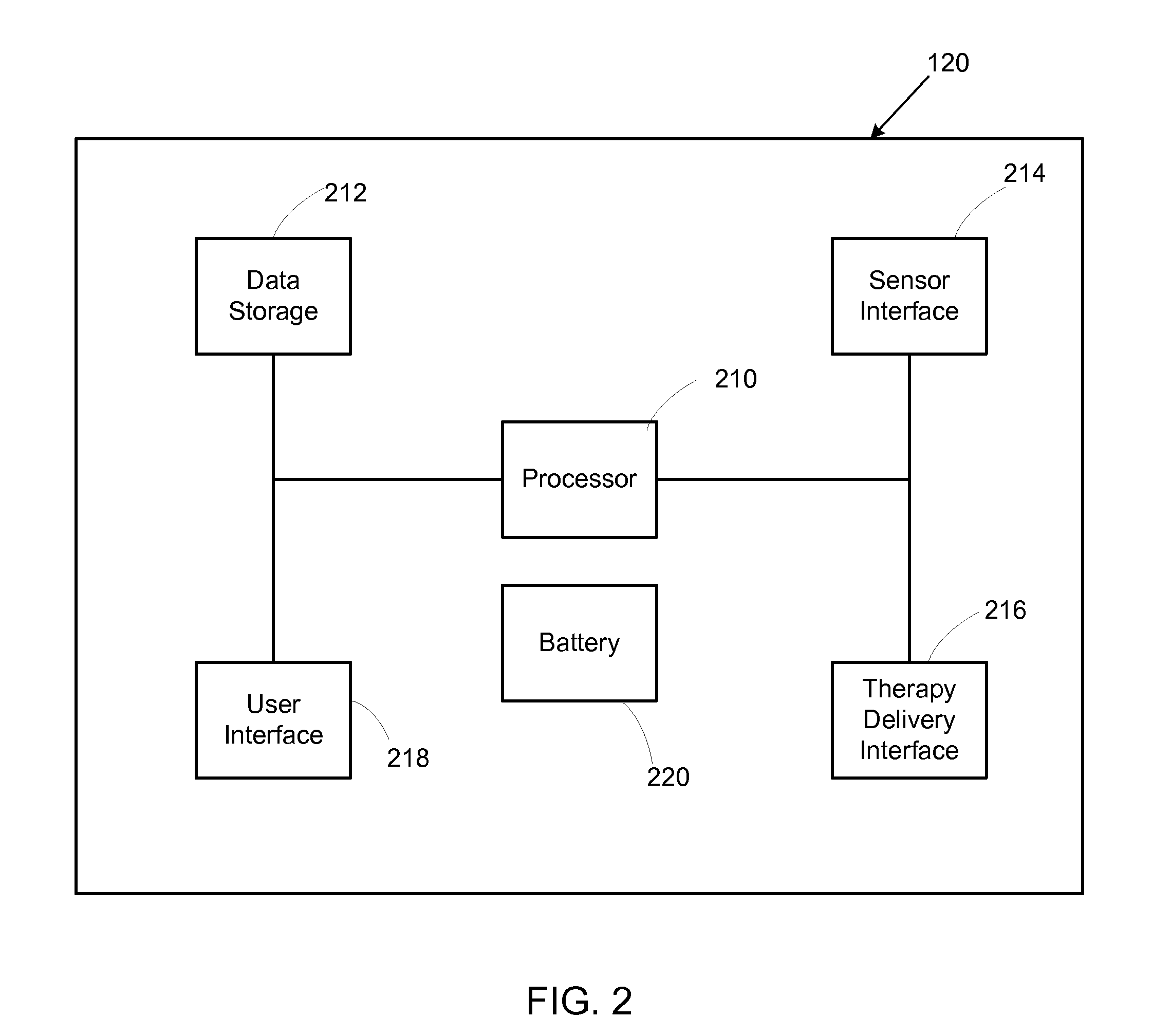
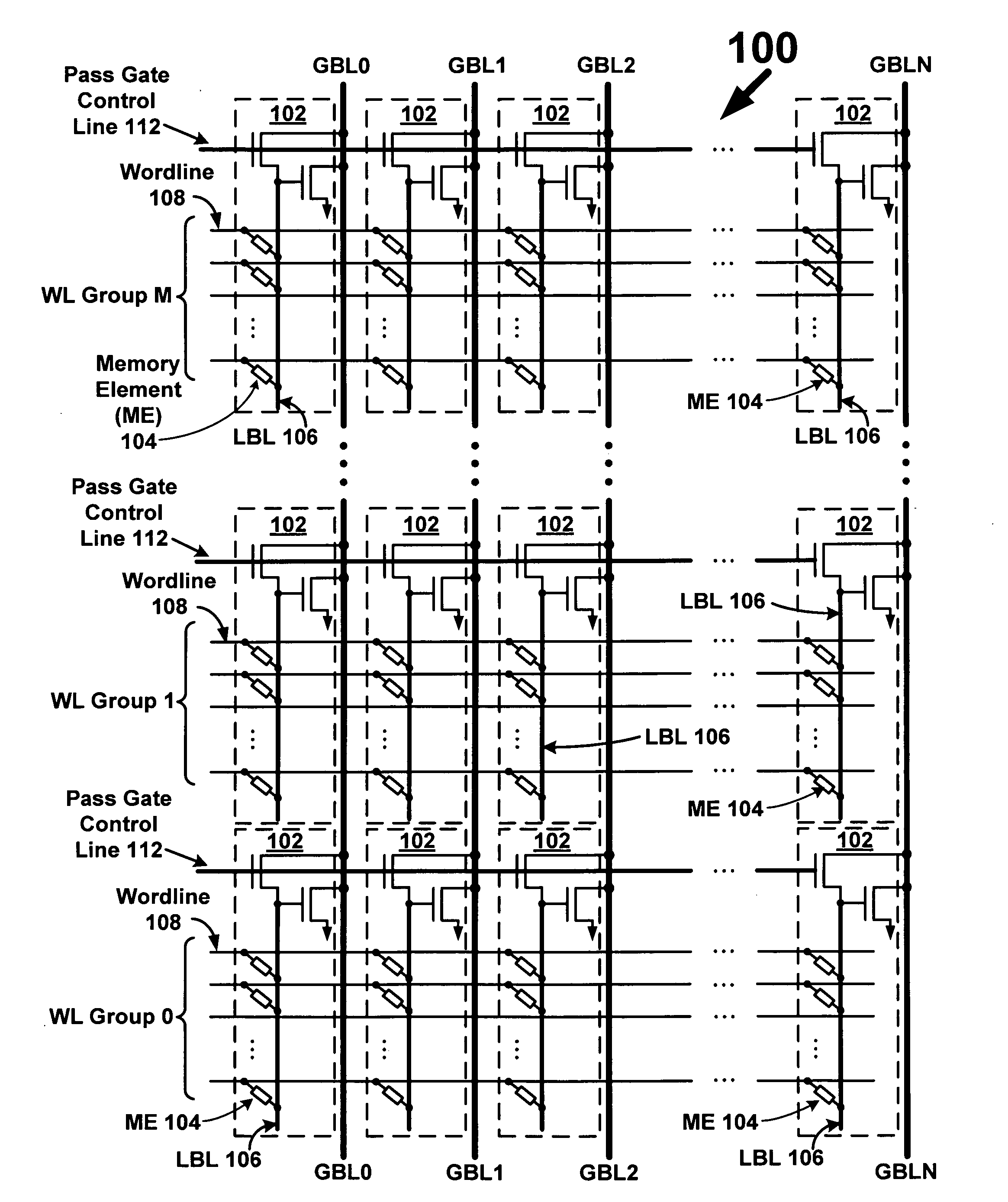
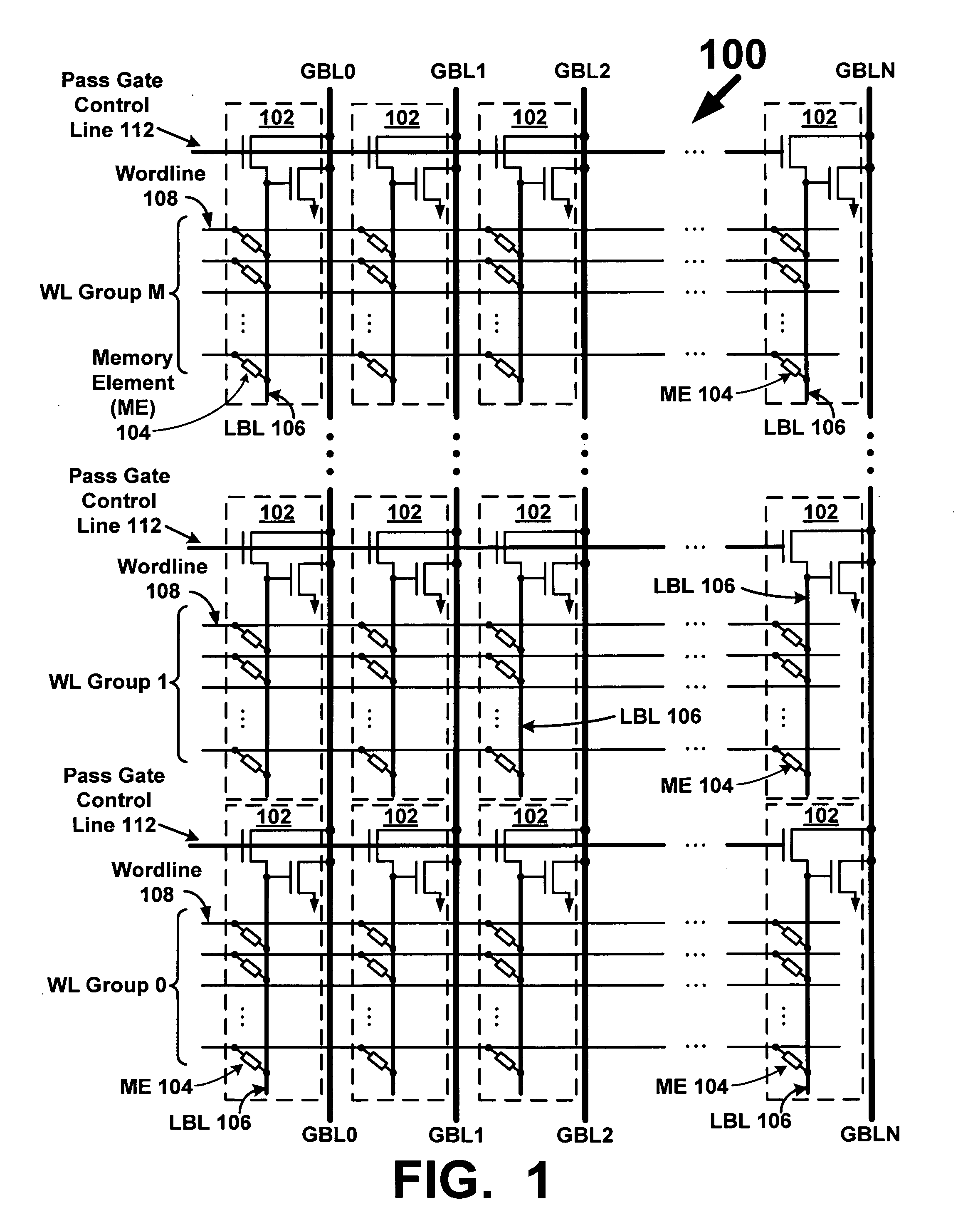
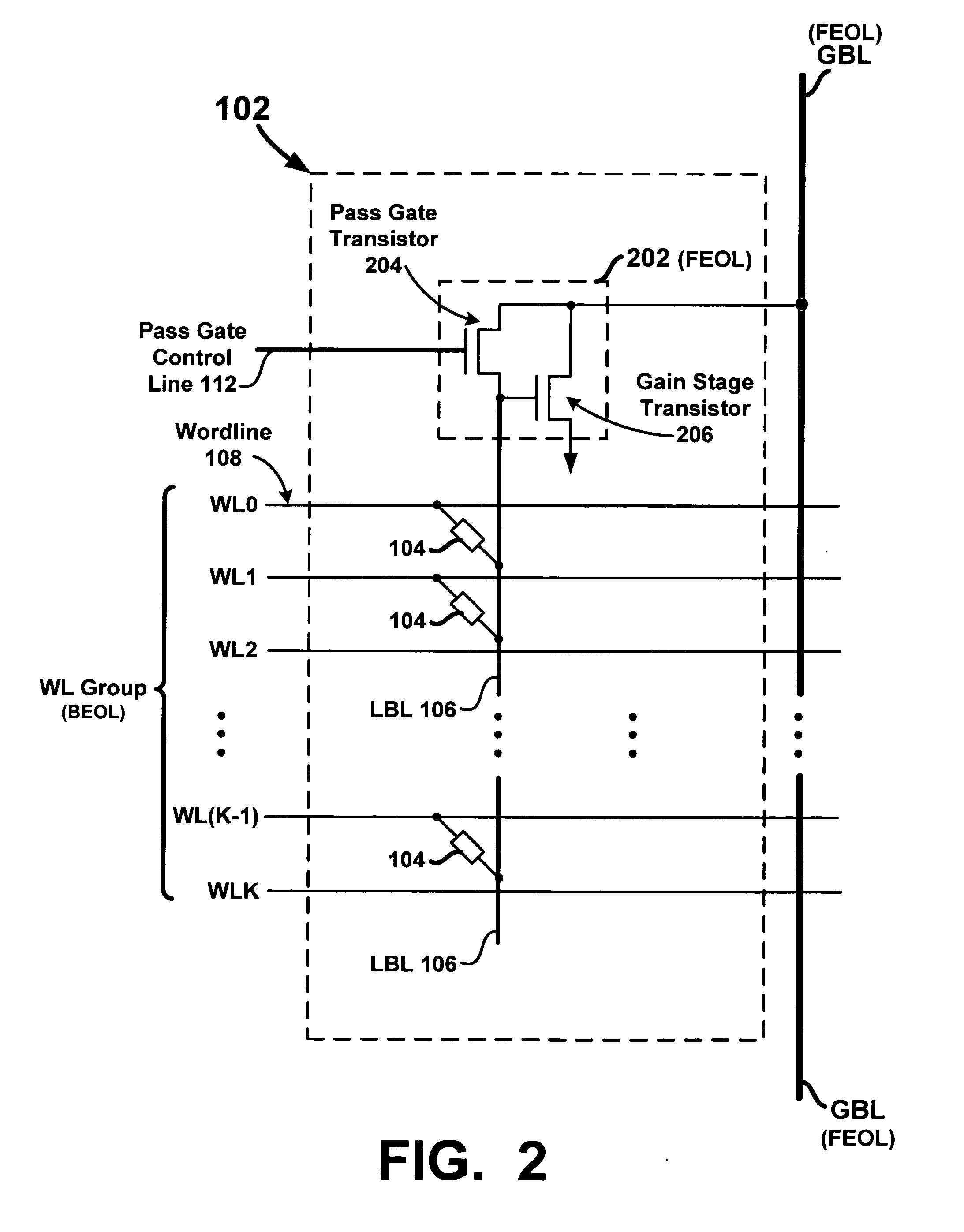
Memory array with local bitlines and local-to-global bitline pass gates and gain stages
ActiveUS20120314468A1Increase chanceCompact integrationNanoinformaticsRead-only memoriesSignal onComputer science
A memory array includes wordlines, local bitlines, two-terminal memory elements, global bitlines, and local-to-global bitline pass gates and gain stages. The memory elements are formed between the wordlines and local bitlines. Each local bitline is selectively coupled to an associated global bitline, by way of an associated local-to-global bitline pass gate. During a read operation when a memory element of a local bitline is selected to be read, a local-to-global gain stage is configured to amplify a signal on or passing through the local bitline to an amplified signal on or along an associated global bitline. The amplified signal, which in one embodiment is dependent on the resistive state of the selected memory element, is used to rapidly determine the memory state stored by the selected memory element.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
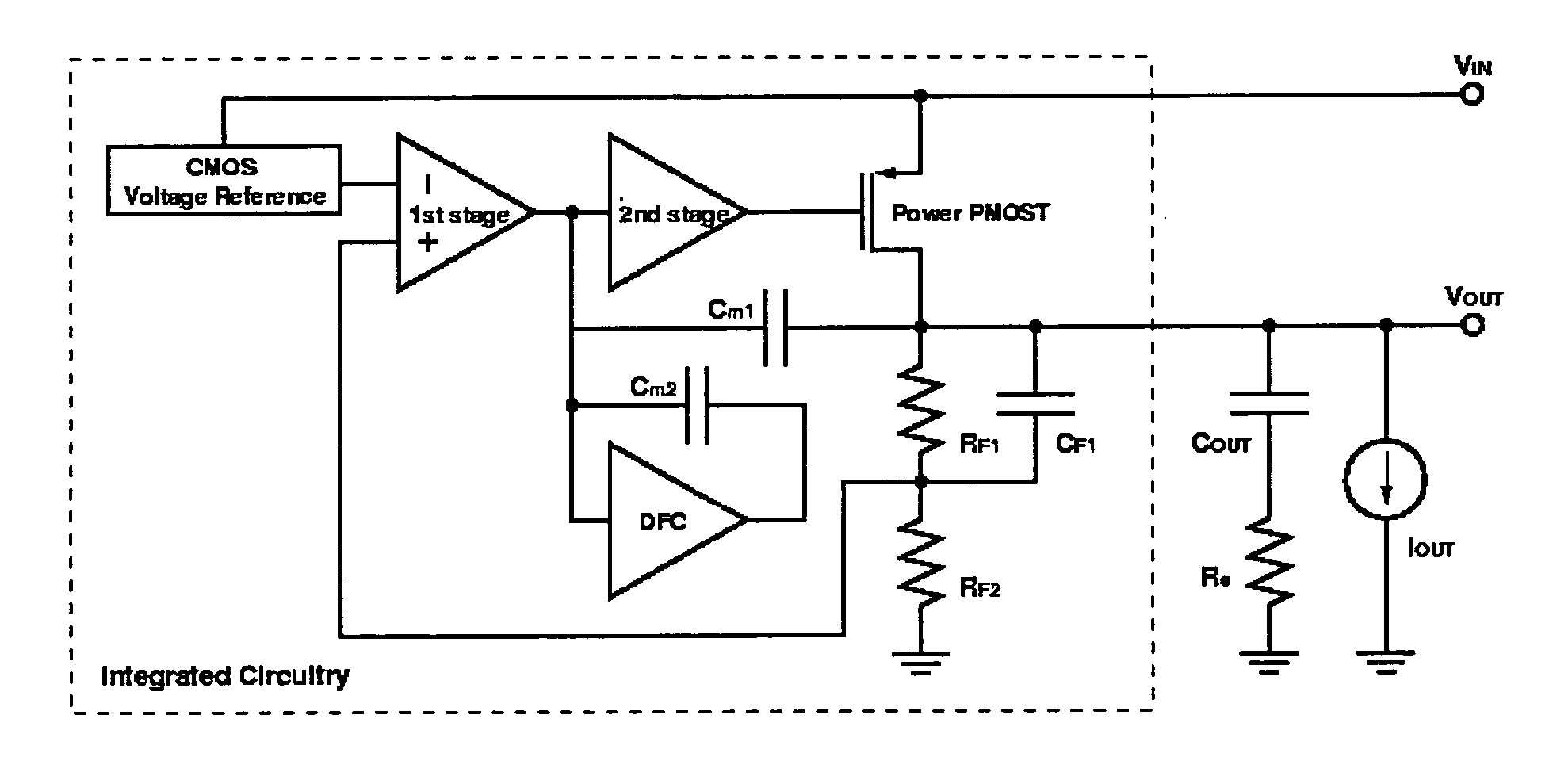
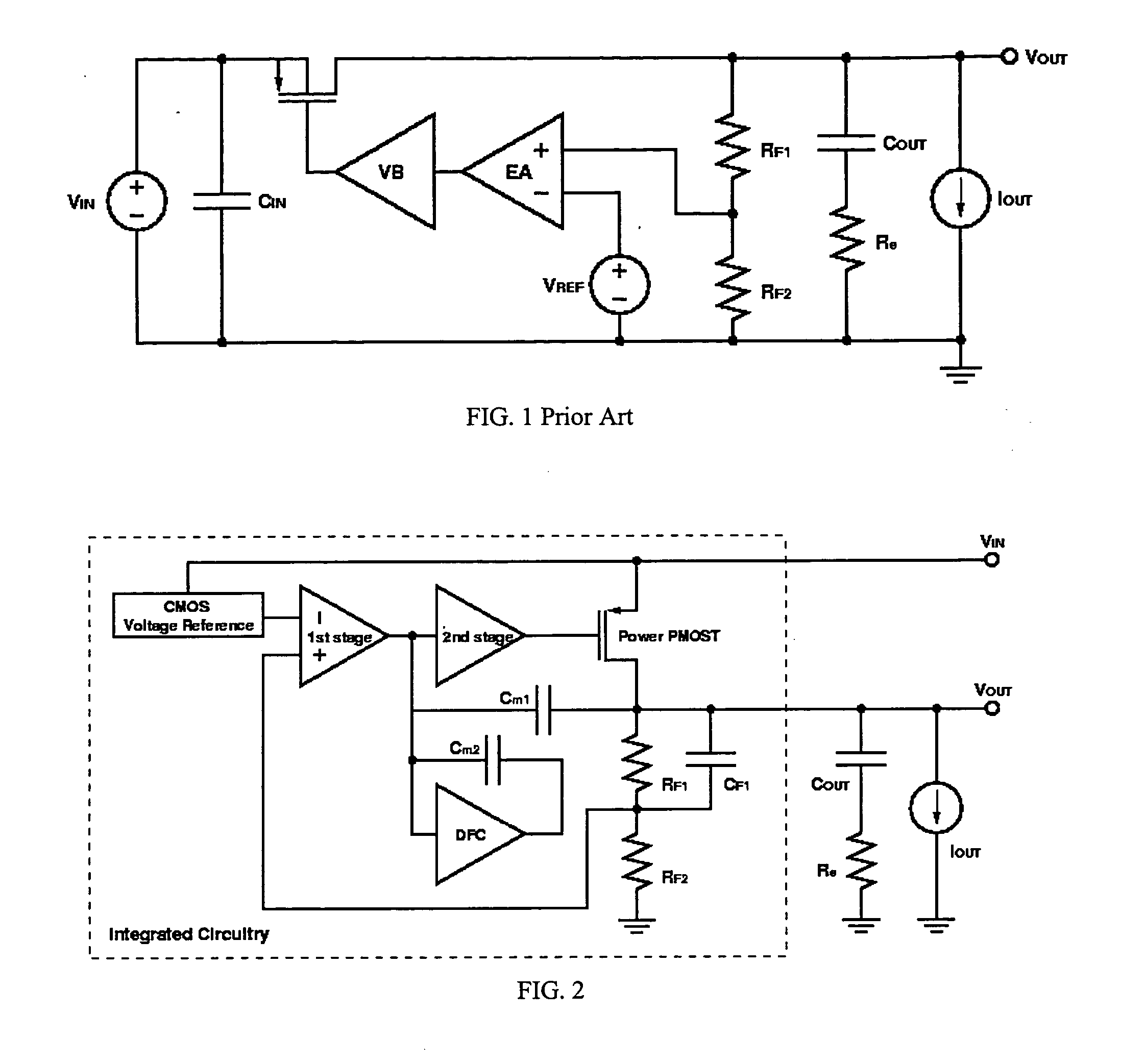
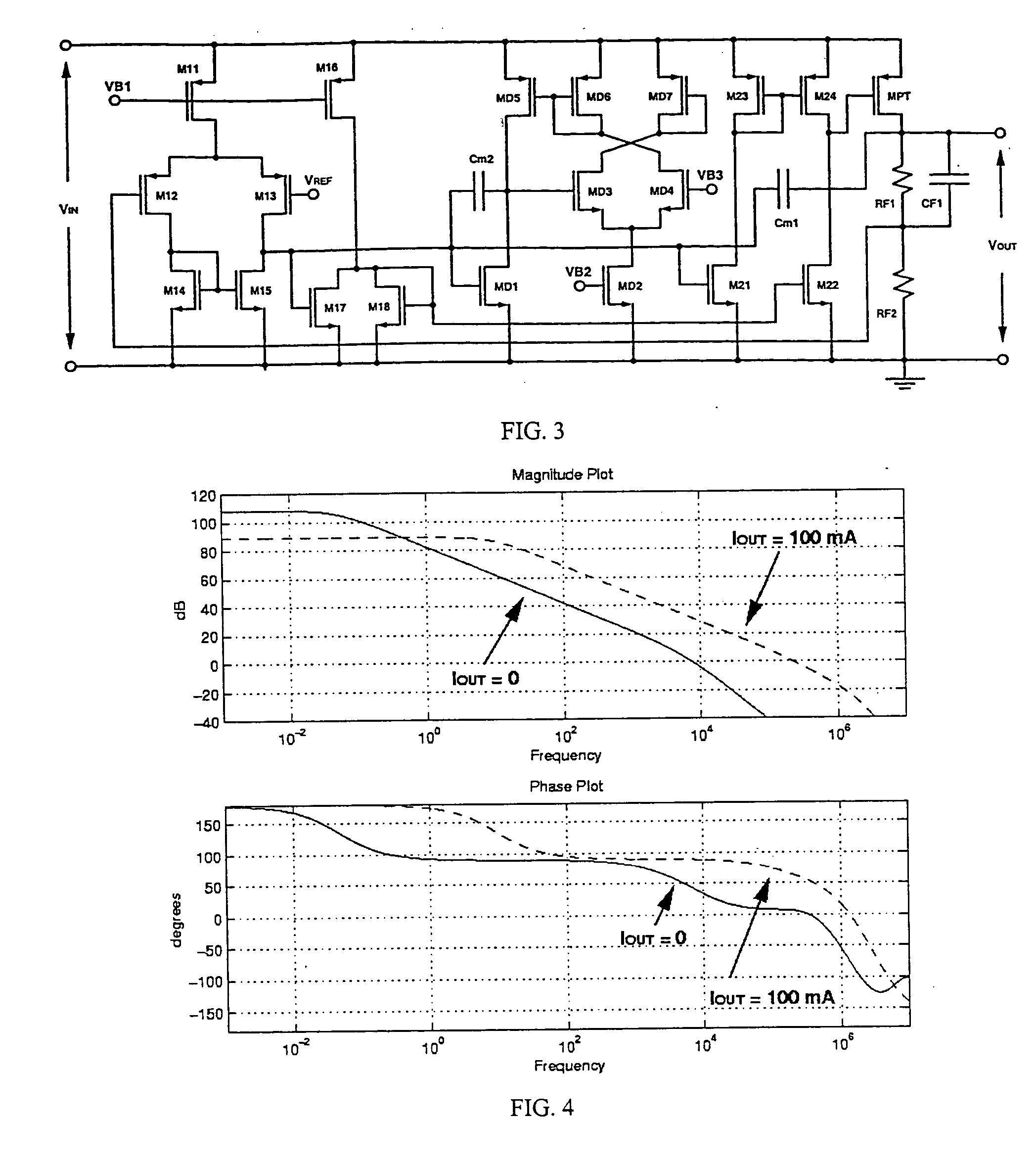
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
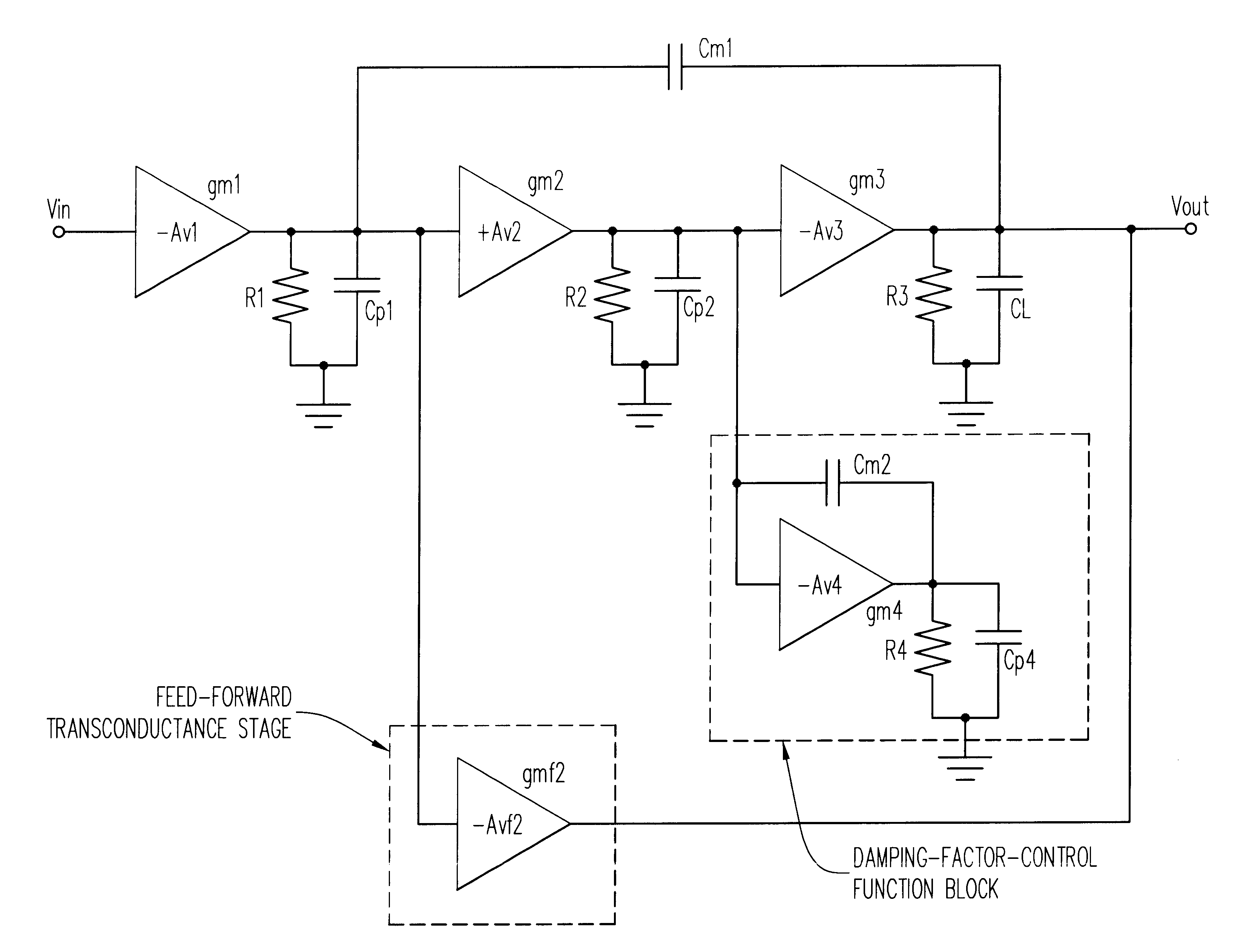
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Class-D amplifier having high order loop filtering
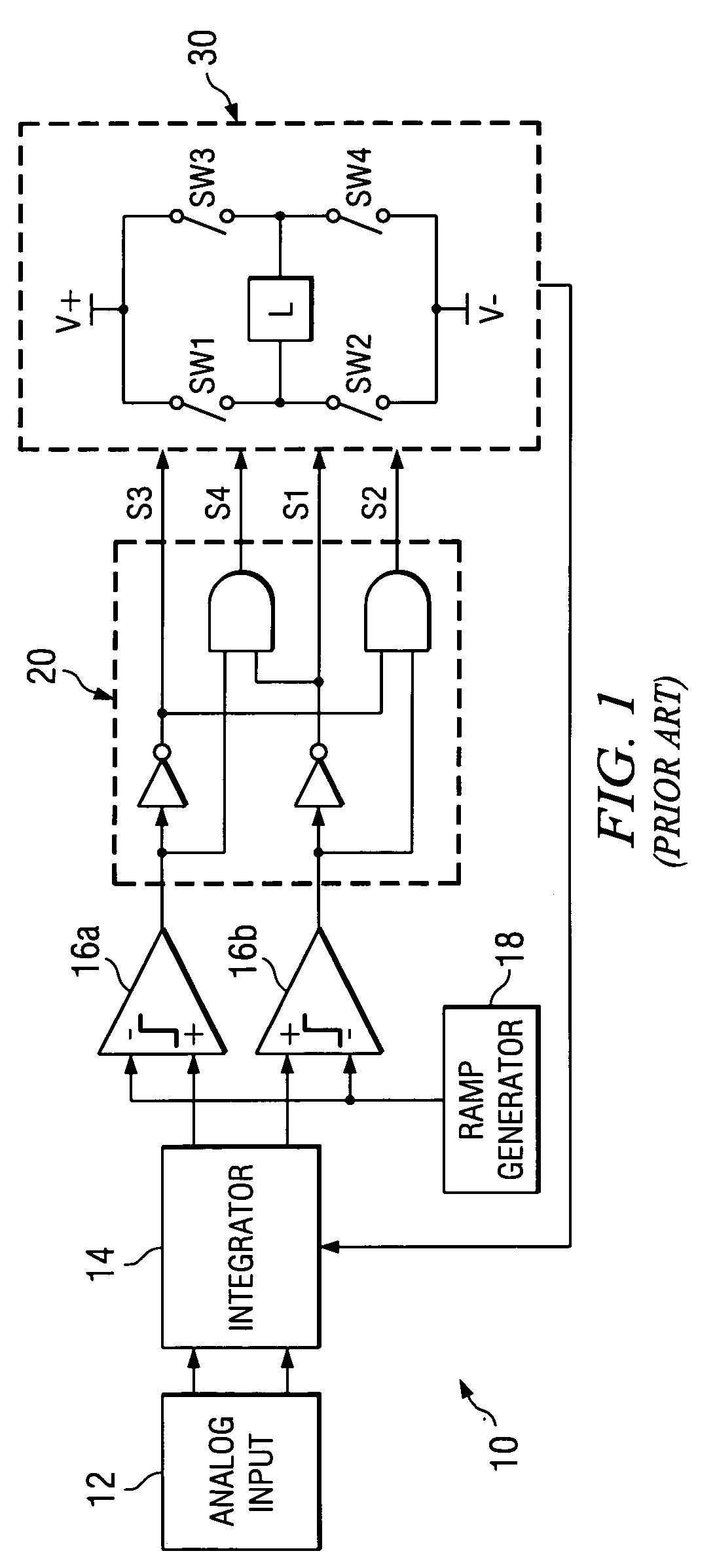
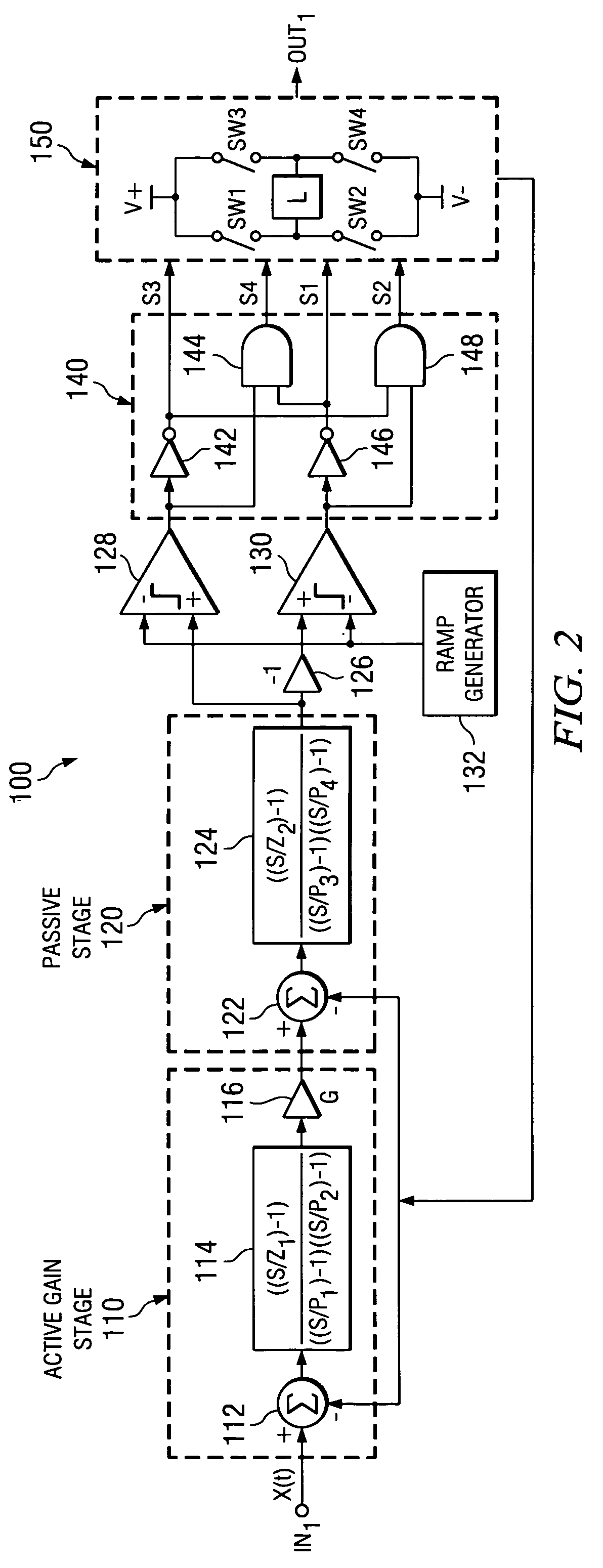
InactiveUS20060044057A1High SNDR performanceImprove PSRRNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorLow-pass filterClass-D amplifier
An amplifier having an active and passive gain stage connect to a load for driving a load according to a system analog input. A first embodiment of the amplifier in accordance with the present invention includes a logic network connected between a comparator network and a switching system, wherein the comparator network connects to the passive gain stage. Specifically, the active gain stage may include an active filter connected to receive an analog or digital input and provide a difference between the analog or digital input and the feedback signal relative to the gain factor of a gain unit connected to the active filter. The passive gain stage includes a passive filter. The logic network generates at least one switching signal which controls the switching system that includes at least one switching device to selectively provide power to the load. An output signal from the switching system provides output for the amplifier and is fed back to the active gain stage. In another embodiment, the output is a two-level signal and the passive and active filters are second order low pass filters, where the gain factor is about 25 or more. In yet another embodiment, the gain factor is approximately 250. Moreover, the amplifier may include a digital delta-sigma modulator connected to supply a two level input.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
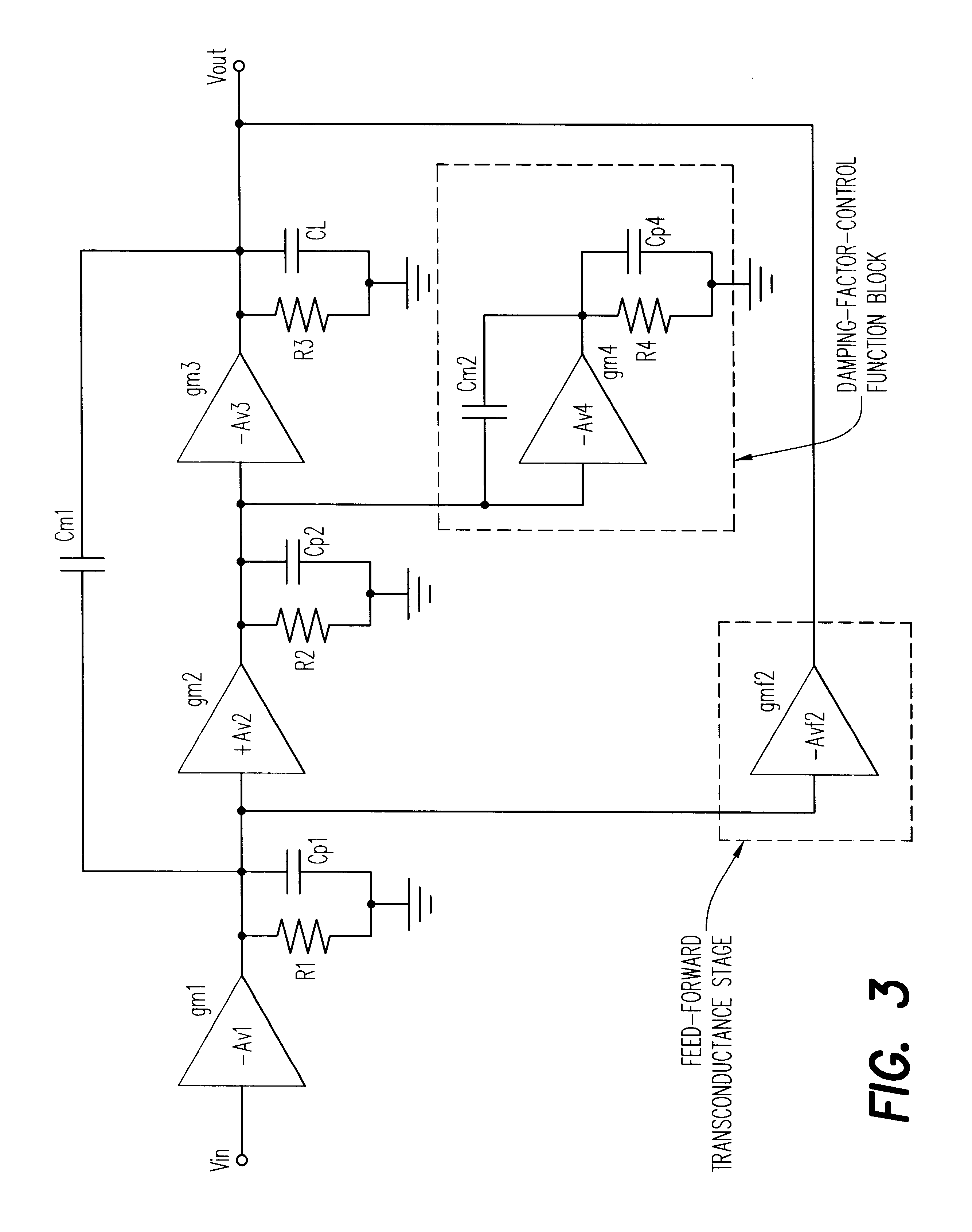
Frequency compensation techniques for low-power multistage amplifiers
InactiveUS6208206B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceDamping factorCapacitance
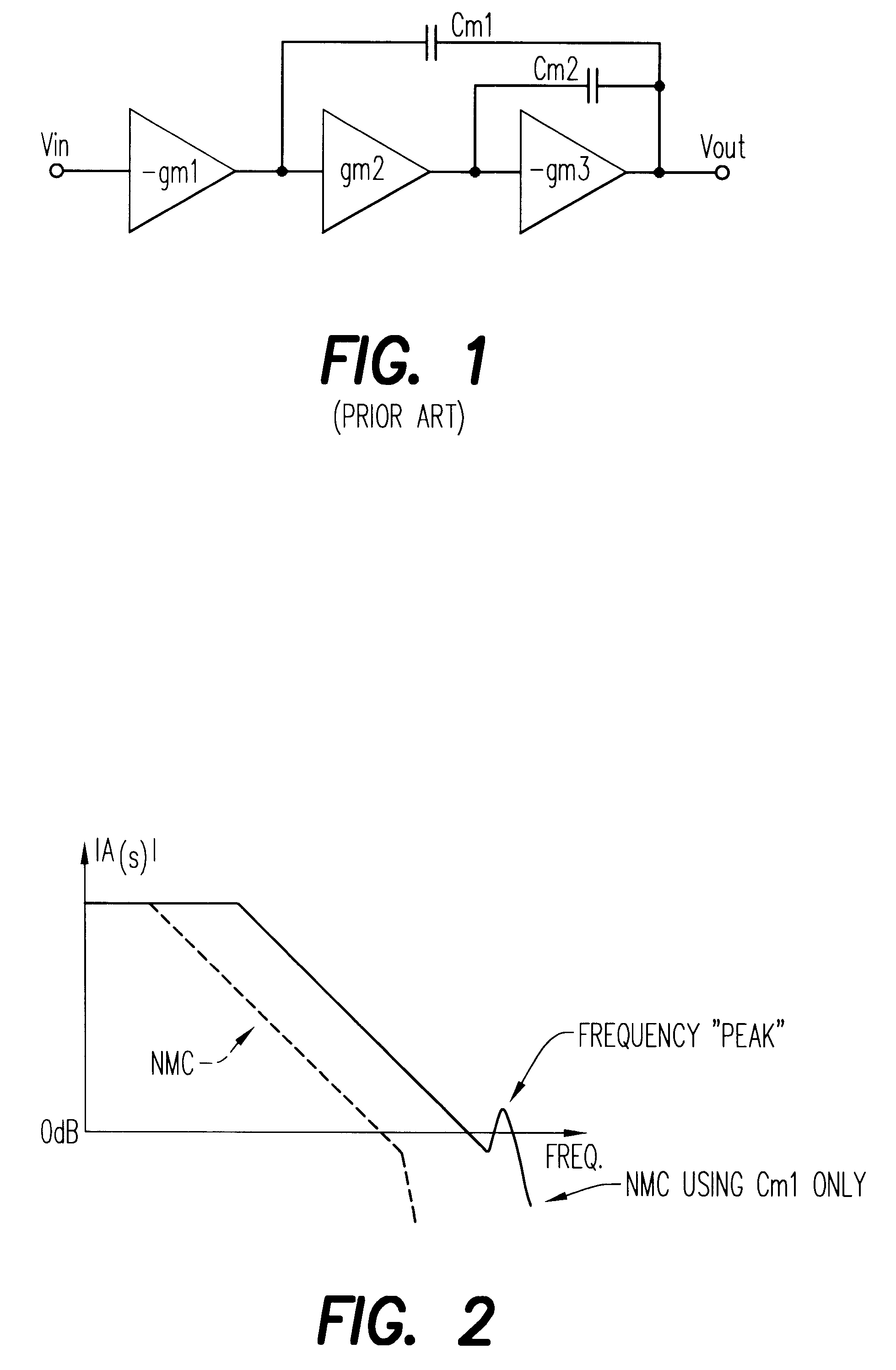
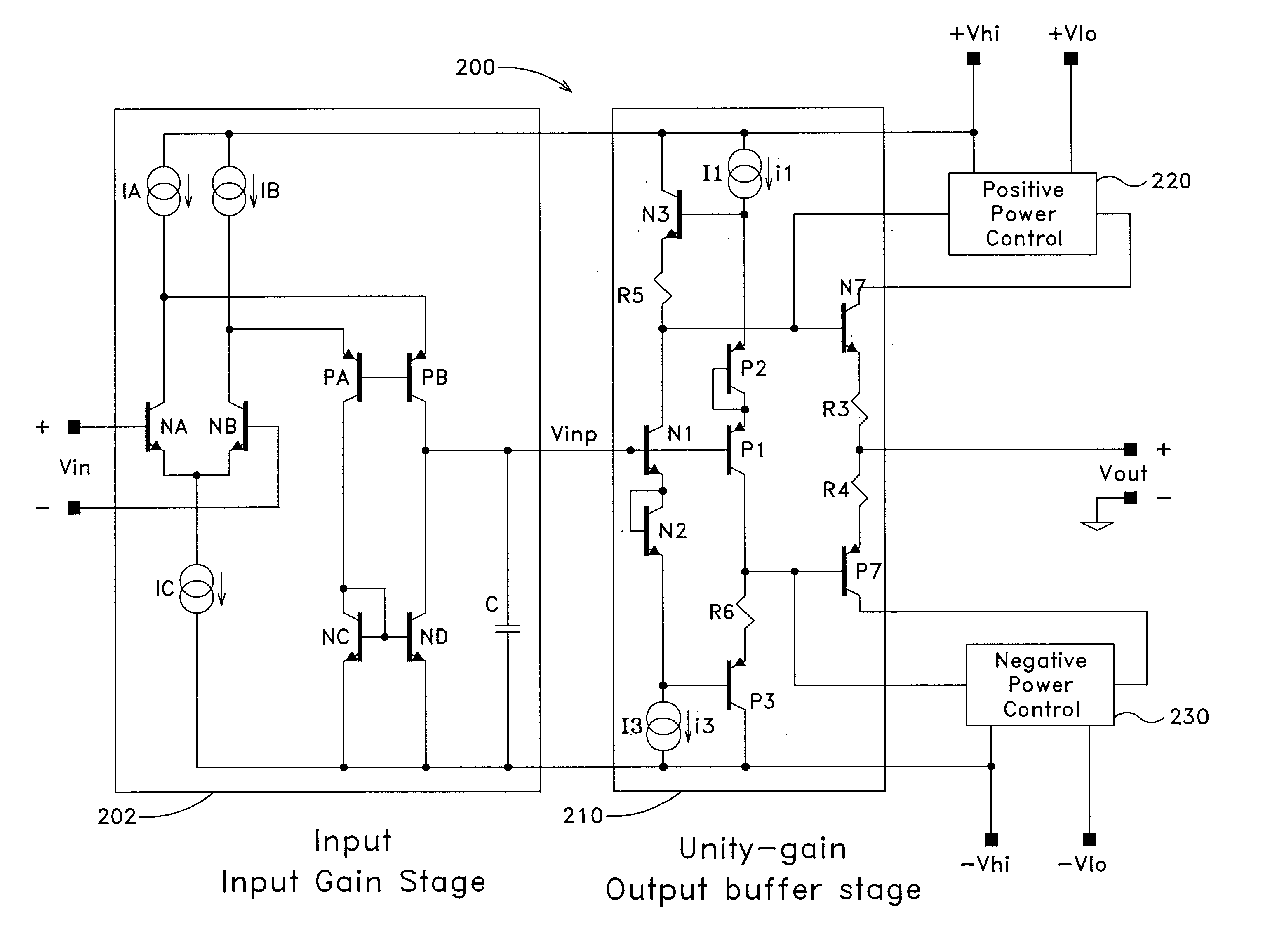
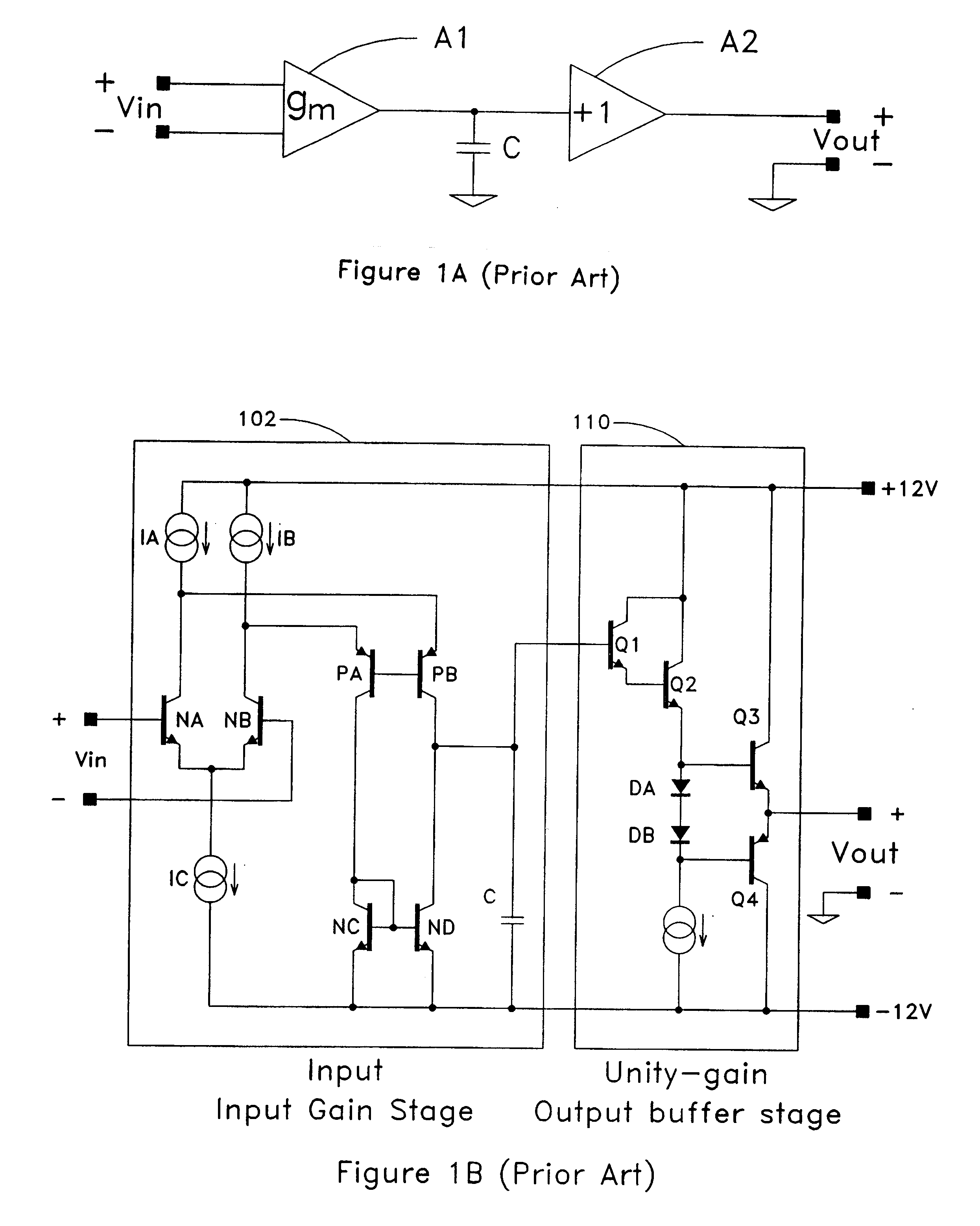
A three stage amplifier is disclosed provided with a novel frequency compensation technique. Only a single feedback loop with a single compensation capacitance is provided. Instead of a conventional nested compensation technique, damping factor control is provided by means of a fourth gain stage in order to stabilize the amplifier. The resulting amplifier is particularly useful to drive large capacitive loads for low-voltage low-power applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bias circuit for transconductance amplifier
InactiveUS6023196AModulation transference balanced arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationSignificant errorVoltage reference
In low-voltage circuits, there is often insufficient voltage to use a current source to bias a transconductance amplifier stage. This is particularly true in mixers where a switching circuit must be stacked on top of the transconductance input stage. One way around this problem is to get "double-duty" out of the input differential pair, using it both for gain stage and for DC bias. This is done by AC coupling in a high-frequency input signal, while using a low-frequency, DC-coupled circuit to establish the proper bias level. One common technique is to use a simple current mirror scheme to establish the DC level. Proper biasing using this technique requires good matching of resistance. In some implementations of transconductance amplifiers, particularly those that use inductors as degeneration elements, series resistance of the inductor and interconnect resistance can cause significant errors in the bias current. This invention addresses that problem by using an operational amplifier with a current-sensing resistor and a low-frequency feedback loop to compensate automatically for any resistance errors. The operational amplifier drives the feedback voltage (generated in accordance with the sensed voltage at the current-sensing resistor and applied to one input of the operational amplifier) towards a reference voltage that is applied to the other input of the operational amplifier to bias the transistor(s) in the transconductance amplifier for desired operating conditions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
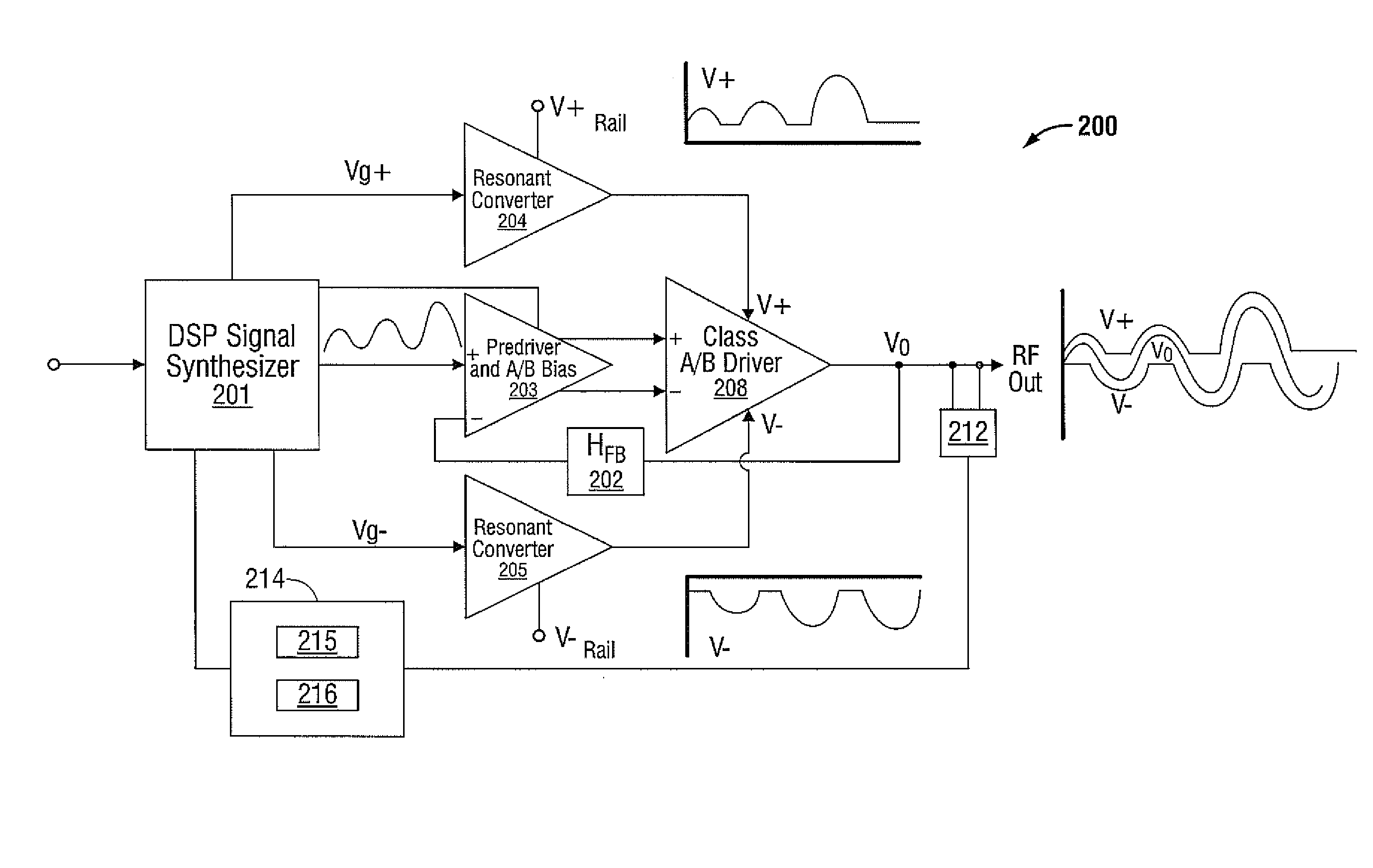
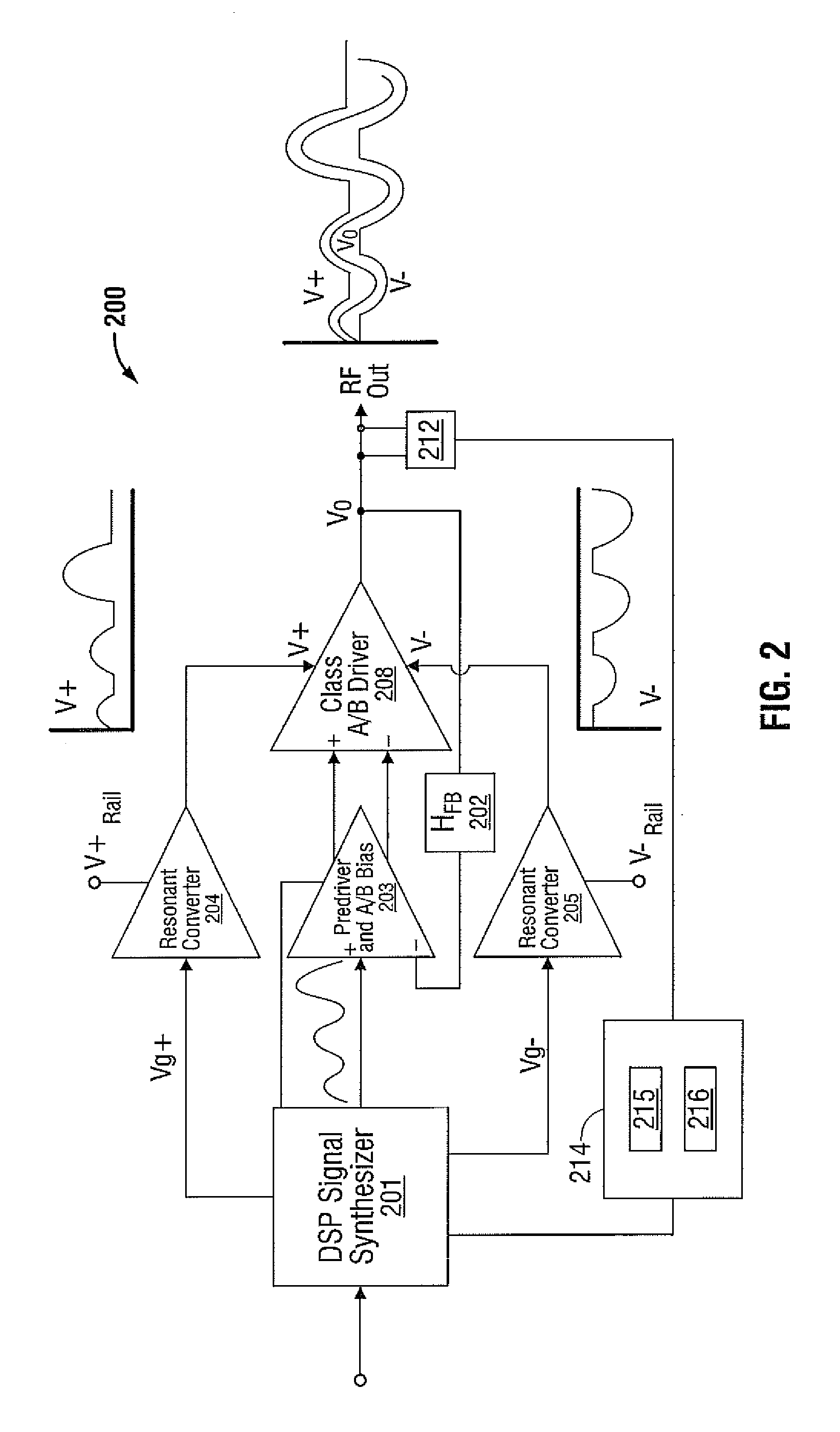
Class Resonant-H Electrosurgical Generators
A generator for use with an electrosurgical device is provided. The generator has a gain stage electrically disposed between a first voltage rail and a second voltage rail, wherein the gain stage includes an input and an output. A voltage source operably coupled to the gain stage input and configured to provide an input signal thereto responsive to a drive control signal is also provided. The generator also has one or more sensors configured to sense an operational parameter of the amplifier and to provide a sensor signal corresponding thereto and a controller adapted to receive the sensor signal(s) and in response thereto provide a drive control signal to the voltage source. The generator has an amplifier output configured to supply an output voltage corresponding to the first voltage rail and the second voltage rail when the output of the gain stage falls between a voltage of the first voltage rail and a voltage of the second voltage rail and is configured to supply a peak voltage output when the voltage output is falls greater than the voltage of the first voltage rail or less than the voltage of the second voltage rail.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Current sensor with calibration for a current divider configuration
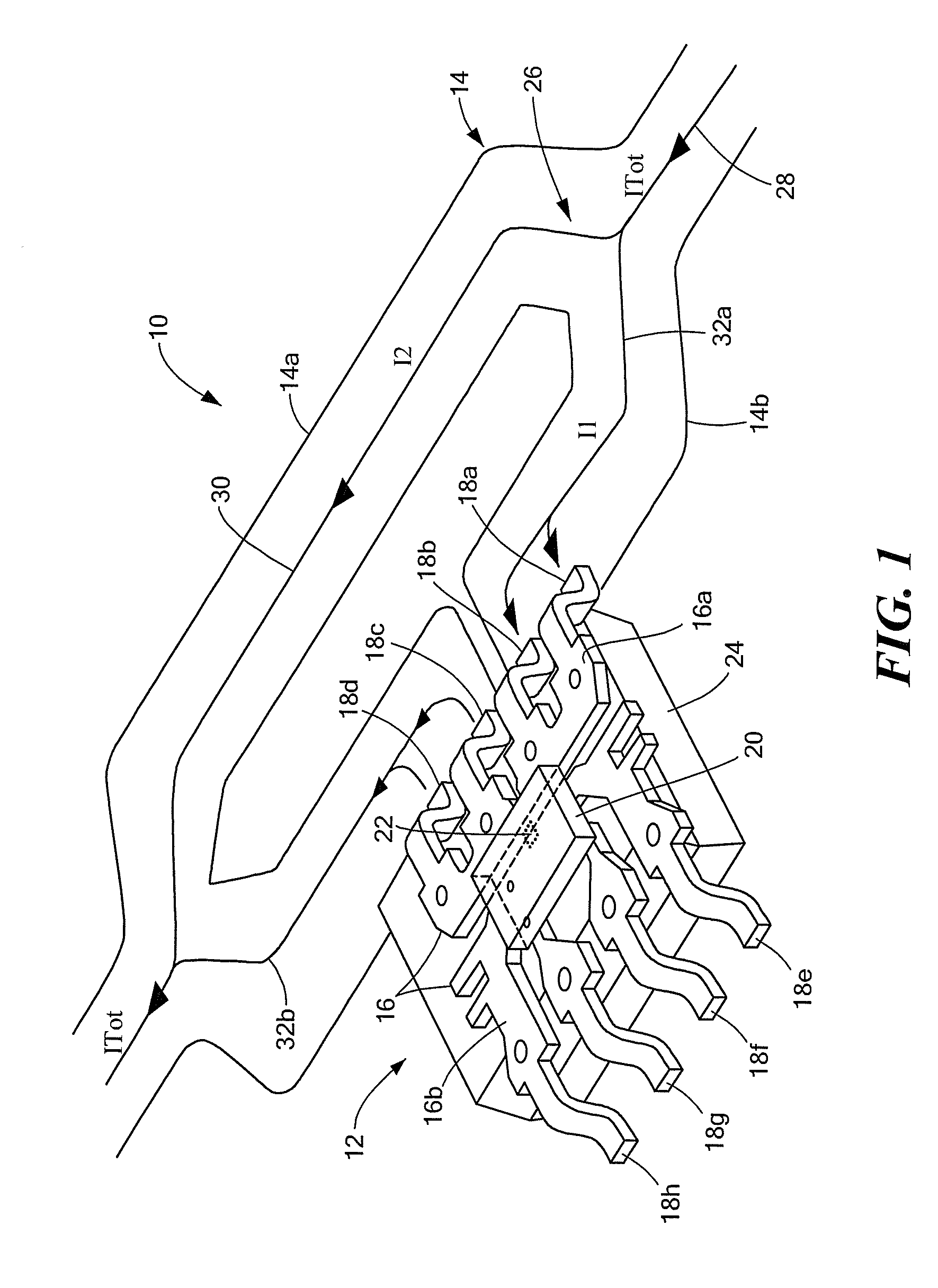
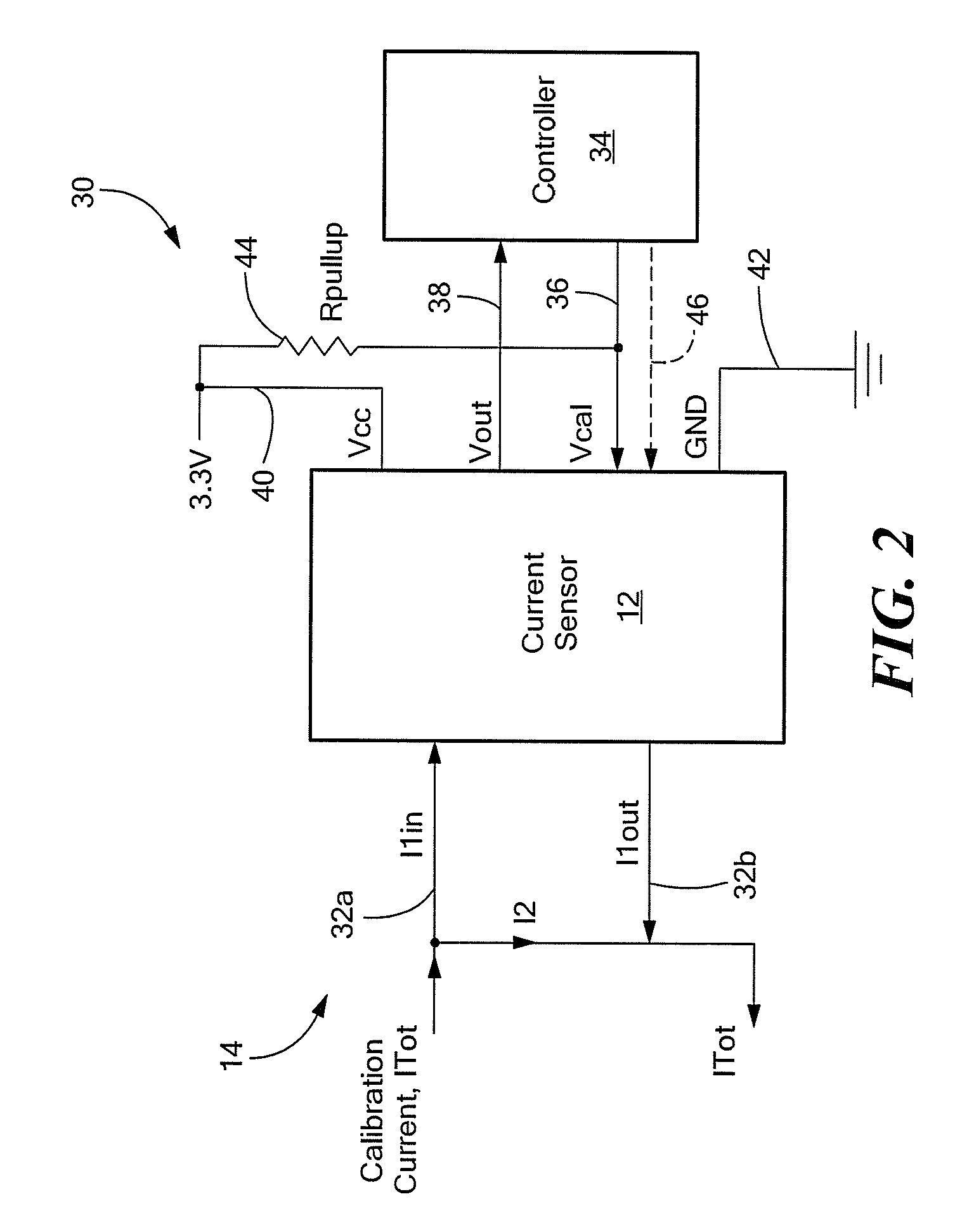
ActiveUS20130015843A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesBase element modificationsShunt DeviceElectrical conductor
An integrated circuit (IC) current sensor that self-calibrates to adjust its signal gain when employed in a current divider configuration is presented. The current sensor includes an integrated current conductor, a magnetic field transducer, a controllable gain stage and a calibration controller. The integrated current conductor is adapted to receive a portion of a calibration current. The calibration current corresponds to a full scale current. The magnetic field transducer, responsive to the calibration current portion, provides a magnetic field signal having a magnitude proportional to a magnetic field generated by the calibration current portion. The controllable gain stage is configured to amplify the magnetic field signal with an adjustable gain to provide an amplified magnetic field signal. The calibration controller is responsive to a calibration command signal to adjust the adjustable gain of the controllable gain stage to a calibrated gain in order to provide the amplified magnetic field signal at a predetermined voltage level that corresponds to a desired current sensor output signal voltage level if the full scale current were received by the integrated current conductor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Multiple-voltage supply power amplifier with dynamic headroom control
InactiveUS6417736B1Reduce circuit areaHigh voltagePush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersAudio power amplifierVoltage source
A monolithic integrated circuit amplifier has a gain stage and a buffer stage. The buffer stage includes an output stage and two separate voltage supplies, the second of which has a greater magnitude than the first. Switching circuitry is included that is connected to the output stage via a regulator bus. When an output demand voltage is less than a switch-over threshold, current to the output stage is provided substantially from the first voltage supply; when the output demand voltage is greater than the switch-over threshold, current to the output stage is provided substantially from the second voltage supply. Collector voltage at the output stage is dynamically controlled to be greater than the emitter voltage by a difference voltage that increases proportionally as output voltage increases above the switch-over threshold. This difference voltage is commonly referred to as "headroom." The dynamic headroom control circuitry preferably includes means for predictably setting and controlling the headroom voltage at switch-over and smoothly increasing the headroom voltage up to maximum output voltage.
Owner:LEWYN CONSULTING
Gain linearizer for variable gain amplifiers
InactiveUS6711391B1Improve performanceResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
Techniques to linearly (in dB) adjust the gains of variable gain elements (i.e., variable gain amplifiers or VGAs) in a receiver or transmitter. An input control signal is provided to a conditioning circuit that conditions the control signal to achieve various signal characteristics. The input control signal is limited to within a particular range of values, temperature compensated, scaled (or normalized) to the supply voltages, shifted with an offset, or manipulated in other fashions. The conditioned signal is then provided to an input stage of a linearizer that generates a set of exponentially related signals. This is achieved using, for example, a differential amplifier in which the conditioned control signal is applied to the inputs of the differential amplifier and the collector currents from the differential amplifier comprises the exponentially related signals. An output stage within the linearizer receives the exponentially related signals and, in response, generates a gain control signal. By approximately matching the output stage to a gain stage of the variable gain element and by using the gain control signal generated by output stage, the gain transfer function of the VGA approximates that of the exponentially related signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
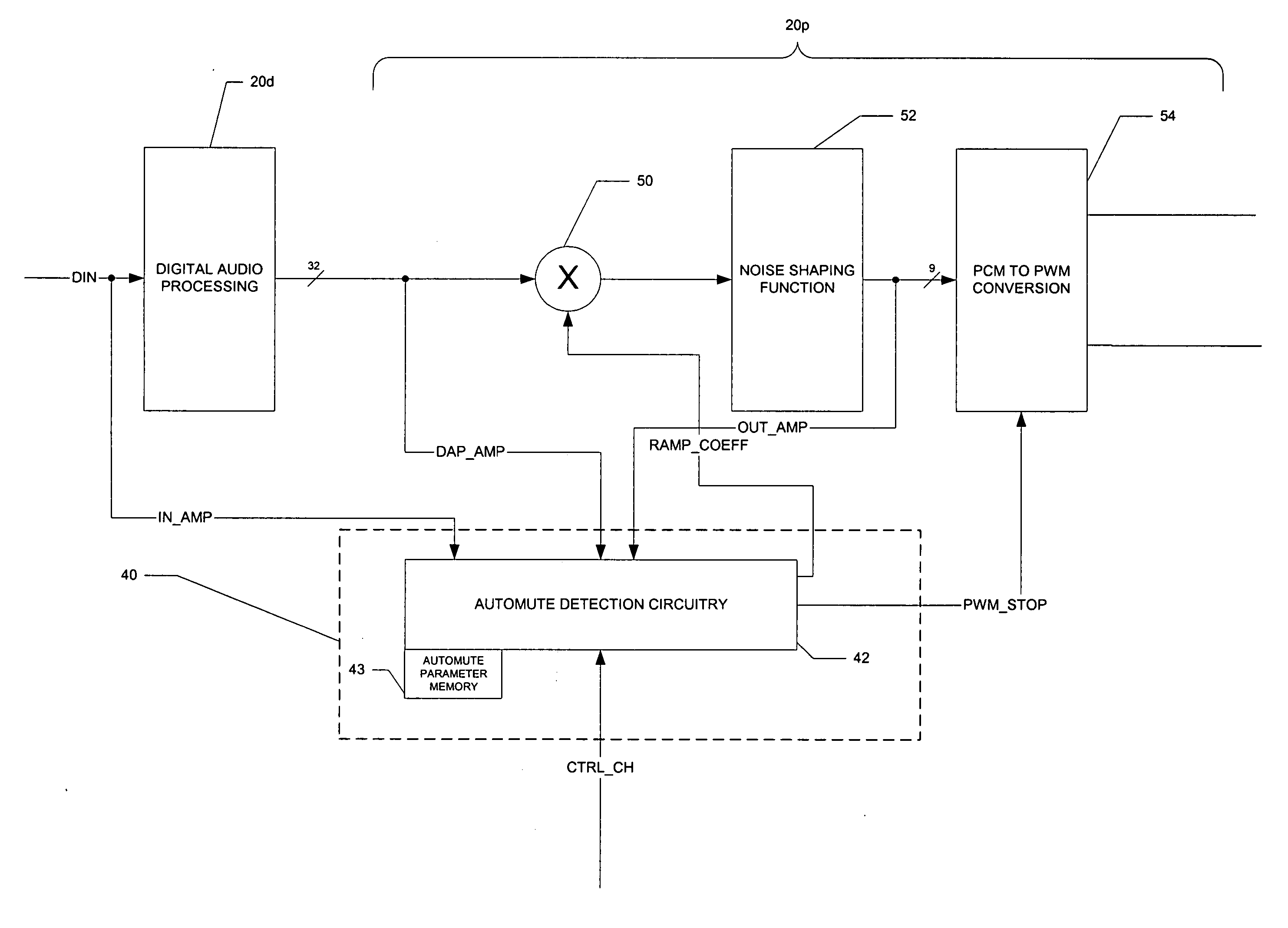
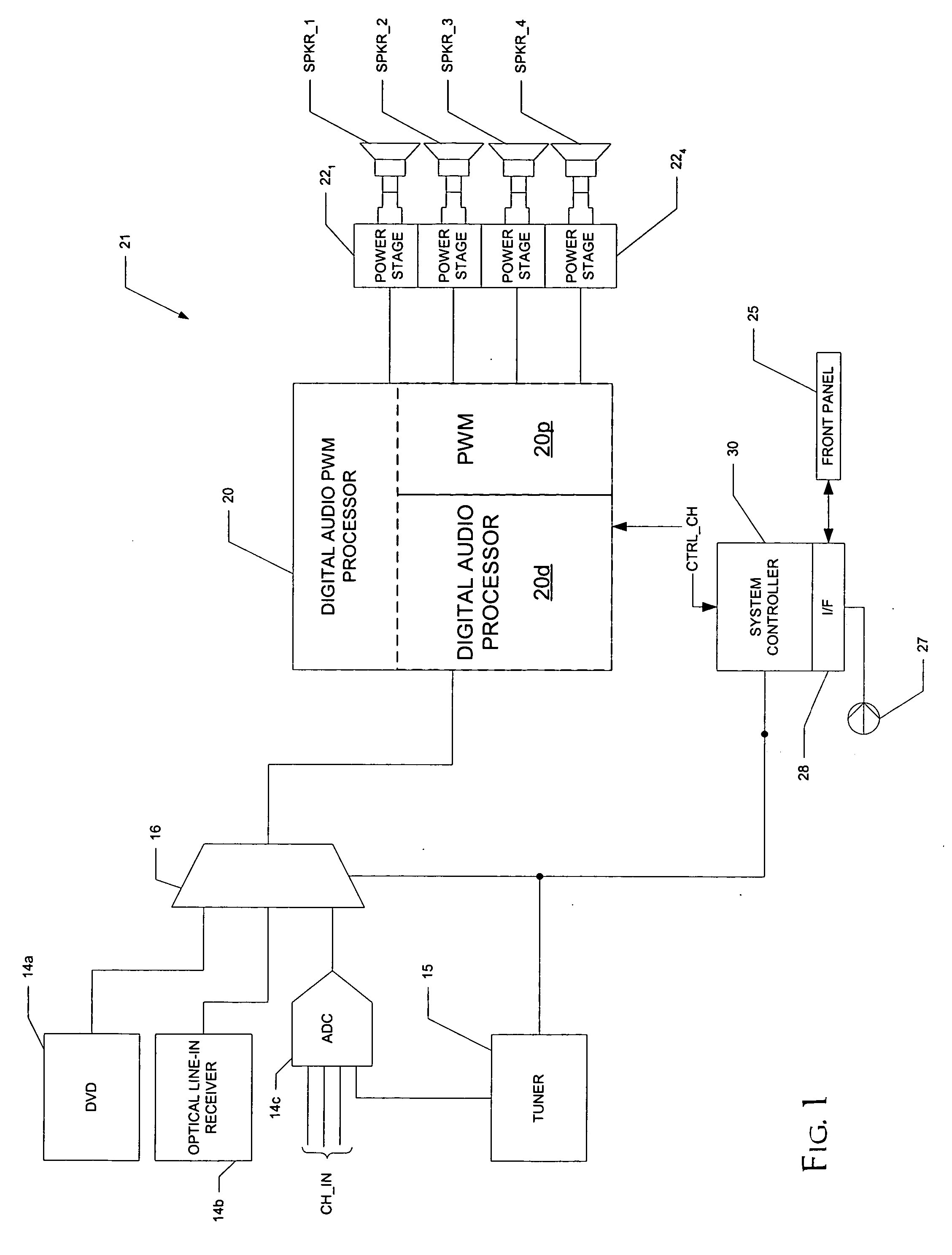
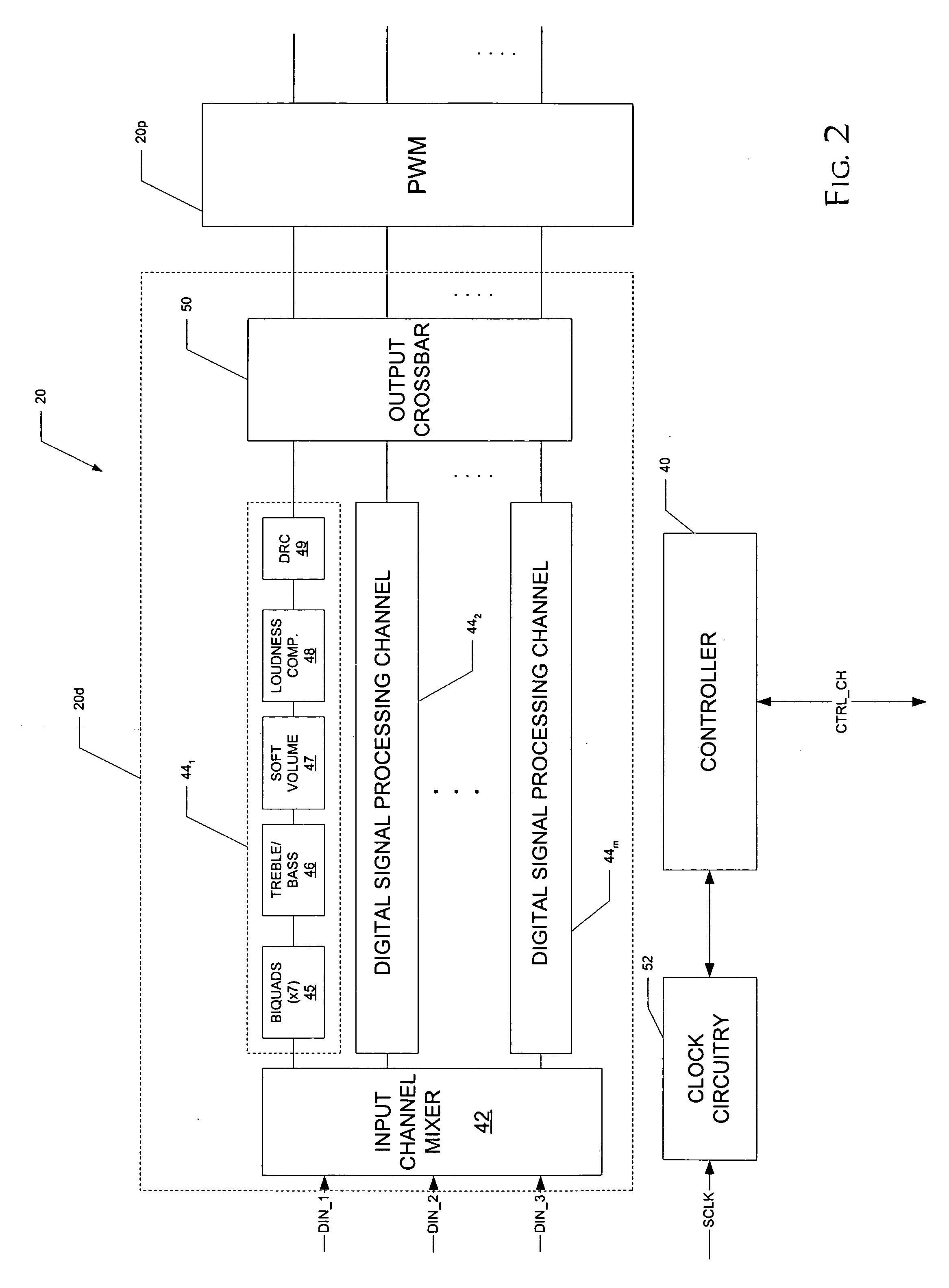
Automute detection in digital audio amplifiers
ActiveUS20070005160A1Rapidly automuteRapidly unmuteAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlHysteresisDigital filter
A digital audio processor (20) for a digital audio receiver (21) having an improved automute sequence is disclosed. The digital audio processor (20) includes automute detection circuitry (42) that monitors the amplitude of digital audio signals before and after the application of digital filters by digital audio processing circuitry (20d). The amplitude of the input signals are compared against a first threshold level, while the amplitude of the output signals are compared against a second threshold level. In response to the amplitude of the input signals for all of the audio channels (44) falling below the first threshold for a selected time period, a gain stage (50) in each channel ramps down the volume to a mute level, and pulse-width-modulation circuitry (54) is disabled. If the output signal amplitude falls below a second threshold for a channel, the pulse-width-modulation circuitry (54) for that channel is disabled. Hysteresis for the input signal amplitude is preferably added into the automute exit determination.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
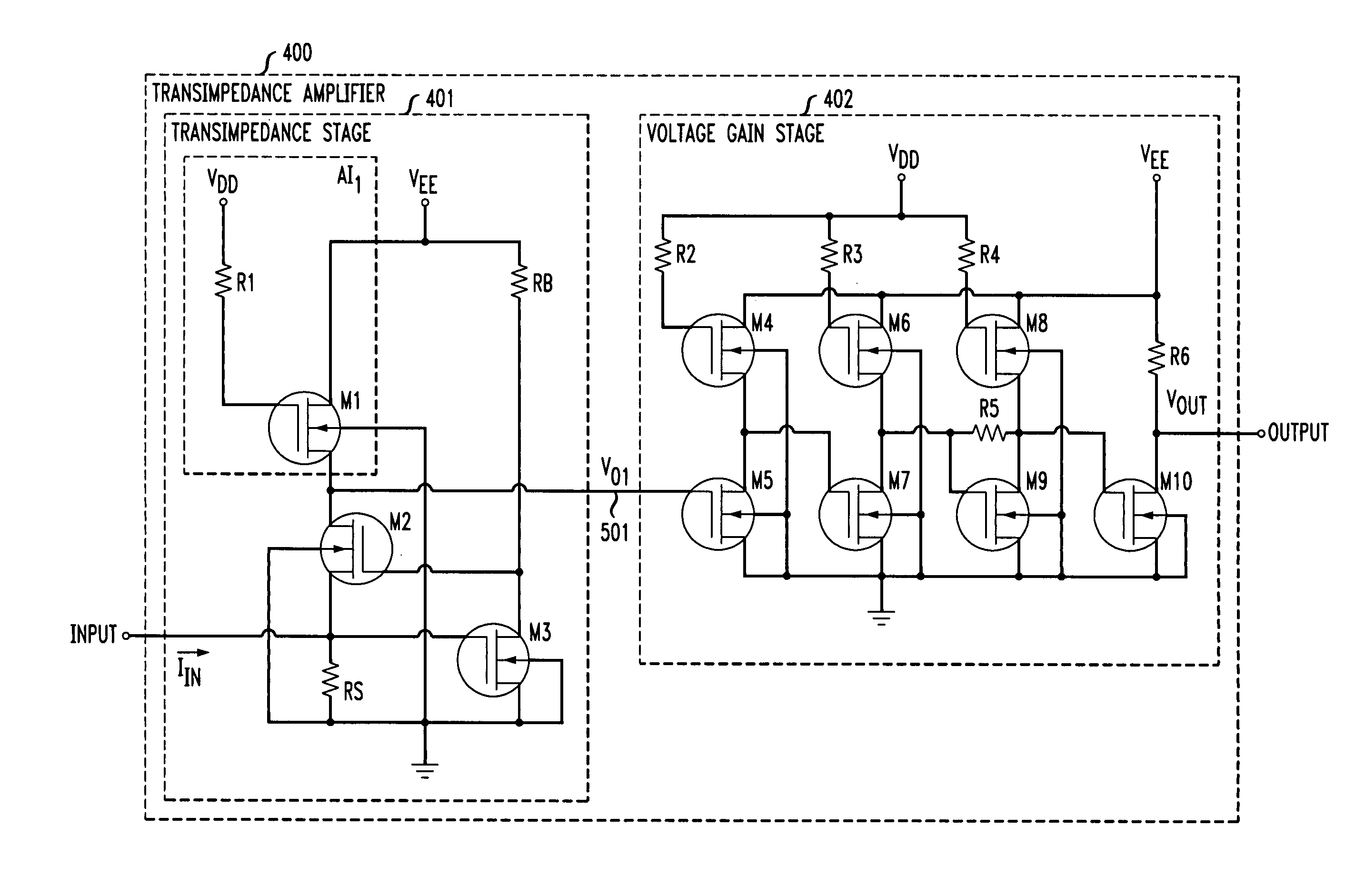
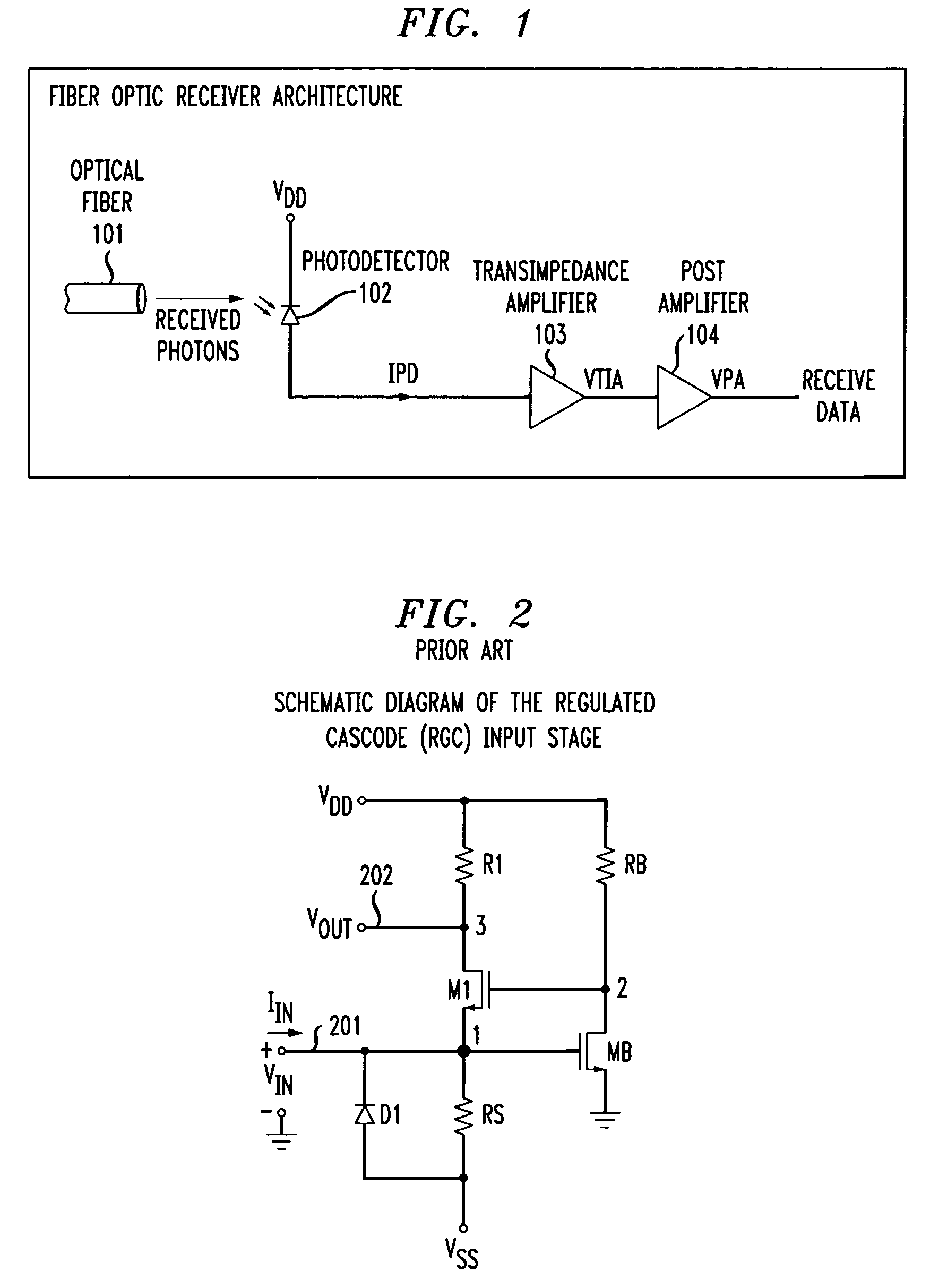
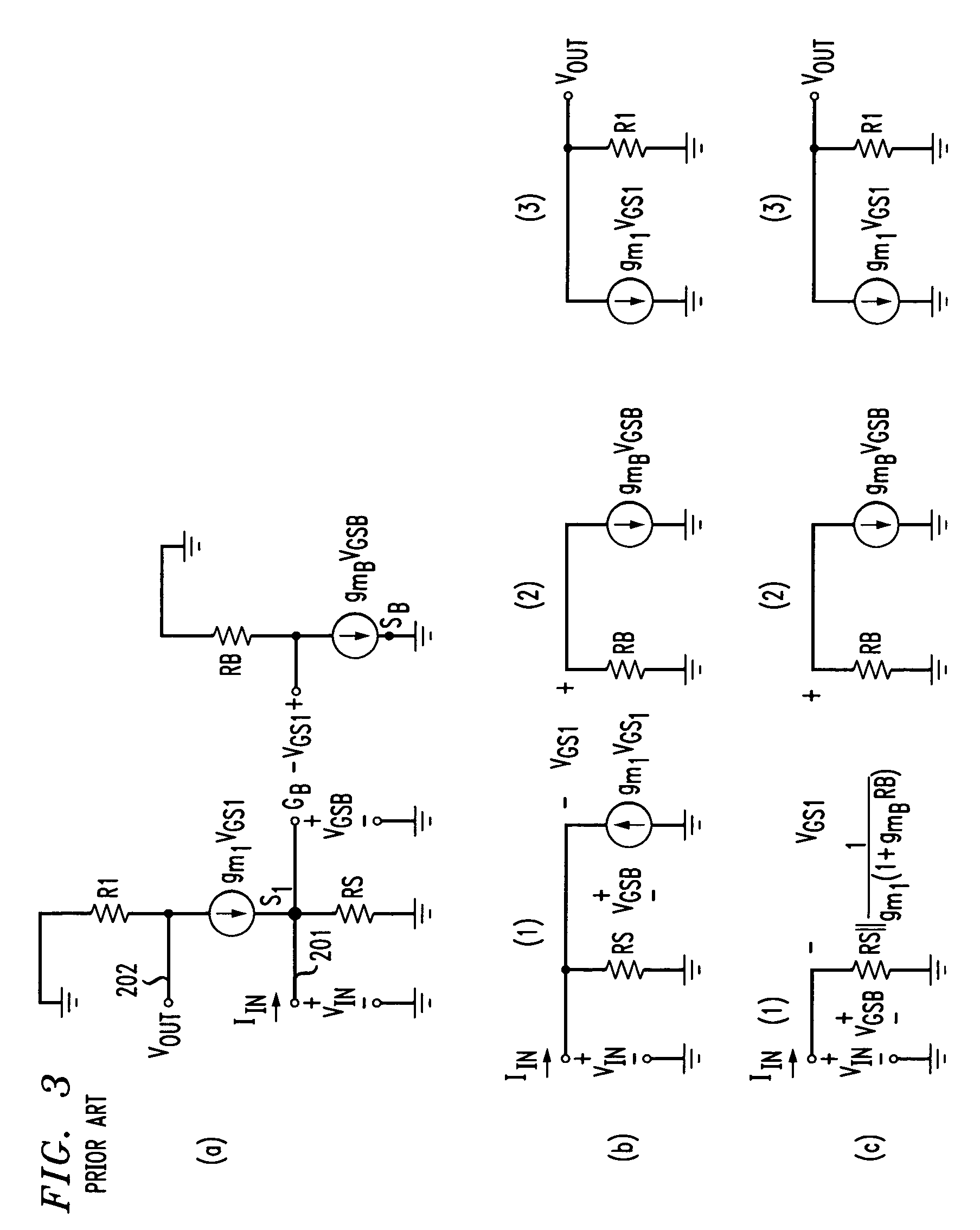
Transimpedance amplifier
InactiveUS7135932B2Minimise currentWide bandwidthAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierEngineering
A transimpedance amplifier, which is useful as an optical fiber preamplifier, is disclosed. The illustrative embodiment exhibits four characteristics. First, it minimizes the equivalent input noise current. Second, it has a wide bandwidth. Third, it has a reasonably large output voltage, and fourth, it is stable over wide temperature and voltage ranges. The illustrative embodiment comprises a transimpedance stage and a gain stage. Both stages employ a pure NMOS design which contributes to the above four advantages. Bandwidth is further increased over the prior art by the use of inductive loads. The inductive loads of the illustrative embodiment are not physical inductors, but transistor-based “active” inductors: the combination of a resistor connected in series with the gate of an NMOS transistor.
Owner:SIRES LABS
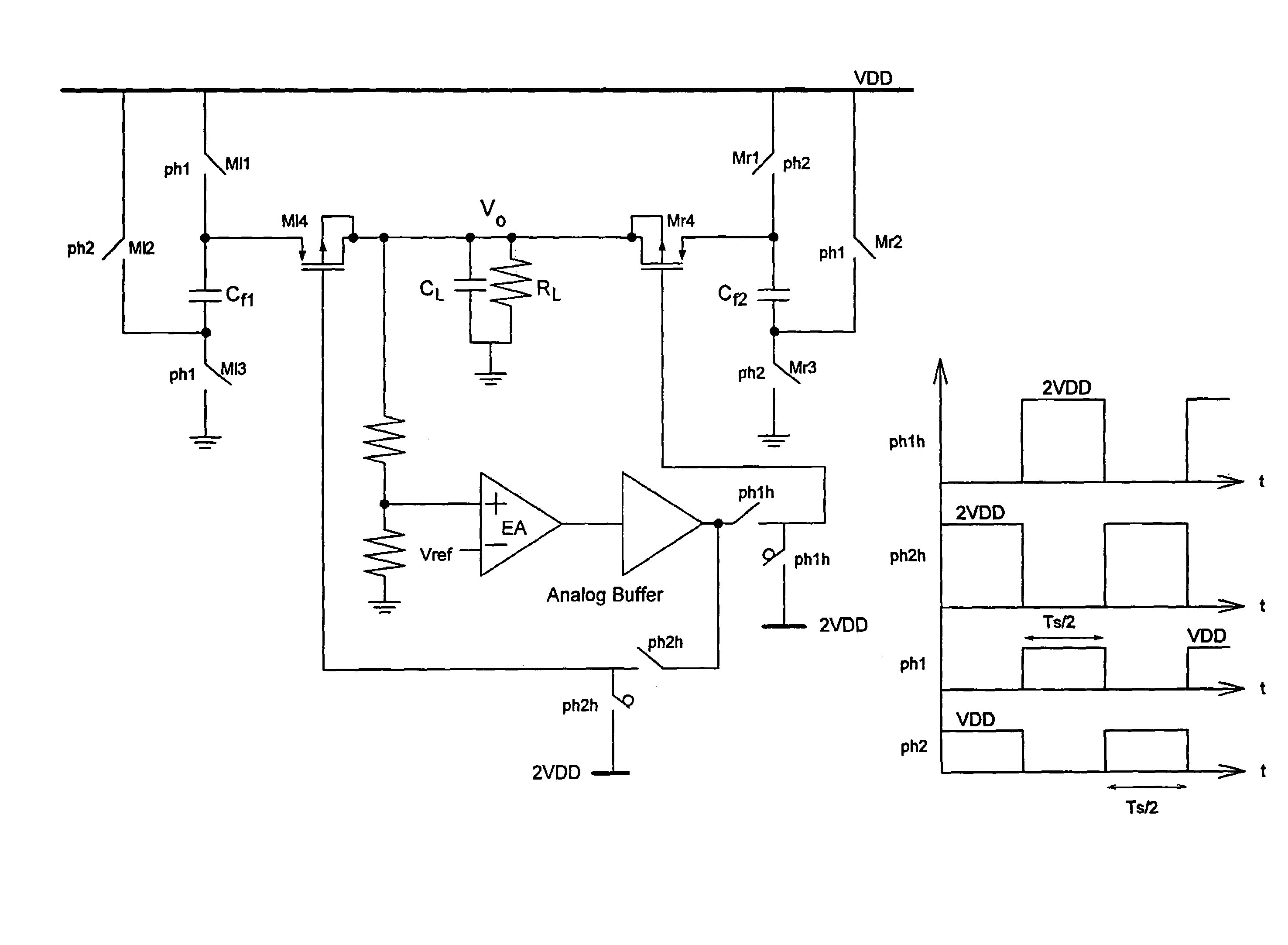
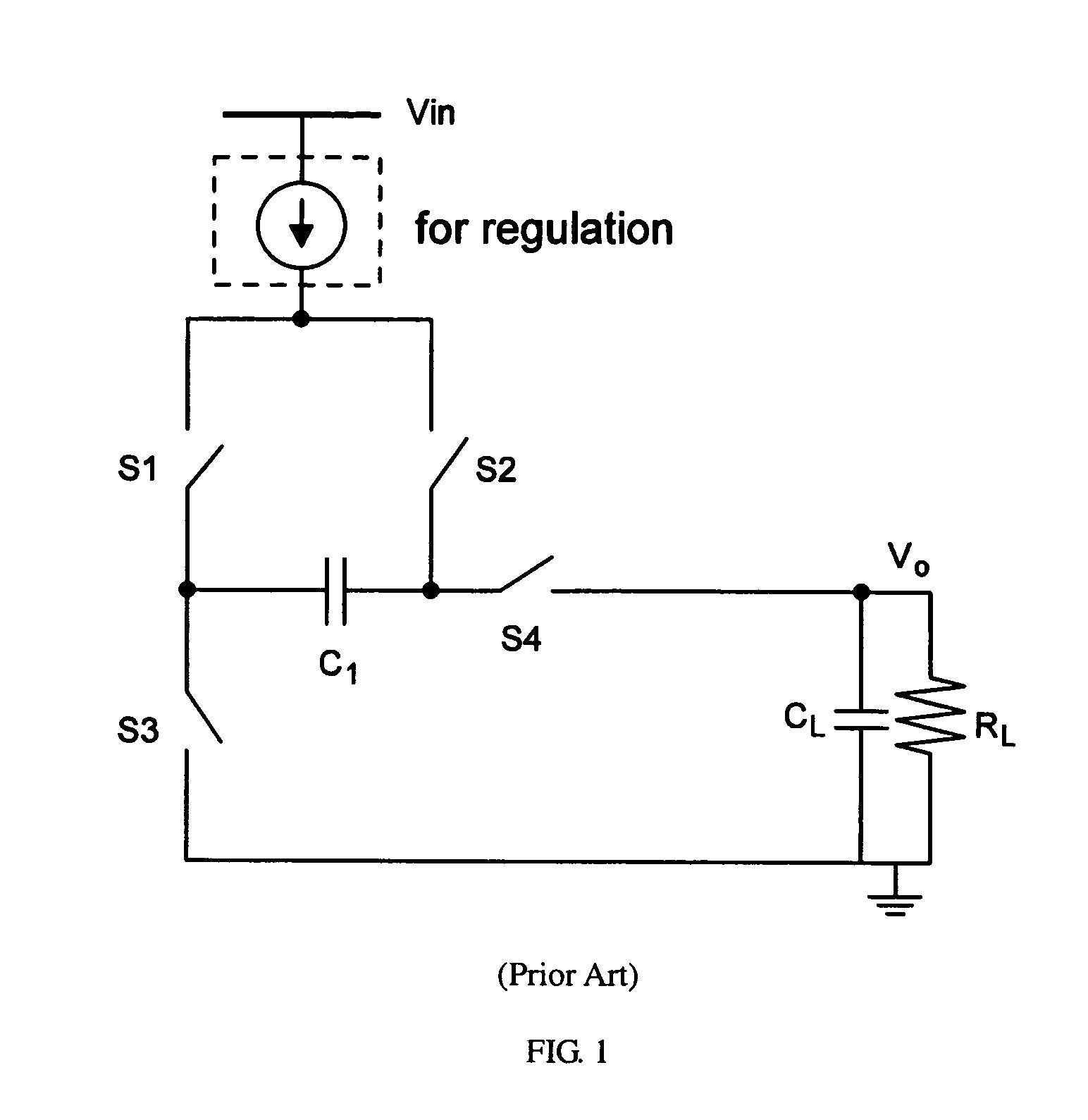
Switched-capacitor regulators
ActiveUS7375992B2Improve area efficiencyIncreases magnitudeAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitancePole splitting
A switched-capacitor regulator is provided for regulating the output voltage of a voltage supply. The switched-capacitor regulator includes a supply input terminal capable of receiving a supply voltage, two or more flying capacitors, a regulation switch located between each flying capacitor and the supply input terminal, and a voltage control circuit. The activity of the regulation switches is controlled by the voltage control circuit. In one embodiment of the invention, the voltage control circuit includes a feedback resistance area having one or more feedback resistors located between the output of the flying capacitors and a ground terminal, a first gain stage connected to the feedback resistance area, and two or more second switchable gain stages, which are each connected to a regulation switch and the first gain stage. The switched-capacitor regulator operates in pseudo-continuous regulator mode using three-stage switchable operational amplifiers with time-multiplexed pole-splitting compensation.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
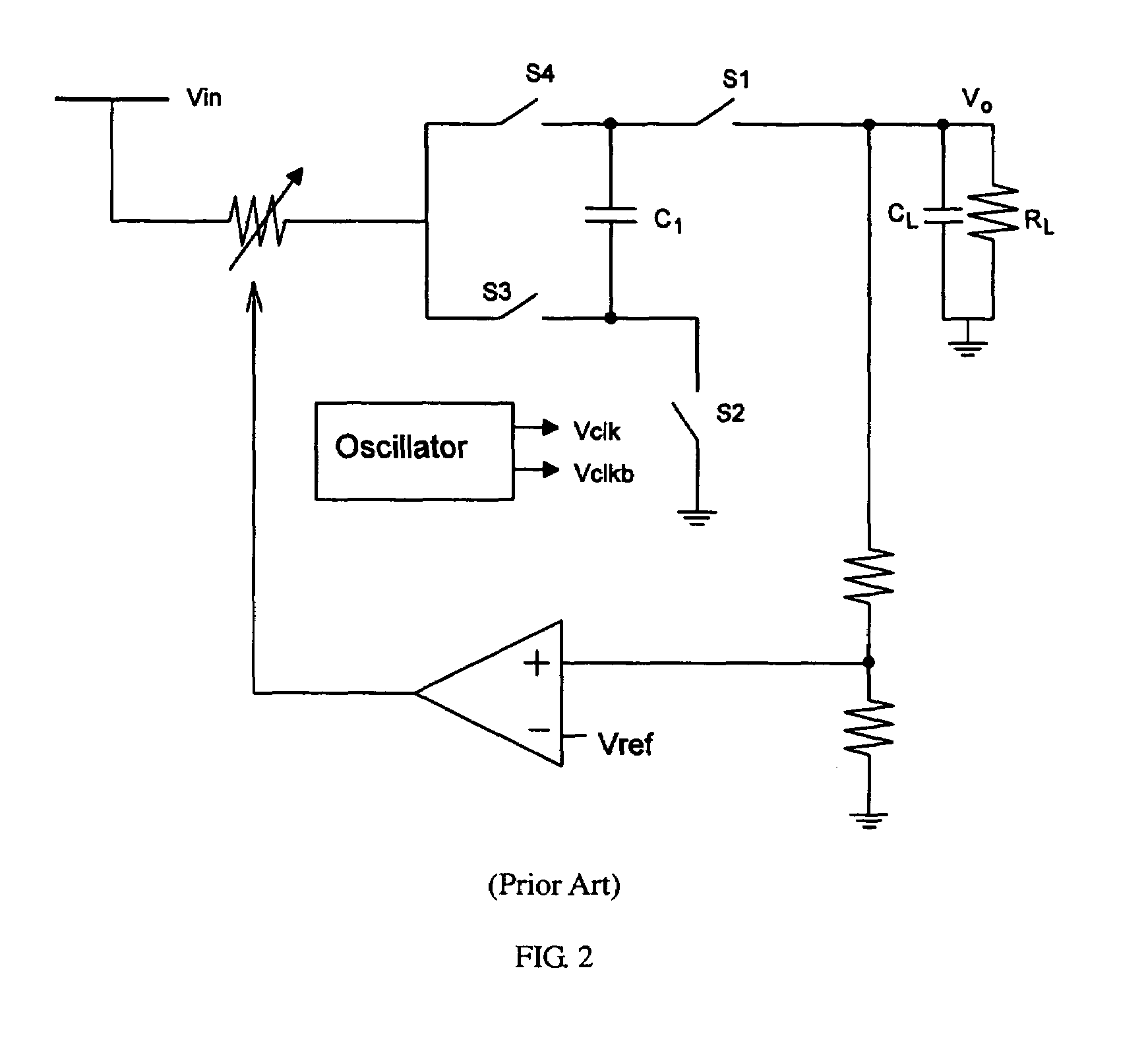
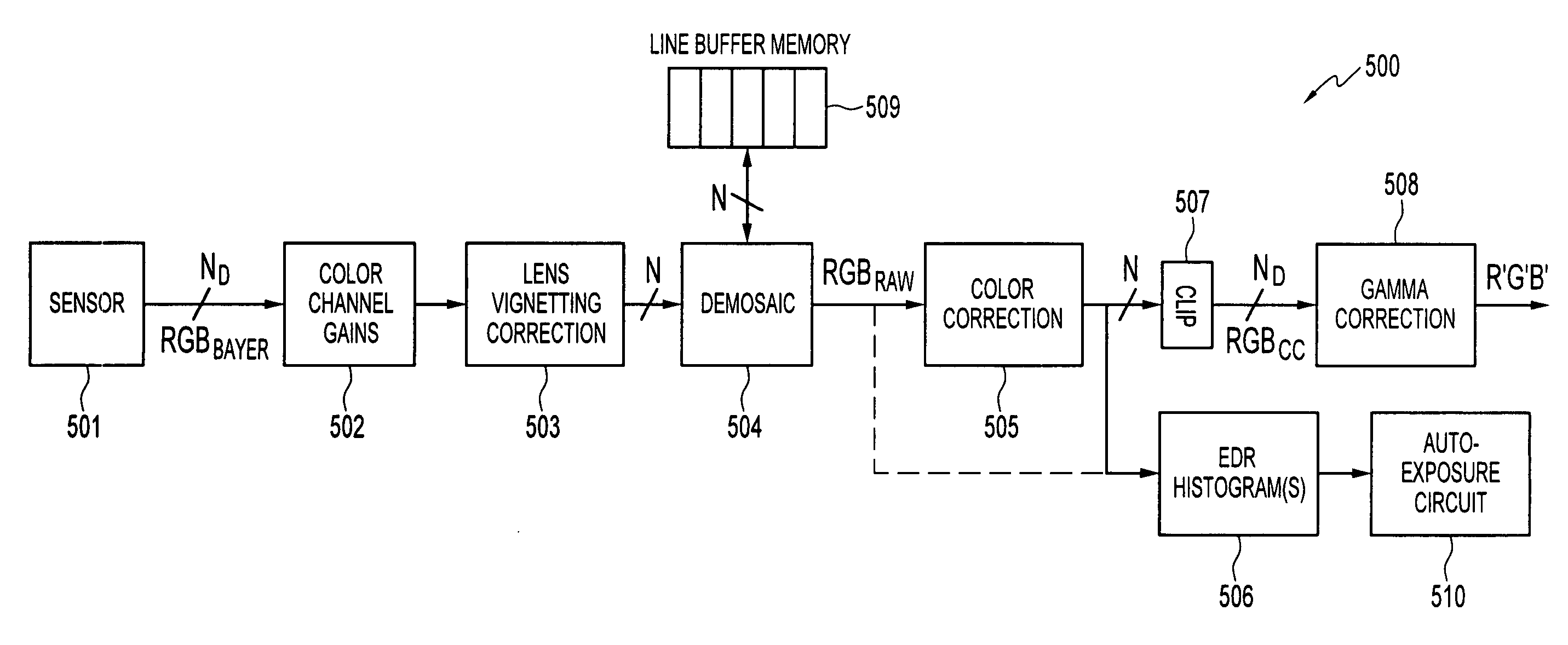
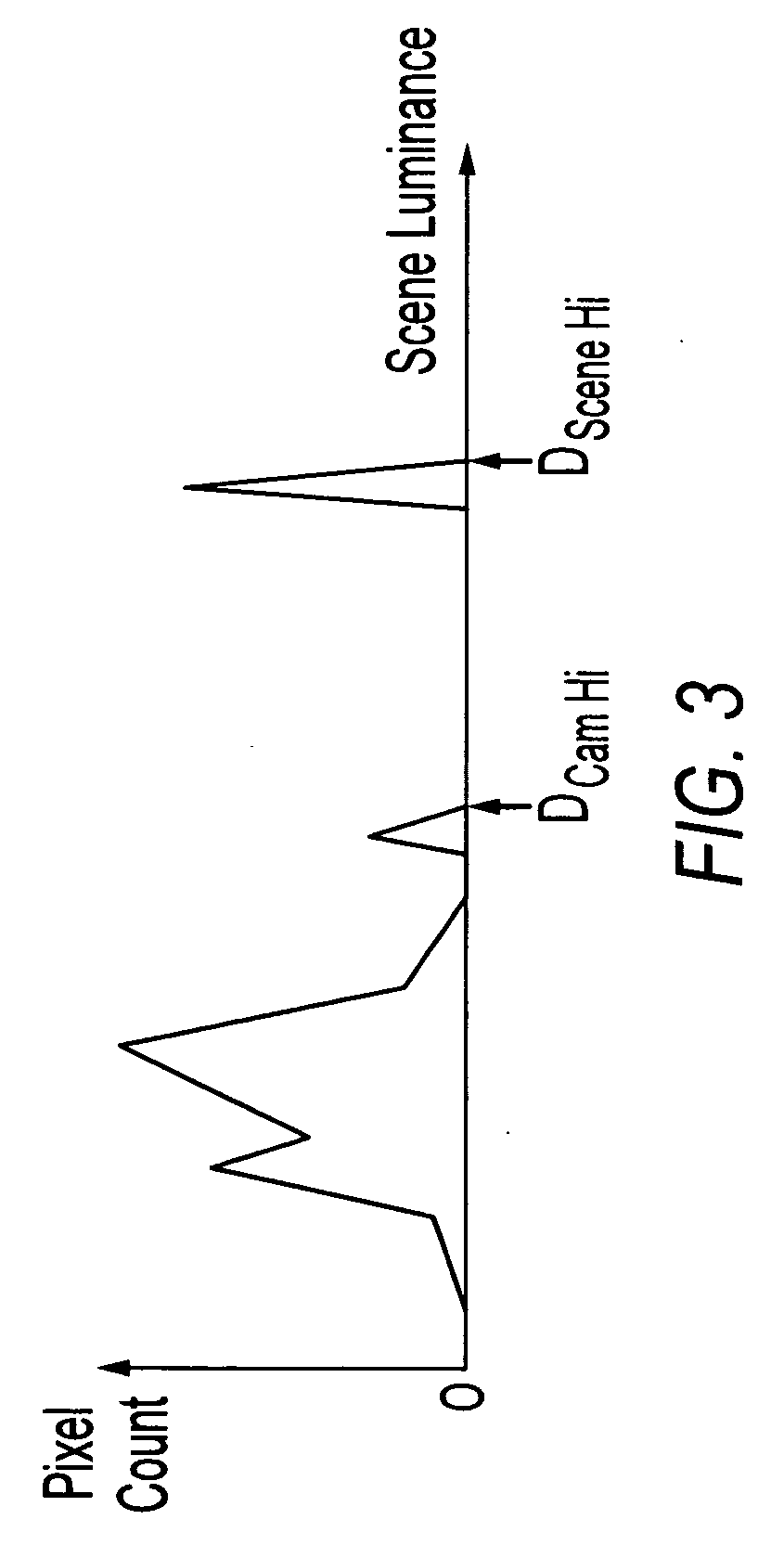
Method, apparatus and system for dynamic range estimation of imaged scenes
ActiveUS20080056704A1Television system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensExposure Elapsed Time
A method, apparatus, and system for dynamic range estimation of imaged scenes for automatic exposure control. For a given exposure time setting, certain areas of a scene may be brighter than what a camera can capture. In cameras, including those experiencing substantial lens vignetting, a gain stage may be used to extend dynamic range and extract auto-exposure data from the extended dynamic range. Alternatively, dynamic range can be extended using pre-capture image information taken under reduced exposure conditions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
DC offset correcting in a direct conversion or very low IF receiver
InactiveUS7136431B2Reduce cancellationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationEngineeringLow IF receiver
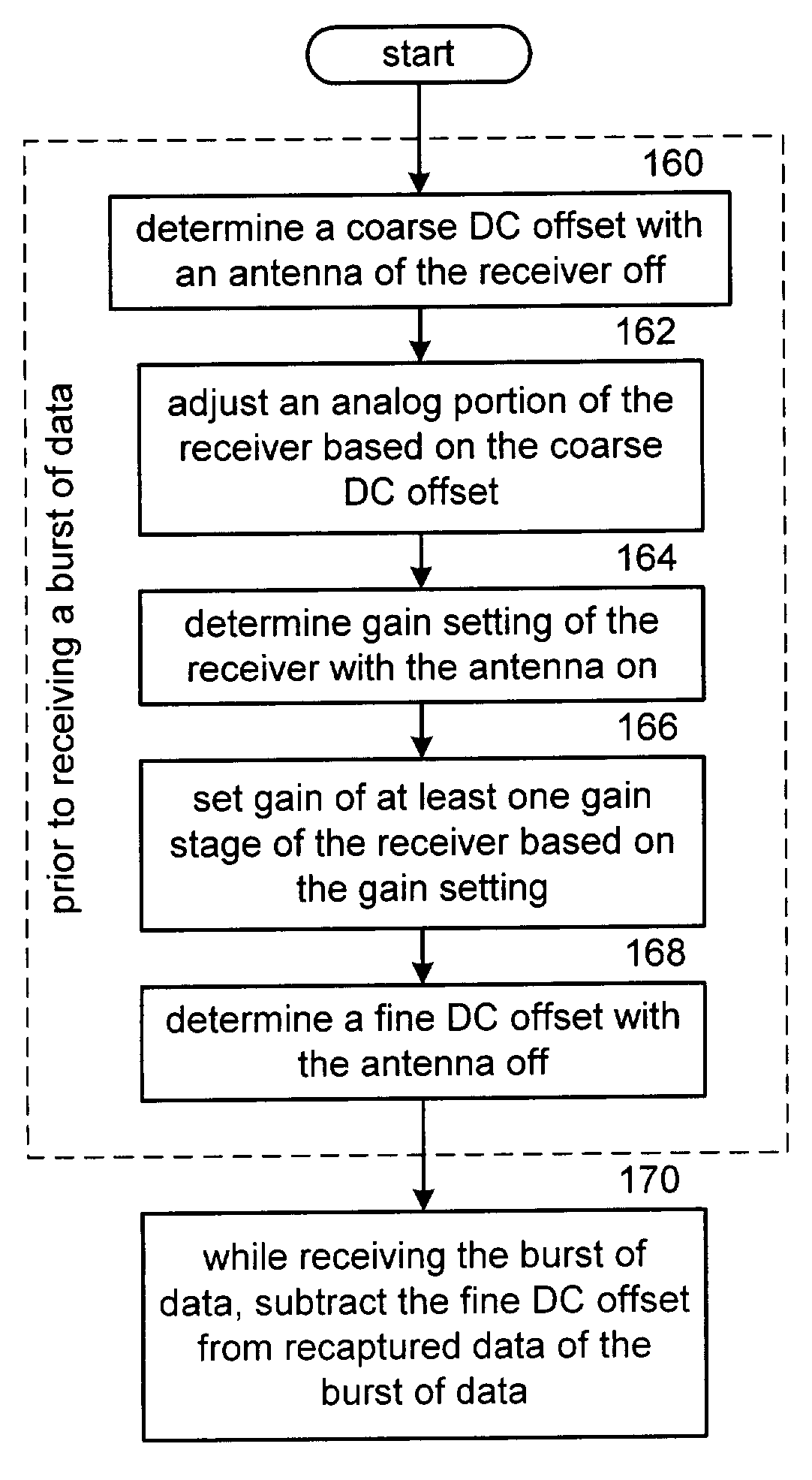
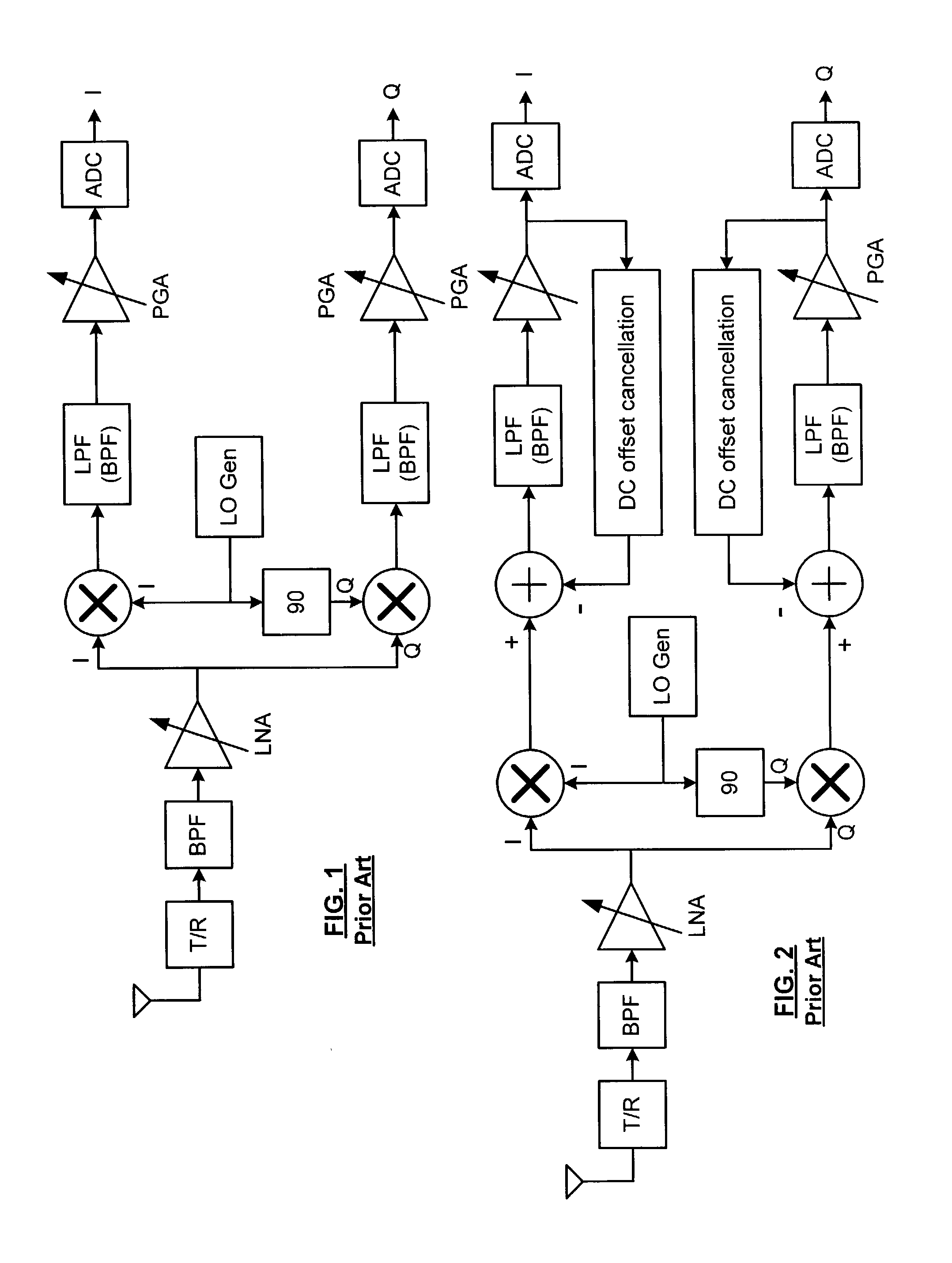
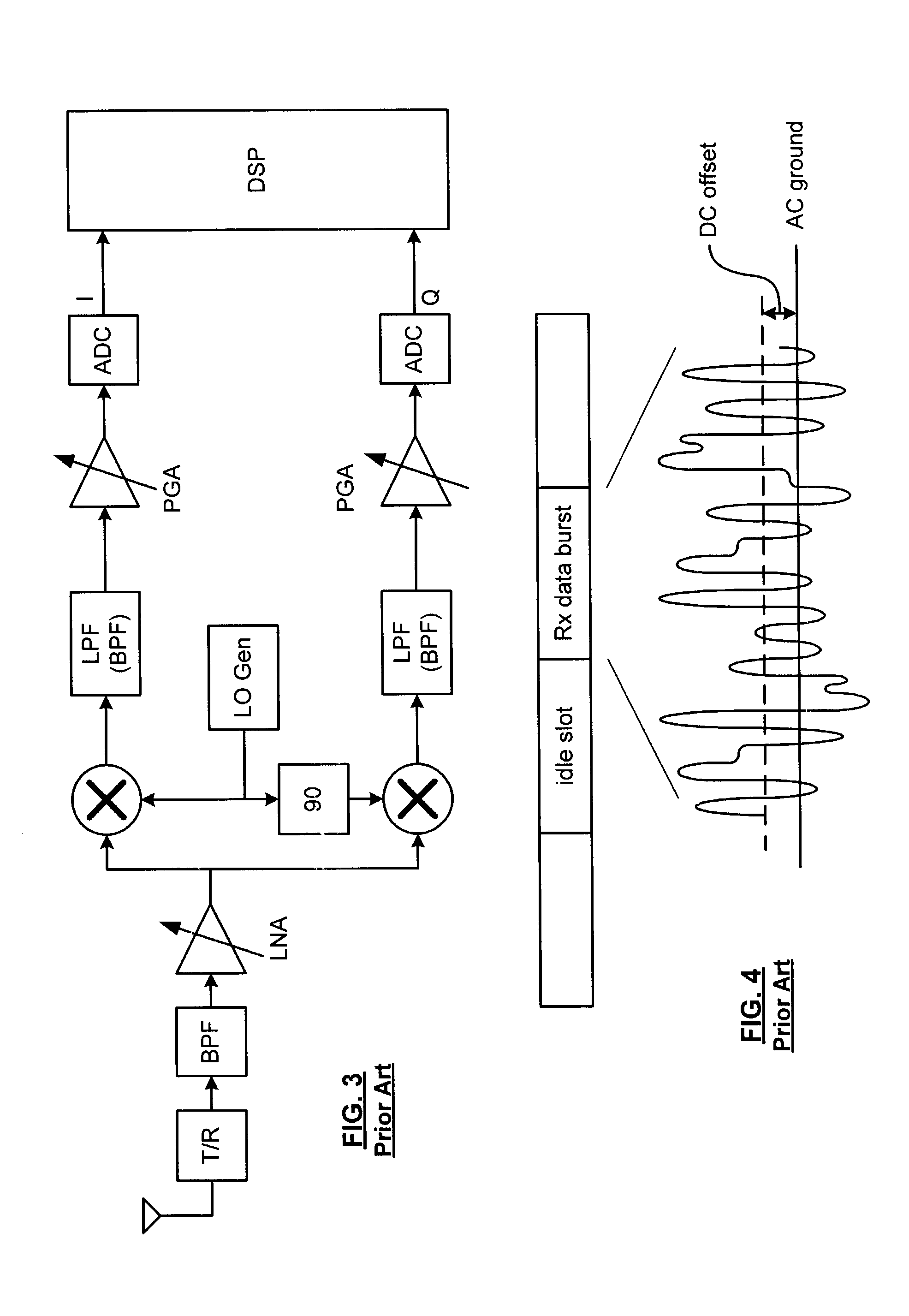
A direct conversion or VLIF receiver corrects DC offset by, prior to receiving a burst of data, the receiver determines a coarse DC offset with the antenna of the receiver switched off. The receiver then adjusts an analog portion of the receiver (e.g., the output of the mixers) based on the coarse DC offset. The receiver then determines a gain setting of the receiver (e.g., for the low noise amplifier and / or programmable gain amplifiers) with the antenna on. The receiver then sets the gain of at least one gain stage of the receiver based on the gain setting. The receiver then determines a fine DC offset with the antenna off. The receiver then, while receiving a burst of data, subtracts the fine DC offset from the digital baseband or low IF signal prior to data recovery.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
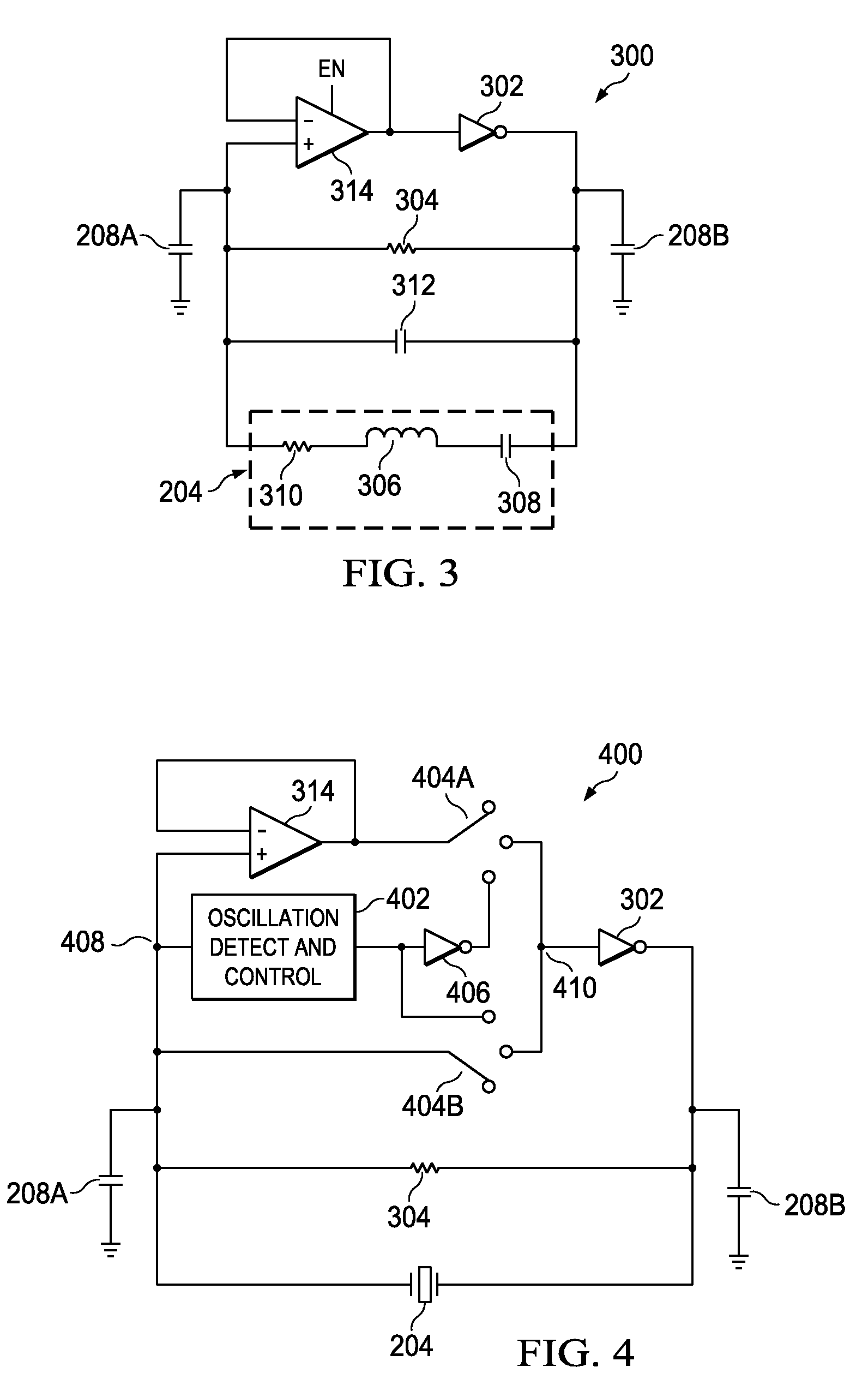
Fast start-up crystal oscillator
ActiveUS20110037527A1Reduce startup timeImprove the immunityPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsStart up timeSnubber
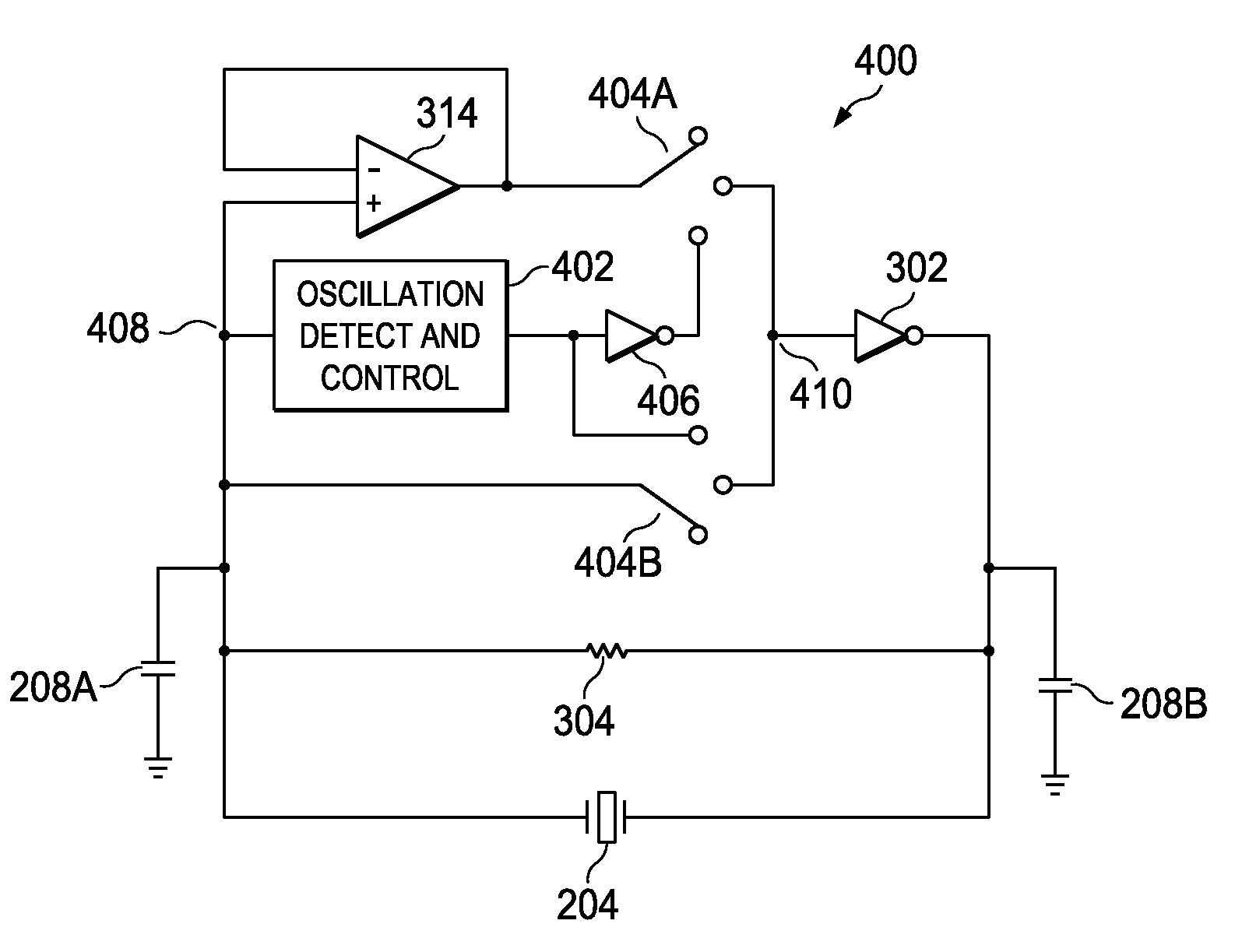
An exemplary fast start-up crystal oscillator with reduced start-up time. The exemplary oscillator reduces the start-up time (i.e., the time taken to attain sustained stable oscillations after the power is turned on) by increasing the negative resistance of a circuit. Increasing the negative resistance increases the rate of growth of the oscillations, thereby reducing start-up time. The exemplary crystal oscillator includes a gain stage with negative resistance. A crystal with shunt capacitance is placed in the feedback loop of the gain stage. A buffer is coupled to the gain stage such that it blocks the crystal shunt capacitance from loading the gain stage, effectively increasing the negative resistance of the gain stage. Further, an oscillation detection and control circuit is coupled between the crystal and the gain stage. The oscillation detection and control circuit connects the buffer during start-up, and disconnects the buffer once an oscillation signal attains sustained stable oscillations.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com