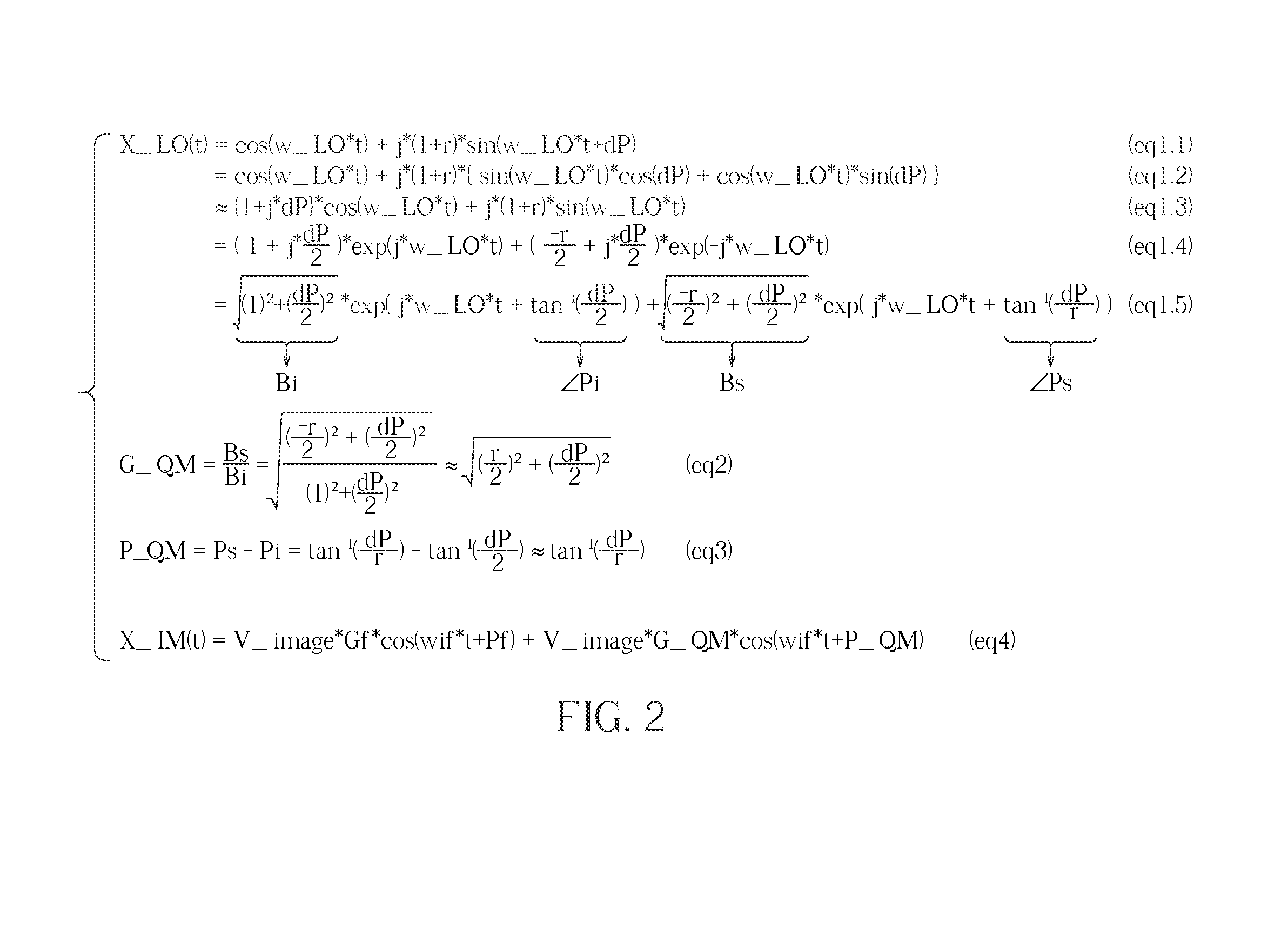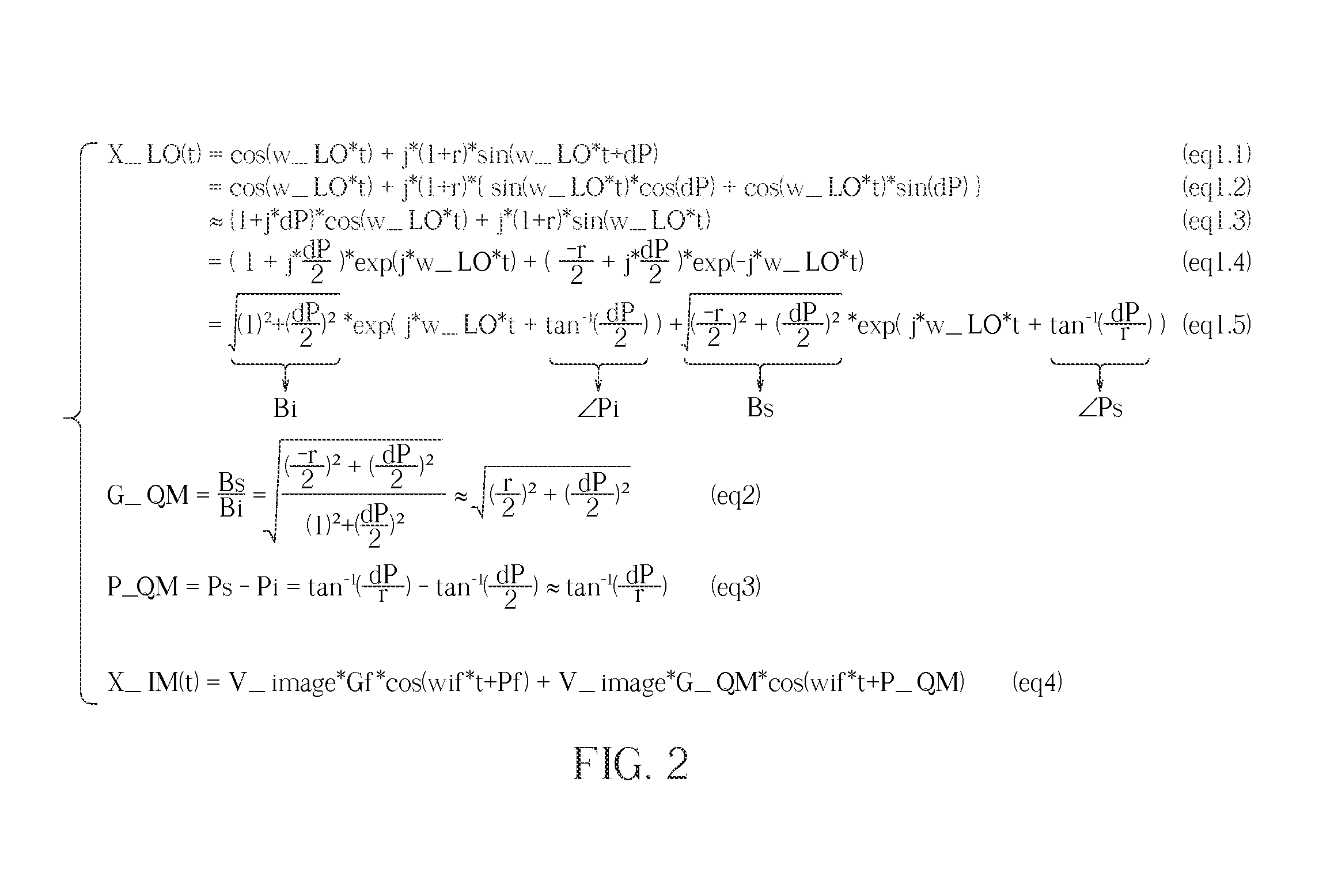Patents
Literature
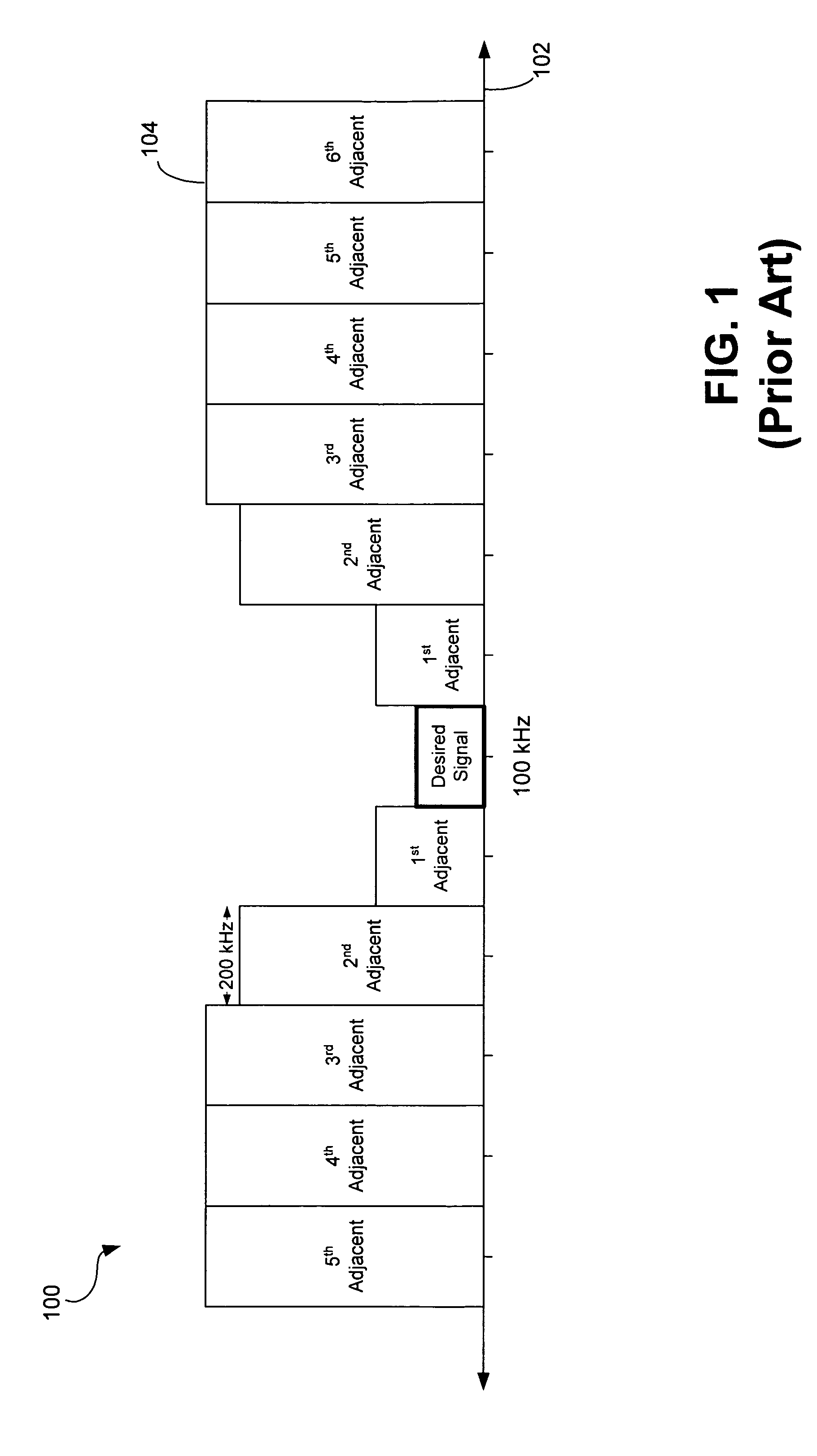
40 results about "Low IF receiver" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
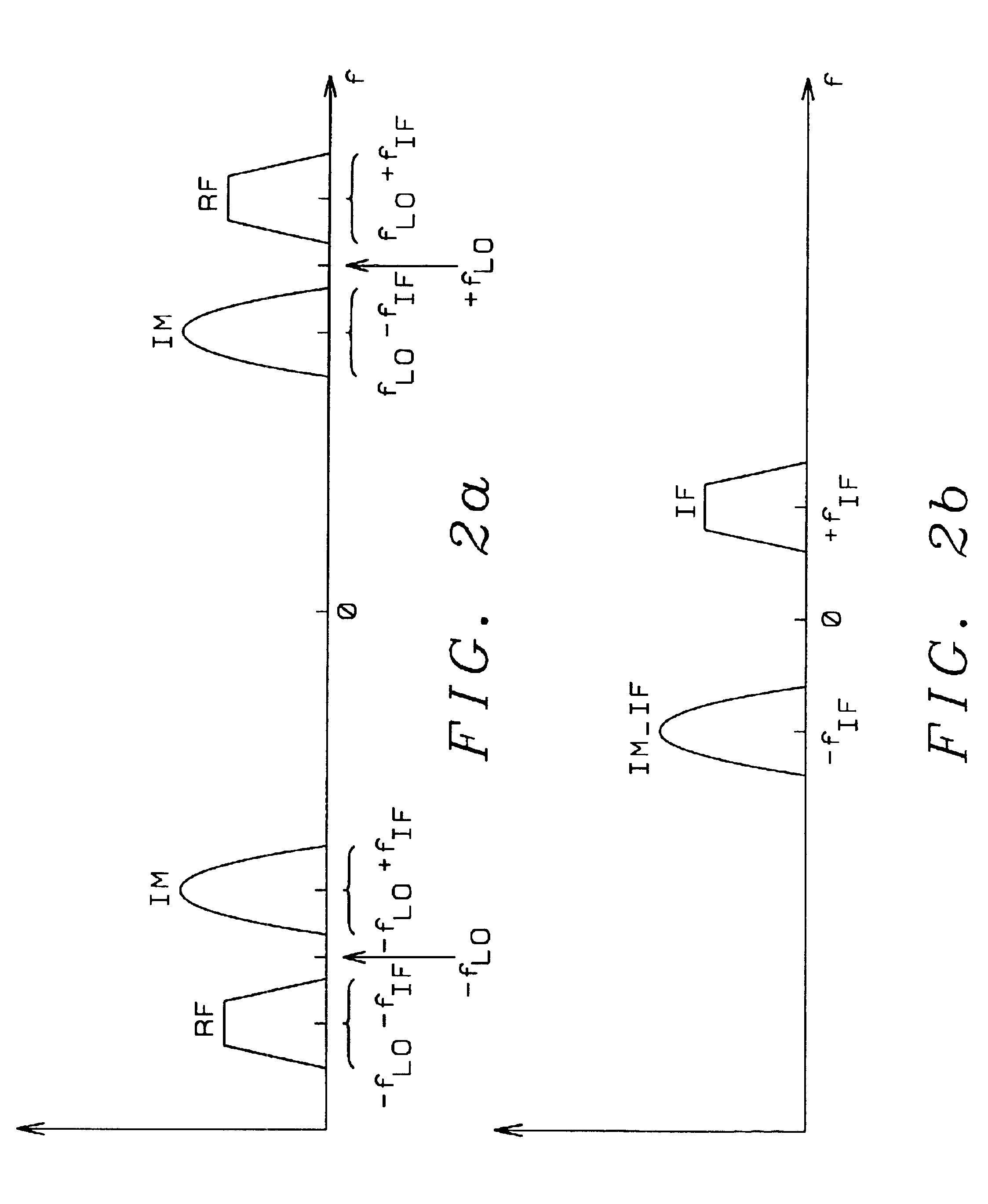
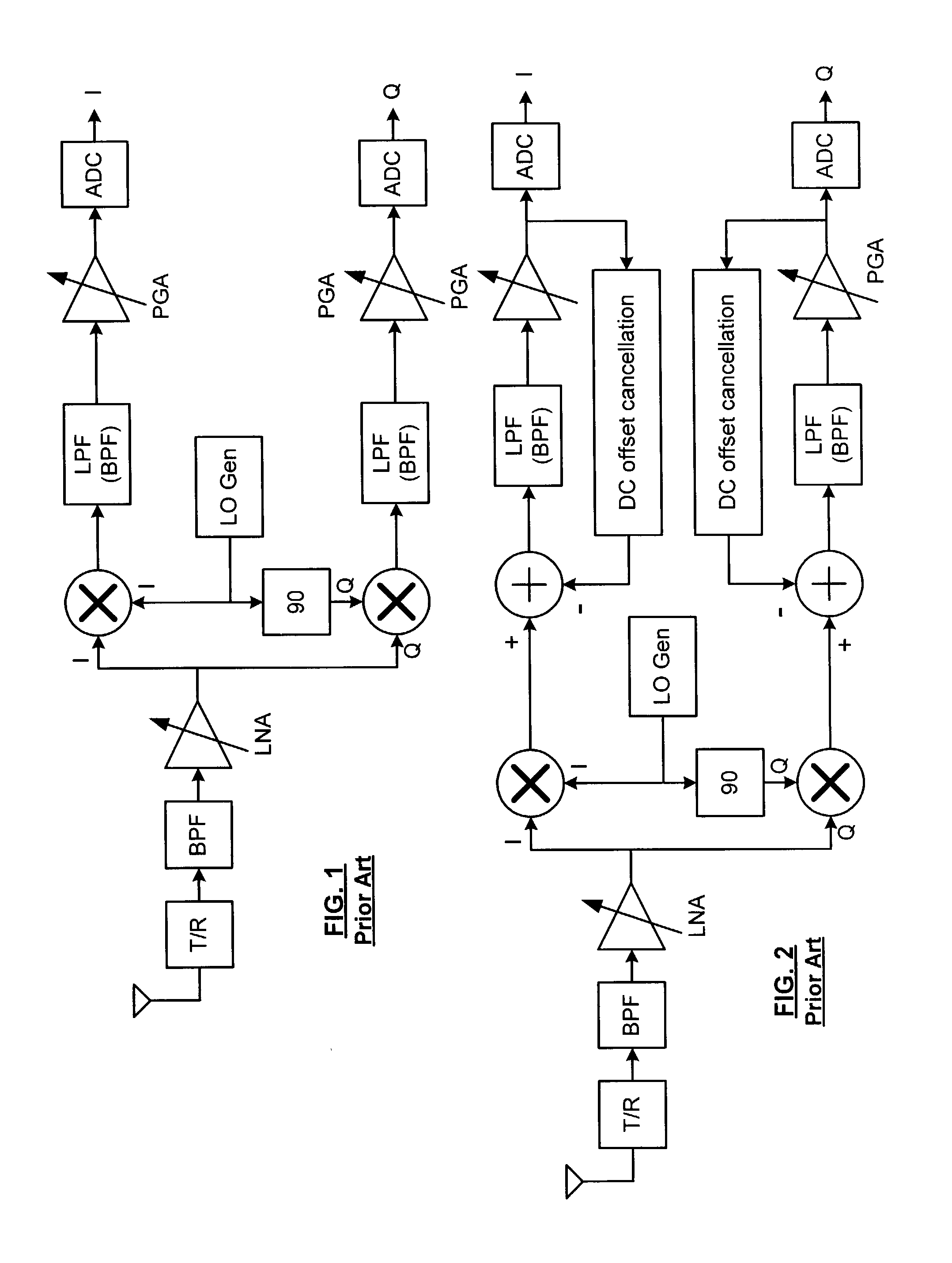
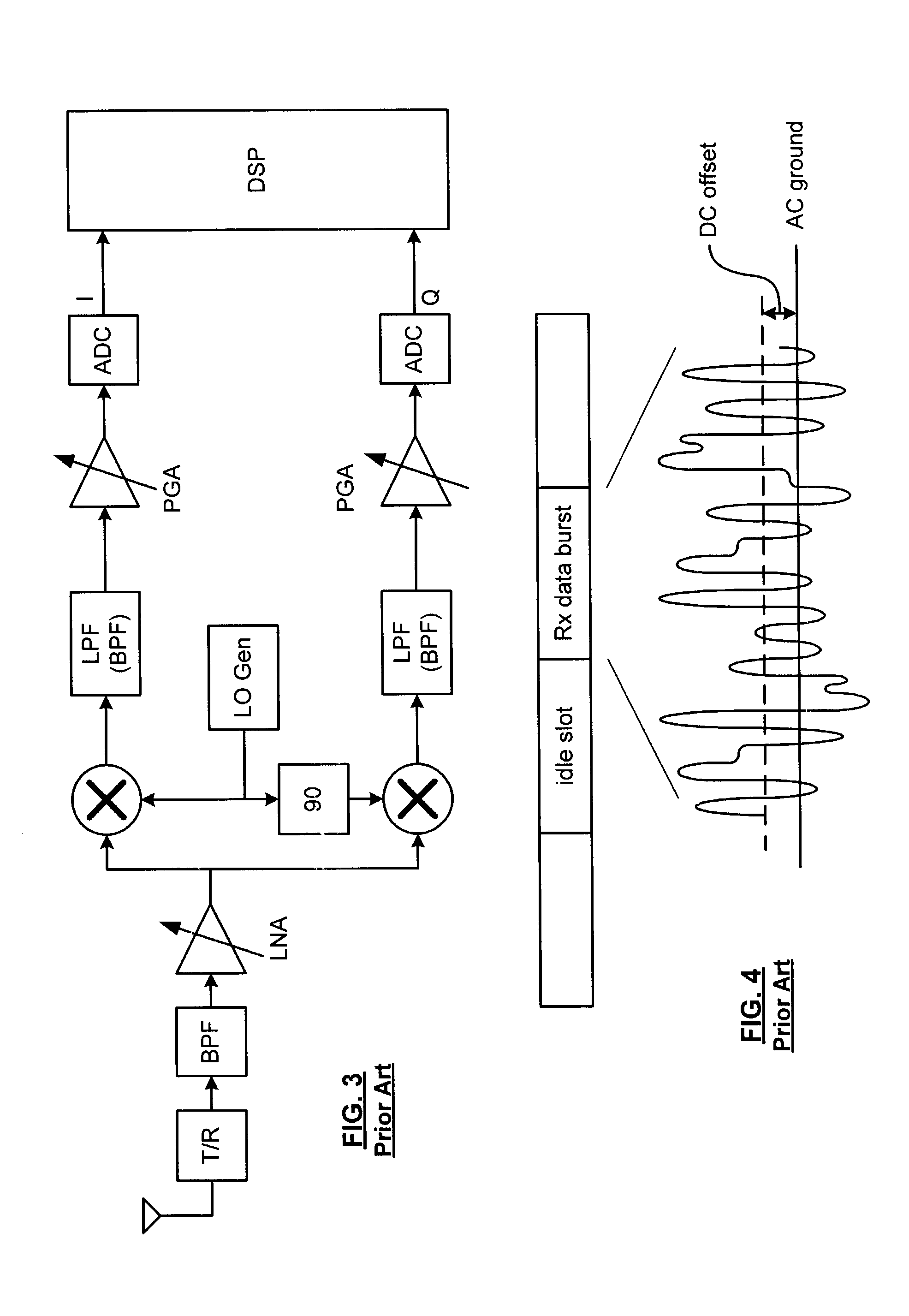
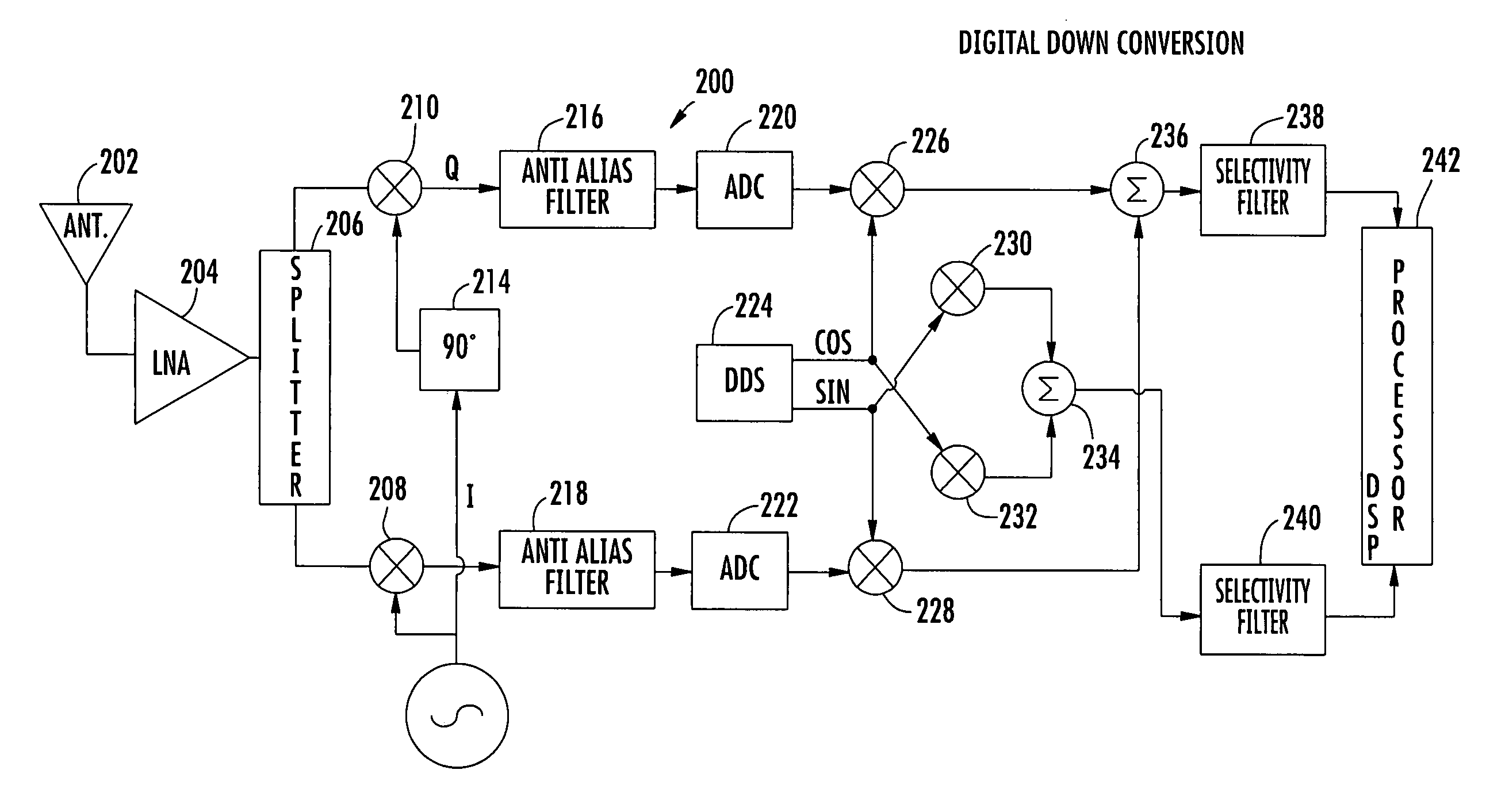
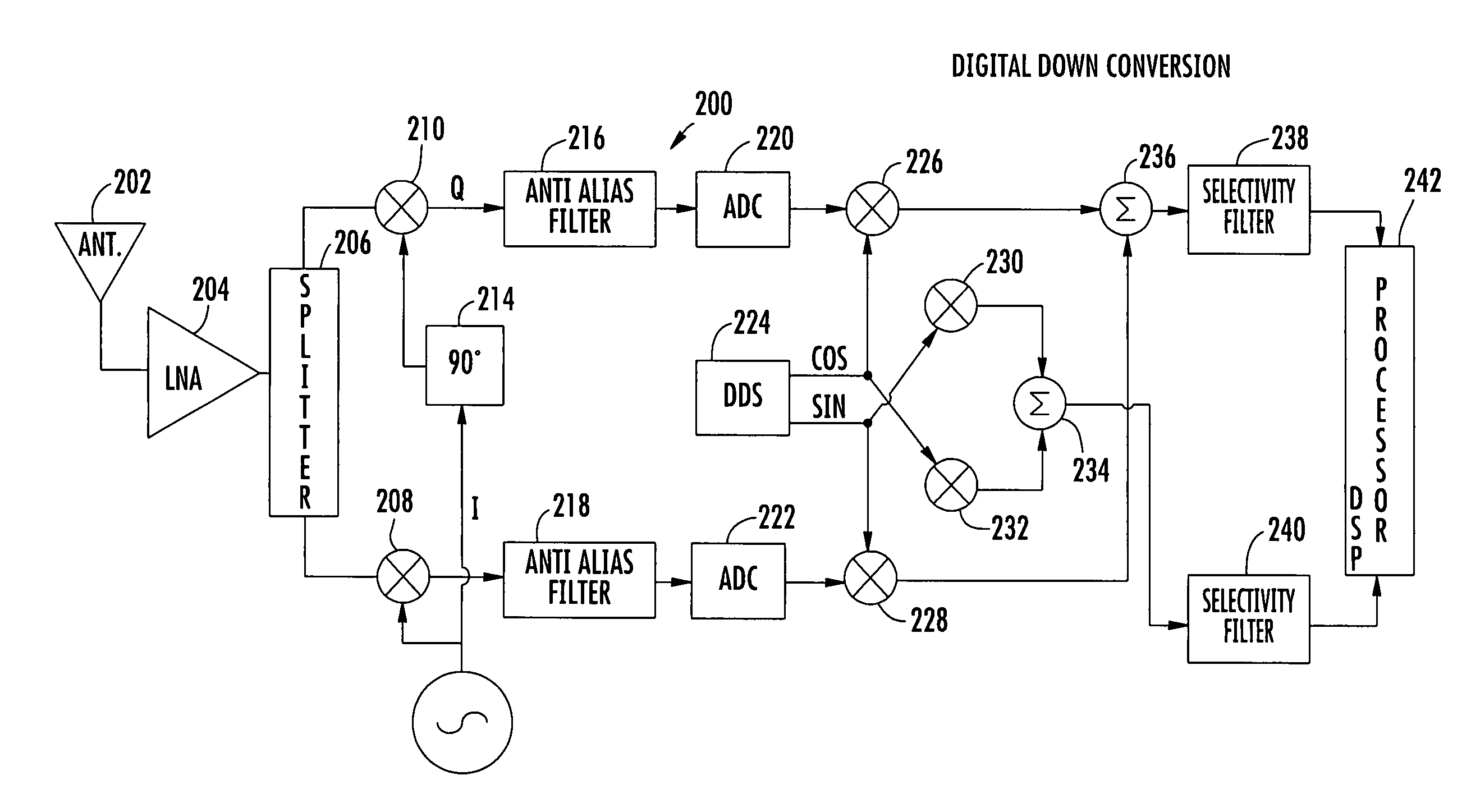
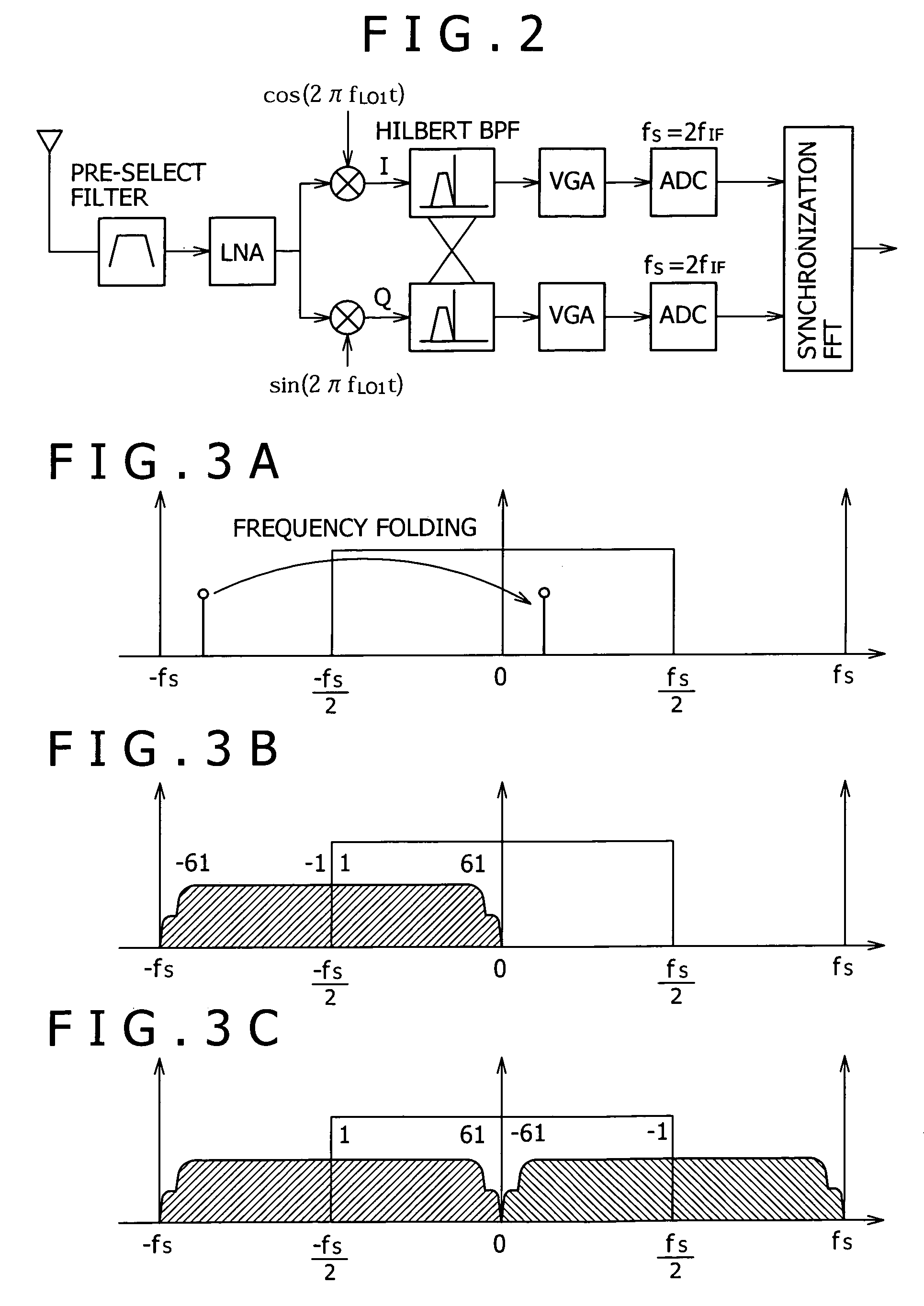
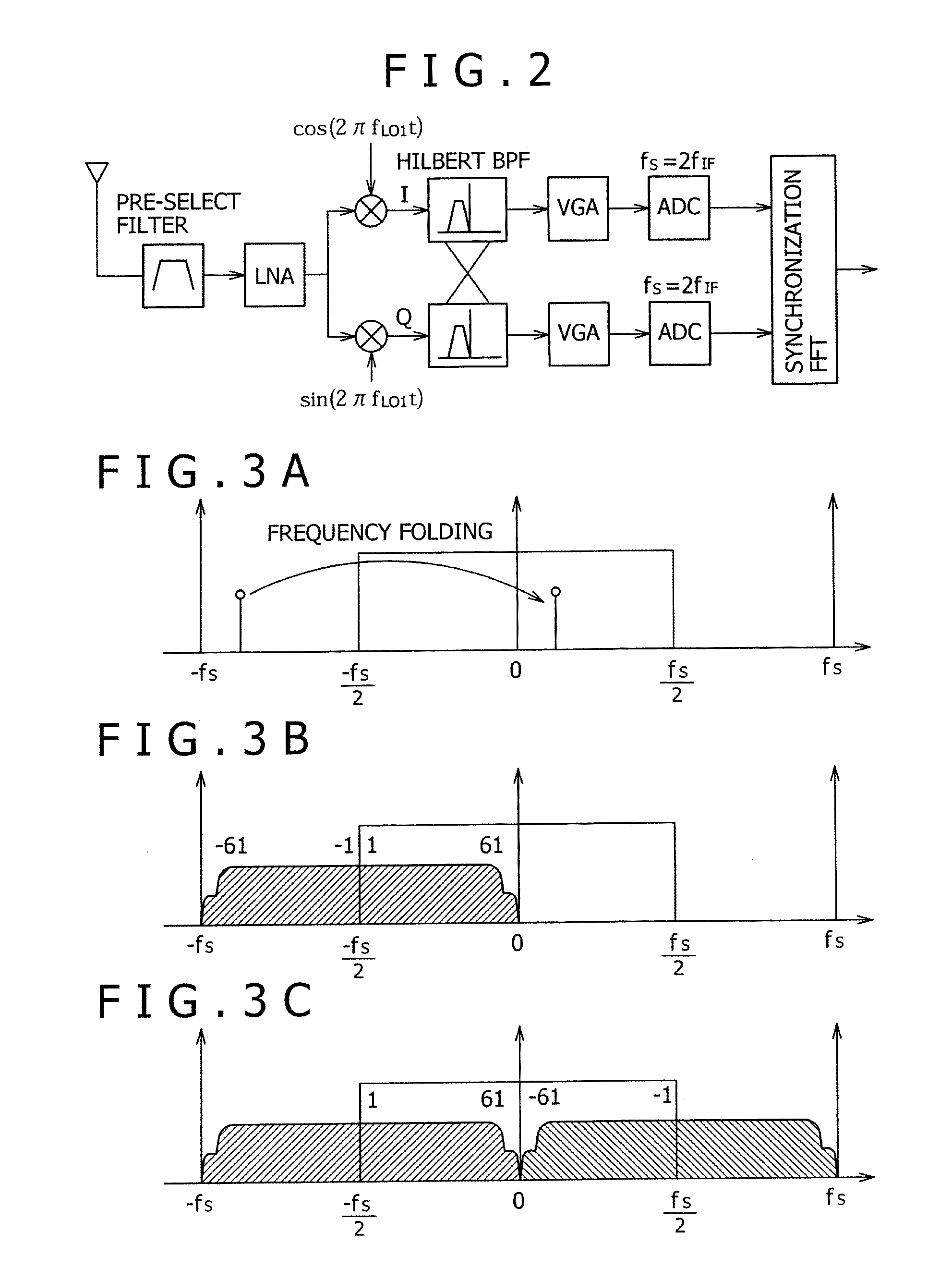
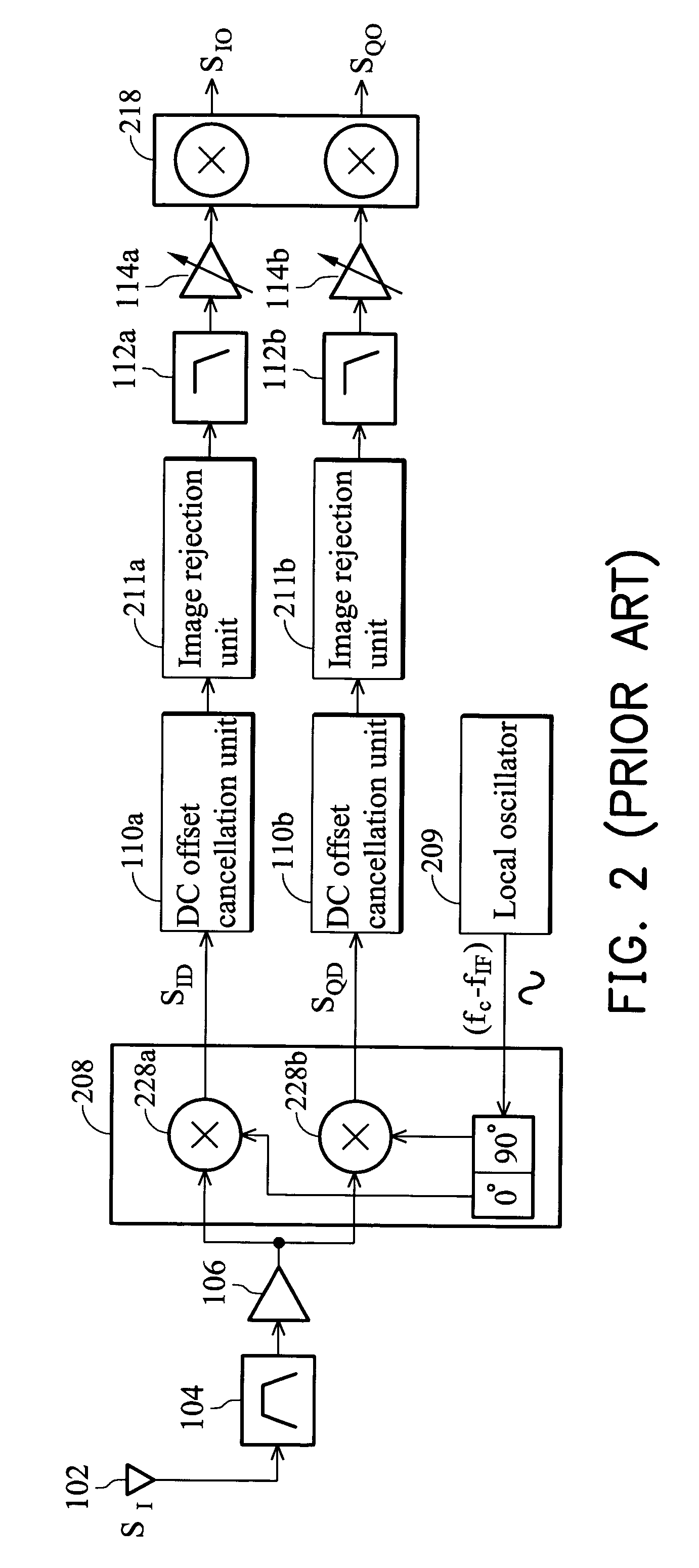
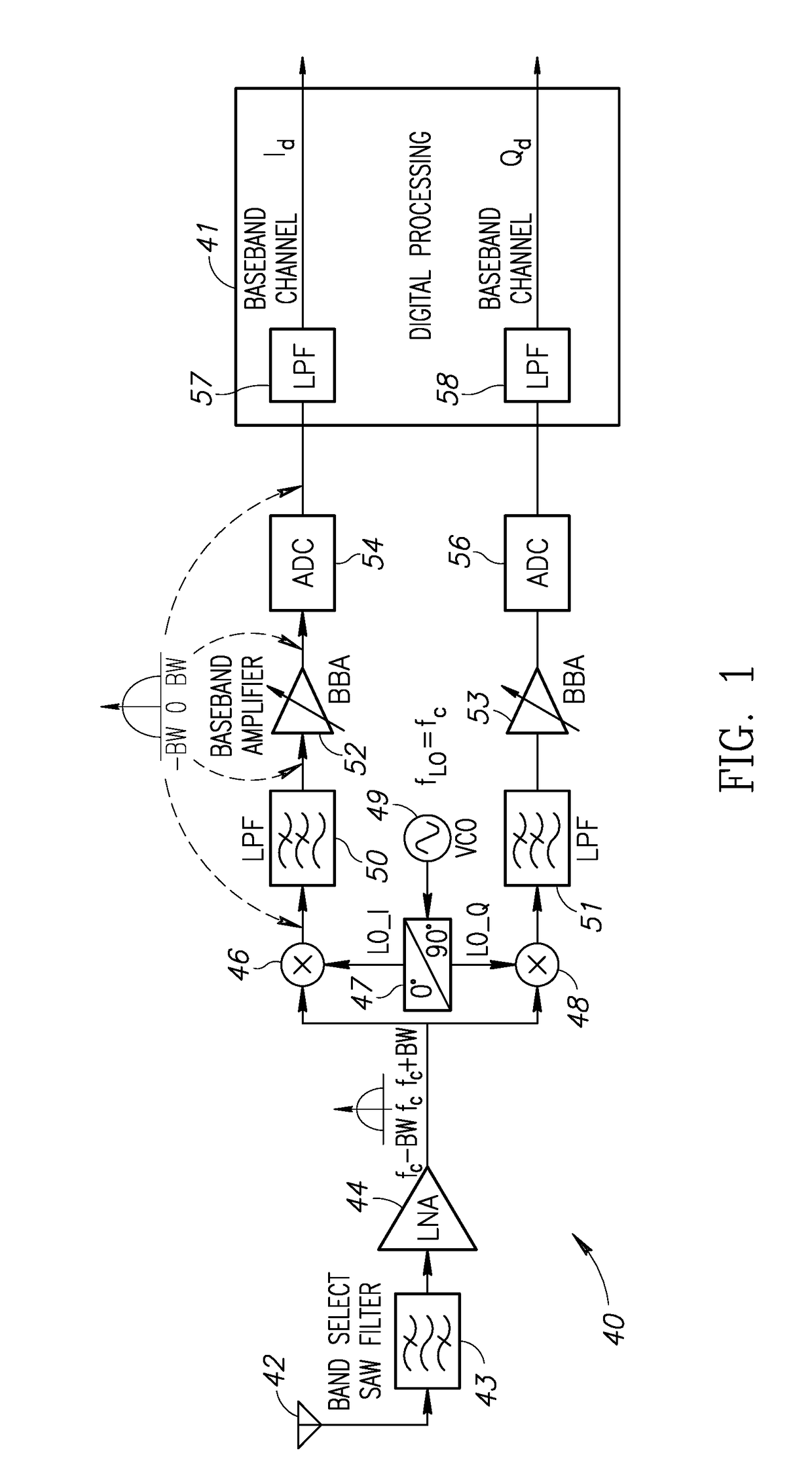
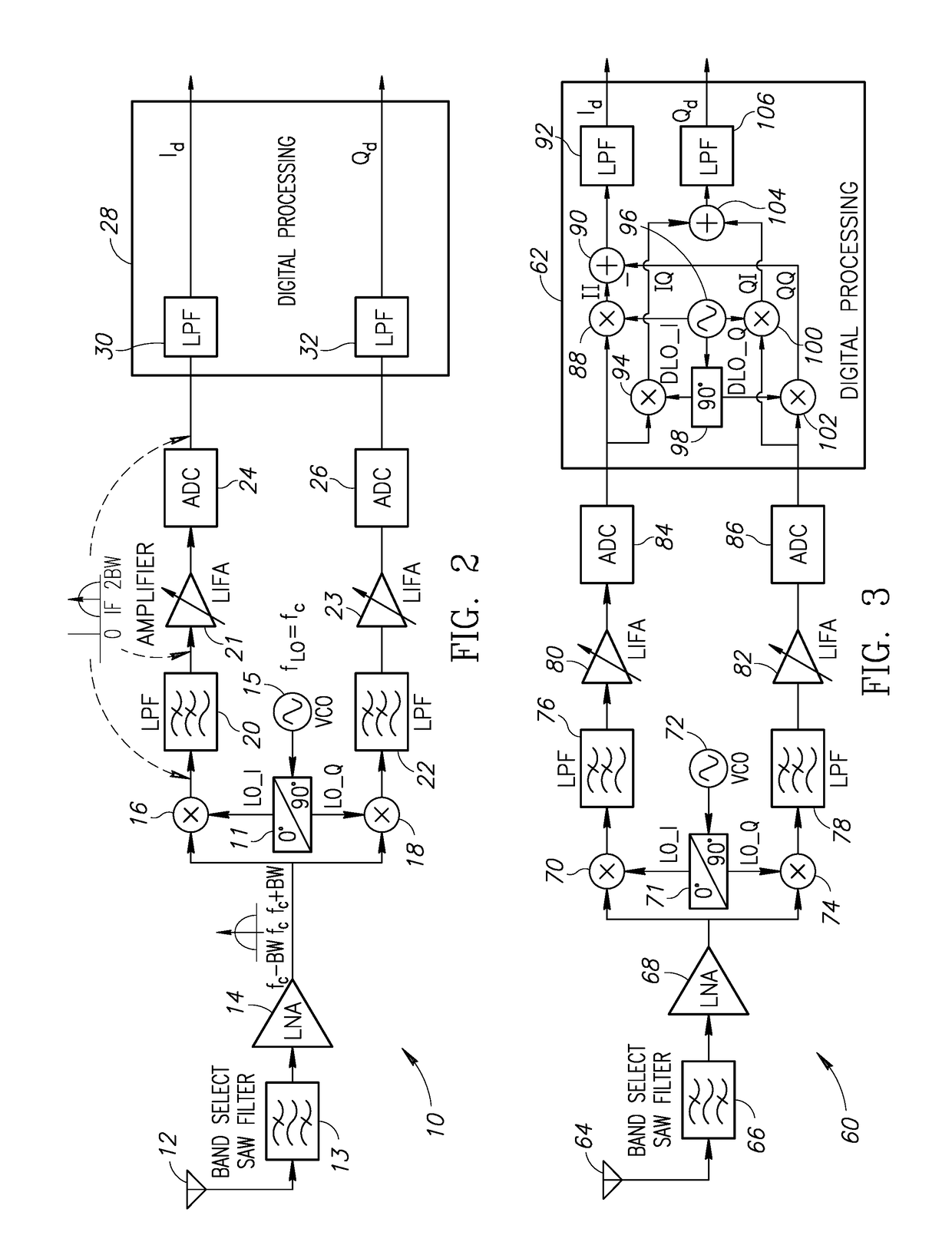
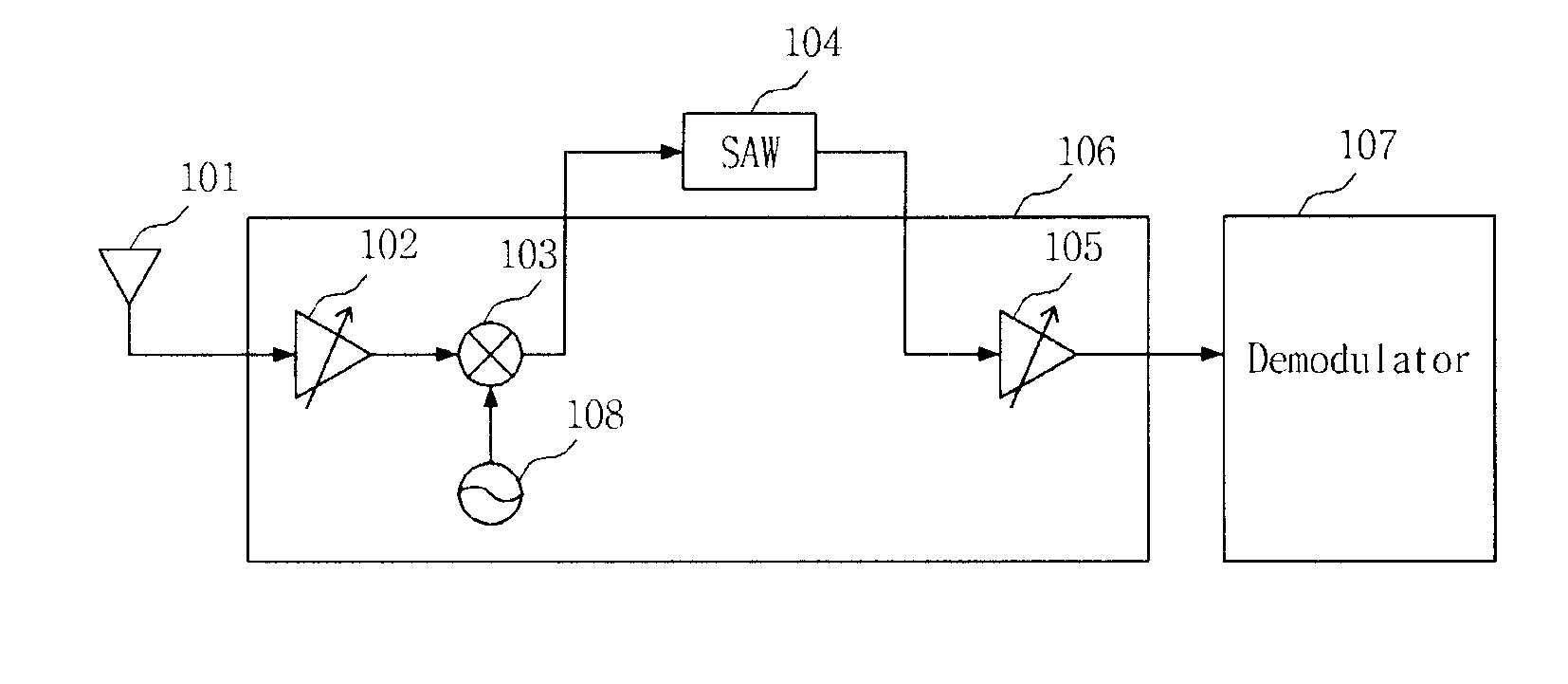
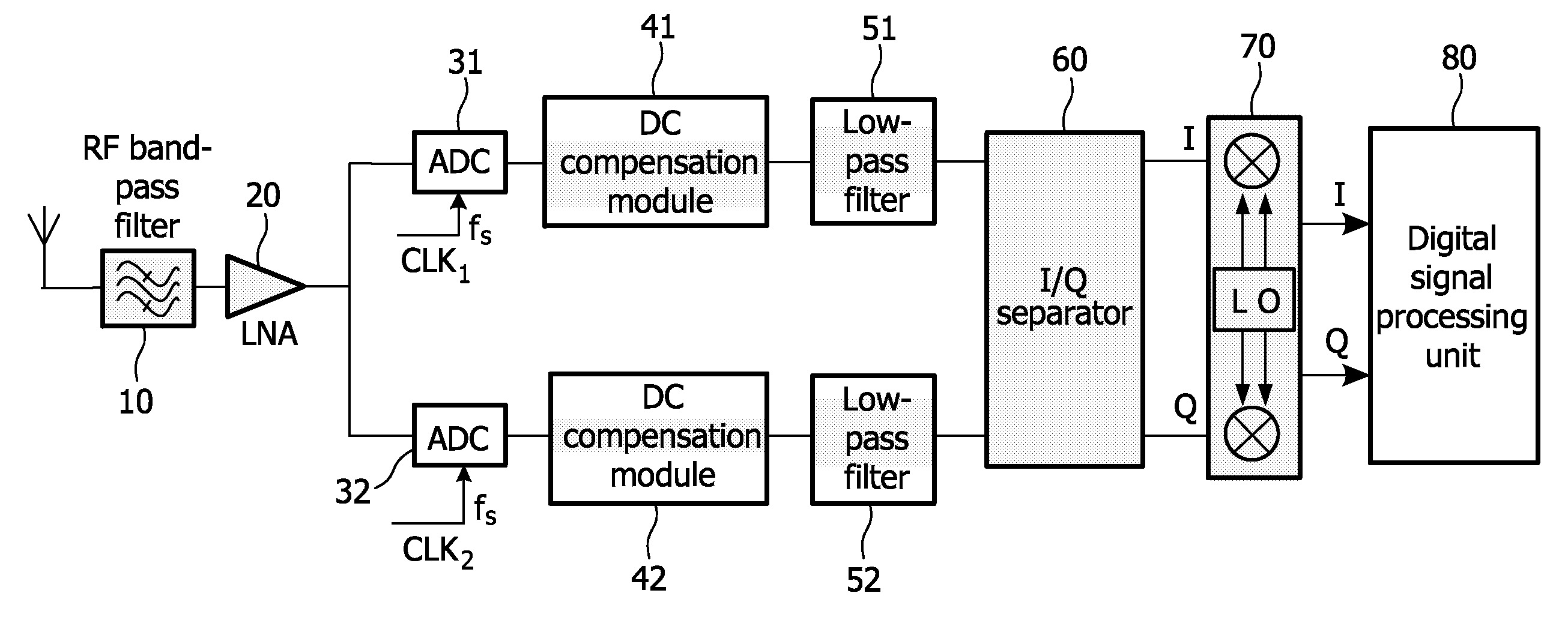
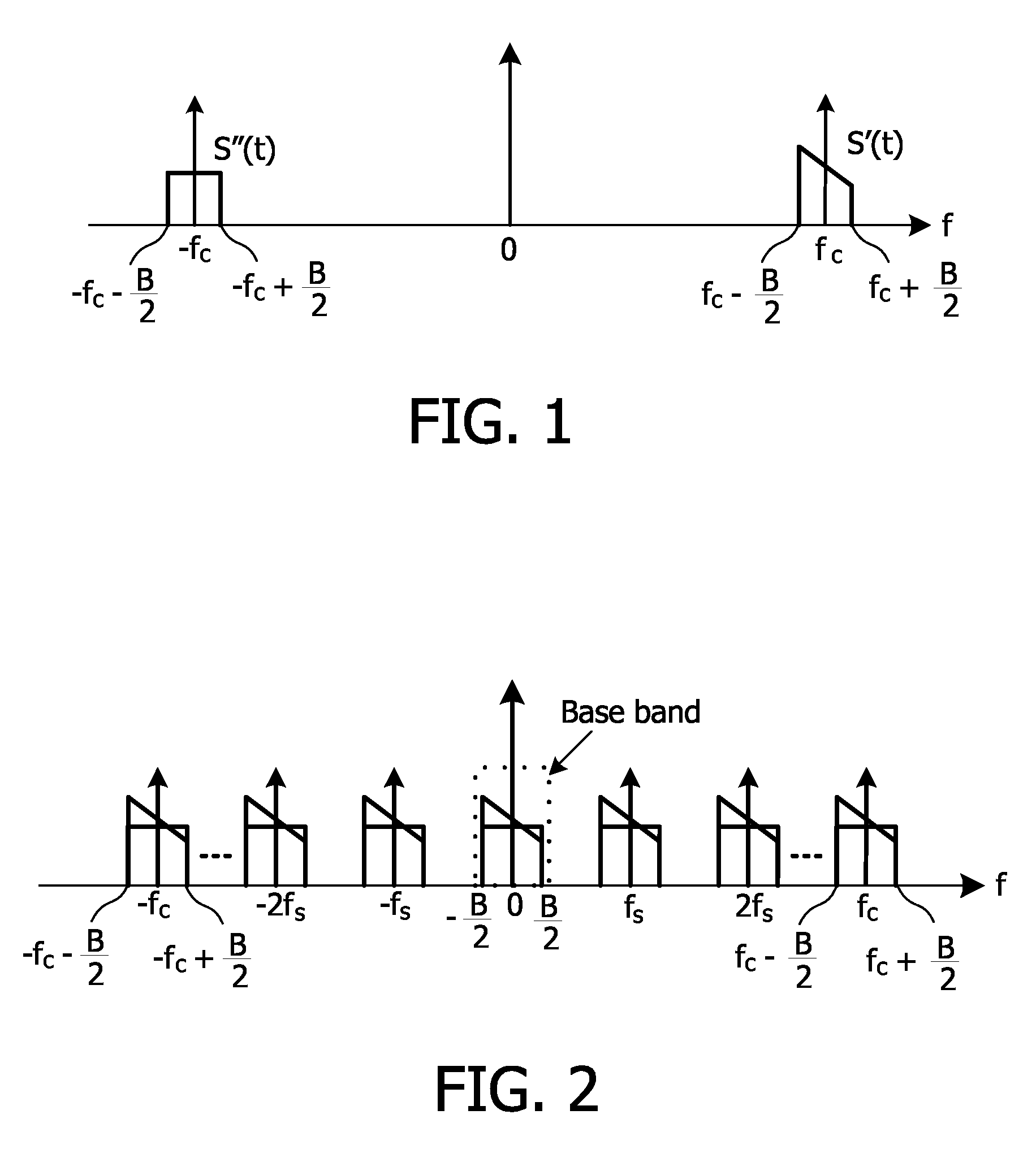
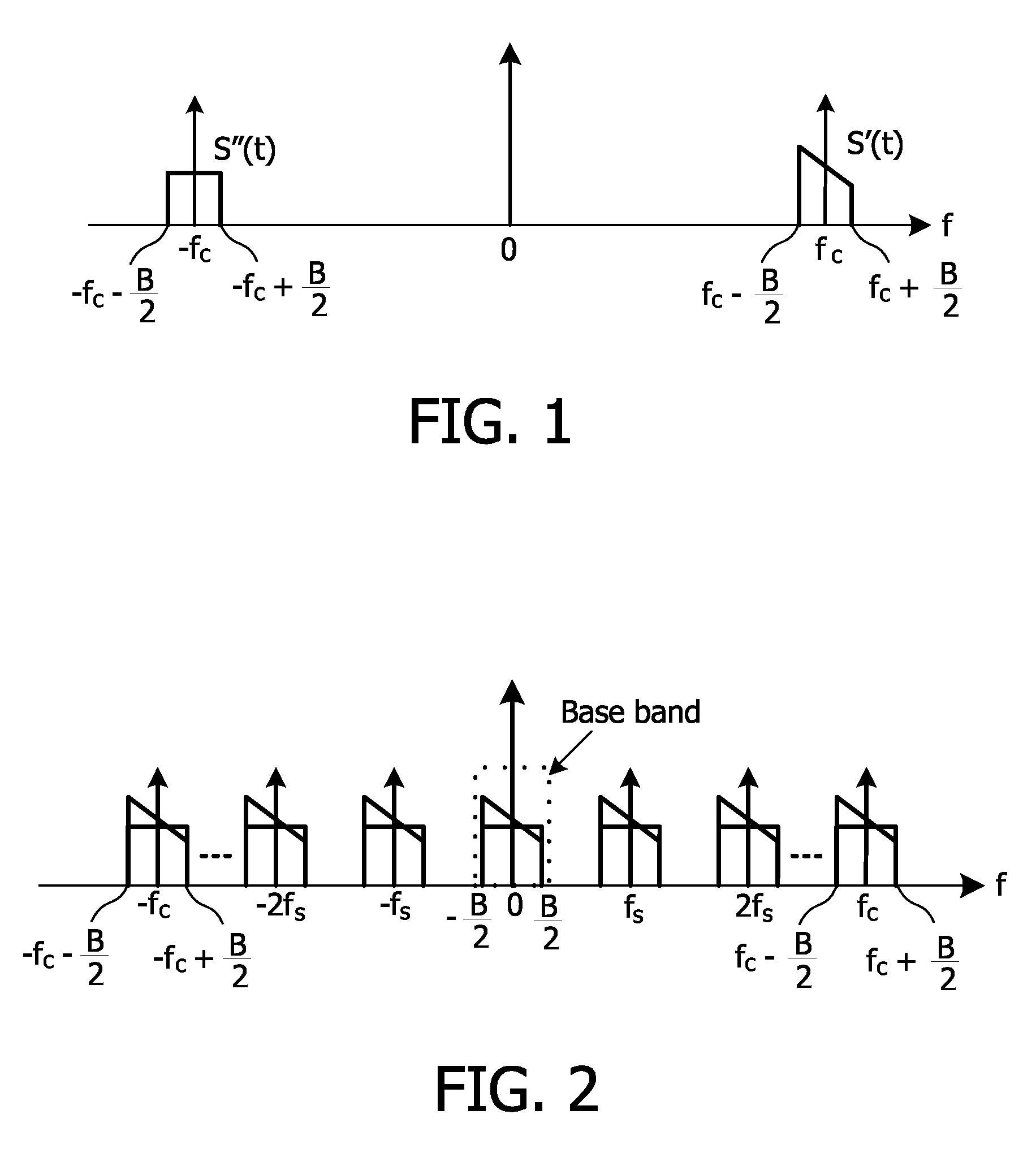
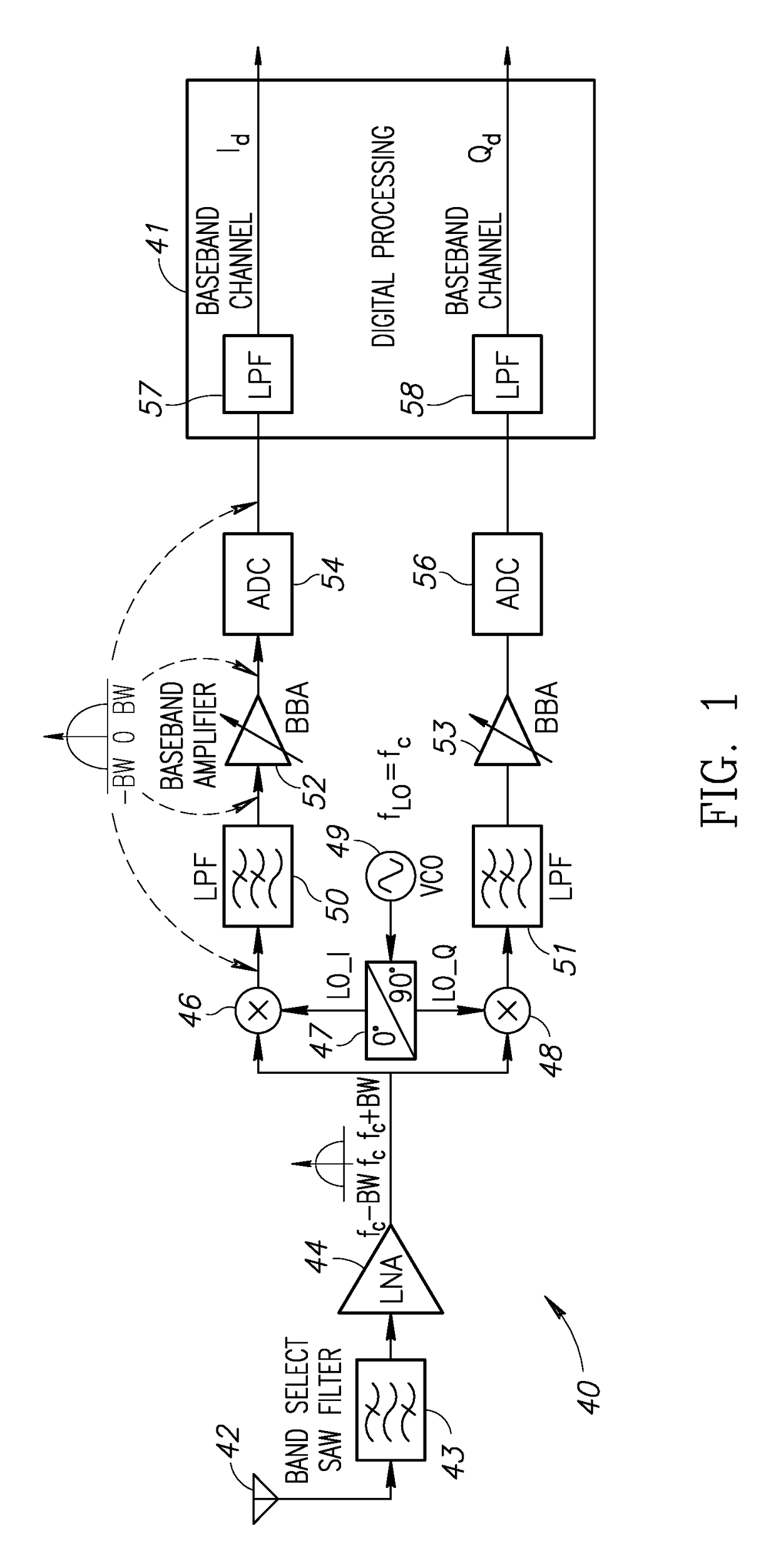
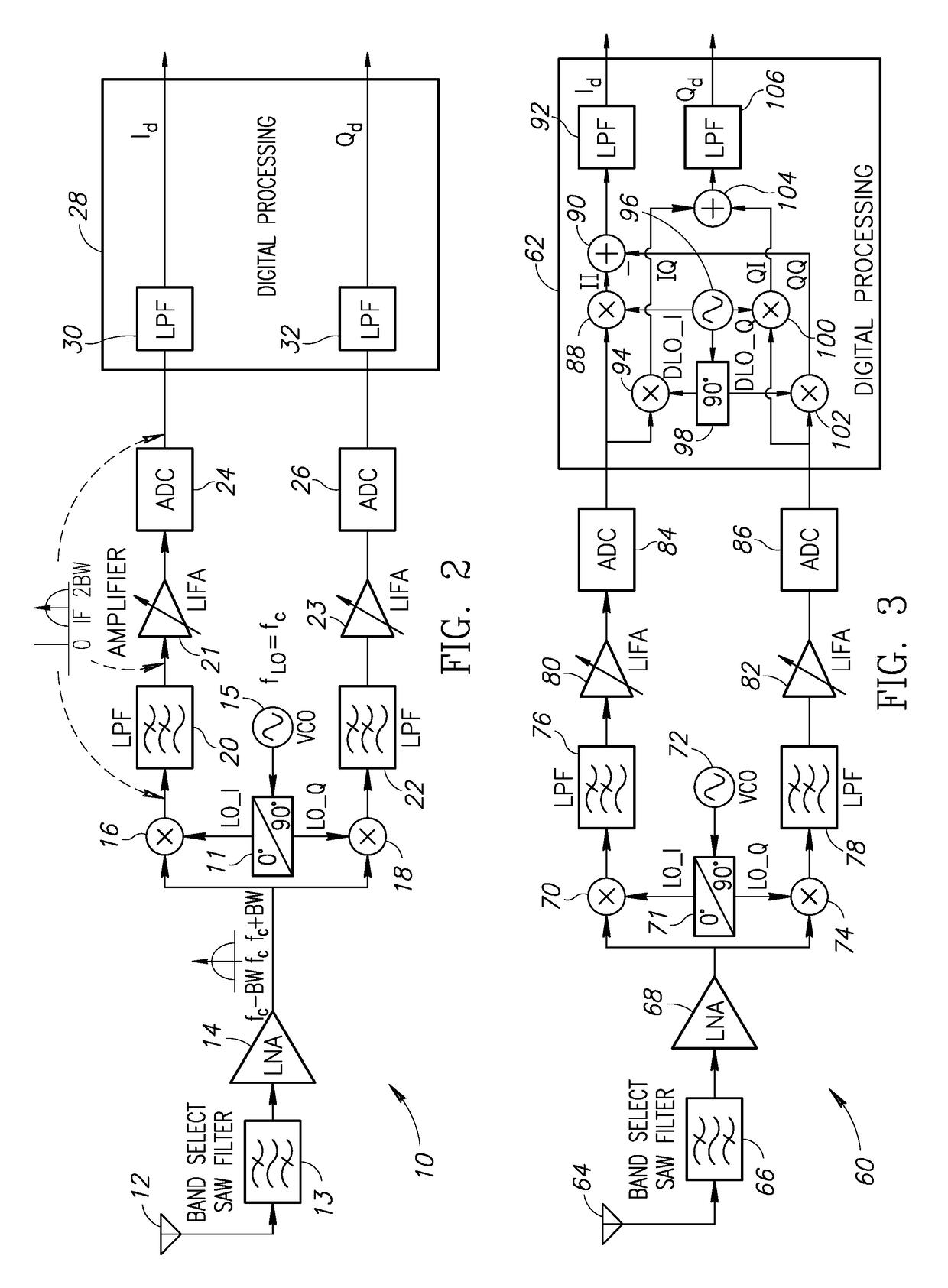
In a low-IF receiver, the RF signal is mixed down to a non-zero low or moderate intermediate frequency, typically a few megahertz (for TV), and even lower frequencies (typically 120-130kHz) in the case of FM radio band receivers. Low-IF receiver topologies have many of the desirable properties of zero-IF architectures, but avoid the DC offset and 1/f noise problems.
Fully integrated self-tuned image rejection downconversion system
InactiveUS6892060B2Low costEasily integrated into single chip RF+IFError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionQuadrature mixerLow IF receiver
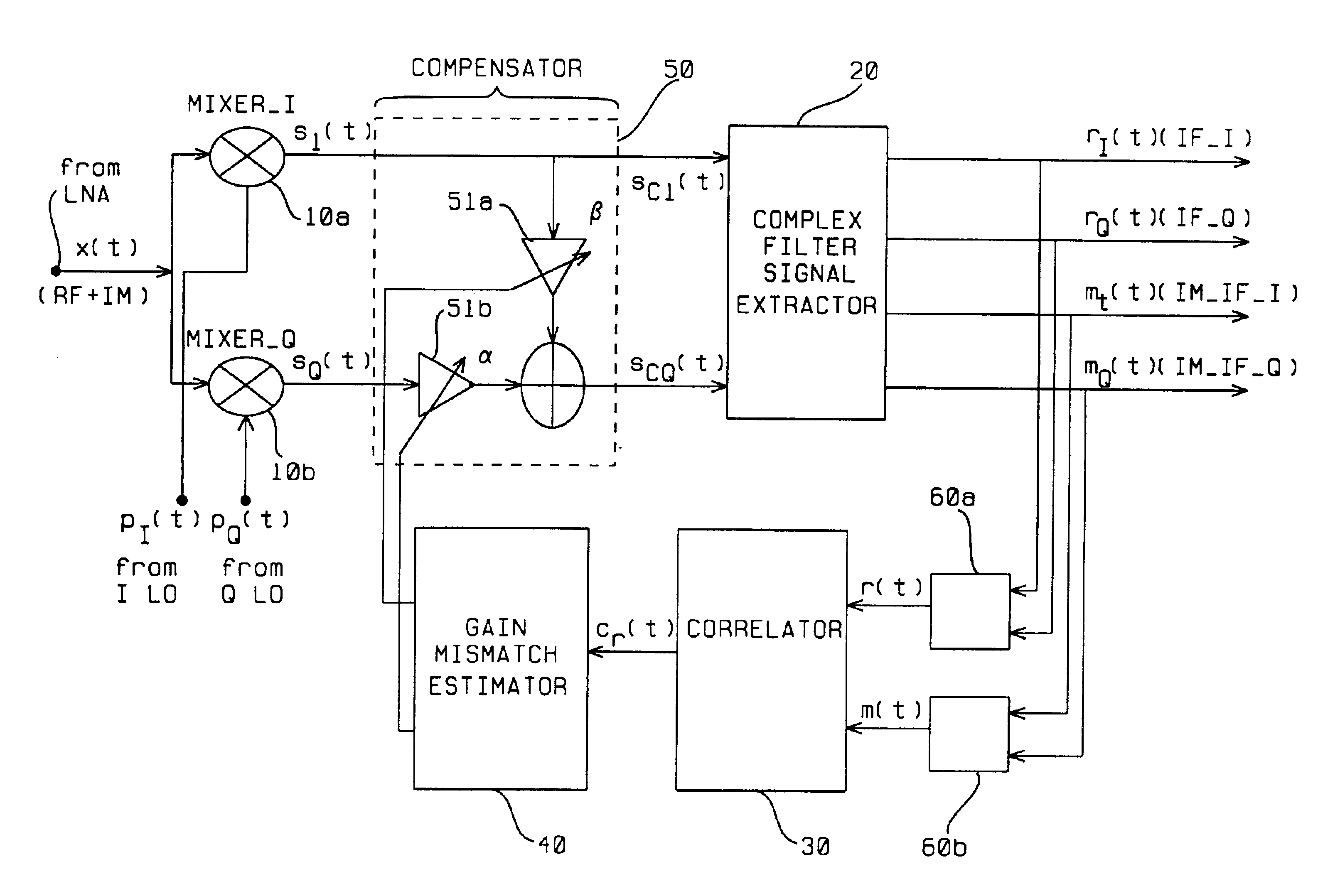
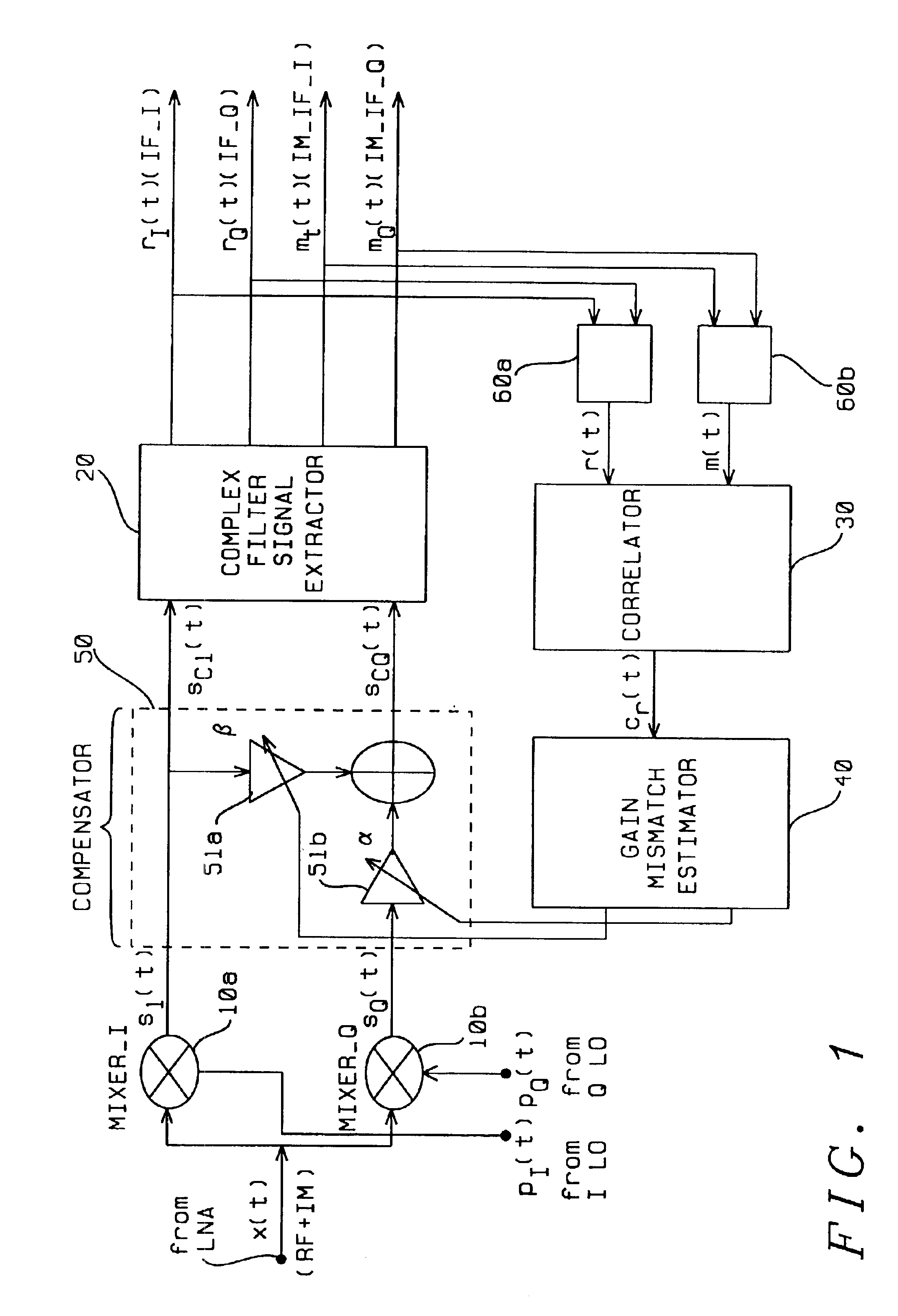
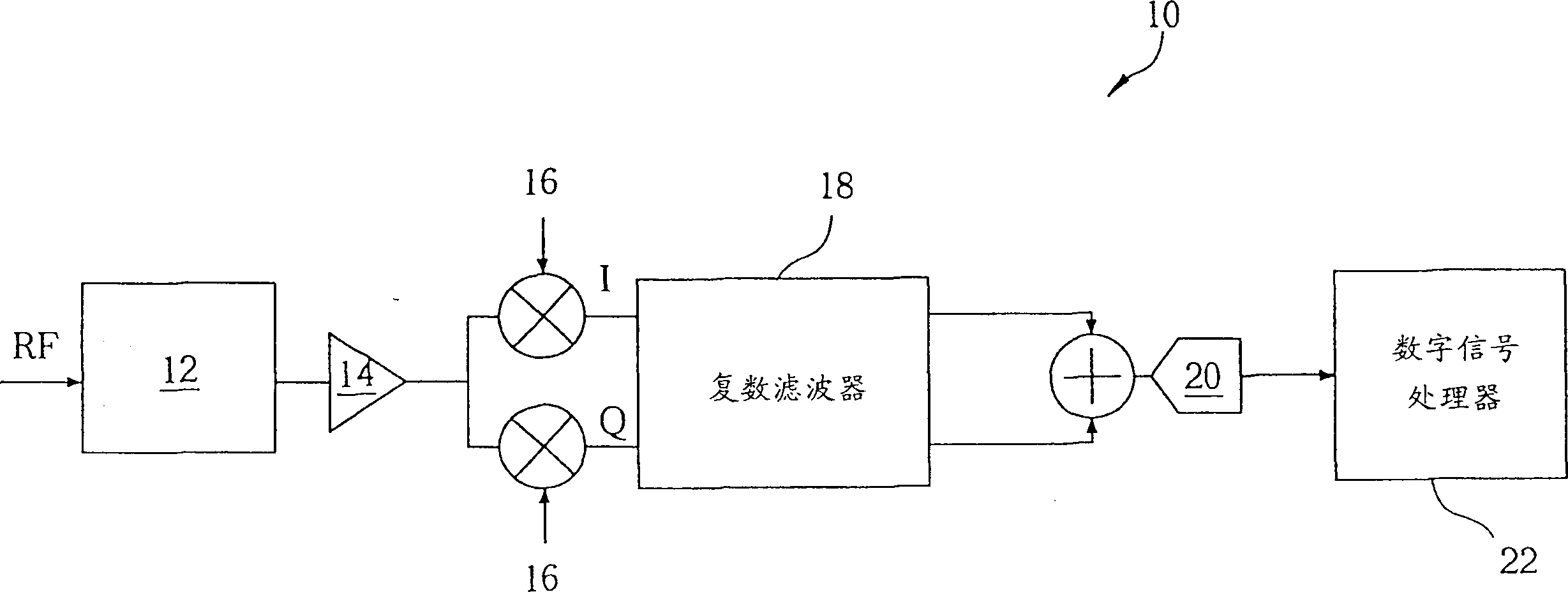
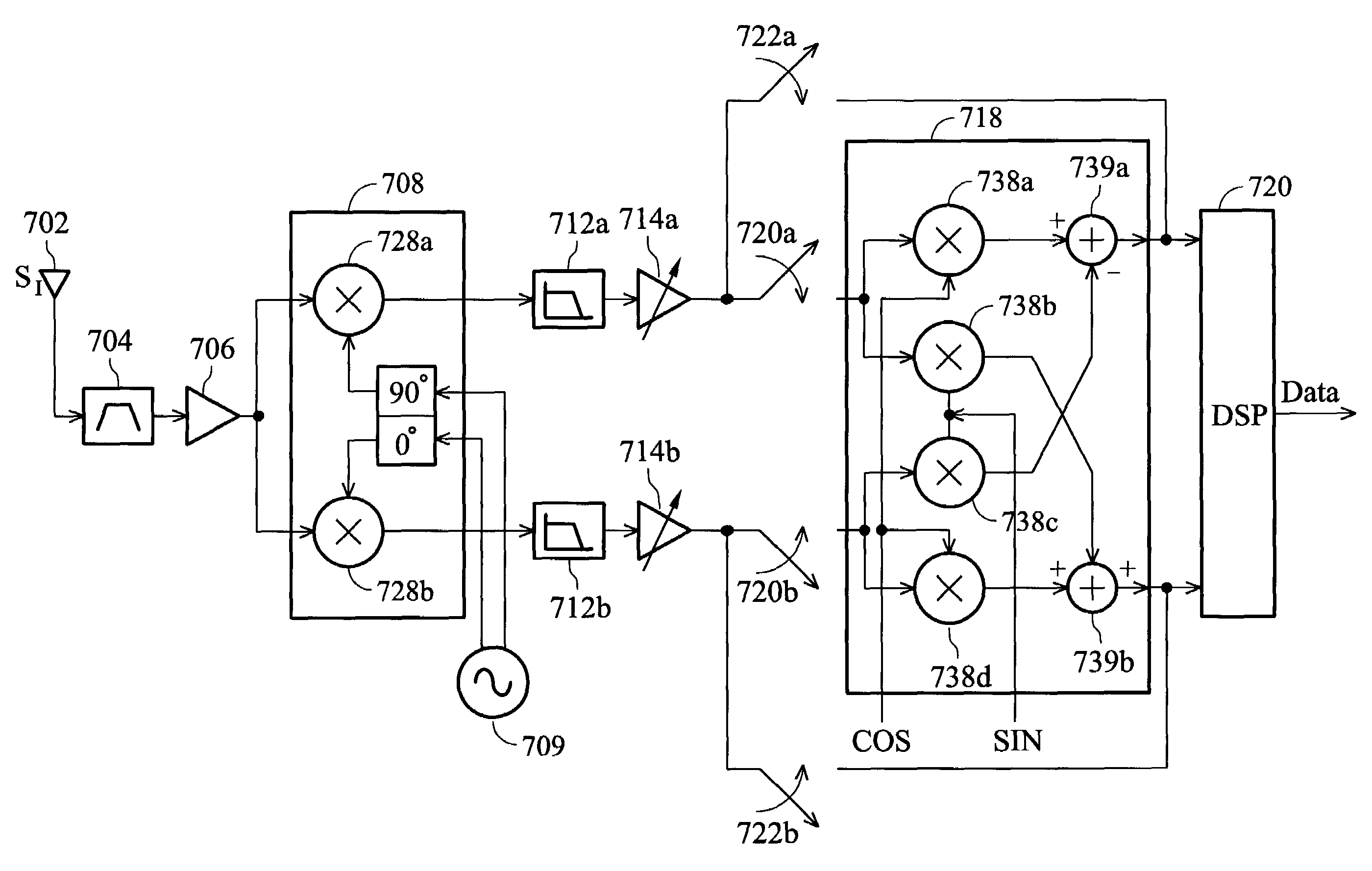
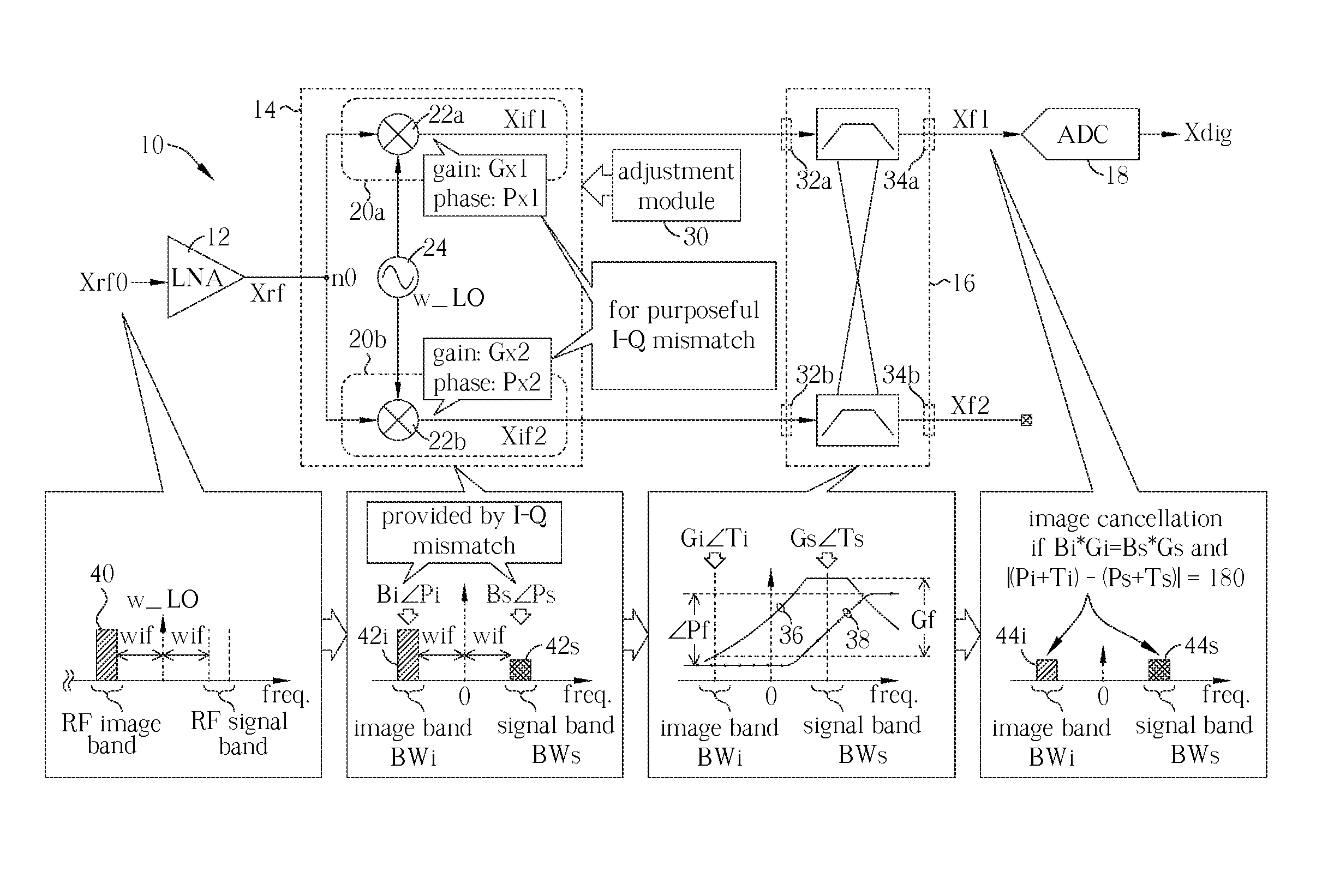
A feedback image rejection downconversion system is described, which can be used in low IF receivers with good performance and completely integrated. In the forward path of the system, quadrature mixers and complex filters are used for frequency downconversion and separation of the RF signal from the image signal. In the feedback path, a correlator, a gain mismatch estimator and two VGAs have been used to detect, estimate and compensate the amplitude and phase mismatch between the forward I and Q path signals. The whole system is self-tuned and can operate in both closed and open loop mode. A very high and robust image rejection ratio (over 60 dB) has been achieved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
DC offset correcting in a direct conversion or very low IF receiver
InactiveUS7136431B2Reduce cancellationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationEngineeringLow IF receiver
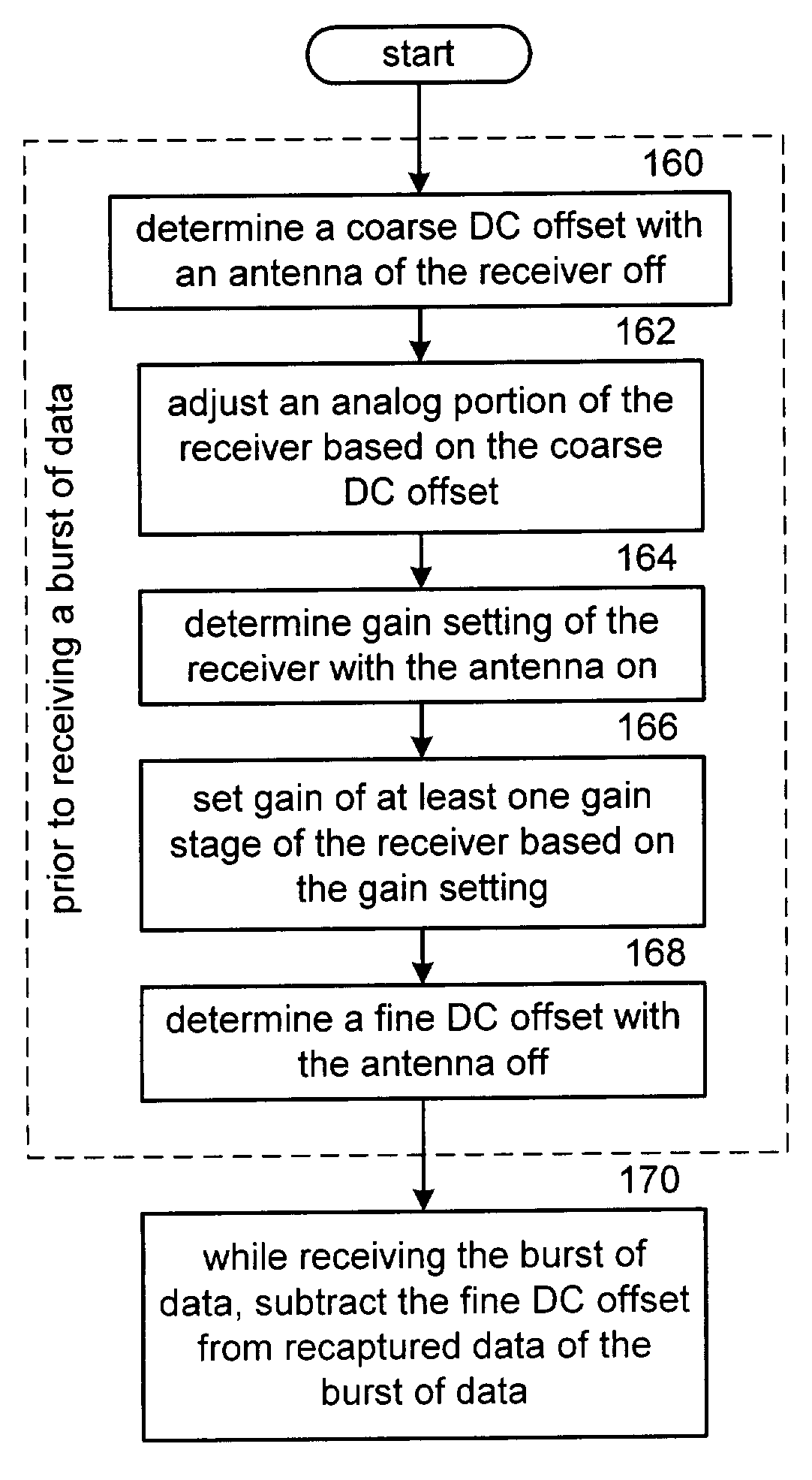
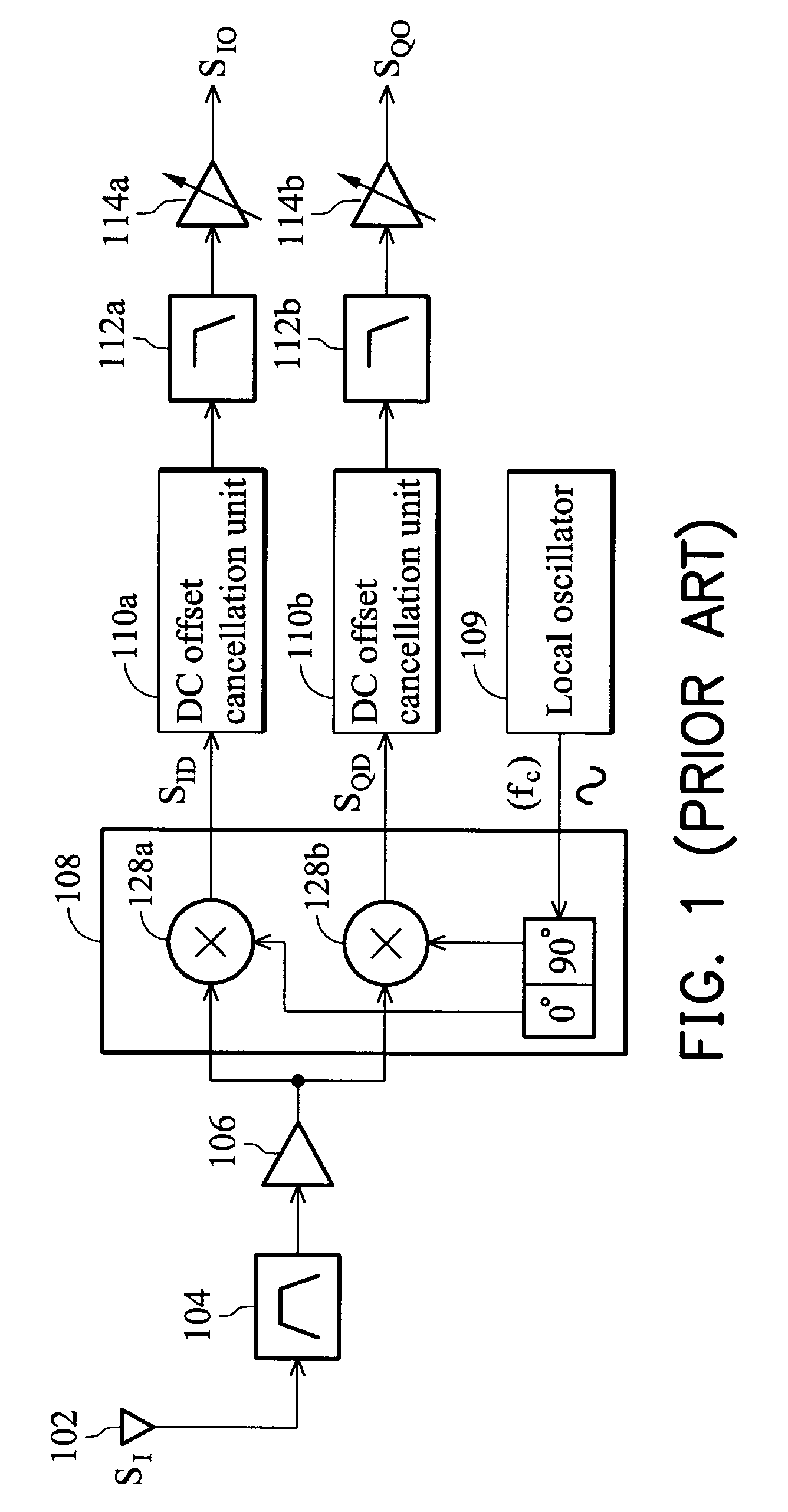
A direct conversion or VLIF receiver corrects DC offset by, prior to receiving a burst of data, the receiver determines a coarse DC offset with the antenna of the receiver switched off. The receiver then adjusts an analog portion of the receiver (e.g., the output of the mixers) based on the coarse DC offset. The receiver then determines a gain setting of the receiver (e.g., for the low noise amplifier and / or programmable gain amplifiers) with the antenna on. The receiver then sets the gain of at least one gain stage of the receiver based on the gain setting. The receiver then determines a fine DC offset with the antenna off. The receiver then, while receiving a burst of data, subtracts the fine DC offset from the digital baseband or low IF signal prior to data recovery.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for calibrating frequencies-amplitude and phase mismatch in a receiver
InactiveUS7783273B2Reduce componentsReduce equipmentElectric signal transmission systemsRadio transmissionQuadrature demodulationLow IF receiver
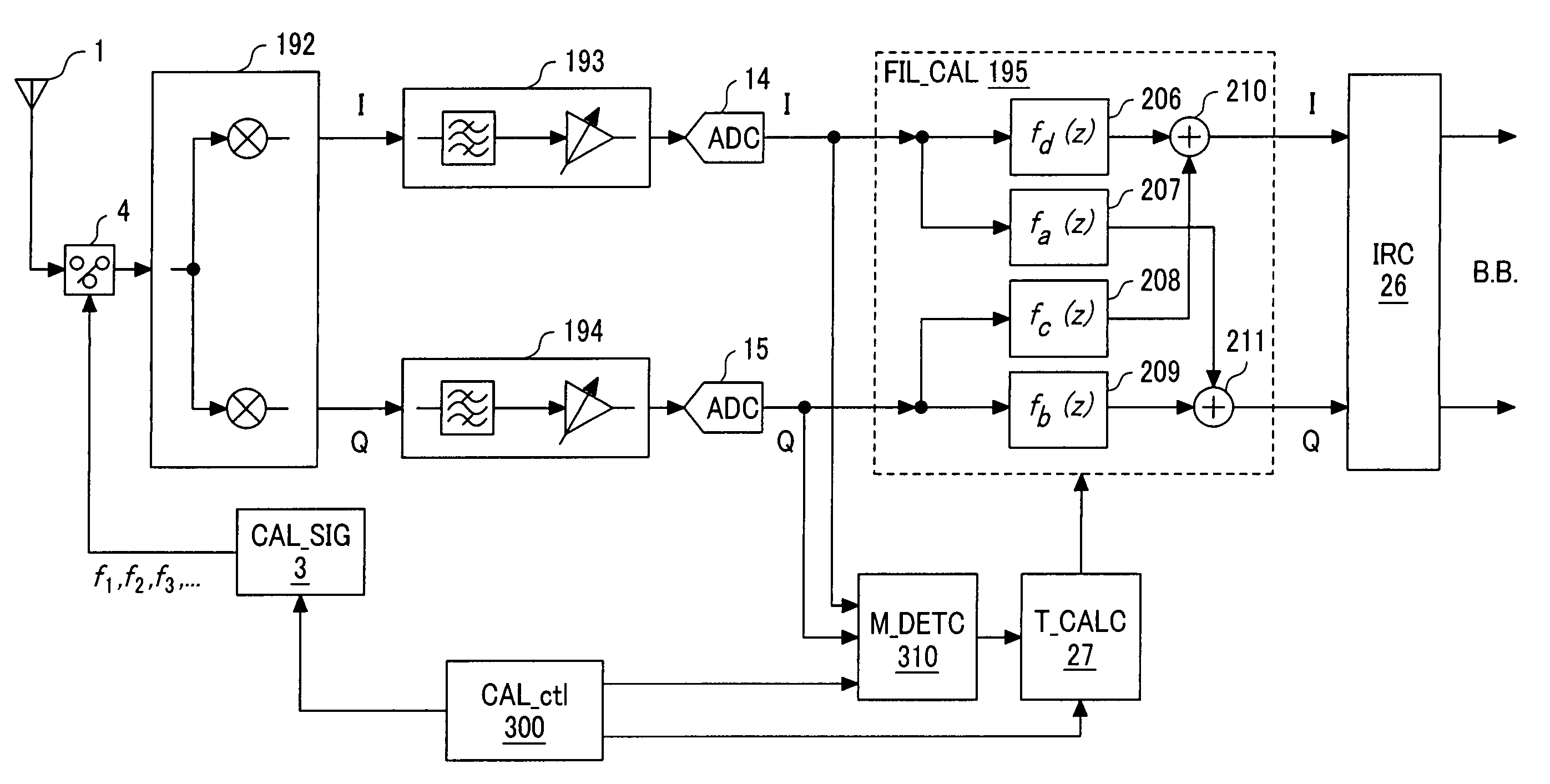
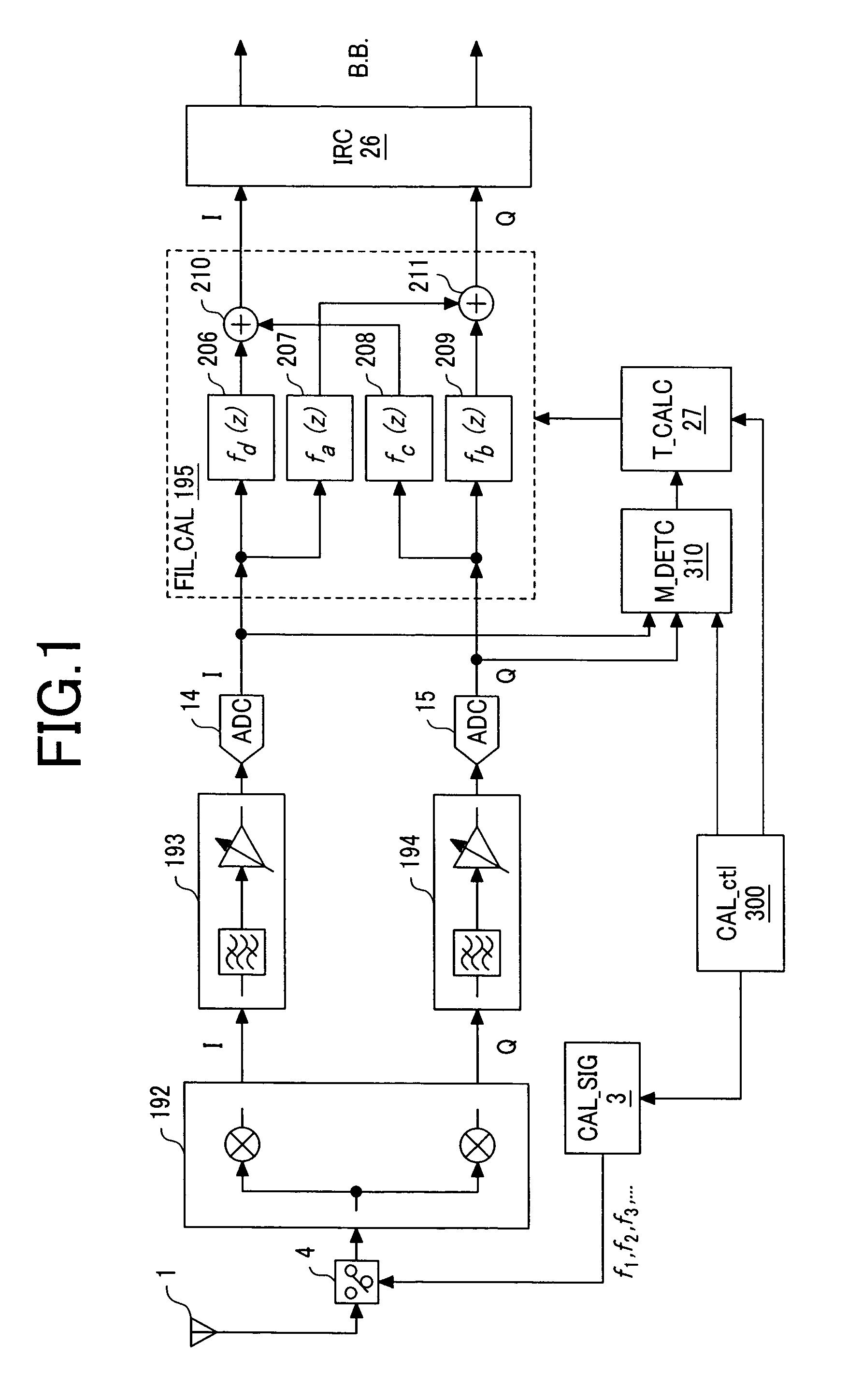
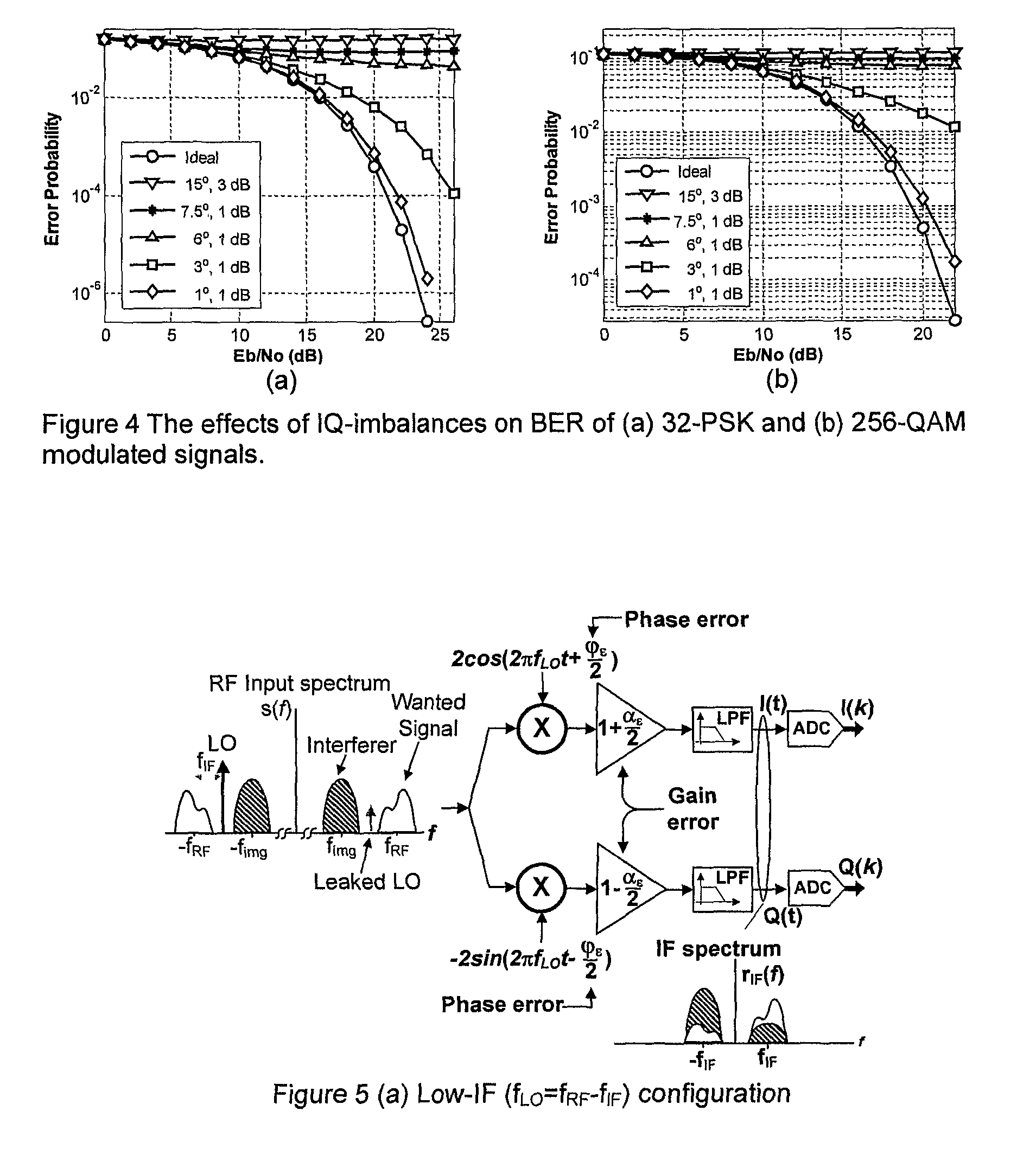
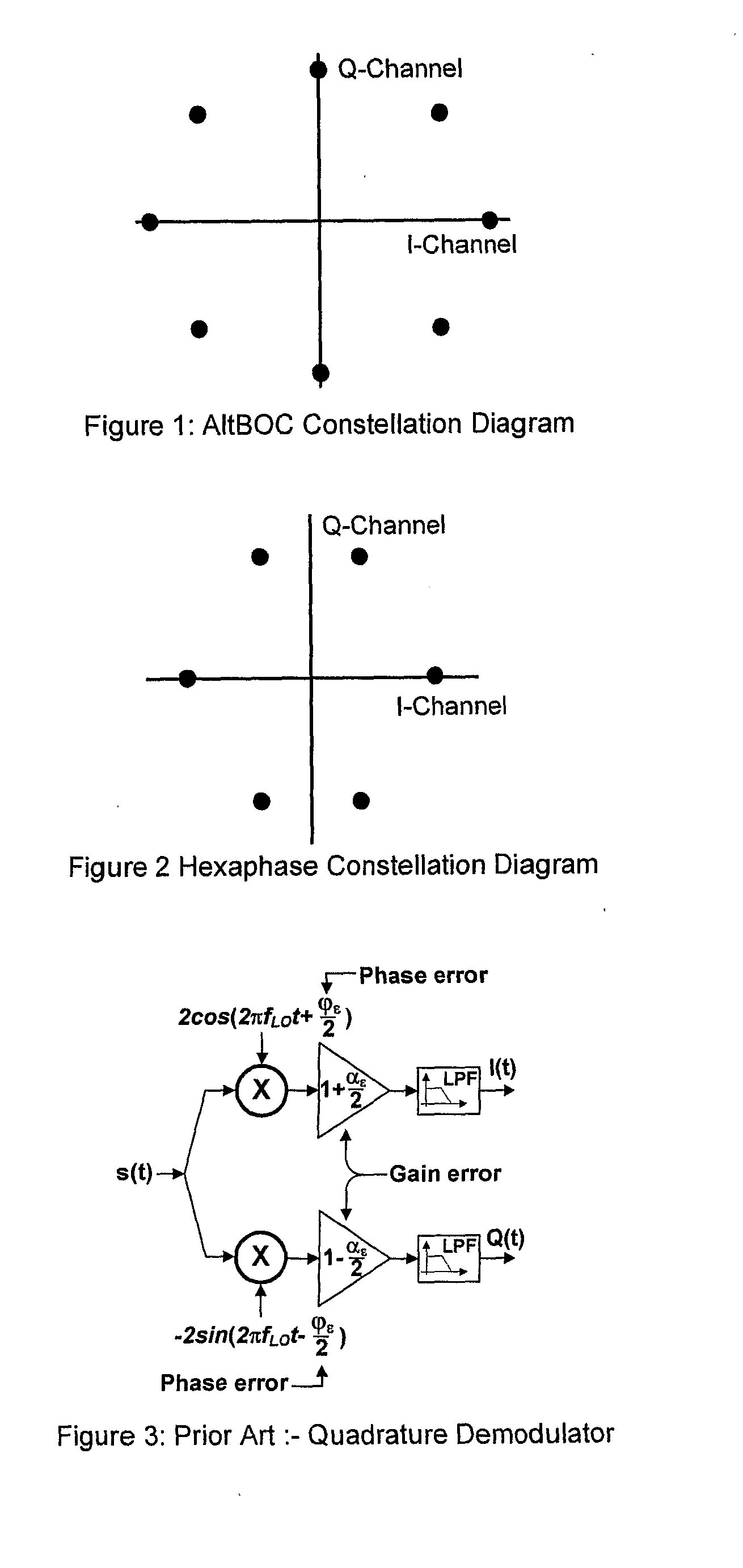
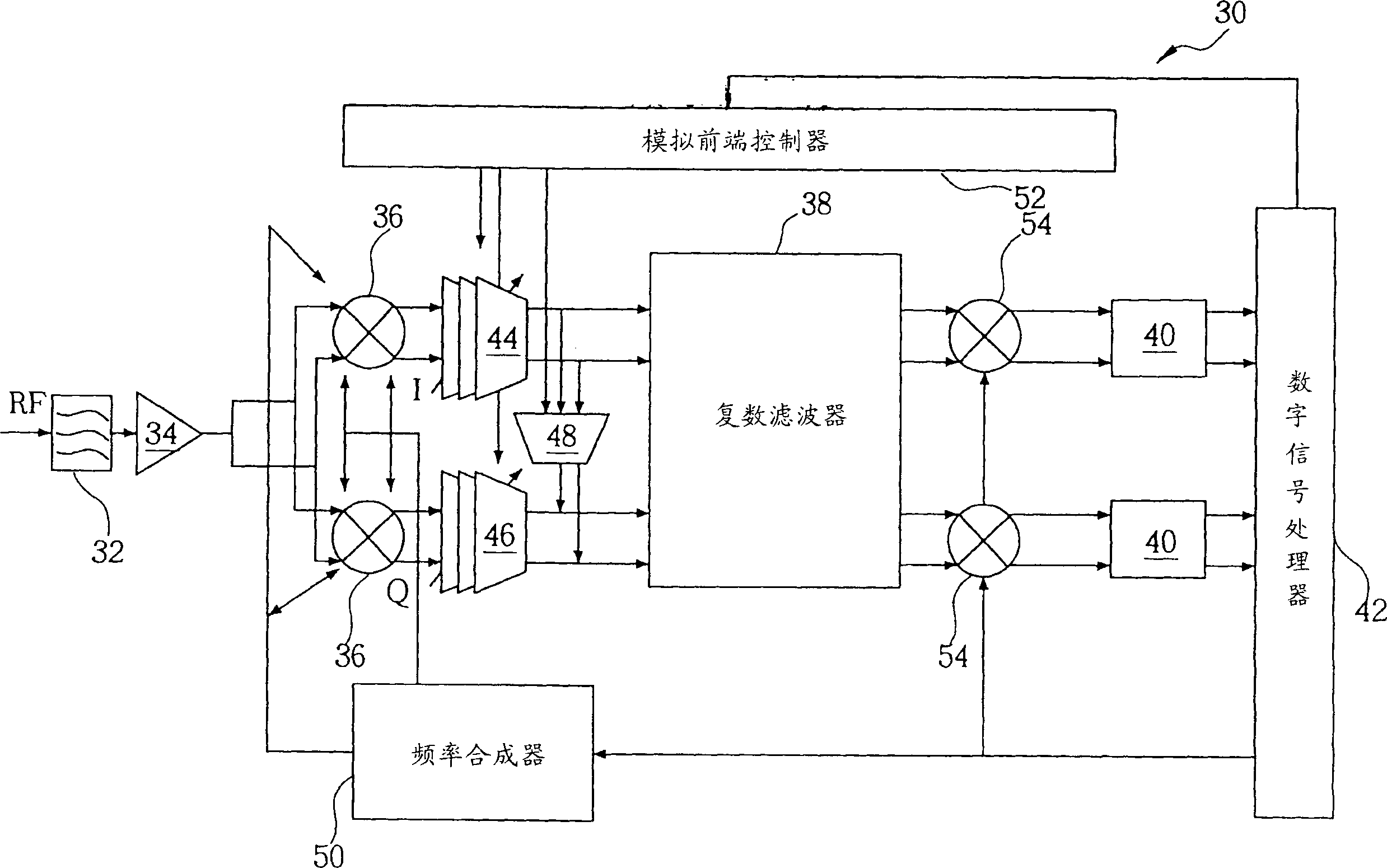
The receiver, which enables rejection of image signals with higher accuracy over wider frequency band, can be provided as a low IF receiver by inputting a calibration signal of frequency fi (1≦i≦N) before reception of signals and determining the frequency response fa(z) to fd(z) of a calibrating filter in a filter mismatch calibrating circuit (FIL_CAL) 195 to make zero amplitude and phase mismatches between the I component and Q component of the quadrature demodulation signal at the frequency fIFi.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Satellite radio navigation receiver
InactiveUS7839314B2Reduce RF impairmentEasy to integrateElectric signal transmission systemsEqual length code transmitterSatellite radioTime domain
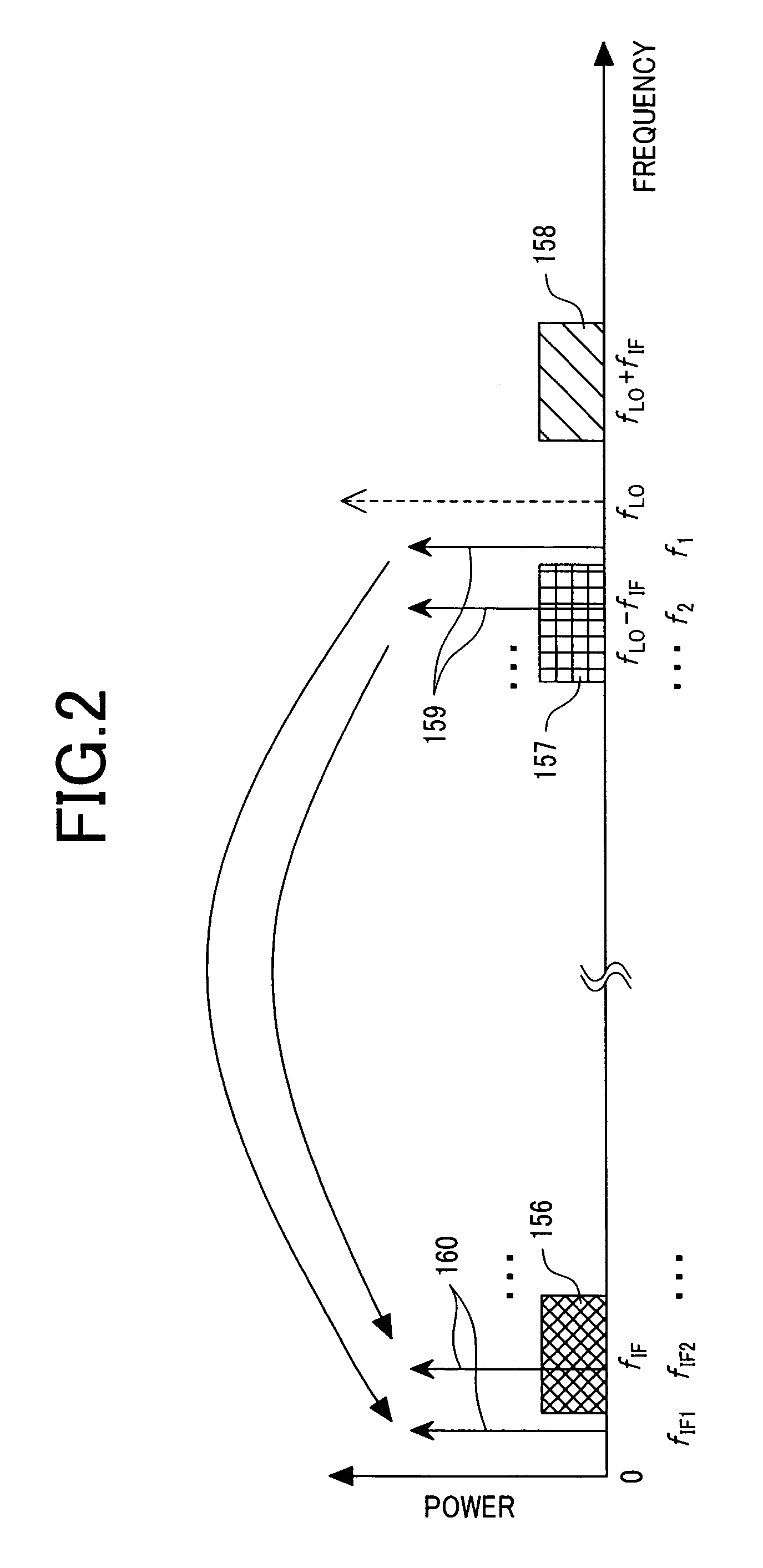
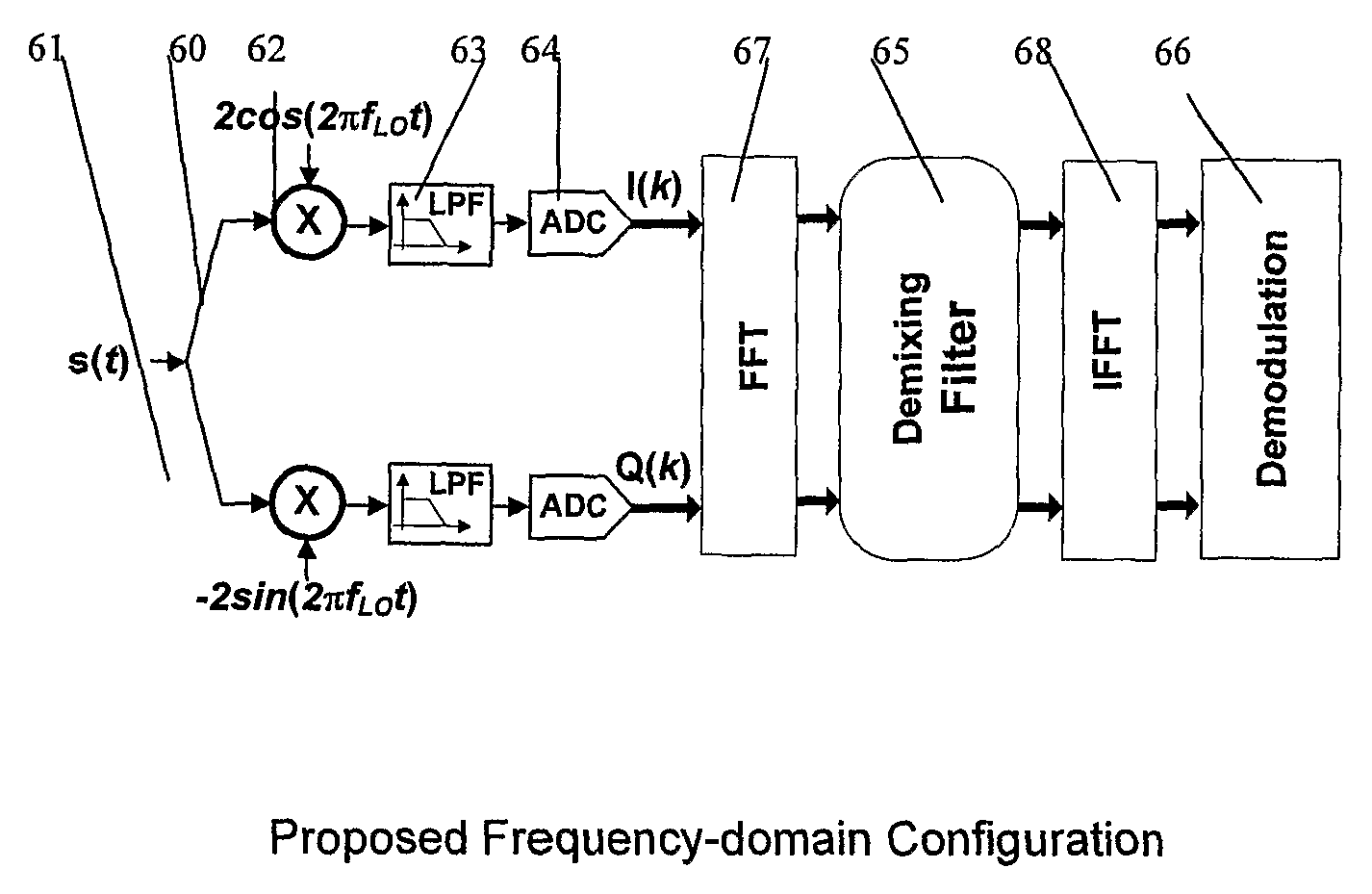
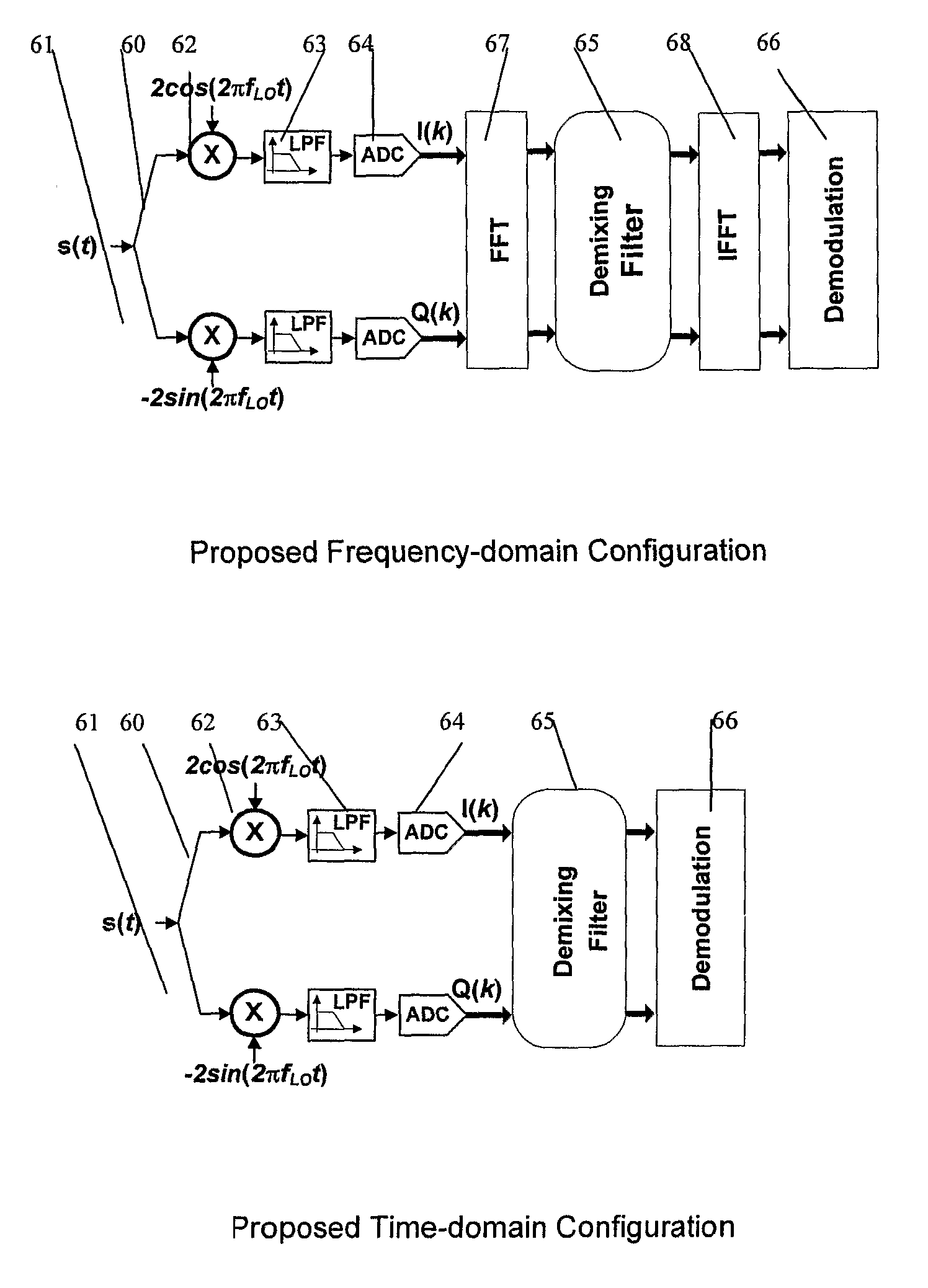
In a satellite radio navigation receiver receiving a transmitted radio navigation signal, a method of removing I / Q-mismatches in the received signal, comprising: resolving the received signal into I and Q signal component, and providing them as inputs to a demixing stage which removes unwanted signals, the demixing stage including first and second cross-coupled adaptive filters, whose coefficients are updated by the outputs of the demixing stage, the outputs of the demixing stage representing an IQ mismatch corrected signal. The coefficients are updated only by the polarity values of the outputs, resulting in great simplification. The receiver may be a zero-IF or low-IF receiver, and may operate on time domain or frequency domain signals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WESTMINSTER
Satellite Radio Navigation Receiver
InactiveUS20090058705A1Reduce RF impairmentEasy to integrateElectric signal transmission systemsEqual length code transmitterTime domainSatellite radio
In a satellite radio navigation receiver receiving a transmitted radio navigation signal, a method of removing I / Q-mismatches in the received signal, comprising: resolving the received signal into I and Q signal component, and providing them as inputs to a demixing stage which removes unwanted signals, the demixing stage including first and second cross-coupled adaptive filters, whose coefficients are updated by the outputs of the demixing stage, the outputs of the demixing stage representing an IQ mismatch corrected signal. The coefficients are updated only by the polarity values of the outputs, resulting in great simplification. The receiver may be a zero-IF or low-IF receiver, and may operate on time domain or frequency domain signals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WESTMINSTER
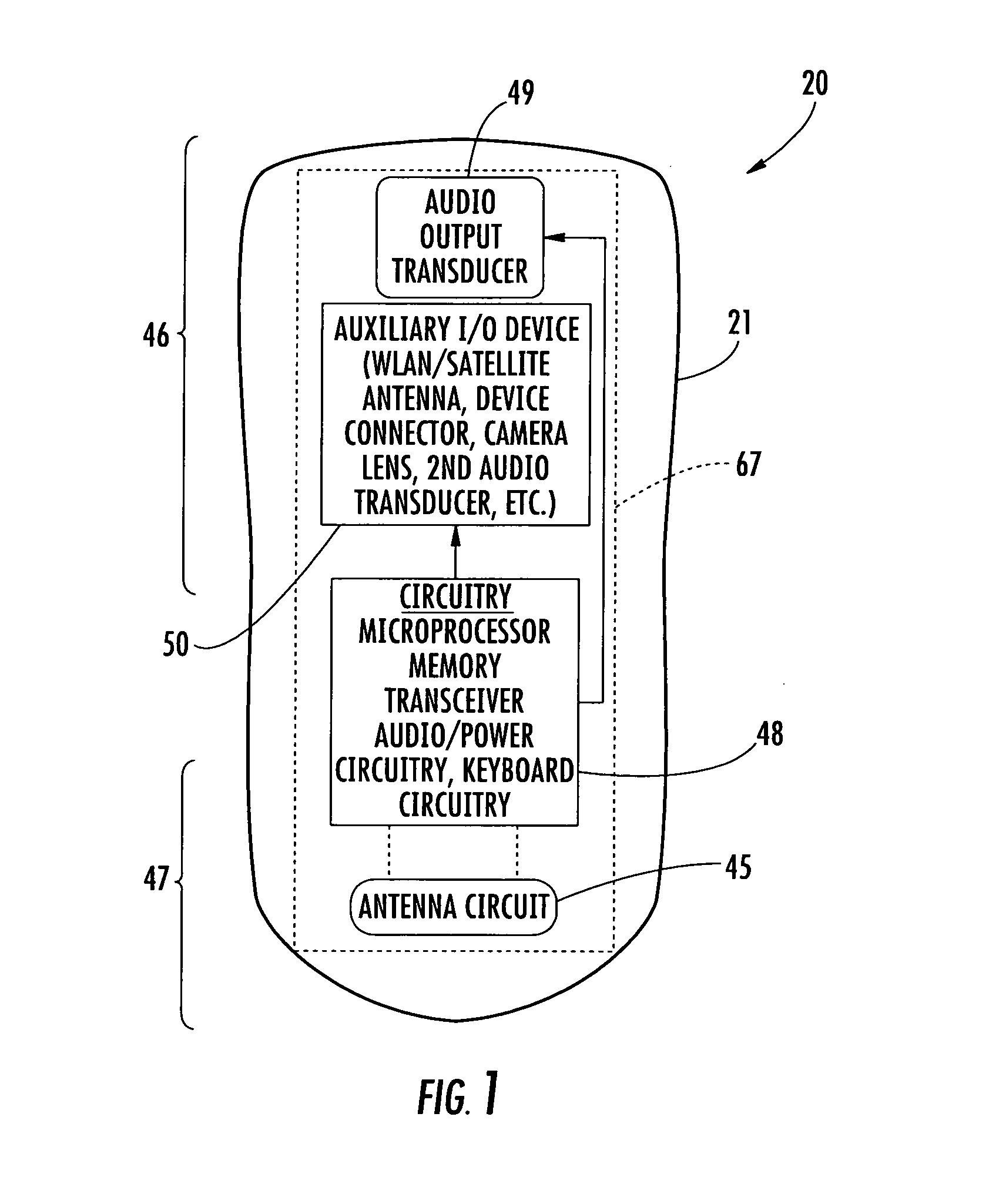
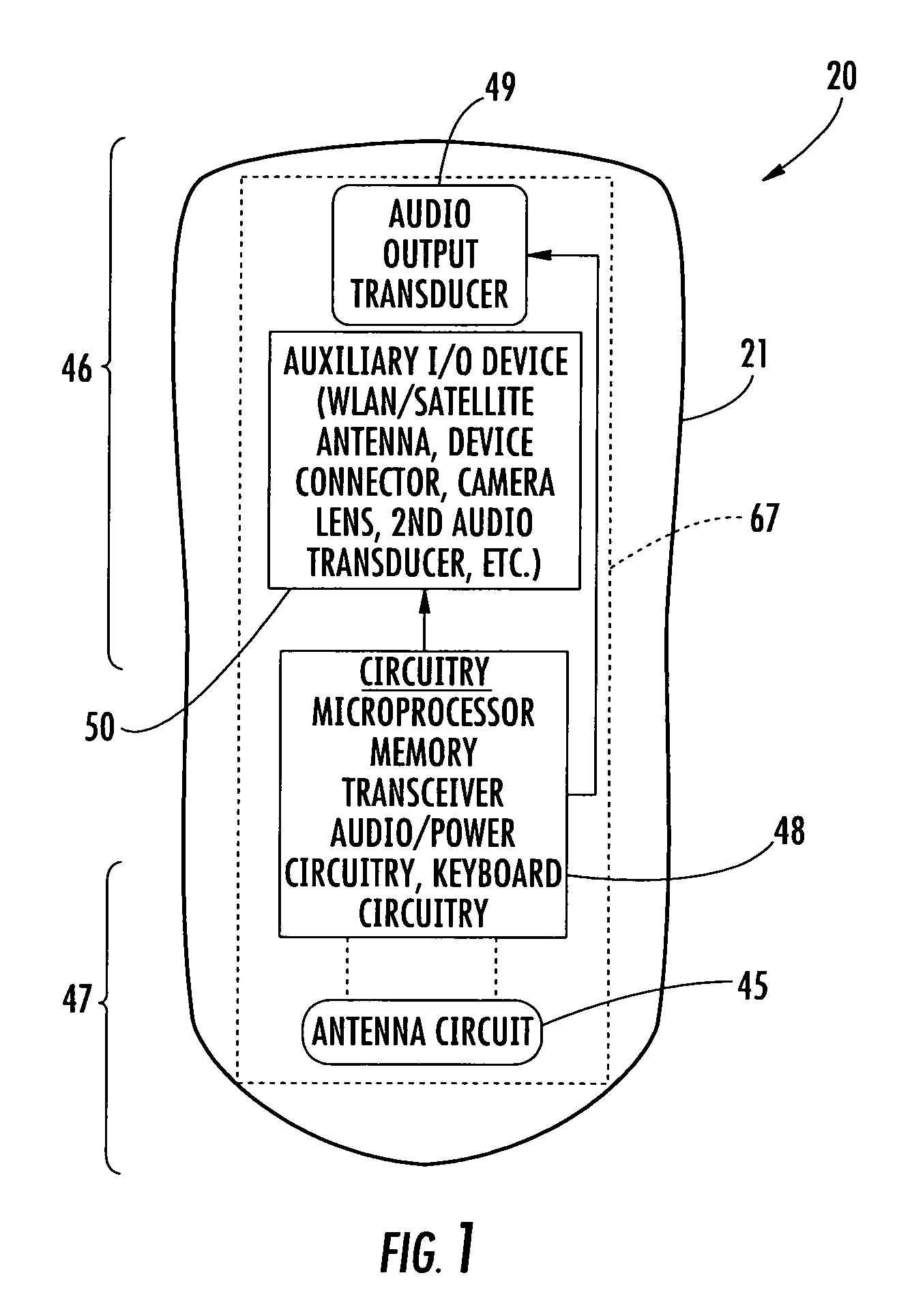
Mobile wireless communications device having low-if receiver circuitry that adapts to radio environment
A mobile wireless communications device, system and associated method includes a housing and circuit board that includes radio frequency (RF) circuitry and processor operative with each other. The RF circuitry includes a low-IF receiver circuit that is operative for maintaining an interferer signal at a same frequency side as a wanted signal relative to a local oscillator frequency setting, creating an interferer image signal, and filtering the image signal as substantially baseband frequency.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Mobile wireless communications device having low-IF receiver circuitry that adapts to radio environment
A mobile wireless communications device, system and associated method includes a housing and circuit board that includes radio frequency (RF) circuitry and processor operative with each other. The RF circuitry includes a low-IF receiver circuit that is operative for maintaining an interferer signal at a same frequency side as a wanted signal relative to a local oscillator frequency setting, creating an interferer image signal, and filtering the image signal as substantially baseband frequency.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Wireless communication device
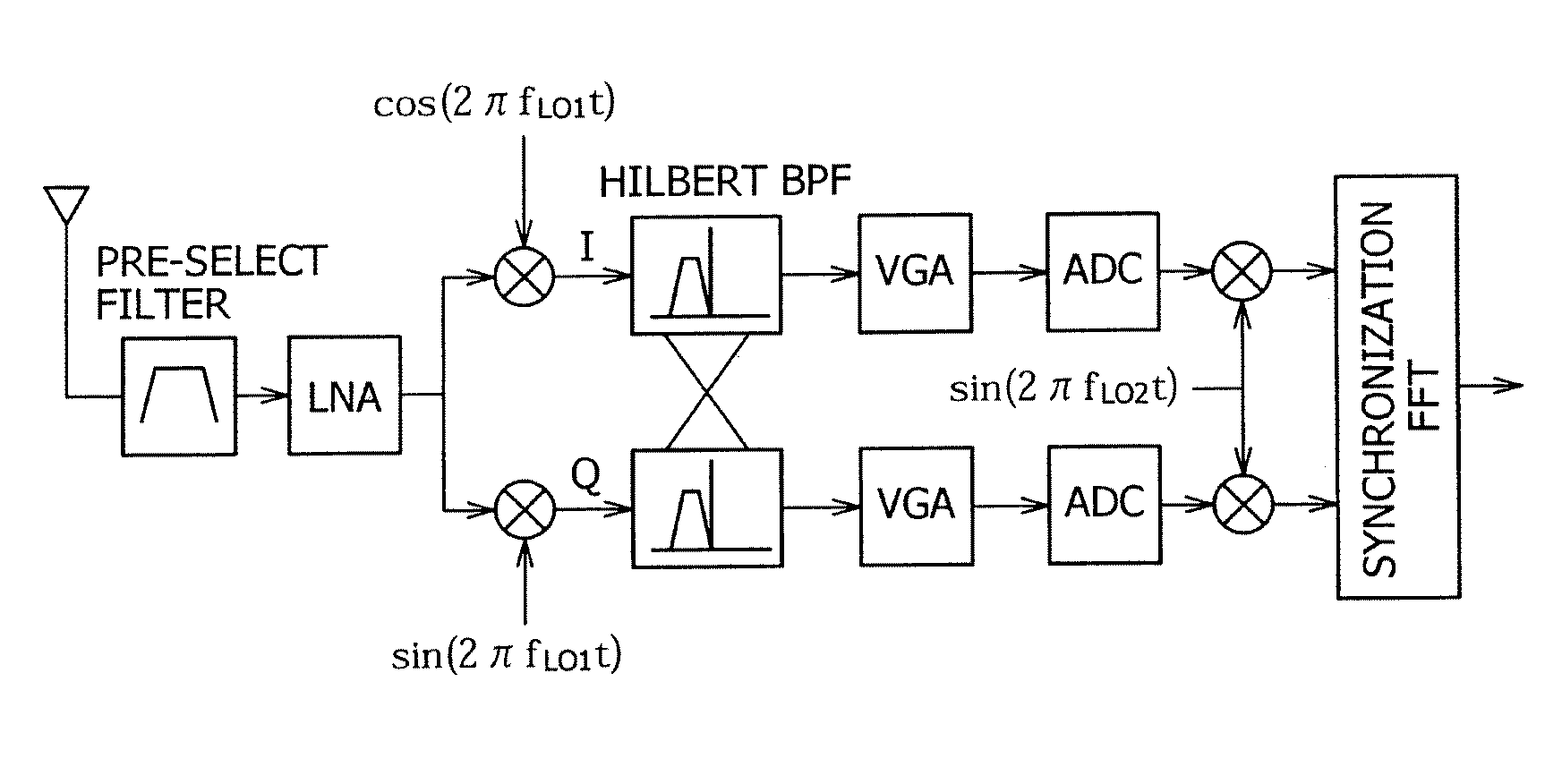
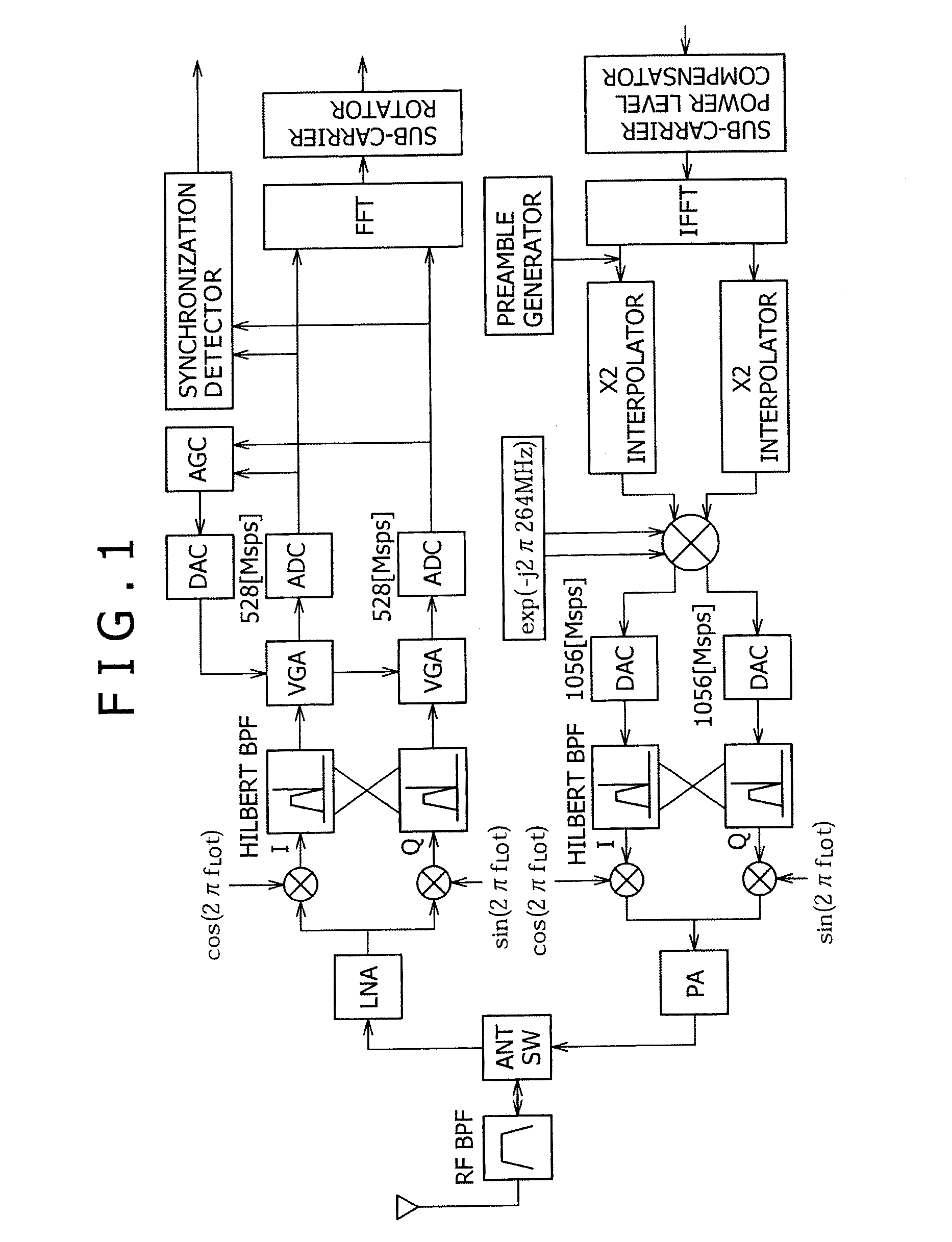
InactiveUS20070110171A1Promote generationEliminate needPolarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionIntermediate frequencyFrequency conversion
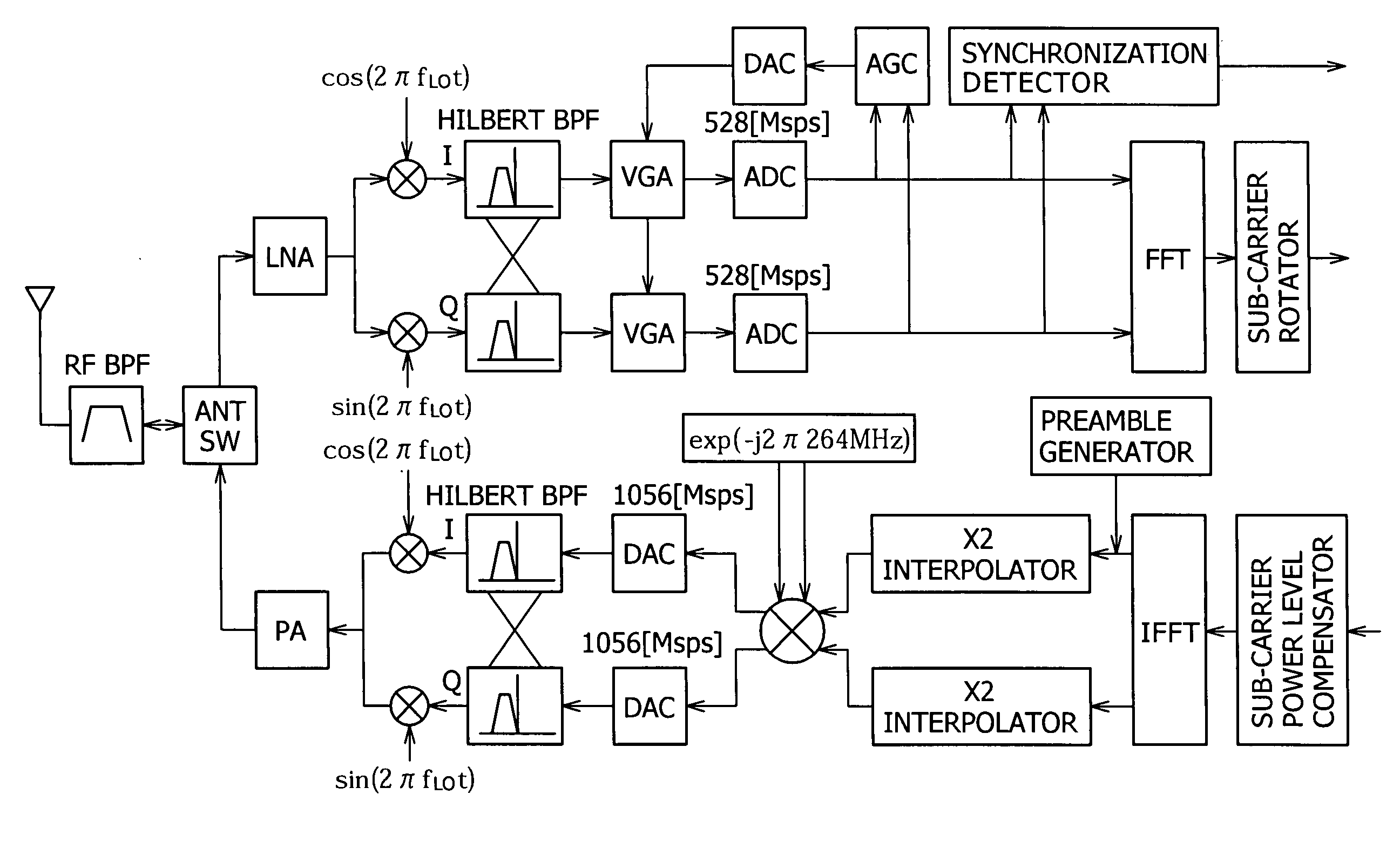
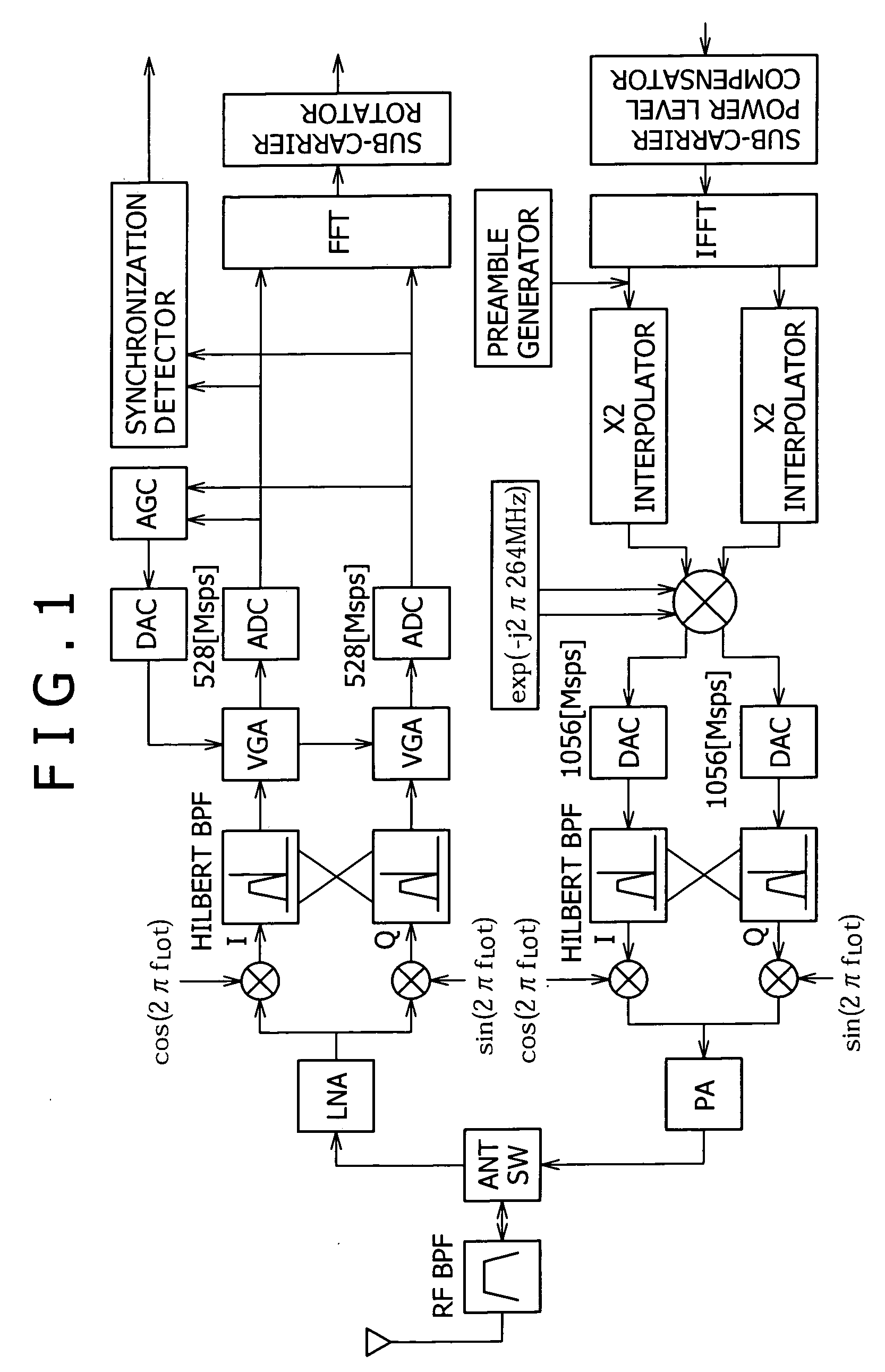
A multiband OFDM_UWB transmitting and receiving apparatus is provided in Low-IF configuration to solve problems attributed to a direct-conversion transmitting and receiving apparatus. A Low-IF receiver performs sorting by rotating a sub-carrier after FFT to eliminate the need for frequency conversion using a second local signal and uses the same AD conversion clock as that for a direct conversion receiver. An FFT-free preamble can be detected by using a sequence resulting from previously multiplying an original preamble pattern and an IF frequency together.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for eliminating mirror image interference in low-intermediate frequency receiver and relevant apparatus
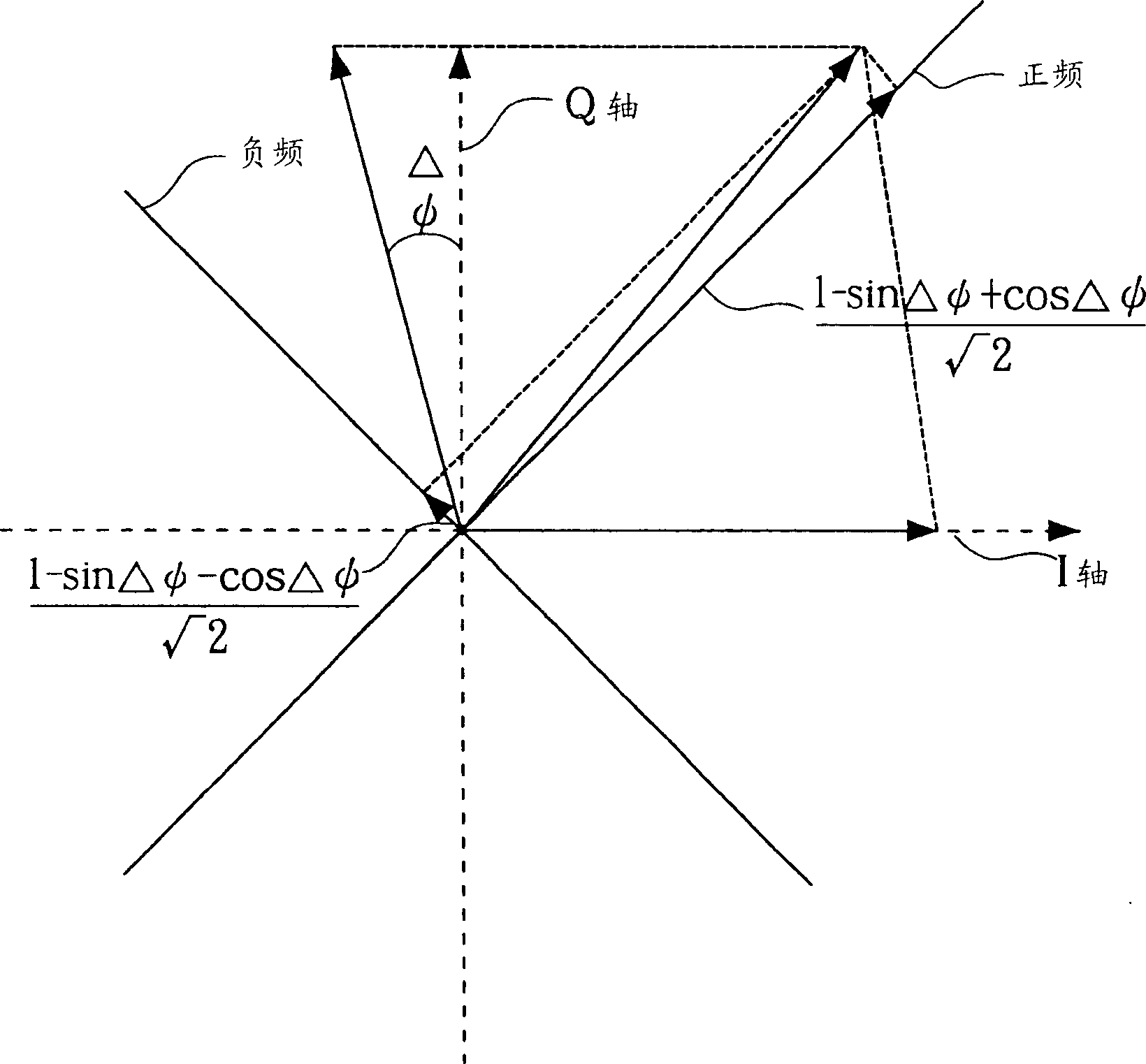
This invention provides a method for eliminating an amplitude mismatch and a phase mismatch in a pair of quadrature signals to eliminate image interference, in which, the said pair of quadrature signals includes an in-phase signal and a quadrature-phase signal. The said method includes compensating part of the in-phase signals into the quadrature-phase signals to make the compensated phase differ from the phase of in-phase signal by 90 deg. to eliminate phase difference of the pair and regulate the amplitude of the in-phase signal and the quadrature phase signal to a same value to eliminate its amplitude difference.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC +1
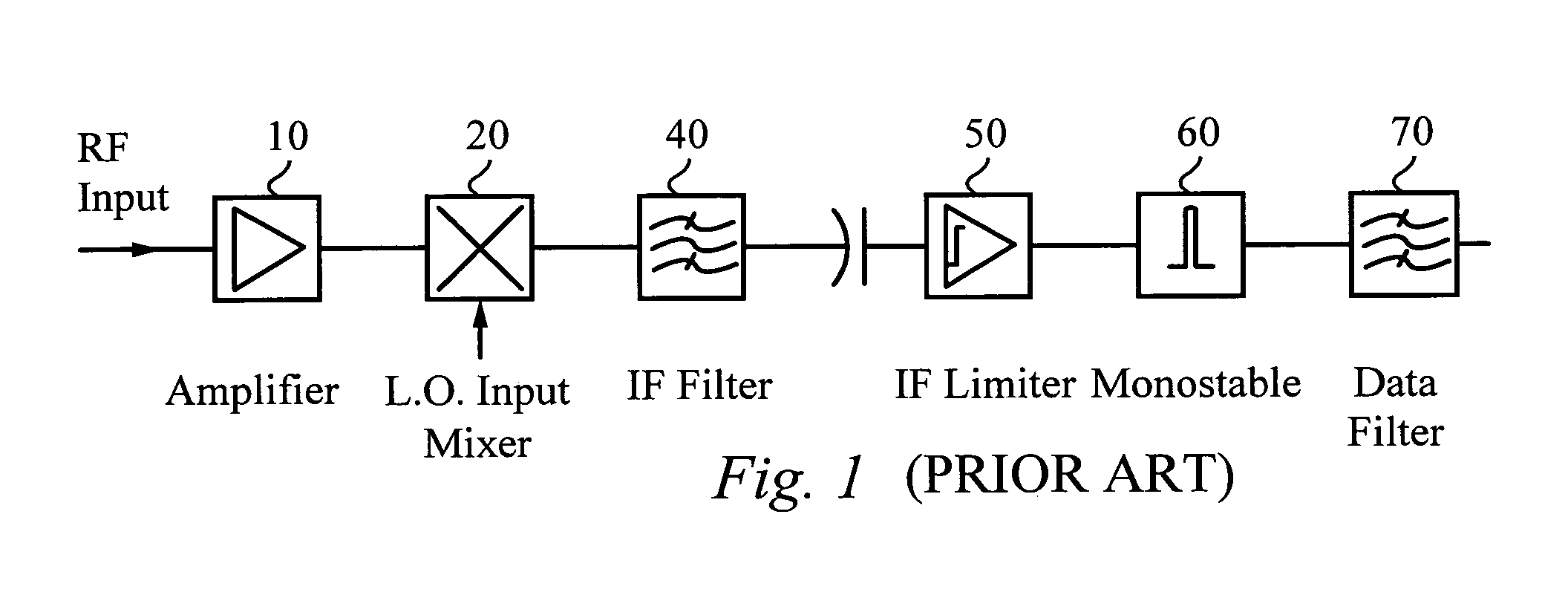
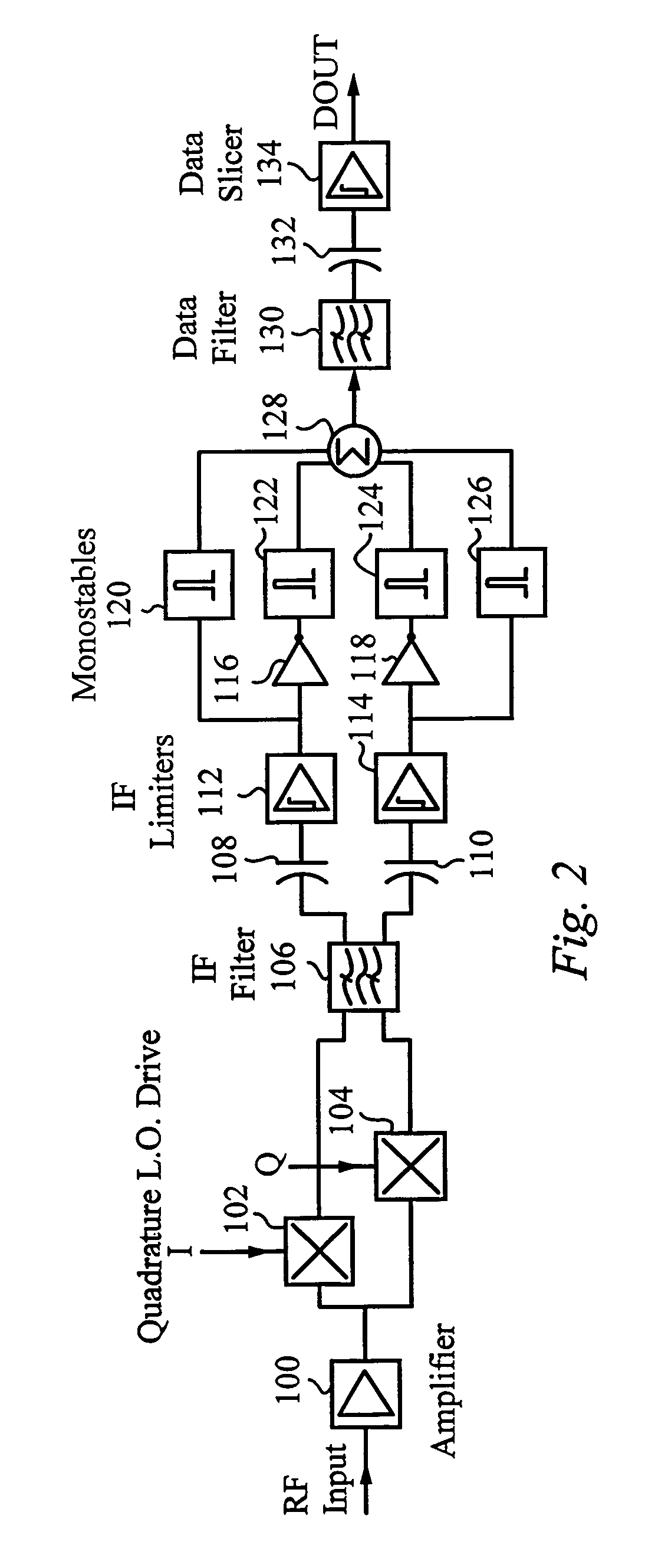
FM demodulator for a low IF receiver
InactiveUS6985541B1Modulated-carrier systemsSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsRadio receptionRadio receiver
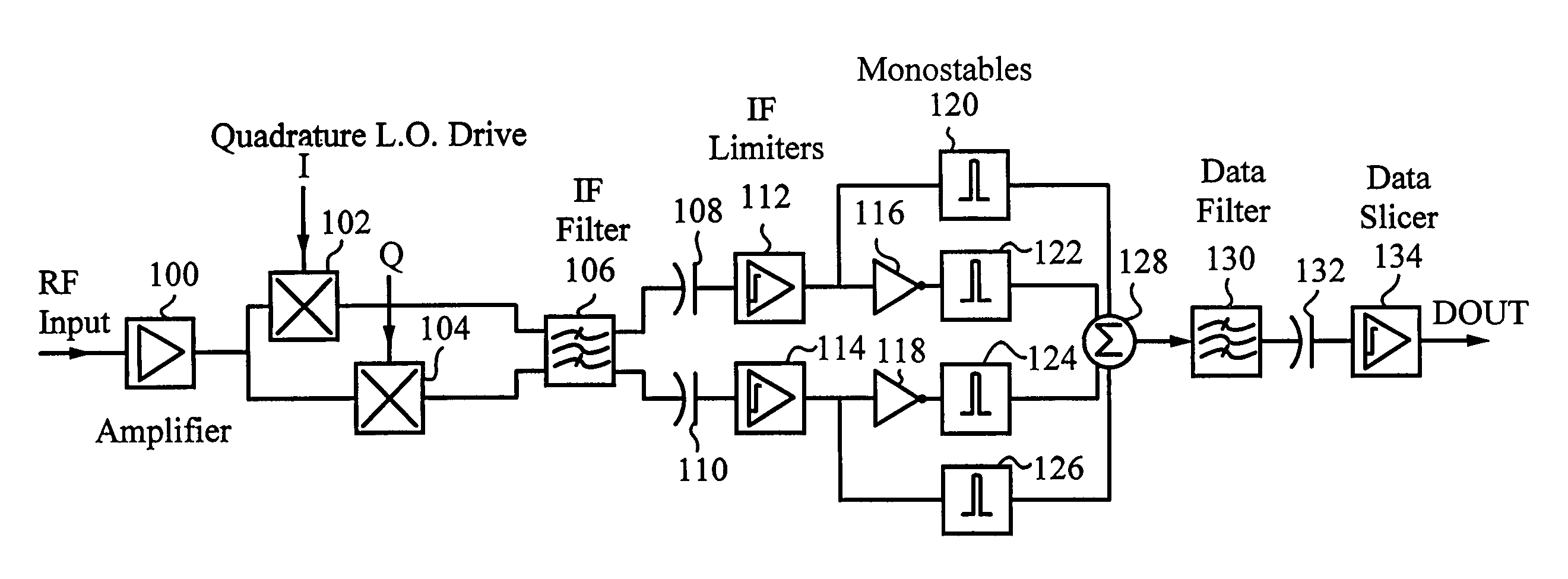
A superhet receiver with quadrature IF and improved demodulator is configured to recover a modulated signal from a low IF in a radio receiver. A superhet receiver receives a FM radio-frequency signal, converts the input RF signal to an in-phase IF signal and an IF signal in phase quadrature to the in-phase signal, and outputs the IF signals. A plurality of monostables receive the IF signals and each monostable generates a corresponding output pulse. By combining the monostable output pulses, a complex waveform is generated. The complex waveform includes the demodulated signal and a carrier signal at a significantly higher IF. The complex waveform is filtered to recover the desired modulated signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Wireless communication device
ActiveUS20090232246A1Promote generationSolve the real problemPolarisation/directional diversityModulation with suppressed carrierFrequency conversionCarrier signal
A multiband OFDM_UWB transmitting and receiving apparatus is provided in Low-IF configuration to solve problems attributed to a direct-conversion transmitting and receiving apparatus. A Low-IF receiver performs sorting by rotating a sub-carrier after FFT to eliminate the need for frequency conversion using a second local signal and uses the same AD conversion clock as that for a direct conversion receiver. An FFT-free preamble can be detected by using a sequence resulting from previously multiplying an original preamble pattern and an IF frequency together.
Owner:SONY CORP
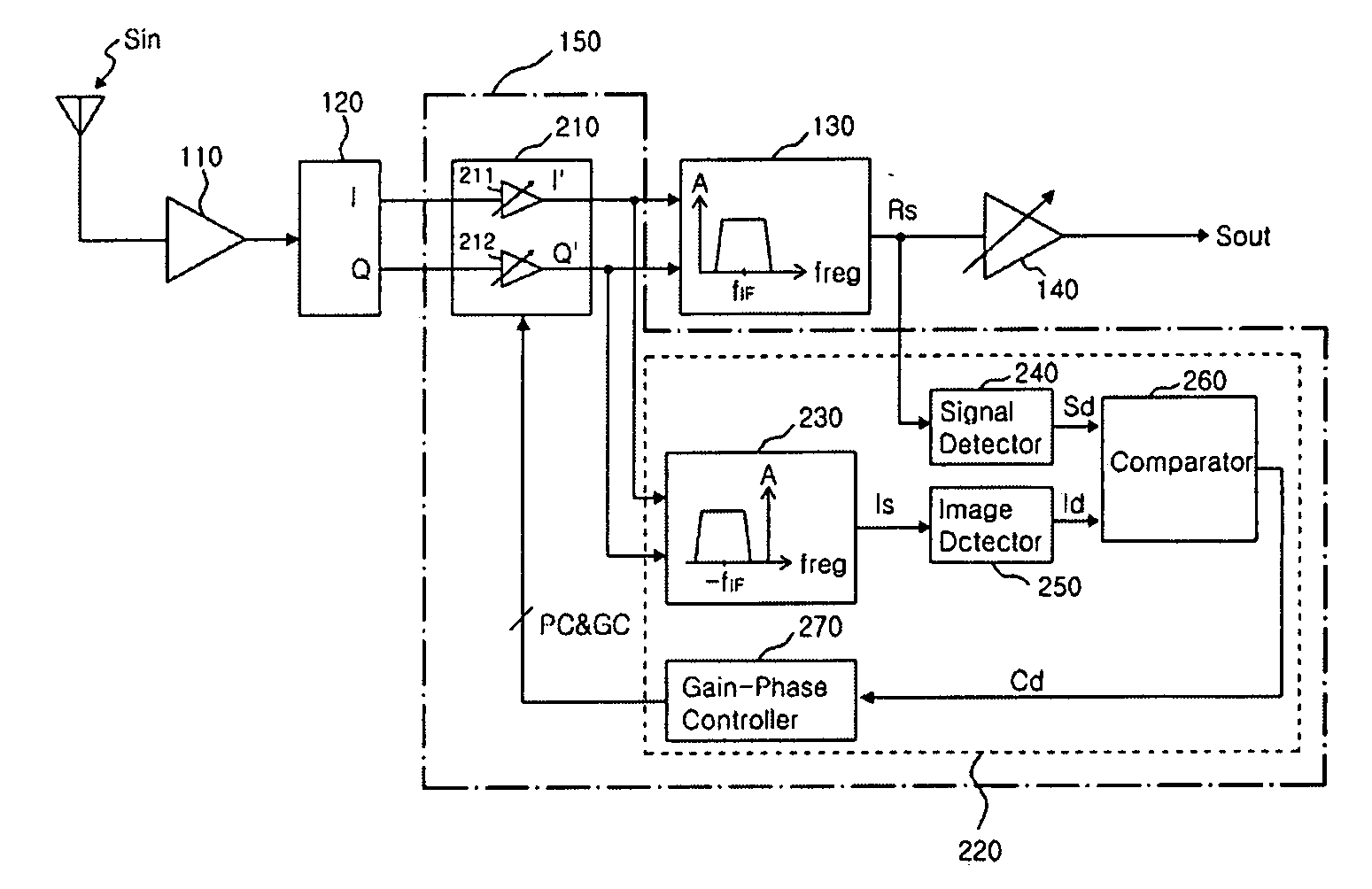
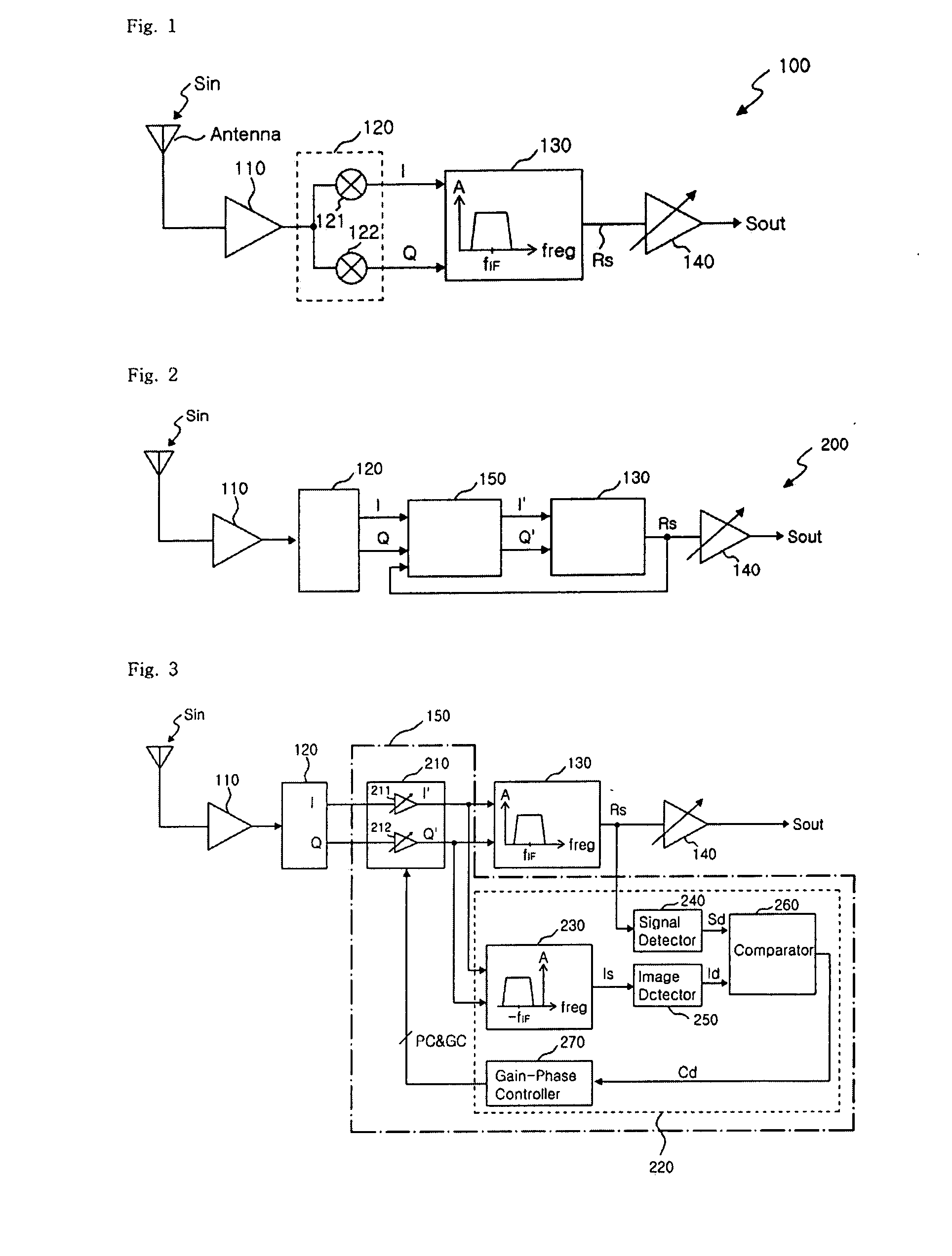
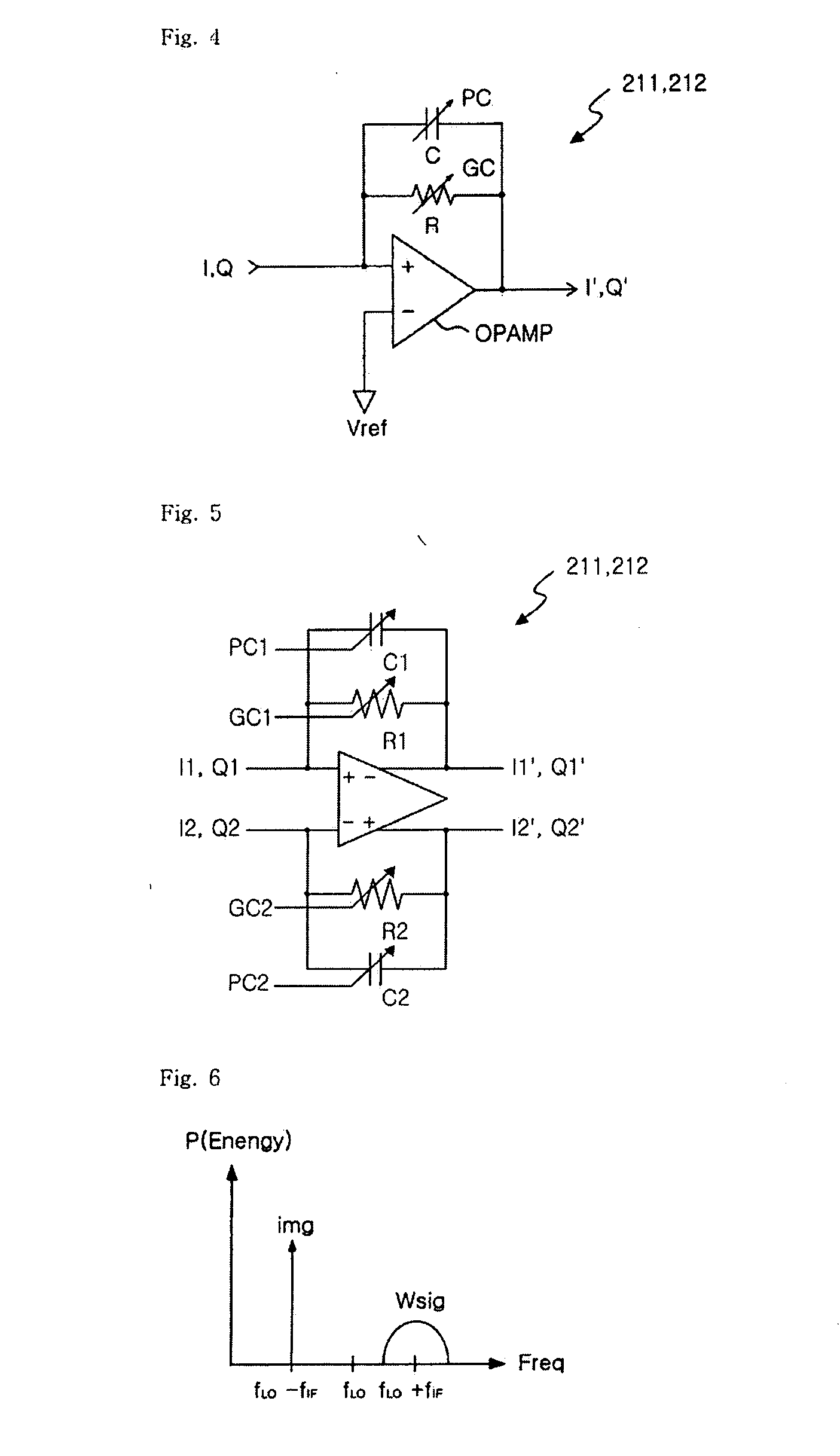
Low IF receiver of rejecting image signal and image signal rejection method
InactiveUS7873342B2Avoiding demodulationReduce noiseCommunication jammingTransmissionAudio power amplifierSignal Repression
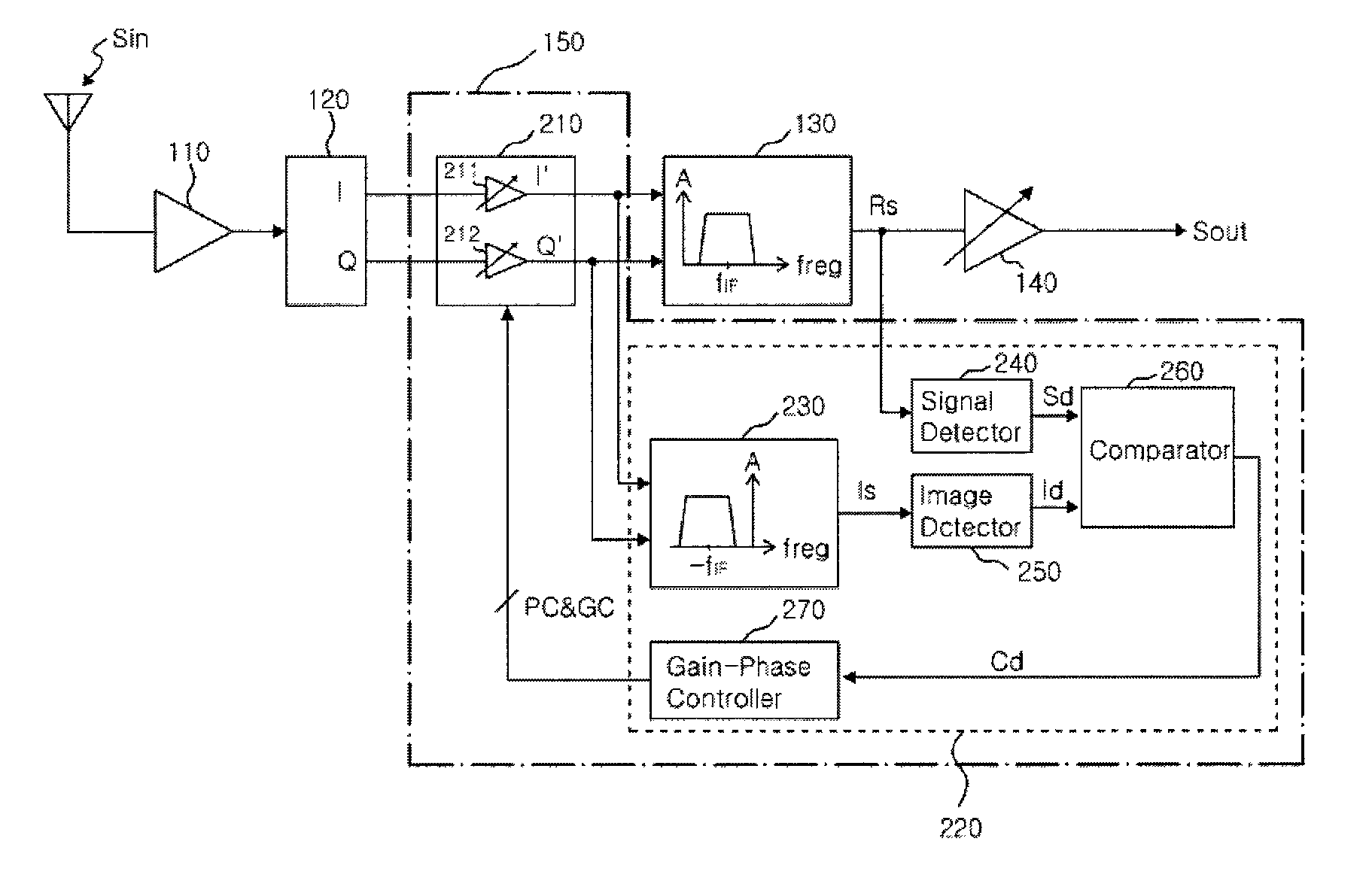
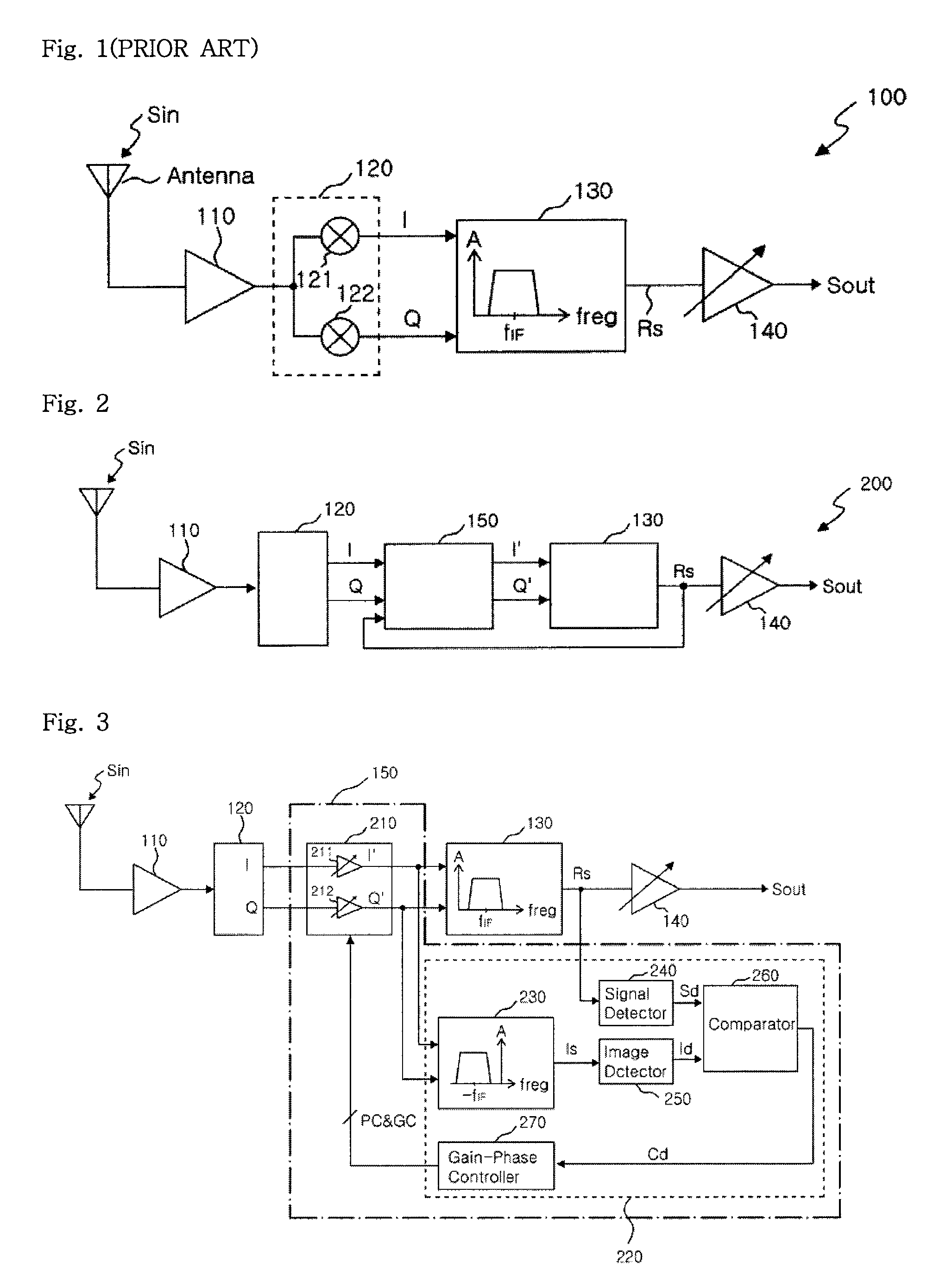
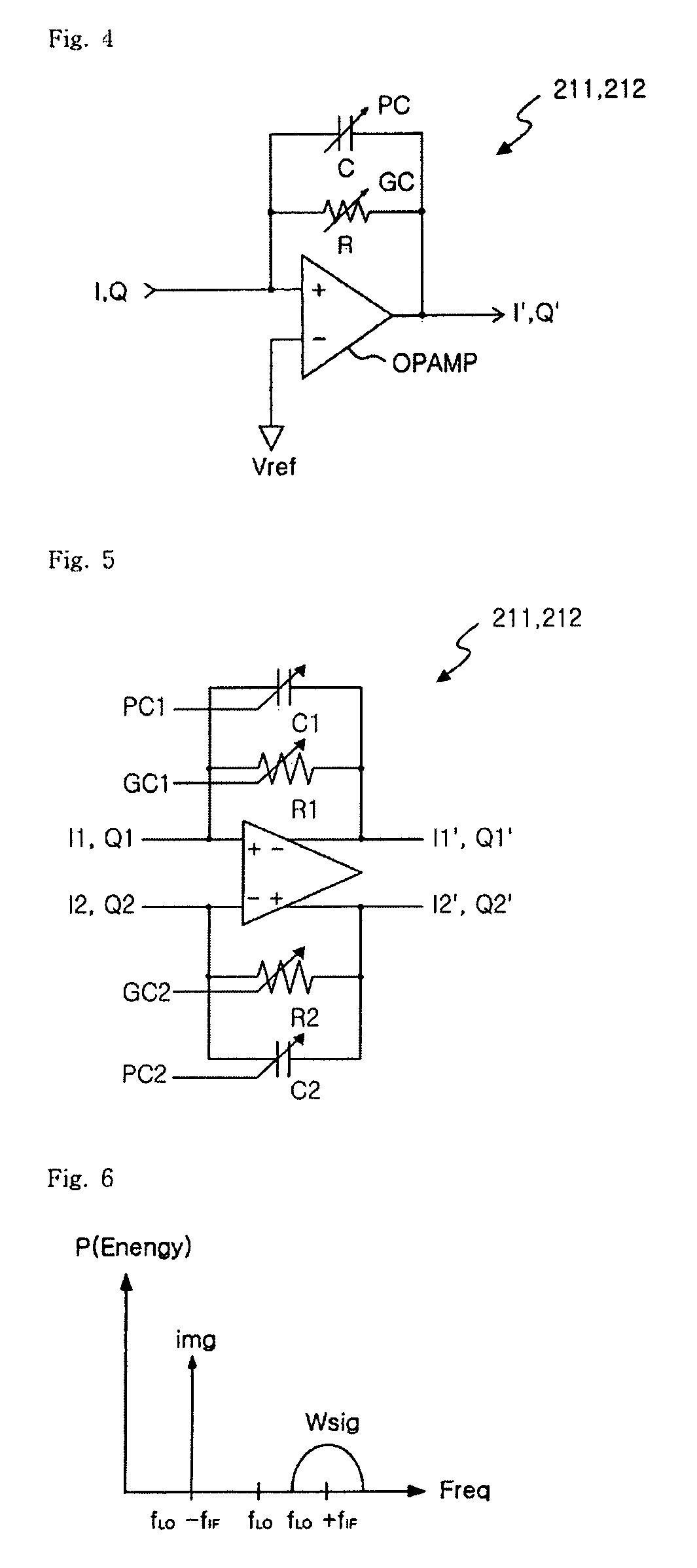
Provided are an image signal rejection method capable of avoiding demodulation of an image signal along with a real signal in a radio frequency (RF) signal and a low IF receiver of rejecting an image signal by using the method. The low IF receiver of rejecting an image signal includes a low noise amplifier, a quadrature I / Q mixer, a signal complex filter, and a phase and gain control block. The low noise amplifier amplifies a radio frequency (RF) signal. The quadrature I / Q mixer generates an I signal and a Q signal by down-converting the amplified RF signal into an IF signal. The phase and gain control block generates an I′ signal and a Q′ signal which are obtained by changing phases and amplitudes of the I signal and the Q signal by using a real signal. The signal complex filter minimizing the image signal in the IF signal and passing the real signal by performing filtering on the I′ signal and the Q′ signal.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON KOREA INC
Low if receiver of rejecting image signal and image signal rejection method
InactiveUS20080096513A1Avoiding demodulationReduce noiseRadio transmissionAudio power amplifierReal signal
Provided are an image signal rejection method capable of avoiding demodulation of an image signal along with a real signal in a radio frequency (RF) signal and a low IF receiver of rejecting an image signal by using the method. The low IF receiver of rejecting an image signal includes a low noise amplifier, a quadrature I / Q mixer, a signal complex filter, and a phase and gain control block. The low noise amplifier amplifies a radio frequency (RF) signal. The quadrature I / Q mixer generates an I signal and a Q signal by down-converting the amplified RF signal into an IF signal. The phase and gain control block generates an I′ signal and a Q′ signal which are obtained by changing phases and amplitudes of the I signal and the Q signal by using a real signal. The signal complex filter minimizing the image signal in the IF signal and passing the real signal by performing filtering on the I′ signal and the Q′ signal.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON KOREA INC
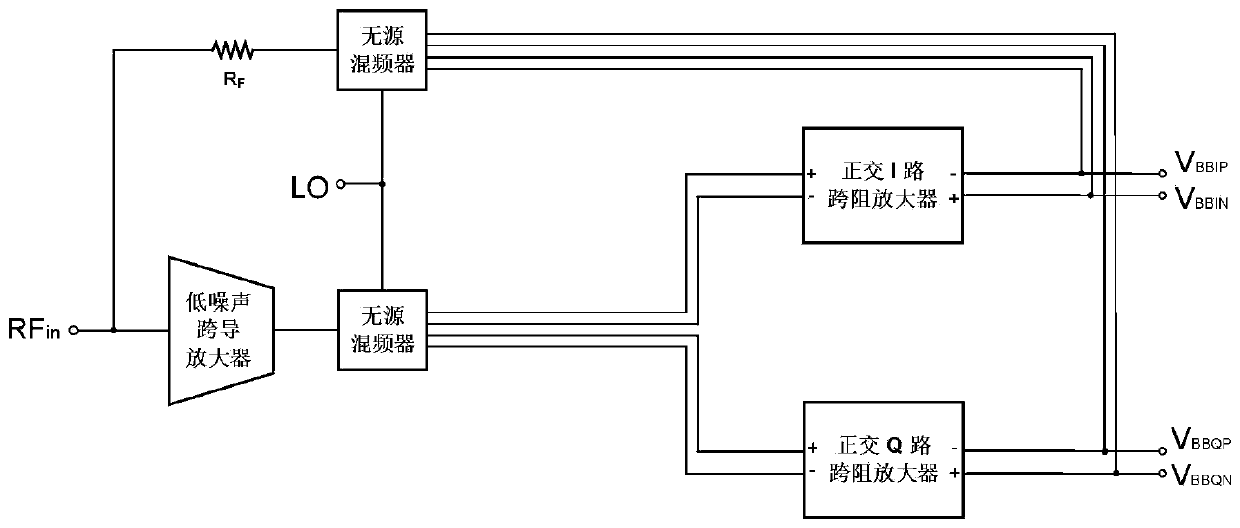
Broadband receiver circuit with adjustable impedance matching frequency
ActiveCN111384902AImprove frequency selectivityImprove anti-interference abilityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersLow noiseNoise (radio)
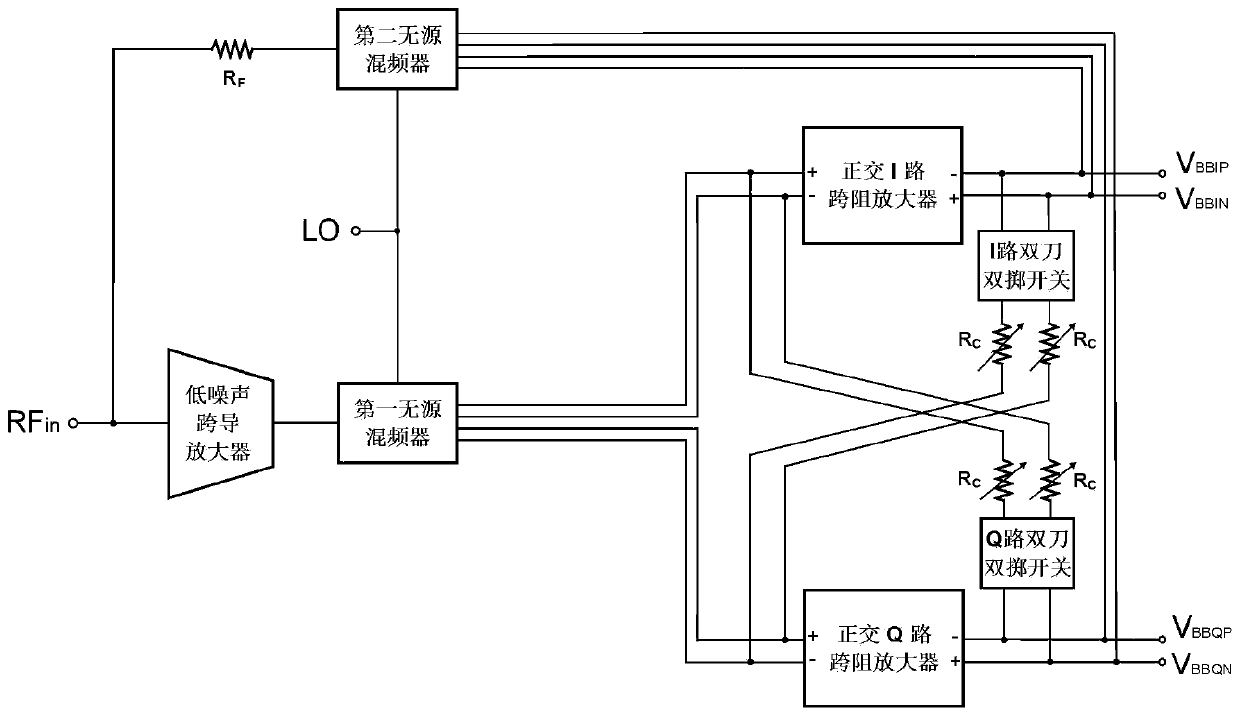
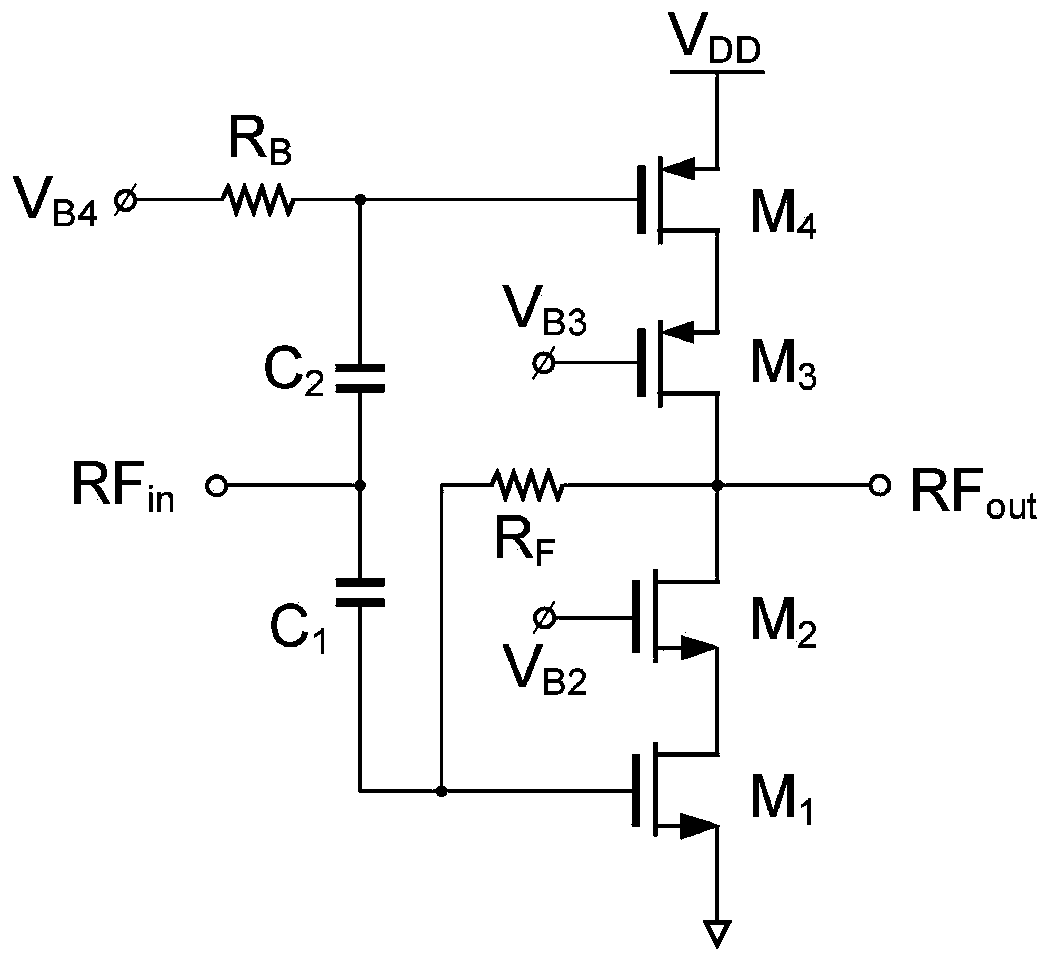
The invention relates to a broadband receiver circuit with adjustable impedance matching frequency, which belongs to the field of radio frequency integrated circuits. The broadband receiver circuit comprises a low-noise transconductance amplifier, two passive frequency mixers, a quadrature trans-impedance amplifier I path, a quadrature trans-impedance amplifier Q path, a feedback resistor, two double-pole double-throw switches and four variable resistors, wherein a radio frequency input signal is connected with an input end of the low-noise transconductance amplifier and is connected with an input end of the second passive mixer through using the feedback resistor; an output end of the low-noise transconductance amplifier is connected with a signal input end of the first passive mixer; clock input ends of the two passive mixers are connected with four-phase non-overlapping clock signals; a signal output end of the first passive mixer is connected with a differential input end of the Ipath and a differential input end of the Q path; differential output signal ends of the I path and the Q path are connected with a four-phase input end of the second passive mixer; and the four variable resistors are bridged at input ends and output ends of the I path and the Q path through using the two double-pole double-throw switches. The broadband receiver circuit is suitable for zero-intermediate-frequency and low-intermediate-frequency receiver schemes.
Owner:NEWRADIO TECH CO LTD
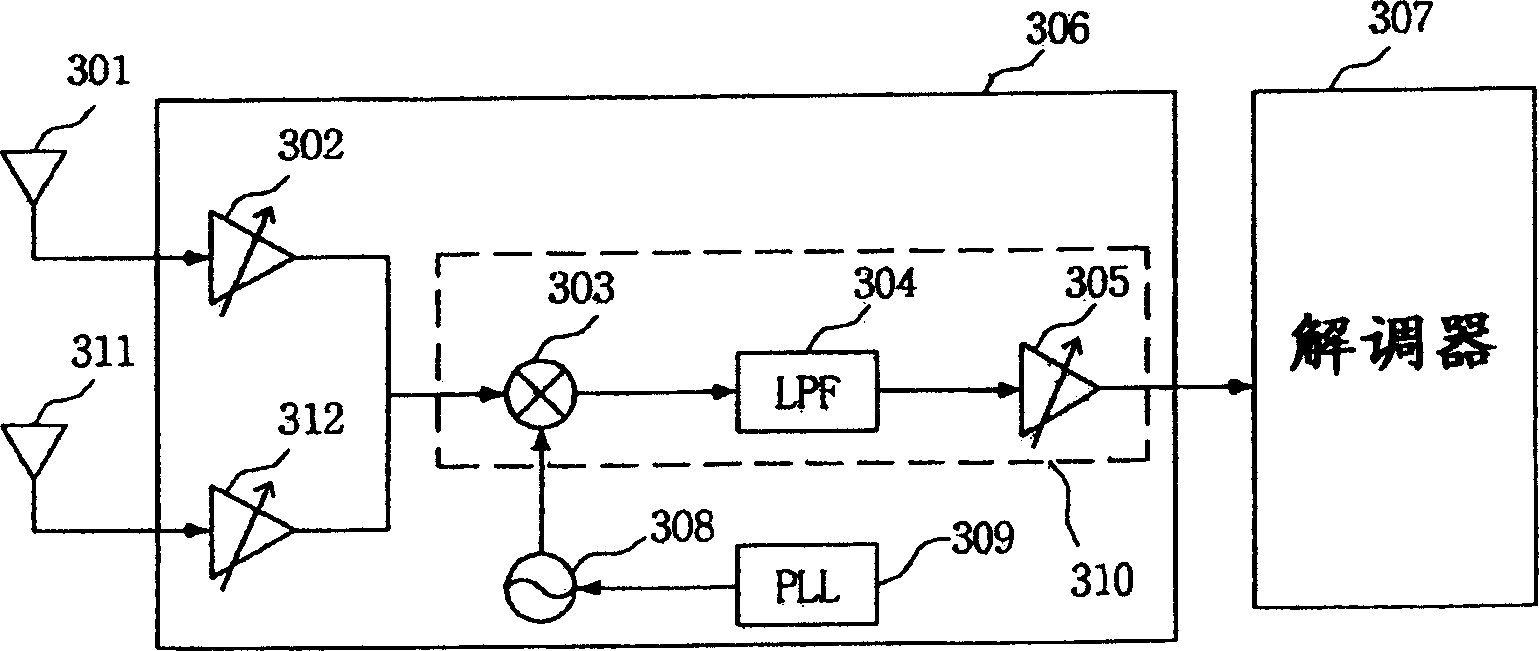
Dual-mode receiver and receiving method thereof
ActiveUS7346128B2Quality improvementReduce manufacturing costModulated-carrier systemsPulse demodulatorDual modeDirect-conversion receiver
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
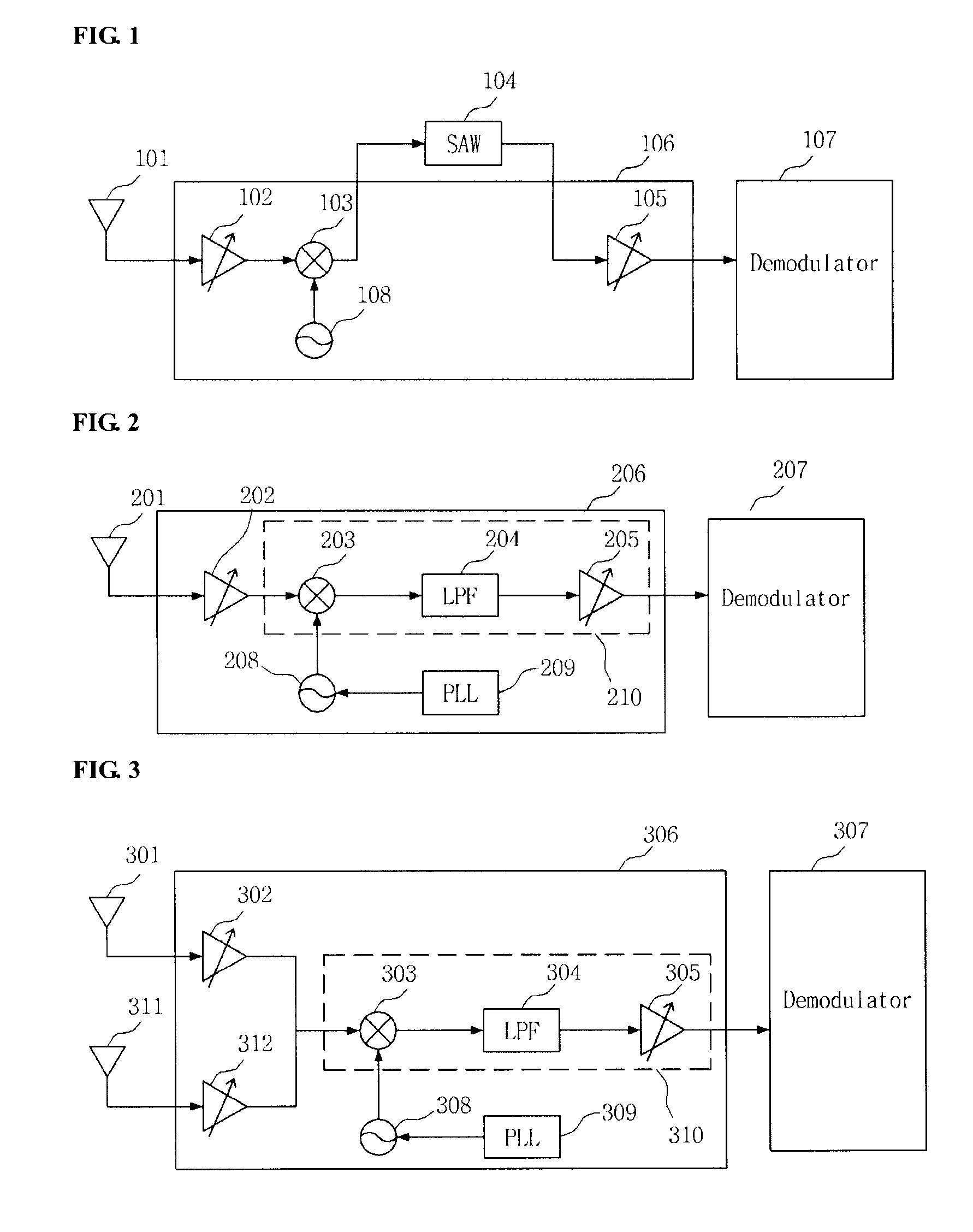
Low intermediate frequency receiver
InactiveUS20090103654A1Well formedDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationPhase shiftedIntermediate frequency
One embodiment relates to a low intermediate frequency (IF) receiver. The low-IF receiver includes an analog front end that is configured to receive a modulated IQ data signal and provide an in-phase signal and a quadrature signal, where the in-phase signal is phase shifted by approximately 90° relative to the quadrature signal. The low-IF receiver further includes a digital processing block, and a single path that provides only one of the in-phase signal and the quadrature signal to the digital processing block. Other receivers and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method of reducing power consumption in a low intermediate frequency radio receiver
ActiveUS20190020310A1Reduce power consumptionBad link qualityPower managementModulation transferenceTransceiverRadio receiver
A novel and useful apparatus and method for an image-interferer aware single quadrature RF downconversion (SQRD) low intermediate frequency (LIF) receiver and related power reduction techniques utilized therein. The invention applies zero-margin adaptive transceiver (ZMAT) design principles to considerably reduce the receiver's power consumption in an adaptive fashion in accordance with the instantaneous reception conditions. In a low IF dual-branch (i.e. quadrature) downconversion receiver, the radio monitors the image strength and shuts off the receiver's Q branch (or I branch) when image rejection is not needed (i.e. when the relative image strength is below a threshold), thus significantly reducing power consumption in the RF receiver. A zero IF receiver is switched to a SQRD low IF receiver of lower power consumption when the image interferer strength is low enough to allow for a given required level of performance.
Owner:SHORT CIRCUIT TECH LLC
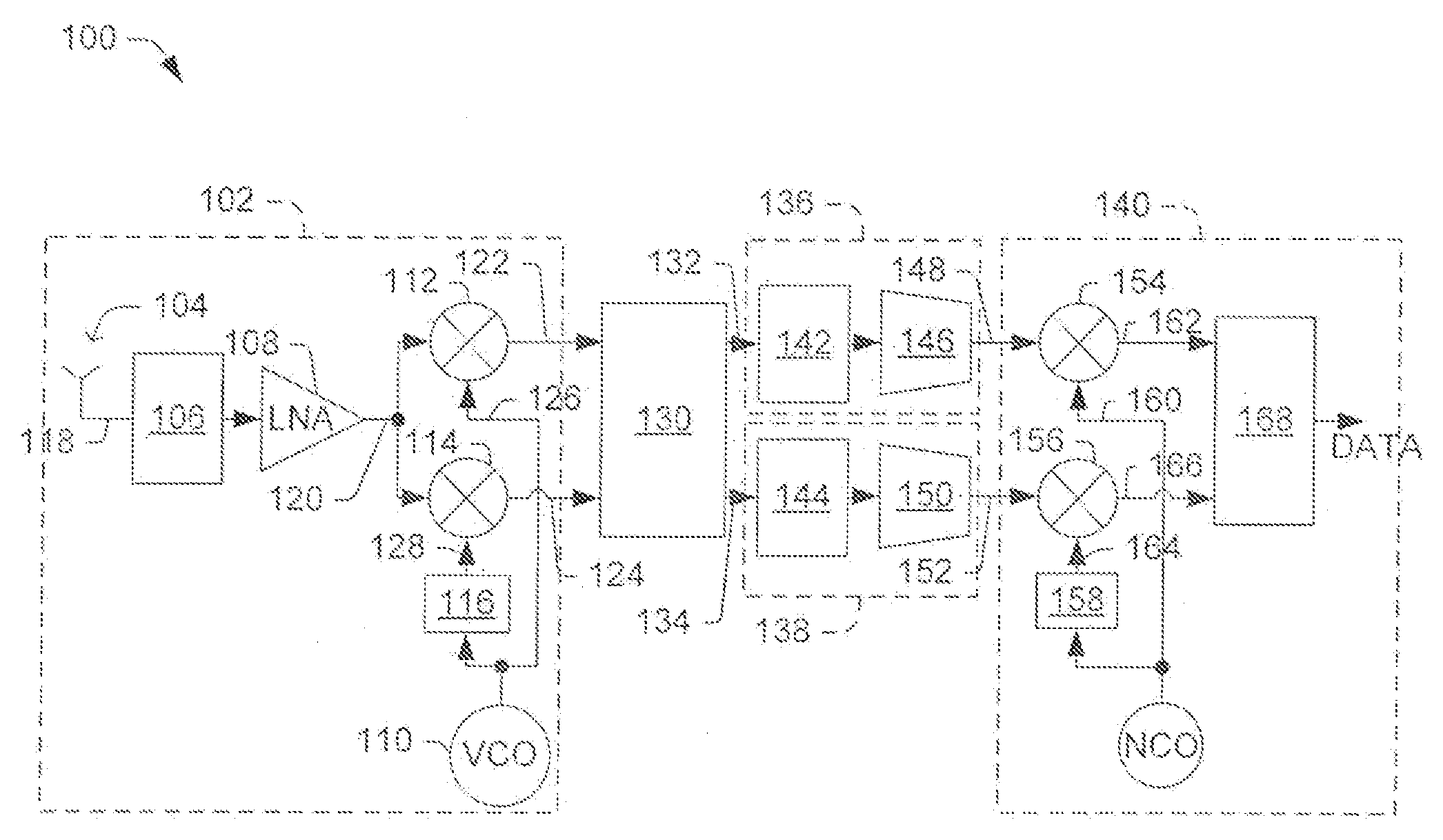
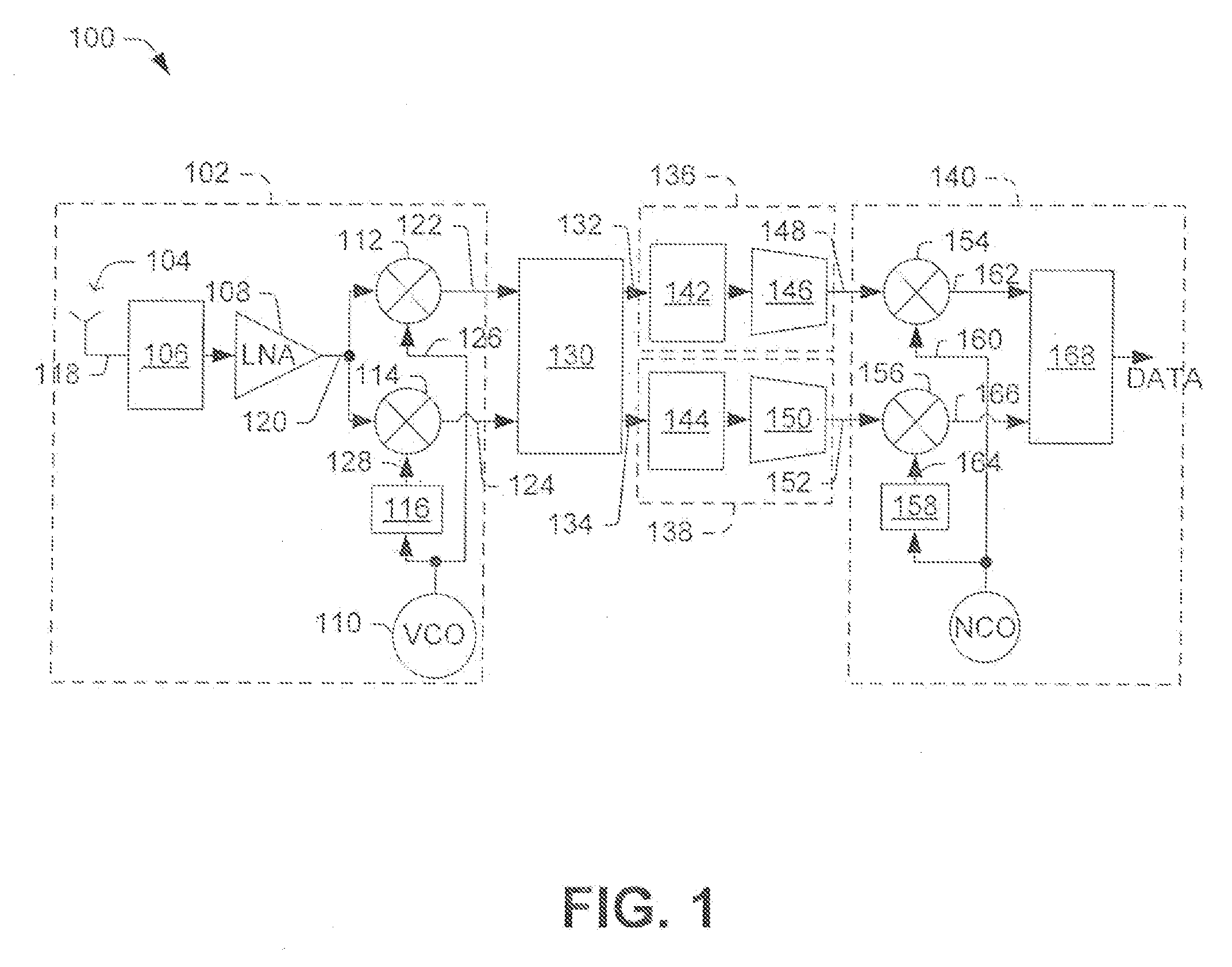
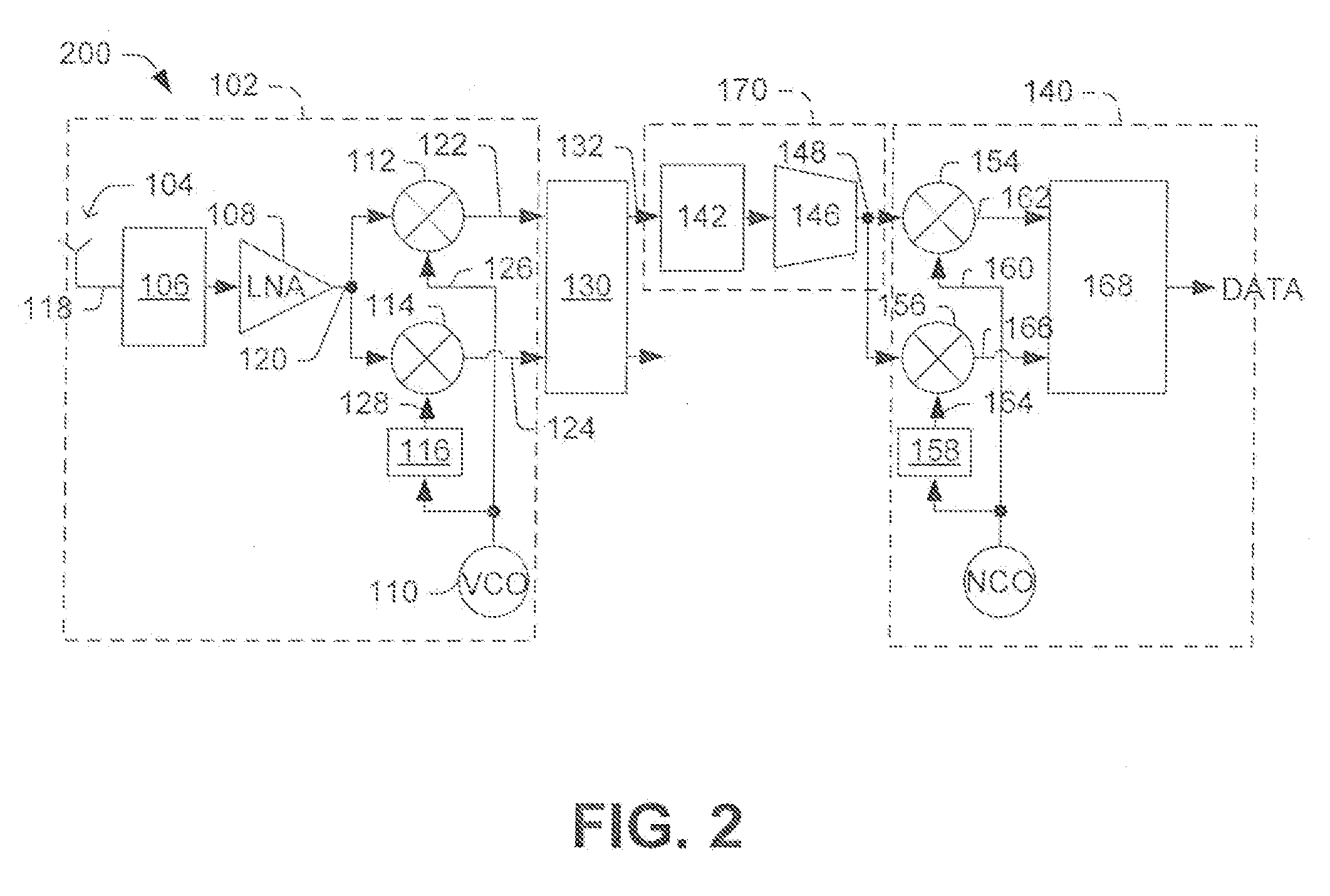
Low IF receiver systems and methods
ActiveUS7480349B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsPhase imbalanceIntermediate frequency
Owner:INTEL CORP
Terrestrial-Digital Multimedia Broadcasting And Digital Audio Broadcasting Low Intermediate Frequency Receiver
InactiveUS20070042730A1Easy to integrateReduce manufacturing costTelevision system detailsReceivers monitoringIntermediate frequencyDown conversion mixer
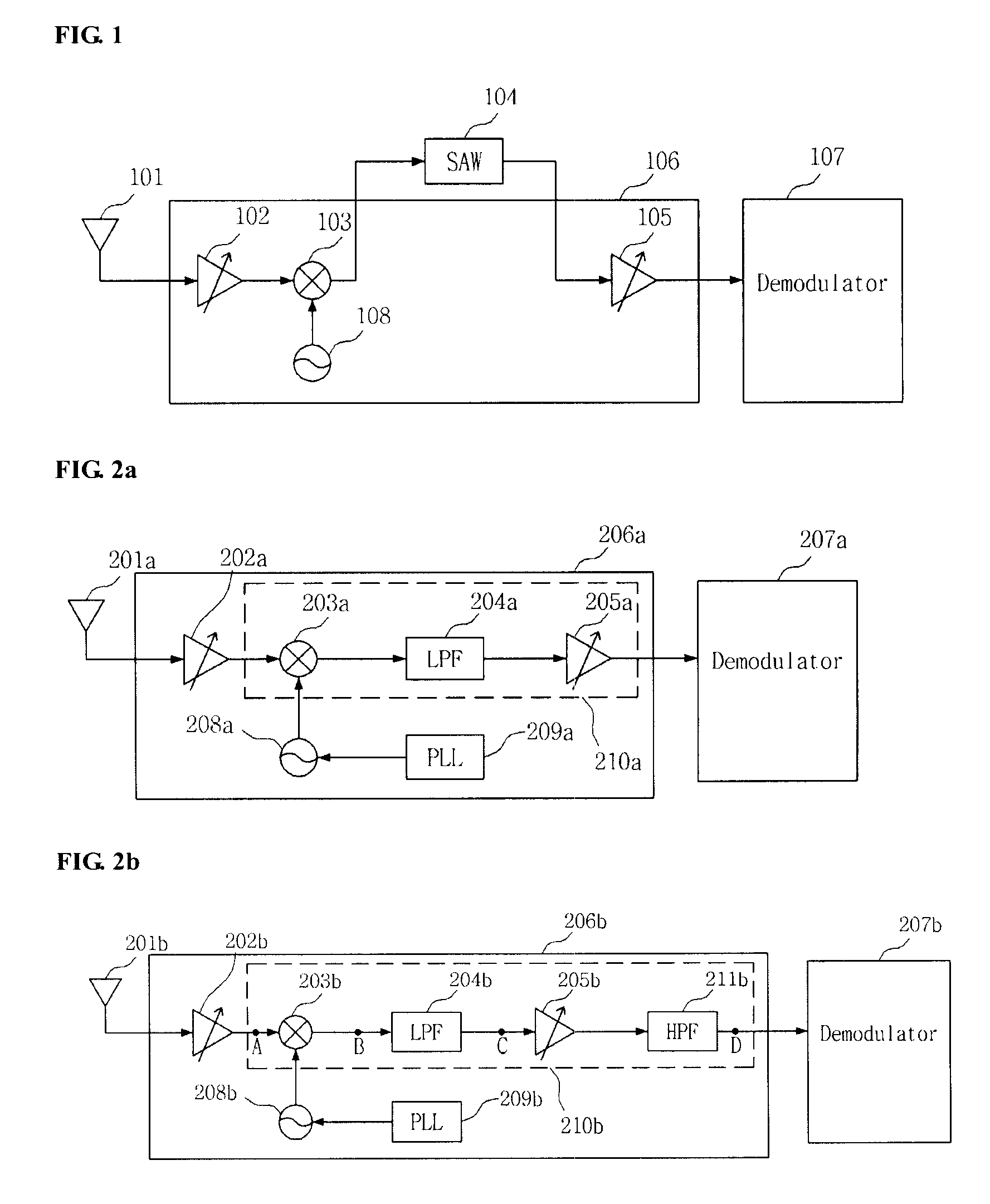
Provided is a terrestrial-digital multimedia broadcasting (T-DMB) and digital audio broadcasting (DAB) low intermediate frequency (IF) receiver. A T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver comprises a low noise amplifier (LNA), an image rejection down-conversion mixer, a low pass filter, an amplifier, a local oscillator, a phase-locked loop, and at least one high pass filter. Particularly, the LNA, the image rejection down-conversion mixer, the low pass filter, the amplifier, the local oscillator, the phase-locked loop, and the high pass filter are integrated in a monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit substrate. The T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver allows a removal of a conventional SAW filter without degrading the performance of the receiver. Thus, the T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver can be easily integrated into a single and manufactured at low costs.
Owner:INTEGRANT TECH
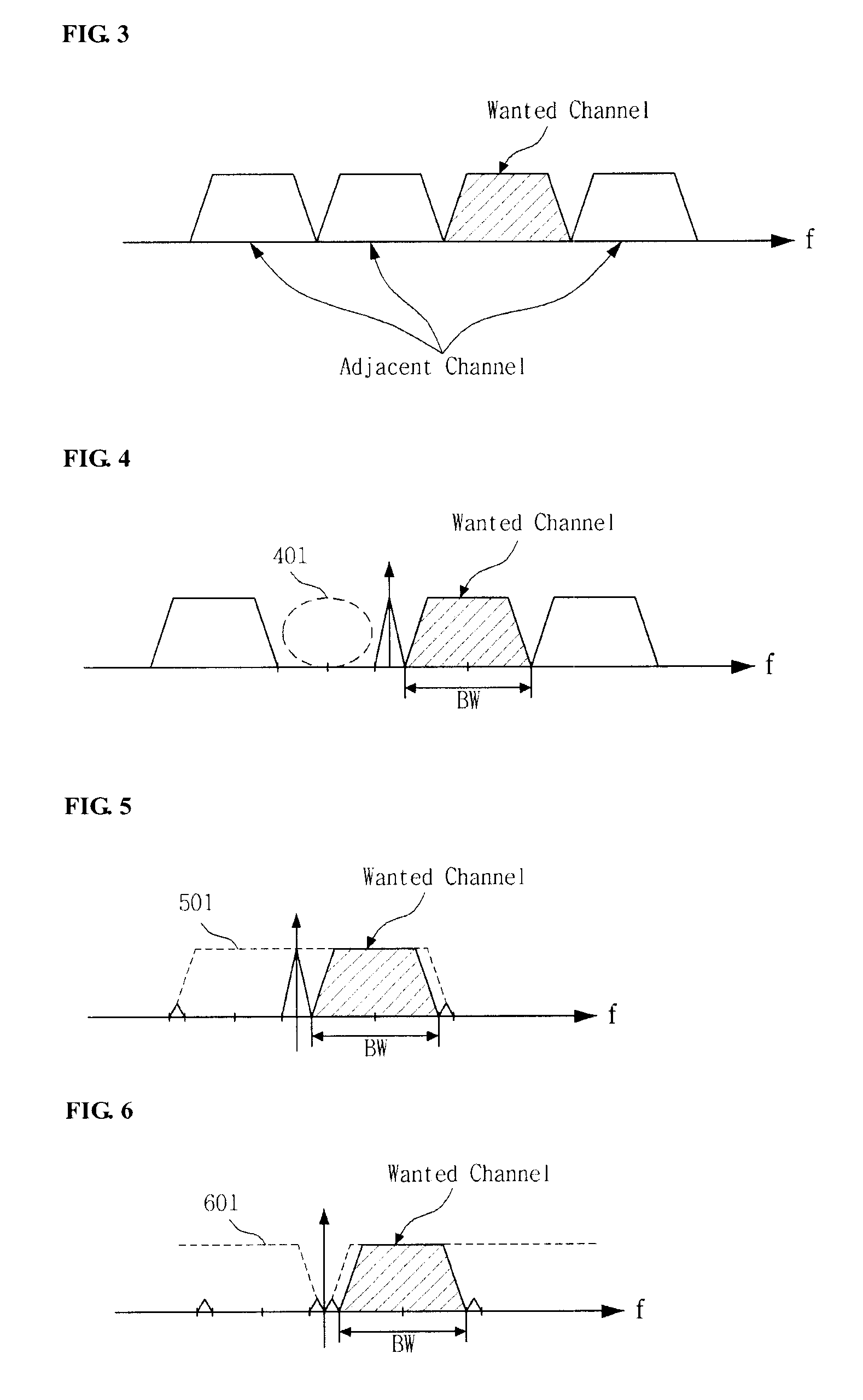
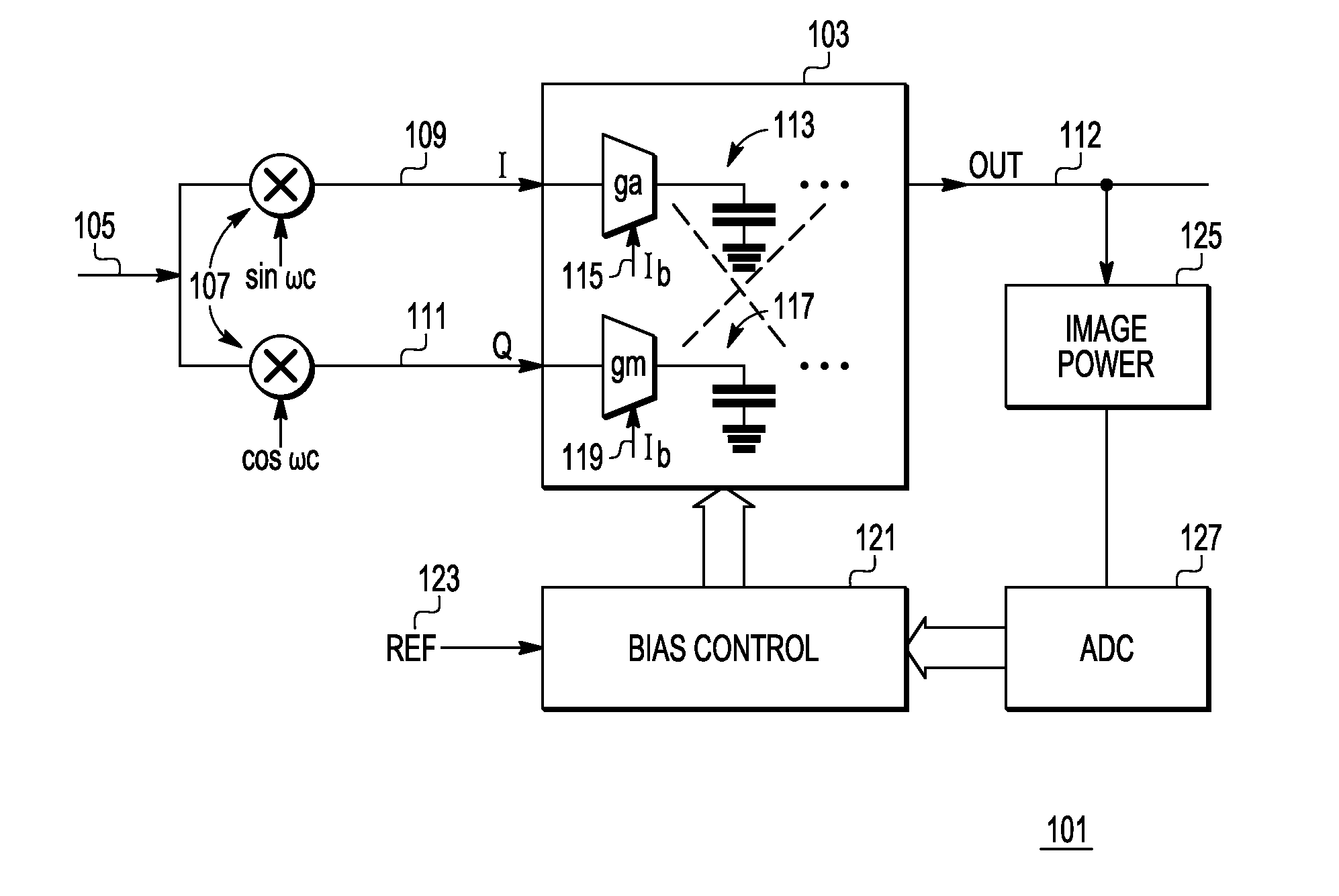
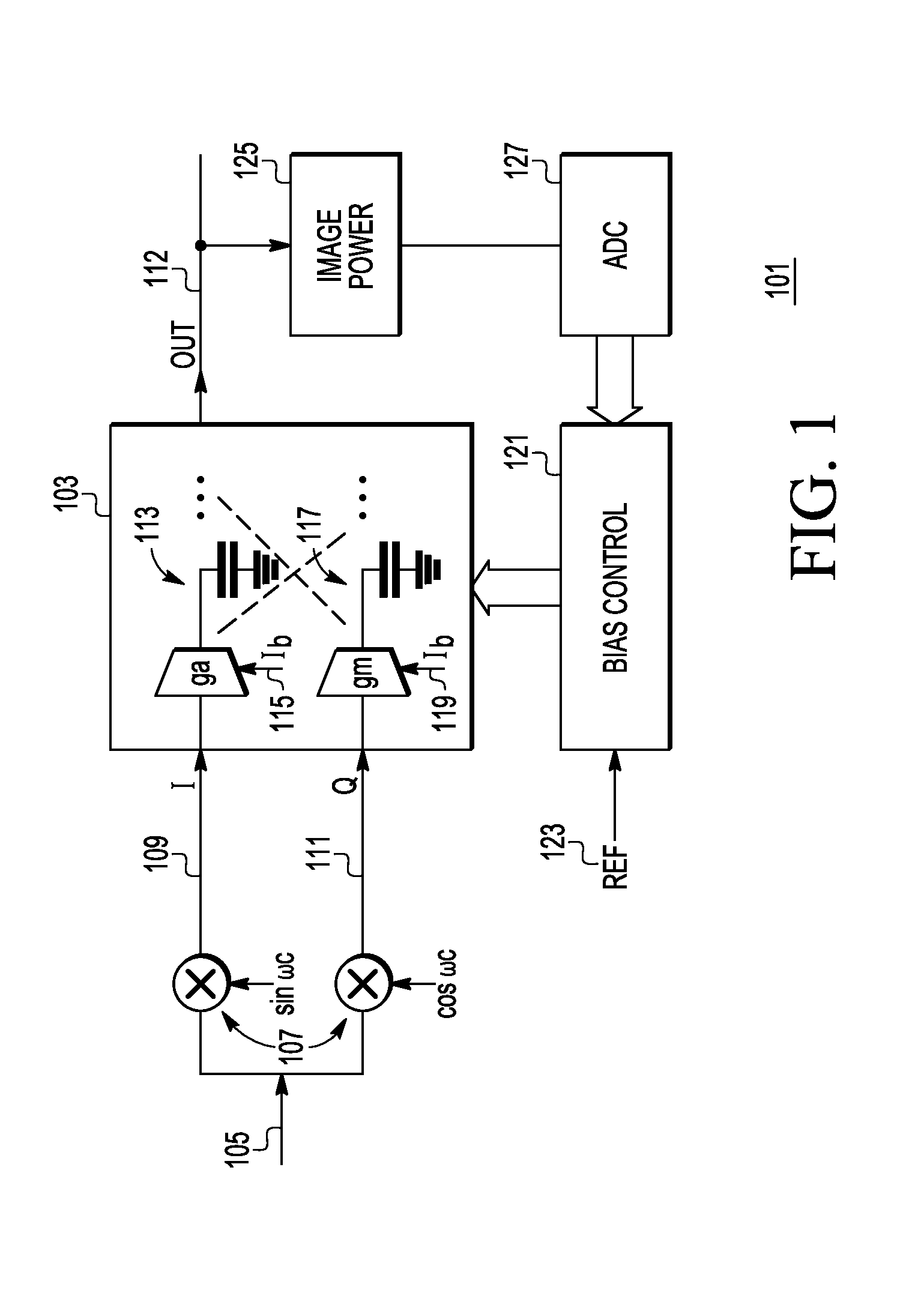
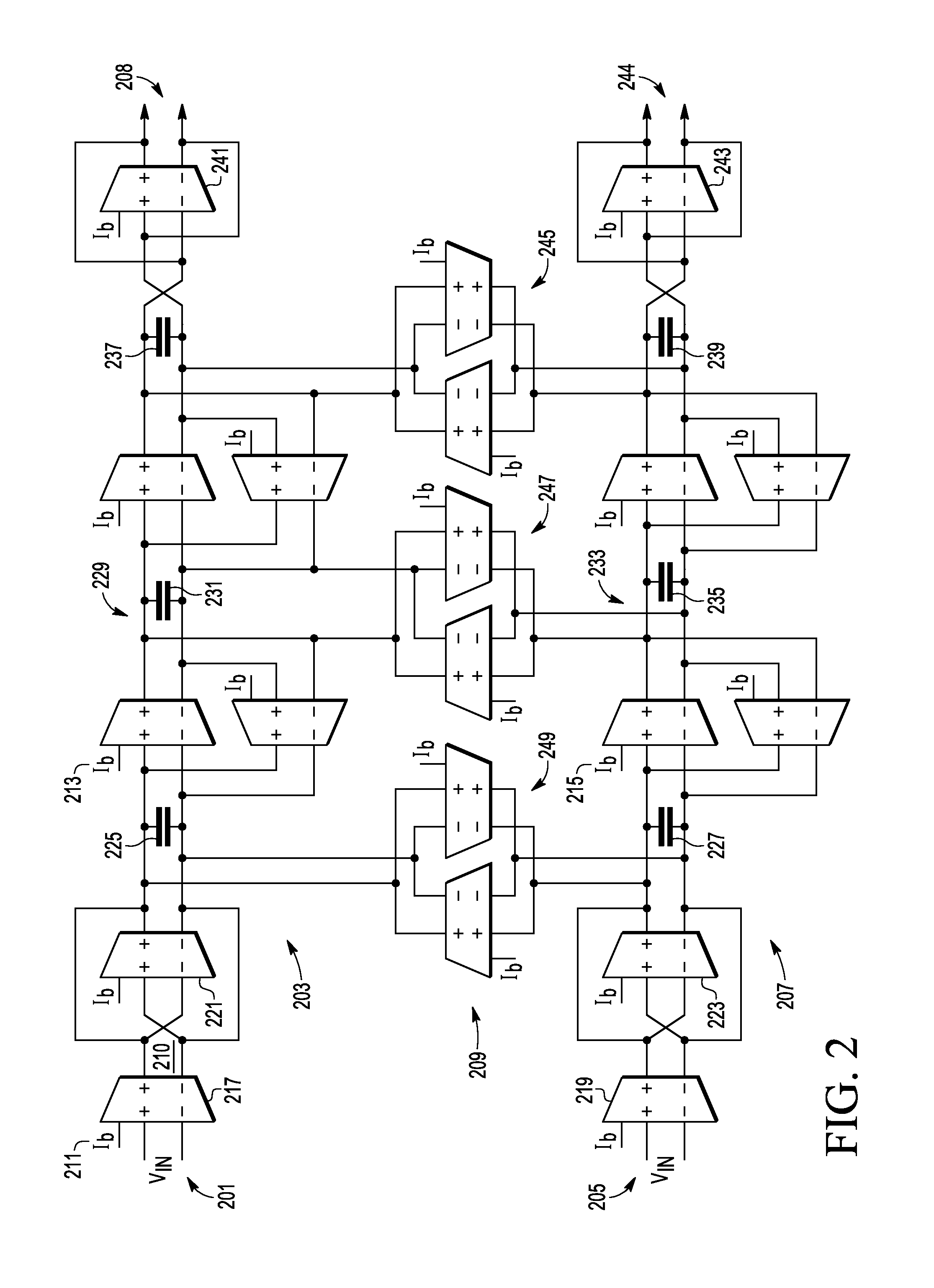
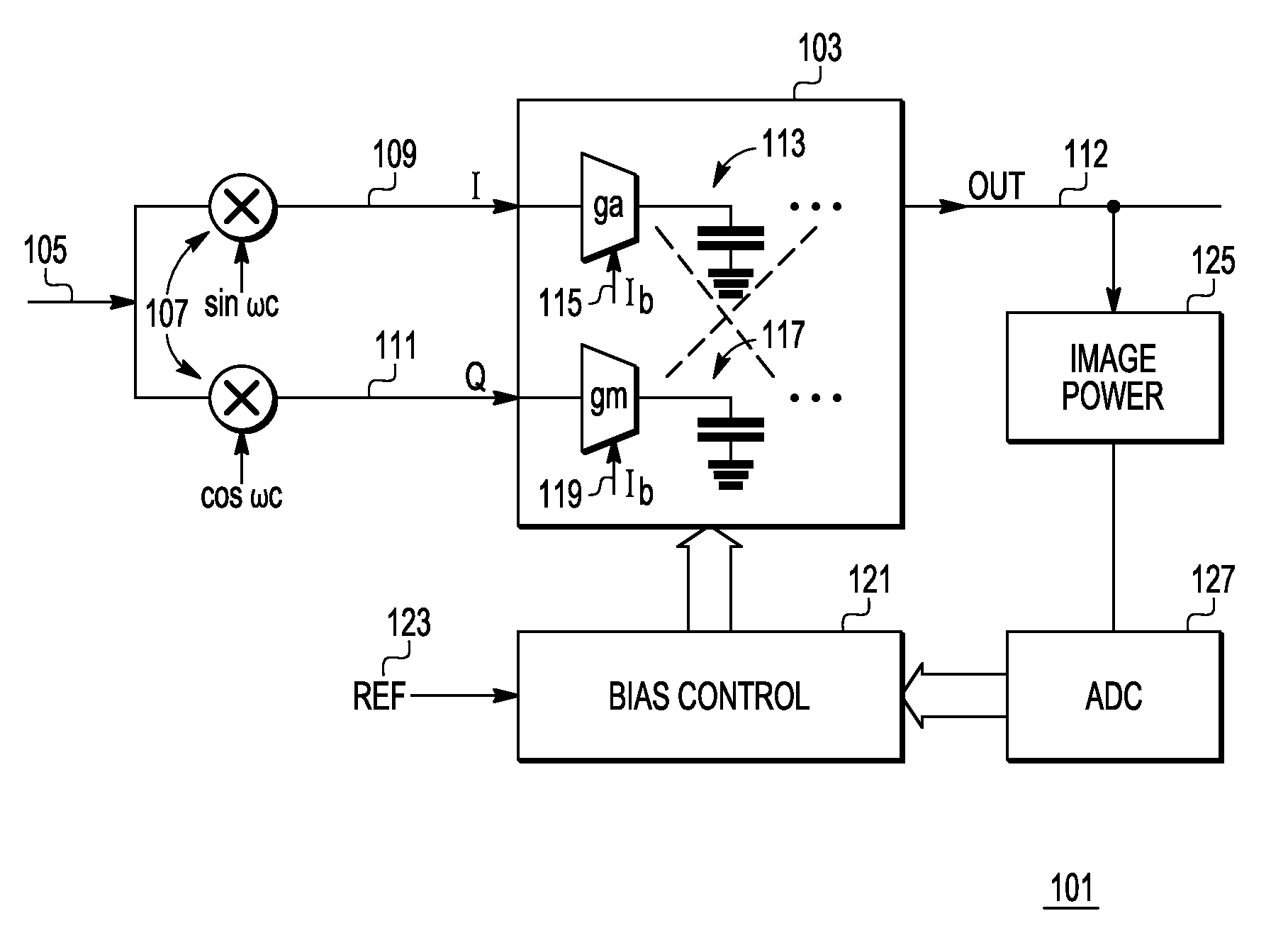
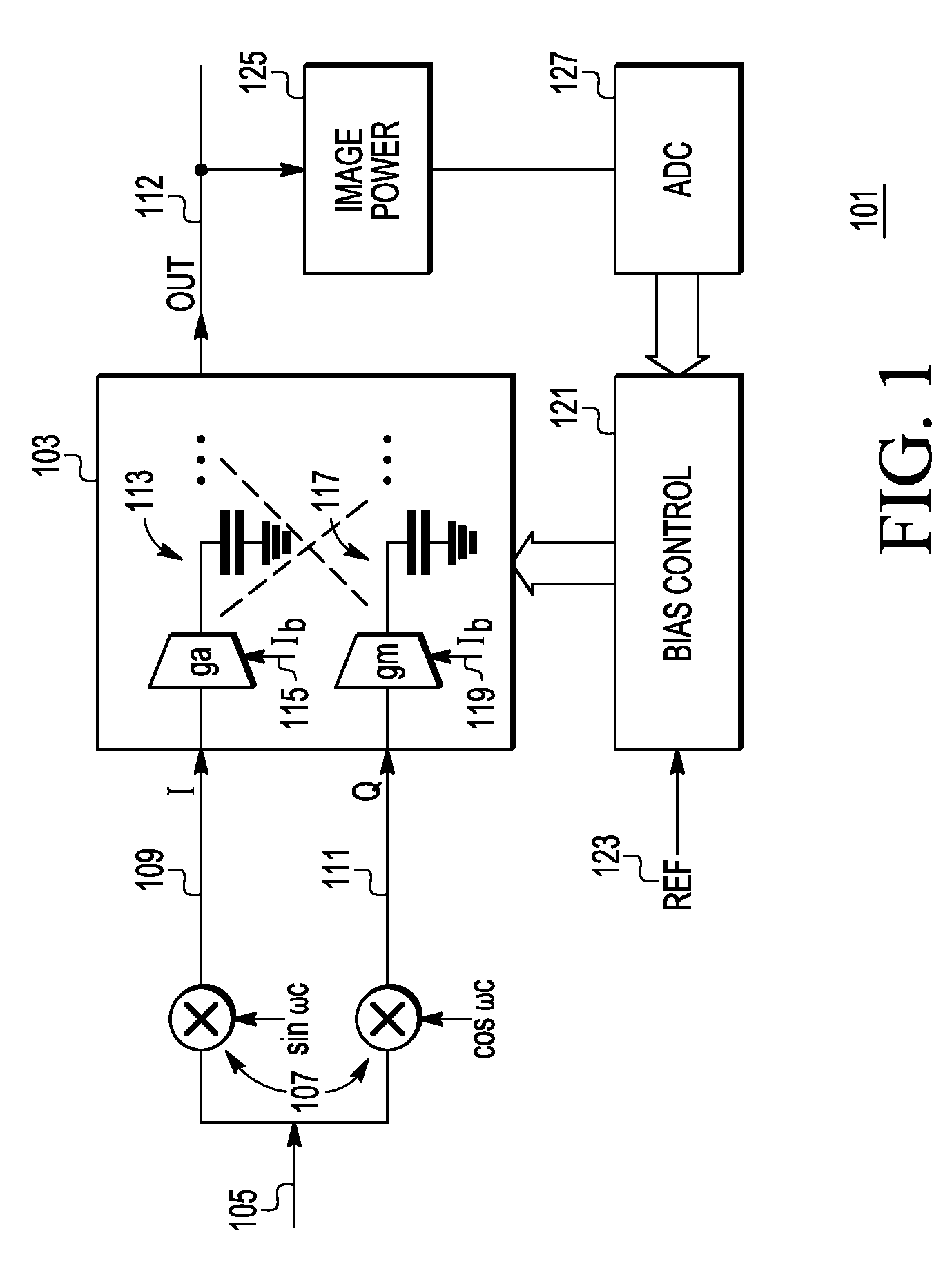
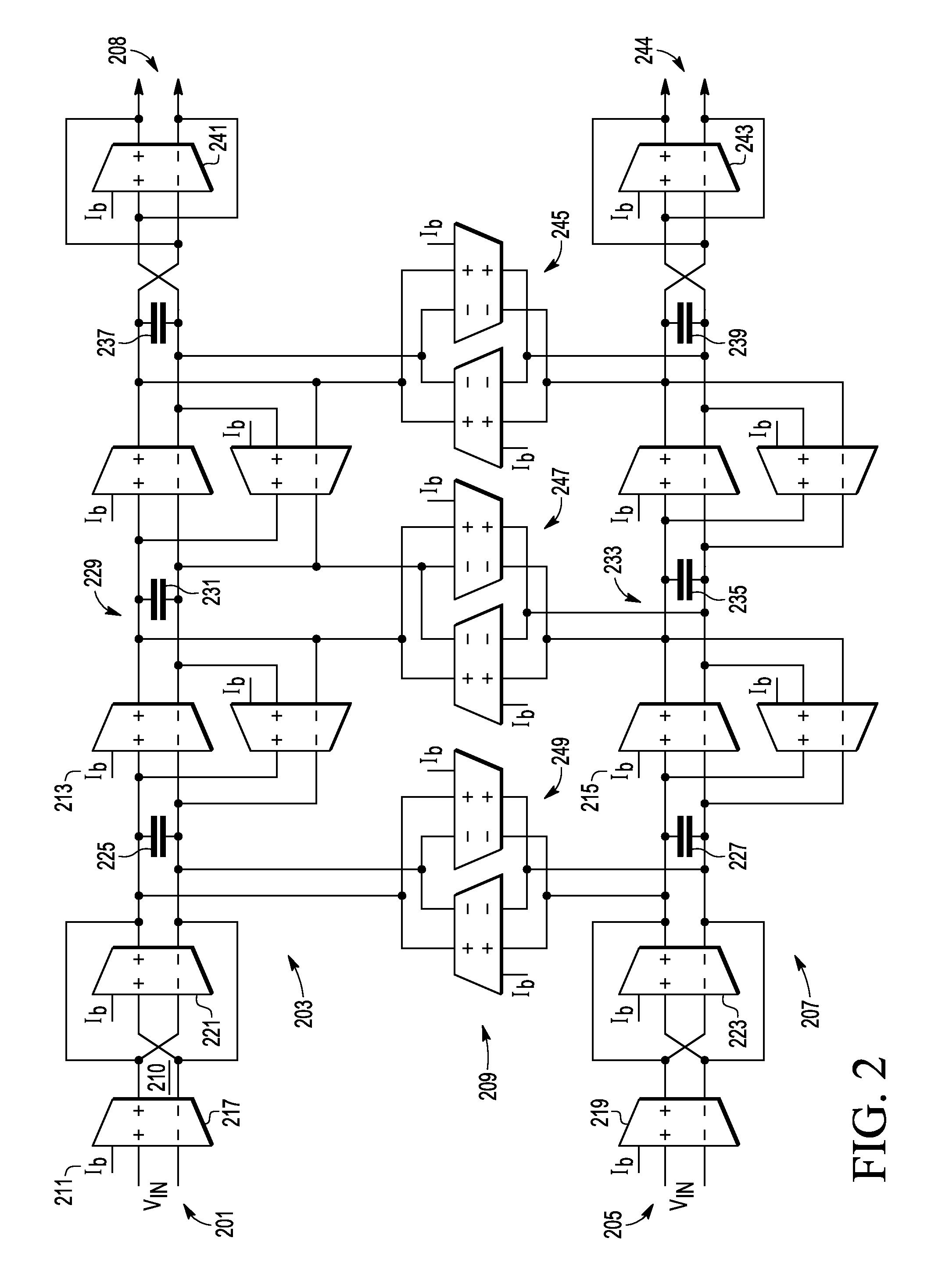
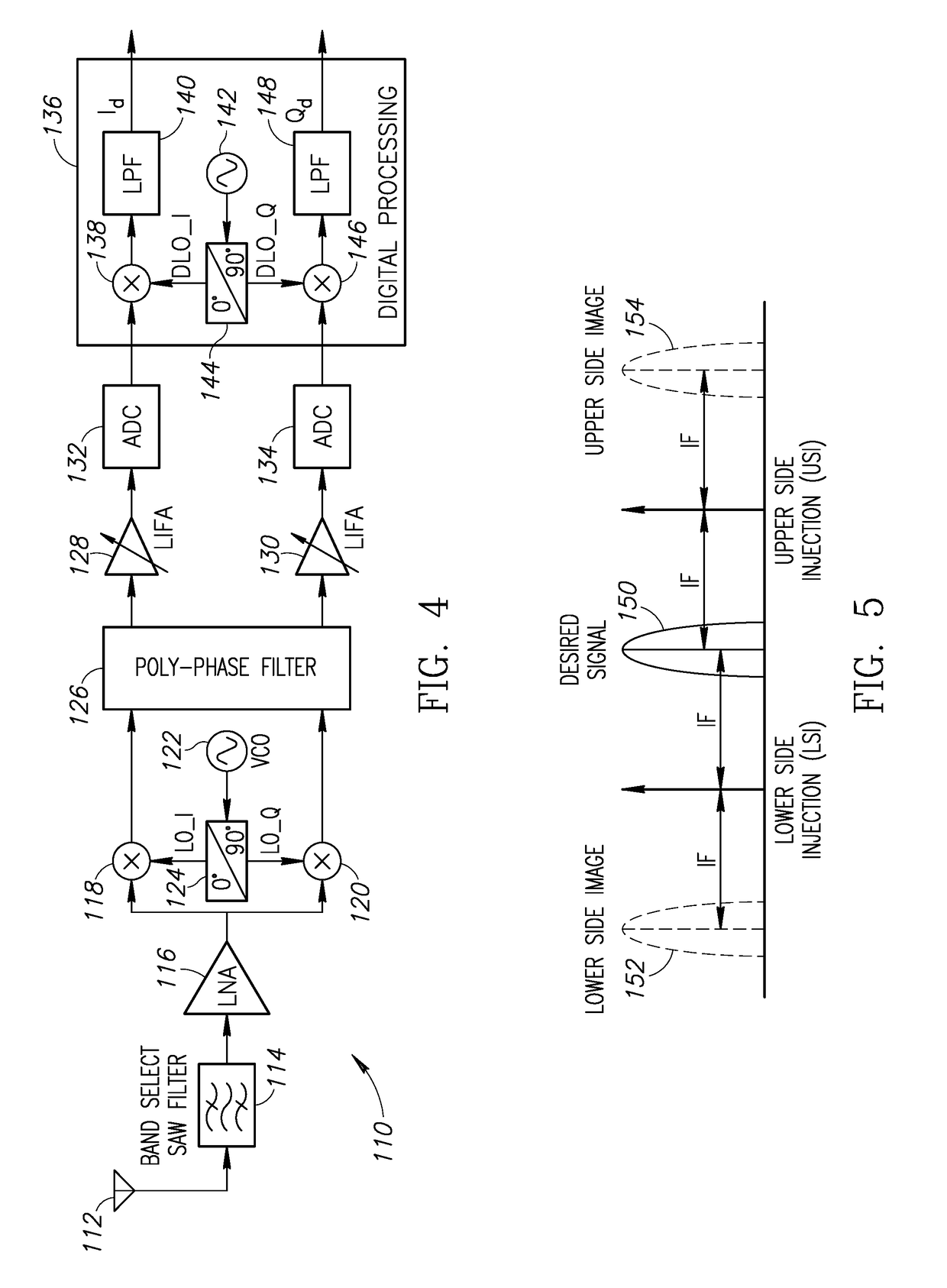
Image rejection for low if receivers
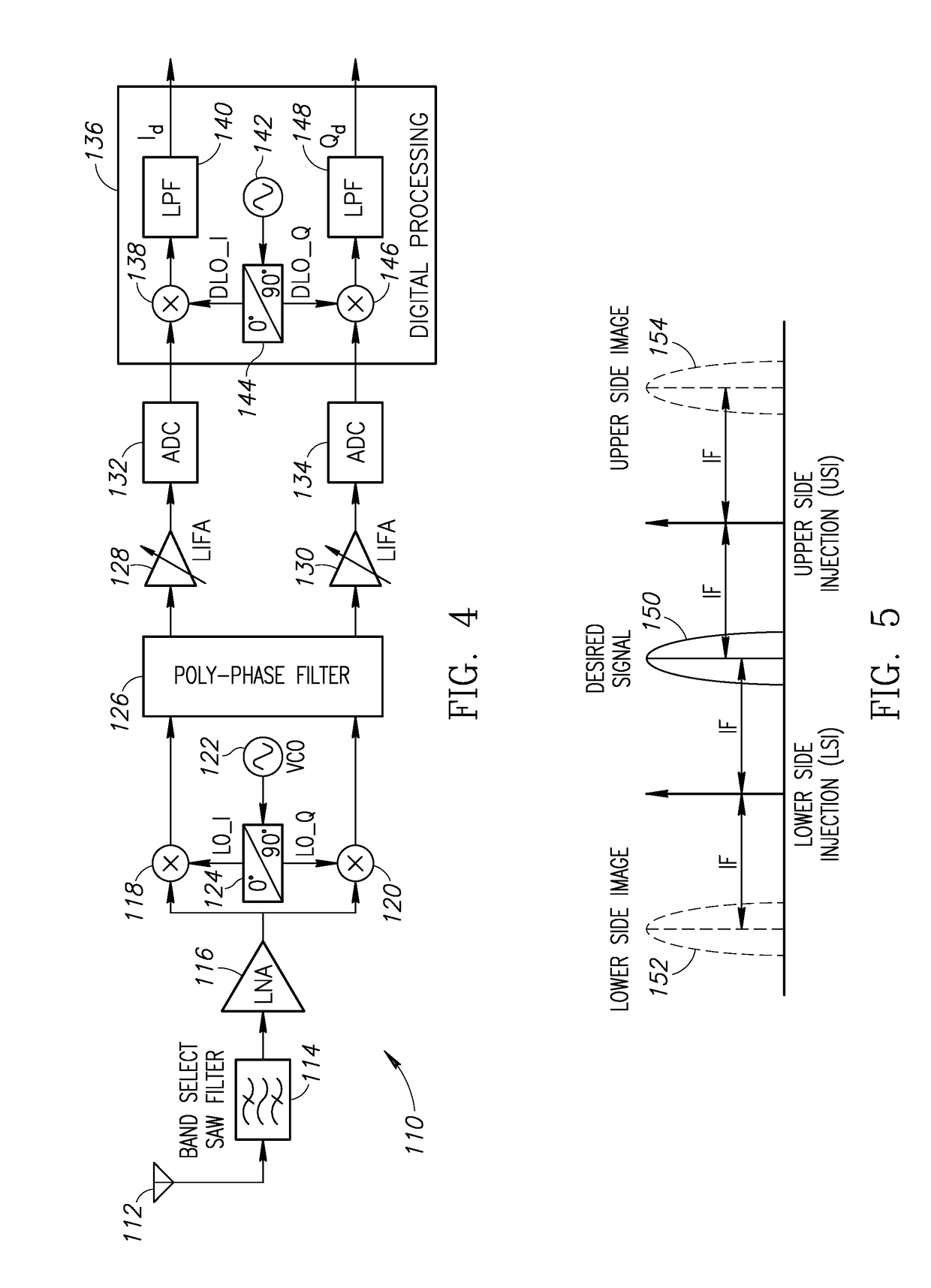
A system that includes a polyphase filter comprises first and second gm-C filters with first and second variable biasing and a bias controller coupled to the first and second gm-C filters and configured to offset the first variable biasing and corresponding first gm of the first gm-C filter relative to the second variable biasing and corresponding second gm of the second gm-C filter to thus improve image rejection in the system. A corresponding method includes processing a signal in a complex polyphase filter and controlling biasing of the first gm-C filter stage relative to the second gm-C filter stage to provide a mismatched gm and thereby improve rejection of the image signal.
Owner:NXP USA INC
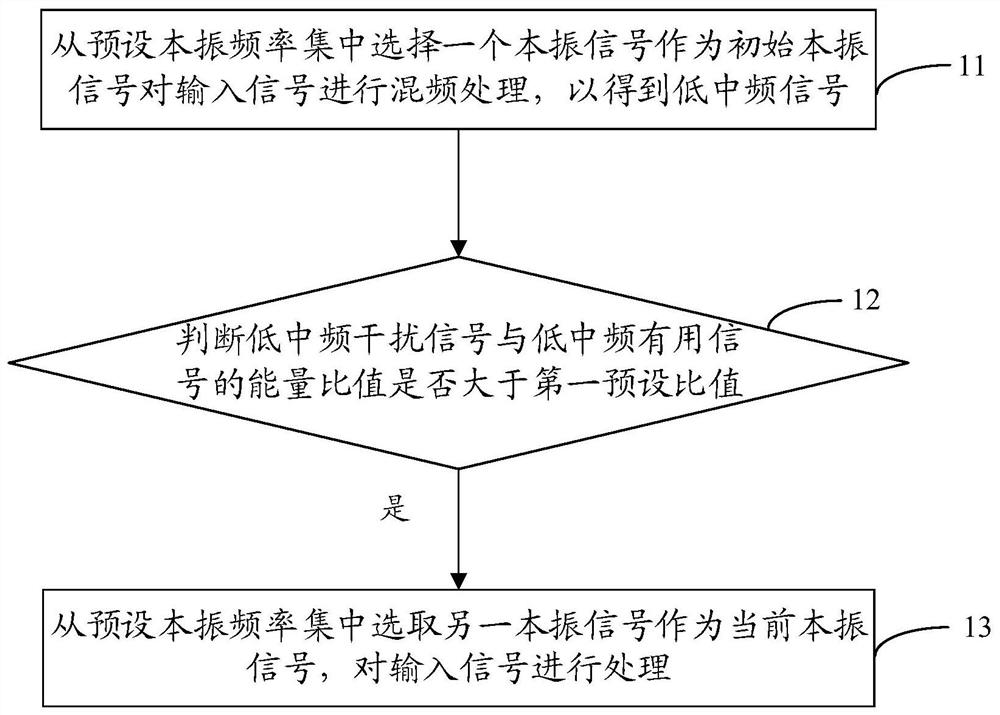
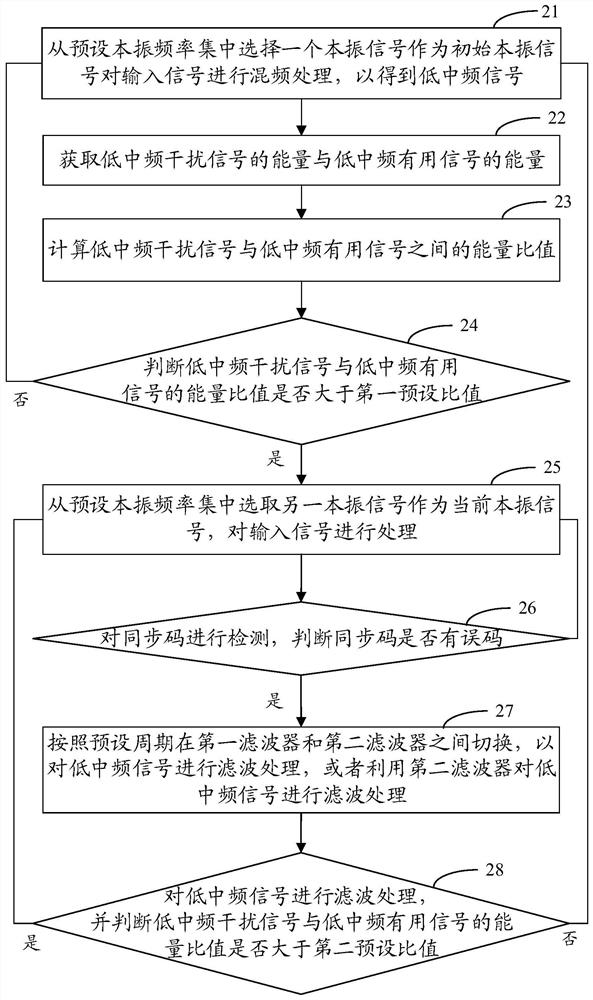
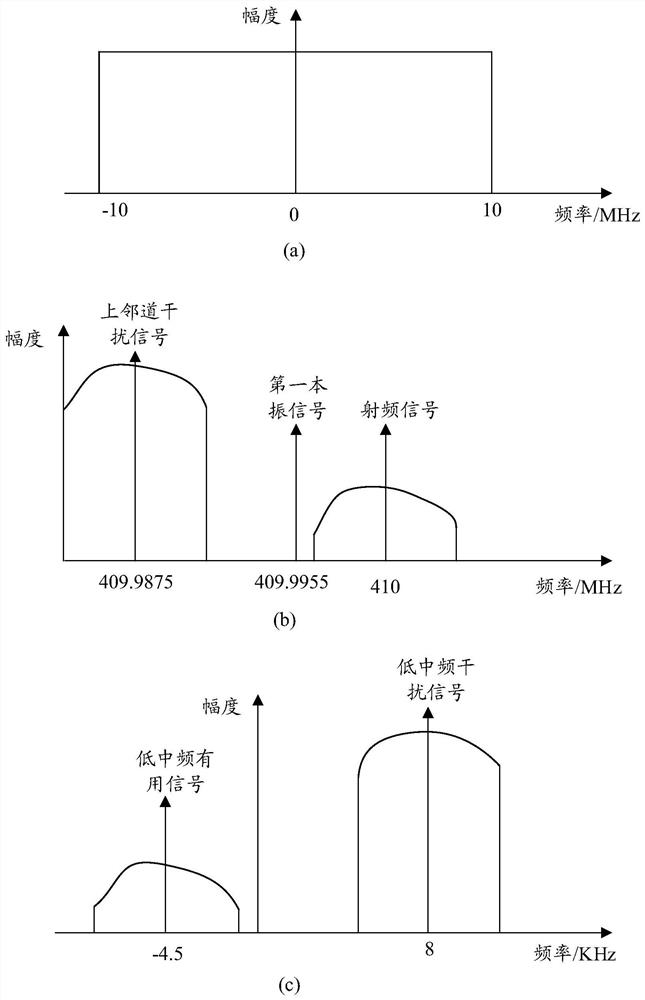
Method for improving performance of low-intermediate frequency receiver, storage medium and receiver
ActiveCN111901002AImprove adjacent channel selectivityTransmissionLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a method for improving the performance of a low-intermediate frequency receiver, a storage medium and the receiver. The method comprises the steps of: selecting a local oscillator signal from a preset local oscillator frequency set to serve as an initial local oscillator signal, so as to carry out frequency mixing processing on an input signal to obtain a low-intermediate frequency signal, wherein the low-intermediate frequency signal comprises a low-intermediate frequency useful signal and a low-intermediate frequency interference signal; judging whether an energy ratio of the low-intermediate frequency interference signal to the low-intermediate frequency useful signal is greater than a first preset ratio; and if the energy ratio of the low-intermediate frequencyinterference signal to the low-intermediate frequency useful signal is greater than the first preset ratio, selecting another local oscillation signal from the preset local oscillation frequency set as a current local oscillation signal, and processing the input signal. In this way, the adjacent channel selectivity of the low-intermediate frequency receiver can be improved.
Owner:HYTERA COMM CORP
Image rejection for low IF receivers
A system that includes a polyphase filter comprises first and second gm-C filters with first and second variable biasing and a bias controller coupled to the first and second gm-C filters and configured to offset the first variable biasing and corresponding first gm of the first gm-C filter relative to the second variable biasing and corresponding second gm of the second gm-C filter to thus improve image rejection in the system. A corresponding method includes processing a signal in a complex polyphase filter and controlling biasing of the first gm-C filter stage relative to the second gm-C filter stage to provide a mismatched gm and thereby improve rejection of the image signal.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Terrestrial-Digital Multimedia Broadcasting And Digital Audio Broadcasting Low Intermediate Frequency Receiver
InactiveUS20070117532A1Easy to integrateReduce manufacturing costTelevision system detailsDigital media broadcastingIntermediate frequencyLow-pass filter
Provided is a terrestrial-digital multimedia broadcasting (T-DMB) and digital audio broadcasting (DAB) low intermediate frequency (IF) receiver. A T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver comprises a low noise amplifier (LNA), an image rejection down-conversion mixer, a low pass filter, an amplifier, a local oscillator, and a phase-locked loop. Particularly, the LNA, the image rejection down-conversion mixer, the low pass filter, the amplifier, the local oscillator, and the phase-locked loop are integrated in a monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit substrate. Using the T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver allows a removal of a conventional SAW filter and the T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver can be easily integrated in the monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit substrate, and manufactured at low costs.
Owner:INTEGRANT TECH
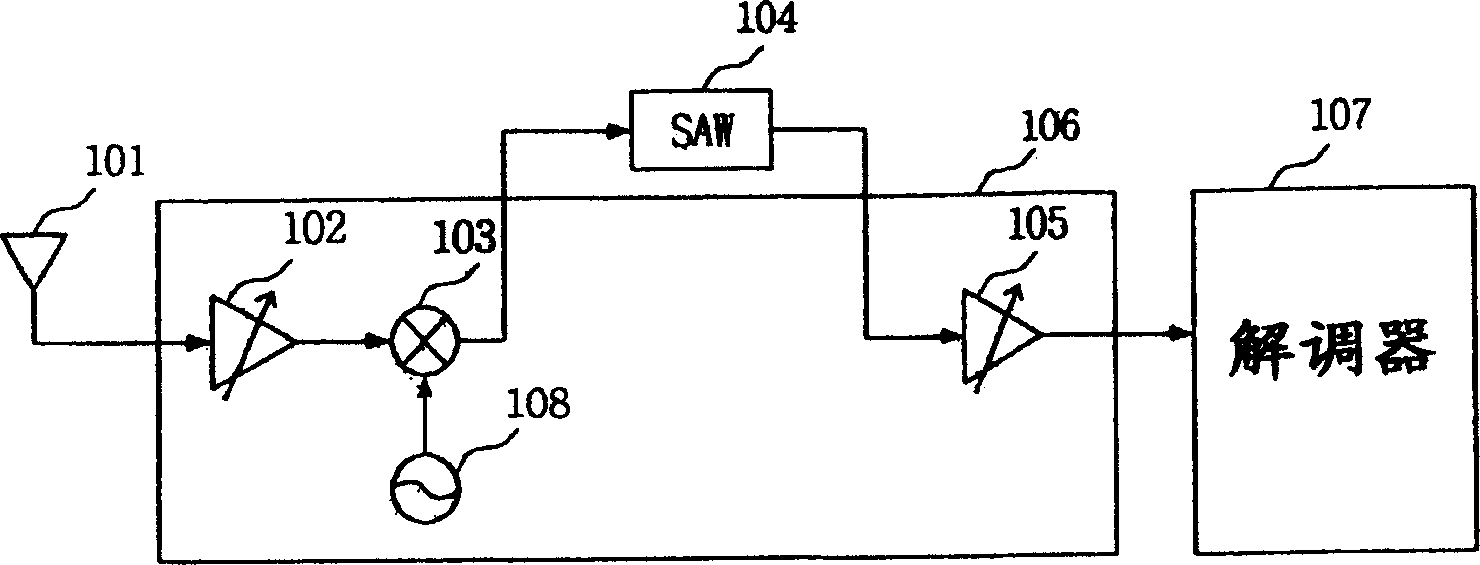
T-dmb and dab low intermediate frequency receiver
InactiveCN1913598ATelevision system detailsDigital media broadcastingLow-pass filterIntermediate frequency
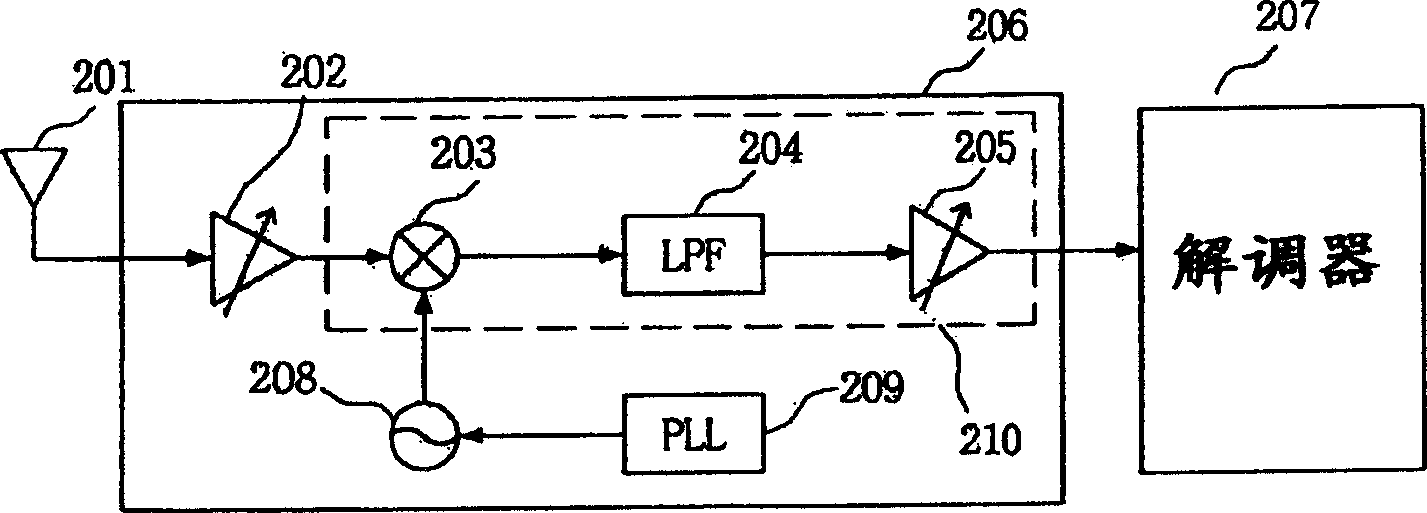
Provided is a terrestrial-digital multimedia broadcasting (T-DMB) and digital audio broadcasting (DAB) low intermediate frequency (IF) receiver. A T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver comprises a low noise amplifier (LNA) 202, an image rejection down-conversion mixer 203, a low pass filter 204, an amplifier 205, a local oscillator 208, and a phase-locked loop 209. Particularly, the LNA, the image rejection down-conversion mixer, the low pass filter, the amplifier, the local oscillator, and the phase-locked loop are integrated in a monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit substrate. Using the T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver allows a removal of a conventional SAW filter and the T-DMB and DAB low IF receiver can be easily integrated in the monolithic semiconductor integrated circuit substrate, and manufactured at low costs.
Owner:INTEGRANT TECH
Mobile wireless communications device having low if receiver circuitry that adapts to radio environment
ActiveCN101075818ARadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionLocal oscillatorLow IF receiver
A mobile wireless communications device, system and associated method includes a housing and circuit board that includes radio frequency (RF) circuitry and processor operative with each other. The RF circuitry includes a low-IF receiver circuit that is operative for maintaining an interferer signal at a same frequency side as a wanted signal relative to a local oscillator frequency setting, creating an interferer image signal, and filtering the image signal as substantially baseband frequency.
Owner:RES IN MOTION LTD
Low intermediate frequency receiver and the same method thereof
InactiveUS7983648B2Effectively filter out interference of DC driftModulation transferenceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsIntermediate frequencyRadio frequency signal
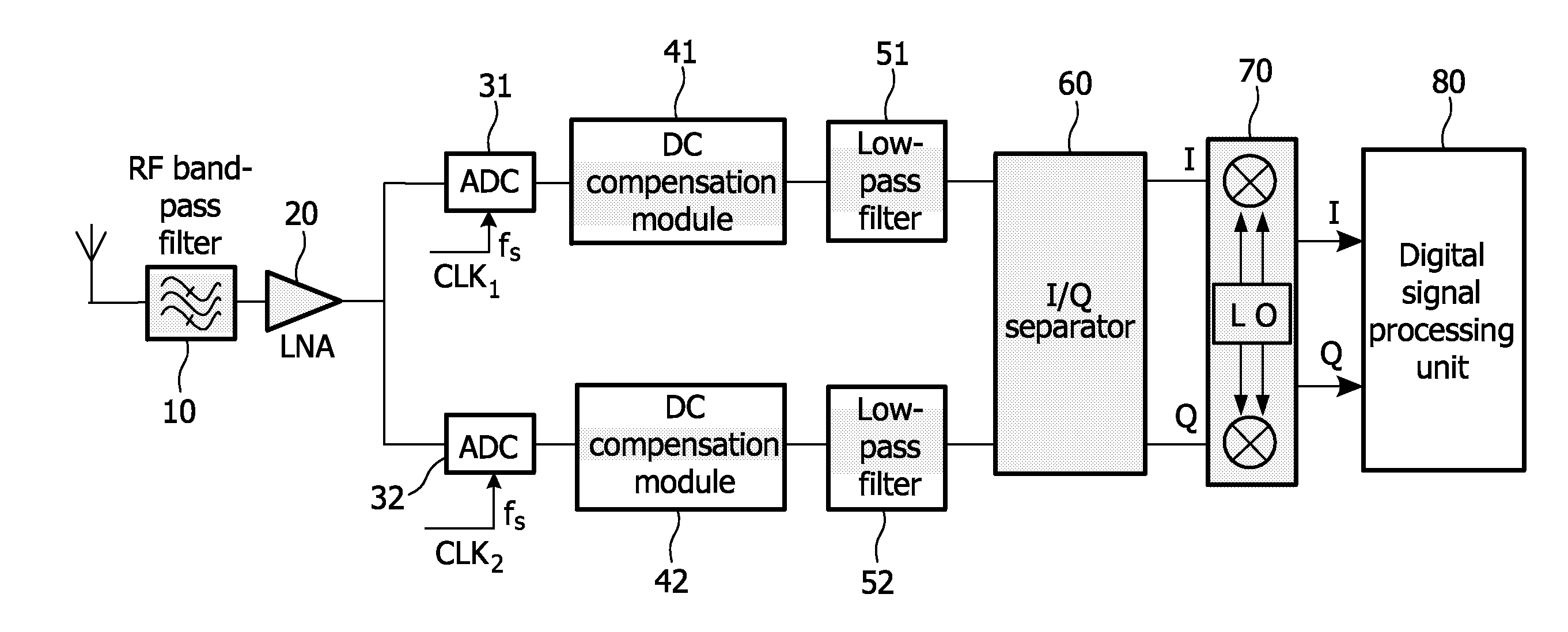
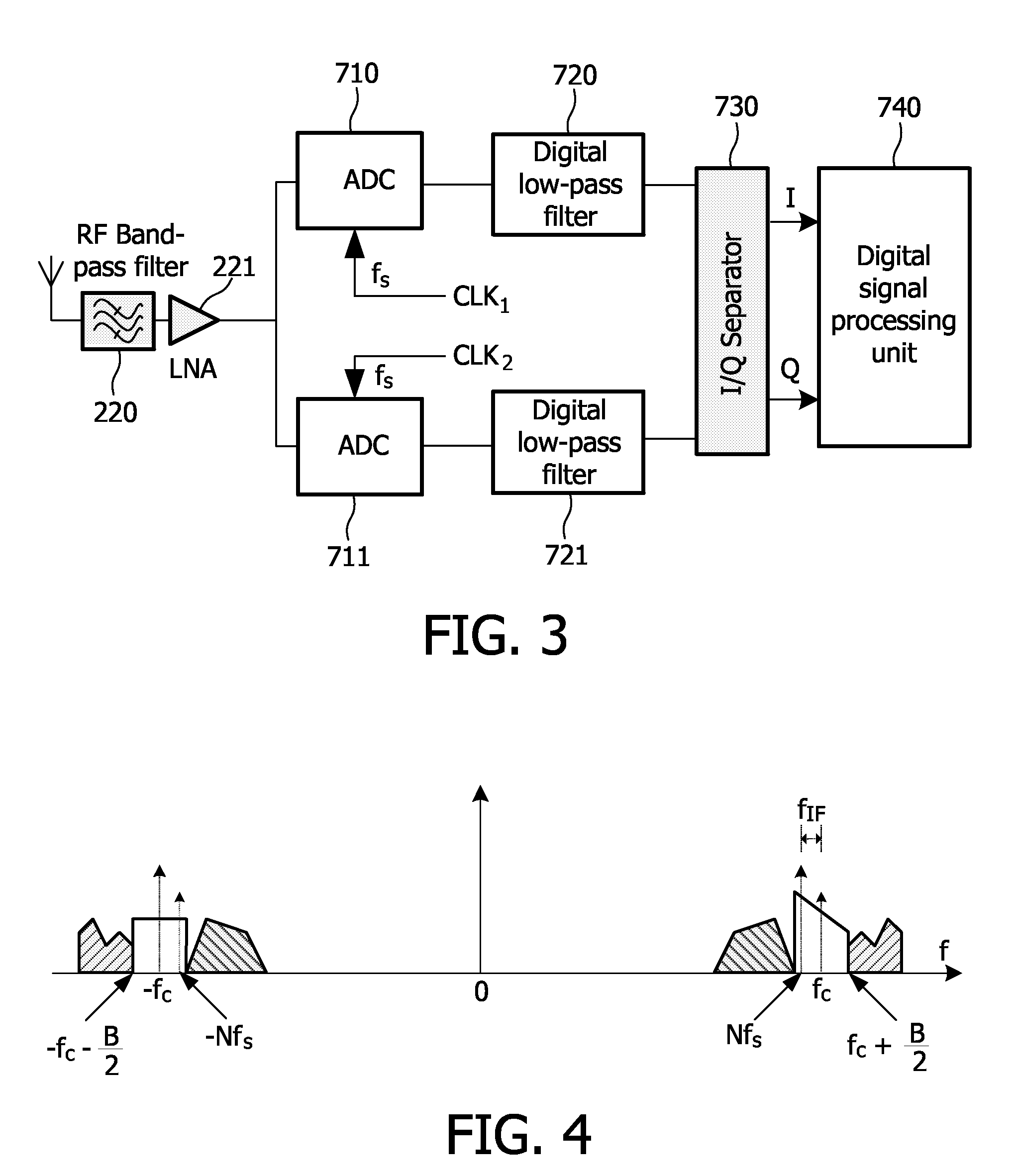
The present invention provides a low intermediate frequency receiver for receiving radio frequency signal and provides the sampling method thereof. The low intermediate frequency receiver firstly samples the radio frequency signal so as to convert it into digital signal of non-zero frequency domain. Secondly it compensates the digital signal of non-zero frequency domain to filter out the interfering signal therein. Finally, the compensated digital signal is frequency-shifted to the zero frequency domain. By using the low intermediate frequency receiver and the sampling method thereof according to the present invention, the interference at the zero frequency, like DC drift and intermodulation component, could be easily filtered out without imposing any great influence on the useful signals.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
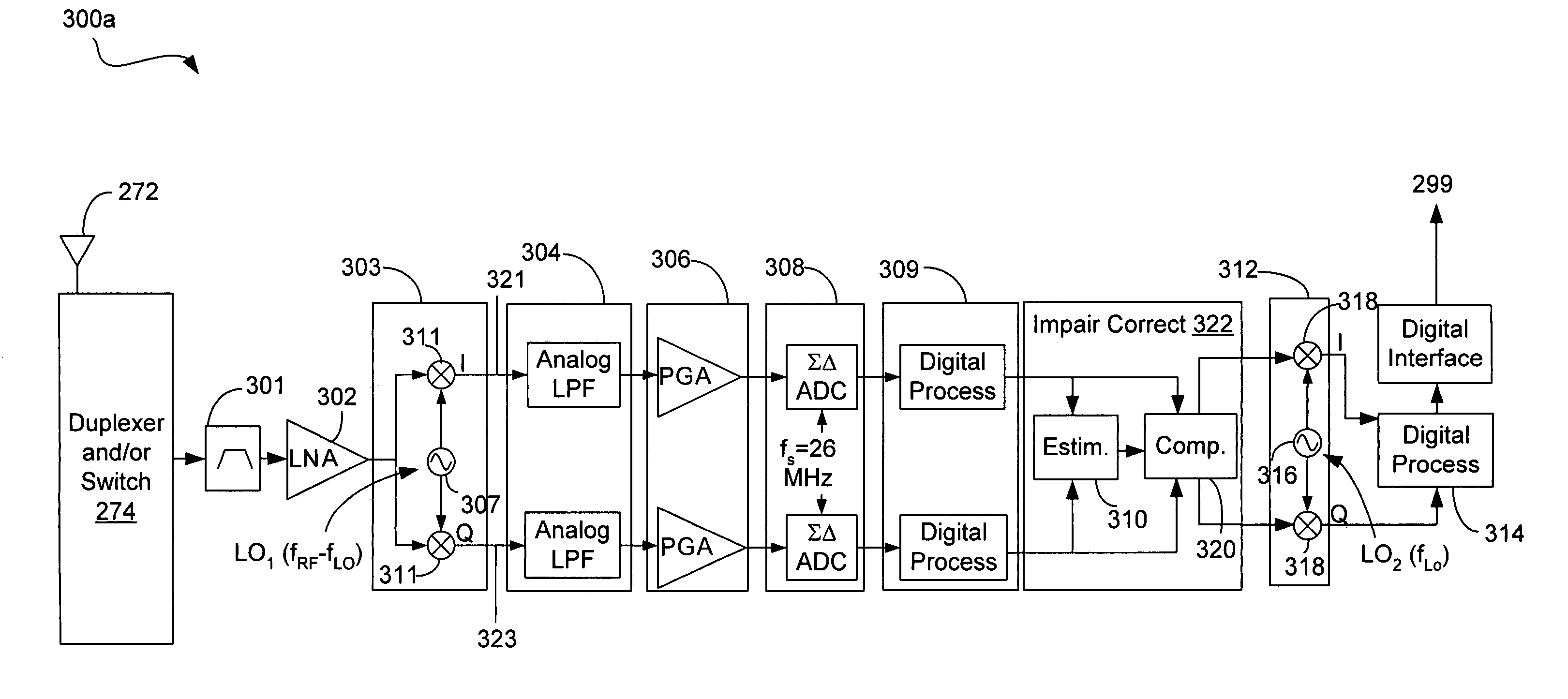
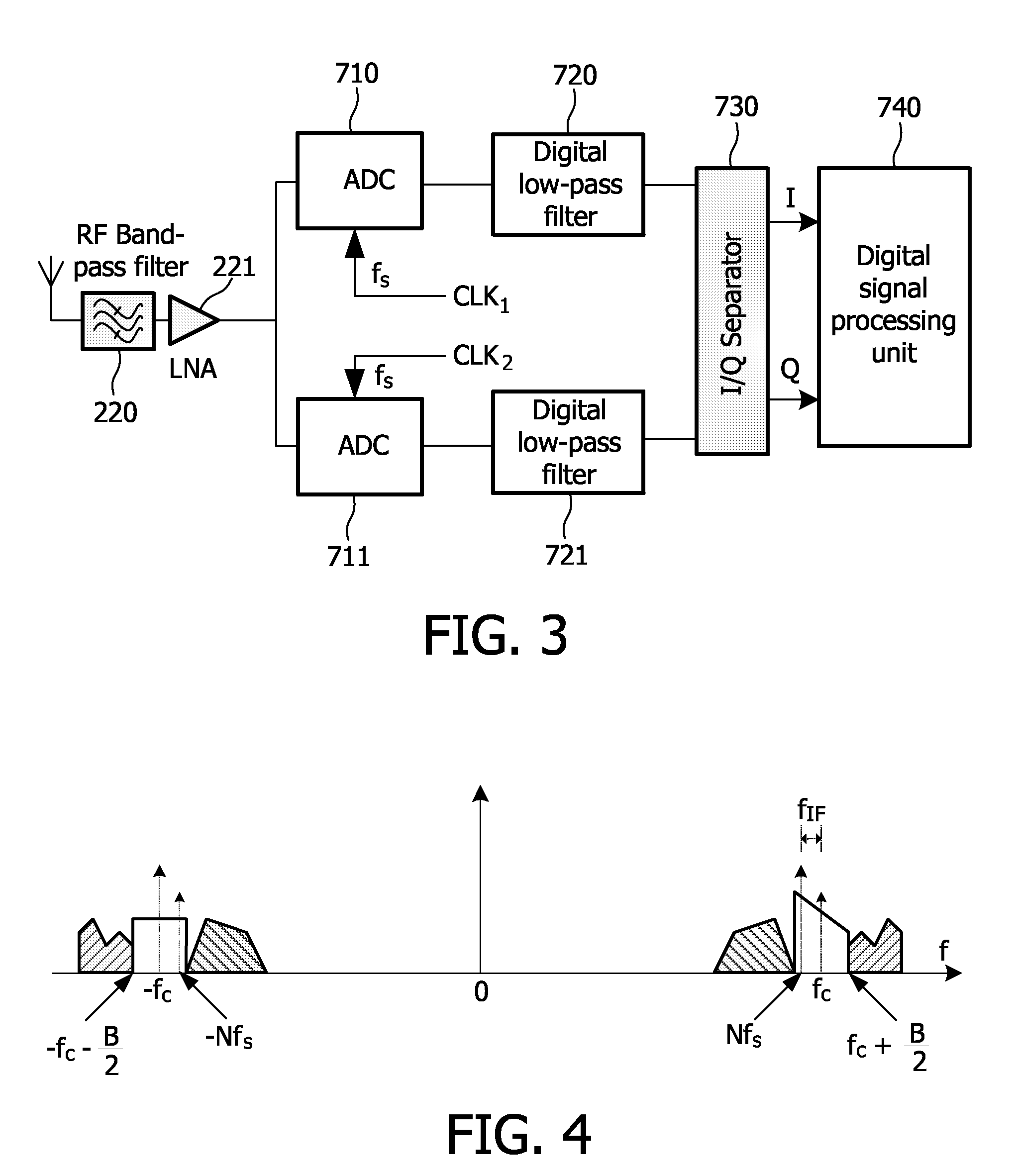
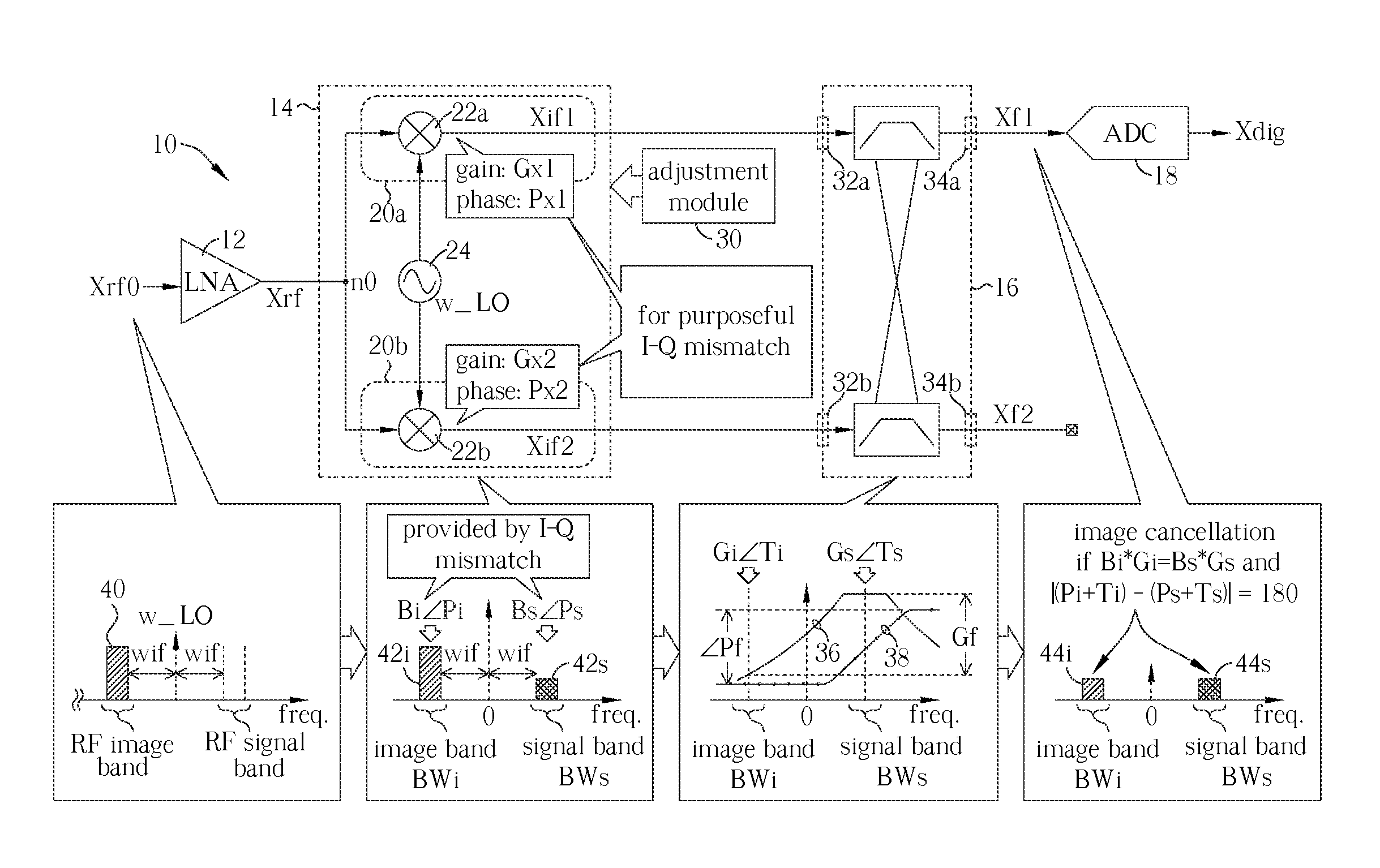
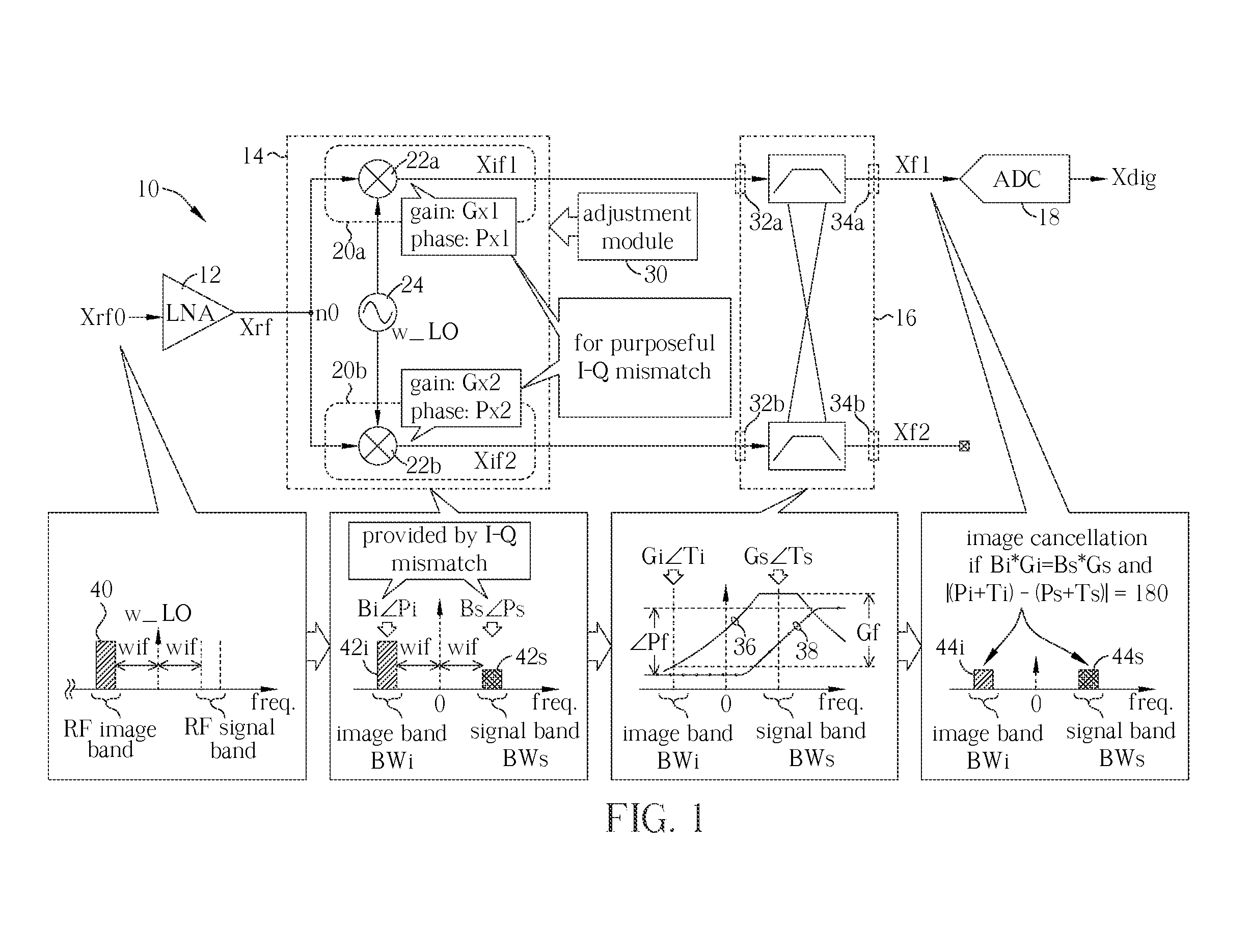
Receiver circuit and associated method
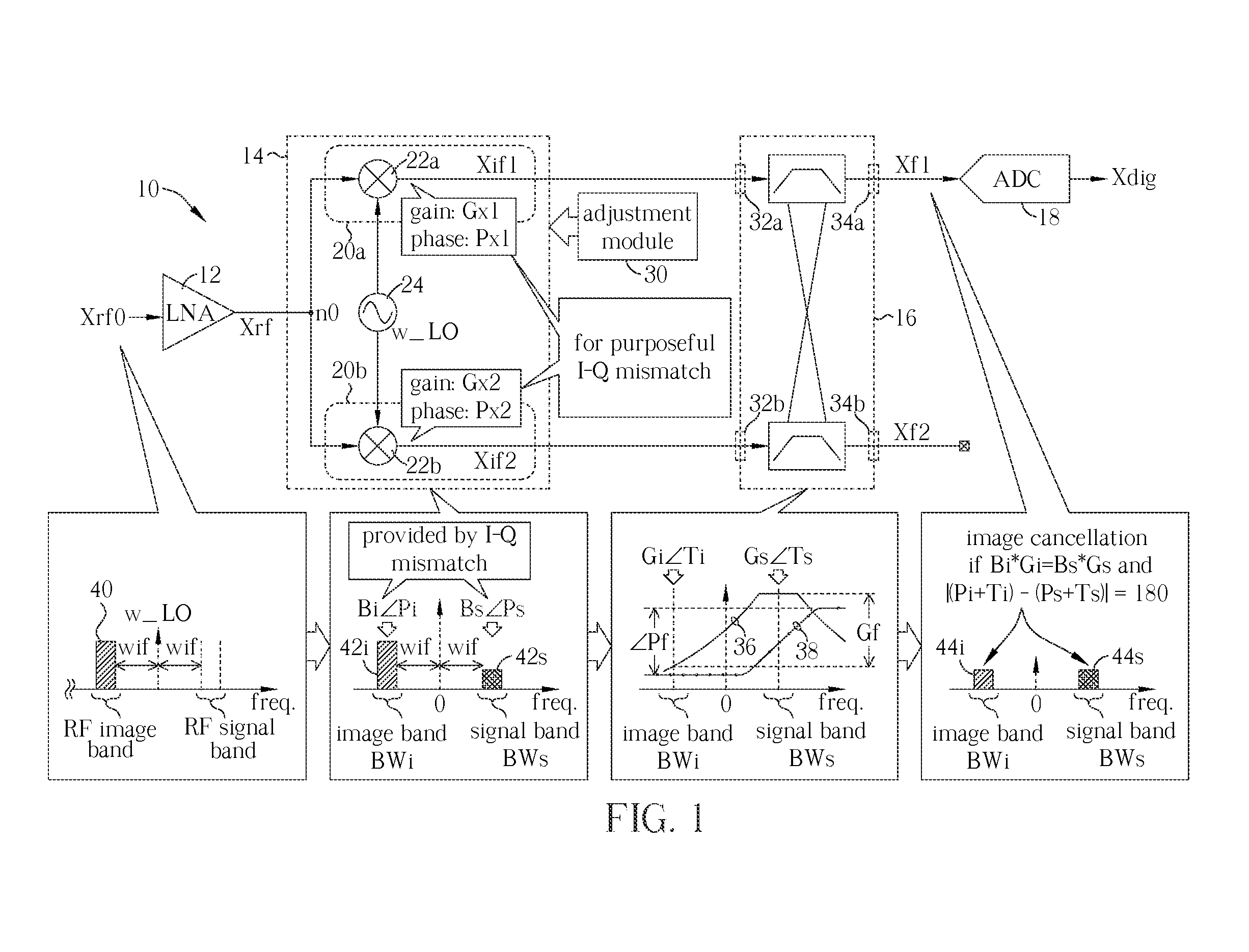
A receiver circuit, e.g., a low-IF receiver, including two mixing paths. The two mixing paths scale an input signal respectively by two mixing gains and shift phase of the input signal respectively by two mixing phase offsets to provide two mixed signals. The two mixing gains and the two mixing phase offsets are arranged to produce an amplitude adjustment between amplitudes of the two mixed signals and a phase difference of 90 degrees plus a phase adjustment between phases of the two mixed signals. With the amplitude adjustment and / or the phase adjustment properly tuned to nonzero value(s) in association with band-pass response of the receiver circuit, image rejection can be achieved and optimized. Associated method is also disclosed.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Low Intermediate Frequency Receiver and the Same Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080207157A1Effectively filter out interference of DC driftModulation transferenceFrequency-modulated carrier systemsIntermediate frequencyRadio frequency signal
The present invention provides a low intermediate frequency receiver for receiving radio frequency signal and provides the sampling method thereof. The low intermediate frequency receiver firstly samples the radio frequency signal so as to convert it into digital signal of non-zero frequency domain. Secondly it compensates the digital signal of non-zero frequency domain to filter out the interfering signal therein. Finally, the compensated digital signal is frequency-shifted to the zero frequency domain. By using the low intermediate frequency receiver and the sampling method thereof according to the present invention, the interference at the zero frequency, like DC drift and intermodulation component, could be easily filtered out without imposing any great influence on the useful signals.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Receiver circuit and associated method
A receiver circuit, e.g., a low-IF receiver, including two mixing paths. The two mixing paths scale an input signal respectively by two mixing gains and shift phase of the input signal respectively by two mixing phase offsets to provide two mixed signals. The two mixing gains and the two mixing phase offsets are arranged to produce an amplitude adjustment between amplitudes of the two mixed signals and a phase difference of 90 degrees plus a phase adjustment between phases of the two mixed signals. With the amplitude adjustment and / or the phase adjustment properly tuned to nonzero value(s) in association with band-pass response of the receiver circuit, image rejection can be achieved and optimized. Associated method is also disclosed.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Apparatus and method of detection of image interference in a radio frequency receiver
ActiveUS10181916B1Reduce power consumptionSave powerCarrier regulationTransmission monitoringTransceiverIntermediate frequency
A novel and useful apparatus and method for an image-interferer aware single quadrature RF downconversion (SQRD) low intermediate frequency (LIF) receiver and related power reduction techniques utilized therein. The invention applies zero-margin adaptive transceiver (ZMAT) design principles to considerably reduce the receiver's power consumption in an adaptive fashion in accordance with the instantaneous reception conditions. In a low IF dual-branch (i.e. quadrature) downconversion receiver, the radio monitors the image strength and shuts off the receiver's Q branch (or I branch) when image rejection is not needed (i.e. when the relative image strength is below a threshold), thus significantly reducing power consumption in the RF receiver. A zero IF receiver is switched to a SQRD low IF receiver of lower power consumption when the image interferer strength is low enough to allow for a given required level of performance.
Owner:SHORT CIRCUIT TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com