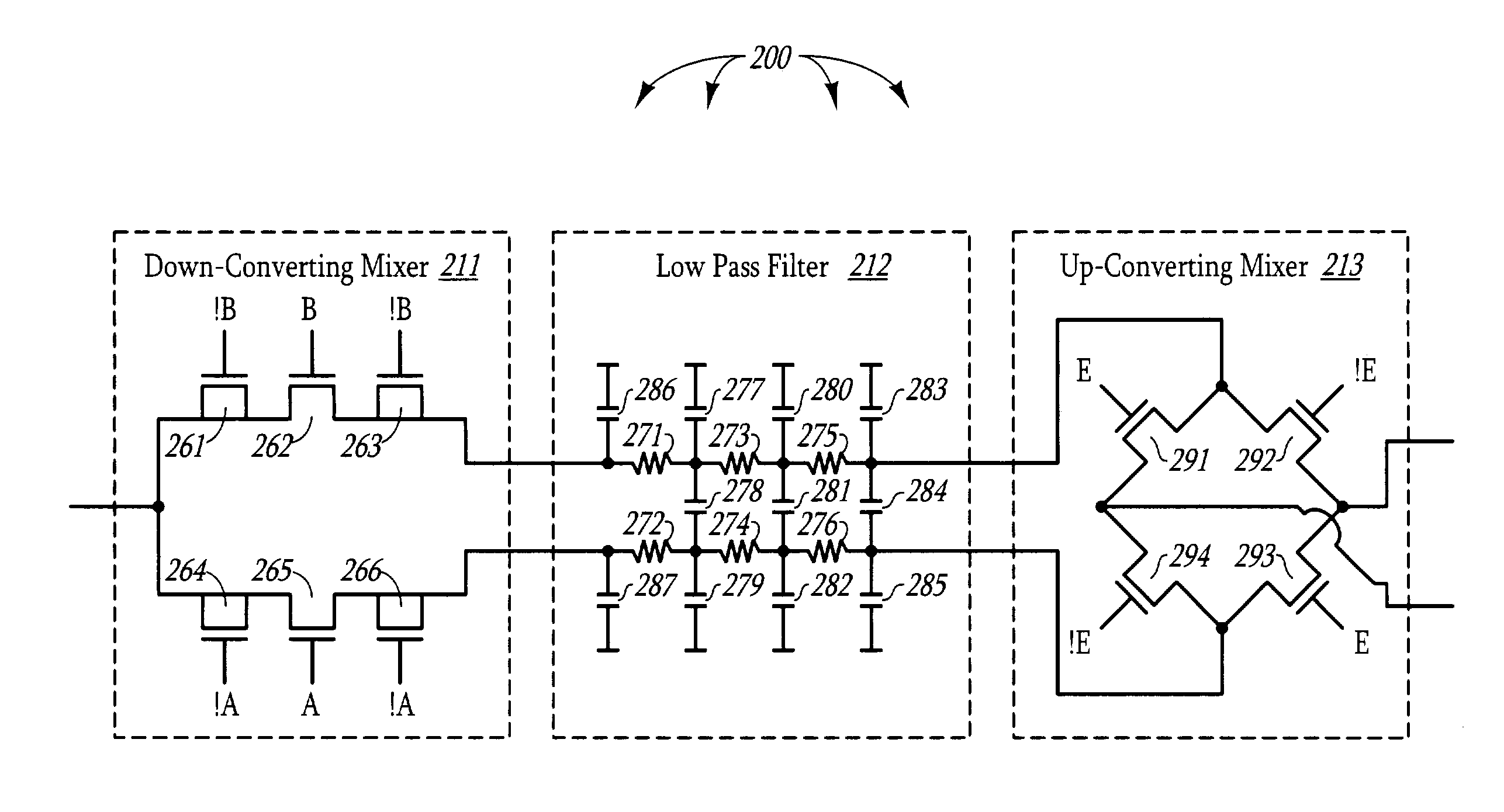
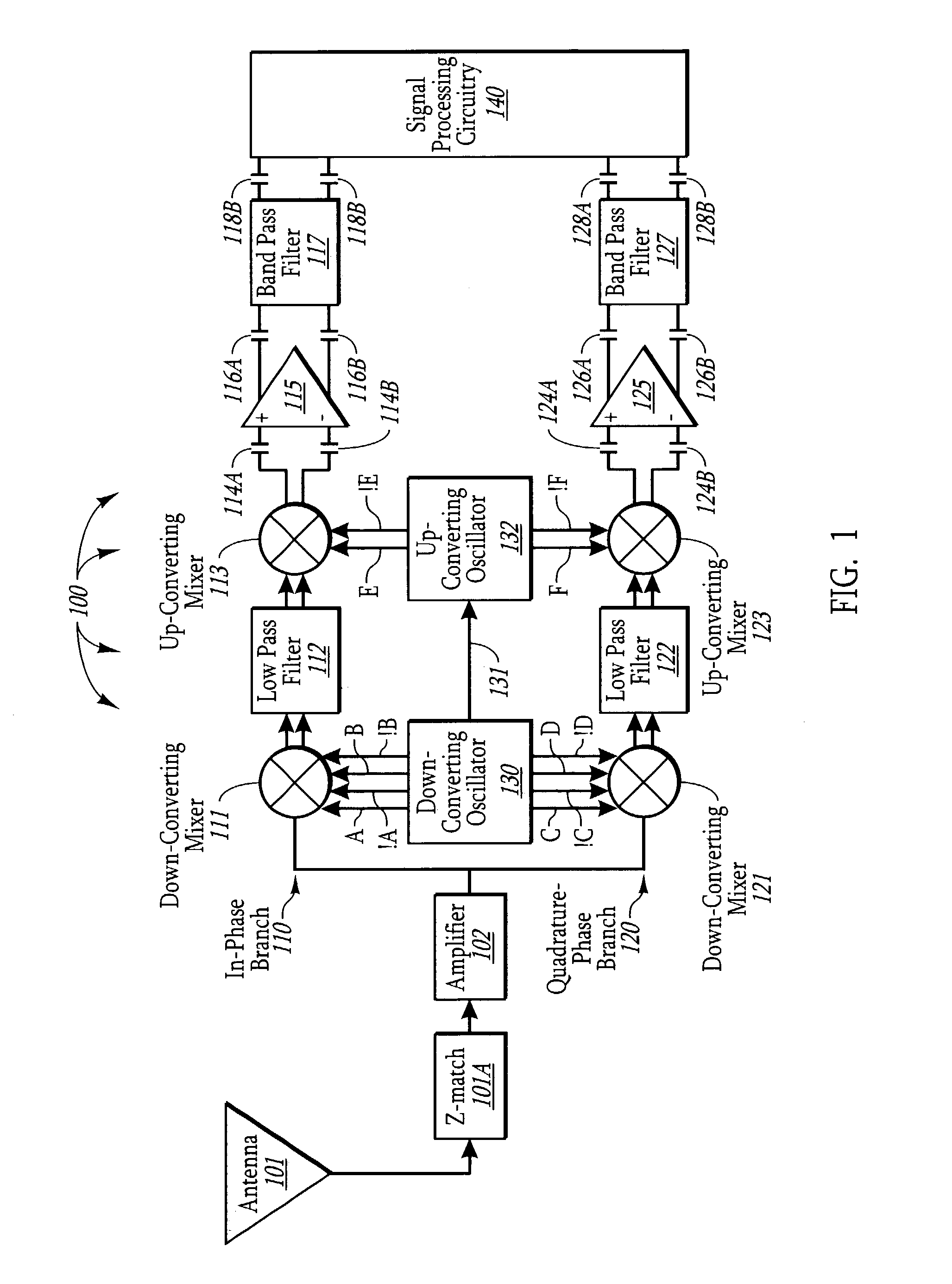
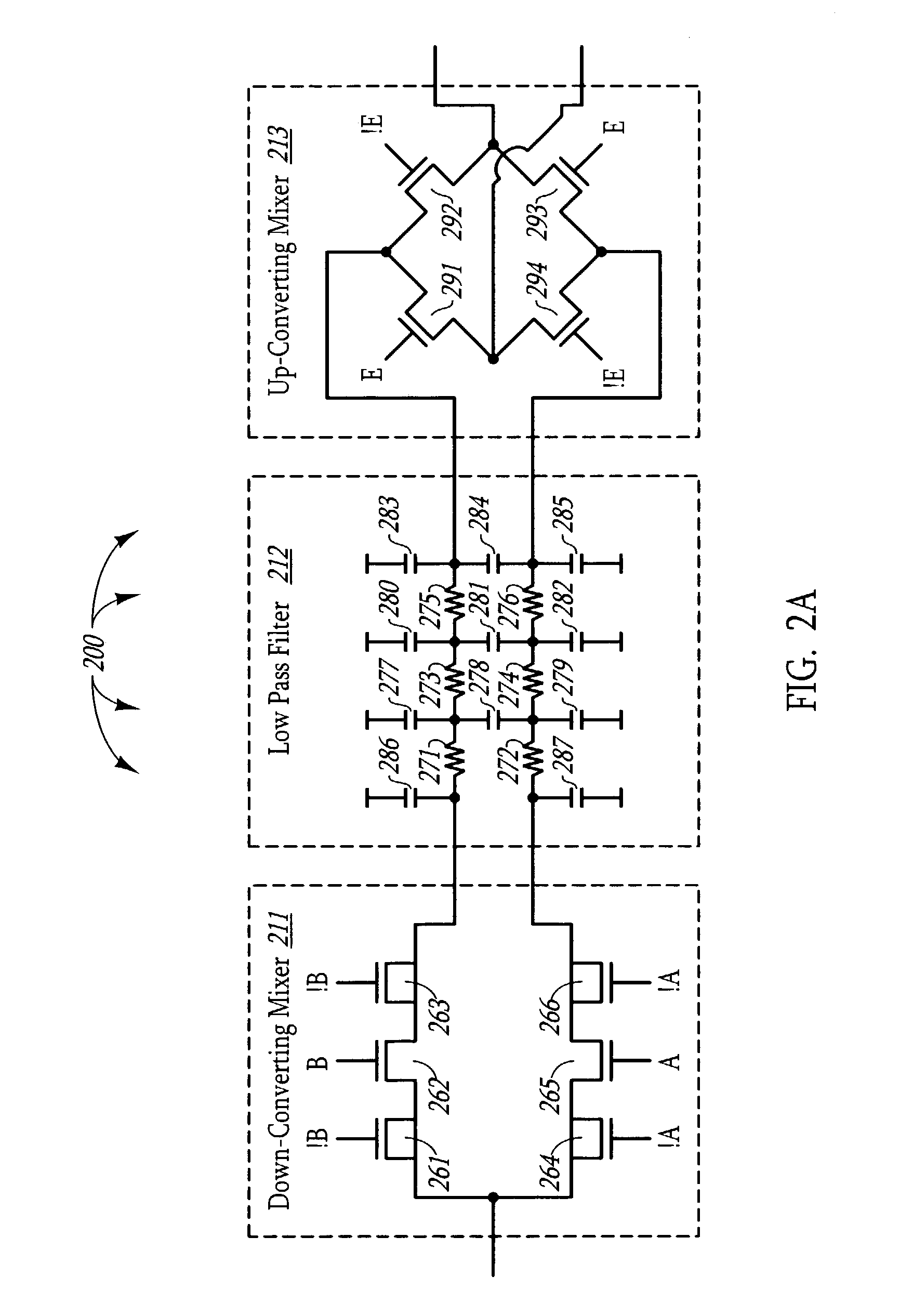
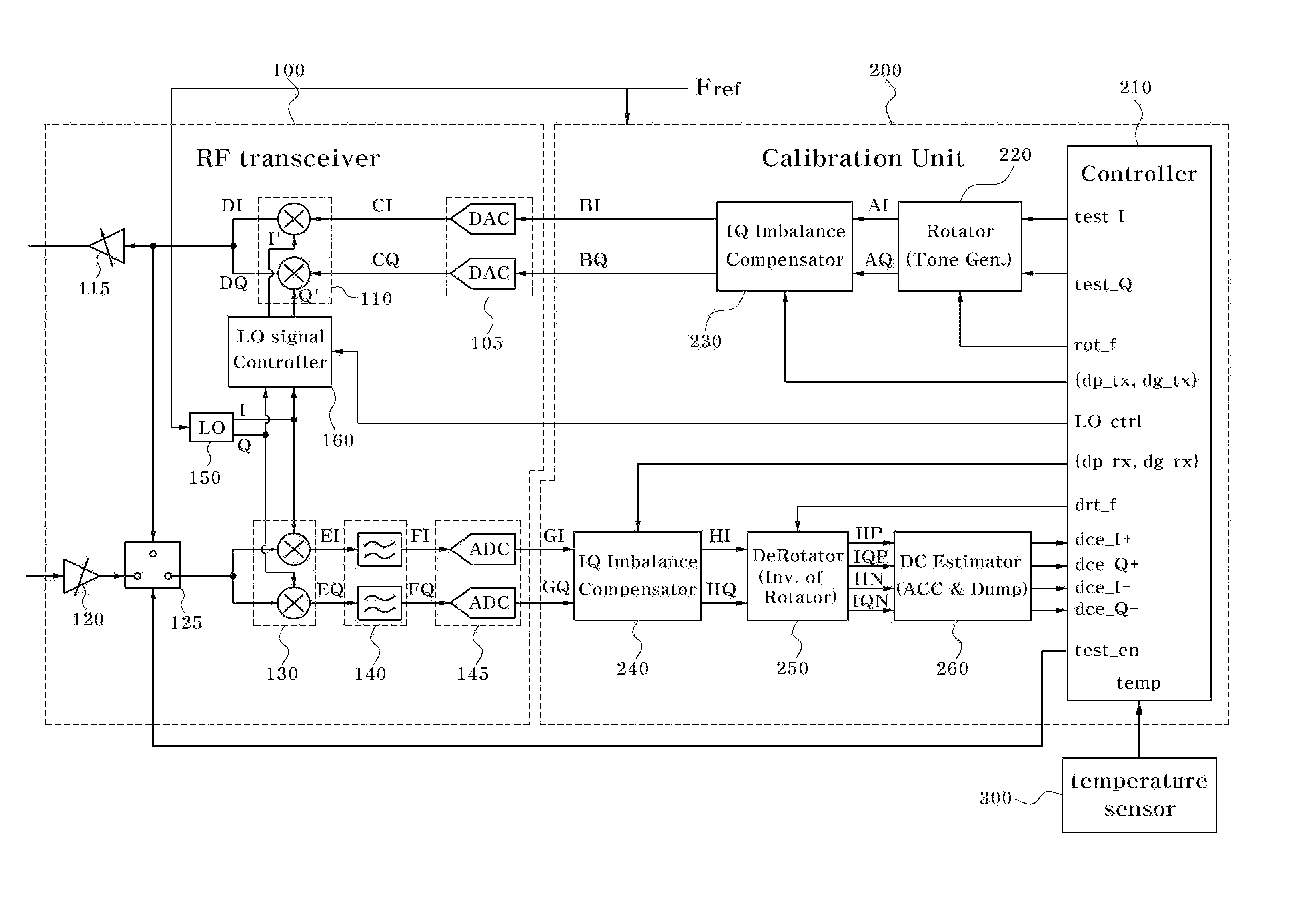
Patents
Literature
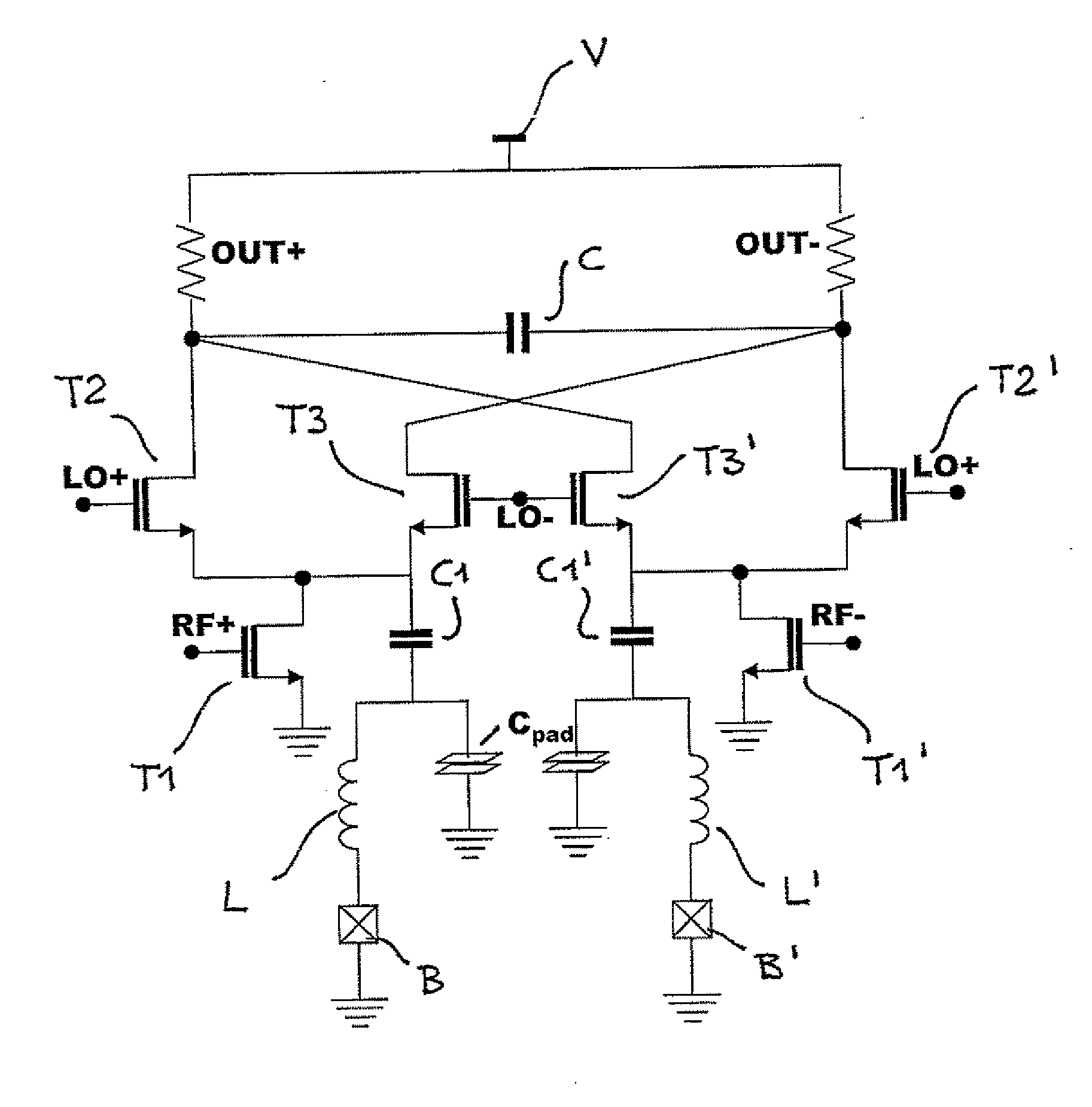
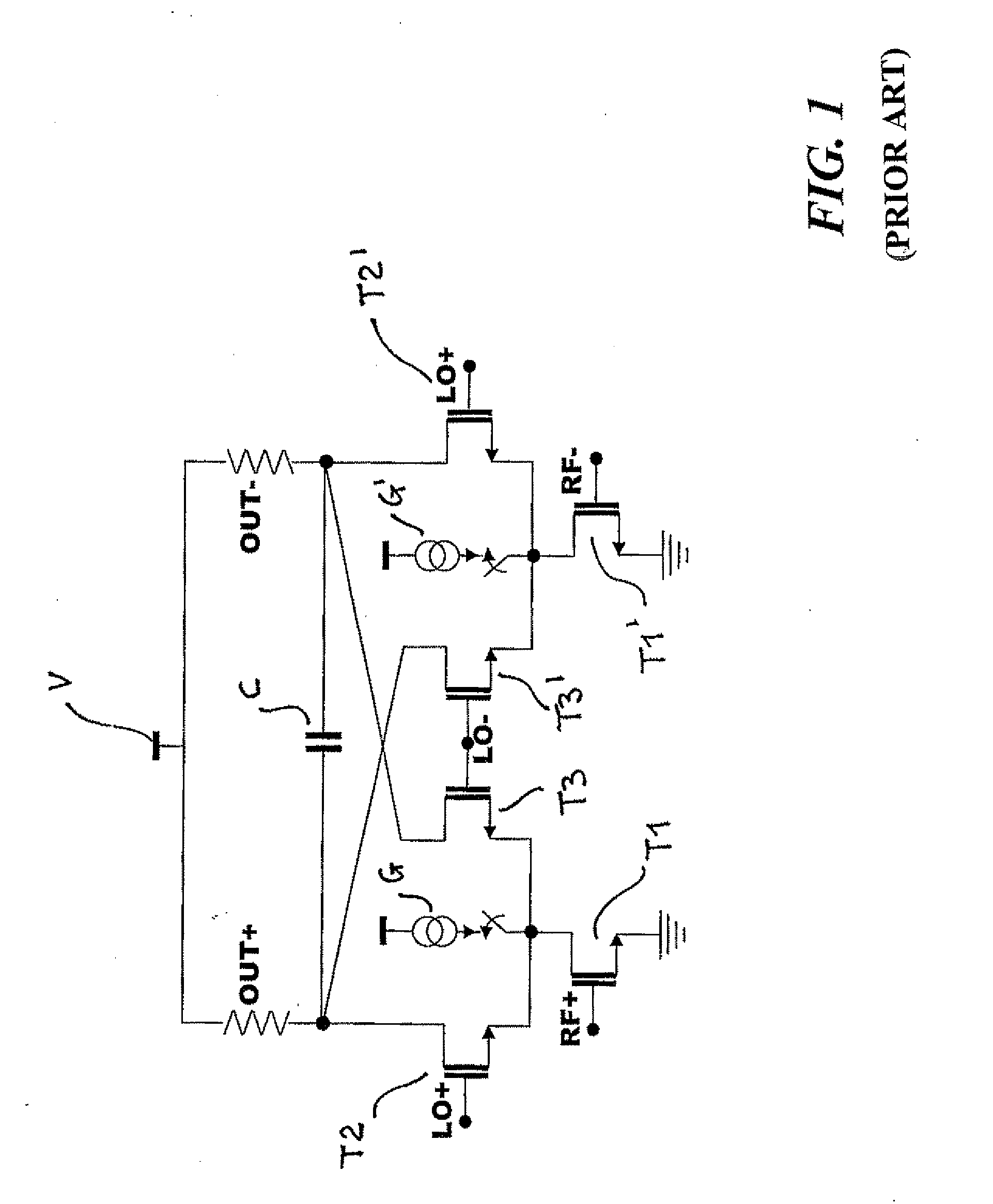
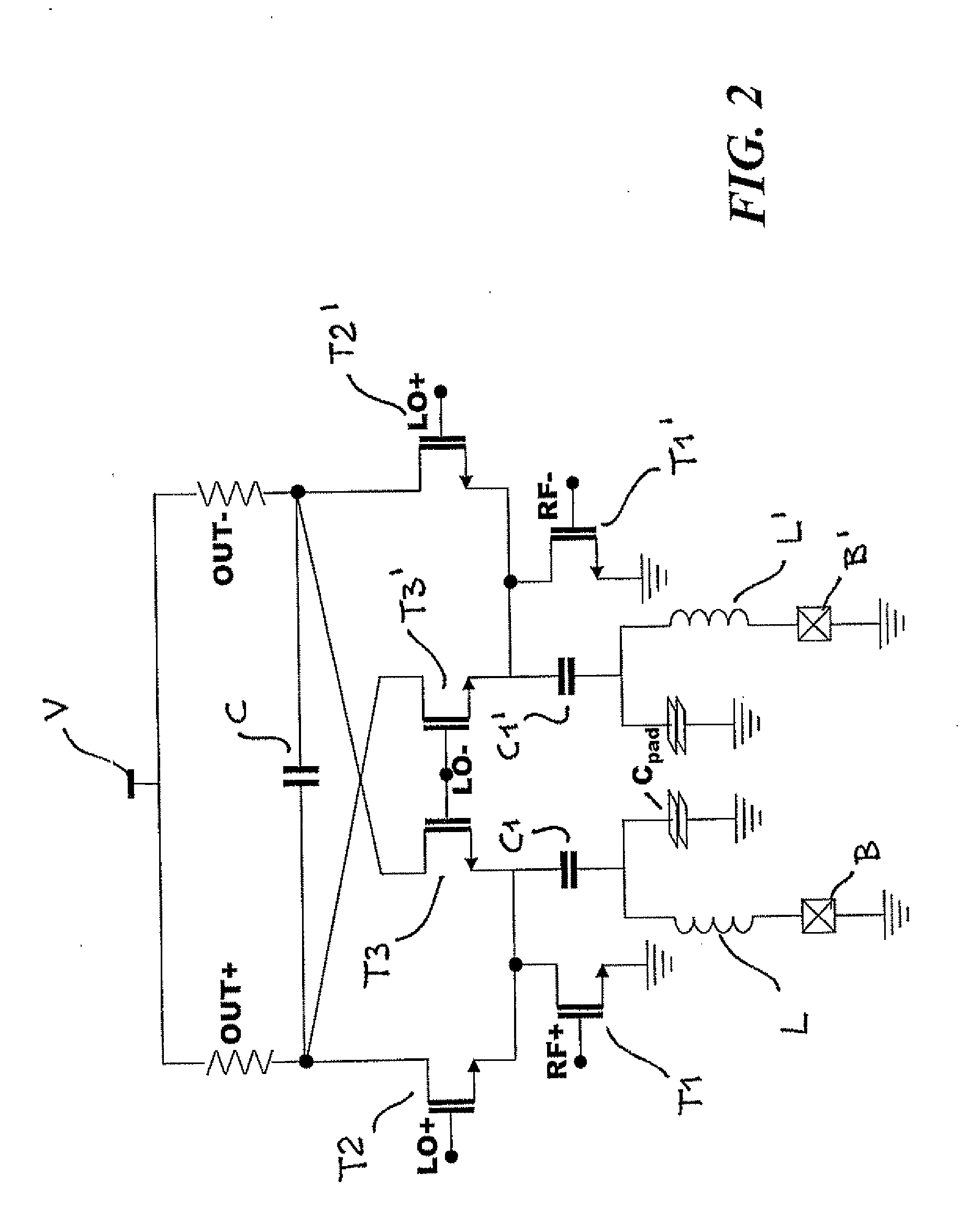
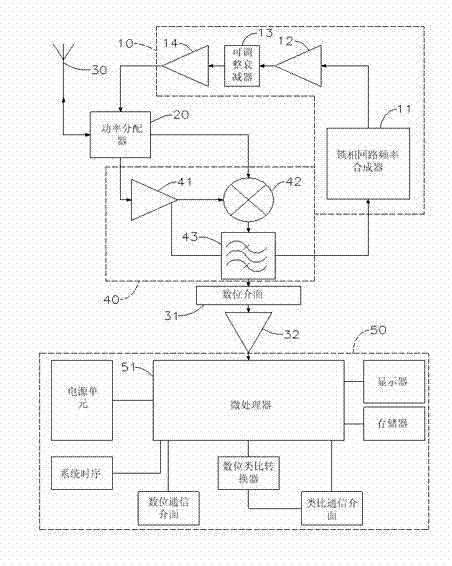
119 results about "Down conversion mixer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
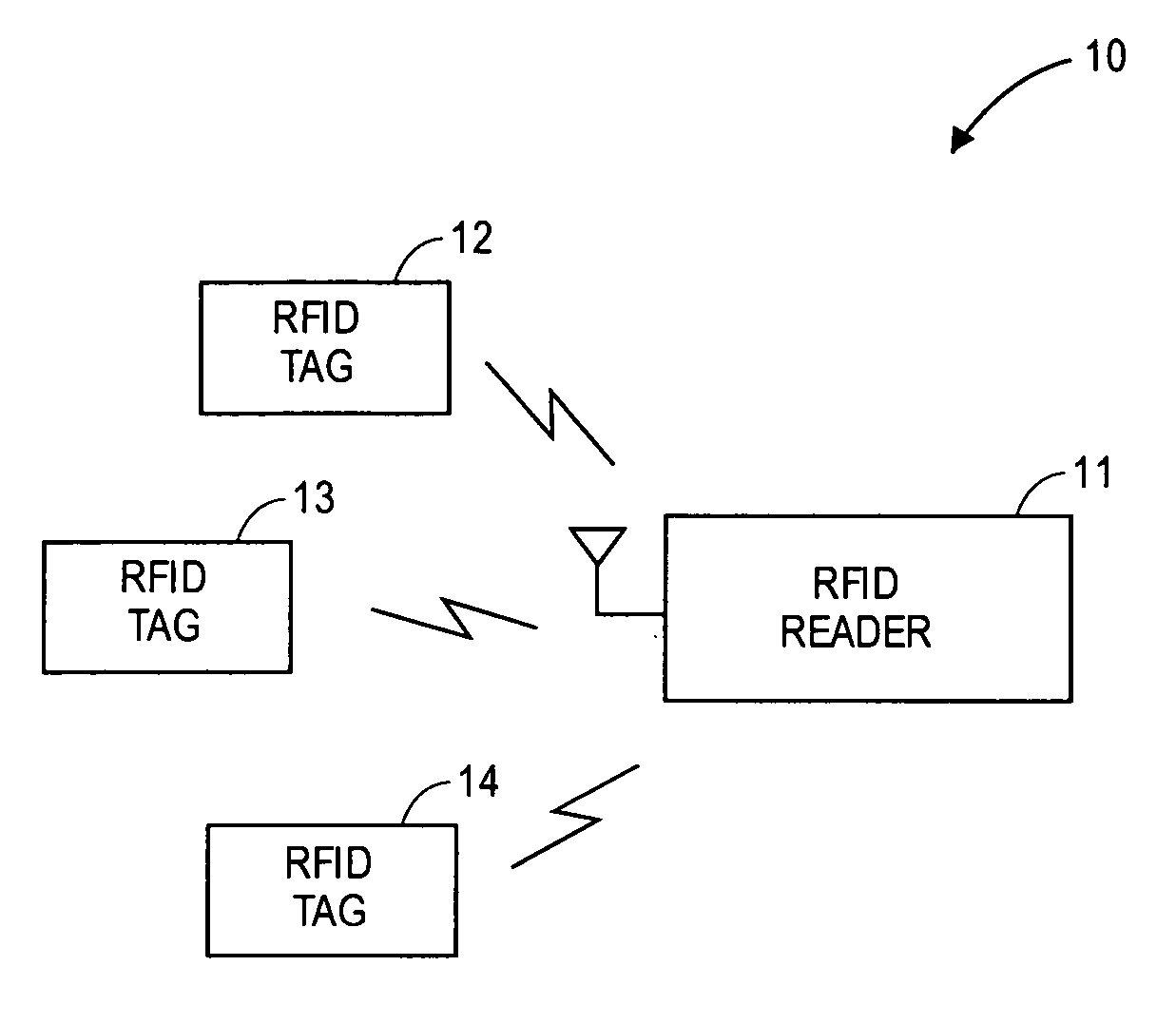
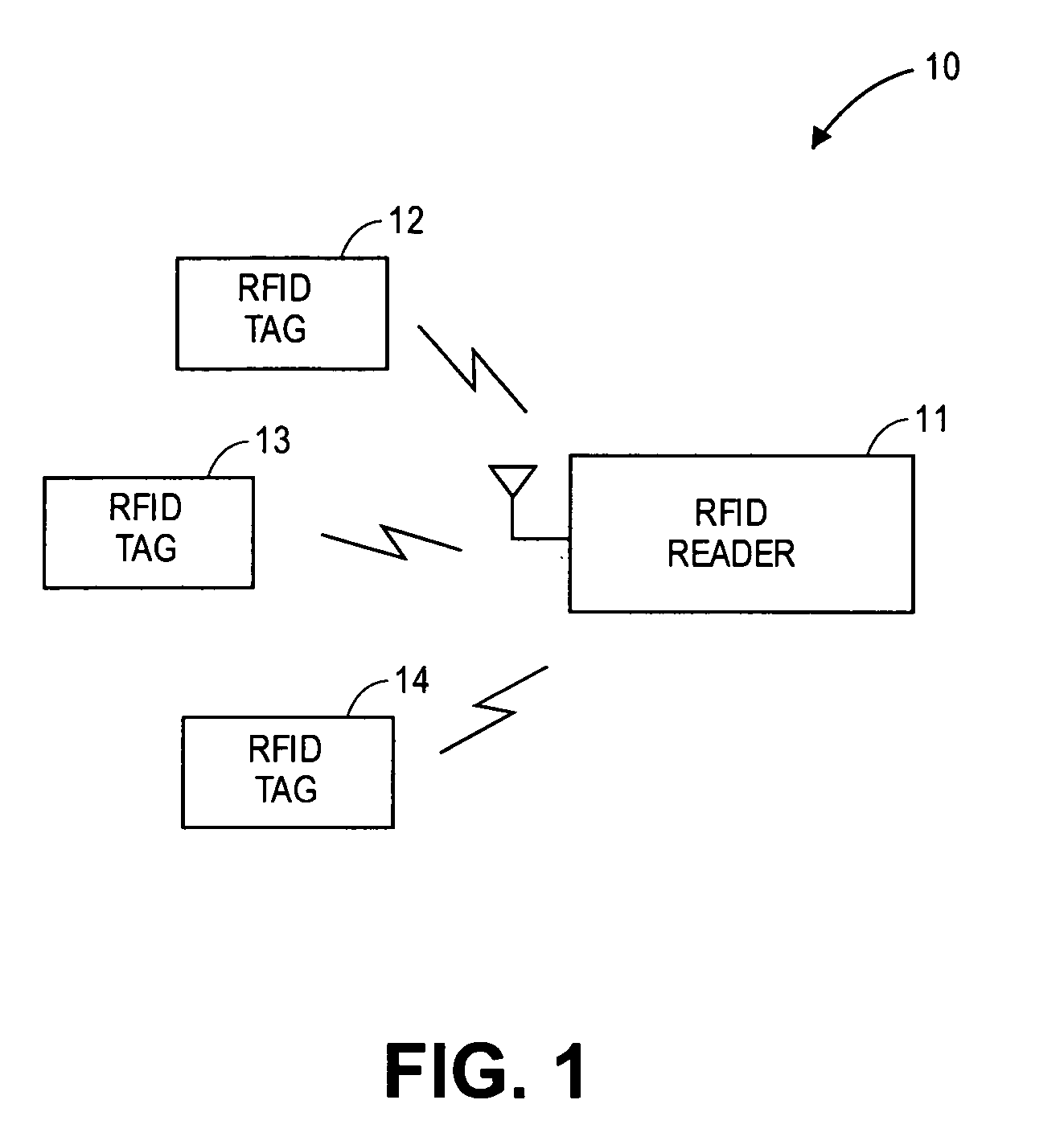
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification transponder transceiver
ActiveUS20060238301A1Memory record carrier reading problemsNear-field in RFIDTransceiverIn-phase and quadrature components
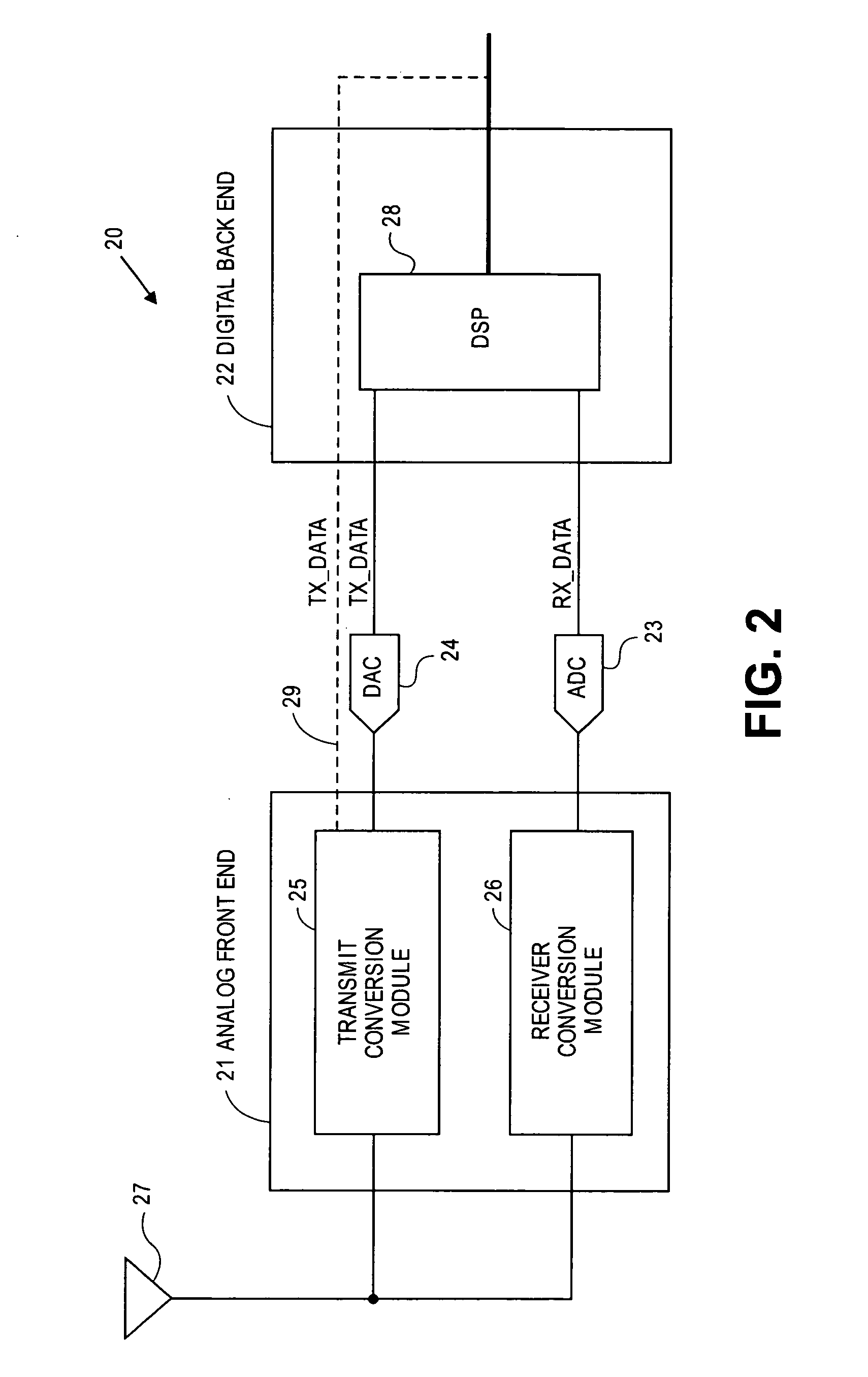
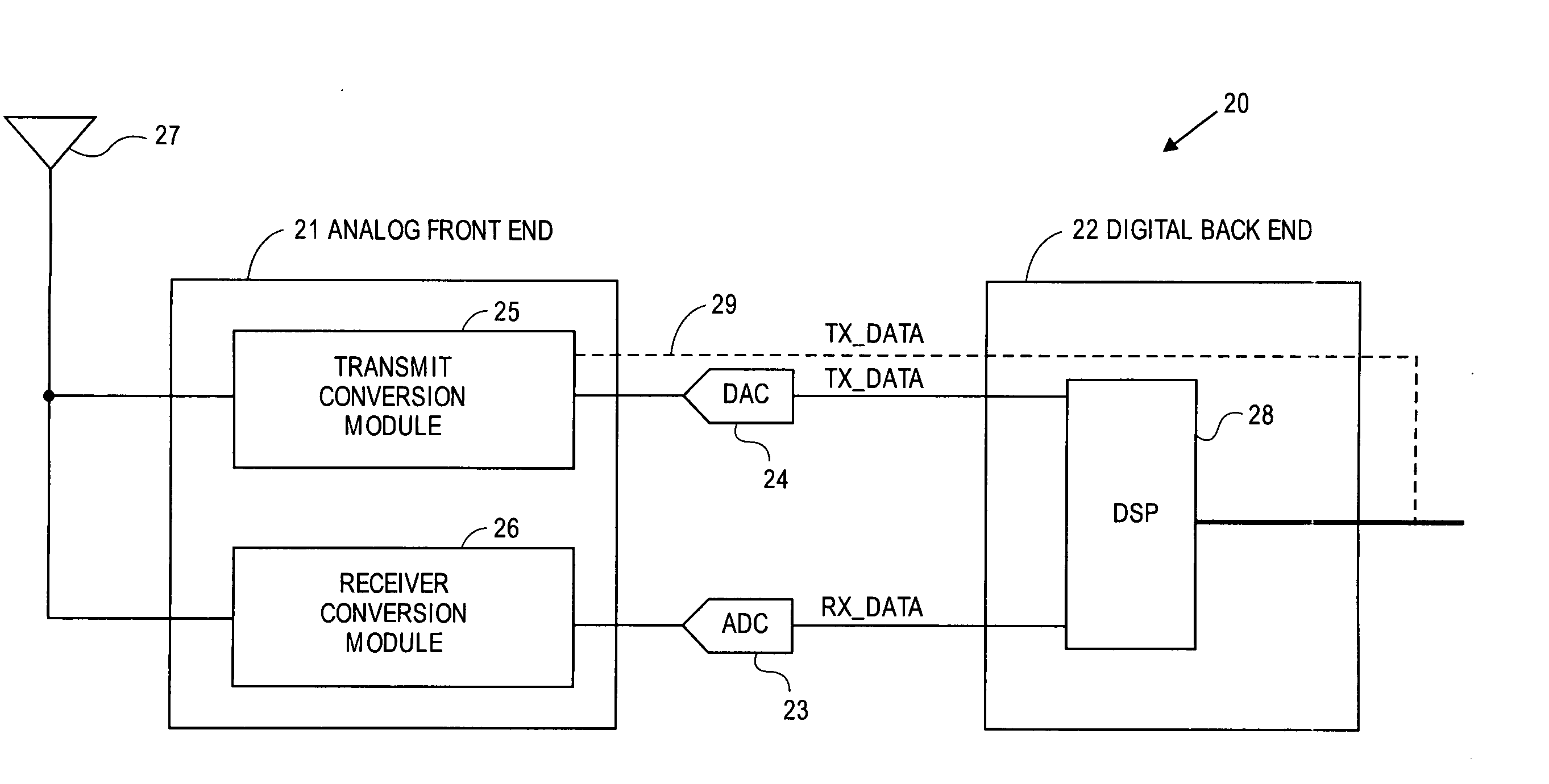
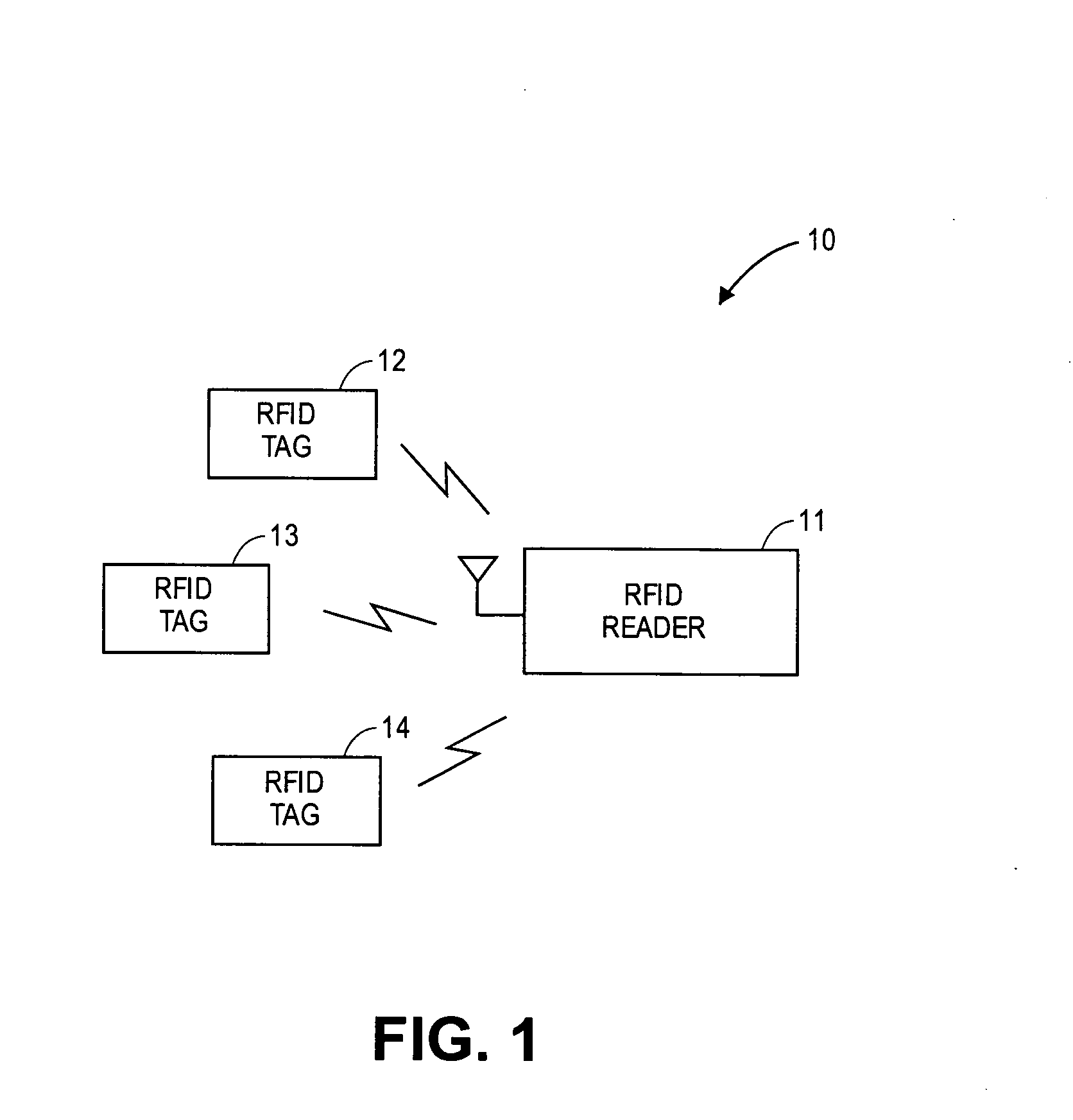
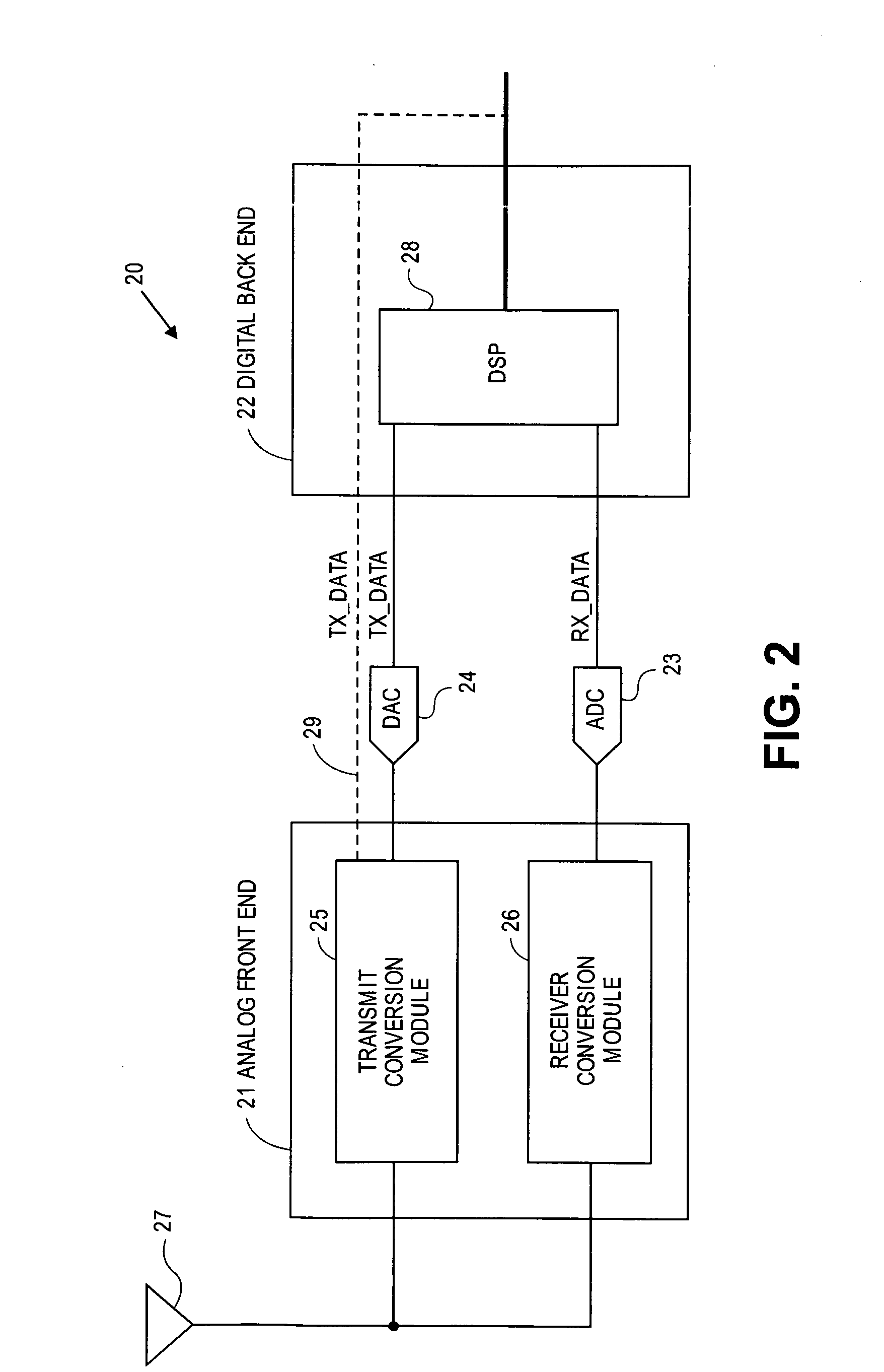
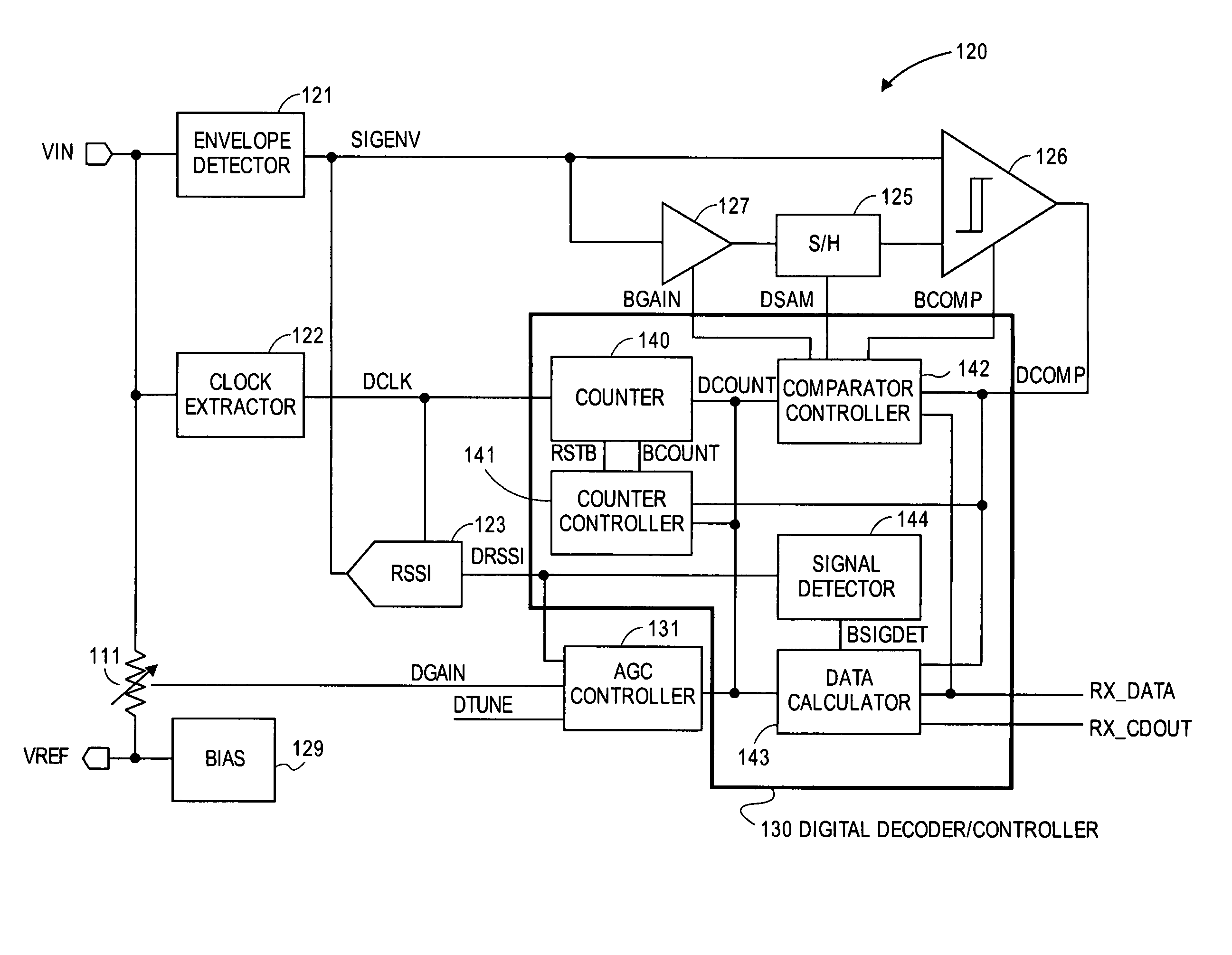
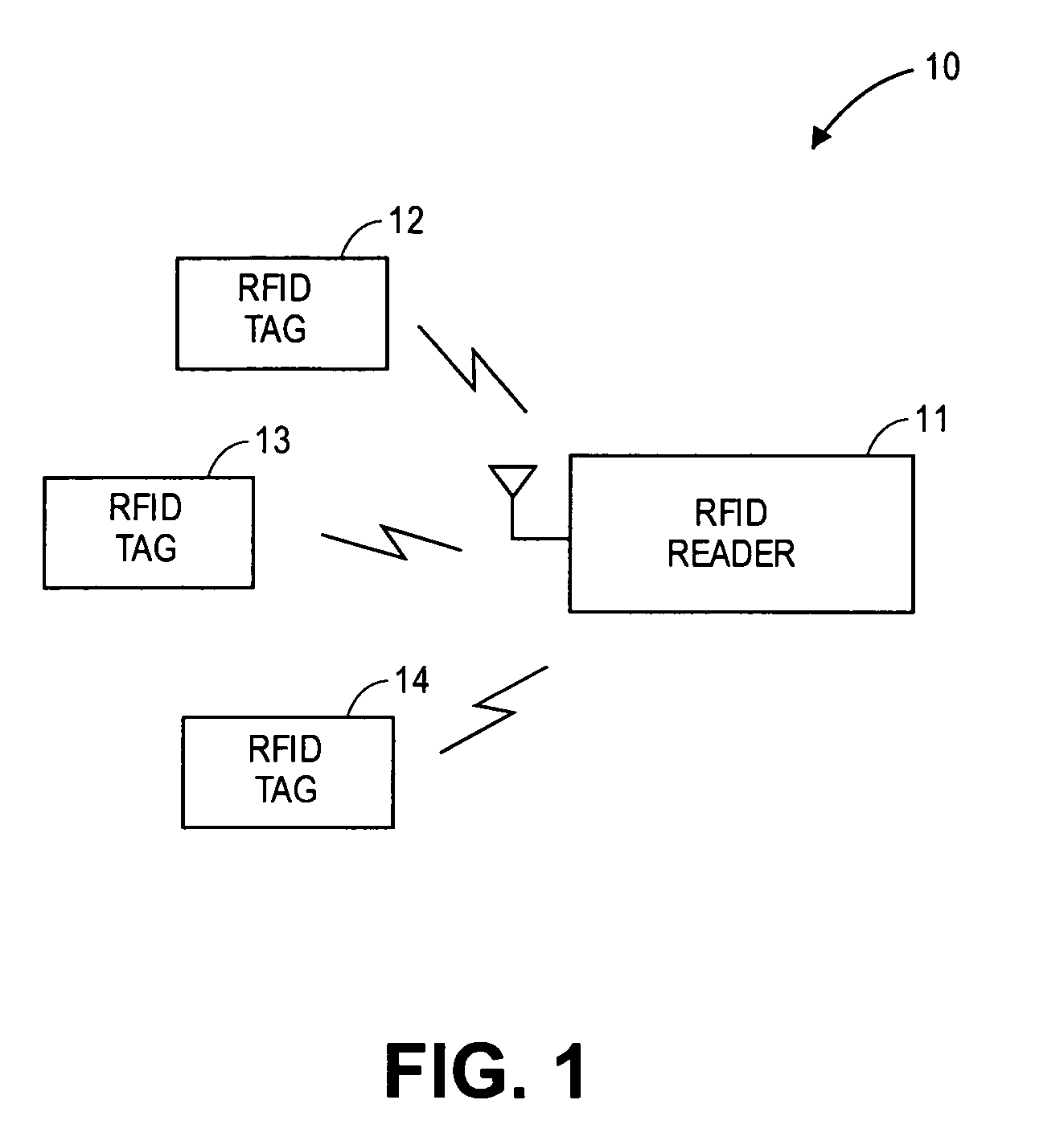
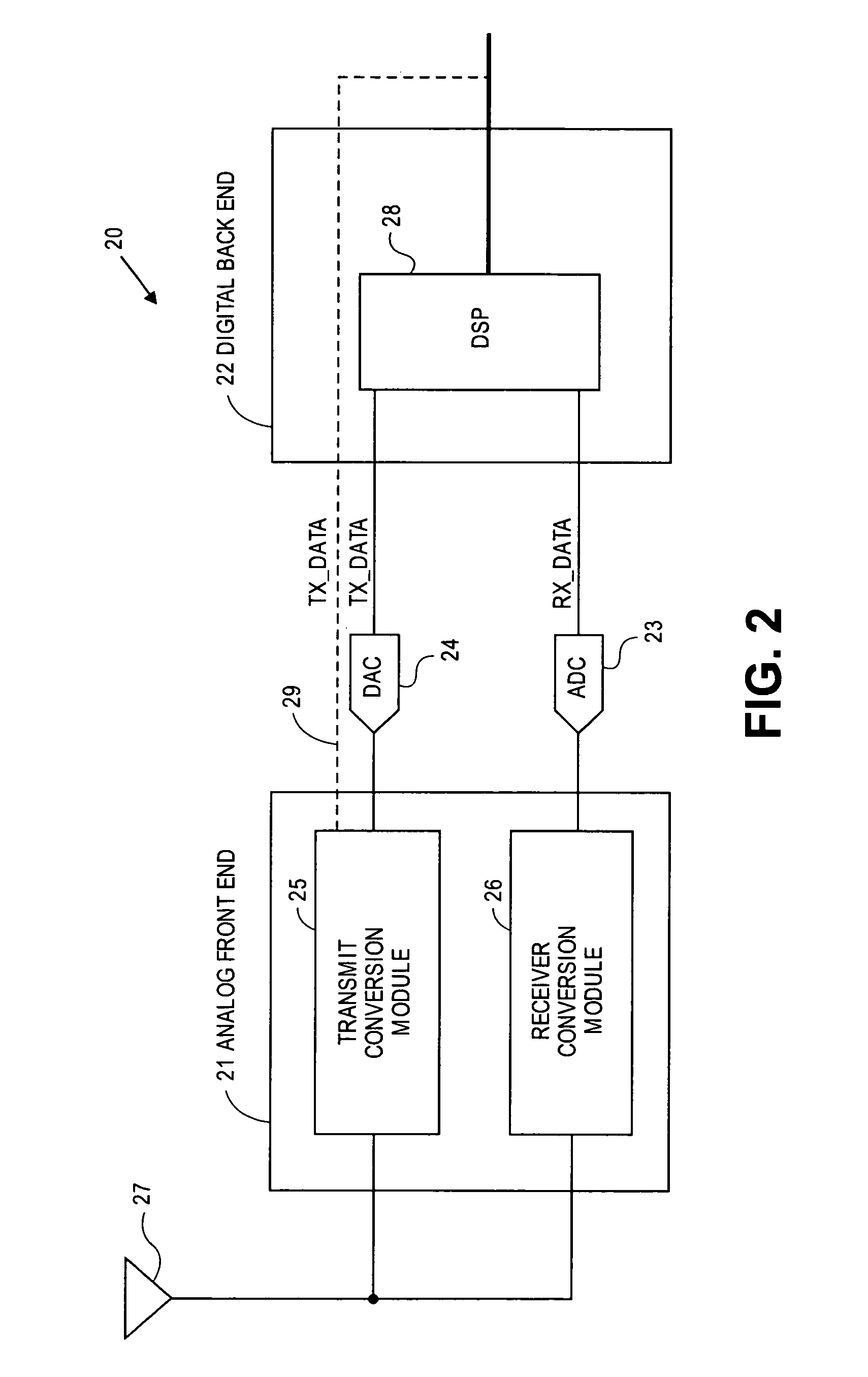
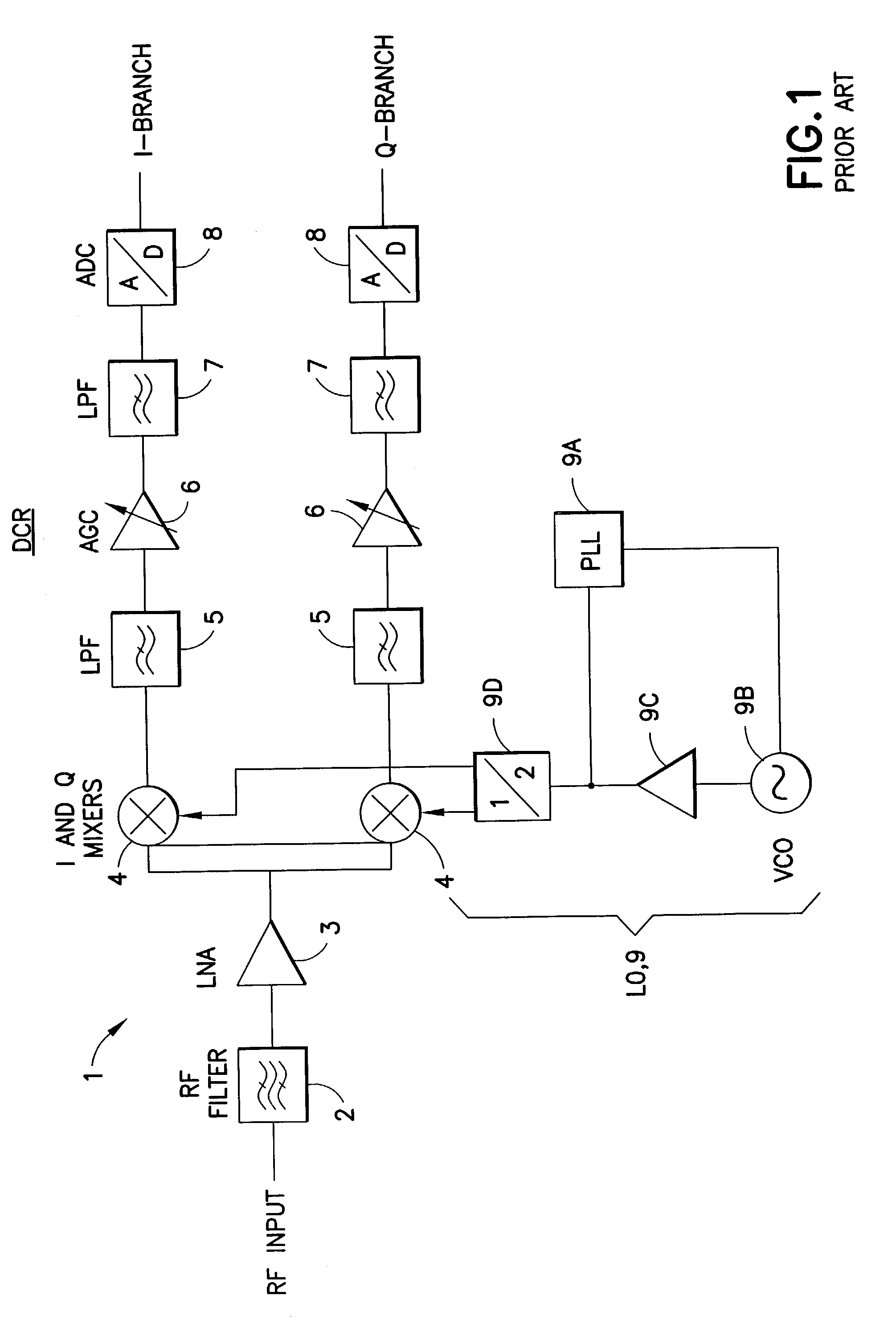
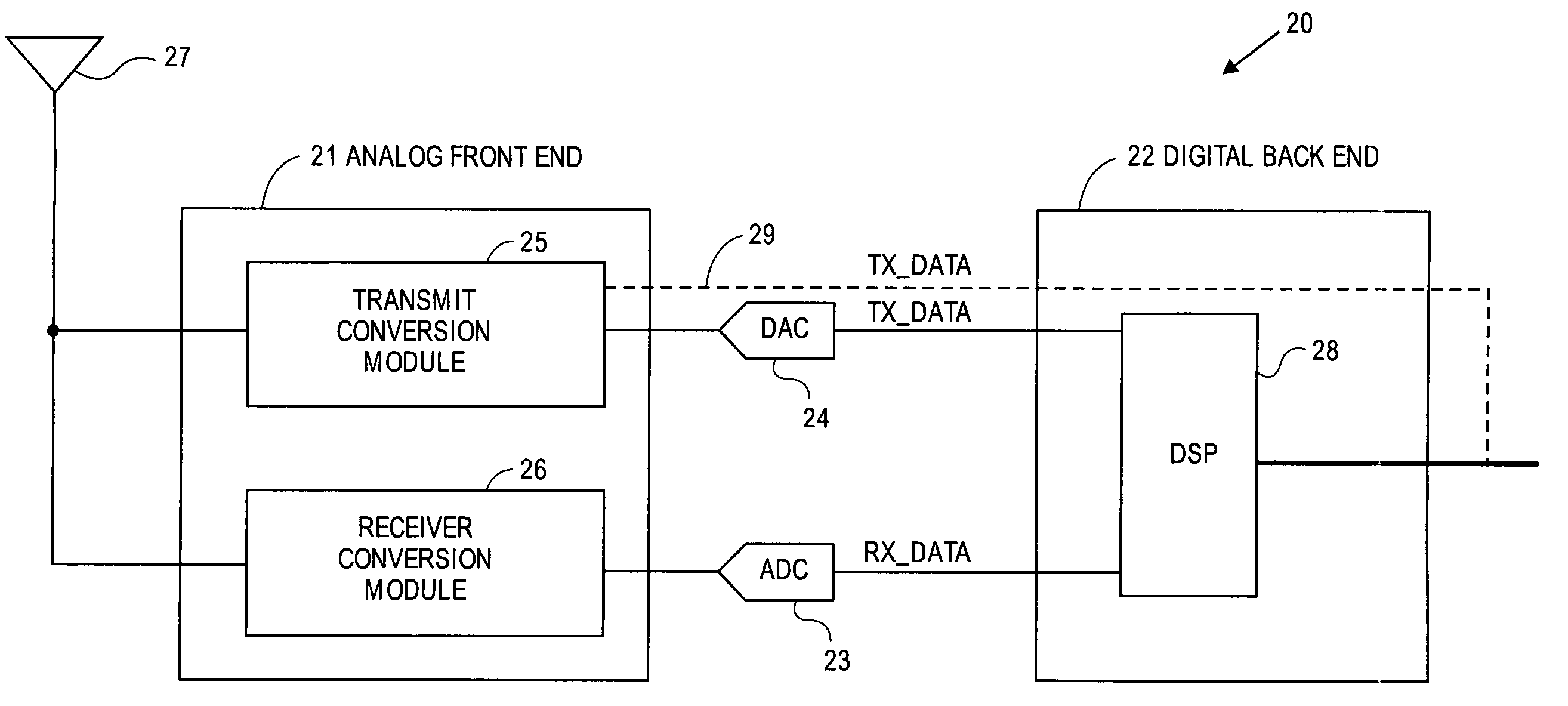
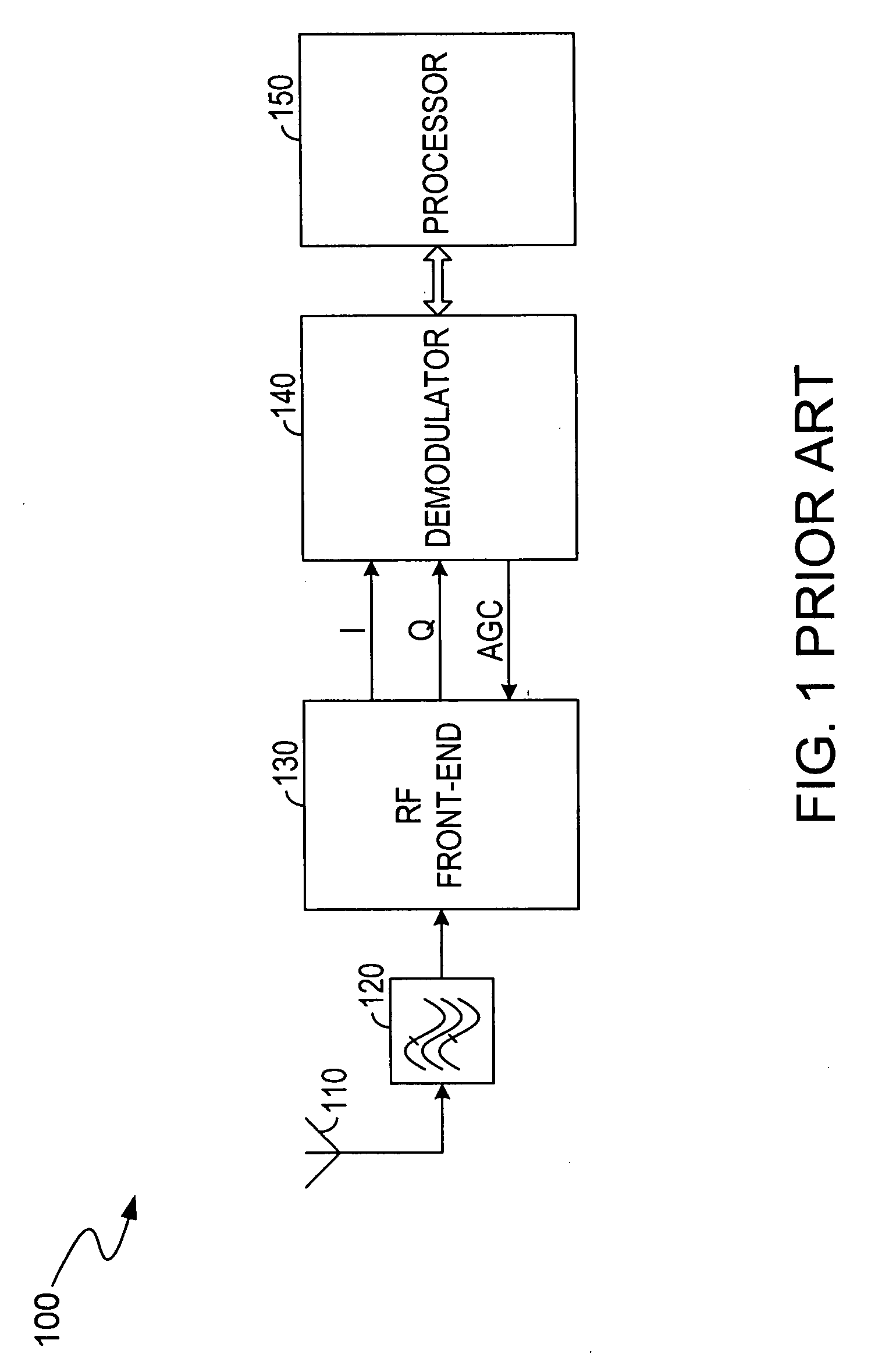
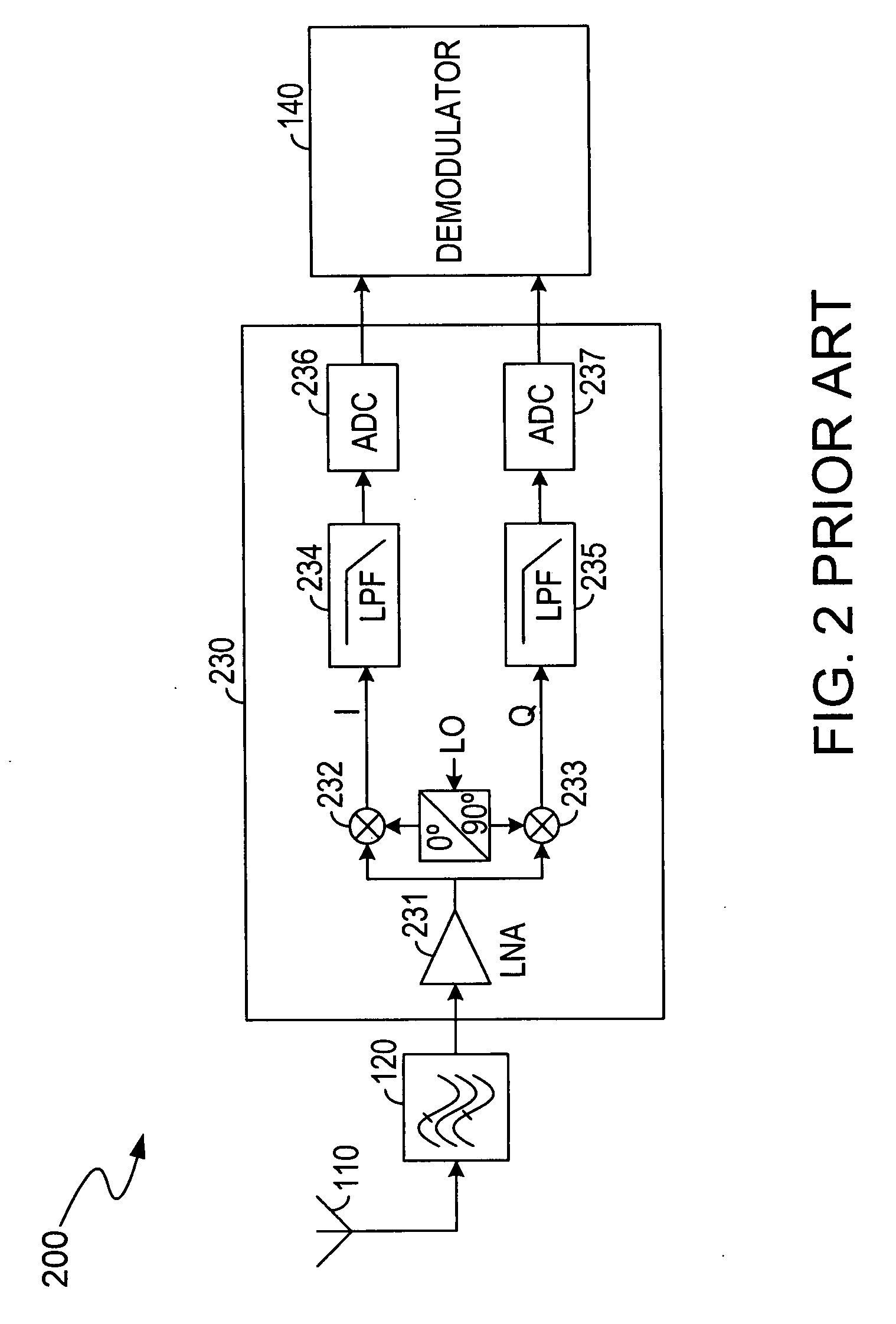
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification reader transceiver
ActiveUS20060186995A1Electric signal transmission systemsError preventionTransceiverDown conversion mixer
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification transponder transceiver
ActiveUS7689195B2Electric signal transmission systemsMemory record carrier reading problemsDigital signal processingTransceiver
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Broadband integrated tuner
InactiveUS7079195B1Low costImprove manufacturabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFrequency mixerDown conversion mixer
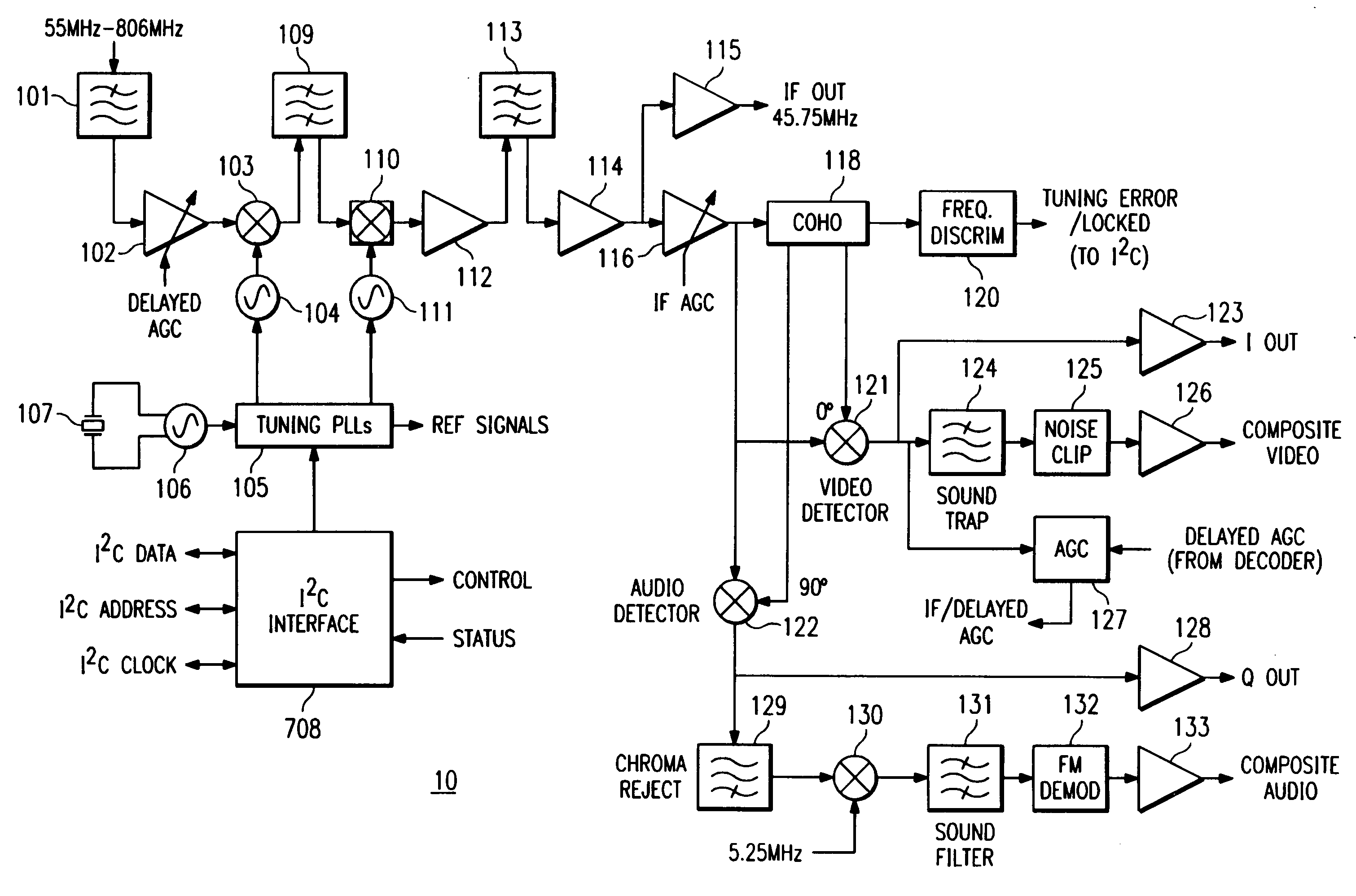
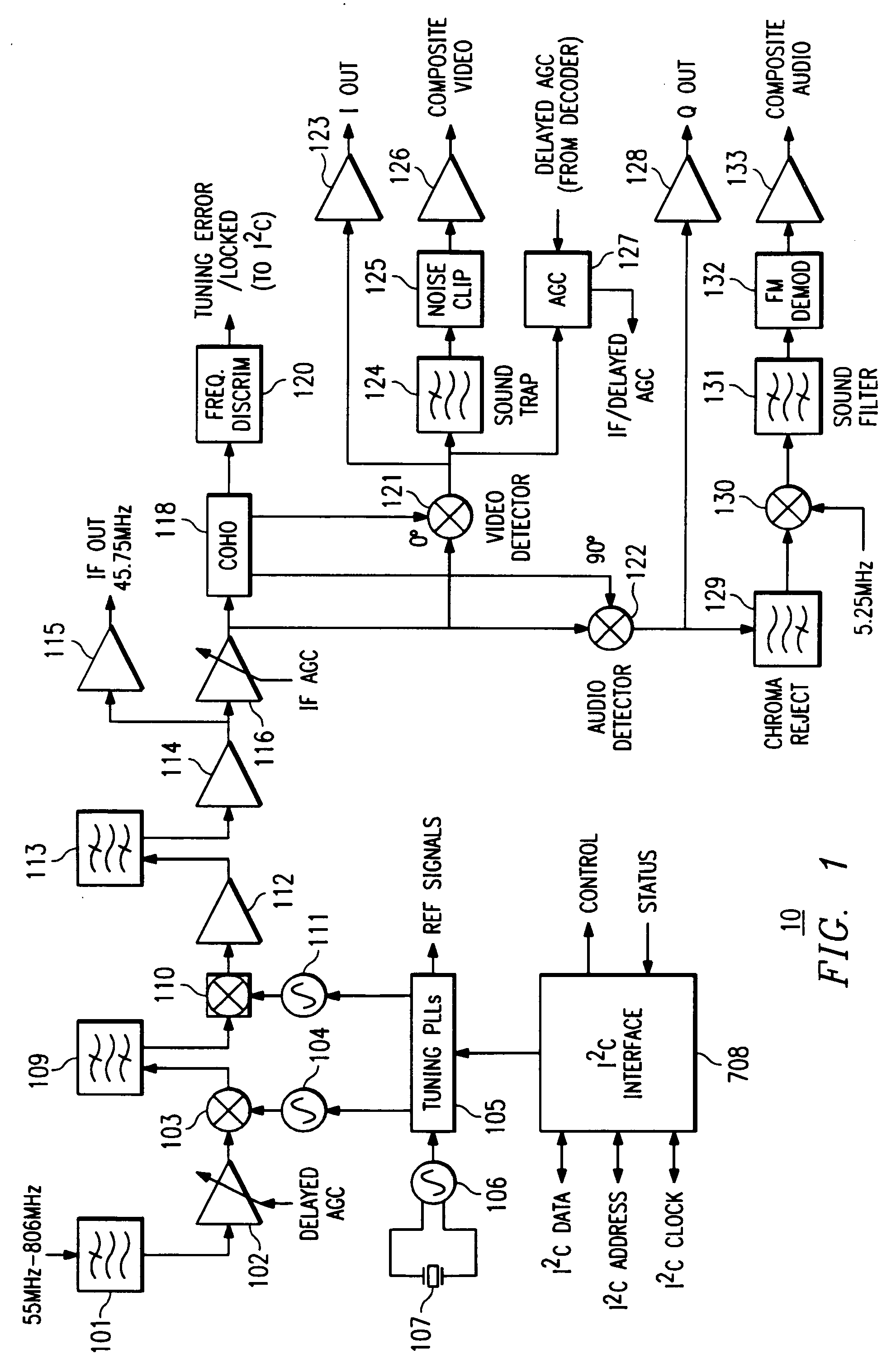
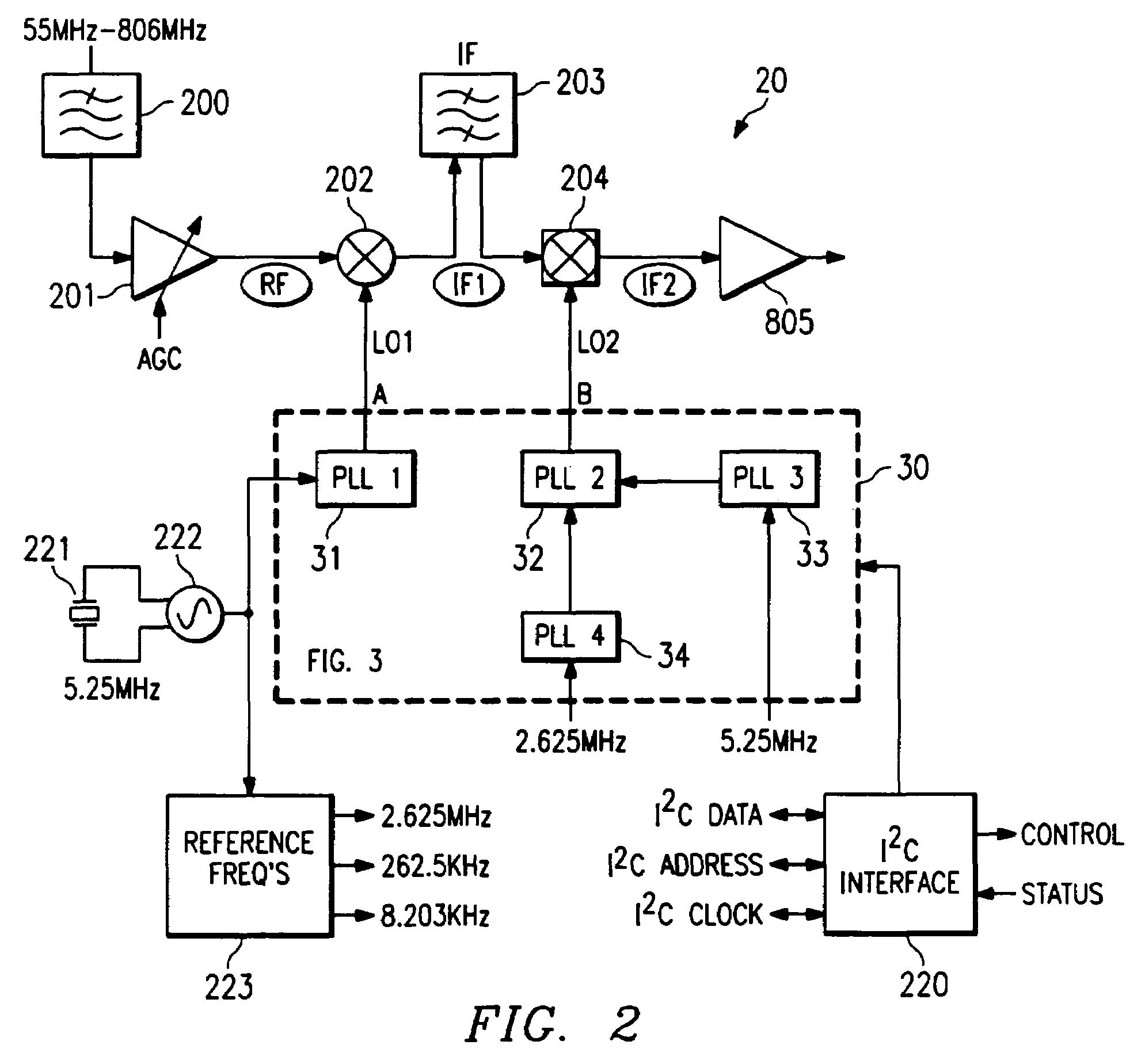
A broadband integrated receiver for receiving input signals and outputting composite video and audio signals is disclosed. The receiver employs an up-conversion mixer and a down-conversion mixer in series to produce an intermediate signal. An intermediate filter between the mixers performs coarse channel selection. The down-conversion mixer may be an image rejection mixer to provide additional filtering.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
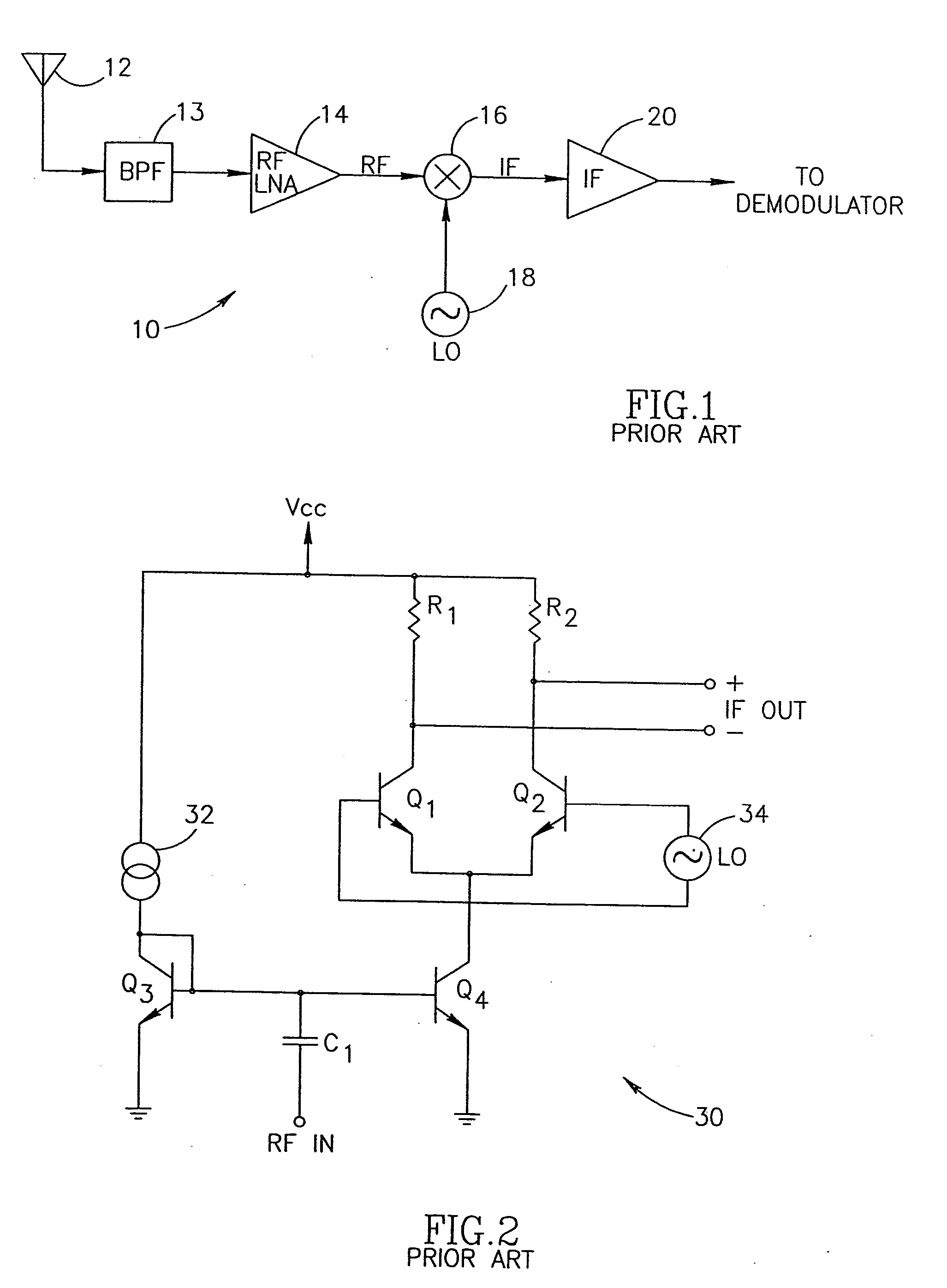
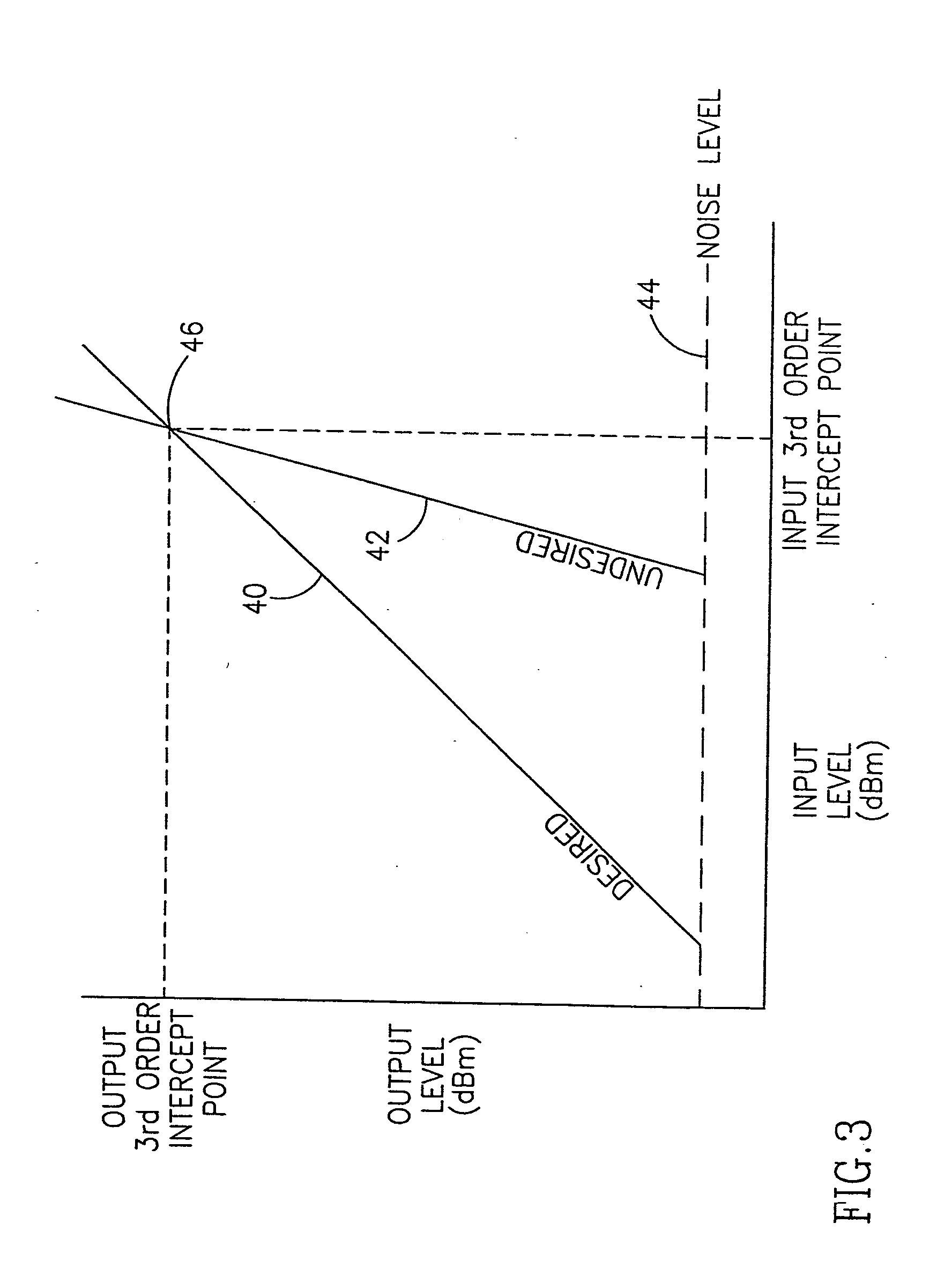
Apparatus for and method of optimizing the performance of a radio frequency receiver in the presence of interference
InactiveUS6965655B1Improve linearityIncrease flexibilityGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTuned radio frequency receiverFrequency mixer
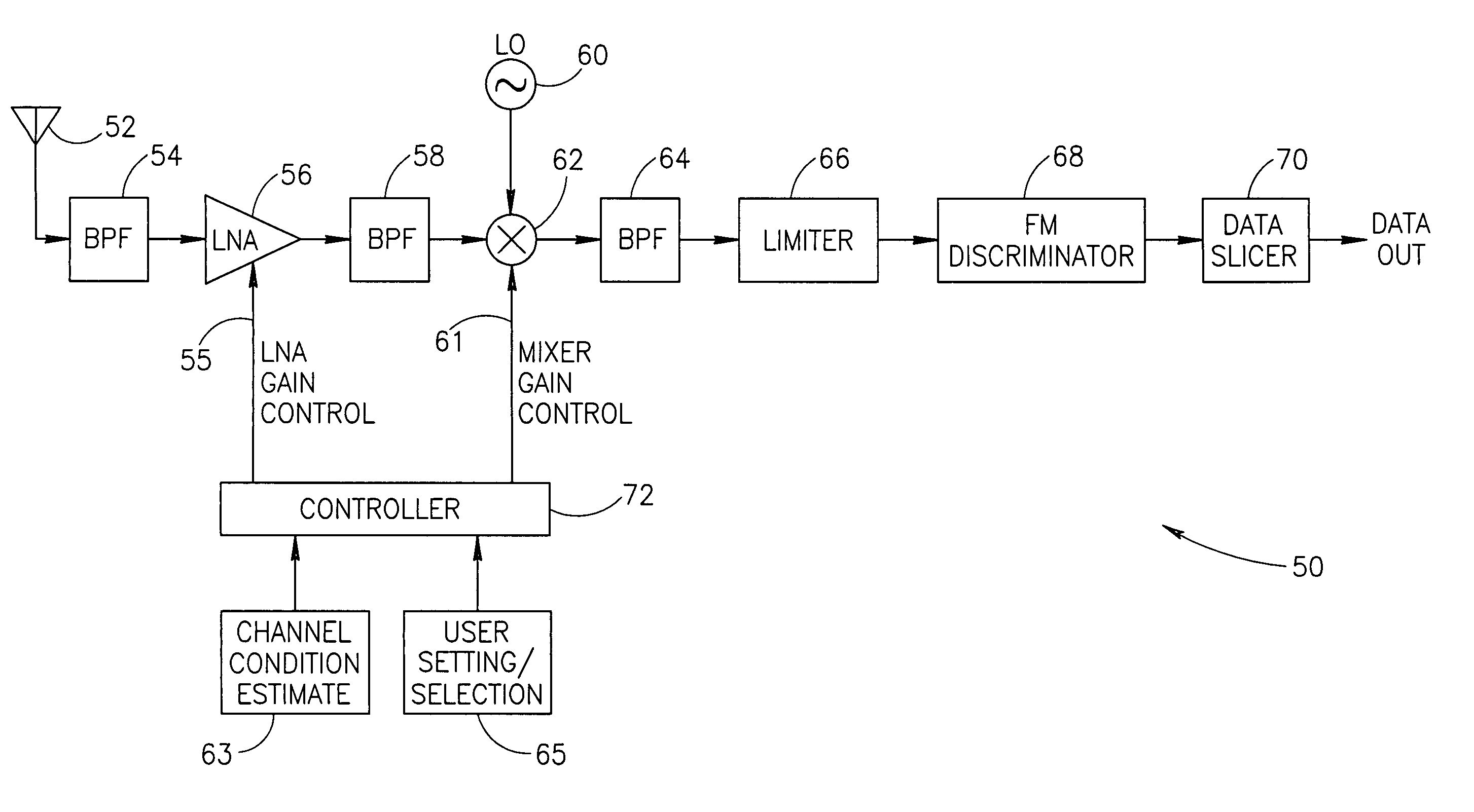
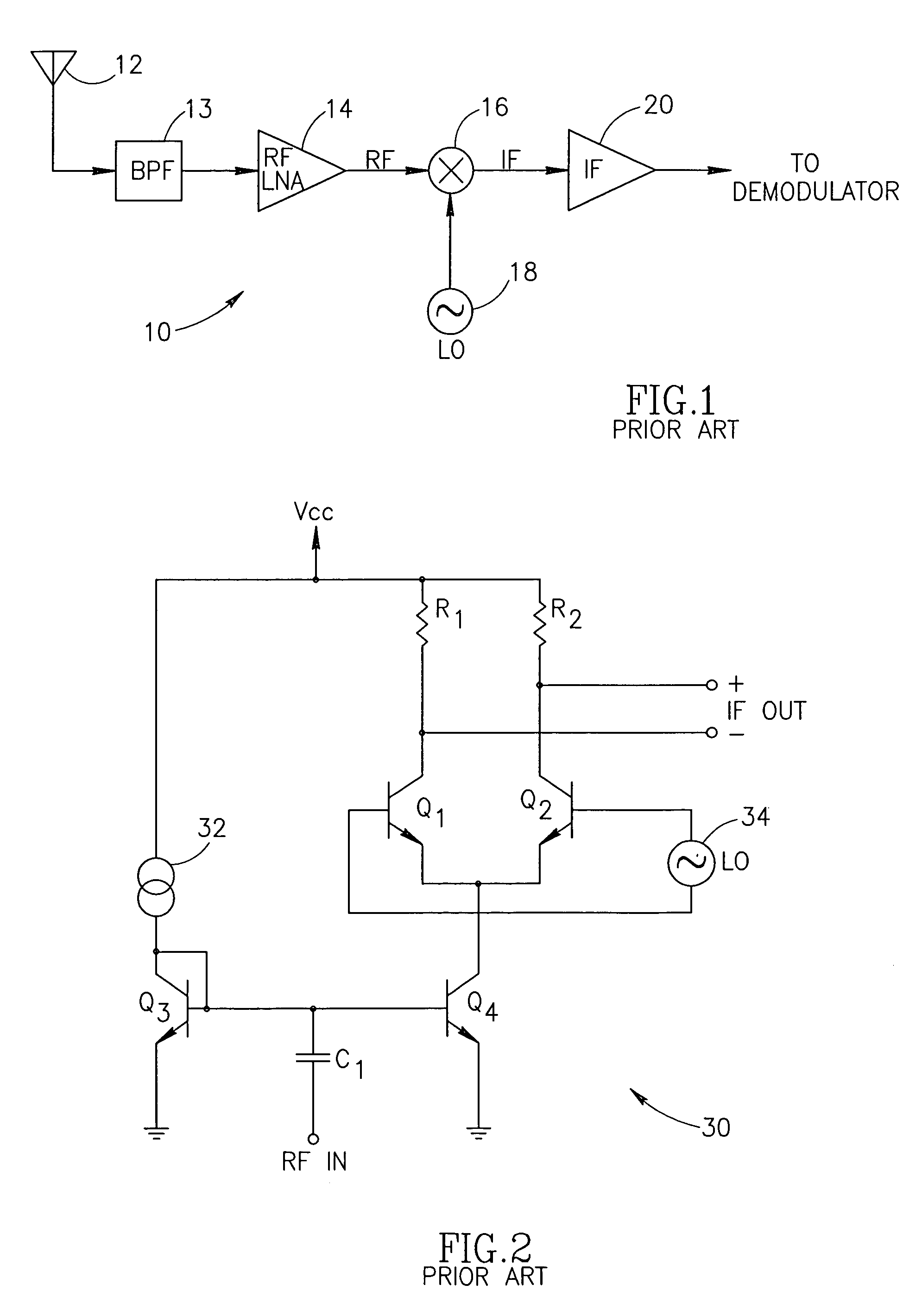
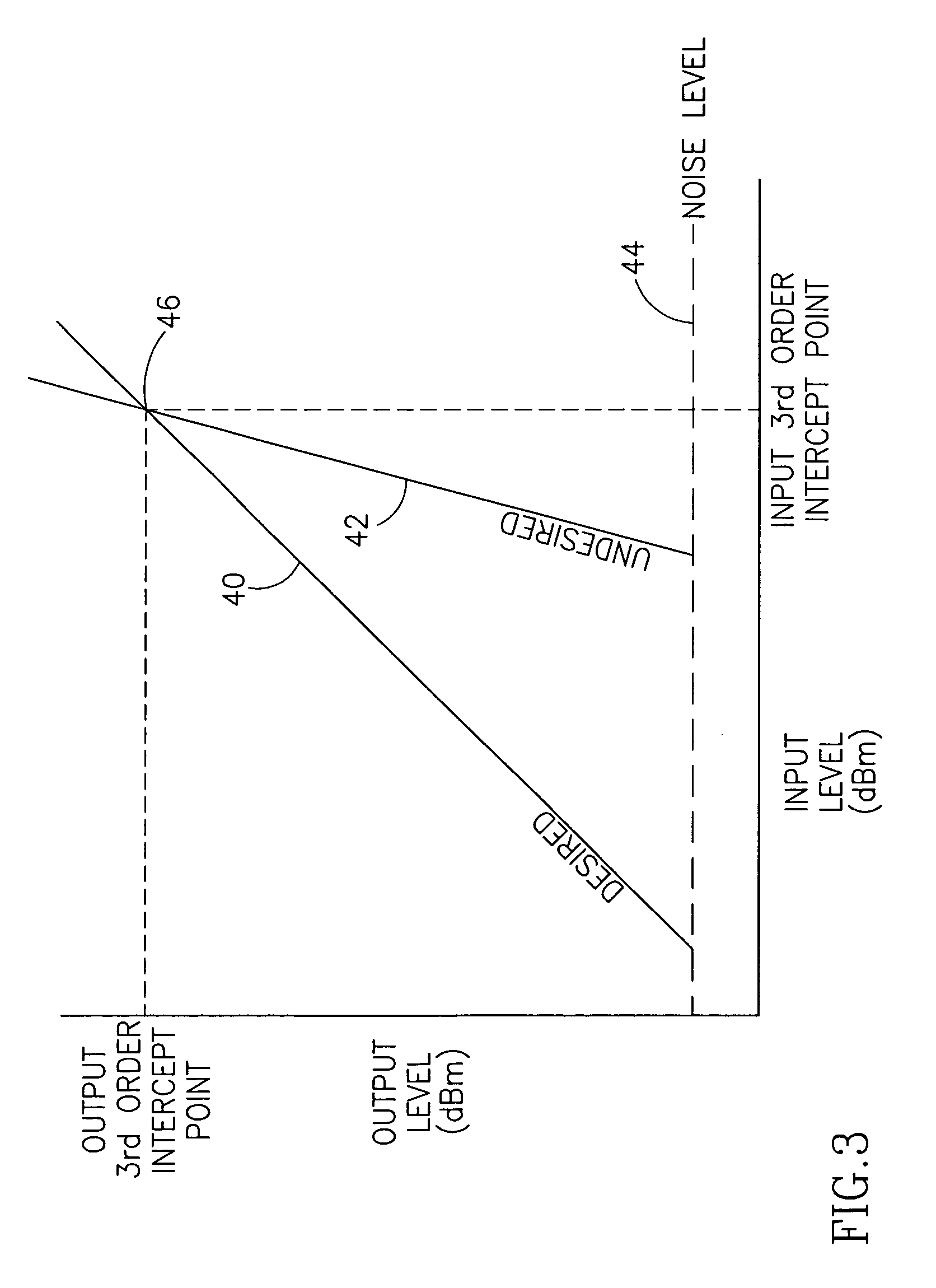
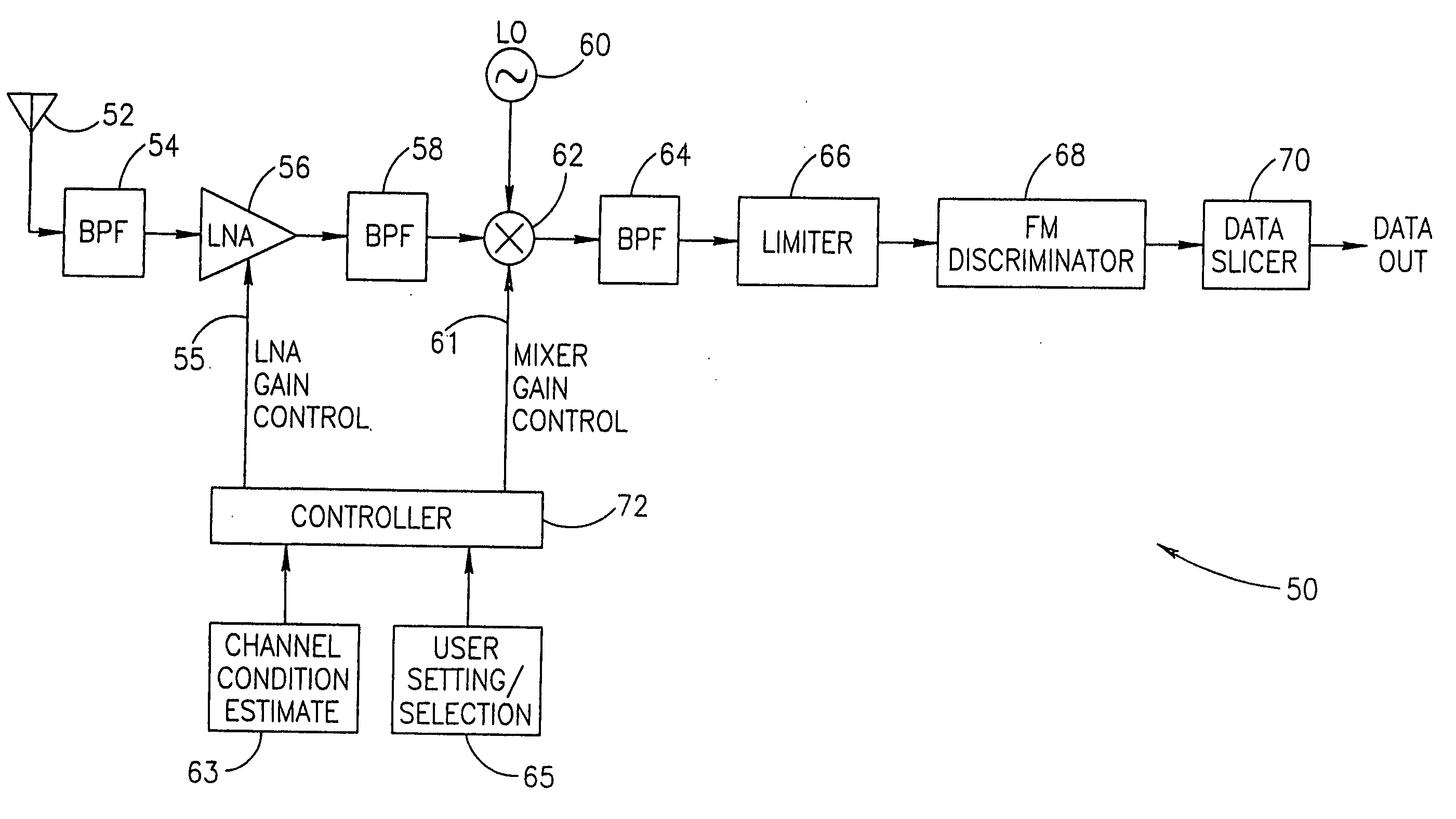
An apparatus for and method of extending the dynamic range of a RF communications receiver. The invention provides a mechanism for controlling the gain of both the LNA and down conversion mixer in the front end portion of an RF receiver. Both the LNA and the mixer are adapted to have both low and high gain modes of operation. The control mechanism typically comprises a two bit gain control that places both the LNA and mixer in one of four operating gain mode states. The selection of the most appropriate operating gain mode state, is preferably determined in accordance with various metrics such as the received levels of the desired signal, levels of interference signals, bit error rate and receiver RSSI.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Current-mode direct conversion receiver
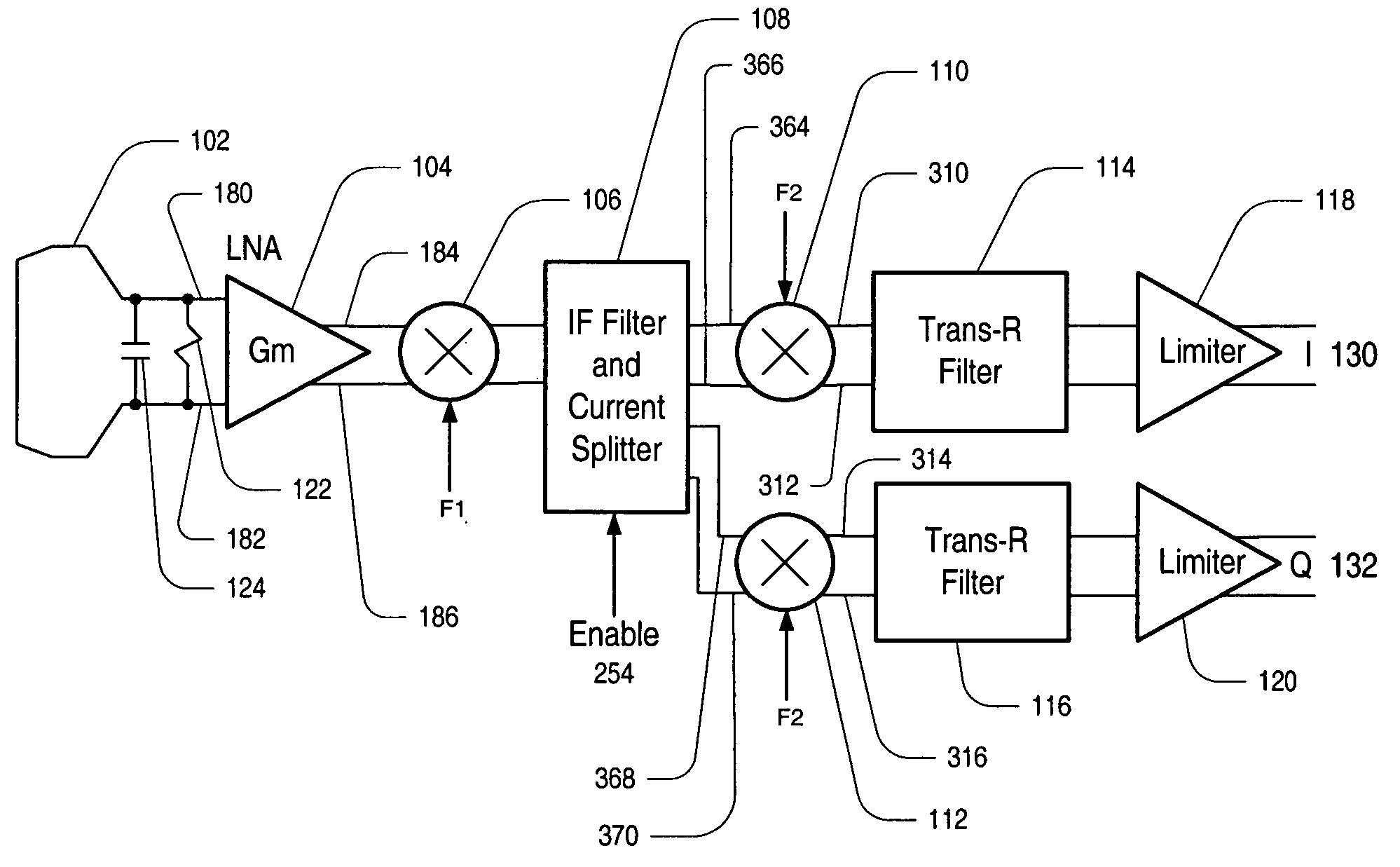
A current-mode direct conversion RF receiver is presented. In one set of embodiments the RF receiver comprises a simple transconductor input stage to create a current-mode modulated signal from a voltage-mode modulated signal. A downconversion mixer may be coupled to the transconductor input stage via a low impedance current cascode stage, and may operate to create a set of current-mode quadrature baseband signals from the current-mode modulated signal. The downconversion mixer may be implemented with a transistor-switching network, which may be driven by a phase locked loop (PLL) with quadrature outputs. The set of current-mode quadrature baseband signals may be converted back to the voltage domain by a transimpedance filter, which may perform channel selection for the receiver. The transimpedance filter may additionally include a low frequency zero to remove DC offsets. The receiver may be implemented using CMOS design technologies and operated with minimal self-mixing effects, minimal DC offset in the baseband signal, and utilizing low voltages.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Adaptive receiver system that adjusts to the level of interfering signals
InactiveUS6980786B1Reduce signalingReduce modulationTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionIntegratorTransmitted power
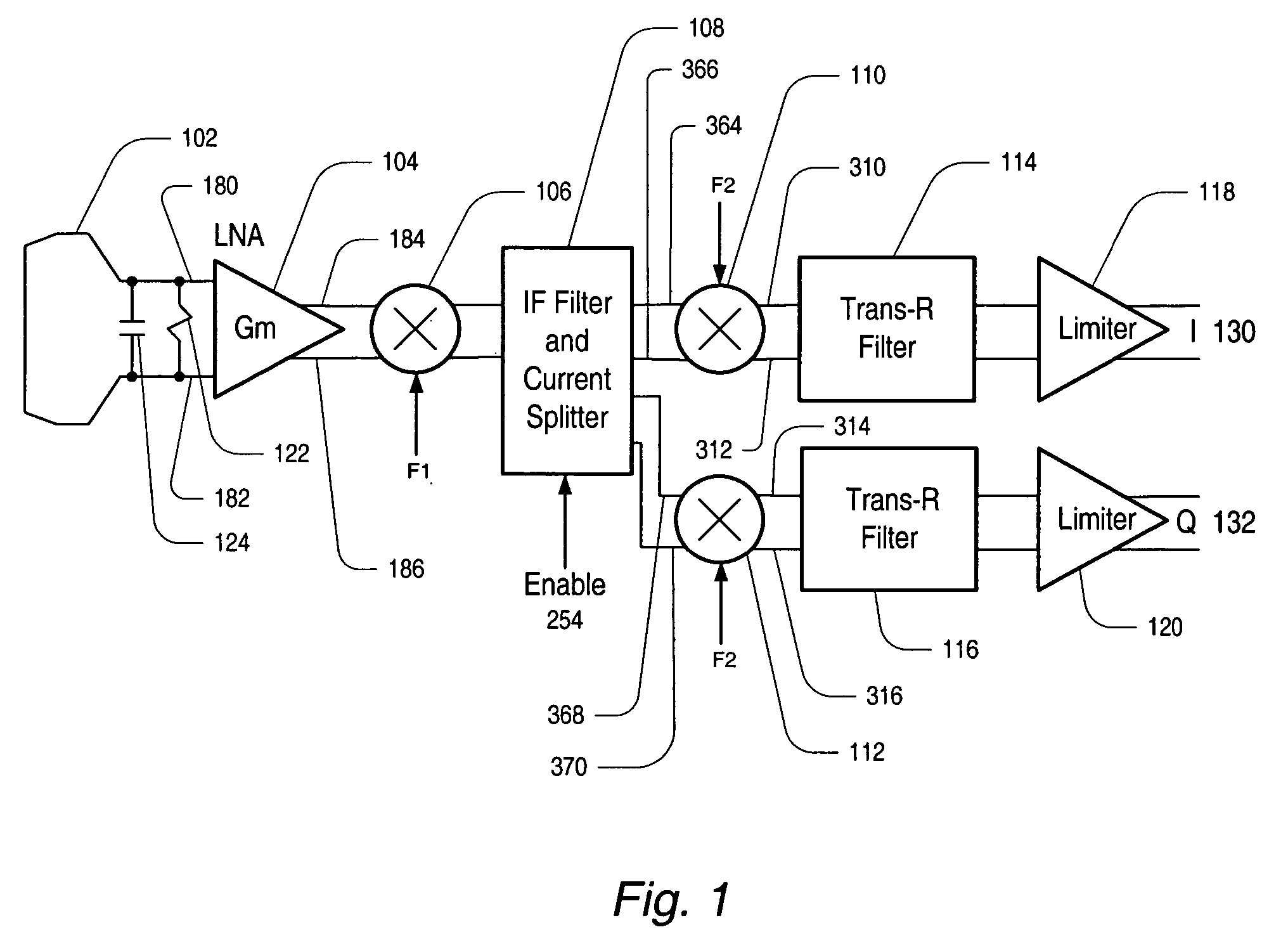
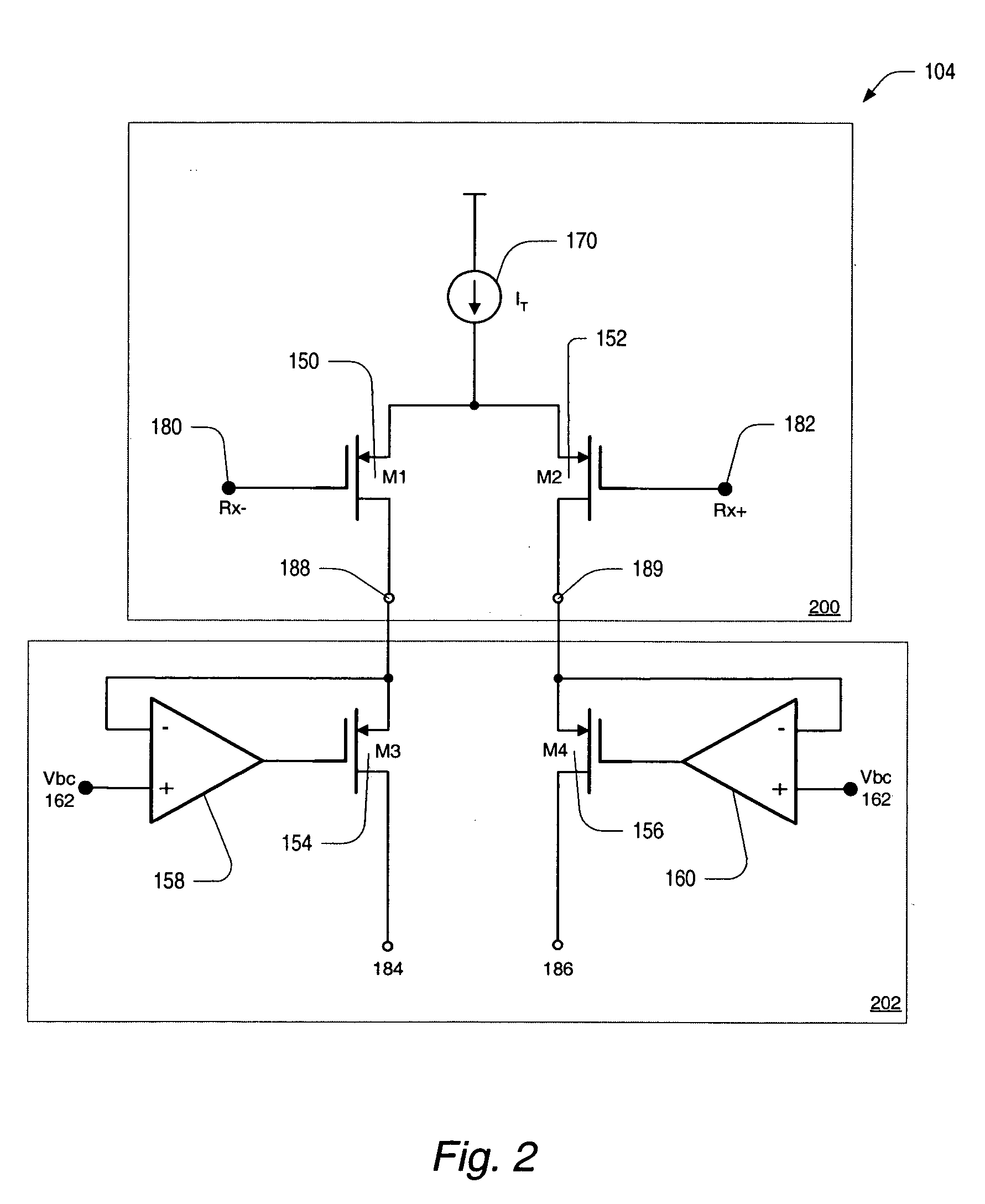
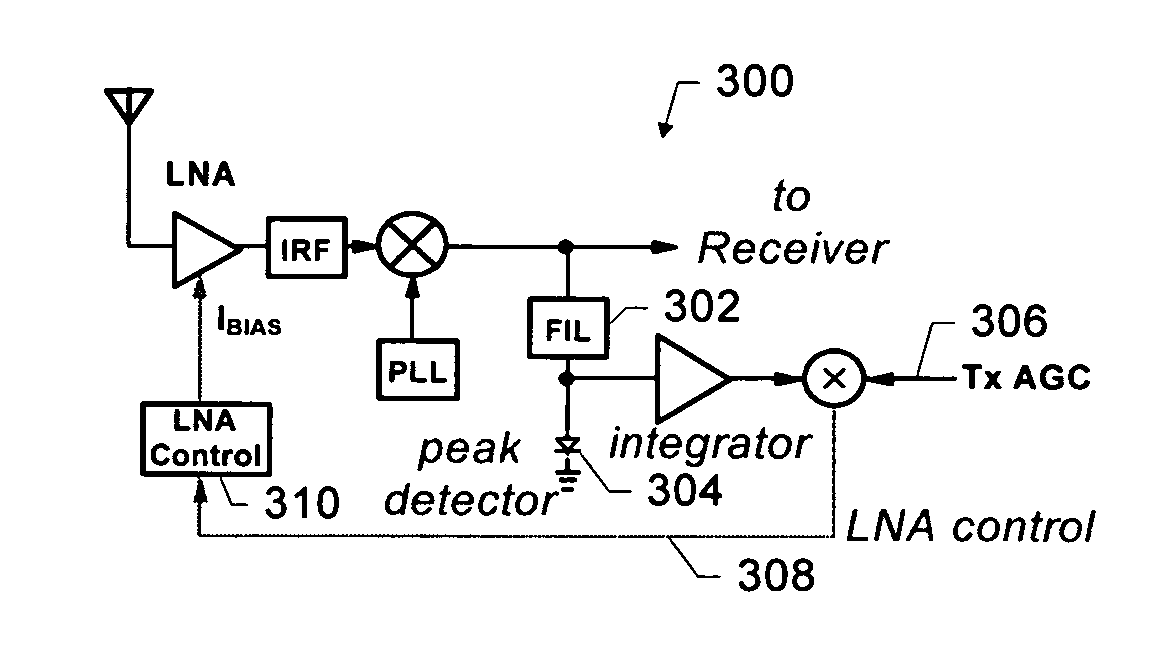
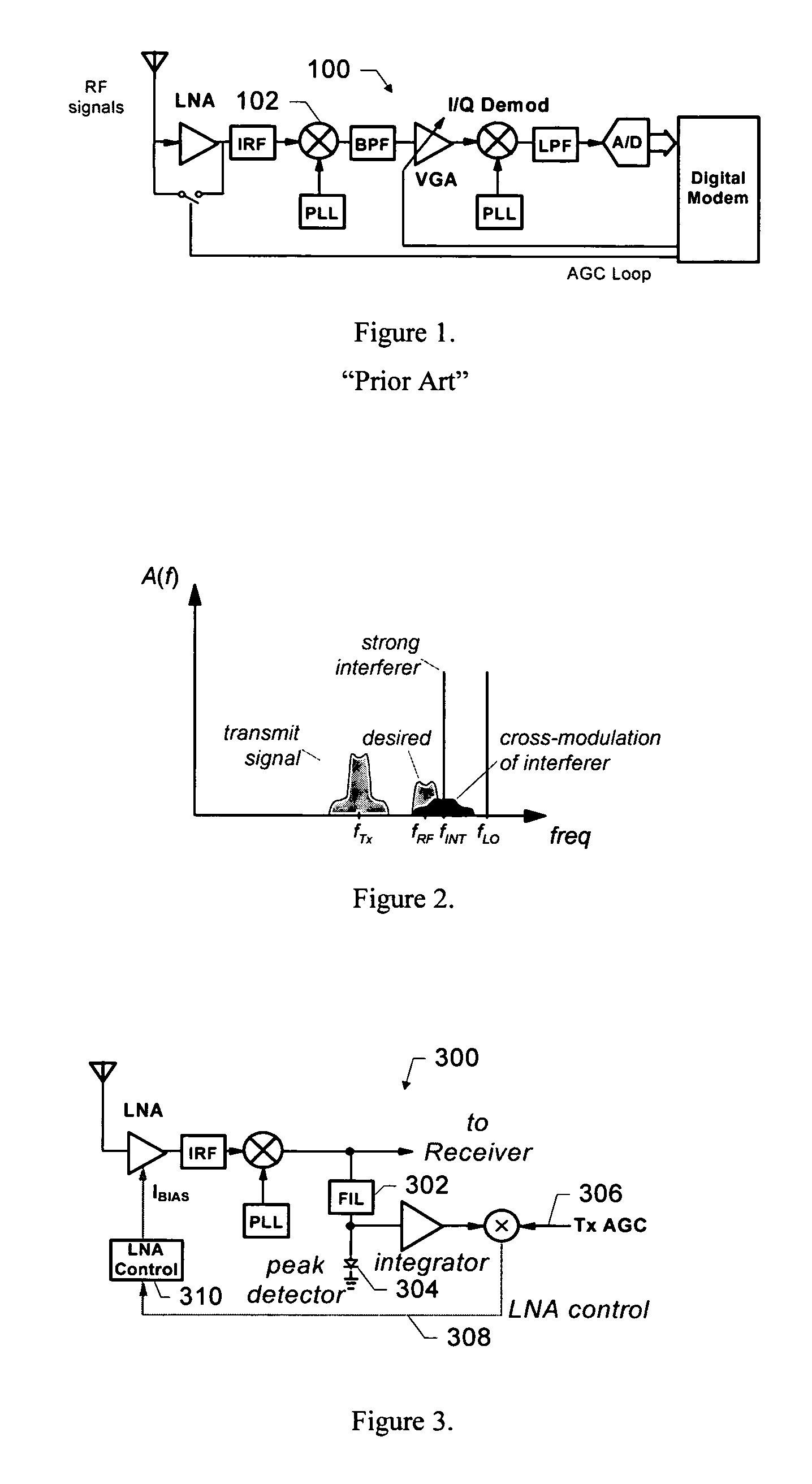
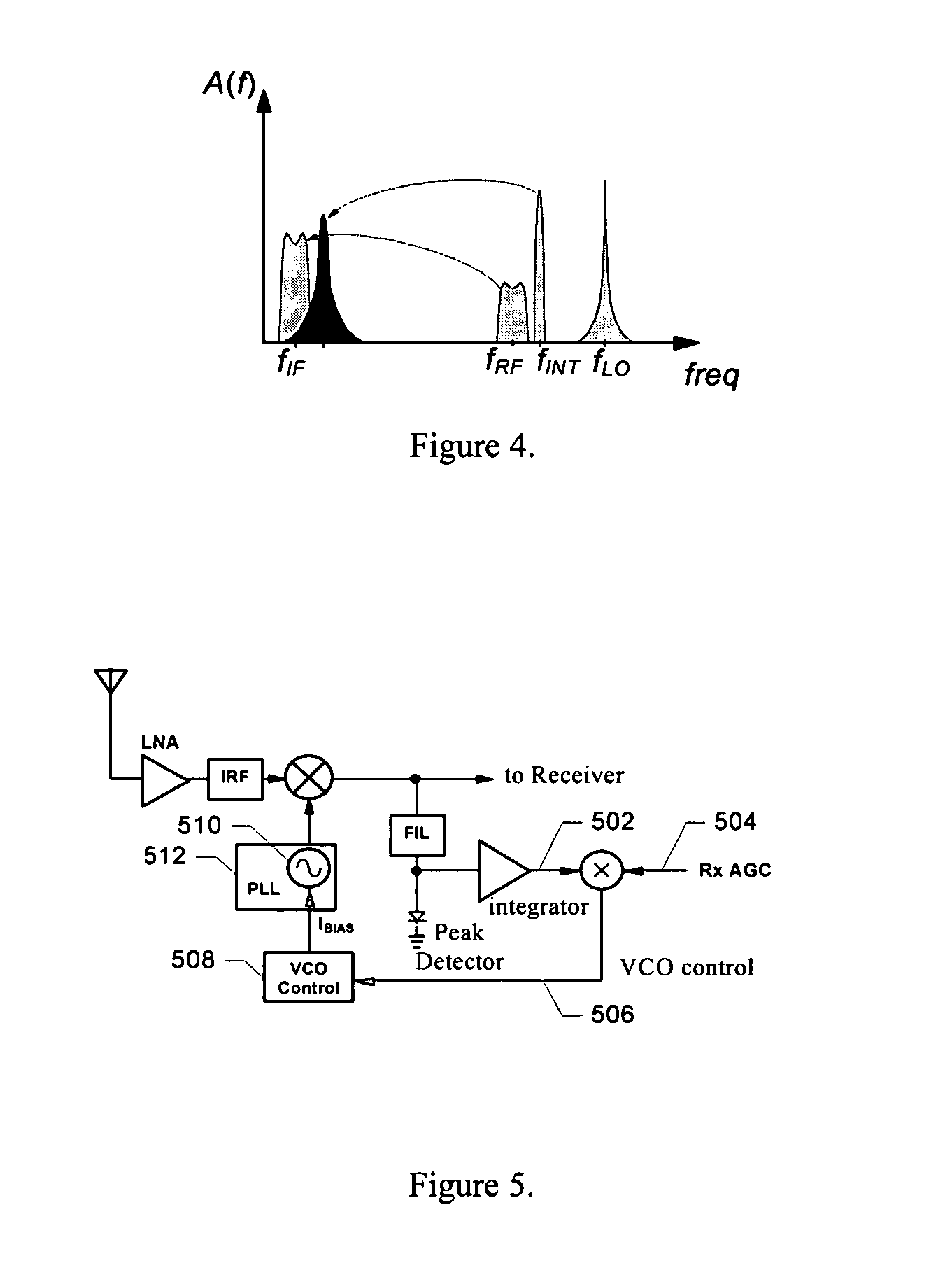
Adaptive receiver system that adjusts to the level of interfering signals. An adaptive system is provided for use with a radio receiver to adapt to interfering signals associated with a received RF signal. The radio receiver includes a LNA to receive the RF signal and produce an amplified signal that is coupled to a down-converting mixer that produces a mixer output. A peak detector is coupled to receive the mixer output to produce a peak signal. An integrator is coupled to the peak detector to receive the peak signal and produce an integrated signal and a mixer is coupled to receive the integrated signal and a transmit power indicator to produce a current control signal that is coupled to the LNA. The current control signal is used to control a bias current of the LNA, so that cross modulation associated with the received RF signal is reduced.
Owner:NXP BV
Direct conversion receiver having a low pass pole implemented with an active low pass filter
ActiveUS7062248B2Reduce component countLow costDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationTransceiverLow-pass filter
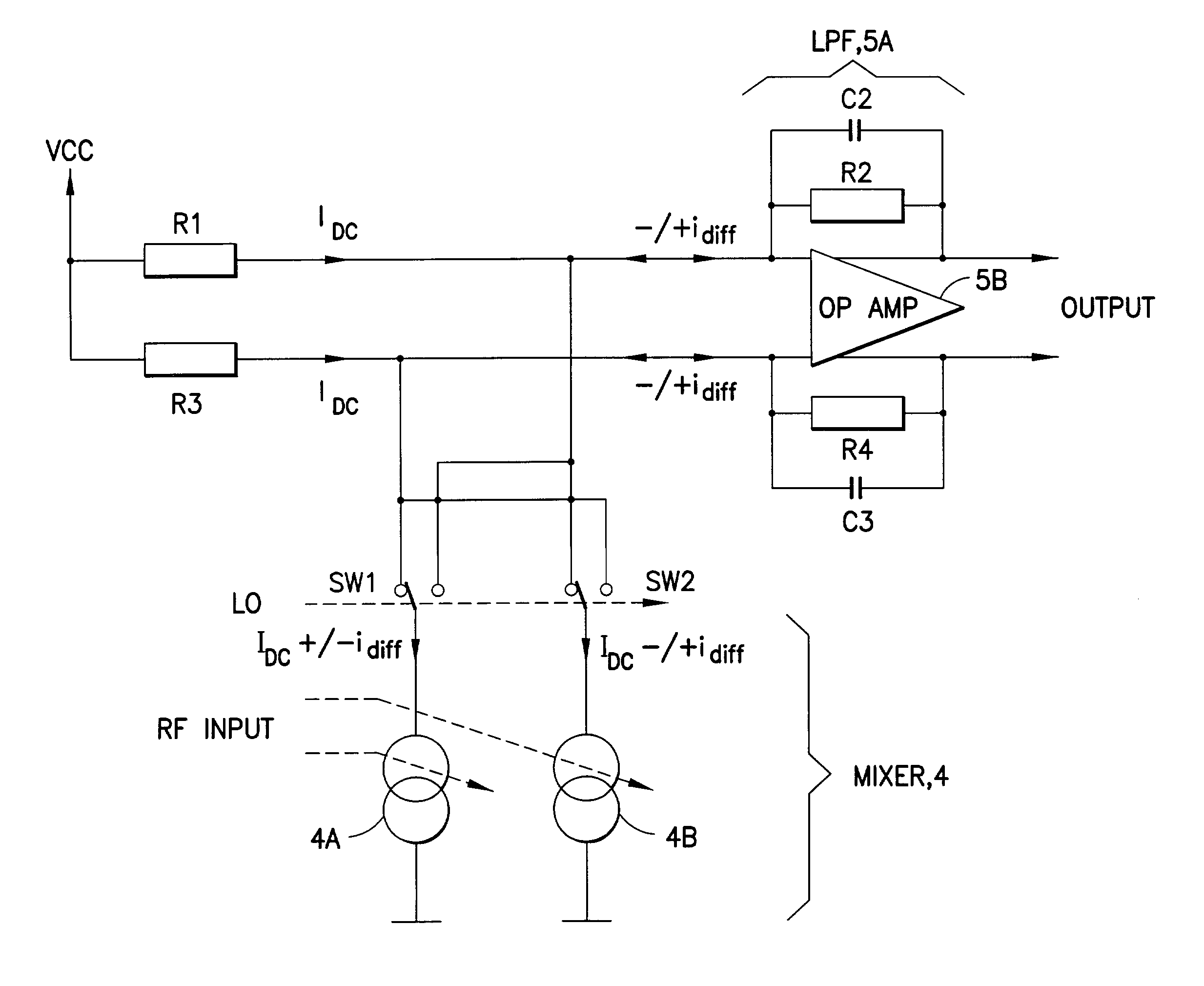
A wireless communications mobile station (10) includes at least one antenna (240) and a RF transceiver (210,220) containing a direct conversion receiver (1) coupled to the antenna. The direct conversion receiver contains a low noise amplifier (3) for amplifying a received RF signal and for outputting the amplified RF signal to a current switching down-conversion mixer (4). The down-conversion mixer has a first input node for receiving the amplified RF signal, a second input node for receiving a local oscillator (LO) signal for mixing with the amplified RF signal and an output node coupled to an input of an operational amplifier forming a low pass filter (5A). In accordance with an aspect of this invention the low pass filter has a low pass pole generated by a resistor R and a capacitor C coupled in parallel in a feedback path of the operational amplifier, where a low pass comer frequency of the low pass filter is inversely proportional to the product of R and C. In a preferred embodiment at least the down-conversion mixer and the low pass filter are implemented as part of an integrated circuit, and the resistor and the capacitor are fabricated within the integrated circuit.
Owner:HMD GLOBAL
Radio frequency automatic gain control amplifier
ActiveCN102868369AReduce signal to noise ratioSimple designAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow-pass filterIntermediate frequency
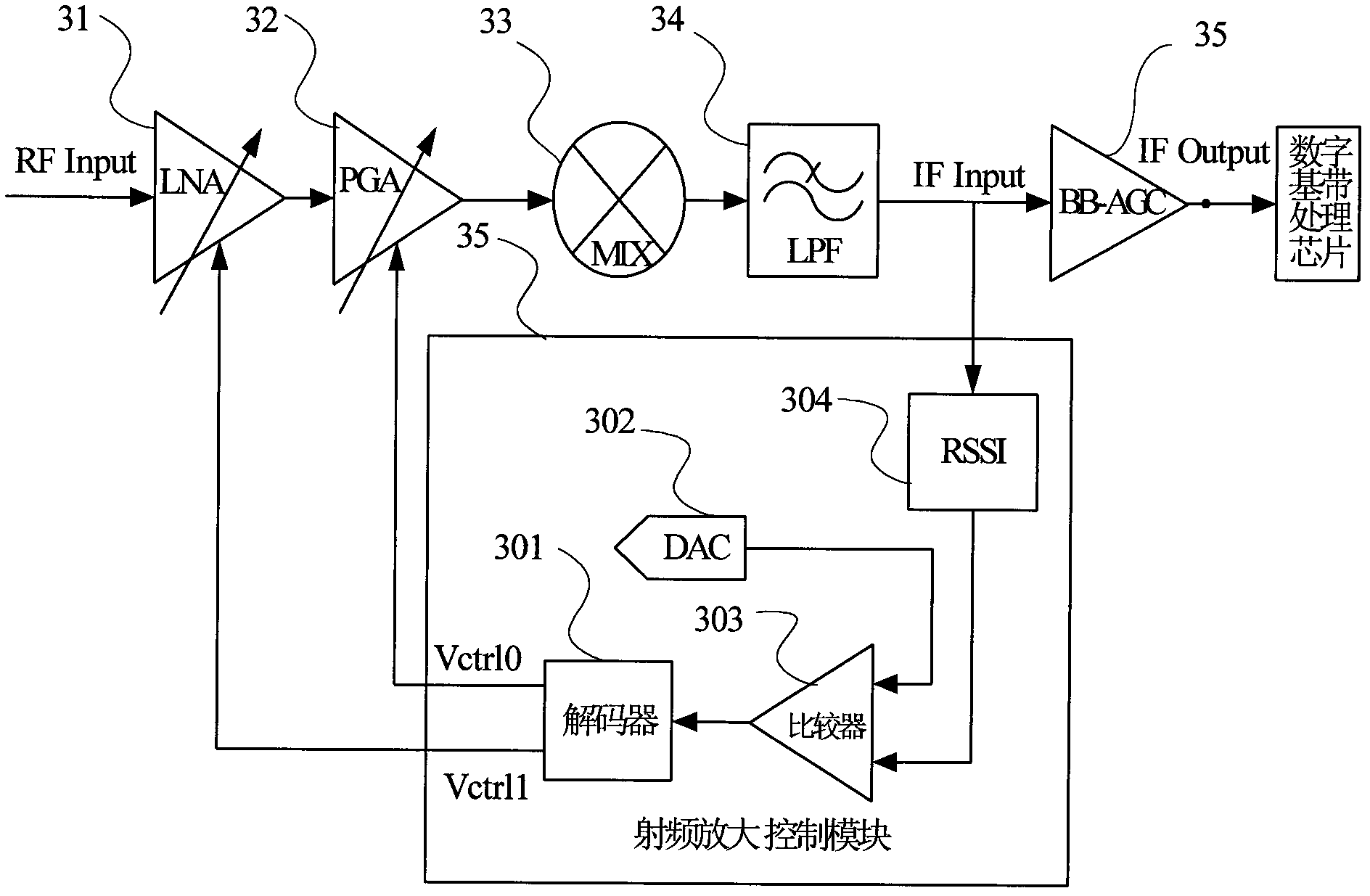
The invention discloses a radio frequency automatic gain control amplifier. The radio frequency automatic gain control amplifier comprises a radio frequency receiving unit, a radio frequency amplifier control unit and an intermediate frequency amplifier, wherein the radio frequency receiving unit is composed of an adjustable low noise amplifier (LNA), a programmable gain amplifier (PGA), a down-conversion frequency mixer and a low-pass filter; the radio frequency amplifier control unit comprises a signal strength detector, a DAC (digital-to-analog converter), a comparator and a decoder; the signal strength detector is used for detecting the strength of an intermediate frequency signal; a comparator circuit is used for comparing an output signal of the signal strength detector with a fixed comparing level output from the DAC so as to output a comparison result; the decoder is used for inputting the comparison result into a gain control digital module and outputting a digital control signal so as to carry out the feedback control to the signal at the front end of the radio frequency, so that the gains of the LNA and the PGA are controlled, the signal to noise ratio of a receiving system is increased, and the requirements on dynamic ranges and high linearity of an input signal are met. The automatic gain control amplifier can be used in various radio frequency receiving chips flexibly, and particularly is applicable to radio frequency front-end circuit which has a wider input range of a radio frequency signal.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Receiver system and method for receiver testing
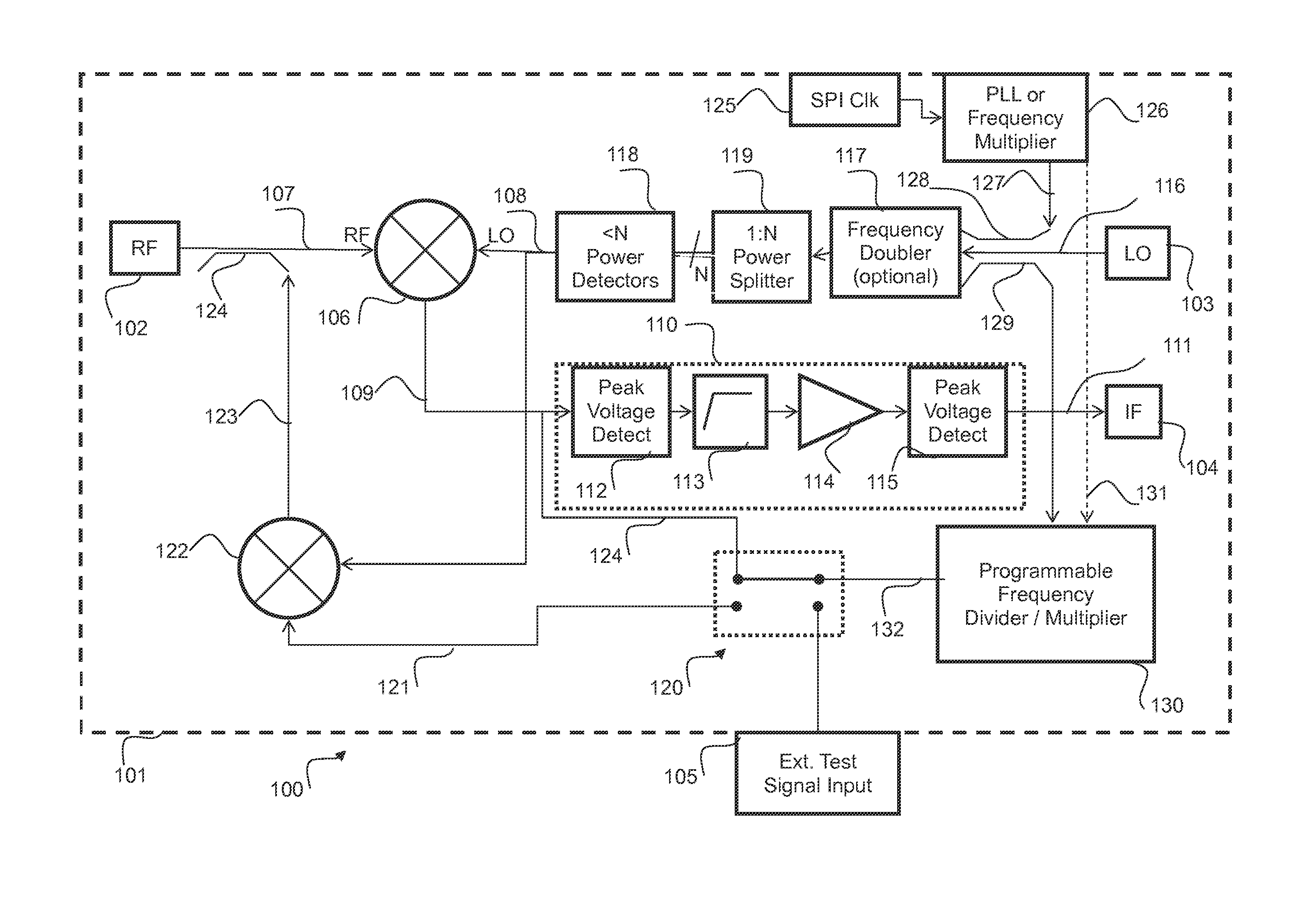
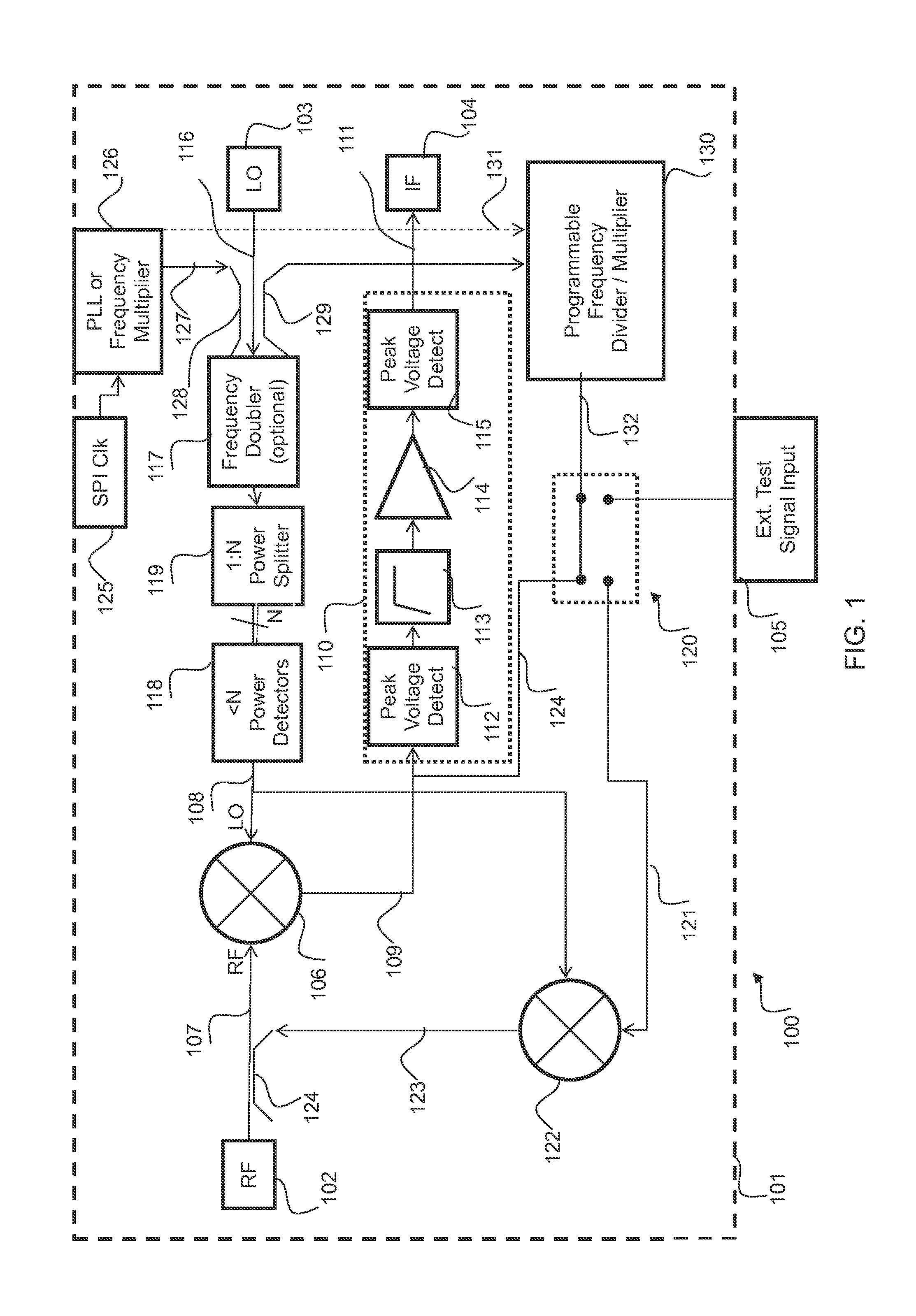
InactiveUS20160077196A1Receivers monitoringRadiofrequency circuit testingOn boardDown conversion mixer
A receiver system which may be implemented in an integrated circuit device and suitable for use in automotive radar systems such as collision avoidance systems, includes self test circuitry whereby a local oscillator test signal is generated by an on-board frequency multiplier and mixed in a down-conversion mixer with an RF test signal. The RF test signal is generated on the device by up-conversion of an externally generated low-frequency test signal with the local oscillator test signal. Baseband components may also be checked using test signals of suitable frequency divided down from the local oscillator test signal by a programmable frequency divider. This self test arrangement obviates any need for applying externally generated RF test signals to the IC device.
Owner:NXP USA INC
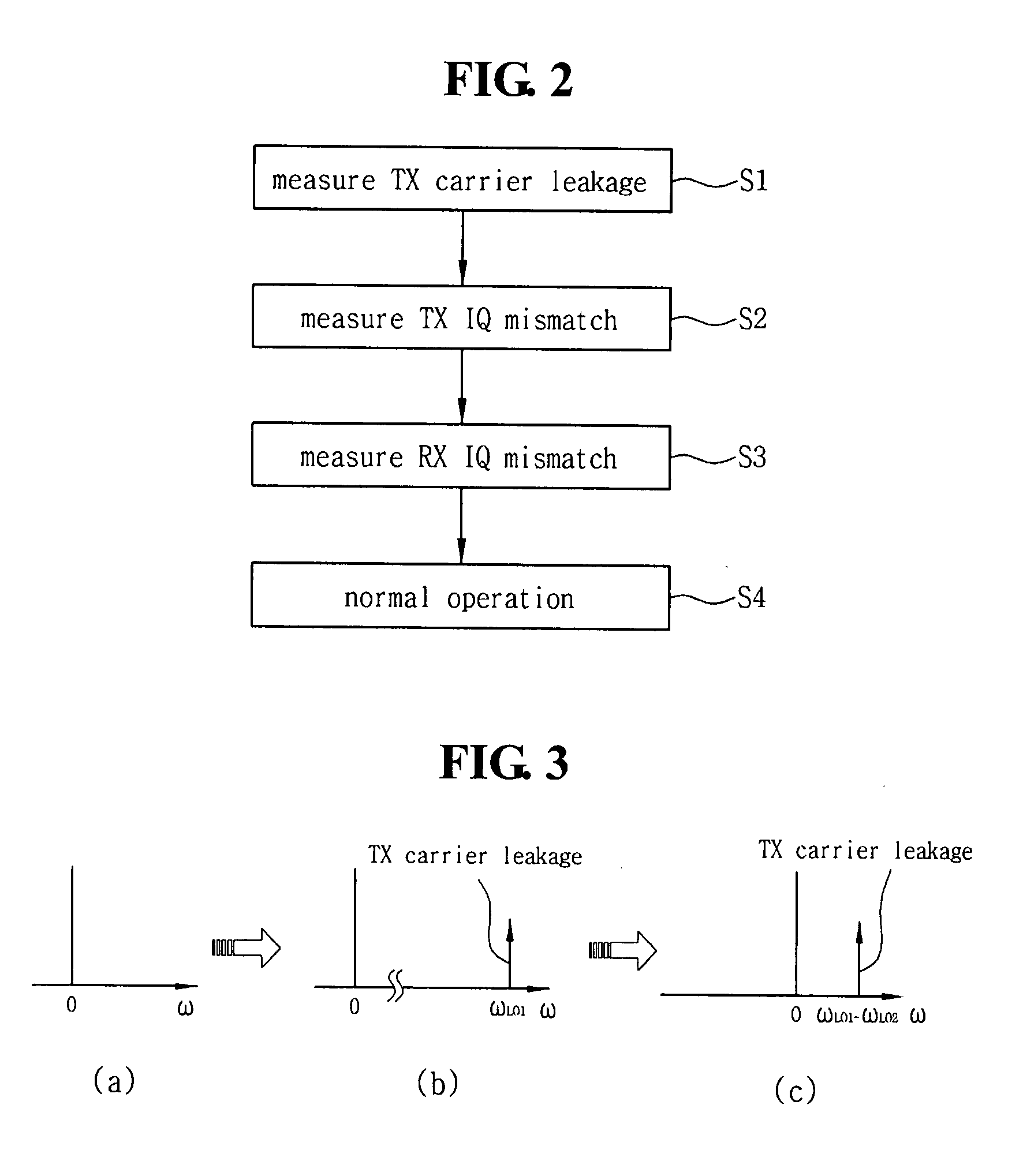
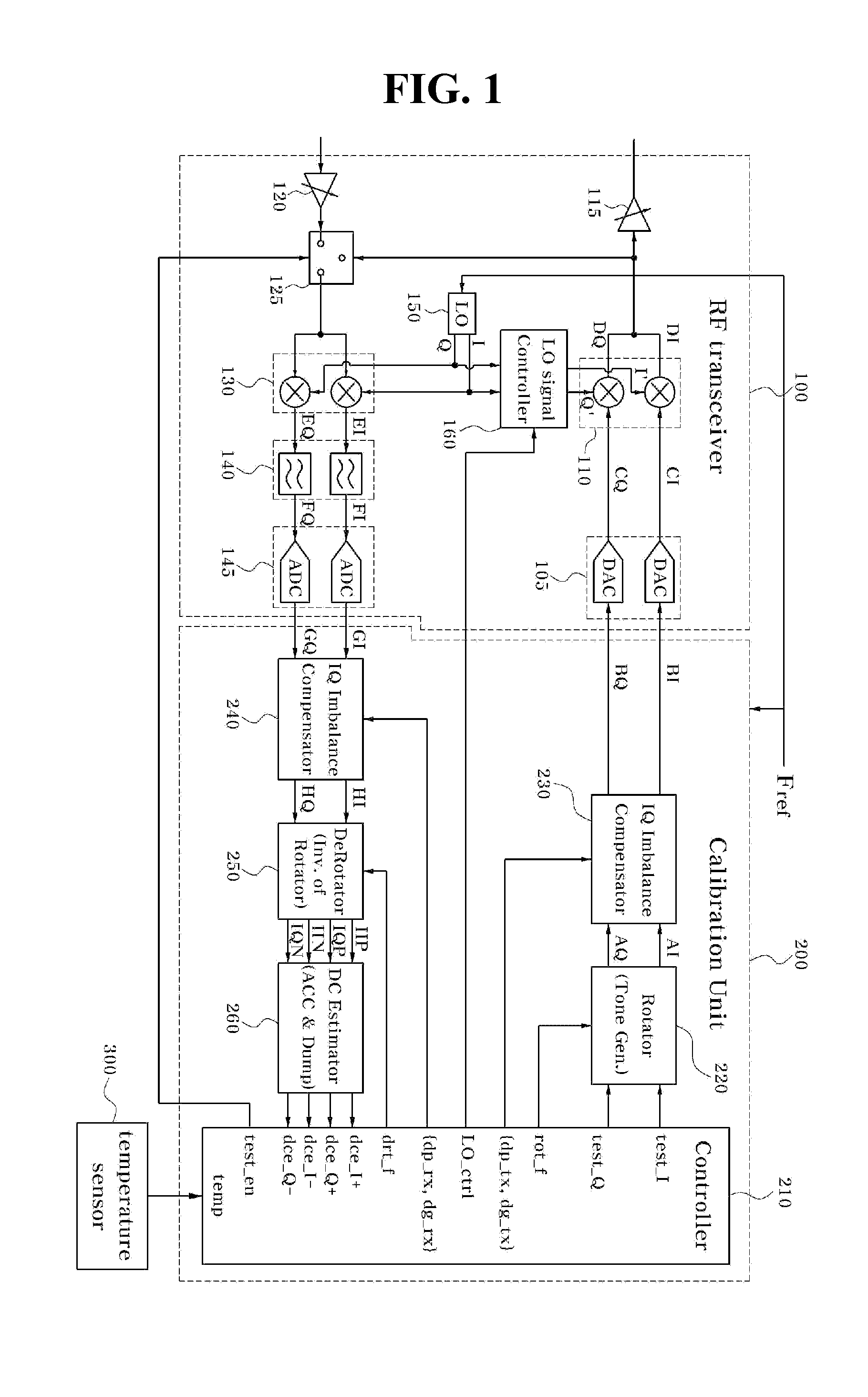
Tranceiver circuit for compensating IQ mismatch and carrier leakage and method for controlling the same
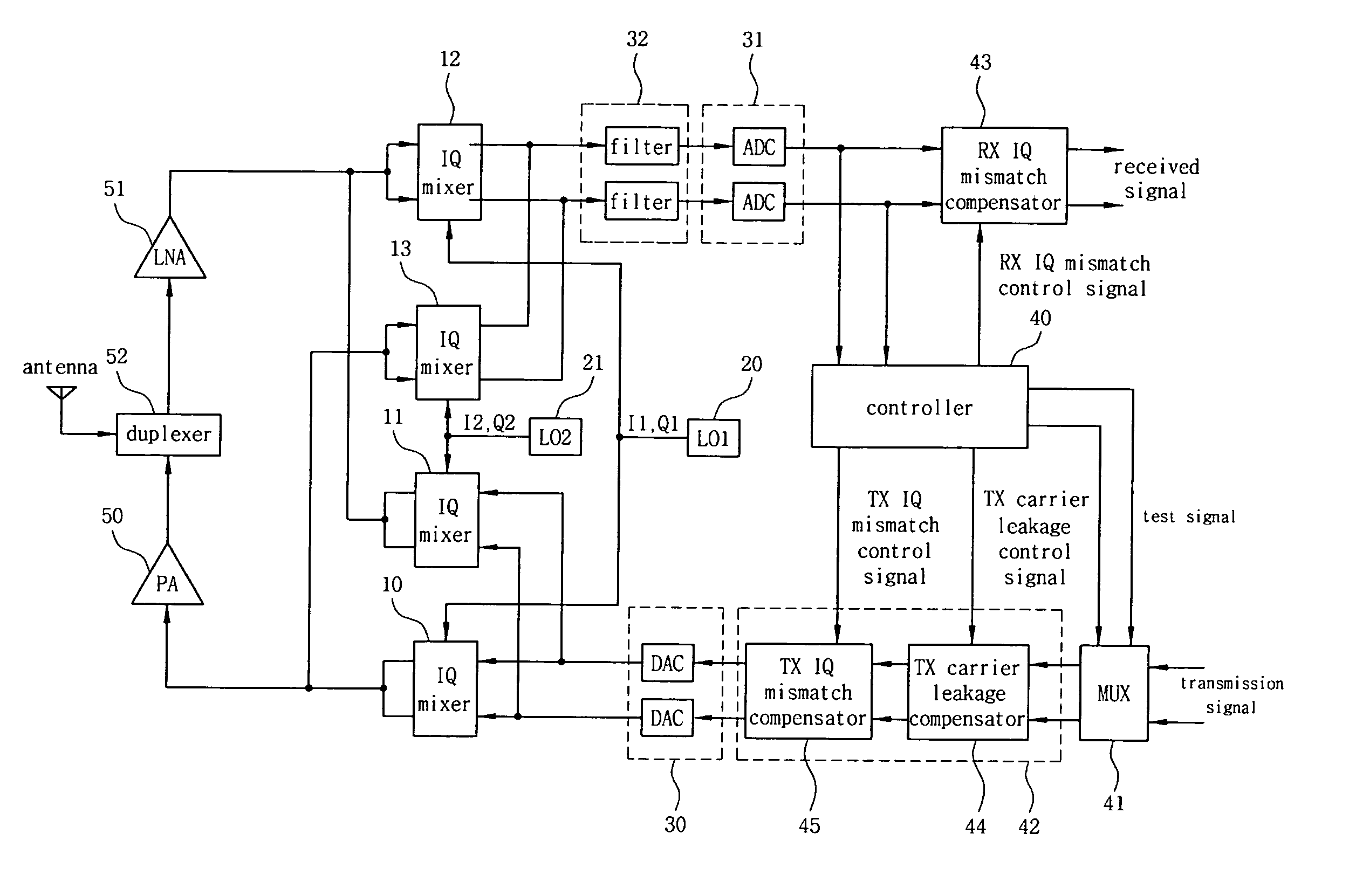
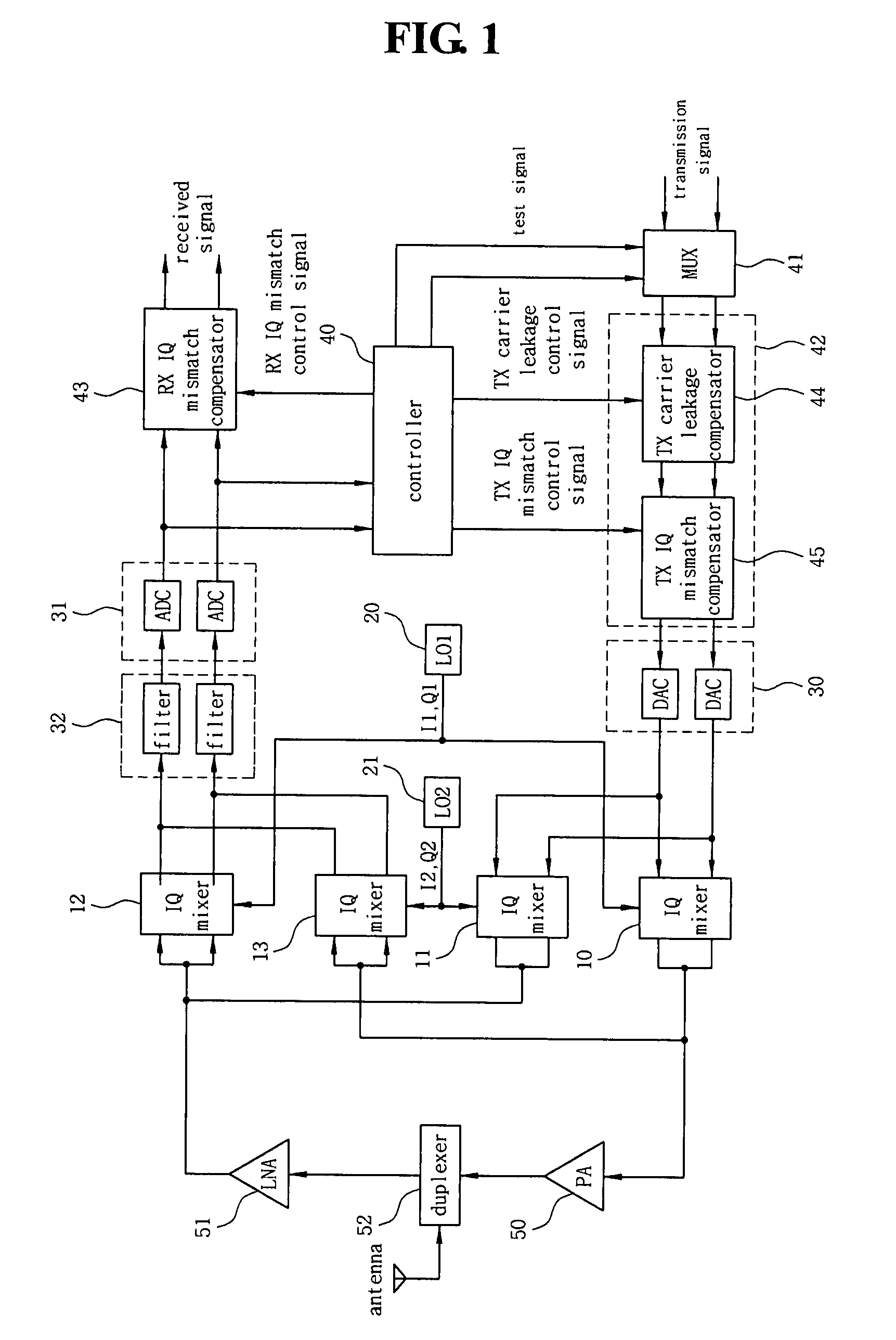
ActiveUS20070202812A1Improve efficiencyReduce measurement errorResonant long antennasAngle modulationTransceiverTelecommunications
Embodiments of methods, transceiver circuits, and systems can compensate an IQ mismatch (e.g., Tx or Rx) or a carrier leakage using a plurality of local oscillators. One embodiment of a transceiver can include a first up-conversion IQ mixer, a second up-conversion IQ mixer, a first down-conversion IQ mixer with an input to receive an output of the second up-conversion IQ mixer, a second down-conversion IQ mixer with an input to receive an output of the first up-conversion IQ mixer, a first local oscillator to generate a first IQ LO signal for the first up-conversion IQ mixer and the first down-conversion IQ mixer, and a second local oscillator to generate a second IQ LO signal for the second up-conversion IQ mixer and the second down-conversion IQ mixer.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Apparatus for and method of optimizing the performance of a radio frequency receiver in the presence of interference
InactiveUS20060040630A1Improve linearityIncrease flexibilityGain controlAmplifier combinationsFrequency mixerMode control
An apparatus for and method of extending the dynamic range of a RF communications receiver. The invention provides a mechanism for controlling the gain of both the LNA and down conversion mixer in the front end portion of an RF receiver. Both the LNA and the mixer are adapted to have both low and high gain modes of operation. The control mechanism typically comprises a two bit gain control that places both the LNA and mixer in one of four operating gain mode states. The selection of the most appropriate operating gain mode state, is preferably determined in accordance with various metrics such as the received levels of the desired signal, levels of interference signals, bit error rate and receiver RSSI.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Beam steerable communication apparatus
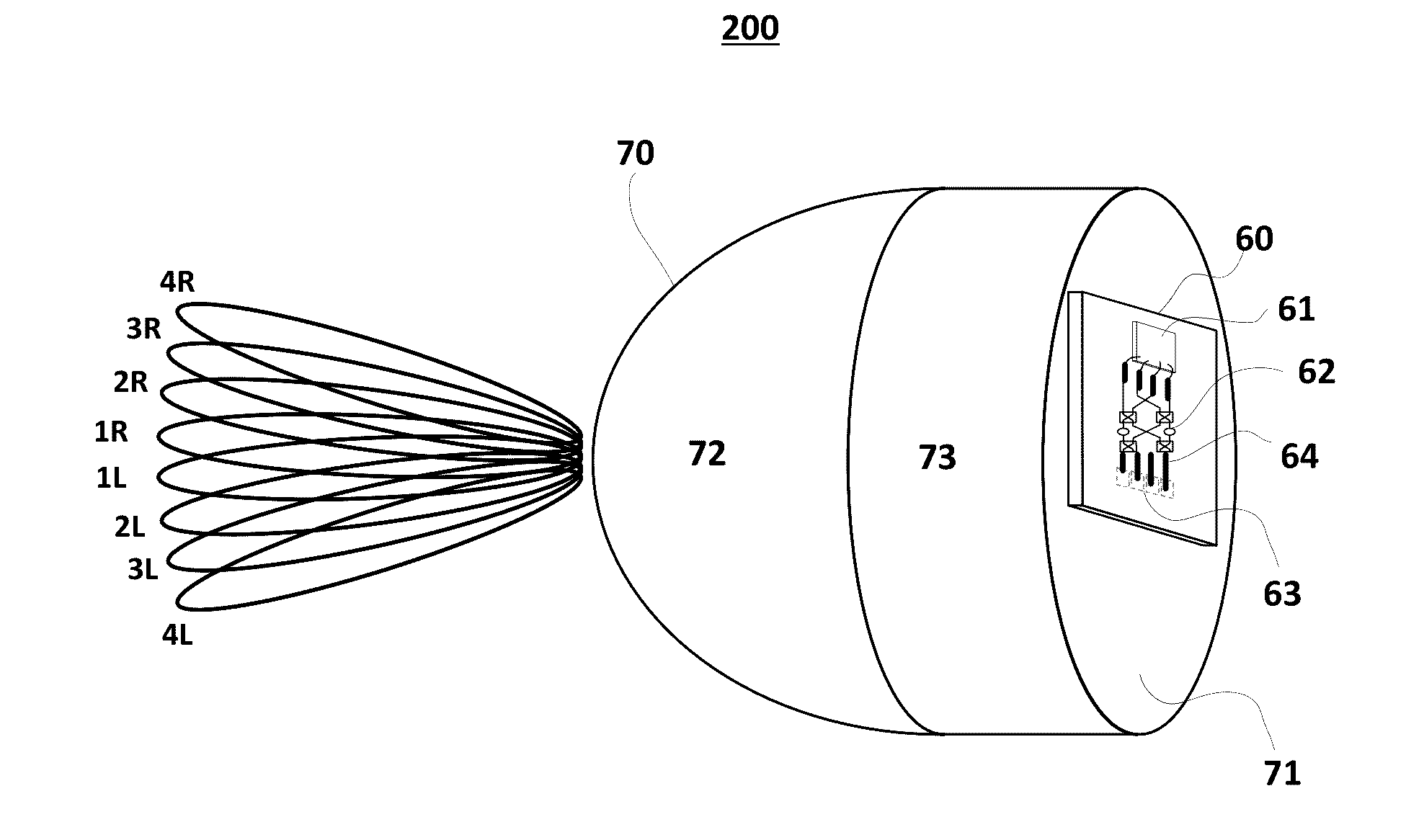
ActiveUS20170062948A1Improve dynamic rangeIncrease lossSpatial transmit diversityAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverModem device
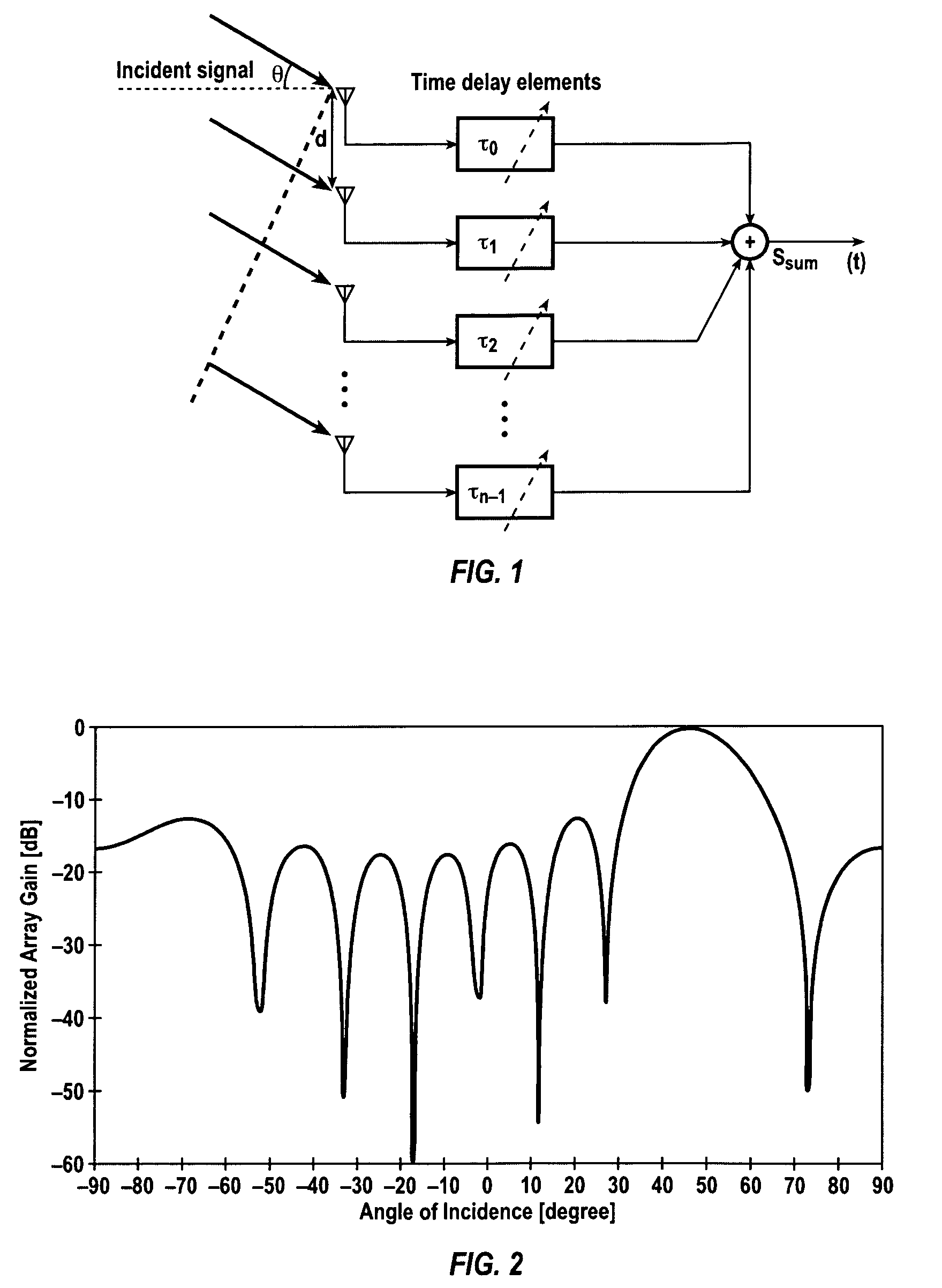
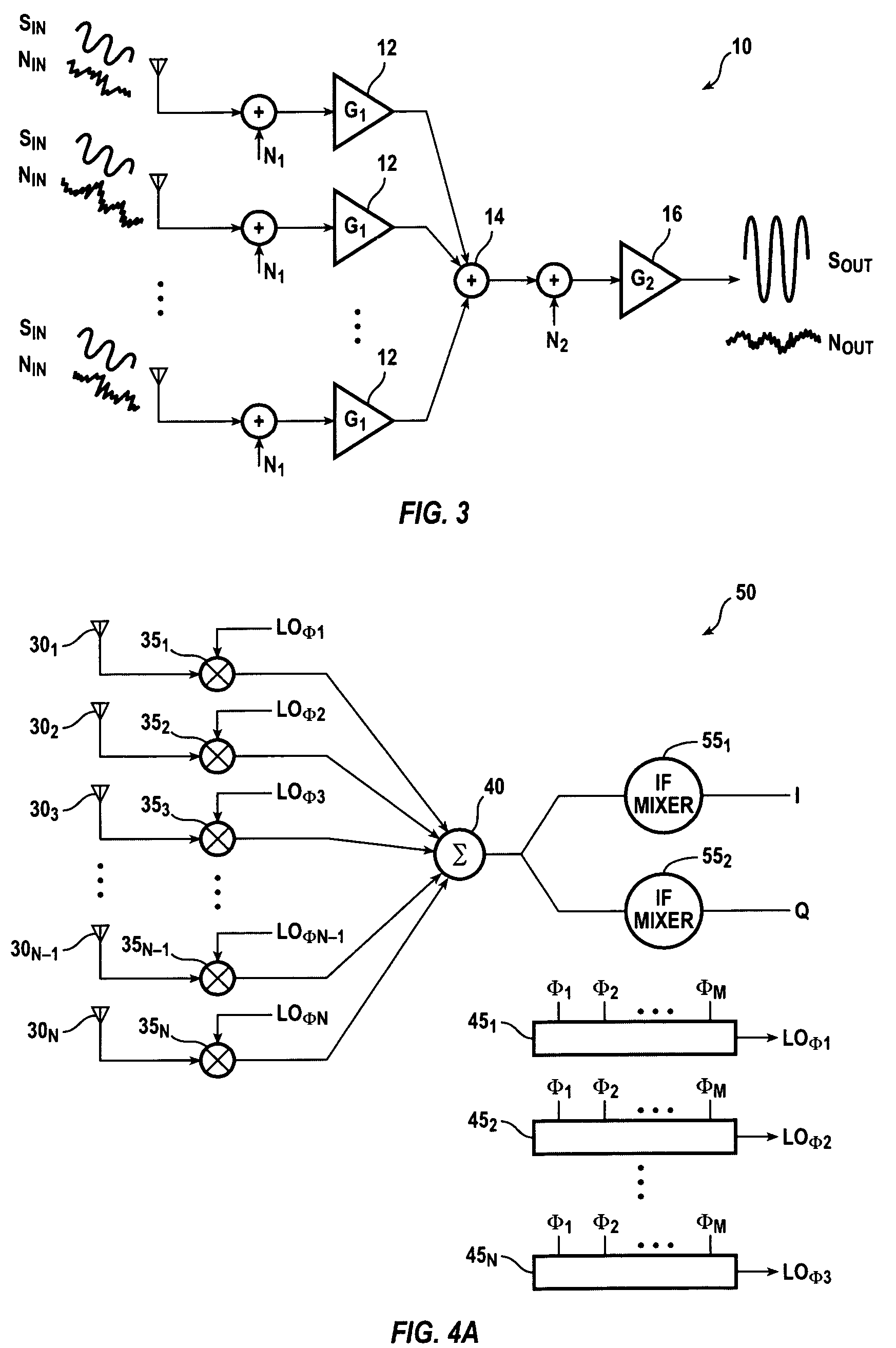
Disclosed is a beam steerable communication apparatus comprising a focusing element with a focal plane, a plurality of antenna elements disposed on the focal plane of the focusing element, a beamforming network which has a plurality of antenna ports and a plurality of beamforming ports, at least one radio frequency transceiver capable to control the phase of carrier frequency signals on its independent outputs, and a baseband modem, wherein each antenna port of the beamforming network is coupled to at least one antenna element, each beamforming port of the beamforming network is coupled to an independent transceiver output, and the phase distribution law formed on the beamforming ports is determined by a baseband modem control commands to the transceivers, said phase distribution law is to combine or distribute signal power on all beamforming ports from or to at least one antenna port of the beamforming network, wherein each radio frequency transceiver includes at least a phase shifter, a Tx / Rx switch, LNA, PA, up and down-conversion mixers, LO generation circuit, receive power combining and transmit power distribution schemes. The technical result of the invention is in the capability of providing efficient beam steering with high gain antennas with all the prospect features of phased antenna arrays, such as the ability to combine / distribute signal power between several RF amplifiers, thus, facilitating linearity requirements and increasing an output power of a transmitter. The present invention can be used, without limitations, in radio relay point-to-point communication systems, e.g. for forming backhaul networks of cellular mobile communication, in car radars and other radars, in local and personal communication systems, in satellite and intersatellite communication systems, etc.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification reader transceiver
ActiveUS7583179B2Electric signal transmission systemsError preventionDigital signal processingTransceiver
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Monolithic silicon-based phased arrays for communications and radars
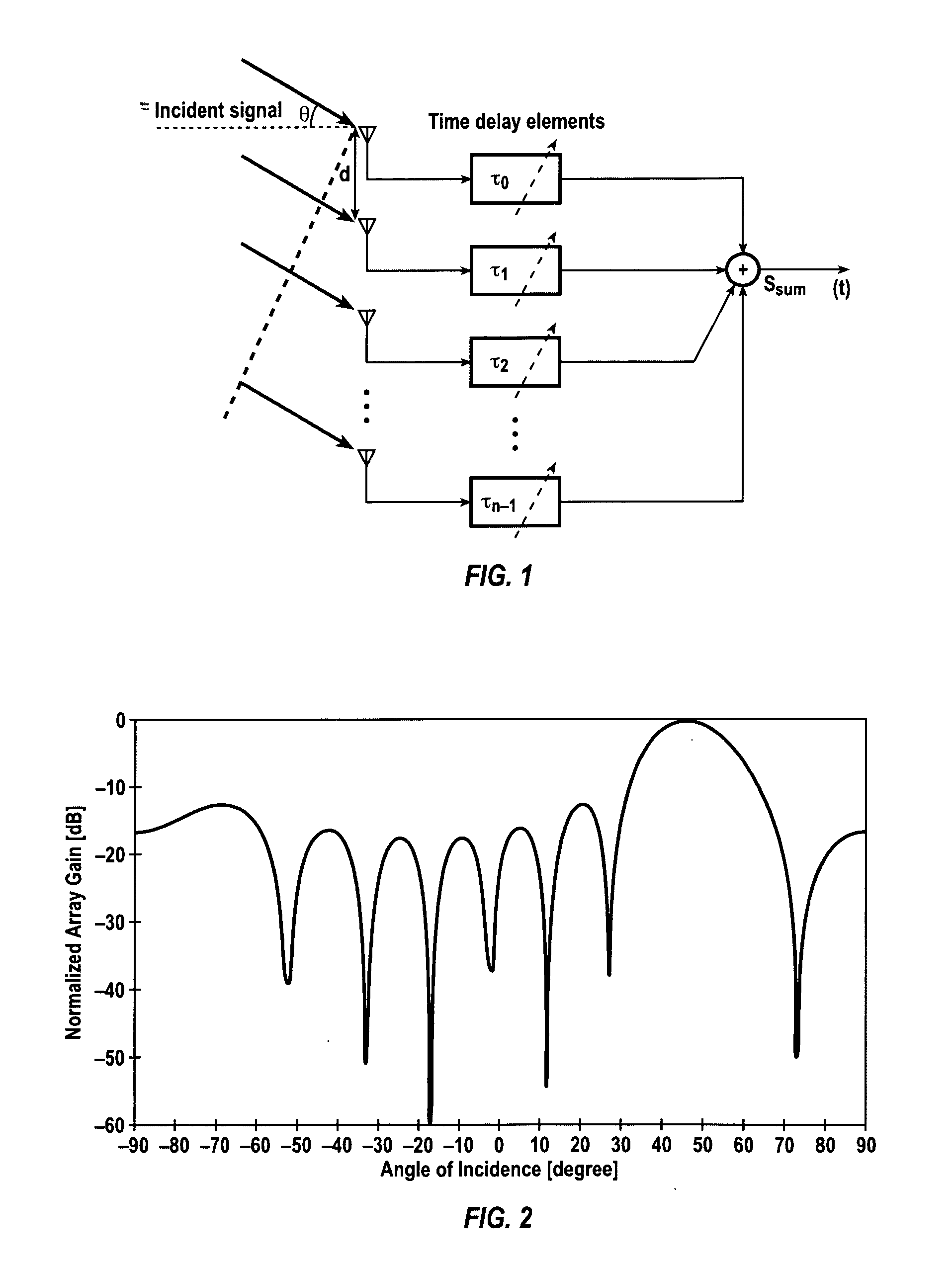
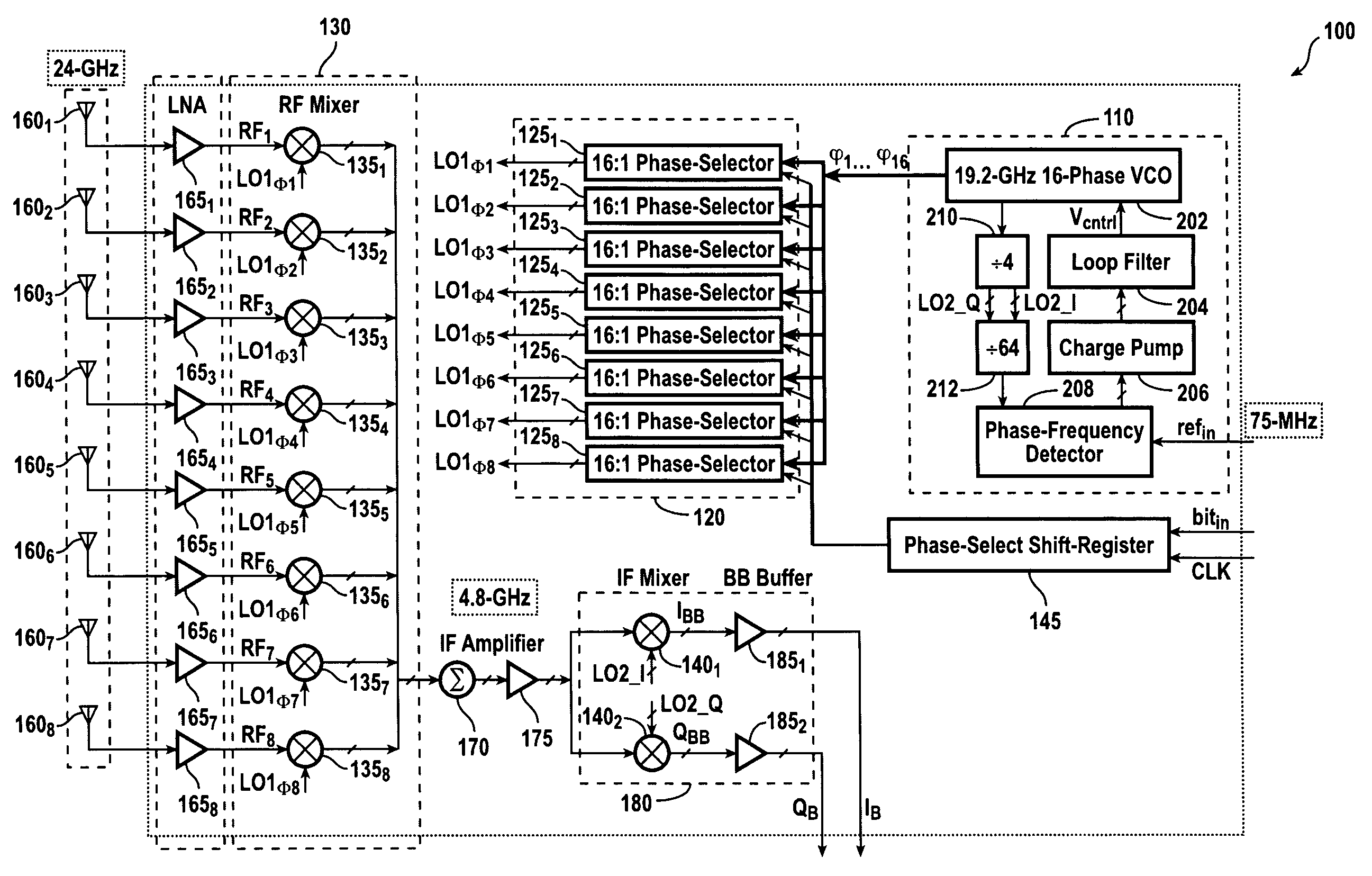
A phased-array receiver is adapted so as to be fully integrated and fabricated on a single silicon substrate. The phased-array receiver is operative to receive a 24 GHz signal and may be adapted to include 8-elements formed in a SiGe BiCMOS technology. The phased-array receiver utilizes a heterodyne topology, and the signal combining is performed at an IF of 4.8 GHz. The phase-shifting with 4 bits of resolution is realized at the LO port of the first down-conversion mixer. A ring LC VCO generates 16 different phases of the LO. An integrated 19.2 GHz frequency synthesizer locks the VCO frequency to a 75 MHz external reference. Each signal path achieves a gain of 43 dB, a noise figure of 7.4 dB, and an IIP3 of −11 dBm. The 8-path array achieves an array gain of 61 dB, a peak-to-null ratio of 20 dB, and improves the signal-to-noise ratio at the output by 9 dB.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Circuit arrangement provided with a phase-locked loop and transmitter-receiver with said circuit arrangement
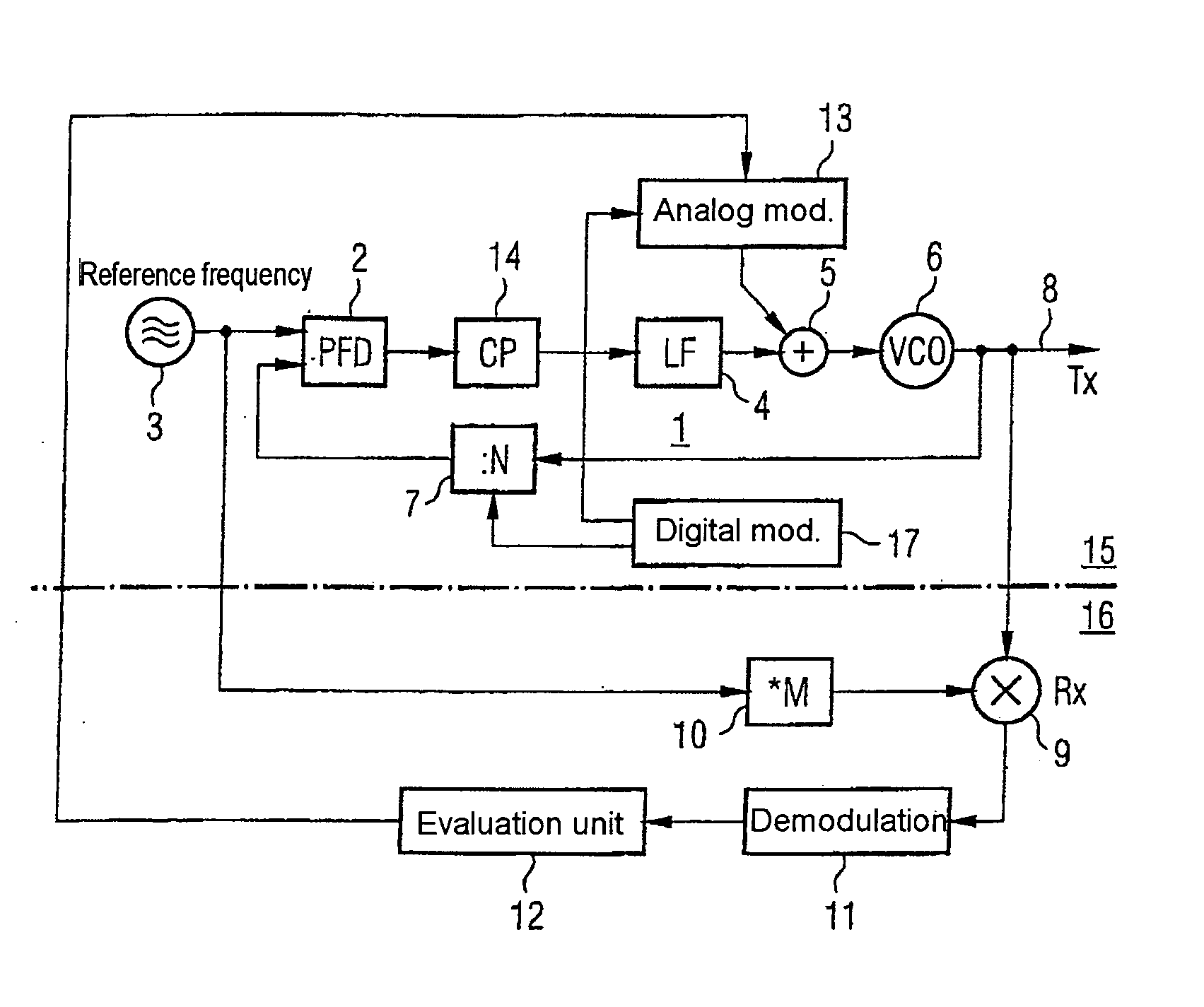
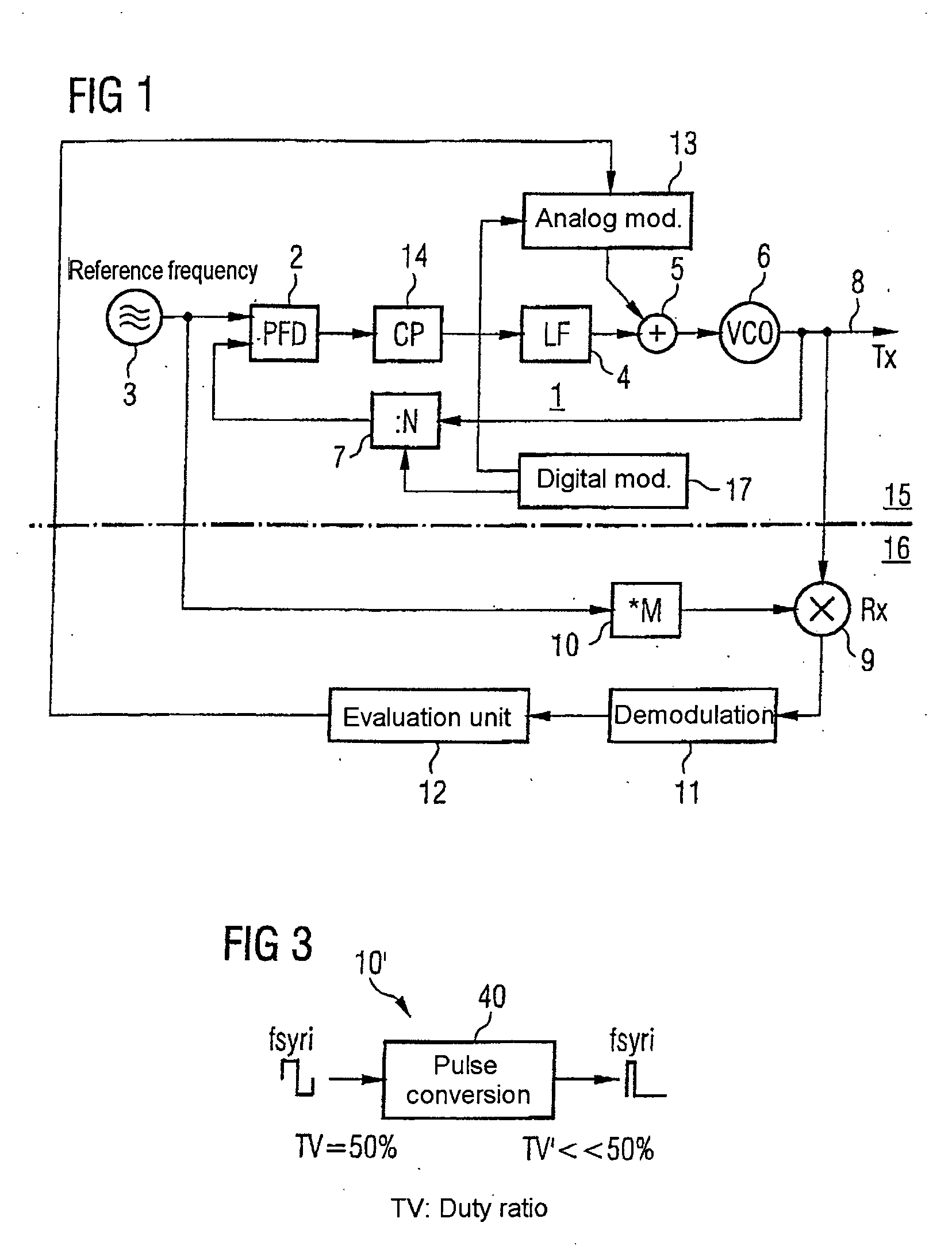
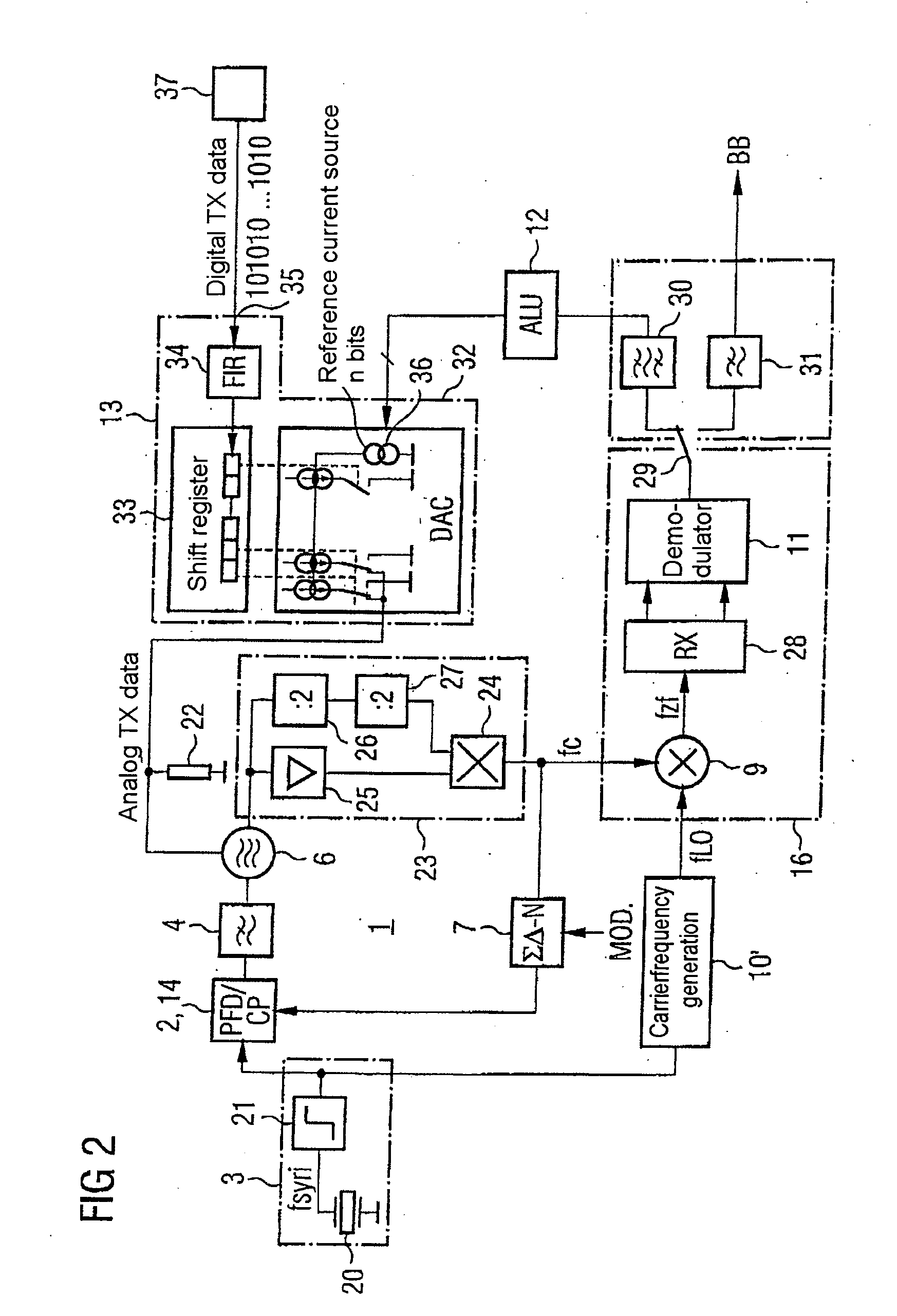
ActiveUS20050185749A1Simple processReduce the amplitudeAngle modulation detailsTransmissionIntermediate frequencyDown conversion mixer
The invention specifies a circuit arrangement with a phase locked loop (1), which can be used as a mobile radio transmitter, in particular. The reference frequency for the PLL (1), which is provided by means of the source (3), is multiplied by a multiplier (10) and is down-converted to an intermediate-frequency level in a down-conversion mixer (9) using the output signal from the PLL, and is evaluated such that a modulator (13) connected to the input of the oscillator (6) can be trimmed. The inventive principle is used to advantage in two-point modulators and allows inexpensive, integratable mobile radio transmitters with good noise characteristics.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Monolithic silicon-based phased arrays for communications and radars
A phased-array receiver is adapted so as to be fully integrated and fabricated on a single silicon substrate. The phased-array receiver is operative to receive a 24 GHz signal and may be adapted to include 8-elements formed in a SiGe BiCMOS technology. The phased-array receiver utilizes a heterodyne topology, and the signal combining is performed at an IF of 4.8 GHz. The phase-shifting with 4 bits of resolution is realized at the LO port of the first down-conversion mixer. A ring LC VCO generates 16 different phases of the LO. An integrated 19.2 GHz frequency synthesizer locks the VCO frequency to a 75 MHz external reference. Each signal path achieves a gain of 43 dB, a noise figure of 7.4 dB, and an IIP3 of −11 dBm. The 8-path array achieves an array gain of 61 dB, a peak-to-null ratio of 20 dB, and improves the signal-to-noise ratio at the output by 9 dB.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Adaptive wireless receiver
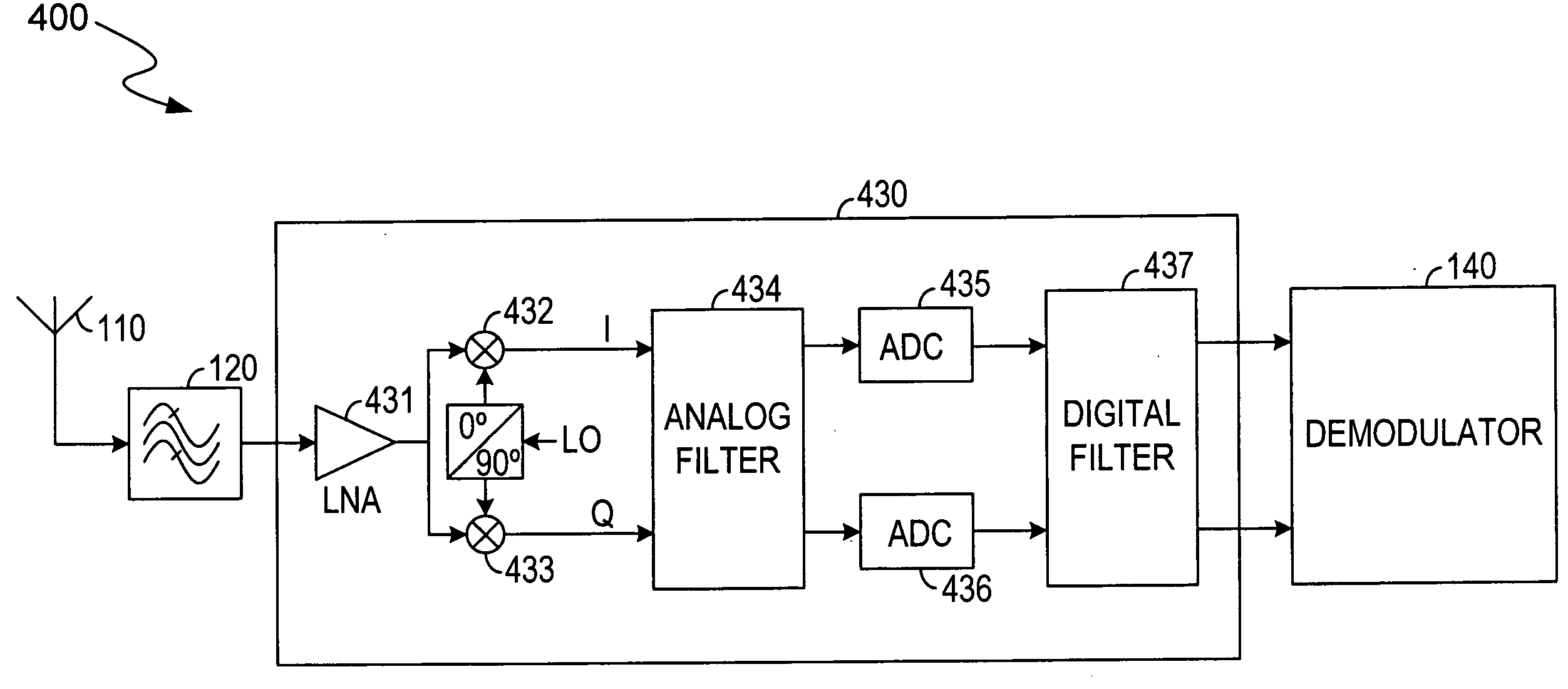
An adaptive wireless receiver and method thereof is disclosed in the present invention. The receiver includes an antenna, a bandpass filter, a front-end unit and a demodulator. Elements inside the front-end unit can be reused when the receiver operates in a zero intermediate frequency (ZIF) mode and in a low intermediate frequency (LIF) mode. The front-end unit includes a first and second down-conversion mixer, an analog filter, a first and second analog-to-digital converter (ADC), and a digital filter.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
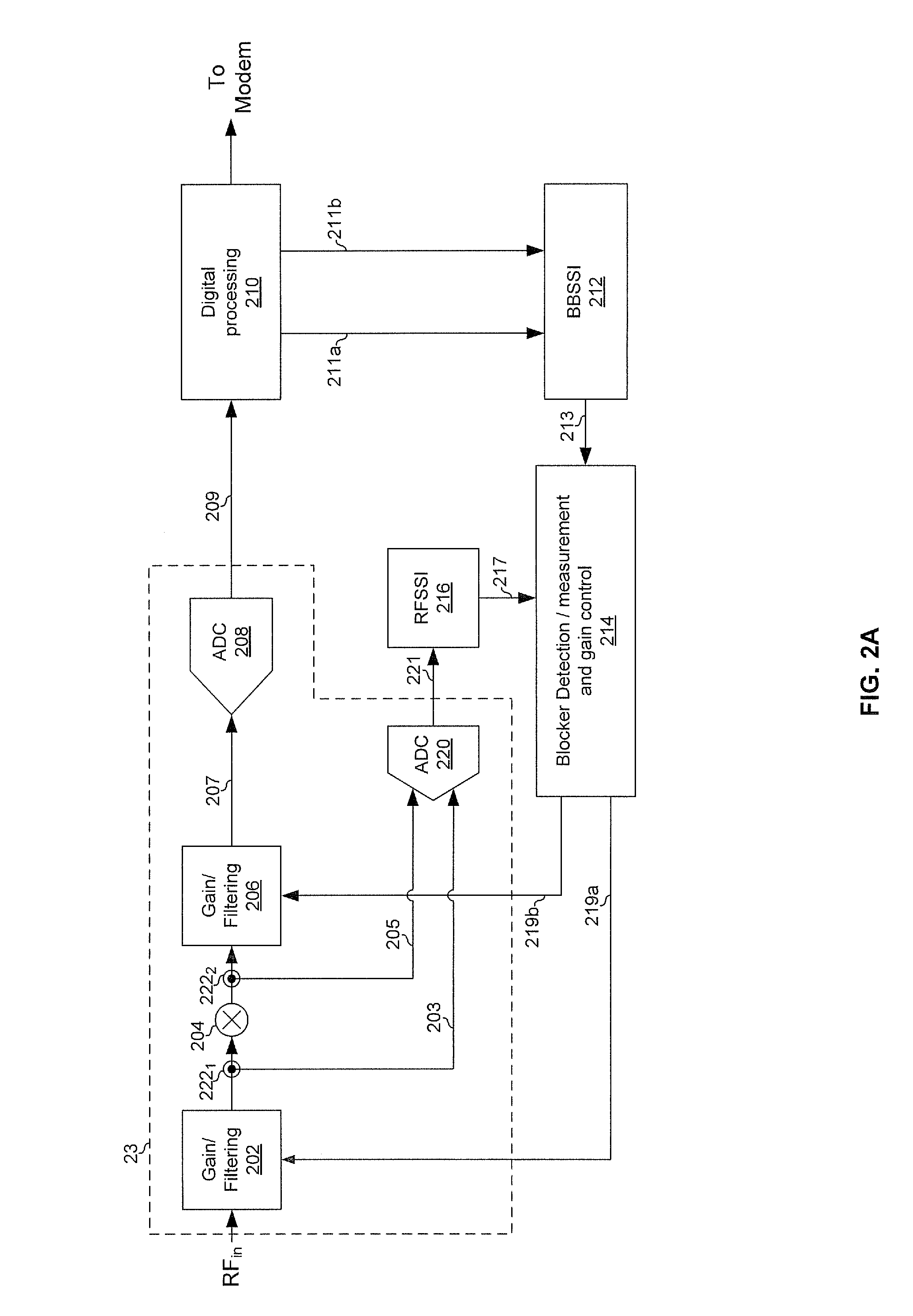
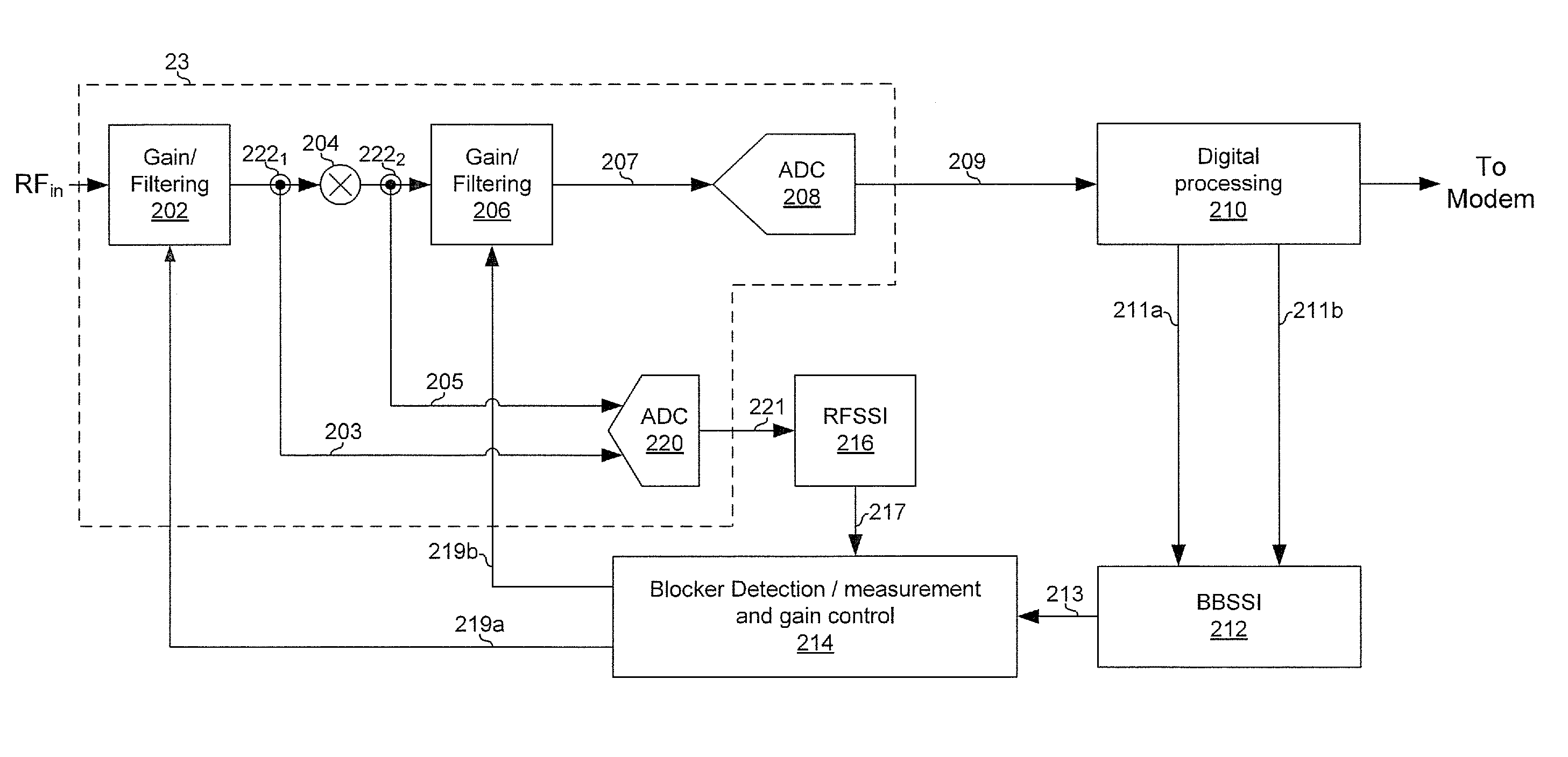
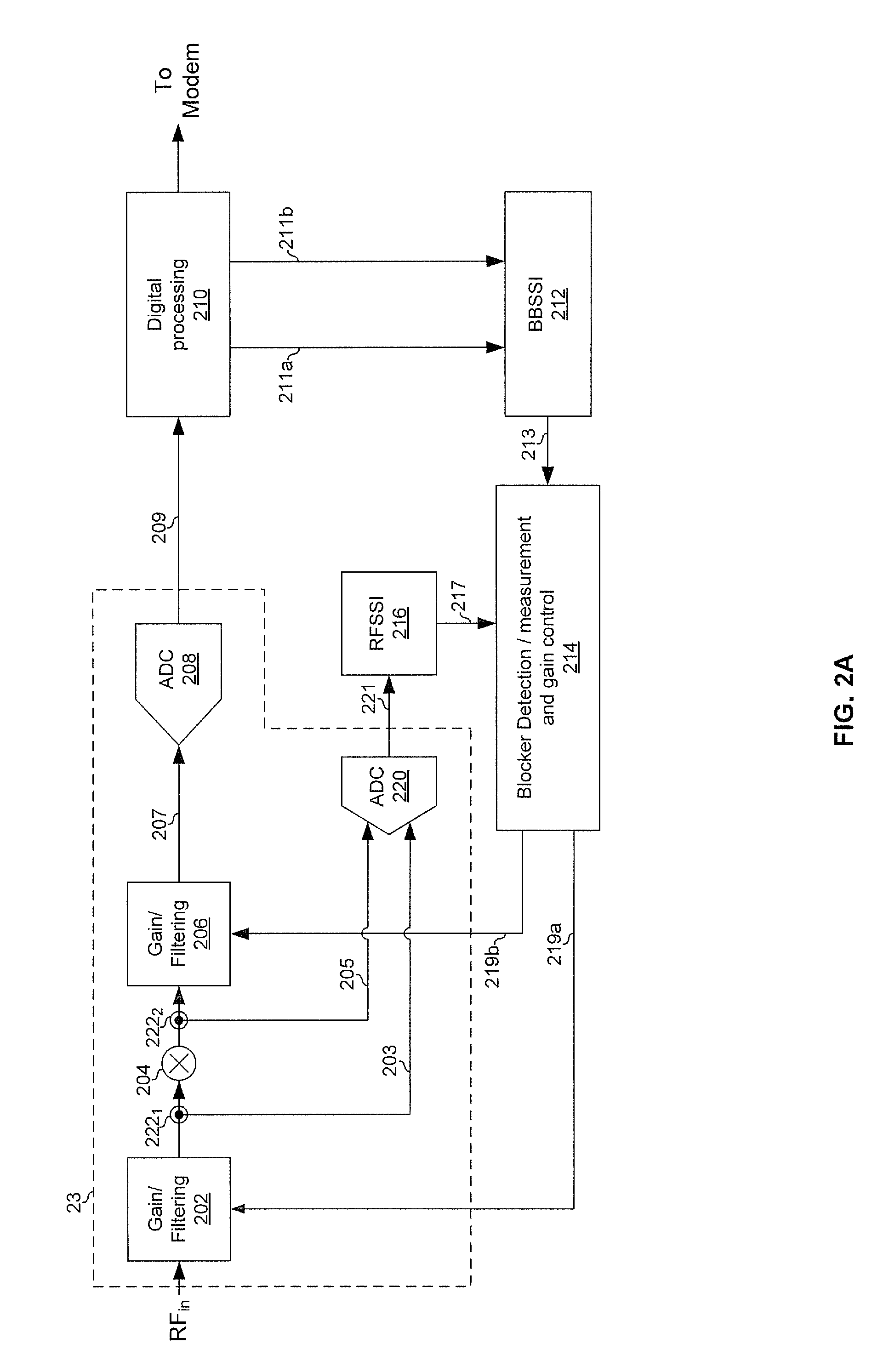
Method and system for blocker detecton and automatic gain control
Aspects of a method and system for integrated blocker detection and automatic gain control are provided. In this regard, a communication device may generate one or more first signal strength indications based on a strength of a received signal at a first point in the analog front-end of the communication device. The communication device may generate one or more second signal strength indications based on a strength of the received signal at a second point in a digital processing module of the communication device. The first point in the analog front-end may be an input or an output of a down-conversion mixer. The second point in the digital processing module may be an output of an analog-to-digital converter or an output of a channel selection filter. The communication device may control, utilizing the first signal strength indication(s) and the second signal strength indication(s), a gain of one or more components of the communication device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for blocker detecton and automatic gain control
Aspects of a method and system for integrated blocker detection and automatic gain control are provided. In this regard, a communication device may generate one or more first signal strength indications based on a strength of a received signal at a first point in the analog front-end of the communication device. The communication device may generate one or more second signal strength indications based on a strength of the received signal at a second point in a digital processing module of the communication device. The first point in the analog front-end may be an input or an output of a down-conversion mixer. The second point in the digital processing module may be an output of an analog-to-digital converter or an output of a channel selection filter. The communication device may control, utilizing the first signal strength indication(s) and the second signal strength indication(s), a gain of one or more components of the communication device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Up-conversion of a down-converted baseband signal in a direct conversion architecture without the baseband signal passing through active elements
ActiveUS7139546B1High frequency componentLesser or no amounts of 1/f noiseOscillations generatorsTransmission noise suppressionAudio power amplifierDown conversion mixer
A direct conversion circuit that not only down-converts the received modulated signal using a down-converting mixer into a baseband signal, but also, after performing a passive low pass filtering to remove higher-order components, performs up-conversion of the baseband signal using an up-converting mixer. Active elements such as highly sensitive amplifiers do not operate on the baseband signal itself, but on the up-converted version of that baseband signal, thereby reducing the 1 / f noise introduced by those active elements. The downstream circuitry after the up-conversion may be coupled by intervening capacitors since the downstream circuitry is operating on a higher frequency signal. Accordingly, the DC offset introduced by the downstream active elements is reduced.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Apparatus for measuring iq imbalance
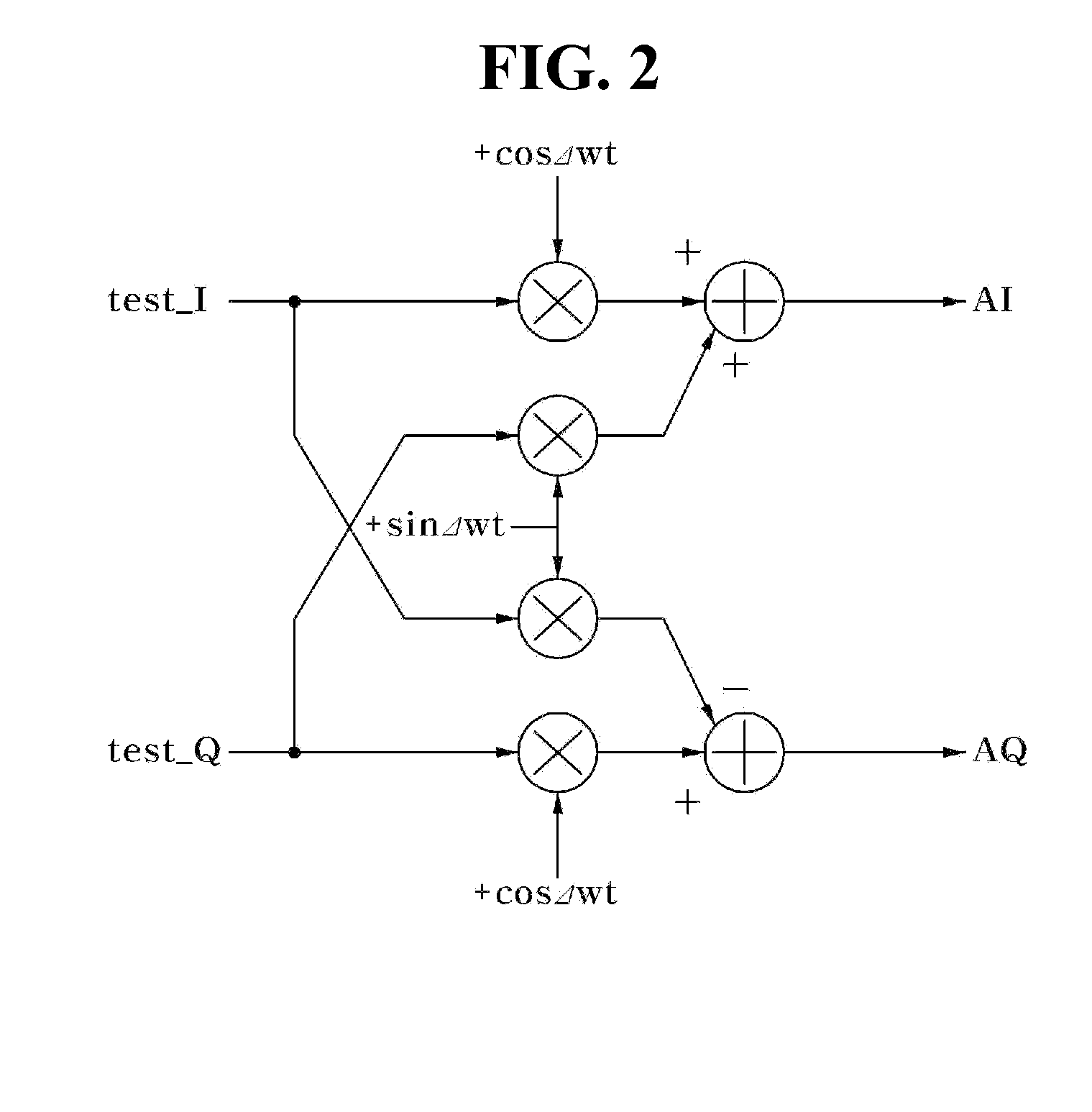
ActiveUS20090028231A1Easy to measureReduce noiseModulation with suppressed carrierAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDown conversion mixerEngineering
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for measuring an IQ imbalance. One embodiment according to the present general inventive concept can provide a method for measuring a Tx IQ imbalance generated in an IQ up-conversion mixer and an Rx IQ imbalance generated in an IQ down-conversion mixer, that includes measuring a first IQ imbalance corresponding to a first combination of the Rx IQ imbalance with the Tx IQ imbalance, measuring a second IQ imbalance corresponding to a second combination of the Rx IQ imbalance with the Tx IQ imbalance and obtaining the Tx IQ imbalance and the Rx IQ imbalance from the first IQ imbalance and the second IQ imbalance.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
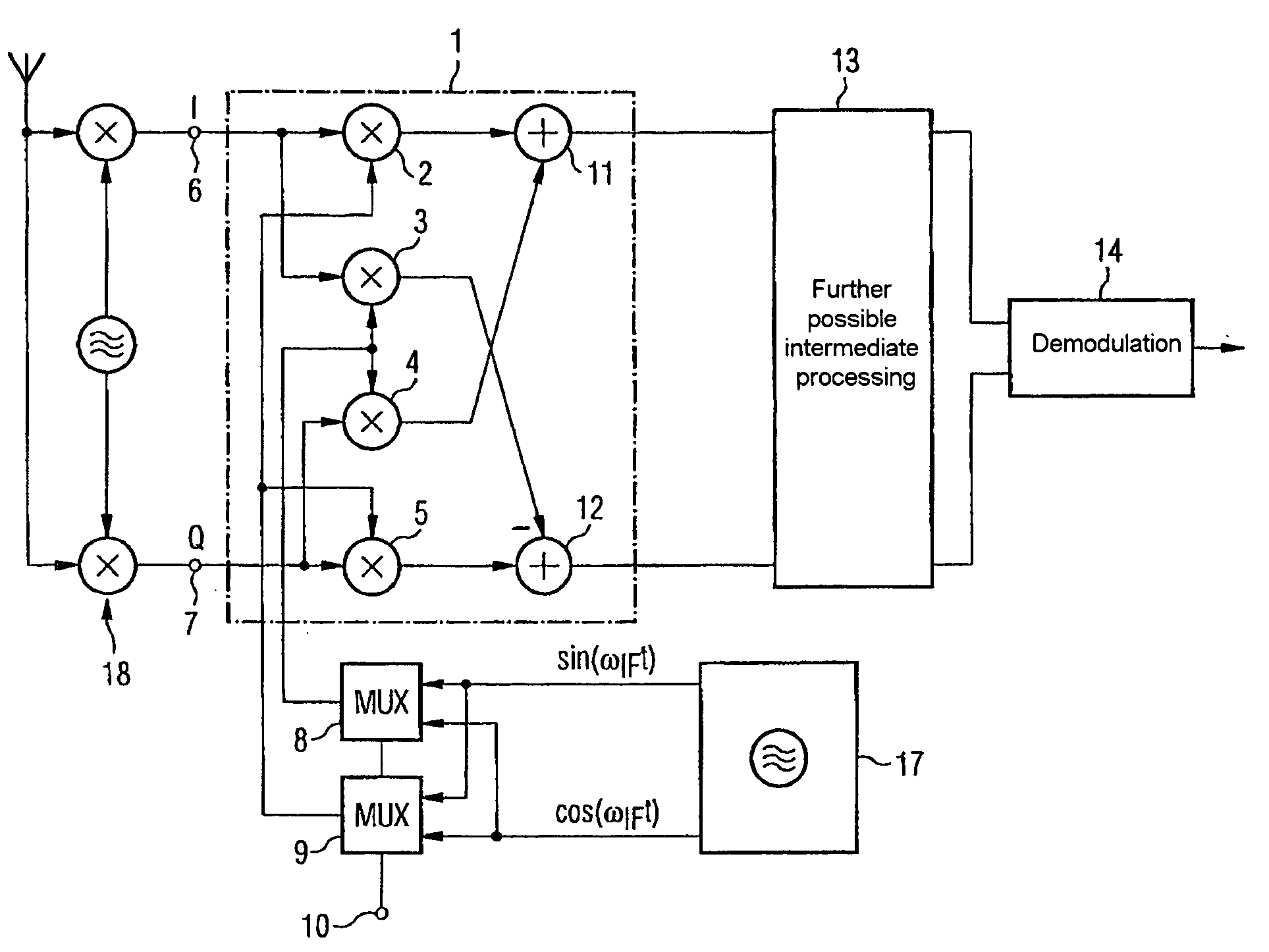
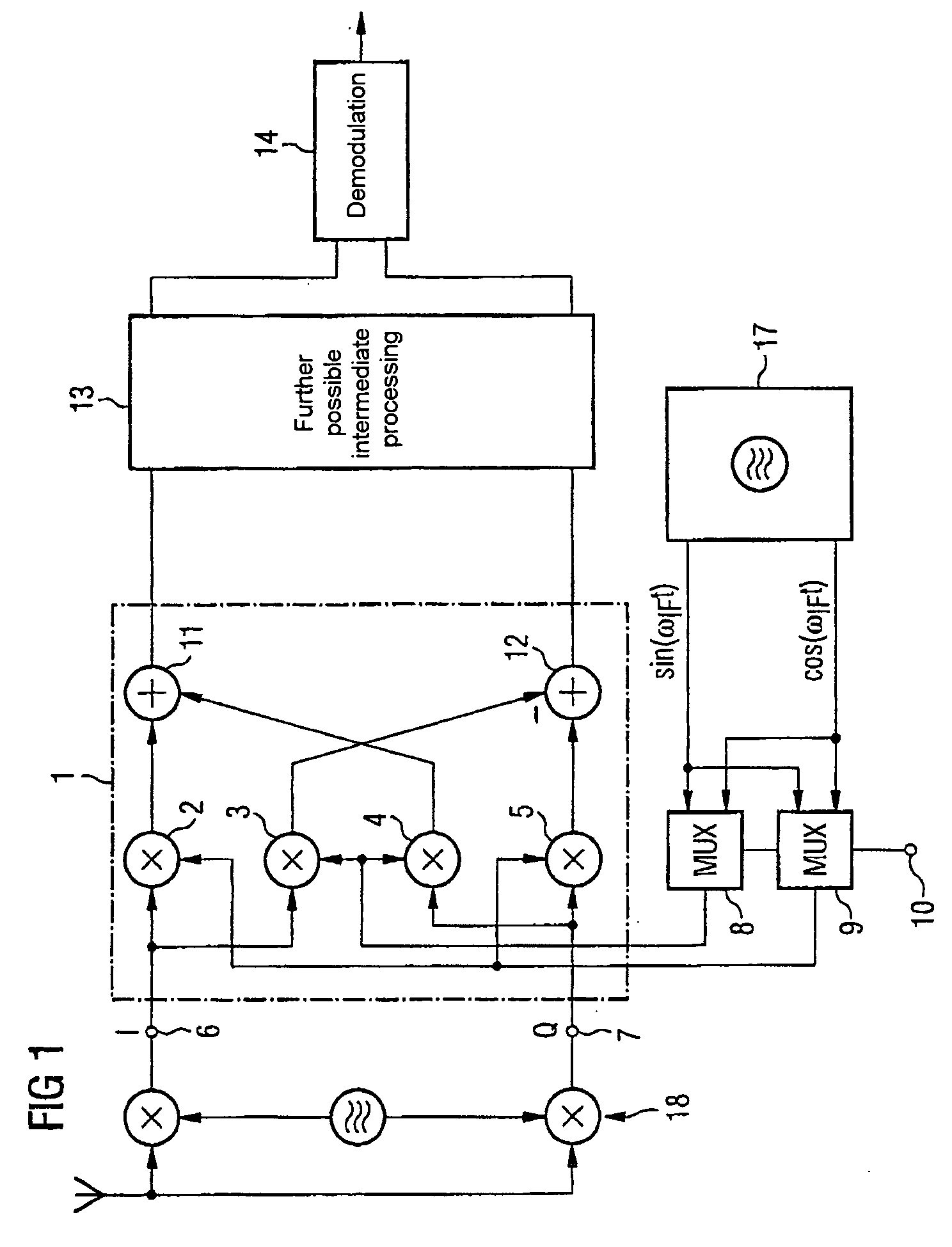
Mobile radio receiver device
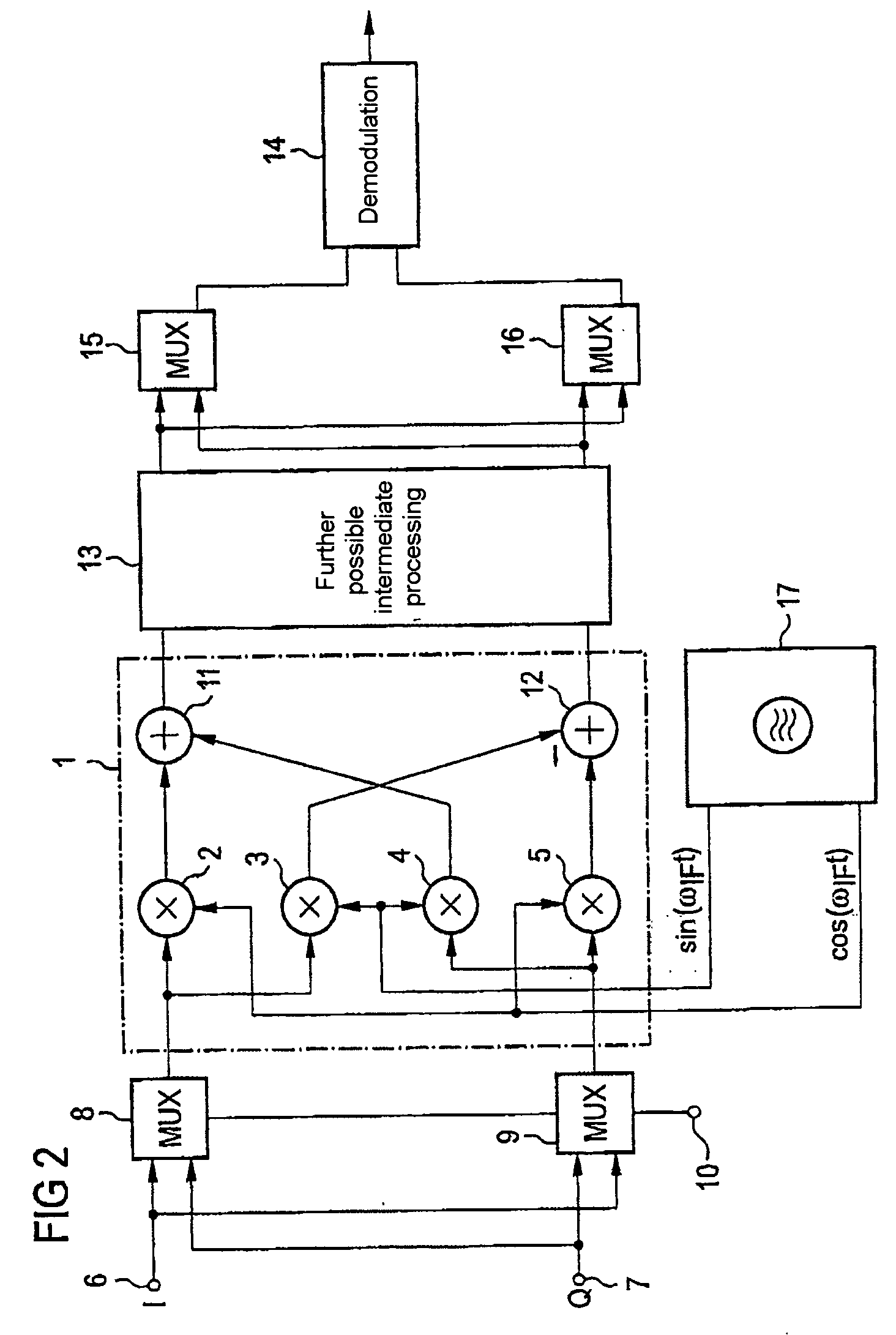
ActiveUS20050170805A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionSidebandDown conversion mixer
The invention is directed to a receiver arrangement, for example, in a mobile radio, which allows the use of slowly locking phase locked loops for a point-to-point connection between two transceivers, even in the case of a heterodyne receiver structure. The need to change channels between a transmission slot and a reception slot is avoided by virtue of a changeover device being provided for the purpose of interchanging the in-phase and quadrature components at the input side on a down-conversion frequency mixer. This advantageously allows either the upper sideband or the lower sideband of a useful signal to be down-converted without the need to change channel.
Owner:APPLE INC
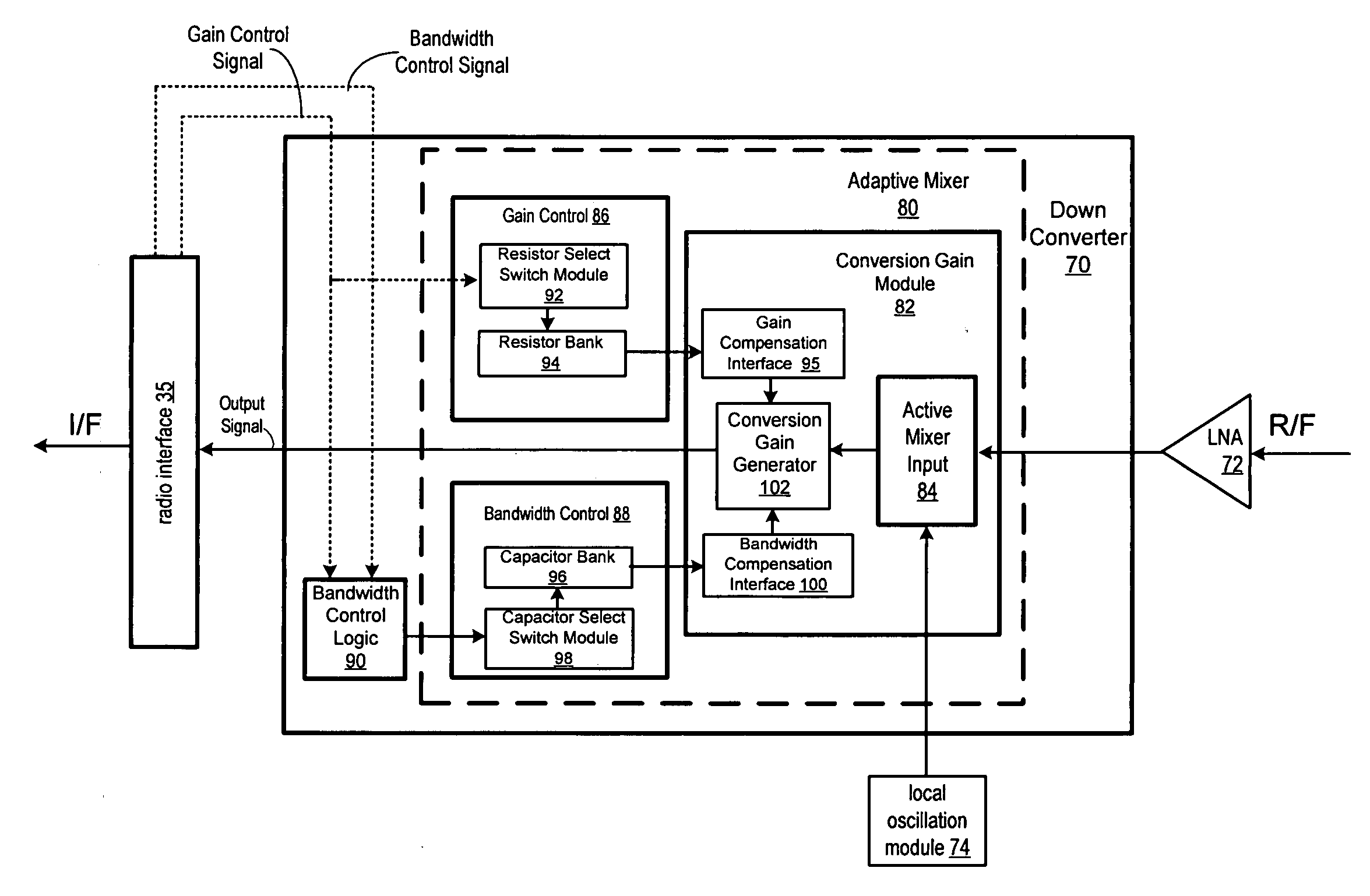
Adaptive mixer output filter bandwidth control for variable conversion gain down-conversion mixer
An improved adaptive mixer for use in the down conversion module of a wireless transceiver. The adaptive mixer comprises a conversion gain module that is operable to receive a radio frequency signal and to generate an intermediate frequency that is provided to a radio interface in a wireless transceiver. The radio interface is operable to generate a gain control signal and a bandwidth control signal. The gain control signal is provided to a gain control module that is operable to select a combination of load resistance values that will provide a predetermined gain level for the output of the conversion gain module. Bandwidth control logic in the adaptive mixer uses the bandwidth control signal to operably connect a plurality of bandwidth control capacitors to the conversion gain module to control the bandwidth of the output signal. By selecting predetermined values for the load resistance and for the bandwidth control capacitors, the method and apparatus of the present invention makes it possible to generate an intermediate frequency output signal having a predetermined gain and a predetermined bandwidth.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Single-chip multi-mode digital television tuner
InactiveCN101557476ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsLow noiseIntermediate frequency
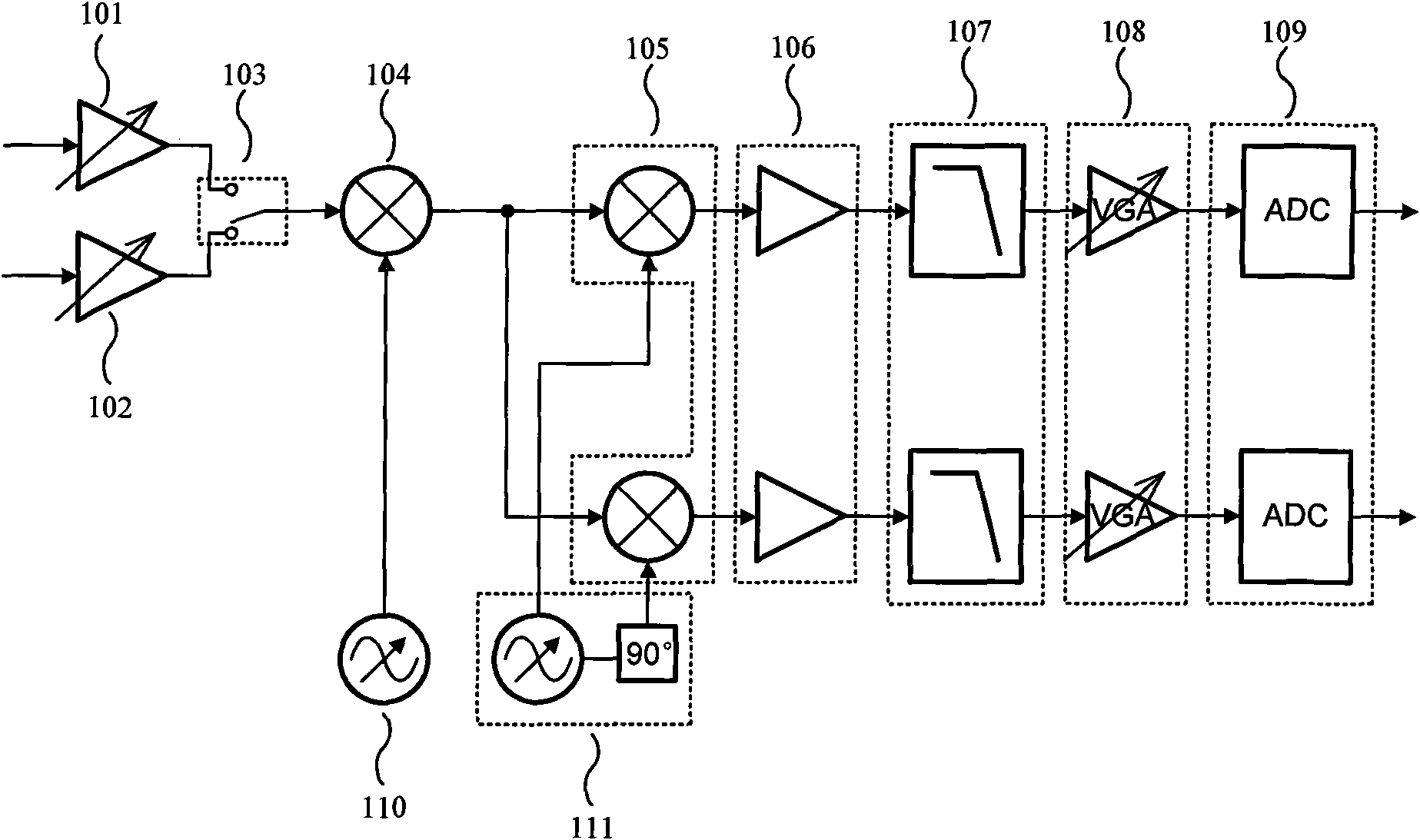
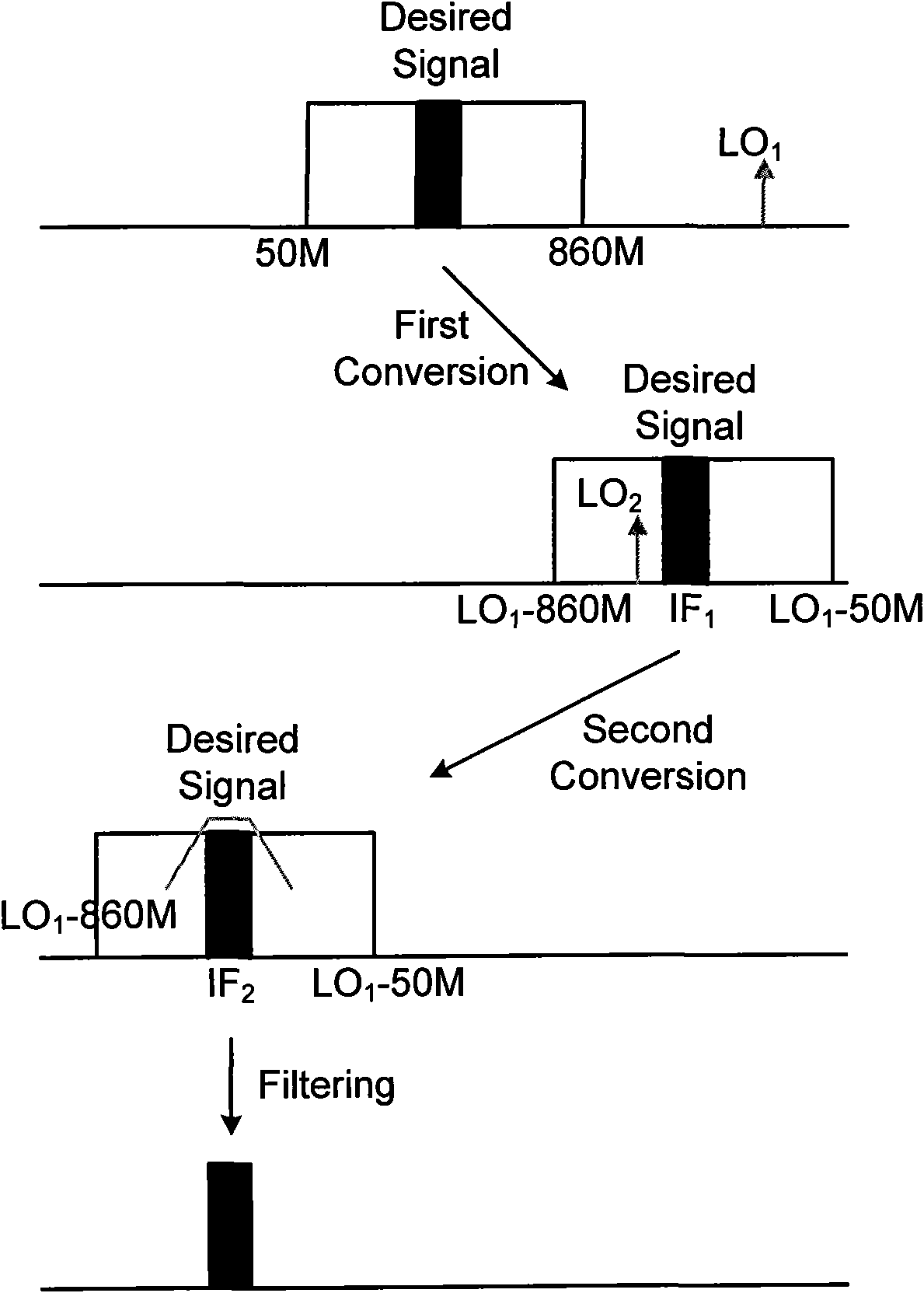
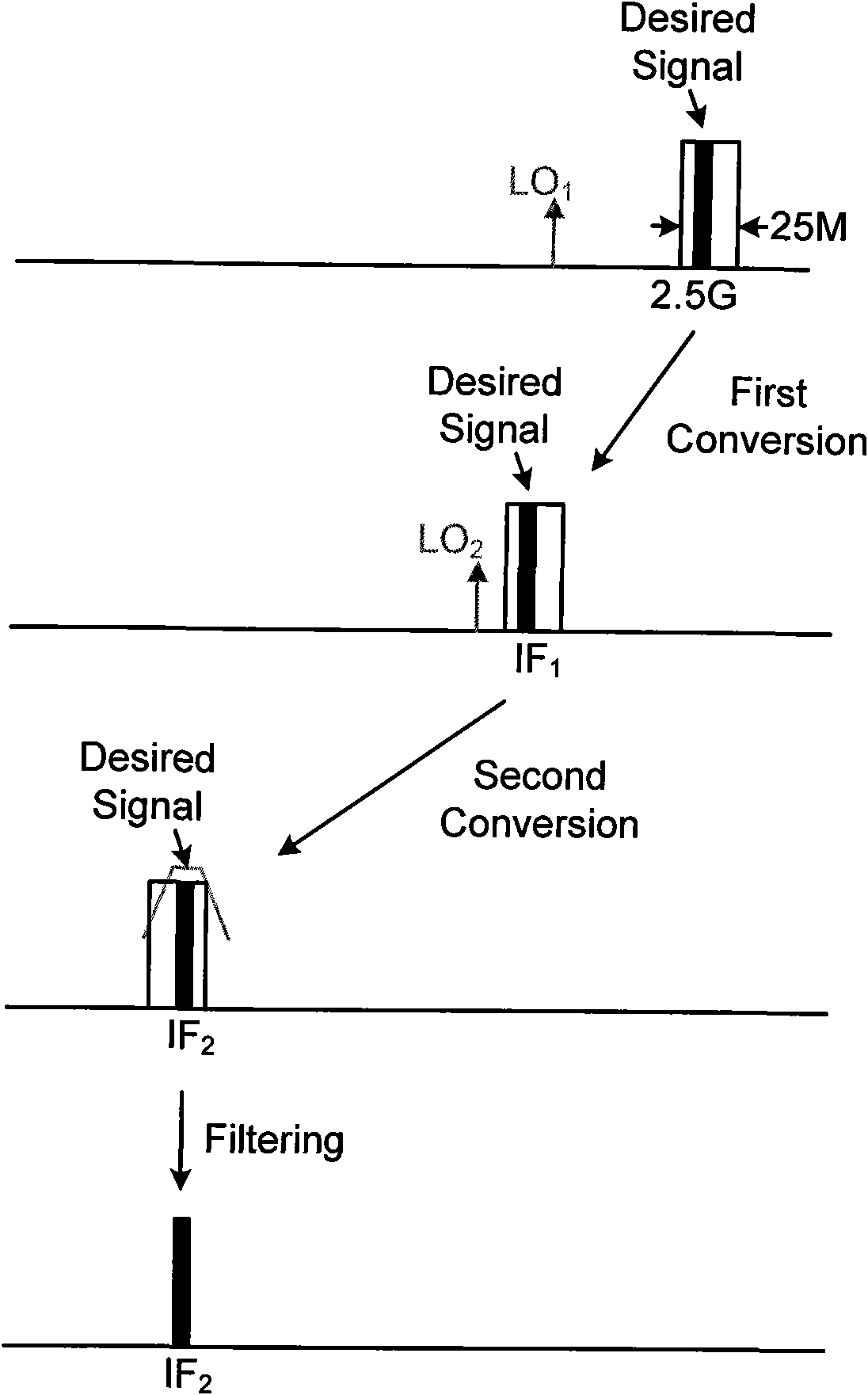
The invention discloses a system structure of a single-chip multi-mode digital television tuner compatible with various domestic and foreign digital television standards such as DVB-T / C / H, DMB-T / H, CMMB, and the like. By adopting a double low-middle frequency conversion way, the structure realizes the inception and the amplification of multi-standard digital television signals with different frequencies through two low noise amplifiers respectively working at frequency bands of 50-860MHz and 2.5GHz and finally obtains the needed middle frequency signals through modules such as an up-conversion mixer, an orthogonal down-conversion mixer, a preliminary amplifier, a filter, a variable gain amplifier, and the like, thereby achieving the function of signal tune. The invention mainly aims to achieve a single-chip fully integrated digital television tuner compatible with the internationally universal DVB-T / C / H standard and homemade DMB-T / H, CMMB standard; in addition, the area and the power consumption of a chip are reduced due to the sharing of the modules.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUIXIE MICROELECTRONICS TECH
Direct conversion receiver with direct current offset correction circuitry
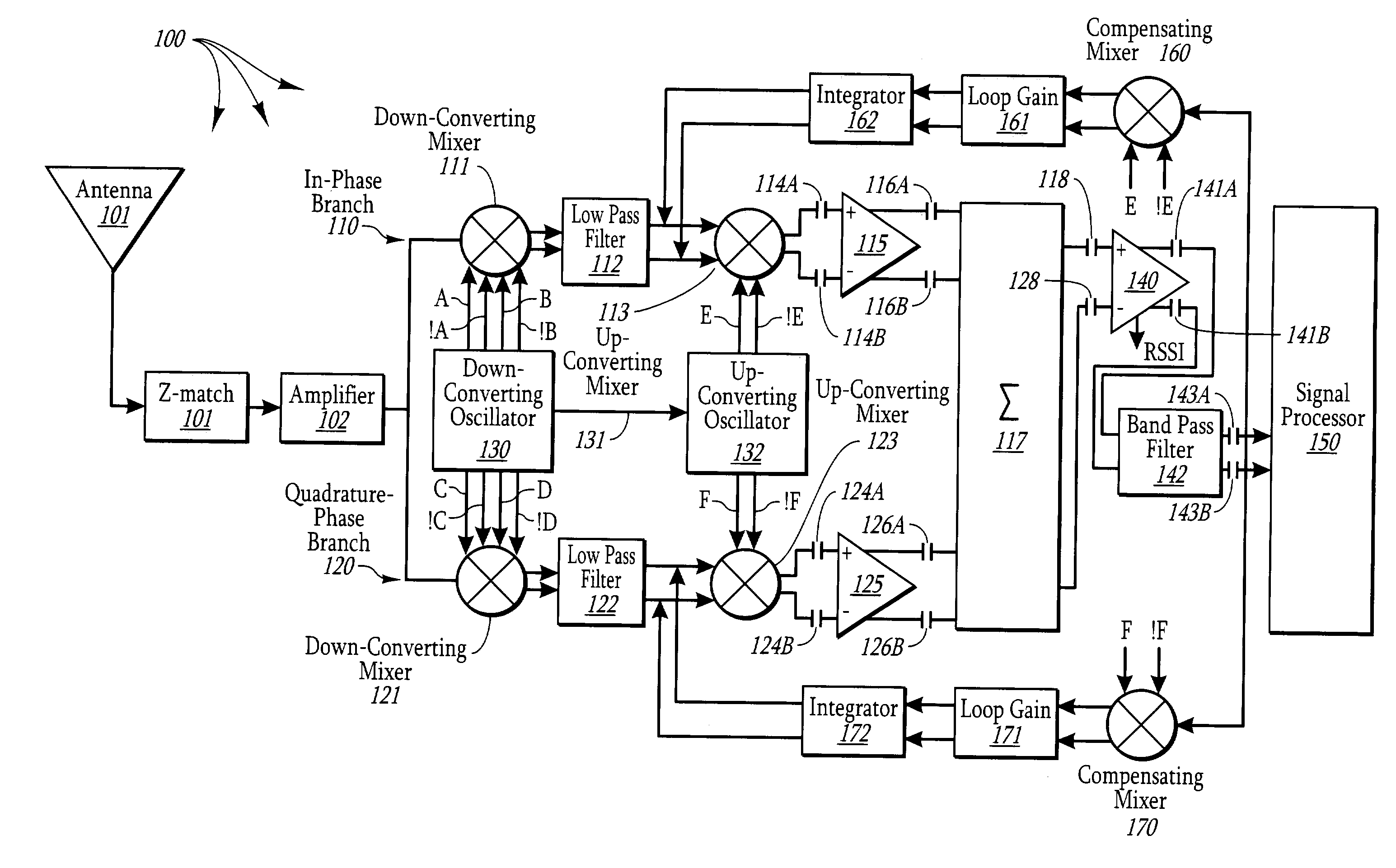
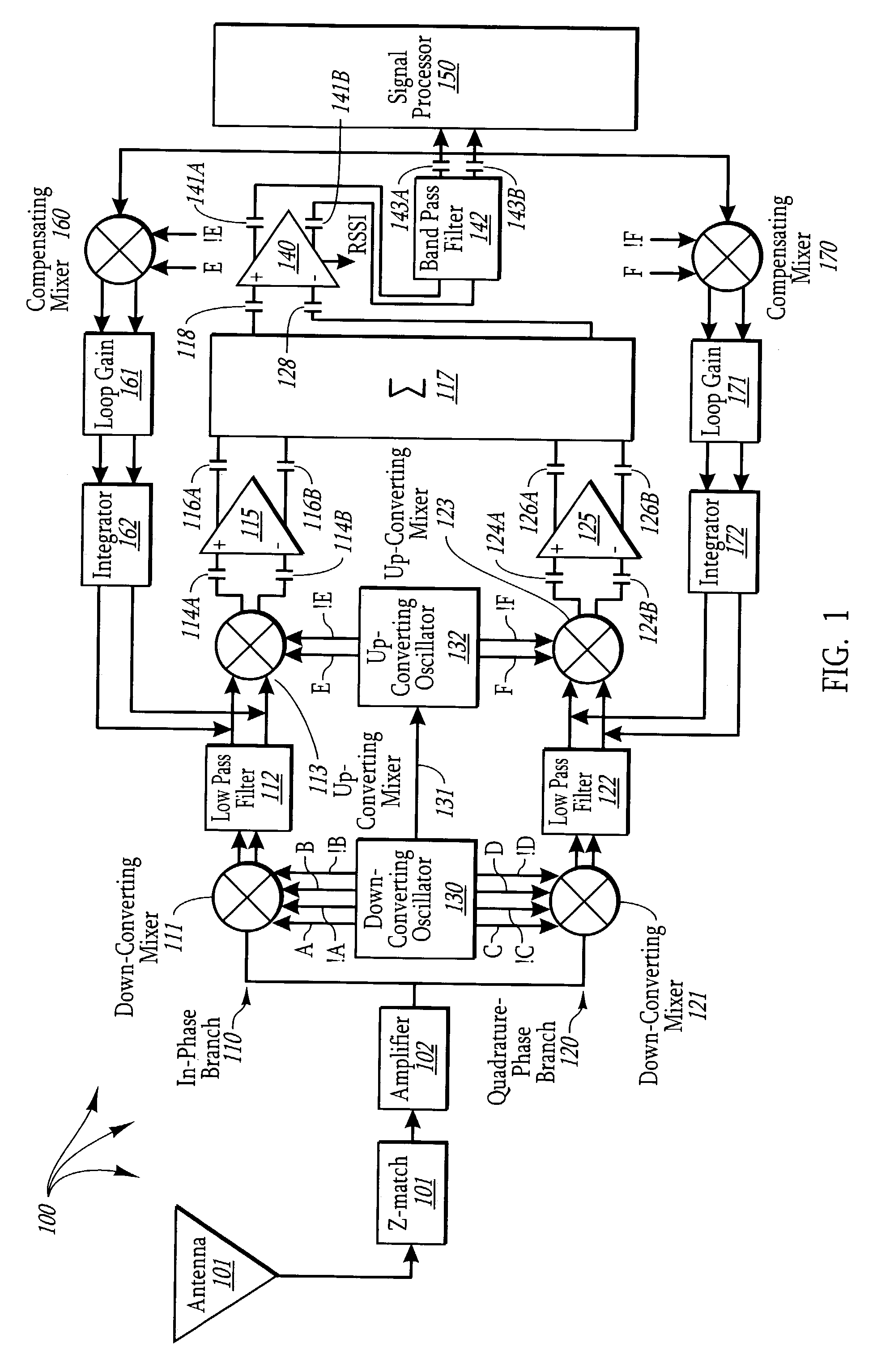
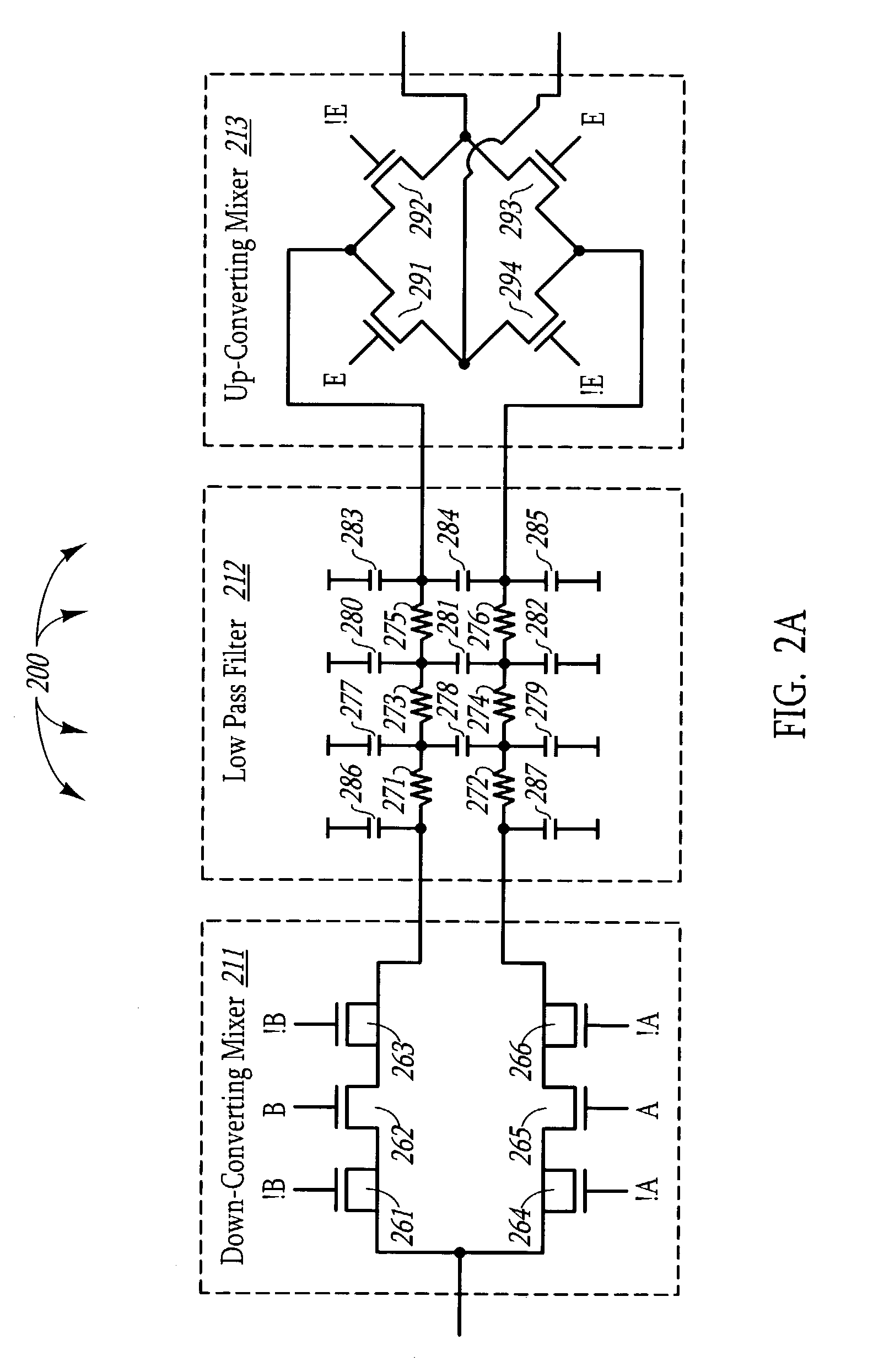
ActiveUS7197091B1Reduce noiseDirect currentElectric signal transmission systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsIntegratorFrequency mixer
A direct conversion circuit that includes an in-phase and quadrature-phase feedback path that reduces Direct Current (DC) offset. Each feedback path includes a compensating mixer that generates an error correction voltage that is passed through a loop gain circuit and an integrator. The integrated signal is applied to the output of a low pass filter that operates on the down-converted baseband signal. The direction conversion circuit may not only down convert the received modulated signal using a down-converting mixer into a baseband signal, but also, after performing a passive low pass filtering to remove higher-order components, performs up-conversion of the baseband signal using an up-converting mixer. This allows active elements operating on the up-converted signal to introduce less 1 / f noise.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
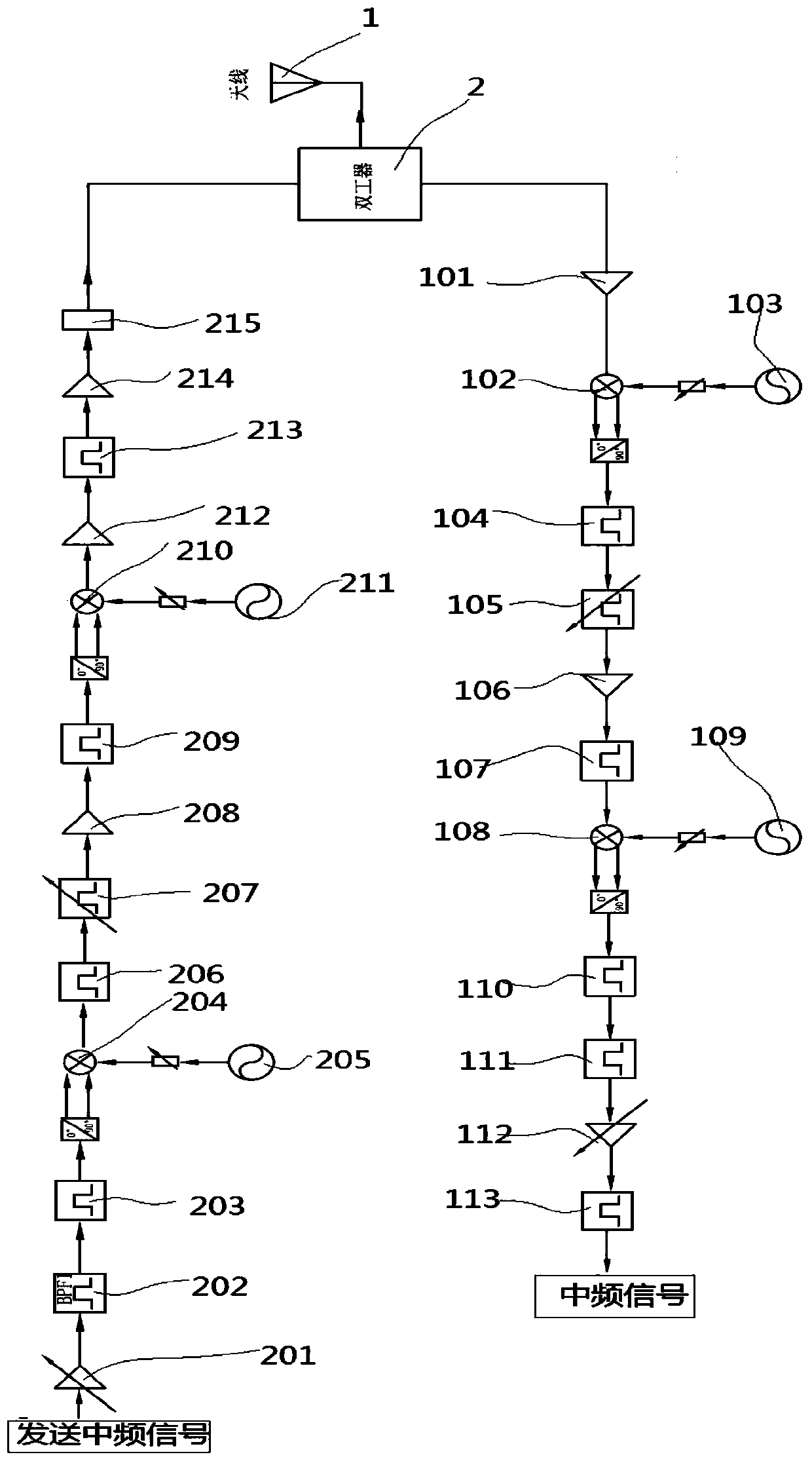
Ku waveband comprehensive radio frequency transceiving system
PendingCN110429952AImprove receiver sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeModifications by conduction heat transferTransmissionIntermediate frequencyDown conversion mixer
The invention provides a Ku waveband comprehensive radio frequency transceiving system. The Ku waveband comprehensive radio frequency transceiving system comprises an antenna, a radio frequency receiver, a radio frequency transmitter and a frequency source. The antenna is respectively connected with the radio frequency receiver and the radio frequency transmitter through a duplexer for isolating transmitted and received radio frequency signals. The radio frequency transmitter comprises an up-converter, wherein The up-converter comprises a first-stage up-conversion mixer for up-converting an intermediate frequency signal into a modulation signal with the center frequency of 280HMz and the bandwidth of 40MHz to increase the frequency to an L waveband, a second-stage up-conversion mixer for up-converting the modulation signal with the L waveband to increase the frequency to a Ku waveband. The radio frequency receiver comprises a down converter, and the down converter comprises a first-stage down-conversion mixer for down-converting a received Ku-waveband radio frequency signal into an L-waveband modulation signal and a second-stage down-conversion mixer for down-converting the L-waveband modulation signal into a 200MHz intermediate frequency for output. The Ku-band comprehensive radio frequency transceiving system has the advantage of Ku-band communication transmission.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGDA ELECTRONICS
Intermittent rubidum atomic clock microwave frequency synthesizer
ActiveCN102394647AImprove phase noiseImprove filtering effectPulse automatic controlLow noiseRubidium
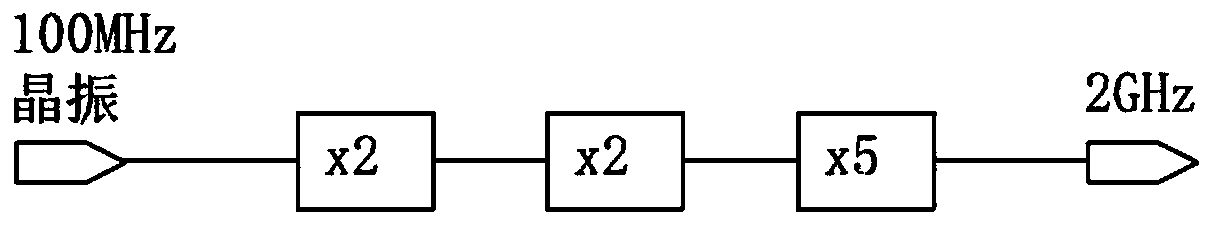
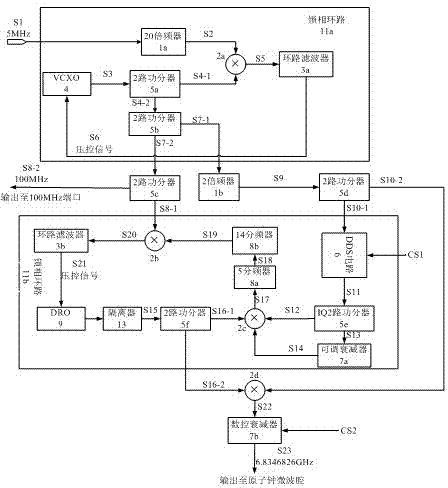
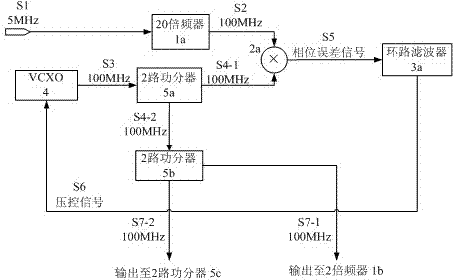
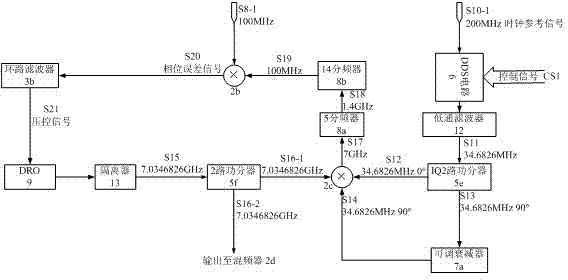
An intermittent rubidum atomic clock microwave frequency synthesizer comprises a first phase-locked loop, a second phase-locked loop, a third two-path power divider, two frequency multipliers, a lower frequency conversion mixer, and a digitally controlled attenuator. The frequency synthesizer provided by the invention has low noise, high frequency resolution factor and power resolution factor, and reliable and simple structure, and is also applicable to other intermittent rubidium atomic clocks.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Down-converter mixer
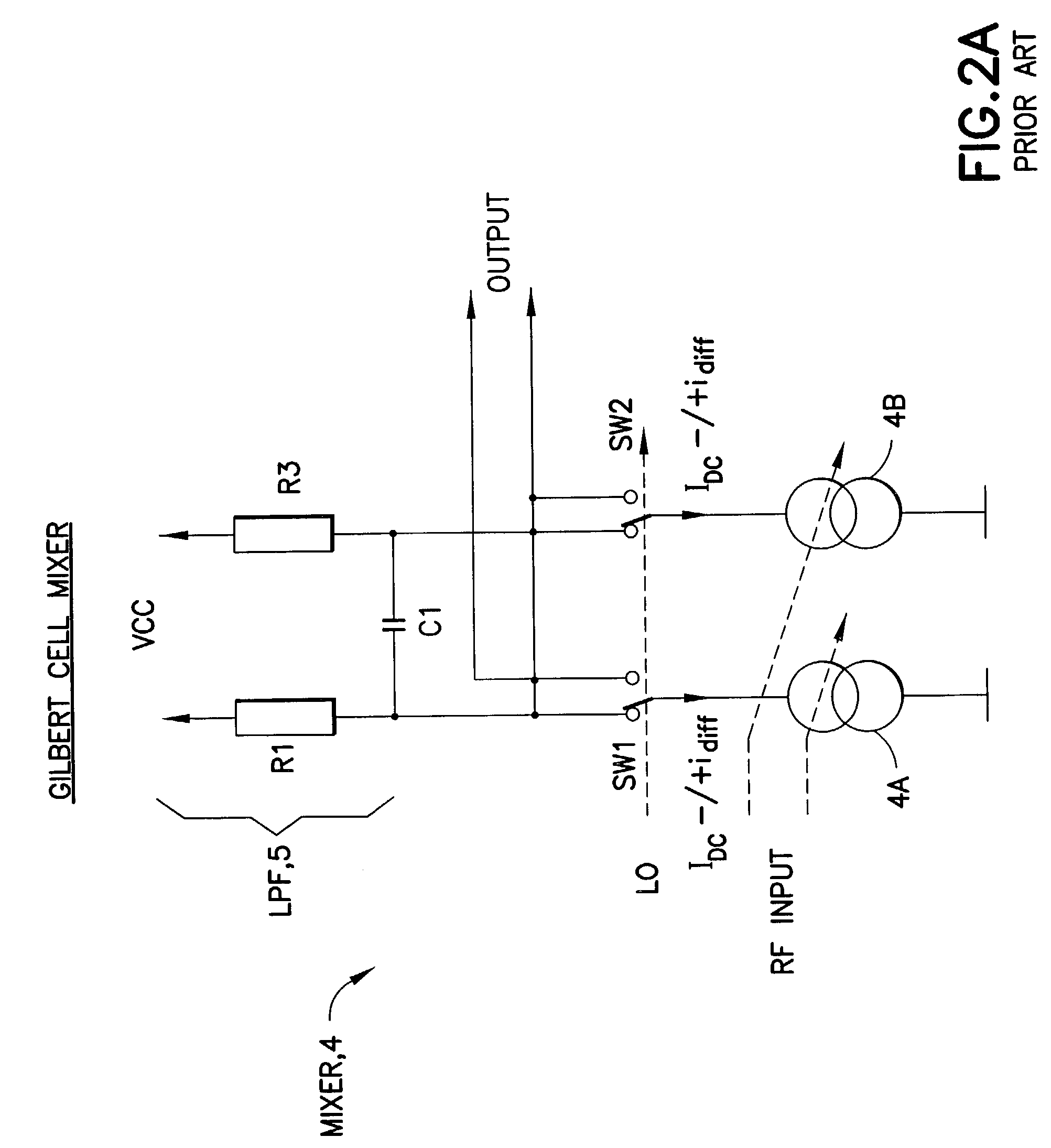
InactiveUS20100164595A1Increase output impedanceImproving impedanceModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesComputations using contact-making devicesLocal oscillator signalGilbert cell
A down-converter mixer may include a Gilbert cell, two transistor differential pairs, which drive output loads, and transistors defining respective tail generators coupled to common source nodes of the differential pairs. The transistors may receive a radio-frequency signal mixable with a local oscillator signal applied symmetrically between the differential pairs to produce in the loads, a signal deriving from down-converting the radio-frequency signal of an amount given by the frequency of the local oscillator signal. An inductor may be coupled to the common source nodes and which resonates with a capacitive load also coupled to the common source nodes, increases the impedance of such common nodes at the local oscillator signal frequency. The inductor may be in an open loop configuration in the absence of feedback from the mixer, and thus may be active both against noise at radio-frequency and distortion at low frequency.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Radar level meter and method for processing signals thereof
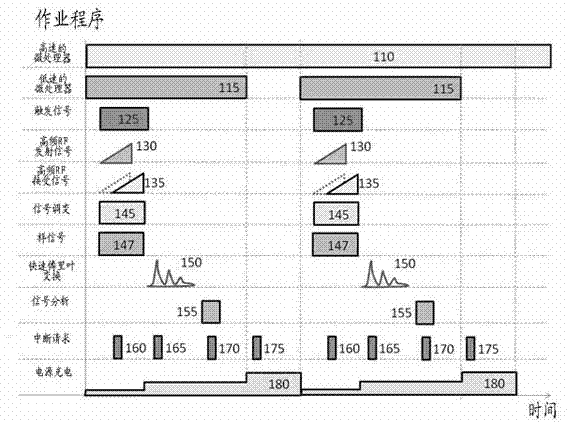
InactiveCN103090930AOvercome the shortcomings of the two-wire control update rate being too slowReduce power consumptionMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsLow speedFrequency spectrum
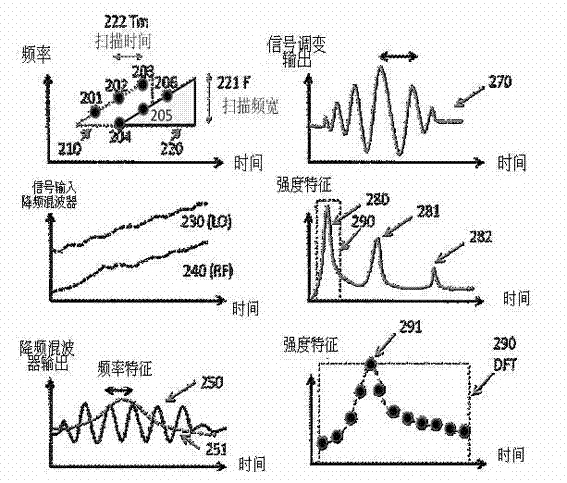
Disclosed are a radar level meter and a method for processing signals thereof. The radar level meter is provided with a micro control unit architecture, the architecture comprises a high-speed microprocessor, a low-speed microprocessor and a power charging and discharging circuit, and requirements on low power consumption and high update rate can be met. The method for processing the signals is a method for modulating the signals of the frequency-modulated continuous-wave radar level meter, and includes generating a high-frequency beat signal and feeding the high-frequency beat signal into a down-conversion mixer; converting the high-frequency signal into an intermediate-frequency periodic signal; converting the intermediate-frequency periodic signals into spectrum characteristics via fast Fourier transfer to obtain an FFT (fast Fourier transfer) signal; performing digital filtering transfer for the FFT signal for at least once to obtain final frequency characteristics; and finally acquiring the level distance by a physical value conversion program to obtain a high-precision distance relation.
Owner:上海凡宜科技电子有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com