Patents
Literature
245results about How to "Improve phase noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
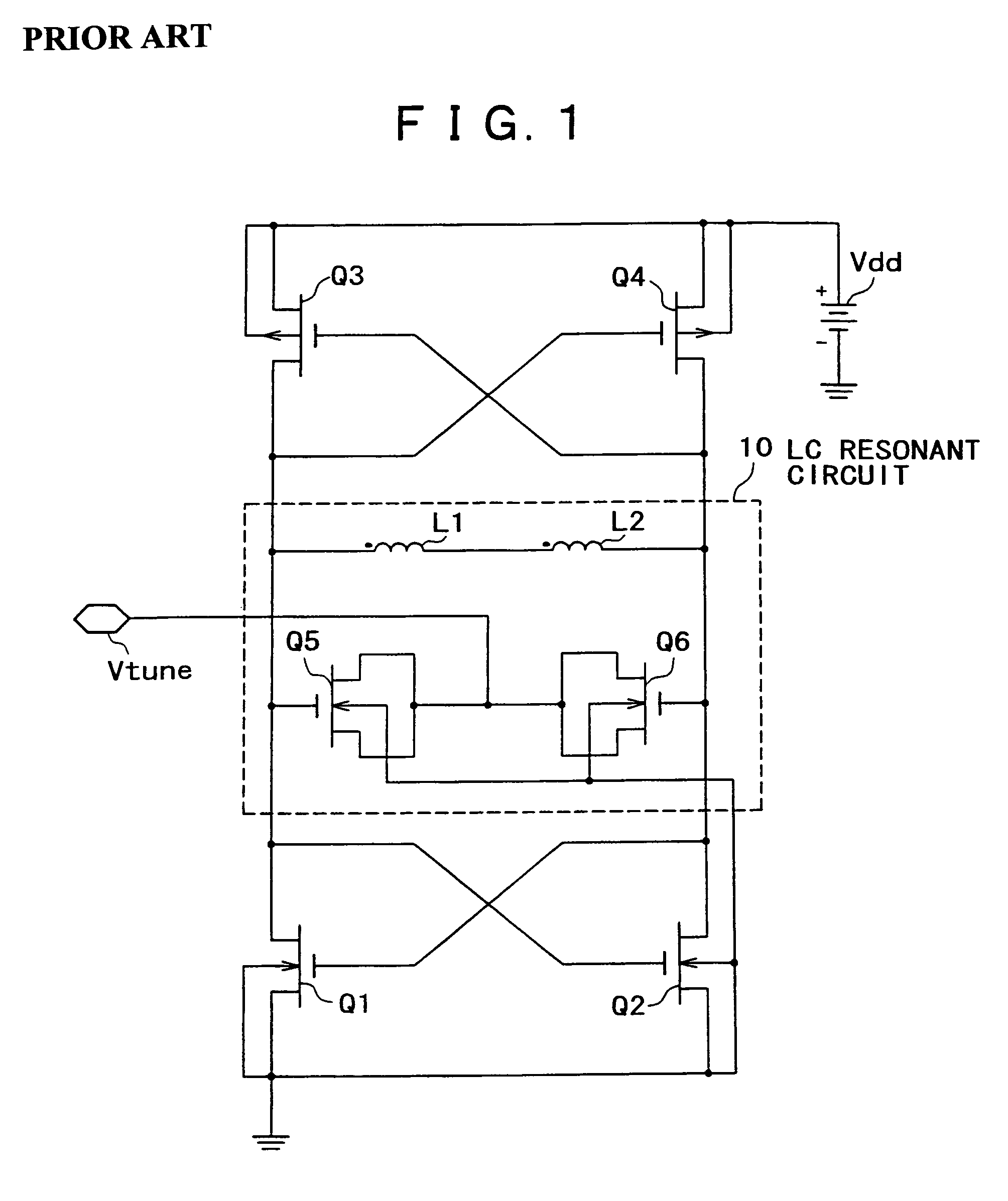
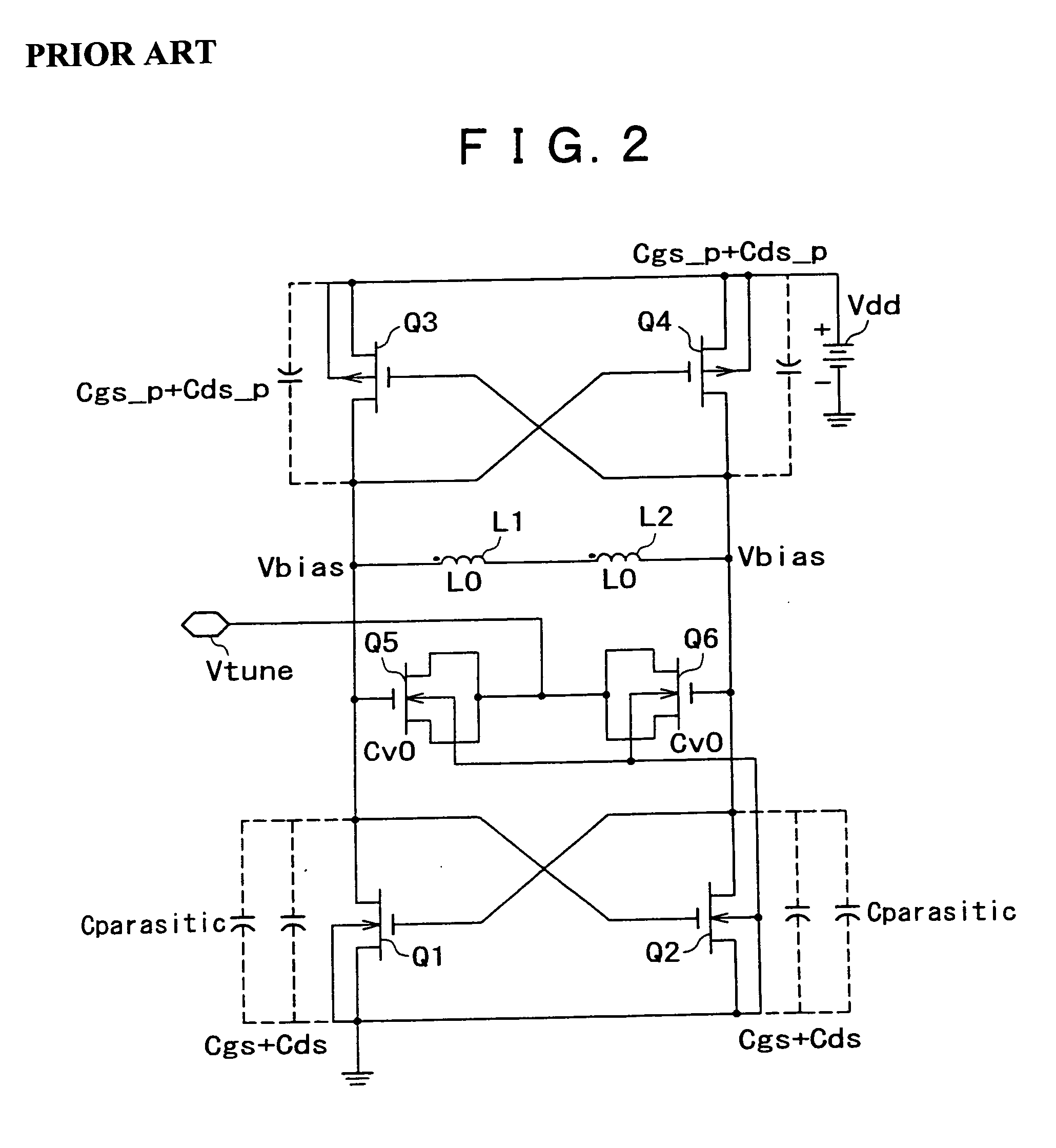
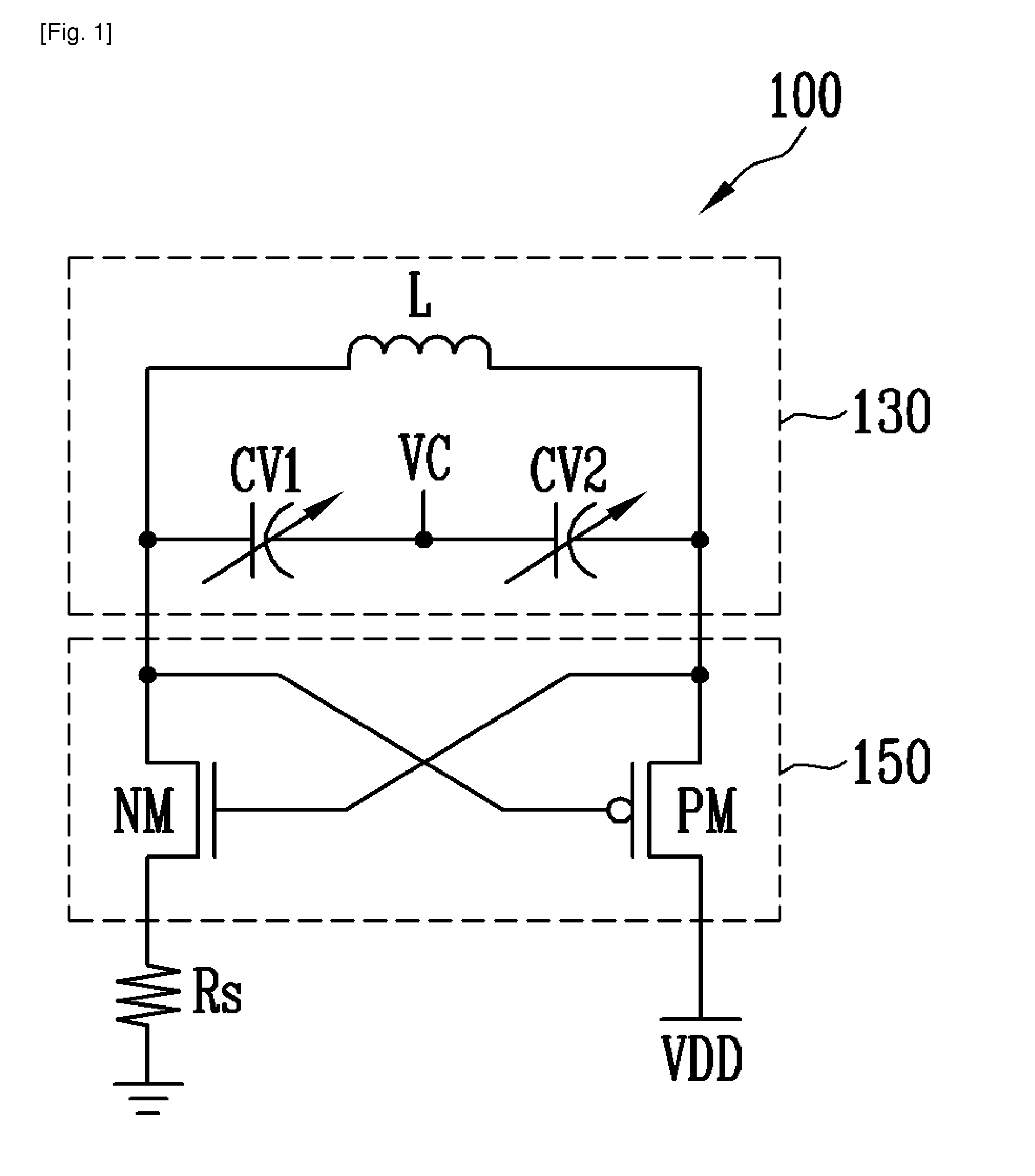
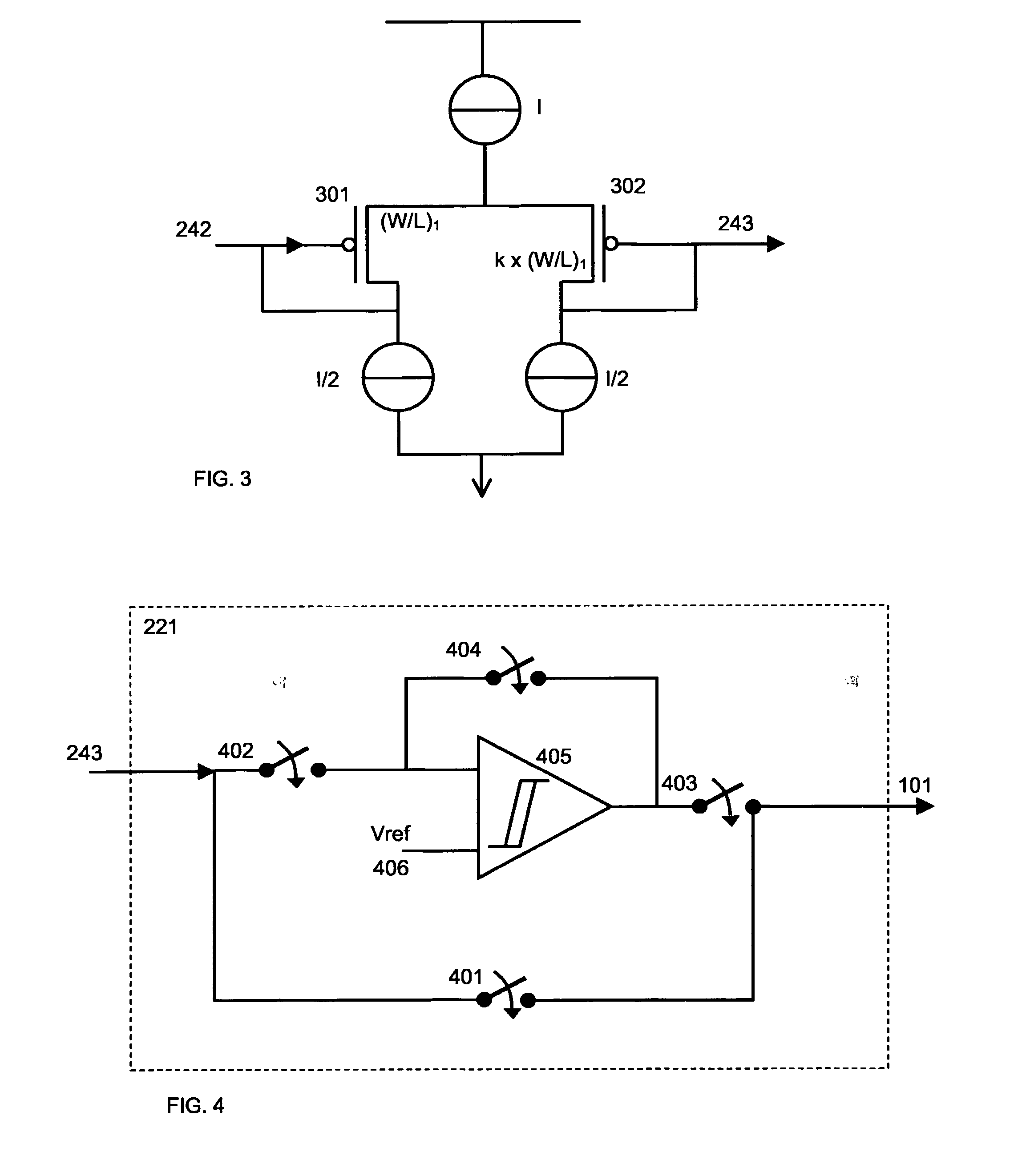
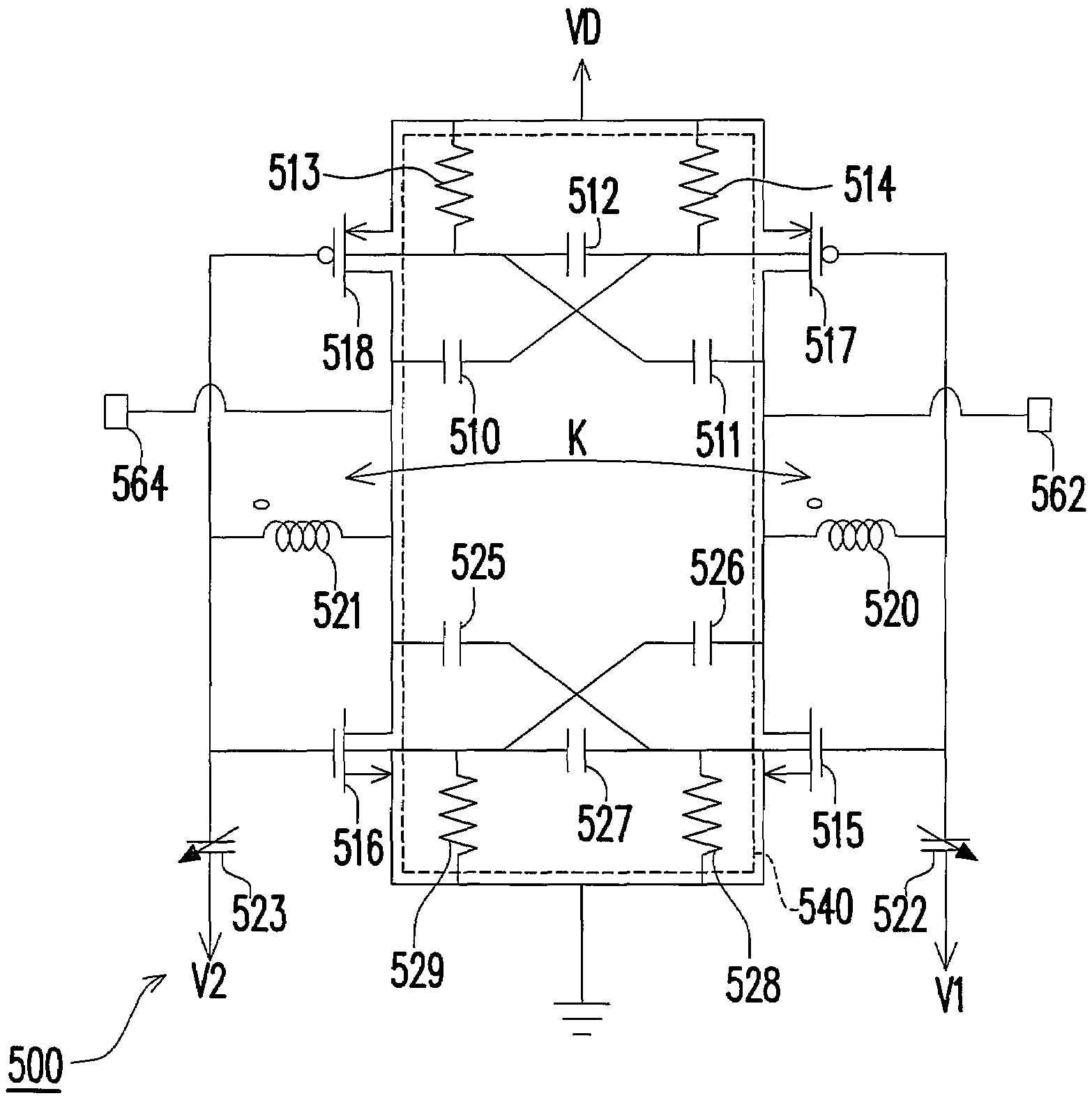
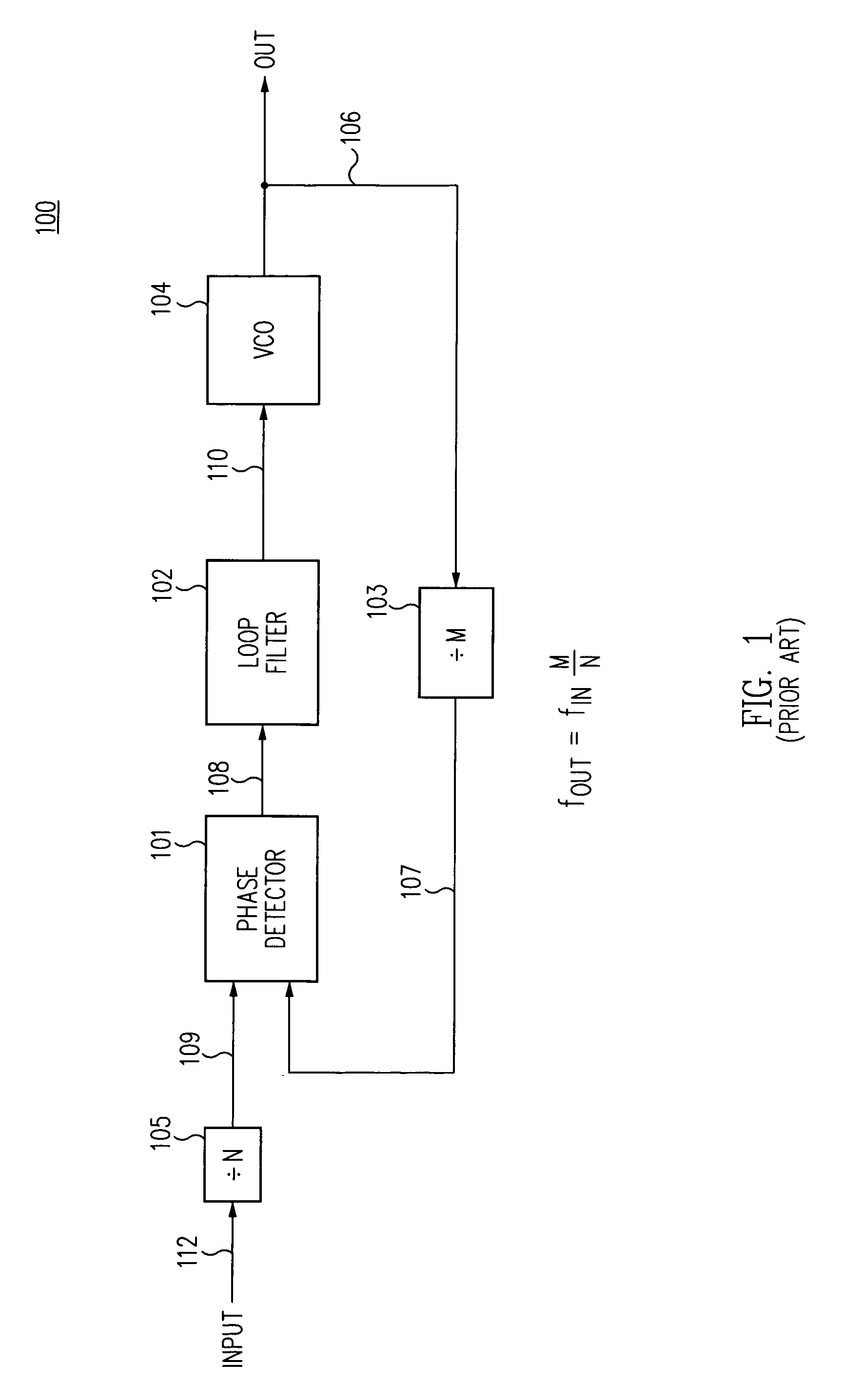
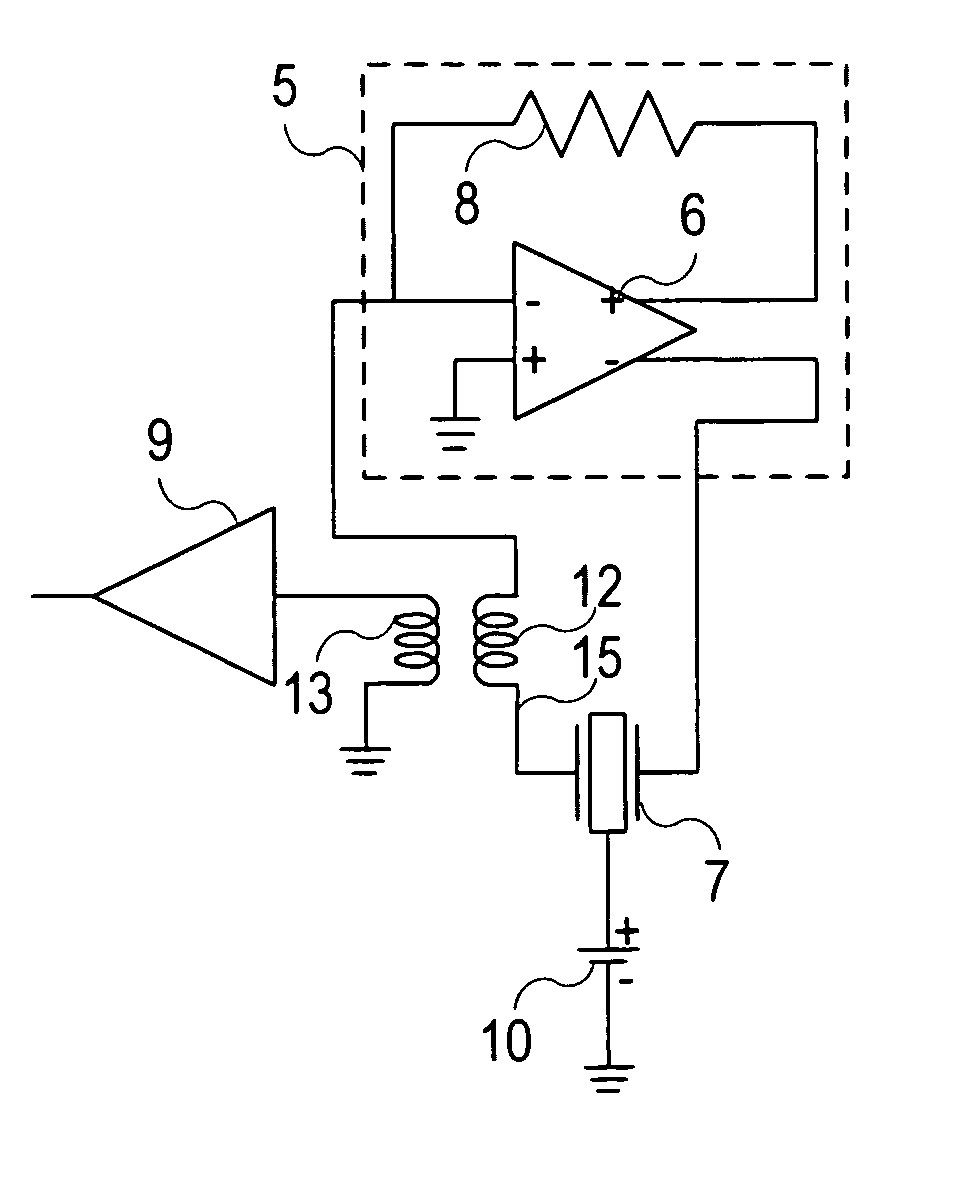
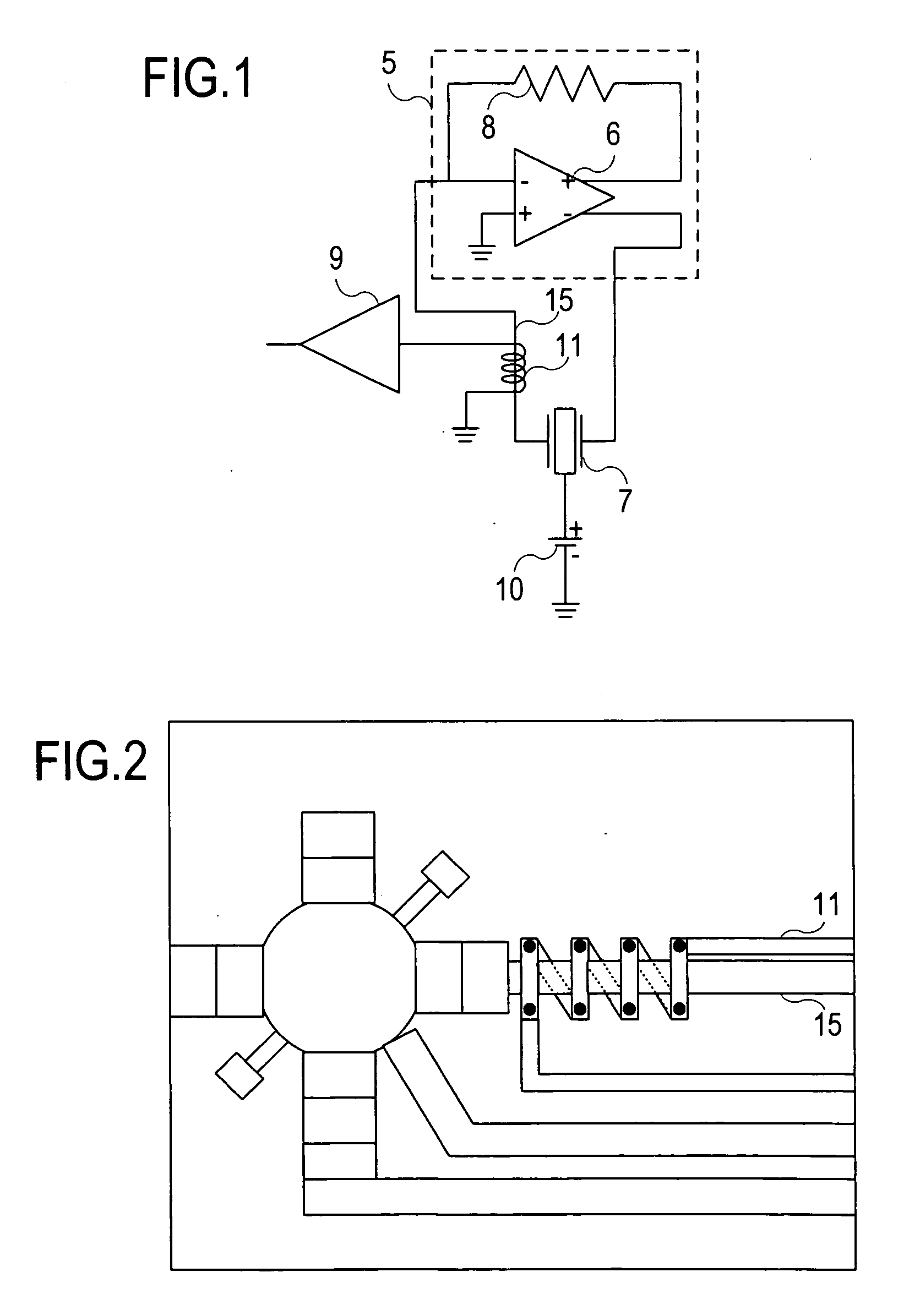
Resonant circuit and a voltage-controlled oscillator
InactiveUS7183870B2Improve phase noiseSimple compositionAngle modulation by variable impedenceAngle modulation detailsCapacitanceVoltage generator
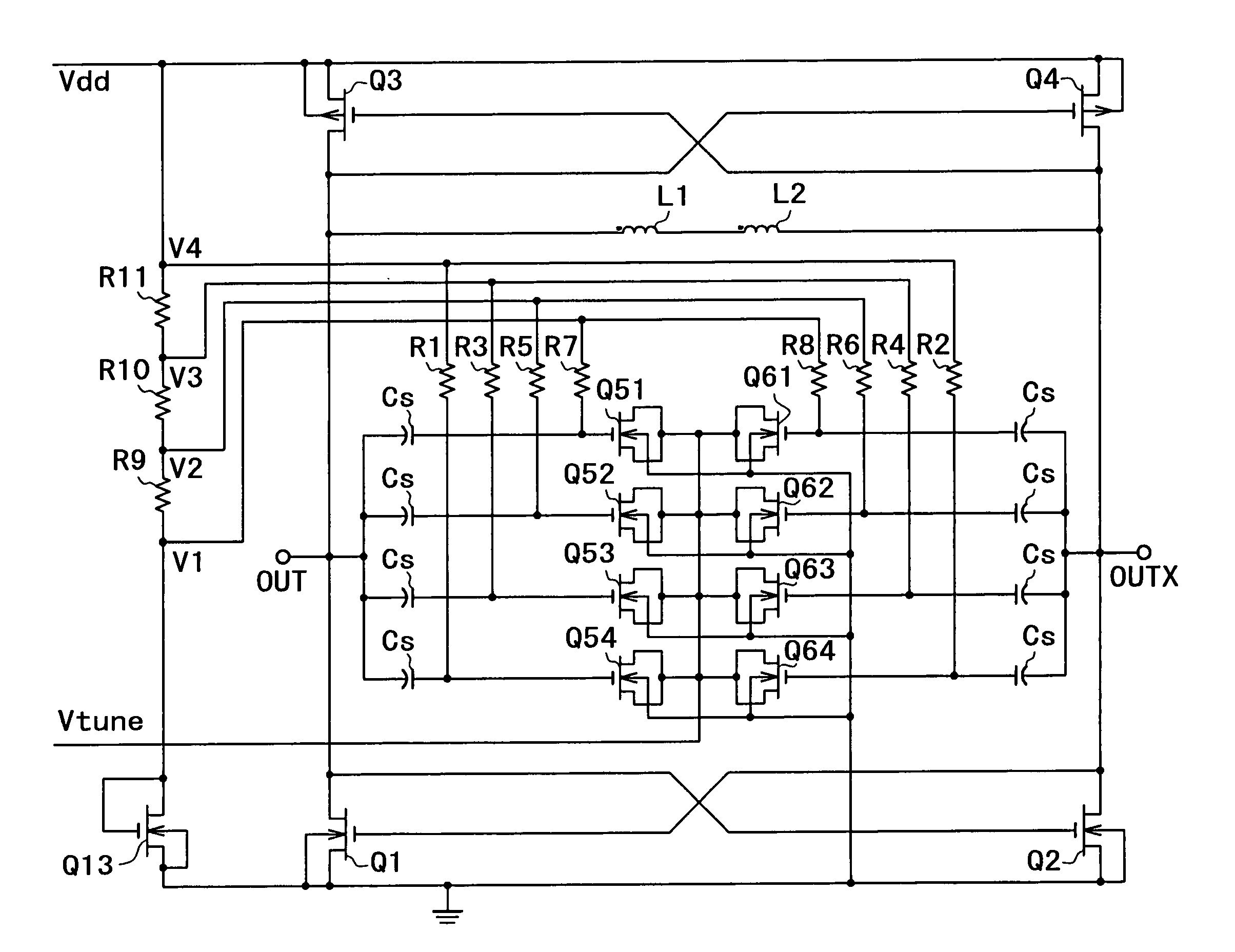
A voltage-controlled oscillator comprising a resonant circuit and MOS transistors which constitute a negative resistance circuit of a differential structure. The resonant circuit consists of an inductance element and a MOS variable capacitance element connected in parallel therewith. The MOS variable capacitance element is divided into plural pairs connected in parallel with each other. A voltage division circuit generates staircase different-step DC bias voltages to be applied respectively to the gates of the plural divided MOS transistors. The divided MOS variable capacitance elements have a common terminal to which a common control voltage is applied. The resonant circuit is capable of reducing a load on the control voltage generator and improving the characteristics of the voltage-controlled oscillator.
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
Frequency synthesizer and frequency synthesizing method
InactiveUS20120112806A1Improve phase noiseFine frequency resolutionPulse automatic controlFrequency synthesisPhase detector
The present invention relates to a frequency synthesizer comprising a main unit and a side unit. The main unit comprises a main phase detector to obtain a main control signal, a main oscillator that generates a main synthesized frequency output signal representing the frequency synthesizer output signal based on said main control signal, and a mixer that mixes said main synthesized frequency output signal with a side synthesized frequency output signal to obtain said mixer output signal. The side unit generates said side synthesized frequency output signal and comprises a frequency signal generation unit that provides a linear frequency sweep signal or a fixed-frequency control signal at a fine frequency resolution from said fixed-frequency side reference signal, and a side oscillator that generates said side synthesized frequency output signal based on said frequency sweep signal or said fixed-frequency control signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
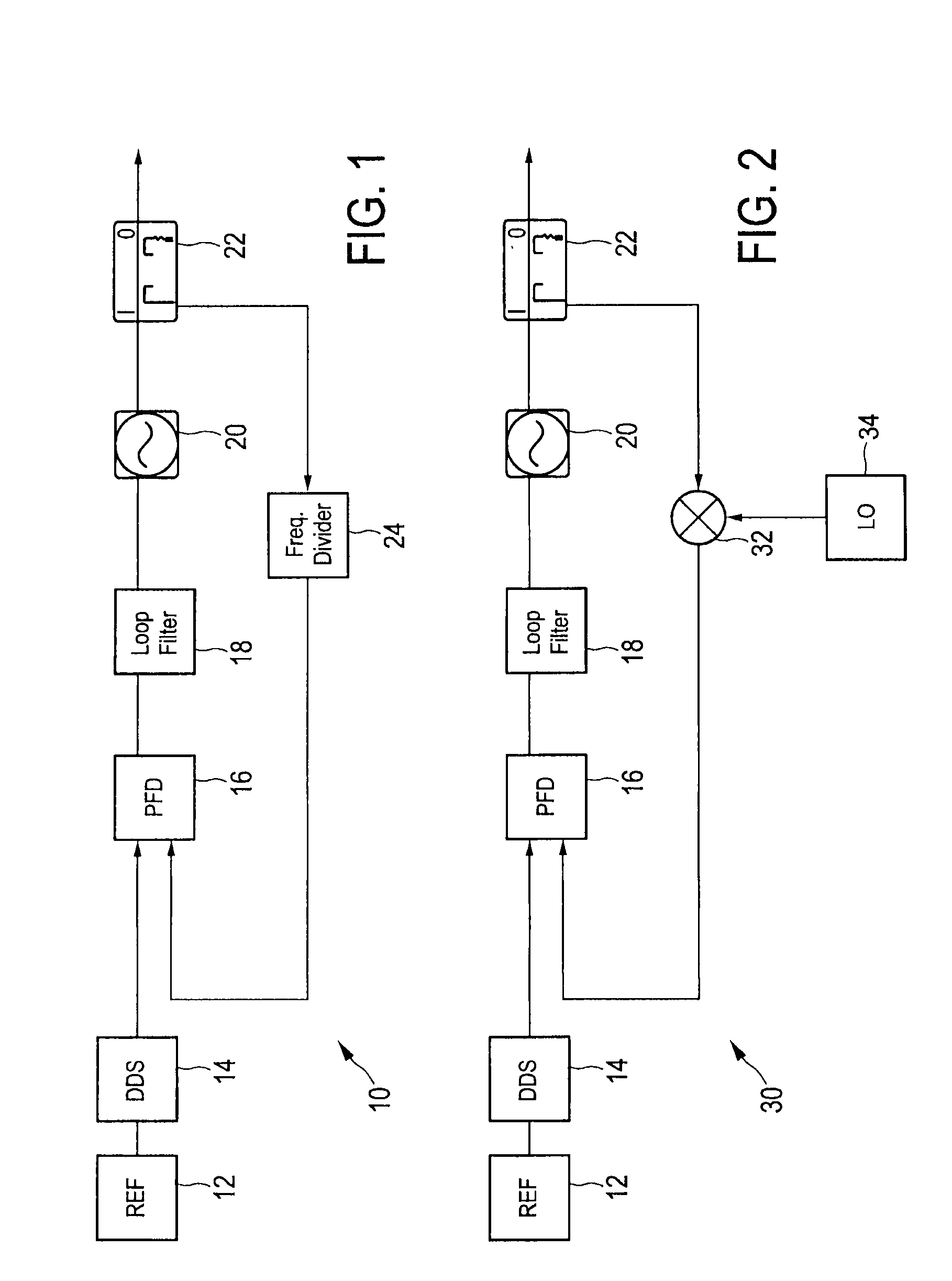
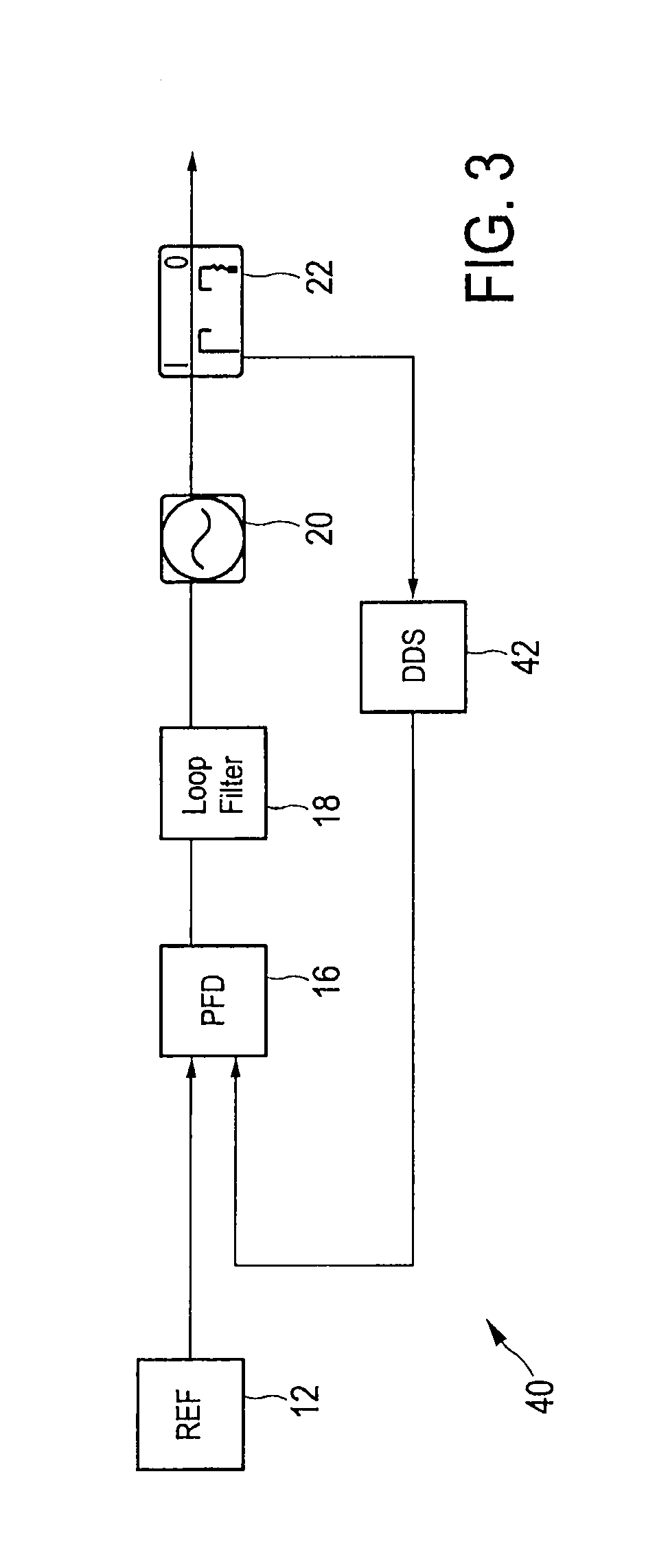
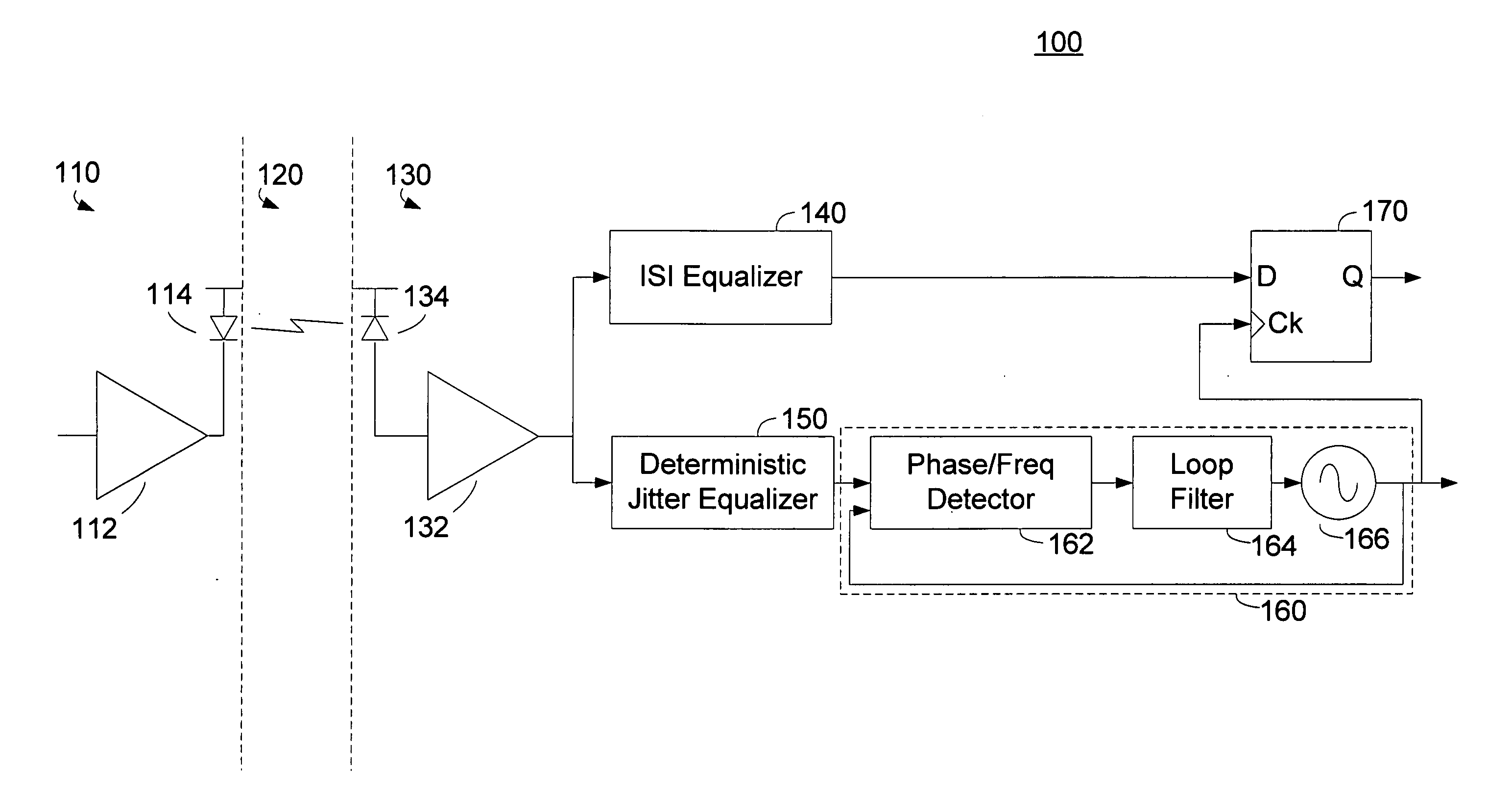
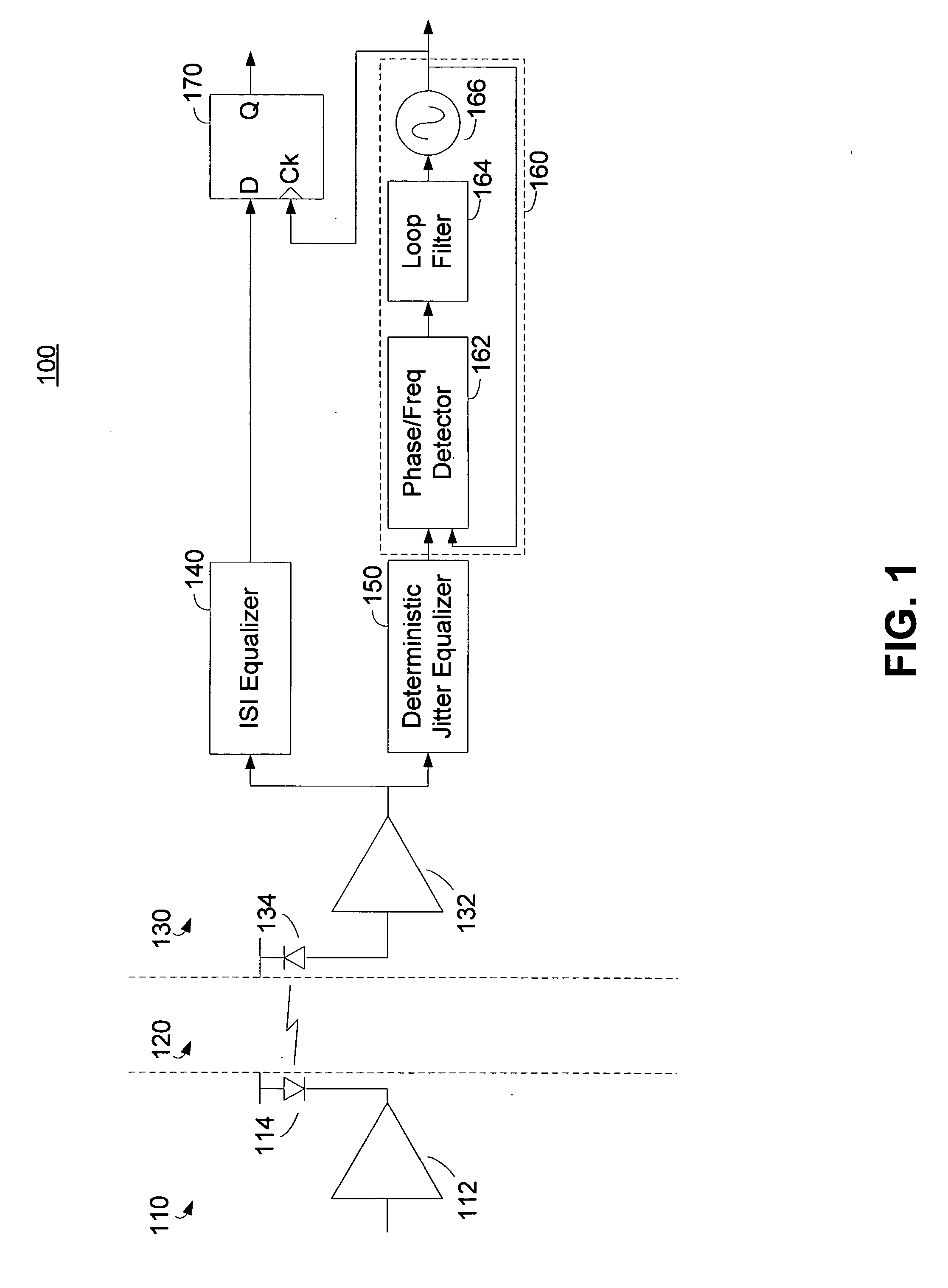
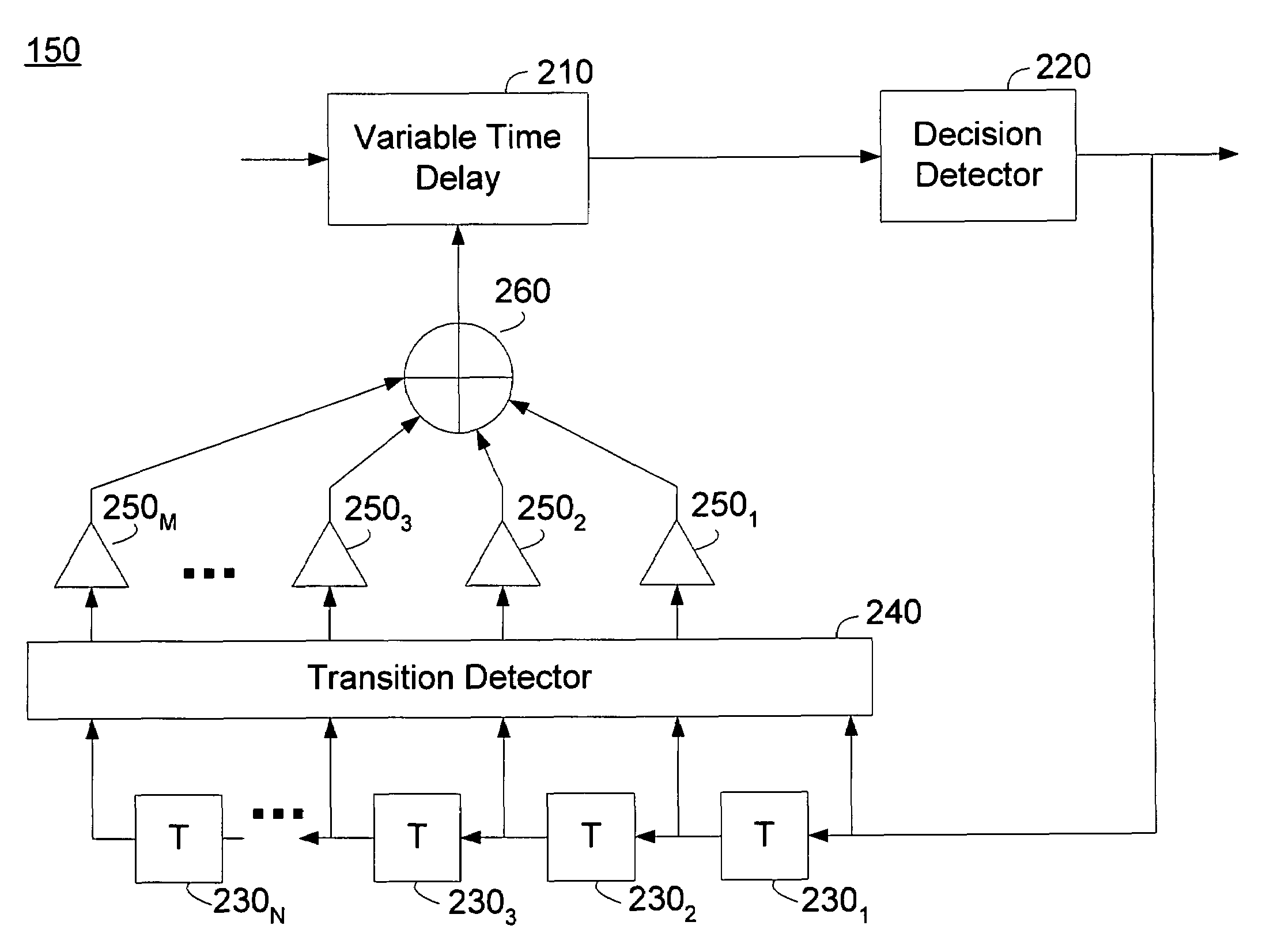
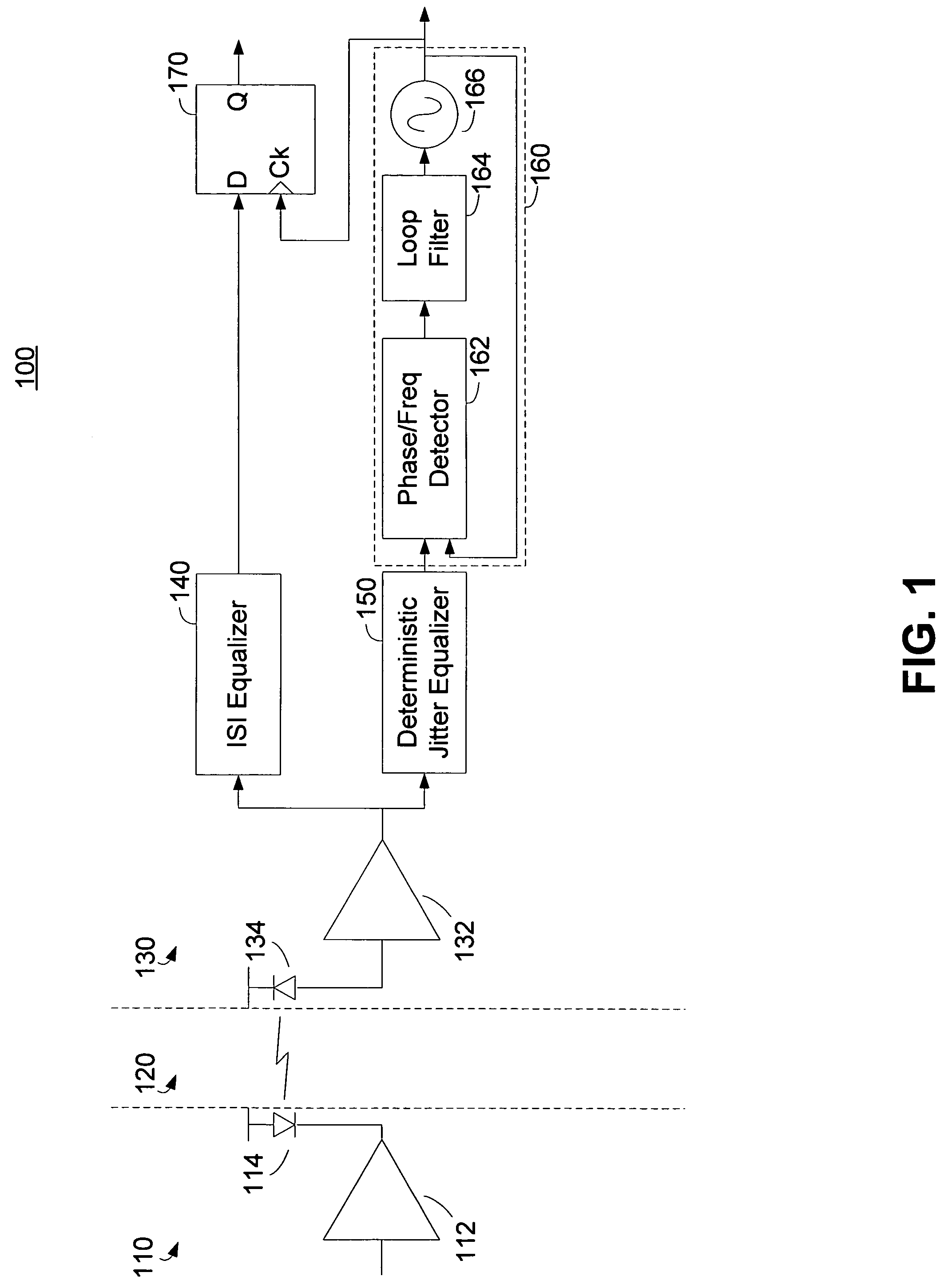
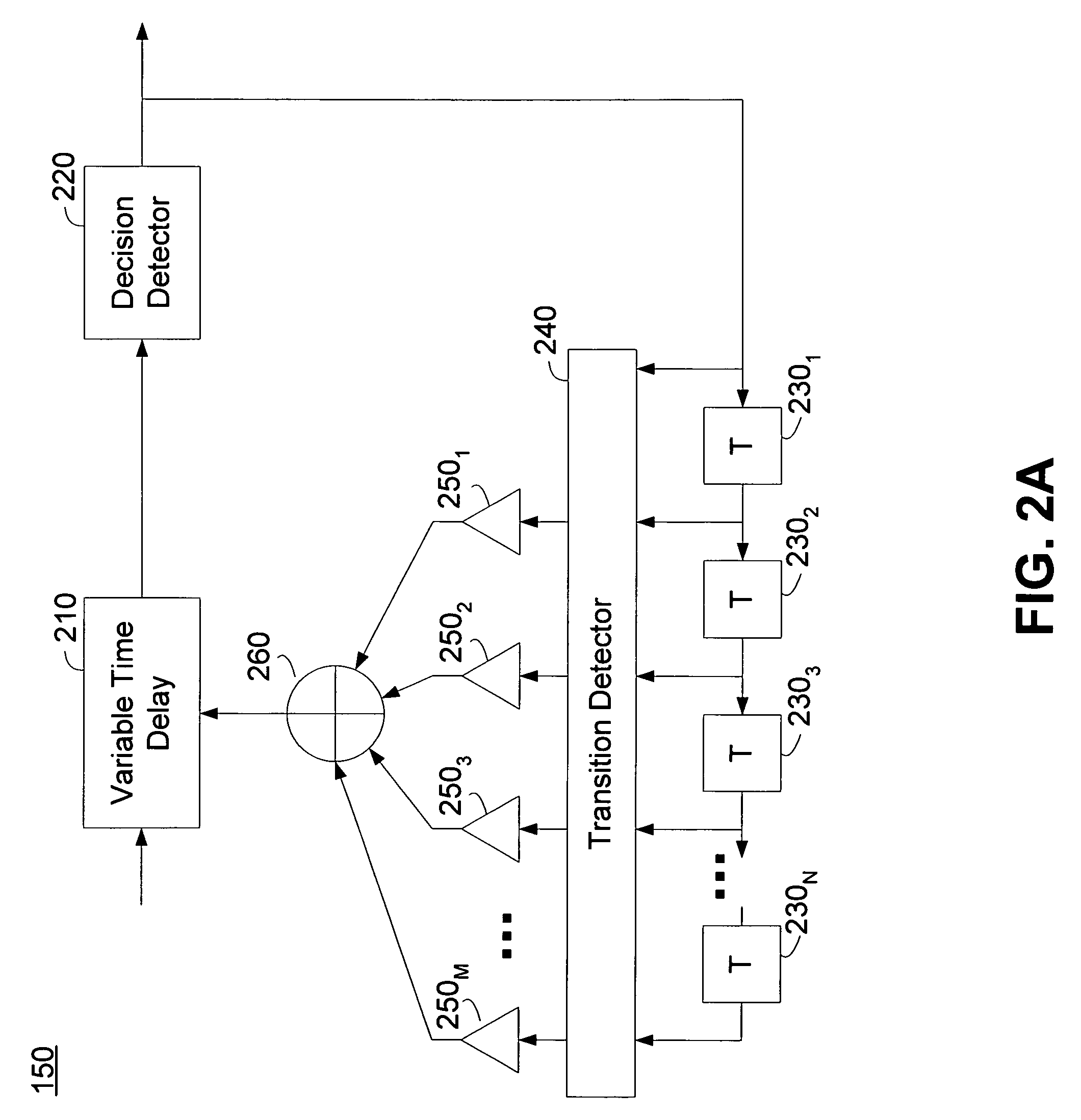
Deterministic jitter equalizer
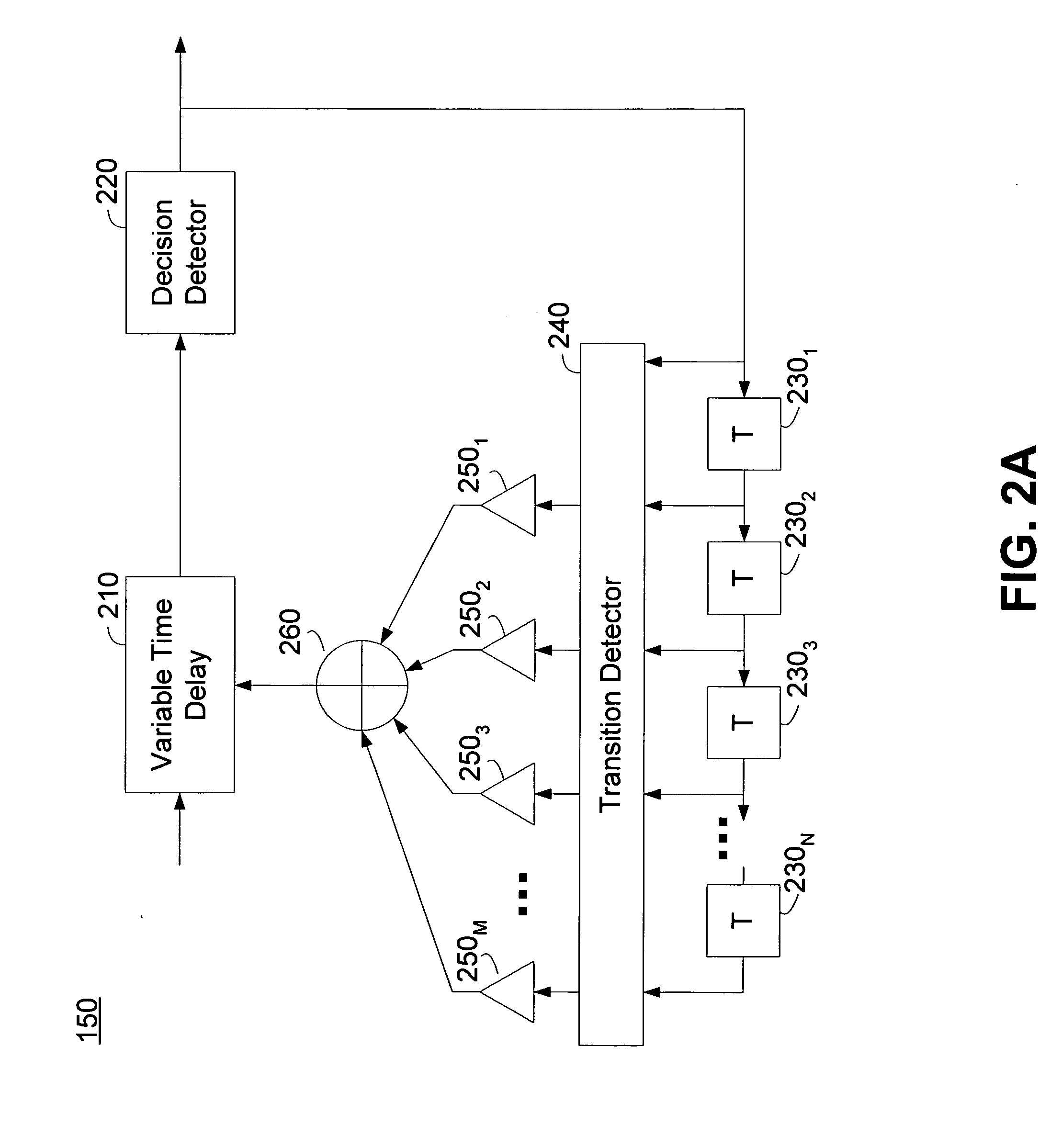
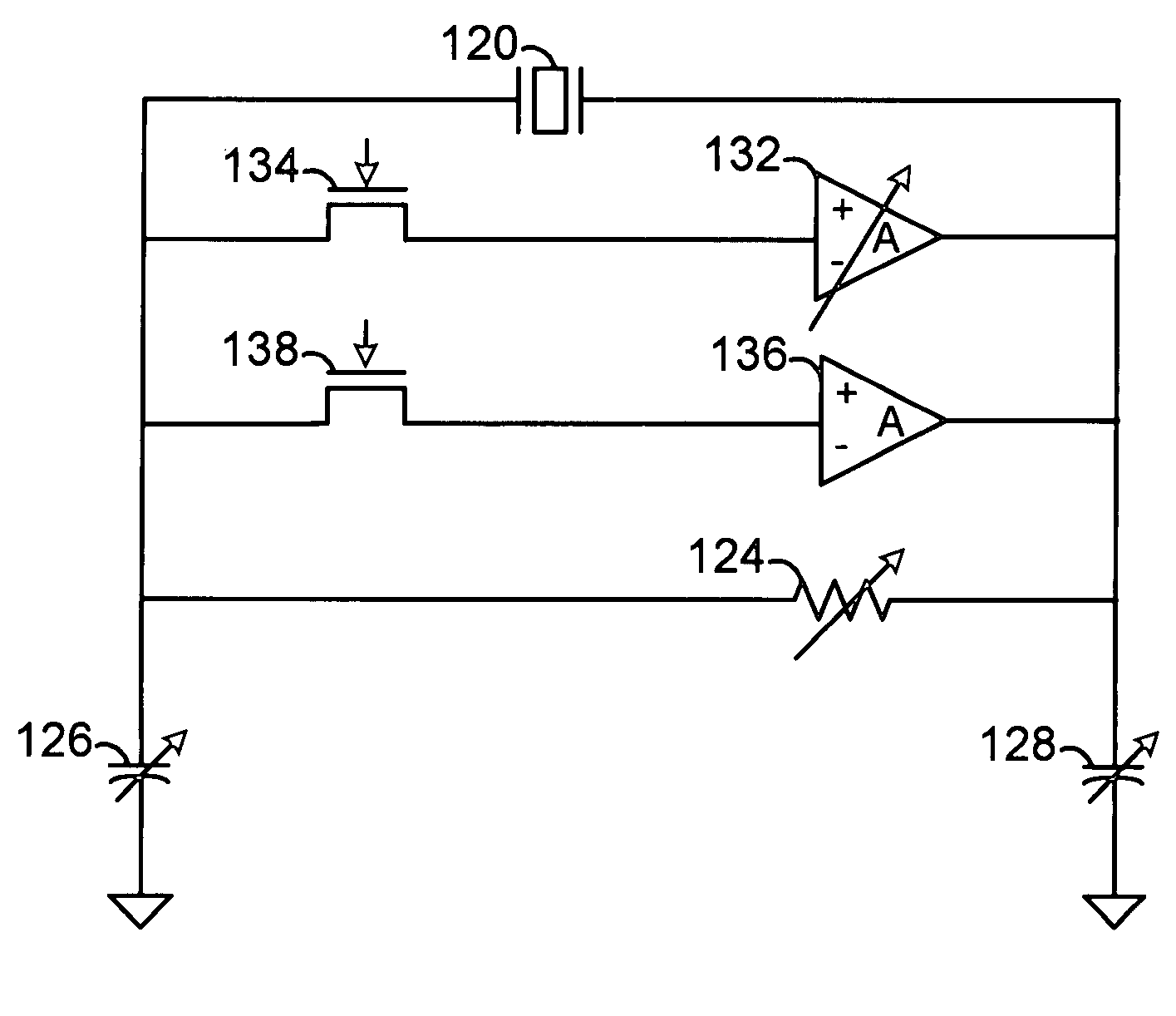
ActiveUS20050152488A1Easy to implementImprove phase noiseMultiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorData streamDuty cycle distortion
An equalizer for serial data communications can be configured to compensate for the effects of deterministic jitter. The equalizer can be configured to compensate a received serial data stream for the effects of data-dependent jitter as well as duty cycle distortion jitter. The equalizer can be configured to determine the value of one or more previously received symbols and compare them to a recovered symbol. The equalizer can adjust a variable delay positioned in the serial data path to introduce a delay into the data path that is based in part on the received data stream. The equalizer can be configured to vary the delay when any of the one or more previously received symbols is different from the recovered symbol, and can be configured to maintain a constant delay if the one or more previously received symbols is the same as the recovered symbol.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
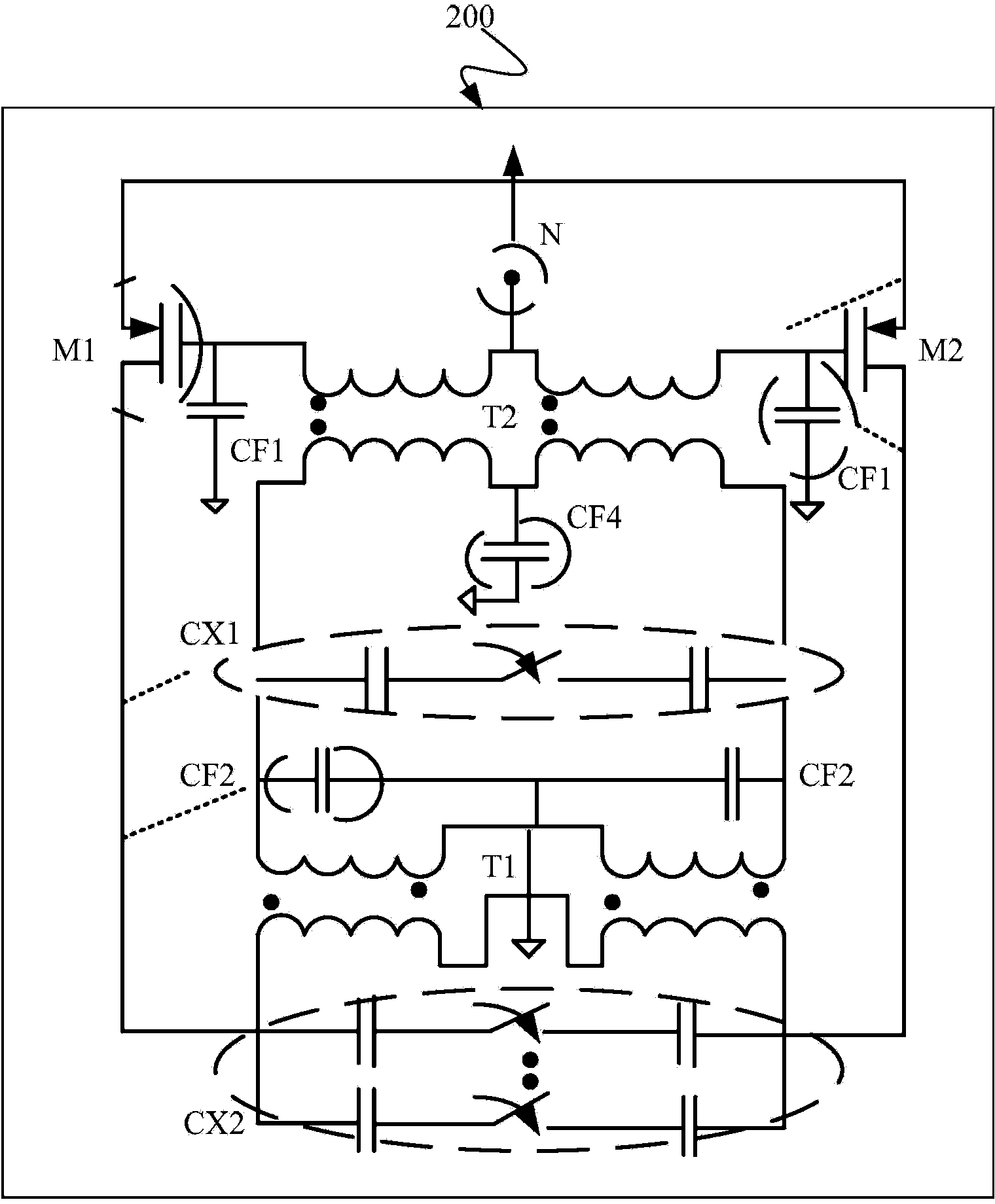
Low phase noise differential LC tank VCO with current negative feedback
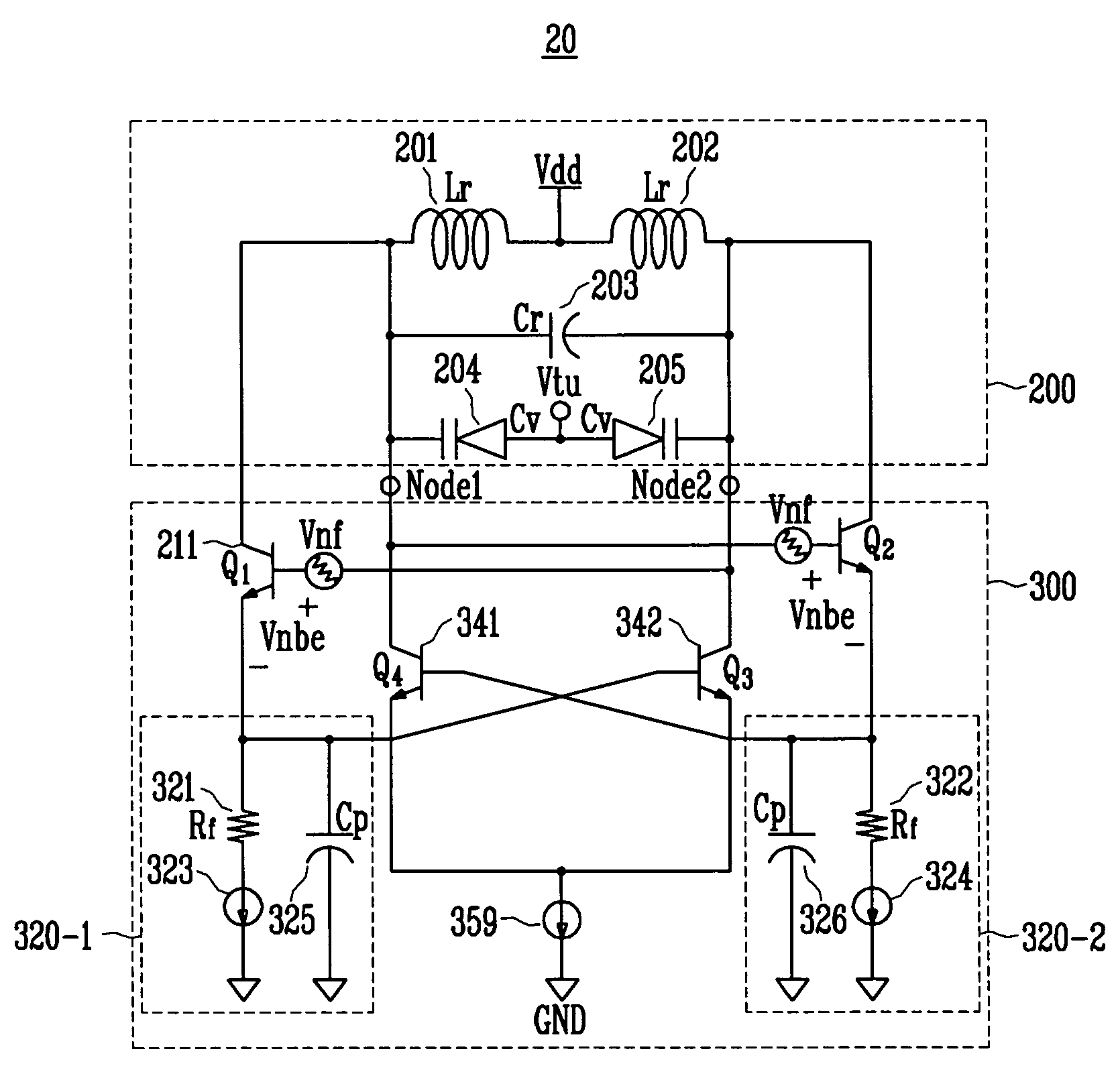
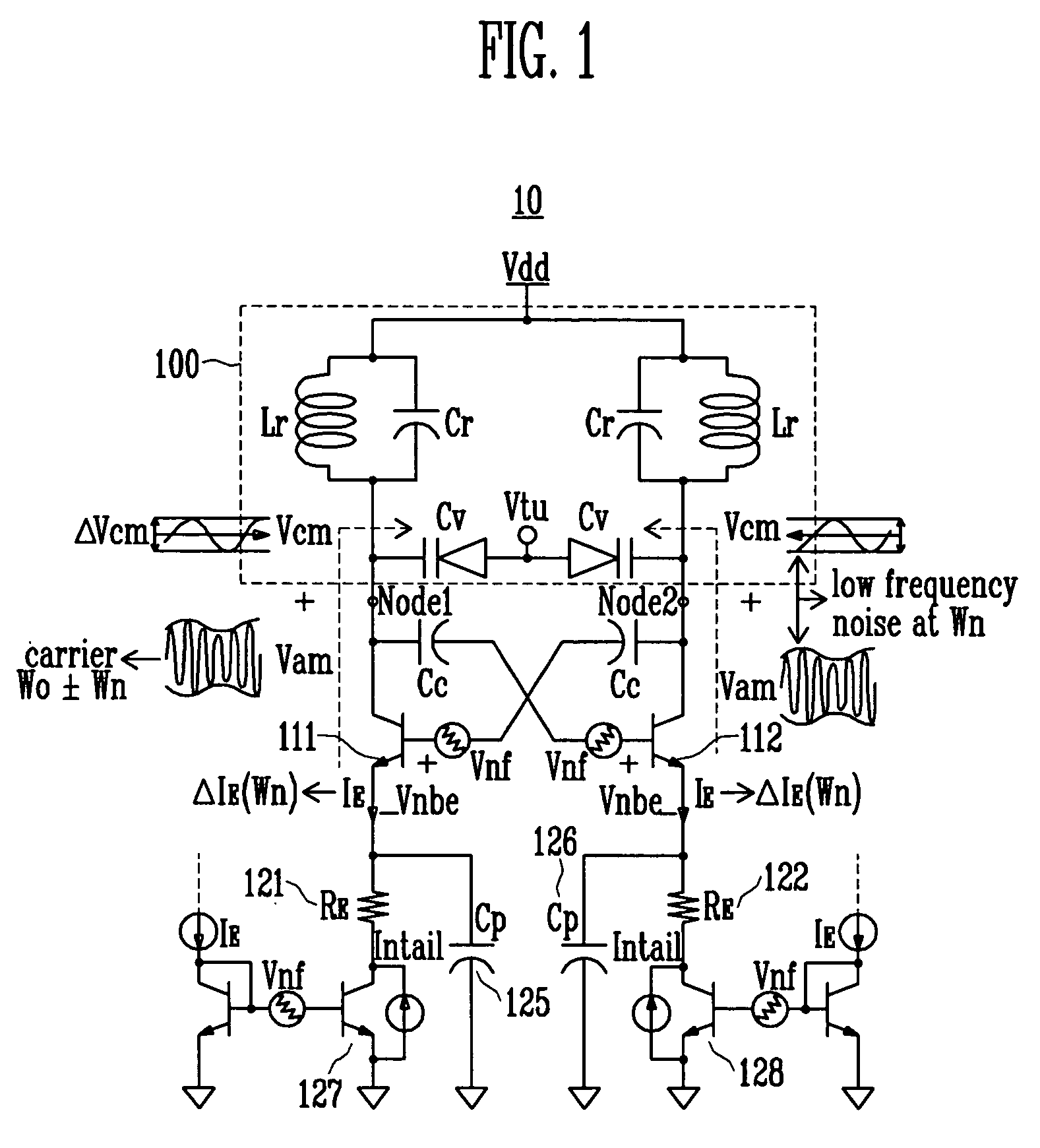
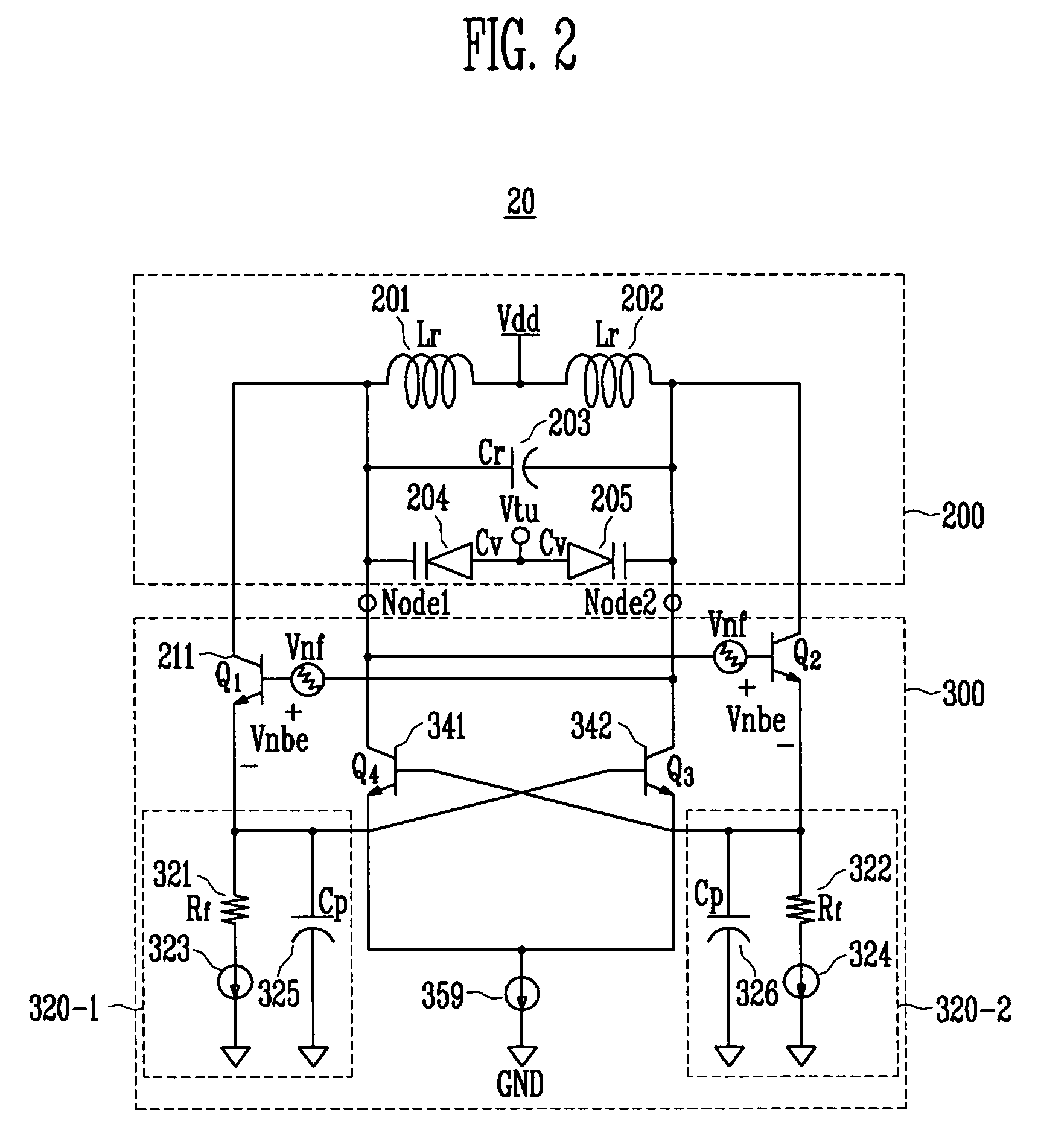
ActiveUS20070132521A1Good phase noise characteristicsEliminate Phase NoiseOscillations generatorsCapacitancePhase noise
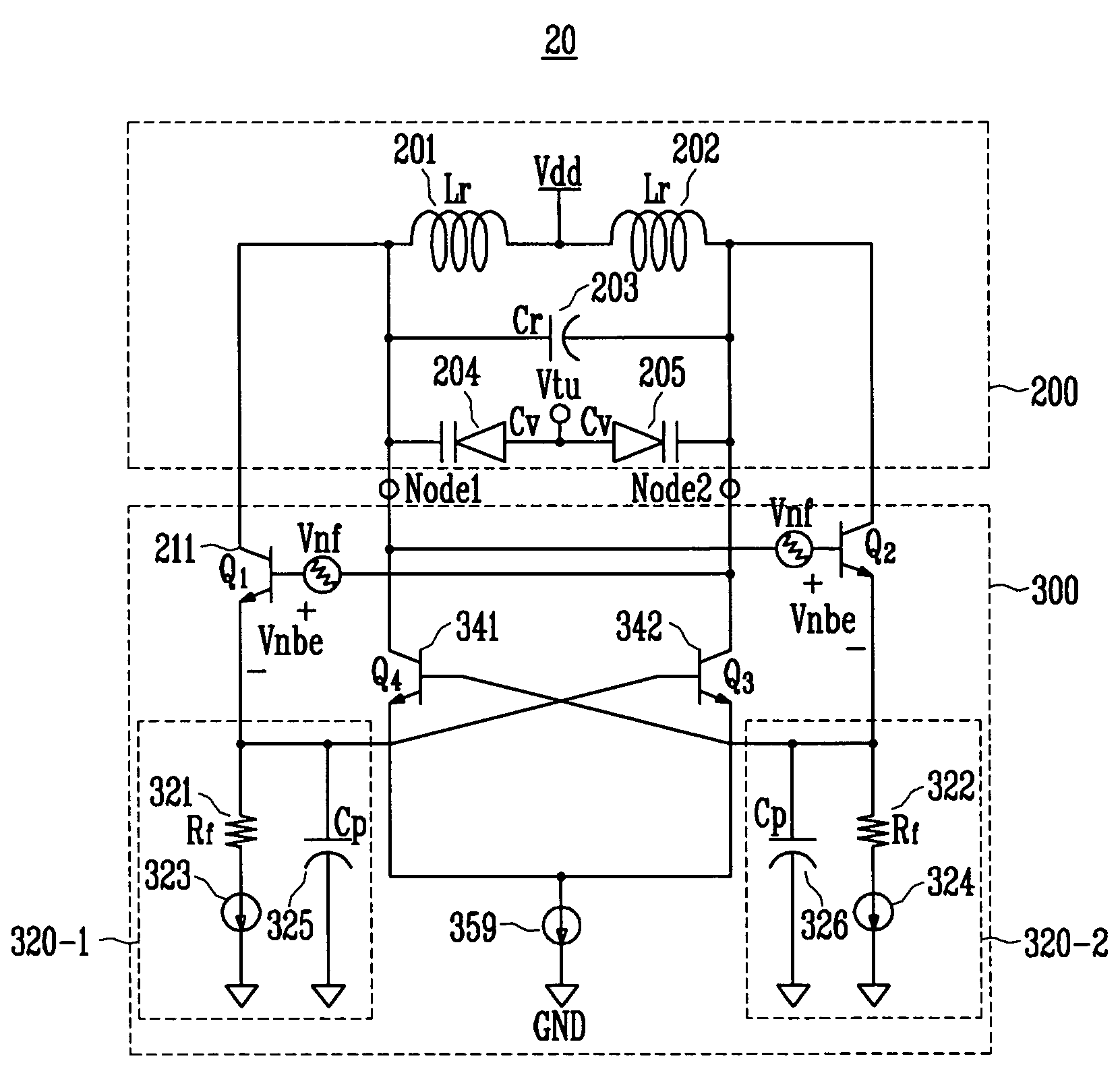
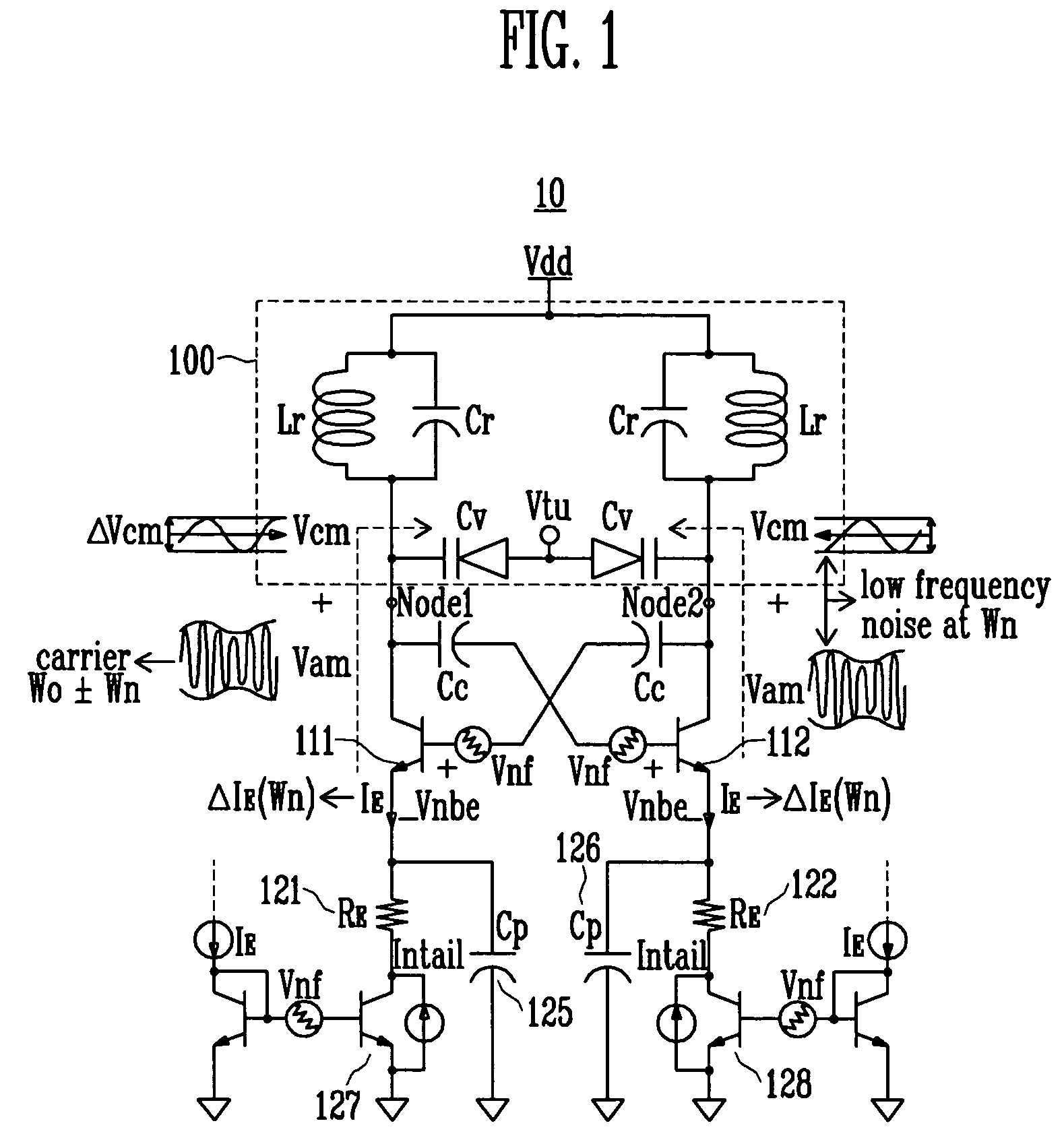
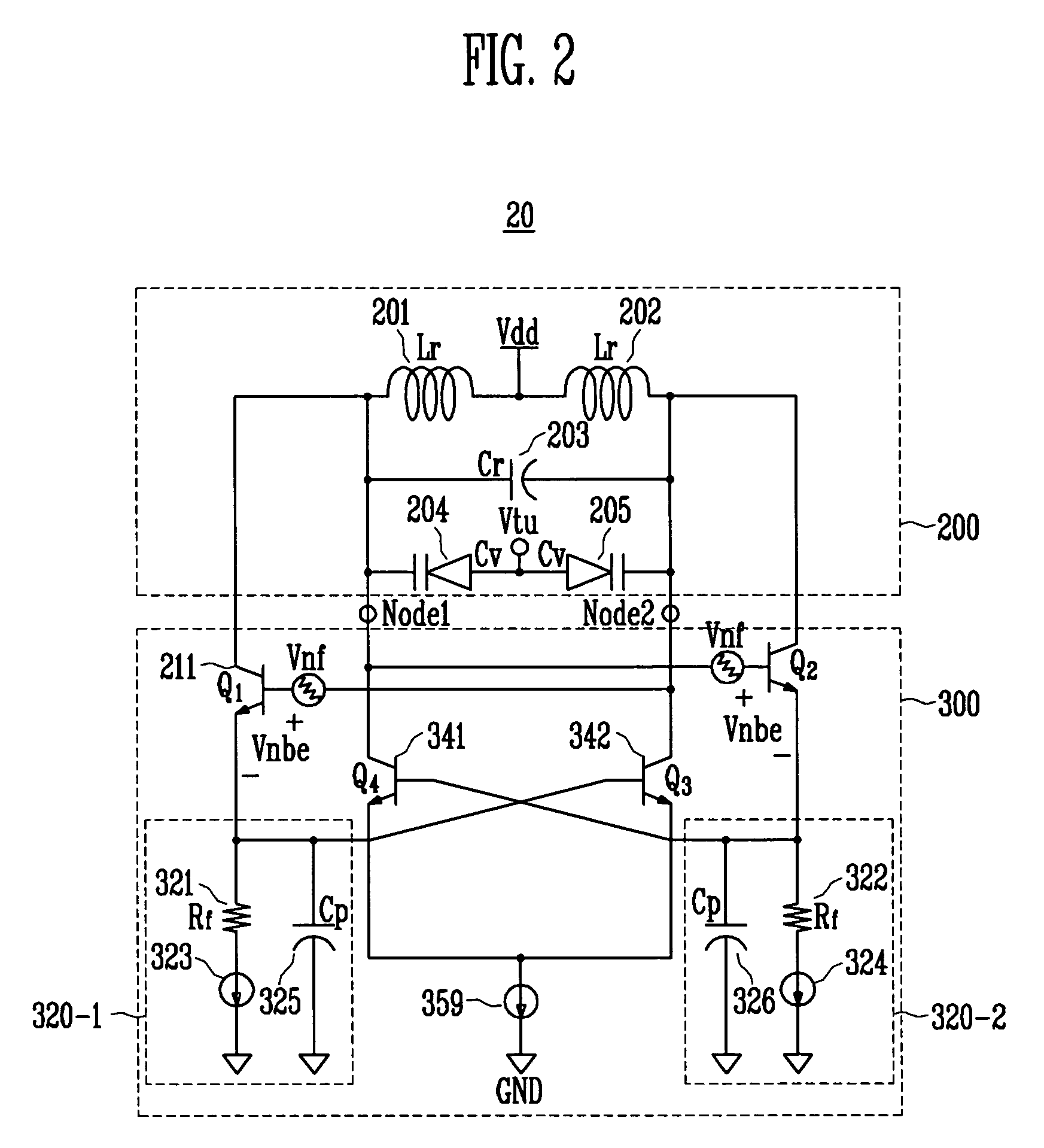
A differential voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) employed in a frequency synthesizer used as a local oscillator of a wireless communication on-chip transmitter / receiver is provided. More particularly, a differential current negative feedback VCO equipped with a current-current negative feedback circuit that suppresses low- and high-frequency noise is provided. A differential current negative feedback VCO includes a resonator determining oscillation frequency, and an oscillator generating negative resistance. In the oscillator of the differential current negative feedback VCO, transistors Q1 and Q2 form a cross-coupled pair, and negative resistance is generated by positive feedback of the cross-coupled pair. And, transistors Q1 and Q3 together with an emitter resistor and a capacitor form a current negative feedback part, and transistors Q2 and Q4 together with an emitter resistor and a capacitor form another current negative feedback part which is disposed opposite to a resonator. Thus, the VCO operates differentially. In the oscillator of the differential current negative feedback VCO, emitter noise currents generated by base noise voltages of Q1 and Q2 induced by low- and high-frequency noise sources in the bases of Q1 and Q2 are sampled by emitter resistors, amplified through bases of Q3 and Q4, and thus return to the bases of the Q1 and Q2 and suppress the base noise voltages. Measurement of the phase noise of the differential current negative feedback VCO reveals a phase noise reduction of approximately 25 dB compared to a conventional differential VCO.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Broadband low-phase noise frequency synthesizer without frequency divider based on harmonic mixing
ActiveCN103762978AReduce the frequency division ratioImprove phase noisePulse automatic controlPhase noiseMeasuring instrument
The invention relates to a broadband low-phase noise frequency synthesizer without a frequency divider based on harmonic mixing. The frequency synthesizer comprises a harmonic extraction module, a phase-locked loop, a direct frequency digital synthesizer and a reference source. The harmonic extraction module is used for extracting multiple-harmonic components of the reference source; appropriate components are elected and provided for an interpolation mixer; meanwhile, a reference clock of the direct frequency digital synthesizer is provided. The phase-locked loop is used for locking output signals and reference signals of a voltage-controlled oscillator. A feedback loop of the phase-locked loop comprises a frequency mixer which is used for guaranteeing broadband frequency outputting. By adopting the broadband low-phase noise frequency synthesizer without the frequency divider based on harmonic mixing, the broadband output frequency range of over one octave can be realized; the frequency divider is thoroughly omitted in the feedback loop, so that phase noise is reduced greatly; the frequency synthesizer supports wide bands and can be applied to a signal source, a frequency spectrograph and other high-performance measuring instruments, thereby having a wider application range.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Multi-mode crystal oscillator
InactiveUS7266349B2Reduce phase noiseImprove accuracyPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
In one embodiment of the present invention, two crystal oscillator circuits are coupled in parallel to provide differing performance according to mode. Generally, a first circuit provides low phase noise and high accuracy while a second circuit provides greater phase noise within an acceptable tolerance while consuming significantly less power in a low power mode of operation. The second circuit includes an entirely separate amplifier for the low power operation that tolerates a relatively smaller input signal swing but that consumes even less power. The first circuit, which comprises selectable amplification elements, and the second circuit are coupled in parallel with selectable resistive elements and capacitive elements to provide varying amounts of amplification and filtering according to whether an operational mode is in a startup mode, a normal mode, or a low power mode of operation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
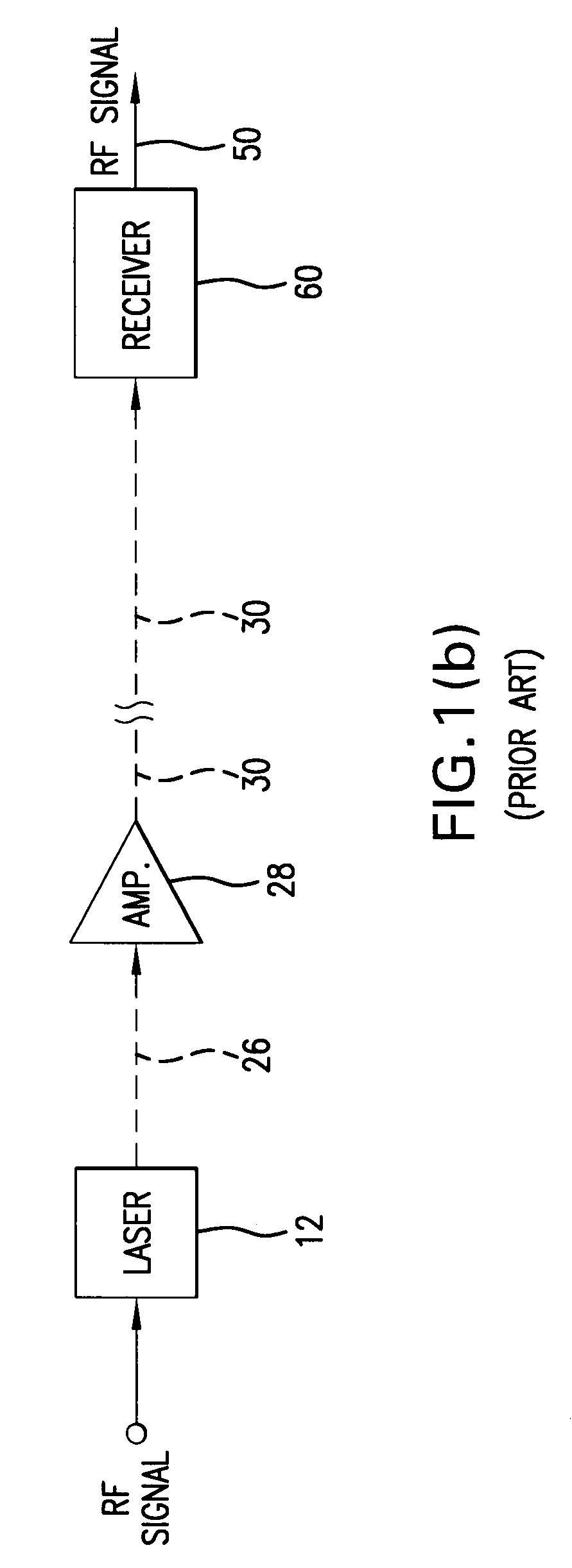
Directly modulated or externally modulated laser optical transmission system with feed forward noise cancellation
InactiveUS20070206961A1Produce some attenuationReduce phase noiseElectromagnetic transmittersFiberTransfer system
An optical transmitter for generating a modulated optical signal for transmission over a fiber optic link to a remote receiver including a laser; a modulator for directly amplitude modulating the laser with an analog RF signal to produce an optical signal including an amplitude modulated information-containing component; and a phase modulator coupled to the output of the laser for canceling the noise signals generated in the laser.
Owner:EMCORE INC
Deterministic jitter equalizer
ActiveUS7463680B2Easy to implementImprove phase noiseMultiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorData streamDuty cycle distortion
An equalizer for serial data communications can be configured to compensate for the effects of deterministic jitter. The equalizer can be configured to compensate a received serial data stream for the effects of data-dependent jitter as well as duty cycle distortion jitter. The equalizer can be configured to determine the value of one or more previously received symbols and compare them to a recovered symbol. The equalizer can adjust a variable delay positioned in the serial data path to introduce a delay into the data path that is based in part on the received data stream. The equalizer can be configured to vary the delay when any of the one or more previously received symbols is different from the recovered symbol, and can be configured to maintain a constant delay if the one or more previously received symbols is the same as the recovered symbol.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
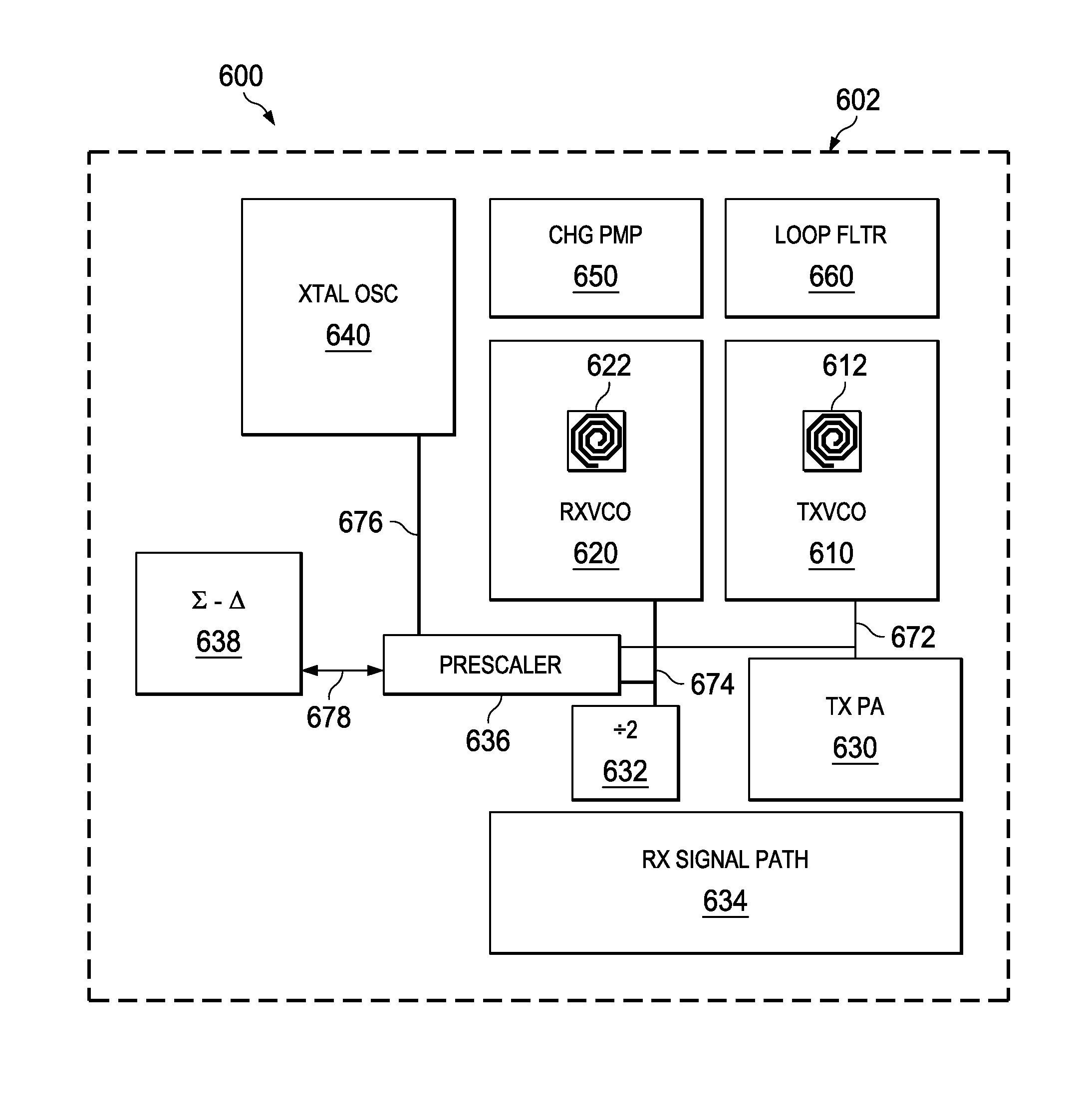
Self-calibrating shared-component dual synthesizer
ActiveUS20150180594A1Reducing substrate areaReduced Power RequirementsTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringPhase noiseFrequency synthesizer
A self-calibrating shared-component dual synthesizer includes, for example, two frequency synthesizers that are adapted to operate (respectively) in transmit (TX) and receive (RX) modes. Each synthesizer can be selectively arranged to vary and optimize the phase noise in accordance with the TX and RX requirements associated with each mode as well as independently optimized for flexible low area floorplan to achieve low power, spectral fidelity and reduced test time, low cost built in self-calibration. The two frequency synthesizers are also adapted to provide a built-in self-test signals used for intermodulation testing and calibration.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
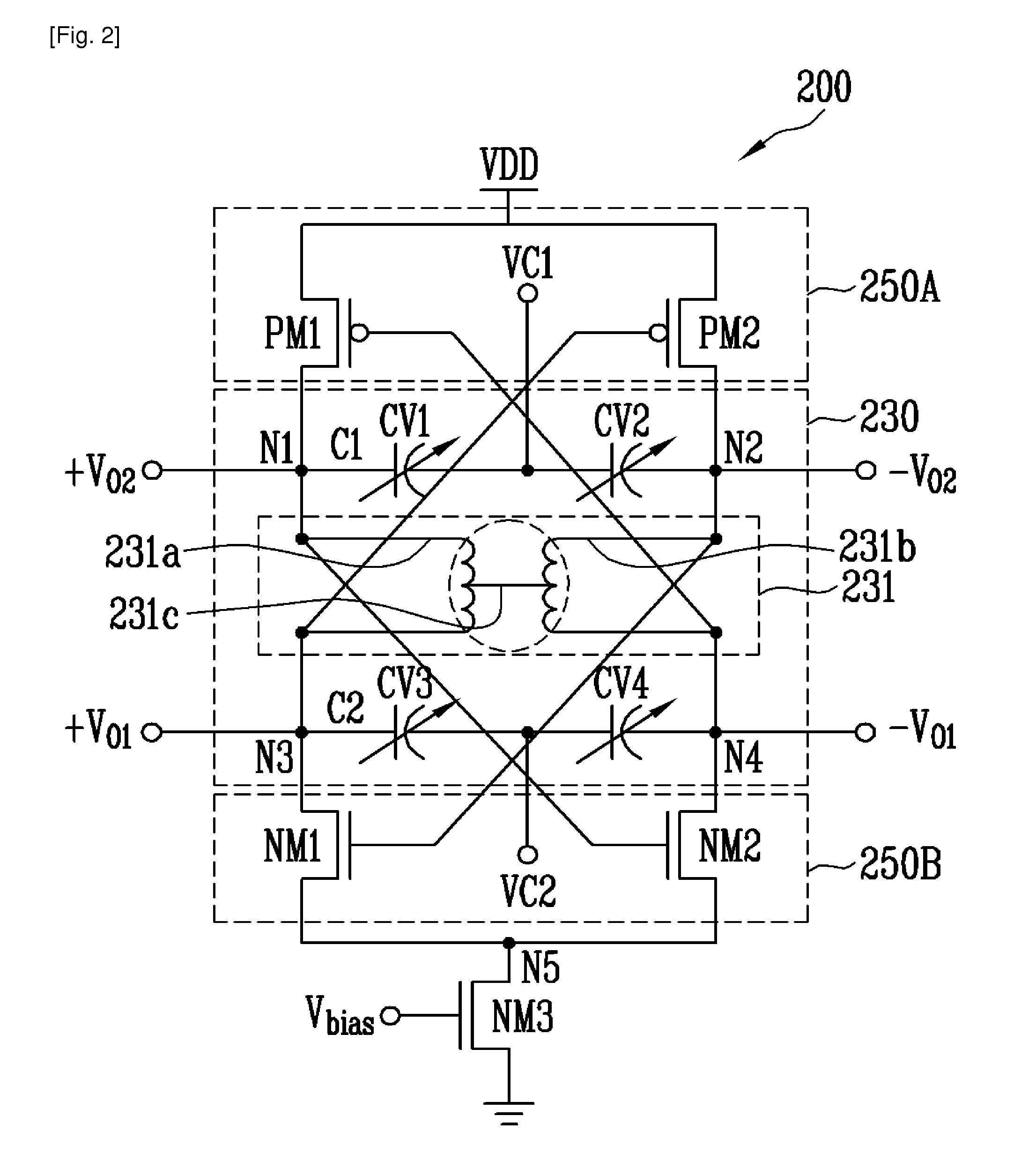
The differential vco and quadrature vco using center-tapped cross-coupling of transformer
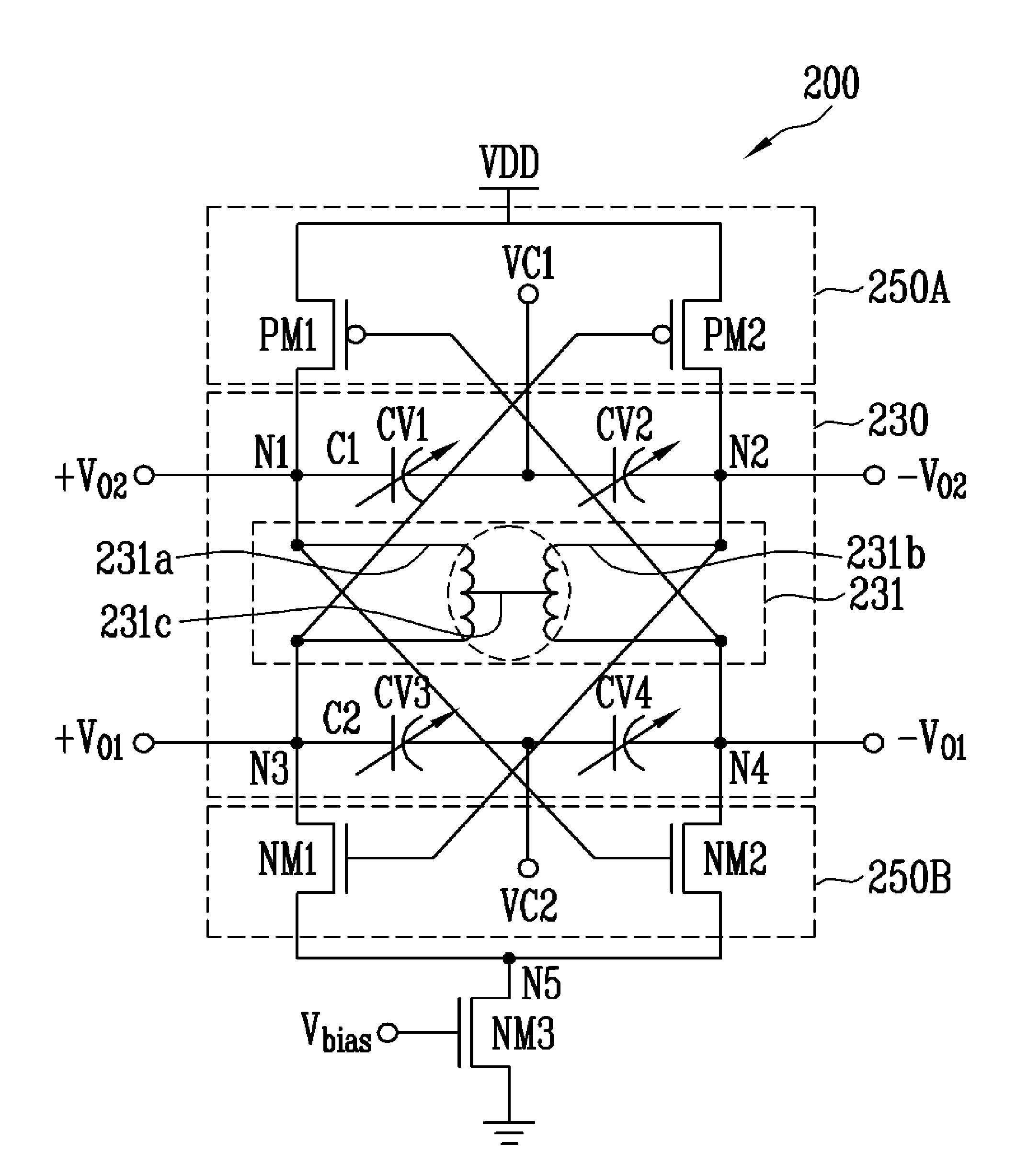
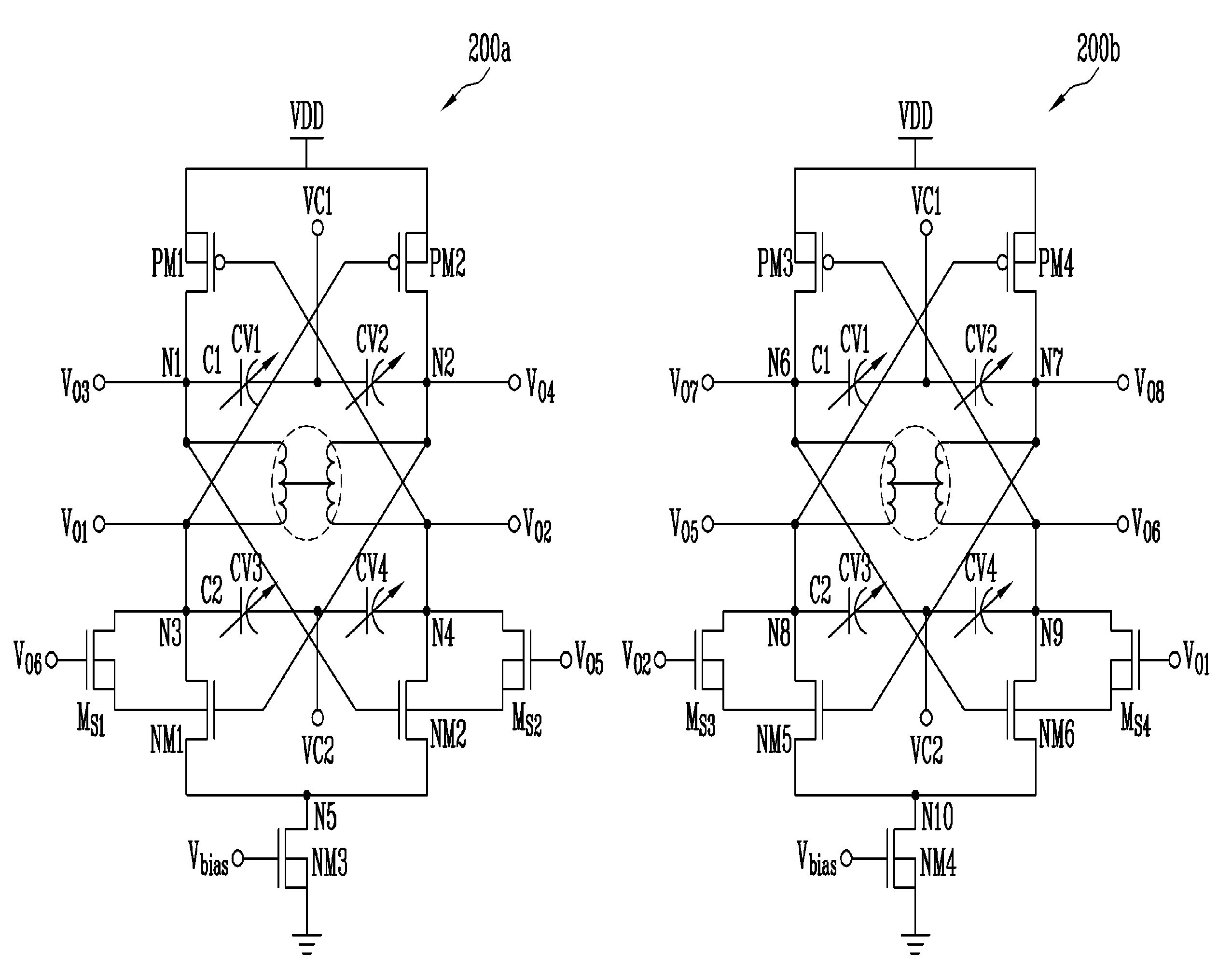
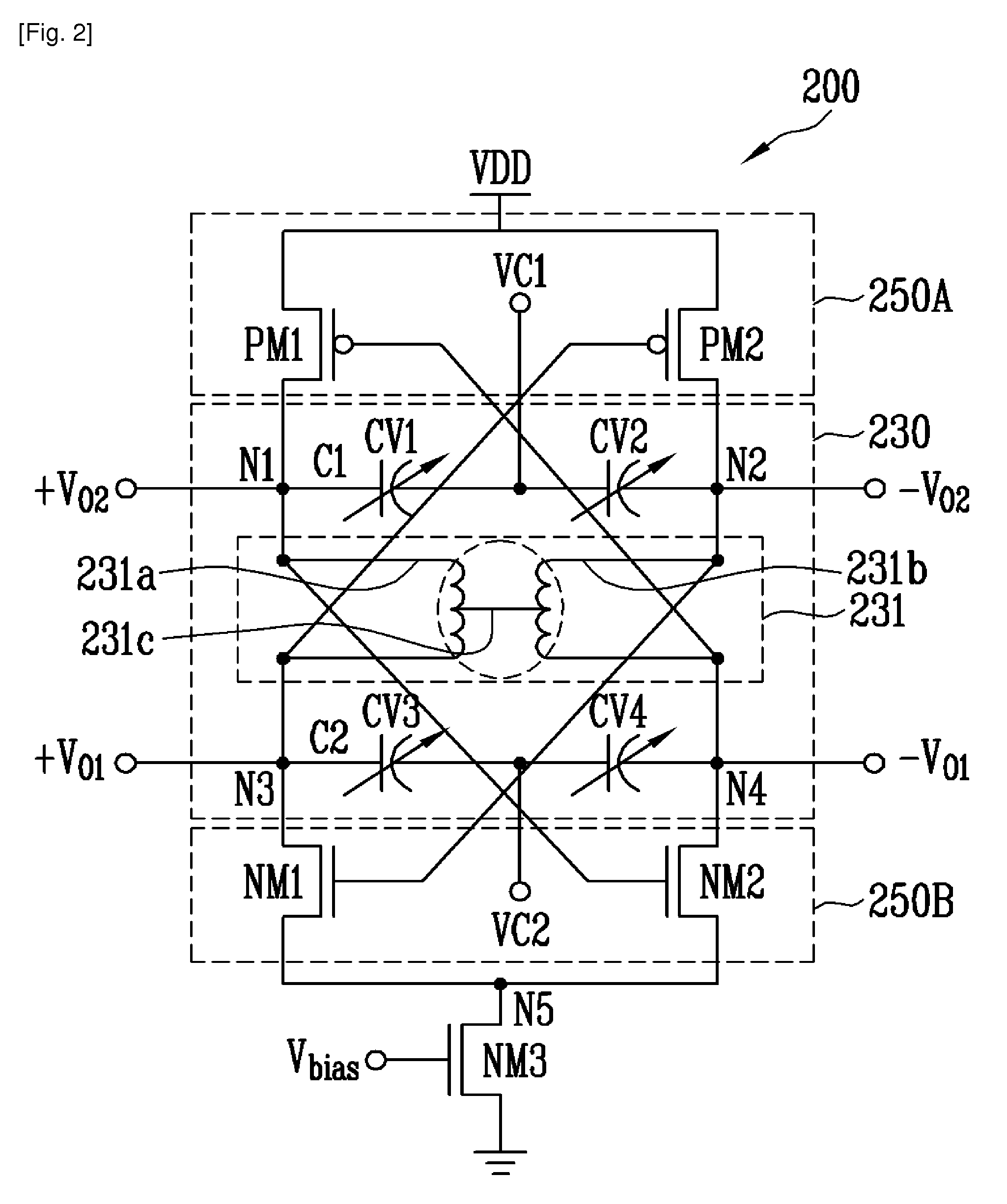
InactiveUS20110032044A1Low powerExcellent phase noise characteristicElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsCenter tapCapacitance
Provided are a differential voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) and a quadrature VCO using center-tapped cross-coupling of a transformer. The differential VCO and the quadrature VCO can be driven by low power through a current reuse structure and have an excellent phase noise characteristic by center-tapped cross-coupling through a transformer. Further, variable capacitance units for frequency variation are divided into variable capacitance units for coarse tuning and variable capacitance units for fine tuning. Therefore, it is possible to obtain a wide tuning range while voltage oscillation gain is reduced. Further, the differential VCO and the quadrature VCO are configured in such a manner that the respective variable capacitance units operate linearly throughout the entire capacitance region due to control voltage distribution by resistors. Accordingly, it is possible to obtain a linear control voltage-oscillation frequency characteristic. The quadrature VCO according to the present invention can output four-phase quadrature signals while having an excellent phase noise characteristic, without substrate loss and current consumption caused by the switching transistors.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
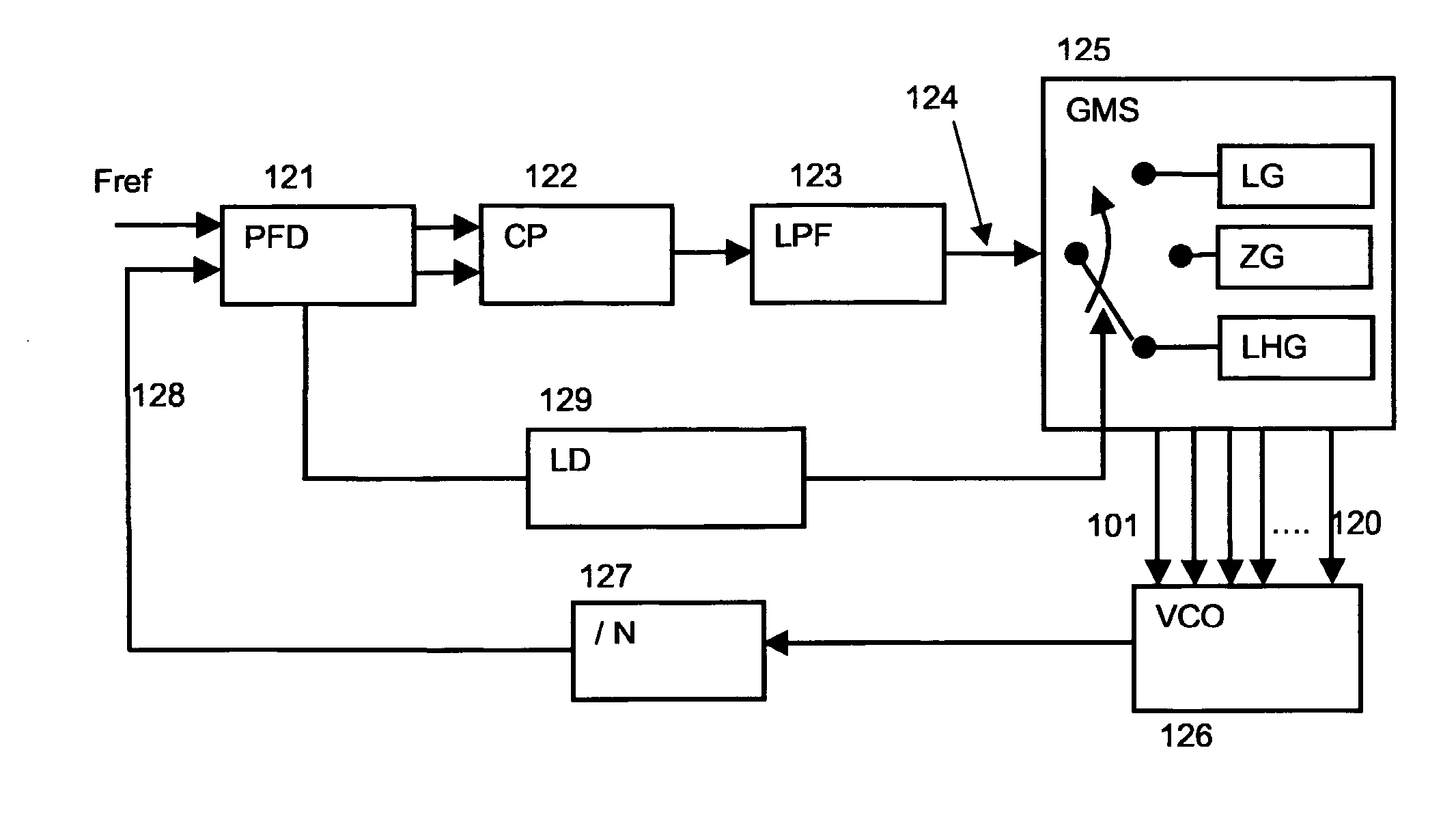
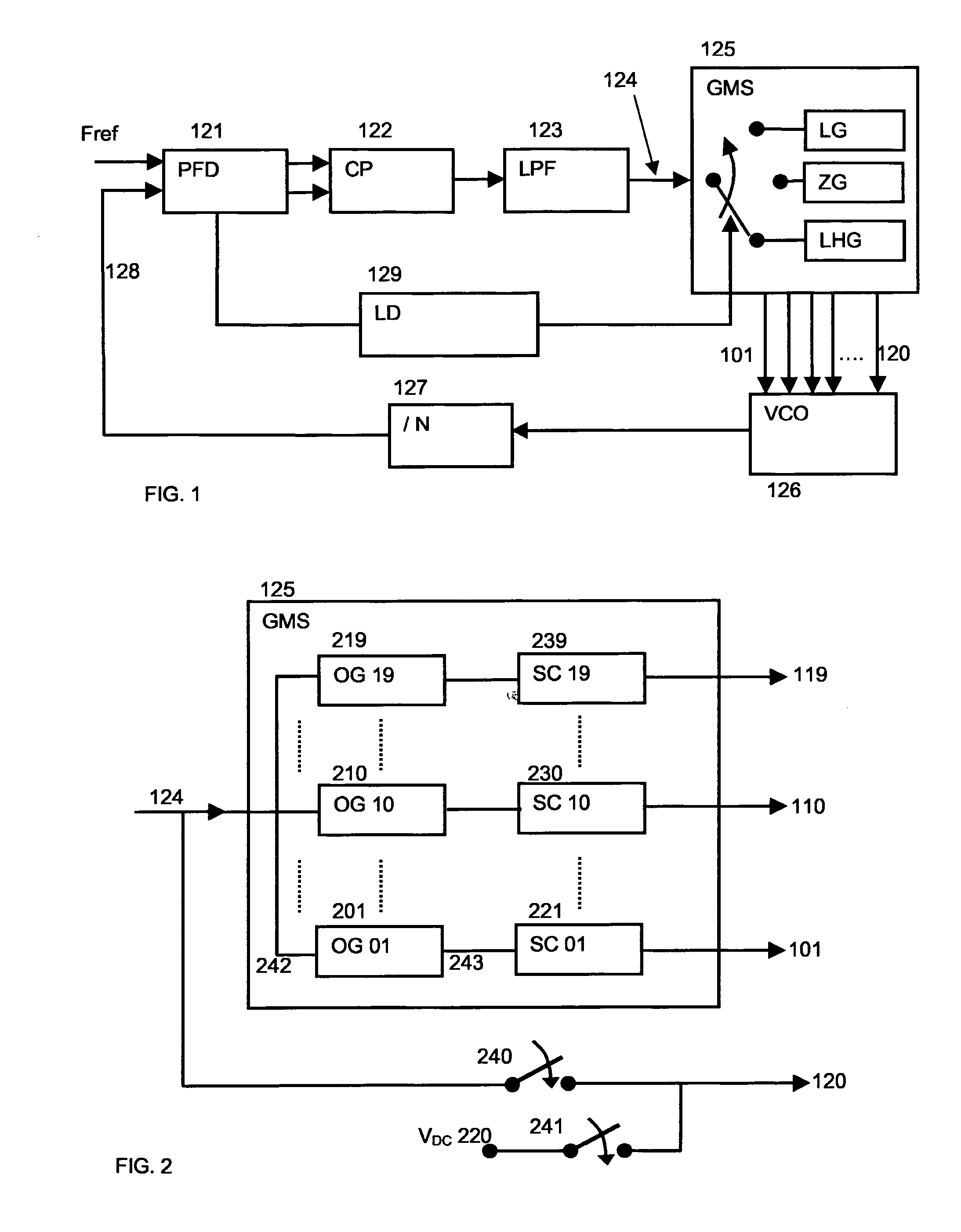
Analogue self-calibration method and apparatus for low noise, fast and wide-locking range phase locked loop
InactiveUS20070040617A1Improve Noise PerformanceWithout usingResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlLow noisePhase noise
A method and apparatus for a fast and automatic setting of the phase locked loop (PLL) output frequency that significantly improves linearity, locking range as well as spectrum purity, jitter and phase noise performances is disclosed. In one embodiment, a PLL frequency synthesizer is disclosed having a reconfigurable voltage controlled oscillator VCO with three modes of operation: a Linear-High-gain, Zero-gain, and Low-gain mode. During a first tuning operation, the VCO work in a linear high gain mode, enabling a totally analogue self-calibration of the PLL over a wide frequency tuning range and with a fast settling time. During this operation the control voltage at the input of the VCO is varied by the PLL until the appropriate output frequency is found. A method for providing a linear variation of the frequency over all the voltage tuning range during this mode is disclosed. When the loop is locked, the VCO is automatically switched to the Zero-gain mode while keeping its frequency unchanged. Its sensitivity to the noise in the control path is then practically eliminated and its phase noise performances significantly improved. If the frequency error and phase noise are sufficiently small for the considered application the tuning is stopped. If the error and phase noise are not sufficiently small the VCO is switched again to Low-gain mode and fine-tuning adjustment of the output frequency is achieved.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Lc oscillator with tail current source and transformer-based tank circuit
ActiveCN104272583ALower quality factorImprove reliabilityPulse automatic controlActive element networkTransformerInductance
An oscillator, comprising: a pair of transistors to which source terminals are interconnected and to which drain and gate terminals are coupled by a positive feedback loop comprising an oscillator tank, wherein the source terminals of the transistors are connected to a current source configured to control physical parameters of the oscillator.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
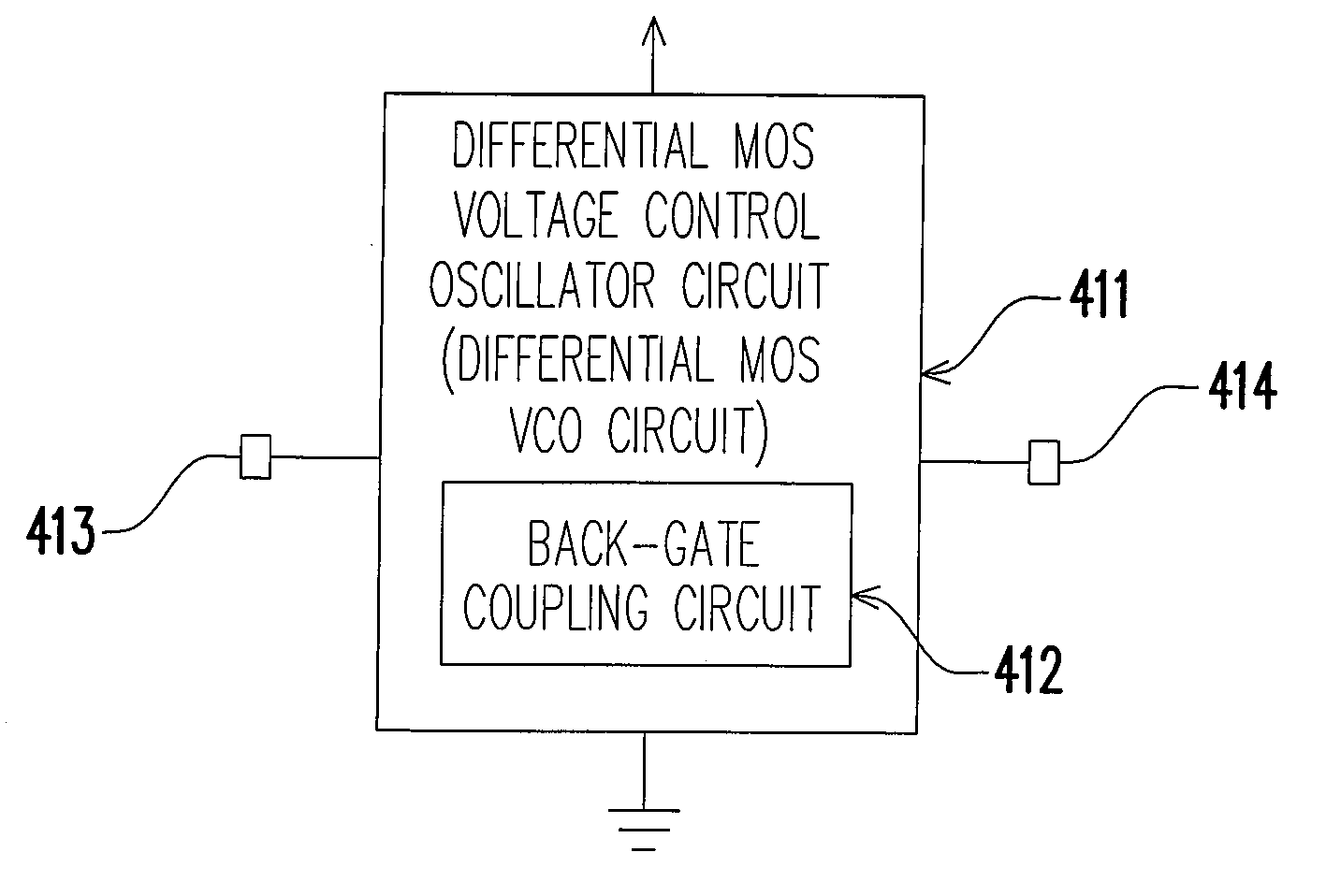
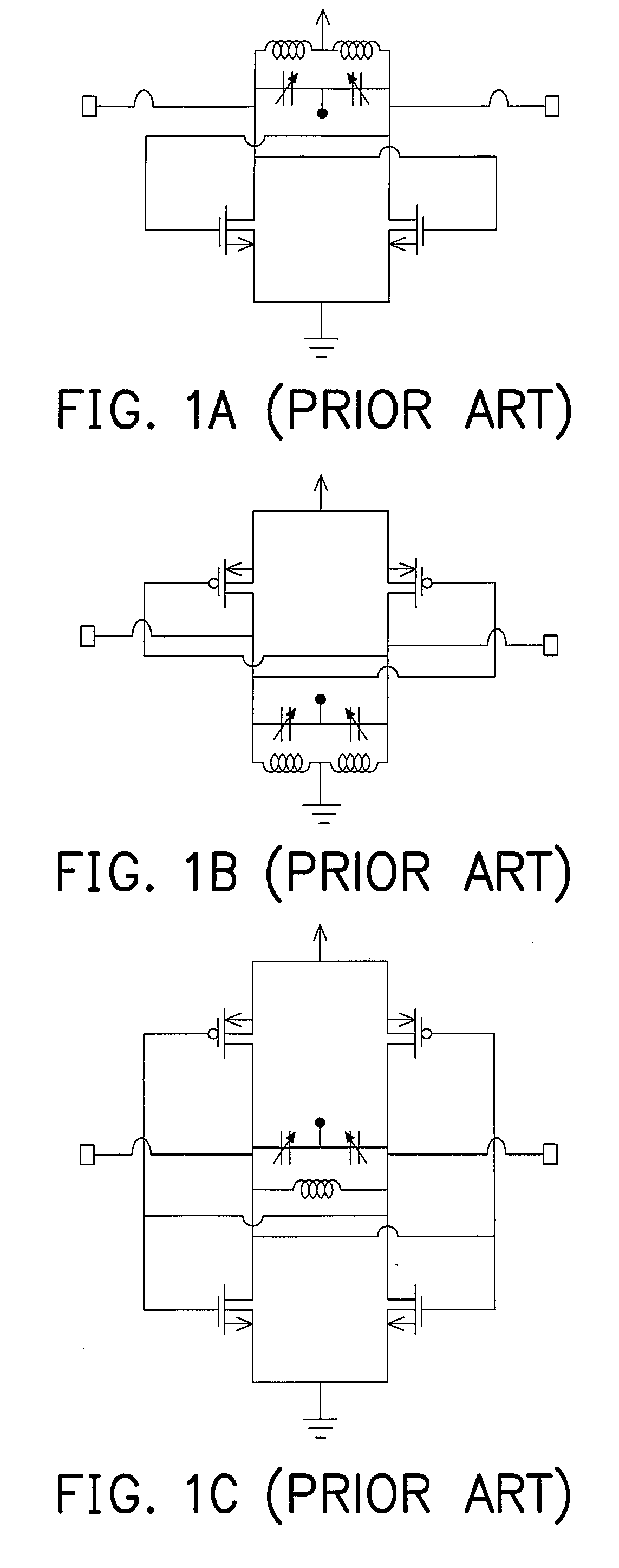
Back-gate coupling voltage control oscillator
InactiveUS7545230B2Improve phase noiseReduce circuit areaAngle modulation by variable impedenceAngle modulation detailsResonant cavityPhase noise
A voltage control oscillator (VCO) includes a VCO circuit and a back-gate coupling circuit, wherein the VCO circuit includes at least a first transistor, a second transistor and a resonant cavity formed by an inductor and a capacitor. The back-gate coupling circuit is formed by a plurality of capacitors and a plurality of resistors. In the embodiments of the present invention, the capacitors are coupled to the back-gate terminals of the first transistor and the second transistor, so as to reduce the power consumption and the phase noise of the VCO.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
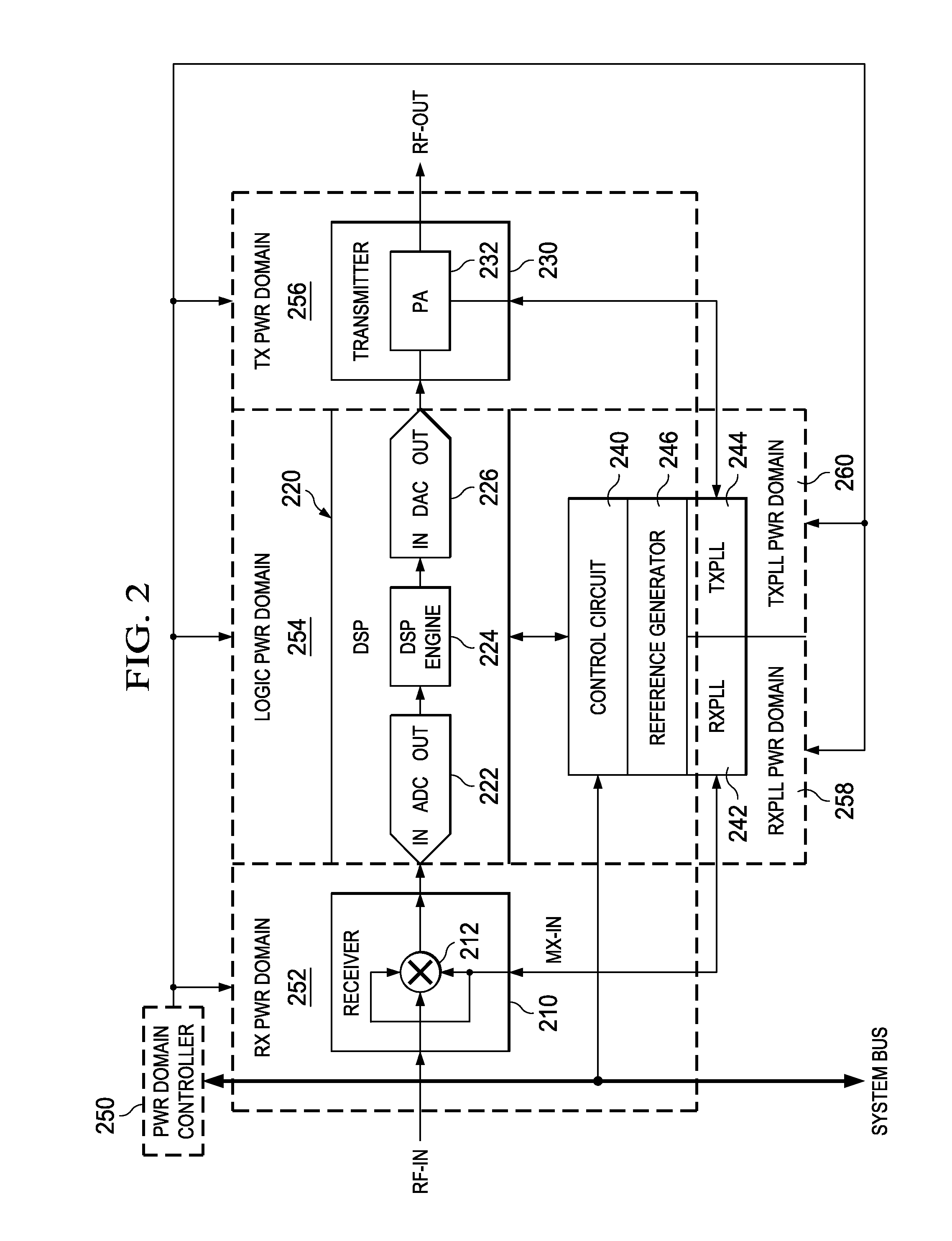
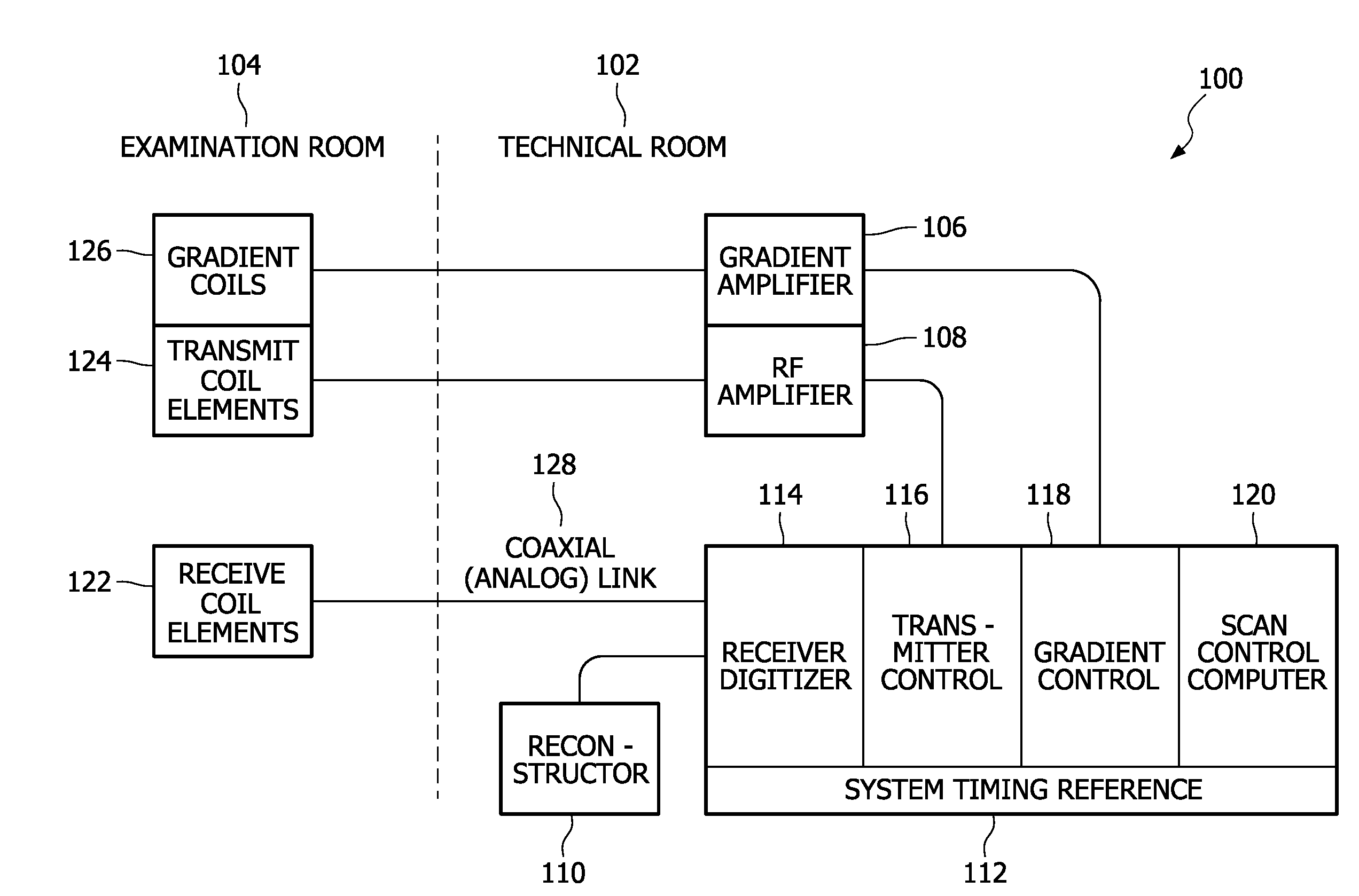
Clock generation in MRI receivers
ActiveUS20100260293A1Improve phase noiseQuality improvementAnalogue/digital conversionMagnetic measurementsTelecommunications linkEngineering
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging radio frequency receiver, the receiver being adapted to receive analogue signals from at least one radio frequency receiver coil unit (122; 204; 306), the radio frequency receiver comprising an analogue-digital converter (408) to convert the analogue magnetic resonance signal into a first digital signal, a resampling and demodulation unit (414) to convert the first digital signal into a second digital signal, a communication interface (400: 600; 602) adapted for transmitting the second digital signal via a communication link (202), and a first clock generator (406) for generating a sampling clock, the sampling clock being the direct clock source for the analogue-digital converter (408), the first clock generator (406) being adapted to generate the sampling clock using a digital timing reference, the digital timing reference being received digitally via the communication link (202) by the communication interface (400: 600; 602), wherein the receiver further comprises a second clock generator (410) for generating a system clock, the system clock being the direct clock source for the resampling and demodulation unit (414), the second clock generator (410) being adapted to generate the system clock using the sampling clock.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Full-light-control phased array radar transmitter based on broadband light source
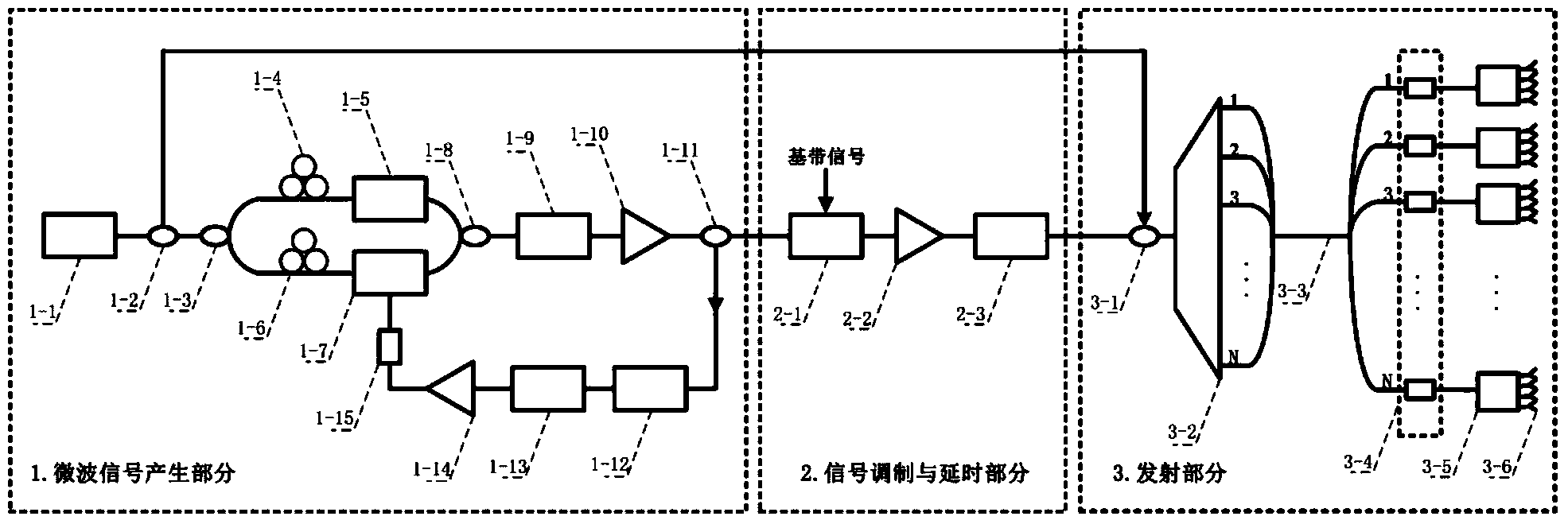
ActiveCN104297731AReal-time latencySimple structureWave based measurement systemsDetector arrayPhased array
A full-light-control phased array radar transmitter based on a broadband light source comprises a microwave signal generating part, a signal modulation and delay part and a transmitting part. The microwave signal generating part comprises the broadband light source, a first optical divider, a second optical divider, a first polarization controller and the like. The signal modulation and delay part comprises a second electrooptical modulator, a second optical amplifier, an optical fiber delay network, a second optical combiner. The transmitting part comprises a first wavelength division multiplexer, an optical fiber or an optical cable, a photoelectric detector array and the like. According to the full-light-control phased array radar transmitter based on the broadband light source, microwave signals are generated through an optoelectronic oscillator based on the broadband light source, an external microwave source is omitted, the broadband light source is used for replacing a multi-wavelength laser array, the structure that the wavelength division multiplexer is used for dividing the broadband light source enables the full-light-control phased array radar transmitter to be simple and compact in structure, and cost is lowered.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Multi-mode crystal oscillator
InactiveUS20060030358A1Easy to adjustReduce phase noiseEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCapacitancePower mode
In one embodiment of the present invention, two crystal oscillator circuits are coupled in parallel to provide differing performance according to mode. Generally, a first circuit provides low phase noise and high accuracy while a second circuit provides greater phase noise within an acceptable tolerance while consuming significantly less power in a low power mode of operation. The second circuit includes an entirely separate amplifier for the low power operation that tolerates a relatively smaller input signal swing but that consumes even less power. The first circuit, which comprises selectable amplification elements, and the second circuit are coupled in parallel with selectable resistive elements and capacitive elements to provide varying amounts of amplification and filtering according to whether an operational mode is in a startup mode, a normal mode, or a low power mode of operation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
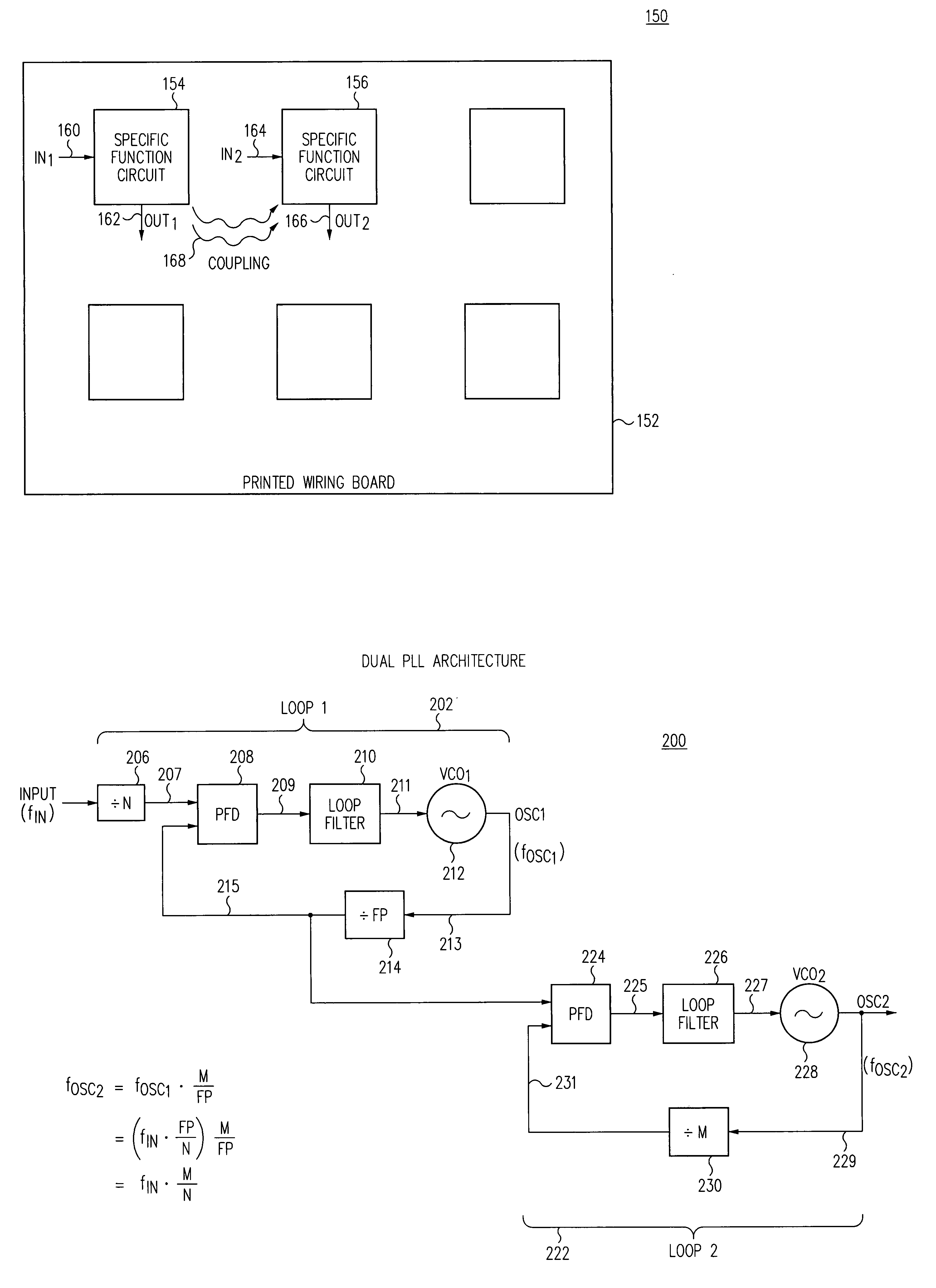
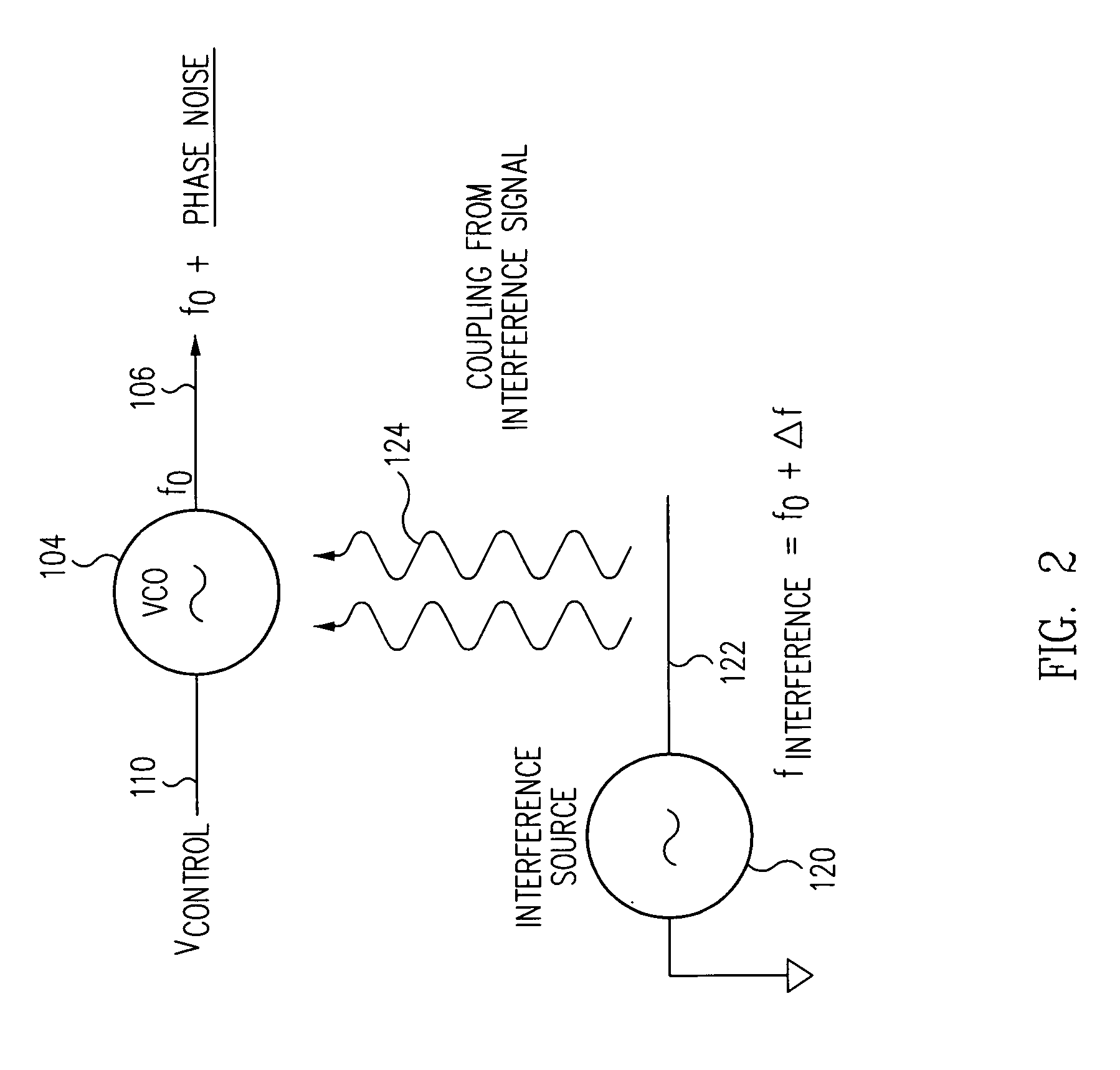
Dual phased-locked loop structure having configurable intermediate frequency and reduced susceptibility to interference
InactiveUS6970030B1Add phase noisePhase noise be largePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorIntermediate frequencyDual loop
A PLL function may be implemented as a dual-loop structure having a first PLL circuit which generates an intermediate signal from the reference signal, and a second PLL circuit which generates an output signal from the intermediate signal. The intermediate signal frequency is preferably chosen at a value in which potential interference signals do not have much energy. The first loop preferably has low bandwidth to provide good input jitter attenuation, while second loop preferably has higher bandwidth to reduce phase noise of the output signal. The circuit preferably provides for a choice of several different intermediate frequencies to allow use where different intermediate frequencies may exist in each system. Moreover, in a system having two such dual-loop PLL circuits, each can be configured with a different intermediate frequency, so that interference from one to the other is reduced.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Frequency synthesizer and frequency synthesizing method
InactiveCN102468849AImprove phase noiseFine frequency resolutionPulse automatic controlPhase detectorFrequency mixer
Owner:SONY CORP
True random number generator and realization method thereof
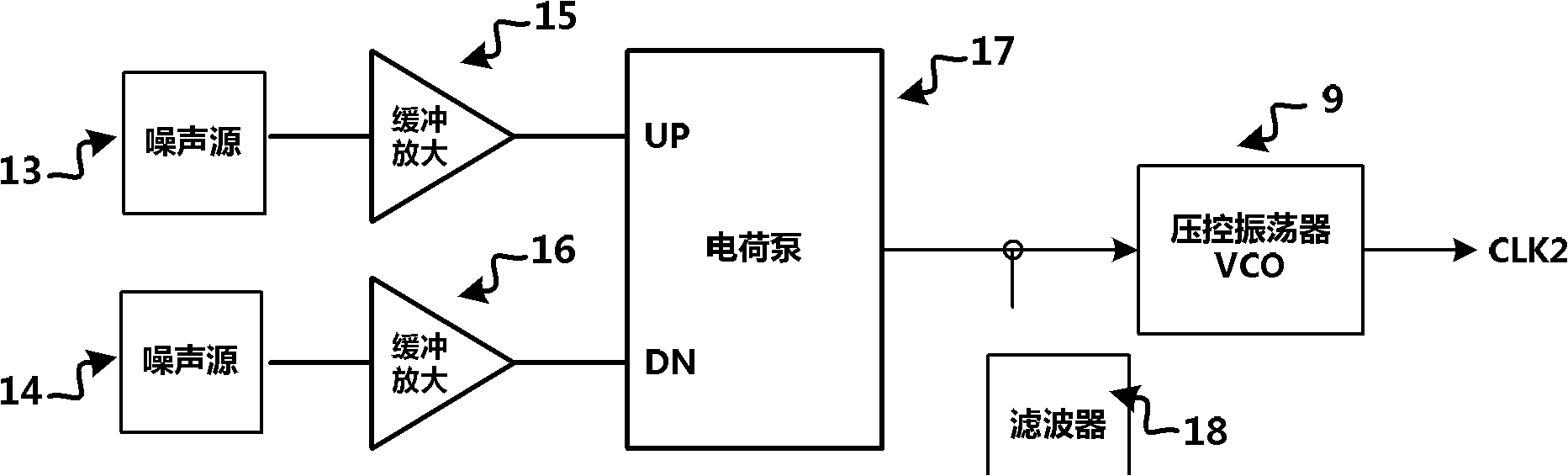
InactiveCN102662625AImprove randomnessReduce correlationRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationVIT signalsRandom test generator
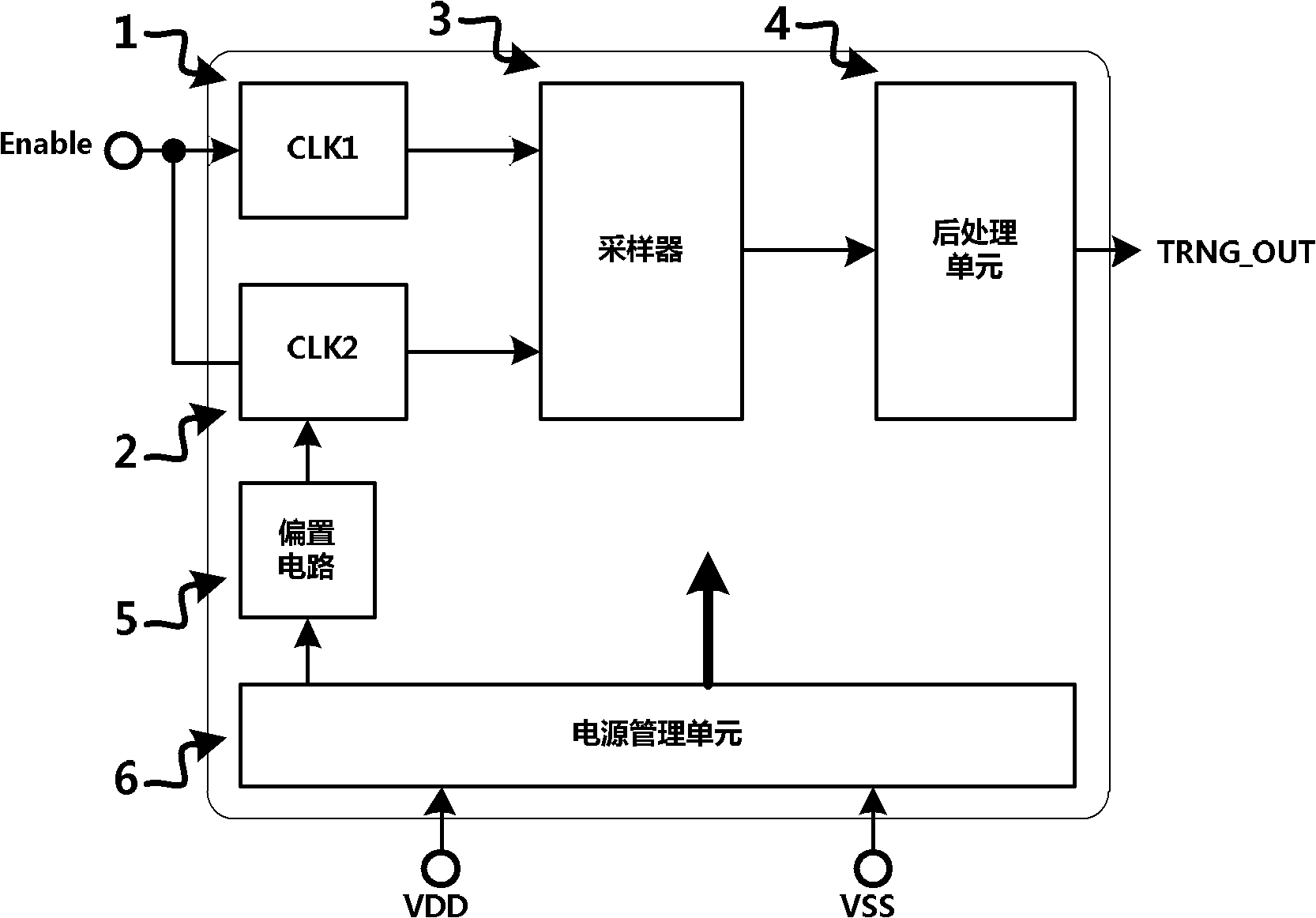
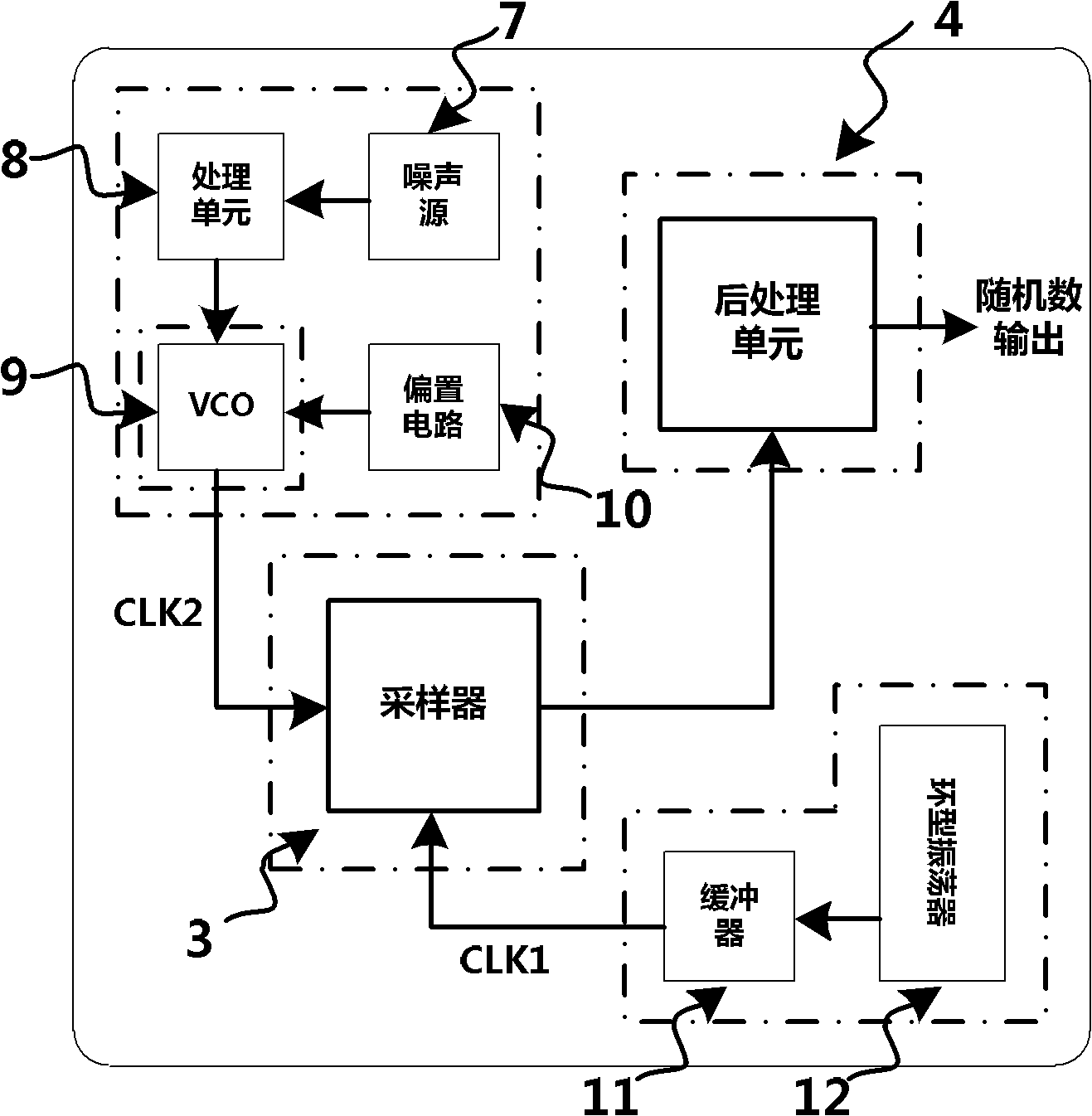
The invention provides a true random number generator and a realization method of the rue random number generator. The realization method comprises the steps: after a VDD / VSS is electrified, a power management unit starts working and provides voltage for all units of the true random number generator; a biasing circuit provides a biasing voltage signal for a second clock source; the biasing circuit in the second clock source provides a biasing voltage for a voltage-controlled oscillator; after being processed by a processing unit, a signal generated from a noise source is used as a voltage signal of an input signal of the voltage-controlled oscillator, and an output signal of the voltage-controlled oscillator is used as the output CLK2 of the second clock source; a signal generated from a circular oscillator is processed by a buffer to obtain a signal which is used as the output CLK1 of a first clock source; digital mixing on the received CLK1 and CLK2 is conducted by a sampler (3) to generate random data; and a post-processing unit processes the received random data of the sampler and outputs a random sequence. With the adoption of true random number generator and the realization method, the phase noise of the oscillation signals can be improved, and the random characteristic of the generated random data is greatly enhanced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Oscillator
InactiveUS20120068776A1Low production costReduce the number of layersOscillations generatorsVoltage converterAudio power amplifier
Provided is an oscillator using an MEMS resonator, which can reduce an influence of noise of a TIA and improve phase noise characteristics of an oscillator output. The oscillator includes an MEMS resonator, a TIA, a buffer amplifier, and a current / voltage converter that couples, by electromagnetic induction, with a wiring line via which an output of the MEMS resonator is fed to the TIA, so as to convert a current flowing in the wiring line to a voltage and output the voltage to the buffer amplifier. Thus, the oscillator output is extracted from the current / voltage converter. Further, the current / voltage converter is provided in the form of an oscillation output coil provided so as to surround the wiring line in a noncontact manner, in which oscillation output coil one end is connected to ground and the other end is connected to the buffer amplifier.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
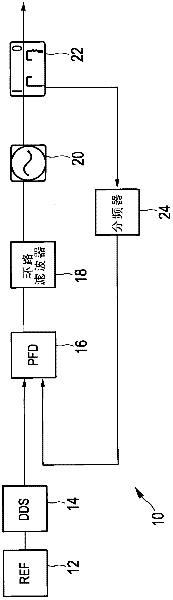
Rational frequency synthesizers
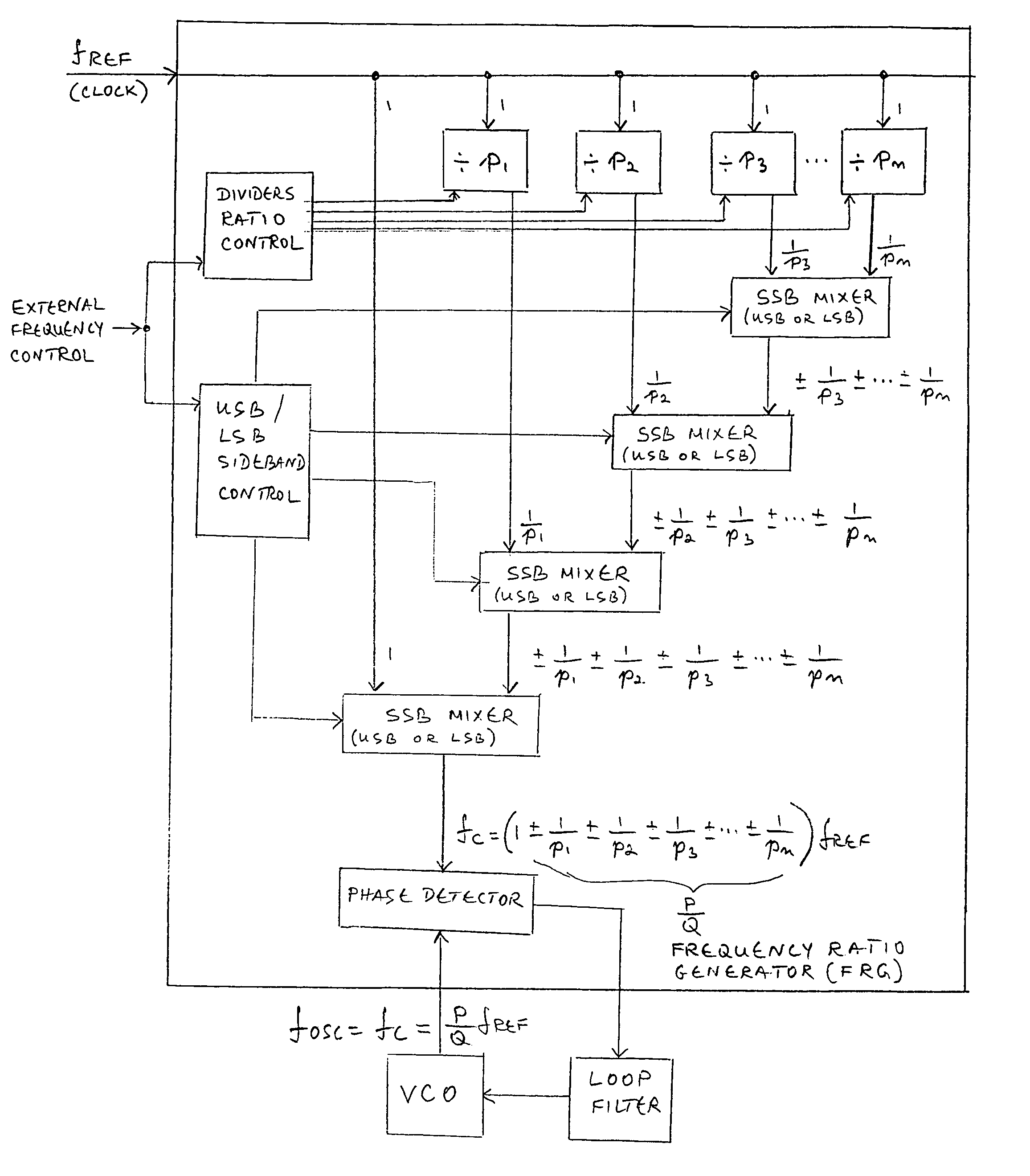
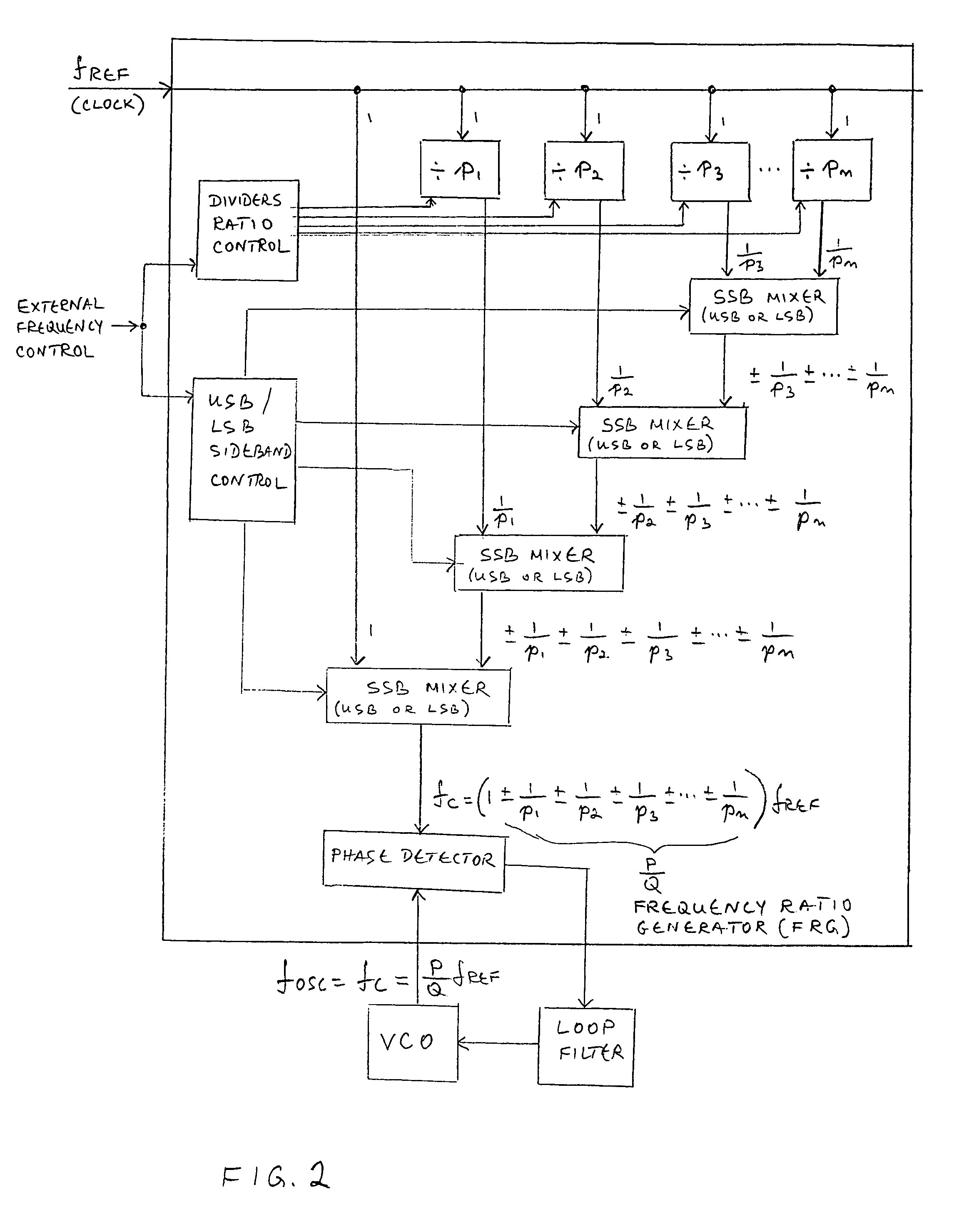
InactiveUS6977556B1Improve phase noiseReduce the ratioPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsSidebandFrequency mixer
A single loop PLL frequency synthesizer for operation in the MHz to GHz range, suitable for integration in integrated circuits, operates at high comparison frequencies thus achieving superior phase noise performance, having wide loop bandwidths while able to tune in small frequency steps. It is based on the fact that the output frequency and the reference clock frequency always have a rational relationship, and so can always be represented as a ratio of two integer numbers. This ratio is expanded into various expressions of equivalent fraction expansions taking the form of a series of divided, added or subtracted terms, each being a rational number in itself. This ratio is realized in hardware through stages of frequency conversions using single sideband mixers (either the upper or lower sideband, and frequency dividers. This process of frequency translation thus generates the comparison frequency to which the PLL phase-locks the VCO.
Owner:WI LAN INC
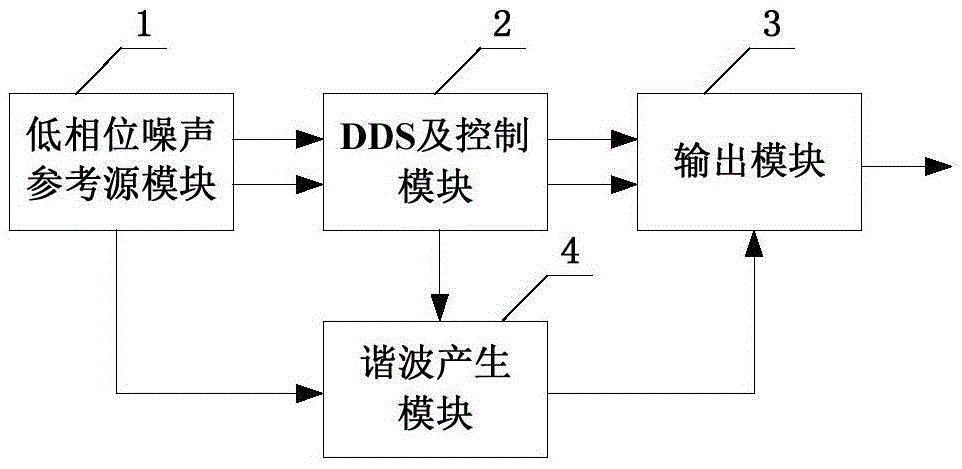
Low-phase noise frequency source
InactiveCN105553469AImprove Phase Noise PerformanceLow spuriousPulse automatic controlPhase noiseHarmonic
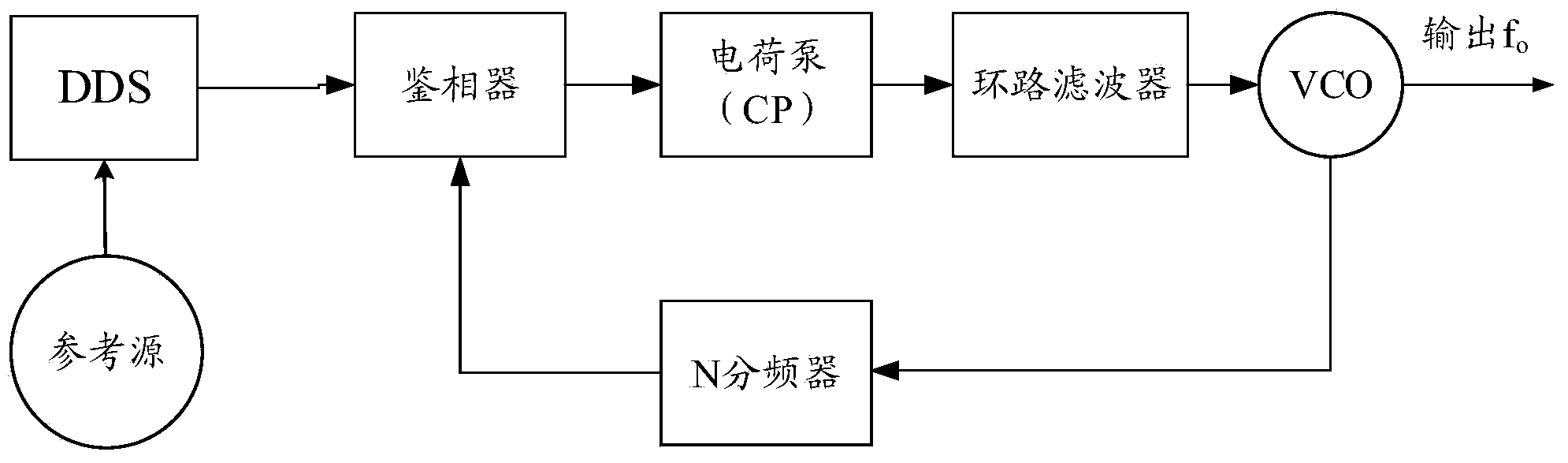
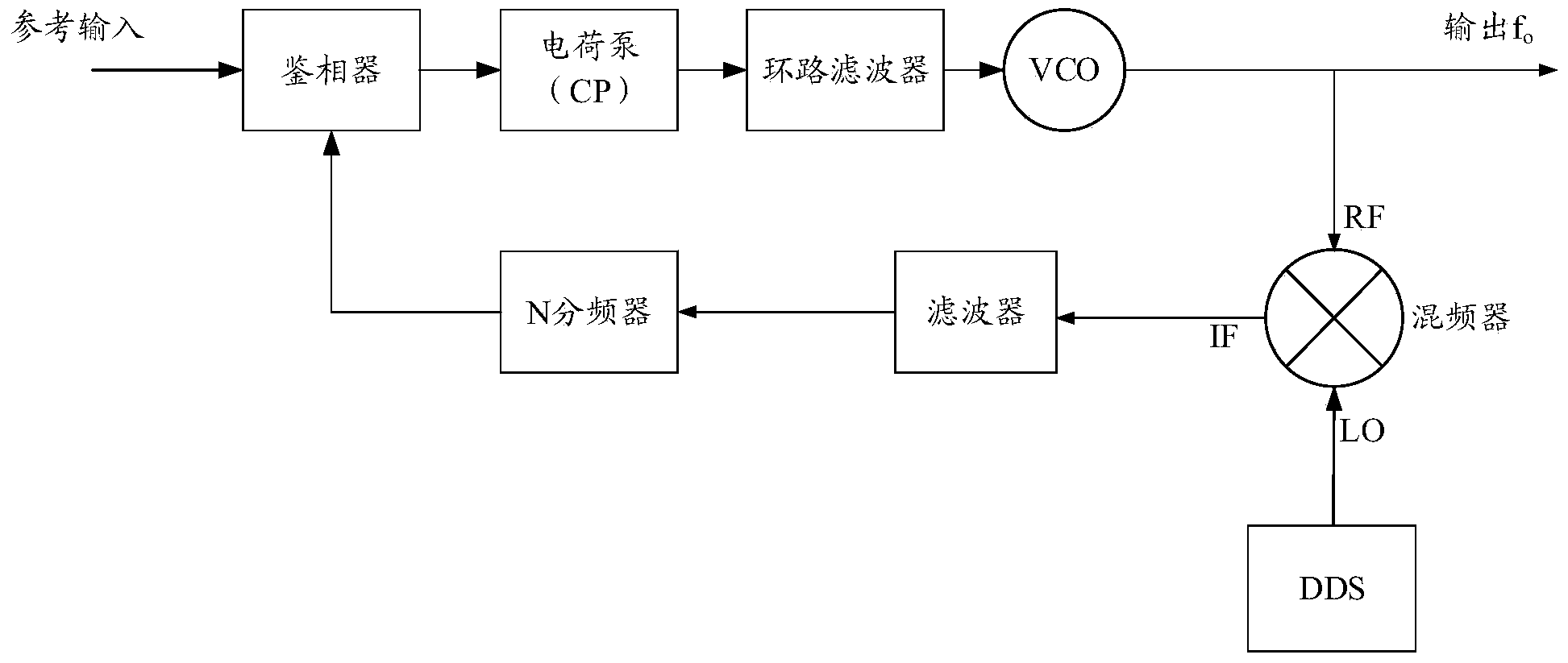
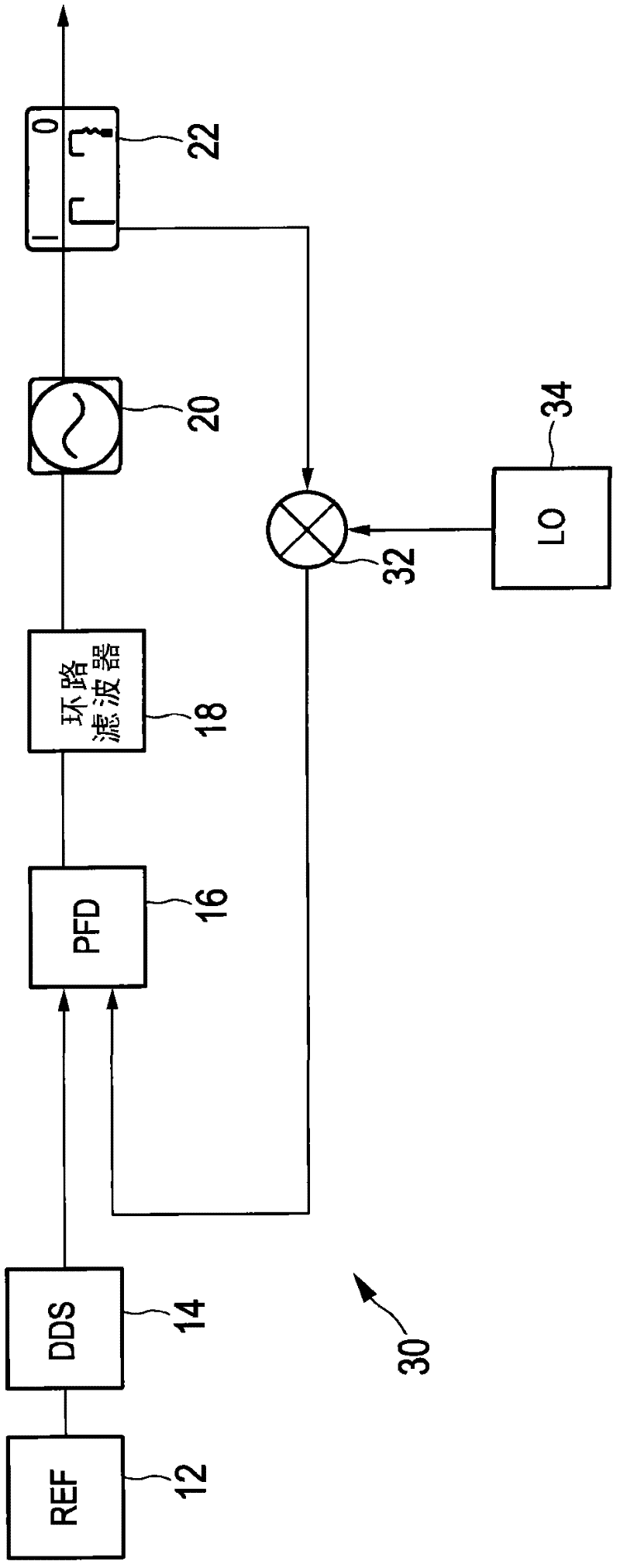
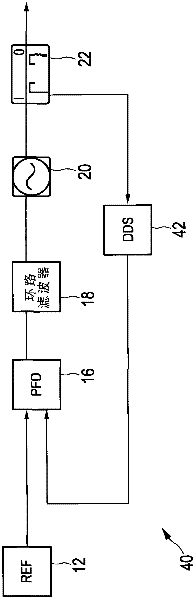
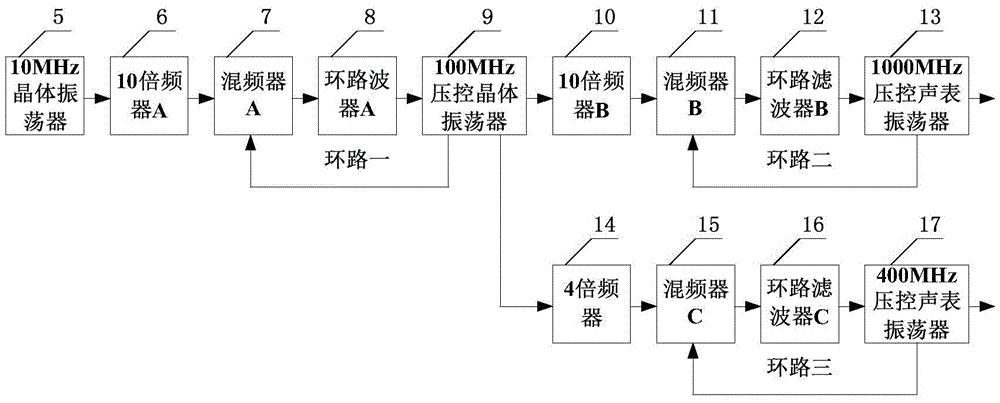
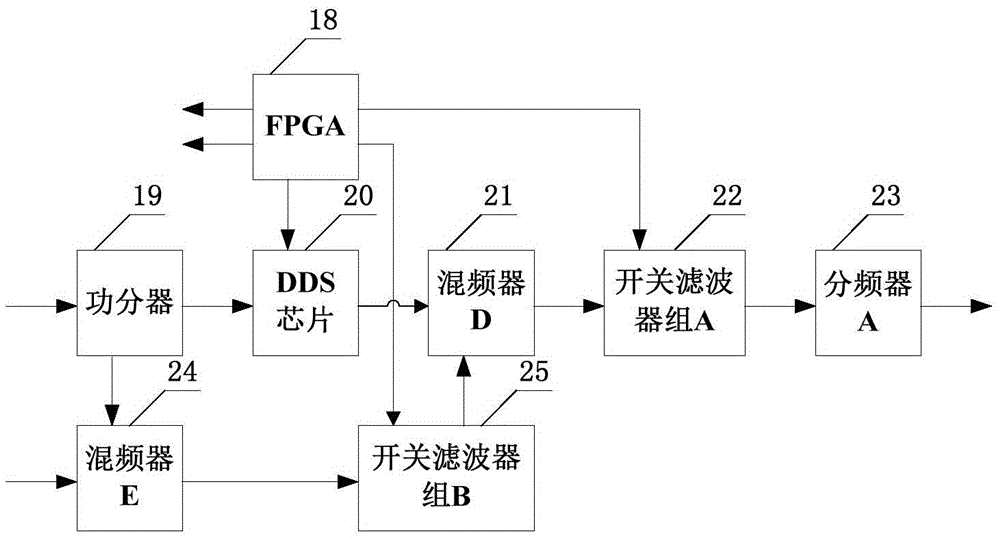
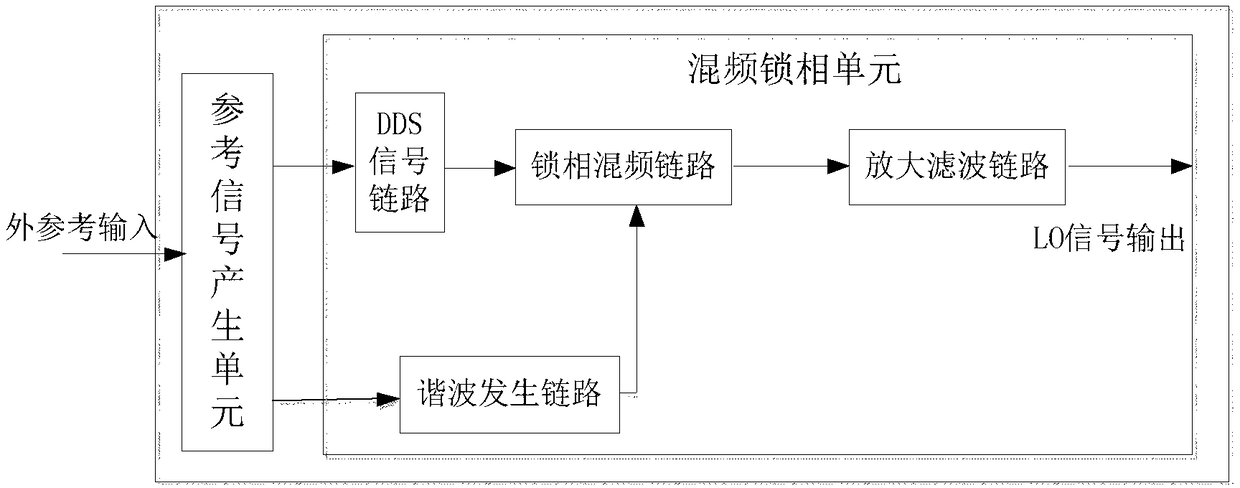
The invention relates to a low-phase noise frequency source. The low-phase noise frequency source includes a low-phase noise reference source which sends low-phase noise 400MHz reference signals and low-phase noise 1000MHz reference signals to a DDS and control module and sends low-phase noise 400MHz excitation signals to a harmonic generation module, the DDS and control module which sends low-phase noise baseband signals to an output module and sends control signals to the output module and the harmonic generation module, the harmonic generation module which sends low-phase noise local vibration signals to the output module, and the output module which performs frequency mixing, filtering and frequency division on the baseband signals and the local vibration signals so as to obtain low-phase noise 5MHz-1000MHz signals which are adopted as output signals. The low-phase noise frequency source of the invention has the advantages of wide band, low stray degree, fine resolution and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
Back-gate coupling voltage control oscillator
InactiveUS20080111644A1Improve phase noiseEffectively reducingOscillations generatorsResonant cavityPhase noise
A voltage control oscillator (VCO) includes a VCO circuit and a back-gate coupling circuit, wherein the VCO circuit includes at least a first transistor, a second transistor and a resonant cavity formed by an inductor and a capacitor. The back-gate coupling circuit is formed by a plurality of capacitors and a plurality of resistors. In the embodiments of the present invention, the capacitors are coupled to the back-gate terminals of the first transistor and the second transistor, so as to reduce the power consumption and the phase noise of the VCO.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Injection locking millimeter wave frequency divider based on self-oscillation optical frequency comb and frequency division method thereof
ActiveCN110034758ALarge frequency division factorReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlOptical elementsInjection lockedPhase noise
The invention discloses an injection locking millimeter wave frequency divider based on a self-oscillation optical frequency comb and a frequency division method of the injection locking millimeter wave frequency divider. The frequency divider comprises a photoelectric hybrid oscillator, an optical comb modulator is arranged in an optical link of the photoelectric hybrid oscillator, and a band-pass filter is arranged in an electric link of the photoelectric hybrid oscillator; a millimeter wave signal to be subjected to frequency division is injected into the photoelectric hybrid oscillator; wherein the central frequency of the millimeter wave signal is an integral multiple of the central frequency of the band-pass filter, the optical frequency comb sideband generated by the photoelectric hybrid oscillator and the modulation sideband of the signal to be converted output a fundamental frequency signal in a beat frequency mode, and the fundamental frequency signal is located within the locking bandwidth range of the photoelectric hybrid oscillator. When a super-harmonic signal is injected into the oscillation loop and locked, the frequency division function of the injected millimeterwave signal can be realized, and the frequency divider has the characteristics of wide band, low phase noise and large frequency division ratio.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Temperature compensation and coarse tune bank switches in a low phase noise vco
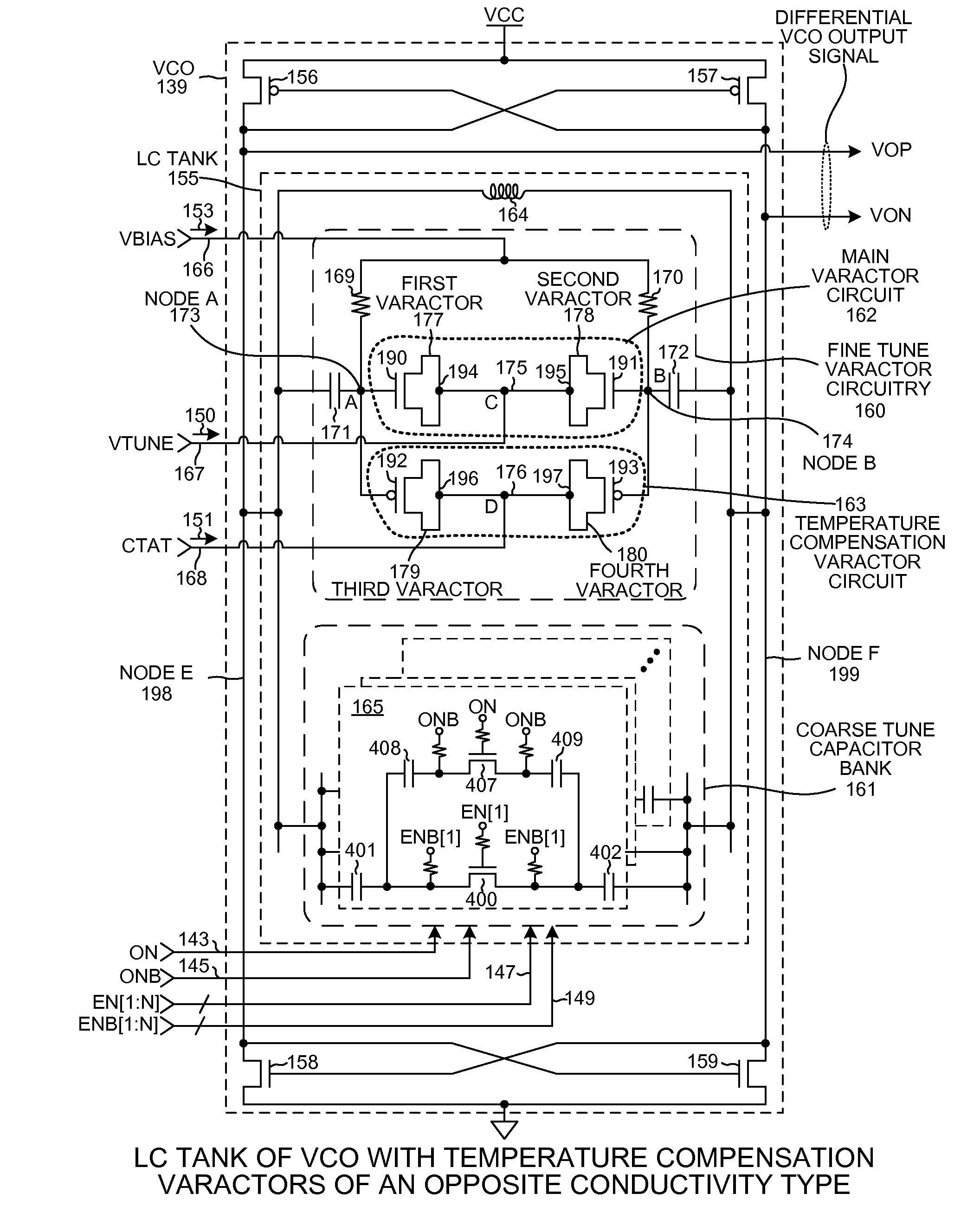
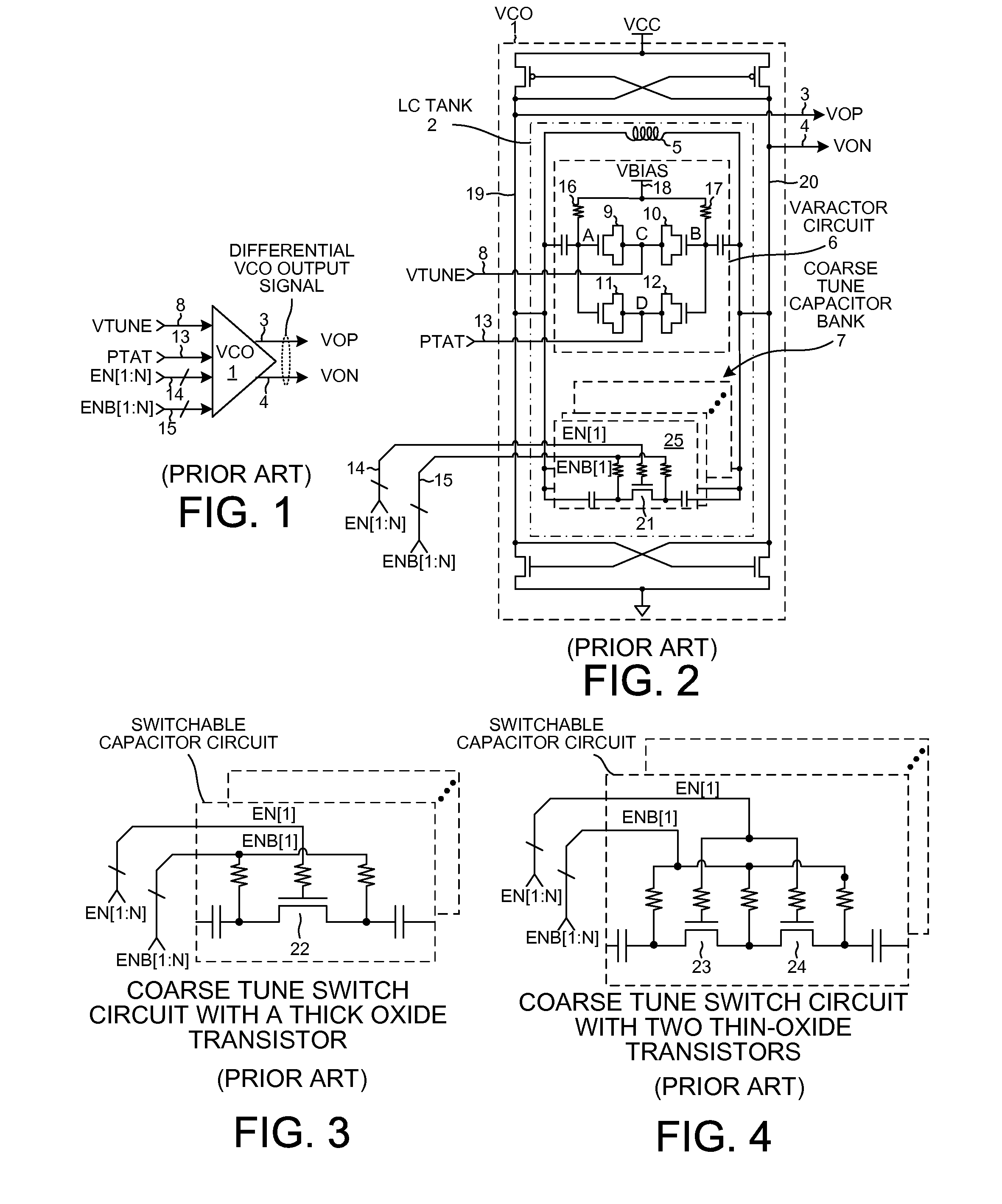
ActiveUS20120223771A1Improves VCO phase noiseReduces VCO susceptibilityPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationThin oxidePhase noise
The LC tank of a VCO includes a main varactor circuit and temperature compensation varactor circuit coupled in parallel with the main varactor circuit. The main varactor is used for fine tuning. The temperature compensation varactor circuit has a capacitance-voltage characteristic that differs from a capacitance-voltage characteristic of the main varactor circuit such that the effects of common mode noise across the two varactor circuits are minimized. The LC tank also has a plurality of switchable capacitor circuits provided for coarse tuning. To prevent breakdown of the main thin oxide switch in each of the switchable capacitor circuits, each switchable capacitor circuit has a capacitive voltage divider circuit that reduces the voltage across the main thin oxide switch when the main switch is off.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Double-conversion television tuner using a Delta-Sigma Fractional-N PLL
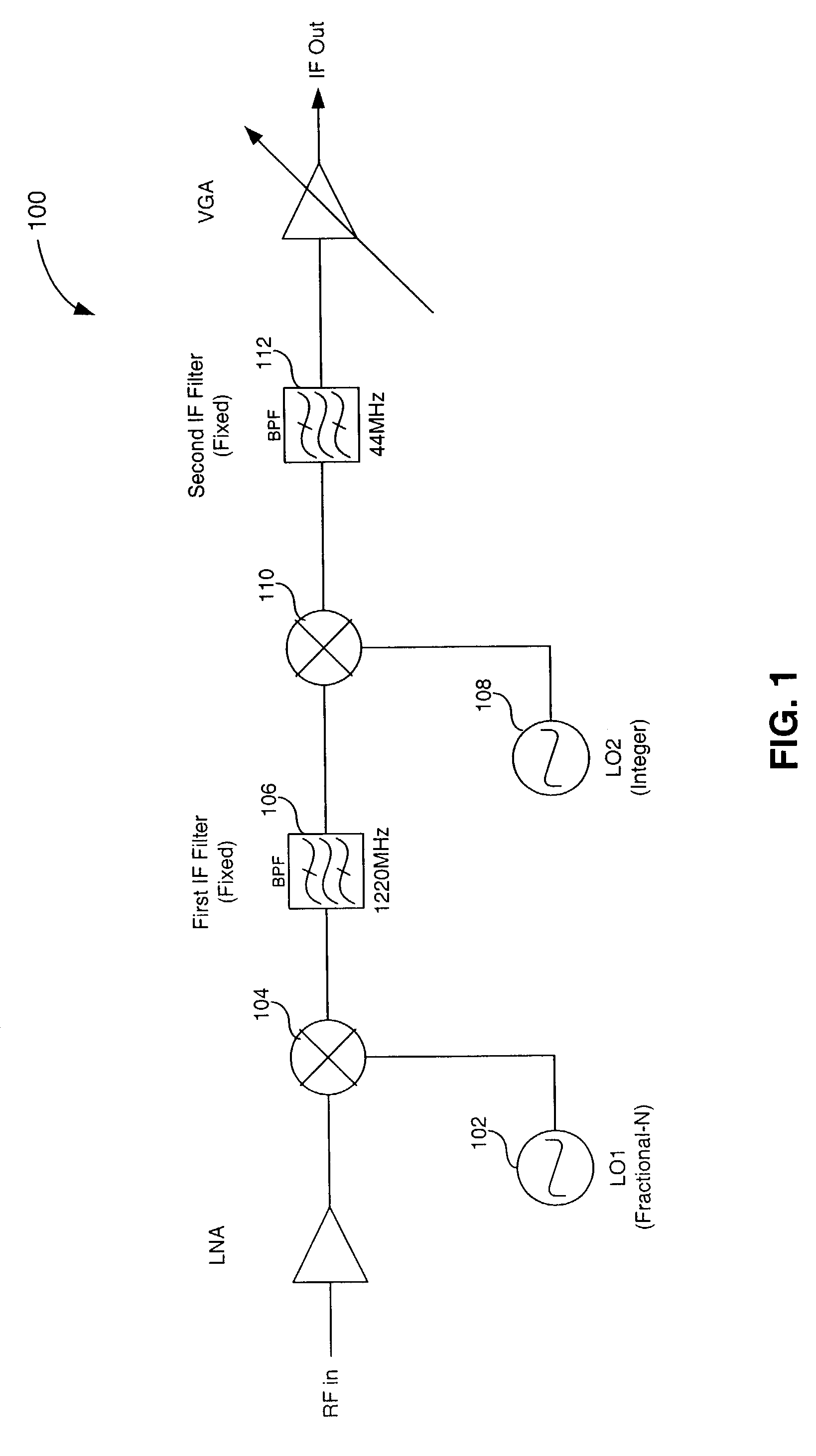
InactiveUS7072633B2Improve phase noisePulse automatic controlFrequency diversityBandpass filteringLocal oscillator signal
A double-conversion tuner receives an RF signal having a number of channels and down-converts a selected channel from the plurality of channels. The double-conversion tuner includes a first mixer configured to up-convert the RF signal to a first IF signal using a first local oscillator signal. A first local oscillator includes a delta-sigma fractional-N phase lock loop to produce the first local oscillator signal. The delta-sigma fractional-N phase lock loop is configured to perform fine-tuning of the first local oscillator signal and to have a wide tuning range sufficient to cover the number of channels. A bandpass filter is configured to select a subset of channels from said first IF signal. A second mixer is configured to down-convert the subset of channels to a second IF signal using a second local oscillator signal. A second local oscillator generates the second local oscillator signal. The second local oscillator is configured to perform coarse frequency tuning of the second local oscillator signal and has a narrow tuning range relative to said first local oscillator. The delta-sigma fractional-N phase lock loop in the first local oscillator permits implementation of a double-conversion tuner with improved phase noise for a given amount of power and complexity.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Differential VCO and quadrature VCO using center-tapped cross-coupling of transformer
InactiveUS8212625B2Improve phase noiseEnhanced oscillationAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse generation by logic circuitsCapacitanceLinear control
Provided are a differential voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) and a quadrature VCO using center-tapped cross-coupling of a transformer. The differential VCO and the quadrature VCO can be driven by low power through a current reuse structure and have an excellent phase noise characteristic by center-tapped cross-coupling through a transformer. Further, variable capacitance units for frequency variation are divided into variable capacitance units for coarse tuning and variable capacitance units for fine tuning. Therefore, it is possible to obtain a wide tuning range while voltage oscillation gain is reduced. Further, the differential VCO and the quadrature VCO are configured in such a manner that the respective variable capacitance units operate linearly throughout the entire capacitance region due to control voltage distribution by resistors. Accordingly, it is possible to obtain a linear control voltage-oscillation frequency characteristic. The quadrature VCO according to the present invention can output four-phase quadrature signals while having an excellent phase noise characteristic, without substrate loss and current consumption caused by the switching transistors.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
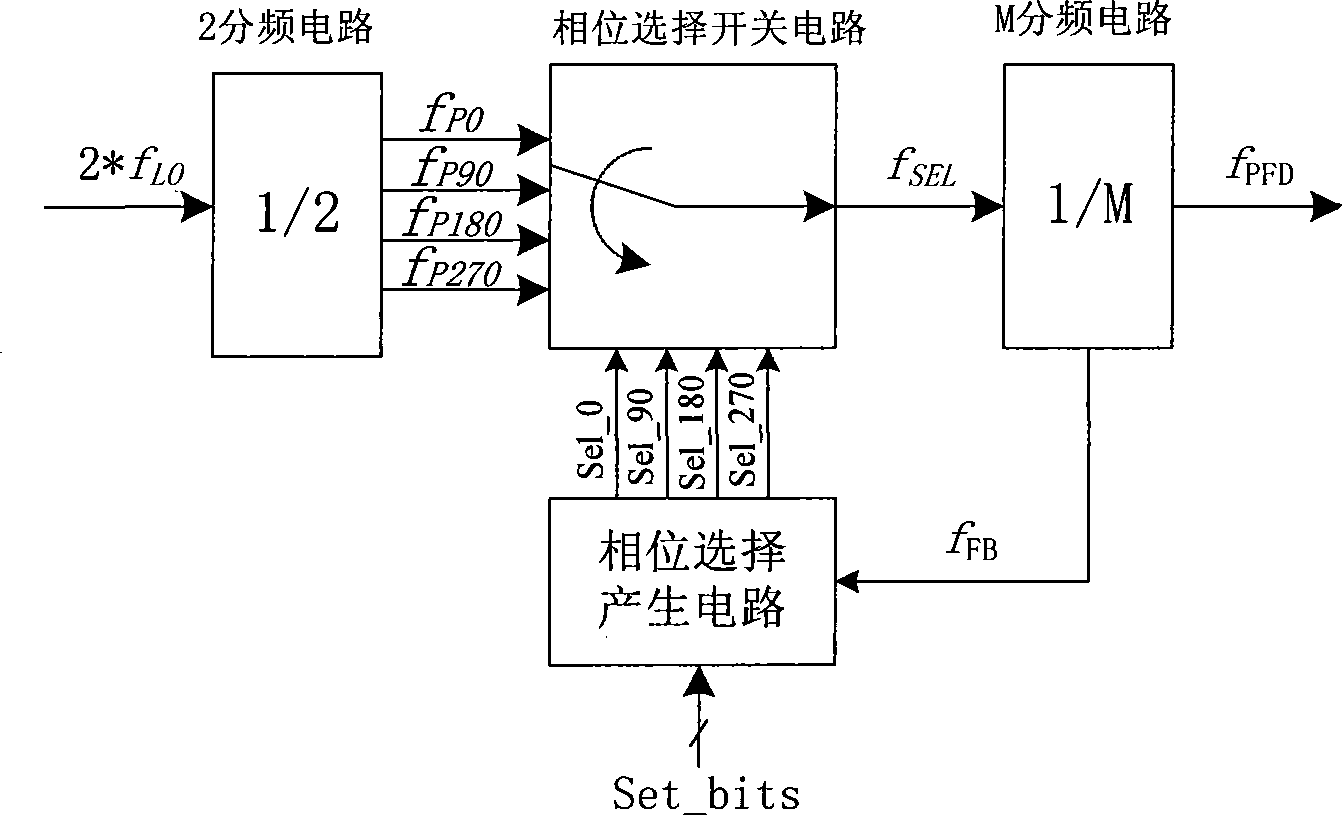
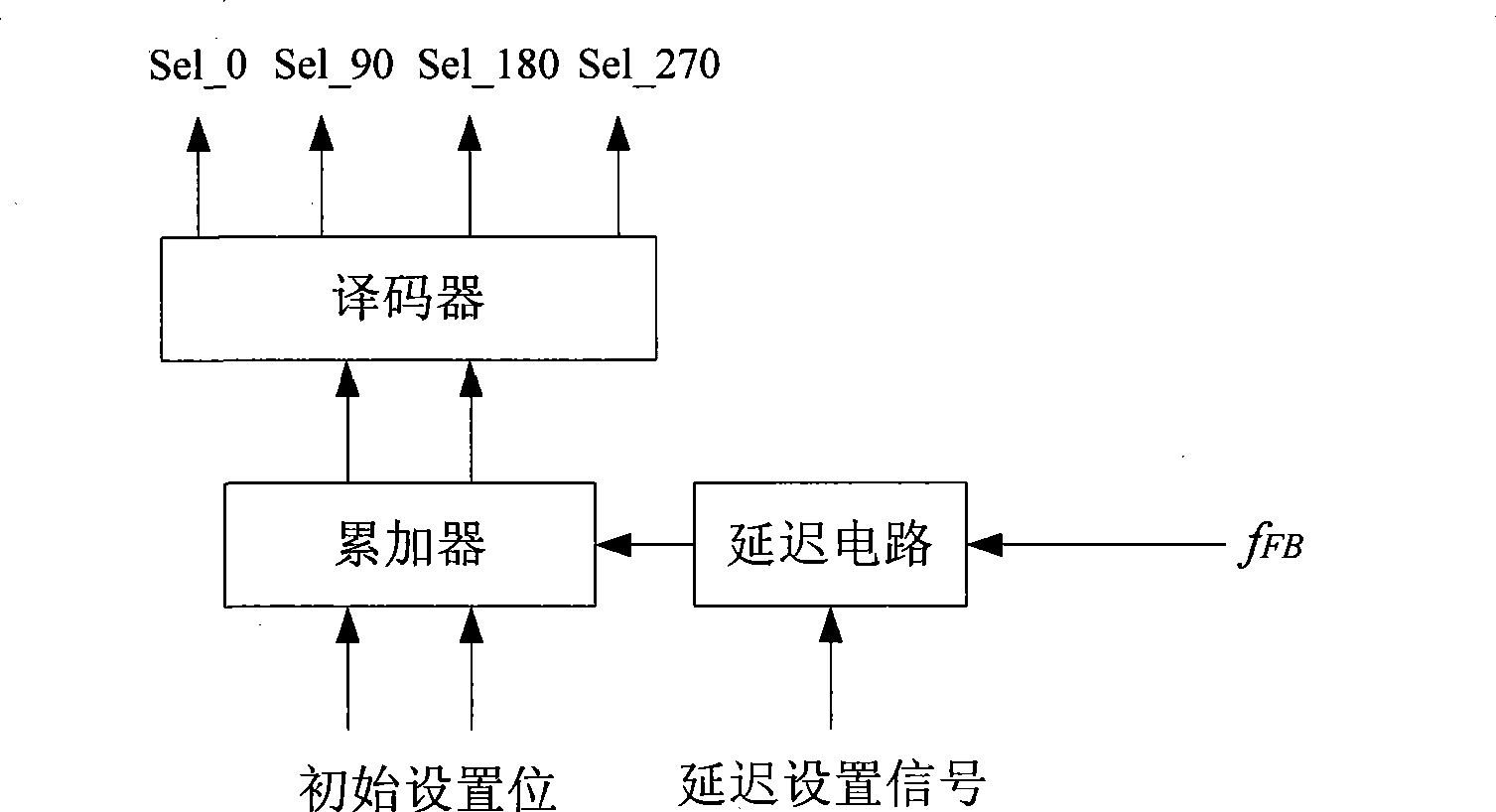
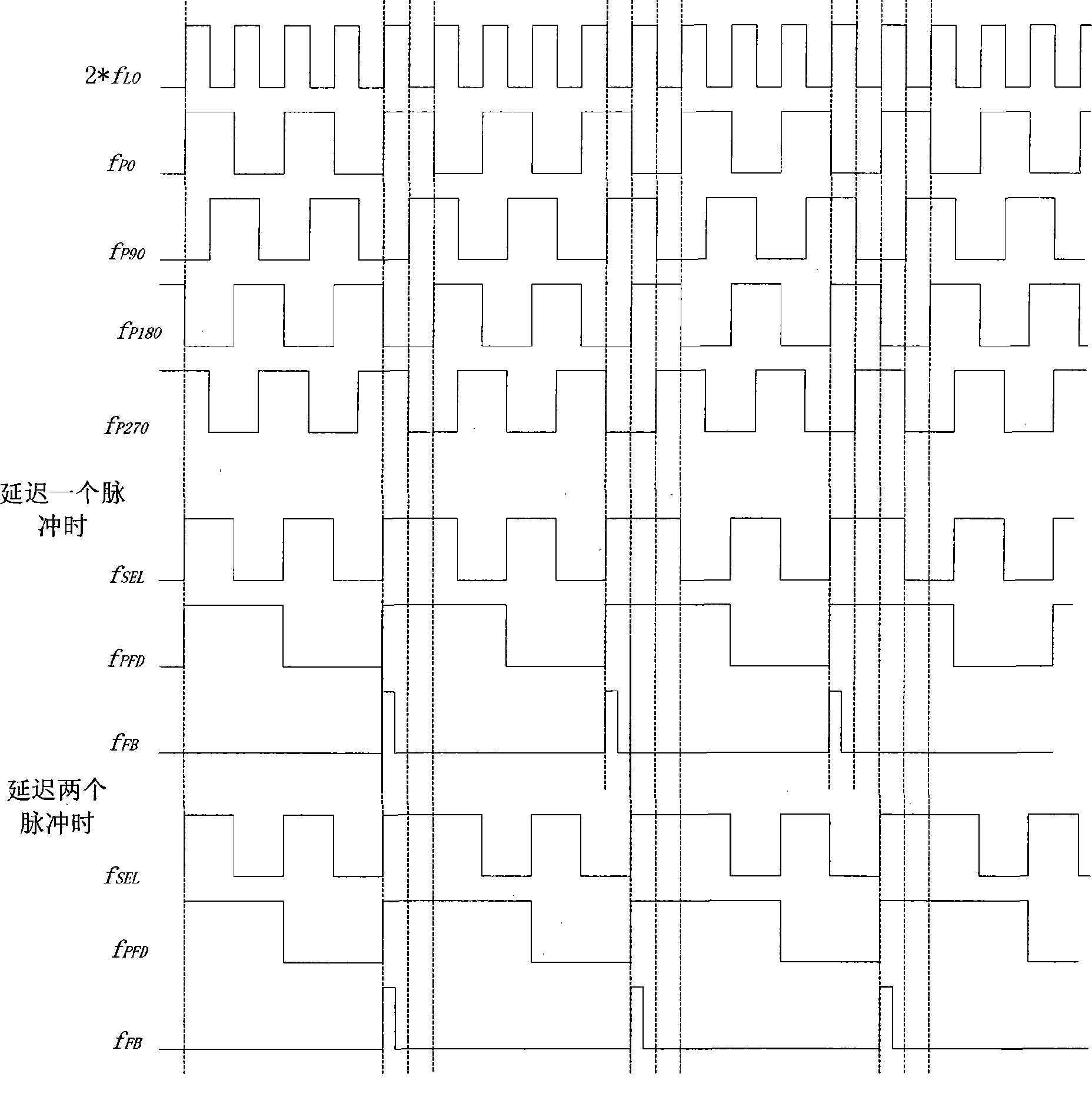
Phase selection programmable frequency divider
InactiveCN101378259AThe production process is simpleImprove stabilityPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersGeneration processPhase noise
The invention discloses a phase selection programmable frequency divider, only an accumulator is needed in a phase selection generating circuit, thus simplifying the producing process of phase selection logic, improving the stability of the whole frequency divider, avoiding the generation of burrs in the phase selection process, and reducing the error possibility of the whole frequency divider; meanwhile, by pre-obtaining four signals working at the actual system working frequency and with the phase difference of 90 degrees, and causing the phase selection generating circuit to output a switching control signal used for controlling the phase selection switching circuit to be switched from the signal of one phase into the signal of another phase under the control of a trigger signal output by the M frequency divider, the frequency dividing value with the minimum value of 0.25 is realized, thus causing reference clock frequency to be improved to be four times of the prior one, namely, the sampling frequency of a Sigma-Delta modulator is improved to be four times of the prior one, thereby effectively reducing the in-band phase noise of a phase-locking loop and improving the entire phase noise of a frequency synthesizer.
Owner:RDA MICROELECTRONICS SHANGHAICO LTD
Low phase noise differential LC tank VCO with current negative feedback
ActiveUS7414488B2Good phase noise characteristicsEliminate Phase NoiseElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsPhase noiseFeedback circuits
A differential voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) employed in a frequency synthesizer used as a local oscillator of a wireless communication on-chip transmitter / receiver is provided. More particularly, a differential current negative feedback VCO equipped with a current-current negative feedback circuit that suppresses low- and high-frequency noise is provided.A differential current negative feedback VCO includes a resonator determining oscillation frequency, and an oscillator generating negative resistance. In the oscillator of the differential current negative feedback VCO, transistors Q1 and Q2 form a cross-coupled pair, and negative resistance is generated by positive feedback of the cross-coupled pair. And, transistors Q1 and Q3 together with an emitter resistor and a capacitor form a current negative feedback part, and transistors Q2 and Q4 together with an emitter resistor and a capacitor form another current negative feedback part which is disposed opposite to a resonator. Thus, the VCO operates differentially.In the oscillator of the differential current negative feedback VCO, emitter noise currents generated by base noise voltages of Q1 and Q2 induced by low- and high-frequency noise sources in the bases of Q1 and Q2 are sampled by emitter resistors, amplified through bases of Q3 and Q4, and thus return to the bases of the Q1 and Q2 and suppress the base noise voltages. Measurement of the phase noise of the differential current negative feedback VCO reveals a phase noise reduction of approximately 25 dB compared to a conventional differential VCO.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Low-spurious/low-phase noise frequency synthesizer
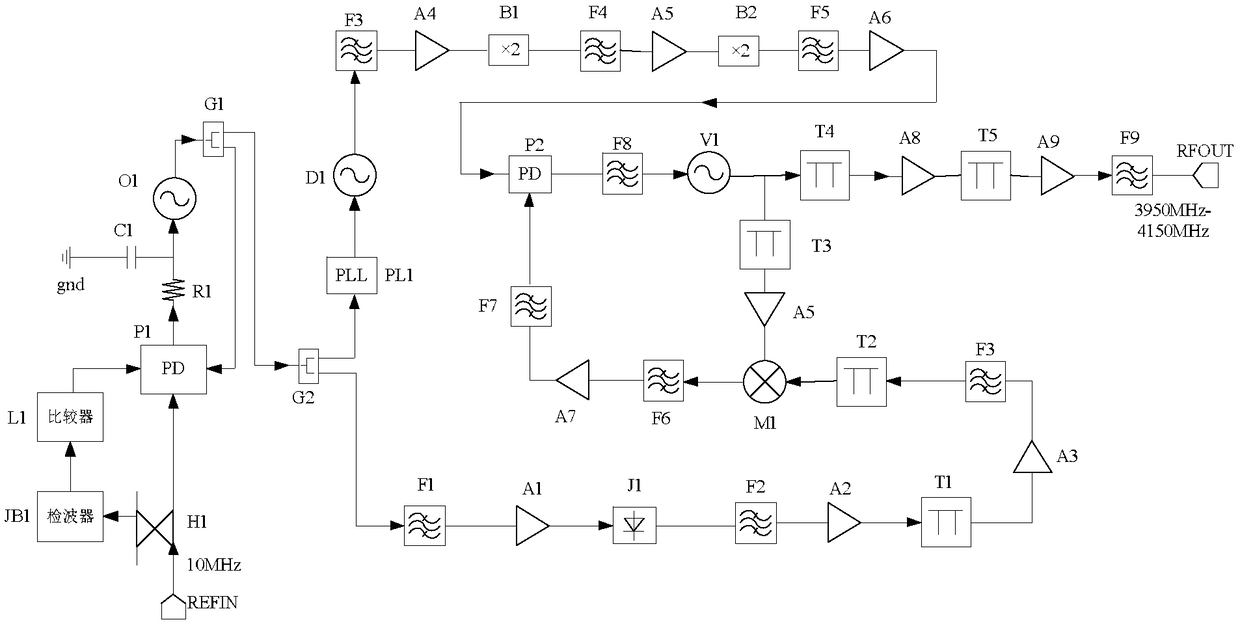
ActiveCN108736889AHigh precisionImprove performancePulse automatic controlLocal oscillator signalPhase noise
The invention discloses a low-spurious / low-phase noise frequency synthesizer, and aims at providing the frequency synthesizer which is thin in stepping, low in spurious signal, low in phase noise, stable and reliable in work and fast in frequency switching speed. The low-spurious / low-phase noise frequency synthesizer is implemented by the technical scheme as follows: a reference signal generationunit uses an externally received reference input signal as unified reference frequency, the reference frequency uses an output signal of a DDS as a reference signal of a phase-locked loop (PLL) via adirect digital frequency synthesizer (DDS), and output frequency is controlled through changing a frequency control word of the DDS. The signal output by the DDS is fed into a phase-locked frequency mixing unit after being subjected to frequency multiplication for two times to be subjected to phase-locked frequency mixing with a local oscillator signal generated by a harmonic generation link at the phase-locked frequency mixing unit, the phase-locked frequency-mixing signal passes through an amplifying and filtering link and is filtered by a band-pass filter to acquire the needed local oscillator signal.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com