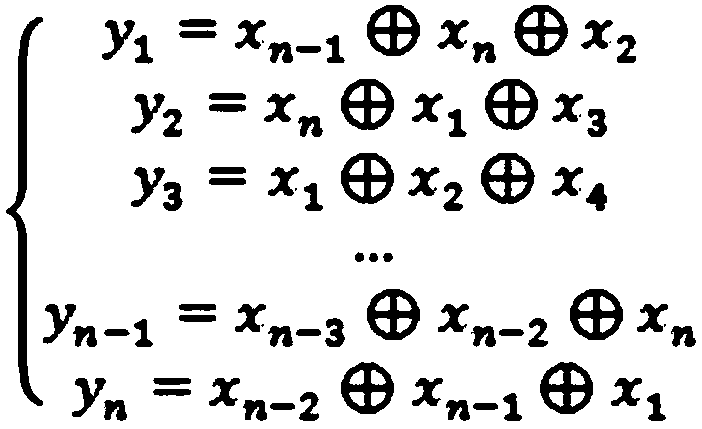Patents
Literature
35 results about "Random test generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Random test generators (often abbreviated RTG or ISG for Instruction Stream Generator) are a type of computer software that is used in functional verification of microprocessors. Their primary use lies in providing input stimulus to a device under test.
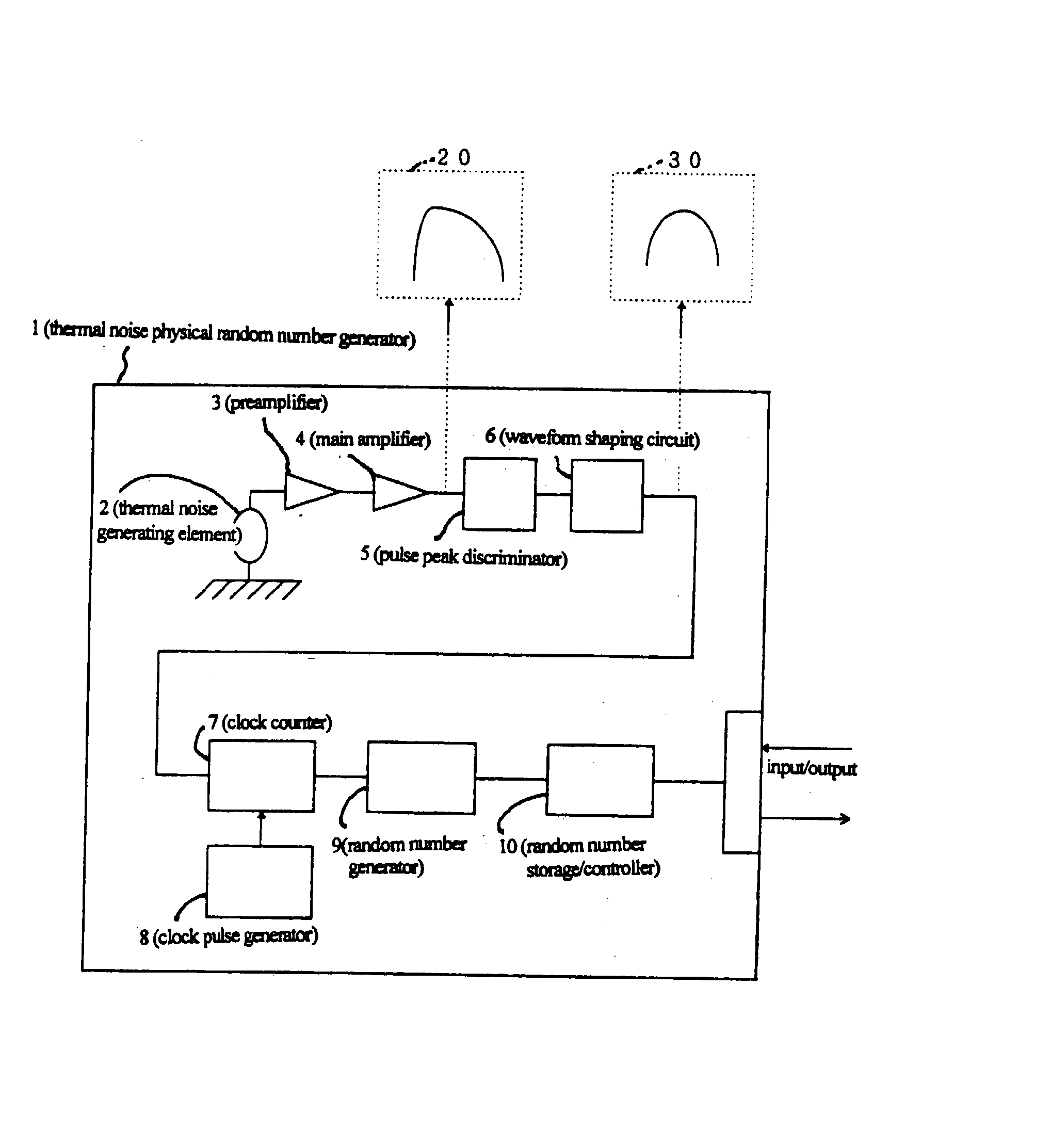
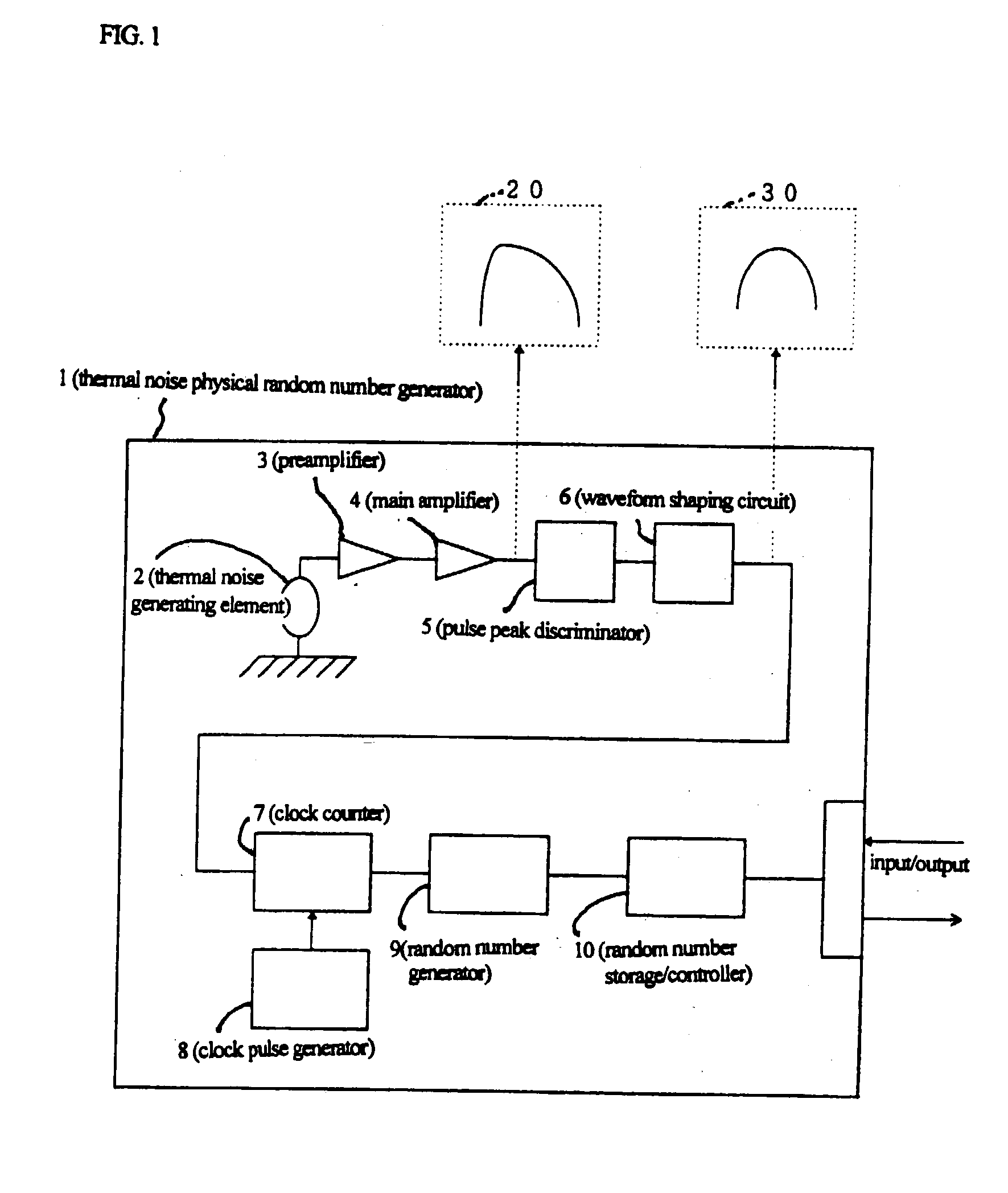
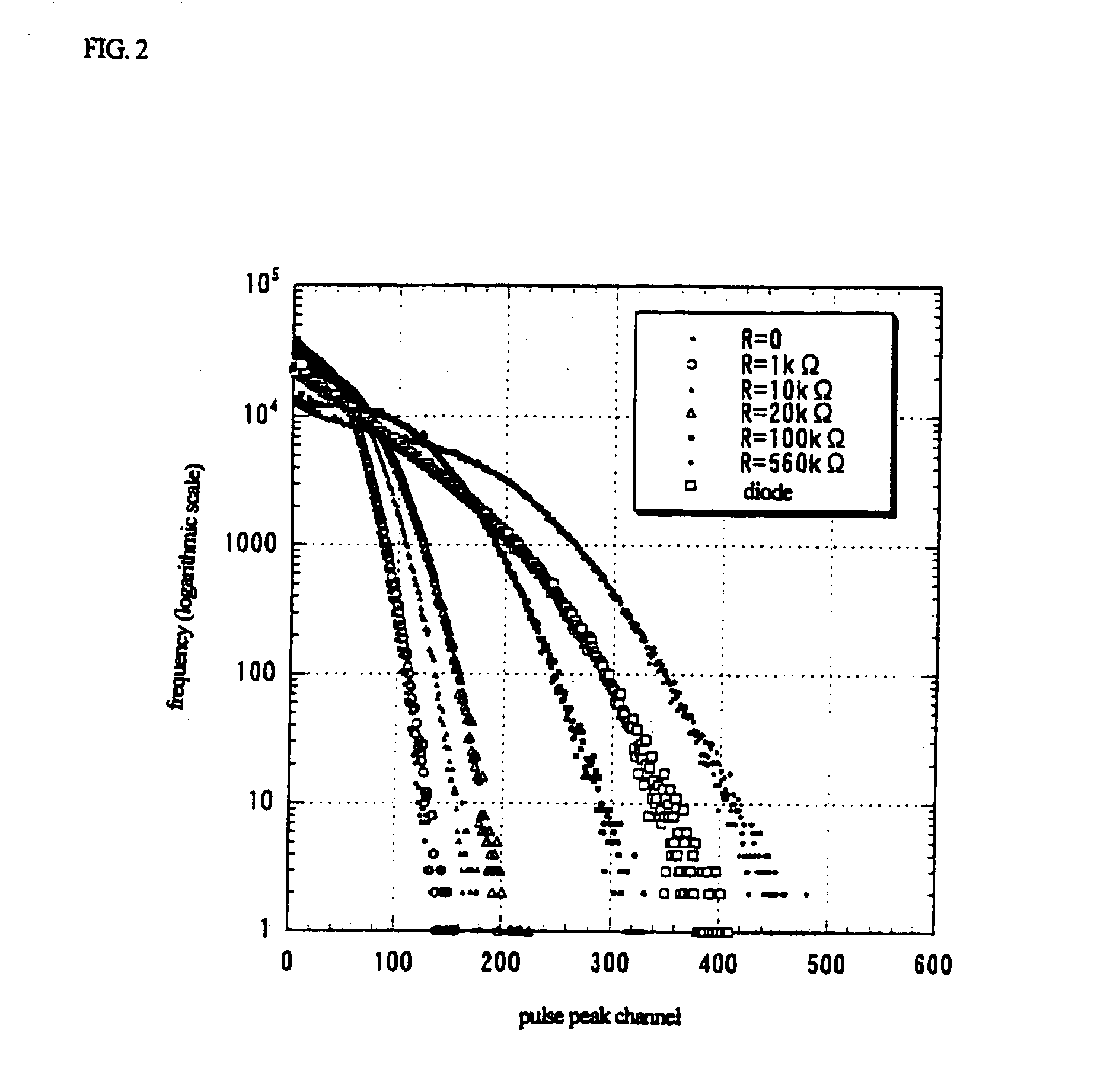
Thermal noise random pulse generator and random number generator
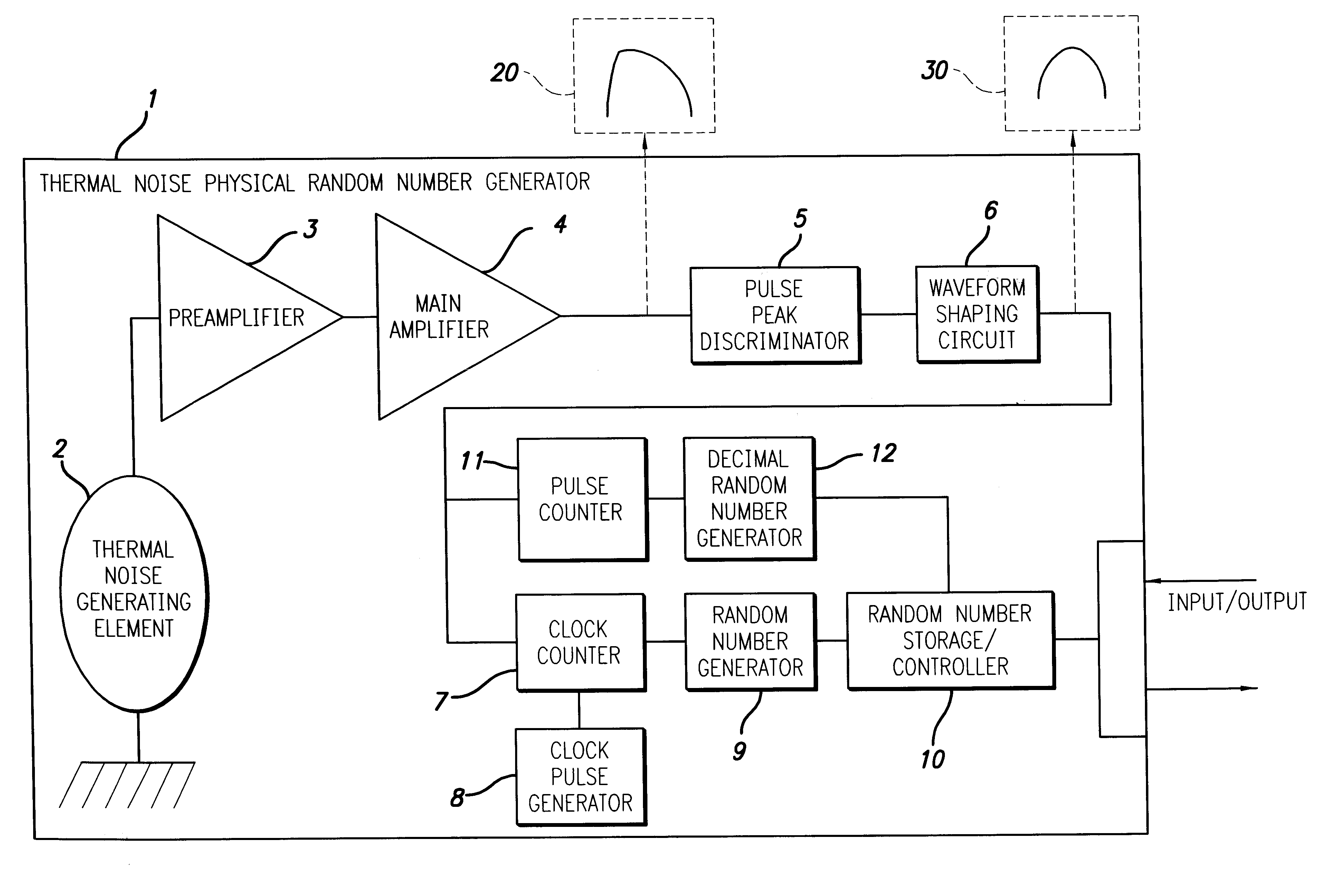
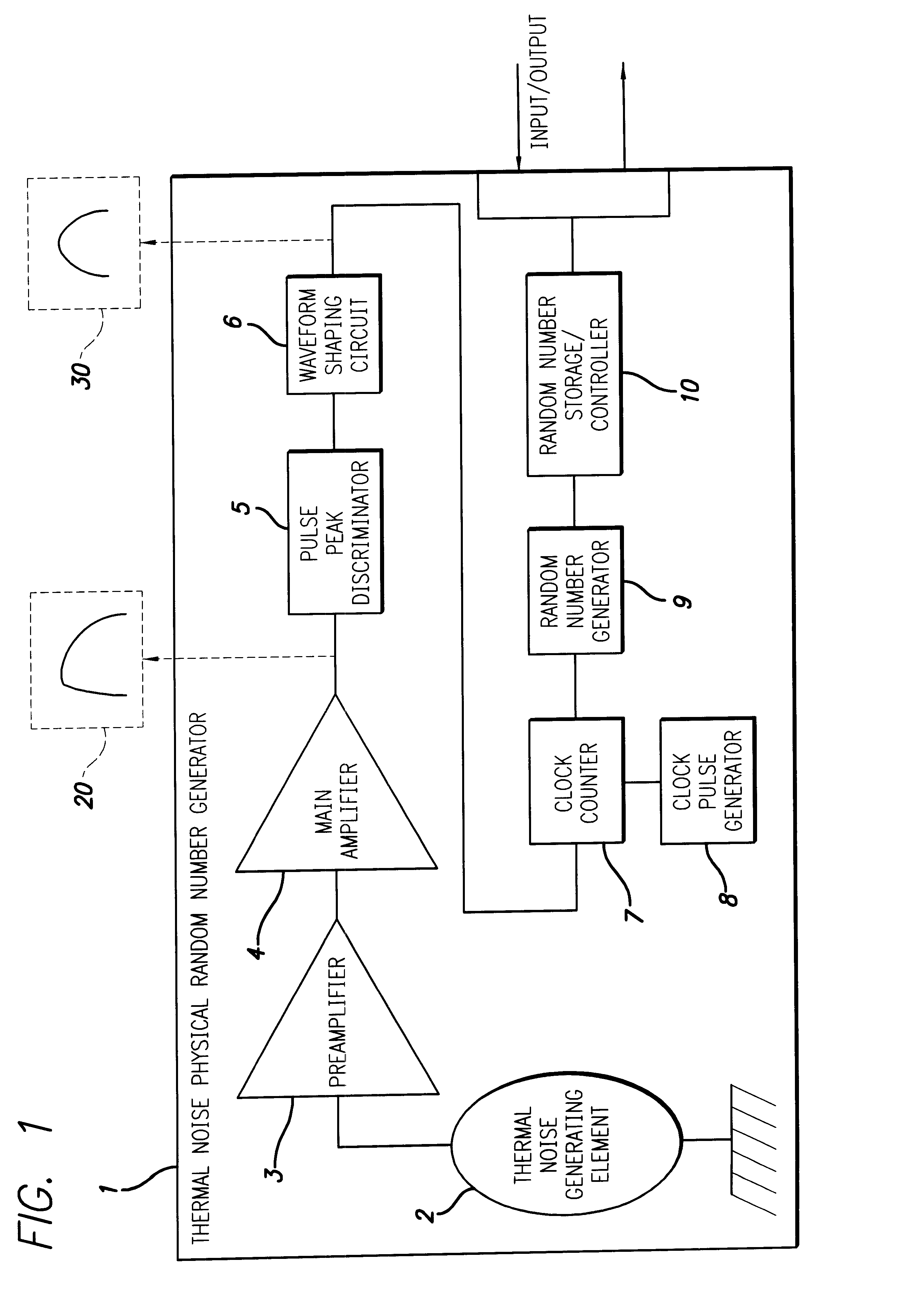
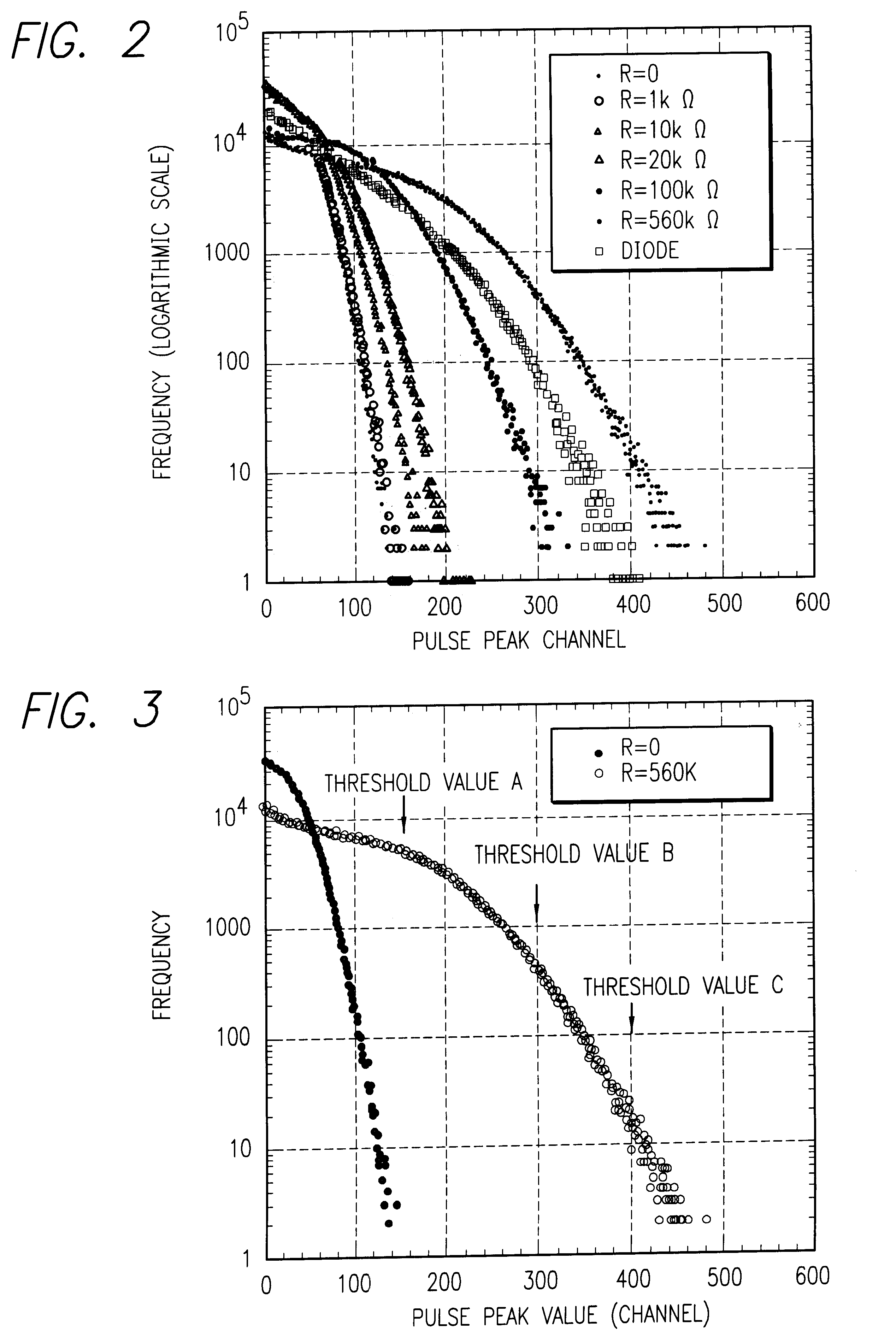
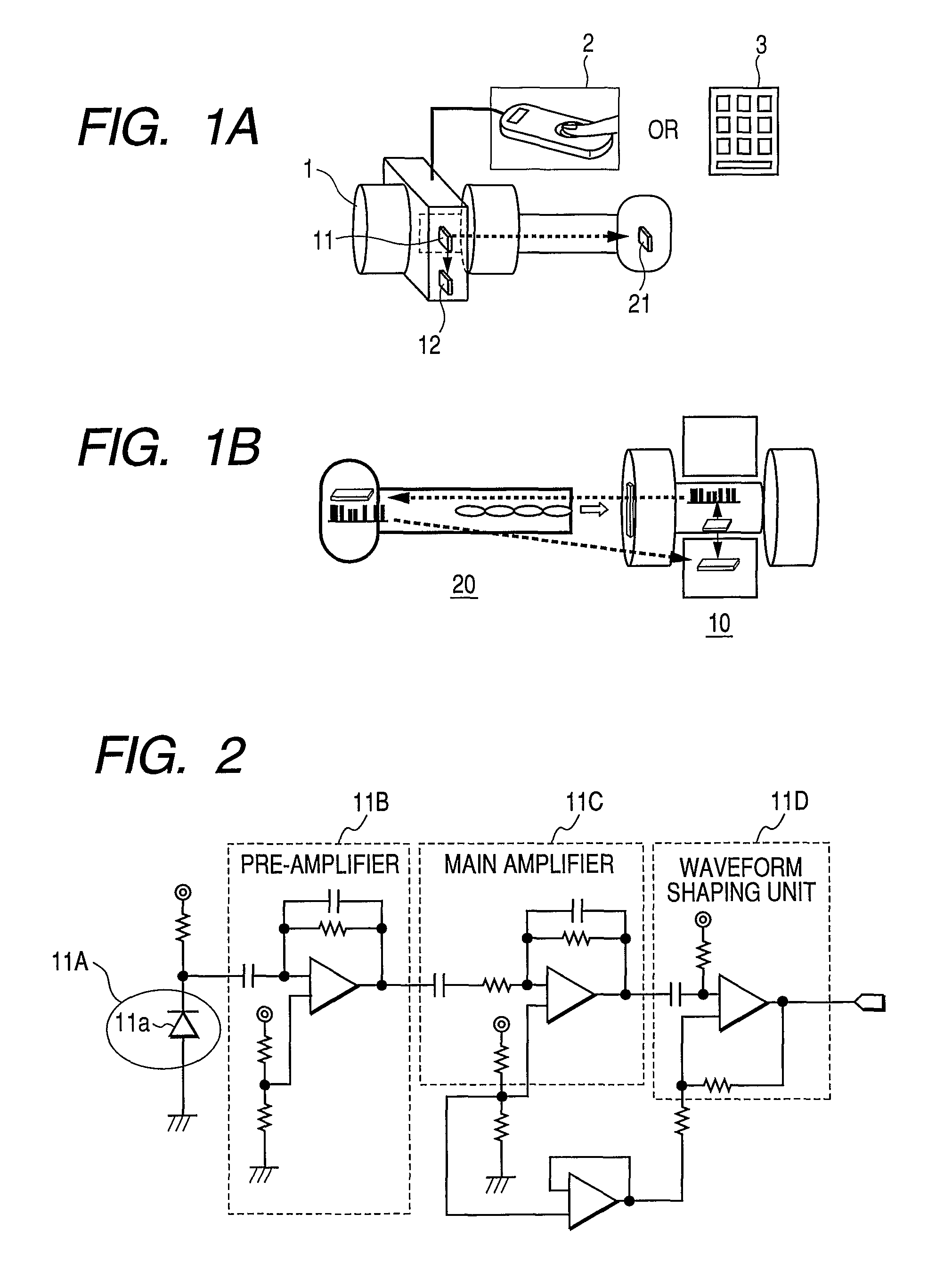
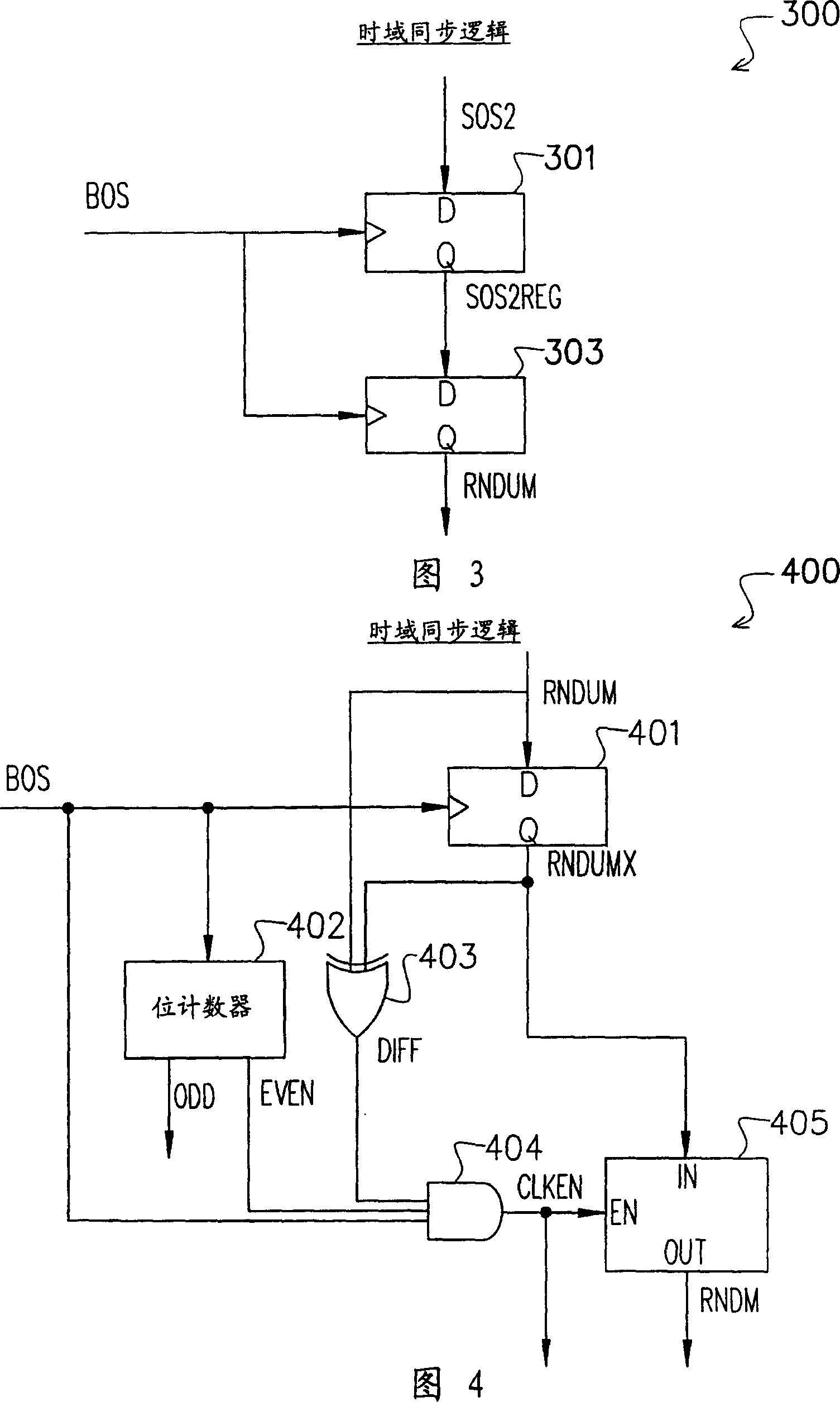
A random number generator has a simple configuration using know inexpensive electronic parts and can generate the true physical random numbers at a required generation speed. Such a random number generator can provide the true physical random numbers to any sectors of society at dramatically low cost A random pulse generator comprises a thermal noise generating element (2) having a resistor, a conductor or a semiconductor such as a diode adapted to generate thermal noises Hen no electric current is supplied to them, an analog-amplifier circuit for amplifying the irregular potential generated from the thermal noise generating element and a waveform shaping circuit (6) adapted to take out the output of the amplifier circuit as random rectangular pulse signals. A thermal noise random number generator comprises, in addition to the above components, an n-bit counter (n being an integer) for measuring the time interval between a random pulse signal output from the waveform shaping circuit (6) and the immediately succeeding random pulse signal and is adapted to output the count of the n-bit counter as natural random number.
Owner:L E TECH
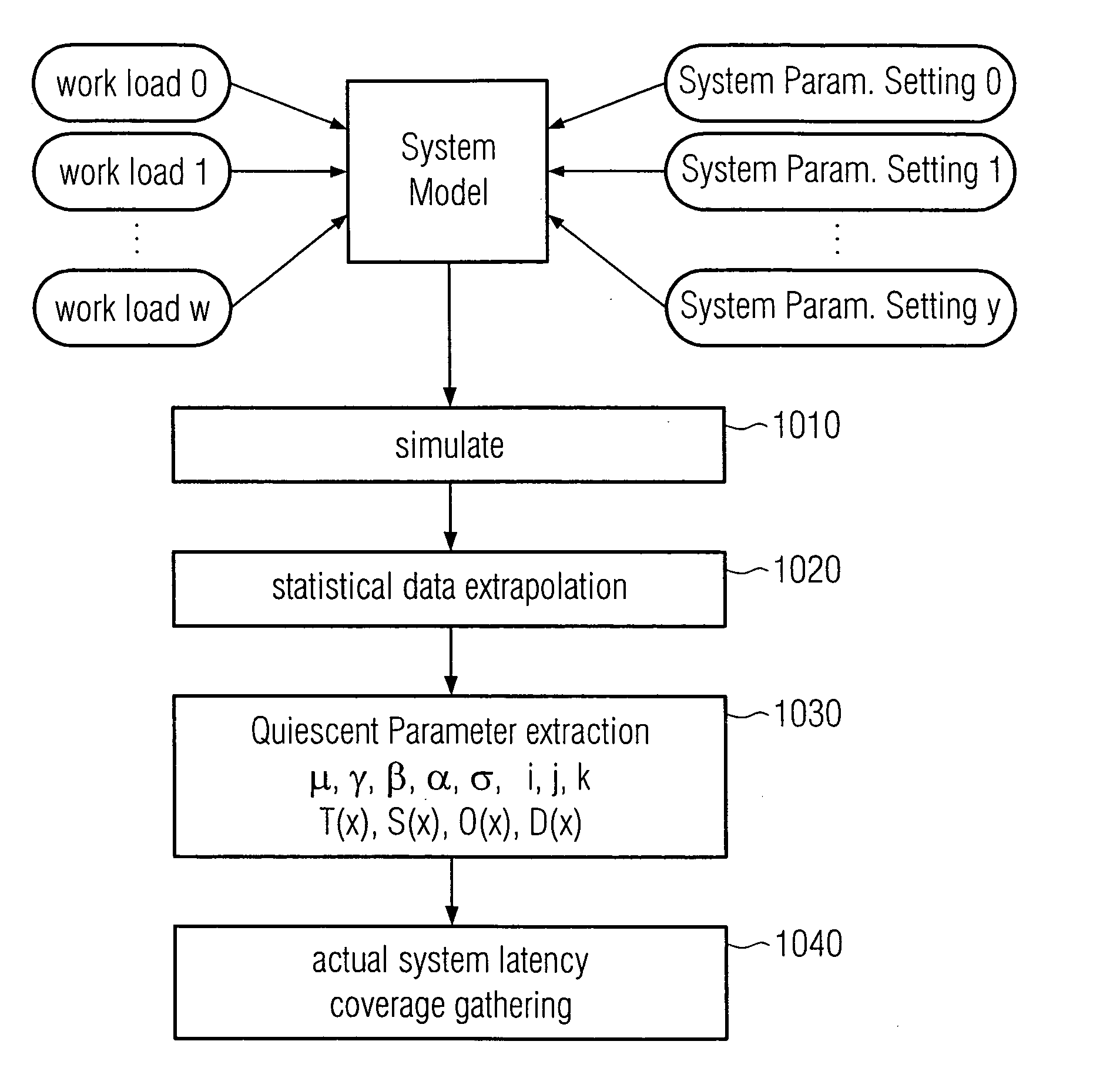
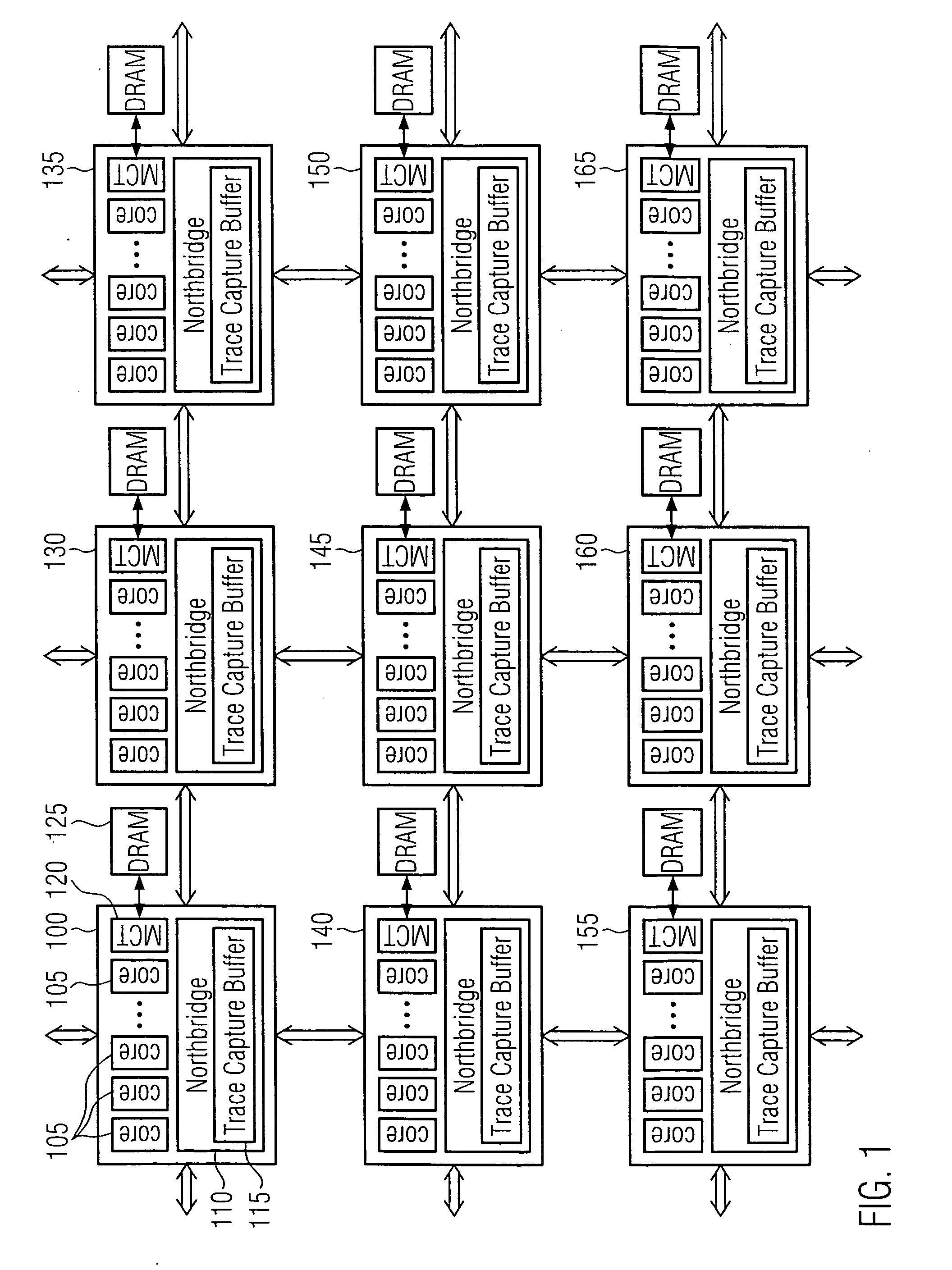
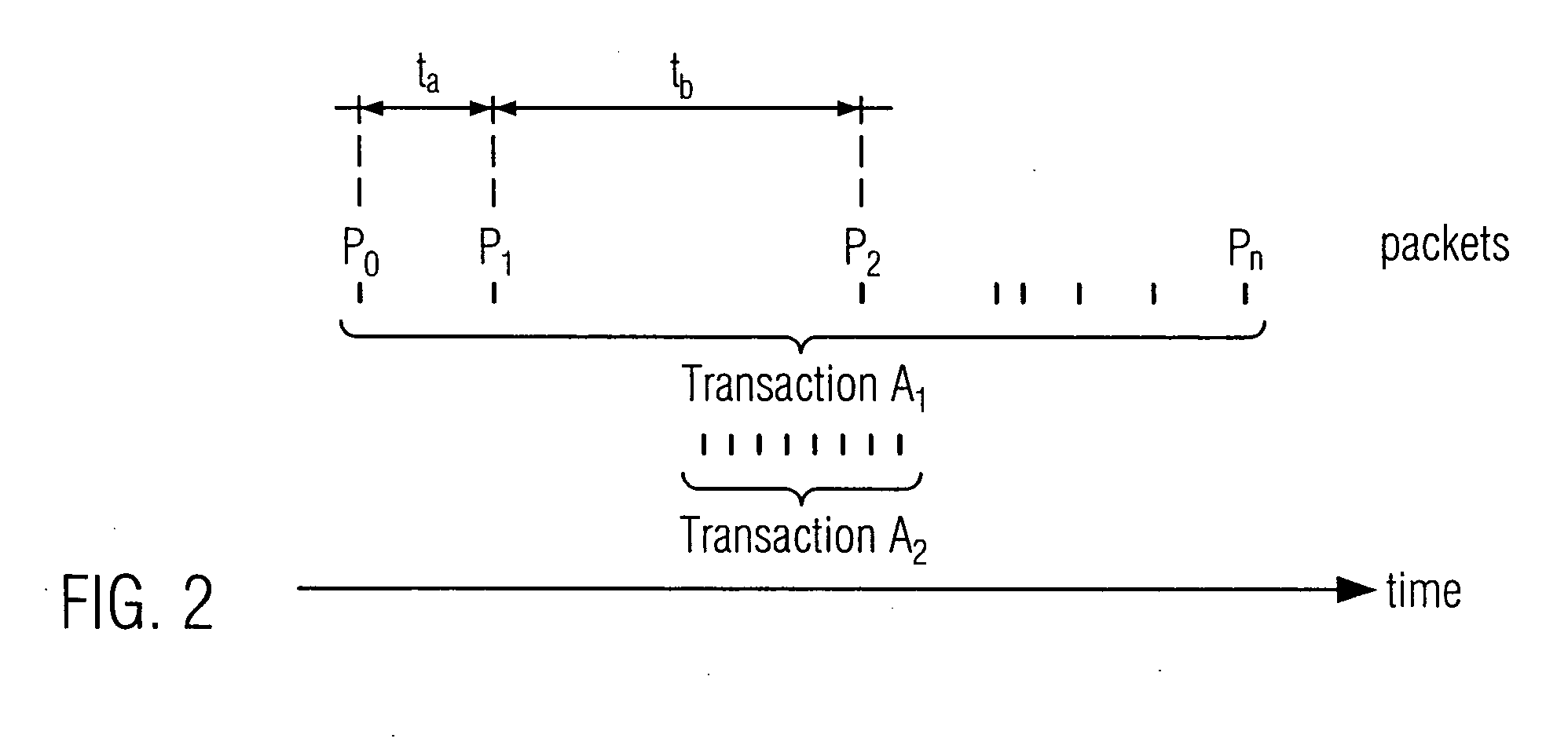
Latency coverage and adoption to multiprocessor test generator template creation
InactiveUS20090064149A1Easy to measureEasy to captureError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsMulti processorTransaction data
A multi-core multi-node processor system has a plurality of multiprocessor nodes, each including a plurality of microprocessor cores. The plurality of microprocessor nodes and cores are connected and form a transactional communication network. The multi-core multi-node processor system has further one or more buffer units collecting transaction data relating to transactions sent from one core to another core. An agent is included which calculates latency data from the collected transaction data, processes the calculated latency data to gather transaction latency coverage data, and creates random test generator templates from the gathered transaction latency coverage data. The transaction latency coverage data indicates at least the latencies of the transactions detected during collection of the transaction data having a pre-determined latency, and includes, for example, four components for transaction type latency, transaction sequence latency, transaction overlap latency, and packet distance latency. Thus, random test generator templates may be created using latency coverage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
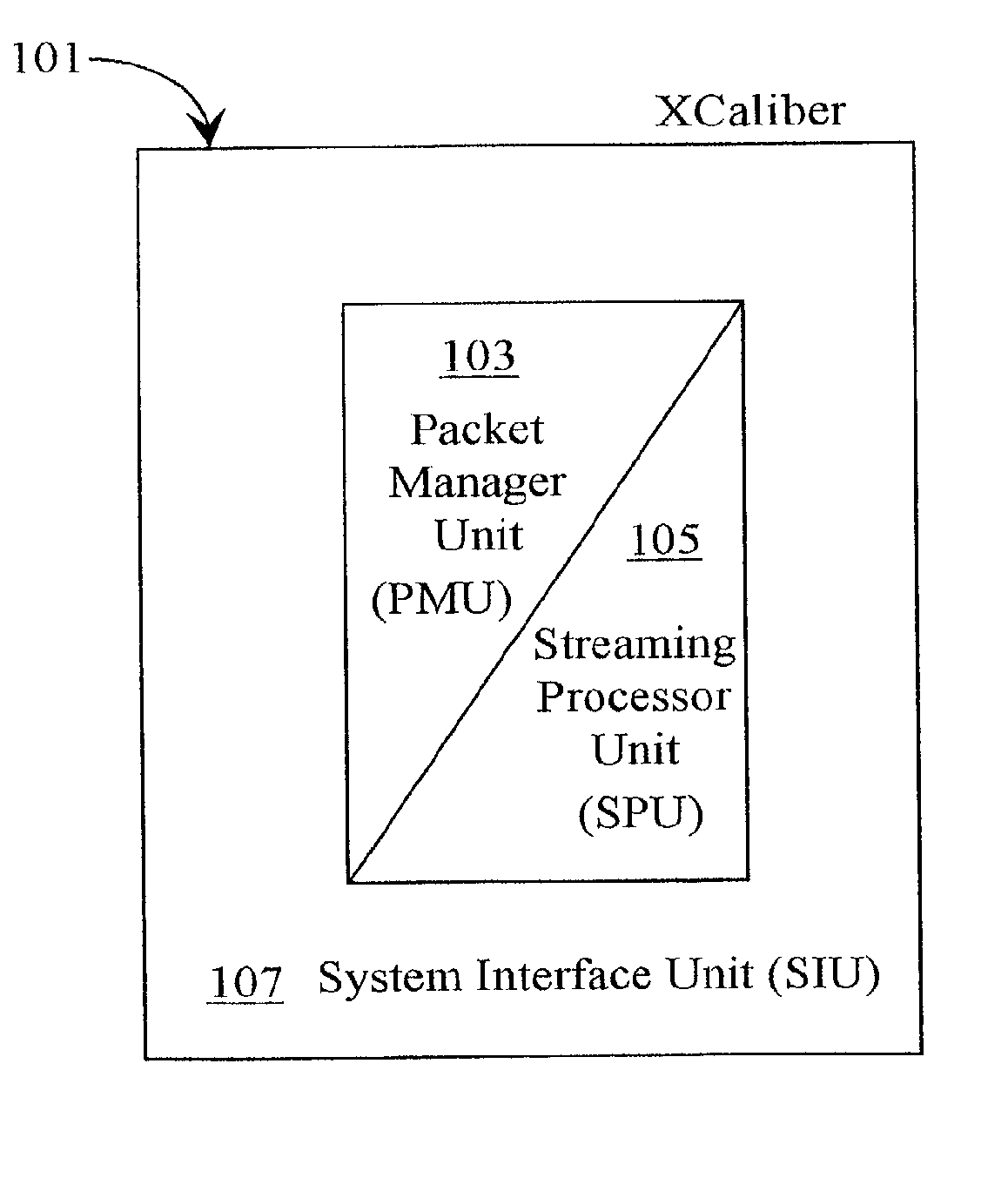
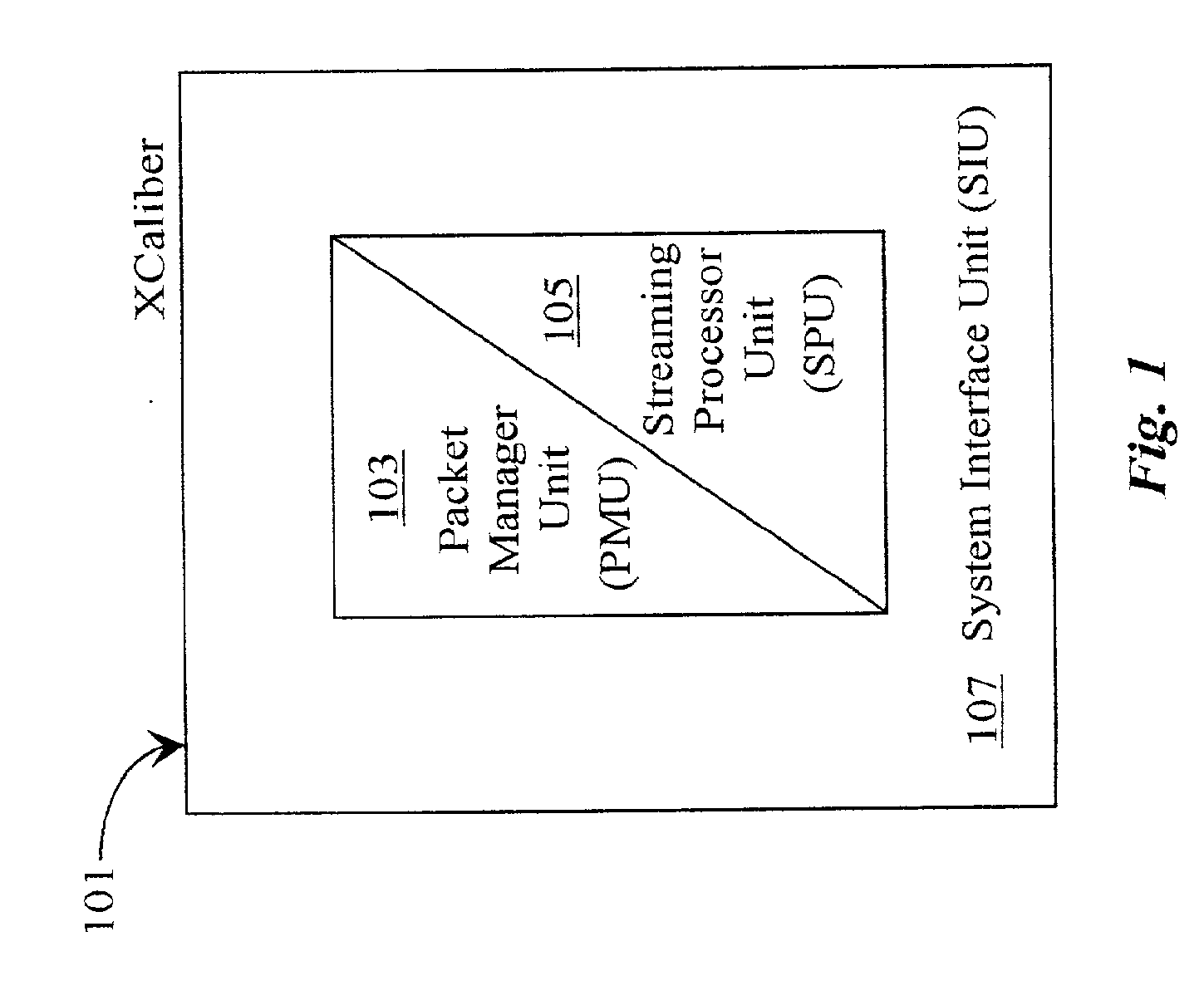
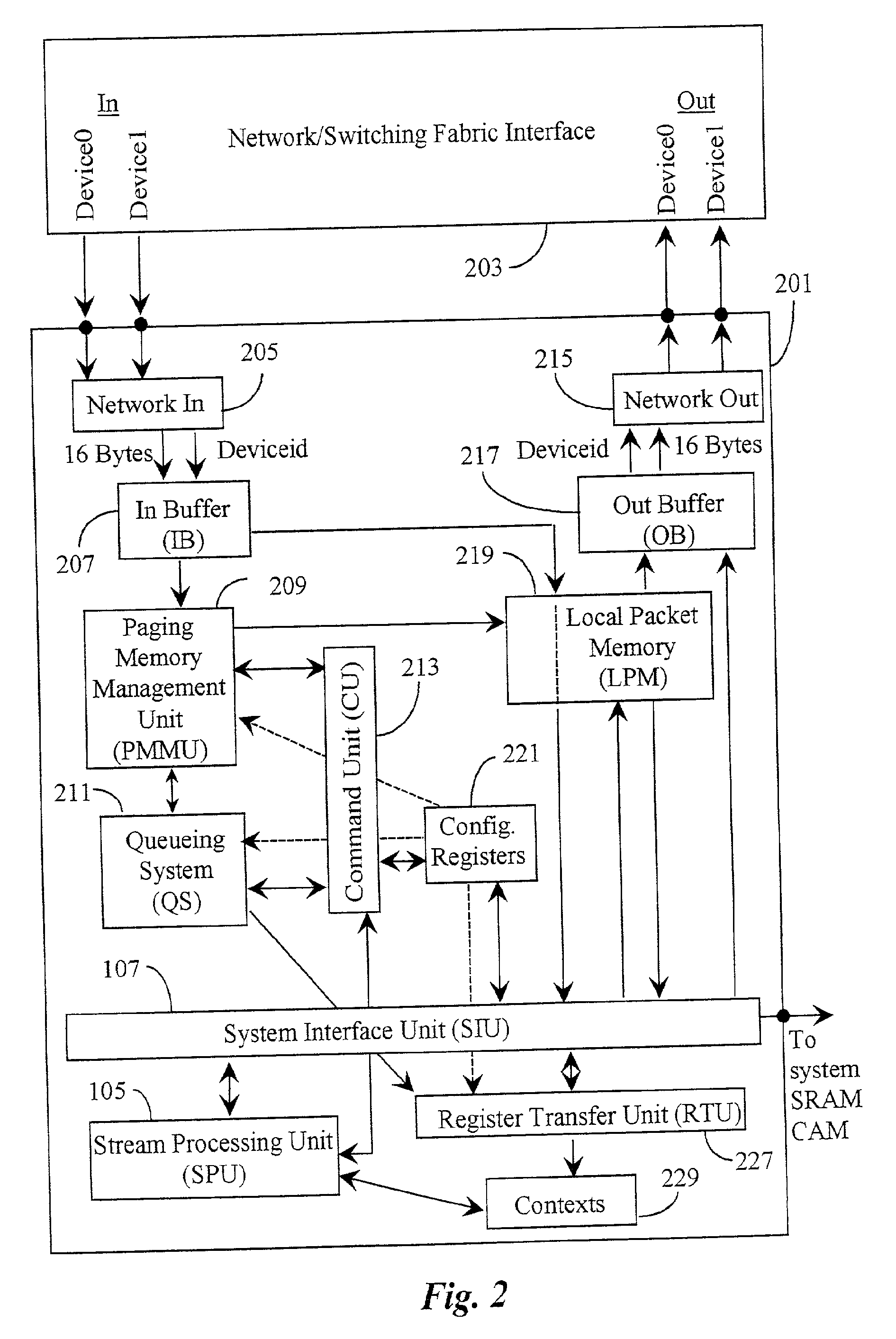
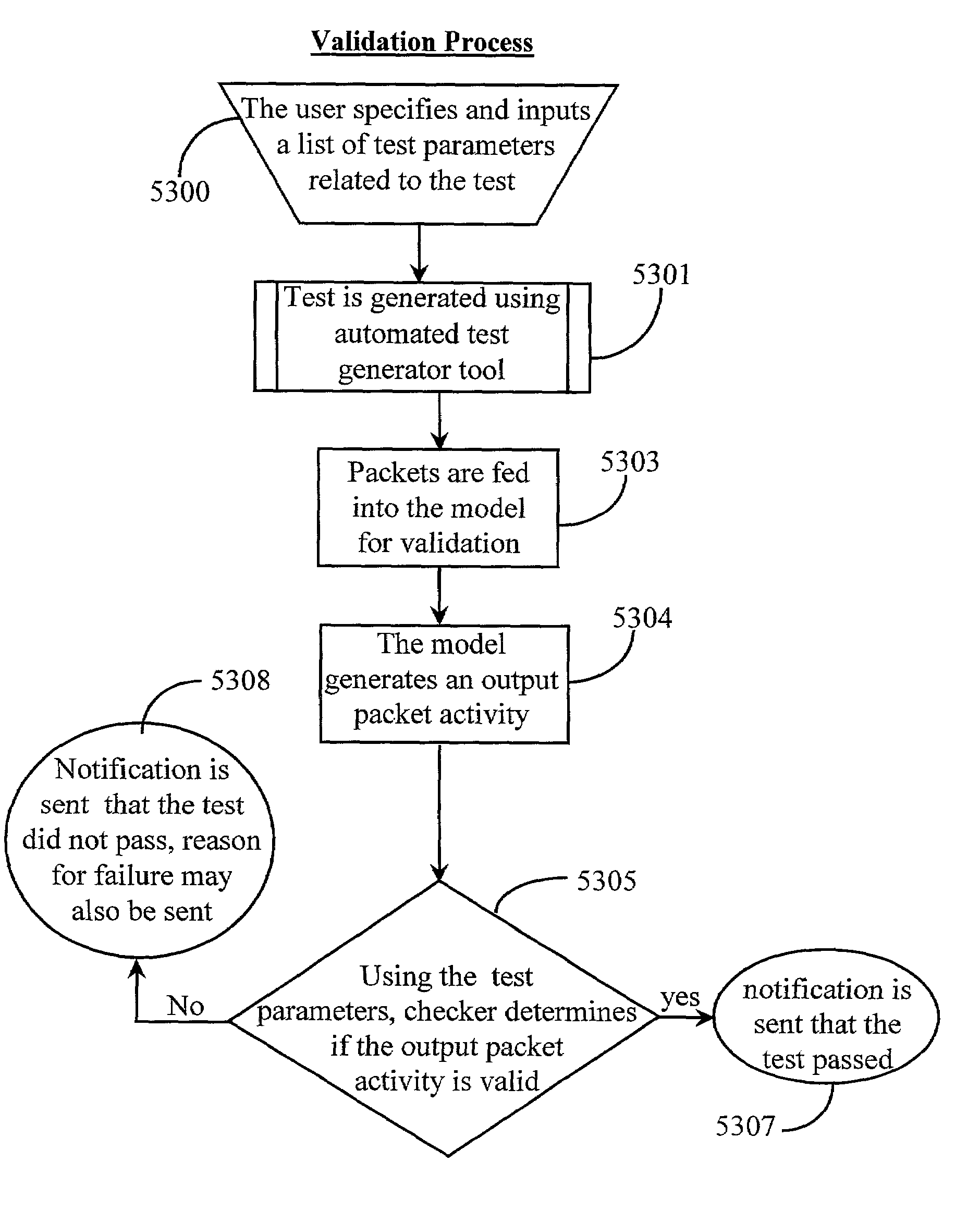
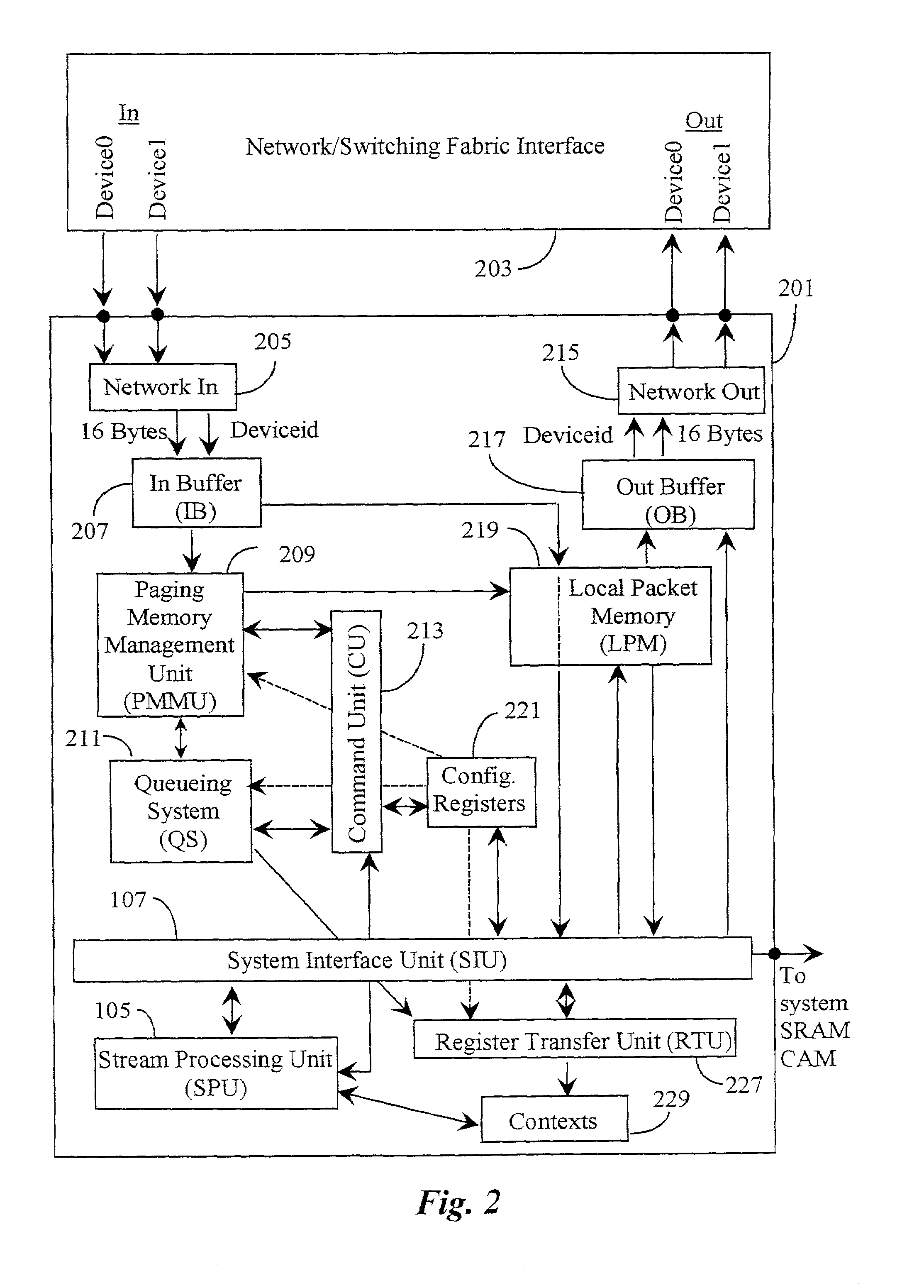
Functional validation of a packet management unit
InactiveUS20070168748A1Cost-effective and reliablePrecise designError detection/correctionProgram controlRandom test generatorUser interface
A validation system is disclosed for validating function of a packet-management unit operationally coupled through a system interface to a processing unit of a processor system. The validation system comprises a user interface for creating an inputting test parameters and test code into the system, a test generator coupled to the user interface, the test generator for generating input packet activity in the form of a packet stream, a model coupled to the test generator for emulating separate and integrated function of the packet management unit, the system interface, and a stream-processing unit and an evaluation software for checking and validating or not validating results. The system validation function relies, in a preferred embodiment, on comparing output results with criteria of the selected test code resulting in an indication of pass or failure of the test. In a preferred embodiment, the system also notifies to cause of failure.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Thermal noise random pulse generator and random number generator
InactiveUS20030090306A1Random number generatorsPulse generation with predetermined statistical distributionElectrical conductorWaveform shaping
A random number generator has a simple configuration using known inexpensive electronic parts and can generate the tine physical random numbers at a required generator speed. Such a random number generator can provide the true physical random numbers to any sectors of society at dramatically low cost A random pulse generator comprises a thermal noise generating element (2) having a resistor, a conductor or a semiconductor such as a diode adapted to generate thermal noises when no electric current is supplied to them, an analog-amplifier circuit for amplifying the irregular potential generated from the thermal noise generating element and a waveform shaping circuit (6) adapted to take out the output of the amplifier circuit as random rectangular pulse signals. A thermal noise random number generator comprises, in addition to the above components, an n-bit counter (n being an integer) for measuring the dine interval between a random pulse signal output from the waveform shaping circuit (6) and the immediately succeeding random pulse signal and is adapted to output the count of the n-bit counter as natural random number.
Owner:SAITO TAKESHI
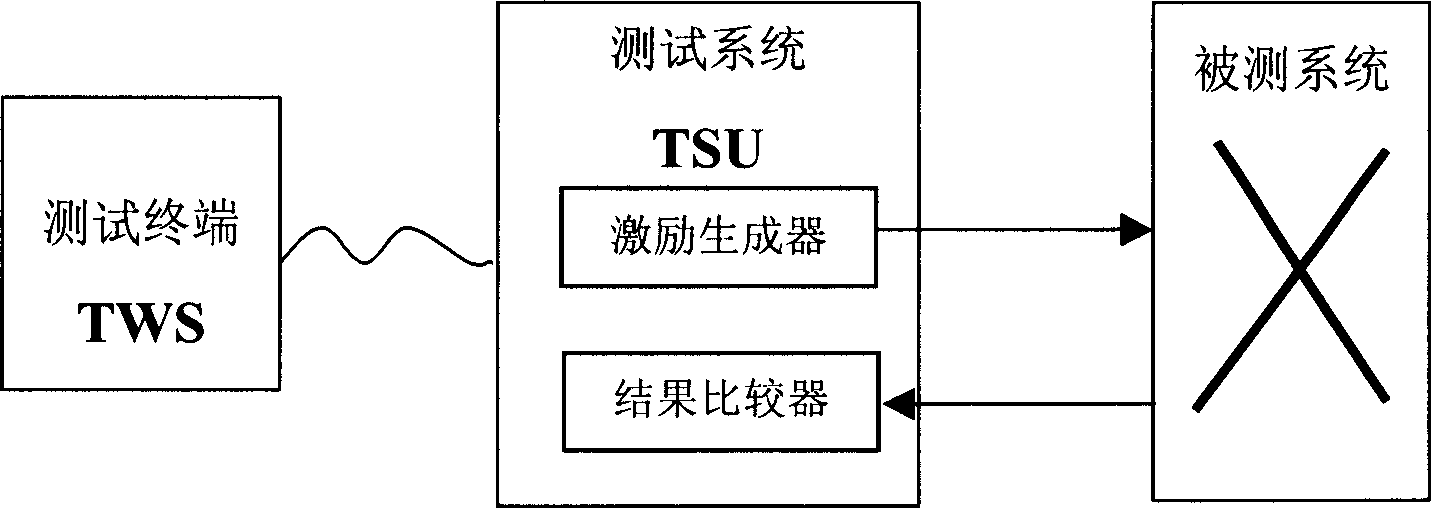
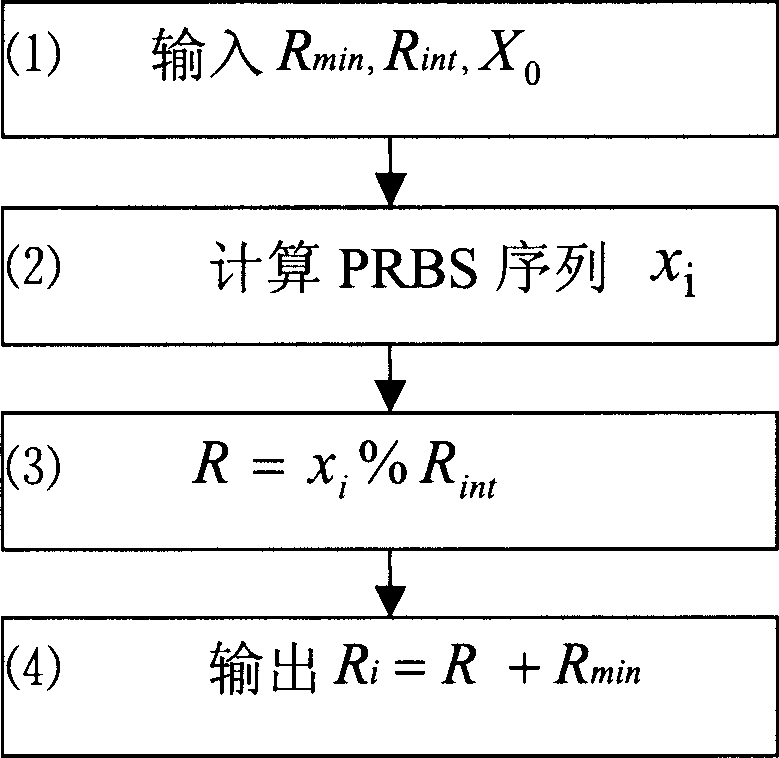
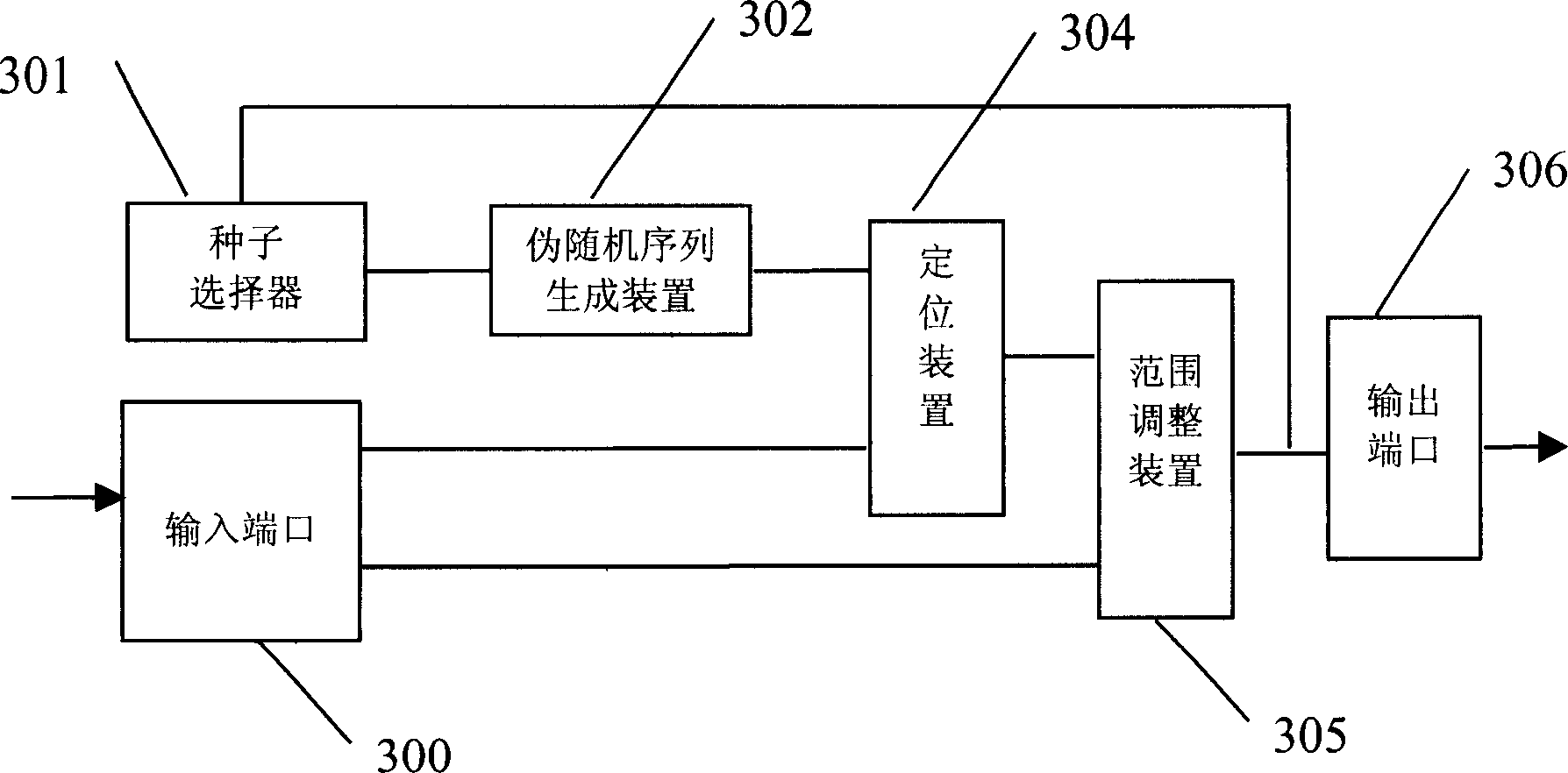
Pseudo-random number generator and test system using it
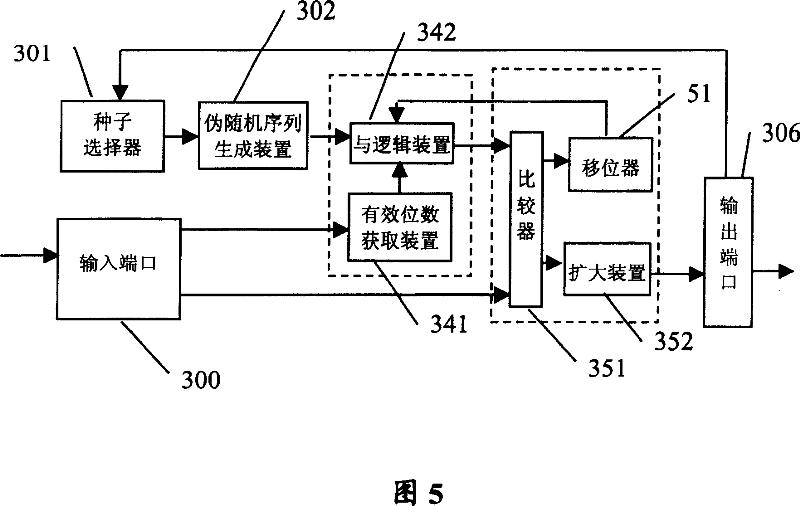
ActiveCN1725714AEasy to produceProduce quicklyData switching networksNumber generatorRandom test generator
A pseudo-random number generating unit consists of input and output ports for inputting random number sampling range , seed selector , pseudo - random sequence generating unit for generating any length of pseudo - random sequence , positioning device for determining effective bit of random sequence and range adjusting unit for adjust random sequence value . The test device realized by above-said unit can quickly generate large amount of message with different length required by test to let system simulate real data flow accurately for raising test effect.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
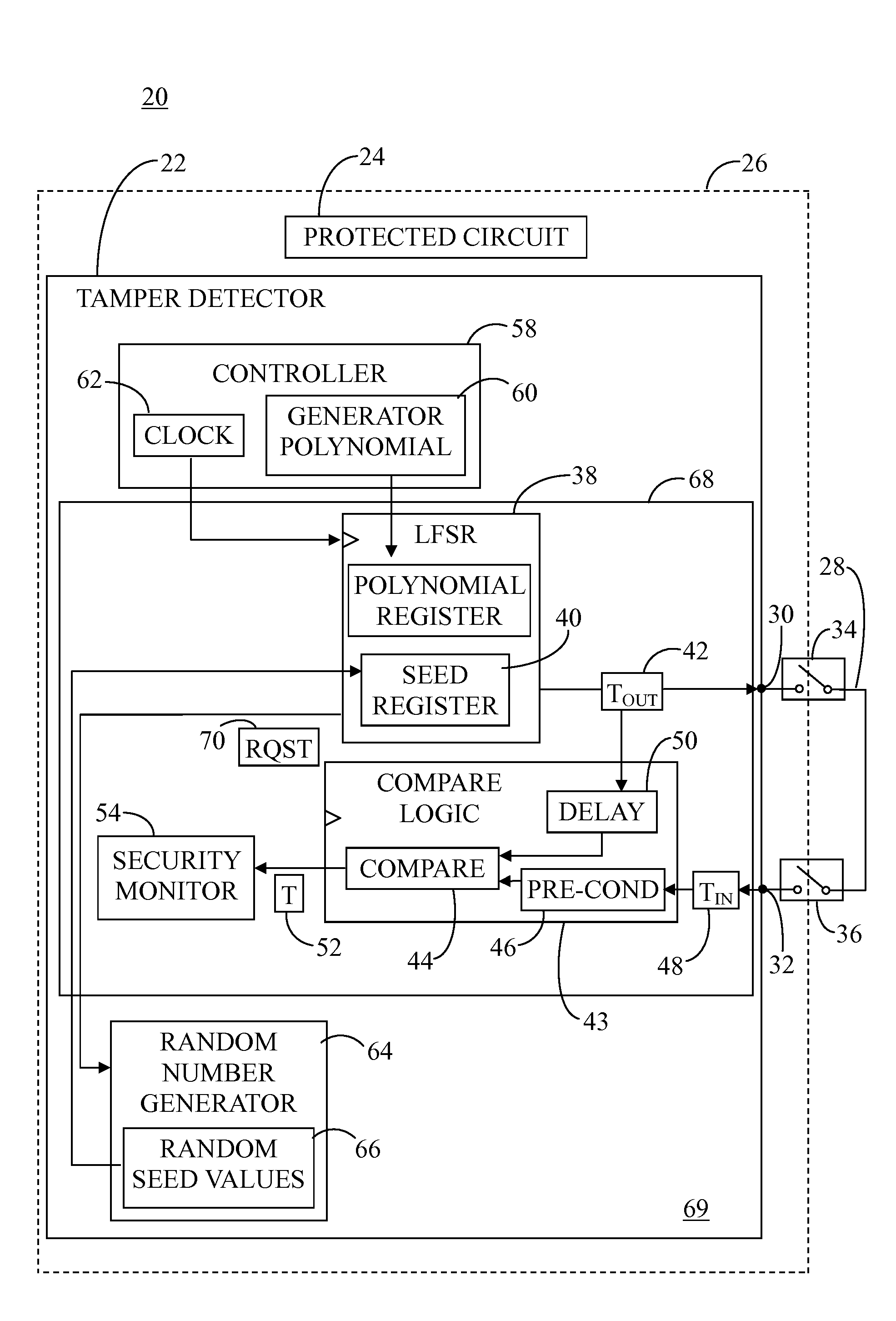
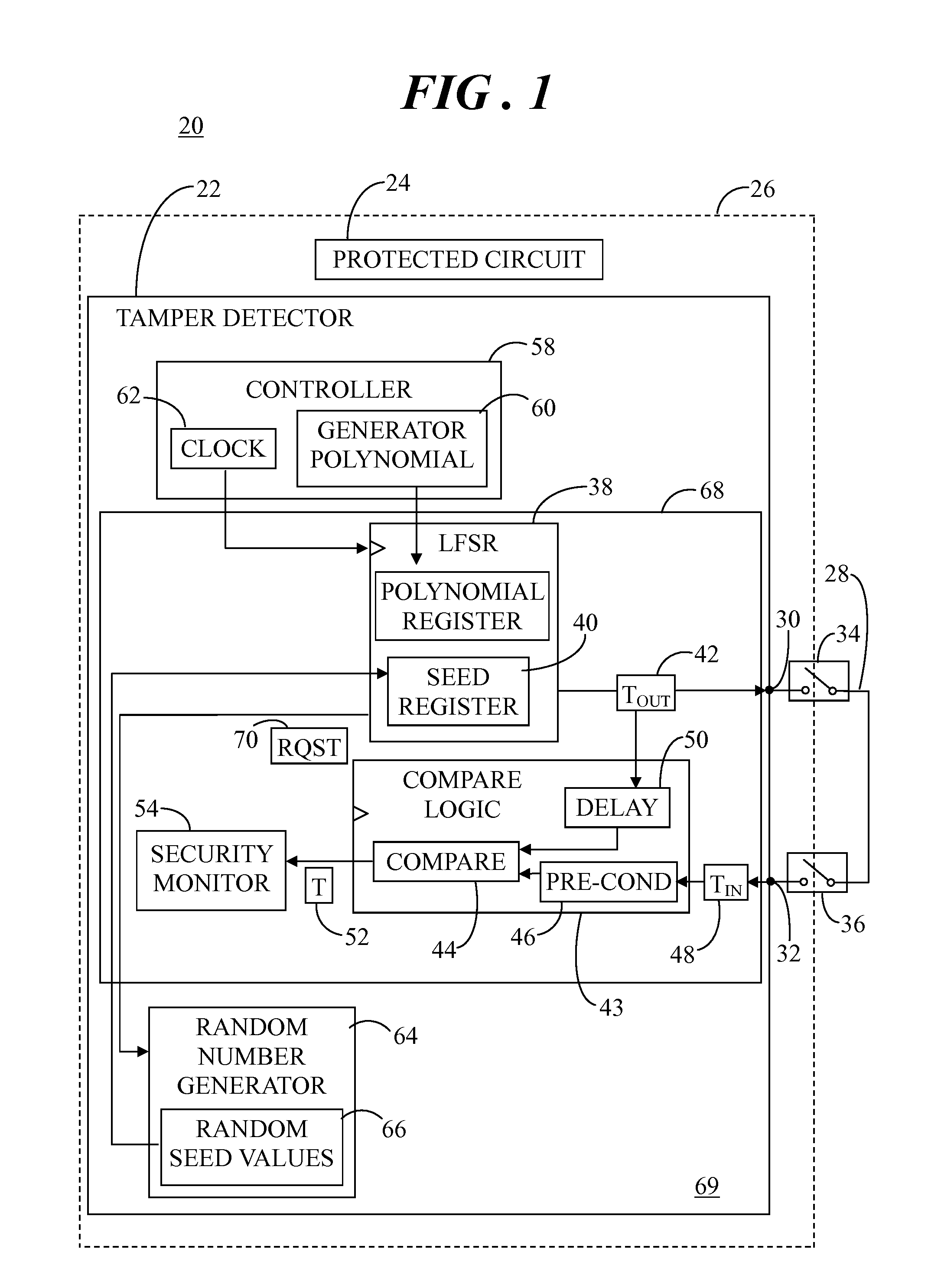
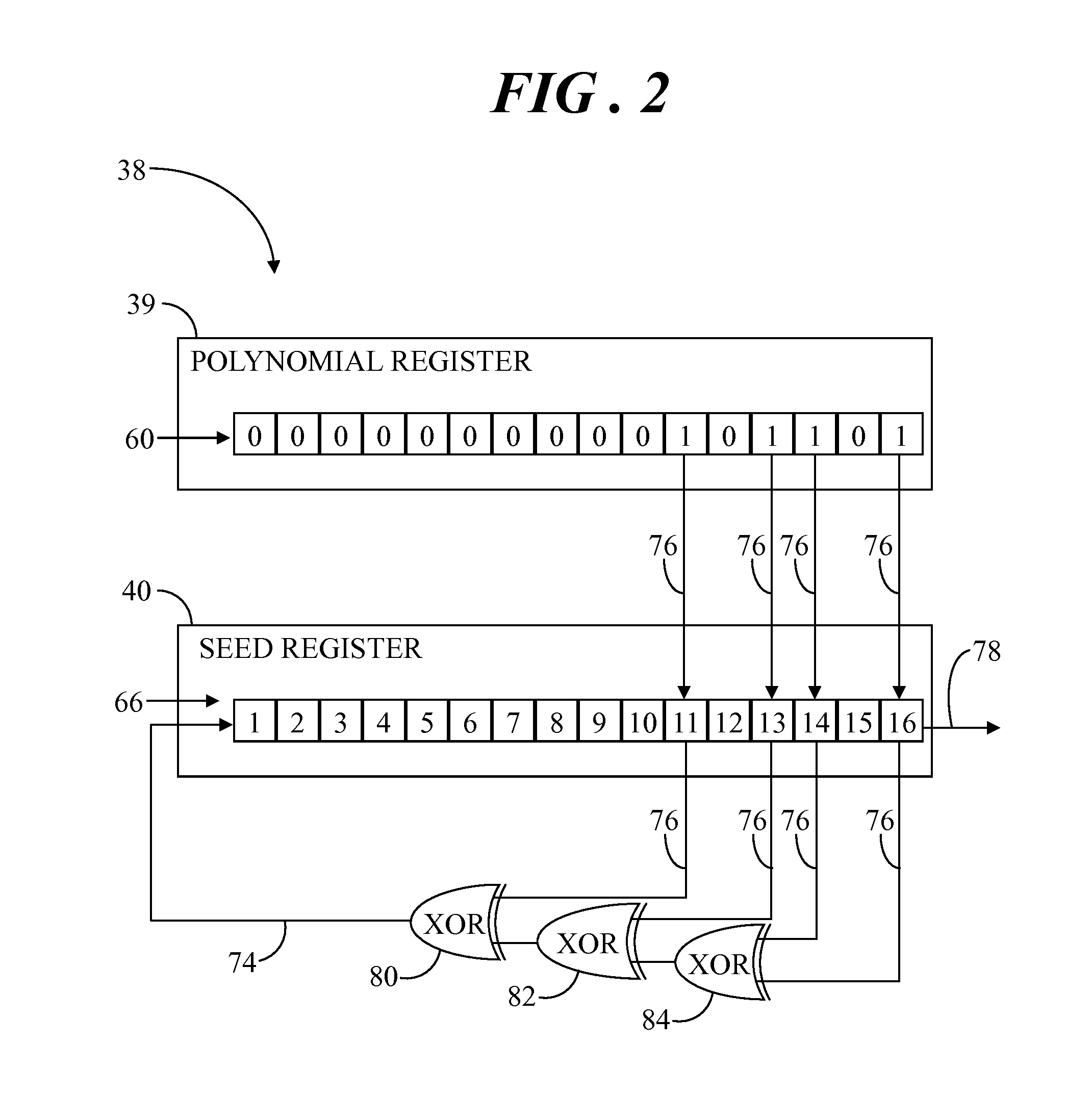
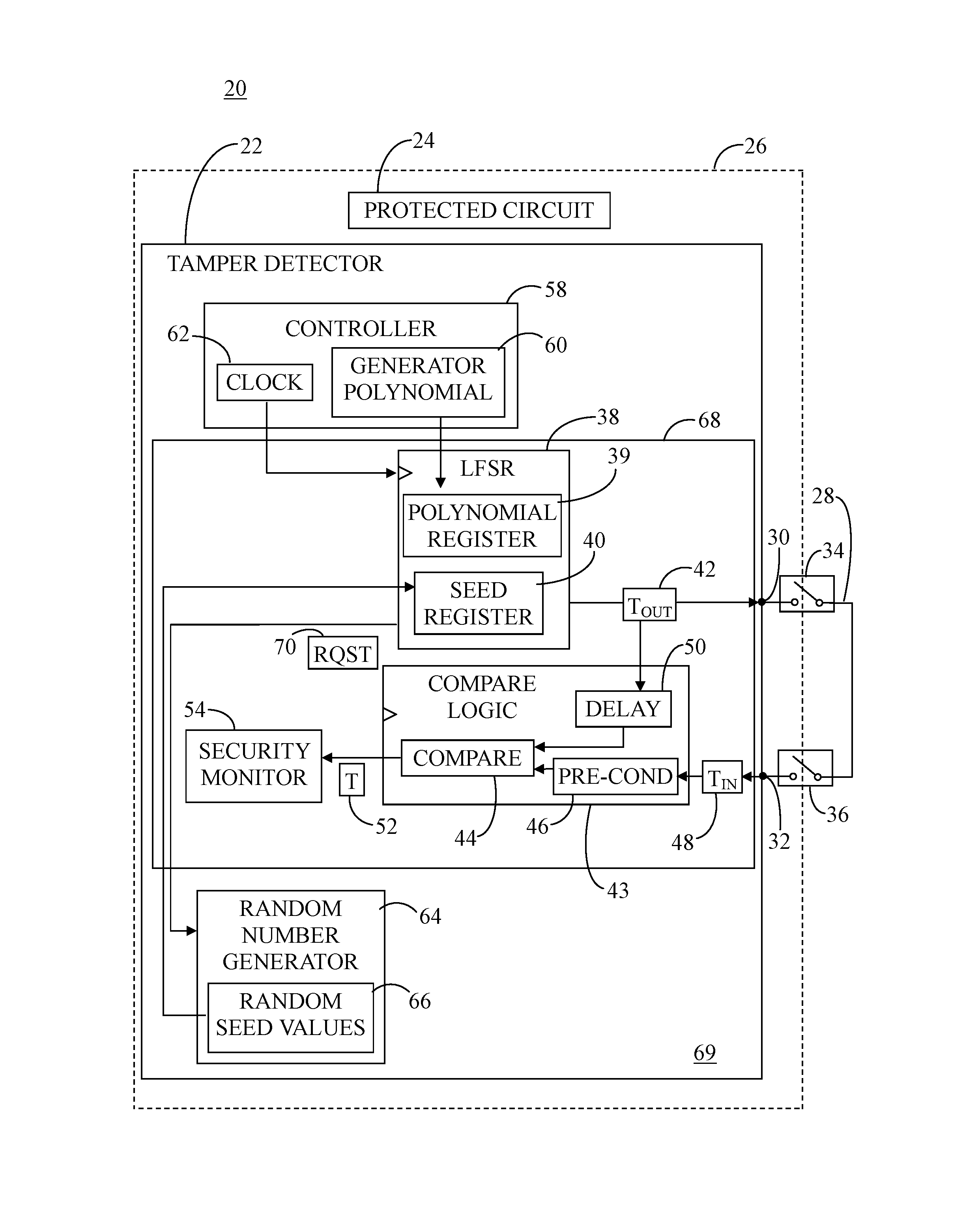
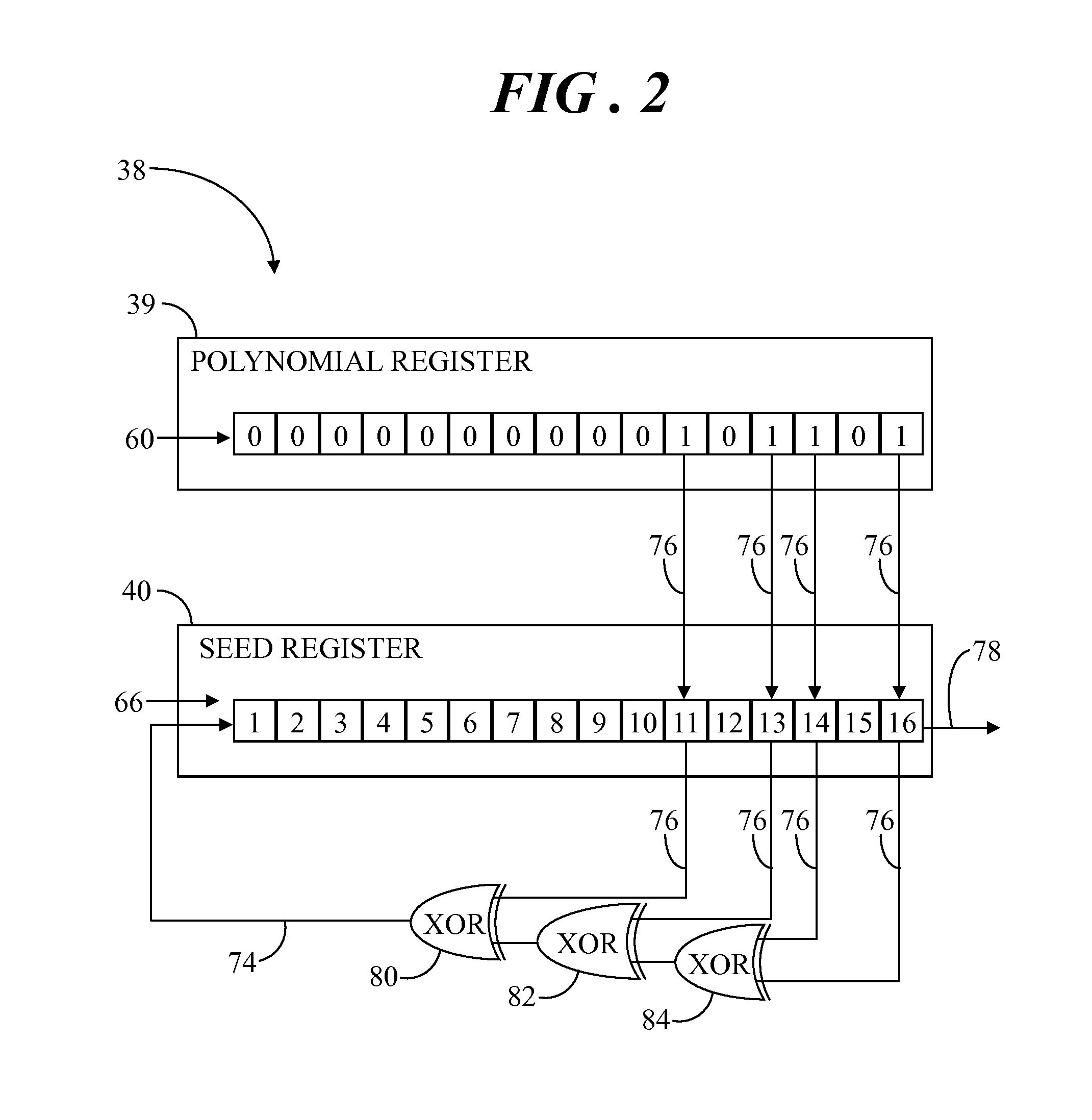
Tamper detector with hardware-based random number generator
A system includes a tamper detector that includes a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) for generating pseudorandom coded detection signals as a function of seed values and a generator polynomial. The generator polynomial is loaded from a controller to the LFSR via software, and the seed values are directly loaded from a hardware-based random number generator to the LFSR. The tamper detector has output and input elements for connection to ends of a tamper detection circuit, wherein the detection circuit is linked with a physical closure surrounding an electronic circuit. The detection signals are applied to the output element and incoming signals are received from the tamper detection circuit at a comparator via the input element. Comparison of the incoming signals with the coded detection signals is performed to detect interference with the detection circuit in an attempt to tamper with the electronic circuit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Random number generator with random sampling
InactiveUS7904494B2Electric signal transmission systemsRandom number generatorsAudio power amplifierDigital number
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
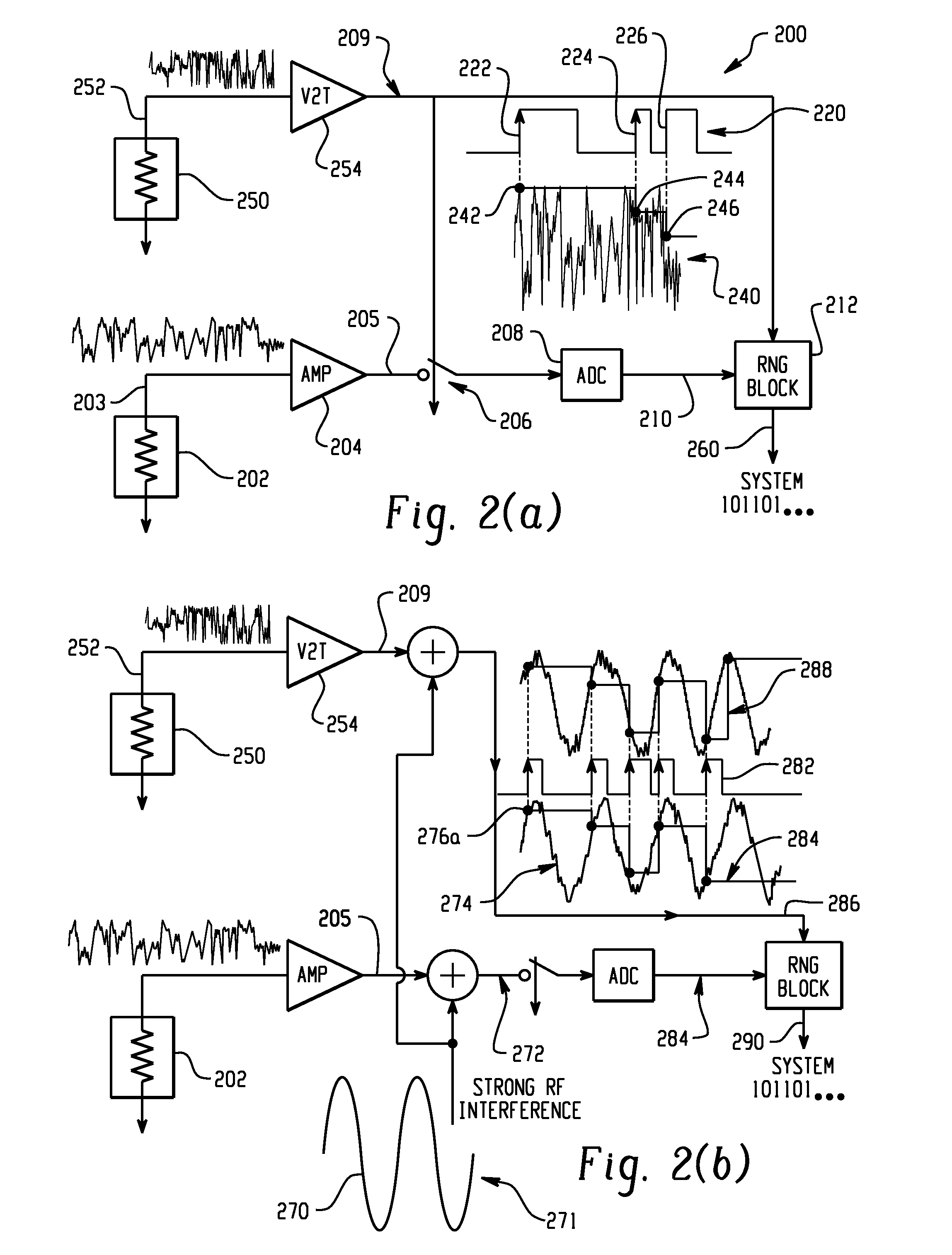
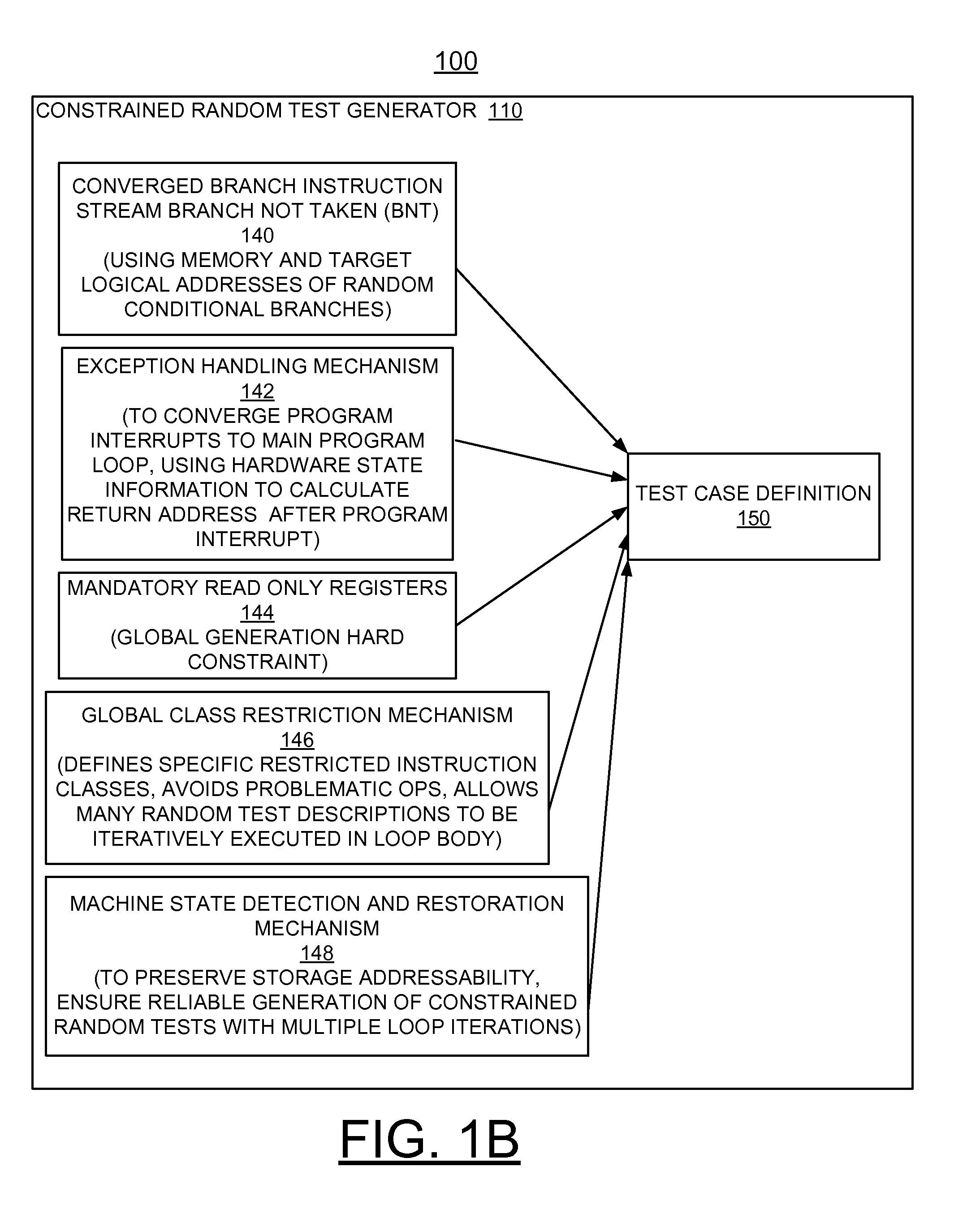
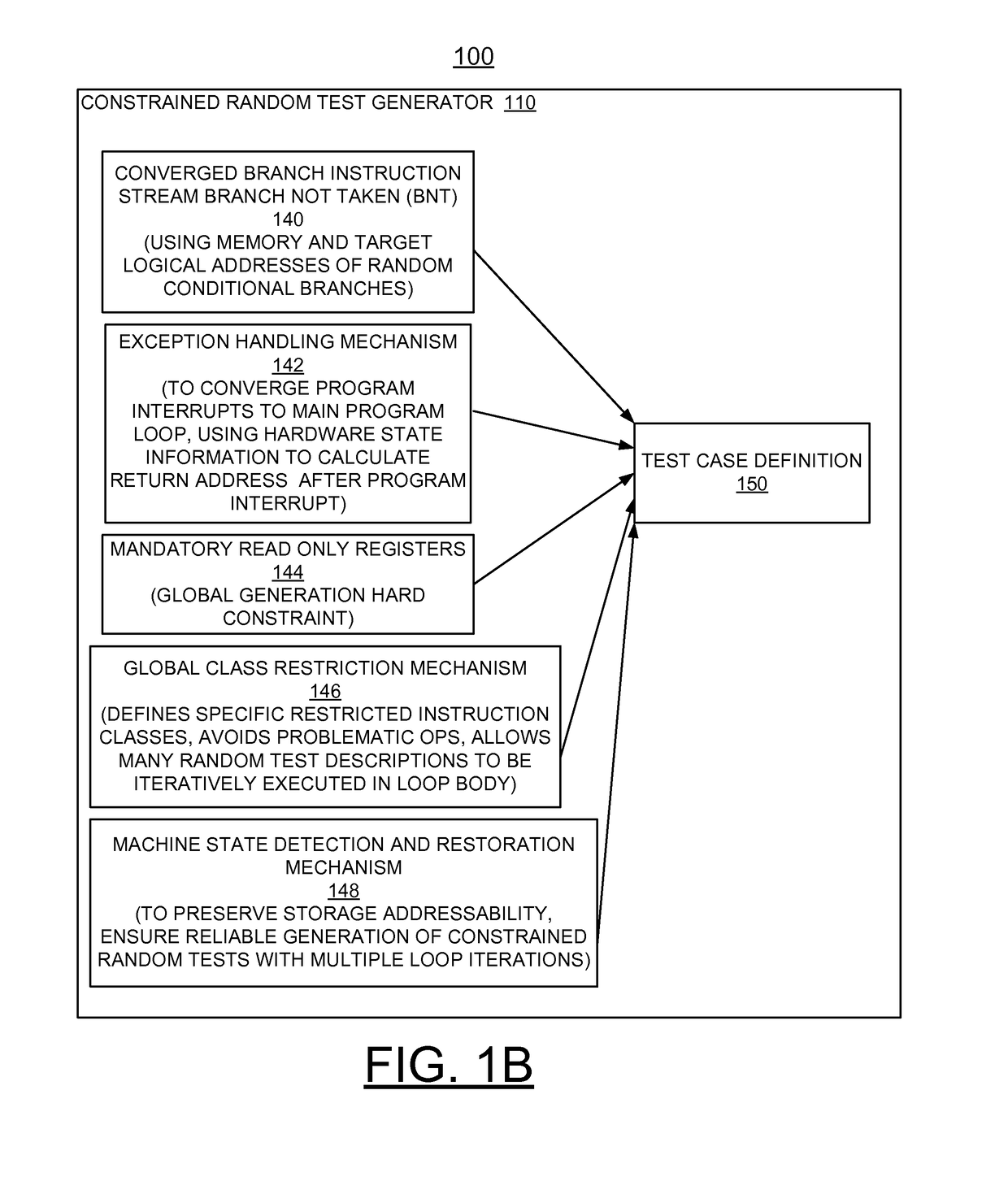
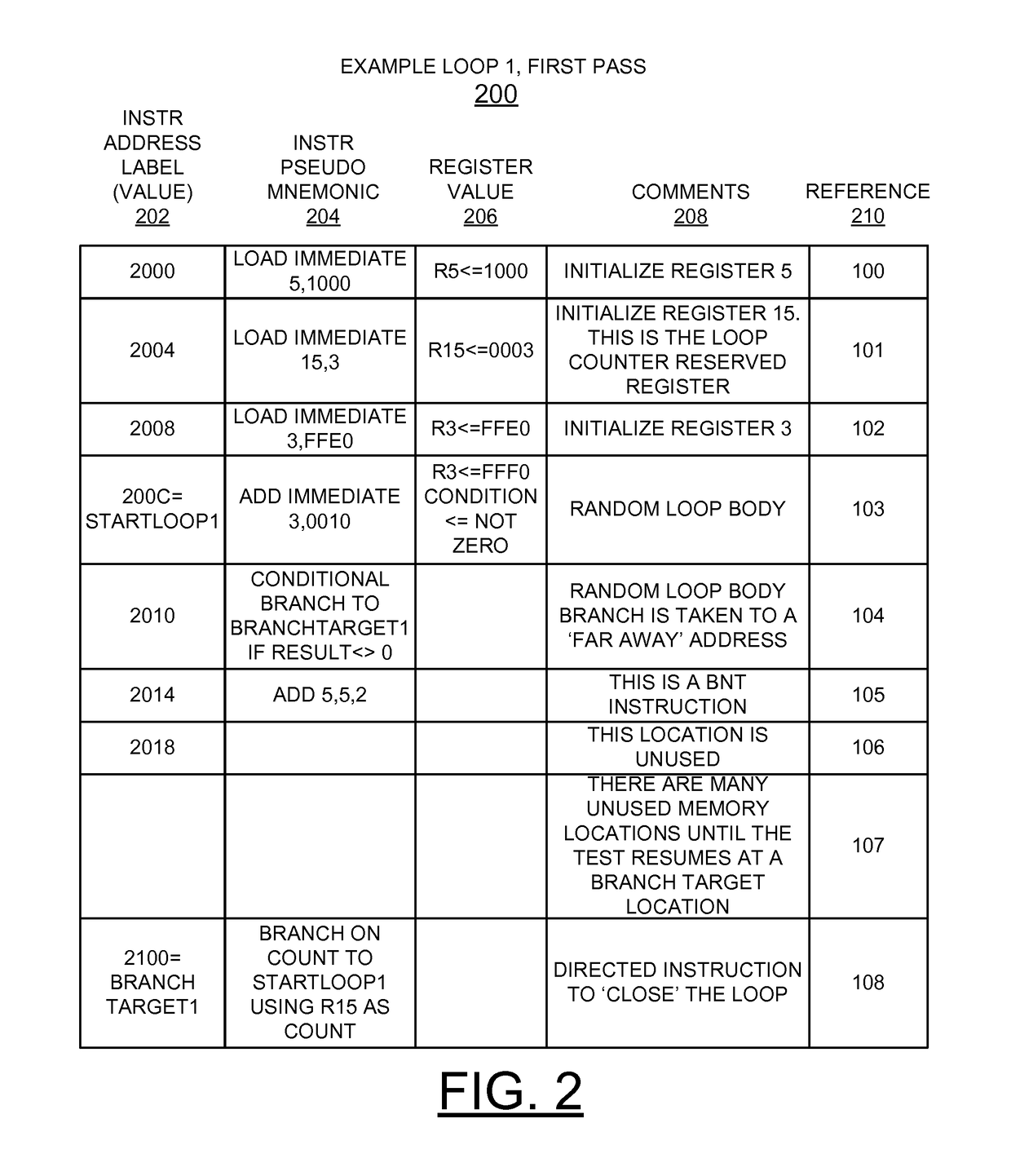
Implementing random content of program loops in random test generation for processor verification
ActiveUS20140257739A1Negative effectAvoids inherently problematic operationError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork address translationRandom test generator
A method and apparatus are provided for implementing random content of program loops in random test generation for processor verification. A converged branch instruction stream is used by a test generator to ensure that all random conditional branches converge to a main program loop. A built in exception handling mechanism of the test generator enables program interrupts to converge to the main program loop. Mandatory read only registers applied to the test generator allow all register based storage addresses to use registers that maintain a value and thus stabilize the storage address translations through subsequent iterations of the loop. A global class restriction mechanism defines specific restricted instruction classes applied to the test generator avoids inherently problematic operations for the program loops. Machine state detection and restoration mechanisms in the test generator are provided to preserve storage addressability.
Owner:IBM CORP
Tamper detector with hardware-based random number generator
ActiveUS9418250B2Random number generatorsInternal/peripheral component protectionEngineeringNumber generator
A system includes a tamper detector that includes a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) for generating pseudorandom coded detection signals as a function of seed values and a generator polynomial. The generator polynomial is loaded from a controller to the LFSR via software, and the seed values are directly loaded from a hardware-based random number generator to the LFSR. The tamper detector has output and input elements for connection to ends of a tamper detection circuit, wherein the detection circuit is linked with a physical closure surrounding an electronic circuit. The detection signals are applied to the output element and incoming signals are received from the tamper detection circuit at a comparator via the input element. Comparison of the incoming signals with the coded detection signals is performed to detect interference with the detection circuit in an attempt to tamper with the electronic circuit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
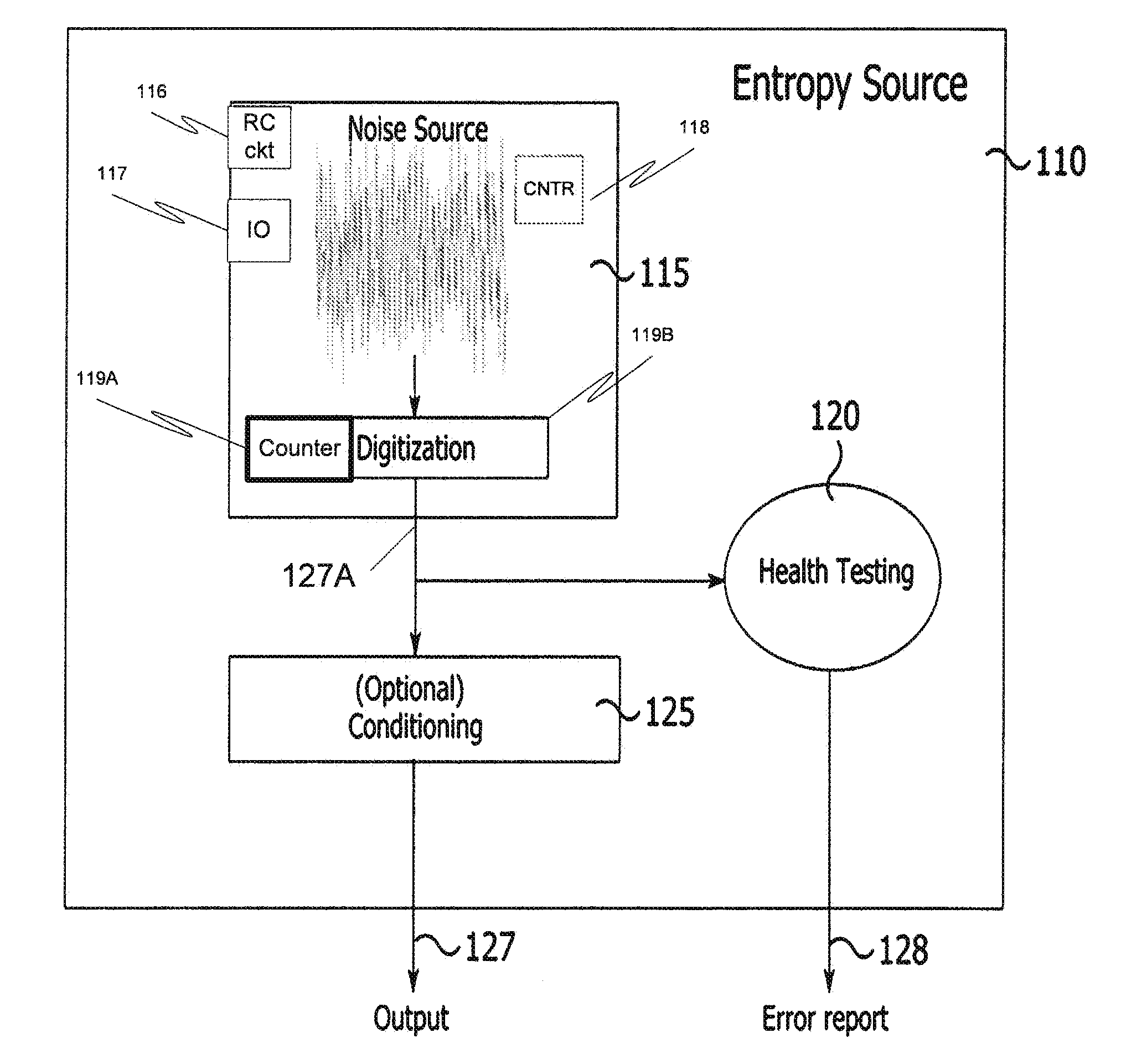
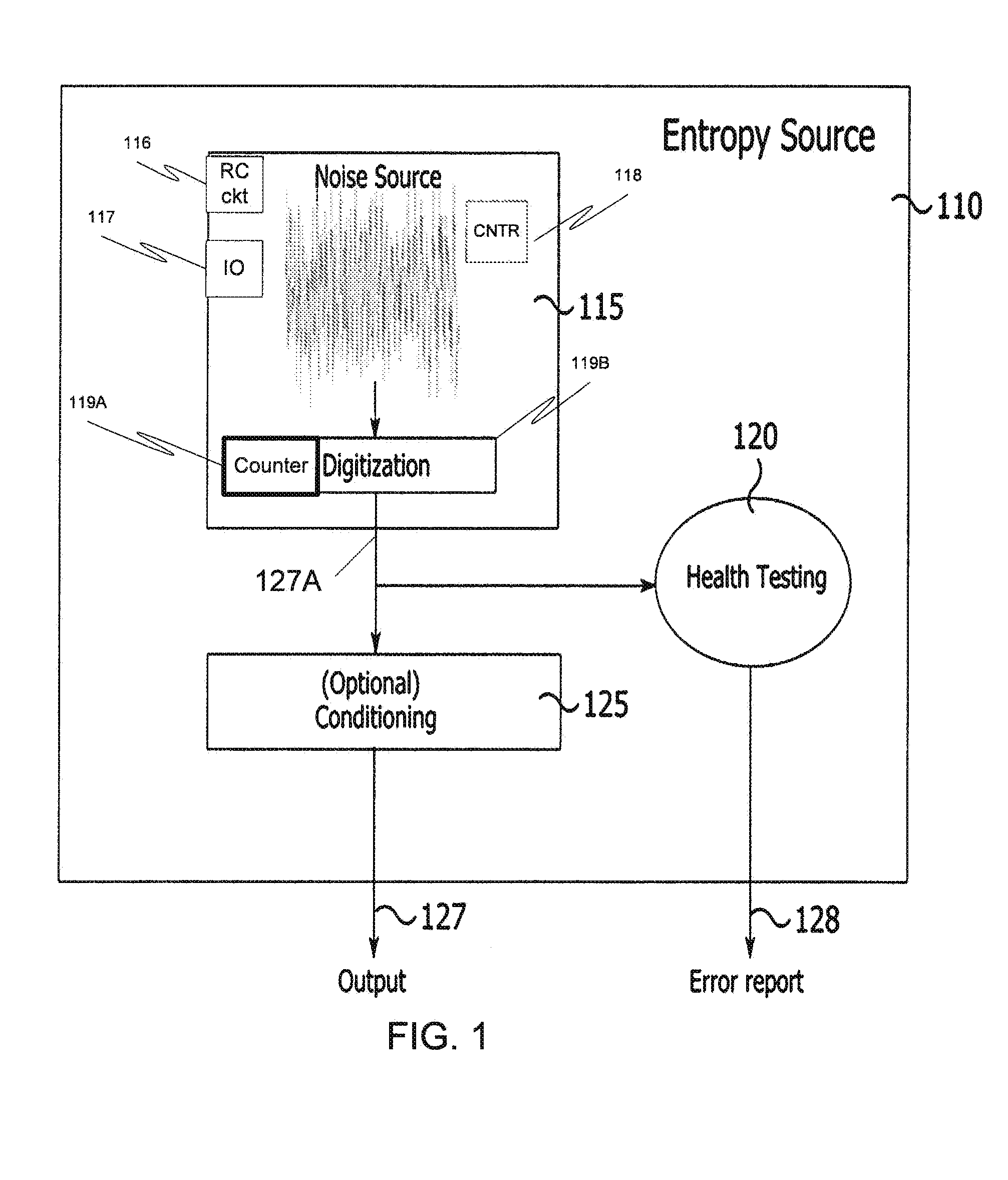
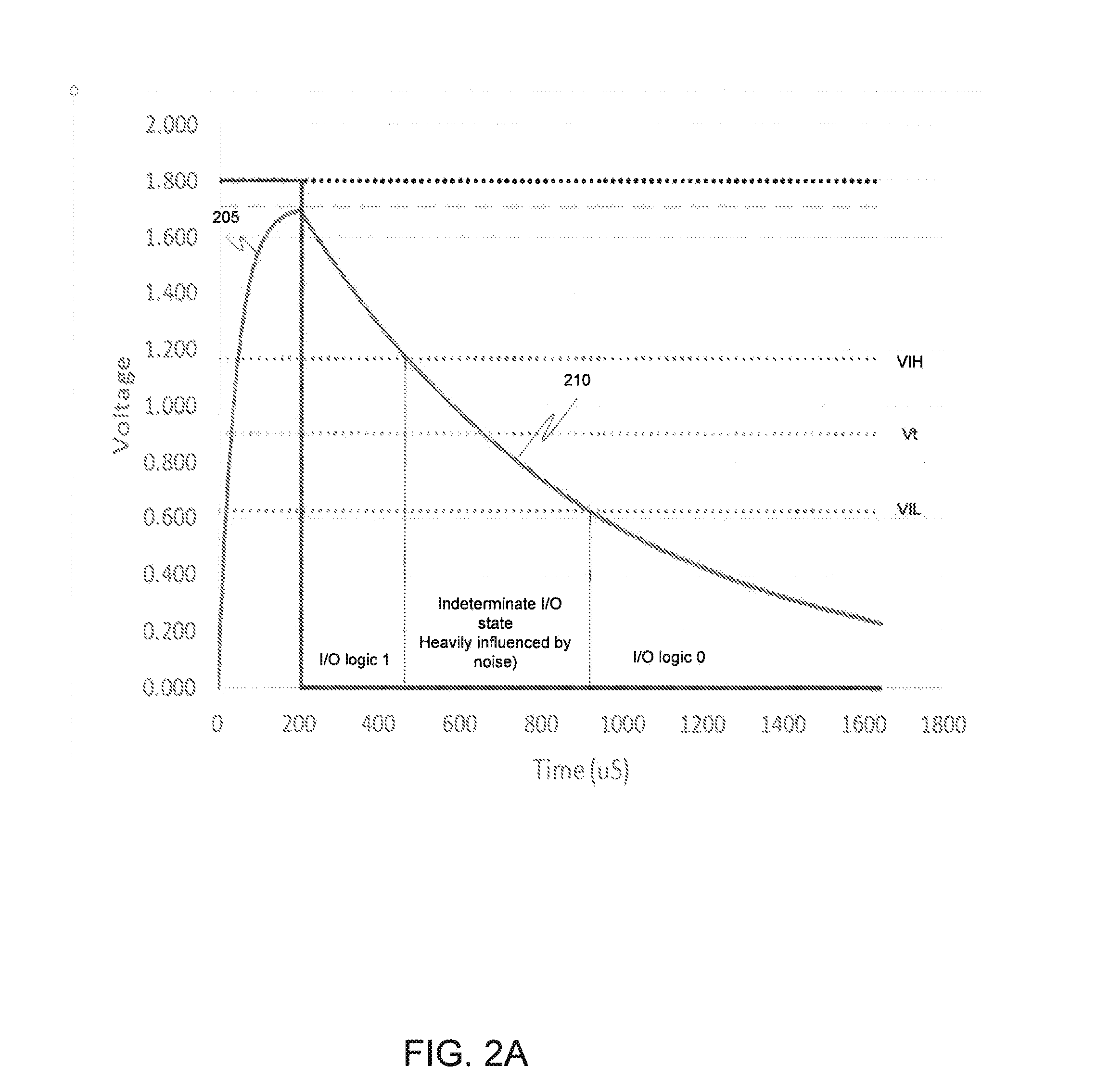
Entropy source for random number generator
An entropy source extracts noise associated with the sampling of an RC circuit. The decay time of the RC circuit and other parameters are selected so that a buffer used to sample the voltage remains in an indeterminate voltage region over multiple clock cycles to generate random transitions. The entropy source may be implemented to be compliant with government standards for entropy sources utilized to generate random numbers.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Functional validation of a packet management unit
InactiveUS7082552B2Cost-effective and reliablePrecise designError detection/correctionTime-division multiplexRandom test generatorUser interface
A validation system is disclosed for validating function of a packet-management unit operationally coupled through a system interface to a processing unit of a processor system. The validation system comprises a user interface for creating an inputting test parameters and test code into the system, a test generator coupled to the user interface, the test generator for generating input packet activity in the form of a packet stream, a model coupled to the test generator for emulating separate and integrated function of the packet management unit, the system interface, and a stream-processing unit and an evaluation software for checking and validating or not validating results. The system validation function relies, in a preferred embodiment, on comparing output results with criteria of the selected test code resulting in an indication of pass or failure of the test. In a preferred embodiment, the system also notifies to cause of failure.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
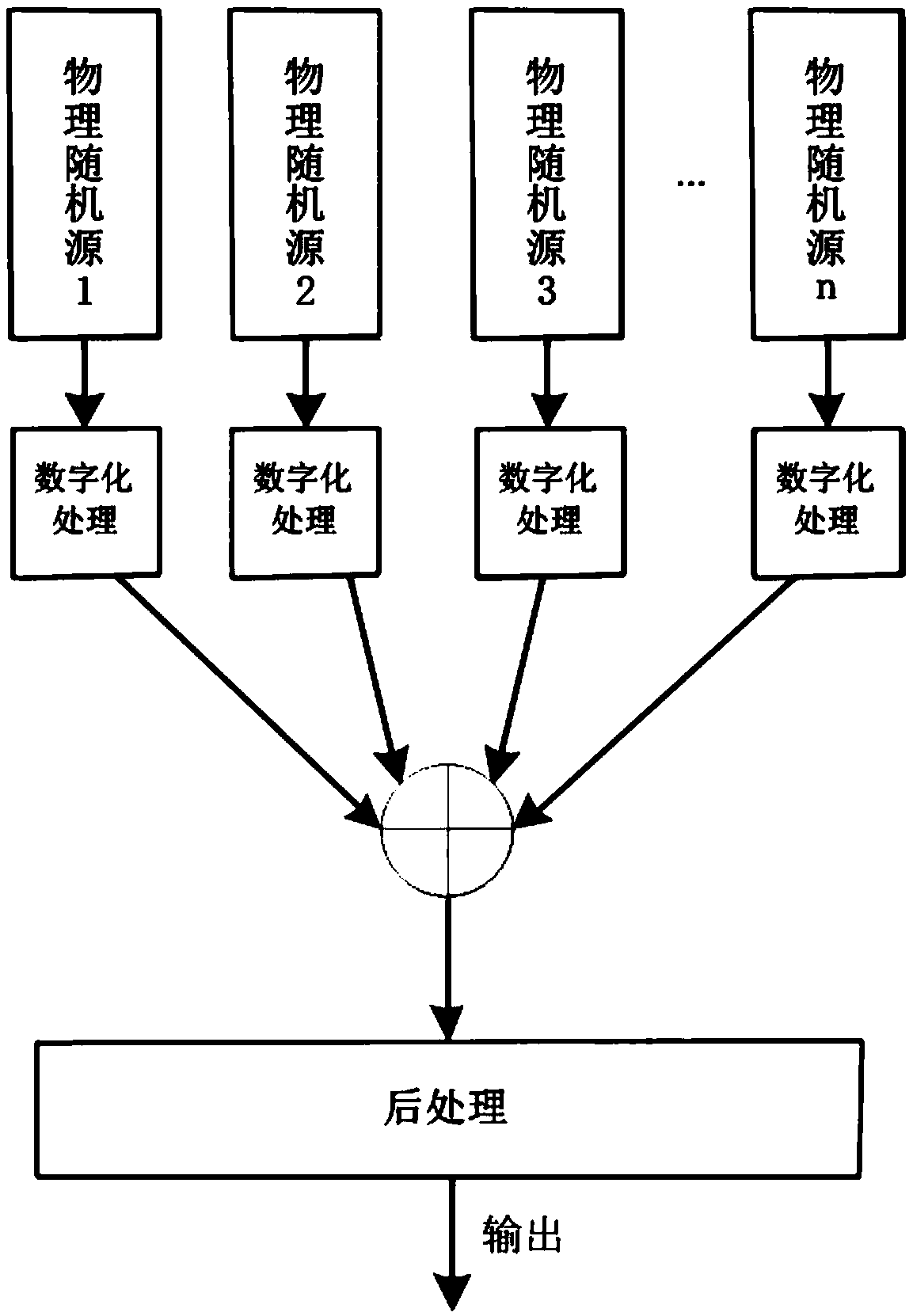
True random number generator
InactiveCN108664234AAddressing VulnerabilityImprove robustnessRandom number generatorsExclusive orComputer module
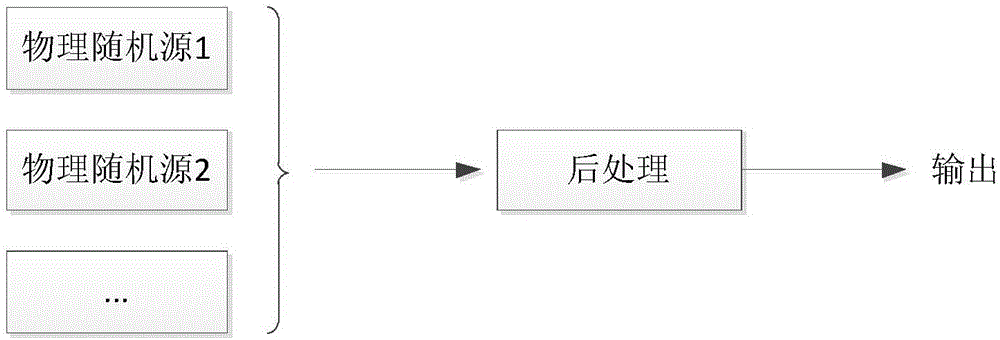
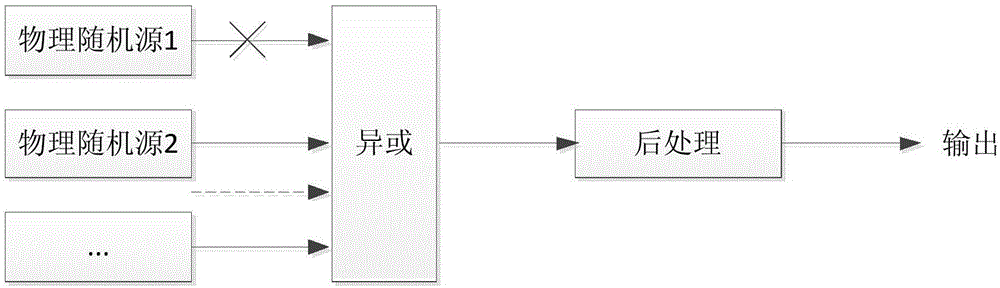
The present invention discloses a true random number generator, which adopts an SP structure. The true random number generator comprises: n physical random sources, n digital processing modules, a diffusion layer, an aliasing layer and a post-processing module. The n physical random sources are used to generate n physical signals; the n digital processing modules are used to respectively match andreceive the n physical signals, and convert the n physical signals into n digital signals; the diffusion layer is used to receive the n digital signals, perform an exclusive-OR operation on the n digital signals, and output n-channel signals, wherein each-channel signals comprise physical signals of at least three physical random sources; the aliasing layer is used to receive the n-channel signals, mix the n-channel signals to realize repeated mix among the n-channel signals, and output mix results; and the post-processing module is used to receive the mix results output by the aliasing layer, and eliminate the deviation and dependence of the mix results. Thus, according to the random number generator disclosed by the present invention, the robustness of the random number generator can beimproved.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +2
Efficient testing of direct memory address translation
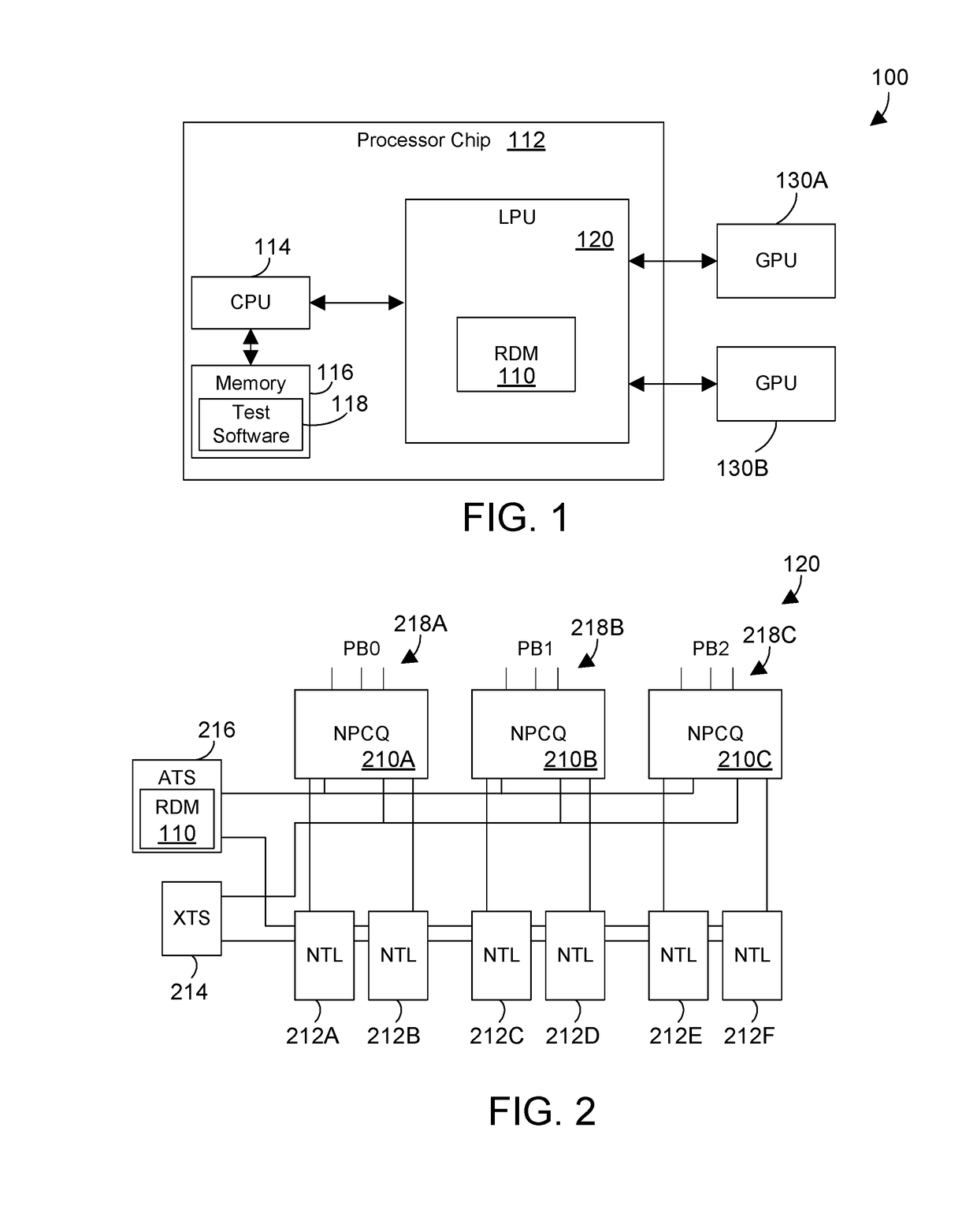
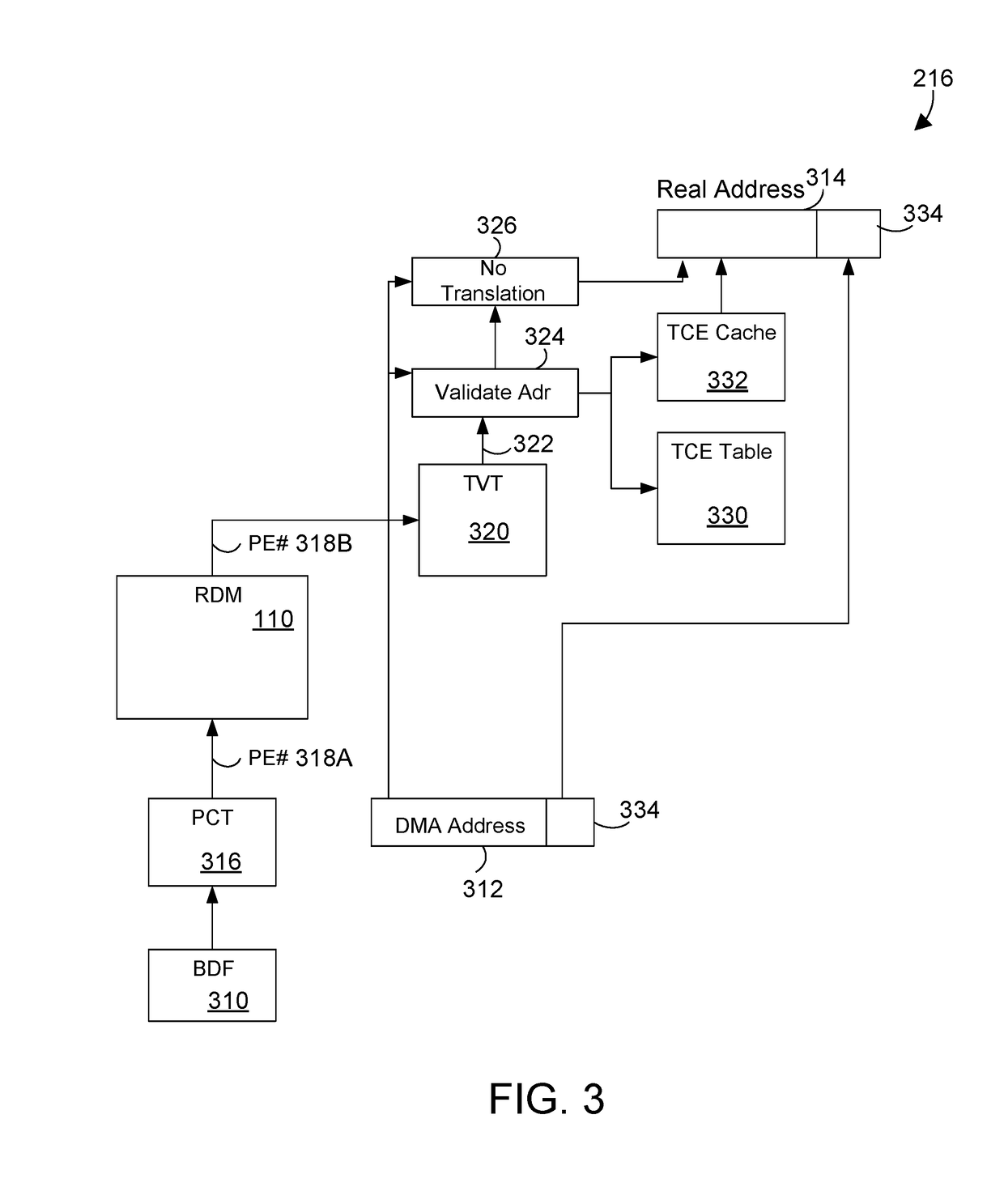
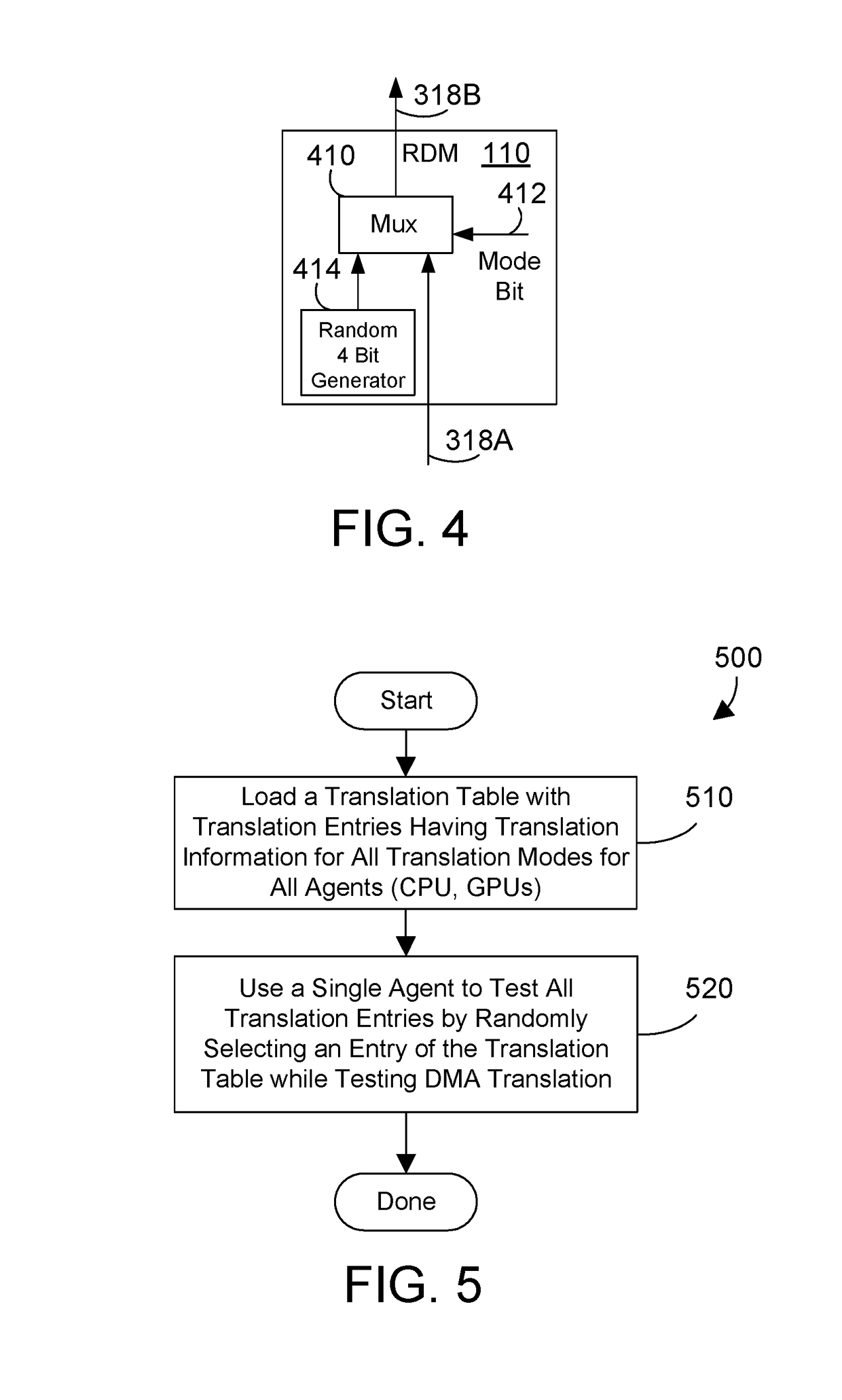
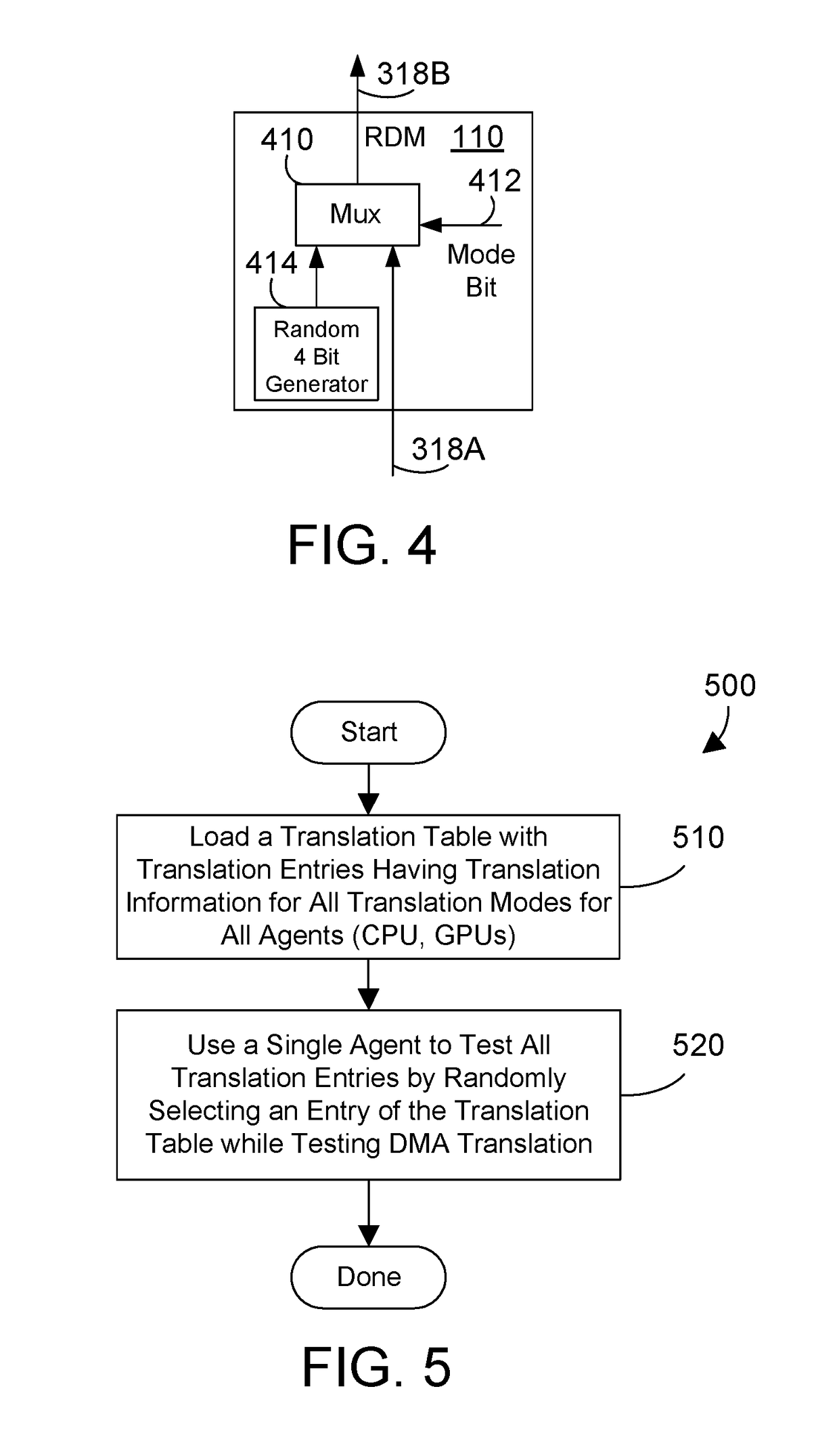
ActiveUS10169186B1Efficient stress testing address translationMemory architecture accessing/allocationHardware monitoringMemory addressMain processing unit
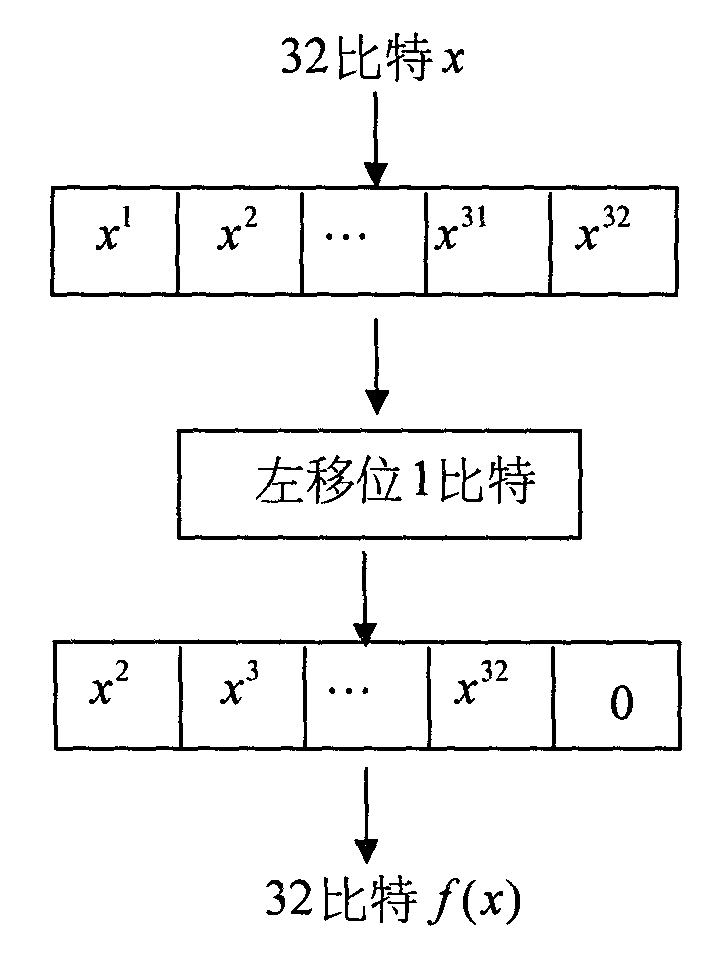
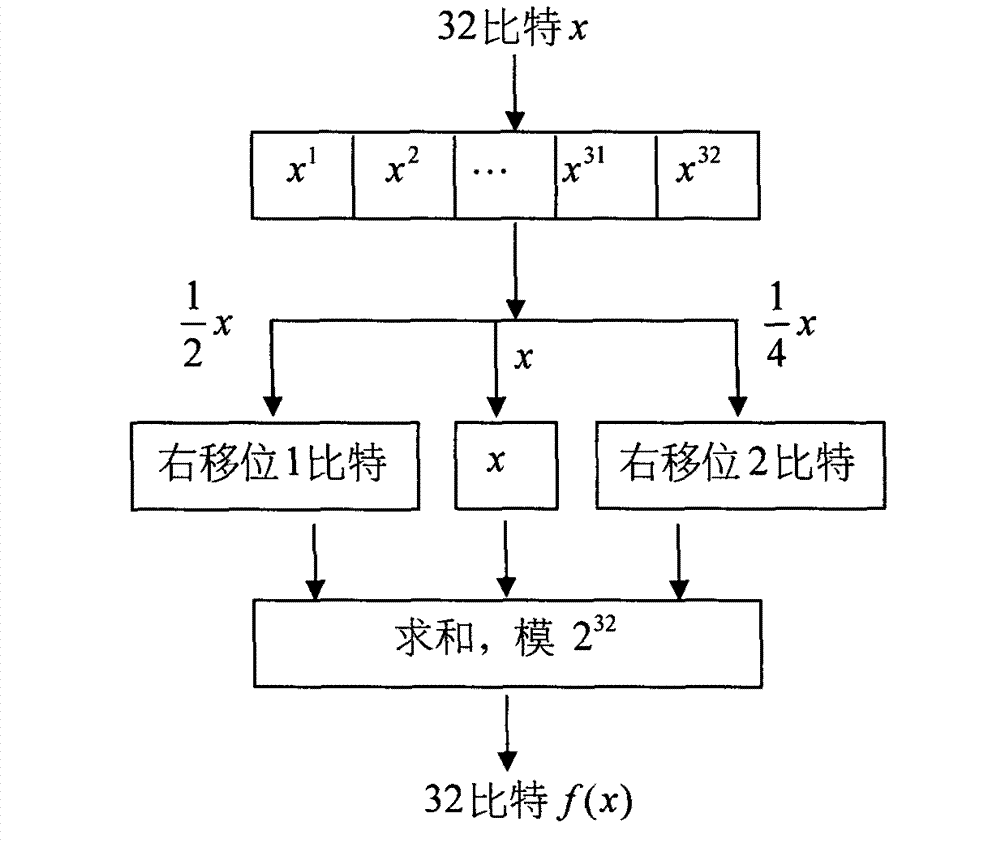
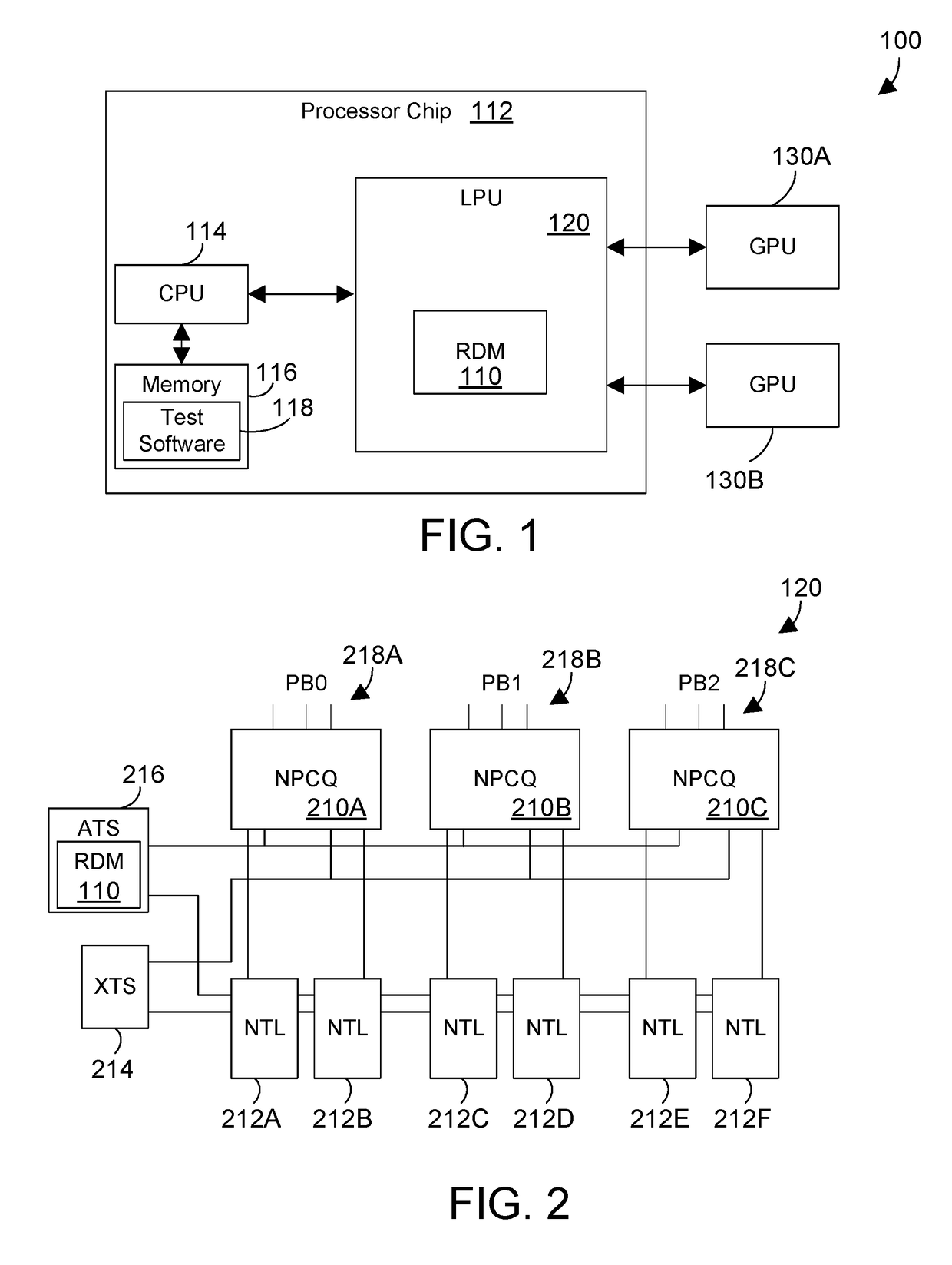
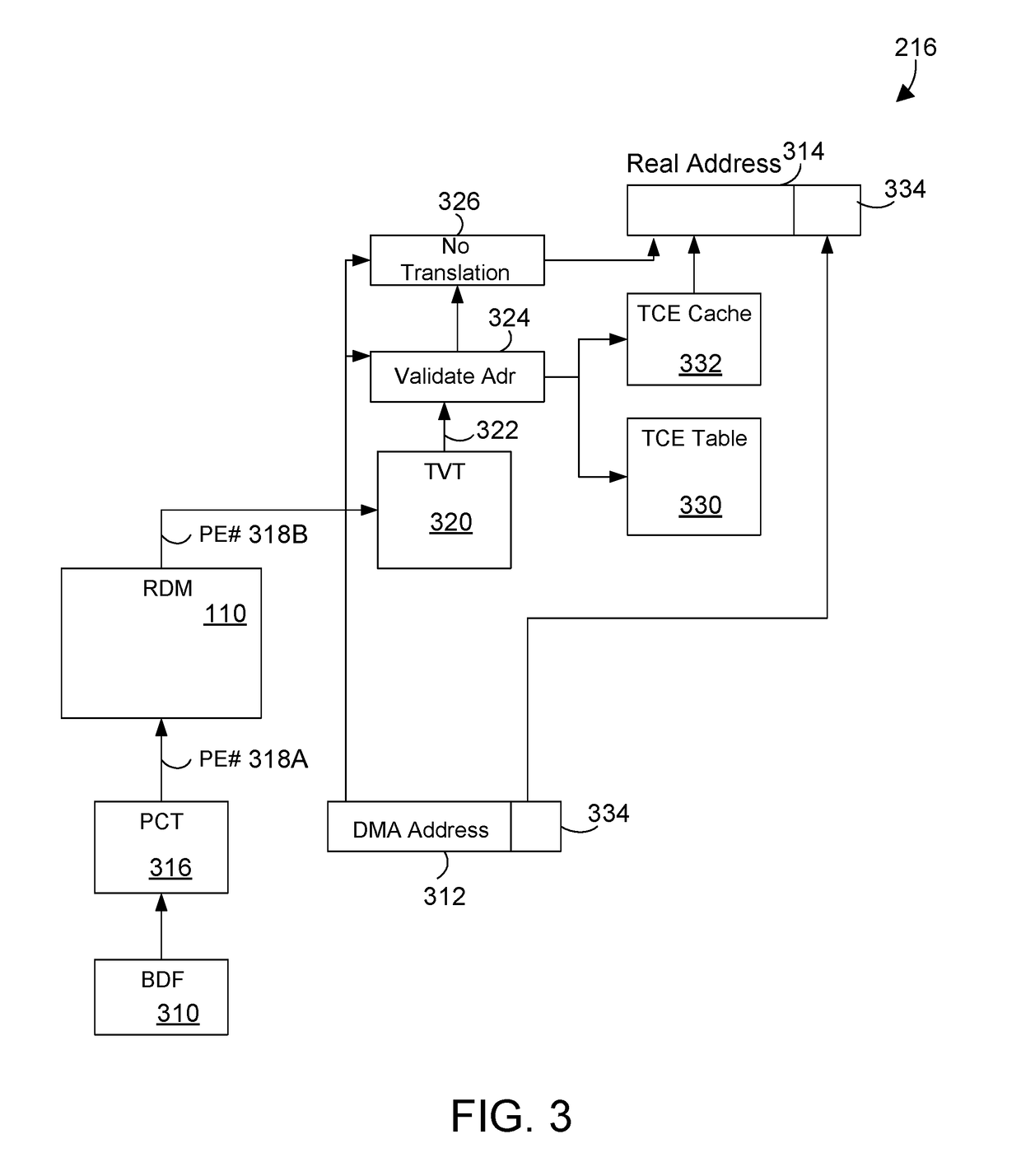
A circuit and method provide efficient stress testing of address translations in an integrated circuit such as a link processing unit. A random DMA mode (RDM) circuit provides a random input to index into a translation validation table (TVT) that is used to generate the real memory address. The RDM circuit allows testing all entries of the TVT, and thus all DMA modes, regardless of what bus agents are connected to the link processing unit. The RDM circuit may use a multiplexer to select between a runtime input and a random test input provided by the random bit generator. When the link processing unit is in a test mode a mode selection bit is asserted to select the random test input.
Owner:IBM CORP
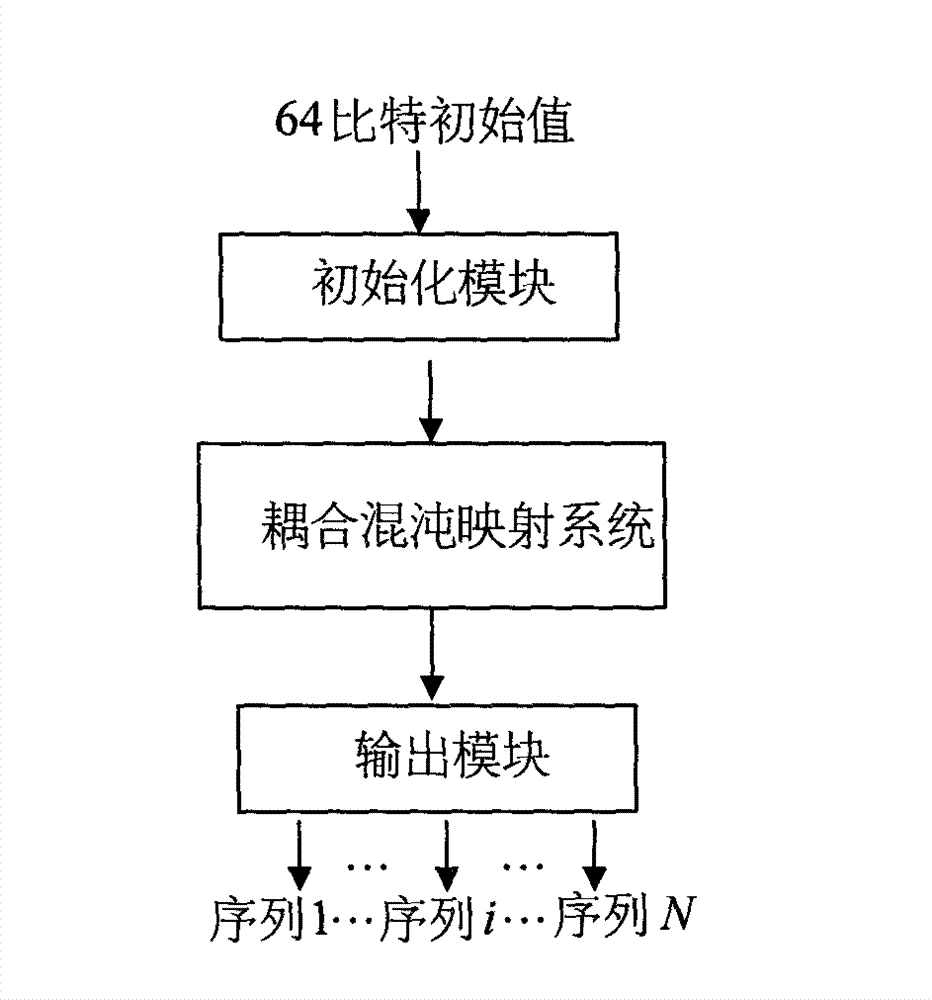
Parallel pseudorandom bit generator based on coupling chaotic mapping system
InactiveCN102904715AEasy to implementSecuring communicationTheoretical computer scienceHardware implementations
The invention aims at designing a pseudorandom bit generator which is efficient and can be used for hardware implementation and parallel operation and particularly relates to a parallel pseudorandom bit generator based on a coupling chaotic mapping system. According to the parallel pseudorandom bit generator, by means of an initialization module, initial values (also called seeds) of a random bit generator are subjected to nonlinear transformation expansion to generate initial values of the coupling chaotic mapping system; the initial values of the coupling chaotic mapping system, which are generated by expanding, are input into the coupling chaotic mapping system, and multi-path chaotic sequences are parallelly output by means of actions of the coupling chaotic mapping system; and the output chaotic sequences are processed by an output module, and pseudorandom bit sequences which meet an NIST SP800-22 revise testing standard are parallelly output.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Efficient testing of direct memory address translation
ActiveUS10169185B1Efficient stress testing address translationMemory architecture accessing/allocationHardware monitoringMemory addressMain processing unit
A circuit and method provide efficient stress testing of address translations in an integrated circuit such as a link processing unit. A random DMA mode (RDM) circuit provides a random input to index into a translation validation table (TVT) that is used to generate the real memory address. The RDM circuit allows testing all entries of the TVT, and thus all DMA modes, regardless of what bus agents are connected to the link processing unit. The RDM circuit may use a multiplexer to select between a runtime input and a random test input provided by the random bit generator. When the link processing unit is in a test mode a mode selection bit is asserted to select the random test input.
Owner:IBM CORP
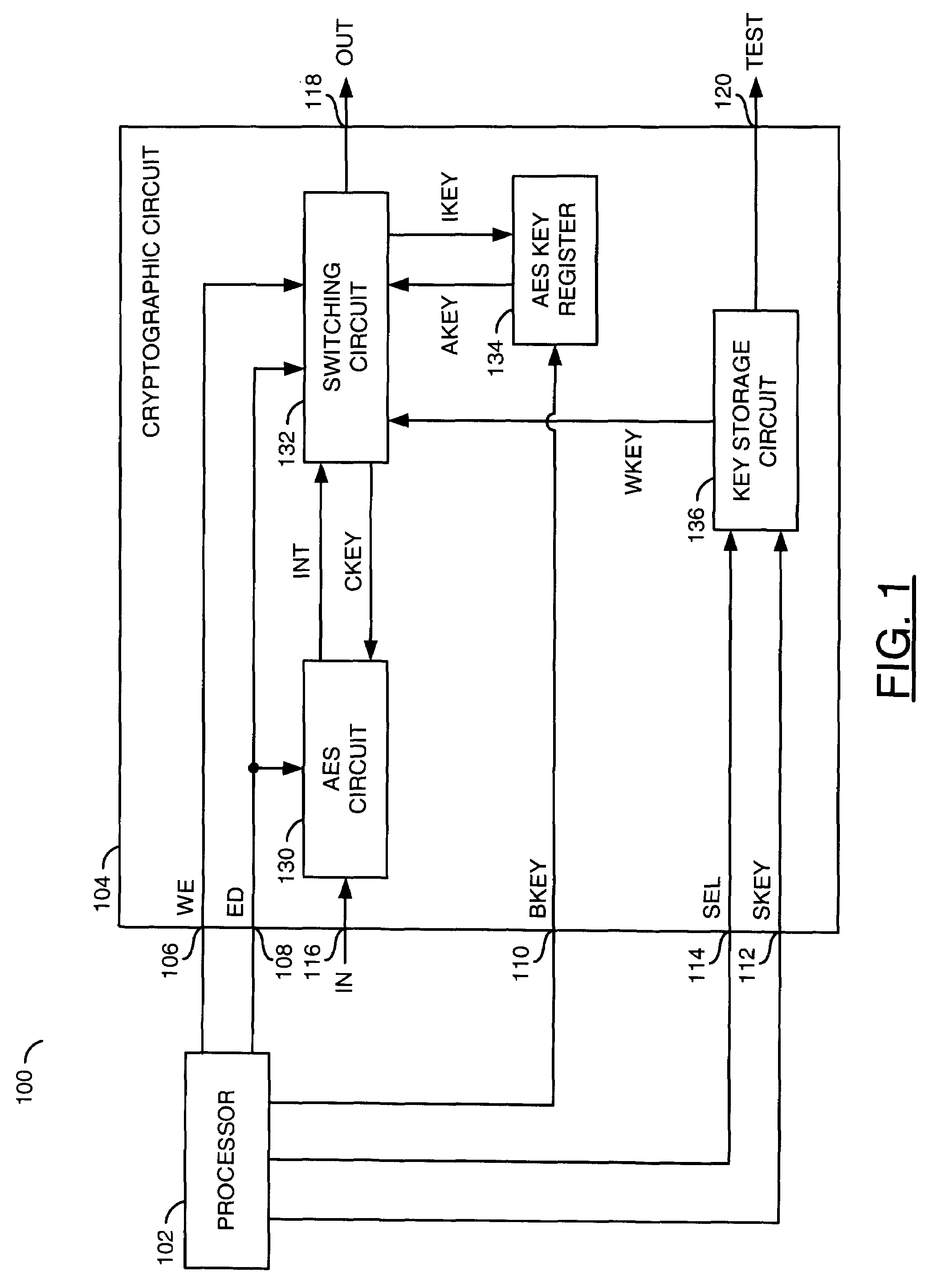
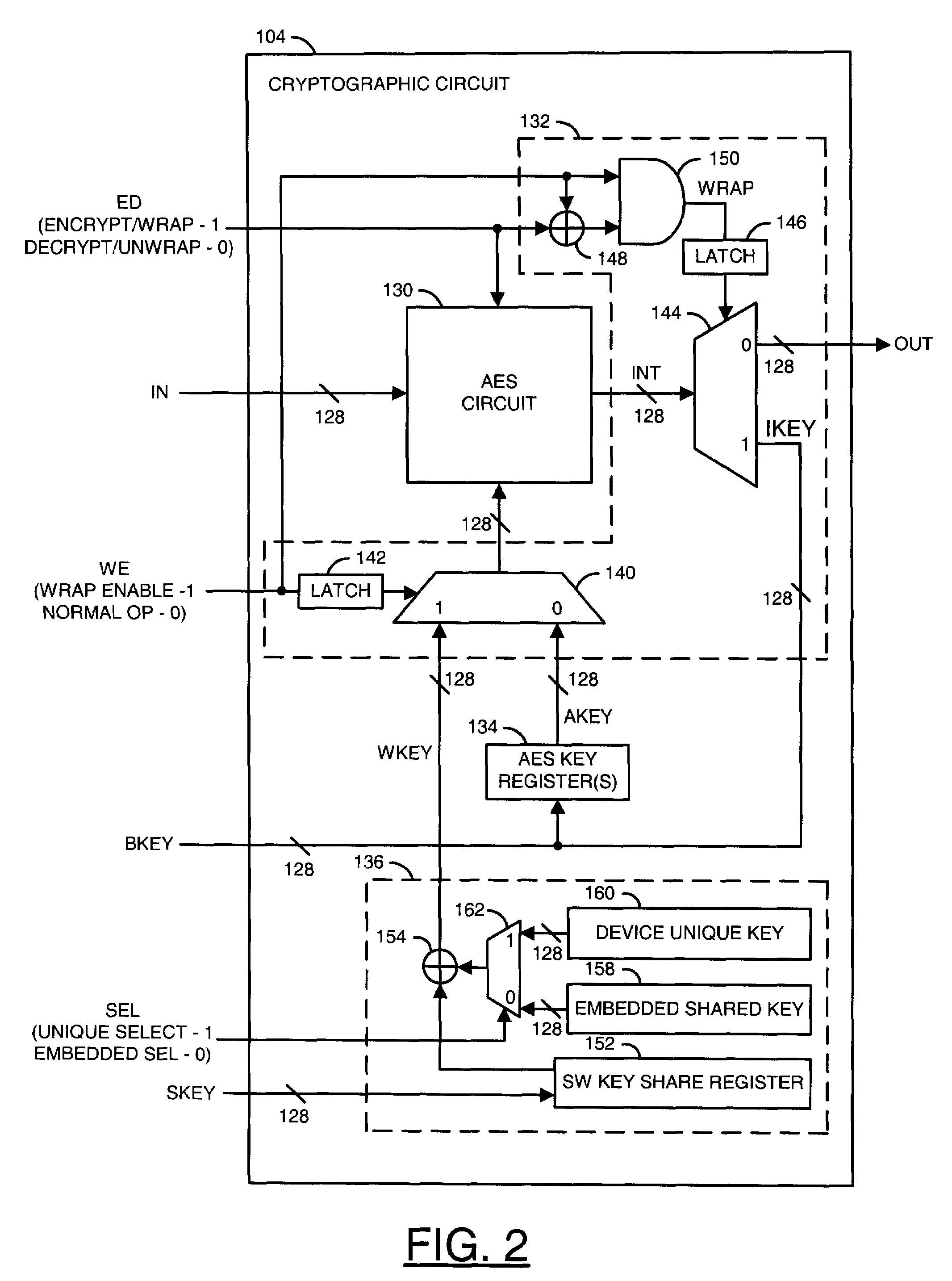
Manufacturing embedded unique keys using a built in random number generator
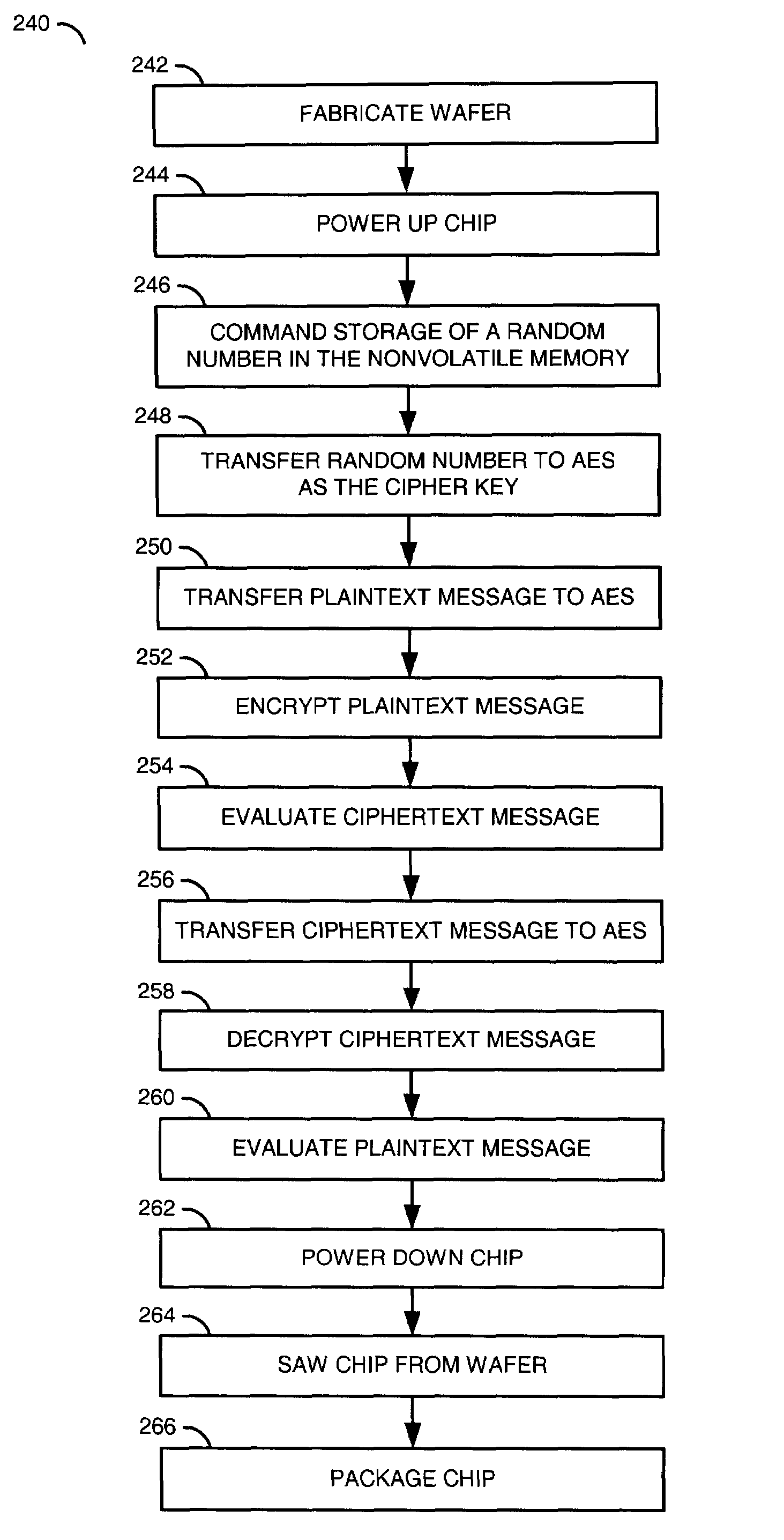
InactiveUS7978850B2Reduce manufacturing costEliminate a reliance on manufacturing equipmentError detection/correctionVolume/mass flow measurementNumber generatorPseudorandom number generator
A method of manufacturing a device containing a key is disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) fabricating a chip comprising a random number generator, a nonvolatile memory and a circuit, (B) applying electrical power to the chip to cause the random number generator to generate a signal conveying a sequence of random numbers, (C) commanding the chip to program a first arbitrary value among the random numbers into the nonvolatile memory, wherein the device is configured such that the first arbitrary value as stored in the nonvolatile memory is unreadable from external to the device and (D) packaging the chip.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
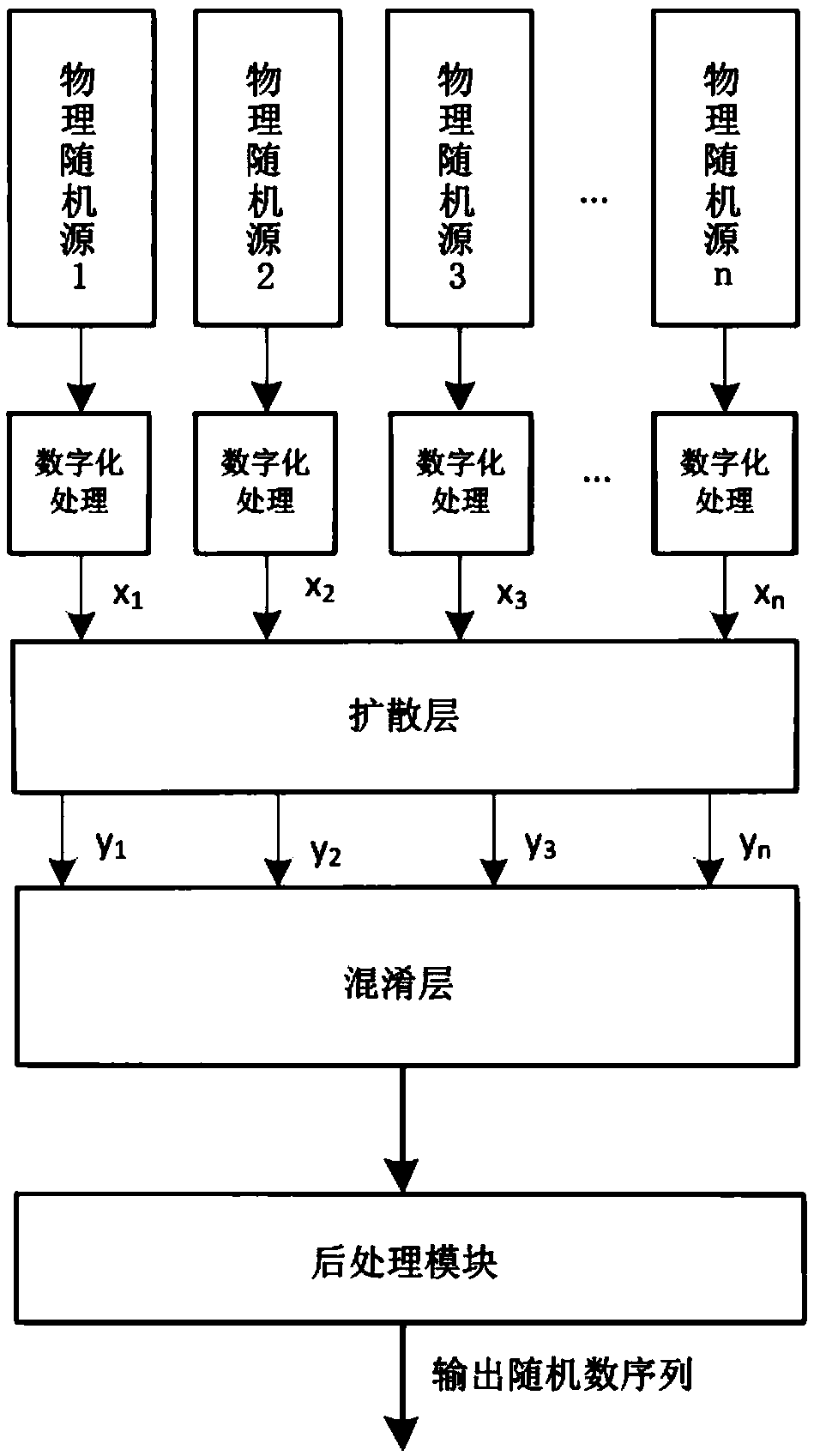
Random number generation method and random number generator
InactiveCN106383691ASolve the problem of XOR attackRandom number generatorsDigital signal processingS-box
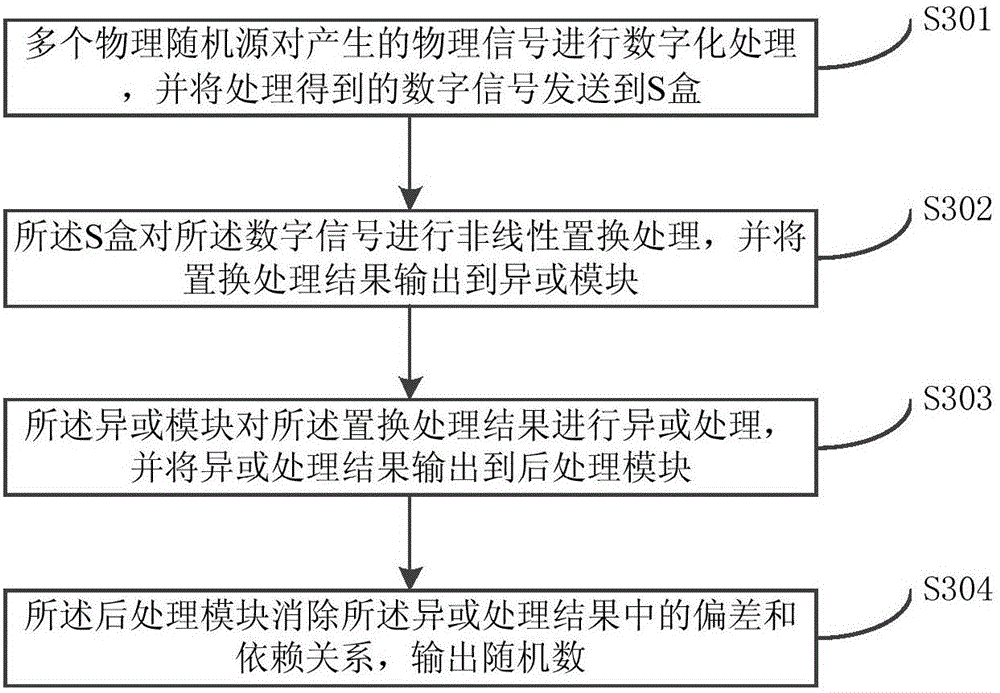
The invention relates to a random number generation method and a random number generator. The method comprises the steps that a plurality of physical random sources perform digital processing on a generated physical signal and sends a digital signal obtained by processing to an S box; the S box performs nonlinear replacement processing on the digital signal and outputs a replacement processing result to an XOR module; the XOR module performs XOR processing on the replacement processing result and outputs an XOR processing result to a post-processing module; and the post-processing module eliminates a deviation and a dependency relationship in the XOR processing result and outputs a random number. According to the random number generation method and the random number generator provided by embodiments of the invention, the problem of XOR attack of the physical random sources is effectively solved; and even if an attacker attacks an input of a physical random source in the XOR position, an input of post-processing still contains information of the random source because the S box has the characteristic of a confusion property.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +4
Dynamic generation of test segments
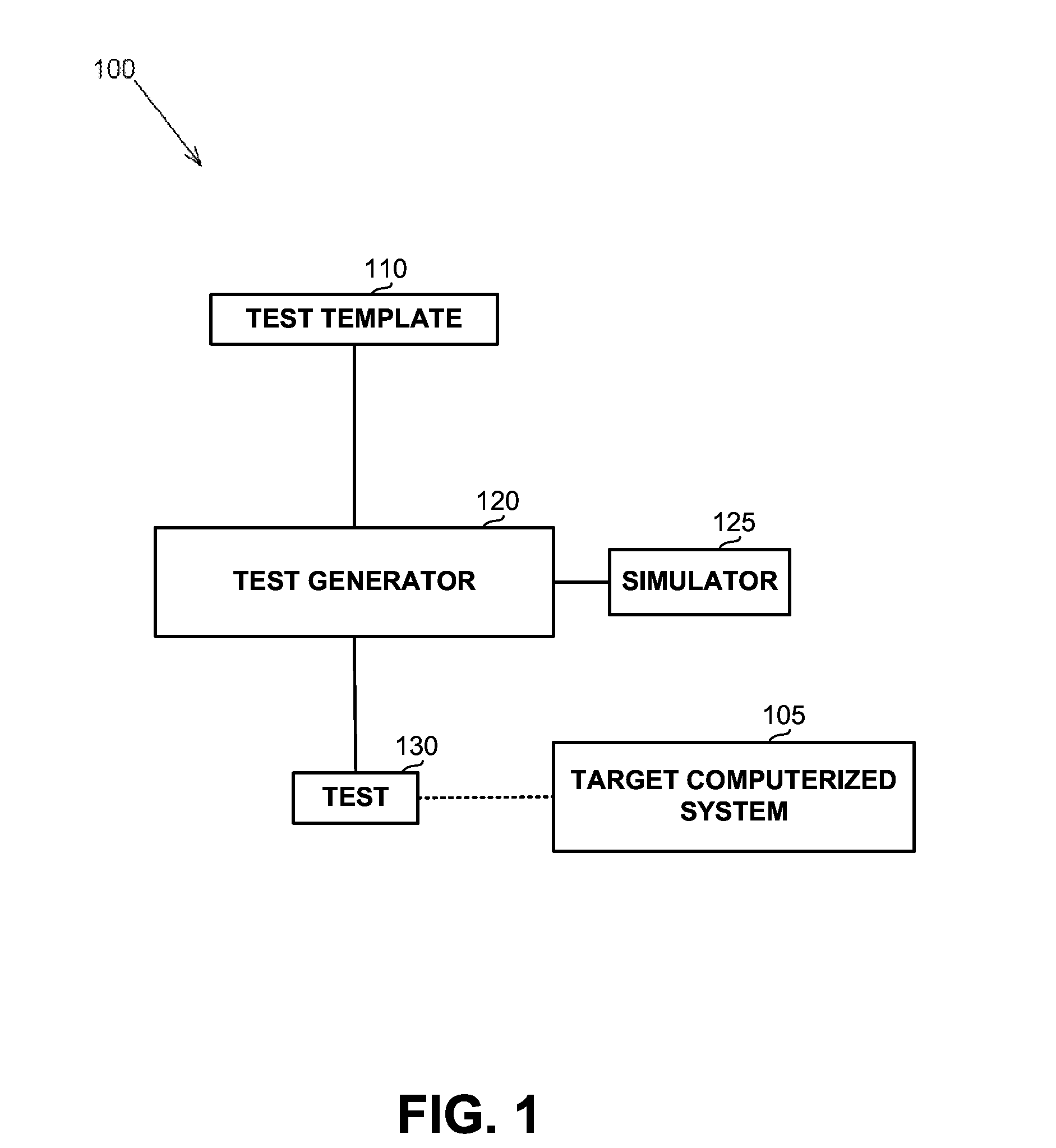
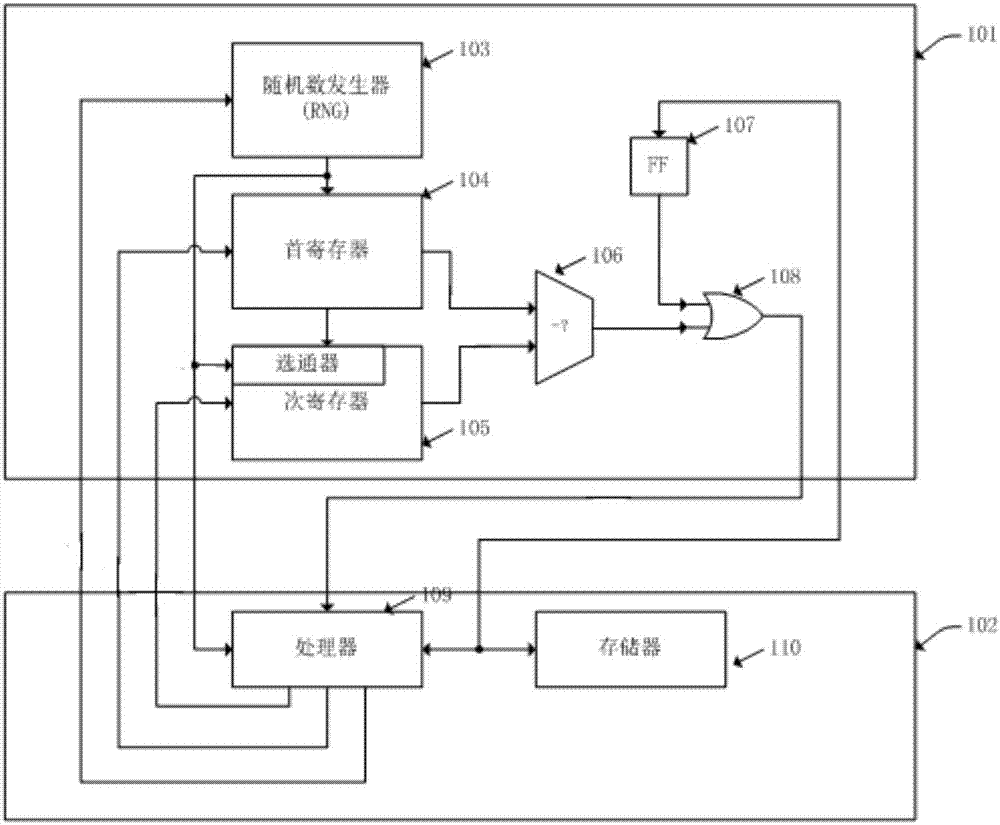
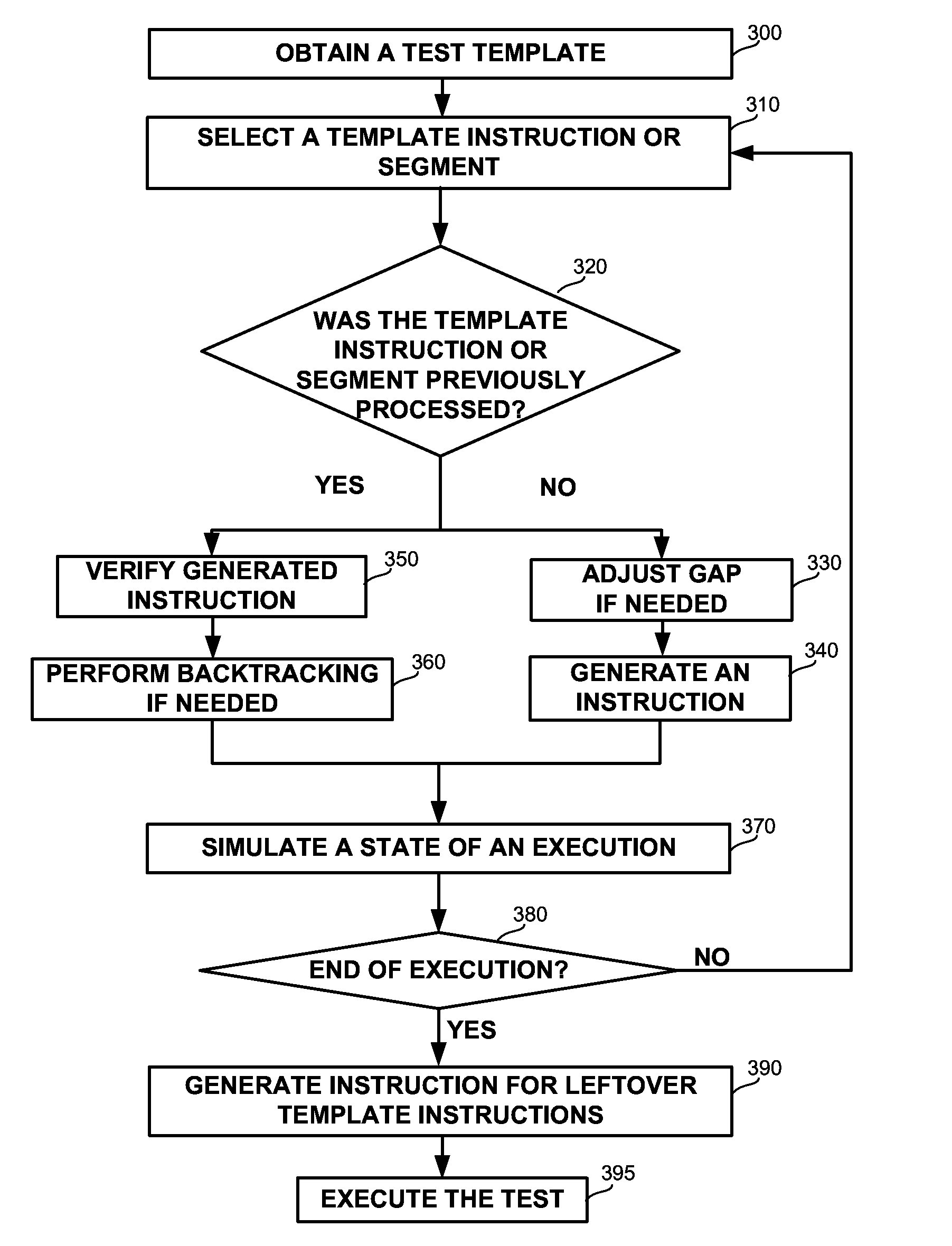
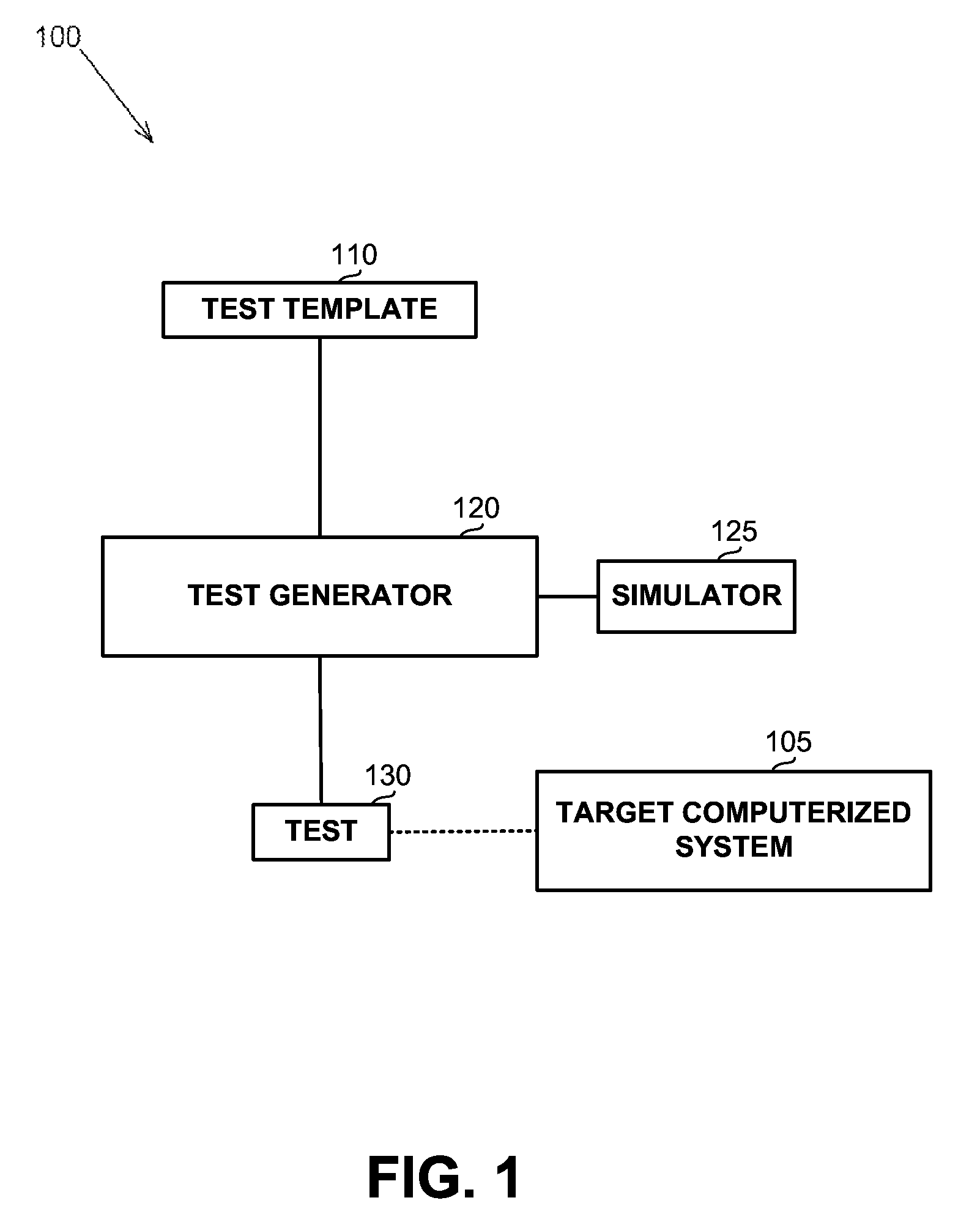
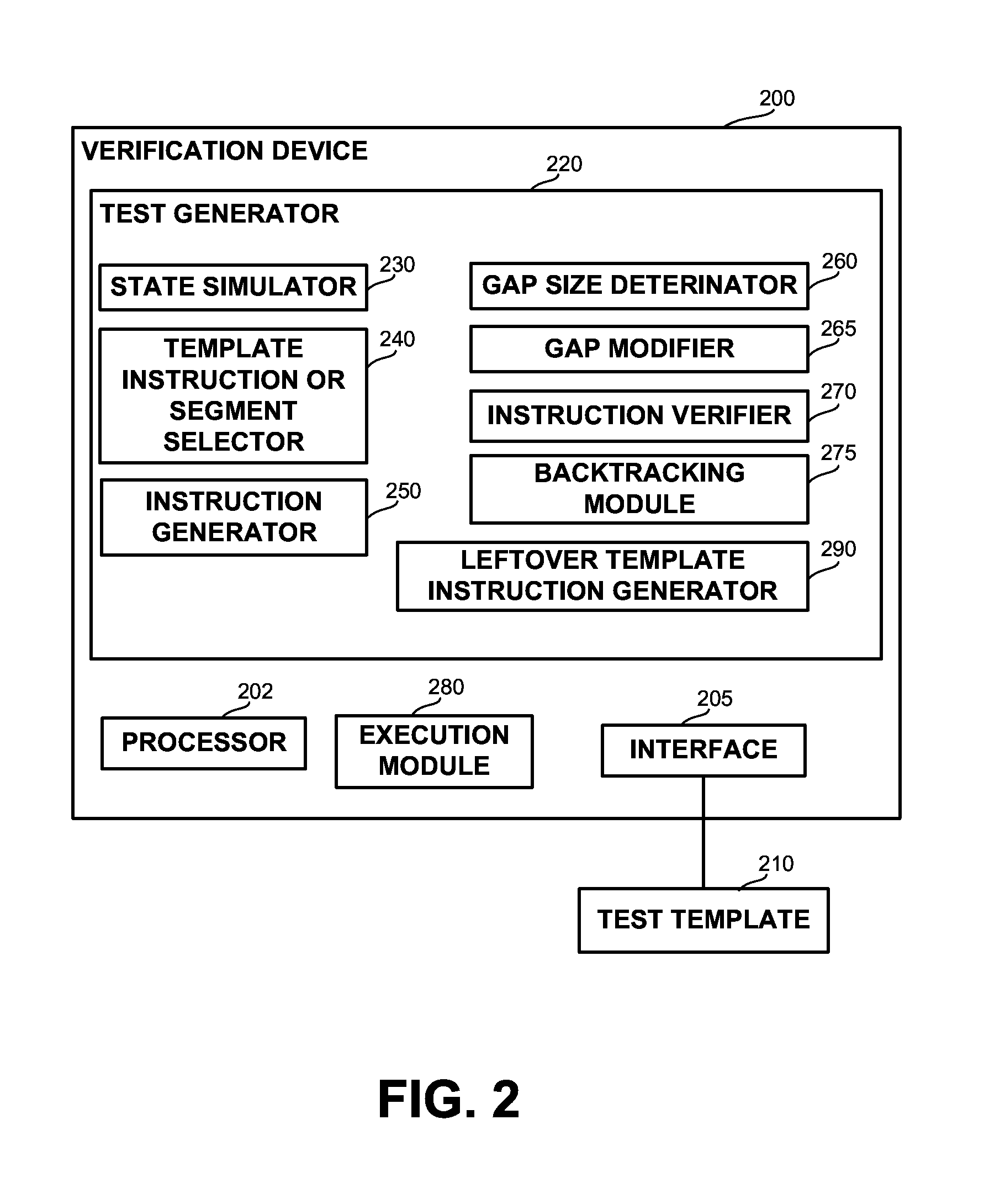
InactiveUS20130311164A1Software testing/debuggingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProgramming languageComputerized system
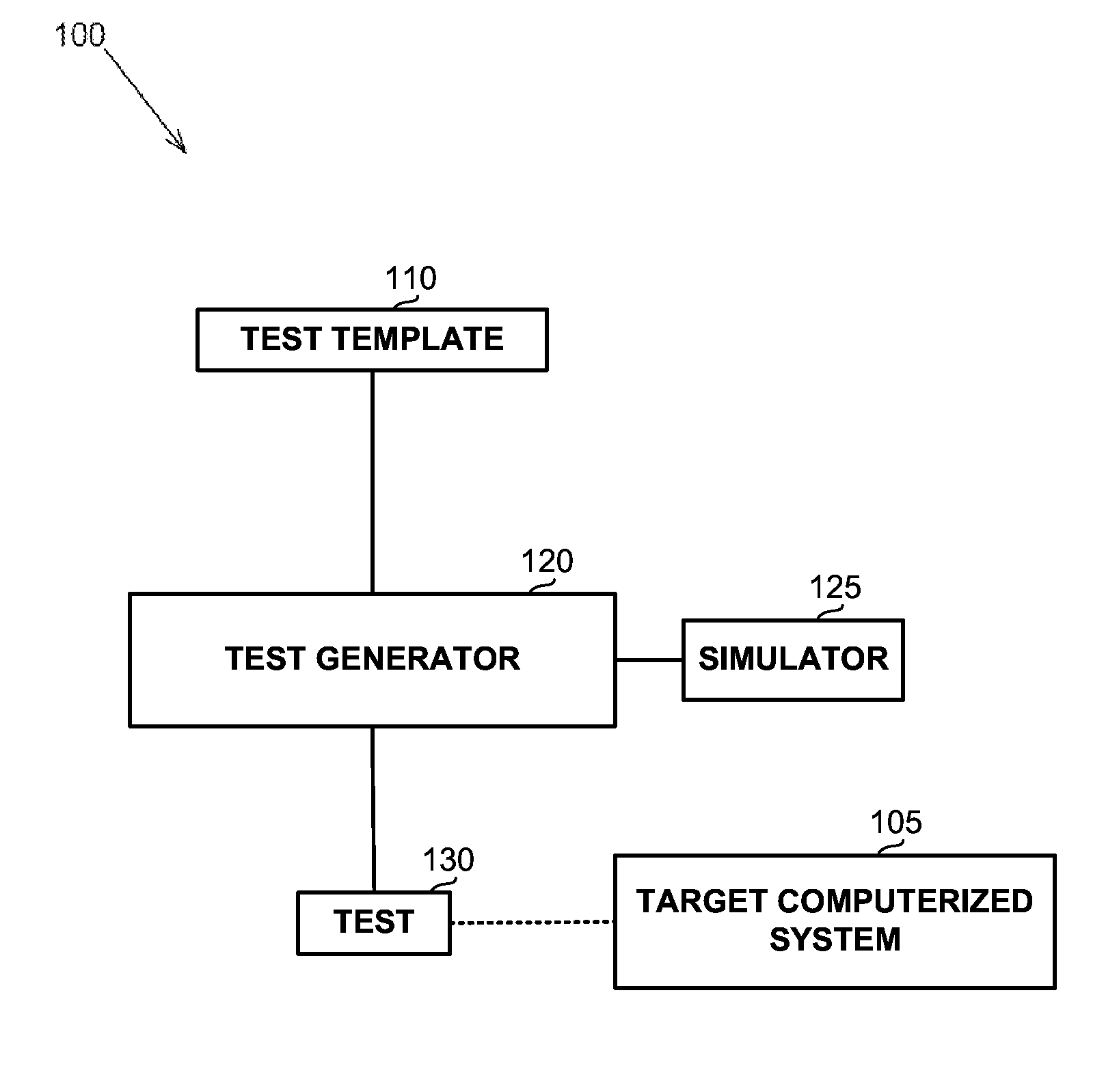
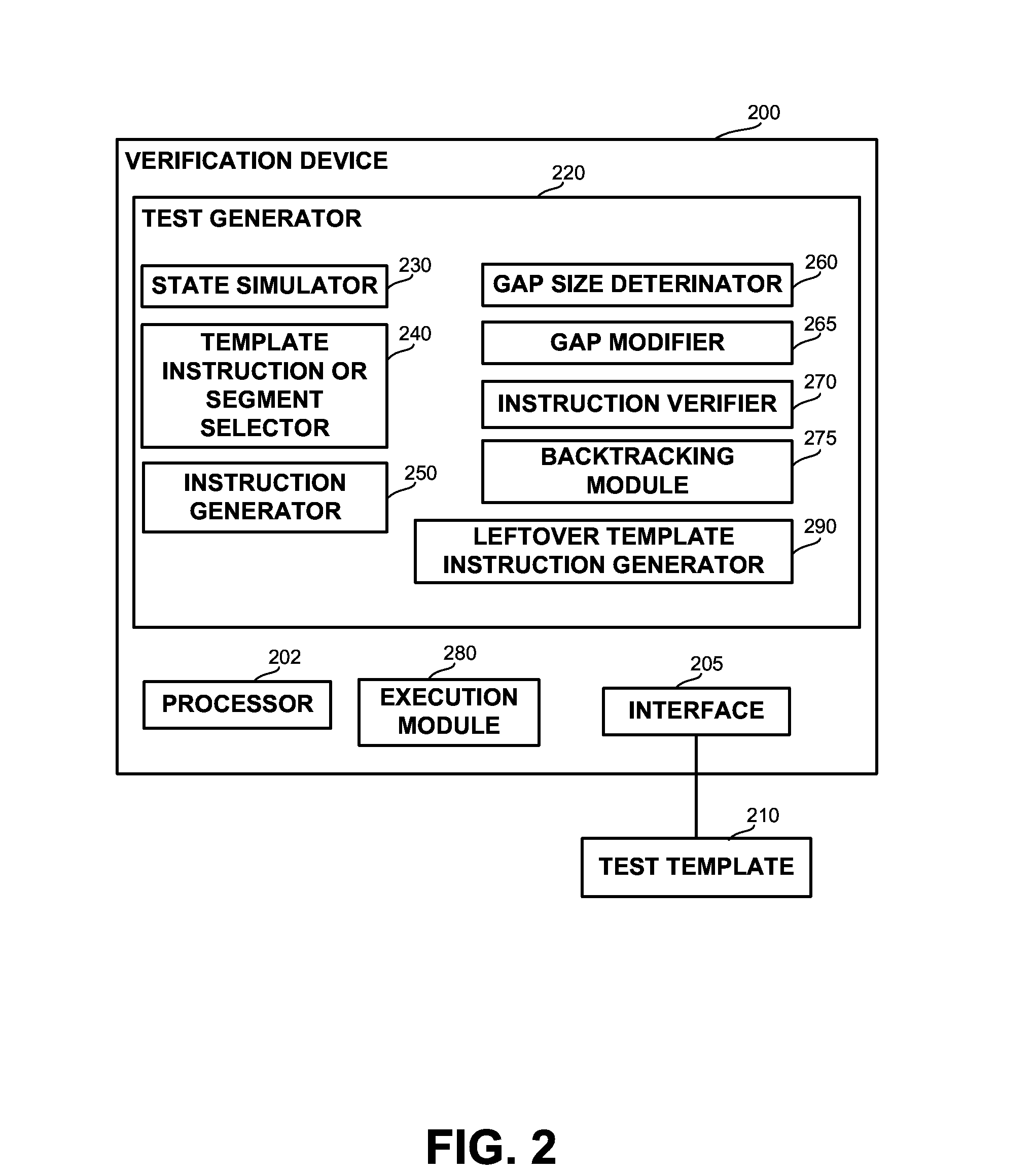
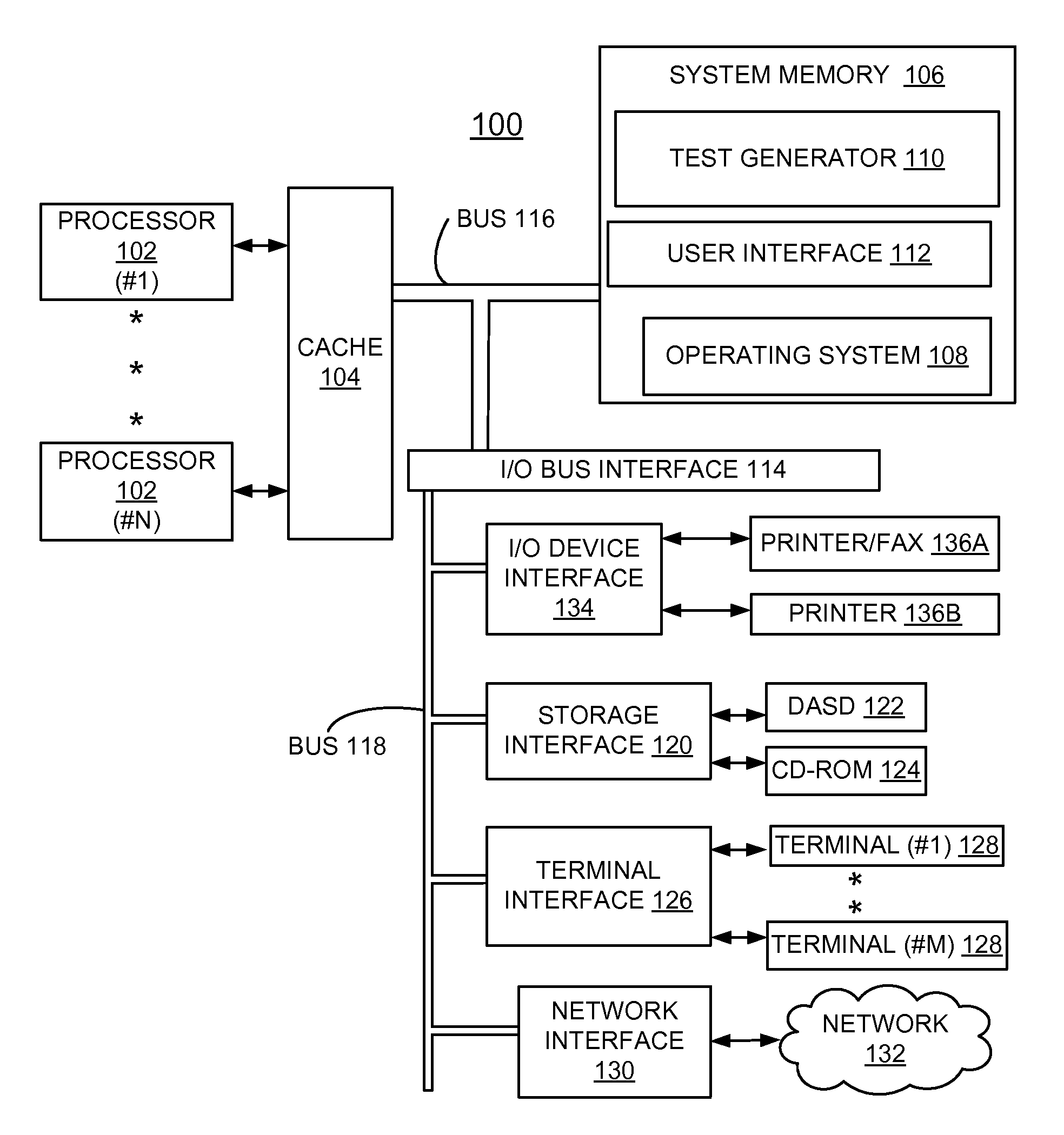
A computerized apparatus, method and computer product for generating tests. The apparatus comprises: a processor; an interface for obtaining a test template associated with a target computerized system, the test template comprises a template segment, the template segment comprising one or more instruction and one or more directives or control constructs related to the instructions; a test generator for generating a test associated with the template segment, said test generator comprises: a state simulator for determining a state of the target computerized system associated with an execution of the test; a template instruction or segment selector for selecting a template instruction or segment from the test template based on the state of the target system determined by said state simulator; and an instruction template segment generator configured to generate a multiplicity of instructions based on the state of the target computerized system and the template segment selected by said template instruction selector, wherein the test generator further comprises an instruction verifier configured to verify that a previously generated instruction is in line with the current state of the target computerized system and with the template instruction or segment selected by said template instruction or segment selector.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
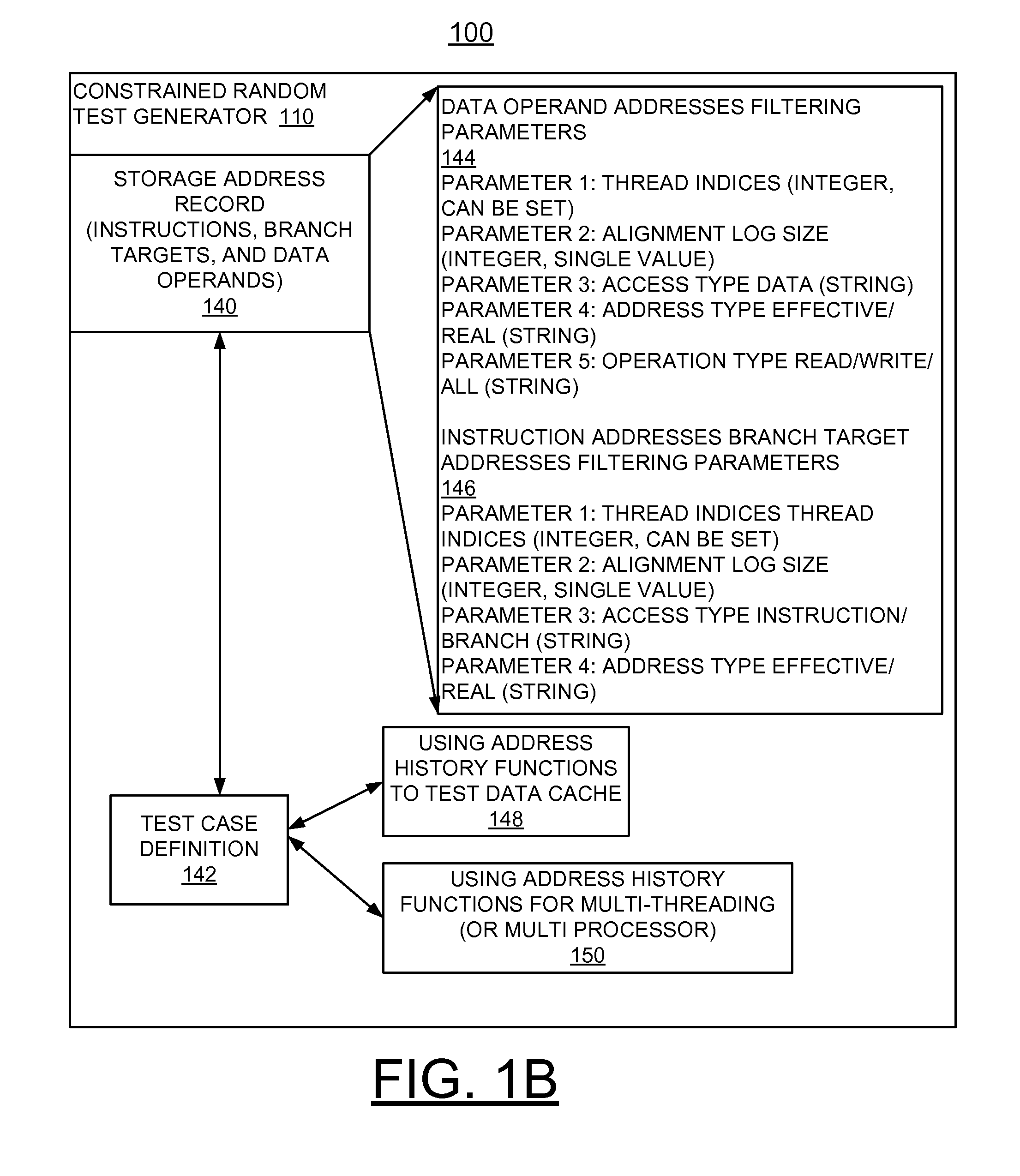
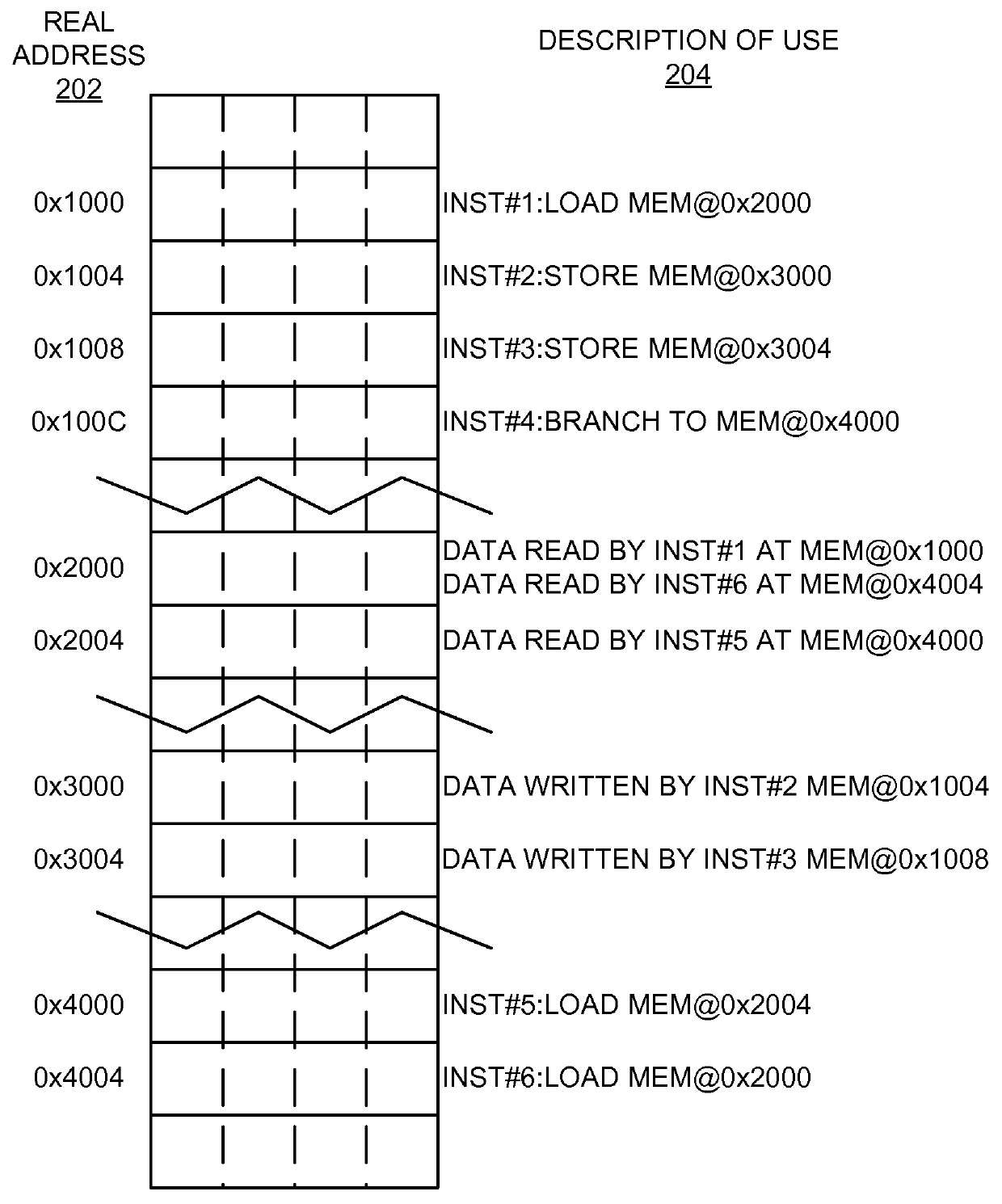
Implementing automated memory address recording in constrained random test generation for verification of processor hardware designs
InactiveUS20140257736A1Negative effectEliminate requirementsDetecting faulty computer hardwareElectrical measurementsComputer hardwareMemory address
A method and apparatus are provided for implementing automated memory address recording in constrained random test generation for verification of processor hardware designs. A test generation program includes a built in feature to keep track of storage addresses used and to make the addresses available to the test definition. This built in feature of a constrained random test generator allows storage addresses used in the past to be accessed by the current instruction generation eliminating the requirement of deliberately establishing target addresses first. This allows separate test events to interact with the same storage addresses without having to write a special test.
Owner:IBM CORP
Implementing random content of program loops in random test generation for processor verification
ActiveUS10061672B2Negative effectAvoids inherently problematic operationDetecting faulty computer hardwareNetwork address translationRandom test generator
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Test circuit for testing random number generator
InactiveCN107957543AAbility to continuously checkTamper-resistantRandom number generatorsElectronic circuit testingTamper resistanceError prevention
The invention provides a test circuit for testing a random number generator. The random number generator generates a first random number and stores it in a primary register, and then enables a test mode of a random number generator circuit; meanwhile, the random number generator further generates a group of random numbers and stores them in a secondary register, and then compares the random numberstored in the primary register with the random numbers stored in the secondary register; and an output signal of the random number generator circuit is regarded as an identification signal for judging whether operation of the random number generator is abnormal after the comparison is finished. The test circuit has the capability of continuous detection and is implemented in a hardware manner, sothat the test circuit has stable function and tamper-proof capability; and the test circuit can realize real-time testing of the random numbers generated by the random number generator, ensure that abnormal operation of the random number generator can be discovered in time when it occurs, and prevent the wrong random numbers from being used by the system.
Owner:天津国芯科技有限公司
Dynamic generation of test segments
InactiveUS9117023B2Software testing/debuggingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProgramming languageTemplate based
A computerized apparatus, method and computer product for generating tests. The apparatus comprises: a processor; an interface for obtaining a test template associated with a computerized system that comprises a template segment comprising instructions and directives or related control constructs; a test generator for generating a test associated with the template segment, comprising: a simulator for determining a state of the system associated with an execution of the test; a selector for selecting a template instruction or segment from the test template based on the state of the system; and a generator configured to generate a multiplicity of instructions based on system's state and on the selected template segment, wherein the test generator further comprises a verifier configured to verify that a previously generated instruction is in line with the current state of the system and with the selected template instruction or segment.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
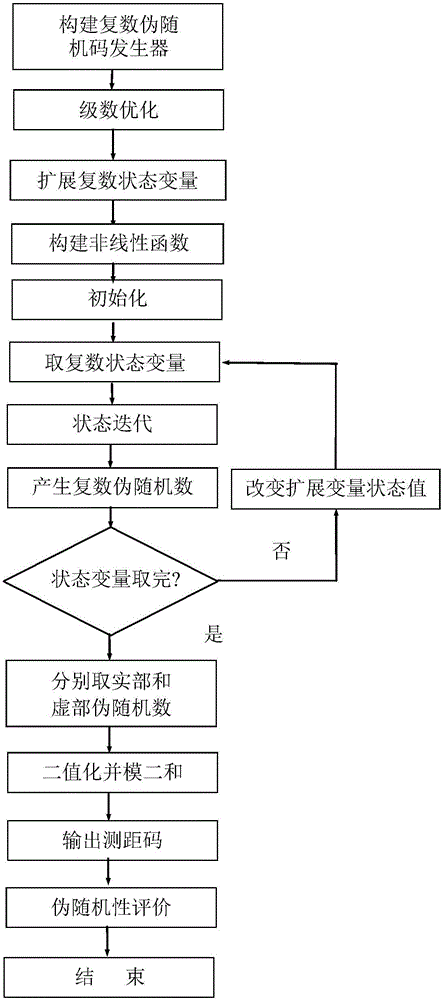
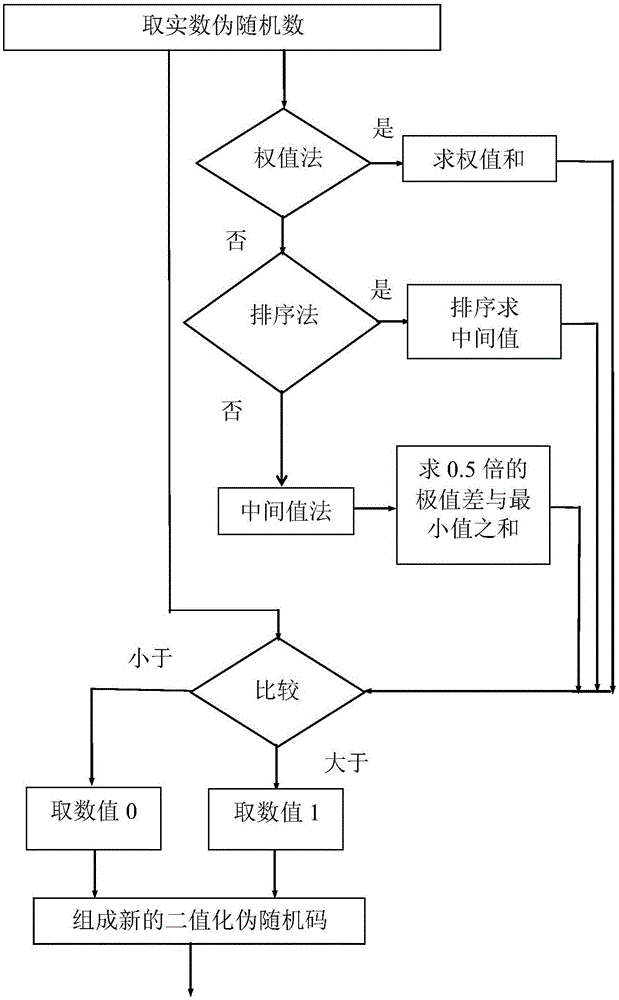
Method and system for realizing multi-state-variable spatial-temporal chaotic complex pseudo-random code generator
ActiveCN106301753AIncreased complexityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecuring communication by chaotic signalsDiffusionCommunications system
The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing a multi-state-variable spatial-temporal chaotic complex pseudo-random code generator. A complex pseudo-random code generator composed of a series of sequentially-arranged and coupled complex state variables is built. First, different nonlinear functions are used to act on the current state values of the current positions and deviation positions of the real part and the imaginary part of the complex state variables, and a complex pseudo-random number sequence distributed over time is generated through mixed operation of addition, subtraction, multiplication or division with the diffusion coefficient as a weight and through state iteration. Then, a real pseudo-random number sequence is extracted from the real part and imaginary part taps of related variables, and binarization and mod-2 sum operation are performed to get a needed ranging code. The method and the system can be widely applied to satellite navigation systems, and can be used in all sorts of ranging systems, communication systems, broadcasting systems, control systems, and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Authentication apparatus and authentication method using random pulse generator
ActiveUS8536979B2Easy to decodeEasy to makeElectric signal transmission systemsRandom number generatorsComputer hardwareCommunication unit
This invention provides an authentication apparatus and an authentication method using a random pulse generator for generating completely random pulses and using a completely random signal as an authentication signal. The authentication apparatus includes: a random pulse generator (hereinafter referred to as the RPG), arranged in a body or a partner side or in both the body and the partner side which generates random pulses; a unit which outputs an authentication signal based on the random pulses generated by the RPG; a unit which stores the authentication signal; a communication unit which transmits / receives an authentication signal; and a control unit which controls the communication of an authentication signal and collate an authentication signal, whereby a complete security can be maintained and safety can be established on the part of the user.
Owner:TSUYUZAKI NORIYOSHI
Random variation analog bias signal device in random number generator
InactiveCN1655451ARandom number generatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRandom noiseLogic state
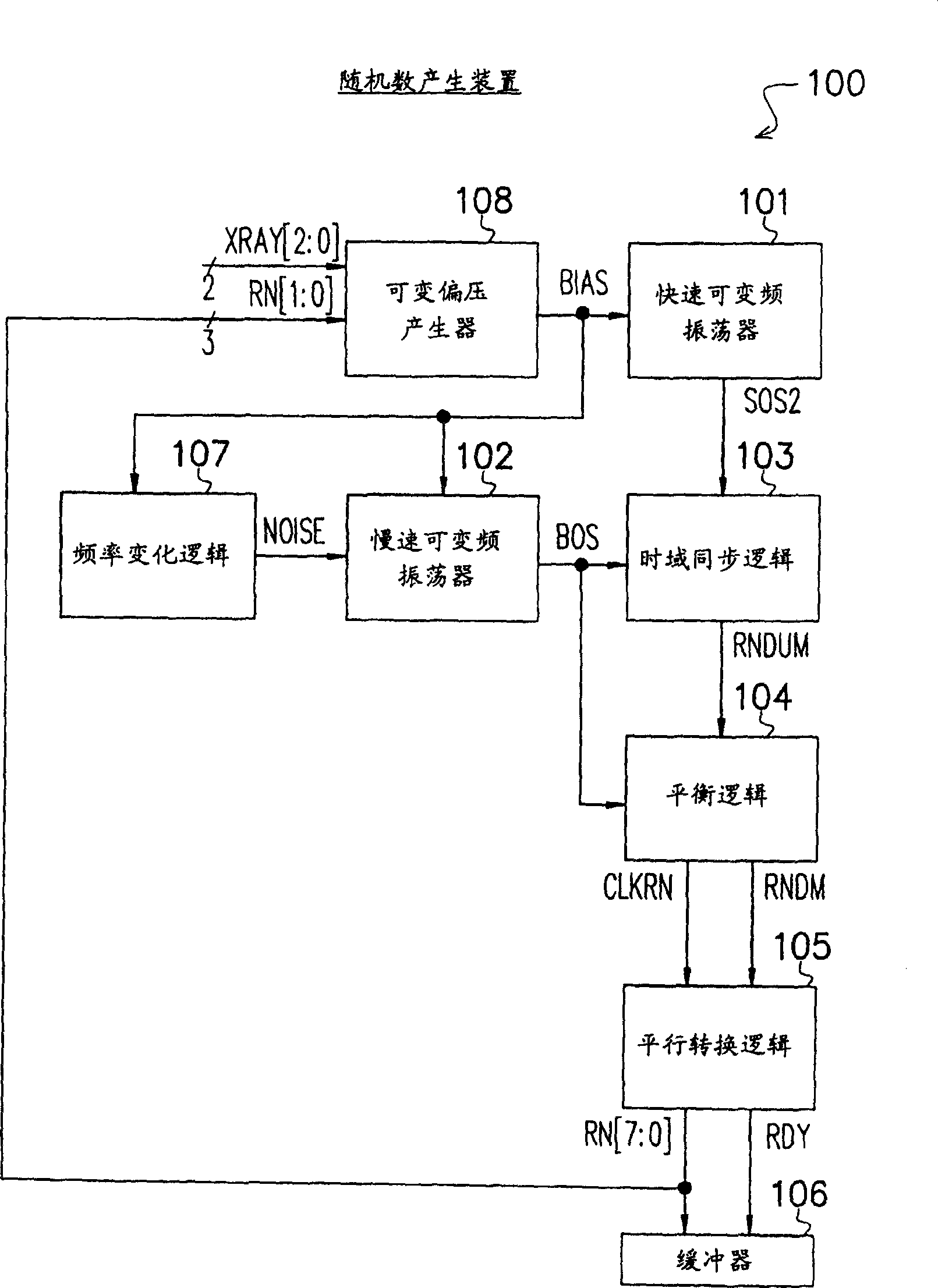
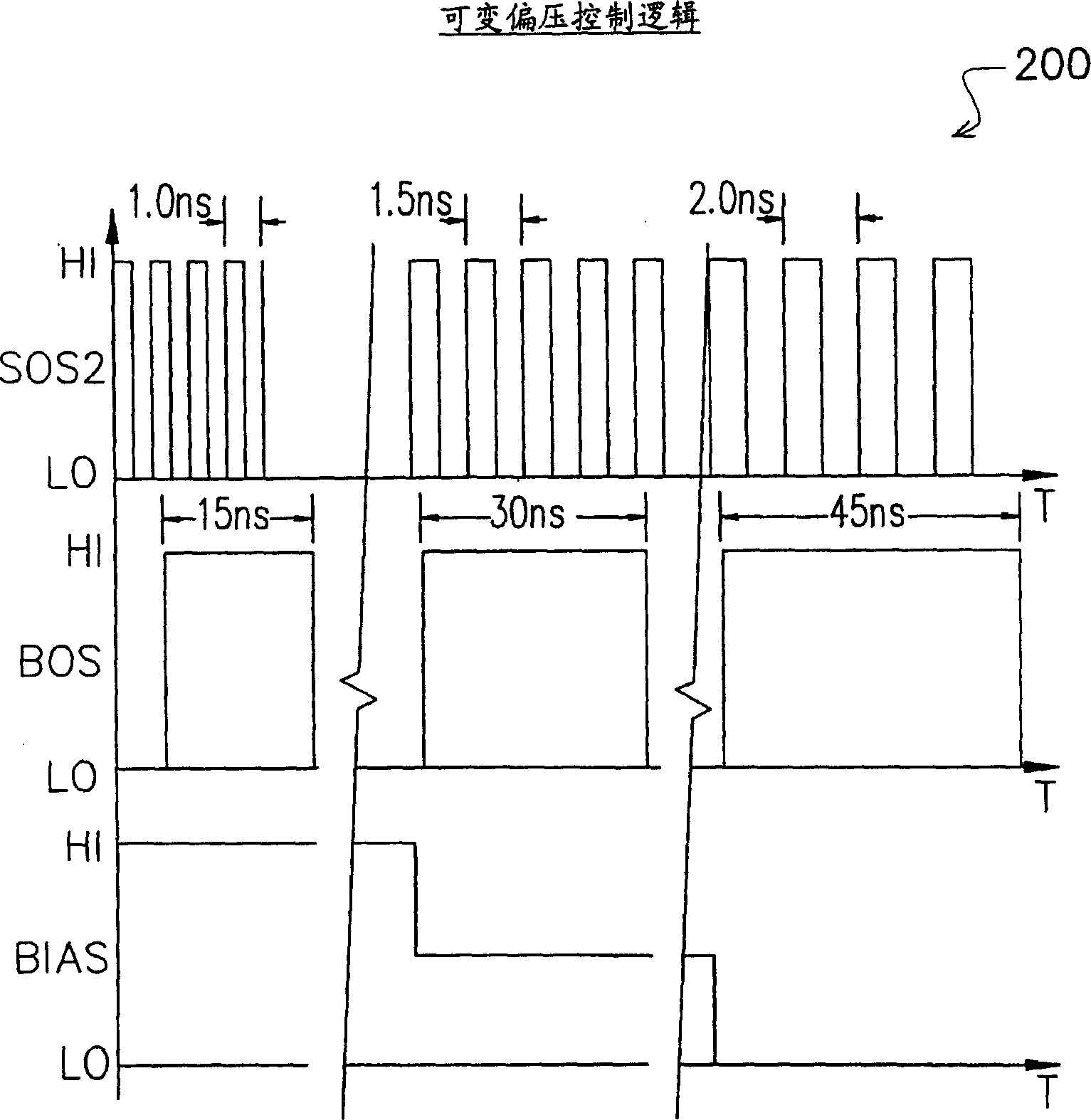
Discloses is a random variation simulation voltage bias signal apparatus in a random number generating device. The apparatus comprises an aggregate logic used for aggregating a state voltage bias signal and a stochastic noise signal to generate a simulation voltage bias signal, and a mechanism used for generating the stochastic noise signal, wherein, the mechanism is coupled with the aggregate logic, and when a random number is allocated in the random number generating device, the stochastic noise signal is varied according to a plurality of logic states of the random number in a bit group.
Owner:IP FIRST
Pseudo-random squence generator and associated method
InactiveCN1540917ARandom number generatorsCoding/ciphering apparatusTheoretical computer scienceRandom test generator
A method, and associated apparatus, for generating a pseudo-random number sequence. Determinations are made of compatible configurations of windmill generators for a selected windmill polynomial. Implementation of a windmill generator is made through use of word-oriented memory elements. Words stored in the memory elements are selectively outputted to form portions of a pseudo-random number sequence.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Chip automatic simulation verification system
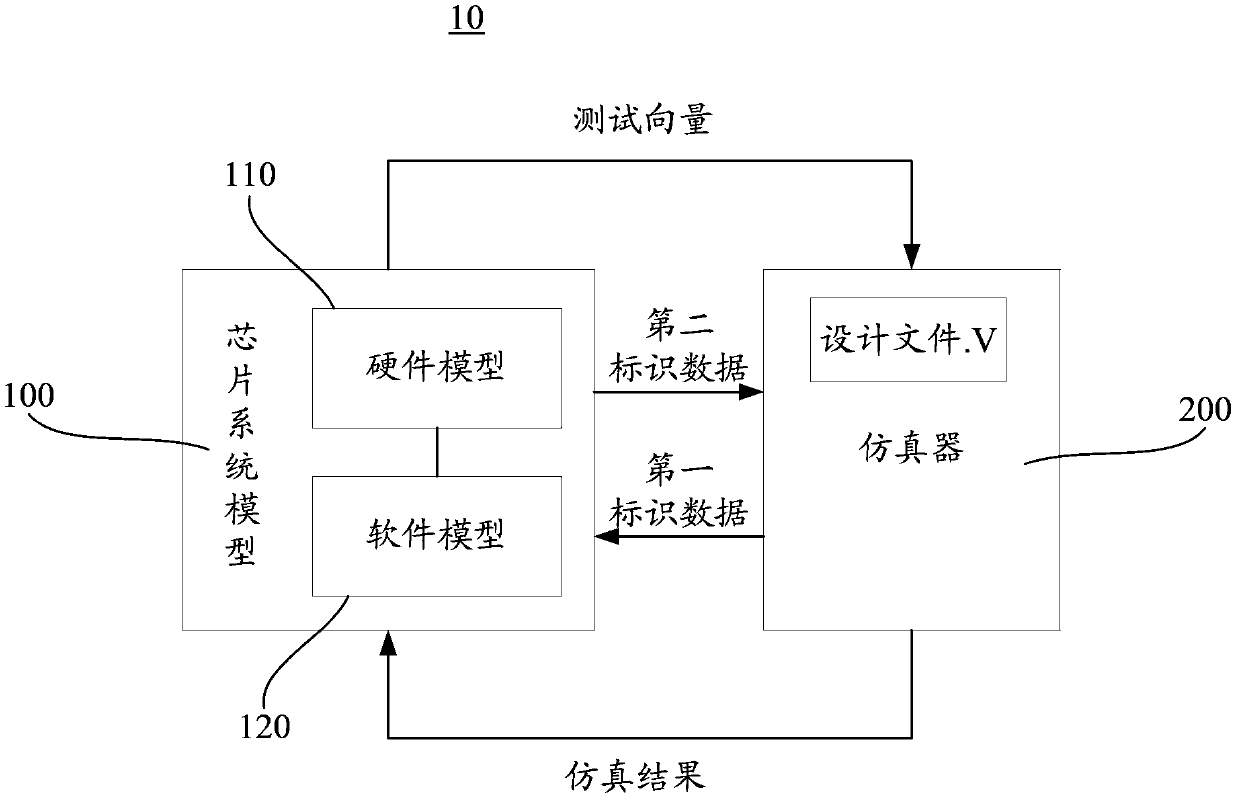
ActiveCN104346272BImplement auto-fulfillmentImprove efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingCommunications systemChIP-on-chip
The invention discloses a chip automatic simulation verification system, comprising: a chip system model corresponding to a system-on-chip chip, wherein a hardware model and a software model corresponding to the system-on-chip chip are established; the chip system model randomly generates test vectors and Running the test vector to obtain a test result; the emulator receives and runs a design file corresponding to the SoC; the emulator communicates with the chip system model, receives the test vector and uses the test vector for test verification to obtain a simulation result; The system-on-chip model also compares the test result with the simulation result, if the test result is consistent with the simulation result, then continue to generate the next random test vector, and perform the next round of testing and comparison, otherwise stop the test. A corresponding chip automatic simulation verification method is also disclosed. The above system and method for automatic chip simulation verification are simpler and more efficient during test verification.
Owner:WUXI CHINA RESOURCES MICROELECTRONICS
Pseudo-random code generator and its generation method based on generalized information domain
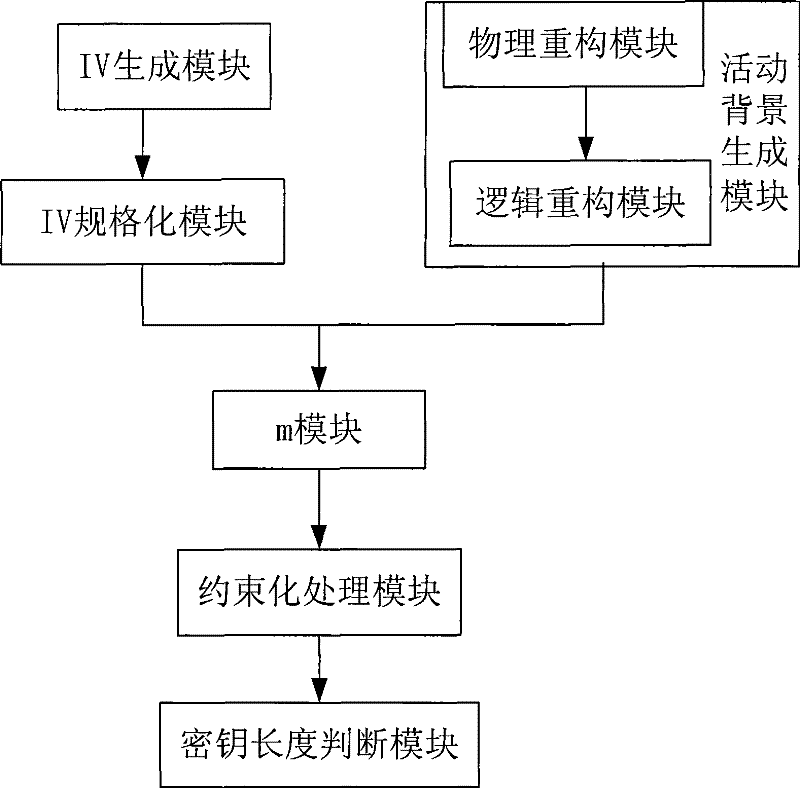
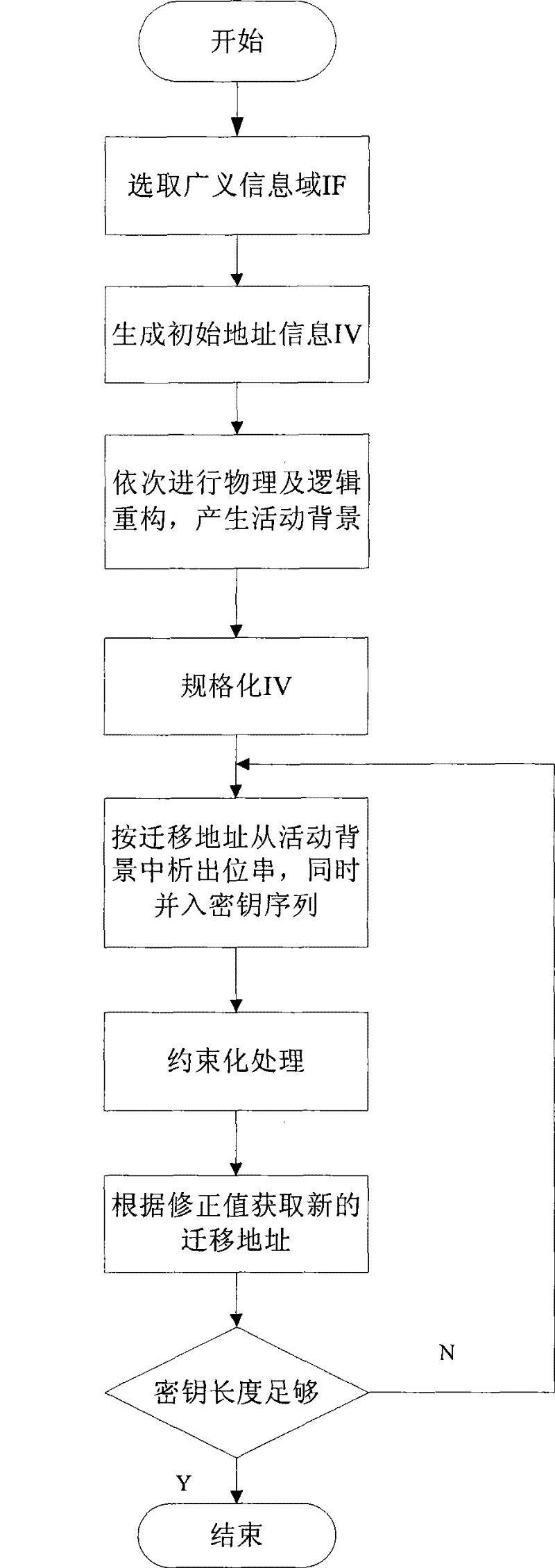
InactiveCN101364868BImplement one-time padEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesKey sizeConfidentiality
The present invention provides a pseudo-random code generator based on a generalized information domain, which includes an initial address information (IV) generation module, an IV normalization module, a key generation algorithm (m) module, a constrained processing module, and an encryption module connected in sequence. A key length judging module, the m module is also connected with the activity background generation module at the same time, and the activity background generation module is mainly composed of a physical reconstruction module and a logic reconstruction module. The present invention breaks through the binary limitation of traditional cryptography, introduces the concept of generalized information domain, expands it into a triple structure, realizes the transfer of key security issues to generalized information domain security issues, improves the strength of resistance to cryptanalysis, and further improves information security. confidentiality. The invention can quickly generate very long pseudo-random codes, can increase the size of the key space when used as a key, and can provide specific keys according to different purposes. The generated pseudo-random code has initial value sensitivity and good randomness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Pseudo-random number generator and test system using it
ActiveCN100356735CEasy to produceProduce quicklyData switching networksNumber generatorRandom test generator
A pseudo-random number generating unit consists of input and output ports for inputting random number sampling range , seed selector , pseudo - random sequence generating unit for generating any length of pseudo - random sequence , positioning device for determining effective bit of random sequence and range adjusting unit for adjust random sequence value . The test device realized by above-said unit can quickly generate large amount of message with different length required by test to let system simulate real data flow accurately for raising test effect.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Implementing automated memory address recording in constrained random test generation for verification of processor hardware designs
InactiveUS9251023B2Negative effectEliminate requirementsError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsMemory addressComputer hardware
A method and apparatus are provided for implementing automated memory address recording in constrained random test generation for verification of processor hardware designs. A test generation program includes a built in feature to keep track of storage addresses used and to make the addresses available to the test definition. This built in feature of a constrained random test generator allows storage addresses used in the past to be accessed by the current instruction generation eliminating the requirement of deliberately establishing target addresses first. This allows separate test events to interact with the same storage addresses without having to write a special test.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com