Patents
Literature
581results about "Pulse generation with predetermined statistical distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
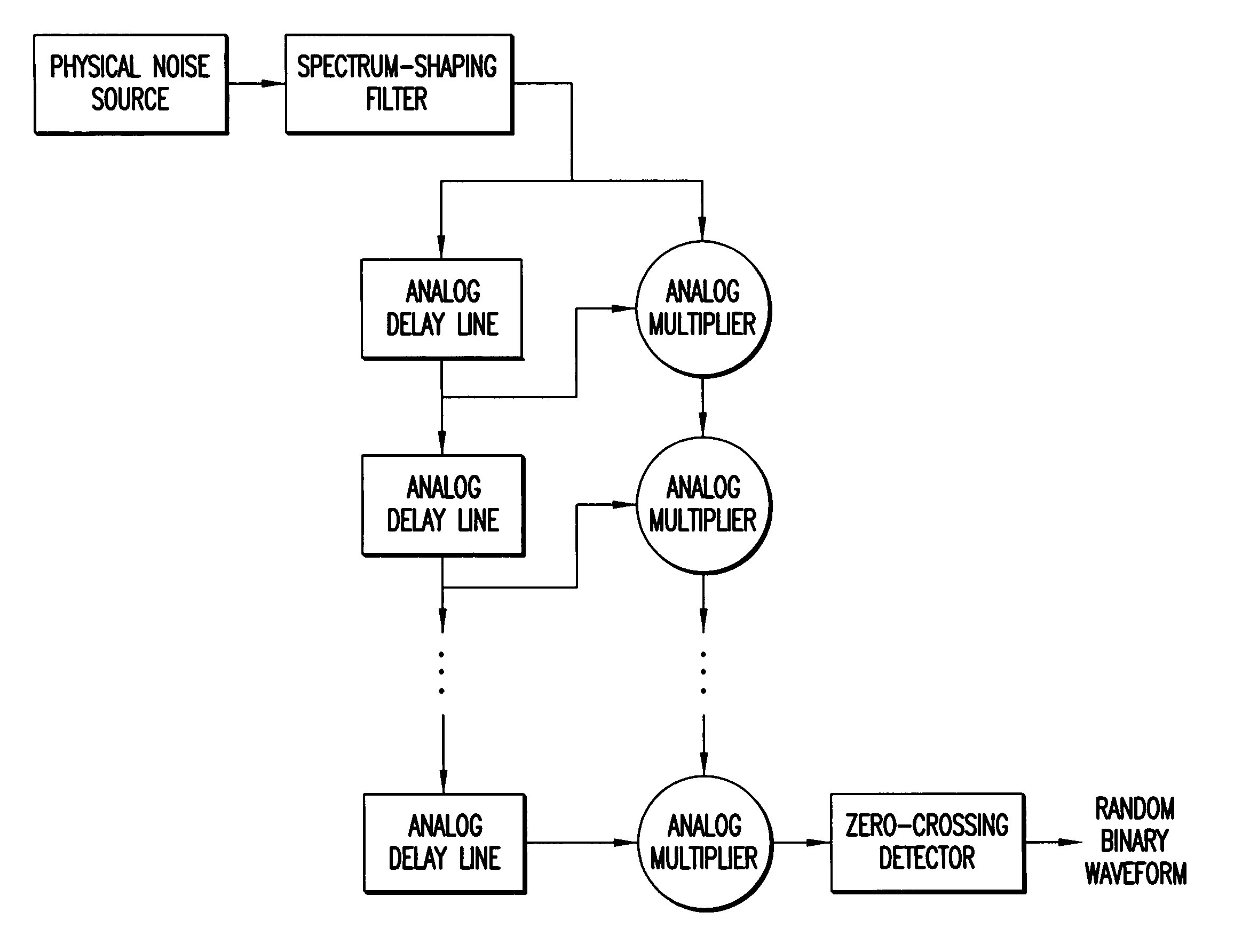
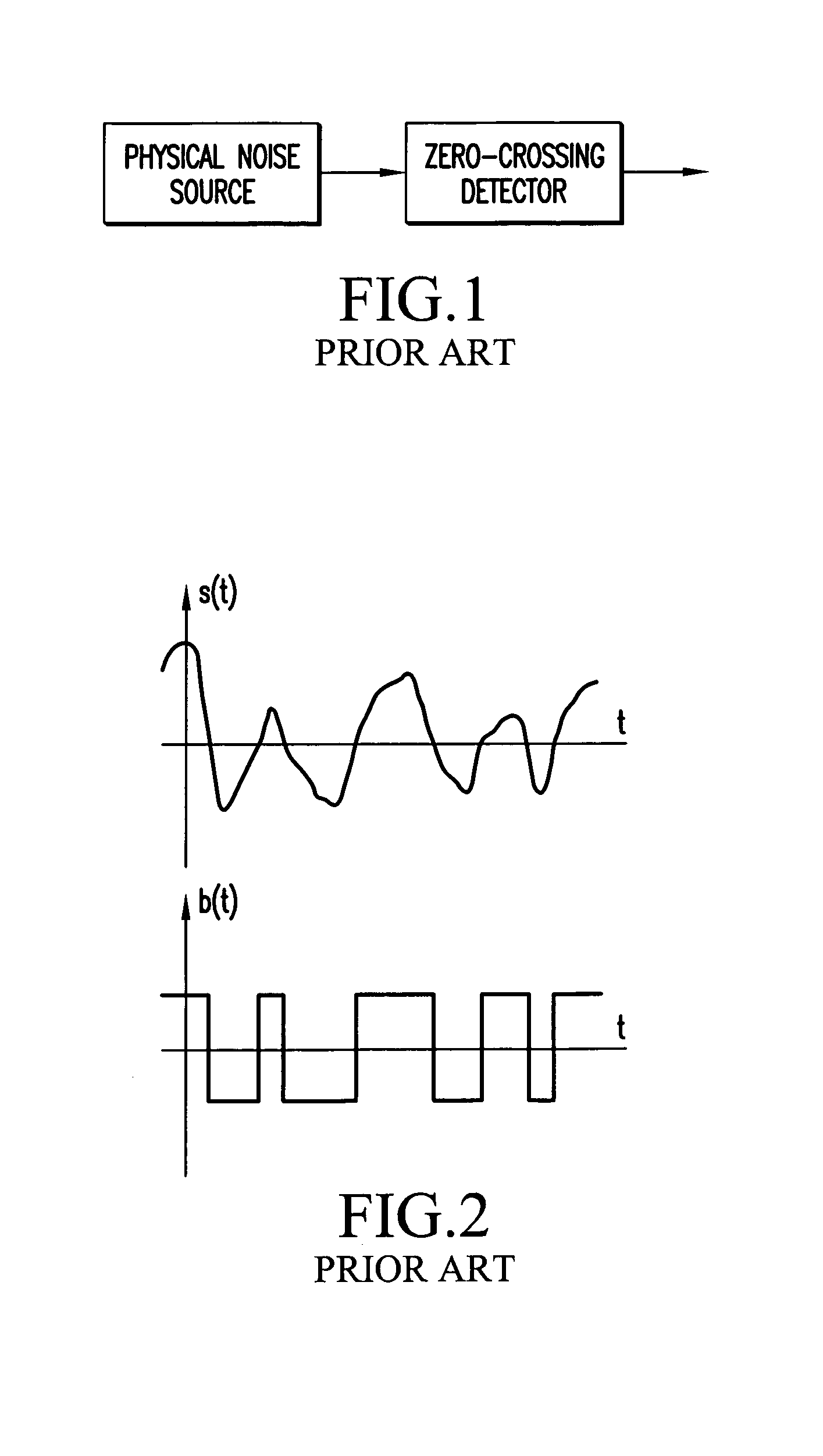
Method and apparatus for generating random signals
InactiveUS7145933B1Reduce probabilityRandom number generatorsTransmissionRandom intervalComputer science
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
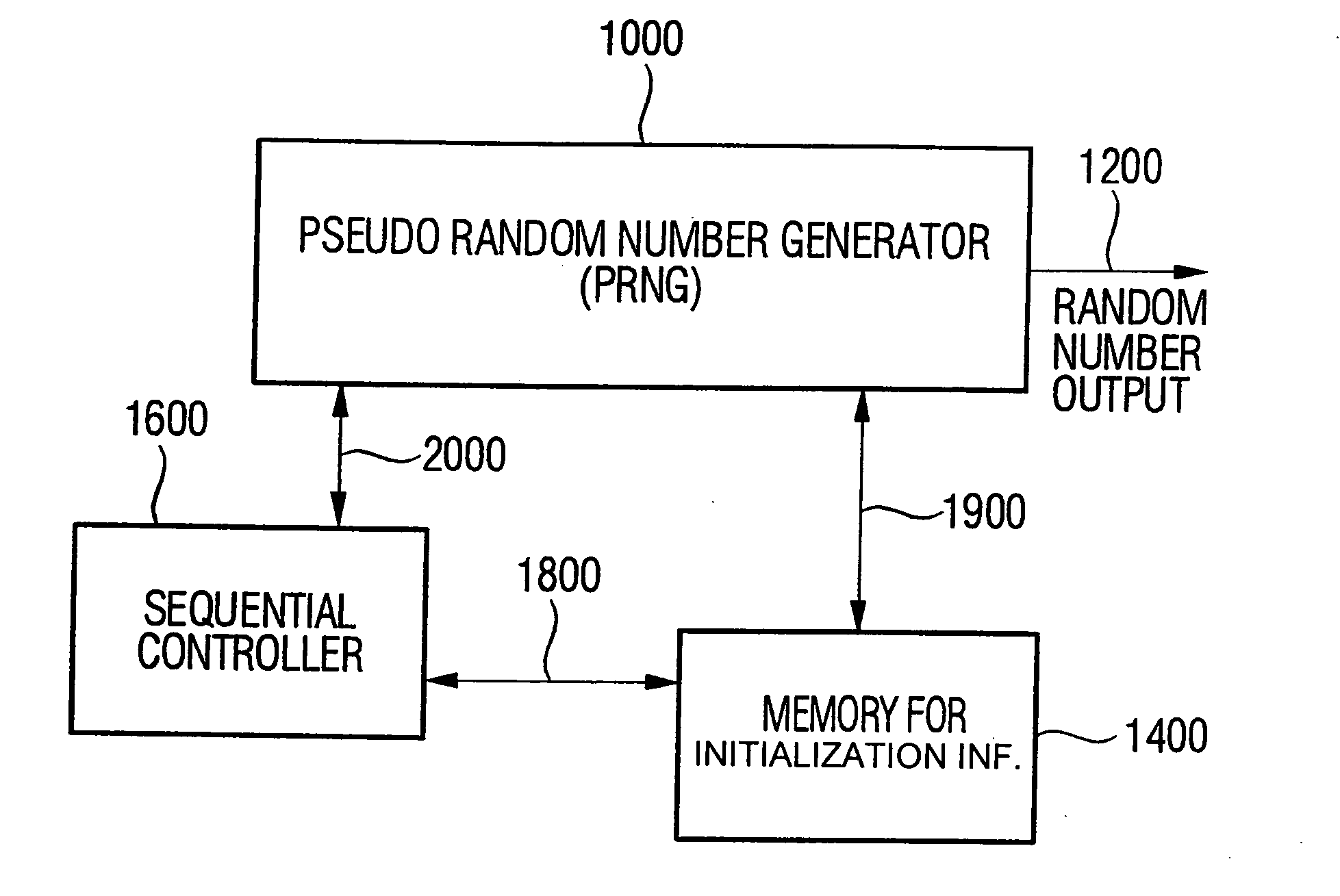
Device and method for generating random numbers using a pseudo random number generator
InactiveUS20050129247A1Simpler and more practicableQuality improvementKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsIntermediate stateNumber generator
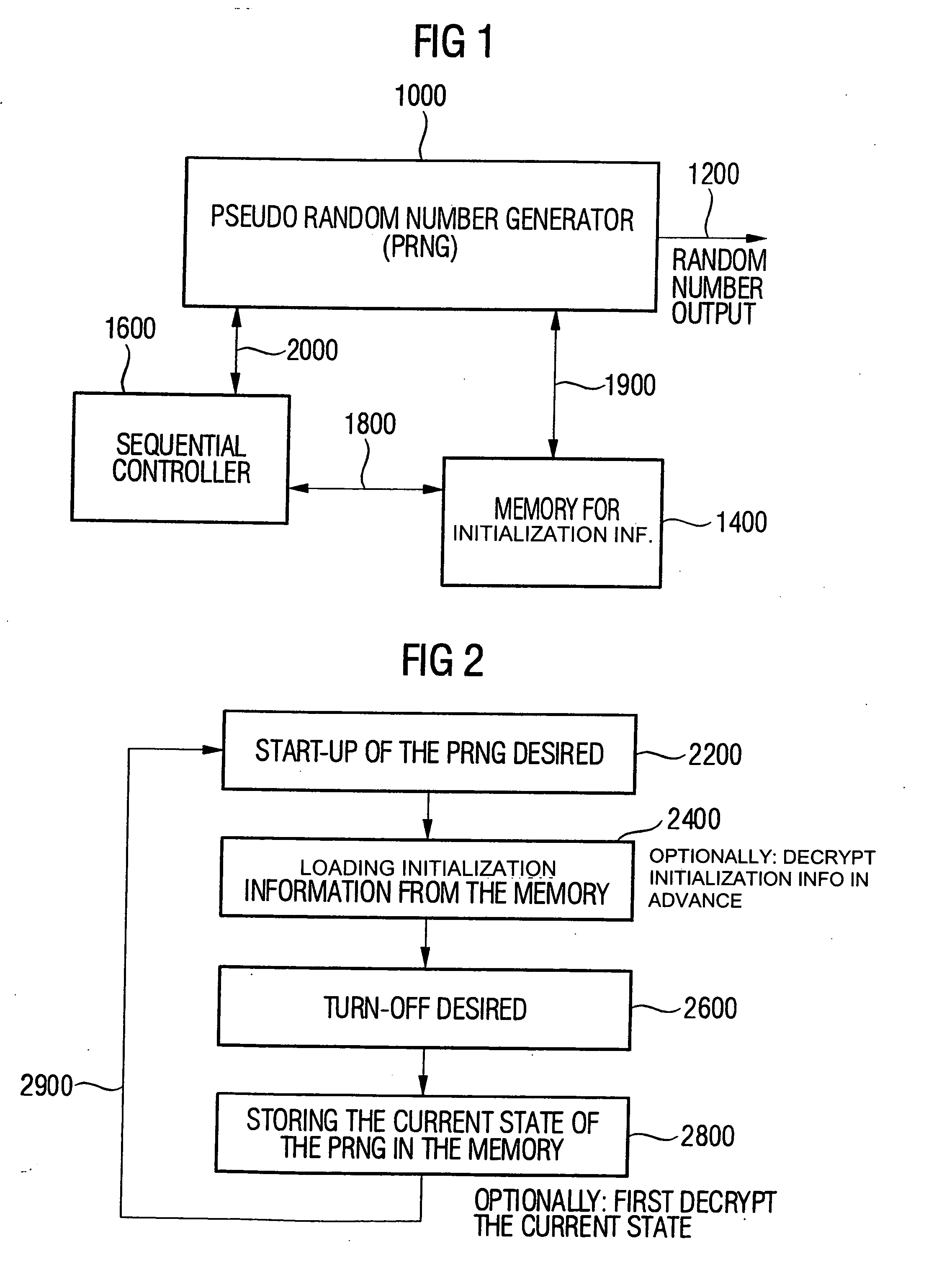
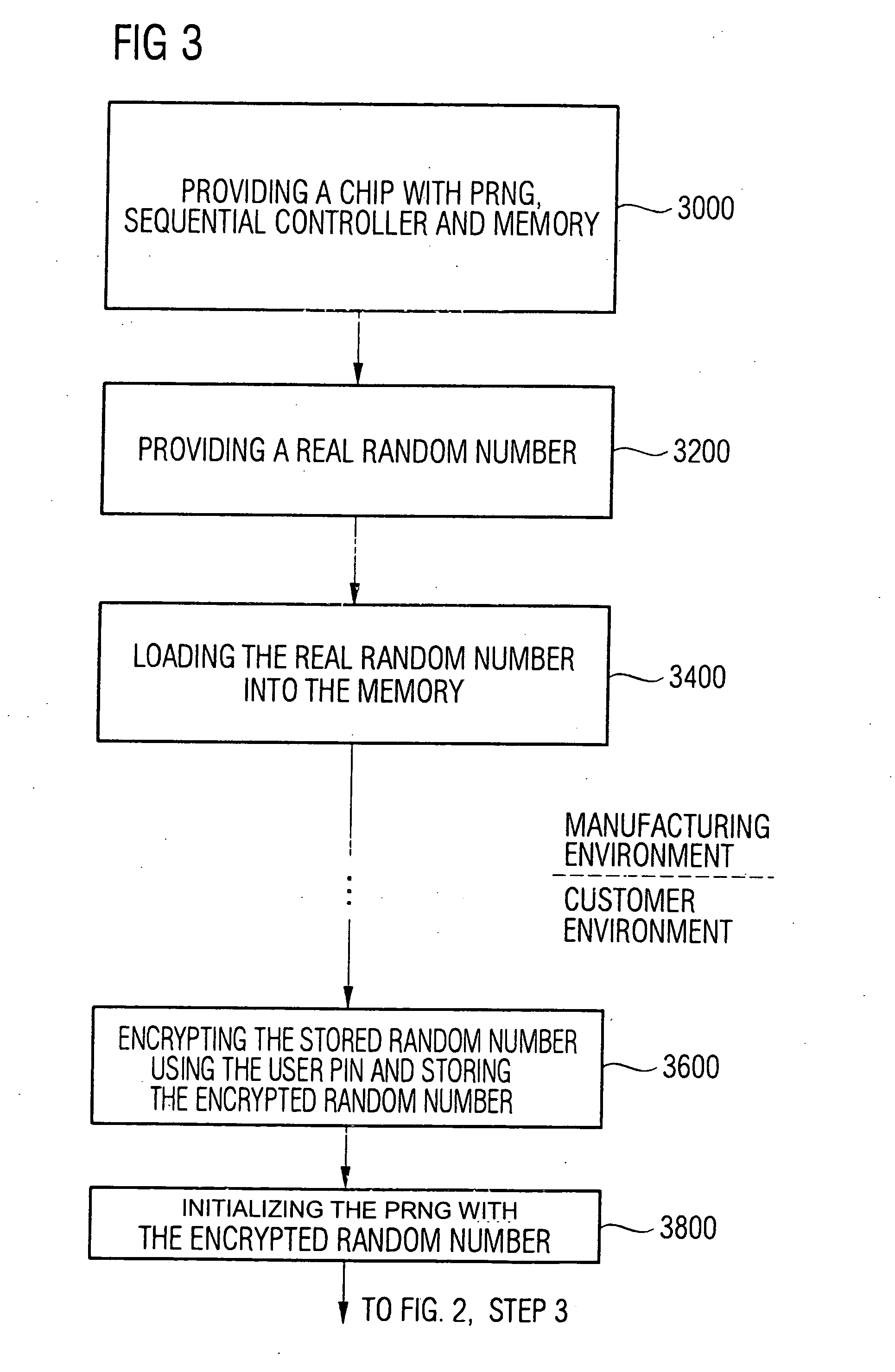
Device for generating random numbers having a pseudo random number generator, a memory and a sequential controller. The pseudo random number generator generates a deterministic random number sequence after an initialization using an initialization value. The memory stores initialization information, wherein the initialization information is derived from a true random number or corresponds to the true random number. The sequential controller initializes the pseudo random number generator at start-up using the initialization information or the information derived from the initialization information, stores an intermediate state of the pseudo random number generator or information derived from the intermediate state in the memory at a turn-off of the pseudo random number generator, and uses the intermediate state or the information derived from the intermediate state for an initialization of the pseudo random number generator at a renewed start-up.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
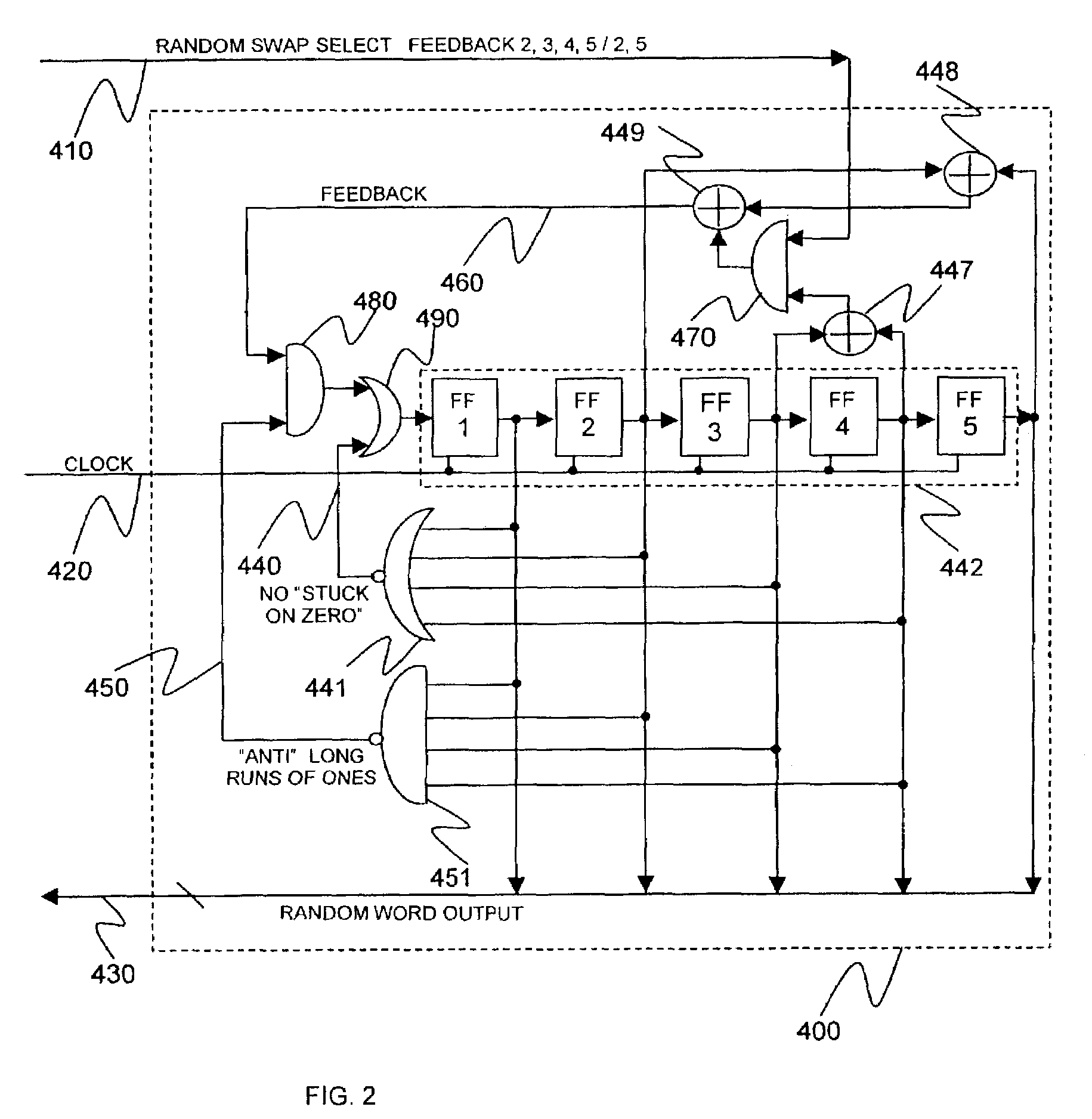
Random number slip and swap generators
InactiveUS7206797B2Increase unpredictabilityIncrease randomnessRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsAlgorithmElectronic equipment
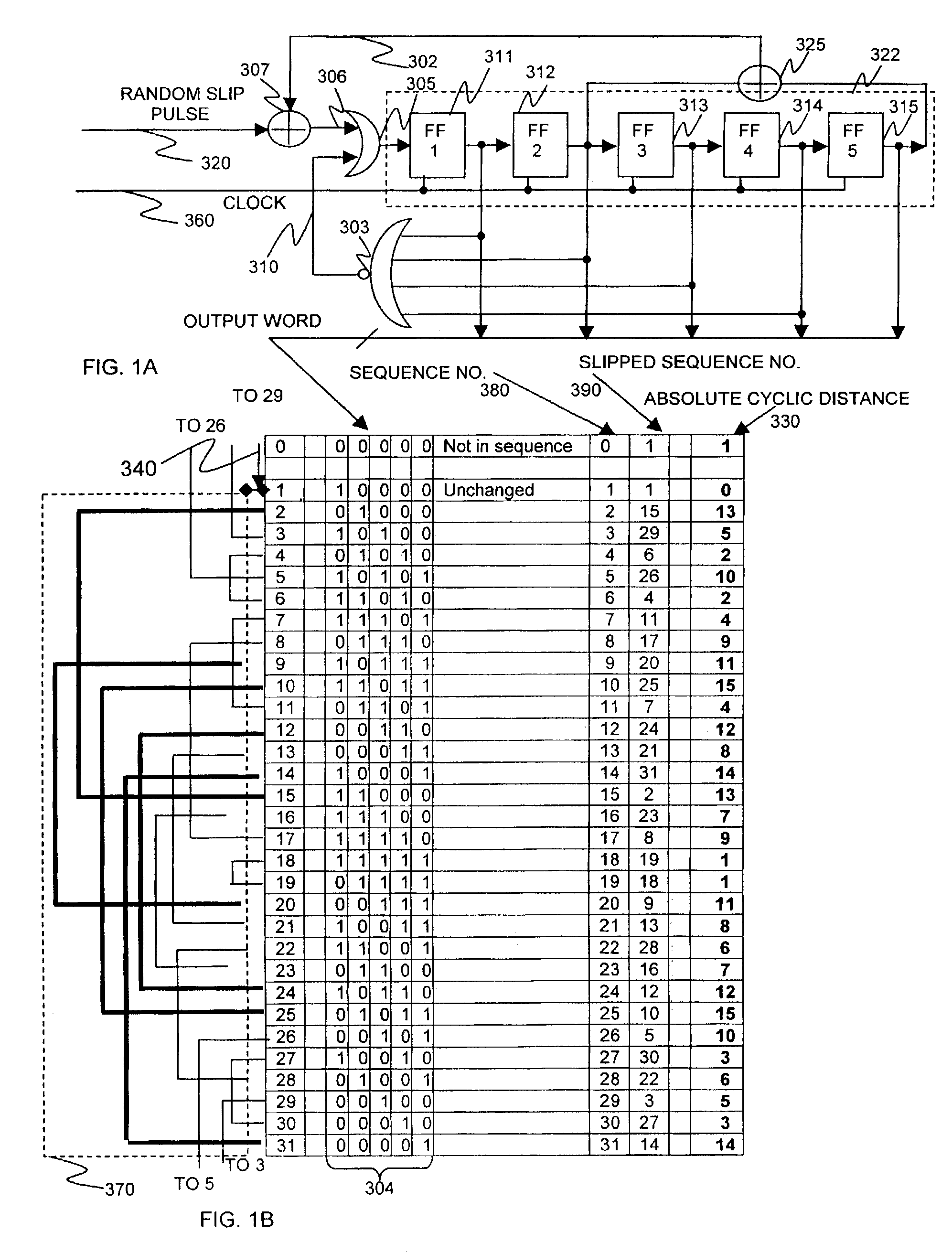
A microelectronic apparatus and method for generating random binary words including at least one clocked pseudorandom binary number sequence generator normally operative to generate a cyclic output sequence of binary numbers, each number including a string of binary symbols, the cyclic output sequence including a basic sequence which is generated repeatedly, at least one bit stream generator generating a clocked bit stream including a stream of binary symbols of a first type occasionally interrupted by a binary symbol of a second type, wherein a first varying time interval between the occasional interruptions is intractably correlated to the output sequence of the number sequence generator, wherein each occurrence of an interruption of the stream of binary symbols of the first type by a binary symbol of the second type causes a pseudorandom modification of the cyclic output sequence of the number sequence generator and a sampling device operative to sample the cyclic output sequence of binary numbers thereby to generate a sampled output sequence including at least one sampled binary word.
Owner:SANDISK IL
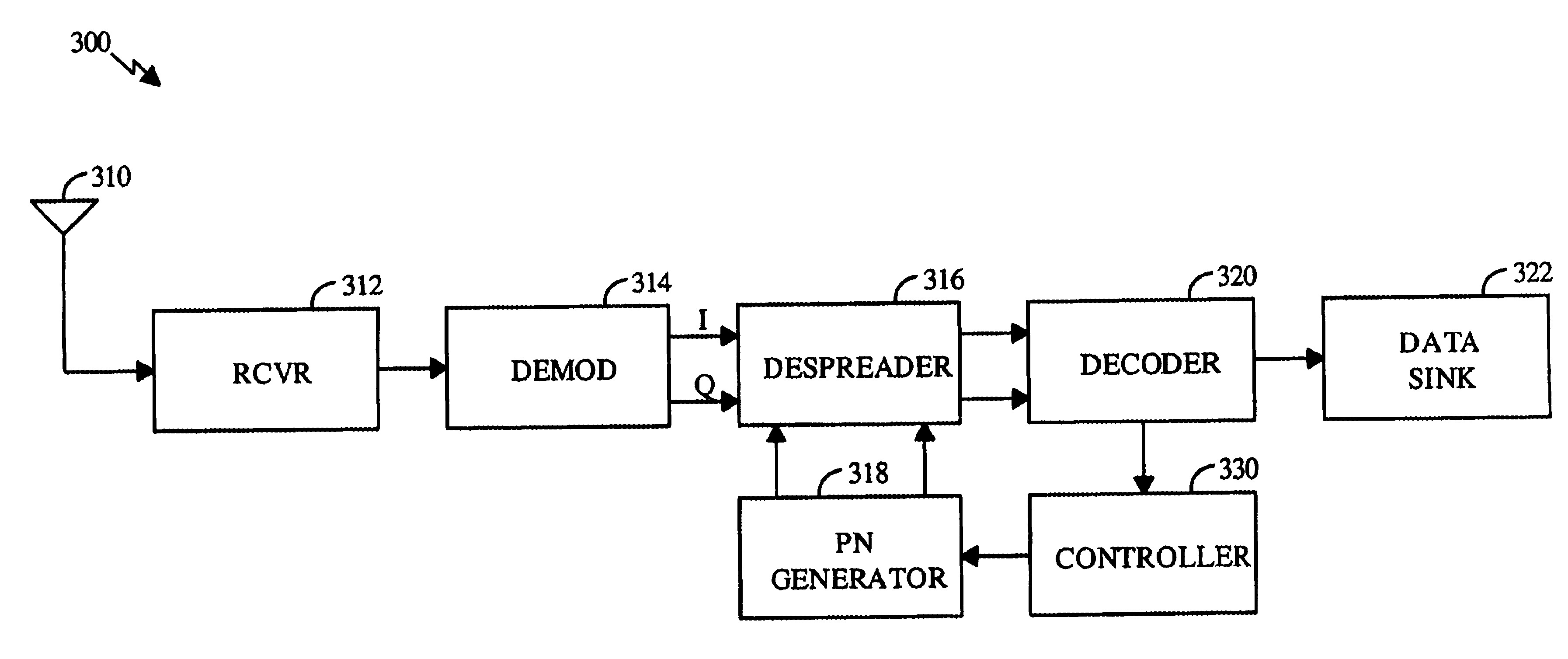
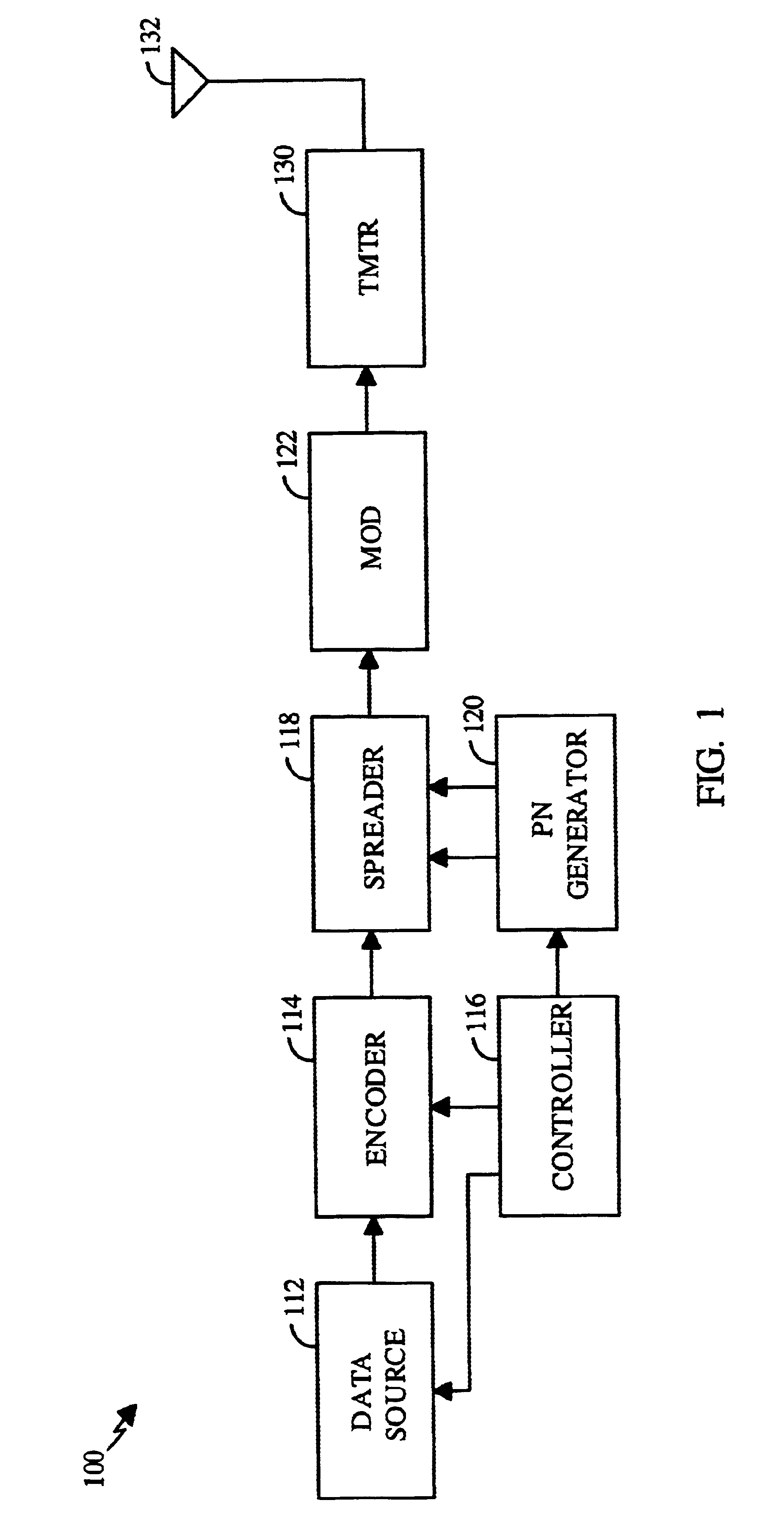
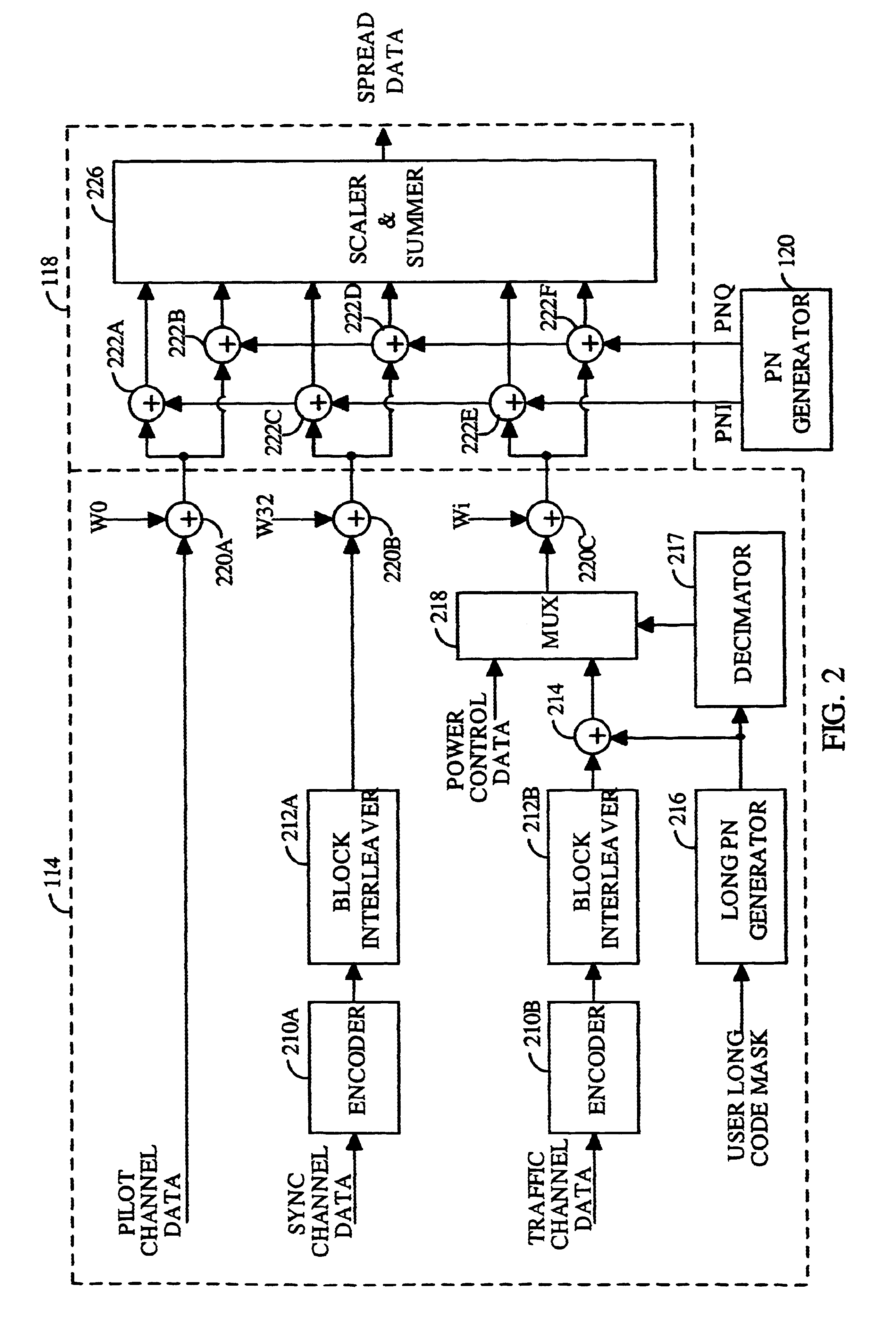
PN generators for spread spectrum communications systems
InactiveUS6661833B1Random number generatorsMultiplex code generationCommunications systemMobile station
Techniques to improve the acquisition process in a spread spectrum environment. The signals from different CDMA systems are spread with different sets of PN sequences, with the PN sequences in each set being uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the other sets. By using uncorrelated PN sequences, the likelihood of detecting a pilot signal from an undesired system is reduced or minimized, and the mean time to acquisition of the pilot signal from the desired system is improved. The mobile station can attempt to acquire the pilot signal by processing the received signal with a first set of PN sequences corresponding to a first hypothesis of the particular signal being acquired. If acquisition of the pilot signal fails, a second set of PN sequences corresponding to a second hypothesis is selected and used to process the received signal. The PN sequences in the second set are uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the first set. The PN sequences for the first set can be generated based on the characteristic polynomials defined by IS-95-A, and the PN sequences for the second set can be the reverse of the PN sequences for the first set.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
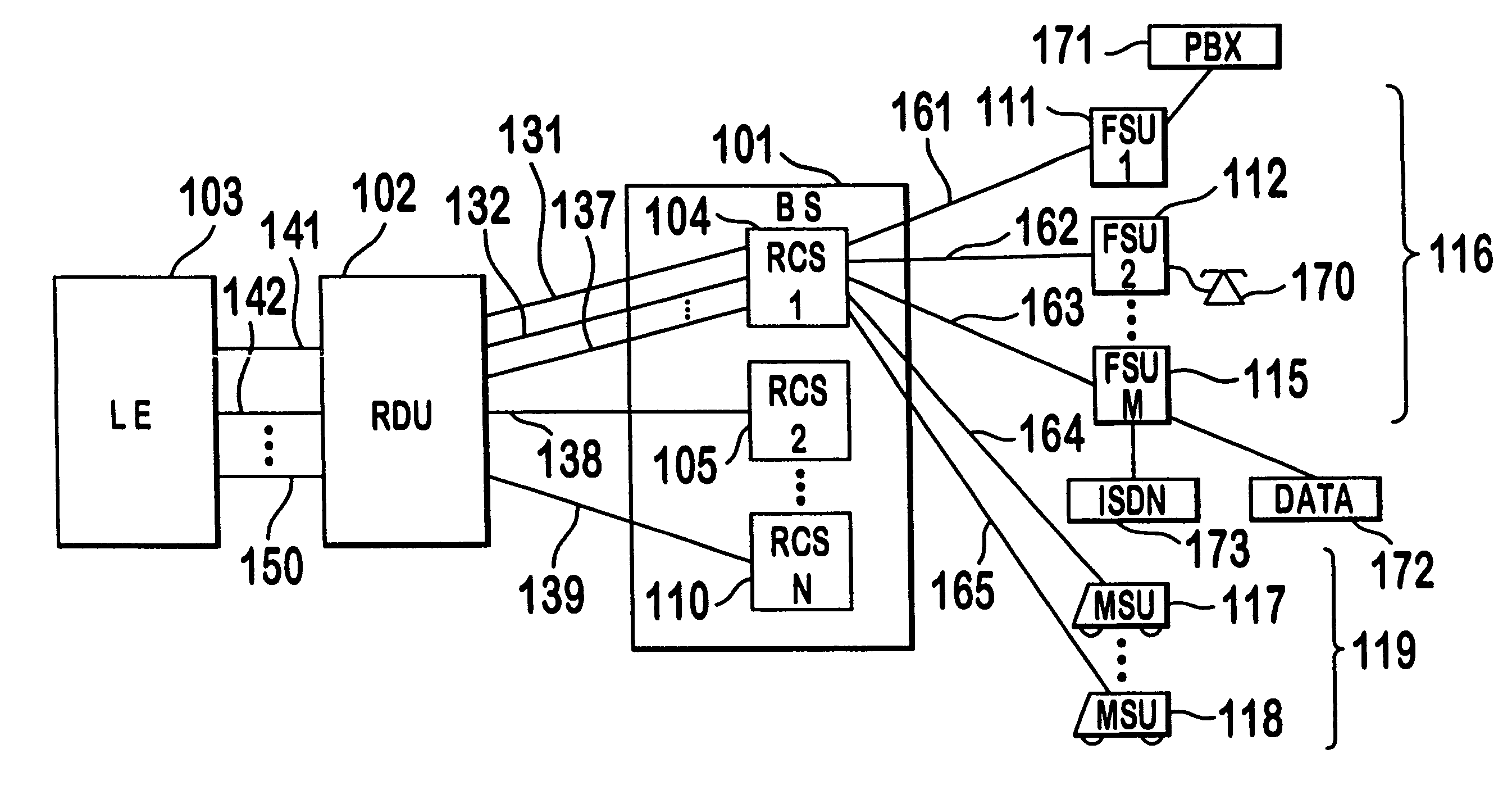
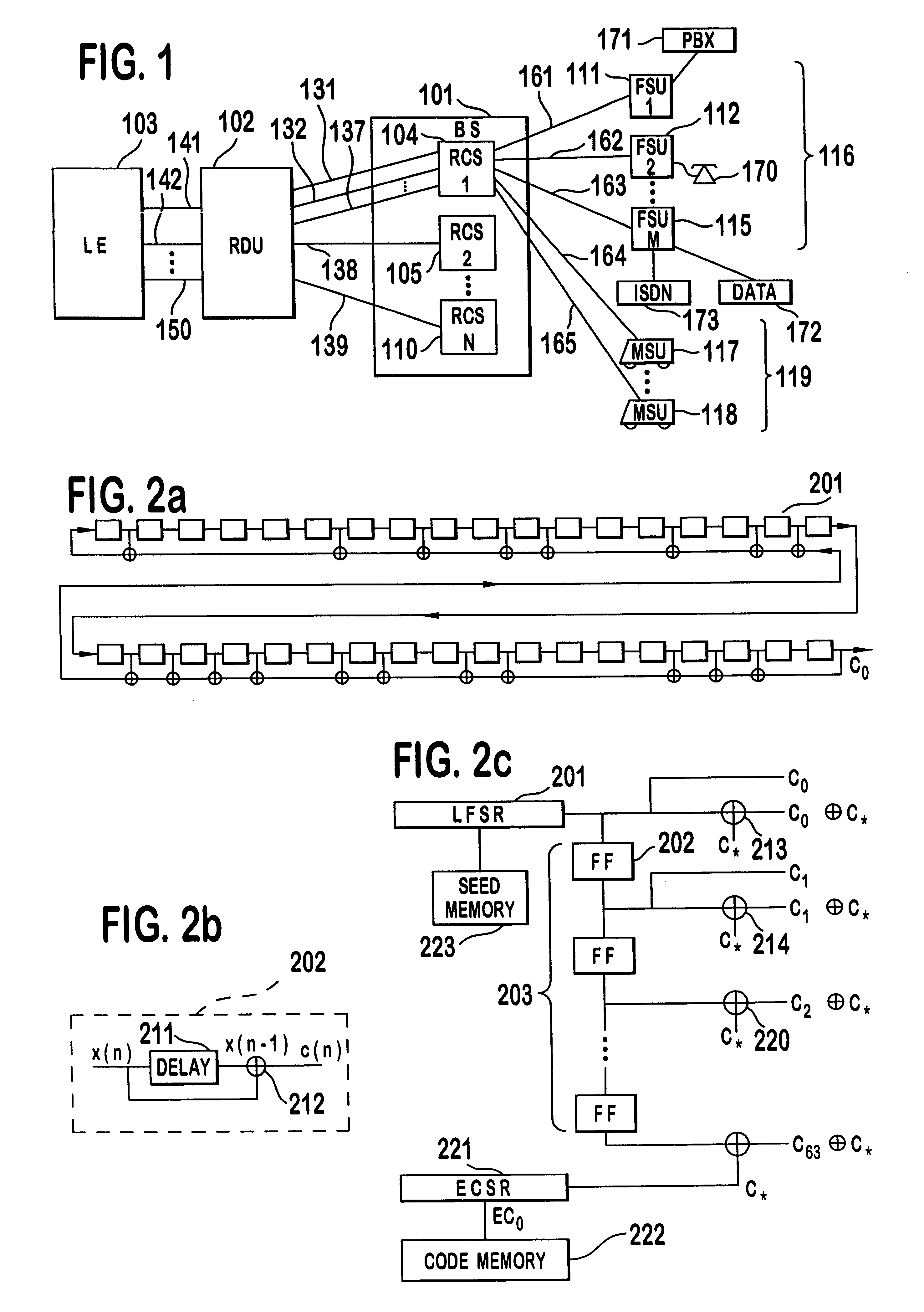
Capacity management method for a code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a Radio Carrier Station (RCS) over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency (RF) channel as a code-division-multiplexed (CDM) signal to a group of Subscriber Units (SUs). The RCS receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The RCS includes a plurality of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a CDM processed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. An RF transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the CDM processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a CDM signal. The RF transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the CDM signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through an RF communication channel to the SUs. Each SU includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the CDM signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the RCS and the SUs, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active SUs for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Random number generator and method for generating random numbers
InactiveUS20060069706A1AutocorrelationReduced sampling rate requirementsRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationNumber generatorComputer science
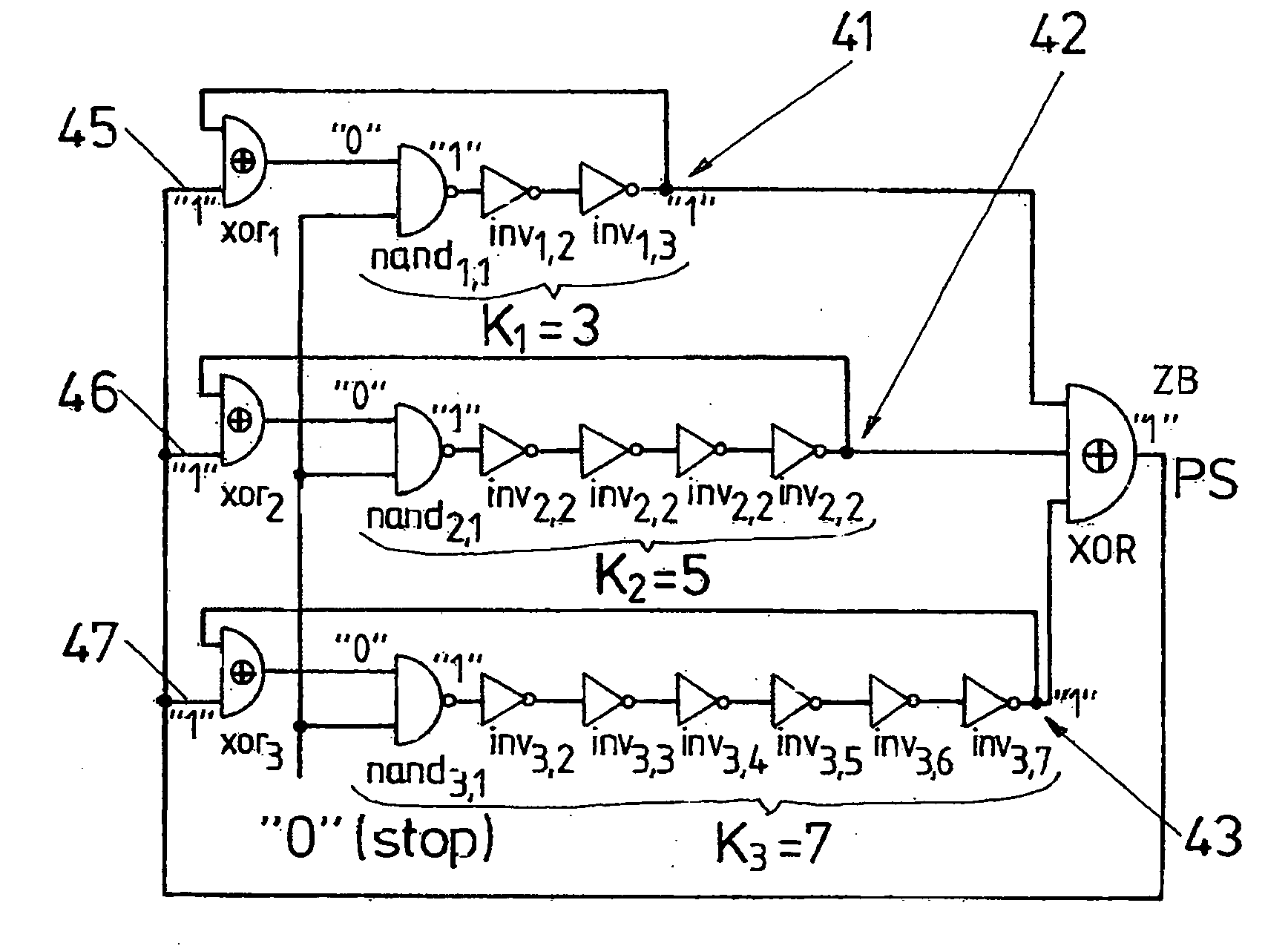
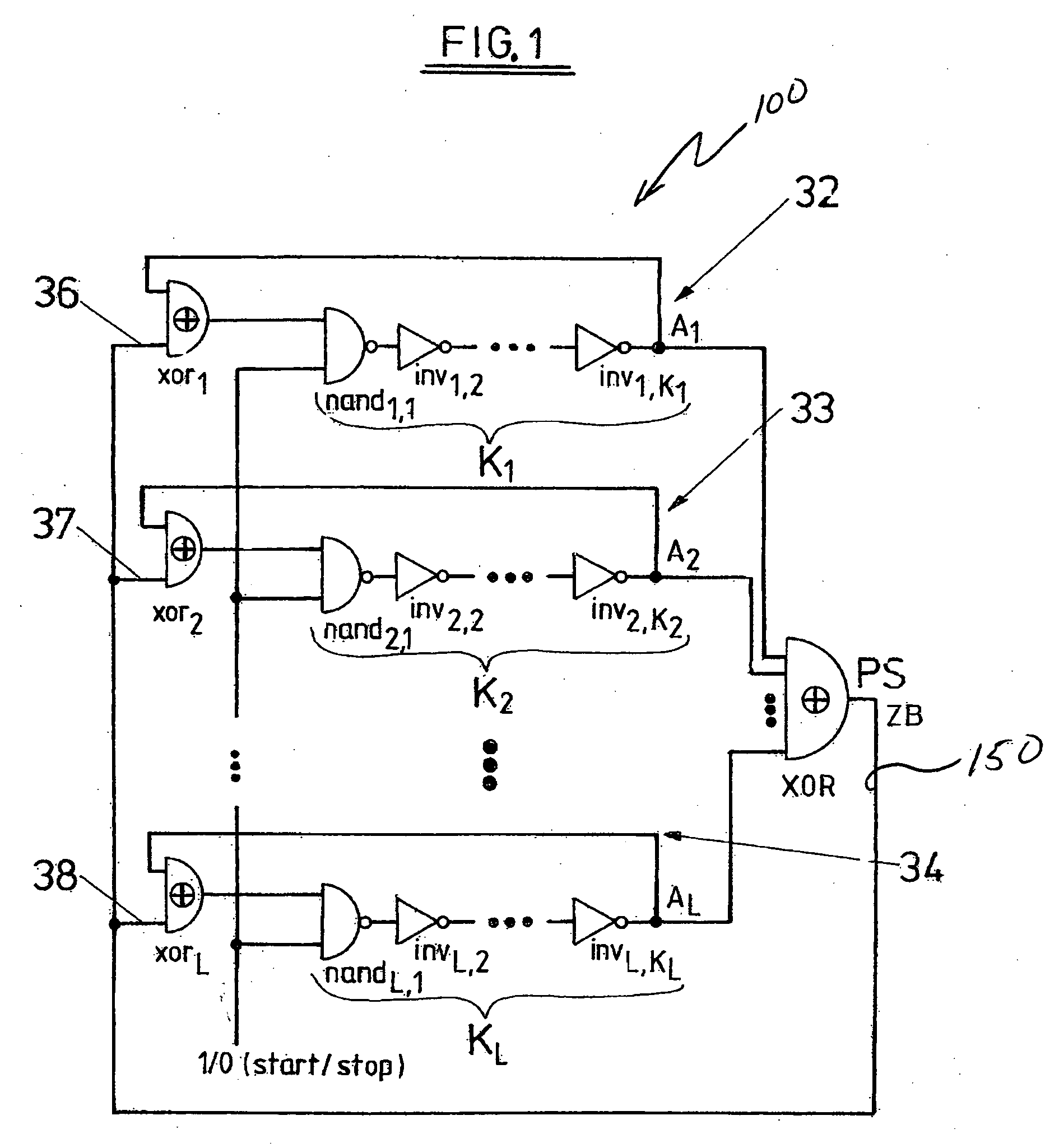
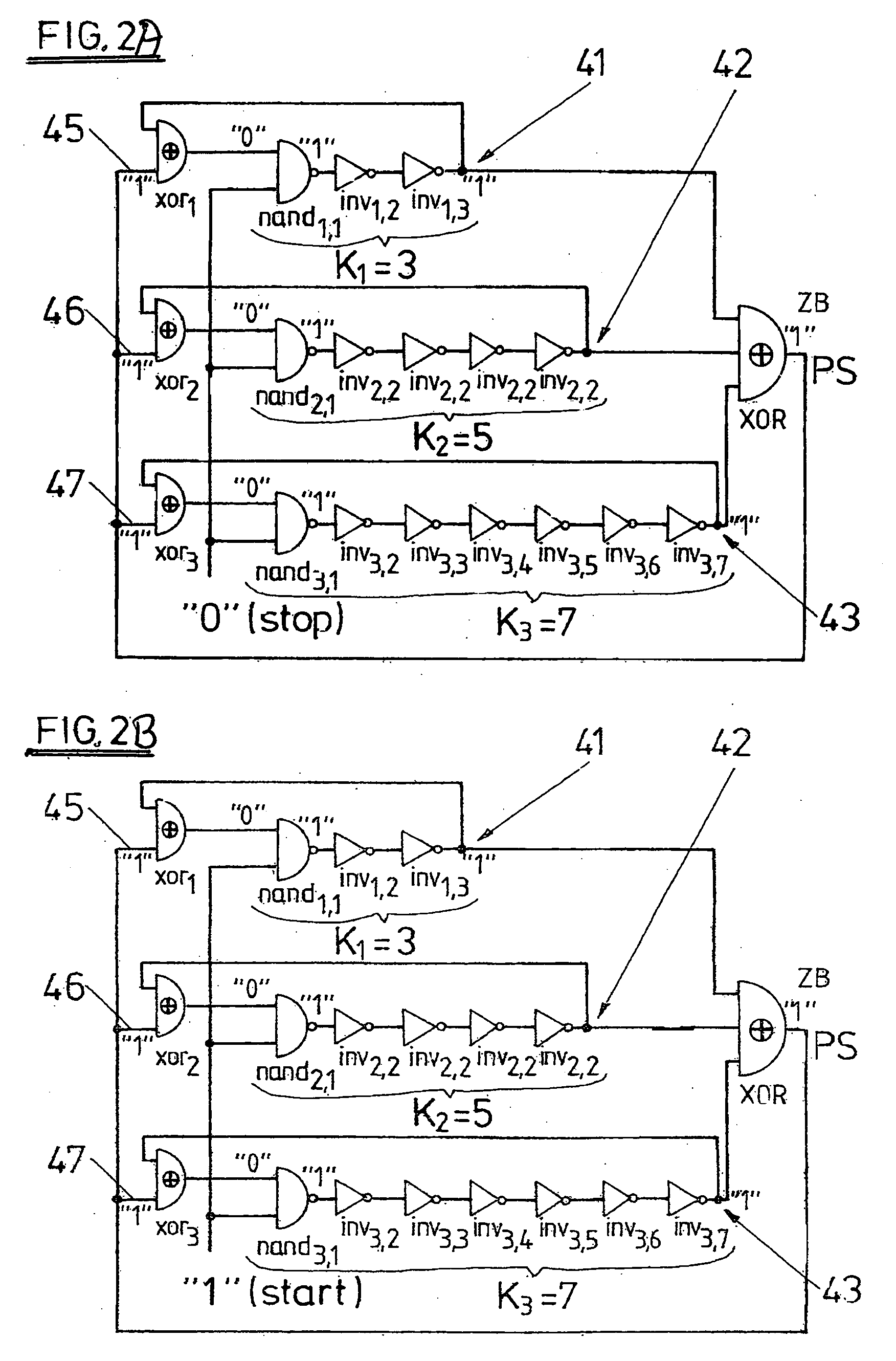
The invention relates to a method for generating random numbers in which oscillating digital output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) of unequal or equal periodicity are generated by at least two ring oscillators (32, 33, 34), an external parity signal (PS) representing a logical state (“0,”“1”) being generated when an odd number of the output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) take on a specified logical state (“1”). According to the invention, the external parity signal (PS) is fed back to an external parity input (36, 37, 38) of each of the respective ring oscillators (32, 33, 34). The invention further relates to a random number generator having at least two ring oscillators (32, 33, 34), made up in particular of independently free-running inverter chains with feedback having an odd number (K) of series-connected inverters (inv1,2, inv2,1, inv3,1, . . . , invi,j, . . . , invL,KL) that generate oscillating digital output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) of unequal or equal periodicity, and having first parity signal generating means (XOR) that generate an external parity signal (PS) representing a logical state (“0,”“1”) when an odd number of the output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) take on a specified logical state (“1”). According to the invention, there are feedback means (xor1, xor2, xor3, xor4, . . . , xorL) that feed back the external parity signal (PS) to an external parity input (36, 37, 38) of each of the respective ring oscillators (32, 33, 34). In this invention the cooperation of chaotic dynamics (feedback of the parity signal) and true randomness (jitter due to thermal noise) in digital circuits, a novel theoretical principle for generating random numbers, has been made into an efficient practical solution.
Owner:TDK MICRONAS GMBH
Pilot adaptive vector correlator
A CDMA modem includes a modem transmitter having: a code generator which provides an associated pilot code signal and which generates a plurality of message code signals; a spreading circuit which produces a spread-spectrum message signal by combining each of the information signals with a respective one of the message code signals; and a global pilot code generator that provides a global pilot code signal to which the message code signals are synchronized. The CDMA modem also includes a modem receiver having an associated pilot code generator and a group of associated pilot code correlators for correlating code-phase delayed versions of the associated pilot signal with a receive CDM signal to produce a despread associated pilot signal. The code phase of the associated pilot signal is changed responsive to an acquisition signal value until a pilot signal is received. The associated pilot code tracking logic adjusts the associated pilot code signal in phase responsive to the acquisition signal so that the signal power level of the despread associated pilot code signal is maximized. Finally, the CDMA modem receiver includes a group of message signal acquisition circuits, each including a plurality of receive message signal correlators which correlate respective local received message code signal to the CDM signal to produce a respective despread received message signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Random number generator
ActiveUS8380768B2Random number generatorsDigital function generatorsElectricityAudio power amplifier
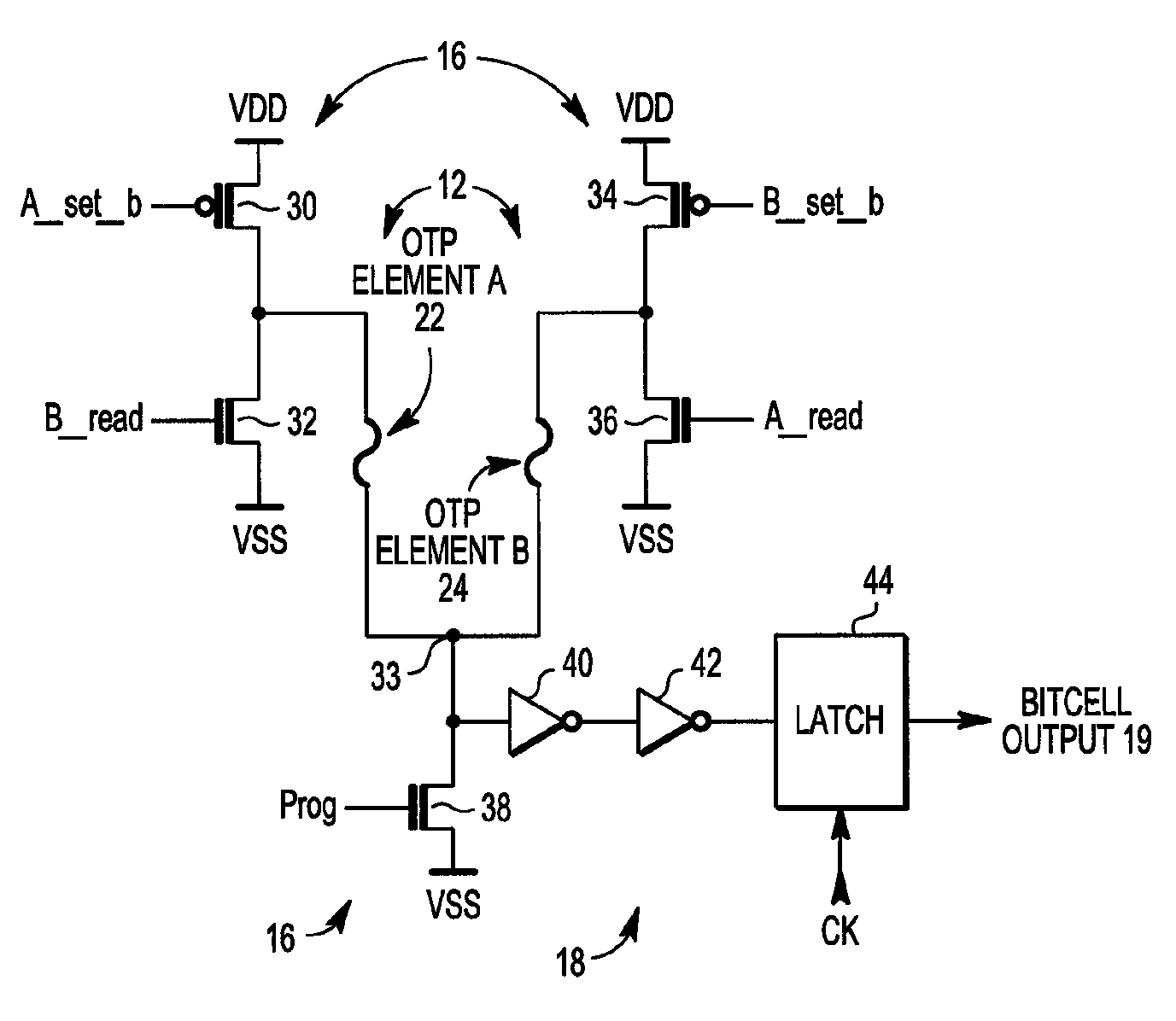
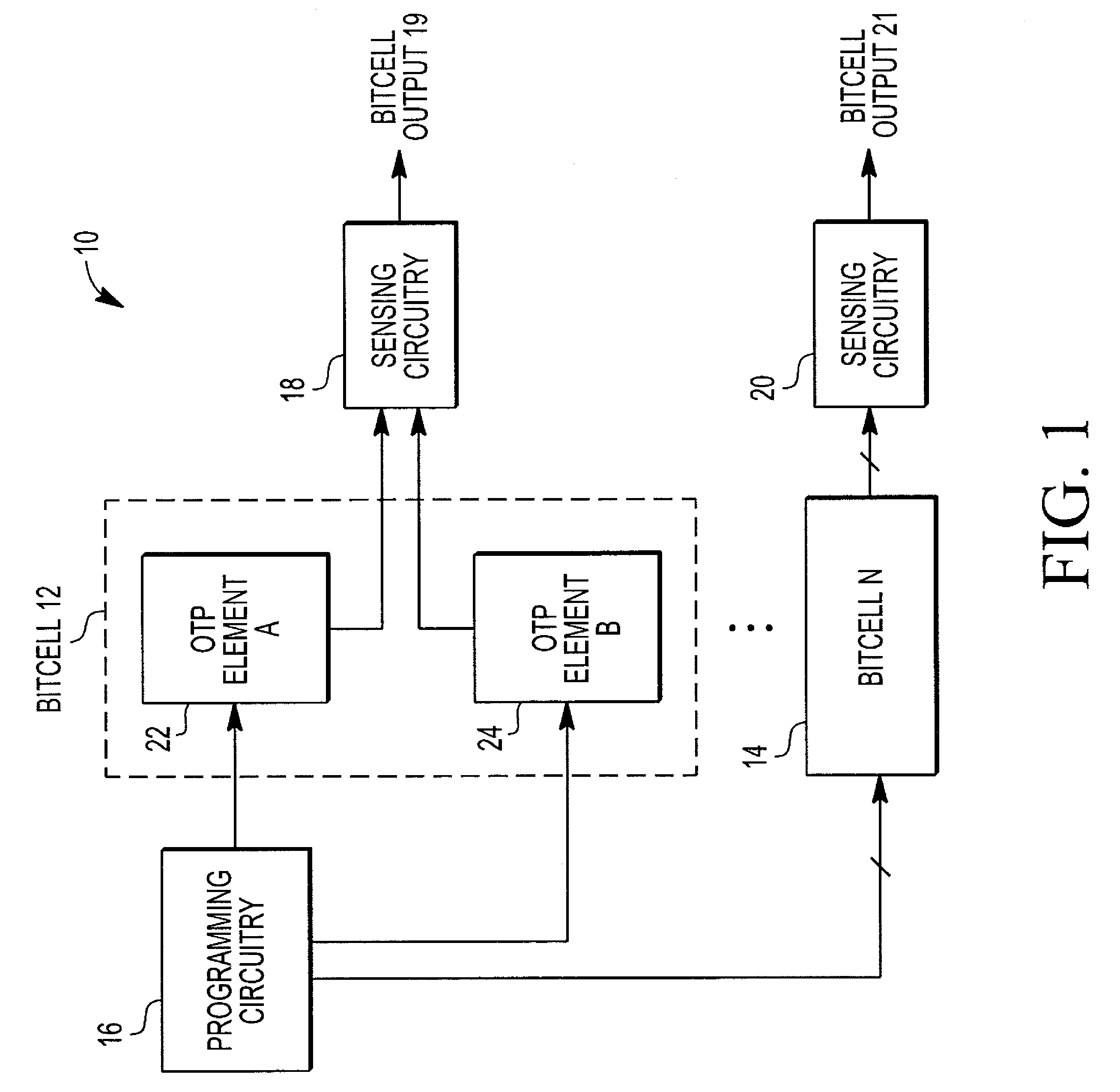
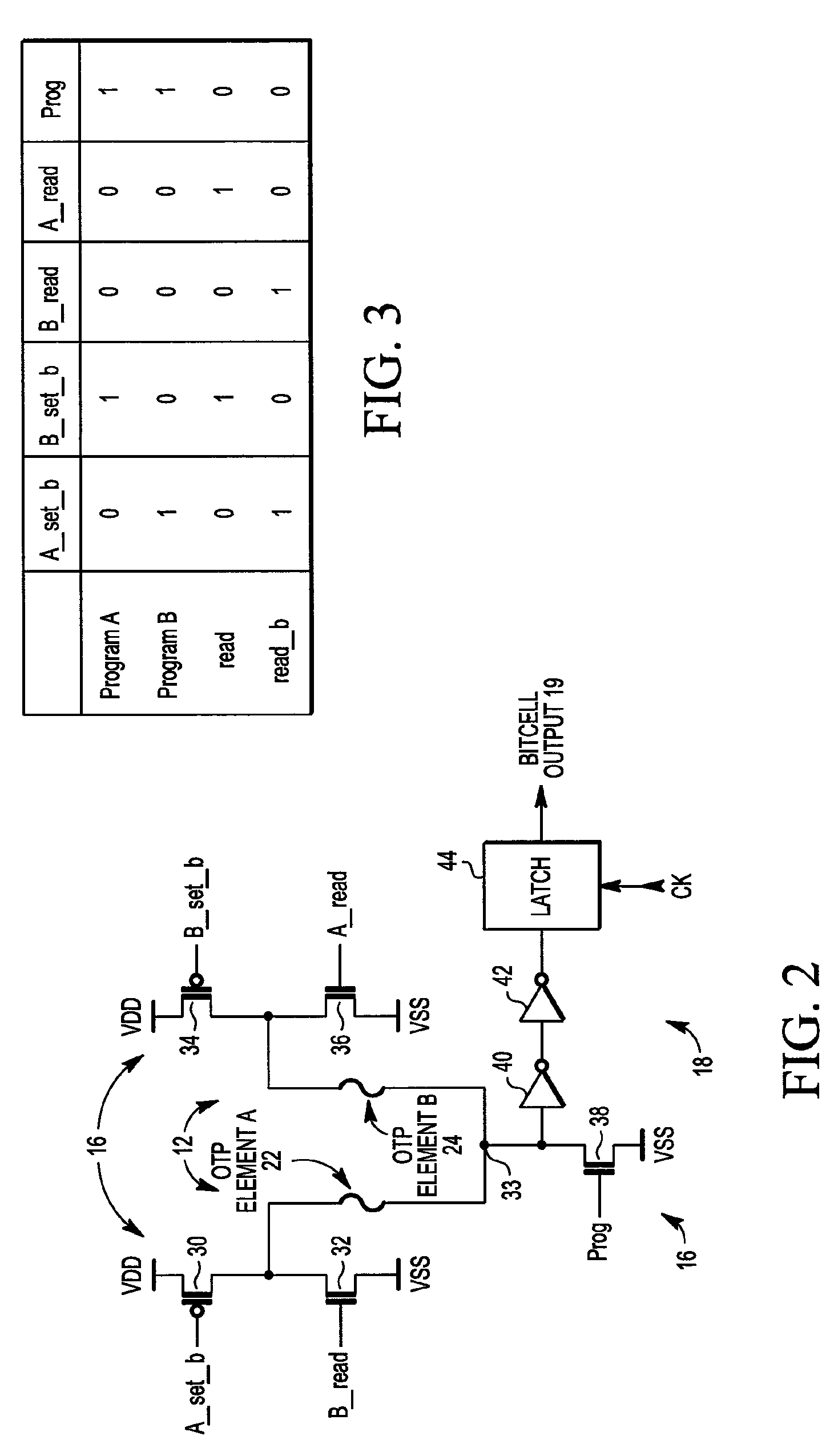
A random number generator includes a first one time programmable (OTP) element and a second OTP element. The first OTP element and second OTP element have a first distribution of probable values for an electrical characteristic when unprogrammed and a second distribution of probable values when programmed. A programming circuit applies a programming signal to the first OTP element and to the second OTP element that causes the first OTP element to switch from being unprogrammed to being programmed and having a first value for its electrical characteristic and the second OTP element to switch from being unprogrammed to being programmed and having a second value for its electrical characteristic. A sense amplifier provides an output signal at a first logic state when the first value exceeds the second value and at a second logic state when the second value exceeds the first value.
Owner:NXP USA INC
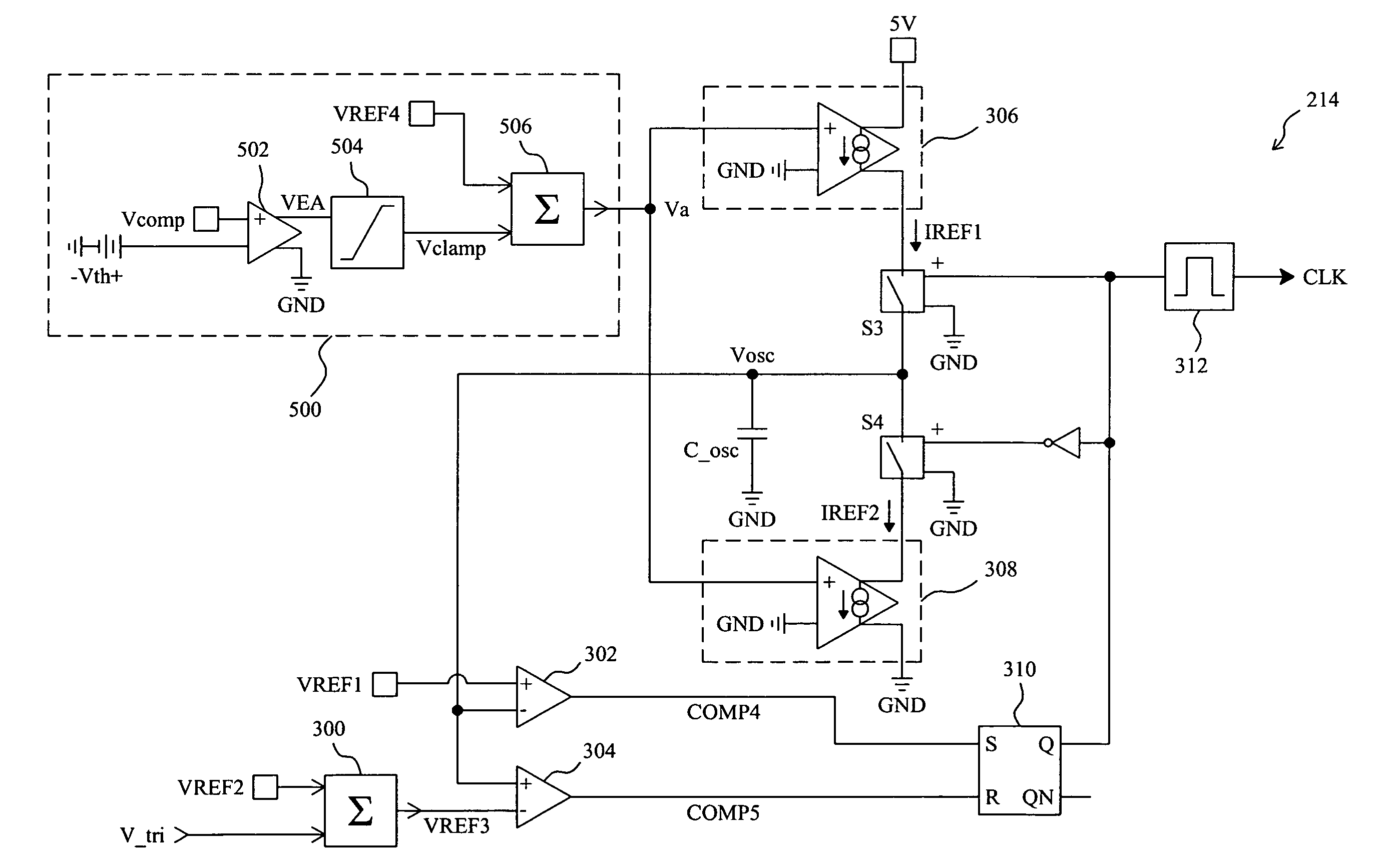
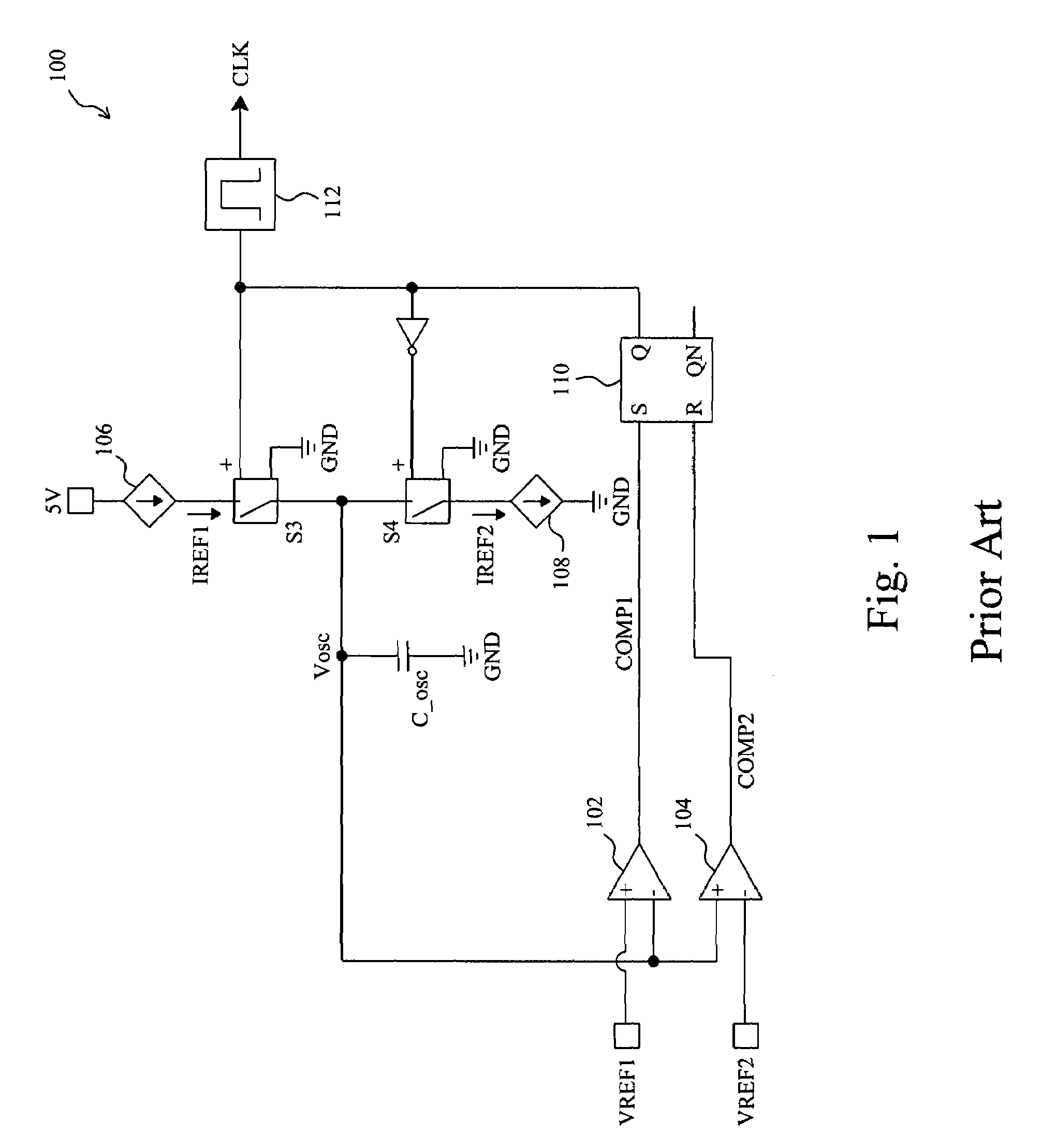
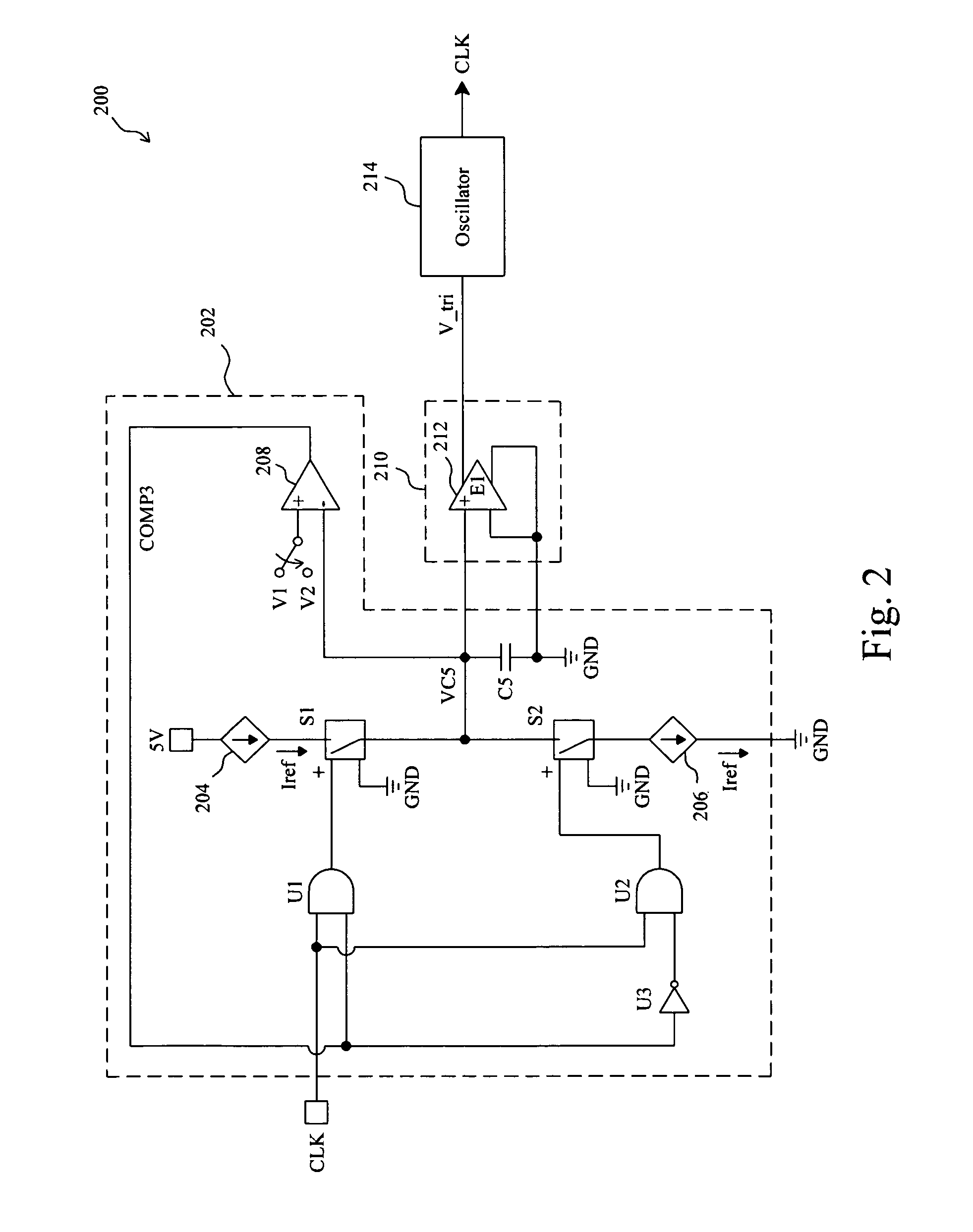
Frequency jittering control for varying the switching frequency of a power supply
ActiveUS7701305B2Digital data processing detailsTransmission noise reductionEngineeringSwitching frequency
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
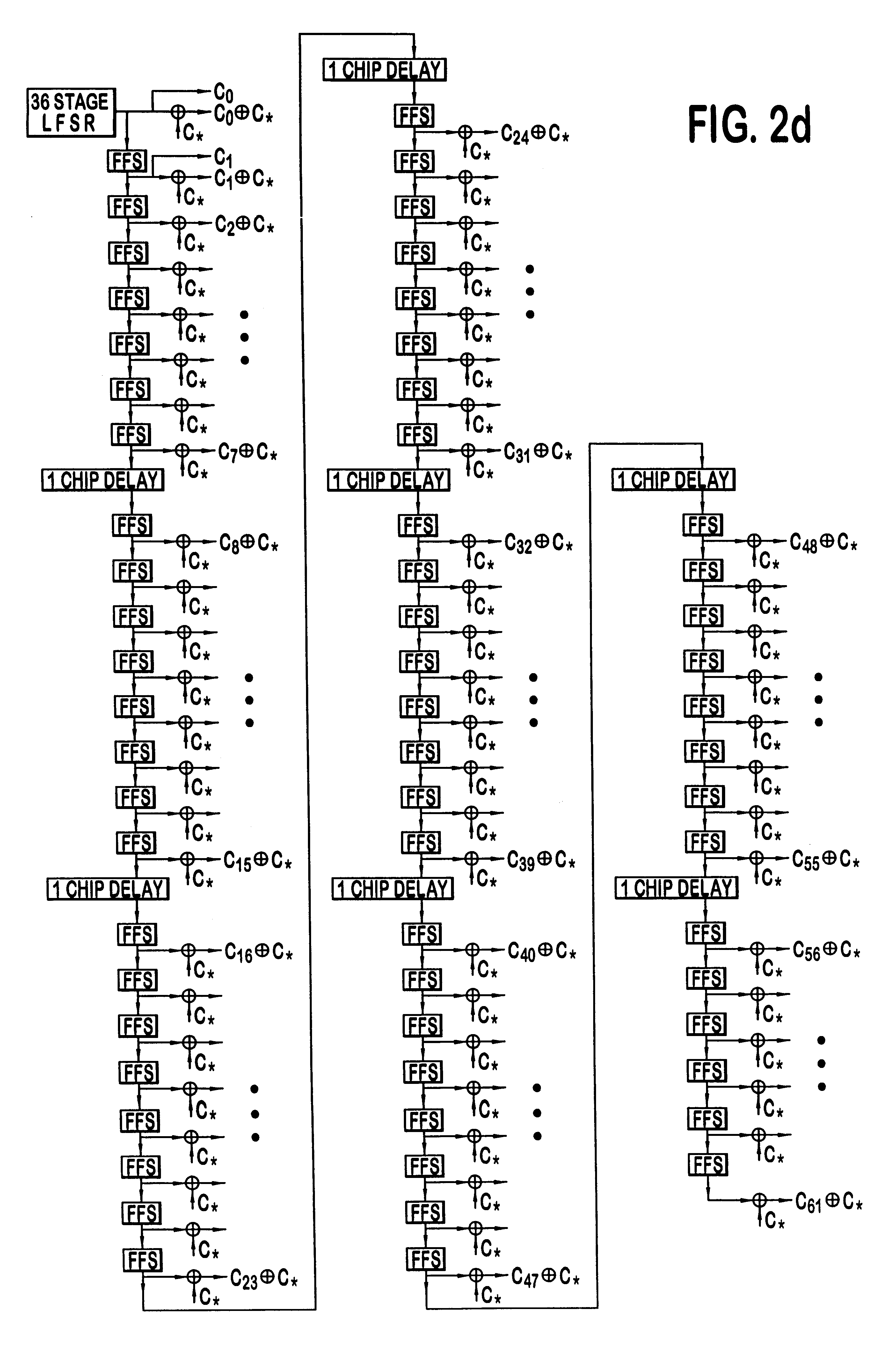
Method for synthesizing linear finite state machines
InactiveUS7260591B2Random number generatorsDigital function generatorsCellular automationVirtual finite-state machine
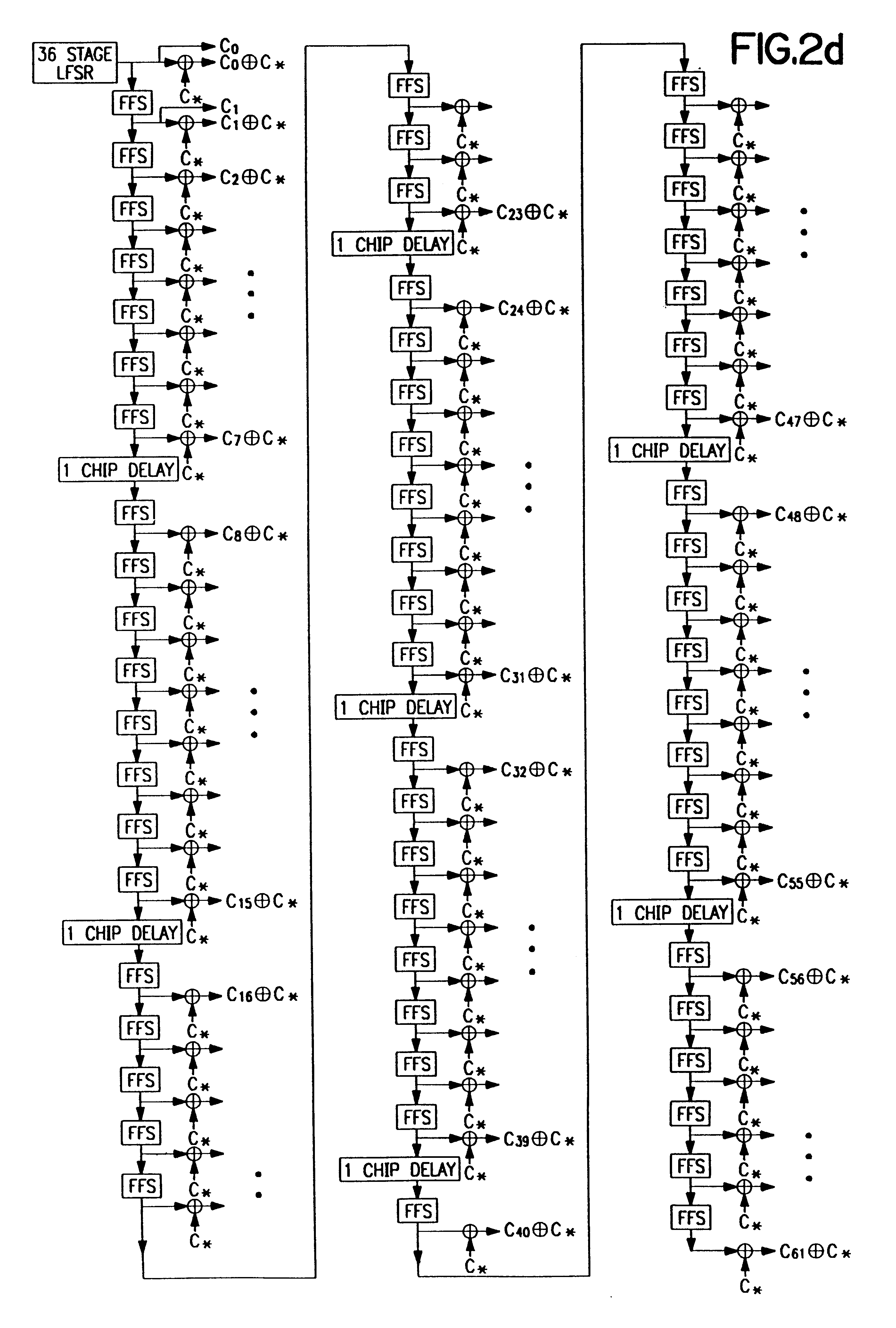
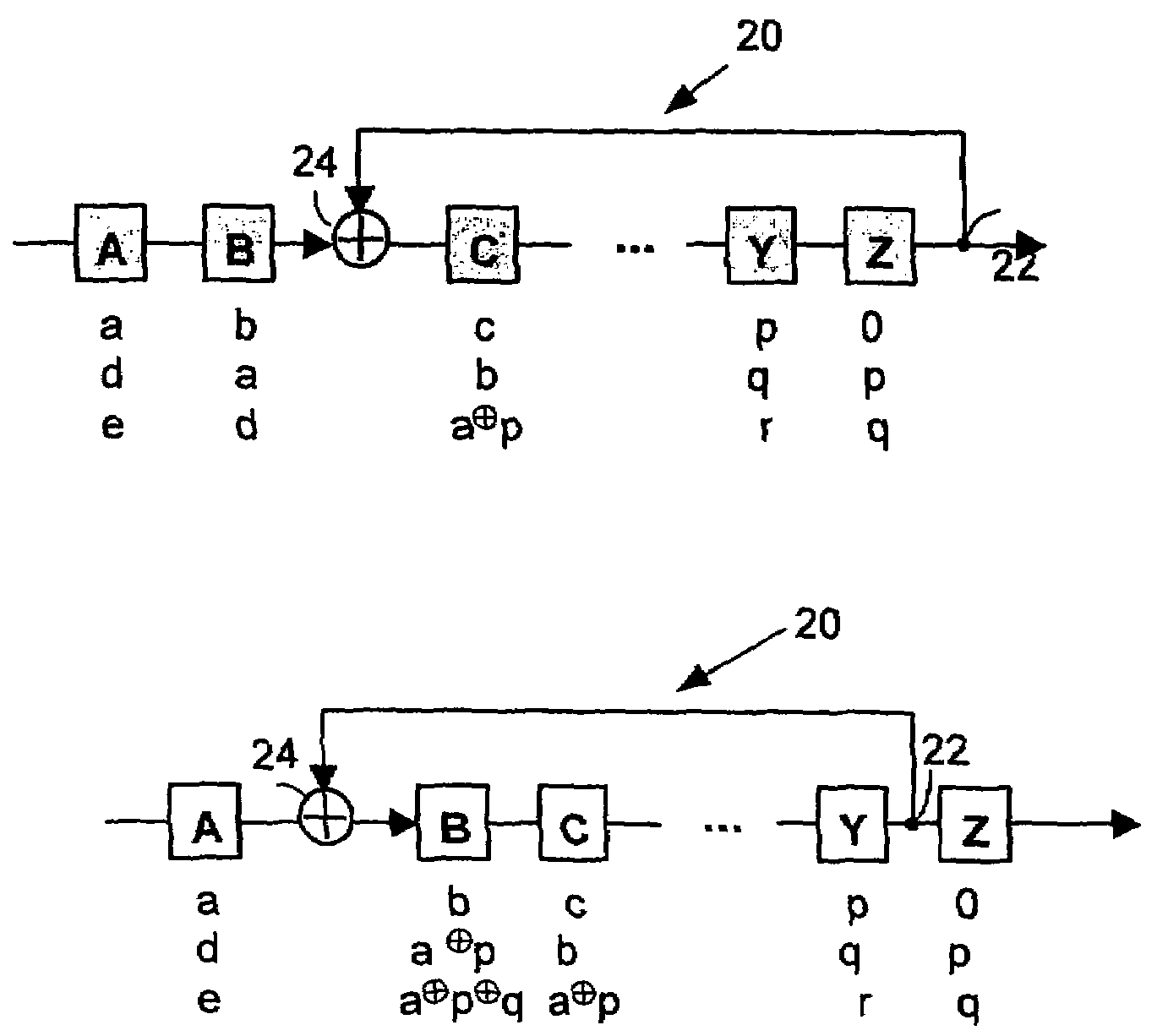
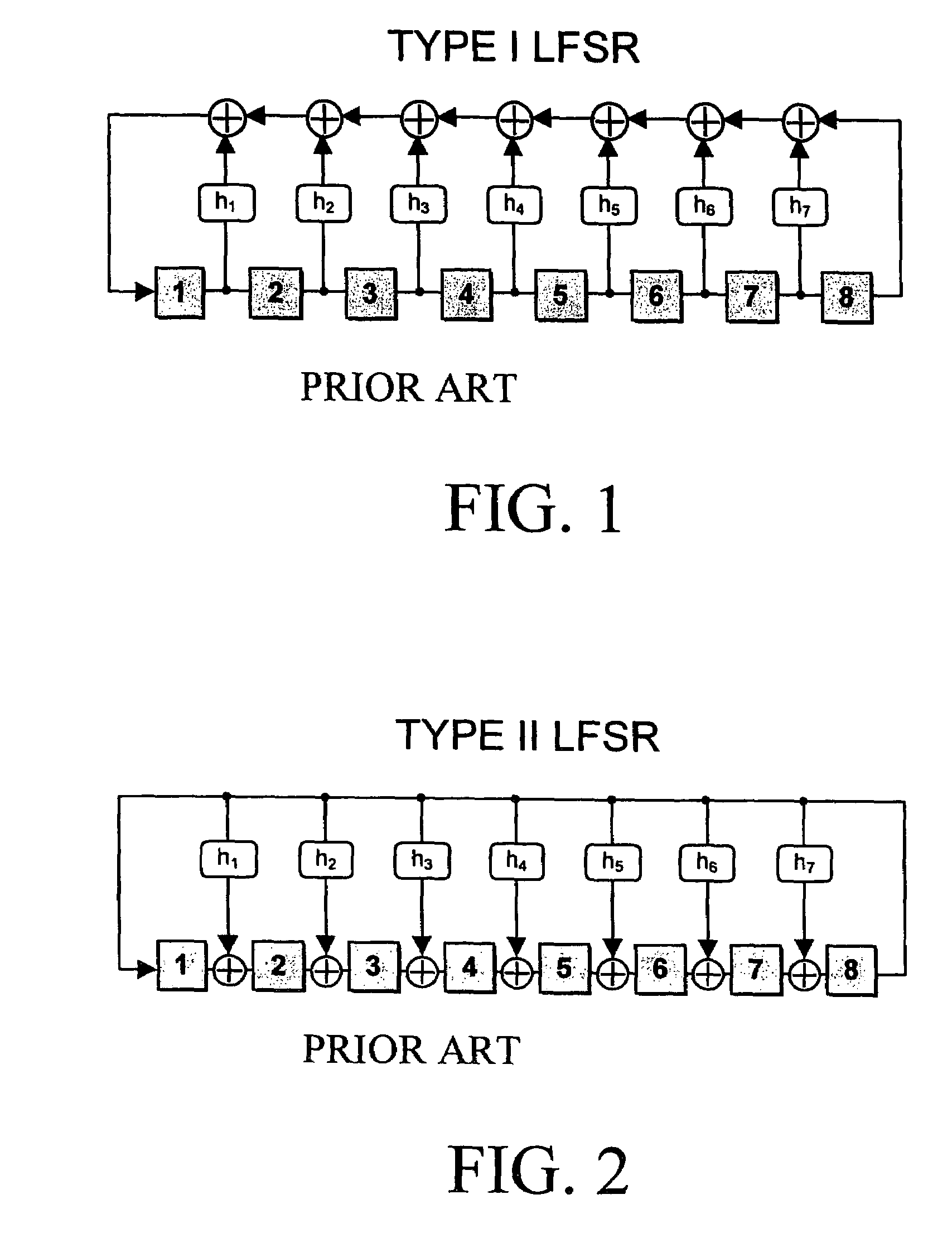
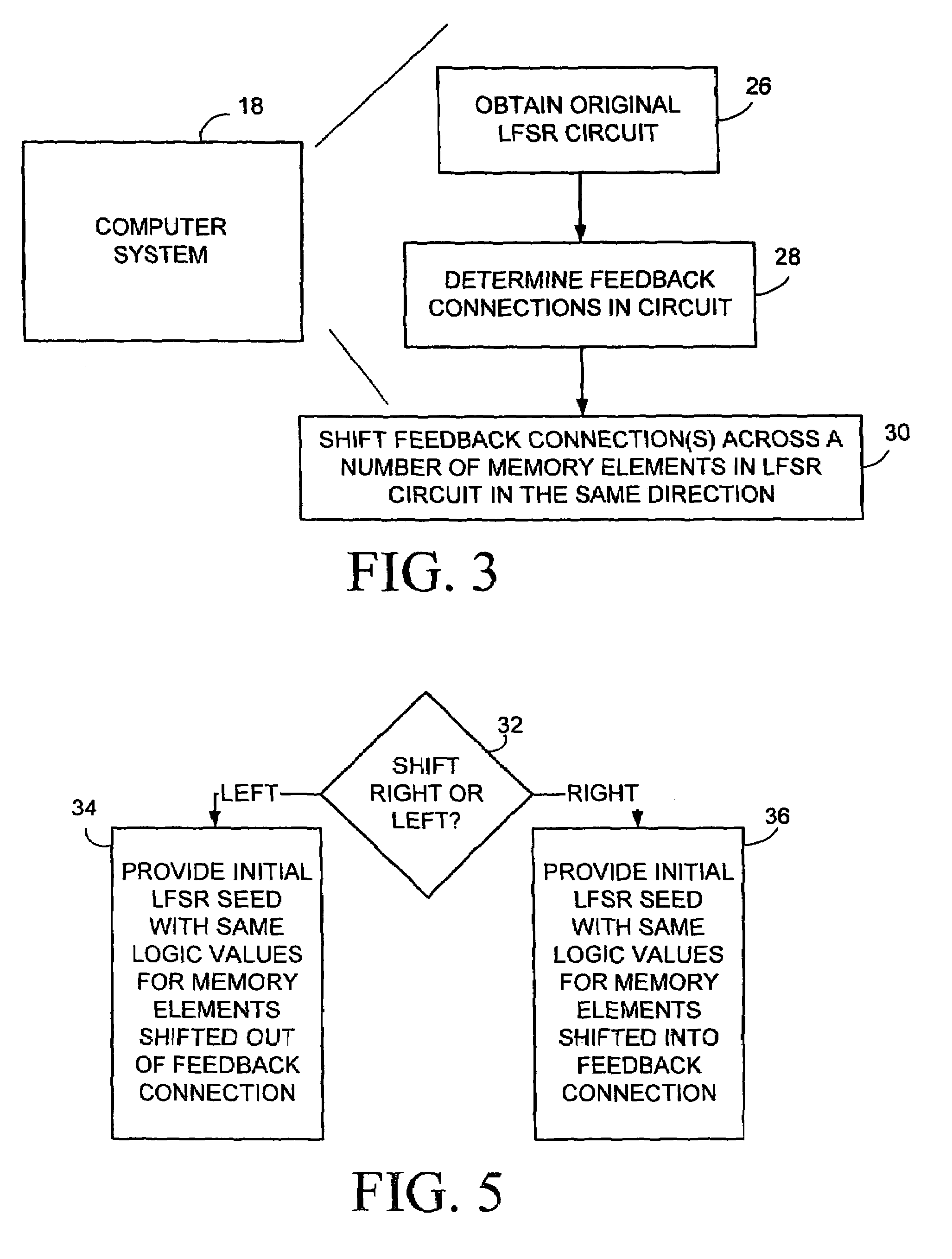
Method and apparatus for synthesizing high-performance linear finite state machines (LFSMs) such as linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs) or cellular automata (CA). Given a characteristic polynomial for the circuit, the method obtains an original LFSM circuit such as a type I or type II LFSR. Feedback connections within the original circuit are then determined. Subsequently, a number of transformations that shift the feedback connections can be applied in such a way that properties of the original circuit are preserved in a modified LFSM circuit. In particular, if the original circuit is represented by a primitive characteristic polynomial, the method preserves the maximum-length property of the original circuit in the modified circuit and enables the modified circuit to produce the same m-sequence as the original circuit. Through the various transformations, a modified LFSM circuit can be created that provides higher performance through shorter feedback connection lines, fewer levels of logic, and lower internal fan-out.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Method and apparatus for dynamic modulation
InactiveUS8085106B2Angle modulation detailsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency spectrumHarmonic
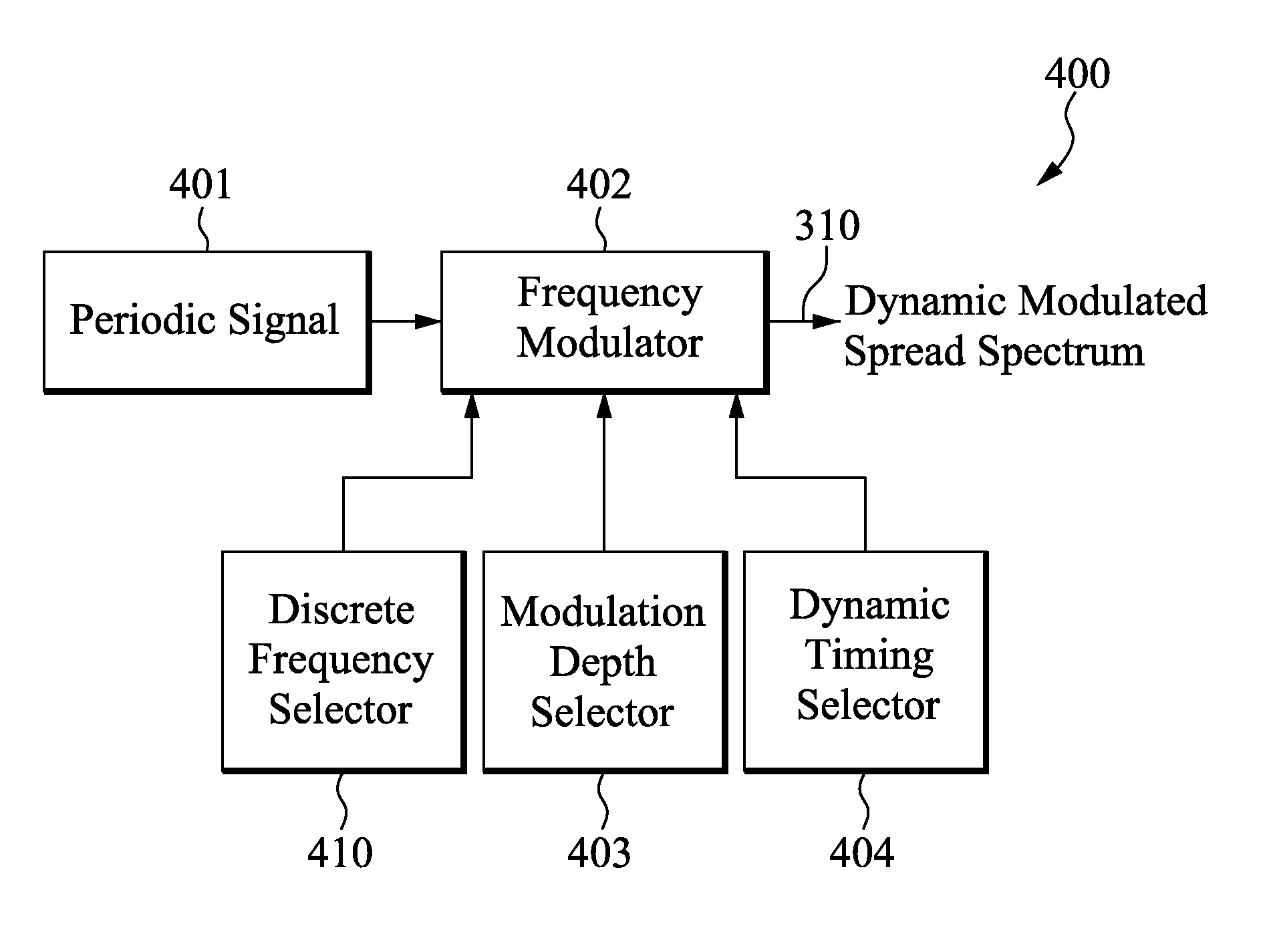
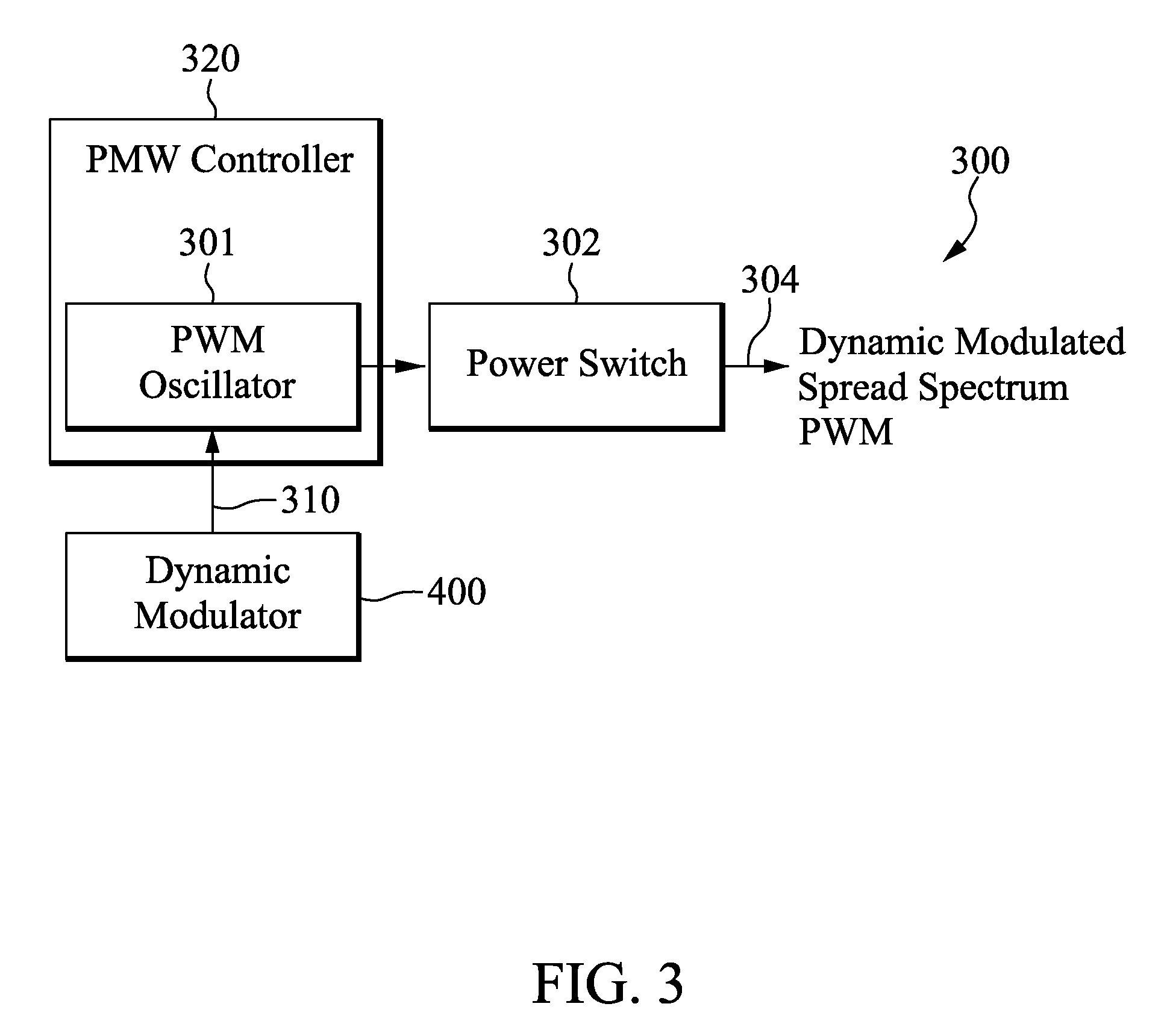
Circuits and methods of dynamic modulation are disclosed. A dynamic modulator is used to reduce measurable conducted and / or radiated electromagnetic interference (EMI). The dynamic modulator is configured to generate either a set of optimal frequency modulation depths or discrete frequencies or both, and dynamically selects them to use over a series of programmable time durations (dwell time). Together with the utilization of Peak, Average or Quasi-Peak (QP) method of measurement, the dynamic modulator can reduce the spectral amplitude of EMI components, in particular the lower harmonics, to effectively pass regulatory requirements. In alternative embodiments, the dynamic modulator is used in a closed loop system to continuously adjust the frequency and the duty cycle of a PWM signal to reduce conducted and / or radiated EMI.
Owner:HUDA MUZAHID BIN +1
Randomized value generation
InactiveUS20120030268A1Effective monitoringMaximize lengthRandom number generatorsSecuring communication by chaotic signalsRandomizationVoltage
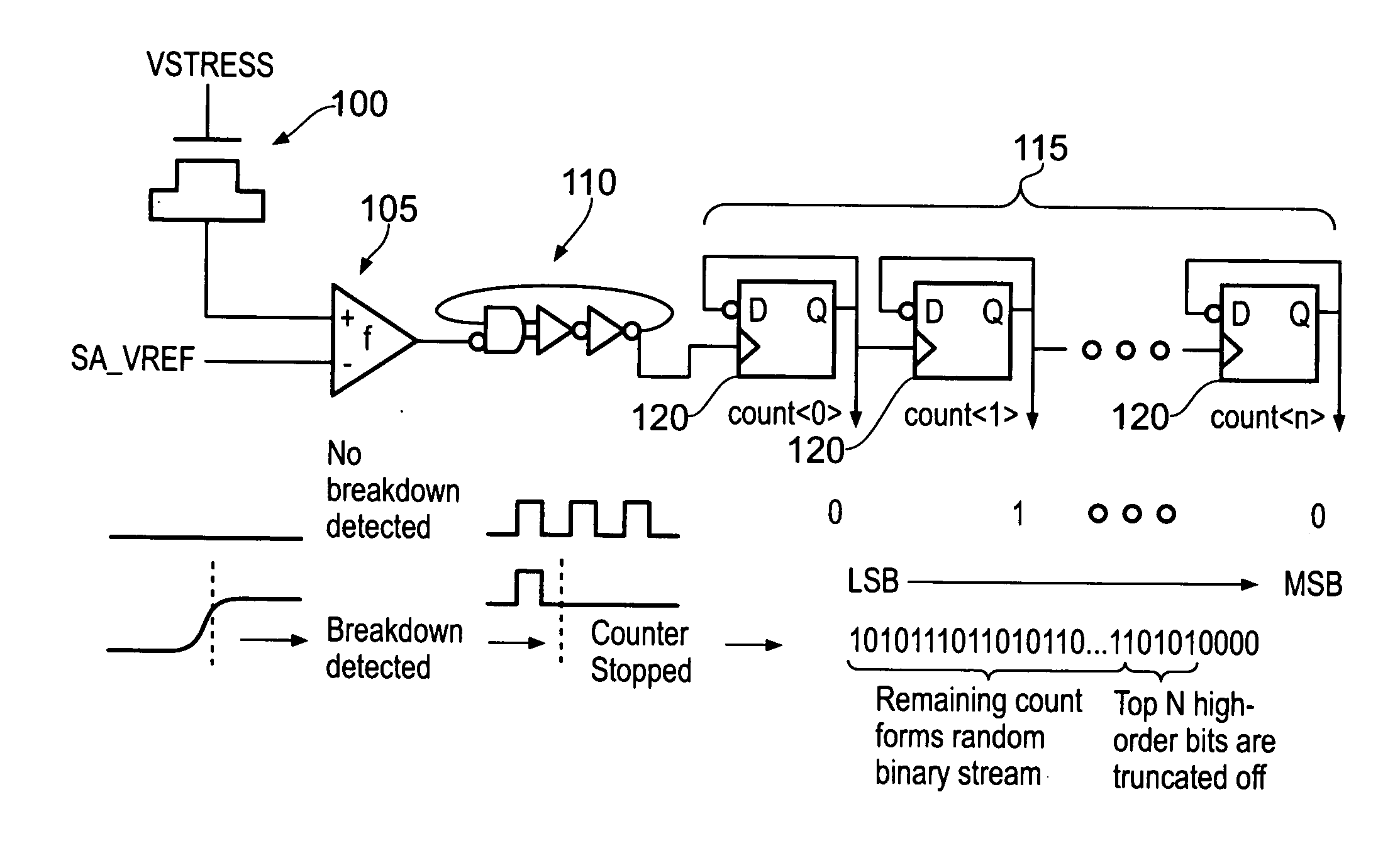
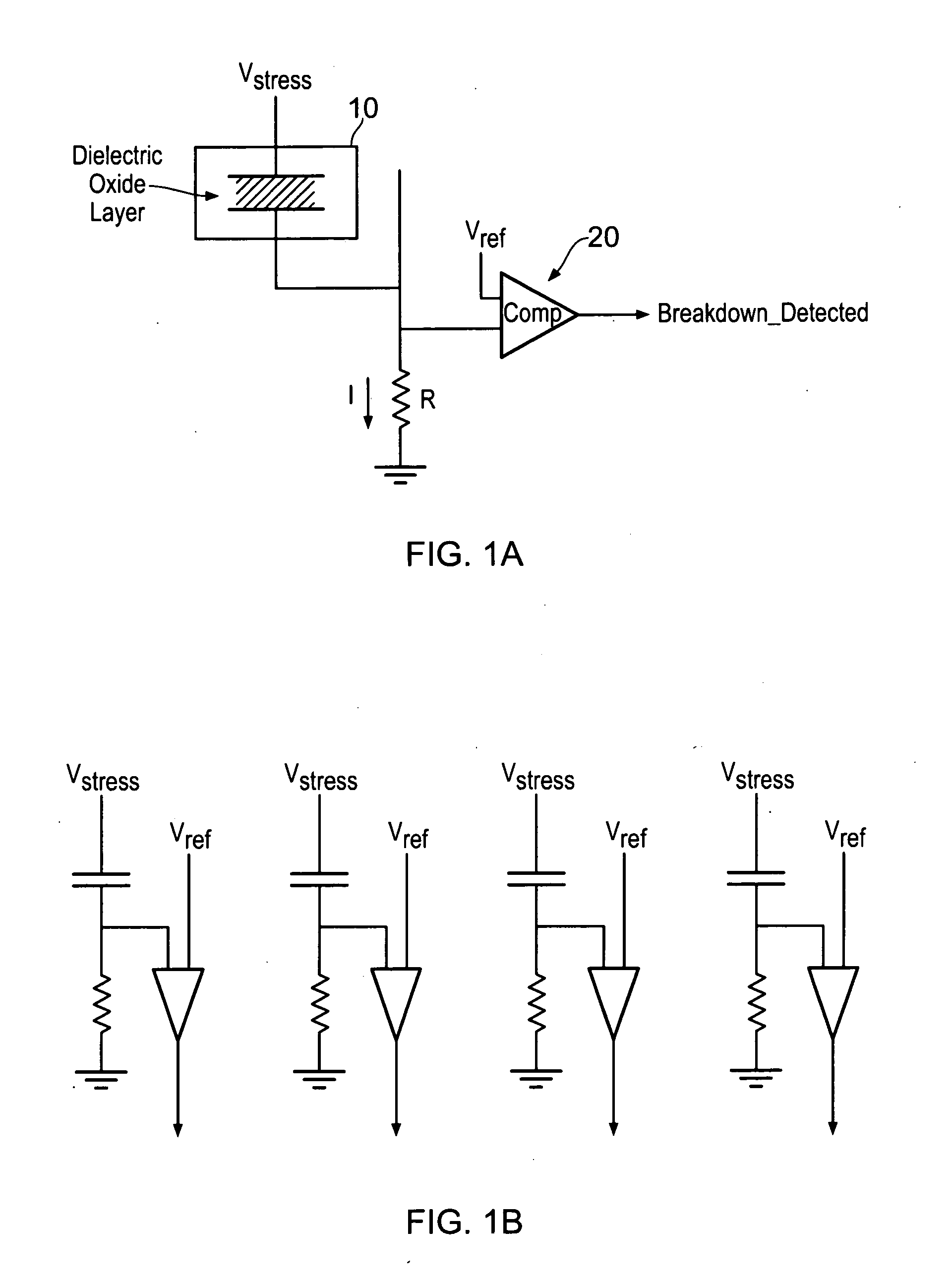
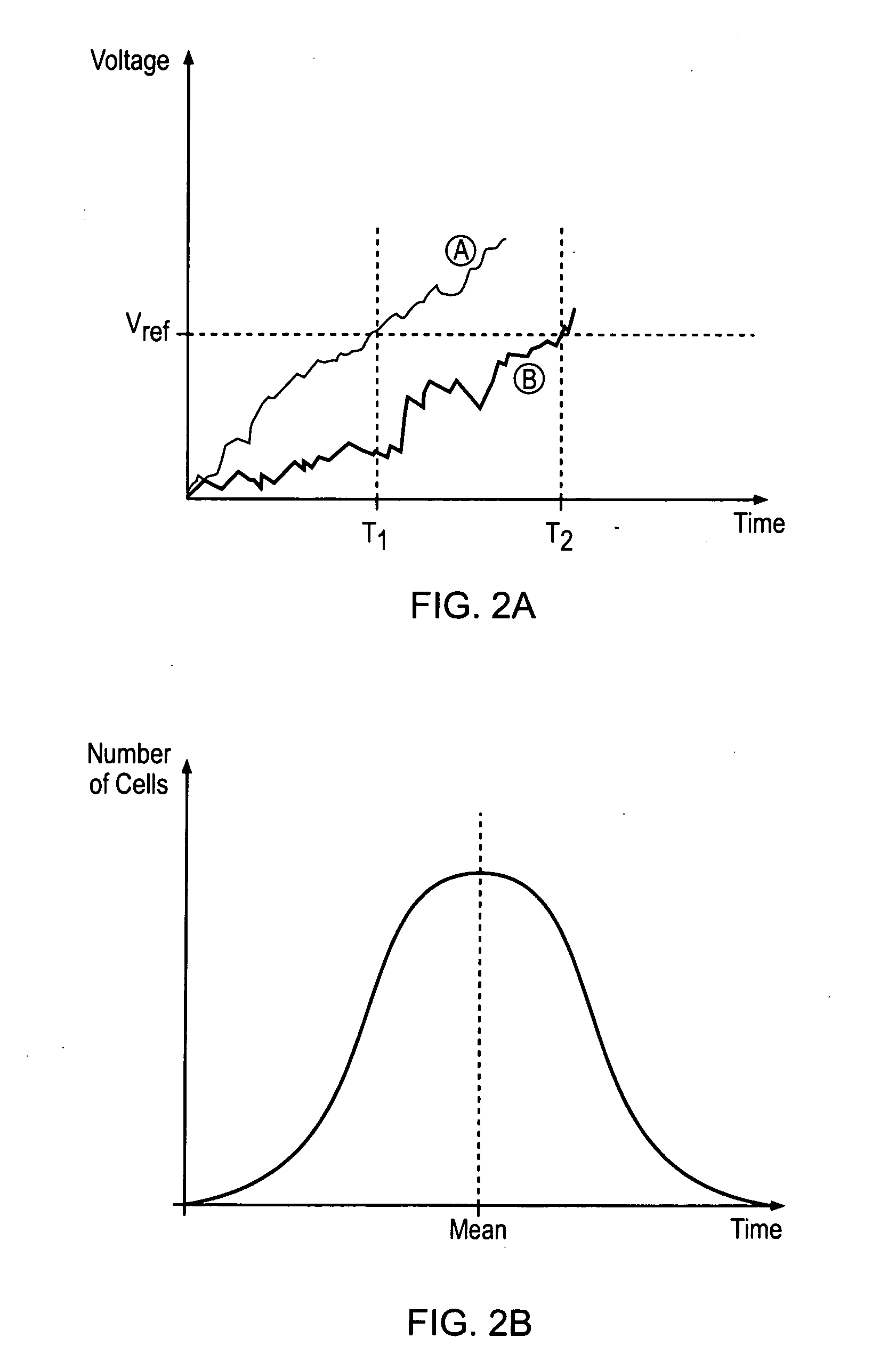
A data processing apparatus is provided for producing a randomized value. A cell in the data processing apparatus comprises a dielectric oxide layer and stress voltage circuitry is configured to apply a stress voltage across the dielectric oxide layer of the cell to cause an oxide breakdown process to occur. Oxide breakdown detection circuitry is configured to determine a current extent of the oxide breakdown process by measuring a response of the dielectric oxide layer to the stress voltage and randomized value determination circuitry is configured to determine a randomized value in dependence on the current extent of the oxide breakdown process.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
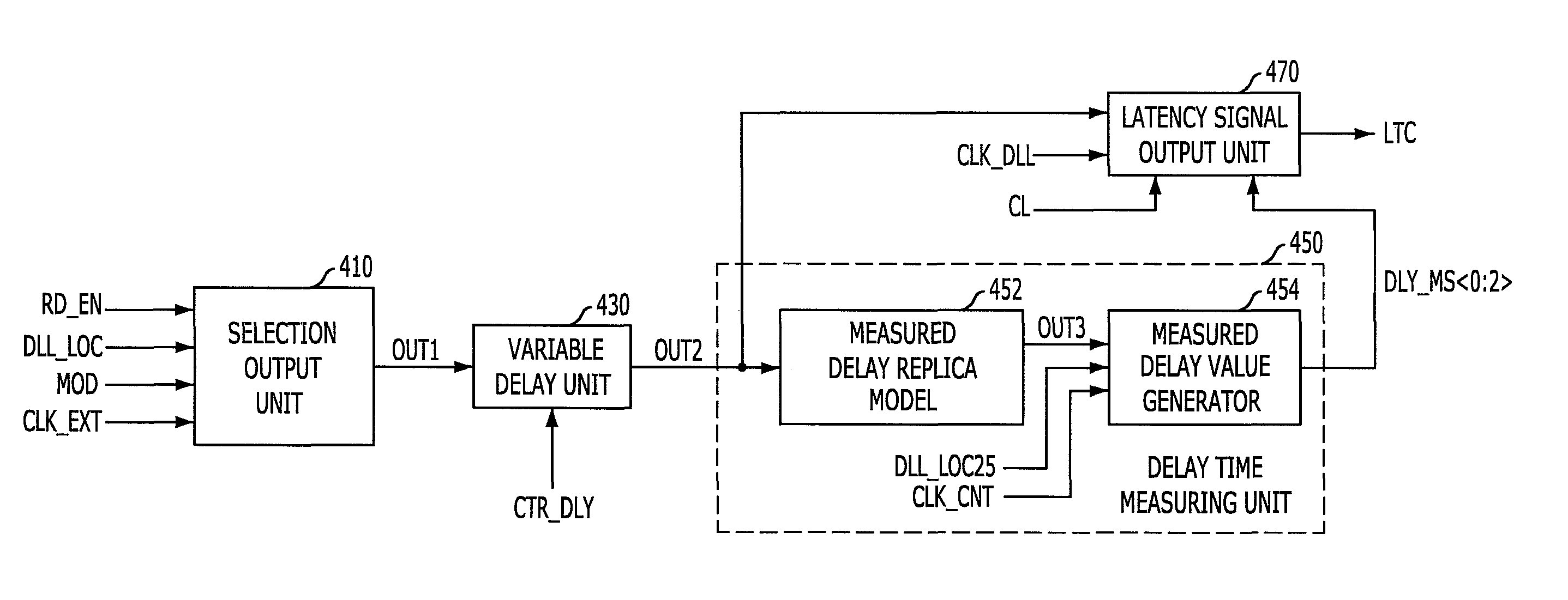
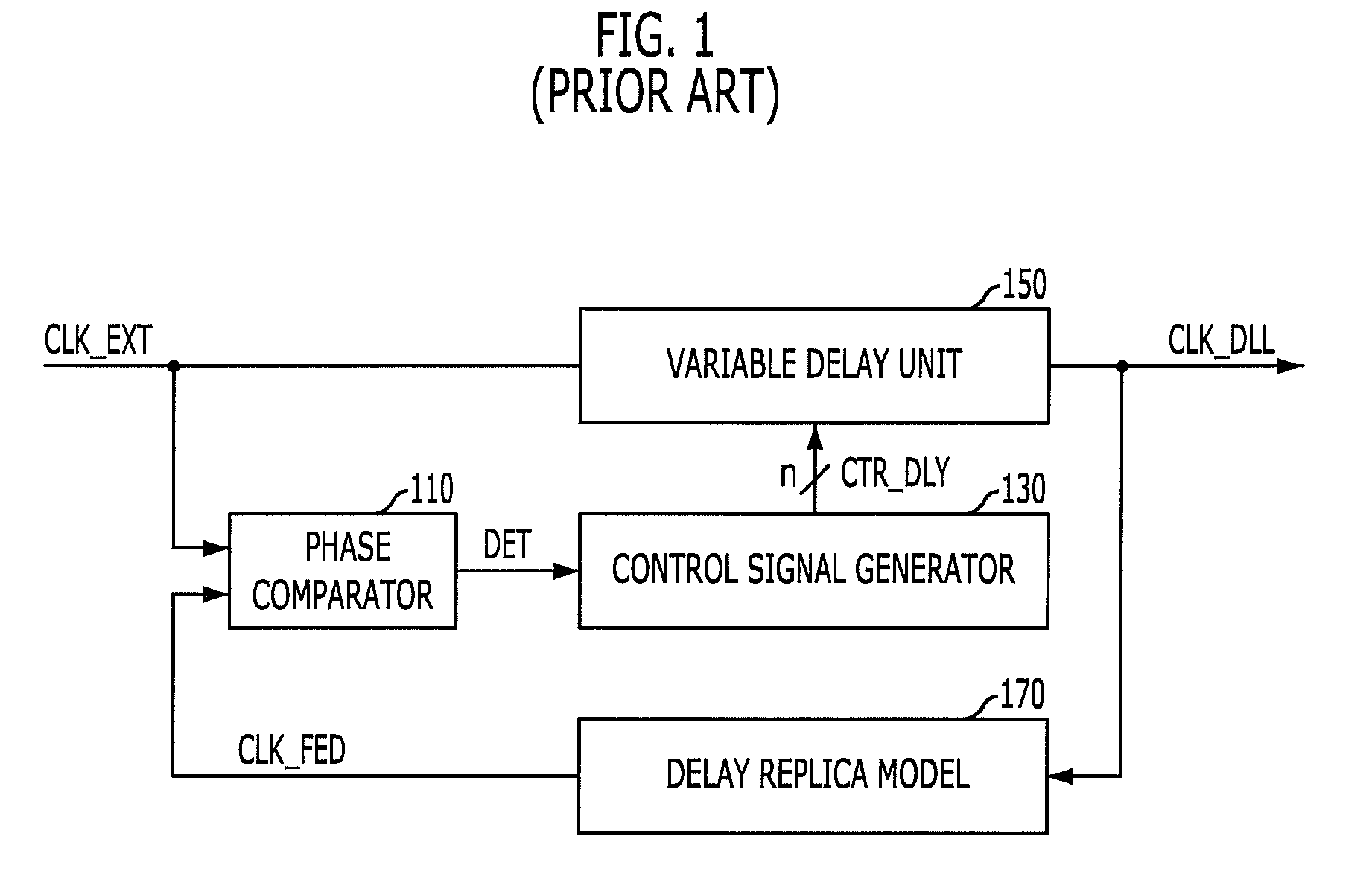
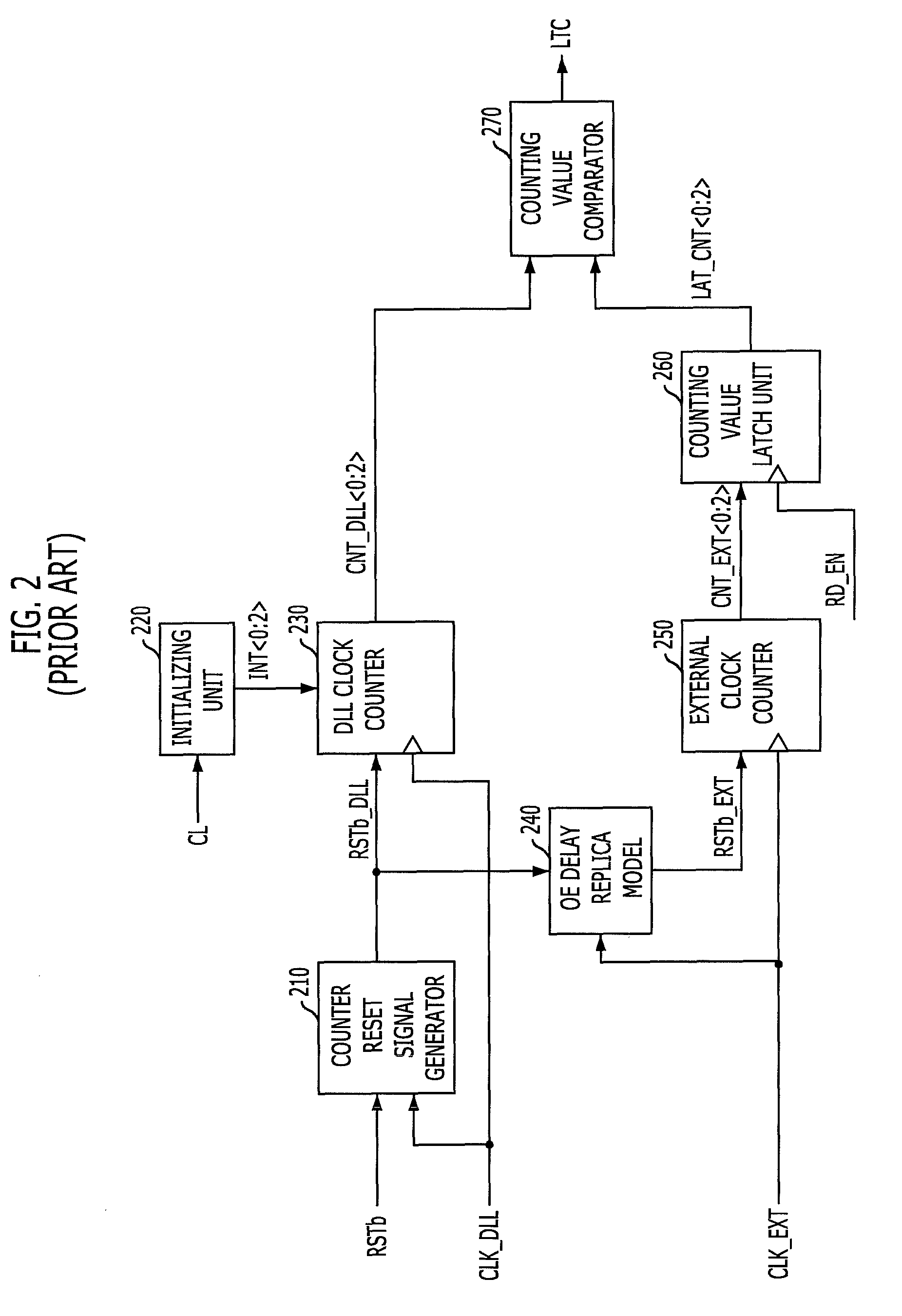
Latency signal generating circuit and semconductor device having the same
InactiveUS8030981B2Guaranteed high speed operationReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlDigital storageDelay-locked loopInput control
A semiconductor device includes a latency signal generating circuit for generating a latency signal corresponding CAS latency by measuring a delay amount reflected at a delay locked loop and reflecting the measured delay amount at a read command signal, and a delay locked loop for controlling an internal clock signal applied to the latency signal generating circuit corresponding to the read command and the latency signal. The semiconductor device includes an internal clock signal generating block configured to generate an internal clock signal, a latency generating block configured to generate a latency signal by synchronizing a read command signal with the internal clock signal at a time corresponding to a CAS latency value and a measured delay value, and an input controlling block configured to activate the reference clock signal using an external clock signal in response to the read command signal and the latency signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
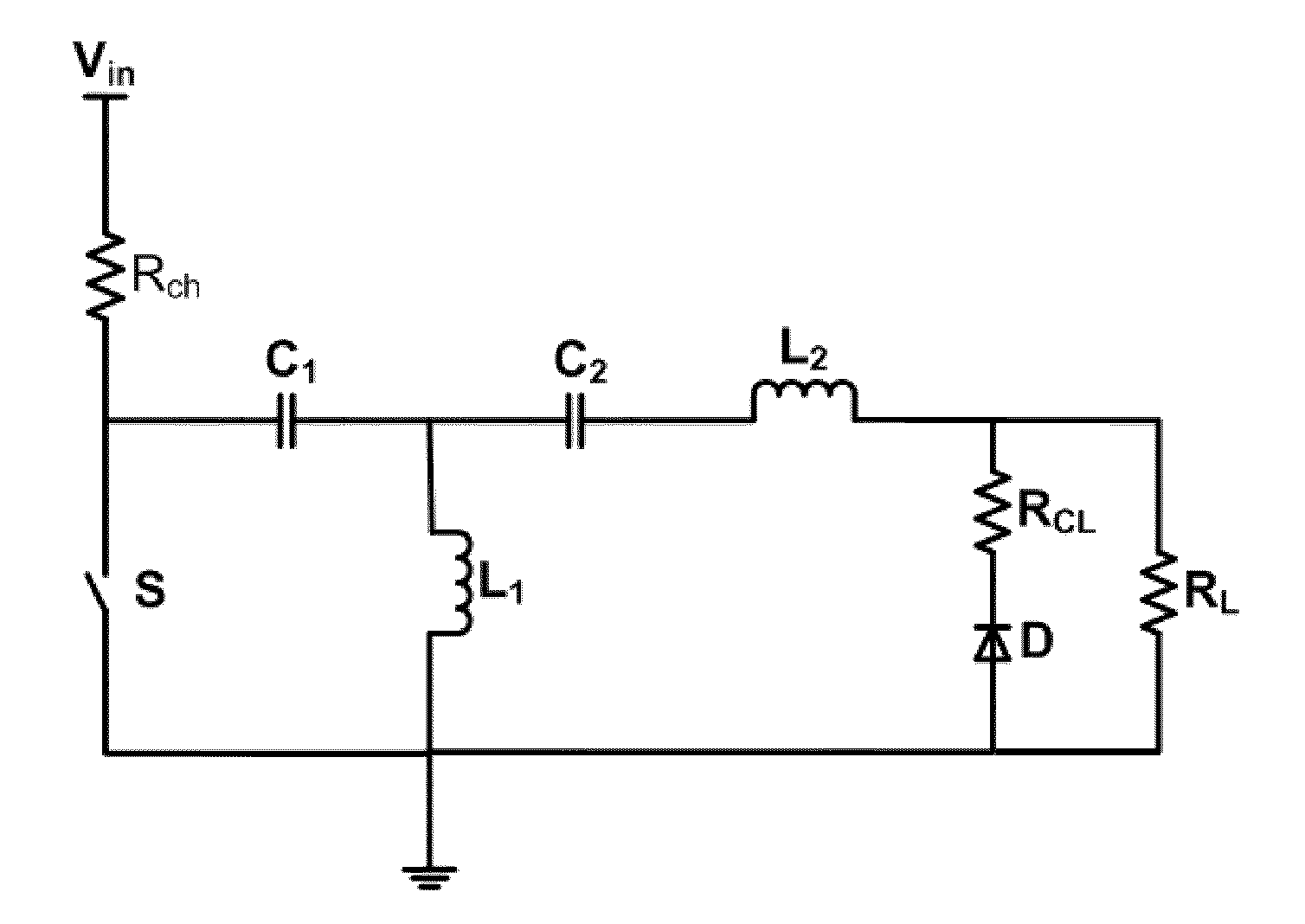
Nanosecond pulse generator
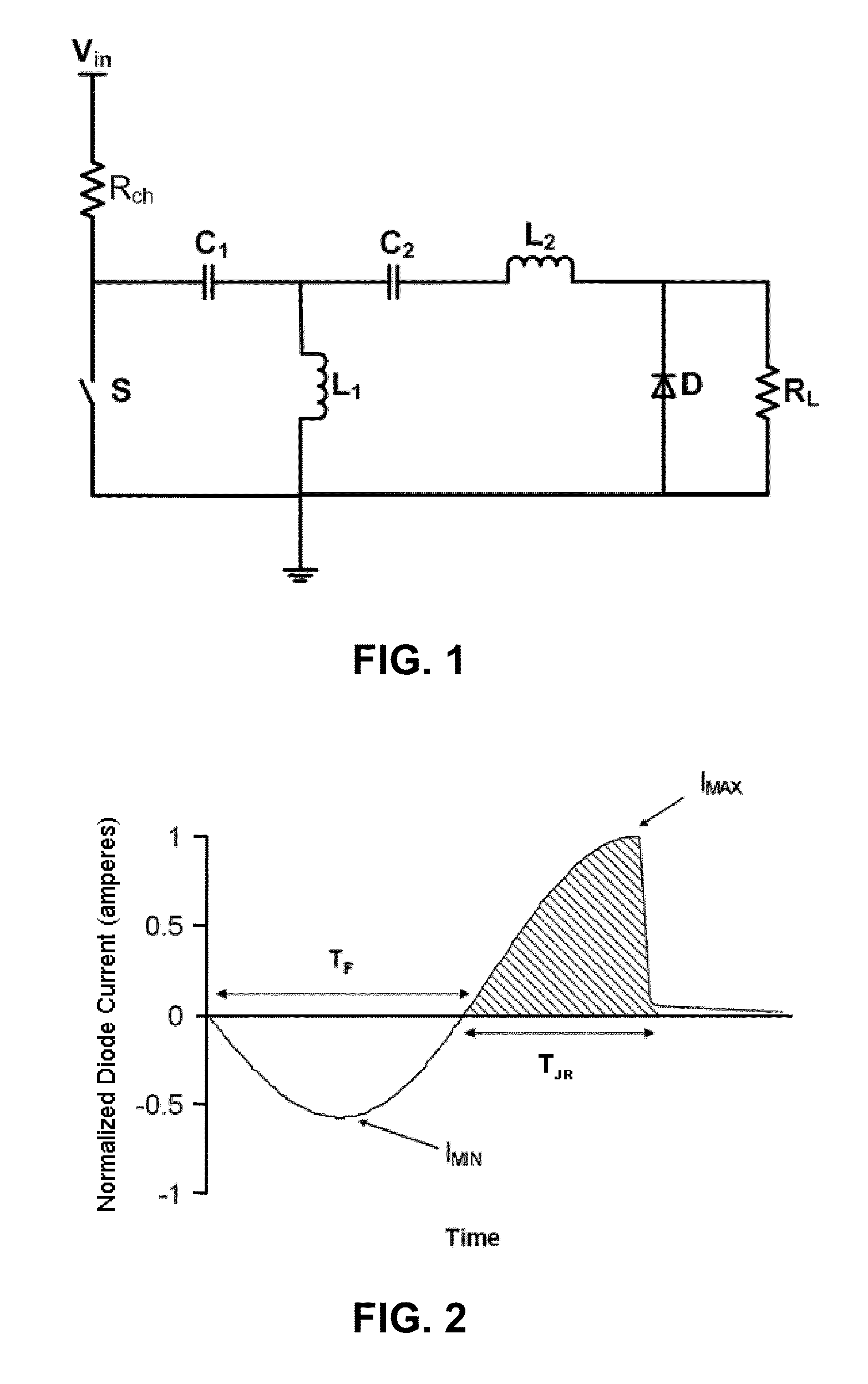
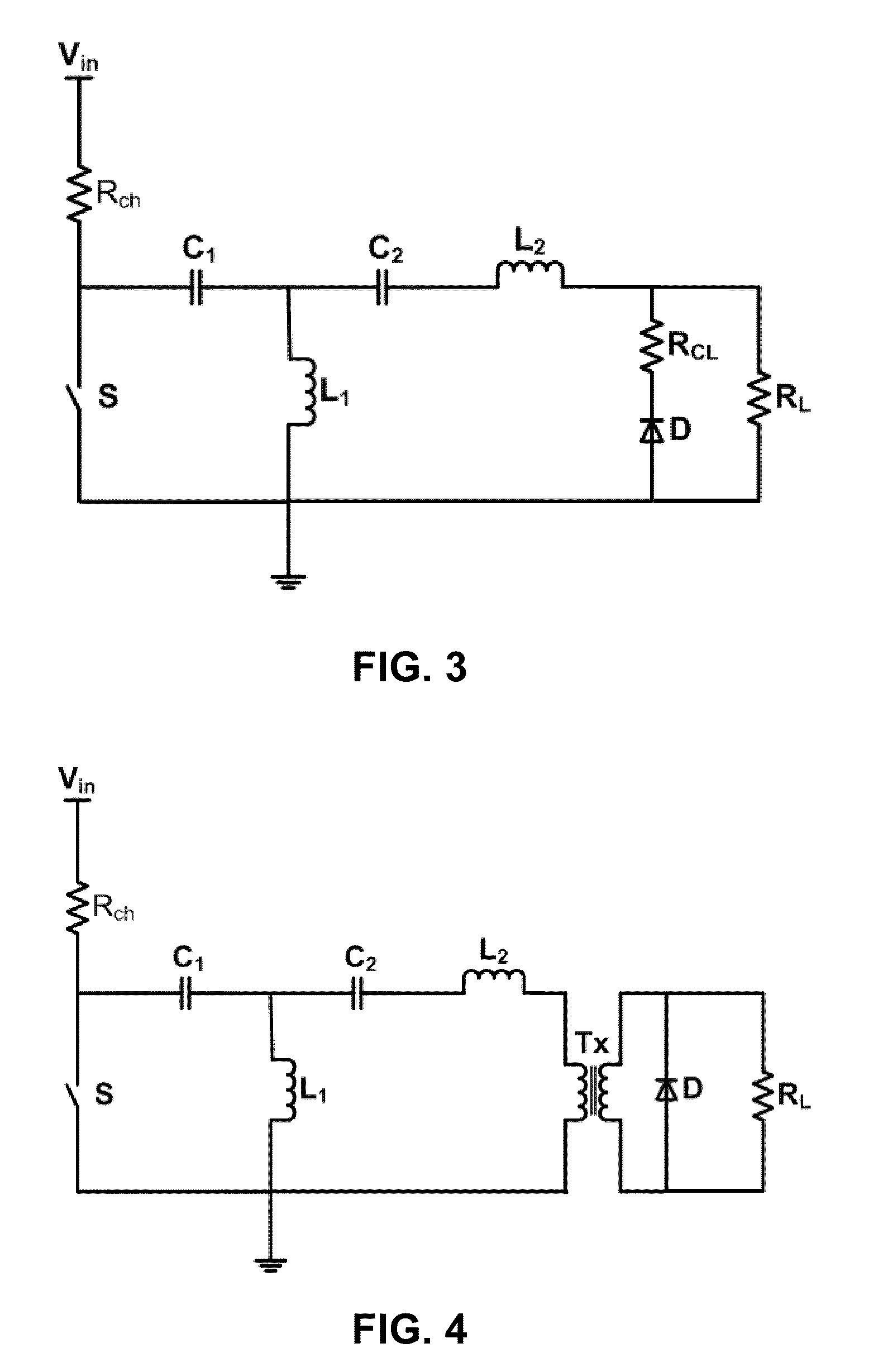
ActiveUS20100038971A1DiodePulse generation by energy-accumulating elementFull width at half maximumPhysics
This invention relates to a pulse generator circuit for delivering a short high current pulse to a load. This pulse generator comprises a junction recovery diode, a switch, a first resonant circuit and a second resonant circuit. The diode may be configured to store charges in its depletion layer when there is a forward flow of a current and to rapidly switch open after the depletion layer is discharged by a reverse flow of a current. After the diode rapidly switch opens, the pulse generator may provide a reverse current to the load. This pulse generator may be configured to generate at least one pulse that is having a length of no more than 100 nanoseconds at the full-width-at-half-maximum and an amplitude of at least 1 kilovolt. Electrodes may be connected to the pulse generator to deliver one pulse or plurality of pulses to biological cells such as tumor cells.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
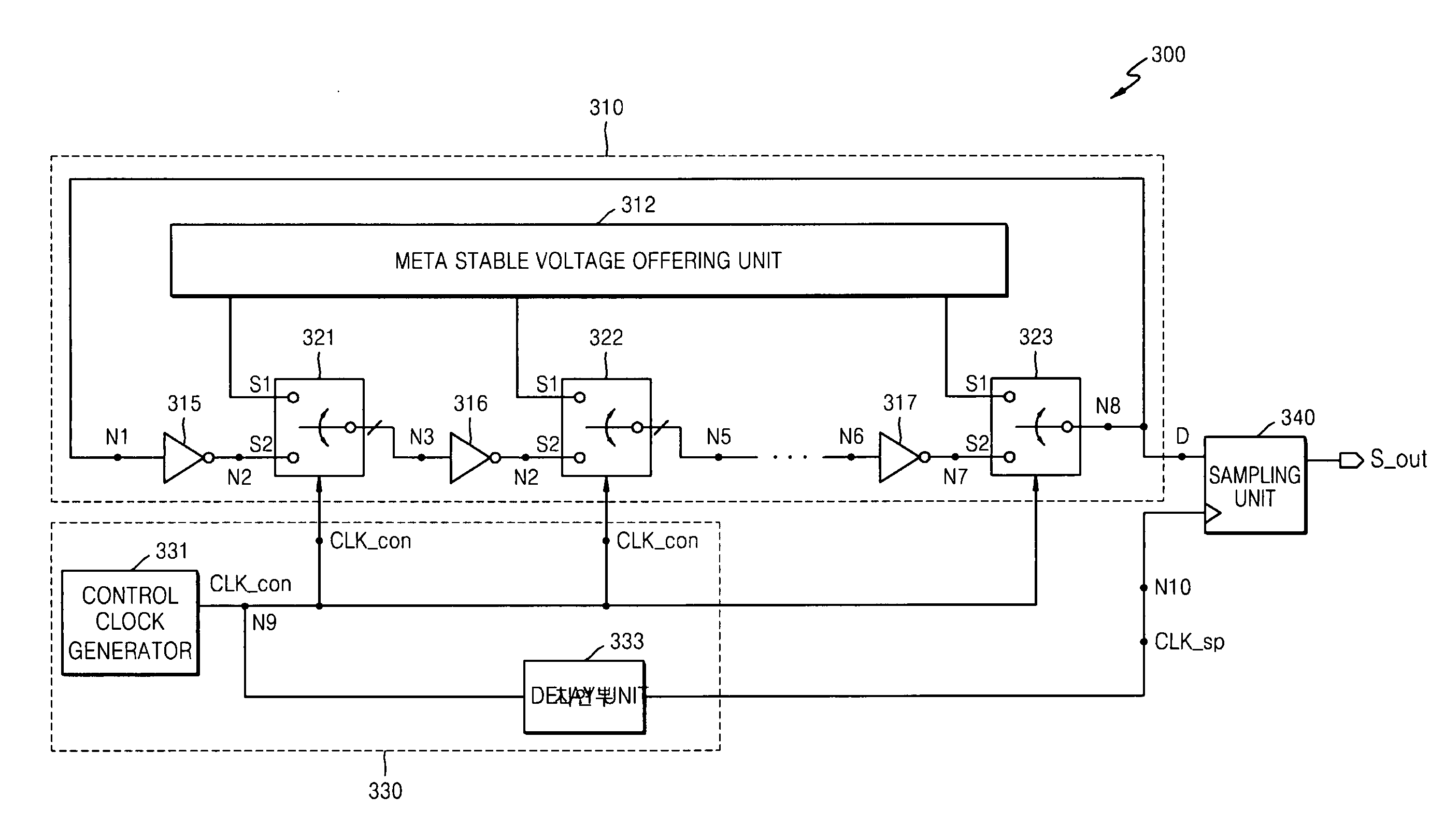
Random number generator
ActiveUS20090106339A1Improve throughputIncrease in areaRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsControl signalEngineering
Provided is a random number generator including: a clock generator outputting first and second control signals; a ring oscillator (RO) block receiving a meta stable voltage and performing an oscillation operation using the meta stable voltage in response to the first control signal; and a sampling unit sampling an output signal according to the oscillation operation in response to the second control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Random number generation device and vehicle control device
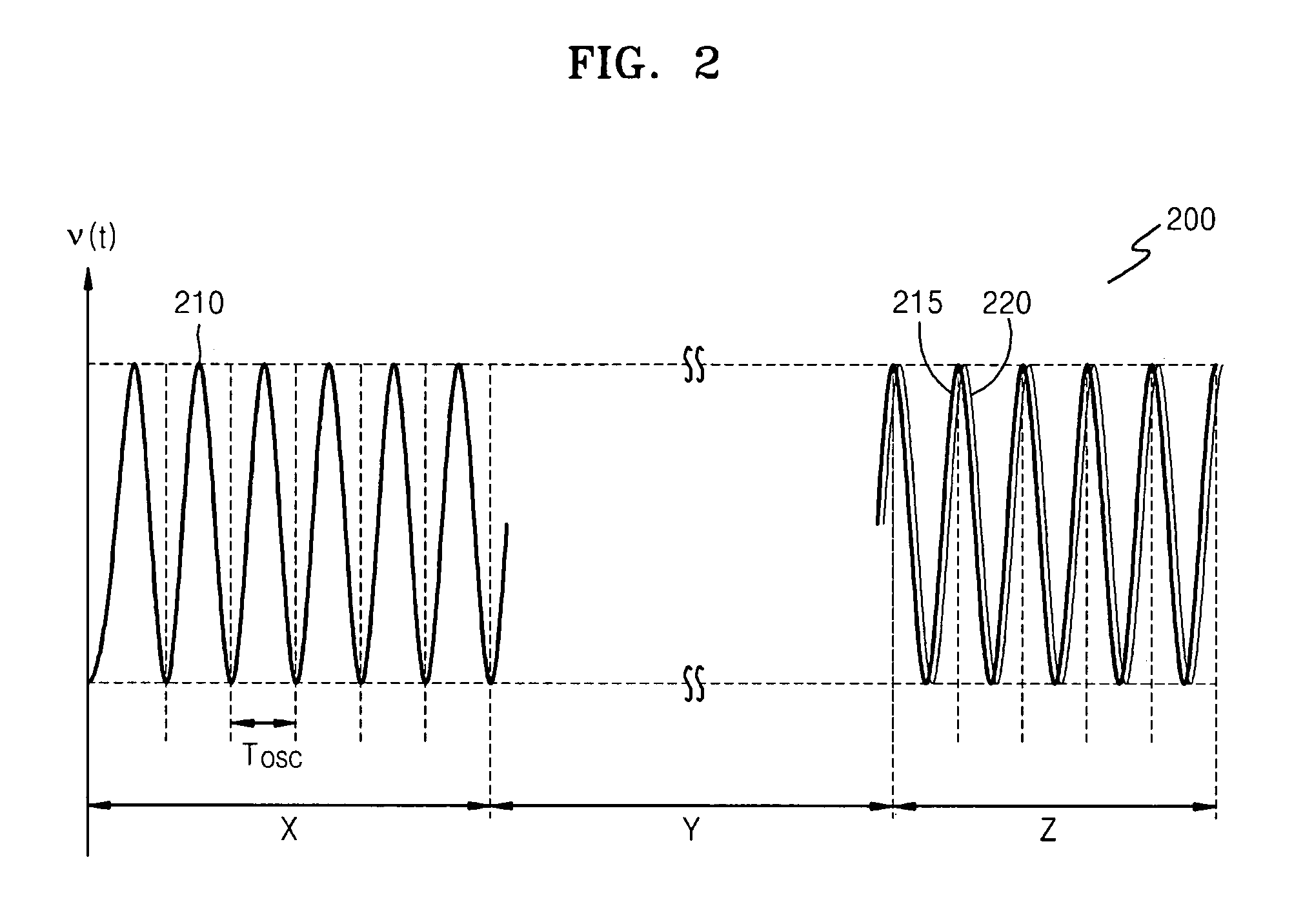
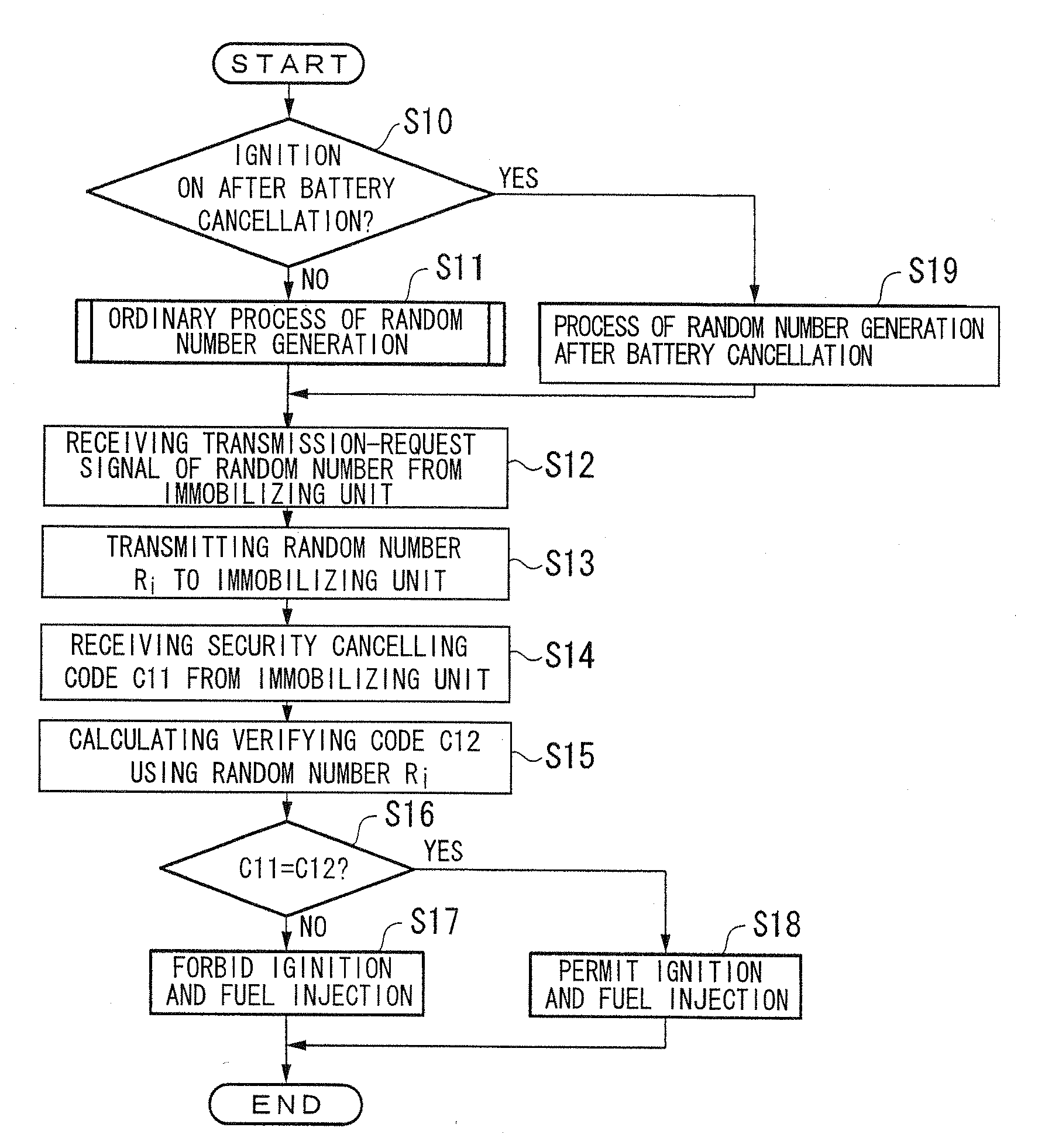
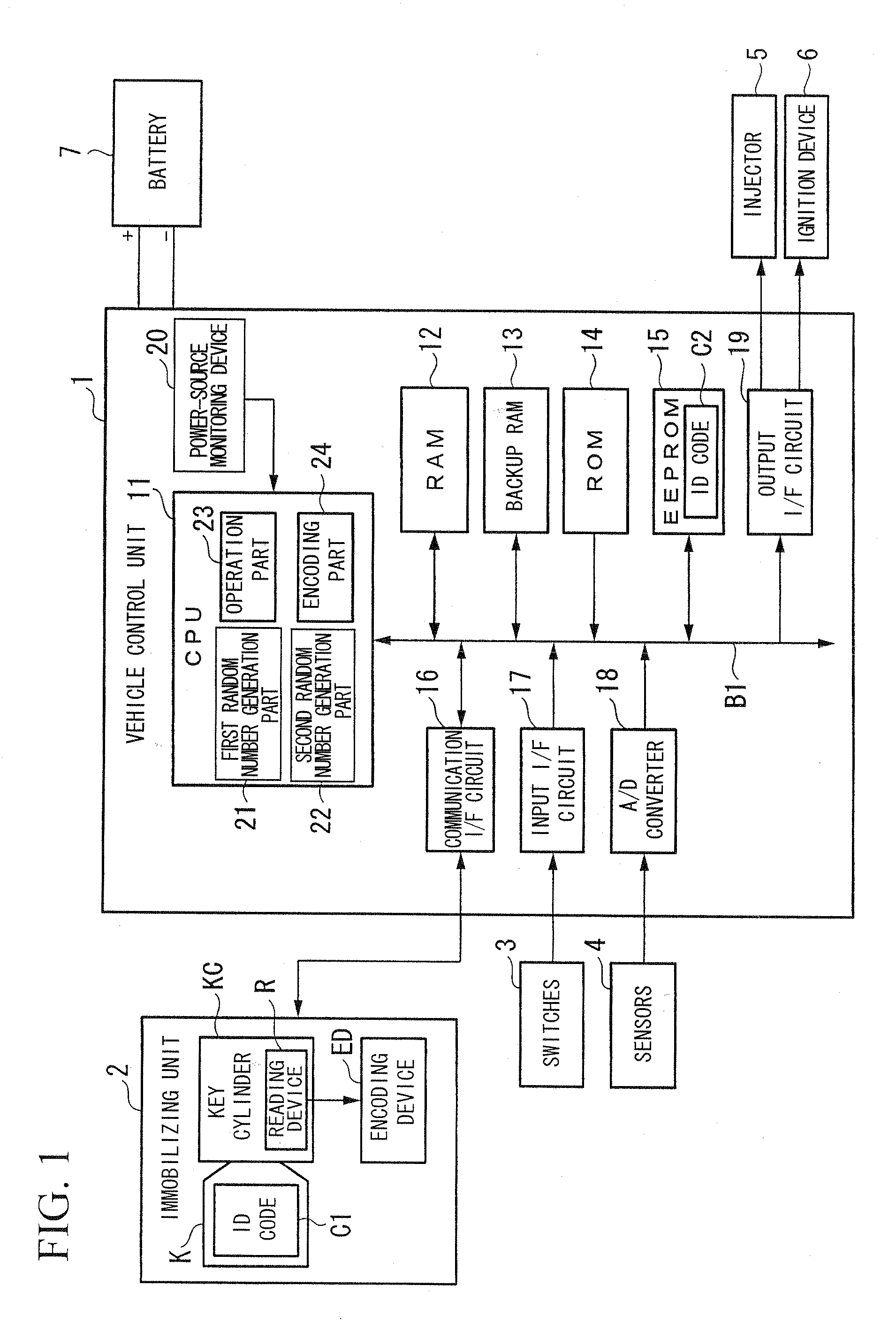
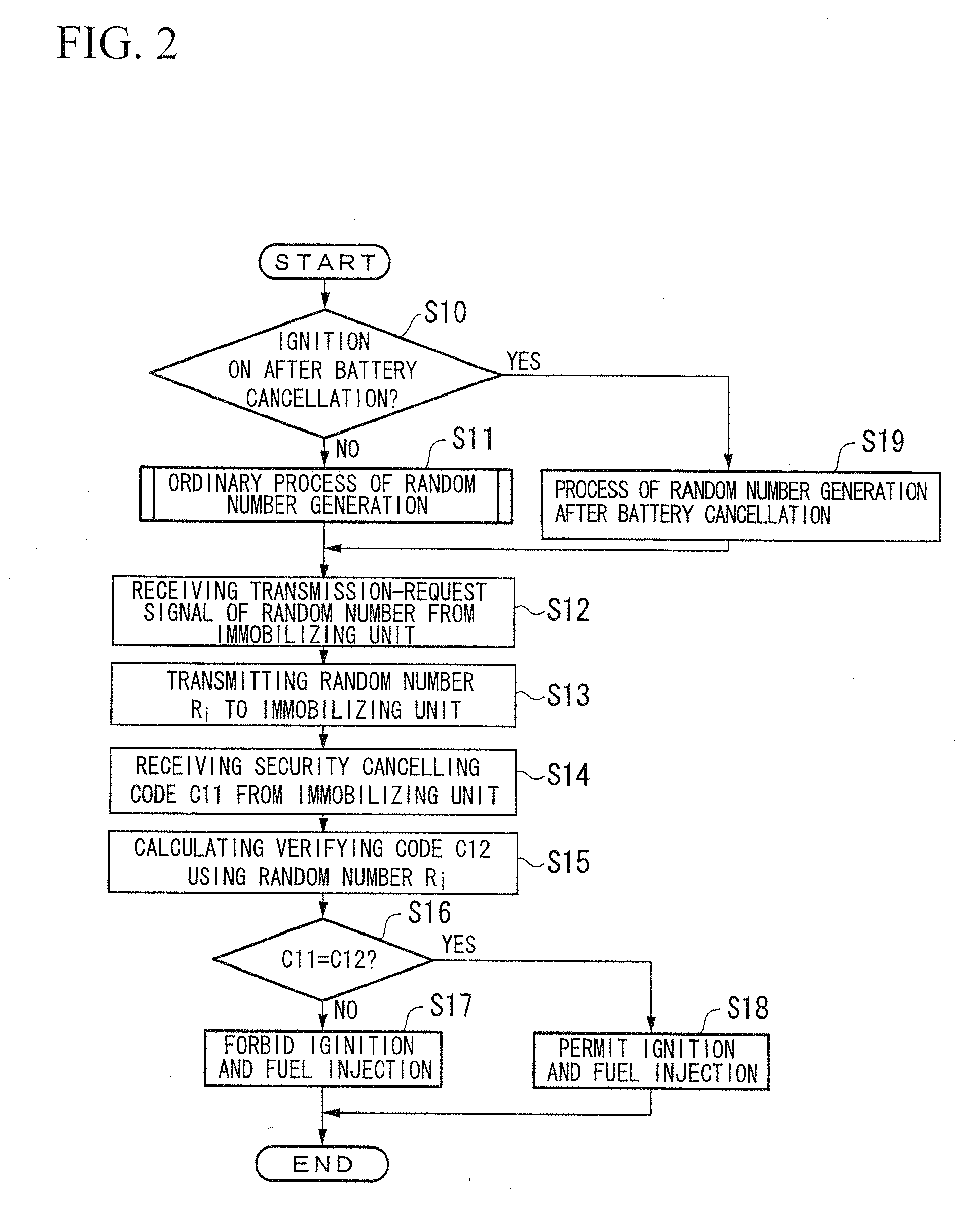
ActiveUS20080294707A1Reduce frequencyImprove securityAnalogue computers for vehiclesRandom number generatorsComputer scienceElectric power
A random number generation device including a first random number generation part which generates a new random number based on a random number which was previously generated and which outputs the random number generated by the first random number generation part, the random number generation device includes: a second random number generation part which generates a random number different from the random number generated by the first random number generation part; and an operation part which outputs a random number obtained by a prescribed operation using a random number generated by the second random number generation part on a random number generated by the first random number generation part when generating a first random number after start of supplying electric power.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD +1
Integrated circuit with a true random number generator
InactiveUS20090132624A1Effective quantityGenerate efficientlyRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationSmart cardNumber generator
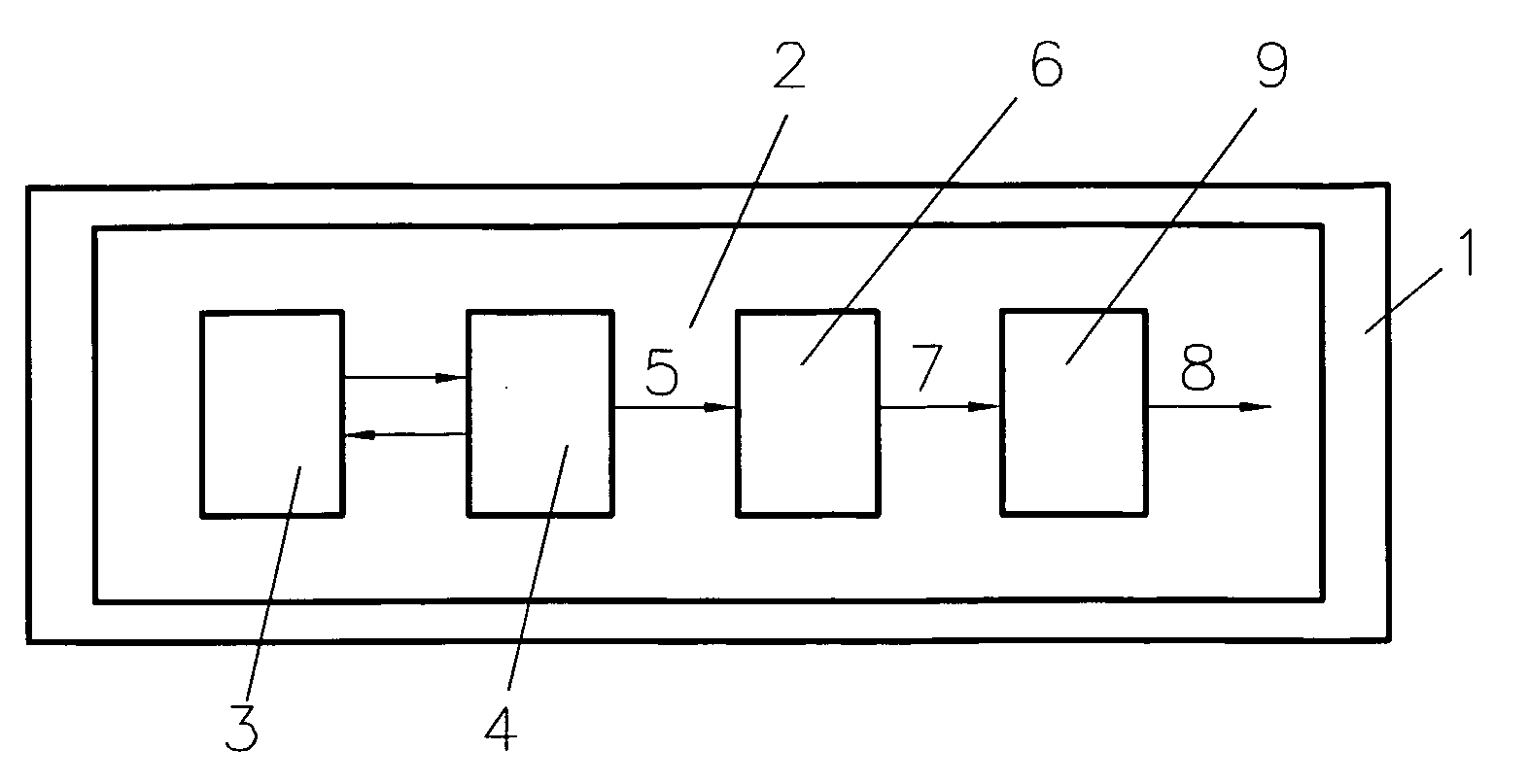
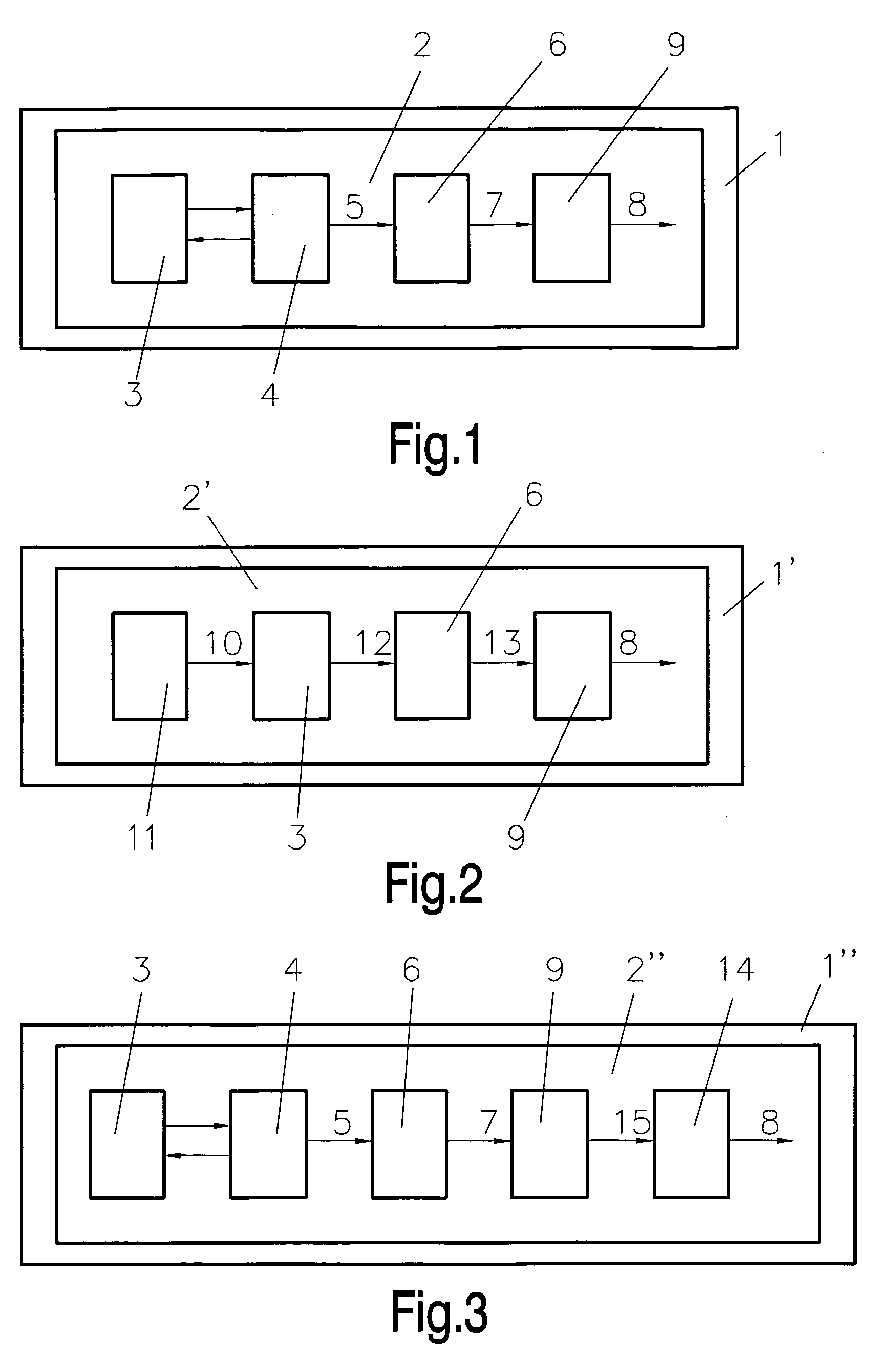
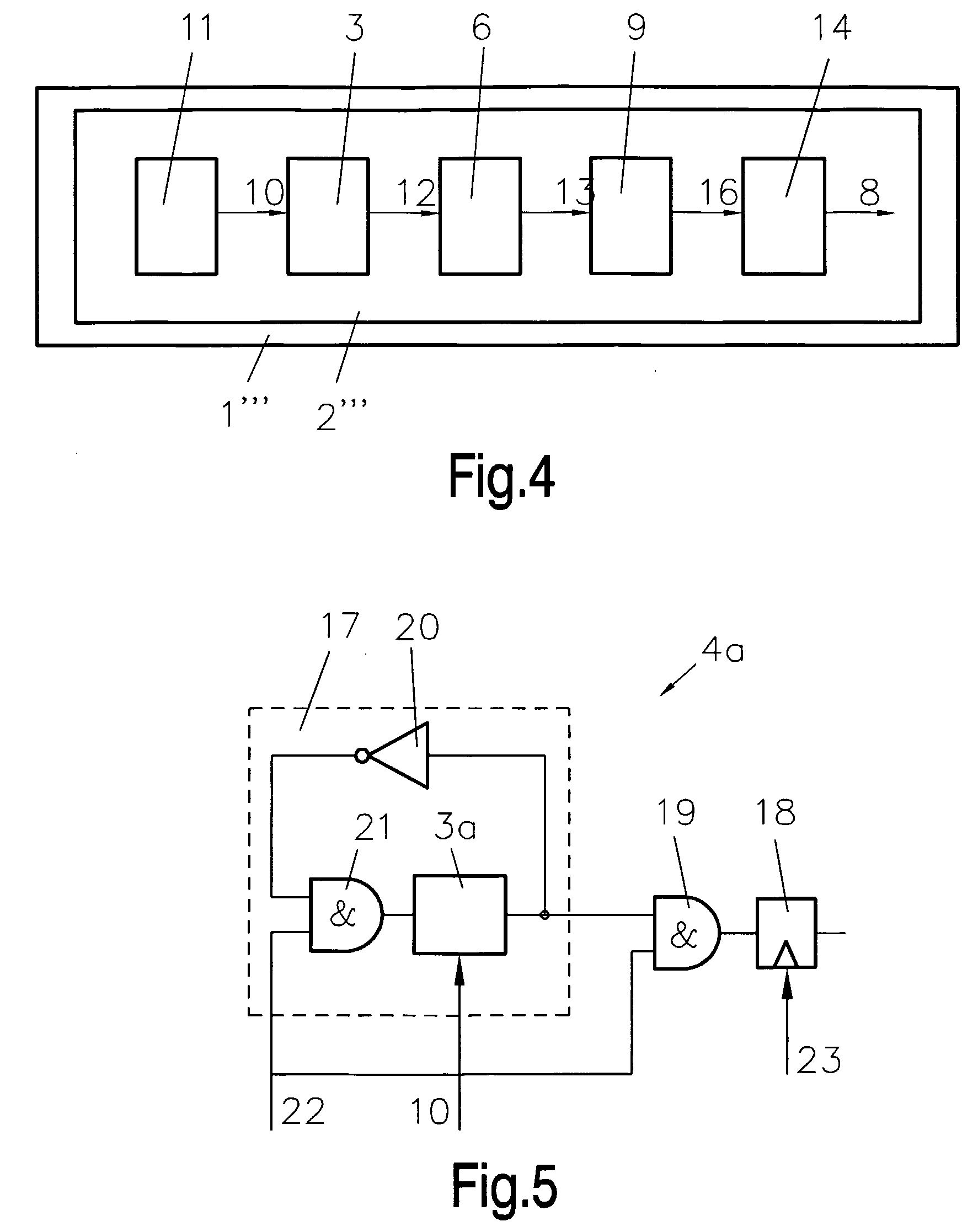
An integrated circuit (1 . . . 1′″, 1a . . . I c) with a true random number generator (2 . . . 2′″), which true random number generator (2 . . . 2″) comprises at least one instable physically uncloneable function (3 . . . 3′″, 3a, 3a′) for generating true random numbers (8). Hence, each device of a group of devices can be provided with a unique true random generator, so that each device of the group is provided with different true random numbers even when said devices are applied to identical environmental conditions. Such a random number generator (2 . . . 2′″) may be part of a smart card as well as of a module for near field communication, for example.
Owner:NXP BV
Circuit and method for reducing electromagnetic interference
ActiveUS20070290894A1Electric signal transmission systemsAc-dc conversionLinear regulatorElectromagnetic interference
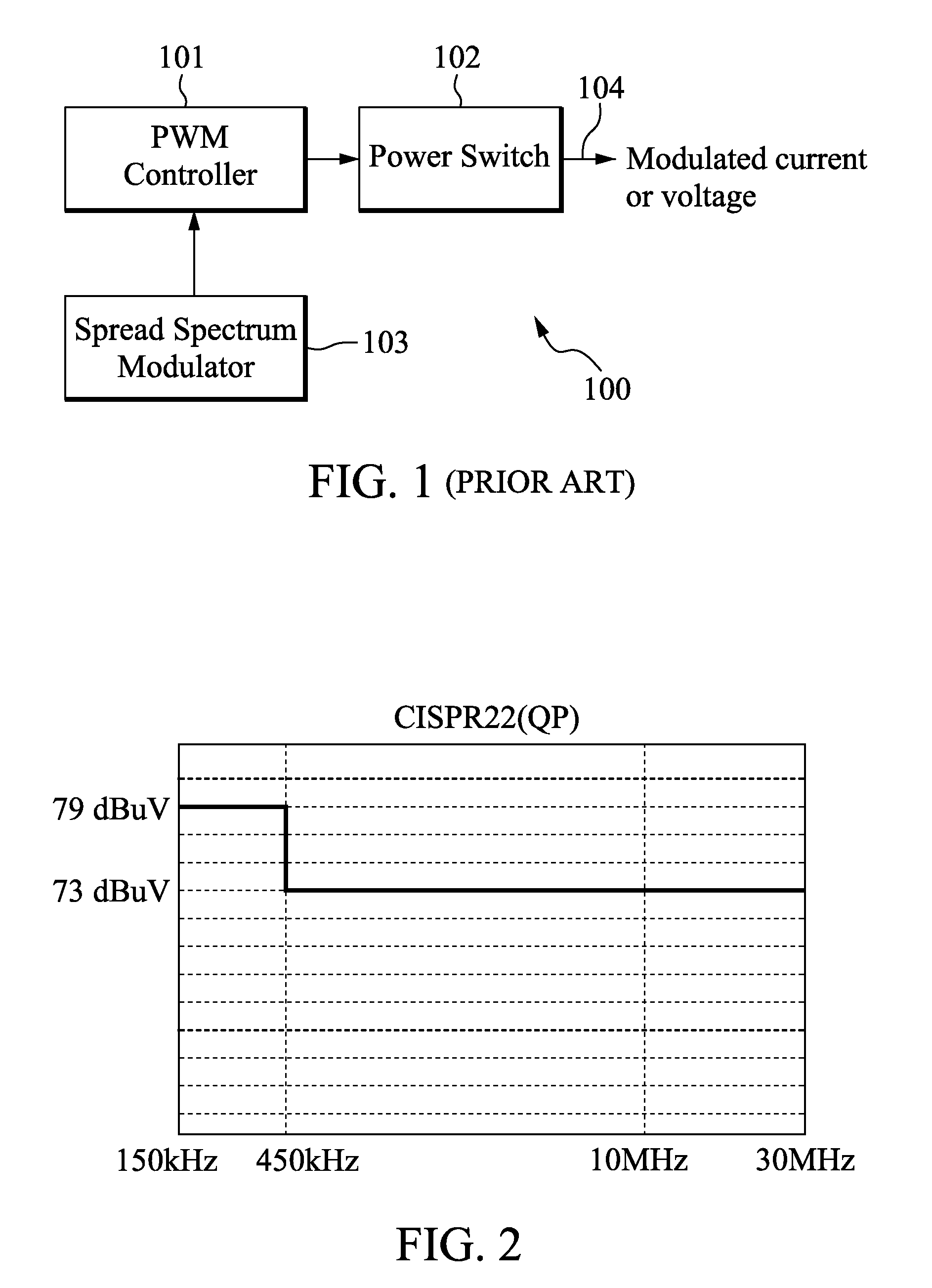
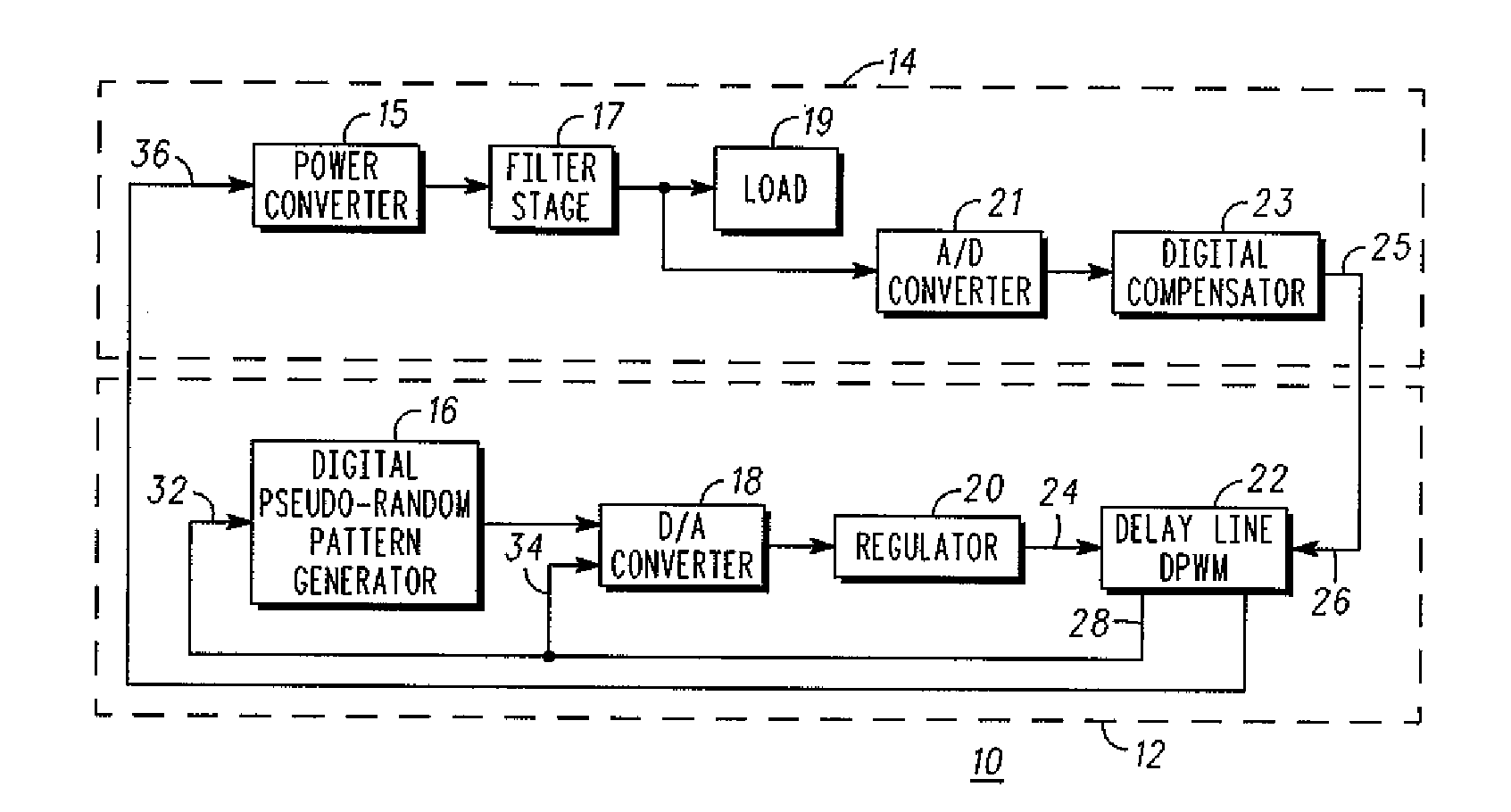
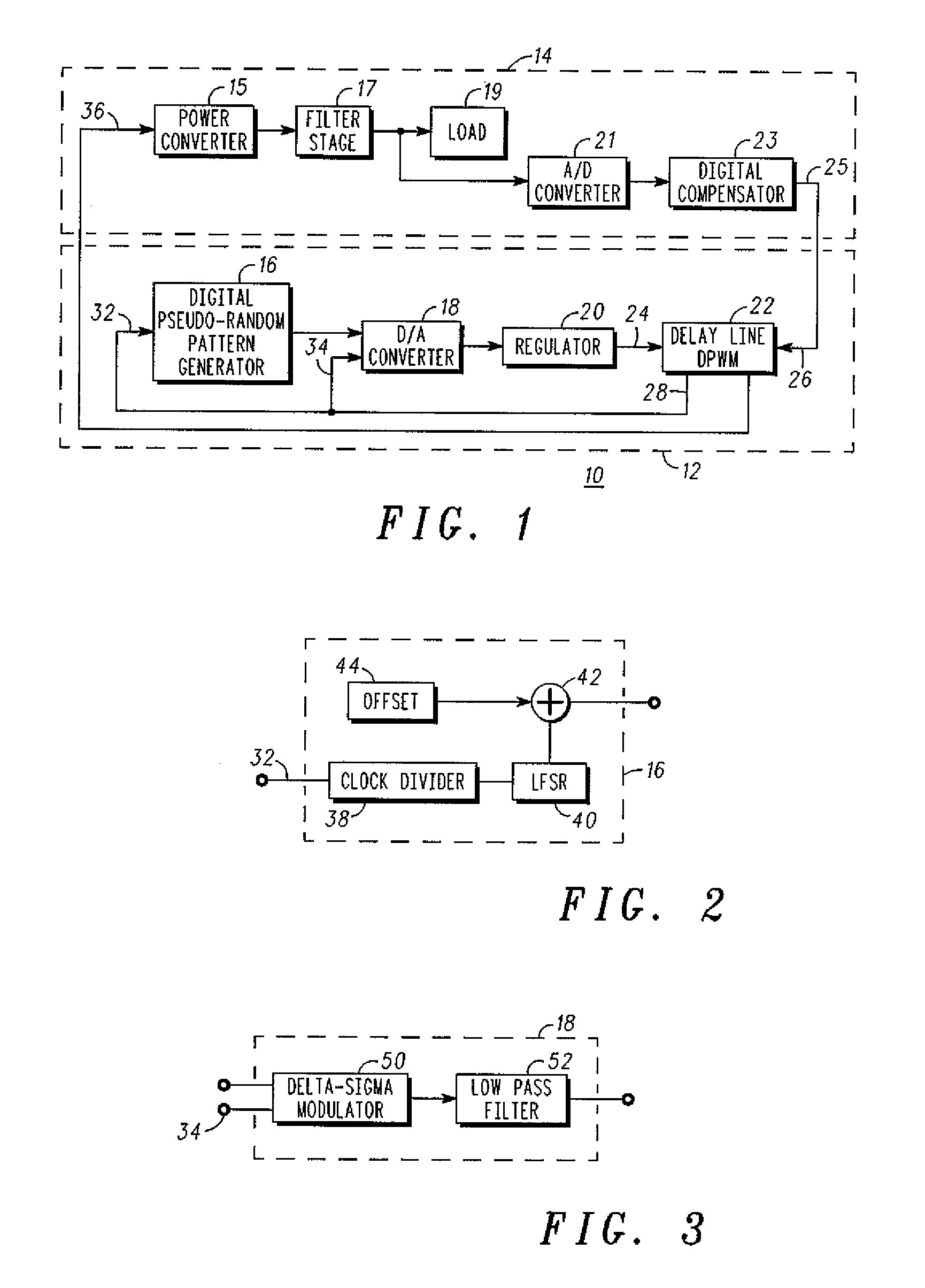
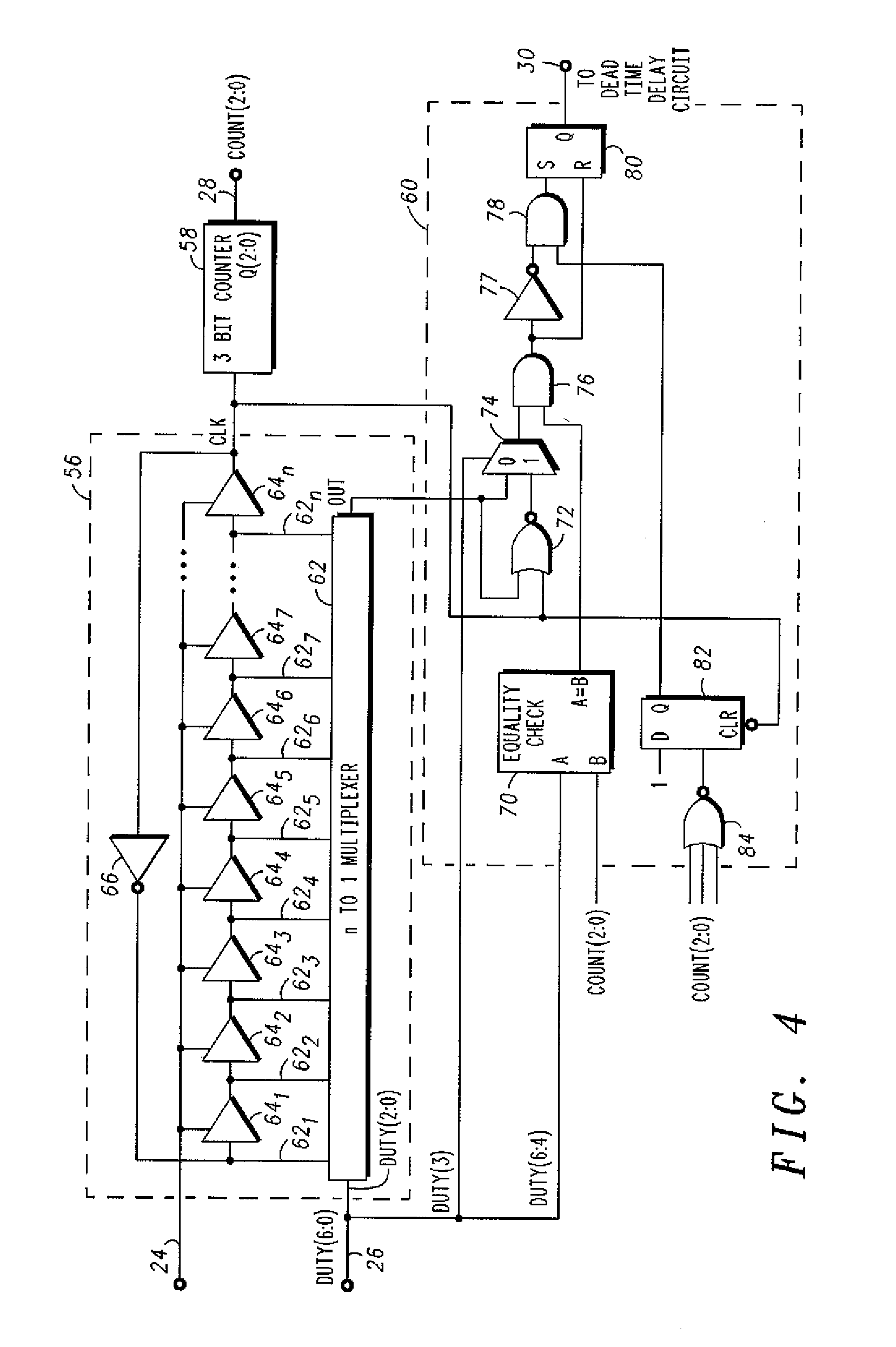
A spread spectrum system having a self-oscillating delay-line digital pulse width modulator and a method for mitigating electromagnetic interference. The spread spectrum system has a pseudo-random pattern generator connected to a digital-to-analog converter, which in turn is connected to a linear regulator. The linear regulator receives a reference voltage from the digital-to-analog converter and creates a frequency varying voltage that serves as an input voltage for delay elements of a delay-line based digital pulse width modulator. In response to frequency varying input signal, the delay-line based digital pulse width modulator generates a frequency varying voltage that is input to a switching network to vary its switching frequency.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Spread-period clock generator
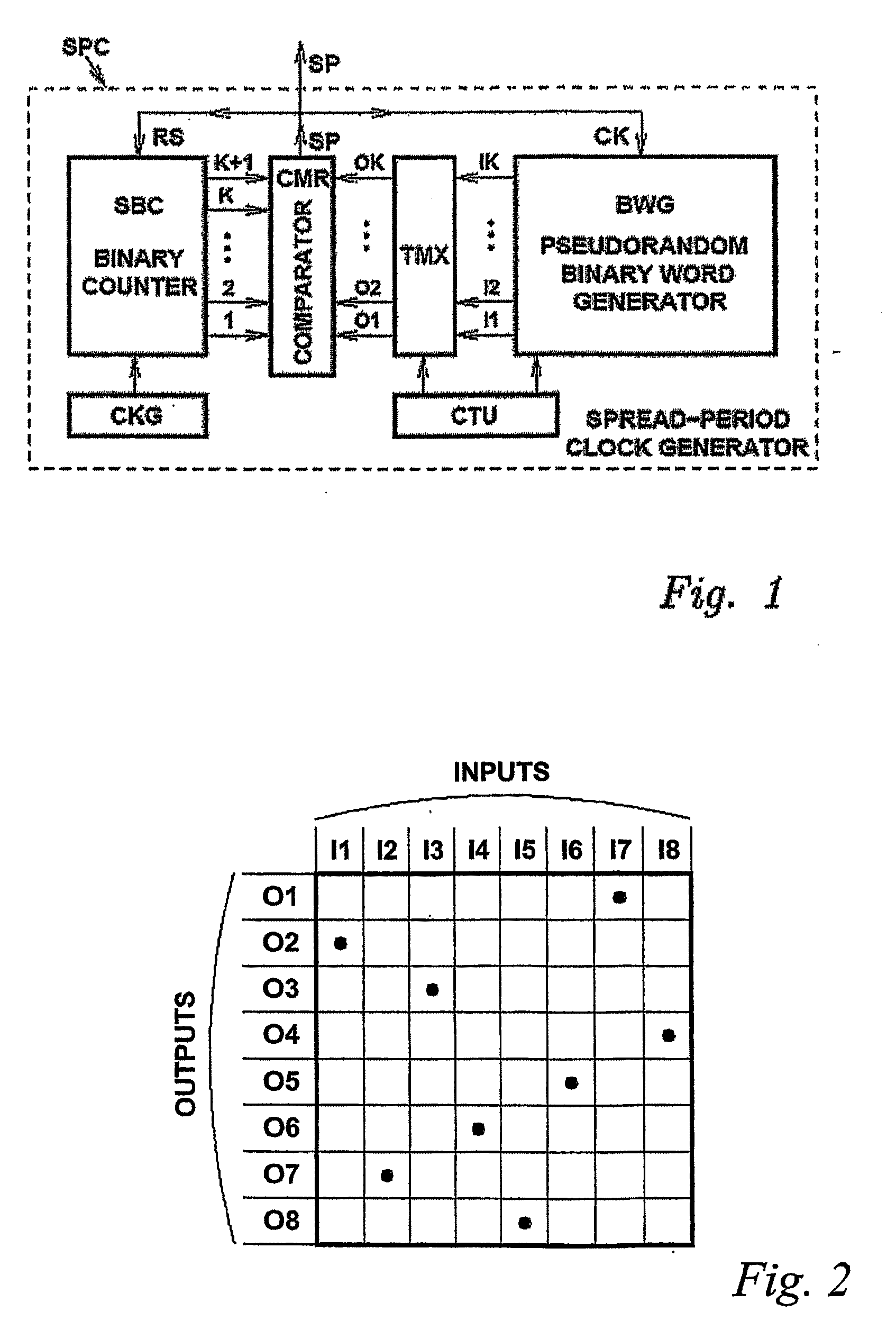
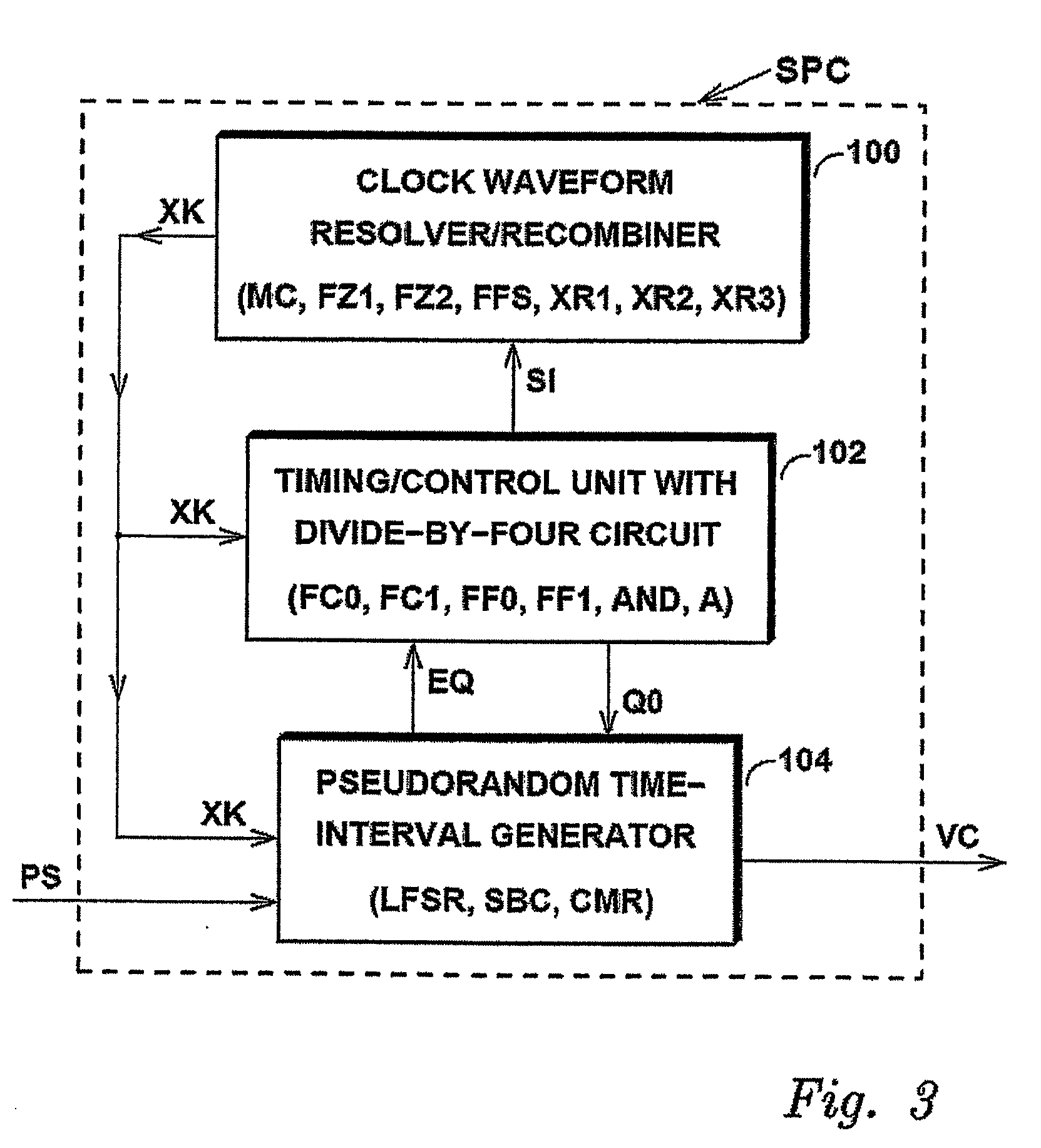
InactiveUS20100141317A1Increase the number ofPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersLeading edgeClock rate
A spread-period clock generator (SPC) counts basic clock pulses (XK) to generate output pulses (EQ) with varying periods, and has means (controlled by signal QS) for switching between a first mode, in which counting is carried out in response to the leading edges of the basic clock pulses (CK), and a second mode, in which counting is carried out in response to the trailing edges of the basic clock pulses (CK). Accordingly, if mode switching (signal QS) is carried out during a counting operation, the counting period is altered by a portion of a basic clock period (CK). Thus, the number of different periods of the output pulses can be increased without increasing the basic clock frequency (input WC, signal LK, CK).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and system of reducing electromagnetic interference emissions
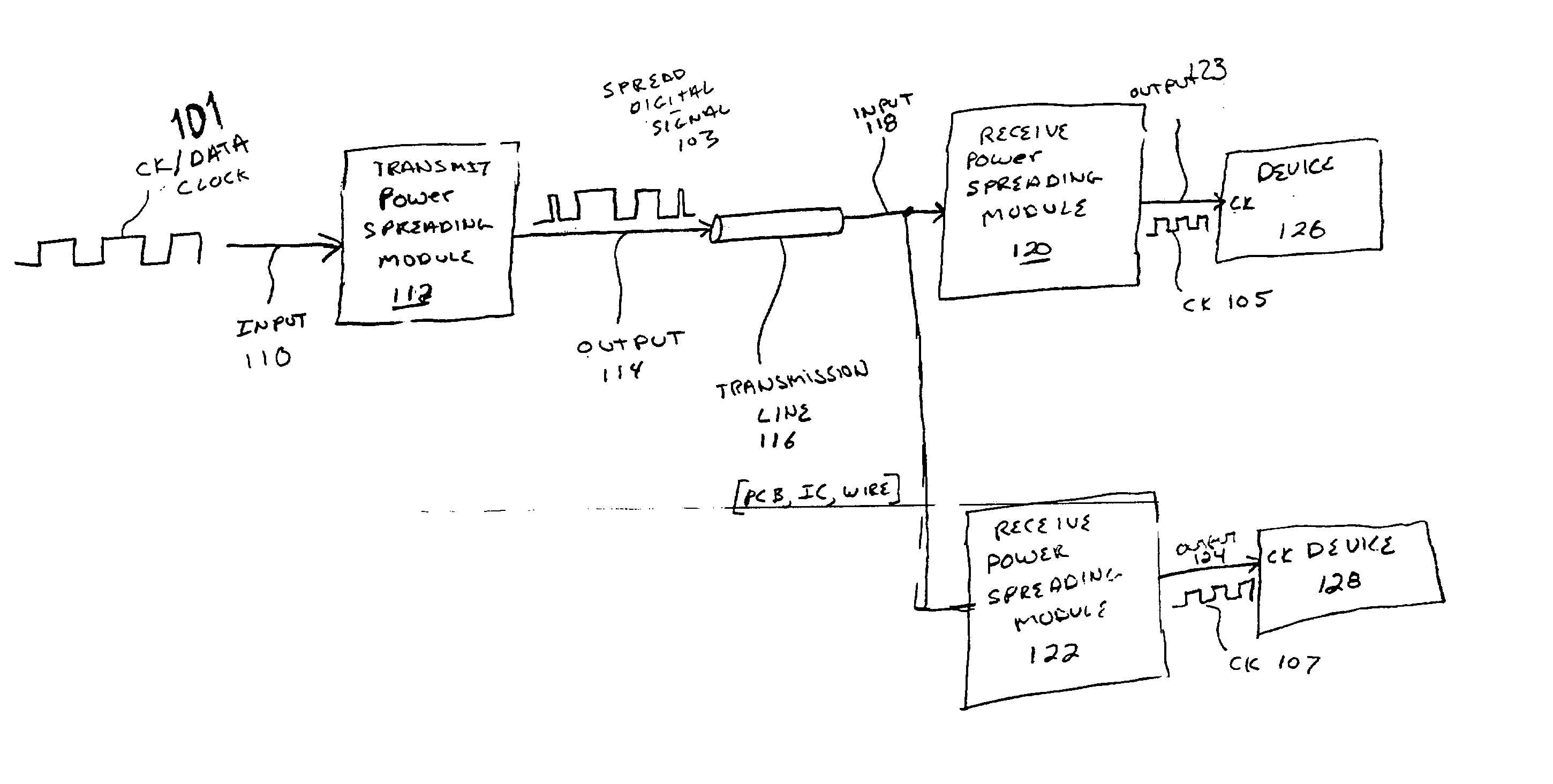
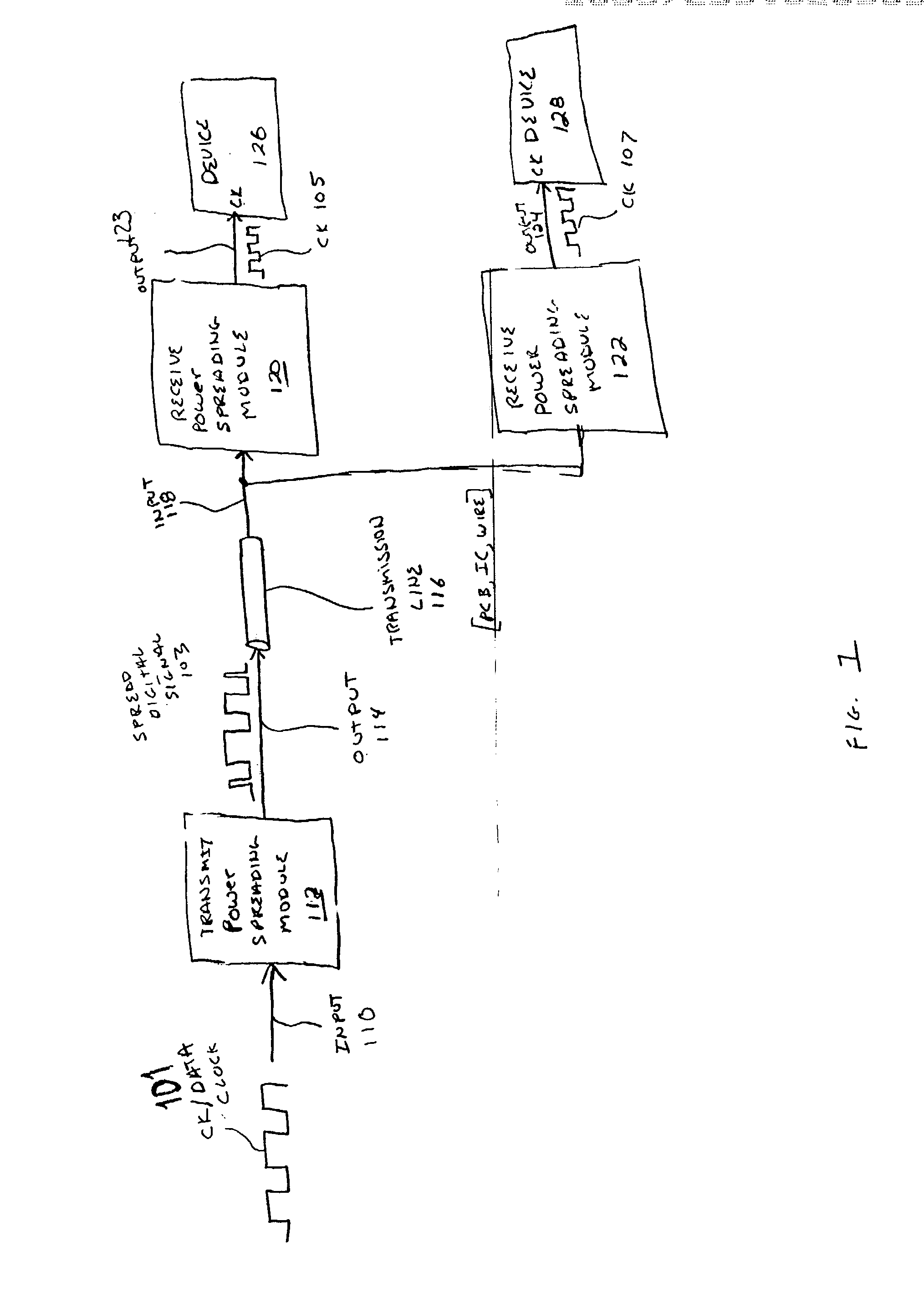
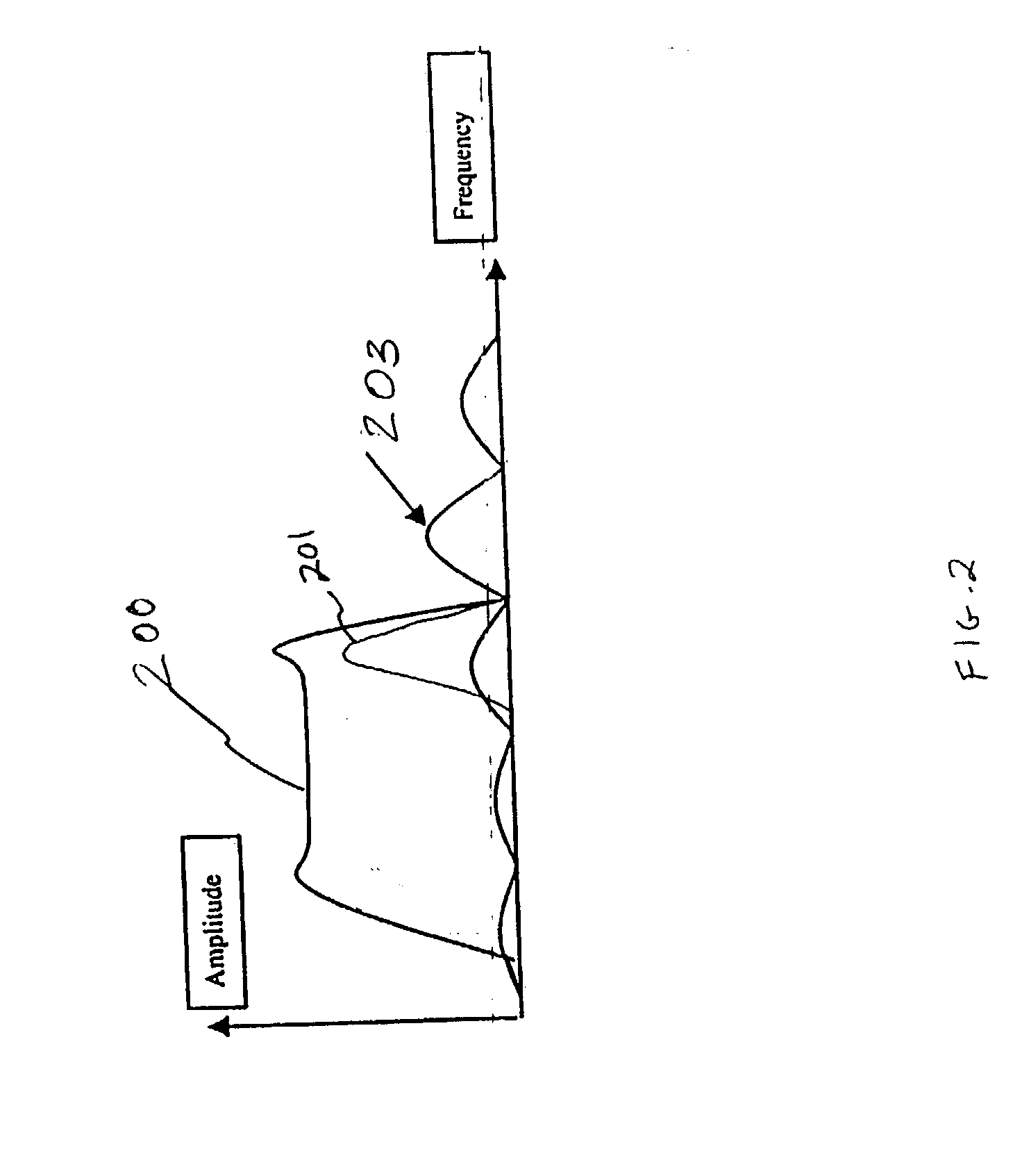
InactiveUS20040001533A1Code division multiplexDigital processing power distributionElectromagnetic interferenceDigital signal
A method and system is disclosed for spreading the power associated with digital signals being transmitted to lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) emissions. After being transmitted across a transmission line, a representation of the original digital signal is recovered and provided to a destination device.
Owner:XEMI
Thermal noise random pulse generator and random number generator
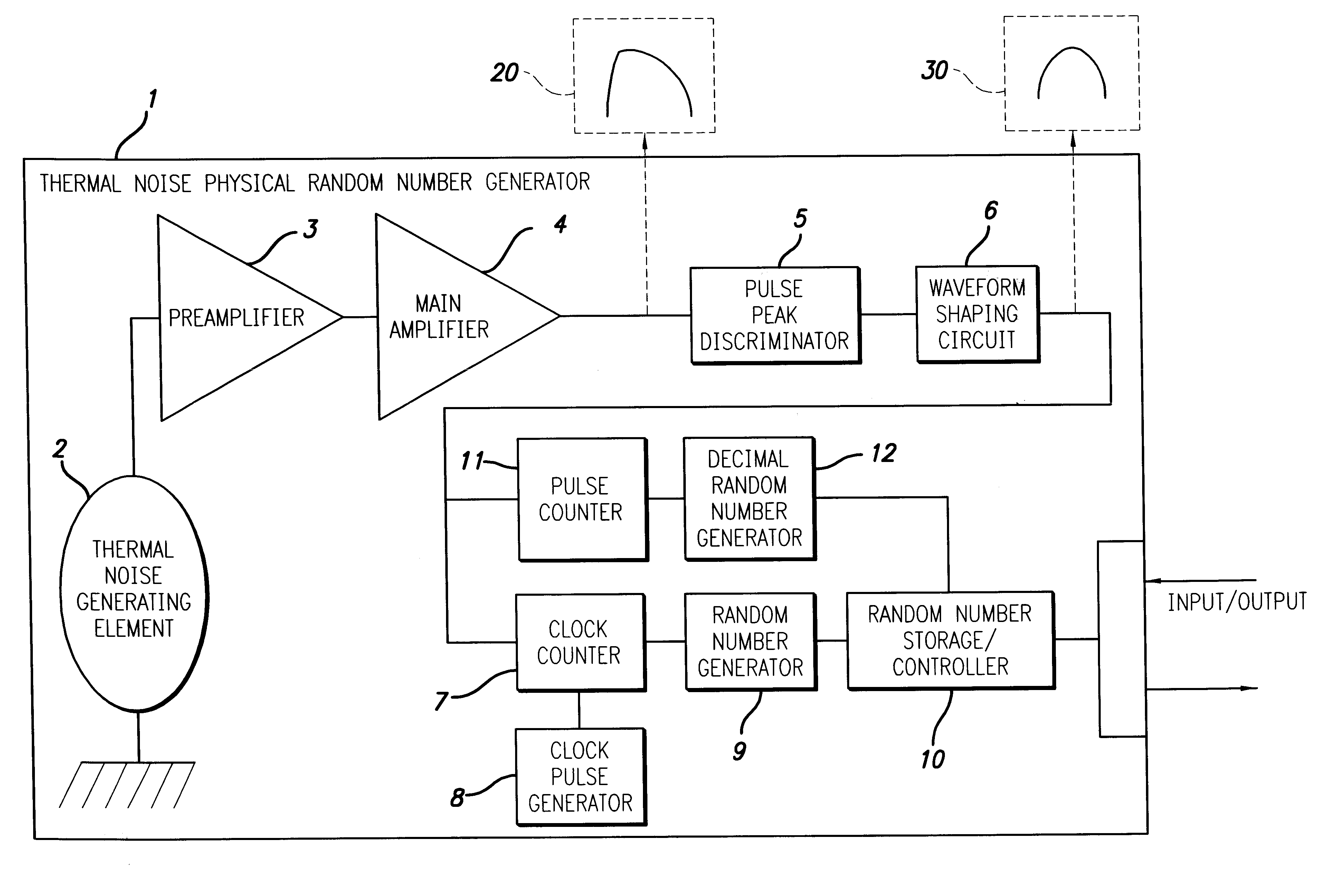
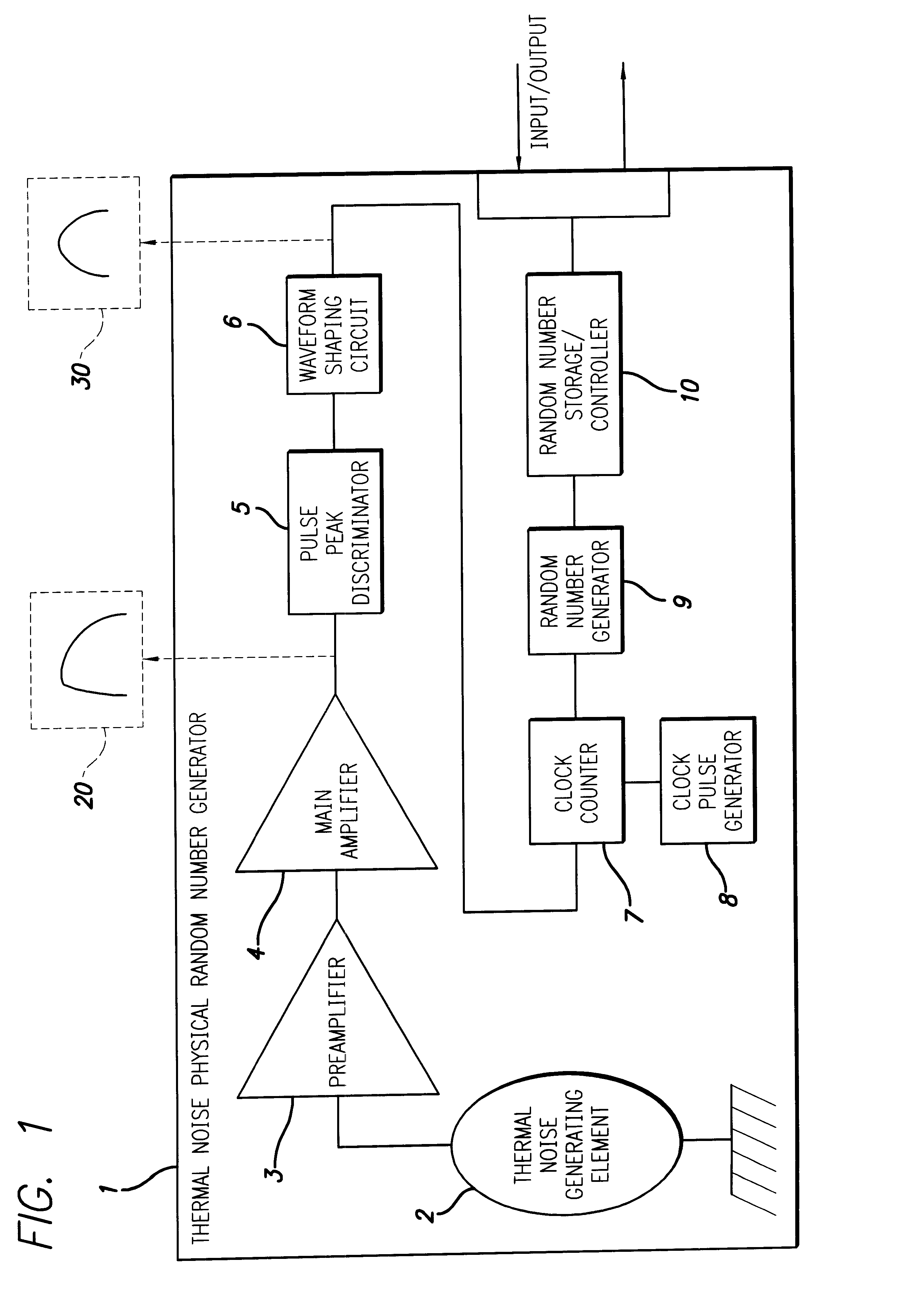
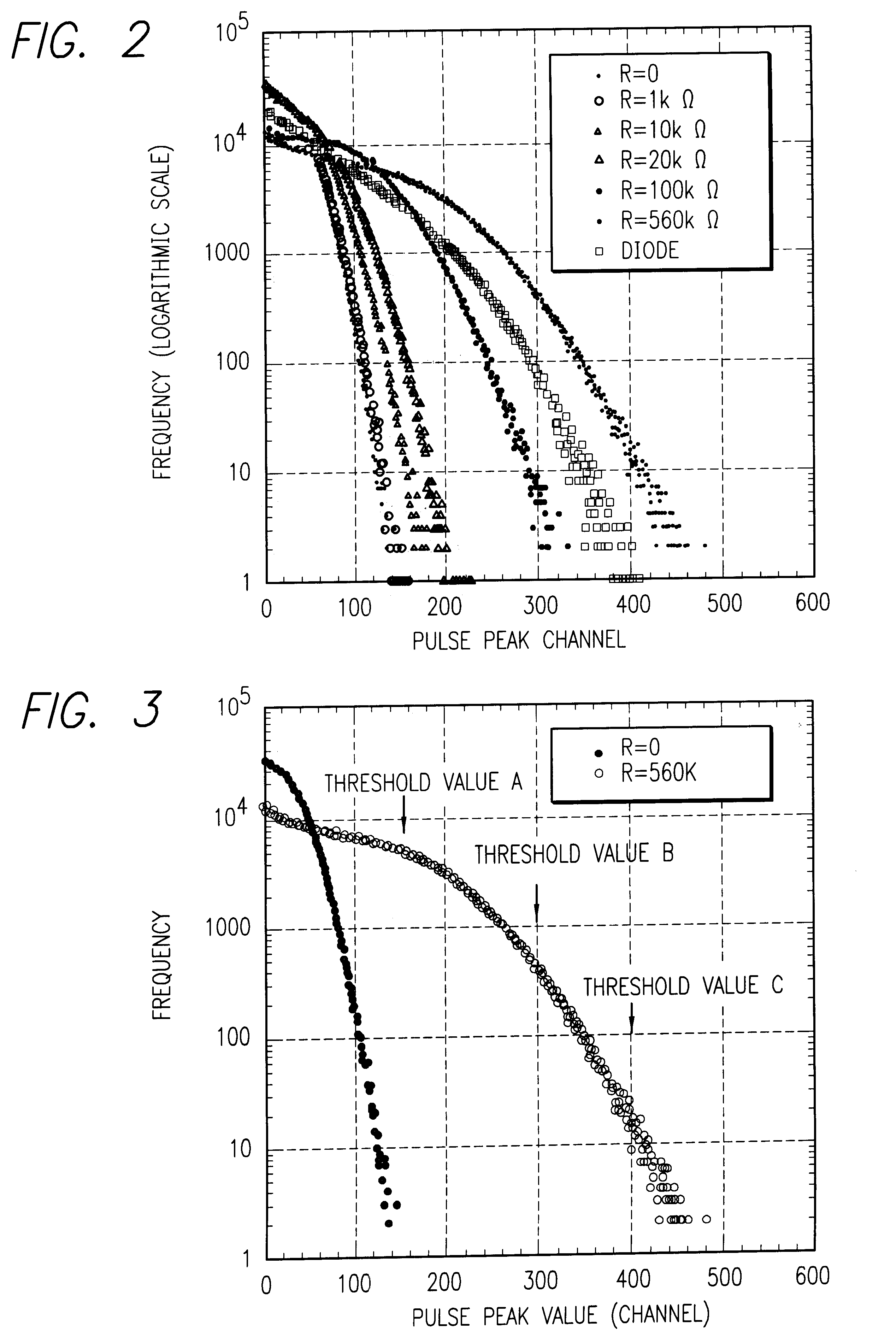
A random number generator has a simple configuration using know inexpensive electronic parts and can generate the true physical random numbers at a required generation speed. Such a random number generator can provide the true physical random numbers to any sectors of society at dramatically low cost A random pulse generator comprises a thermal noise generating element (2) having a resistor, a conductor or a semiconductor such as a diode adapted to generate thermal noises Hen no electric current is supplied to them, an analog-amplifier circuit for amplifying the irregular potential generated from the thermal noise generating element and a waveform shaping circuit (6) adapted to take out the output of the amplifier circuit as random rectangular pulse signals. A thermal noise random number generator comprises, in addition to the above components, an n-bit counter (n being an integer) for measuring the time interval between a random pulse signal output from the waveform shaping circuit (6) and the immediately succeeding random pulse signal and is adapted to output the count of the n-bit counter as natural random number.
Owner:L E TECH
Spread Spectrum Clock Interoperability Control and Inspection Circuit
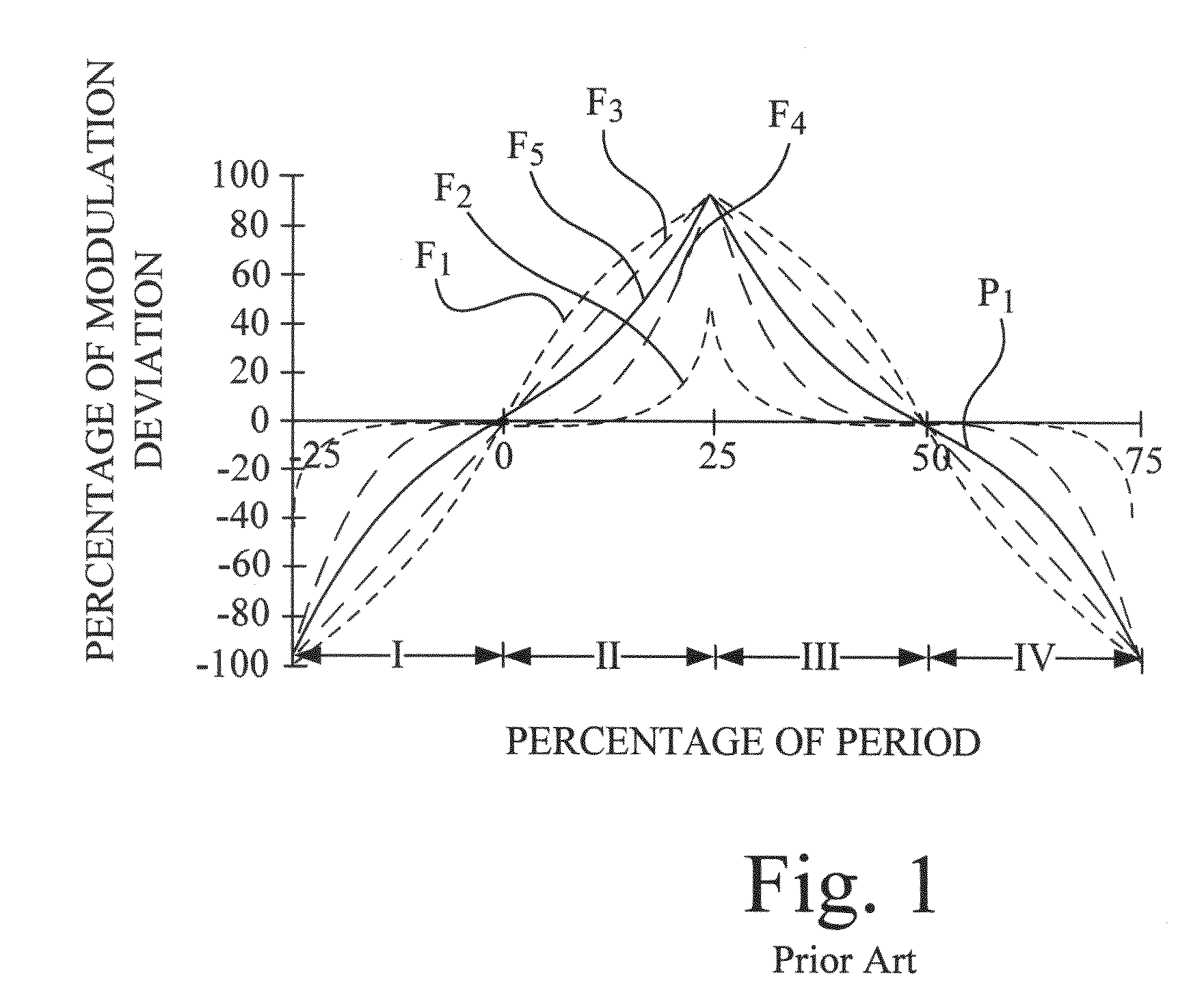
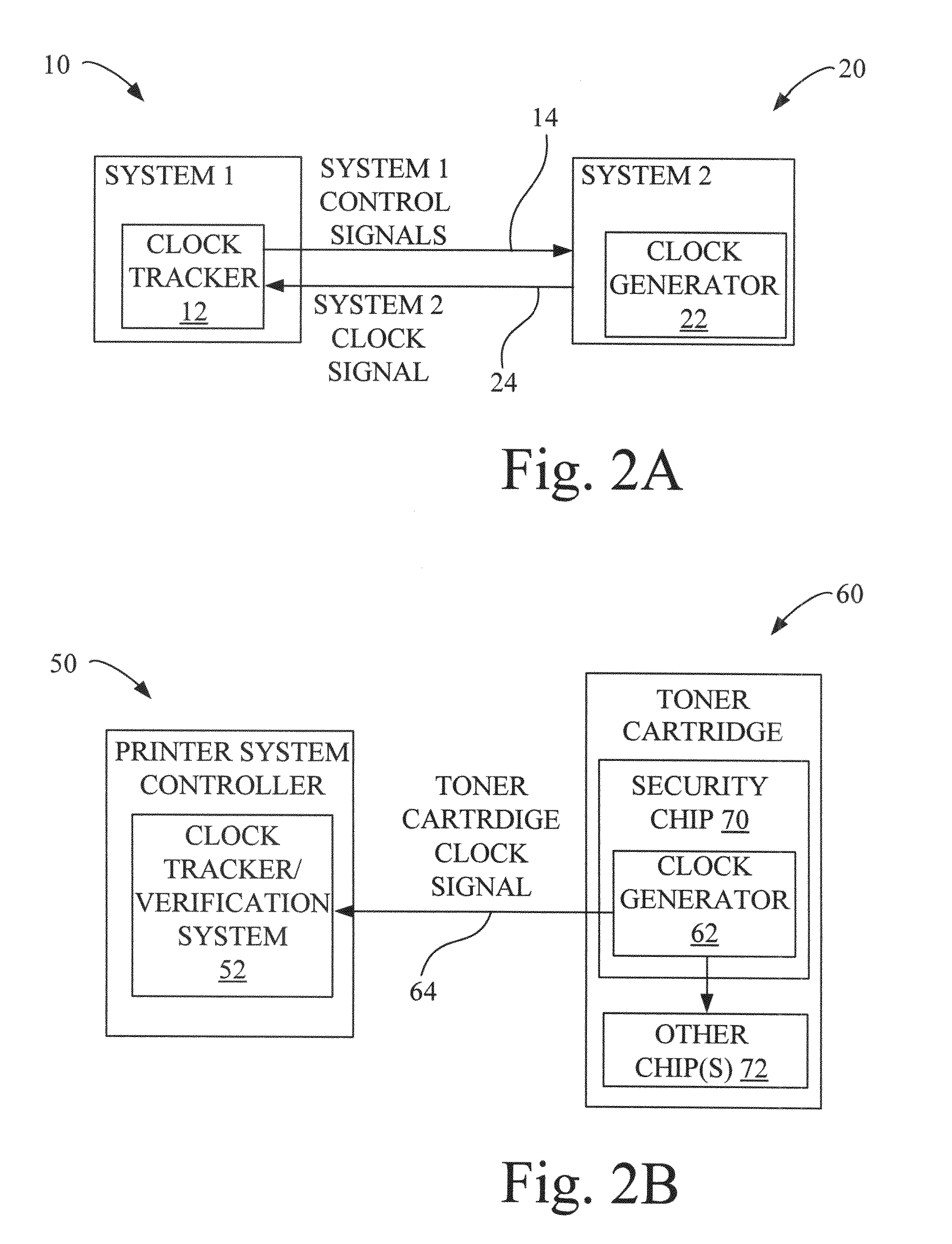
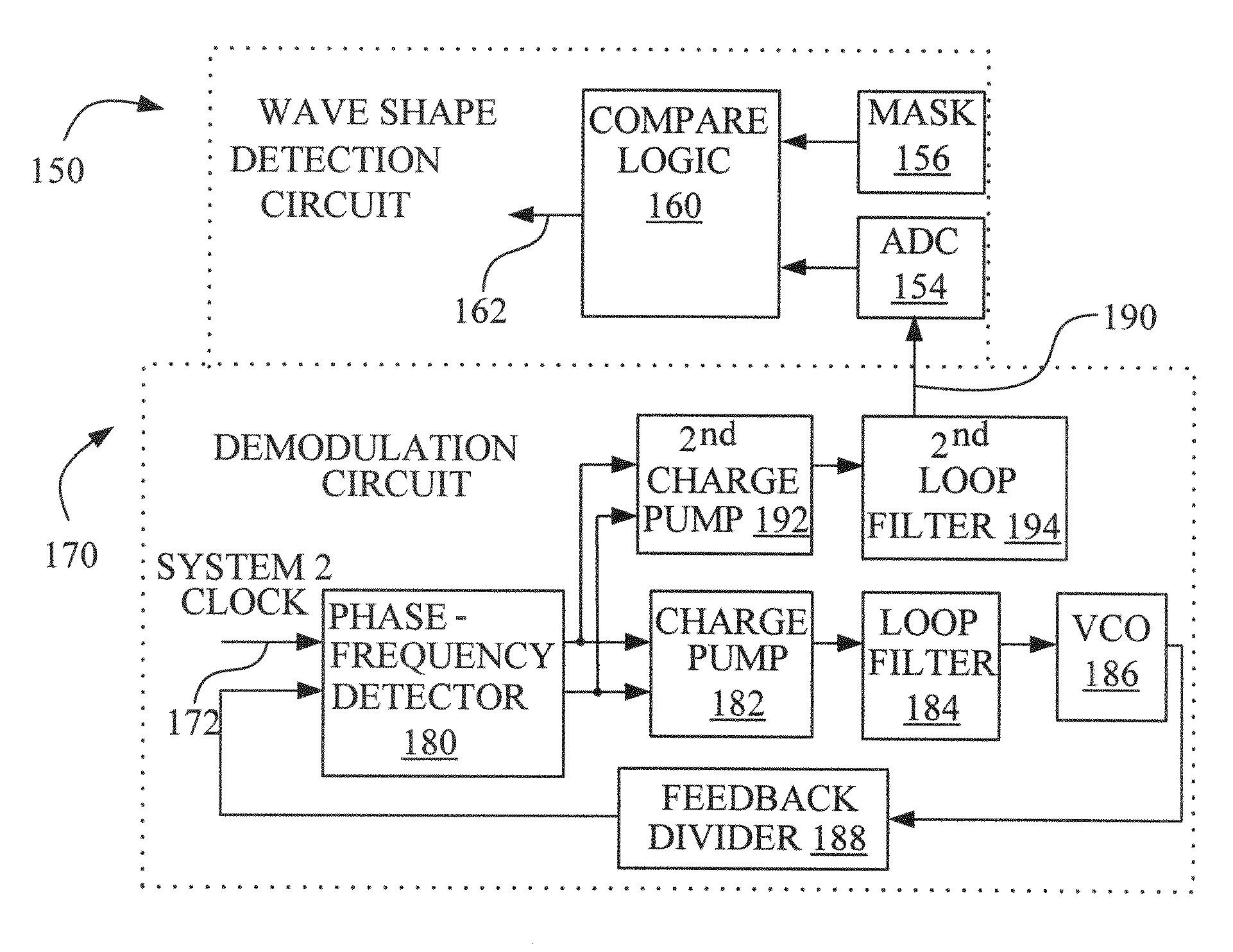
ActiveUS20090179678A1Prevent frequency overlapAvoid frequencyComputer security arrangementsPulse shapingMagnetic tapeModularity
A spread spectrum clock generator (SSCG) control and inspection circuit provides a system and method for inspecting and controlling an external SSCG, and for verifying the modulation profile waveform of an external SSCG. An electronic circuit is included that can check for the presence of an optimal SSCG modulation profile in product subsystems, and in attached modular systems, including electronic plug-in features such as internal network adapters and cartridges. In one mode of the invention, an electronic circuit ensures continued radiated emissions compliance for field replaceable units or consumable parts within a product, such as a printer, a scanner, or a combination (or all-in-one) printer / scanner. In another mode of the invention, an electronic circuit may also act as a secondary security device for consumable products, such as toner cartridges or ink jet cartridges. In yet another mode of the invention, an electronic circuit may also adjust the attached SSCG clock.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Randomness test utilizing auto-correlation
InactiveUS6947960B2Random number generatorsCoding/ciphering apparatusNumber generatorComputer science
Owner:NXP BV
Clock and data recovery circuit and clock control method thereof
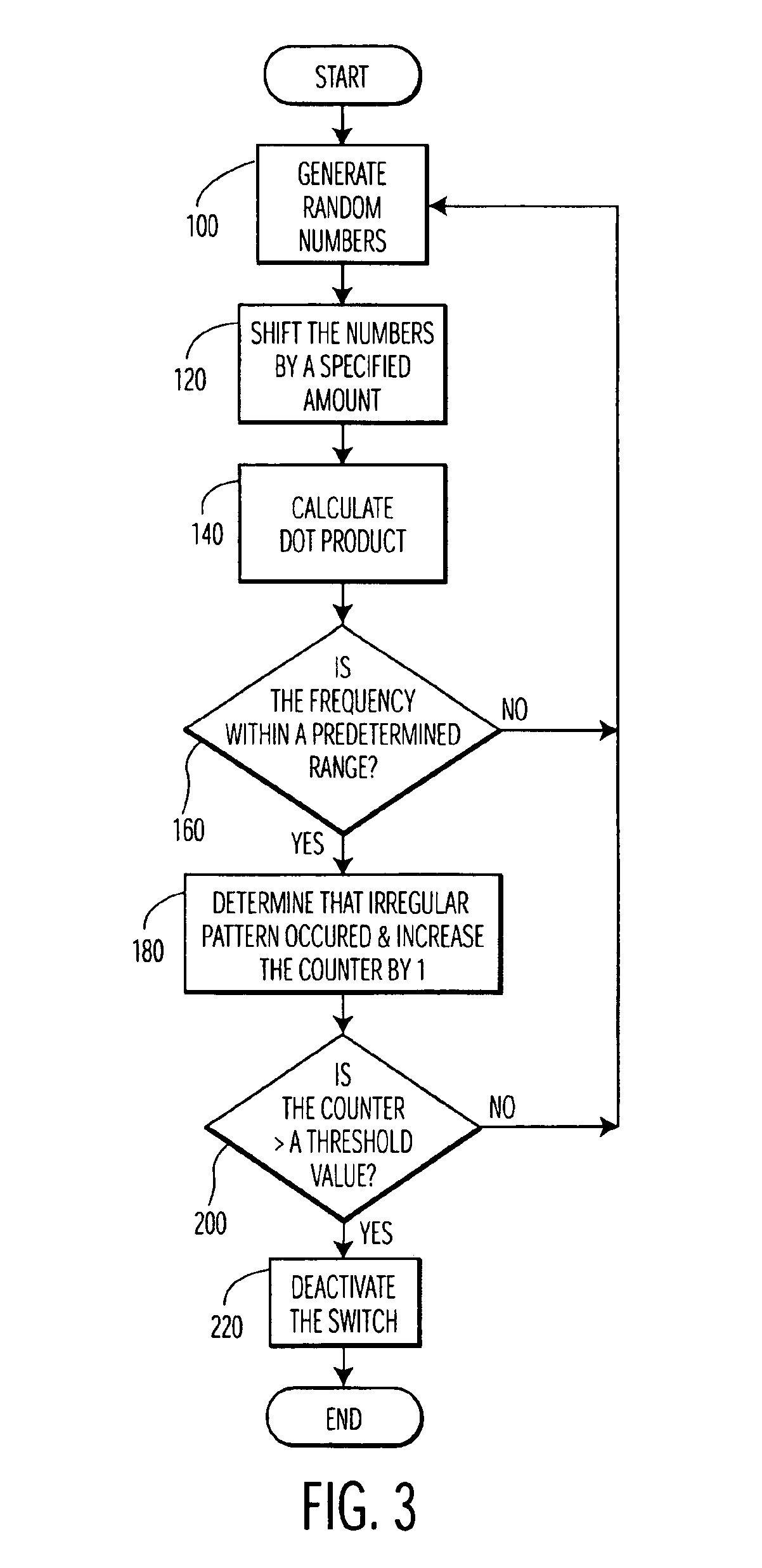
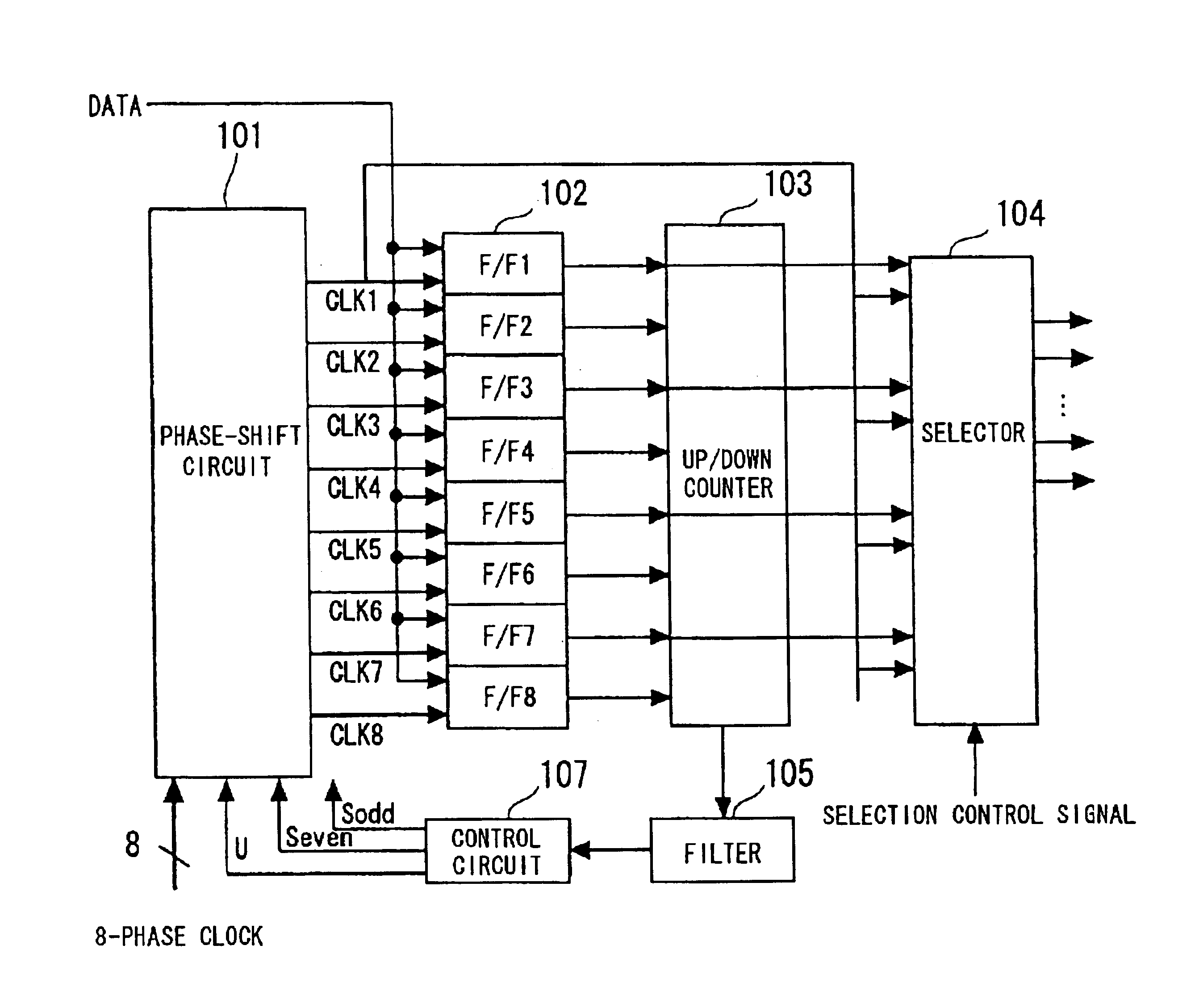
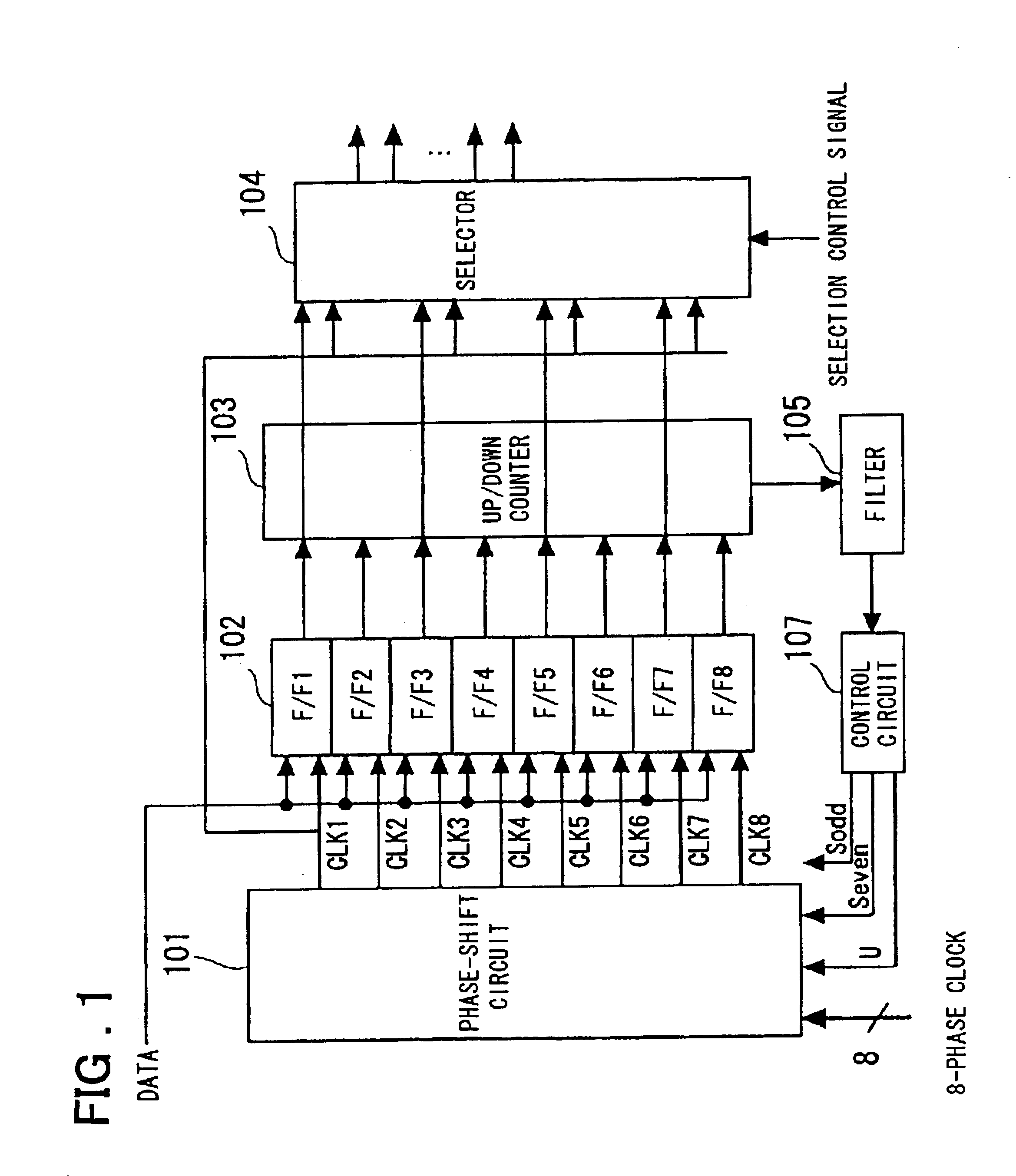
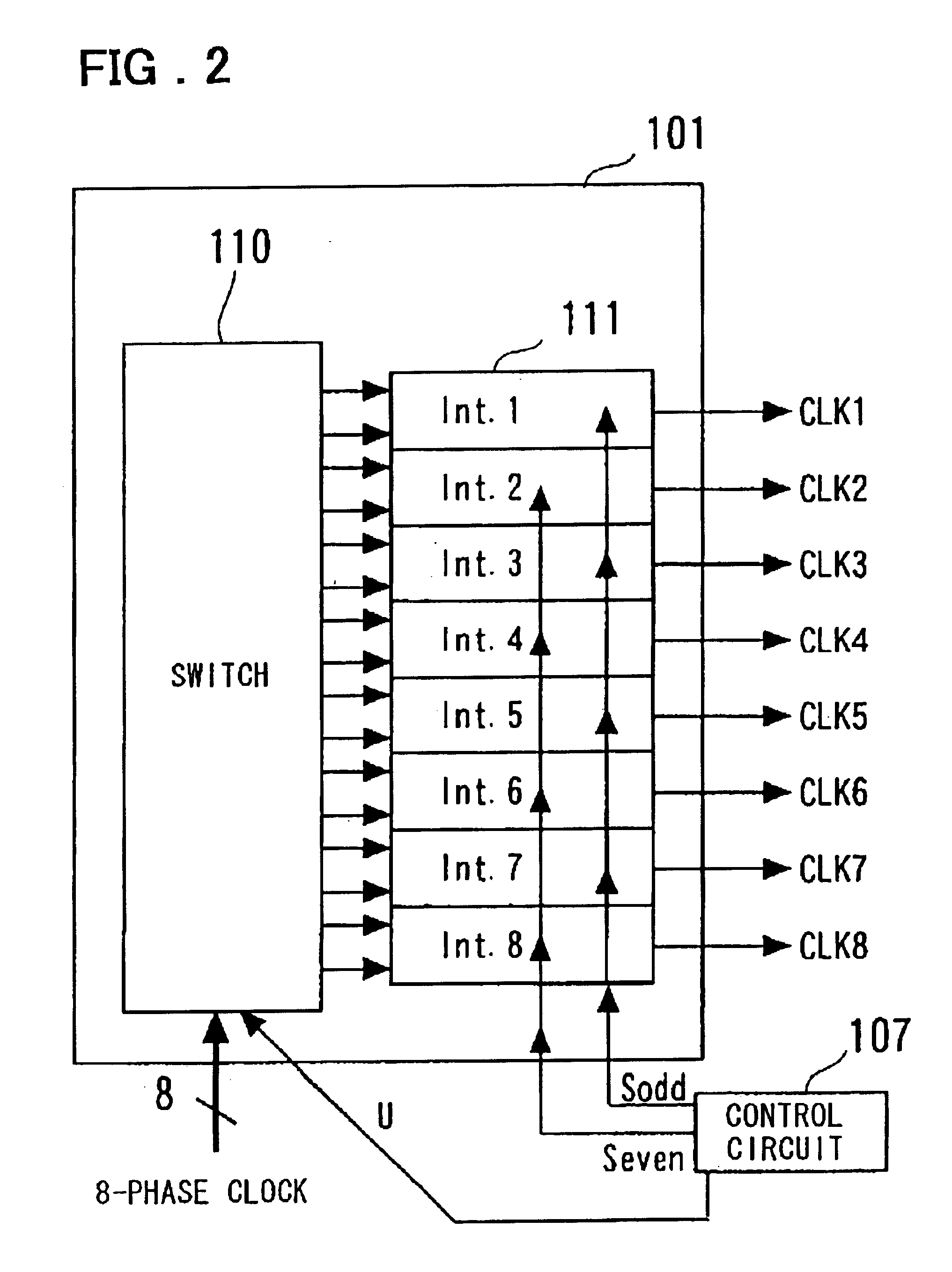
InactiveUS6753712B2Eliminate the effects ofAccurate dataPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsPhase shiftedControl signal
A clock and data recovery circuit includes a phase-shift circuit having a switch, which receives multiphase clocks, for selecting and outputting a plurality of clock pairs from among the multiphase clocks, and a plurality of interpolators, which receive the plurality of clock pairs output from the switch, for outputting clock signals in which delay time is stipulated by time obtained by performing interior division of the phase difference between the clocks of the pair; a plurality of latch circuits which receive input data in common; a phase detecting circuit for detecting and outputting phase, with respect to the clock, of a transition point of the input data from the outputs of the plurality of latch circuits; a filter for smoothing the output of the phase detecting circuit; and a control circuit for controlling clock phase by outputting control signals for controlling the interpolators and / or switch of the phase-shift circuit based upon the filter output.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Pseudo-random number sequence output unit, transmitter, receiver, communication system and filter unit
InactiveUS20070098054A1Eliminate redundant calculationsMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkCommunications systemArtificial intelligence
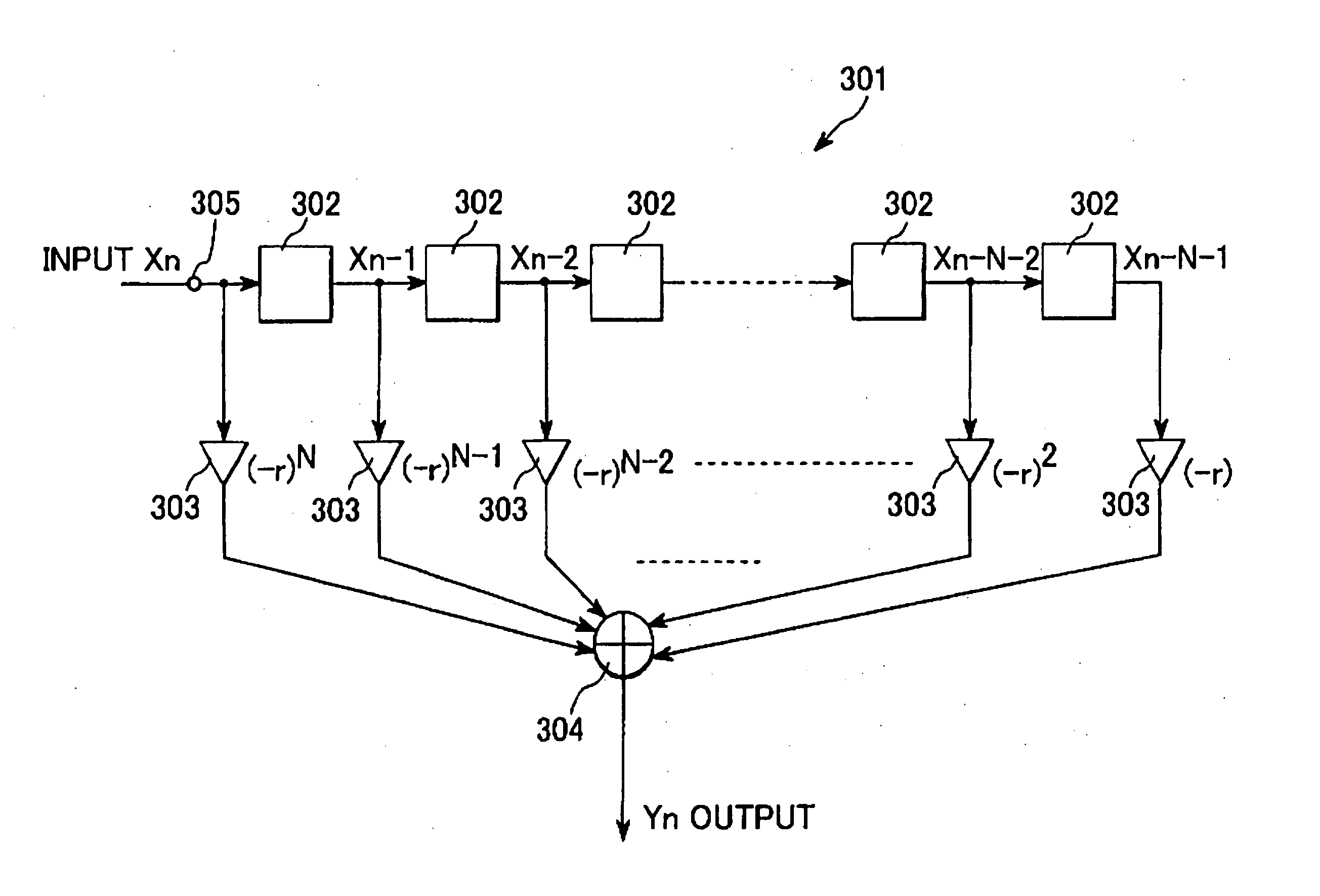
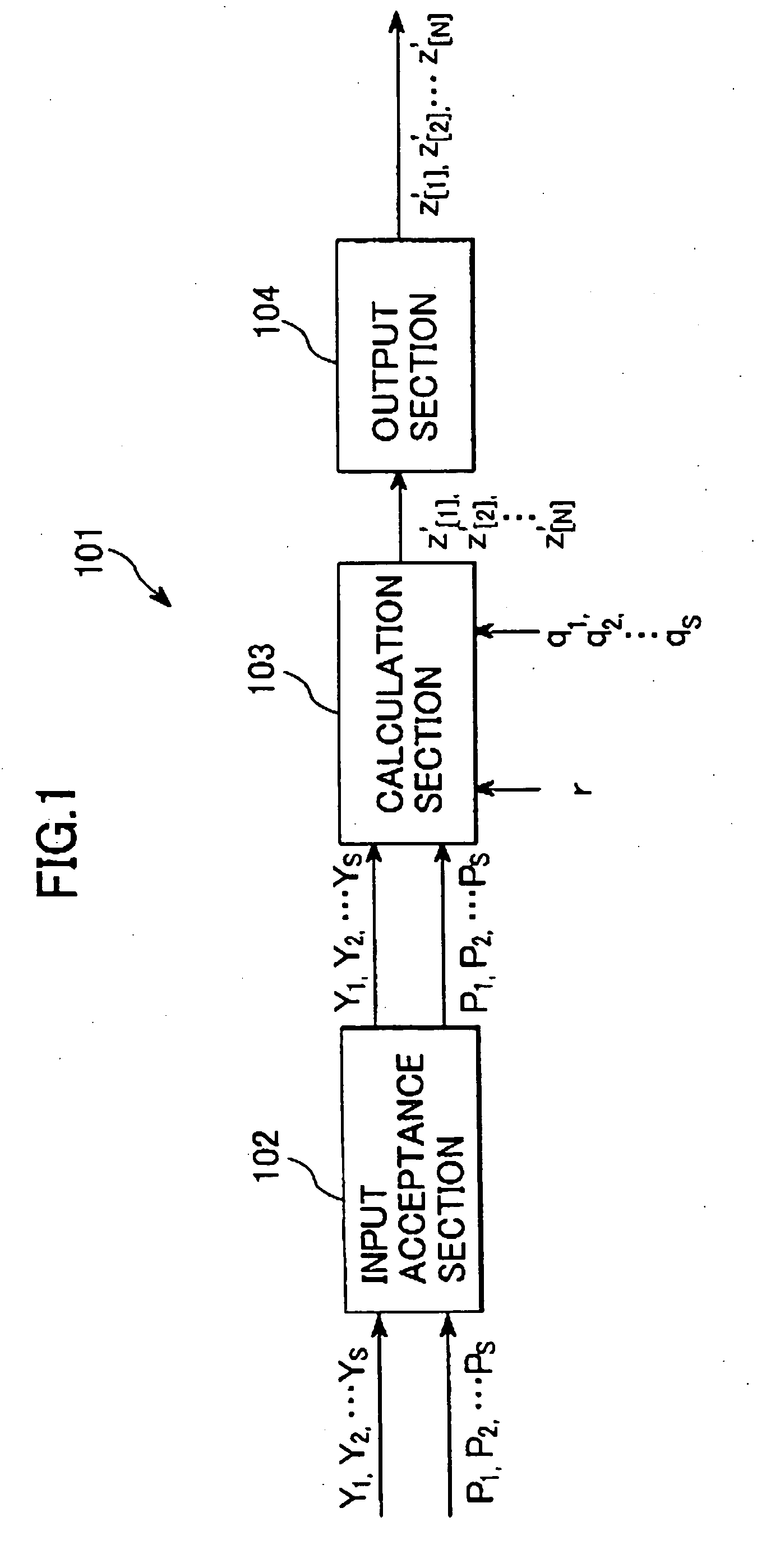
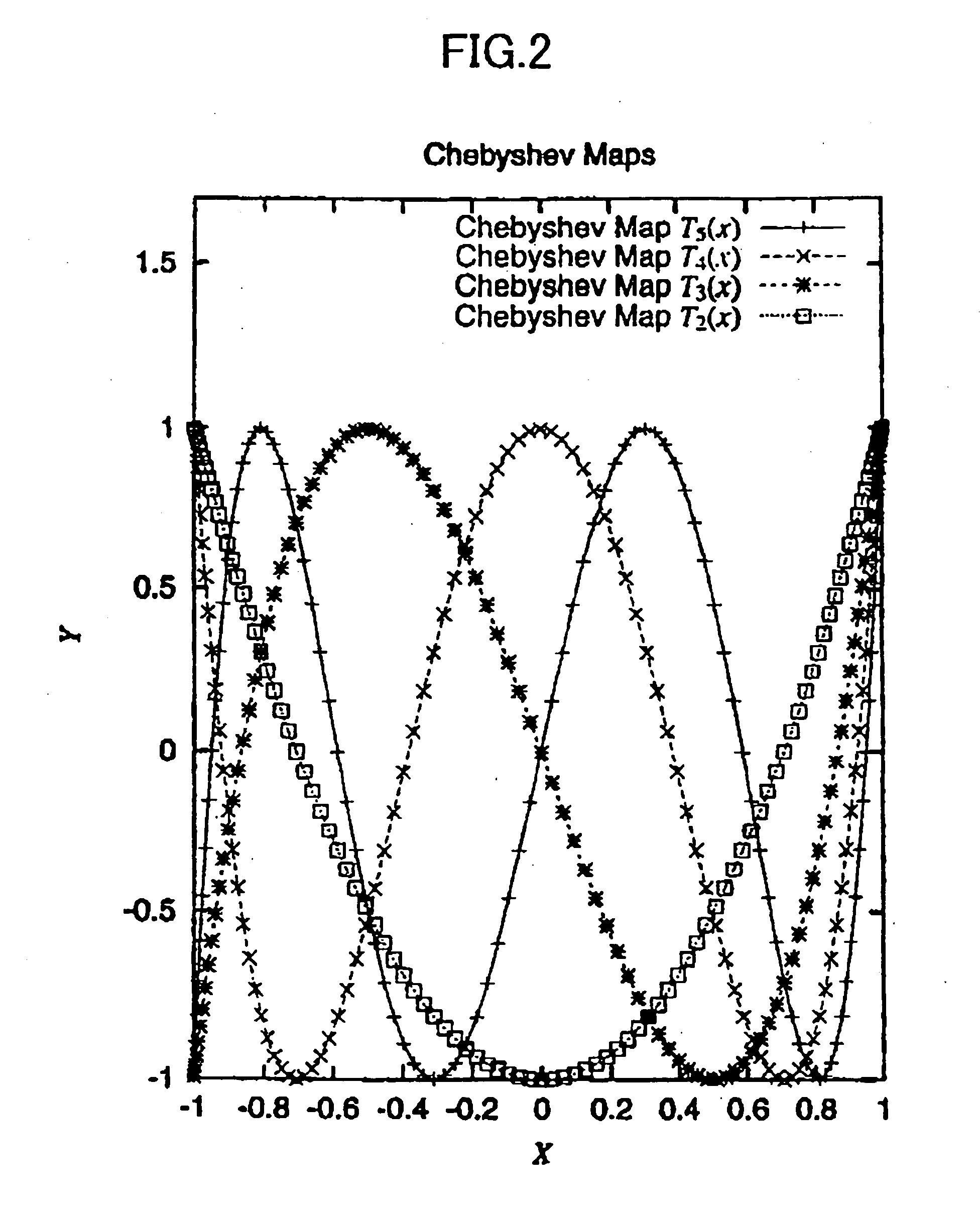
A pseudo-random number sequence output unit responsive to s (1<=s) number of prescribed positive integers q1, q2, . . . , qs, a prescribed real impulse constant r (-1<r<1), and a prescribed non-zero real constant C for outputting a pseudo-random number sequence of length N (1<=N), which output unit includes: an input acceptance section that accepts input of s (1<=s) number of real number sequence initial values Y1, Y2, . . . , Ys (-1<Y1<1, -1<Y2<1, . . . , -1 Ys<1), and s number of integer parameters p1, p2, . . . , ps (2<=P1, 2<=P2, . . . 2<=Ps) for which q1 mod p1<>0, q2 mod p2<>0 . . . , qs mod ps<>0 respectively hold with respect to the prescribed positive integers q1, q2 . . . qs; a calculation section that uses the prescribed real impulse constant r, the prescribed non-zero real constant C, the sequence initial values Y1, Y2, . . . , Ys, the integer parameters p1, p2, . . . , ps, the prescribed positive integers q1, q2, . . . , qs and integers j (1<=j<=s), m (1<=m<=2N-2) and n (1<=n<=2N-1) to calculate from the recurrence formula T p ( cos theta ) = T ( p , cos theta ) = cos ( p theta ) y j [ 1 ] = Y j y j [ m + 1 ] = T ( p j , y j [ m ] ) z [ n ] = ∏ j = 1 s T ( q j , y j [ n ] ) a pseudo-random number sequence z'[1], z'[2], . . . , z'[N] of length N that satisfies z ' [ 1 ] = C ∑ j = 1 N ( - r ) j z [ j ] , z ' [ 2 ] = C ∑ j = 1 N ( - r ) j z [ j + 1 ] , ⋮ z ' [ N ] = C ∑ j = 1 N ( - r ) j z [ j + N - 1 ] ; and an output section that outputs the pseudo-random number sequence z'[1], z'[2], . . . , z'[N]. A transmitter, receiver and communication system that utilize the output unit, a filter unit, a pseudo-random number sequence output method, transmission method, receiving method and filtering method are provided. A computer-readable data recording medium recorded with a program for operating the transmitter, receiver, communication system and implementing the output, transmission and receiving methods is also provided.
Owner:UMENO KEN +1
Random Number Generation Based on Logic Circuits with Feedback
ActiveUS20070273408A1Improve robustnessIncrease productionRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsTheoretical computer scienceFinite-state machine
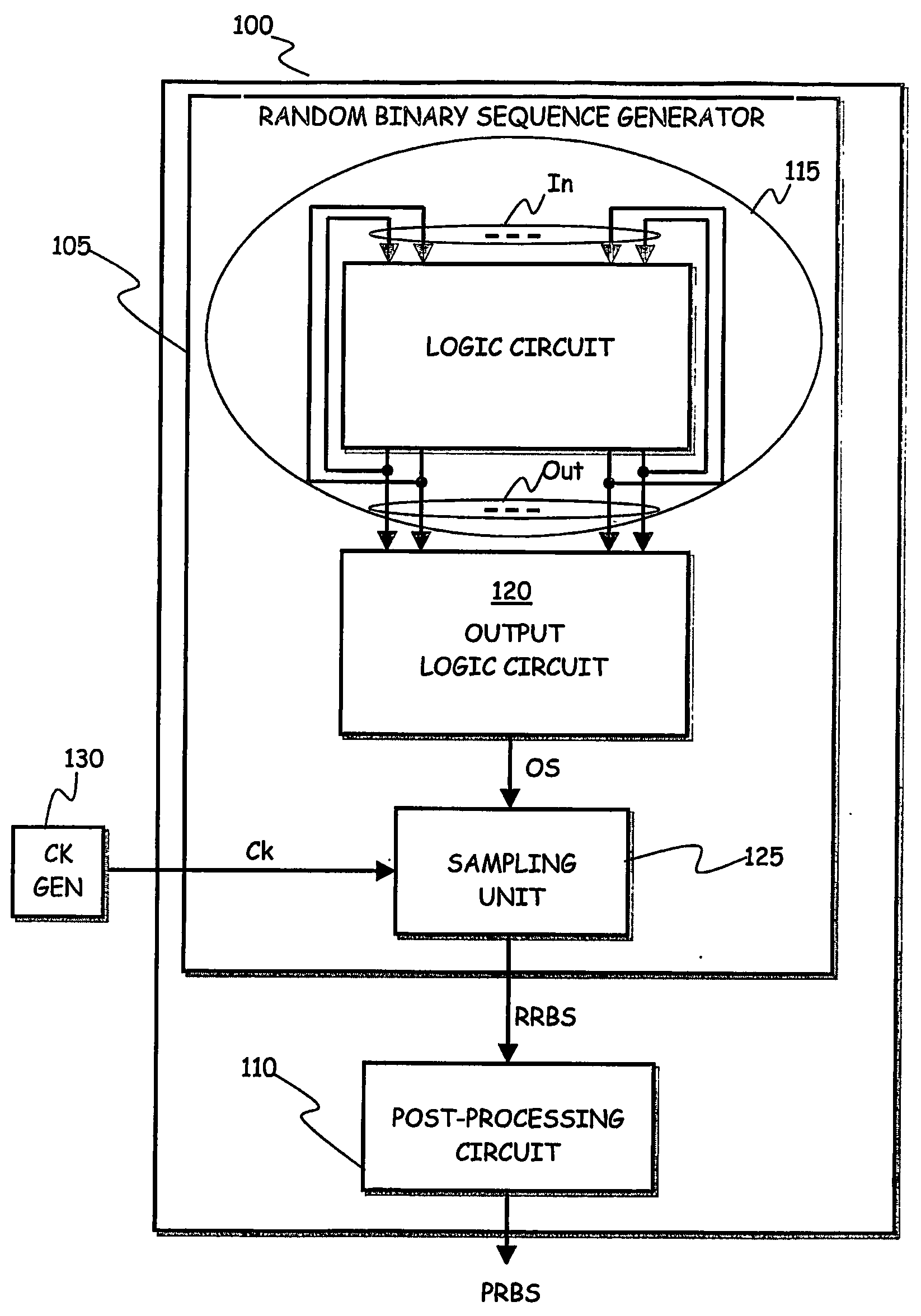
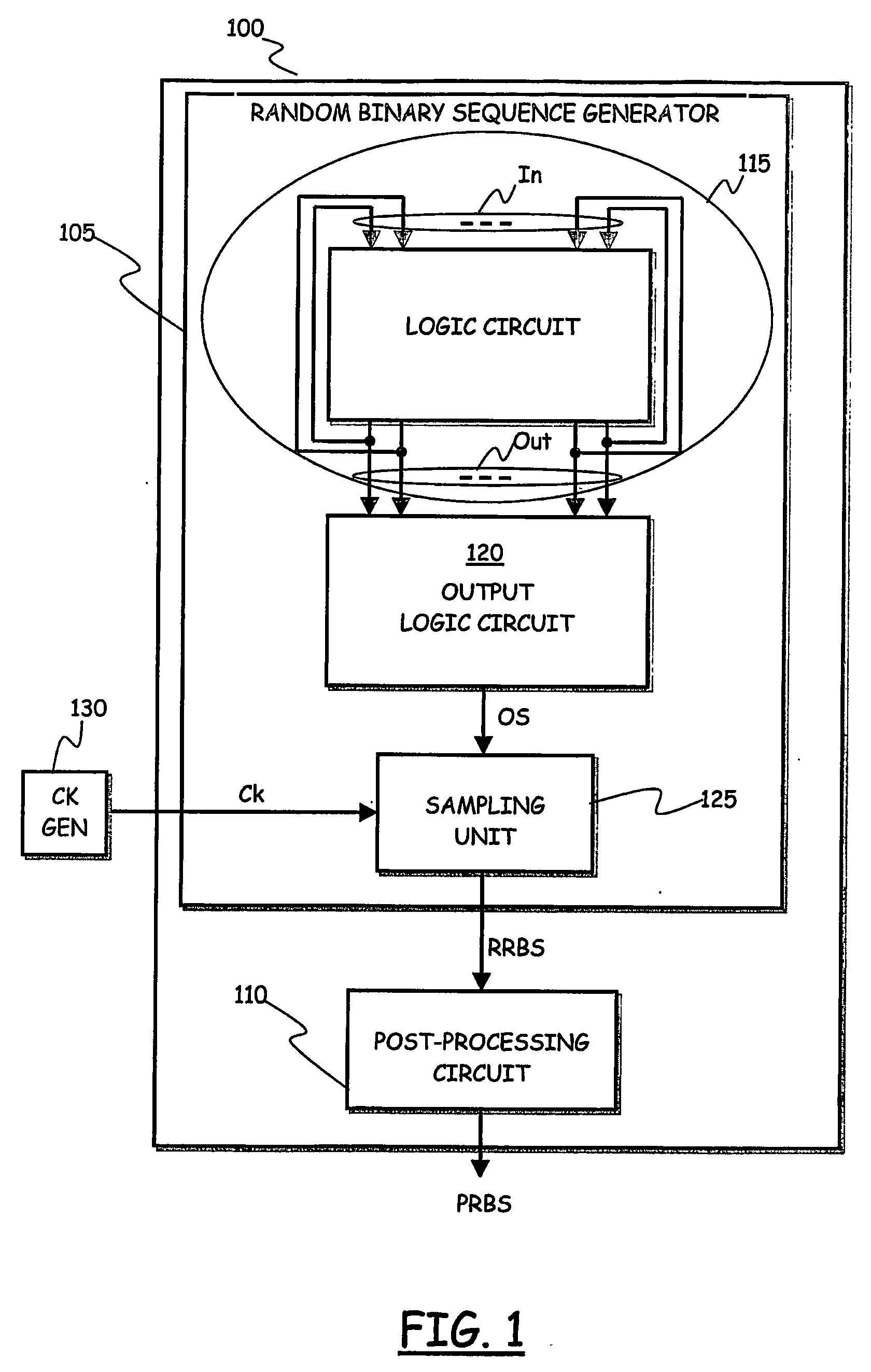
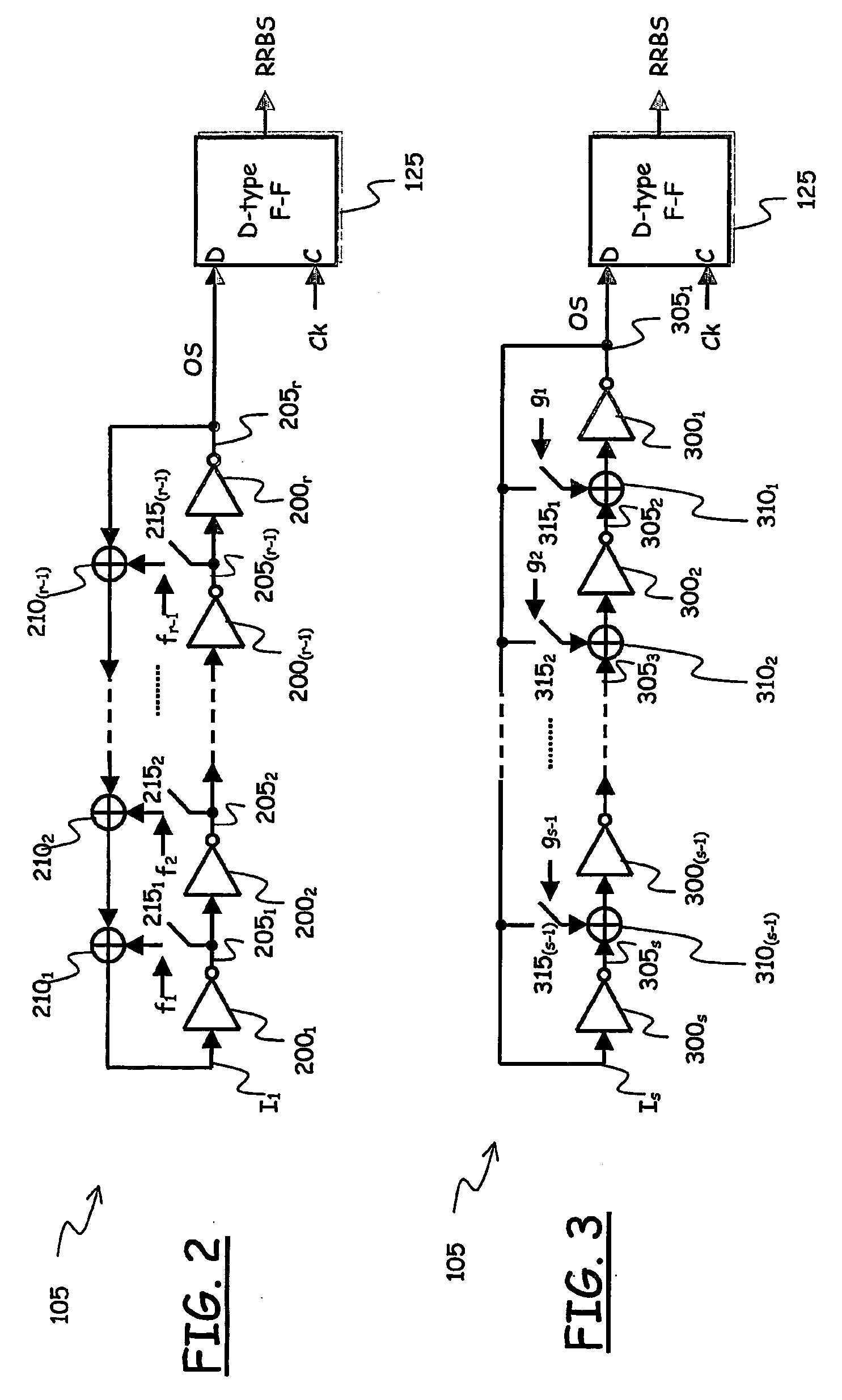
A random binary sequence generator for generating a random binary sequence adapted to be used for producing random numbers, includes at least one logic circuit corresponding to an associated finite-state machine having a state-transition function including states arranged to form cycles of states, wherein the at least one logic circuit has a set of logic circuit inputs and a set of logic circuit outputs fed back to the logic circuit inputs; the associated finite-state machine is autonomous and asynchronous; the state-transition function is void of loops; and any of the cycles of states has either a minimum length equal to three states, in case the cycle is stable, or a minimum length of two states, in case the cycle is meta-stable.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
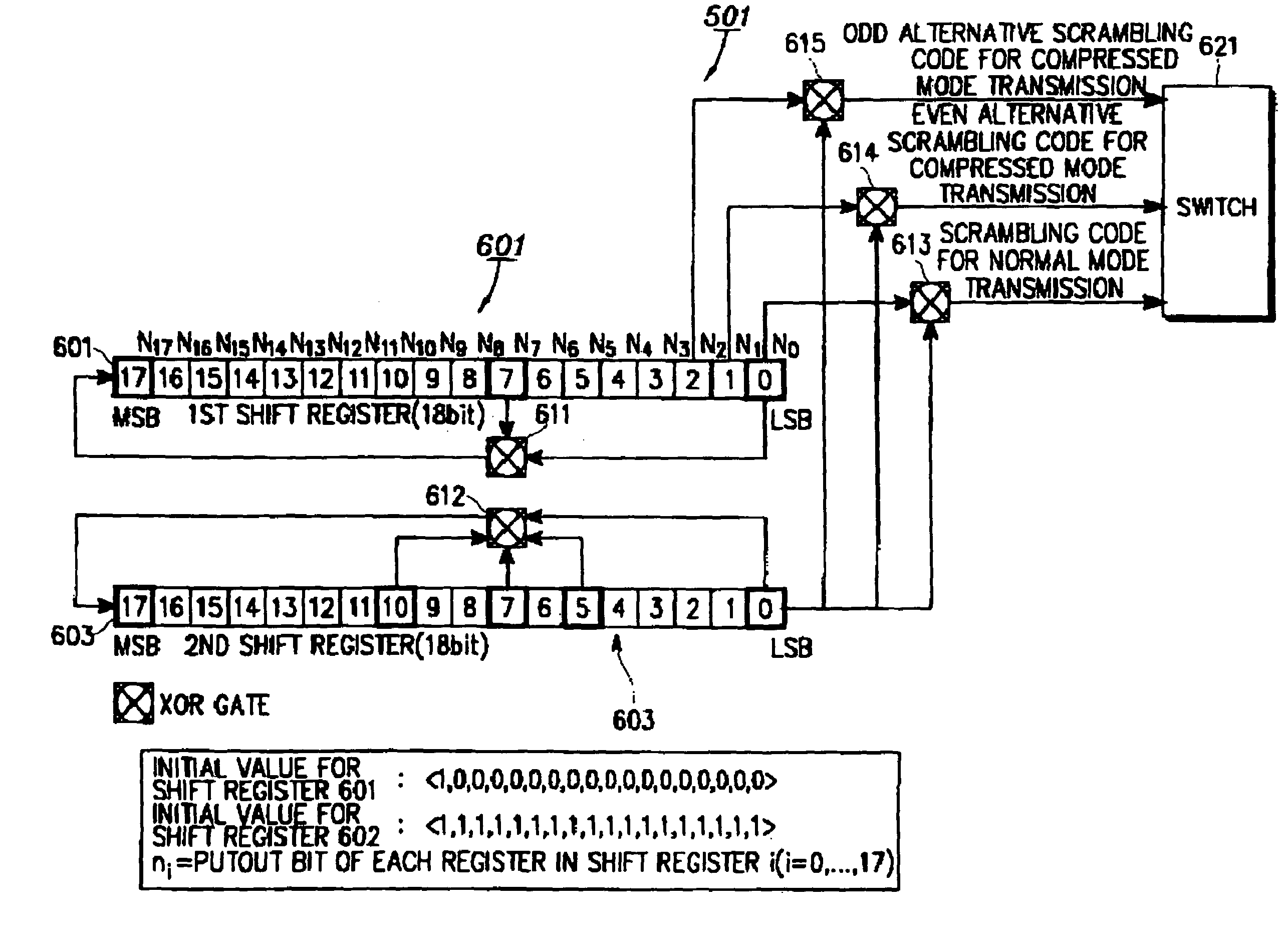
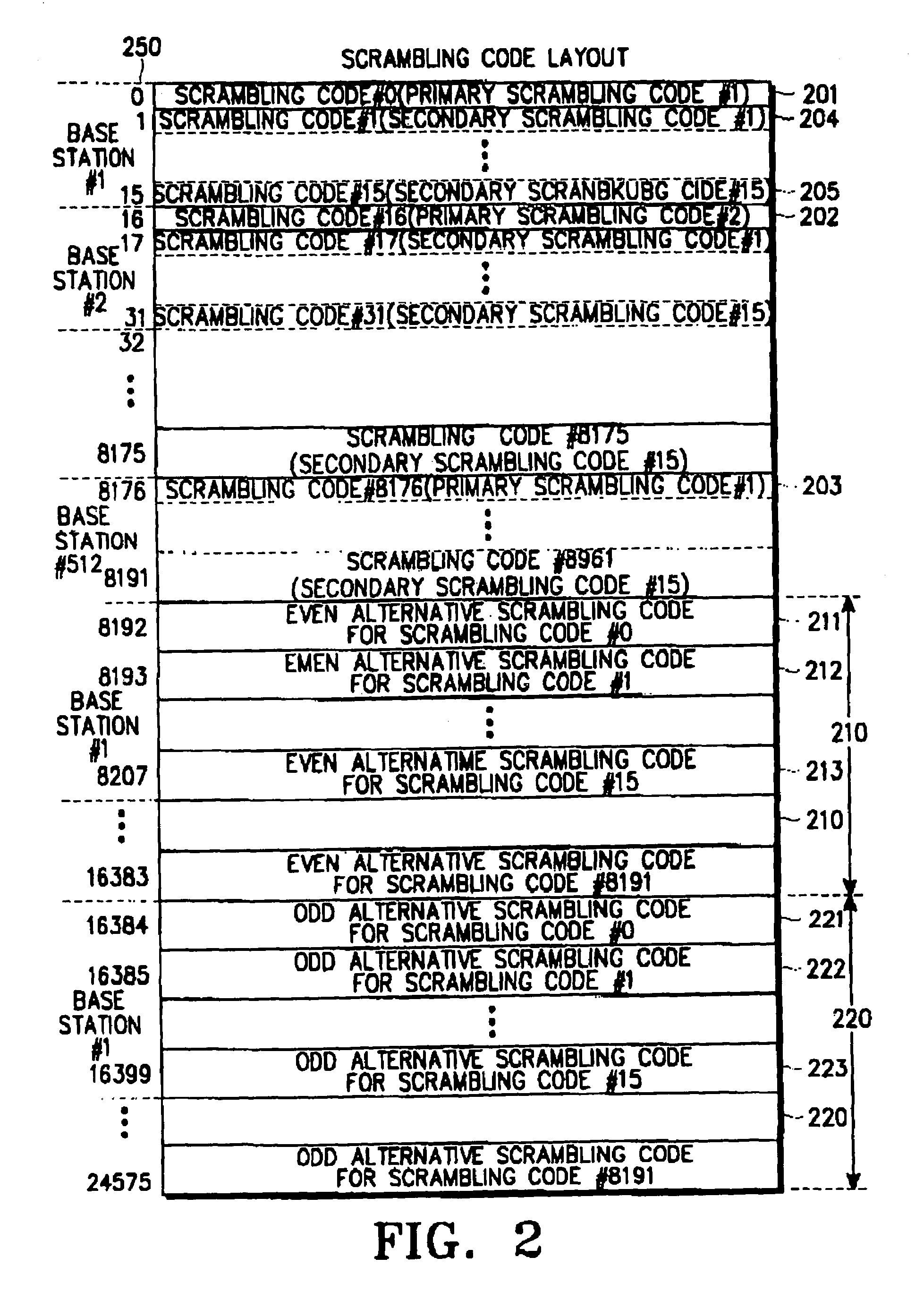
Apparatus and method for generating multiple scrambling codes in asynchronous mobile communication system
An apparatus and method for generating multiple scrambling codes in an asynchronous mobile communication system. In a scrambling code generating apparatus for generating a current scrambling code and a compressed mode scrambling code for compressed mode transmission in a base station device having a spreader for spreading an input data sequence with one of a plurality of OVSF codes and a scrambler for scrambling the spread data sequence with a primary scrambling code used as a default or one of a plurality of secondary scrambling codes according to the number of mobile stations in communication, a first feedback linear shift register generates an m-sequence from first predetermined initial bits, a second feedback linear shift register generates another m-sequence from second predetermined initial bits, a first adder generates the current scrambling code by adding the outputs of the first and second linear feedback shift registers, a second adder adds the output of the second linear feedback register and an m-sequence one bit delayed from the output of the first linear feedback register, and a third adder adds the output of the second linear feedback register and an m-sequence two bits delayed from the output of the first linear feedback register. Here, the compressed mode scrambling code is one of the outputs of the second and third adders and provided to the scrambler to scramble the spread data sequence.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for circuit testing
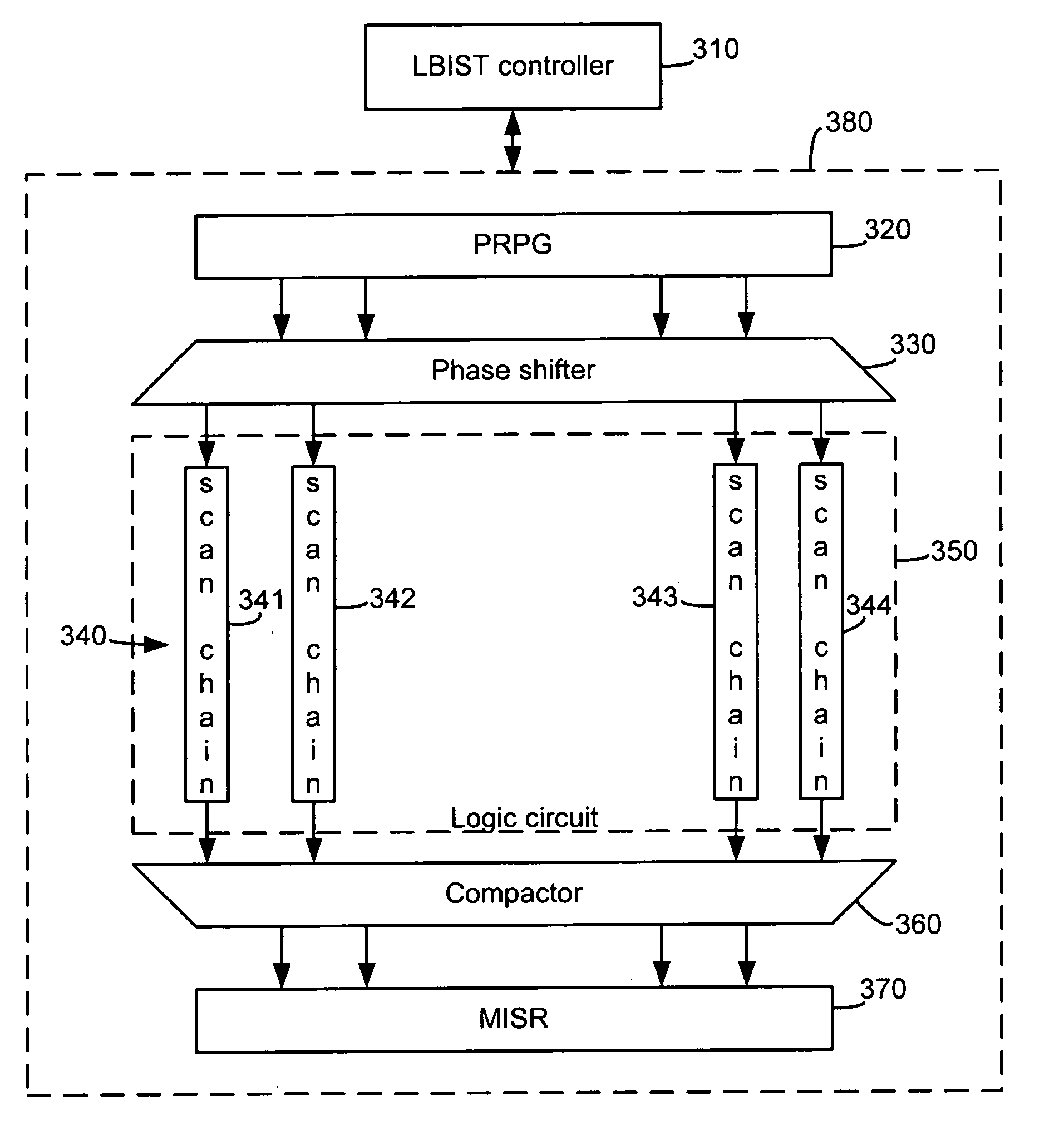
ActiveUS20050138509A1Improve performanceImprove test coverageElectronic circuit testingSolid-state devicesCircuit under testEngineering
Systems and methods for improved performance of built-in-self-tests (BISTs) in integrated circuits, where variability is introduced into the self tests to improve the coverage of the tests. In one embodiment, an LBIST system includes scan chains interposed between levels of functional logic in a circuit under test. An exemplary method includes the steps of, for each of one or more initial scan chains, filling the initial scan chains with data comprising a pseudorandom pattern of bits, determining a number of levels of functional circuitry and corresponding subsequent scan chains through which to propagate the data and propagating the data from the initial scan chains through the determined number of levels of functional circuitry and corresponding subsequent scan chains. The number of levels of circuitry through which data is propagated is varied from one test cycle to another based upon a pseudorandom input signal.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Spread spectrum clock interoperability control and inspection circuit
ActiveUS7970042B2Prevent frequency overlapAvoid frequencyComputer security arrangementsPulse shapingMagnetic tapeModularity
A spread spectrum clock generator (SSCG) control and inspection circuit provides a system and method for inspecting and controlling an external SSCG, and for verifying the modulation profile waveform of an external SSCG. An electronic circuit is included that can check for the presence of an optimal SSCG modulation profile in product subsystems, and in attached modular systems, including electronic plug-in features such as internal network adapters and cartridges. In one mode of the invention, an electronic circuit ensures continued radiated emissions compliance for field replaceable units or consumable parts within a product, such as a printer, a scanner, or a combination (or all-in-one) printer / scanner. In another mode of the invention, an electronic circuit may also act as a secondary security device for consumable products, such as toner cartridges or ink jet cartridges. In yet another mode of the invention, an electronic circuit may also adjust the attached SSCG clock.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Countermeasure method and device against an attack by fault injection in an electronic microcircuit
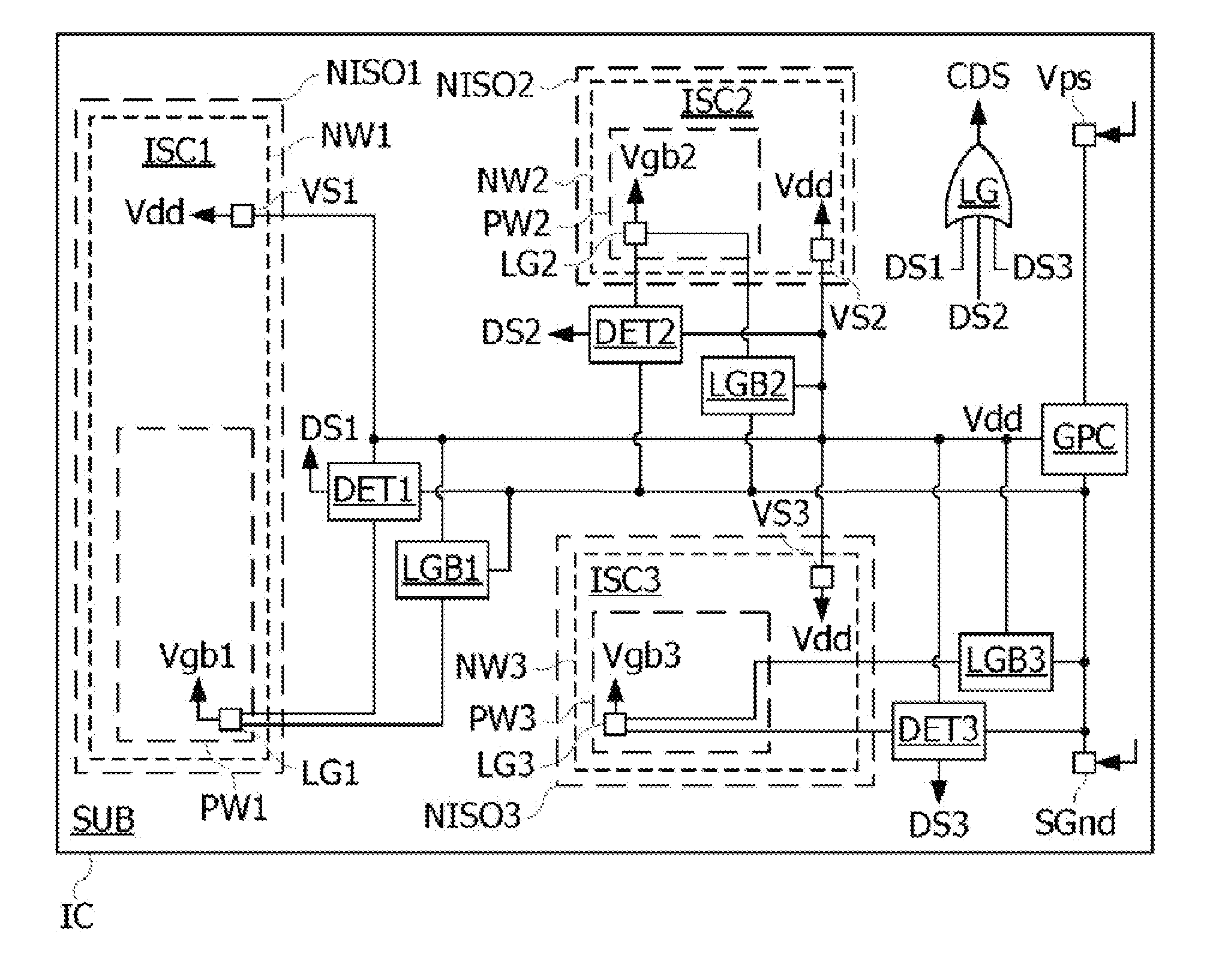
InactiveUS20110234307A1Increased complexityIncrease consumptionReliability increasing modificationsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityCountermeasure
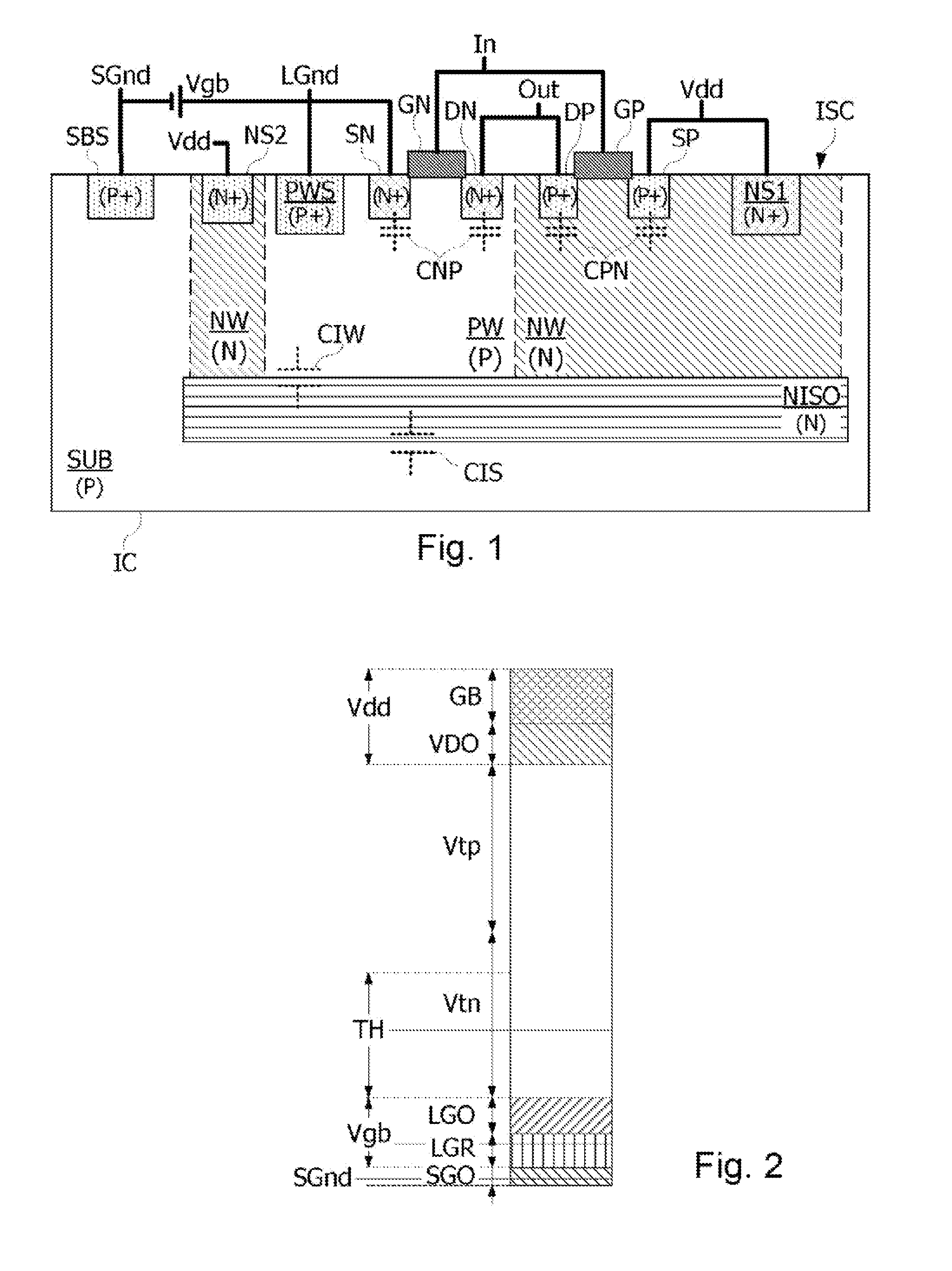
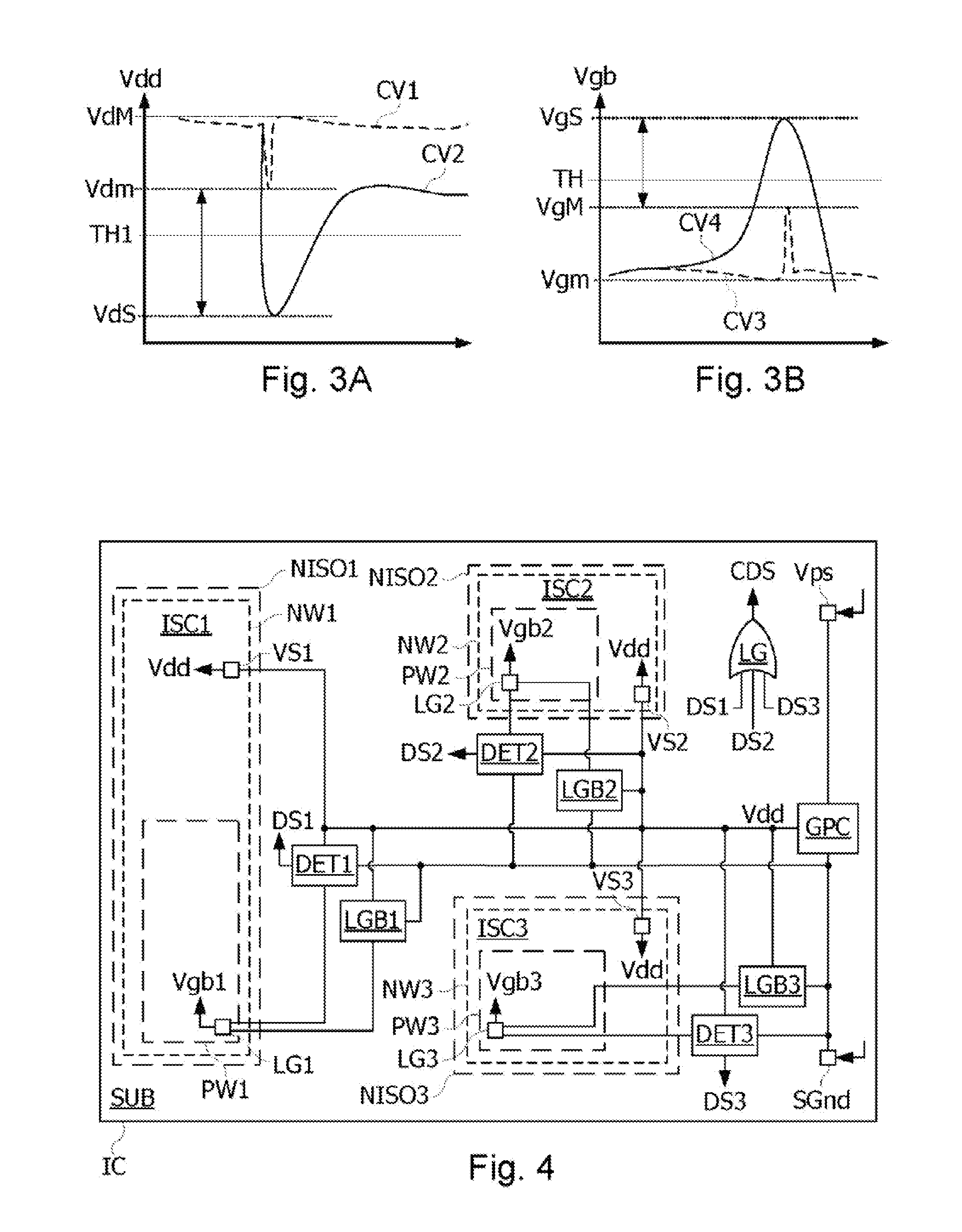
The disclosure relates to a method for detecting an attack in an electronic microcircuit, comprising: forming the microcircuit in a substrate, forming in the substrate a first well electrically isolated from the substrate, by a second well and an embedded well, forming in the first and second wells a data processing circuit comprising a ground terminal formed in the first well and a power supply terminal formed in the second well, and activating a detection signal when a voltage at the ground or power supply terminal of the data processing circuit crosses a threshold voltage.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
Popular searches
Radio wave reradiation/reflection Pulse generation with predetermined statistical distribution Payment architecture Coded identity card or credit card actuation Radio transmission Wireless communication Radio transmission for post communication Orthogonal multiplex Link quality based transmission modification Duplex signal operation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com