Patents
Literature
408 results about "Circuit under test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
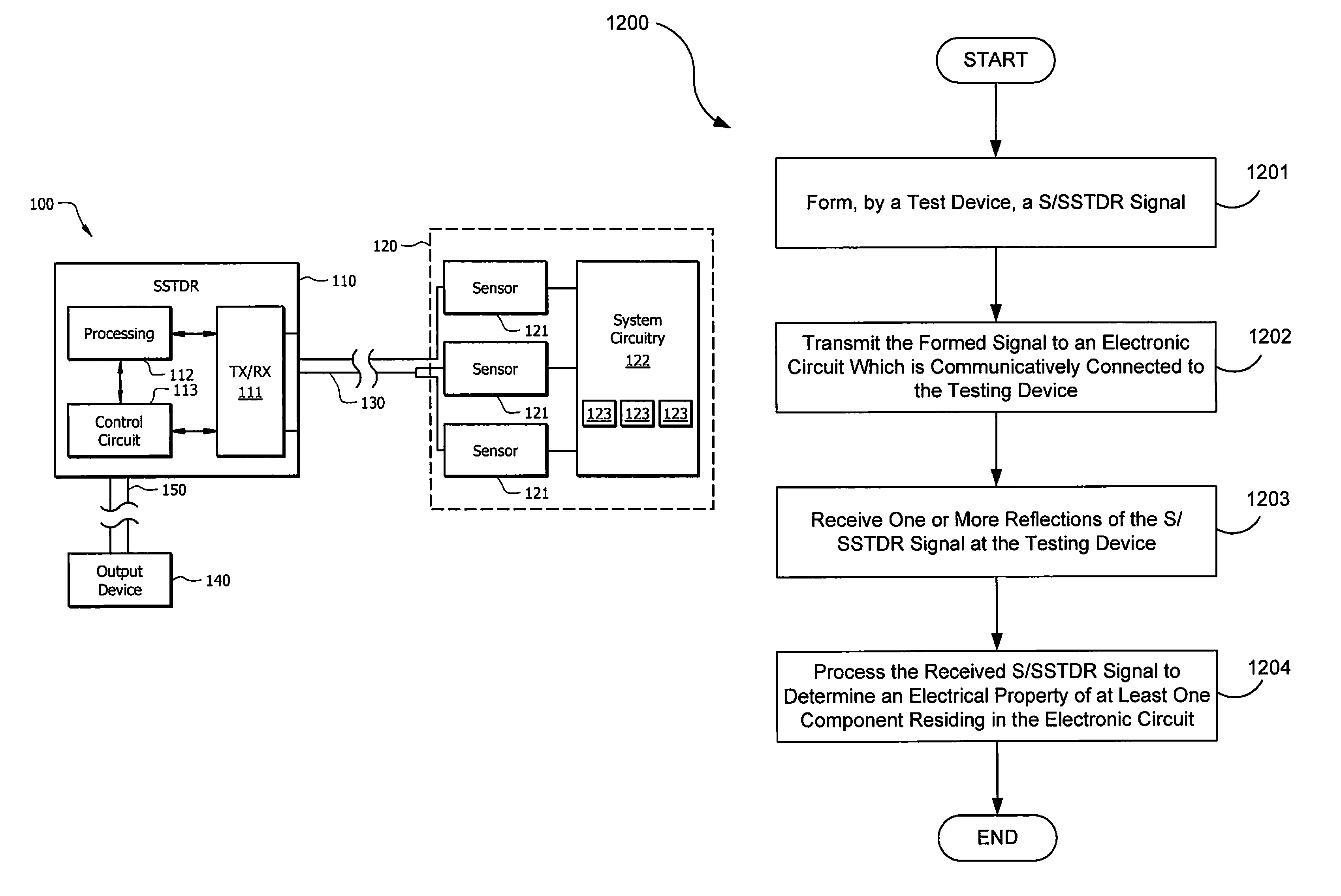
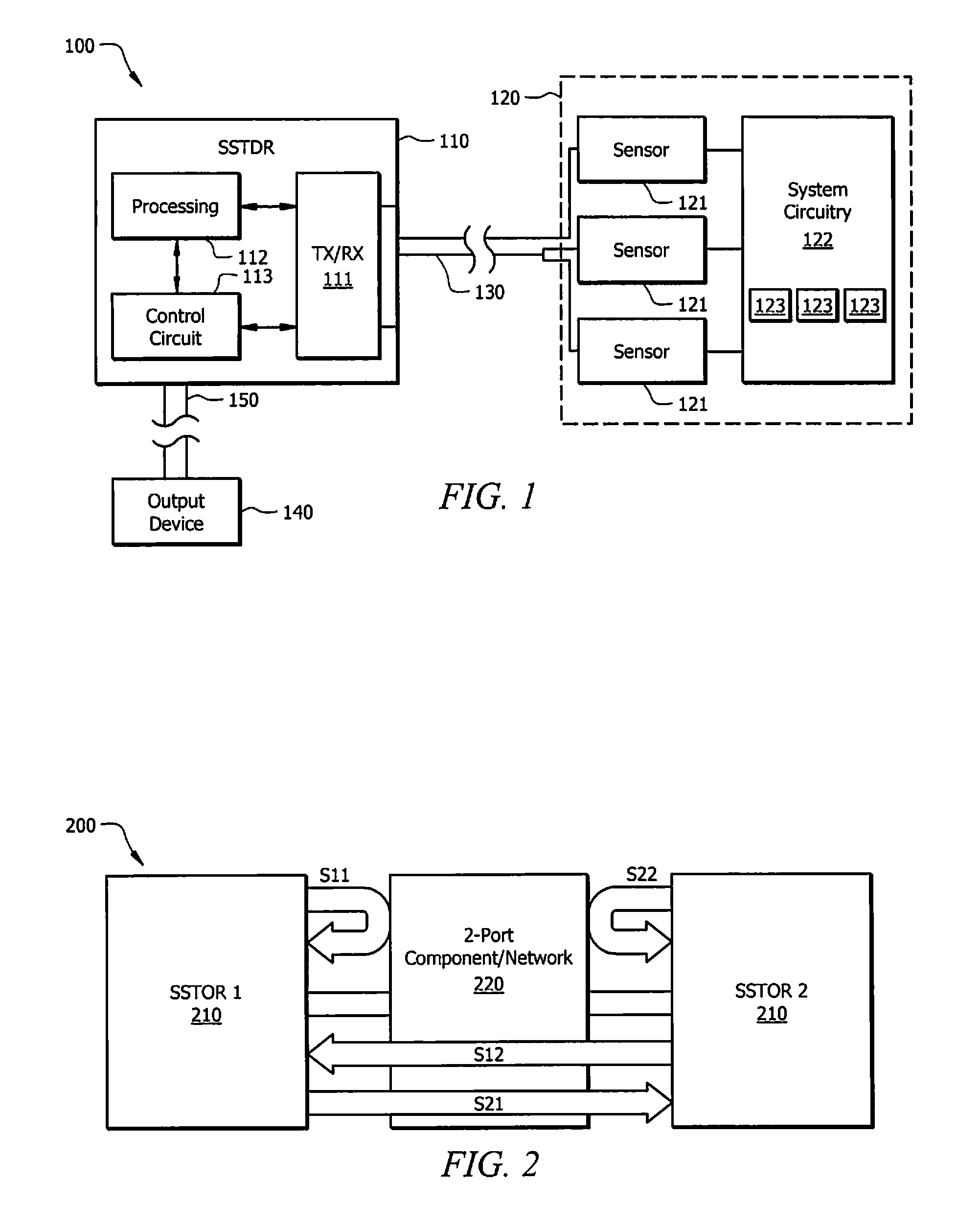
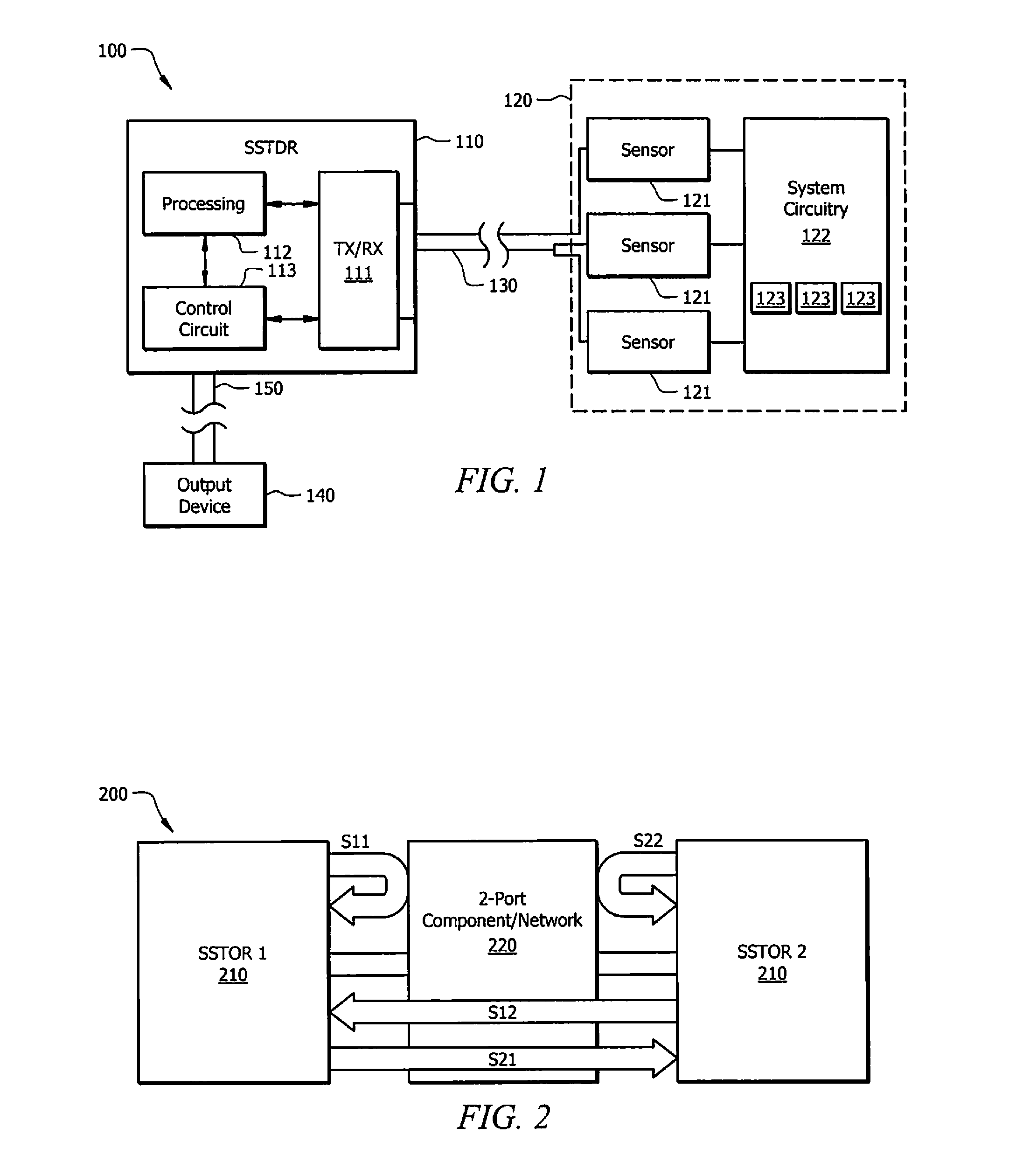
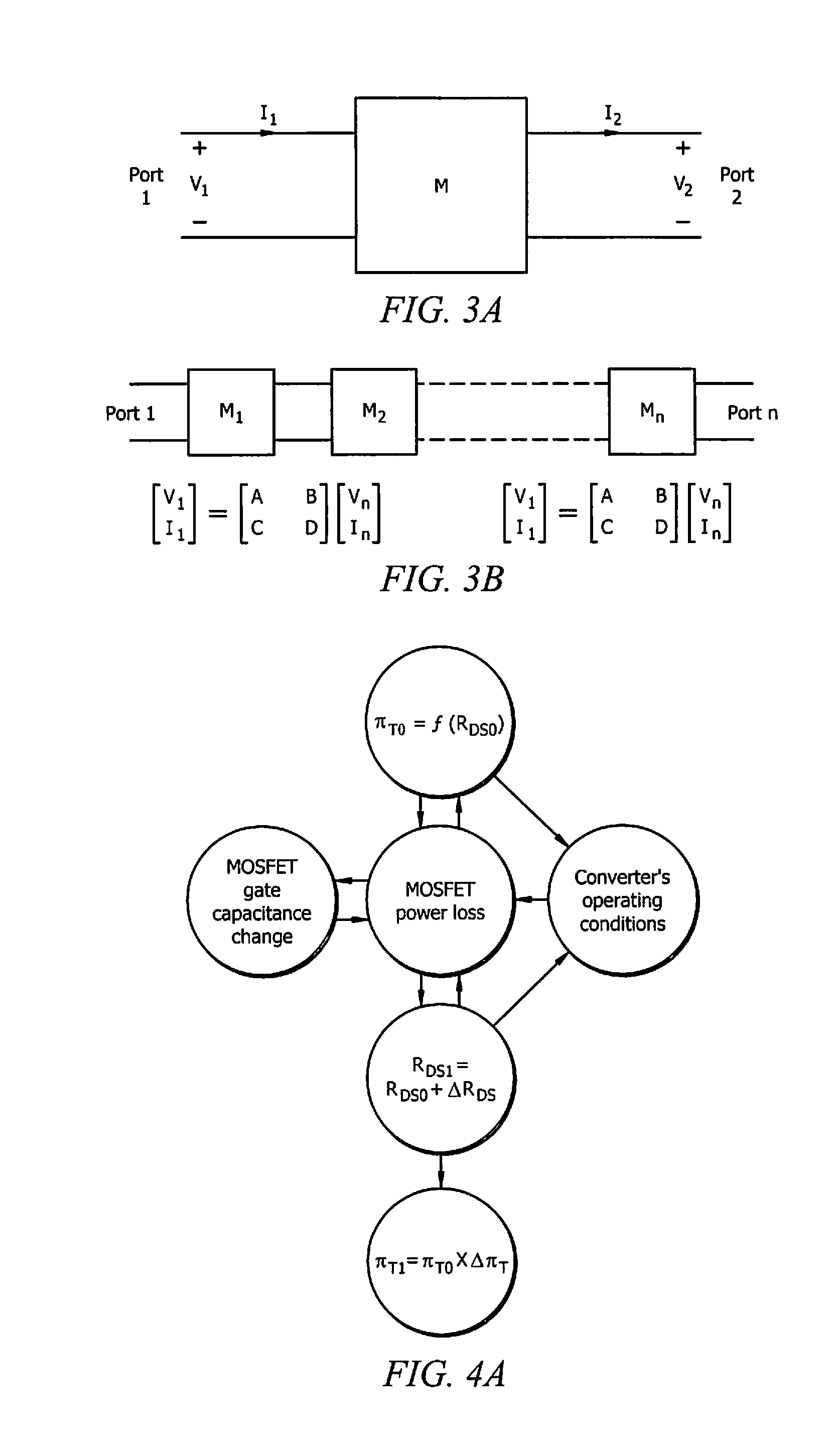
Systems and methods for implementing S/SSTDR measurements
ActiveUS9244117B2Shorten the timeAccurate measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingCircuit under testSpread spectrum
Systems and methods which utilize spread spectrum sensing on live circuits to obtain information regarding a circuit under test are provided. In some embodiments S / SSTDR testing may be utilized to obtain R, L, C and Z measurements from circuit components. In yet further embodiments, these measurements may be utilized to monitor the output of sensors on a circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
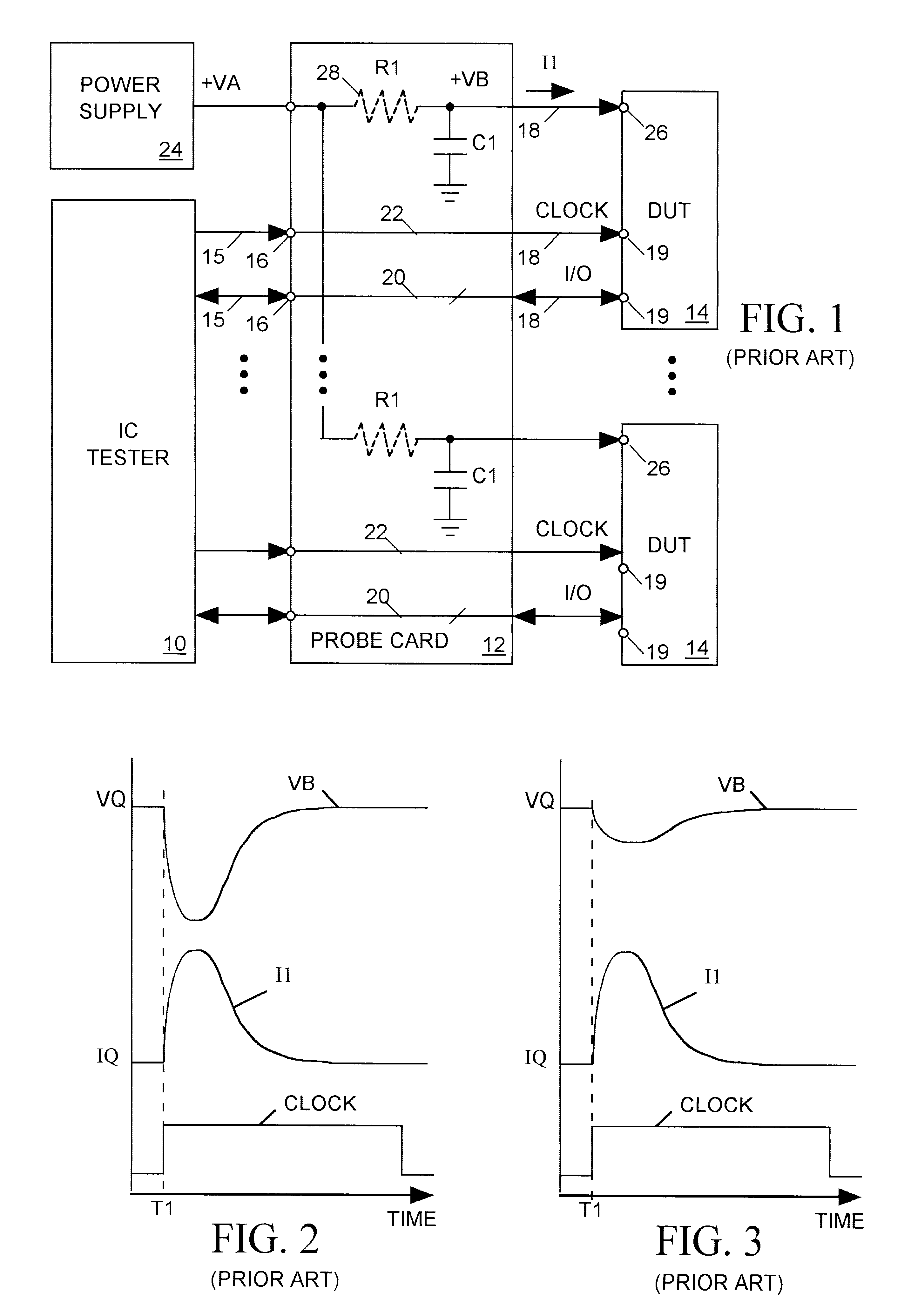
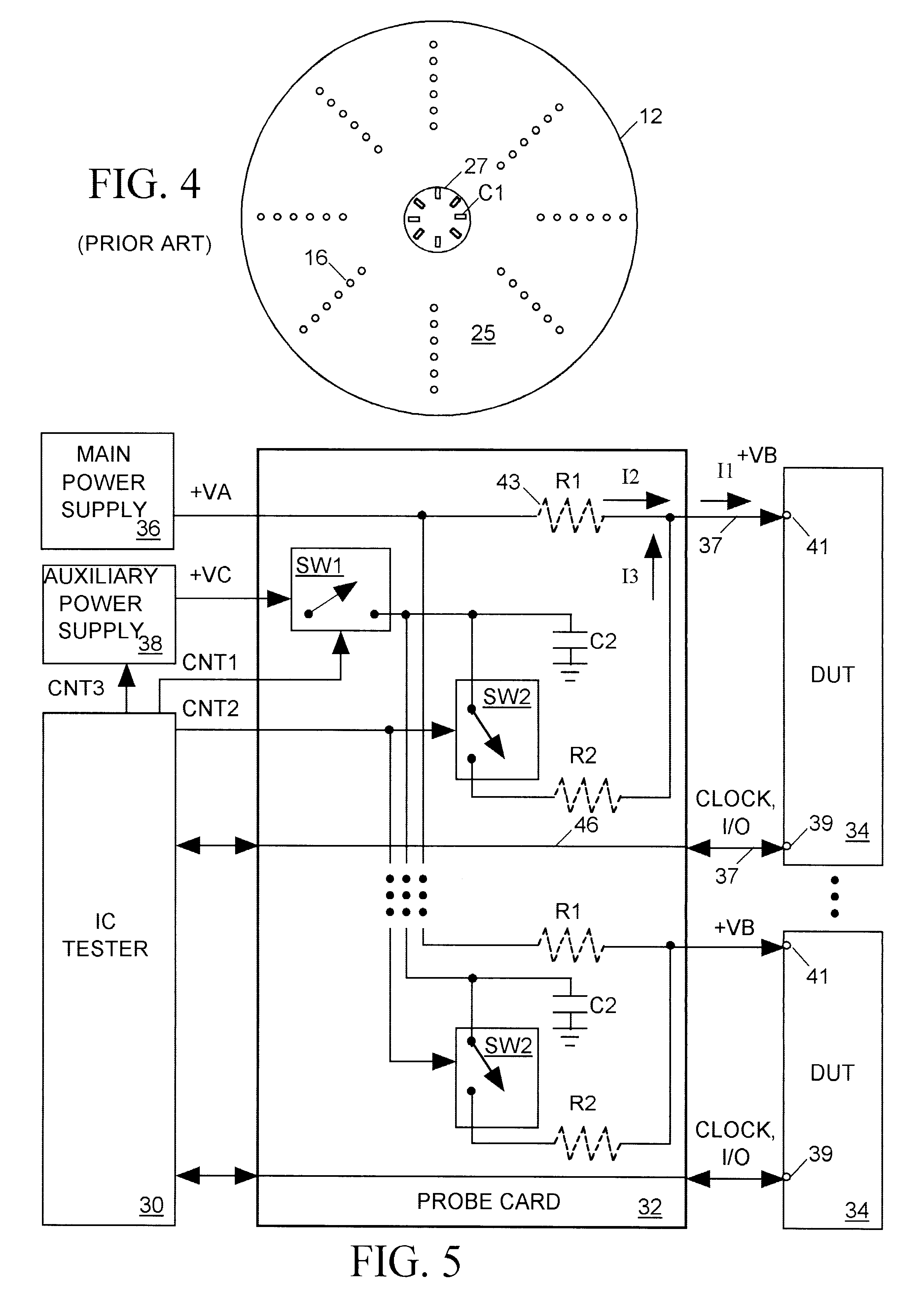
Predictive, adaptive power supply for an integrated circuit under test
InactiveUS6657455B2Suppress mutationReduce noiseDigital circuit testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPower flowFeedback circuits
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
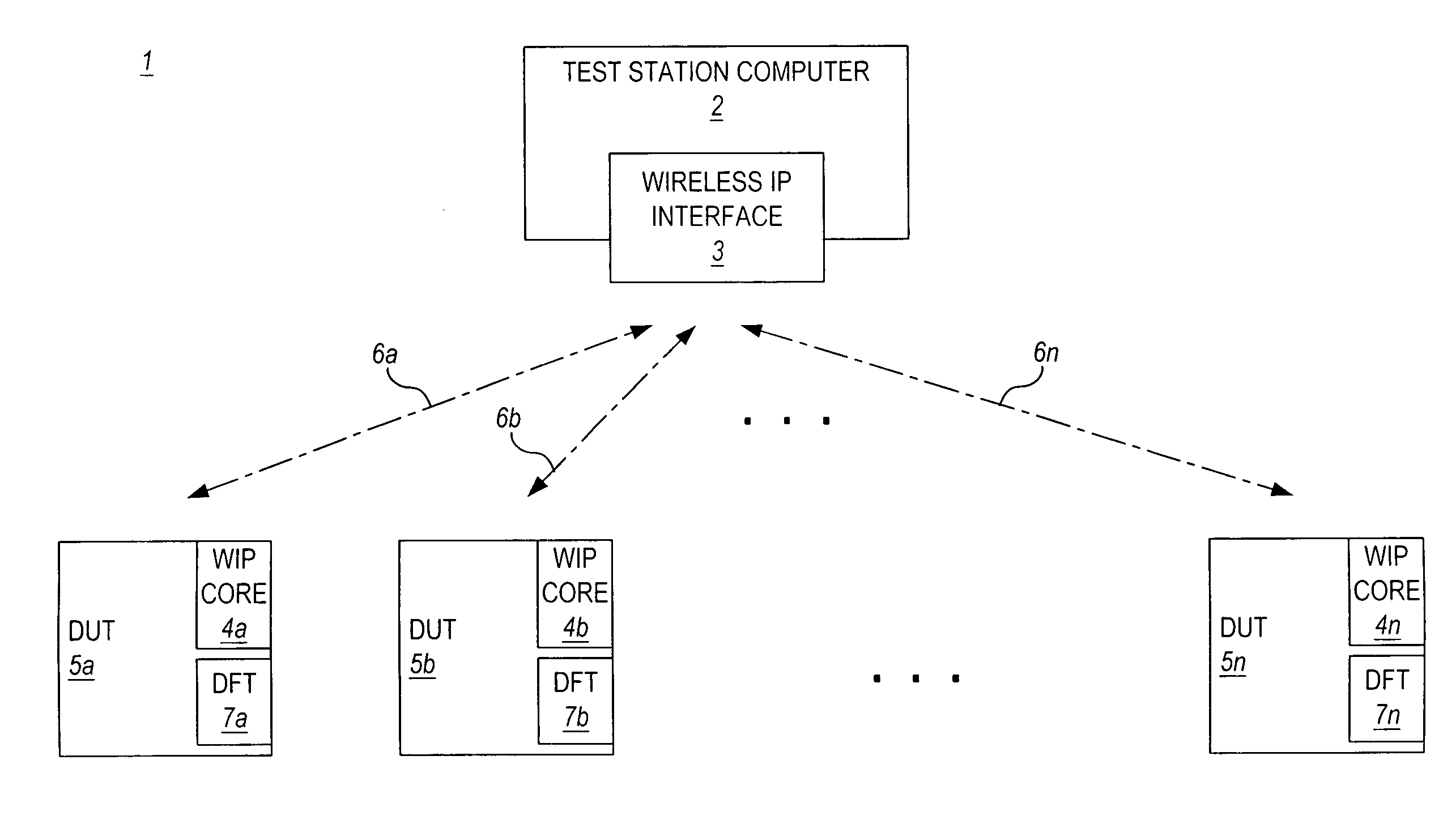
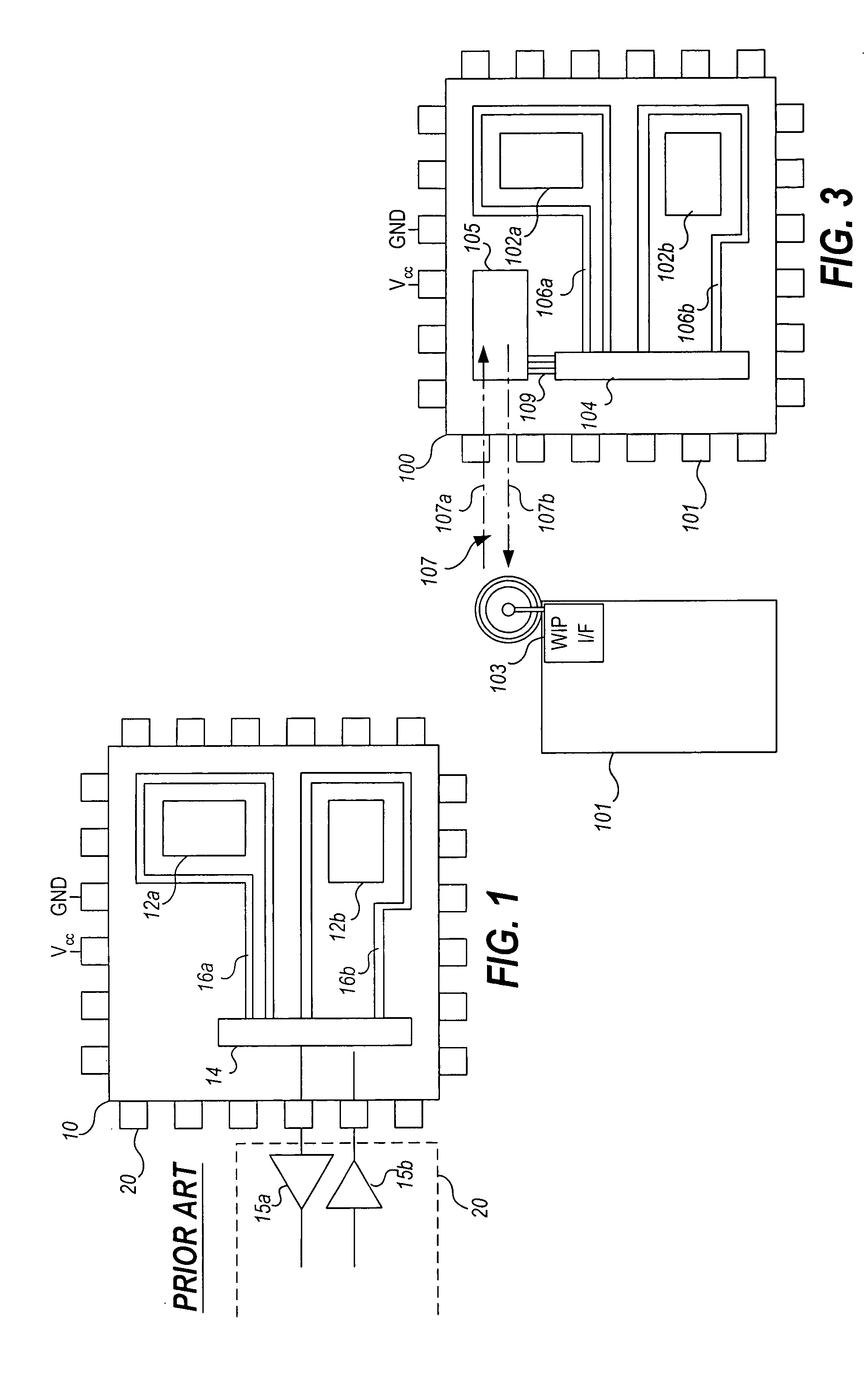
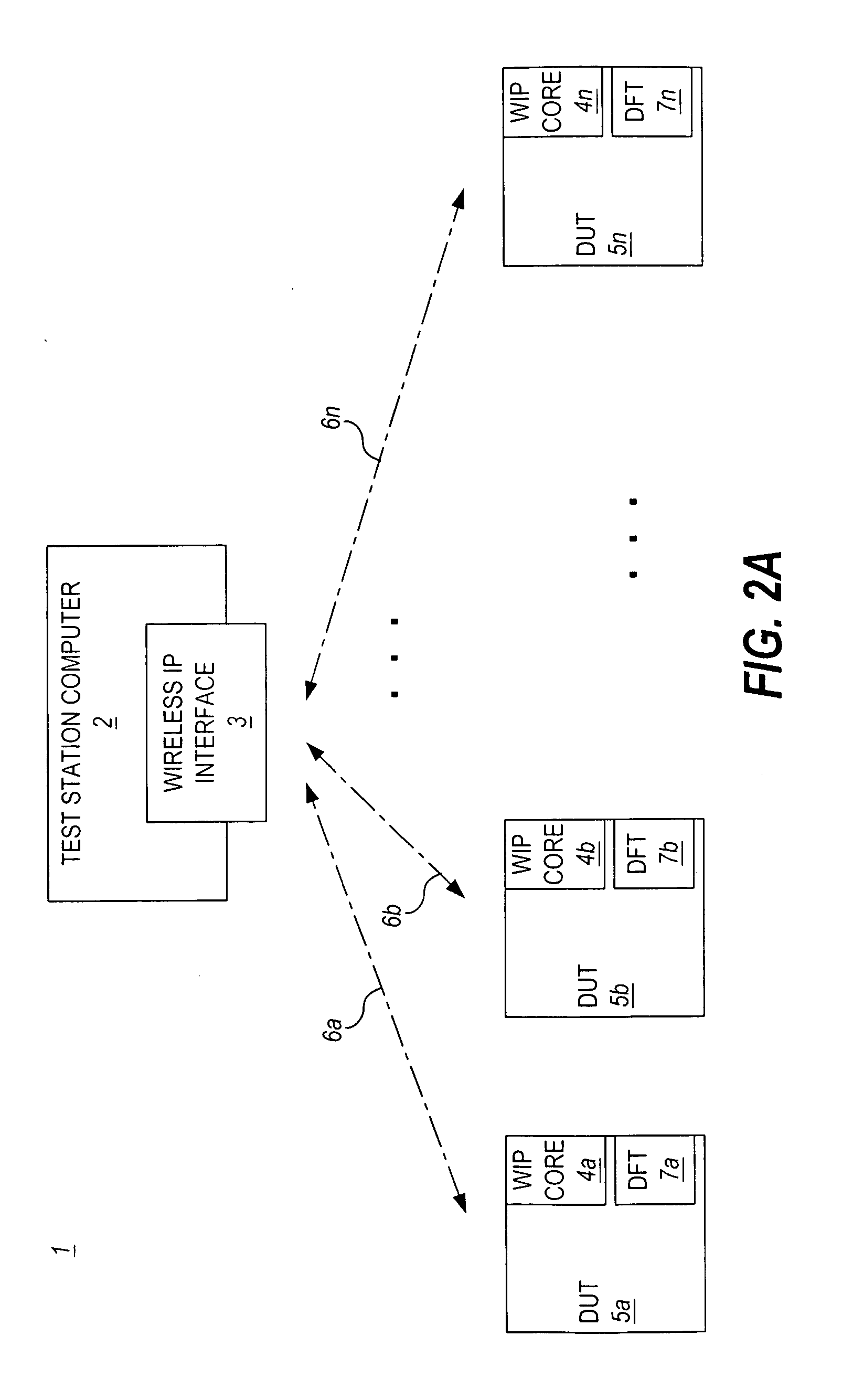
Wireless no-touch testing of integrated circuits
ActiveUS20050193294A1Immediate cost-reduction impactIncrease speedDigital circuit testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementCircuit under testEngineering
A wireless integrated circuit test method and system is presented. The invention allows testing of one or more integrated circuits configured with a wireless interface and a test access mechanism which controls input of test data received over a wireless connection from a test station to test structures which test functional blocks on the integrated circuit. Via the wireless connection, multiple integrated circuits or similarly equipped devices under test can be tested simultaneously. The invention also enables concurrent testing of independently testable functional blocks on any given integrated circuit under test.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
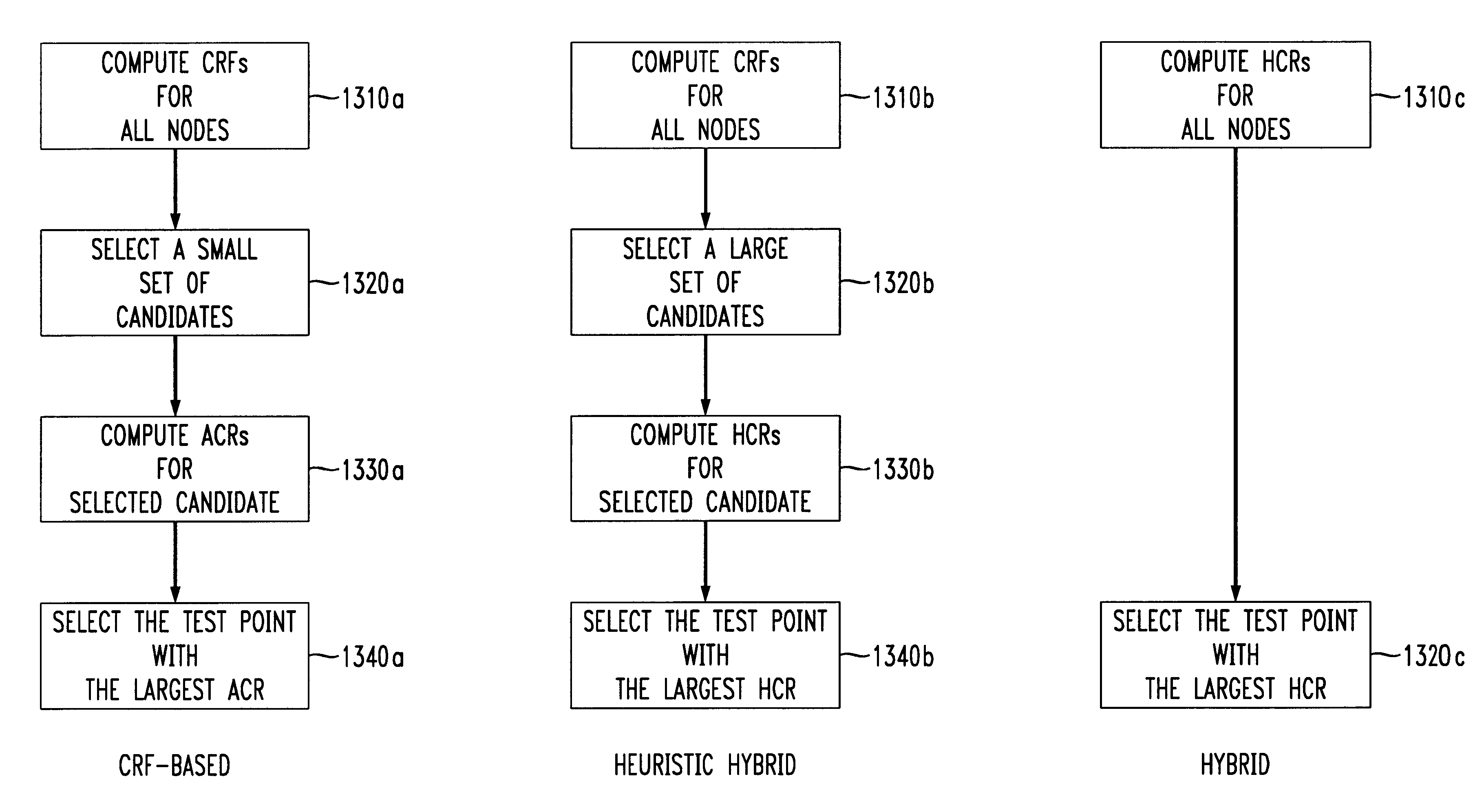
Hybrid algorithm for test point selection for scan-based BIST
A test point selection method for scan-based built-in self-test (BIST). The method calculates a hybrid cost reduction (HCR) value as an estimated value of the corresponding actual cost reduction for all nodes in a circuit under test. A test point is then selected having a largest HCR. This iterative process continues until the fault coverage of the circuit under test reaches a desired value or the number of test points selected is equal to a maximum number of test points. In an alternative embodiment, the cost reduction factor is calculated for all nodes in the circuit under test, the HCR is calculated for only a selected set of candidates, and the candidate having the largest HCR is selected as the test point. The test point selection method achieves higher fault coverage results and reduces computational processing relative to conventional selection methods.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
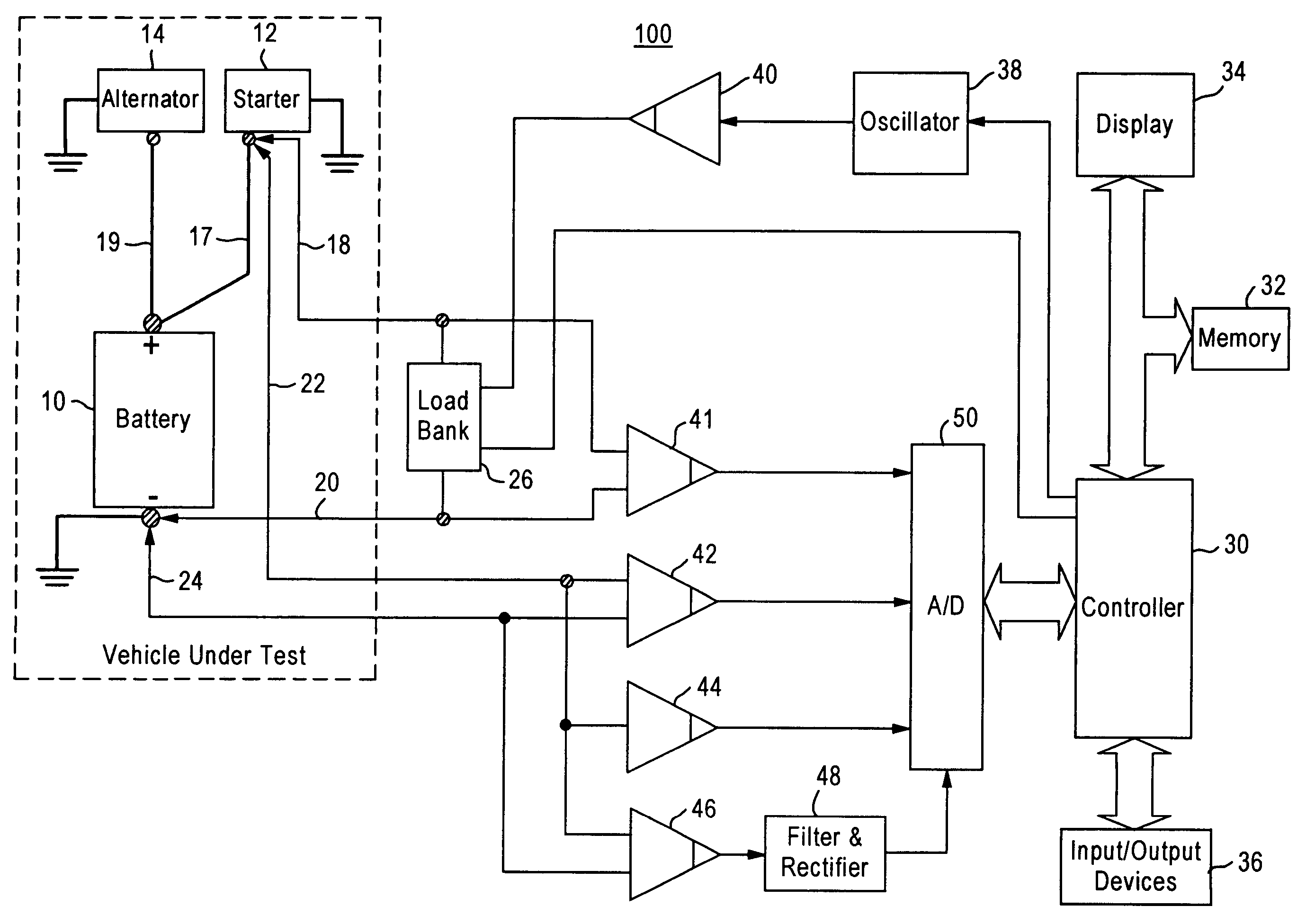
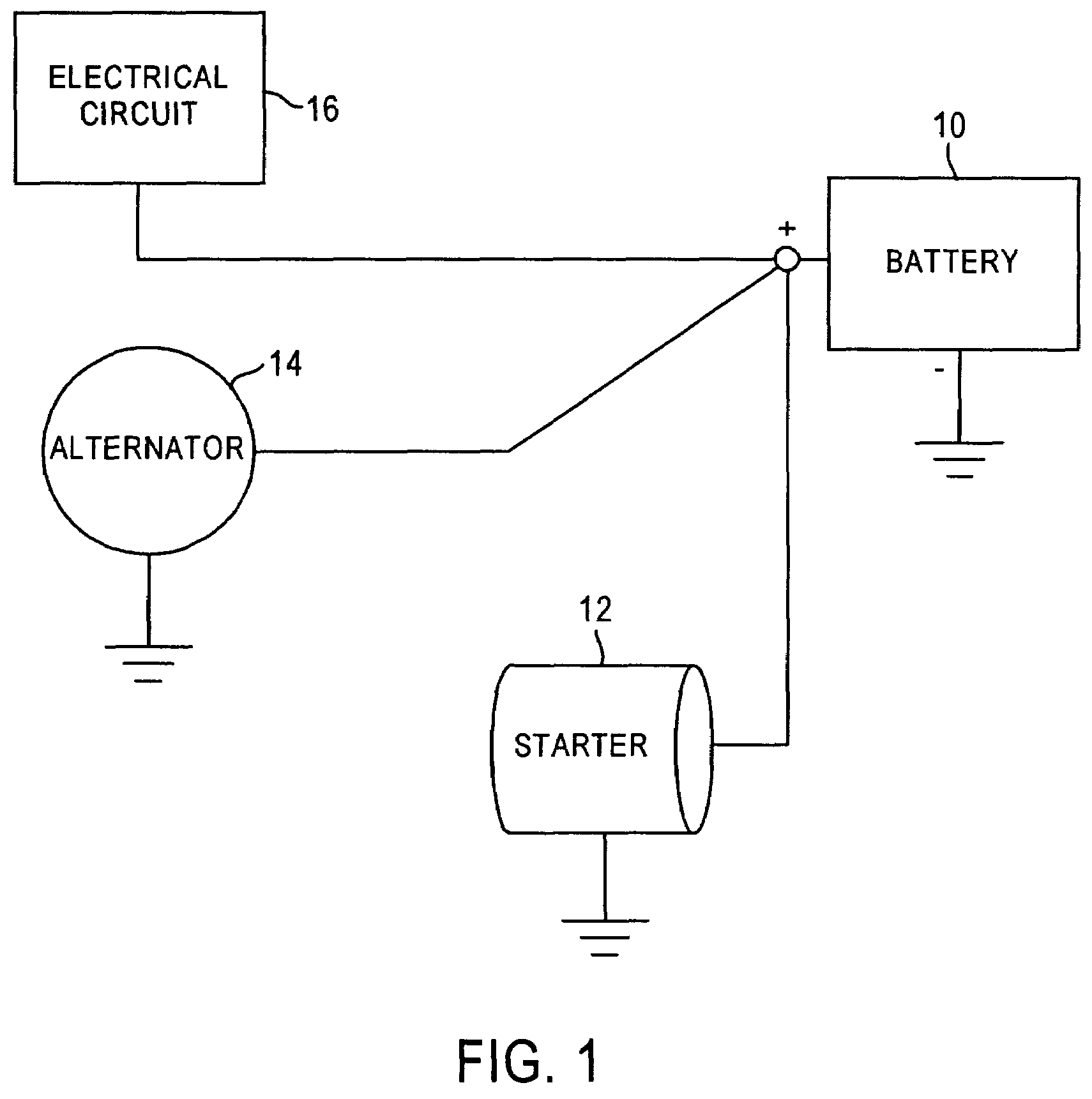
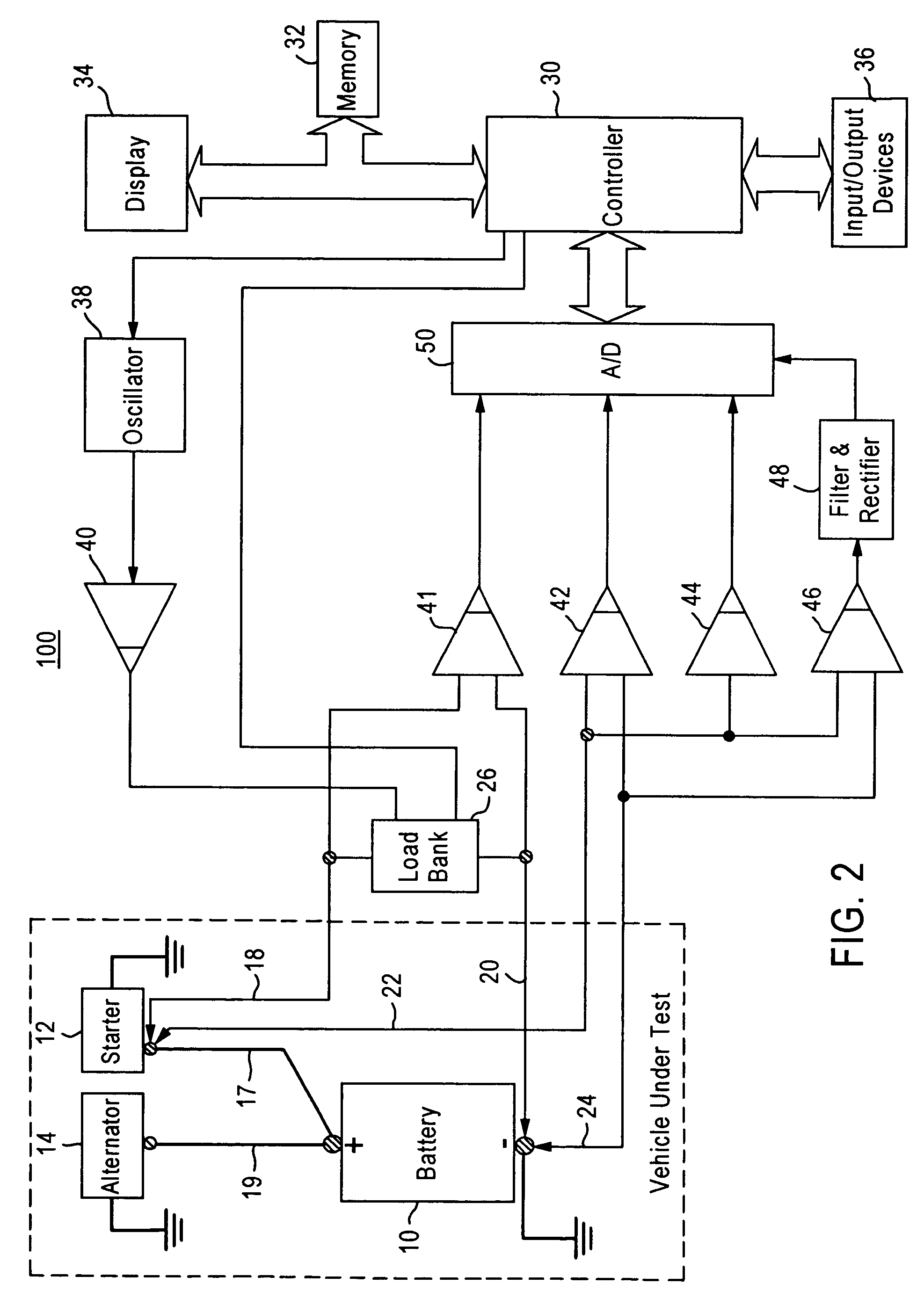
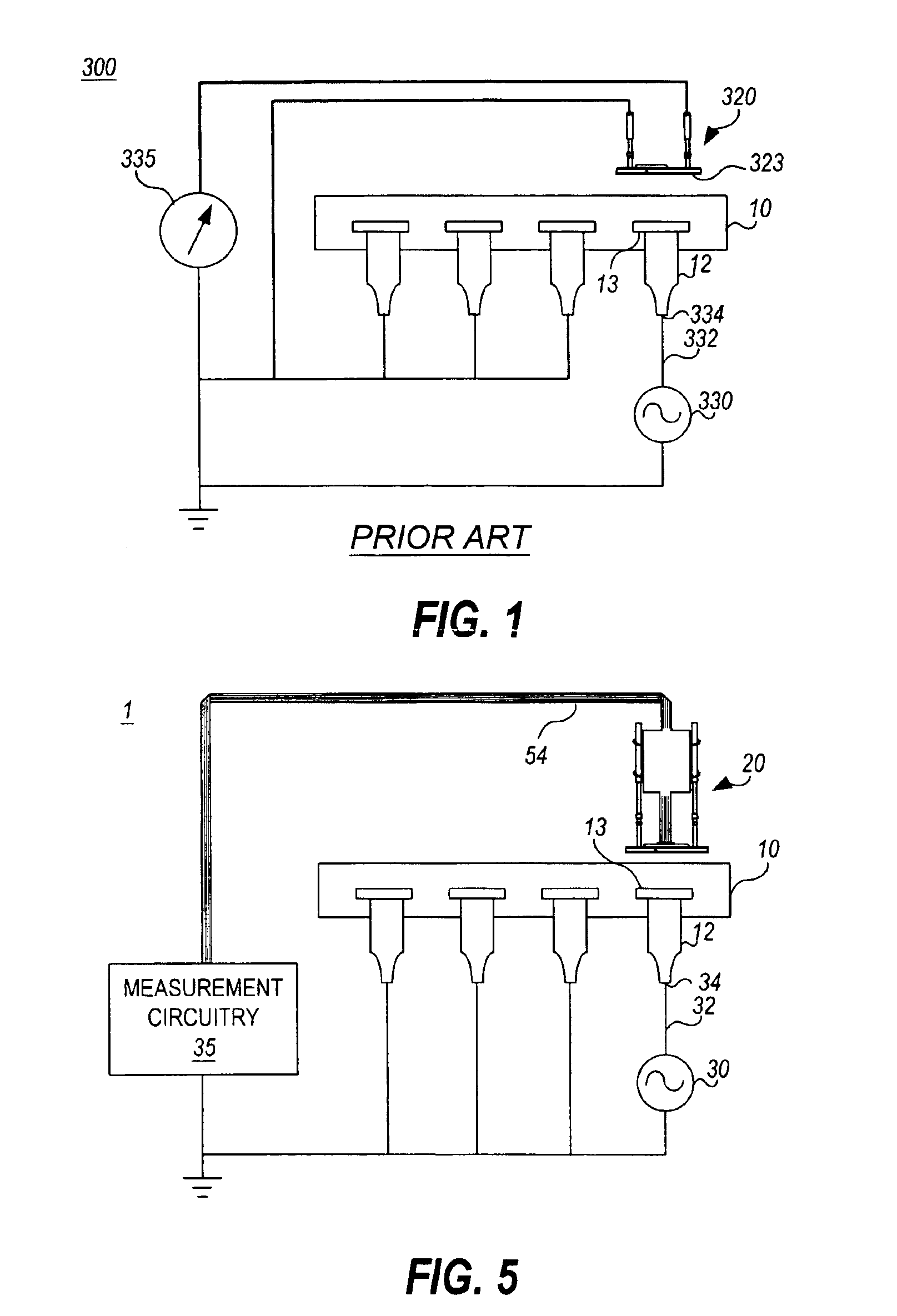
Active tester for vehicle circuit evaluation
InactiveUS7209850B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementCircuit under testComputer terminal
Owner:SNAP ON INC
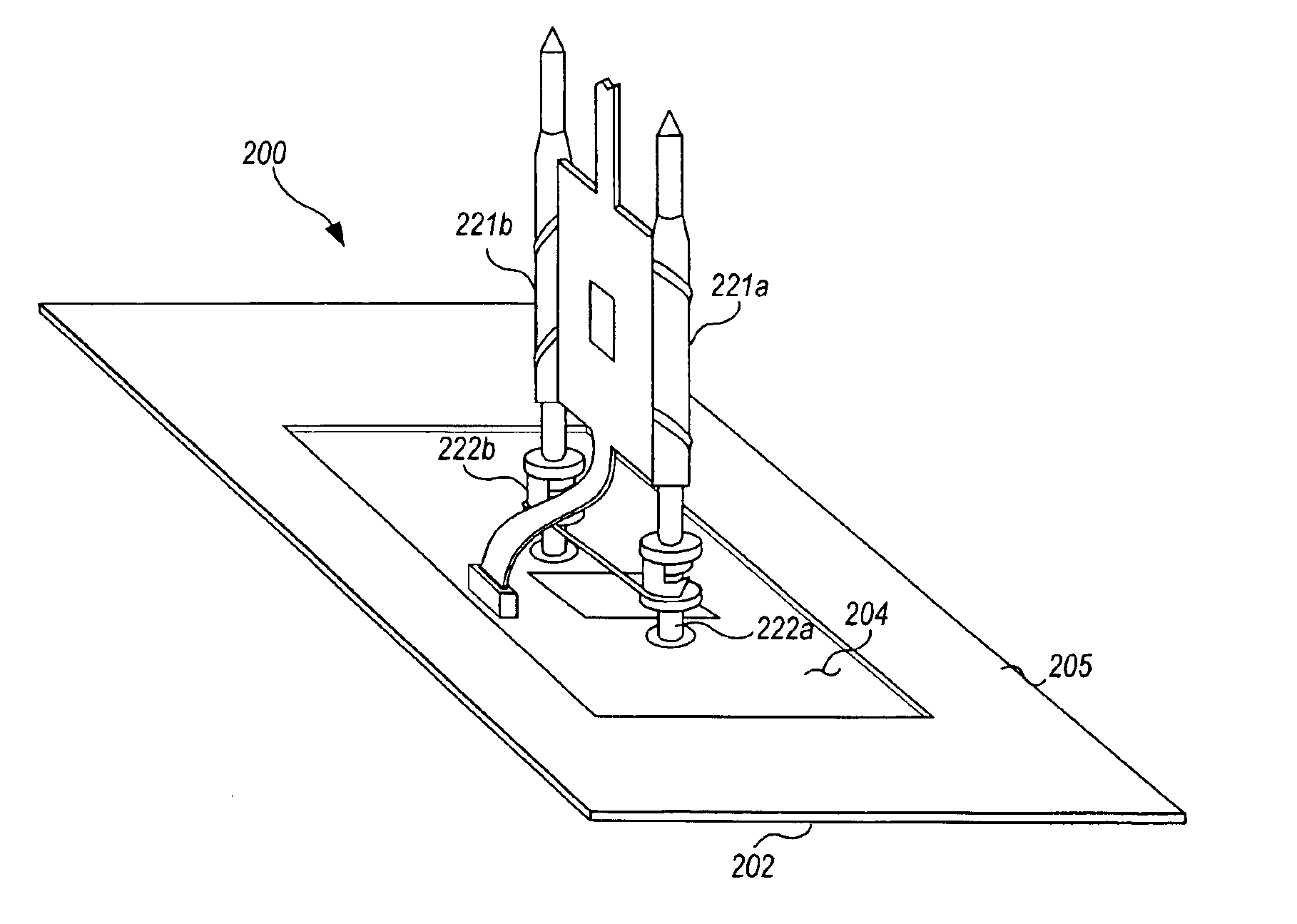
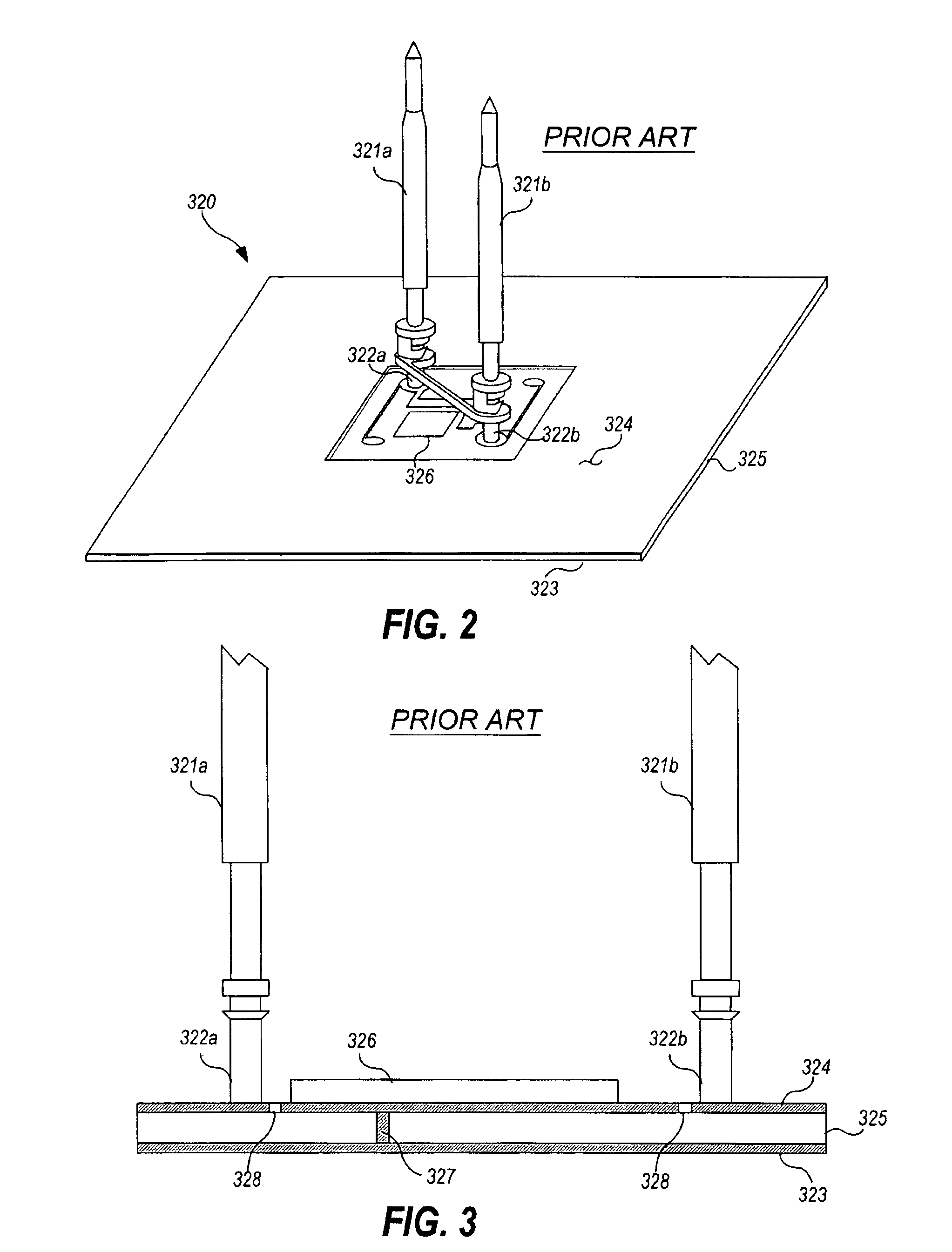
Capacitive probe assembly with flex circuit
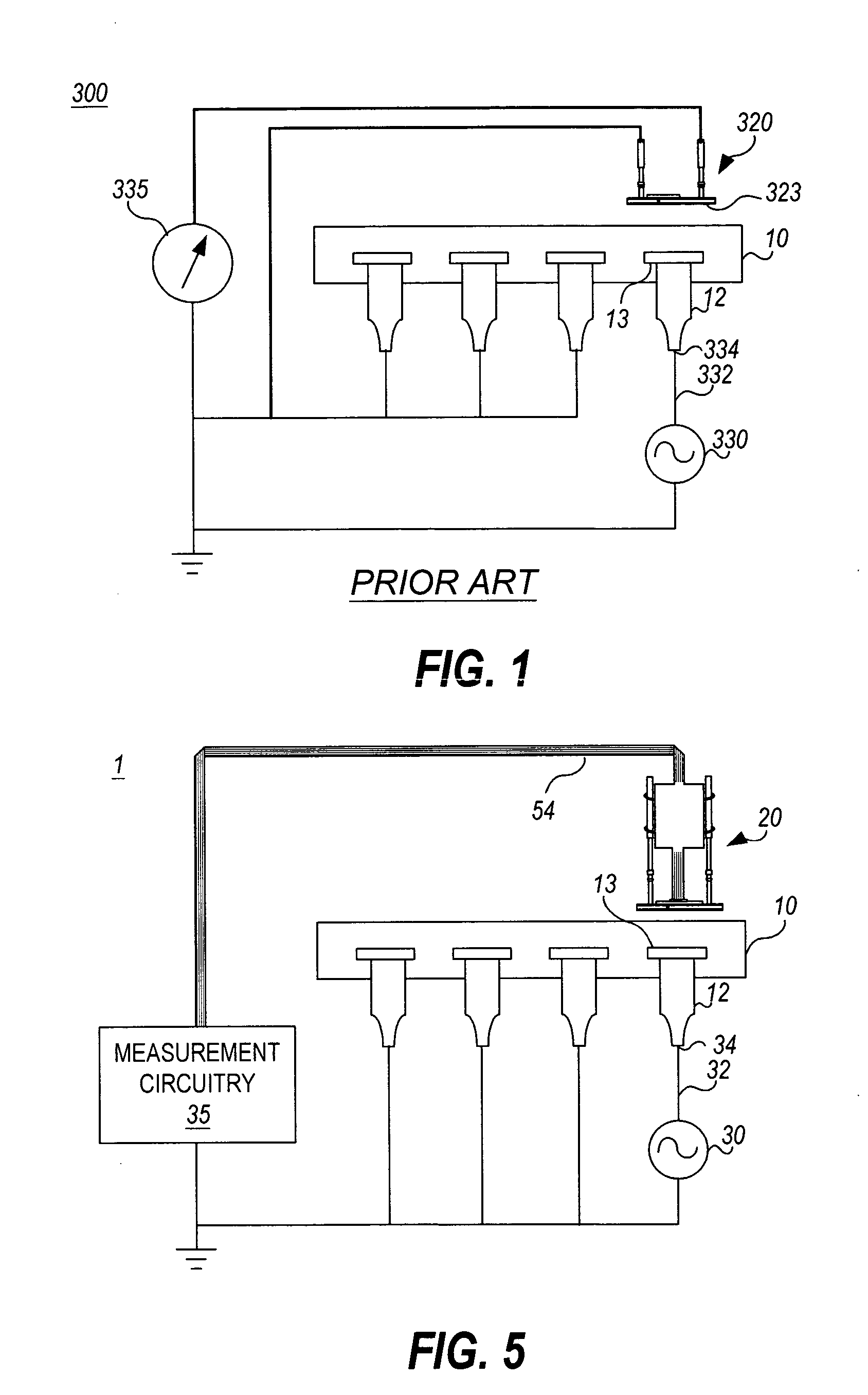
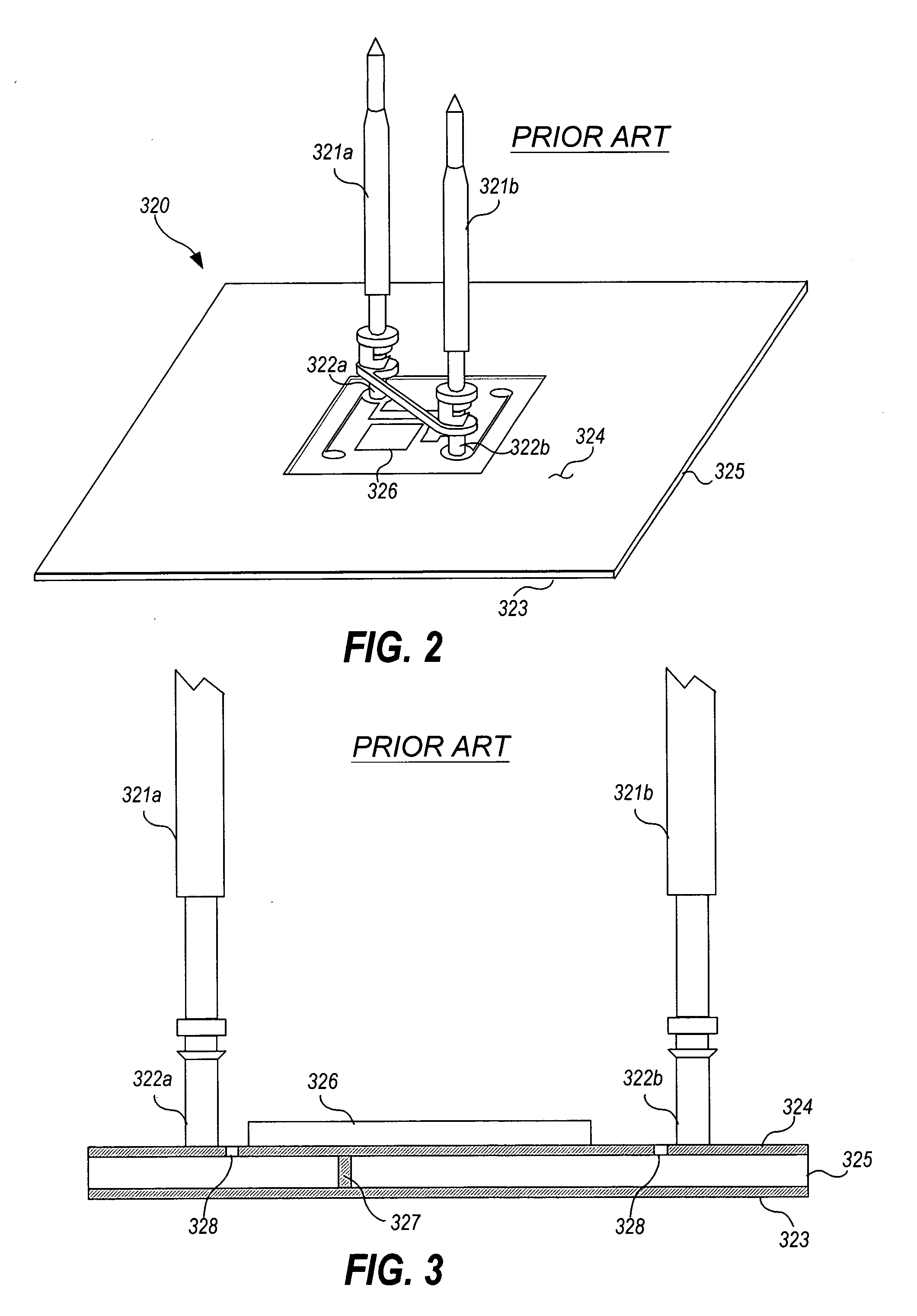
InactiveUS6930494B2Reduce complexityReduce in quantityResistance/reactance/impedenceElectric connection testingAudio power amplifierFlexible circuits
A novel capacitive sensor assembly that utilizes a flex circuit for amplification of capacitively sensed signals and for separating the power, ground, and measurement signals is presented. The use of a flex circuit in the capacitive probe assembly allows implementation of multiple capacitive sensors for respectively capacitively coupling multiple signals from respective multiple test points of a circuit under test. The invention integrates the sensor plate, amplifier, and return wiring for each capacitive sensor all onto one flex circuit.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
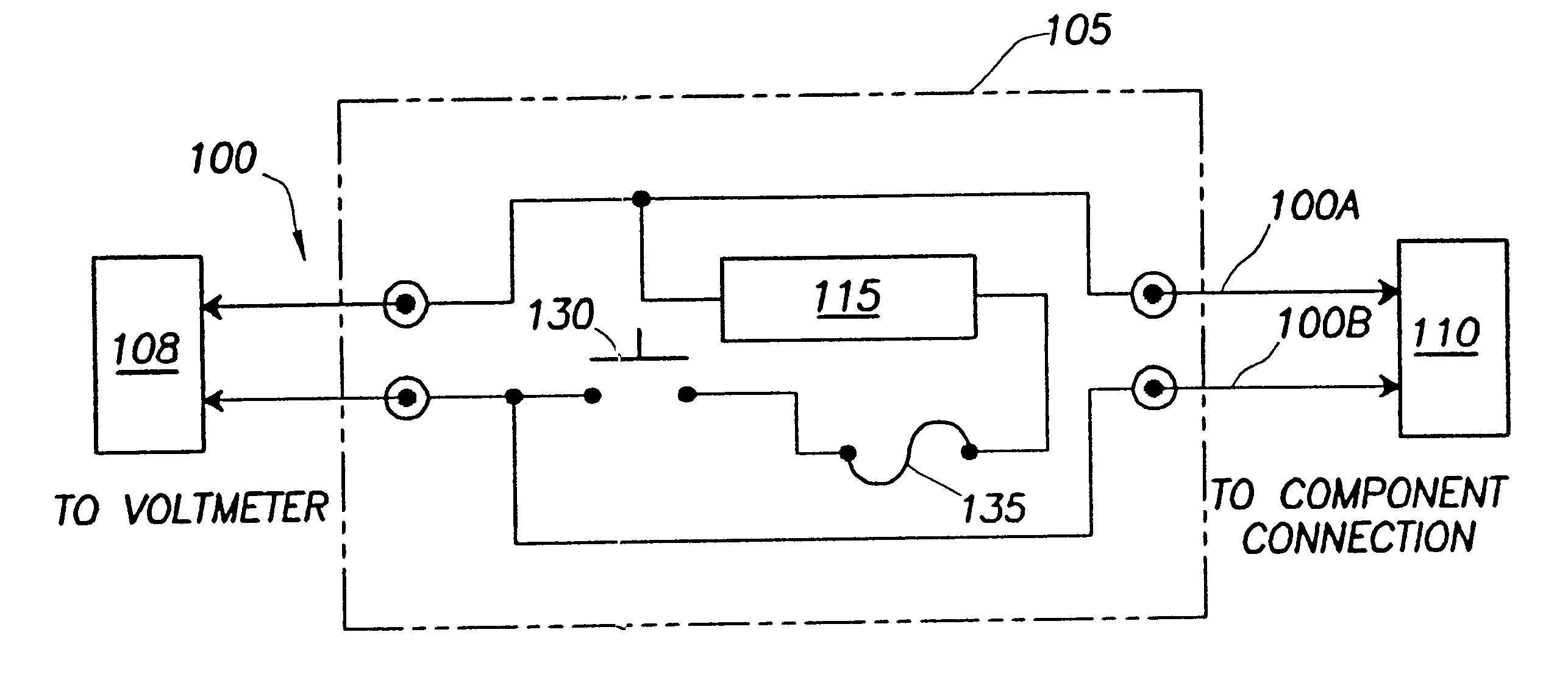
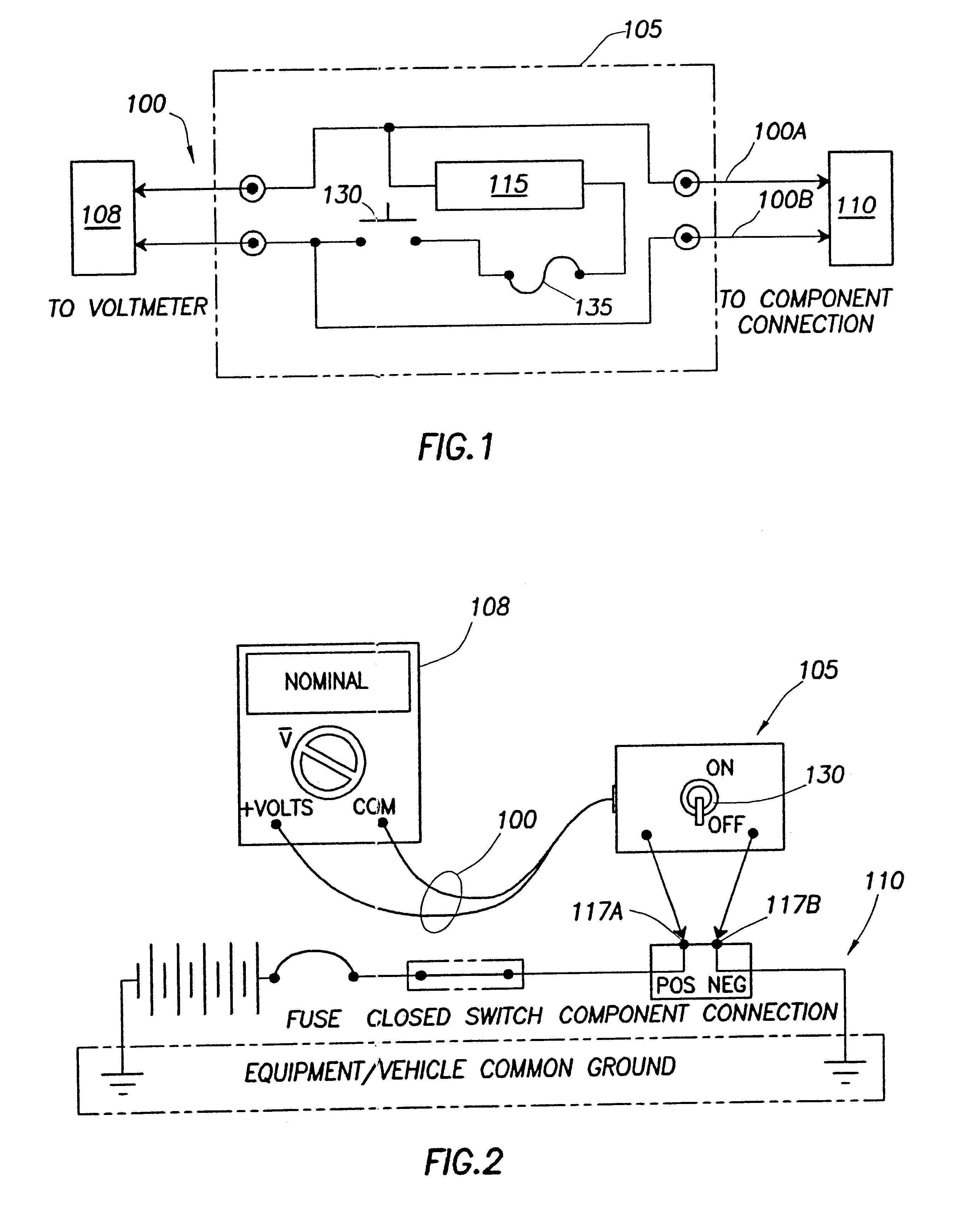
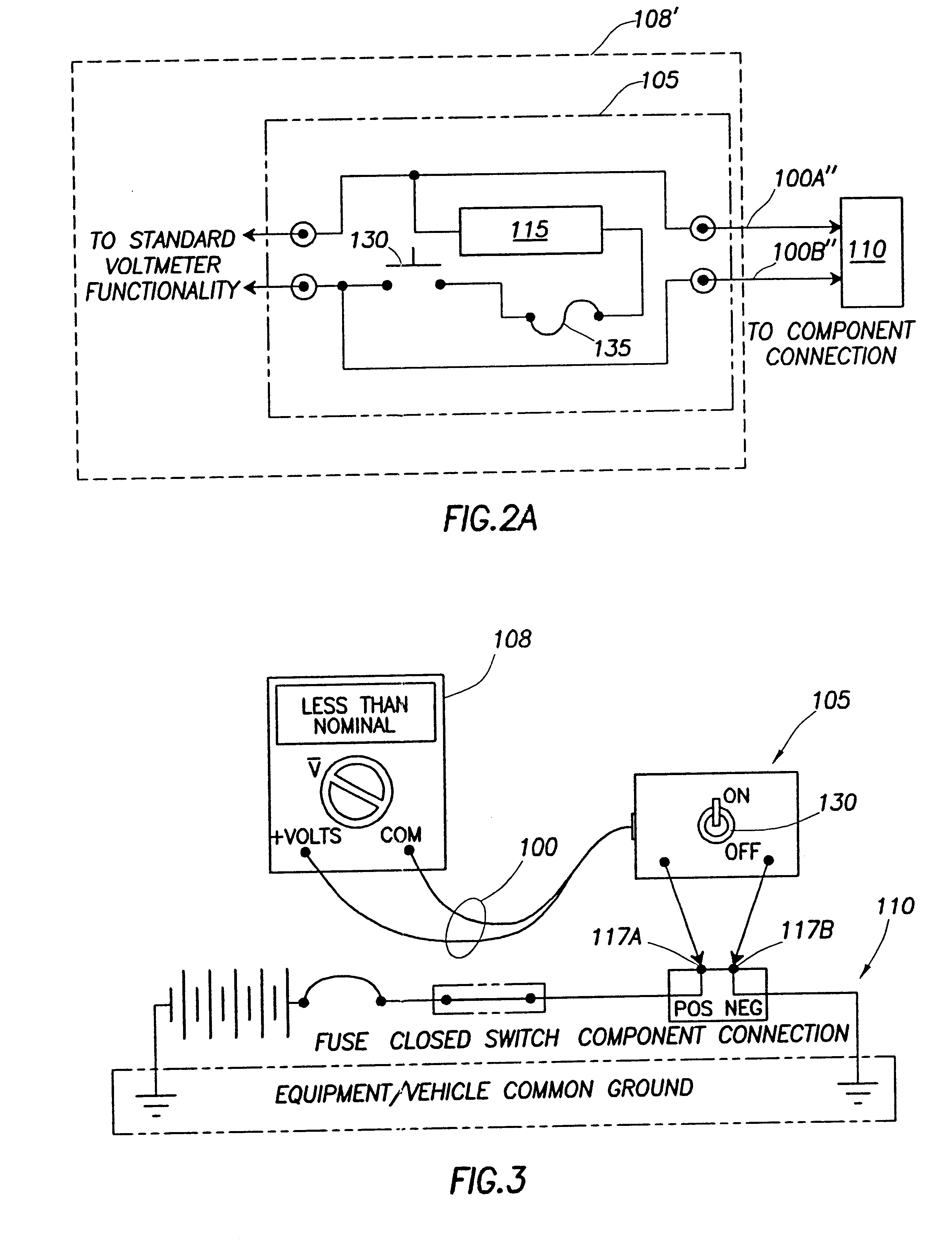
Enhancing voltmeter functionality
InactiveUS6356853B1Overload protection arrangementsResistance/reactance/impedenceLoad circuitValue set
Enhanced voltmeter leads includes load circuitry having a test load that can be switchably coupled between the leads to help identify faults in a circuit under test. In certain embodiments, the value of the test load can be any appropriate value set according to parameters or characteristics of the circuit under test. In these embodiments, the value of the test load can be set manually or automatically or both. The types of faults that can be identified include a short-to-ground, an open circuit, and a high (e.g., corrosive) resistance. The leads include a switch whose setting is adjustable to couple and decouple the test load between the leads. The switch can be located in the leads or in a lead handle of the leads for easy access by a user / technician. The leads can also include a fuse or circuit breaker for safety reasons. The leads can be used systematically to help identify the type and location of a fault from voltage readings. The voltage readings are obtained at various points in the circuit under test with the switch both closed and open. Conventional test leads or the leads that include the switch to couple / decouple the test load can be used if the load circuitry is integrated into the voltmeter or if the load circuitry has a separate coupling or connection to the voltmeter inputs.
Owner:SULLIVAN DANIEL B
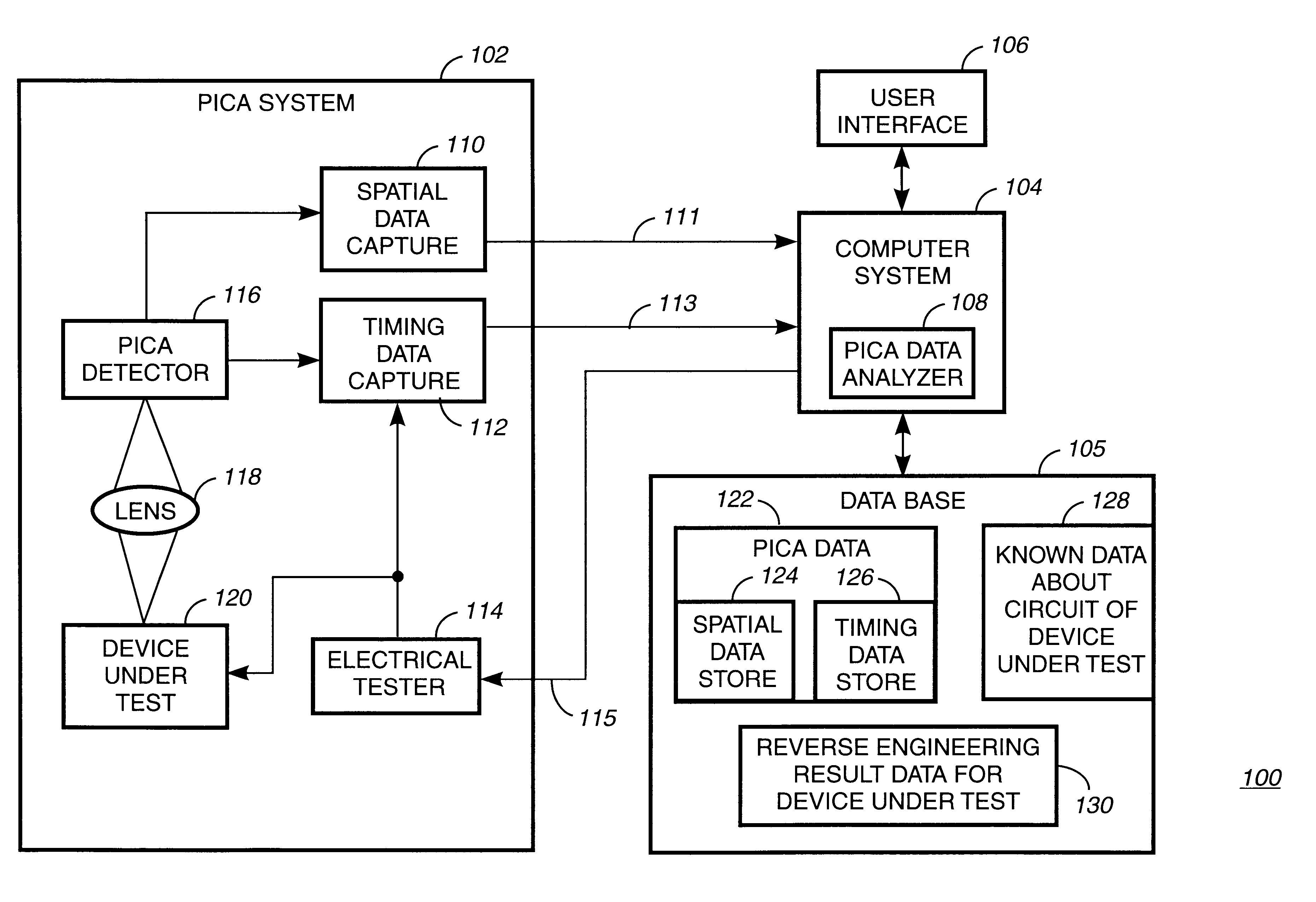
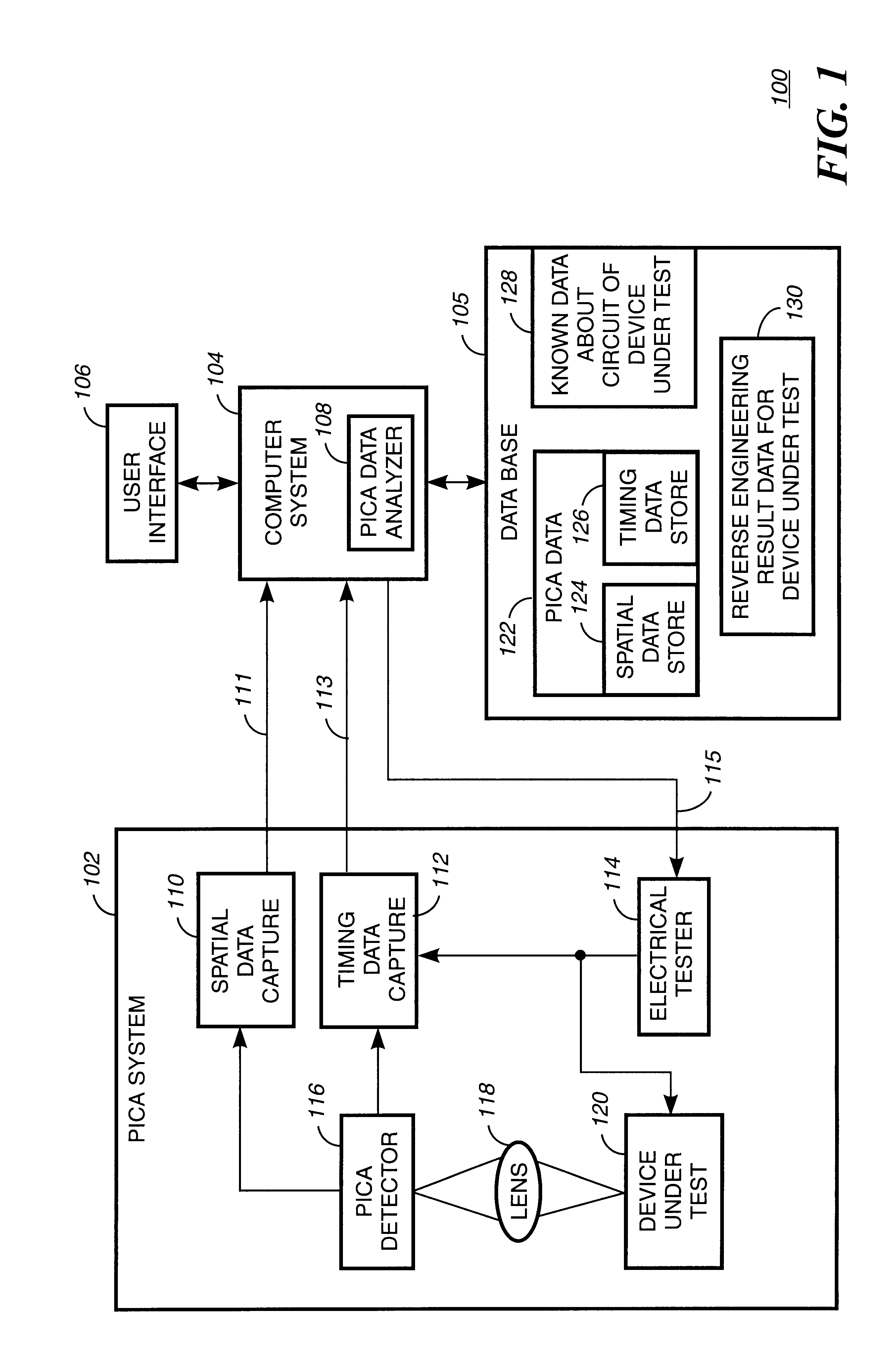
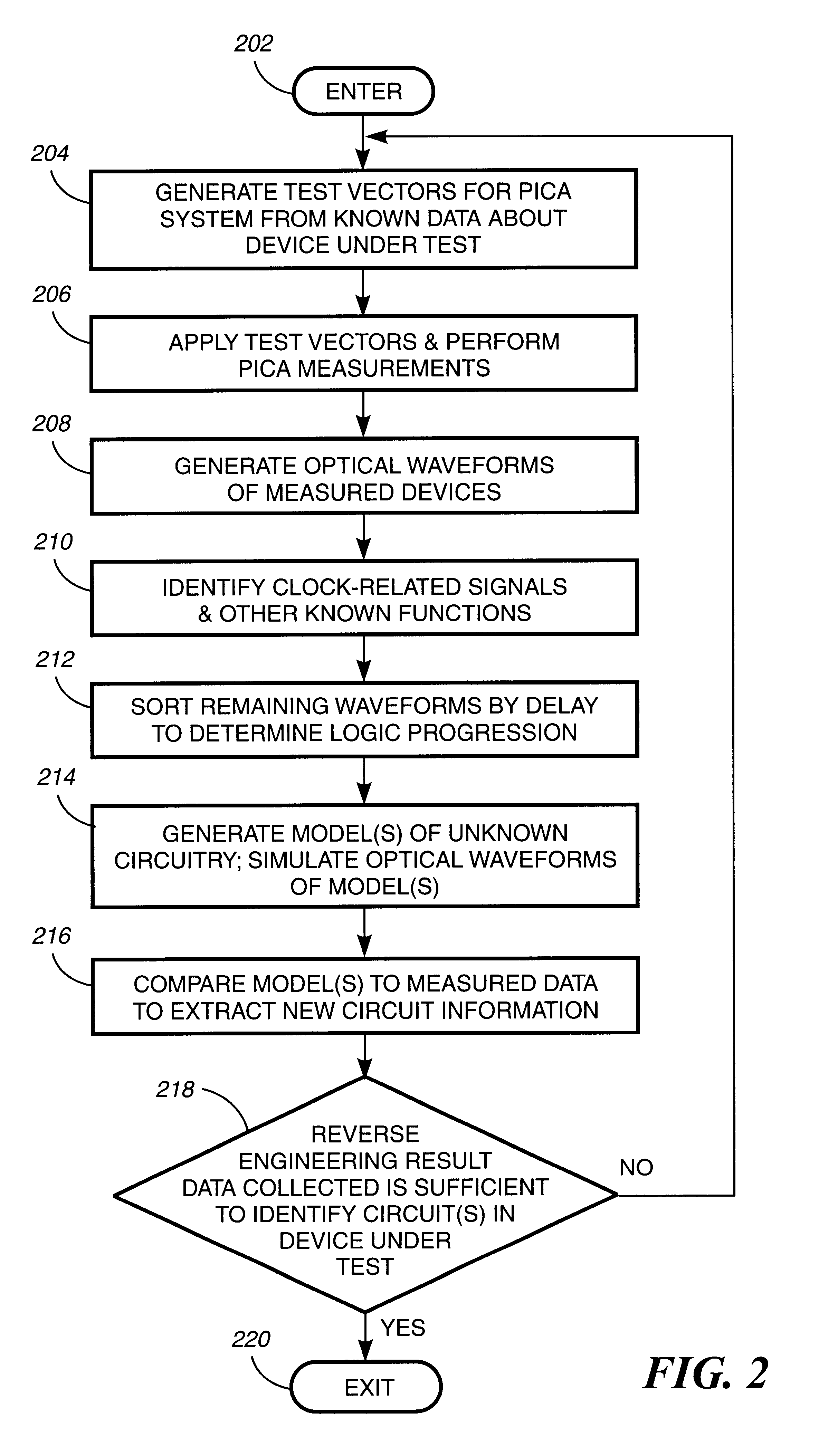
Method and apparatus for reverse engineering integrated circuits by monitoring optical emission
InactiveUS6496022B1Individual semiconductor device testingContactless circuit testingElectricityTime information
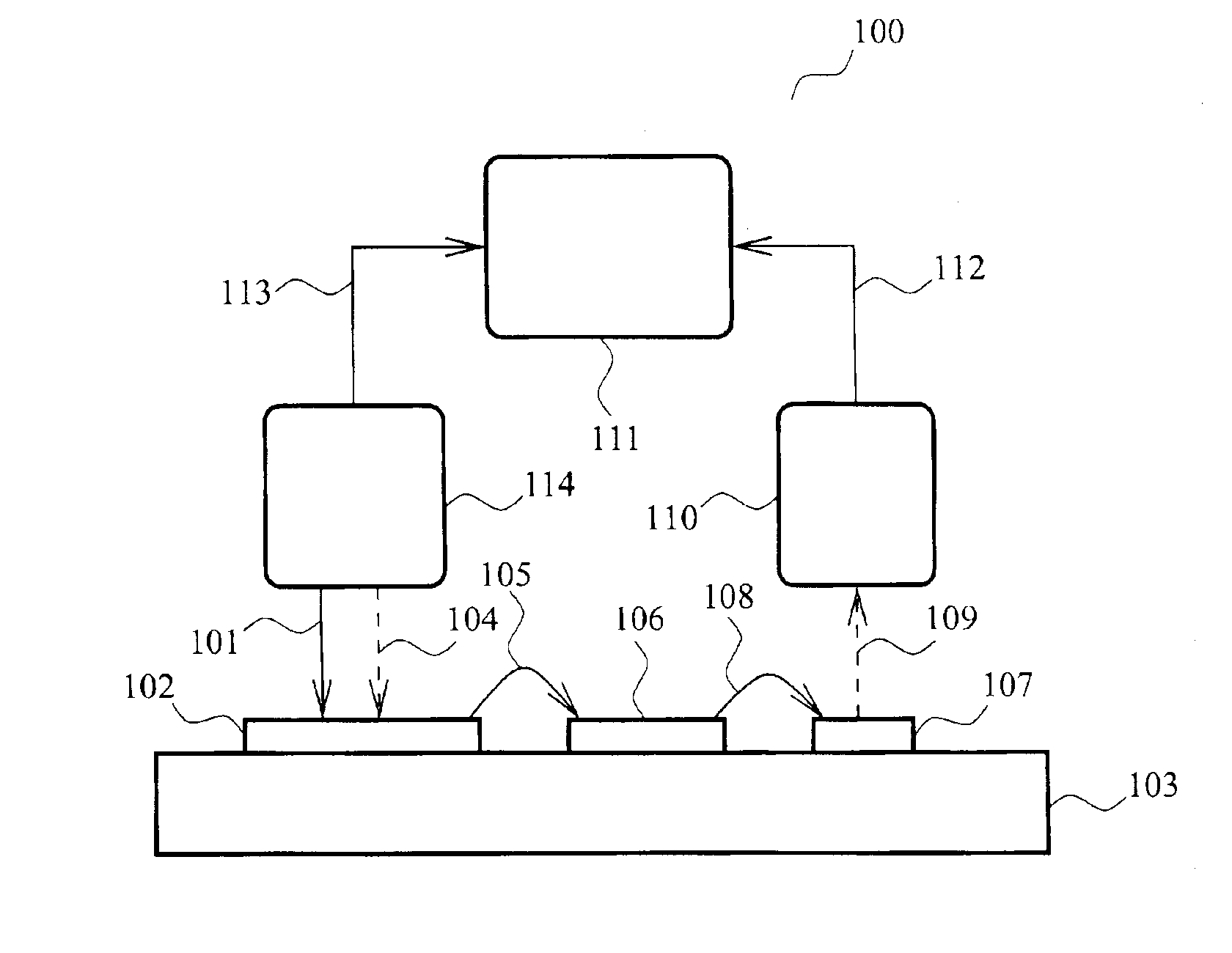
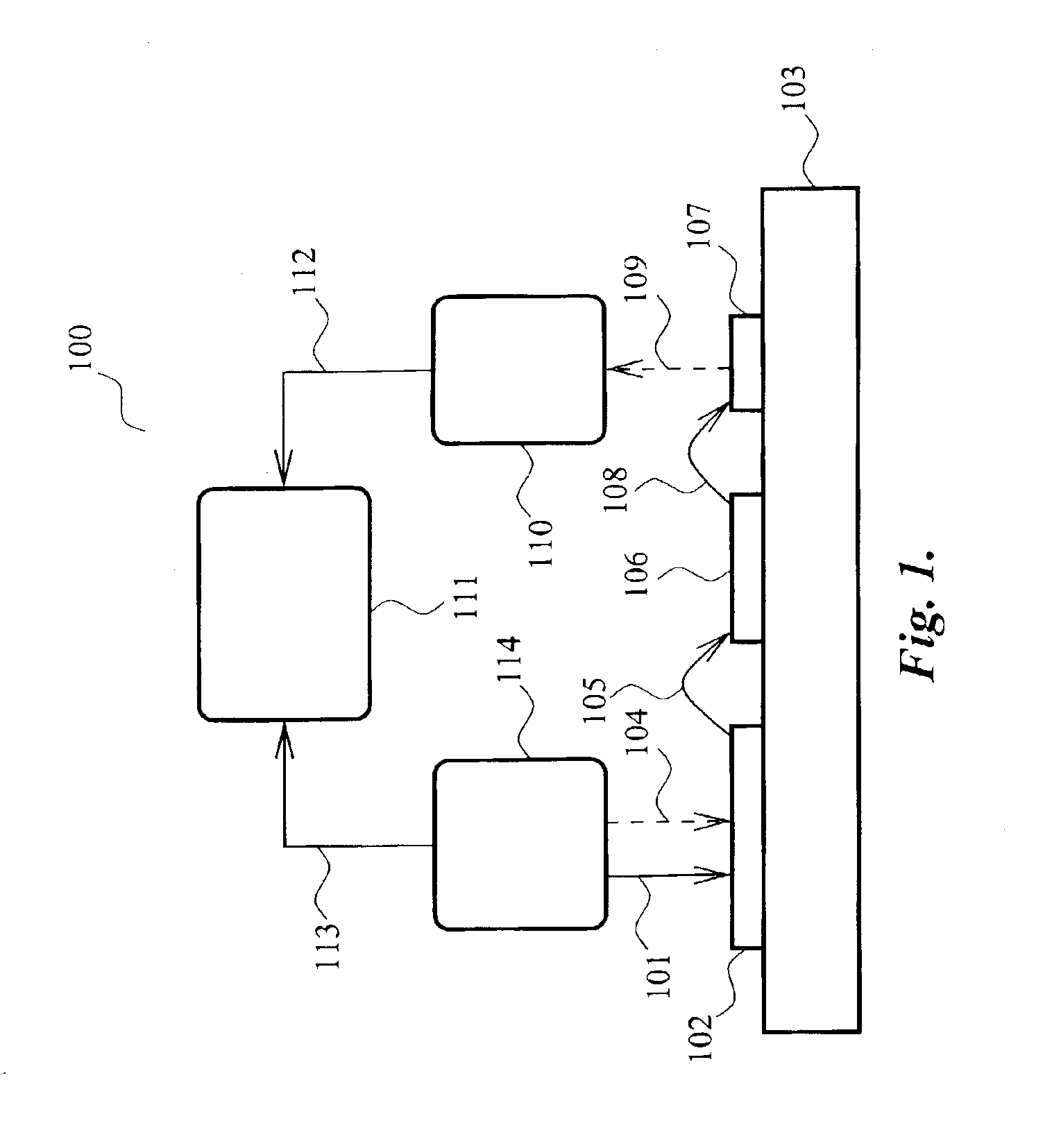
A method and apparatus for reverse engineering an integrated circuit chip (IC chip) (120) utilizes an electrical circuit tester (114) for injecting a triggering signal into the IC chip (120) to exercise a circuit under test. In synchronization thereto, a PICA detector (116) monitors optical emissions from the circuit under test. A spatial data extractor, electrically coupled to the PICA detector, collects space information (124) from patterns of light emissions emitted by the circuit under test, and a timing data extractor, electrically coupled to the electrical circuit tester and to the PICA detector (116), collects time information (126) from the patterns of light emissions emitted by the circuit under test. A database memory (105) includes known data about the circuit under test and also includes at least one reference pattern for comparing a captured light emission pattern thereto to identify at least one circuit element in the circuit under test. A PICA data analyzer (108), electrically coupled to the database memory (105) and to the PICA detector (116), determines at least one of whether the circuit under test comprises a circuit element with a light emission pattern that matches one of the at least one reference pattern in the database memory (105), and the value contained in a memory in the IC chip (120).
Owner:IBM CORP
Adaptive fault diagnosis of compressed test responses
ActiveUS7302624B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionCircuit under testSelf adaptive
Methods, apparatus, and systems for diagnosing failing scan cells from compressed test responses are disclosed herein. For example, in one nonlimiting exemplary embodiment, one or more signatures are received that indicate the presence of one or more errors in one or more corresponding compressed test responses. Scan cells in the circuit-under-test that caused the errors are identified by analyzing the signatures. In this exemplary embodiment, the analysis includes selecting a scan cell candidate that potentially caused an error in a compressed test response based at least partially on a weight value associated with the scan cell candidate, the weight value being indicative of the likelihood that the scan cell candidate caused the error. Tangible computer-readable media comprising computer-executable instructions for causing a computer to perform any of the disclosed methods are also provided. Tangible computer-readable media comprising lists of failing scan cells identified by any of the disclosed methods are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Systems and Methods for Implementing S/SSTDR Measurements
ActiveUS20140266238A1Shorten the timeImprove accuracyResistance/reactance/impedenceTesting electric installations on transportCircuit under testSpread spectrum
Systems and methods which utilize spread spectrum sensing on live circuits to obtain information regarding a circuit under test are provided. In some embodiments S / SSTDR testing may be utilized to obtain R, L, C and Z measurements from circuit components. In yet further embodiments, these measurements may be utilized to monitor the output of sensors on a circuit.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
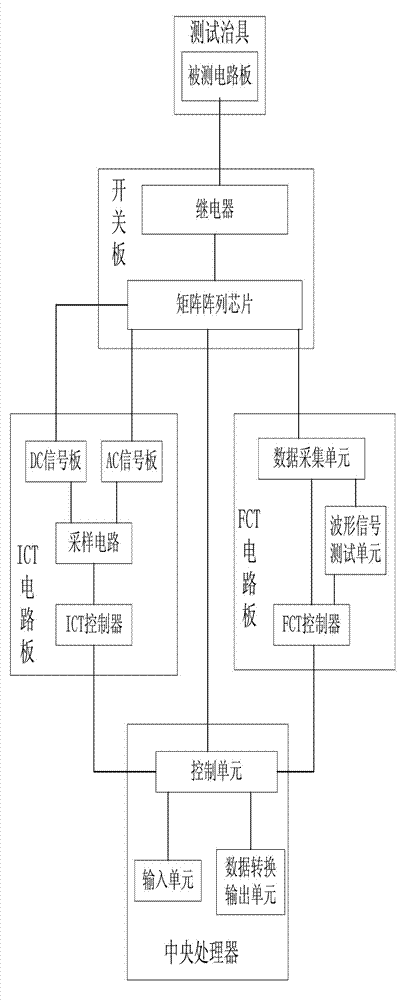
Automatic test system for circuit board
ActiveCN103033738AReduce work intensitySimplify work proceduresElectronic circuit testingCircuit under testEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of a test for installed circuit boards, in particular to an automatic test system for a circuit board. The automatic test system for the circuit board comprises a central processing unit, text fixtures, an integrated circuit test (ICT) circuit board, a final circuit test (FCT) circuit board, and a switch board for achieving the conversion between a component level test and a board test. The central processing unit comprises an input unit, a control unit, and a data conversion output unit. The control unit is connected with the input unit and the data conversion output unit. One end of the switch board is connected with the text fixtures, and one end of the ICT circuit board and one end of the FCT circuit board are both connected with the other end of the switch board. The other end of the switch board, the other end of the ICT circuit board, and the other end of the FCT circuit board are all connected with the control unit. The automatic test system for the circuit board can test the component level and functionally test the circuit board at the same time, and therefore work intensity of testers can be reduced, efficiency is improved, and testing man-made errors are reduced. The practical value of the automatic test system for the circuit board is high.
Owner:APM TECH DONGGUAN
Systems and methods for circuit testing
ActiveUS20050138509A1Improve performanceImprove test coverageElectronic circuit testingSolid-state devicesCircuit under testEngineering
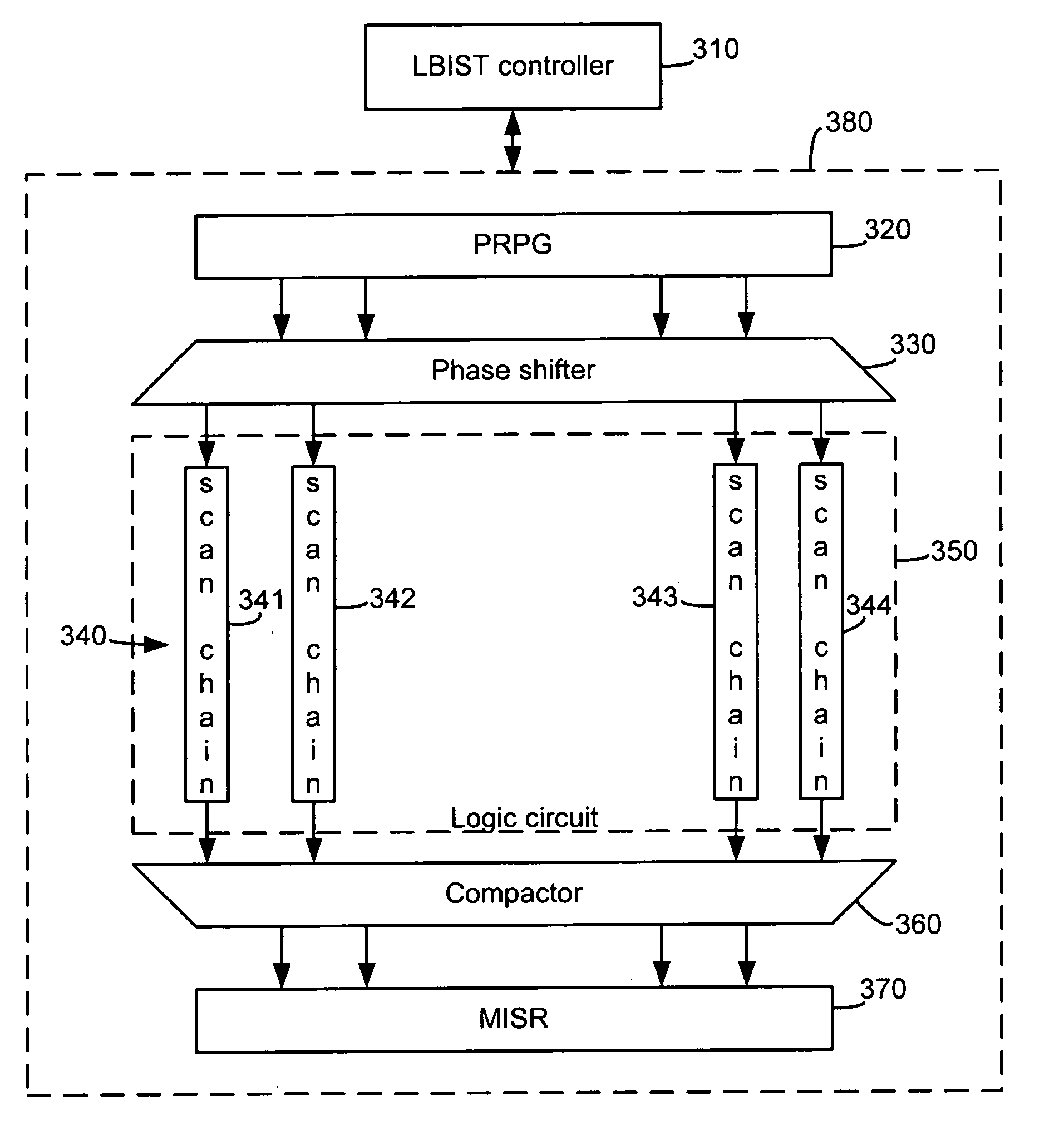
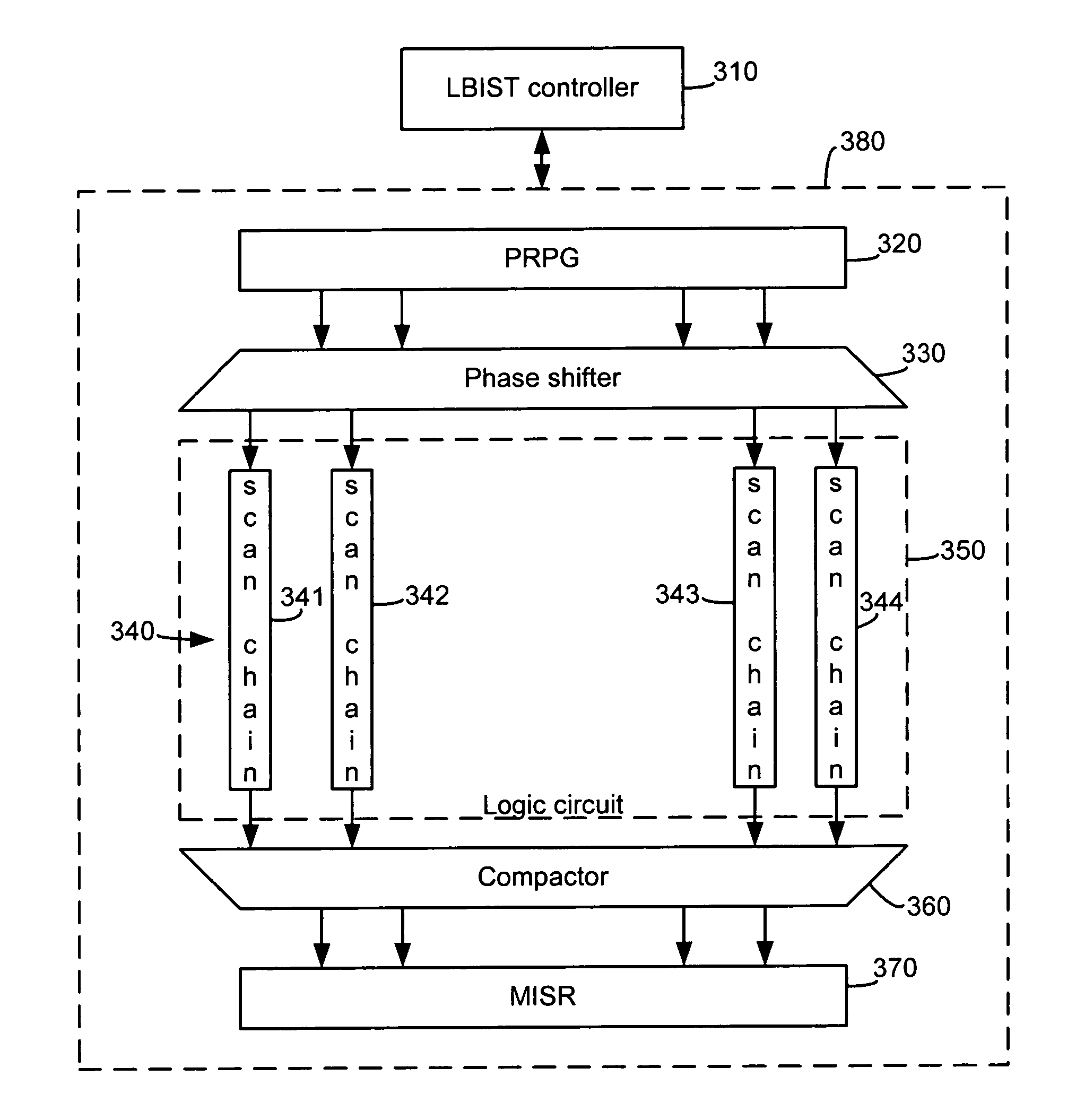
Systems and methods for improved performance of built-in-self-tests (BISTs) in integrated circuits, where variability is introduced into the self tests to improve the coverage of the tests. In one embodiment, an LBIST system includes scan chains interposed between levels of functional logic in a circuit under test. An exemplary method includes the steps of, for each of one or more initial scan chains, filling the initial scan chains with data comprising a pseudorandom pattern of bits, determining a number of levels of functional circuitry and corresponding subsequent scan chains through which to propagate the data and propagating the data from the initial scan chains through the determined number of levels of functional circuitry and corresponding subsequent scan chains. The number of levels of circuitry through which data is propagated is varied from one test cycle to another based upon a pseudorandom input signal.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
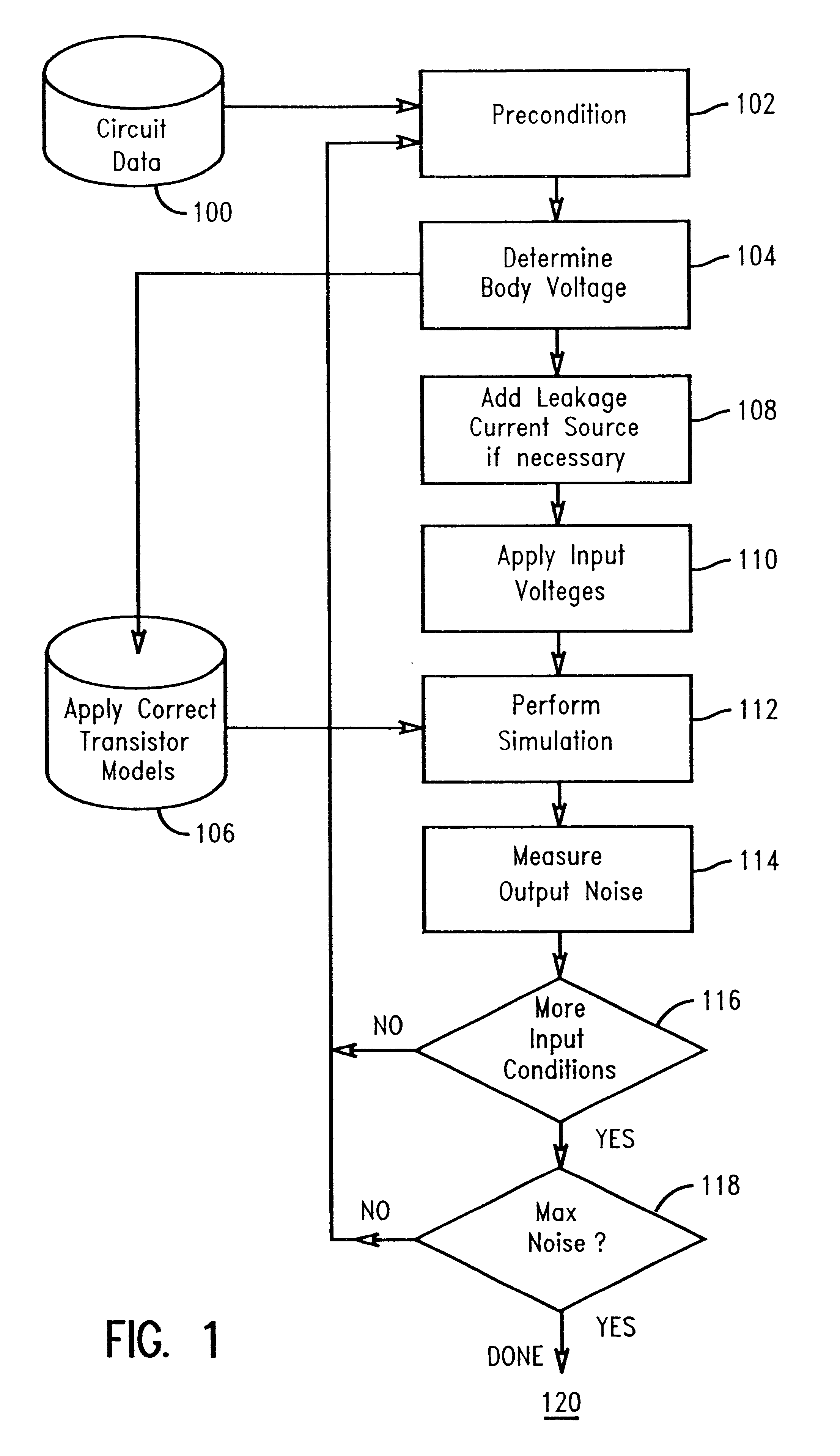
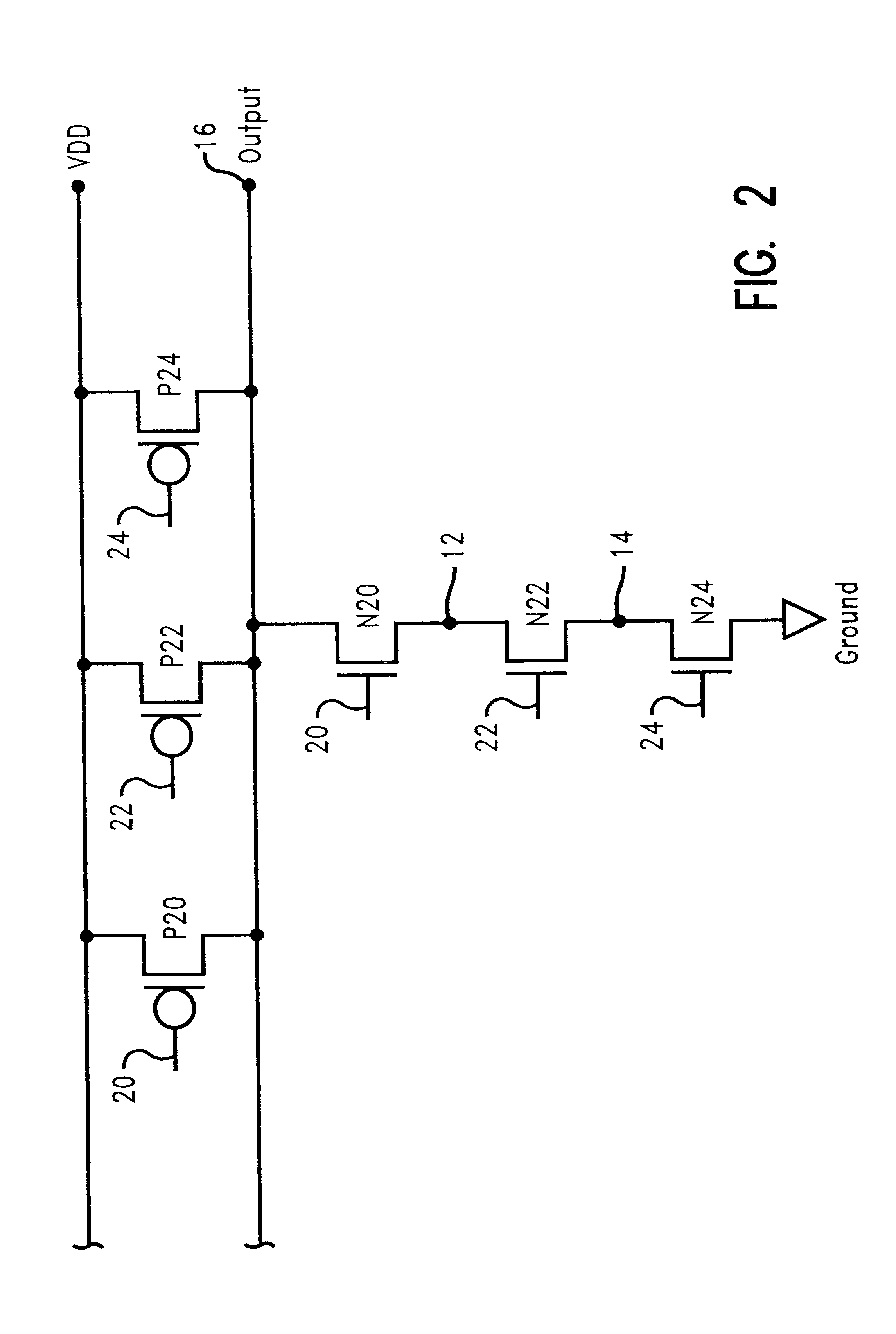
Use of static noise analysis for integrated circuits fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator process technology
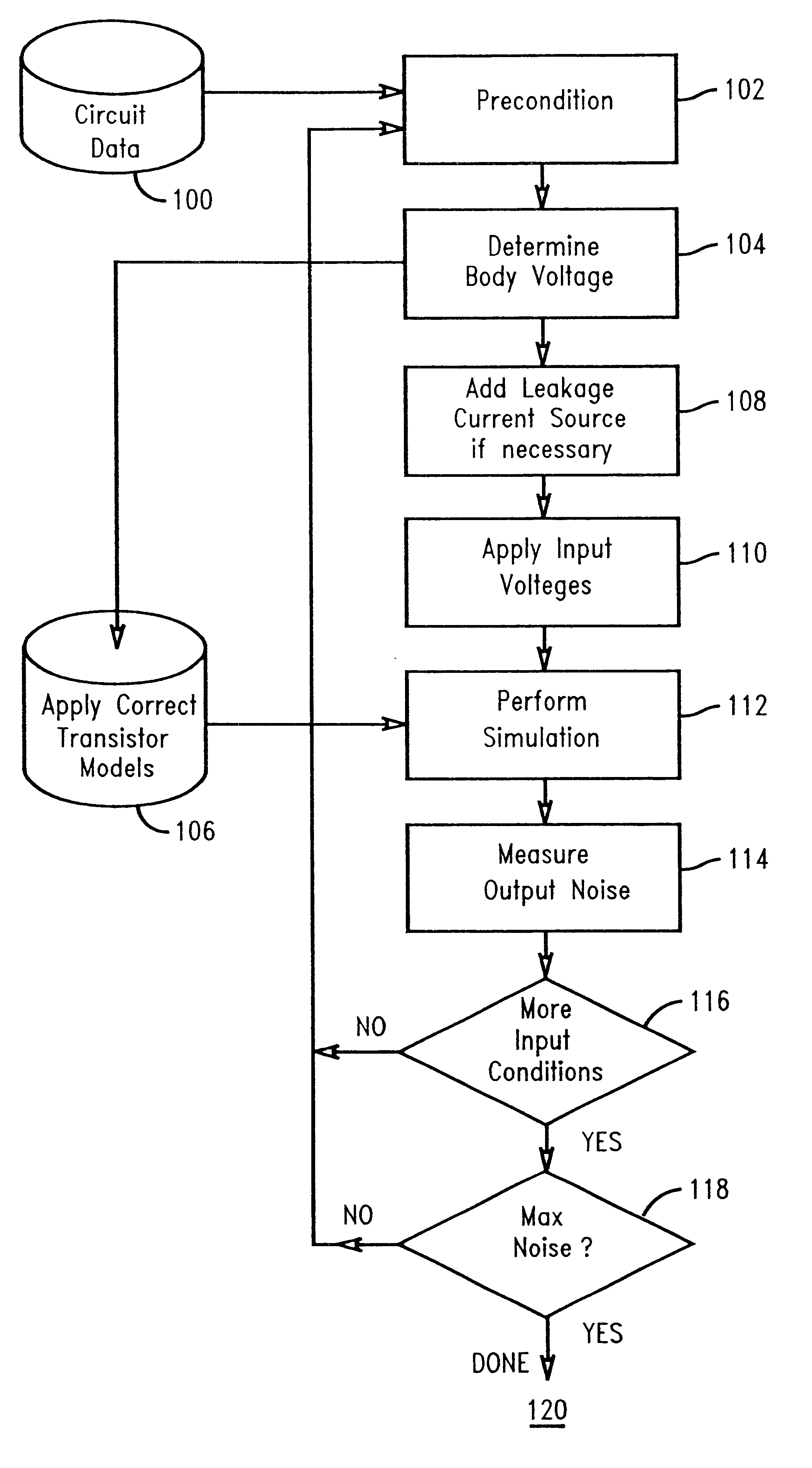
A method and structure for analyzing the effect of electrical noise in an integrated circuit fabricated in a silicon-on-insulator ("SOI") technology. The present invention uses a static noise analysis to evaluate an integrated circuit's response to electrical noise, taking into account hysteresis effect and parasitic bipolar current voltage, both of which are unique to integrated circuits fabricated in a SOI technology process. The present invention also includes a computer, computer storage device, computer program and software incorporating the method steps and simulating the testing and analysis of the circuit under test.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
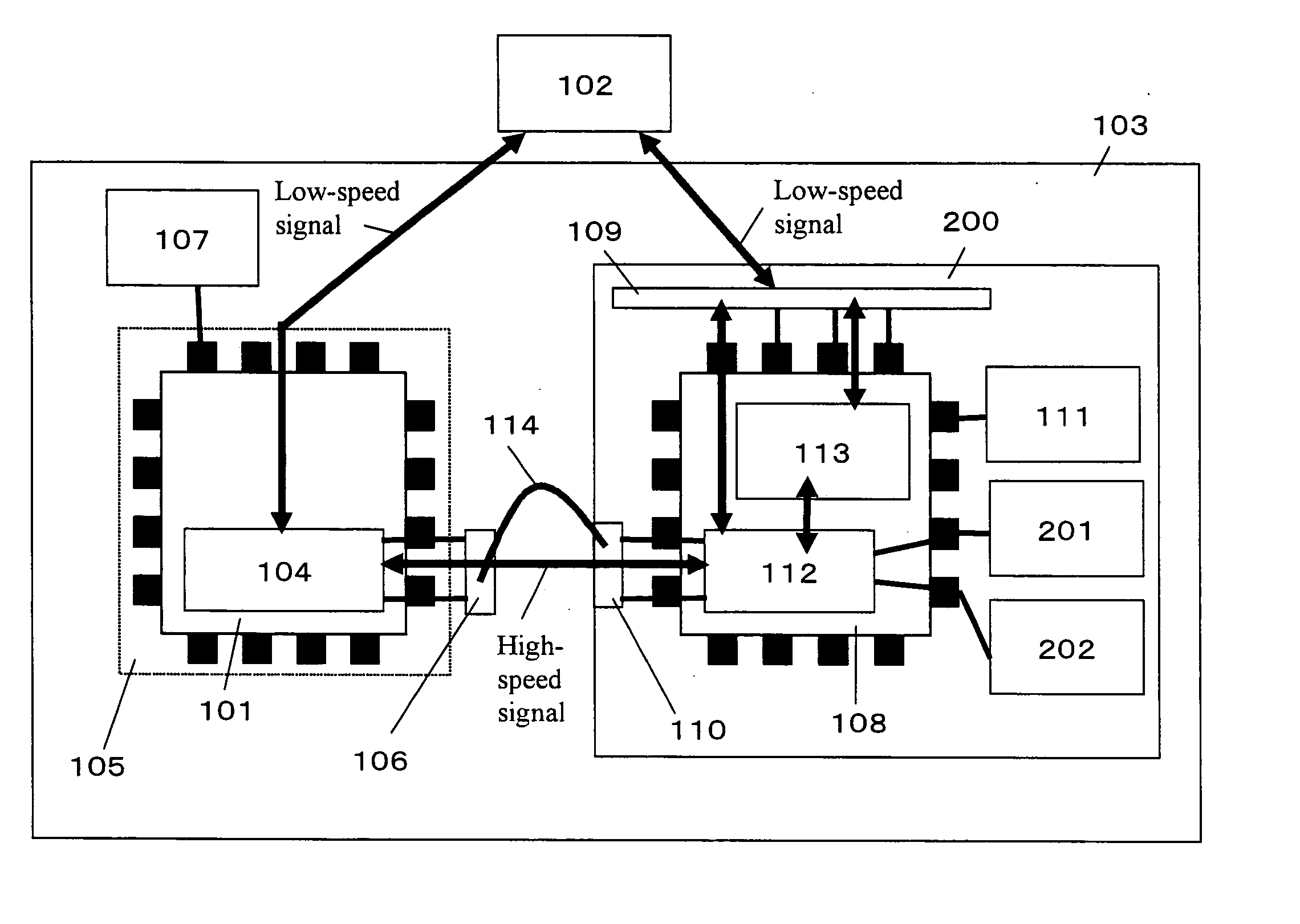
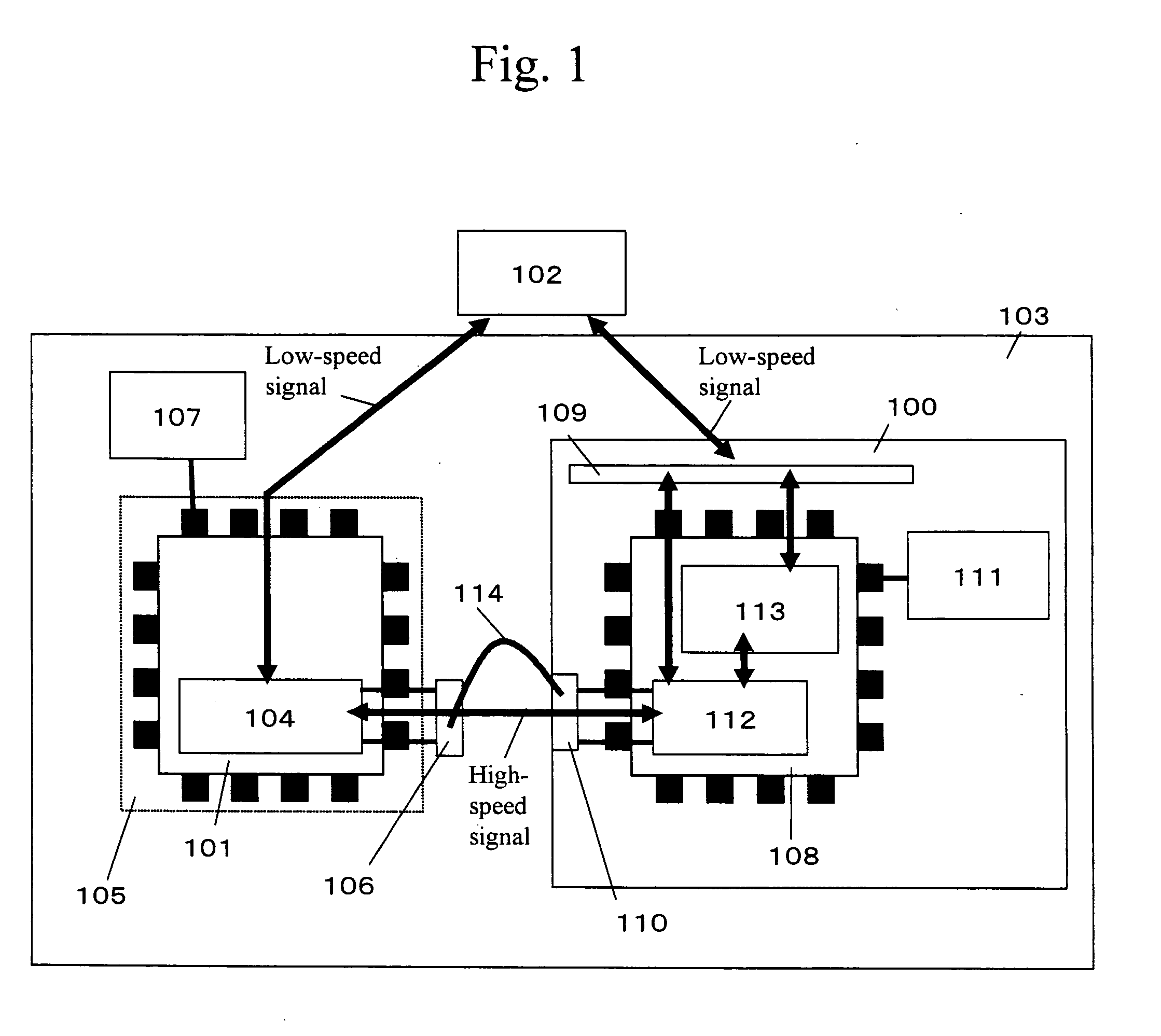
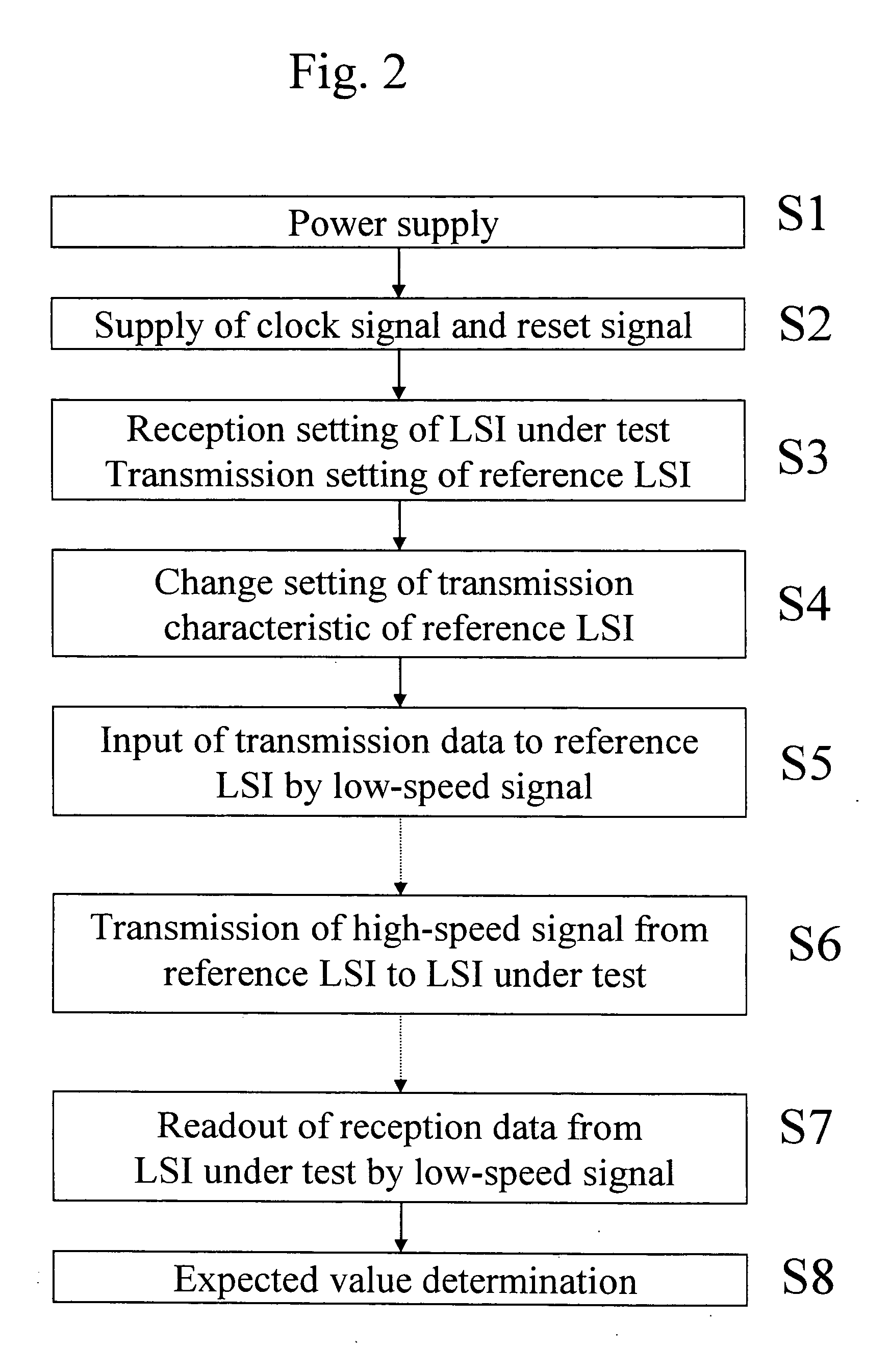
High-speed interface circuit test module, module under high-speed interface circuit test, and high-speed interface circuit test method
InactiveUS20050258856A1Efficient executionReduce test costsDigital circuit testingData switching networksLow speedComputer module
In the shipment test of an LSI provided with a high-speed interface circuit, both cost reduction and a high test guarantee level are realized. The following are provided: a high-speed interface circuit that is mounted on a load board interfacing with an LSI tester, is provided with a circuit converting the signal speed, and is capable of changing the transmission and reception characteristics; a controller that controls the transmission and reception characteristics of the high-speed interface circuit; a clock generator that generates the clock supplied to the high-speed interface circuit; a first connector provided specifically for the high-speed interface, connected to the high-speed interface circuit and provided with a signal port for performing high-speed signal communication with a circuit under test; and a second connector connected to the high-speed interface circuit and the LSI tester and provided with a signal port and a power port for performing low-speed signal communication with the high-speed interface circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
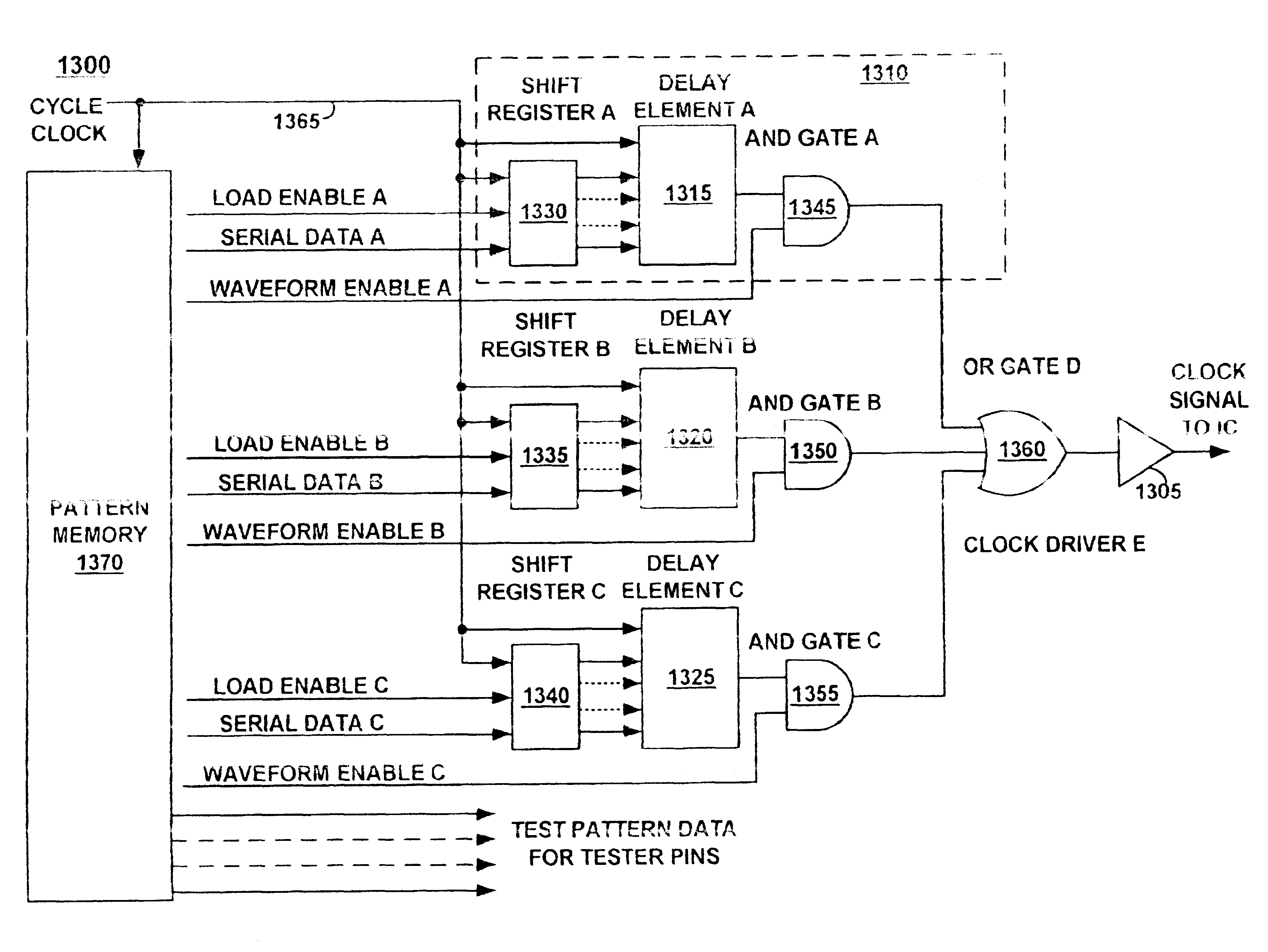
Dynamically reconfigurable precision signal delay test system for automatic test equipment
InactiveUS6880137B1Efficient memory usageGenerate efficientlyResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingAutomatic test equipmentCircuit under test
A programmable time event and waveform generator for the application of precise timing patterns to a logic circuit and the capture of response data from the logic circuit. The time event and waveform generator comprises a programmable delay element that is programmed with values stored in pattern memory. For scan based testing, the time event and waveform generator is programmed between test pattern scan sequences by serial loading from the test pattern memory. The generator may be used to generate precise signal transitions to input pins of a circuit under test, and to capture at precise times the signal states from the output pins of a circuit under test. The data for programming the delay element is accessed from test pattern memory.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Integrated excitation/extraction system for test and measurement
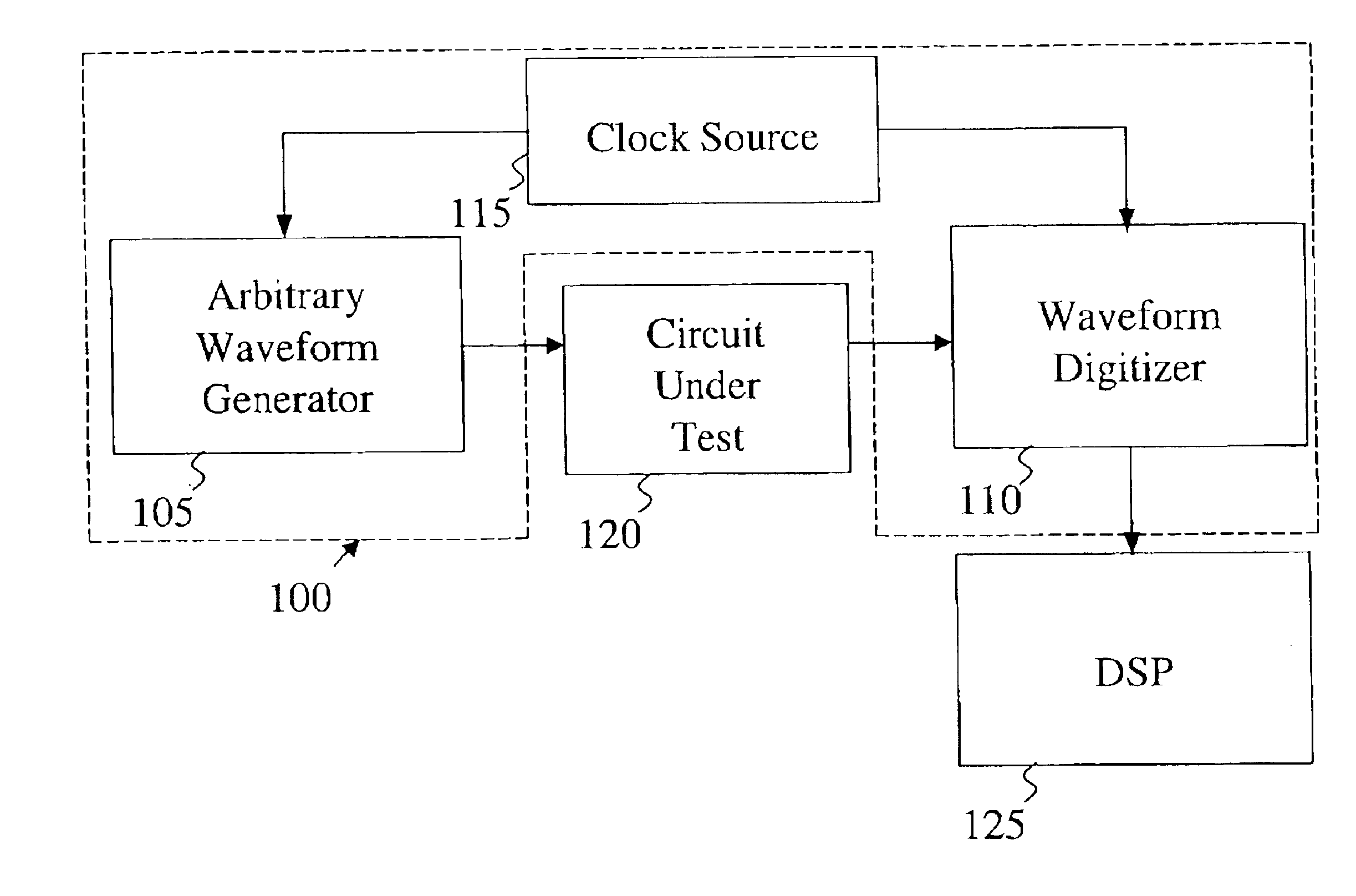
InactiveUS6931579B2Convenient verificationElectronic circuit testingTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesVoltage generatorReconstruction filter
An integrated test core for mixed-signal circuits comprises a periodic waveform generator capable of generating arbitrary band-limited waveforms for excitation purposes and a waveform digitizer for extracting an arbitrary waveform from the test circuit's analog response signal. The digitized response may be tested and measured using DSP techniques. Preferably, the waveform generator and digitizer are synchronously controlled. The core is a nearly all digital implementation with the exception of a reconstruction filter (optional) for sending the test signal to the circuit under test (CUT) and the comparator for extracting the digitized waveform from the CUT's response. The periodic waveform generator may comprise a ΣΔ modulator and, optionally, a reconstruction filter between the modulator and CUT. The waveform digitizer may comprise a programmable reference voltage generator for providing a variable voltage reference signal, a comparator for generating a comparison signal from the CUT's analog response signal and the reference signal and means for controlling the reference voltage generator.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
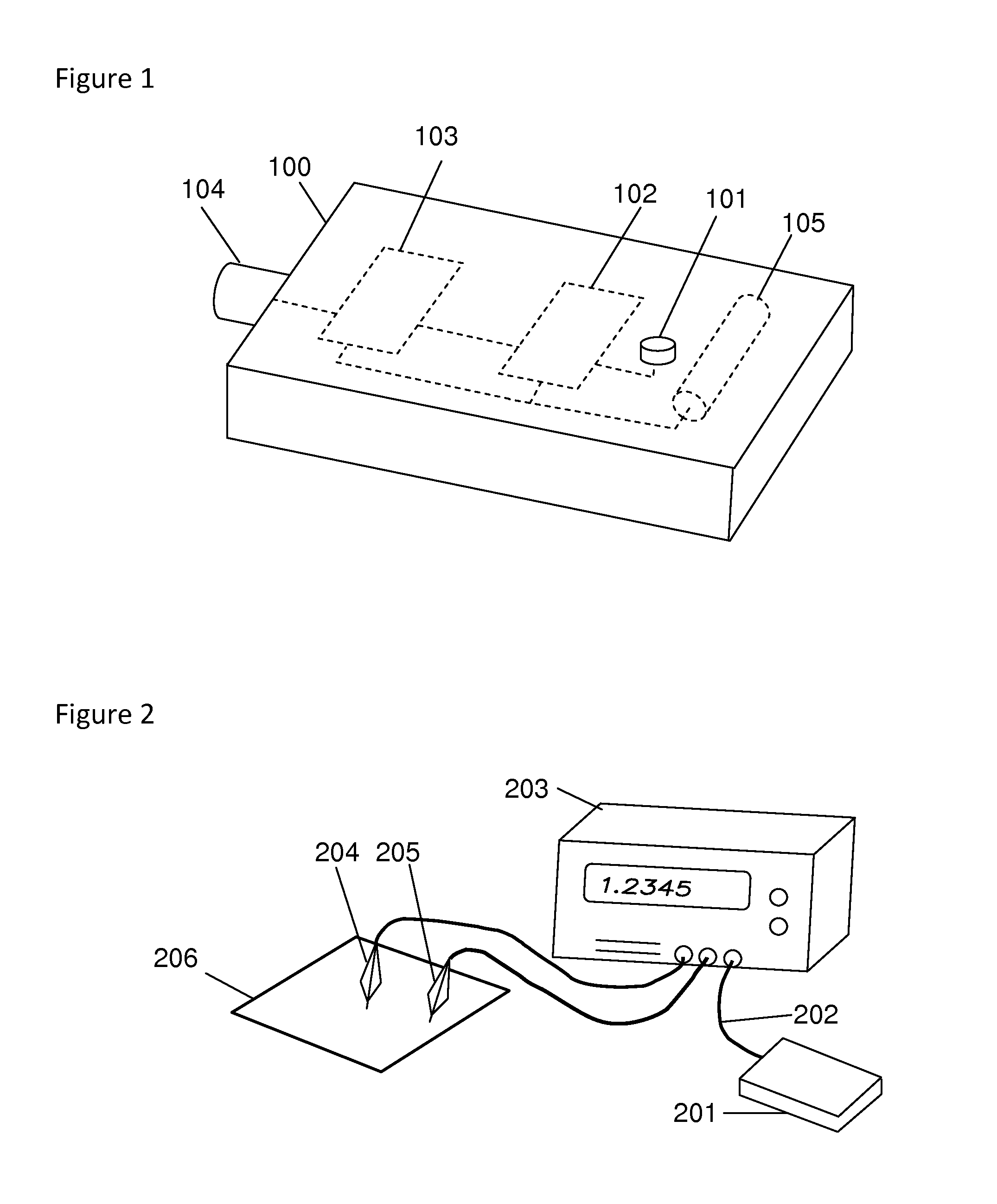
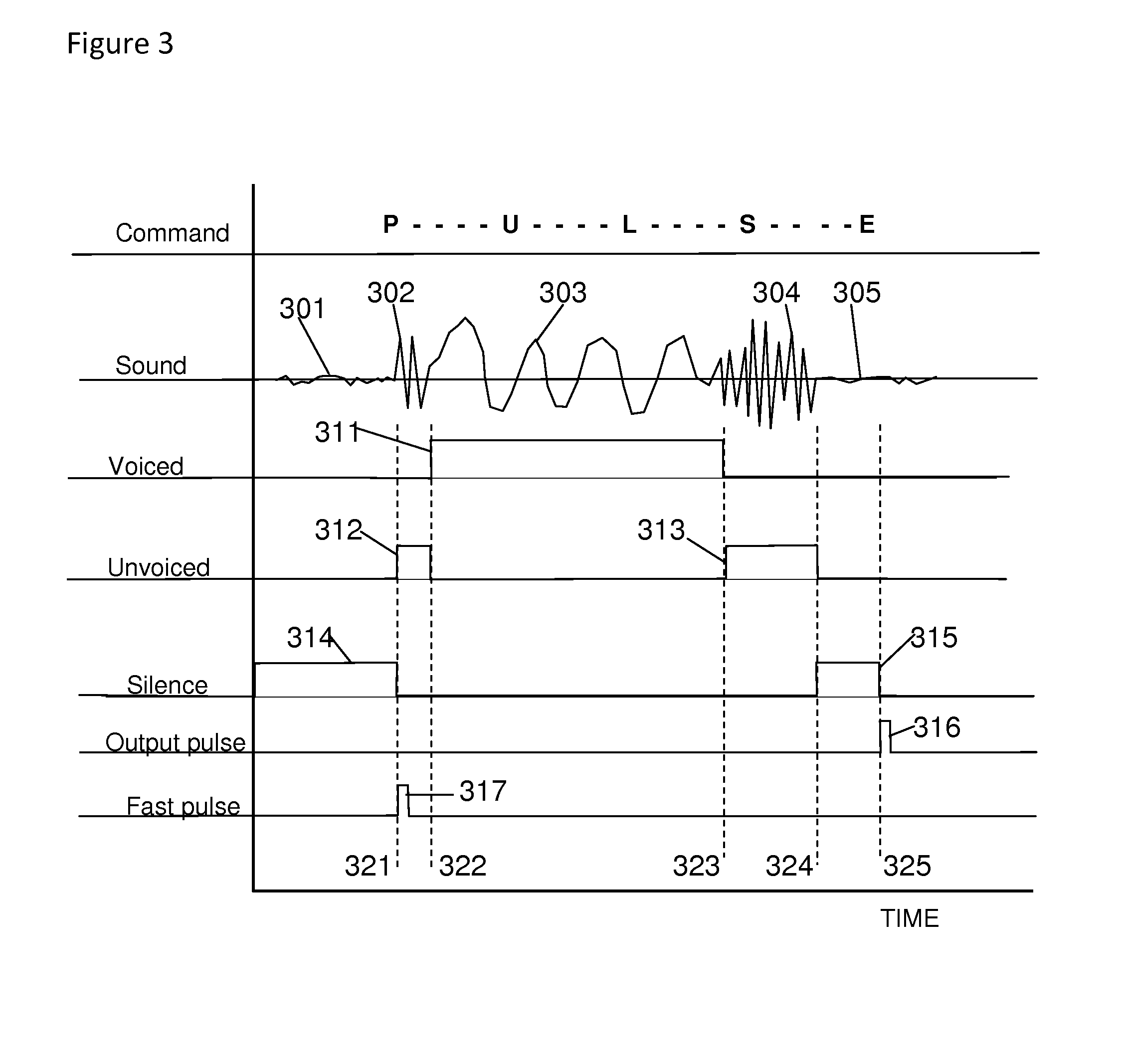
Voice-Activated Signal Generator
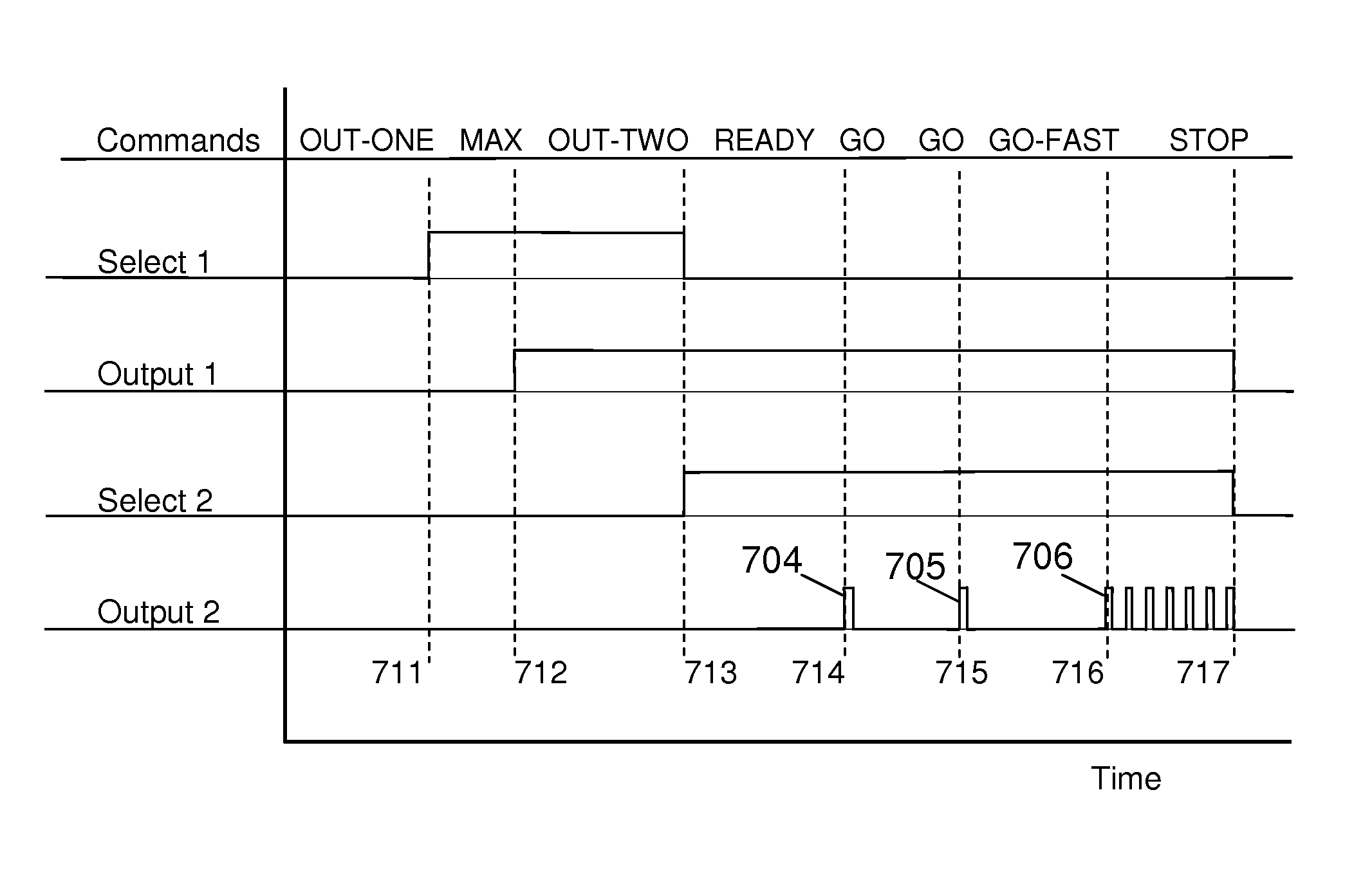
InactiveUS20140142949A1Control process safetyUnprecedented operational flexibilitySpeech recognitionCircuit under testEngineering
A voice-activated signal generator is a device to produce output signals responsive to spoken commands. The device accepts only predetermined commands and responsively generates specific output signals such as a pulse, a series of pulses, a voltage level, or a periodic waveform. The device is suitable for triggering an oscilloscope, or controlling a circuit under test, or activating another instrument. The invention also enables safely controlling a hazardous system such as a high voltage system, hands-free and with precise timing determined by the user. Also disclosed are fast, compact, robust algorithms for analyzing spoken commands, and particularly for detecting voiced and unvoiced sound, and for identifying commands by comparing the order of sound intervals in the spoken command to templates that represent the predetermined commands. The device may have one output or multiple outputs in parallel, all controlled by voice commands with precision output timing.
Owner:ELOQUI VOICE SYST LLC
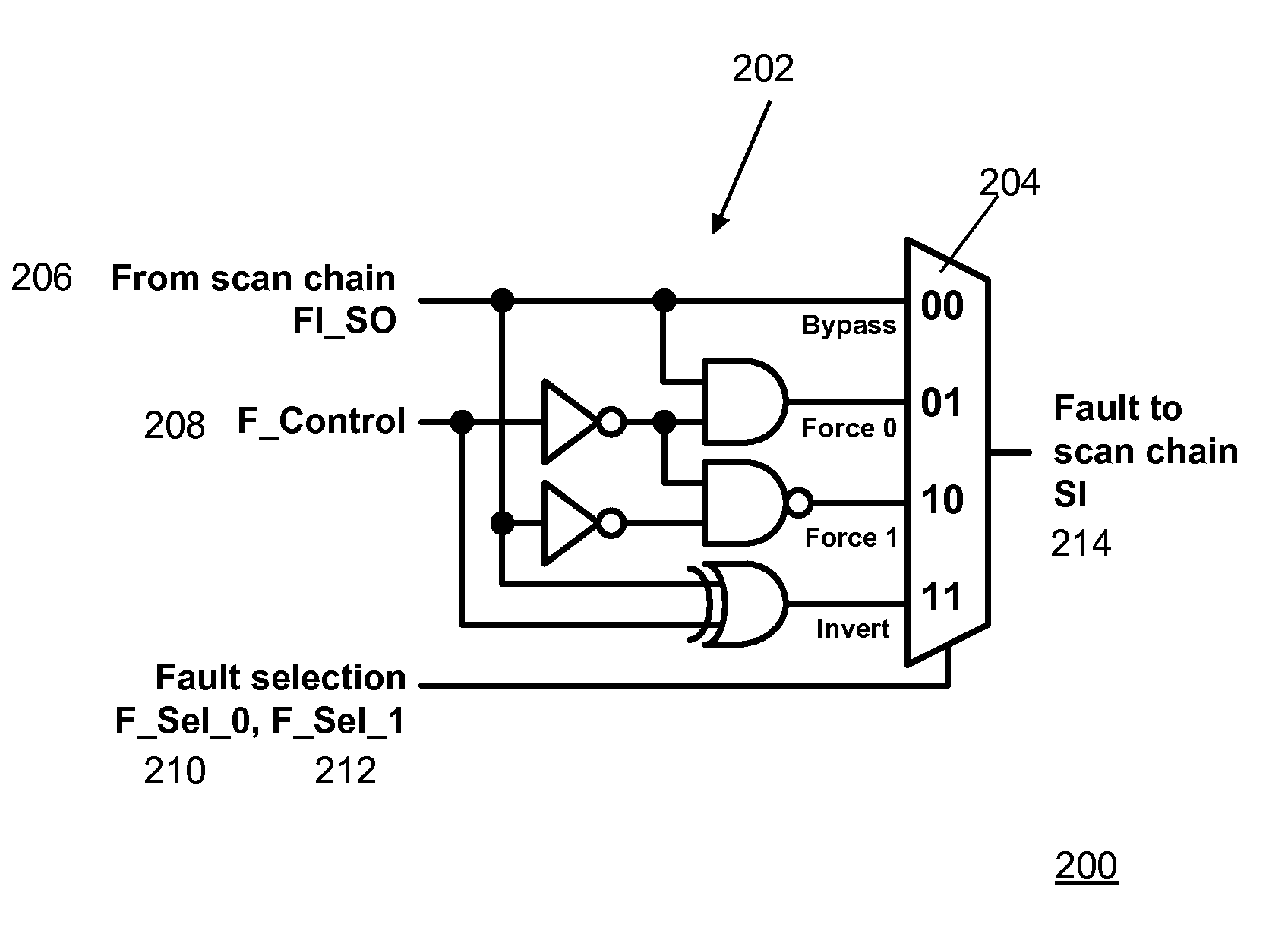
Method and Apparatus for Fault Injection
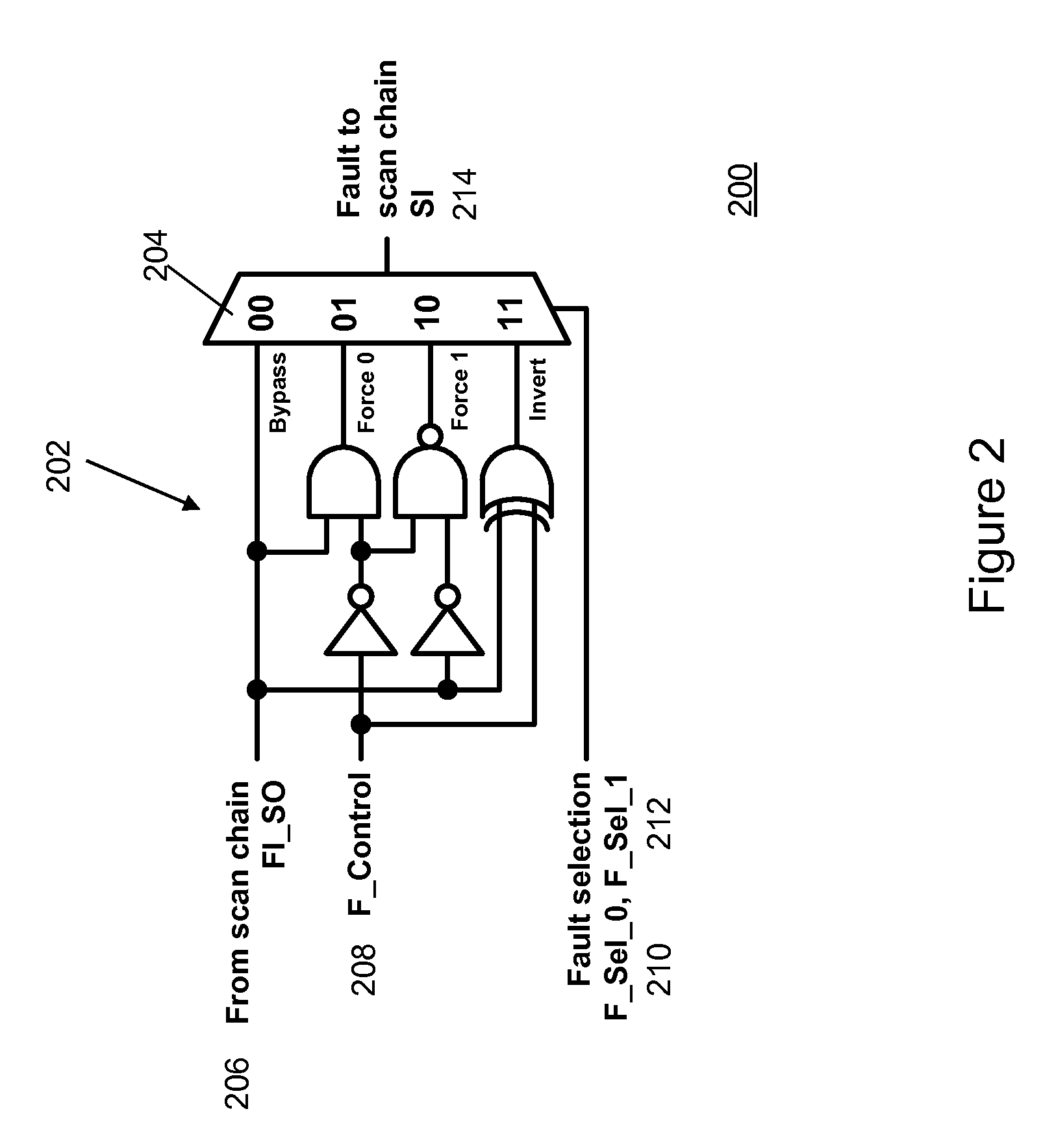
InactiveUS20120239993A1Redundant hardware error correctionContactless circuit testingCircuit under testEngineering
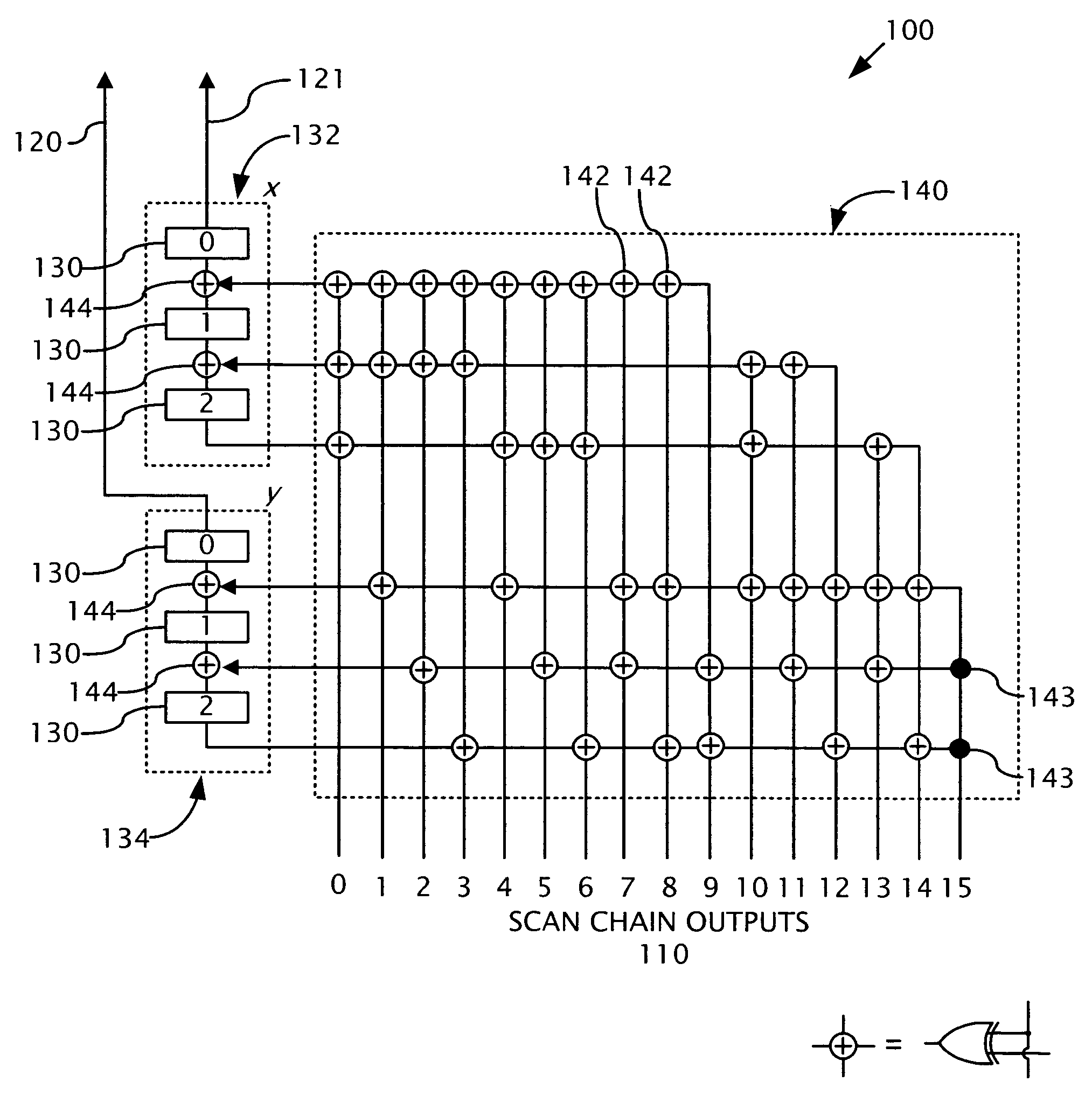
The present invention provides various circuits for injecting faults into a larger circuit, sometimes called circuit under test, or CUT. One type of fault injection circuit is a clock controlled fault injection circuit. This type of circuit uses internal scan chains as a way by which a fault injection operation is performed while a system clock is in the off state. Another type of fault injection circuit is a concurrent fault injection circuit. This type of fault injection circuit uses dedicated fault injection scan chains in parallel with or without internal scan chains. Yet another type of fault injection circuit is a hybrid fault injection circuit that uses both clock controlled and concurrent fault injection circuits. Other embodiments are disclosed and still other embodiments would be obvious to those of ordinary skill in the art upon understanding the full scope of the present disclosure.
Owner:EIGENIX
Circuit and method for measuring delay of high speed signals
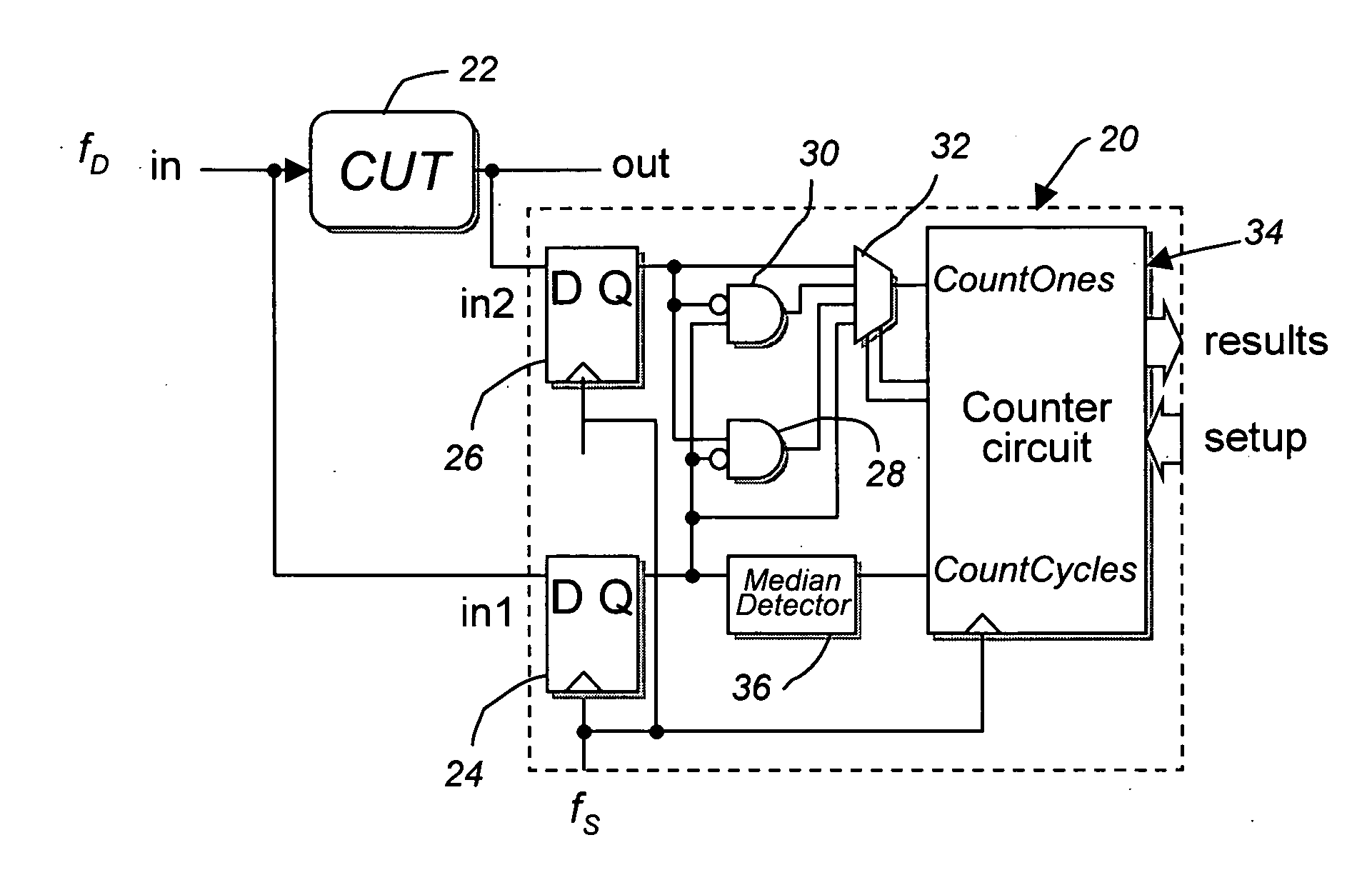
ActiveUS20050111537A1Measurement performanceNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCurrent/voltage measurementCircuit under testElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method and circuit for measuring a time interval between transitions of periodic signals at nodes of a circuit-under-test (CUT), the signals having a periodic clock frequency, the method comprises periodically latching a digital value of a first periodic signal at edges of an undersampling clock, simultaneously periodically latching a digital value of a second periodic signal at edges of the undersampling clock, combining the latched digital values of the first and second periodic signals to produce a combined output whose duty cycle is proportional to the time interval between a median edge of latched digital values of the first periodic signal and a median edge of latched digital values of the second periodic signal; and counting the number of undersampling clock cycles in which the combined output is a predetermined logic value within a predetermined time interval whereat the number is proportional to a time interval between a transition of the first periodic signal and a transition of the second periodic signal.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Systems and methods for signature circuits
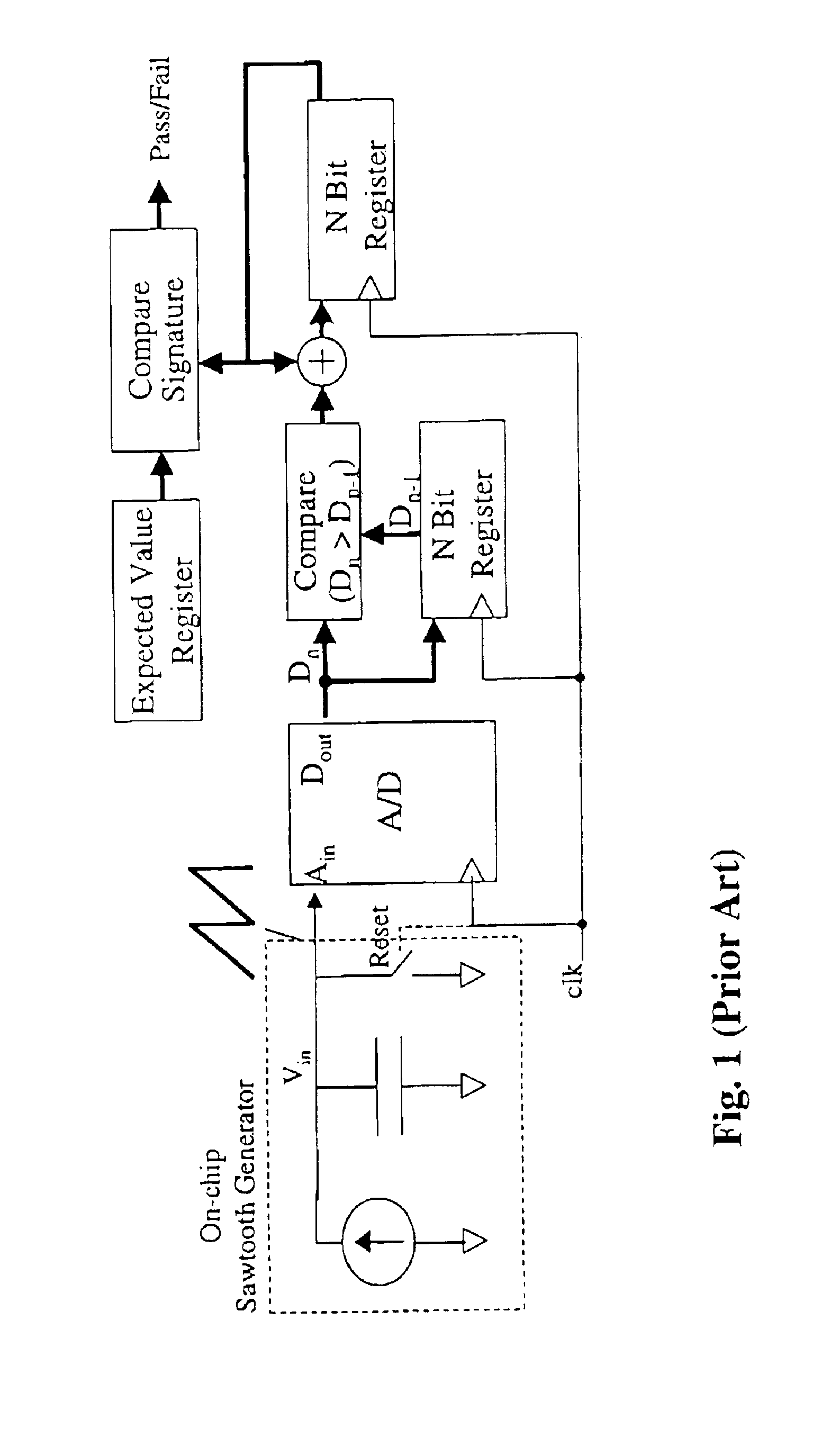
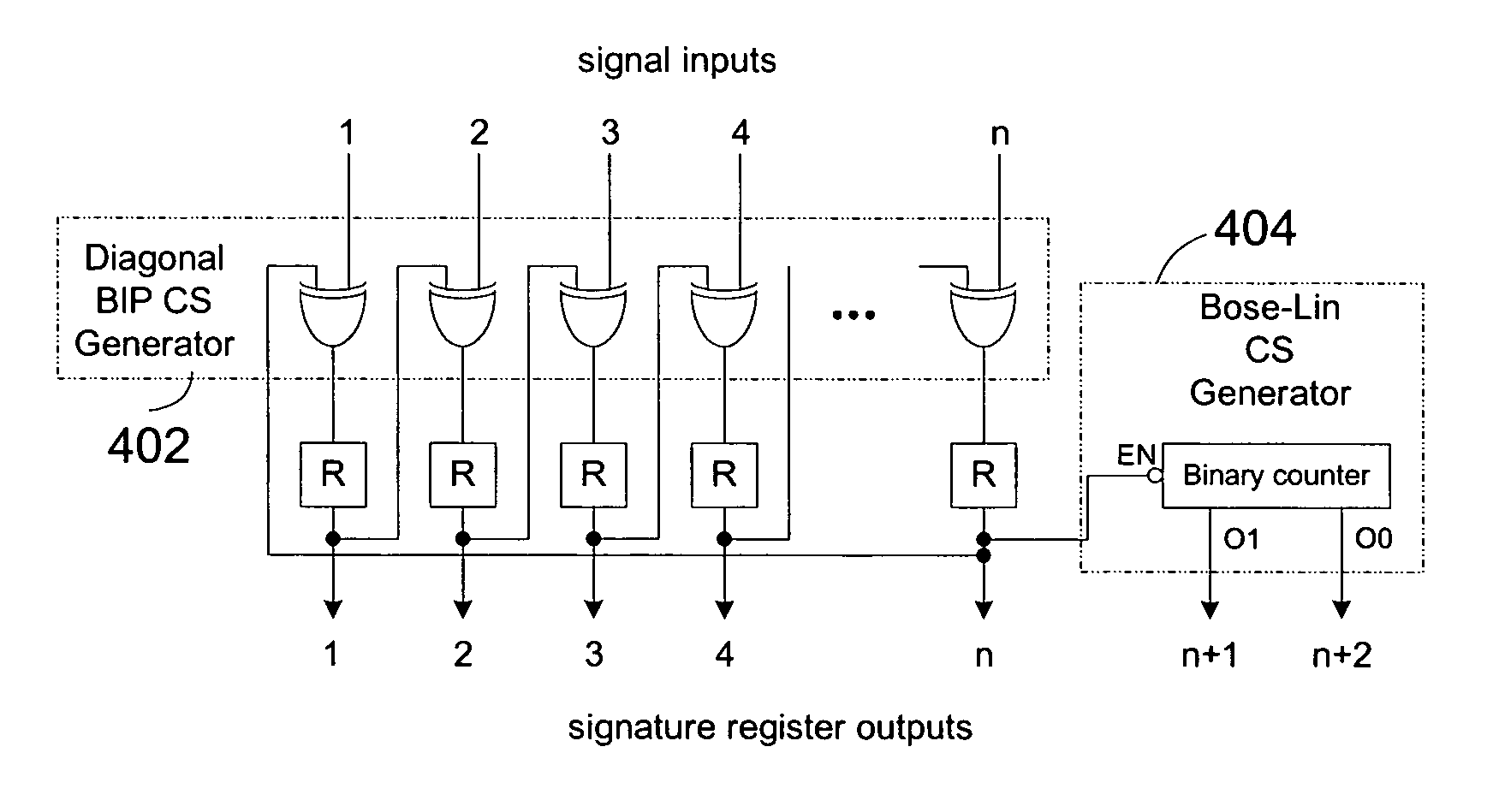
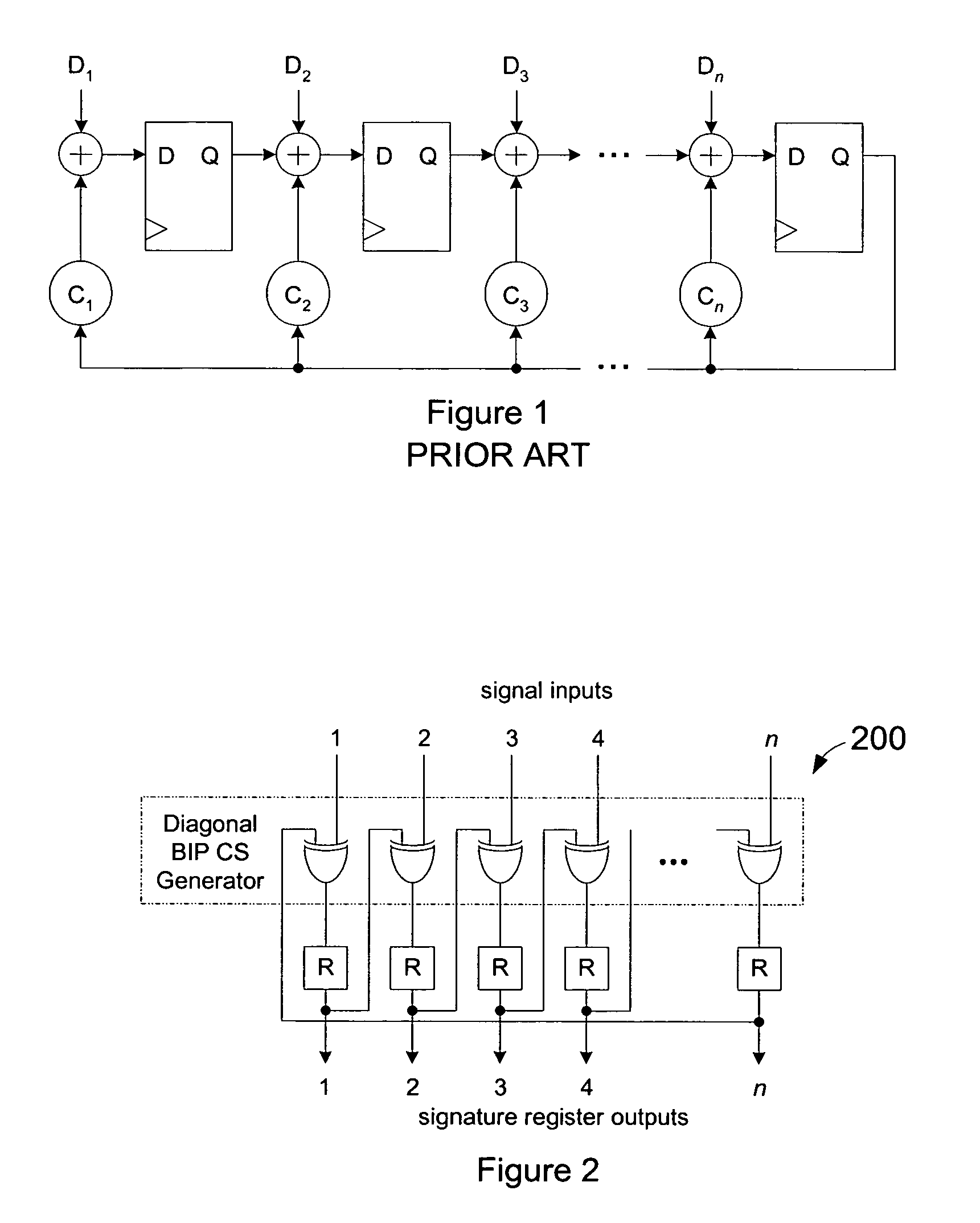
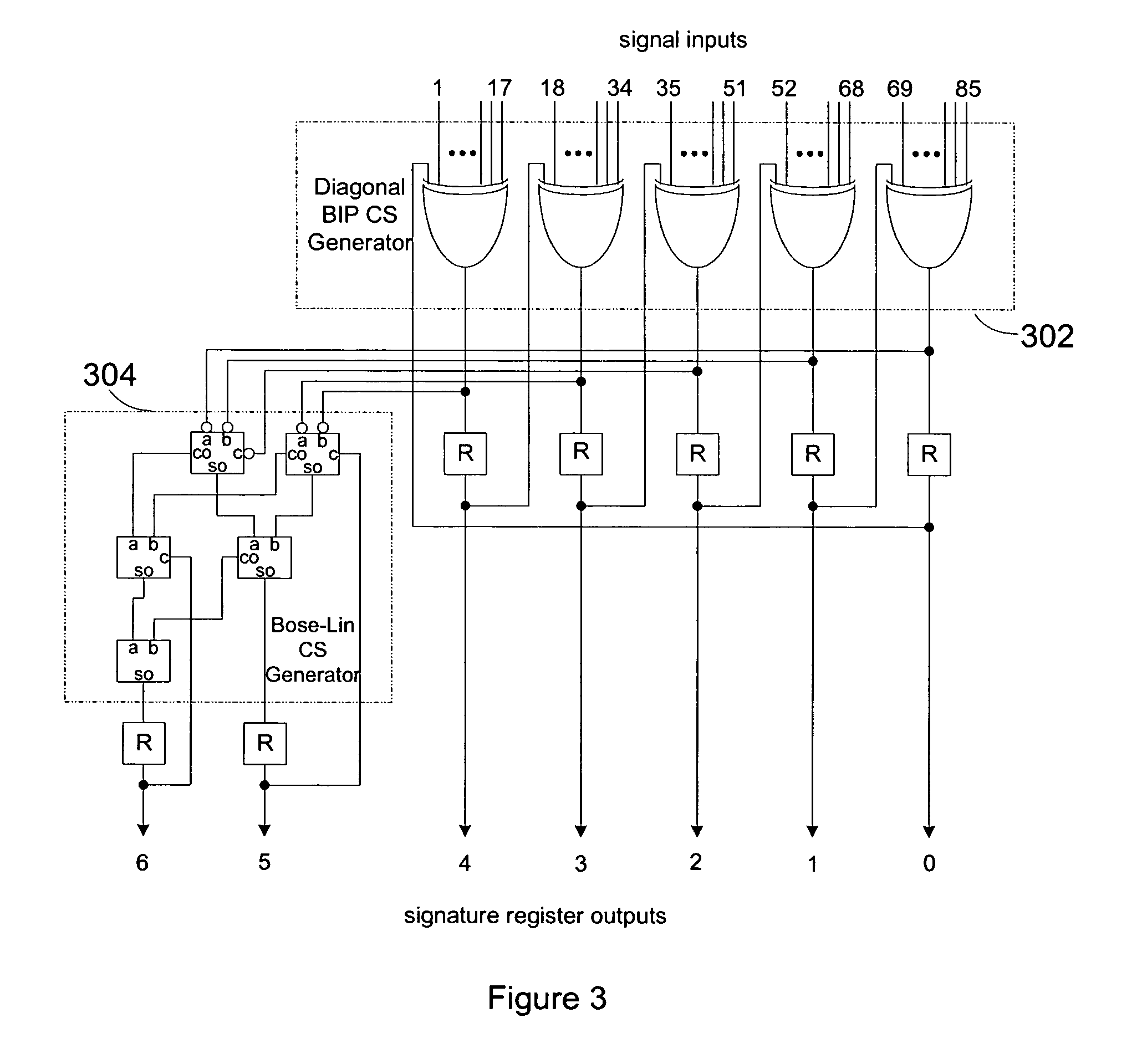
ActiveUS7437641B1Reduce loadExceed capacityElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionProcessor registerCircuit under test
Signature circuits are used during testing of an integrated circuit. Test vectors are applied as inputs to a circuit under test. A signature circuit stores a “signature” for the circuit under test based on a combination of signals from the circuit under test in response to test vectors and a previous stored state of the signature register. The value contained in the signature register at the end of the test is the signature. A fault-free circuit generates a particular signature for the applied test vectors. Faults can be determined by detecting variances from the expected signature. In one embodiment, the signature circuit uses a combination of two error detection codes.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Architecture for generating adaptive arbitrary waveforms
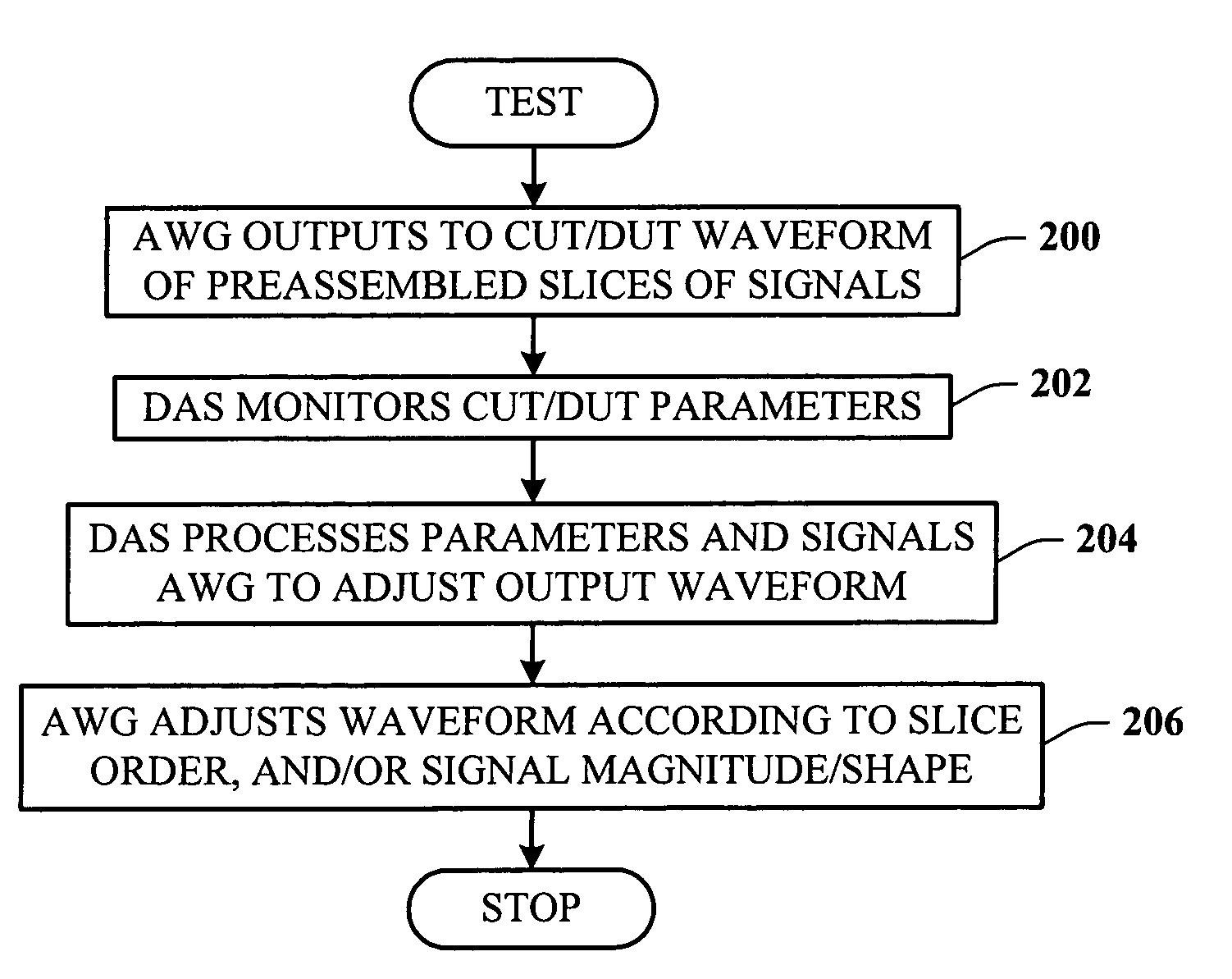
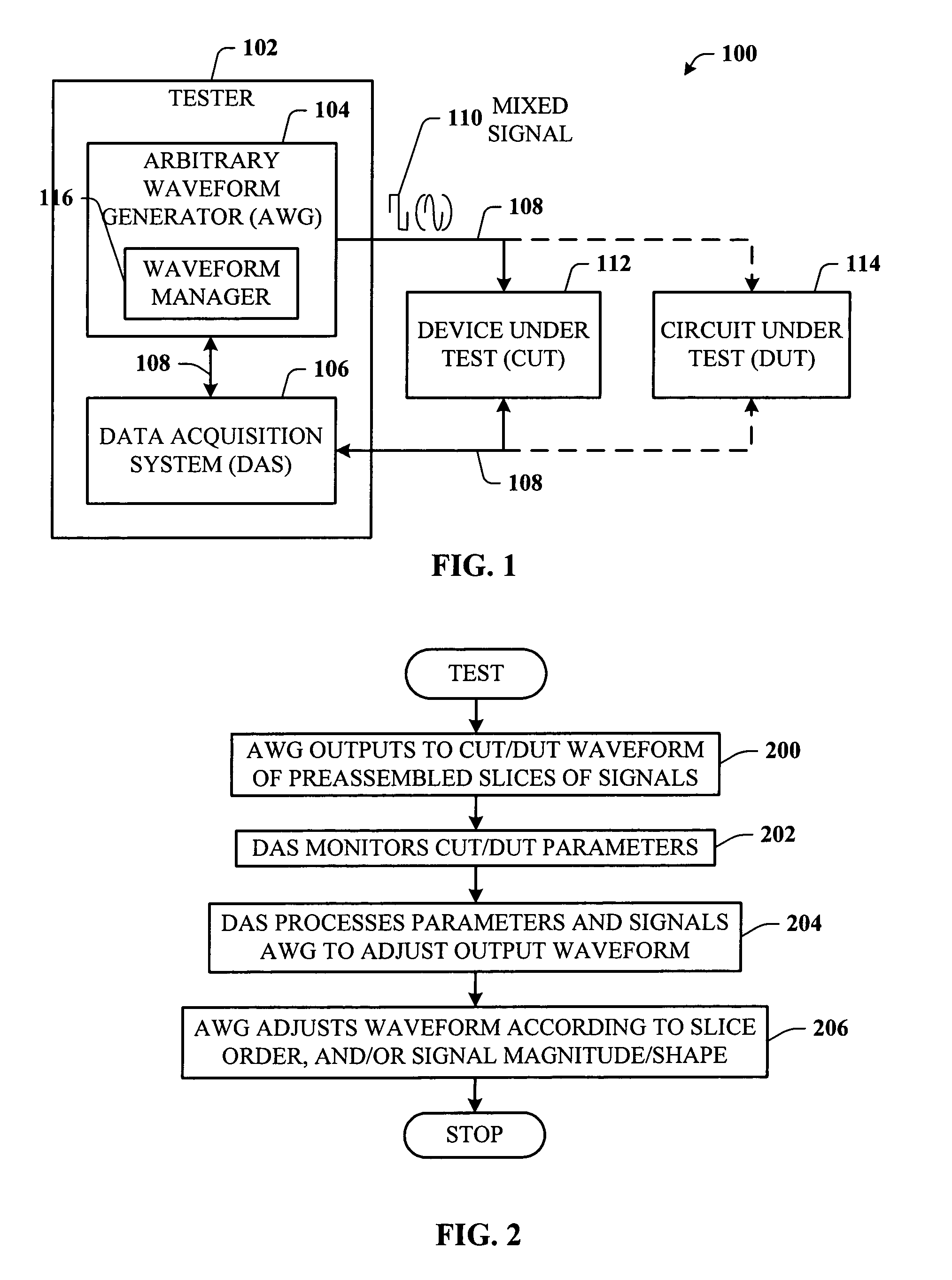
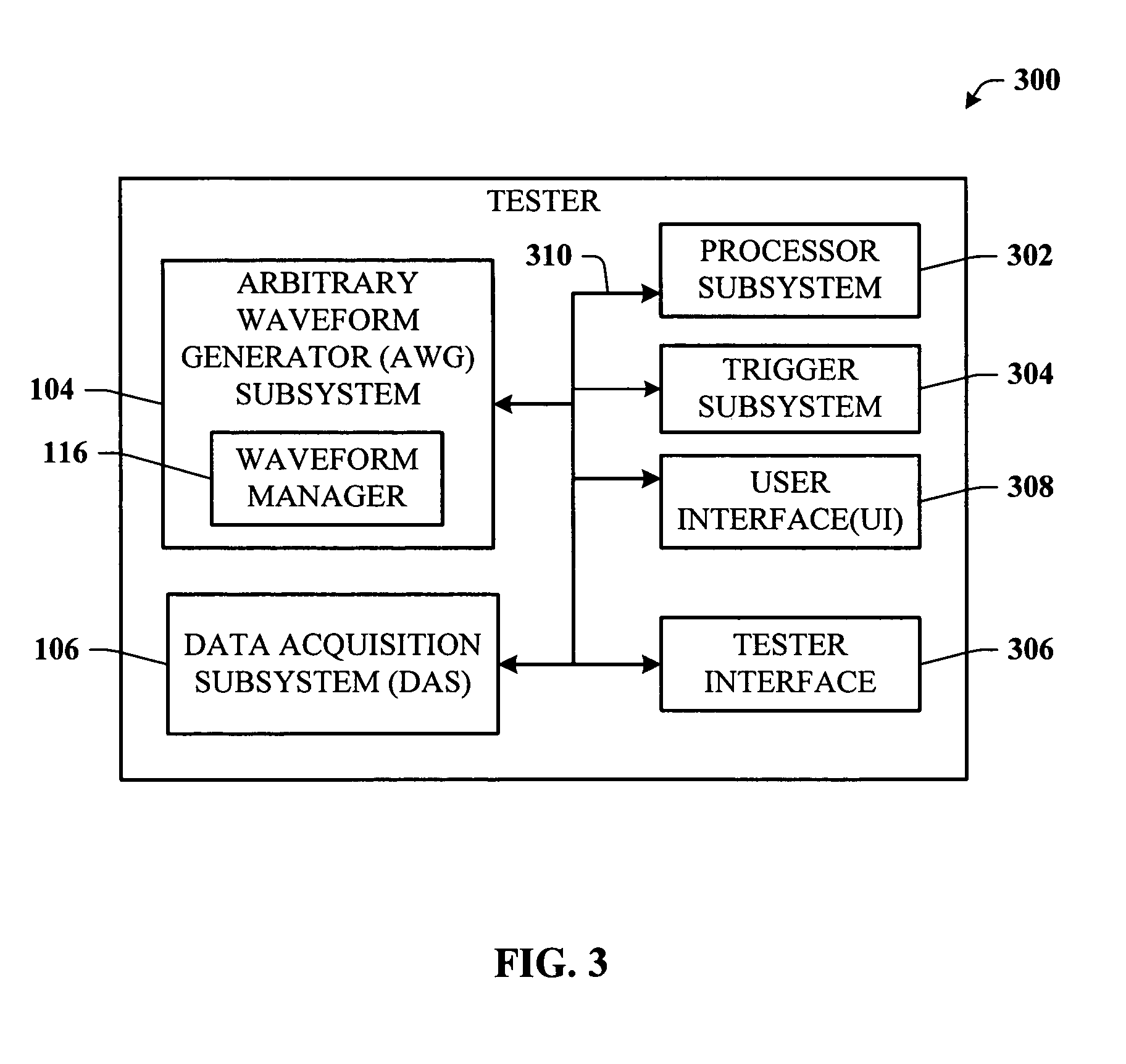
InactiveUS7072781B1Change in numberEasy to changeResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCircuit under testData acquisition
A test system having a feedback loop that facilitates adjusting an output test waveform to a DUT / CUT (Device Under Test / Circuit Under Test) on-the-fly according to changing DUT / CUT parameters. The system includes a tester having an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) and a data acquisition system (DAS) that monitors the status of the DUT / CUT. The AWG and DAS connect to the DUT / CUT through a feedback loop where the AWG outputs the test waveform to the DUT / CUT, the DAS monitors the DUT / CUT parameters, and the DAS analyzes and communicates changes to the AWG to effect changes in the output waveform, when desired. The AWG builds the output waveform in small slices (or segments) that are assembled together through a process of selection and calibration. The feedback architecture facilitates a number of changes in the output waveform, including a change in the original order of the preassembled slices, and changes in the magnitude / shape of the output waveform.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Apparatus and method for measuring characteristics of dynamic electrical signals in integrated circuits
InactiveUS6976234B2Digital circuit testingSpecial data processing applicationsCircuit under testHemt circuits
Systems and methods consistent with principles of the present invention allow contactless measurements of voltage characteristics of dynamic electrical signals in integrated circuits. The invention utilizes a signal analysis circuit, such as a voltage comparator, disposed with the circuit under test, which is optically coupled with the external timing measurement equipment. The signal analysis circuit changes its state depending on the characteristics of the measured electrical signal applied thereto. The changes in the condition of the signal analysis circuit are sensed by the external timing measurement equipment provided outside the circuit under test. To this end, the signal analysis circuit is optically coupled with the external measurement equipment registering specific changes in the condition of the signal analysis circuit. The information on the condition of the signal analysis circuit registered by the external measurement equipment is used to study the characteristics of the dynamic electrical signals within the circuit.
Owner:DCG SYST
Adaptive fault diagnosis of compressed test responses
ActiveUS20060041813A1Increasing hardware overheadEffective diagnosisElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionCircuit under testTest response
Methods, apparatus, and systems for diagnosing failing scan cells from compressed test responses are disclosed herein. For example, in one nonlimiting exemplary embodiment, one or more signatures are received that indicate the presence of one or more errors in one or more corresponding compressed test responses. Scan cells in the circuit-under-test that caused the errors are identified by analyzing the signatures. In this exemplary embodiment, the analysis includes selecting a scan cell candidate that potentially caused an error in a compressed test response based at least partially on a weight value associated with the scan cell candidate, the weight value being indicative of the likelihood that the scan cell candidate caused the error. Tangible computer-readable media comprising computer-executable instructions for causing a computer to perform any of the disclosed methods are also provided. Tangible computer-readable media comprising lists of failing scan cells identified by any of the disclosed methods are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Test method of semiconductor intergrated circuit and test pattern generator
InactiveUS6922803B2Avoid problemsEliminate overheadElectronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareFault coverageGraphics
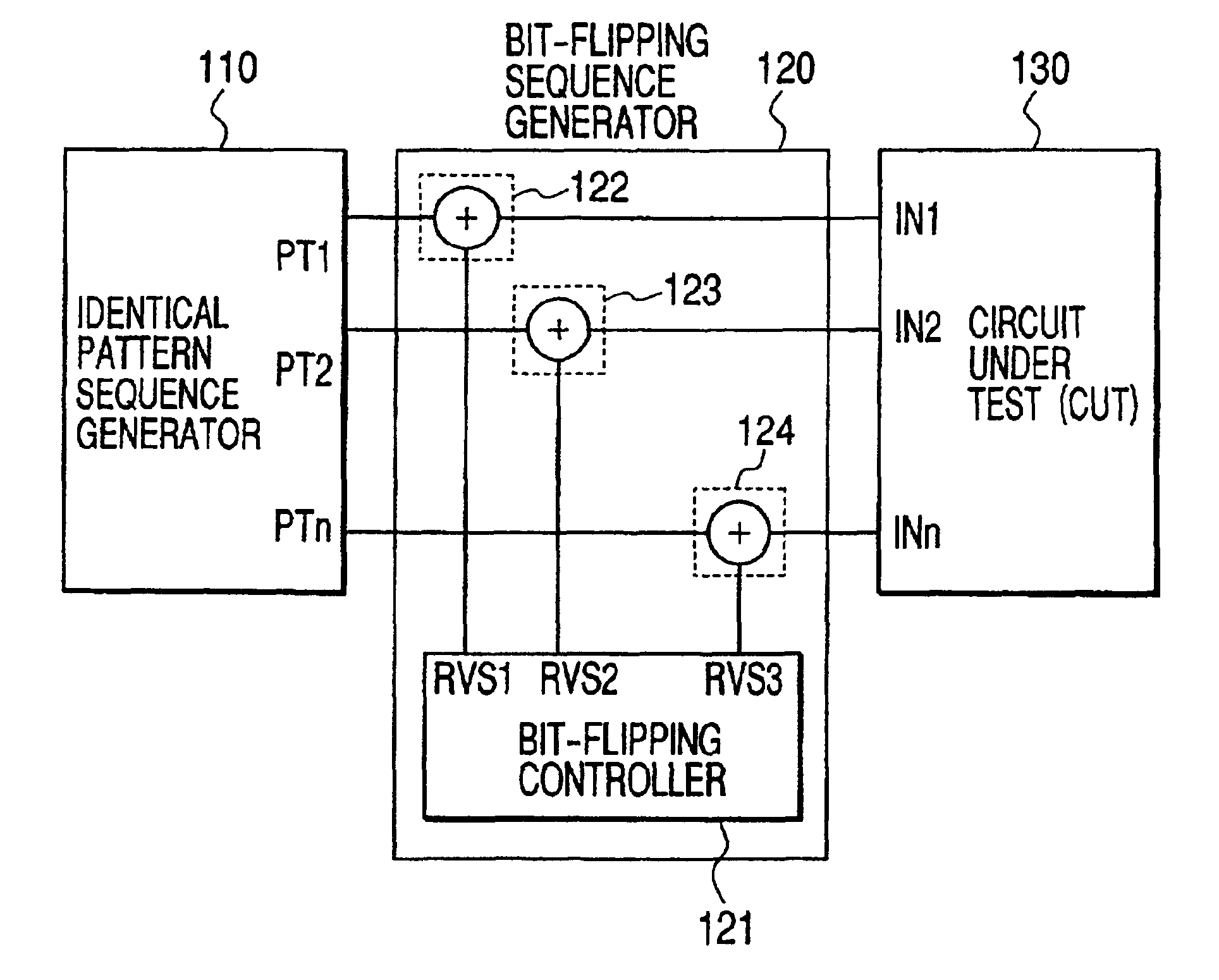
A semiconductor integrated circuit test method which reduces the required data volume for testing and efficiently detects faults in a circuit to be tested, the method comprising means 110 to generate identical pattern sequences repeatedly and means 120 to control flipped bits in pattern sequences, in order to generate neighborhood pattern sequences and use the neighborhood patterns to test the circuit under test 130. The neighborhood patterns include, in whole or in part, such pattern sequences as ones without flipped bits, ones with all or some flipped bits in one pattern and ones with all or some flipped bits in consecutive patterns or patterns at regular intervals, the interval being equivalent to a given number of patterns. Because a test pattern generator is provided independently of the circuit to be tested, the problem of a prolonged design period can be eliminated, a loss in the operating speed of the circuit under test is minimized and a high fault coverage can be achieved with less hardware overhead and a smaller volume of test data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for circuit testing
ActiveUS7055077B2Improve performanceImprove test coverageElectronic circuit testingSolid-state devicesCircuit under testEngineering
Systems and methods for improved performance of built-in-self-tests (BISTs) in integrated circuits, where variability is introduced into the self tests to improve the coverage of the tests. In one embodiment, an LBIST system includes scan chains interposed between levels of functional logic in a circuit under test. An exemplary method includes the steps of, for each of one or more initial scan chains, filling the initial scan chains with data comprising a pseudorandom pattern of bits, determining a number of levels of functional circuitry and corresponding subsequent scan chains through which to propagate the data and propagating the data from the initial scan chains through the determined number of levels of functional circuitry and corresponding subsequent scan chains. The number of levels of circuitry through which data is propagated is varied from one test cycle to another based upon a pseudorandom input signal.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
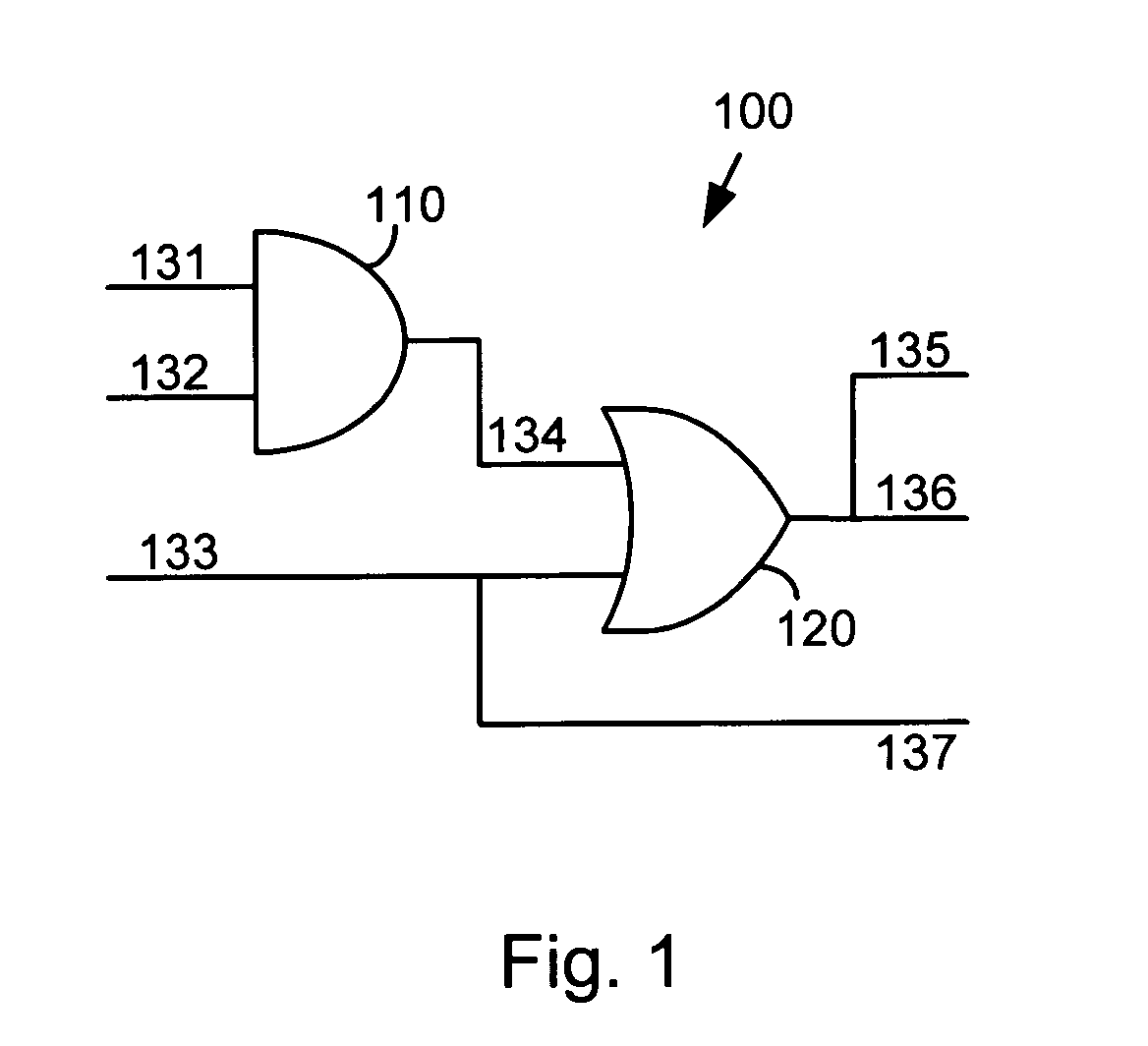
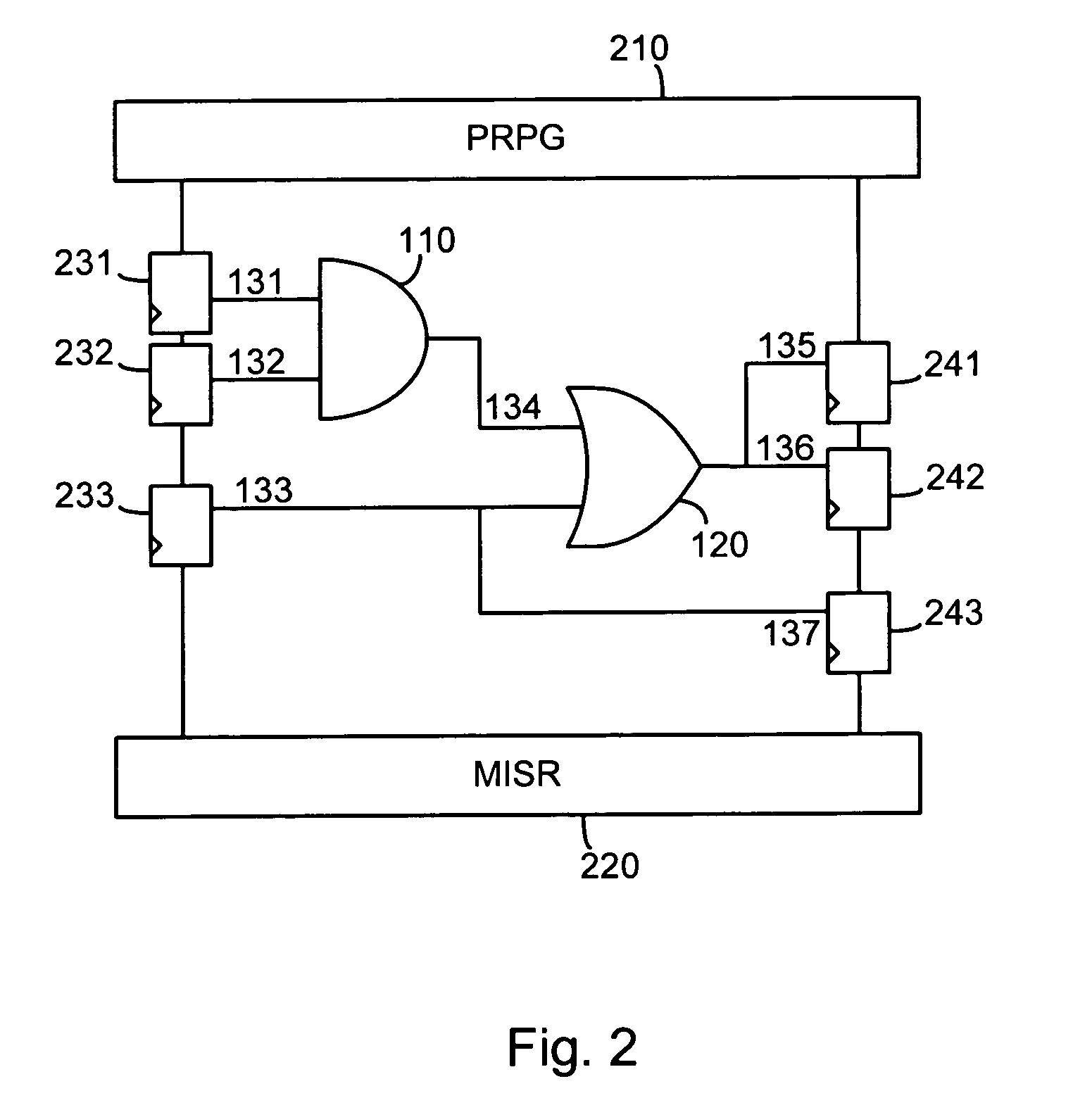
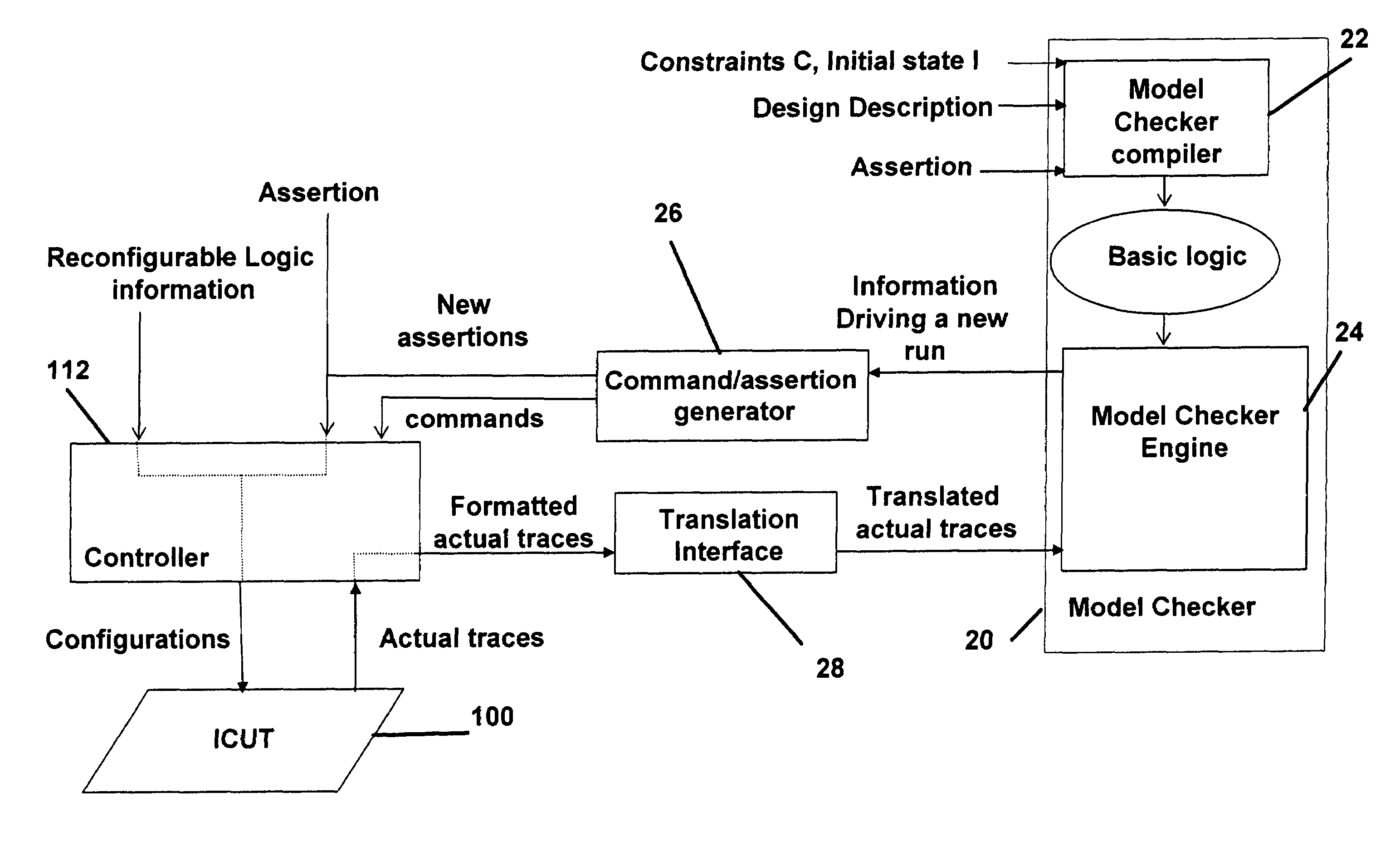
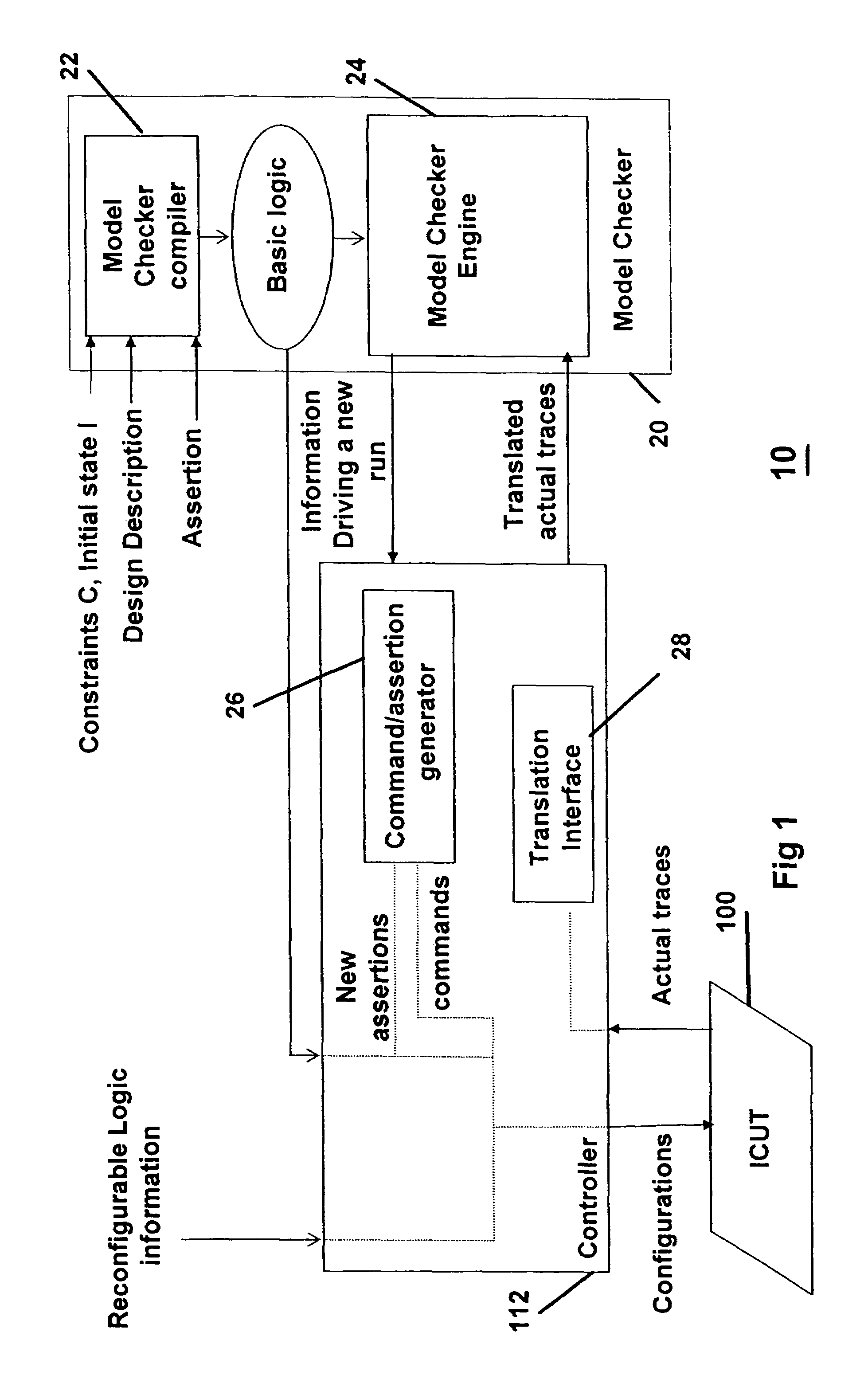
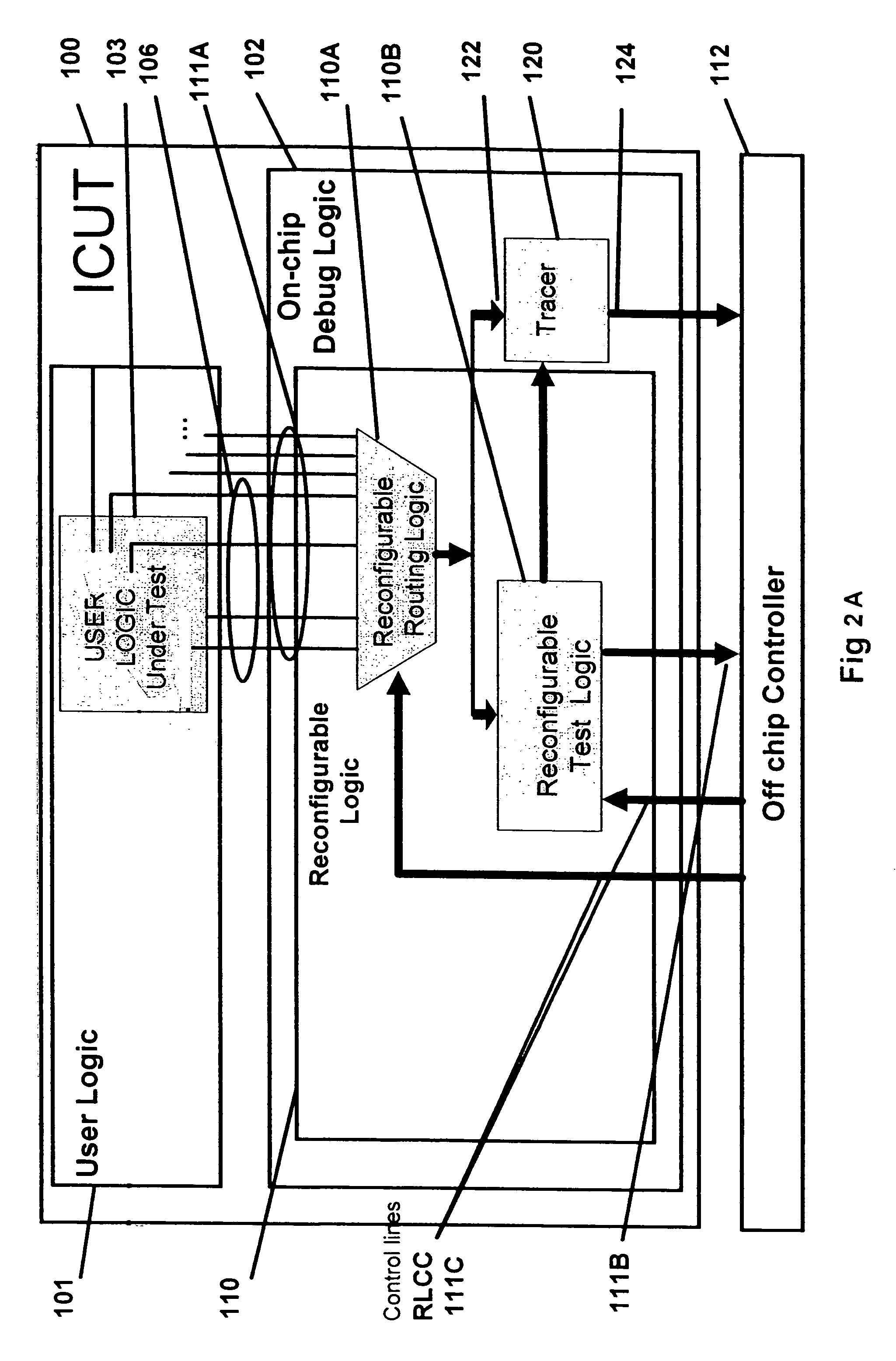
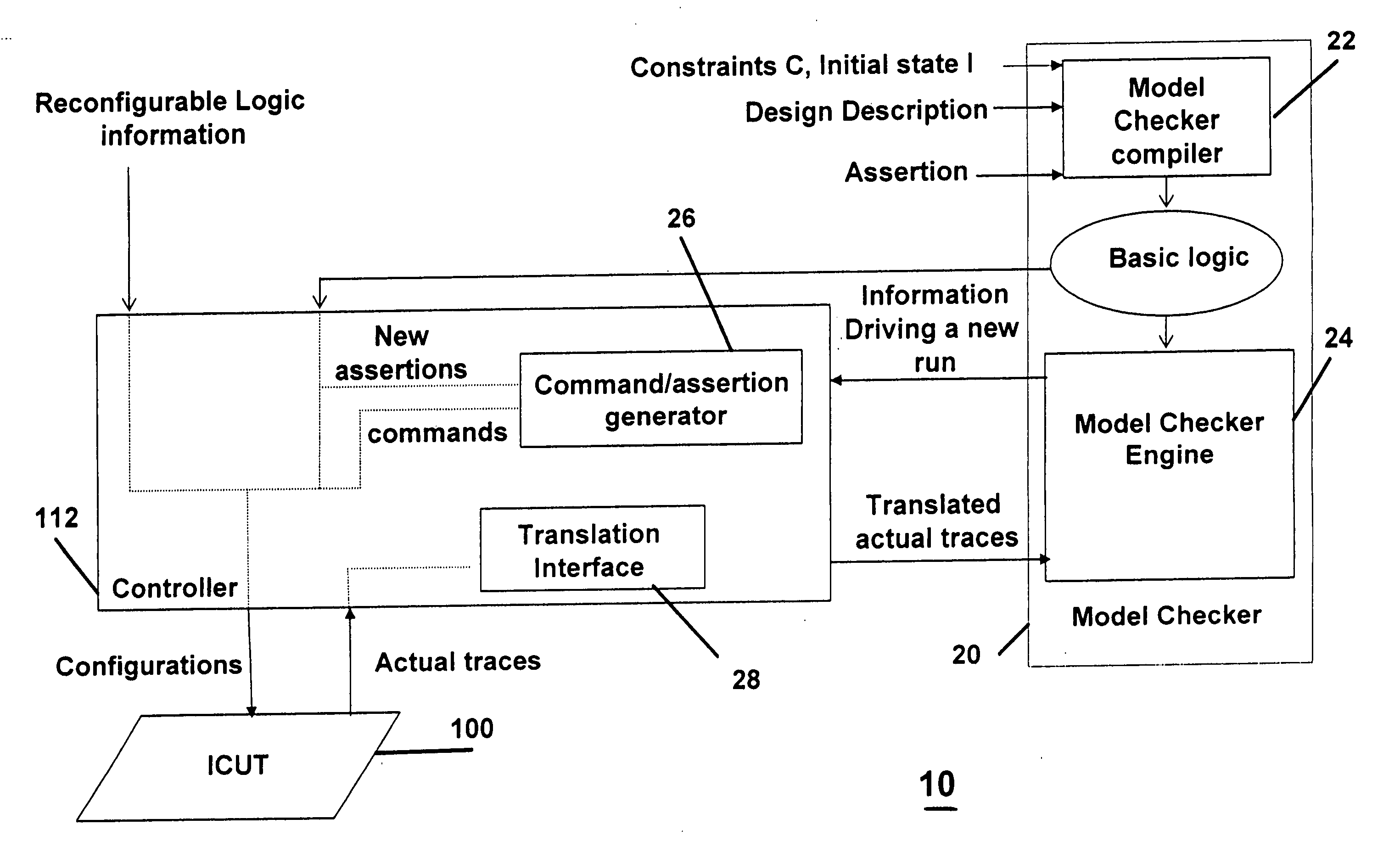
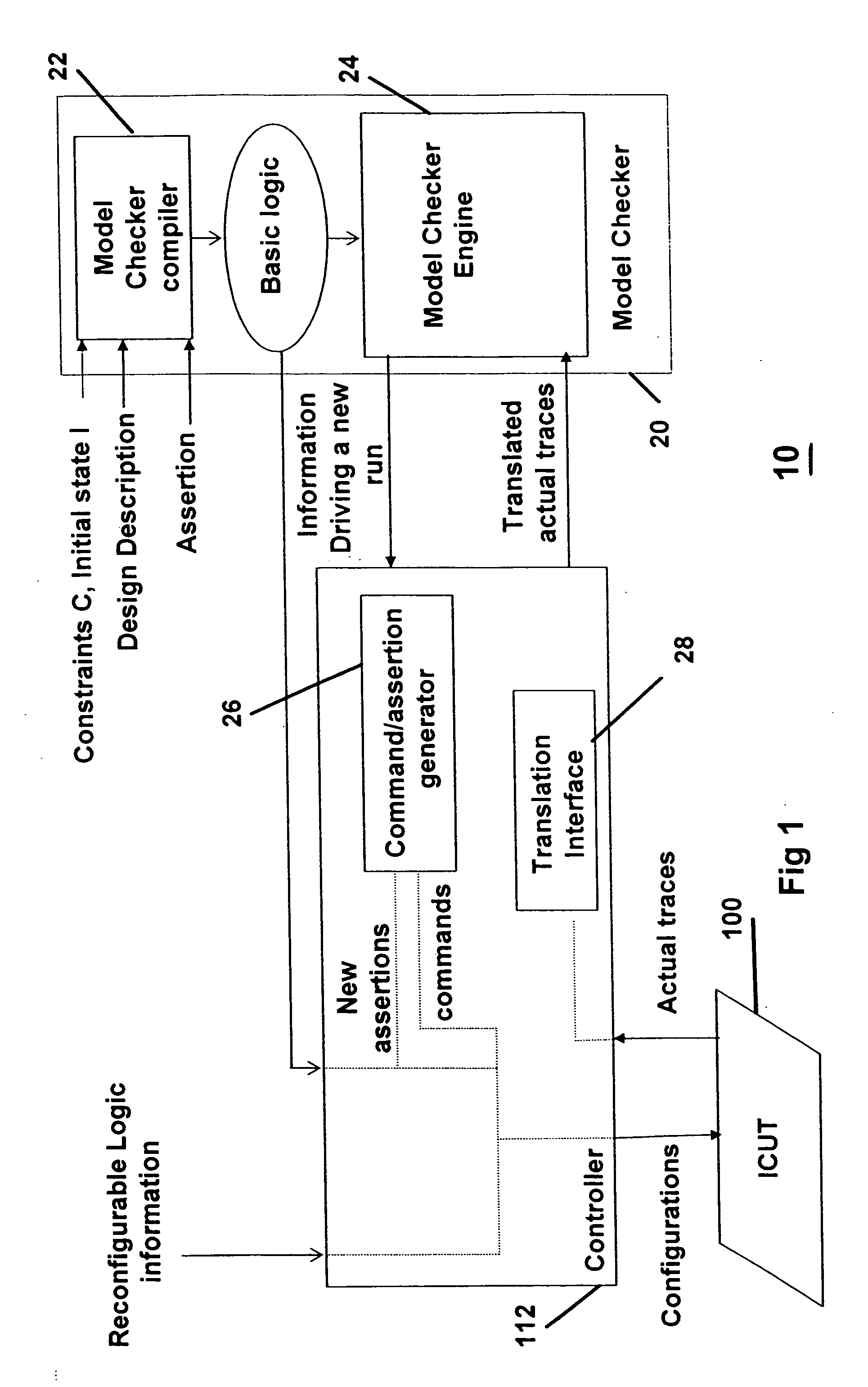
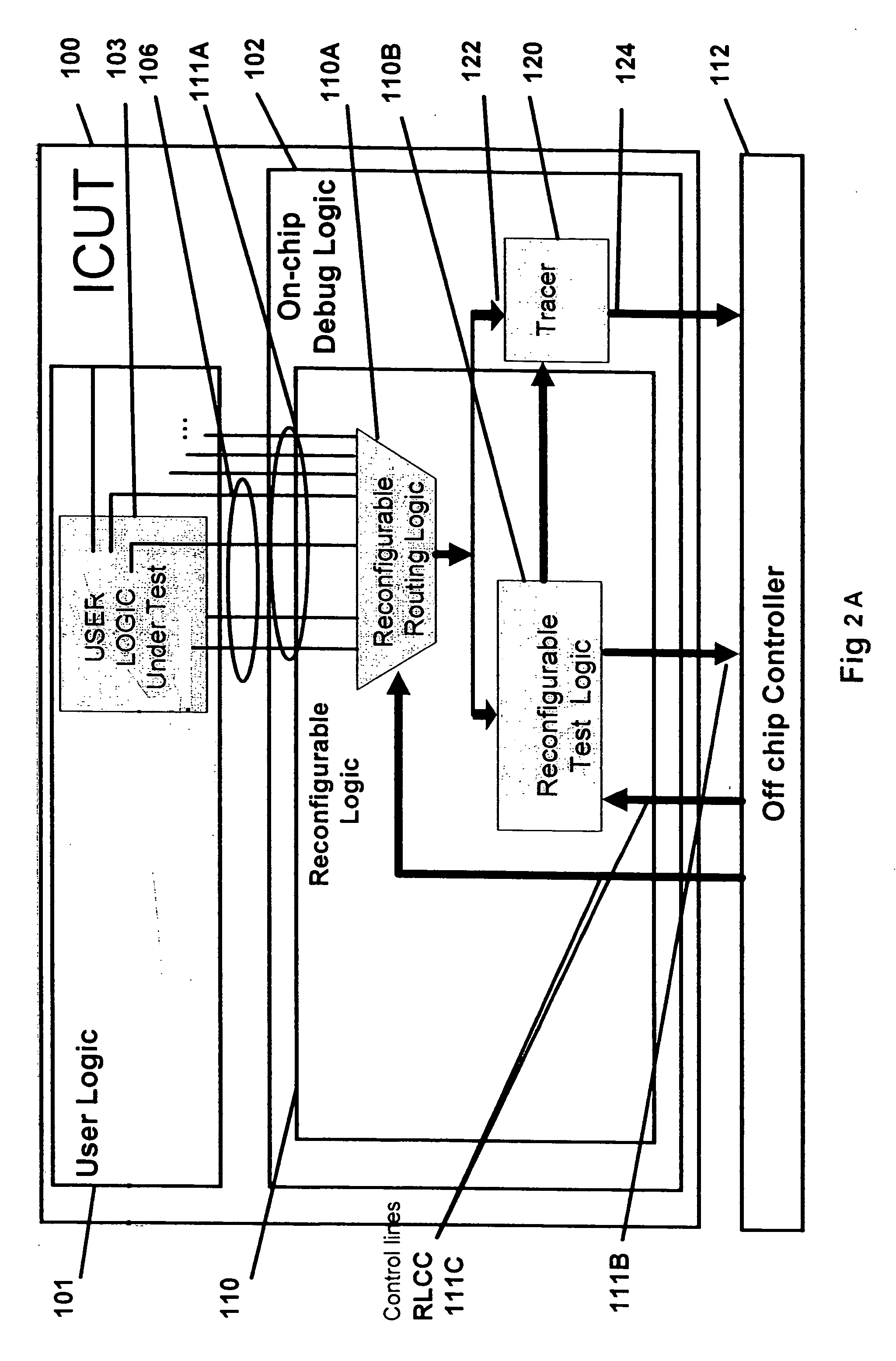
Integrated circuit analysis system and method using model checking
A method and system for verifying an integrated circuit using a Model Checker at post-silicon time to improve post-silicon assertion-based verification. A dialog is established between the Model Checker and a fabricated integrated circuit under test (ICUT), to increase the state space which is explored. ICUT-based traces from the integrated current are generated, in part based on initial states and assertions provided by the Model Checker or by a user. The Model Checker verifies the integrated circuit by generating Model Checker-based traces from basic logic, which are reproductions of the ICUT-based traces.
Owner:DAFCA
Integrated circuit analysis system and method using model checking
A method and system for verifying an integrated circuit using a Model Checker at post-silicon time to improve post-silicon assertion-based verification. A dialog is established between the Model Checker and a fabricated integrated circuit under test (ICUT), to increase the state space which is explored. ICUT-based traces from the integrated current are generated, in part based on initial states and assertions provided by the Model Checker or by a user. The Model Checker verifies the integrated circuit by generating Model Checker-based traces from basic logic, which are reproductions of the ICUT-based traces.
Owner:DAFCA
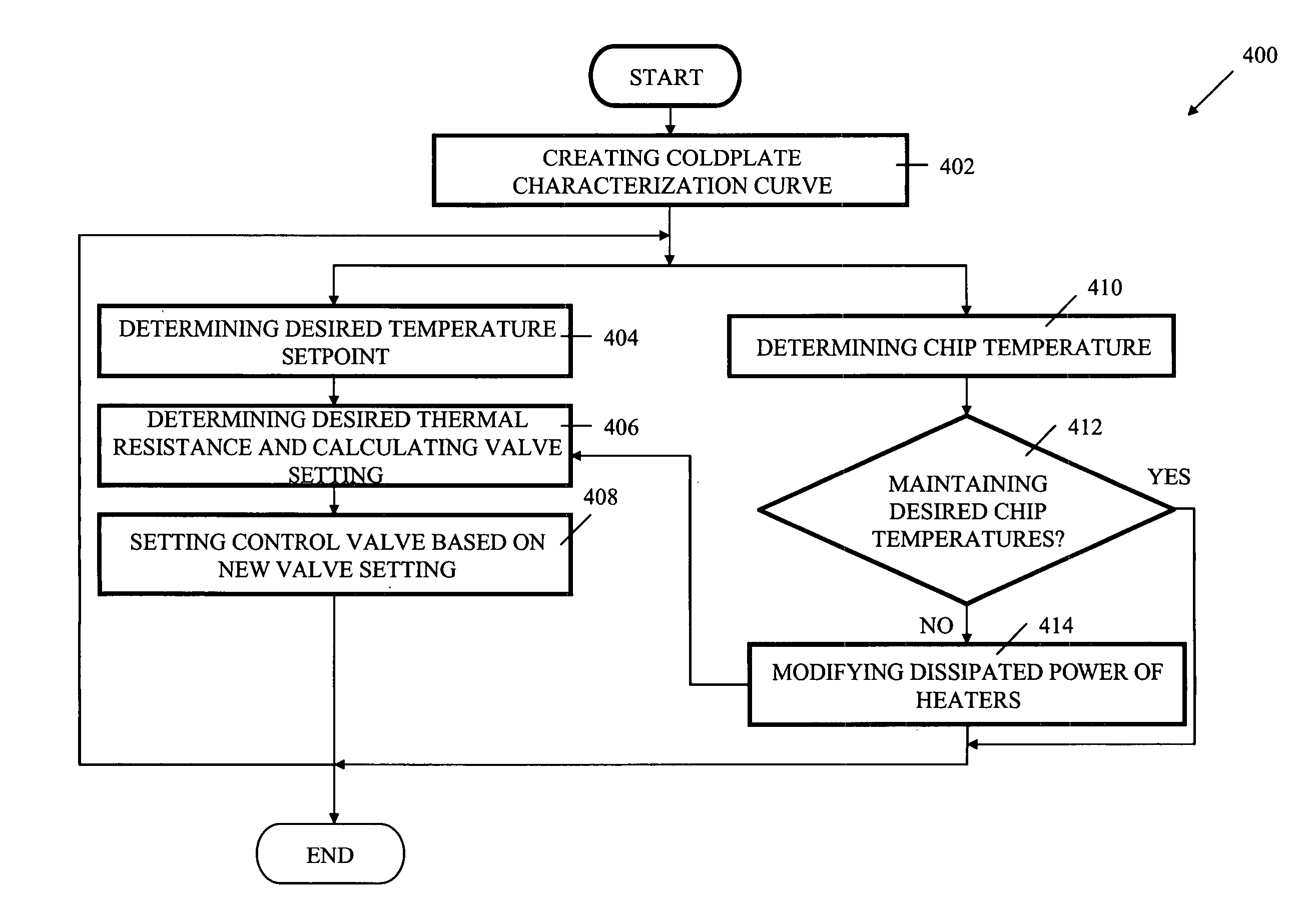
System, apparatus and method for controlling temperature of an integrated circuit under test
InactiveUS20060152238A1Fault location by increasing destruction at faultProportional controlCircuit under test
A system, apparatus and method for controlling temperature of an integrated circuit in a chip tester is disclosed. Embodiments include supplying a chilled fluid to a cold plate at a first flowrate, where the first flowrate is associated with a first valve setting based on at least a desired temperature setpoint and an applied power. Embodiments may determine a change in applied power and modify the chilled fluid flowrate in response to a change in testing conditions to a second flowrate associated with a second valve setting associated with at least the desired temperature setpoint and the changed testing conditions. This feed forward loop may be supplemented by a feedback loop that includes modifying the energy supplied to a cold plate heater in response to a comparison of a current temperature and the temperature setpoint. The valve may be a proportional control valve or the like.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Capacitive probe assembly with flex circuit
InactiveUS20050046428A1Reduce complexityReduce in quantityResistance/reactance/impedenceElectric connection testingAudio power amplifierCapacitive coupling
A novel capacitive sensor assembly that utilizes a flex circuit for amplification of capacitively sensed signals and for separating the power, ground, and measurement signals is presented. The use of a flex circuit in the capacitive probe assembly allows implementation of multiple capacitive sensors for respectively capacitively coupling multiple signals from respective multiple test points of a circuit under test. The invention integrates the sensor plate, amplifier, and return wiring for each capacitive sensor all onto one flex circuit.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Inductively coupled direct contact test probe
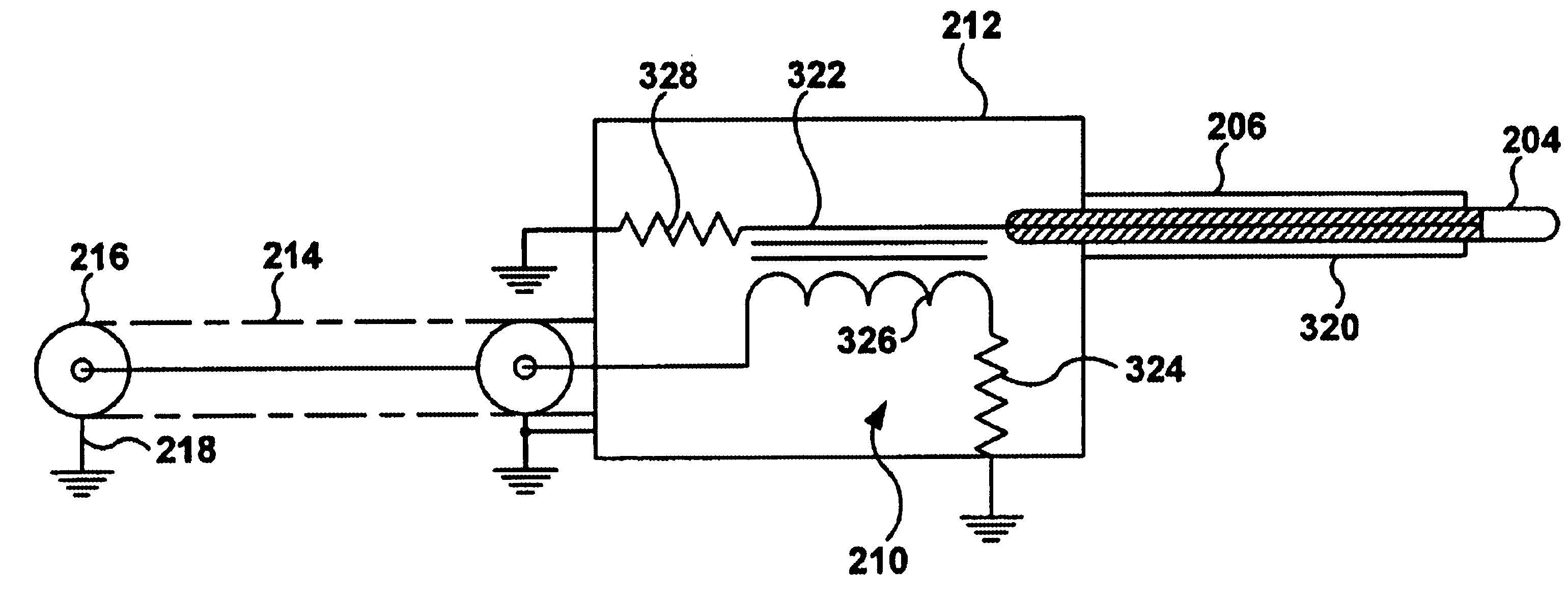
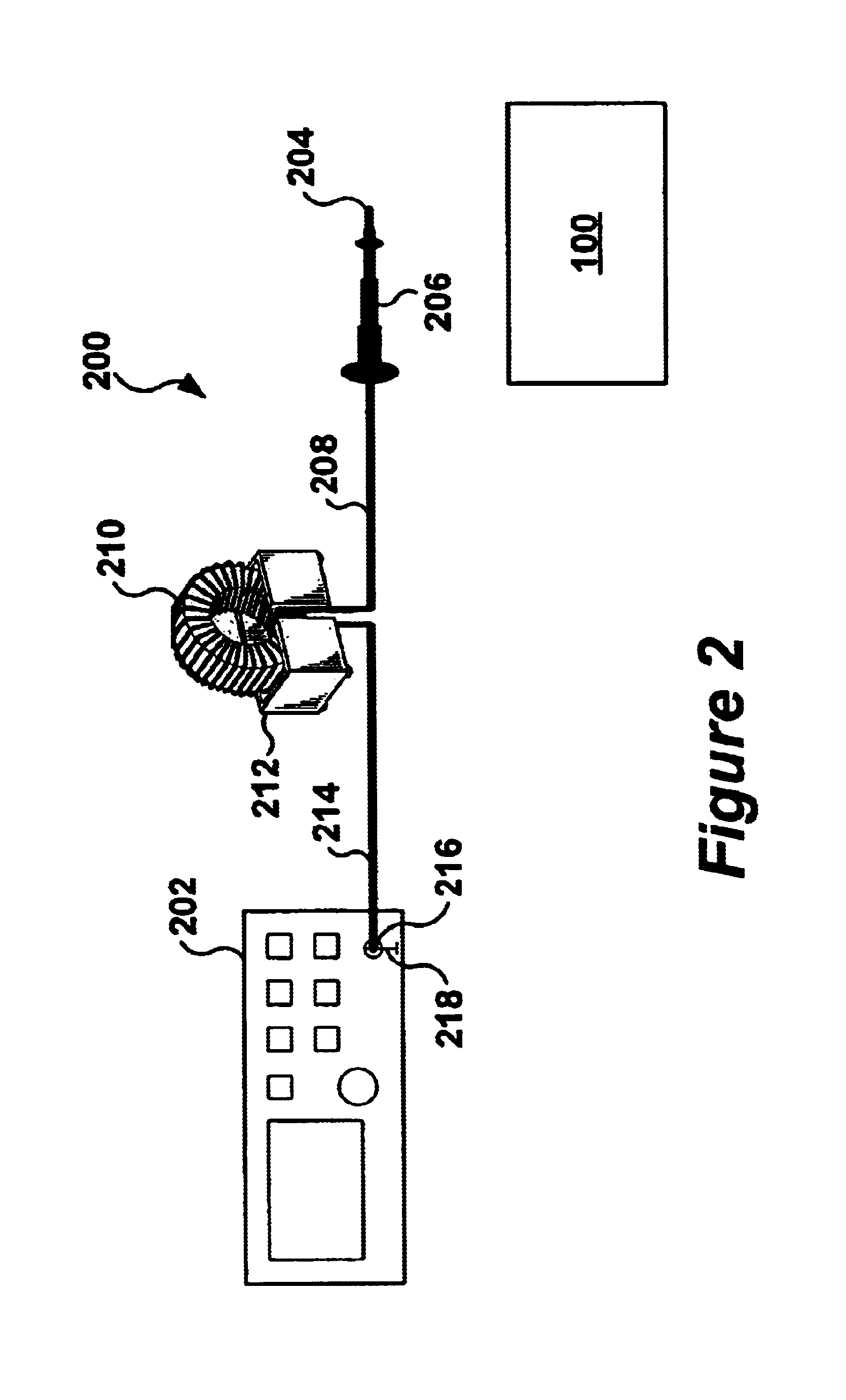
ActiveUS6841986B1Minimize pickupWithout risk of damageResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsDielectricElectrical conductor
A probe for measuring radio frequency / electromagnetic interference (RF / EMI) is used in combination with a spectrum analyzer or oscilloscope (measuring equipment) to measure and / or test for EMI in electronic equipment. The RF / EMI probe has high dielectric transformer isolation between the input of the measuring equipment and the circuit under test so as to prevent damaging the measuring equipment if a high voltage or current is encountered in the circuit being tested. The RF / EMI probe comprises a measurement tip connected to a shielded sense line, the shielded sense line is electro-magnetically coupled to a toroid forming a RF transformer, a high impedance termination load is connected to the shielded sense line, a shielded coaxial cable having a center conductor connected to a secondary winding on the toroid transformer, the shielded coaxial cable being adapted for connection to an input of the measuring equipment. The shield of the coaxial cable is continuous between the input connector of the measuring equipment and a shielded enclosure surrounding the toroid transformer. The coaxial cable may terminate in a RF connector, e.g., BNC and the like, for quick connection to and disconnection from the measuring equipment.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com