Patents
Literature
467 results about "Arbitrary waveform generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) is a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate electrical waveforms. These waveforms can be either repetitive or single-shot (once only) in which case some kind of triggering source is required (internal or external). The resulting waveforms can be injected into a device under test and analyzed as they progress through it, confirming the proper operation of the device or pinpointing a fault in it.
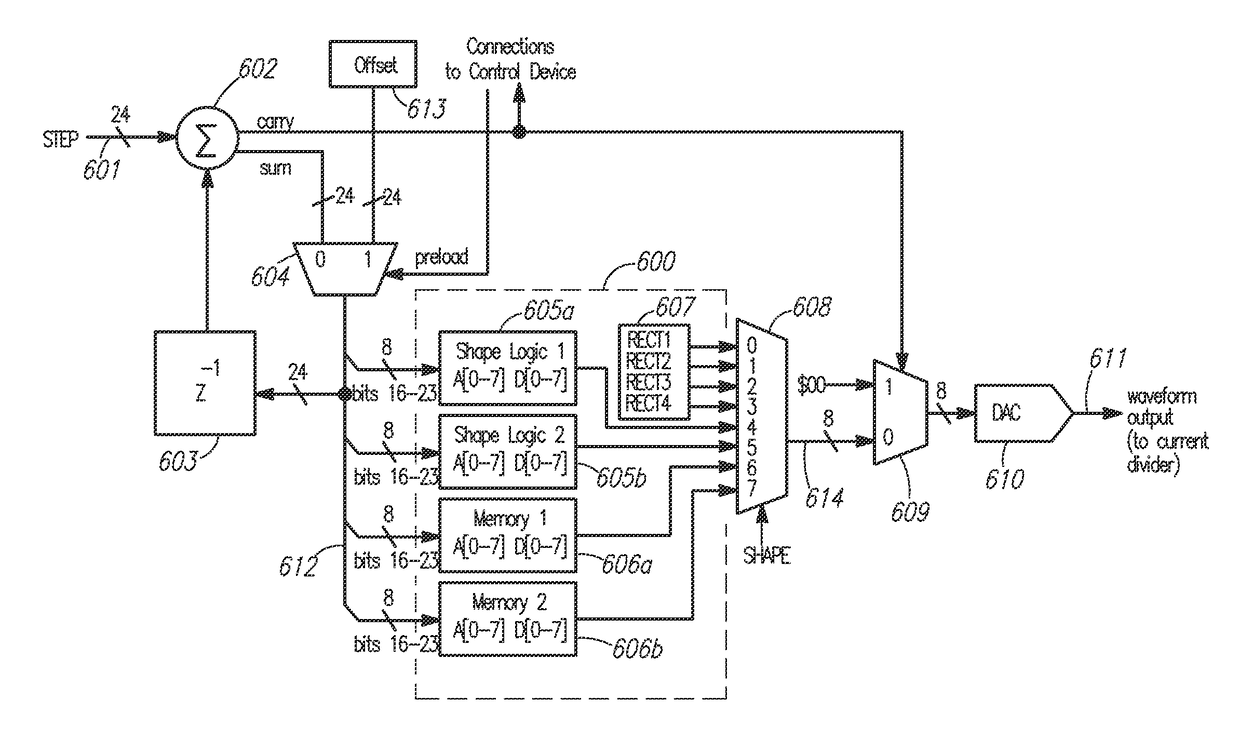
Arbitrary waveform generator having programmably configurable architecture
InactiveUS6356224B1Electric signal transmission systemsOscillations generatorsDigital analog converterMultiplexer
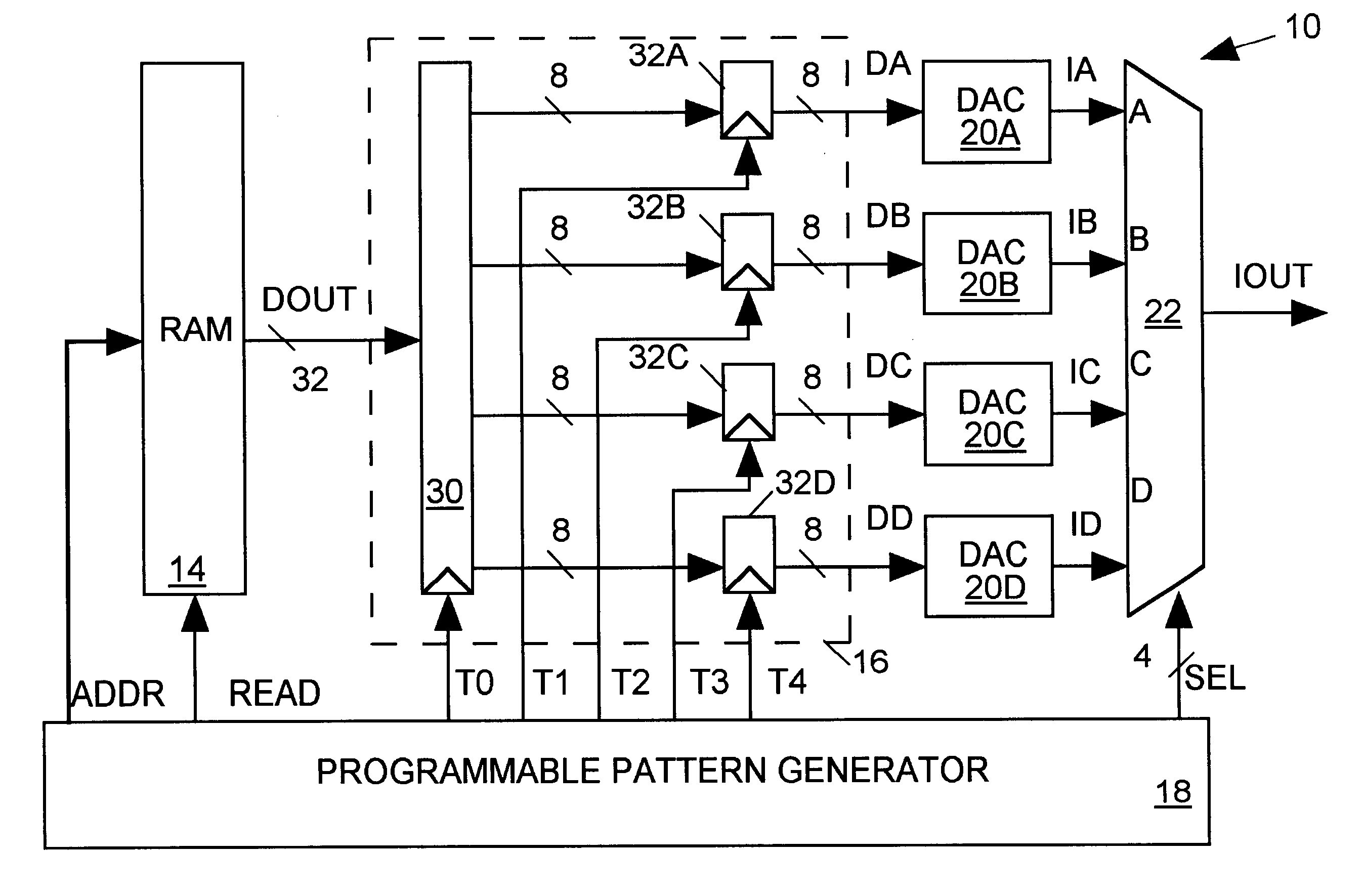
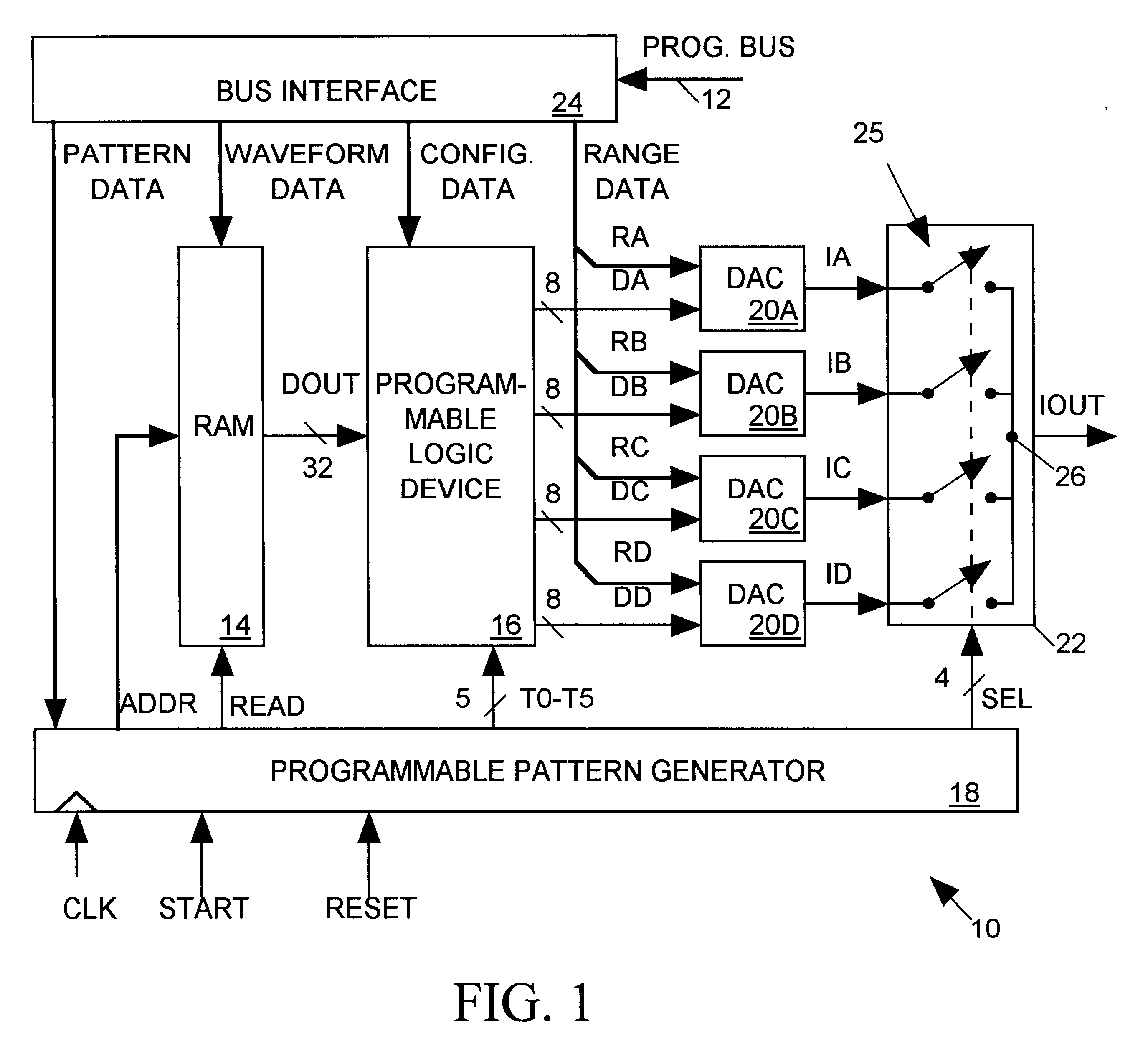
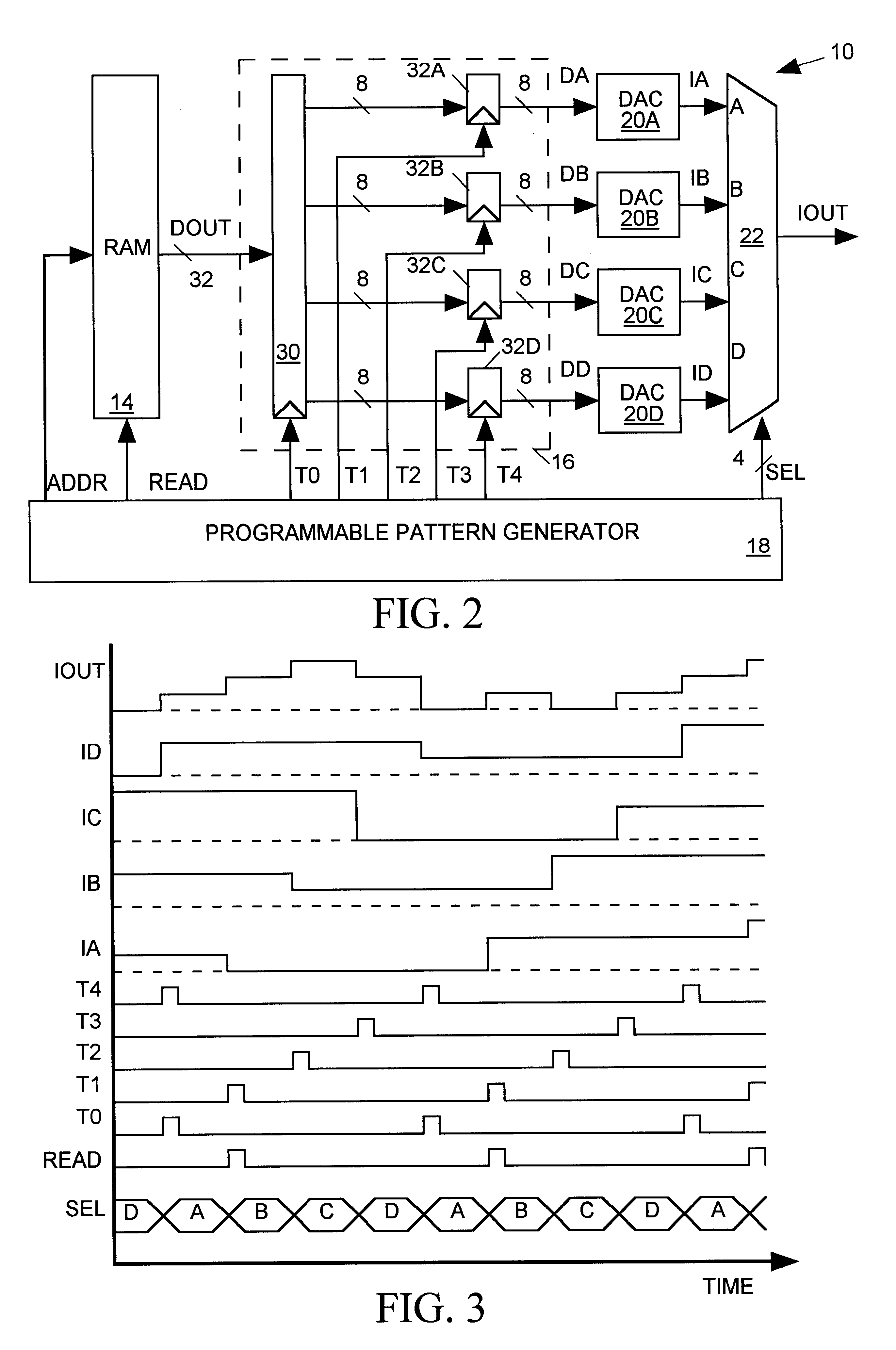
An arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) for producing an analog output current signal includes a random access memory (RAM), a programmable logic device (PLD), a programmable pattern generator, several digital-to analog converters (DACS) and a current multiplexer. The RAM store data sequences representing the analog waveform to be generated. The pattern generator read addresses the RAM causing it to sequentially read out its stored data sequence to the PLD. The PLD routes selected fields of each data sequence word to one or more of the DACs in response to timing signals provided by the pattern generator. Each DAC produces an output current of magnitude determined by its input waveform and range data. The pattern generator also signals the analog multiplexer to sum currents produced by one or more selected DACs to produce the AWG output waveform. The nature of the AWG output waveform is flexibly determined by the nature of the data sequence and the frequency at which it is read out of the RAM, the manner in which the PLD routes the data sequence to the DACs, the value of the range data supplied to each DAC, and the output pattern generated by the pattern generator. The flexible AWG architecture permits the AWG to be appropriately configured for various combinations of output waveform frequency, bandwidth and resolution requirements.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Advanced arbitrary waveform generator
InactiveUS20070067123A1Digital variable displayDigital data processing detailsSequence memoryComputer science
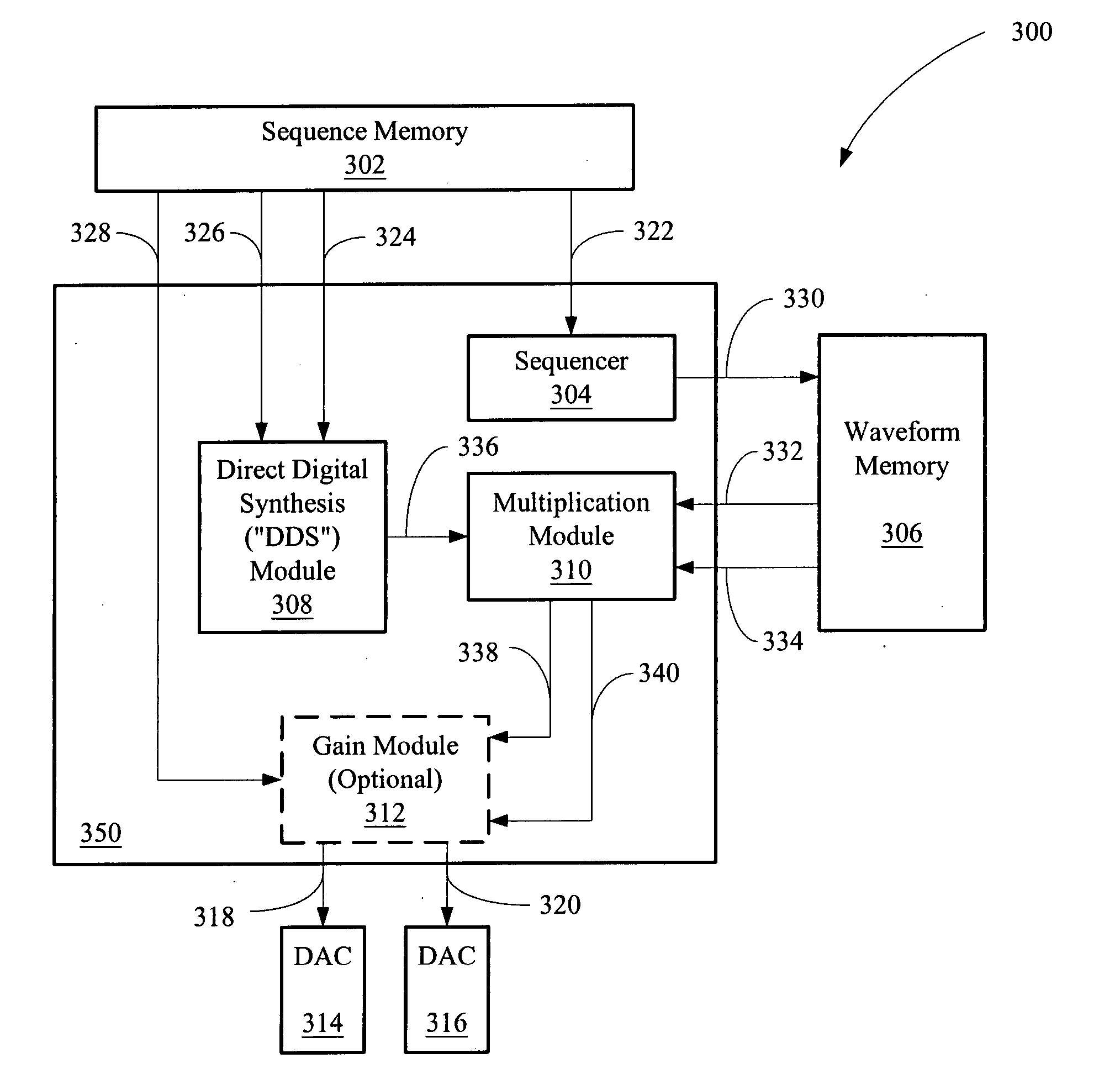
An advanced arbitrary waveform generator (“AAWG”) for producing an arbitrary waveform is disclosed. The AAWG may include a direct digital synthesis (“DDS”) module in signal communication with a sequence memory and a multiplication module in signal communication with both the DDS module and a waveform memory, where the multiplication module receives signal waveform data from the waveform memory and multiplies the received signal waveform data with a DDS output signal to produce the arbitrary waveform signal.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Enhanced test and measurement instruments using compression and decompression
InactiveUS7071852B1Less bandwidthLess storageDigital variable displayElectric signal transmission systemsMeasuring instrumentParallel compression
An enhancement that improves the performance of test and measurement equipment such as digital oscilloscopes and arbitrary waveform generators through the use of compression and decompression is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or cannot effectively be compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention improves digital oscilloscopes by compressing the sampled version of an analog waveform under observation in real time, allowing a significantly longer duration of the waveform to be stored in the oscilloscope's capture memory, when compared with the duration of the same signal's uncompressed waveform stored in the same memory. Similarly, the present invention improves arbitrary waveform generators by storing a compressed version of a desired arbitrary waveform, instead of the uncompressed version of the arbitrary waveform, in the signal generator's waveform memory. During signal generation, the compressed waveform is decompressed in real time. The uncompressed waveform drives a D / A converter that generates the desired analog waveform. The present invention's simplicity, and its ability to be implemented using parallel compression and decompression elements, allows its use at the high sampling rates of test and measurement instruments. Using the present invention, storage elements in test and measurement equipment can hold significantly longer waveforms in a fixed amount of memory. Users of the present invention can also determine the proper balance between the fidelity and the duration of the decompressed waveform by adjusting various compression and decompression control parameters.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
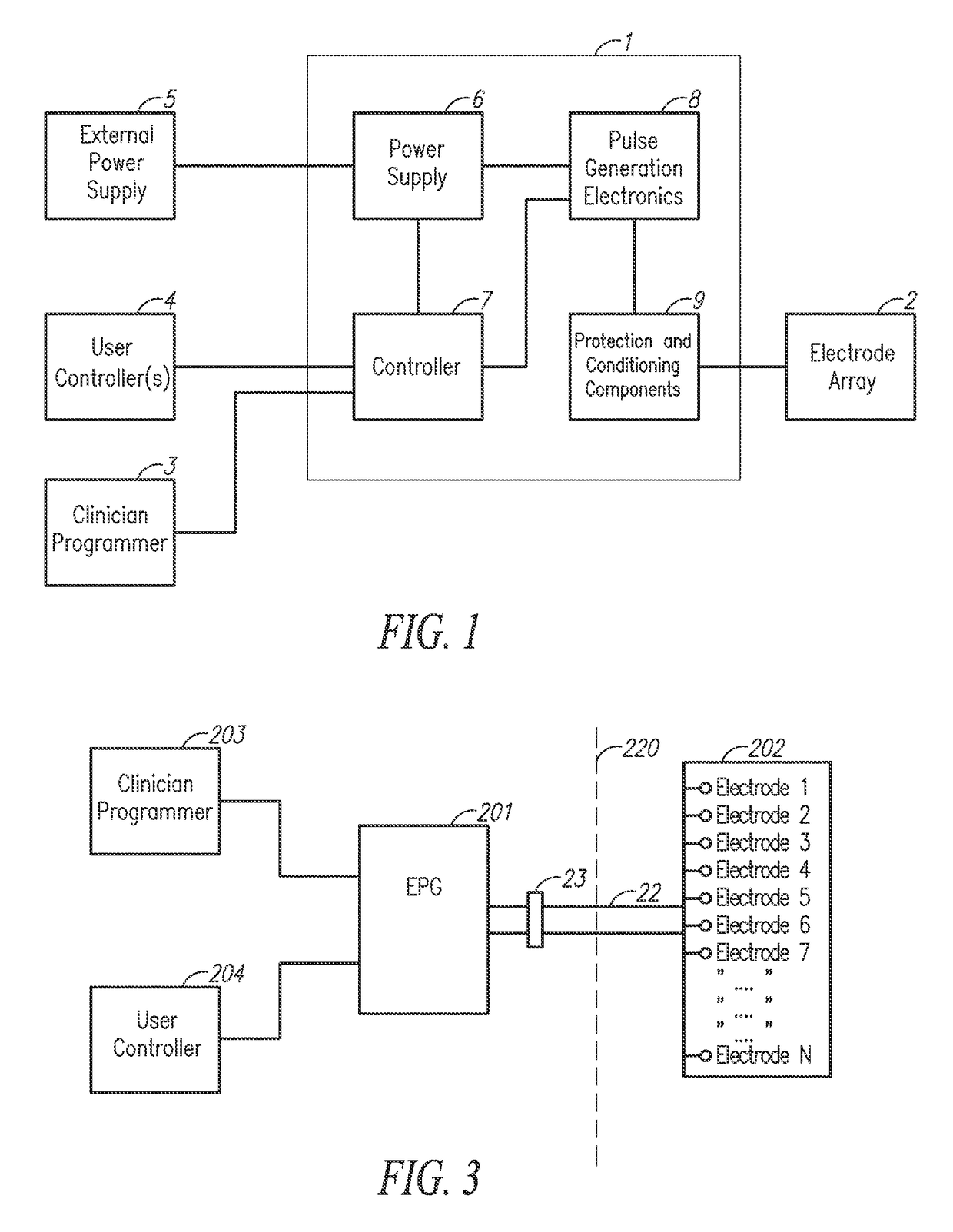
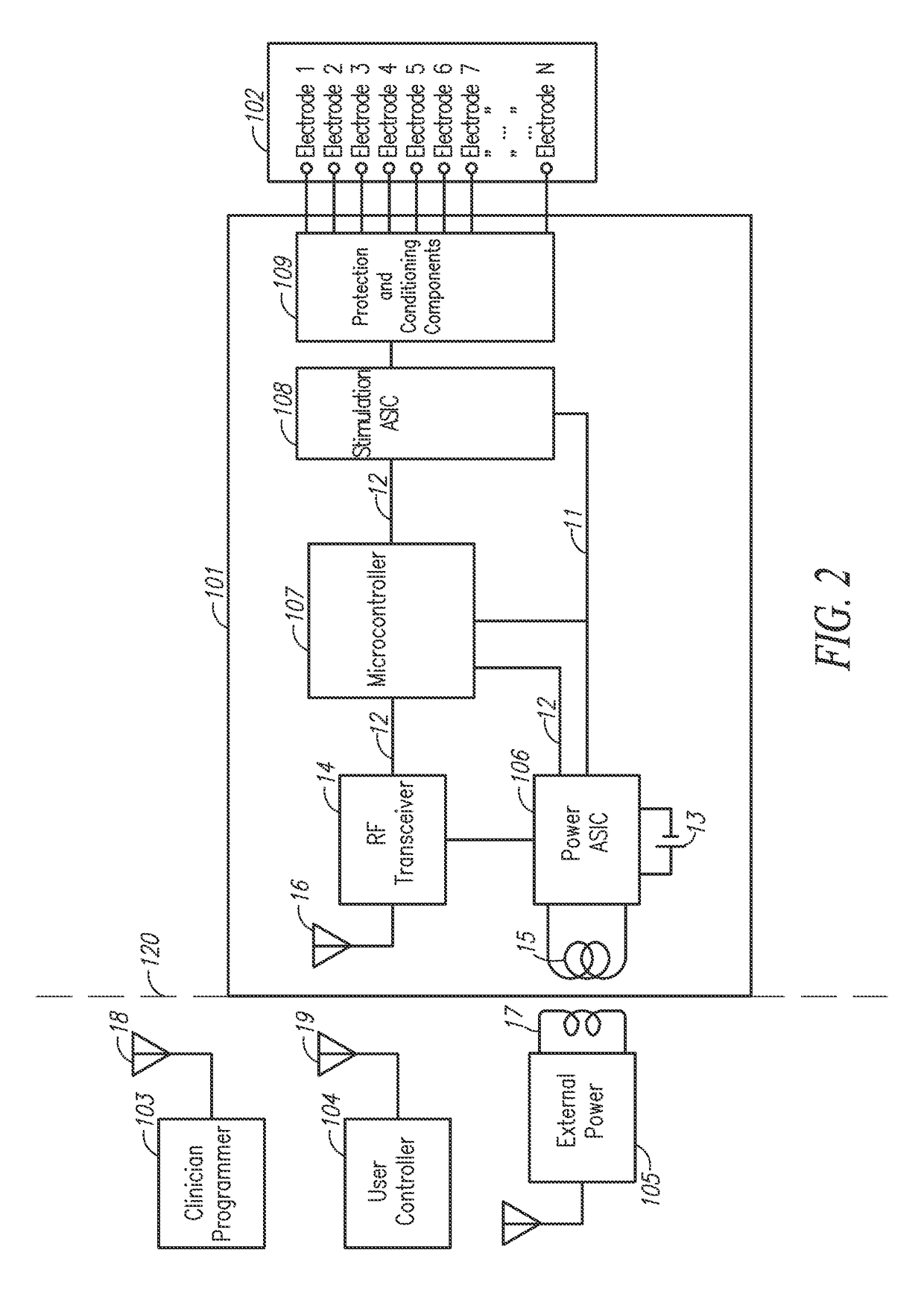
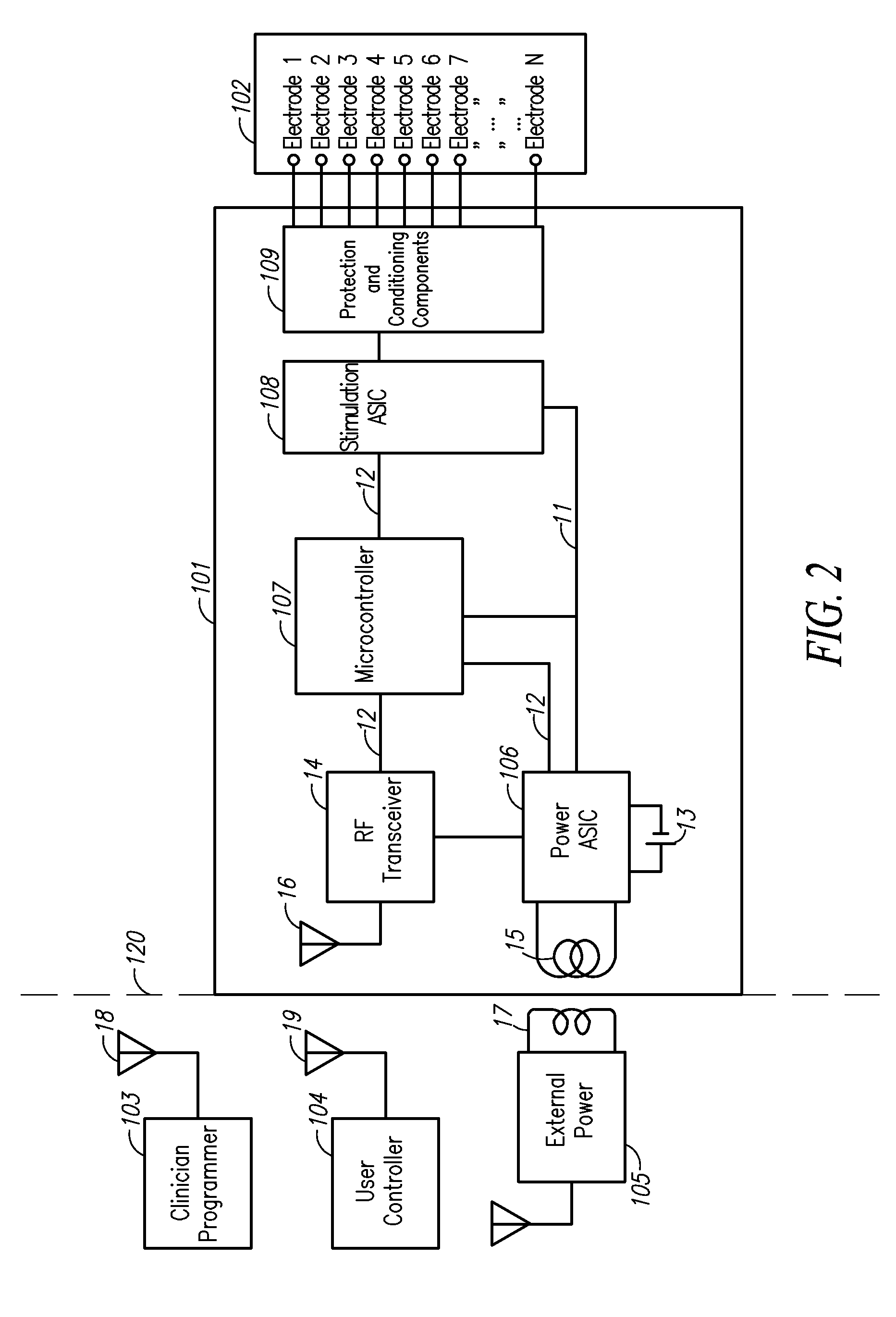
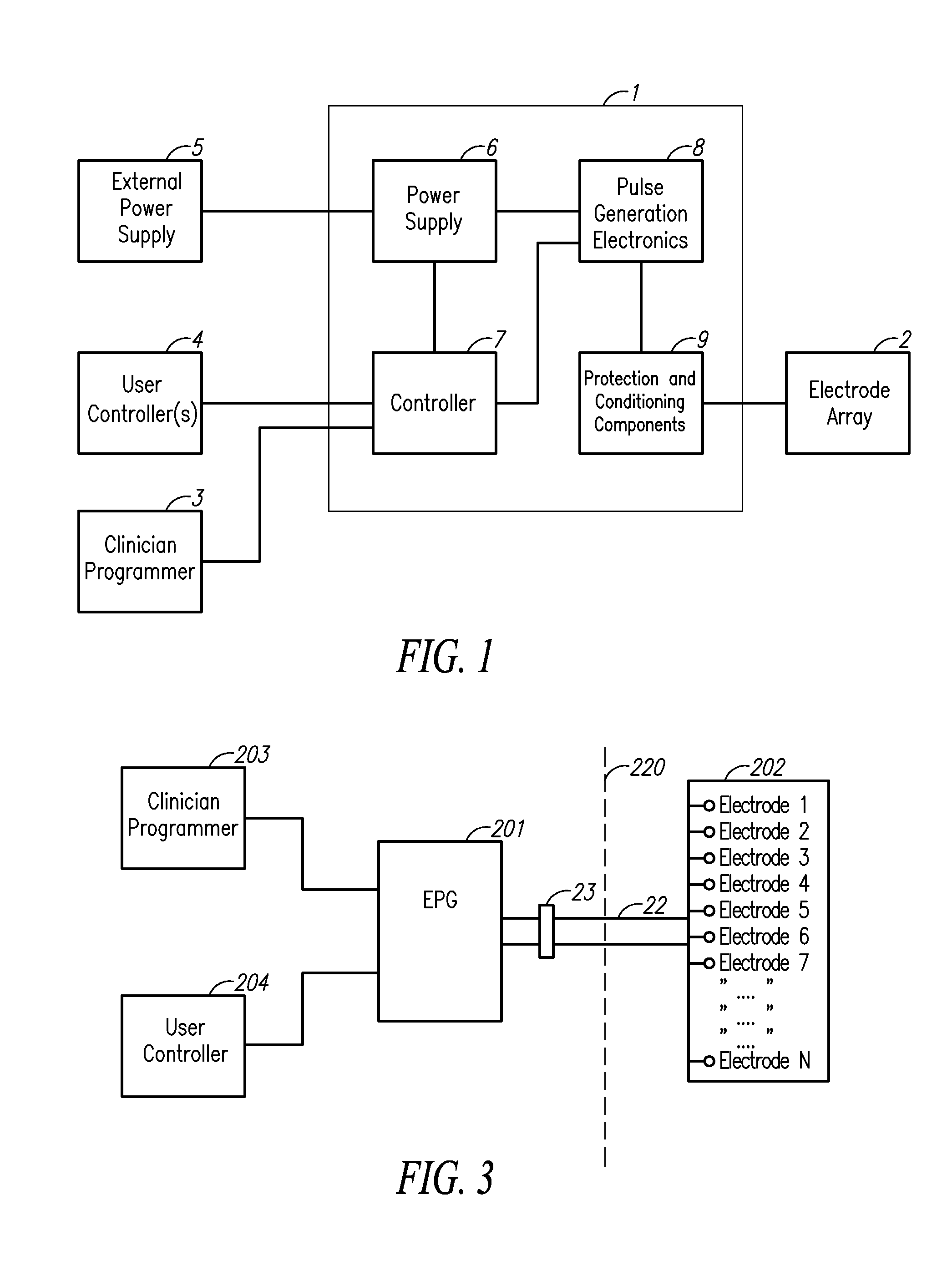
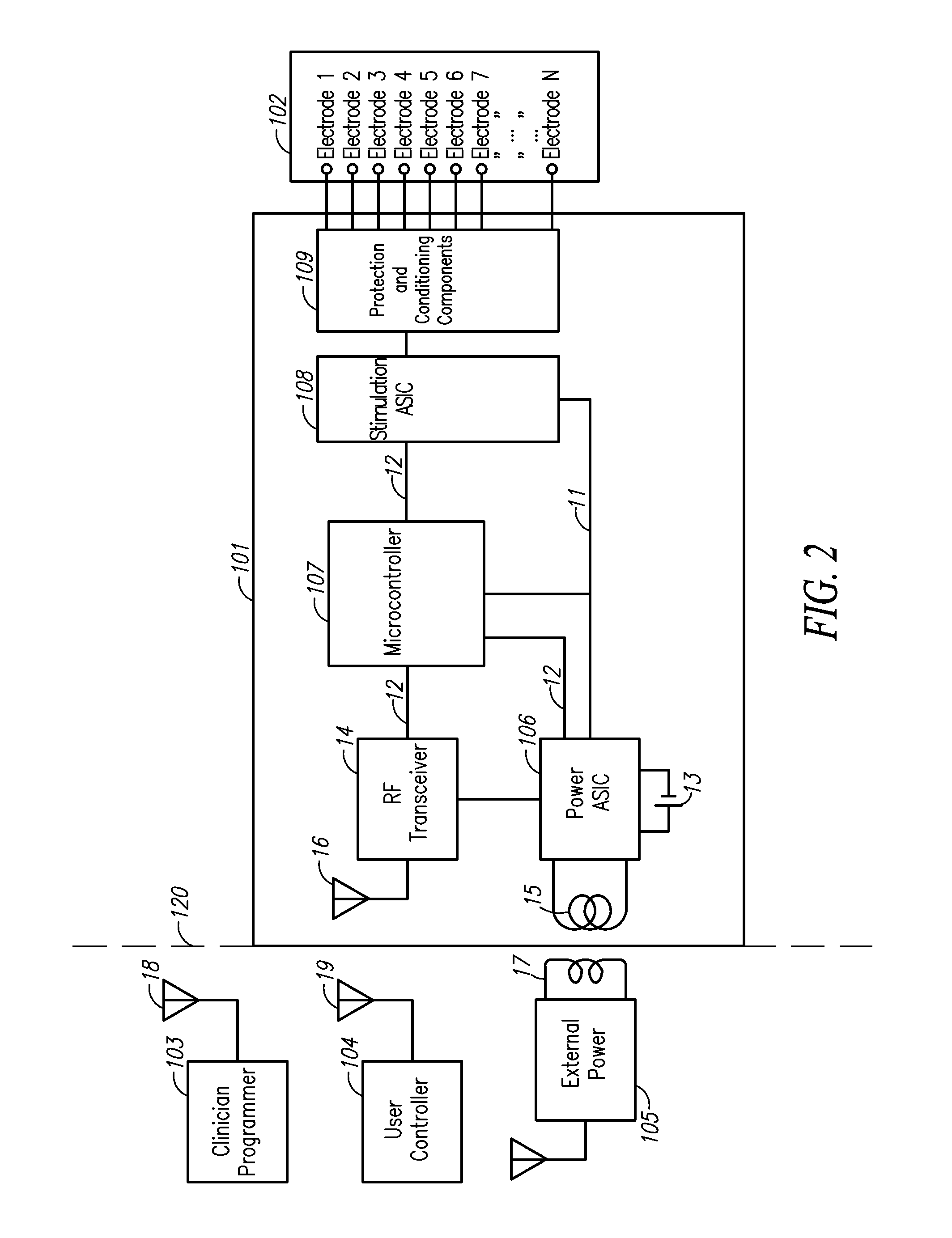
Charge balancing for arbitrary waveform generator & neural stimulation application
ActiveUS20120259382A1Adjusting amplitudes and pulsewidths simply and efficientlyEliminate needElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMedicineNeural stimulation
A method, device and / or system for generating arbitrary waveforms of a desired shape that can be used for generating a stimulation pulse for medical purposes such as for spinal cord stimulation therapy, where such arbitrary waveforms can also be used for charge balancing purposes.
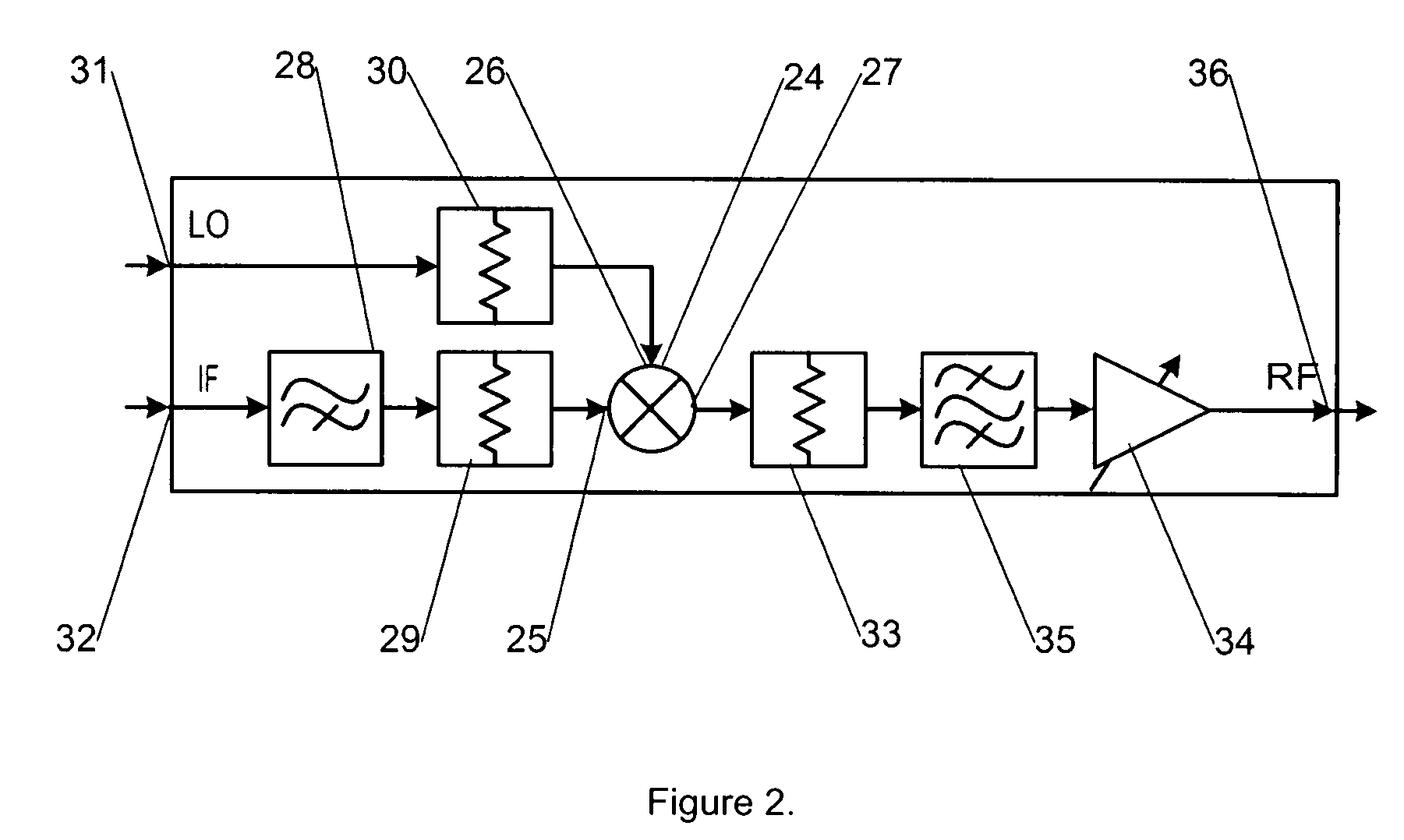
Owner:CIRTEC MEDICAL CORP
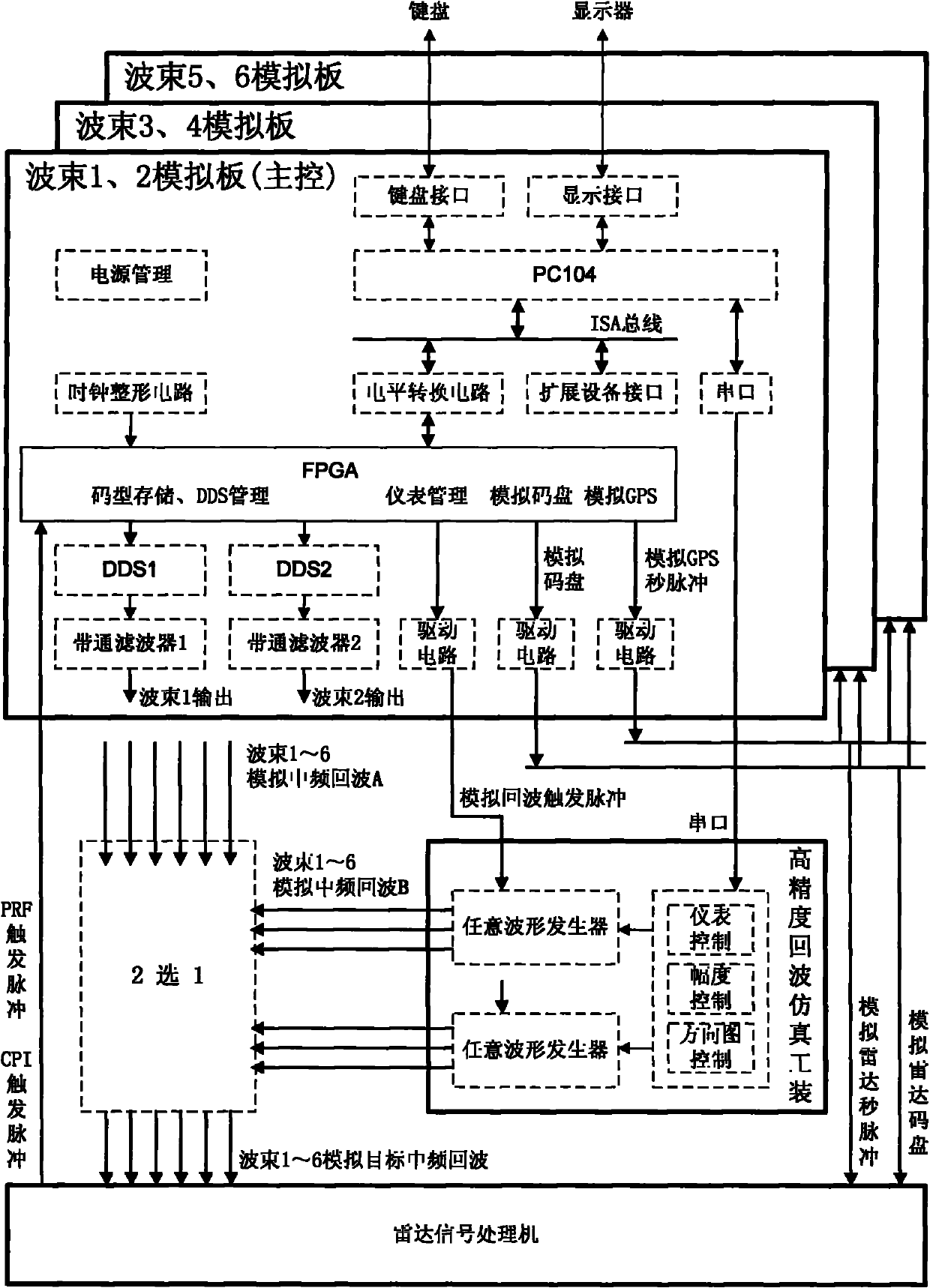
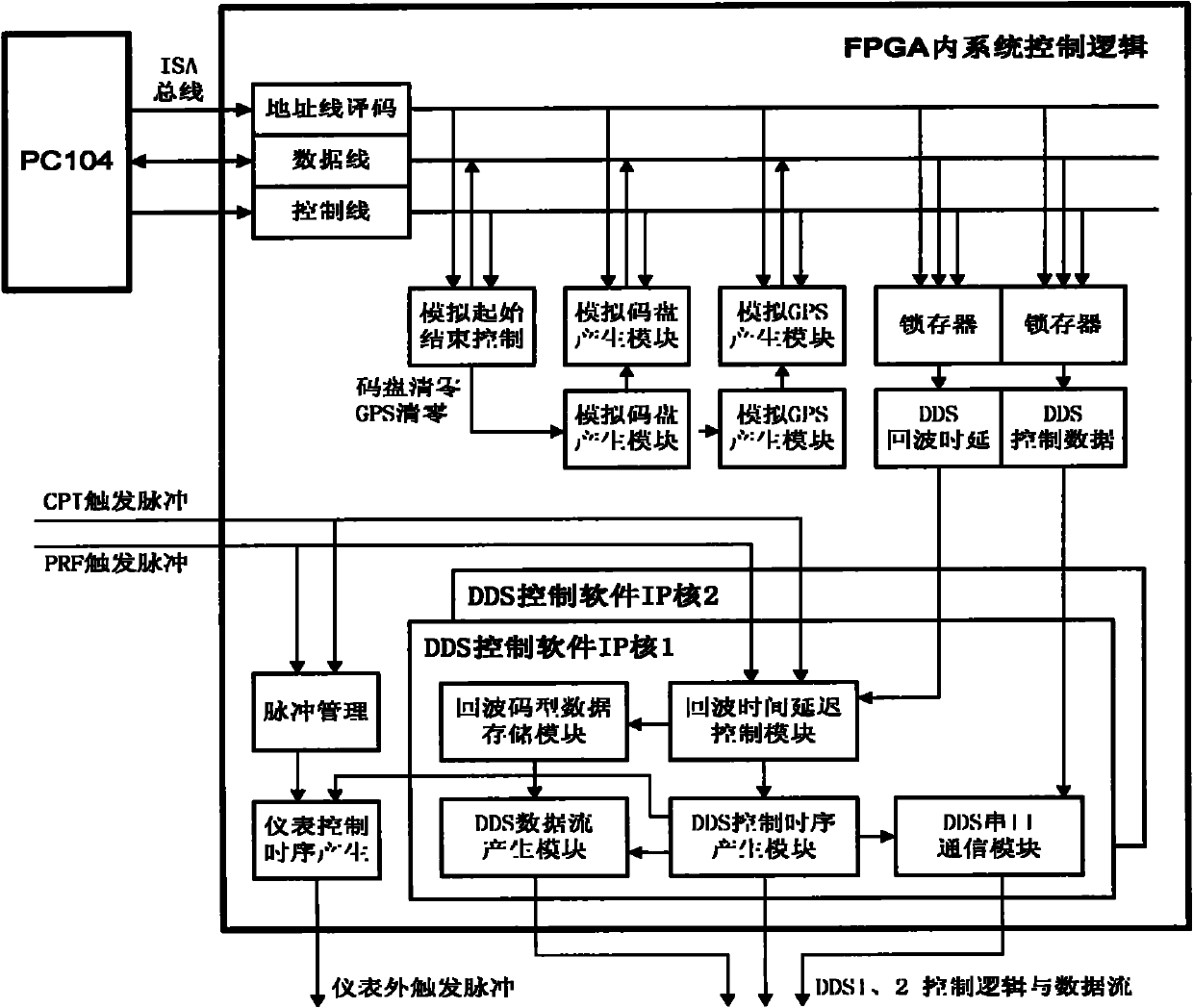
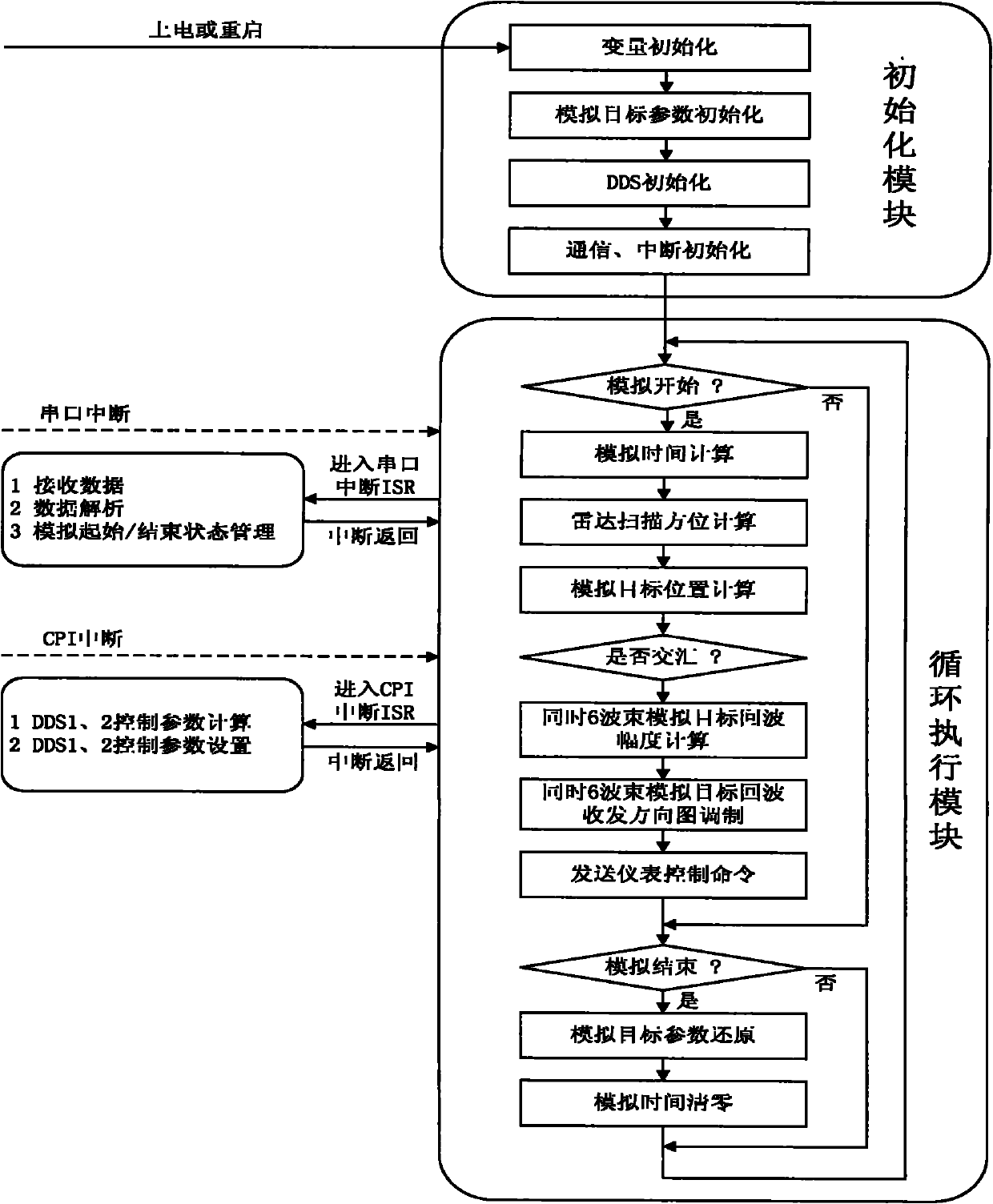
Radar target intermediate frequency (IR) echo simulation system based on multi-beam amplitude-comparison angle measurement and control method thereof
InactiveCN102023293AEasy to controlDensity controllableWave based measurement systemsIntermediate frequencyRadar signal processing
The invention relates to a radar target intermediate frequency (IR) echo simulation system based on multi-beam amplitude-comparison angle measurement and a control method thereof, relating to the field of radar target echo simulation. The system comprises three target echo simulation boards and an arbitrary waveform generator instrument fixture, wherein the echo simulation boards are designed with a computer module PC104, a field programmable gate array (FPGA), direct digital synthesis (DDS) technique and a simulation circuit as cores; and the arbitrary waveform generator instrument fixture is designed with instrument programming control as the core. According to the invention, simultaneous 6-channel simulated target IR echo simulation of the radar of the multi-beam amplitude-comparison angle measurement system is realized, parameters of the simulated target echo such as distance, delay, echo amplitude, Doppler shift, pattern, direction pattern modulation, noise superposition and the like can be controlled, single-channel switching and output of dual-beam echo is realized, and the test use requirement of the radar signal processor of the system is met. In the invention, the arbitrary waveform generator instrument frock is utilized, thus improving the amplitude precision of the output echo signals; and the control program in the FPGA in the target echo simulation boards is designed by the soft IP core, thus providing convenience for hardware transplanting and clipping.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二0六研究所
Arbitrary waveform generator and neural stimulation application with scalable waveform feature and charge balancing
ActiveUS9656076B2Adjusting amplitudes and pulsewidths simply and efficientlyEliminate needElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMedicineNeural stimulation
A method, device and / or system for generating arbitrary waveforms of a desired shape that can be used for generating a stimulation pulse for medical purposes such as for spinal cord stimulation therapy, including the option of using such arbitrary waveforms for charge balancing purposes.
Owner:CIRTEC MEDICAL CORP
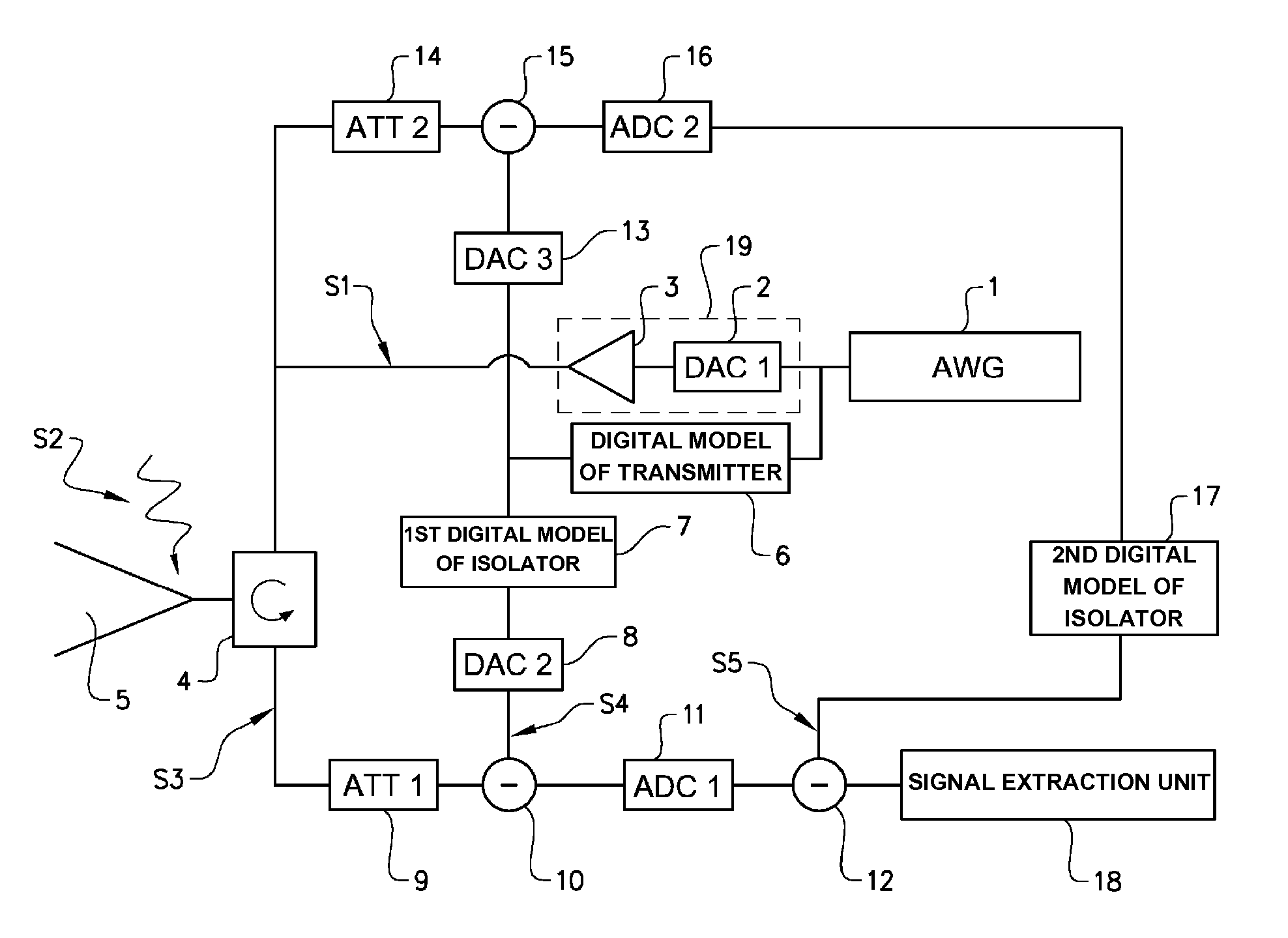
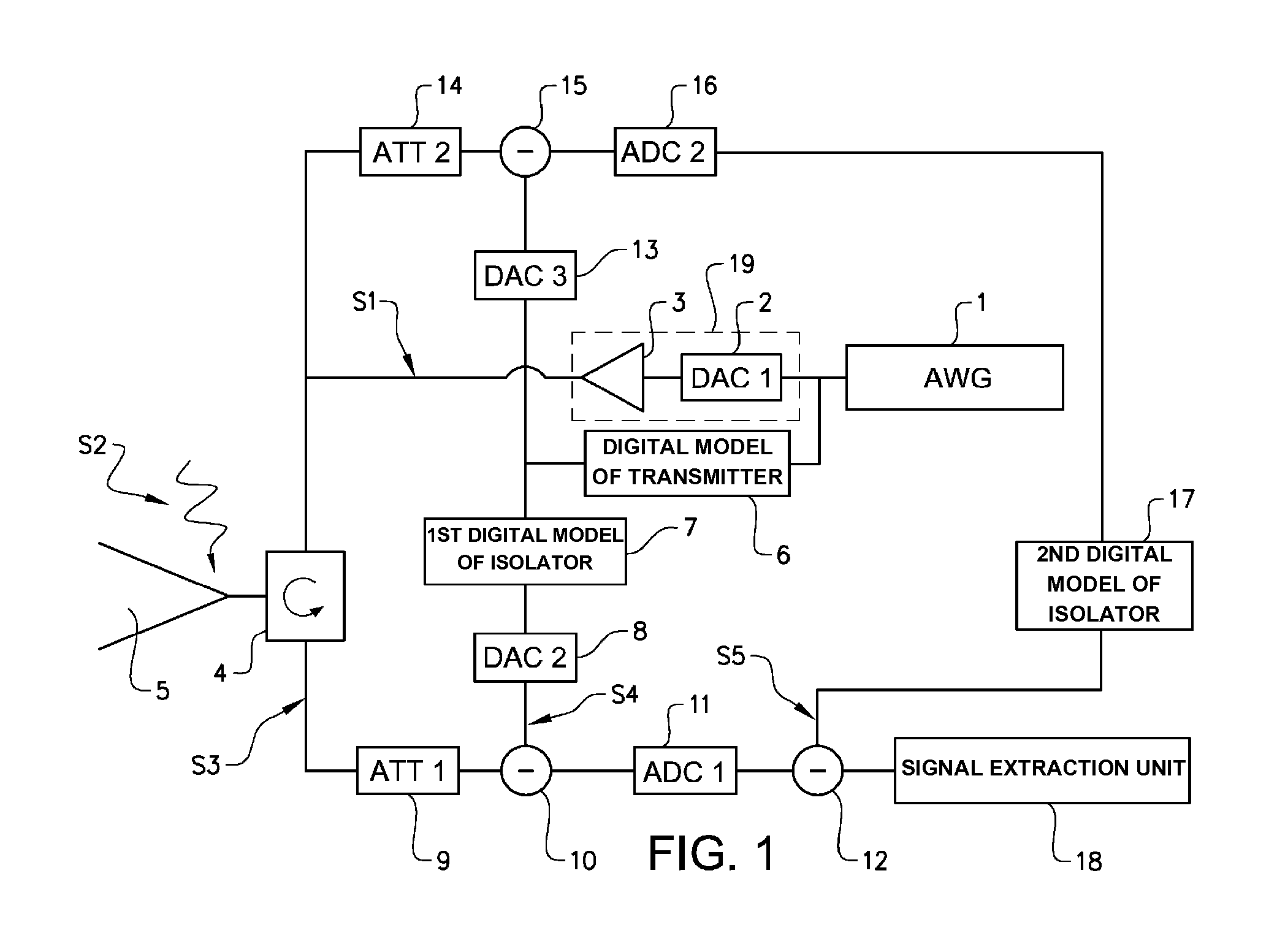
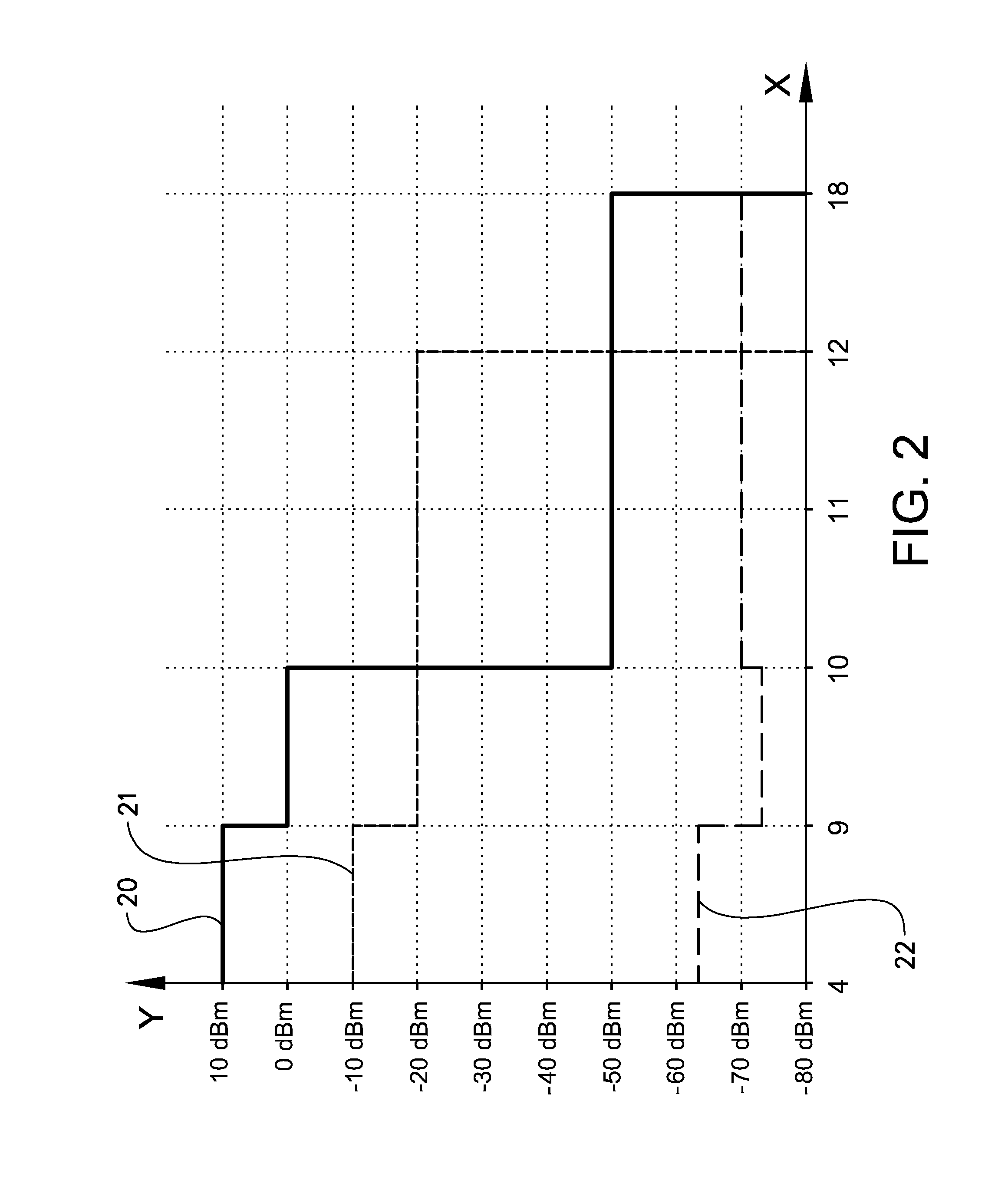
Wideband transmitter/receiver arrangement for multifunctional radar and communication
ActiveUS20130201050A1Reduce decreaseExcellent leakage cancellationDuplex signal operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarEngineering
A transmitter / receiver arrangement comprises a digital arbitrary waveform generator AWG connected to a transmitter. Said waveform generator is configured to generate an arbitrary waveform within a given bandwidth. Said transmitter / receiver arrangement further comprises an antenna arrangement configured to emit a transmitter signal, and to receive an incident signal, a receiver configured to receive a receiver signal, and an analogue isolator connected to said antenna arrangement, said transmitter, and said receiver. Said analogue isolator is adapted to route said transmitter signal from said transmitter to said antenna arrangement, and said incident signal from said antenna arrangement to said receiver, and to isolate said transmitter signal from said receiver signal. Said receiver is adapted to cancel any residual transmitter signal in said receiver signal by means of at least one digital model of at least said isolator, said antenna arrangement, and said transmitter.
Owner:SAAB AB
High speed arbitrary waveform generator based on FPGA
InactiveCN101017383ASolve the problem of working frequency mismatchLower working clockDigital function generatorsWave shapeParallel processing
This invention relates to one high speed random wave generator based on FPGA, which adopts DDS technique with data sample rate more than 1GHz and comprises CPU, parallel data phase generation part, wave shape memory part, plug and filter part, parallel and series conversion circuit and DAC, wherein, the parallel data phase generation adopts parallel process to generate multiple data phase In one time clock to get multiple data; then it uses FPGA series and parallel conversion circuit to output the data to DAC into virtual volume.
Owner:王文华
Fast Switching Arbitrary Frequency Light Source for Broadband Spectroscopic Applications
ActiveUS20130228688A1Enlarged cavityQuick switchRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using multiple reflectionSpectroscopySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
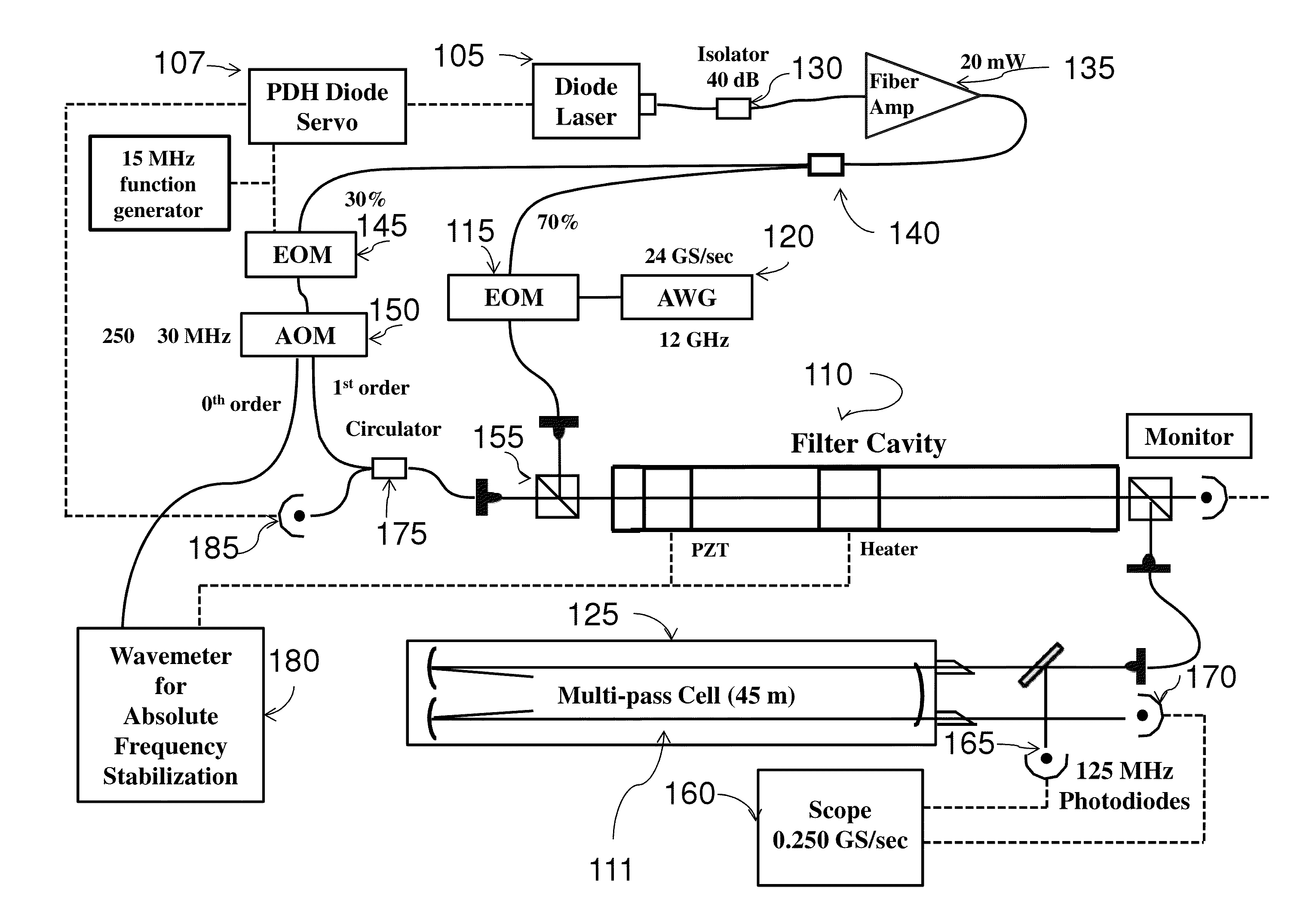
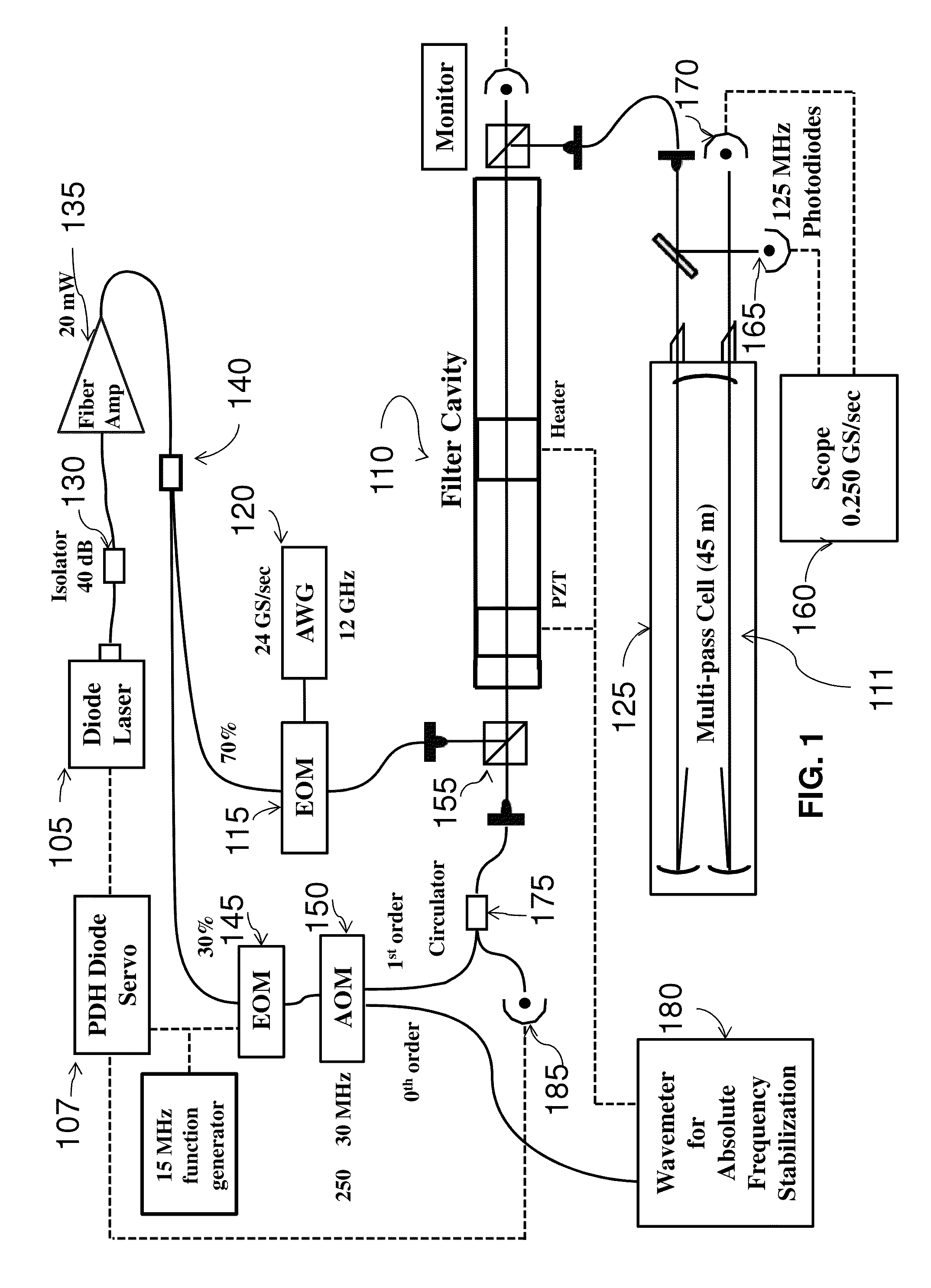
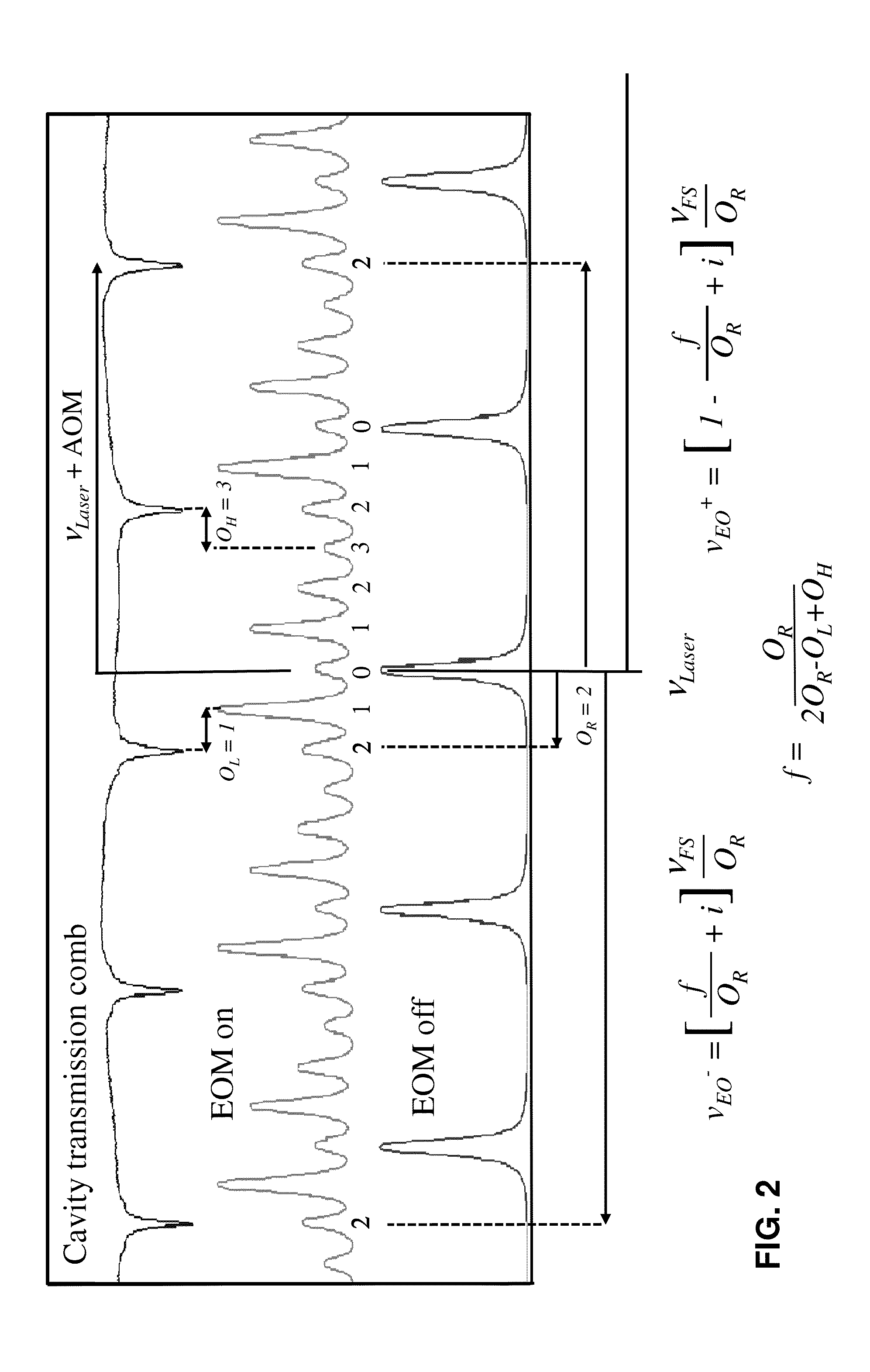
A fast switching arbitrary frequency light source for broadband spectroscopic applications. The light source may operate near 1.6 um based on sideband tuning using an electro-optic modulator driven by an arbitrary waveform generator. A Fabry-Perot filter cavity selects a single sideband of the light source. The finesse (FSR / ΔνFWHM) of the filter cavity may be chosen to enable rapid frequency switching at rates up to 5 MHz over a frequency range of 40 GHz (1.3 cm−1). The bandwidth, speed and spectral purity are high enough for spectroscopic applications where rapid and discrete frequency scans are needed. Significant signal-to-noise advantages may be realized using the rapid and broadband scanning features of this system in many areas of spectroscopy, e.g., process monitoring and control, reaction dynamics, and remote sensing (e.g., greenhouse gas monitoring, biological / chemical agent screening).
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY
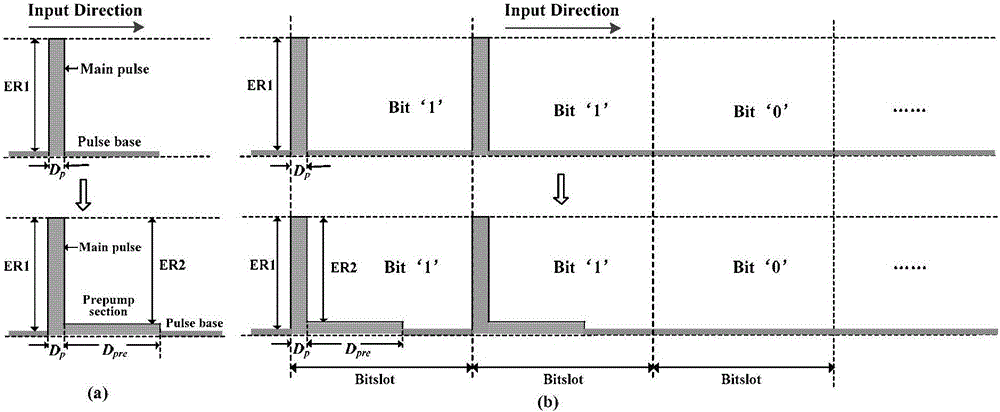
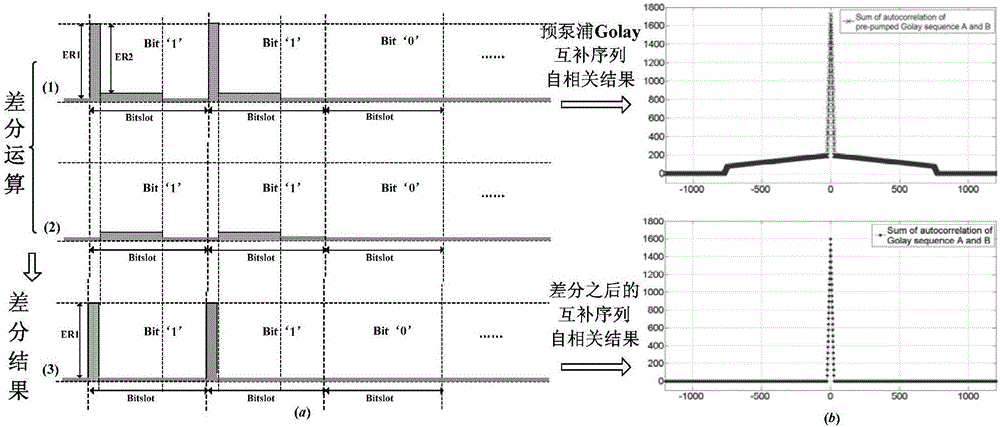
Pre-pumped pulse and Gray code based BOTDA (Brillouin Optical Time Domain Analysis) instrument
ActiveCN105675031ALong sensing distanceKeep unstretchedForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesErbium dopingSemiconductor sensor
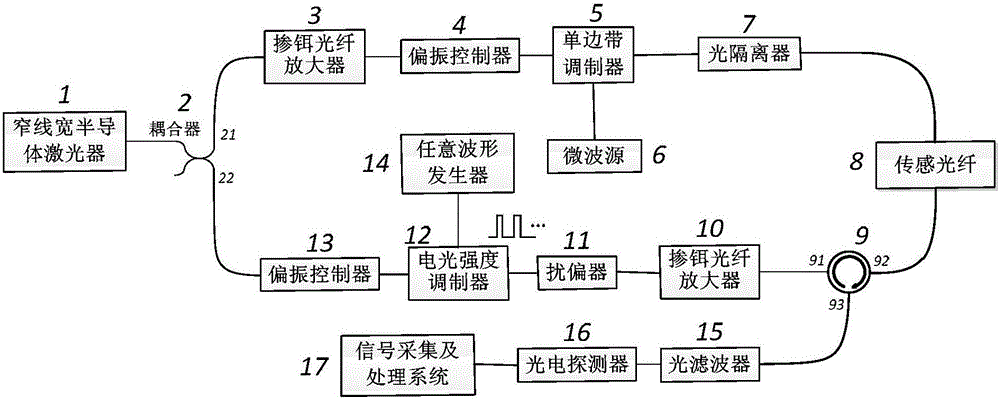
The invention relates to the technical field of fiber sensing, and especially to a pre-pumped pulse and Gray code based BOTDA instrument. The BOTDA instrument comprises a narrow-linewidth semiconductor sensor, a coupler, a first erbium doped fiber amplifier, a first polarization controller, a single sideband modulator, a microwave source, an optical isolator, a sensing fiber, an optical annular device, a second erbium doped fiber amplifier, a polarization scrambler, an electro-optical intensity modulator, a second polarization controller, an arbitrary waveform generator, an optical filter, a photoelectric detector and a signal collecting and processing system. On the premise that the high spatial resolution of a BOTDA system is maintained, the BOTDA instrument ensures the sensing distance and the measuring precision of the system, and improves the sensing performance of the system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Arbitrary waveform generator and neural stimulation application
ActiveUS8874219B2Adjusting amplitudes and pulsewidths simply and efficientlyLess memoryHeart stimulatorsDigital function generatorsMedicineNeural stimulation
Owner:QIG GRP +1
Phase-light time domain reflection device and method based on heterodyne detection phase demodulation
ActiveCN104819770AHigh sensitivityAccurate identificationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansErbium dopingOptical fiber coupler
The invention relates to the field of optical fiber sensing, specifically a phase-light time domain reflection device and method based on heterodyne detection phase demodulation. The device consists of a narrow linewidth laser, an optical fiber coupler with a coupling model of 1*2, a polarization controller, a sound-light modulator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a narrow-band optical fiber filter, a first variable optical attenuator, a three-port circulator, a sensing optical fiber, an optical fiber coupler with a coupling model of 2*1, a photoelectric detector, a signal collection and processing module, an arbitrary waveform generator, a power amplifier, and a second variable optical attenuator. The device and method enable the heterodyne detection phase demodulation to be combined together, achieve external vibration sensing through direct phase demodulation, and are higher in sensitivity. In addition, the device and method employ a brand new direct phase modulation method to sense the external vibration, so the positioning method, compared with a conventional method, of each vibrating point is different.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
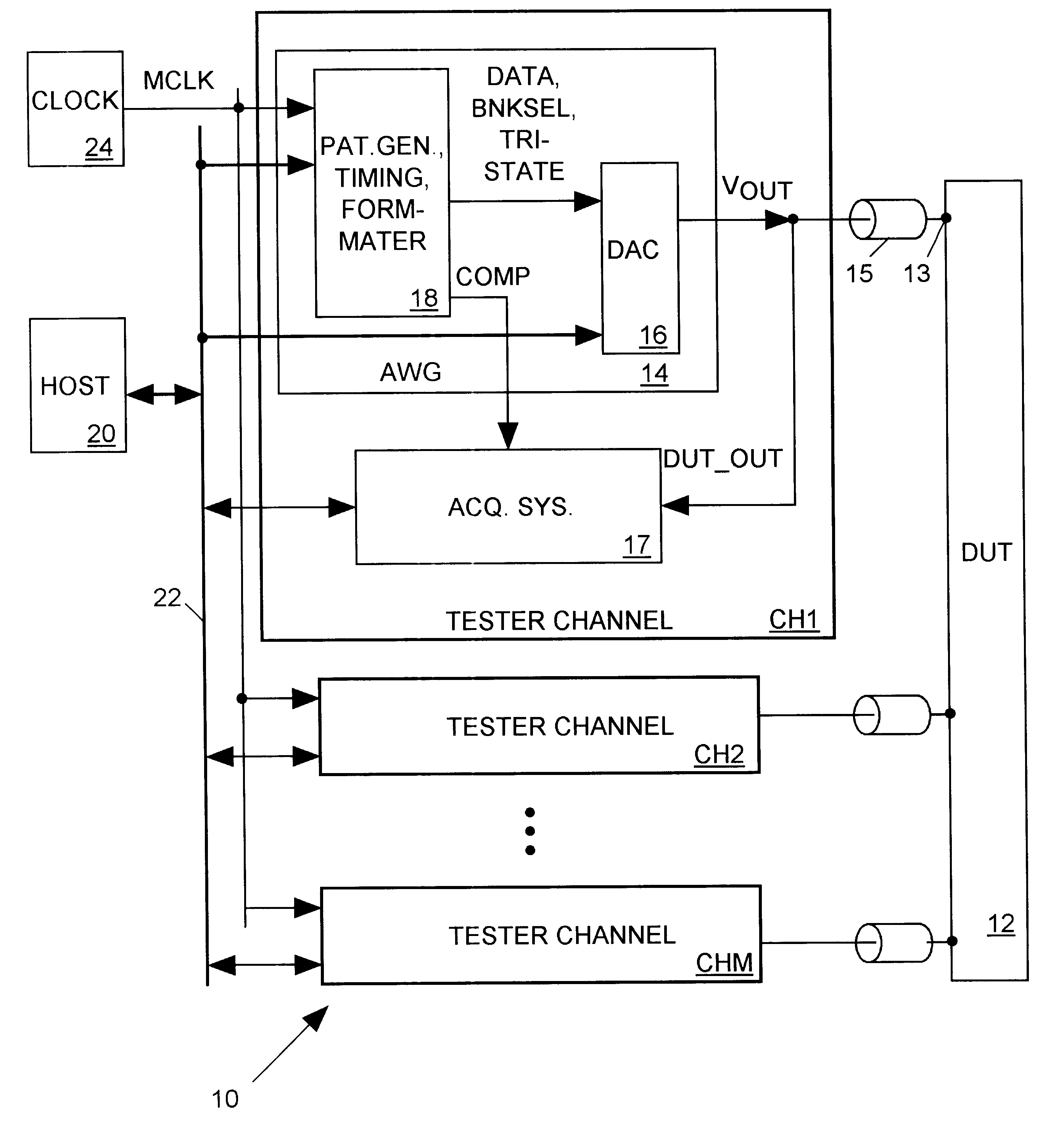
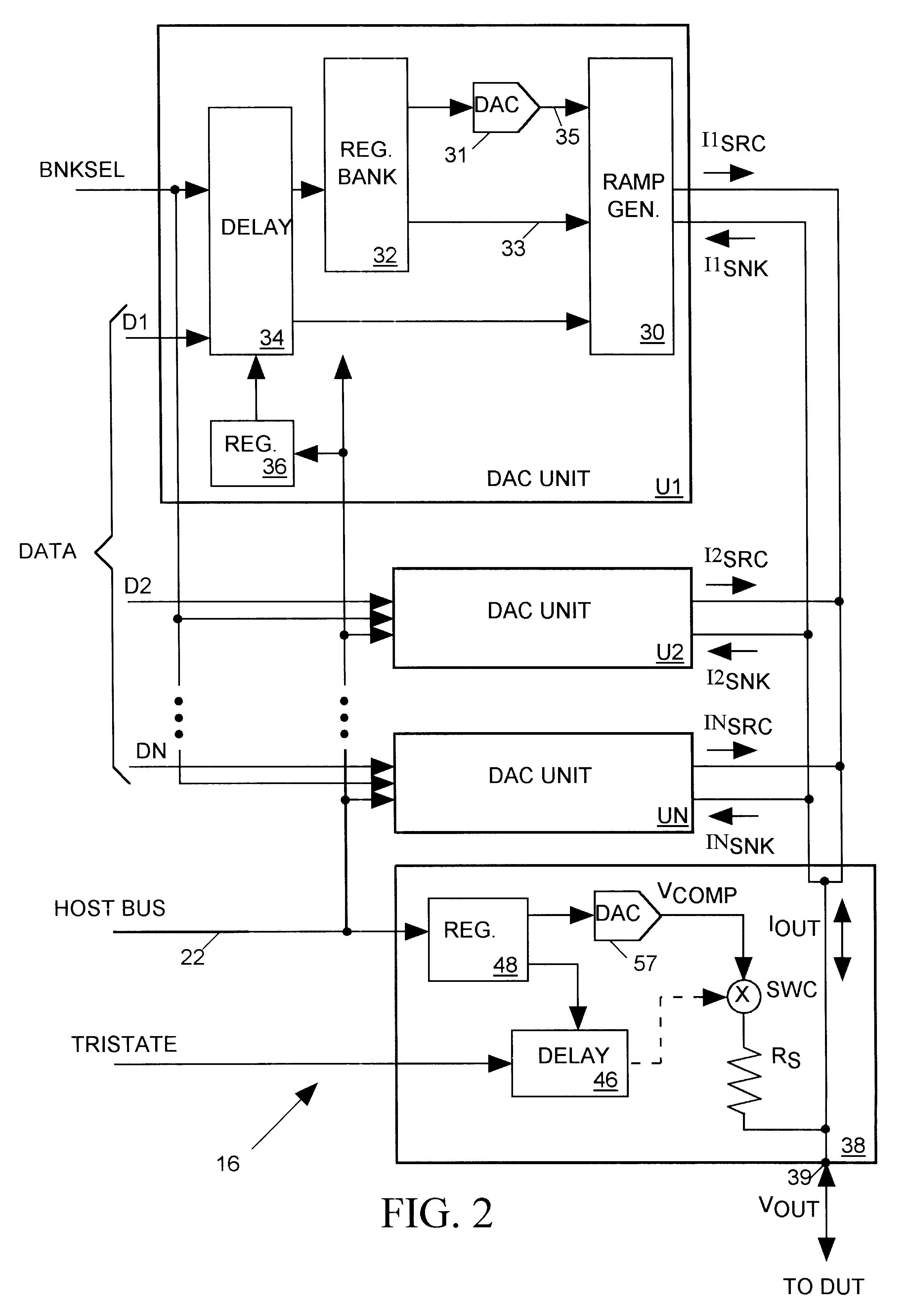
Linear ramping digital-to-analog converter for integrated circuit tester
InactiveUS6232759B1Digital circuit testingError detection/correctionDigital analog converterEngineering
An integrated circuit (IC) tester includes a separate arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) for each input terminal of an IC to be tested. Each AWG generates a test signal input to the IC terminal that linearly ramps between discrete levels to approximate a smoothly varying waveform. Each AWG includes a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) formed by a set of N ramp generators, with each ramp generator producing output currents that ramp at adjustable rates between discrete levels in response to a change in state of an input waveform data bit. The output currents of all N ramp generators of the DAC, which have separately weighted magnitude levels, are summed and converted to a proportional voltage to produce the AWG's test signal.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
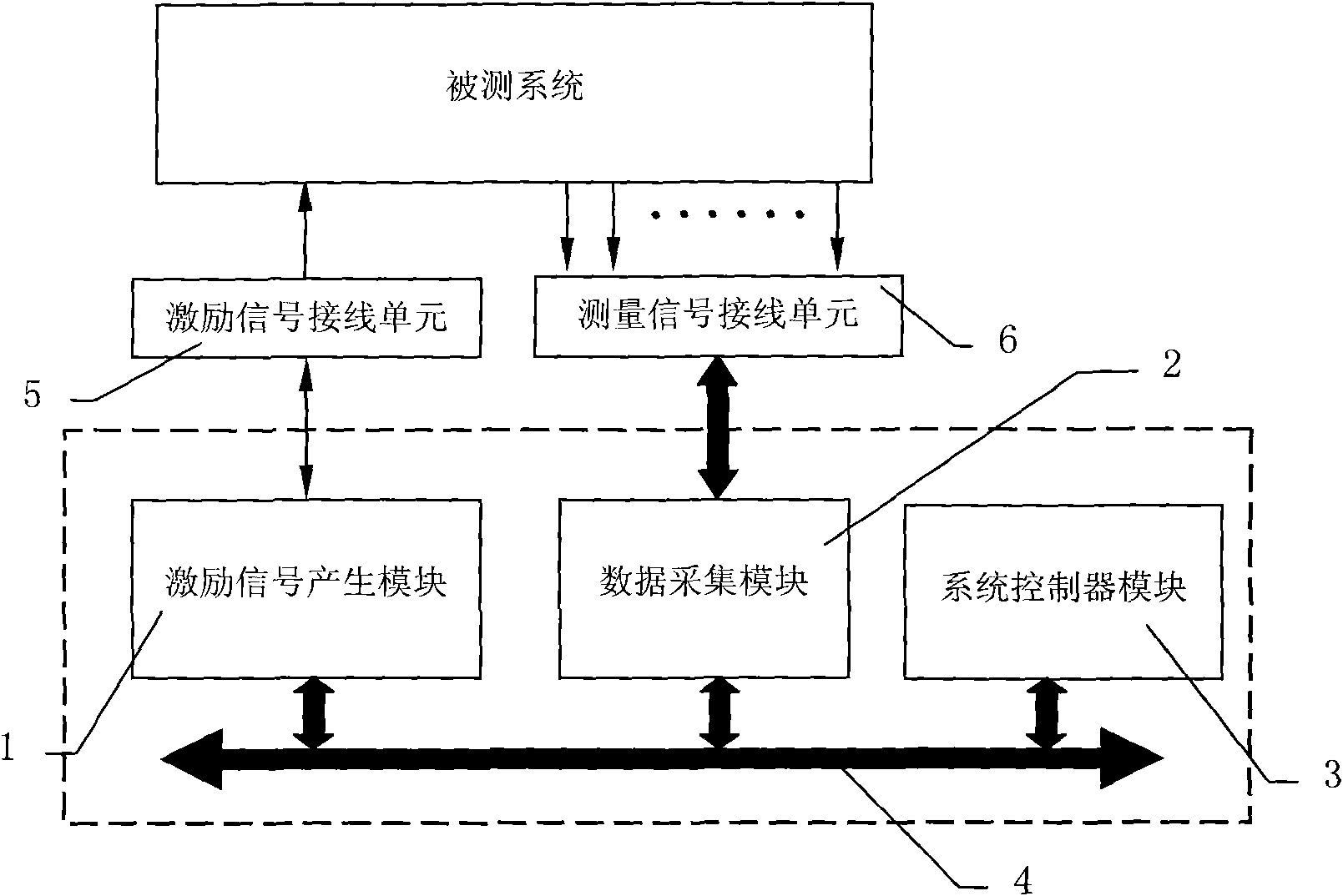
Multi-channel frequency response analysis system and method thereof
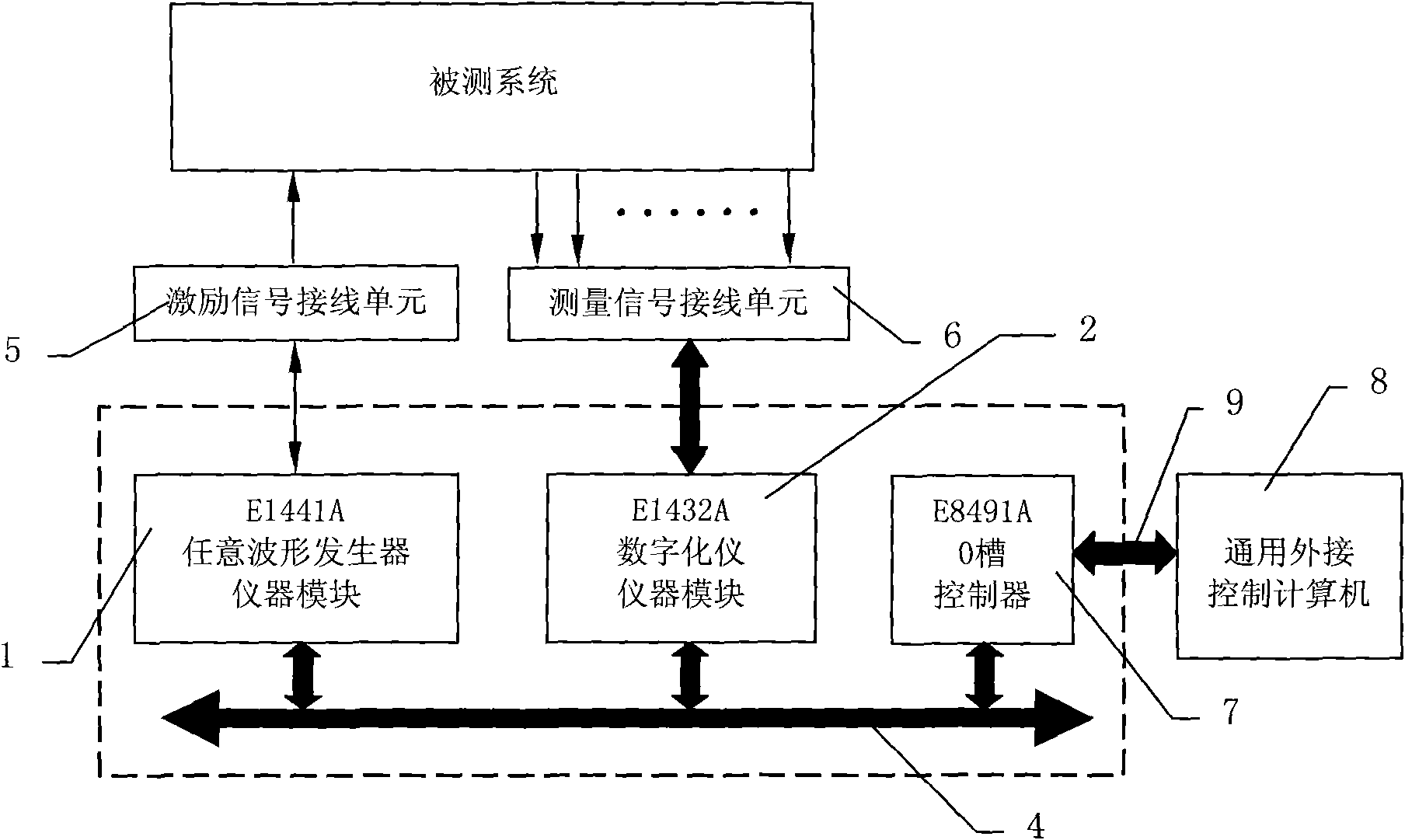
InactiveCN101806833AImprove test accuracyPowerful data processing functionSpectral/fourier analysisData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-channel frequency response analysis system and a method thereof. The system comprises an actuating signal generation module [1], data acquisition modules [2], a system controller module [3], an instrument control bus [4], an actuating signal wiring unit [5] and a measuring signal wiring unit [6], wherein the actuating signal generation module [1] is an instrument module of any-waveform generator; the data acquisition modules [2] are a plurality of multi-channel parallel data acquiring instrument modules or a plurality of multi-channel digitalized instrument modules; the system controller module [3] communicates with the actuating signal generation module [1] and the data acquisition modules [2] through the instrument control bus [4] of a case backboard or a bottom board; a signal of the actuating signal generation module [1] is output by the actuating signal wiring unit [5]; and an external measuring signal accesses the data acquisition modules [2] through the measuring signal wiring unit [6]. The invention has the advantages of more measuring channels, compact structure, strong data processing capacity, high test precision and favorable expansibility and tailorability.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
High speed arbitrary waveform generator
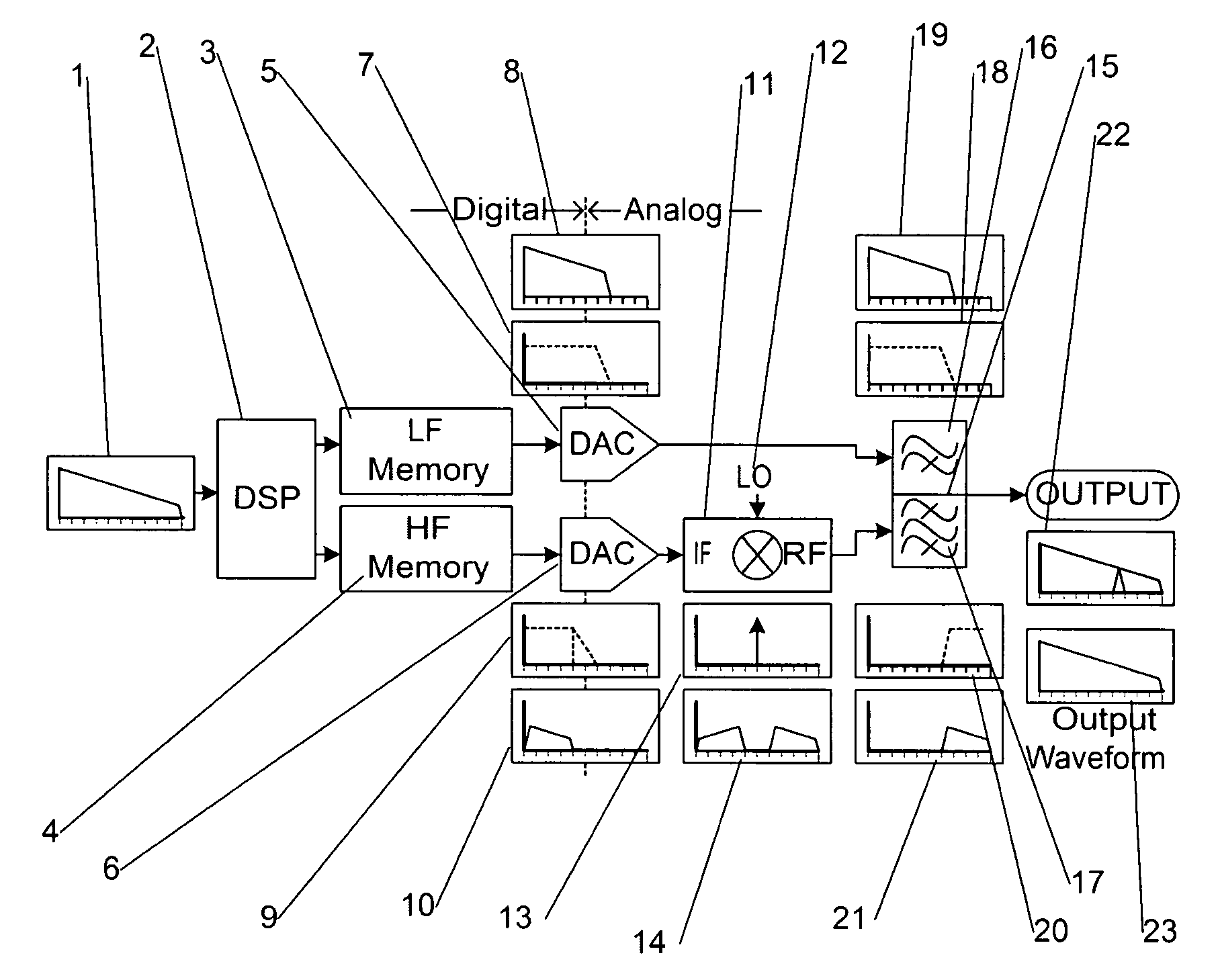
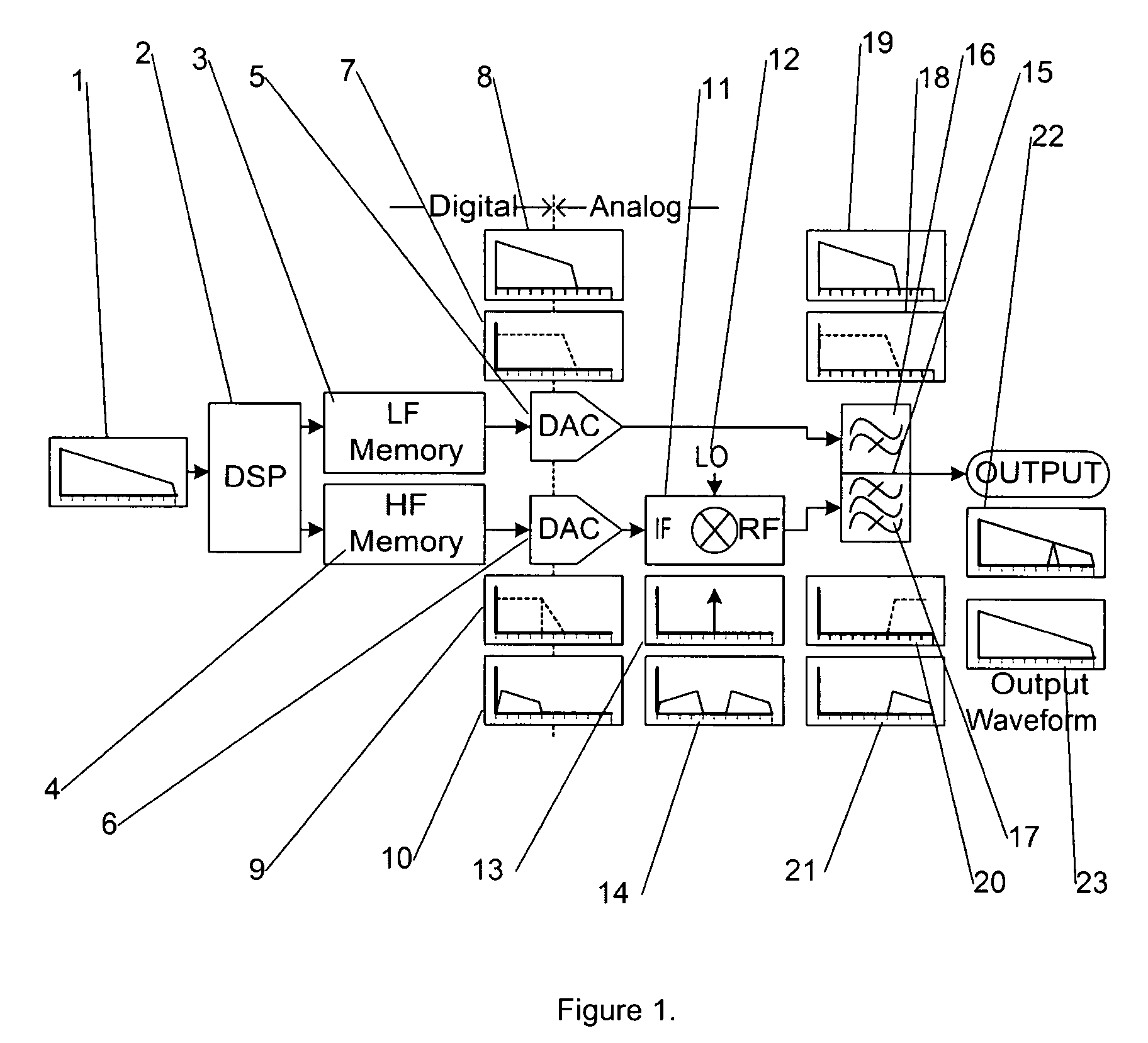
ActiveUS7535394B2Electric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsDigital analog converterWave shape
A high-speed arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) that utilizes multiple digital-to-analog converters (D / A converters) and overcomes bandwidth limitations of individual D / A converters to produce high-speed waveforms.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
Device for compensating non-linear damage of optical fiber
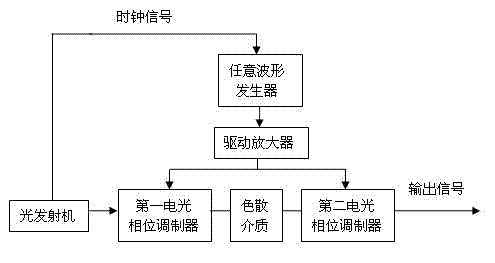
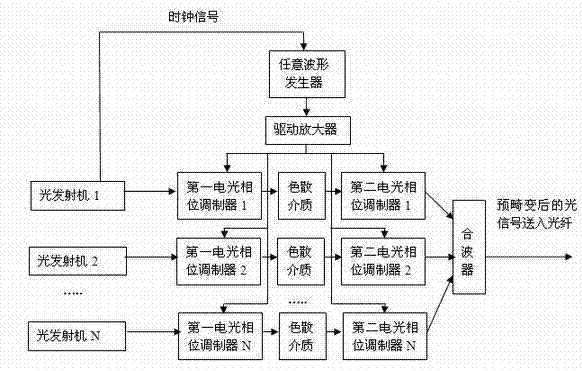
InactiveCN102420661AReduce power consumptionReduce bit error rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionEngineeringCommunication device
The invention discloses a device for compensating a non-linear damage of optical fiber, belongs to an optical fiber communication device, solves the problem of limitation on transmission speed rate or higher complexity of the conventional restraint device, and guarantees the transmission speed rate of an optical fiber system during compensation of the non-linear damage of the optical fiber. The device comprises an arbitrary waveform generator, a driving amplifier, a first electro-optical phase modulator, a dispersion medium and a second electro-optical phase modulator, wherein a clock signal is input to a trigger end of the arbitrary waveform generator; the arbitrary waveform generator outputs a periodic parabola type waveform signal, and the periodic parabola type waveform signal is amplified by using the driving amplifier into an electric driving signal and sent to driving ends of the first electro-optical phase modulator and the second electro-optical phase modulator at the same time; an optical transmitter outputs a data signal to an input end of the first electro-optical phase modulator; and an output end of the second electro-optical phase modulator is connected with an optical fiber link. The invention has the advantages that: an adopted optical device is simple; the bit error rate of signal receiving reaches 10<-7> to 10<-9>; optical power cost is reduced by about 3 dB; and the device is applicable to a long-distance high-capacity and ultra-high-speed optical fiber communication system of all kinds of modulation formats and transmission speed rate.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Architecture for generating adaptive arbitrary waveforms
InactiveUS7072781B1Change in numberEasy to changeResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCircuit under testData acquisition
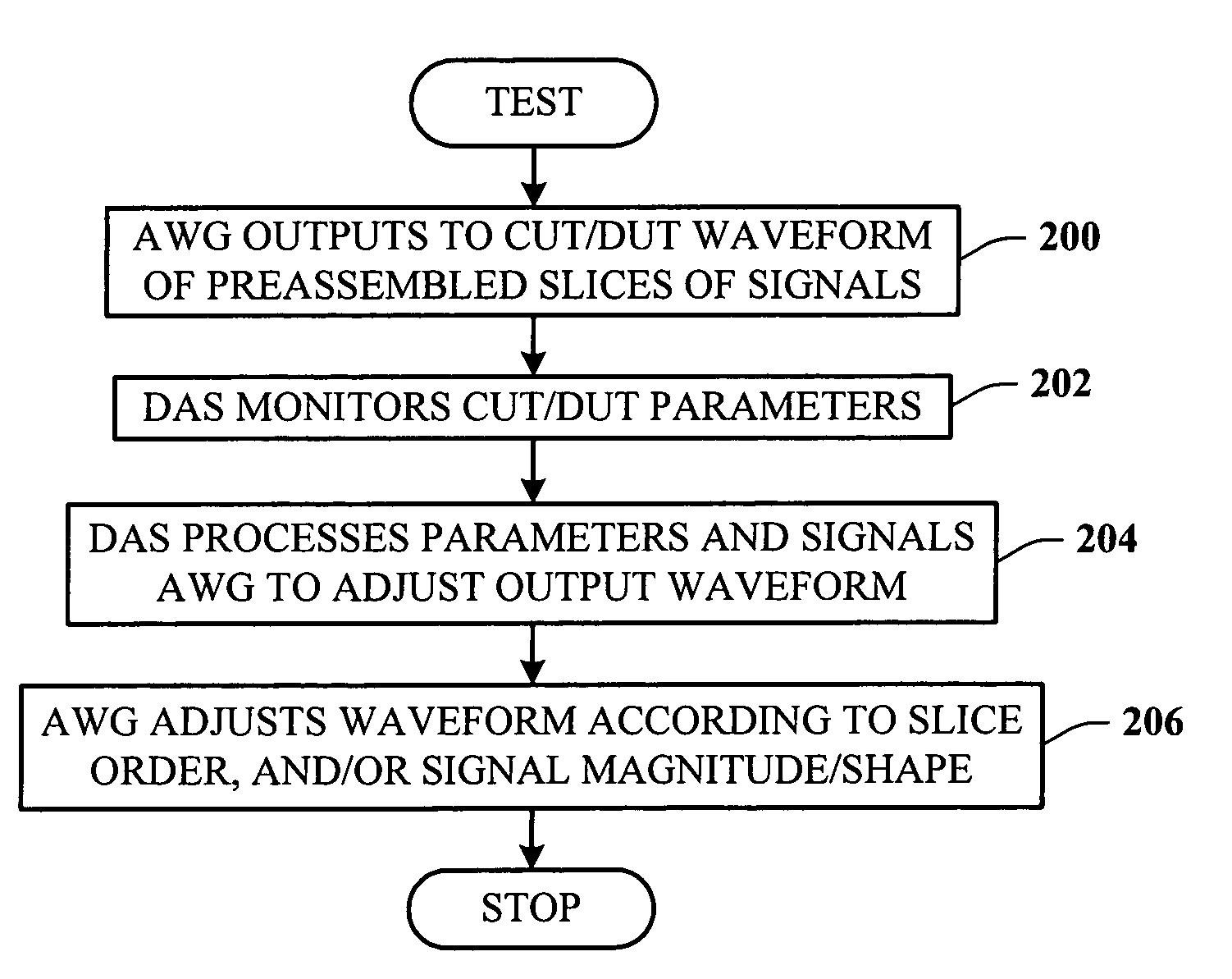
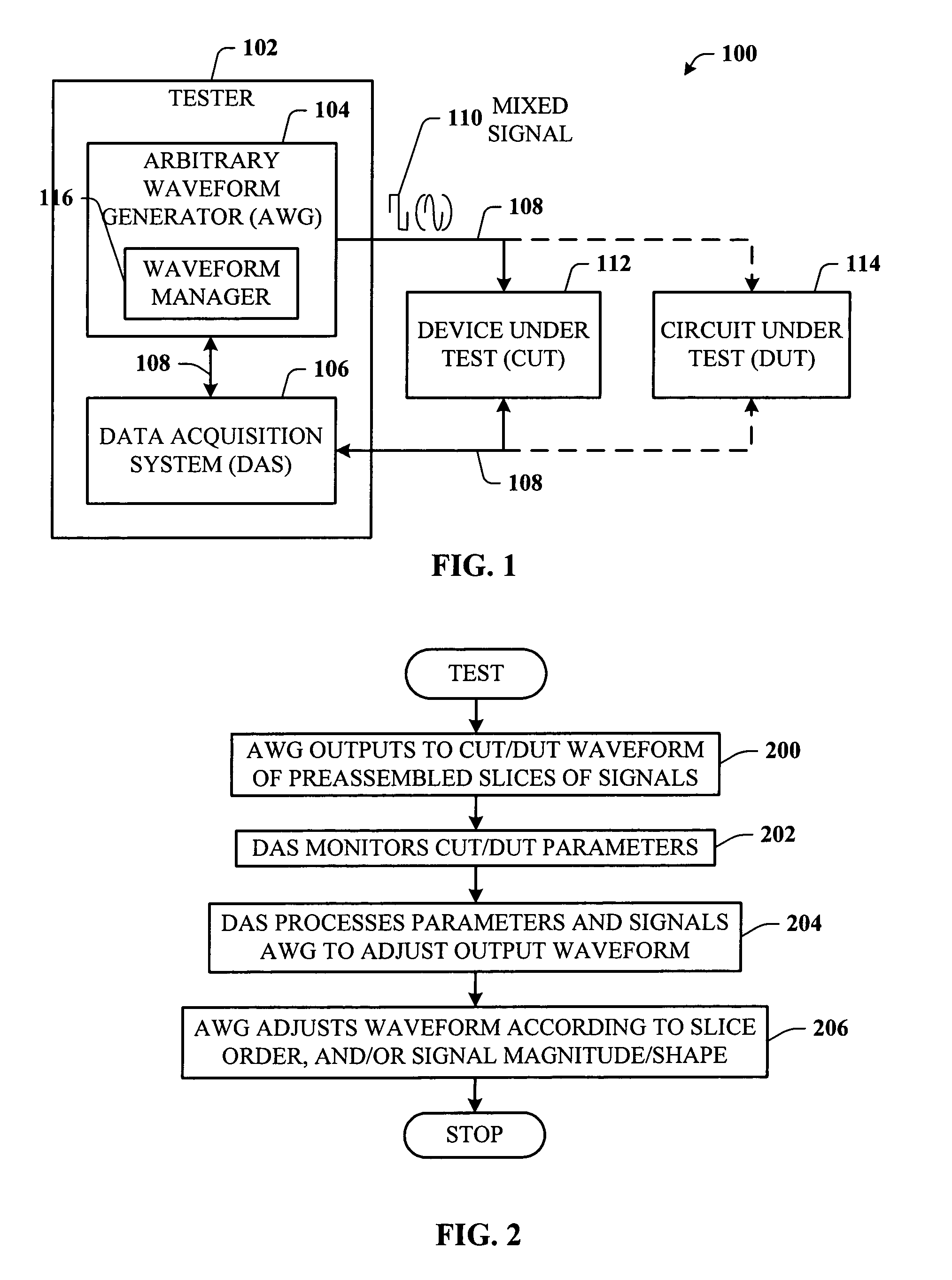
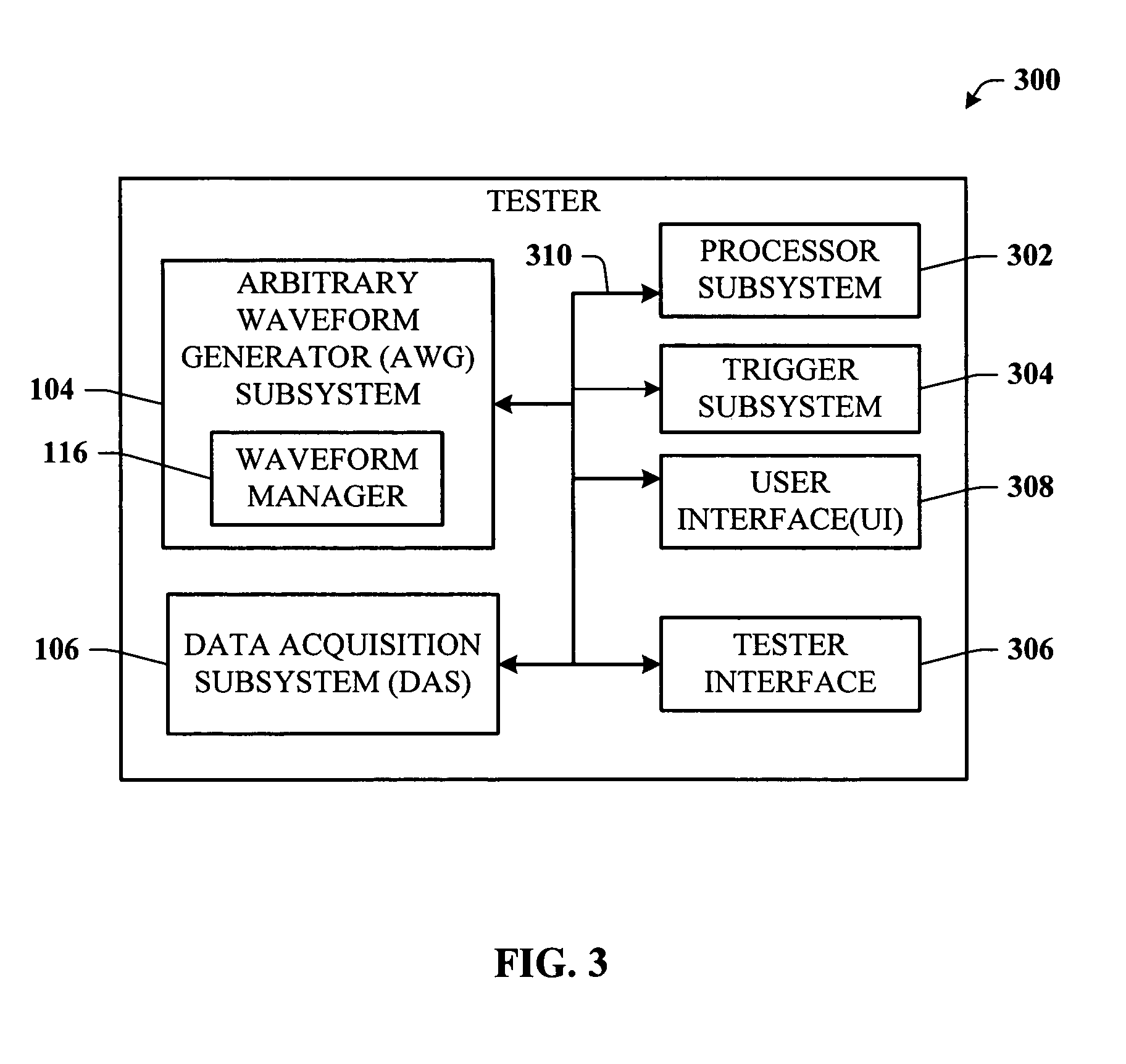
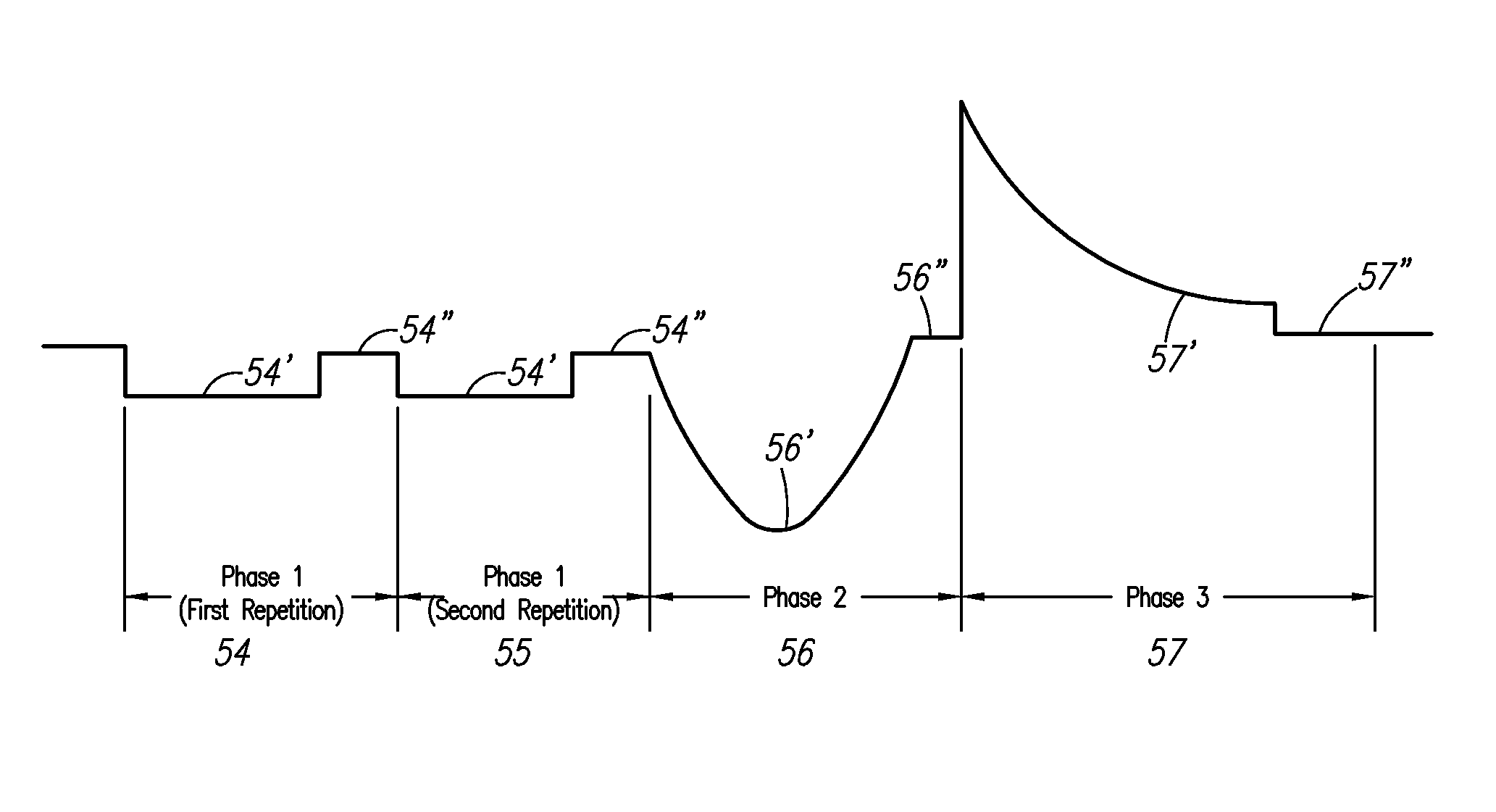
A test system having a feedback loop that facilitates adjusting an output test waveform to a DUT / CUT (Device Under Test / Circuit Under Test) on-the-fly according to changing DUT / CUT parameters. The system includes a tester having an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) and a data acquisition system (DAS) that monitors the status of the DUT / CUT. The AWG and DAS connect to the DUT / CUT through a feedback loop where the AWG outputs the test waveform to the DUT / CUT, the DAS monitors the DUT / CUT parameters, and the DAS analyzes and communicates changes to the AWG to effect changes in the output waveform, when desired. The AWG builds the output waveform in small slices (or segments) that are assembled together through a process of selection and calibration. The feedback architecture facilitates a number of changes in the output waveform, including a change in the original order of the preassembled slices, and changes in the magnitude / shape of the output waveform.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Charge balancing for arbitrary waveform generator and neural stimulation application
ActiveUS8996115B2Adjusting amplitudes and pulsewidths simply and efficientlyEliminate needElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMedicineDual purpose
Owner:CIRTEC MEDICAL CORP
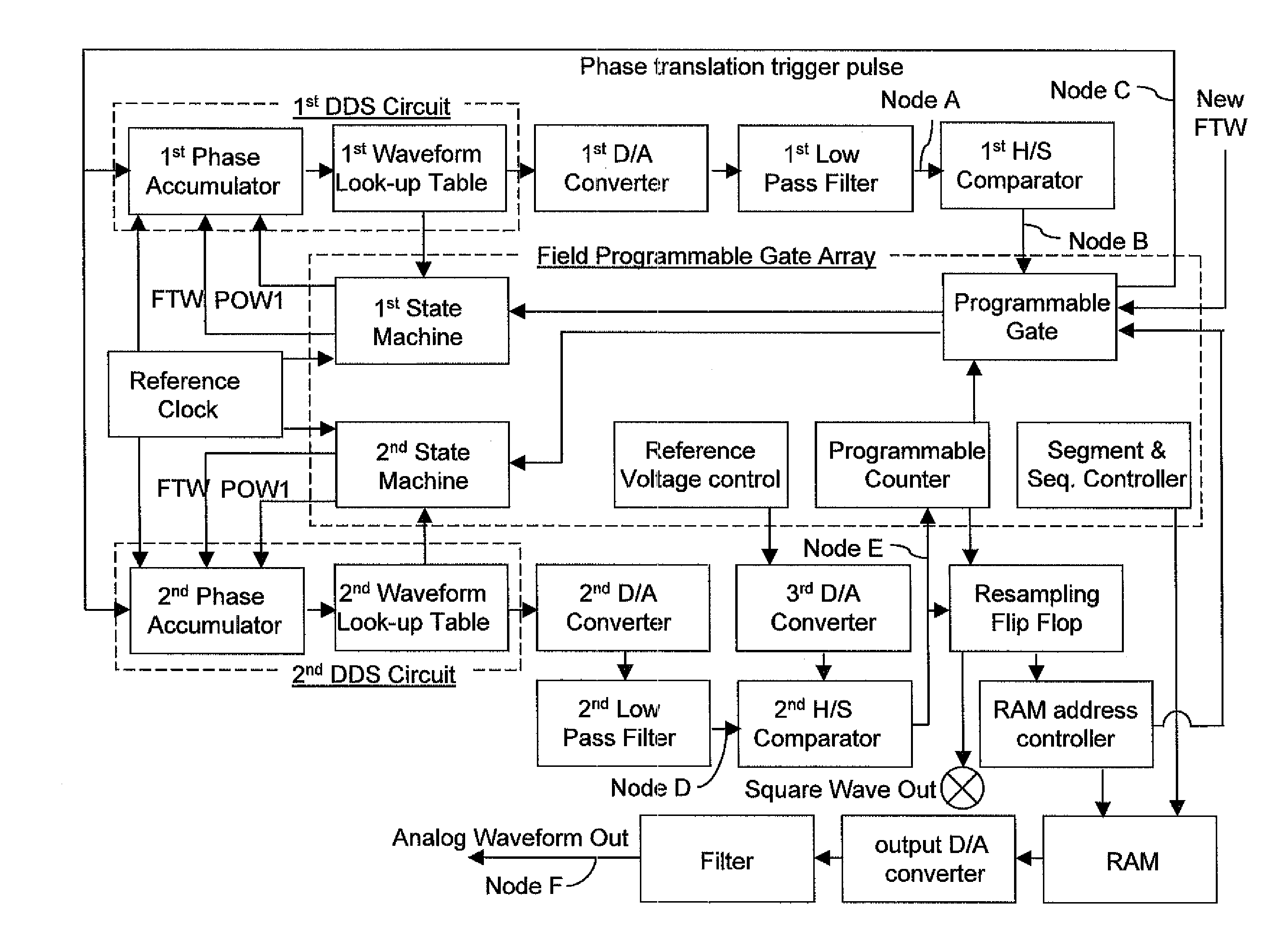
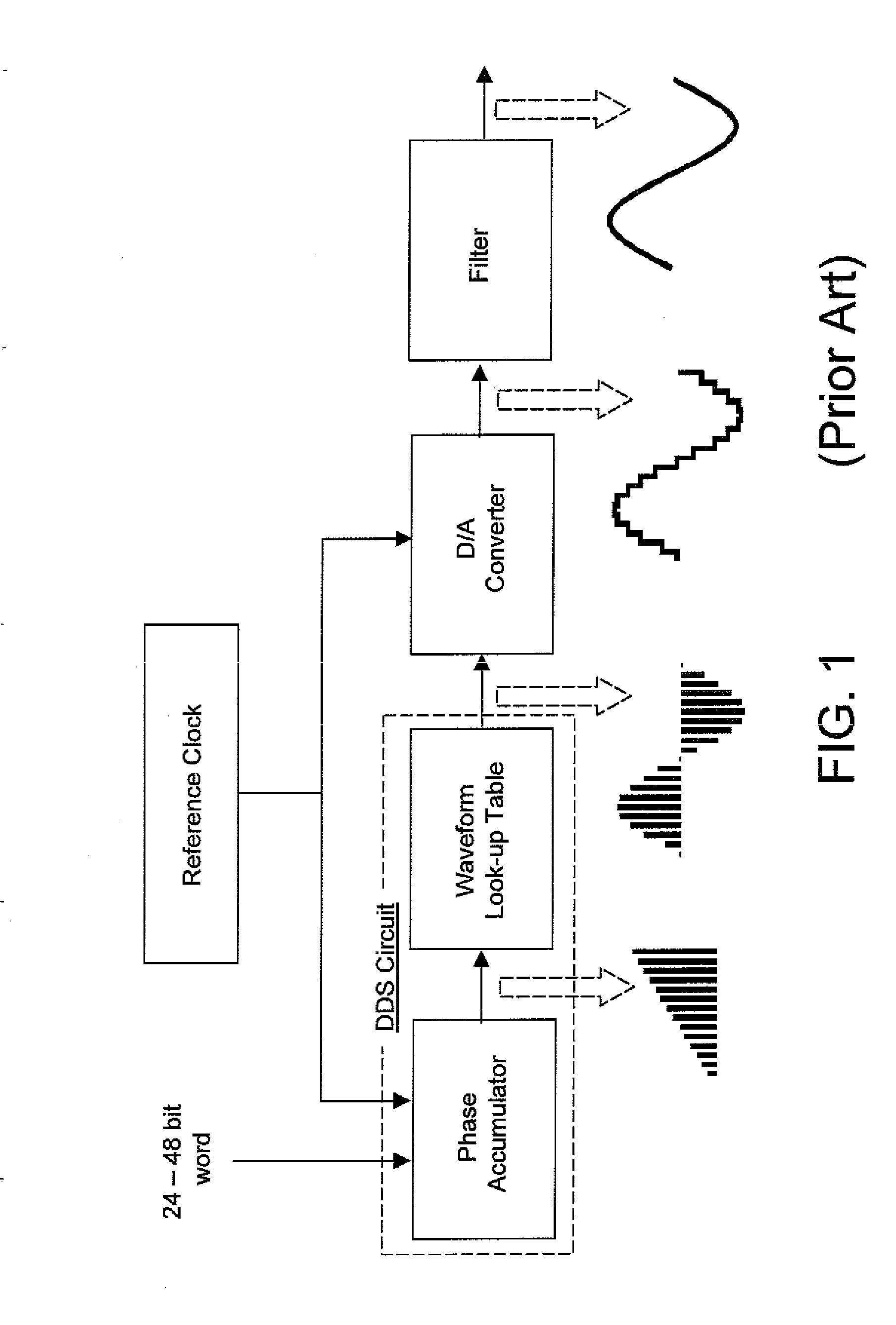
Agile high resolution arbitrary waveform generator with jitterless frequency stepping
InactiveUS20090256640A1Digital data processing detailsOscillations generatorsArbitrary waveform generatorHigh resolution
Jitterless transition of the programmable clock waveform is generated employing a set of two coupled direct digital synthesis (DDS) circuits. The first phase accumulator in the first DDS circuit runs at least one cycle of a common reference clock for the DDS circuits ahead of the second phase accumulator in the second DDS circuit. As a phase transition through the beginning of a phase cycle is detected from the first phase accumulator, a first phase offset word and a second phase offset word for the first and second phase accumulators are calculated and loaded into the first and second DDS circuits. The programmable clock waveform is employed as a clock input for the RAM address controller. A well defined jitterless transition in frequency of the arbitrary waveform is provided which coincides with the beginning of the phase cycle of the DDS output signal from the second DDS circuit.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Digital enhanced interference-based high-sensitivity quasi-distributed fiber bragg grating vibration sensor
InactiveCN105157812ASuppress noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiber couplerGrating
The invention discloses a digital enhanced interference-based high-sensitivity quasi-distributed fiber bragg grating vibration sensor, which comprises a narrow linewidth laser, a first fiber coupler, an electro-optic modulator, an acousto-optic modulator, a circulator, a weak reflection fiber bragg grating array, a second fiber coupler, a double-balanced detector, an arbitrary waveform generator, an electrical amplifier, n electrical delayers, n multipliers and a phase demodulator, wherein the output port of the narrow linewidth laser is connected with the input port of the first fiber coupler; the first output port of the first fiber coupler is connected with the light signal input end of the electro-optic modulator; the output port of the electro-optic modulator is connected with the light signal input port of the acousto-optic modulator; the light signal output port of the acousto-optic modulator is connected with the first port of the circulator; and the second port of the circulator is connected with the input port of the weak reflection fiber bragg grating array.
Owner:NANJING PIONEER AWARENESS INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
System and method of perfusion imaging and ultrasonic control releasing based-on capsule microbubble
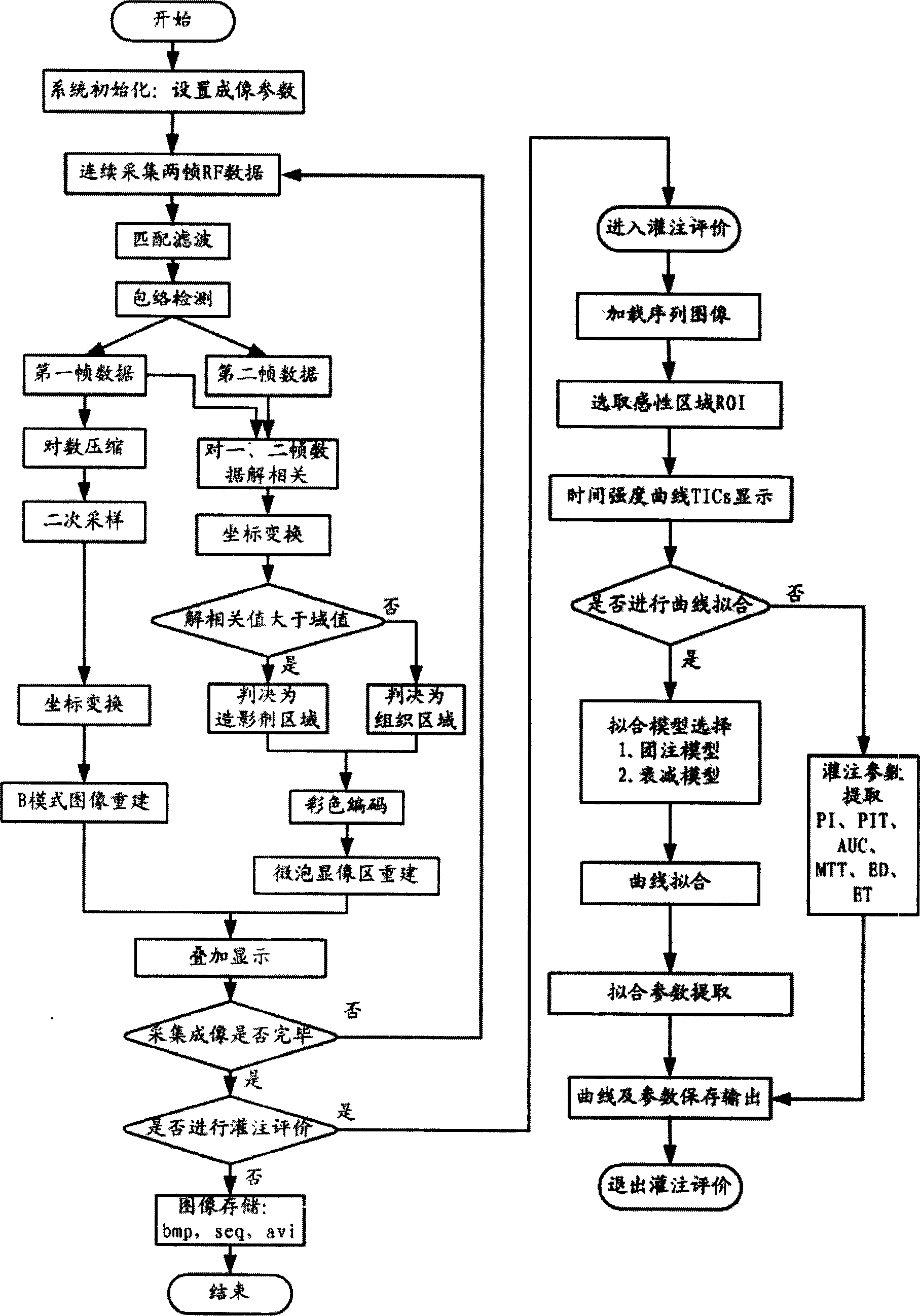
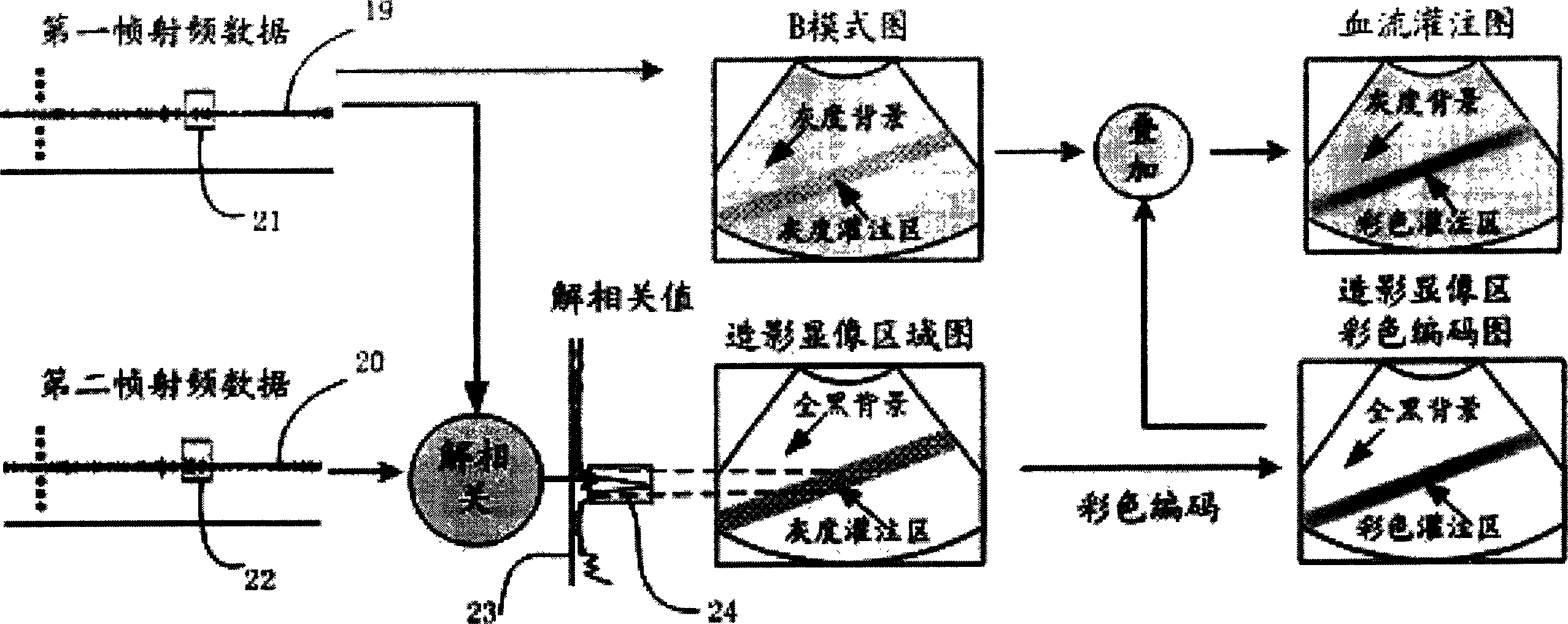
InactiveCN1792334AAggregation easeOvercome attractionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMicrovesicleSonification
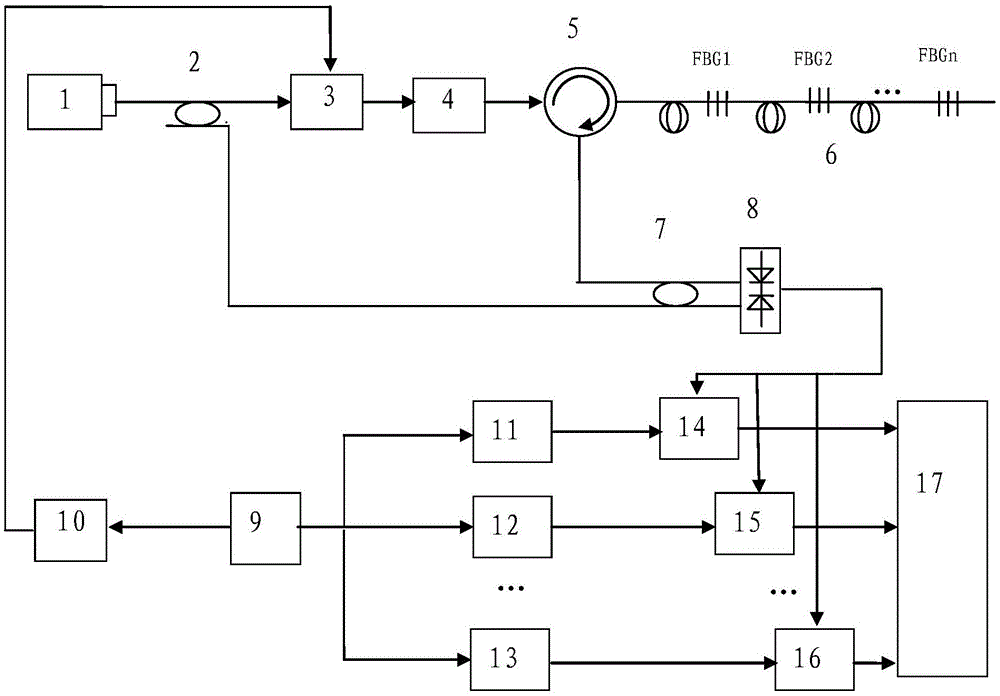
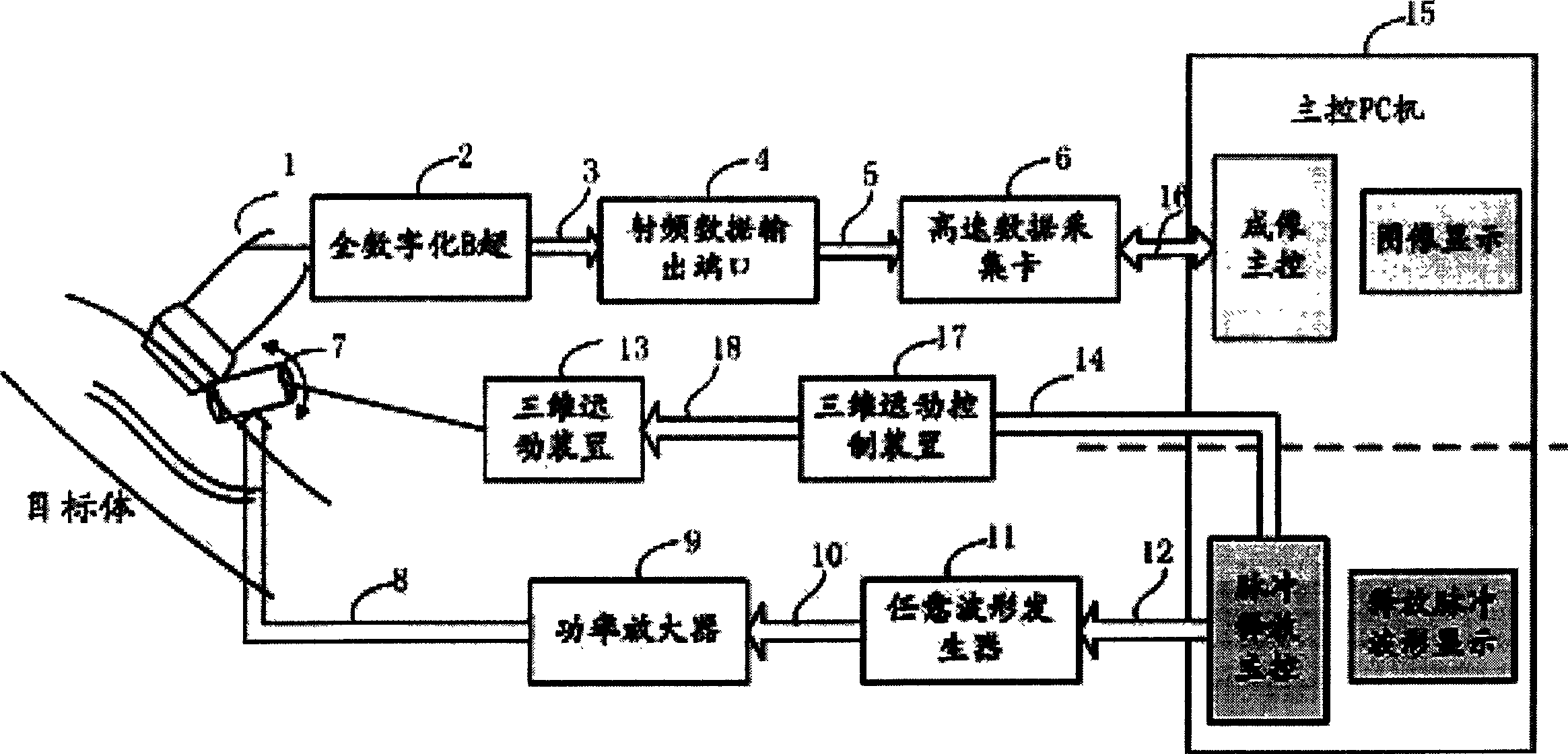
A system based on envelope microvesicle for perfusion imaging and ultrasonic controlled release is composed of ultrasonic imaging probe, fully digitalized ultrasonography B, RF data output port, high-speed data acquisition card, PC as main controller, any waveform generator, 3D moving unit, moving controller and single-cell transducer. On the basis of fully digitalized ultrasonography B, a blood perfusion imaging algorithm is used for making a decision to obtained original RF data and performing real-time imaging. Under the guide of perfusion image, the release of envelope microvesicles is controlled.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ultrasonic guided wave device and method for detecting defect at rail bottom of steel rail at long distance
InactiveCN102043015AAccurate judgmentSolve the problem that rapid non-destructive testing cannot be performedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesSonificationAudio power amplifier
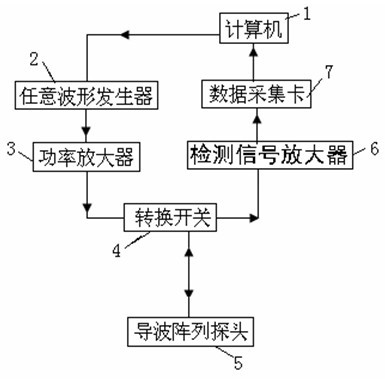
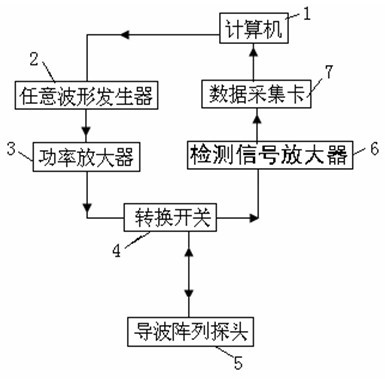
The invention discloses an ultrasonic guided wave device for detecting a defect at the rail bottom of a steel rail at a long distance, which comprises a computer, a data acquisition card, a detection signal amplifier, an arbitrary waveform generator, a power amplifier, a change-over switch and a guided wave array probe. The ultrasonic guided wave device is characterized in that: the computer serves as a control center of the device, and controls the arbitrary waveform generator to generate a single-audio frequency signal of which central frequency is selected detection frequency; the single-audio frequency signal is transmitted to the guided wave array probe after passing through the power amplifier to excite guided waves of a vertical bending mode in the rail bottom of the steel rail; and under the regulation and control of the change-over switch, the guided wave array probe receives a defect reflection echo signal which is transmitted to the computer for processing and display after passing through the detection signal amplifier and the data acquisition card. The ultrasonic guided wave device realizes the rapid nondestructive detection of the defect at the rail bottom of the steel rail.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
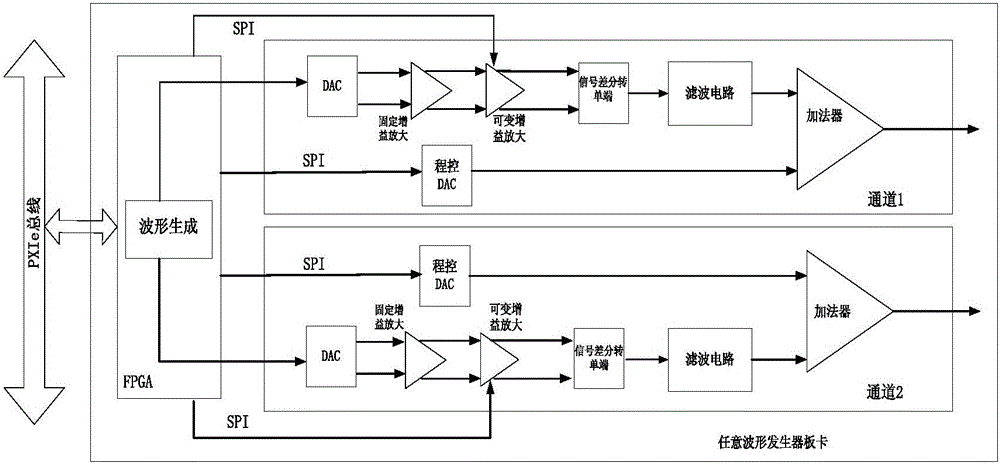
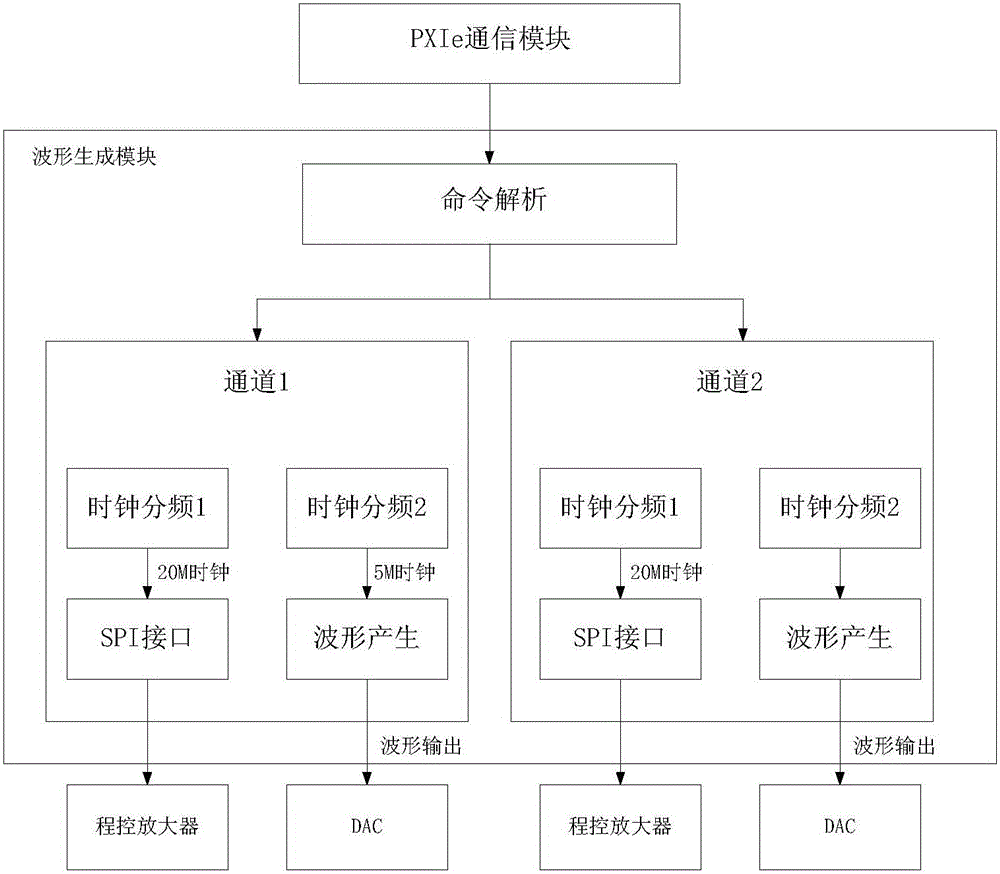
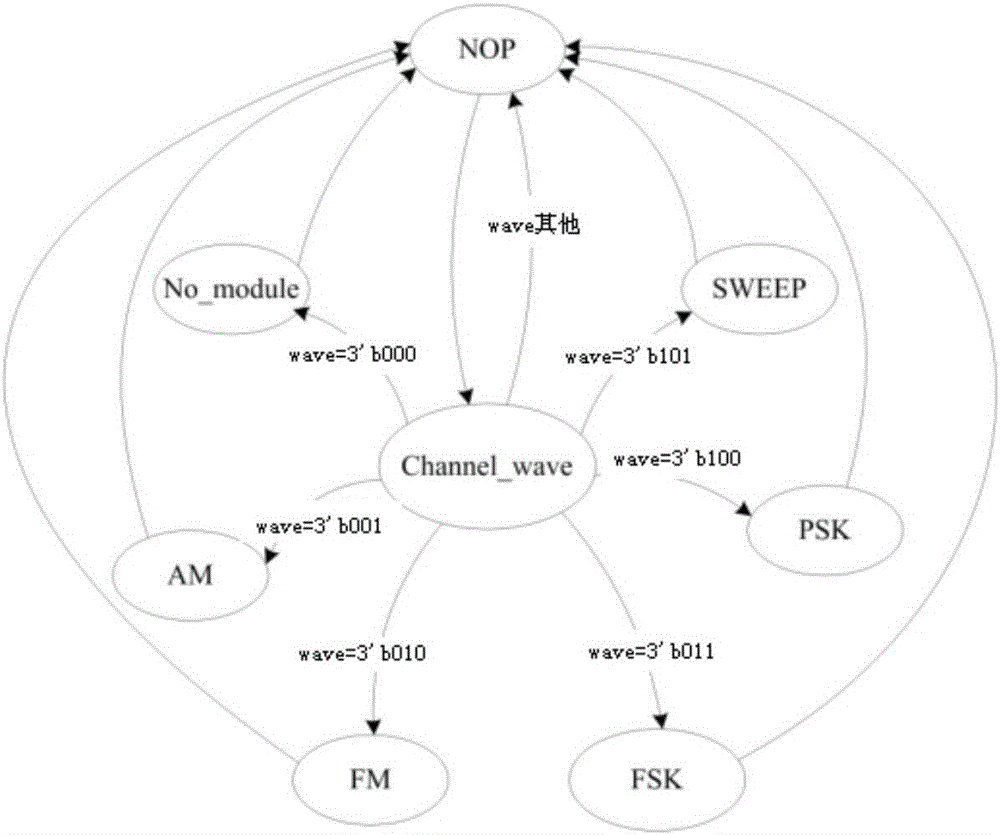
Arbitrary waveform generator based on PXIe bus
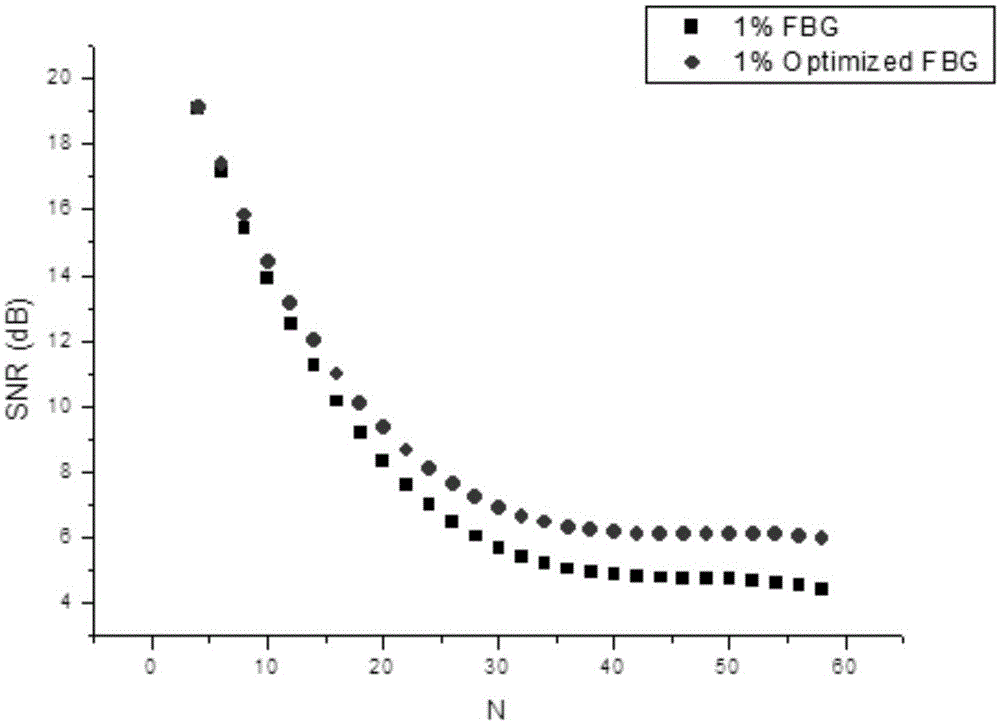
ActiveCN105866482AGuaranteed integrityGood attenuation characteristicsElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingSmall amplitudeSignal quality
The invention relates to the field of signal generator, and specifically relates to an arbitrary waveform generator based on a PXIe bus. The generator comprises a waveform generation part and a waveform conditioning part. The waveform generation part comprises an FPGA and a crystal oscillator. The waveform conditioning part comprises a 16-bit DAC, an operational amplifier, an SPI program control amplifier, a filter circuit, an SPI program control DAC, a differential operational amplifier, and a subtracter. The generator employs the PXIe bus as a channel which is used by an upper computer for transmitting waveform data. The FPGA continuously process the waveform data transmitted by the upper computer in a waveform generation process, so as to guarantee the integrity of high-frequency signal quality. In a waveform conditioning process, the generator respectively employs a Bessel filter and an elliptic filter according to the frequency characteristics of signals and the difference of anti-noise capabilities, and meets the filtering requirements of different types of signals. For a signal with the amplitude being less than 50mV, a small signal processing branch circuit is designed, thereby guaranteeing that a signal with a small amplitude value cannot be flooded by noise. The generator employs a mode of internal and external synchronization adjustment for signal amplitude and bias, and guarantees the accuracy of a signal.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING CHANGCHENG AVIATION MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH INST +2
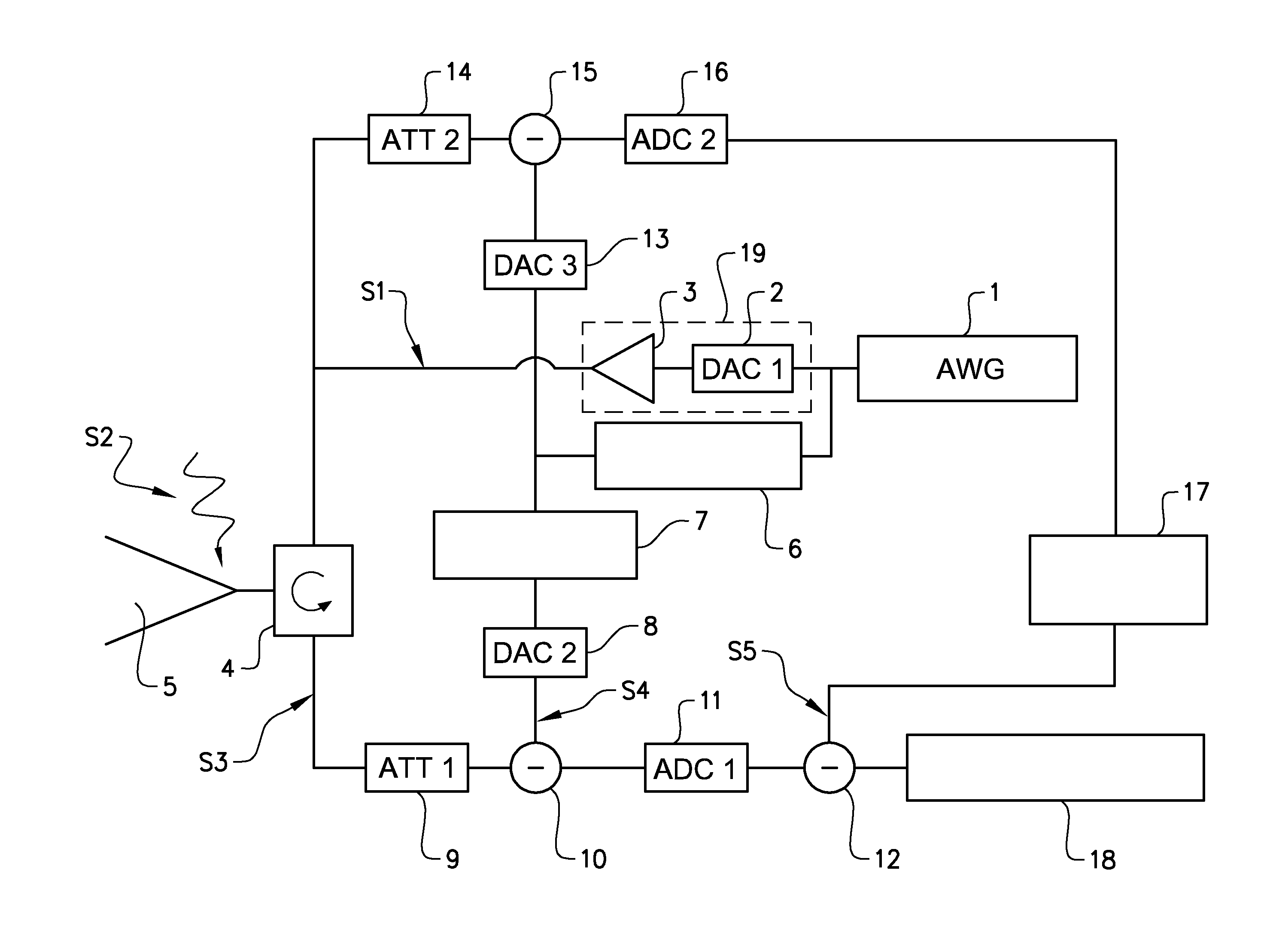
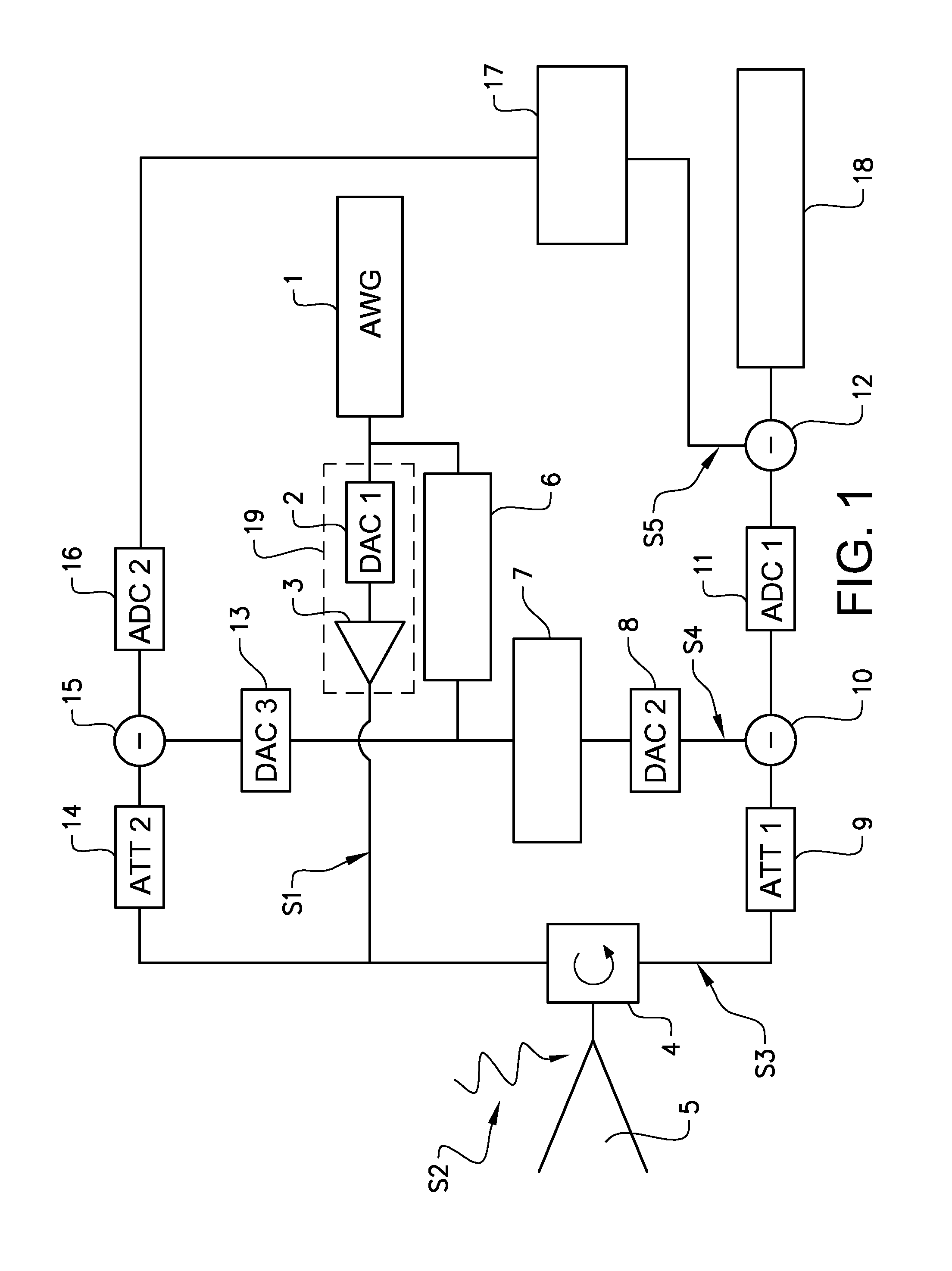
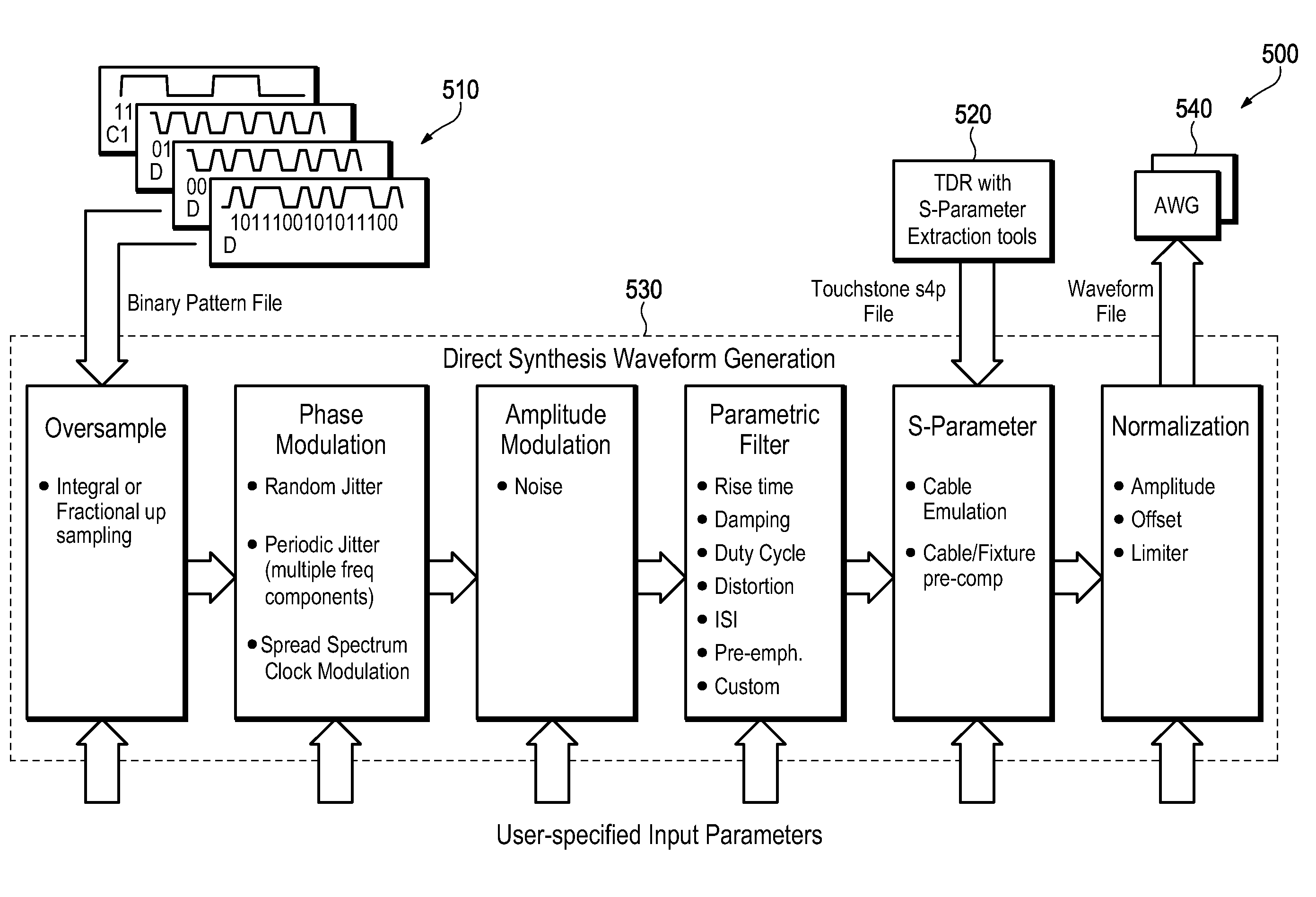
Synthesis and generation of arbitrary waveforms with isi components for jitter tolerance
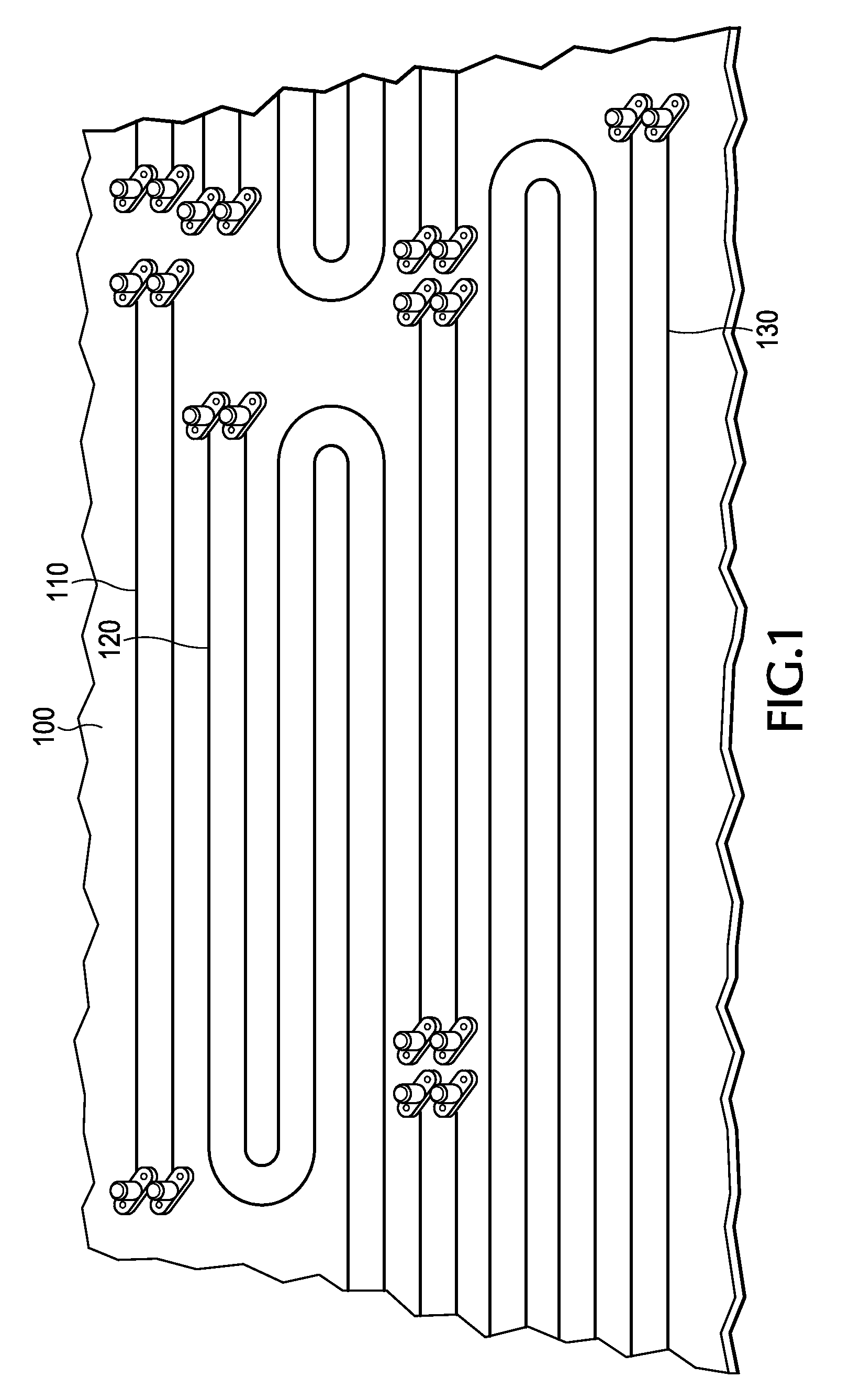
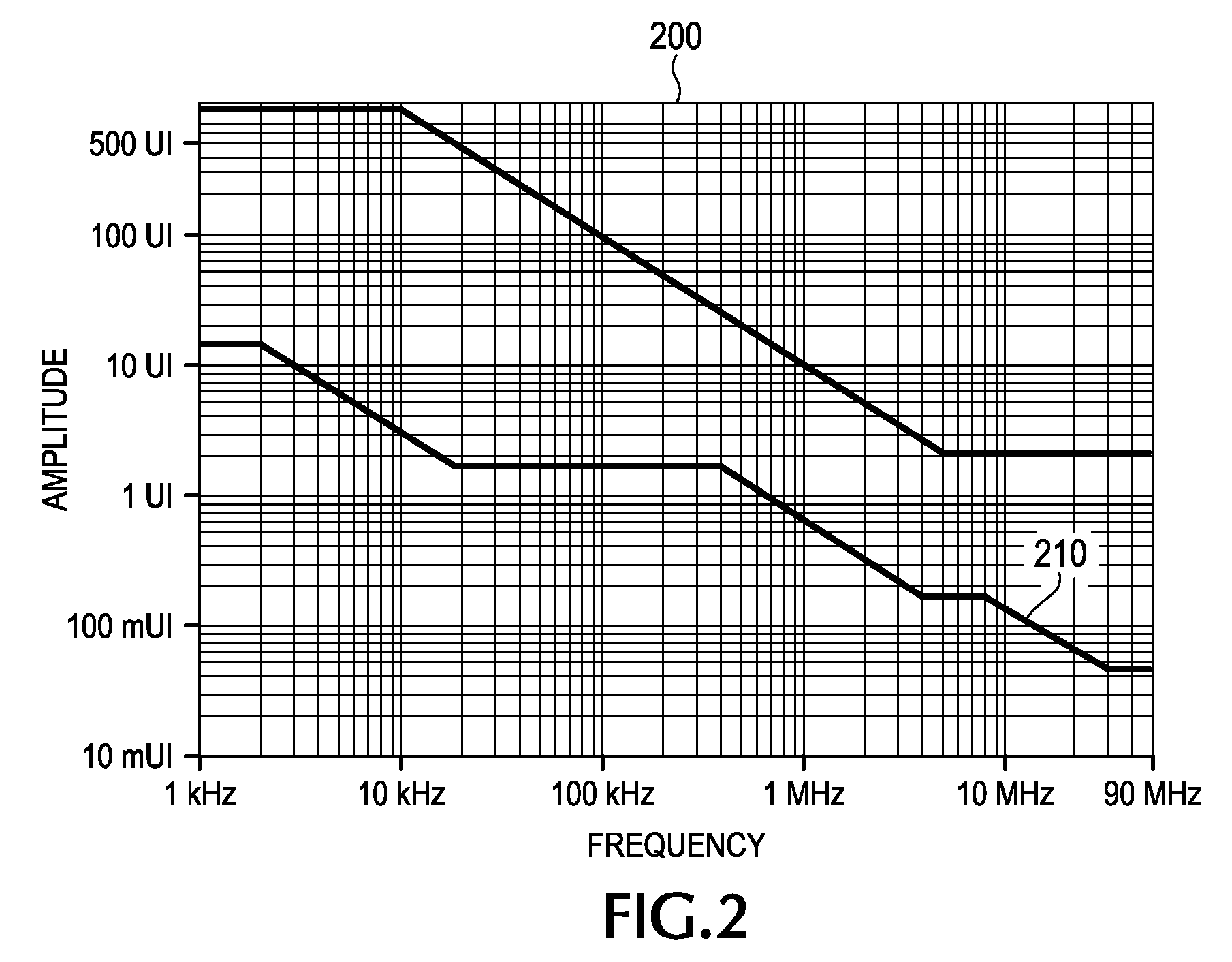
An Arbitrary Waveform Generator has a controller programmed to generate a sequence of test waveforms using previously-defined waveform data files. The controller generates this series of test waveforms by direct synthesis to cause said each waveform to contain a respective different predetermined amount of Rj, Sj and ISI jitter components. In this way, the Arbitrary Waveform Generator produces a sequence of waveforms incorporating varying amounts of ISI to sweep said ISI jitter components from a an initial amount of ISI, for example, zero ISI, and continually increment said amount of ISI to a full unit interval of ISI in predetermined increments, for example, 0.1 UI steps.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
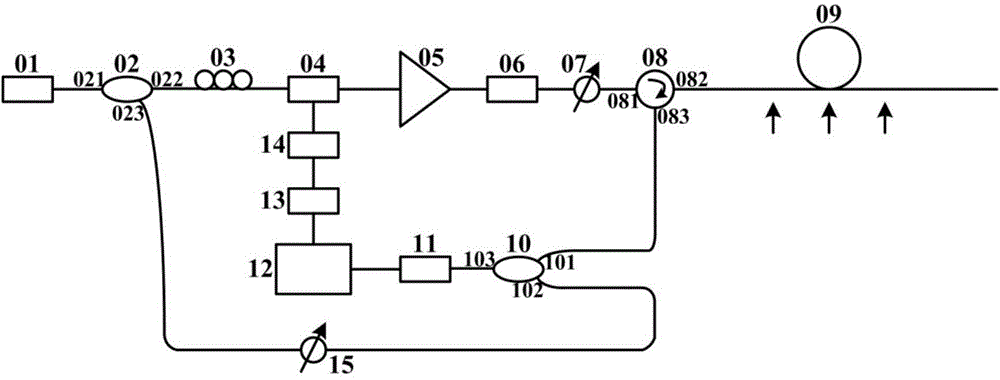
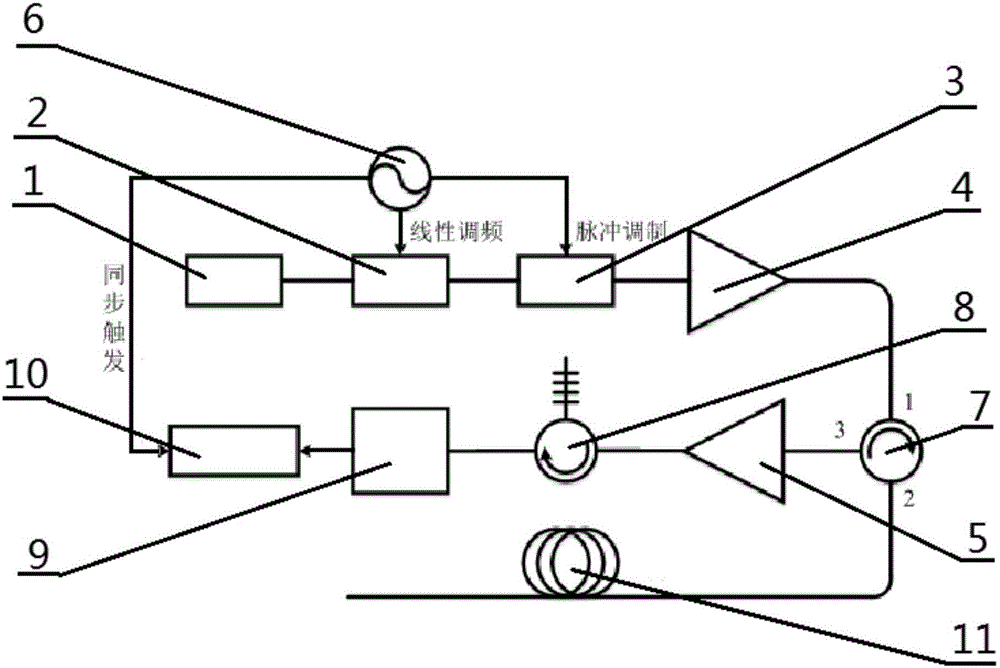
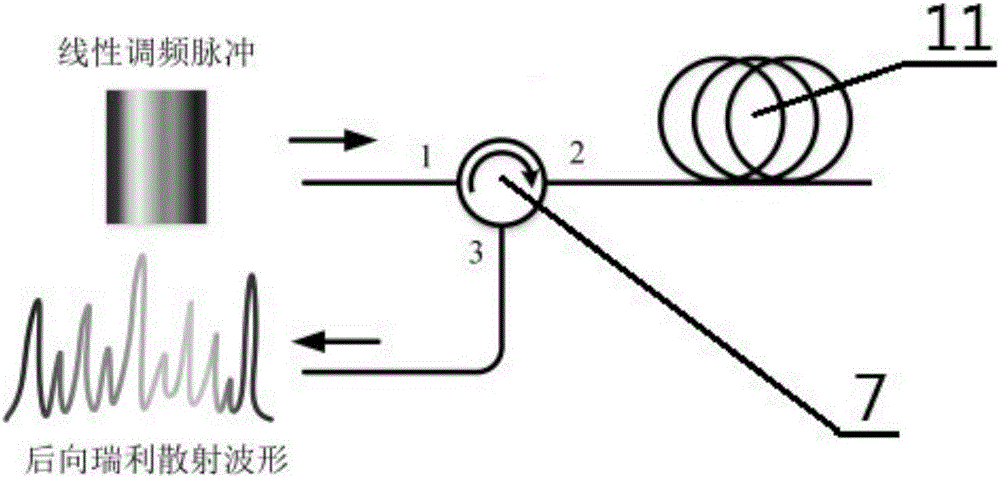
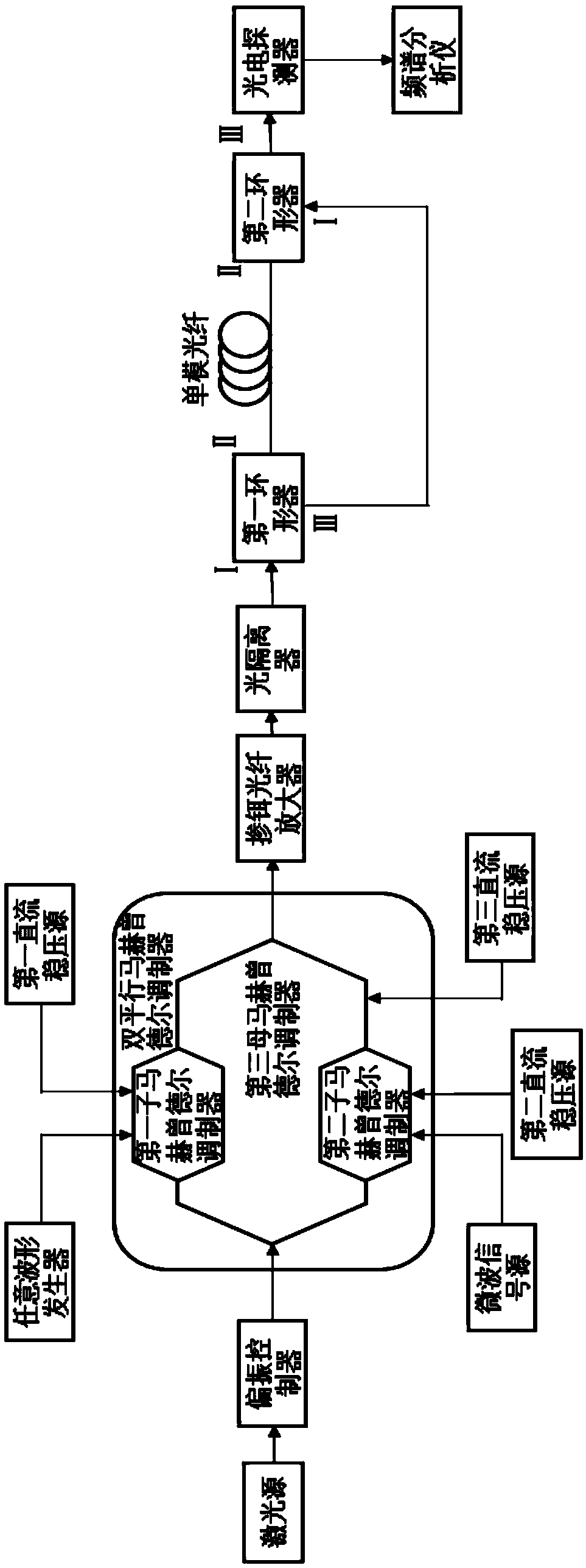
Phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometer based on linear frequency-modulation pulse and measurement method of phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometer
PendingCN106643832AImprove linearityHigh measurement accuracyConverting sensor output opticallyRayleigh scatteringGrating
The invention relates to a phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometer based on a linear frequency-modulation pulse and a measurement method of the phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometer. The phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometer comprises a laser device, a single side band modulator SSBM, an acoustic optical modulator AOM, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier EDFAI, an EDFAII, an arbitrary waveform generator AWG, an optical fiber circulator, a fiber Bragg grating filter FBG, a photoelectric detector, a data collection module and a to-be-measured optical fiber, wherein laser enters the single side band modulator SSBM and is modulated into pulsed light by virtue of the acoustic optical modulator AOM, and the pulsed light is amplified by virtue of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier EDFAI and enters the to-be-measured optical fiber through the optical fiber circulator; and a backward Rayleigh scattering signal is output through the optical fiber circulator, a backward Rayleigh scattering optical signal is amplified by virtue of the erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier EDFAII and is detected and converted into an electric signal through the fiber Bragg grating filter FBG, and the data collection module executes data collection and data analysis. By the utilizing linear frequency-modulation pulse, the measurement time is shortened, and the dynamic performance of a system is improved; and the scheme provided by the invention is convenient and feasible, and the structure of the system is relatively simple.
Owner:ANSHAN REALPHOTONICS TECH CO LTD
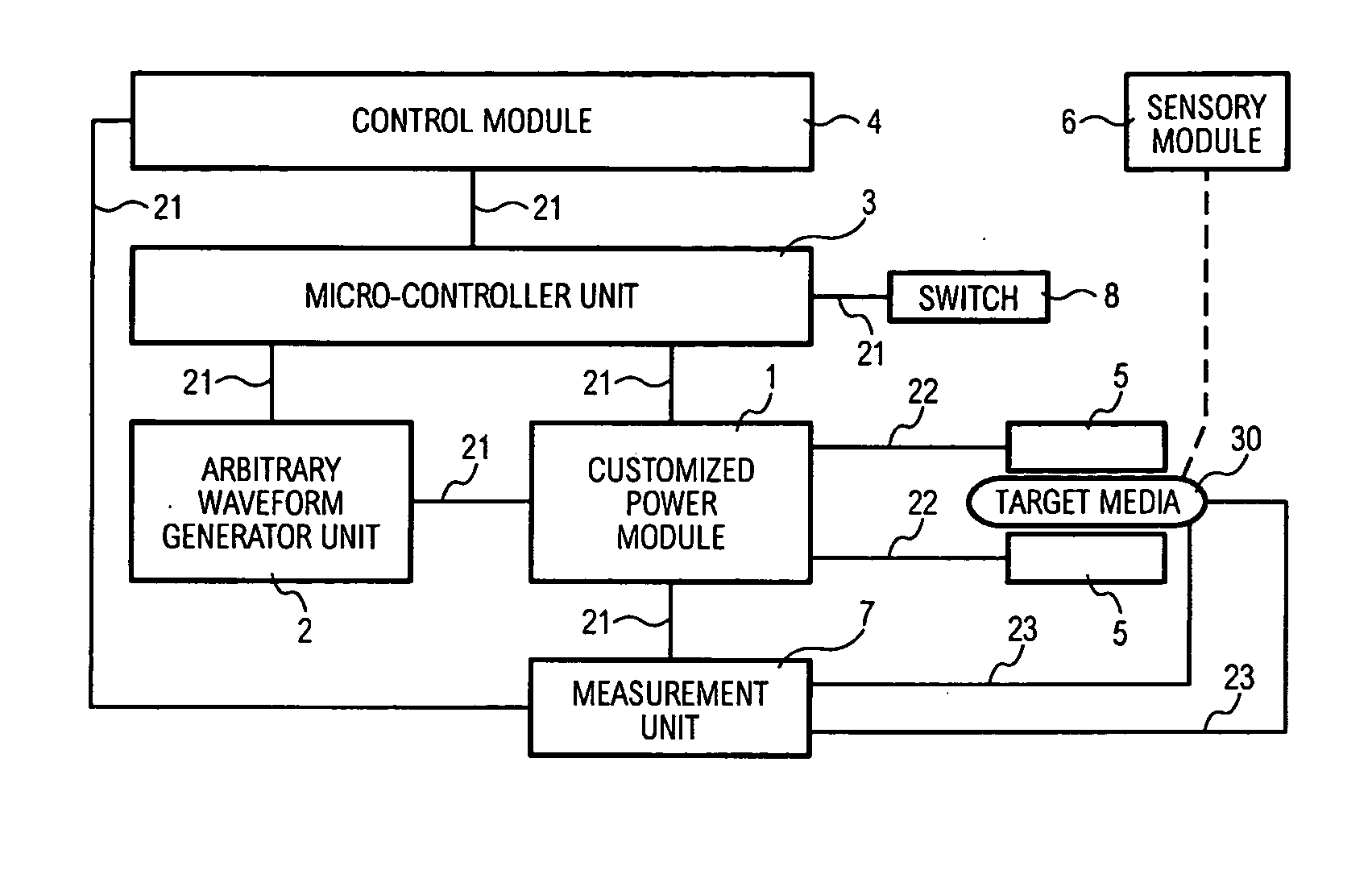
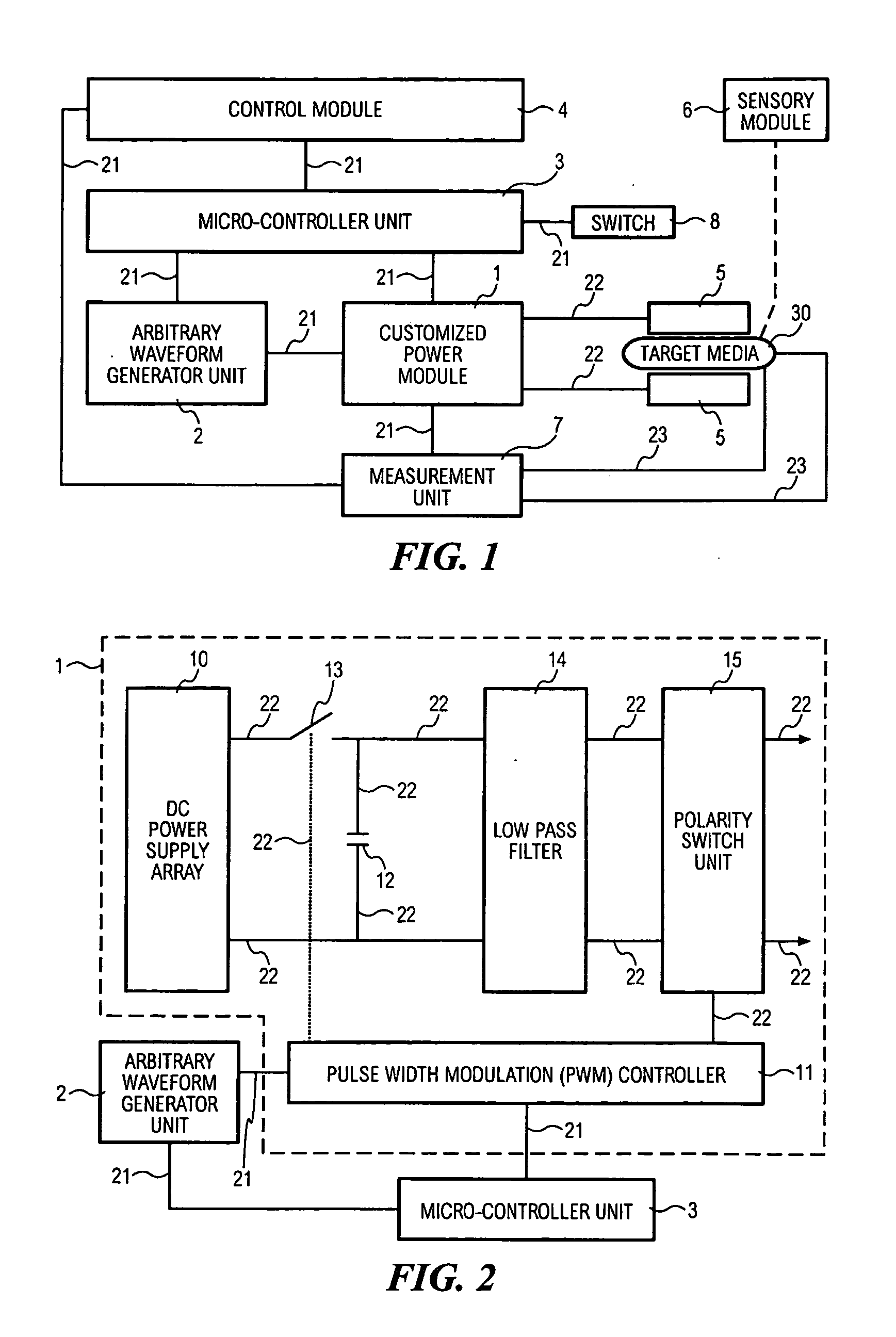
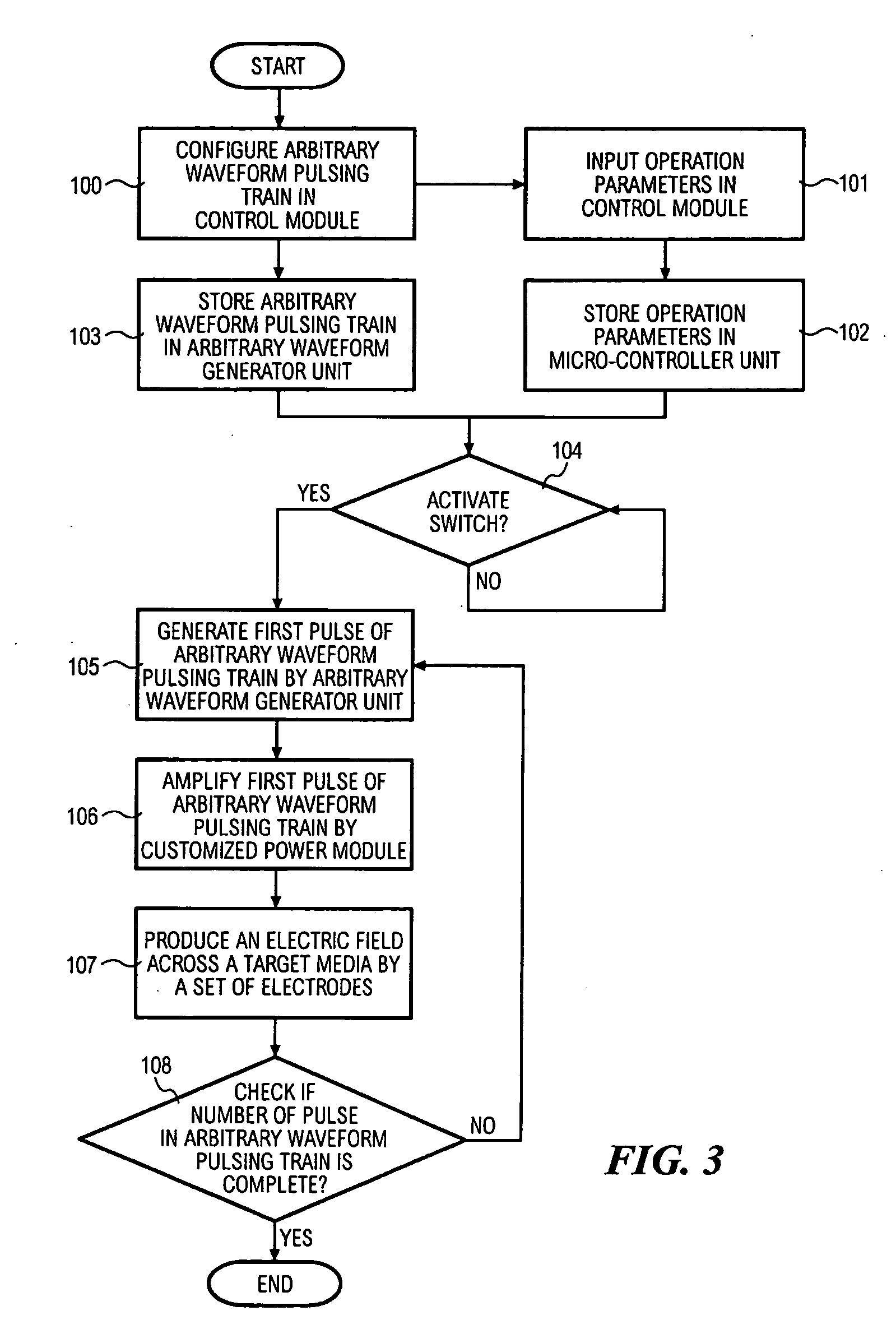
Programmable apparatus and method for optimizing and real time monitoring of gene transfection based on user configured arbitrary waveform pulsing train
InactiveUS20060142688A1ElectrotherapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentElectricityComputer module
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for generating and applying an electric field according to a user configured arbitrary waveform pulsing train. A control module allows the user to input operation parameters and configure the arbitrary waveform pulsing train for the electroporation process. A micro-controller unit coupled to the control module controls an arbitrary waveform generator unit and a customized power module. During the electroporation process, the arbitrary waveform generator unit produces the arbitrary waveform pulsing train that is amplified by the customized power module. The customized power module is coupled to at least two electrodes, wherein the at least two electrodes will produce an electric field across a target media.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT OF SINGAPORE PTE
Dynamic distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensing device and method
ActiveCN103335666AAchieve frequency agilityRealize dynamic sensingConverting sensor output opticallyData acquisitionErbium doping
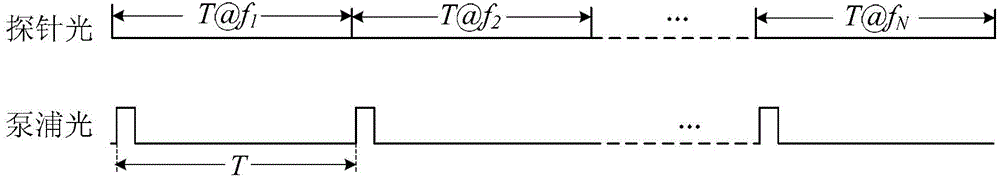
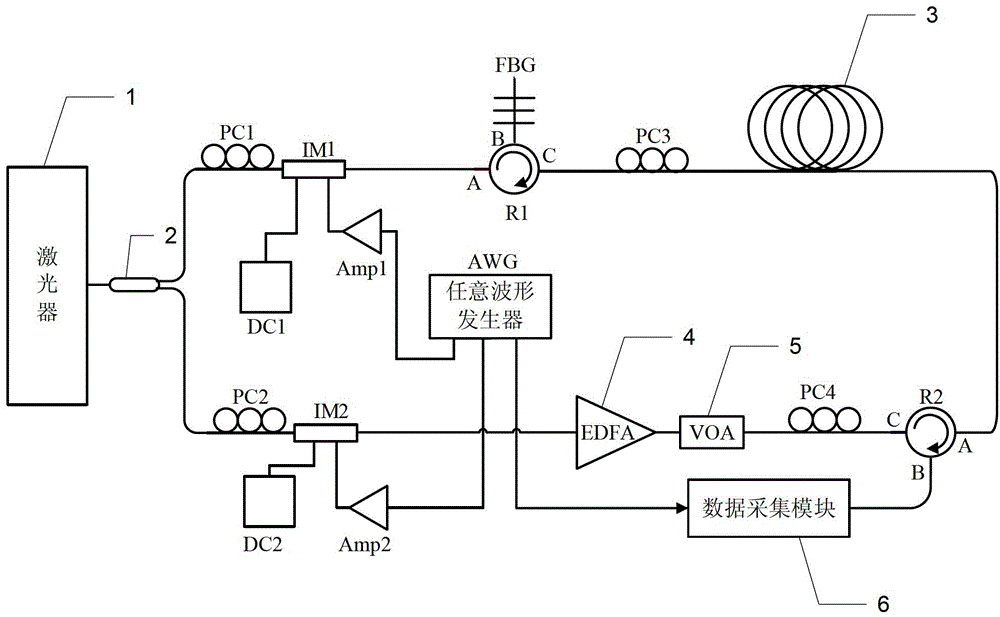
The invention discloses a dynamic distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensing device and method, belongs to the optical field, and solves the problem of small strain measurement range in a dynamic sensing technology based on a Brillouin gain slope method. The dynamic distributed Brillouin optical fiber sensing device comprises a laser, a coupler, a to-be-measured polarization maintaining optical fiber, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier, an adjustable optical attenuator, a data acquisition module, a first polarization controller PC1, a second polarization controller PC2, a third polarization controller PC3, a fourth polarization controller PC4, a probe light intensity modulator IM1, a pump light intensity modulator IM2, an arbitrary waveform generator (AWG), a first circulator R1, a second circulator R2, a first signal amplifier Amp1 and a second signal amplifier Amp2. According to the invention, the intensity modulators can be driven by arbitrary waves, so that the frequency agility of probe light is realized, the fast frequency scan problem is solved, the distributed Brillouin dynamic sensing is achieved, and the strain of the to-be-measured polarization maintaining optical fiber is measured.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A microwave photon millimeter wave ultra-wideband signal generation method and device based on up-conversion
ActiveCN109039464ASimple structureEasy to implementElectromagnetic transmittersUltra-widebandFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a microwave photon millimeter wave ultra-wideband signal generation method and device based on up-conversion, belonging to the technical field of microwave photonics. A lasersource, a polarization controller, an arbitrary waveform generator, a microwave signal source, a dual-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator, an erbium-doped fib amplifier, an optical isolator, a first annulator, a single-mode optical fiber, a second annulator, a photodetector and a spectrum analyzer constitute the device. The invention is based on the up-conversion technology to generate the signal at 22GHz-29GHz millimeter wave UWB signal, the upconversion realized by SSB modulation can overcome the dispersion effect in single-mode fiber, so that the UWB signal can be transmitted over long distance. Single sideband modulation using secondary Brillouin scattering is simple and easy to implement. Moreover, the amplification of Brillouin gain and the attenuation of loss make the spectrum of the generated UWB signal satisfy the power spectral density mask specified by the Federal Communications Commission of the United States.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Kelvin probe force microscope synchronously measuring multiple parameters
ActiveCN106645808ACompensation errorImprove usabilityScanning probe microscopyElectricityAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a Kelvin probe force microscope synchronously measuring multiple parameters and relates to a Kelvin probe force microscope. The invention aims to solve the problem that surface appearance, mechanical property and surface local potential of a sample cannot be synchronously represented by using a conventional Kelvin probe force microscope. In the invention, a direct current power supply is used for generating a direct current signal and loads the same between a conductive probe and the sample, a signal generator generates three-path same signals, the frequency of which is the same as a second order resonant frequency of the conductive probe, and the first-path signal is overlaid with a signal generated by an arbitrary waveform generator for controlling a #3 piezoelectric controller, so that the #3 piezoelectric controller drives a piezoelectric ceramic on a probe hand; the second-path signal as a reference signal is sent to a lock phase amplifier; the third-path signal which is shifted by 90 degrees by a phase shifter is loaded between the conductive probe and the sample; and a signal output by the lock phase amplifier is sent to an upper computer. The Kelvin probe force microscope disclosed by the invention is suitable for measuring the surface appearance, the mechanical properties and the surface local potential of the sample.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wideband transmitter/receiver arrangement for multifunctional radar and communication
ActiveUS9071337B2Excellent leakage cancellationReduce volumeDuplex signal operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWave shapeRadar
A transmitter / receiver arrangement comprises a digital arbitrary waveform generator AWG connected to a transmitter. Said waveform generator is configured to generate an arbitrary waveform within a given bandwidth. Said transmitter / receiver arrangement further comprises an antenna arrangement configured to emit a transmitter signal, and to receive an incident signal, a receiver configured to receive a receiver signal, and an analog isolator connected to said antenna arrangement, said transmitter, and said receiver. Said analog isolator is adapted to route said transmitter signal from said transmitter to said antenna arrangement, and said incident signal from said antenna arrangement to said receiver, and to isolate said transmitter signal from said receiver signal. Said receiver is adapted to cancel any residual transmitter signal in said receiver signal by means of at least one digital model of at least said isolator, said antenna arrangement, and said transmitter.
Owner:SAAB AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com