Patents
Literature
1651 results about "Gas monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
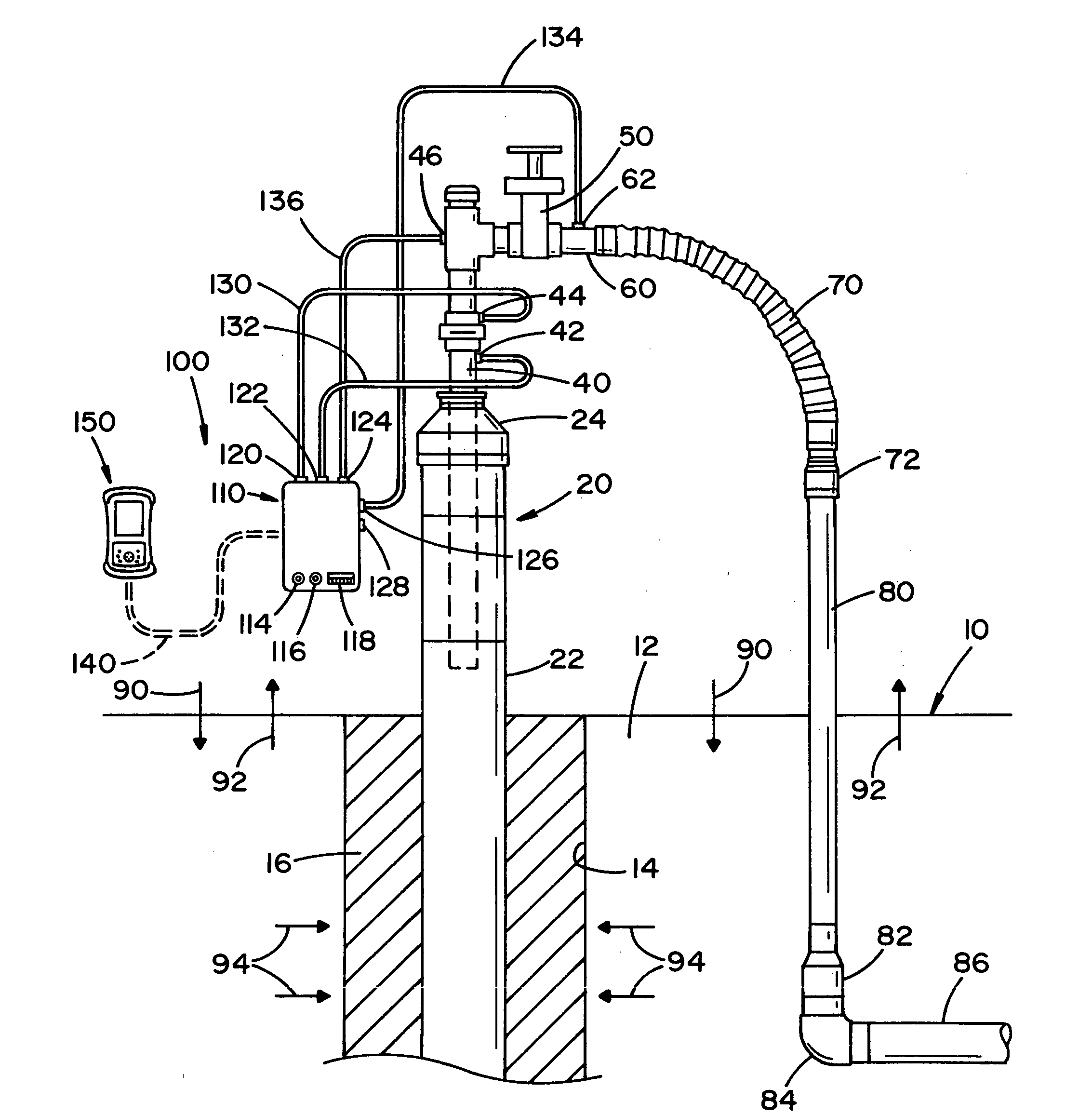
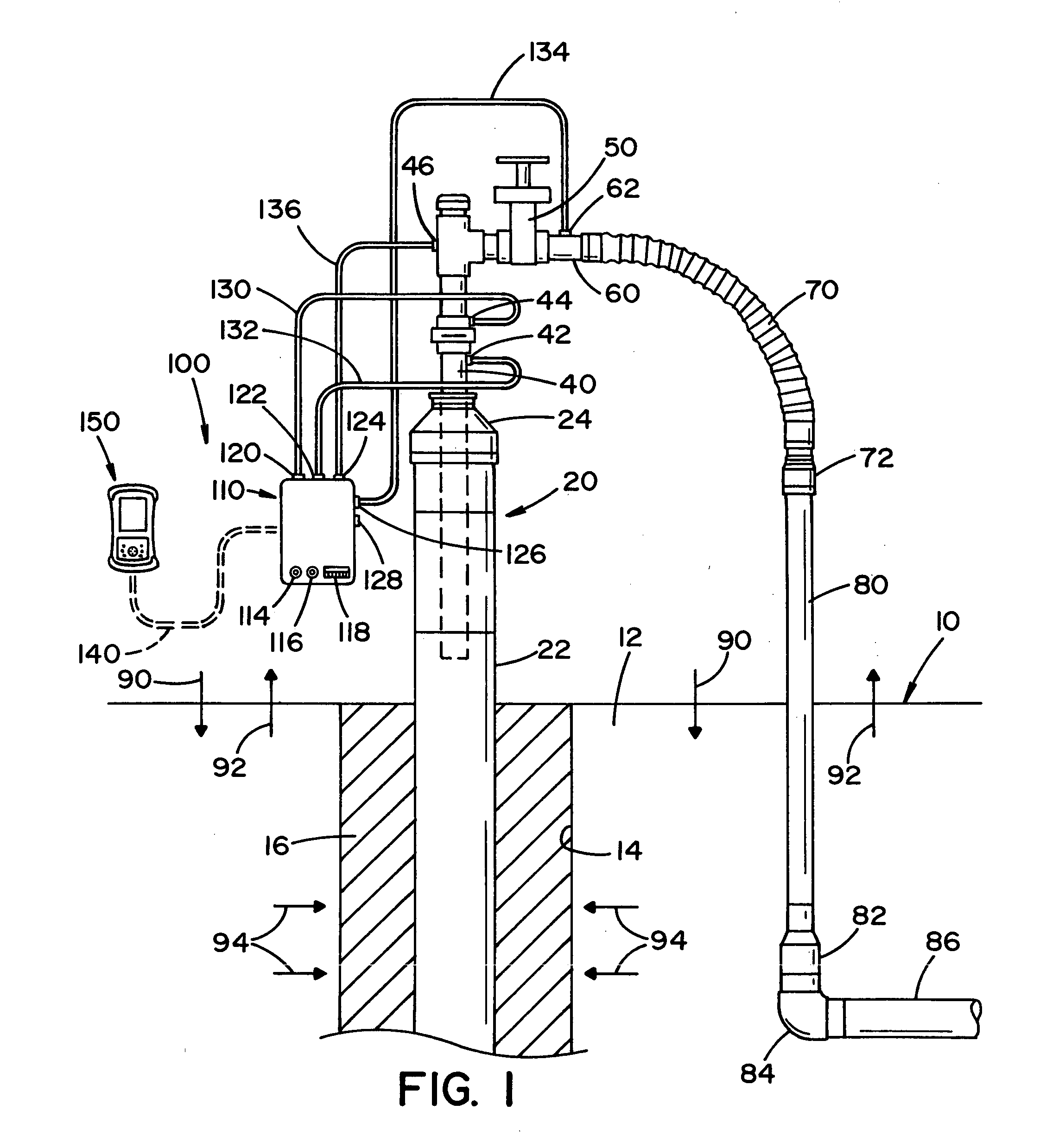
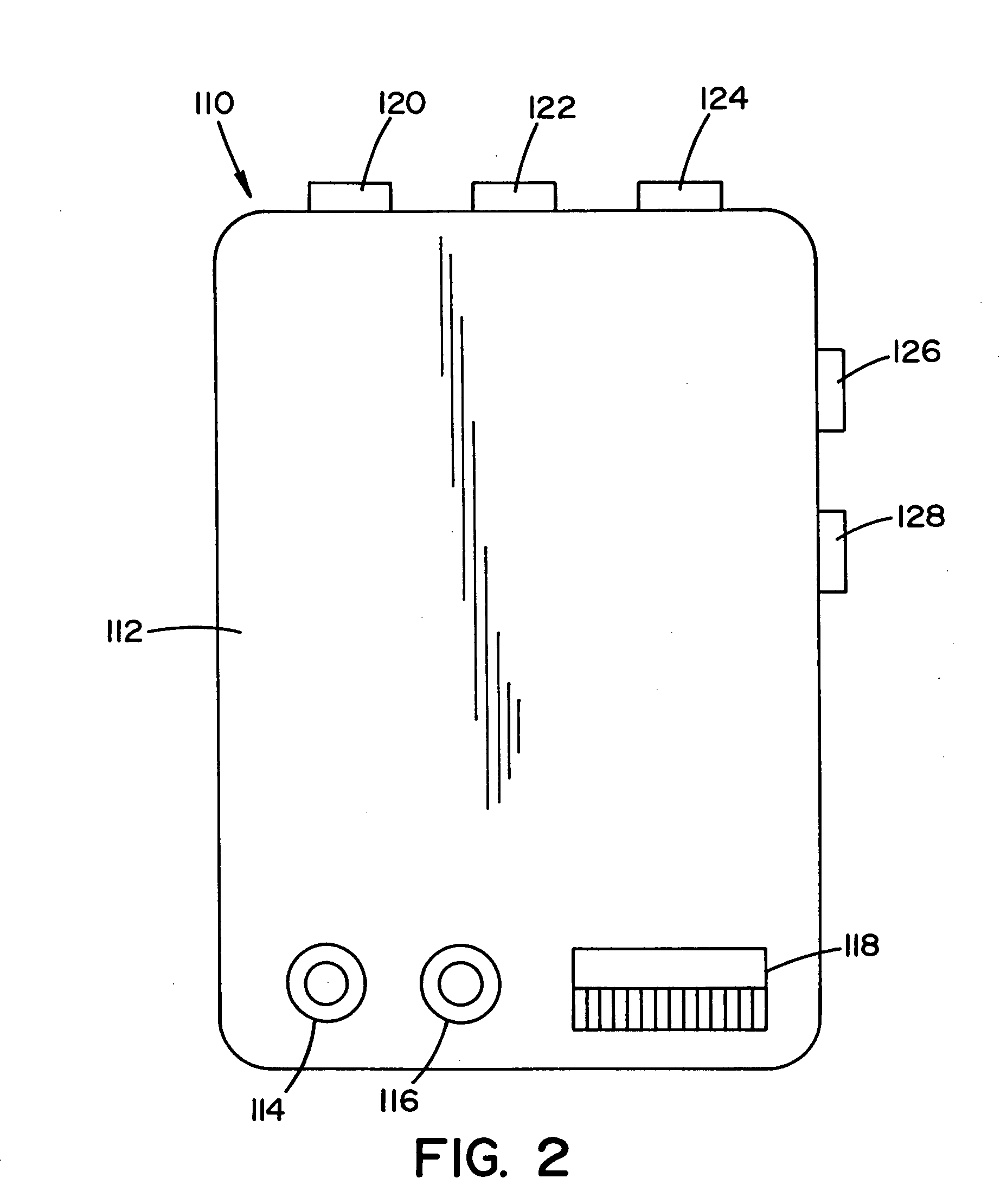
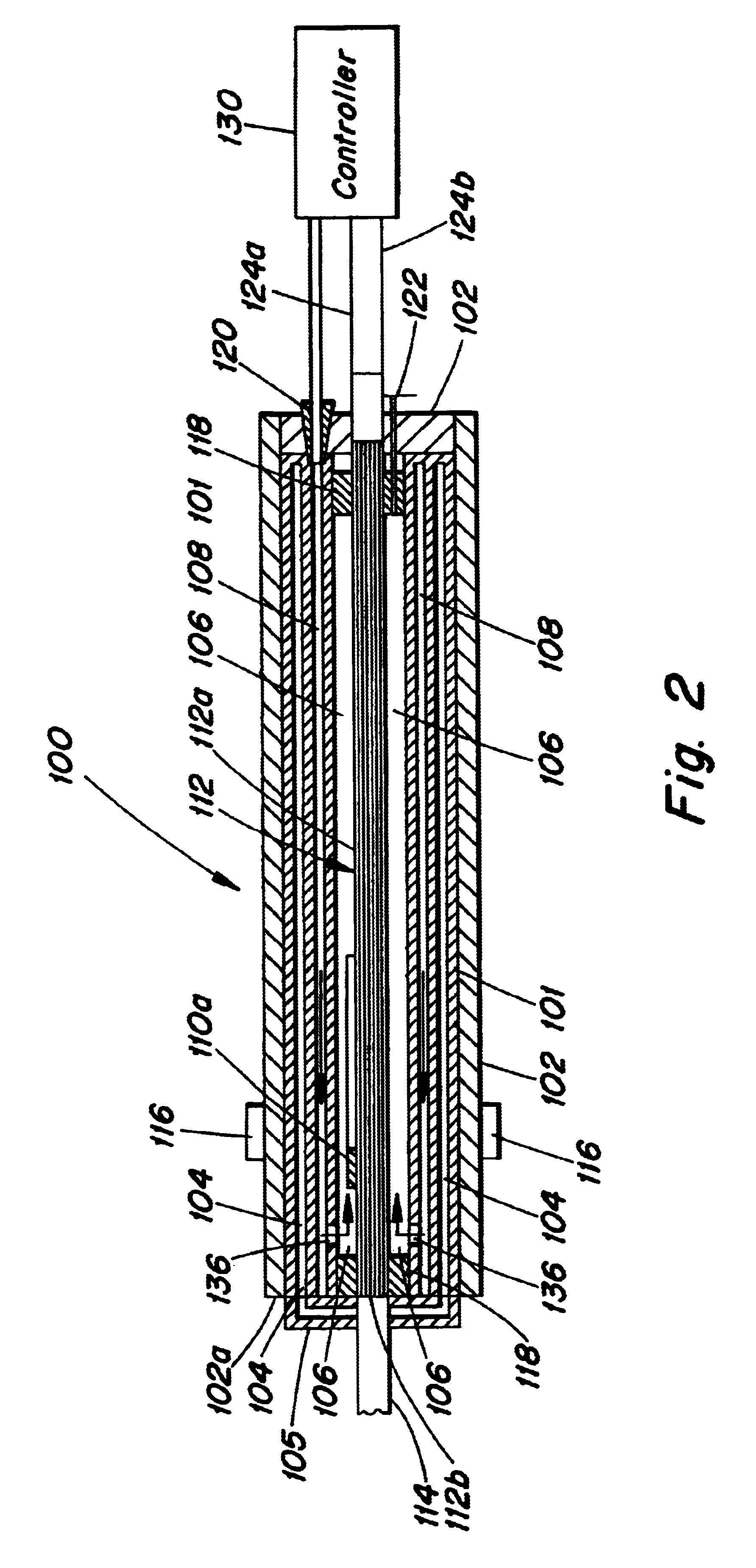
Method and apparatus for improving measuring accuracy in gas monitoring systems
InactiveUS20060108221A1Accurate and repeatable measurementFacilitate the monitoring of such speciesGas analyser construction detailsMaterial electrochemical variablesLine tubingEngineering
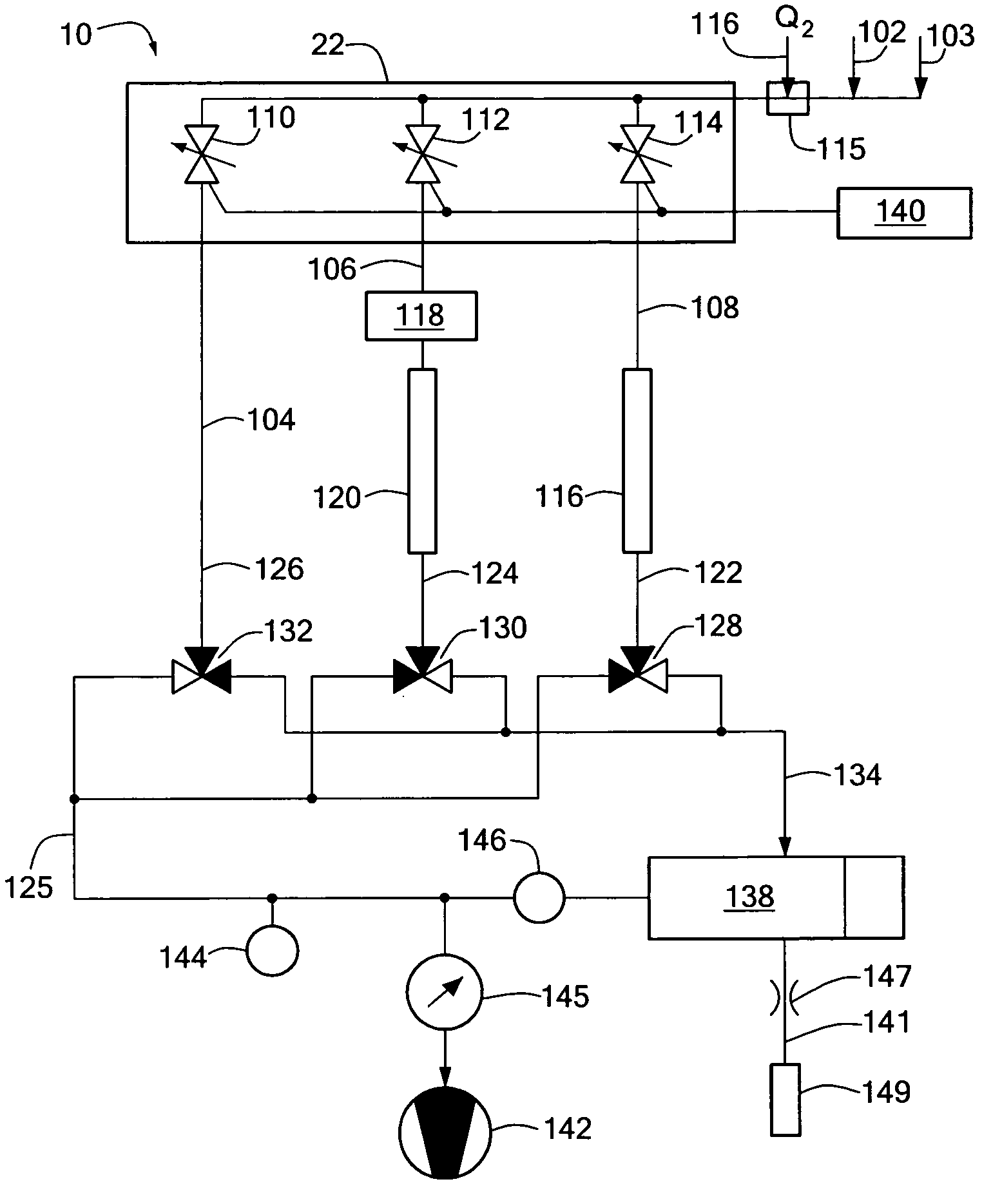
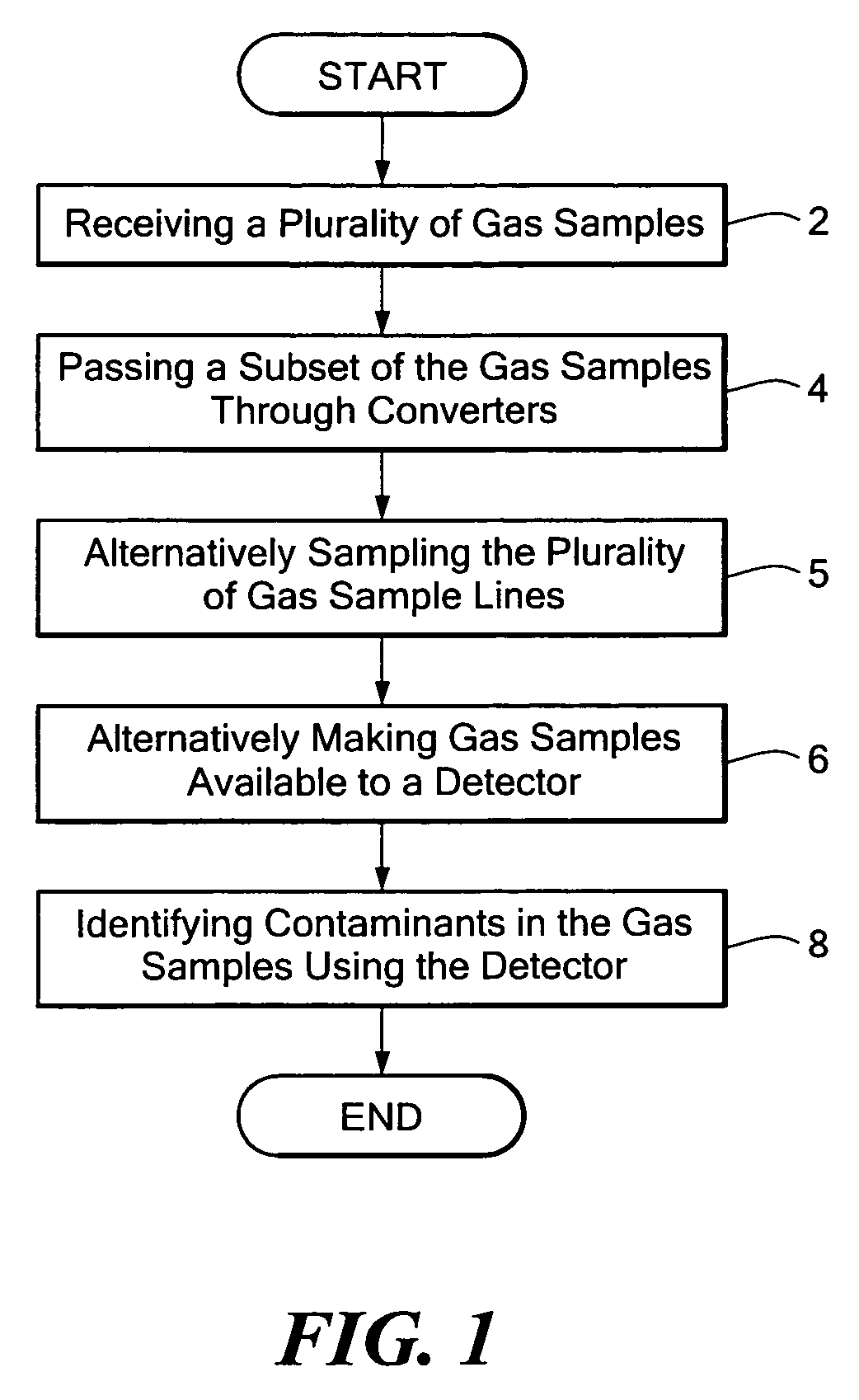
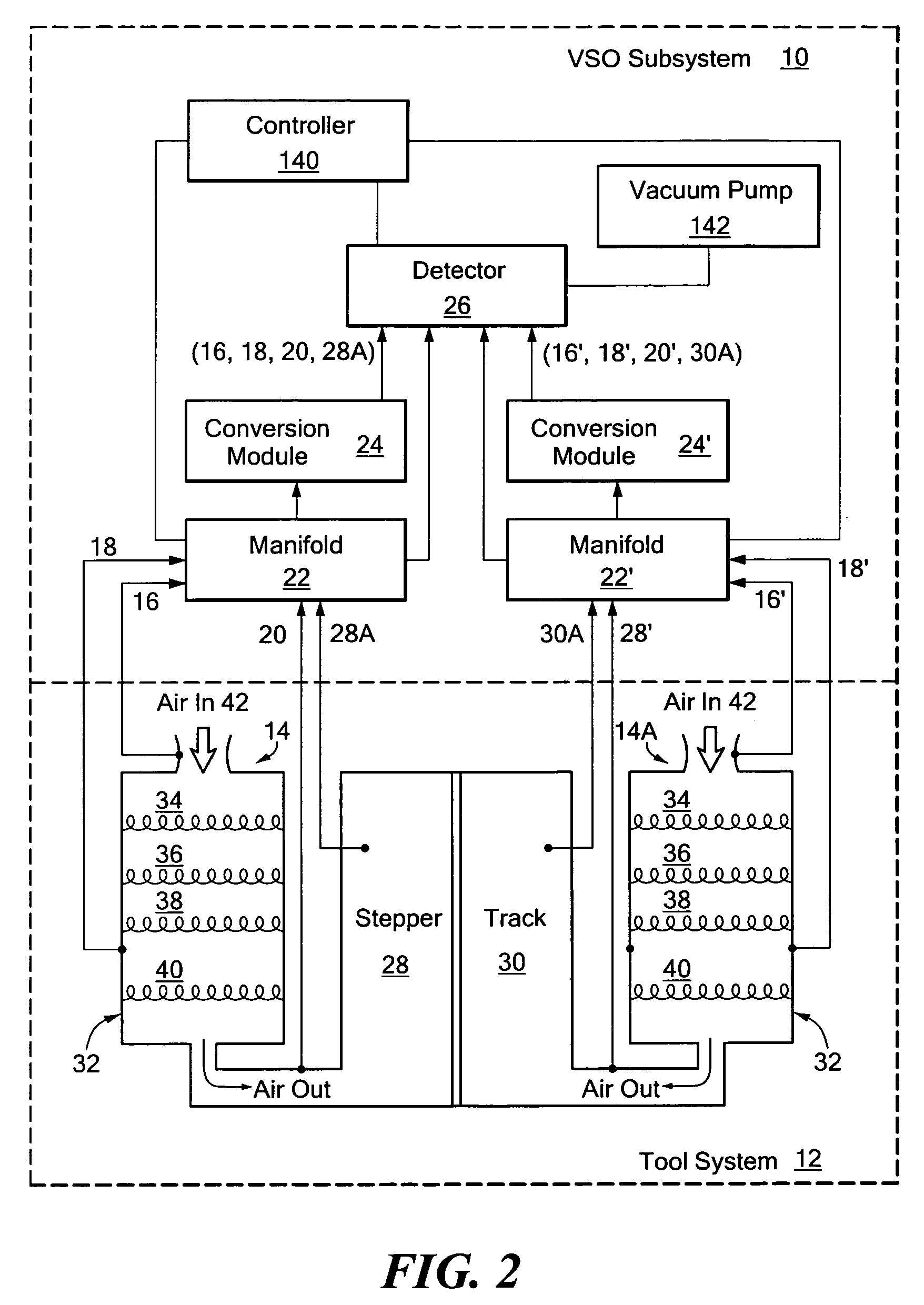
A method and apparatus for improving measurement accuracy in a gas monitoring system is provided. The apparatus can be connected to a plurality of gas sample lines each containing a gas sample. The gas samples are routed through a number of delivery channels which are fewer in number than the plurality of sample lines. Each delivery channel is alternatively coupled to a detector which identifies contaminants present in the gas samples. Each delivery channel includes a voltage sensitive orifice (VSO). The VSO's are operated by a controller and provide gas samples at a constant flow and a constant pressure to the detector independent of the length of the gas sample line being measured.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Gas sampling line
ActiveUS20110237969A1Improve accuracyReduce distortion problemsDispersed particle separationRespiratory organ evaluationGas analysisPolyethylene oxide
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Gas monitor
InactiveUS20060044562A1Less componentsReduce needColor/spectral properties measurementsA d converterProcessing element
Gas detection or monitoring apparatus mainly comprising, an optical source unit including a tunable diode laser, an optical detection unit including a light sensitive detector, the source and the detector being arranged so that light from the source propagates through a gas measurement volume prior to being received by the detector, and the source being adapted to scan the light wavelength across one or more expected absorption lines of gases in the measurement volume, a control and processing unit for control and modulation of the source and processing of the detected signal and for calculating at least one digital value representing (a) gas concentrations in the gas measurement volume, wherein said control and processing unit is coupled to the source via a digital-to-analogue (D / A) converter, and the detector output signal is coupled to the input of an analogue-to-digital (A / D) converter, and the output of the A / D converter is coupled to the processing unit.
Owner:NORSK ELEKTRO OPTIKK
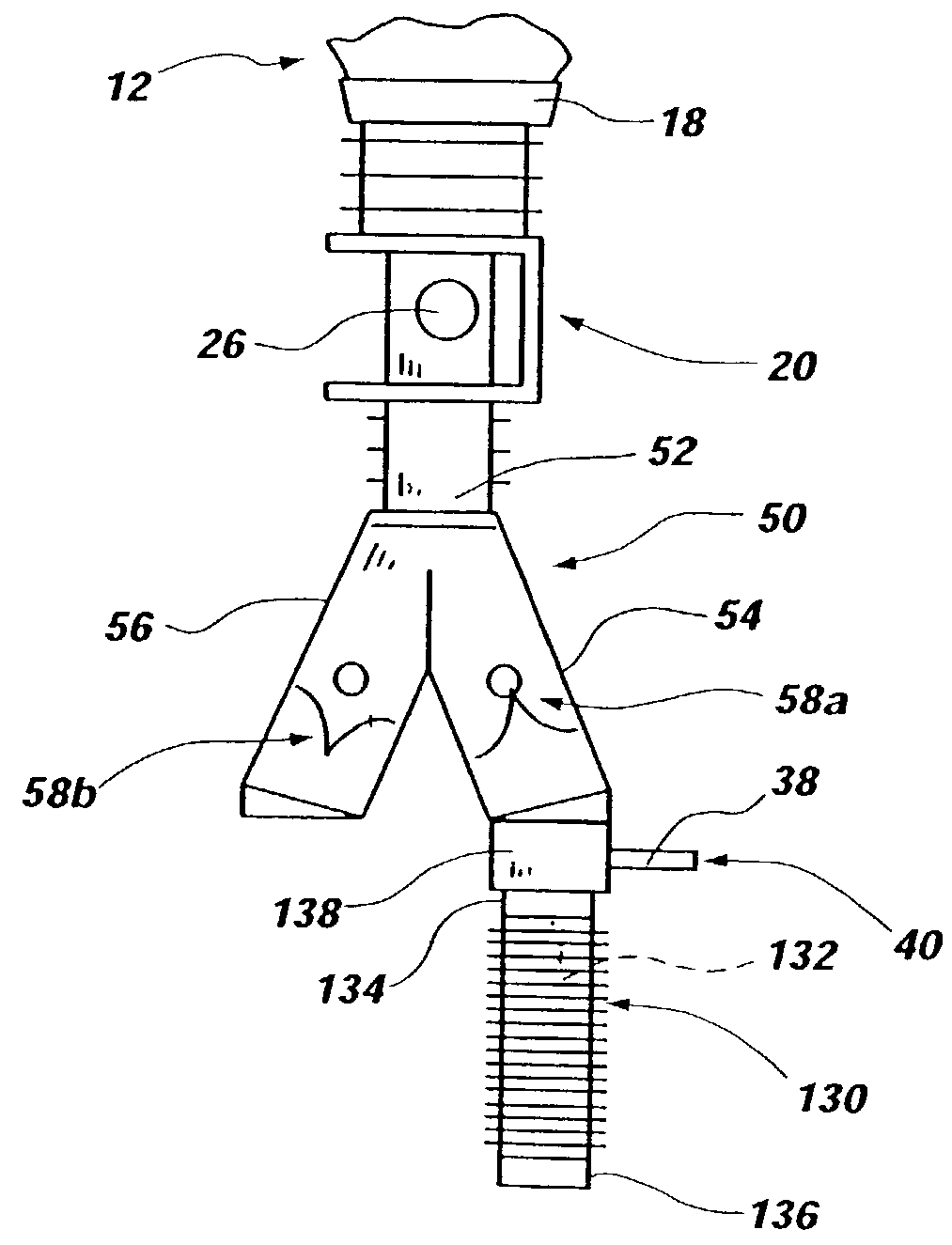
Face mask for gas monitoring during supplemental oxygen delivery
InactiveUS7004168B2Efficient detectionAccurate measurementOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksNasal cavityPatient management
A face mask including a gas monitoring capability for improved patient management in combination with improved efficiency of supplemental oxygen delivery to the patient is provided. The face mask of the present invention is configured to direct substantially all of the inspiratory and expiratory gas streams to and from the patient through a gas measuring device and to efficiently deliver supplemental oxygen. As such, the face mask permits measurement of both oral and nasal gas exchange.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Quartz crystal microbalance sensors and semiconductor manufacturing process systems comprising same
InactiveUS6295861B1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProcess systemsQuartz crystal microbalance
A sensor device for detecting the presence of a gas species in a gas environment susceptible to the presence of same. The sensor device may include a piezoelectric crystal coated with a sensor material having adsorptive affinity for the gas species, with an electric oscillator arranged for applying an oscillating electric field to the piezoelectric crystal to generate an output frequency therefrom indicative of the presence of the gas species when present in the gas environment, when the gas environment is exposed to the piezoelectric crystal. Another aspect of the invention involves a porous polymeric material that may be employed as a sensor material on a piezoelectric crystal sensor device, as well as a quartz microbalance holder that enables reactor gas monitoring. The sensor device alternatively may comprise an optical sensor arranged in a non-contaminating fashion in relation to the gas environment being monitored.
Owner:LIFE SAFETY GERMANY
Apparatus and method for wireless gas monitoring
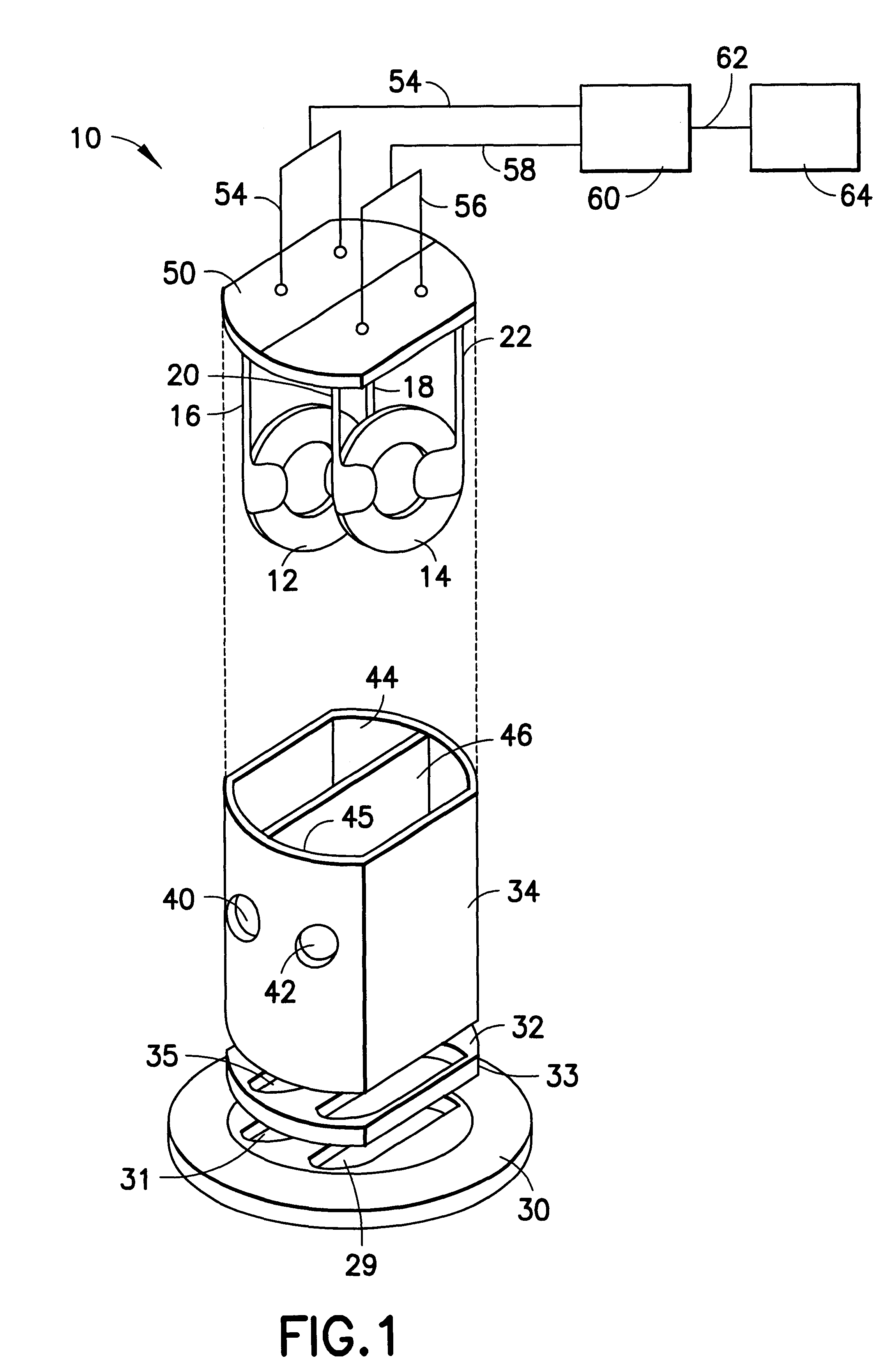
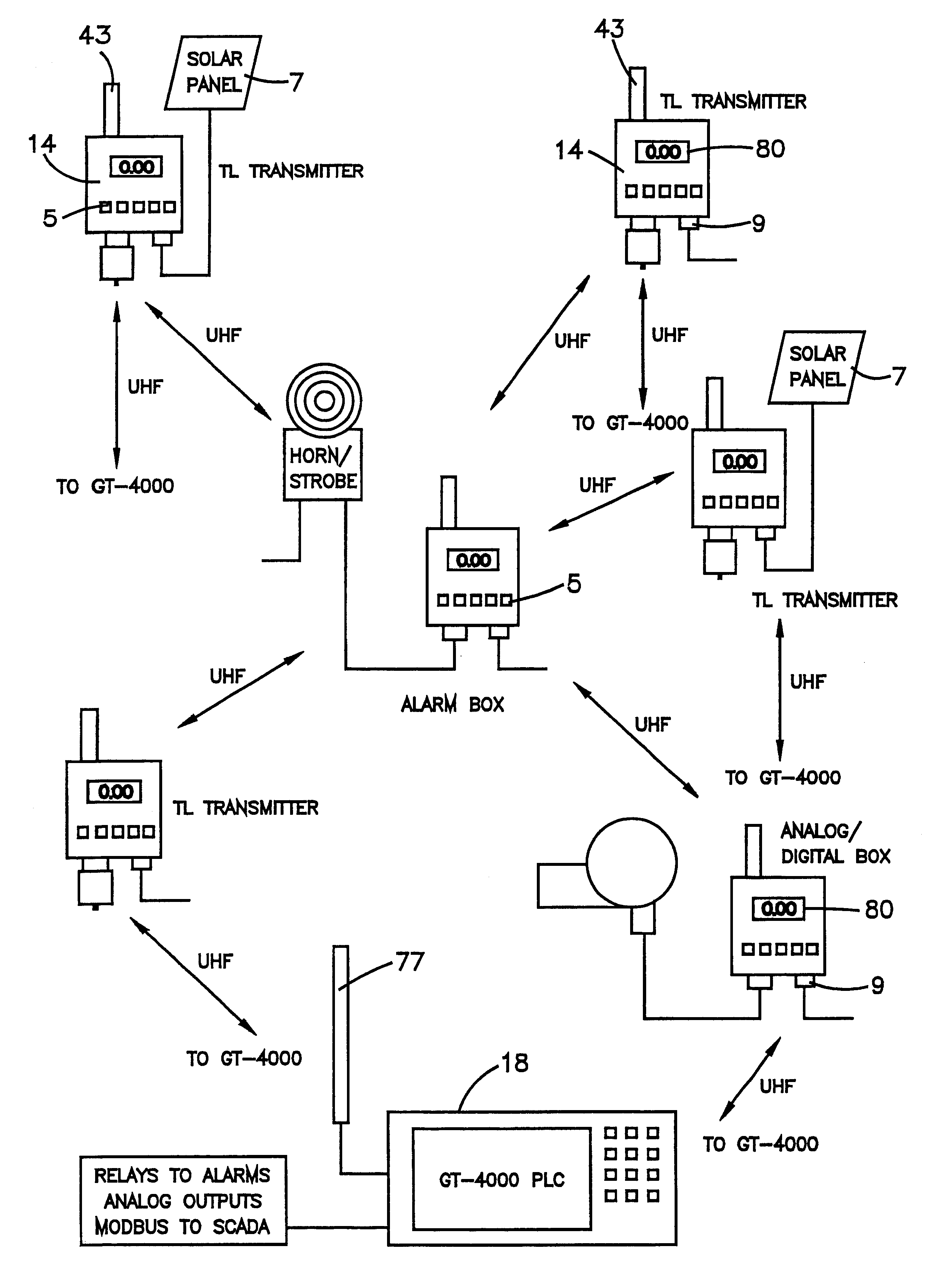
InactiveUS6670887B2Electric signalling detailsFire alarm smoke/gas actuationSatellite technologyTransceiver
The current invention provides a wireless monitoring system. The system has one or more monitoring devices. Each device can transmit data and receive messages from an output center or alarm system. The output center can also transmit and receive messages. Both the output center and each device preferably have a transceiver that enables both the transmission and receipt of messages. No remote terminal units hardwiring is required for the system to function. The system is truly a wireless gas monitoring system. The system may use low earth orbit satellite technology, or licensed radio frequencies or any other means to wirelessly transmit and receive messages.
Owner:GASTRONICS
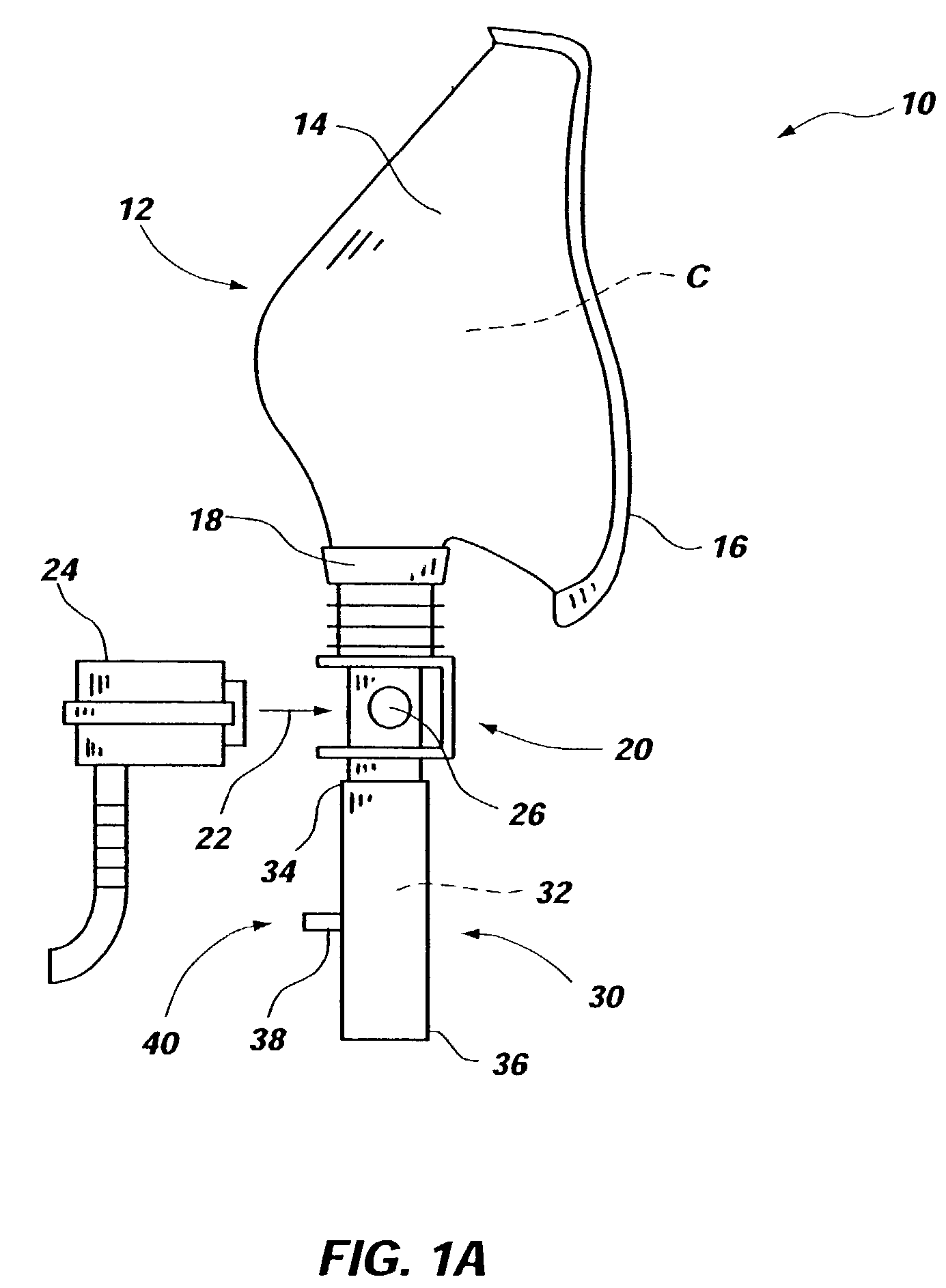
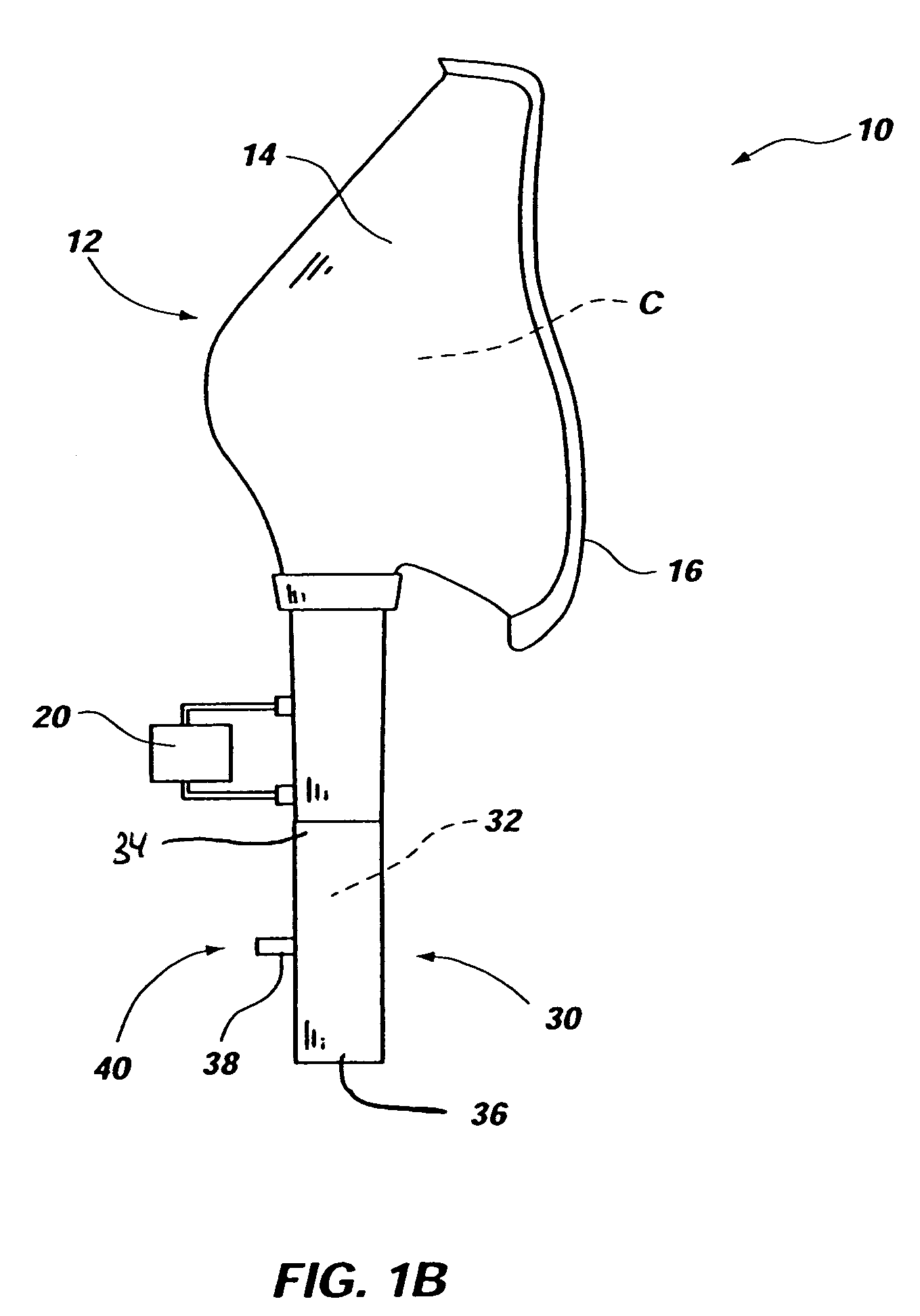
Patient interface with respiratory gas measurement component
InactiveUS20060249160A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing filtersAirway adaptorCatheter
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Low-Power Fast Infrared Gas Sensor, Hand Held Gas Leak Detector, and Gas Monitor Utilizing Absorptive-Photo-Acoustic Detection
InactiveUS20080277586A1Low possible costLow costDetection of fluid at leakage pointRadiation pyrometryHand heldEngineering
A gas sensor for sensing the presence of a gas includes an IR source, a microphone, a reference gas substantially similar to the gas to be detected, a reference body defining a reference chamber therein, the reference chamber having a pressure port coupled to the microphone, and a broad-band optical window through which at least IR wavelengths corresponding to absorption peaks of the predetermined gas may pass. The window is disposed between the IR source and reference chamber. The reference gas is contained within the reference chamber between the optical window and the microphone. The sensor can be included in a hand-held gas detection instrument having power supply, an outer shell, a circuit board assembly including sensor circuitry, a suction pump, actuation controls and status indicators. A probe defining a lumen therethrough supplies the sample gas.
Owner:CARDINALE DENNIS
Portable gas monitor
InactiveUS20110231099A1Easy to identifyEasily obtain informationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsEngineeringControl unit
A portable monitor used to measure landfill gas and landfill well parameters. The portable monitor includes a control unit and a measuring unit that can communicate wirelessly with one another. The control unit and / or measuring unit can include a heating arrangement to increase the temperature of one or more components in the control unit and / or measuring unit in cold environments.
Owner:ELKINS EARTHWORKS
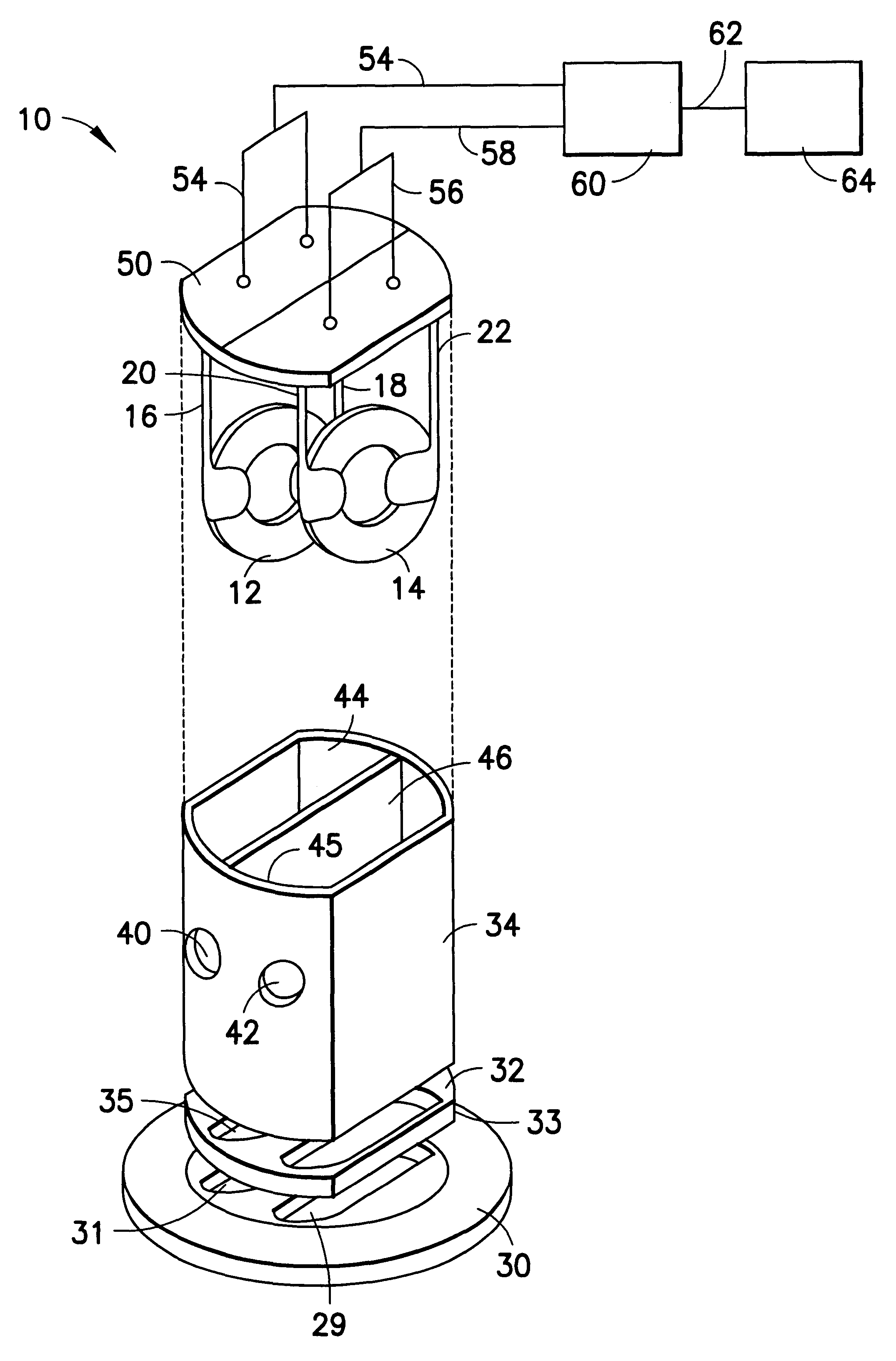
Gas monitoring system and sidestream gas measurement system adapted to communicate with a mainstream gas measurement system
InactiveUS6954702B2Overcomes shortcomingChemical analysis using combustionRespiratory organ evaluationProduct gasProcess engineering
A method and apparatus for interfacing a plurality of gas measurement systems, including a mainstream and a sidestream gas measurement system, to a host system via an interface unit. The present invention also pertains to a sidestream gas measurement system that output signals emulating the signals output by a mainstream gas measurement system or portion thereof, so that the sidestream gas measurement system can seamlessly communicate with a host system configured to communicate only a mainstream gas measurement system or a portion thereof.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Apparatus and method for wireless gas monitoring
InactiveUS20040056771A1Fire alarm smoke/gas actuationMaterial analysisSatellite technologyTransceiver
The current invention discloses a wireless monitoring system. The system has one or more monitoring devices. Each device can transmit data and receive messages from an output center or alarm system. The output center can also transmit and receive messages. Both the output center and each device preferably have a transceiver that enables both the transmission and receipt of messages. No remote terminal units or hardwiring is required for the system to function. The system is truly a wireless gas monitoring system. The system may use low earth orbit satellite technology, or licensed radio frequencies or any other means to wirelessly transmit and receive messages.
Owner:GASTRONICS
Portable gas monitor
ActiveUS20080127726A1Easy to identifyEasily obtain informationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSolid waste disposalControl unitElectrical and Electronics engineering
A portable monitor used to measure landfill gas and landfill well parameters. The portable monitor includes a control unit and a measuring unit that can communication wirelessly with one another. The control unit and / or measuring unit can includes a heating arrangement to increase the temperature of one or more components in the control unit and / or measuring unit in cold environments.
Owner:ELKINS EARTHWORKS
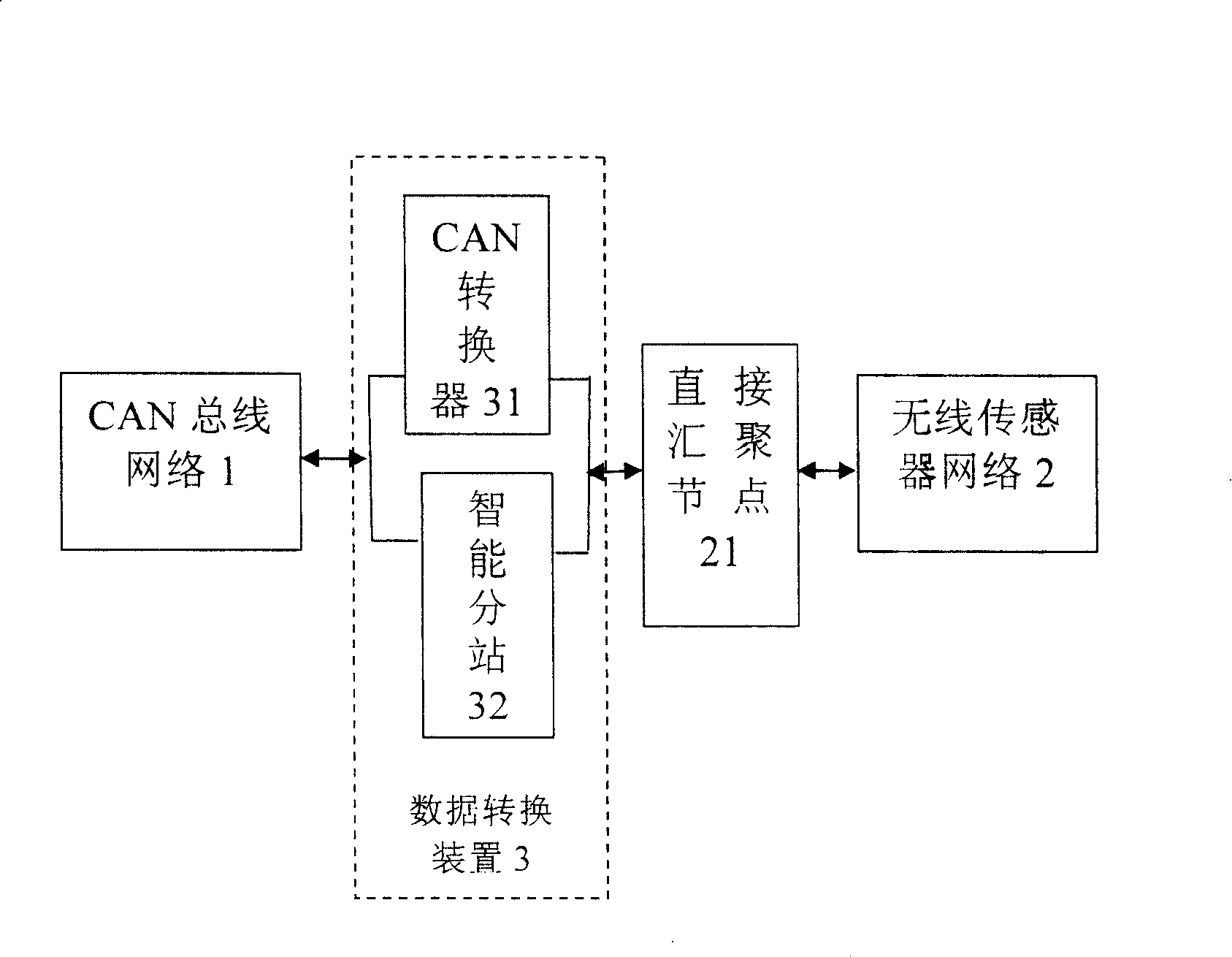
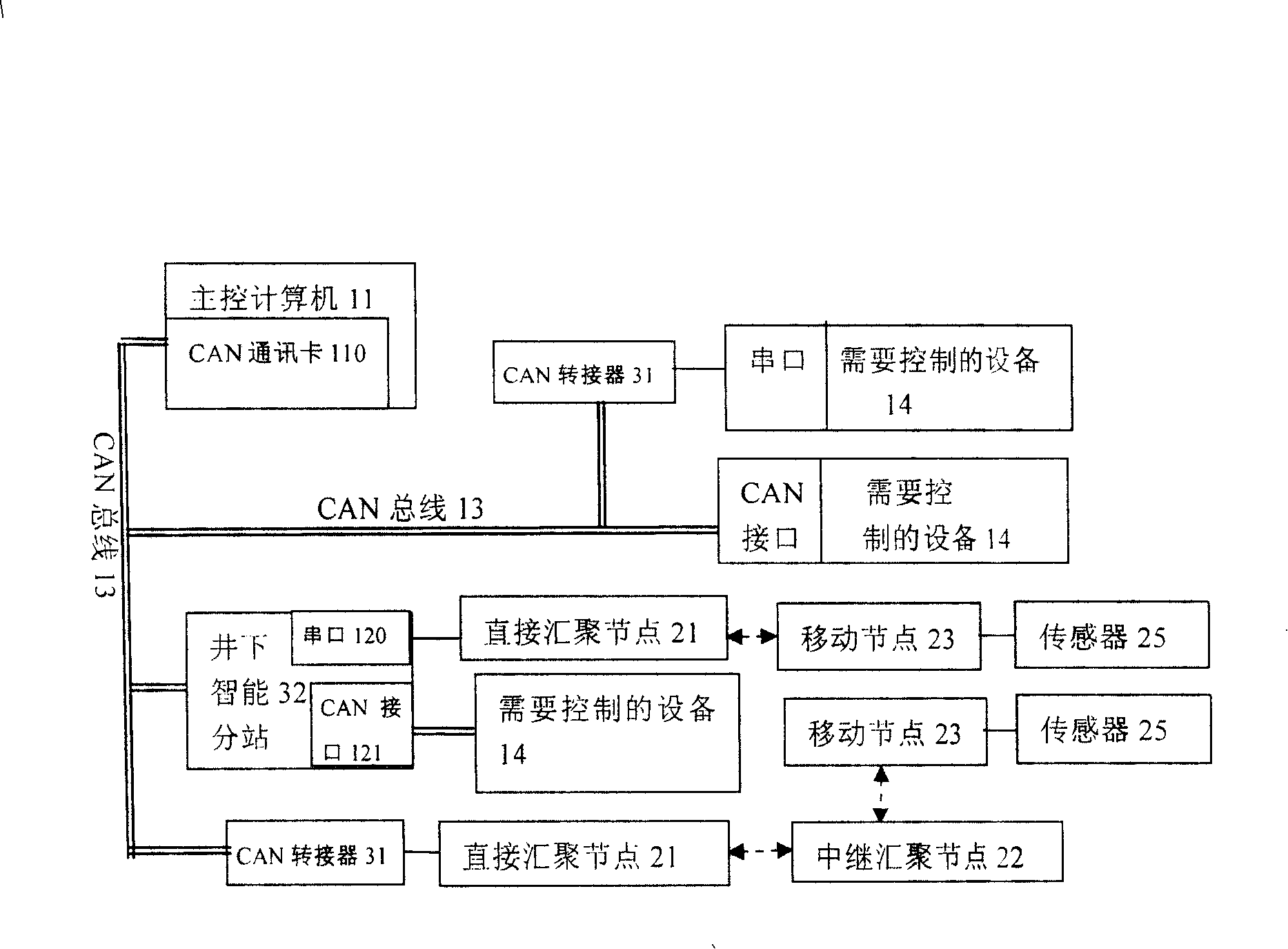
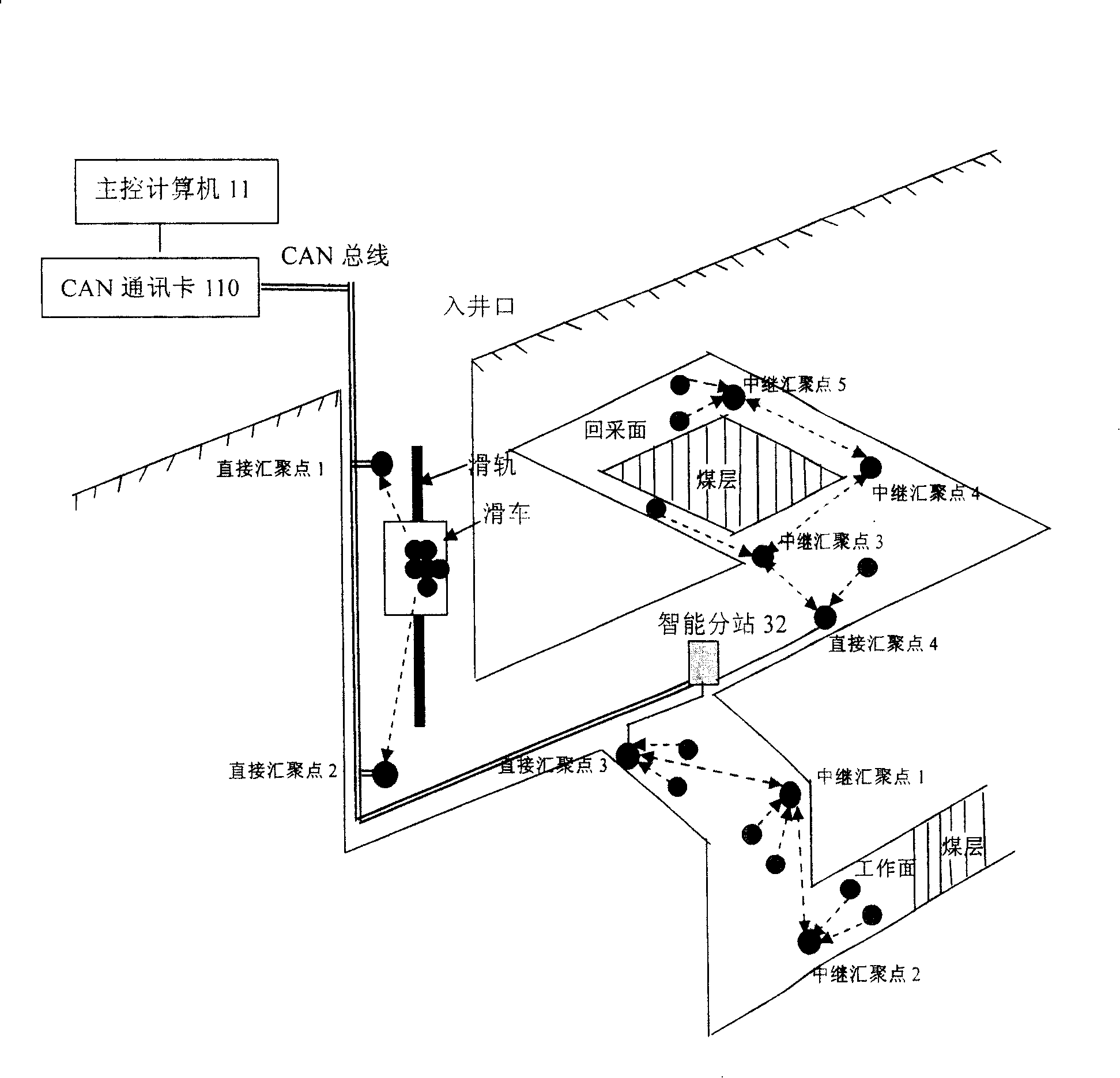
Coal mine down-hole personnel positioning and mash gas concentration dynamic monitoring method and system
InactiveCN101240717AReduce usageReduce investmentMining devicesTransmission systemsNetwork connectionDynamic monitoring
The present invention discloses methods and system for coal mine downhole personnel locating and mash gas concentration dynamic monitoring, the system includes: CAN bus network, wireless sensor network and data conversion device. CAN network connects with wireless transducing network connections by data switching device, and by using wireless sensor network self-organizing, multi- skip, data acquisition and processing, and wireless communicating characteristic, the invention designs a system about out-in well personnel work attendance and moving vehicle zone location in coal mine well, and a system for monitoring gas dynamic concentration. The system and method overcome the current deficiency of operating gas monitoring system and personnel position location system respectively, not only personnel zone location and dynamic gas testing is realized, but also allocation is obtained about personnel arrangement and moving mechanical equipment before the accident, this provides reliable data for rescuing miner and avoiding second disaster.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
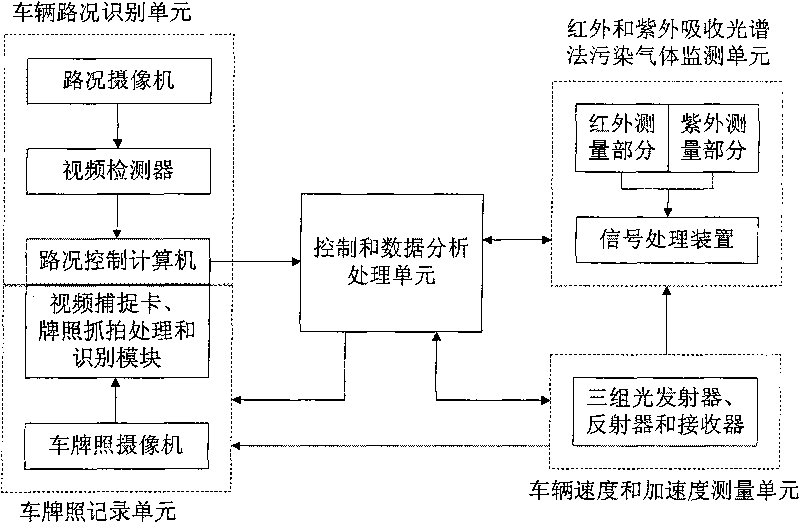
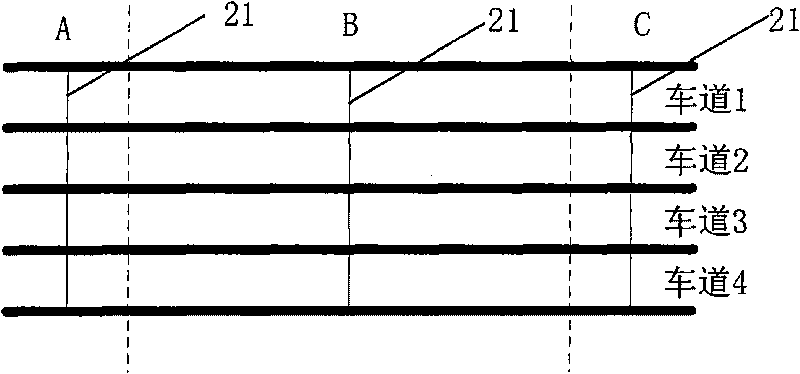
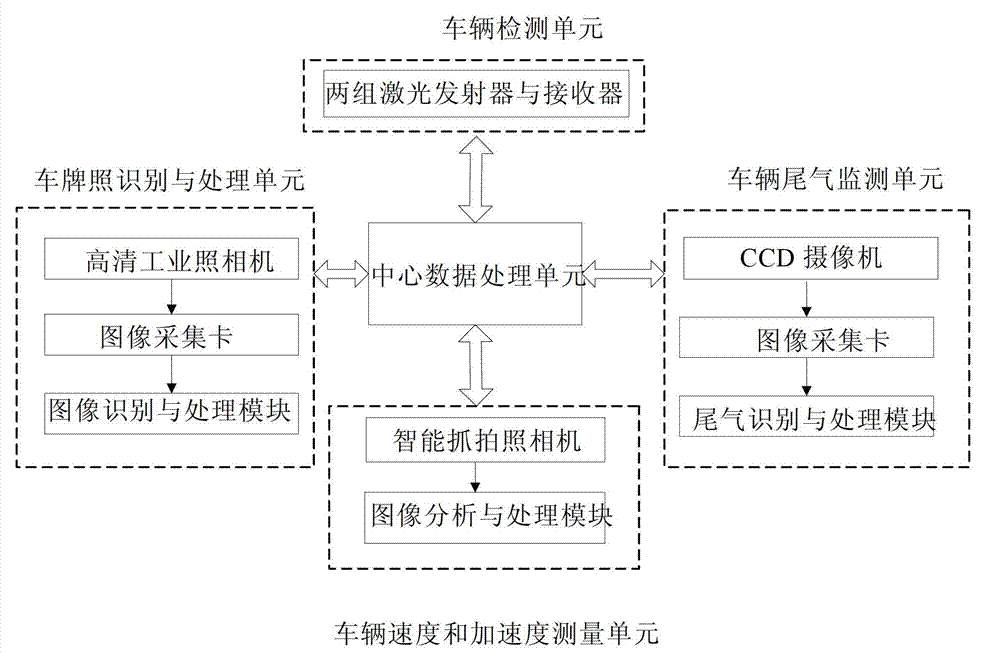
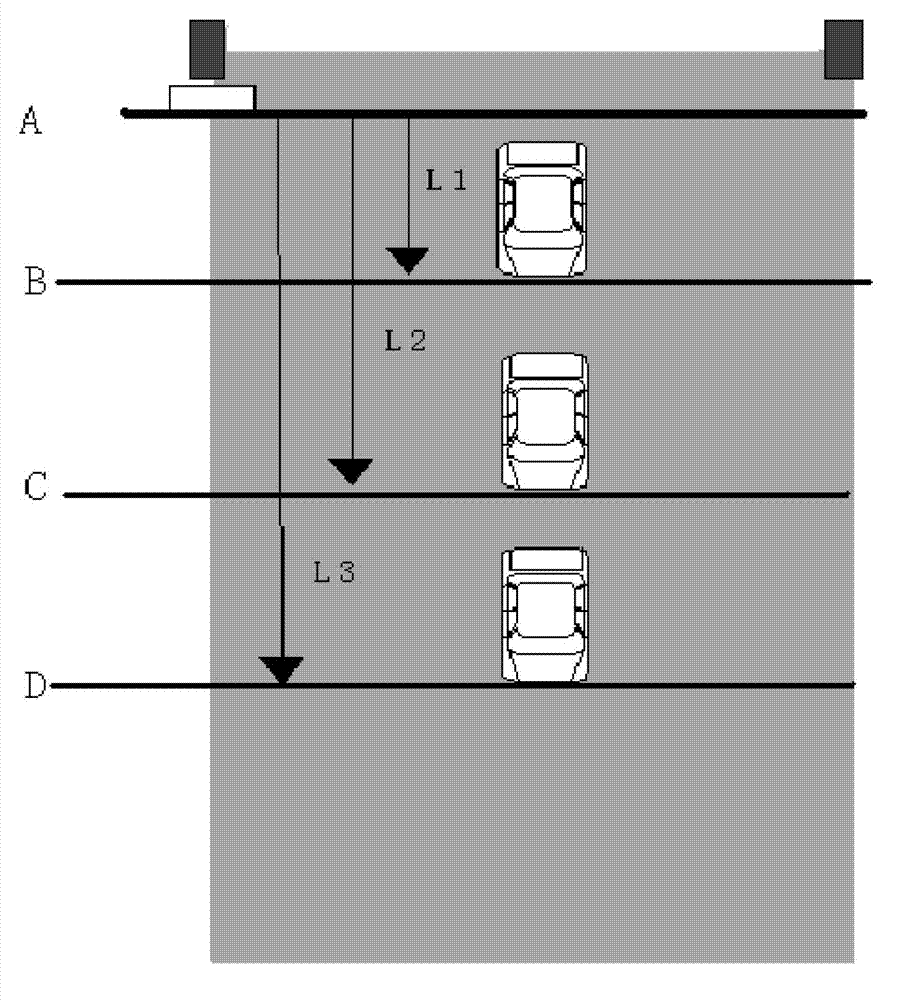
Multilane motor vehicle exhaust remote measuring device
ActiveCN101726466AGet real-time statusAccurately obtain the concentrationTelevision system detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlTime conditionEngineering
A multilane motor vehicle exhaust remote measuring device comprises a vehicle road condition recognizing unit, a license plate recording unit, a vehicle velocity and acceleration measuring unit, a polluted gas monitoring unit by using infrared and ultraviolet absorption spectrometry and a control and data analysis / processing unit. The device can obtain the real-time condition of vehicle driving on one-way or two-way multilane pavement, accurately obtain various exhaust concentrations, velocity, acceleration and license plate number when only one vehicle drives on multiple lanes in a short time and complete preliminary exhaust analysis and license plate obtainment when a plurality of vehicles drive on multiple lanes simultaneously.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
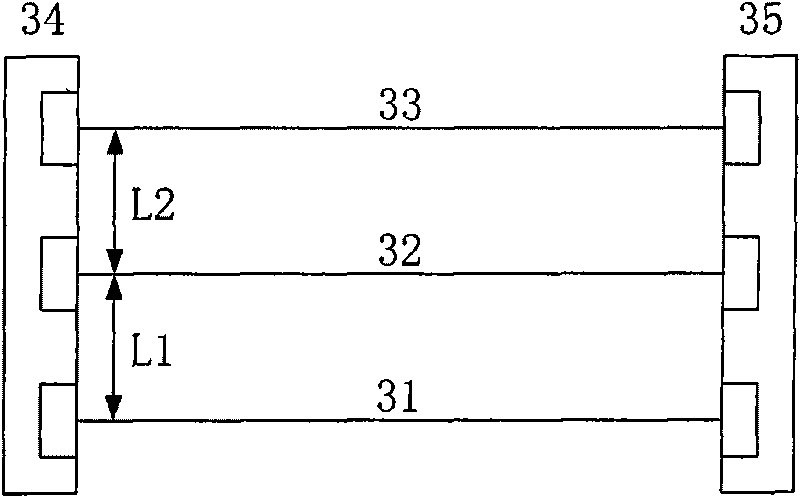
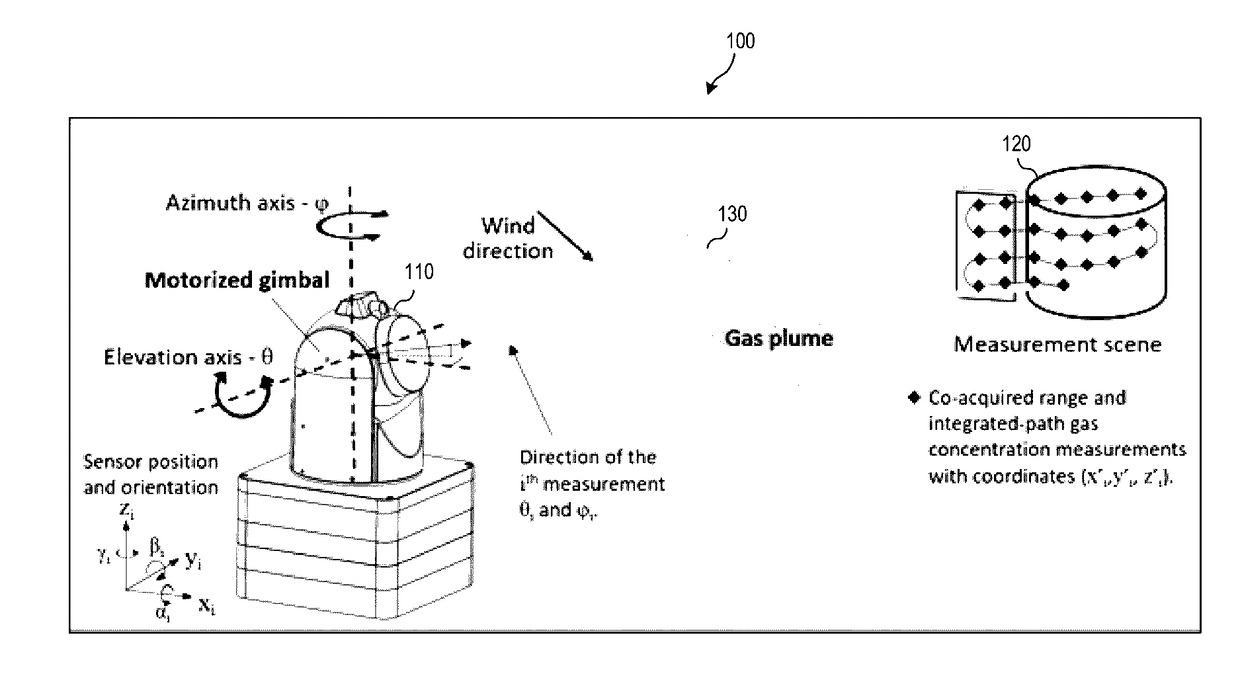
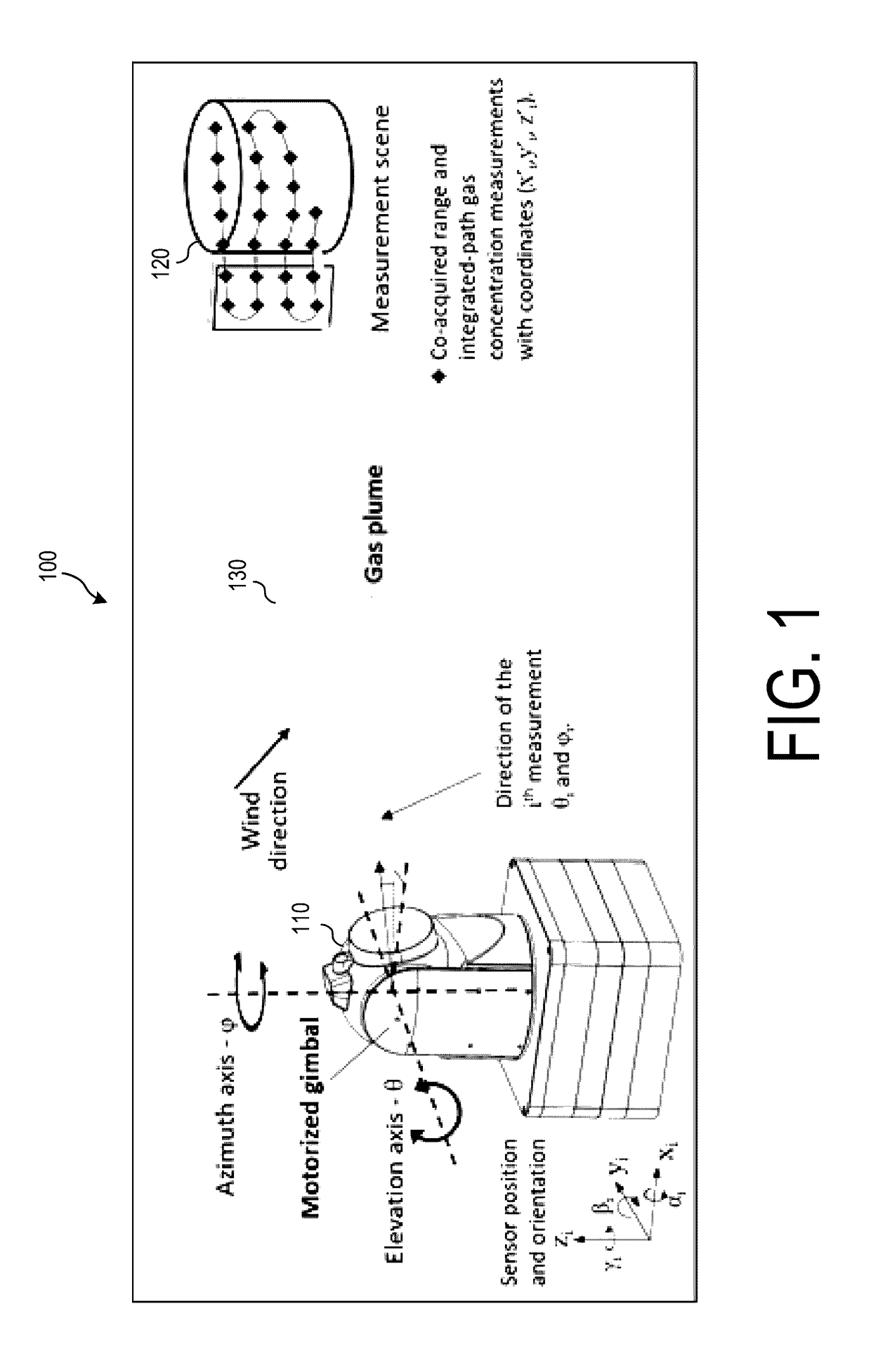
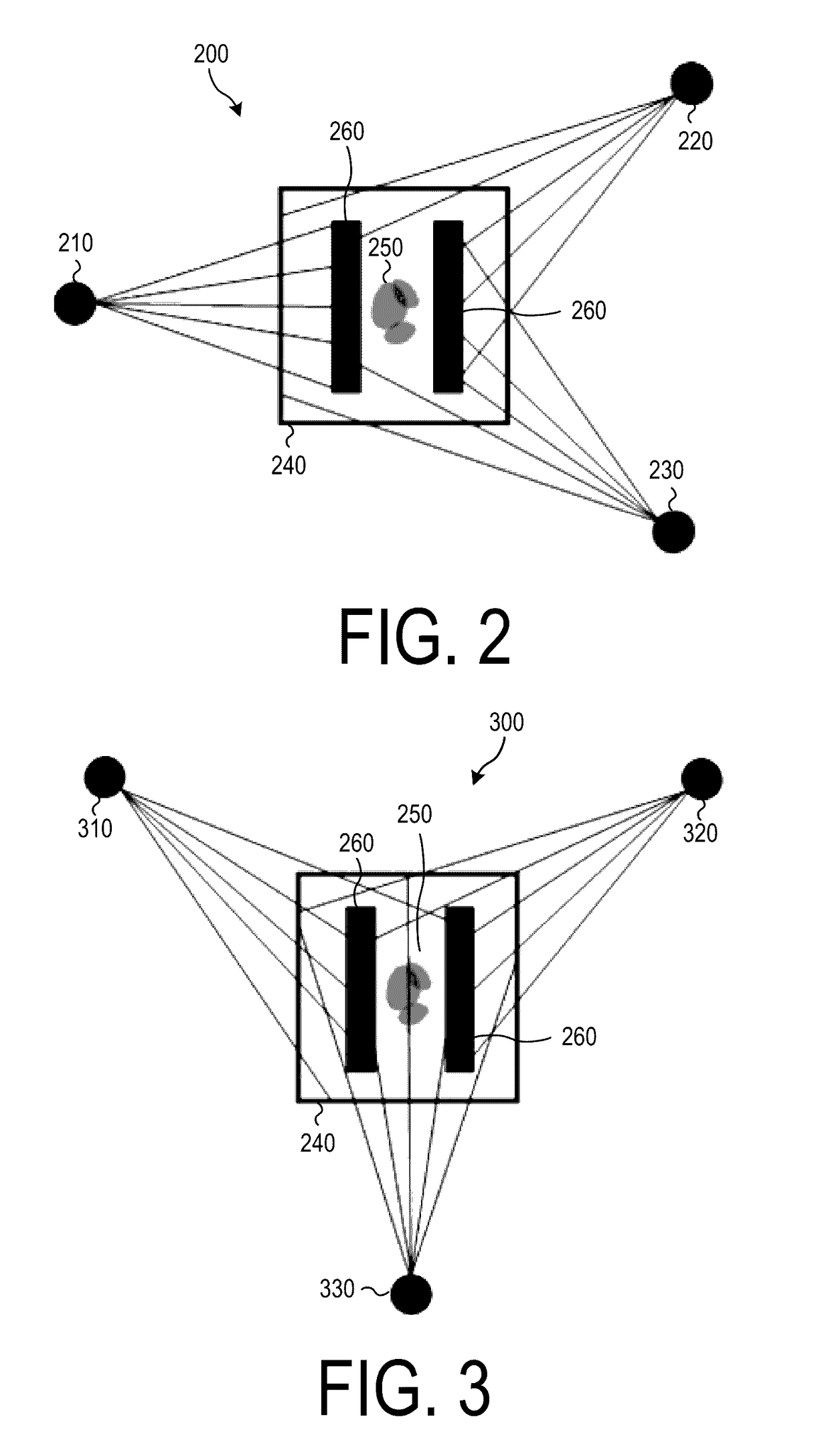
Gas-mapping 3D imager measurement techniques and method of data processing
ActiveUS20170097274A1Shorten the timeReduced measurement timeMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateScattering properties measurementsConfidence metricEngineering
Measurement approaches and data analysis methods are disclosed for combining 3D topographic data with spatially-registered gas concentration data to increase the efficiency of gas monitoring and leak detection tasks. Here, the metric for efficiency is defined as reducing the measurement time required to achieve the detection, or non-detection, of a gas leak with a desired confidence level. Methods are presented for localizing and quantifying detected gas leaks. Particular attention is paid to the combination of 3D spatial data with path-integrated gas concentration measurements acquired using remote gas sensing technologies, as this data can be used to determine the path-averaged gas concentration between the sensor and points in the measurement scene. Path-averaged gas concentration data is useful for finding and quantifying localized regions of elevated (or anomalous) gas concentration making it ideal for a variety of applications including: oil and gas pipeline monitoring, facility leak and emissions monitoring, and environmental monitoring.
Owner:BRIDGER PHOTONICS
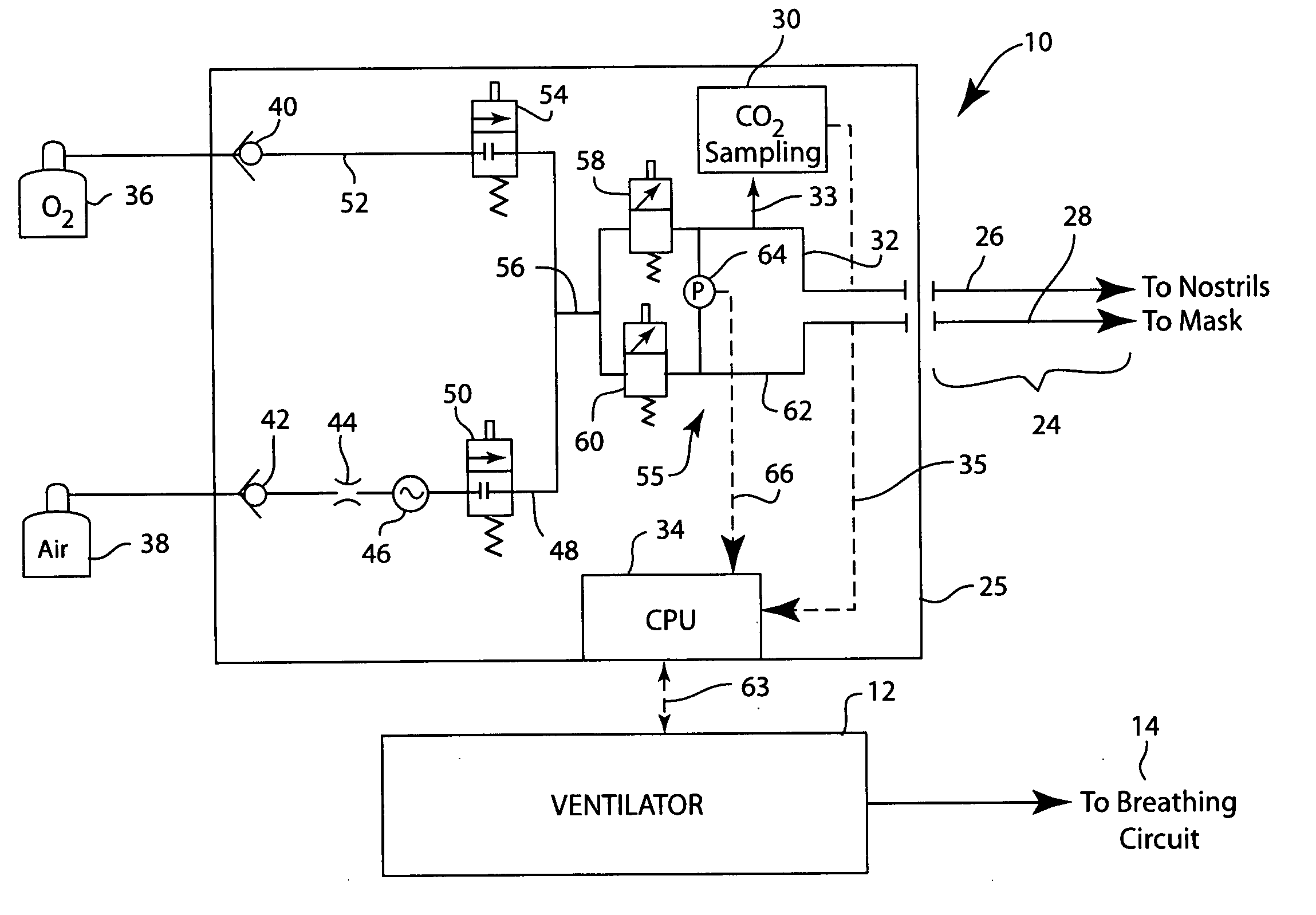
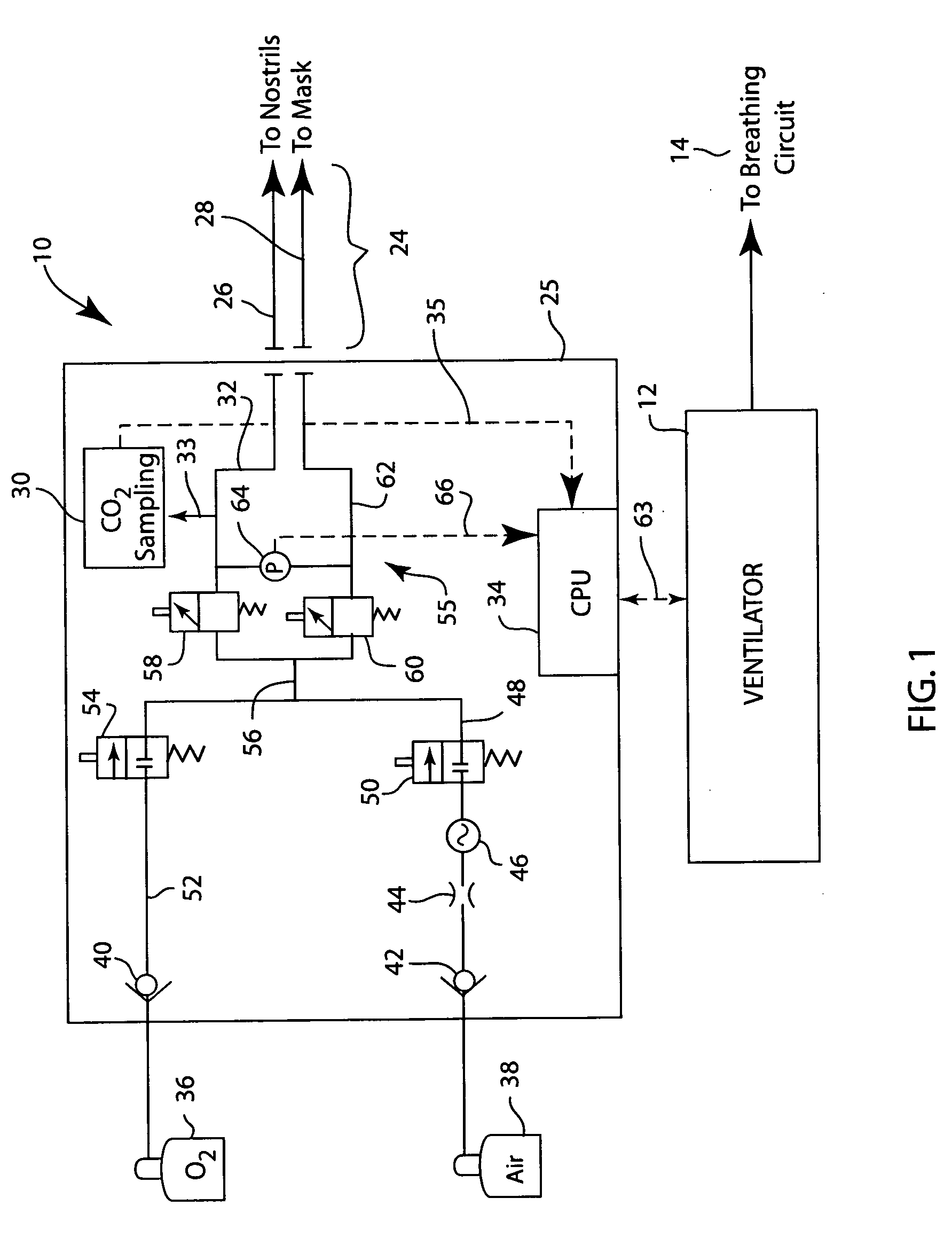
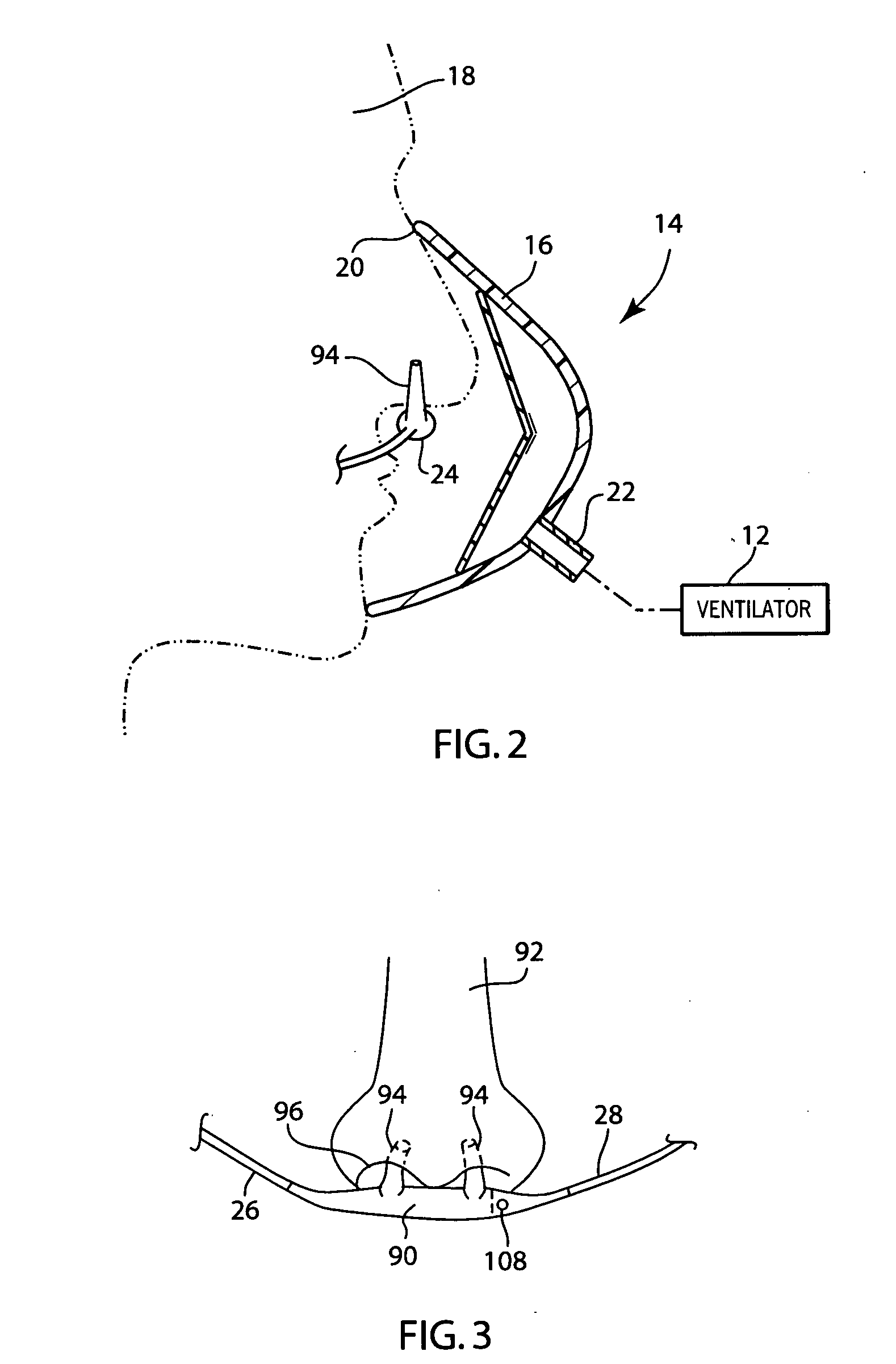
Integrated ventilator nasal trigger and gas monitoring system
ActiveUS20070144518A1Efficient combinationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksNostrilDifferential pressure
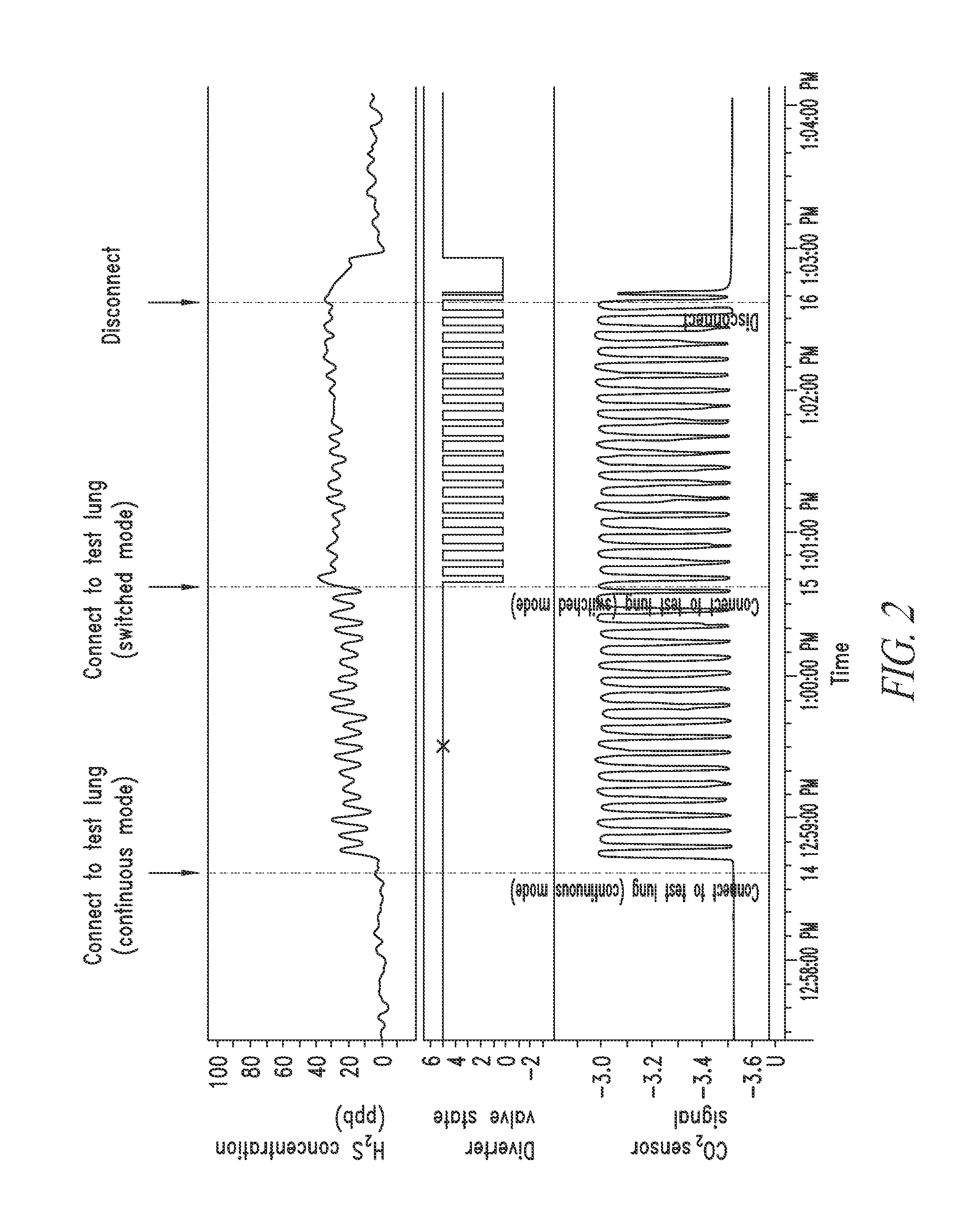
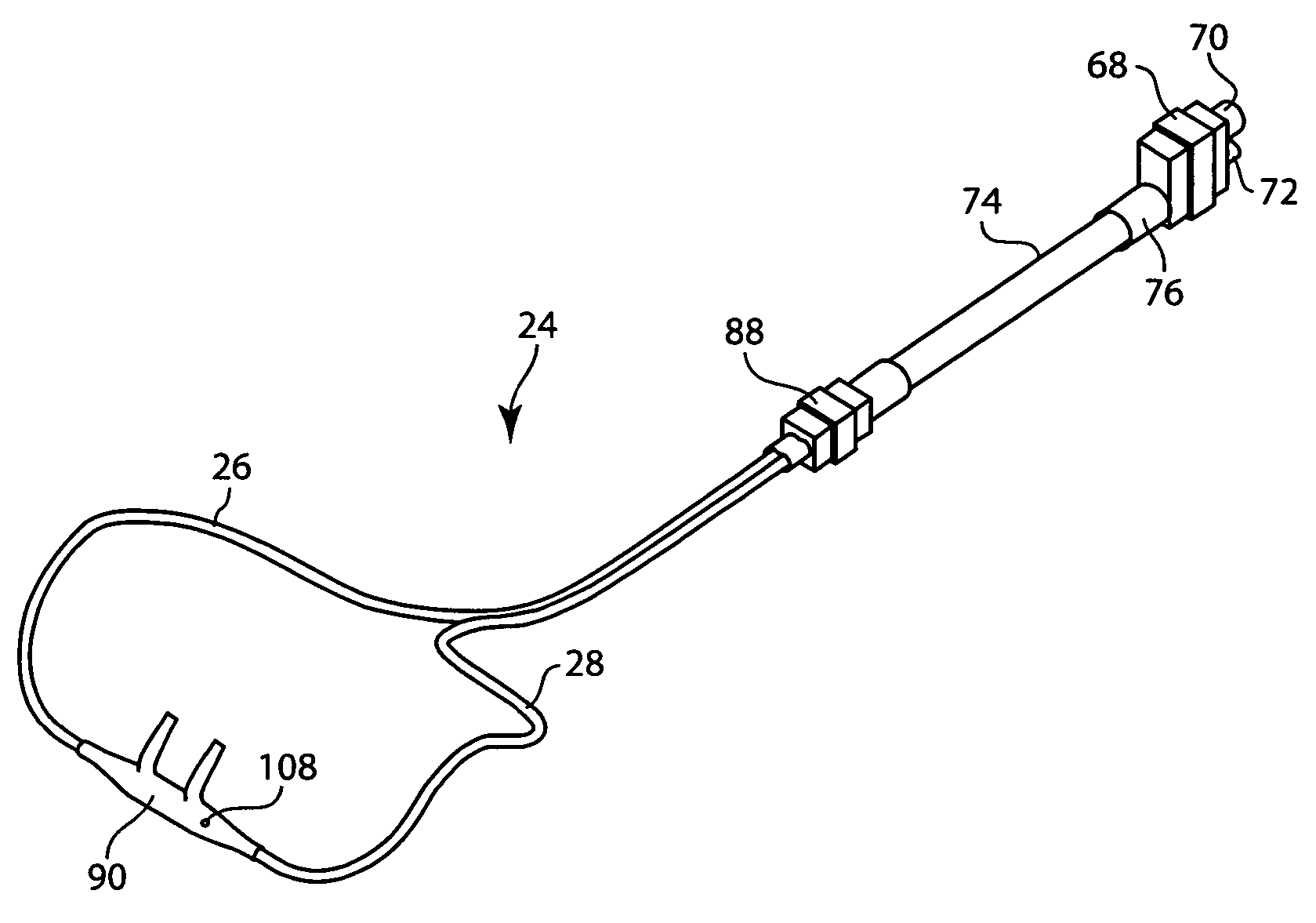
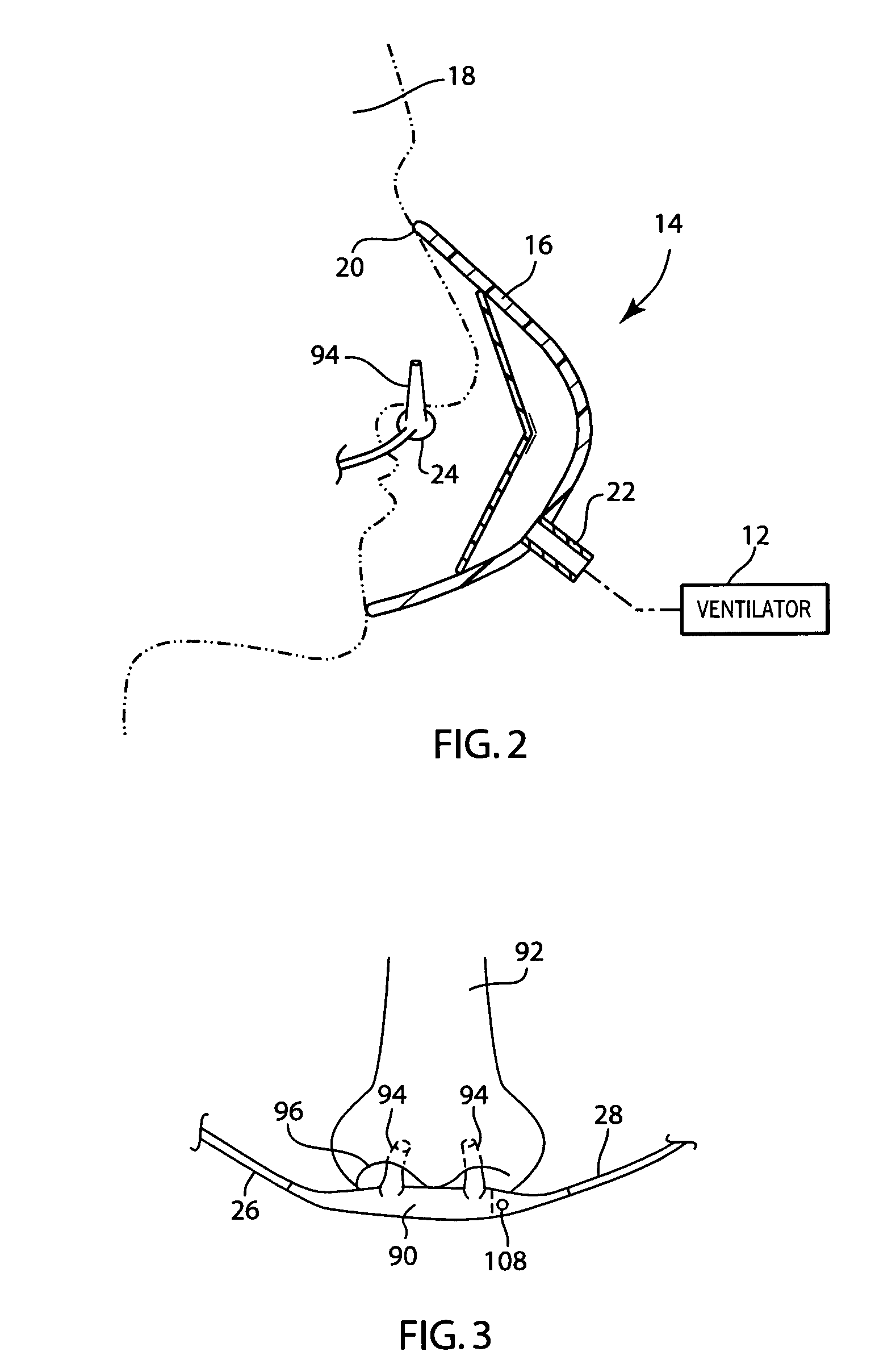
An arrangement and method for detecting spontaneous respiratory effort of a patient receiving ventilatory support by a breathing circuit. The nasal cannula control system includes a nasal cannula assembly having two distinct lumens. A different pressure sensor is positioned to detect the pressure difference between each of the two lumens, thereby determining the differential pressure from within the patient's nostrils and within a breathing mask. The nasal cannula control system includes a gas sampling system such that the amount of a monitored gas discharged or exhaled by the patient can be monitored using the same nasal cannula assembly used to generate the differential pressure signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
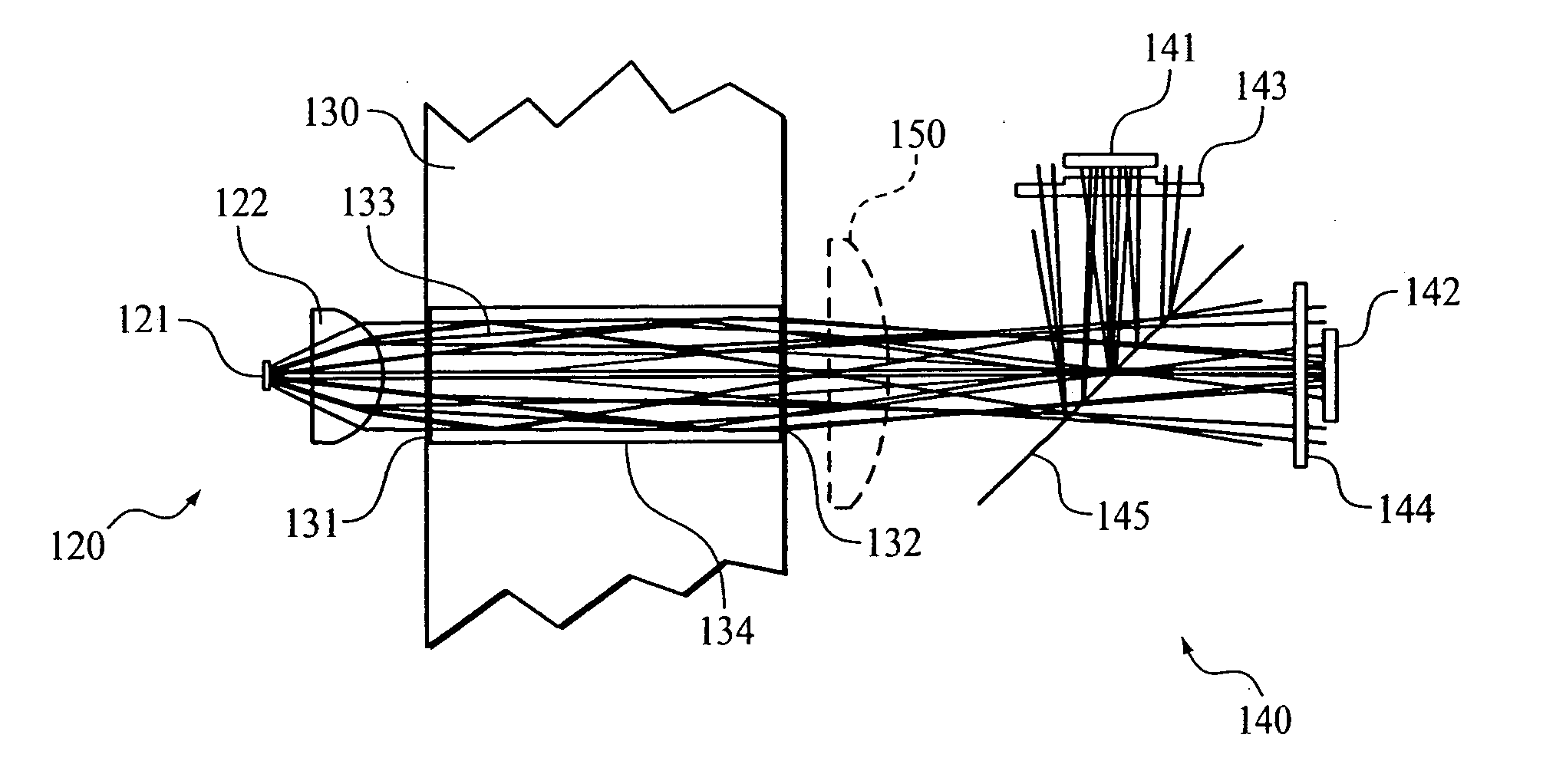
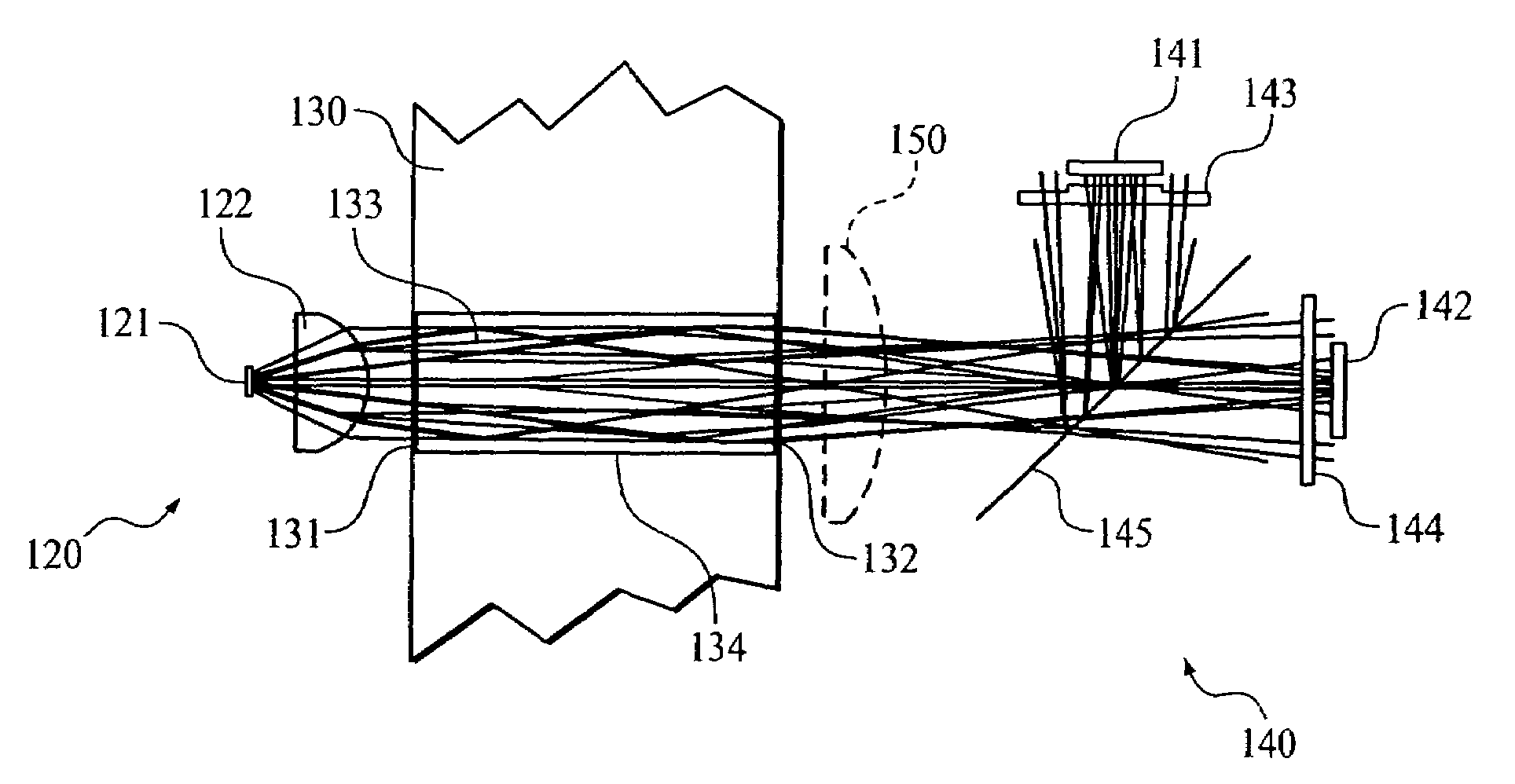
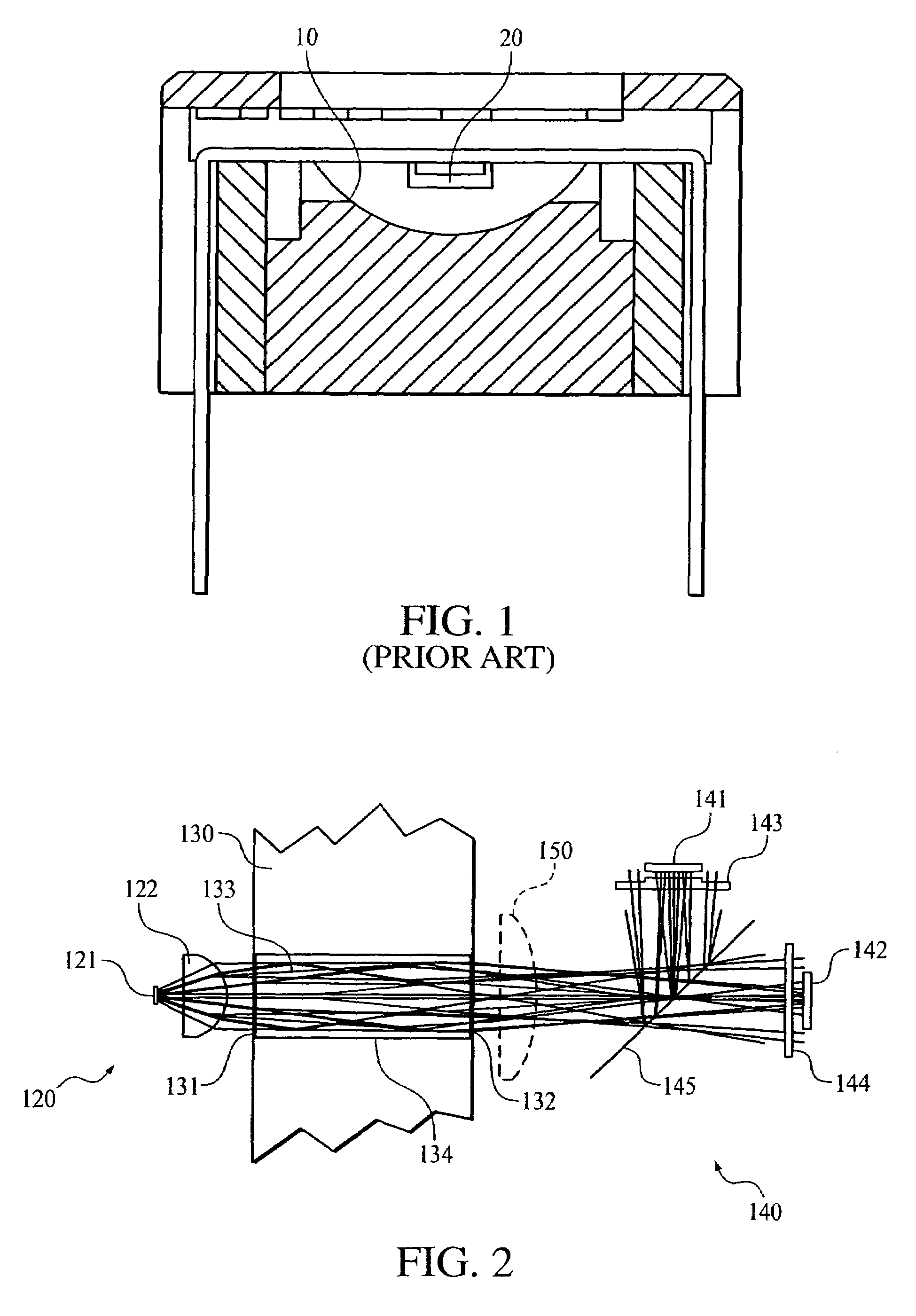
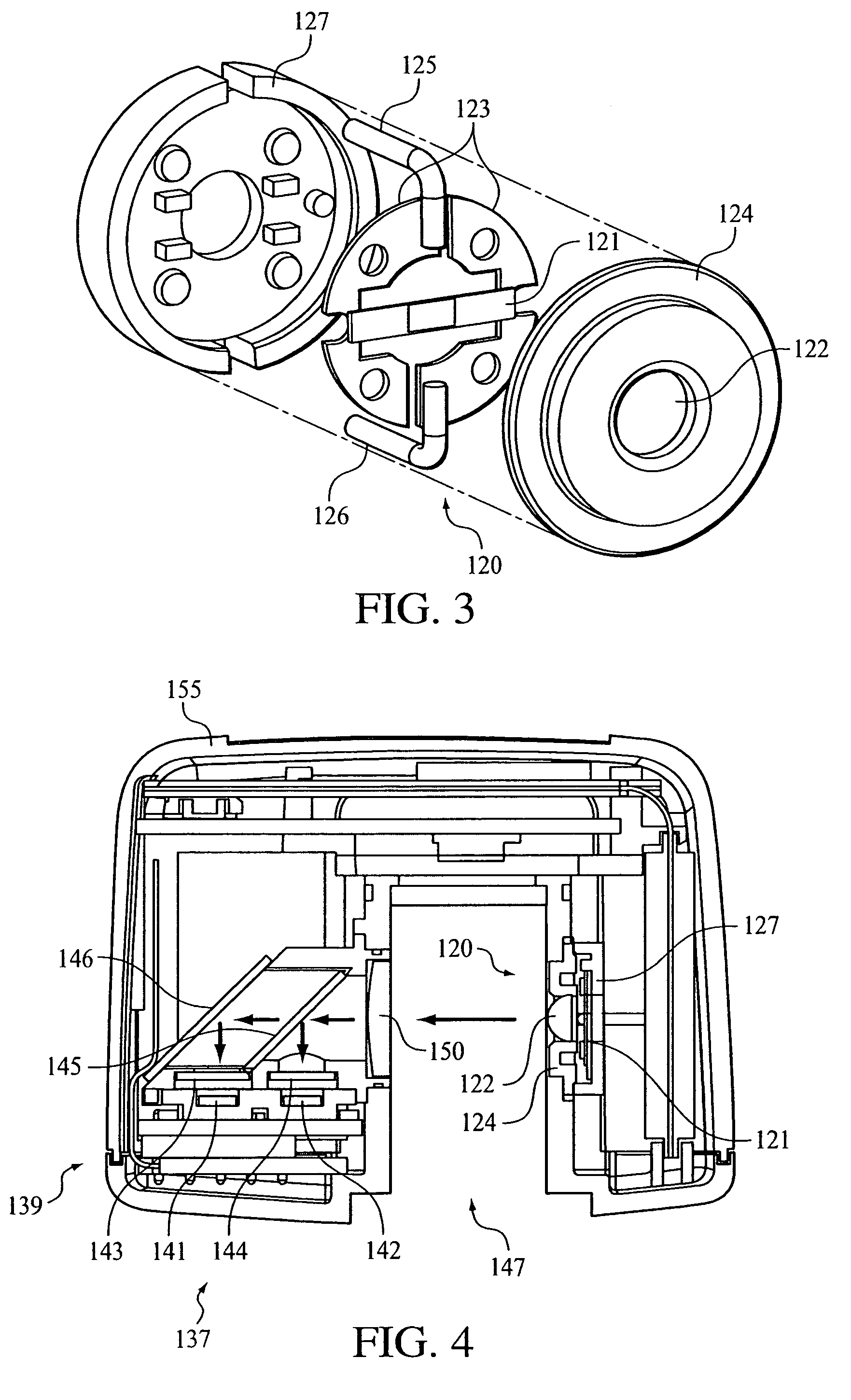
Optical system for a gas measurement system
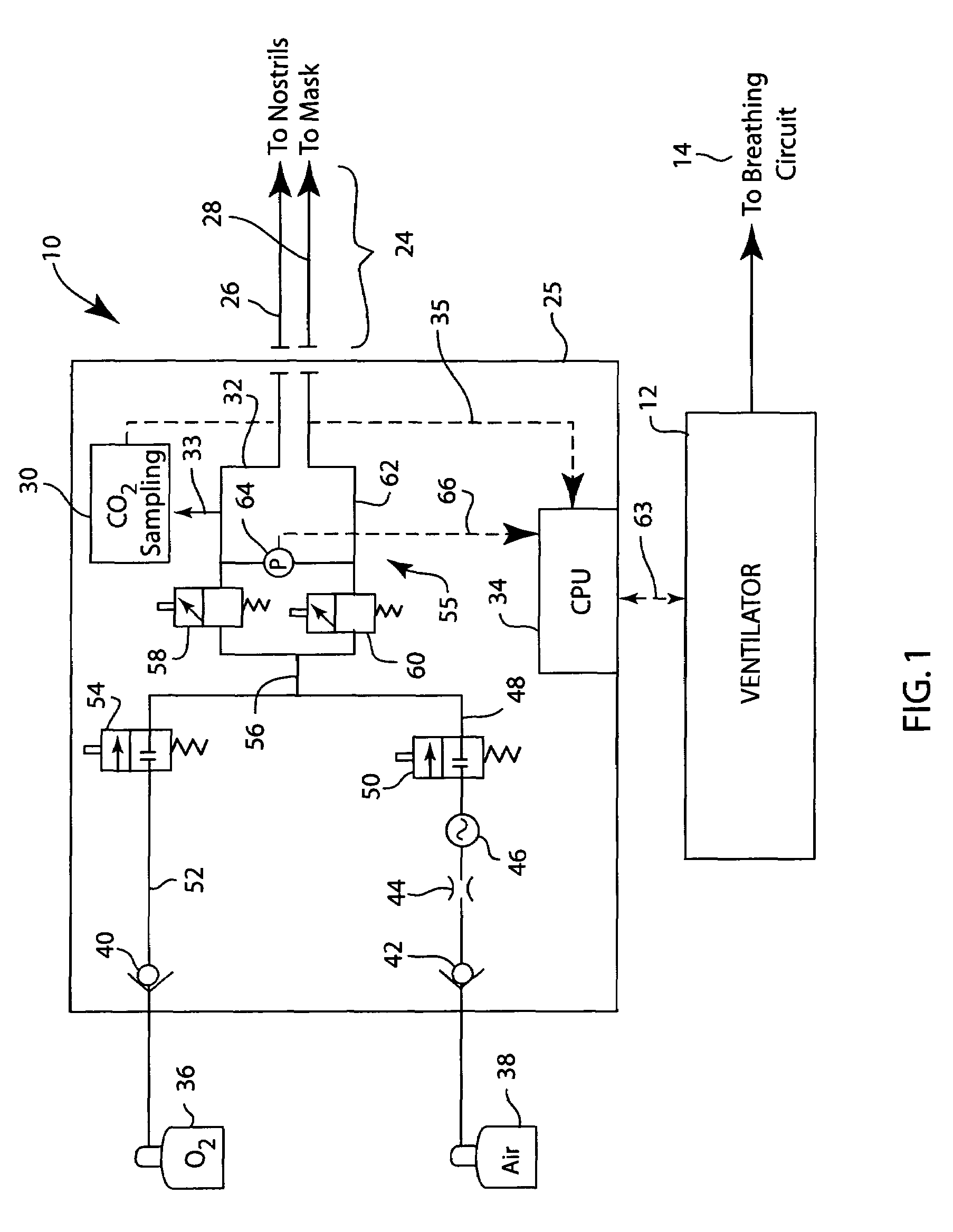
An improved optical configuration for use in a gas monitoring system. The optical system uses a high numerical aperture lens that maximizes capture of relatively large angle rays, thereby increasing the measured signal at the infrared radiation detector. In one embodiment of the present invention, a half-ball-type lens is provided proximal to the infrared radiation source in the gas measurement system. To further increase the measured signal at the infrared radiation detector and allow more efficient capture of the larger angle rays, materials that are reflective in the infrared band of interest are used, so that the walls of the sample cell act as a hollow light pipe.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
End-tidal gas monitoring apparatus
InactiveUS20150032019A1Increased blood levelsIncreasing therapeutic doseRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsBreathing gasNon invasive
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Integrated ventilator nasal trigger and gas monitoring system
ActiveUS7305988B2Efficient combinationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksNostrilDifferential pressure
An arrangement and method for detecting spontaneous respiratory effort of a patient receiving ventilatory support by a breathing circuit. The nasal cannula control system includes a nasal cannula assembly having two distinct lumens. A different pressure sensor is positioned to detect the pressure difference between each of the two lumens, thereby determining the differential pressure from within the patient's nostrils and within a breathing mask. The nasal cannula control system includes a gas sampling system such that the amount of a monitored gas discharged or exhaled by the patient can be monitored using the same nasal cannula assembly used to generate the differential pressure signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical system for a gas measurement system
ActiveUS7183552B2Enhanced signalIncrease the number ofDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLight pipeHigh numerical aperture
An improved optical configuration for use in a gas monitoring system. The optical system uses a high numerical aperture lens that maximizes capture of relatively large angle rays, thereby increasing the measured signal at the infrared radiation detector. In one embodiment of the present invention, a half-ball-type lens is provided proximal to the infrared radiation source in the gas measurement system. To further increase the measured signal at the infrared radiation detector and allow more efficient capture of the larger angle rays, materials that are reflective in the infrared band of interest are used, so that the walls of the sample cell act as a hollow light pipe.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Thermoelectrically cooled water trap
InactiveUS7000490B1Low detection sensitivityEasy to removeWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationThermoelectric coolingWater vapor
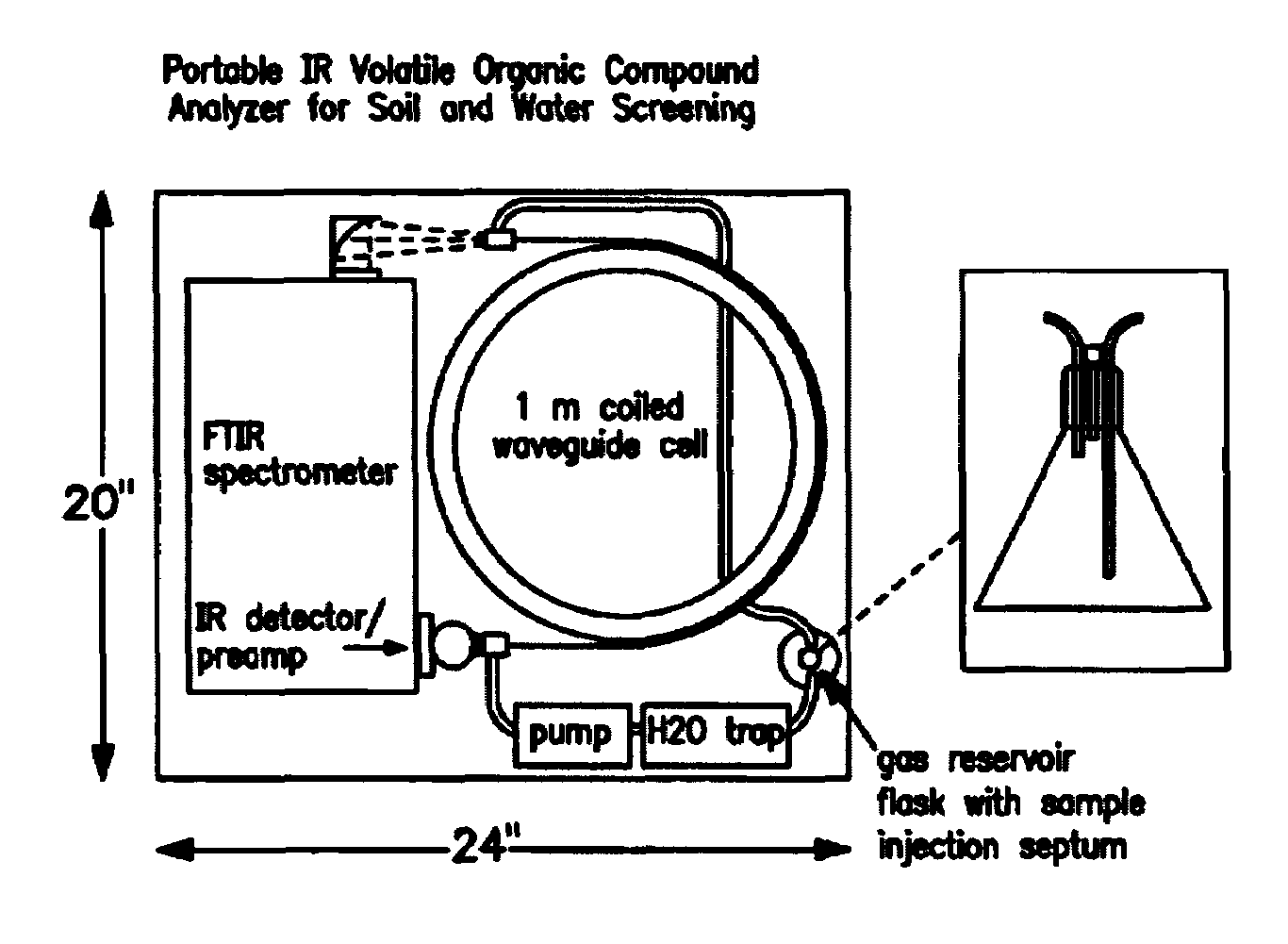
A water trap system based on a thermoelectric cooling device is employed to remove a major fraction of the water from air samples, prior to analysis of these samples for chemical composition, by a variety of analytical techniques where water vapor interferes with the measurement process. These analytical techniques include infrared spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, ion mobility spectrometry and gas chromatography. The thermoelectric system for trapping water present in air samples can substantially improve detection sensitivity in these analytical techniques when it is necessary to measure trace analytes with concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) or ppb (parts per billion) partial pressure range. The thermoelectric trap design is compact and amenable to use in a portable gas monitoring instrumentation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Oxygen monitoring device
InactiveUS6925852B2Minimizing introductionAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOxygen monitoringThermal conduction
A gas monitoring device for monitoring gas levels within a chamber is provided. The gas monitoring device includes a housing having a probe with a sensor disposed on the probe. The probe extends through the housing and into a chamber such that the sensor is within the chamber. The housing includes a first passageway disposed about the probe and second passageway disposed about the first passageway. During operation of the gas monitoring device, a temperature adjusting medium enters the second passageway through an inlet of the housing and then enters into the first passageway via the second passageway. As the temperature adjusting medium travels through the first passageway, the temperature adjusting medium adjusts the temperature of the probe. The temperature adjusting medium adjusts the temperature of the probe through thermal conduction. As the temperature of the probe adjusts, the temperature of the sensor also adjusts through thermal conduction.
Owner:SUSKO KENNETH
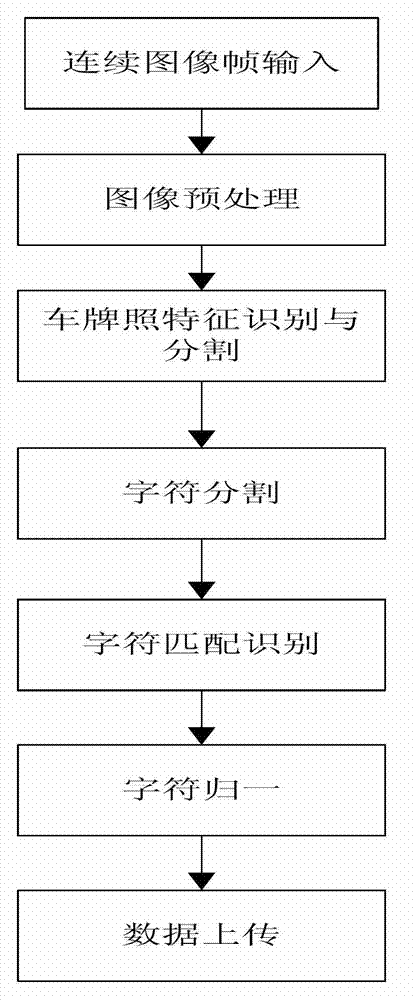
Identification system of smoke intensity image of tail gas of diesel vehicle
The invention relates to an identification system of a smoke intensity image of tail gas of a diesel vehicle. The identification system consists of a vehicle detection unit, a license plate identifying and processing unit, a vehicle velocity and acceleration measuring unit, a vehicle tail gas monitoring unit and a central data processing unit. The identification system provided by the invention can acquire the real-time condition of a vehicle running on the roadway, and accurately acquire tail gas smoke intensity level, velocity, acceleration and license plate number of the vehicle running on the roadway in a short time.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
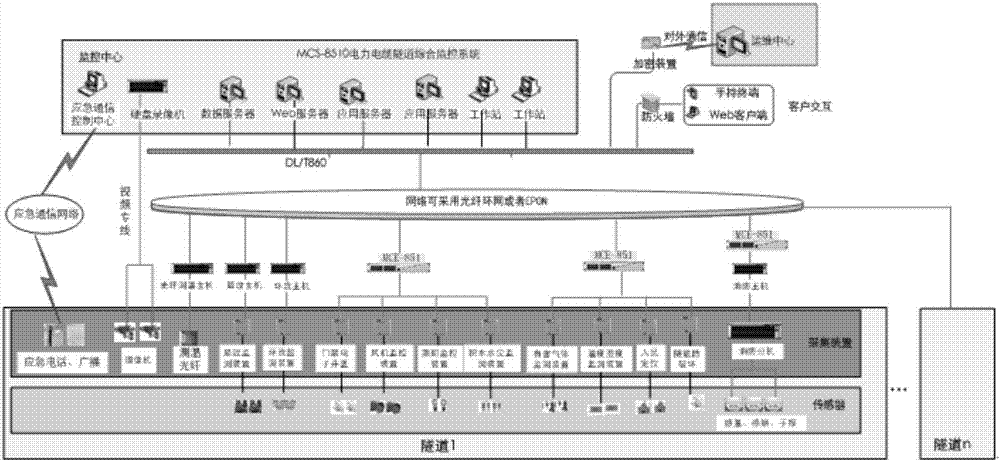
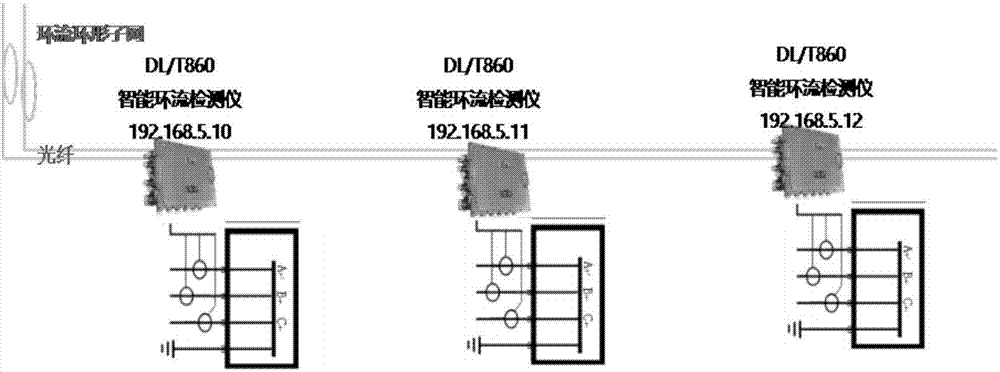
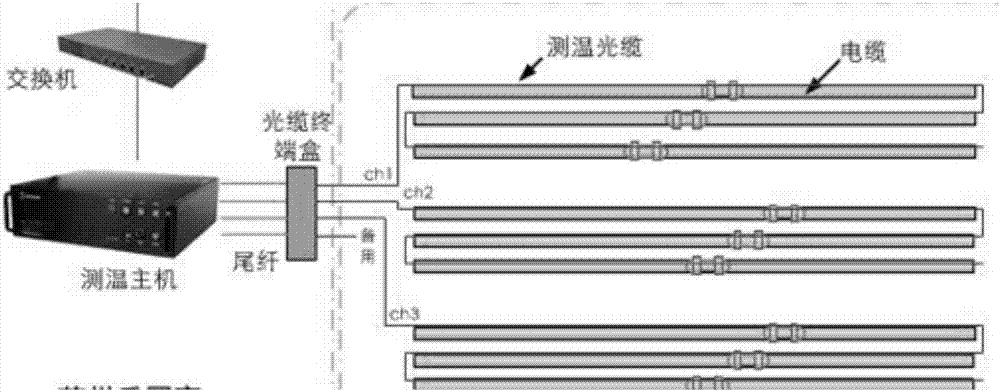
Comprehensive monitoring system and method for power cable tunnel
InactiveCN107991999AFully automatedImprove operation and maintenance levelProgramme total factory controlVideo monitoringTamper resistance
An embodiment of the invention discloses a comprehensive monitoring system and method for a power cable tunnel, wherein the system comprises: a cable body information monitoring mechanism and a tunnelenvironment monitoring auxiliary mechanism, wherein the cable body information monitoring mechanism comprises a ring current monitoring subsystem, a local discharge monitoring subsystem, and a fibertemperature measuring subsystem, wherein the tunnel environment monitoring auxiliary mechanism comprises a video monitoring subsystem, a security subsystem, a firefighting subsystem, a fan / water pump / lighting control subsystem, a toxic harmful gas monitoring subsystem, a personnel positioning subsystem, a robot inspection subsystem, a wireless communication subsystem, and a tunnel tamper-proof monitoring subsystem.
Owner:BEIJING XJ ELECTRIC +1
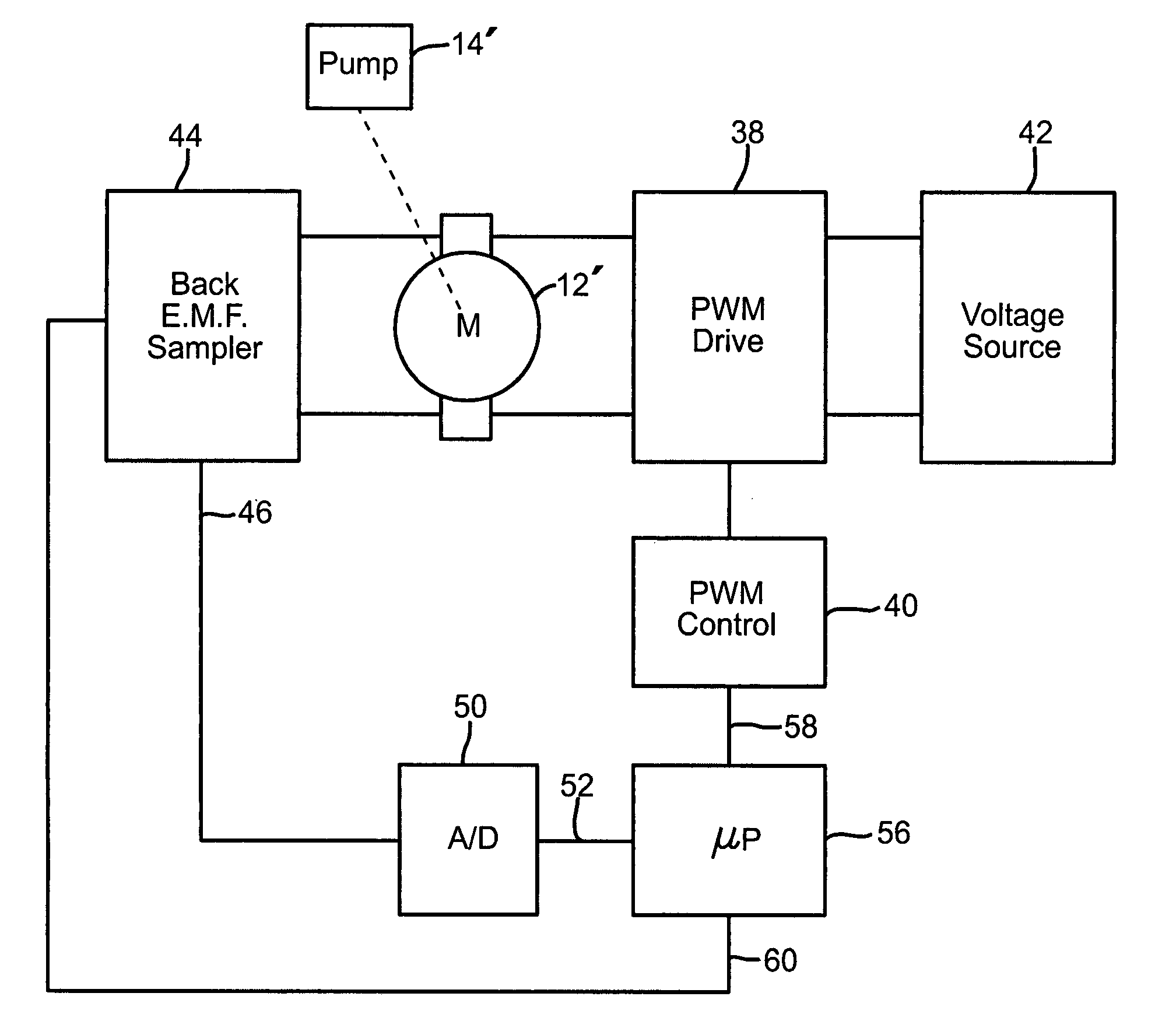
Speed and fluid flow controller
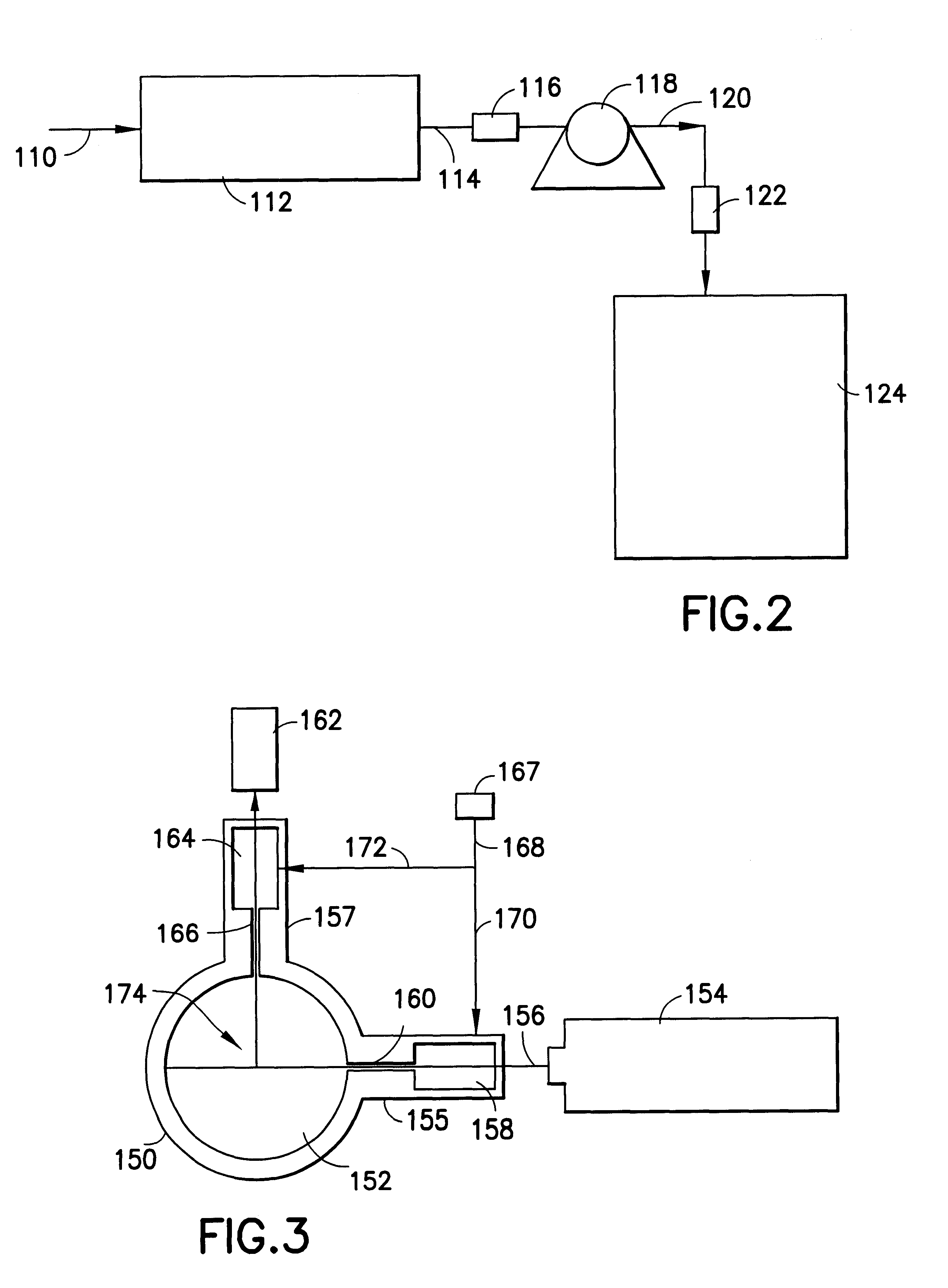
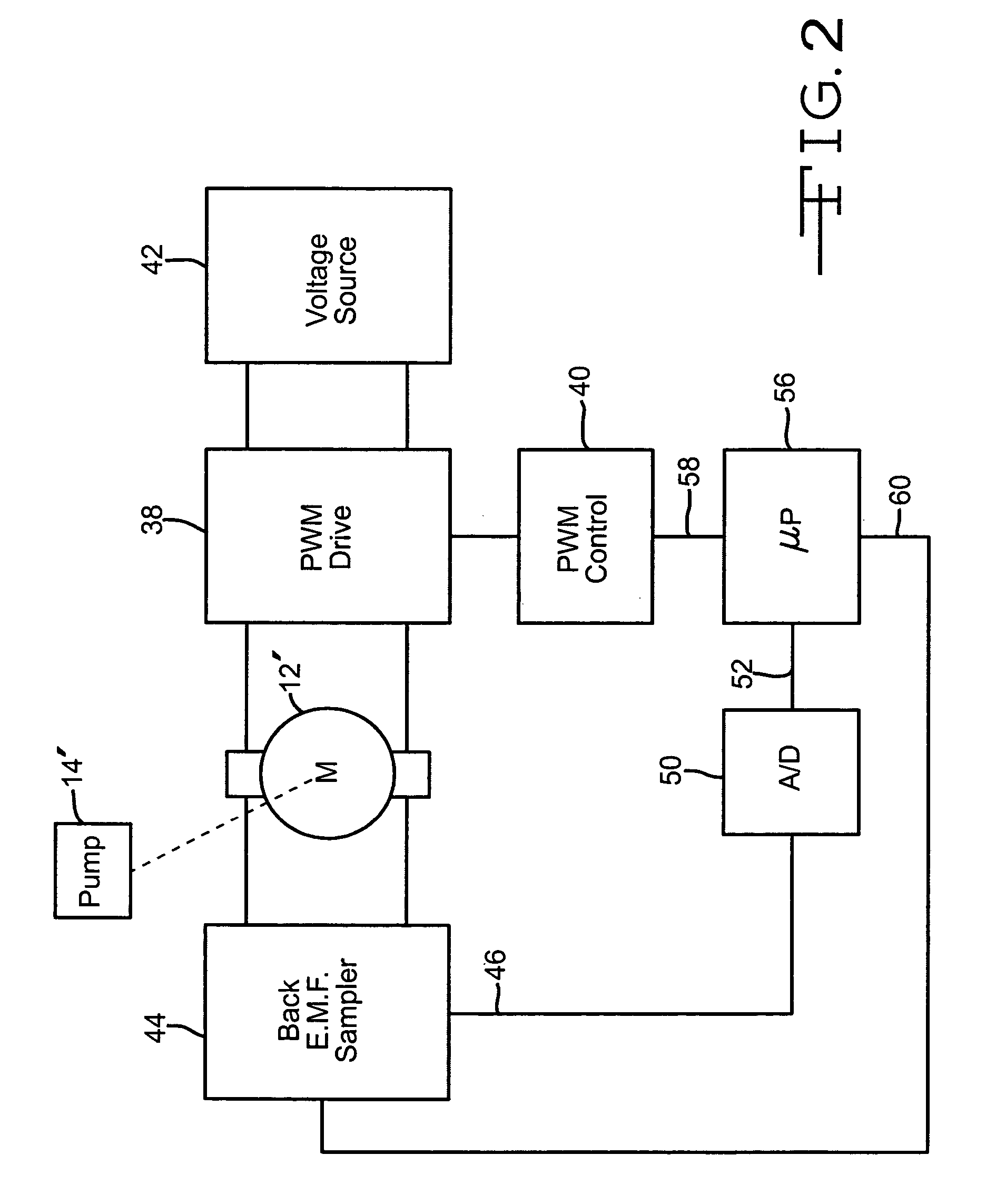
InactiveUS6981402B2Reduced sampling rate requirementsEasy to useFlow controlProgramme controlMotor speedVoltage source
A system and method for measuring fluid flow rate in a system where fluid is pumped, such as a gas monitoring instrument where gas is pumped from a space such as a room or enclosure through a conduit to a sensor. The flow of gas through a pump is determined by measuring motor back-e.m.f. which is proportional to motor speed. In a system where motor speed is regulated by pulse width modulation of the motor drive voltage, the back-e.m.f. is sampled during intervals between the drive pulses applied to the motor, and in a further aspect the sampling is done at selected, spaced-apart or infrequent intervals such as once for every ten or once for every hundred motor drive pulses. Advantageously, in an instrument that uses a microprocessor and analog-to-digital converter to measure gas-concentration, the same microprocessor and converter can provide the PWM control of the pump, in response to the back-e.m.f. generated by the pump motor between the drive pulses. The microprocessor compares the output of the analog-to-digital converter, corresponding to the back-e.m.f., which in turn corresponds to the pump motor speed, to a set-point value, representative of the desired pump motor speed. The processor then adjusts the PWM to control the pump motor to achieve and maintain the desired speed. As a result, in a gas monitor, the gas-flow rate may be maintained close to a desired gas flow rate regardless of the voltage supplied by the battery or other voltage source, regardless of the degree to which the gas is filtered, and under a wide range of operating conditions.
Owner:TELEDYNE DETCON INC
Low-power fast infrared gas sensor, hand held gas leak detector, and gas monitor utilizing absorptive-photo-acoustic detection
InactiveCN101303298ADetection of fluid at leakage pointTransmissivity measurementsInfraredGas detector
Owner:丹尼斯·卡迪纳尔 +1
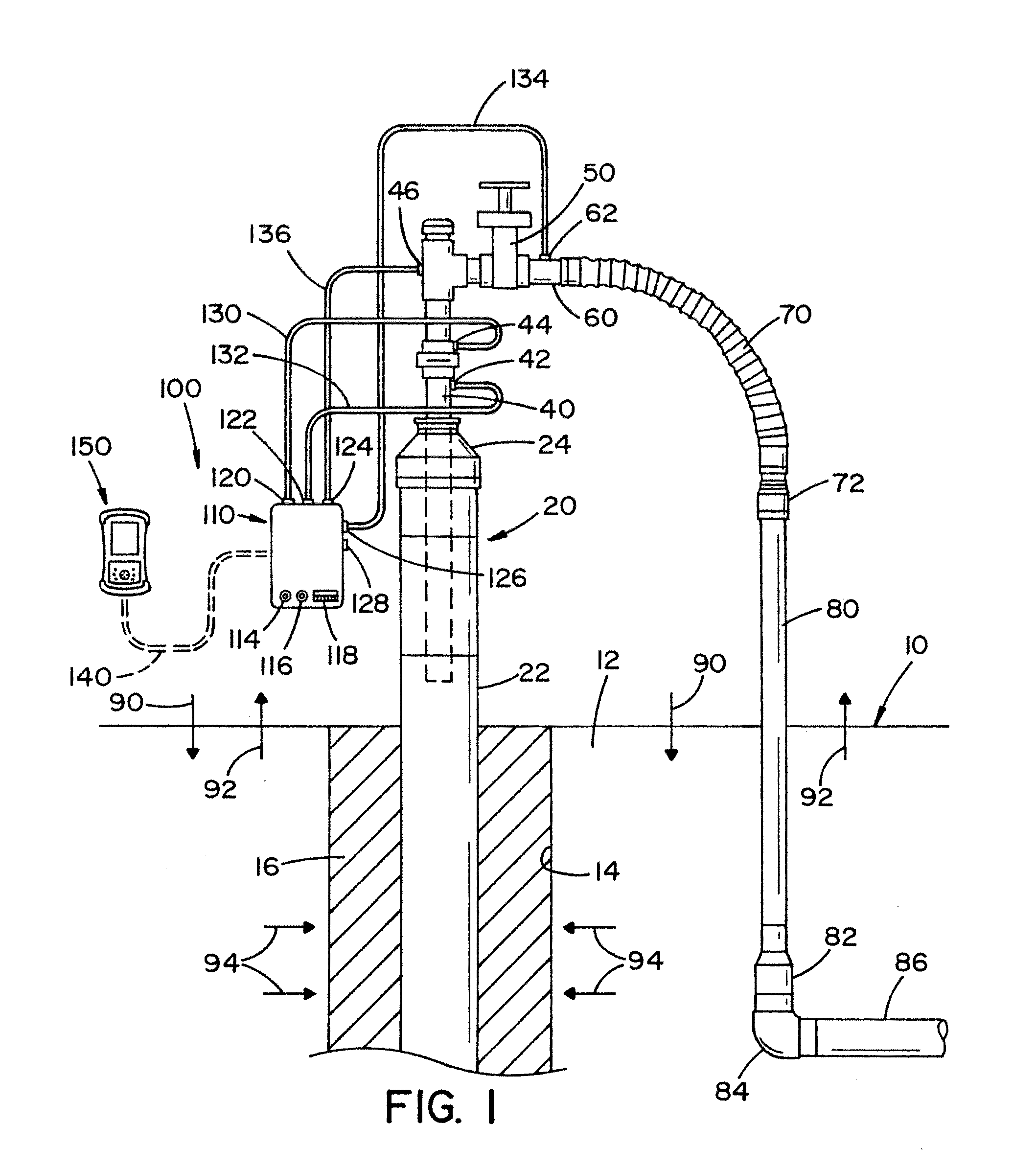
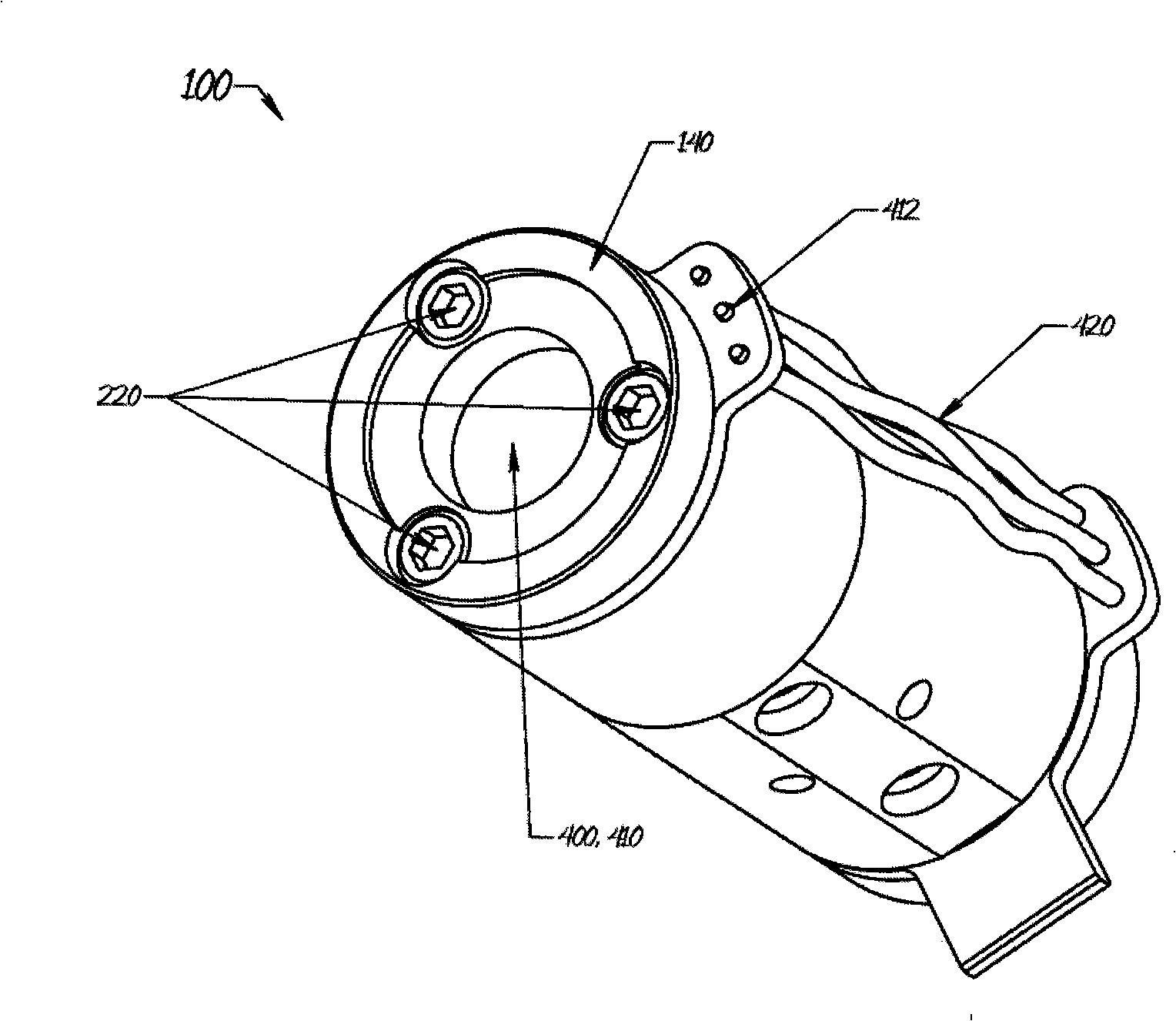
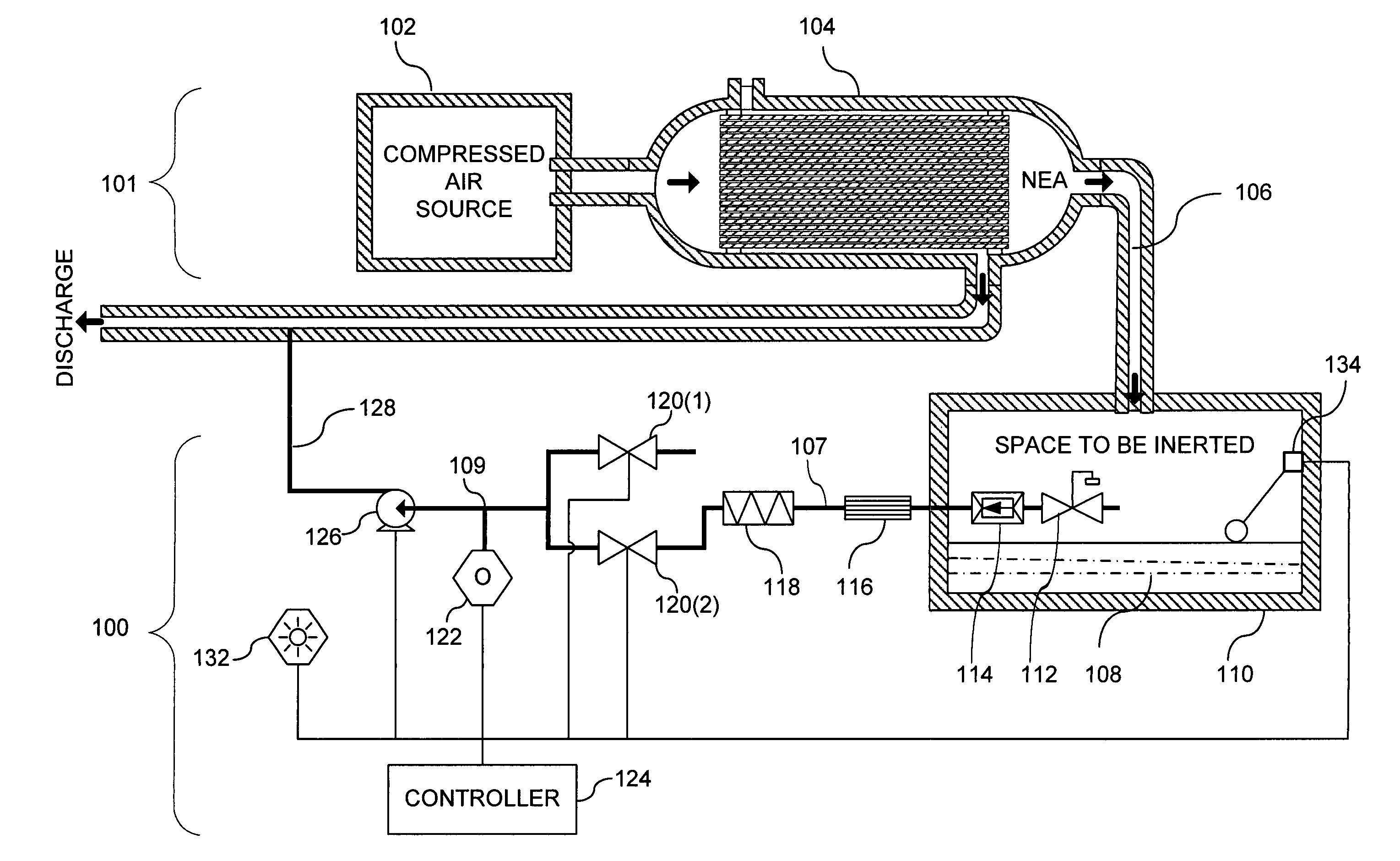
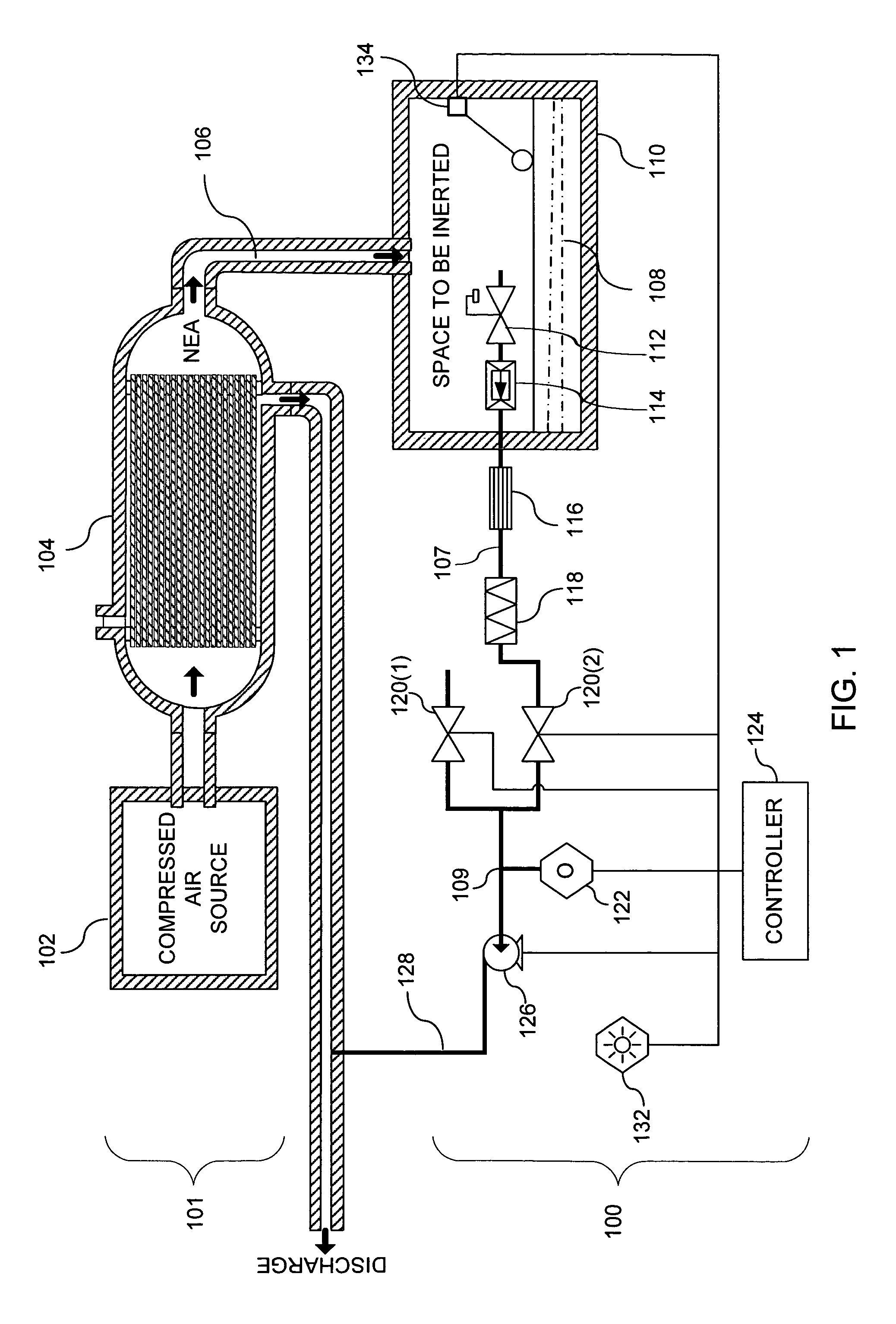
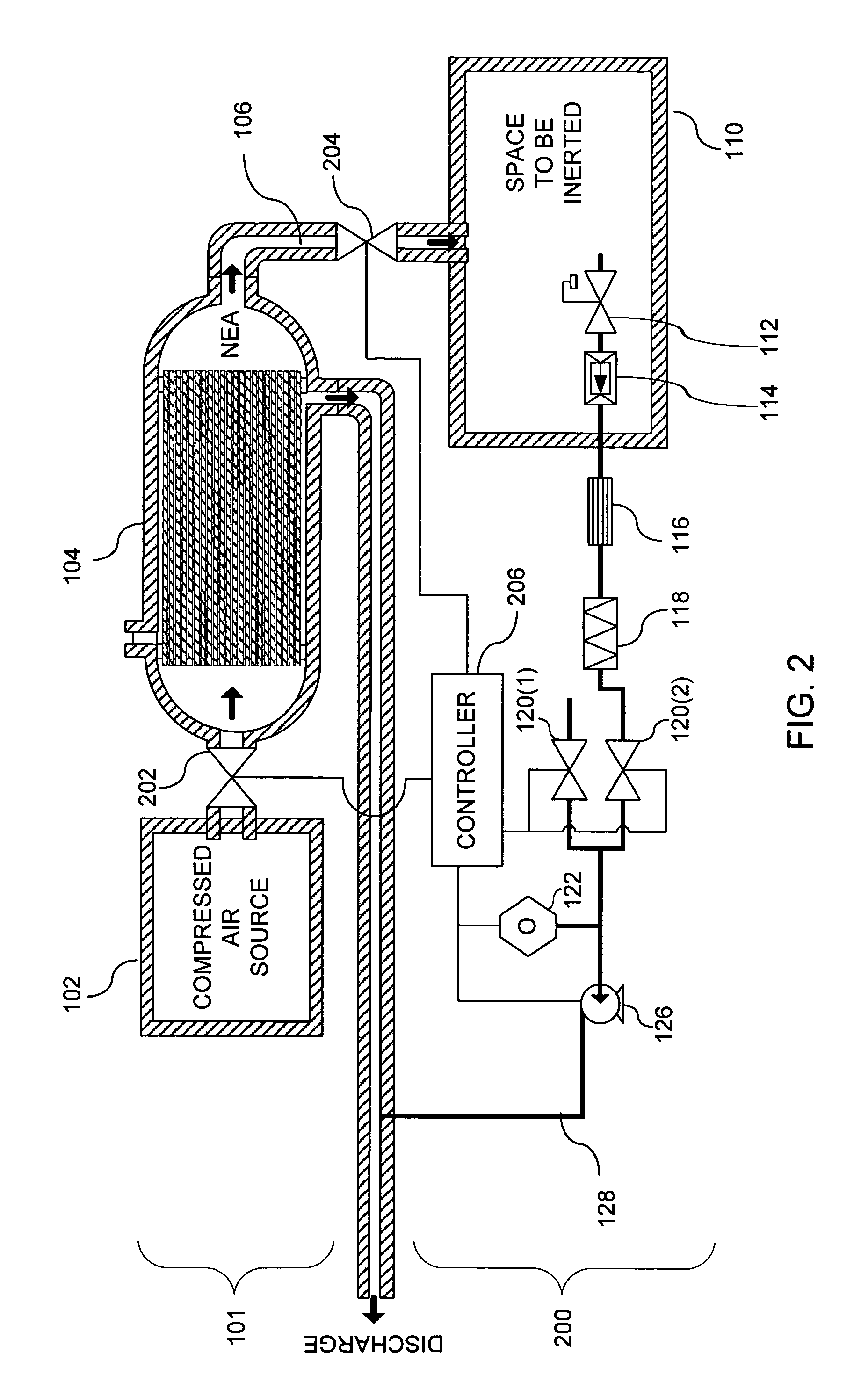
System and method for monitoring the performance of an inert gas distribution system
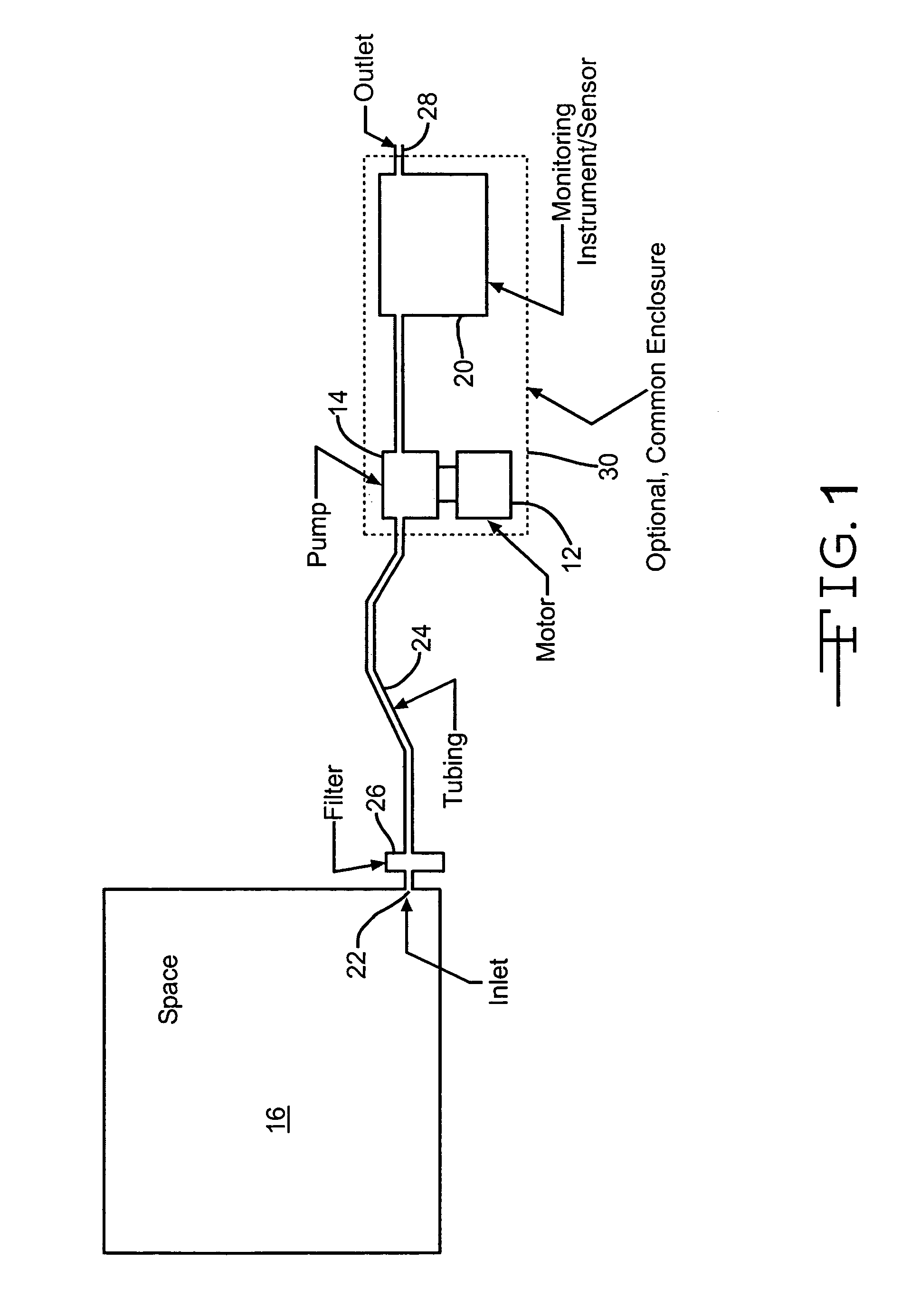
ActiveUS7013905B2Convenient verificationReduce misreadingAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesValve arrangementsElectricityLine tubing
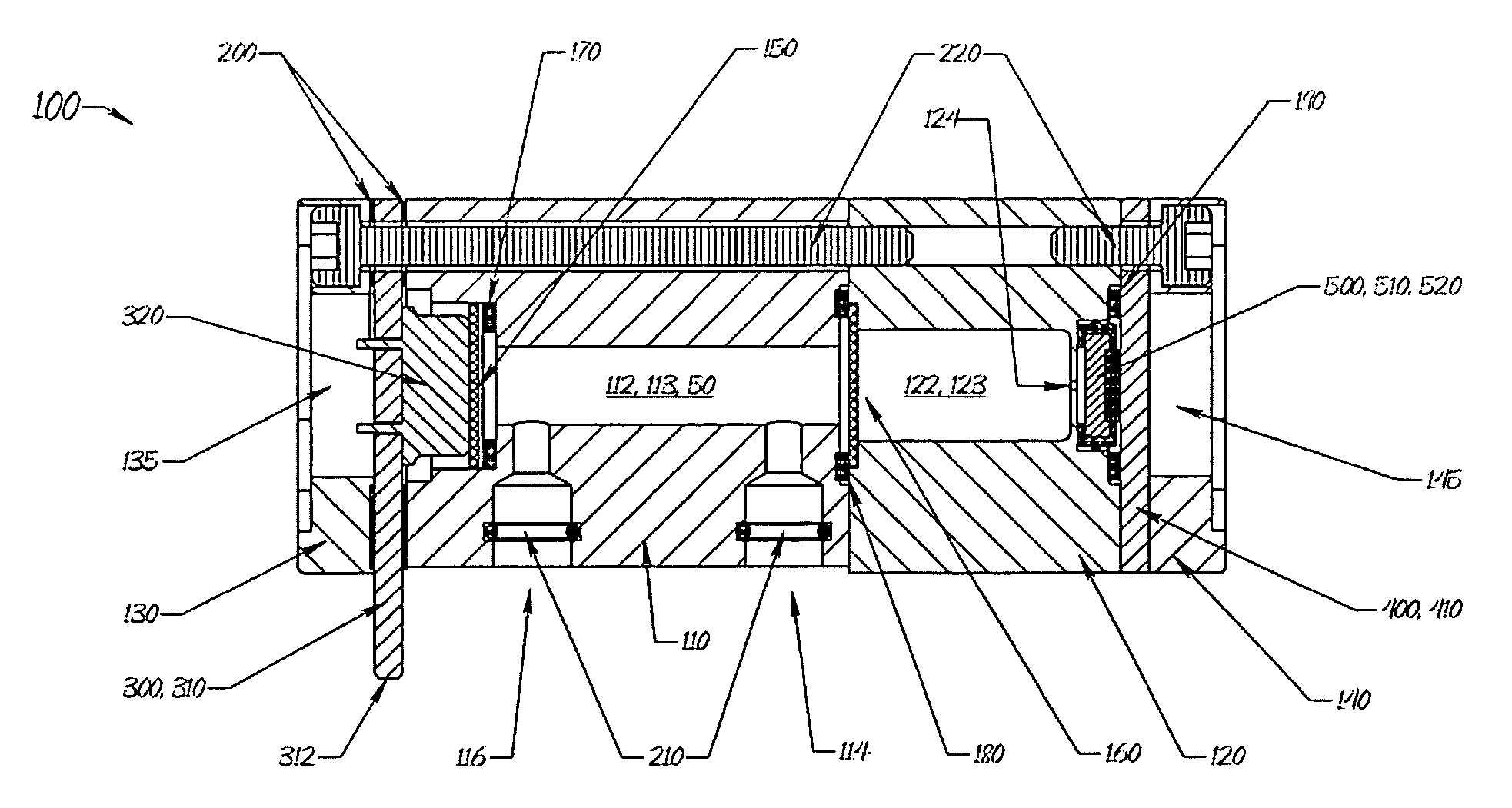
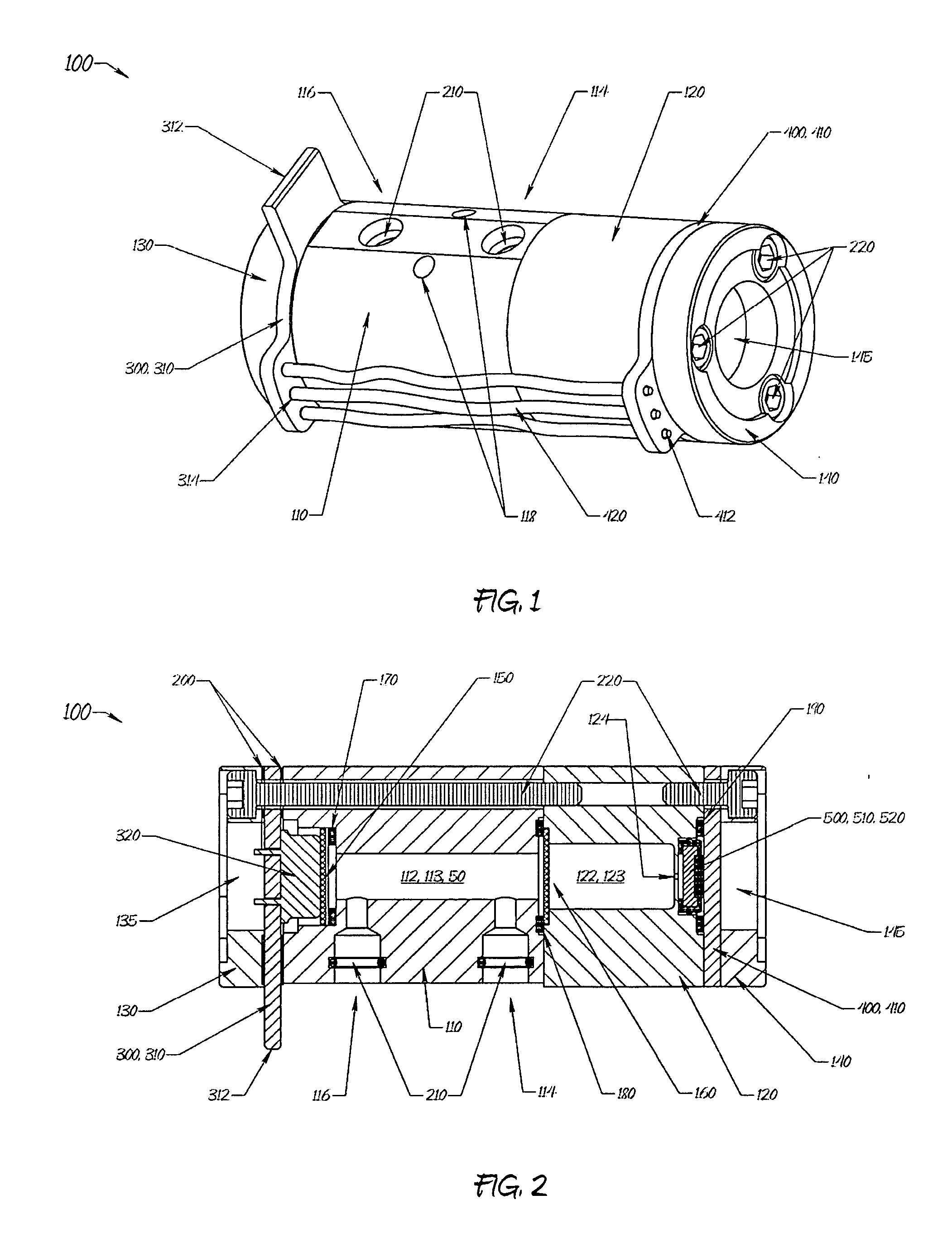
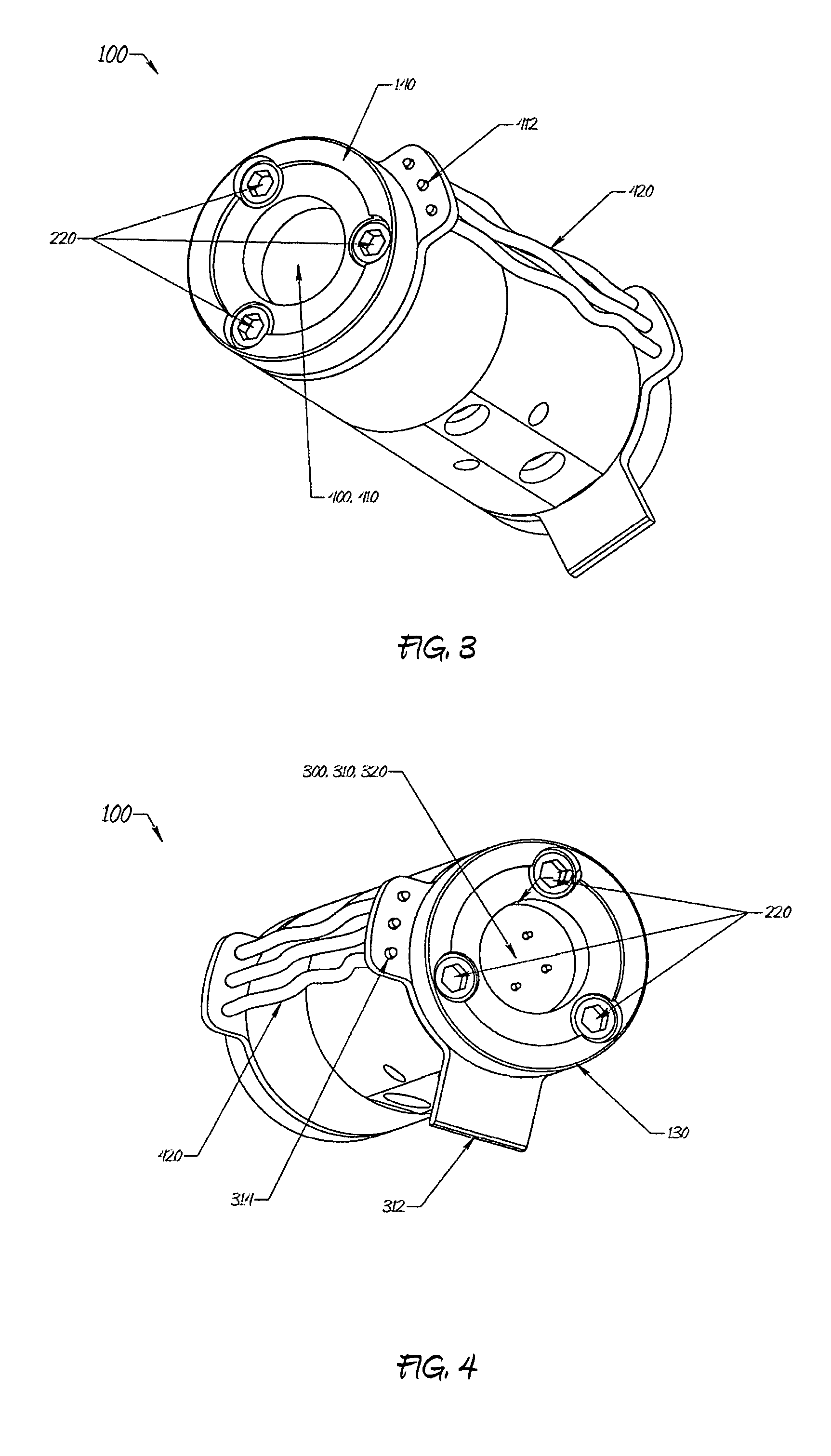
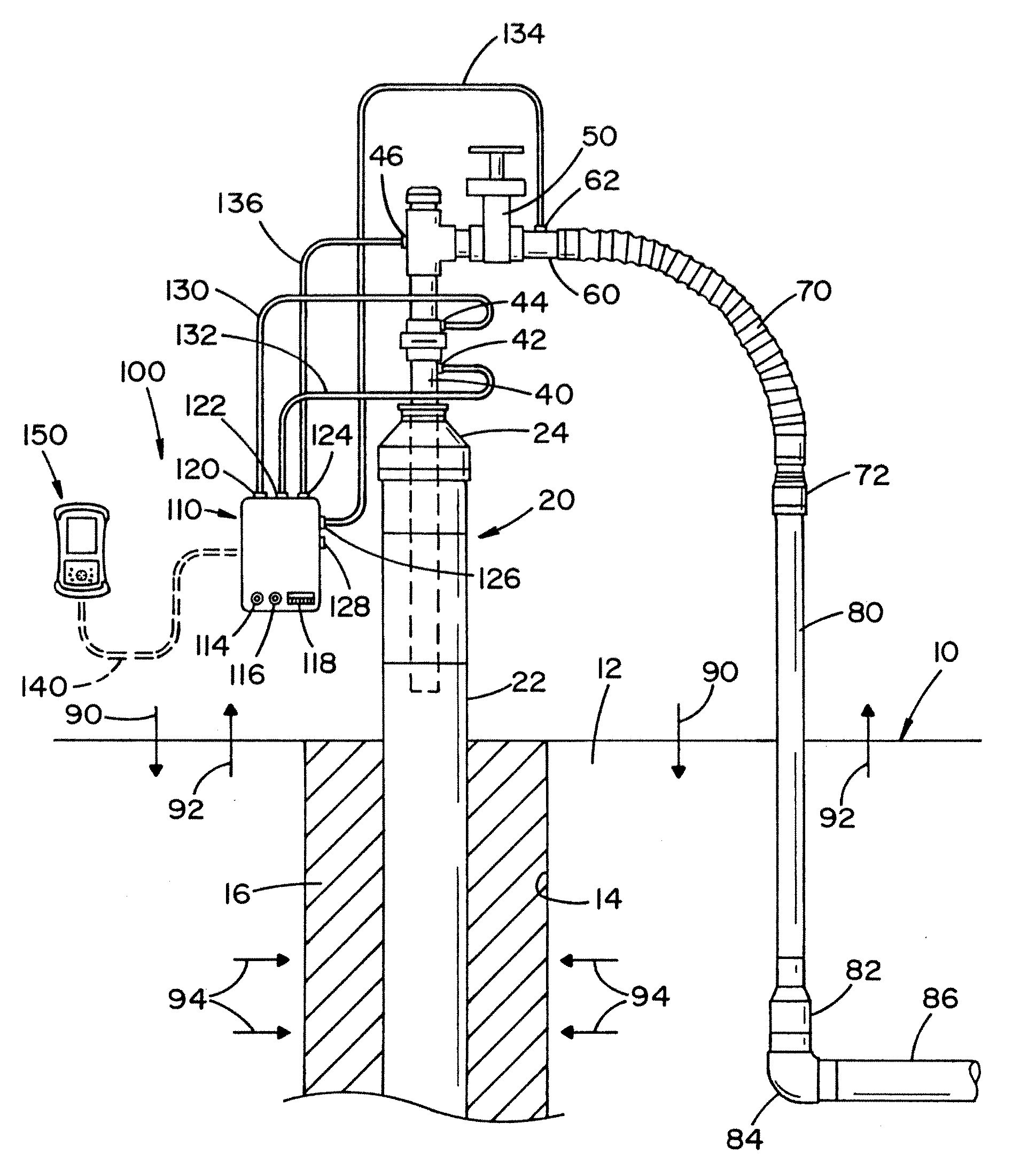
The gas monitoring system may include a gas line, an oxygen sensor, a filter, a pump, a indicator, and a controller. The gas line is configured to convey gas from a space configured to receive inert gas to a location remote from the space. The oxygen sensor is fluidly coupled to the gas line at the location. The oxygen sensor is configured to determine a partial pressure of oxygen present in the gas. The filter is fluidly coupled to the gas line between the space and the location. The filter is configured to remove combustible contaminants from the gas before it reaches the oxygen sensor. The controller is electrically coupled to the oxygen sensor and to the indicator. The controller is configured to activate the indicator when the partial pressure of oxygen exceeds a predetermined level.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Continuous prediction method of gas emission dynamic characteristic outburst of tunneling surface
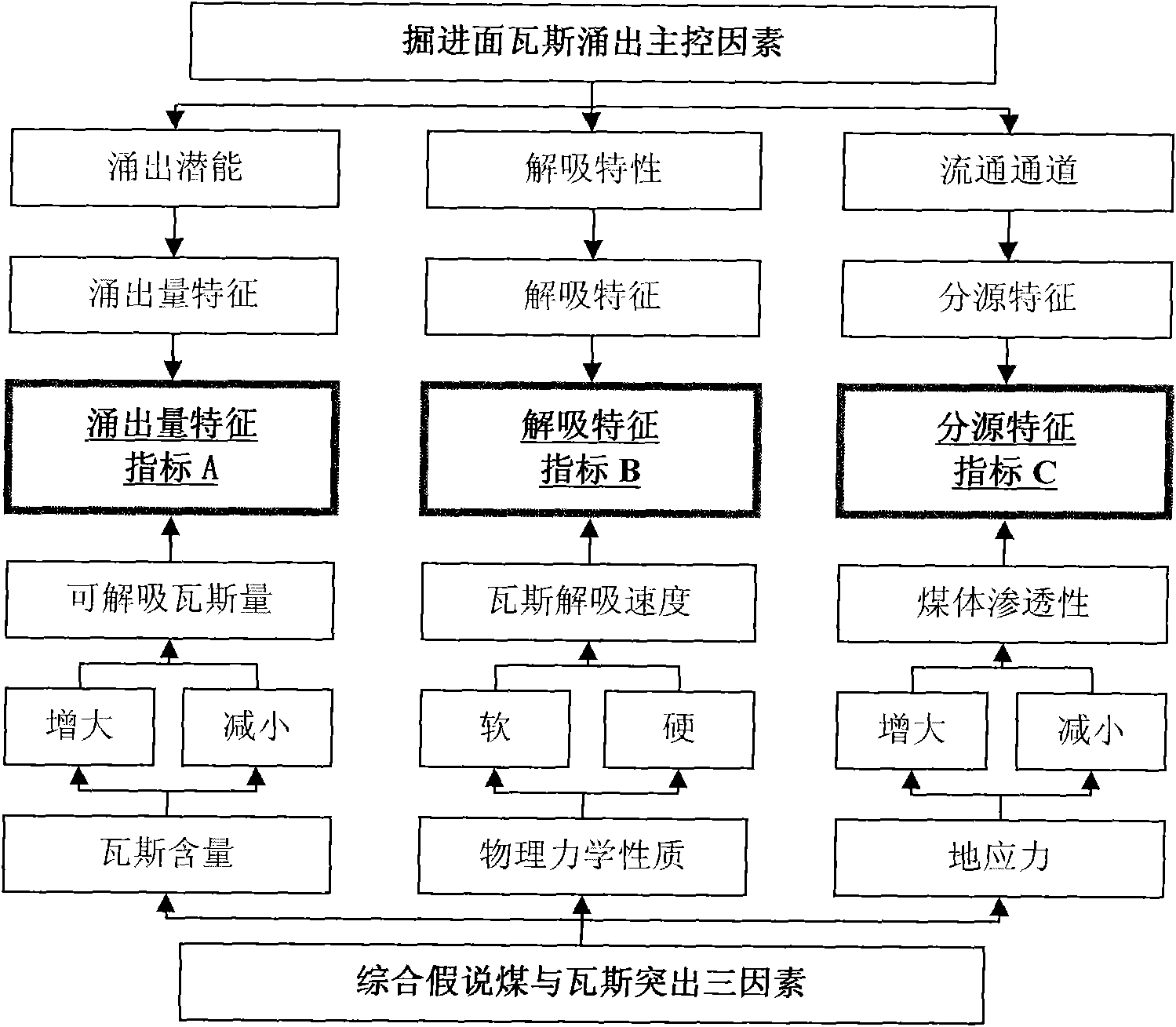
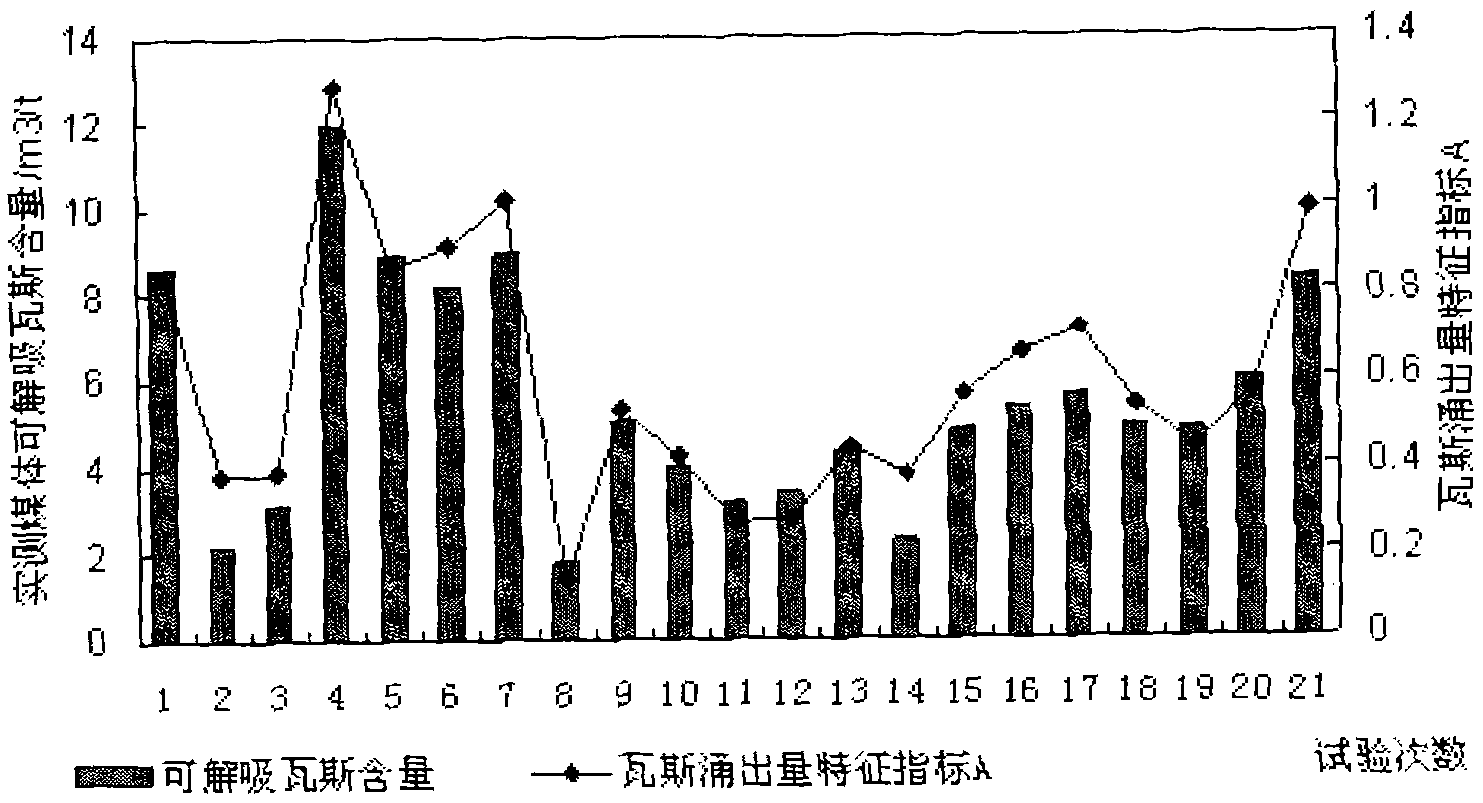
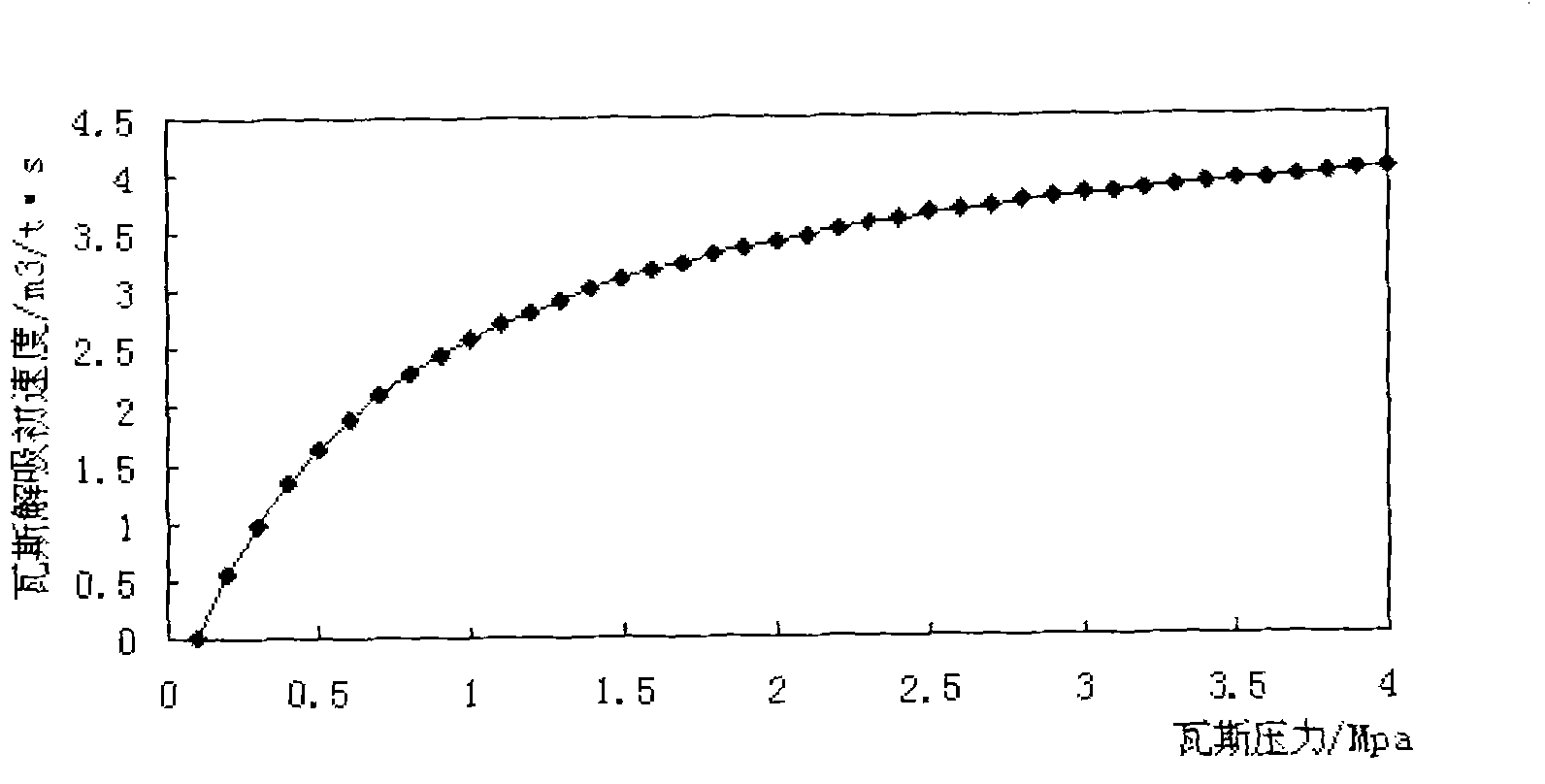
The invention relates to the technical field of coal mine safety, in particular to a continuous prediction method of gas emission dynamic characteristic outburst of a tunneling surface, which utilizes the development state and the development trend of three factors of outburst comprehensive hypothesis of the tunneling surface of gas emission dynamic characteristic reaction of the tunneling surface and realizes the non-contact type continuous prediction technology of coal of the tunneling surface and gas outburst; and the method comprises the following steps: acquiring real-time gas emission monitoring data of an underground gas sensor from a coal mine gas monitoring system; extracting dynamic characteristics of gas emission of the tunneling surface, including average value of frequency ofthe monitoring data of the gas emission, the maximum value of the frequency per minute of the monitoring data of the gas emission and the movement minimum value of the frequency per t minutes of the gas emission; and acquiring the shape design characteristic parameters of a lane, the original desorbable gas content of a coal layer, wind rate and frequency time, sequentially acquiring characteristic index of the gas emission rate of the tunneling surface, gas desorption index and gas dividing source characteristic index, and carrying out real-time prediction and forecast of outburst risk of a working surface according to the states and the trends of the three characteristic indexes.
Owner:CHINA COAL TECH & ENG GRP CHONGQING RES INST CO LTD
Smoke gas on-line monitoring system and smoke gas on-line monitoring method
ActiveCN104407161AAnalysis and detection are accurateStable flow rateMaterial analysisGas analysisParticulates
The invention relates to a smoke gas on-line monitoring system and a smoke gas on-line monitoring method, and aims at providing the smoke gas monitoring system and the monitoring method which have the advantages of being simple in structure, high in automation degree and accurate in monitoring. The system comprises a pitot pitometer, a smoke gas sampler, a particulate matter monitor, sampling pipelines and demarcating pipelines, wherein the pitot pitometer, the smoke gas sampler and the particulate matter monitor are all provided with anti-purging devices, signal receiving terminals of all the anti-purging devices are respectively connected with a central controller, and all the anti-purging devices are controlled by the central controller to regularly purge. Smoke gas collected by the smoke gas sampler successively passes through a first refrigerator, a gas filter, a second refrigerator and a membrane type filter, the collected smoke gas is cooled and filtered by the first refrigerator, the gas filter, the second refrigerator and the membrane type filter, and the rest smoke gas finally obtained is fed into a multicomponent gas analysis instrument to be analyzed and detected. For the system, whole calibrated pipelines and partial calibrated pipelines are also arranged, so that the analysis instrument in a line can be wholly calibrated and partially calibrated.
Owner:汇众翔环保科技股份有限公司
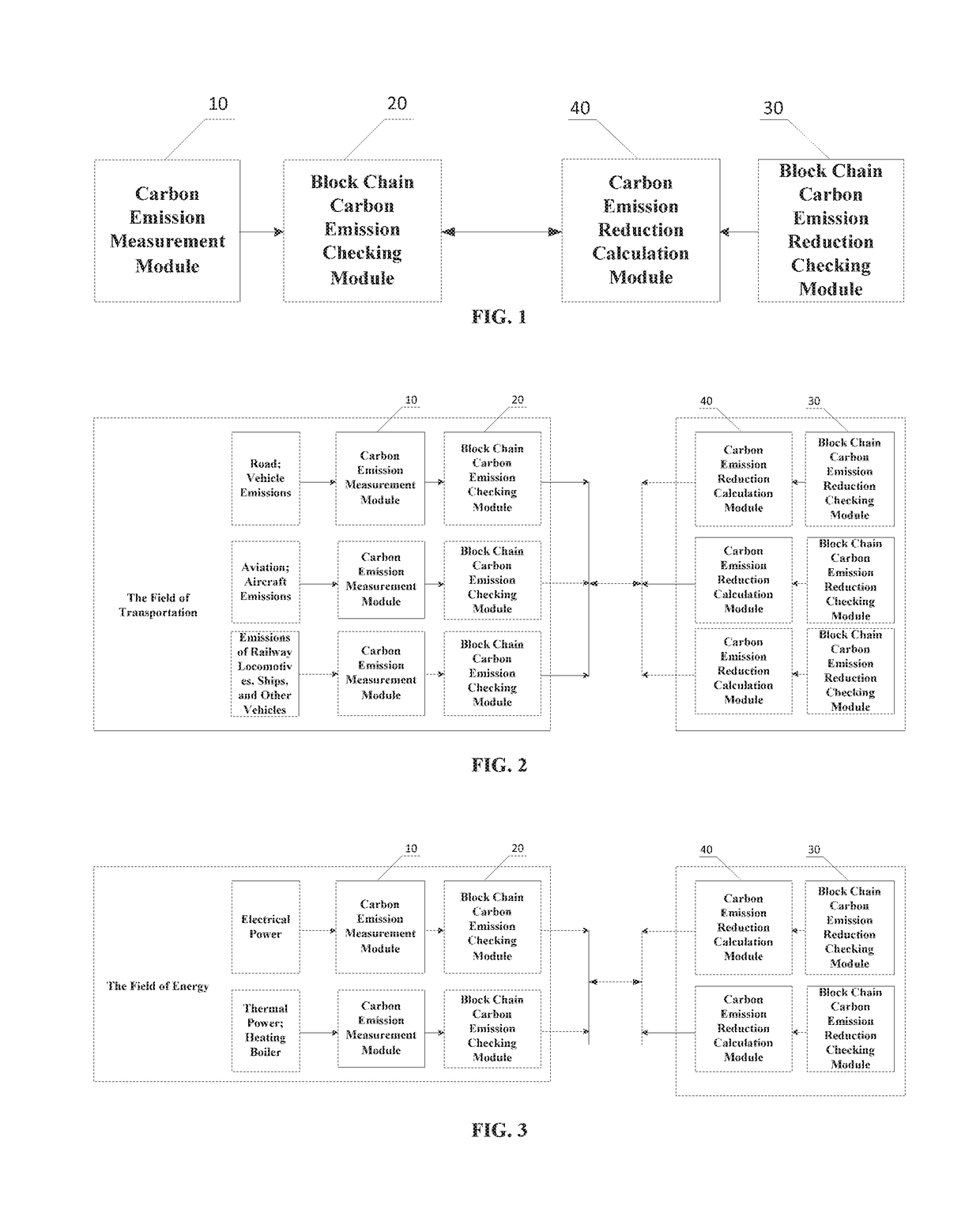
Blockchain-based carbon trading system
InactiveUS20190057396A1Increase credibilityImprove efficiencyFinanceCryptography processingTimestampMaterials science
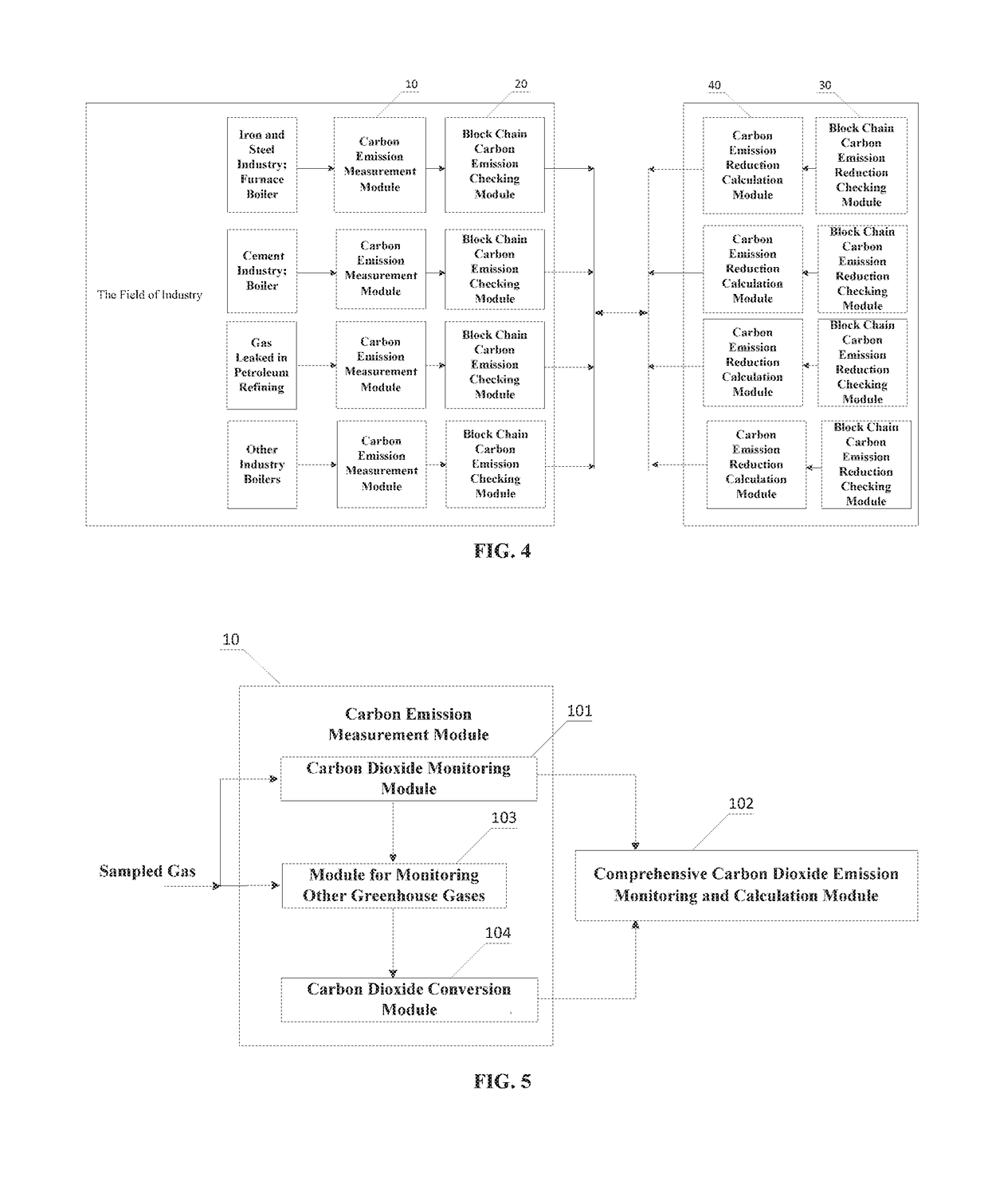
The present invention discloses a blockchain-based carbon trading system, relates to the technical field of greenhouse gas monitoring and block chains. The carbon trading system comprises: a carbon emission measurement module configured to measure carbon emission of greenhouse gas to generate carbon emission data, a block chain carbon emission checking module configured to add a timestamp onto the carbon emission data to generate carbon emission information, a carbon emission reduction calculation module configured to measure carbon emission reduction of reduced greenhouse gas to generate carbon emission reduction data, and a block chain carbon emission reduction checking module configured to add a timestamp onto the carbon emission reduction data to check the generated carbon emission reduction information.
Owner:HEPU TECH DEV BEIJING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com