Patents
Literature
7583 results about "Pulse-width modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pulse width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with MPPT maximum power point tracking, it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because they have inertia to react slow. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible.
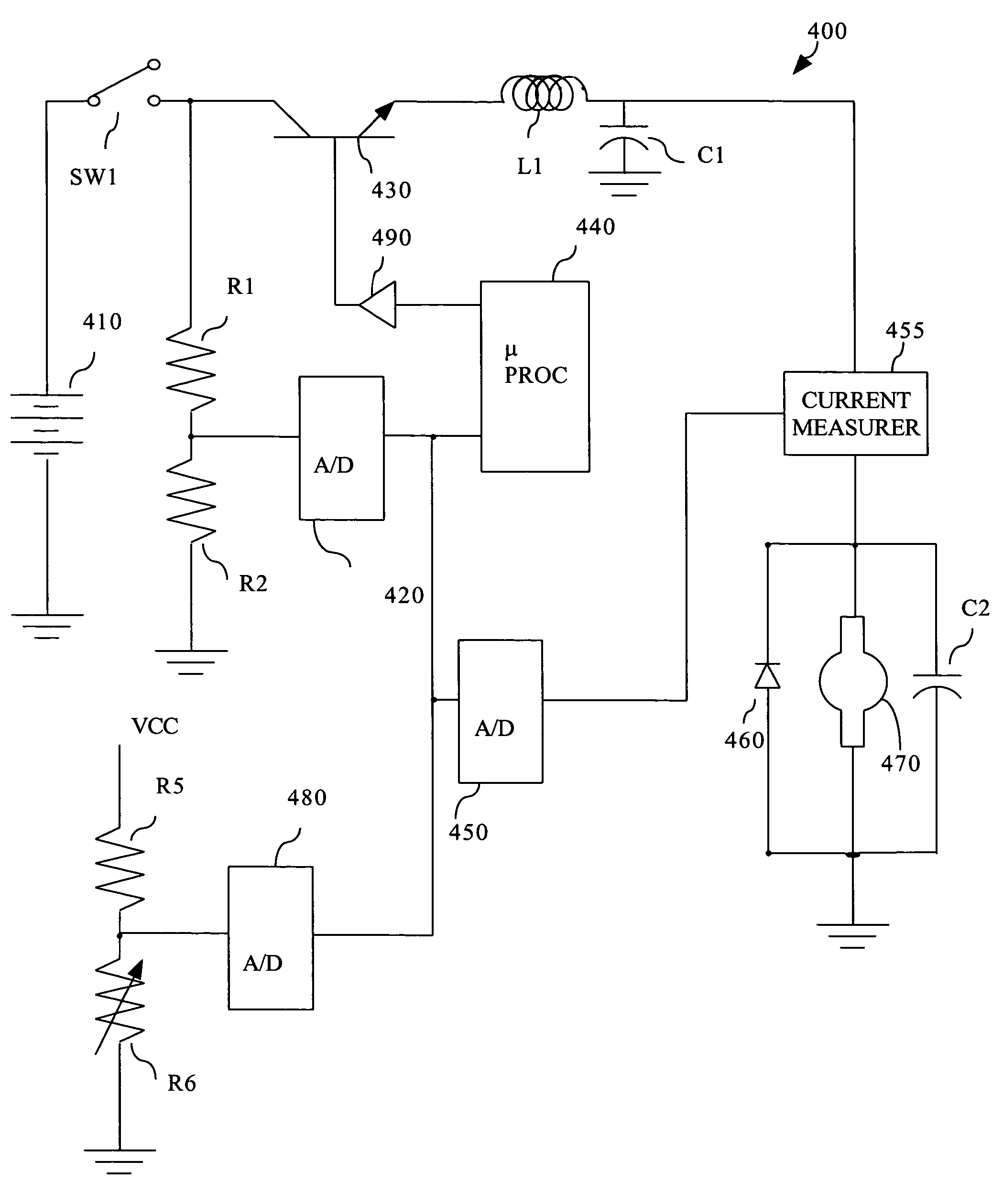
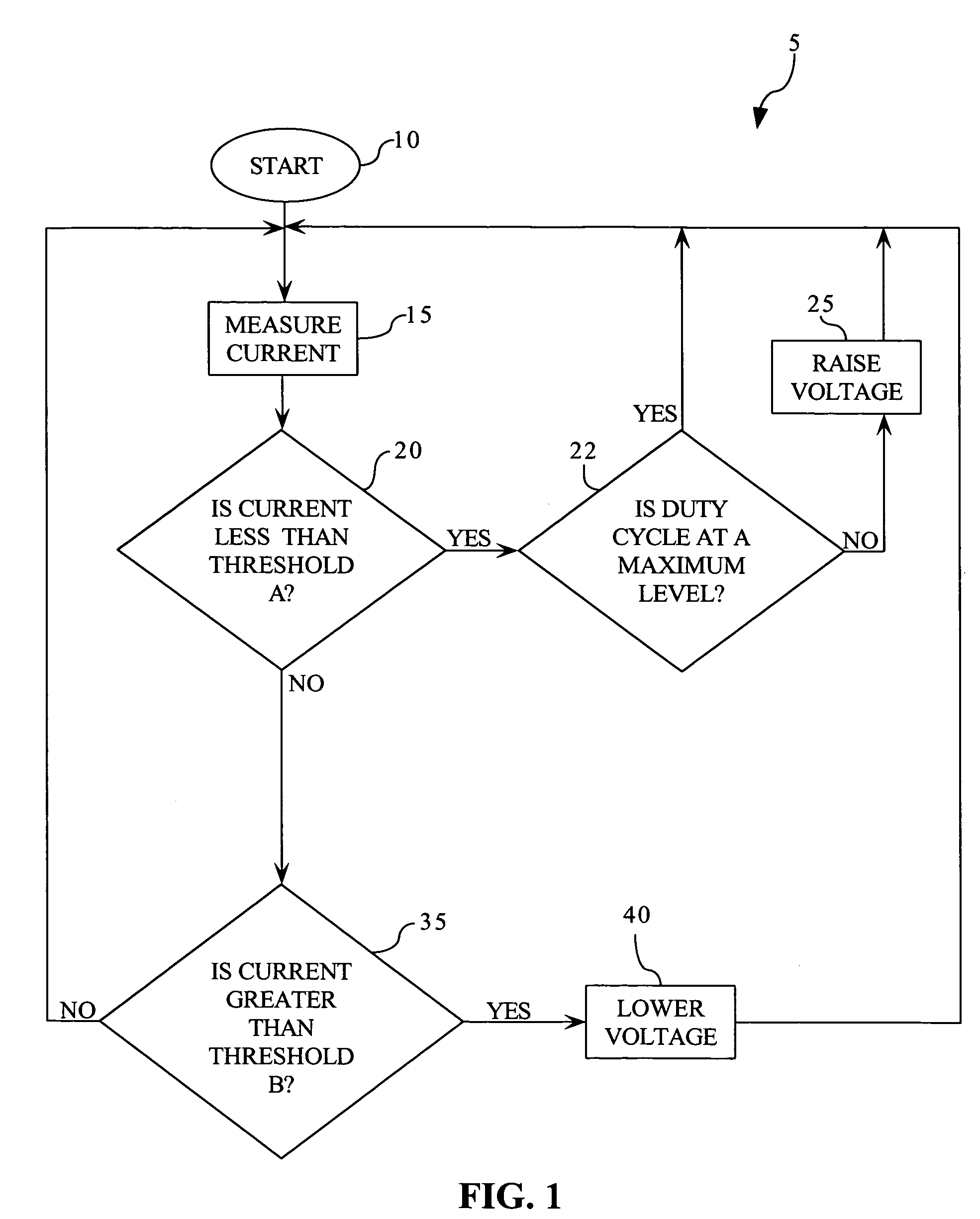
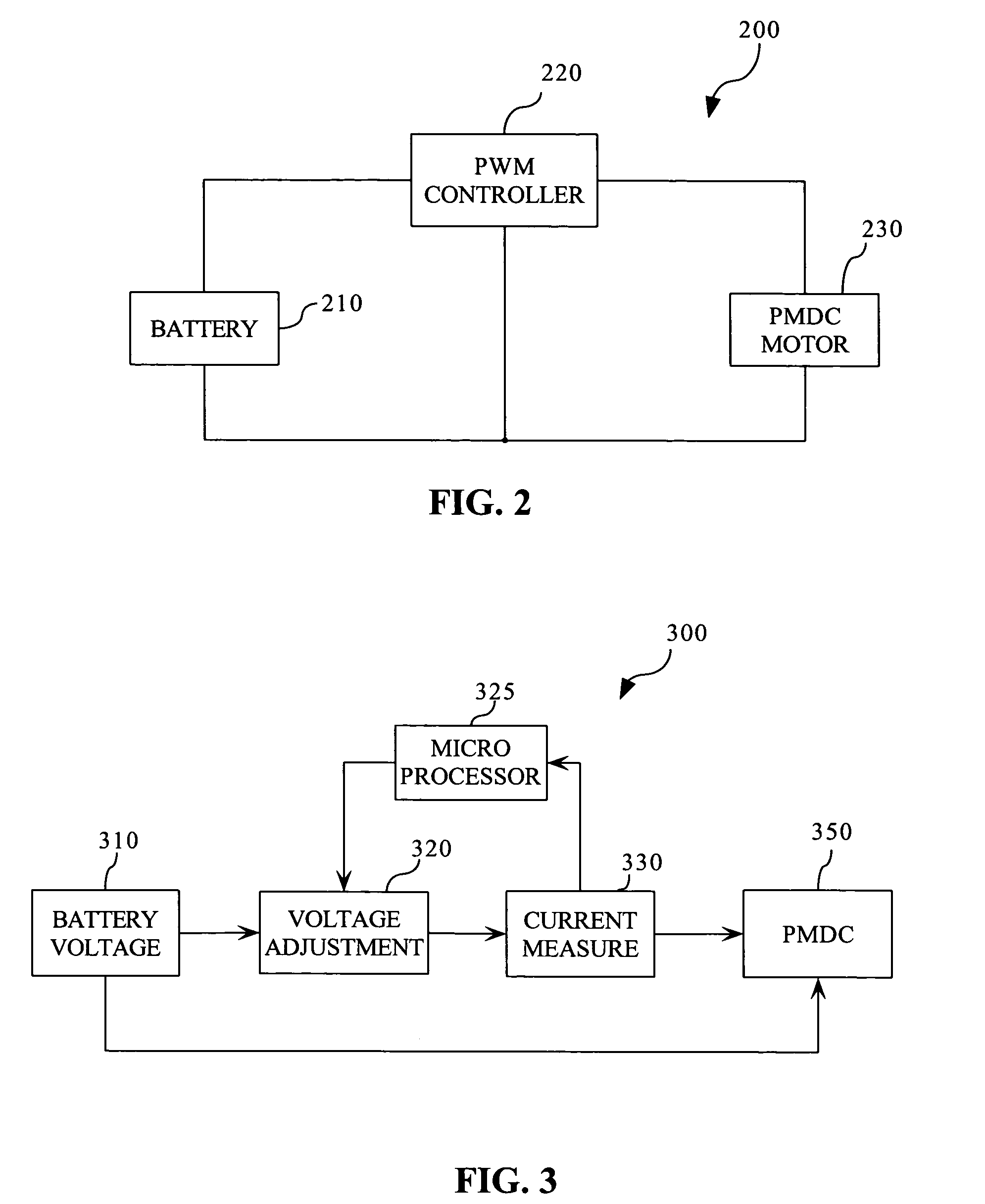
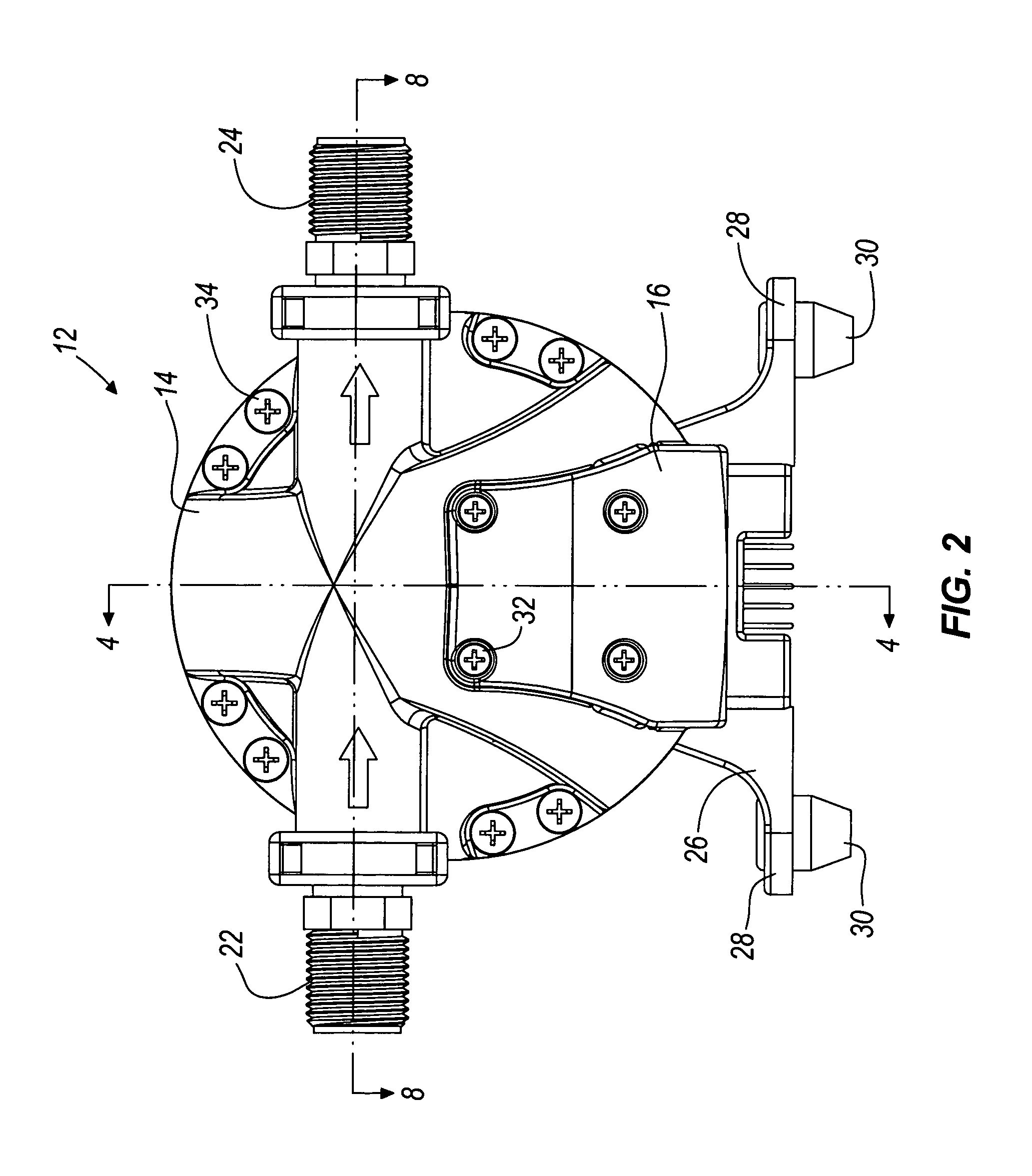
Amperage control for protection of battery over current in power tools
InactiveUS7133601B2Battery protectionHigh currentAC motor controlElectric motor controlLithiumNickel cadmium
Amperage control of a power tool motor is provided by pulse width modulation of current from a power supply. The pulse width modulation may be varied according to the determined motor current and measured power supply voltage. The power supply preferably includes a battery, such a lithium ion or nickel cadmium.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
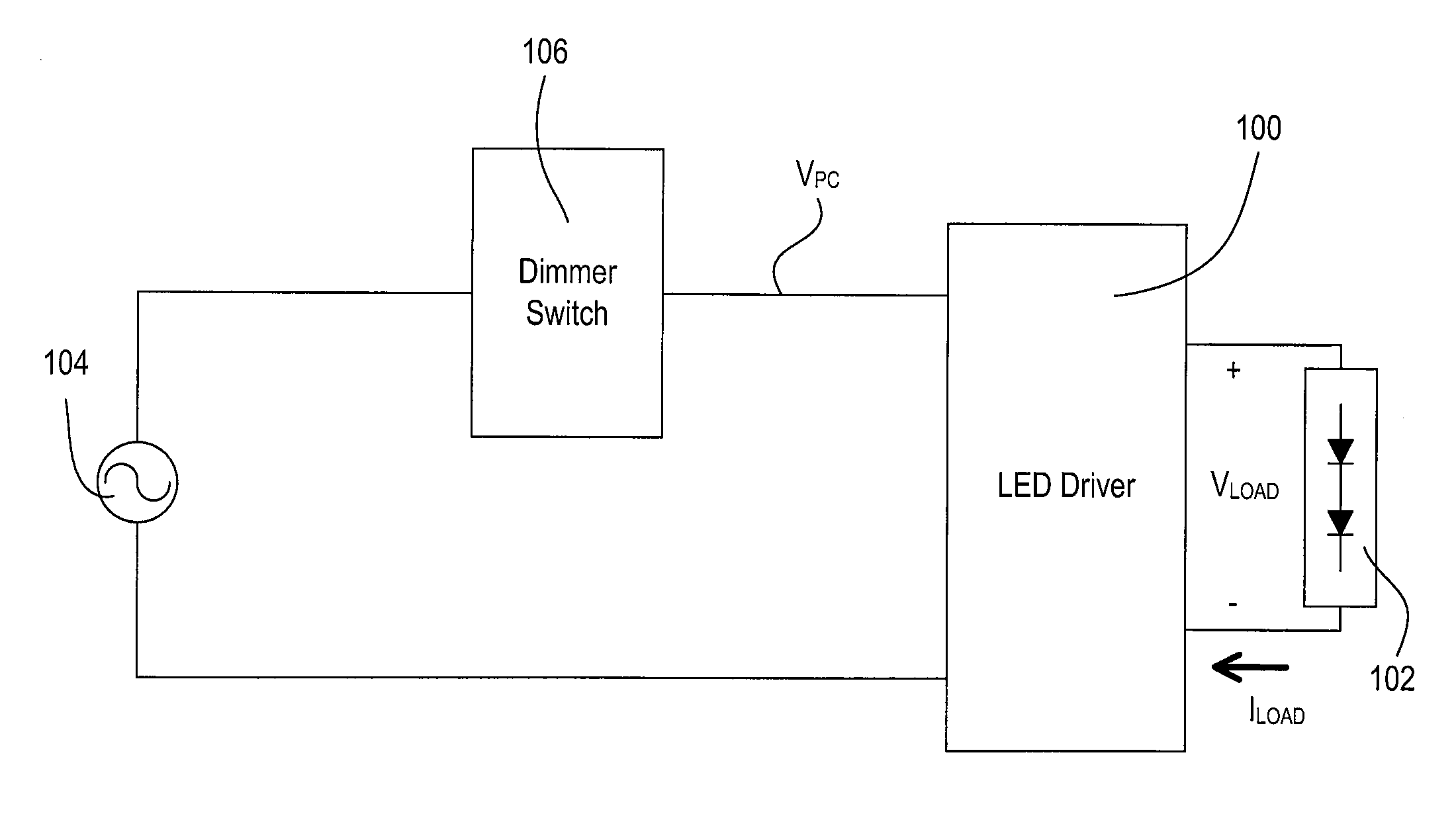
Load control device for a light-emitting diode light source
ActiveUS20110080110A1Reduce power consumptionControlling the magnitude of a load current conductedElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLinear regulatorEngineering
A light-emitting diode (LED) driver is adapted to control either the magnitude of the current conducted through a LED light source or the magnitude of a voltage generated across the LED light source. The LED driver comprises a power converter circuit for generating a DC bus voltage, and an LED drive circuit for receiving the bus voltage and adjusting the magnitude of the current conducted through the LED light source. The LED driver is operable to dim the LED light source using either a pulse-width modulation technique or a constant current reduction technique. The LED drive circuit may comprise a controllable-impedance circuit, such as a linear regulator. The LED driver may be operable to control the magnitude of the bus voltage to optimize the efficiency and reduce the power dissipation in the LED drive circuit, as well ensuring that the load voltage and current do not have any ripple.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Compositions, devices, and methods for nicotine aerosol delivery
ActiveUS20140345635A1Reduce degradationConstant efficiencyTobacco treatmentTobacco devicesSolventElectron
The present disclosure generally relates to compositions, and related devices and methods, useful in vaporizing devices such as electronic cigarettes. The composition may comprise nicotine, at least one solvent, and at least one ion pairing agent, and may be vaporized to form a condensation aerosol, wherein inhalation of the aerosol allows for deposition of nicotine with the respiratory system, including deep lung deposition. The vaporizing device may comprise a vaporization unit, a battery, and an integrated circuit coupled to the battery, wherein the integrated circuit is configured to control the battery for rapid initial vaporization without overheating, producing thermal degradation products, or draining battery energy. The battery may operate with pulse width modulation for at least a portion of the time the vaporizing device is being used.
Owner:NJOY LLC
Power line communication using power factor correction circuits
ActiveUS7205749B2Systems using filtering and bypassingAc-dc conversion without reversalElectronic systemsPower MOSFET
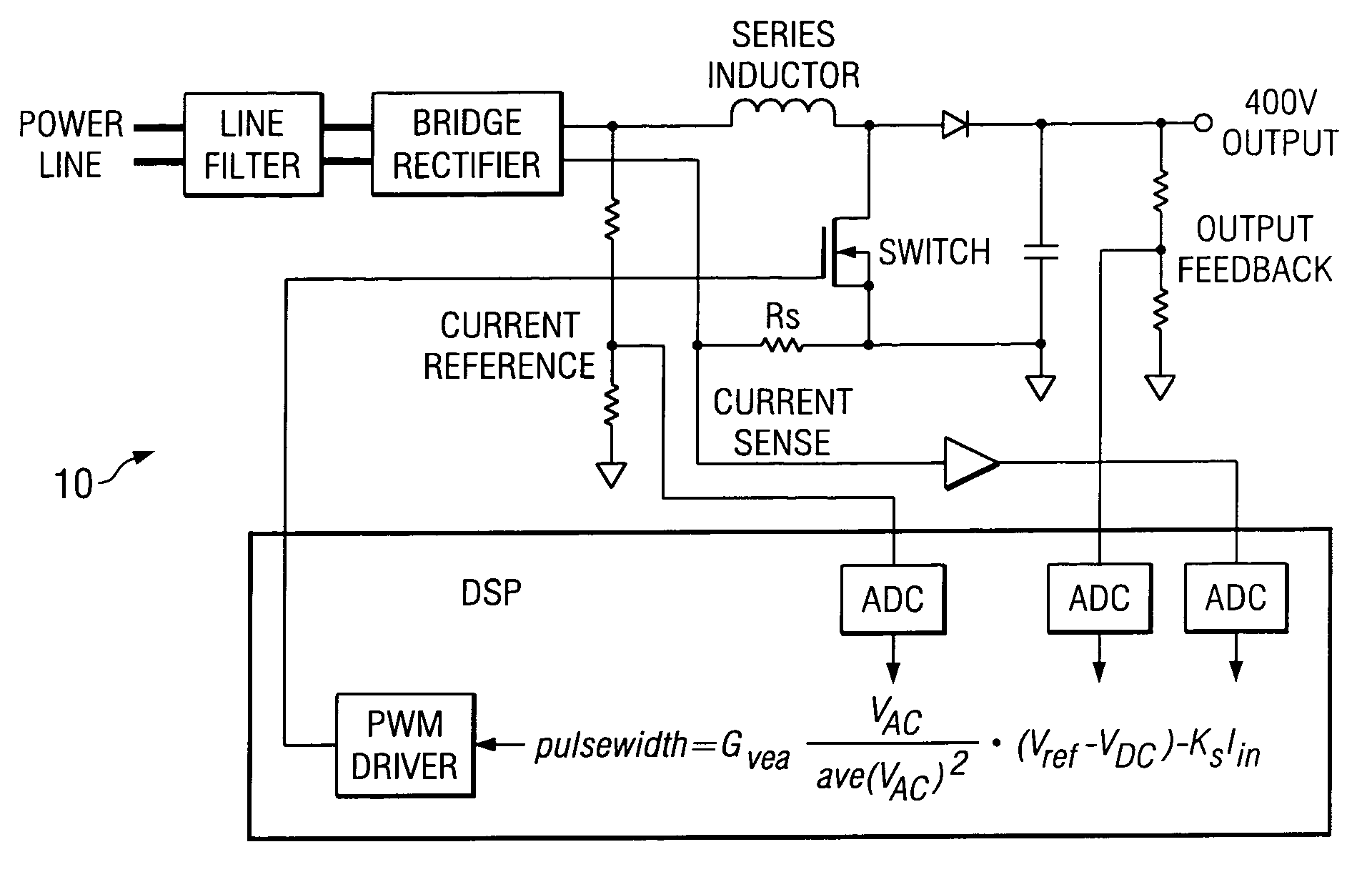
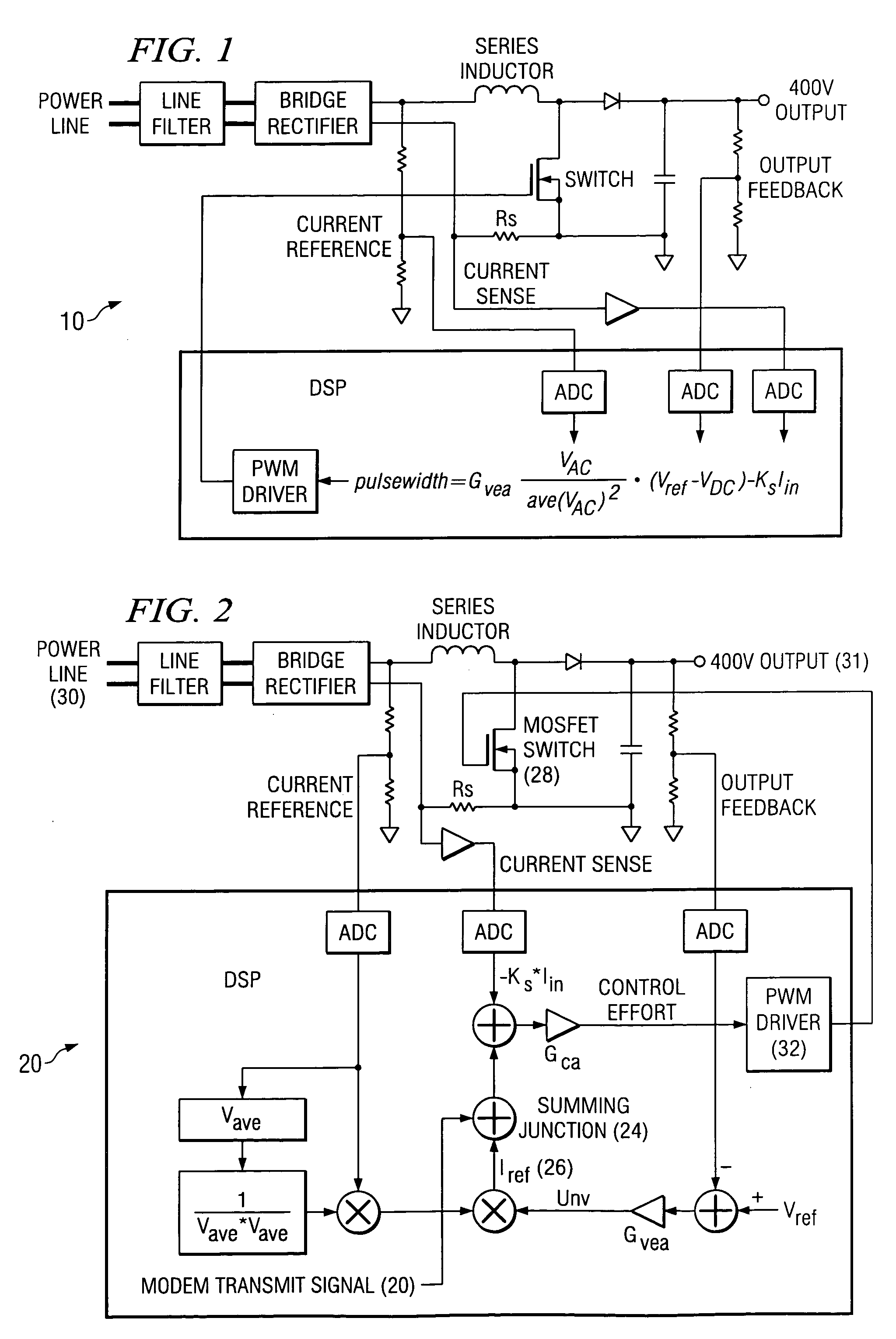
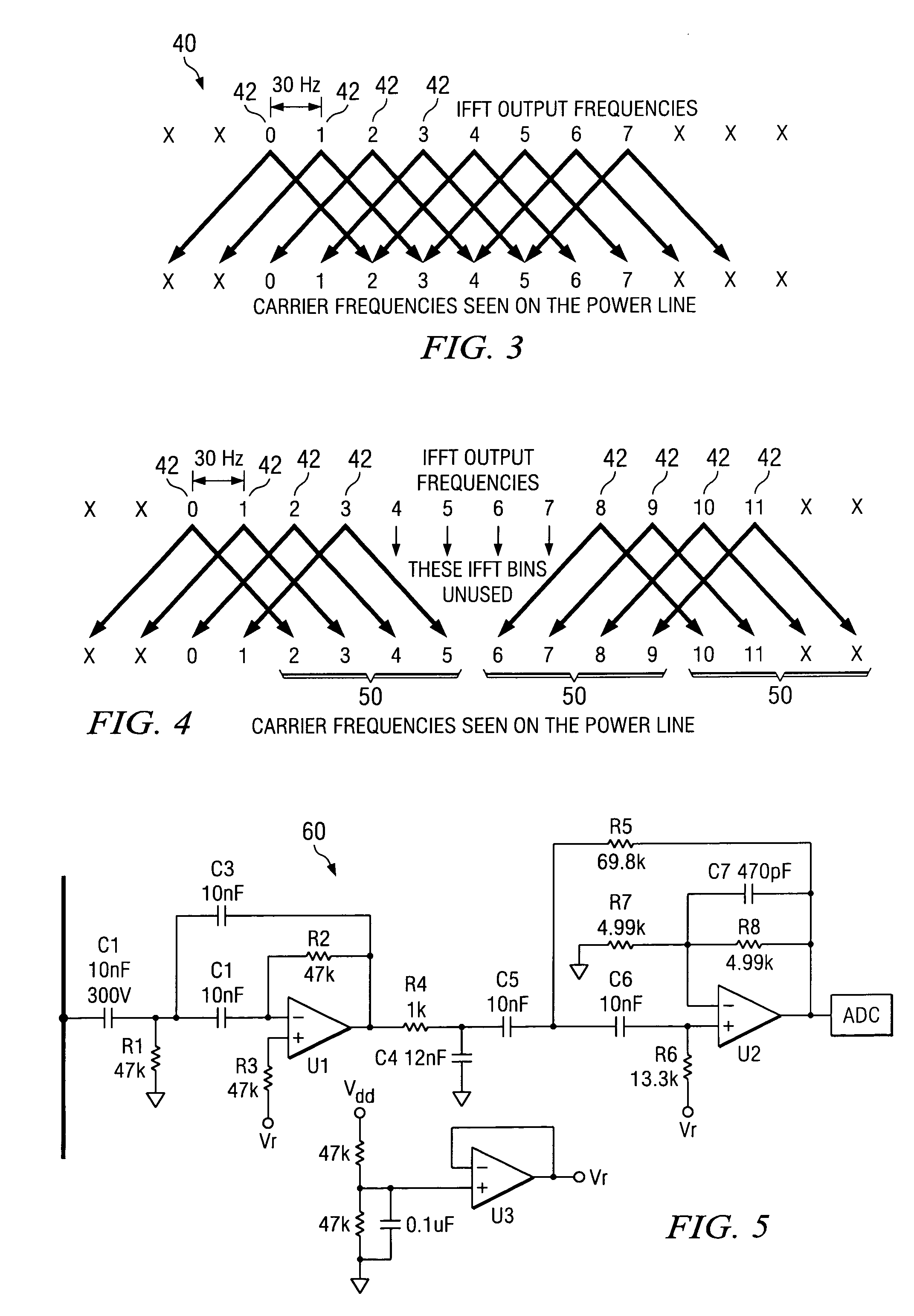
A PFC circuit modulating a power line using pulse width modulation (PWM) to drive a power MOSFET and series inductor across the power line. Since many modern electronic systems include a power factor correction circuit (PFC) that already includes a series inductor and power MOSFET, a PLC is incorporated into a controller to inject a PLC transmit signal into a control loop for the PFC circuit. This can be done using either an analog PFC controller, such as the UCC28517, the UCC2819A, or a digital PFC controller such as based on a TMS320C24xx DSP.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Power supply driver circuit
InactiveUS7138786B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A power supply driver circuit with low power losses and desired response characteristics with respect to changes in output and its miniaturization is provided. In a driver IC constituting a switched-mode power supply equipment controlling the switching, by pulse width modulation, of first and second power transistors passing a current in a coil, and outputting a voltage bucked or boosted from an input voltage, current sensing with desired responsiveness is enabled by providing a switching transistor between an inverted input terminal and a non-inverted input terminal of an operational amplifier, preventing, while the second power transistor is ON, the generation of a potential which is undefined when first power transistor is ON, i.e. when the second power transistor is OFF, and maintaining a node potential in a state in which the potential is well defined.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
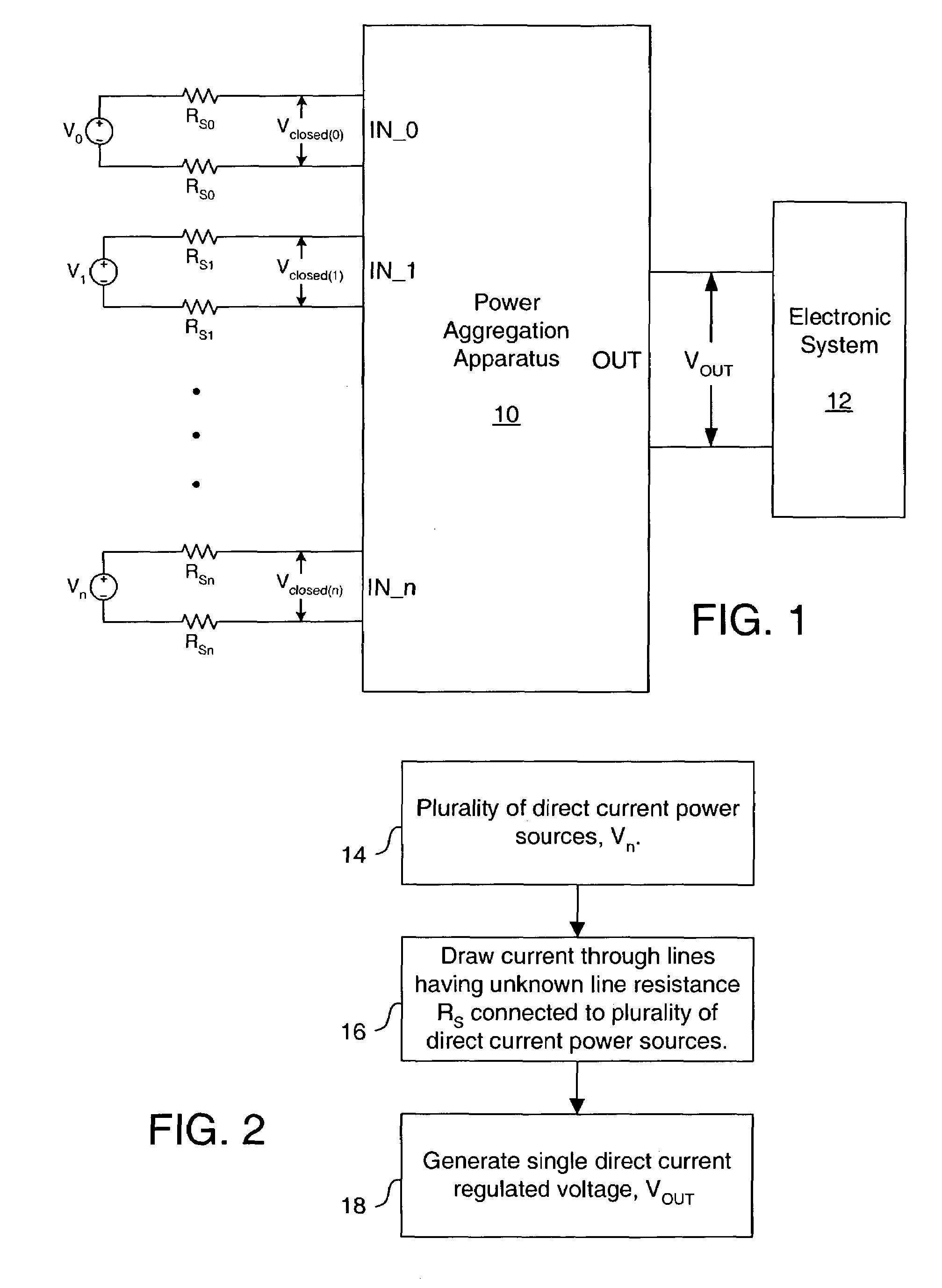
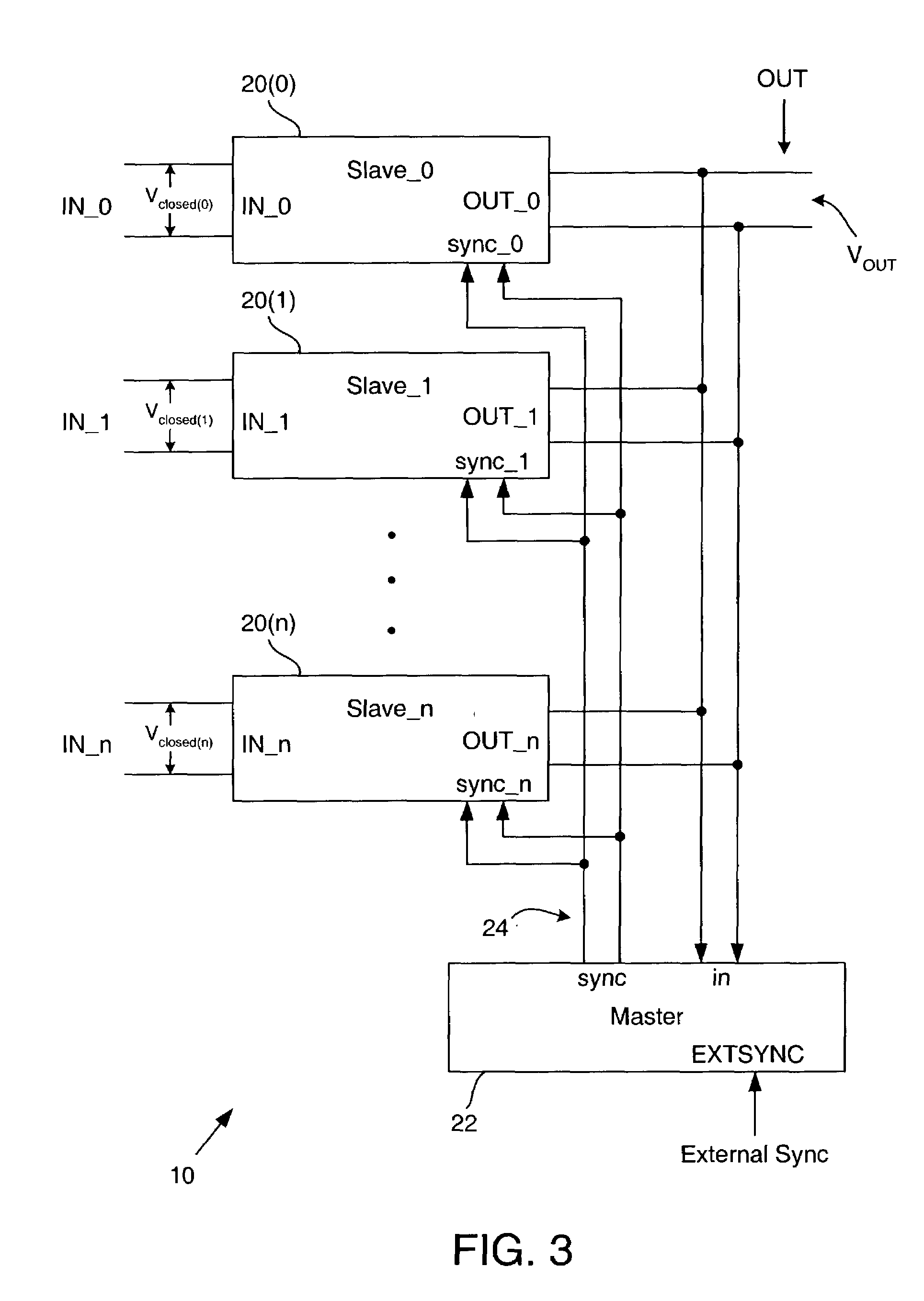
Method and apparatus for aggregating power from multiple sources
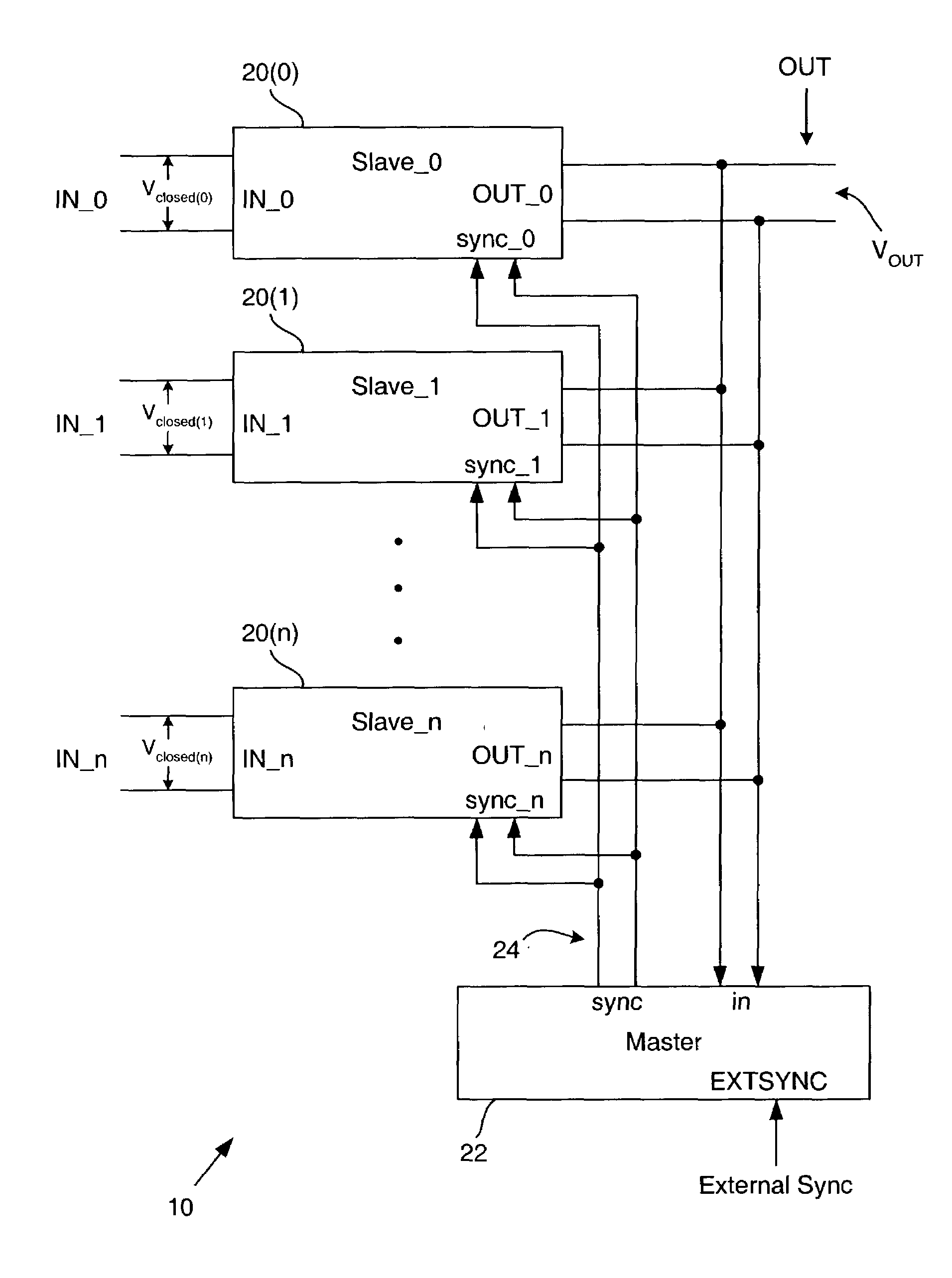
ActiveUS7259474B2Large line resistanceLimit maximum power drainedBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVoltage converterLine resistance
A method and apparatus for aggregating power from multiple sources generates a single direct current regulated voltage. The apparatus comprises a plurality of slave voltage converters and a master pulse width modulator circuit. Providing a plurality of direct current power sources, current is drawn through a plurality of lines connected to the plurality of direct current power sources. An open circuit voltage for each direct current power source is unknown. Each line of the plurality of lines has a line resistance. The line resistance of at least some of the plurality of lines may be unknown. The line resistance of at least some of the plurality of lines is large. The single direct current regulated voltage is generated from the drawn current.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
Method and apparatus for illumination and communication
InactiveUS7689130B2Electroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageData signalCarrier signal
The present invention provides a method and apparatus of using light-emitting elements for illumination as well as communication of data, wherein potential flicker due to sub-fusion frequency data correlations can be reduced compared to prior art techniques, while reducing redundancy in the data transmission. The intensity of the illumination from the light-emitting elements is controlled by a dimming signal such as a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal or a pulse code modulation (PCM) signal, for example. An amplitude-modulated data signal is then superimposed on the dimming signal for communication of data. The dimming signal thus acts as a carrier signal for the data signal. A sensing means is then used to receive the data signal by detecting all or part of the illumination from the light-emitting elements. The data signal can subsequently be extracted from the detected illumination.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
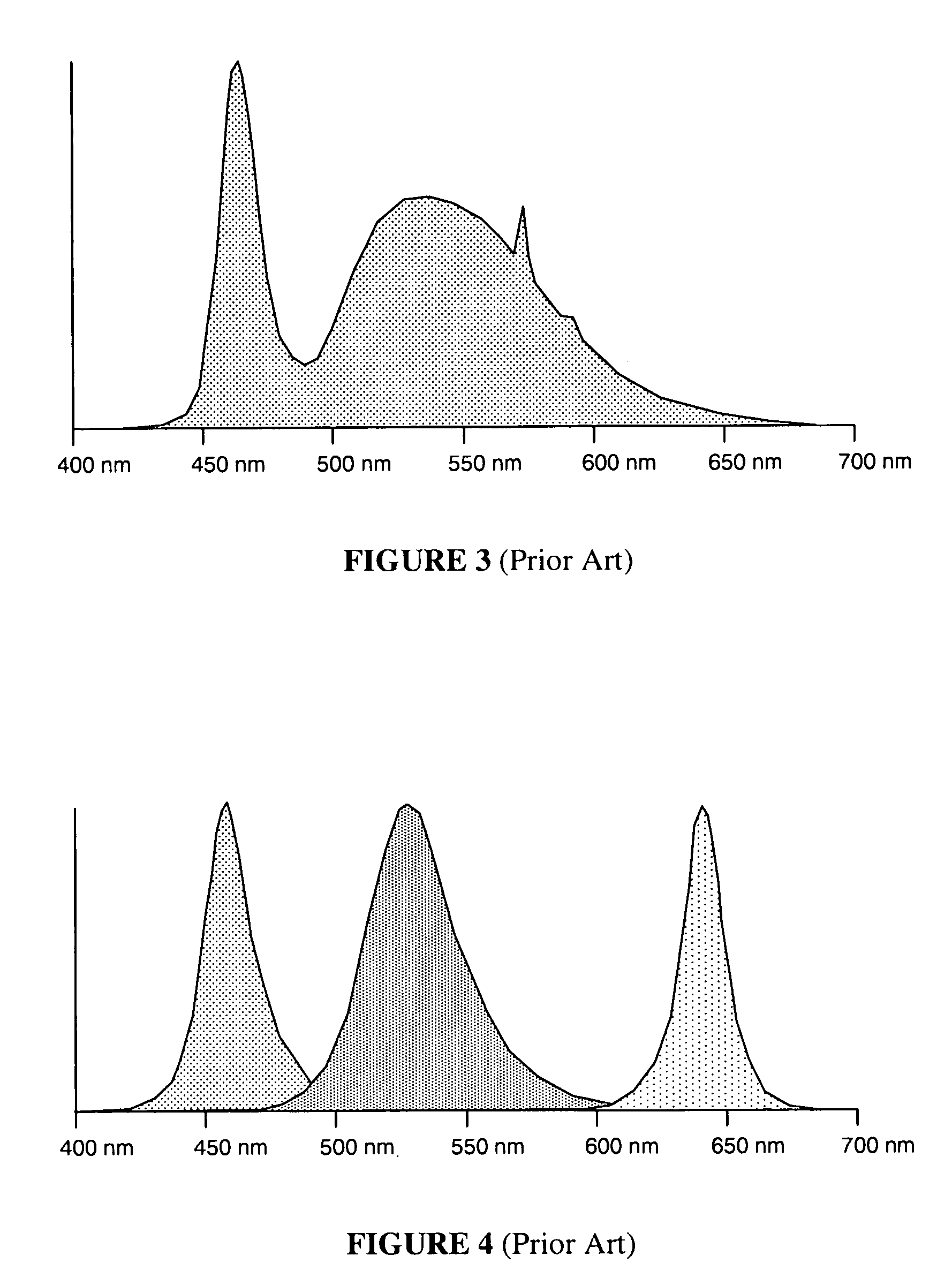
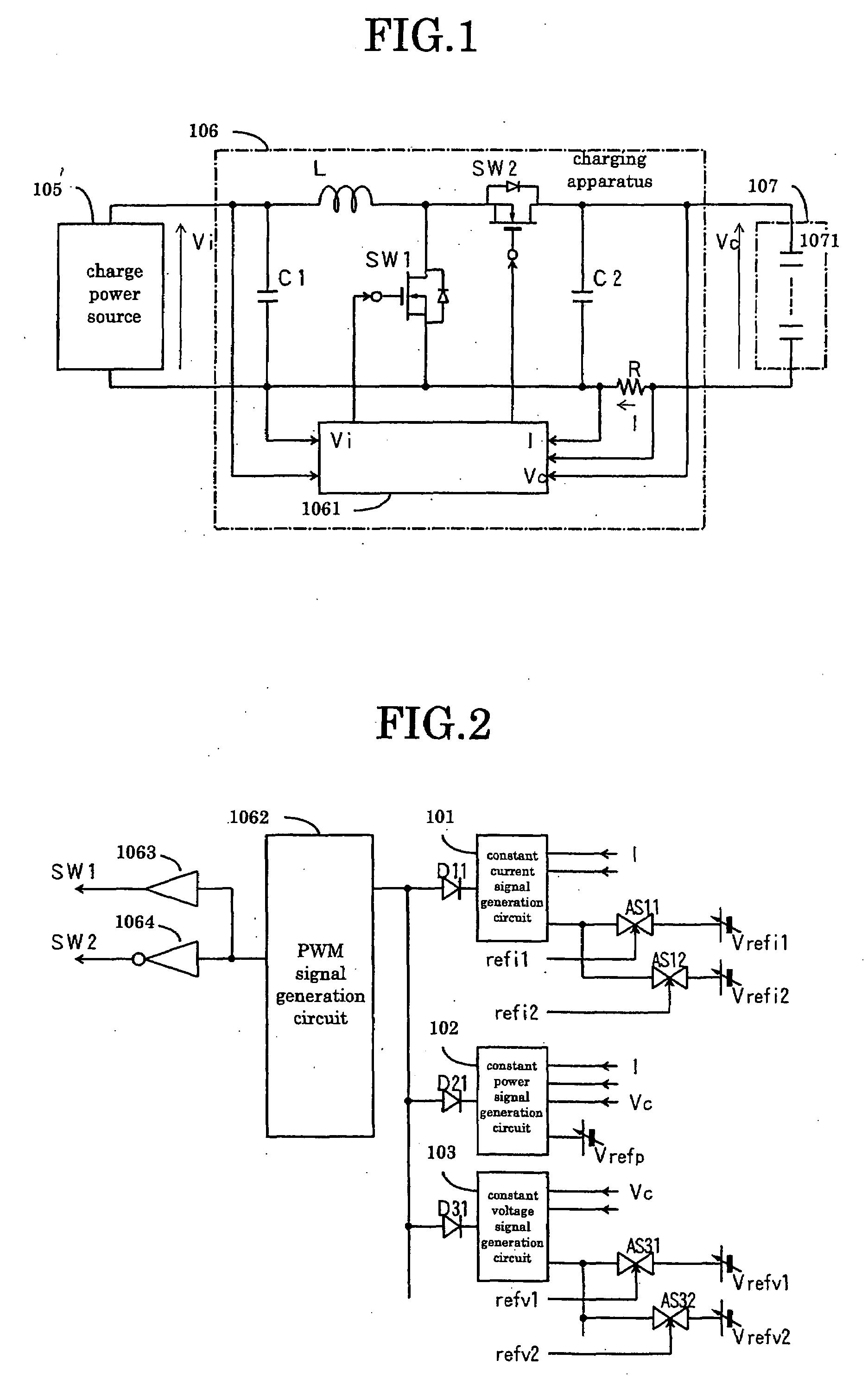
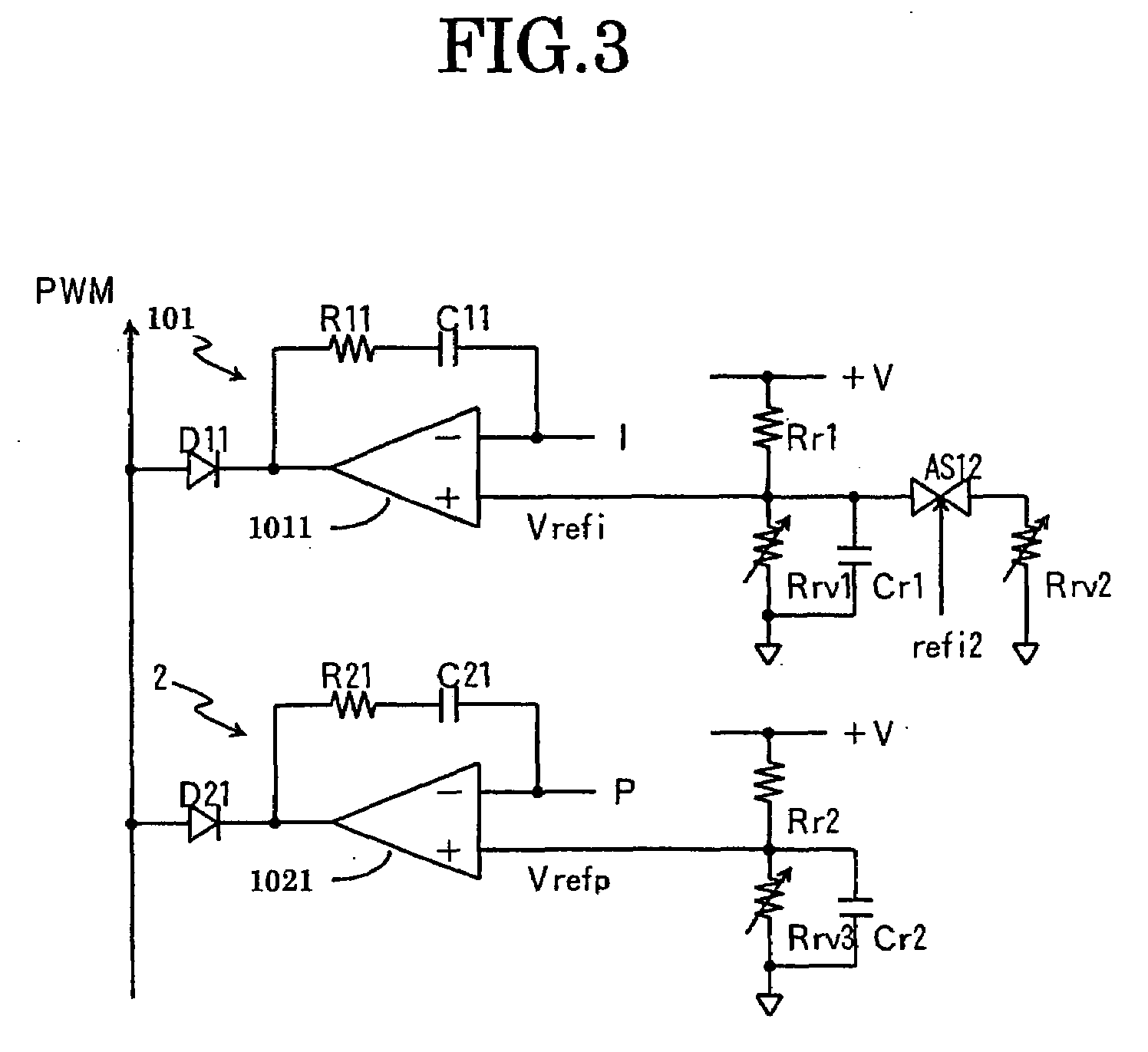
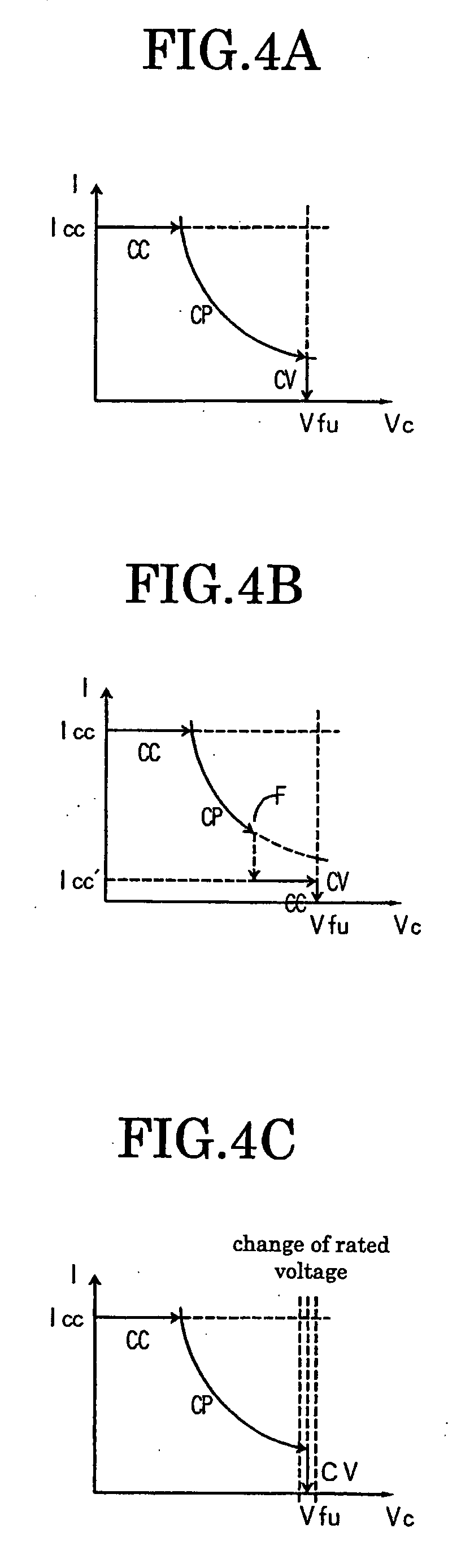
Charging apparatus for capacitor storage type power source and discharging apparatus for capacitor storage type power source
InactiveUS20070194759A1MinimizeImprove efficiencyCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerCharge currentVoltage reference
A charging apparatus for electrically charging a capacitor storage type power source comprises a switching circuit for turning on / off the charge current, a current detection circuit for detecting the charge current, a voltage detection circuit for detecting the voltage of power source, a constant current control circuit for outputting an error amplifying signal according to the current value, a power control circuit for outputting an error amplifying signal according to the current value, the voltage value-and a power reference value, a constant voltage control circuit for outputting an error amplifying signal according to the voltage value and a voltage reference value, an OR circuit for selecting one of the error amplifying signals and a control circuit for generating a pulse width modulation signal according to the error amplifying signal output from the OR circuit to turn on / off the switching circuit and control the charge current.
Owner:POWER SYST KK
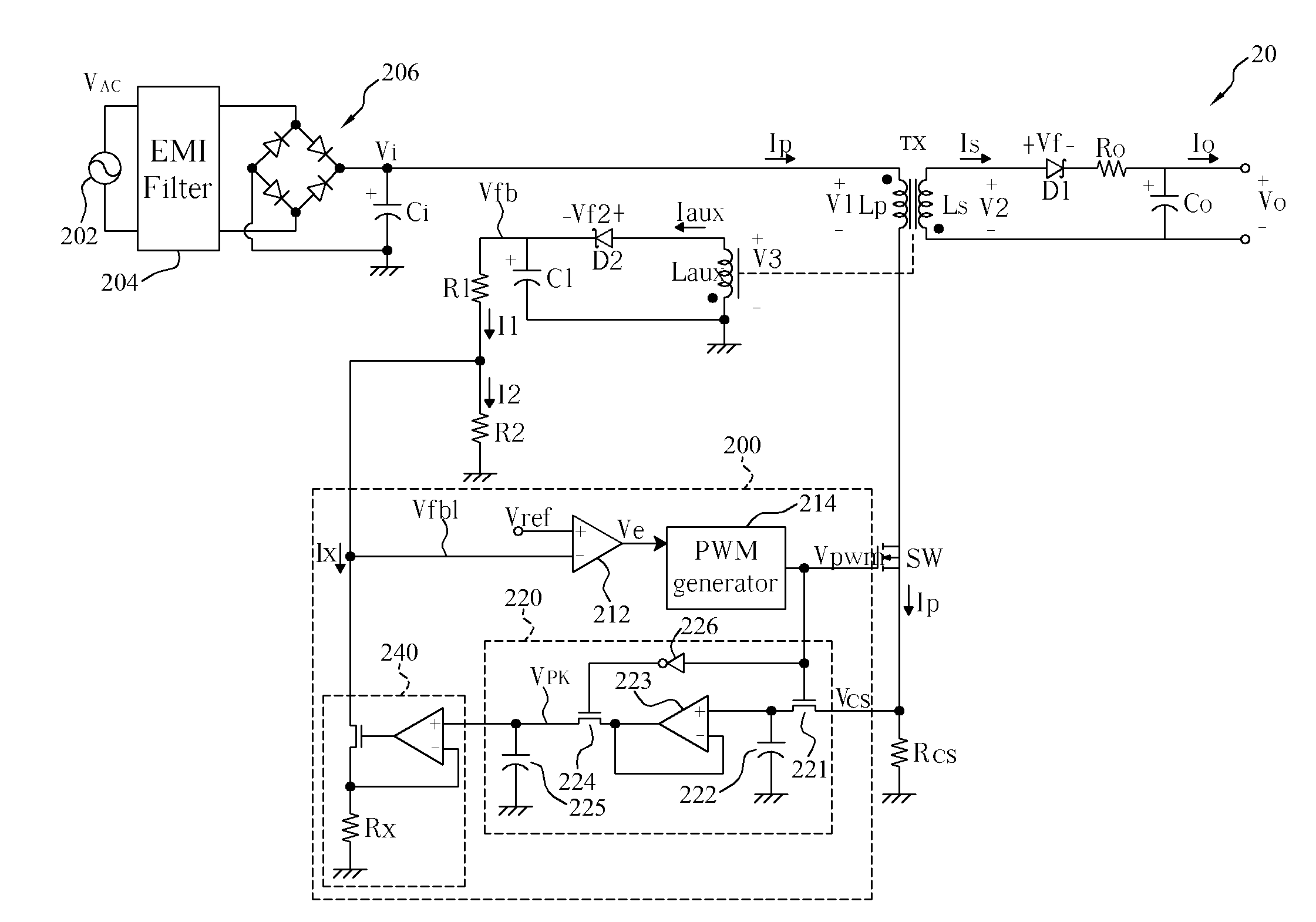
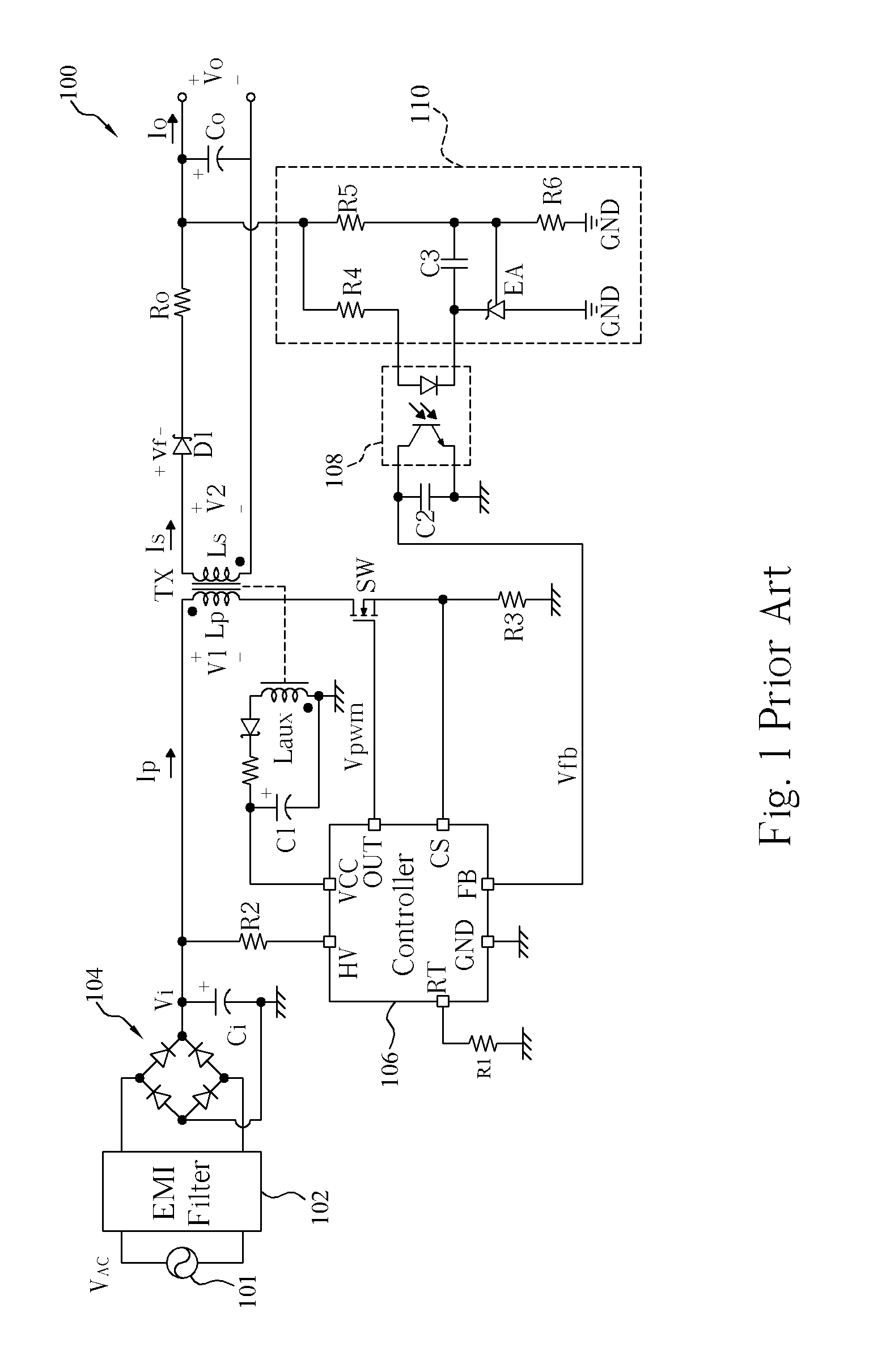
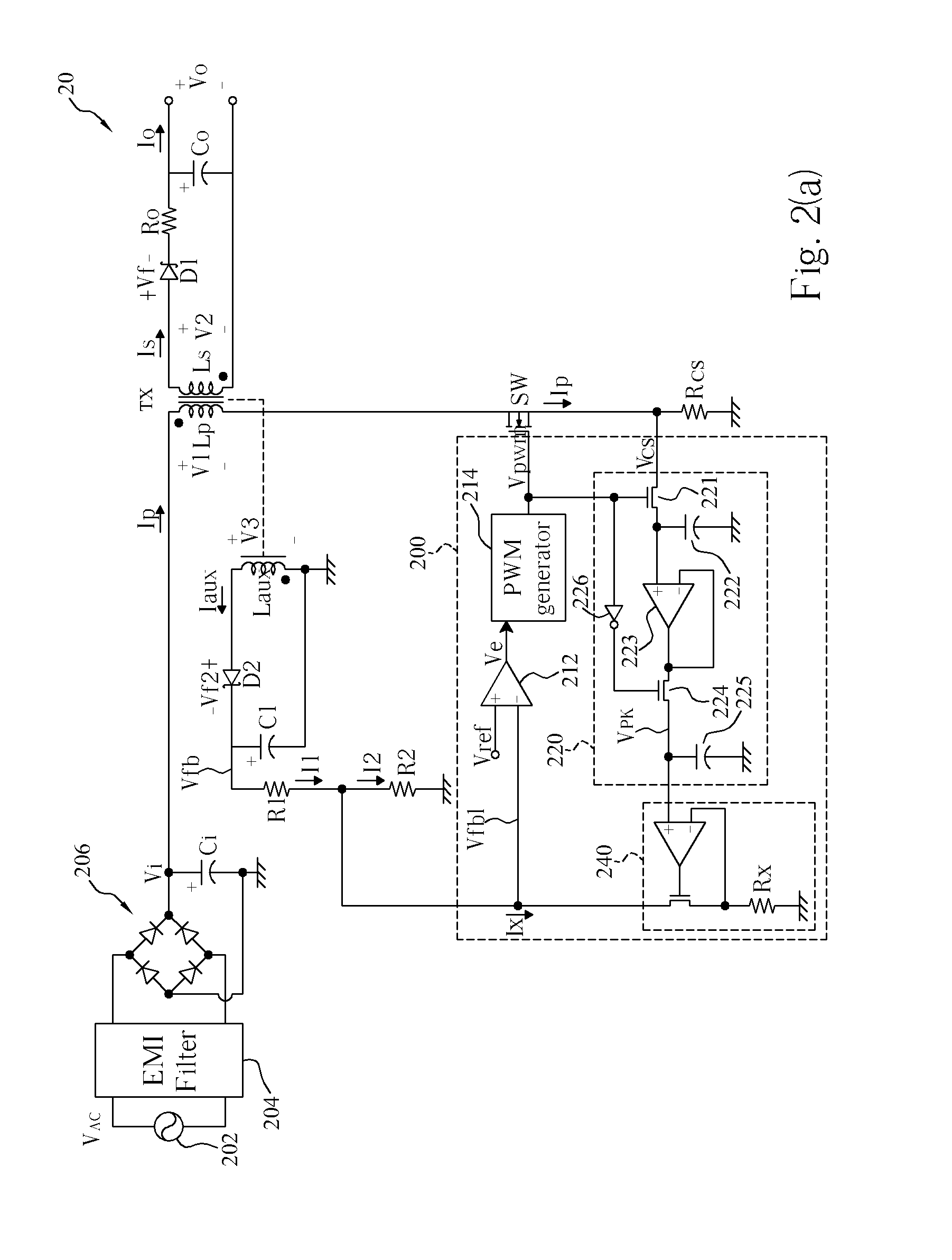
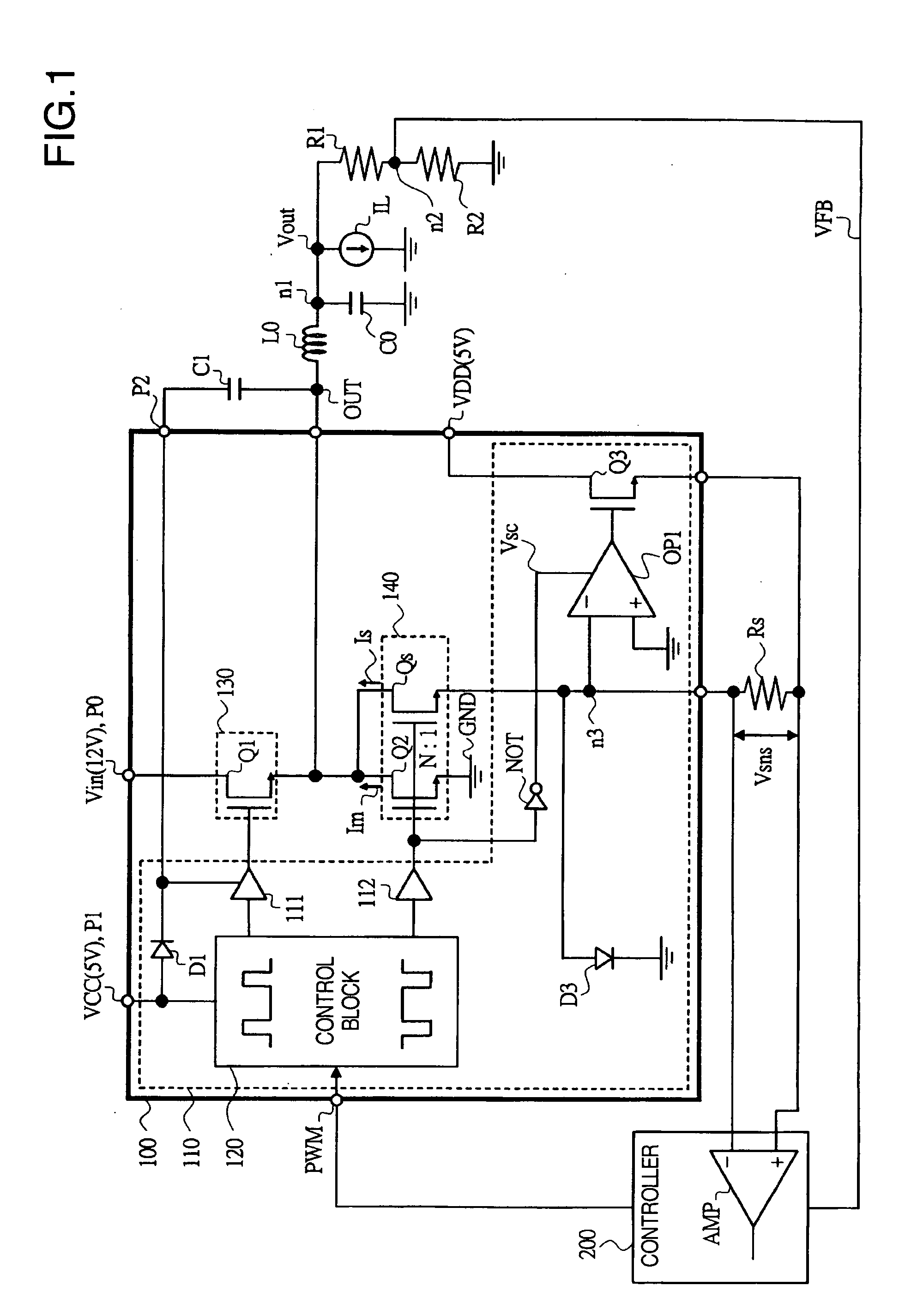
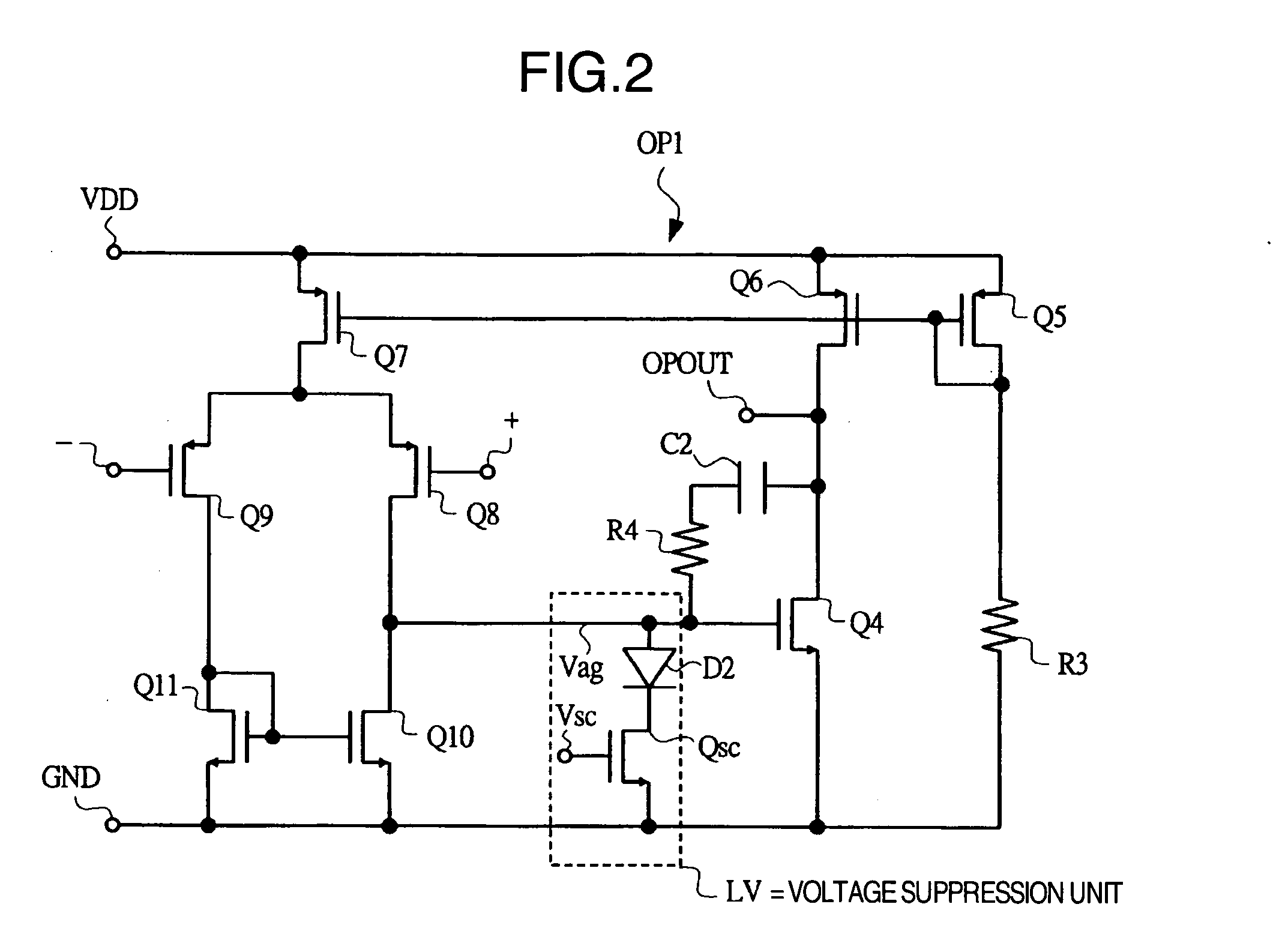
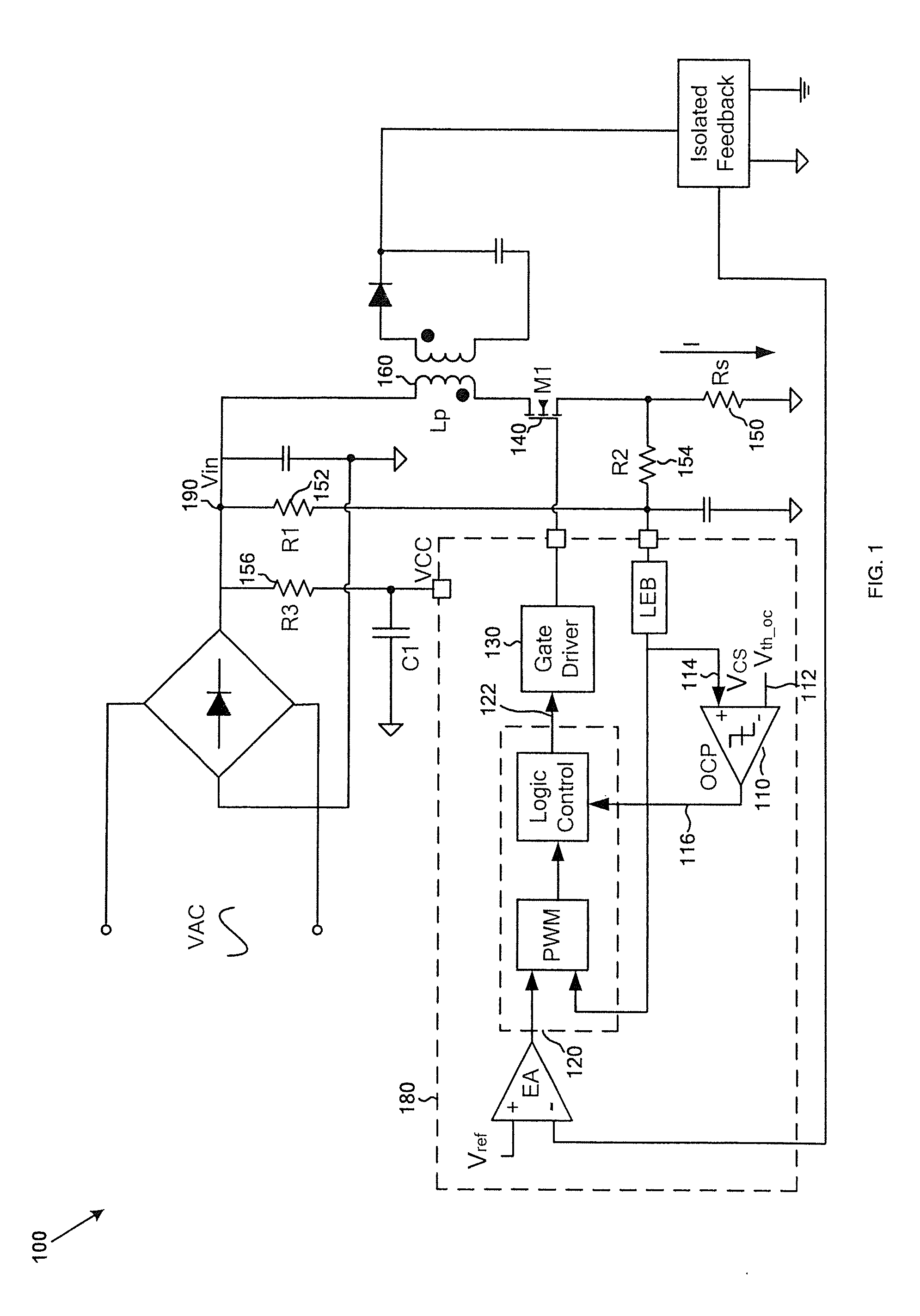
Switching-mode power converter and pulse-width-modulation control circuit with primary-side feedback control
A pulse-width-modulation control circuit of a switching-mode power converter with a primary-side feedback control is disclosed. The switching-mode power converter includes a transformer, a power switch, a current sensing resistor and the pulse-width-modulation control circuit. The transformer includes a primary-side winding, a secondary-side winding and an auxiliary winding. The pulse-width-modulation control circuit includes a sample and hold circuit, a transconductor circuit, an error amplifier and a pulse-width-modulation generator.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
Power supply driver circuit
InactiveUS20060113979A1Improve responseImproving Current Sensing AccuracyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A power supply driver circuit with low power losses and desired response characteristics with respect to changes in output and its miniaturization is provided. In a driver IC constituting a switched-mode power supply equipment controlling the switching, by pulse width modulation, of first and second power transistors passing a current in a coil, and outputting a voltage bucked or boosted from an input voltage, current sensing with desired responsiveness is enabled by providing a switching transistor between an inverted input terminal and a non-inverted input terminal of an operational amplifier, preventing, while the second power transistor is ON, the generation of a potential which is undefined when first power transistor is ON, i.e. when the second power transistor is OFF, and maintaining a node potential in a state in which the potential is well defined.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Feedback based apparatus, systems and methods for controlling emissive pixels using pulse width modulation and voltage modulation techniques
The present invention provides techniques for emissive pixels of flat panel displays. Specifically, pixel feedback and a combination of voltage modulation and pulse width modulation are used to improve the quality and consistency of aging pixels. Based on feedback, an image frame is divided into sub-frames of various time periods. Also based on feedback, a voltage, or voltages of different voltage levels, is (are) applied to the selected sub-frames to generate an image frame of a particular gray level. The human eye integrates the effects of the voltage and pulse width modulation techniques that are applied to the various sub-frames of the image frame, over the duration of the image frame.
Owner:LEADIS TECH
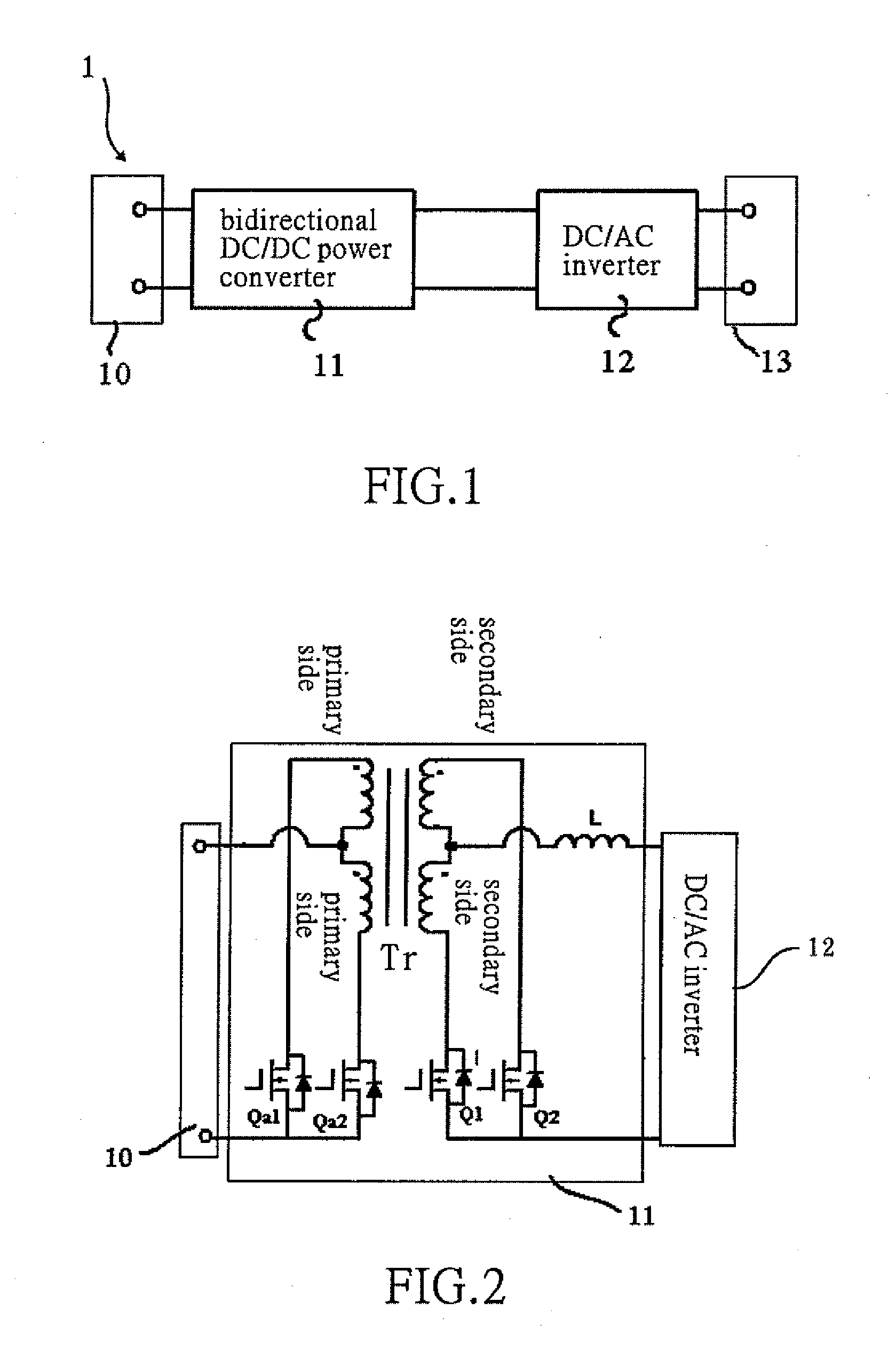
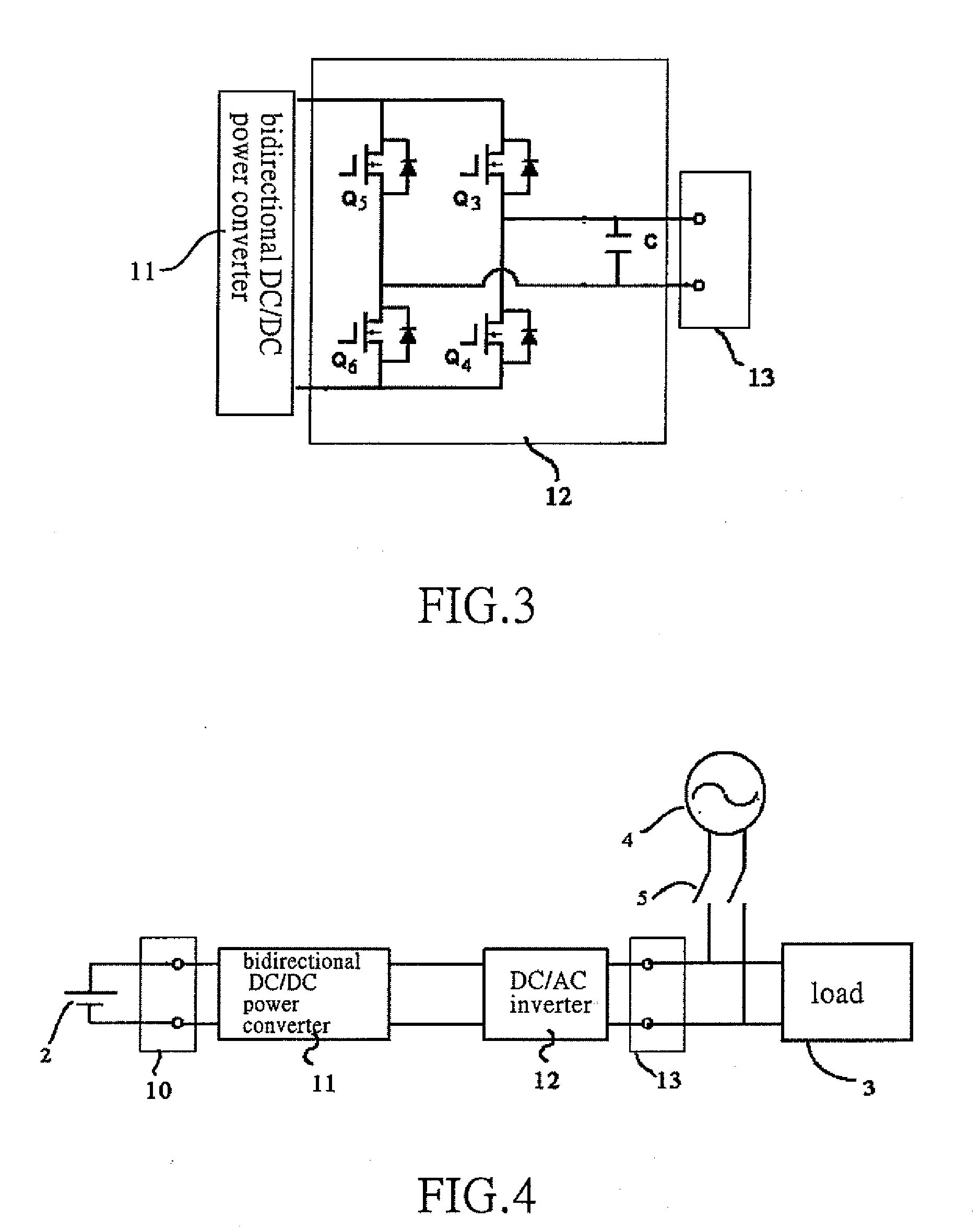
Bidirectional active power conditioner
InactiveUS20080062724A1Reduce switching lossesImprove power efficiencyDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsPower conditionerDc current
A bidirectional active power conditioner includes a DC side, a bidirectional DC / DC power converter, a DC / AC inverter and an AC side. The DC side electrically connects with a DC source while the AC side electrically connects with a load and an AC source. The bidirectional DC / DC power converter is controlled via high-frequency pulse width modulation (PWM) switching so as to generate a predetermined DC voltage or DC current while the DC / AC inverter is controlled to convert the predetermined DC voltage or DC current into a predetermined AC voltage or AC current.
Owner:ABLEREX ELECTRONICS CO LTD
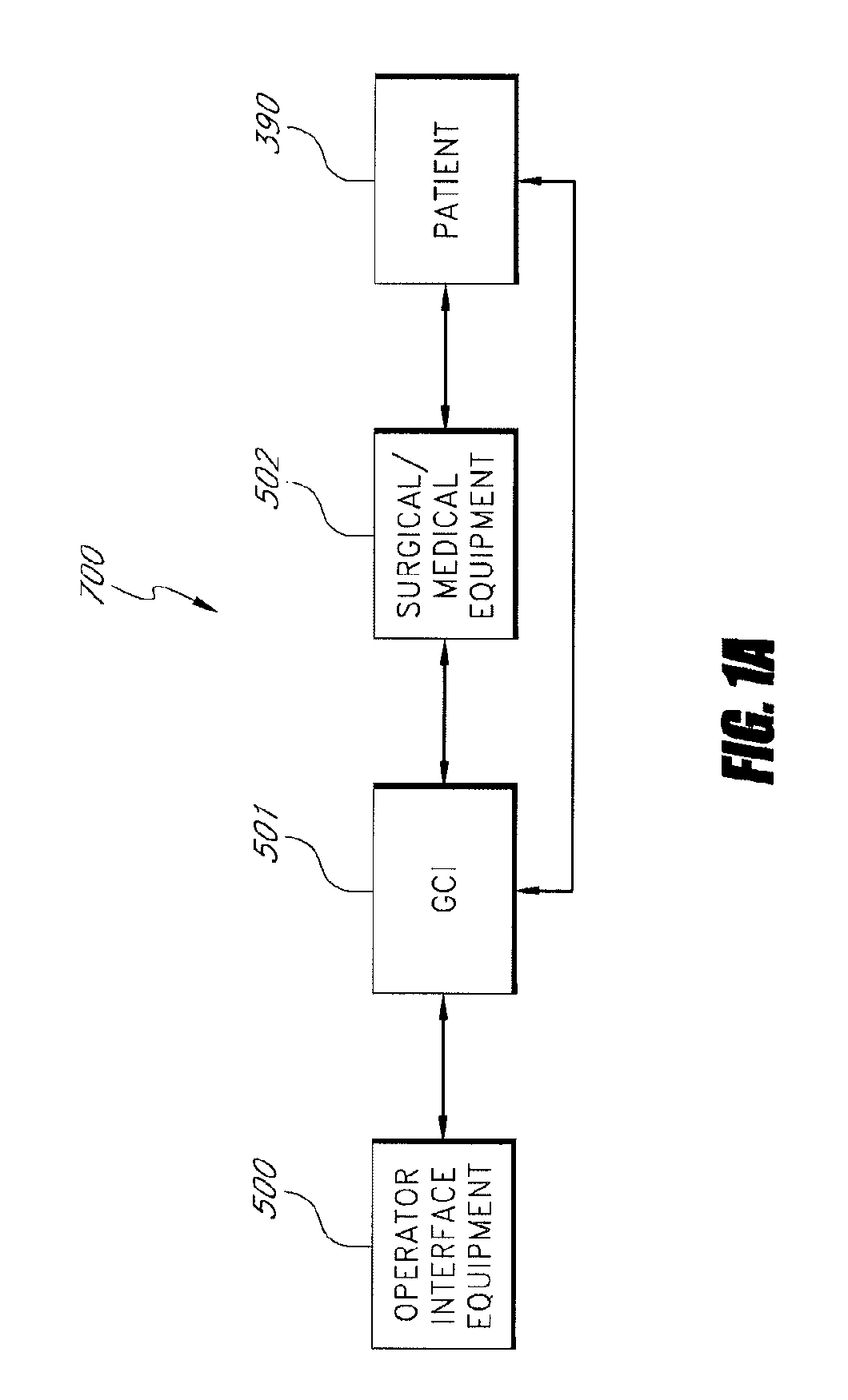
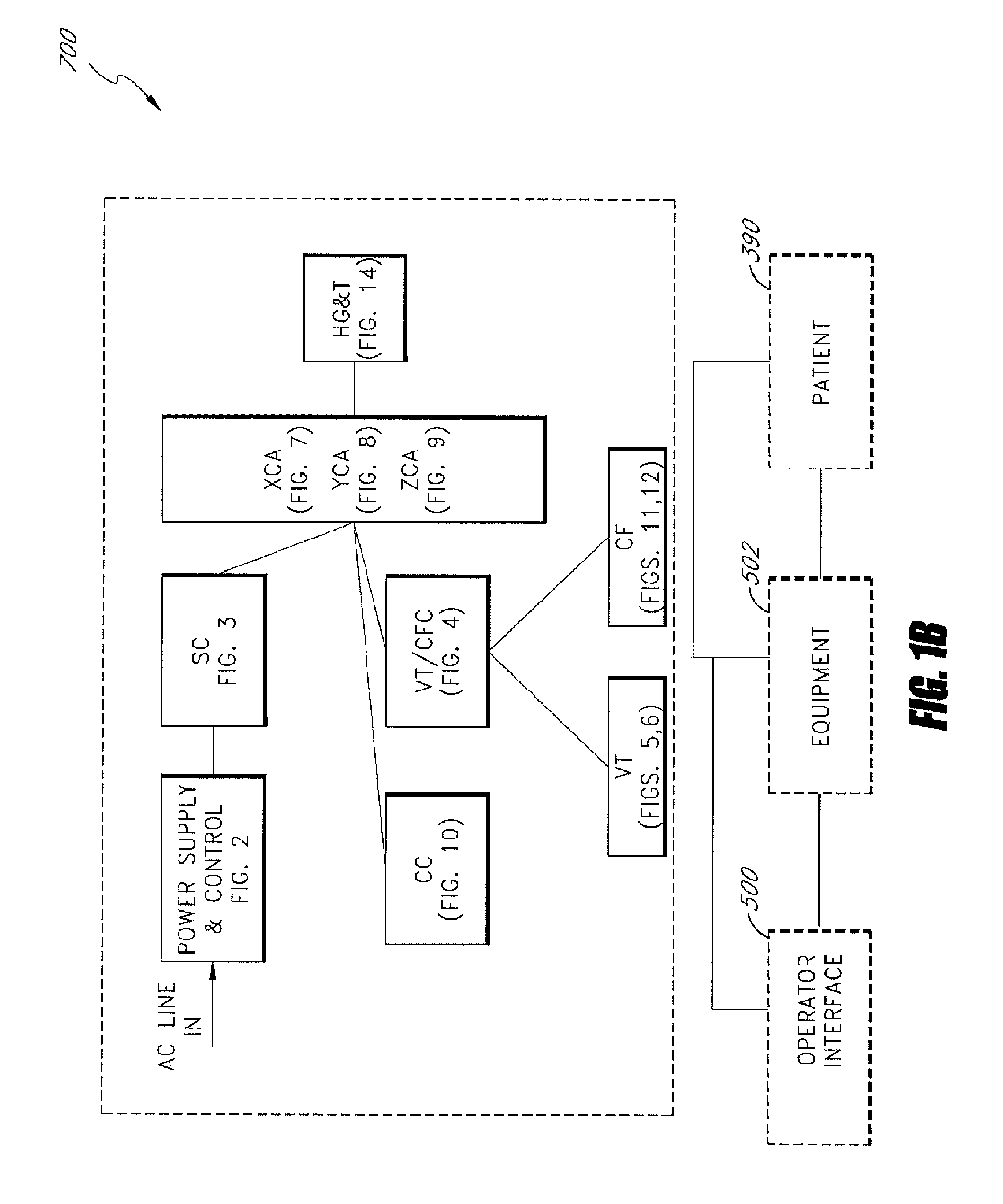
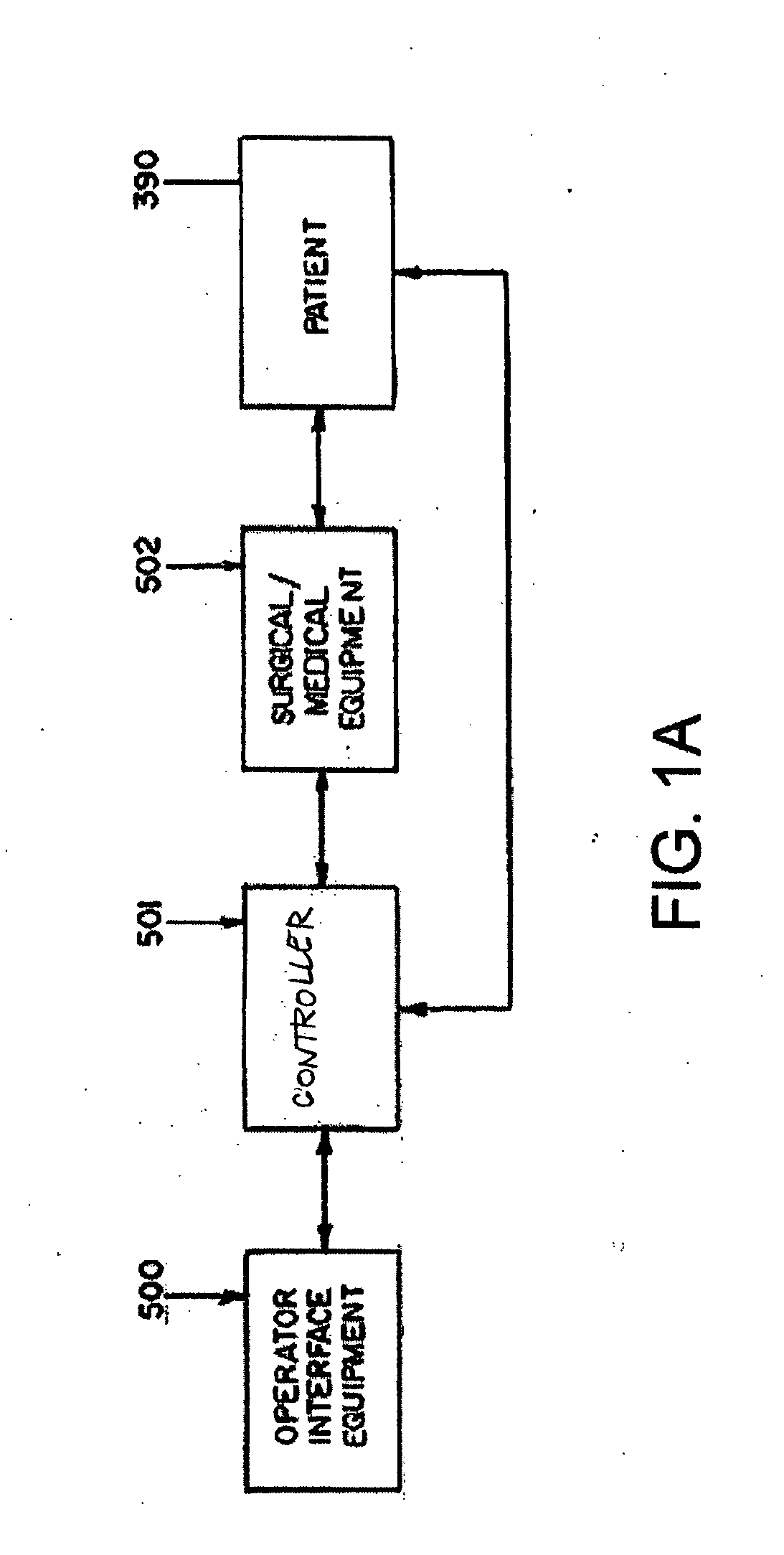
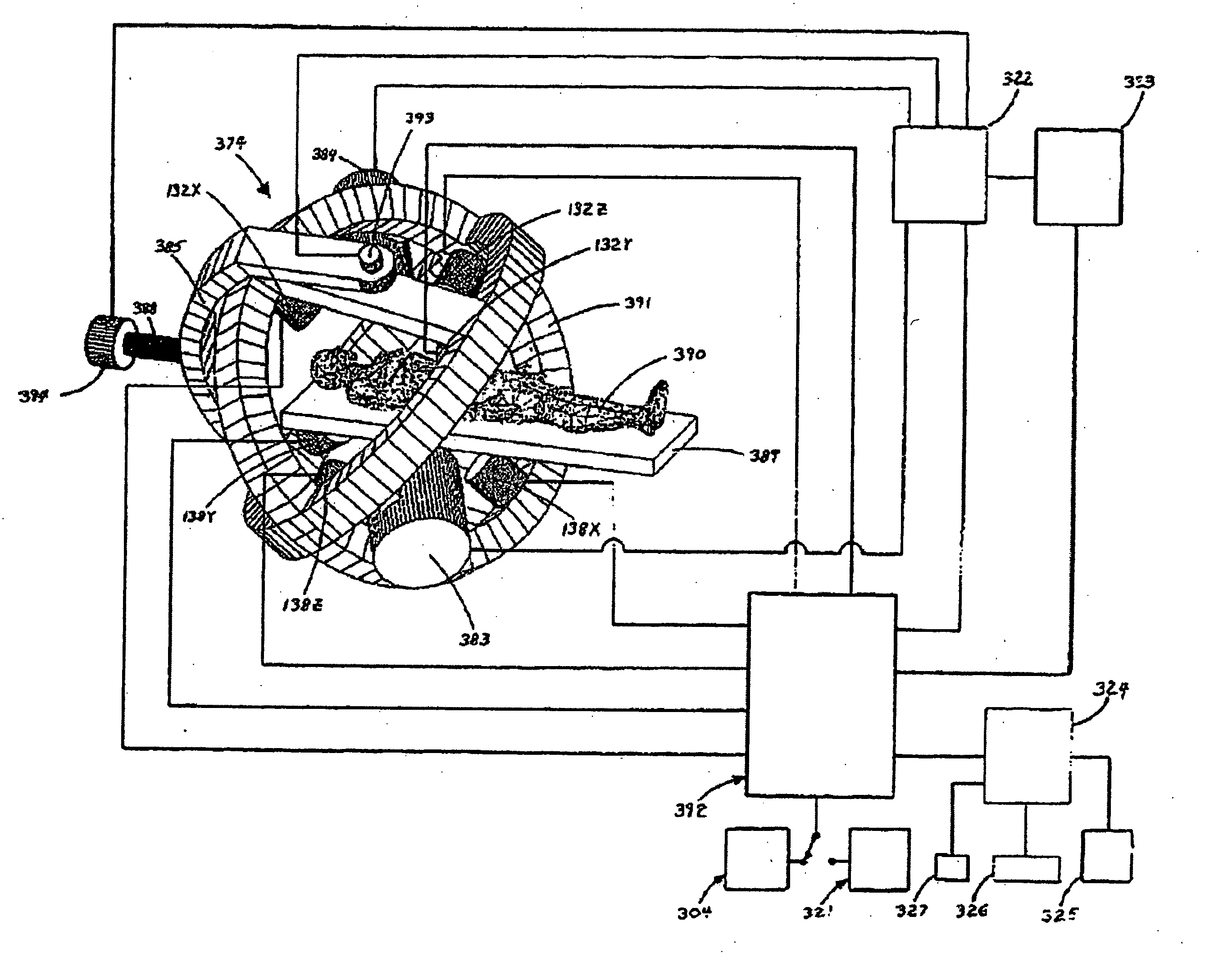
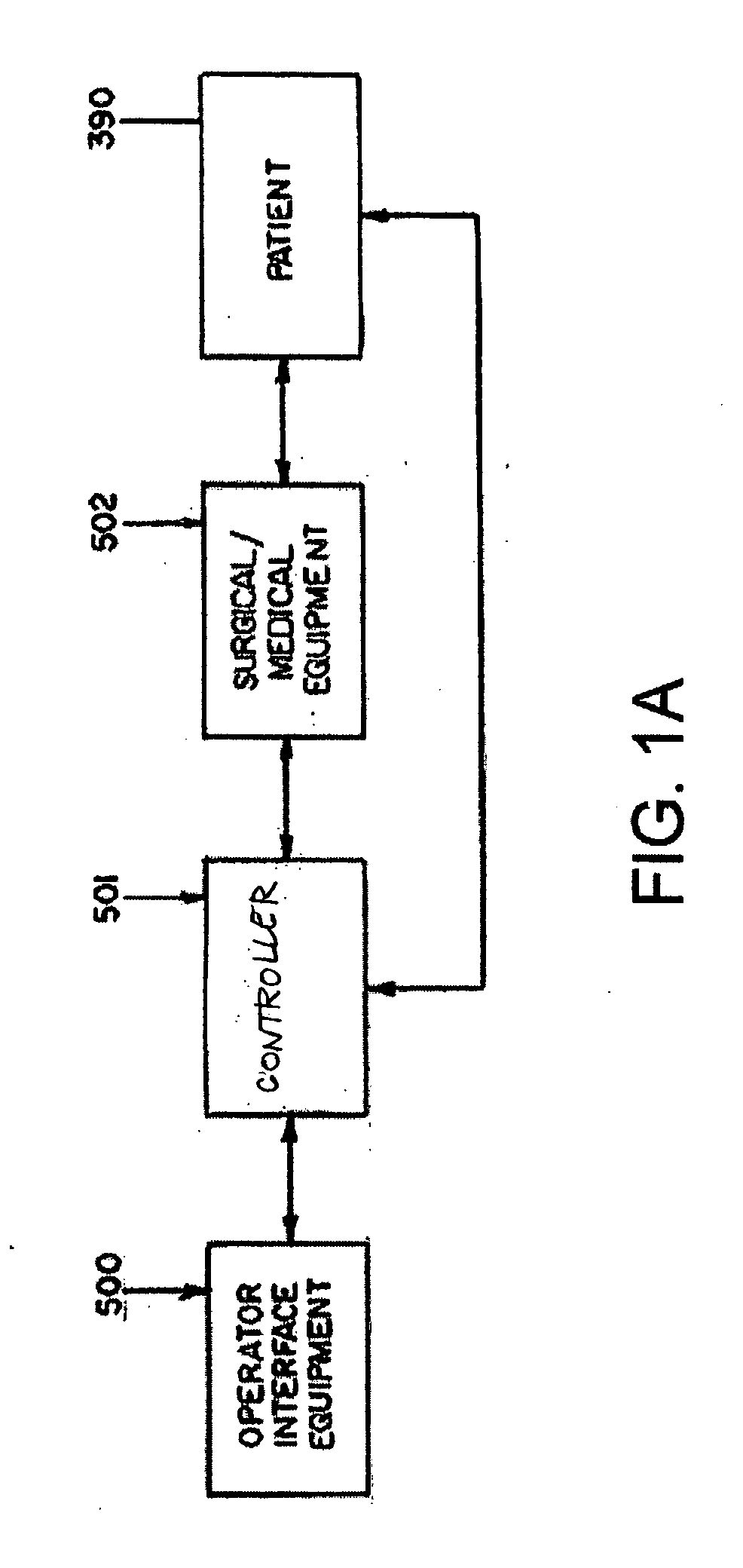
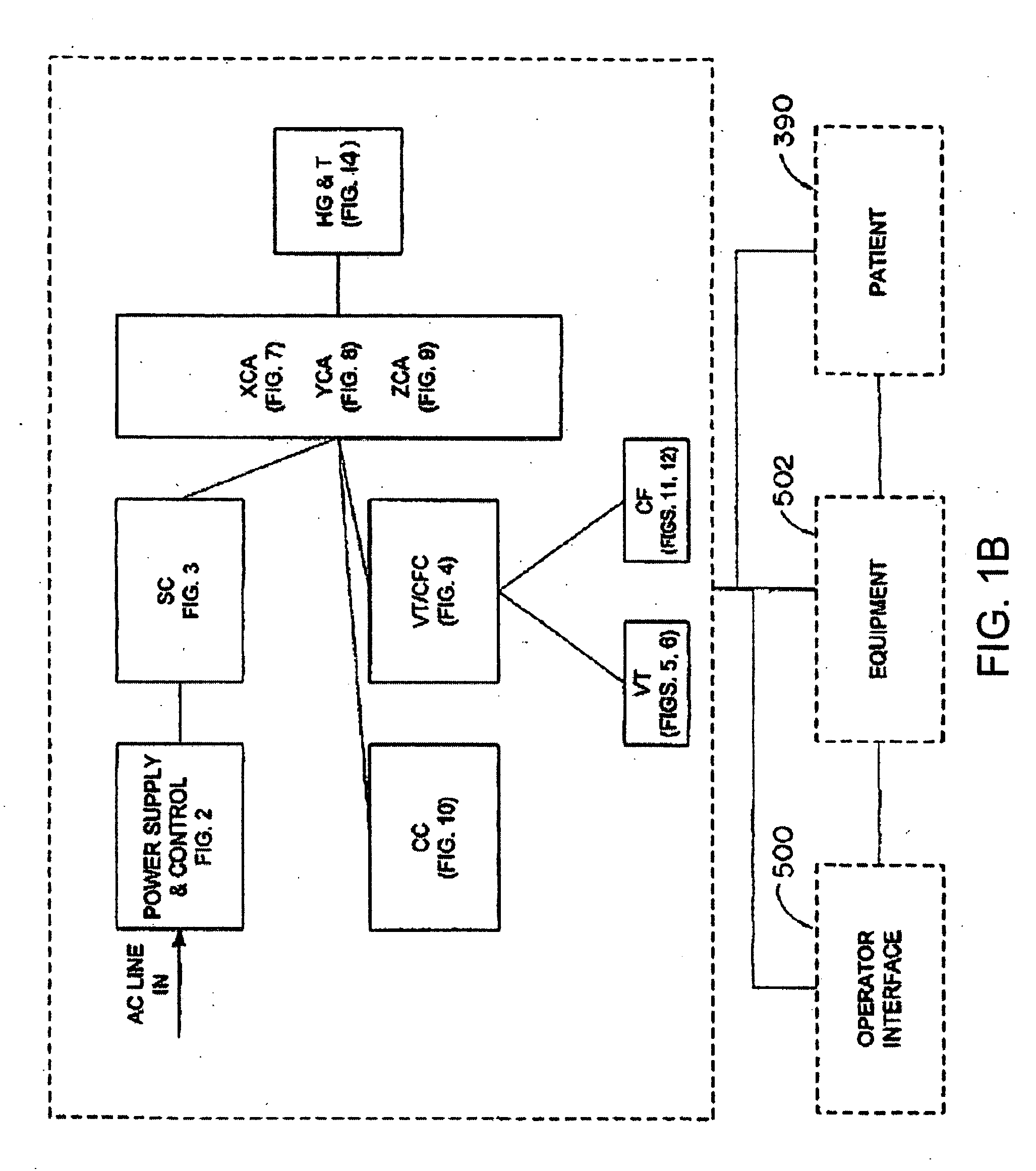
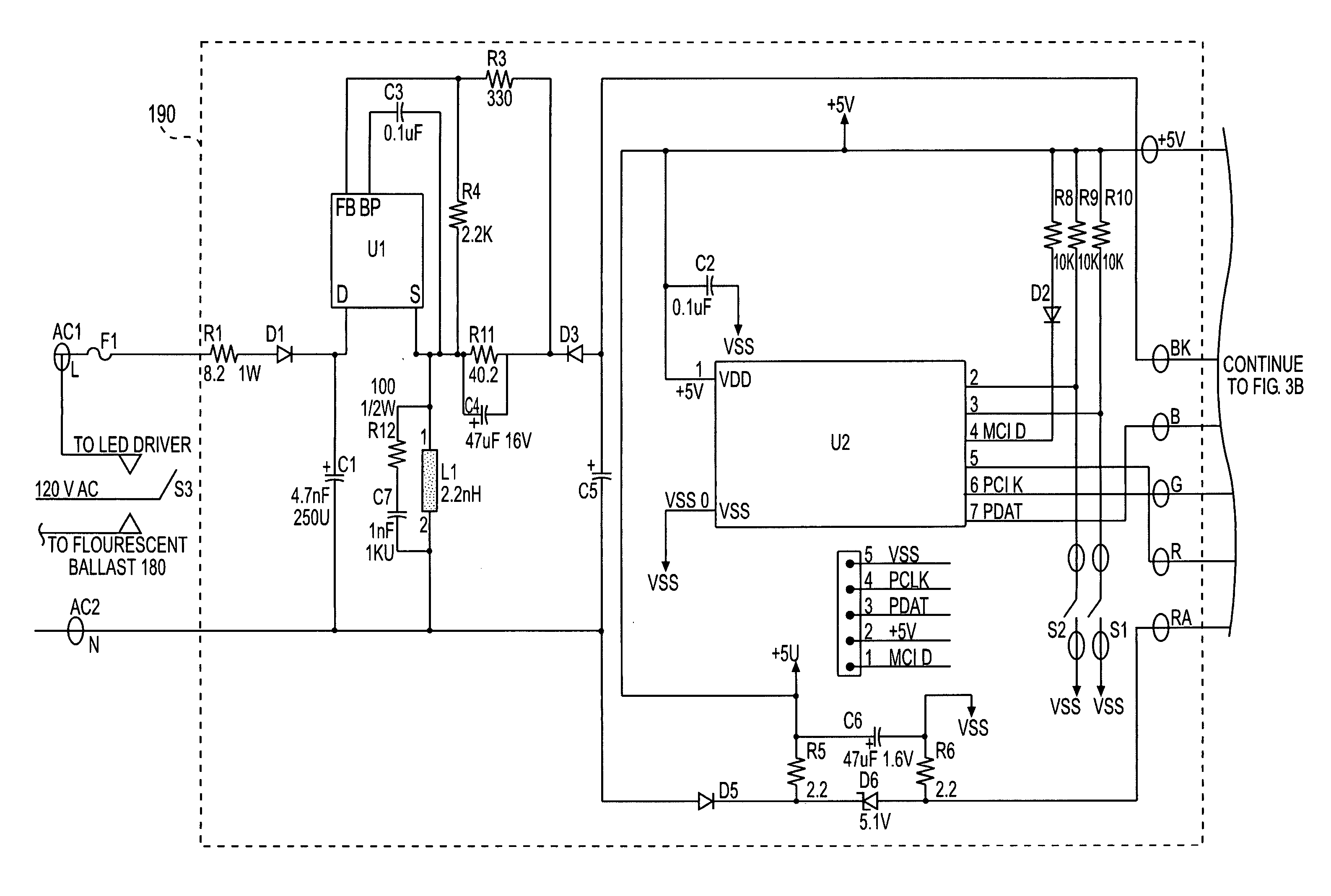
Apparatus and method for catheter guidance control and imaging
InactiveUS7769427B2Less trainingLess skillSurgical navigation systemsCatheterTip positionGuidance control
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and positioned. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
System and method for a magnetic catheter tip
InactiveUS20060116633A1Less trainingMinimizing x-raySurgical navigation systemsMedical devicesTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Constant current driving device, backlight light source device, and color liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20050231459A1Electroluminescent light sourcesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentLiquid-crystal display
A constant current driving device for constant current driving of a plurality of elements connected in series with each other by a pulse width modulation constant current driving circuit includes: switching elements respectively connected in parallel with the plurality of elements connected in series with each other; a control circuit for performing control to bypass a driving current flowing through the other elements than an arbitrary element to be measured via the respective switching elements and pass a measuring driving current through only the element to be measured; and a detecting circuit for identifying an element at a faulty position by detecting the driving current flowing through the plurality of elements connected in series with each other.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for generating a magnetic field
InactiveUS20060114088A1Less trainingMinimizing x-raySurgical navigation systemsMagnetsTip positionDisplay device
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
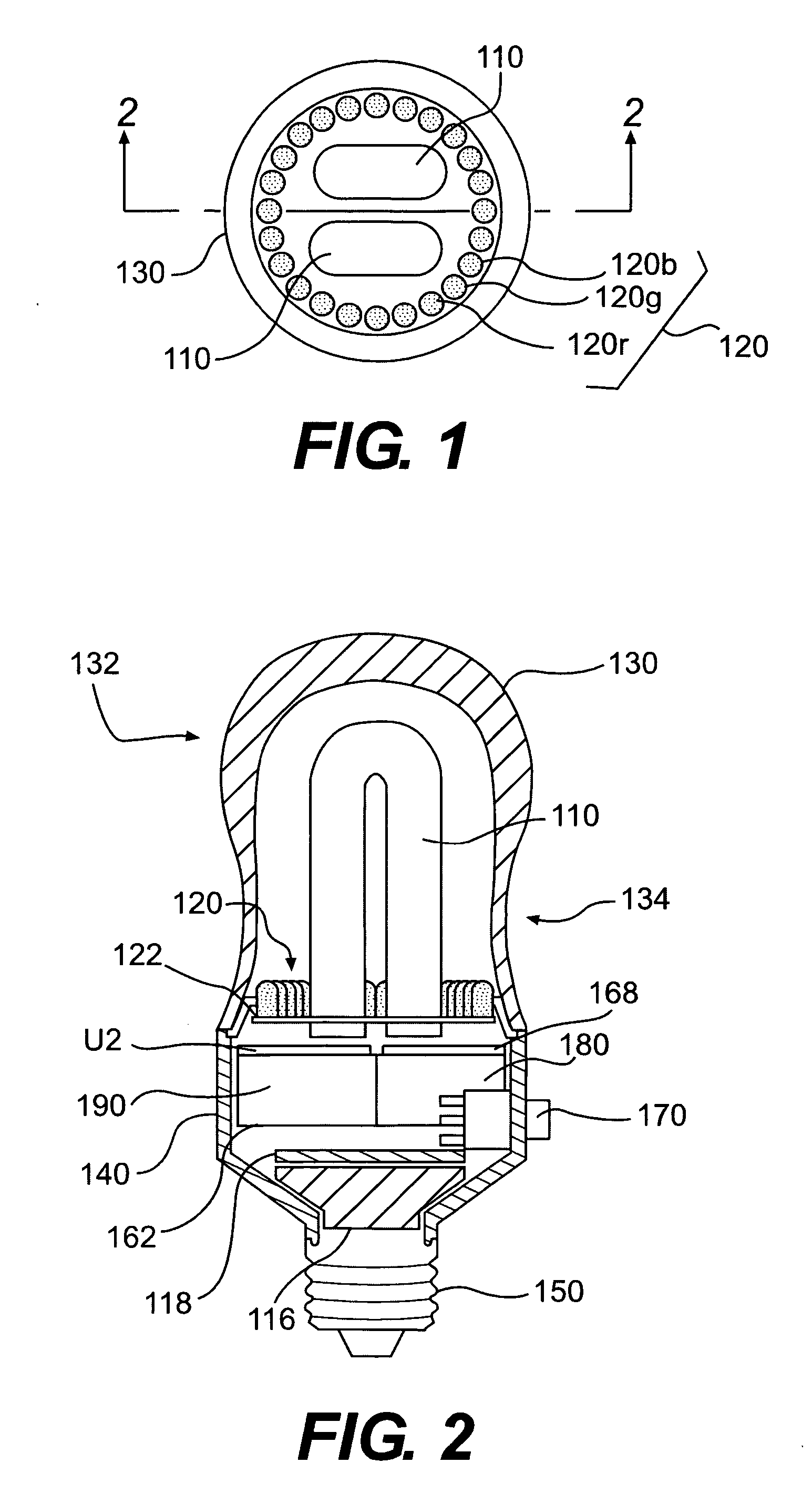
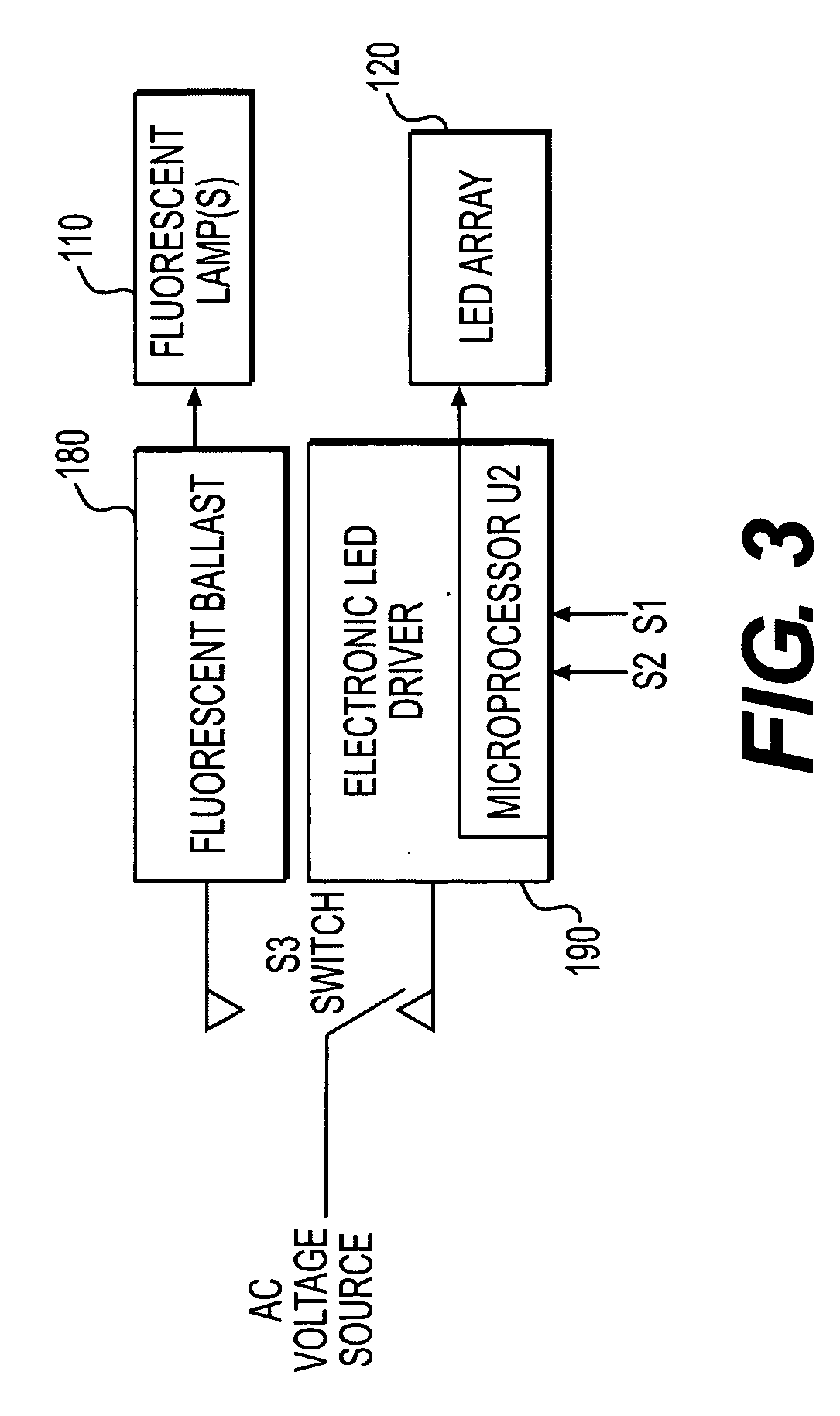
Lighting device having a circuit including a plurality of light emitting diodes, and methods of controlling and calibrating lighting devices
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
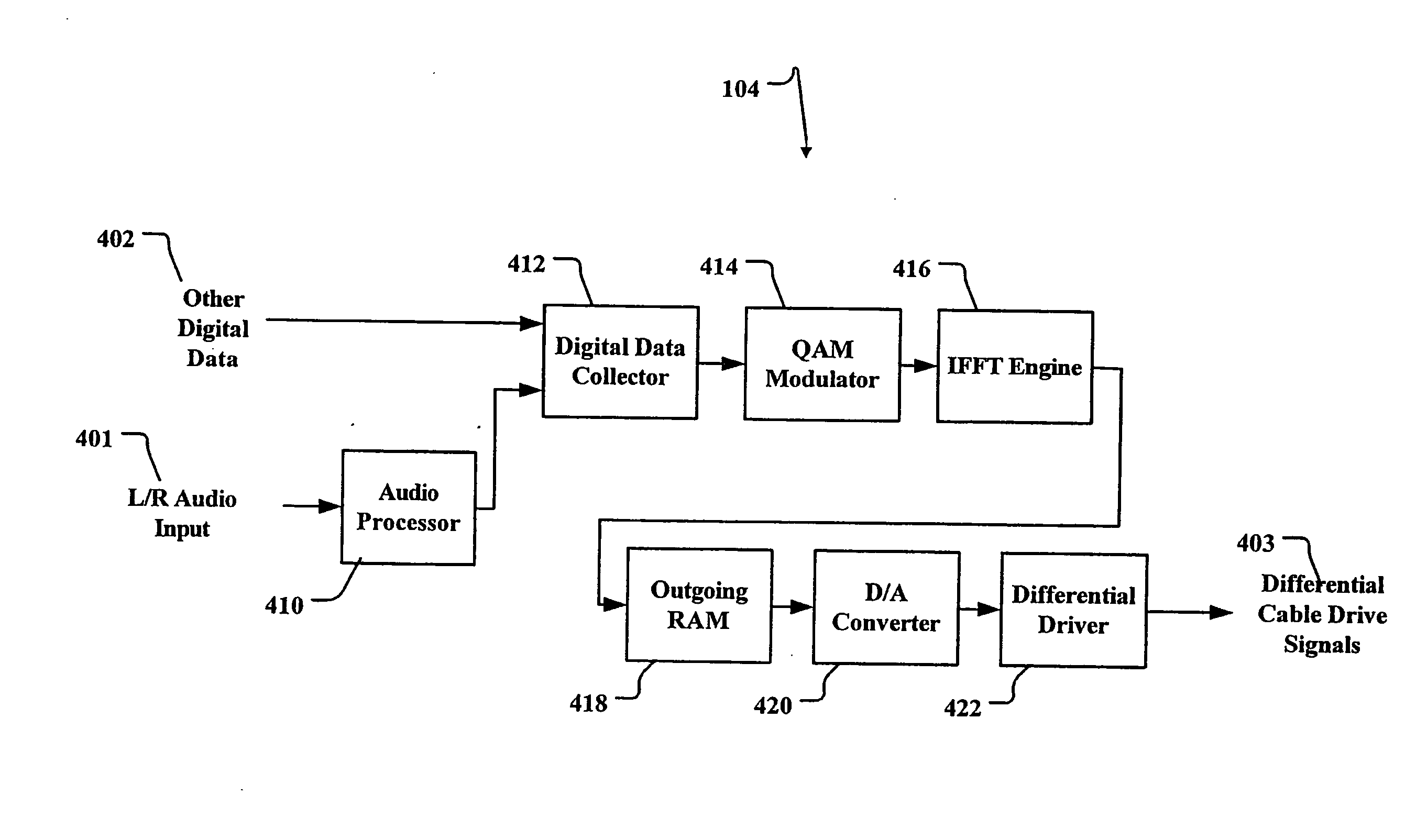
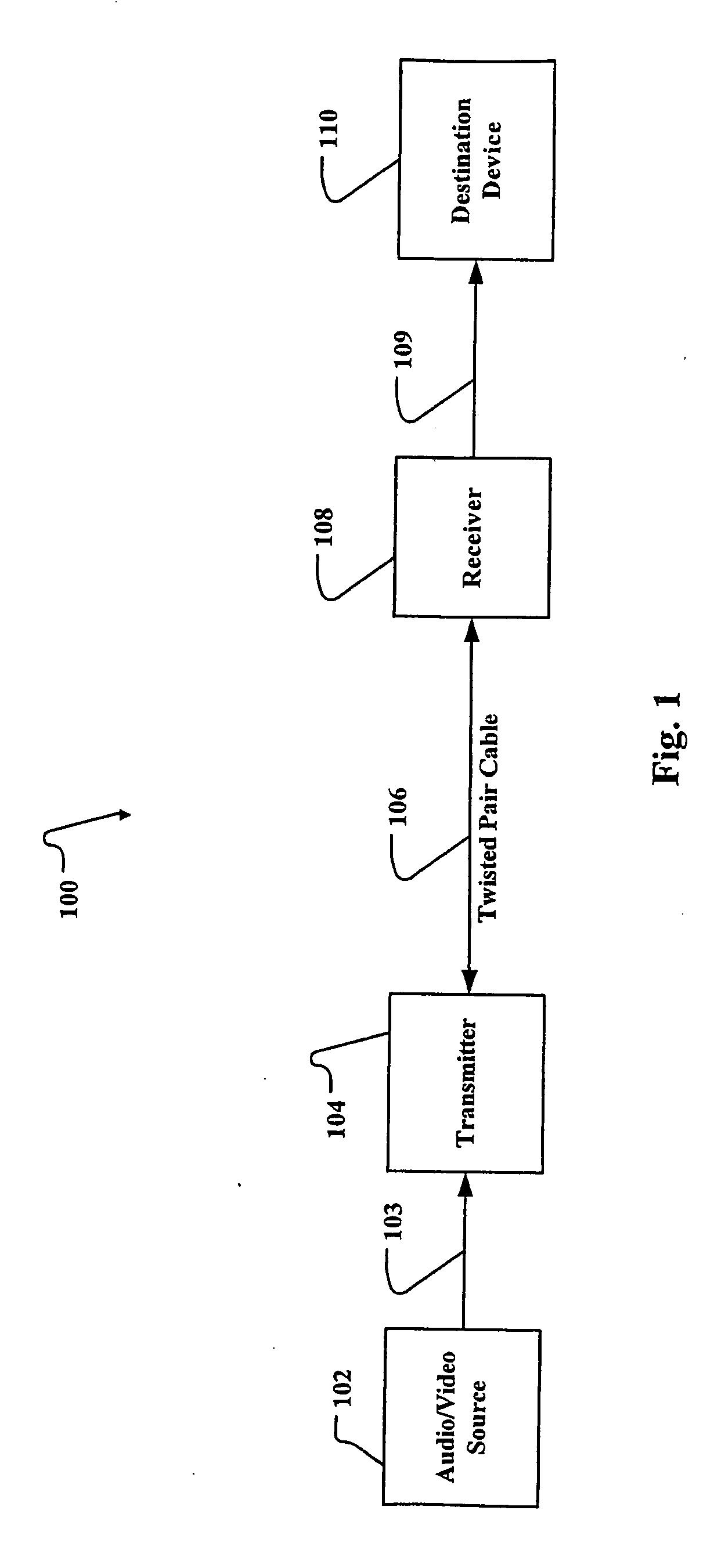
Method and apparatus for extending the transmission capability of twisted pair communication systems
InactiveUS20090059782A1Improve transmission performanceDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemClosed loop feedback
A closed loop feedback system is employed in a receiver to automatically compensate the communication signal from twisted pair cables for AC and DC losses. This is accomplished through the use of a reference pulse signal which is sent along with other digital information. At the receiver, the reference pulse signal is restored to its proper level through a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)-controlled variable compensation amplifier circuit. The received reference signal is compared to a known reference value and the duty cycle of the PWM circuit is adjusted until the proper level reference signal is achieved. Thereafter, the digital signal is extracted. OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) with pilot tones are used to maximize payload while minimizing crosstalk effects. The pilot tones locate the OFDM symbols in time while supplying compensation information concerning the transmission medium.
Owner:RGB SYST INC
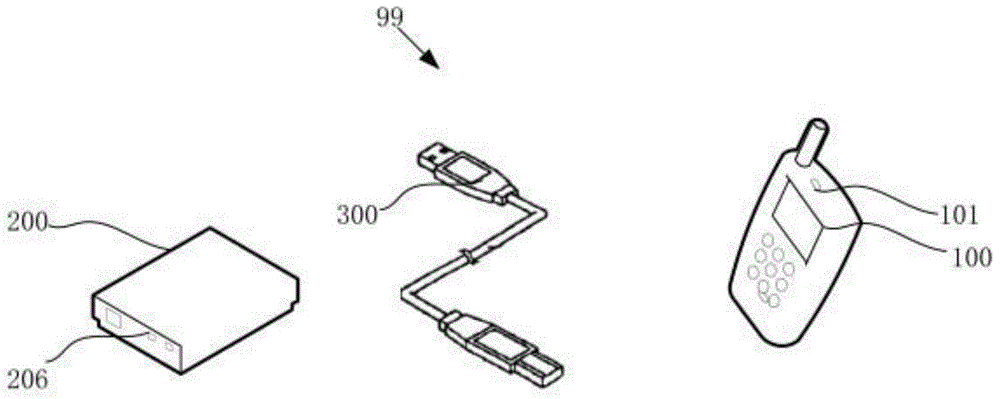
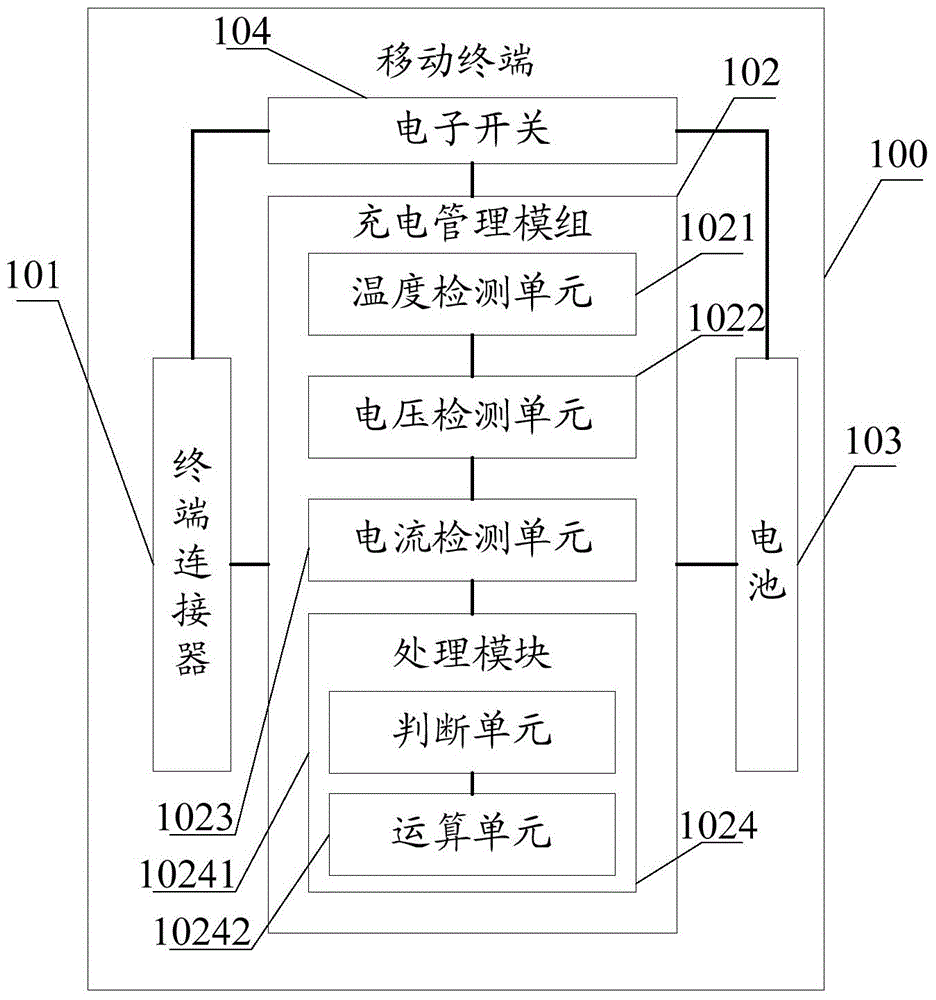
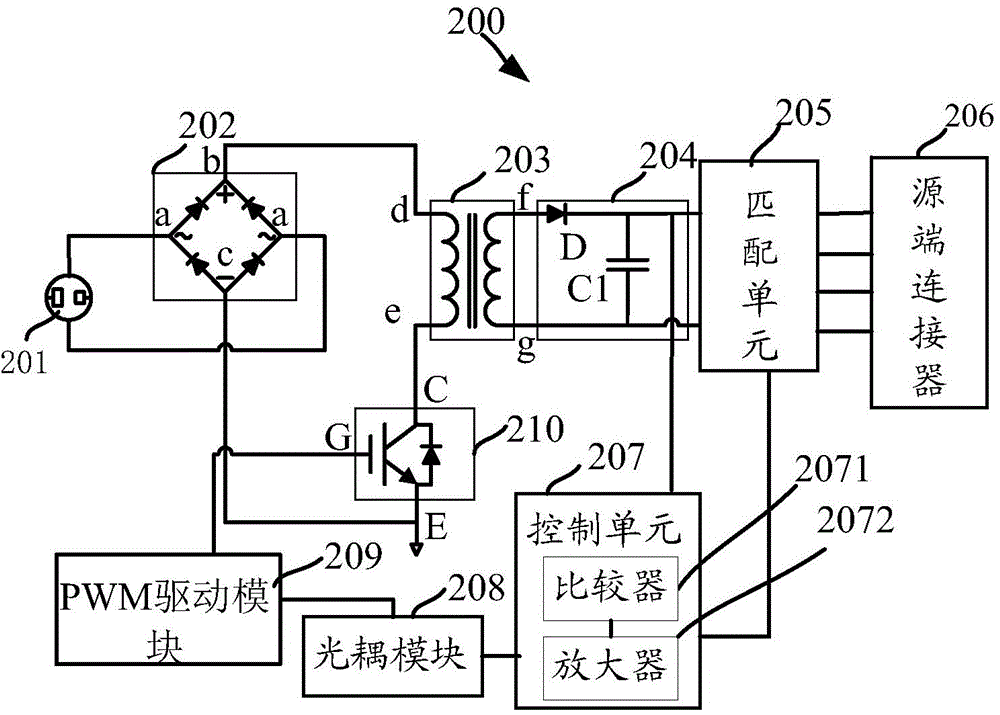
Adapter
The invention discloses an adapter. A mobile terminal is charged through a data line, and a source end connector is used for receiving required charging voltage and required charging current from the mobile terminal. A control unit is used for obtaining the charging voltage and the charging current. The control unit is used for comparing the charging voltage and the charging current with the required charging voltage and the required charging current respectively, and a control signal is generated when the charging voltage and the charging current are different from the required charging voltage and the required charging current. A PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) driving module is used for adjusting an output pulse signal according to the control signal so as to control the start frequency of a switch unit and change a third alternating current, and thus the charging voltage and the charging current are adjusted to the required charging voltage and the required charging current. In the charging process of the adapter, the adapter outputs voltage and current matched with the required charging voltage and the required charging current of the mobile terminal, and thus the charging effect of the mobile terminal is better.
Owner:李昊
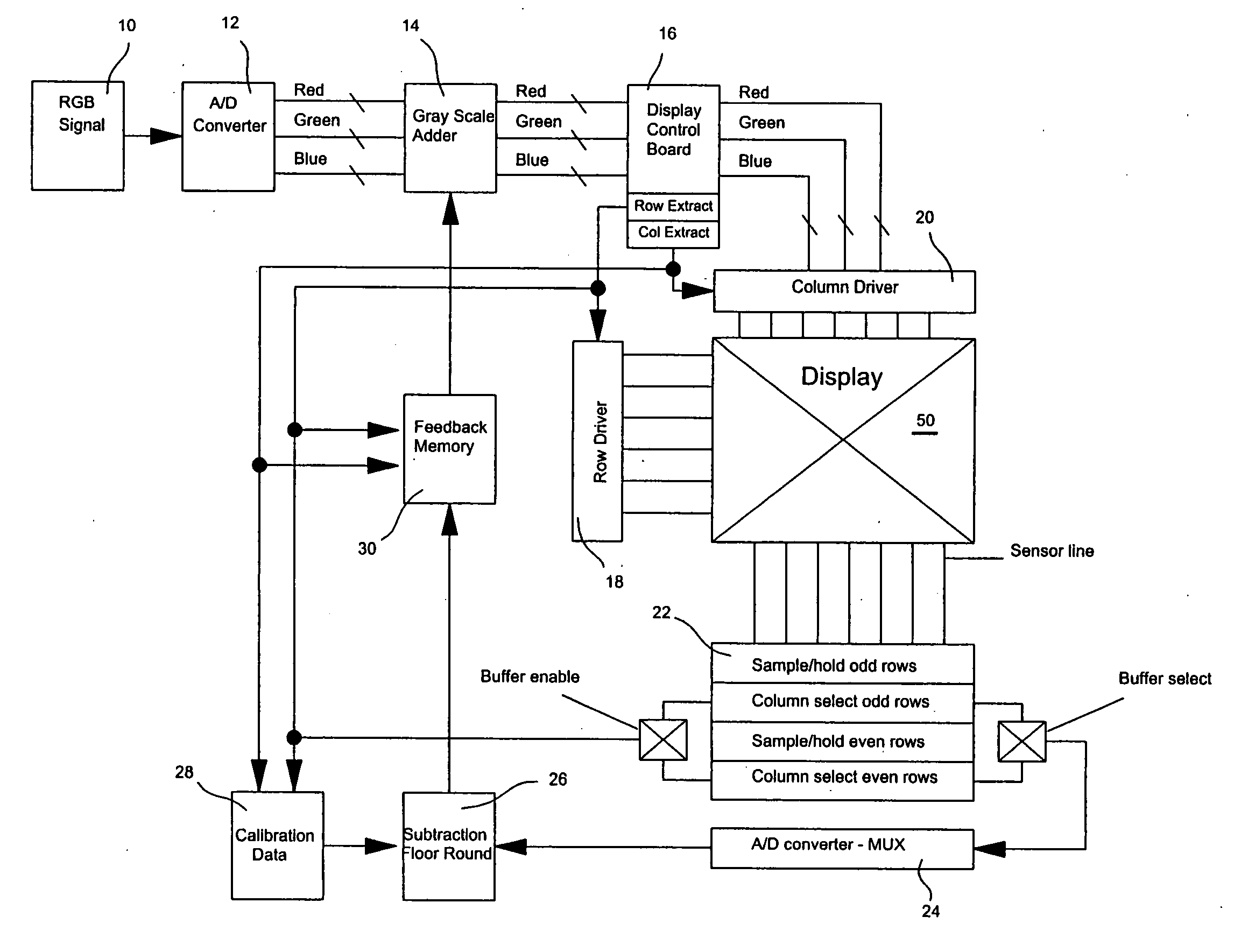
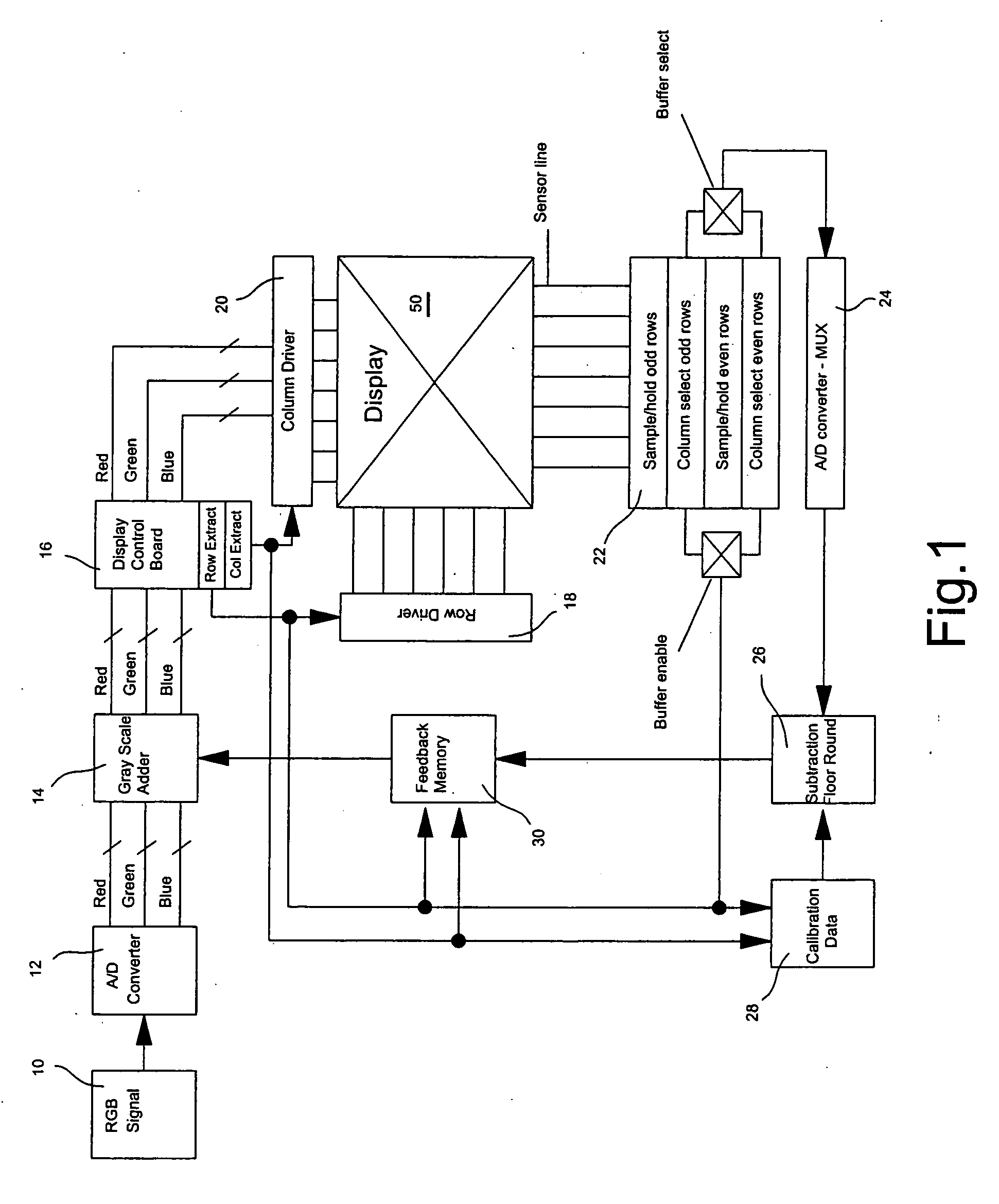
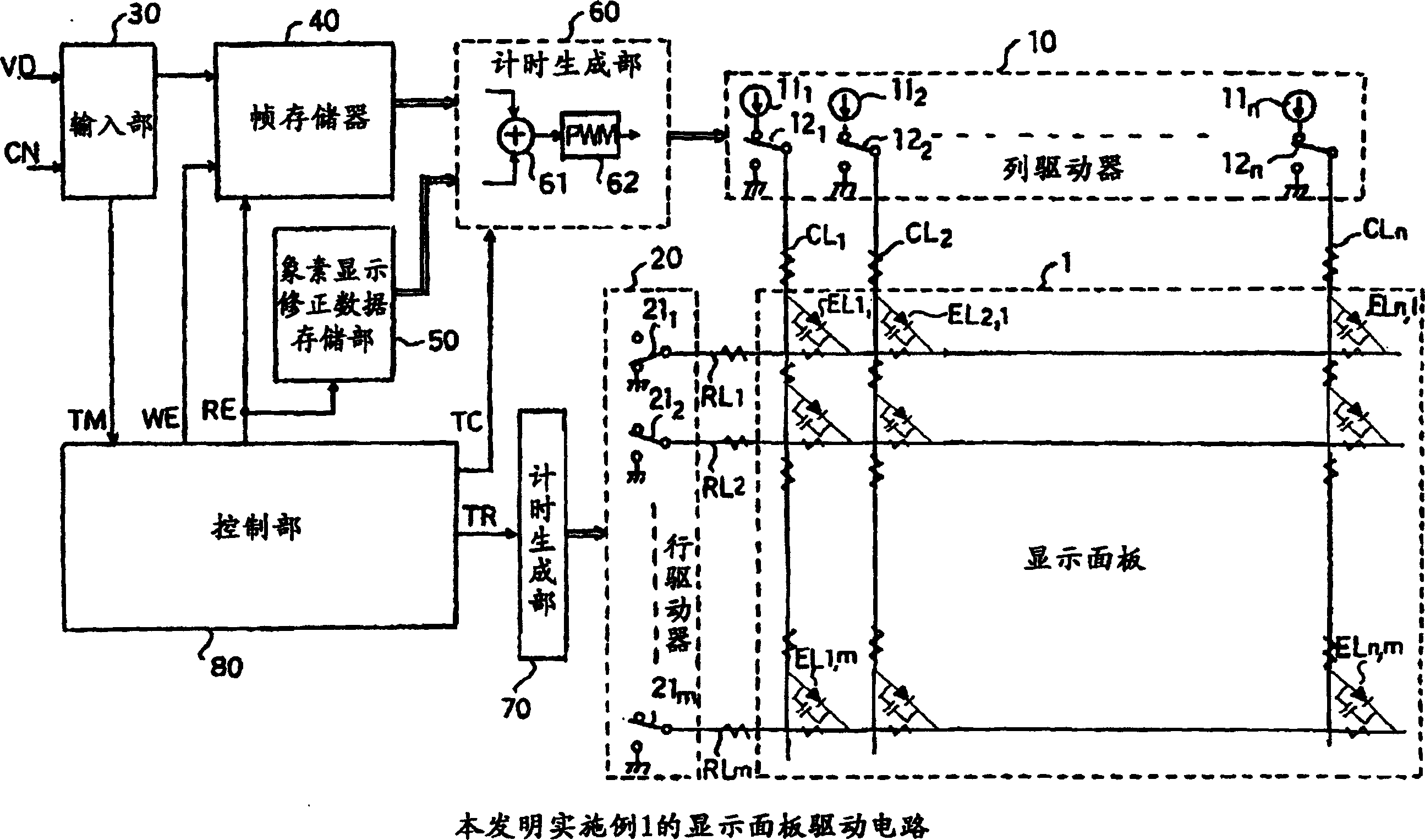
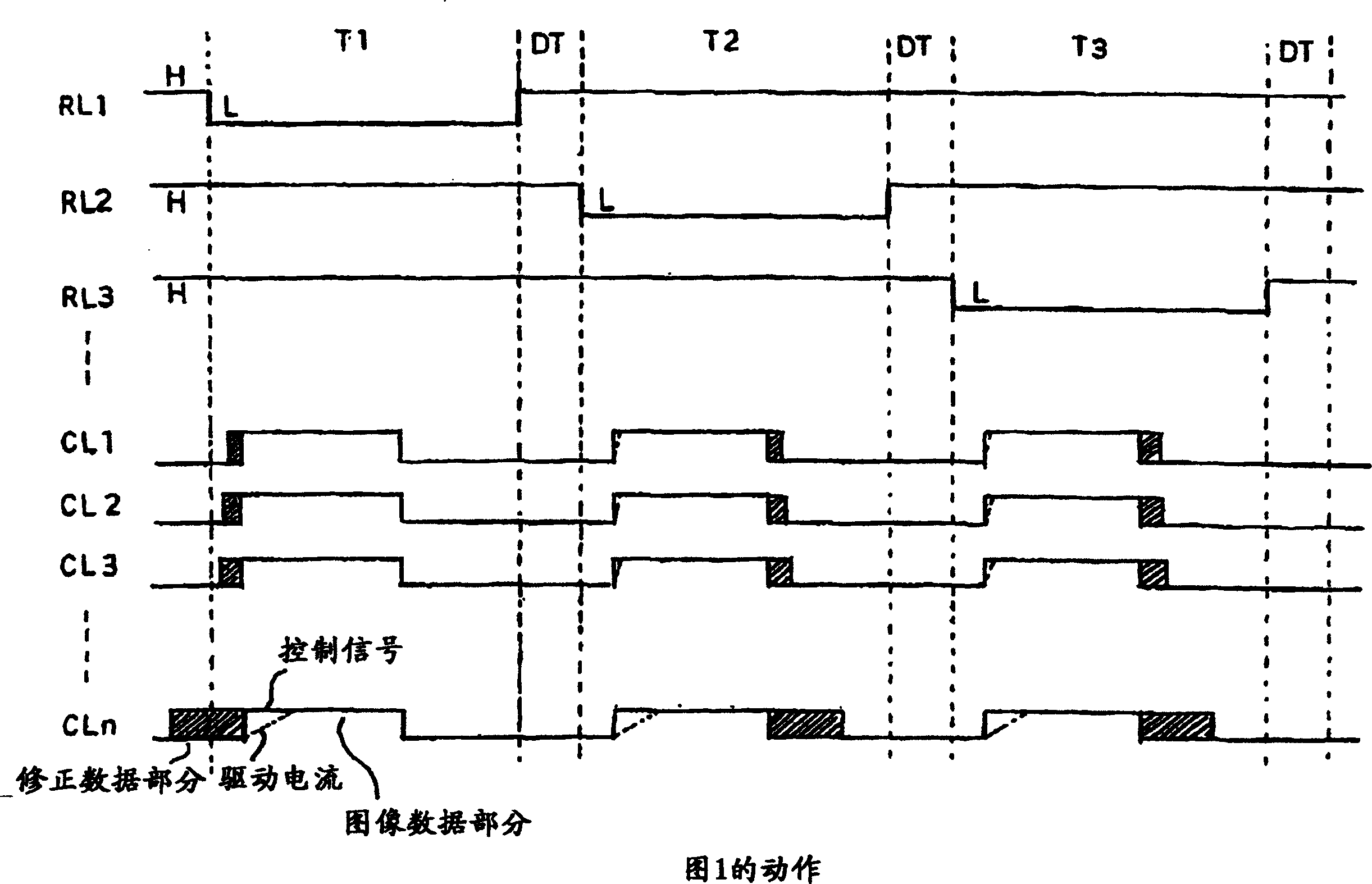
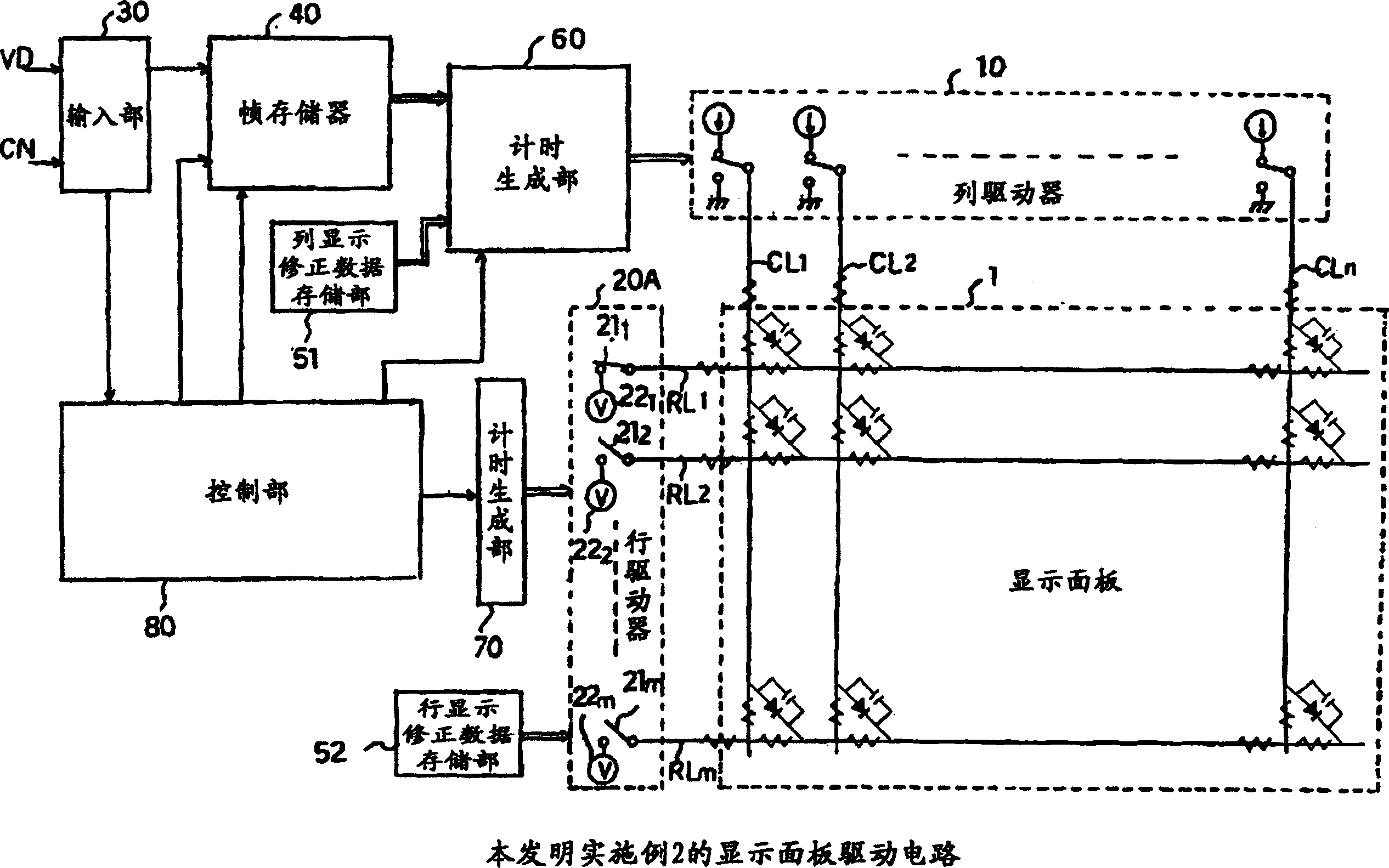
Display panel driving circuit and driving method
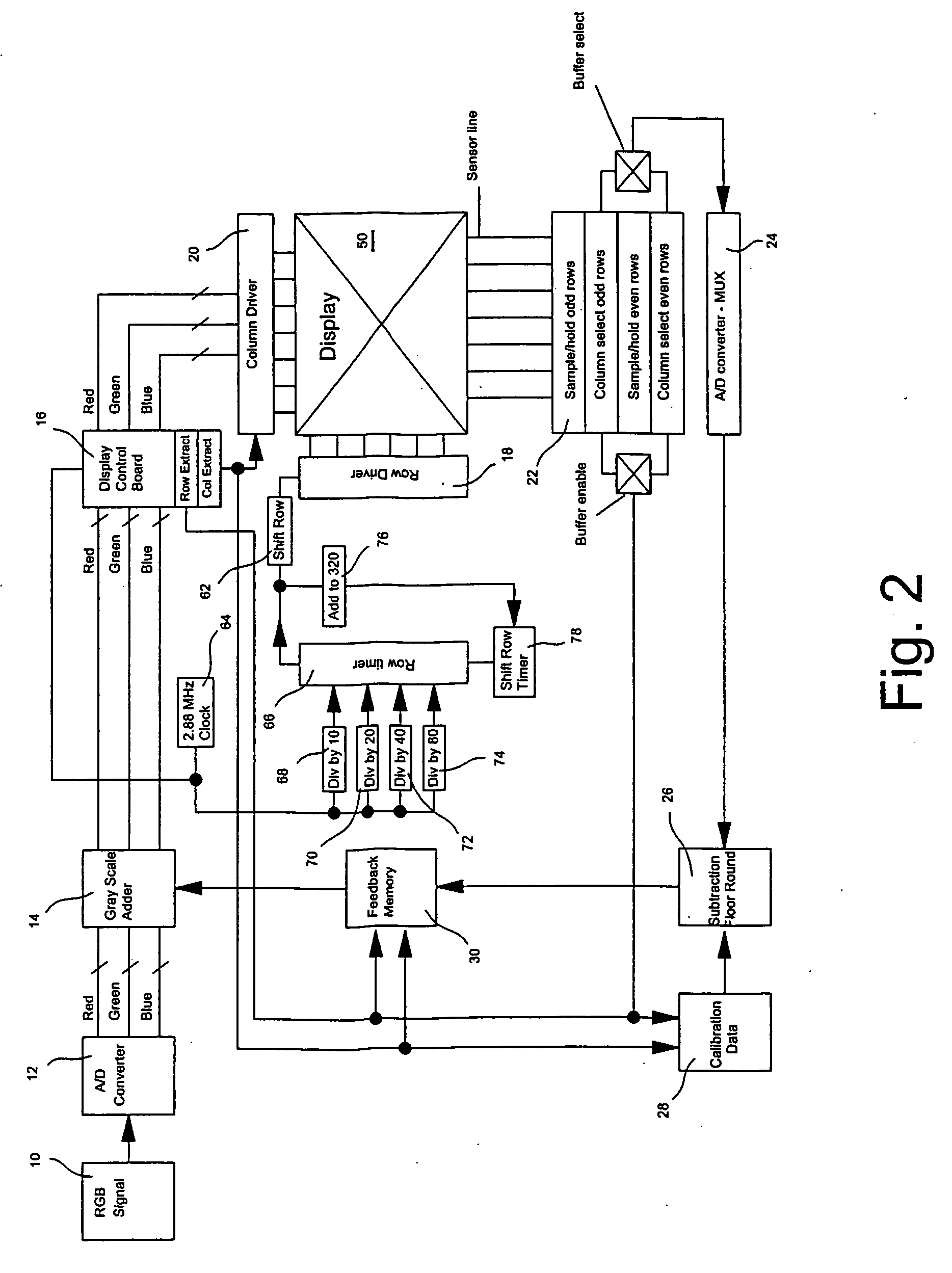
The invention provides a display panel driving circuit capable of making display free of unevenness by correcting the nonuniformity of luminance due to a difference in the resistance etc., of a row line and column line of a display panel and to provide a driving method. Such correction data to attain the same luminance by increasing or decreasing the driving time for light emitting elements varying in the luminance on the basis of the light emitting element EL outputting the average luminance when the image data of the same luminance level is given is set, and is previously stored in a pixel display correction data storage section 50. The actual image data for the one line component stored in a frame memory 40 and the corresponding correction data for the one line component stored in the pixel display correction data storage section 50 are read out and are added by each pixel in a timing generation section 60 and the on-off of each driving switch 12 of a column driver 10 is controlled with the pulse width modulation signal by the result of the addition as a control signal.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
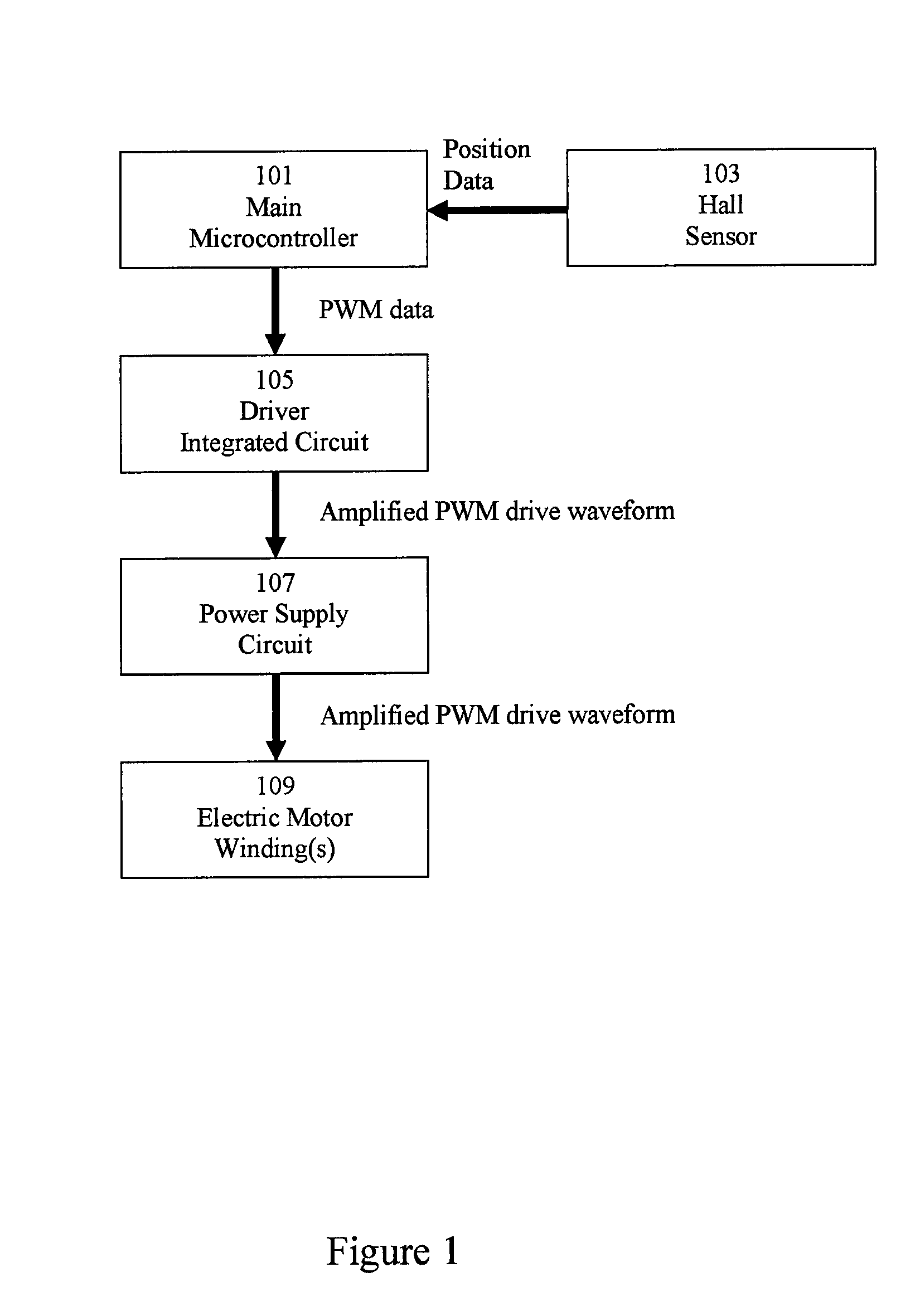
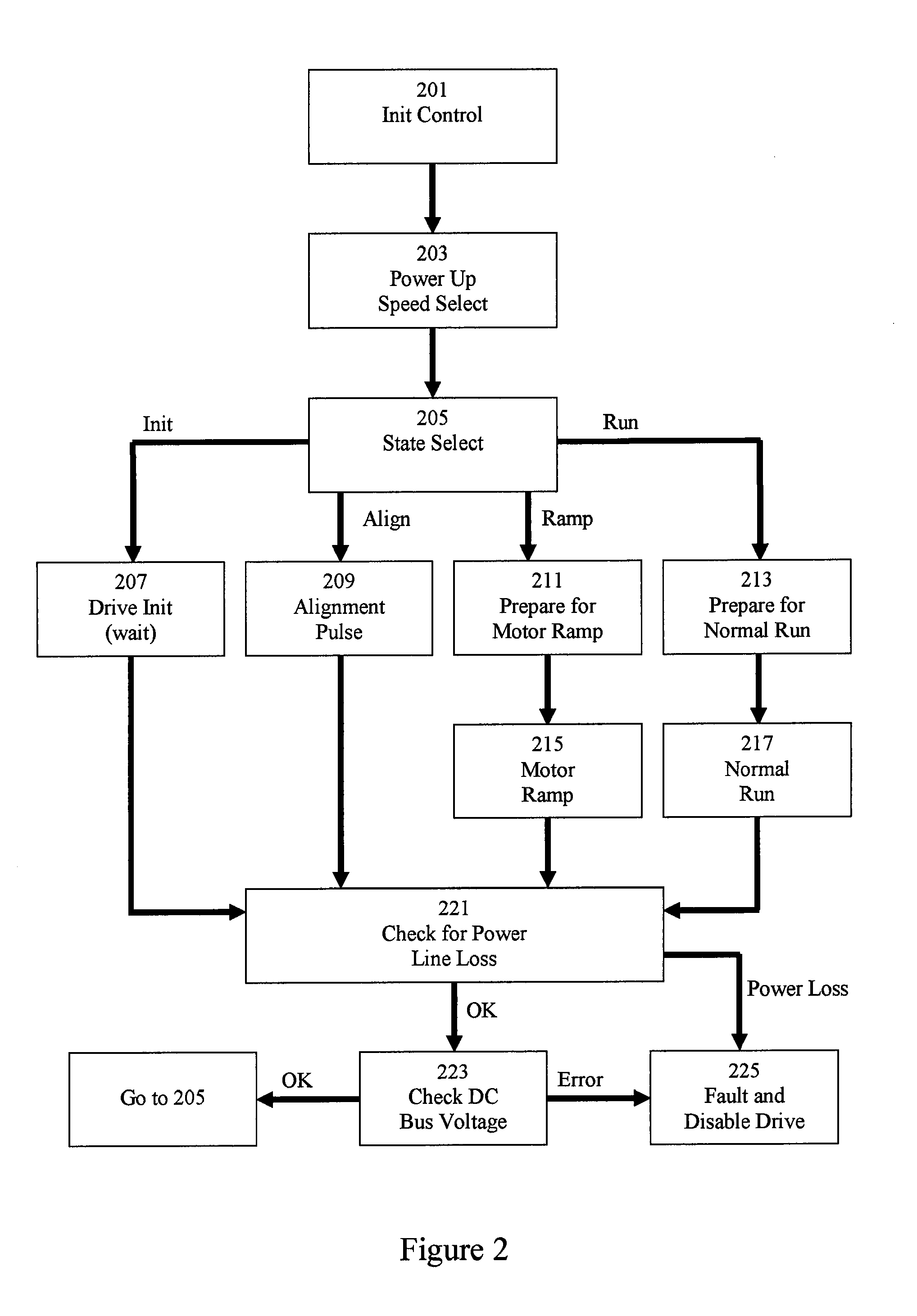
Electric motor and motor control
InactiveUS8575873B2Reduce noiseHigh complexitySingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlElectric machinePermanent magnet motor
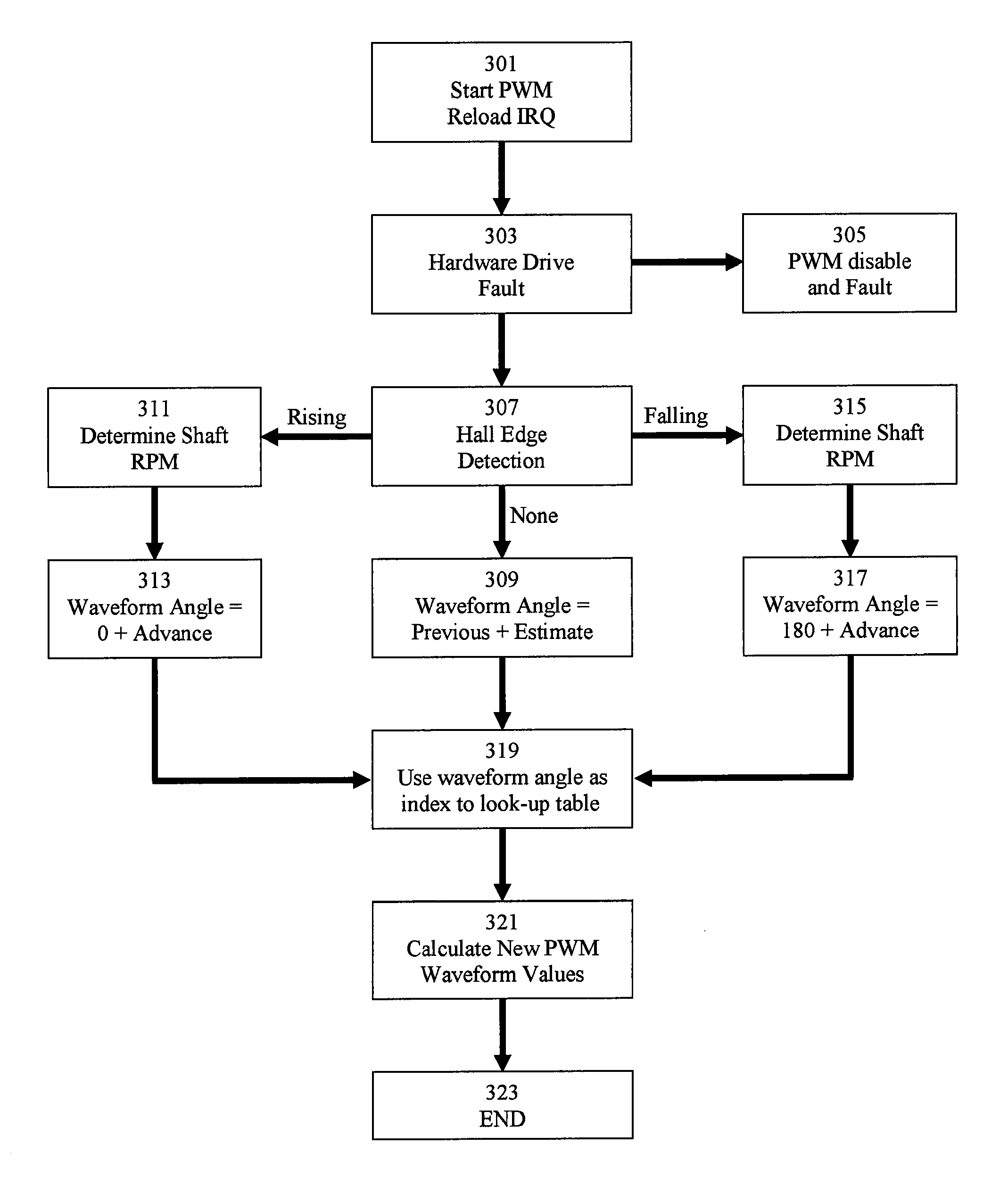
Various embodiments of an electric motor and electronic control for an electric motor are disclosed. An exemplary electric motor comprises a single-phase brushless permanent magnet electric motor. In exemplary embodiments, the electronic motor control is configured to commutate an electric motor at a frequency other than line frequency, perform pulse width modulation, and drive the electric motor with a drive waveform that approximates the counter-electromotive force of the motor.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
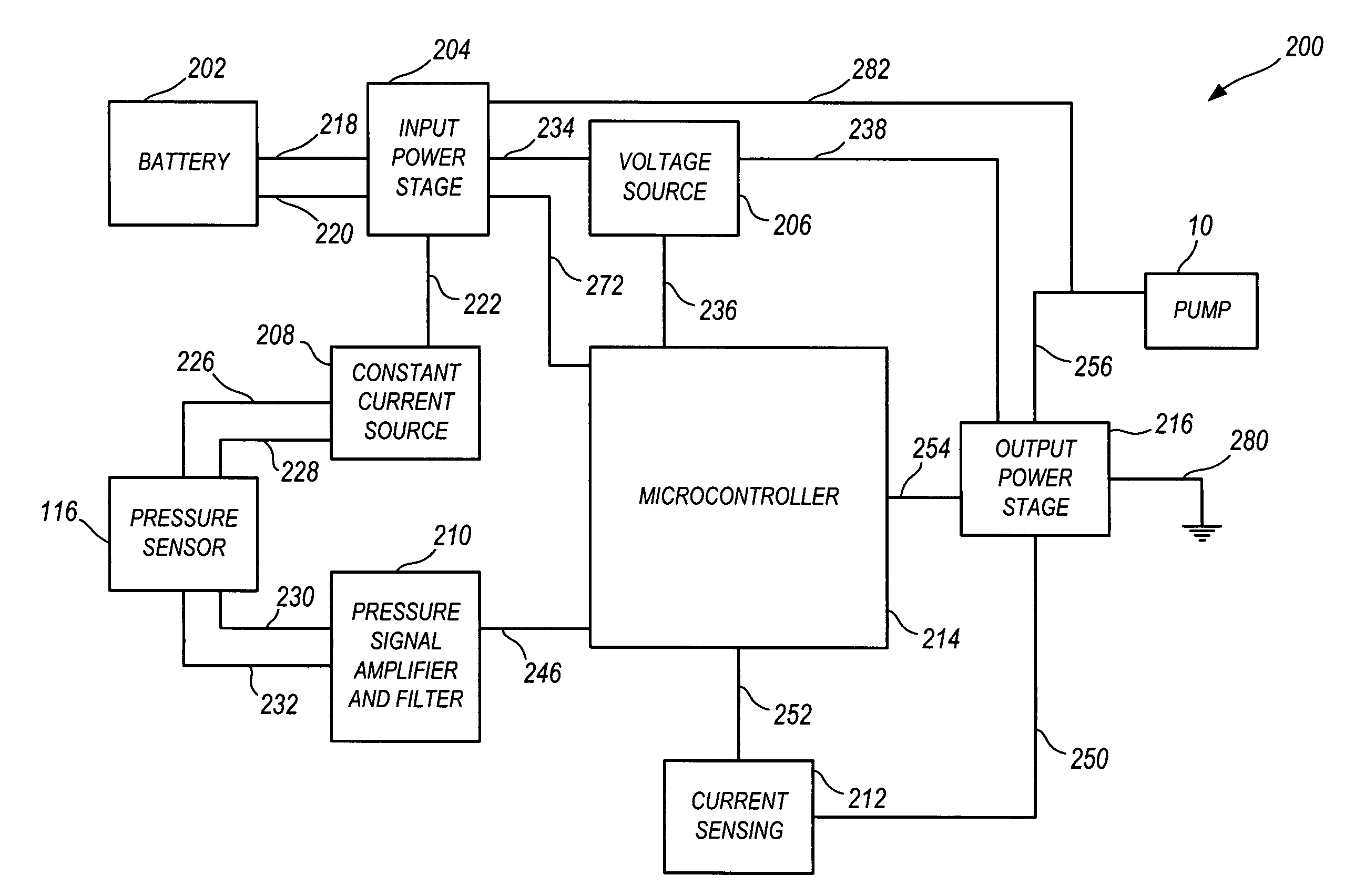
Pump and pump control circuit apparatus and method
InactiveUS7083392B2Large range of motionReduce diaphragm stressFluid parameterFlexible member pumpsMicrocontrollerControl system
A method and apparatus for a pump and a pump control system. The apparatus includes pistons integrally formed in a diaphragm and coupled to the diaphragm by convolutes. The convolutes have a bottom surface angled with respect to a top surface of the pistons. The apparatus also includes an outlet port positioned tangentially with respect to the perimeter of an outlet chamber. The apparatus further includes a non-mechanical pressure sensor and a temperature sensor coupled to a pump control system. For the method of the invention, the microcontroller provides a pulse-width modulation control signal to an output power stage in order to selectively control the power provided to the pump. The control signal is based on the pressure within the pump, the current being provided to the pump, the voltage level of the battery, and the temperature of the pump.
Owner:SHURFLO
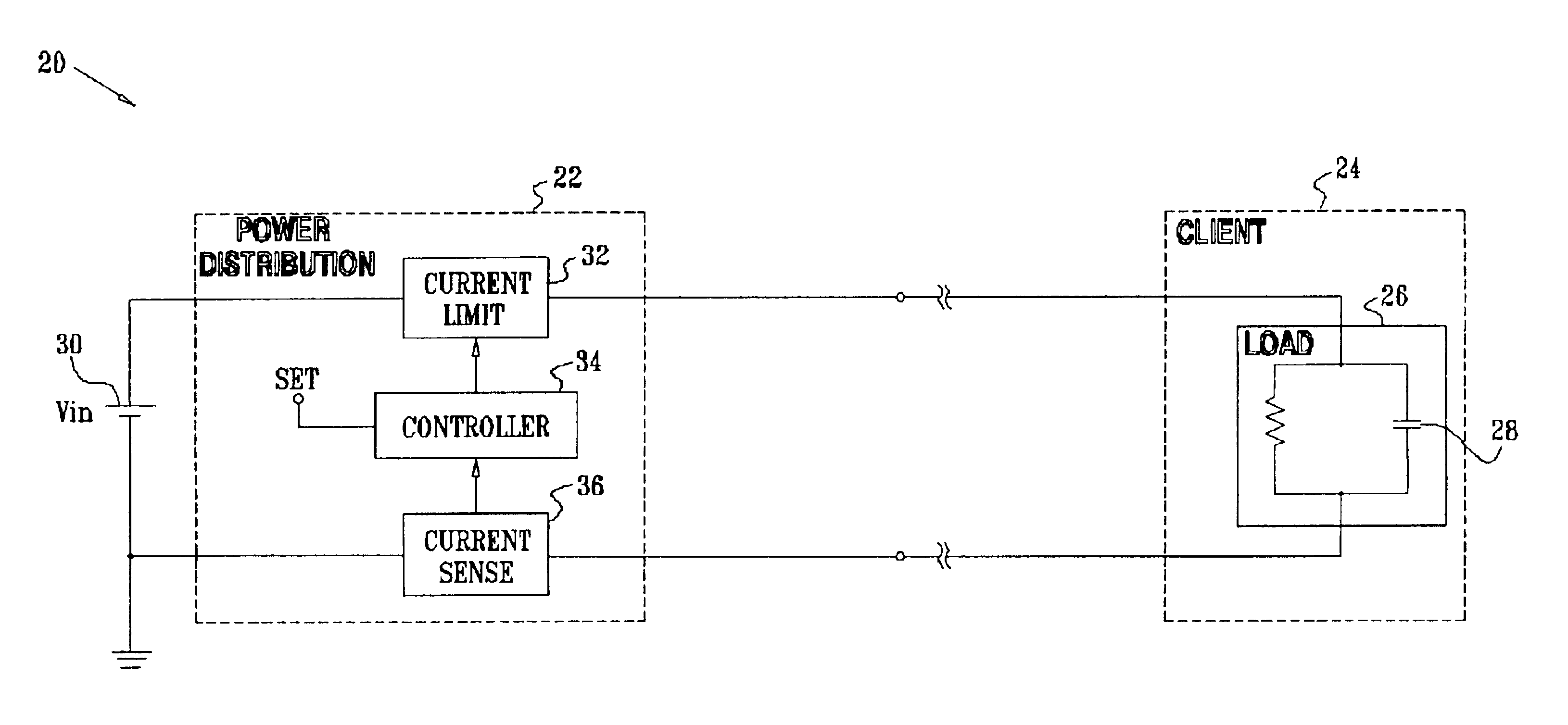
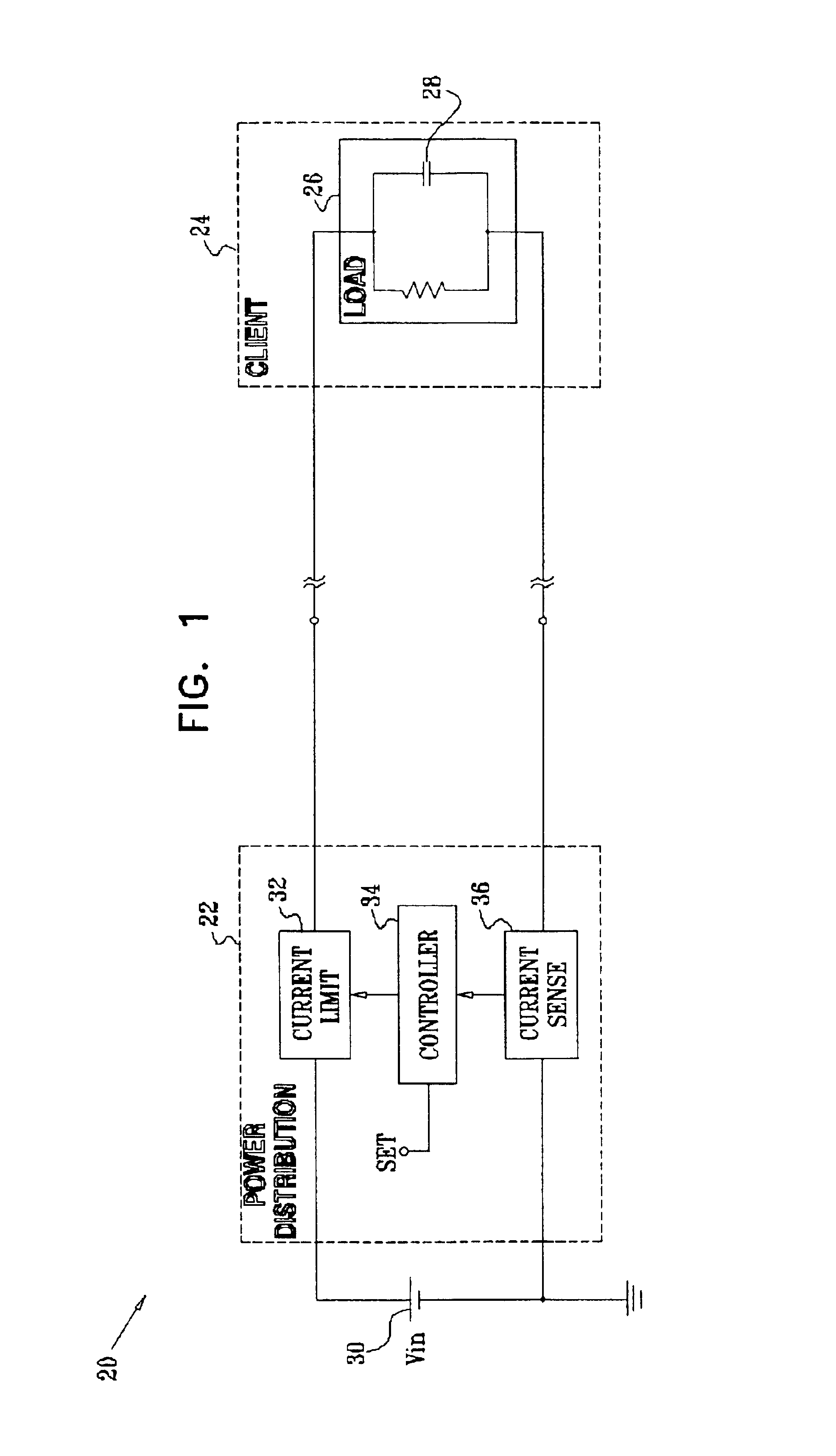
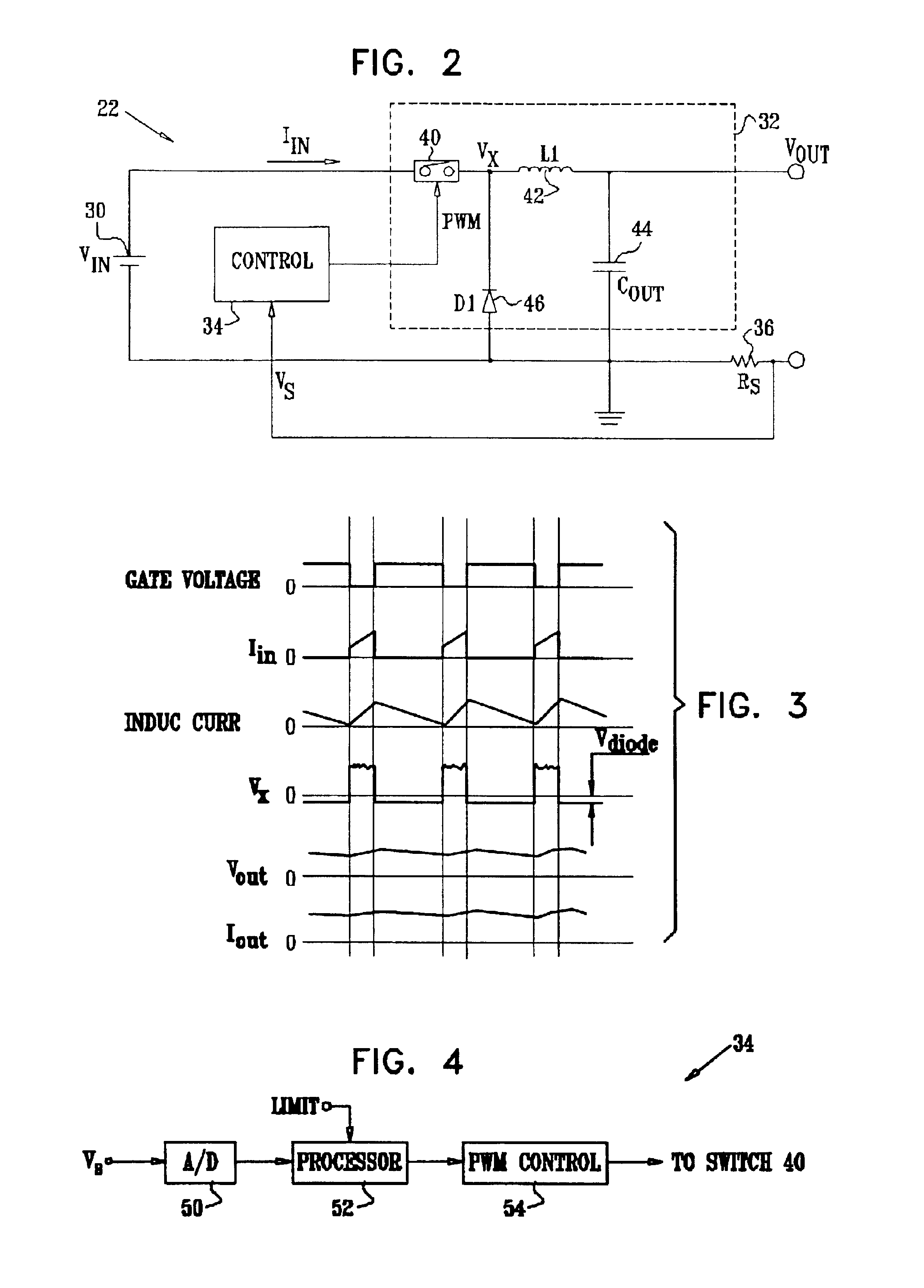
Power distribution with digital current control
InactiveUS6841979B2Minimum power consumptionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionControl powerCurrent sensor
Power distribution apparatus, for controlling supply of a current from an electrical power source to at least one load, includes a current sensor, which is coupled to provide an indication of a magnitude of the current flowing to the at least one load. A current limiter is adapted, responsive to the indication, to apply a pulse width modulation to the current drawn from the source so as to maintain the magnitude of the current flowing to the at least one load within a predetermined limit.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
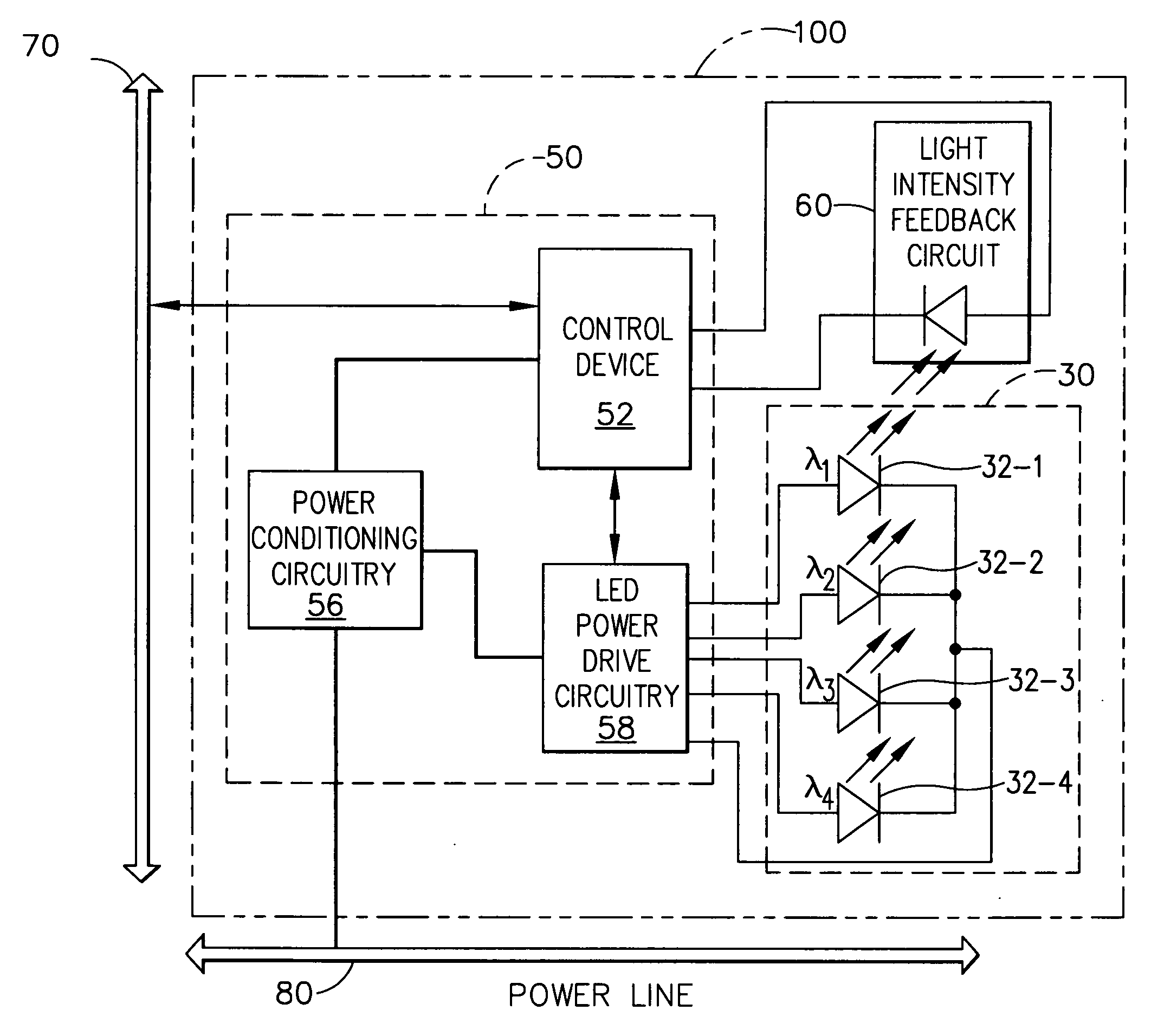
LED-based luminaire utilizing optical feedback color and intensity control scheme
InactiveUS20060006821A1Electric signal transmission systemsPoint-like light sourceLight equipmentEngineering
A system and method for implementing an LED-based luminaire (100) incorporates one or more color channels (32-n). The luminaire includes a controller (50) that uses optical sensing and feedback to control LEDs (30A) in each channel to deliver a consistent intensity and / or color output. The optical feedback loop may provide measured intensity and / or color of the luminaire's output to the luminaire controller. The controller may then adjust the current, pulse width modulation (PWM) duty cycle, or both, which are delivered to discrete color channels of the luminaire to obtain the desired intensity and / or color.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
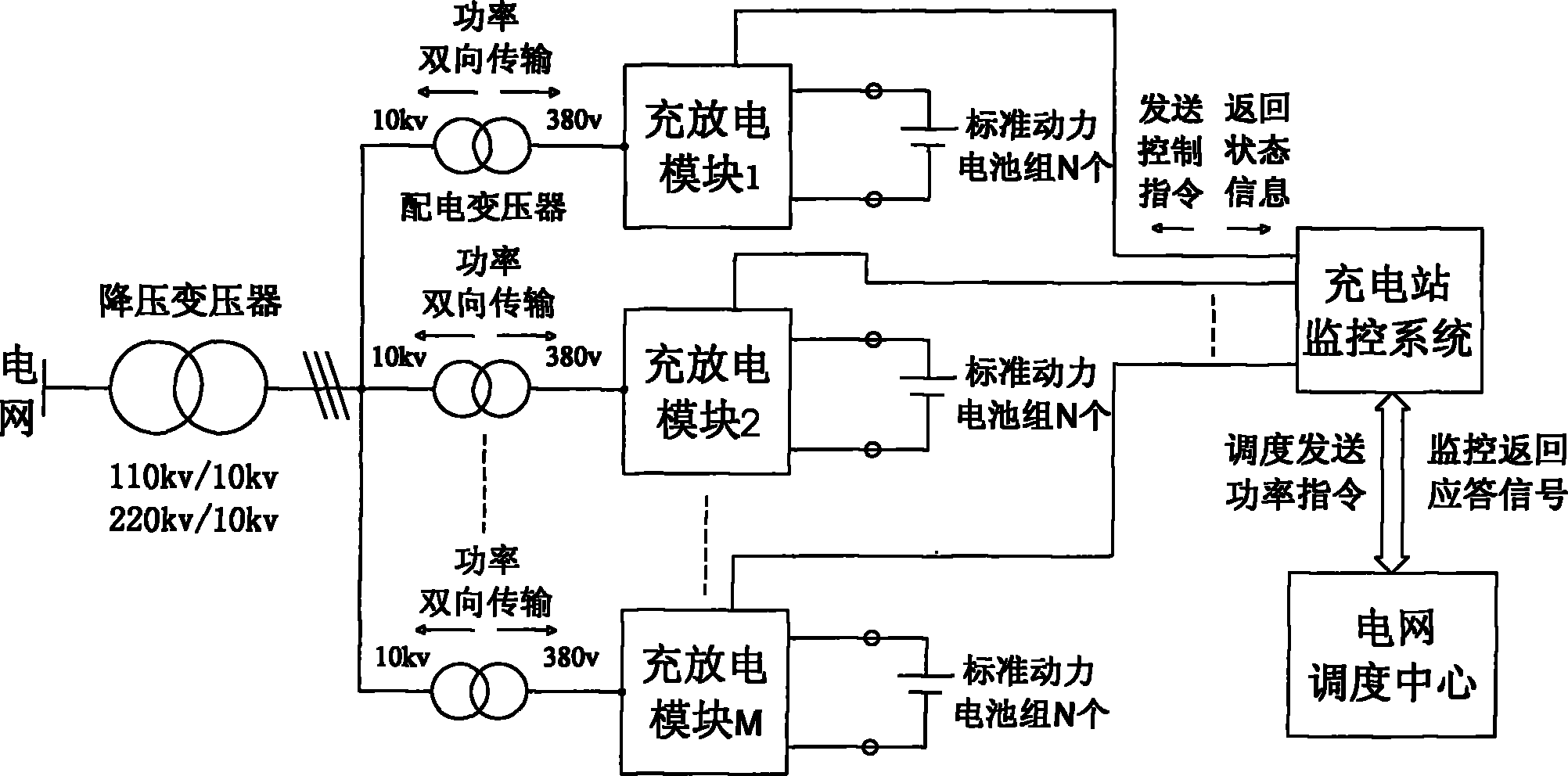
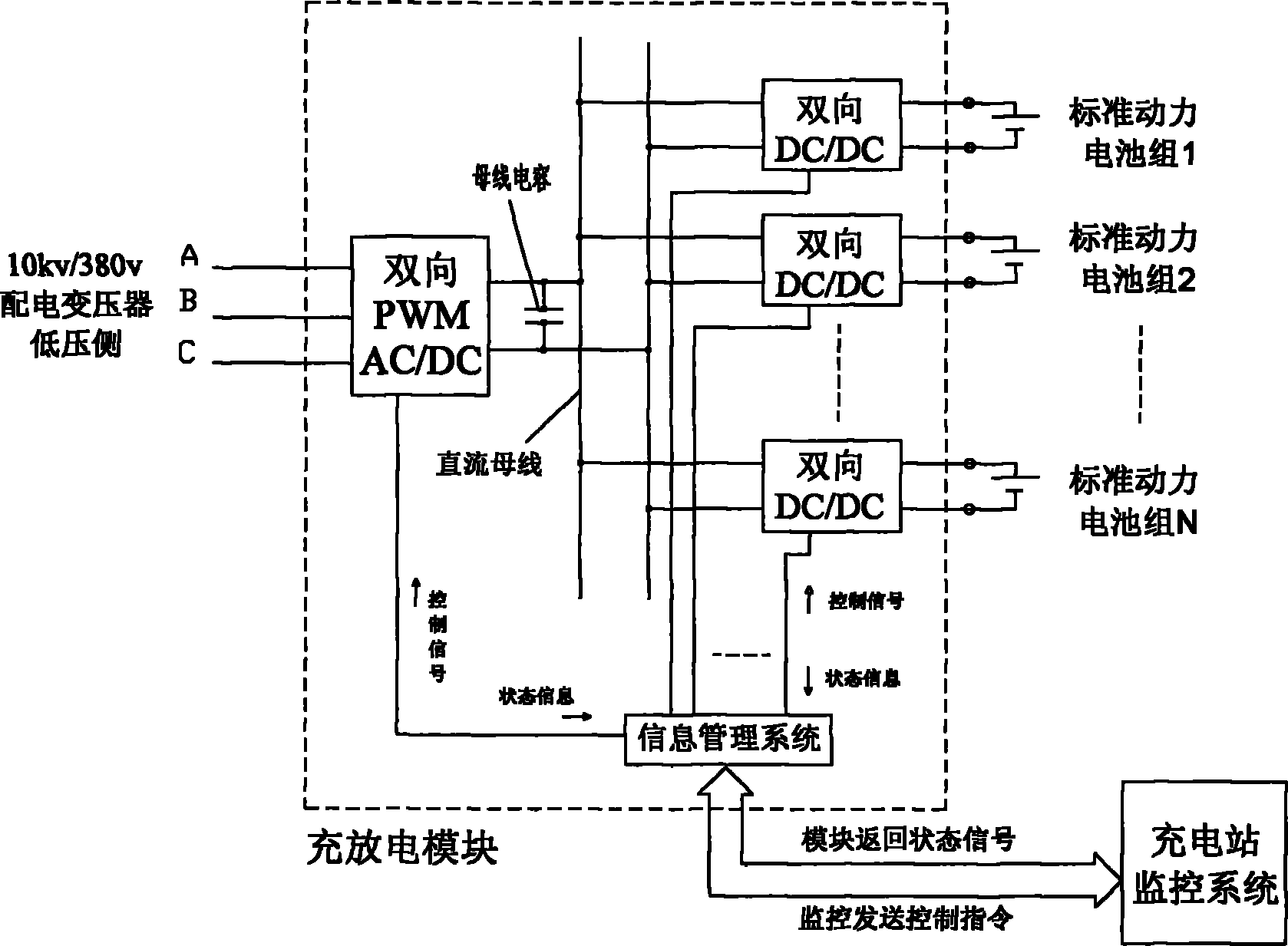
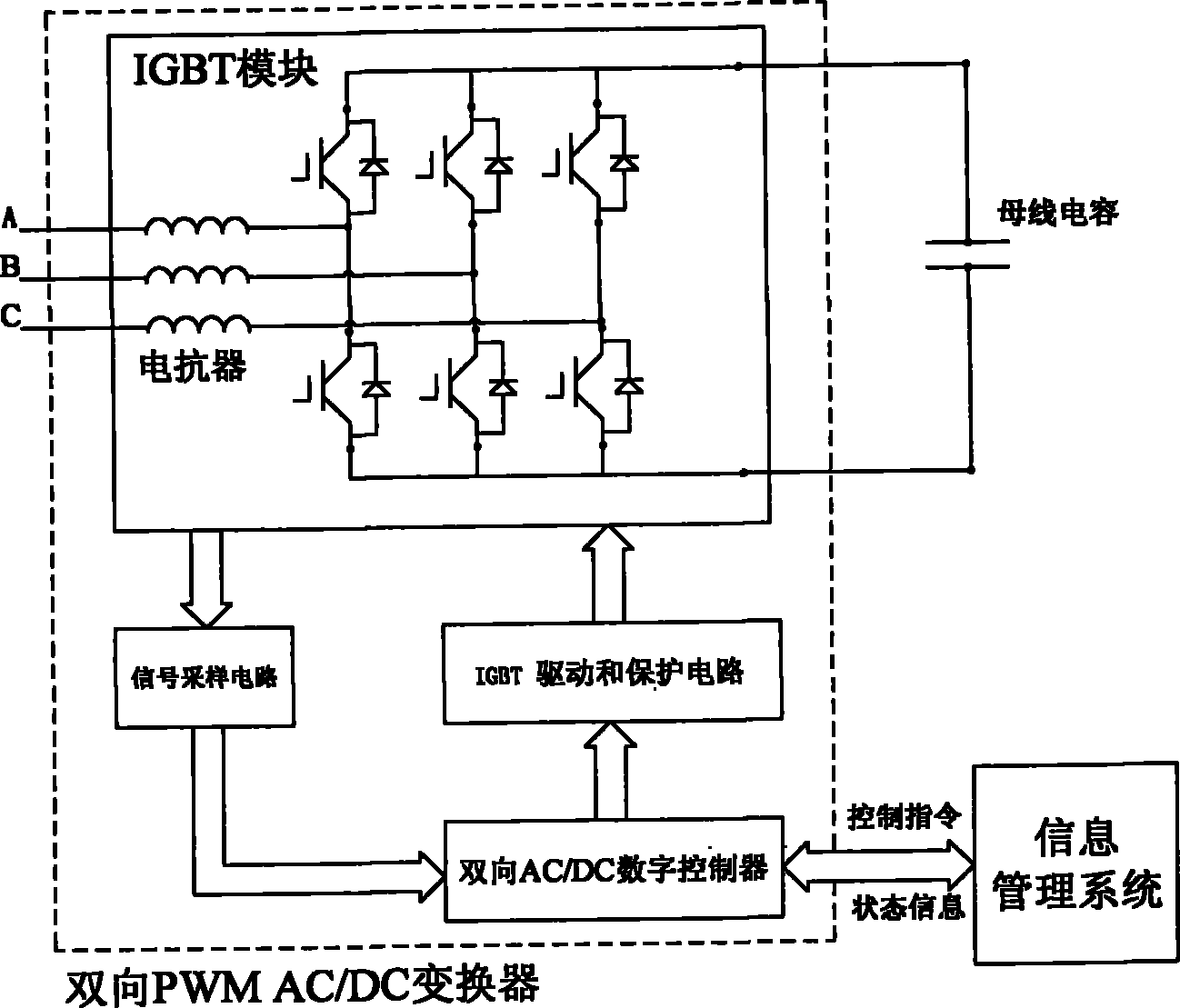
Modular charging/discharging system of power battery pack of multifunctional electromobile
InactiveCN102025182AExtend your lifeImprove charge and discharge efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsAc network load balancingElectric power transmissionLow voltage
The invention relates to a modular charging / discharging system of a power battery pack of a multifunctional electromobile, which aims to provide a system which can effectively meet the requirement for the bi-directional power transmission of a charging station and can exert the functions of peak clipping and valley filling as well as peak modulation and frequency modulation of a power grid. The technical scheme is as follows: the modular charging / discharging system of the power battery pack of the multifunctional electromobile comprises a charging-station monitoring system and an information management system, wherein the charging-station monitoring system is composed of a computer and a network communication system. The modular charging / discharging system is characterized by also comprising a three-phase step-down transformer, wherein the high voltage side of the three-phase step-down transformer is connected with a power grid, and the low voltage side of the three-phase step-down transformer is connected in parallel with a plurality of charging / discharging branches; each branch comprises a three-phase distribution transformer and a charging / discharging module, and the three-phase distribution transformer is connected in series with the charging / discharging module; and each charging / discharging module comprises a pulse-width modulation alternating current / direct current (PWM AC / DC) converter with the function of bi-directional power transmission, a plurality of electromagnetic isolation type DC / DC transform modules with the function of bi-directional power transmission and the information management system, and the electromagnetic isolation type DC / DC transform modules are connected in parallel.
Owner:梁一桥
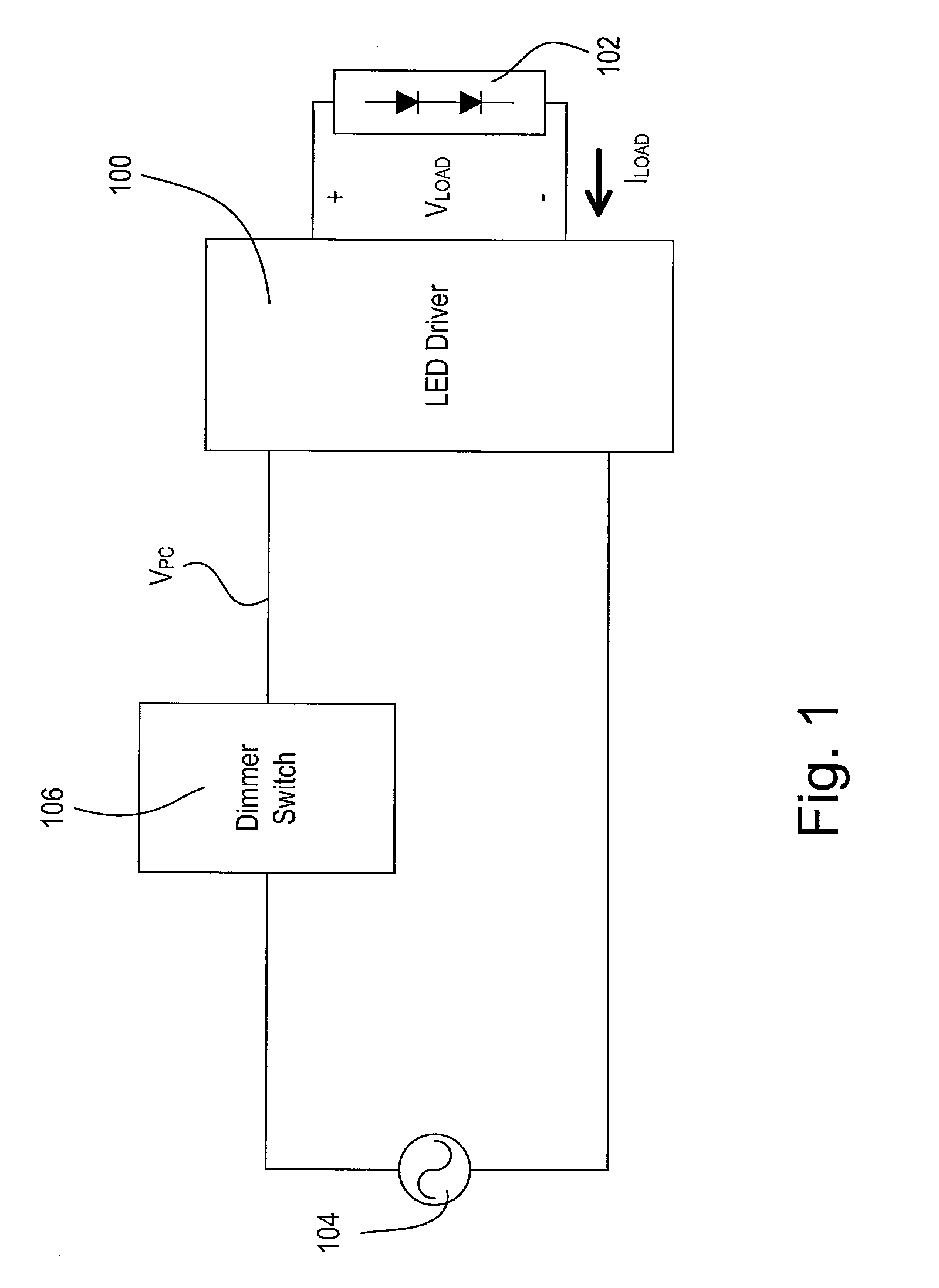
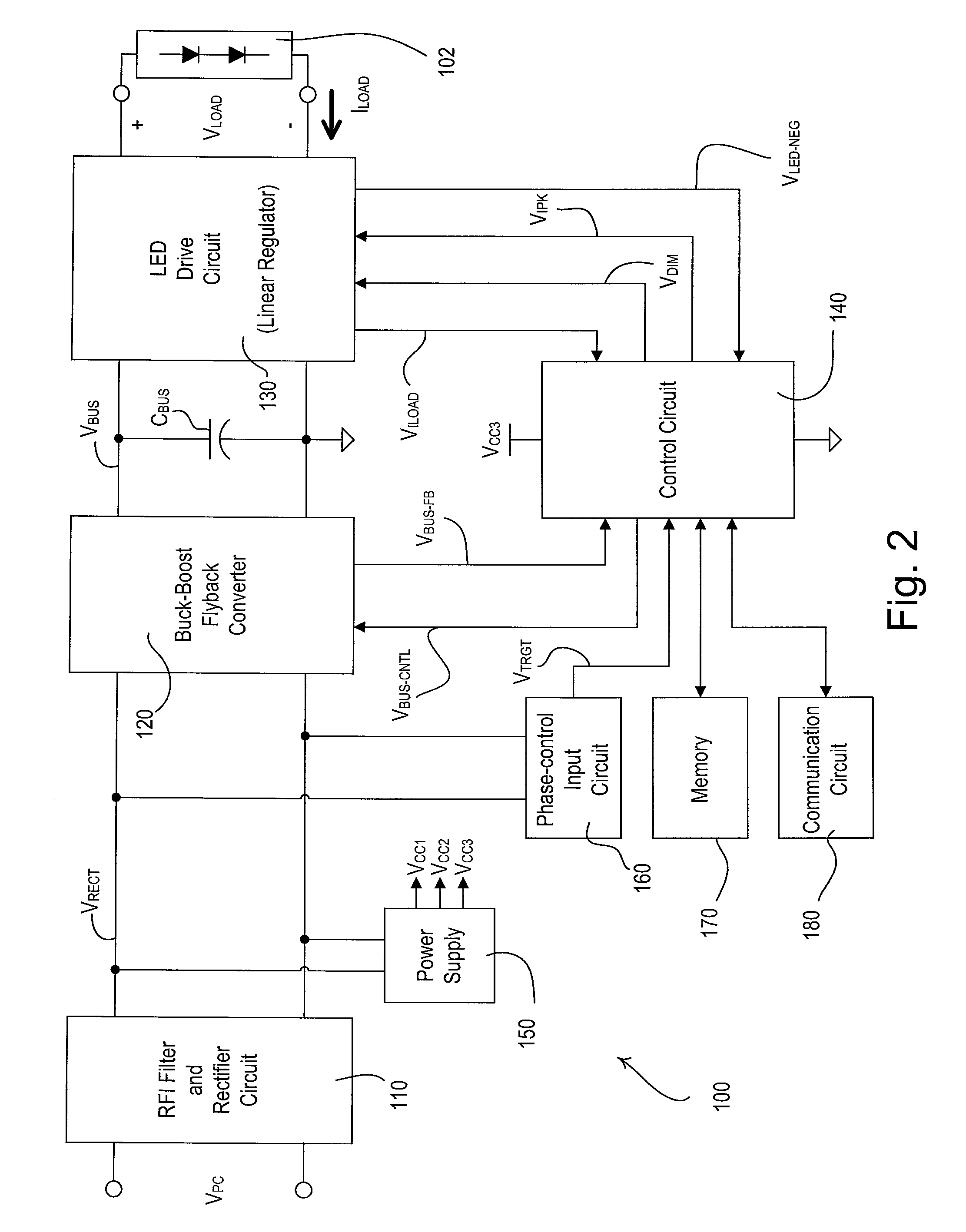
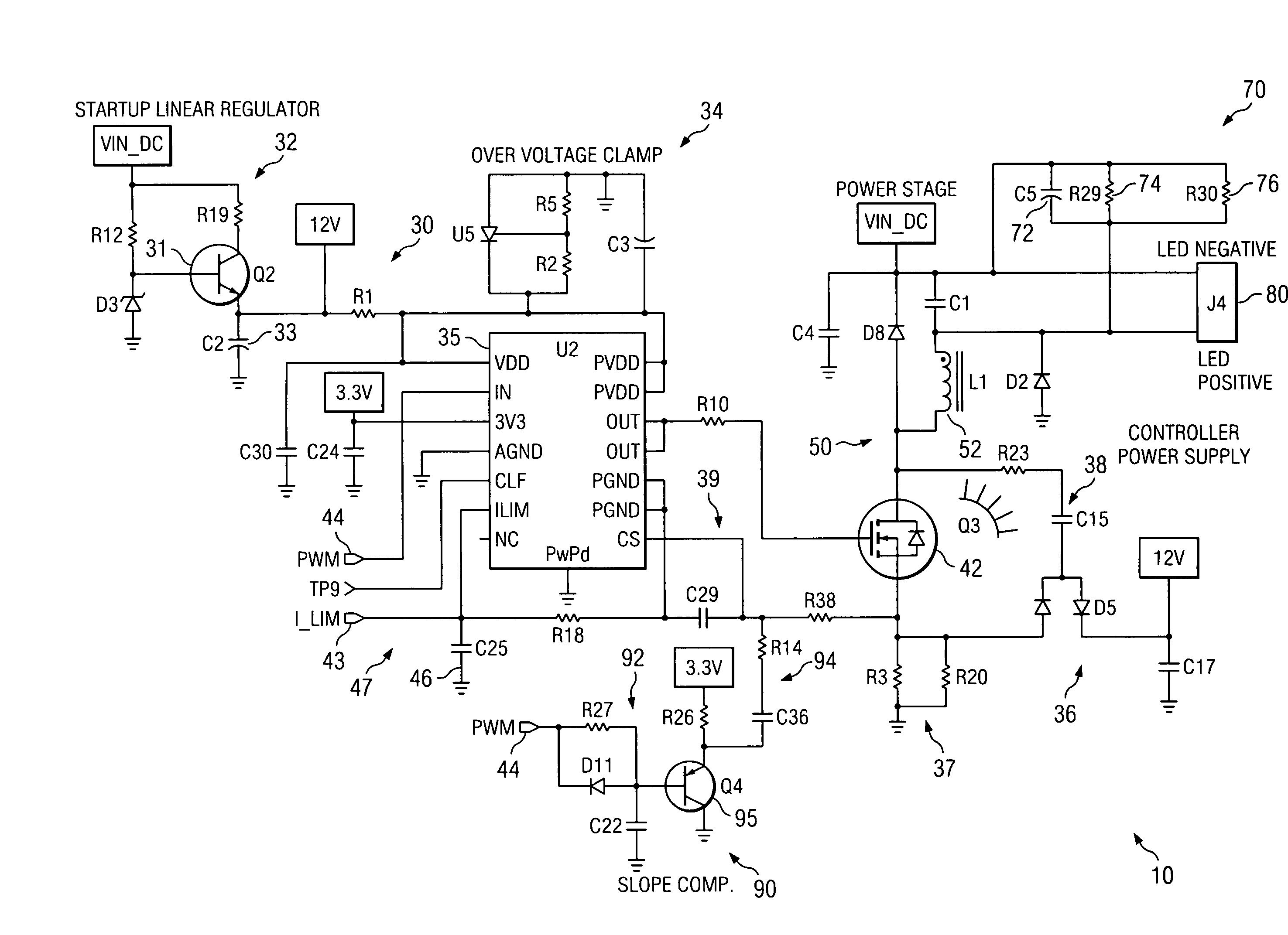
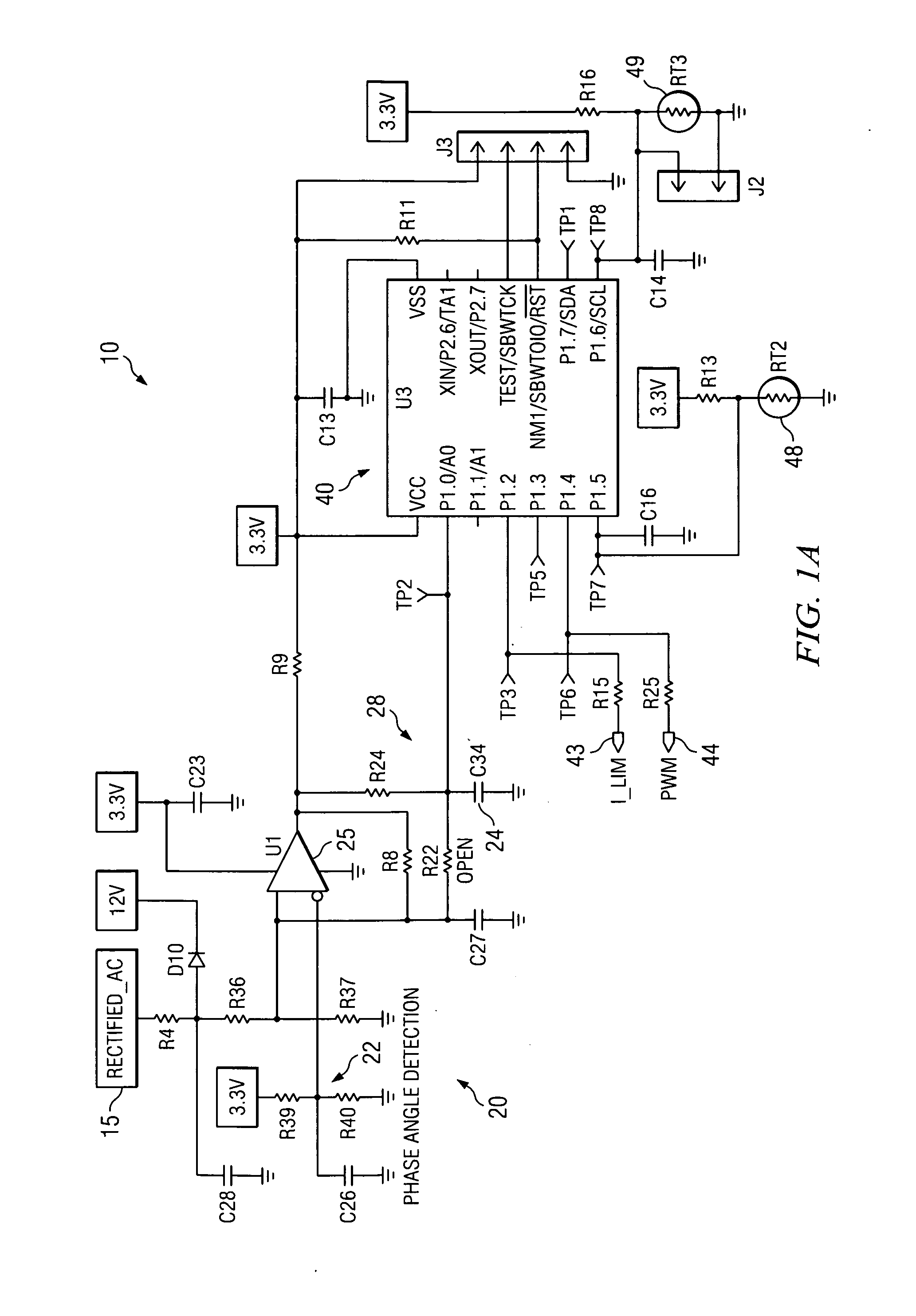
AC-powered, microprocessor-based, dimming LED power supply
ActiveUS20090167203A1Level of audible noise may increaseTotal current dropDc network circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesNoise levelAverage current
A dimmable, light-emitting diode (LED) power supply adapted to provide a direct current (DC), constant current (“constant current source”) from a conventional, phase-controlled 120 VAC, 60 Hz power source is disclosed. The constant current source of the present invention utilizes two processes to control dimming. In a first process, the phase angle of the input voltage is used to control the duty cycle of a line frequency pulse width modulation (PWM). In a second process, a proportional-current limit adjustment is used to control the average current to the LED during the ON time of the line frequency by PWM. As a result, at relatively low phase angles, peak currents can be lowered, reducing flicker and improving the audible noise levels generated by the circuit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
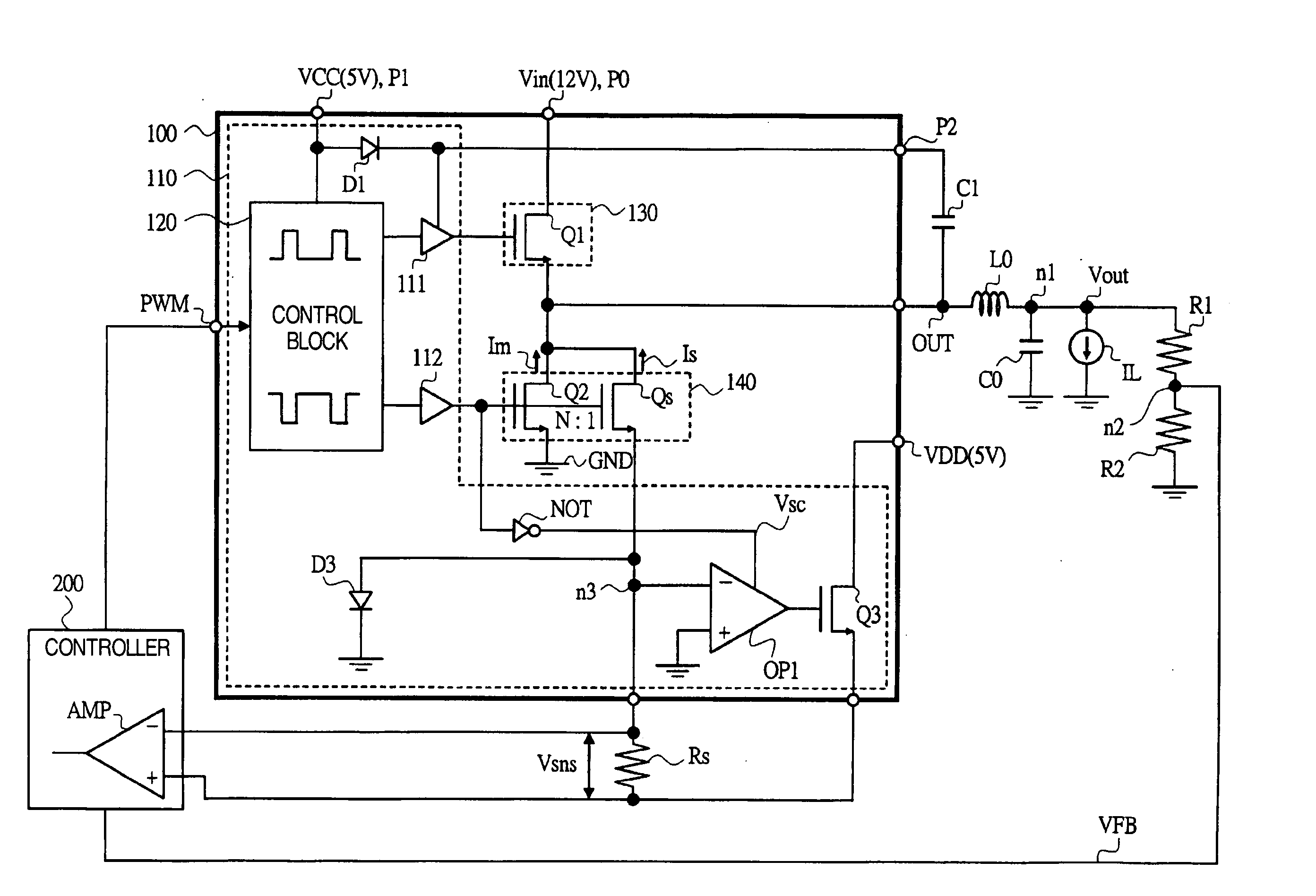
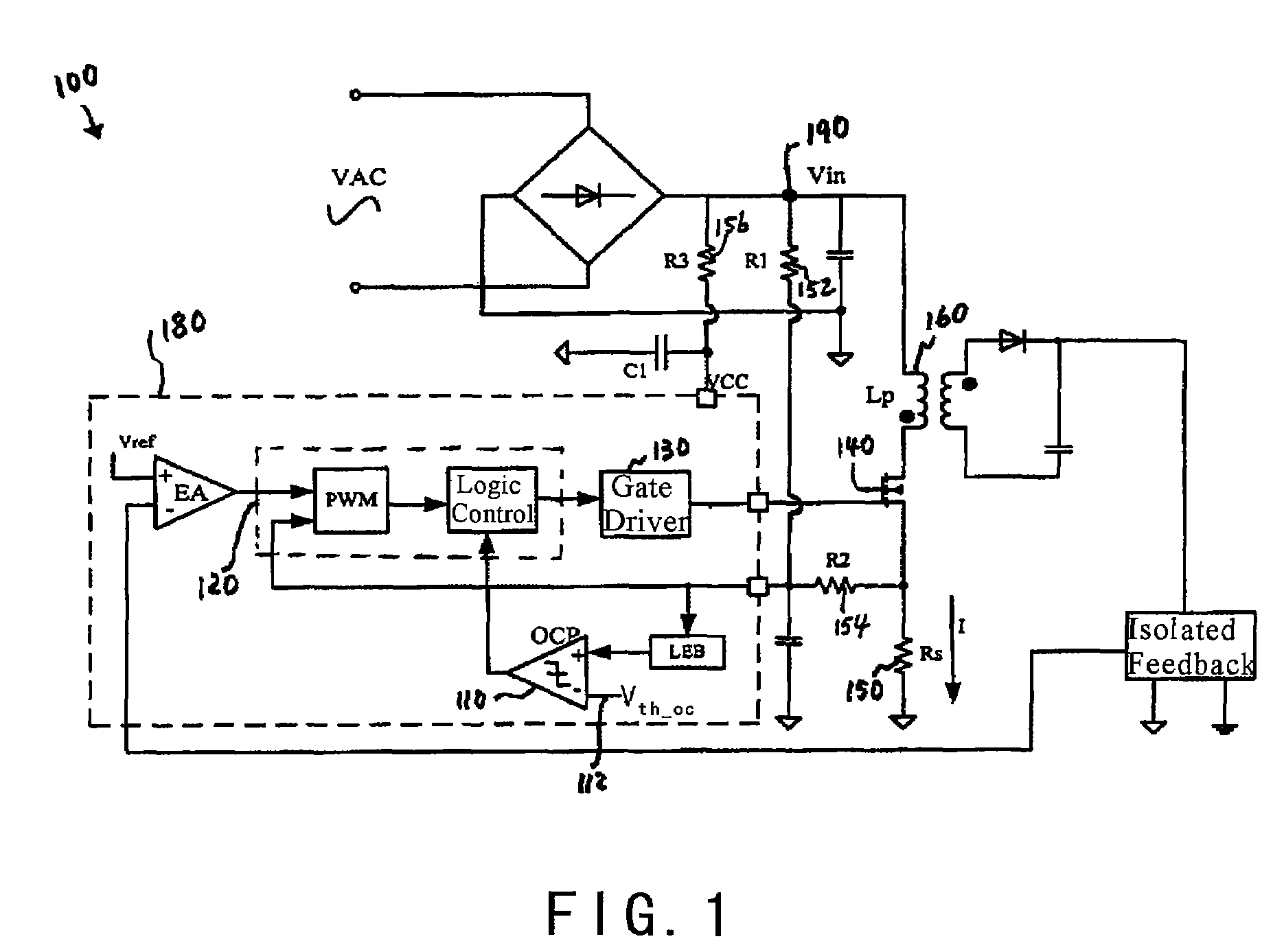
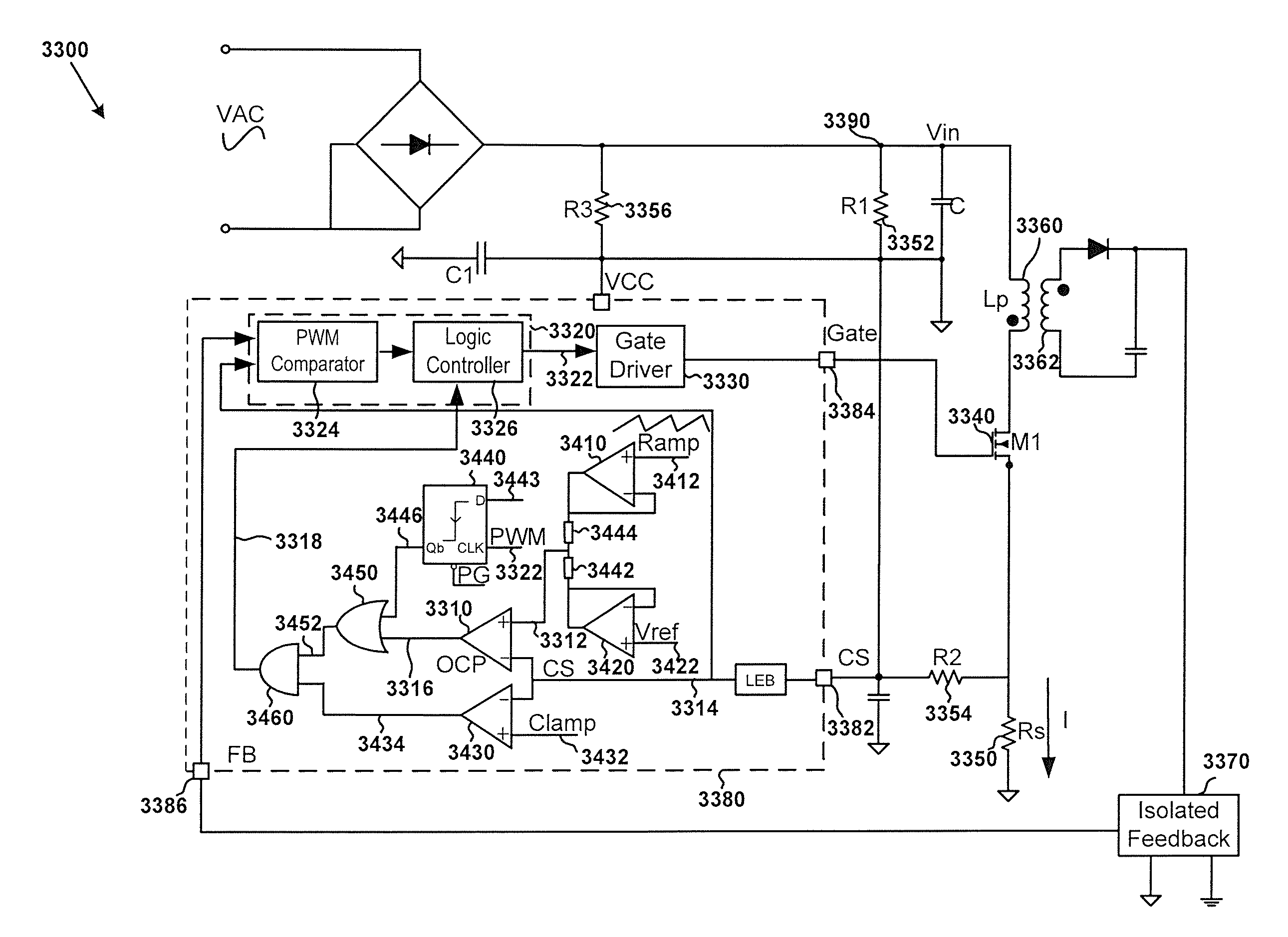
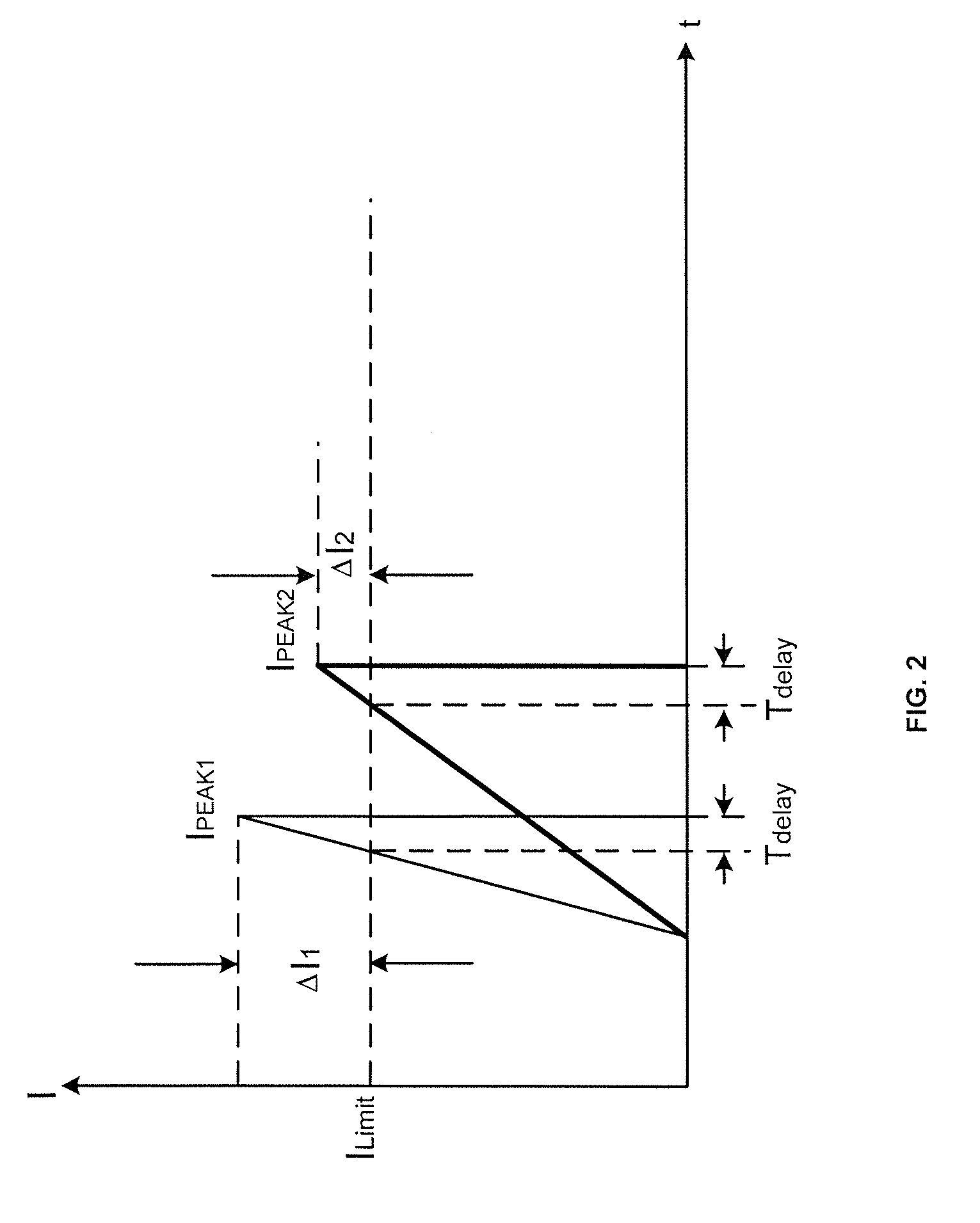
System and method providing over current and over power protection for power converter
ActiveUS7684220B2Good compensationEasy to adjustArrangements responsive to excess currentEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentEngineeringComparator
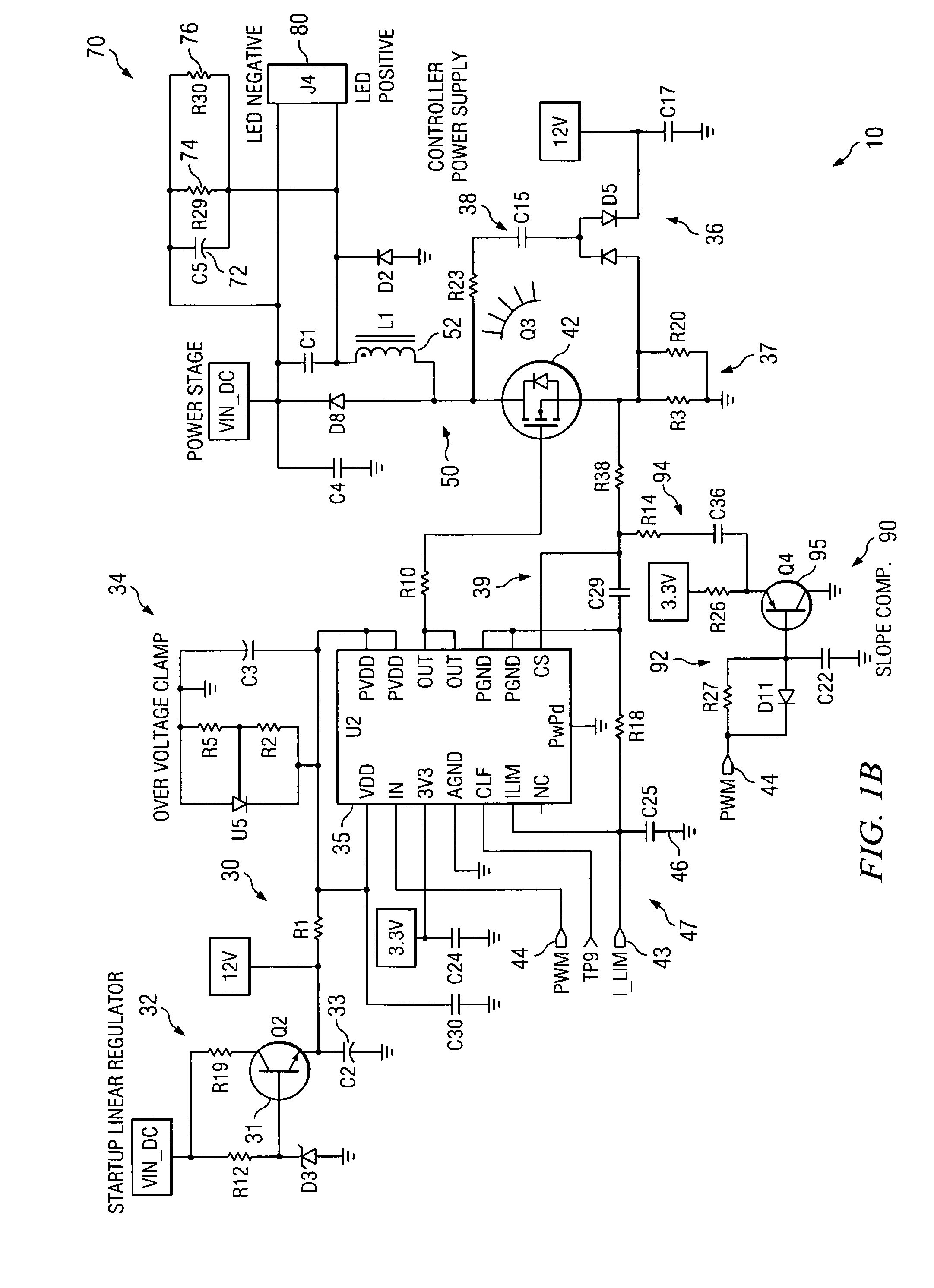
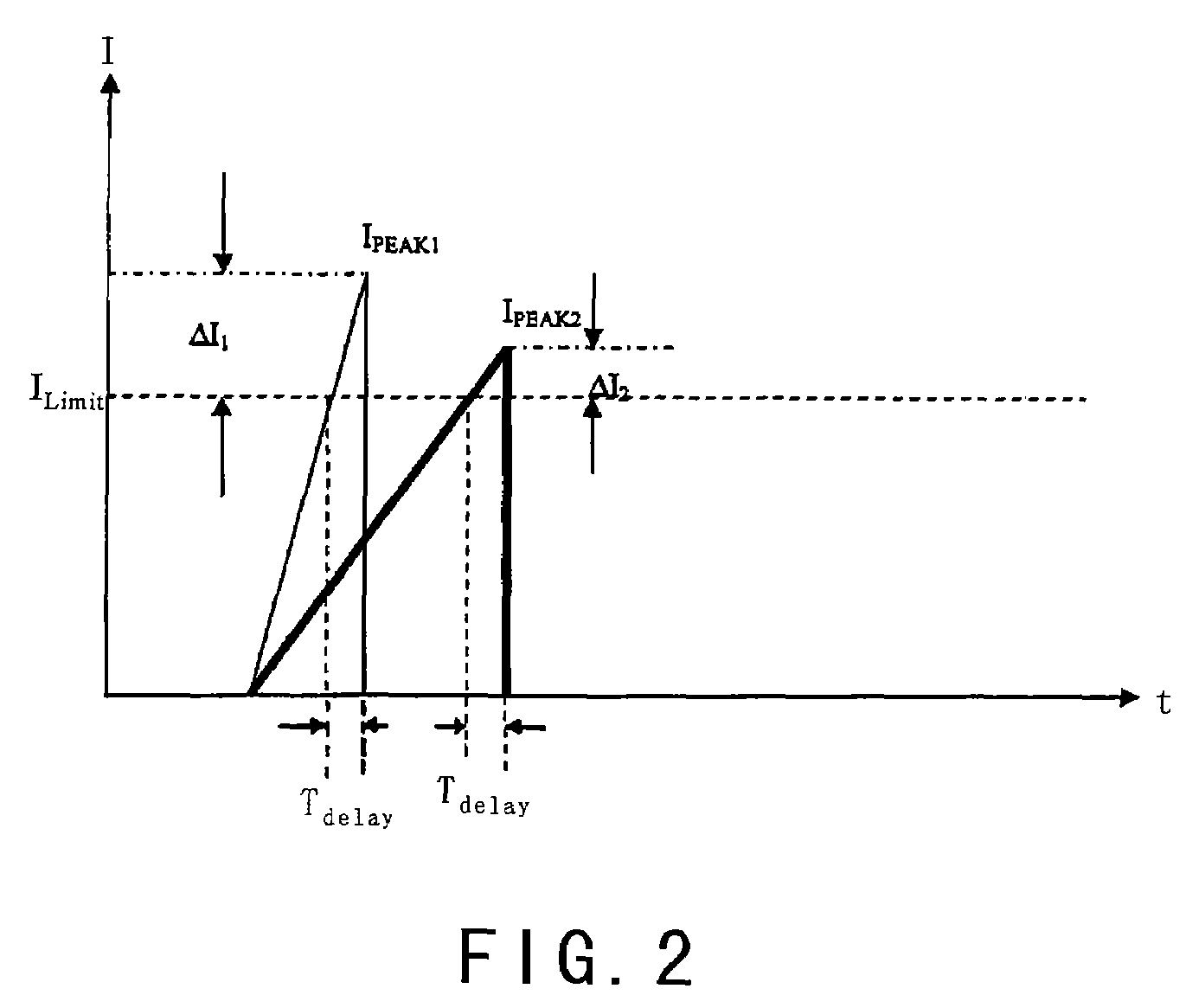
System and method for protecting a power converter. A system includes a threshold generator configured to generate a threshold signal, and a first comparator configured to receive the threshold signal and a first signal and to generate a comparison signal. The first signal is associated with an input current for a power converter. Additionally, the system includes a pulse-width-modulation generator configured to receive the comparison signal and generate a modulation signal in response to the comparison signal, and a switch configured to receive the modulation signal and adjust the input current for the power converter. The threshold signal is associated with a threshold magnitude as a function of time. The threshold magnitude increases with time at a first slope during a first period, and the threshold magnitude increases with time at a second slope during a second period. The first slope and the second slope are different.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Phase-shifted dual-bridge DC/DC converter with wide-range ZVS and zero circulating current
ActiveUS20090196072A1Solve insufficient storage spaceMinimizes voltage ringingAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionFull wavePhase difference
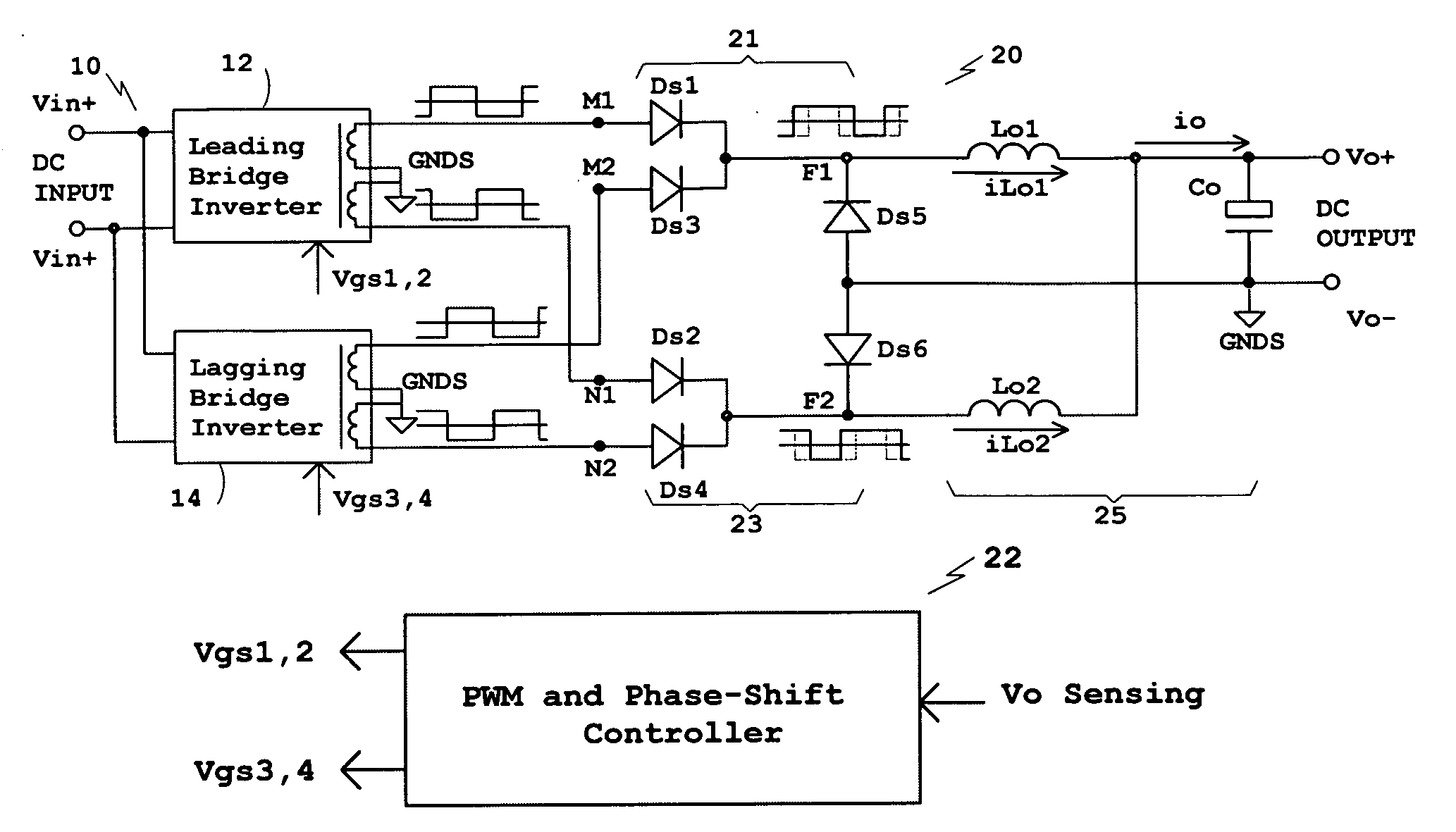
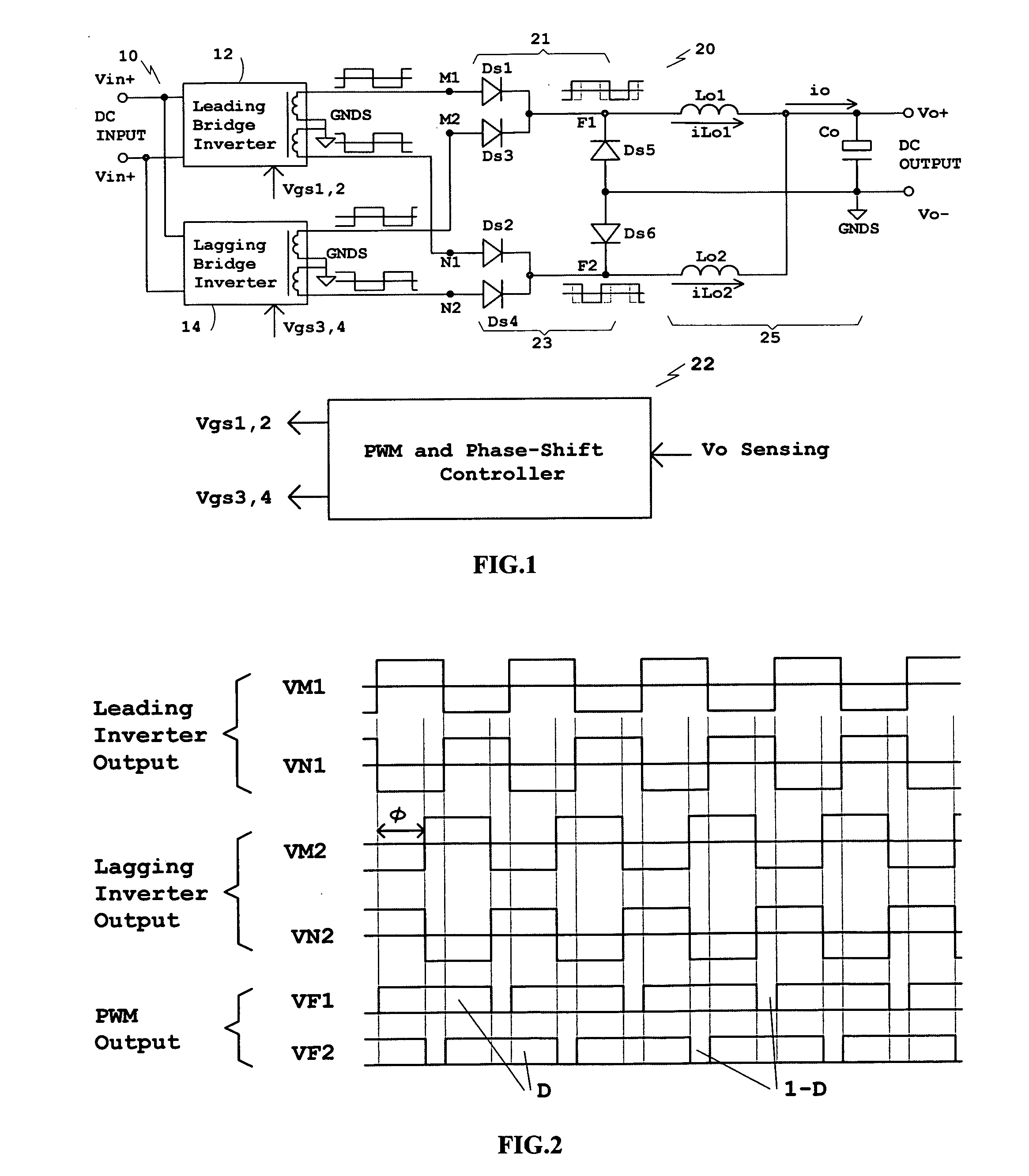
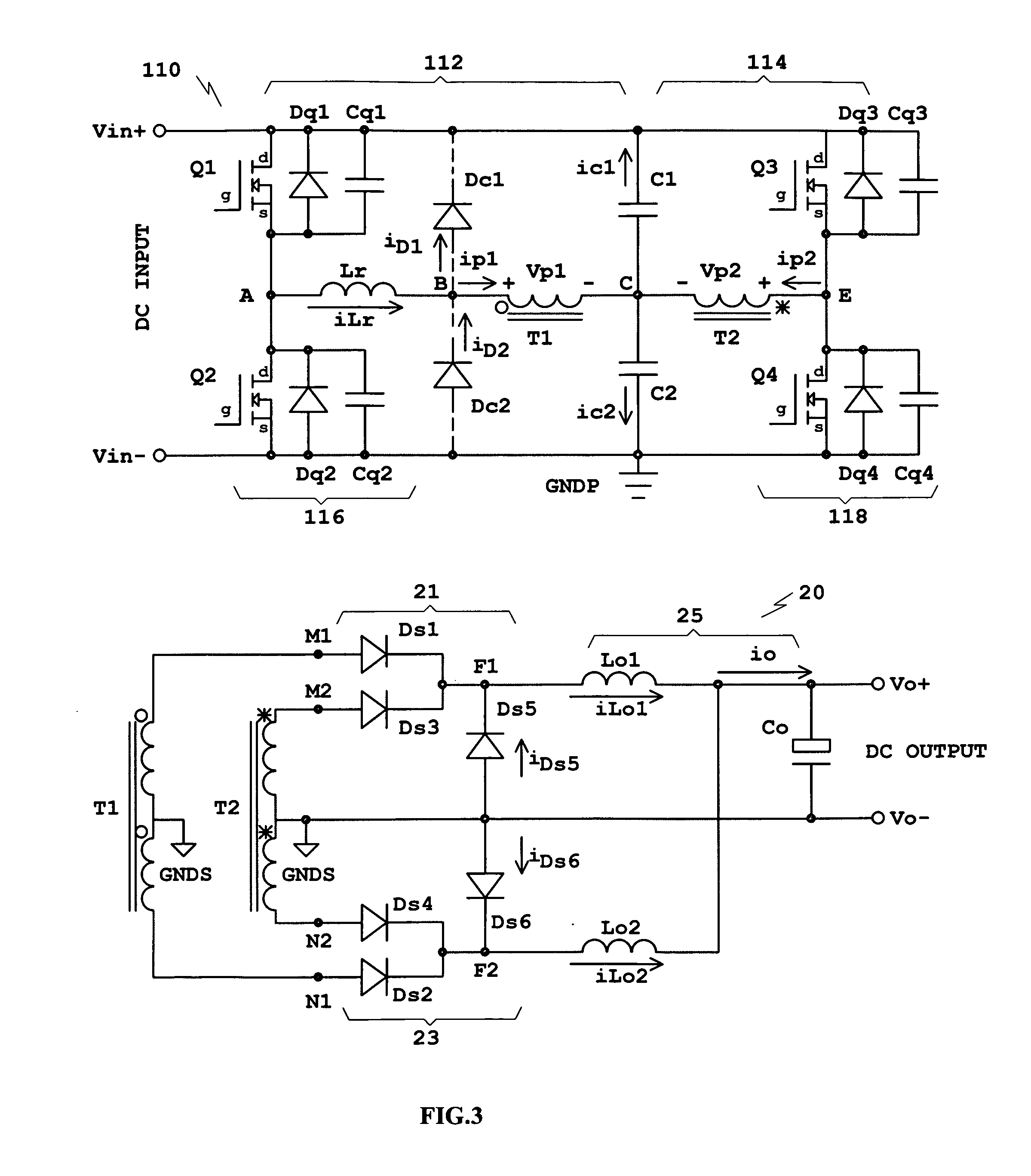
Disclosed is a family of new DC / DC converters and a new control method. The converter comprises two bridge inverters, two full-wave rectification circuits and a current-doubler filter. Each inverter is able to generate a symmetrical and isolated AC output voltage. Phase-shift control is employed to control the phase difference between the two bridge inverters. By shifting the phase, the converter changes the two inverters' output voltage overlapping area to regulate its output voltage. The bridge inverters always operate at 50% duty cycle, like an open loop Bus Converter, to achieve wide-range zero voltage switching and eliminate circulating current for normal operation. For low output voltage regulation and soft start, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control is used. The converters and the control method improve power conversion efficiency, maximize magnetic component utilization, reduce semiconductor stress and decrease EMI emission.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method providing over current protection based on duty cycle information for power converter
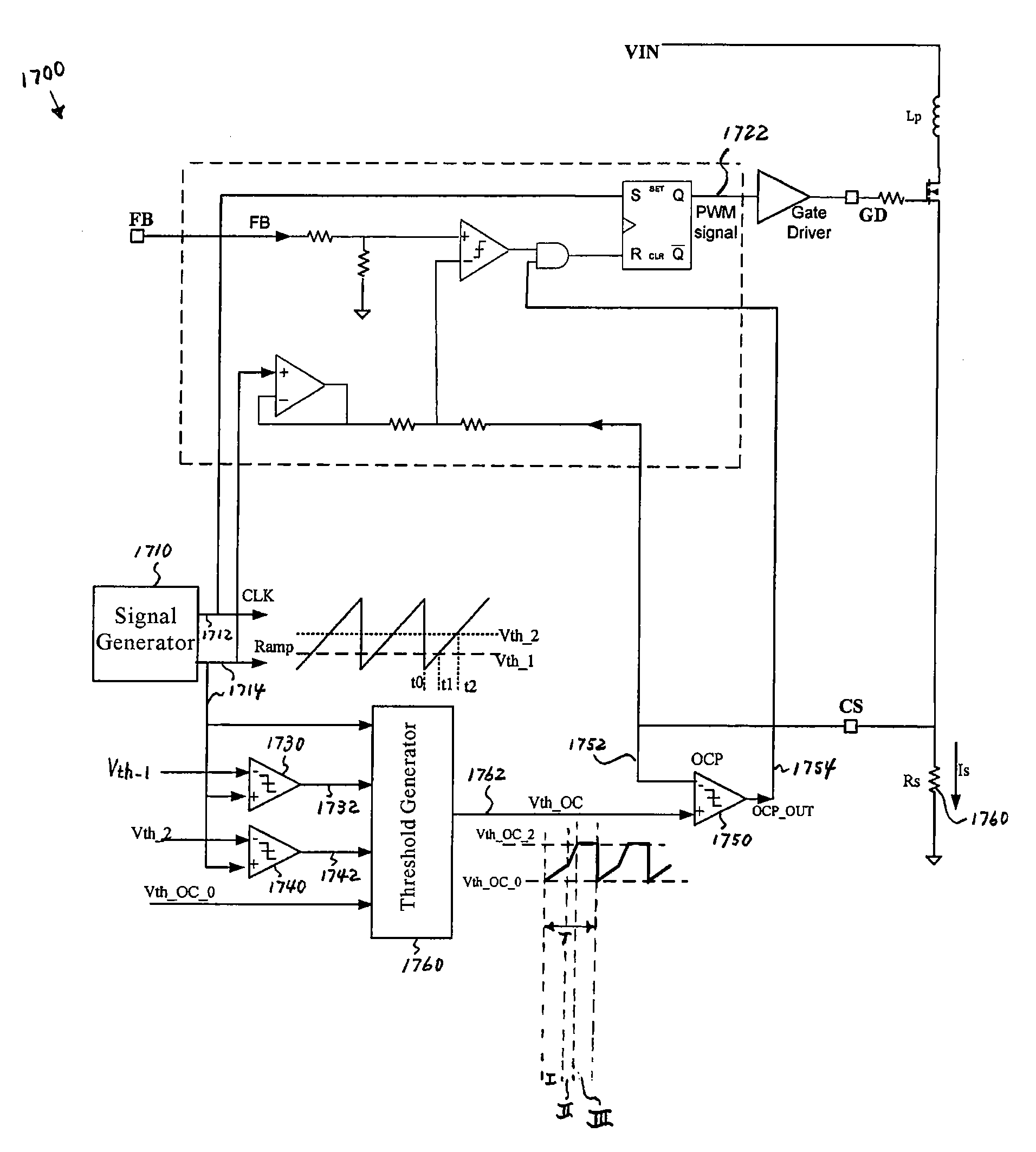
System and method for protecting a power converter. The system includes a duty-cycle detection component configured to receive a modulation signal, determine a first duty cycle corresponding to a first period of the modulation signal, compare the first duty cycle with a threshold duty cycle, and generate a duty-cycle comparison signal. Additionally, the system includes a threshold generator configured to receive the duty-cycle comparison signal and generate a threshold signal corresponding to a second period of the modulation signal, the second period being after the first period, and a comparator configured to receive the threshold signal and a first signal and to generate a first comparison signal. The first signal is associated with an input current for a power converter. Moreover, the system includes a pulse-width-modulation component configured to receive the first comparison signal and generate the modulation signal for adjusting the input current for the power converter.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Apparatus and method for high-speed transfer and centering of wafer substrates
InactiveUS6116848AGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolenoid valveElectromotive force
An apparatus for centering and gripping semiconductor wafers. A solenoid is used to actuate two or three curved contacts. Power to the solenoid, and position information from the solenoid is transmitted along a pair of wires. To center the wafer, the solenoid is actuated and the contacts move radially towards the center of the wafer. The contacts grip the edge of the wafer and a pulse-width-modulation signal is used to determine solenoid position as a function of back electromotive force value or waveform. During handling, the contacts hold the wafer such that the wafer does not move relative to the apparatus.
Owner:BROOKS AUTOMATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com