Patents
Literature
15875results about "Electric motor control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for quiet variable motor speed control
ActiveUS7330004B2Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor speedEngineering
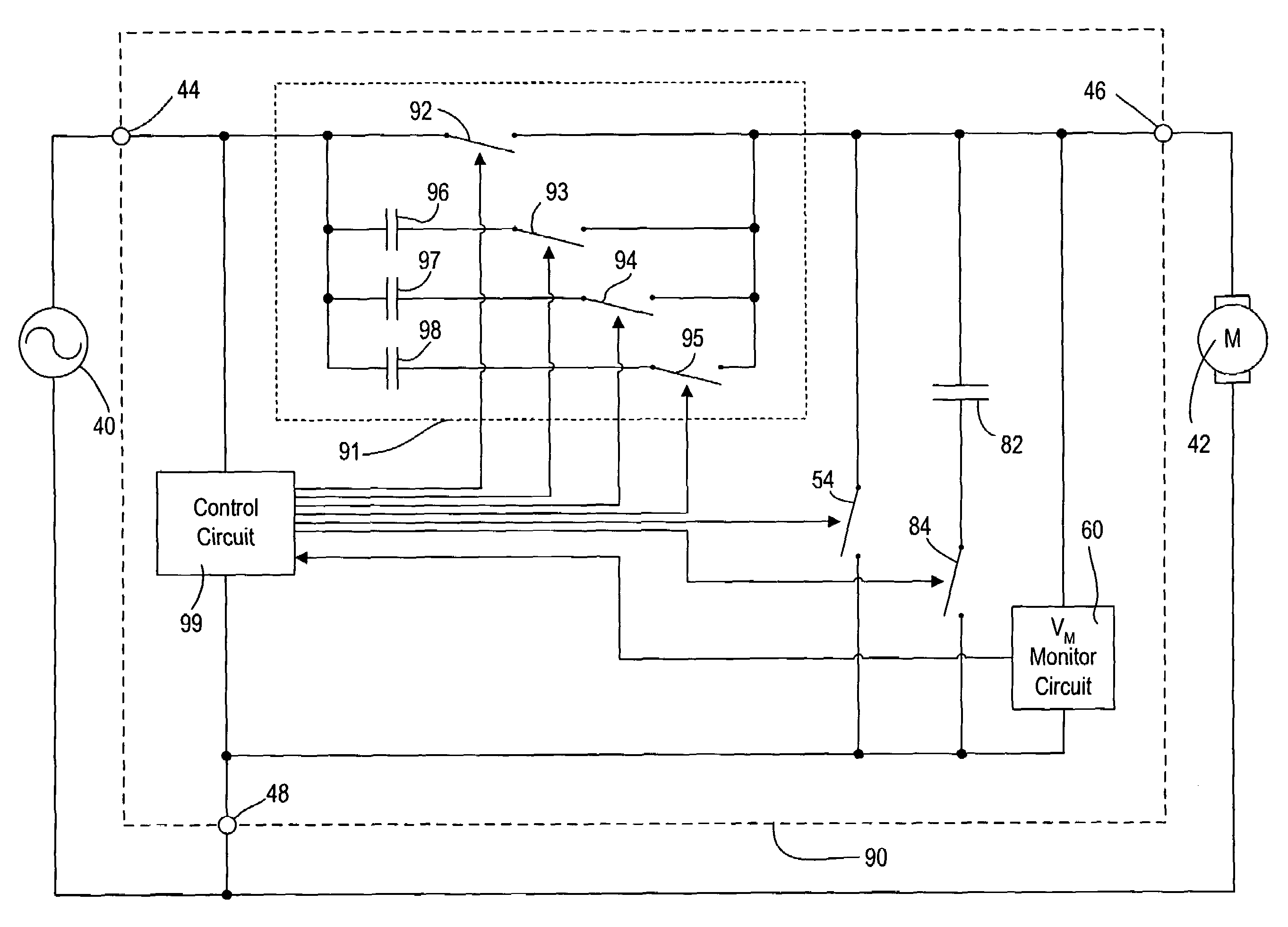
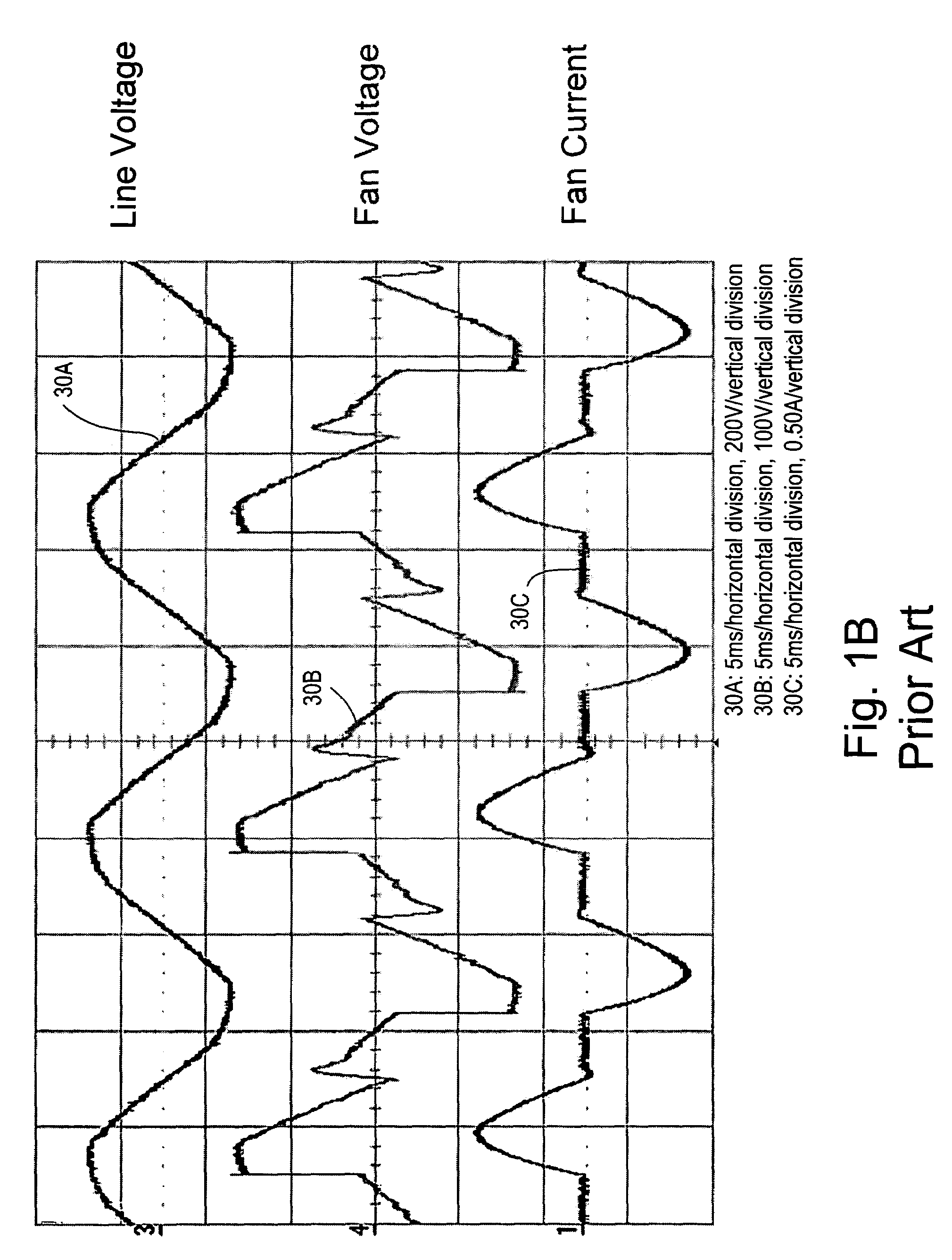
An apparatus for controlling the speed of an AC motor comprising a switch adapted to be coupled in parallel with power terminals for the AC motor; a capacitor coupled in series with the parallel combination of the switch and the motor; the capacitor adapted to provide an AC supply voltage from an AC source to the parallel circuit comprising the motor and the switch; and a control circuit for controlling the conduction time of the switch in order to vary the speed of the motor. The switch is preferably pulse-width modulated at a frequency twice the line frequency of the AC supply voltage, and the switch is turned on when the voltage across the AC motor is zero volts. The apparatus is operable to provide for continuously variable control of the motor speed while minimizing acoustic noise in the motor.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
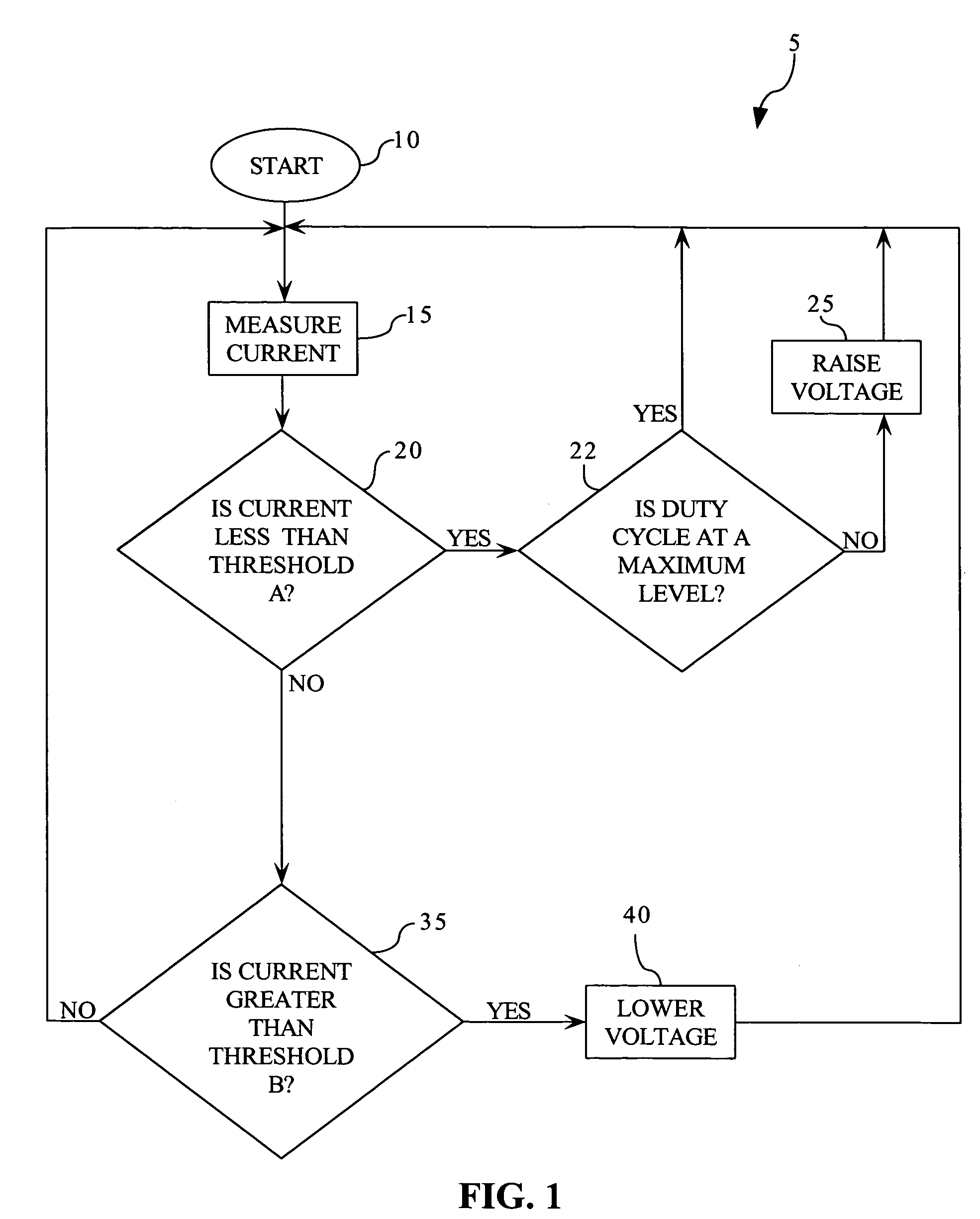
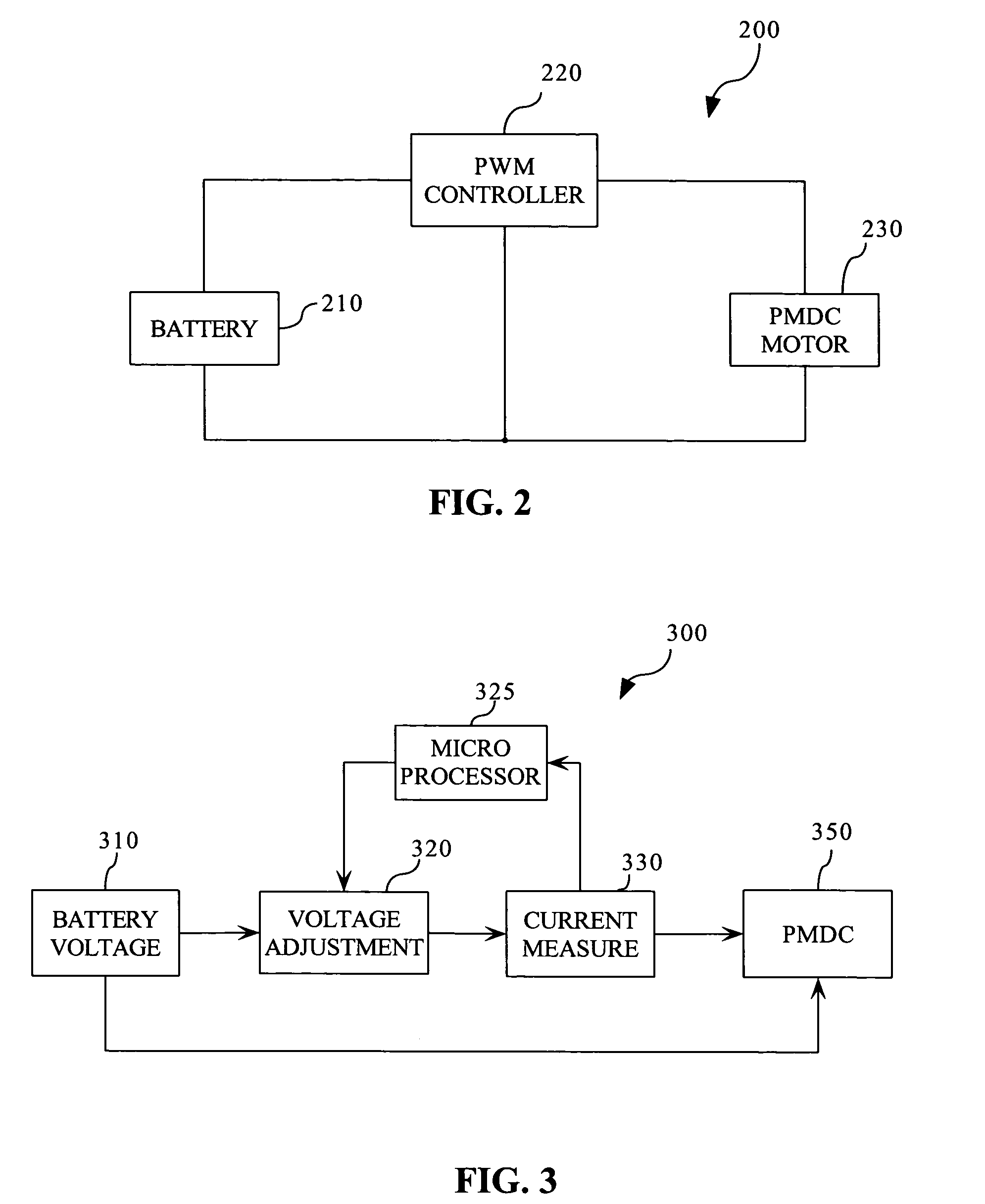
Amperage control for protection of battery over current in power tools
InactiveUS7133601B2Battery protectionHigh currentAC motor controlElectric motor controlLithiumNickel cadmium
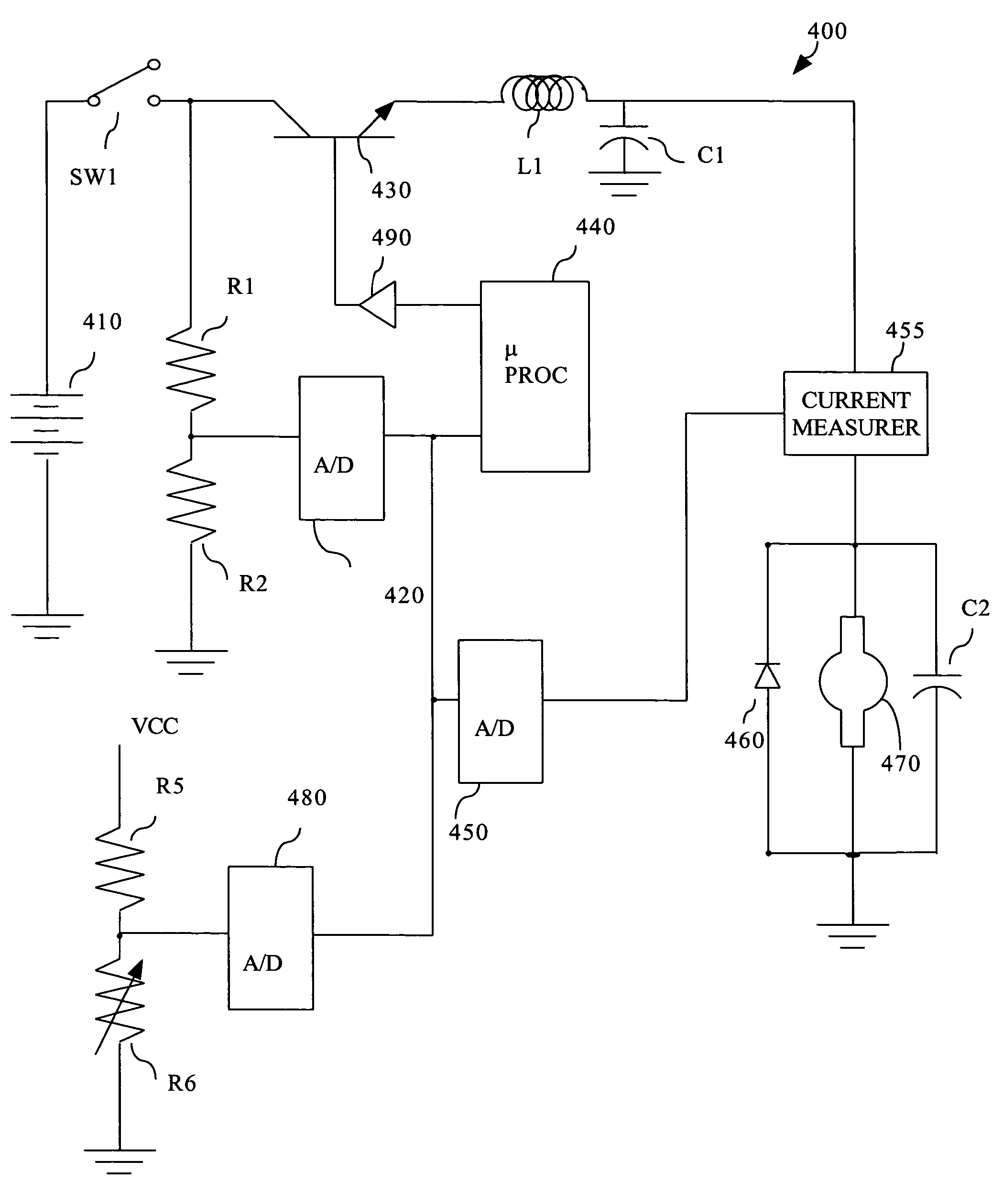
Amperage control of a power tool motor is provided by pulse width modulation of current from a power supply. The pulse width modulation may be varied according to the determined motor current and measured power supply voltage. The power supply preferably includes a battery, such a lithium ion or nickel cadmium.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
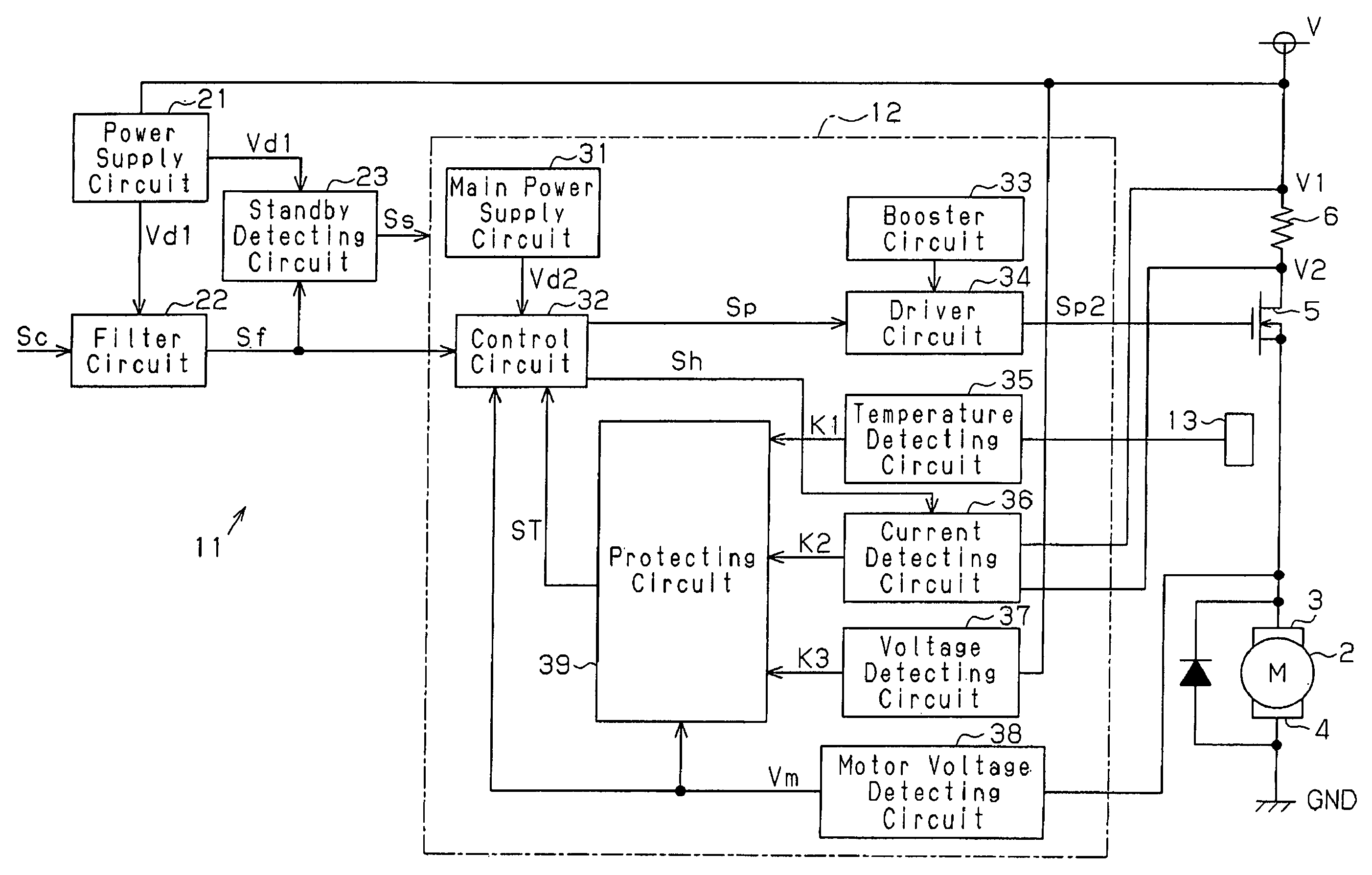
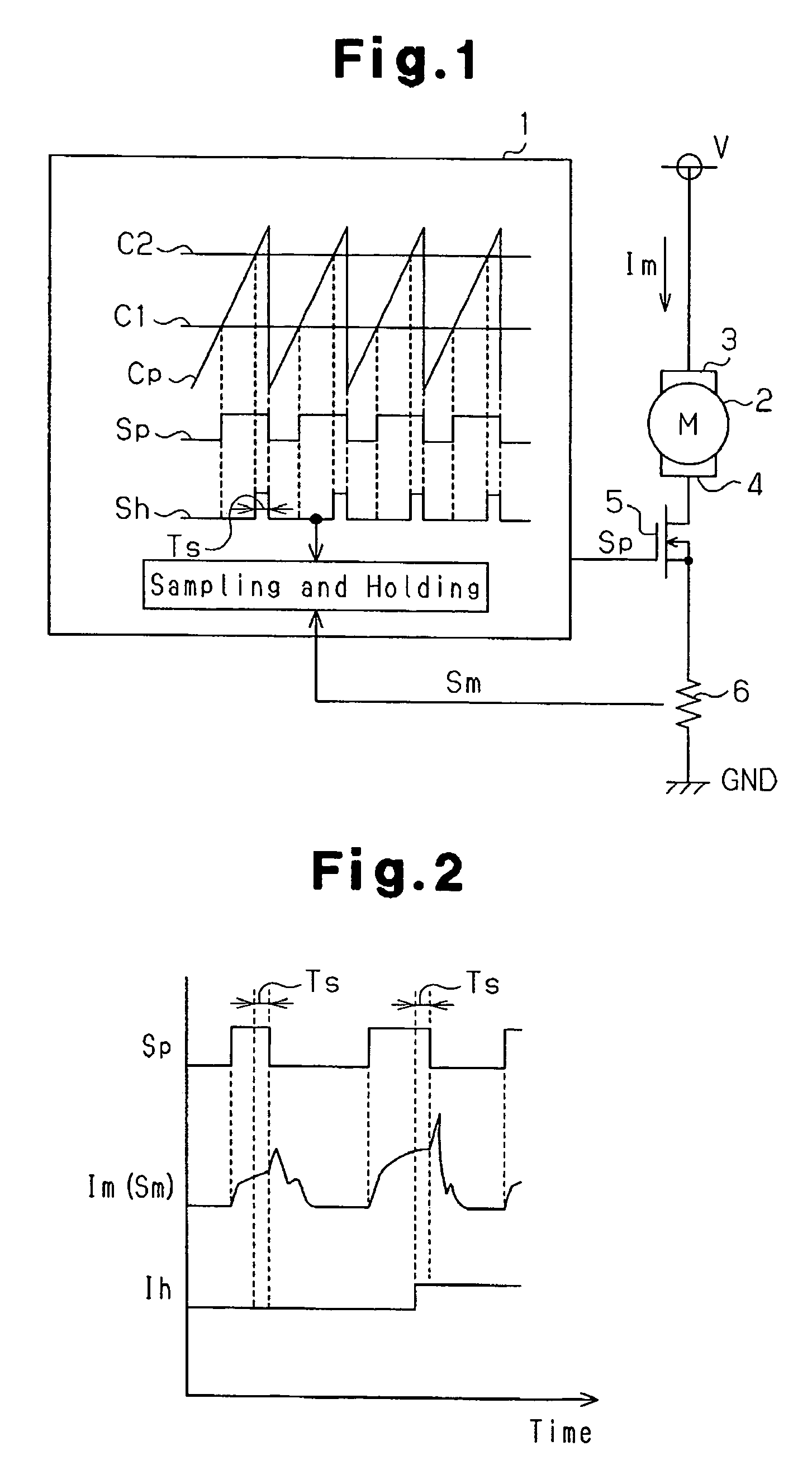
Motor control device and motor control method
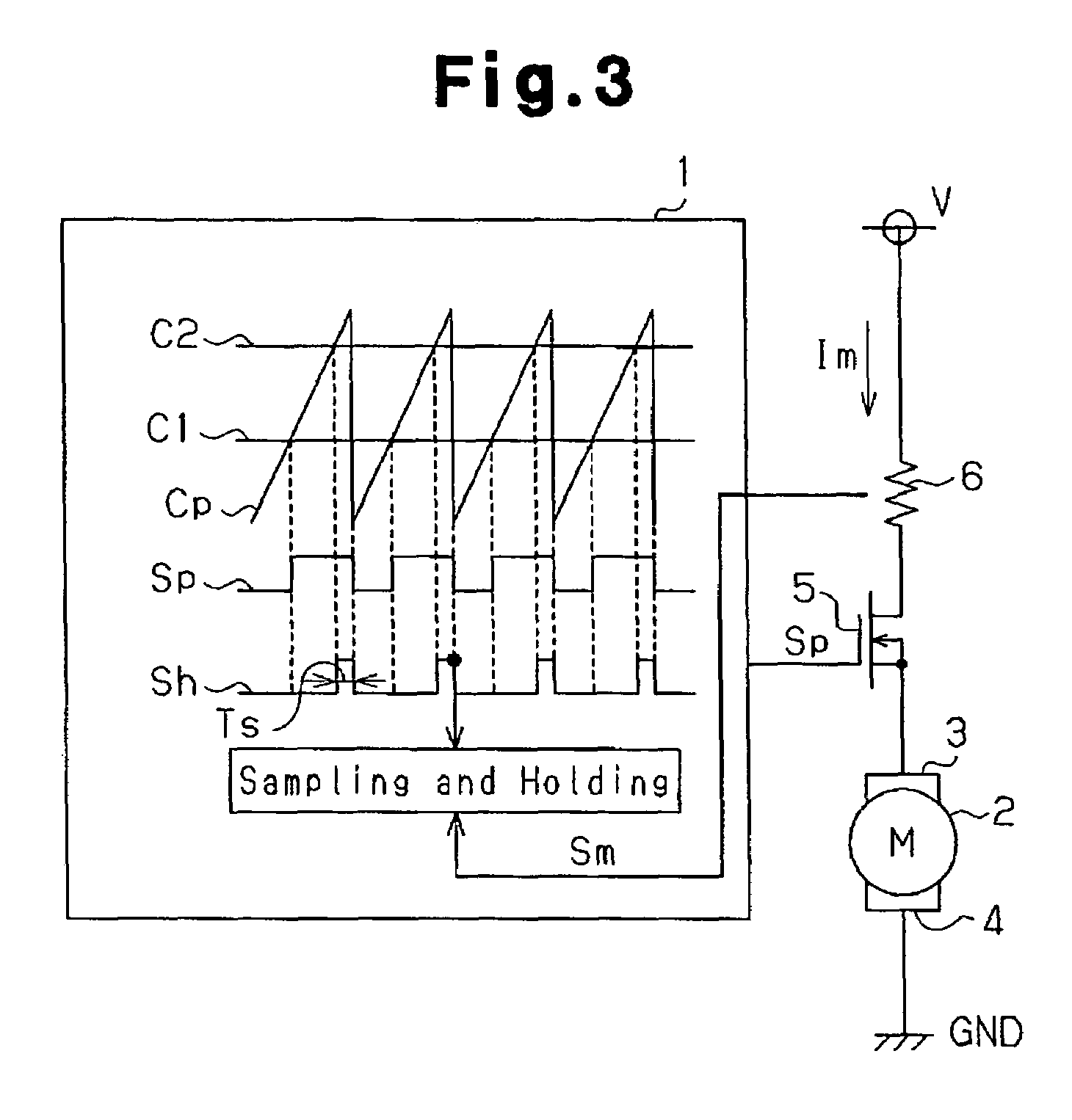
InactiveUS7183737B2Improve accuracyCurrent detectionAC motor controlElectric motor controlDriving currentControl signal
A motor control device selectively turns on or off a drive transistor in-accordance with a PWM control signal Sp, such that a drive current Im supplied to a motor is adjusted. The device also samples and holds a motor current Sm for obtaining a motor current value Ih. With reference to the motor current value Ih, the device protects the motor from an overcurrent. Sampling and holding of the motor current Sm is performed for a sampling and holding time Ts. The sampling and holding time Ts corresponds to a time period between a first point in time when the level of the PWM control signal Sp is switched for turning off the drive transistor and a second point in time that precedes the first point in time by a predetermined period. As a result, the motor current value Ih is detected with high accuracy.
Owner:ASMO CO LTD
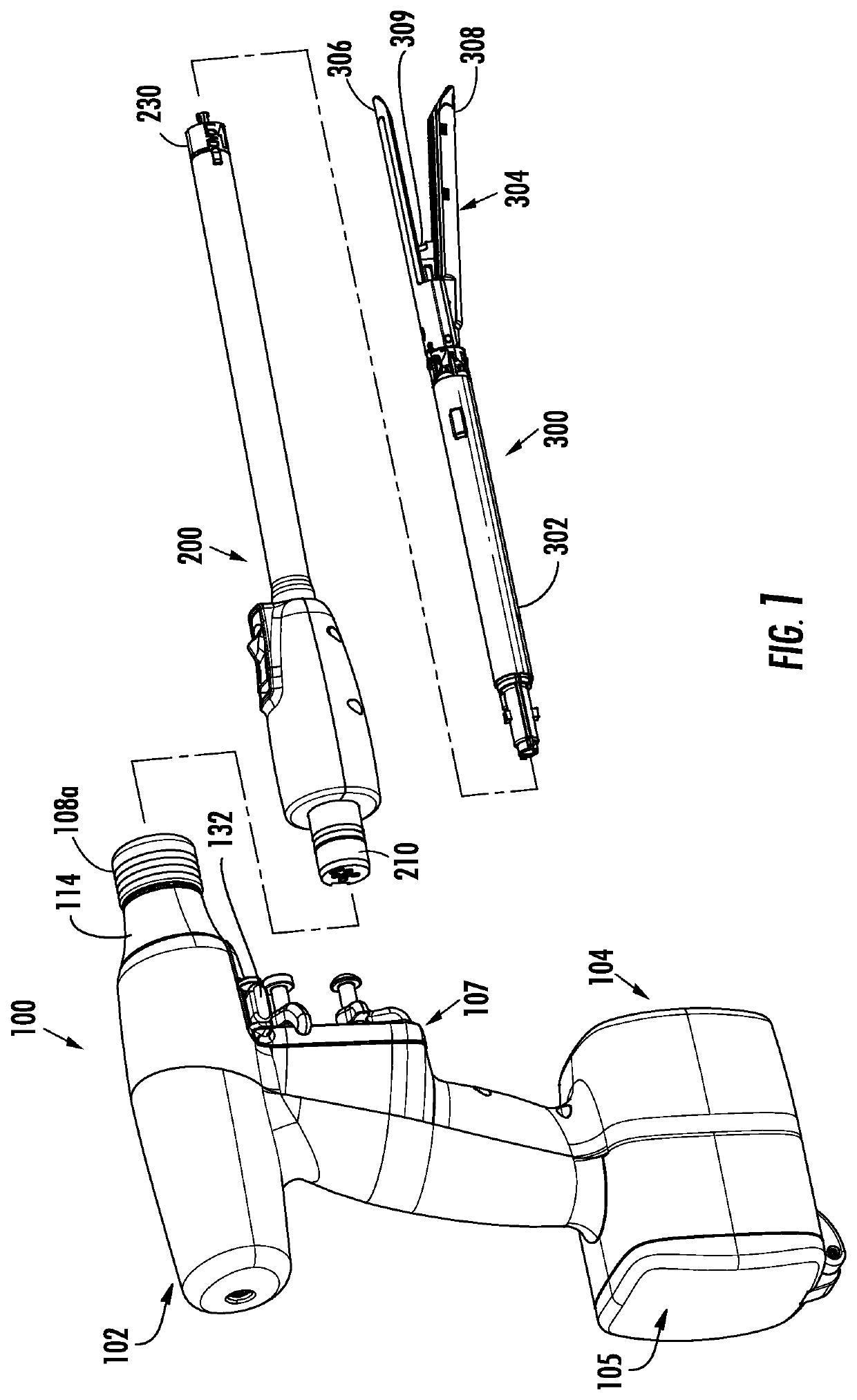
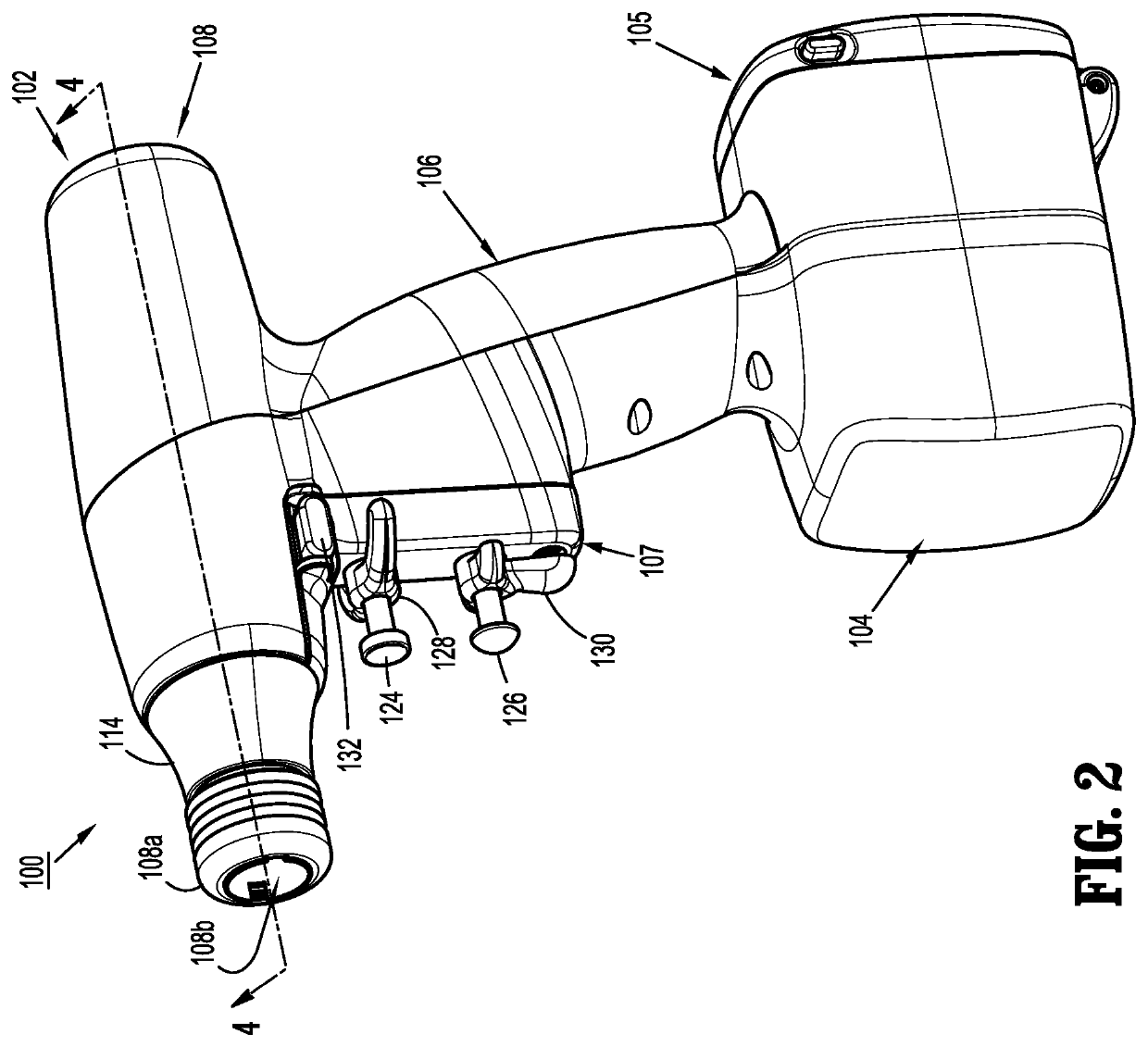
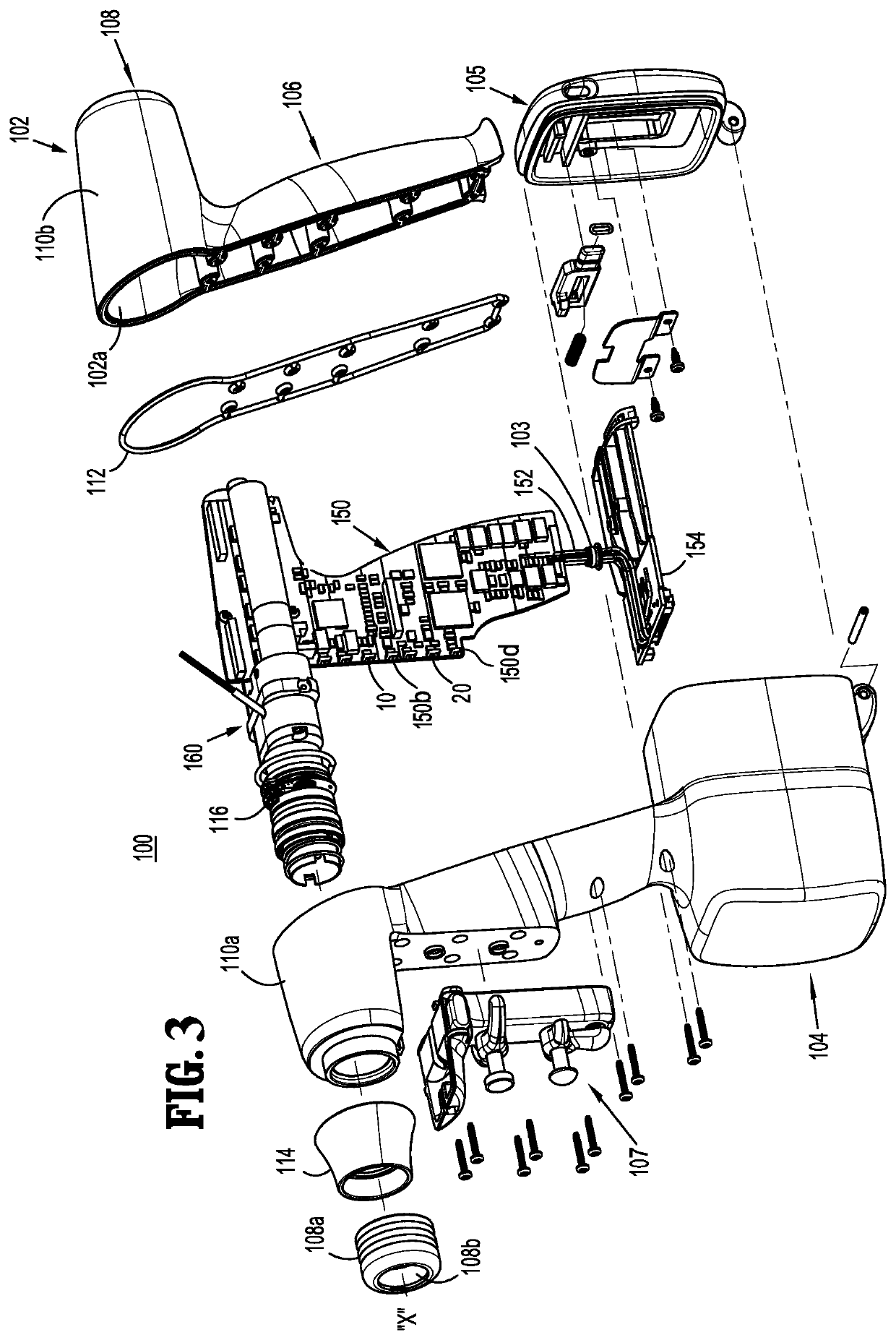
Surgical machine and method for controlling and/or regulating a surgical machine
ActiveUS8029510B2Easy to disassembleSimplified detachmentElectric motor controlDiagnosticsEngineering
Owner:AESCULAP AG
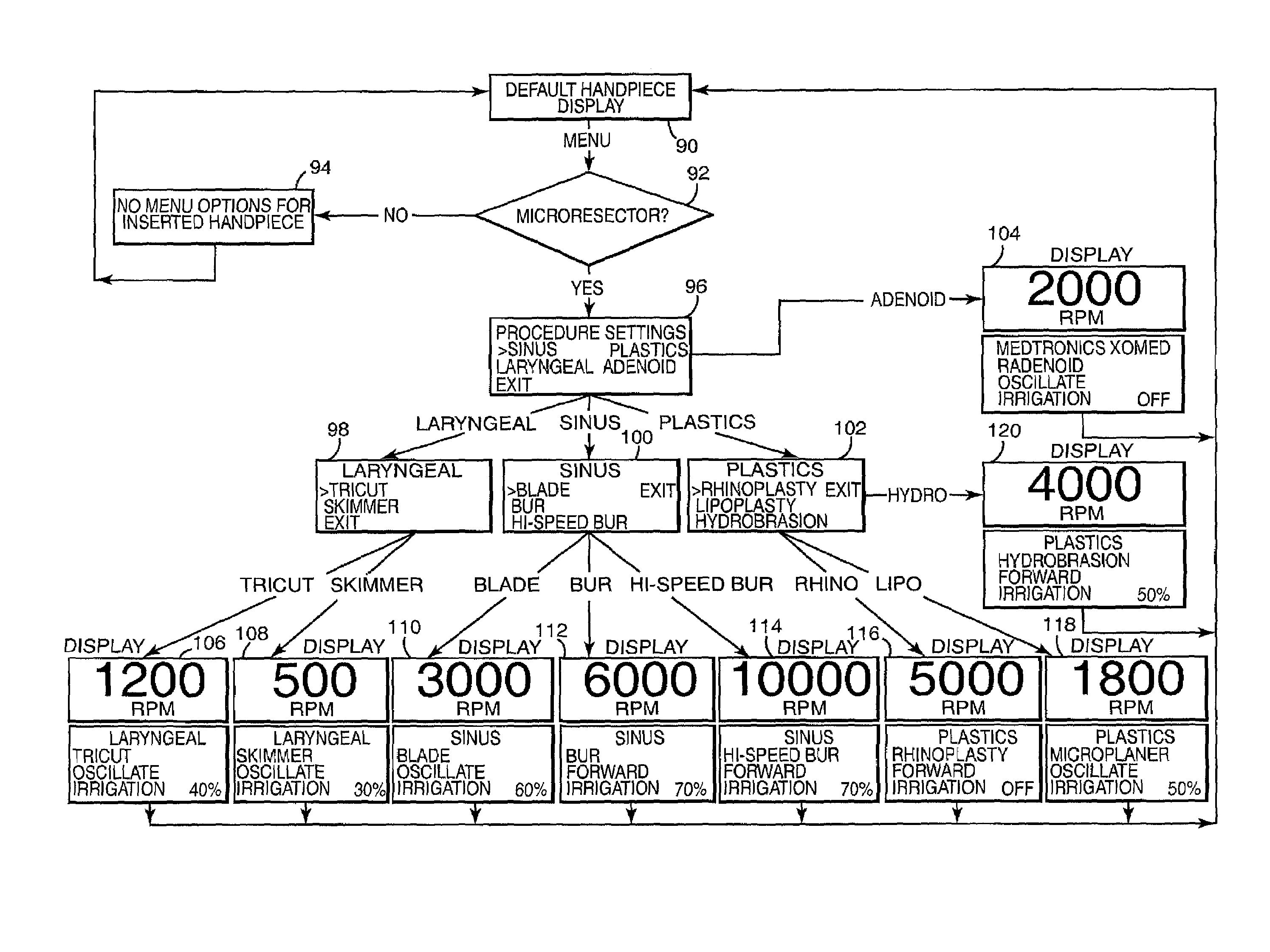
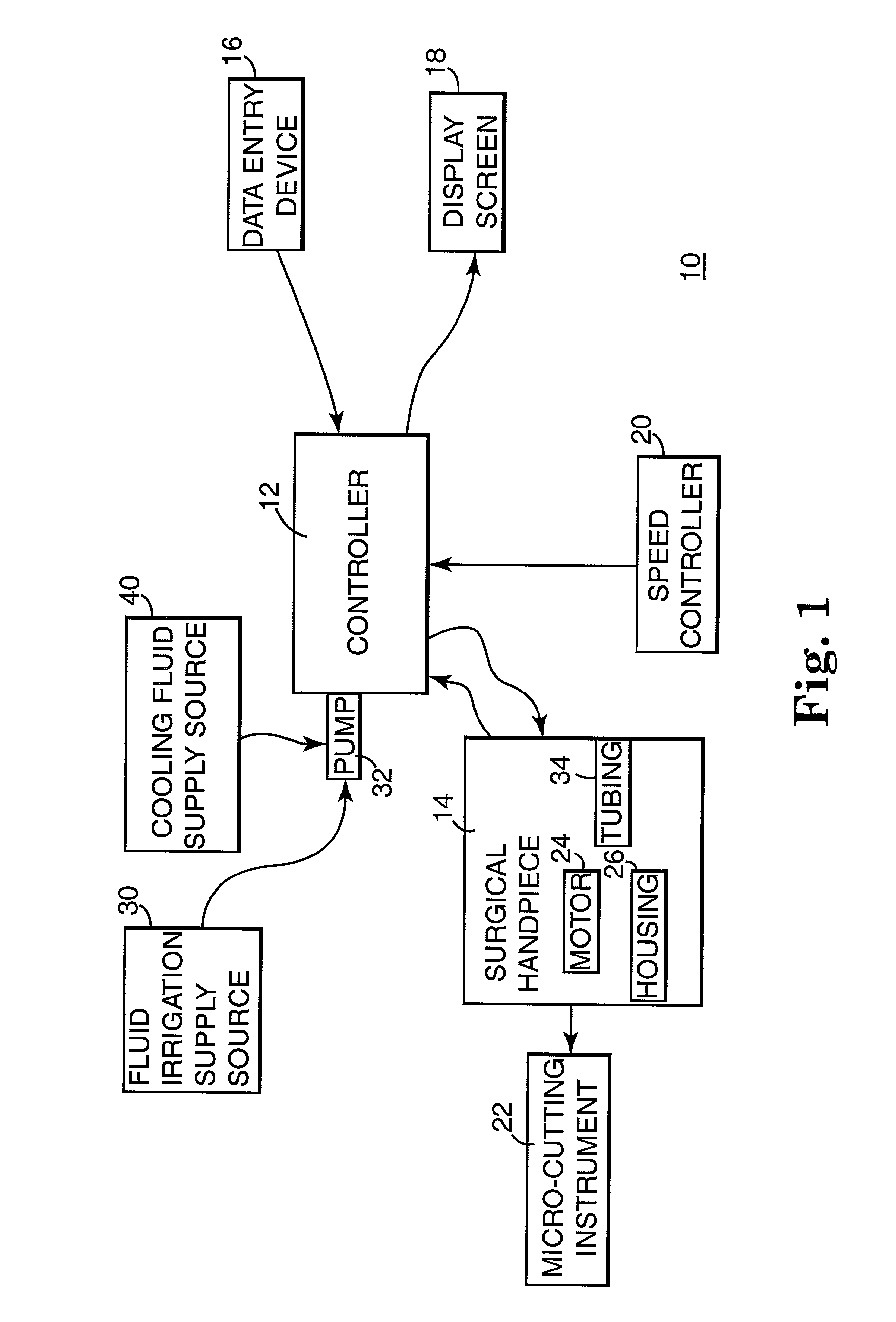
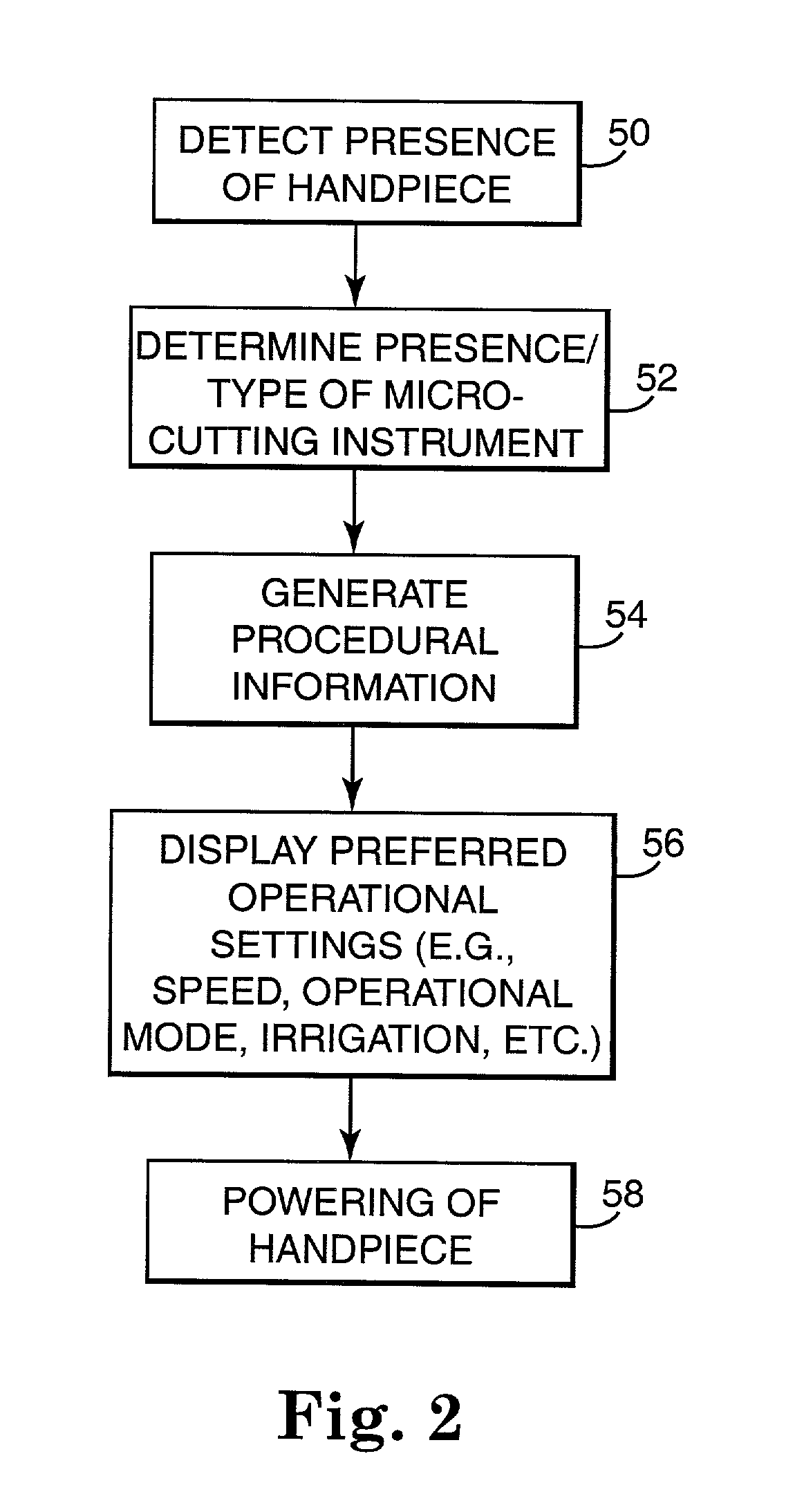
Motor control system for a surgical handpiece
A system and method for powered surgical handpiece capable of powering various micro-cutting instruments is described. The system is comprised of a controller adapted for controlling / interfacing with a powered surgical handpiece based upon user-defined procedural information. A data entry device is used for entering the user-defined procedural information used by the controller for configuring and operating the motor control system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
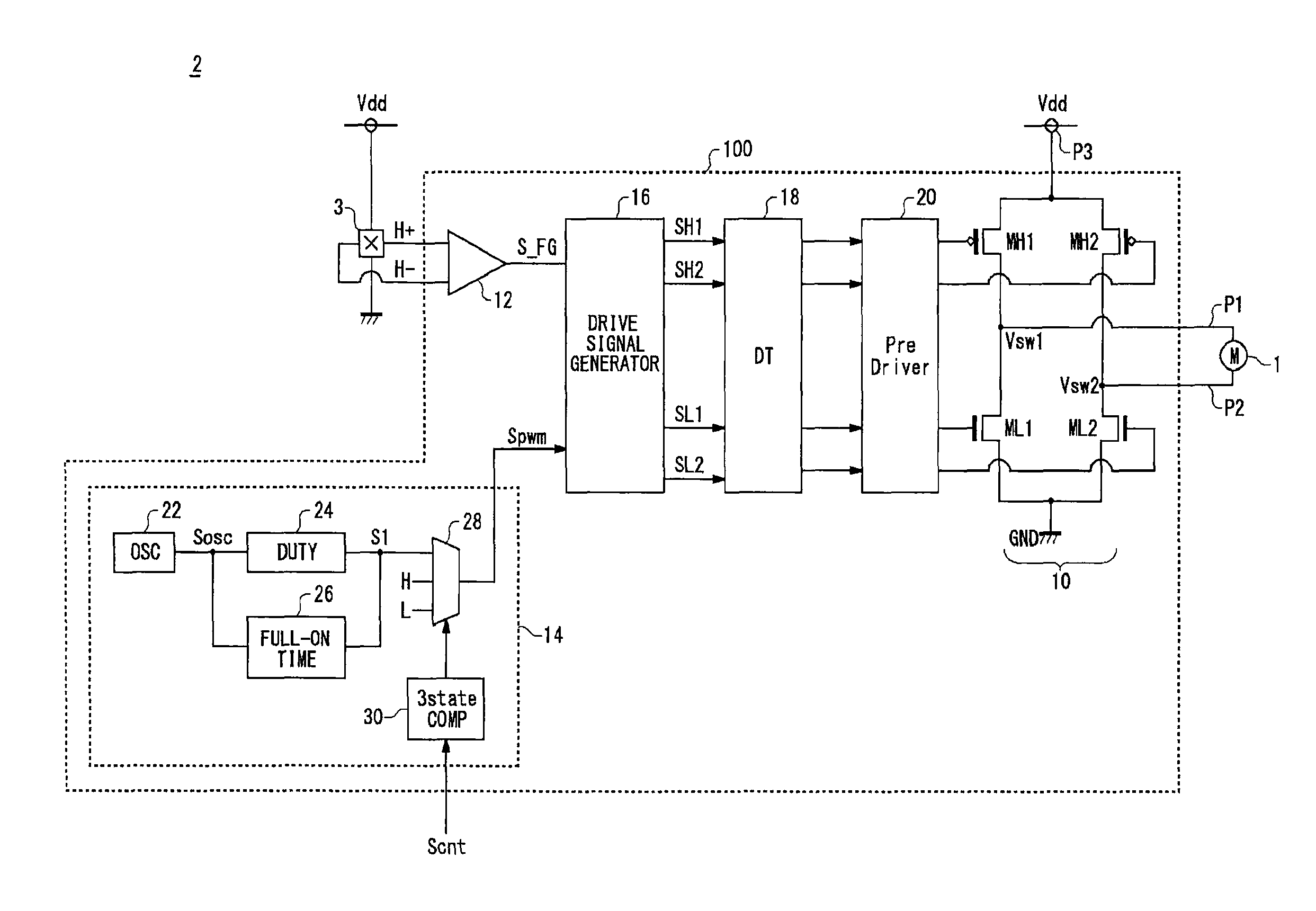
Motor drive circuit with short startup time
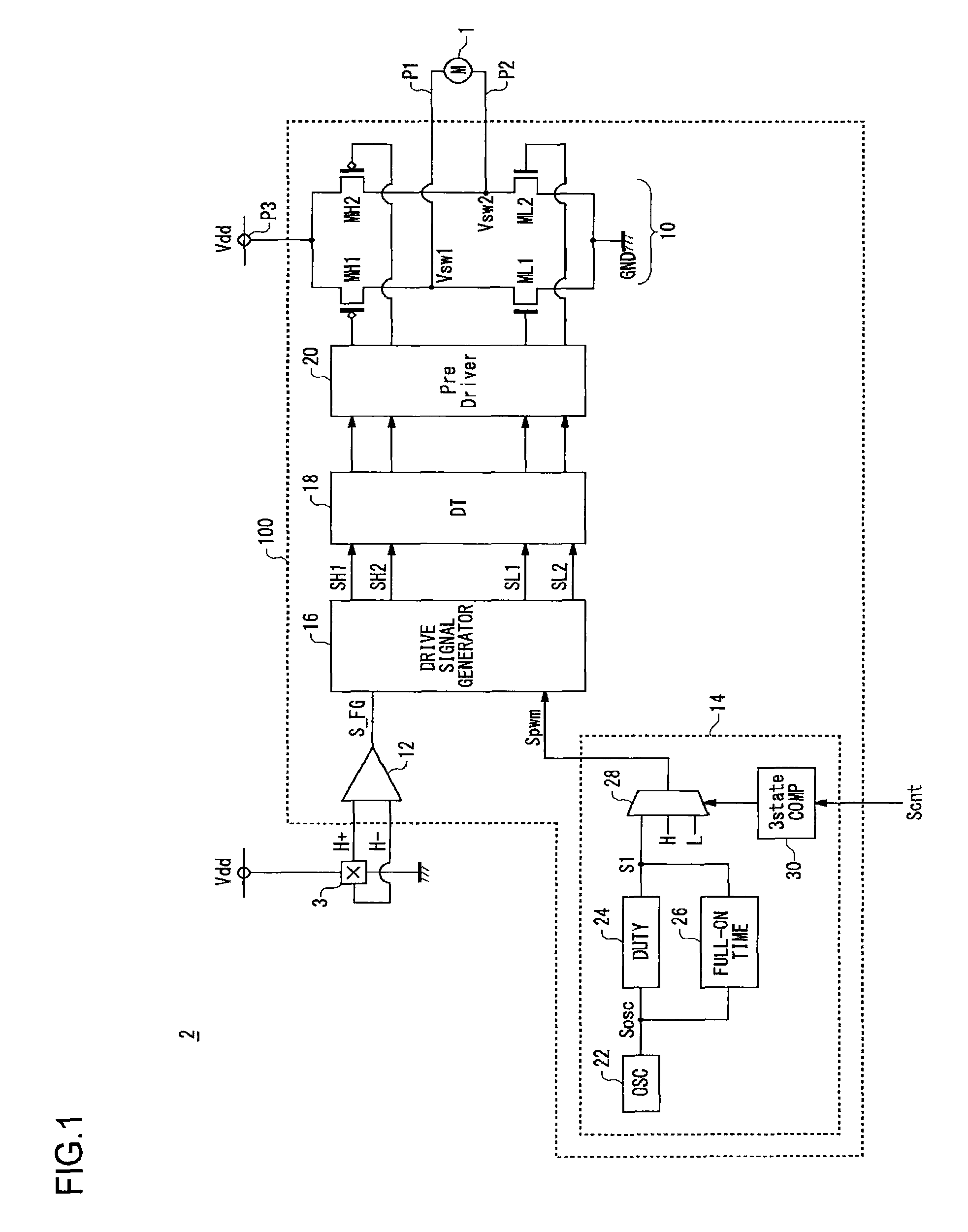
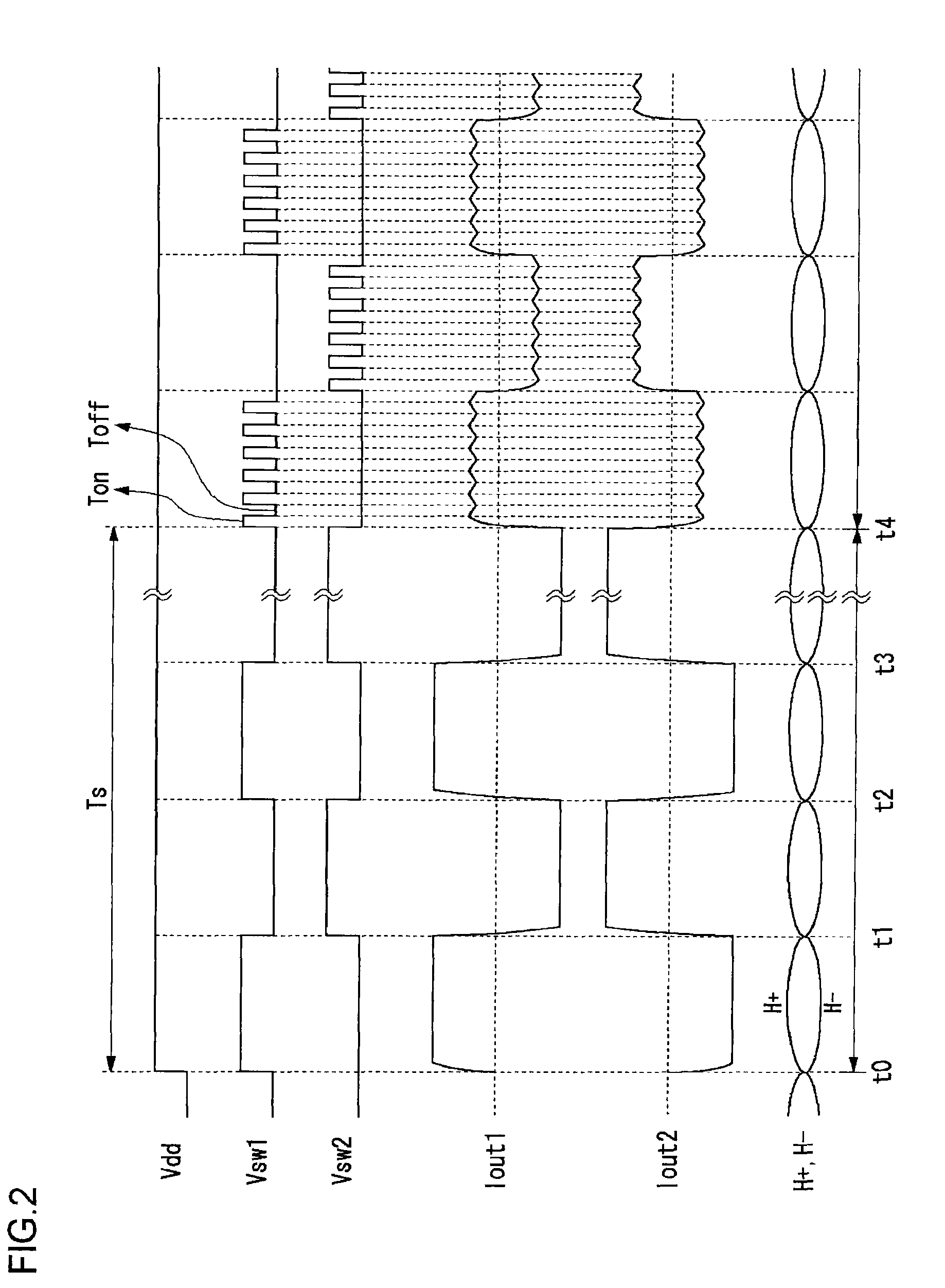
An H-bridge circuit is connected to a coil of the vibration motor that is to be driven. A comparator receives Hall signals indicating position information of a rotor of the vibration motor, and converts to an FG signal. A pulse width modulator generates a pulse-modulated pulse signal specifying energization time of the coil of the vibration motor. The pulse width modulator, in a first mode, after commencing start-up of the vibration motor, sets a duty ratio of the pulse signal to 100%, and after that, switches the duty ratio to a predetermined value in accordance with rotational frequency of the motor. In a second mode, the duty ratio of the pulse signal continues to be set to 100%. In a third mode, frequency and the duty ratio of the pulse signal are set based on a control signal of a pulse form inputted from outside. The control signal is used also in switching mode.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Portable drilling device
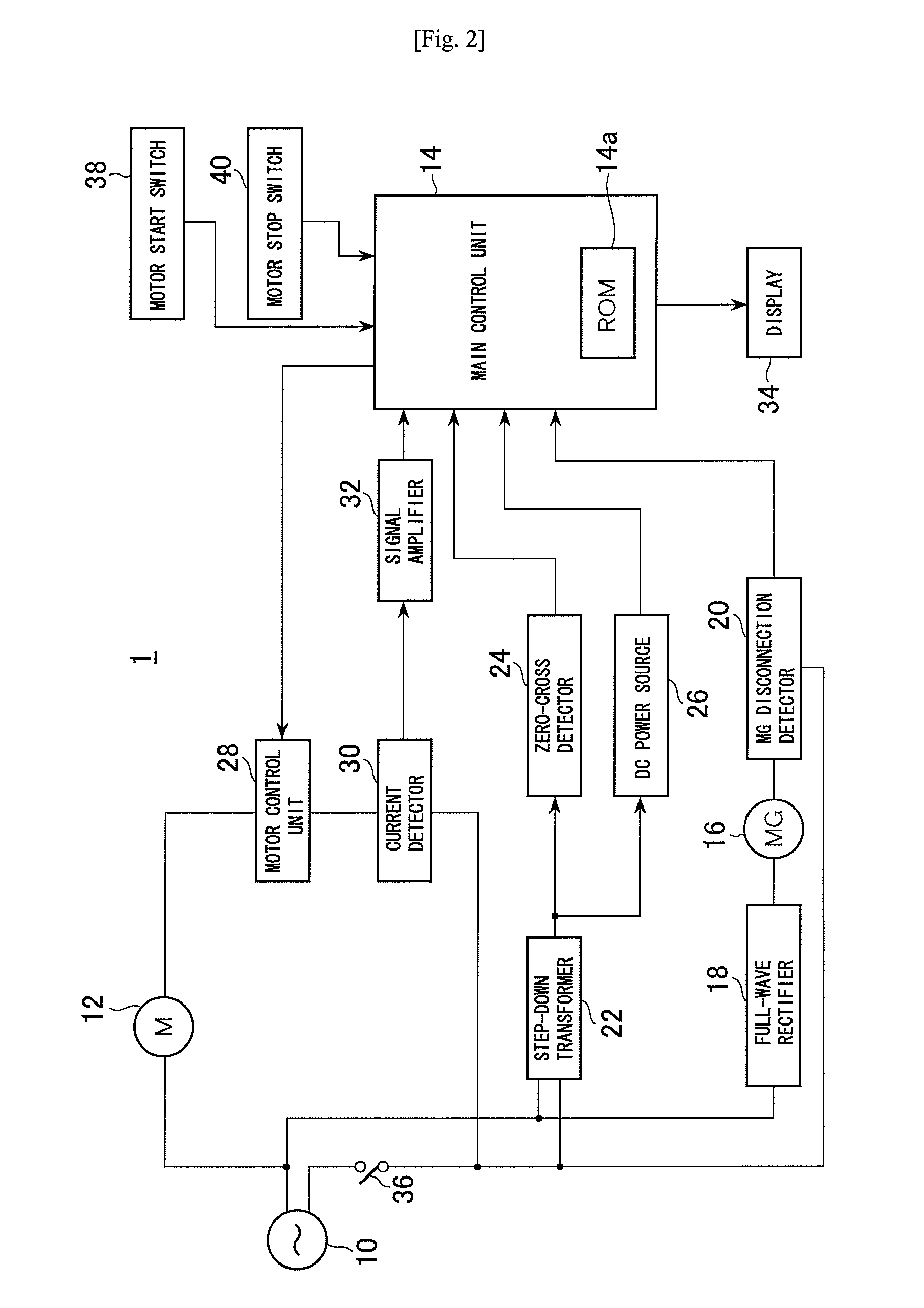
ActiveUS7936142B2Easy to operateImprove securityAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlFull waveEngineering
A drilling device prevents recurrence of an overload condition after occurrence of the overload condition, thereby improving operability and safety in the drilling device. A motor for rotating a drill is connected to an AC power source through a motor control unit, a current detector, and a power switch. A magnet is also connected to the AC power source through the power switch and a full-wave rectifier. The motor control unit rotationally drives the motor on the basis of a signal sent from a main control unit according to a state in which a motor start switch is on. The main control unit controls the motor control unit to gradually reduce a supply voltage to the motor when the motor becomes overloaded, to gradually increase the voltage to the normal power supply condition when the overload condition is vanished, and to stop power supply to the motor if the overload condition continues for a predetermined period.
Owner:NITTO KOHKI CO LTD
Apparatus and method for controlling hybrid motor
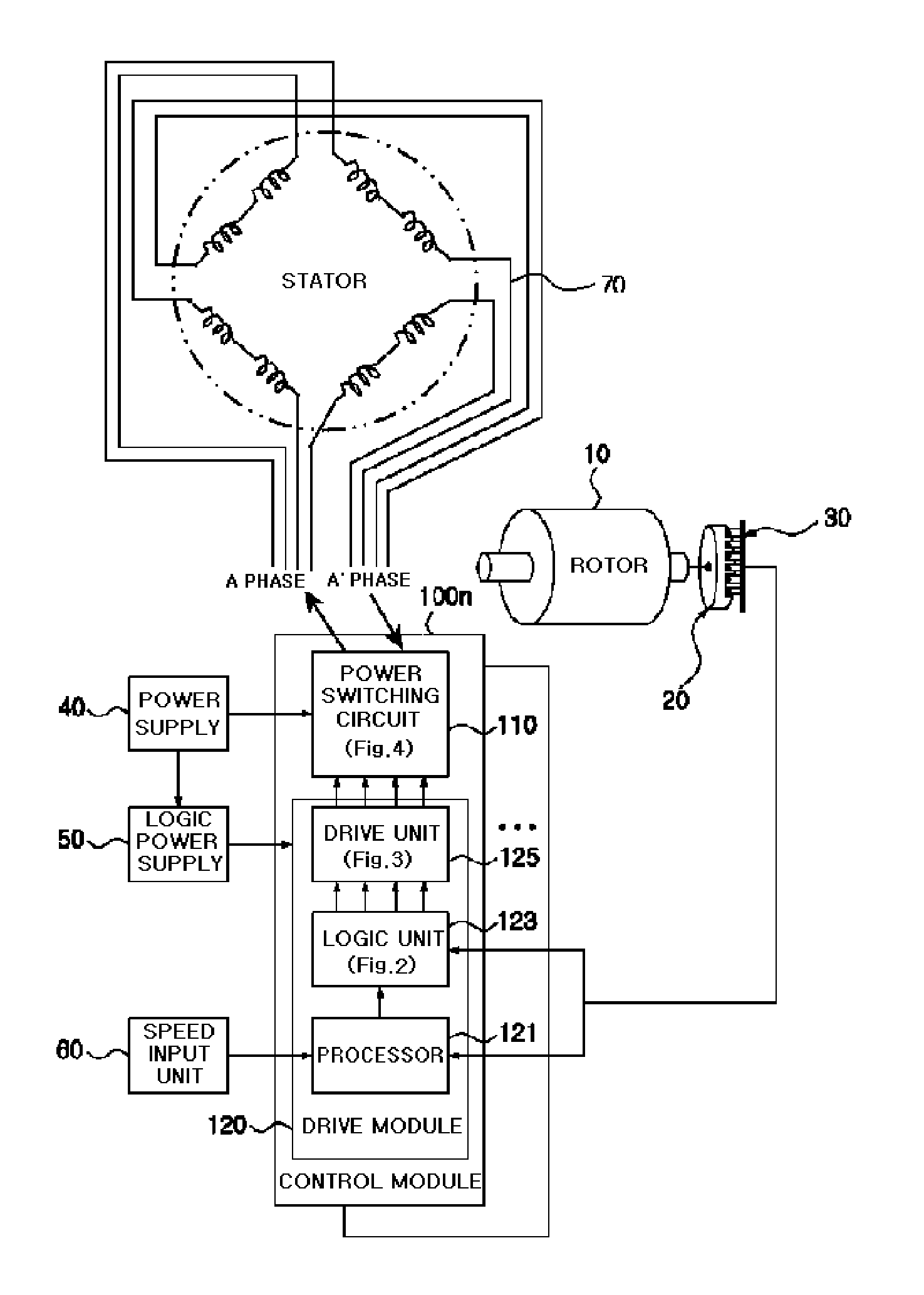
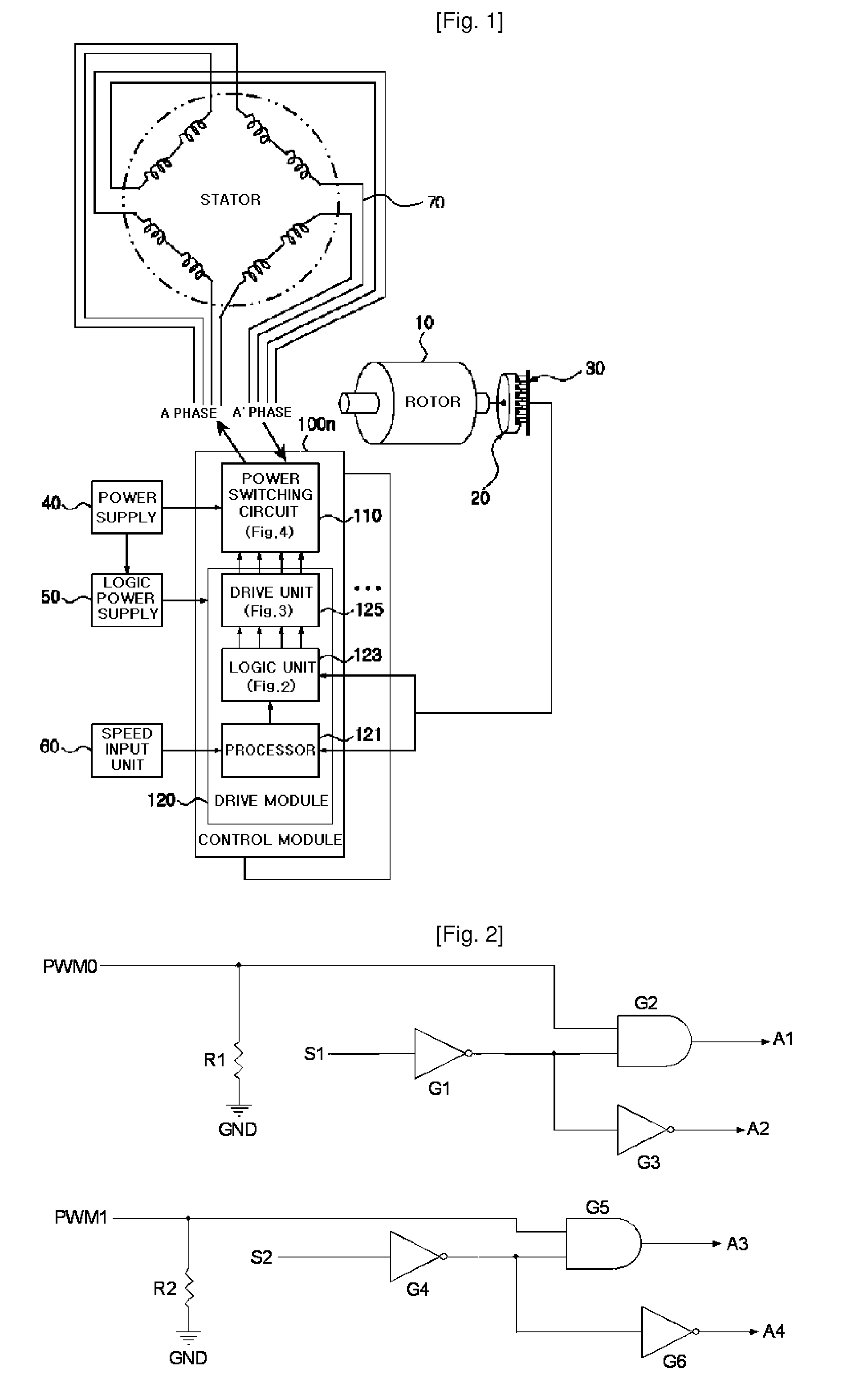
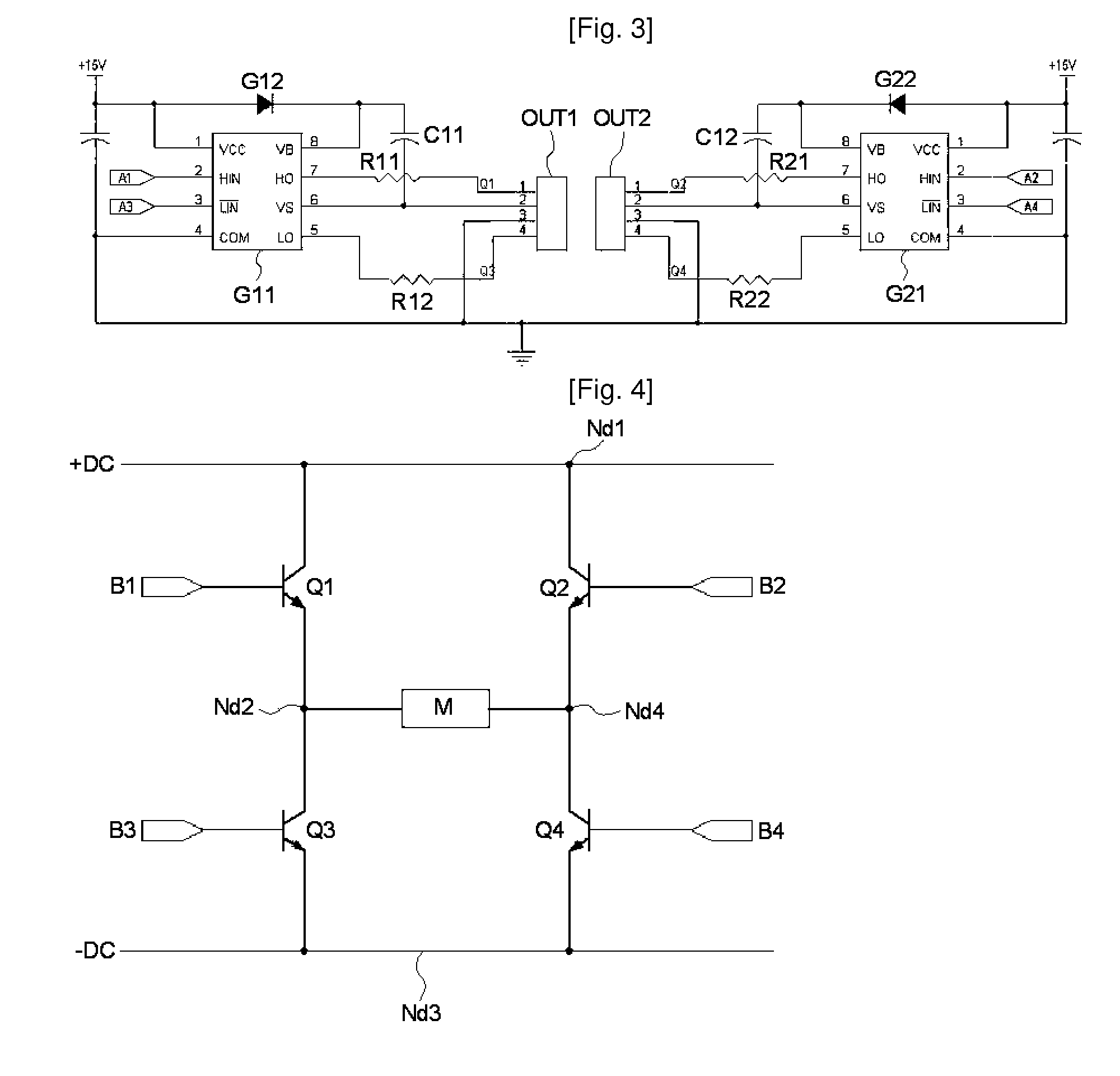
ActiveUS8228020B2Reduce capacityReduce electricity loadSingle-phase induction motor startersWindingsDriver circuitPower switching
An apparatus and method for controlling a hybrid motor, The hybrid motor, uses a permanent magnet instead of a field coil for a rotor, winds a coil round a stator in a multi-phase independent parallel manner, fixes a rectifying type encoder to the rotor and connects a sensor to a driving circuit. The apparatus comprises: an encoder attached to a rotor in cooperation with a pole sensor a speed input unit for generating a speed instruction signal a power switching circuit to generate motor driving signals; a drive module receiving the speed instruction signal and the sensor signal and outputting the speed instruction signal synchronized with the sensor signal as a driving motor signal; a power supply for applying a DC voltage to the power switching circuit; A logic power supply for converting the DC voltage into a logic voltage, and applying logic voltage to the drive module. The motor has n phases, n power switching circuits and n drive modules.
Owner:NAMYANG NEXMO CO LTD
Powered surgical instrument with pressure sensitive motor speed control
A surgical instrument includes a drive shaft, a motor for rotating the drive shaft, and a motor speed control. The motor speed control includes a first switch and a second switch which are in communication with the motor. The first switch is disposed over and in registration with the second switch. The first switch has an activated state such that the first switch sends a first signal to the motor. The motor rotates the drive shaft in response to the first signal. The second switch sends a second signal to the motor that varies the speed that the motor rotates the drive shaft in response to a force applied to the second switch by the first switch.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
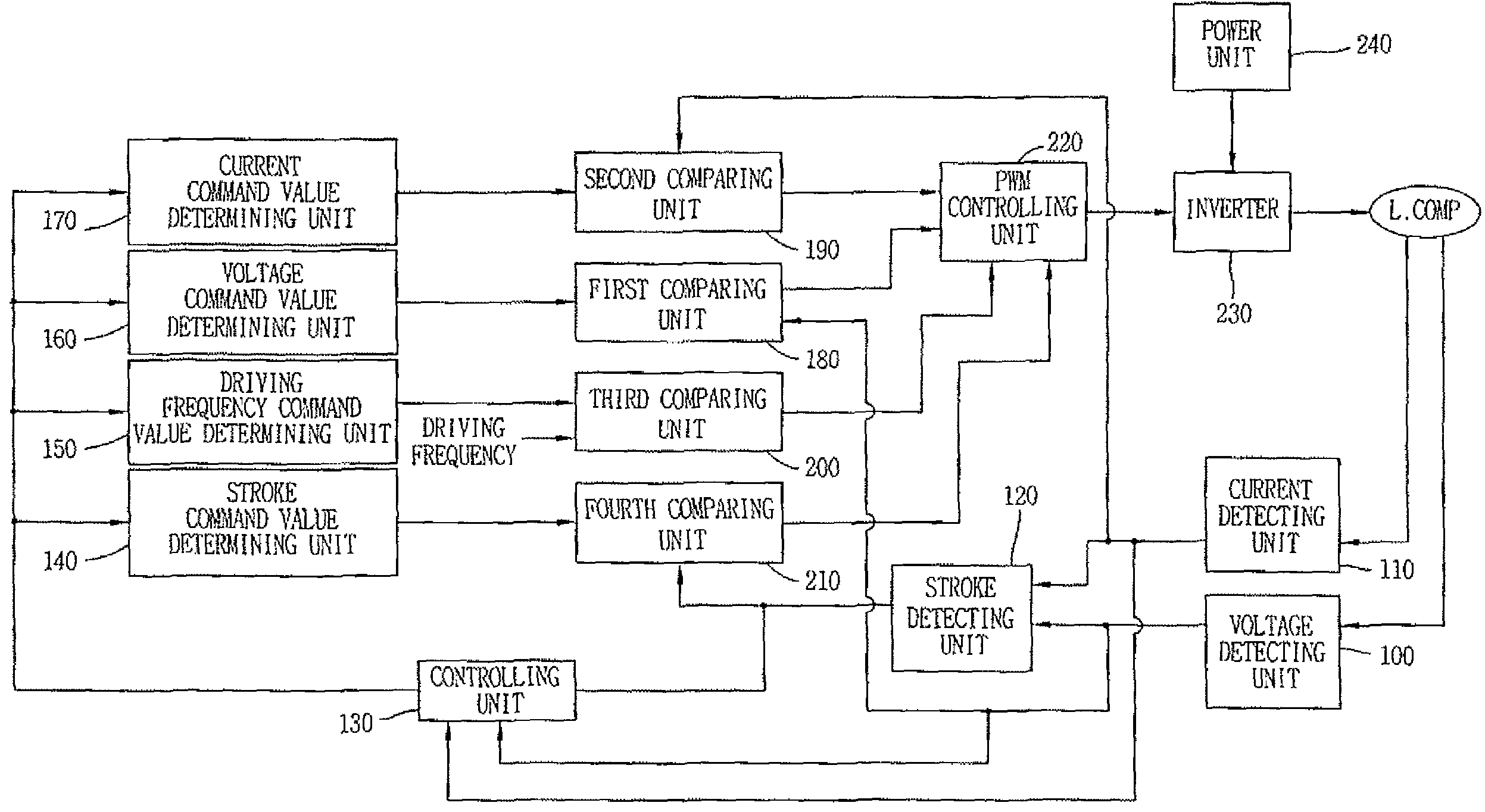
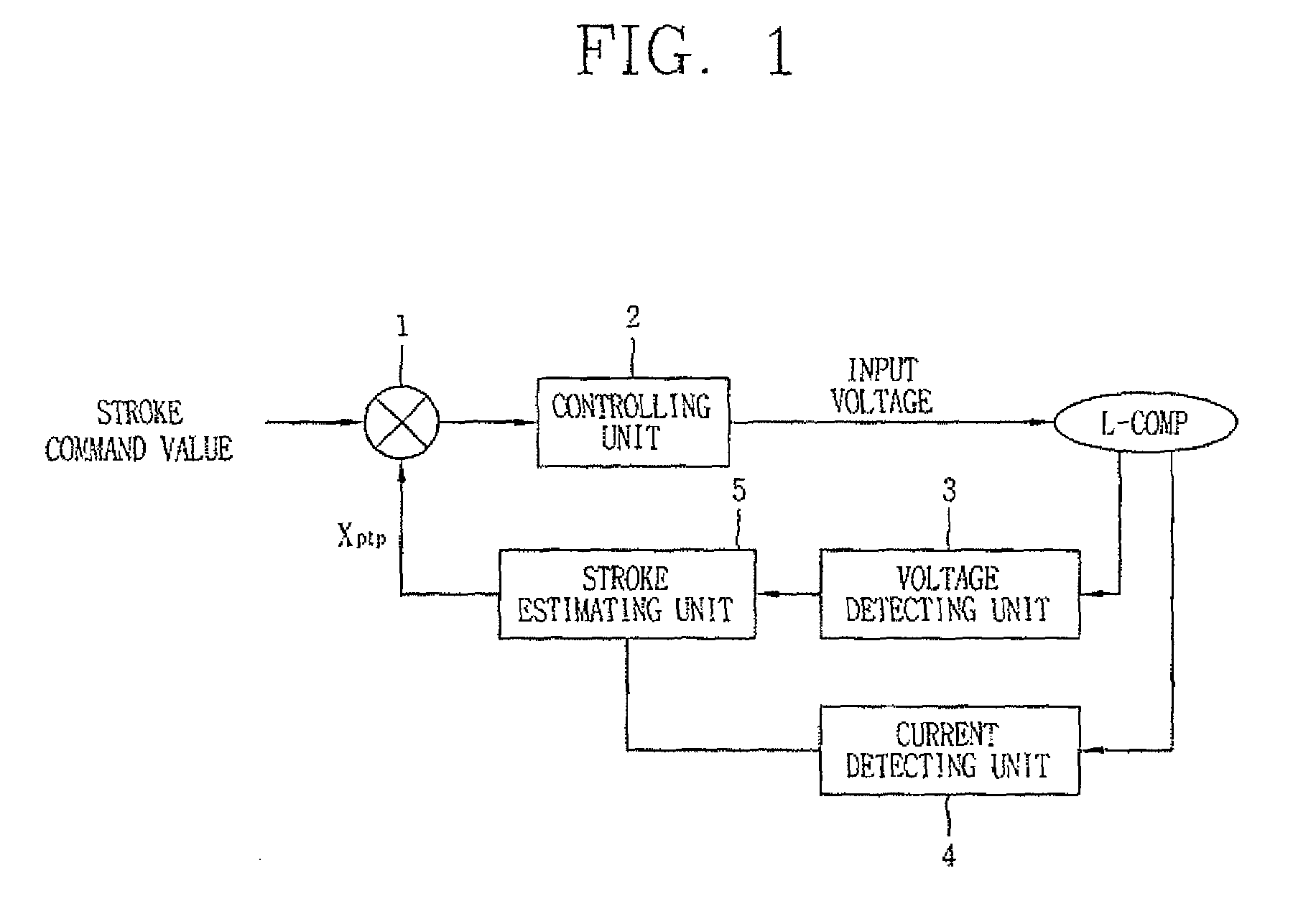
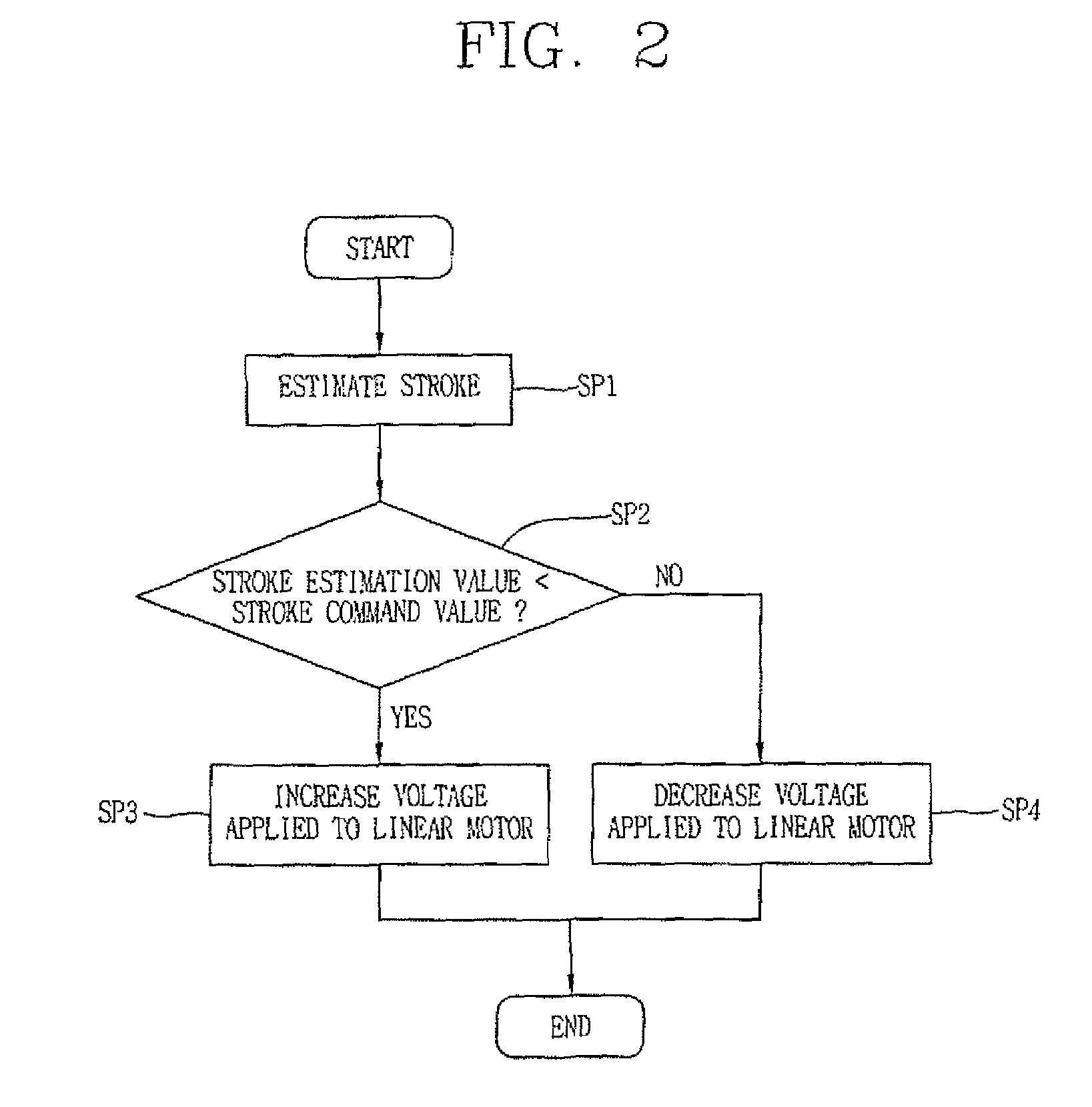
Driving controlling apparatus for linear compressor and method thereof
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
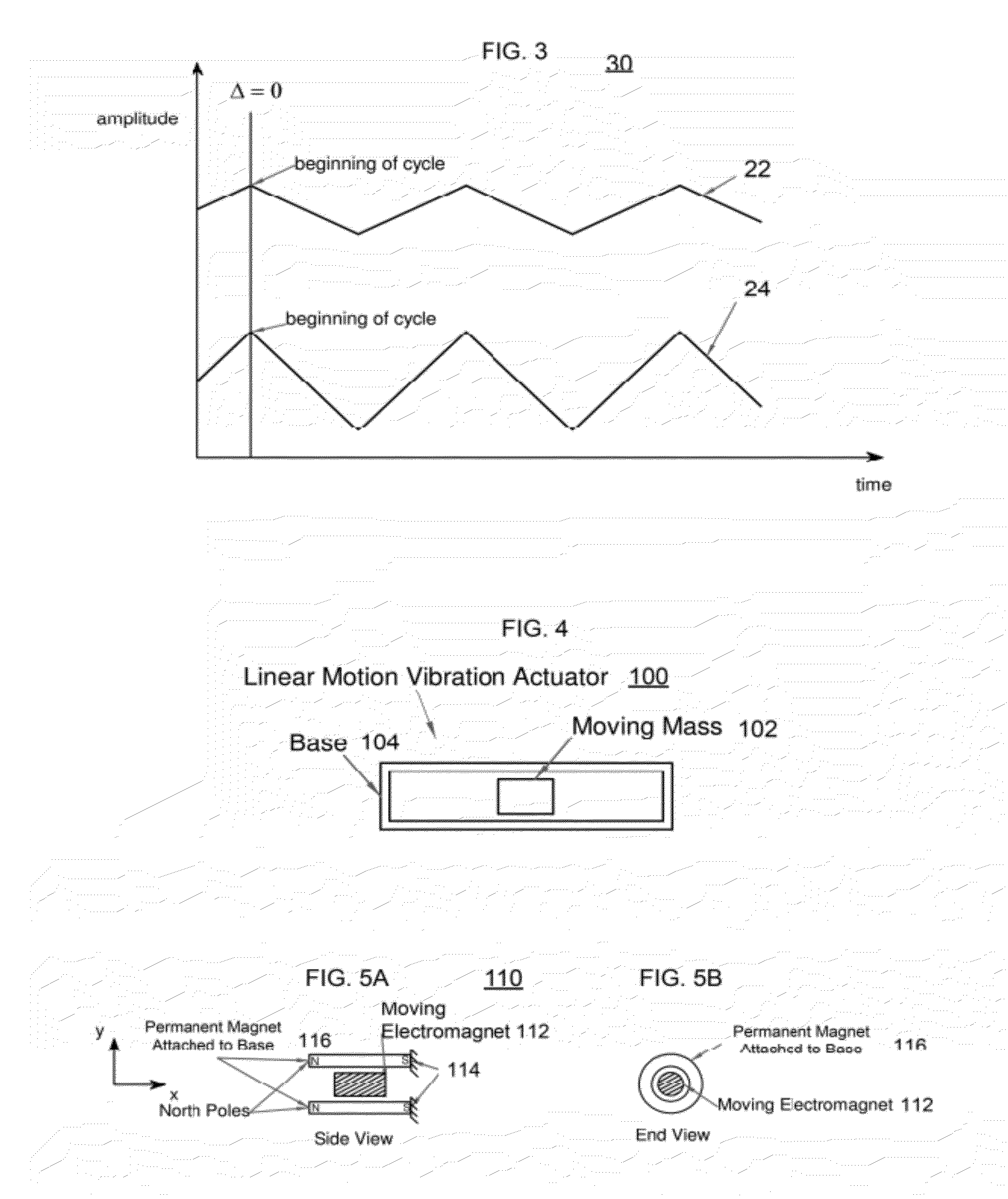
Asymmetric and general vibration waveforms from multiple synchronized vibration actuators
InactiveUS20120232780A1Low costImprove responsivenessDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDriver circuitPeak value
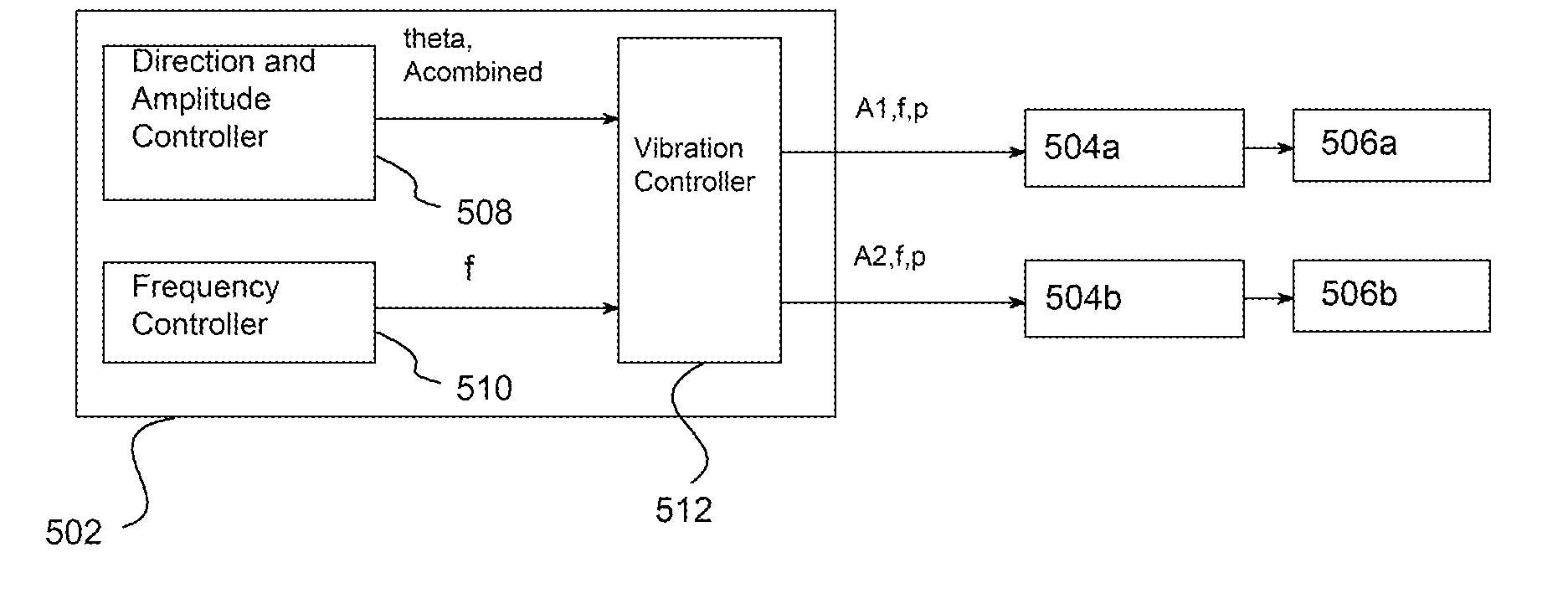
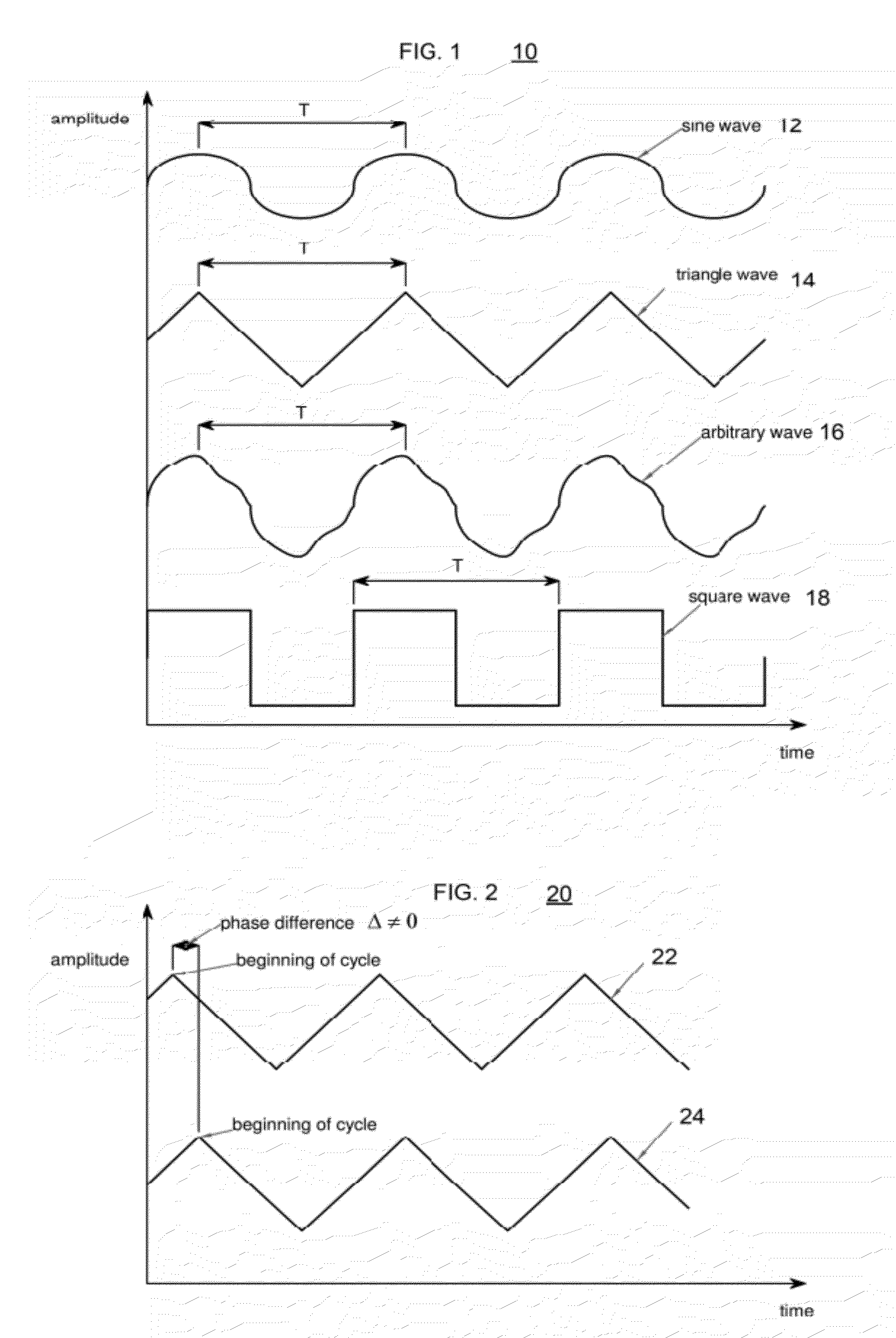
The disclosure relates to General Synchronized Vibration devices that provide haptic feedback to a user and improve the performance of existing vibratory devices. Different actuator types may be employed to provide synchronized vibration, including linear rotary actuators, rotating eccentric mass actuators including interleaved rotating mass actuators, and rocking mass actuators. A controller sends signals to one or more driver circuits to provide adjustment of vibration magnitude, frequency, and direction of the actuators. The system may apply forces onto an object, and a sensor measures a feature(s) of the object. This information is provided to a vibration device controller, which can then modify the vibration waveform to improve overall system performance. Fourier synthesis can be used to approximate arbitrarily shaped waveforms by controlling the phase and frequency of vibration actuators. These waveforms can include asymmetry where the peak force in one direction is higher than the peak force in another direction.
Owner:COACTIVE DRIVE CORP
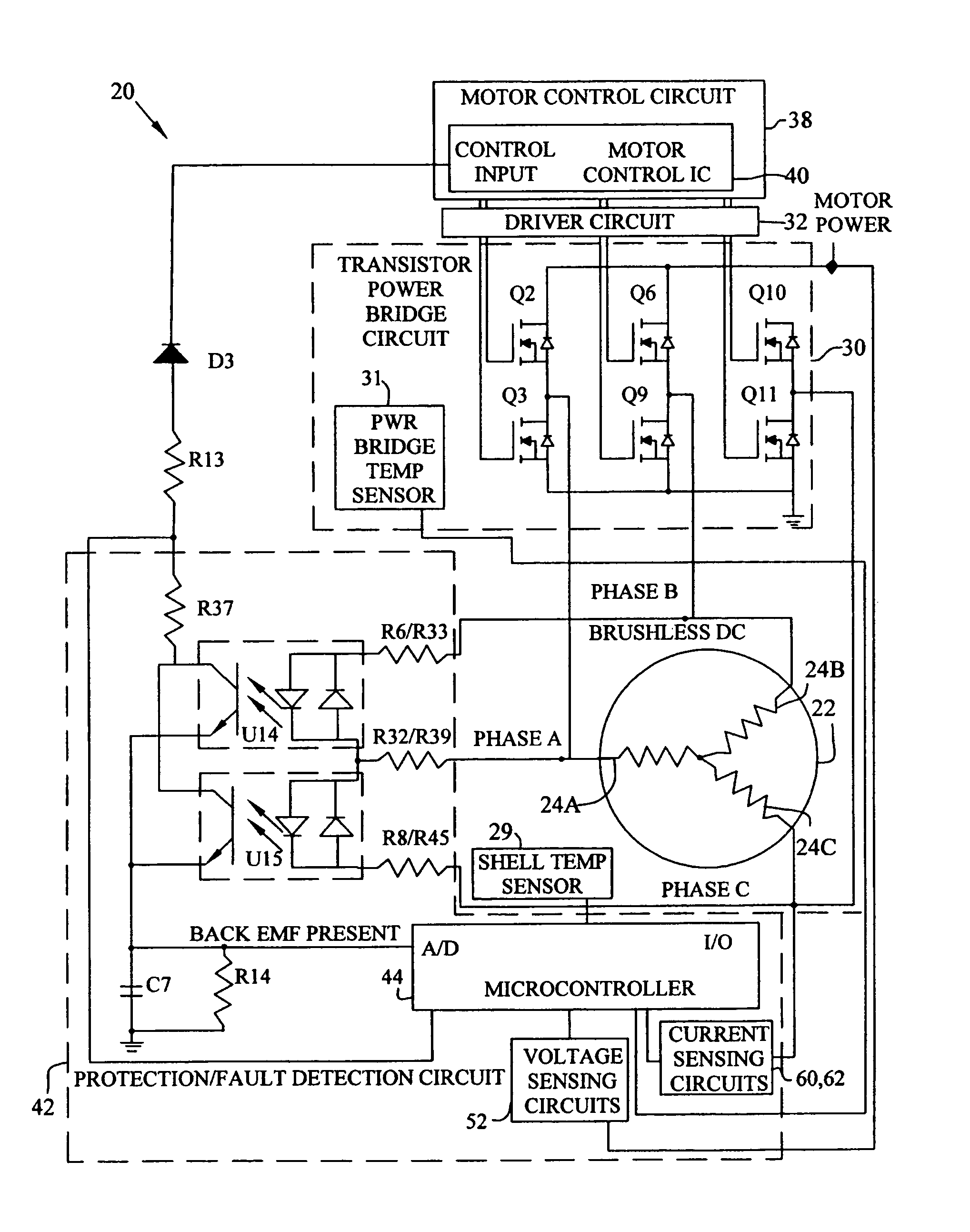
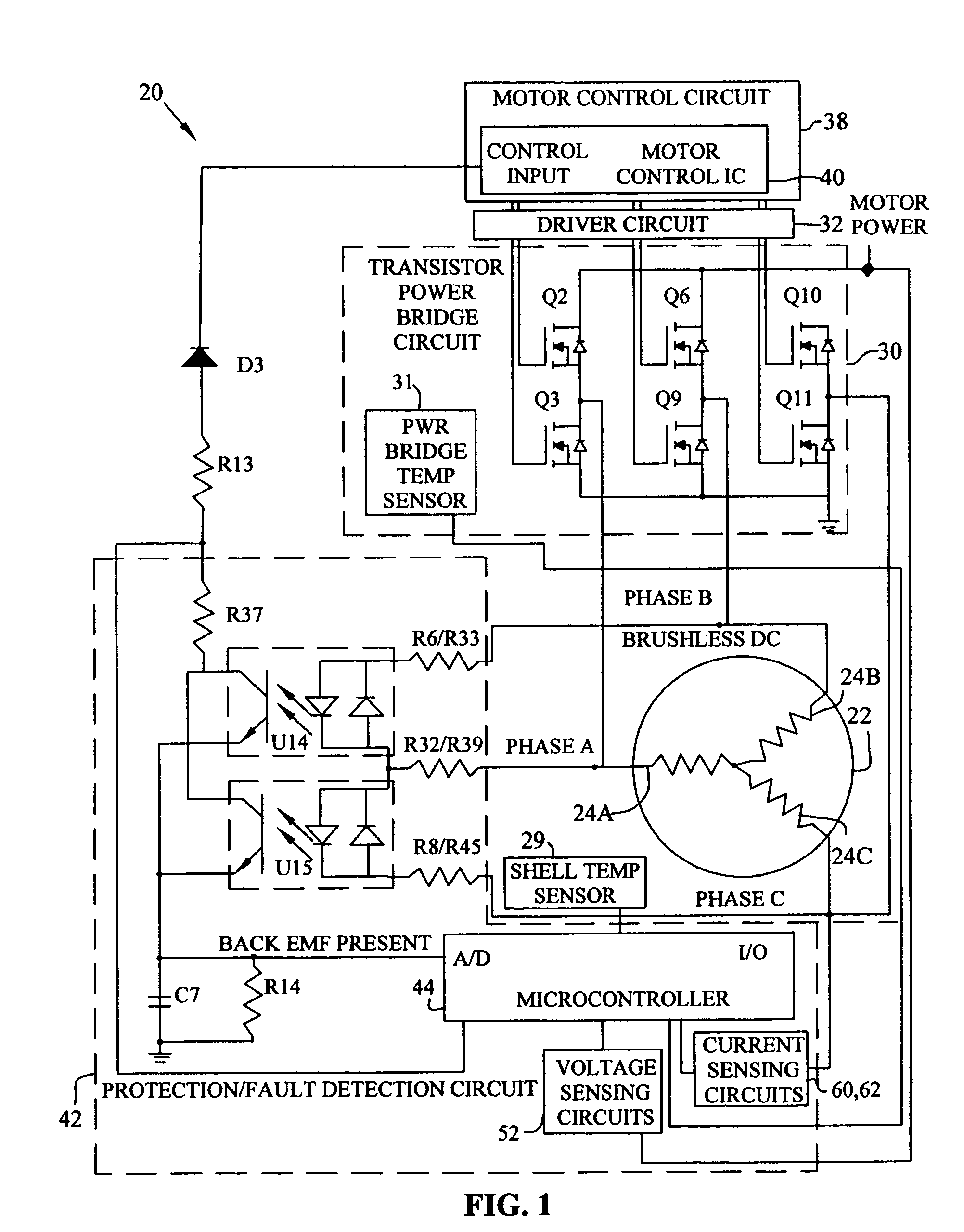
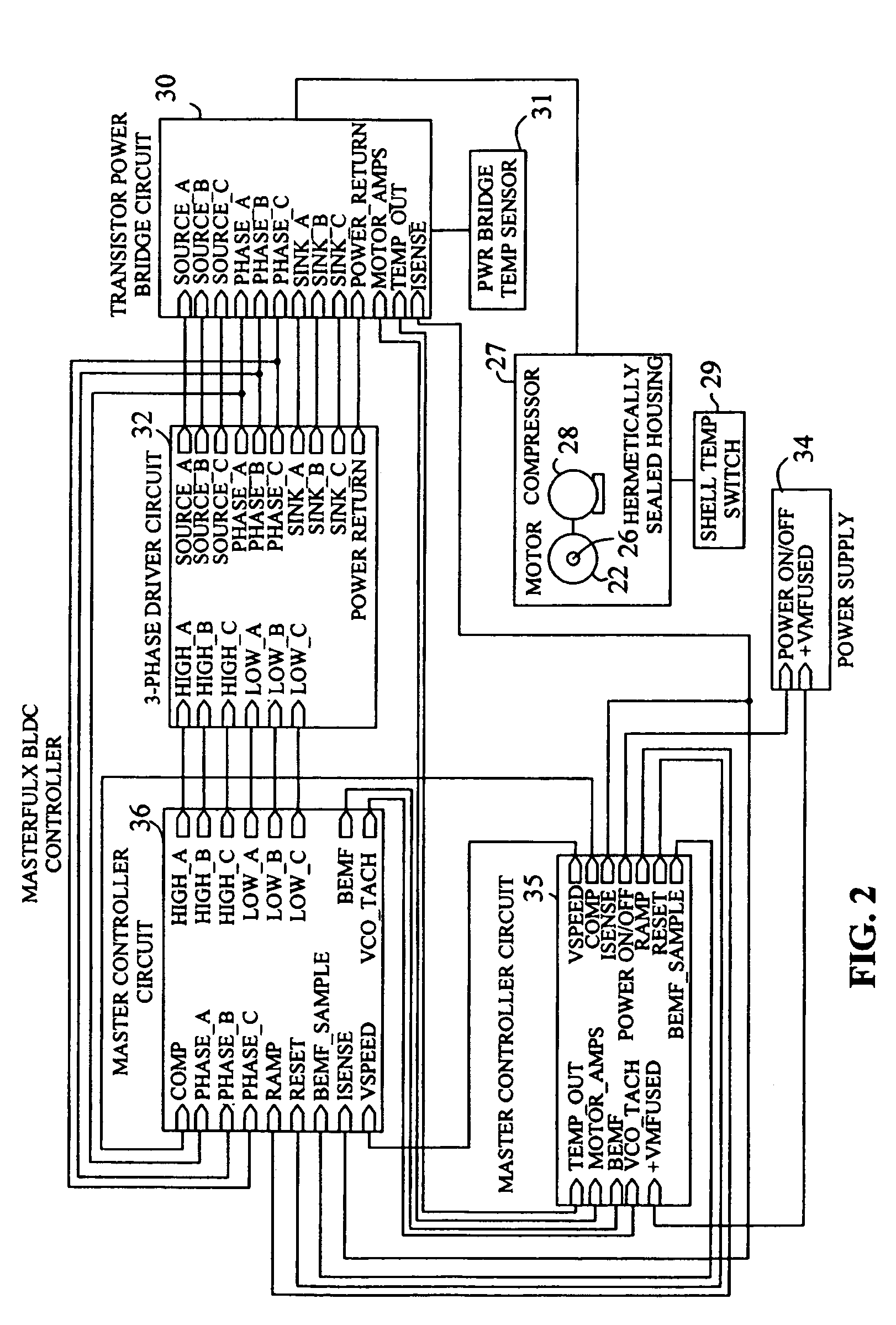
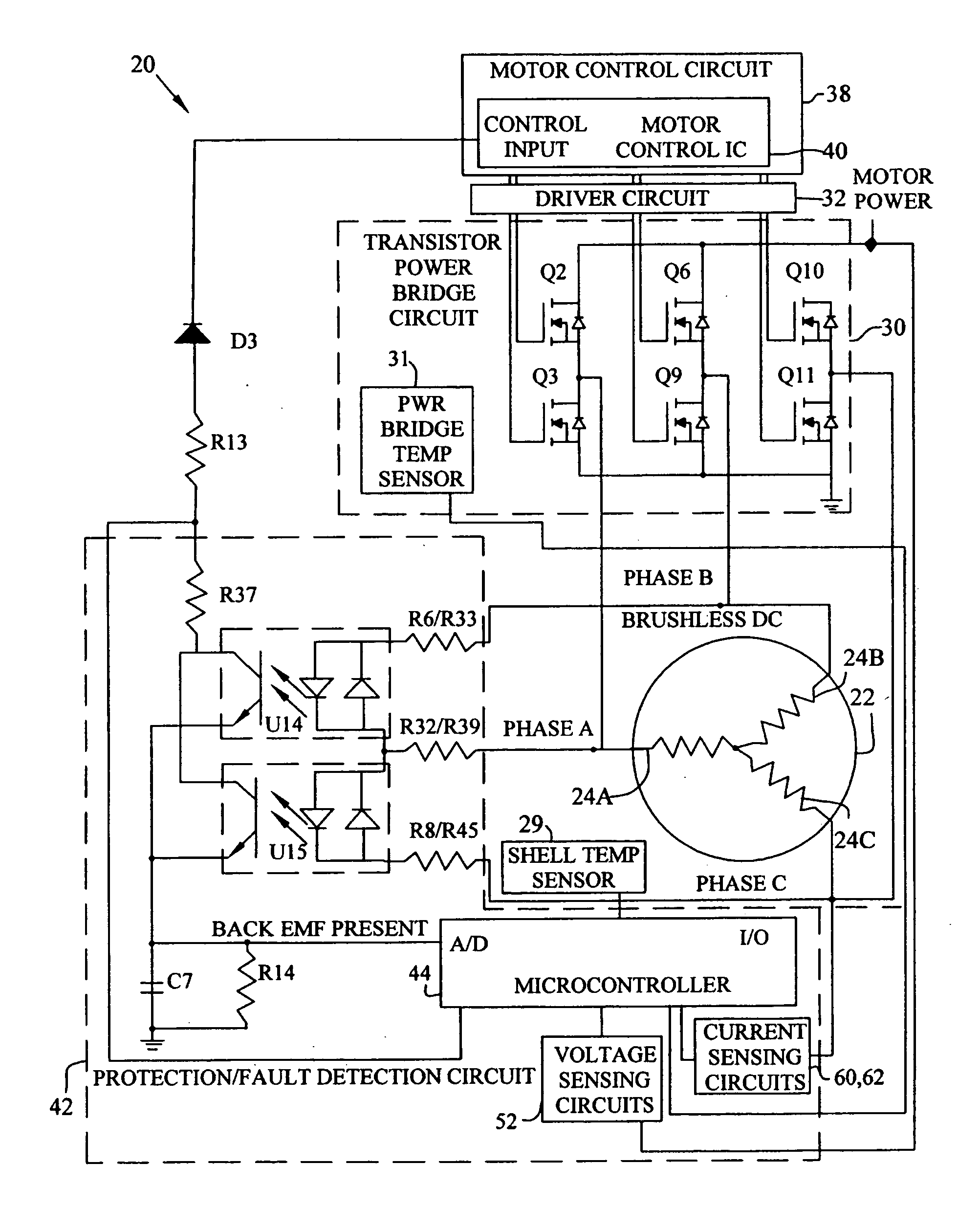
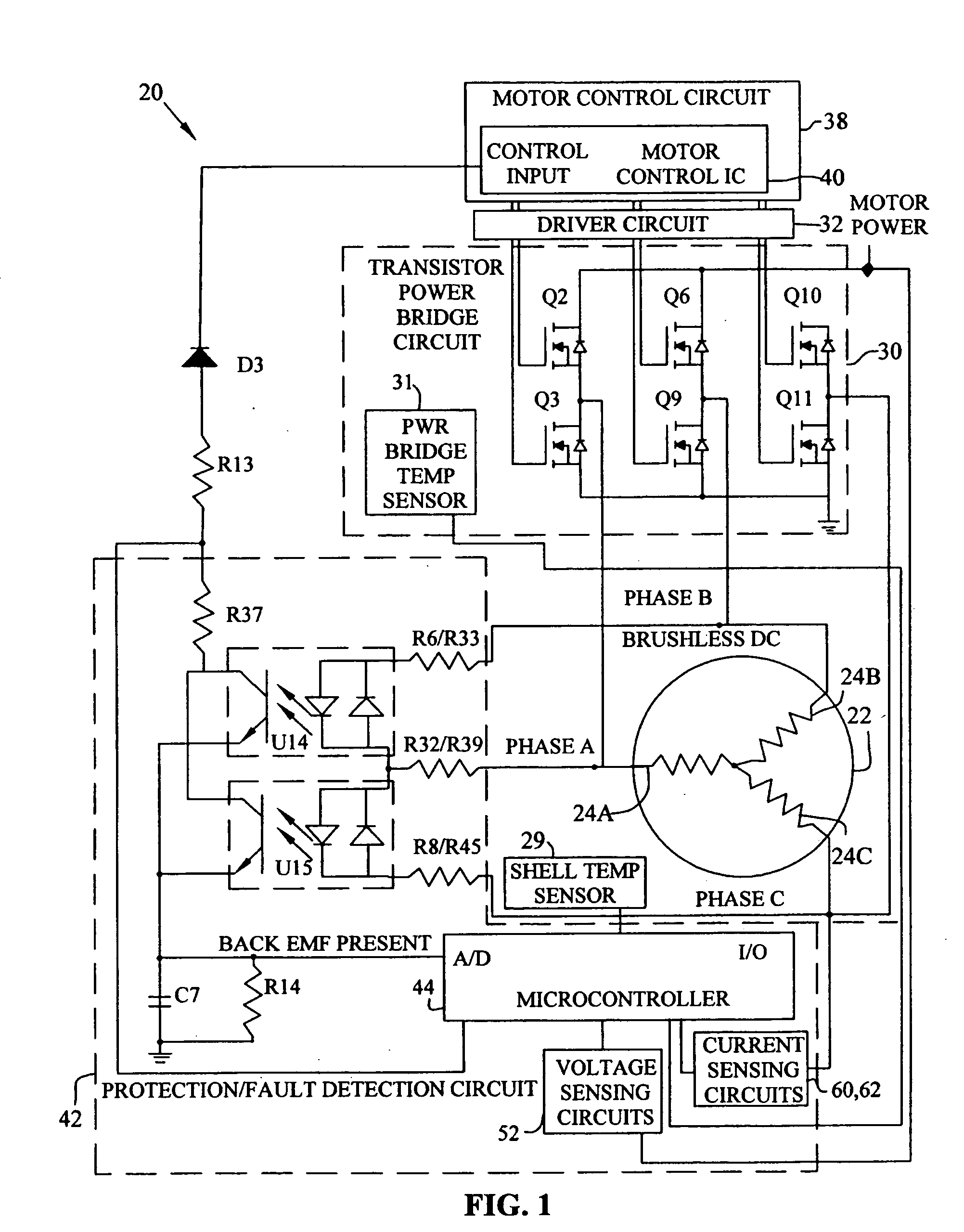
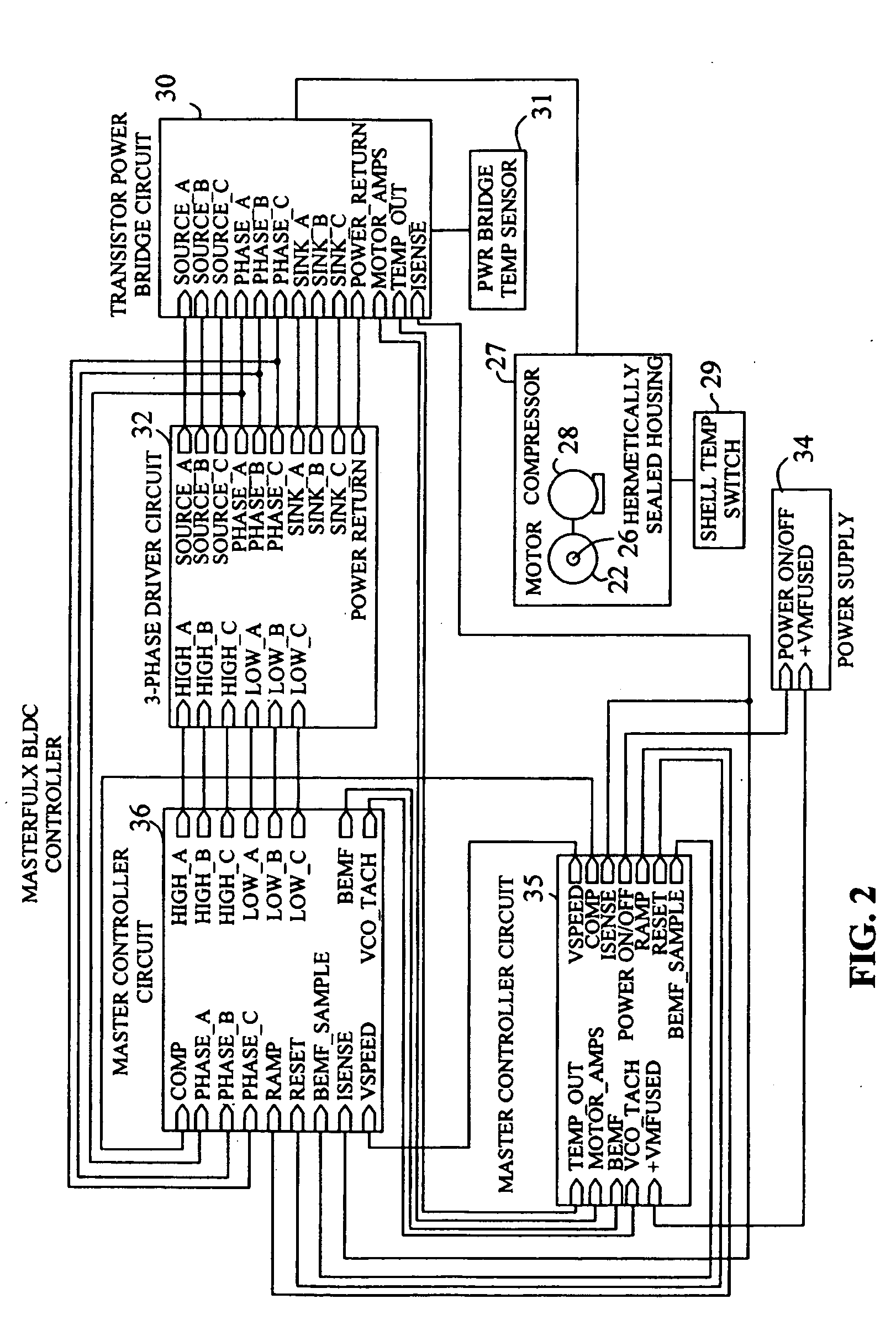
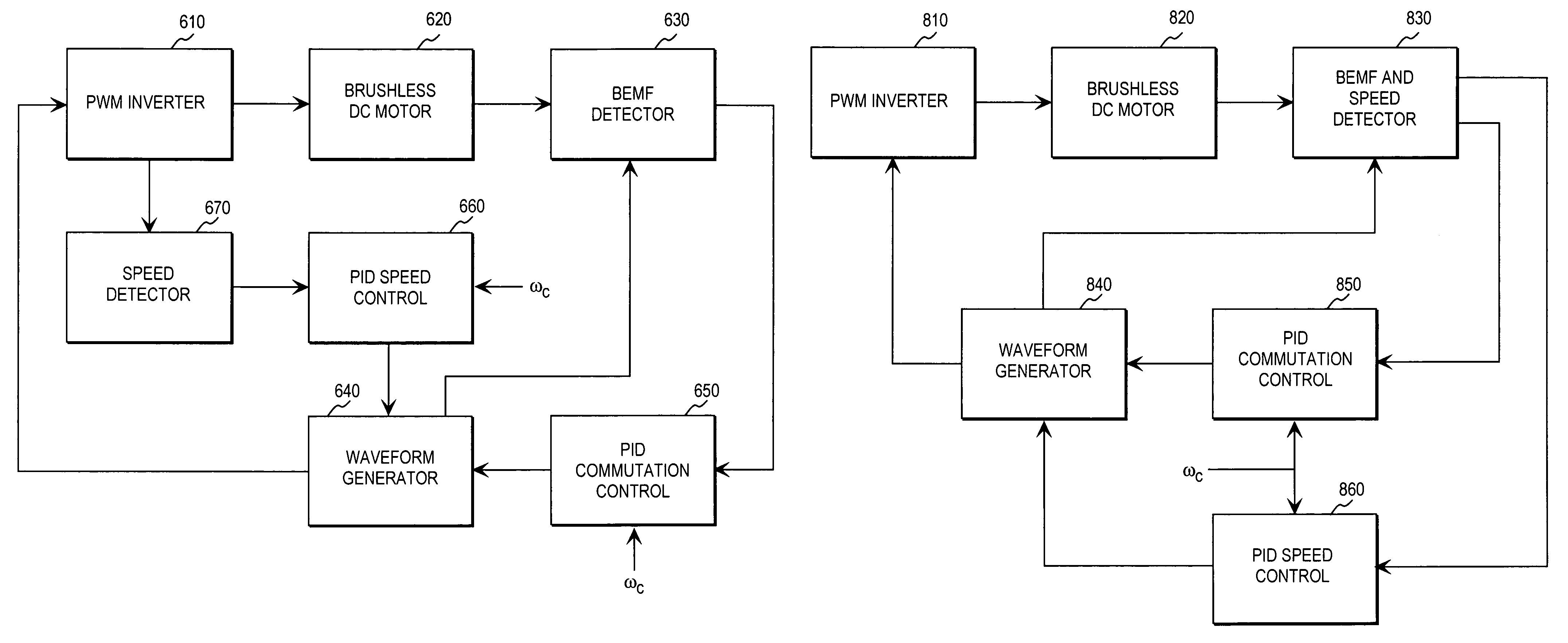
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS7042180B2Simple control methodEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringAC motor controlMotor speedDc motor control
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Integrated torsional mode damping system and method
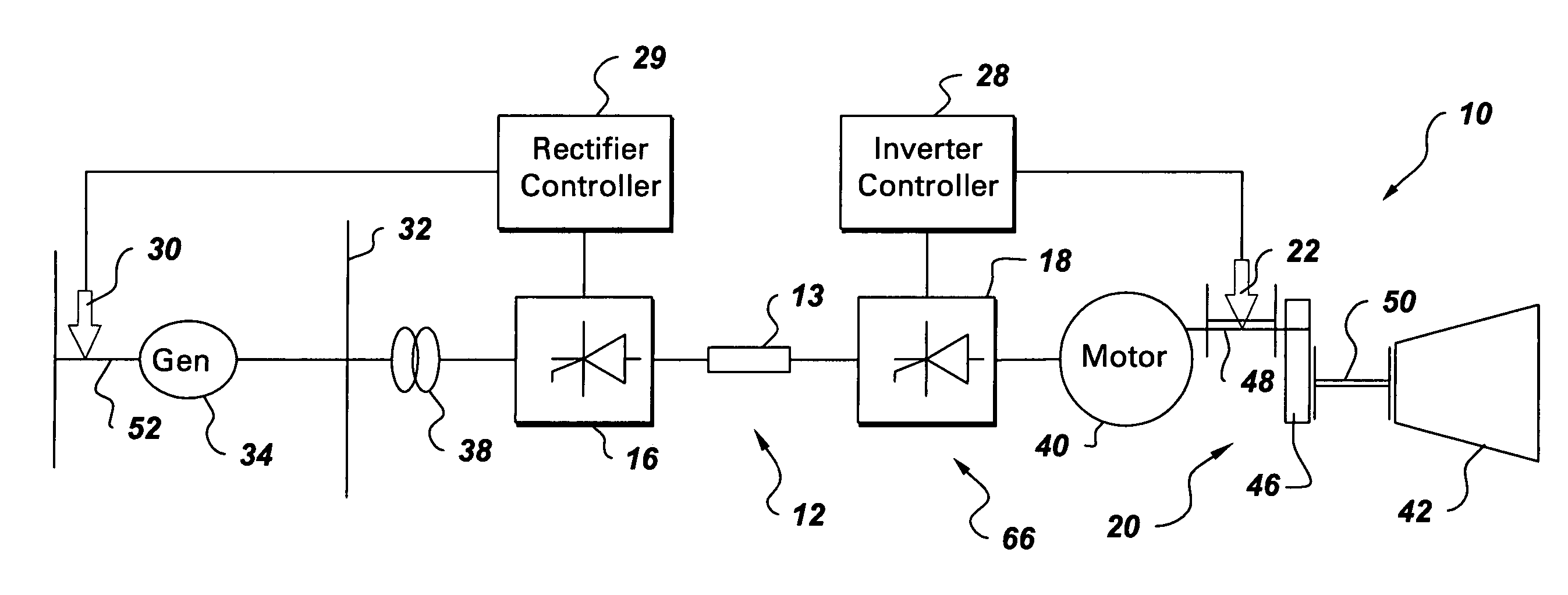
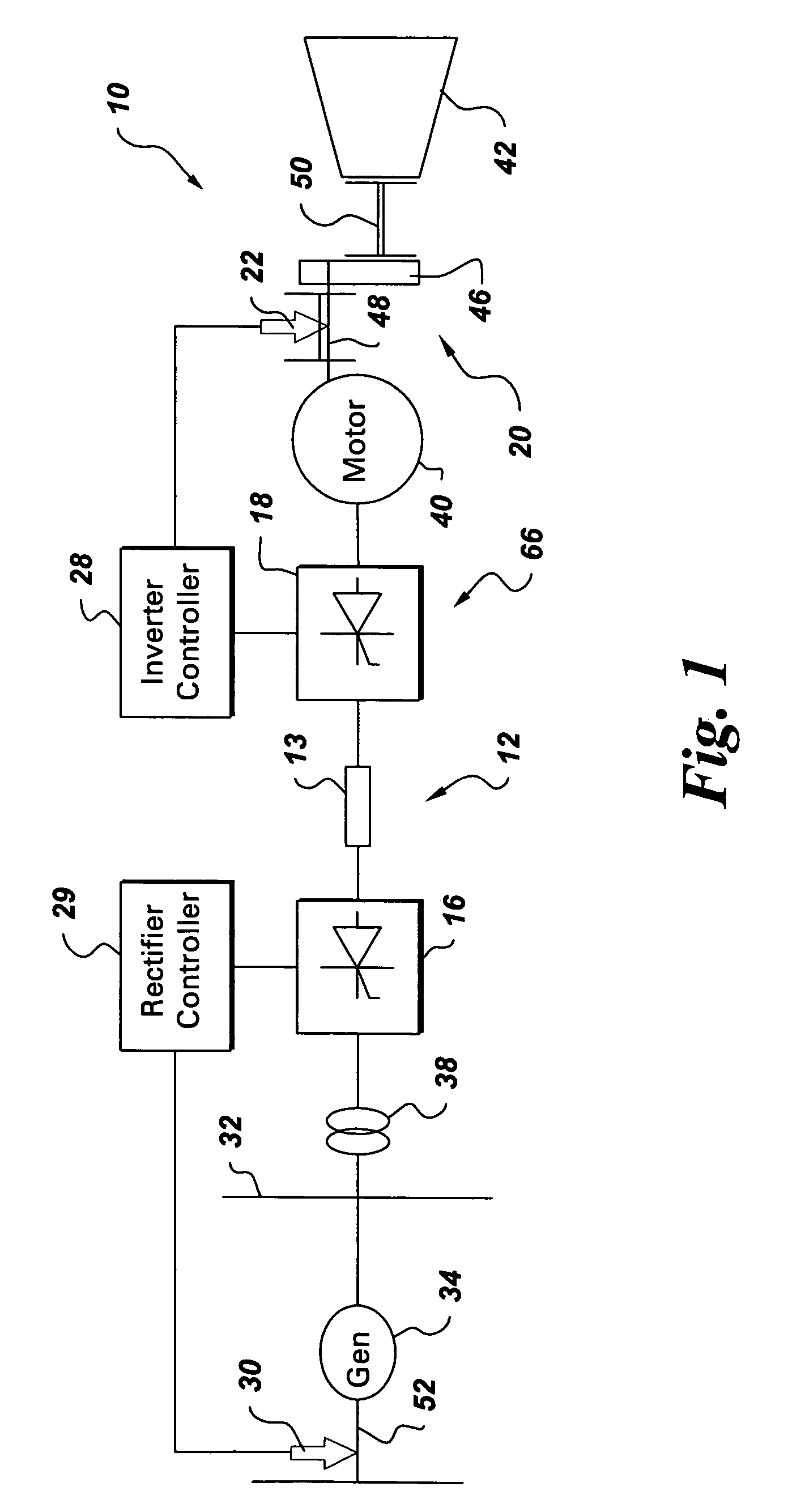
InactiveUS7173399B2DC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsInductorTorsional vibration
An integrated torsional mode damping method for a current source converter, including a rectifier, an inverter, and a DC link inductor coupled between the rectifier and the inverter, includes sensing a signal representative of torque on a shaft coupled to the inverter or rectifier; using the sensed signal for detecting a presence of a torsional vibration on the shaft; and damping the torsional vibration by modulating active power through the respective inverter or rectifier.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
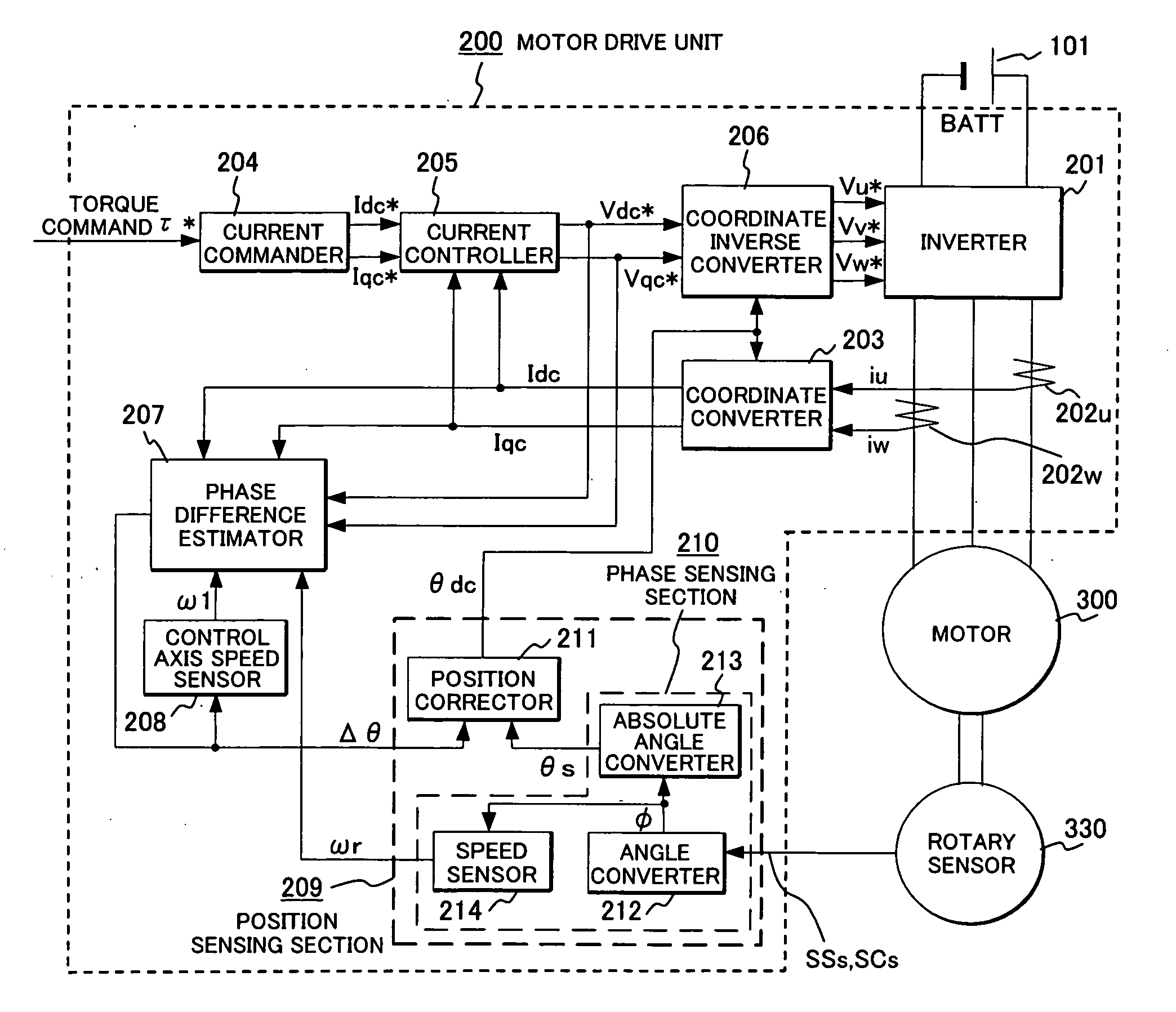
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060125439A1Efficient driveImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorPhase difference
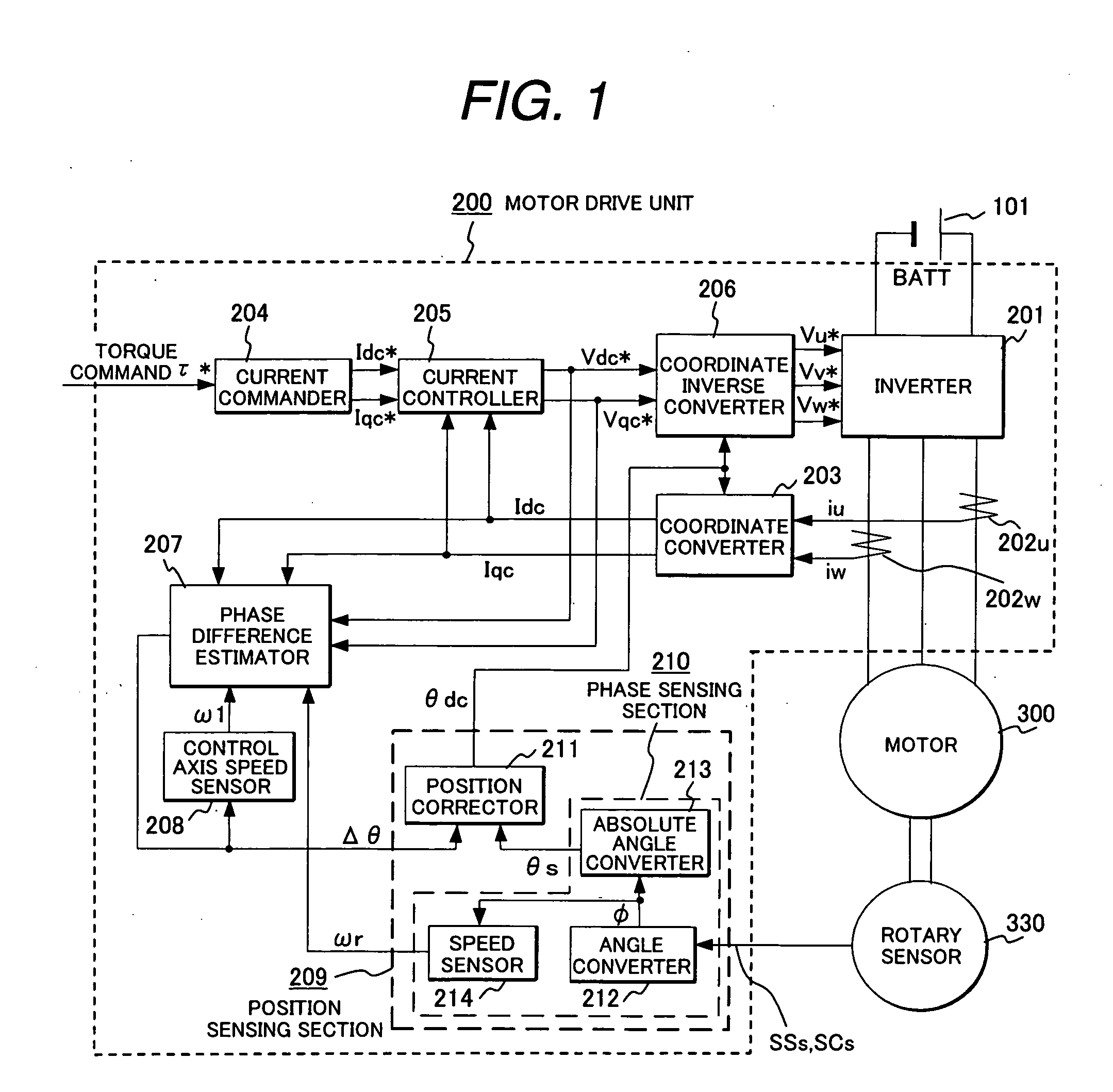
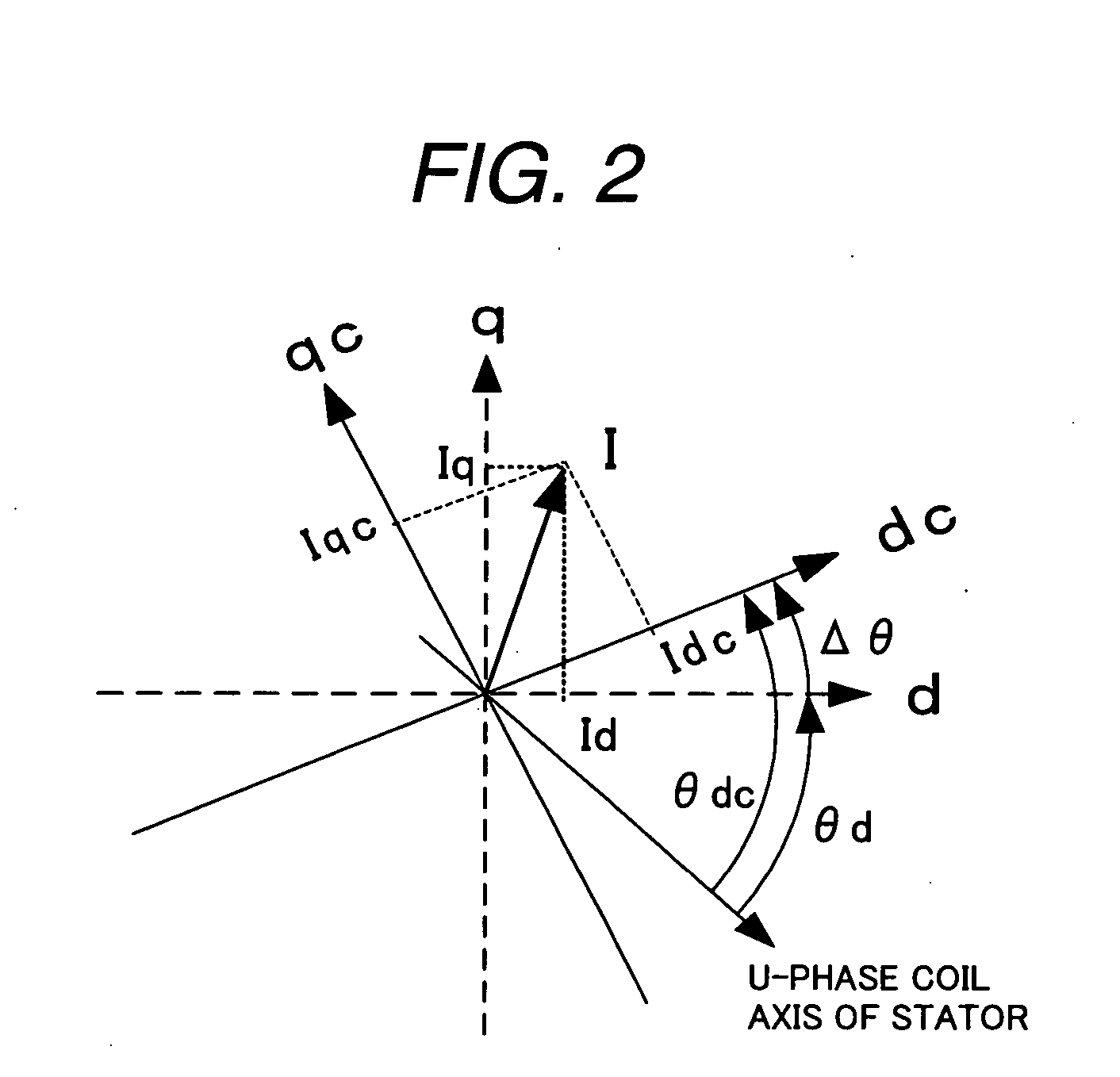
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position. A high-efficiency motor drive unit with improved maintainability of rotary sensor and improved accuracy of sensing the magnet pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor that accelerates and decelerates very quickly in a wide range of speed is realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
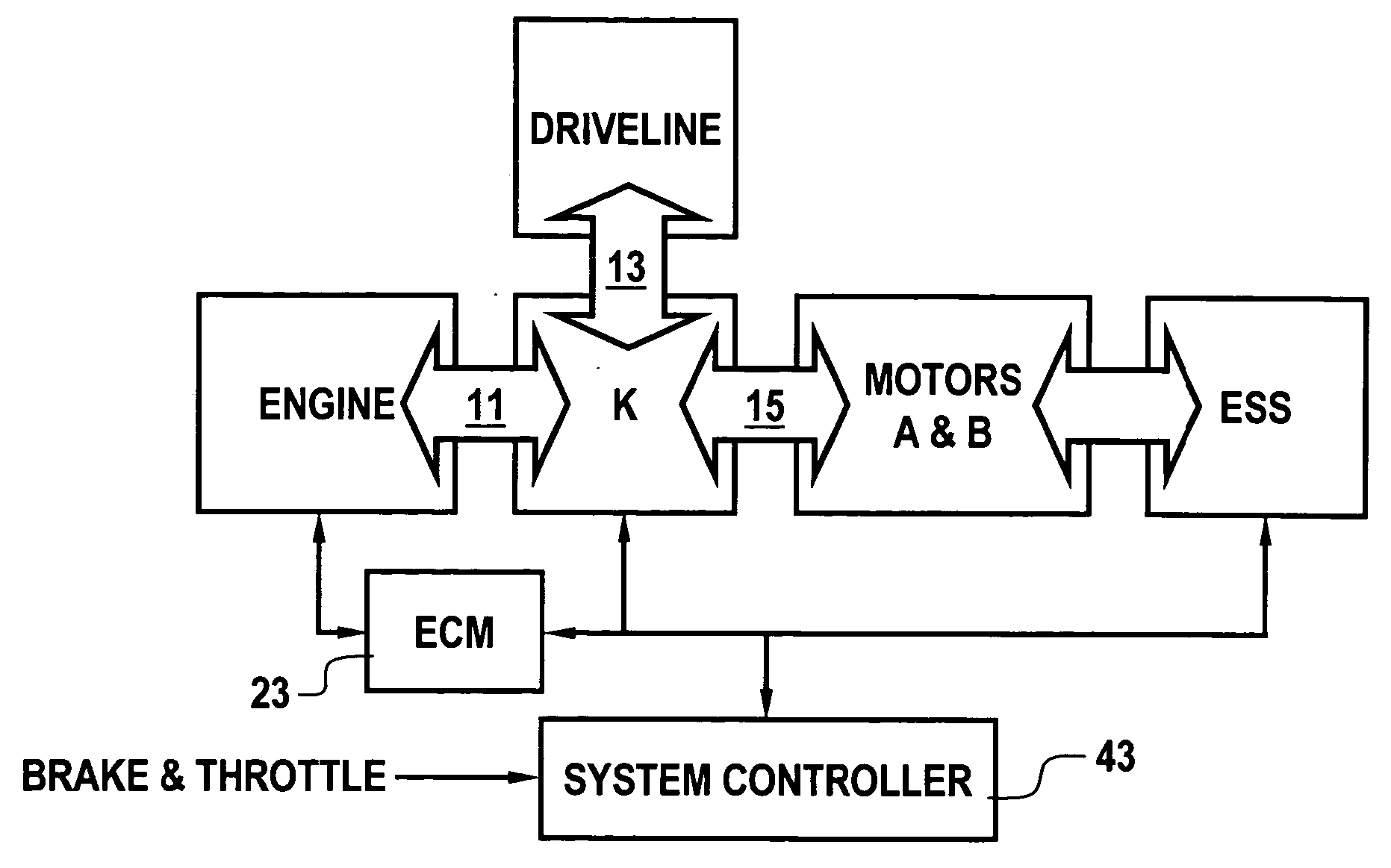
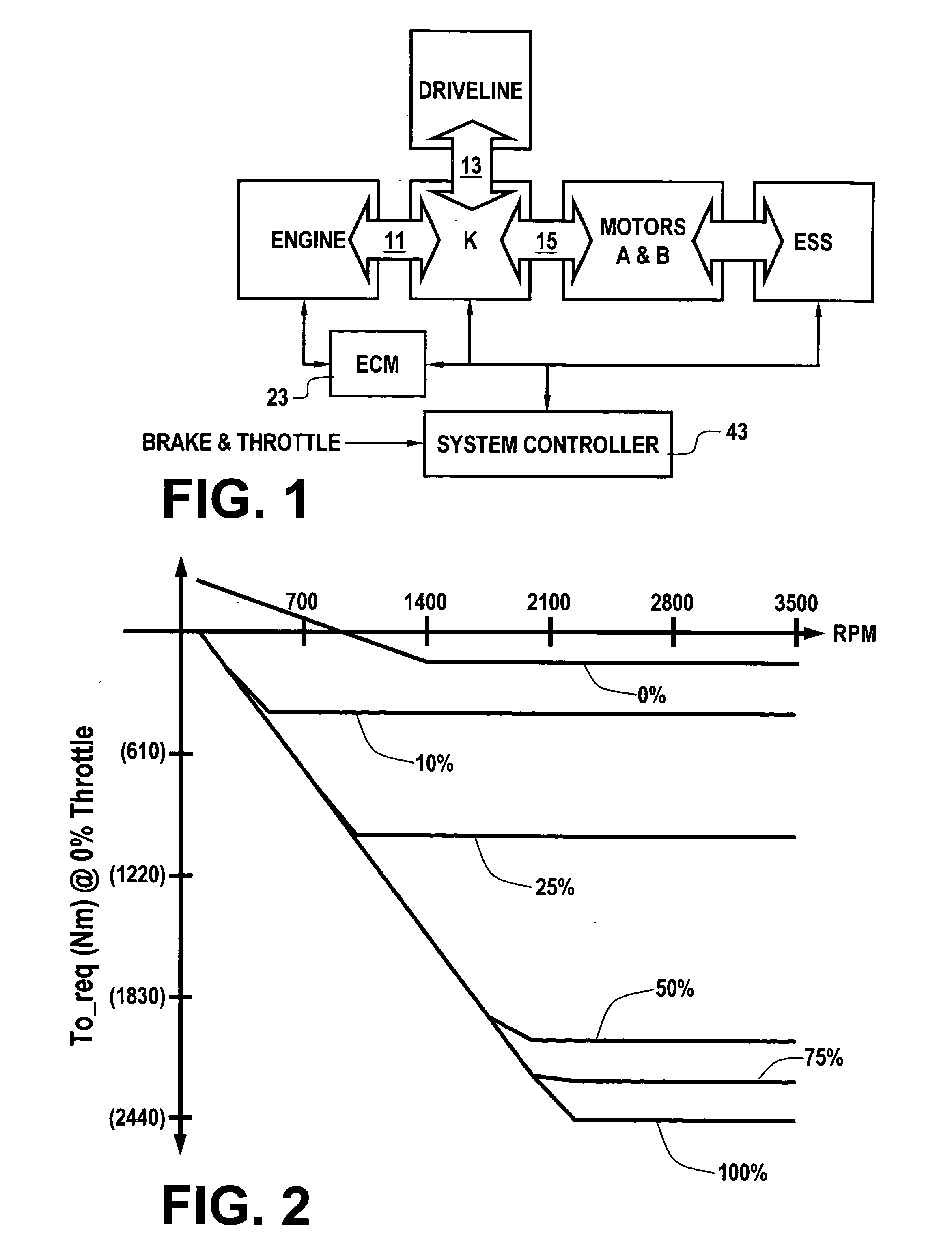
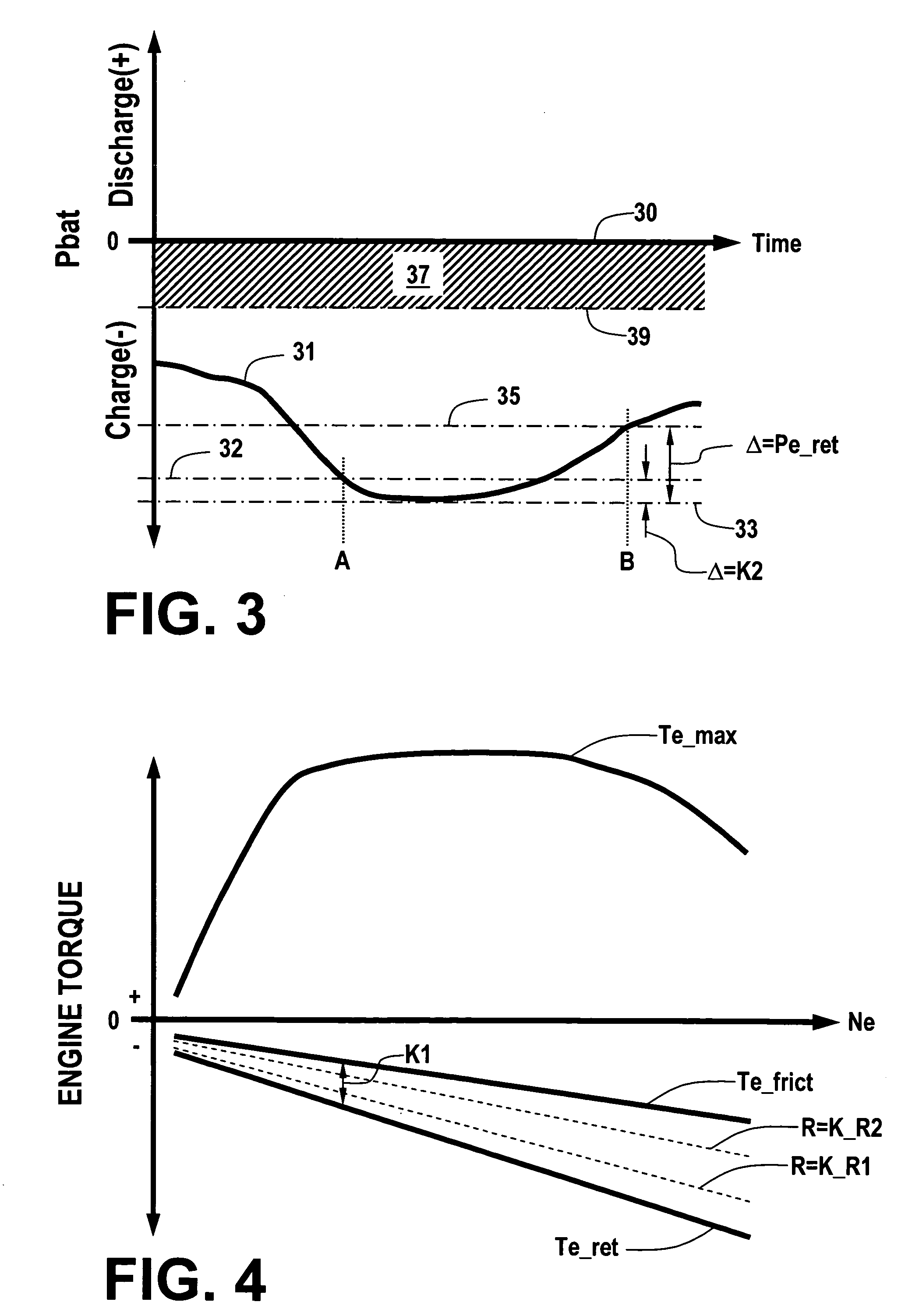
Engine retard operation scheduling and management in a hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20050255966A1Hybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsOperation schedulingElectric machine
A hybrid vehicle includes a powertrain having a retarded diesel engine, an electric machine and energy storage system. The engine and motor are operatively coupled through one or more planetary gearsets and selective coupling paths in accordance with application and release of various torque transfer devices to a drivetrain via an output. Regenerative and retarded engine braking are coordinated to provide priority to energy return to an energy storage system in accordance with predetermined power flow limits.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS20050029976A1Easy to modifyEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlMotor speedDc motor control
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Control device for electric motor
ActiveUS7005828B2Improve artSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlDriving currentAcquired characteristic
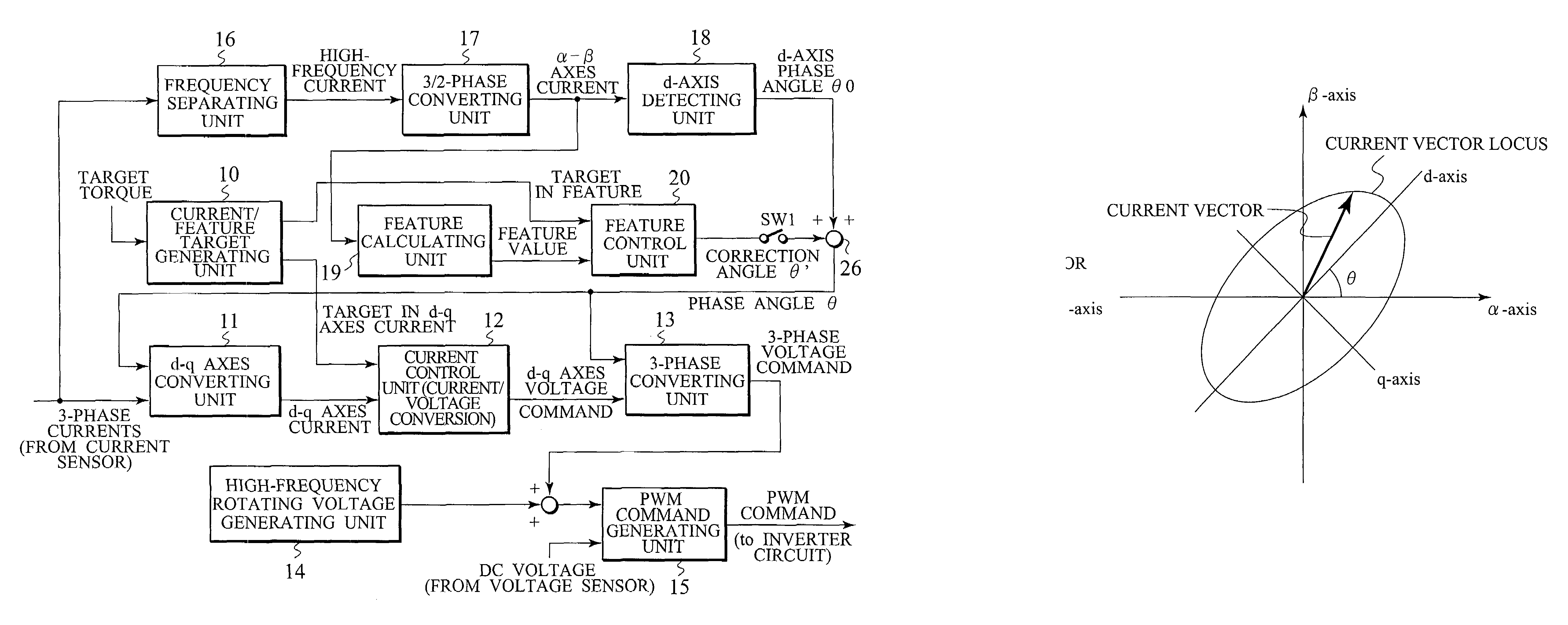
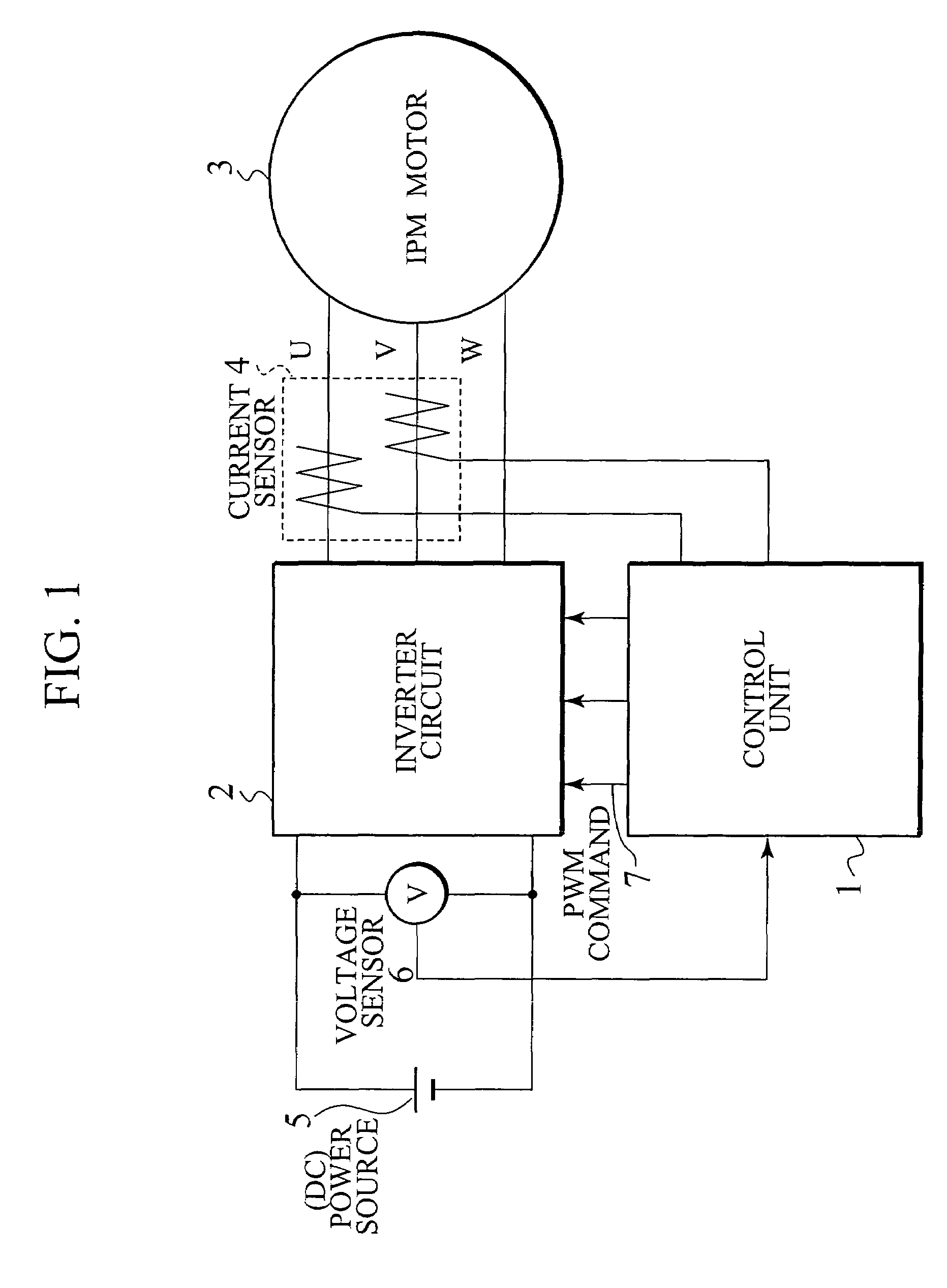
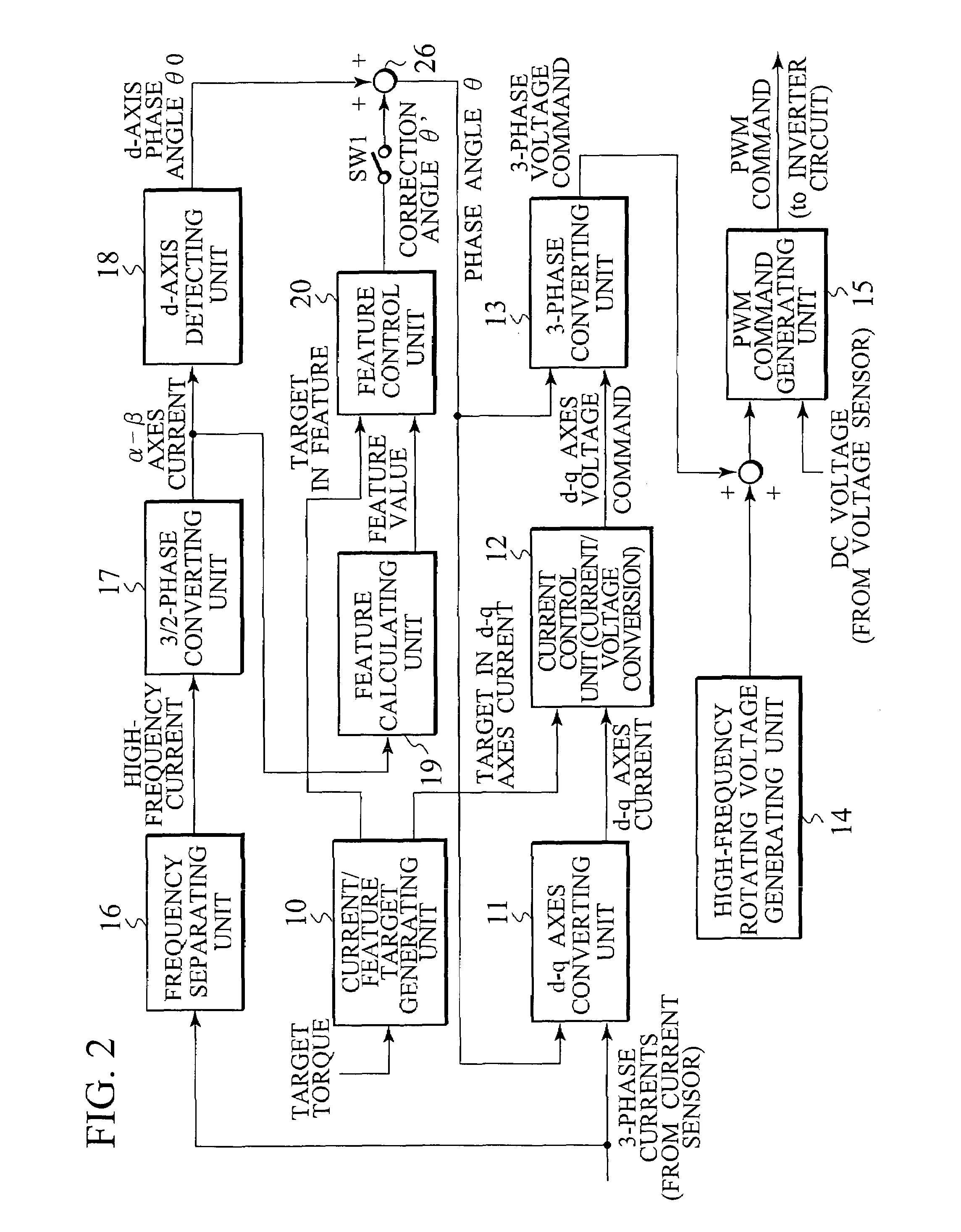
Corresponding to a target torque, the control device calculates a target value of a feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus and the length of the short axis and further superimposes a superimposed current on a drive current for the motor, the superimposed current having a frequency different from the frequency of the drive current. Further, the control device detects an actual value of the feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus of the superimposed current and the length of the short axis of the same and finally detects a phase angle of the motor based on the target value and the actual value for the feature. The manipulation of a detecting phase is performed by feedback of a feature obtained by the magnitude of the superimposed current. That is, when the actual feature is more than the target value, the detecting phase is advanced. Conversely, when the actual feature is less than the target value, the detecting phase is delayed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
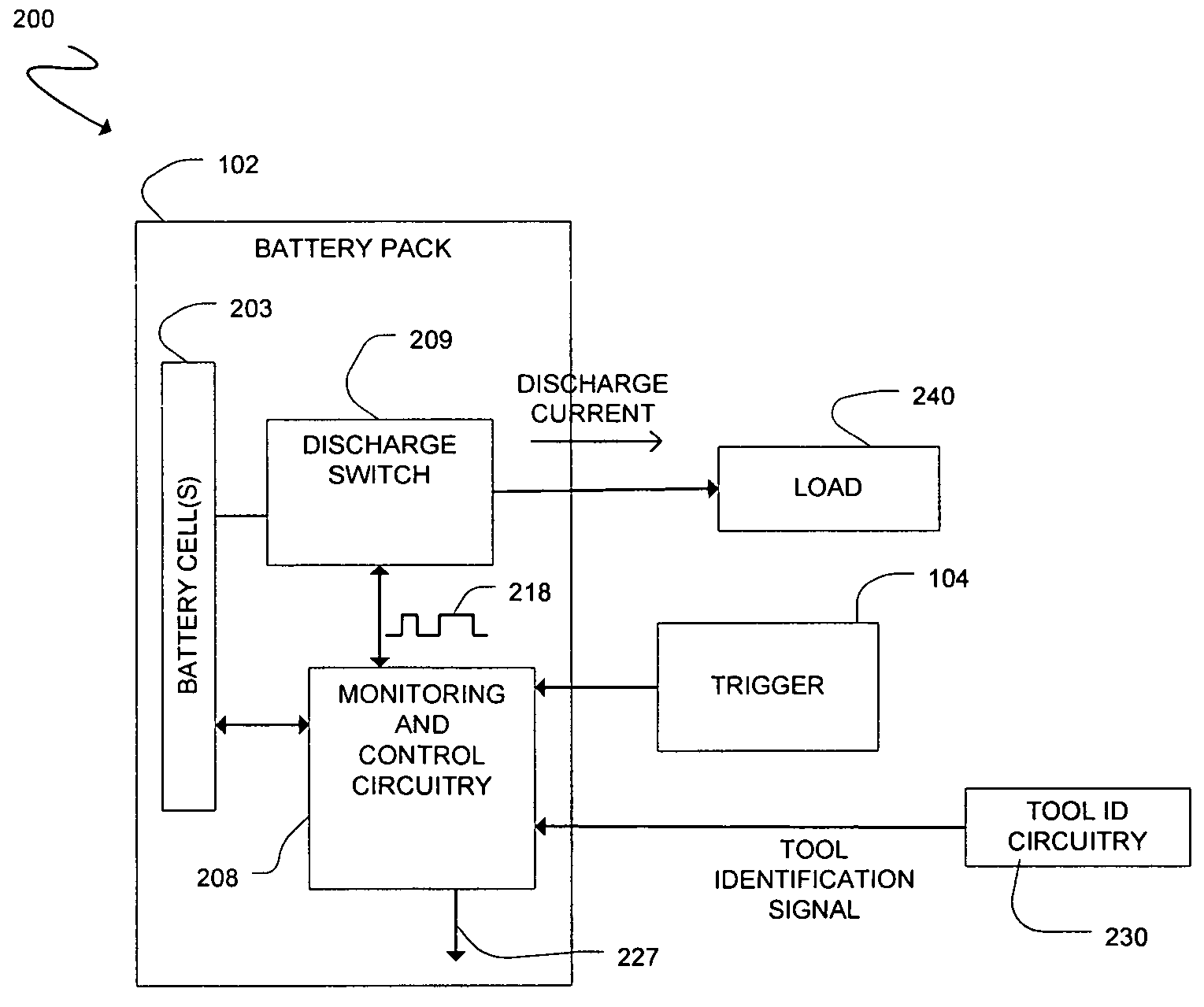
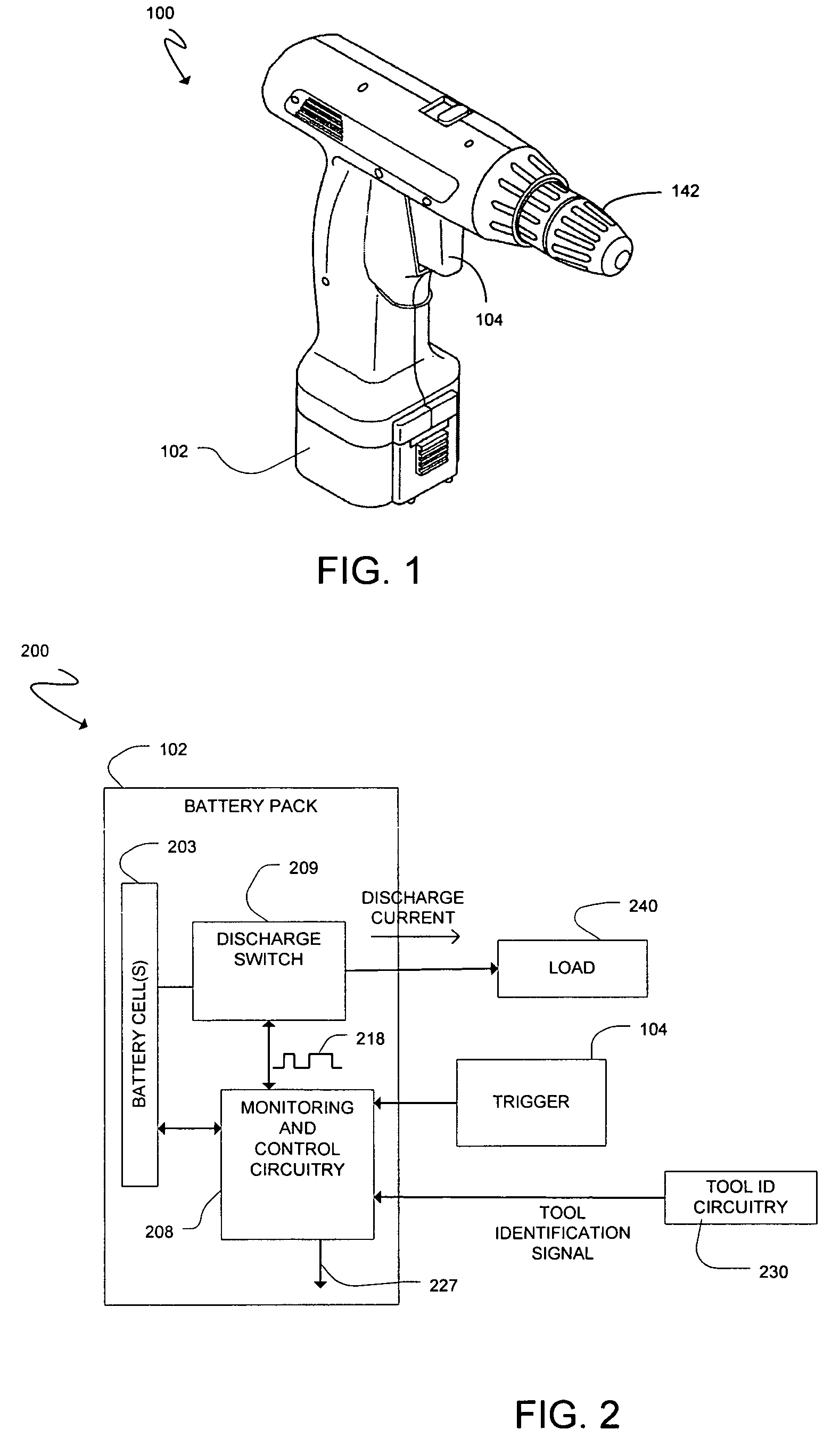
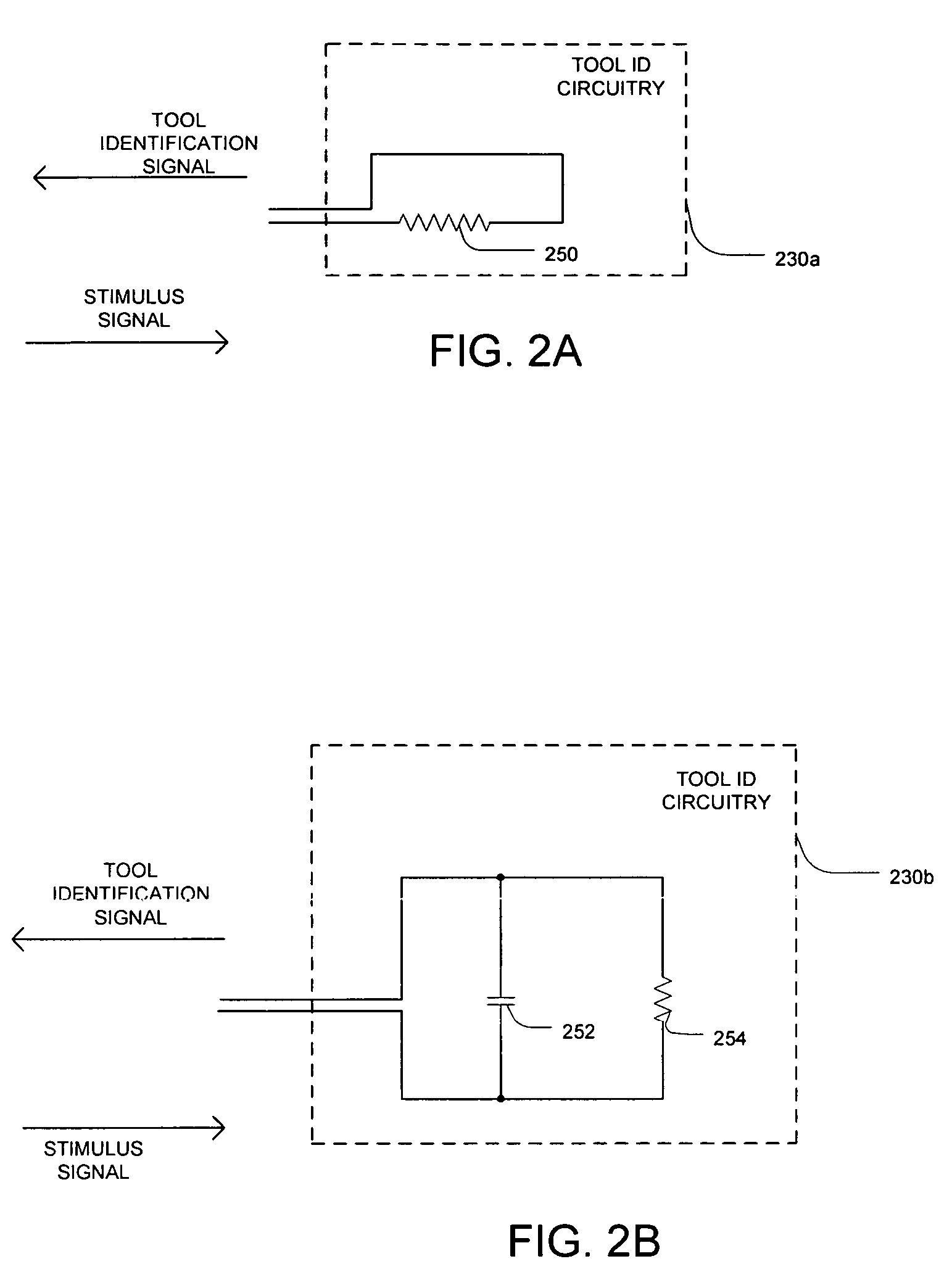
Cordless power tool with tool identification circuitry
ActiveUS7119516B2Electric motor controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringPower tool
A cordless power tool may include tool identification circuitry to provide a tool identification signal to a battery pack. The tool identification signal may be representative of data particular to the cordless power tool. A method may include coupling a battery pack to a cordless power tool, and providing a tool identification signal to the battery pack from the cordless power tool once the battery pack is coupled to the cordless power tool, the tool identification signal representative of data particular to the cordless power tool.
Owner:O2 MICRO INT LTD
System and method for controlling motor using parameter associated with magnetic flux
InactiveUS20080129243A1Reliably graspTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersDriving currentOperating point
A control method for a motor that rotates based on flux linkages to a winding member of the motor when the winding member is energized by a drive current is provided. The method includes storing magnetic-state information indicative of a relationship between each of a plurality of predetermined operating points of the drive current and a magnetic-state parameter associated with the flux linkages. The method includes obtaining at least one of command information associated with an operating state of the motor and detection information associated with the operating state of the motor. The method includes referencing the magnetic-state information with the use of the obtained at least one of the command information and detection information to obtain a value of the magnetic-state parameter based on a result of the reference. The method includes controlling an output of the motor based on the obtained value of the magnetic-state parameter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method for improving estimation accuracy of rotor position of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN106788071AEasy to implementReduce computing burdenElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlControl systemHarmonic
The invention discloses a method for improving the estimation accuracy of the rotor position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of realizing estimation of the rotor position of the permanent magnet synchronous motor by utilizing a pulse-shake high frequency voltage injection method, processing the extracted position estimation error function, eliminating a second harmonic component introduced due to asymmetric motor parameters, so as to obtain a processed position estimation error function, then establishing a phase-locked loop, and adjusting the phase-locked loop to be 0, thus obtaining estimated rotor speed and estimated rotor position. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively inhibit position estimation second harmonic error caused by the asymmetric motor parameters, and the performance of a control system without a position sensor can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Modular remote power generation and transmission for hydraulic fracturing system
ActiveUS10526882B2Avoid damageElectric motor controlFluid removalElectric power equipmentEngineering
A hydraulic fracturing system for fracturing a subterranean formation includes a power generation system, a transmission section, and an equipment load section. The power generation system includes a turbine generator that generates electricity that is used to power equipment in the equipment load section. The equipment in the equipment load section conditions and pressurizes fluid that is injected into a wellbore for fracturing the formation. The power generation and equipment load sections are distal from one another are separated by a long distance. The transmission section connects the power generation and equipment load sections, and thus spans the long distance between these sections.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
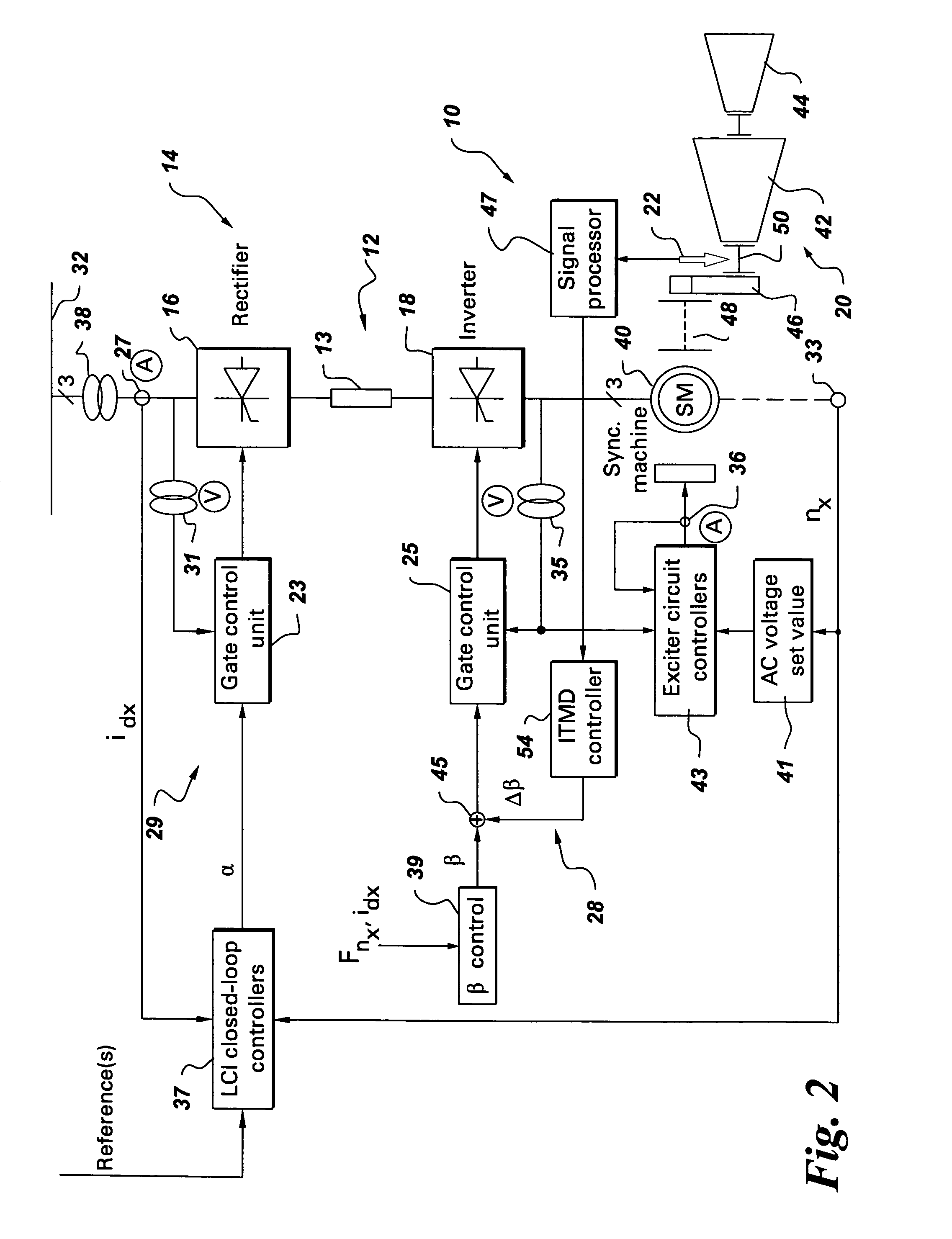
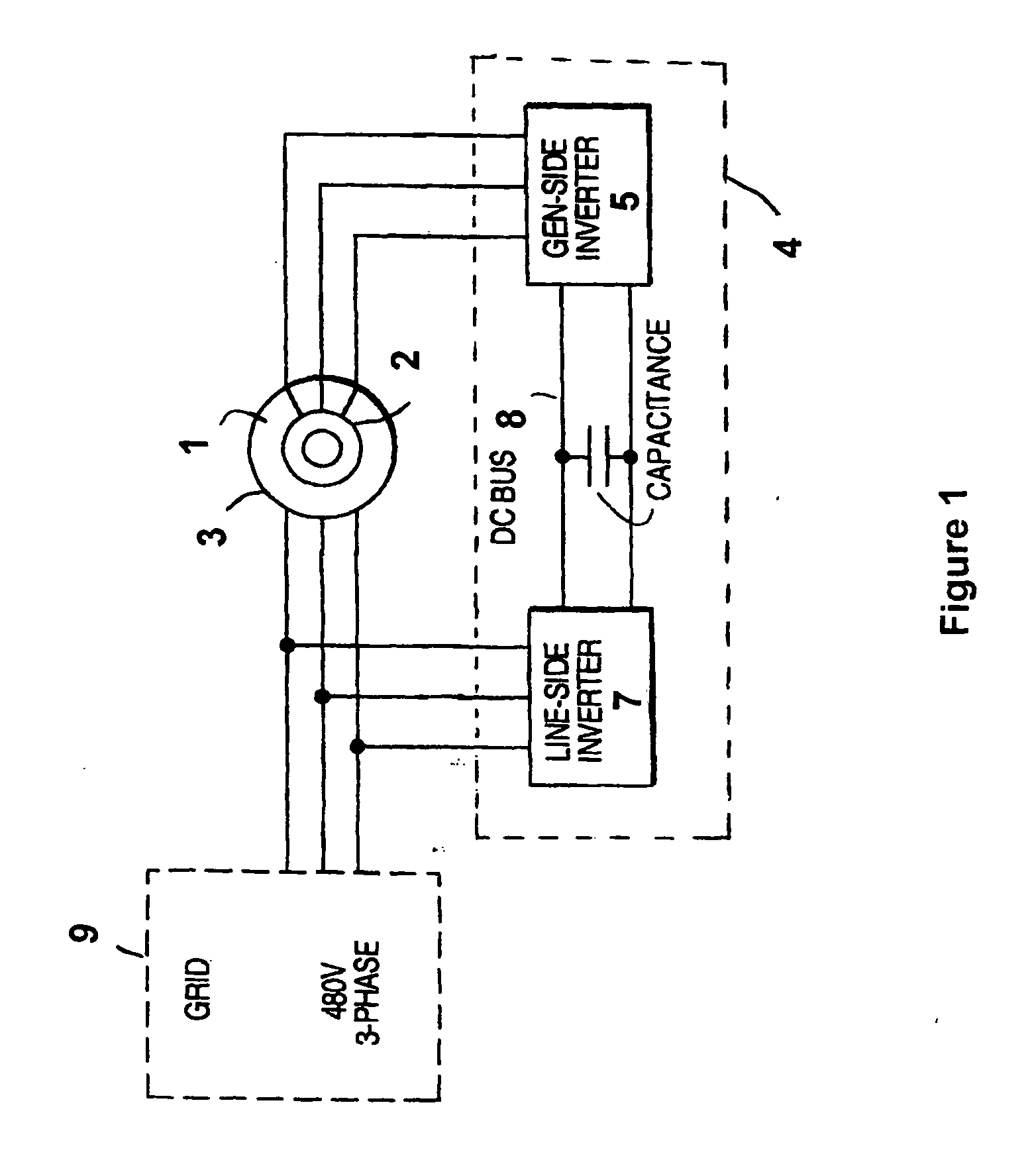
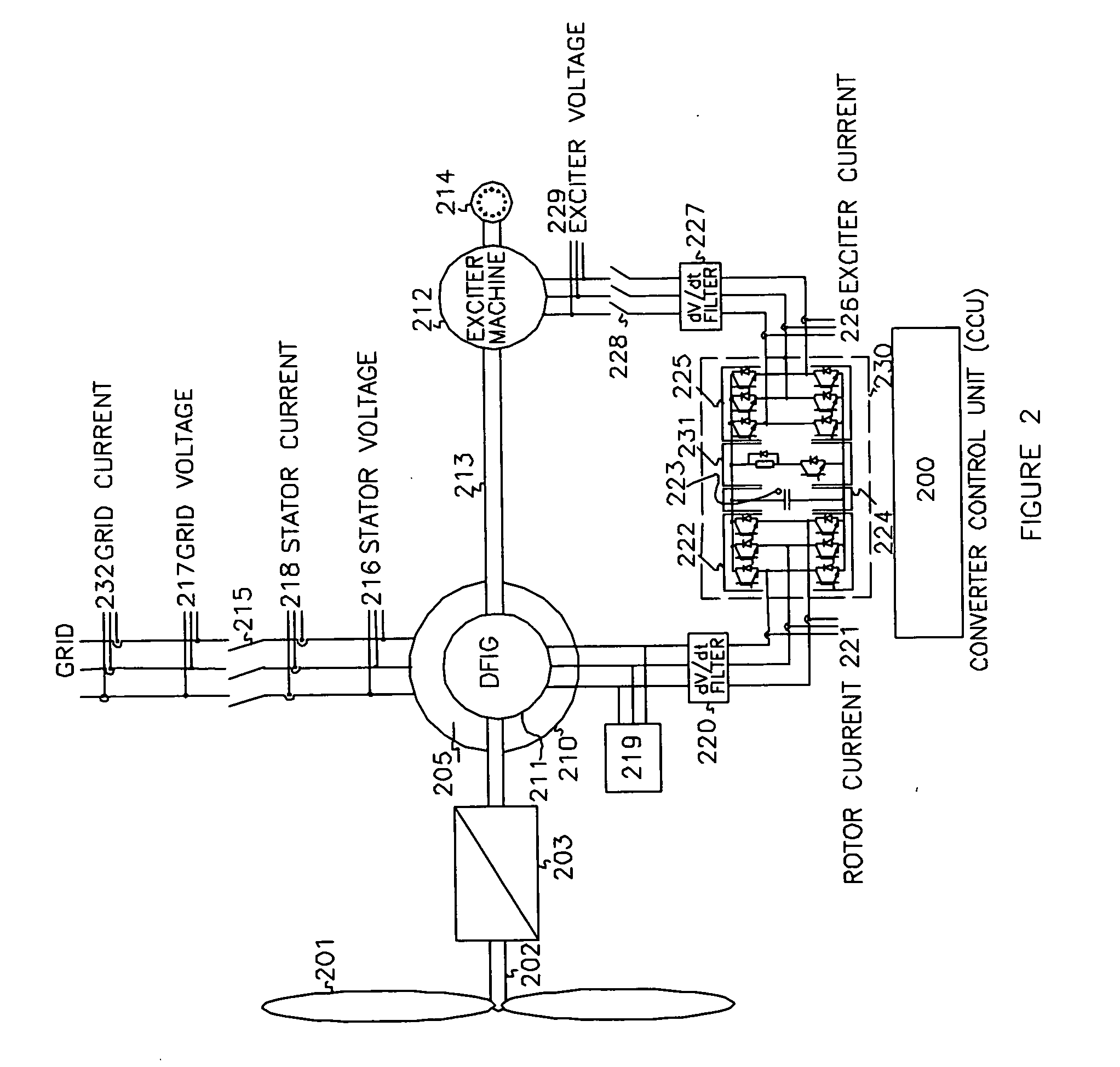
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS20070216164A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityHarmonic
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
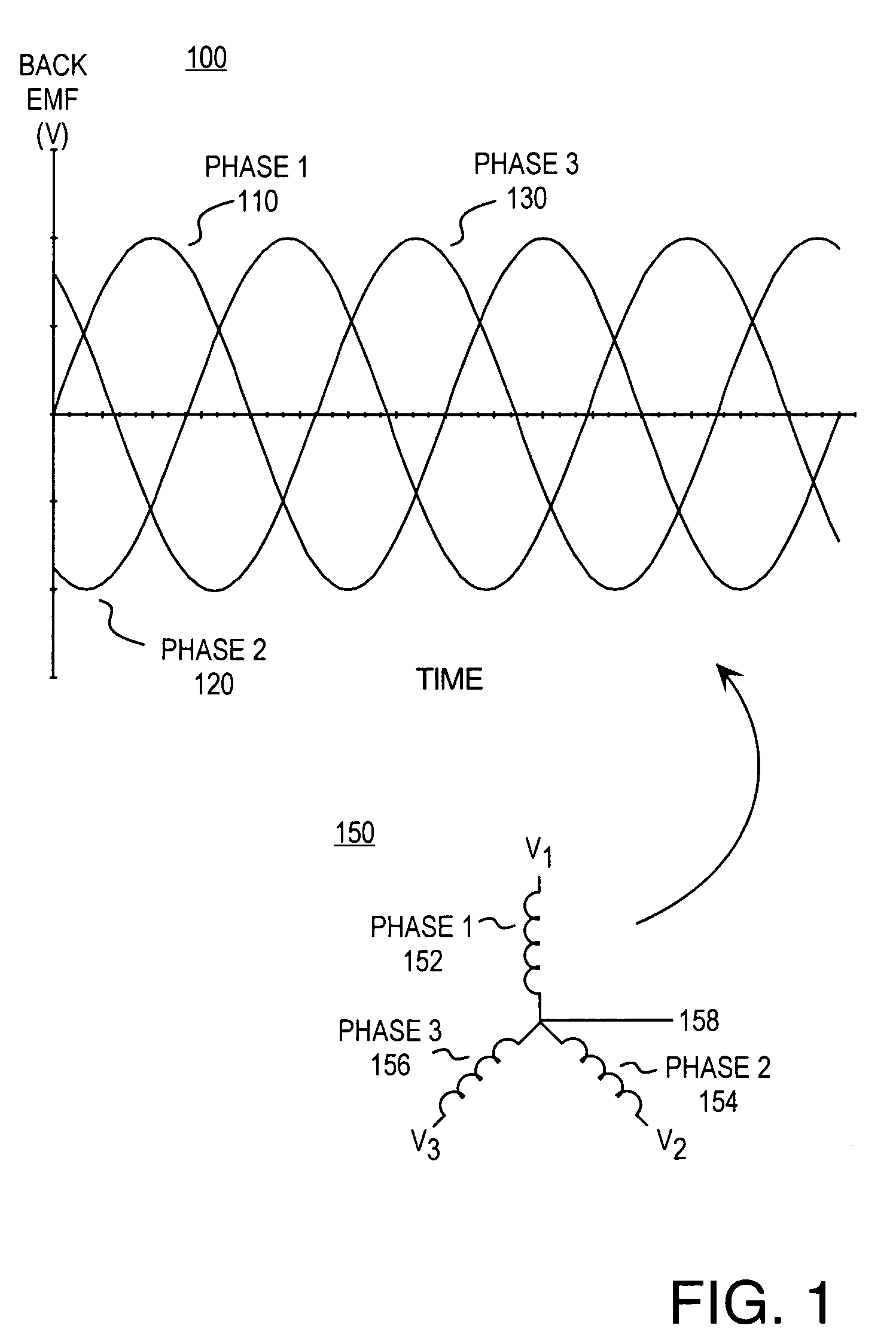
Method and apparatus for controlling brushless DC motors in implantable medical devices
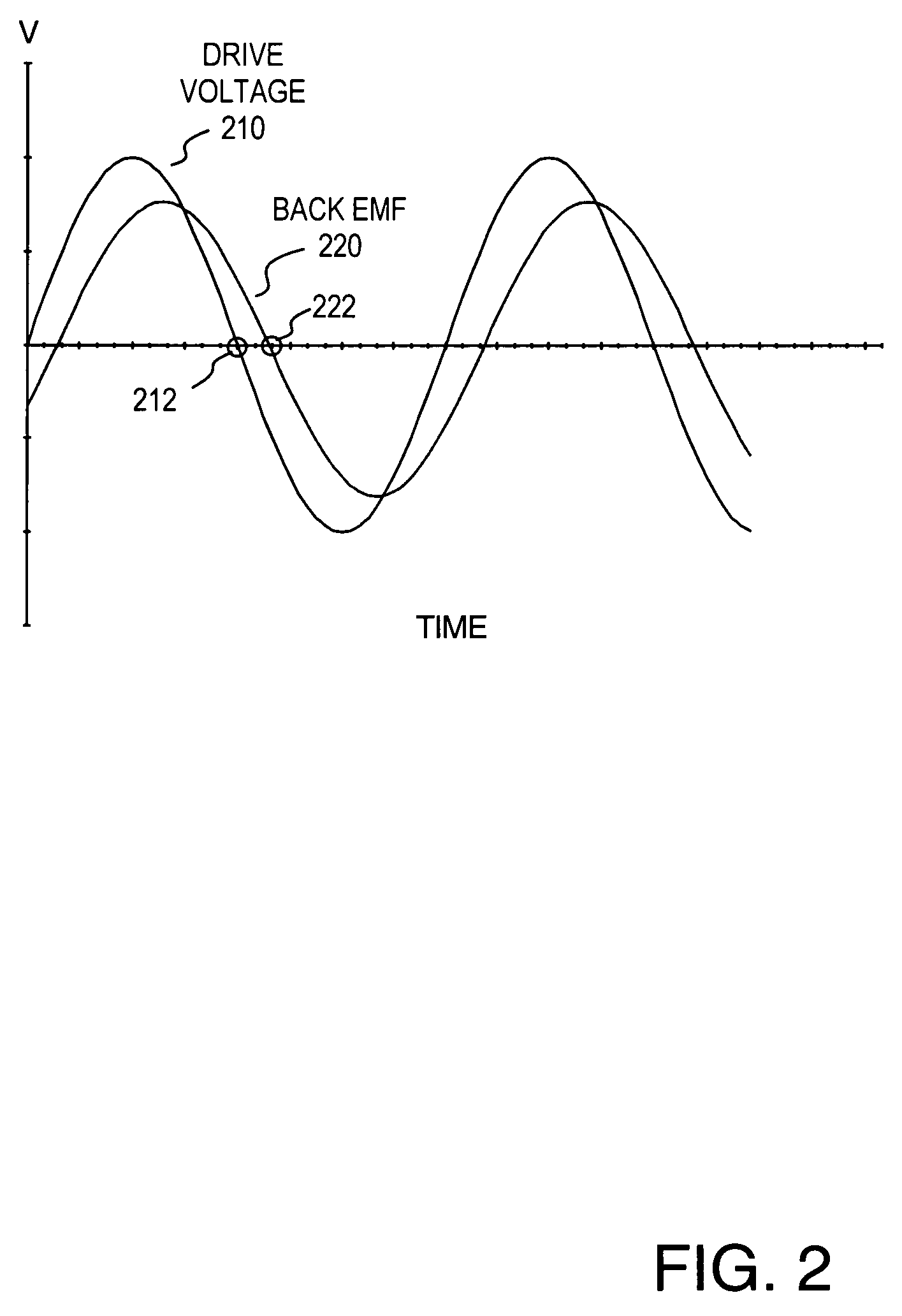
Methods and apparatus for controlling a polyphase motor in implantable medical device applications are provided. In one embodiment, the polyphase motor is a brushless DC motor. The back emf of a selected phase of the motor is sampled while a drive voltage of the selected phase is substantially zero. Various embodiments utilize sinusoidal or trapezoidal drive voltages. The sampled back emf provides an error signal indicative of the positional error of the rotor. In one embodiment, the sampled back emf is normalized with respect to a commanded angular velocity of the rotor to provide an error signal proportional only to the positional error of the motor rotor. The error signal is provided as feedback to control a frequency of the drive voltage. A speed control generates a speed control signal corresponding to a difference between a commanded angular velocity and an angular velocity inferred from the frequency of the drive voltage. The speed control signal is provided as feedback to control an amplitude of the drive voltage. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a brushless DC motor and a commutation control. The commutation control provides a commutation control signal for a selected phase of the motor in accordance with a sampled back electromotive force (emf) of that phase. The back emf of the phase is sampled only while the corresponding drive voltage for the selected phase is substantially zero, wherein a frequency of a drive voltage of the motor is varied in accordance with the commutation control signal.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
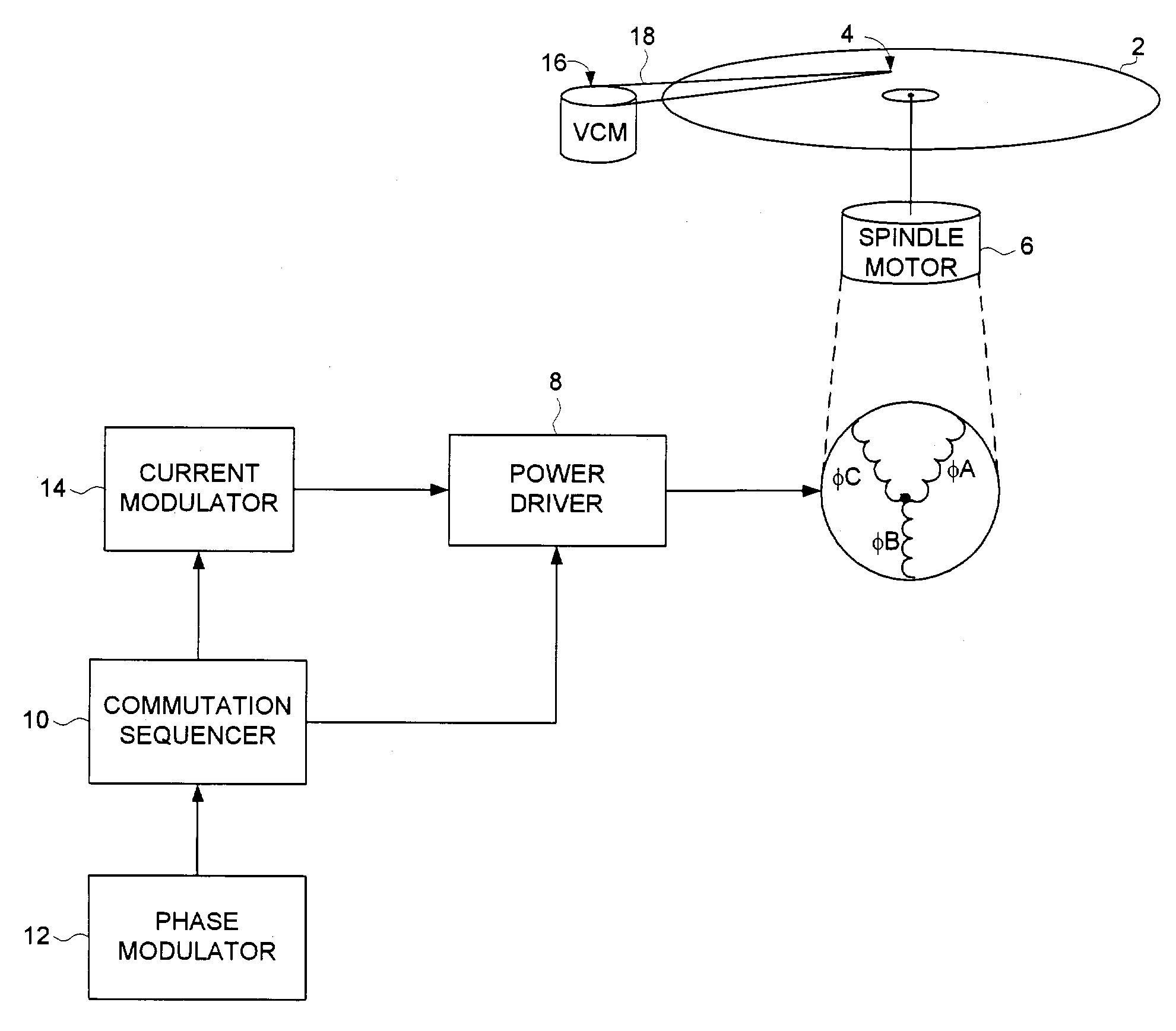
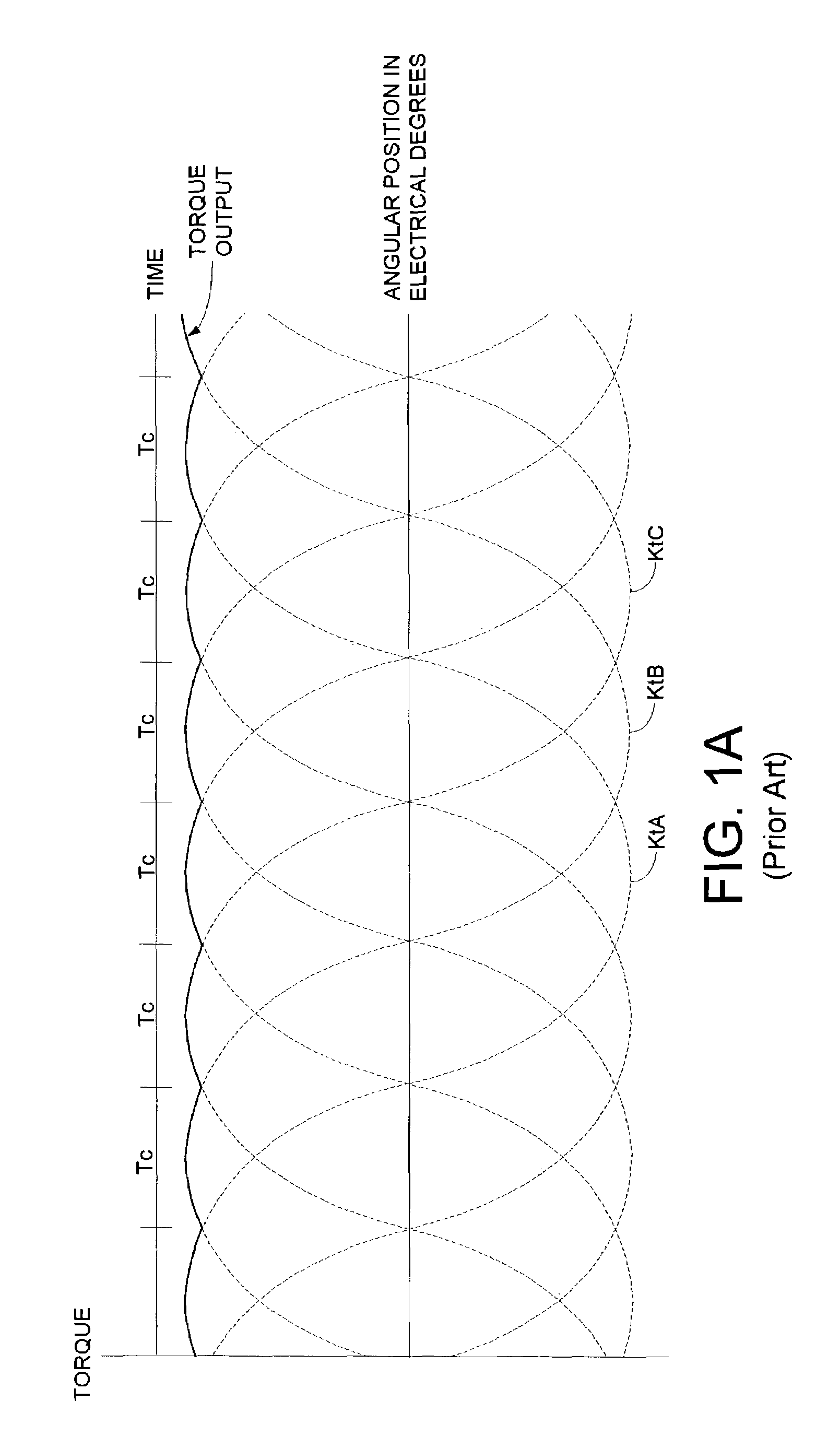
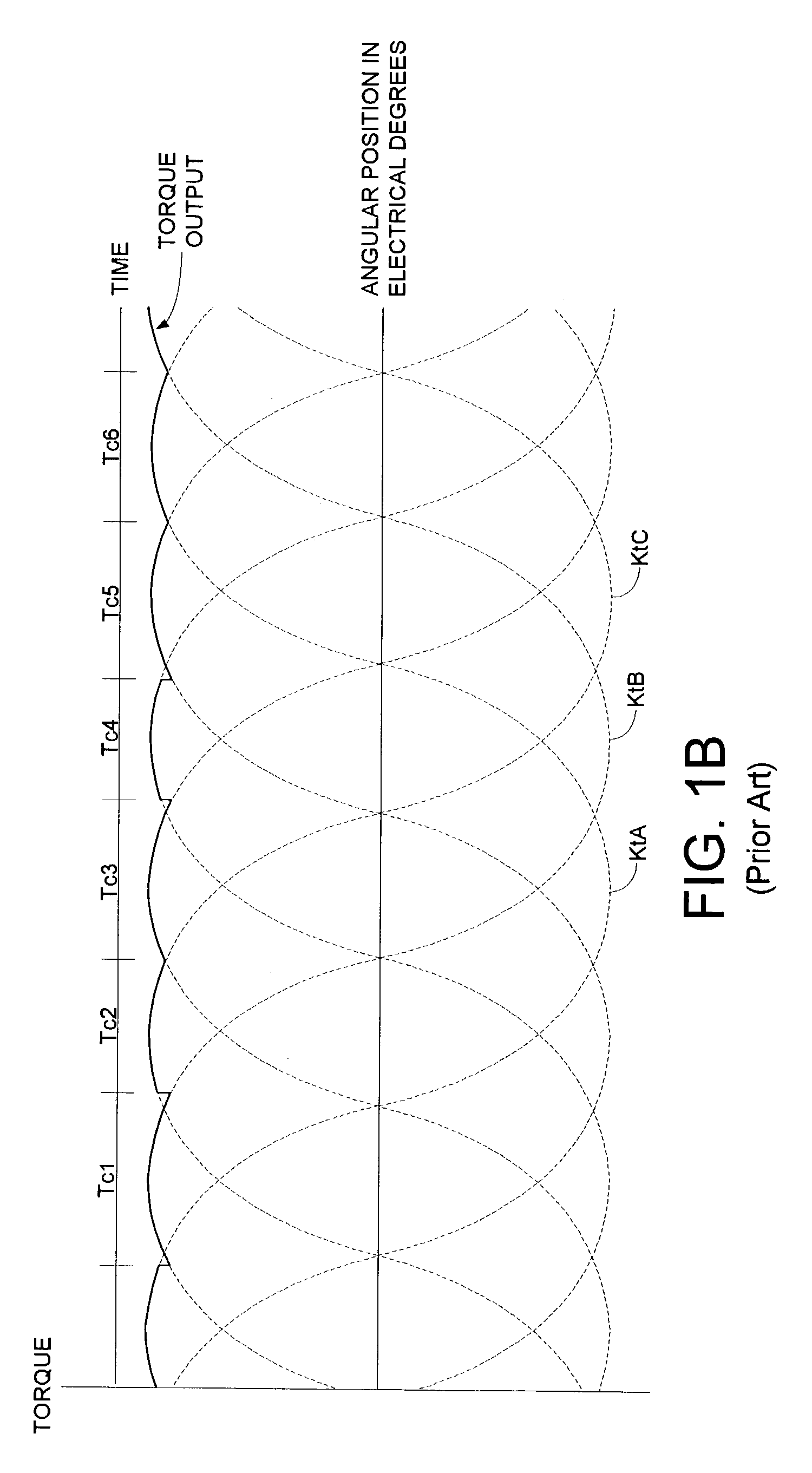
Disk drive employing commutation phase modulation and current modulation of a spindle motor
InactiveUS6972539B1Reduce discontinuityReduce vibrationAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineNoise reduction
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a spindle motor comprising a plurality of windings for rotating a disk. The spindle motor is rotated by commutating the windings over a plurality of commutation states, wherein audible noise generated by the disk drive is reduced by phase modulating the commutation interval. Further audible noise reduction is achieved by modulating a current applied to the windings which substantially reduces discontinuities in the torque output of the spindle motor caused by phase modulation of the commutation intervals.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
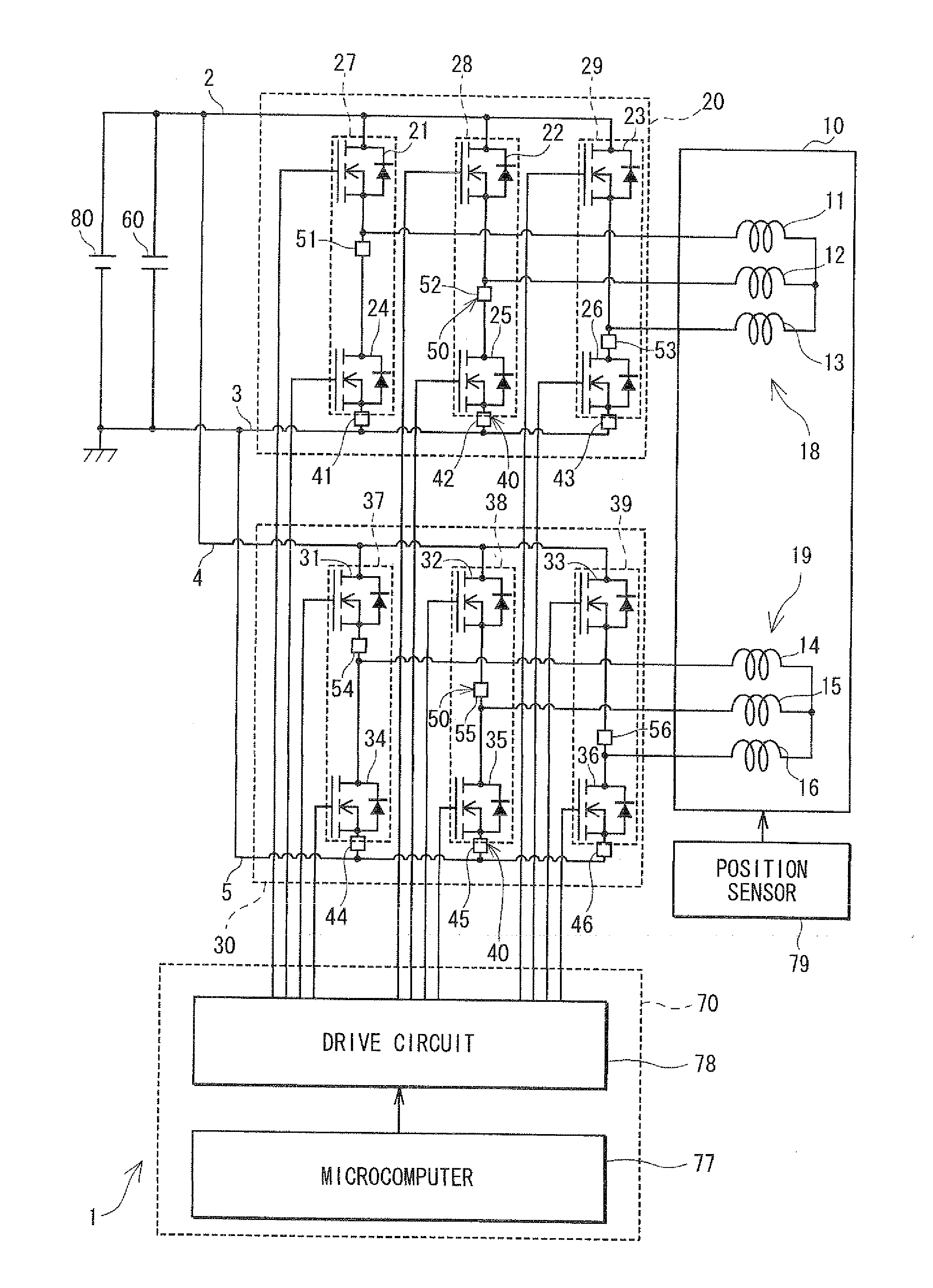
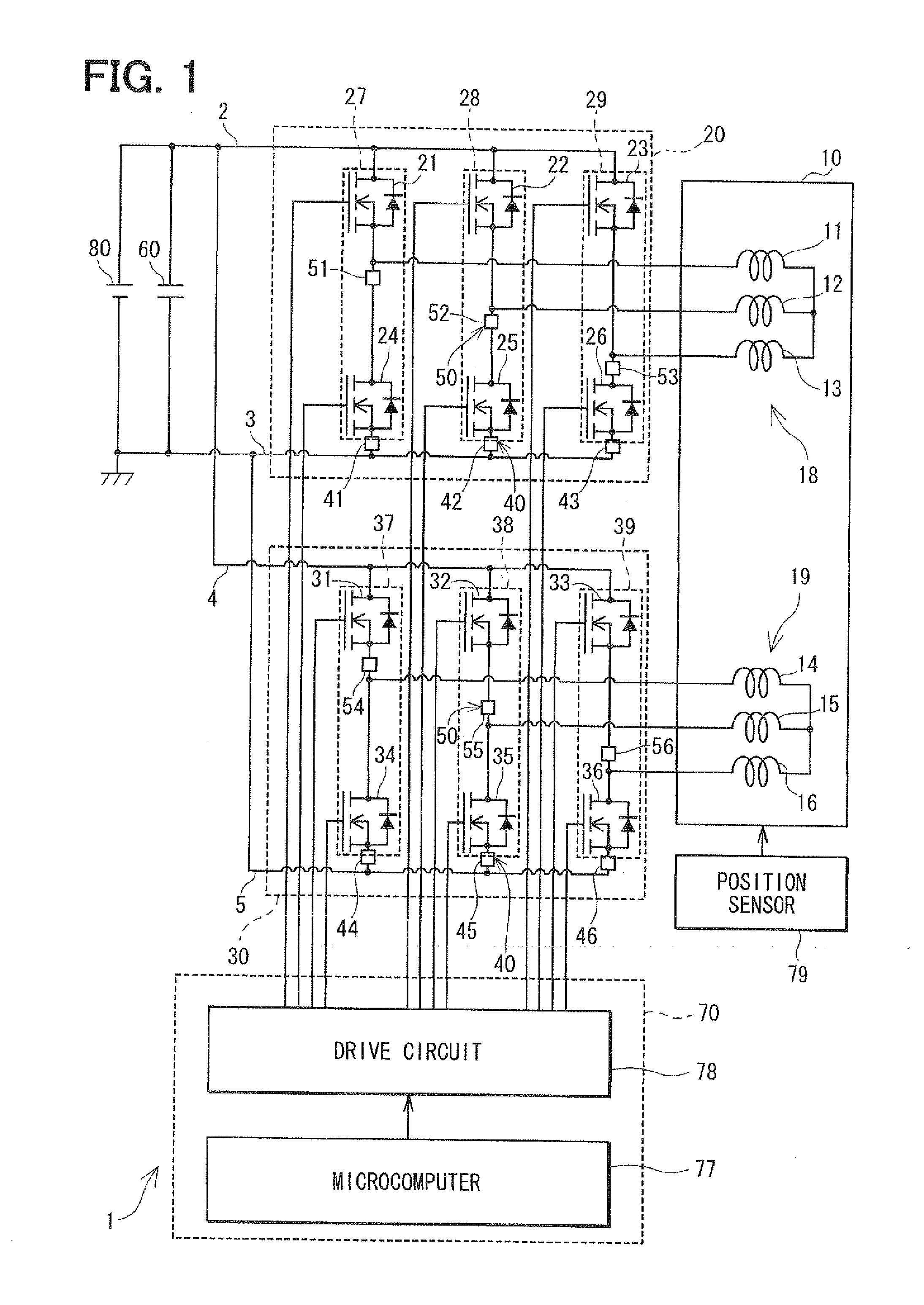
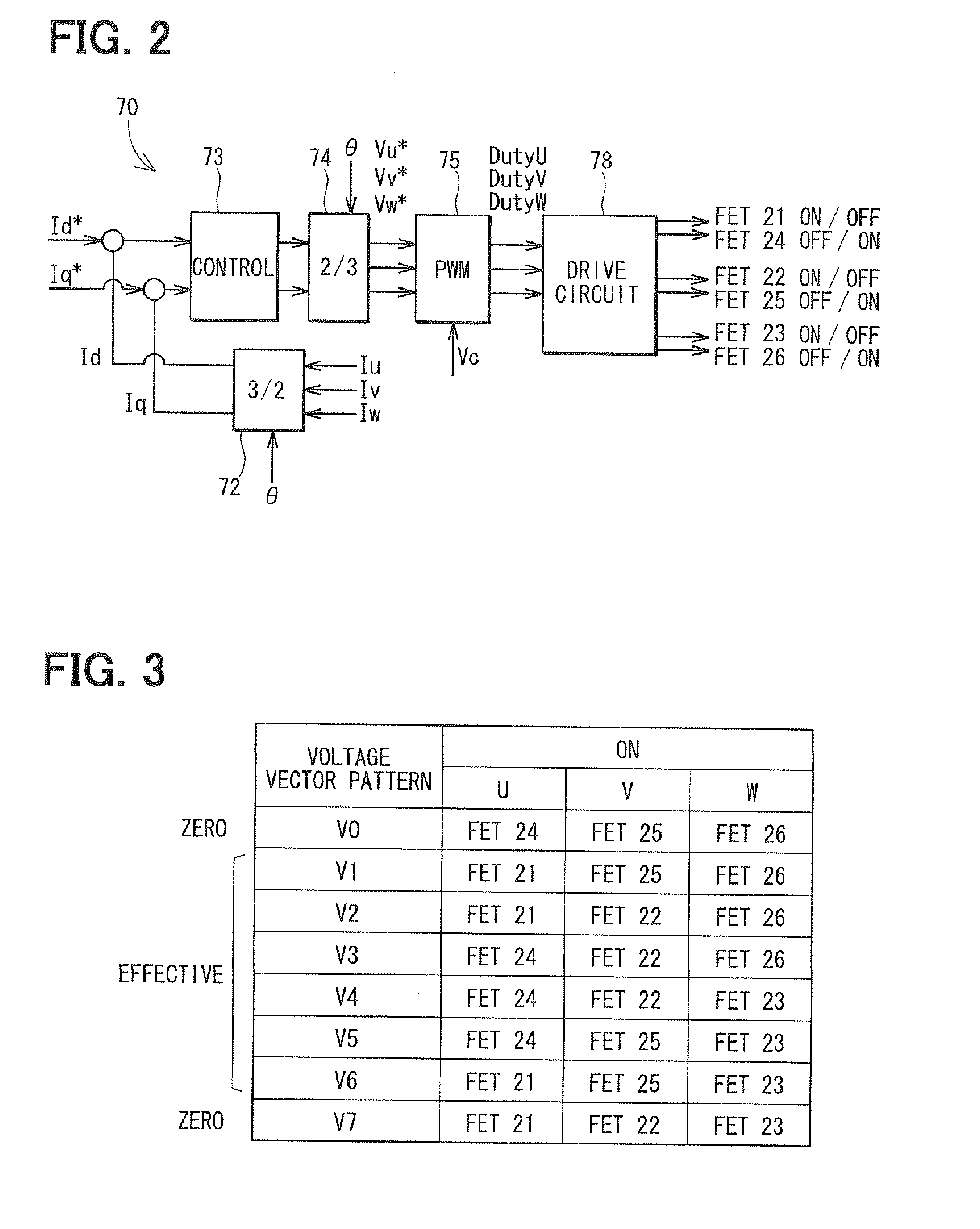
Control apparatus for multi-phase rotary machine and electric power steering system
ActiveUS20110074333A1Smooth rideInhibition effectCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlBrake torqueElectric power steering
A control apparatus for a multi-phase rotary machine includes a control unit and a plurality of power supply systems including respective inverter units. When a short-circuiting failure occurs in one of the systems due to an ON-failure in any one of FETs in an inverter unit of the failure system, the control unit stops driving of the rotary machine by bringing all the FETs in the failure system into the OFF state. The control unit controls FETs of the non-failure system such that a brake torque generated in the failure system is cancelled or the influence of the brake torque exerted on the driving of the motor is reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
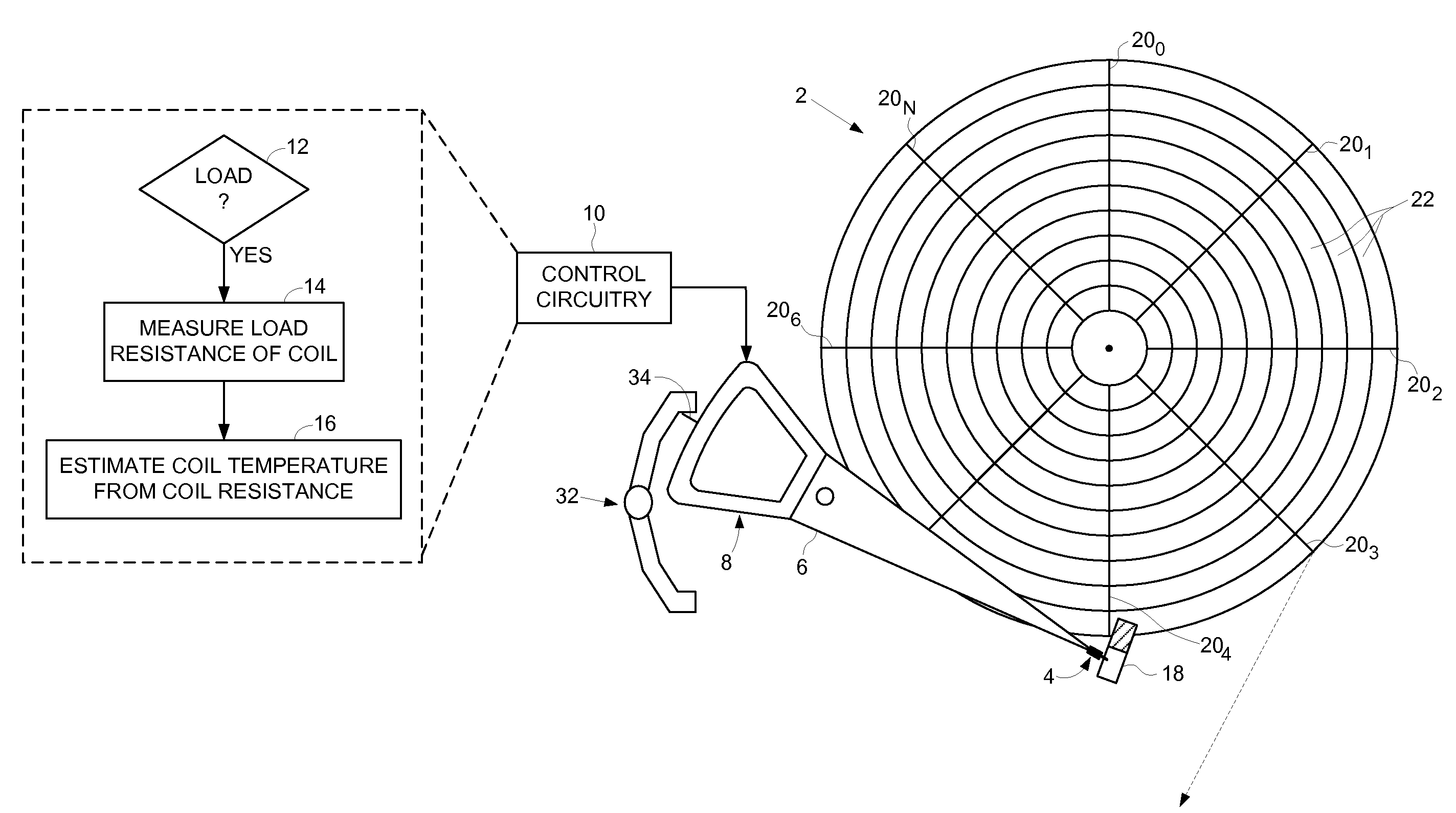
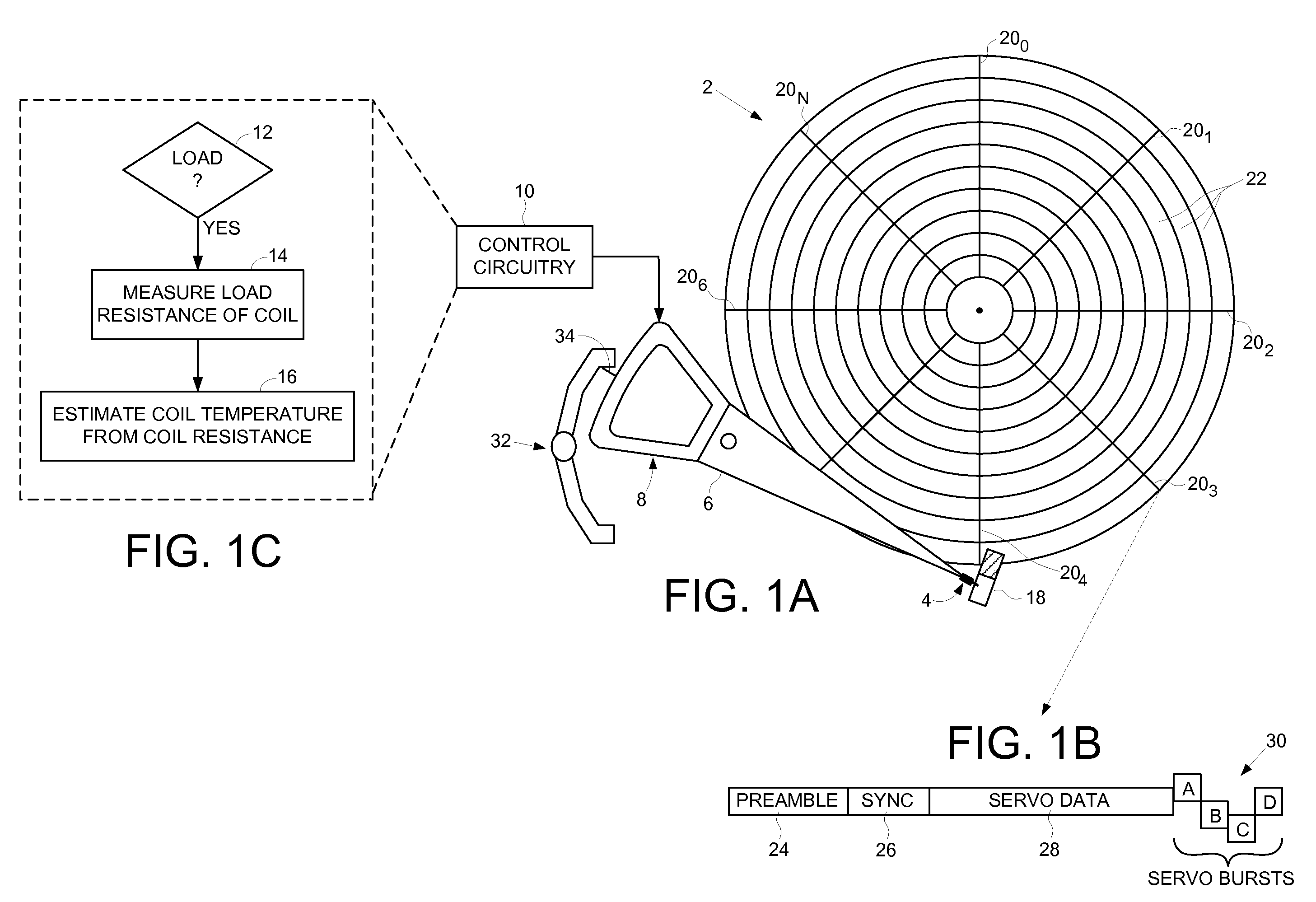
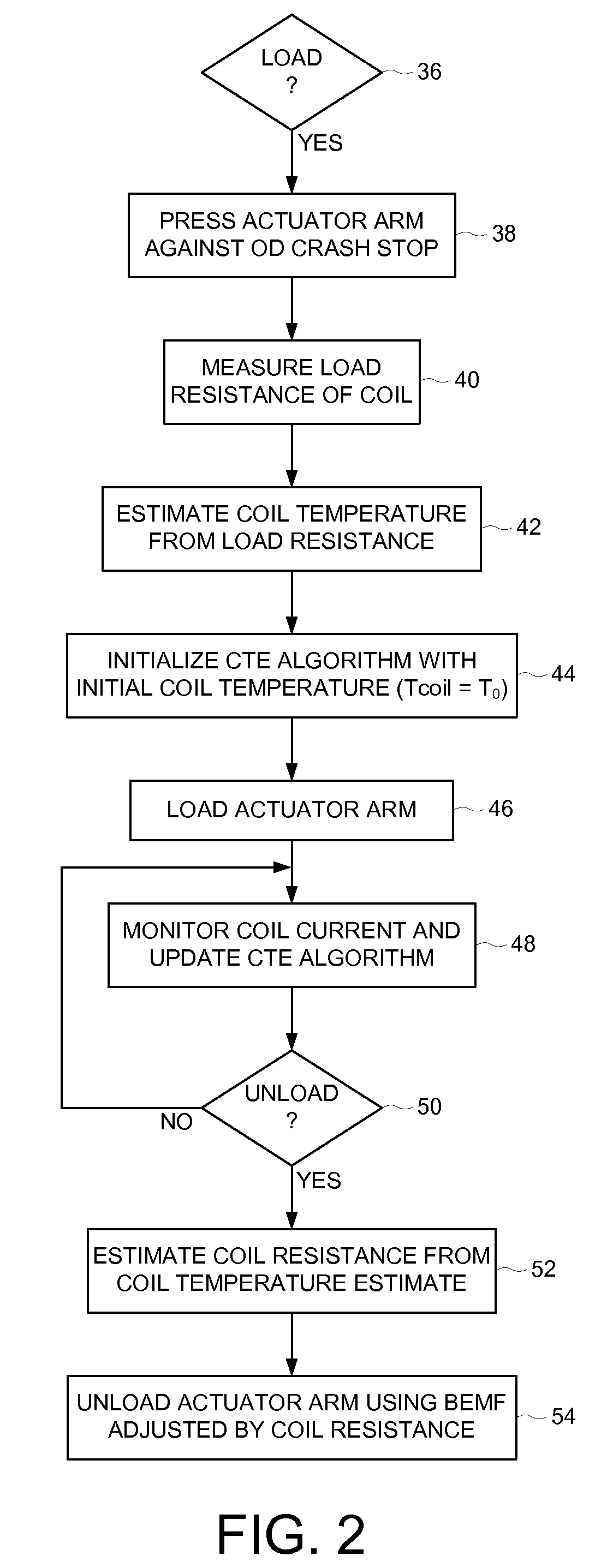
Disk drive initializing a coil temperature estimation algorithm using a resistance of the coil estimated during a load operation
InactiveUS7660067B1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlLoad resistanceElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk, a head coupled to a distal end of an actuator arm, and a voice coil motor (VCM) operable to rotate the actuator arm about a pivot to actuate the head radially over the disk, wherein the VCM comprises a coil. Control circuitry within the disk drive measures a load resistance of the coil prior to executing a load operation, wherein the load operation moves the actuator arm off a ramp to load the head onto the disk. The load resistance of the coil is then converted into an initial coil temperature estimate.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
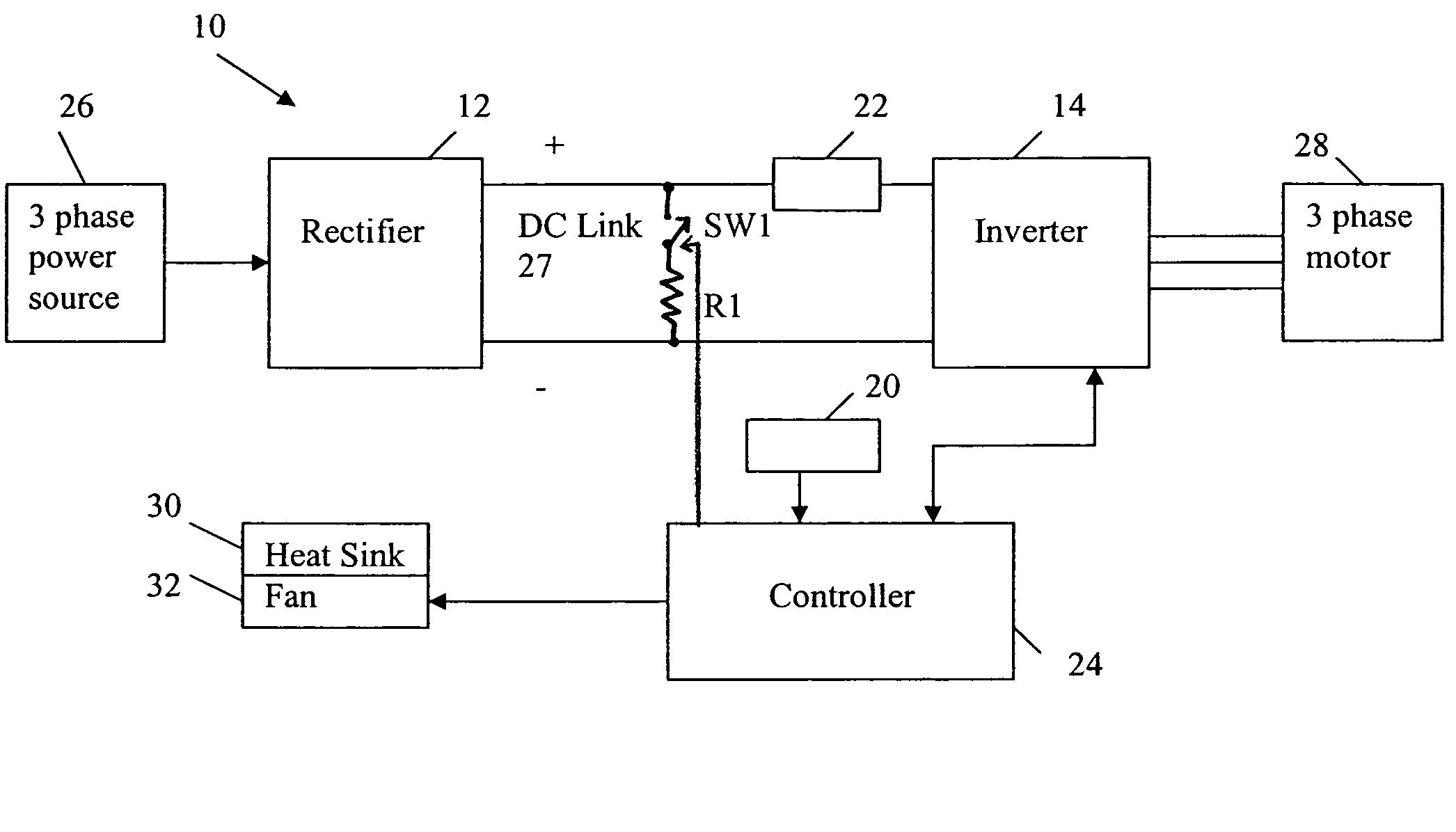
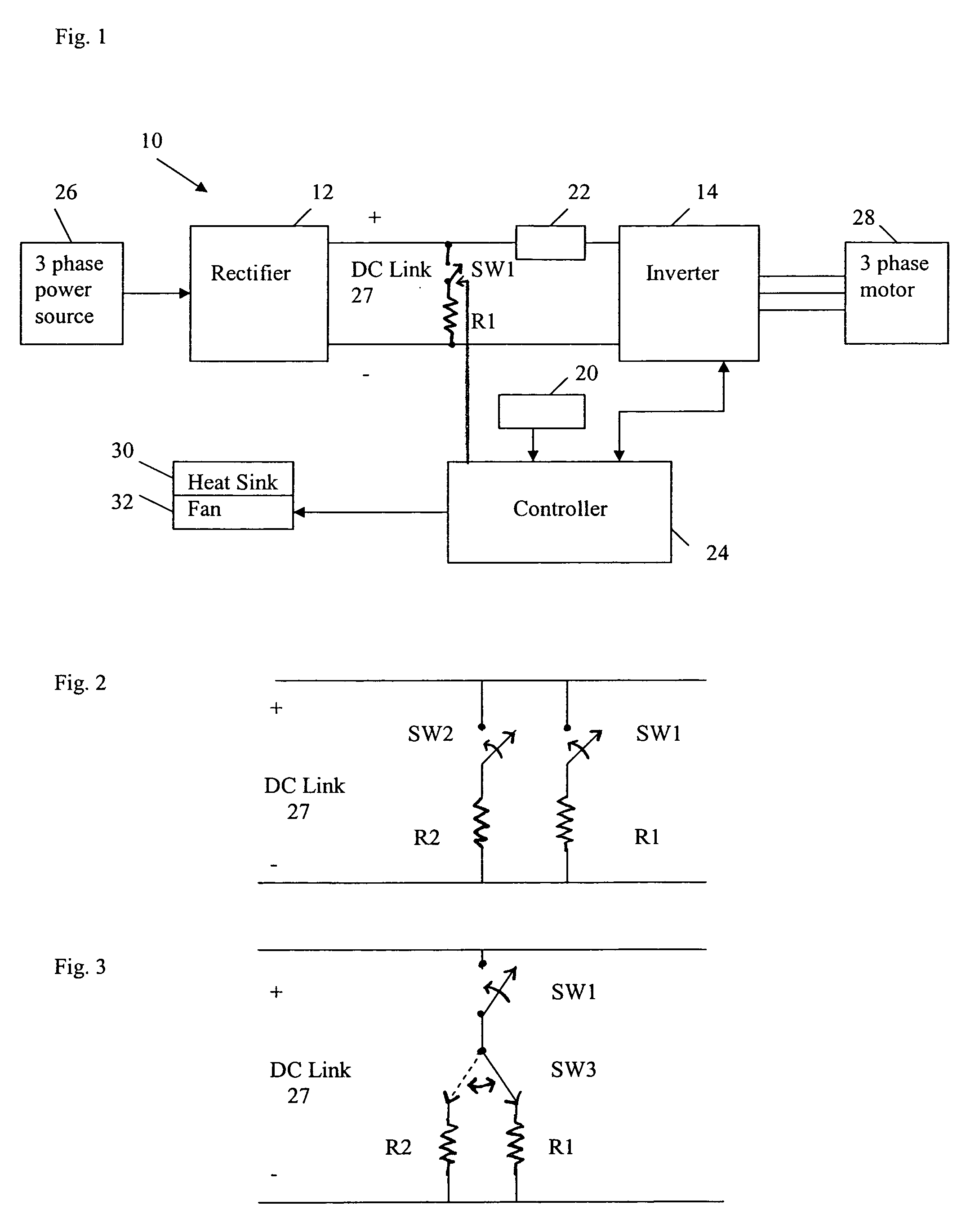
Thermal regulation of AC drive
ActiveUS7312593B1Avoid condensationSimple and cost-effectiveTemperature control using analogue comparing deviceDC motor speed/torque controlEngineeringElectric power
An apparatus for the thermal regulation of an AC drive for providing power to a motor includes a temperature sensor producing a signal indicative of temperature, a heater resistor connectable across a DC link of the AC drive, and a first switch. A controller is operable to monitor the temperature signal and control the first switch to provide power via the DC link to the heater resistor if the sensed temperature is below a predetermined setpoint.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Method and system for fail-safe motor operation
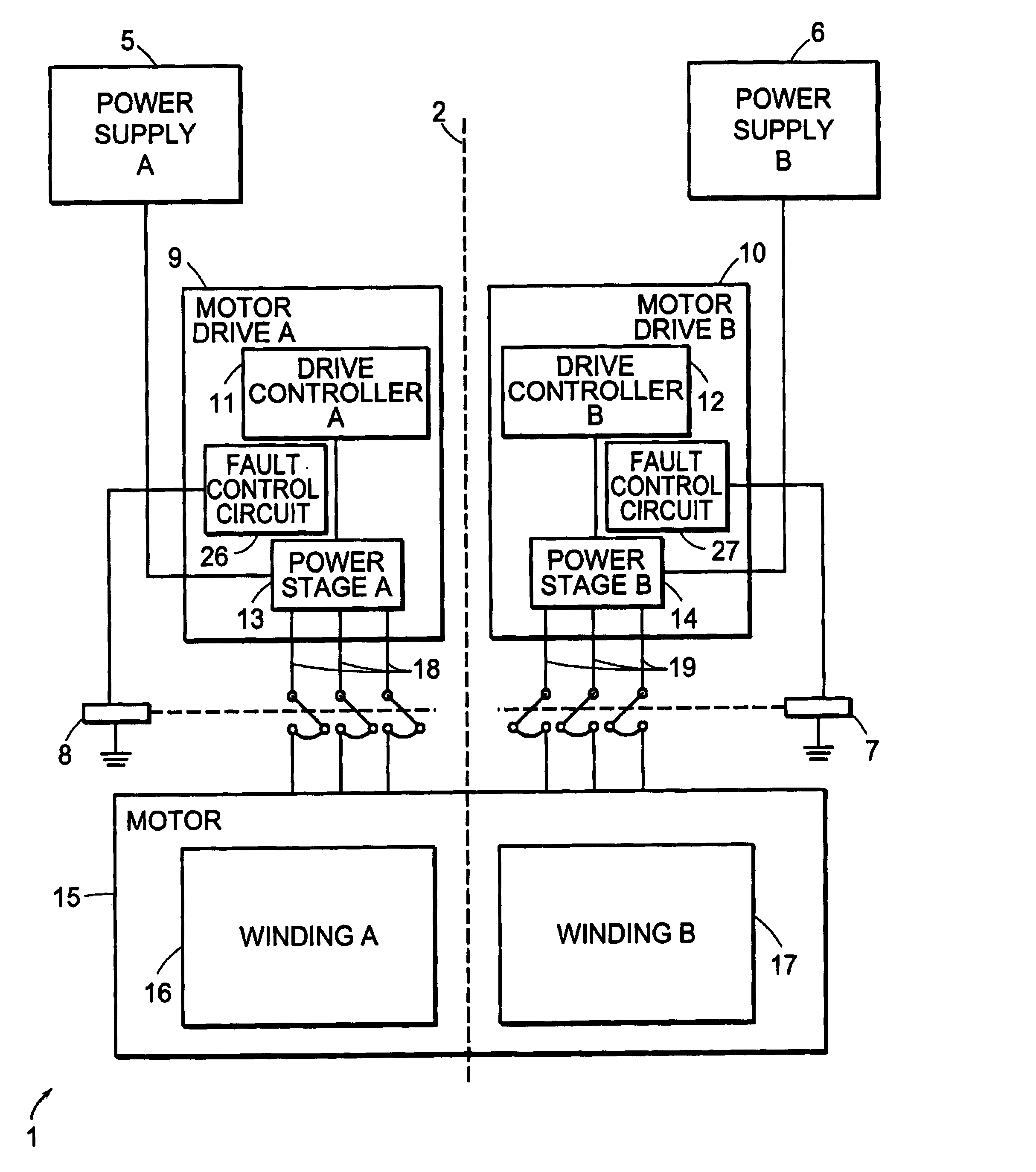
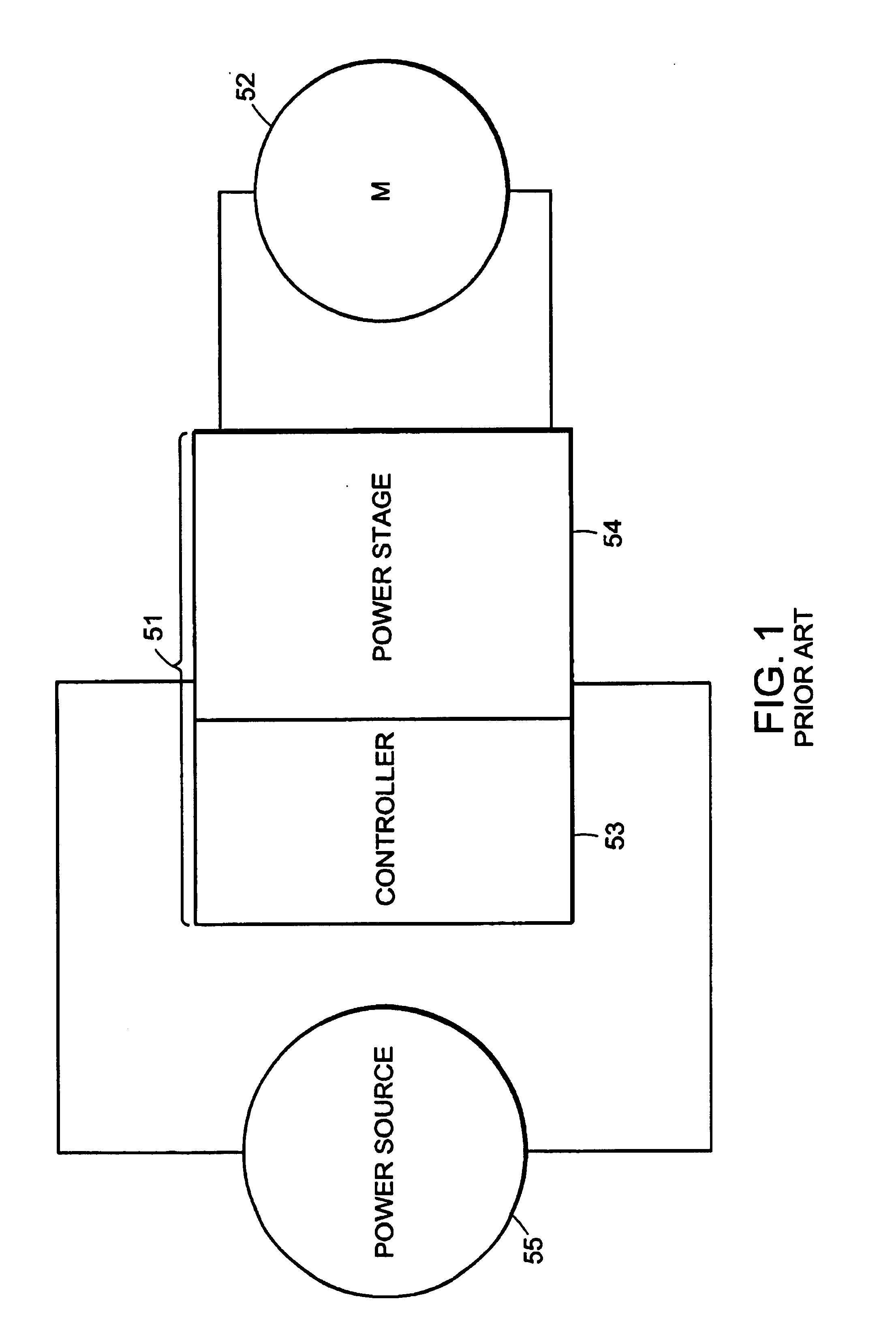
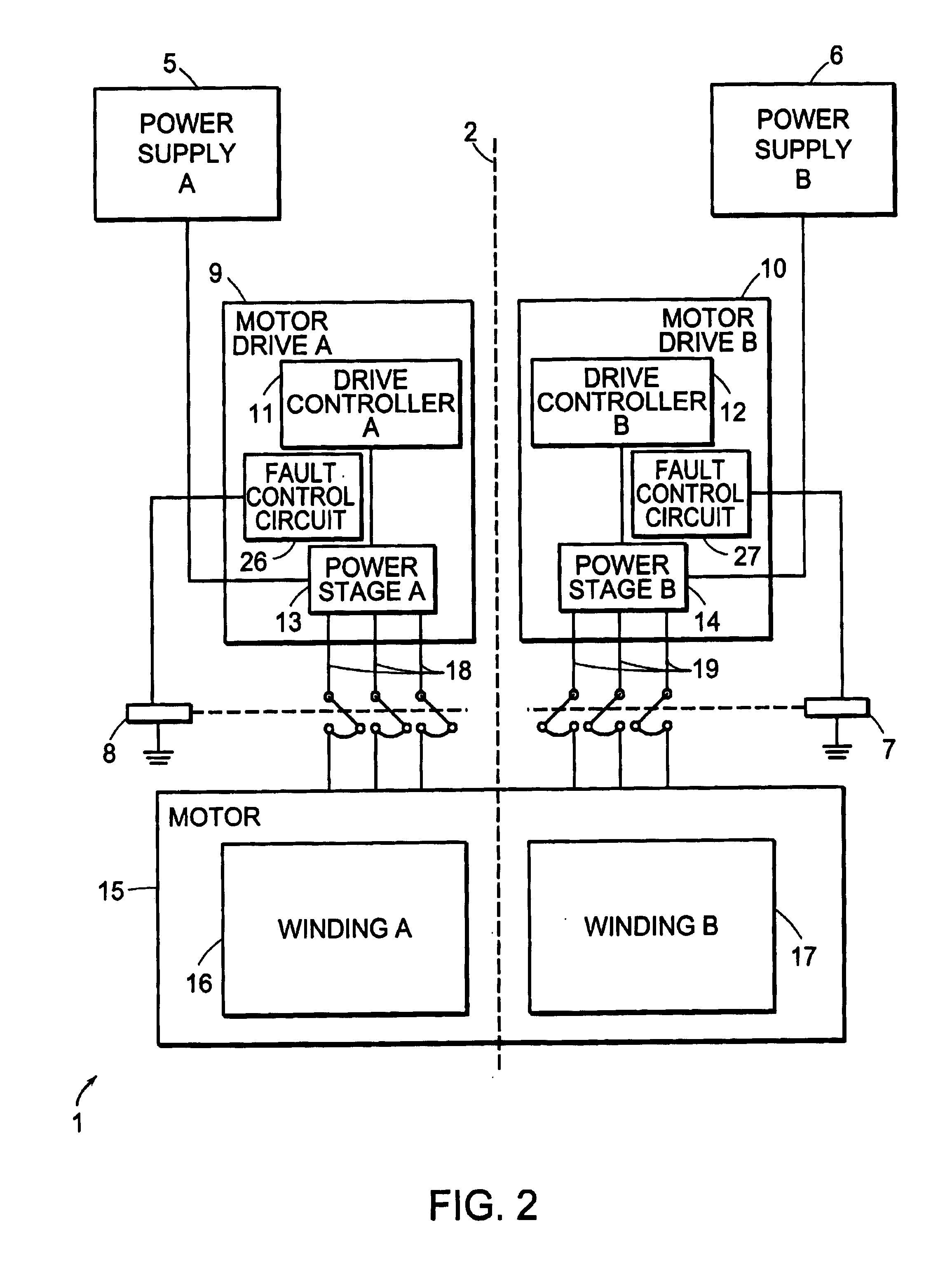
InactiveUS6965206B2Reducing fault torqueEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPropulsion by batteries/cellsMotor driveElectrical devices
An electric device includes a motor and a motor drive for commanding a torque generated by the motor. A fault control circuit detects a fault condition associated with the motor drive. Upon detection of the fault condition, the fault control circuit adjusts the torque commanded by the motor drive.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
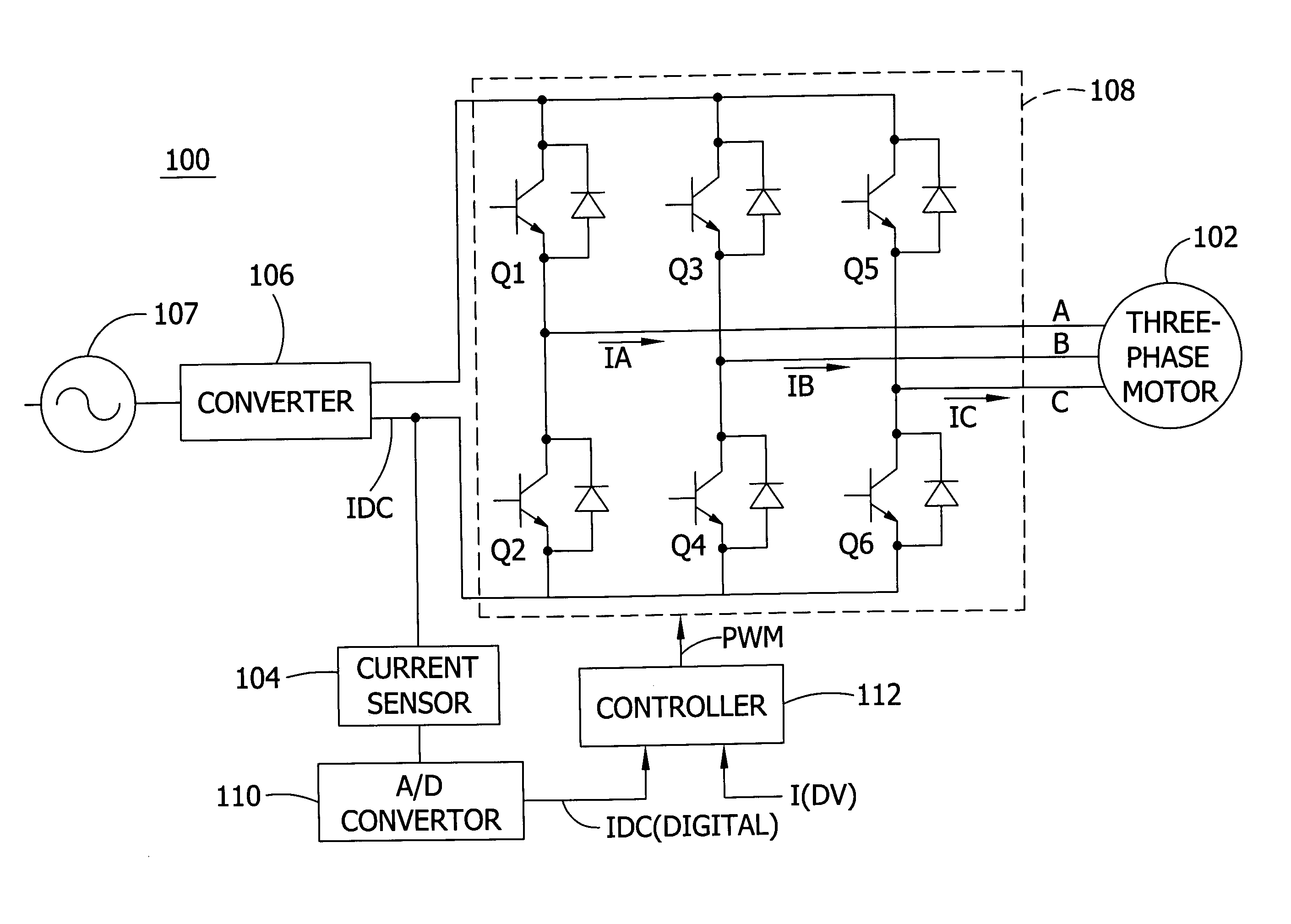
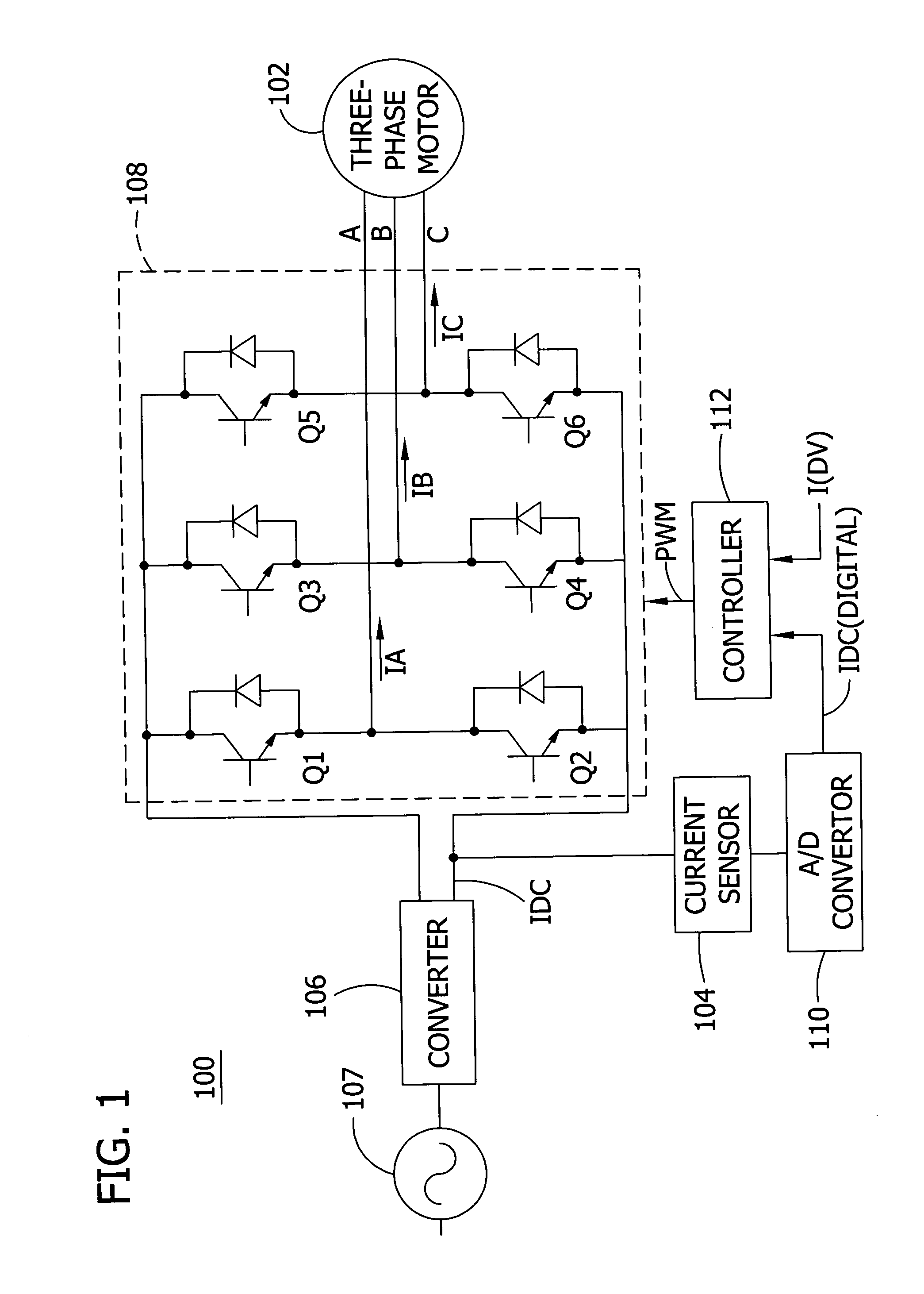
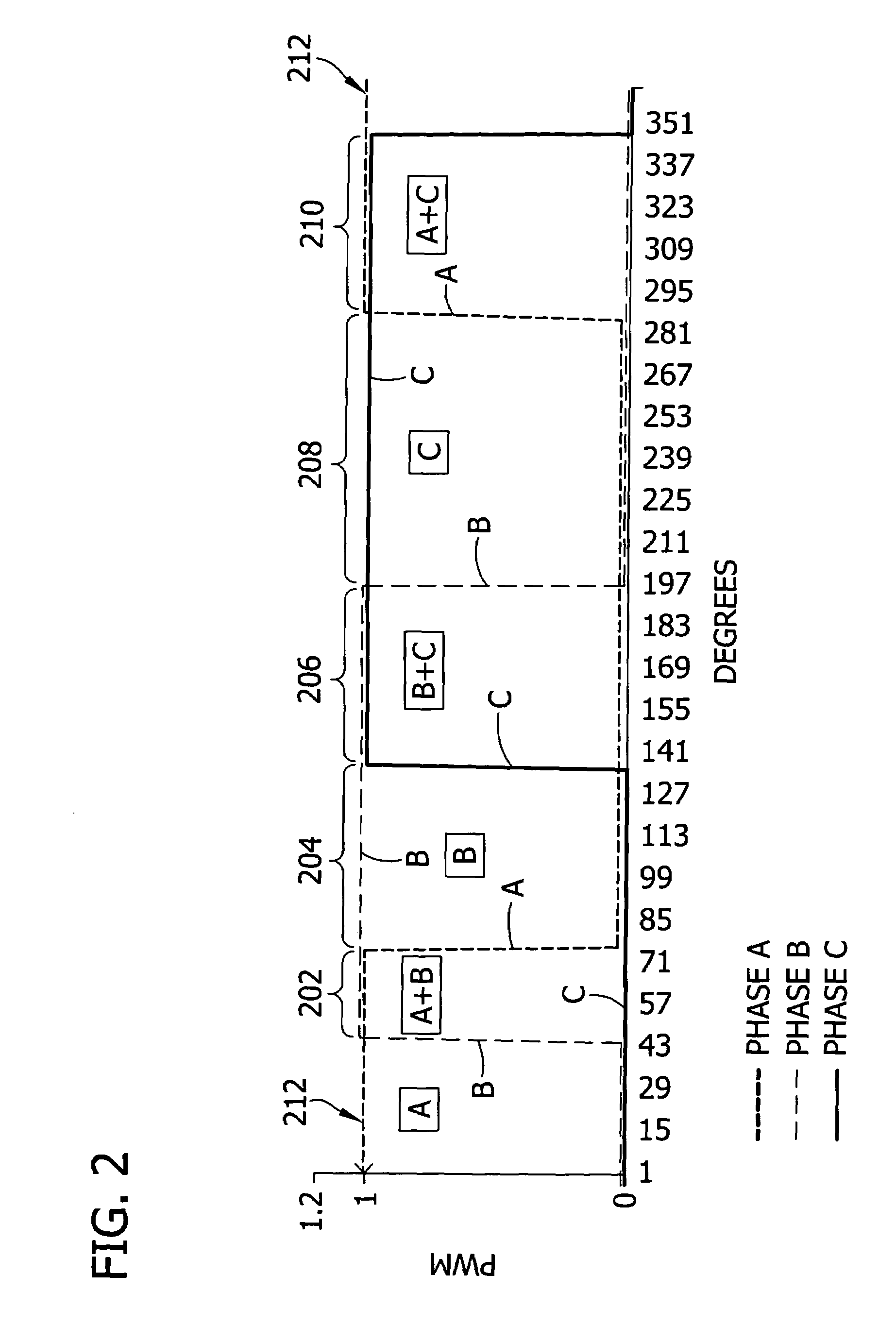
Offset PWM signals for multiphase motor
A multi phase motor includes a switching array for interconnecting a power source to each phase. A current sensor senses current supplied from the power source via the switching array to the winding and a controller generates offset PWM signals for controlling the switching array to supply power to each of the phases of the winding. The offset timing allows the individual phase currents to be determined from a single current sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Electrical power tool having a motor control circuit for providing control over the torque output of the power tool
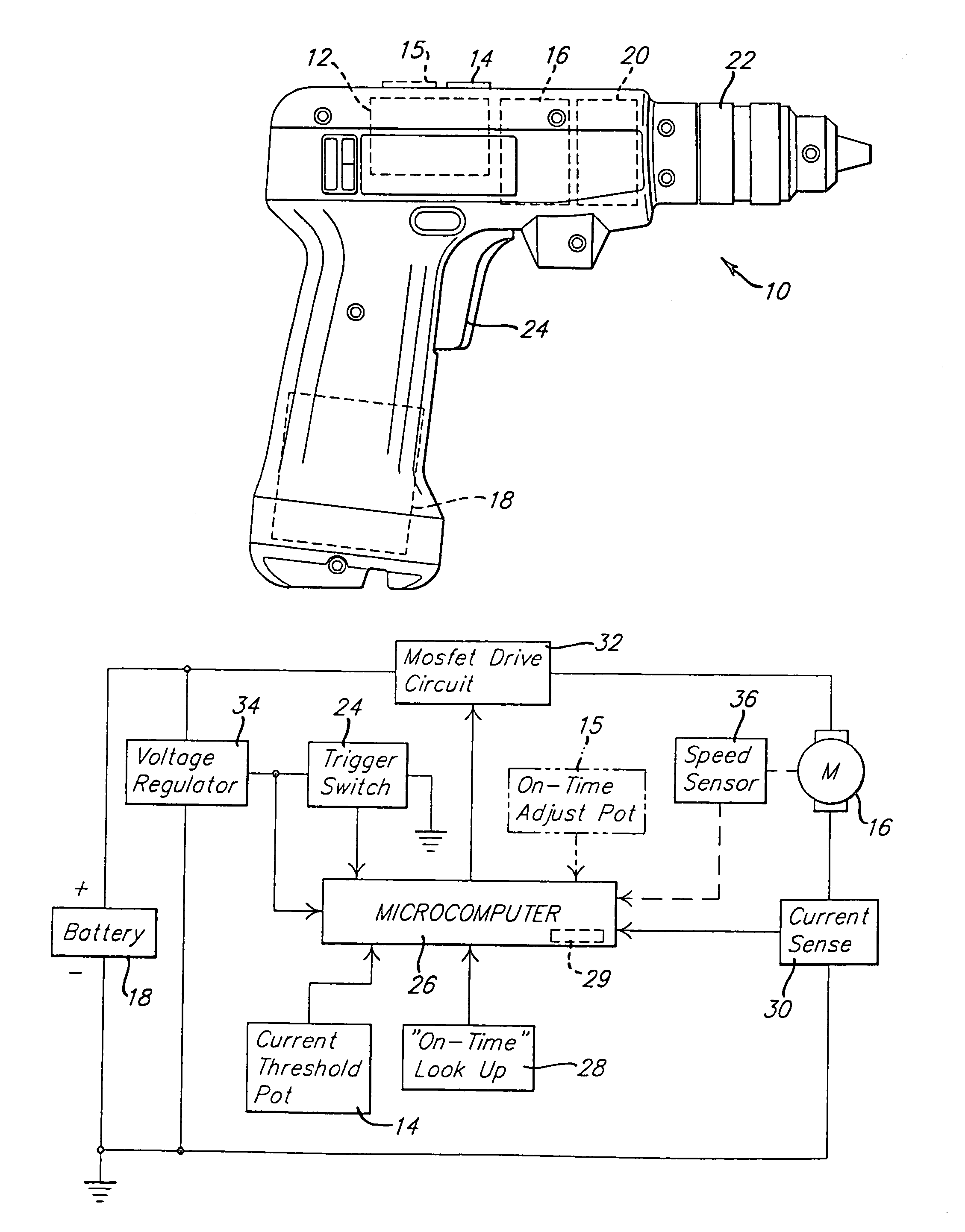
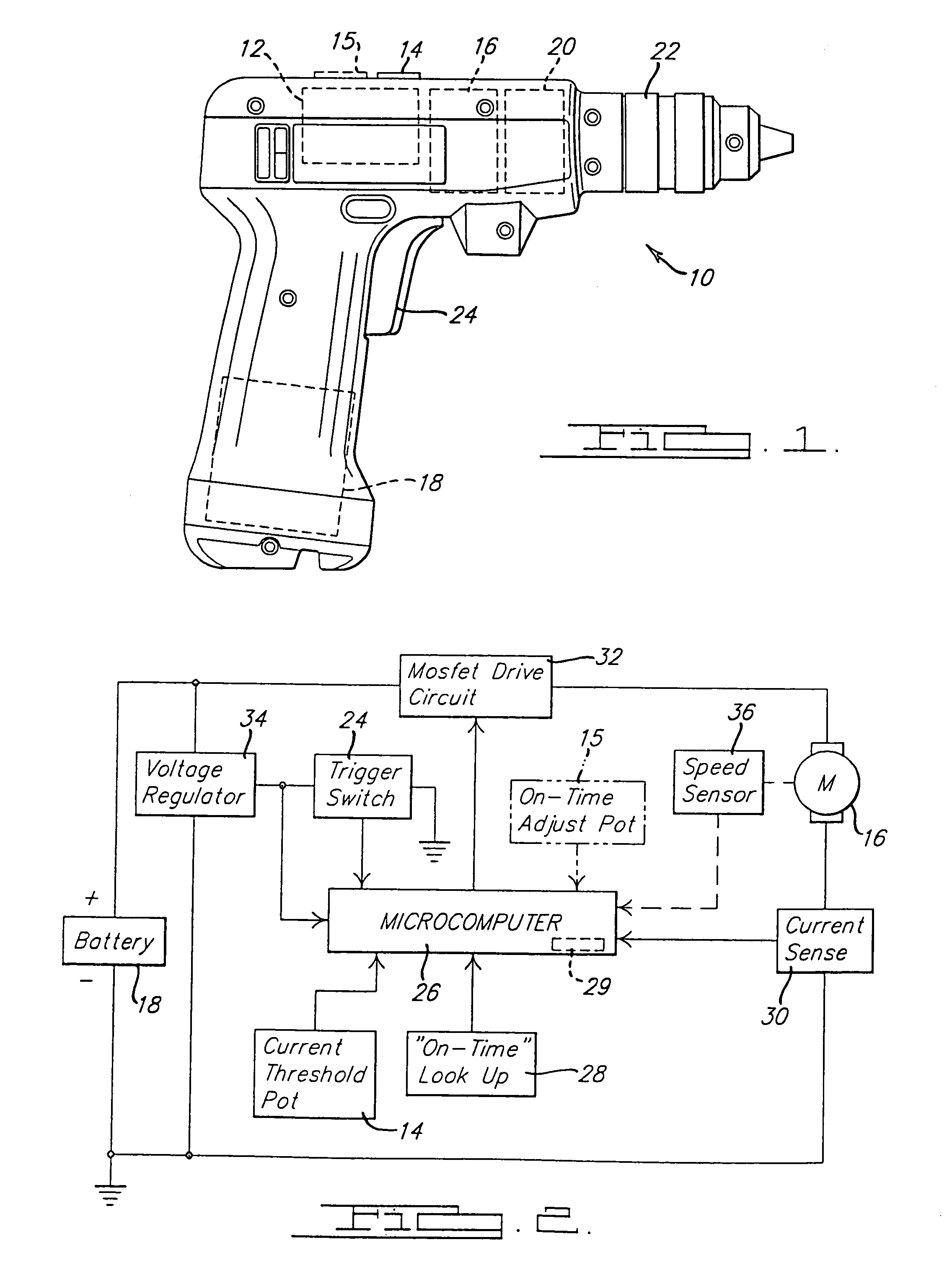
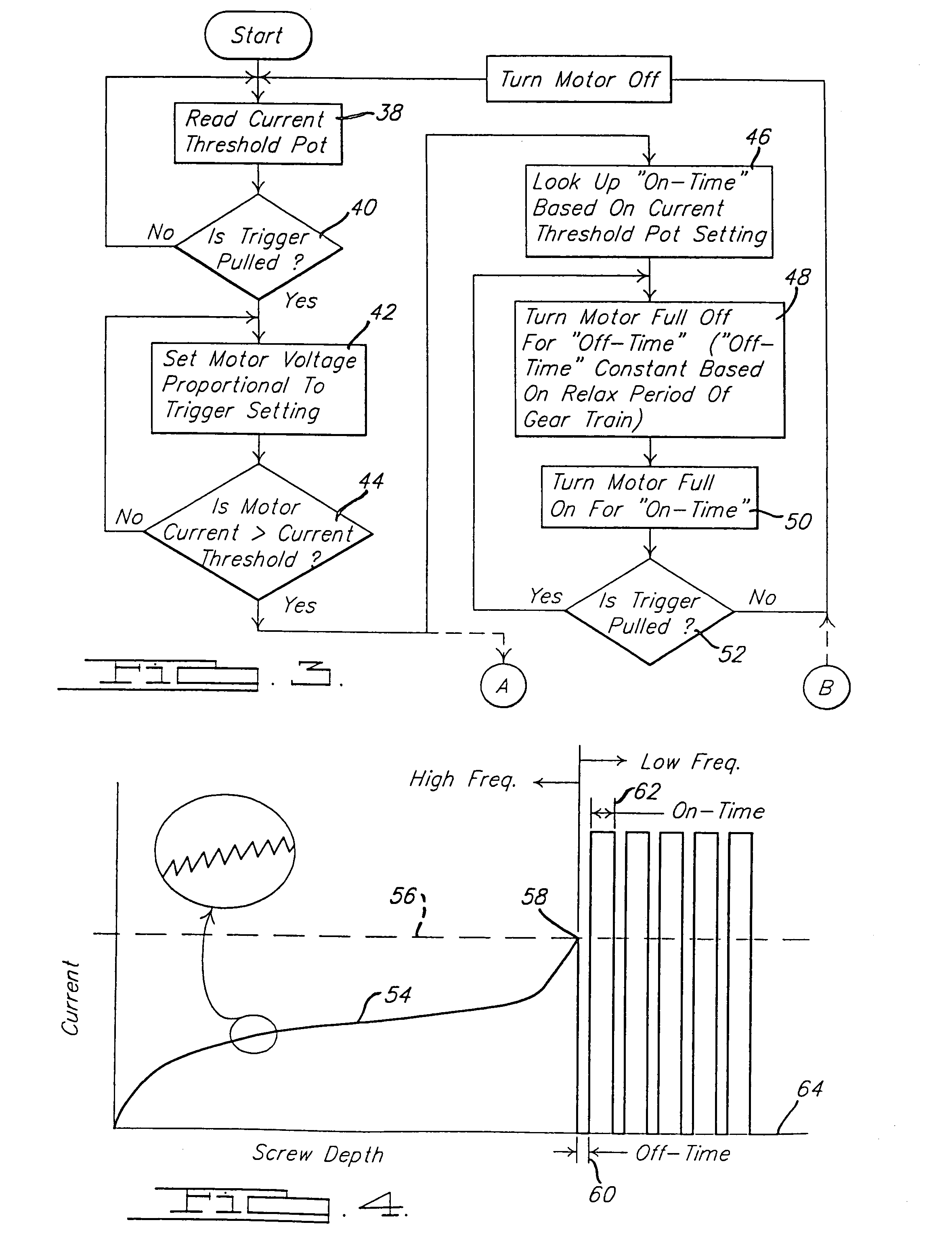
InactiveUS7112934B2Limit magnitudeGreat potential energyDC motor speed/torque controlAsynchronous induction motorsPulsed modeMotor control
A power tool such as an electric drill typically contains a gear train that couples the output spindle of the motor to the tool bit-receiving chuck. The control circuit for the power tool is operable in a ratcheting or pulse mode that causes the output spindle to rotate in discrete incremental amounts. Corresponding methods for controlling the operation of the electric motor of a power tool are also disclosed.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com