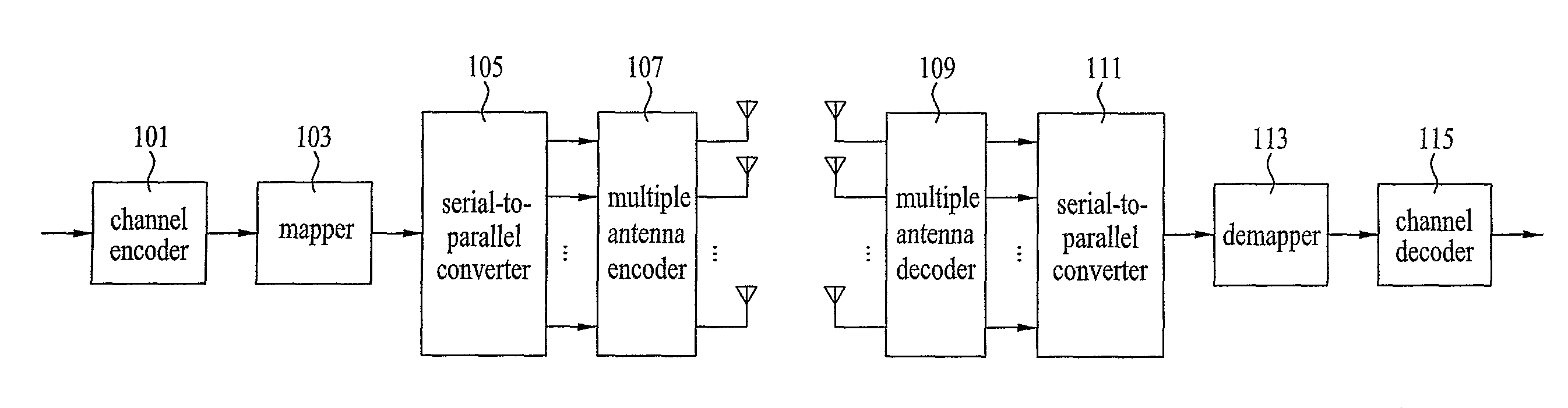
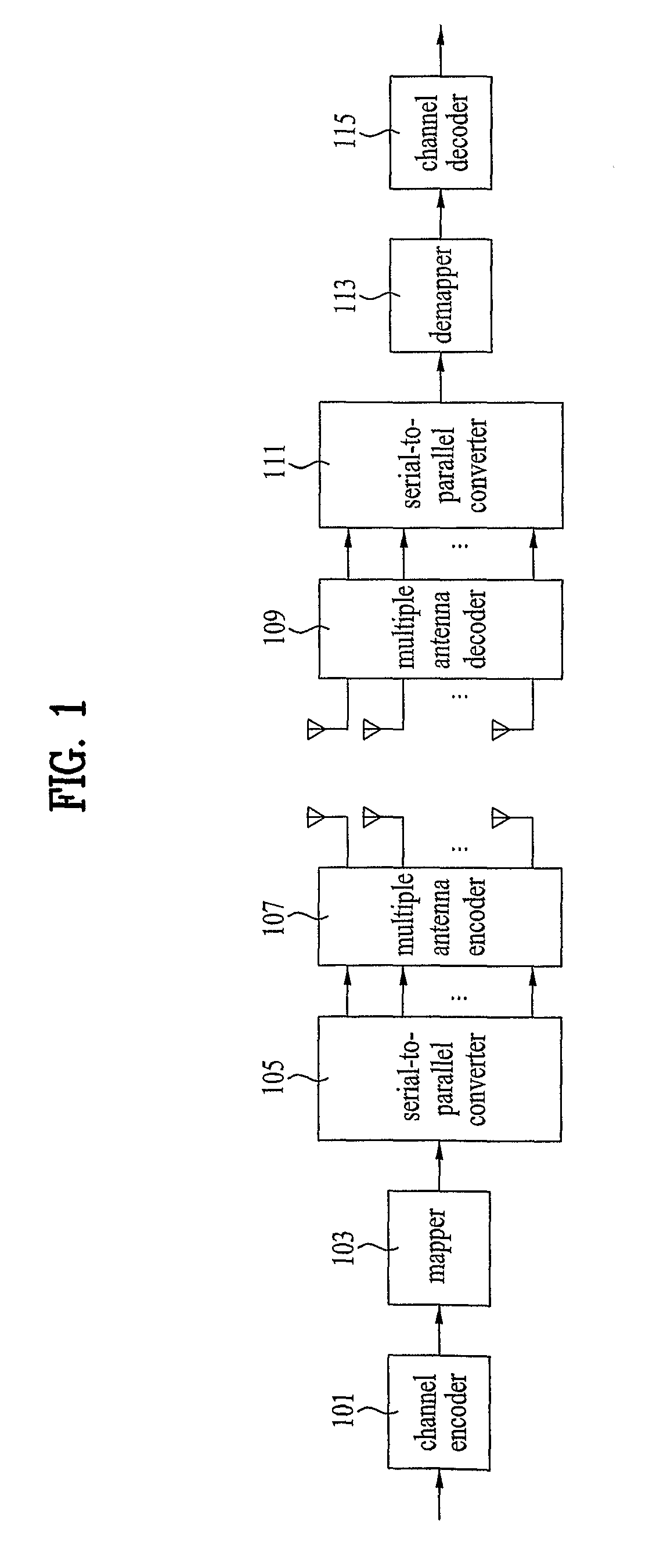
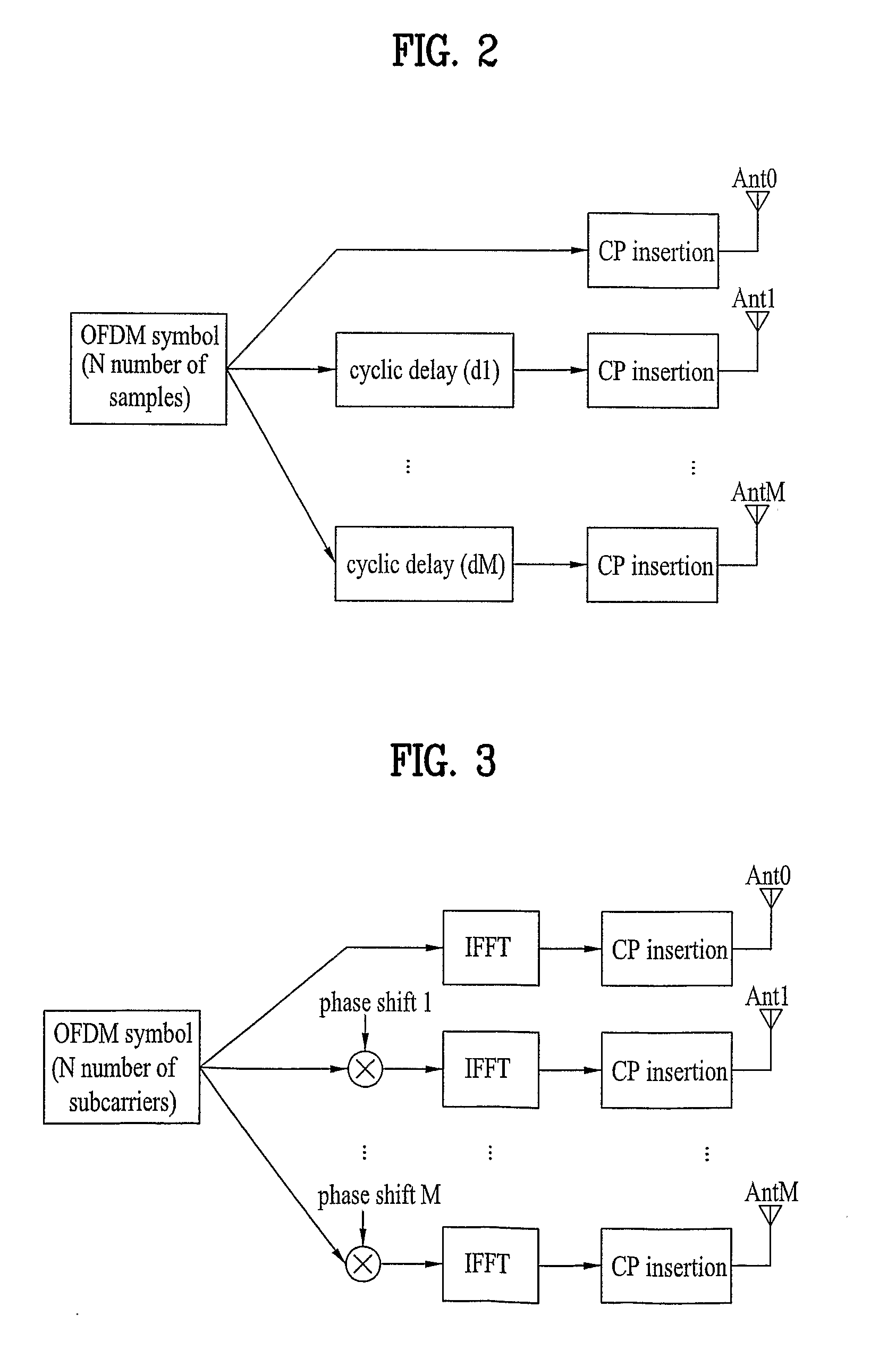
Patents
Literature
4509 results about "Phase angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the context of phasors, phase angle refers to the angular component of the complex number representation of the function. The notation A∠ θ, for a vector with magnitude (or amplitude) A and phase angle θ, is called angle notation. This notation is frequently used to represent an electrical impedance. In this case, the phase angle is the phase difference between the voltage applied to the impedance and the current driven through it.
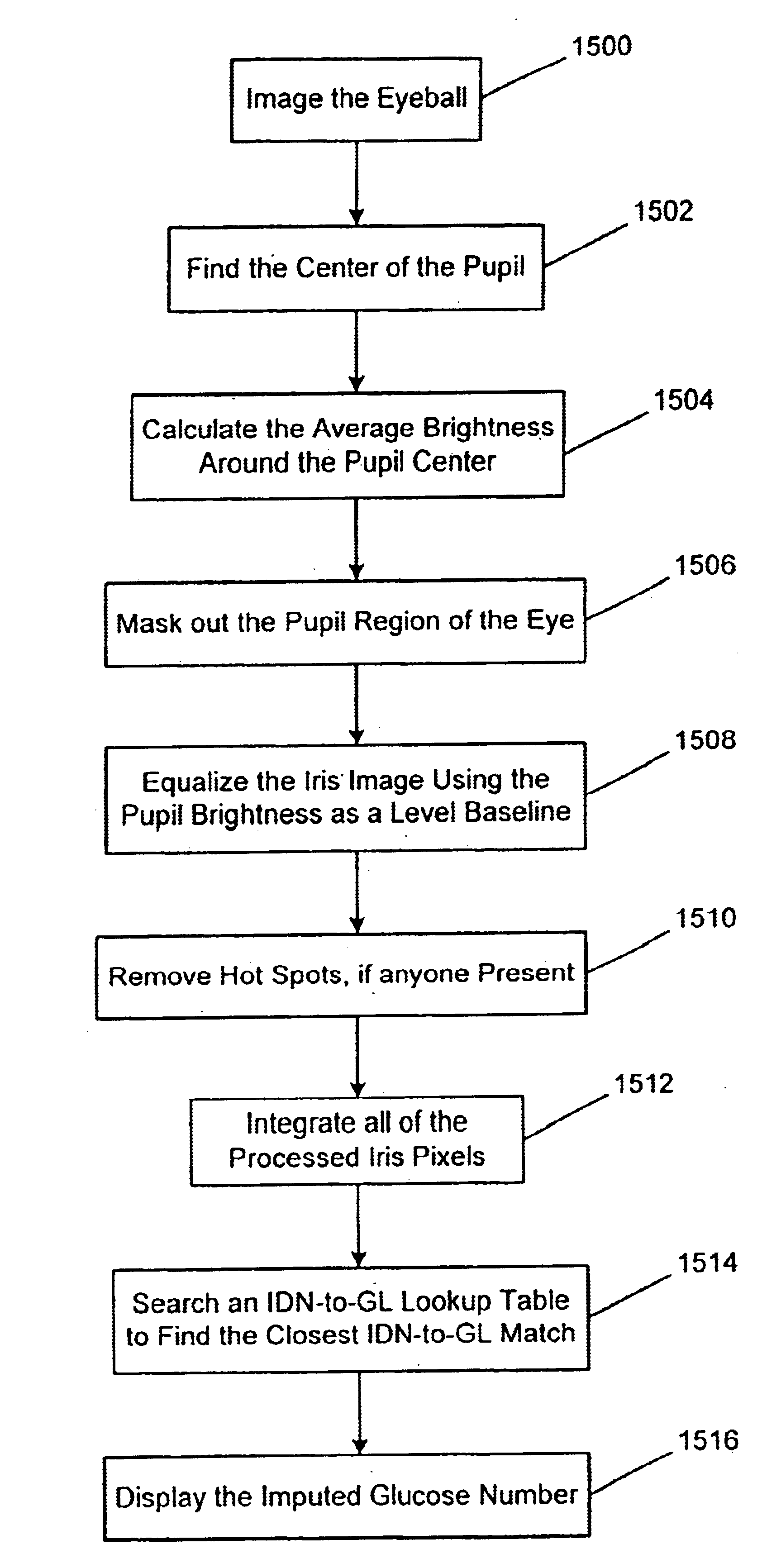
Noninvasive measurement system
InactiveUS6853854B1Value can be obtainedCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringData processing systemReflected waves
The noninvasive measurement system provides a technique for manipulating wave data. In particular, wave data reflected from a biological entity is received, and the reflected wave data is correlated to a substance in the biological entity. The wave data may comprise light waves, and the biological entity may comprise a human being or blood. Additionally, a substance may comprise, for example, a molecule or ionic substance. The molecule may be, for example, a glucose molecule.Furthermore, the wave data is used to form a matrix of pixels with the received wave data. The matrix of pixels may be modified by techniques of masking, stretching, or removing hot spots.Then, the pixels may be integrated to obtain an integration value that is correlated to a glucose level. The correlation process may use a lookup table, which may be calibrated to a particular biological entity. Moreover, an amplitude and phase angle may be calculated for the reflected wave data and used to identify a glucose level in the biological entity.The glucose level may be displayed on a monitor attached to the computer. The computer may be a portable, self-contained unit that comprises a data processing system and a wave reflection capture system. On the other hand, the computer may be attached to a network of other computers, wherein the reflected wave data is received by the computer and forwarded to another computer in the network for processing.
Owner:STI MEDICAL SYST
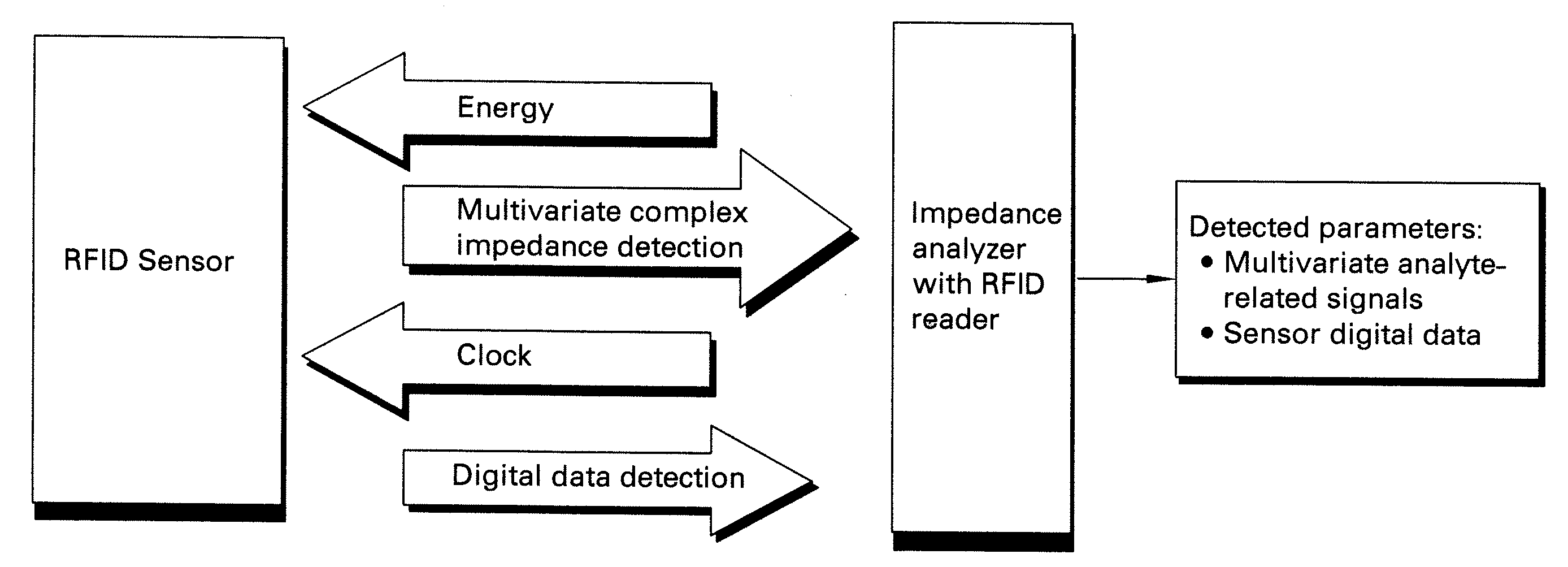
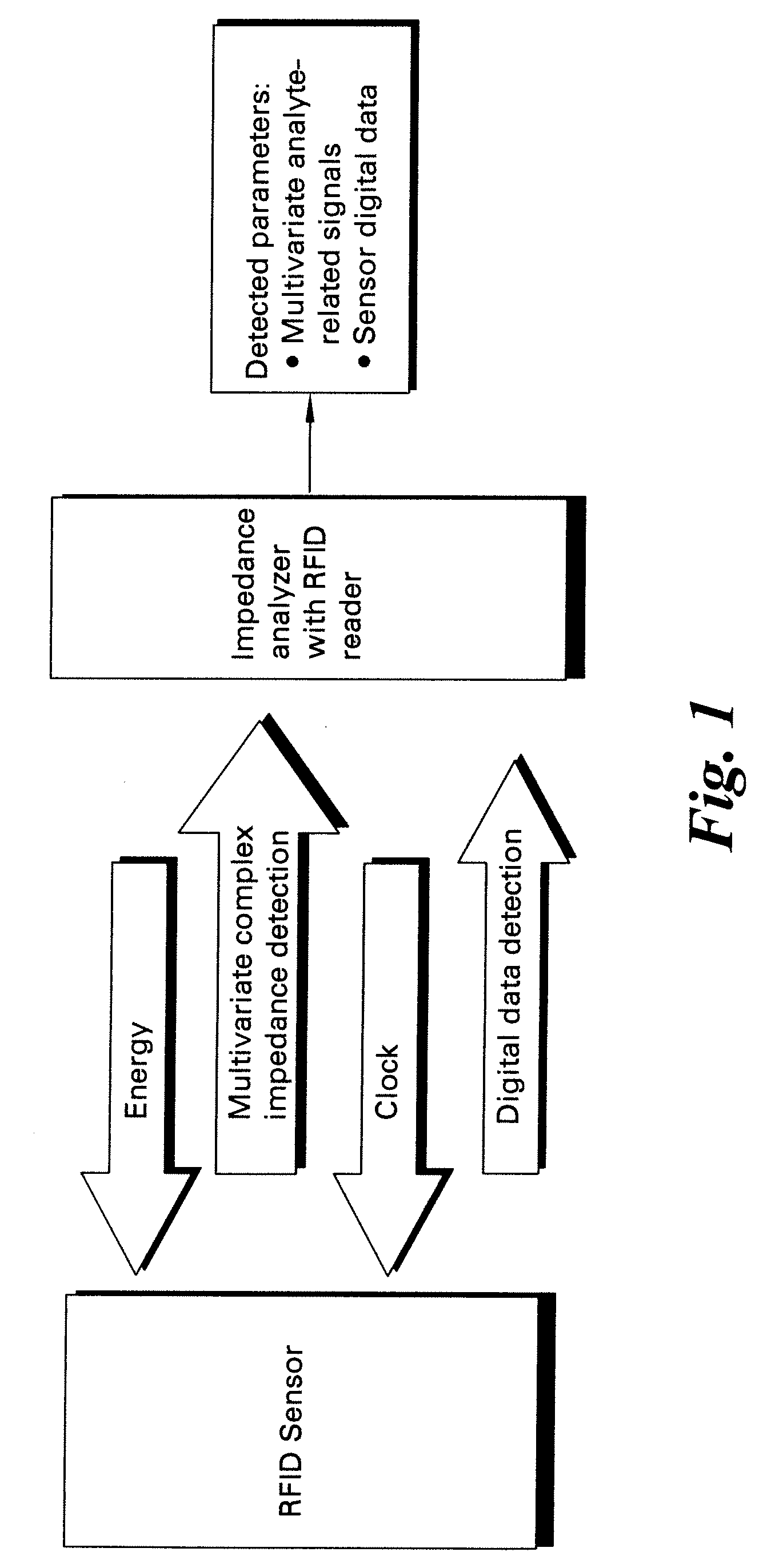
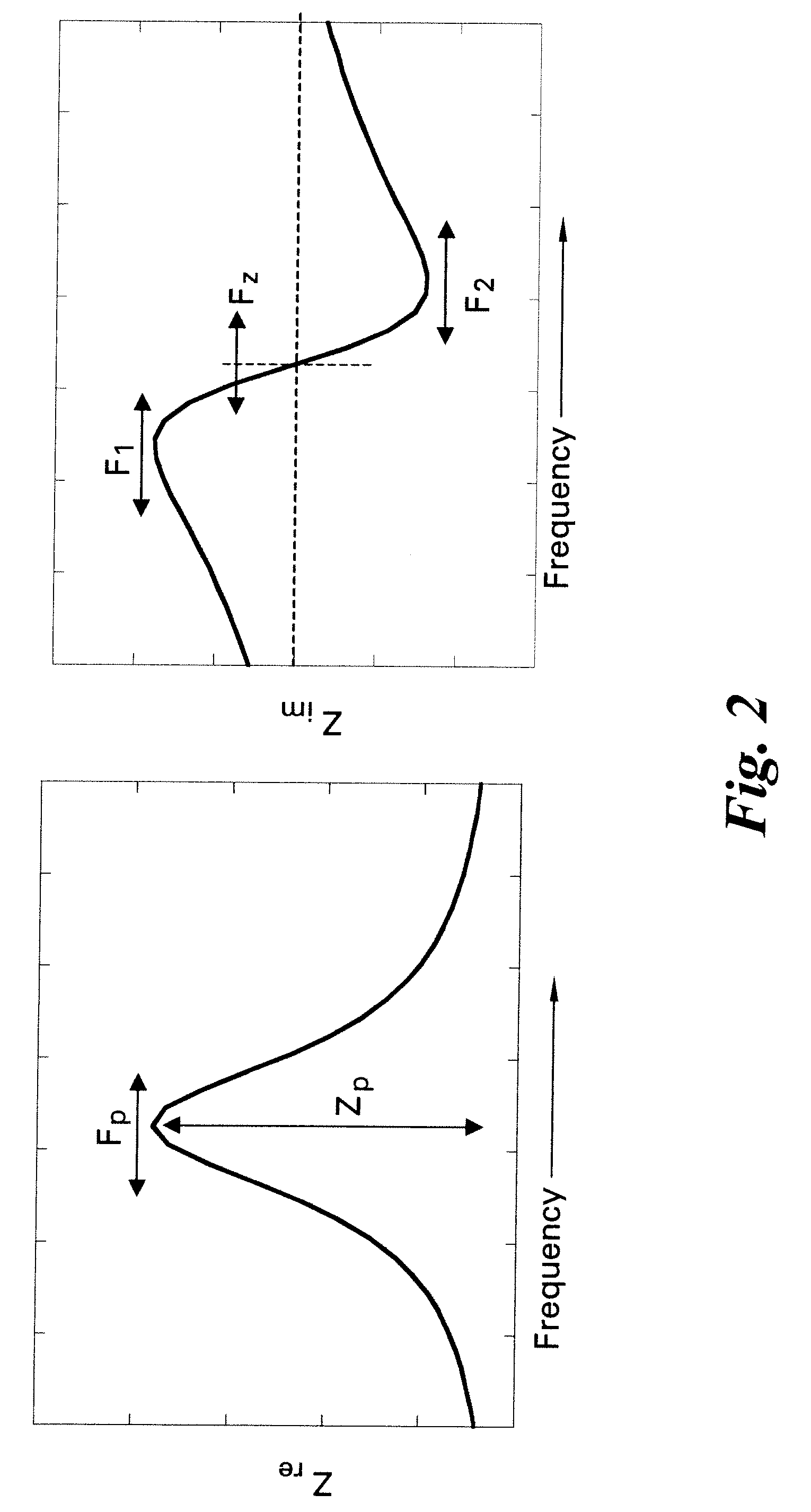
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors
ActiveUS20090278685A1Testing sensing arrangementsGas analyser calibrationMemory chipComplex impedance spectra
Methods and systems for calibration of RFID sensors used in manufacturing and monitoring systems are provided. The methods include measuring impedance of an RFID sensor antenna, relating the measurement of impedance to one or more parameters (such as physical, chemical and biological properties), computing one or more analytical fit coefficients, and storing the one or more analytical fit coefficients on a memory chip of the RFID sensor. Measuring impedance of the RFID sensor may comprise measuring complex impedance which involves measuring complex impedance spectrum, phase angle and magnitude of the impedance, at least one of frequency of the maximum of the real part of the complex impedance, magnitude of the real part of the complex impedance, zero-reactance frequency, resonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance, and antiresonant frequency of the imaginary part of the complex impedance. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a sensing film wherein analytical fit coefficients are stored on the memory chip to allow calibration of the RFID sensor. Also provided are manufacturing or monitoring systems comprised of an RFID sensor wherein the RFID sensor comprises, a memory chip, an antenna, and a complementary sensor attached to the antenna where the complementary sensor in a pre-calibrated fashion predictably affects the impedance of the antenna.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE AIR BRAKE TECH CORP
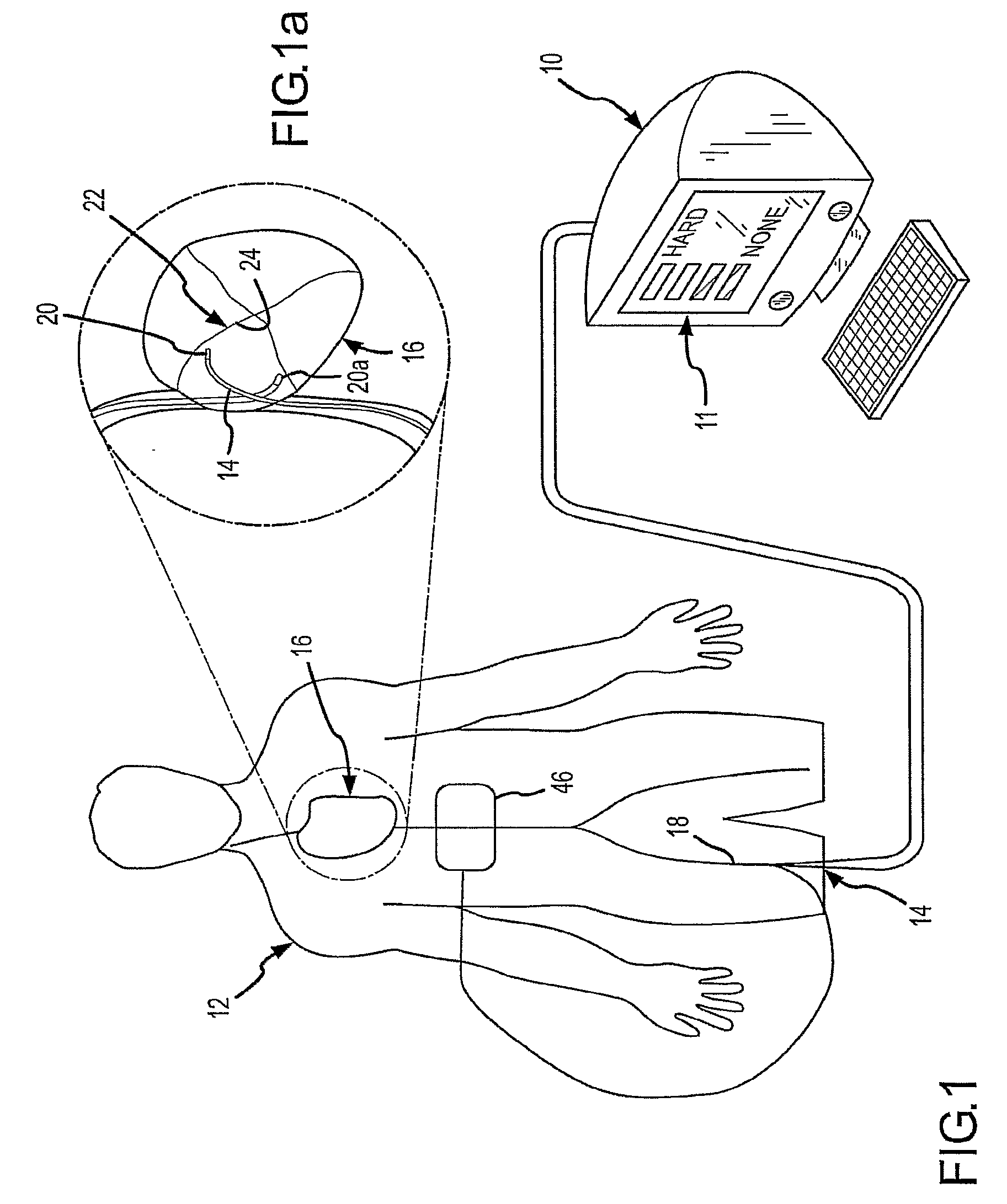
Method and apparatus for controlling contact of biomedical electrodes with patient skin
A method of monitoring the contact of a biomedical electrode to skin of a patient is disclosed, where the phase angle of current flow through one portion of the electrode is compared to the phase angle of current flow through another portion of the electrode. The two portions are both electrical conductors, one having a lossy dielectric surface and the other bare metal. Any monitoring of an electrical interface is possible based on the difference in phase angle. Lift of any portion of the electrode from contact with skin of a patient can be monitored more easily than using conventional Contact Quality Monitoring circuitry and "split plate patient plates."
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Induced power transmission circuit
ActiveUS20100213770A1Efficient transferEasy to calculateMultiple-port networksElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionLoad circuit
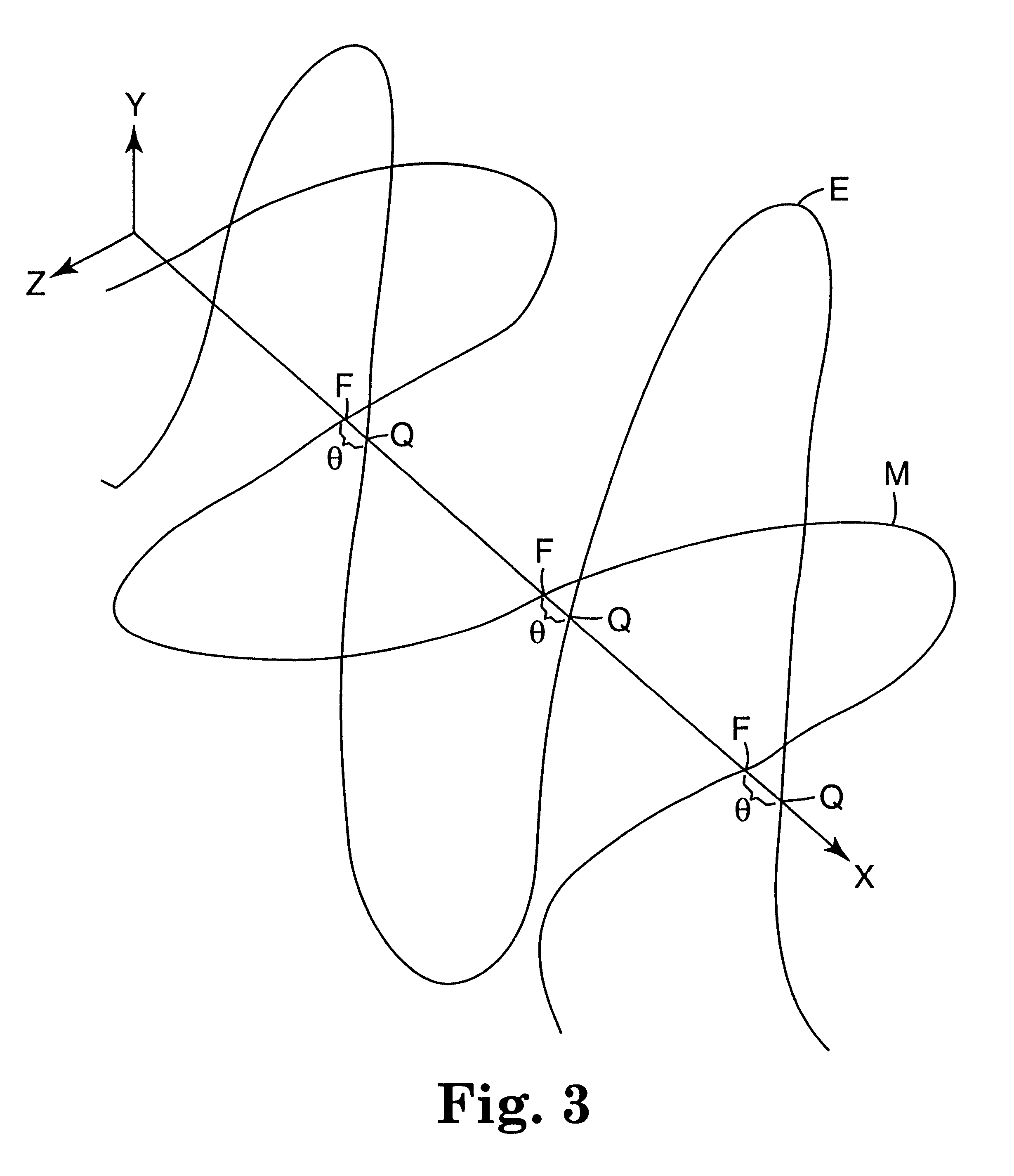
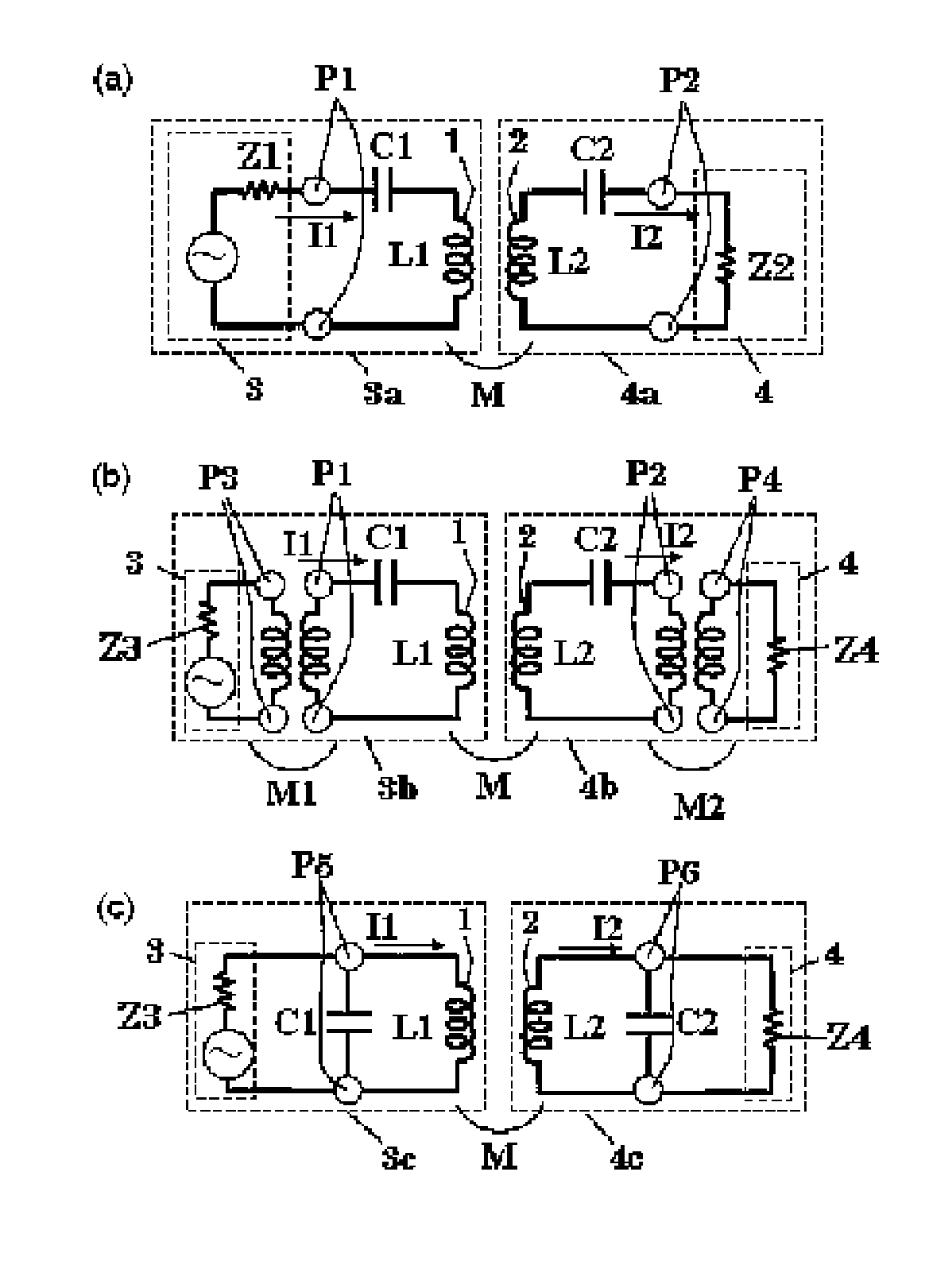
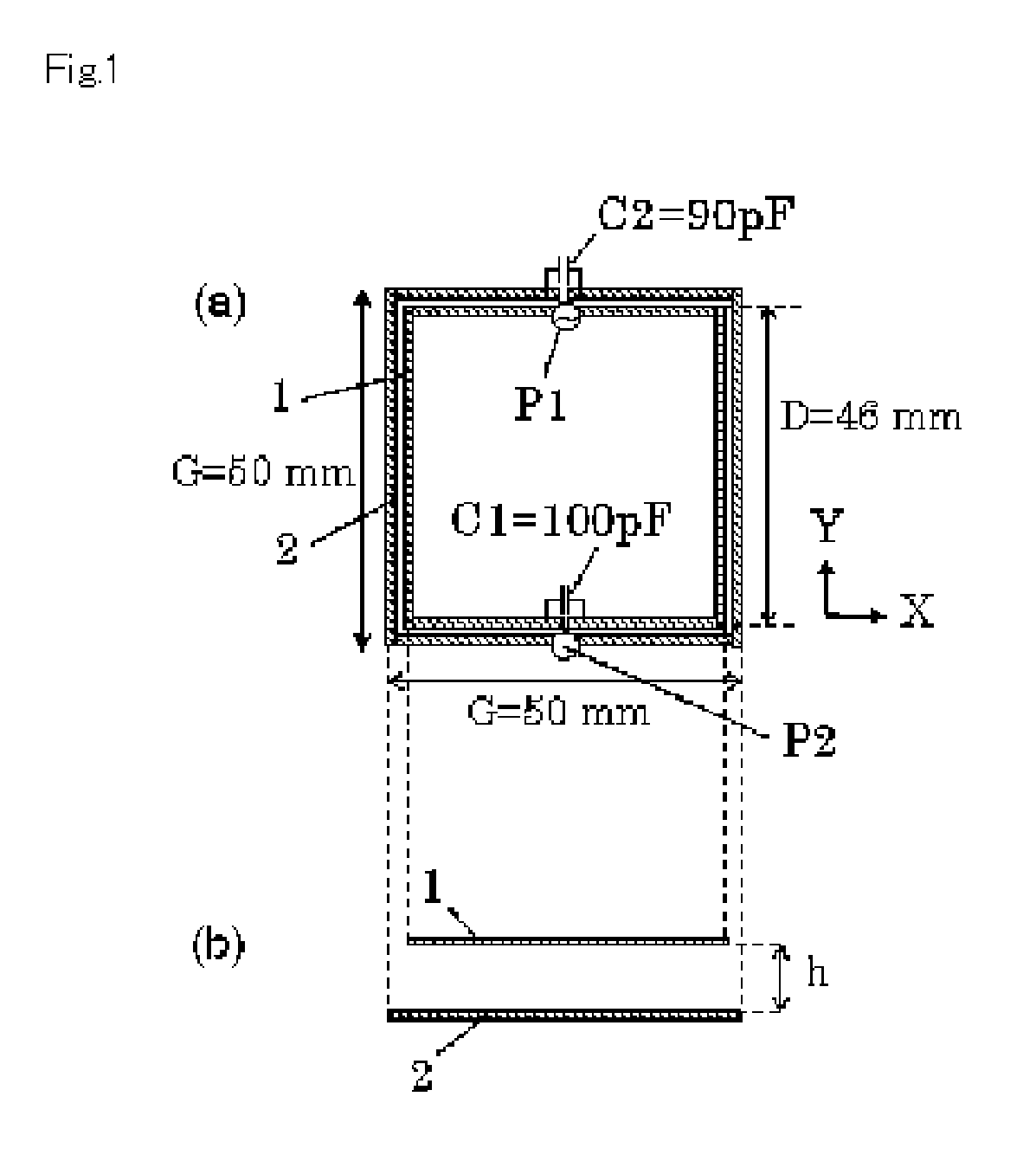
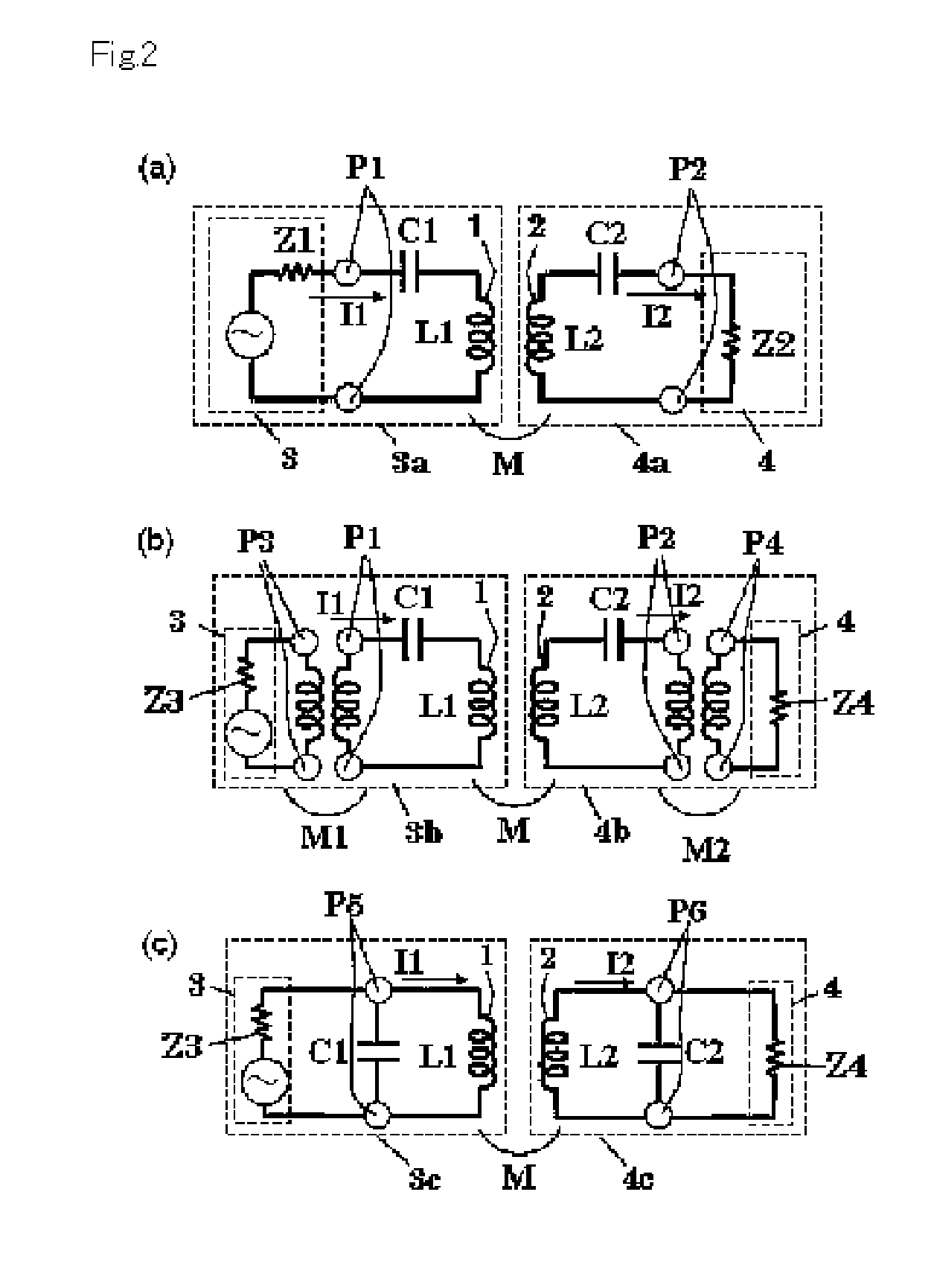
To provide an induced power transmission circuit that transmits, from a transmission antenna (1) connected to a power supply circuit, an AC power having an angular frequency ω to a spaced reception antenna (2) with an excellent efficiency, thereby transmitting it to a load circuit. The induced power transmission circuit comprises a circuit the two ends of which are coupled by a capacitor (C1) and in which the power supply circuit is connected in series to a midway port (1) (P1) of the transmission antenna (1) having an effective self-inductance L1; and a circuit the two ends of which are coupled by a capacitor (C2) and in which the load circuit is connected in series to a midway port (2) (P2) of the reception antenna (2) having an effective self-inductance L2; wherein for a coupling coefficient k of the electromagnetic induction between the antennas and for a phase angle β having an arbitrary value, the angular frequency ω is set to the square root of the reciprocal of a value of L2×C2×(1+k*cos (β)), the output impedance of the power supply circuit is set to approximately kωL1*sin (β), and the input impedance of the load circuit is set to approximately kωL2*sin (β). There is also provided an impedance converting circuit that converts the circuit impedances.
Owner:KIKUCHI HIDEO
Transmission apparatus for remotely indicating position and reception apparatus
InactiveUS20120200399A1High resolutionElectric signal transmission systemsElectric controllersEngineeringTransmitter
A transmitting apparatus and receiving apparatus for indicating a position can be remotely controlled. The transmitting apparatus includes a means for measuring an inclined angle of a transmitter with respect to a gravity axis of the earth to measure and transmit the inclined value of the transmitter in addition to transmitting waveforms having different phase angles and the same frequency simultaneously and the receiving apparatus is configured by a receiving apparatus that receives and ultimately amplifies the transmitted signal and processes the amplified signal so as to acquire positional information regarding a shift of a phase which is shifted from a reference signal.
Owner:CHAE KWANG MUK
Image forming apparatus
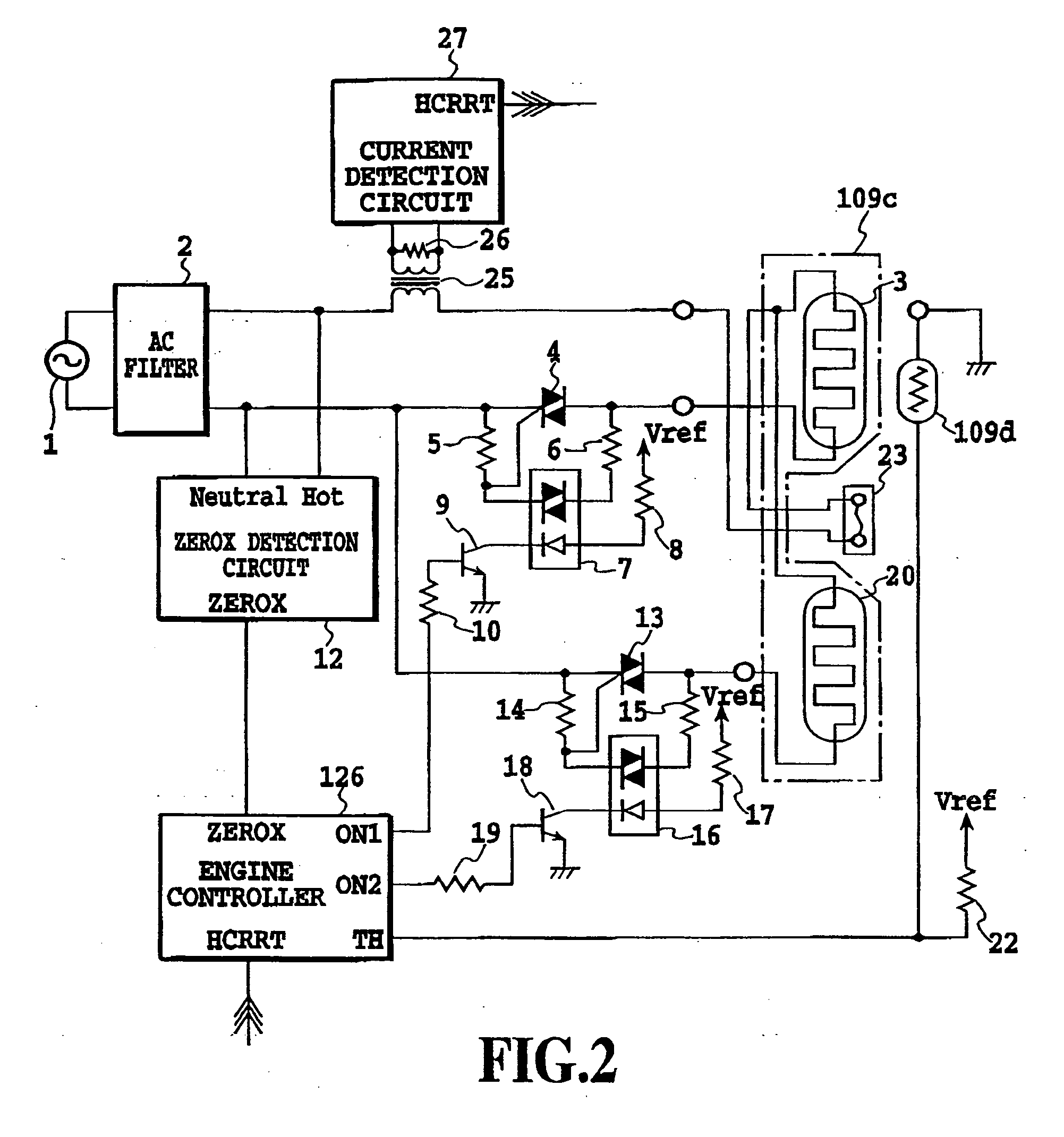
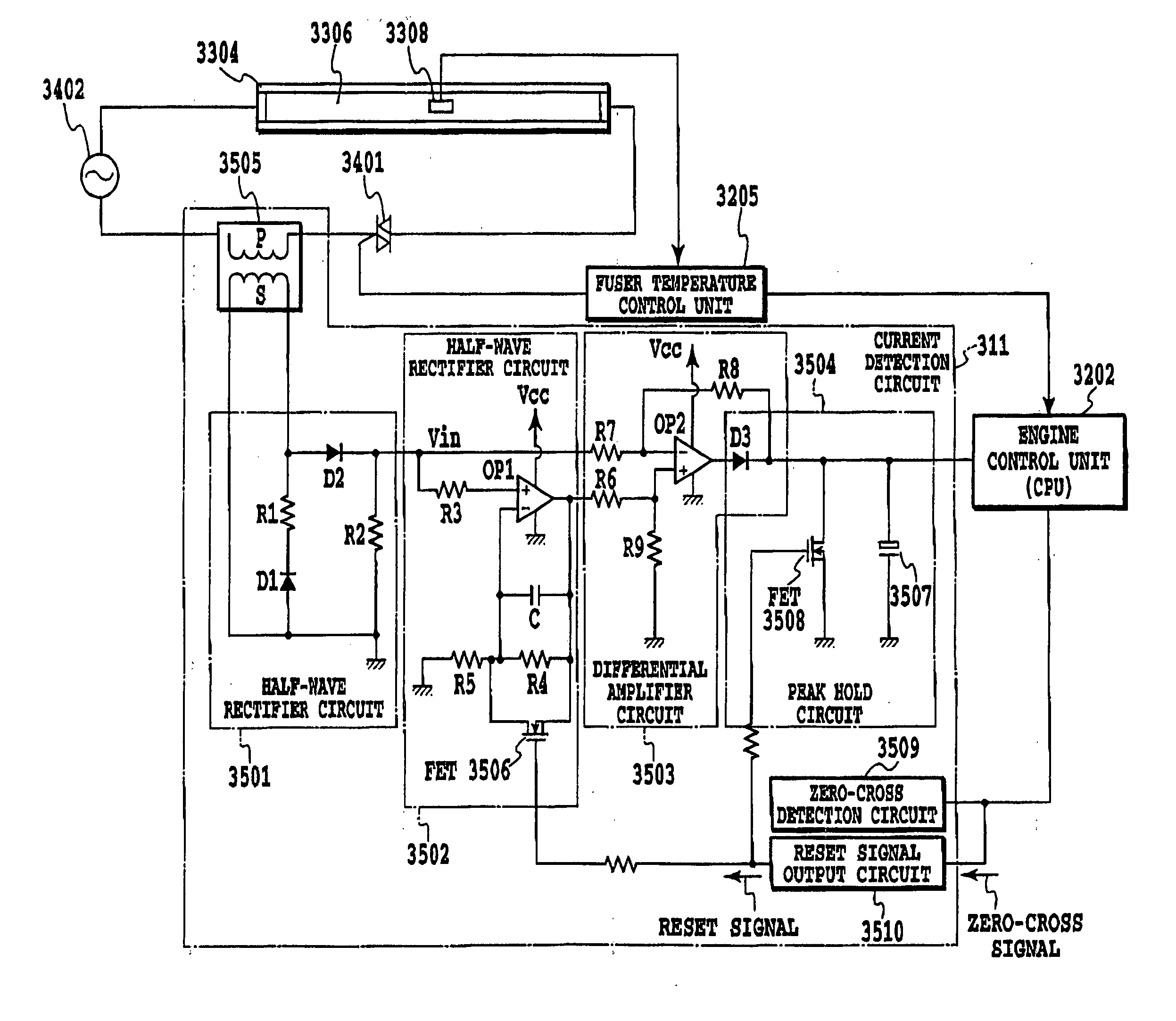
ActiveUS20060078344A1Improve detection accuracyOhmic-resistance heatingElectrographic process apparatusElectricityTemperature control
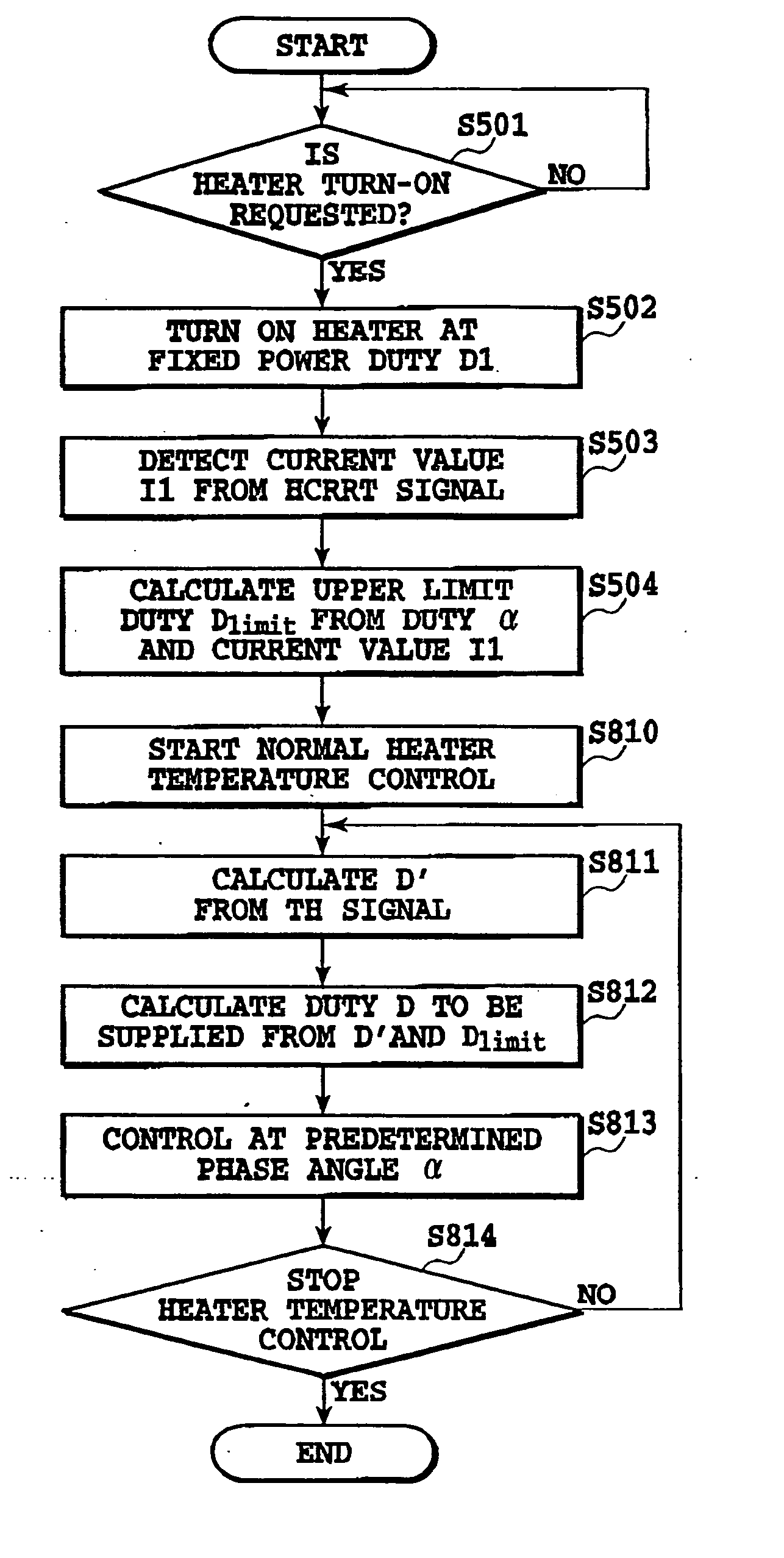
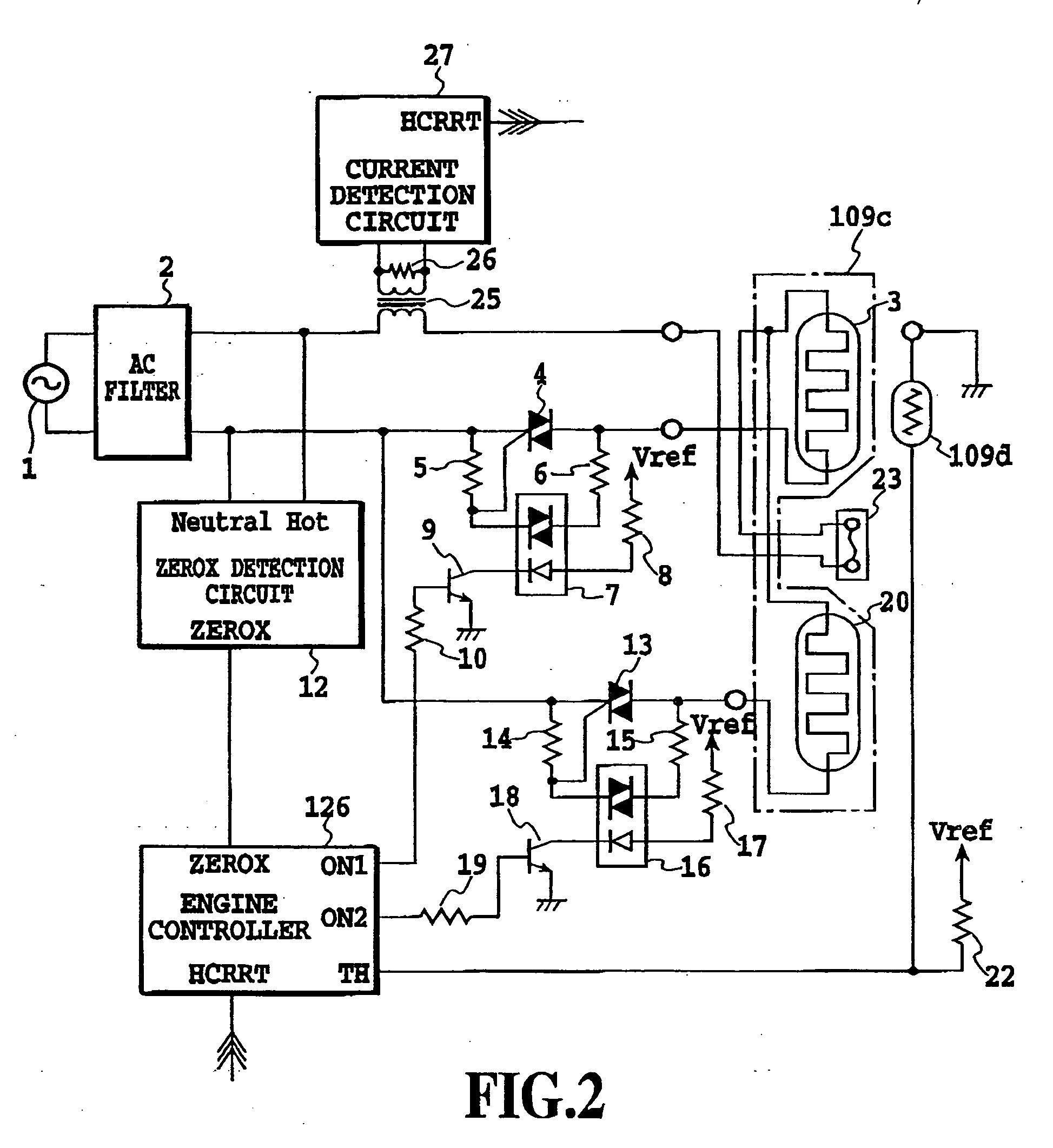
This invention is intended to control the amount of power to be supplied to a fusing heater below a maximum applicable current value. The engine controller supplies electricity to both of two heating bodies at the same fixed duty D1. At a phase angle al corresponding to the fixed duty D1, pulse signals ON1 and ON2 are issued in response to a ZEROX signal as a trigger. A current value I1 is detected based on a HCRRT signal from the current detection circuit. The engine controller calculates an upper limit of applicable power duty Dlimit based on the detected current value I1, the fixed duty D1 and the preset applicable current value Ilimit. Then, a PI temperature control is performed at a duty below the upper-limit duty Dlimit.
Owner:CANON KK
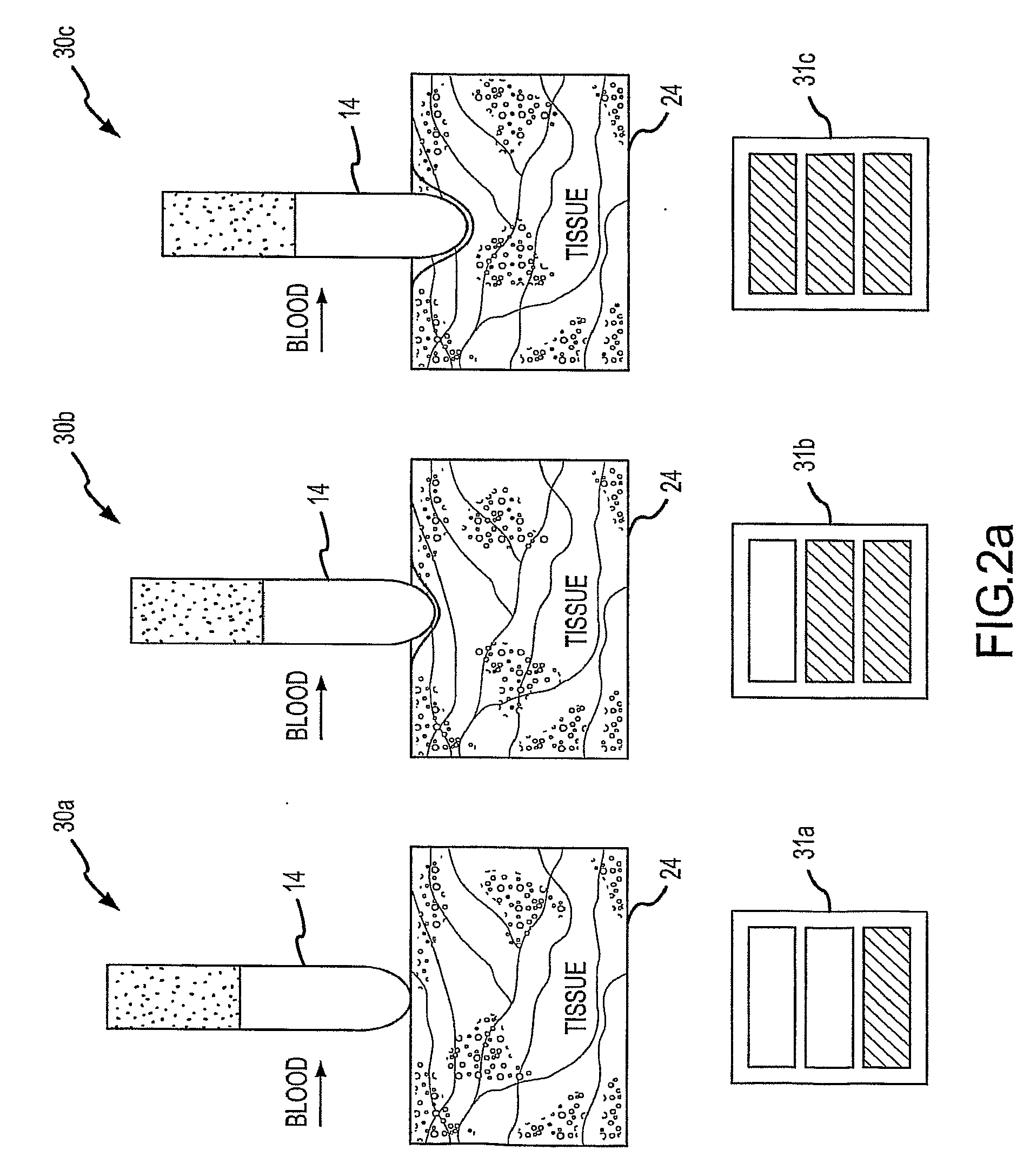
Apparatus and method for assessing transmurality of a tissue ablation
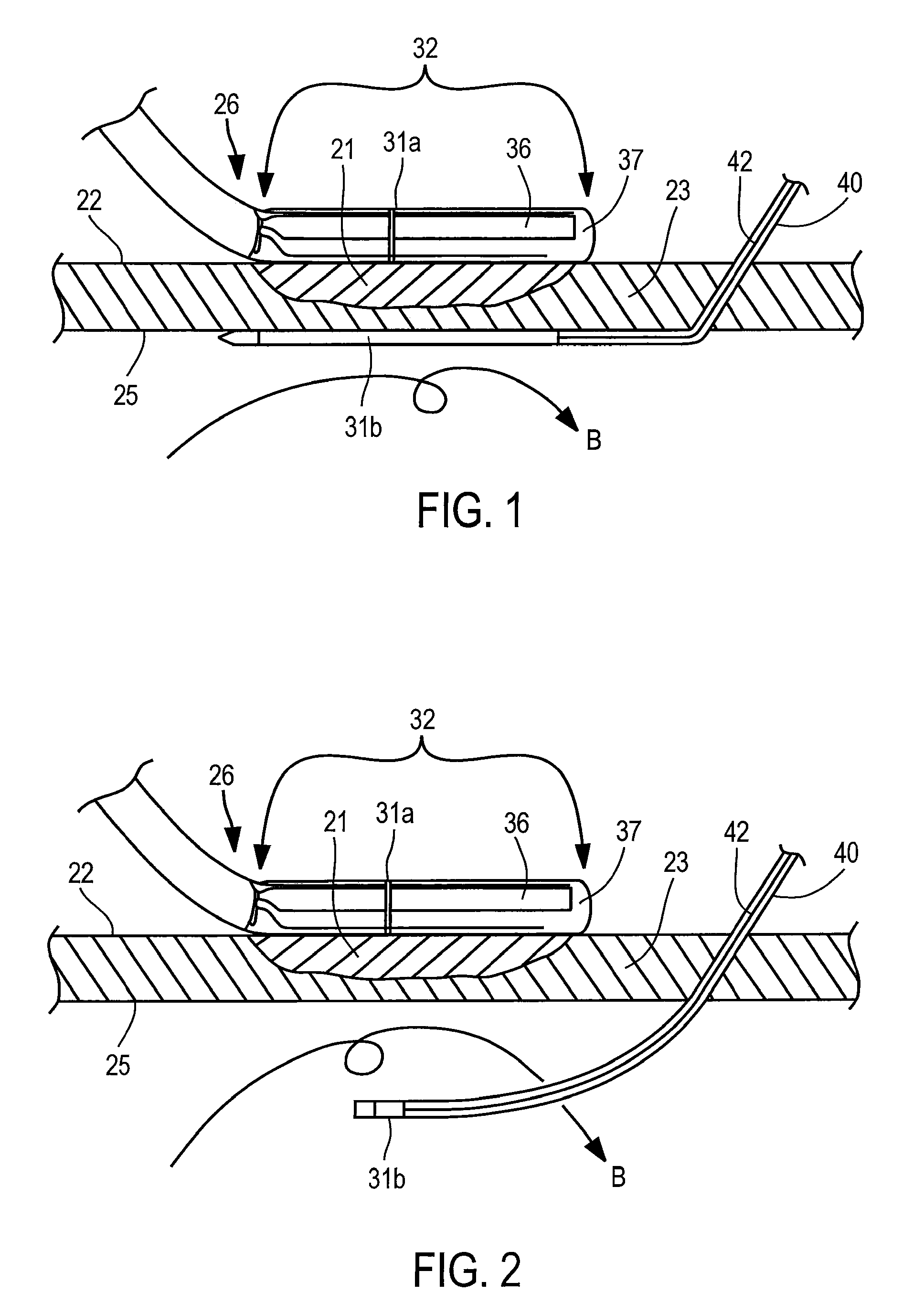
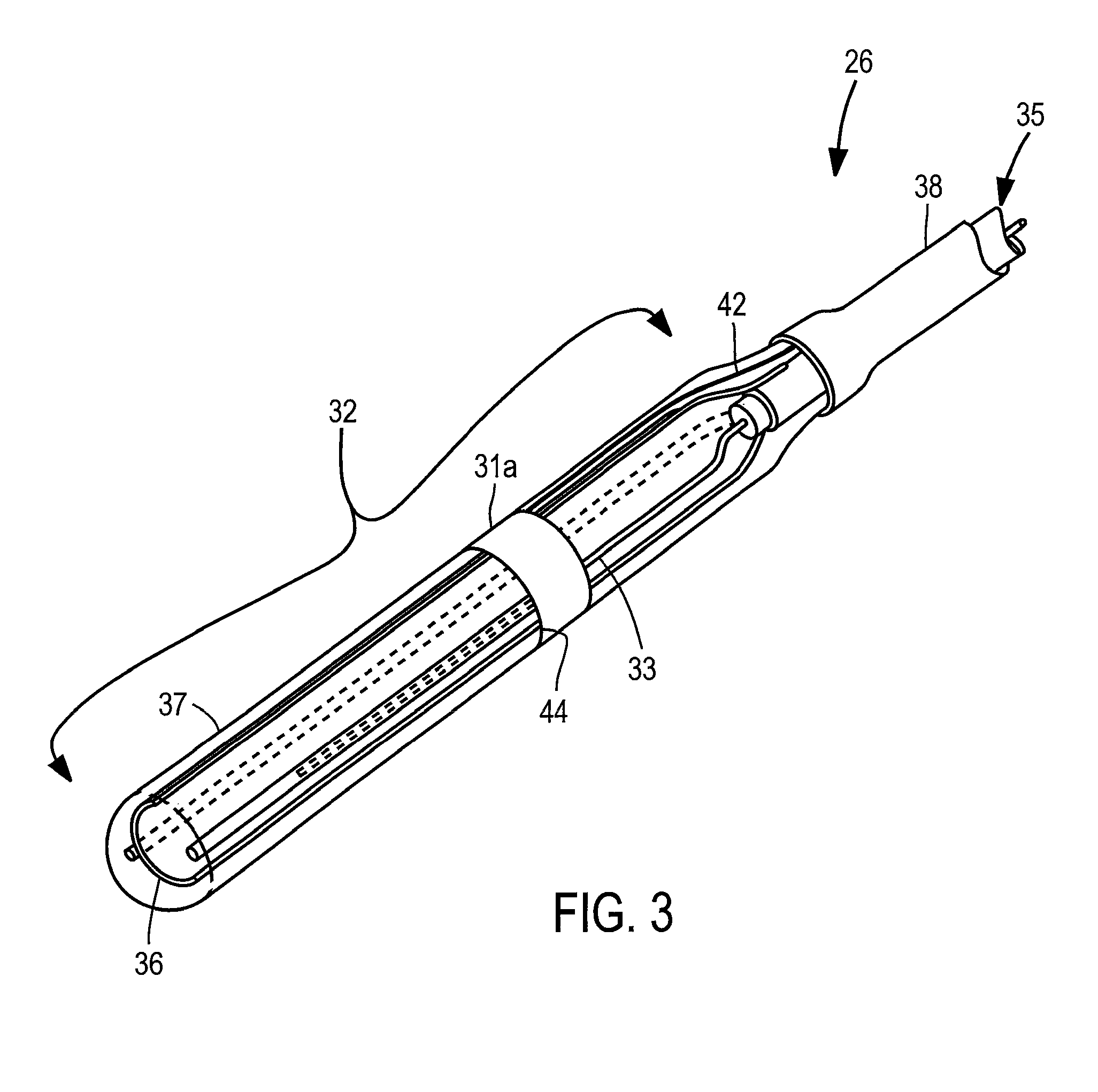
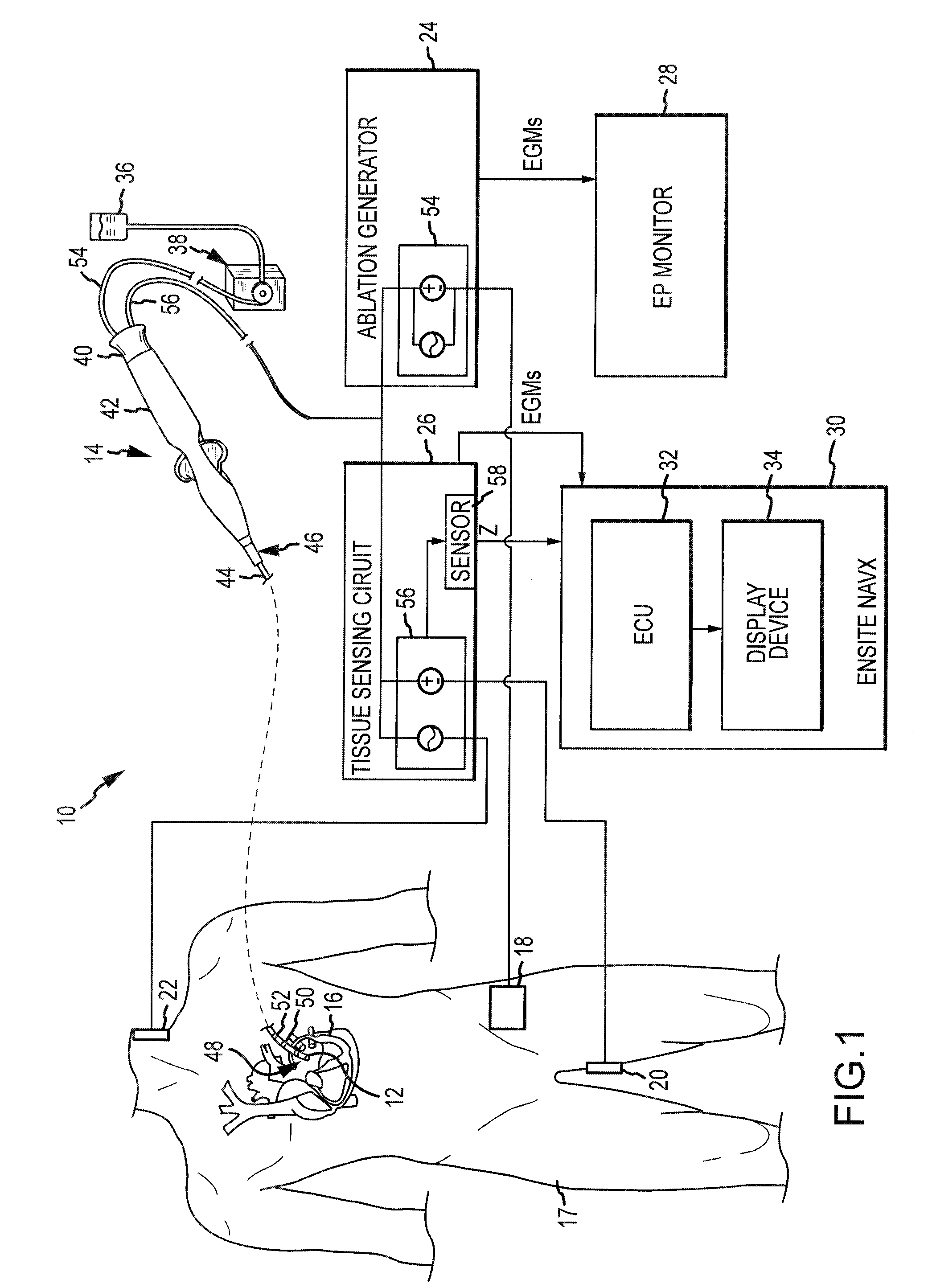
InactiveUS7192427B2Good transmuralityGood signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingConduction timeTissue ablation
An instrument is provided to assess the transmurality of an ablation lesion from a first surface of a targeted biological tissue to an opposed second surface thereof. The instrument includes at least a first electrode operably attached to an ablation instrument adapted to engage a tissue first surface, and at least a second electrode adapted to engage a tissue second surface, the at least second electrode positioned generally opposed to the at least first electrode. Alternatively, the at least second electrode may be adapted to be placed within a chamber of an organ. These electrodes each measure at least one of conduction time, conduction velocity, phase angle, and impedance through at least a portion of the targeted tissue to determine the transmurality of the ablation lesion.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
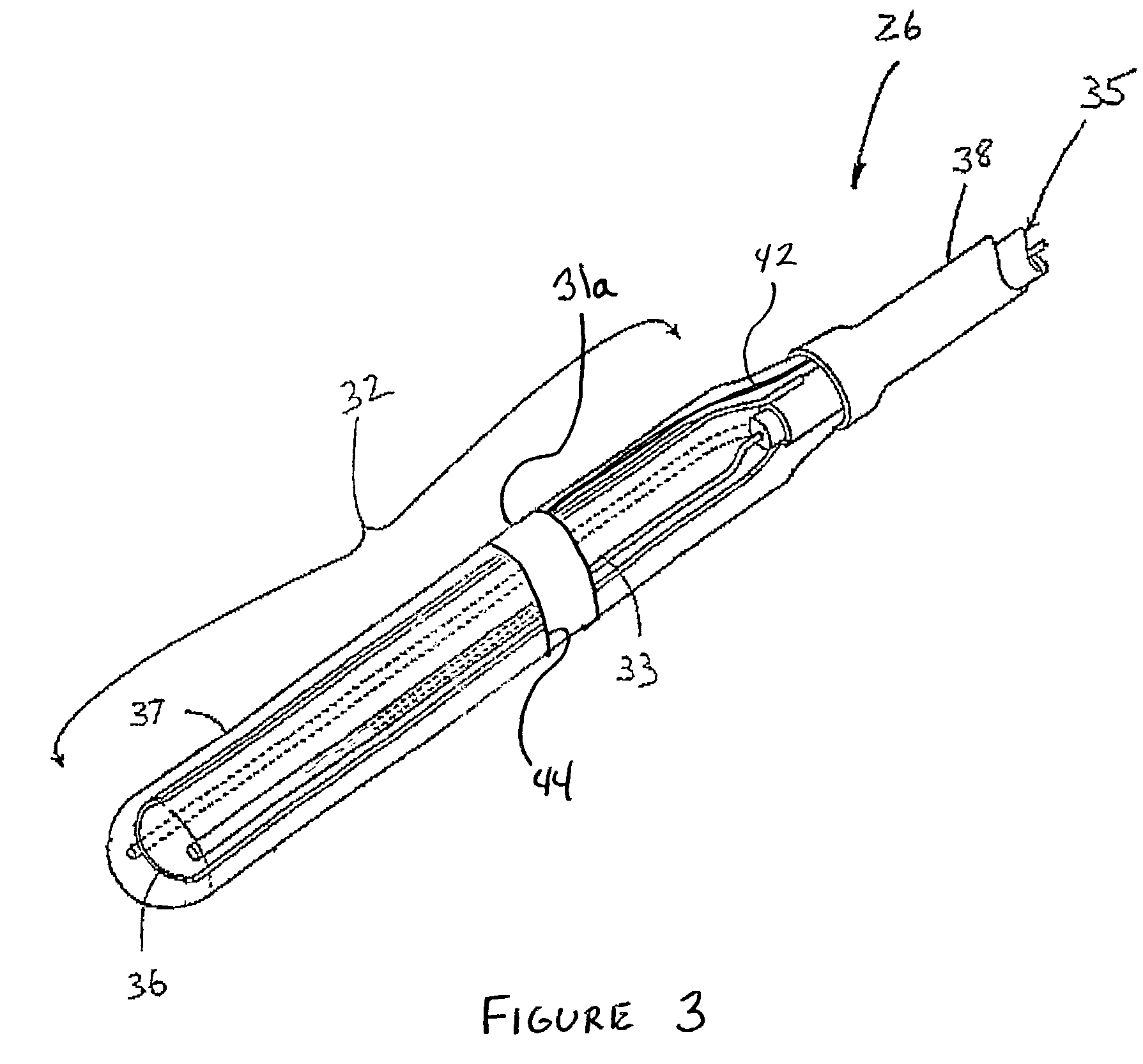
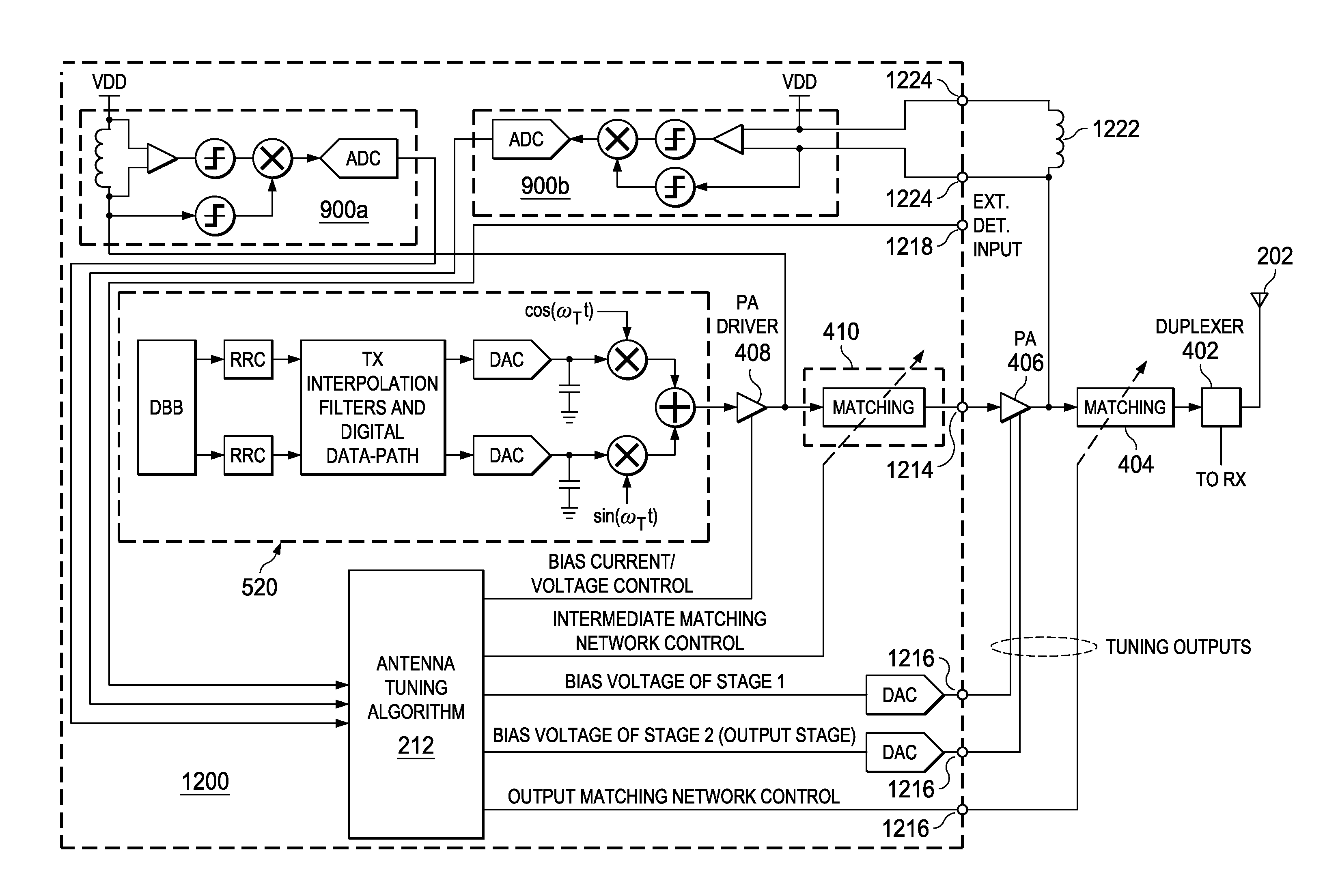
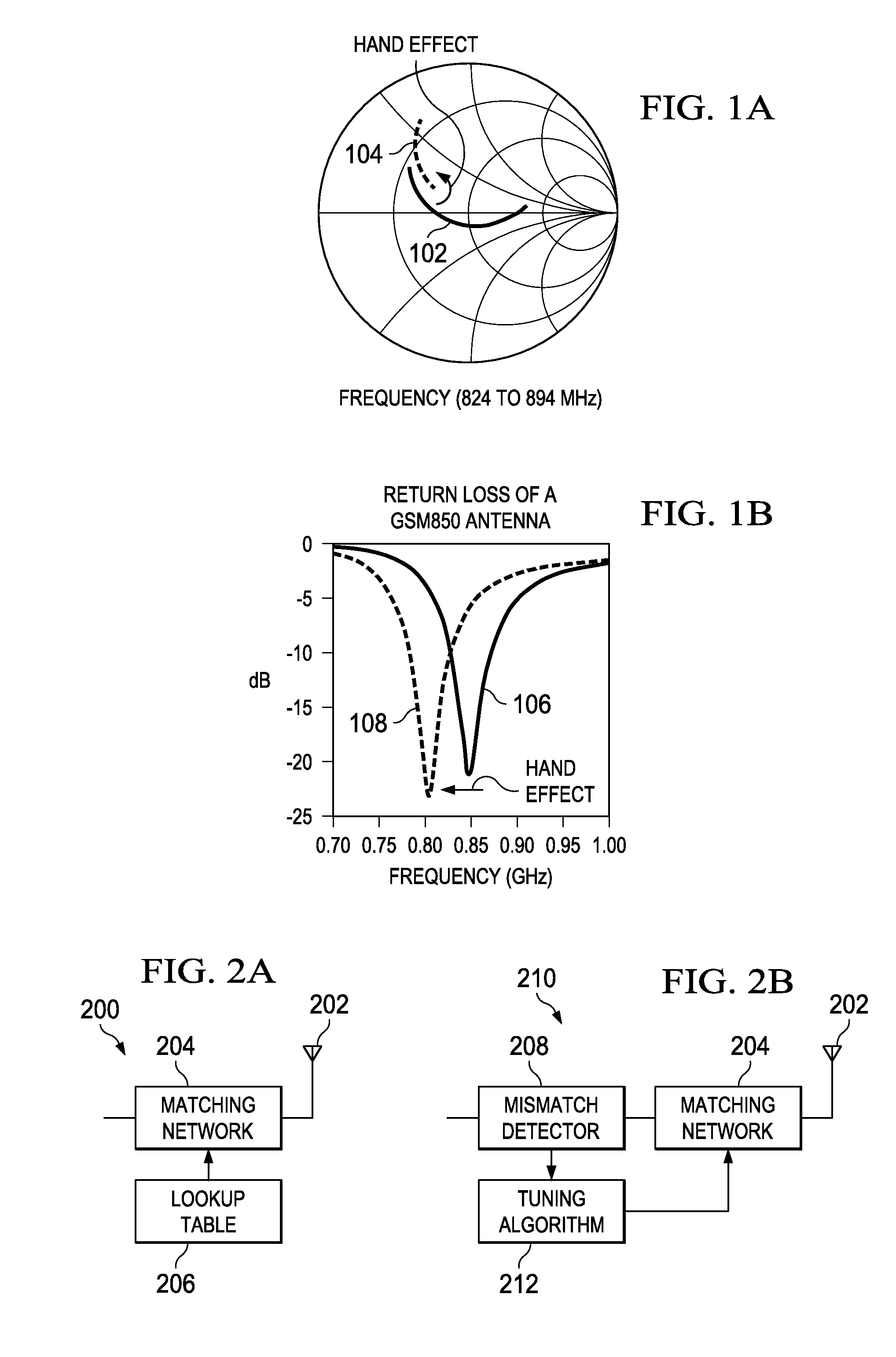
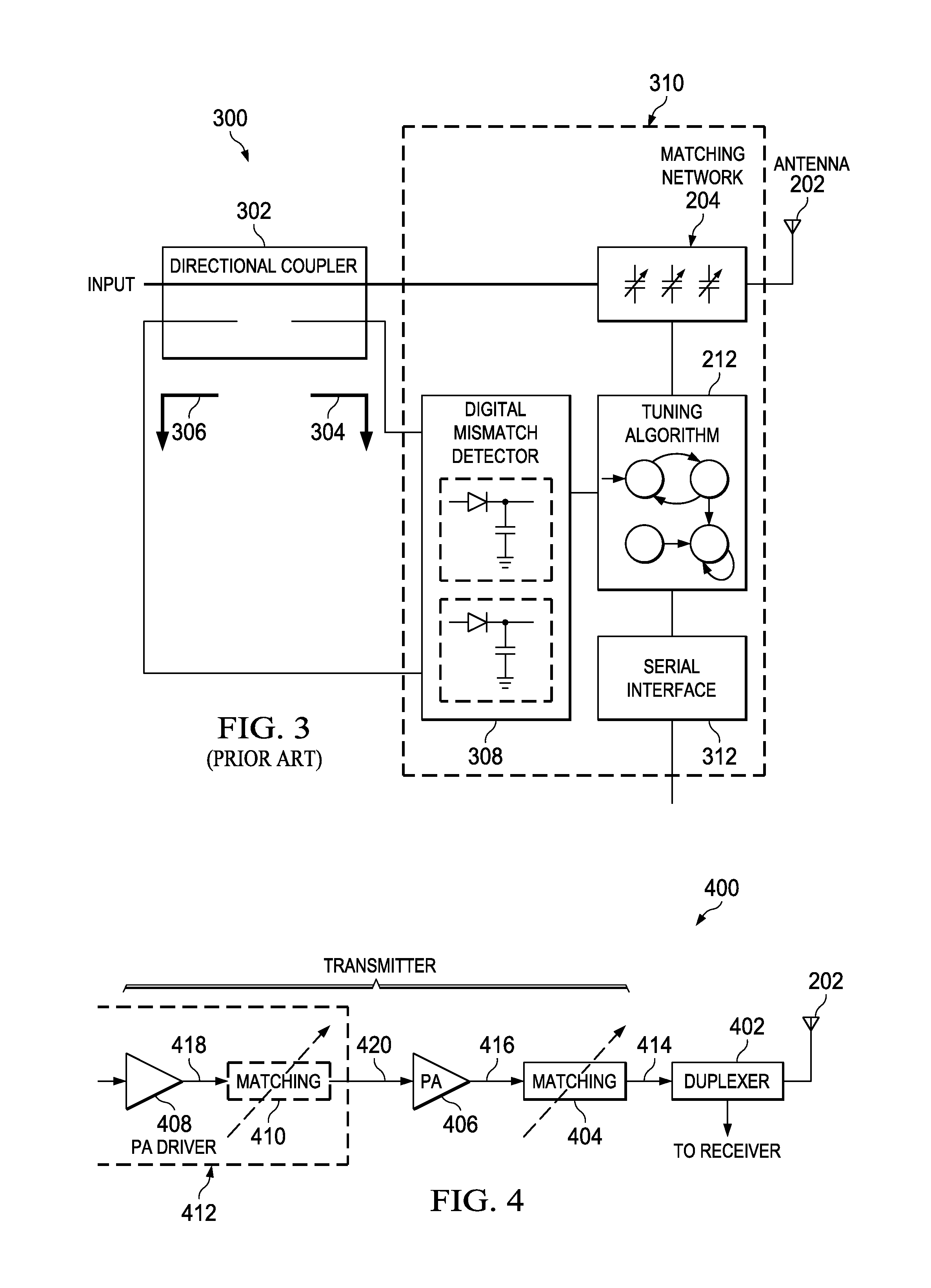
Method and apparatus for antenna tuning
ActiveUS20110086600A1Reduce Impedance MismatchReduce biasResonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsTransceiverOperating point
A method for tuning a transmitter in order to improve impedance matching to an antenna or to intermediate radio frequency stages uses an error detector that senses a deviation of the amplitude or phase angle of a load current of a power amplifier driver or of a power amplifier. A controller calculates a correction and dynamically adjusts tunable transmitter parameters, which may include values of components in matching networks or bias voltages in the power amplifier or the power amplifier driver, so as to reduce the deviation and thereby improve the impedance matching. The load current of the power amplifier may alternatively be sensed by measuring the duty cycle of its switching mode power supply. A transmitter having a power amplifier and one or more tunable circuit elements incorporates an error detector that senses the amplitude or phase of a load current and a controller that adjusts one or more tunable parameters to reduce impedance mismatch. An integrated circuit device suitable for use in a transmitter includes a power amplifier driver circuit and a detector circuit capable of sensing a load current, and a controller circuit that can adjust tunable parameters either within or external to the integrated circuit. By eliminating directional couplers and integrating the detectors and power amplifier drivers, the size, complexity, and cost of wireless transceivers can be reduced, while efficiency and power consumption are improved through the dynamic adjustment of operating points and impedance matching.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
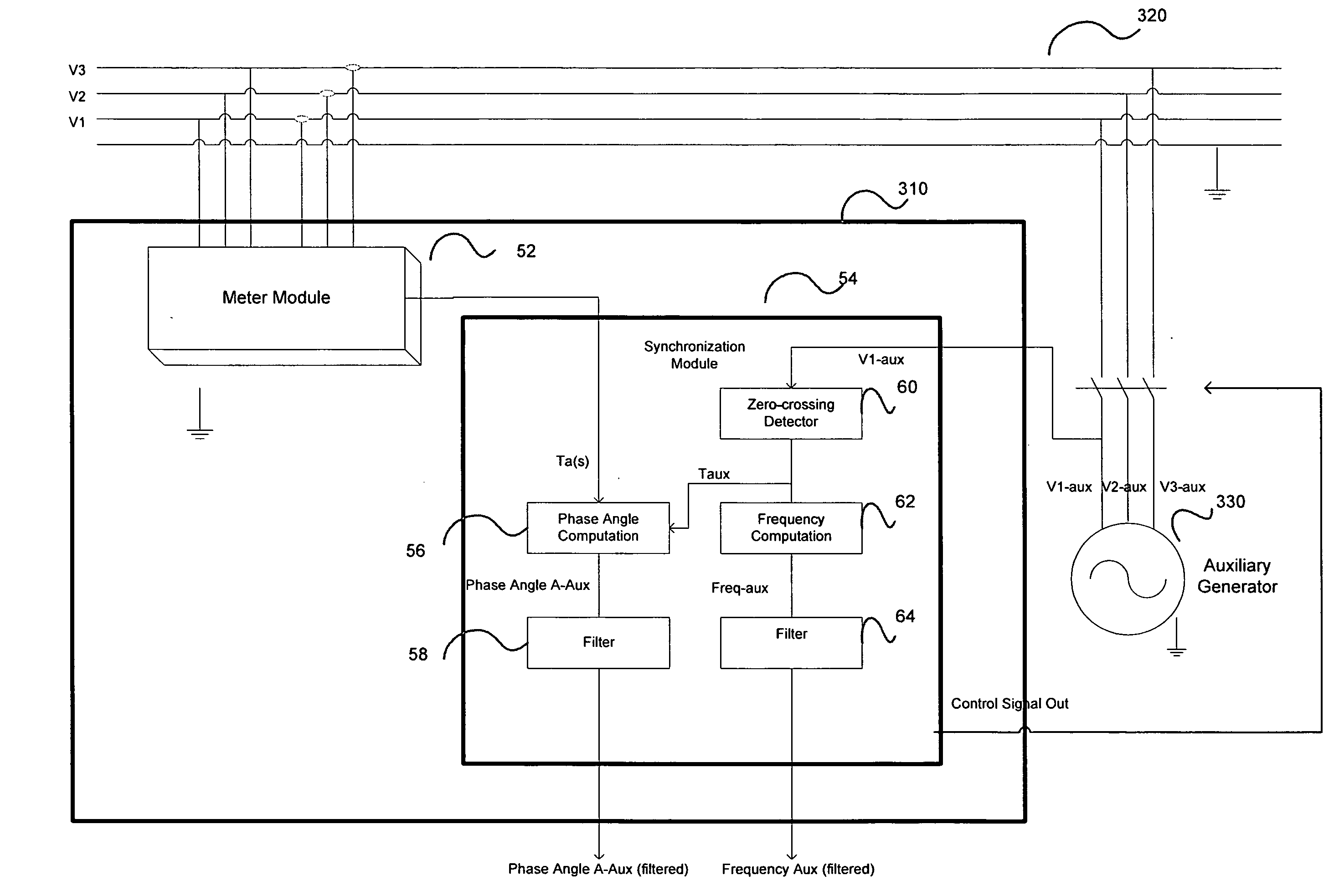
System and method for synchronizing an auxiliary electrical generator to an electrical system
There is provided herein methods and apparatus for apparatus for controlling the interconnection of an auxiliary AC generator with an electrical system, such as an electrical distribution system, e.g., a utility grid. A measuring circuit measures the frequency of an auxiliary AC generator and the phase angle between one voltage phase of the generator and the correspondent voltage phase of the electric utility's electricity supply lines, i.e., the grid, each of which are averaged and filtered. The measured frequency of the auxiliary AC generator is matched to the frequency of the electrical system and the measured phase angle of the generator is matched to the electric utility's electricity supply lines. Once matching is achieved to within a defined tolerance, interconnecting contactors are closed.
Owner:ELECTRO INDUSTRIES GAUGE TECH
Apparatus and method for assessing transmurality of a tissue ablation
InactiveUS7497858B2Good signalGood transmuralityDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingTarget tissueTissue ablation
An instrument assesses the transmurality of an ablation lesion from a first surface of a targeted biological tissue to an opposed second surface thereof. The instrument includes at least a first electrode operably attached to an ablation instrument adapted to engage a tissue first surface, and at least a second electrode adapted to engage a tissue second surface, the at least second electrode positioned generally opposed to the at least first electrode. Alternatively, the at least second electrode may be adapted to be placed within a chamber of an organ. These electrodes facilitate measuring at least one of conduction time, conduction velocity, phase angle, and impedance through at least a portion of the targeted tissue to determine the transmurality of the ablation lesion.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060051122A1Improve detection accuracyDc-dc conversionElectric light circuit arrangementTemperature controlElectricity
This invention is intended to control the amount of power to be supplied to a fusing heater below a maximum applicable current value. The engine controller supplies electricity to both of two heating bodies at the same fixed duty D1. At a phase angle α1 corresponding to the fixed duty D1, pulse signals ON1 and ON2 are issued in response to a ZEROX signal as a trigger. A current value I1 is detected based on a HCRRT signal from the current detection circuit. The engine controller calculates an upper limit of applicable power duty Dlimit based on the detected current value I1, the fixed duty D1 and the preset applicable current value Ilimit. Then, a PI temperature control is performed at a duty below the upper limit duty Dlimit.
Owner:CANON KK
Apparatus and Method for Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis
ActiveUS20130282084A1Big vessel lumenIncrease blood flowSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyInsertion stentCatheter
A catheter and catheter system can use energy tailored for remodeling and / or removal of target material proximate to a body lumen, often of stenotic material or tissue in the luminal wall of a blood vessel of a patient. An elongate flexible catheter body with a radially expandable structure may have a plurality of electrodes or other electrosurgical energy delivery surfaces to radially engage the luminal wall when the structure expands. Feedback using one or parameters of voltage, current, power, temperature, impedance magnitude, impedance phase angle, and frequency may be used to selectively control the delivery of energy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Distance/ranging determination using relative phase data
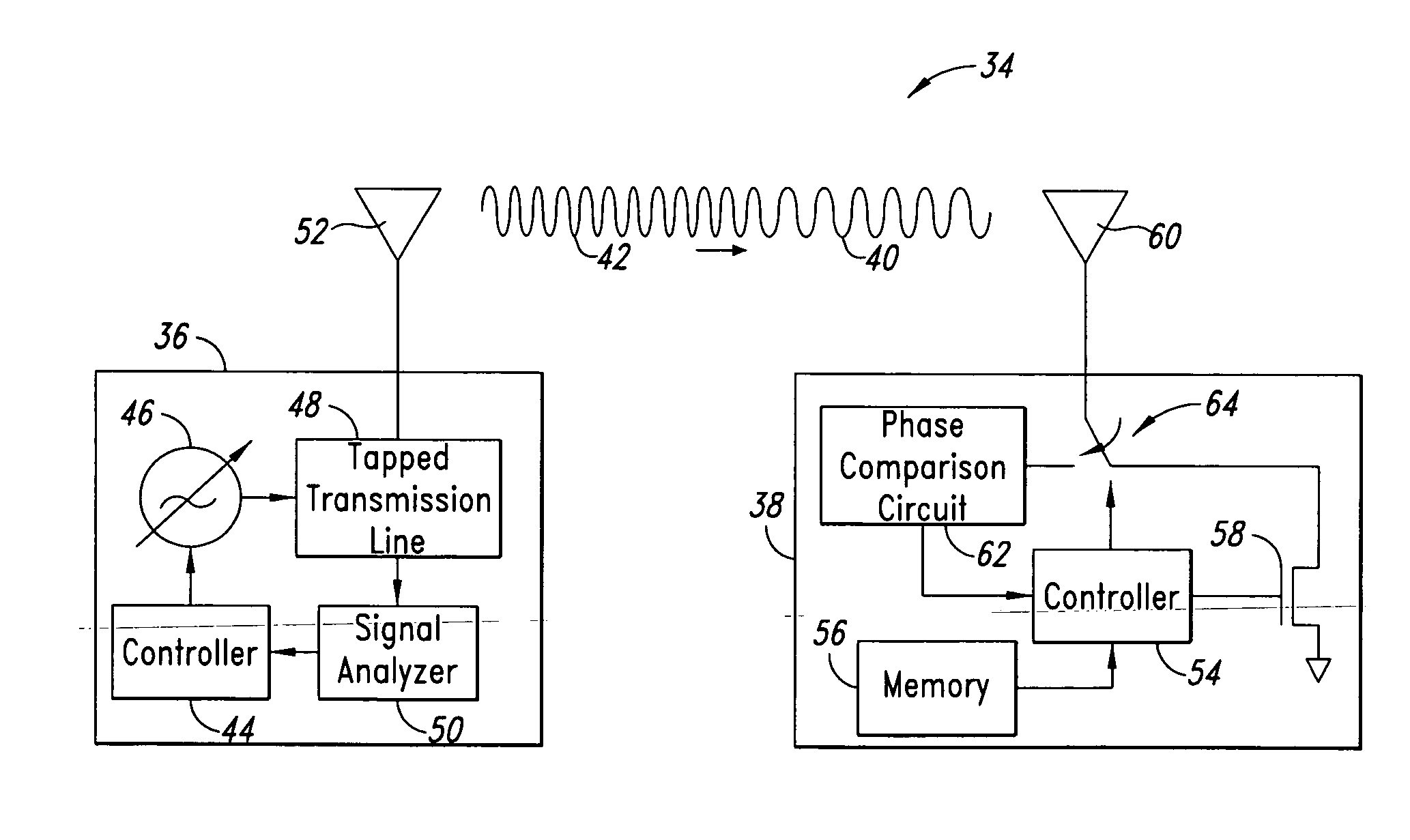
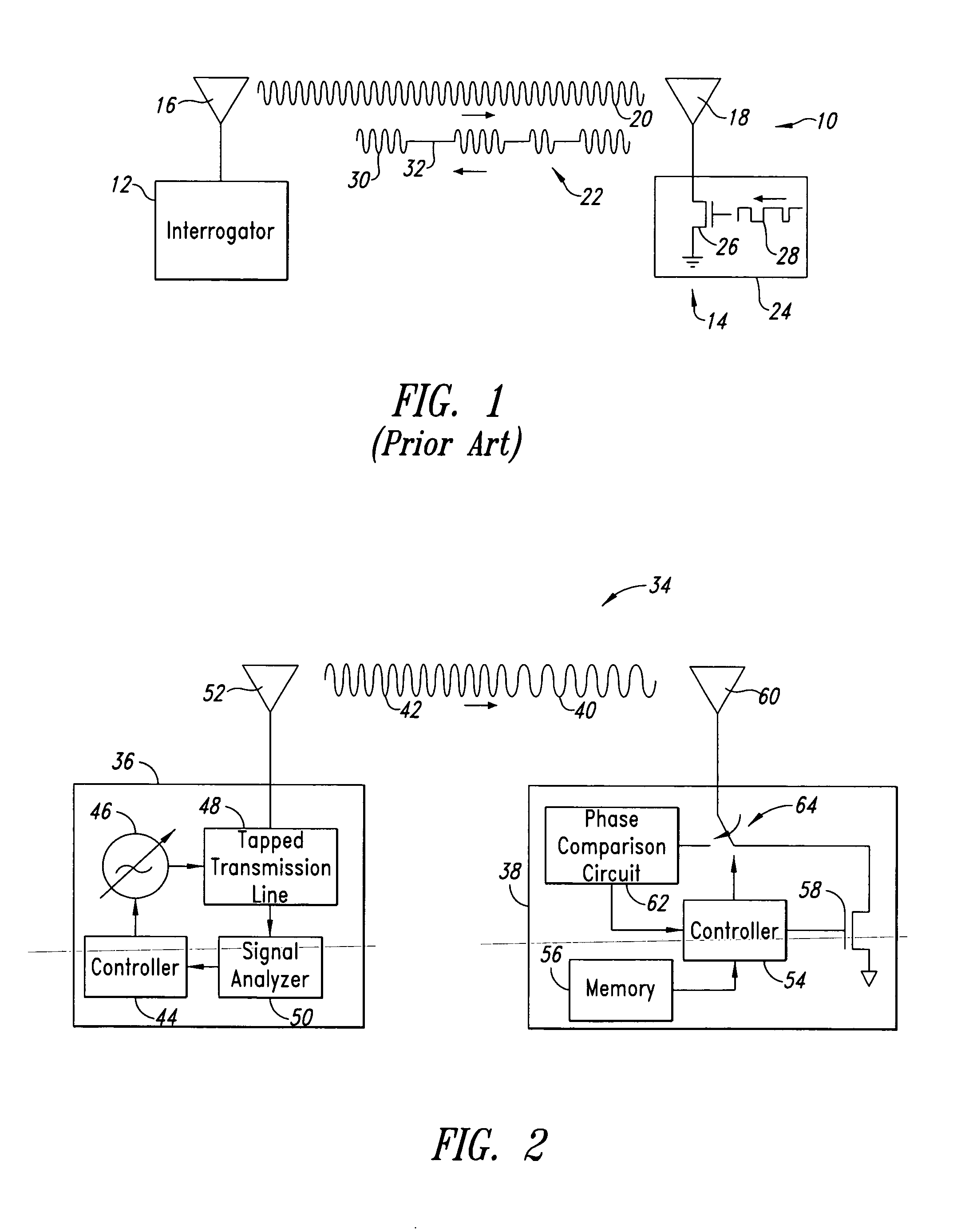
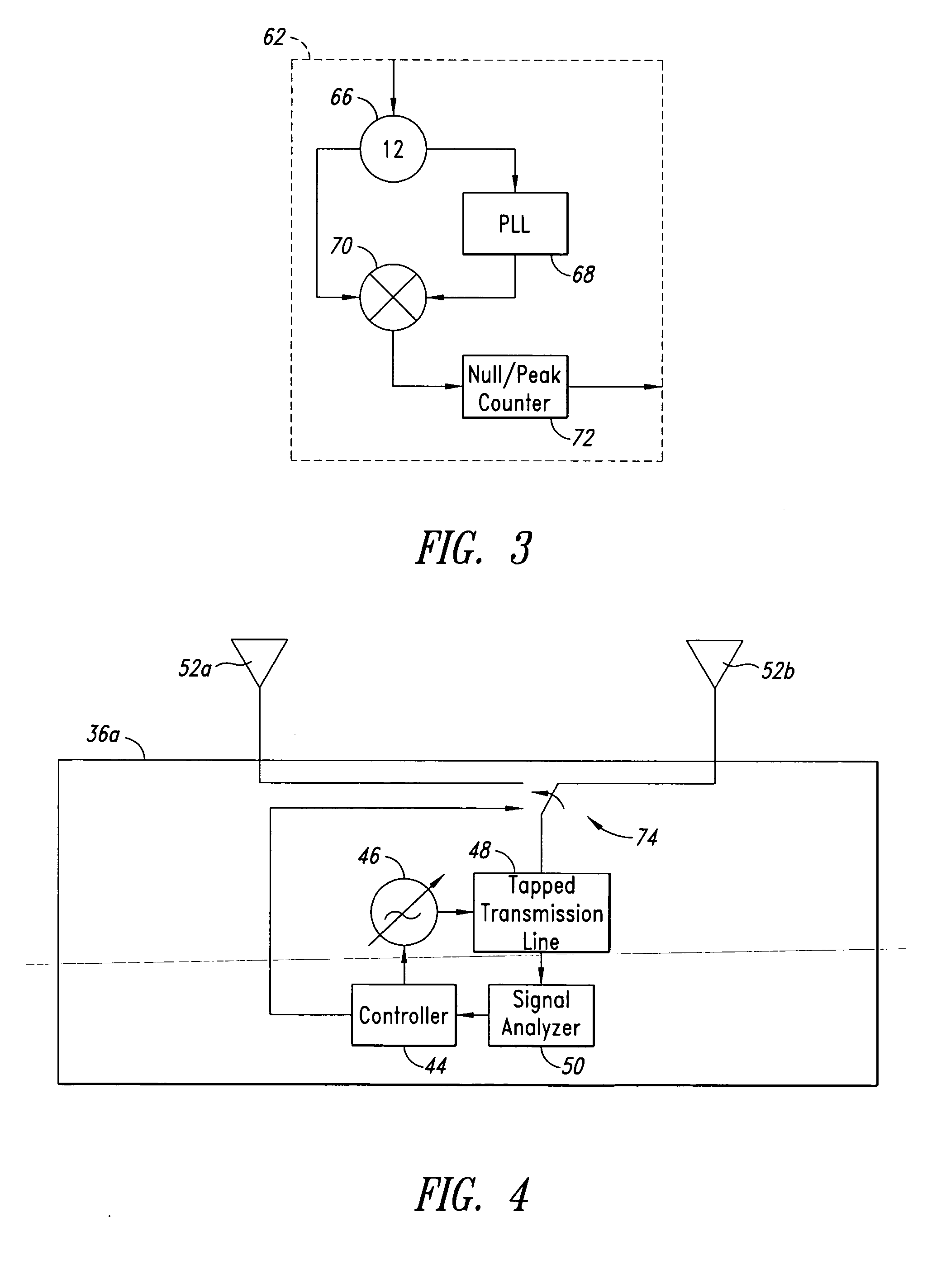
InactiveUS20050237953A1Transmission control/equalisingPosition fixationRelative phasePhase difference
A method and system for locating an RF transponder based on phase differences between signals received from the RF transponder. The method includes receiving a signal from the transponder and calculating distance, relative movement, and position by comparing I-Q phase angle vectors of the signals. Global scroll commands can be used following receipt of signals at first and second frequencies to quickly determine distance.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
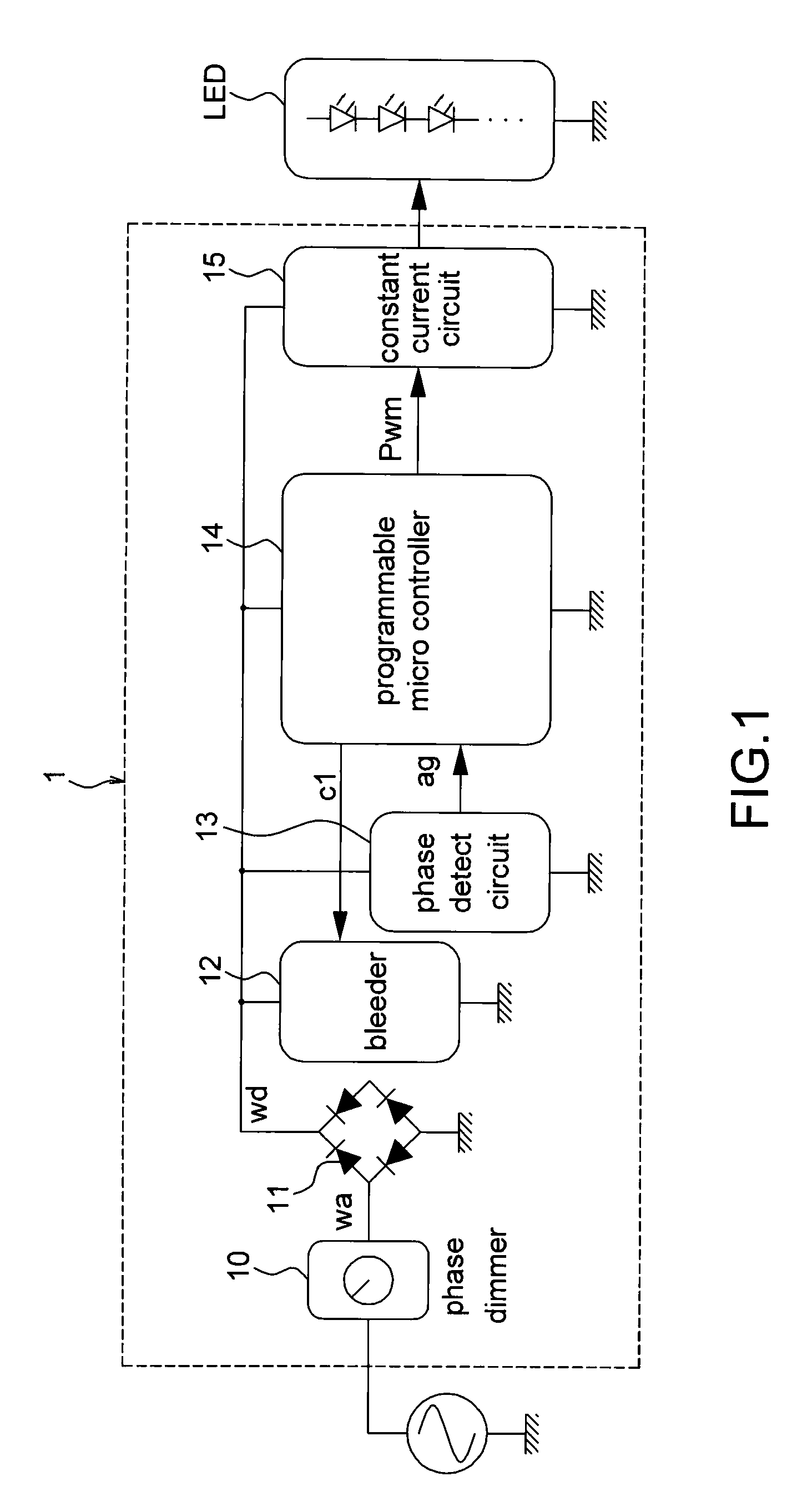
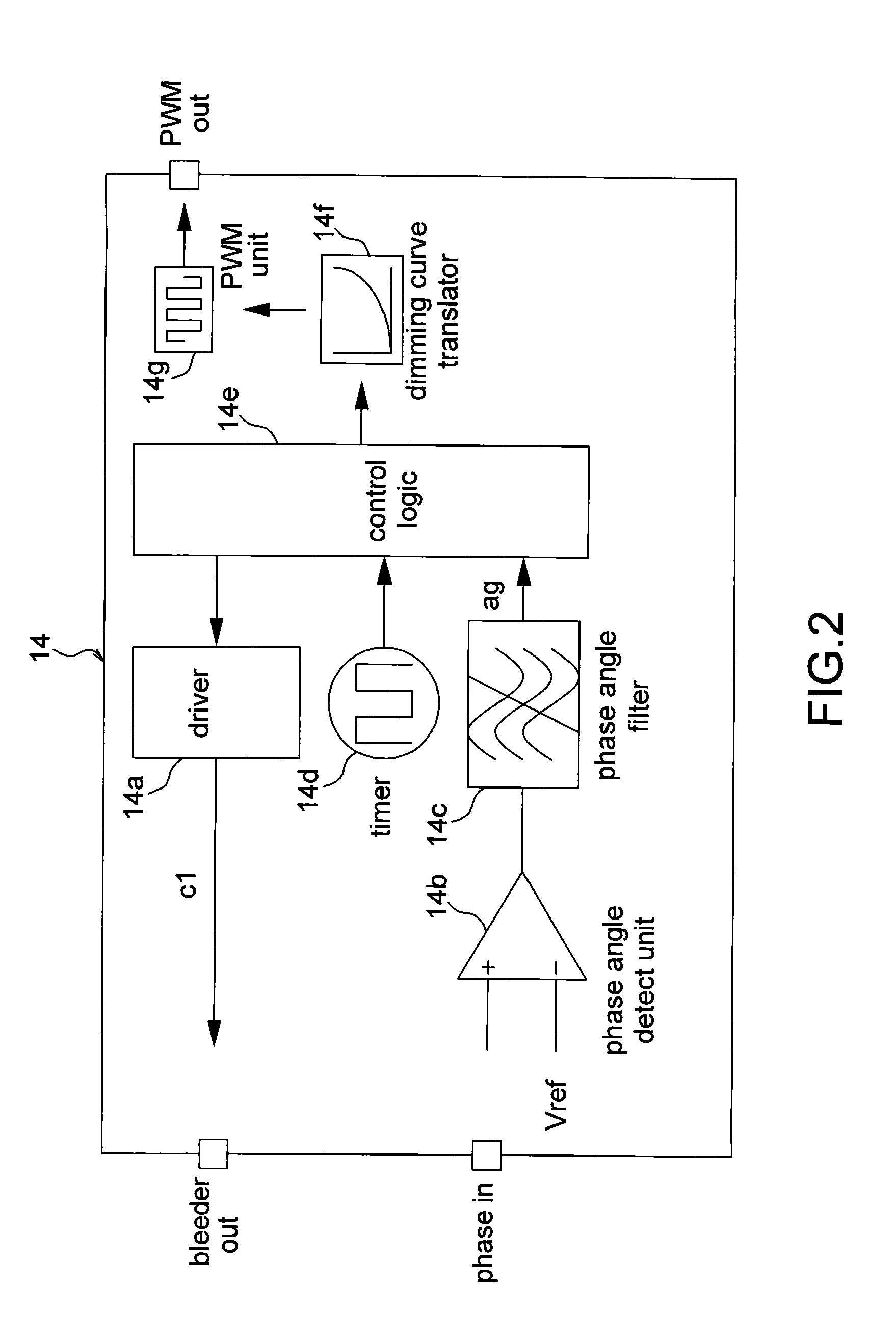
Dimmer circuit applicable for LED device and control method thereof
InactiveUS20110291583A1Improve efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesProgrammable logic controllerProgrammable Interrupt Controller
A dimmer circuit applicable for LED device and control method thereof is disclosed in the embodiments of the present invention. The dimmer circuit is applicable for controlling at least a LED device. The dimmer circuit includes a rectifier, a bleeder, a phase angle detect circuit, a constant current circuit and a programmable micro controller. The phase angle detect circuit couples to the programmable micro controller. The constant current circuit couples to the LED device The programmable micro controller generates a PWM signal according to the output signal of the phase angle detect circuit to adjust current of the constant current circuit.
Owner:UNITED POWER RES TECH CORP
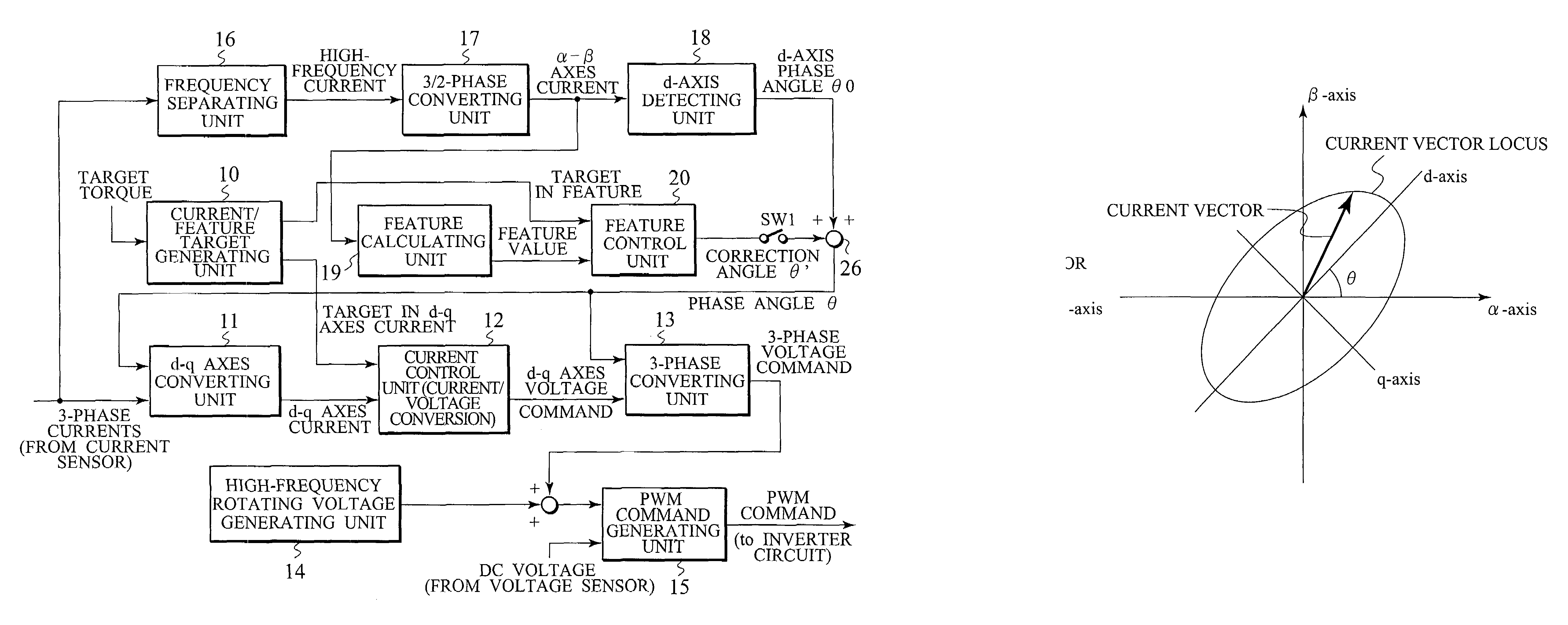
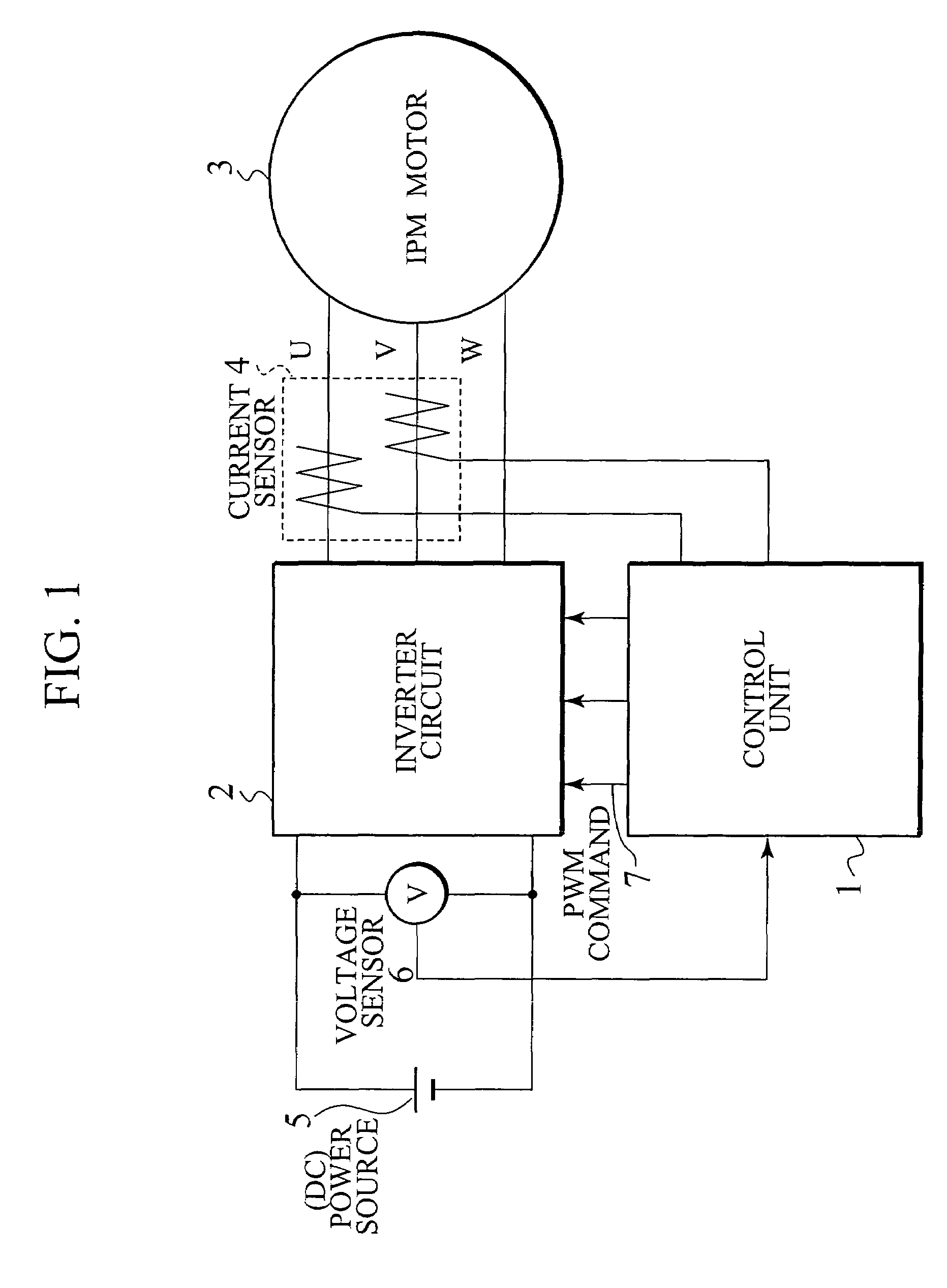
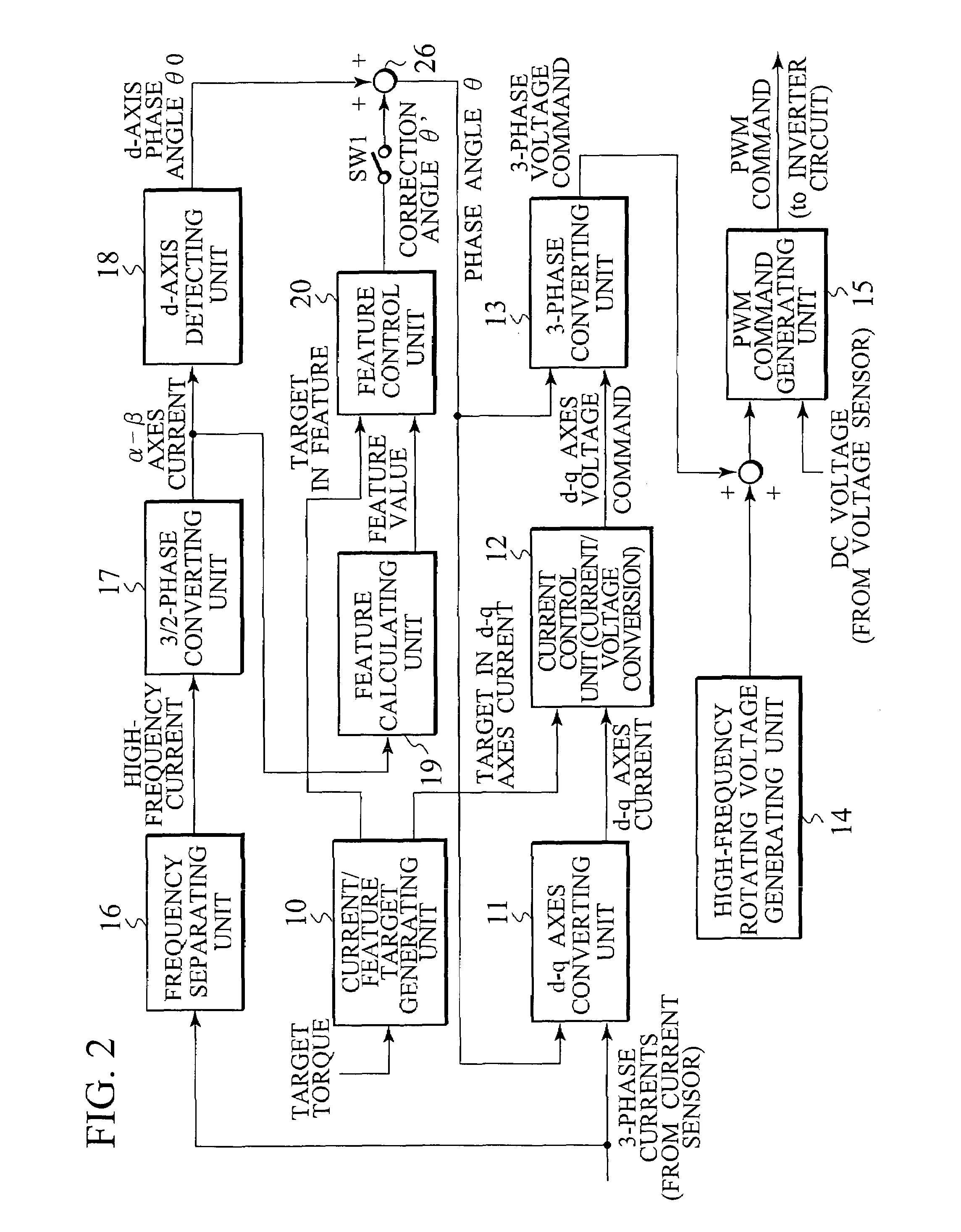
Control device for electric motor
ActiveUS7005828B2Improve artSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlDriving currentAcquired characteristic
Corresponding to a target torque, the control device calculates a target value of a feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus and the length of the short axis and further superimposes a superimposed current on a drive current for the motor, the superimposed current having a frequency different from the frequency of the drive current. Further, the control device detects an actual value of the feature based on at least one of the length of a long axis of a current vector locus of the superimposed current and the length of the short axis of the same and finally detects a phase angle of the motor based on the target value and the actual value for the feature. The manipulation of a detecting phase is performed by feedback of a feature obtained by the magnitude of the superimposed current. That is, when the actual feature is more than the target value, the detecting phase is advanced. Conversely, when the actual feature is less than the target value, the detecting phase is delayed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
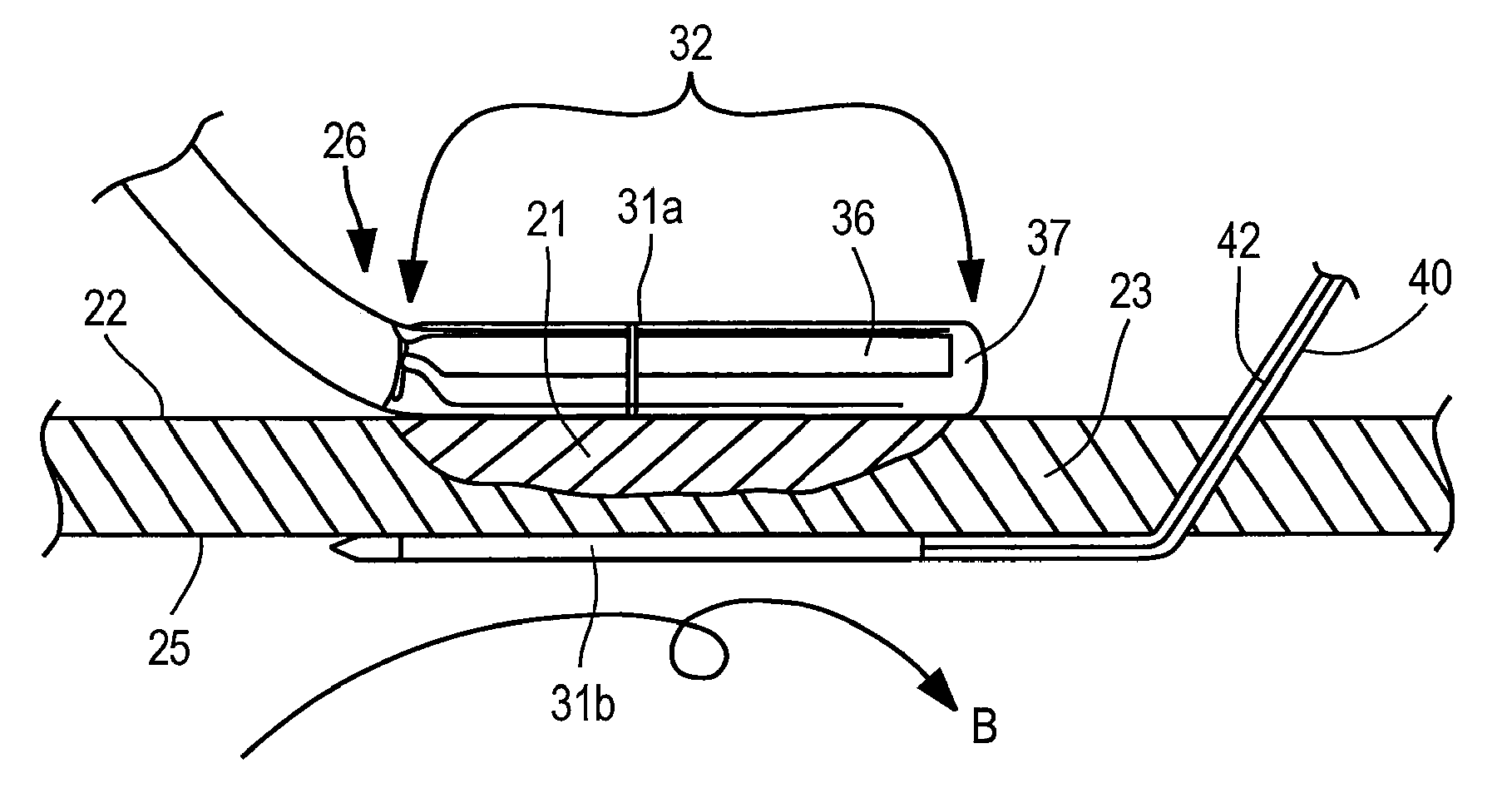
Ablation Device with Sensor
InactiveUS20140194864A1ElectrocardiographySurgical instruments for heatingElectricityConduction time
An electrosurgical device having a distal tip for creating a lesion on tissue includes a first electrode and a second electrode that are parallel for the delivery of RF energy to tissue. A sensor electrode is provided parallel to and spaced away from the first electrode a different distance than the second electrode. When the sensor electrode and at least one of the first and second electrodes are in contact with tissue. The electrosurgical device can perform at least one of the following: ablating tissue, and sensing at least one selected from the group of voltage, tissue impedance, electrical conduction, conduction time, conduction velocity, and signal phase angle.
Owner:ATRICURE
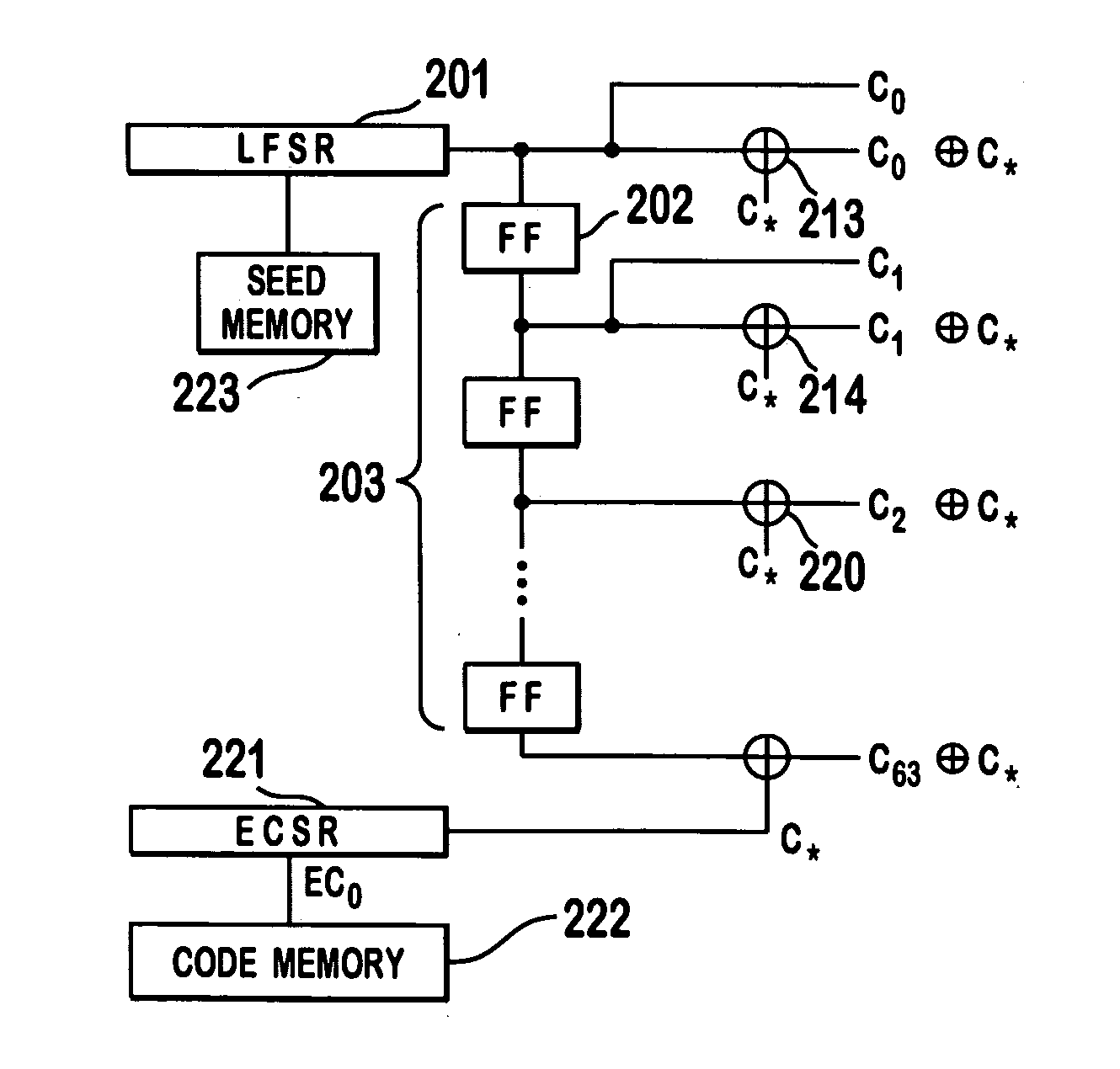
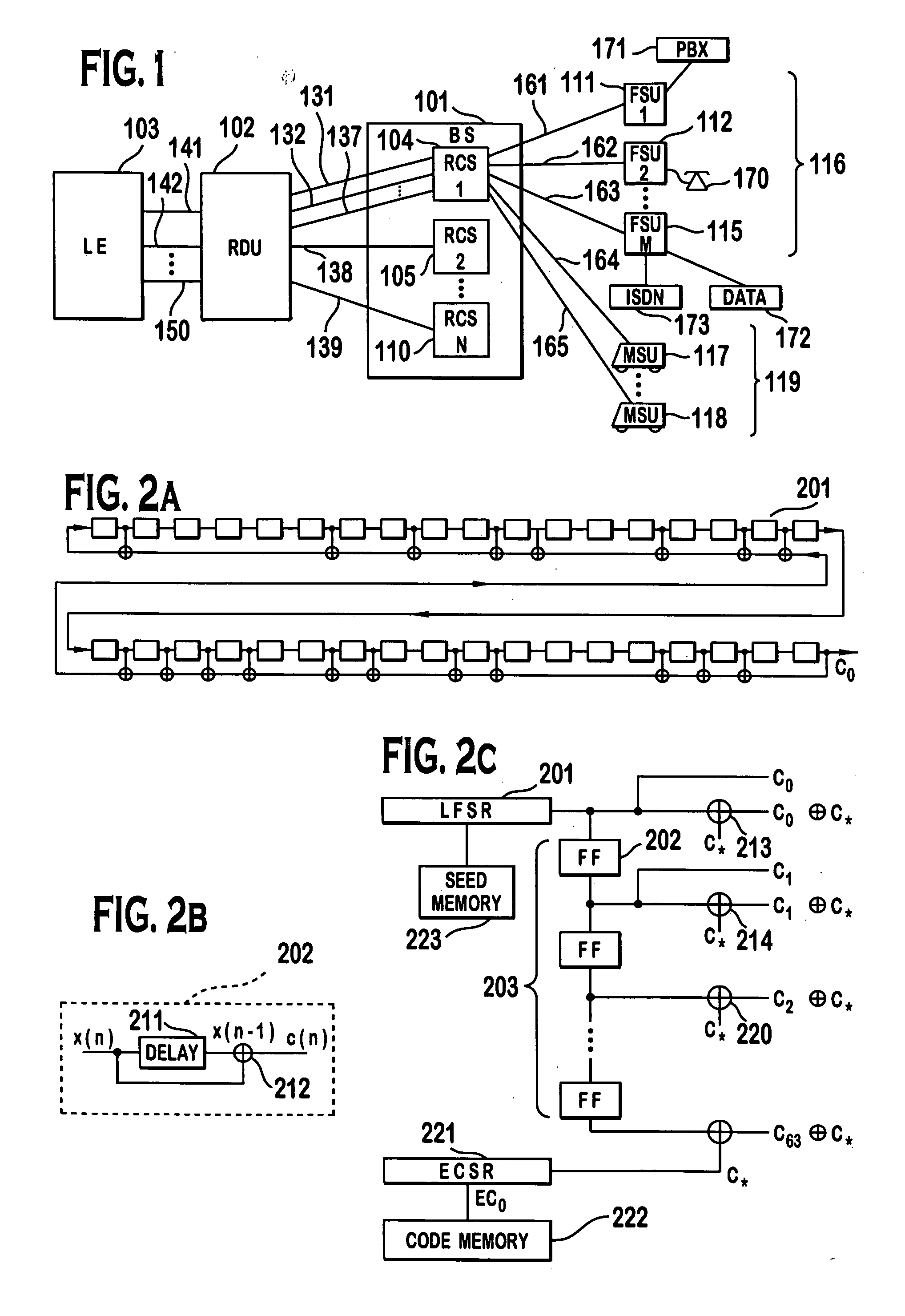
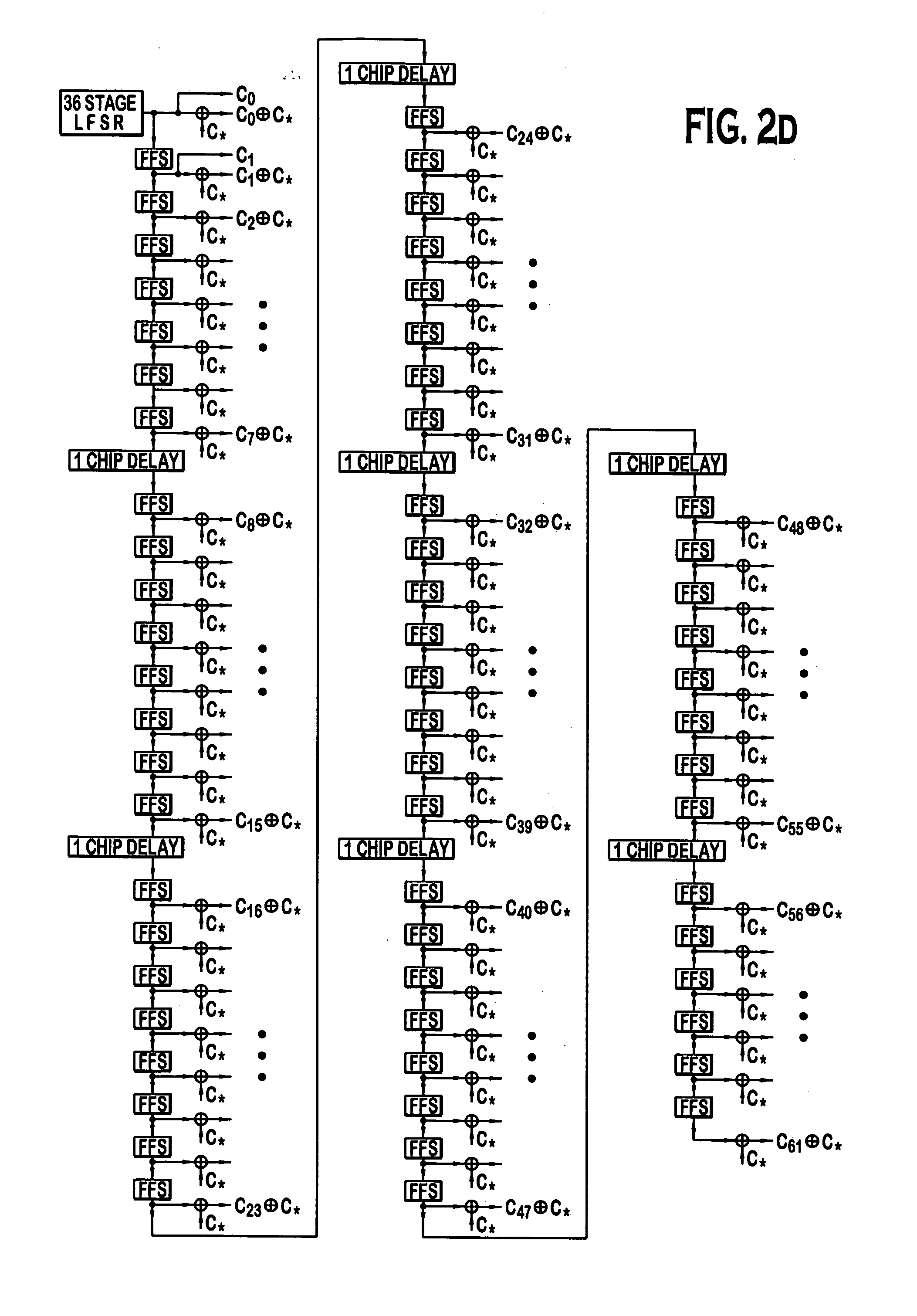
System for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20050265430A1Increase profitEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationCode division multiple accessCarrier signal
A system for rapidly acquiring a spreading code, used in a code division multiple access (CDMA) system, comprises a generator for generating a first long code and a second long code, with each long code having a length of N chips. The first long code is different from the second long code. A transmitter transmits the first long code and the second long code at a first phase angle and at a second phase angle, respectively, on a carrier signal over a communications channel using radio waves. The first long code and the second long code may be transmitted at an in-phase (I) angle and at a quadrature-phase (Q) angle, respectively, on the carrier signal. From the communications channel, an I acquisition circuit and a Q acquisition circuit may acquire, in parallel, the first long code and the second long code from the I angle and the Q angle, respectively, of the carrier signal by searching, in parallel, N / 2 chips of the first long code and the second long code.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
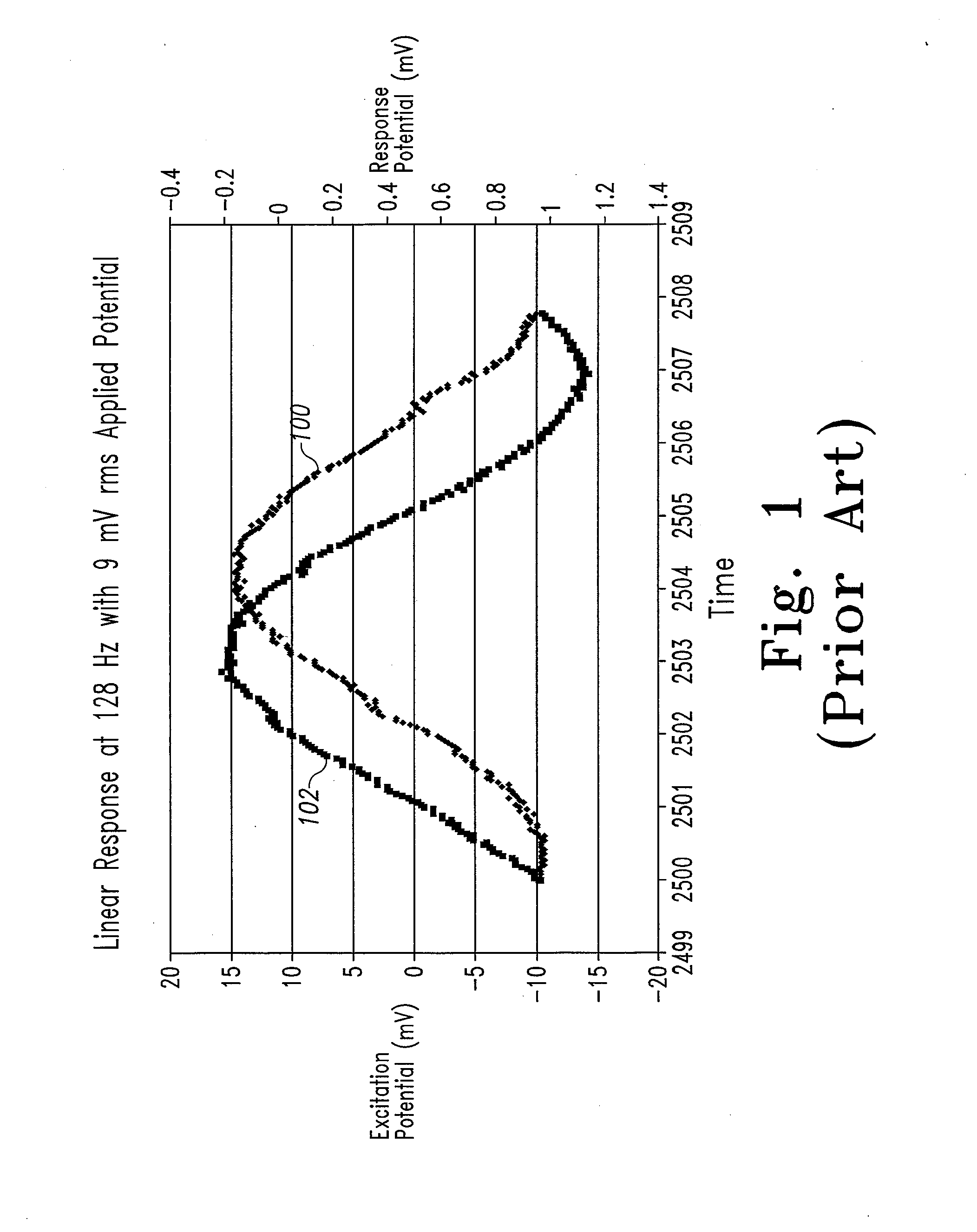
System and method for analyte measurement using a nonlinear sample response
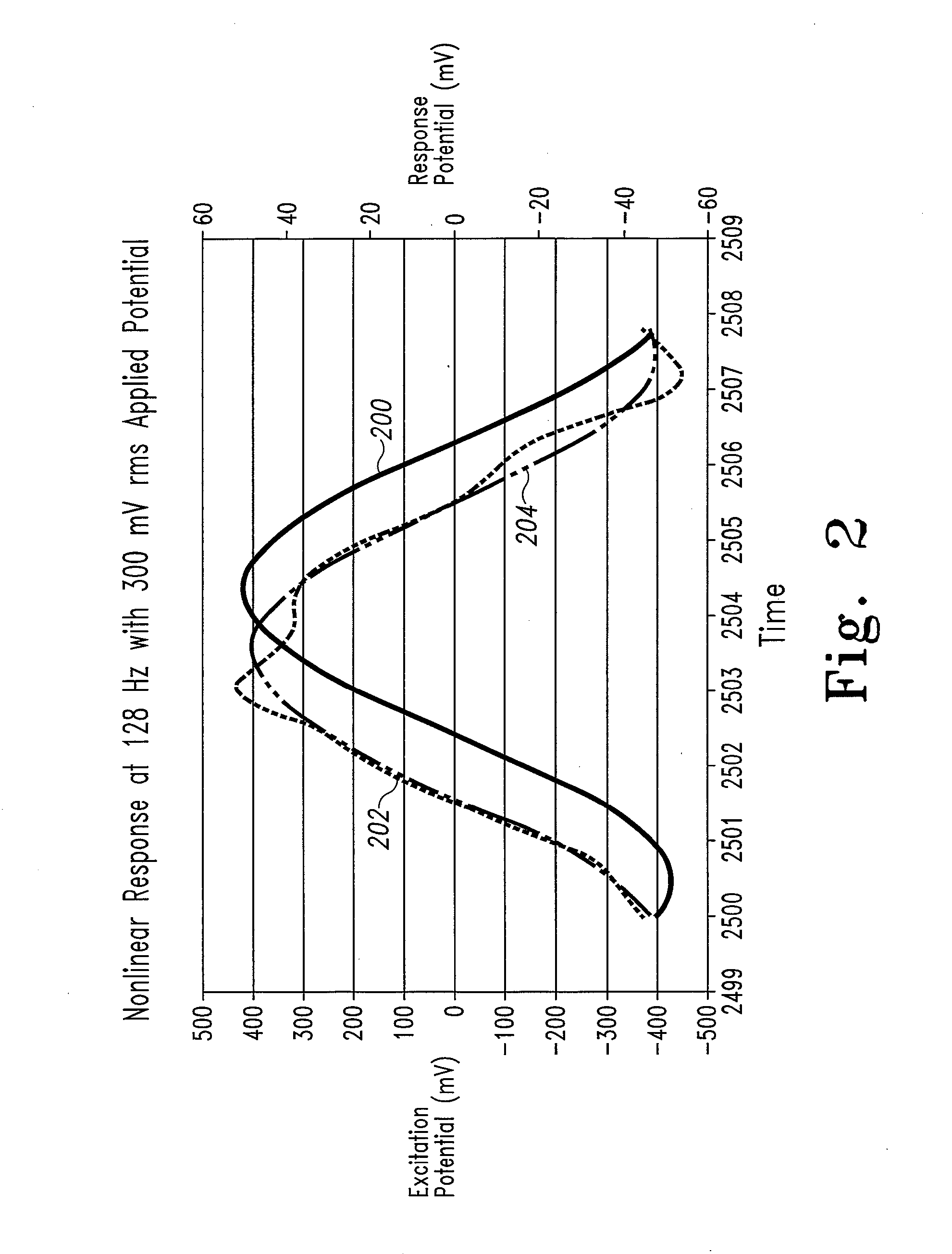
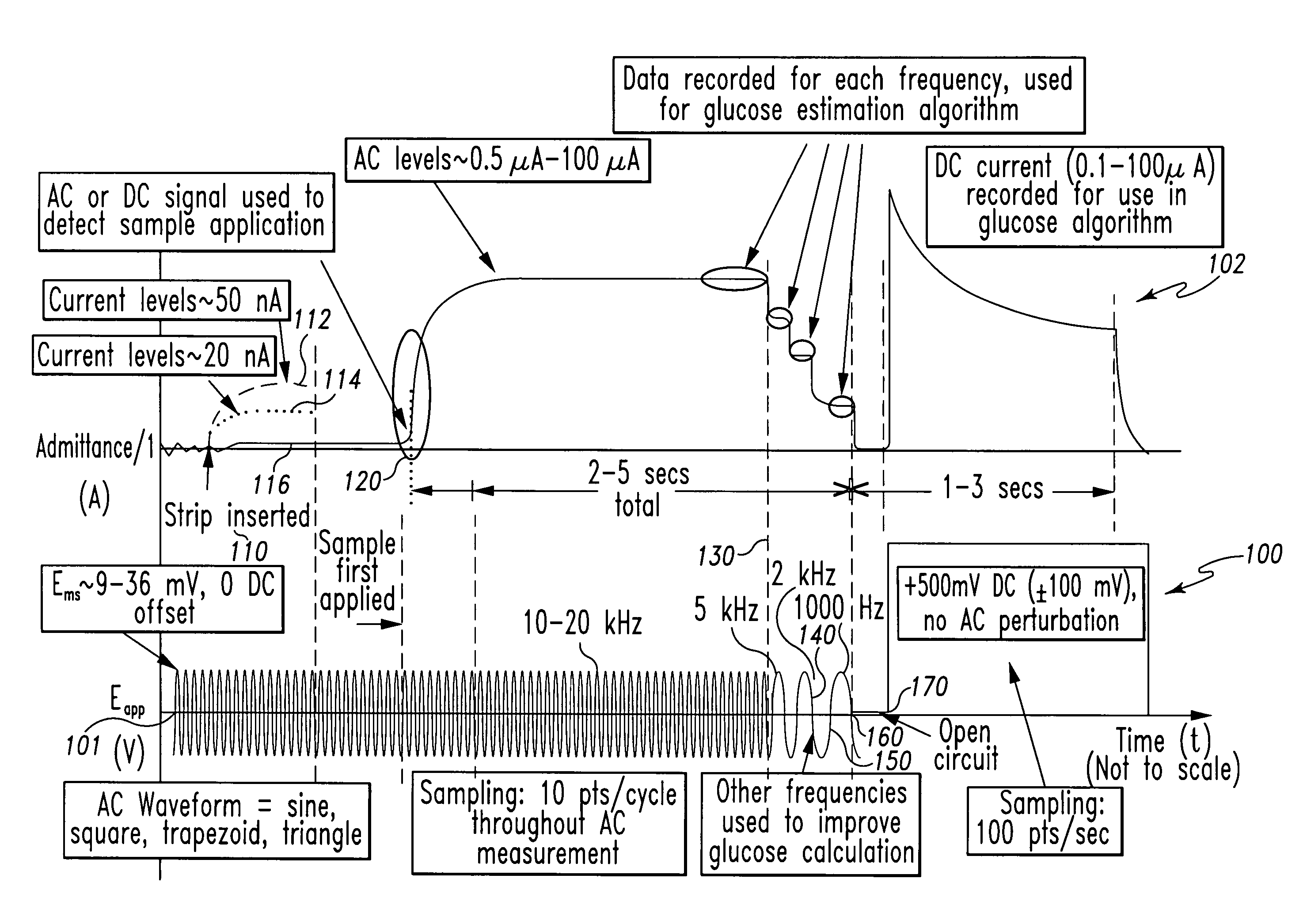
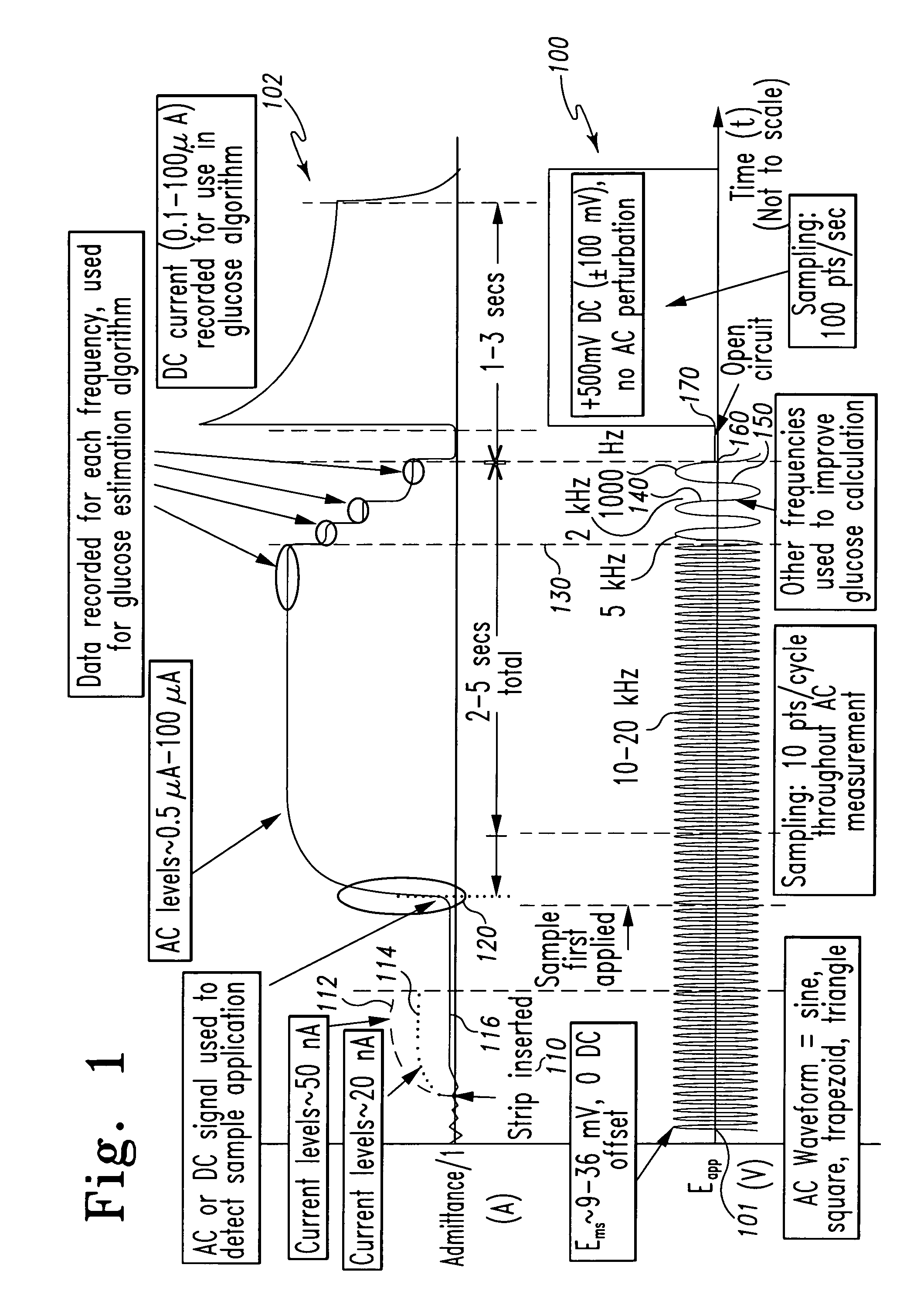
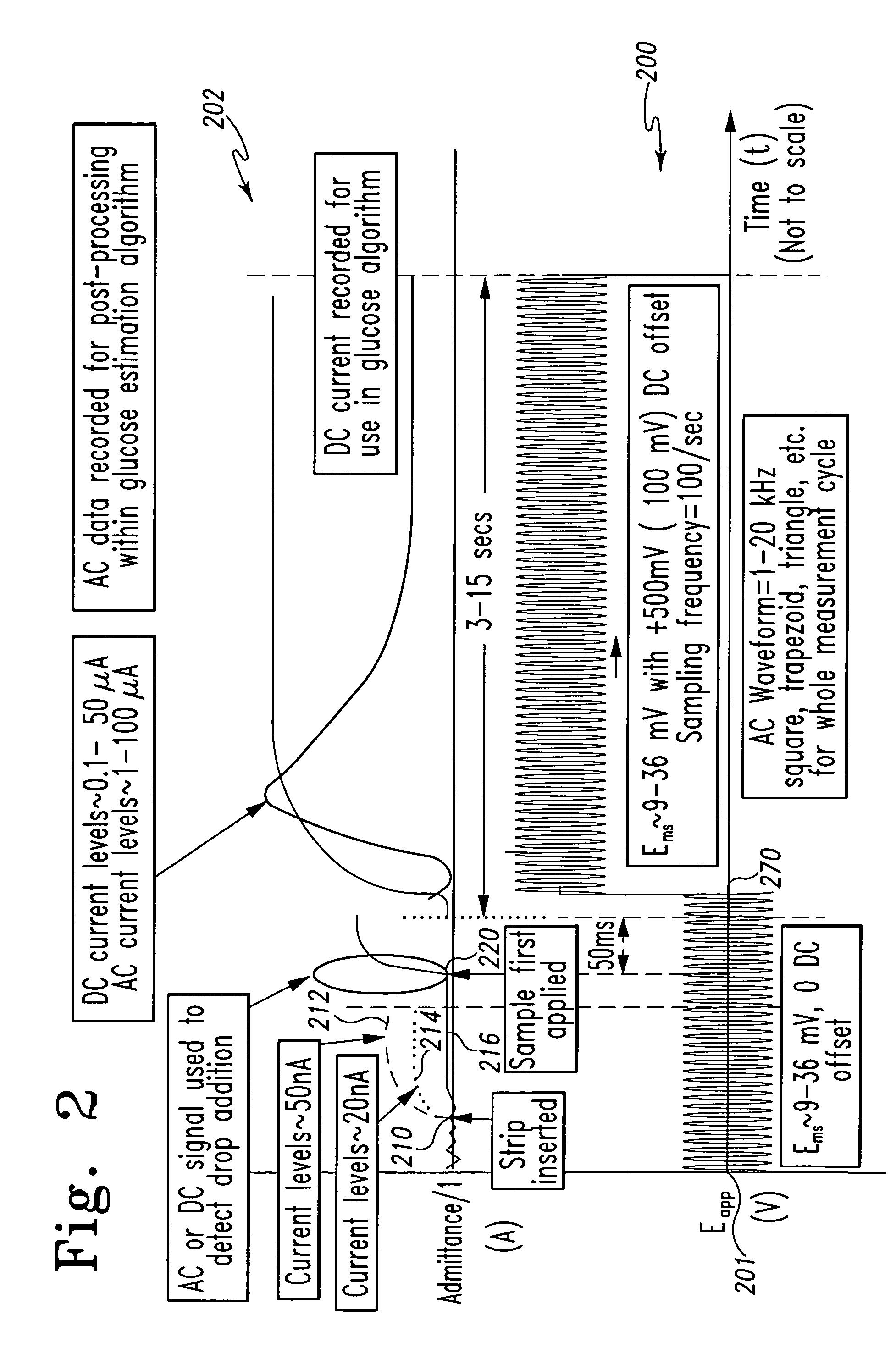
InactiveUS20070264721A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingLinear componentApplied potential
The systems and methods of the present invention utilize a linear component of a non-linear, faradaic current response generated by a biological fluid sample when an AC excitation potential sufficient to produce such a faradaic current response is applied to the sample, in order to calculate the concentration of a medically significant component in the biological fluid sample. The current response is created by the excitation of electrochemical processes within the sample by the applied potential. Typically, the linear component of the current response to an applied AC potential contains phase angle and / or admittance information that may be correlated to the concentration of the medically significant component. Also typically, the fundamental linear component of the current response is utilized in the disclosed systems and methods. Harmonics of the fundamental linear component may also be used. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
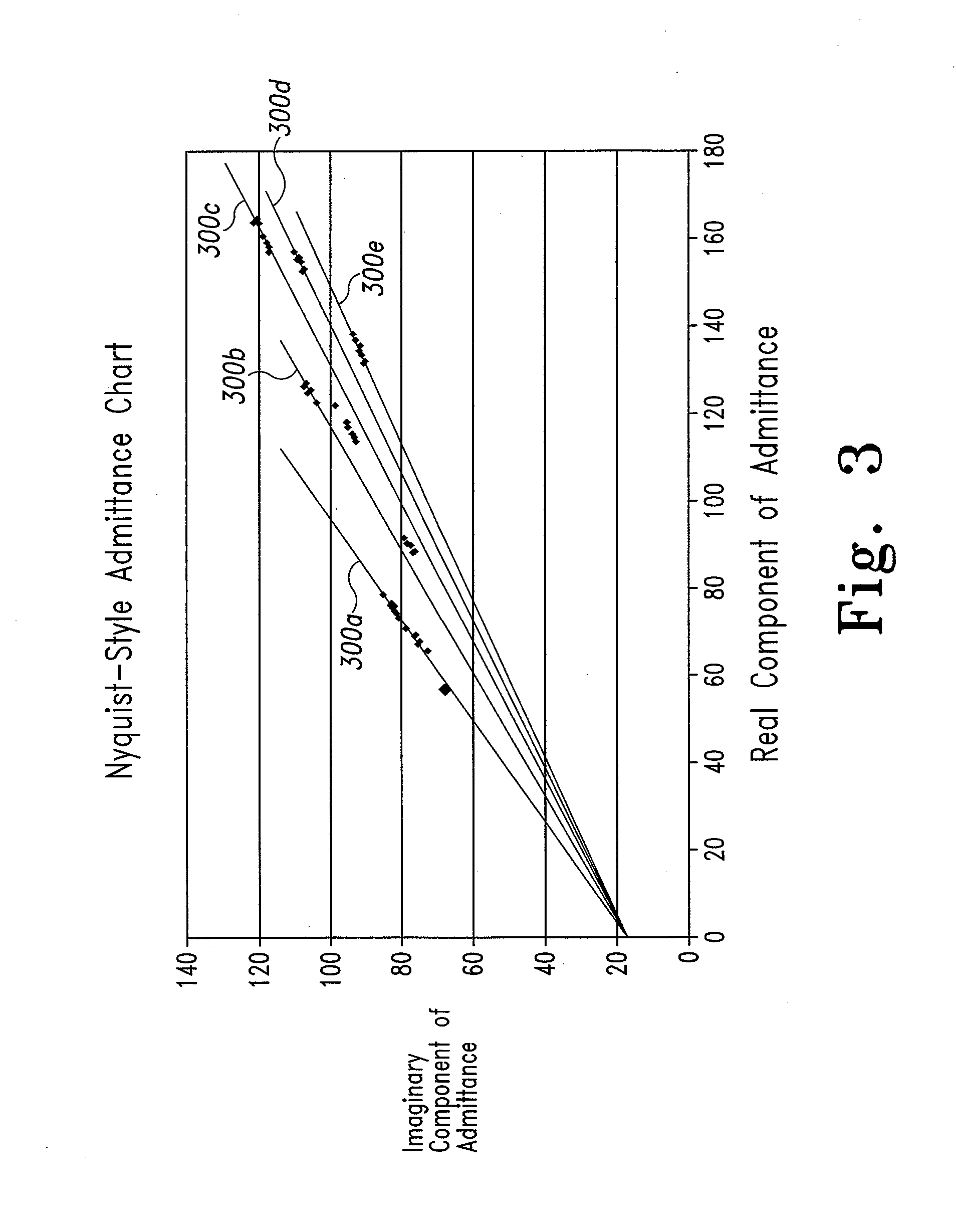
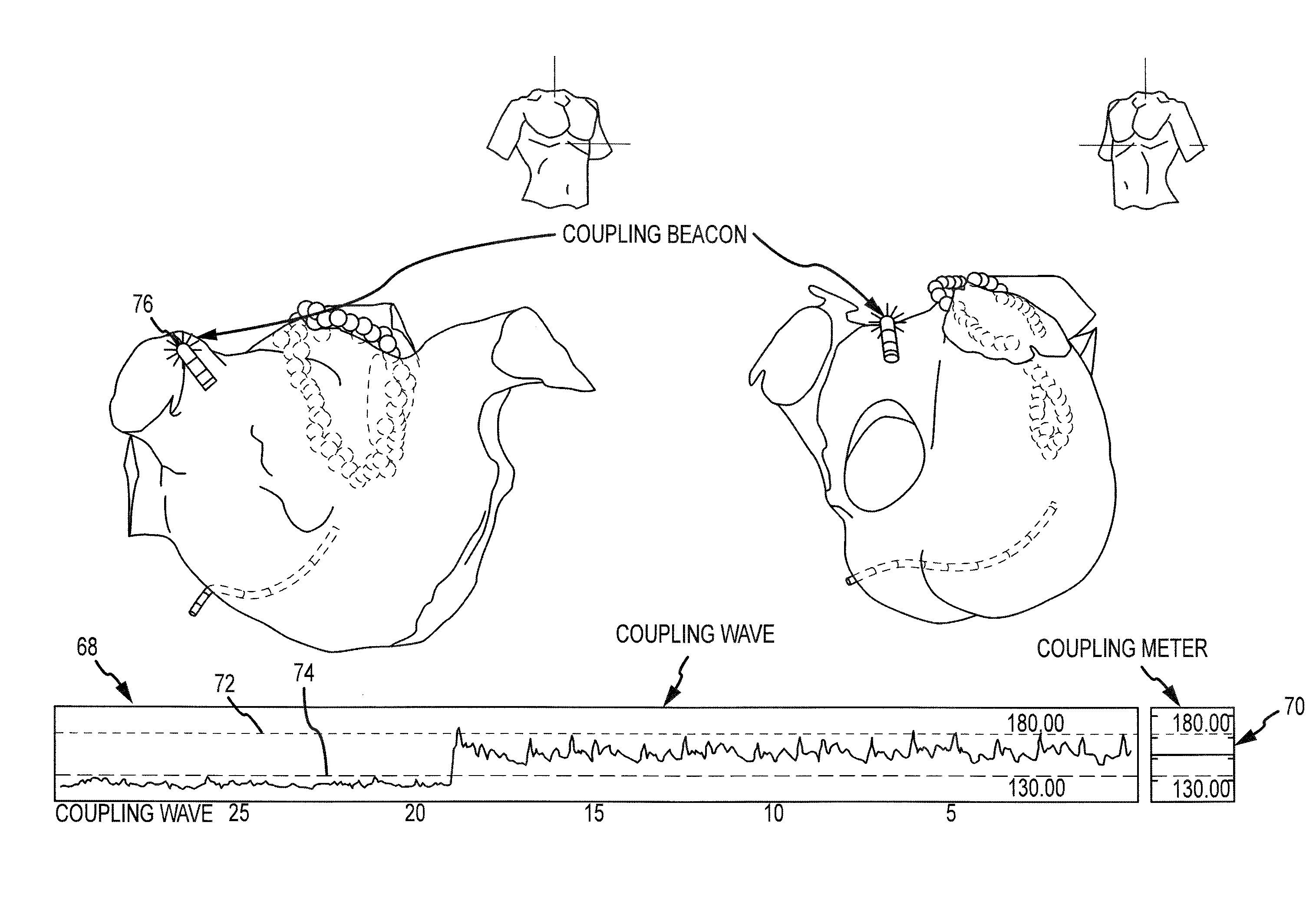
System and method for assessing coupling between an electrode and tissue
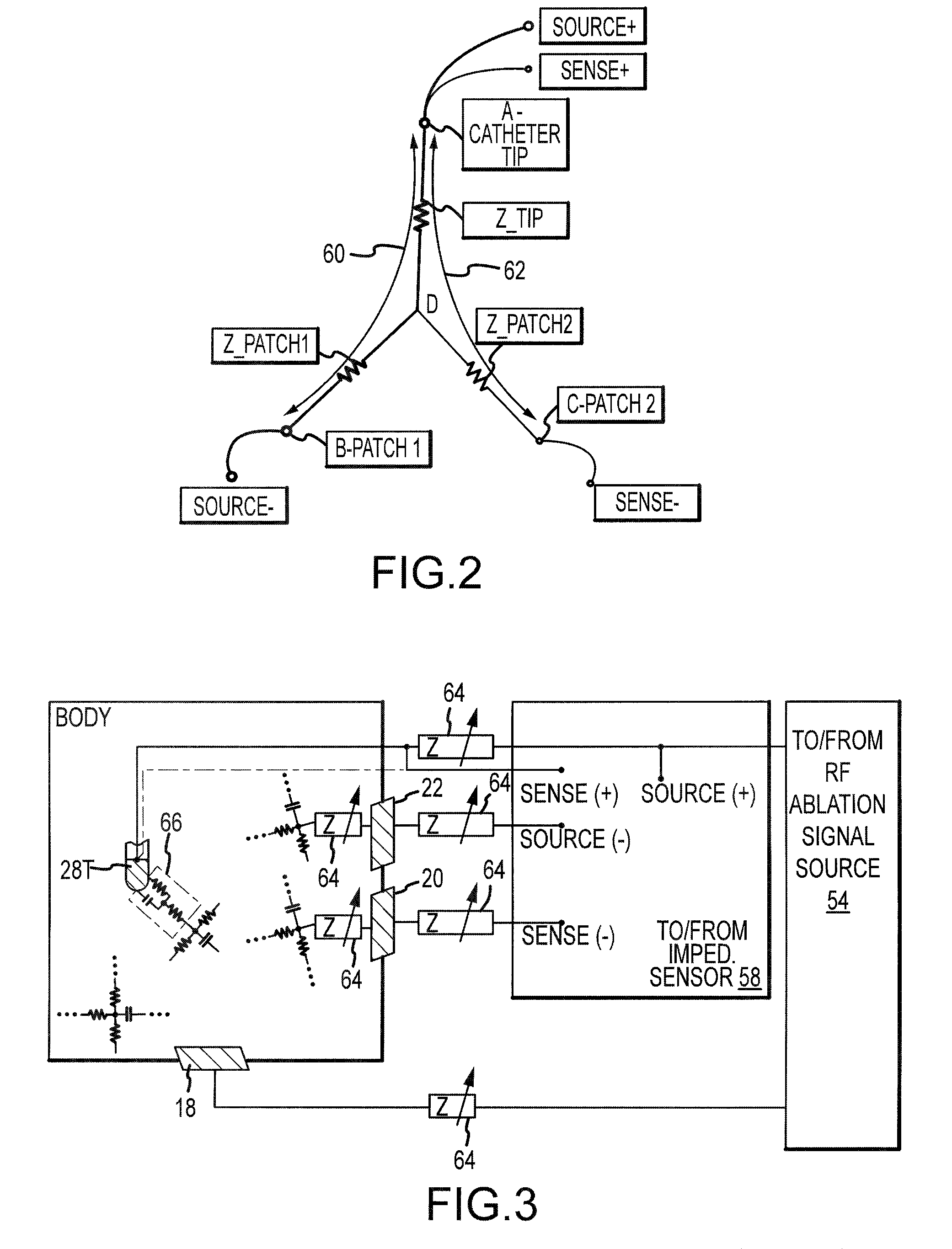
ActiveUS8449535B2Easy interpretation and correlationBetter assessmentResistance/reactance/impedenceCatheterElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System and method for analyte measurement using AC phase angle measurements
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE OPERATIONS +1
Active power factor correction circuit and control method thereof
InactiveUS7295452B1Reduce Higher Harmonic DistortionReduce switching lossesEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDriver circuitPower switching
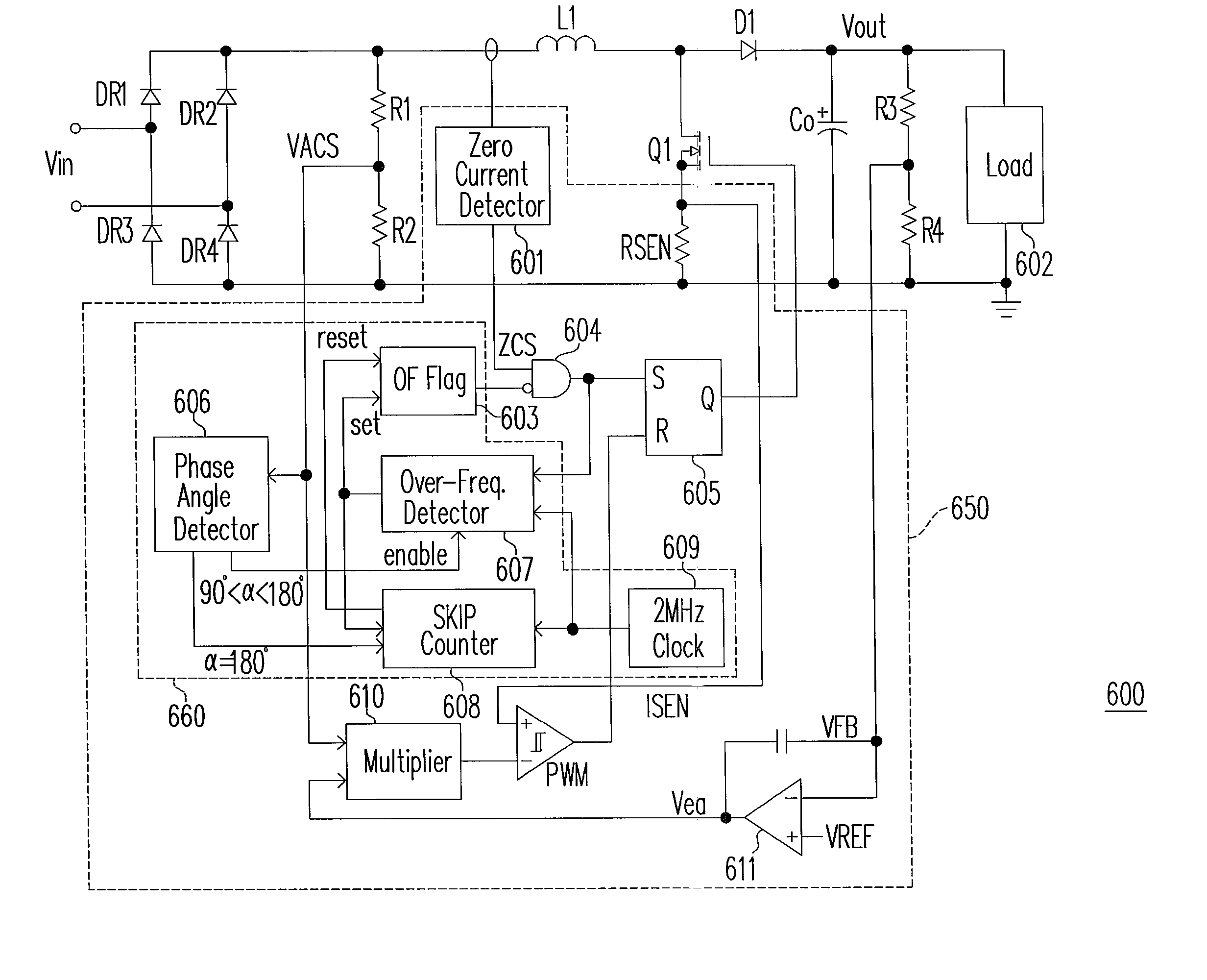
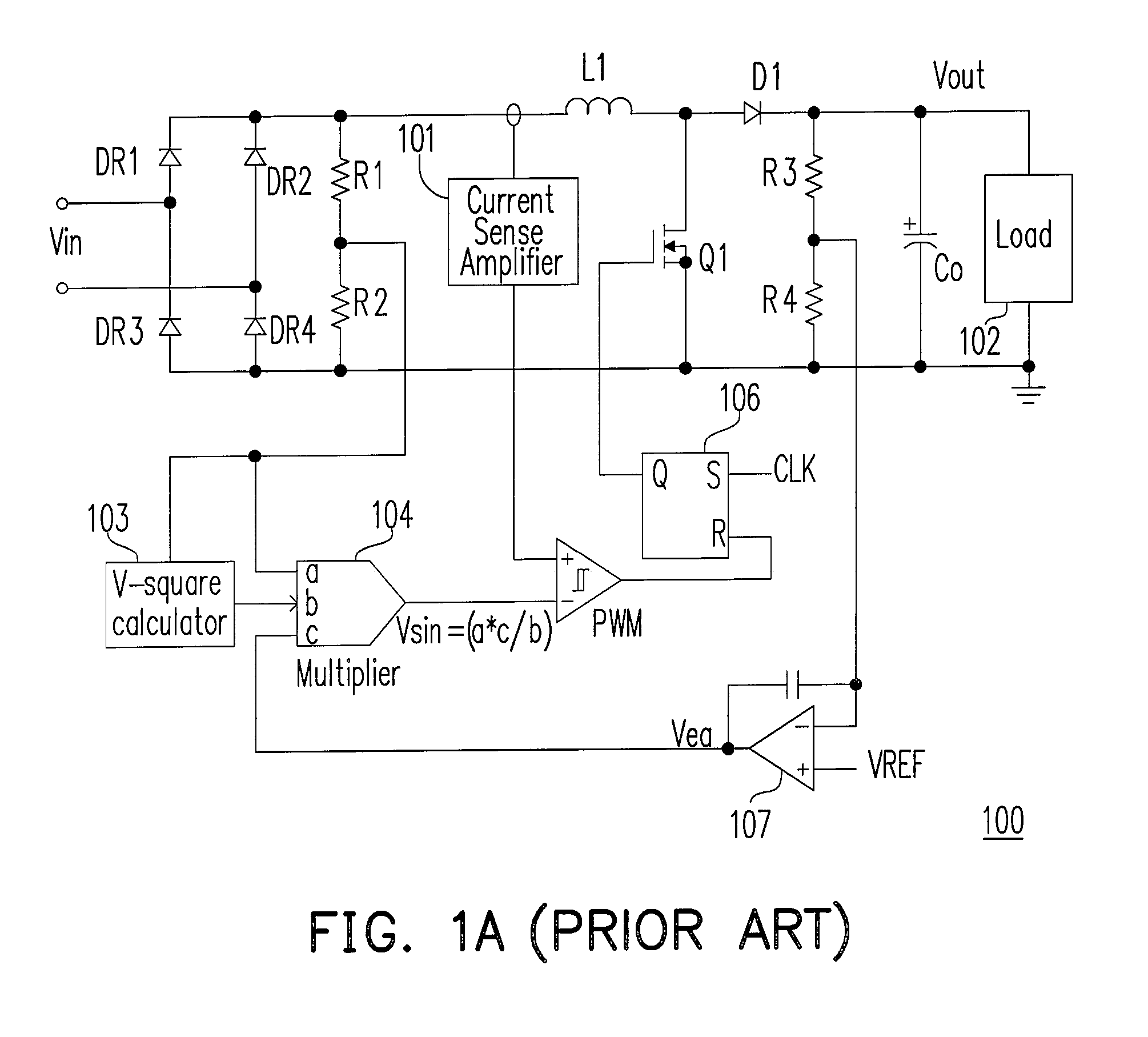
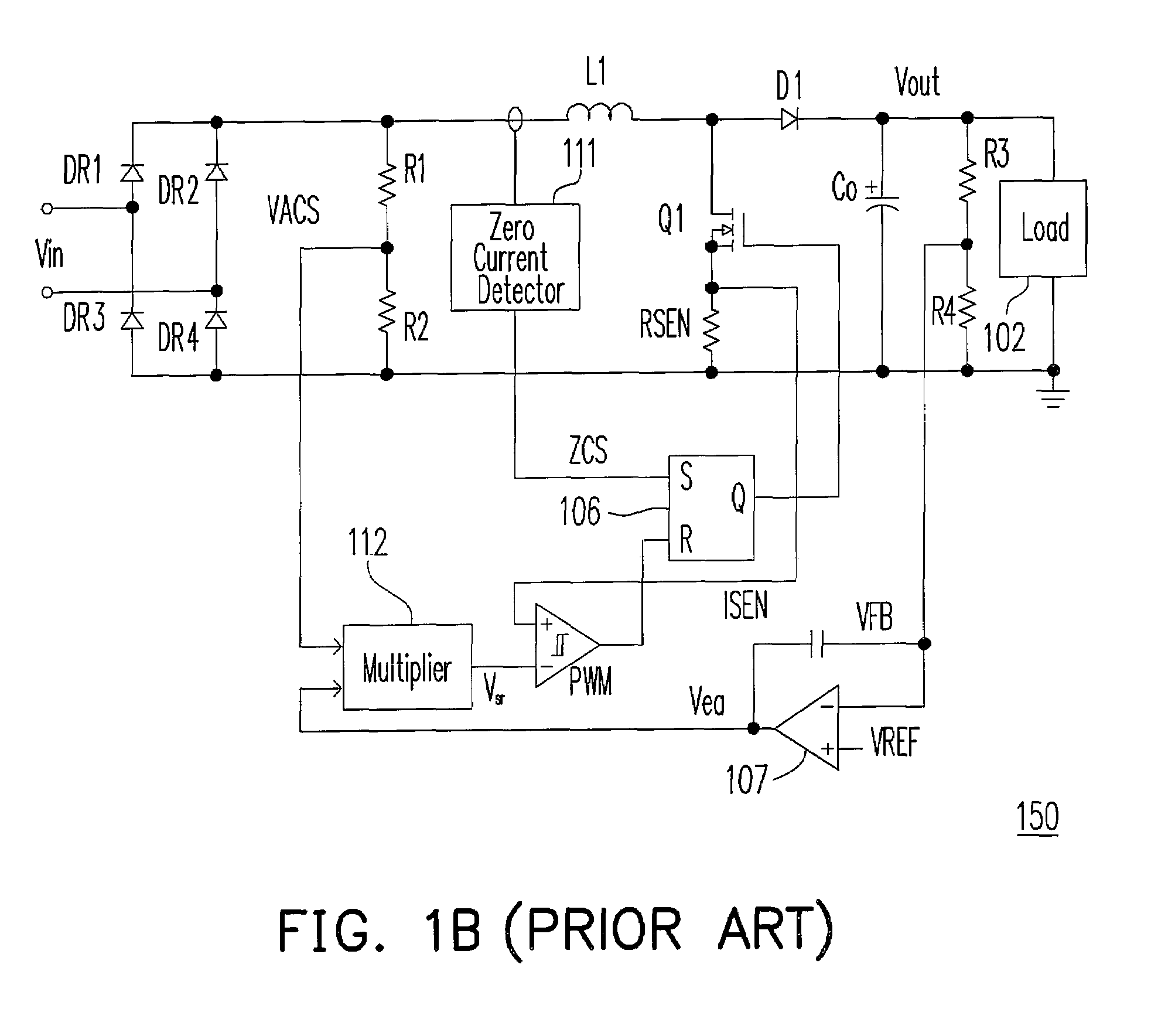
An active power factor correction (PFC) circuit and its controlling method are provided. The method comprises the following steps. Drive the power switch of the circuit so that the average inductor current waveform follows the rectified input voltage waveform. Suspend the operation of the power switch at a first moment in a first line cycle of the rectified input voltage and then resume the operation of the power switch at a second moment in a second line cycle of the rectified input voltage. The first moment is when the phase angle of the rectified input voltage exceeds a predetermined angle and the switching frequency of the power switch exceeds a predetermined frequency. The time span from the first moment to the end of the first line cycle is substantially as long as the time span from the beginning of the second line cycle to the second moment.
Owner:GREEN MARK TECH
Method for operating a wind turbine
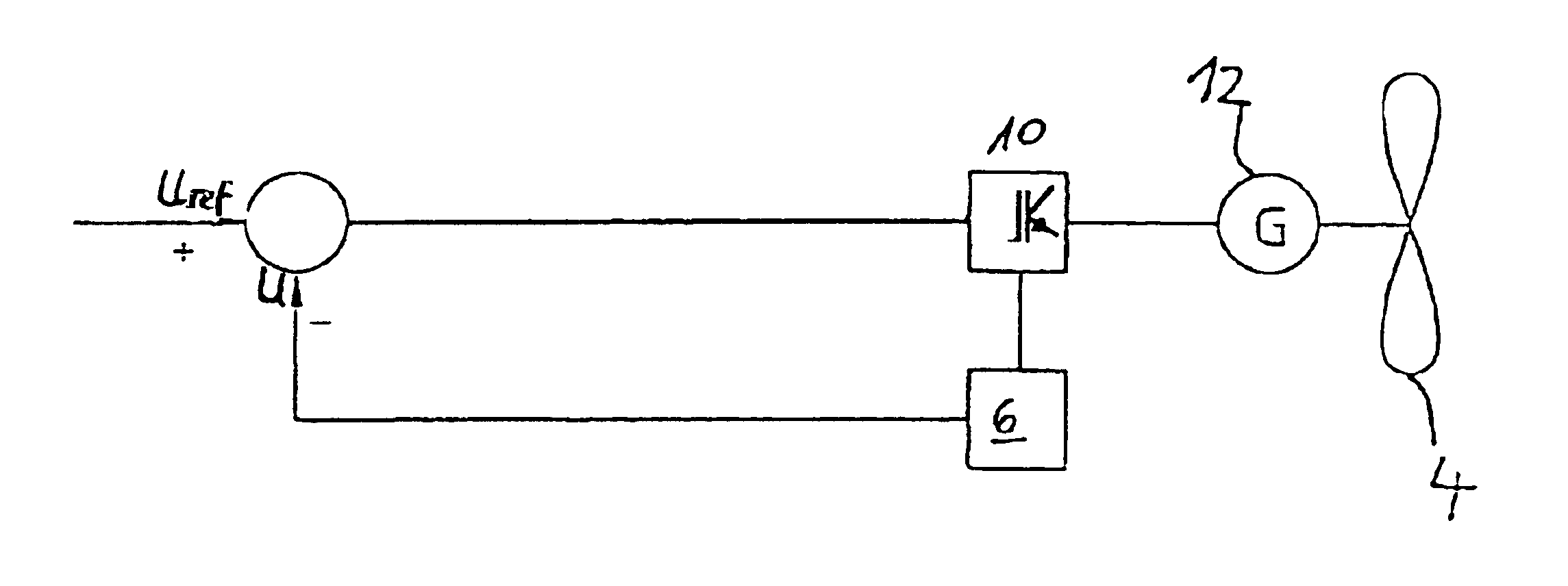
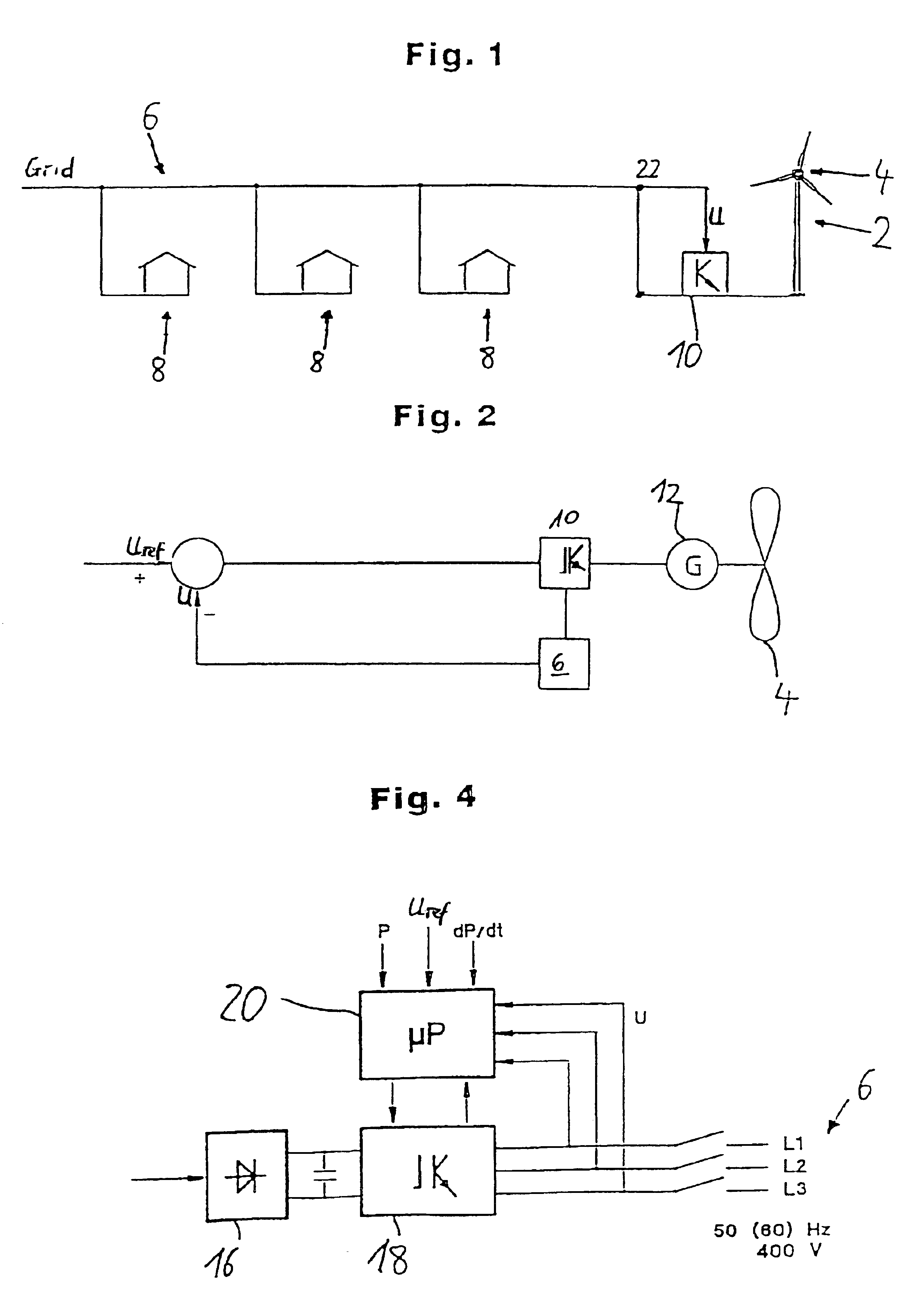
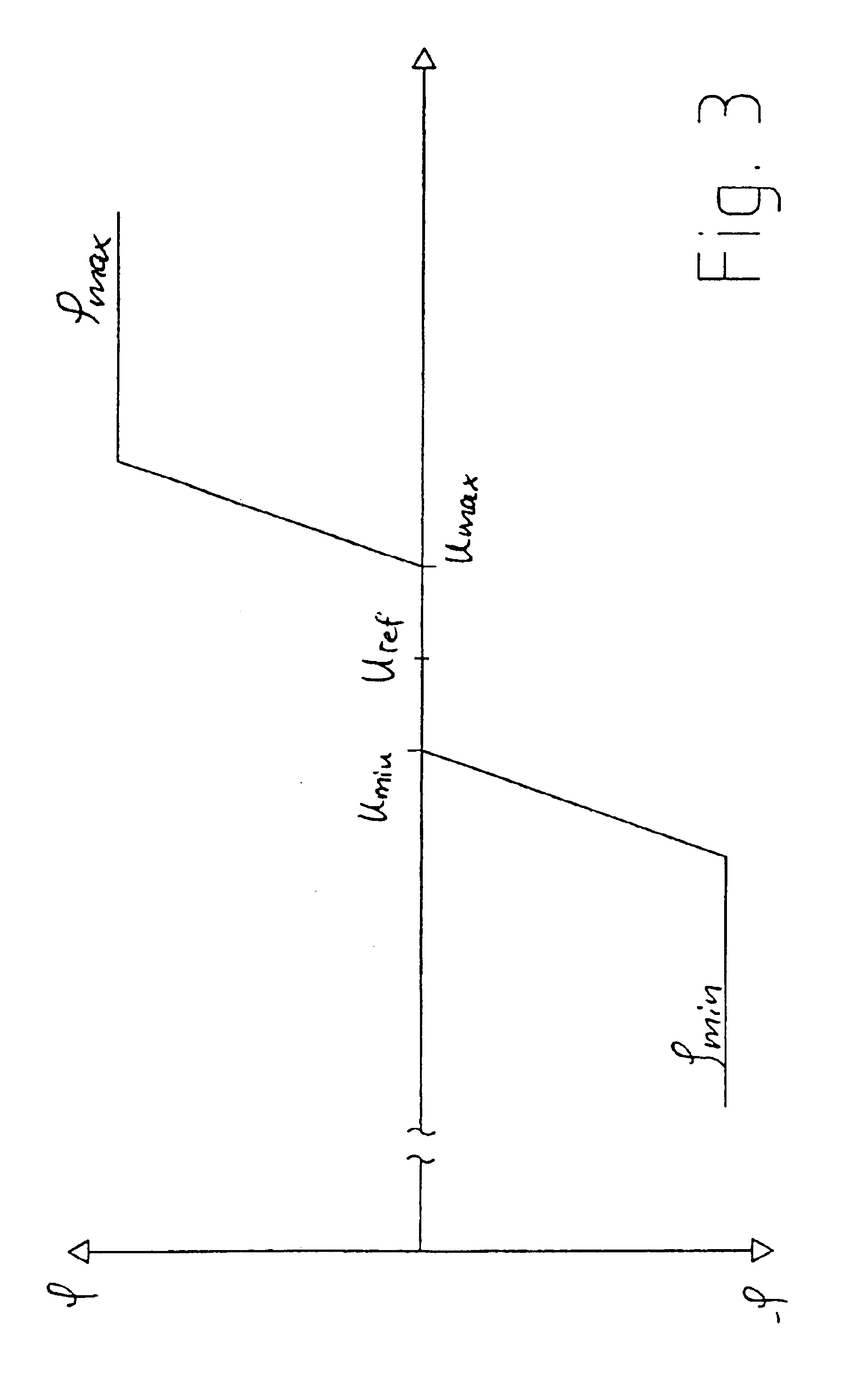
InactiveUS6965174B2Voltage fluctuationUnwanted fluctuationWind motor controlMachines/enginesPower gridWind force
The present invention relates to a method for operating a wind turbine with an electrical generator, drivable by a rotor, for supplying electrical power to an electric grid, in particular to the loads connected thereto. The object of the present invention is to define a method for operating a wind turbine and to provide a wind turbine and / or a wind farm that is capable, even when the output of non-reactive power fluctuates, of reducing or at least of insignificantly increasing the unwanted fluctuation in voltage at a predefined point in the grid compared to the situation with no wind turbine(s). Method for operating a wind turbine with an electrical generator, drivable by a rotor, for supplying electrical power to an electric grid, in particular to the loads connected thereto, characterized in that the phase angle φ is changed in response to at least one voltage measured in the grid.A method for operating a wind turbine and to provide a wind turbine and / or a wind farm that is capable, even when the output of non-reactive power fluctuates, of reducing or at least of insignificantly increasing the unwanted fluctuation in voltage at a predefined point in the grid compared to the situation with no wind turbines. Method for operating a wind turbine with an electrical generator, drivable by a rotor, for supplying electrical power to an electric grid, in particular to the loads connected thereto, characterized in that the phase angle φ is changed in response to at least one voltage measured in the grid.
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
Contact sensitive device
InactiveUS20040133366A1Flow propertiesFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsPhase differenceAcoustics
A contact sensitive device includes a member capable of supporting bending waves and a plurality of sensors mounted on the member for measuring bending wave vibration in the member. The sensors measure the bending wave signals and by calculating a phase angle for each measured bending wave signal and a phase difference between the phase angles of least two pairs of sensors so that at least two phase differences are calculated, the location of the contact can be determined.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC +1
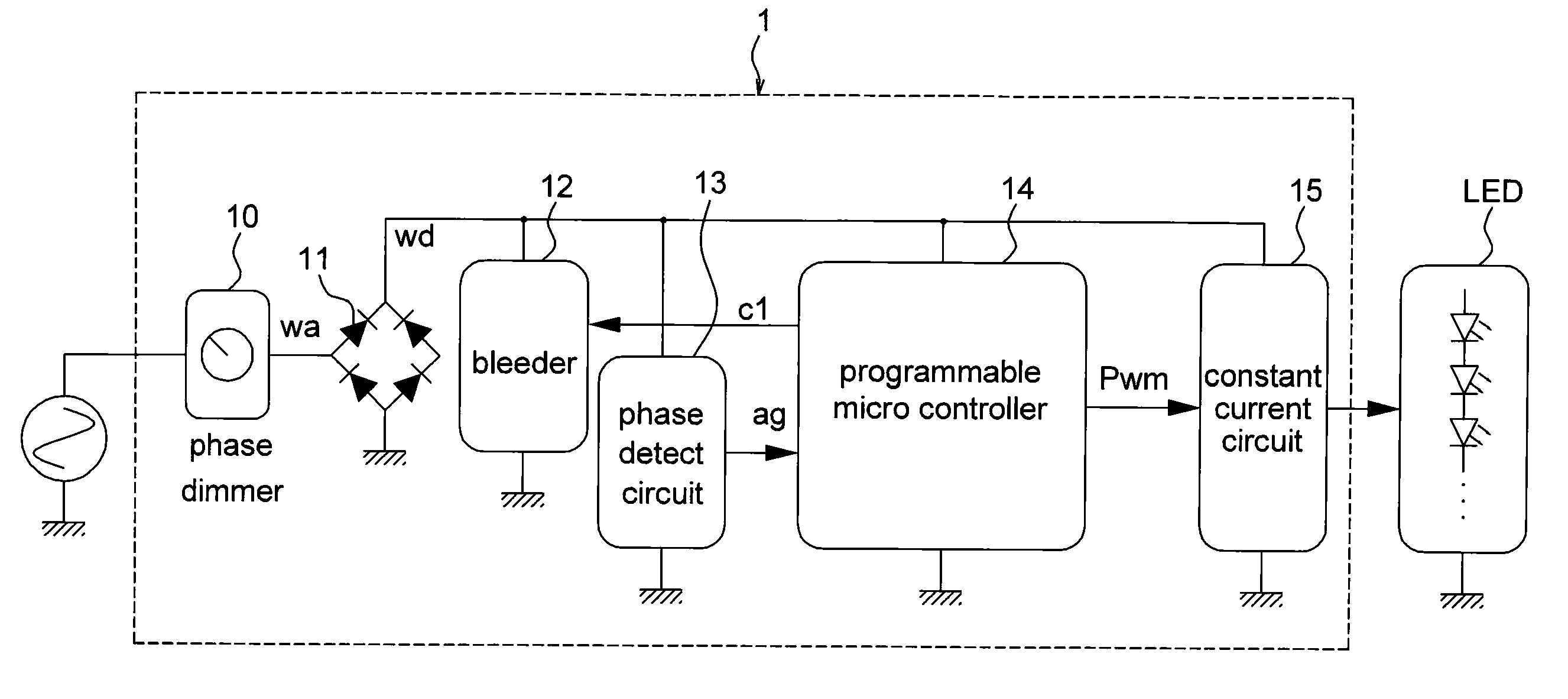
AC-powered, microprocessor-based, dimming LED power supply
ActiveUS20090167203A1Level of audible noise may increaseTotal current dropDc network circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesNoise levelAverage current
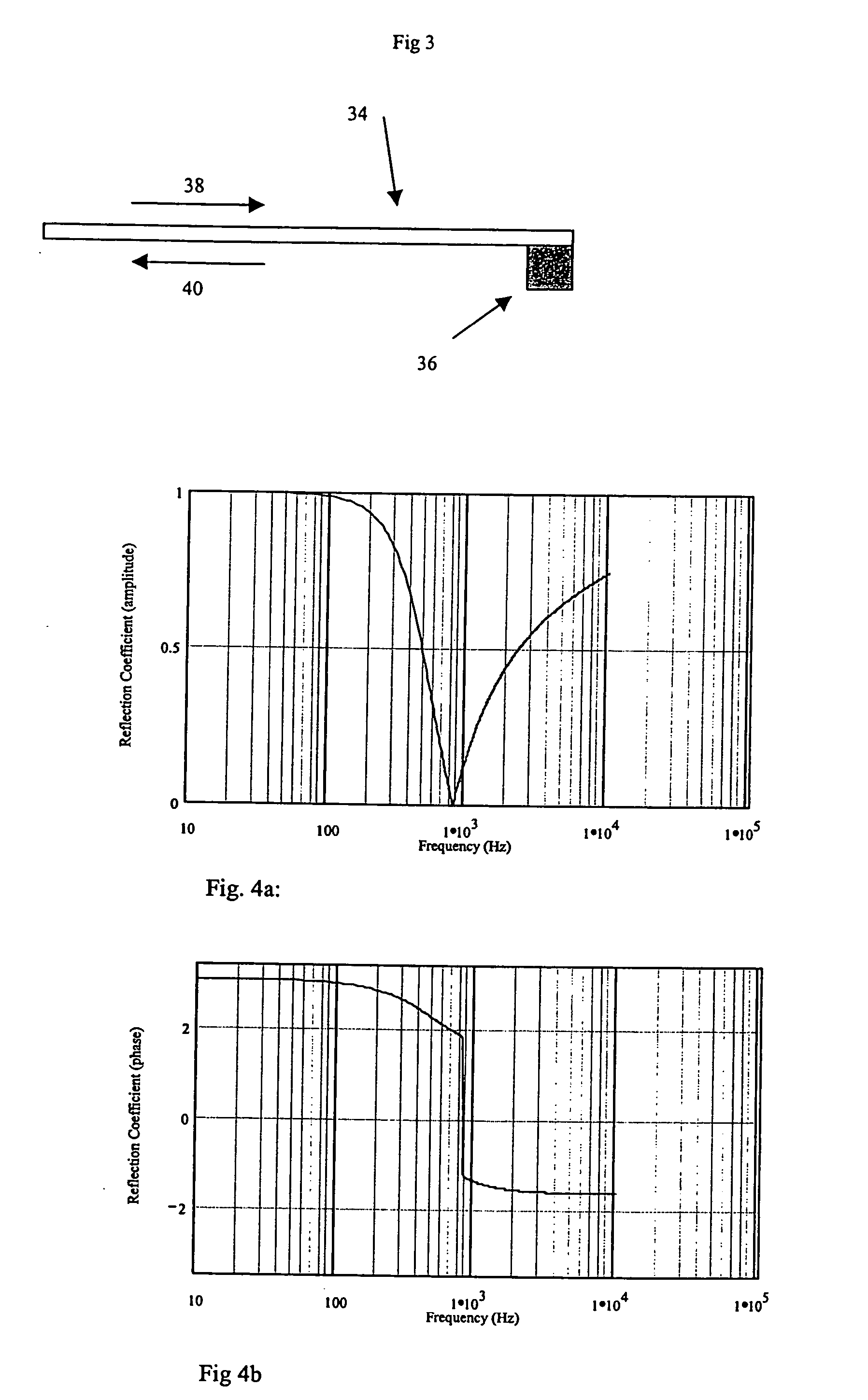
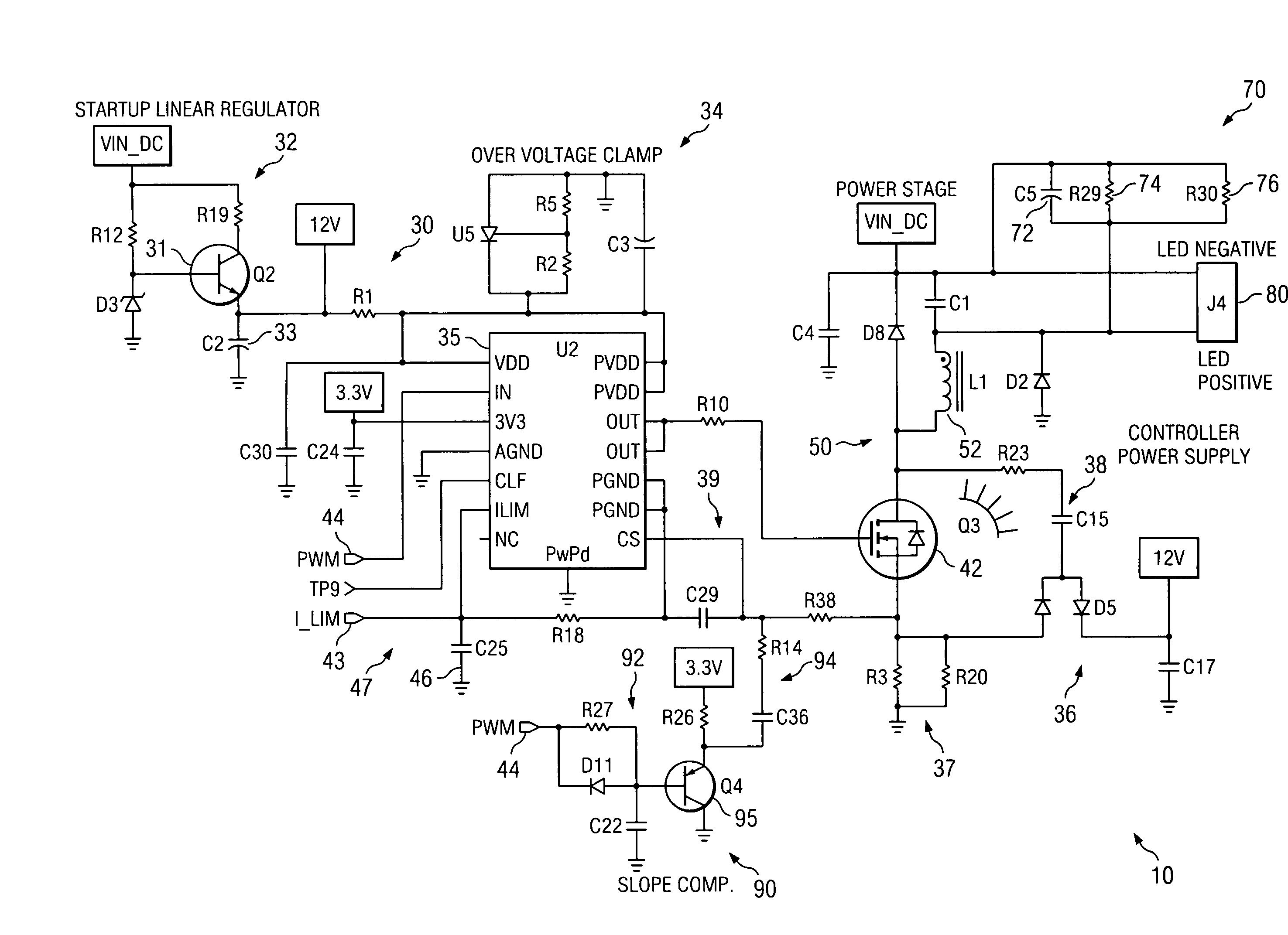
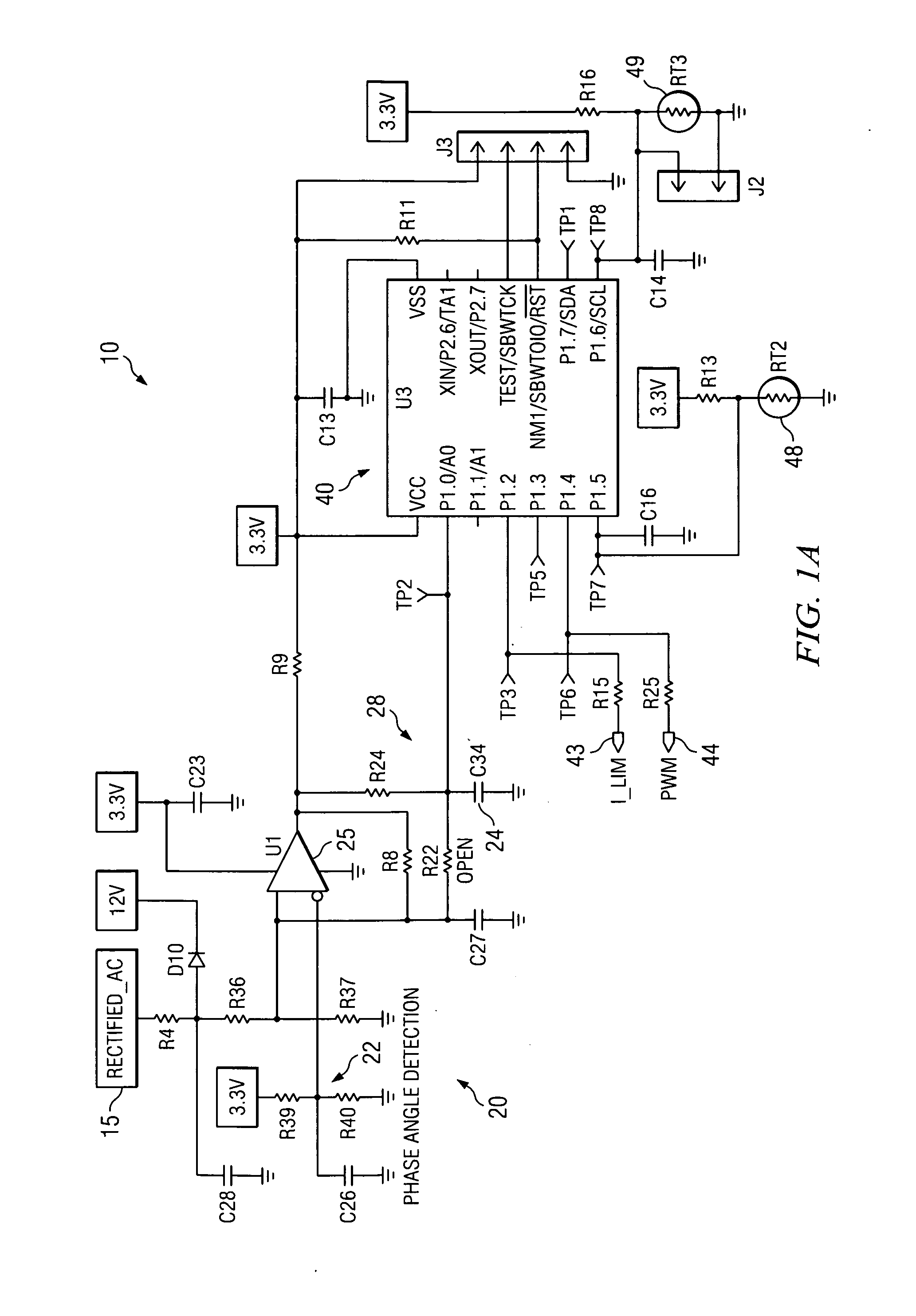
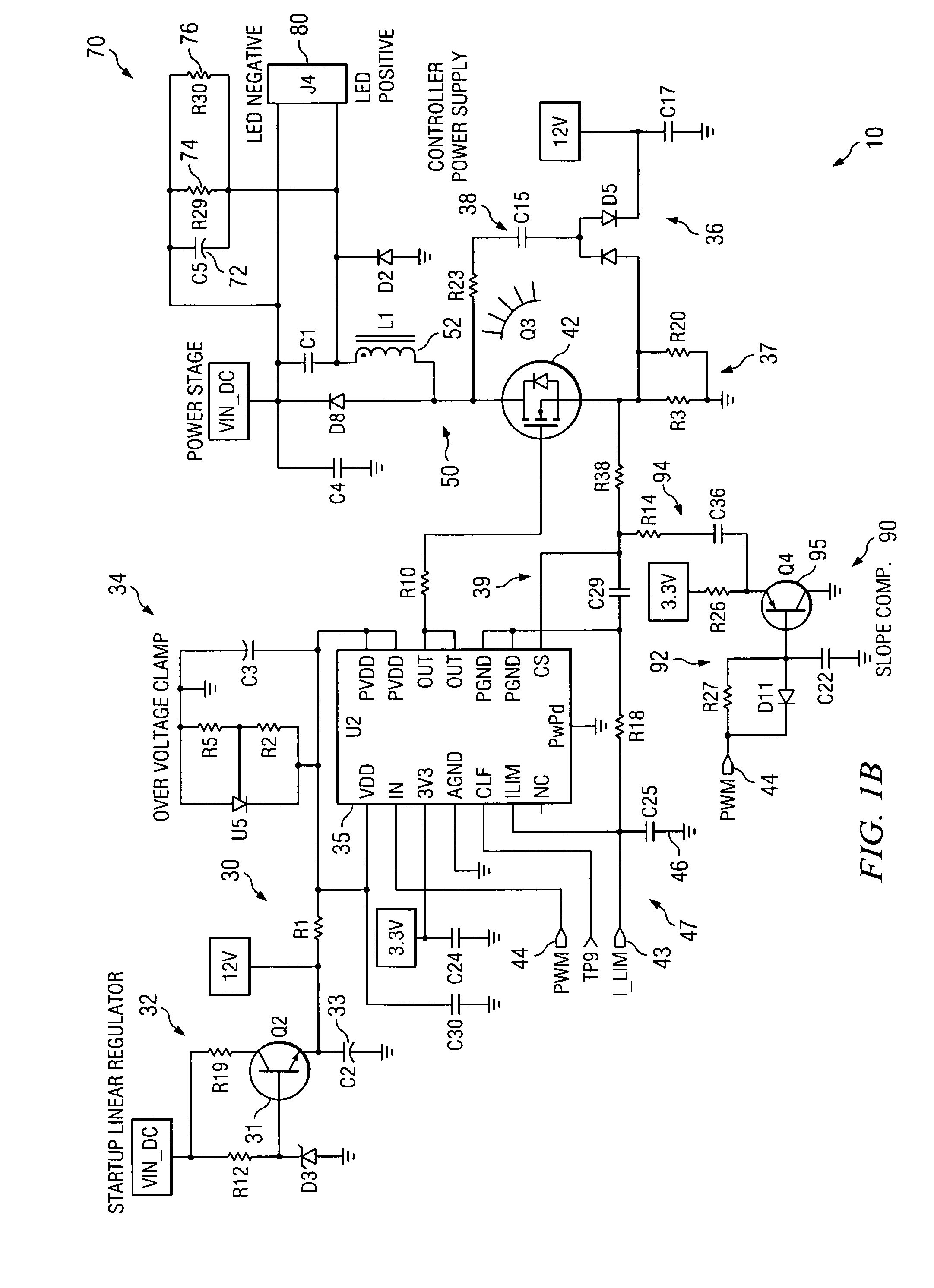
A dimmable, light-emitting diode (LED) power supply adapted to provide a direct current (DC), constant current (“constant current source”) from a conventional, phase-controlled 120 VAC, 60 Hz power source is disclosed. The constant current source of the present invention utilizes two processes to control dimming. In a first process, the phase angle of the input voltage is used to control the duty cycle of a line frequency pulse width modulation (PWM). In a second process, a proportional-current limit adjustment is used to control the average current to the LED during the ON time of the line frequency by PWM. As a result, at relatively low phase angles, peak currents can be lowered, reducing flicker and improving the audible noise levels generated by the circuit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for improving the start up of an ultrasonic system under zero load conditions
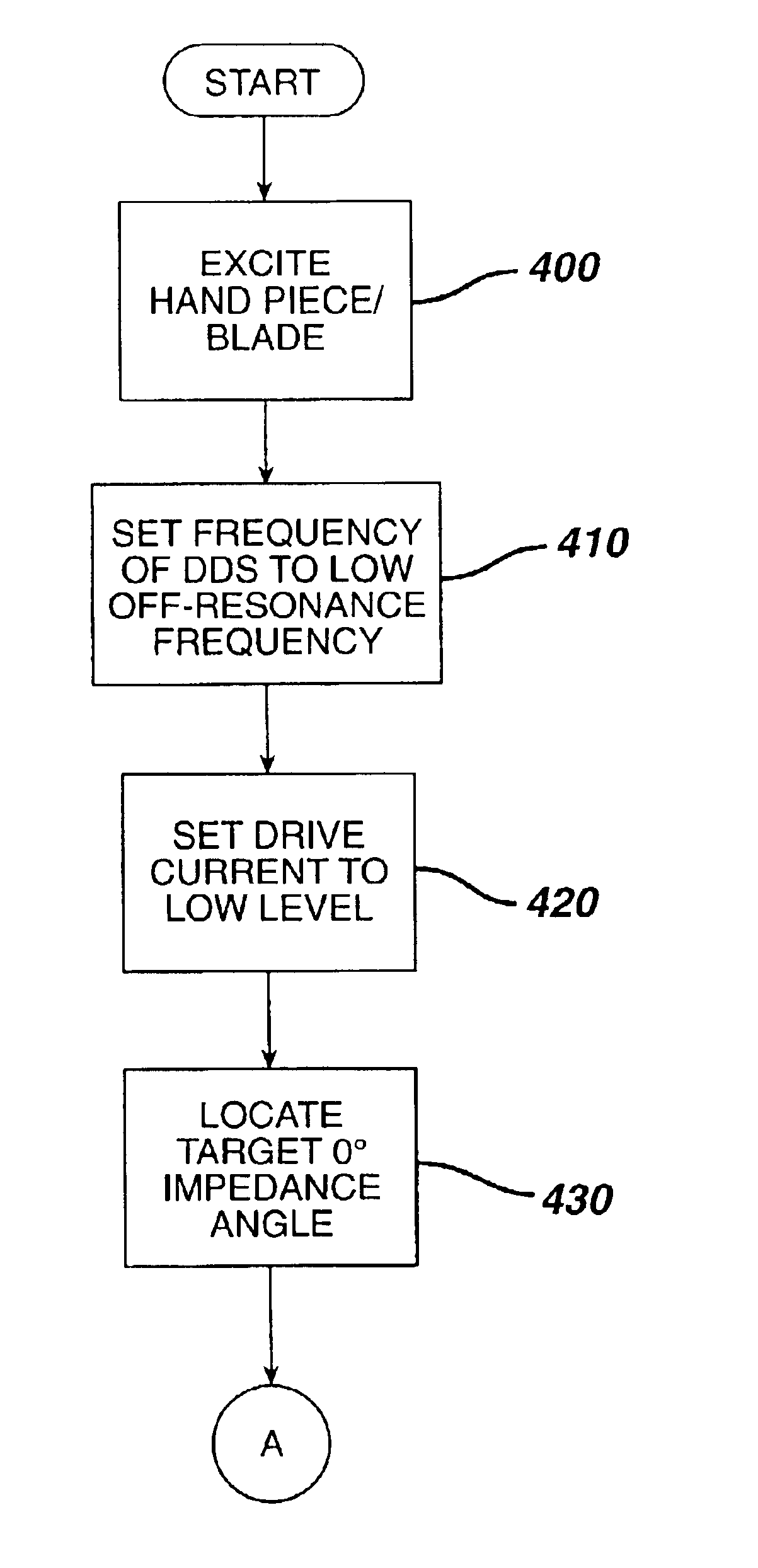
InactiveUS6898536B2Easy to startIncrease flexibilityNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementSurgical instrument detailsDriving currentPower flow
The start up performance of an ultrasonic system under zero load conditions is improved by setting a phase set point in a frequency control loop such that, at start up under zero load conditions, the phase set point intersects a point on a phase-frequency response curve which has a low positive slope. This intersection point on the phase-frequency response curve changes as the load is increased and the system Q is decreased. The controller “seeks” a target 0° impedance phase angle. The frequency of the ultrasonic generator is set to an off-resonance frequency which is lower than the resonance of any known hand piece / blade combination. In order for the drive voltage to not exceed the physical limit of the system, the drive current is set to a low level. The drive frequency is then smoothly increased in steps until the target 0° impedance phase delta is located.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Assessment of Electrode Coupling For Tissue Ablation
ActiveUS20080281319A1Lower potentialRaise the potentialSurgical navigation systemsMechanical features of instrumentMedicineCoupling
An electrode catheter and a method for assessing electrode-tissue contact and coupling are disclosed. An exemplary electrode catheter comprises an electrode adapted to apply electrical energy. A measurement circuit is adapted to measure impedance between the electrode and ground as the electrode approaches a target tissue. A processor determines a contact and coupling condition for the target tissue based at least in part on reactance of the impedance measured by the measurement circuit. In another exemplary embodiment, the electrode catheter determines the contact and coupling condition based at least in part on a phase angle of the impedance.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
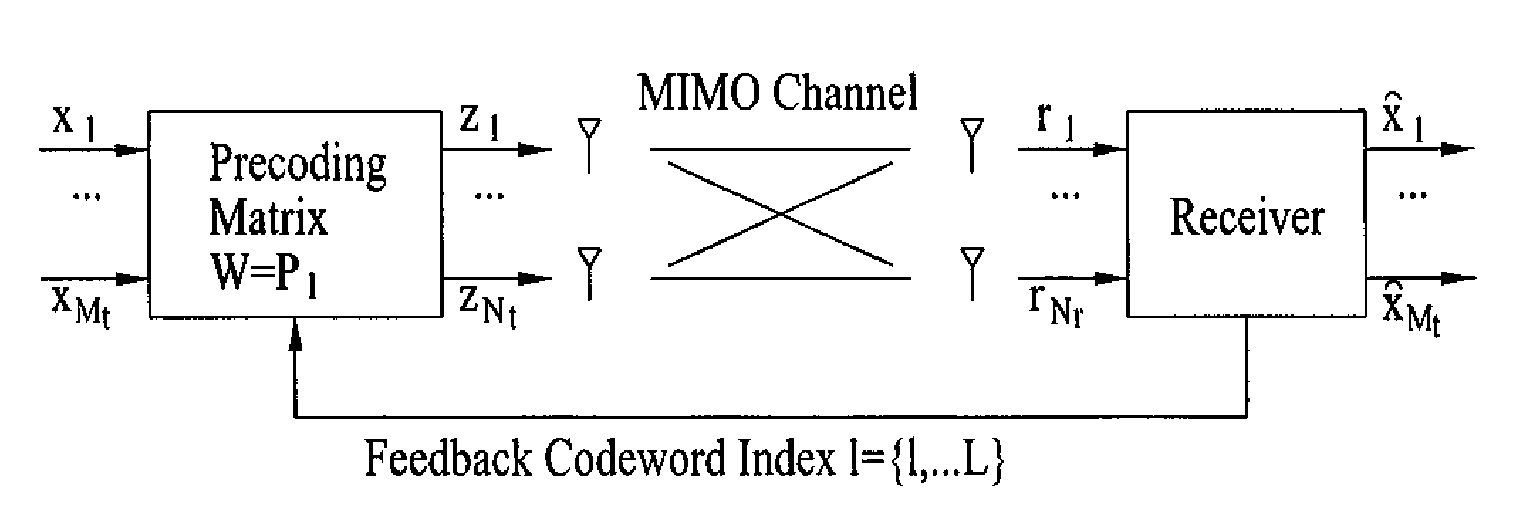
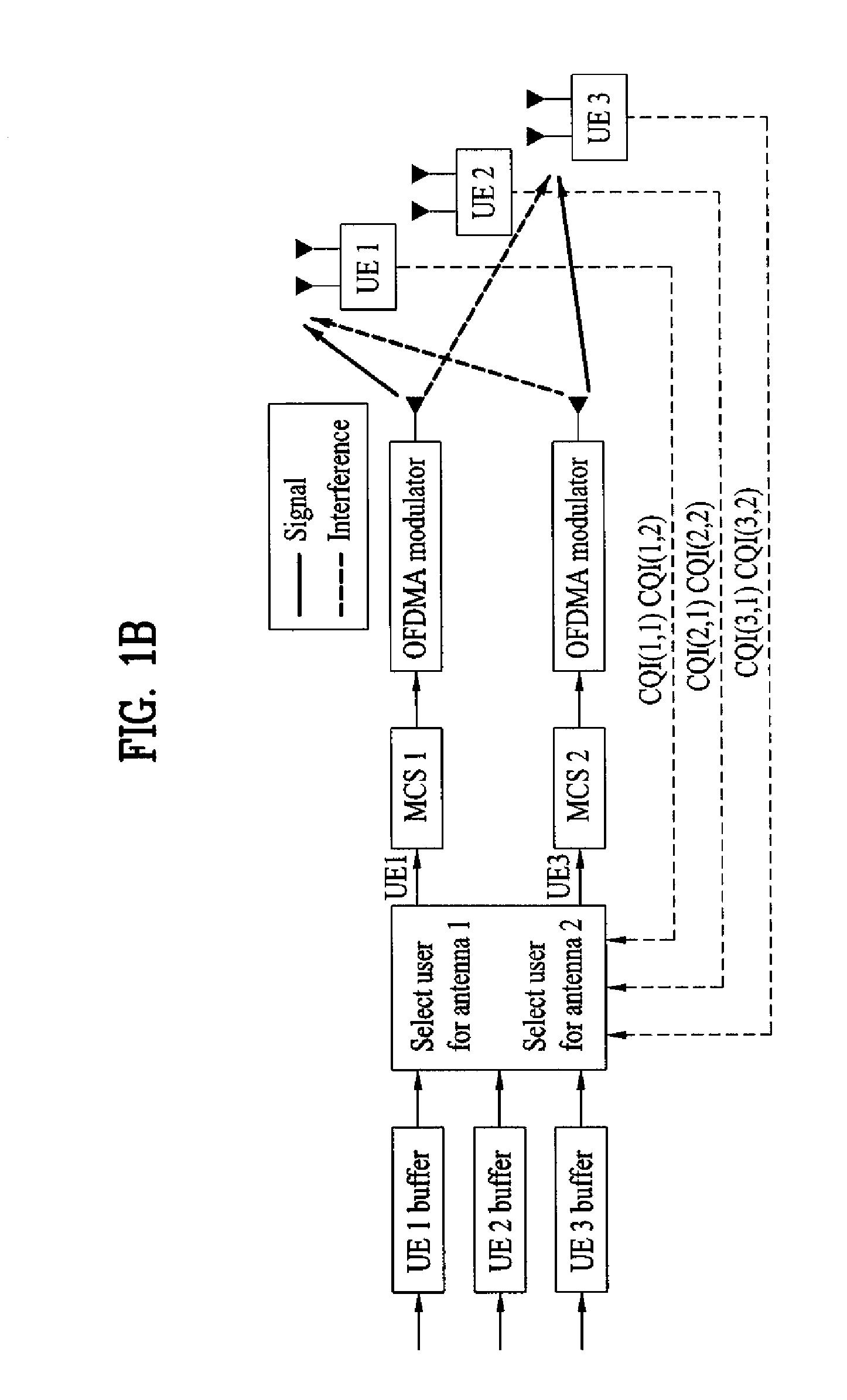
Method of transmitting using phase shift-based precoding and apparatus for implementing the same in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080205533A1Eliminate the problemEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemPhase shifted
A method of transmitting data using a plurality of subcarriers in a multi-antenna wireless communication system is disclosed. More specifically, the method includes receiving feedback information from a mobile station (MS), performing channel encoding and modulation independently on user data to be transmitted by each antenna using the received feedback information, determining a phase shift-based precoding matrix for increasing a phase angle of the user data by a fixed amount, and performing precoding using the determined phase shift-based precoding matrix on the user data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for correcting errors in a multiple subcarriers communication system using multiple antennas
ActiveUS20090307558A1Increase speedImprove reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemPhase shifted
A method for correcting errors in a multiple antenna system based on a plurality of sub-carriers and a transmitting / receiving apparatus supporting the same are disclosed. The method includes determining a phase shift based precoding matrix phase shifted at a predetermined phase angle, initially transmitting each sub-carrier symbol to a receiver in a packet unit by using the phase shift based precoding matrix, reconstructing the phase shift based precoding matrix to reduce a spatial multiplexing rate if a negative reception acknowledgement (NACK) is received from the receiver, and retransmitting the initially transmitted sub-carrier symbol by using the reconstructed phase shift based precoding matrix or by changing the phase shift based precoding matrix using offset information fed back from the receiver or random offset information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
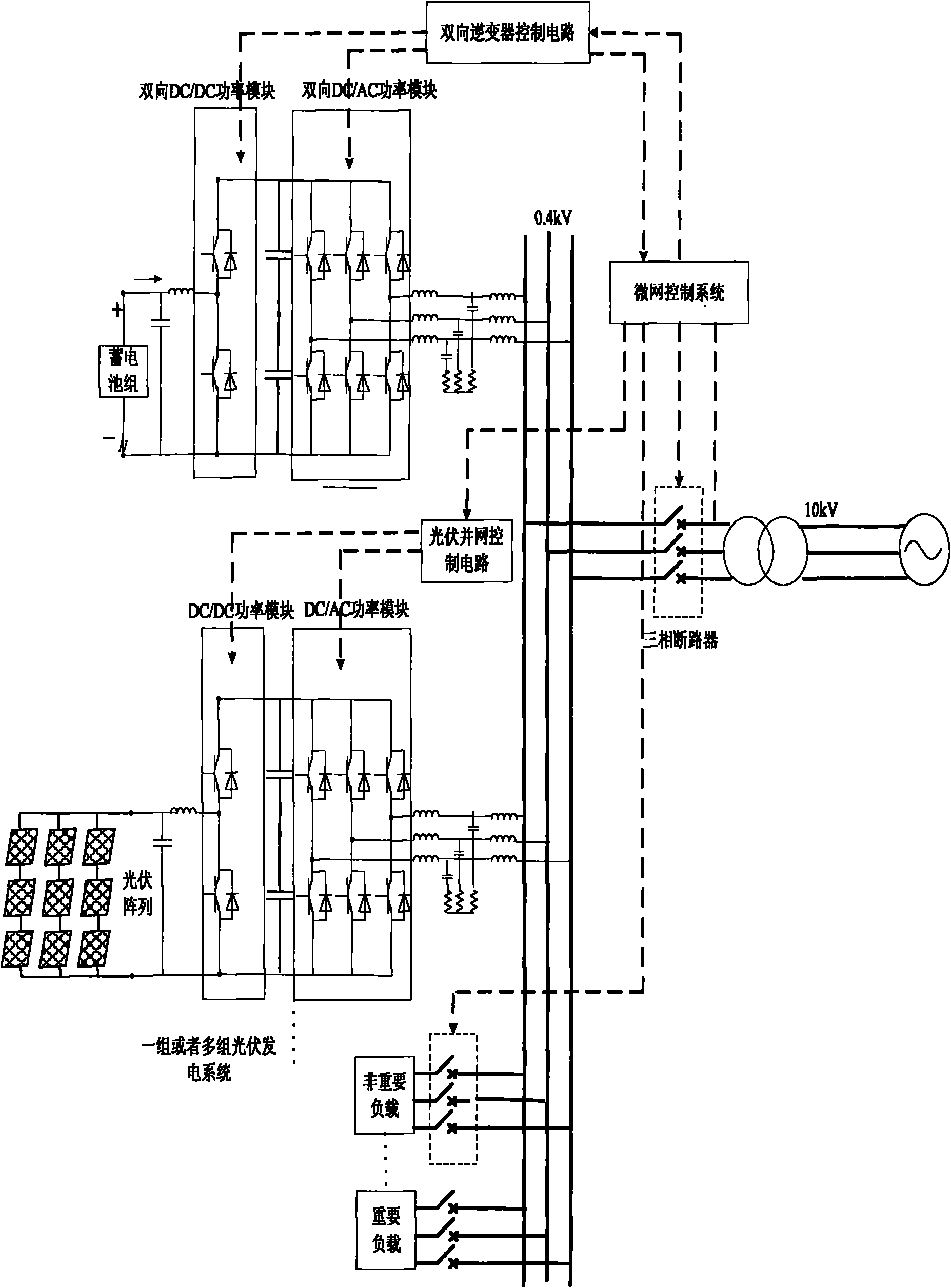
Master-slave strategy-based microgrid system coordination control method
InactiveCN101931238AAchieving two-way flowImprove robustnessSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageMicrogridControl system
The invention discloses a microgrid system coordination control method which takes a storage battery energy storage system as a main power supply. The conventional inversion products and technology hardly form a microgrid and cannot meet the requirement on stable operation of the microgrid system. The storage battery energy storage system in the microgrid is taken as a main power supply when the microgrid independently works, the microgrid frequency and voltage are kept constant, and a distributed power supply controls the power along with the microgrid voltage and a phase angle; and a microgrid control system controls a bidirectional inverter for energy storage to effectively switch between a parallel control mode and an independent operation mode according to the state of an external power grid. The power supply in the microgrid has the advantages of high robustness, high speed, and capacities of realizing bidirectional flow of electric energy and flexible current control and meeting the requirement on stable operation of the microgrid system.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMAPNY +1
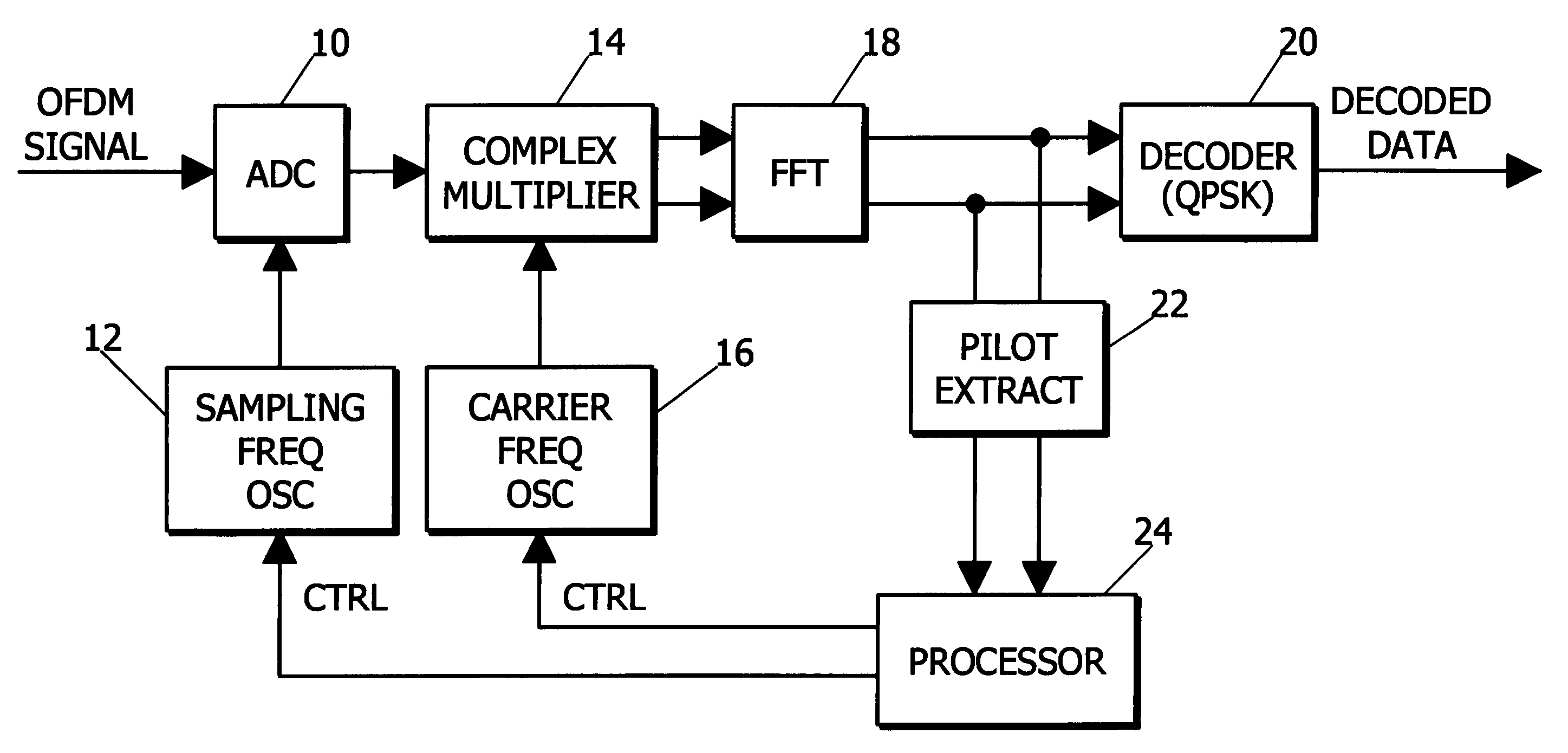
Digital signal demodulation of an OFDM signal with error correction
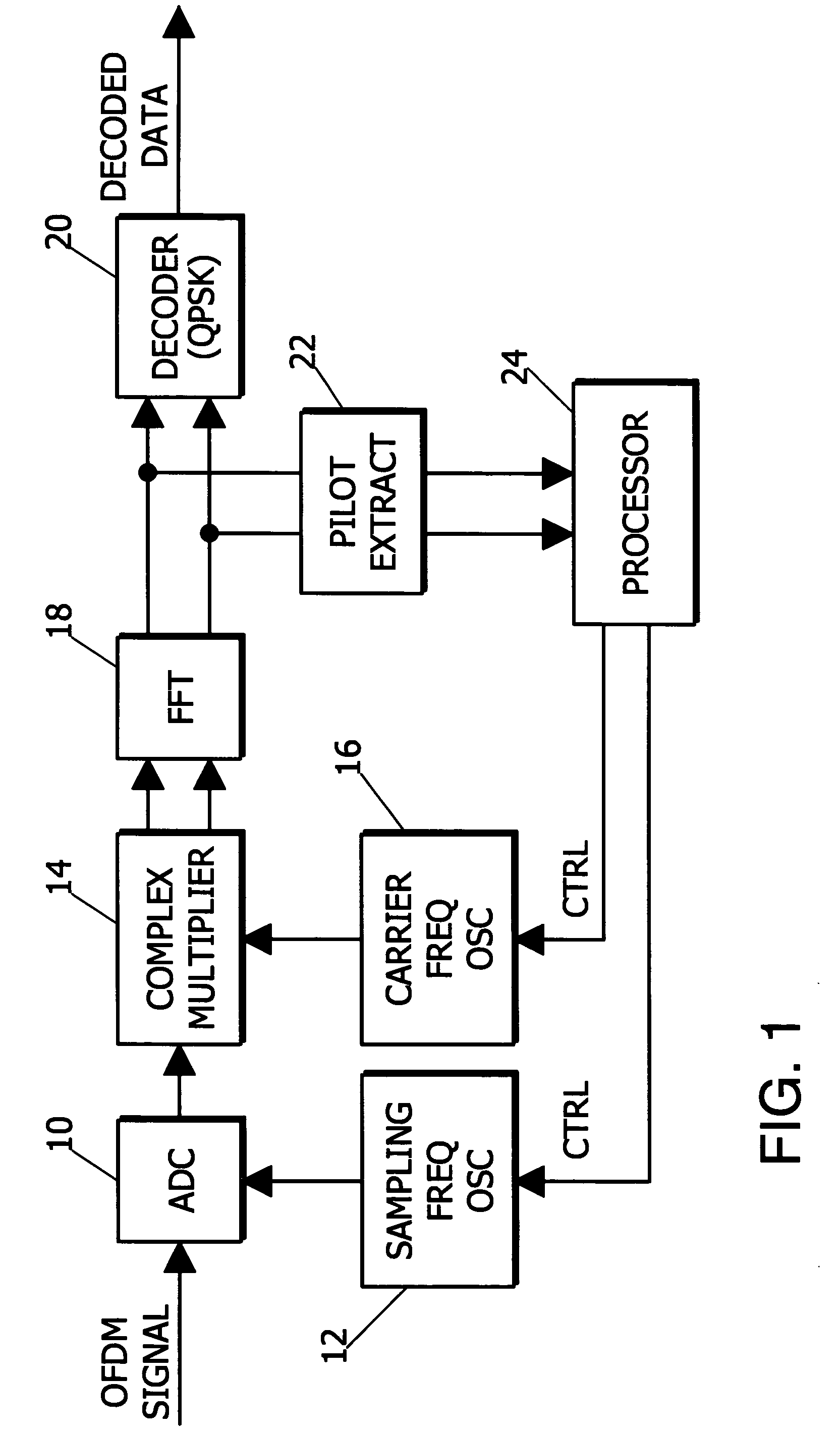
InactiveUS20050175113A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionPhase differenceCarrier signal
A digital signal demodulator digitizes an OFDM signal at a sampling frequency from a sampling oscillator to produce a digital OFDM signal. The digital OFDM signal is converted into I and Q components using a carrier frequency from a carrier oscillator. The IQ components are transformed into digital complex symbols, and pilot signals are extracted from the complex symbols. A processor calculates an inter-symbol difference of phase differences between pilot signals to control the sampling oscillator to correct the sampling frequency; calculates an inter-symbol difference for one of the pilot signals to control the carrier oscillator to correct the carrier frequency; and calculates a phase angle for one of the subcarriers at a frequency in the middle of the plurality of subcarriers for the OFDM signal to control the carrier oscillator to correct the carrier frequency phase.
Owner:OKUYAMA HIDEO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com