Patents
Literature
38 results about "Faradaic current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
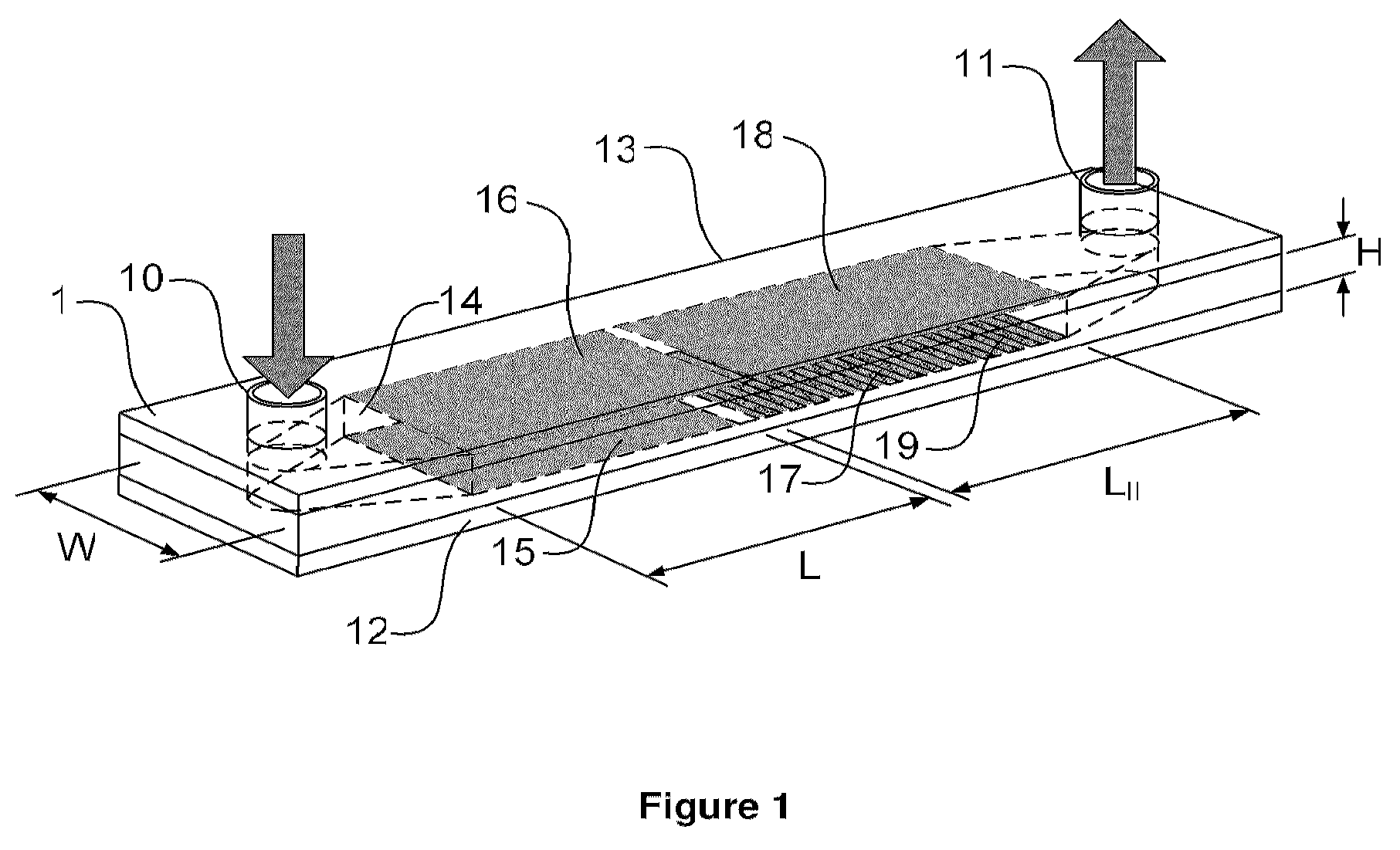
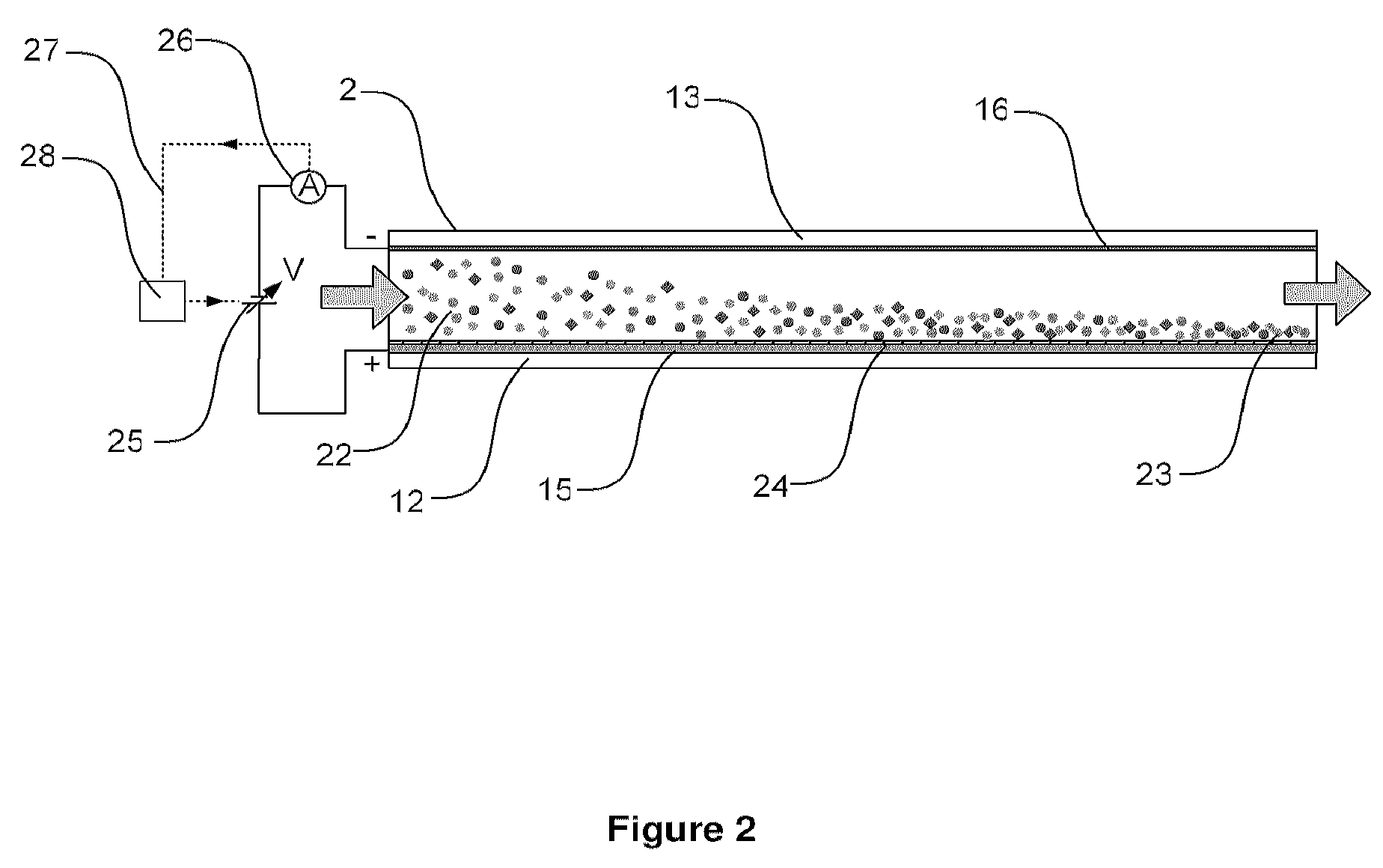
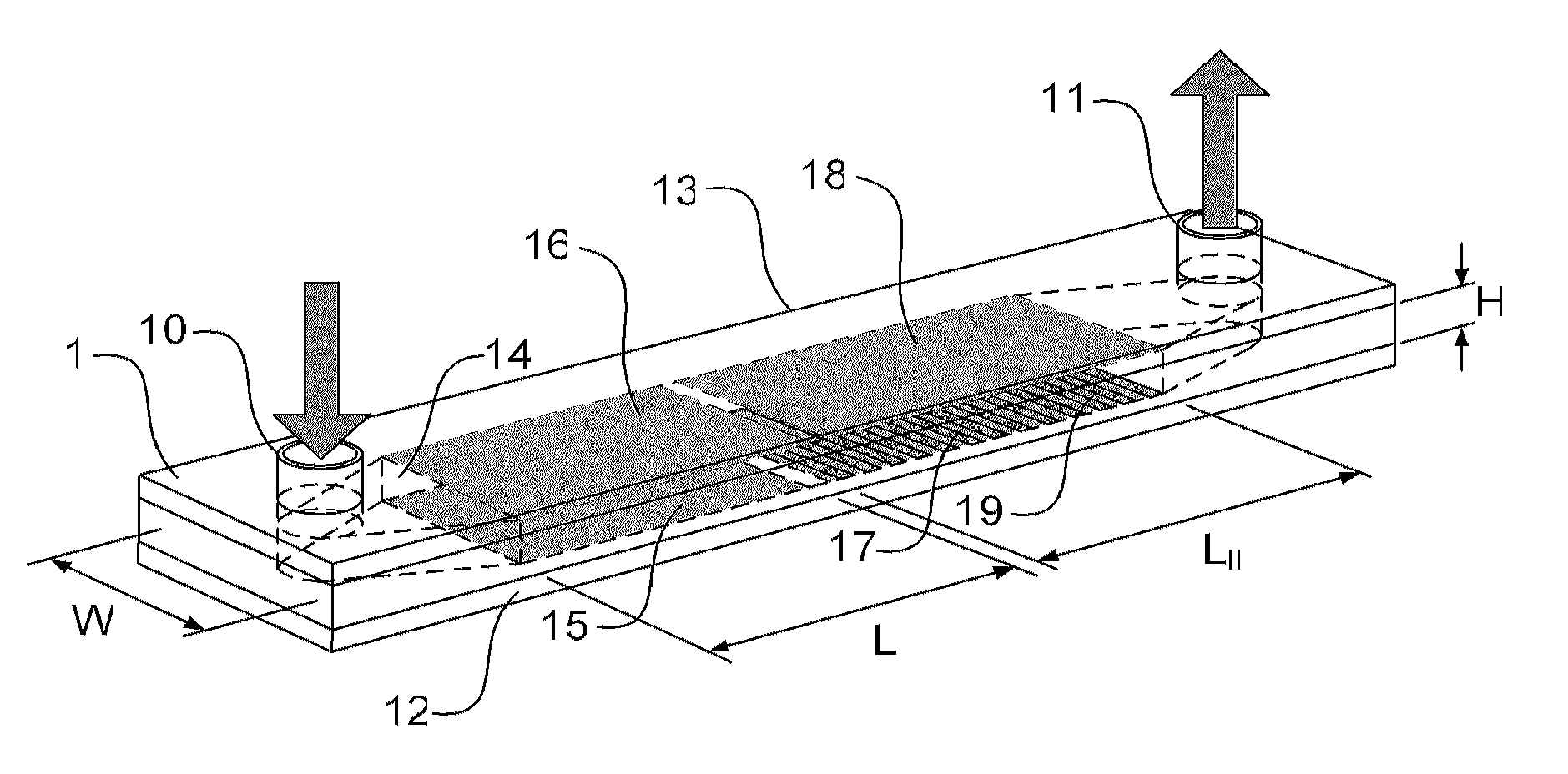
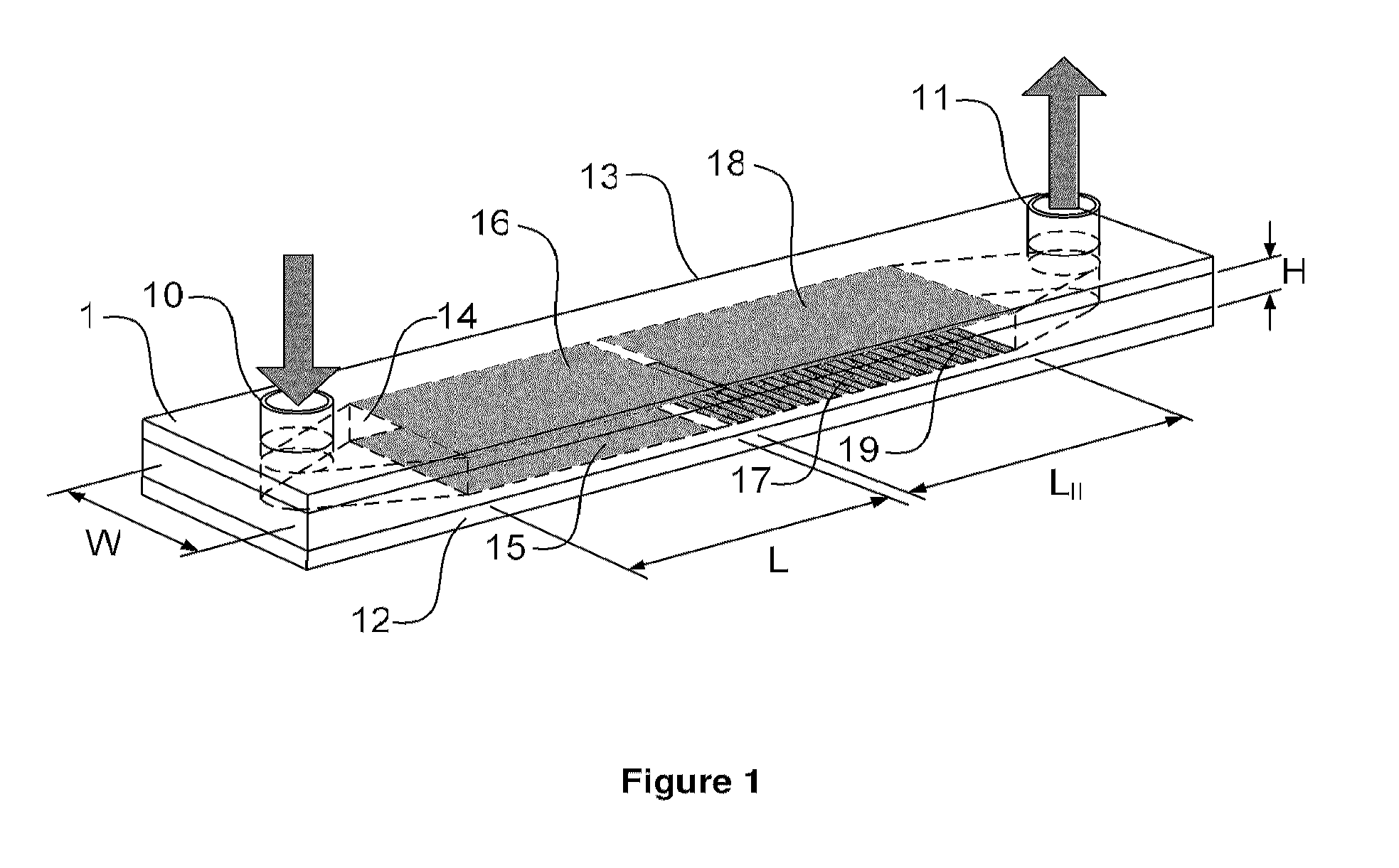
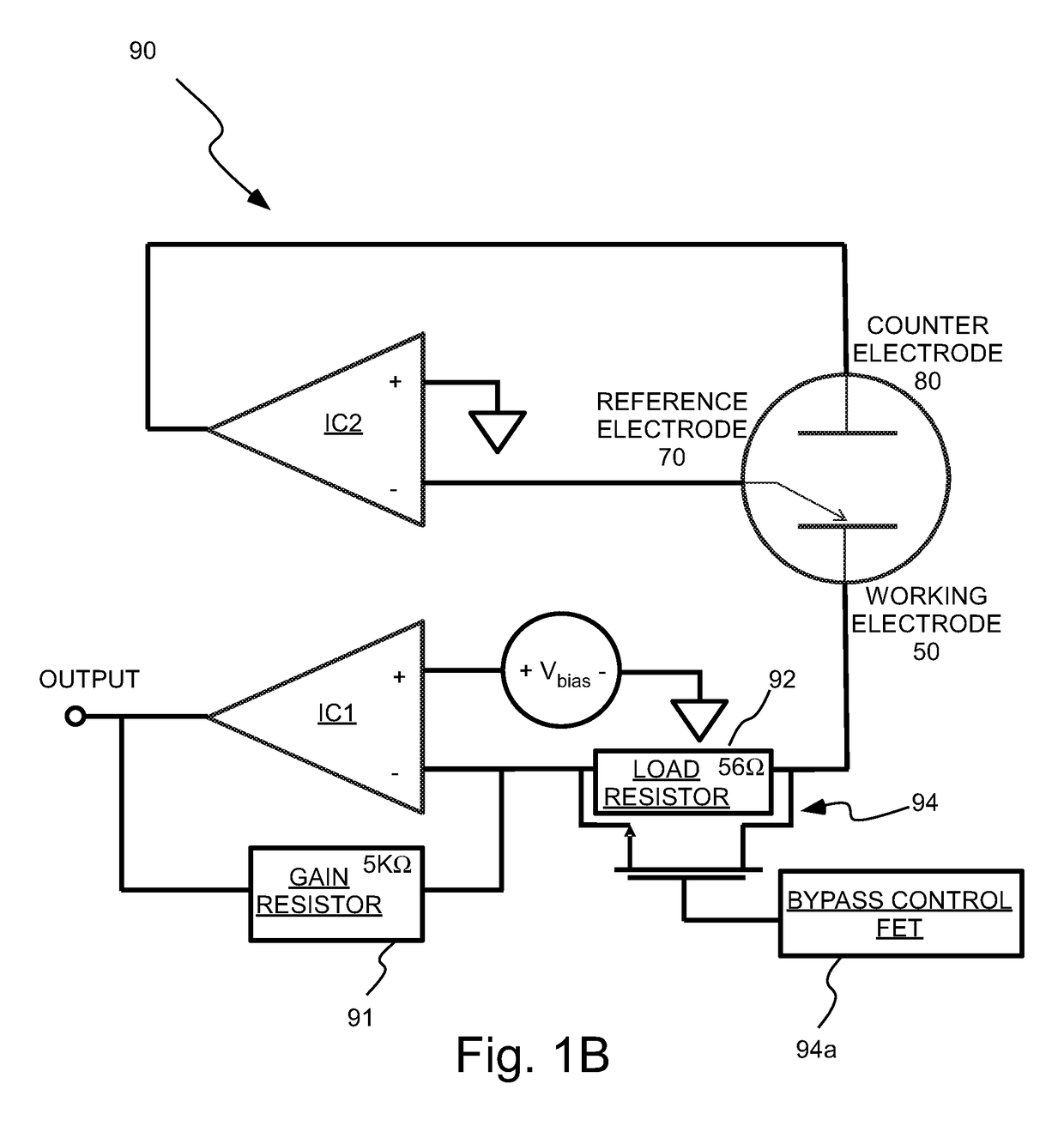
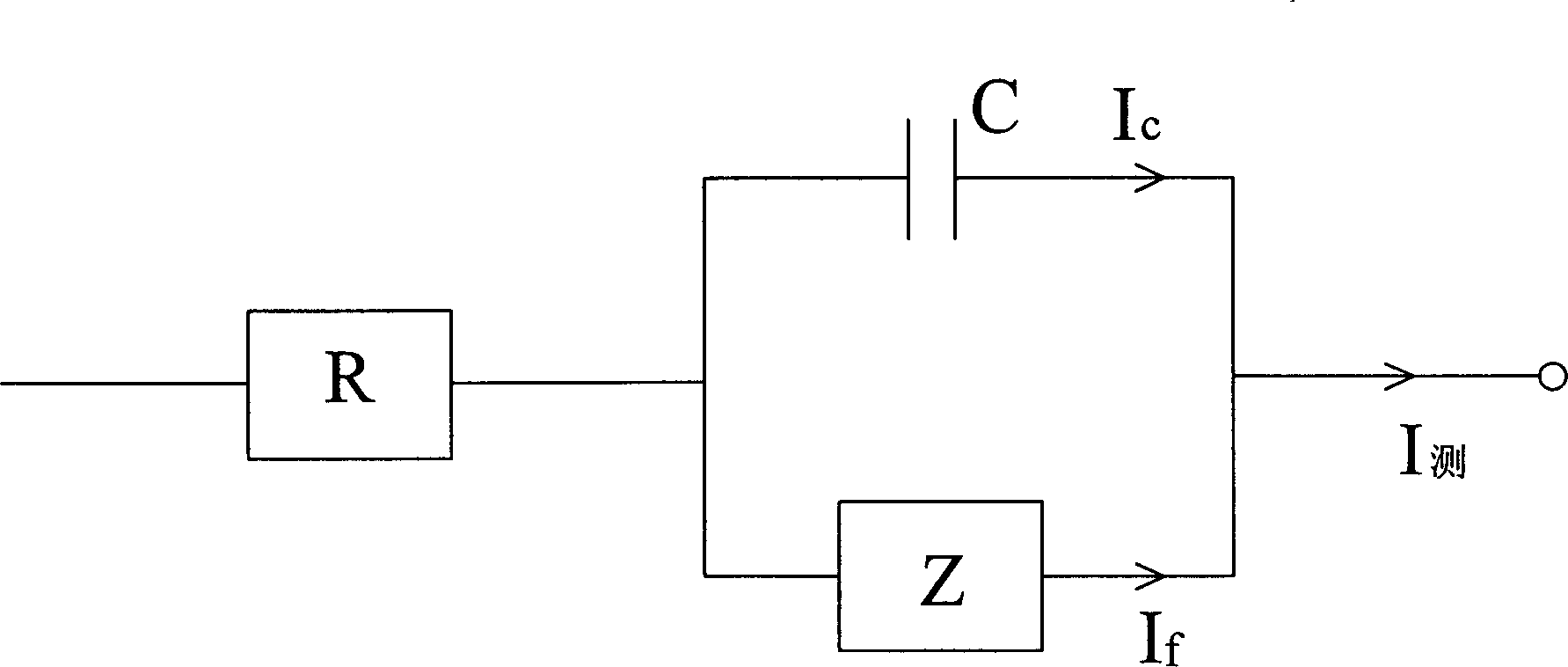
The faradaic current is the current generated by the reduction or oxidation of some chemical substance at an electrode. The net faradaic current is the algebraic sum of all the faradaic currents flowing through an indicator electrode or working electrode.
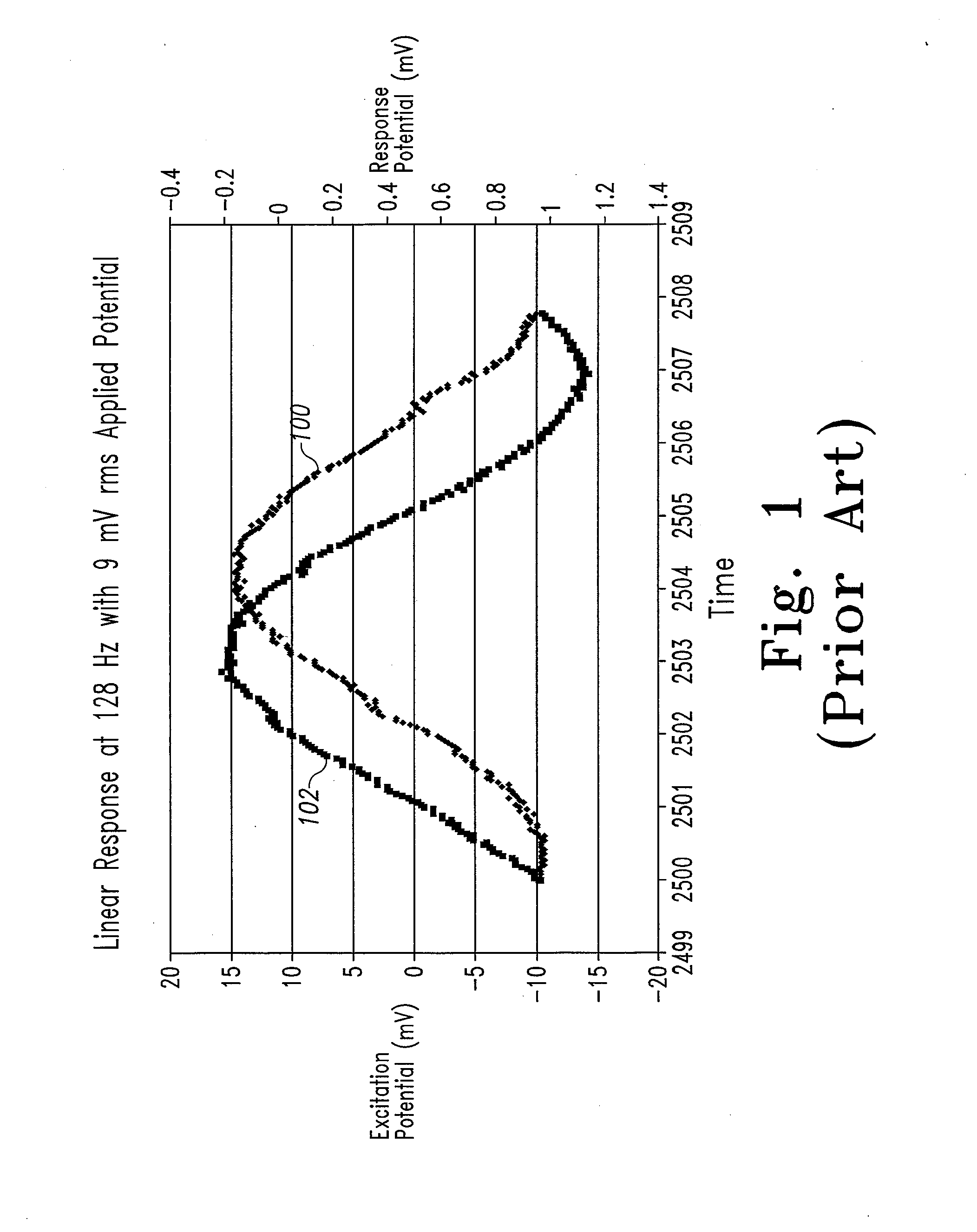
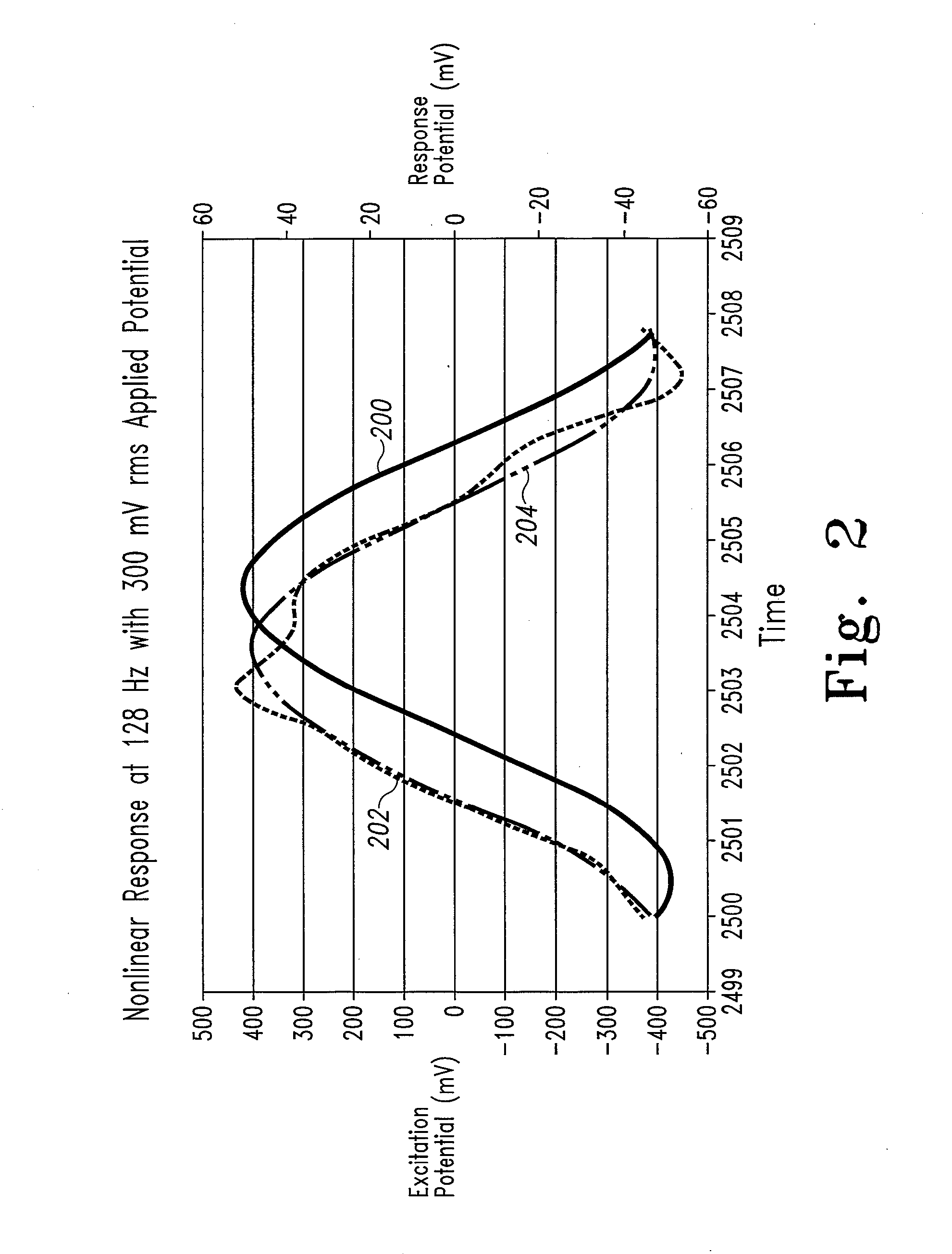
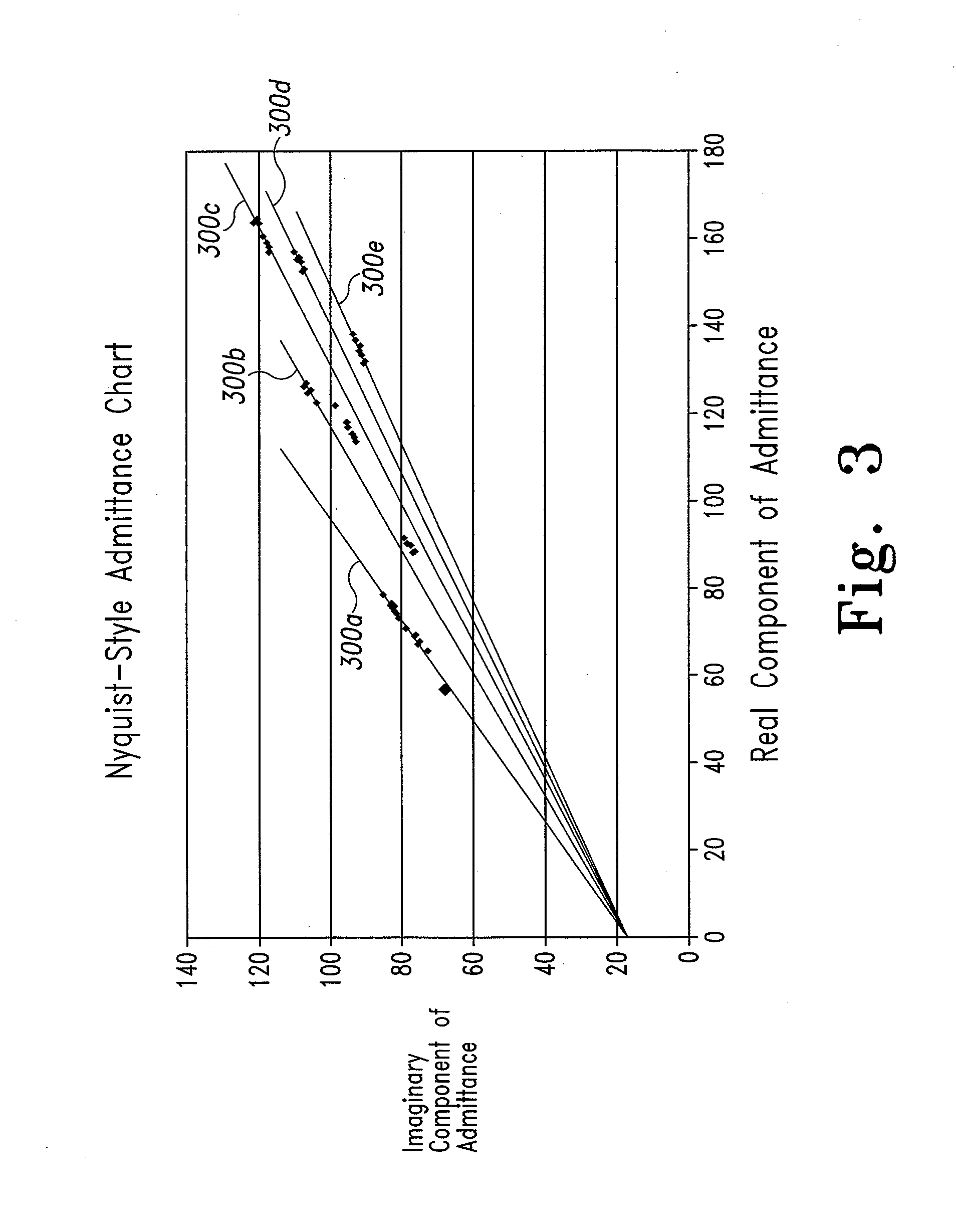
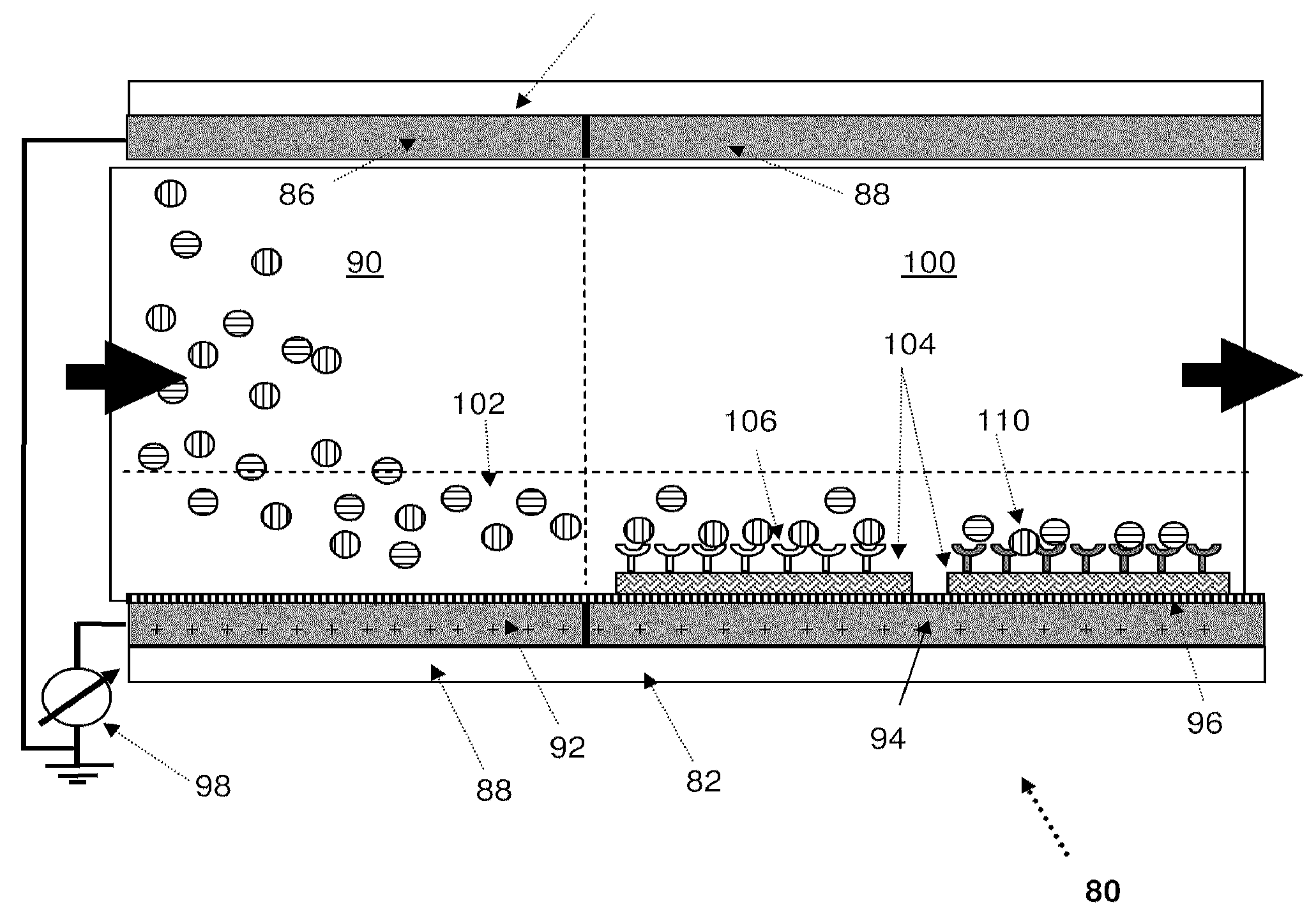
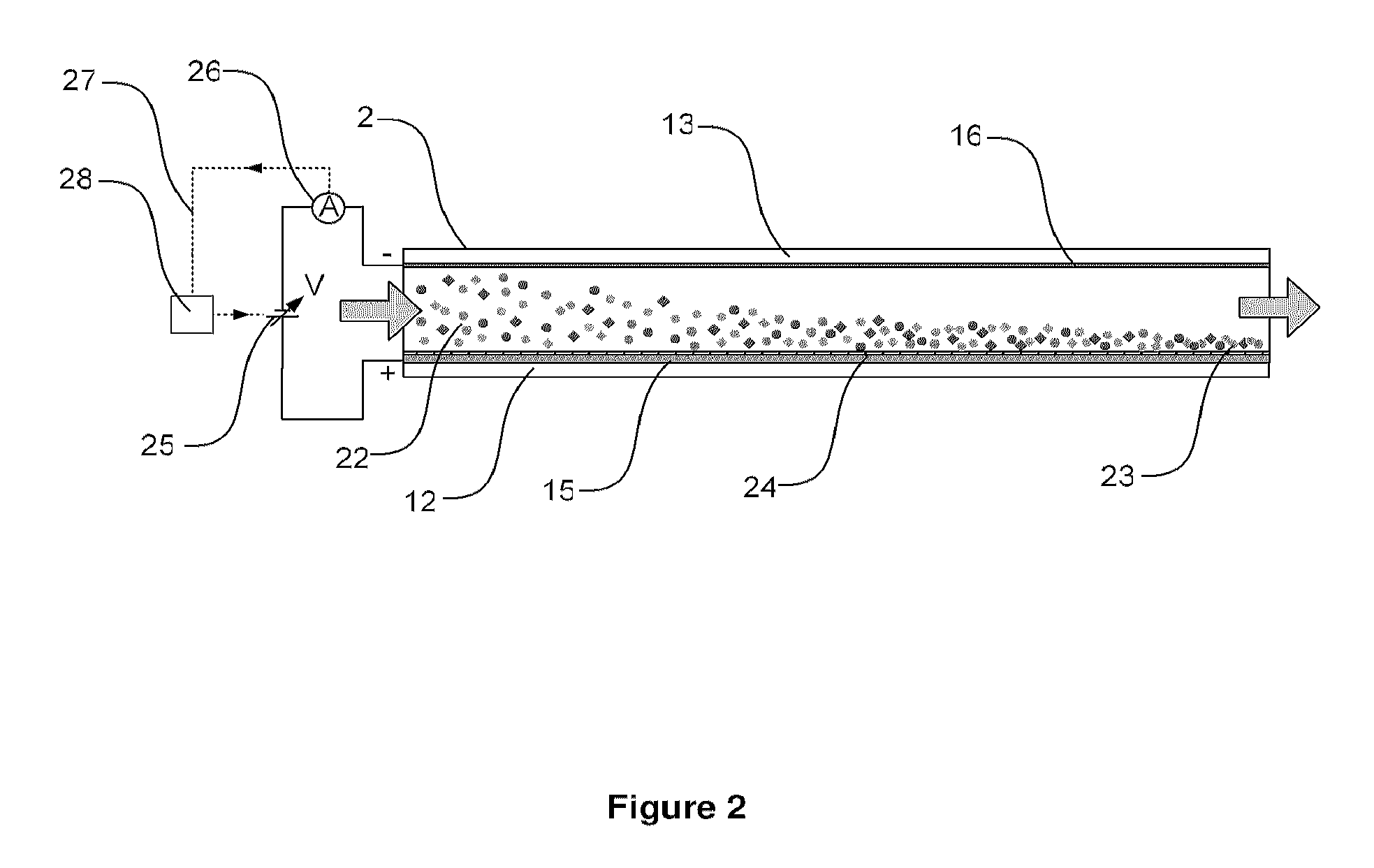
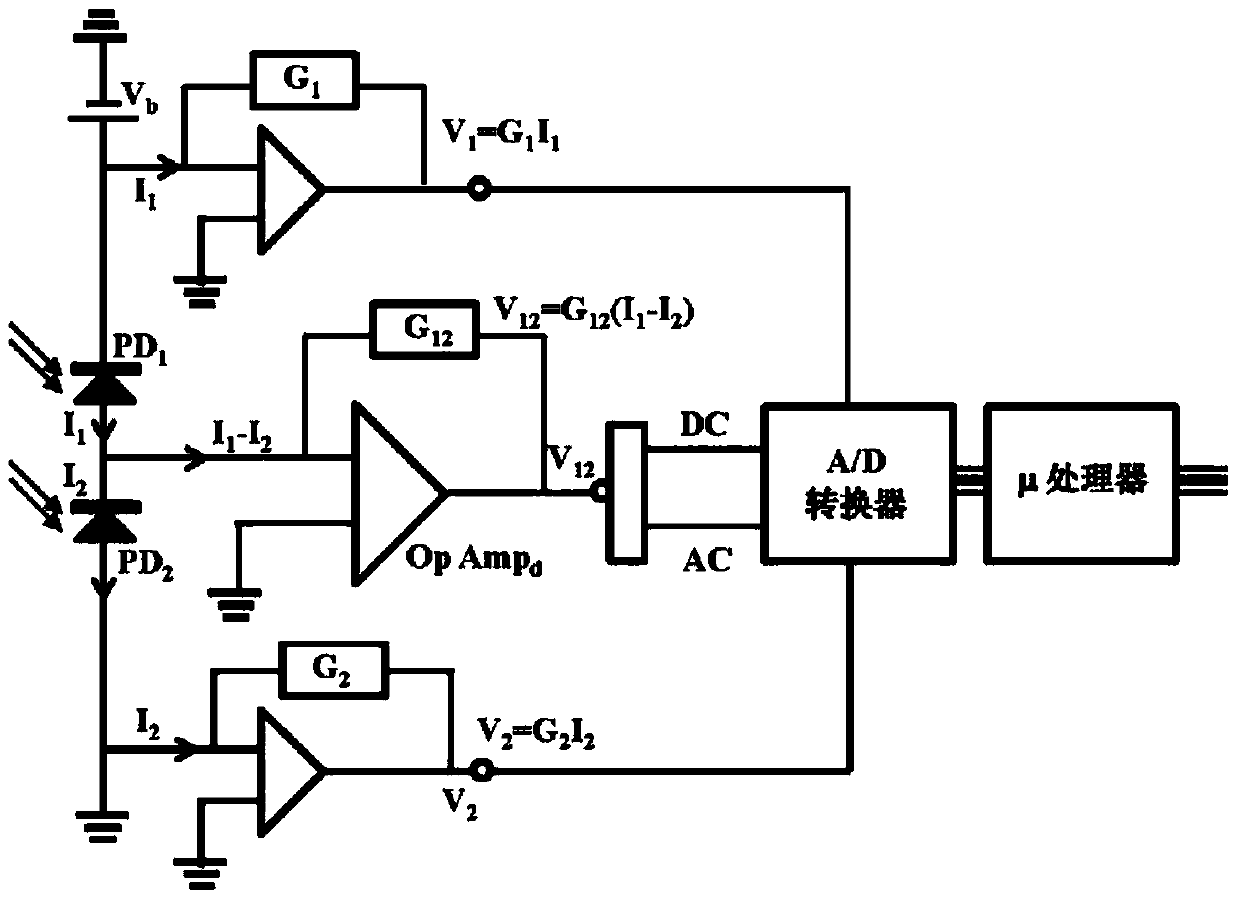
System and method for analyte measurement using a nonlinear sample response
InactiveUS20070264721A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingLinear componentApplied potential
The systems and methods of the present invention utilize a linear component of a non-linear, faradaic current response generated by a biological fluid sample when an AC excitation potential sufficient to produce such a faradaic current response is applied to the sample, in order to calculate the concentration of a medically significant component in the biological fluid sample. The current response is created by the excitation of electrochemical processes within the sample by the applied potential. Typically, the linear component of the current response to an applied AC potential contains phase angle and / or admittance information that may be correlated to the concentration of the medically significant component. Also typically, the fundamental linear component of the current response is utilized in the disclosed systems and methods. Harmonics of the fundamental linear component may also be used. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Cell concentration, capture and lysis devices and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20120190040A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteLysis
The present invention provides a microfluidic devices and methods of use thereof for the concentration and capture of cells. A pulsed non-Faradic electric field is applied relative to a sample under laminar flow, which results to the concentration and capture of charged analyte. Advantageously, pulse timing is selected to avoid problems associated with ionic screening within the channel. At least one of the electrodes within the channel is coated with an insulating layer to prevent a Faradic current from flowing in the channel. Under pulsed application of a unipolar voltage to the electrodes, charged analyte within the sample is moved towards one of the electrodes via a transient electrophoretic force.
Owner:QVELLA CORP
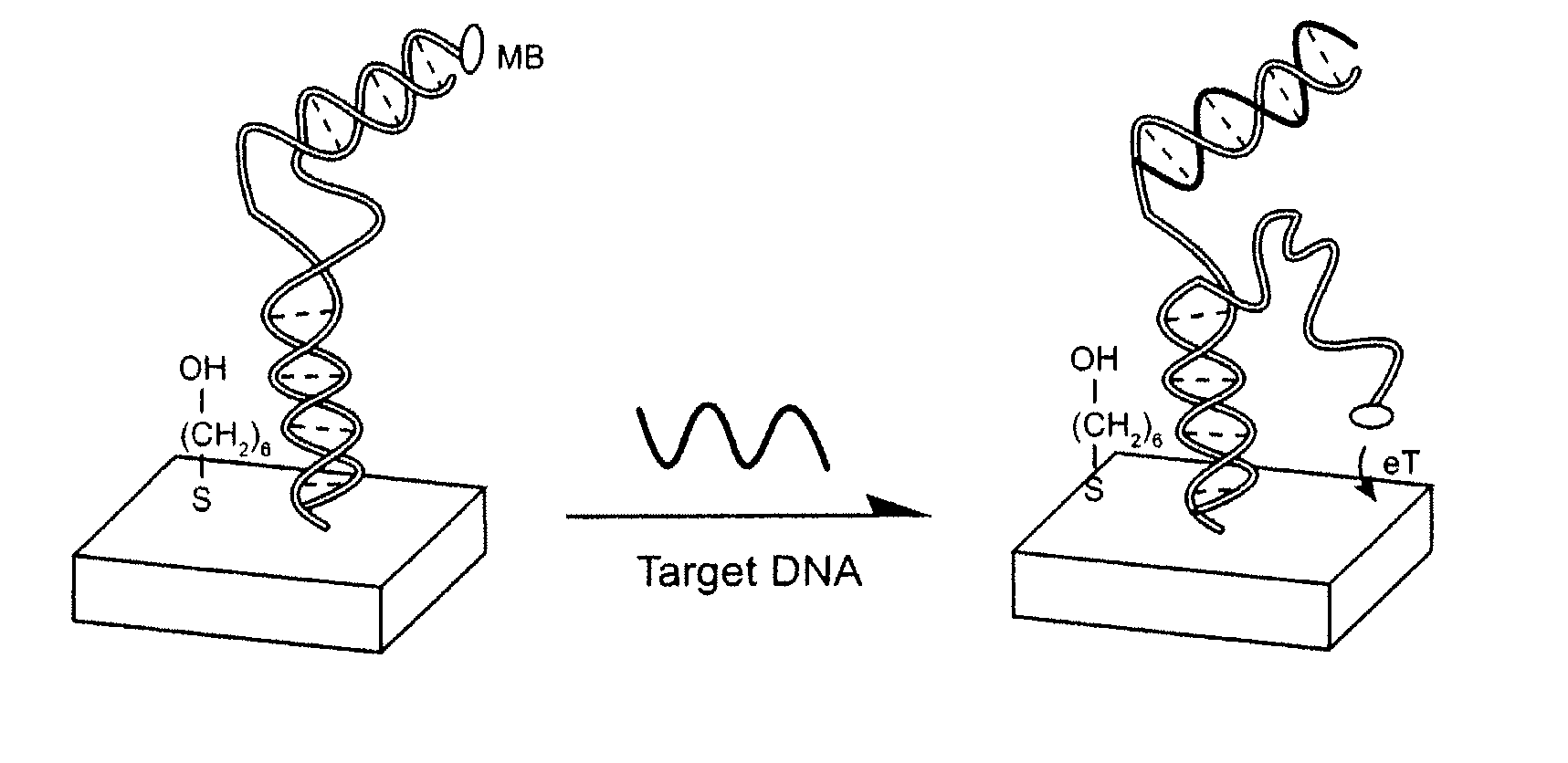
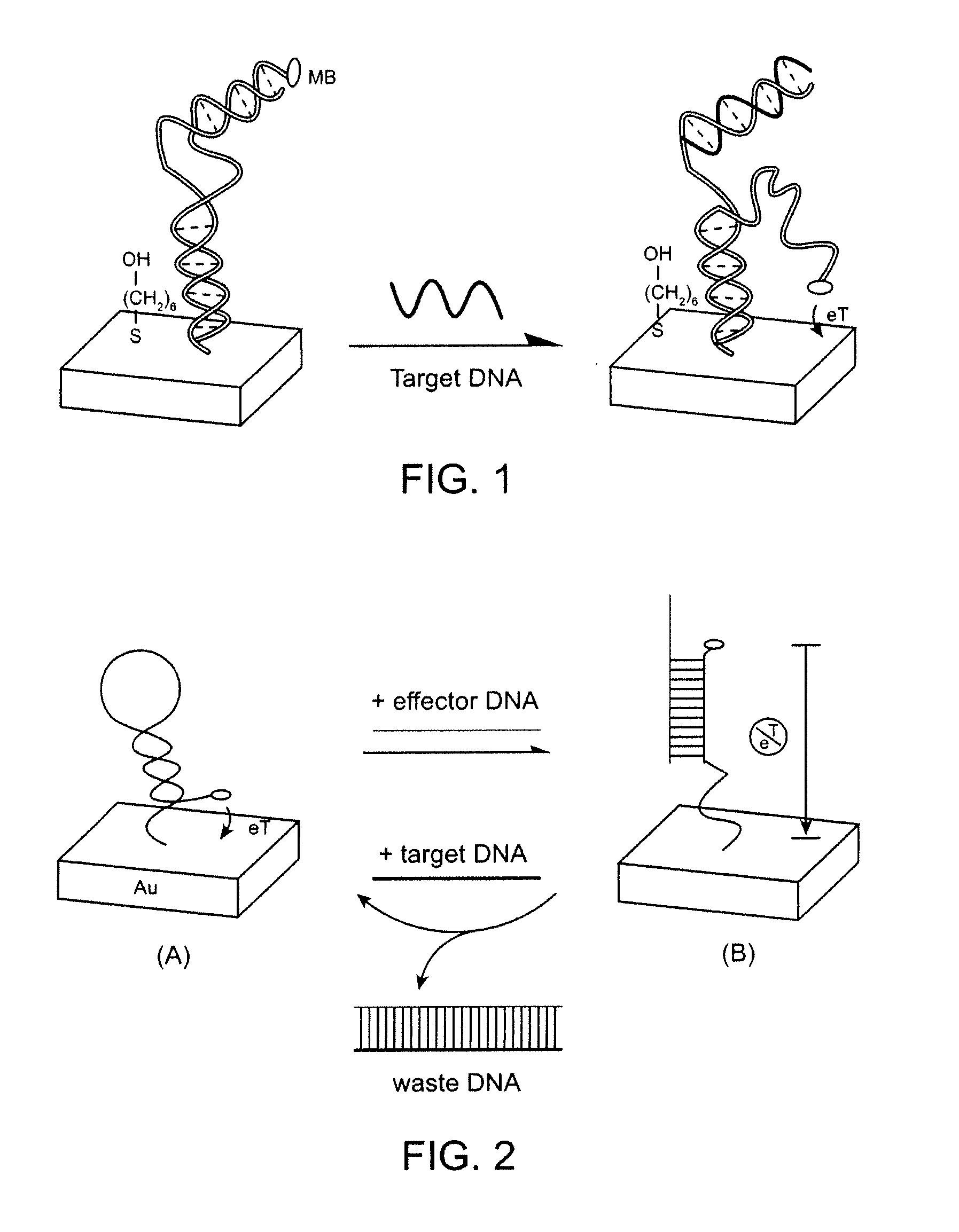
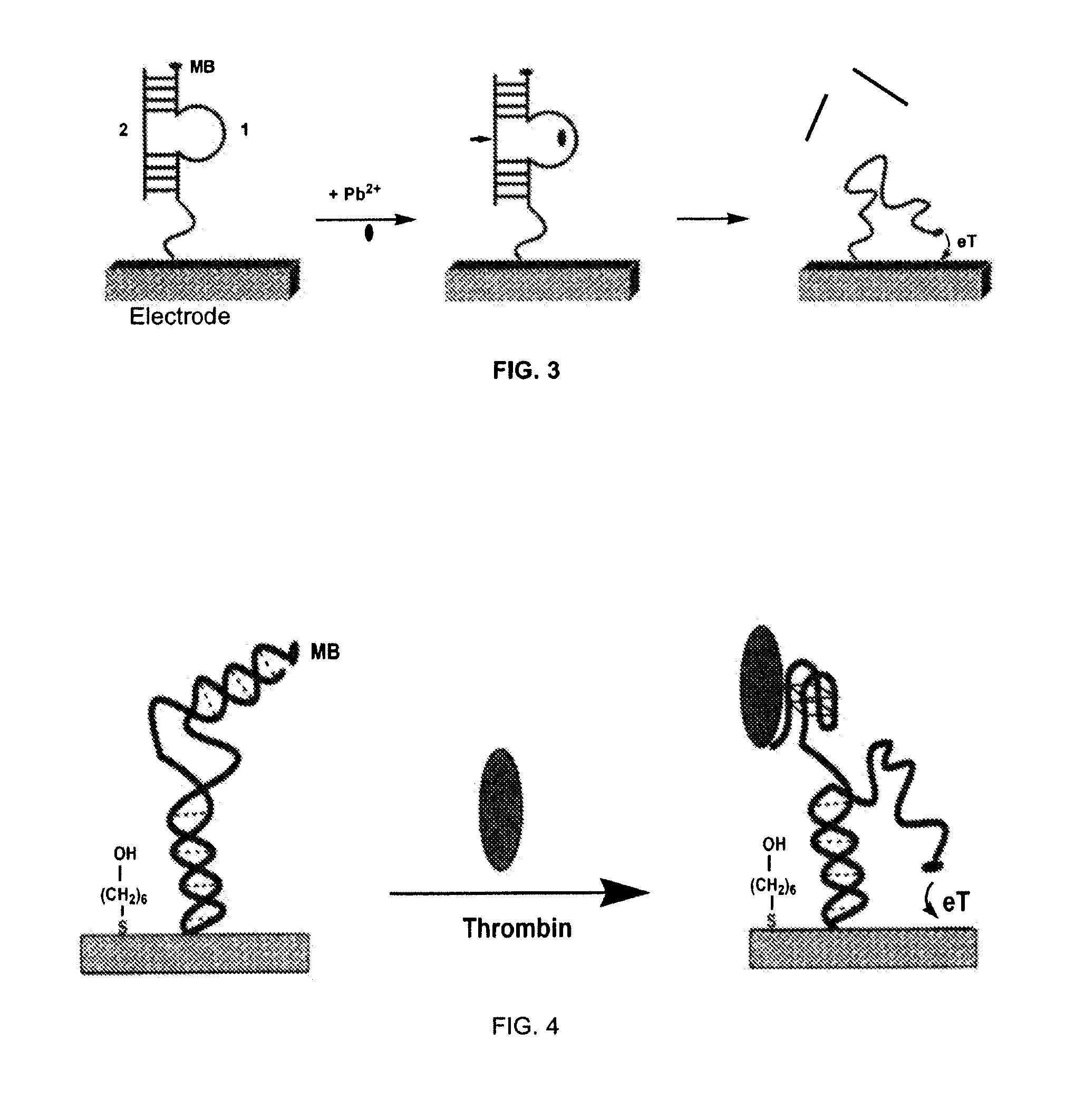
Signal-on architecture for electronic, oligonucleotide-based detectors
ActiveUS20070154909A1Enhanced detection signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal onOxidation-Reduction Agent
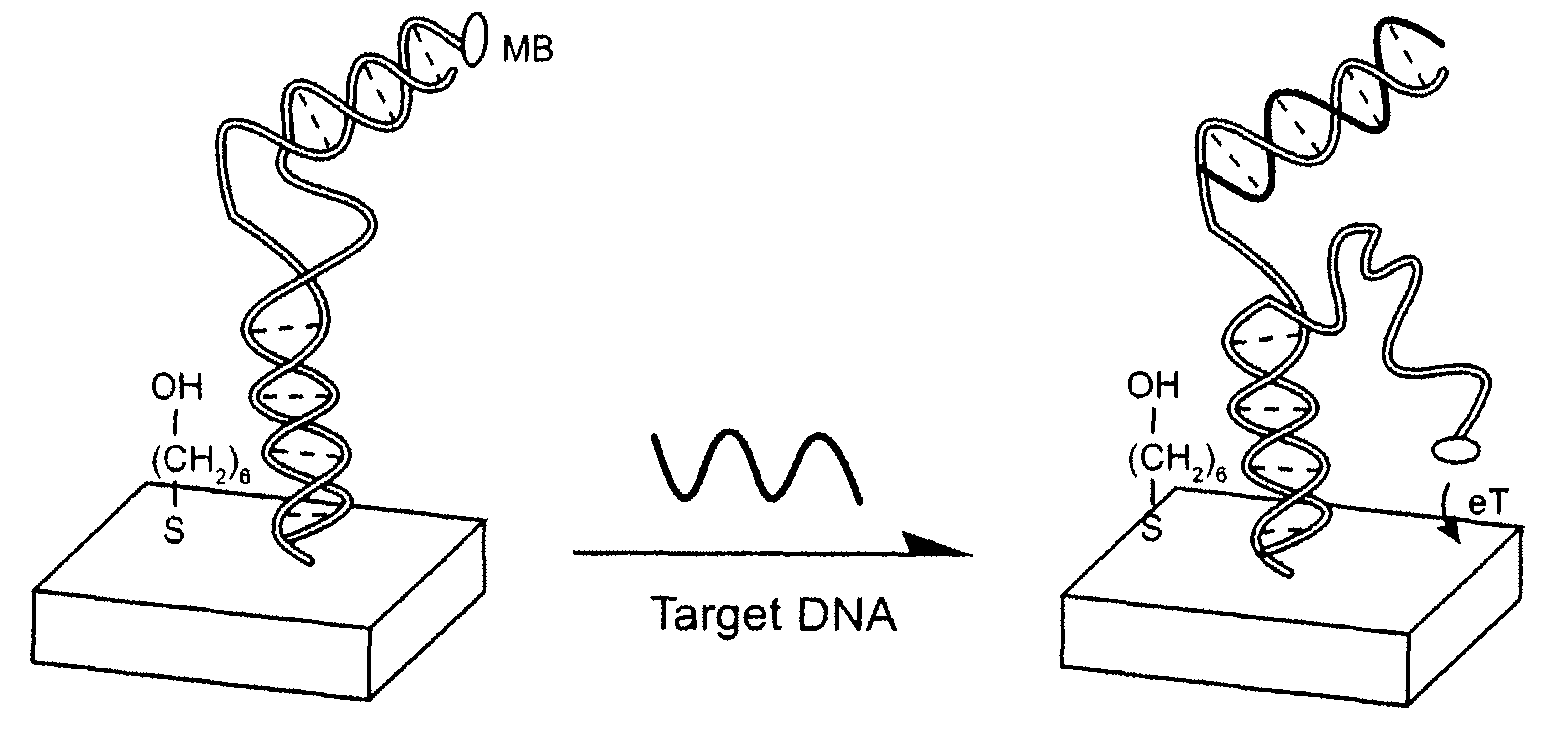
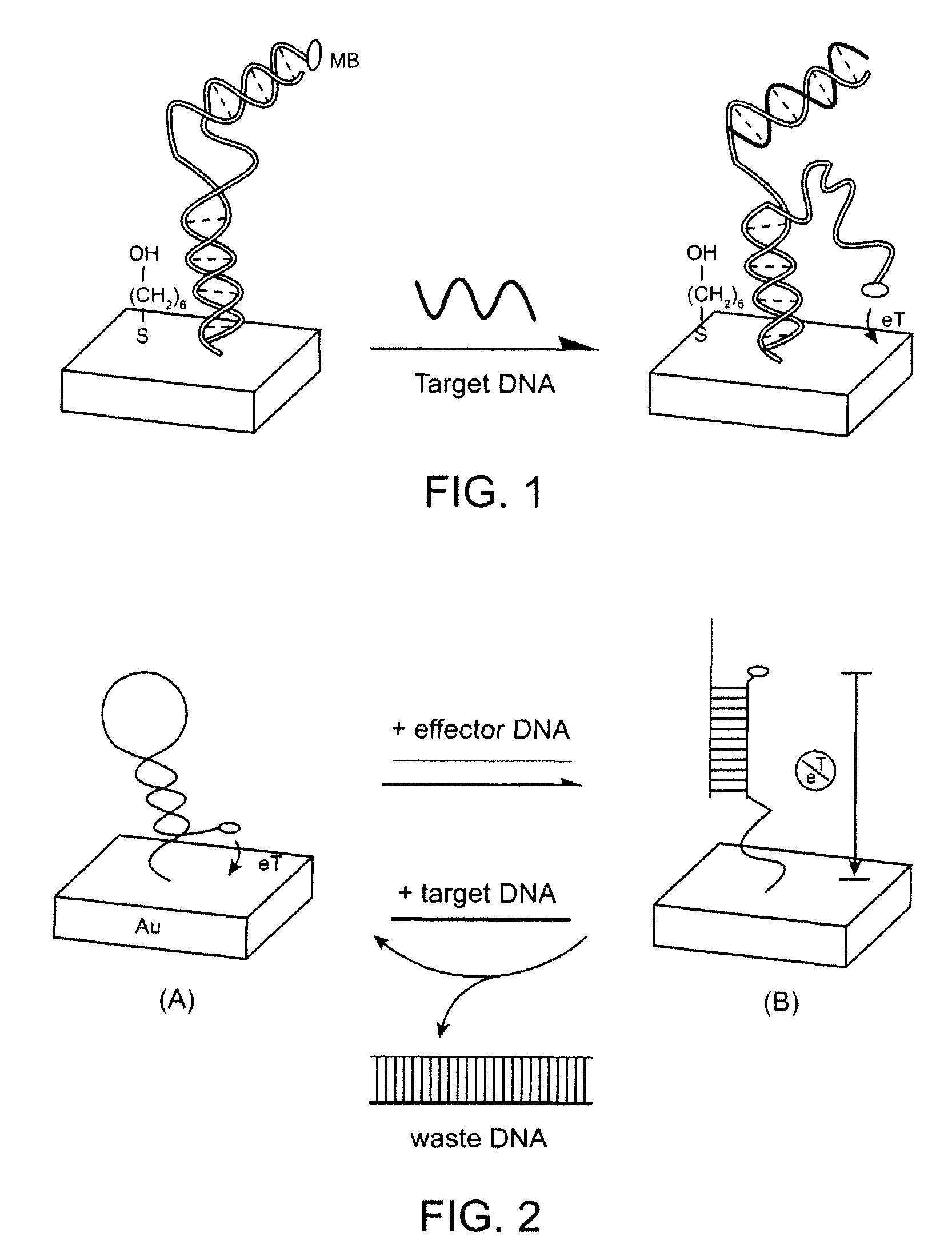
The invention provides a general “signal-on” architecture for oligonucleotide-based detectors that leads to order of magnitude increases in signal gain and sensitivity as compared to prior art detectors. The detectors of the invention rely on base pairing between two oligonucleotide strands, the sensor strand and the blocker strand. In the ‘off’ position of the detector, i.e., in the absence of target, the blocker strand and sensor strand are base-paired. As shown in FIG. 1, the formation of comparatively rigid, duplex DNA prevents the redox moiety from approaching the electrode surface, thereby suppressing Faradaic currents. When target is added to the system, the target displaces the blocker strand, binds to the sensor strand, liberating the end of the redox-labeled oligonucleotide to produce a flexible element. This, in turn, allows the redox moiety to collide with the electrode surface, producing a readily detectable Faradaic current.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Signal-on architecture for electronic, oligonucleotide-based detectors
ActiveUS7803542B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal onOxidation-Reduction Agent
The invention provides a general “signal-on” architecture for oligonucleotide-based detectors that leads to order of magnitude increases in signal gain and sensitivity as compared to prior art detectors. The detectors of the invention rely on base pairing between two oligonucleotide strands, the sensor strand and the blocker strand. In the ‘off’ position of the detector, i.e., in the absence of target, the blocker strand and sensor strand are base-paired. As shown in FIG. 1, the formation of comparatively rigid, duplex DNA prevents the redox moiety from approaching the electrode surface, thereby suppressing Faradaic currents. When target is added to the system, the target displaces the blocker strand, binds to the sensor strand, liberating the end of the redox-labeled oligonucleotide to produce a flexible element. This, in turn, allows the redox moiety to collide with the electrode surface, producing a readily detectable Faradaic current.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Faraday apparatus for angle measurement of parallel beam
InactiveCN101414545ATo prevent danger caused by electrificationMeasurement devicesElectric discharge tubesPeak valueCrystal plane
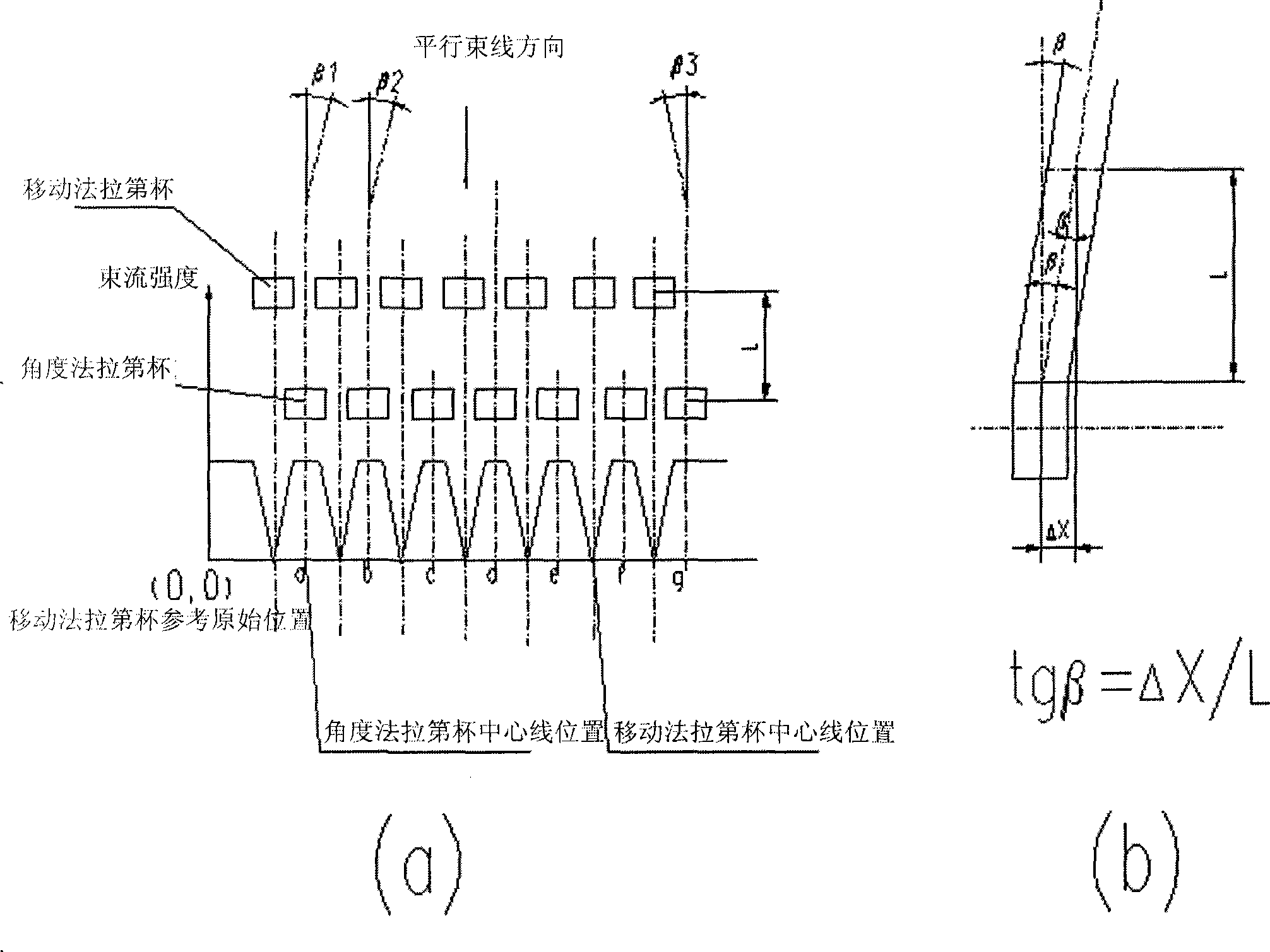
The invention discloses a parallel-beam angle measurement Faraday device of an ion implanter, relates to the ion implanter and belongs to the manufacturing field of semiconductors. The structure is as follows: the parallel-beam angle measurement Faraday device is composed of a Faraday collection frame, an electronic suppression plate, a bottom plate of the collection frame, seven fixed-angle Faraday cups and a moving Faraday cup, the Faraday collection frame collects incident ion beam flow, the electronic suppression plate suppresses the electron overflow generated by the bombardment on metal bodies of the Faraday cups by ion beams, the angle collection bottom plate is used for the vacuum connection and the sealing of the Faraday collection frame and the Faraday cups, the seven fixed-angle Faraday cups measure the current intensity of the ion beams, the central position of the implanted ion beams is determined by being combined with the moving Faraday cup which is arranged in a target room area, when the parallel beams are the incident beams which are perpendicular to a crystal plane, the central position of the blocking beams of the moving Faraday cup is consistent with the center of the measuring beams of the fixed Faraday cups, and the current of the fixed-angle Faraday cups simultaneously achieves the peak value at the position when the current of the moving Faraday cup achieves the peak value.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGKEXIN ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Sensor interrogation with fast recovery
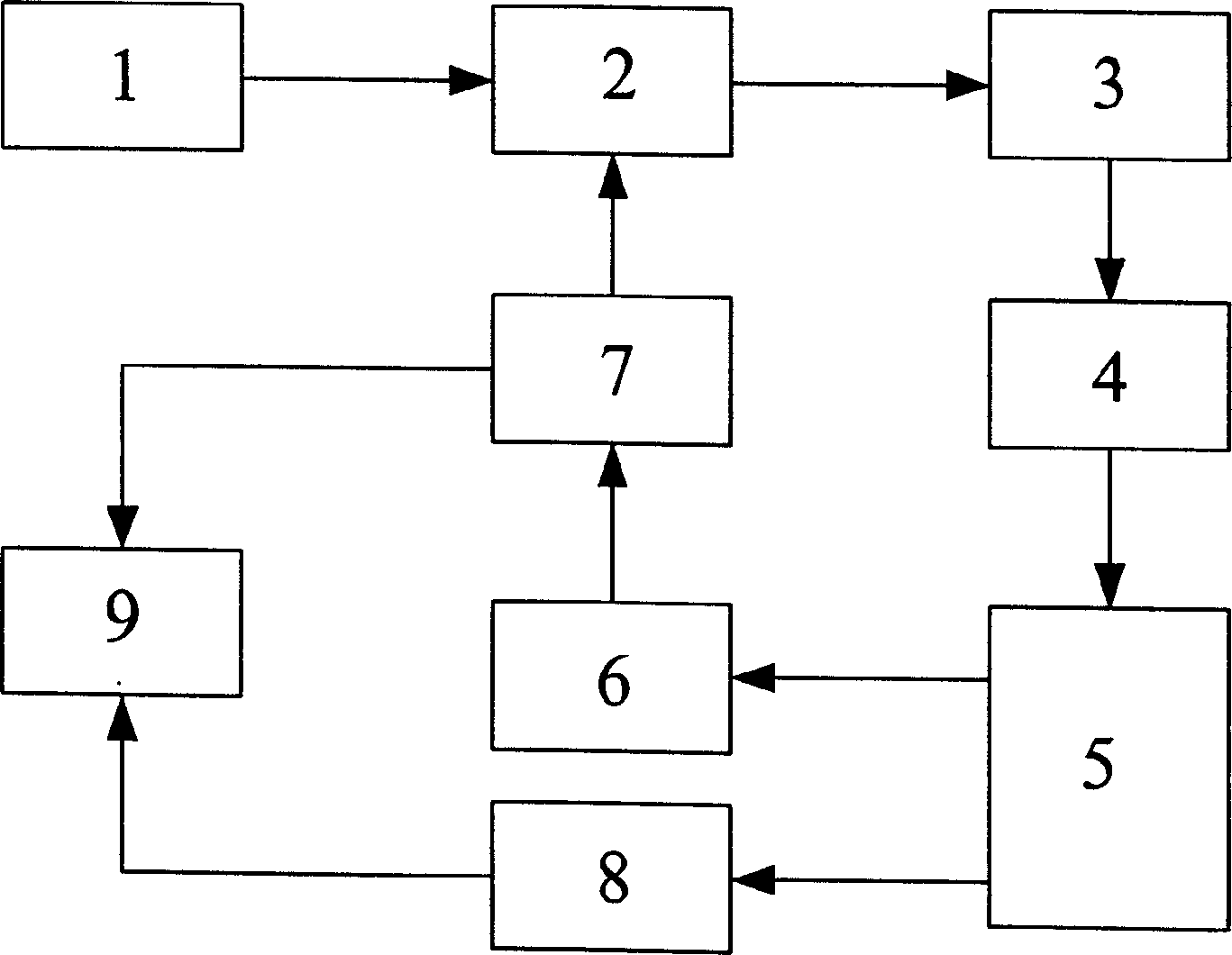
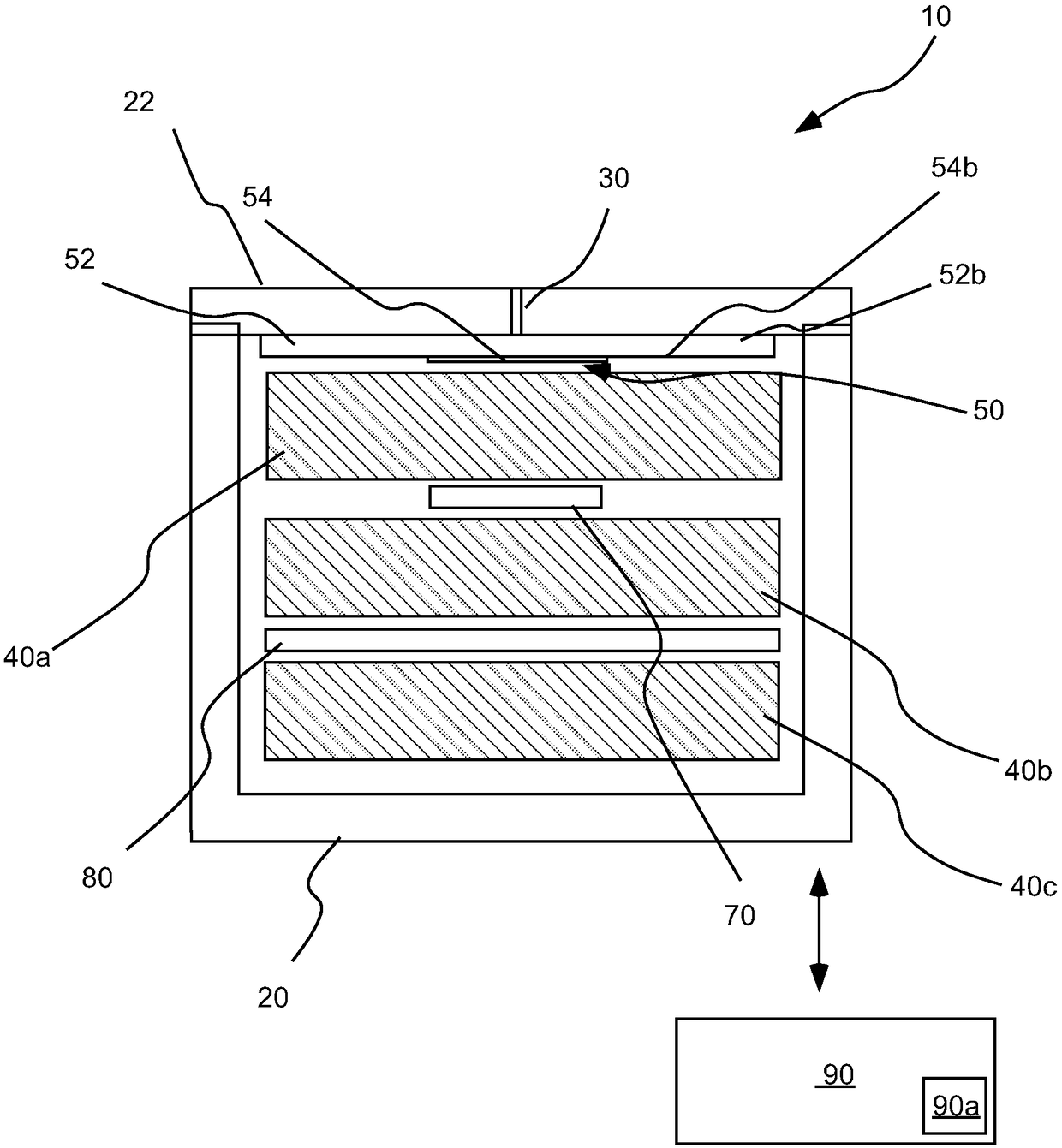
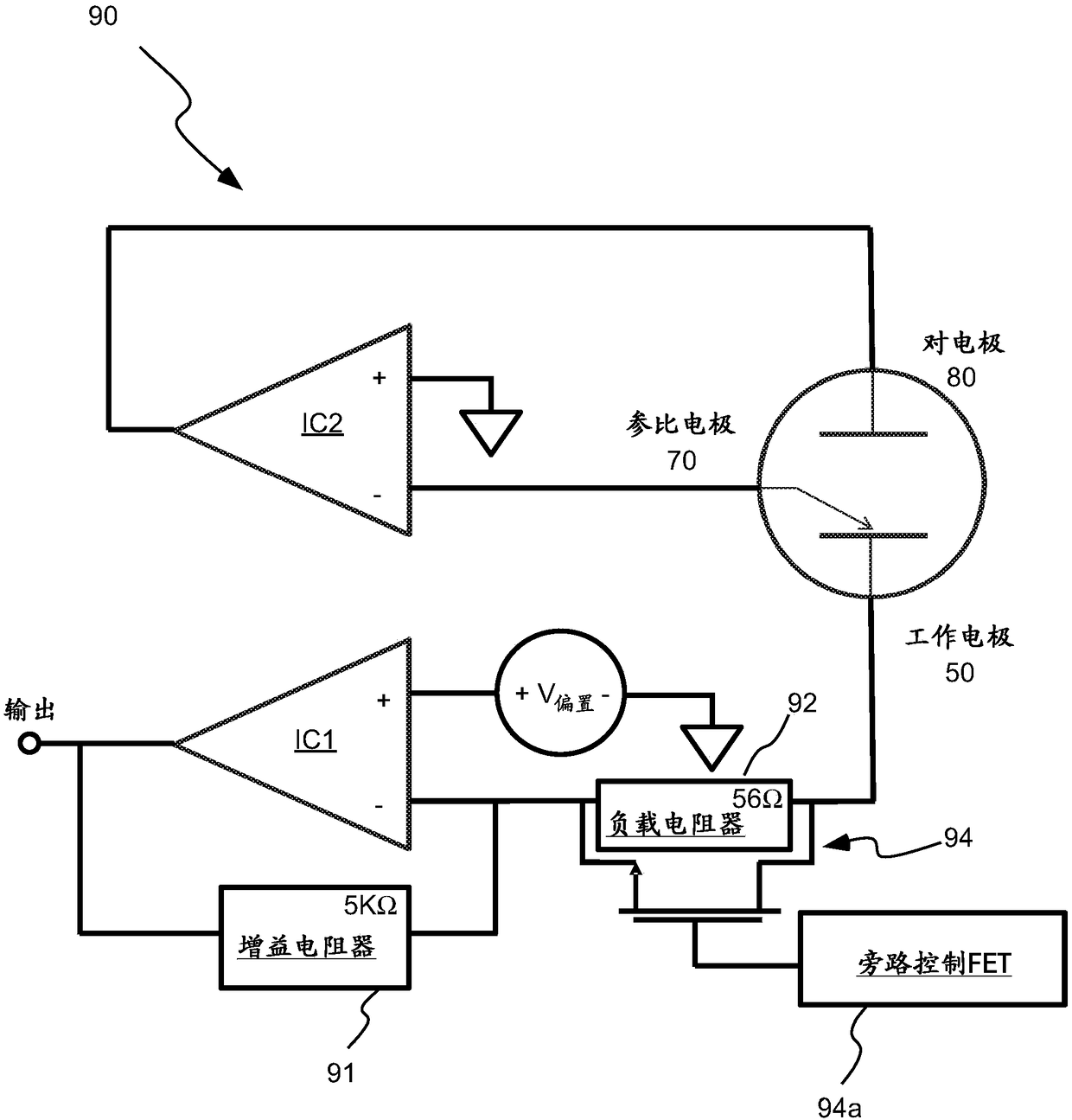
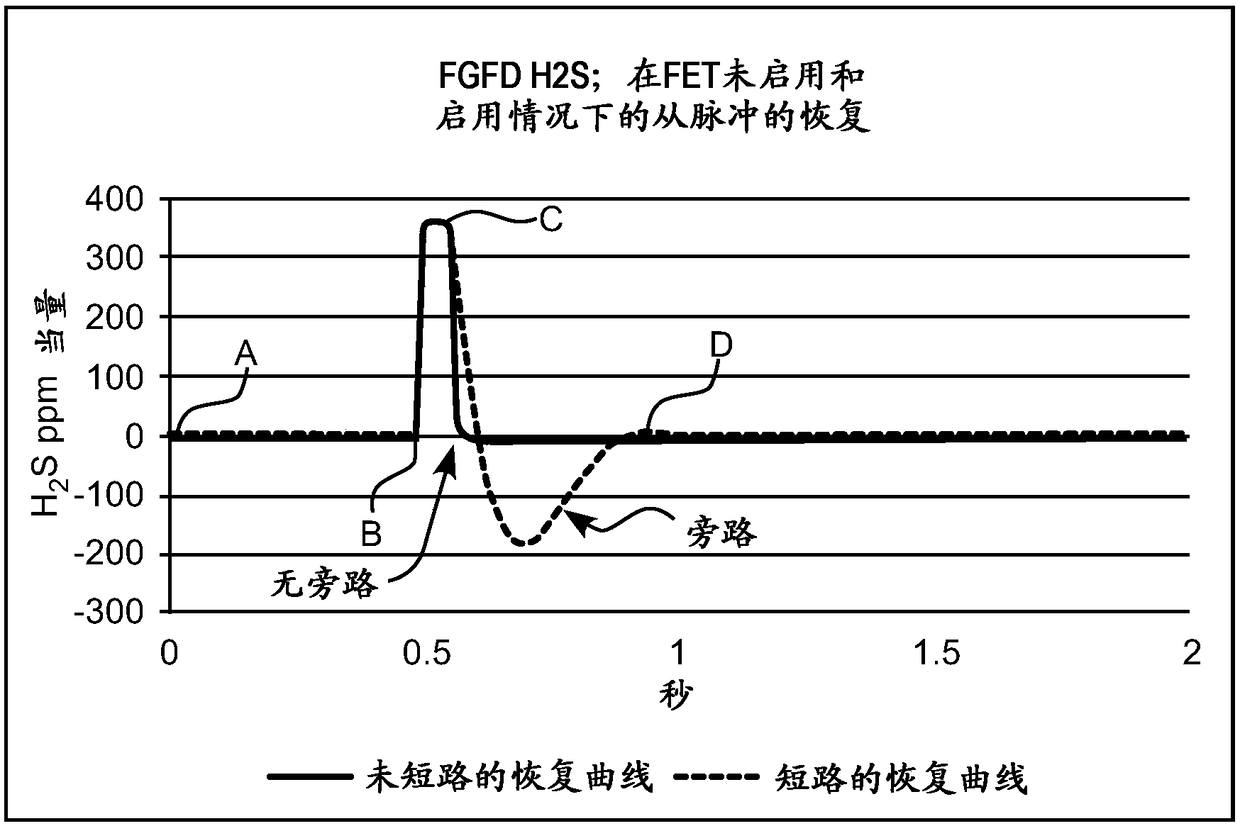
ActiveUS20170219515A1Reduce load resistanceImprove load resistanceWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteEngineering
A method of operating a sensor to detect an analyte in an environment, wherein the sensor includes a working electrode and circuitry in operative connection with the working electrode, includes performing a sensor interrogation cycle including applying electrical energy to the working electrode to generate a non-faradaic current, measuring a response to the generation of the non-faradaic current to determine a state of the sensor, and actively controlling the circuitry to dissipate the non-faradaic current.
Owner:MSA TECH
Method for preparing nano-stick array electrode capable of self-assembling after dispersing
InactiveCN101165213ATake advantage ofImprove electrocatalytic activityActive material electrodesMaterial electrochemical variablesSolventMetal
The present invention relates to nanometer rod array electrode, and is especially nanometer metal rod dispersing and self-assembling process of preparing nanometer rod array electrode with best utilization of surface area. The process includes the following steps: dissolving the template for growing nanometer metal rods, adding dispersant to the solvent and ultrasonically treating for well dispersing nanometer metal rods in the solvent, and regulating the concentration of nanometer metal rods to self-assemble nanometer metal rods onto the surface of electrode base in controllable intervals. The nanometer metal rod array electrode has best utilization of the great surface area of the nanometer metal rods, very high diffusion flux and faraday current, and very high electrically catalytic activity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Device for preparing micron-order and/or millimeter-order coated powder by intermittent electrodeposition and processing method thereof
ActiveCN107552779AUniform and controllable thicknessStir wellElectrolysis componentsEngineeringMetal powder
The invention provides a device for preparing micron-order and / or millimeter-order coated powder by intermittent electrodeposition and a processing method thereof. The device comprises an electroplating tank, a power module, a cathode plate, an anode plate and a power supply; the power module is arranged on one side of a tank body of the electroplating tank; the cathode plate is paved at the bottom of the electroplating tank; the anode plate is arranged at the top of the electroplating tank, and is opposite to the cathode plate; and the power supply is connected with the cathode plate and theanode plate through leads. Through combination of self characteristics of micron-order and / or millimeter-order spherical powder, and through left-right reciprocating rotation of the electroplating tank around a center shaft, the micron-order and / or millimeter-order powder is fully stirred, and the thickness of a plated layer is uniform and controllable. On this basis, the faradic current law is combined, so that the device can be used for large-scale production of the micron-order and / or millimeter-order coated metal powder. The device and the method for preparing the micron-order and / or millimeter-order coated powder have the characteristics of low cost, capability of circulating, easiness in operation and large-scale production, and satisfy the demands in industrial production.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing fuel by synchronously electrolyzing water vapor at high temperature and oxidizing methane
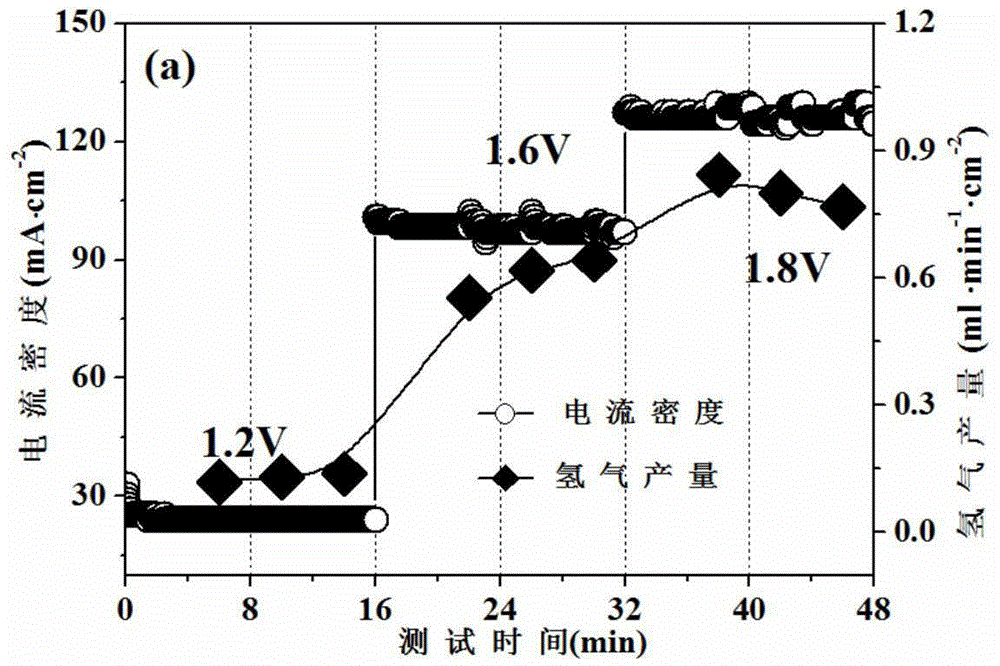
ActiveCN104064792ANo emissionsHigh Faradaic current efficiencyHydrogenElectrolysis componentsWater vaporOxygen ions
The invention discloses a method for preparing fuel by synchronously electrolyzing water vapor at the high temperature and oxidizing methane. According to the method, when oxygen is produced by electrolyzing the water vapor at the high temperature on one side of a cathode based on an oxygen ion type solid oxide electrolysis tank, synthesis gas fuel is produced by electrochemically oxidizing the methane at an anode. By utilizing the method, the synthesis gas fuel can be prepared by oxidizing the methane when the oxygen is prepared by directly electrolyzing the water vapor; an experimental result shows that the Faradic current efficiency of the solid oxide electrolysis tank can be up to 100%; a carbon deposition phenomenon is avoided when the methane is oxidized at the anode of a ceramic substrate; the performance of the water vapor reduced at the cathode of the ceramic substrate. The method can be applied to the fields of reproducible electric energy storage and methane reformation.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Electrochemical thin-film condensation sensor
InactiveCN105606668ASimple structurePracticalMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrical conductorElectrical battery
The present invention discloses an electrochemical thin-film condensation sensor, and solve the problem that a conventional device can not accurately measure surface condensation. The sensor is characterized by comprising a positive electrode, a negative electrode, an insulating layer, an amplifier circuit, an output positive electrode and an output negative output. The positive electrode and negative electrode are disposed on the same side or the opposite sides of the insulating layer; the insulating layer is a substrate for the positive electrode and the negative electrode; the positive electrode and the negative electrode are connected to the output positive electrode and output negative electrode by the amplifier circuit. The sensor uses conductor materials with different potential ordinals to form heterogeneous electrode pair, forms an original battery after surface condensation, and has a Faraday current output. The sensor is simple in structure and convenient for surface mounting in key parts of condensation sensitive equipment and facilities, has good response to the state of condensation, and realizes the monitoring on the amount of surface condensation.
Owner:HUAIBEI POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER +1
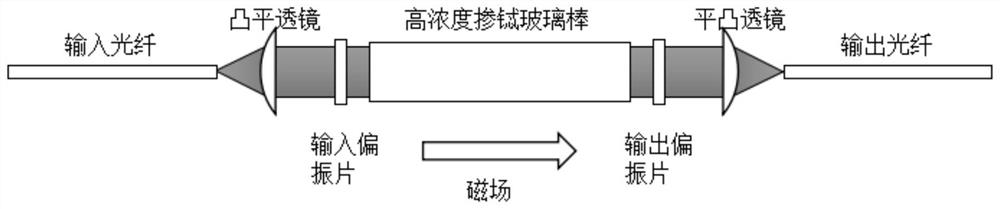
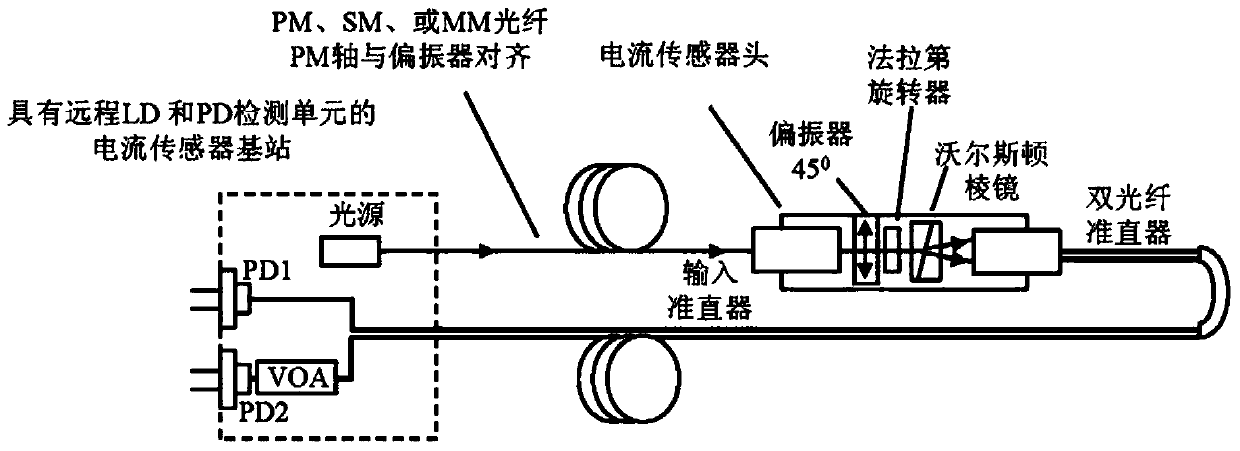
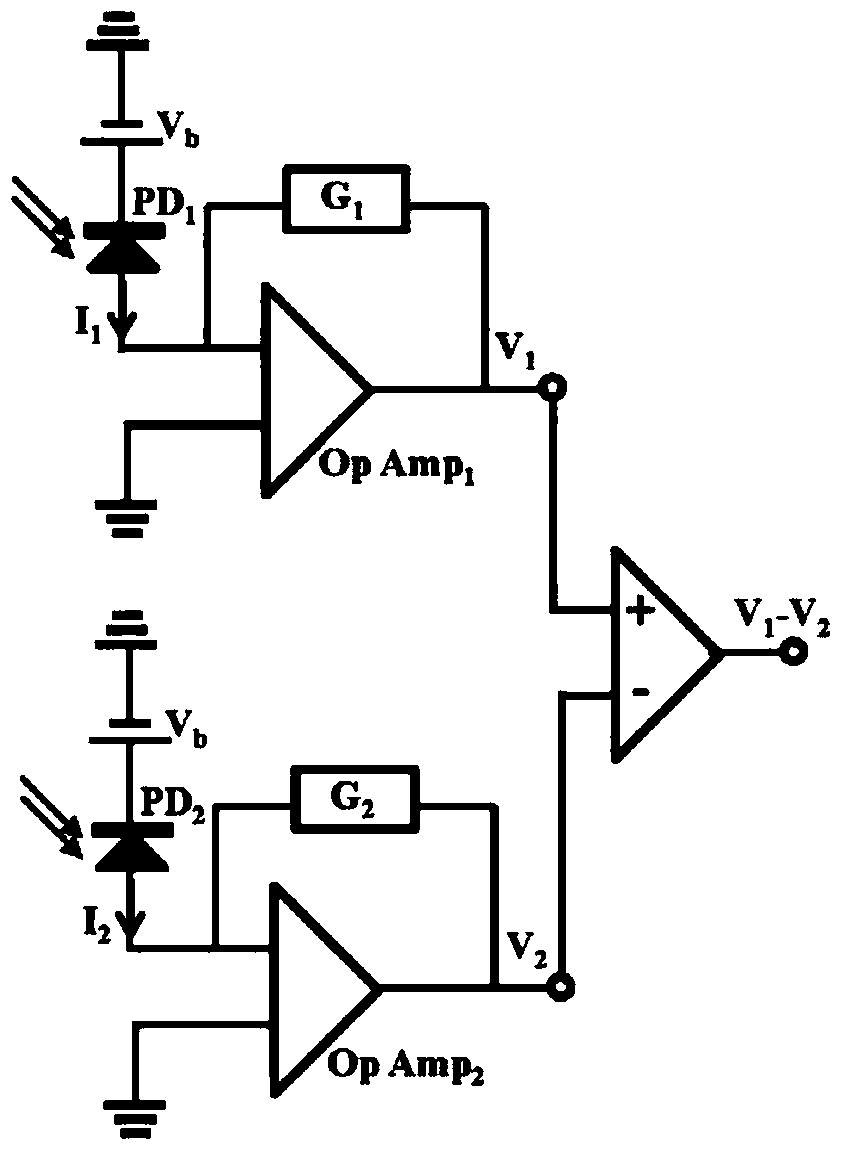
Faraday current and temperature sensors
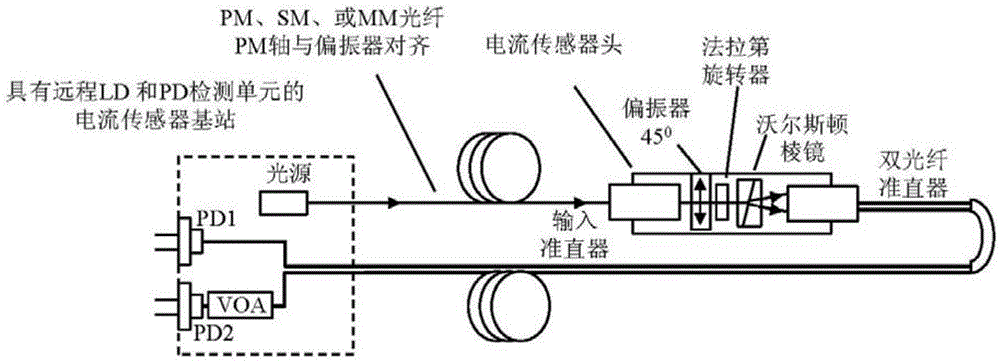
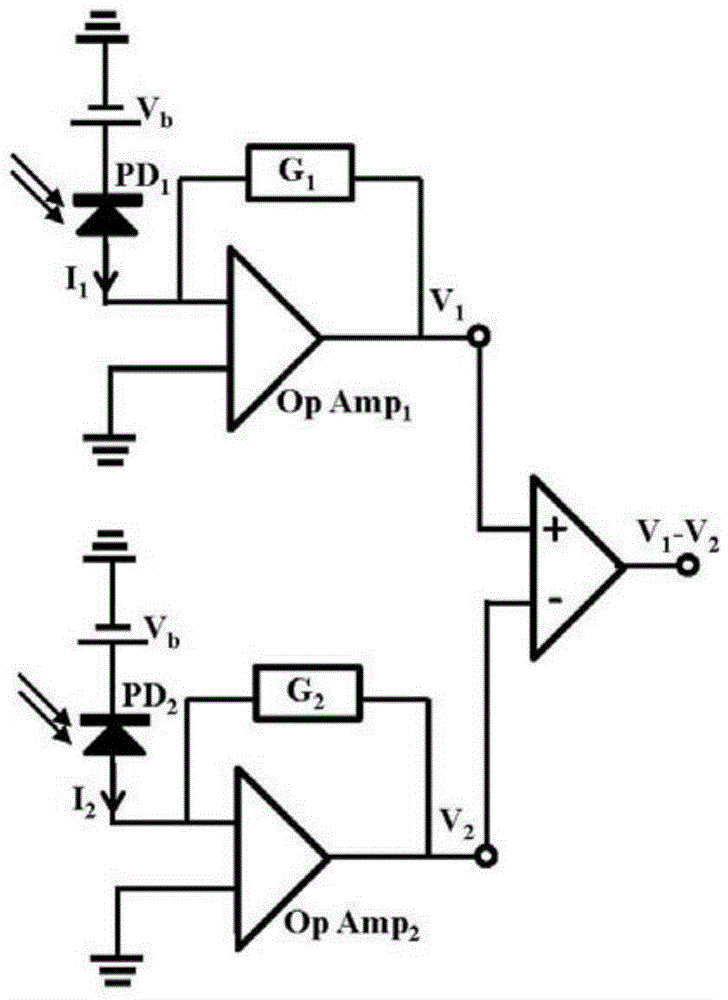
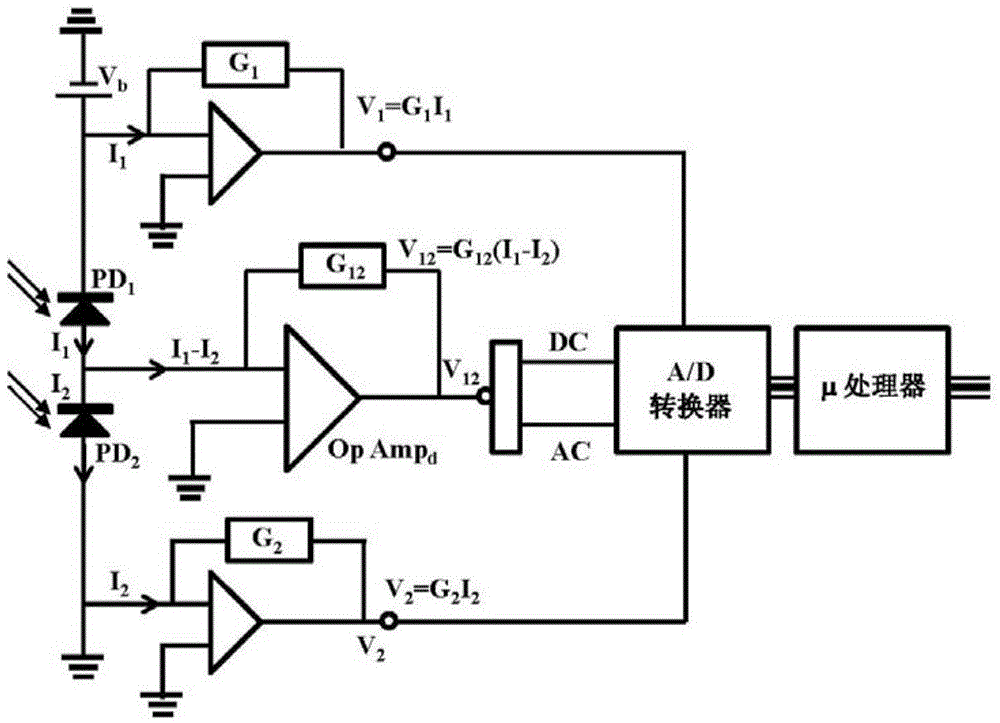
ActiveCN104569544ACurrent/voltage measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesPower flowCurrent sensor
This patent application discloses techniques and devices for sensing or measuring electric currents and / or temperature based on photonic sensing techniques. An optical current sensor head is located near or at a current-carrying conductor so that a magnetic field associated with the current is present at a Faraday material and the optical detection unit detects the light from the Faraday material to determine a magnitude of the current. An optical temperature sensor head is located near or at a location so that the temperature at a temperature-sensing Faraday material is reflected by the optical polarization rotation which is detected to determine the temperature.
Owner:姚晓天
Reduction catalytic material, gas diffusion electrode and preparation method of gas diffusion electrode
ActiveCN108636402AIncrease the catalytic activity of electrochemical reductionGuaranteed contact areaCatalyst activation/preparationElectrolytic organic productionCarbonizationSurface binding
The invention discloses a reduction catalytic material, a gas diffusion electrode and a preparation method of the gas diffusion electrode. The reduction catalytic material comprises carbonized polydopamine particles and Pt nanoparticles bonded to the surfaces of the carbonized polydopamine particles. According to the invention, high-temperature carbonization treatment is carried out on the polydopamine particles with the Pt nanoparticles bonded to the surfaces, and then the specific surface area of the reduction catalytic material can be effectively improved, so that more active sites of the Pt nanoparticles are exposed, the electrochemical reduction catalytic activity of the reduction catalytic material to the reduction of carbon dioxide is increased, and the hydrogen evolution reaction is effectively inhibited. The surface of the gas diffusion electrode provided by the invention is combined with the reduction catalytic material. When the carbon dioxide is reduced by the electrode, the electrode can conduct the current and also can quickly discharge by-products such as H2, CH4 and the like generated by the reduction process out of the working electrode, so that the contact area ofthe CO2 and the reduction catalytic material is ensured, and the Faraday current efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
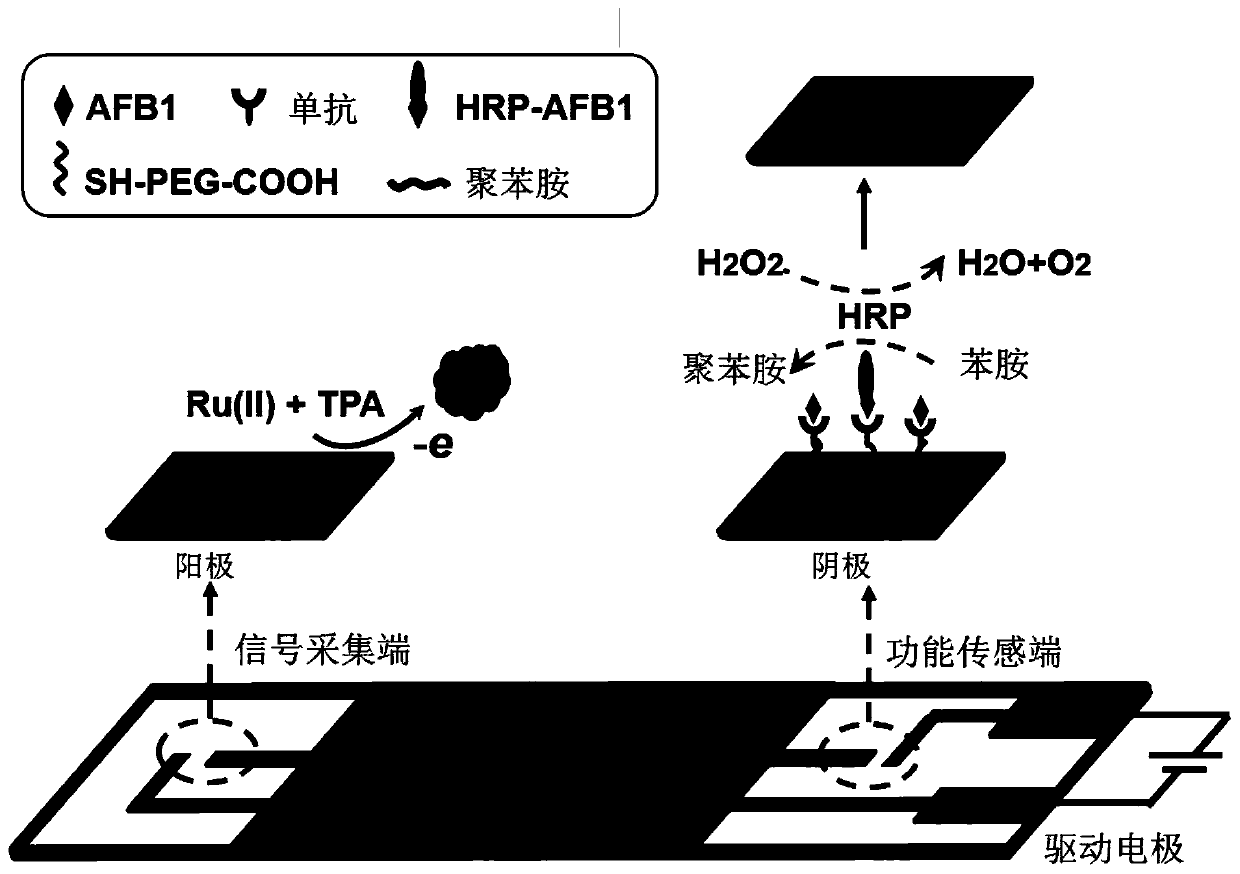
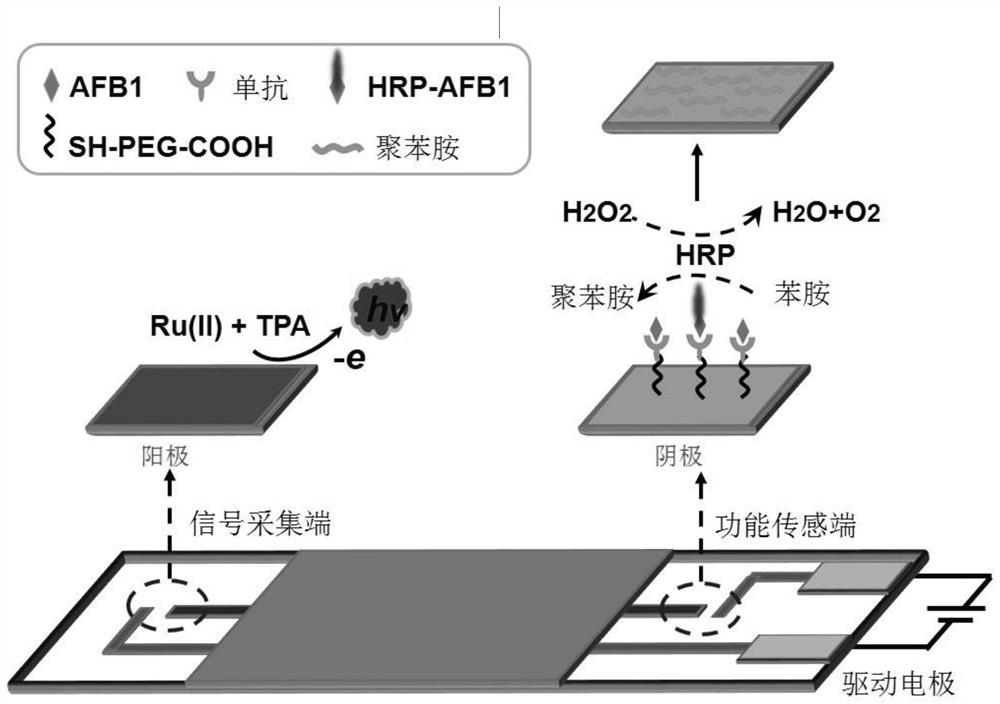
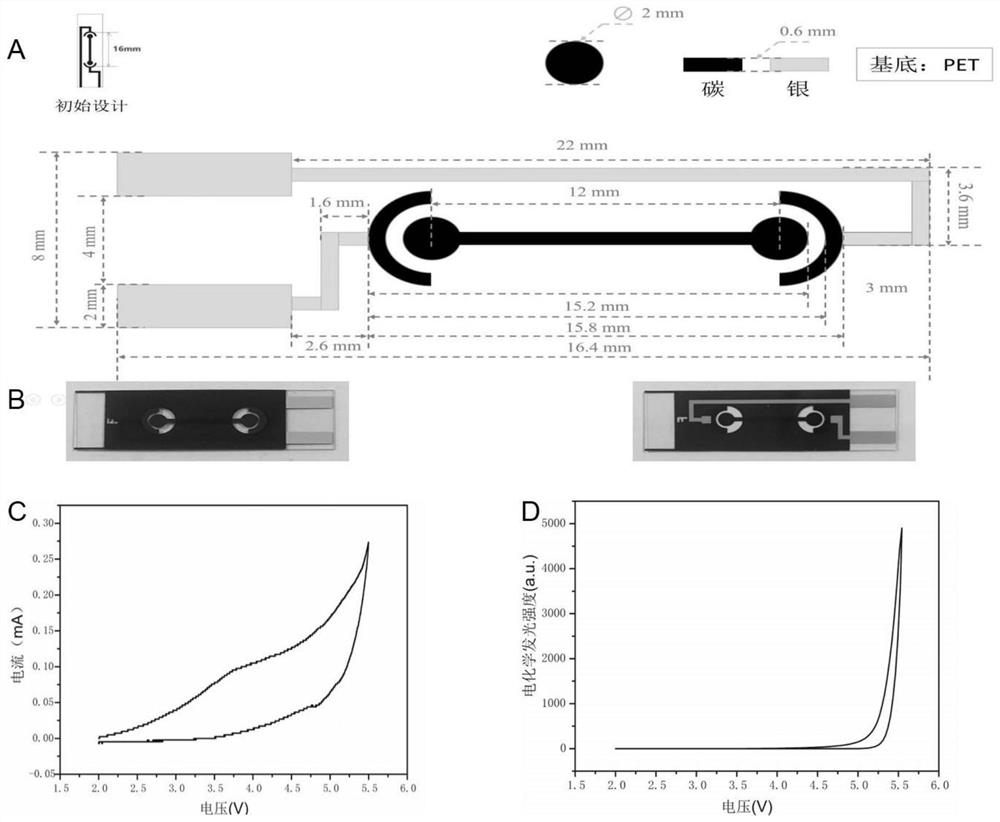
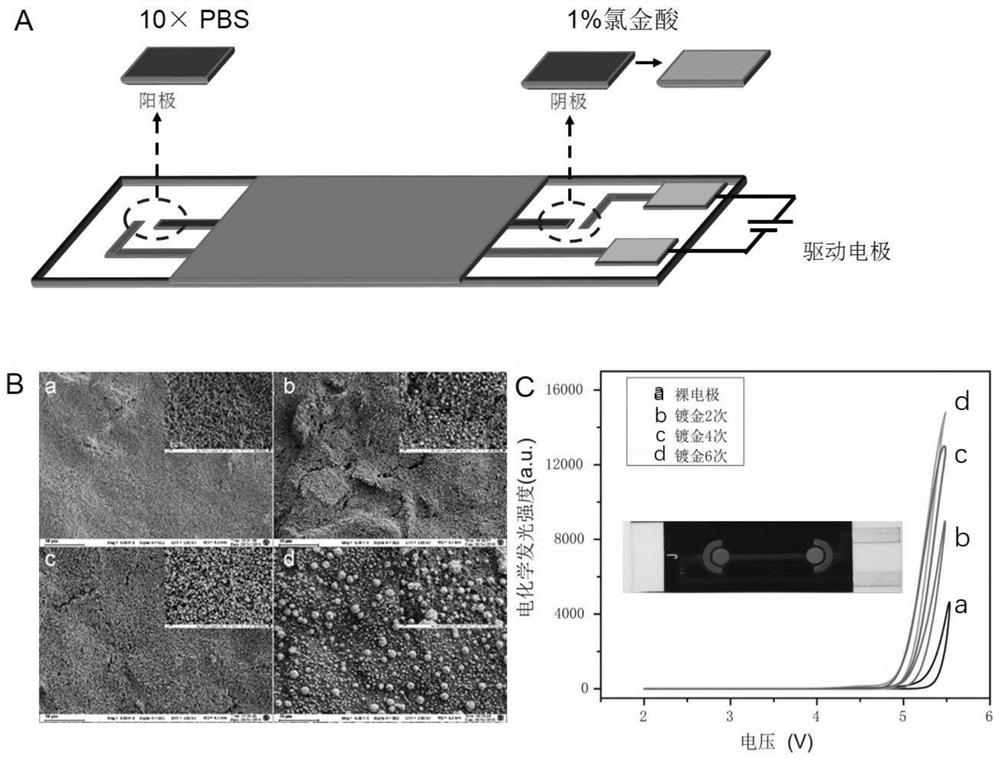
Method for detecting aflatoxin B1 based on visual BPE-ECL technology
ActiveCN110530853AEasy constructionAvoid direct contactChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesChemical reactionSignal on
The invention discloses a method for detecting aflatoxin B1 based on the visual BPE-ECL technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a screen-printed bipolar electrode; 2) constructing a function sensing interface; 3) mixing AFB1 with unknown concentration and HRP-AFB1 with fixed concentration, and then, reacting with an AFB1 monoclonal antibody on the function sensing interface; and 4) detecting an electrochemiluminescence signal on a signal acquisition interface by using a bipolar electrode working principle. An electrochemical signal of chemical reaction is converted into an electrochemiluminescence signal capable of being sensitively detected by utilizing BPE, so that the problem that Faraday current and charging current cannot be distinguished by electrochemistryis solved; the function sensing interface and the signal acquisition interface are physically isolated by utilizing the BPE, so that direct contact between photoactive molecules and a complex reaction system is avoided, the false positive phenomenon is effectively inhibited, the analysis and detection range is expanded, and the detection method is simplified; and the method has the advantages ofbeing simple and convenient and good in sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for regulating and controlling electrochemiluminescence signal by surface charge density of tapered micron-sized hole
InactiveCN110132947ALow costEasy to operateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityResearch model
The invention discloses a method for regulating and controlling electrochemiluminescence detection by surface charge density of a tapered micron-sized hole. According to the method, the micron-sized hole is used as an analysis element; an Ru(phen)32+ / TPrA research model is used for researching that a system current is regulated and controlled by the surface charge density of the tapered micron-sized hole to regulate and control the faraday current transmission efficiency of an Ru(phen)32+ / TPrA oxidation reaction; and different electrochemiluminescence signals are generated. The regulation andcontrol of the electrochemiluminescence signals by the surface charge density of the tapered micro-sized hole are realized for the first time; and an experiment device is simple in structure, low incost and convenient to use, widens the application range of electrochemiluminescence, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
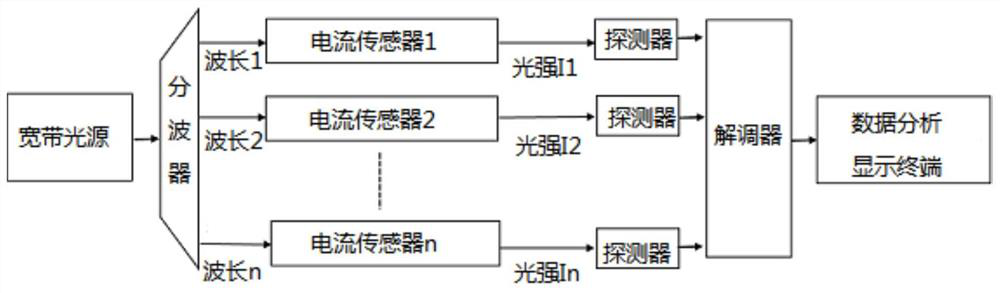
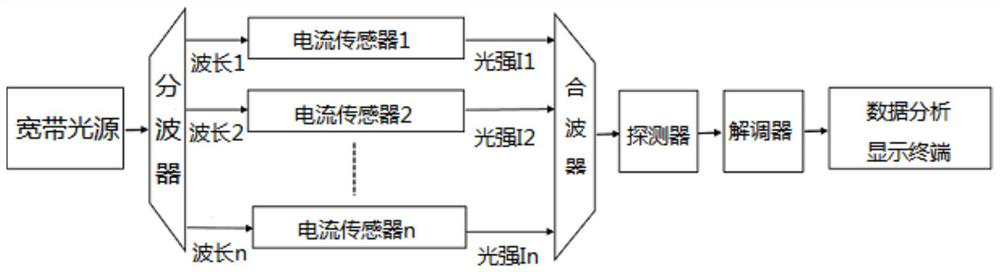
Current detection system of distributed high-voltage power transmission line
PendingCN111751596AEliminate the effect of excitation currentEliminate external electromagnetic interferenceCurrent measurements onlyVoltage/current isolationCurrent sensorMagneto
The invention relates to the technical field of current detection in a high-voltage power transmission line, and provides a current detection system of a distributed high-voltage power transmission line. The system comprises a broadband light source, a wave separator, Faraday current sensors with the same number as a plurality of to-be-measured wires, a detector and a demodulator; the broadband light source emits detection light, and a plurality of detection lights with different wavelengths are formed through the wave separator and transmitted to the Faraday current sensors arranged on the plurality of to-be-measured wires; optical signals are converted into electric signals, the electric signals are input into the demodulator, a magnetic field intensity B is obtained through calculationaccording to the Faraday magneto-optical effect and the Malus theorem, and the current intensity I of the multiple to-be-measured wires is calculated according to the Pitot-Savart theorem and the magnetic field intensity B. The problems that a power transmission line current detection method is large in size, heavy in weight and prone to being interfered by exciting current, a measurement system is complex in structure, and when a power transmission system comprises a plurality of power transmission wires, each power transmission wire needs to be detected respectively are solved.
Owner:贵州江源电力建设有限公司
Electrochemical imaging system and method based on graphene adjustable light scattering property
ActiveCN110376261AAchieving current detection limitLow detection limitMethod using image detector and image signal processingMethods for obtaining spatial resolutionManufacturing technologyCell system
The invention belongs to the optical microscope instrument manufacturing technology and electrochemical imaging technology field and especially relates to an electrochemical imaging system and methodbased on a graphene adjustable light scattering property. The system comprises a graphene electrolytic cell system, a microscope system, an imaging module and an image processing module. The grapheneelectrolytic cell system uses graphene as a working electrode. The microscope system and the imaging module are arranged on a scattered light path of the graphene electrolytic cell system. The image processing module extracts a picture obtained by the imaging module, and carries out operation processing on picture scattered light intensity to obtain the picture representing local surface Faraday and non-faradaic current densities of a target sample so as to realize electrochemical imaging. By using the electrochemical imaging method based on the graphene adjustable light scattering property, local surface electrochemical signals of the multiple target samples in a field of view can be detected simultaneously, sensitivity of current collection is reduced from a nanoampere level in the priorart to an angstrom ampere level by a matched scattering imaging system, and a spatial resolution is significantly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Preparation method for isolated needle point with housing layers wrapped in dual manner
InactiveCN106645809AOutstanding advantagesHighlight technical effectsRaman scatteringChemical vapor deposition coatingIridiumAtomic layer deposition
The invention provides a preparation method for an isolated needle point with housing layers wrapped in dual manner, which relates to a scanning probe. The method comprises the following steps: 1) using a chemical etching method to prepare a needle point; 2) wrapping the surface of the needle point with a housing layer; and 3) using high polymer materials to package the part of the needle point wrapped by the housing layer in step 2 excluding the needle point end for a second time to obtain an isolated needle point with the housing layers wrapped in a dual manner. According to the invention, an atomic layer deposition technique is adopted and different source precursors are used so that the needle point surface can be wrapped by different inert housings. Through the control over the number of circulation turns of different source precursors, the thickness of the housing layer can be accurately controlled. The wrapping in dual manner can prevent the non-analyte molecules in the solution from interfering with the signal generated at the needle point and can isolate the interference of the Faraday current. Therefore, the method can be applied to electrochemical needle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, electrochemical scanning tunneling microscope and electrochemical scanning microscope. Capable of being universally applied, the method can also be used to the wrapping of other needle points, like silver needle points, AFM needle points, and platinum iridium needle points. The method is simple to perform and is suitable for large batch production.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Non-reciprocal phase shift device-based Sagnac interference type high-current optical fiber current transformer measurement method
The invention relates to a non-reciprocal phase shift device-based Sagnac interference type high-current optical fiber current transformer measurement method, and belongs to the technical field of electric measurement. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing a non-reciprocal phase shift device, manufacturing a current sensing head by adoption of a circularly polarized fiber,fixedly arranging a phase modulator at one end of an Sagnac delay coil, and importing a Pi / 2 non-reciprocal phase deviation; (2) carrying out phase detection, and demodulating a circuit by using a phase discrimination manner so as to finally realize a phase demodulation manner unrelated to light intensity; (3) obtaining an output waveform oscillogram and precision of the current by utilizing a Faradic current sensing experiment; and (4) controlling phase interference caused by slow variables such as temperature and light source intensity changes through applying voltages with different frequencies on an electro-optical crystal, so as to improve the phase precision. According to the method, linear birefringence caused by long delay coils is decreased, the system polarization is better kept,the system precision is improved, a modulation circuit and an algorithm required by a phase deviator are decreased, and the sensor reaction time is prolonged.
Owner:STATE GRID JIBEI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD TANGSHAN POWER SUPPLY CO +1
Pulse polarography and electrochemical spectrum method for quick clearing double electric layer charging current error
InactiveCN1588031ALower charge current backgroundSampling is fast and accurateMaterial electrochemical variablesCharge currentPolarography
The invention provides a method of clear the error pulsepolargram and electrochemical spectrum of the two layer charging current. It relates to a new method in electrochemical analysing device and is applied to clearing error of the two layer charging current and solution ohm level drop with electrochemical instrument and electrochemical process detecting instrument. Current of high amplitude and narrow pulse is generated to provide ample two layer charging electrical quantity and two-layer charging toward the tested electrode to the level of the rectangle pulse of the driving signal. The tested electrode potential and command signal potenial are compared when the pulse current is interrupted, when the electrode potential reaches to the command potential and the two layer charging current is 0, the current flowing through the electrode is Faradic current,which make the electrode potential reach the driving signal potential exactly. Now, the two layer charging current is 0, the Faradic current sampling is quick and accurate, capable of measuring the overall curve in the second (subsecond) level.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Sensor interrogation with fast recovery
PendingCN108369206AMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGas analyser calibrationAnalyteHemt circuits
A method of operating a sensor to detect an analyte in an environment, wherein the sensor includes a working electrode and circuitry in operative connection with the working electrode, includes performing a sensor interrogation cycle including applying electrical energy to the working electrode to generate a non-faradaic current, measuring a response to the generation of the non-faradaic current to determine a state of the sensor, and actively controlling the circuitry to dissipate the non-faradaic current.
Owner:MSA TECH
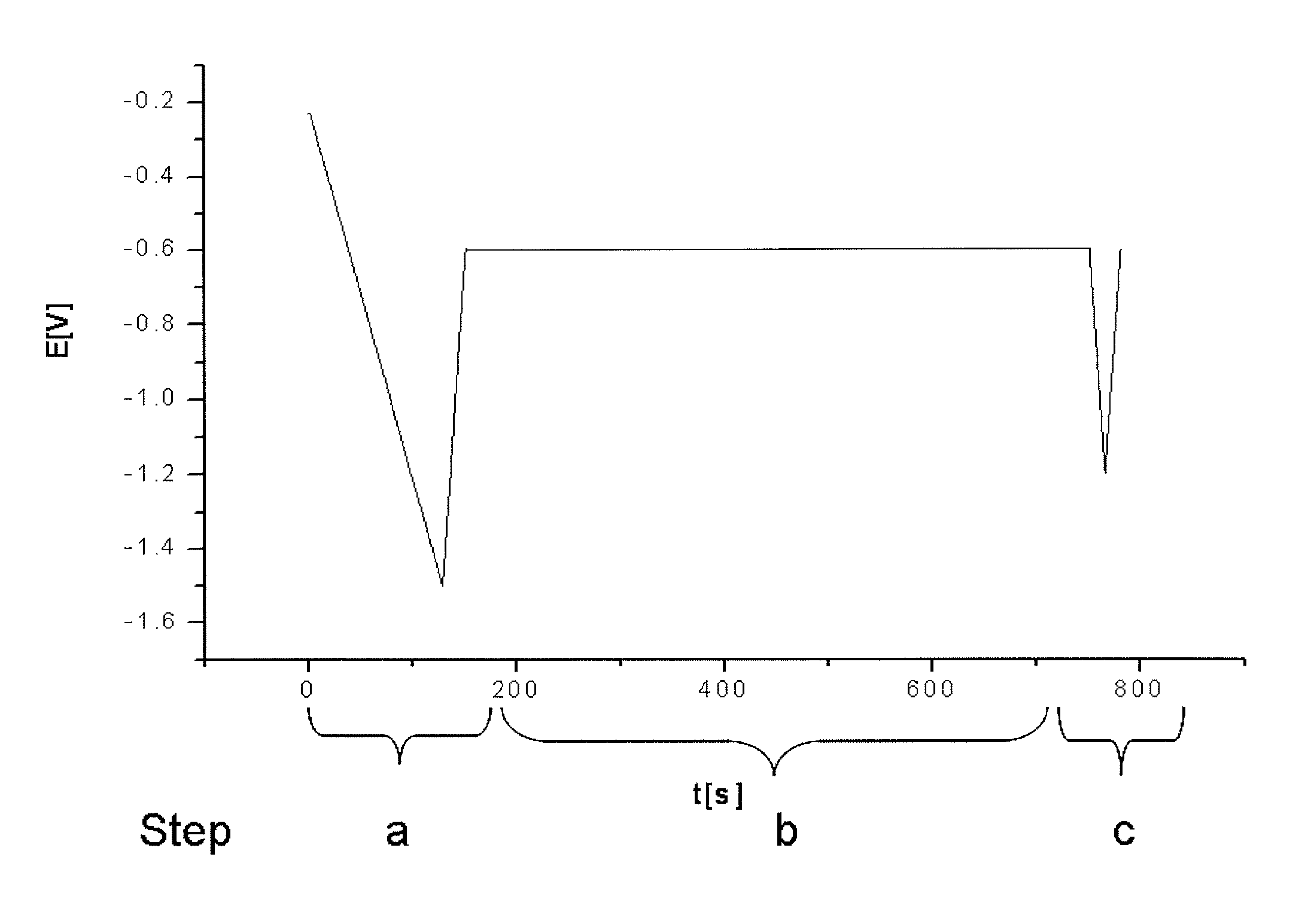
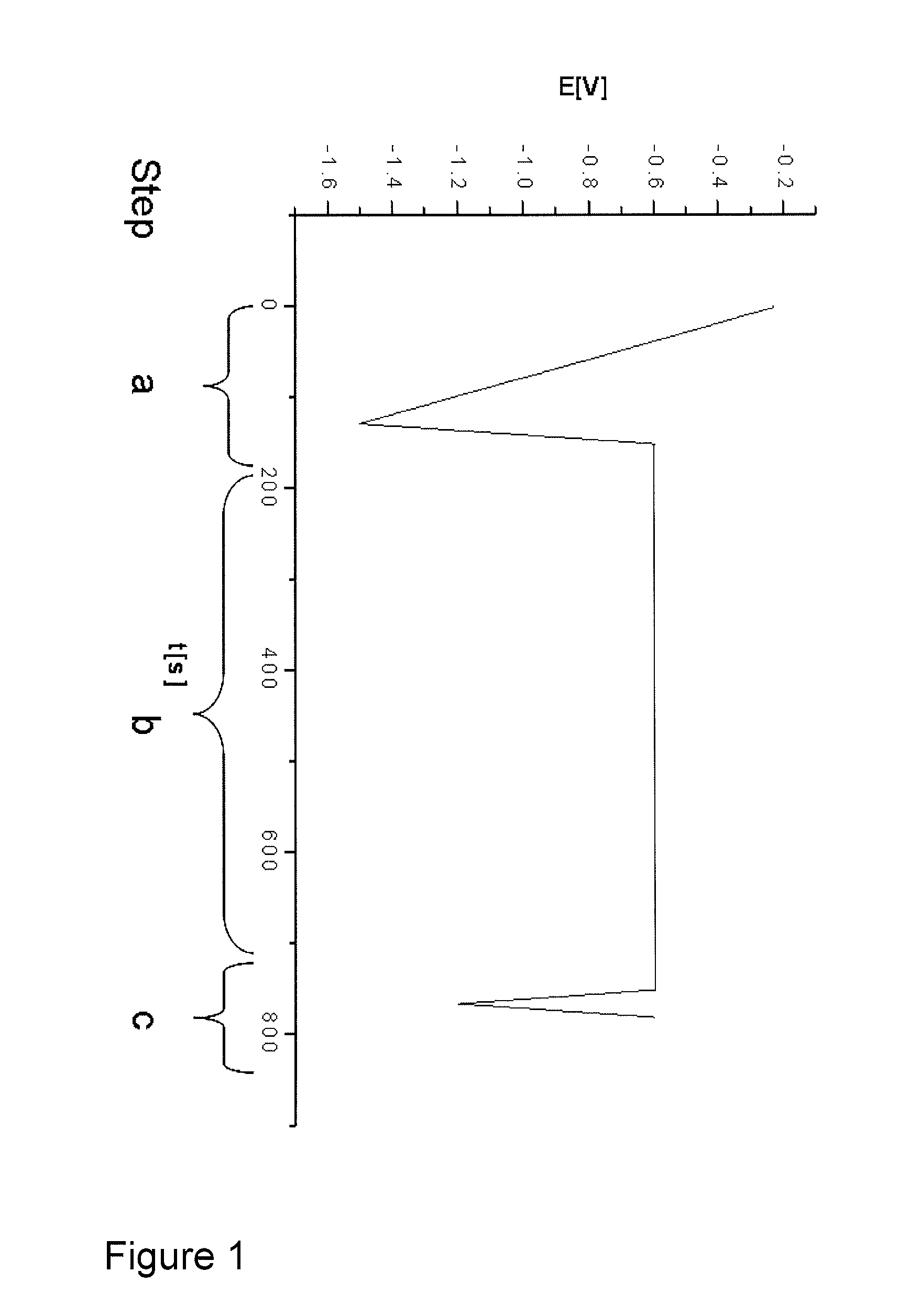
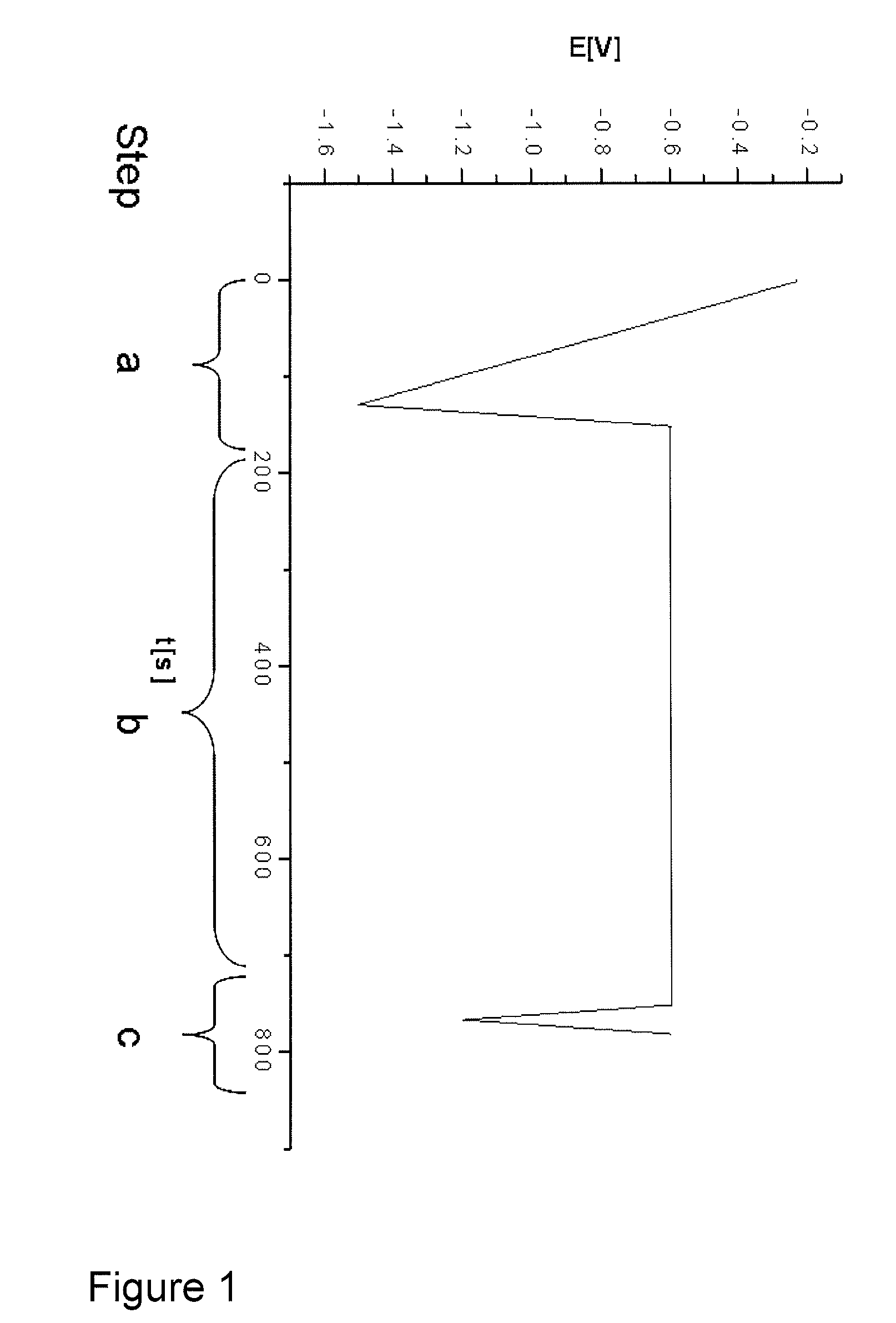
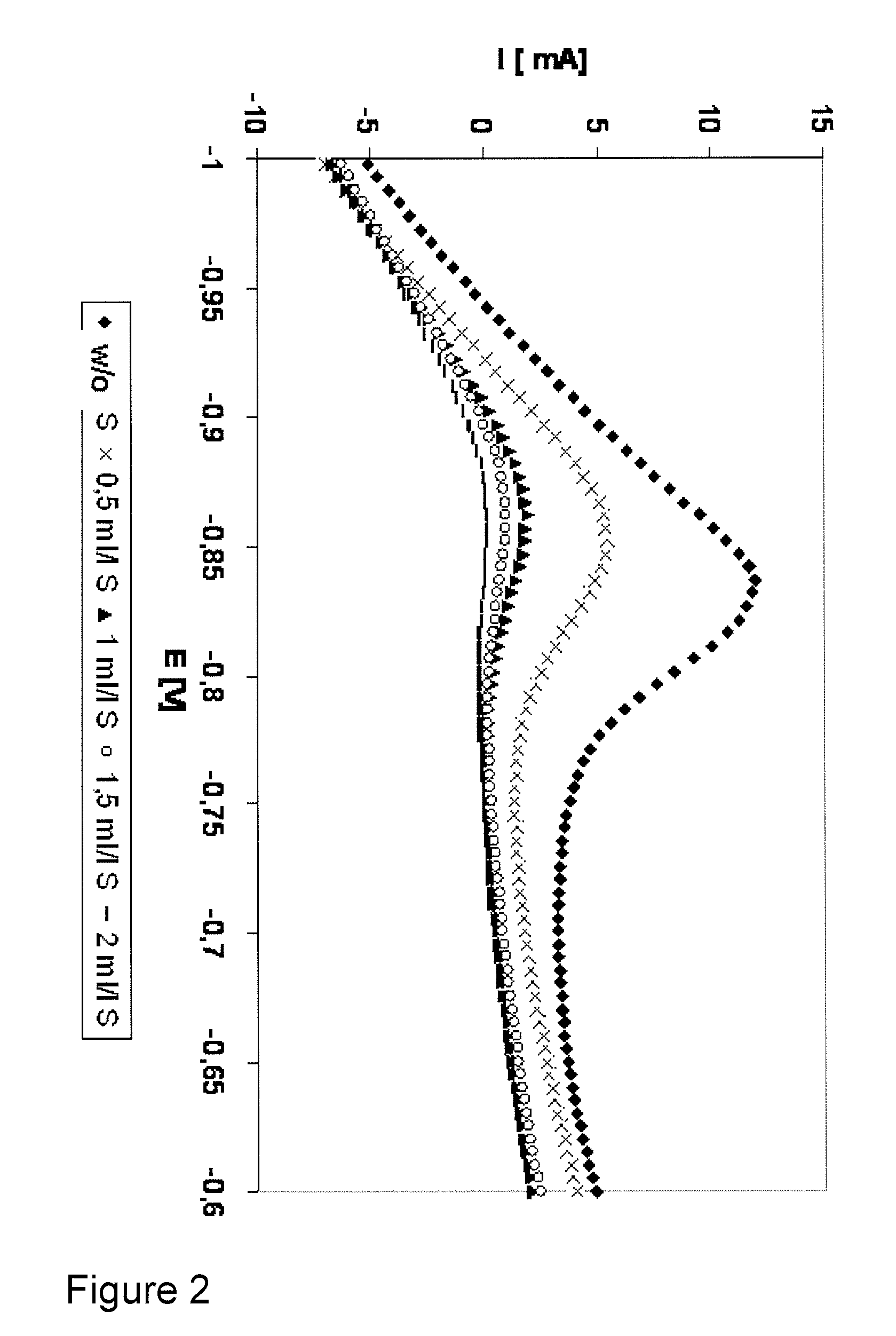
Method for control of stabilizer additives in electroless metal and metal alloy plating electrolytes
InactiveUS20110221445A1Liquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingMaterial electrochemical variablesElectroless nickelMetal alloy
The present invention describes a method for the measurement of the stabilizer additive concentration in electroless metal and metal alloy plating electrolytes comprising a voltammetric measurement. Said method comprises the steps a. conditioning of the working electrode, b. interaction of intermediates on the working electrode, c. measurement of the Faradaic current and d. determining the Faradaic current.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
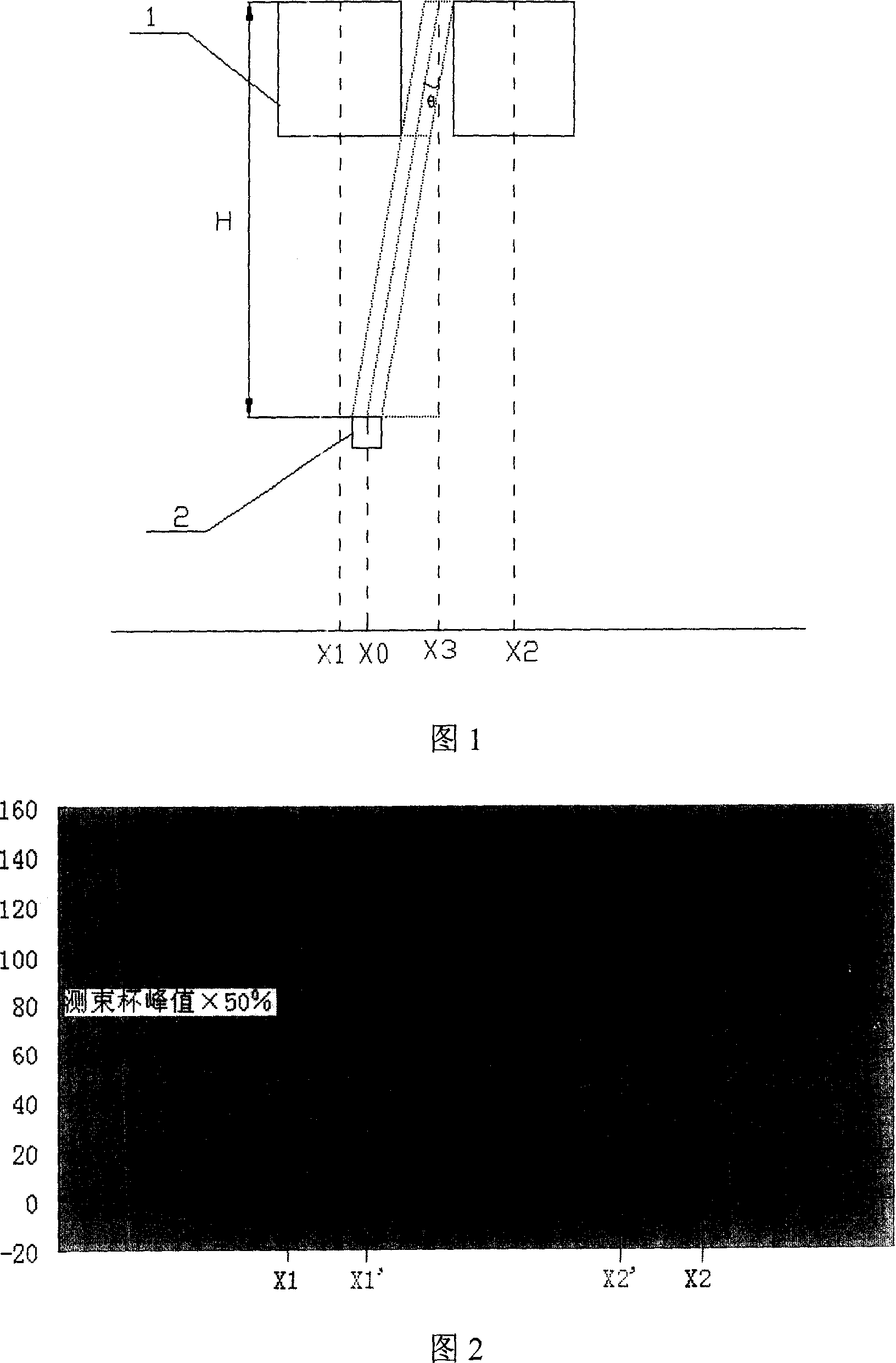
Method for measuring parallel beam injection angle
ActiveCN100378915CSimple methodPractical methodSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesIon beamPeak value
This invention discloses parallel beam injection angle measuring method. Moving faraday and beam faraday are used. The procedures are that (1) the moving faraday method is used to shelter ion beam to make the beam faraday method forming corresponding current curve graph. (2) parallel beam injection angle is computed by formula theta=arctg((X1'+X2') / 2-X0) / (H-h / 2), X1', X2'are 50 percent two points position of beam measuring cup current peak value, X0 is midpoint position of the cup, h is moving faraday height, H is distant between the moving faraday and beam faraday. This invention is simple and practical, its operation is easy and measuring is accurate.
Owner:BEIJING SHUOKE ZHONGKEXIN ELECTRONICS EQUIP CO LTD
Method for detecting aflatoxin b1 based on visual bpe-ecl technology
ActiveCN110530853BEasy constructionAvoid direct contactChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesChemical reactionSignal on
The invention discloses a method for detecting aflatoxin B1 based on visual BPE‑ECL technology, which comprises the following steps: 1) preparation of a screen-printed bipolar electrode; 2) construction of a functional sensing interface; 3) combining unknown concentrations of AFB1 and After mixing a fixed concentration of HRP-AFB1, it interacts with the AFB1 monoclonal antibody on the functional sensing interface; 4) Using the working principle of bipolar electrodes, the electrochemiluminescence signal on the signal acquisition interface is detected. The invention uses BPE to convert the electrochemical signal of the chemical reaction into a sensitively detectable electrochemiluminescence signal, which solves the problem that the electrochemical cannot distinguish the Faraday current and the charging current; uses the BPE to perform a physical connection between the functional sensing interface and the signal acquisition interface. Isolation avoids direct contact between photoactive molecules and complex reaction systems, effectively suppresses false positive phenomena, expands the scope of analysis and detection, and simplifies detection methods. The present invention has the advantages of simplicity, sensitivity and good specificity.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
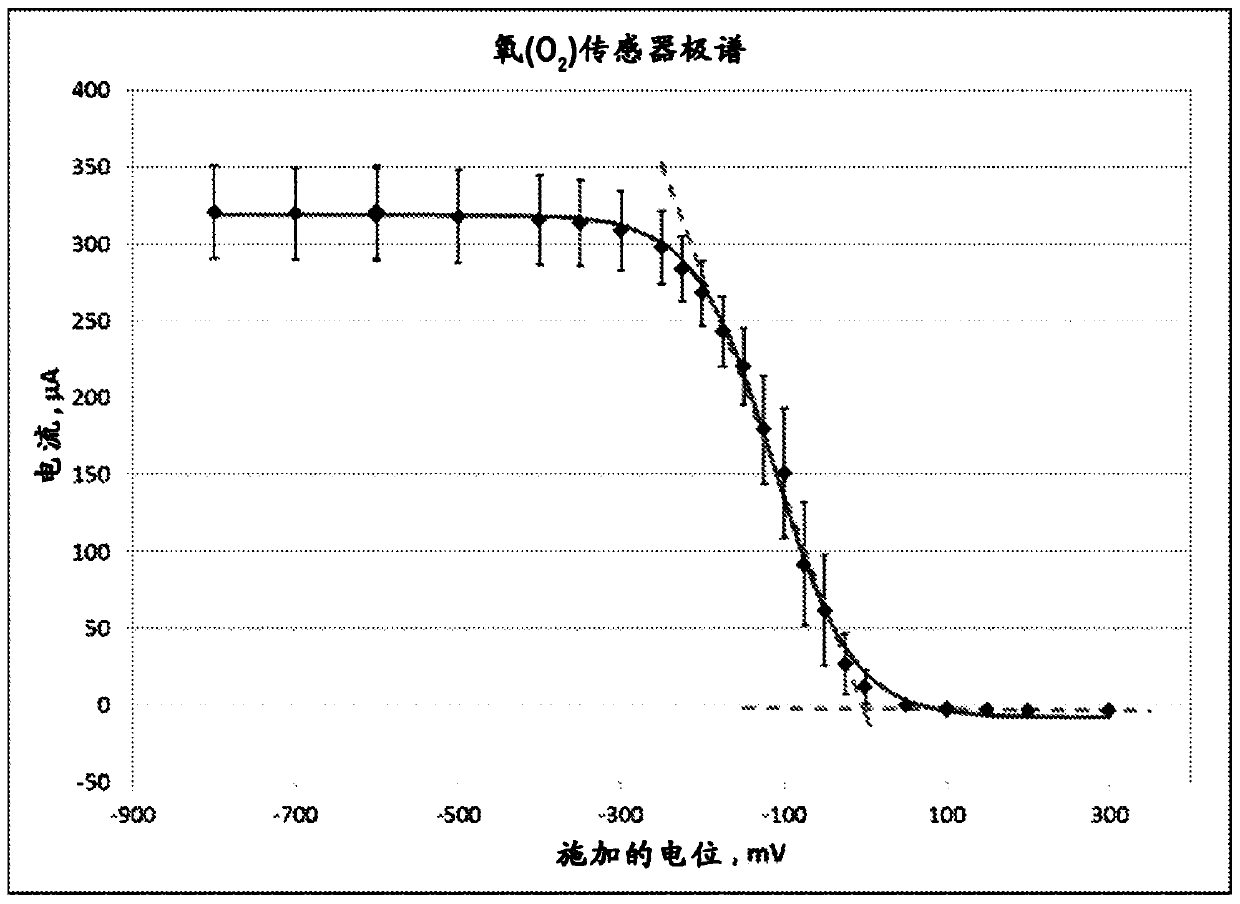
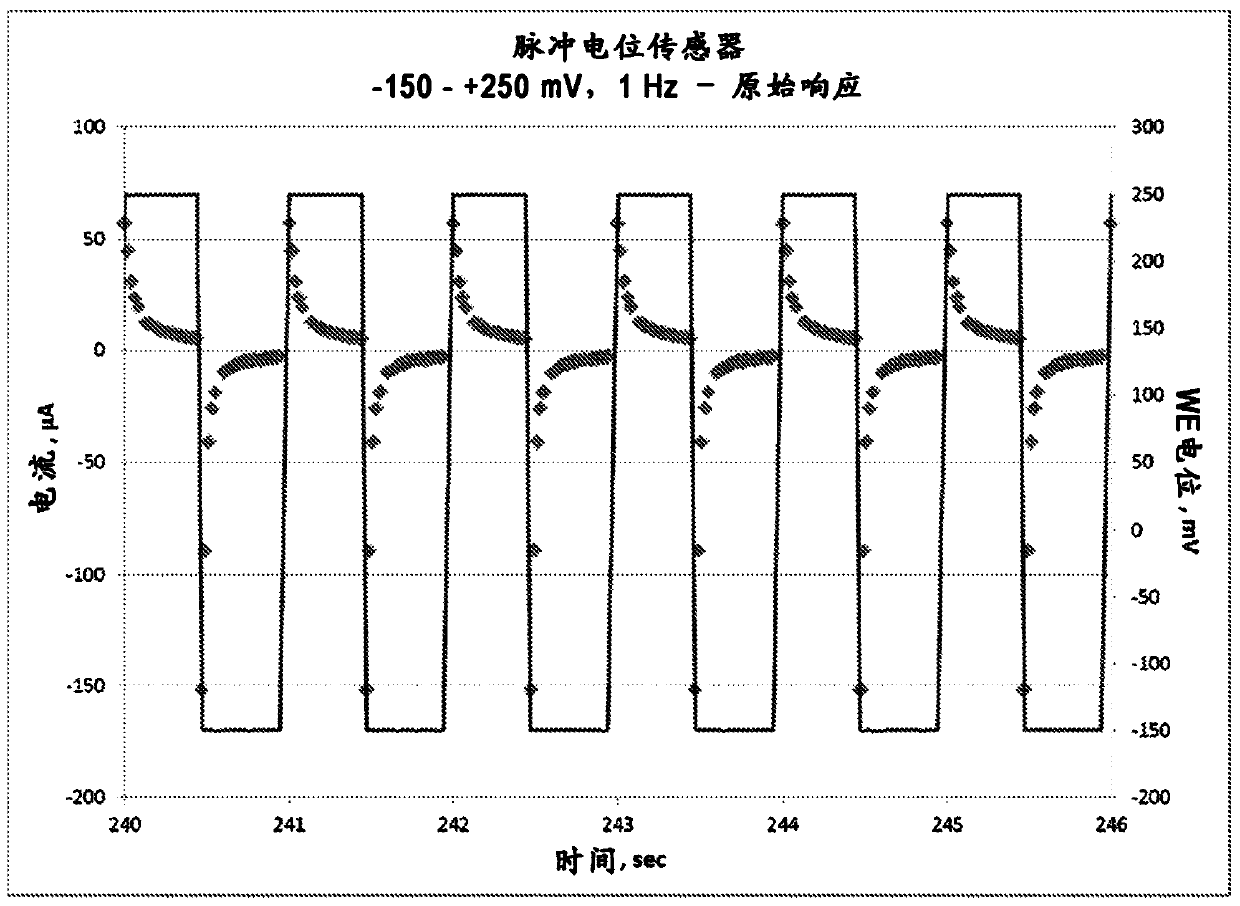
Pulse potentiometric gas sensor
A method of operating an electrochemical gas sensor comprising at least one working electrode comprising an electrocatalyst and having a ratio of total electrochemically accessible surface area to geometric surface area of at least 2:1, the method comprising alternating multiple times biasing the potential of the at least one working electrode to a first potential at which the electrocatalyst is active for catalyzing a redox reaction of a first target gas and a second potential different from the first potential at which the electrocatalyst is active for catalyzing a first target gas substantially inactive for a redox reaction of a target gas; measuring a first output signal resulting from a redox reaction of the first target gas at a first potential; and deconvoluting at least one working electrode biased at the first potential The concentration of the first target gas is determined by separating the portion of the first output signal generated by the non-Faradaic current.
Owner:MSA TECH
Pulse polarography and electrochemical spectrum method for quick clearing double electric layer charging current error
InactiveCN1271407CEliminate the effects ofOvercome the ills affected by the RC constantMaterial electrochemical variablesCharge currentPolarography
The invention provides a method of clear the error pulsepolargram and electrochemical spectrum of the two layer charging current. It relates to a new method in electrochemical analysing device and is applied to clearing error of the two layer charging current and solution ohm level drop with electrochemical instrument and electrochemical process detecting instrument. Current of high amplitude and narrow pulse is generated to provide ample two layer charging electrical quantity and two-layer charging toward the tested electrode to the level of the rectangle pulse of the driving signal. The tested electrode potential and command signal potenial are compared when the pulse current is interrupted, when the electrode potential reaches to the command potential and the two layer charging current is 0, the current flowing through the electrode is Faradic current,which make the electrode potential reach the driving signal potential exactly. Now, the two layer charging current is 0, the Faradic current sampling is quick and accurate, capable of measuring the overall curve in the second (subsecond) level.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fast scanning circuit with background current eliminating function
ActiveCN107918428ACause interferenceMake an impactElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a fast scanning circuit with the background current eliminating function. The fast scanning circuit comprises an alternating-current power source, a first operational amplifier, a second operational amplifier, a third operational amplifier, a fourth operational amplifier, an electrochemical cell, a first resistor, a second resistor, a third resistor, a fourth resistor, a fifth resistor, a sixth resistor, a seventh resistor, an eighth resistor, a ninth resistor, a tenth resistor, a first slide rheostat, a second slide rheostat and a first capacitor, a background currentcompensation generating circuit is formed by the third operational amplifier, the second rheostat, the tenth resistor and the first capacitor, and a background current eliminating circuit is formed bythe fourth operational amplifier, the sixth resistor, the seventh resistor, the eighth resistor and the ninth resistor. The fast scanning circuit has the advantages that no matter how the scanning frequency is improved, background currents are eliminated and do not cause interference or influence on Faradic currents, the signal to noise ratio of output voltage is increased, and the detection sensitivity of the scanning circuit is improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for control of stabilizer additives in electroless metal and metal alloy plating electrolytes
InactiveUS8648601B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceResistance/reactance/impedenceElectroless nickelMetal alloy
The present invention describes a method for the measurement of the stabilizer additive concentration in electroless metal and metal alloy plating electrolytes comprising a voltammetric measurement. Said method comprises the steps a. conditioning of the working electrode, b. interaction of intermediates on the working electrode, c. measurement of the Faradaic current and d. determining the Faradaic current.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Faraday current sensor and Faraday temperature sensor
ActiveCN104569544BCurrent/voltage measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesCurrent sensorPhotonics
The invention relates to a Faraday current sensor and a Faraday temperature sensor. This patent application discloses techniques and devices for sensing or measuring current and / or temperature based on photonic sensing technology. The optical current sensor head is positioned at or near the current carrying conductor such that a magnetic field associated with the current exists at the Faraday material and the optical detection unit detects light from the Faraday material to determine the magnitude of the current. The optical temperature sensor head is located at or near a location such that the temperature at the temperature sensitive Faraday material is reflected by the optical polarization rotation that is detected to determine the temperature.
Owner:姚晓天
Pulsed potential gas sensors
A method of operating an electrochemical gas sensor, which includes at least one working electrode including an electrocatalyst and having a ratio of total electrochemically accessible surface area togeometrical surface area of at least 2: 1, includes alternatively biasing a potential of the at least one working electrode to a first potential at which the electrocatalyst is active to catalyze a redox reaction of a first target gas and to a second potential, different from the first potential, at which the electrocatalyst is substantially inactive to catalyze the redox reaction of the first target gas, a plurality of times, measuring a first output signal arising from the redox reaction of the first target gas at the first potential, and deconvoluting the first output signal while the at least one working electrode is biased at the first potential to separate a portion of the first output signal arising from non-faradaic current to determine a concentration of the first target gas.
Owner:MSA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com