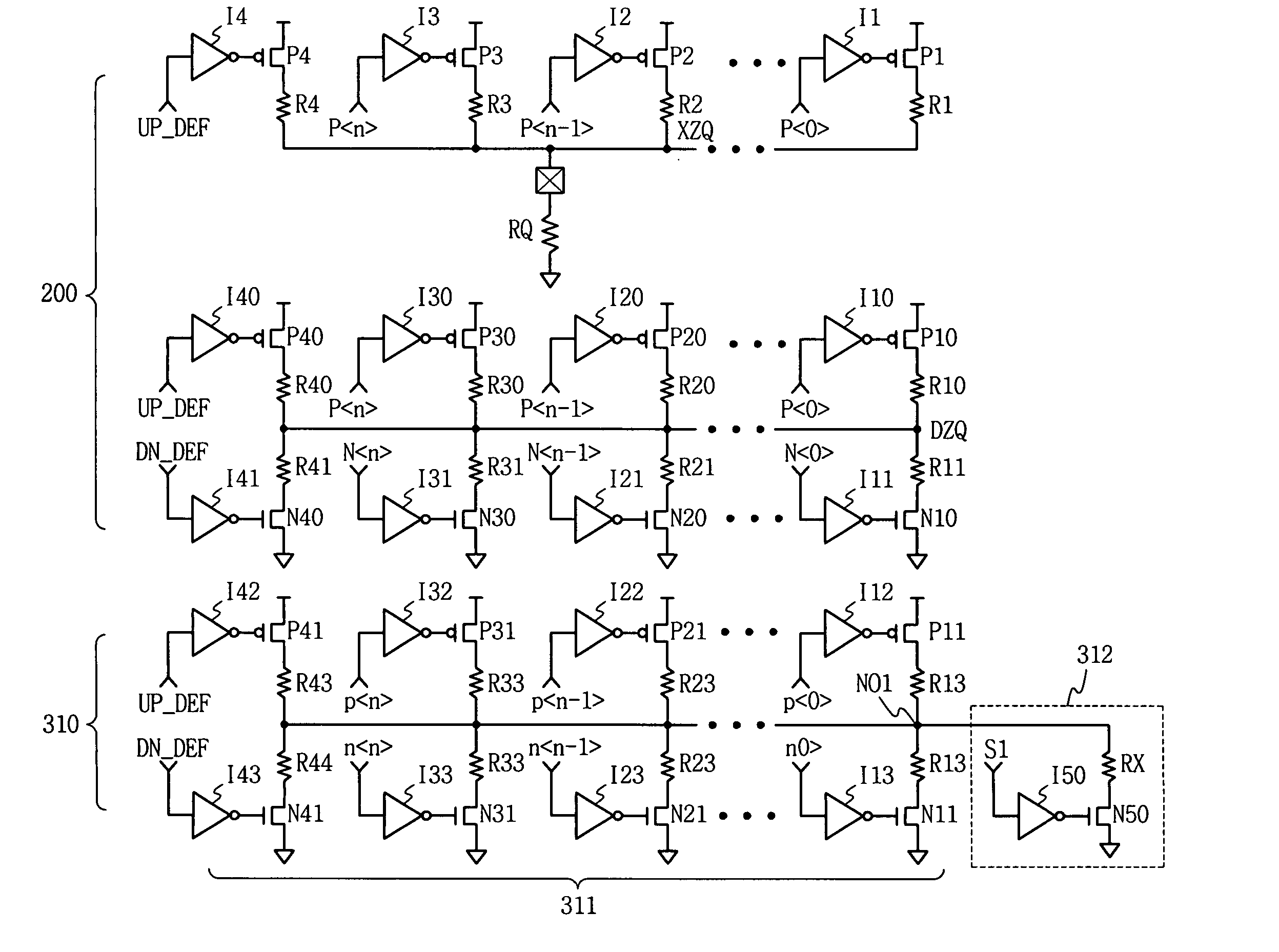Patents
Literature
98results about How to "Reduce Impedance Mismatch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
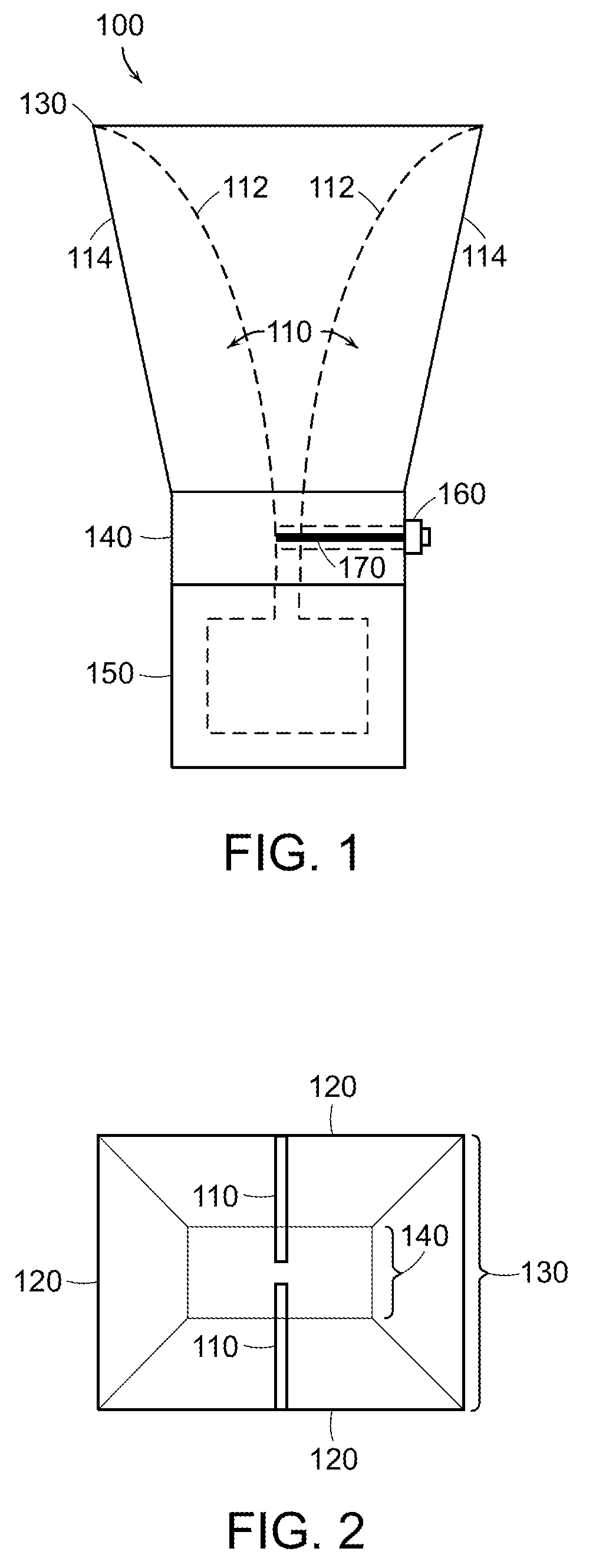
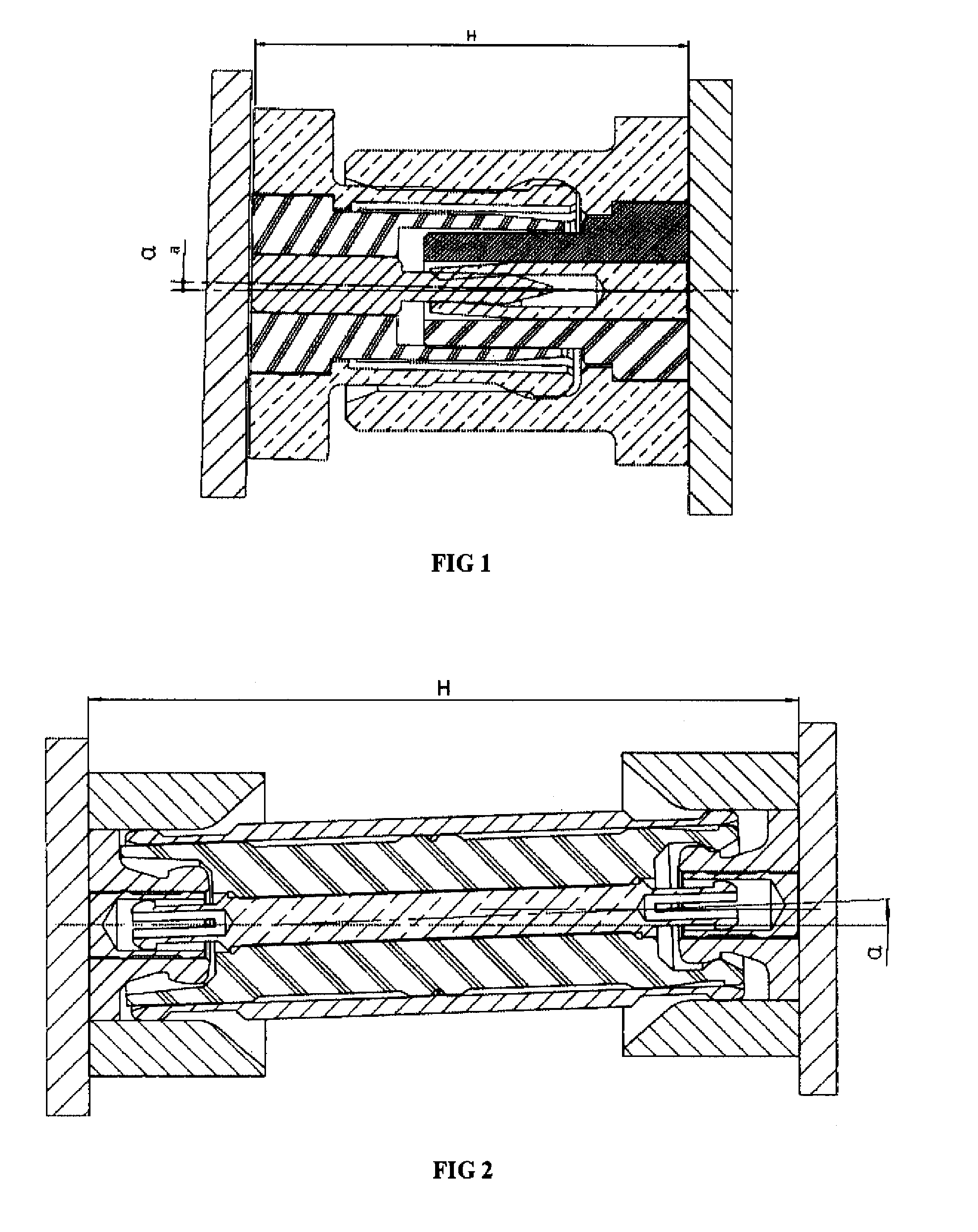
Plastic waveguide-fed horn antenna
InactiveUS20100214185A1Low costReduce Impedance MismatchWaveguide hornsPrintingHorn antennaResonator
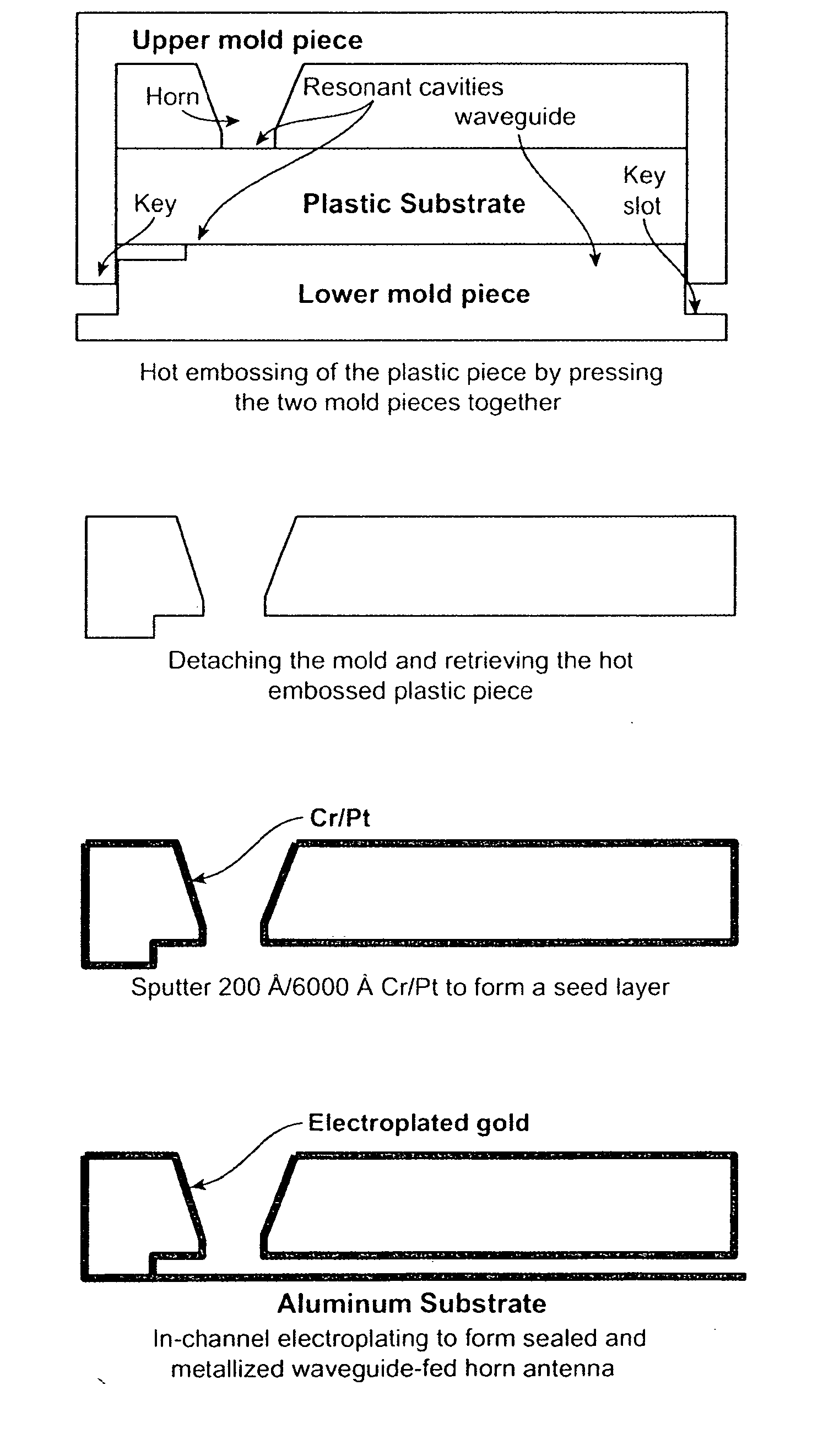
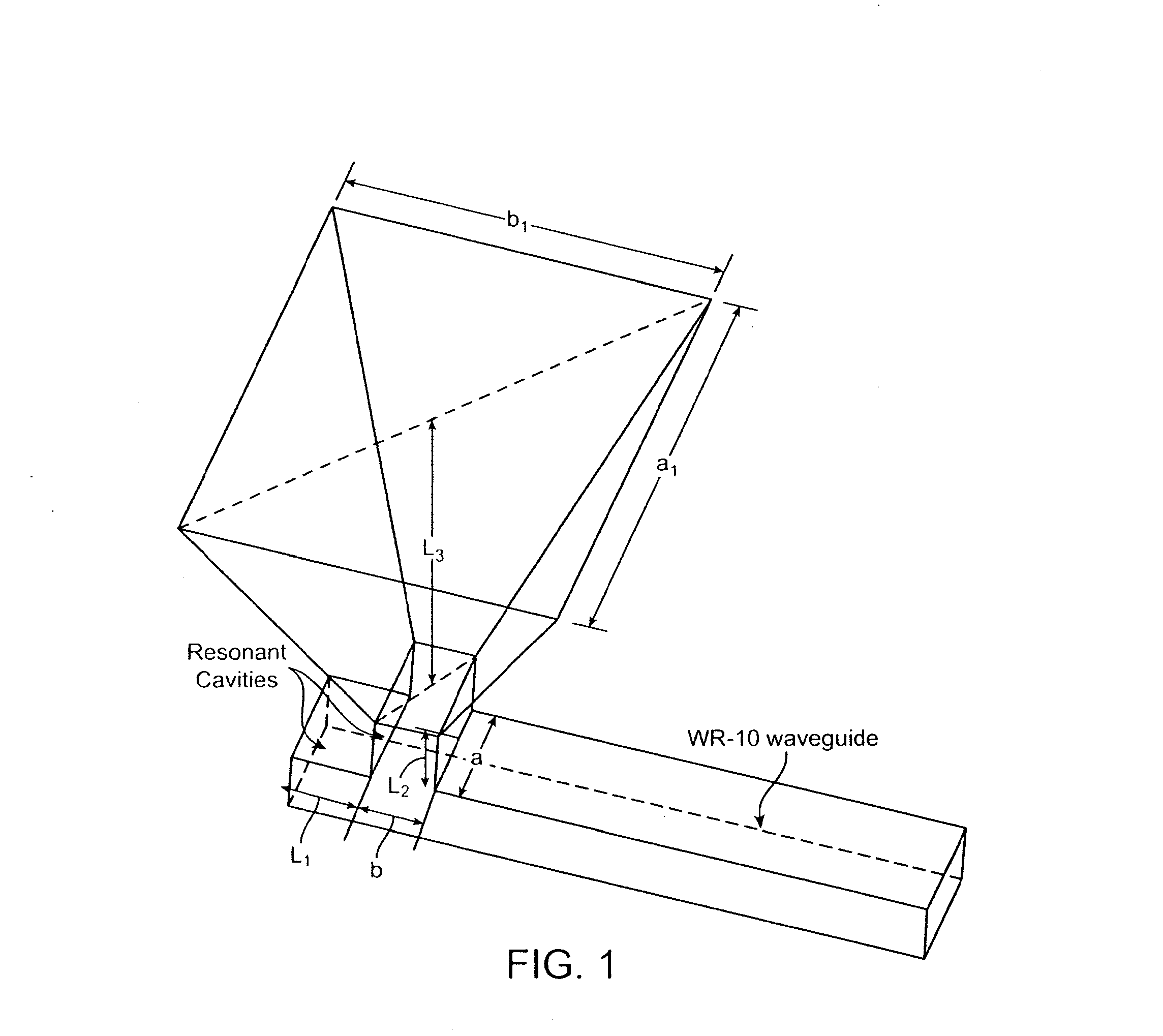
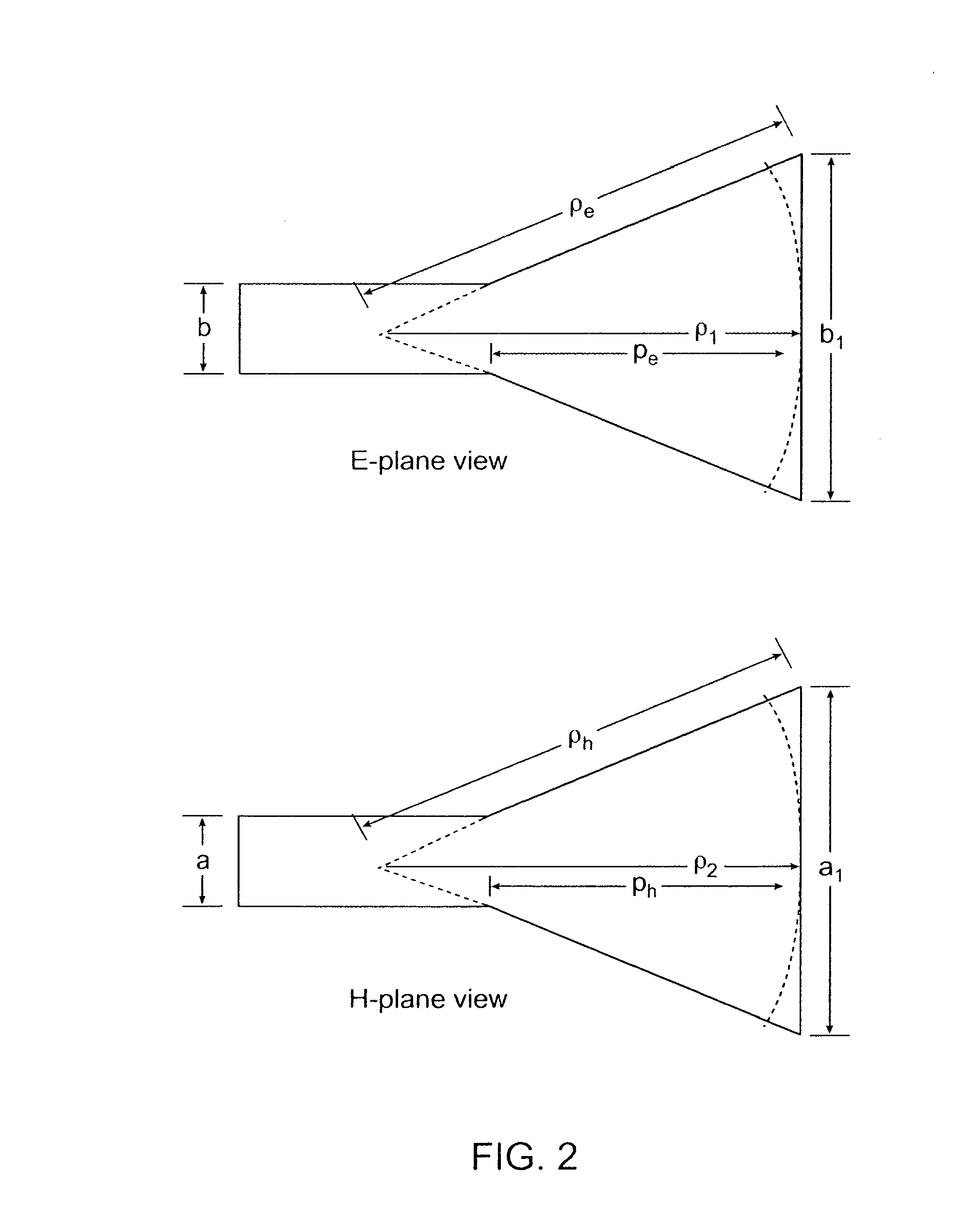
A plastic, waveguide-fed, horn antenna is manufactured using a three-dimensional (3D), polymeric micro hot embossing process. Two cavity resonators may be designed to reduce the impedance mismatch between the pyramidal horn antenna and the feeding waveguide. The waveguide-fed antenna may be fabricated using a self-aligned 3D plastic hot embossing process followed by a selective electroplating and sealing process to coat an approximately 8 μm-thick gold layer around the internal surfaces of the system. As such, this plastic, low-cost manufacturing process may be used to replace the expensive metallic components for millimeter-wave systems and provides a scalable and integrated process for manufacturing an array of antenna.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
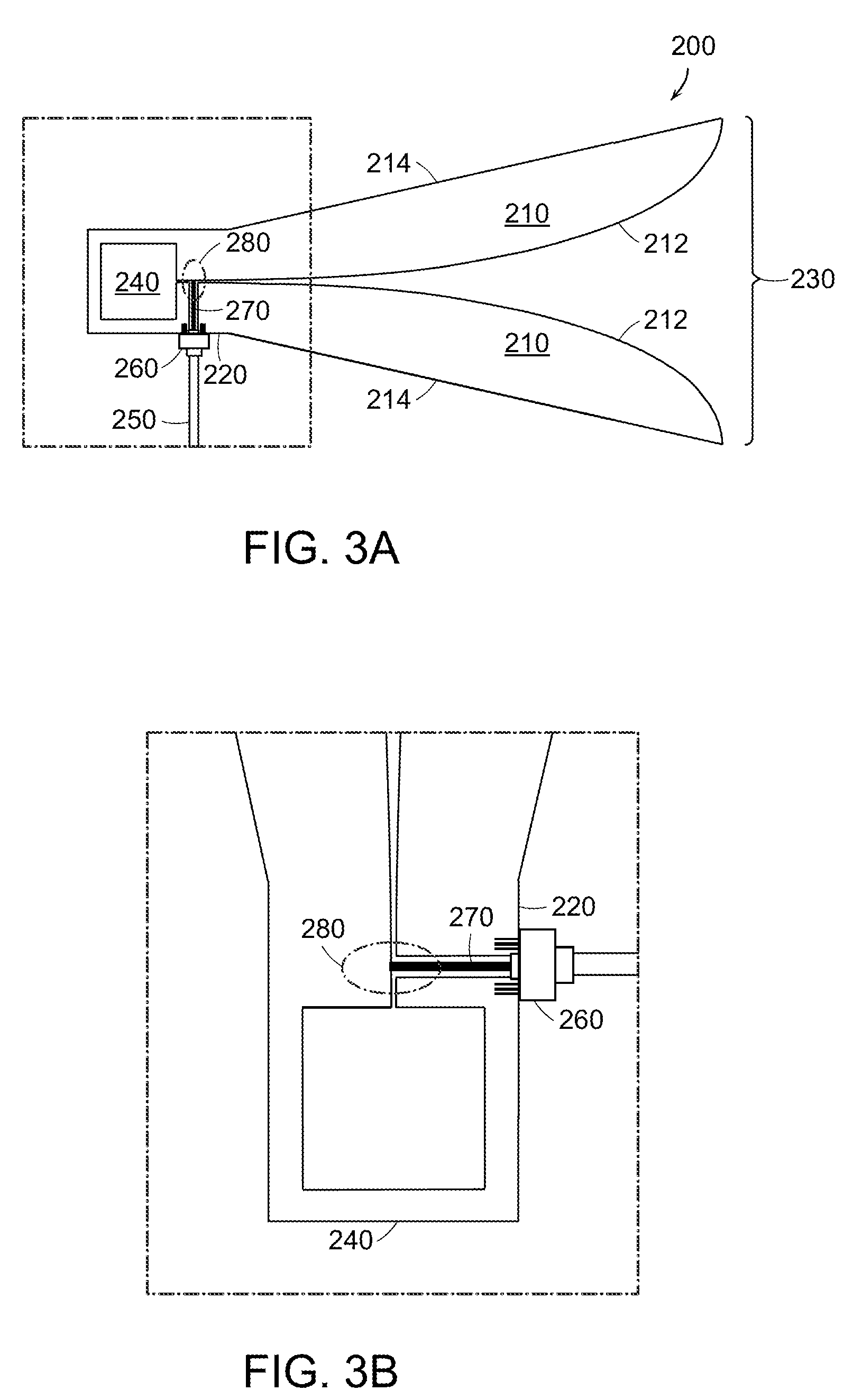
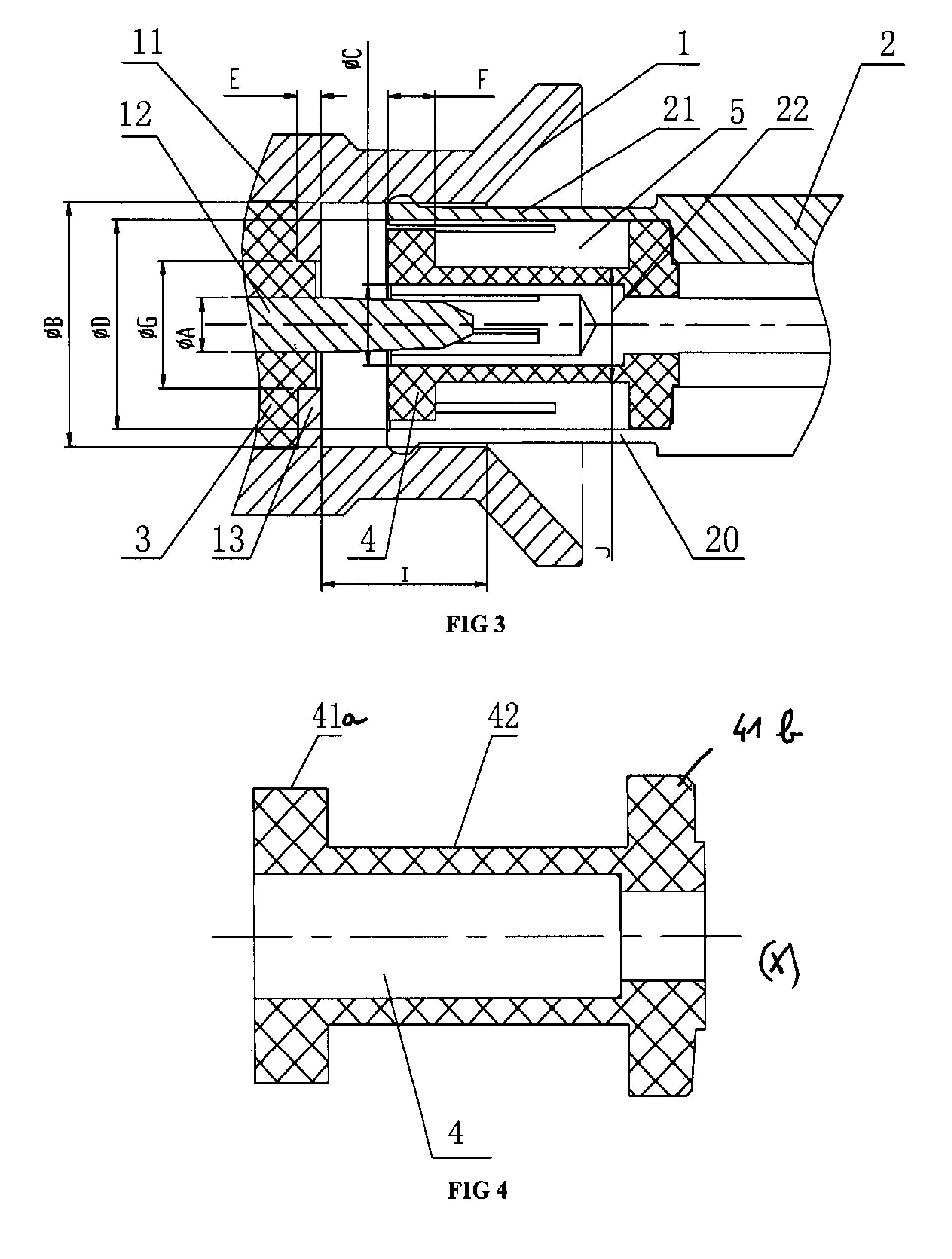
Horn Antenna with Integrated Impedance Matching Network for Improved Operating Frequency Range
ActiveUS20100033391A1Reduce Impedance MismatchReduce mismatchWaveguide hornsWaveguide mouthsCapacitanceHorn antenna
A dual- or quad-ridged horn antenna with an embedded impedance matching network is provided herein. According to one embodiment, the horn antenna may include at least one pair of ridges arranged opposite one another for guiding an electromagnetic wave there between. A transmission line is coupled to a first one of the ridges for supplying power to, or receiving a signal from, a feed region of the horn antenna. To reduce impedance mismatches between the transmission line and the ridges, an impedance matching network is embedded within a second one of the ridges at the feed point. The impedance matching network reduces impedance mismatch and extends the operational frequency range of the horn antenna by providing a sufficient amount of series capacitance between the transmission line and the ridges at the feed region. As set forth herein, the impedance matching network is preferably implemented as an open-circuit transmission line stub or capacitive stub.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
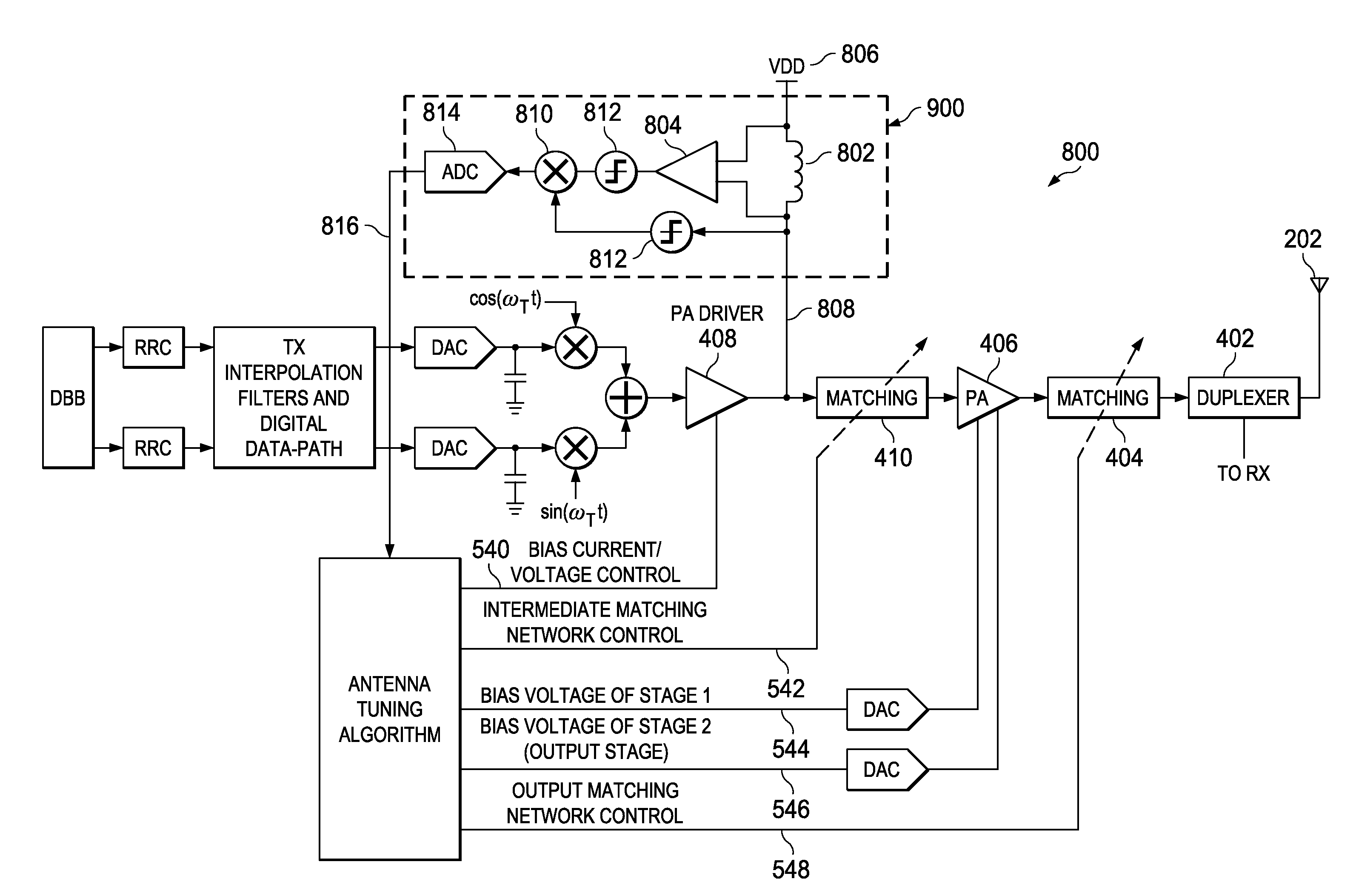
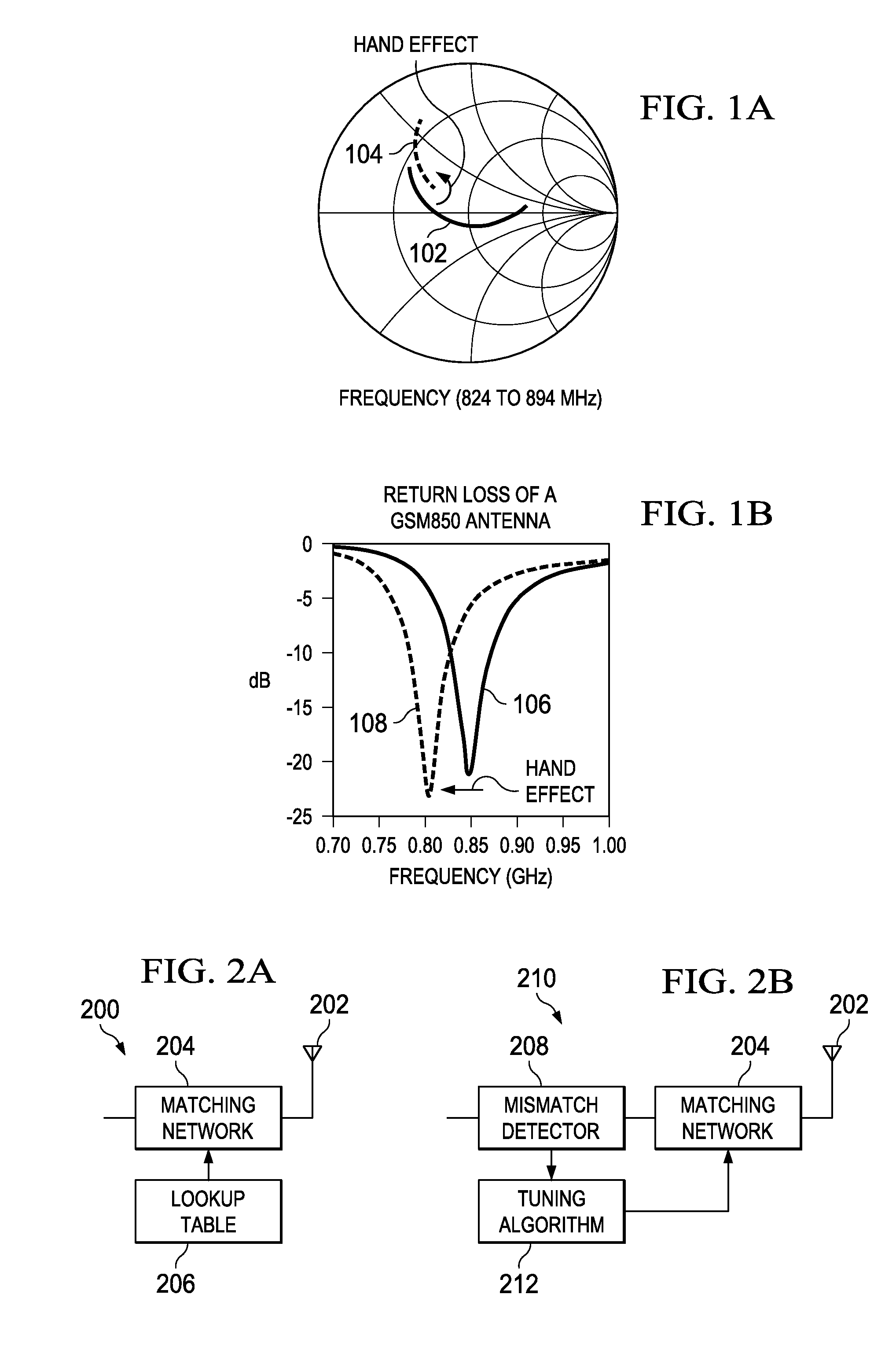
Method and apparatus for antenna tuning
ActiveUS8131232B2Reduce biasReduce Impedance MismatchResonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsTransceiverOperating point
A method for tuning a transmitter in order to improve impedance matching to an antenna or to intermediate radio frequency stages uses an error detector that senses a deviation of the amplitude or phase angle of a load current of a power amplifier driver or of a power amplifier. A controller calculates a correction and dynamically adjusts tunable transmitter parameters, which may include values of components in matching networks or bias voltages in the power amplifier or the power amplifier driver, so as to reduce the deviation and thereby improve the impedance matching. The load current of the power amplifier may alternatively be sensed by measuring the duty cycle of its switching mode power supply. A transmitter having a power amplifier and one or more tunable circuit elements incorporates an error detector that senses the amplitude or phase of a load current and a controller that adjusts one or more tunable parameters to reduce impedance mismatch. An integrated circuit device suitable for use in a transmitter includes a power amplifier driver circuit and a detector circuit capable of sensing a load current, and a controller circuit that can adjust tunable parameters either within or external to the integrated circuit. By eliminating directional couplers and integrating the detectors and power amplifier drivers, the size, complexity, and cost of wireless transceivers can be reduced, while efficiency and power consumption are improved through the dynamic adjustment of operating points and impedance matching.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Compliant printed circuit peripheral lead semiconductor package
InactiveUS20120044659A1Improve mechanical propertiesReduce environmental problemsPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsContact padLead bonding
A compliant printed circuit semiconductor package including a compliant printed circuit with at least a first dielectric layer selectively printed on a substrate with first recesses. A conductive material is printed in the first recesses to form contact members accessible along a first surface of the compliant printed circuit. At least one semiconductor device is located proximate the first surface of the compliant printed circuit. Wirebonds electrically couple terminals on the semiconductor device to the contact members. Overmolding material seals the semiconductor device and the wirebonds to the first surface of the compliant printed circuit. Contact pads on a second surface of the compliant printed circuit are electrically coupled to the contact members.
Owner:HSIO TECH
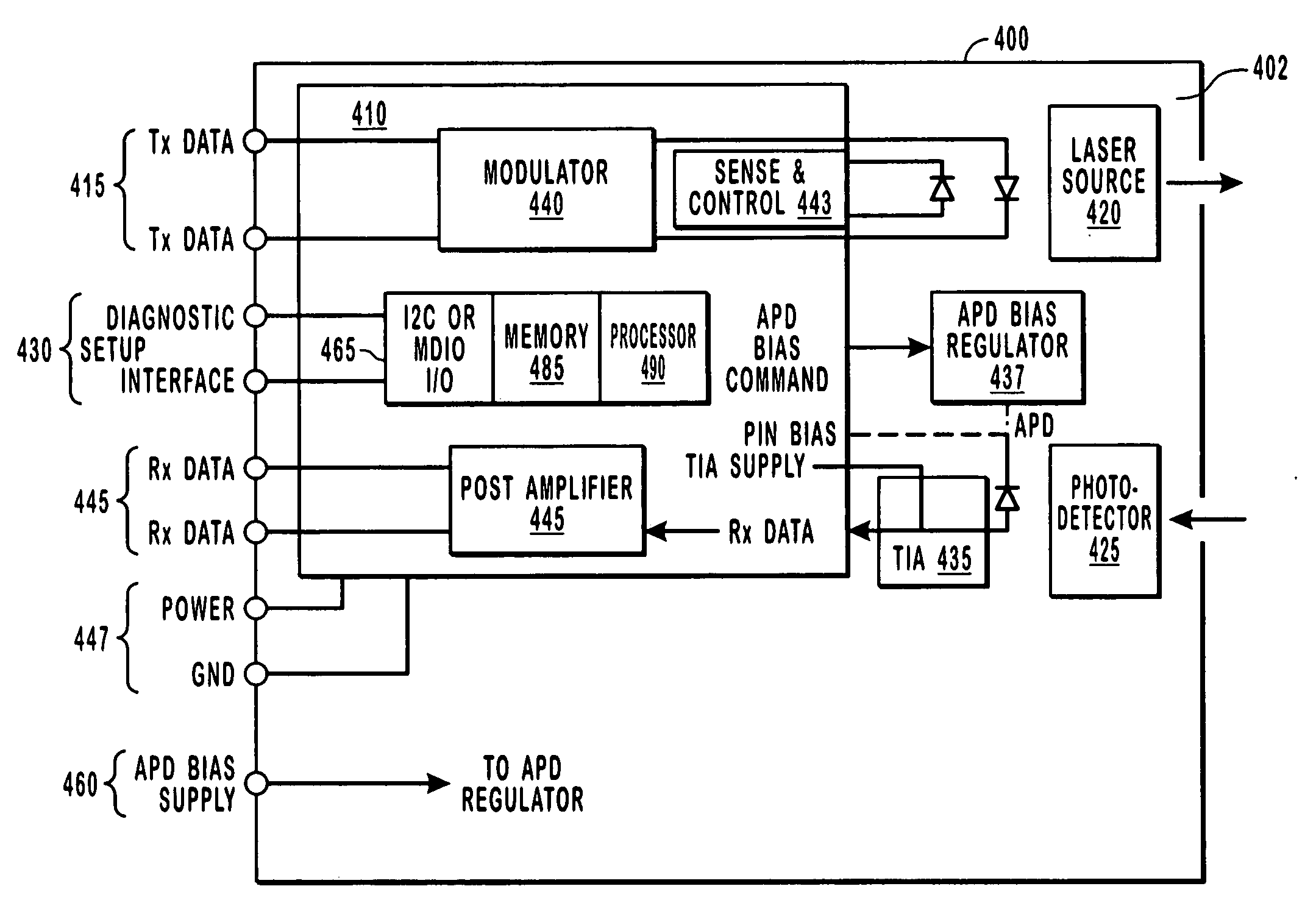
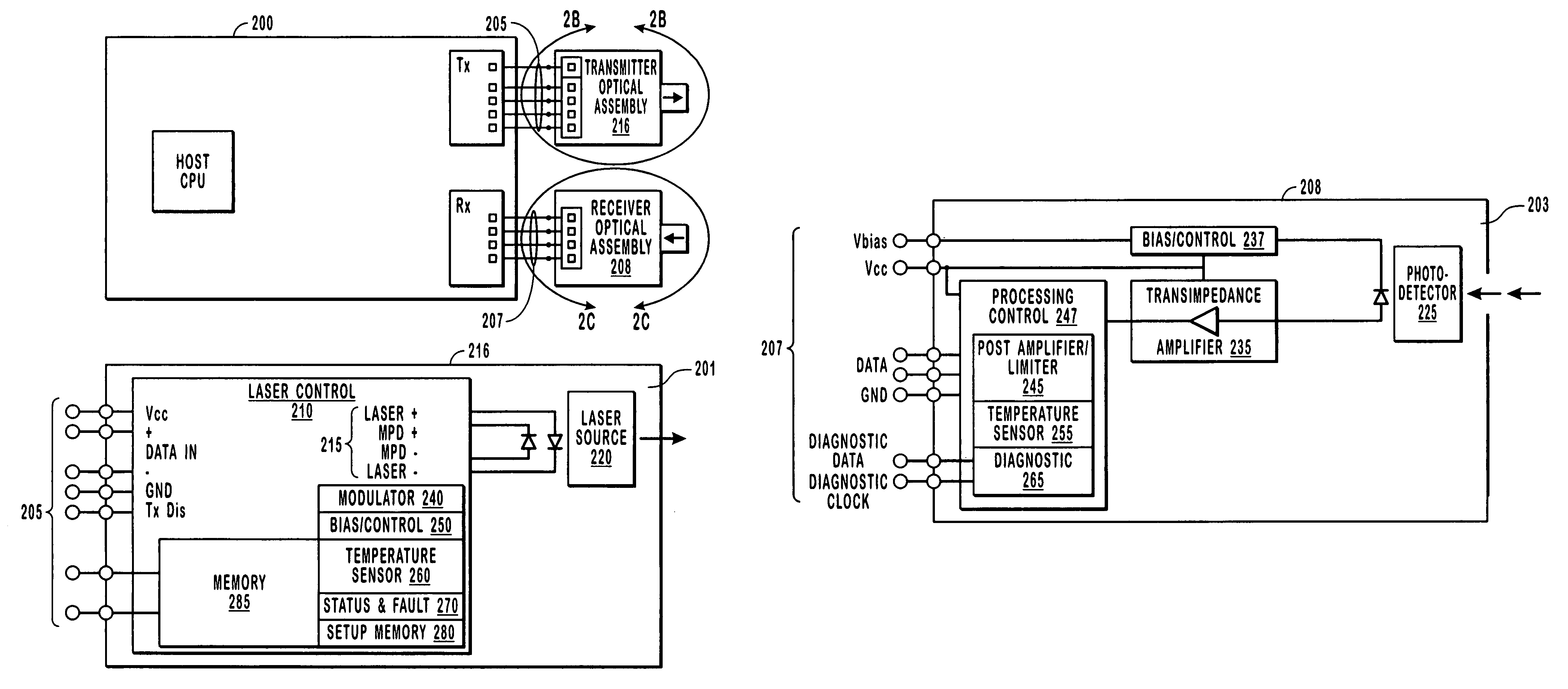
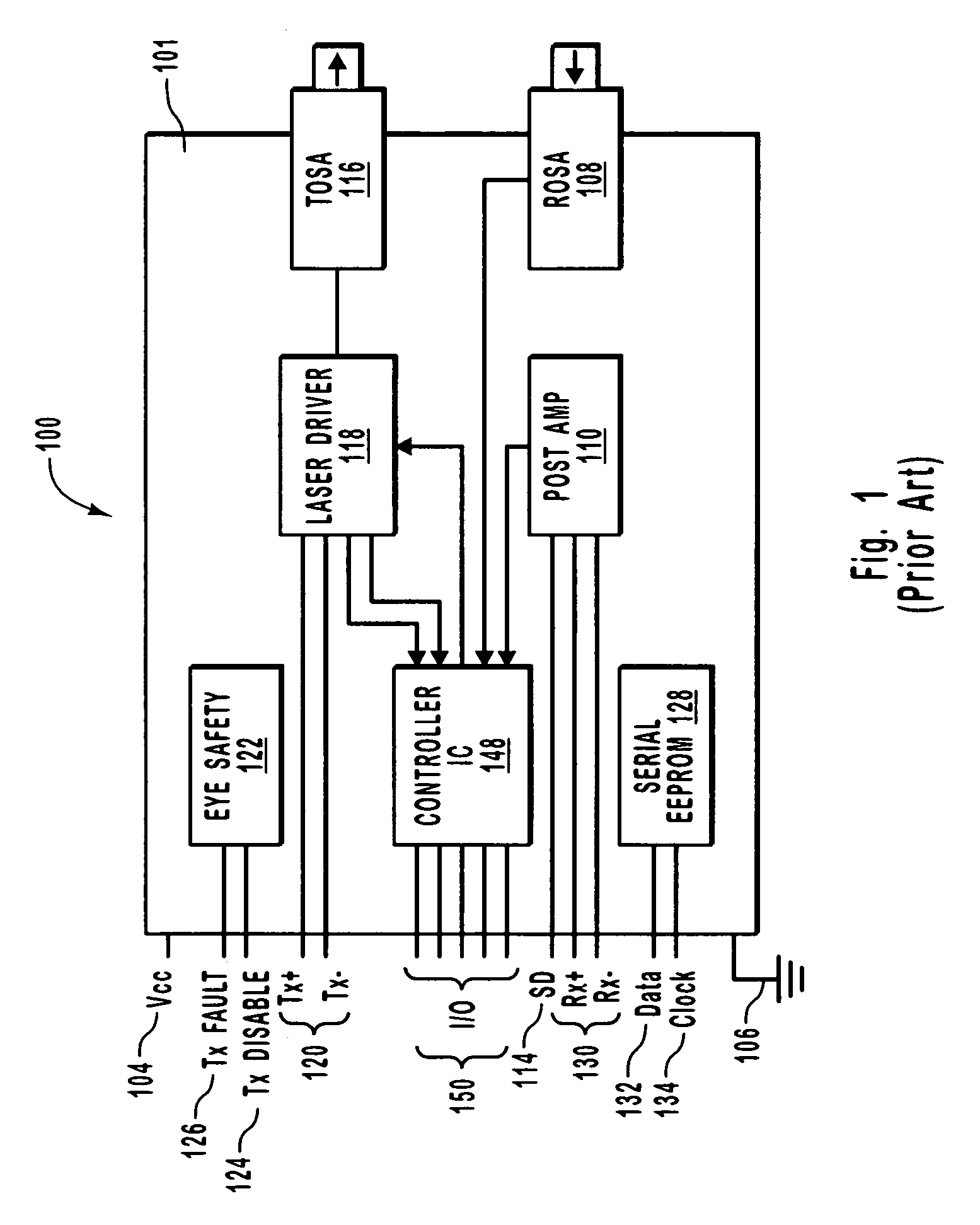
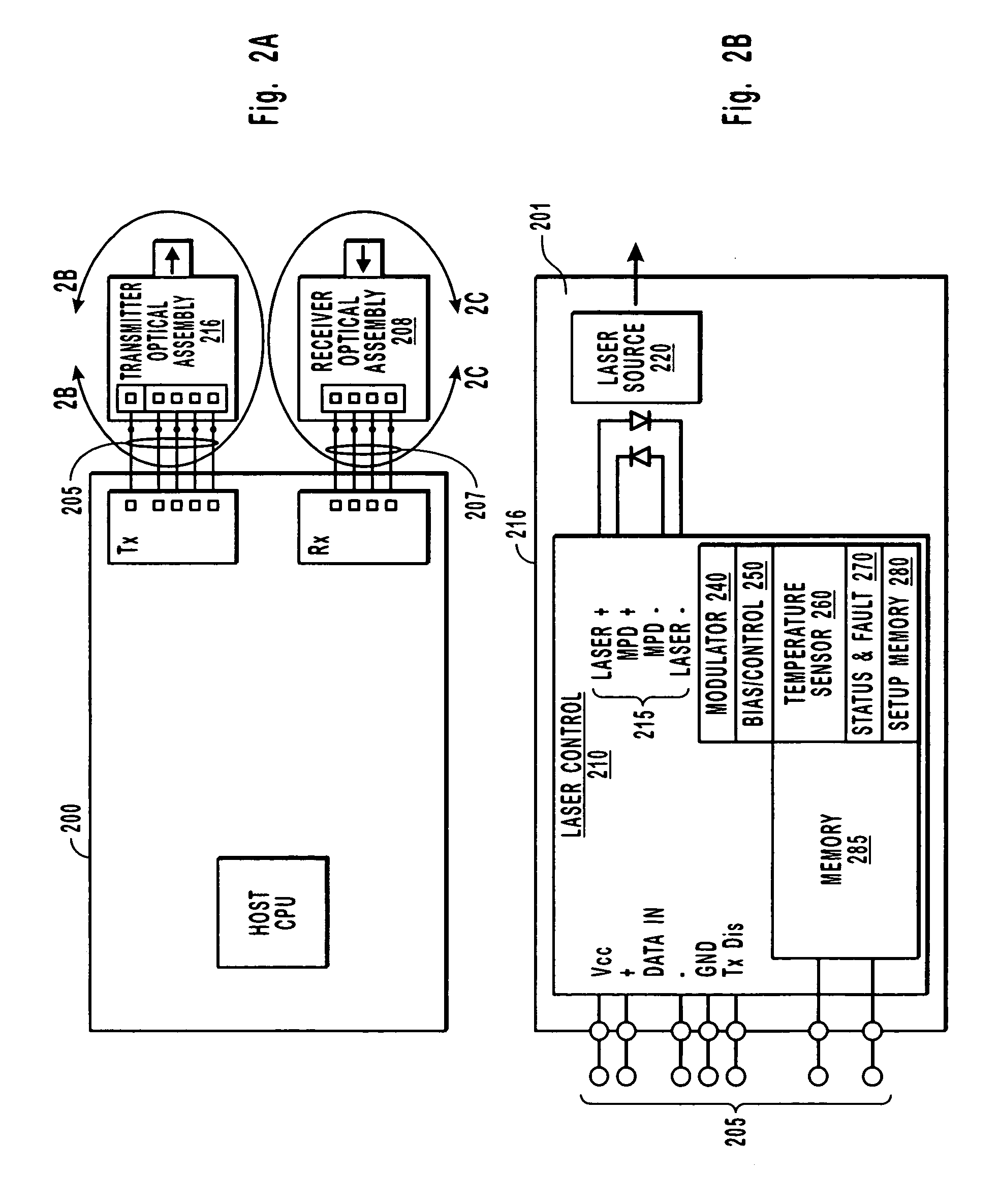
Integrated optical assembly
ActiveUS20050078916A1Minimizing any discontinuityReduce in quantityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideTransceiverPhotodiode
An integrated fiber optic assembly includes some of the active components that are otherwise found in a typical transceiver. For example, a transmitter optical assembly includes a laser source, a laser driver, and a component for administering diagnostic data. A receiver optical assembly includes a photo-diode an optical converter, such as a transimpedance amplifier, and a processing control that can administer, for example diagnostic data associated with the receiver optical assembly. A combination optical assembly includes a photo-diode and a laser source, as well as many of the active components for driving, operating, or administering the laser source. In part since the active components can be placed in close proximity to each other, electrical impedance is reduced that would otherwise be present in a typical transceiver and optical subassembly.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
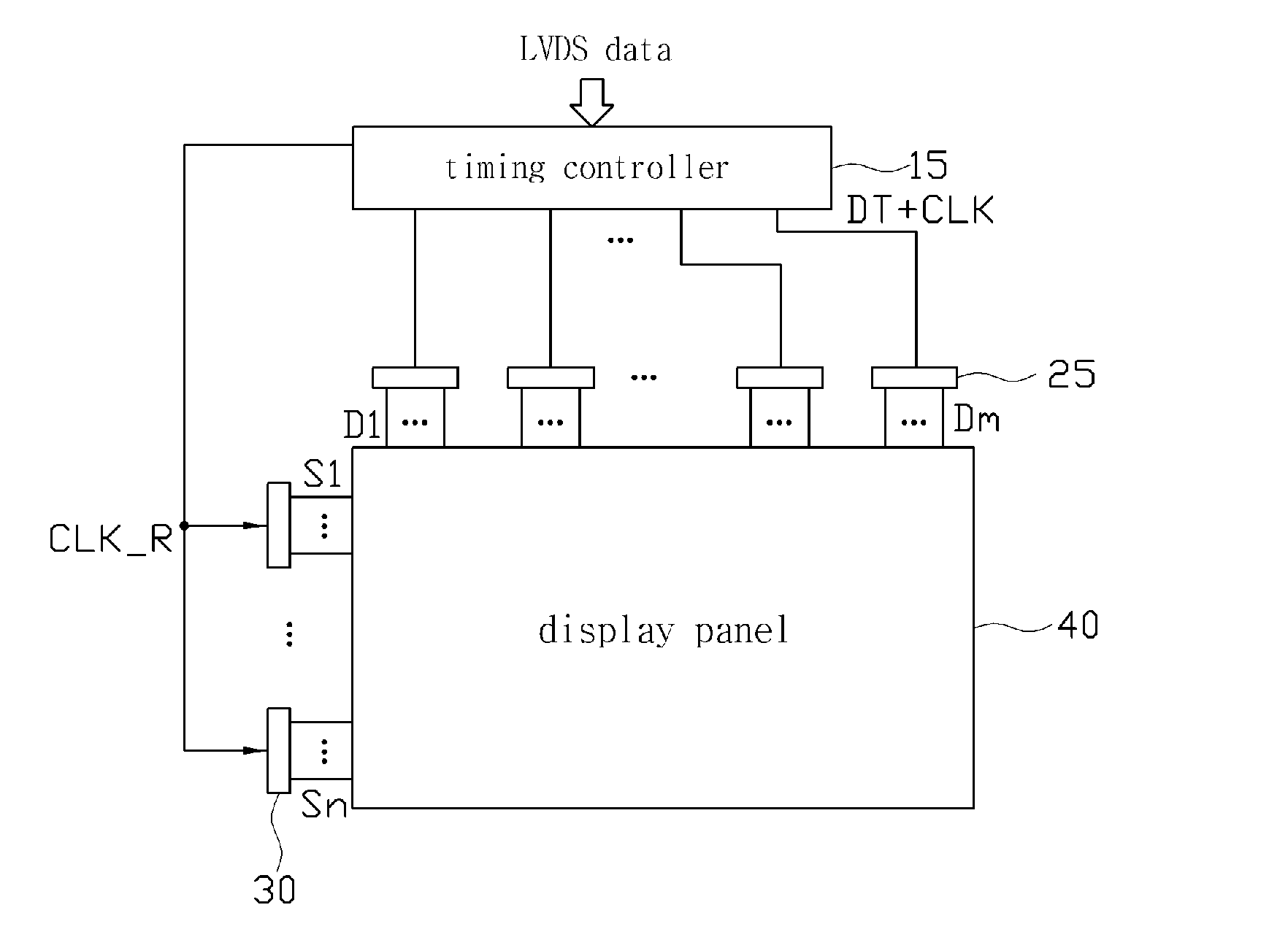
Display, timing controller and data driver for transmitting serialized mult-level data signal
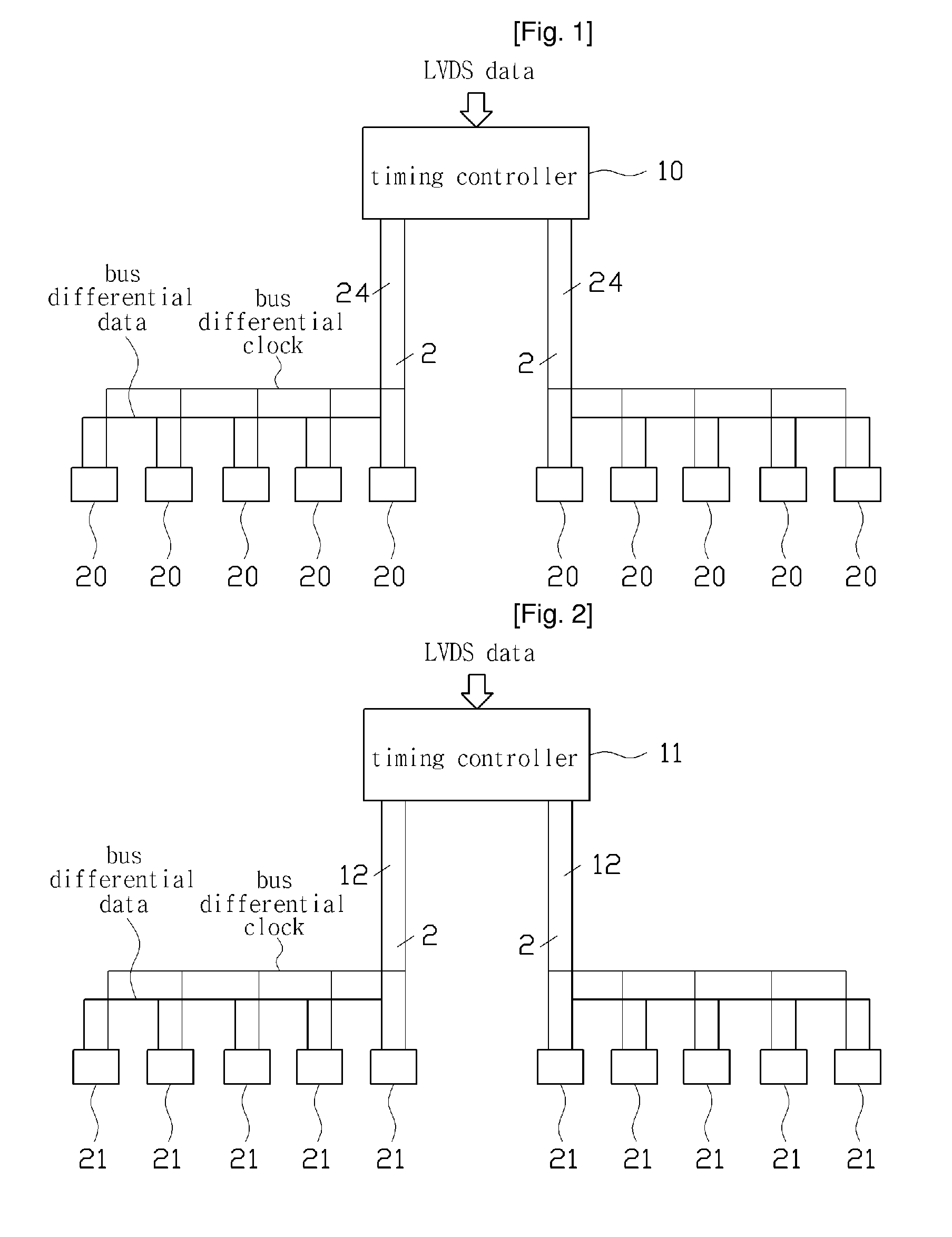
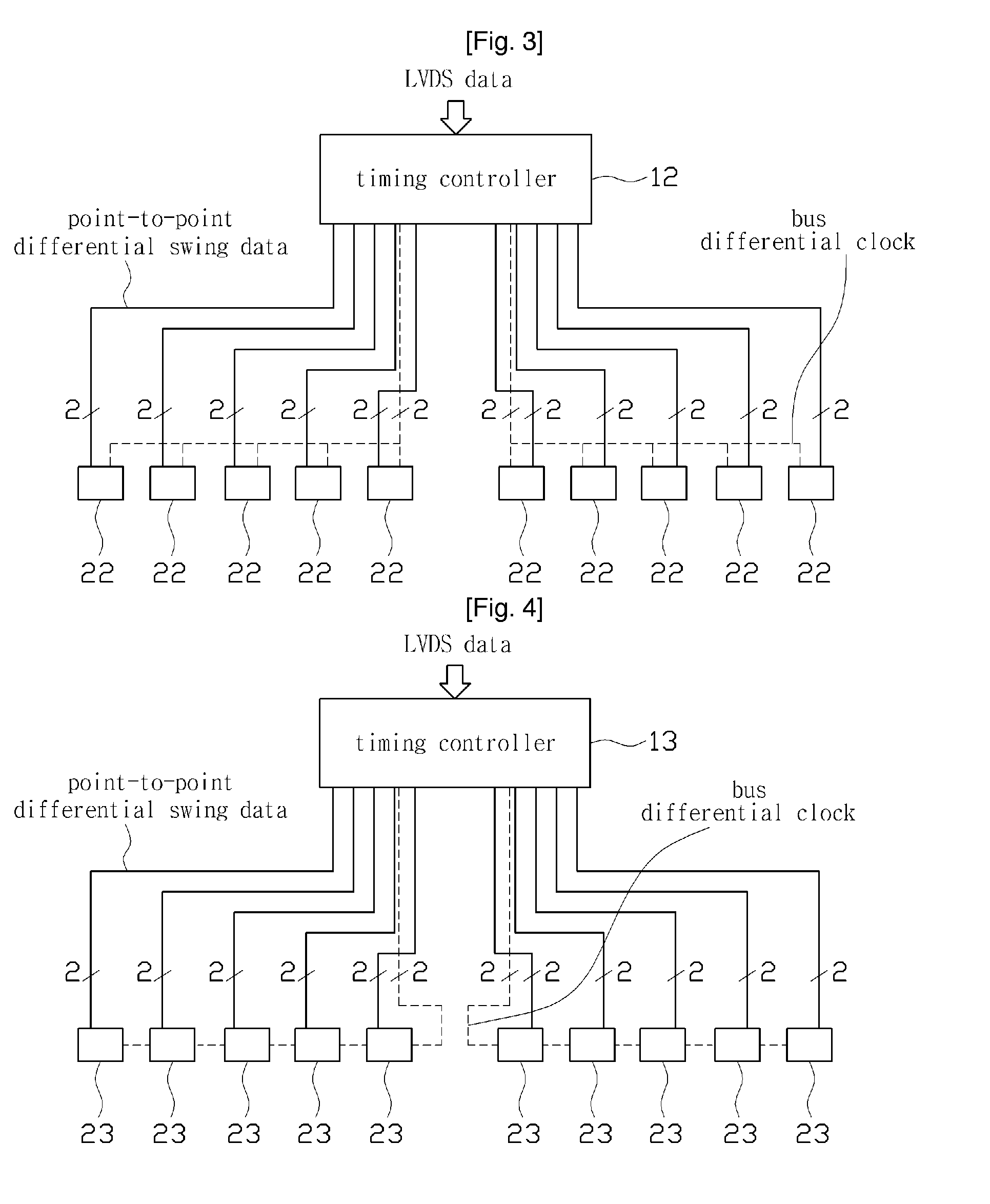
ActiveUS20100225620A1Reduce Impedance MismatchReduce numberCathode-ray tube indicatorsBaseband systemsLevel dataReal-time computing
The present invention relates to a display, a timing controller and a data driver for transmitting a serialized multi-level data signal, and more particularly to a display, a timing controller and a data driver for transmitting a serialized multi-level data signal for reducing the number of wirings between the timing controller and the data driver, and for reducing an EMI component. The display of the present invention comprises a display panel, a scan driver, a timing controller and a plurality of data drivers, wherein the timing controller transmits a transmission signal including a serialized data signal to one of the plurality of the data drivers, wherein a level of the data signal is selected from at least four different levels according to a value of a data having a length of at least two bits, and wherein the data driver restores the data from the transmitted transmission signal.
Owner:ANAPASS
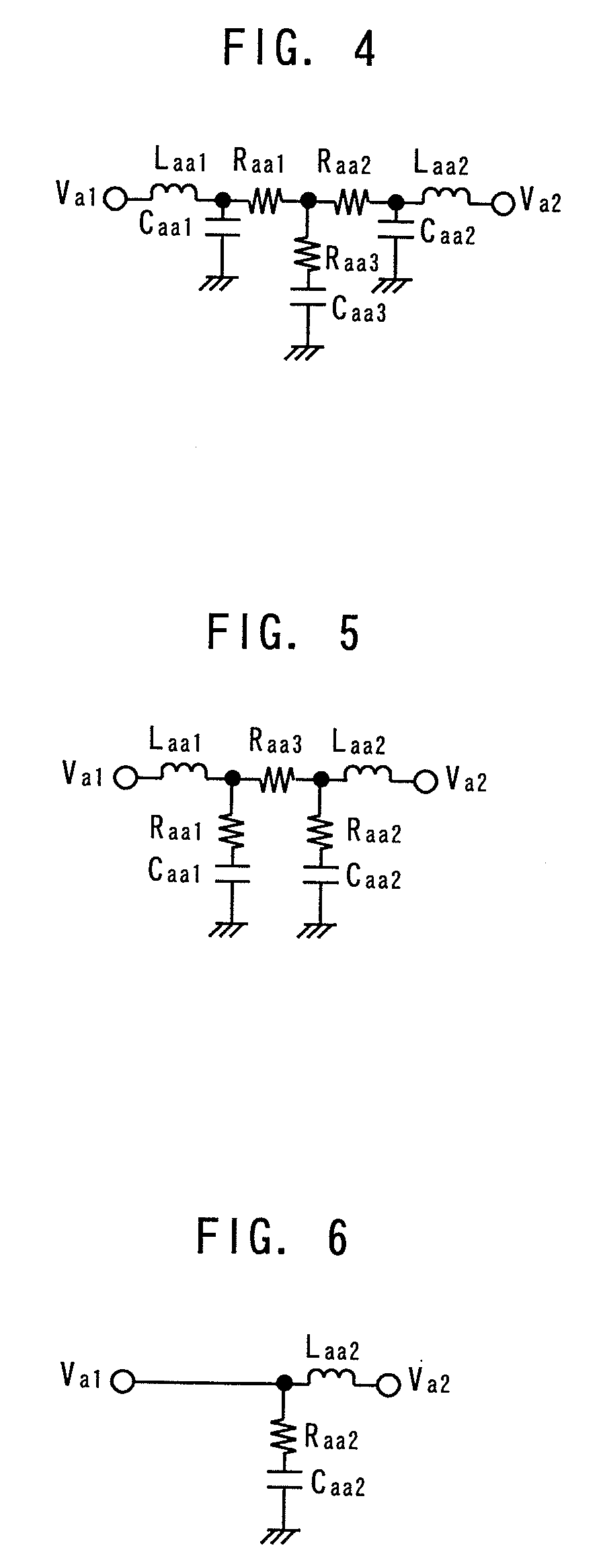
Impedance control circuit and semiconductor device including the same
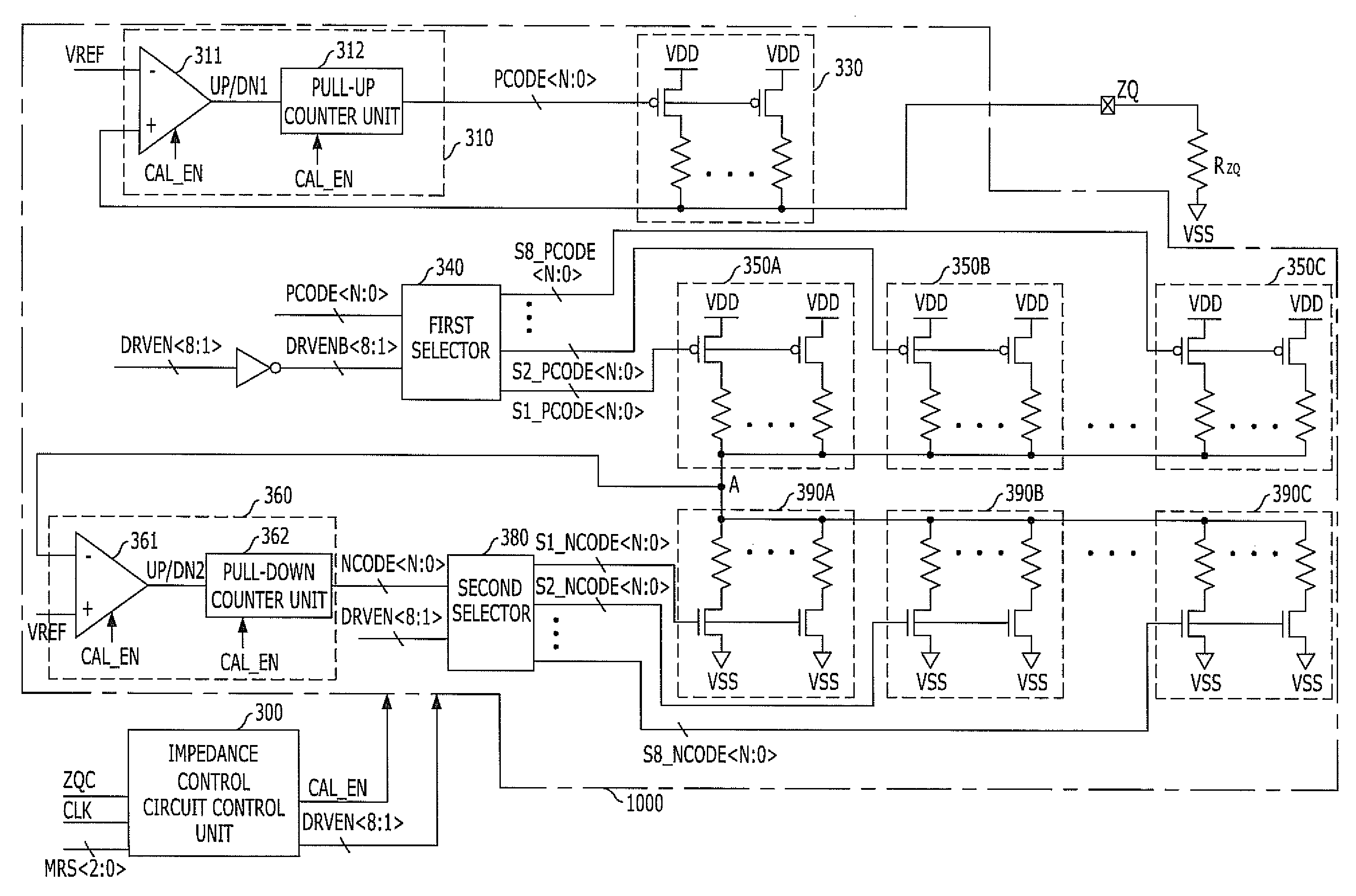
ActiveUS20130113517A1Reduce Impedance MismatchInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsSemiconductorSemiconductor device
An impedance control circuit includes a pull-up code generator configured to generate pull-up impedance control codes using a voltage of a first node, a pull-up impedance unit configured to pull-up-drive the first node in response to the pull-up impedance control codes, a plurality of dummy impedance units enabled in response to respective select signals and each configured to pull-up-drive a second node in response to the pull-up impedance control codes, a pull-down code generator configured to generate pull-down impedance control codes using a voltage of the second node, and a plurality of pull-down impedance units enabled in response to the respective select signals and each configured to pull-down-drive the second node in response to the pull-down impedance control codes.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Fire-retardant type wide-frequency-band high-power compound wave-absorbing material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103347379AImprove flame retardant performanceImprove power enduranceMagnetic/electric field screeningFibre treatmentPentaerythritolEngineering
The invention relates to a fire-retardant type wide-frequency-band high-power compound wave-absorbing material and a preparing method thereof. The material comprises an outer shell, an inner core and a base, wherein the outer shell is a polyhedron formed by a set of pyramids arranged side by side, the wedges of the pyramids are towards the same side, the inner core is located inside the outer shell, the base is located at the bottom of the outer shell, the outer shell is made of non-woven cloths, the inner core and the base are made of polyurethane foams, the inner surface and the outer surface of the outer shell are respectively provided with a first fire-retardant wave-absorbing agent layer in a coating mode, and the inner core and the base are immersed in second fire-retardant wave-absorbing agents. Both the first fire-retardant wave-absorbing agents and the second fire-retardant wave-absorbing agents comprise acetylene black, alpha-SiC, aluminum hydroxide, kaolin, pentaerythritol, and App-3. The corresponding preparing method comprises the steps of preparing the outer shell, preparing the inner core and the base, and inserting the inner core into the outer shell, and therefore the wave-absorbing material is obtained. The wave-absorbing material has good wave absorbing performance and fire retardance, and the preparing method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:NANJING LUOPU TECH CO LTD
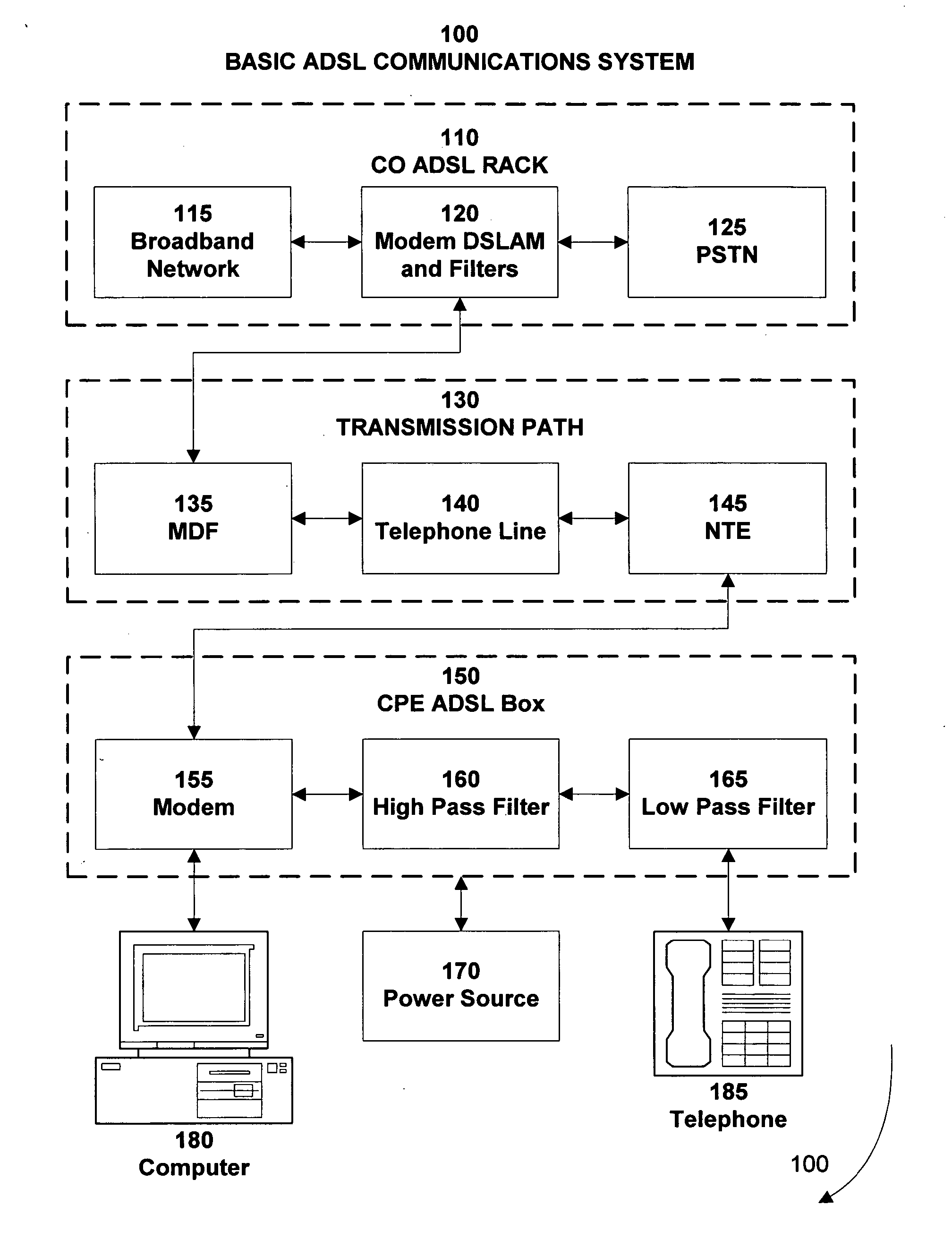
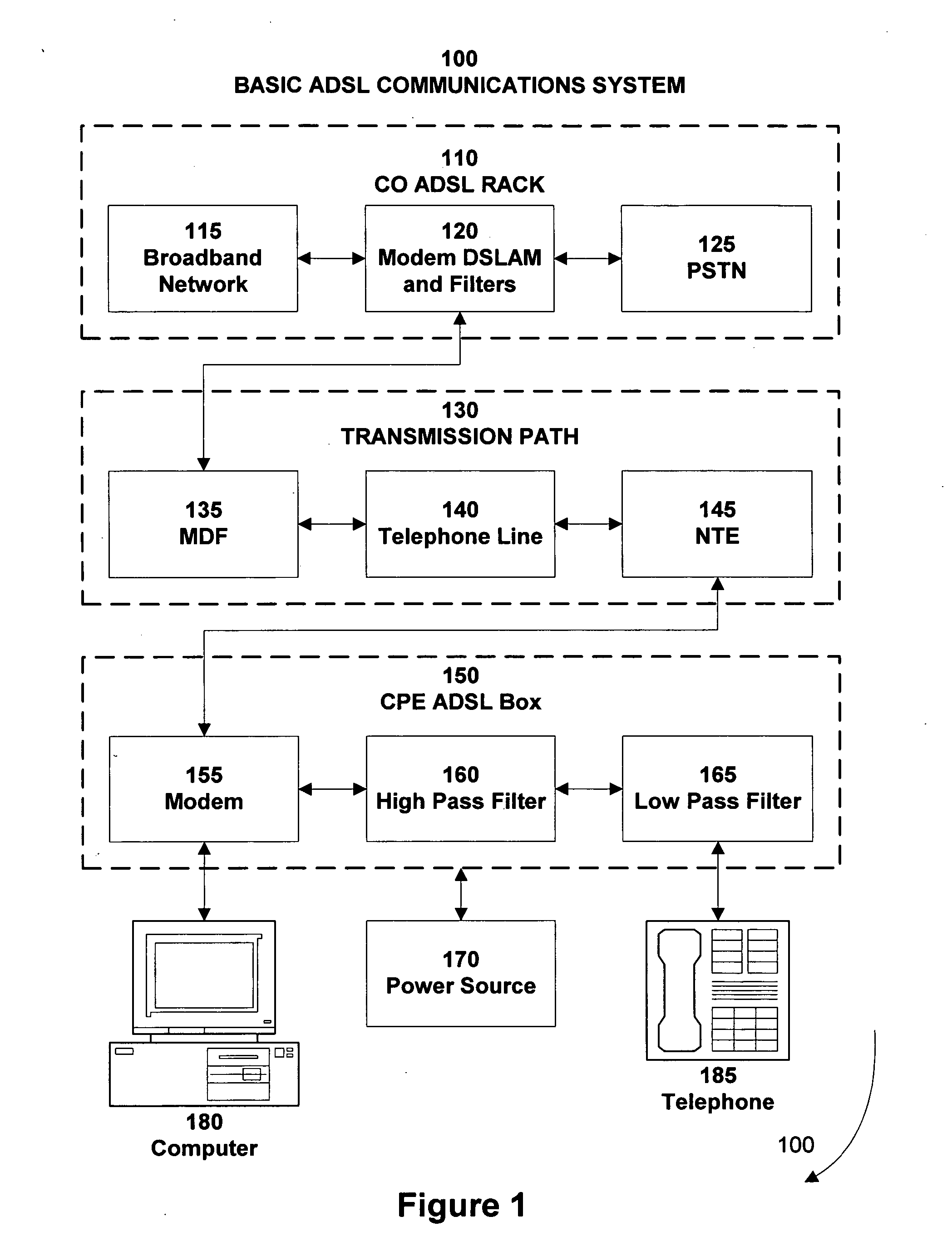
System for crosstalk noise reduction on twisted pair, ethernet, polyphase and shielded wire systems
InactiveUS20050018596A1Reduce crosstalk noiseReduce impedance mismatchFrequency-division multiplex detailsCross-talk reductionDigital signal processingOperating frequency
The present invention is an electronic circuit that reduces crosstalk in communications systems employing twisted pair, Ethernet, polyphase or shielded wire transmission media. The present invention includes three stages of crosstalk noise reduction. Stage 1 filters common mode noise from the transmission media and balances the resistive and reactive parasitic electrical characteristics of the transmission media that couple each line to the local ground over the operating frequency band. The second Stage performs differential crosstalk noise reduction in real time using multiple feedback loops. It can dynamically locate and set optimal system operating conditions for minimal differential crosstalk coupling for the specific environmental and interfering channel utilization conditions. The third Stage utilizes digital signal processing techniques to further reduce any residual crosstalk after analog-to-digital conversion. The third Stage also functions as a digital controller for the entire system as well as portions of subsystems including the feedback loops of Stage 2.
Owner:MASHHOON HAMID R
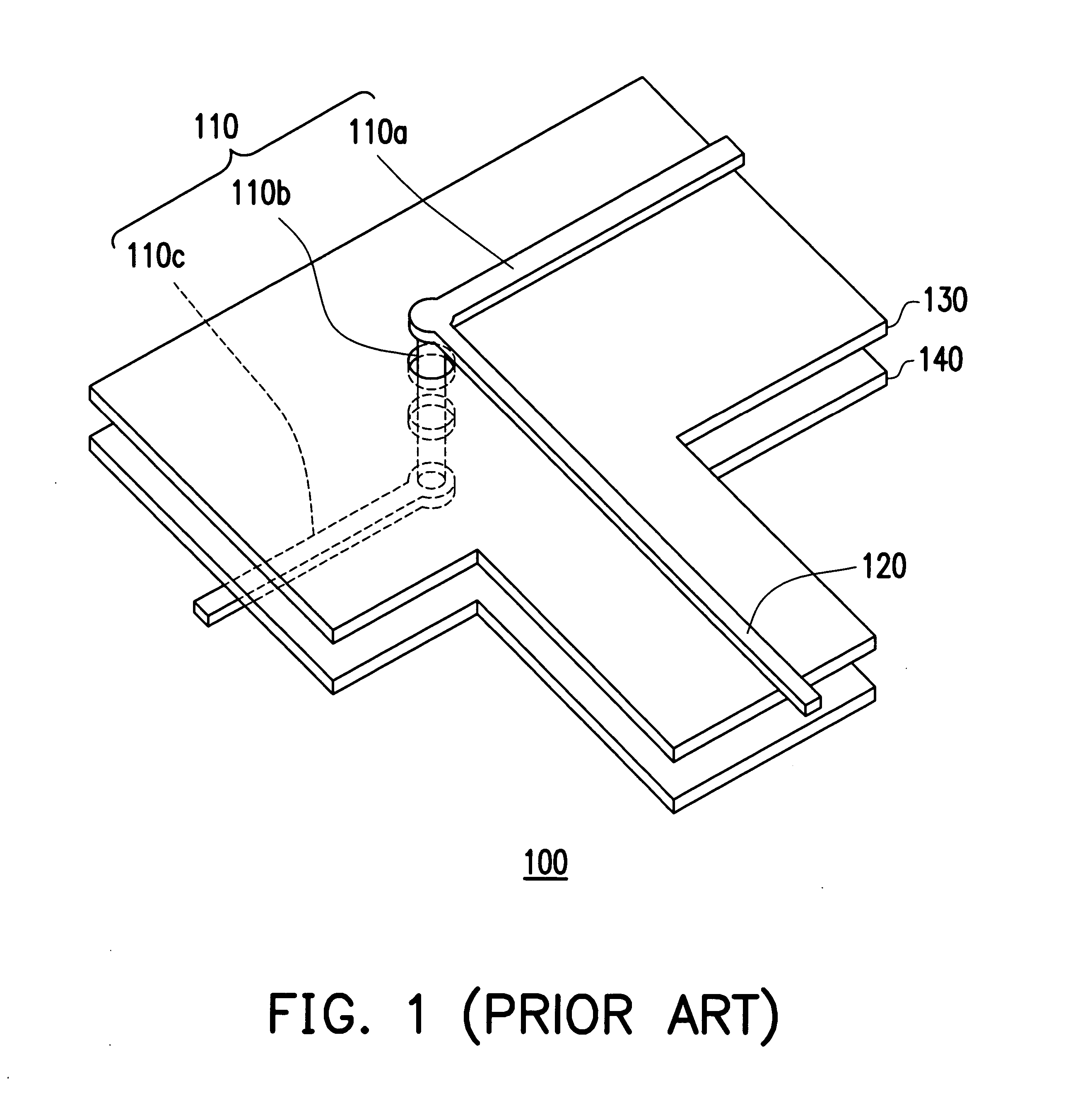
Signal transmission structure having plural reference planes with non-overlapping openings
ActiveUS7202758B2Improve signal transmission qualityReduce noise disturbanceMultiple-port networksPrinted circuit aspectsCouplingResonance
A signal transmission structure including a signal line, a first reference plane with a first opening, and a second reference plane with a second opening is provided. The first reference plane is disposed beside the signal line, and a portion of the signal line passes through a position of the first opening. In addition, the second reference plane is disposed beside the first reference plane, and the second opening is in a position corresponding to the position of the first opening, while the outline of the second opening projected onto the first reference plane does not overlap with the position of the first opening. Therefore, at high frequency-transmission, the above structure can reduce the insertion loss resulted from impedance mismatch as the signal passes through the opening, and reduce the resonance induced by the coupling between two reference planes to enhance the quality of signal transmission.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Apparatus for reducing signal reflection in a circuit board
InactiveUS7230835B1Reduce signal lossReduce widthFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsSignal reflectionContact pad
A circuit board has, in a first signal layer, a signal conductor having a relatively small width and a contact pad having a relatively large width. The relatively large width of the contact pad combined with the relatively narrow signal conductor creates an impedance mismatch between the contact pad and the signal conductor. The circuit board has, in a second signal layer, a ground plane separated from the first signal layer by a nonconductive layer. The circuit board defines an opening in the second signal layer underneath the contact pad. The presence of the ground plane underneath the contact pad typically affects the impedance of the contact pad. The opening in the second signal layer removes a portion the ground plane relative to the contact pad and, therefore, reduces the impedance mismatch between the contact pad and the signal conductor. Such reduction in the mismatch of the impedances between the contact pad and the signal conductor minimizes signal reflection of a signal transmitted through the signal conductor and across the contact pad.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Detection element for detecting an electromagnetic wave
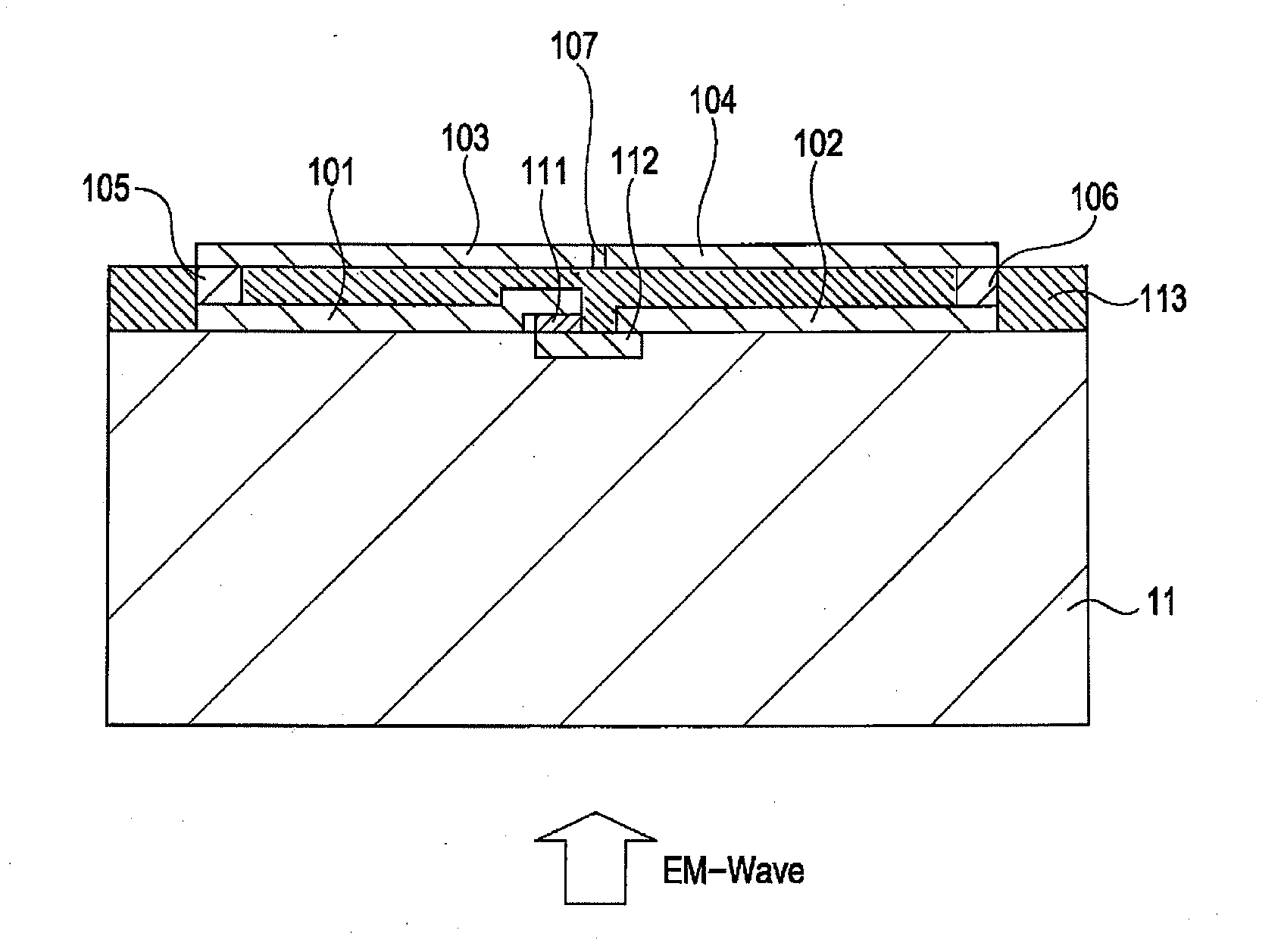
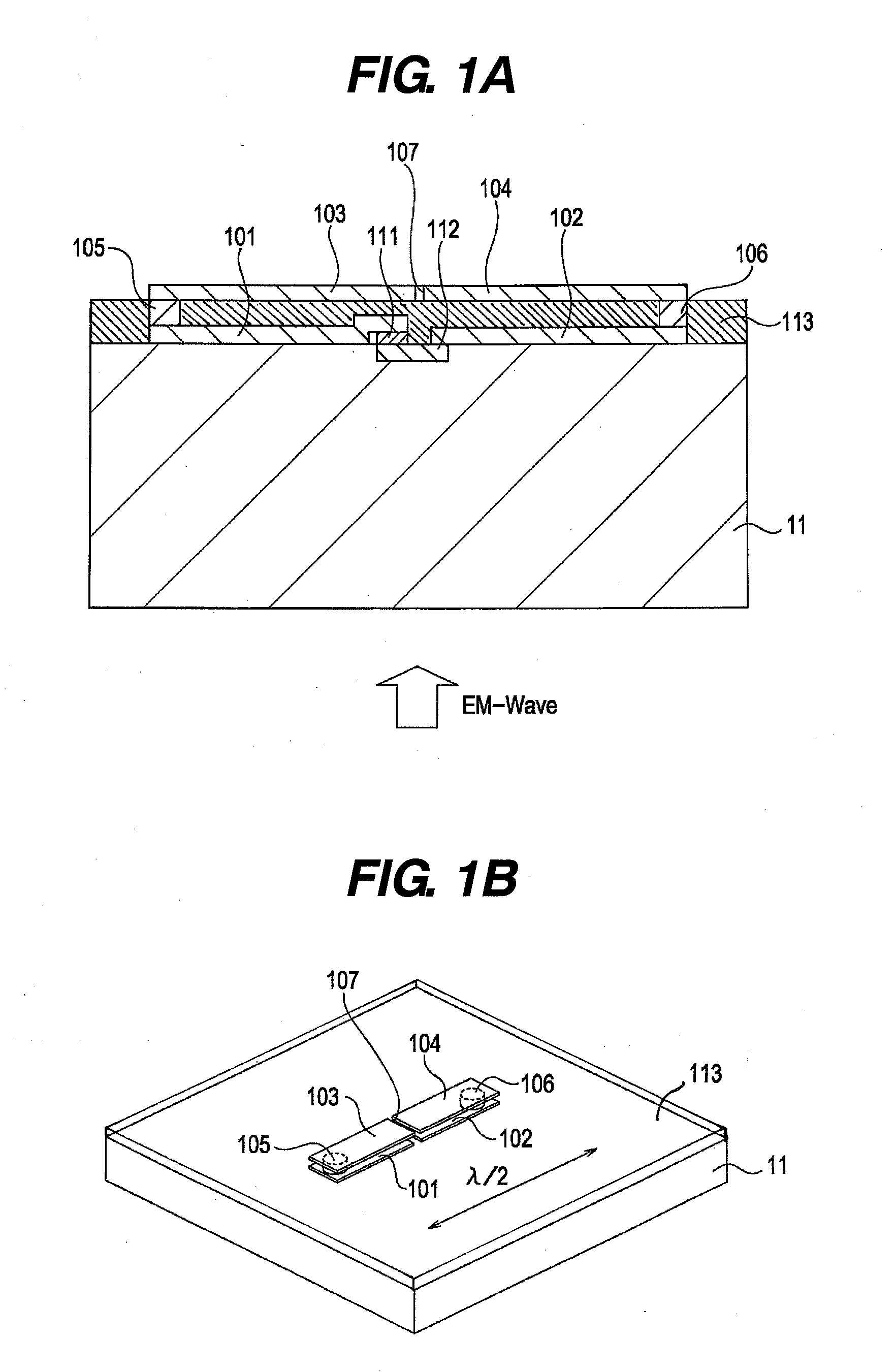
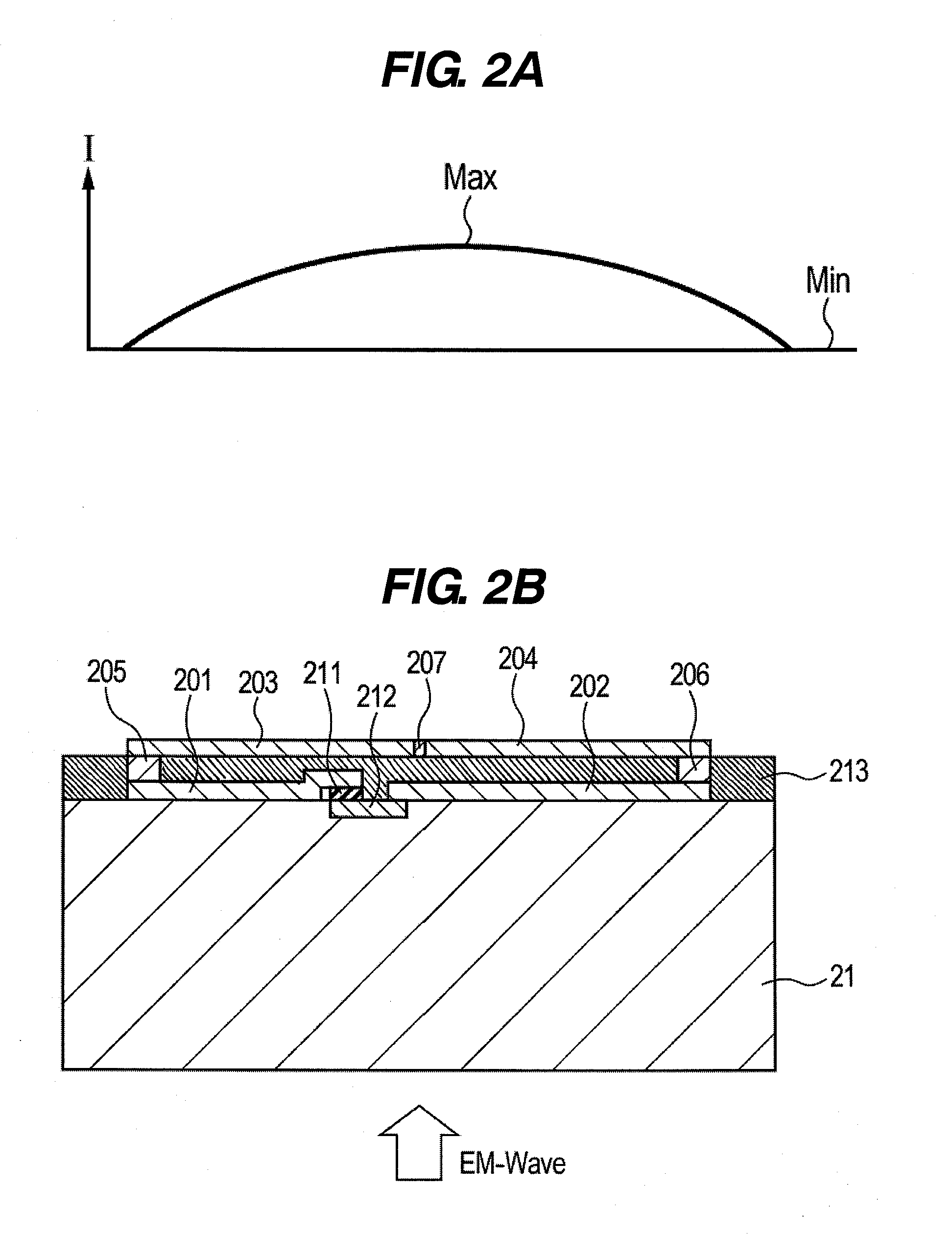
InactiveUS20110248724A1High impedanceReduce Impedance MismatchResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrically short antennasElectricitySchottky barrier
A detection element for detecting an electromagnetic wave includes: a substrate; a schottky barrier diode disposed on the substrate; and an antenna disposed on the substrate, wherein the antenna includes a first conductive element and a second conductive element which are divided, a third conductive element and a fourth conductive element which are divided, a first connecting member that electrically connects the first conductive element and the third conductive element, and a second connecting member that electrically connects the second conductive element and the fourth conductive element, wherein the first conductive element and the second conductive element, and the third conductive element and the fourth conductive element are formed on multiple surfaces of the substrate, which are spaced apart from each other along an incident direction of the electromagnetic wave, respectively, and wherein the schottky barrier diode is electrically connected between the first conductive element and the second conductive element.
Owner:CANON KK
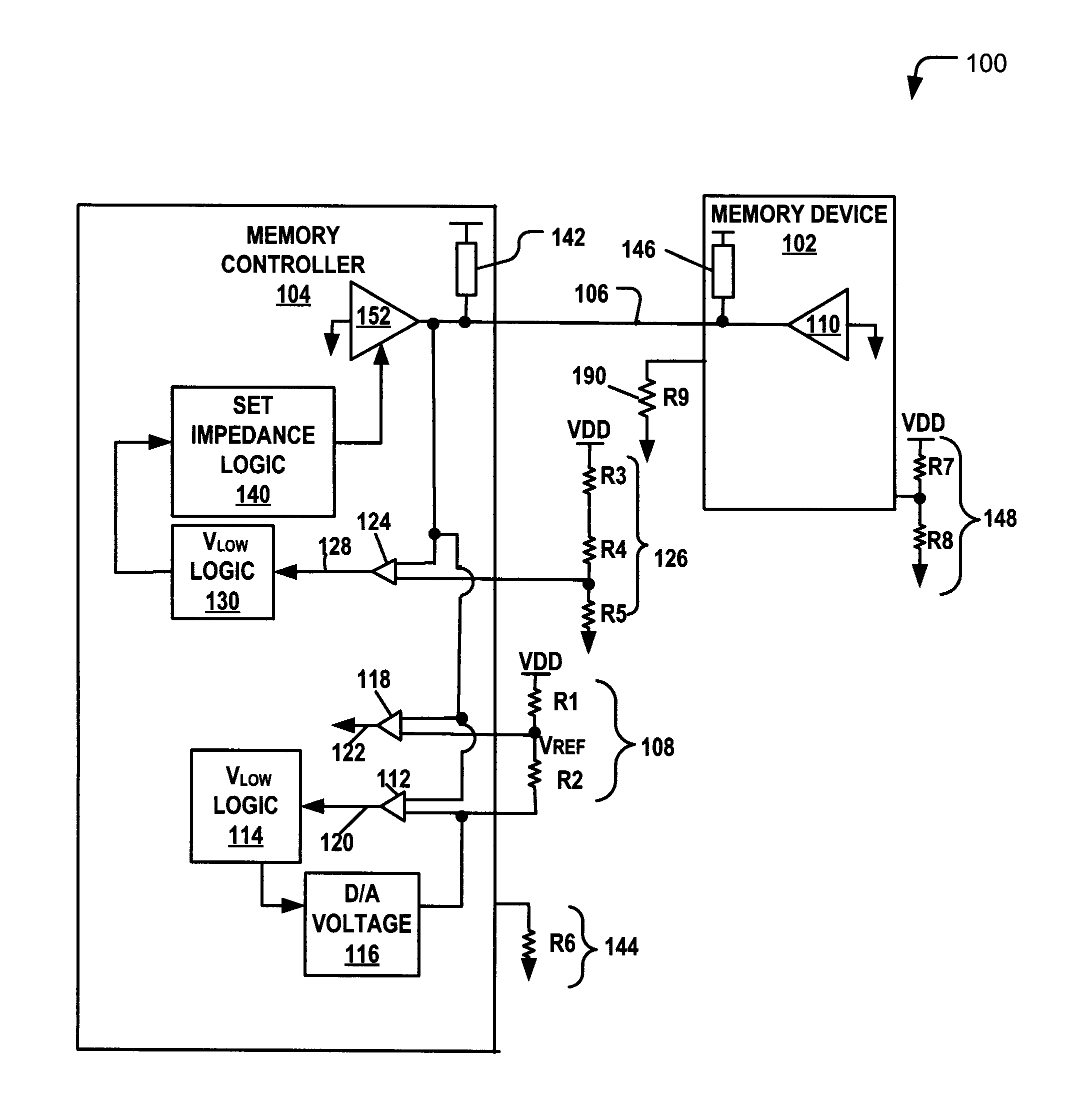
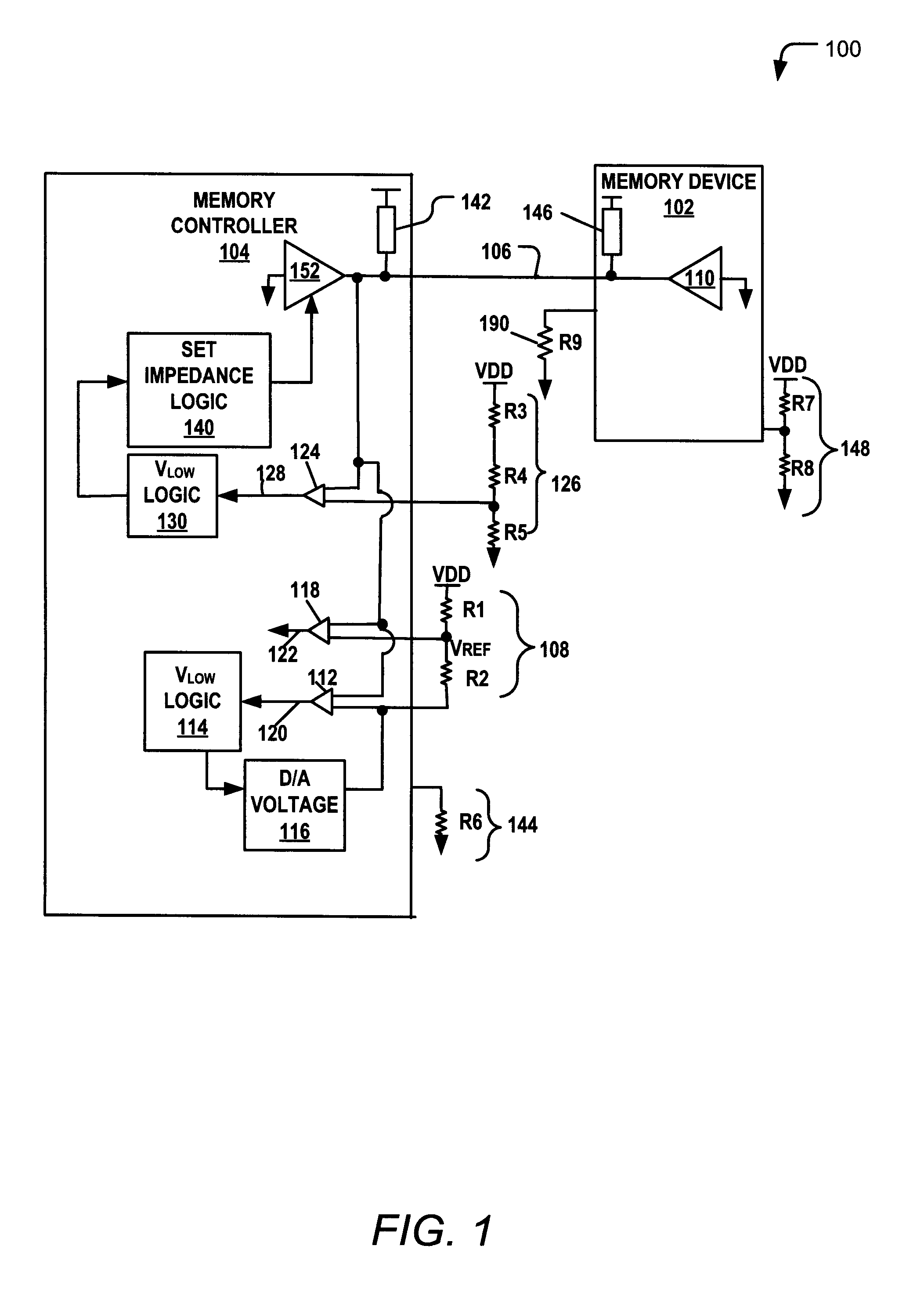
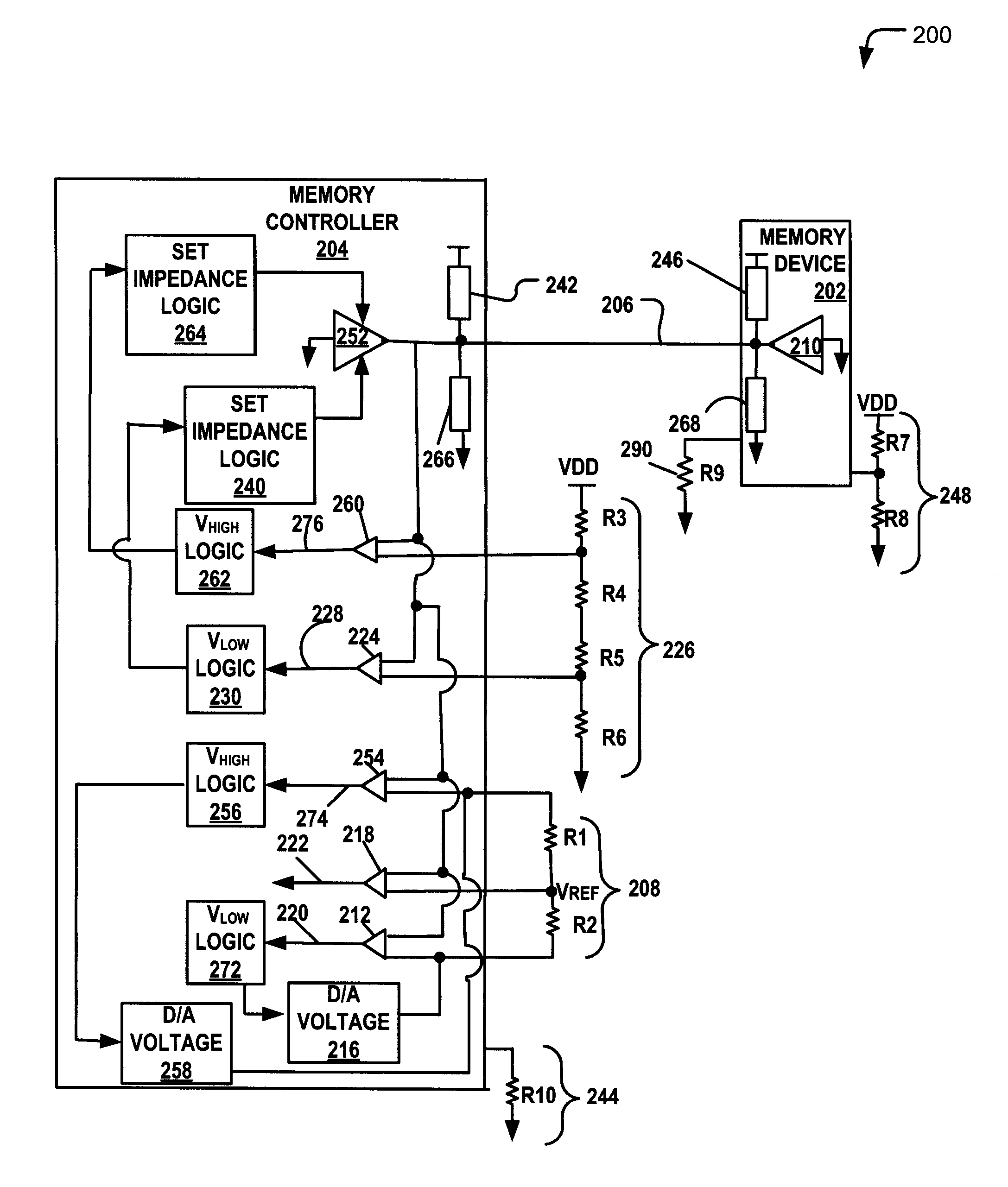
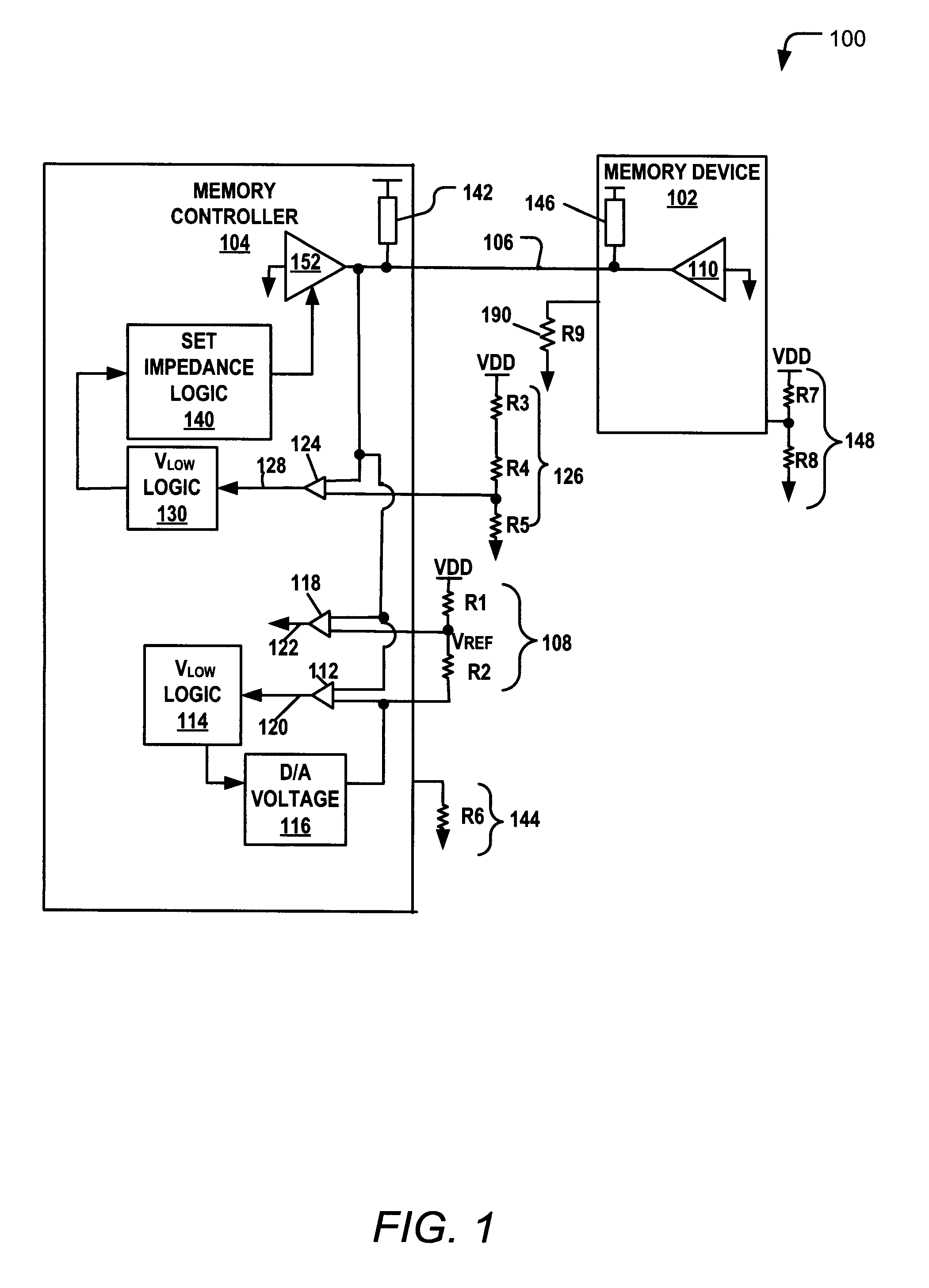
Training a Memory Controller and a Memory Device Using Multiple Read and Write Operations
InactiveUS20110307671A1Reduce Signal ErrorSpeedLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsControl storeMemory controller
Systems and methods to set a voltage value associated with a communication bus that includes memory controller coupled to a memory device are disclosed. A particular method may include performing a first calibration operation associated with first data written from a memory controller to a memory device. A second calibration operation may be associated with second data read at the memory controller from the memory device. The operating parameter may be set based on a result of at least one of the first and the second calibration operations at the memory device or the memory controller.
Owner:IBM CORP
Integrated optical assembly
ActiveUS7440647B2Minimizing any discontinuityReduce in quantityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideFiberTransceiver
An integrated fiber optic assembly includes some of the active components that are otherwise found in a typical transceiver. For example, a transmitter optical assembly includes a laser source, a laser driver, and a component for administering diagnostic data. A receiver optical assembly includes a photo-diode an optical converter, such as a transimpedance amplifier, and a processing control that can administer, for example diagnostic data associated with the receiver optical assembly. A combination optical assembly includes a photo-diode and a laser source, as well as many of the active components for driving, operating, or administering the laser source. In part since the active components can be placed in close proximity to each other, electrical impedance is reduced that would otherwise be present in a typical transceiver and optical subassembly.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Coplanar waveguide transition for multi-band impedance matching
ActiveUS20170093041A1Reducing impedance mismatch lossImproving Impedance MatchingSimultaneous aerial operationsResonant antennasMulti bandCoplanar waveguide
A microstrip antenna including a first substrate, a ground plane disposed on a first side of the first substrate, a first conductive layer disposed on a second side of the first substrate, wherein the first conductive layer is configured to resonate at a first frequency, a second substrate disposed on the first conductive layer, a second conductive layer disposed on a side of the second substrate, wherein the second conductive layer is configured to resonate at a second frequency, a first feed portion extending through the first substrate, and configured to provide first excitation signals to the first conductive layer, a second feed portion extending through the second substrate, wherein the second feed portion is configured to provide second excitation signals to the second conductive layer, and a conductive strip disposed in the first conductive layer and electrically connecting the first feed portion and the second feed portion.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
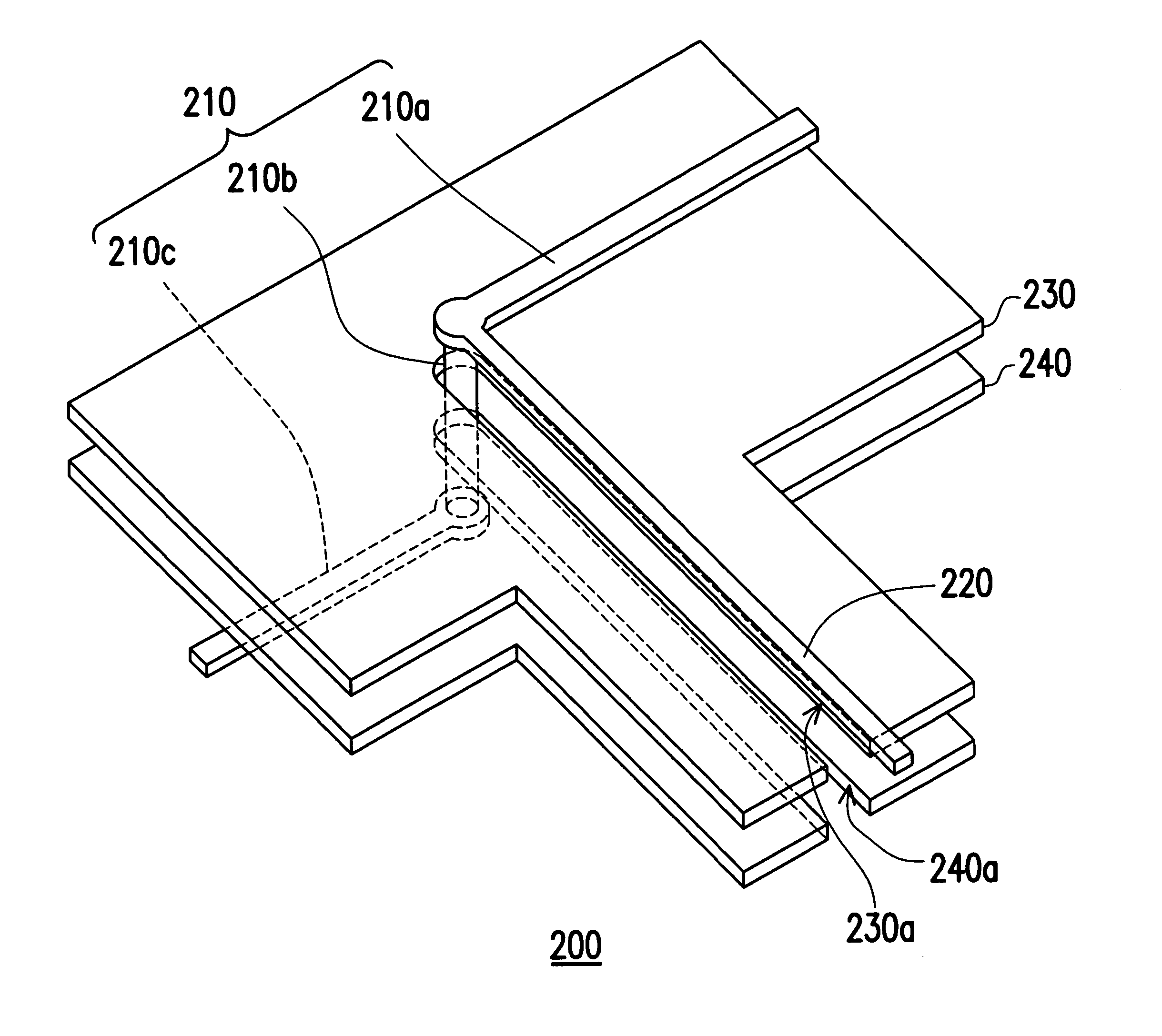
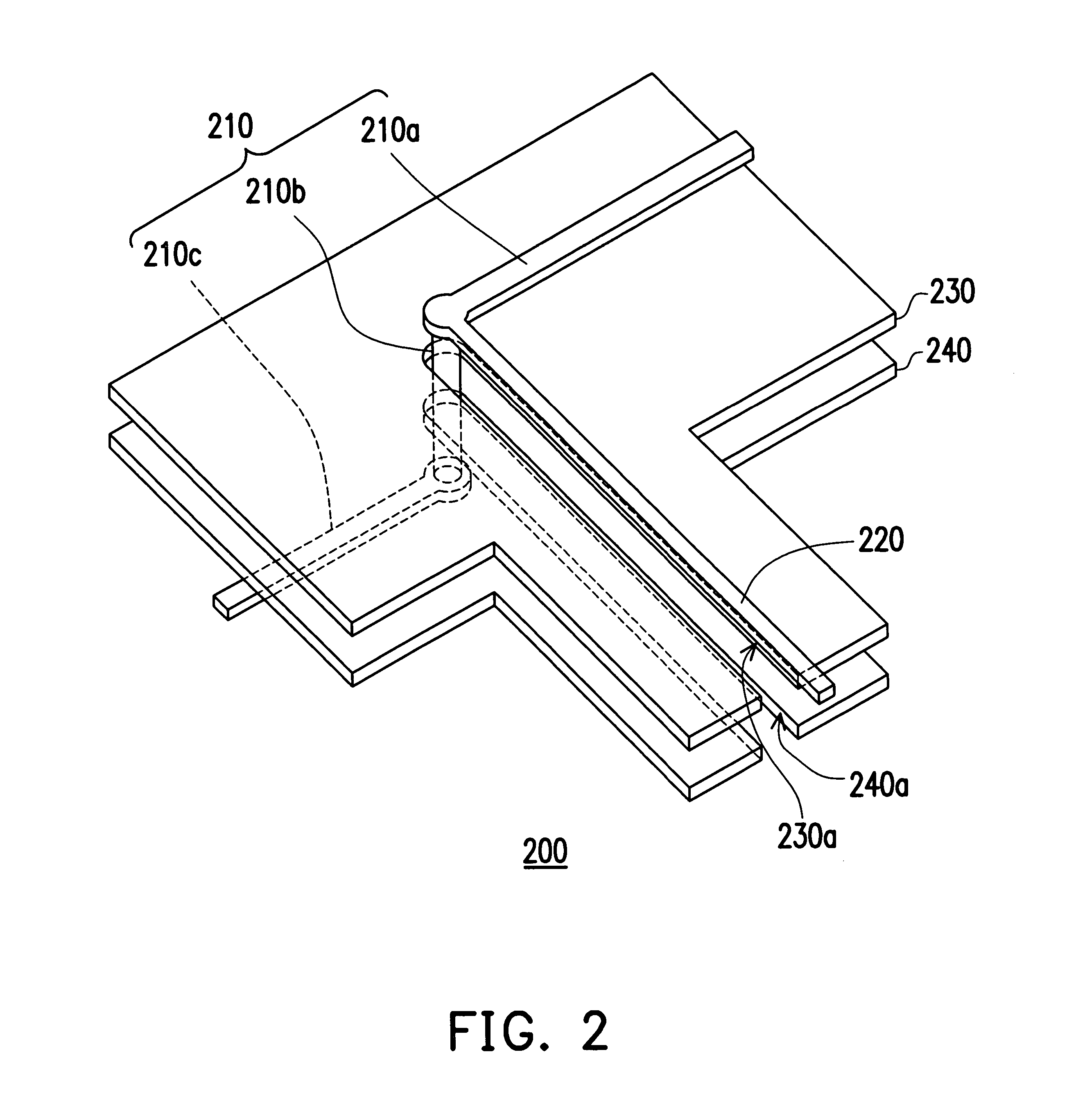
Signal transmission structure
ActiveUS20060071739A1Improve signal transmission qualityReduce noise disturbanceMultiple-port networksHigh frequency circuit adaptationsCouplingResonance
A signal transmission structure including a signal line, a first reference plane with a first opening, and a second reference plane with a second opening is provided. The first reference plane is disposed beside the signal line, and a portion of the signal line passes through a position of the first opening. In addition, the second reference plane is disposed beside the first reference plane, and the second opening is in a position corresponding to the position of the first opening, while the outline of the second opening projected onto the first reference plane does not overlap with the position of the first opening. Therefore, at high frequency-transmission, the above structure can reduce the insertion loss resulted from impedance mismatch as the signal passes through the opening, and reduce the resonance induced by the coupling between two reference planes to enhance the quality of signal transmission.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Simple low-cost test method
InactiveCN104020379AEasy to operateReduce Impedance MismatchElectrical testingTest structureEngineering
The invention discloses a simple low-cost test method. The simple low-cost test method comprises a test fixture and a test plate. Two tested conveying lines with different lengths are designed on the same layer of the test plate and named as X1 and X2 respectively to serve as a test structure A and a test structure B, the length difference of X1-X2 is at least larger than 4 inches, and the two ends of a test line are connected to a test point through passing holes; the short line X2 can not be too short; the parameter S, tested through the conveying line X1, of the structure A comprises that IL (A) = loss of the conveying line X1 + passing hole loss of 2 PCBs + loss of a probe + uncertain influence of the test fixture; the parameter S, tested through the conveying line X2, of the structure B comprises that IL (B) = loss of the conveying line X2 + passing hole loss of the 2 PCBs + loss of the probe + uncertain influence of the test fixture; the loss formula of each inch after difference between the test structure A and the test structure B is calculated is obtained: dB / inch loss = (IL(A) - IL(B)) / (X2-X1), and the loss value of each inch of the conveying lines at different frequency points can be obtained through the formula.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
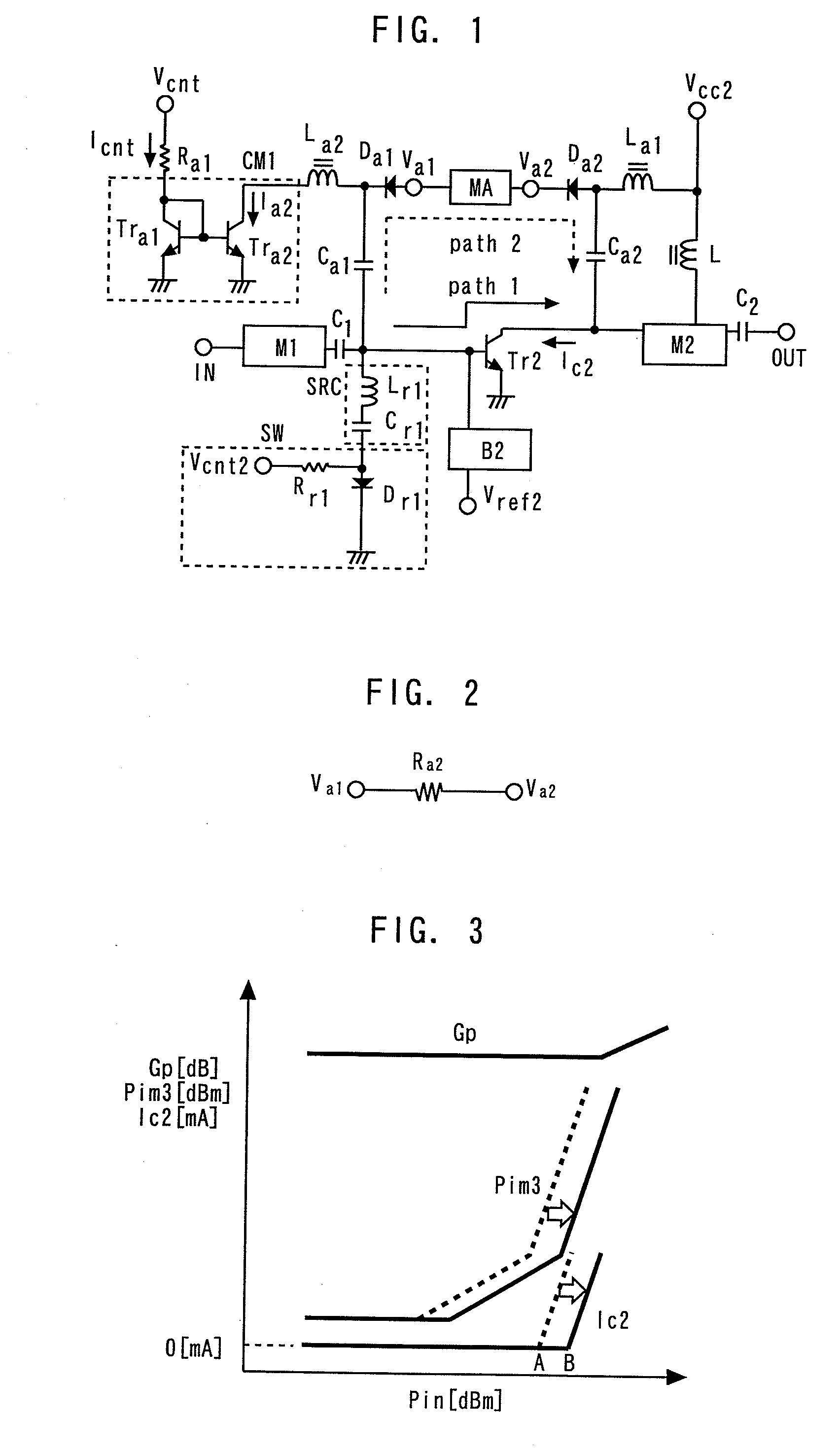
Power amplifier
ActiveUS7688133B2Reduce Impedance MismatchImpedance mismatchAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Impedance control circuit in semiconductor device and impedance control method
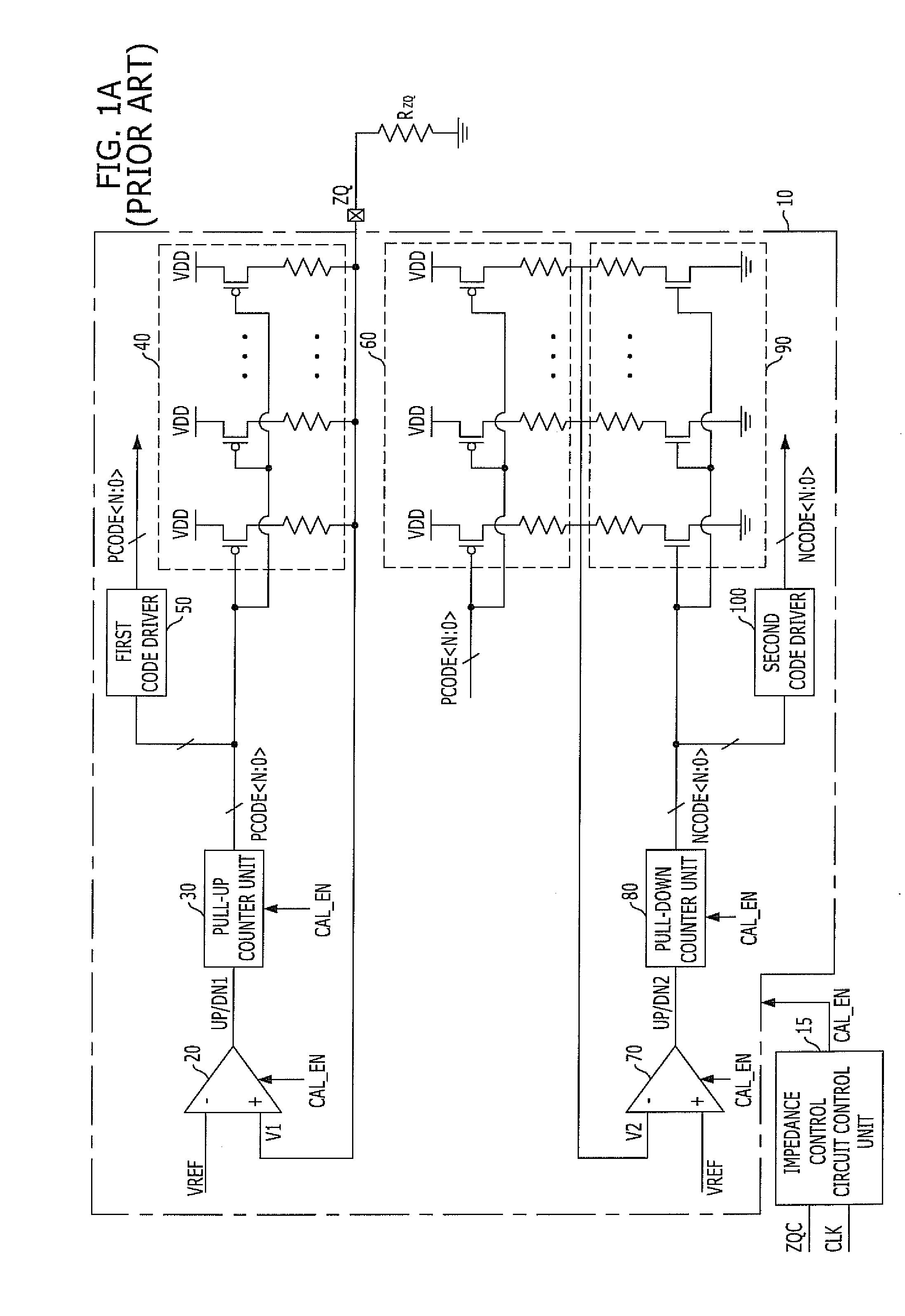
ActiveUS20060261844A1High resolutionImpedance mismatchInput/output impedence modificationReliability increasing modificationsTransistor arrayDevice material
An impedance control circuit for use in a semiconductor device reduces an impedance mismatch between pull-up and pull-down resistances without increasing a resolution. The impedance control circuit includes an impedance detector, an output driver and an impedance controller. The impedance detector generates a first output value to a detection pad connected between an external determination resistor and a pull-up transistor array, and outputs a second output value to a resistance divider terminal commonly connected between a pull-up and pull-down transistor array in response to a pull-up control code data and a pull-down control code data. The output driver has a commonly connected pull-up and pull-down transistor array, and a compensating unit connected to the pull-up and pull-down transistor array of the output driver, to compensate for quantization error of the pull-up and pull-down control code data. The impedance controller performs a comparison and counting operation so that the first and second output values of the impedance detector become approximated to a predetermined reference value, and generates the pull-up and pull-down control code data. Impedance mismatch between pull-up and pull-down resistances is reduced to half of a digital control resolution, substantially reducing transmission error or adverse effects on a setup / hold window of a receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
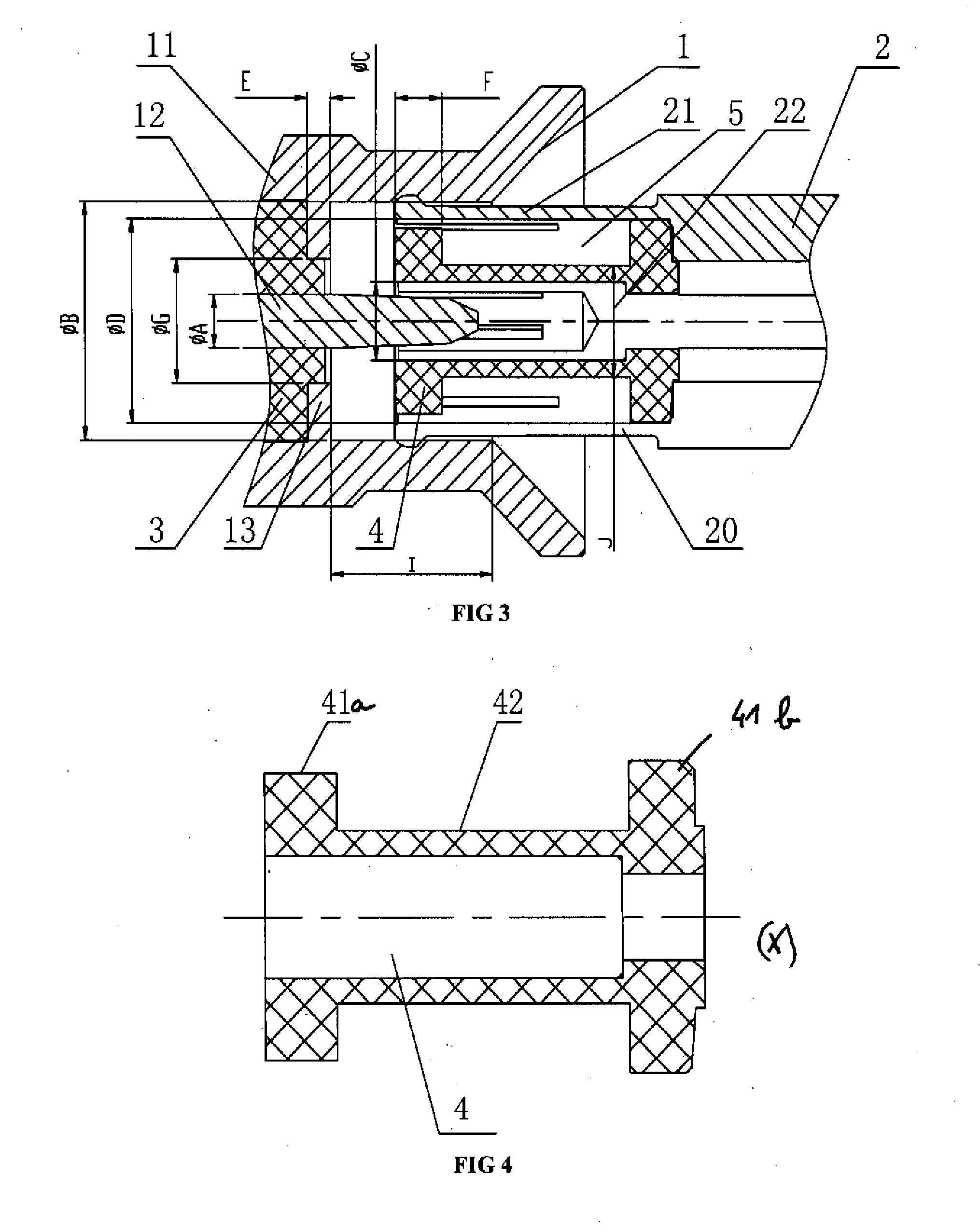
Multipolar connector
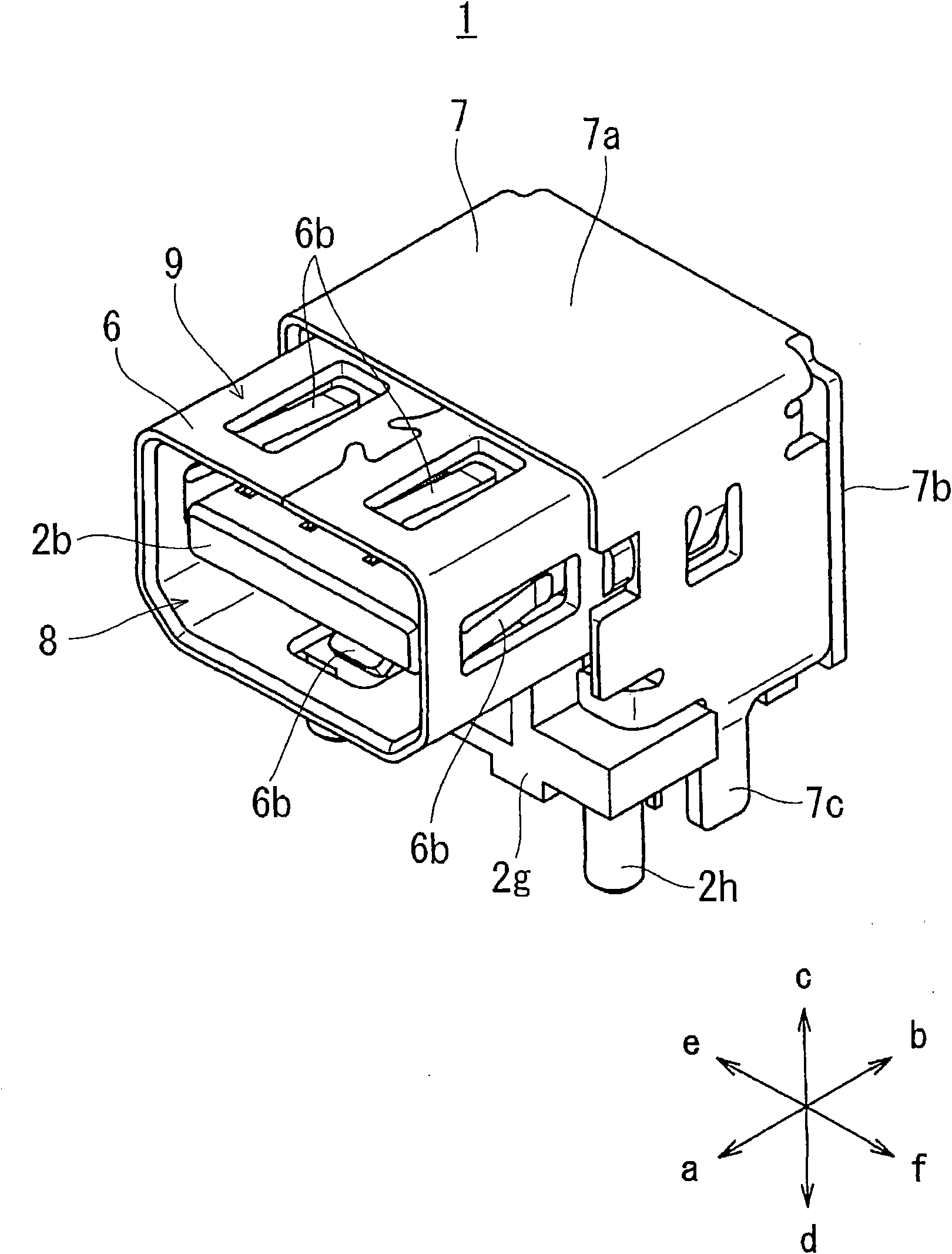
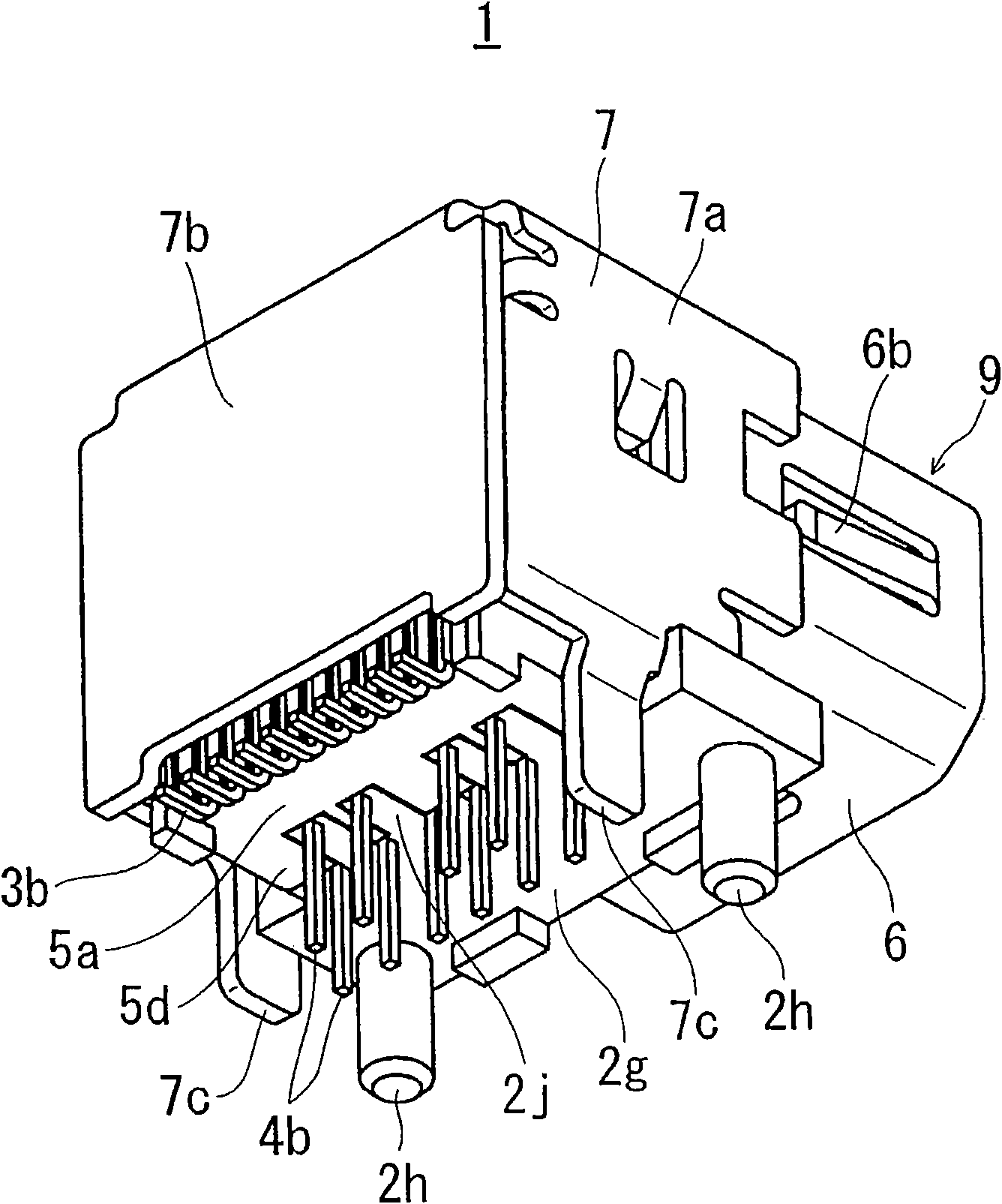
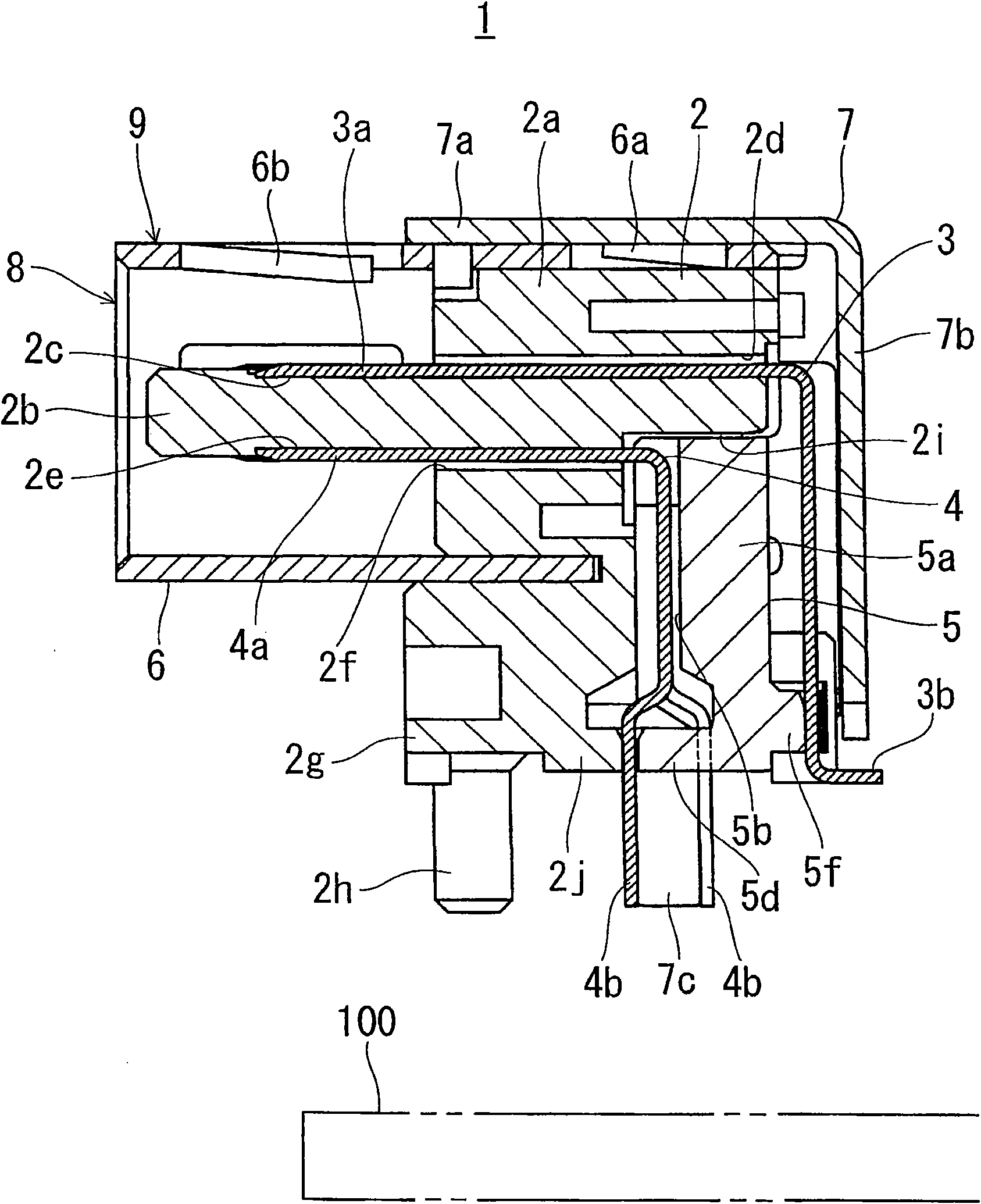
ActiveCN101938053AReduce Impedance MismatchLarge capacityCoupling contact membersTwo-part coupling devicesPrinted circuit board
The invention provides a multipolar connector in which one terminal row can be divided into a plurality of rows (row conversion) while reducing an impedance mismatch. A multipolar connector (1) which is to be insert-mounted on a printed circuit board (100) includes a terminal group (40) in which a plurality of terminals (4) are arranged in one row in contact portions (4a) with respect to terminals of a counter connector, and, while being then passed through a row converting portion (45), one terminal row (41) is divided into a plural-row portion (44) consisting of two rows (42, 43) and functioning as a connecting portion that is opposite to the counter connector, and row-converted to a substantially zigzag arrangement. The terminal group (40) includes two specific terminals (46, 47) in which, in the plural-row portion (44), the terminal width (L1) is wider than the terminal width (L2) of the contact portions (4a). The two specific terminals (46, 47) constitute a terminal pair for transmitting differential signals.
Owner:HOSIDEN CORP
Ultra-wideband planar monopole antenna
ActiveCN108172991ASmall sizeReduce operating frequencyRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsUltra-widebandCapacitance
The invention discloses an ultra-wideband planar monopole antenna. The ultra-wideband planar monopole antenna comprises a dielectric substrate, a monopole radiation patch, a lumped device and a grounding plate, wherein the monopole radiation patch is formed by loading a monopole antenna main body and a top end, a part, near to the grounding plate, of the monopole radiation patch employs a triangular corner and is mainly used for impedance matching of a high-frequency part. A lumped component loaded by the antenna main body is mainly used for reducing a working frequency band of the antenna andgain of a smooth antenna in the whole frequency band, a plurality of rectangular open-circuit branches are loaded at a top end of a monopole, the capacitance between the antenna and floor is improved, and the working frequency band of the antenna is further reduced. By loading the lumped component and additionally arranging open-circuit branches on ground, the antenna size is effectively reducedas well as favorable ultra-wideband characteristic is maintained, and the application of the antenna in the monitoring field is facilitated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
RF coaxial connector
ActiveUS20110117778A1Improve the compensation effectLow regionElectrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsState of artElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a RF coaxial connector, which includes a socket and an adapter. The socket includes an outer conductor and a center conductor. The adapter includes a plug capable of being inserted into the socket. The adapter also includes an outer conductor and a center conductor that can be in contact with the outer conductor and the center conductor of the socket, respectively. A dumbbell-shaped first insulating body is disposed inside the plug of the adapter and filled between the outer conductor and the center conductor of the adapter. The first insulating body has a middle portion narrower than two end portions thereof such that an annular gap is formed between the middle portion of the first insulating body and the outer conductor of the adapter, thereby forming different impedance regions at the connection regions of the plug and the socket. Therefore, a high impedance region and a low impedance region can compensate each other so as to decrease the adverse effect of the high impedance region on the connector performance and improve electrical and RF performance of the product. Compared with the prior art, the connector of the present invention allows a larger axial offset.
Owner:RADIALL SA
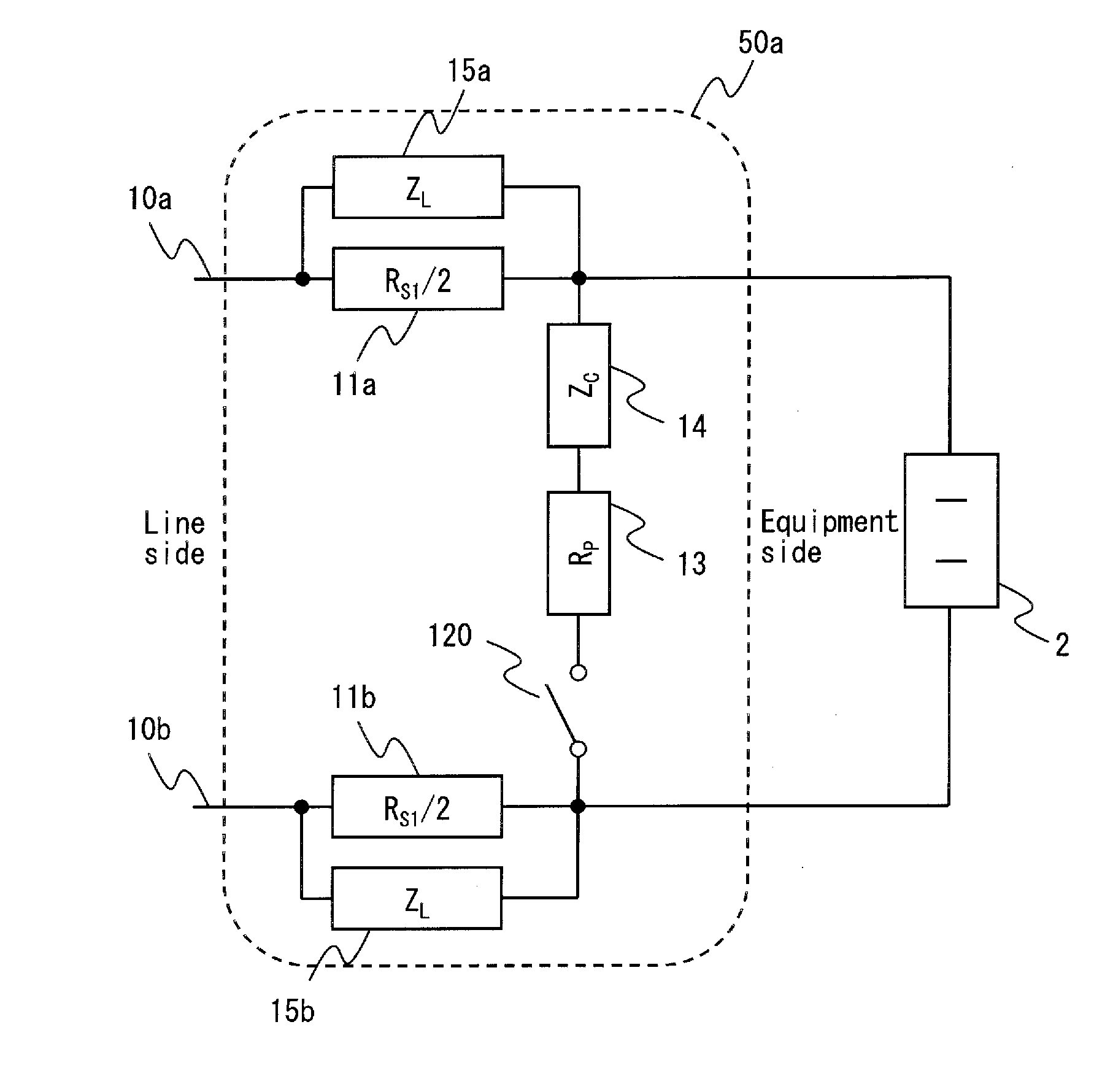
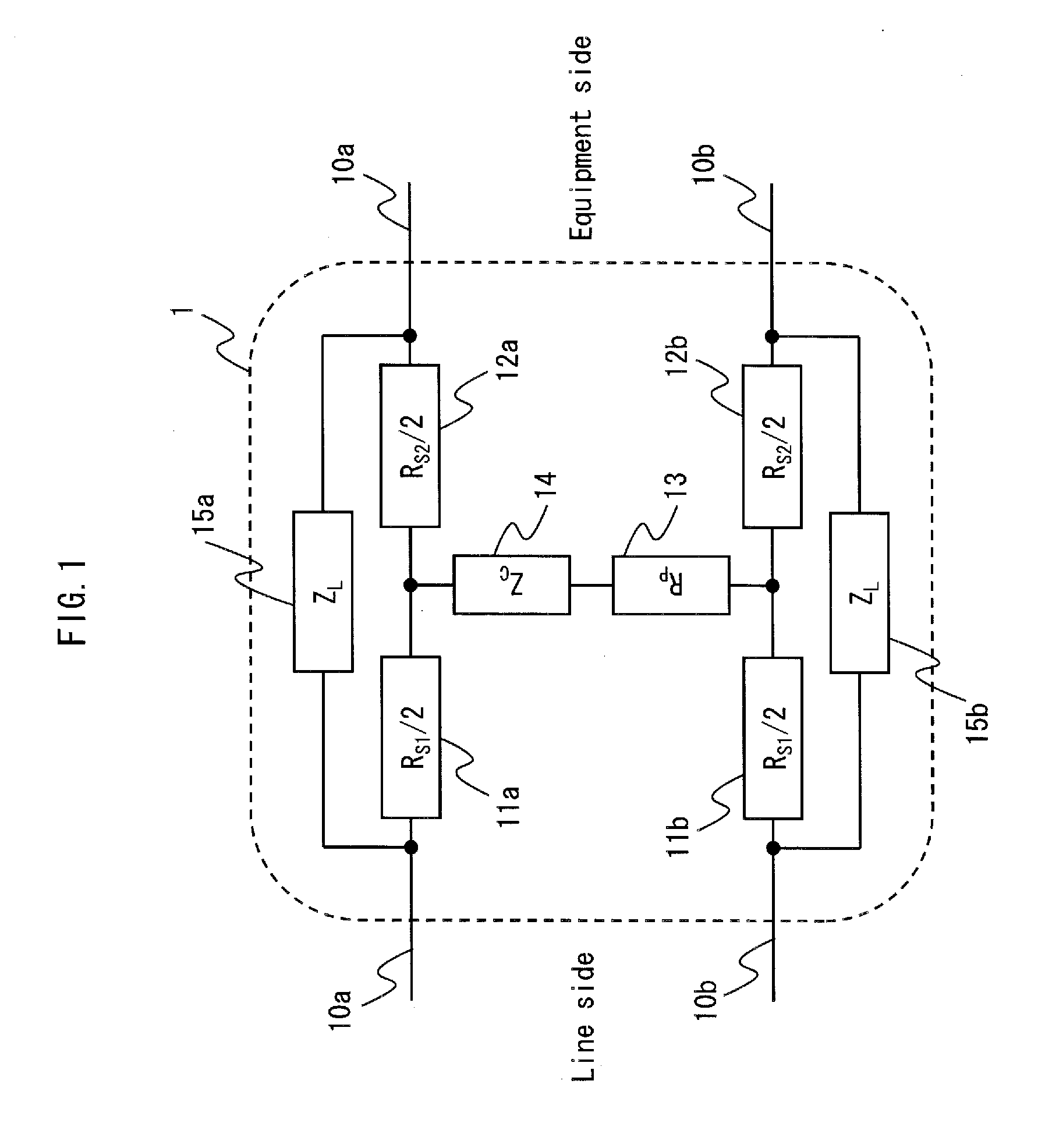
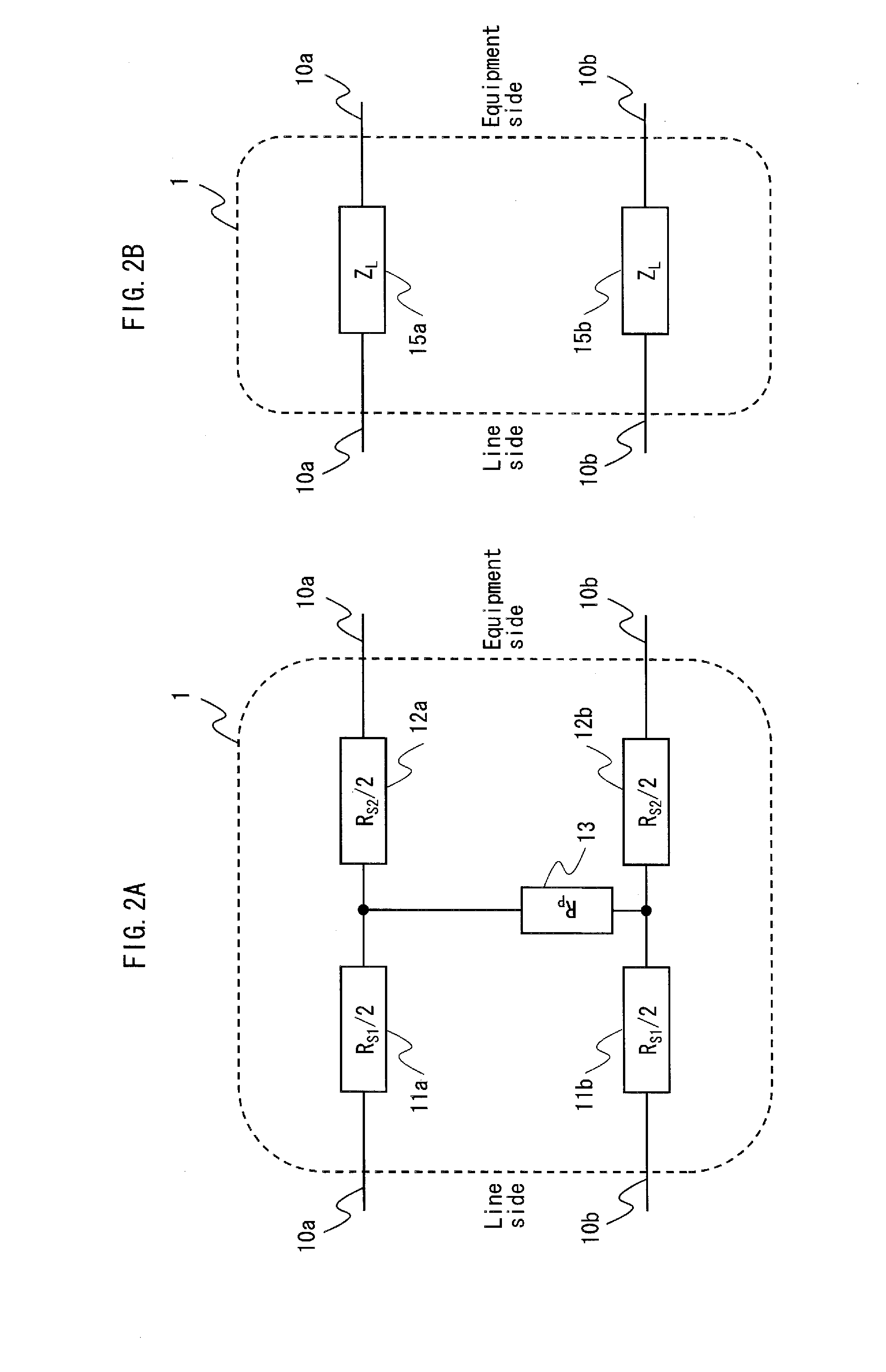
Impedance stabilization device
InactiveUS20120086517A1Reduce Impedance MismatchMultiple-port networksPower distribution line transmissionEngineeringLow frequency
Provided is an impedance stabilization device having a configuration in which a circuit including a series matching impedance element (11a and 12a (11b and 12b)) and a high-frequency blocking element connected in parallel is inserted in series into at least one of lines (10a (10b)) constituting a power line, and the lines (10a and 10b) are connected via another circuit including a parallel matching impedance element (13) and a low-frequency matching element (14) connected in series. A high-frequency signal passes through the series matching impedance element, a power current passes through the high-frequency blocking element, and the parallel matching impedance element functions as a termination resistor when a terminal on an equipment side is an open end.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Signal transmission structure
ActiveUS20050104692A1Reduce Impedance MismatchImprove transmission qualityMultiple-port networksHigh frequency circuit adaptationsTransmission qualitySignal lines
A signal transmission structure is disclosed. The signal transmission structure is adapted for a circuit substrate, including at least a signal line, a plating bar and a reference plane. The plating bar is disposed on a side of the reference plane and connected to the signal line. In addition, the plating bar is disposed on the side of the reference plane, and the reference plane has a non-reference area corresponding to the plating bar. The signal transmission structure can reduce the impedance mismatch at the conjunction of the signal line and the plating bar, and the resonant frequency of the plating bar can be improved as to generate a desired transmission quality of the signal.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
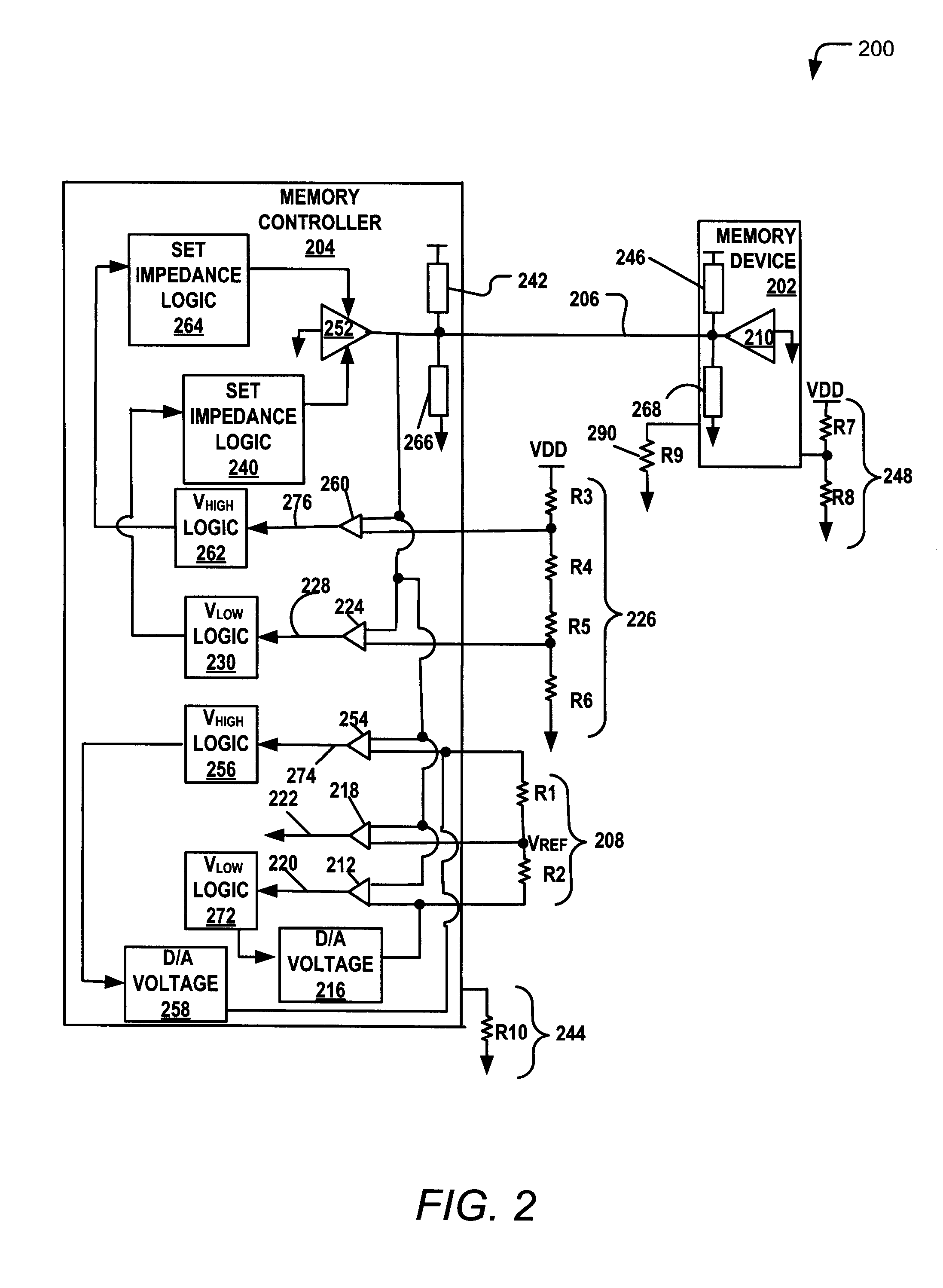
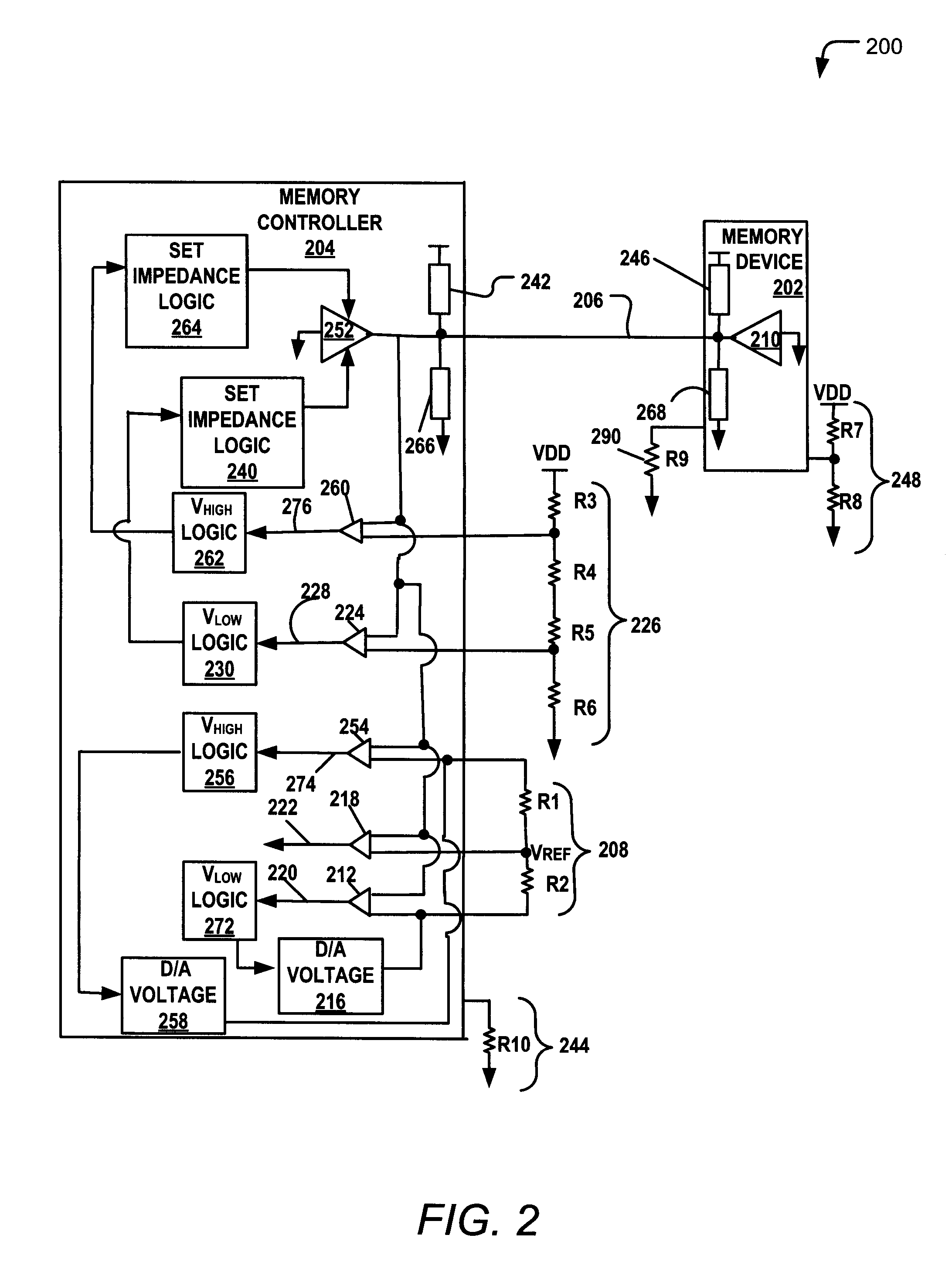
Training a memory controller and a memory device using multiple read and write operations
InactiveUS8681571B2Reduce Signal ErrorSpeedLogic circuit coupling arrangementsReliability increasing modificationsComputer hardwareMemory controller
Systems and methods to set a voltage value associated with a communication bus that includes memory controller coupled to a memory device are disclosed. A particular method may include performing a first calibration operation associated with first data written from a memory controller to a memory device. A second calibration operation may be associated with second data read at the memory controller from the memory device. The operating parameter may be set based on a result of at least one of the first and the second calibration operations at the memory device or the memory controller.
Owner:IBM CORP
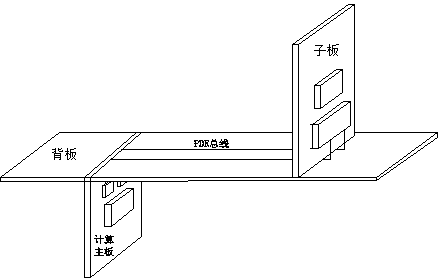
Method for reducing influence of AC coupling capacitor PAD on transmission of high-speed serial signals
InactiveCN103987191AReduce Impedance MismatchReduce lossElectrical connection printed elementsPrinted element electric connection formationCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a method for reducing influence of an AC coupling capacitor PAD on transmission of high-speed serial signals. An AC coupling capacitor additionally arranged on a high-speed serial bus is designed to be in small package so that the line width of a FDR bus passing through the capacitor can approximate the width of the PAD as much as possible to reduce sudden impedance change caused by change from a bonding pad of the capacitor to a transmission line body capacitor structure. Two-layer hollowing-out treatment is carried out on the FDR bus through the bonding pad of the AC coupling capacitor, so that the impedance of the FDR bus at the position of the AC coupling capacitor is kept unchanged, unnecessary reflection is avoided, the loss of a transmission line is reduced, and signal transmission stability is guaranteed.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Multi-element composite microwave absorbent, microwave absorbing coating, microwave absorbing base material and preparation method
ActiveCN103073961AReduce Impedance MismatchReduce reflectionFibre treatmentRadiation-absorbing paintsGreek letter alphaPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to a multi-element composite microwave absorbent, a microwave absorbing coating, a microwave absorbing base material and a preparation method. The multi-element composite microwave absorbent is composed of ACET (acetylene black), alpha-SiC and Ni0.7Zn0.3Fe2O4 based on a weight ratio, wherein the microwave absorbing coating is composed of the microwave absorbent, de-ionized water, a PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) solution, a wetting agent, a dispersing agent, a de-foaming agent and a water-based leveling agent based on a weight ratio; and the microwave absorbing base material comprises a plurality of pyramidal substrates of which both sides are coated with the microwave absorbing coating. According to the invention, the microwave absorbing base material has excellent reflection loss performance for 118 GHz microwaves, and can be used for manufacturing an anechoic chamber.
Owner:NANJING LUOPU TECH CO LTD
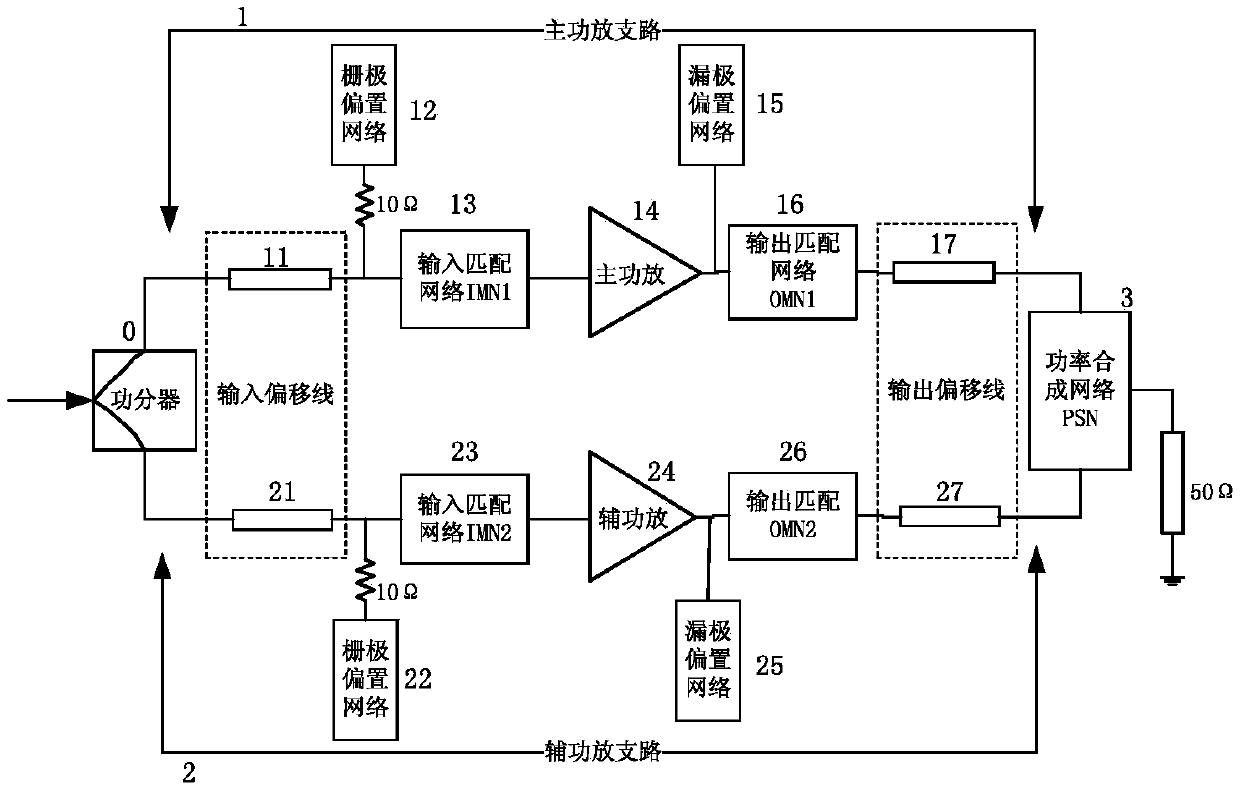
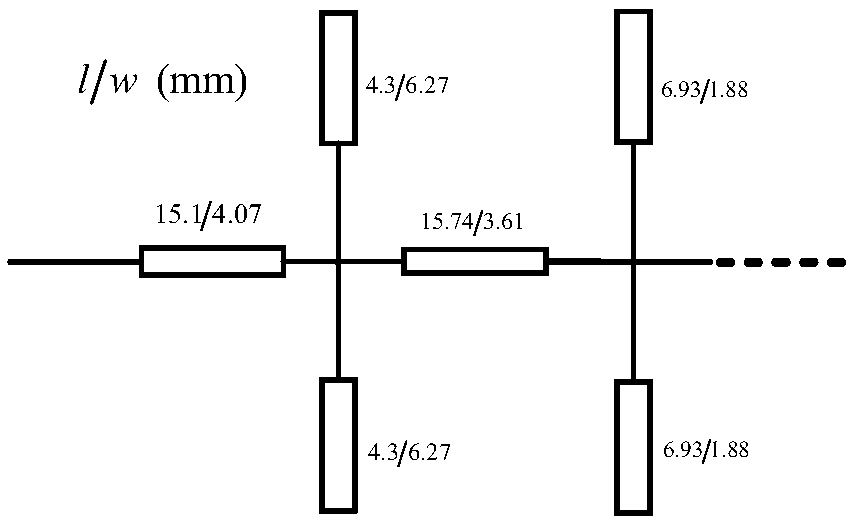
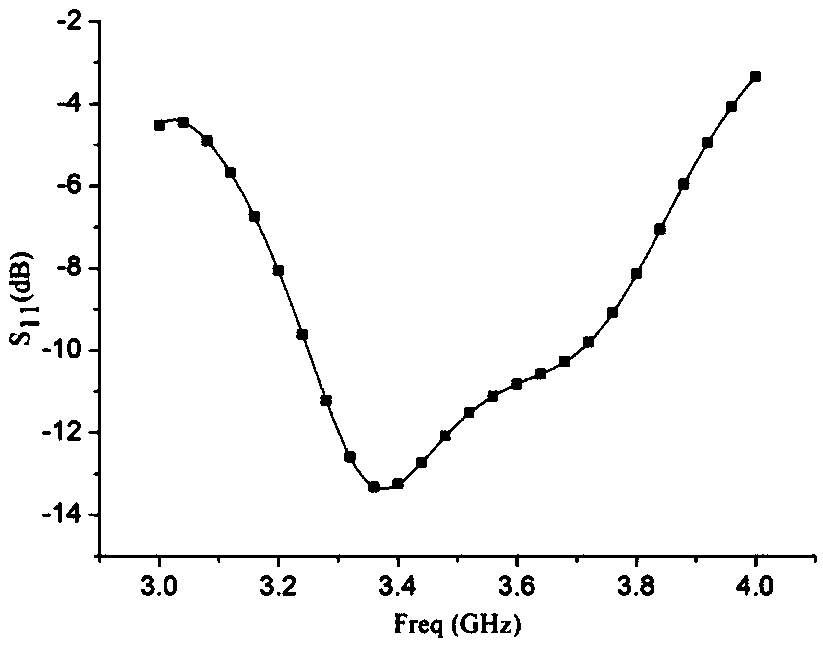
Asymmetric broadband Doherty power amplifier suitable for full frequency band of 5G low frequency band
ActiveCN109672411AEasy inputImprove output matchingAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierLow-pass filter
The invention relates to an asymmetric broadband Doherty power amplifier suitable for a full frequency band of a 5G low frequency band, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The amplifier is composed of a power divider, a main power amplification branch, an auxiliary power amplification branch and a power synthesis network, wherein the main power amplification branch and the auxiliary power amplification branch respectively comprise an input and output offset line, a gate and drain bias network, and an input and an output matching network; the working bandwidth of the Doherty power amplifier is expanded by reducing an impedance transformation ratio of a quarter-wave impedance adjustment line and an impedance transformation line in the power synthesis network; and arequired broadband matching network is designed by a broadband impedance transformation network of a low-pass filter prototype, and the influence on an input matching network is reduced by using gatebias networks of antedisplacement primary and secondary power amplifiers. By adoption of the asymmetric broadband Doherty power amplifier provided by the invention, the working bandwidth of the Doherty power amplifier can be expanded.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
RF coaxial connector
ActiveUS8016614B2High regionHigh impedanceElectrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsState of artElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a RF coaxial connector, which includes a socket and an adapter. The socket includes an outer conductor and a center conductor. The adapter includes a plug capable of being inserted into the socket. The adapter also includes an outer conductor and a center conductor that can be in contact with the outer conductor and the center conductor of the socket, respectively. A dumbbell-shaped first insulating body is disposed inside the plug of the adapter and filled between the outer conductor and the center conductor of the adapter. The first insulating body has a middle portion narrower than two end portions thereof such that an annular gap is formed between the middle portion of the first insulating body and the outer conductor of the adapter, thereby forming different impedance regions at the connection regions of the plug and the socket. Therefore, a high impedance region and a low impedance region can compensate each other so as to decrease the adverse effect of the high impedance region on the connector performance and improve electrical and RF performance of the product. Compared with the prior art, the connector of the present invention allows a larger axial offset.
Owner:RADIALL SA
Power amplifier
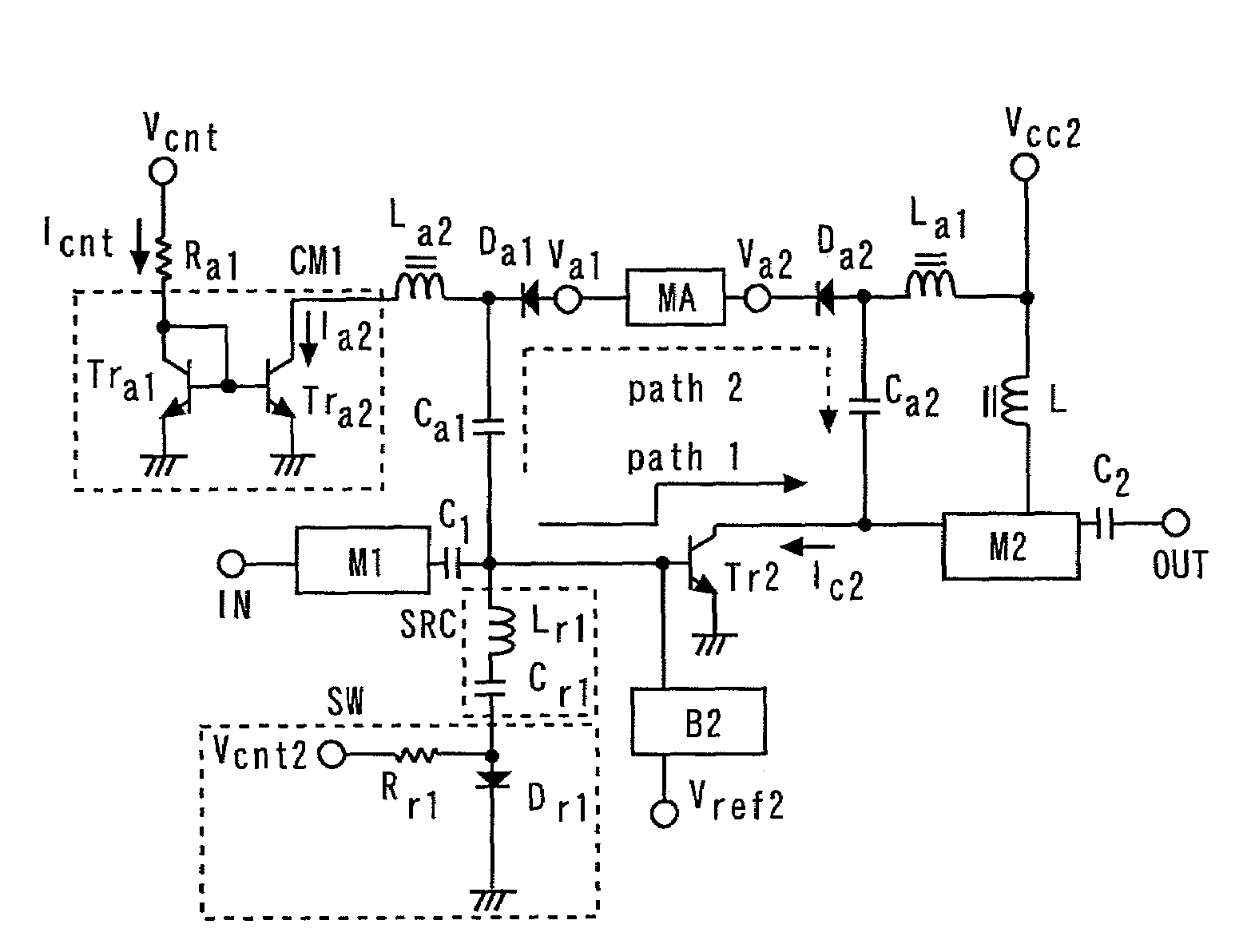
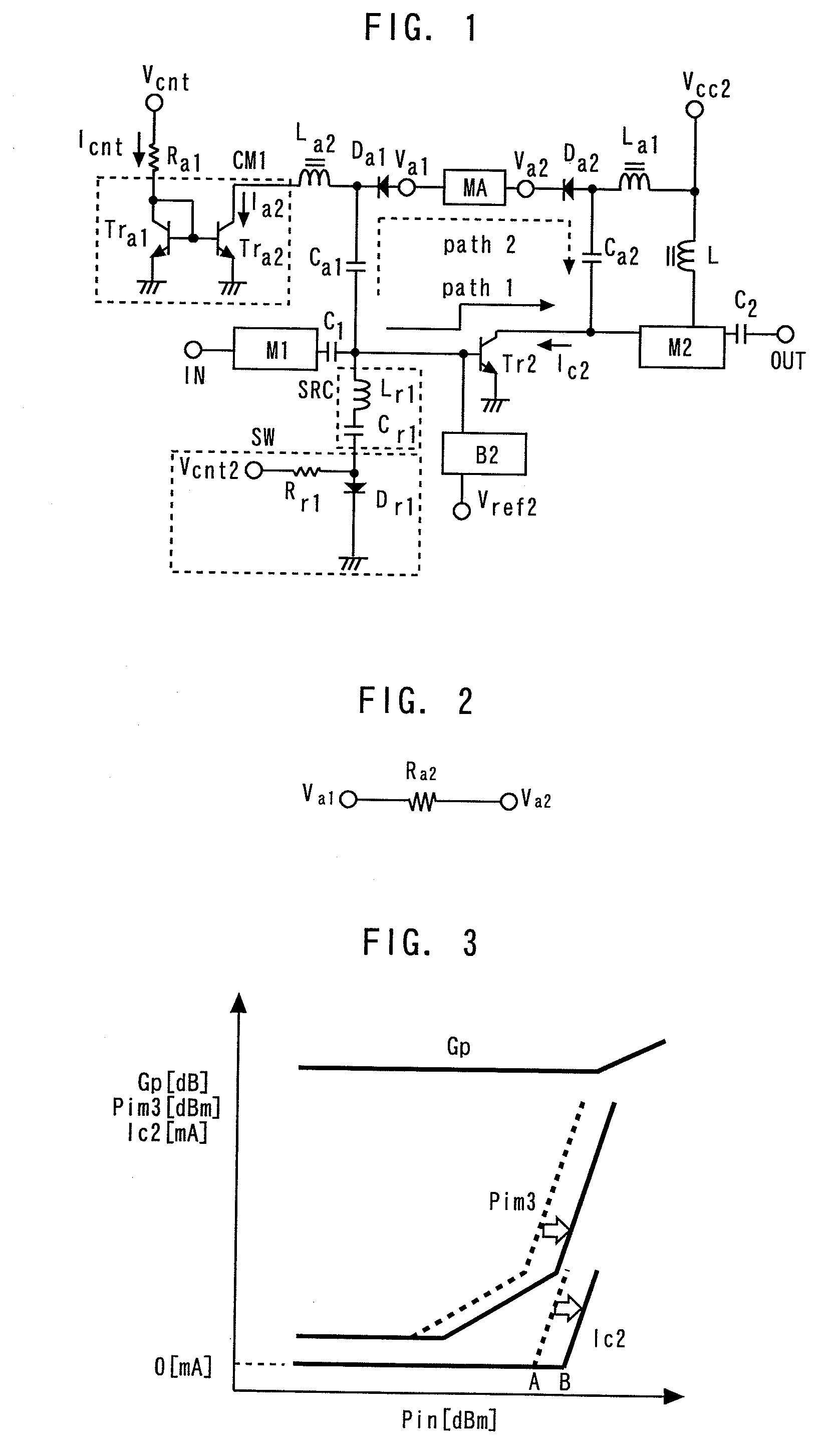
ActiveUS20090309655A1Reduce the minimum operating voltageReduce Impedance MismatchAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierCurrent mirror
A power amplifier includes: an amplifying transistor; a bias circuit; a first diode; a second diode; a matching attenuating circuit; a first current mirror circuit; a serial resonant circuit, and a switch. In an amplification mode, the bias circuit supplies a bias current to the amplifying transistor, and the first current mirror circuit turns off the first and second diodes, and the switch. In an attenuation mode, the bias circuit supplies no bias current to the amplifying transistor, and the first current mirror circuit turns on the first and second diodes, and the switch.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com