Patents
Literature
1018 results about "Horn antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
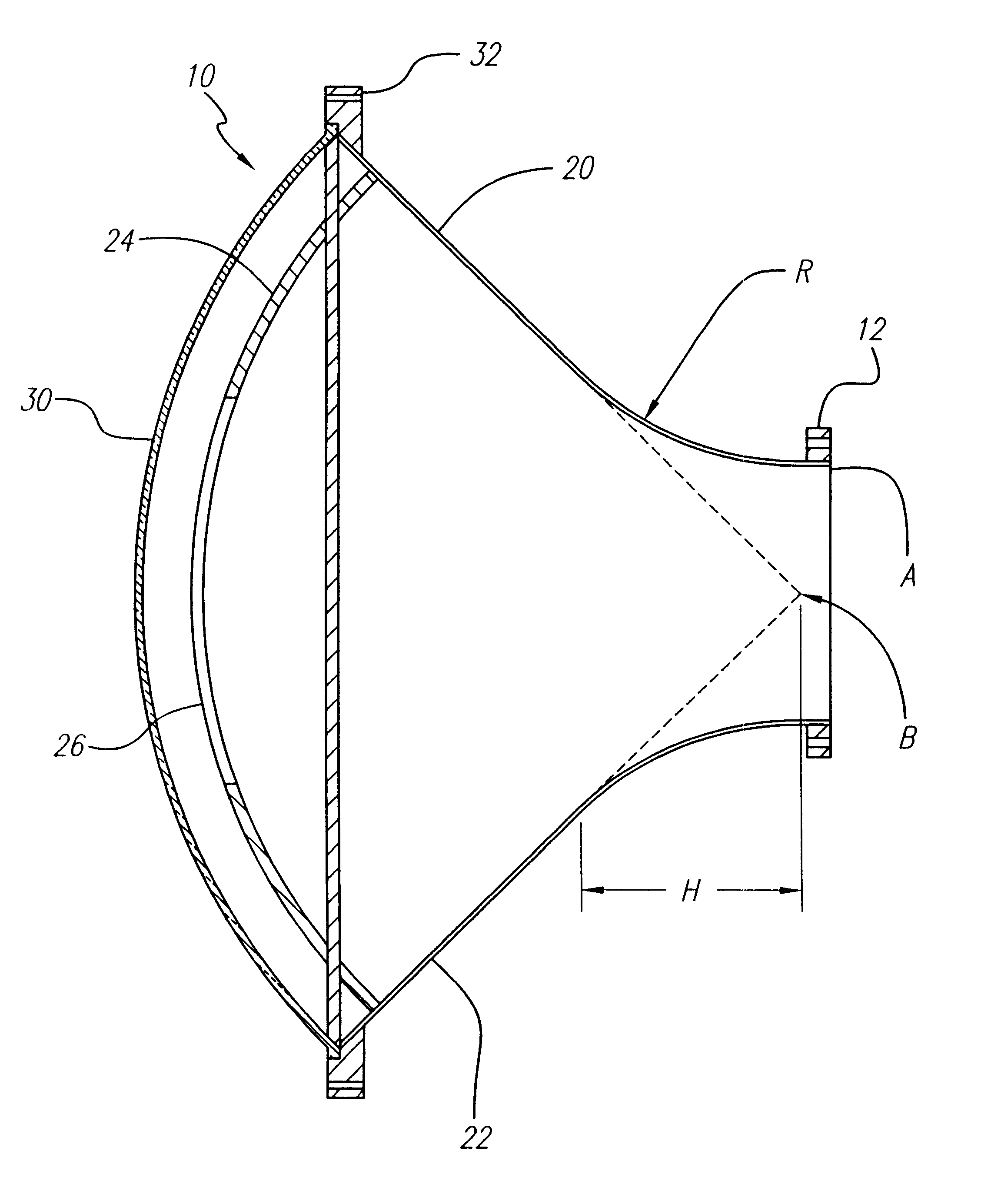
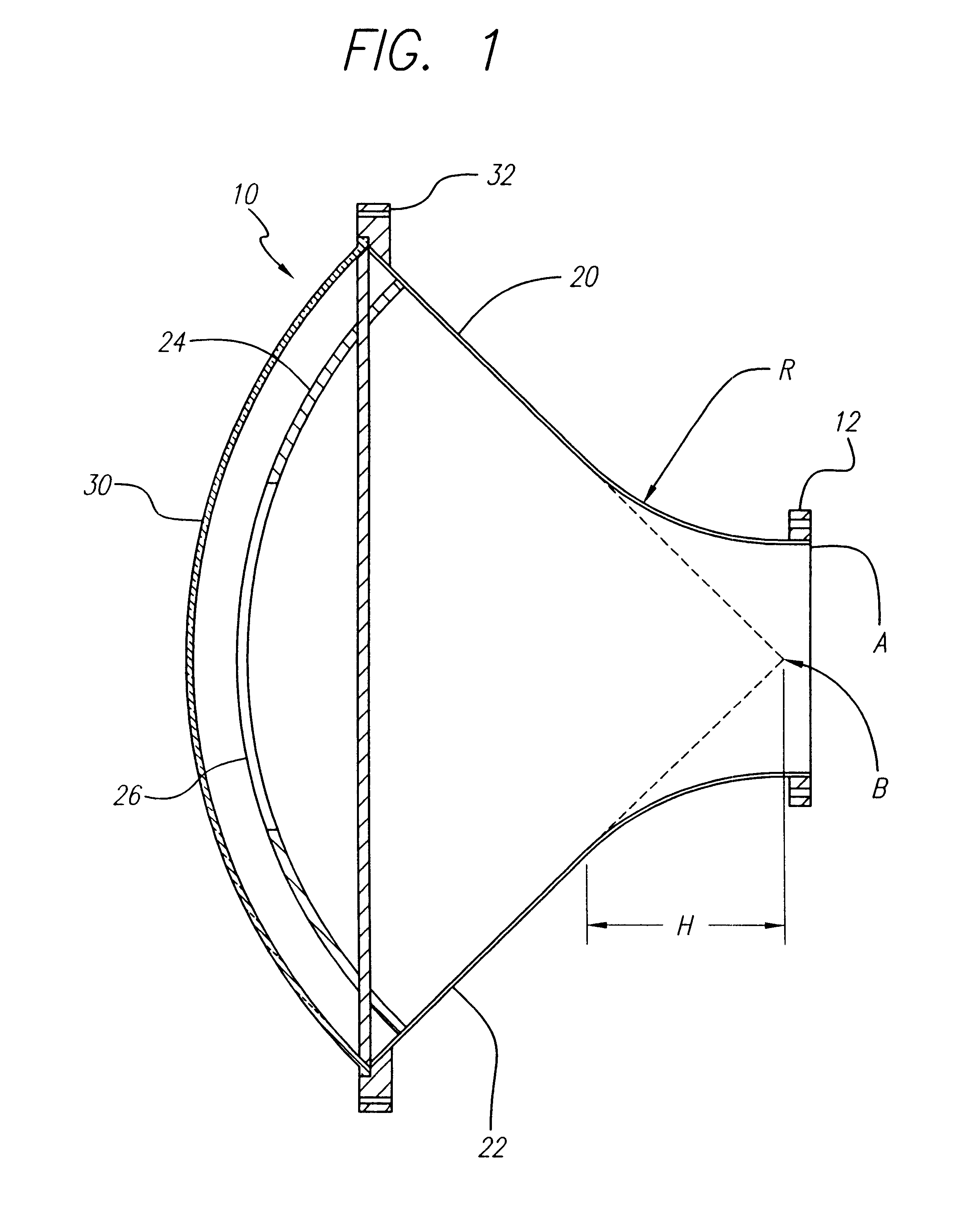
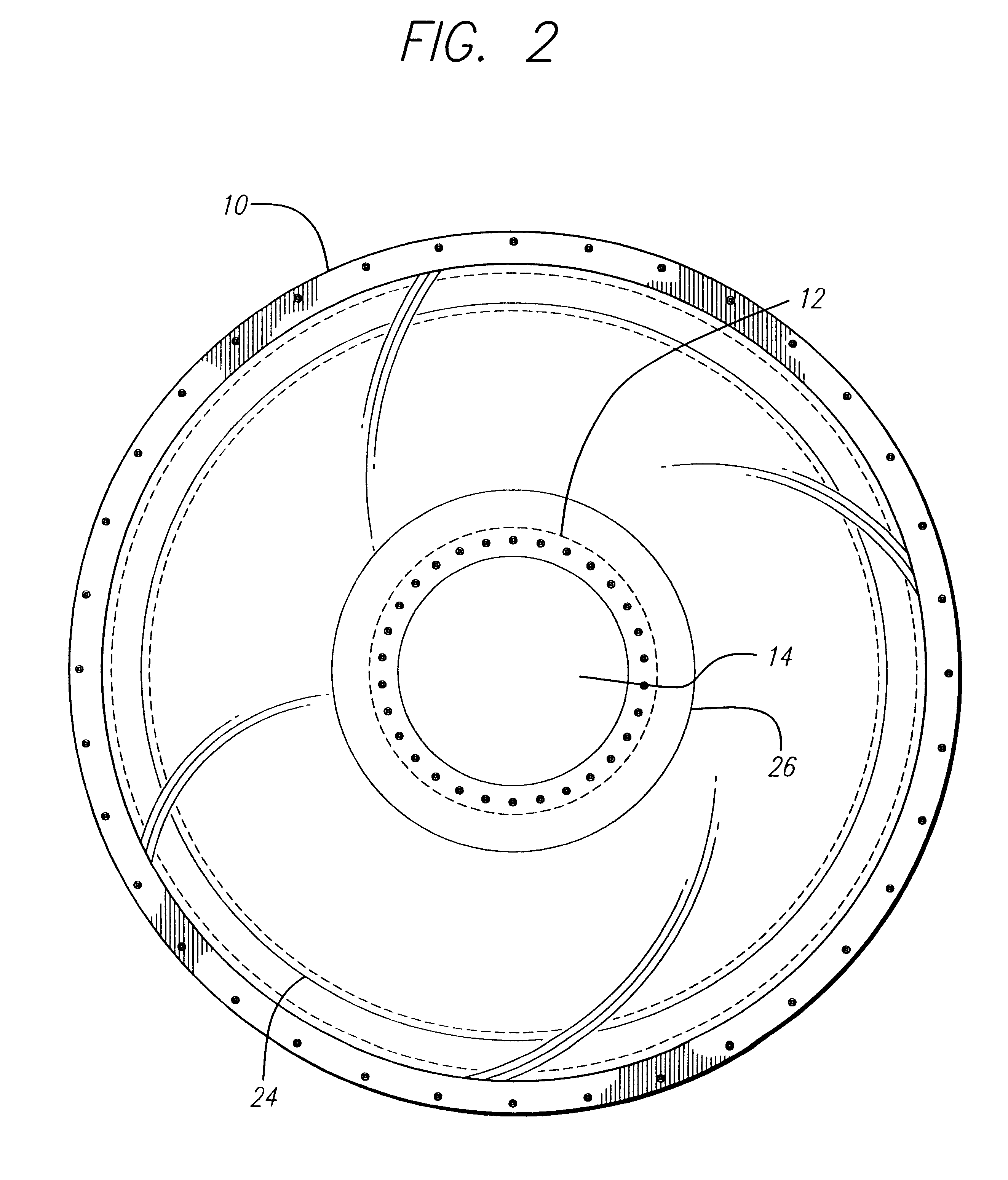
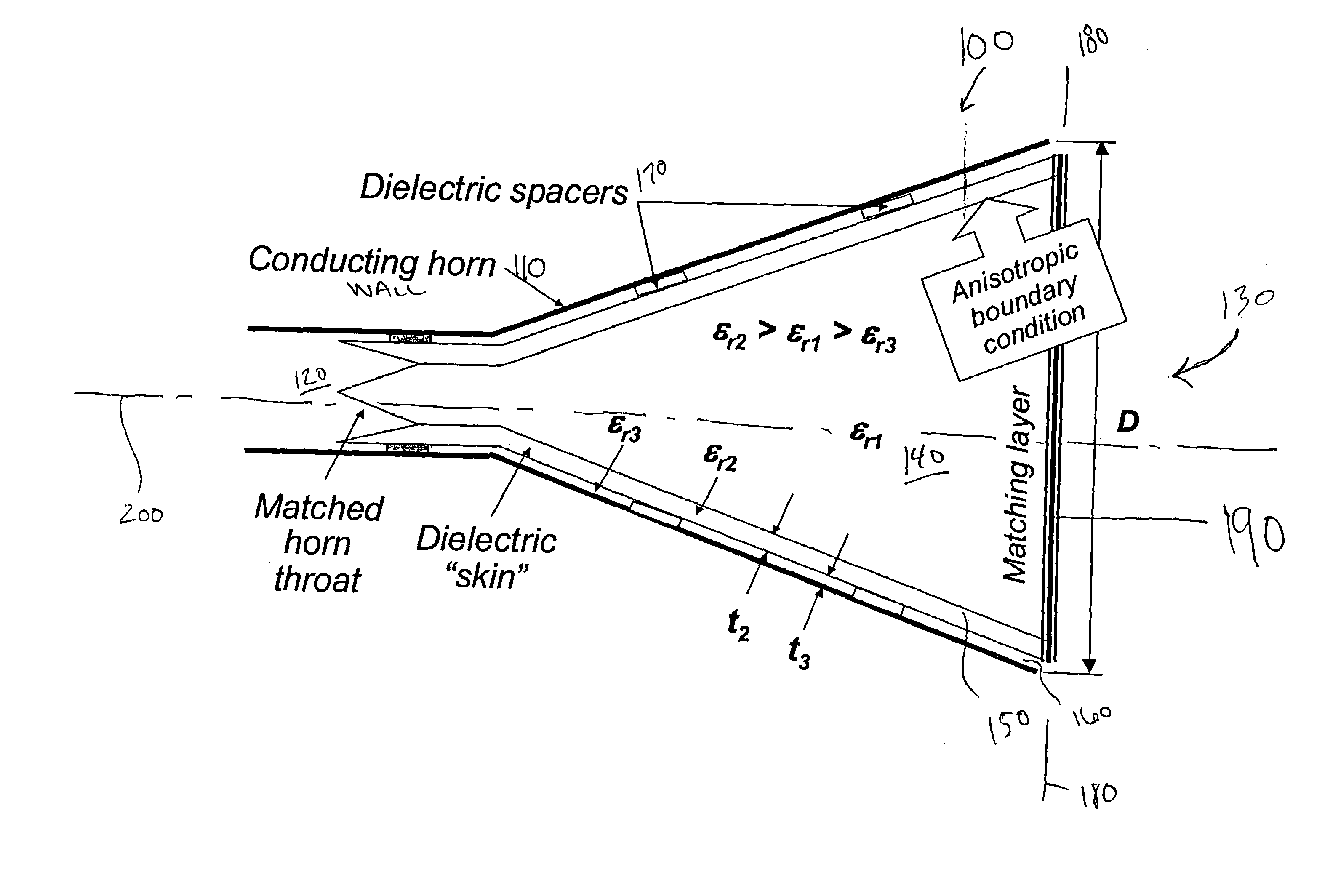
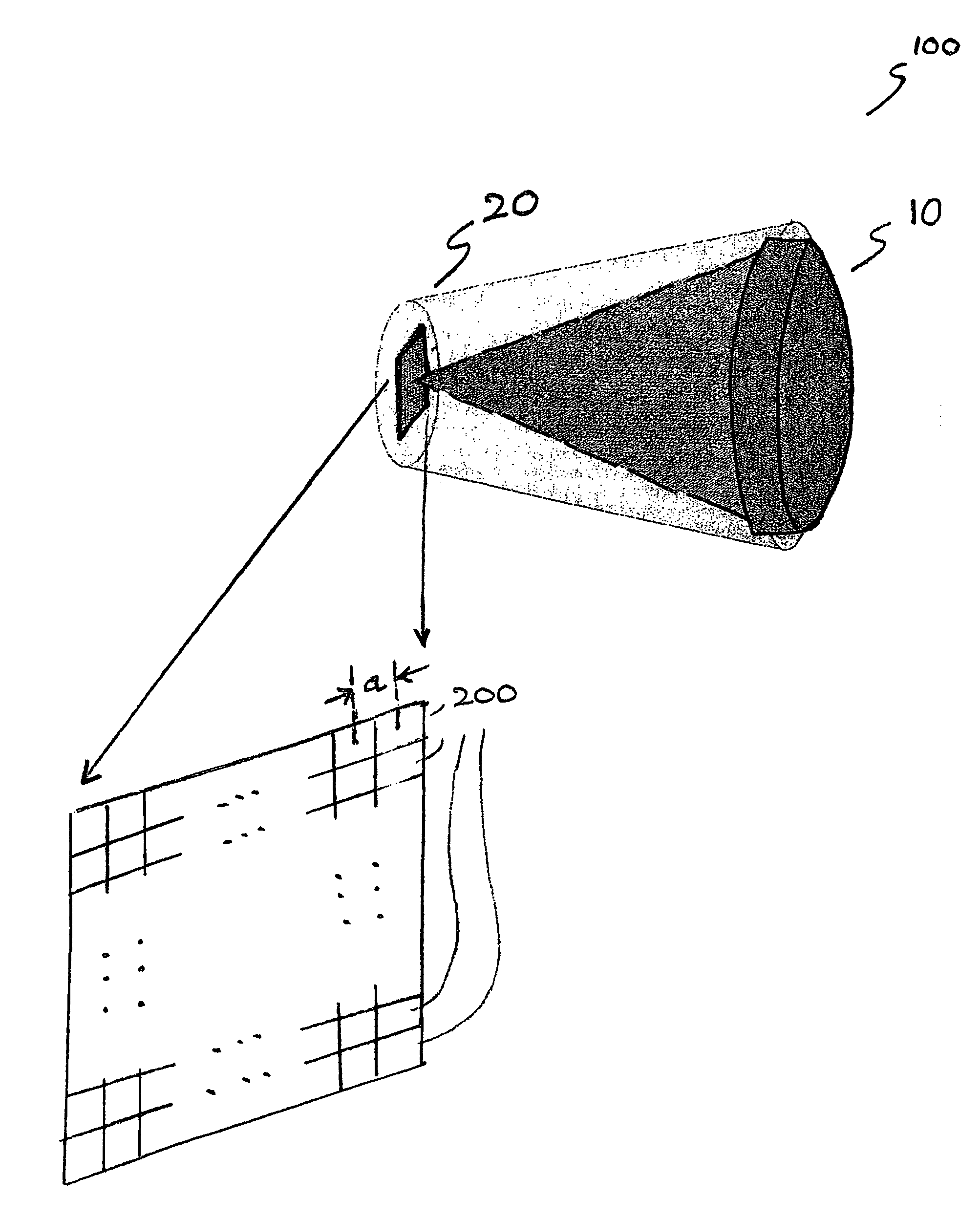
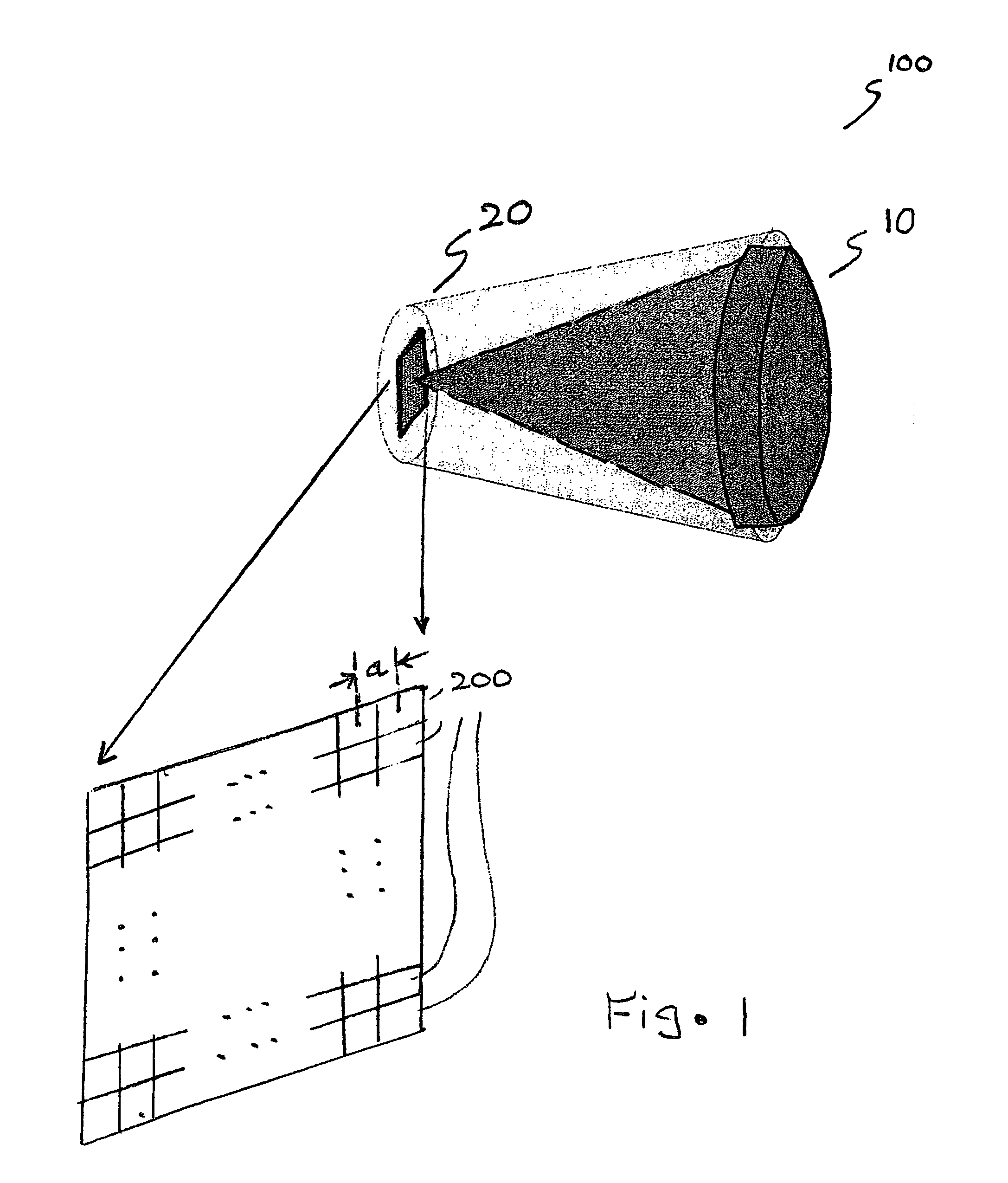
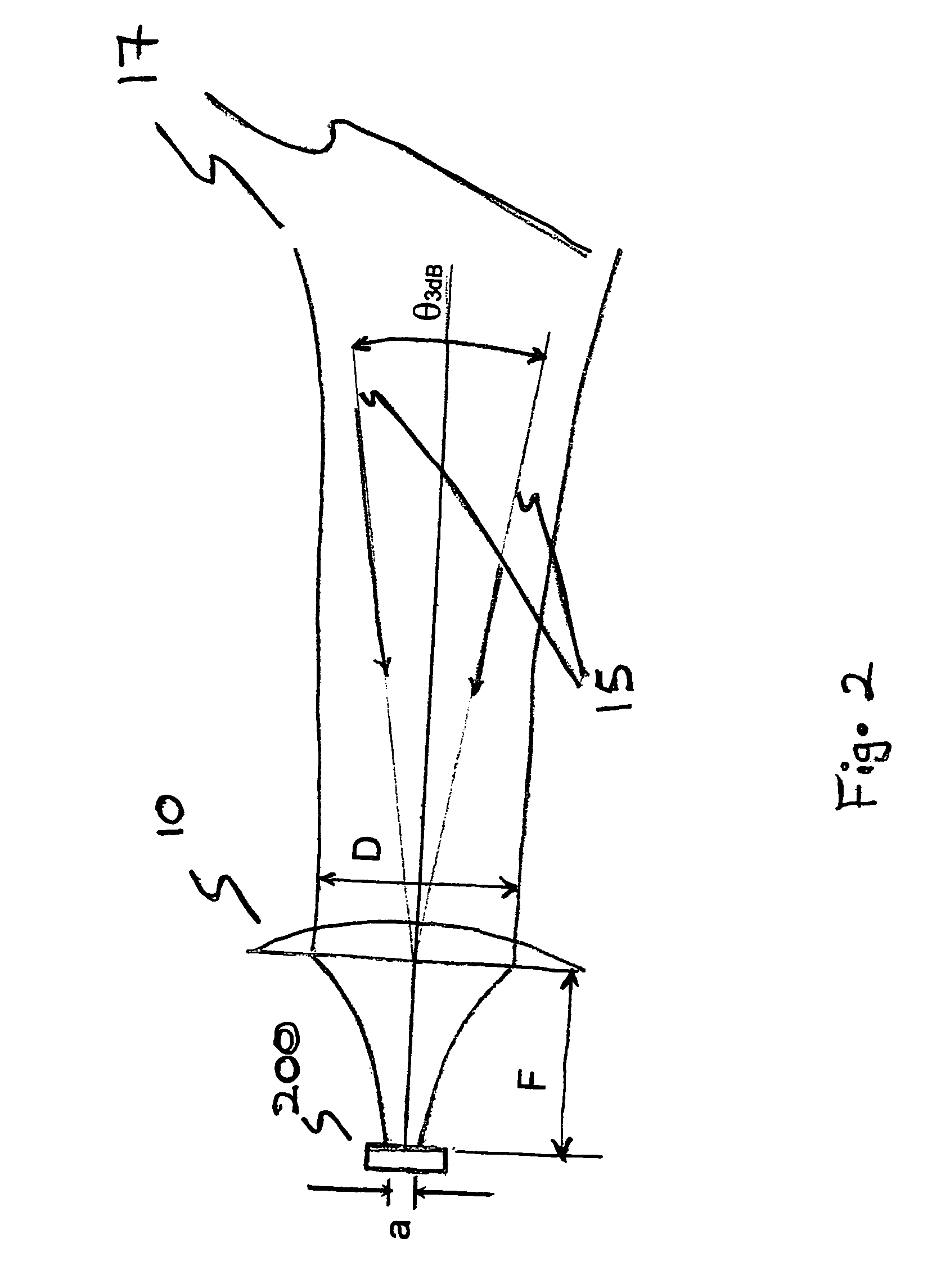
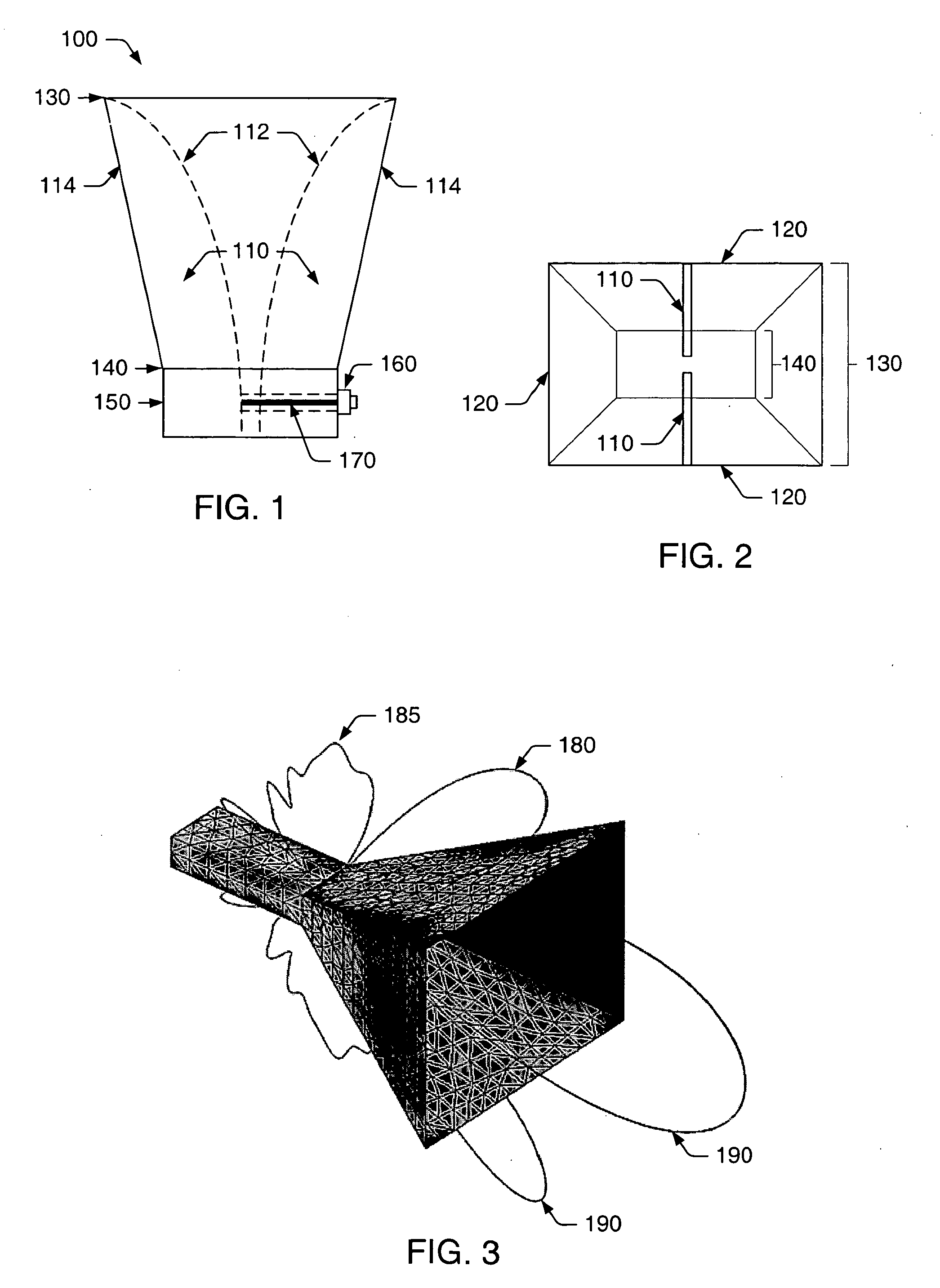
A horn antenna or microwave horn is an antenna that consists of a flaring metal waveguide shaped like a horn to direct radio waves in a beam. Horns are widely used as antennas at UHF and microwave frequencies, above 300 MHz. They are used as feed antennas (called feed horns) for larger antenna structures such as parabolic antennas, as standard calibration antennas to measure the gain of other antennas, and as directive antennas for such devices as radar guns, automatic door openers, and microwave radiometers. Their advantages are moderate directivity, low standing wave ratio (SWR), broad bandwidth, and simple construction and adjustment.
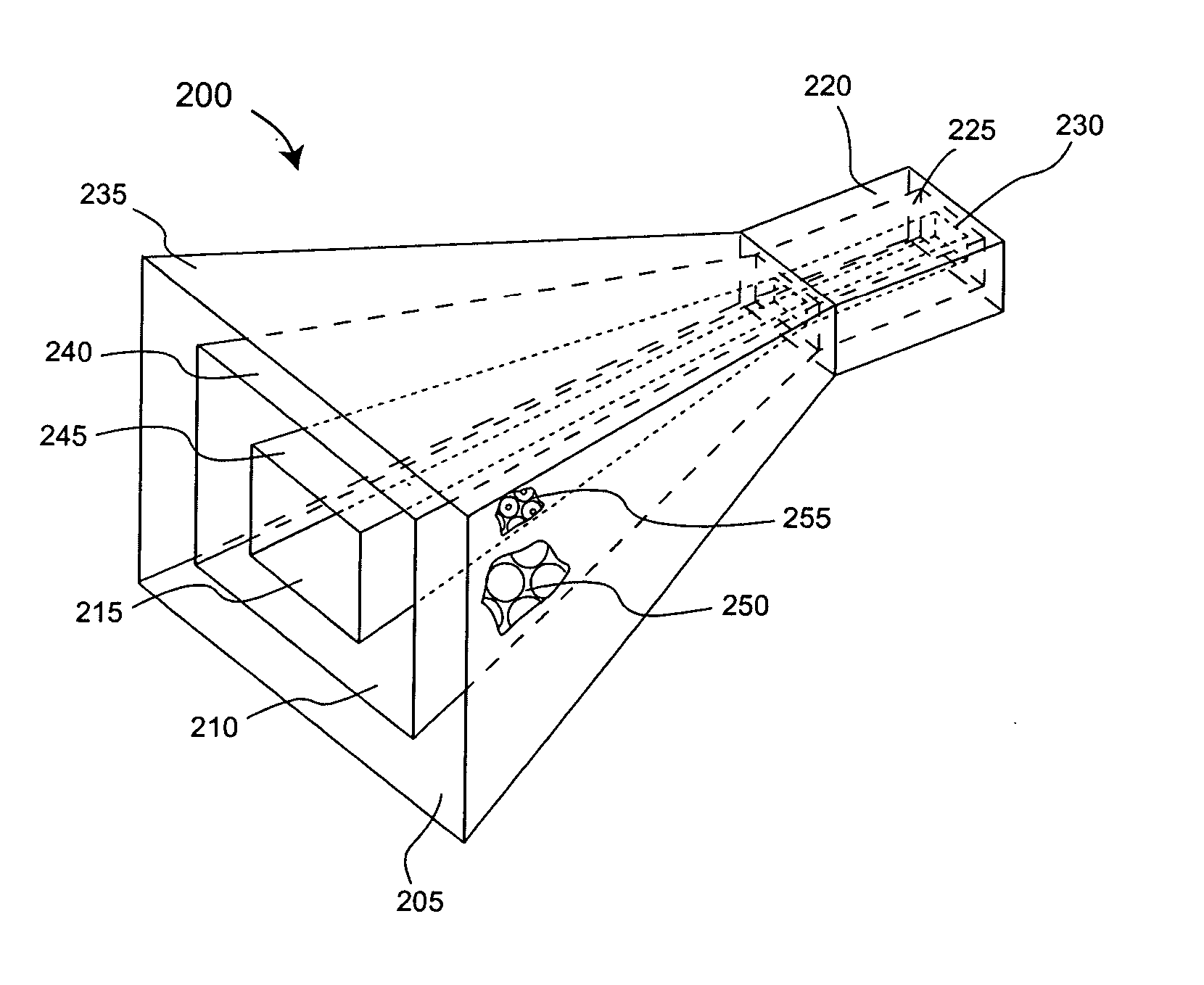
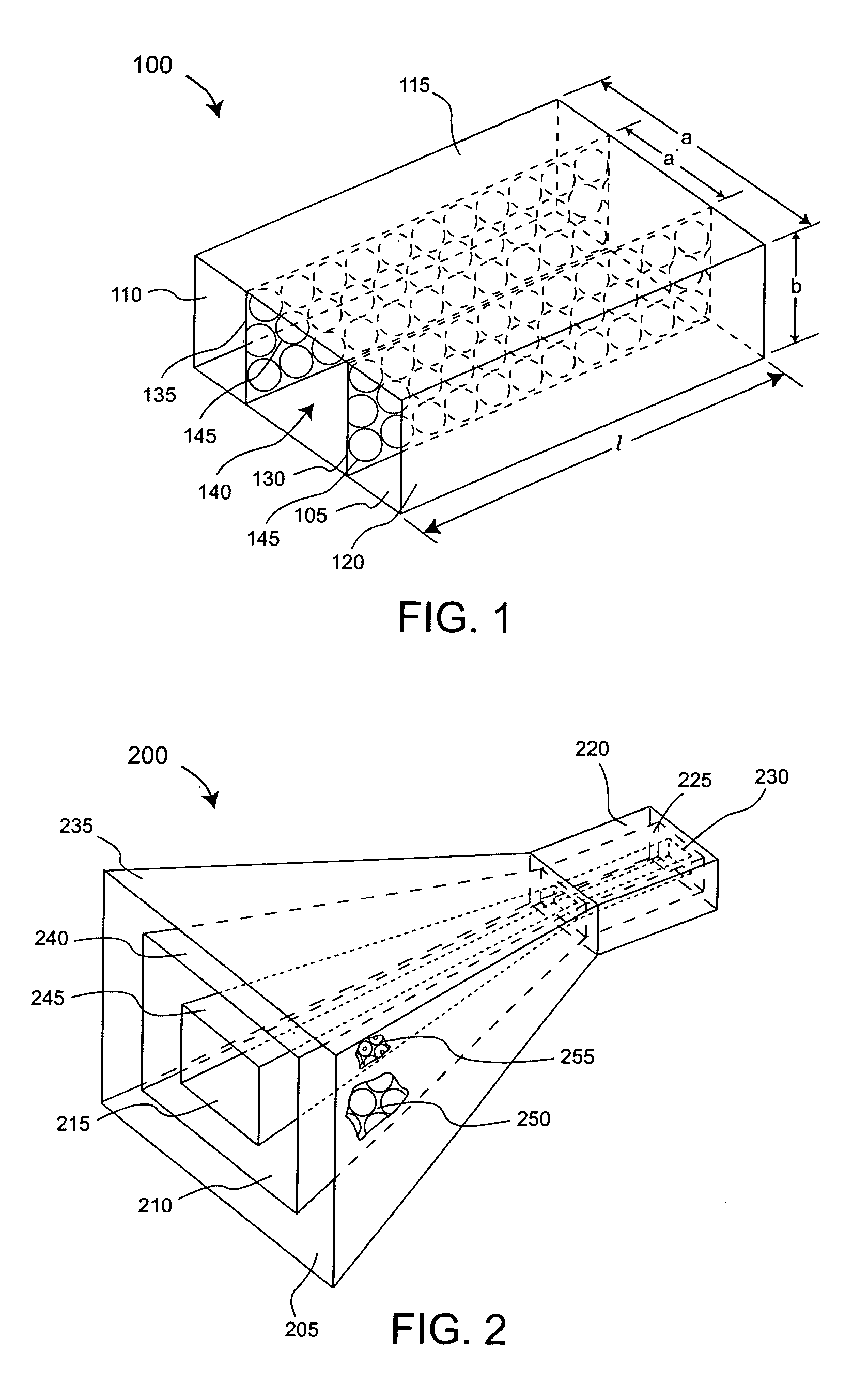
Dual-window high-power conical horn antenna
A high power TM01 mode radio frequency antenna. The inventive antenna comprises a conical horn for receiving an electromagnetic input signal and radiating an output signal in response thereto. An inner window is disposed within the conical horn. An outer window is mounted at an output aperture of the conical horn in alignment with the inner window. The antenna has a gradual taper from a waveguide input to the aperture over a cone angle of 45 degrees. The outer window is mounted at the aperture in concentric alignment with the inner window. For an optimal compact design, the inner and outer windows are of polycarbonate construction.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Hybrid-mode horn antenna with selective gain
ActiveUS6992639B1Designing can be facilitatedMechanically simpleWaveguide hornsHorn antennaMixed mode
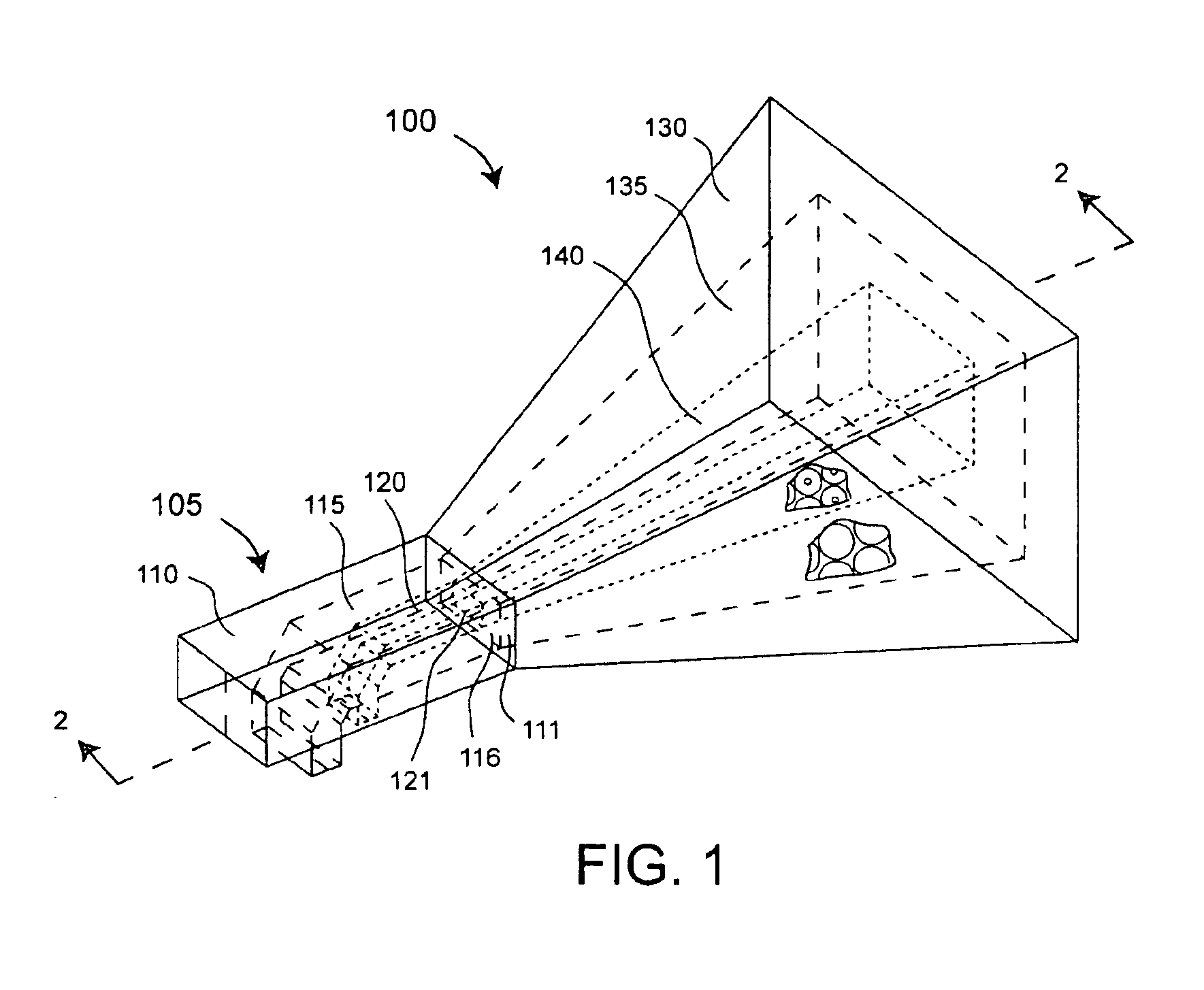
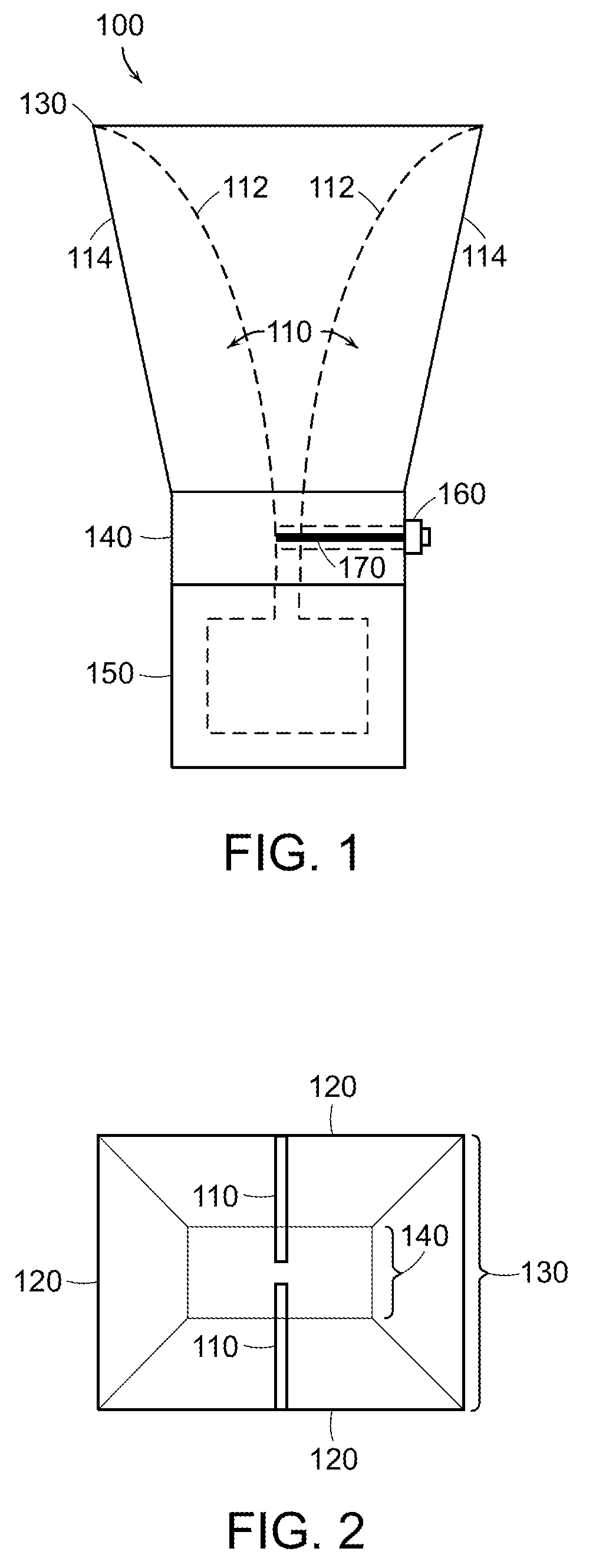
The present invention provides a new class of hybrid-mode horn antennas. The present invention facilitates the design of boundary conditions between soft and hard, supporting modes under balanced hybrid condition with uniform as well as tapered aperture distribution. In one embodiment, the horn antenna (100) is relatively simple mechanically, has a reasonably large bandwidth, supports linear as well as circular polarization, and is designed for a wide range of aperture sizes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Low-cost one-dimensional electromagnetic band gap waveguide phase shifter based ESA horn antenna
A one-dimensional electromagnetic band gap (EBG) waveguide phase shifter electronically scanned array (ESA) horn antenna utilizes a linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters for scanning and radiating a beam. A linear array feed feeds the linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters. A horn directs radiation from the linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters. Each of the EBG waveguide phase shifters is a waveguide with vertical and horizontal sidewalls. EBG devices are located on the vertical waveguide walls to shift phase to scan the beam.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Lens antenna with electronic beam steering capabilities
InactiveUS20150116154A1Improve directivityImprove radiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntenna gainRadio relay
The invention discloses a lens antenna with high directivity intended for use in radio-relay communication systems, said antenna providing the capability of electronic steering of the main radiation pattern beam by switching between horn antenna elements placed on a plane focal surface of the lens. Electronic beam steering allows antenna to automatically adjust the beam direction during initial alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and in case of small antenna orientation changes observed due to the influence of different reasons (wind, vibrations, compression and / or extension of portions of the supporting structures with the temperature changes, etc.). The technical result of the invention is the increase of the antenna directivity with simultaneously provided capability of scanning the beam in a continuous angle range and also the increase of the antenna radiation efficiency and, consequently, the increase of the lens antenna gain. This result is achieved by the implementation of horn antenna elements with optimized geometry.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
Low cost millimeter wave imager
InactiveUS7583074B1Low costUseful sensitivity levelMeasurement using dc-ac conversionMeasurement using ac-dc conversionLow noiseTunnel diode
Low cost millimeter wave imagers using two-dimensional focal plane arrays based on backward tunneling diode (BTD) detectors. Two-dimensional focal arrays of BTD detectors are used as focal plane arrays in imagers. High responsivity of BTD detectors near zero bias results in low noise detectors that alleviate the need for expensive and heat generating low noise amplifiers or Dicke switches in the imager. BTD detectors are installed on a printed circuit board using flip chip packaging technology and horn antennas direct the waves toward the flip chip including the BTD detectors. The assembly of the horn antennas, flip chips, printed circuit board substrate, and interconnects together work as an imaging sensor. Corrugated surfaces of the components prevent re-radiation of the incident waves.
Owner:HRL LAB
Horn antenna for a radar device
A horn antenna for a radar device comprising a metal body having a tubular hollow waveguide section opening into a hollow horn section, a dielectric filling body filling up the inner space of the horn section, and a dielectric cover, wherein the horn antenna is configured to protrude in a measurement environment, protected from highly aggressive process environments and is usable over a wide temperature range.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
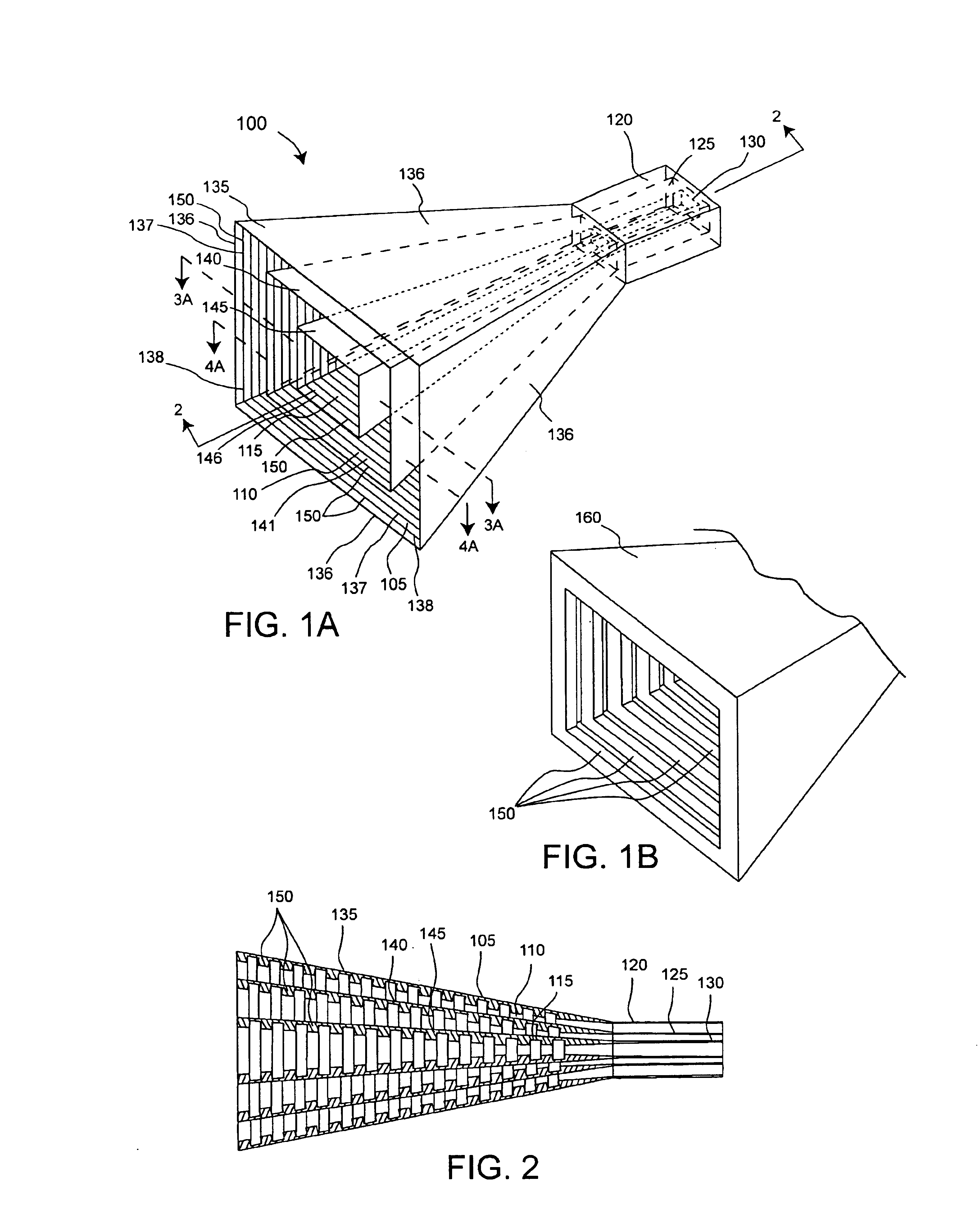
Multi-band horn antenna using frequency selective surfaces
InactiveUS6985118B2Grating lobe of the antenna is reducedImprove permeabilityWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandHorn antenna
A waveguide (100) including at least one outer surface (105, 110, 115, 120) defining a waveguide cavity (140) and at least one inner surface (130, 135) positioned within the waveguide cavity (140). The inner surface (130, 135) includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) having a plurality of FSS elements (145) coupled to at least one substrate. The substrate defines a first propagation medium such that an RF signal having a first wavelength in the first propagation medium can pass through the FSS (130, 135). The FSS (130, 135) is coupled to a second propagation medium such that in the second propagation medium the RF signal has a second wavelength which is at least twice as long as a physical distance between centers of adjacent FSS elements (145). The second wavelength can be different than the first wavelength.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
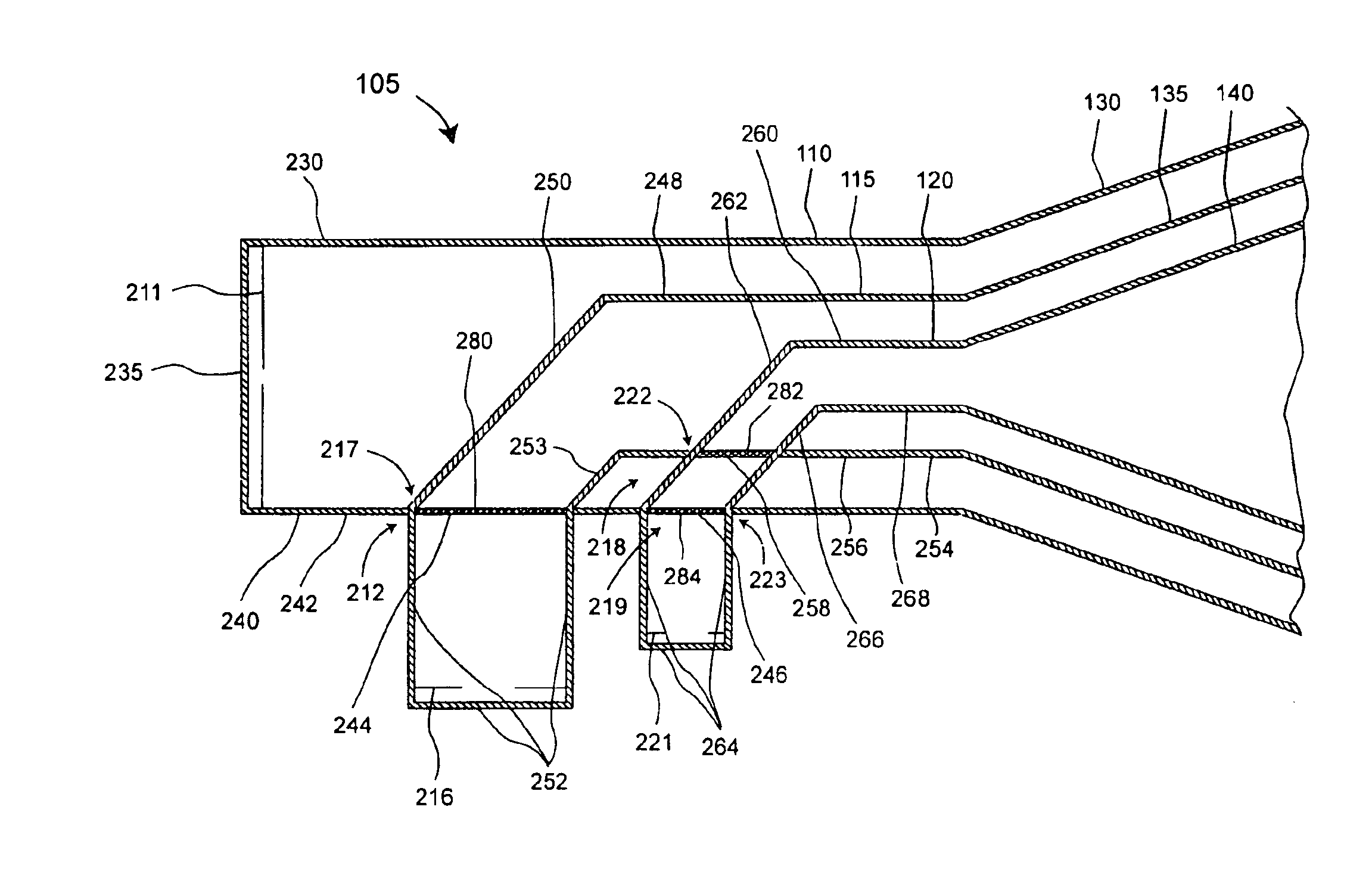
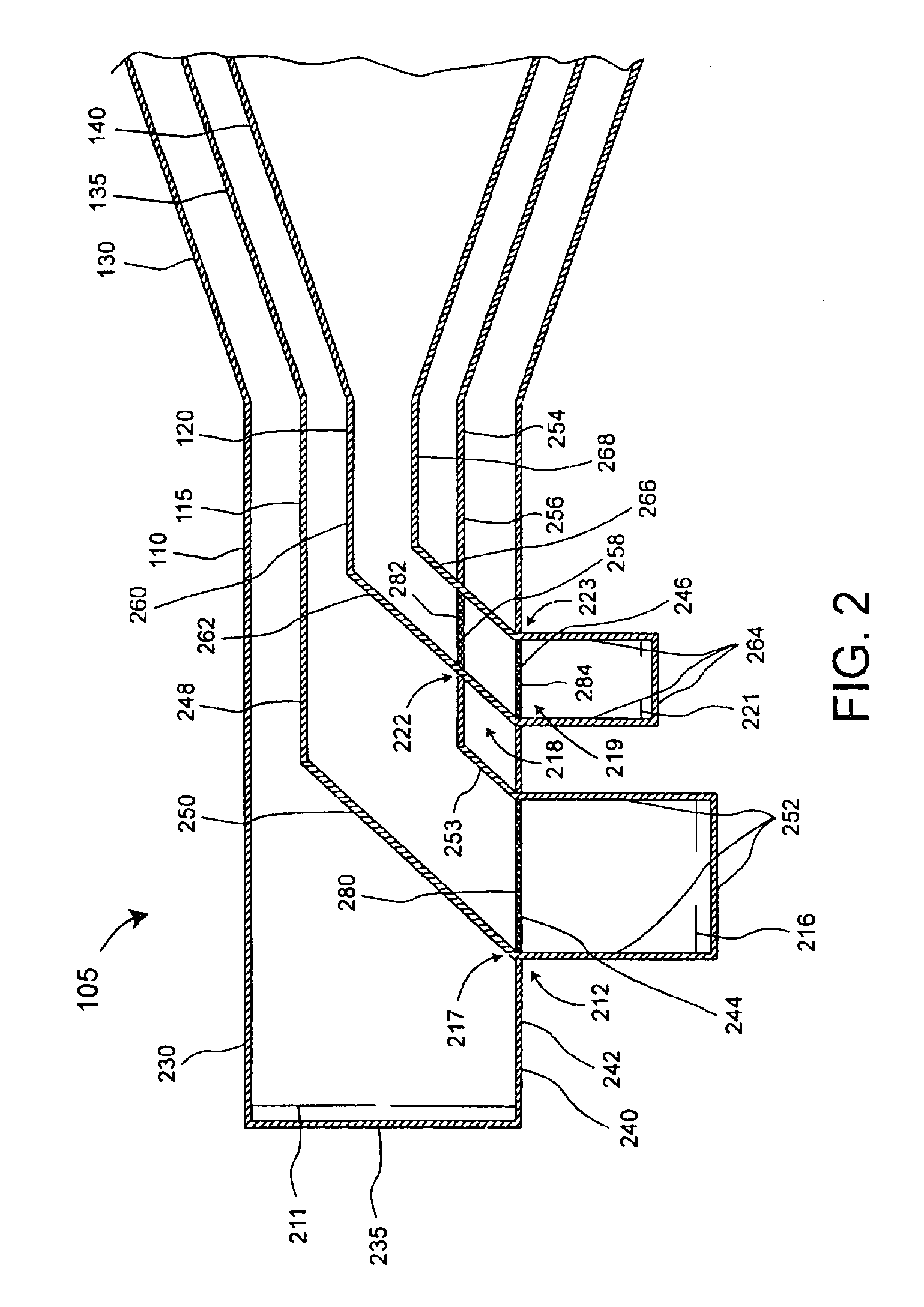
FSS feeding network for a multi-band compact horn
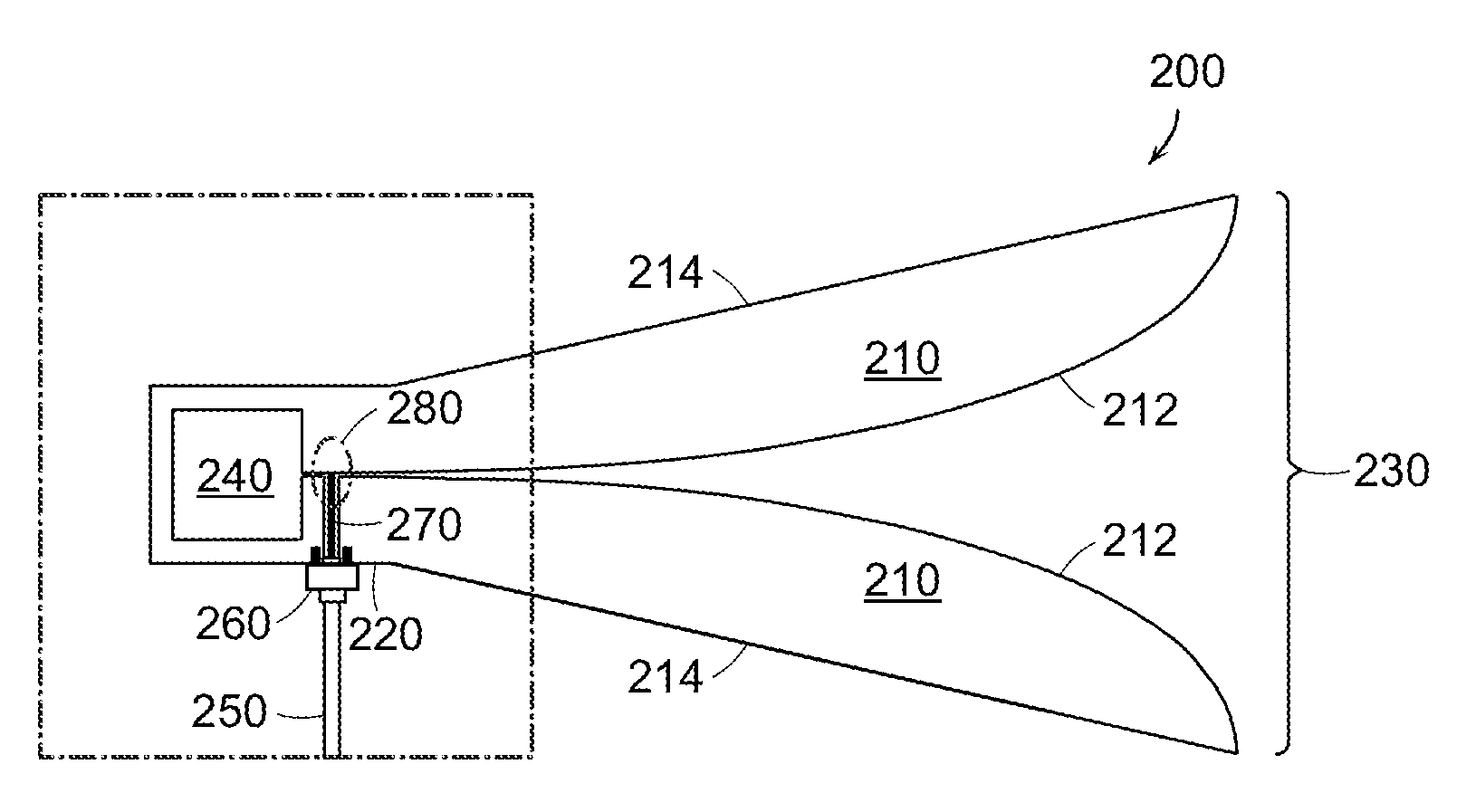
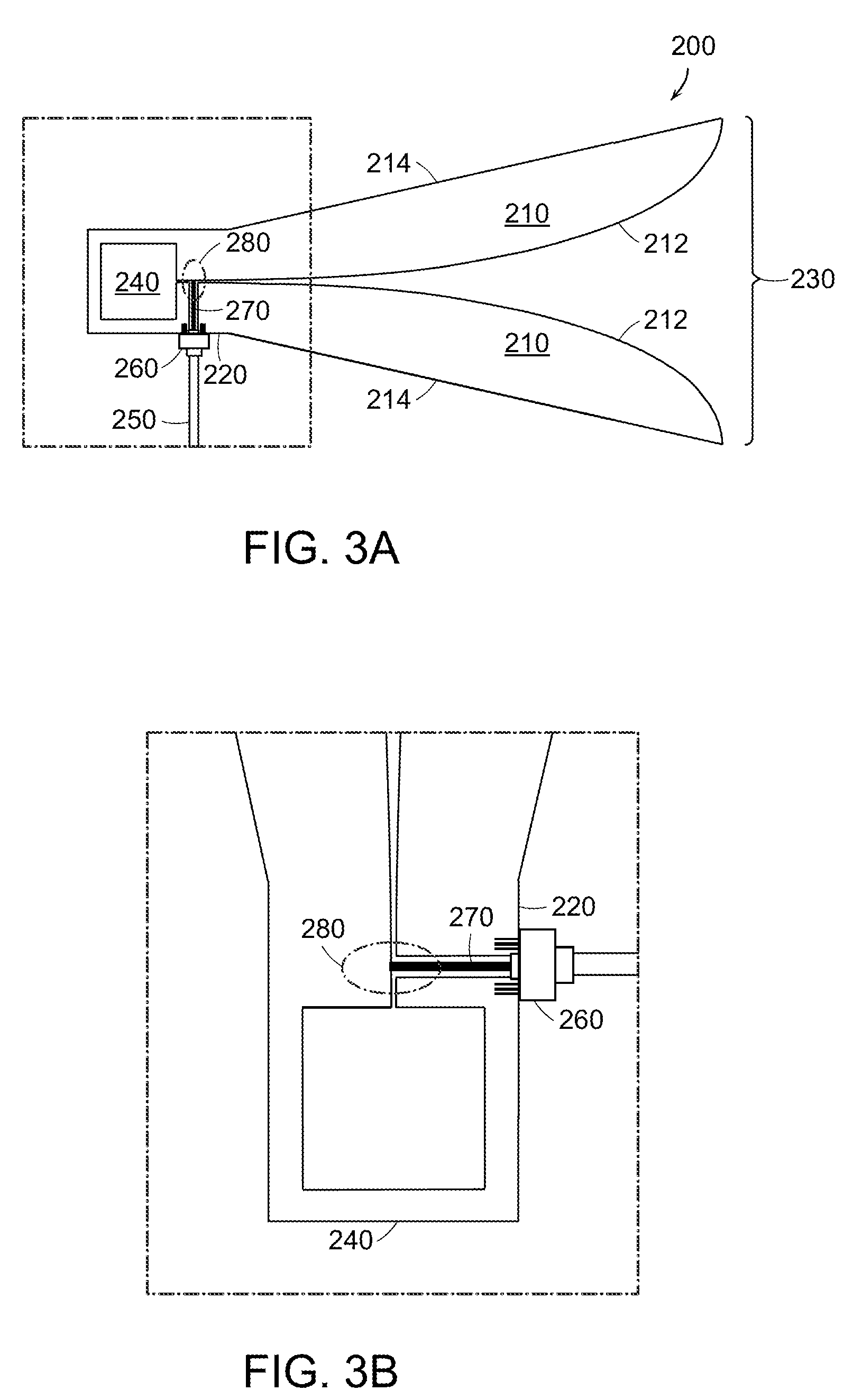
A feed structure (105) for a horn antenna (100). The feed structure can include a first waveguide (110) and a second waveguide (115) having a first portion at least partially disposed within the first waveguide. The second waveguide also can include a second portion intersecting a first wall (240) of the first waveguide. The first wall can include a first frequency selective surface (244) at an intersection (280) of the first wall and the second portion of the second waveguide. The first waveguide can be operatively coupled to a first horn section (130) and the second portion can be operatively coupled to a second horn section (135).
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Compact broad-band admittance tunnel incorporating gaussian beam antennas
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
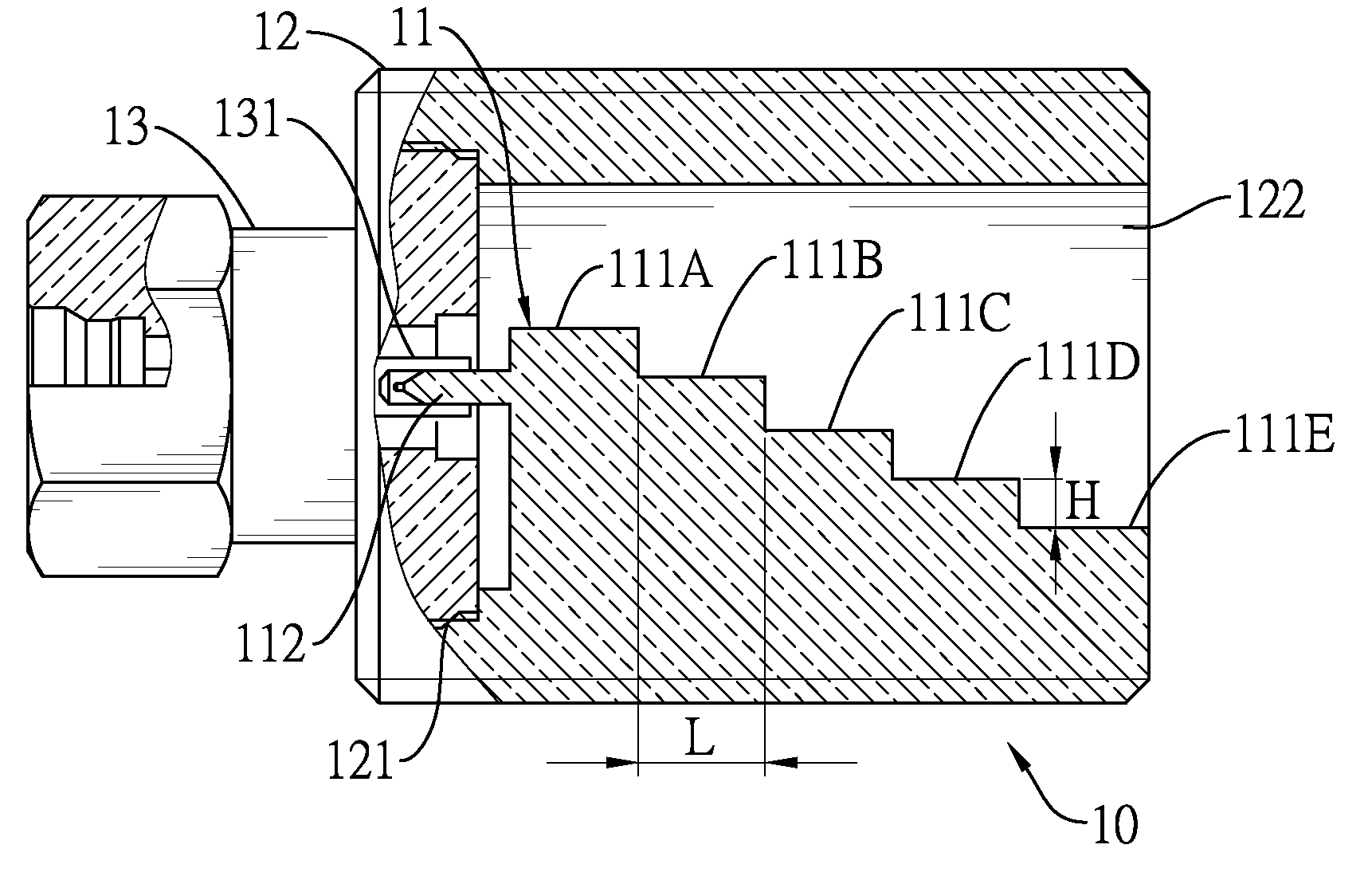
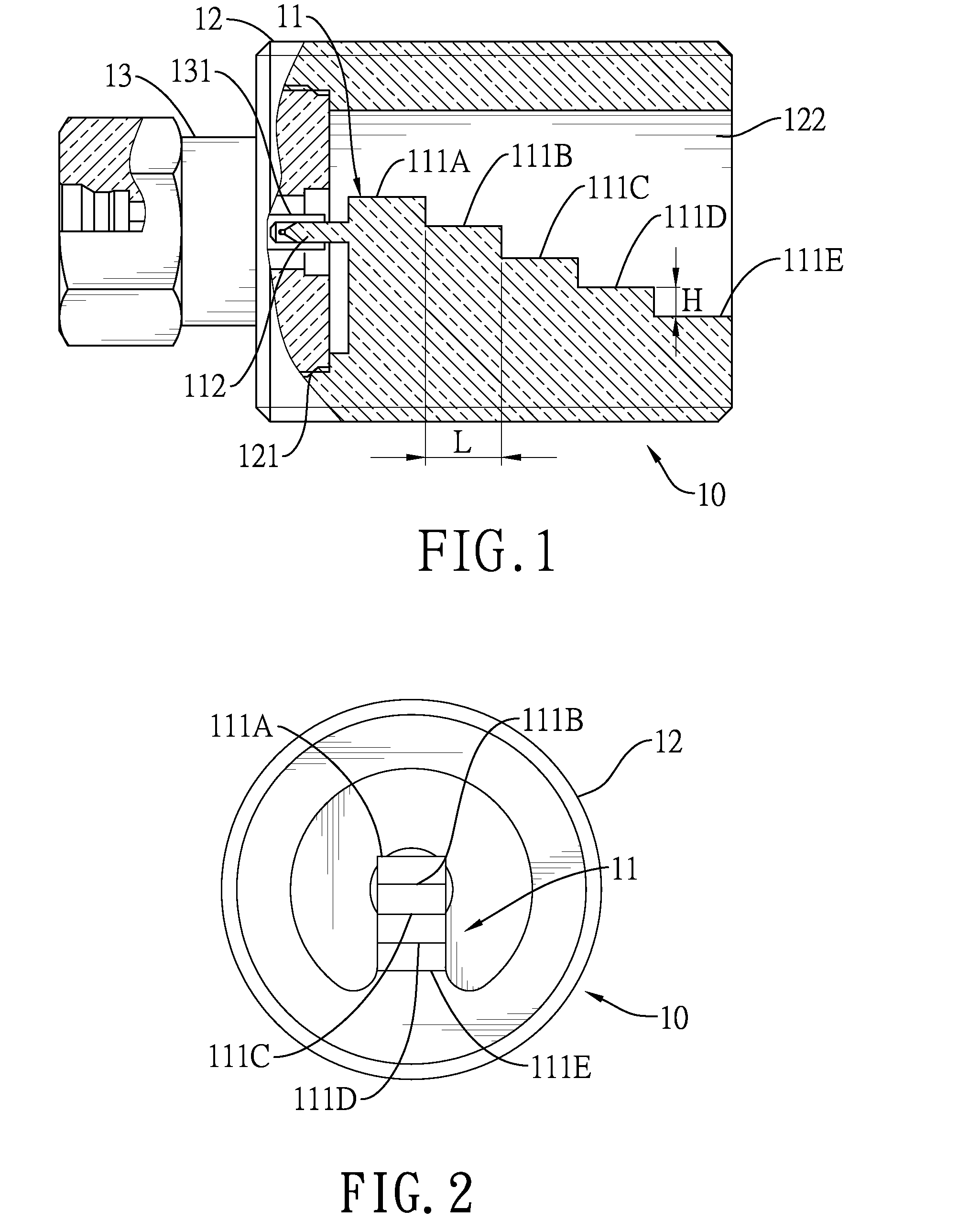
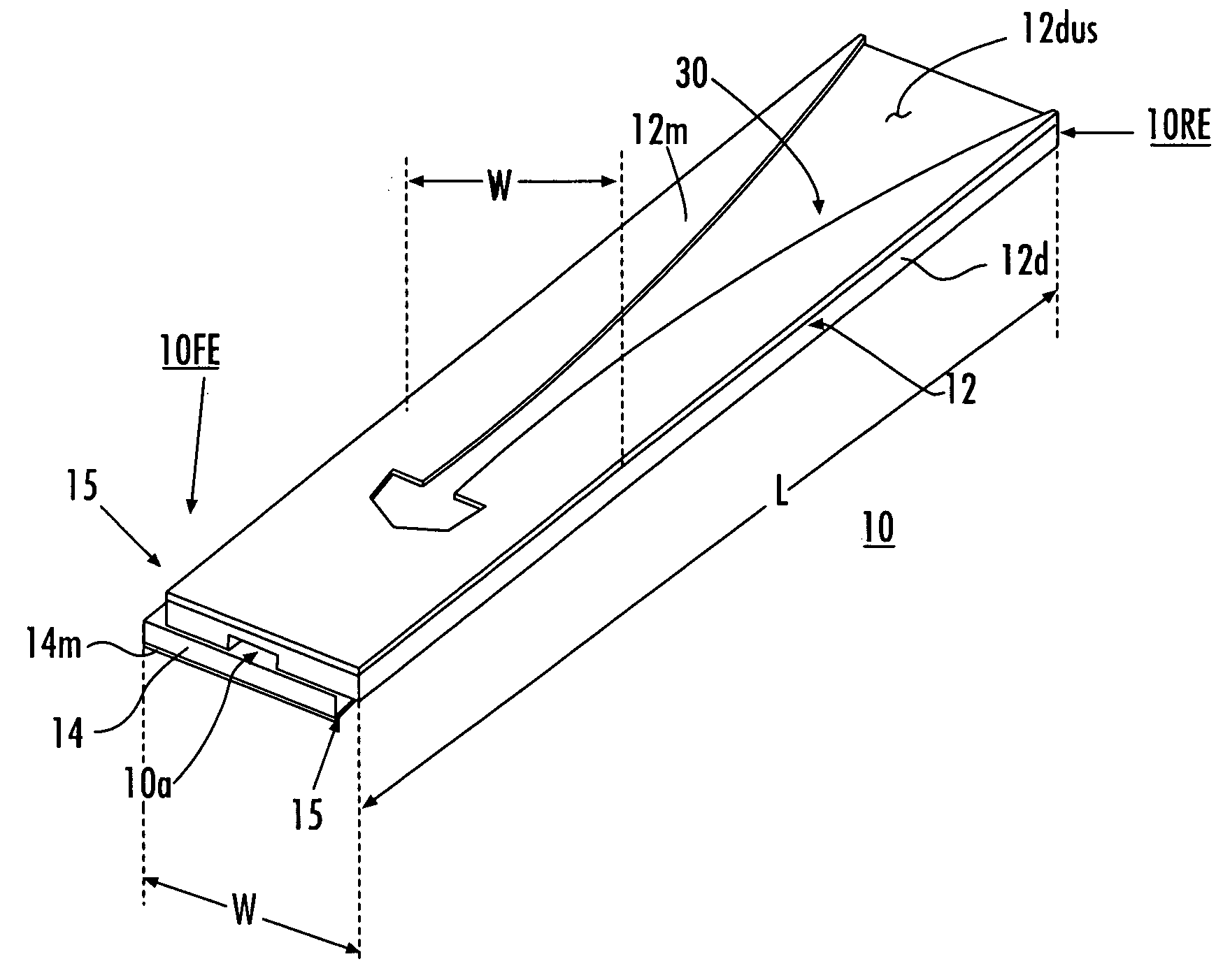
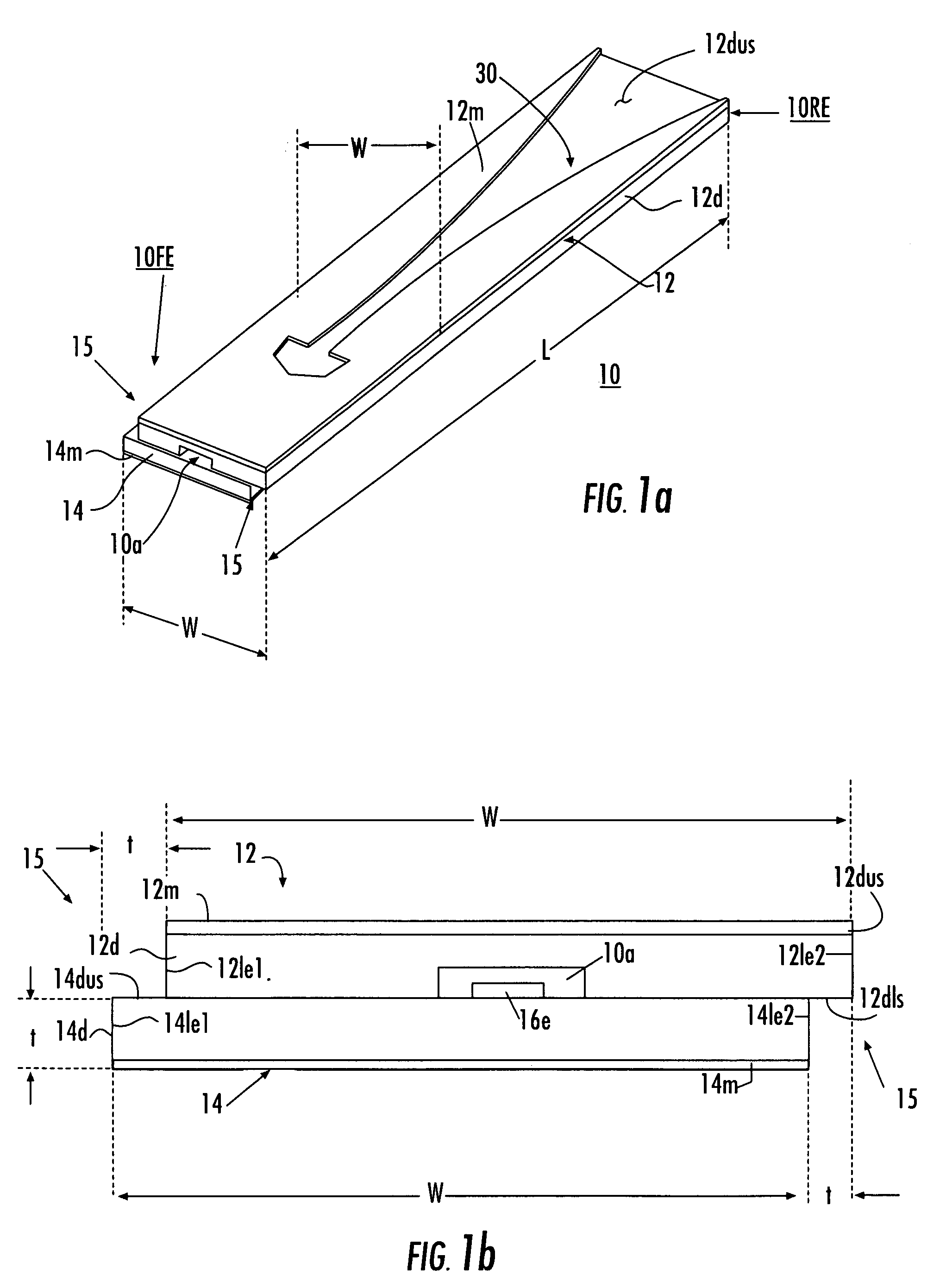
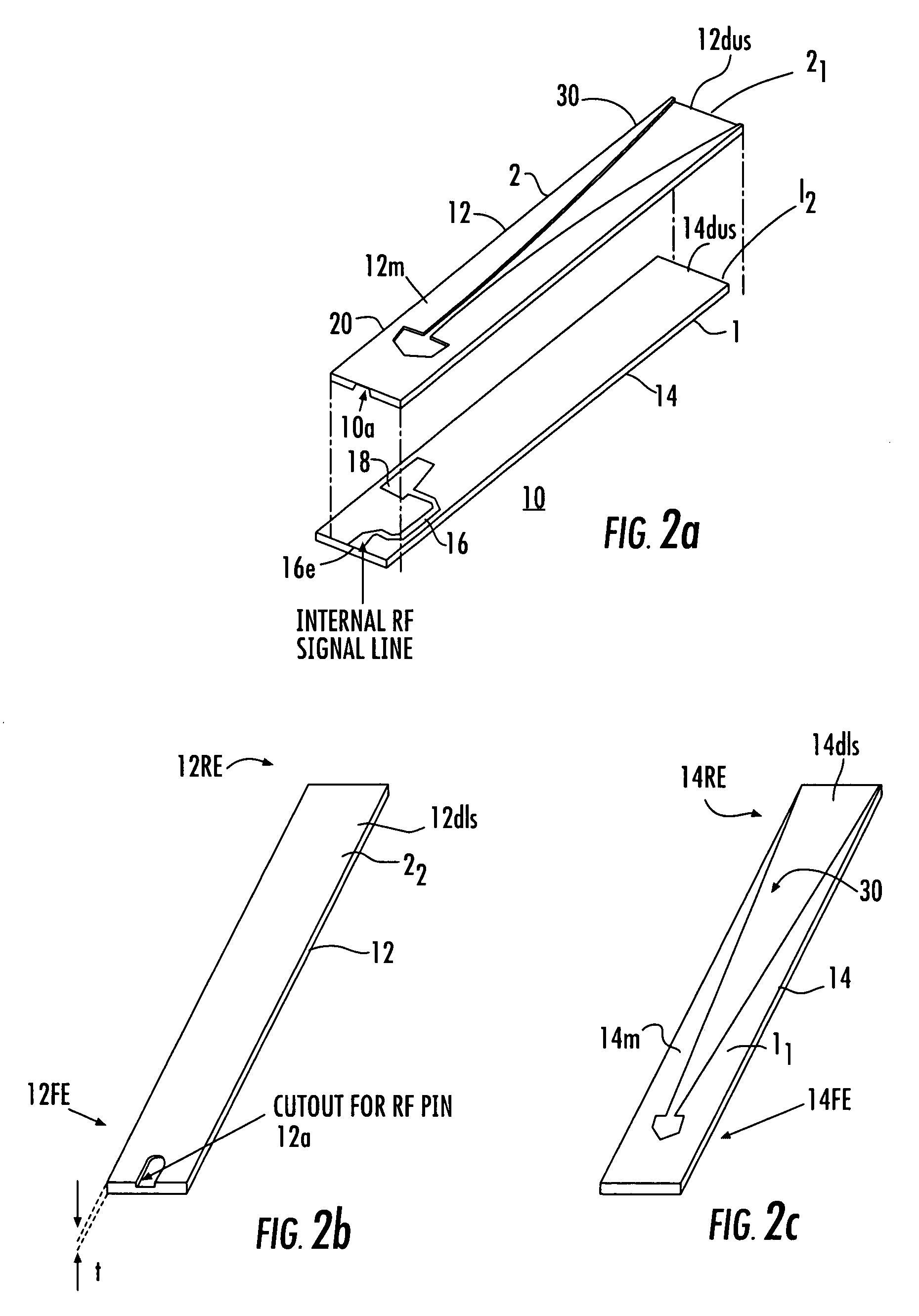
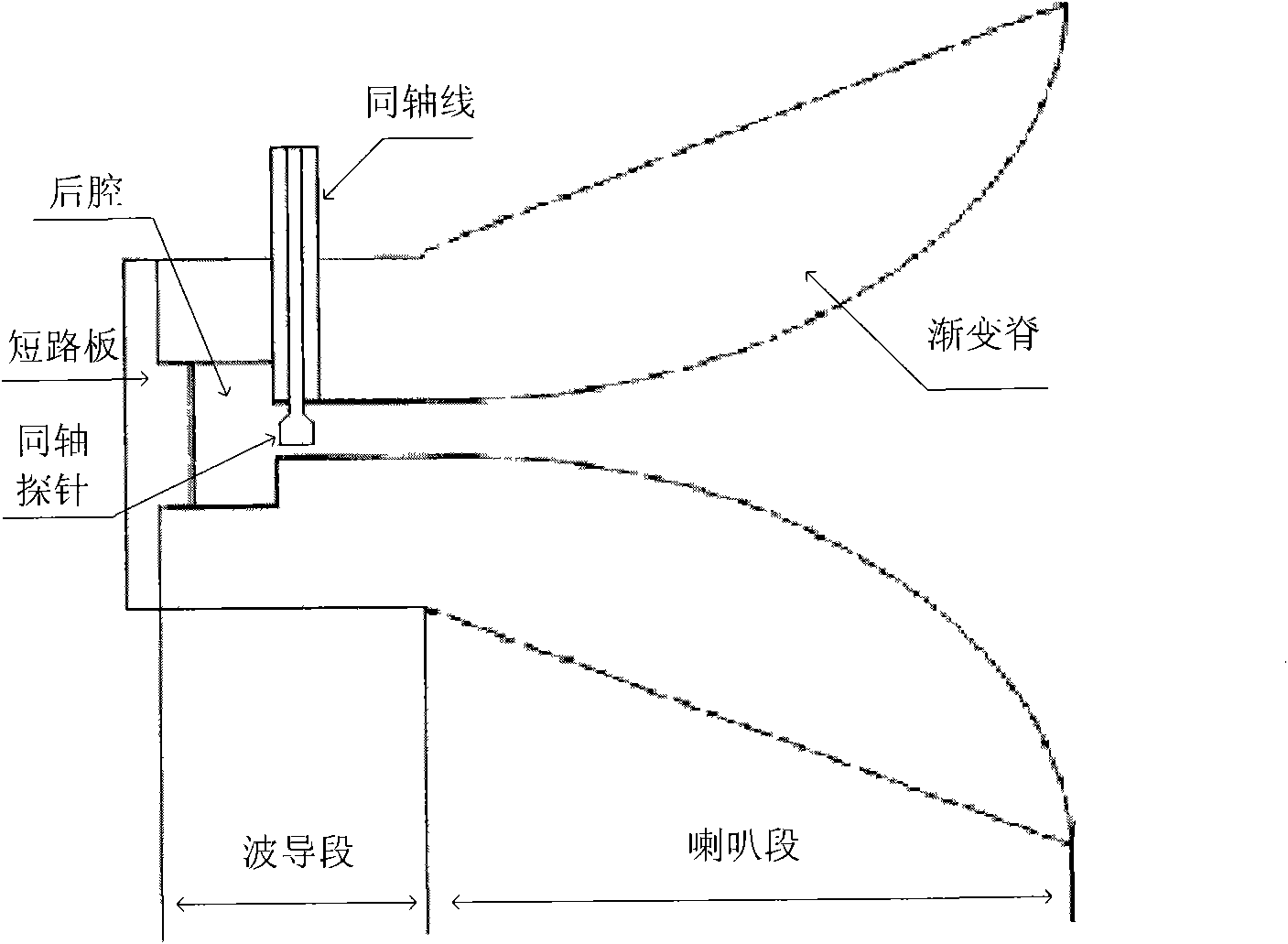
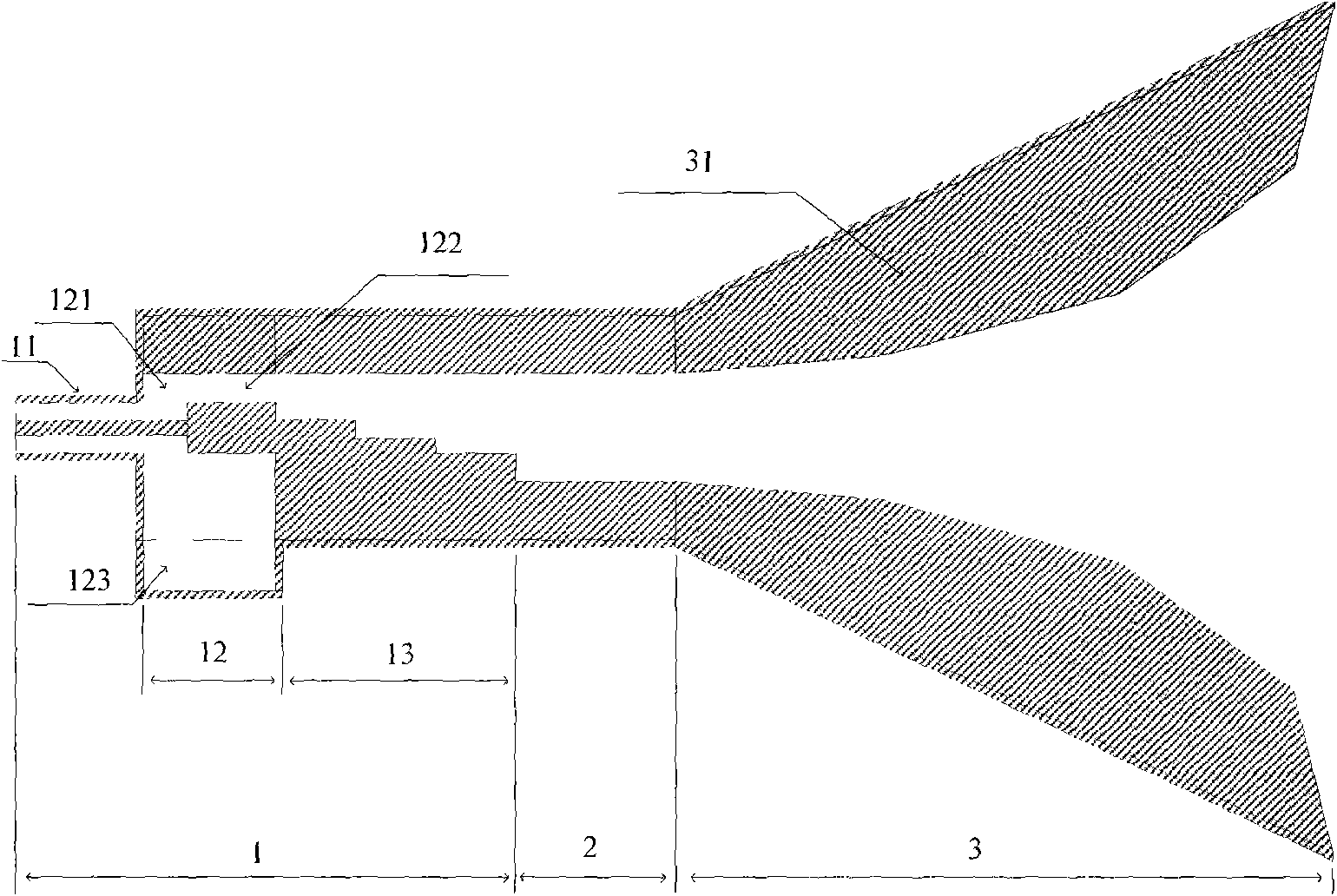
Horn antenna device and step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20150029065A1Sure easyAssembly precisionWaveguide hornsAntennas earthing switches associationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise rate
The present invention relates to a horn antenna device. The horn antenna device has a step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus and a conical horn antenna. The step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus has a stepped body having multiple stairs and a connecting pin. The stepped body is adapted to radiate electromagnetic waves and receive a reflection of the electromagnetic waves. According to the structure of the step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus of the invention, the resonating modes are easy to be determined. The directivity and the signal-to-noise rate are improved. In addition, the connecting pin is directly connected to the stairs for improving the signal stability of the horn antenna device.
Owner:FINETEK CO LTD
Horn antenna
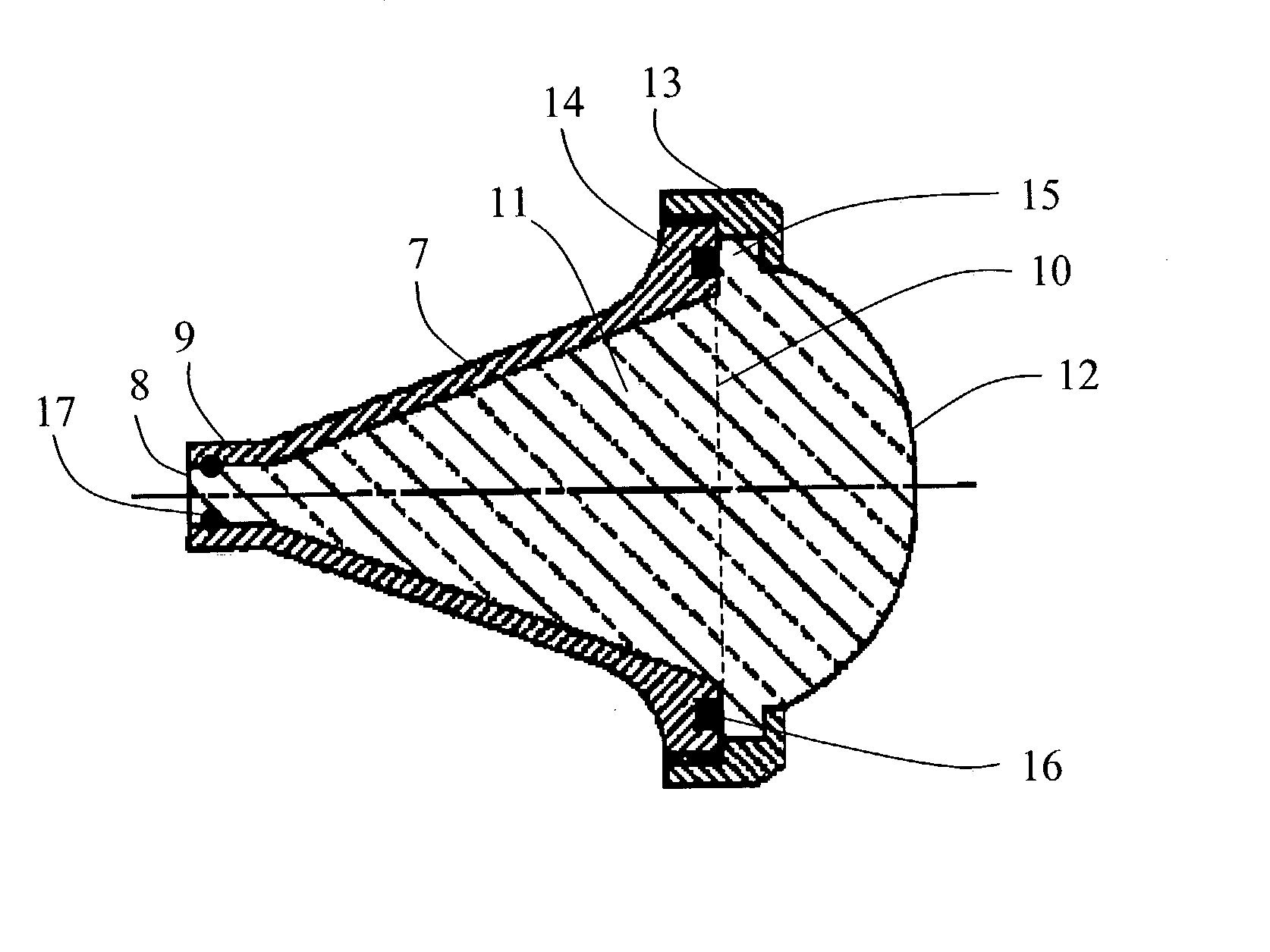
InactiveUS6859187B2Efficient separationImprove performanceWaveguide hornsAntenna supports/mountingsRadarEngineering
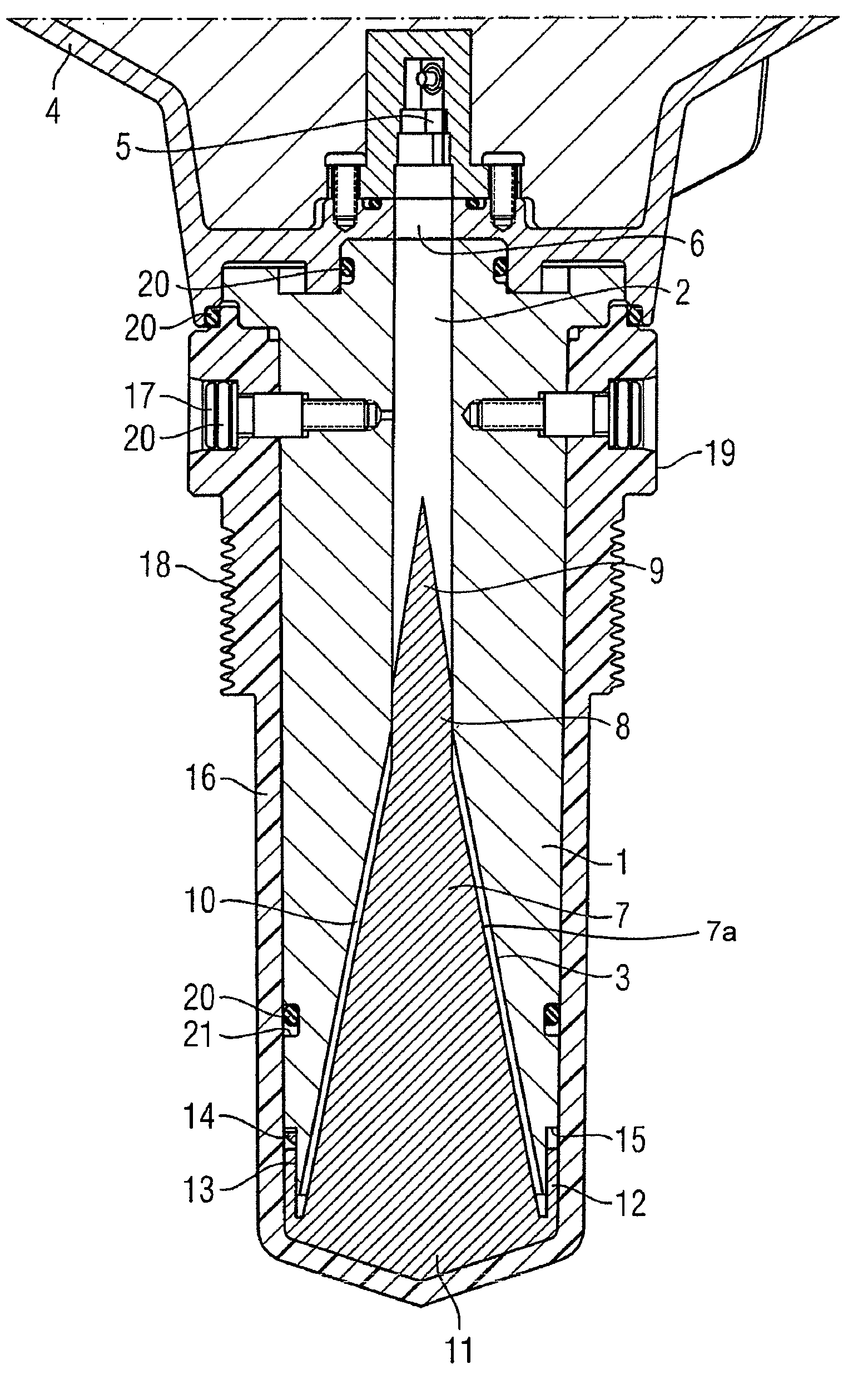
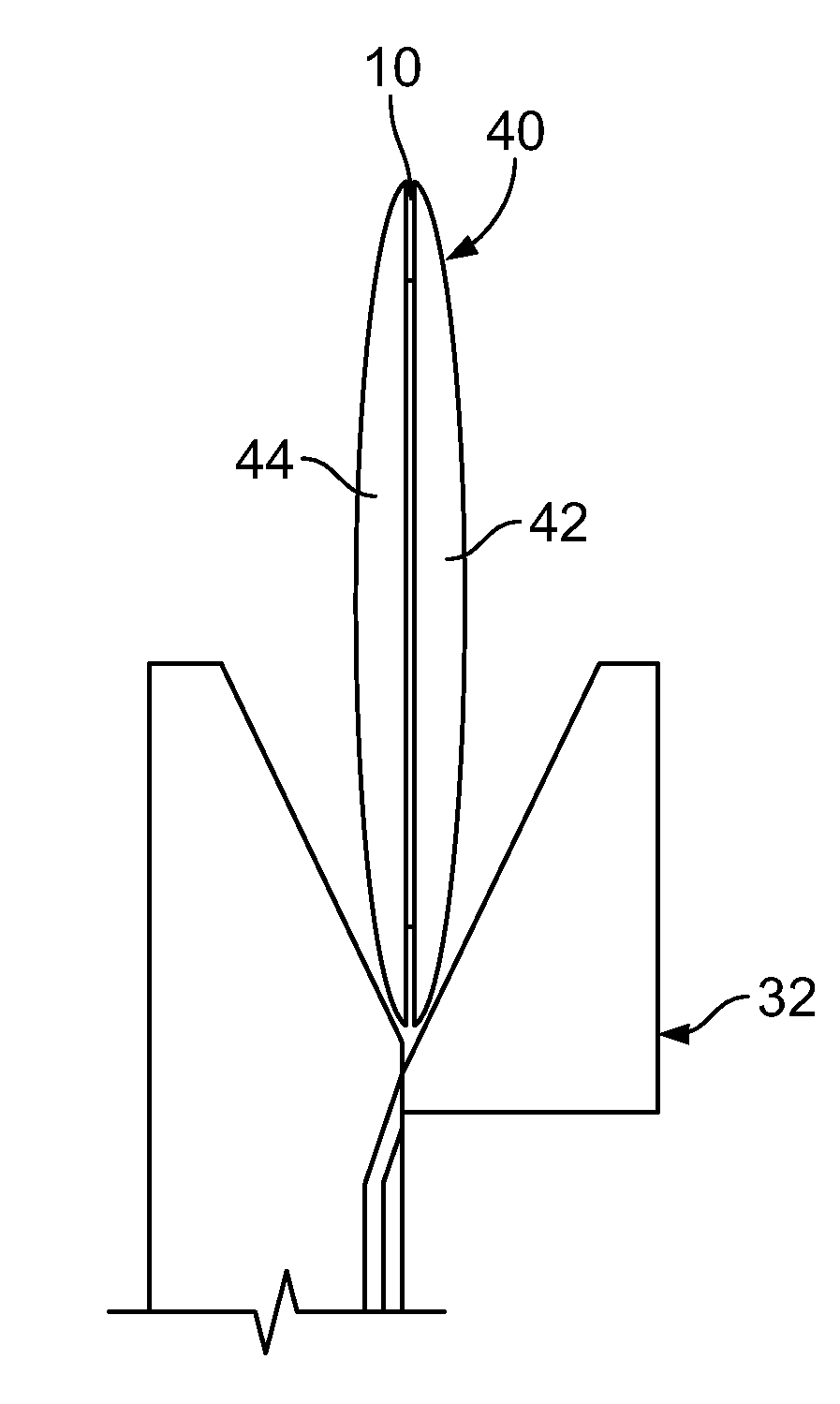
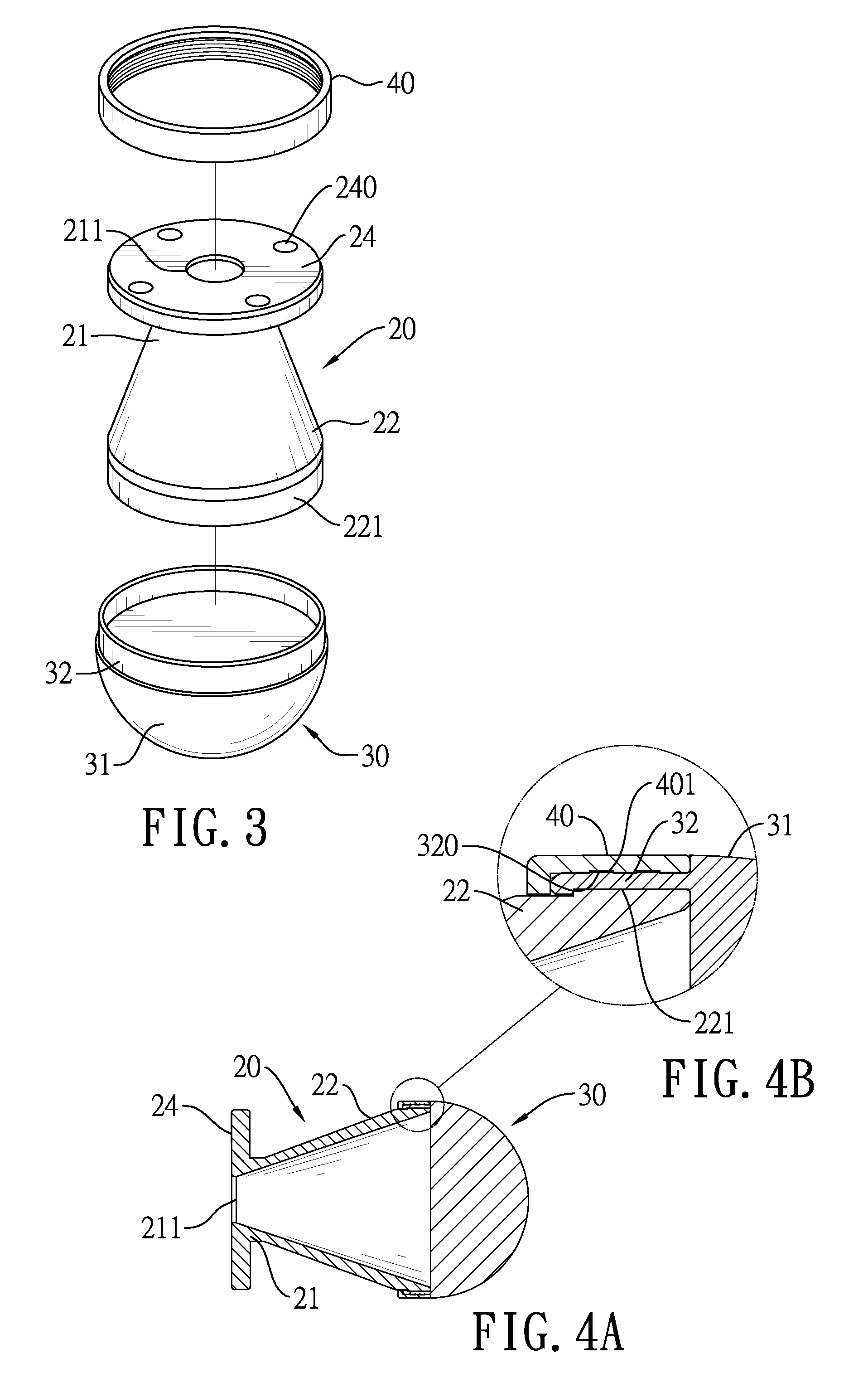
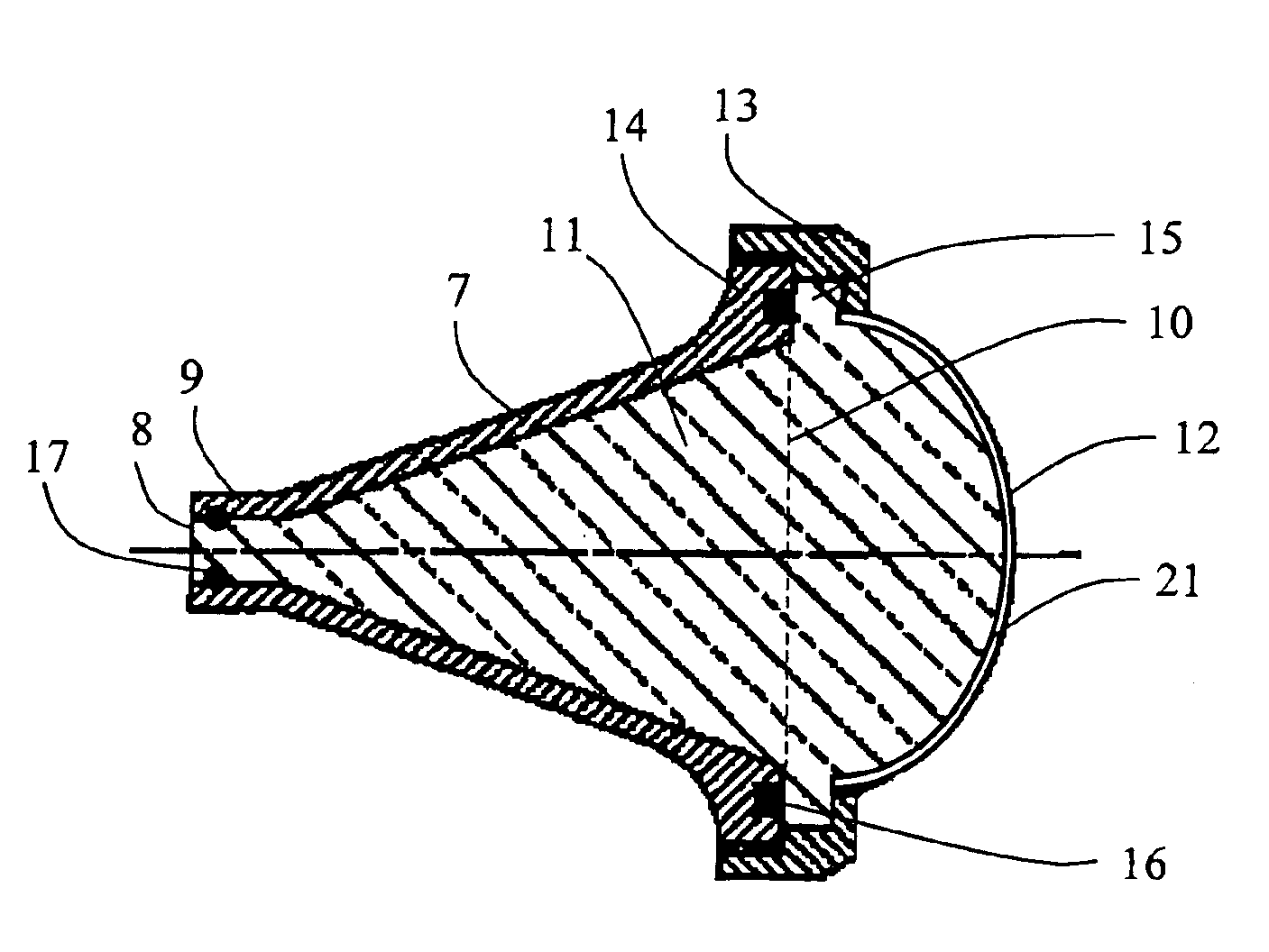
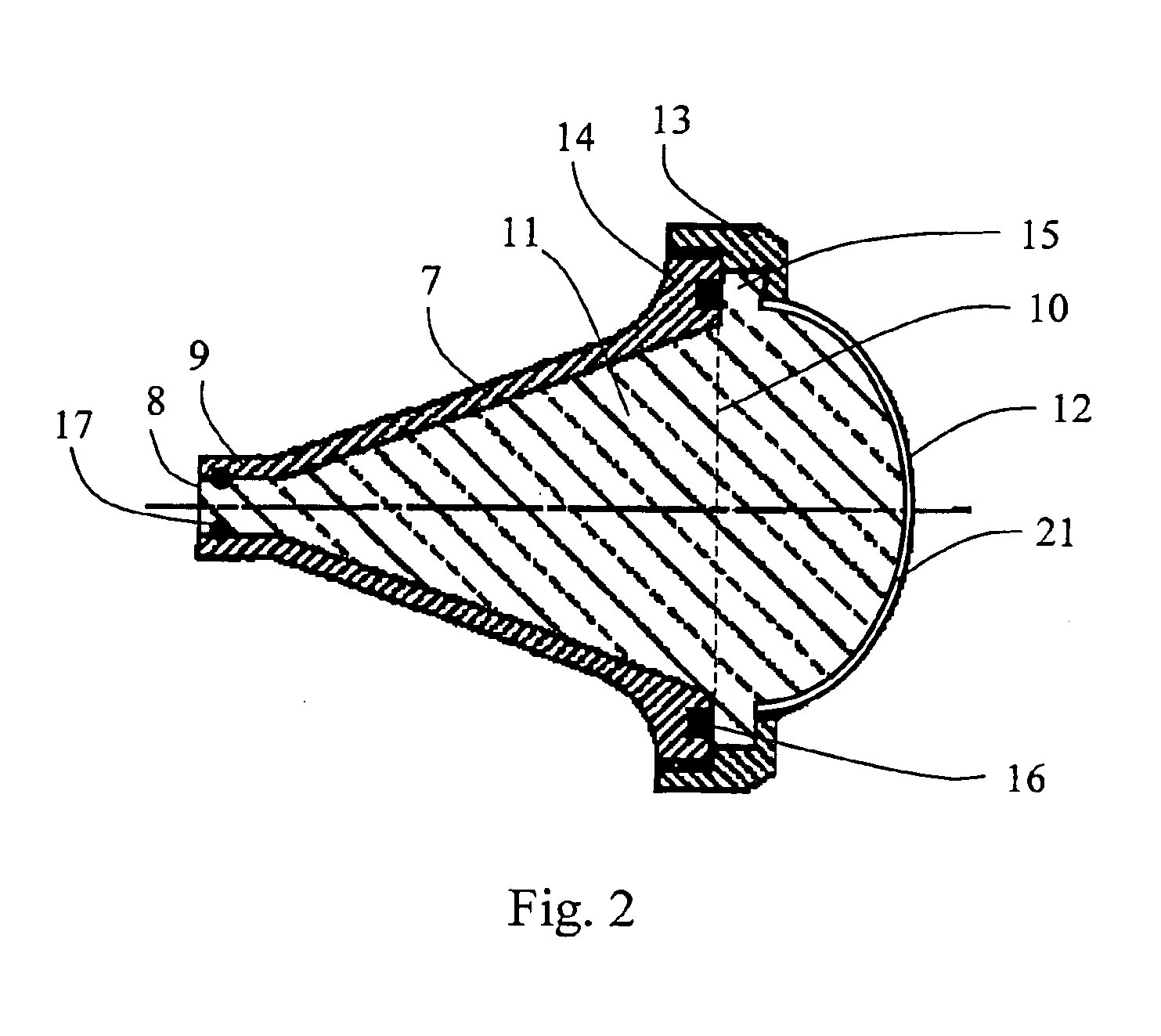
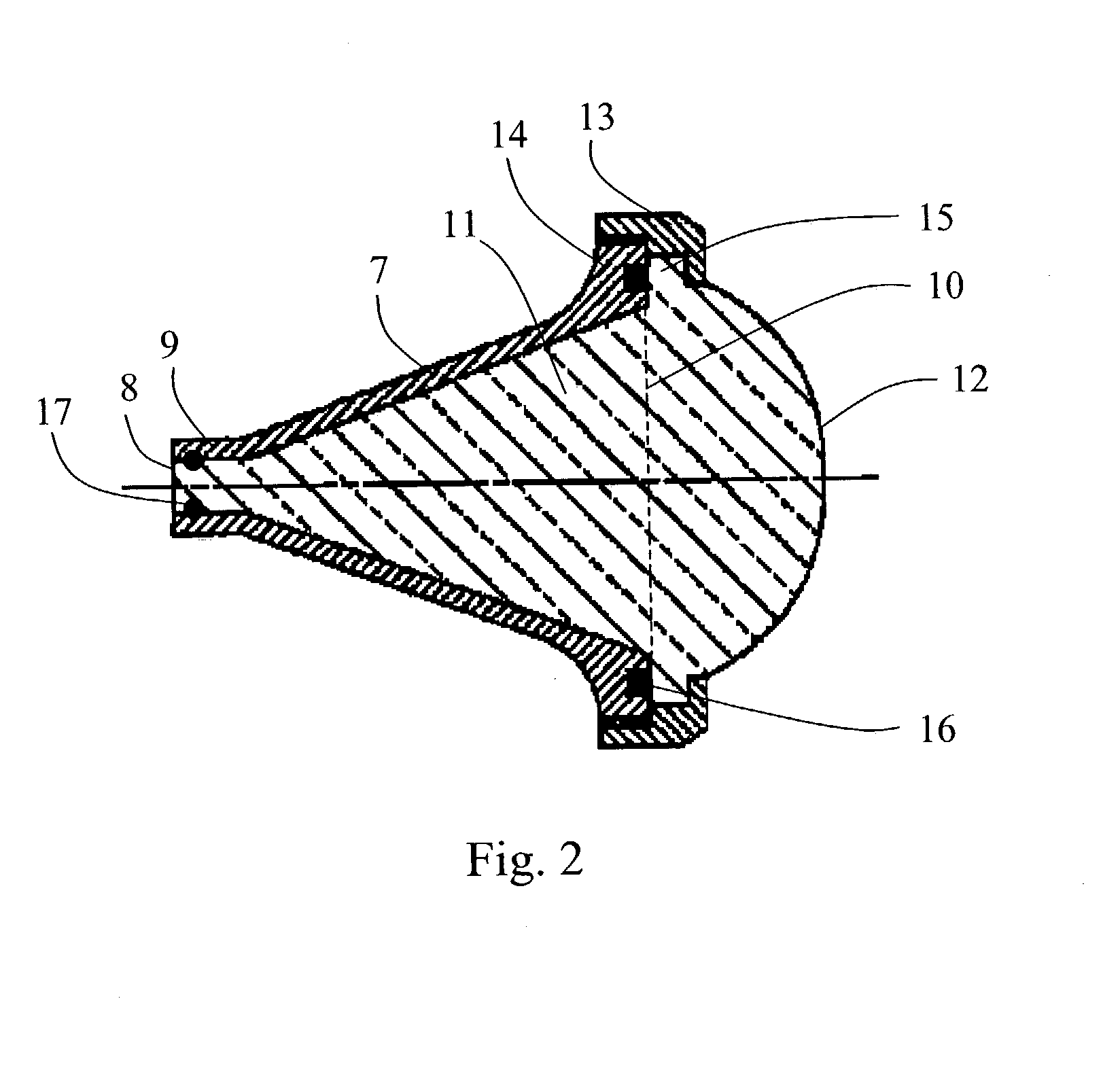
The present invention relate to a horn antenna at a radar level gauge for determination of a level of a surface of a medium stored in a tank and a method of making a horn antenna which is mechanically constituted such that the horn antenna will withstand the environment of the tank interior. The antenna comprises a first conductive housing (7) having a wave guide port (8), which is connectable to a wave guide, a first aperture (10), which is separated from the wave guide port (8) and a fist divergent section between the wave guide port (8) and the first aperture (10). A dielectric body (11) is arranged inside and essentially filling the first conductive housing (7), which body (11) displays a free end (12) in the area of the first aperture (10). The horn antenna is characterized in that around the first aperture (10) is arranged a locking device (13), which is arranged to fix the dielectric body (11) in the first housing (7) and that in the area of the locking device (13) is arranged at least one flexible sealing element (16) between the dielectric body (11) and the first cover (7).
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Substrate embedded horn antenna having selection capability of vertical and horizontal radiation pattern
Substrate embedded horn antenna includes a dielectric, metal patterns, metal vias and a ground plate. The metal patterns are embedded by being stacked in dielectric. Metal patterns are hollow rectangle types or hollow circle types. Metal vias connect layers of metal patterns by being embedded between layers of metal patterns. Ground plate is formed in an upper side of dielectric. Metal patterns form waveguide structure by being stacked in radial shape. Waveguide structure propagates electromagnetic wave by focusing electromagnetic wave. Embedded horn antenna capable of selectively using vertical radiation and horizontal radiation may be implemented using the via and metal pattern in dielectric substrate. Embedded horn antenna may be implemented in small size with high gain. Vertical embedded horn antenna and horizontal embedded horn antenna may be implemented in a substrate. Method of manufacturing embedded horn antenna capable of selectively using vertical radiation and horizontal radiation may be provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Waveguide horn antenna array and radar device
InactiveUS7423604B2Wide range of adjustmentSimple structureLinear waveguide fed arraysElectrical conductorCoupling
A conductor member contains a linear feed waveguide extending in a fixed direction and a plurality of horn antennas coupled to the feed waveguide and set at an interval of about one half of a wavelength in the extending direction of the feed waveguide. The horn antennas are formed by horns and coupling waveguides, and the coupling waveguides are set so as to partially enter the feed waveguide. When the size of the spatial coupling portion formed by the entrance is changed, the degree of coupling between the feed waveguide and each of the coupling waveguides changes.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Semi-coaxial horn antenna
InactiveUS6538615B1Short antennas for non-sinusoidal wavesResonant antennasDielectricElectrical conductor
A semi-coaxial horn antenna transmits and receives electromagnetic waves, including impulse radio waves. The antenna includes an inner conductor that is surrounded by a cone-shaped dielectric, and an outer conductor that is conformally attached to the cone shaped dielectric. In embodiments, the inner conductor is a hollow metallic cylinder that is able to slide over a separate metal shaft, which may be part of a portable hand-tool device. The dielectric constant of the cone shaped dielectric may be selected to match a target medium. The outer conductor has a cross-section that is substantially an arc shape, and defines a sector angle phi that determines an impedance along the length of the antenna.
Owner:TDC ACQUISITION HLDG
Small Aperture Interrogator Antenna System Employing Sum Difference Azimuth Discrimination Techniques
InactiveUS20090267852A1Low costSuppresses grating lobeWaveguide hornsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesHorn antennaPhysics
An antenna system comprising a first antenna corresponding to a horn antenna, a second antenna corresponding to a horn antenna disposed such that the E-plane of the second antenna is co-planar with the E-plane of the first antenna an such that an aperture of the first antenna and an aperture of the second antenna are substantially in a common plane; and a third antenna corresponding to a horn antenna disposed such that the E-plane of the third antenna is substantially co-planar with the E-plane of the first antenna and such that an aperture of said third antenna is substantially in the same plane as the aperture of the first and second antennas and wherein the second and third antennas are canted toward each other.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Horn antenna for a radar device
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
Horn Antenna with Integrated Impedance Matching Network for Improved Operating Frequency Range
ActiveUS20100033391A1Reduce Impedance MismatchReduce mismatchWaveguide hornsWaveguide mouthsCapacitanceHorn antenna
A dual- or quad-ridged horn antenna with an embedded impedance matching network is provided herein. According to one embodiment, the horn antenna may include at least one pair of ridges arranged opposite one another for guiding an electromagnetic wave there between. A transmission line is coupled to a first one of the ridges for supplying power to, or receiving a signal from, a feed region of the horn antenna. To reduce impedance mismatches between the transmission line and the ridges, an impedance matching network is embedded within a second one of the ridges at the feed point. The impedance matching network reduces impedance mismatch and extends the operational frequency range of the horn antenna by providing a sufficient amount of series capacitance between the transmission line and the ridges at the feed region. As set forth herein, the impedance matching network is preferably implemented as an open-circuit transmission line stub or capacitive stub.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Multi-probe spherical near field channel calibration device and method
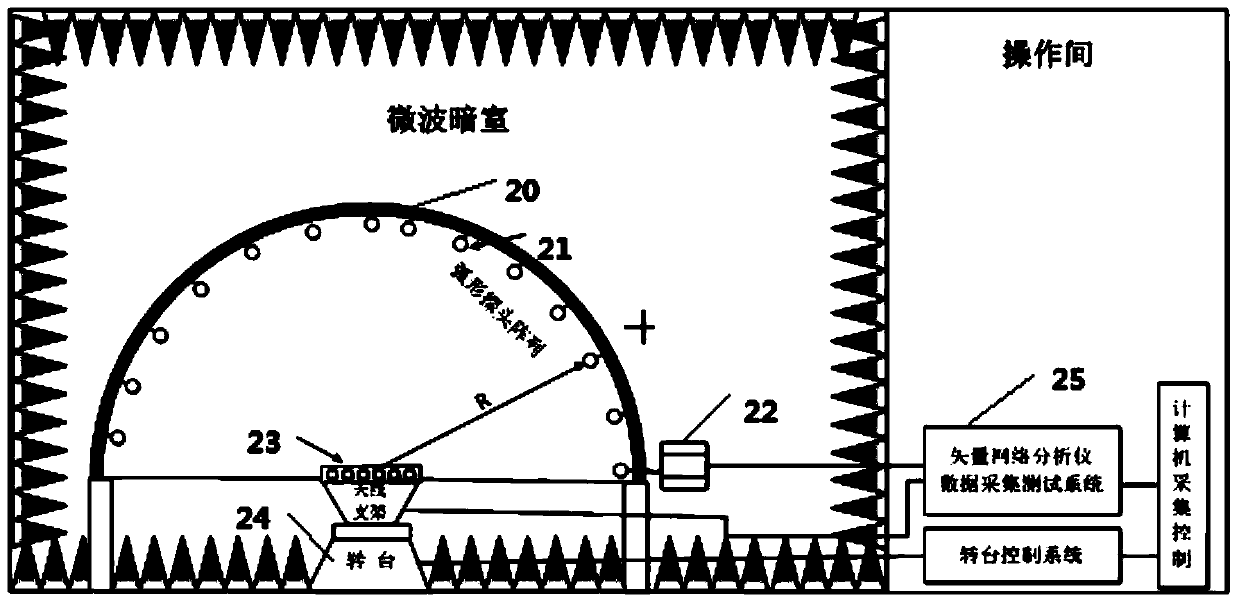
The invention provides a multi-probe spherical near field channel calibration device and method. The device comprises a tool, a rotary shaft, a telescopic arm, an orienting antenna, a laser range finder, a first rotary table control system and a second rotary table control system; the tool is arranged on a rotary table and is provided with the rotary shaft; the telescopic arm is arranged on the rotary shaft and is provided with the orienting antenna; the orienting antenna is provided with the laser ranger finder; the first rotary control system is arranged to be connected with the tool and is used for controlling the tool to move left and right or up and down; the second rotary table control system is connected with the rotary table and is used for controlling the rotary table. By adopting the scheme, the orienting horn antenna is adopted as the calibration antenna to precisely calibrate the multi-probe spherical near field measuring data of the antenna, and the influence to the antenna performance caused by a backward ground when an omnidirectional antenna is used is avoided.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Horn antenna array and methods for fabrication thereof
A method for making a horn antenna array includes the steps of making first and second equal-size printed-circuit half-horn-elements, and offset-juxtaposing element pairs to make horn elements having a dielectric lip or step. A ground plane defining mutually intersecting crossed slot sets is loaded with horn elements with their lips interlocking near the slot crossings, to define the horn antenna array. The horn elements can be fed by pins extending through portions of the ground plane and into an aperture adjacent the feed elements of the horn elements. Electrical connections are made by fusion joining after the array is assembled.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Electrical axis optical calibration system of spaceborne microwave tracking-pointing radar and calibration method thereof
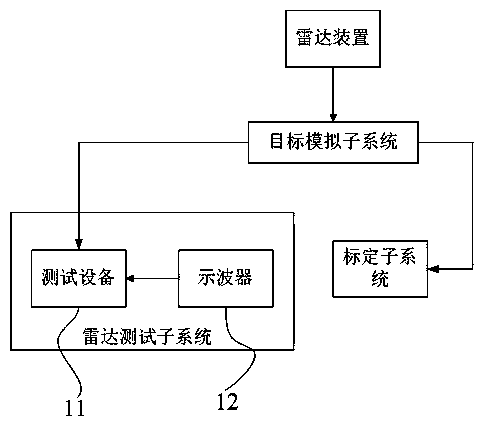
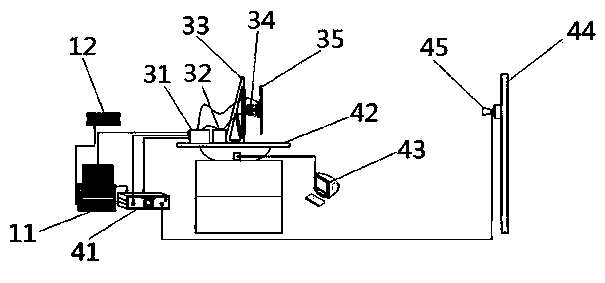
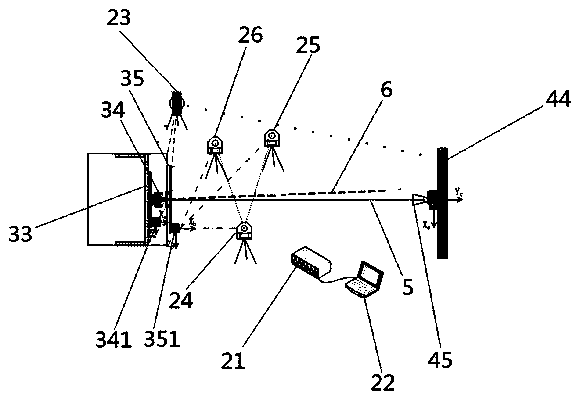
The invention discloses an electrical axis optical calibration system of a spaceborne microwave tracking-pointing radar and a calibration method of the electrical axis optical calibration system. The electrical axis optical calibration system comprises a radar testing subsystem, a calibration subsystem, a radar device and a target simulation subsystem. The target simulation subsystem comprises a target simulation source, a two-dimensional testing rotary table, a two-dimensional testing rotary table controller connected with the two-dimensional testing rotary table, a two-dimensional scanning frame and a target simulation horn antenna arranged on the two-dimensional scanning frame. The calibration method comprises the first step of calibrating the mounting precision of a radar antenna and a driving mechanism, the second step of calibrating the consistency of a radar electric axis and a radar antenna mechanical axis and the third step of correcting the radar according to a calibration result. According to the electrical axis optical calibration system of the spaceborne microwave tracking-pointing radar and the calibration method, high-precision calibration can be carried out on the radar in a compact field, the requirement of the radar for the temperature, the humidity and the cleanliness of used environment is met, the non-contact calibration of the spaceborne microwave tracking-pointing radar is achieved, the used measuring instruments are small in number and high in precision, the calculation of data can be automatically completed, and the high precision and the high reliability of the radar are guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
H face sectoral horn antenna including filter function
InactiveCN101179155AReduce volumeReduce manufacturing costWaveguide hornsWaveguide type devicesHorn antennaPhysics
The invention relates to an H-plane fan-shaped horn antenna including a filter function. The existing horn antenna has a large volume, cannot be integrated in a plane, and has high processing costs. In the invention, a metal layer is plated on both sides of a dielectric substrate, and the upper metal layer is etched for a microstrip line and a microstrip converter for power feeding. Through the upper metal layer, the dielectric substrate and the lower metal layer, a plurality of metallized through holes arranged in a circle are opened to form a substrate integrated waveguide and an H-plane fan-shaped horn. Four perturbation metallization through holes are opened on the central axis of the fan-shaped horn opening area of the H surface through the entire substrate, and are used for adjusting impedance matching and forming filtering functions. The new structure uses substrate-integrated waveguide technology to realize the function equivalent to the traditional metal H-plane fan-shaped horn antenna on a common dielectric substrate, and successfully integrates the filtering function of the traditional inductive metal pillar waveguide filter. The dual-function integrated module has a very compact volume, and the entire structure can be manufactured by a low-cost PCB process, and can be seamlessly integrated with the system.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Planar horn antenna for phase amplitude calibration
InactiveCN103022716AImprove Caliber EfficiencyHigh gainWaveguide hornsDielectric substrateAntenna gain
The invention relates to a planar horn antenna, in particular to a planar horn antenna for phase amplitude calibration. The antenna comprises a micro-strip feeder (1), a substrate integrated waveguide horn antenna (2) and embedded plated-through holes (3) which are integrated on a dielectric substrate (4), the micro-strip feeder (1) is connected with an antenna port (5) and a narrow horn antenna port (6), the horn antenna (2) is composed of a first metal plane (8), a second metal plane (10) and two rows of plated-through hole horn side walls (11), a middle plated-through hole array (12), a left plated-through hole array (16) and a right plated-through hole array (17) which are composed of the plated-through holes (3) form four dielectric-filled waveguides in the horn antenna (2), and one ends of the four dielectric-filled waveguides are close to the narrow antenna port (6) while the other ends of the four dielectric-filled waveguides are disposed on an antenna aperture surface (15). The antenna is capable of increasing antenna gain.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
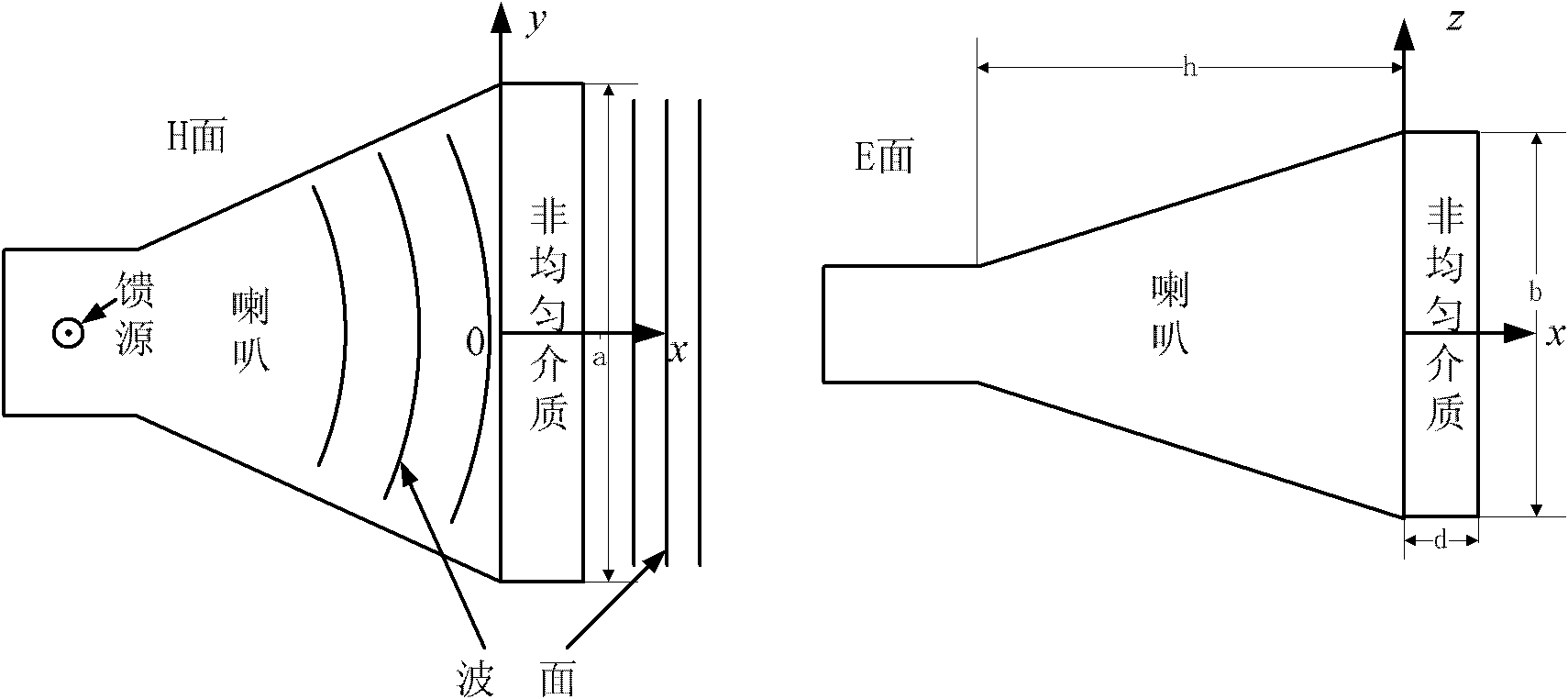
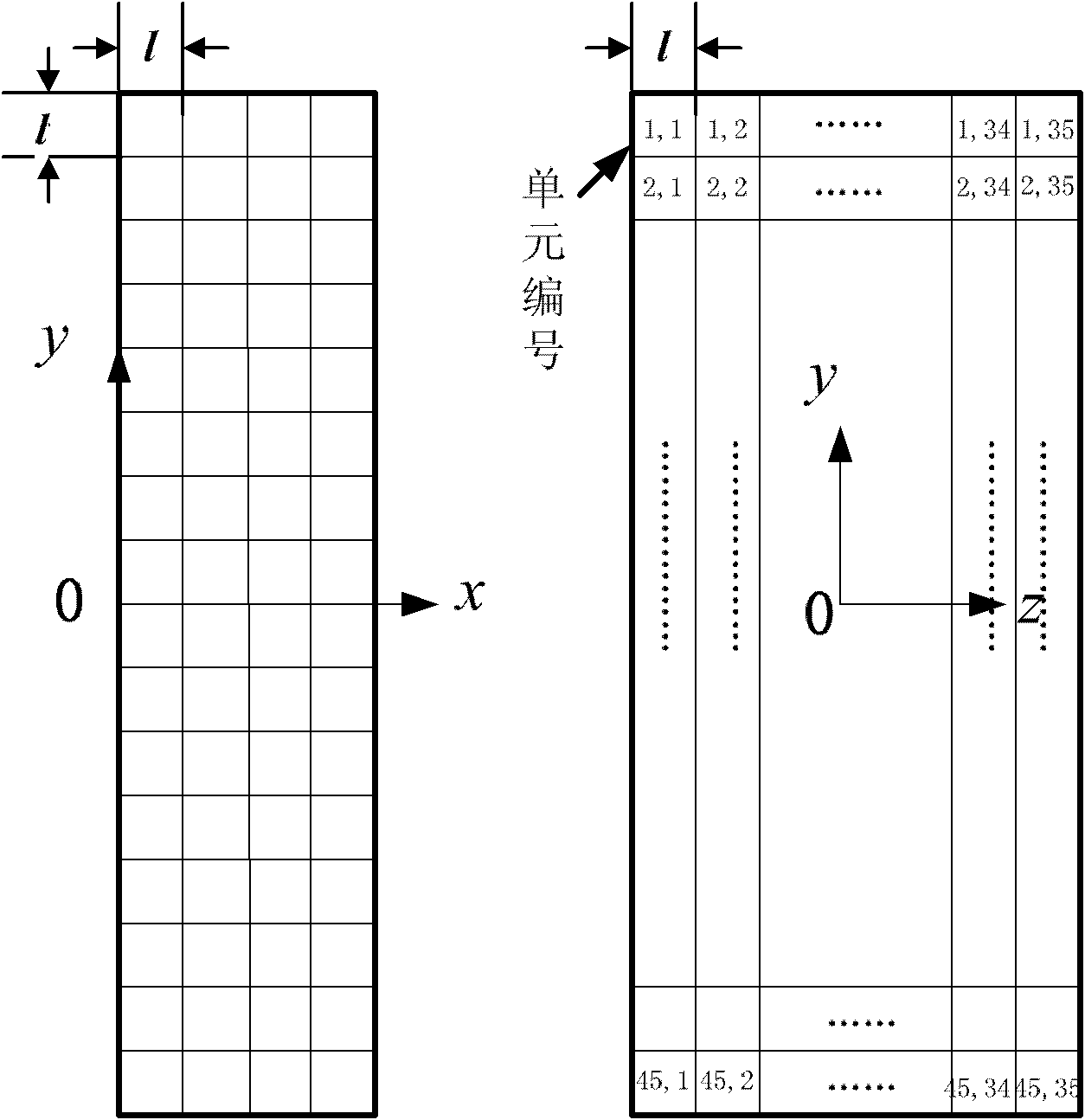
High-gain horn antenna based on inhomogeneous medium
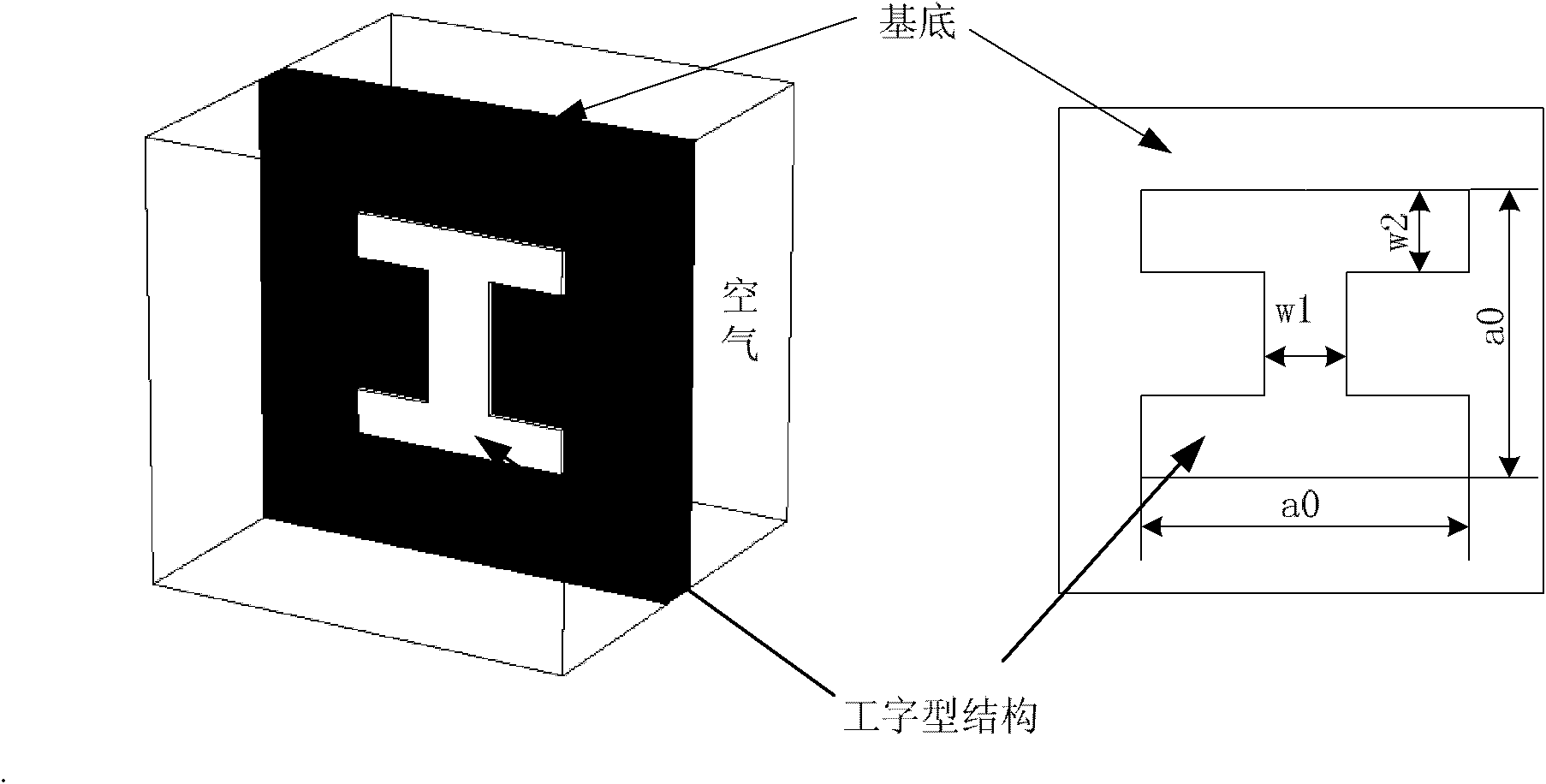
The invention discloses a high-gain horn antenna based on an inhomogeneous medium, which is made by the following steps of: (1) determining a central frequency f for the operation of the antenna; (2) designing the ordinary horn antenna operated in the central frequency according to a general designing method for the horn antenna, wherein the aperture of an H side of the antenna is a, the aperture of an E side is b, and the length of a horn is h; (3) determining a refractive index profile n (x, y) of the inhomogeneous medium placed on a mouth surface of the horn; and (4) building the inhomogeneous medium with refractive indexes distributed according to the n (x, y) by using a reverse H-shaped sub-wavelength artificial structural material, and evaluating the structural size of a reverse H-shaped sub-wavelength artificial structural material unit corresponding to each refractive index in a mode of emulation by finite element software.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
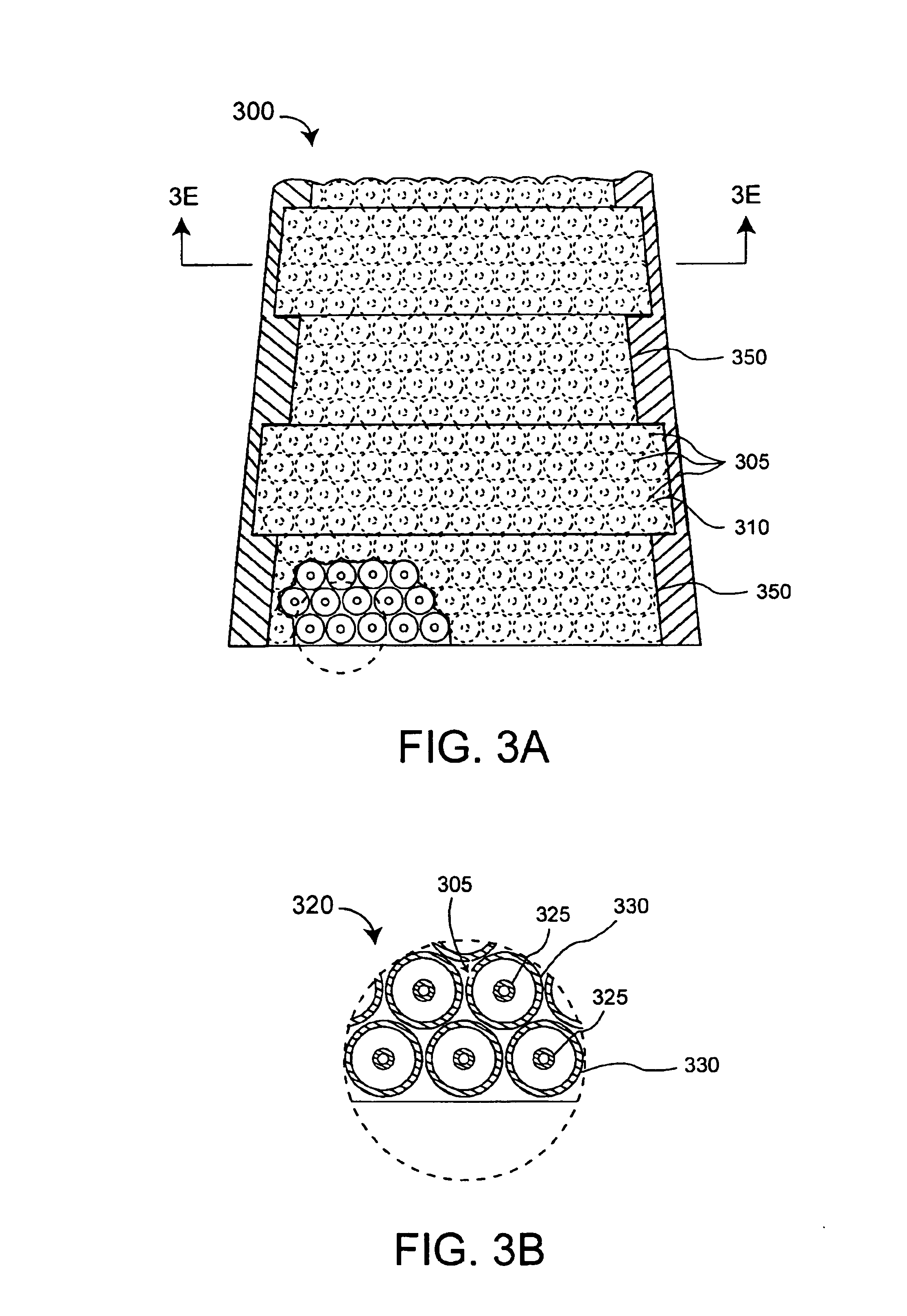
Multi-band horn antenna using corrugations having frequency selective surfaces
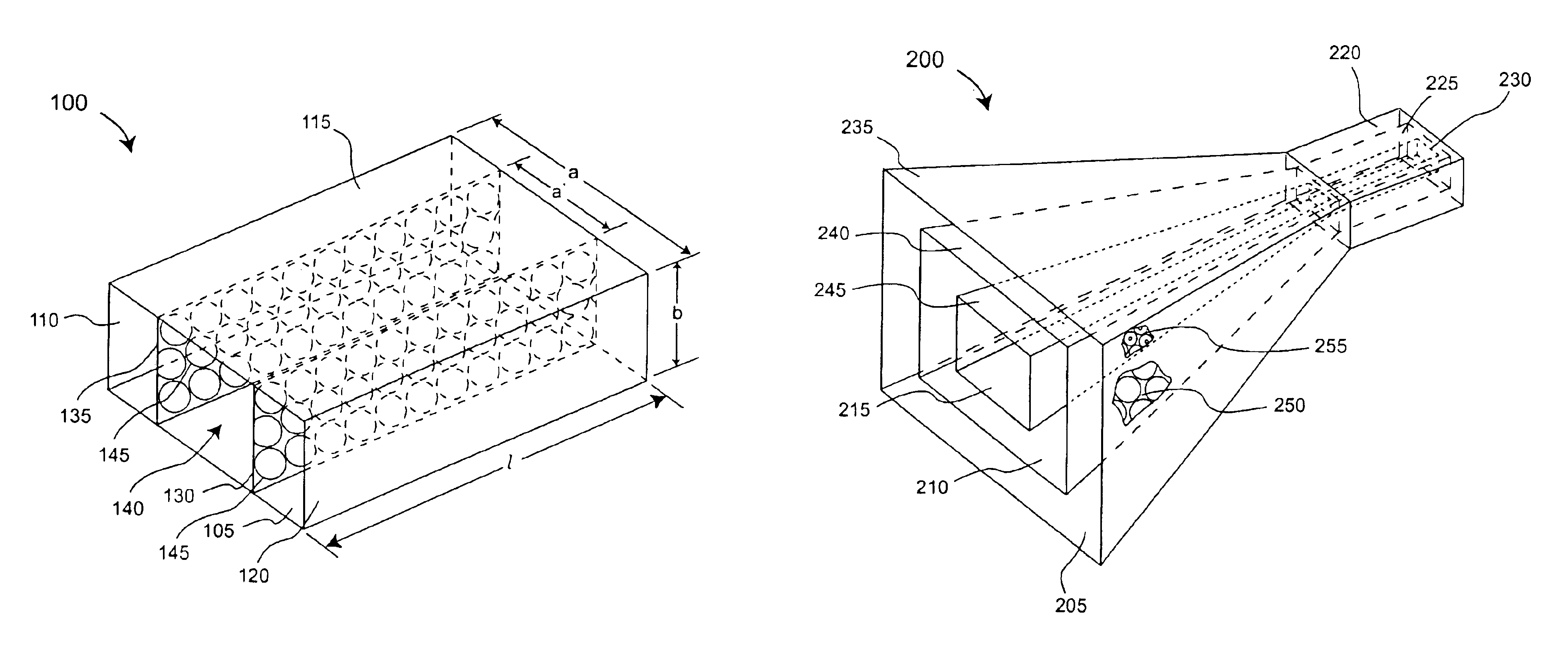
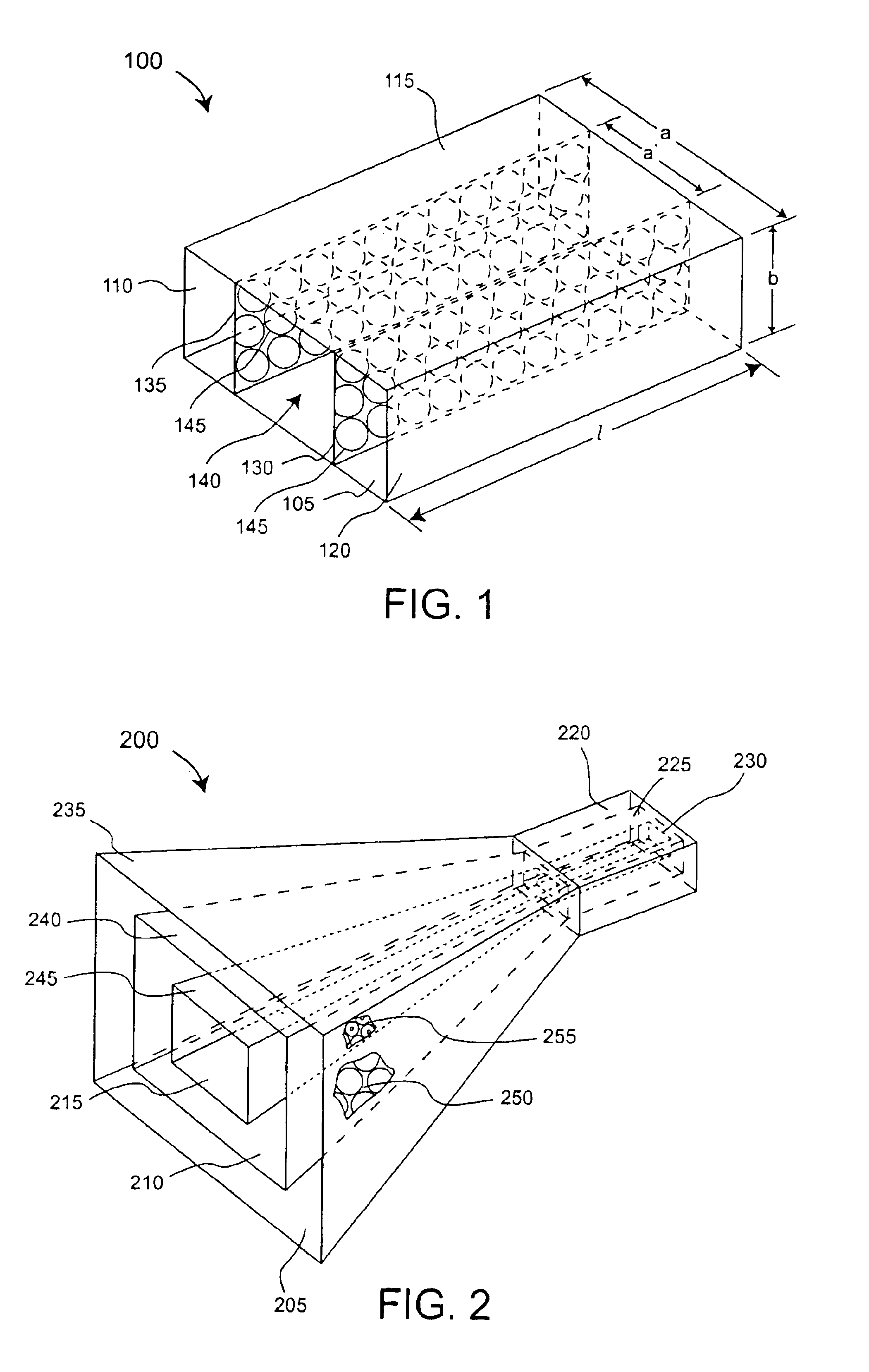
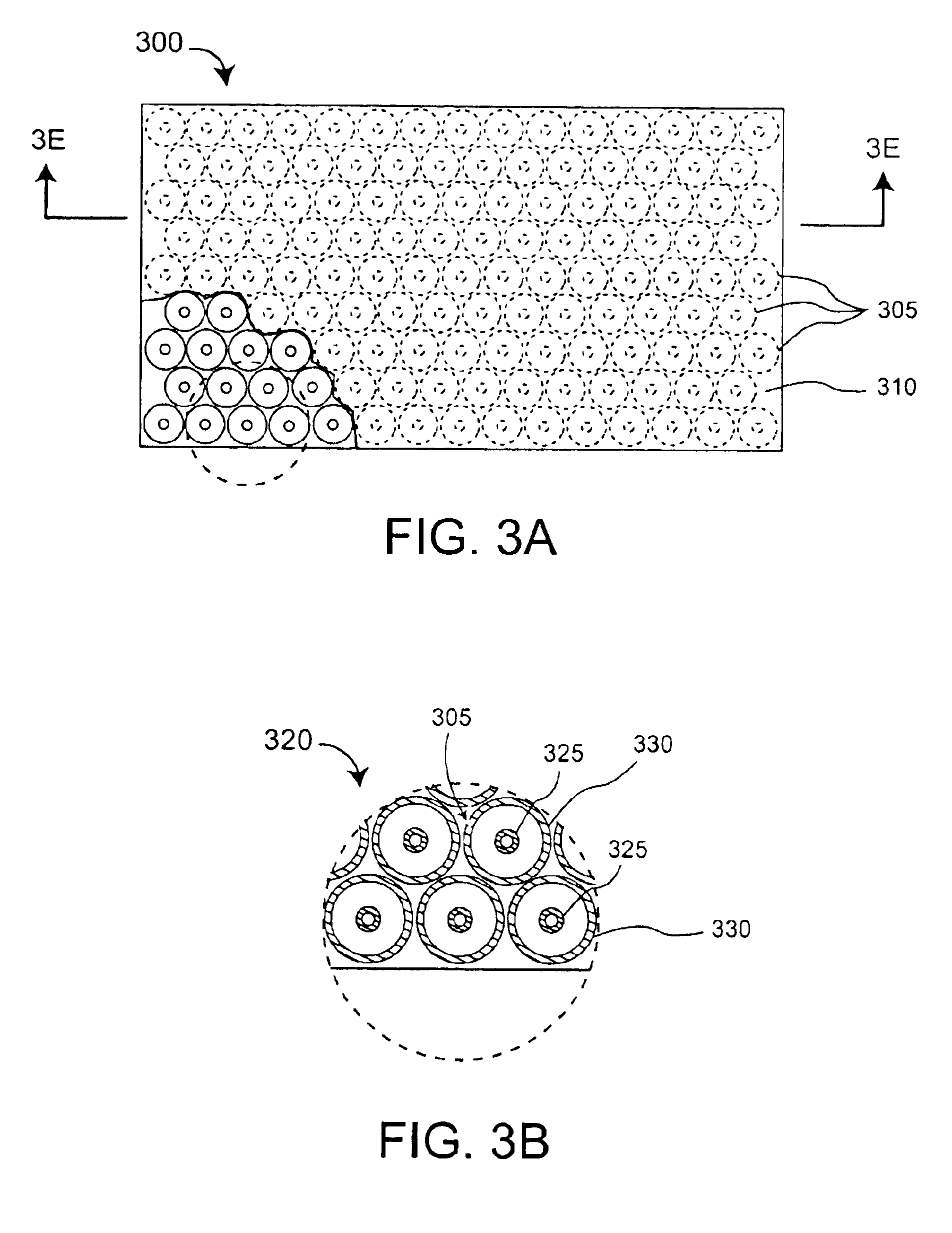
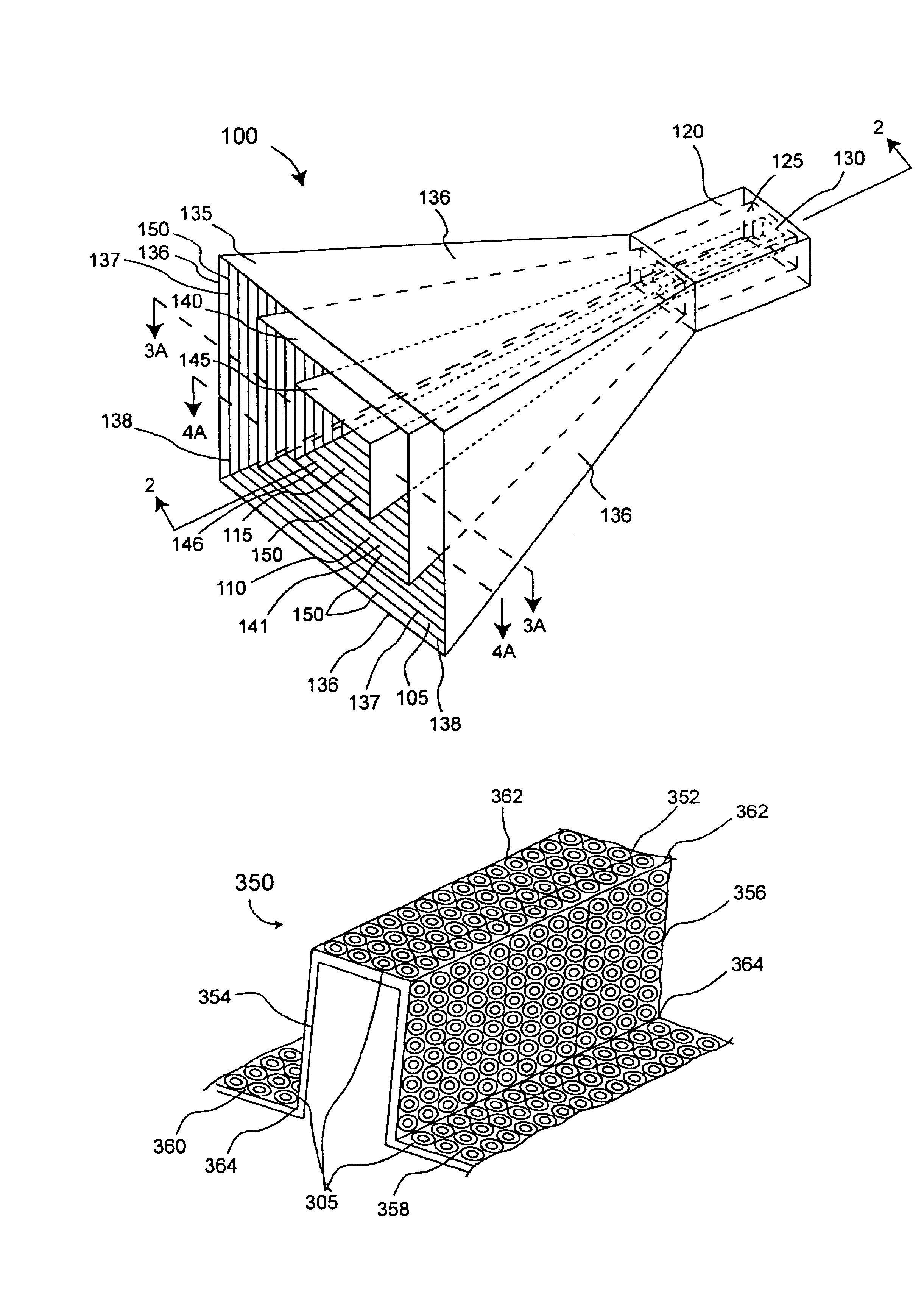
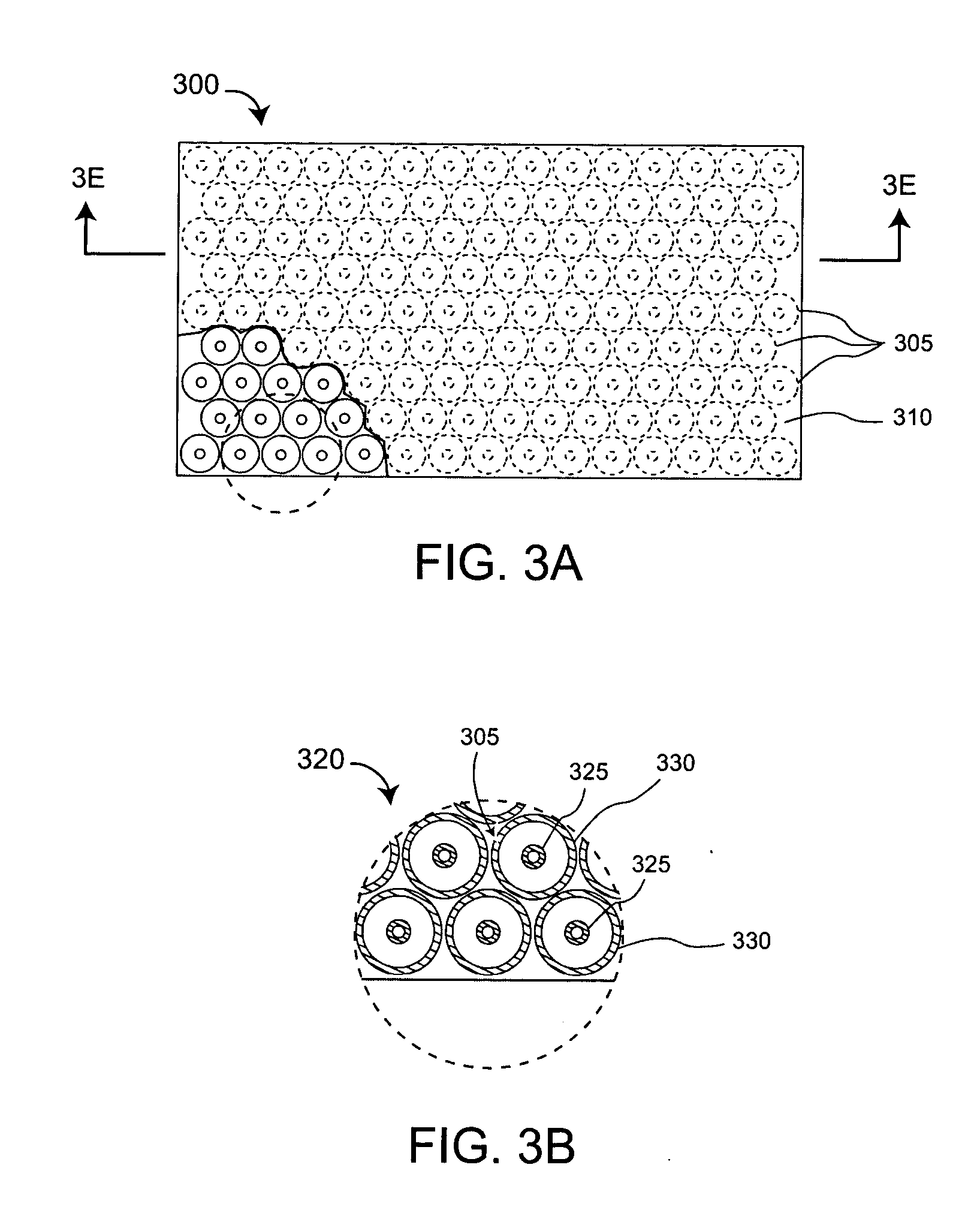
An antenna (100) for microwave radiation including a first horn (135) which includes a plurality of corrugations (150). At least one of the corrugations (150) is formed of a frequency selective surface (FSS) (138). The FSS has a plurality of FSS elements (305) coupled to at least one substrate (310). The substrate (310) can define a first propagation medium such that an RF signal having a first wavelength in the first propagation medium can pass through the FSS (300). The FSS (300) is coupled to a second propagation medium such that in the second propagation medium the RF signal has a second wavelength which is at least twice as long as a physical distance between centers of adjacent FSS elements (305).
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Horn antenna
The present invention relate to a horn antenna at a radar level gauge for determination of a level of a surface of a medium stored in a tank and a method of making a horn antenna which is mechanically constituted such that the horn antenna will withstand the environment of the tank interior. The antenna comprises a first conductive housing (7) having a wave guide port (8), which is connectable to a wave guide, a first aperture (10), which is separated from the wave guide port (8) and a fist divergent section between the wave guide port (8) and the first aperture (10). A dielectric body (11) is arranged inside and essentially filling the first conductive housing (7), which body (11) displays a free end (12) in the area of the first aperture (10). The horn antenna is characterized in that around the first aperture (10) is arranged a locking device (13), which is arranged to fix the dielectric body (11) in the first housing (7) and that in the area of the locking device (13) is arranged at least one flexible sealing element (16) between the dielectric body (11) and the first cover (7).
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Back-fed millimeter wave broadband double ridged horn antenna
The invention provides a back-fed millimeter wave broadband double ridged horn antenna, belongs to the technical field of microwave and millimeter wave signal processing, and relates to a millimeter wave broadband horn antenna. The back-fed millimeter wave broadband double ridged horn antenna comprises a coaxial line excitation part, a ridge waveguide part and a double ridged horn part, wherein the coaxial line excitation part is formed by orderly connecting a coaxial line, a mode converting part and an impedance matching part; the mode converting part is formed by connecting a shielding panel line provided with a ridge and a coaxial line on the ridge side; the impedance matching part is stepped gradient double ridged waveguide; the ridge waveguide part is standard double ridged waveguide; and two ridges of the double ridged horn part are extended from two ridges of the ridge waveguide part to a mouth of a horn. The antenna adopts a back-fed structure, electromagnetic waves are fed in from the back of the ridge waveguide parallel to the ridge waveguide transmission direction, the coaxial line and the waveguide are positioned in the same axes, and a small voltage standing wave ratio can be obtained; and through mode conversion and impedance matching, the antenna can have satisfactory characteristics in a broadband range between 18 and 40GHz, and is characterized by wide frequency band, compact structure and good performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-band horn antenna using frequency selective surfaces
InactiveUS20050007289A1Improve permeabilityIncreasing permittivityWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsMulti bandHorn antenna
A waveguide (100) including at least one outer surface (105, 110, 115, 120) defining a waveguide cavity (140) and at least one inner surface (130, 135) positioned within the waveguide cavity (140). The inner surface (130, 135) includes a frequency selective surface (FSS) having a plurality of FSS elements (145) coupled to at least one substrate. The substrate defines a first propagation medium such that an RF signal having a first wavelength in the first propagation medium can pass through the FSS (130, 135). The FSS (130, 135) is coupled to a second propagation medium such that in the second propagation medium the RF signal has a second wavelength which is at least twice as long as a physical distance between centers of adjacent FSS elements (145). The second wavelength can be different than the first wavelength.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
High-gain layered lens antenna based on optical transformation theory
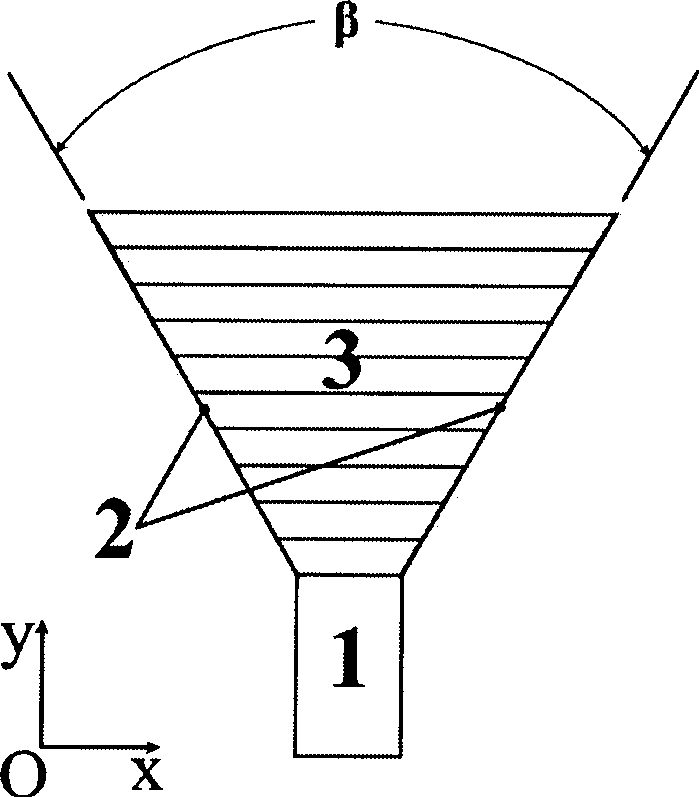
The invention relates to a high-gain layered lens antenna based on optical transform theory, comprising a rectangular feeding waveguide; a metallic conductor horn is connected with the rectangular feeding waveguide and internally embedded with a layered lens; the layered lens is filled with horns and each layer of the lens is parallel to the aperture surface of the horn; the layered lens is composed of non-uniform and anisotropic artificial electromagnetic material, the direction of the electric field is vertical to the paper surface and the k layer meets the following conditions: Mux is equal to Epsilonz which is equal to 1, Muy is equal to 1 / Alphak<2> and Alphak is equal to 1 plus (k minus Deltak)(b-a)(na), wherein, Mux represents the magnetic permeability of the k layer of the lens in the x direction, Muy> is the magnetic permeability of the k layer of the lens in the y direction, Epsilonz is dielectric constant of the k layer of the lens in the z direction which is vertical to the paper surface, Alphak is an intermediate variable related to the k layer of the lens, n is the total number of the layers of the lens and the value range thereof is a certain integer between 10 to 50, k is the layer of the lens and the value thereof is between 1 and the total layers n, Deltak is a certain set constant between 0 to 1, a is the width of the feeding waveguide, and b is the aperture width of the horn antenna. The inclined angle Beta of the horn is between 60 DEG C and 150 DEG C. The invention has simple shape and high gain.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
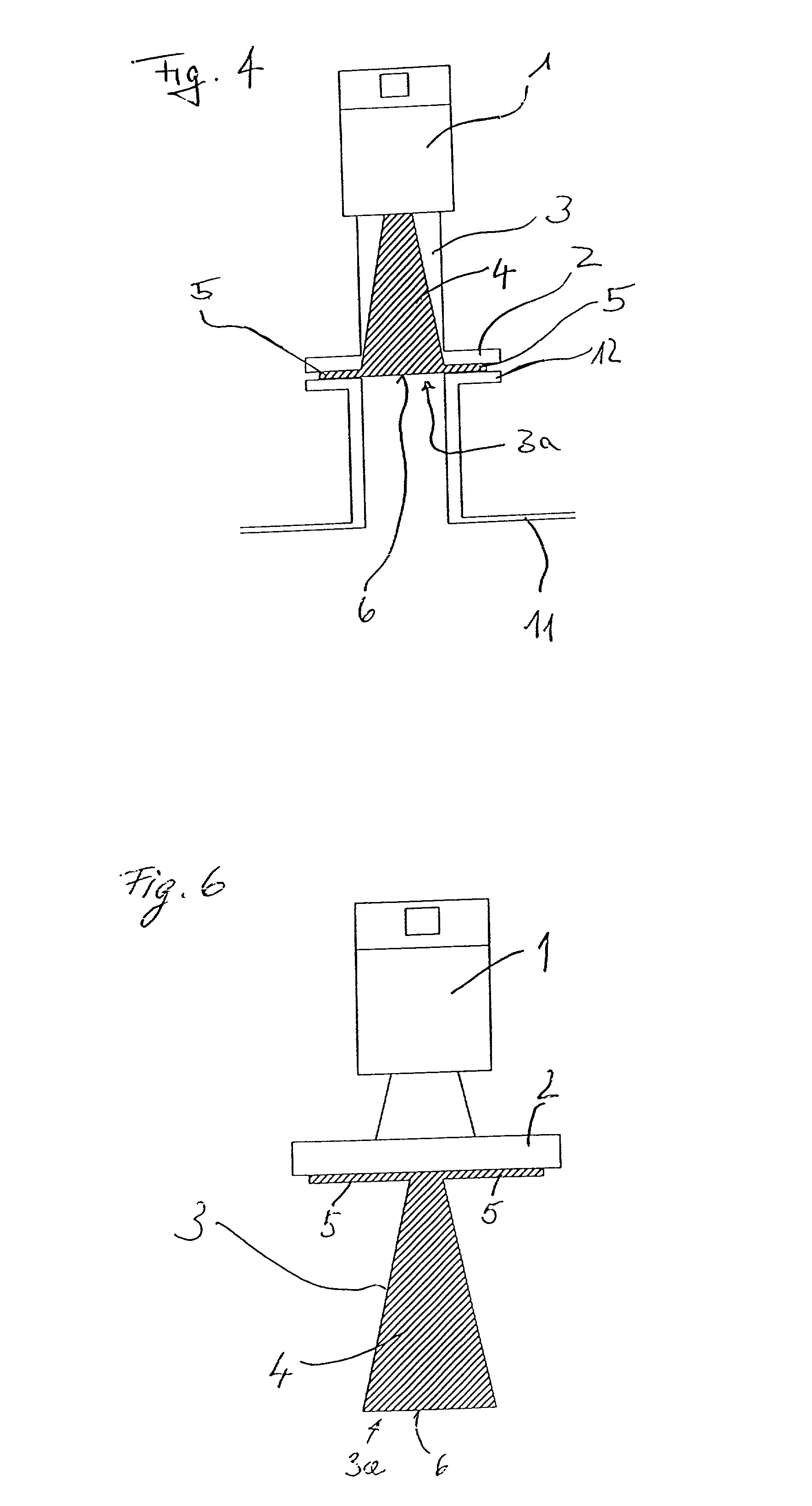
Horn antenna for a radar device
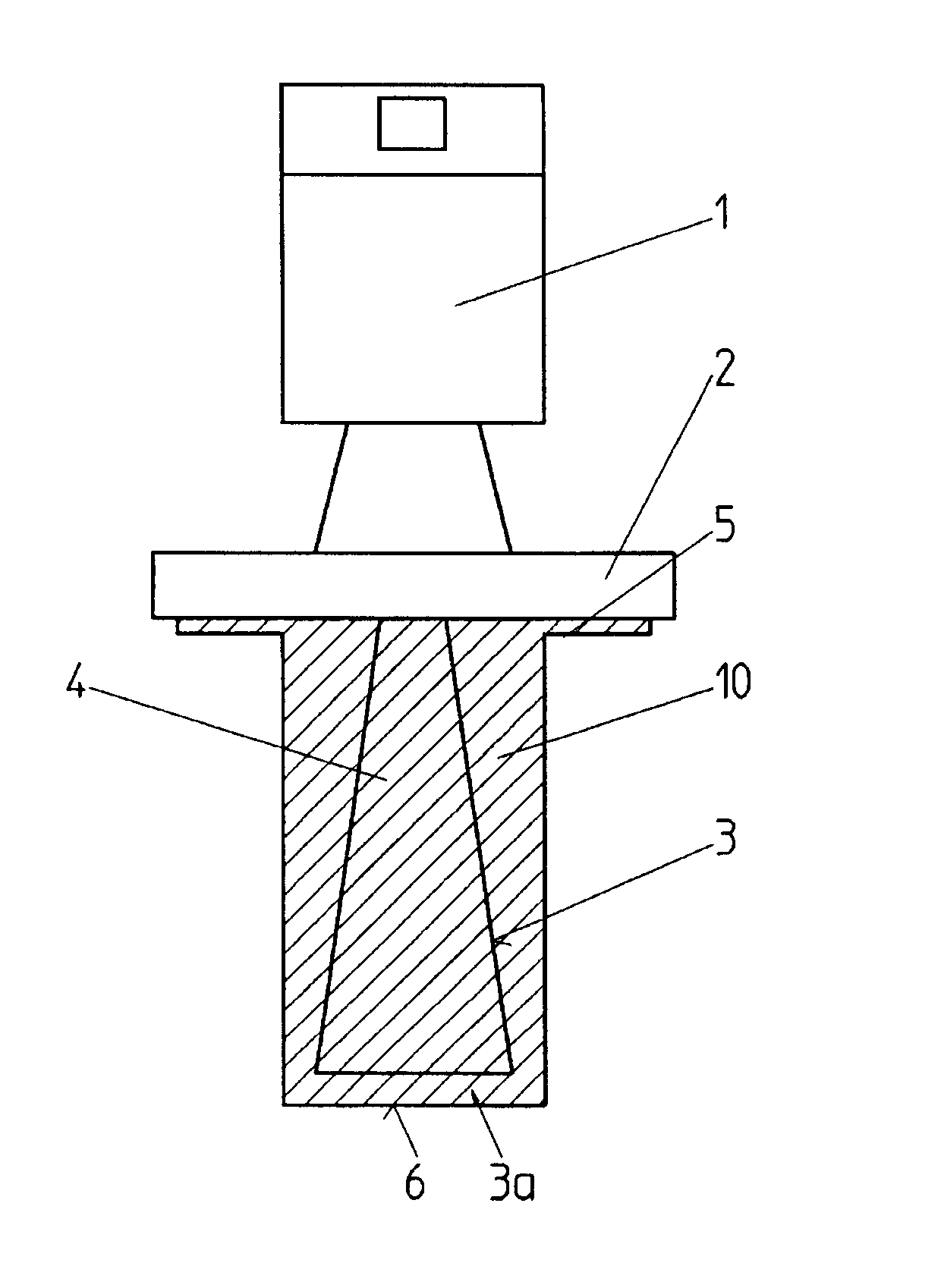
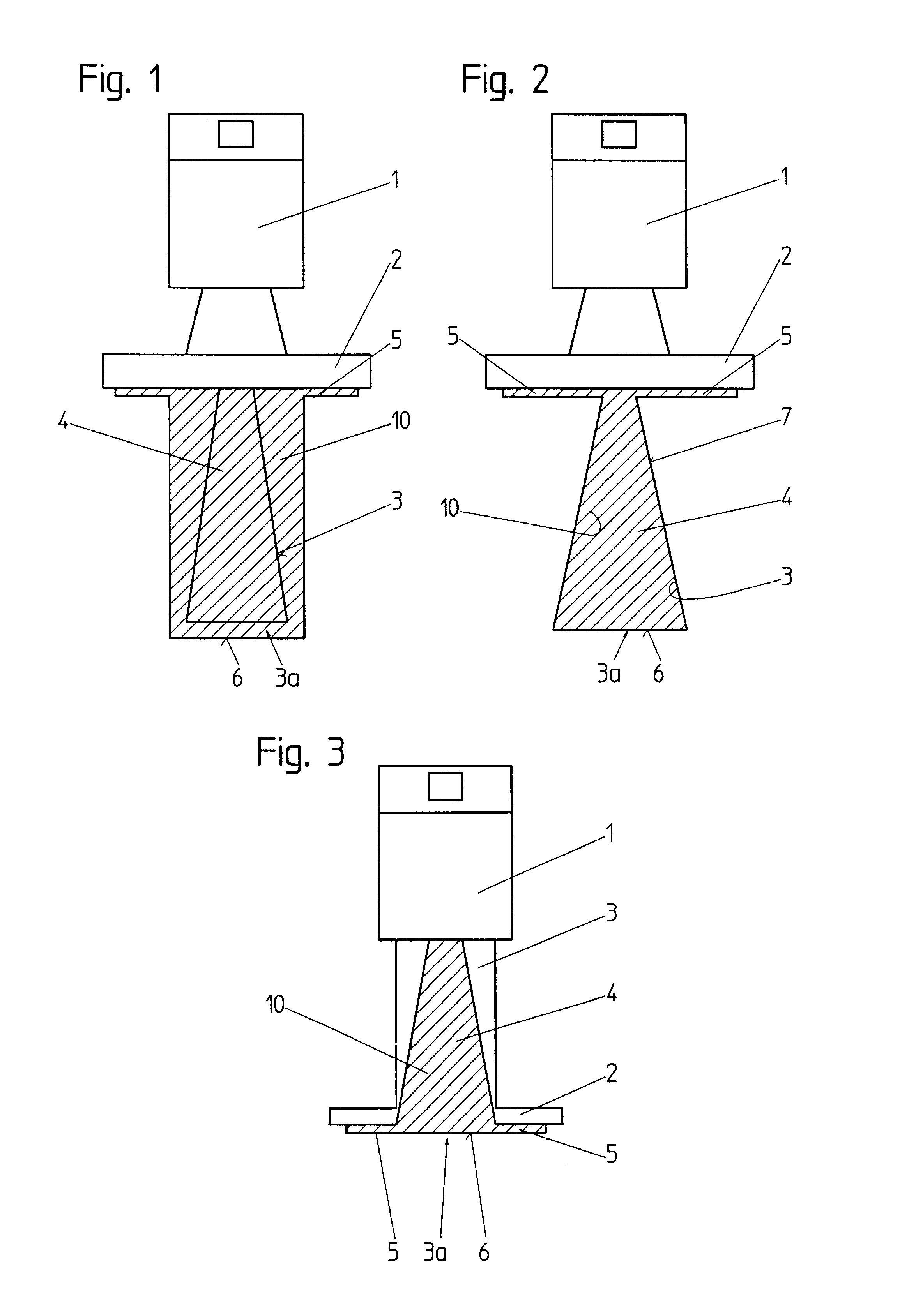
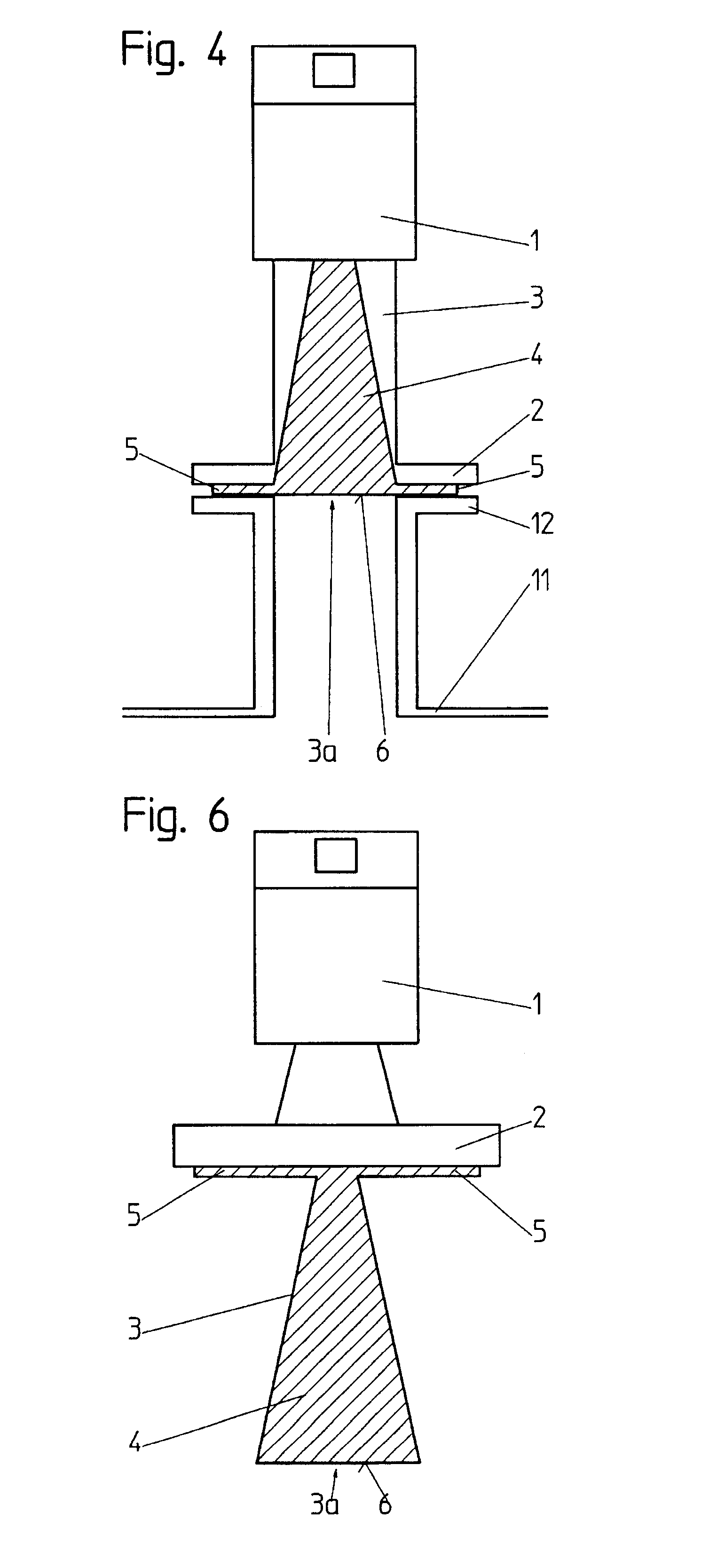
The invention relates to a horn antenna for a radar-filling level measuring device having an antenna envelope (3) that comprises a flaring hollow space (4) of the antenna, in which a filling (10) is present at least in part filling up said hollow space (4) of the antenna, and having an encasing (10, 20) of a dielectric material and enclosing the outside of the antenna envelope (3) and closing the opening (3a) of the hollow space of the hollow space (4) of the antenna.
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
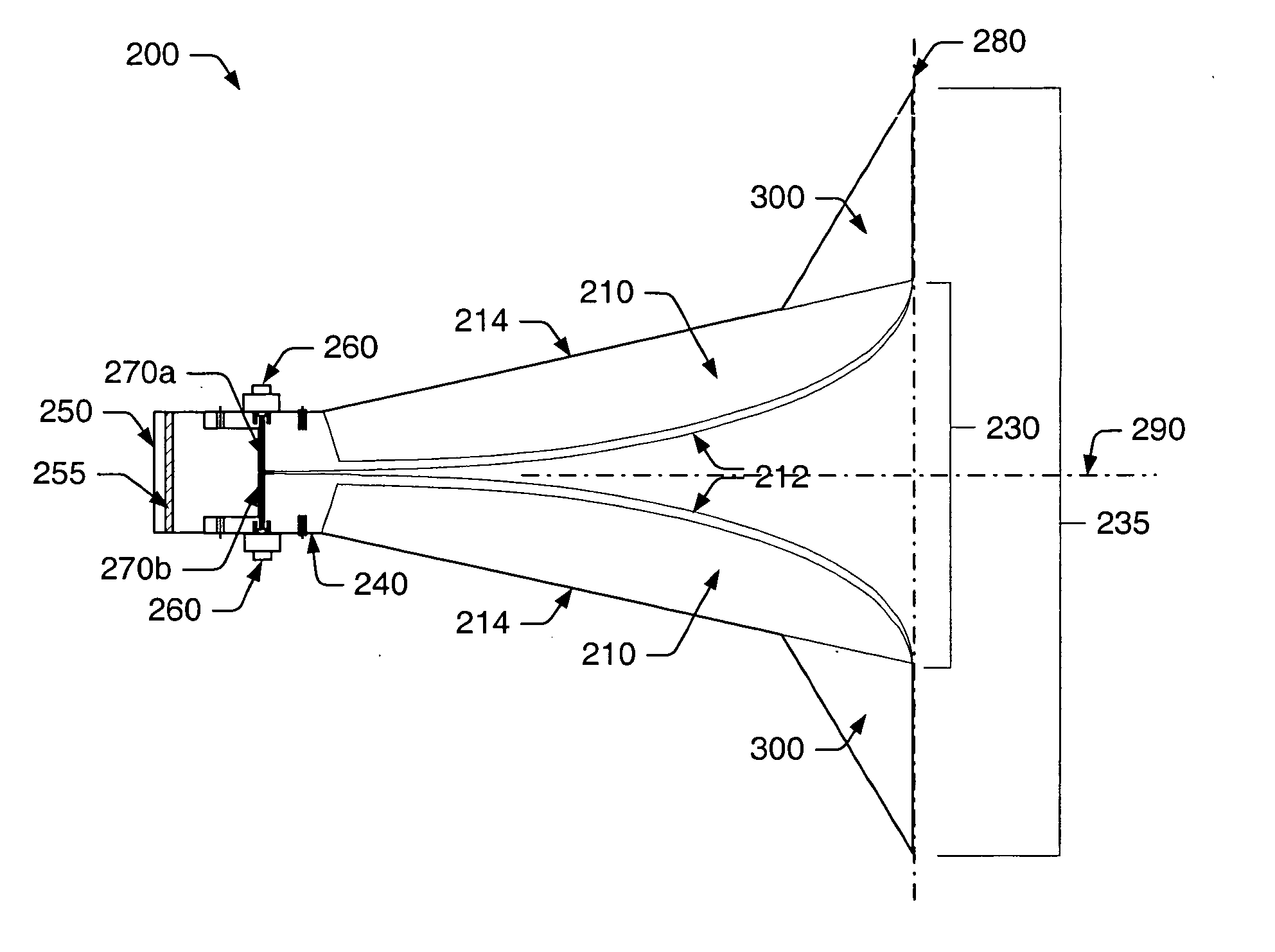
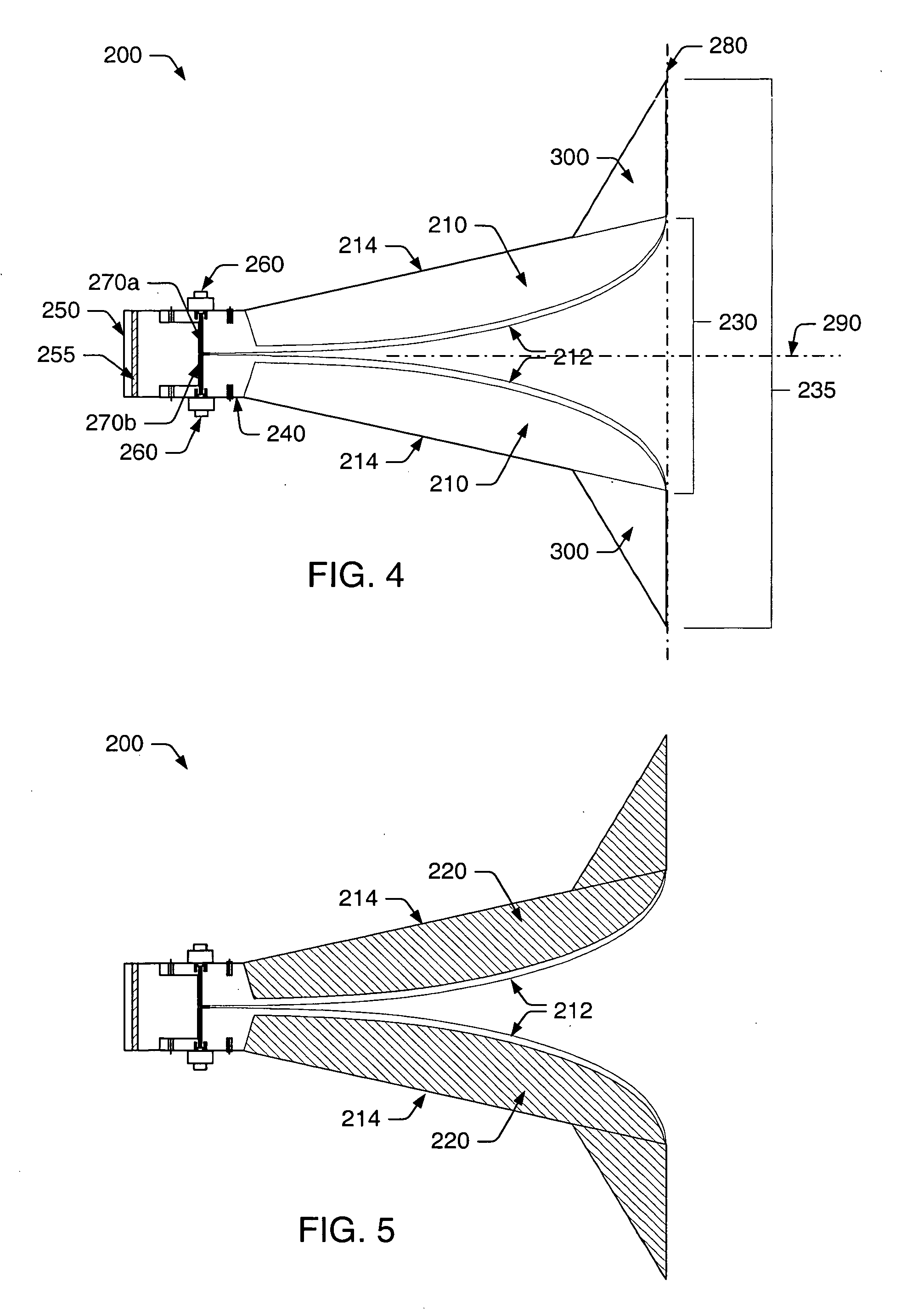
Dual- and quad-ridged horn antenna with improved antenna pattern characteristics
ActiveUS20050231436A1Good radiation characteristicsImproving impedanceWaveguide hornsFiling appliancesBroadbandHorn antenna
As provided herein, a dual- or quad-ridged broadband horn antenna may include a pair of conductive antenna elements arranged opposite one another for guiding an electromagnetic wave in a longitudinal direction through the horn antenna. In some cases, the pair of conductive antenna elements may include substantially convex inner surfaces and appropriately shaped outer surfaces. The convex inner surfaces may generally function to direct or guide the radiated energy without disturbing the intended radiation pattern. To maintain the intended radiation pattern, the broadband horn antenna may also include a pair of tapered extension elements, each coupled to an outer surface of a different one of the antenna elements at one end thereof. In some cases, a magnetic material may be arranged upon at least a portion of the antenna elements to restrict surface currents to flowing along the inner surfaces only. In some cases, longitudinal grooves may be formed within the inner surfaces to restrict surface currents from flowing in a direction transverse to the longitudinal direction.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com