Patents
Literature
130 results about "Hollow waveguide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
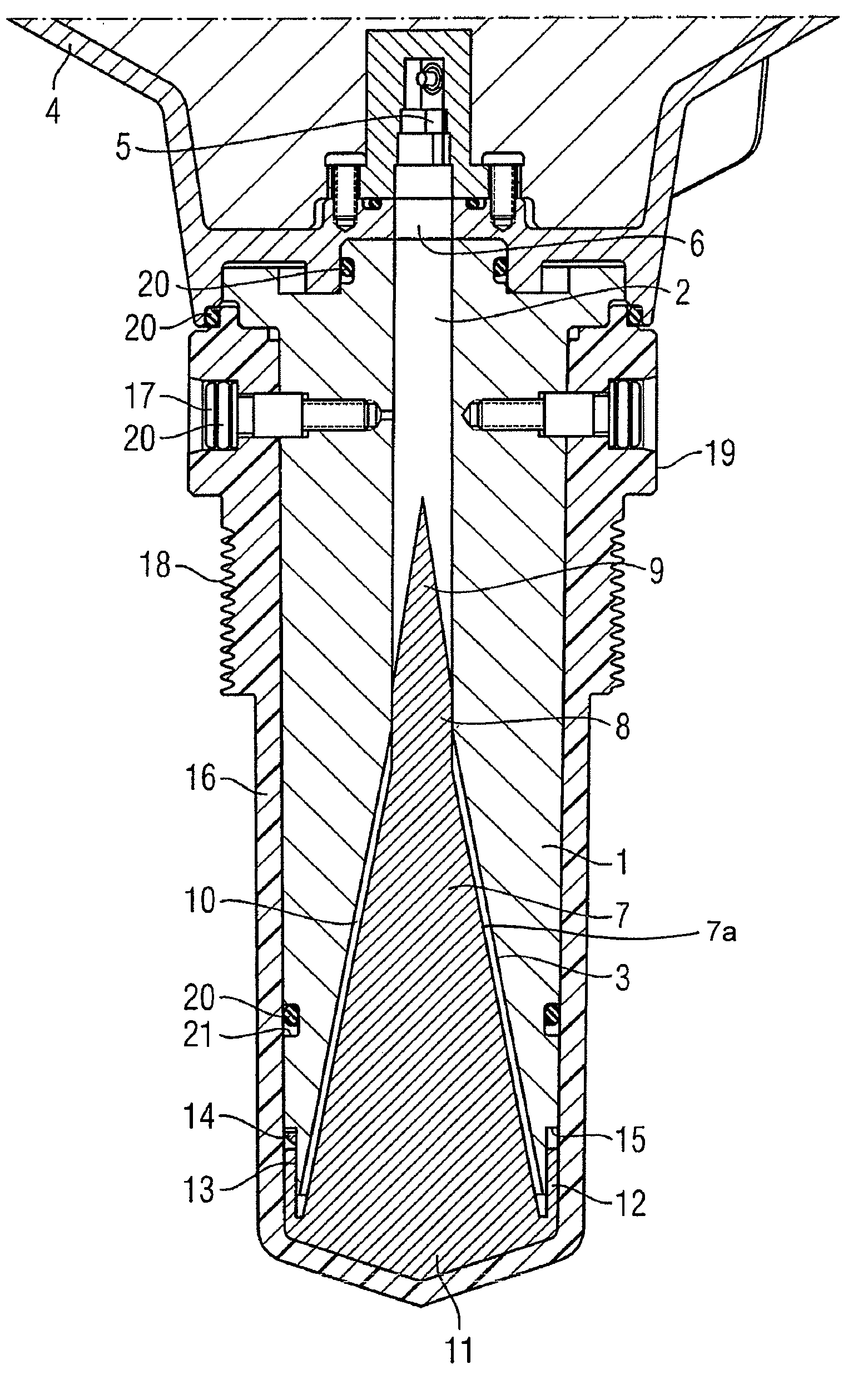
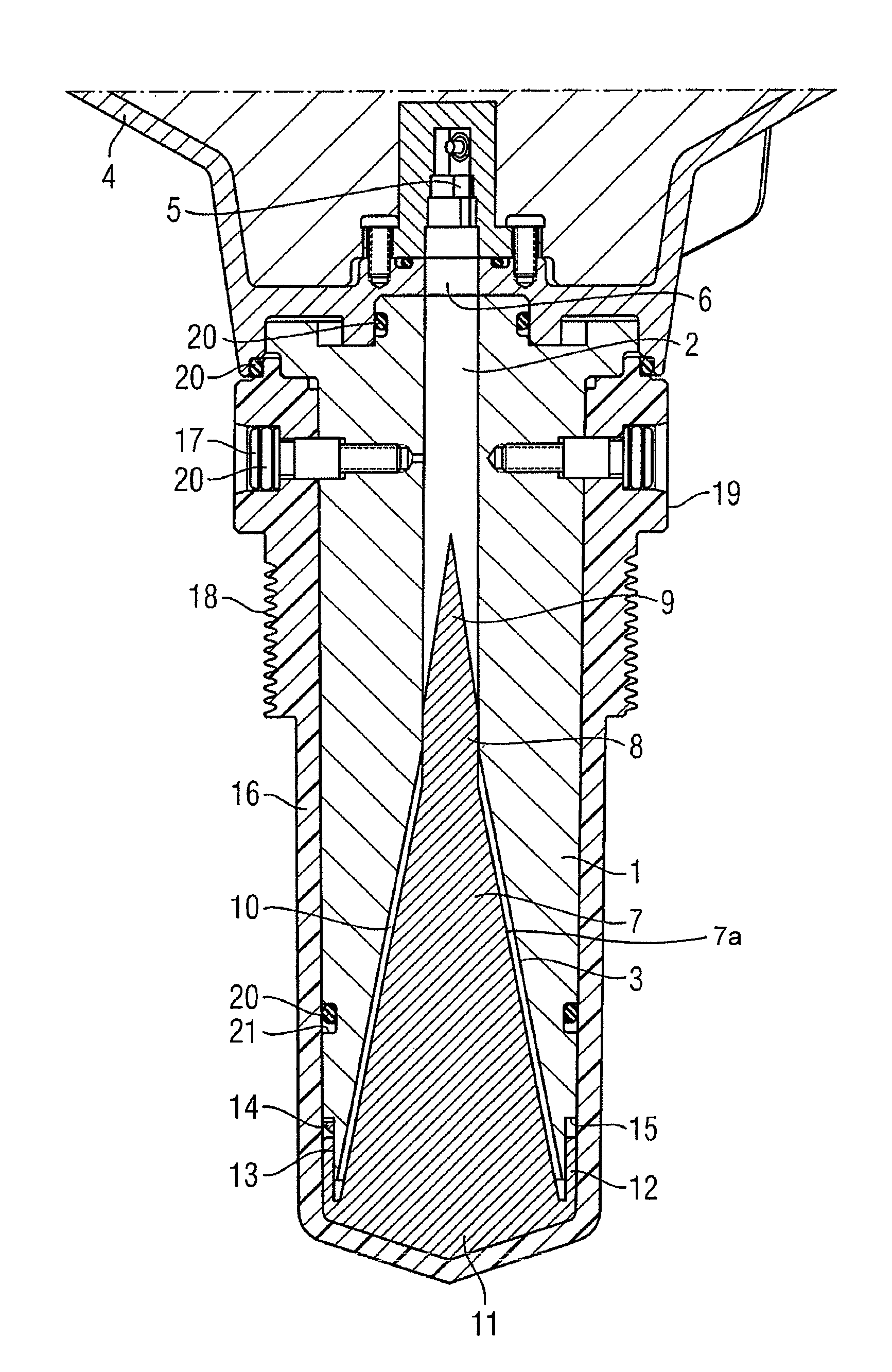
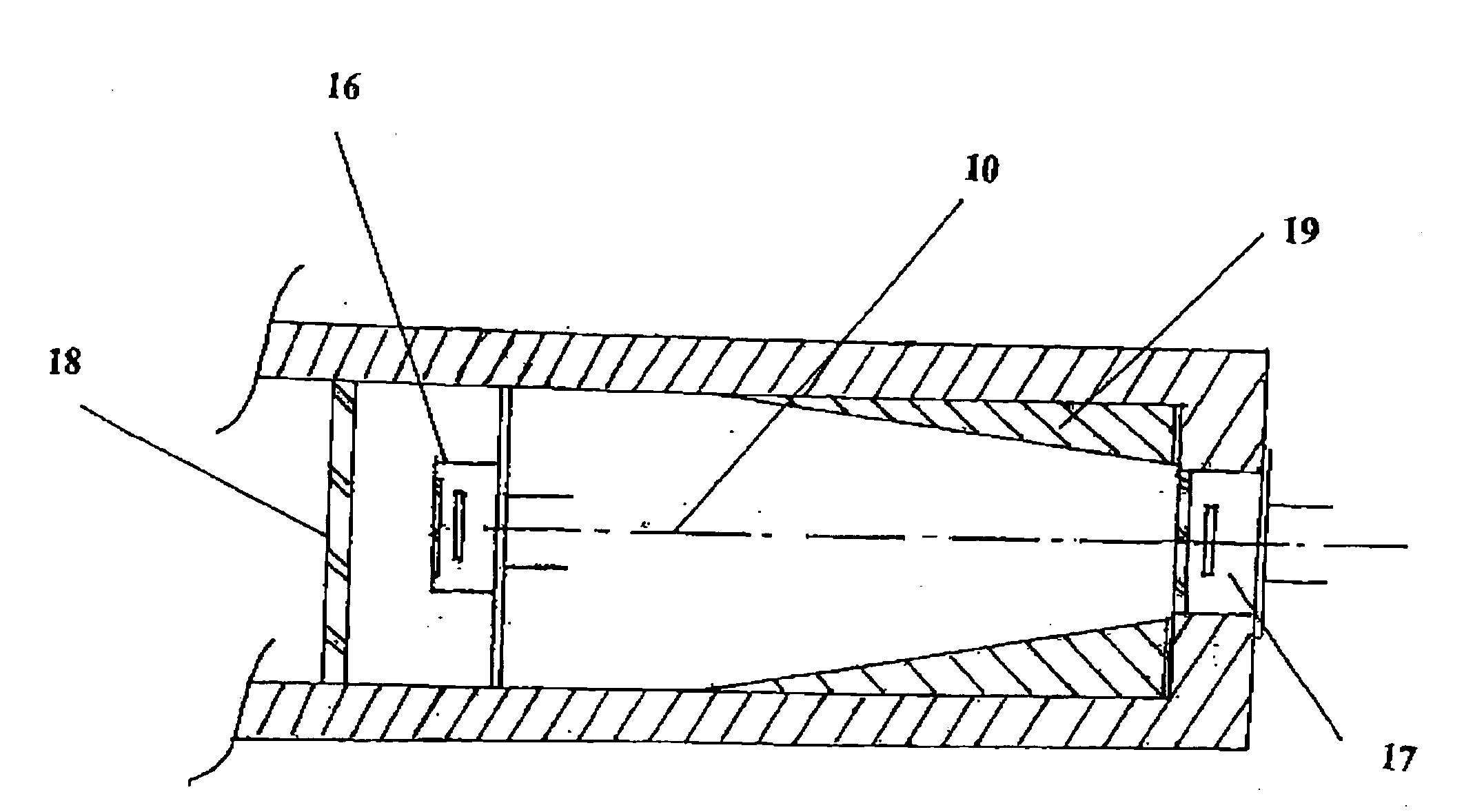
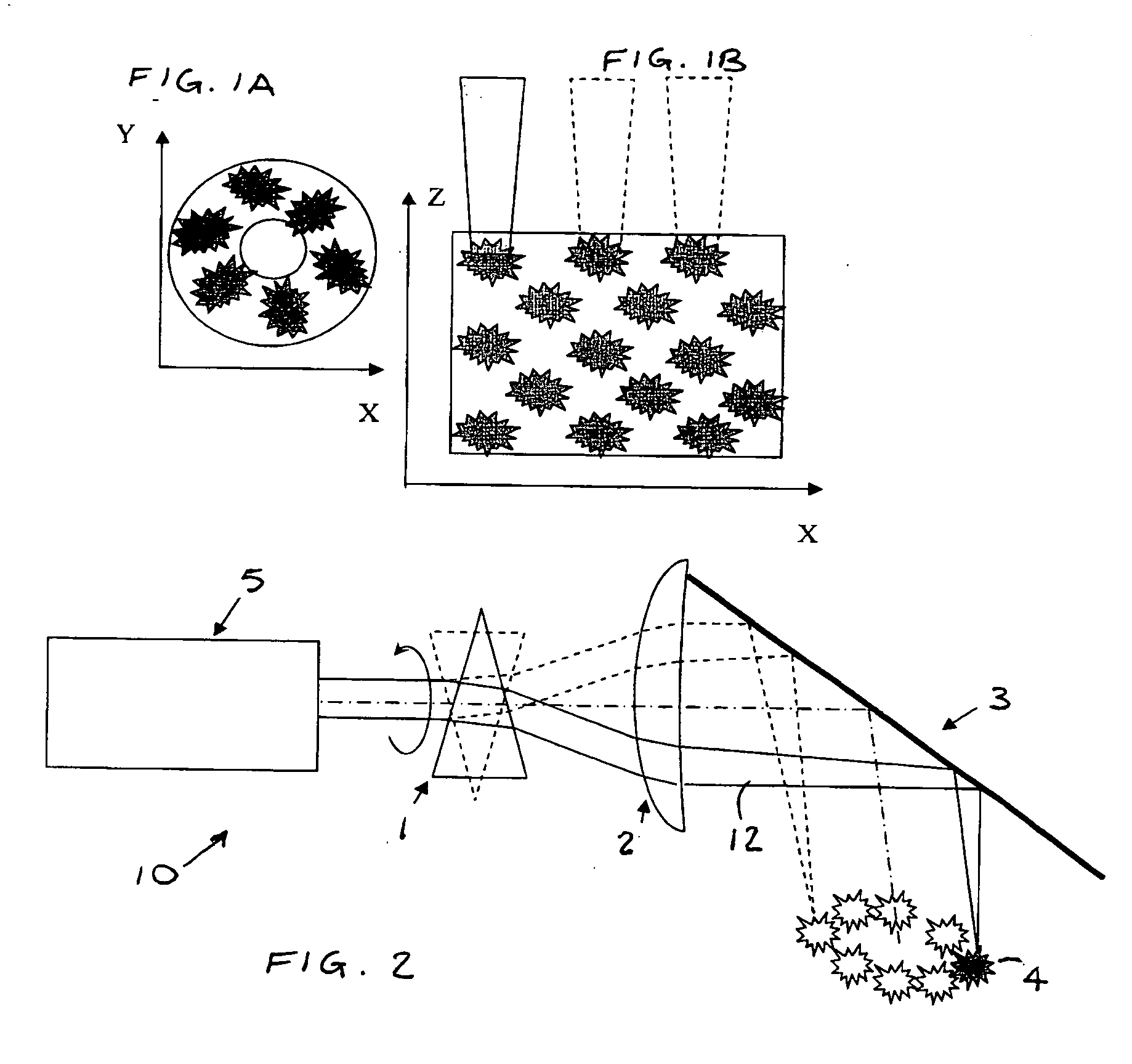
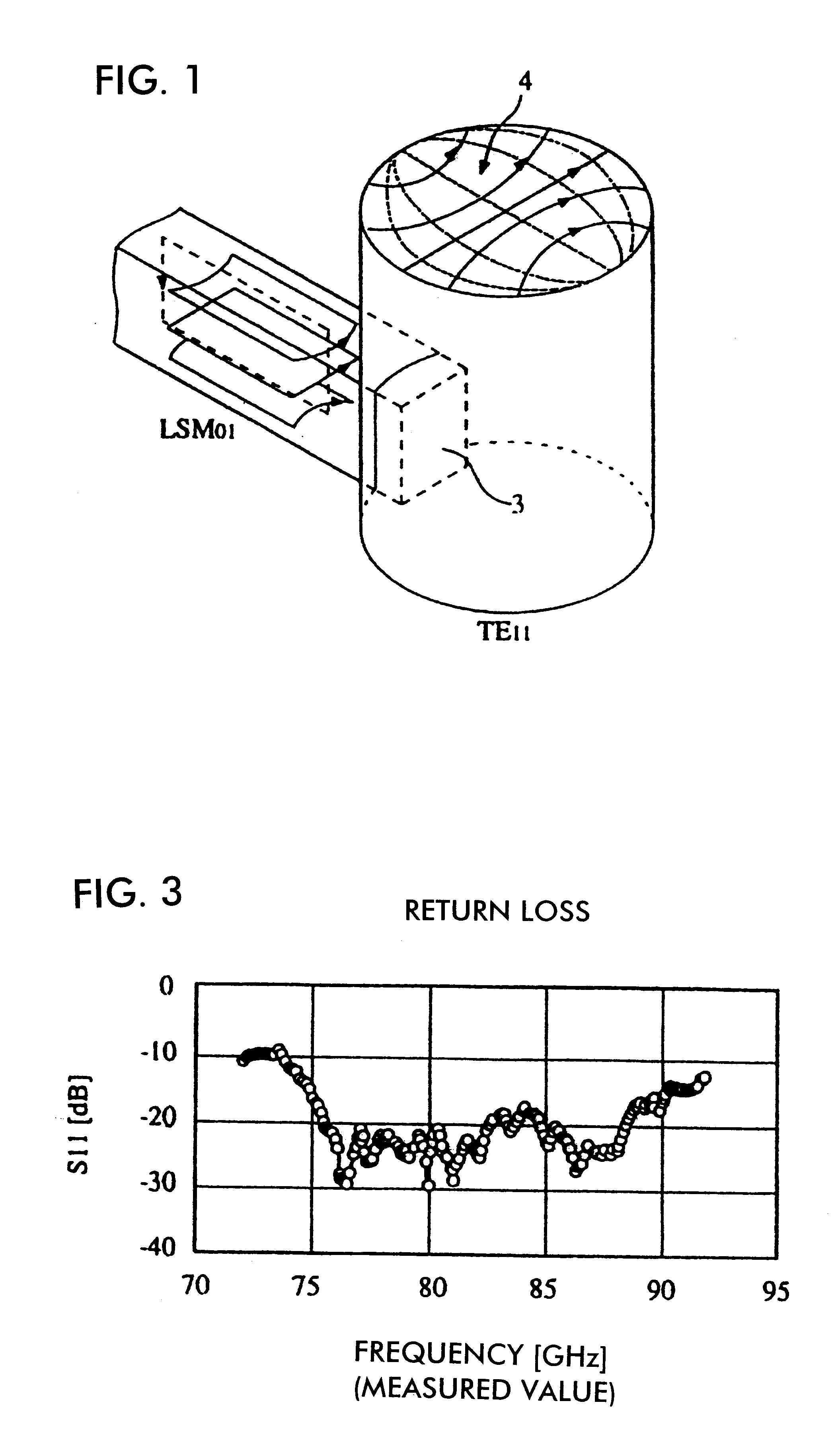
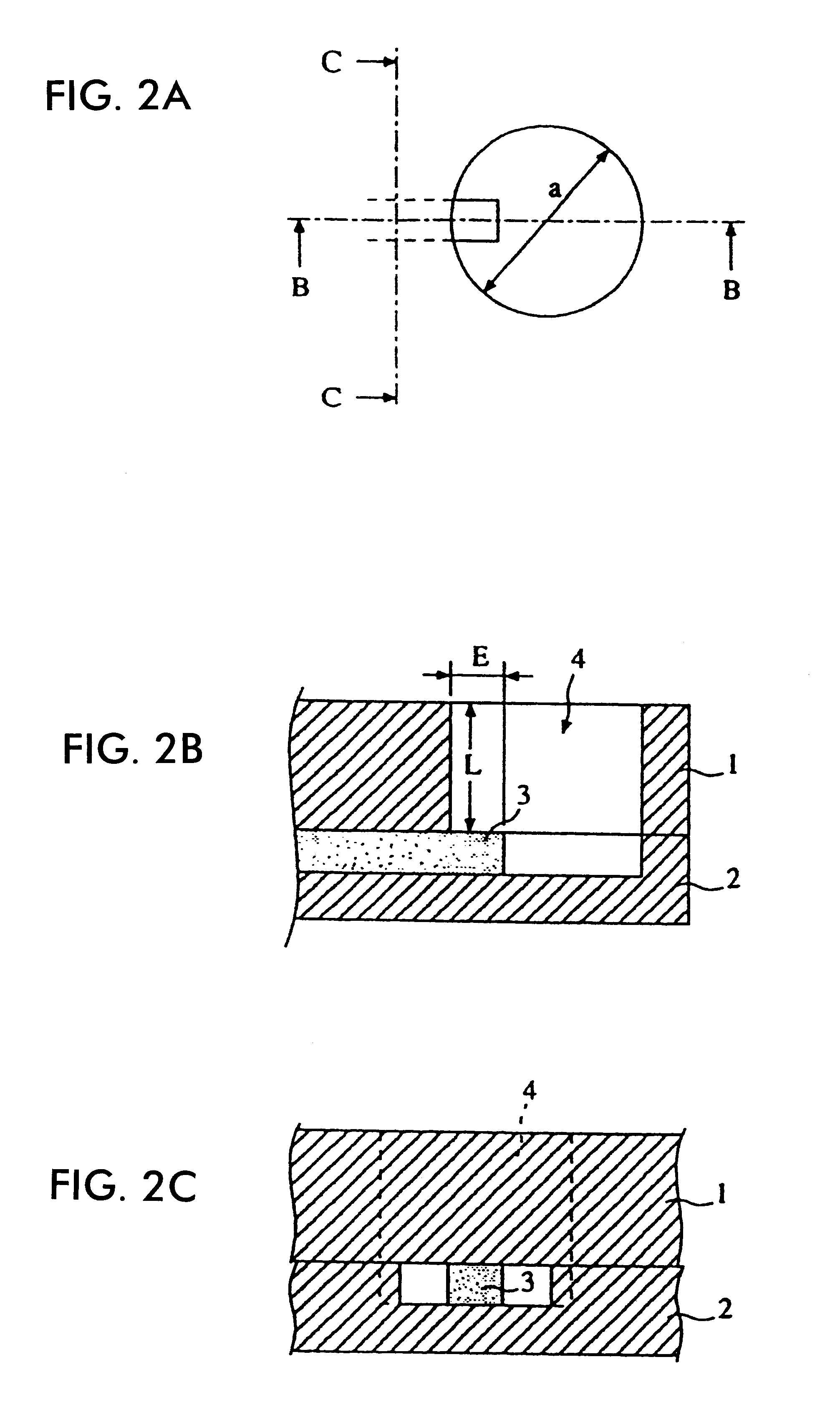
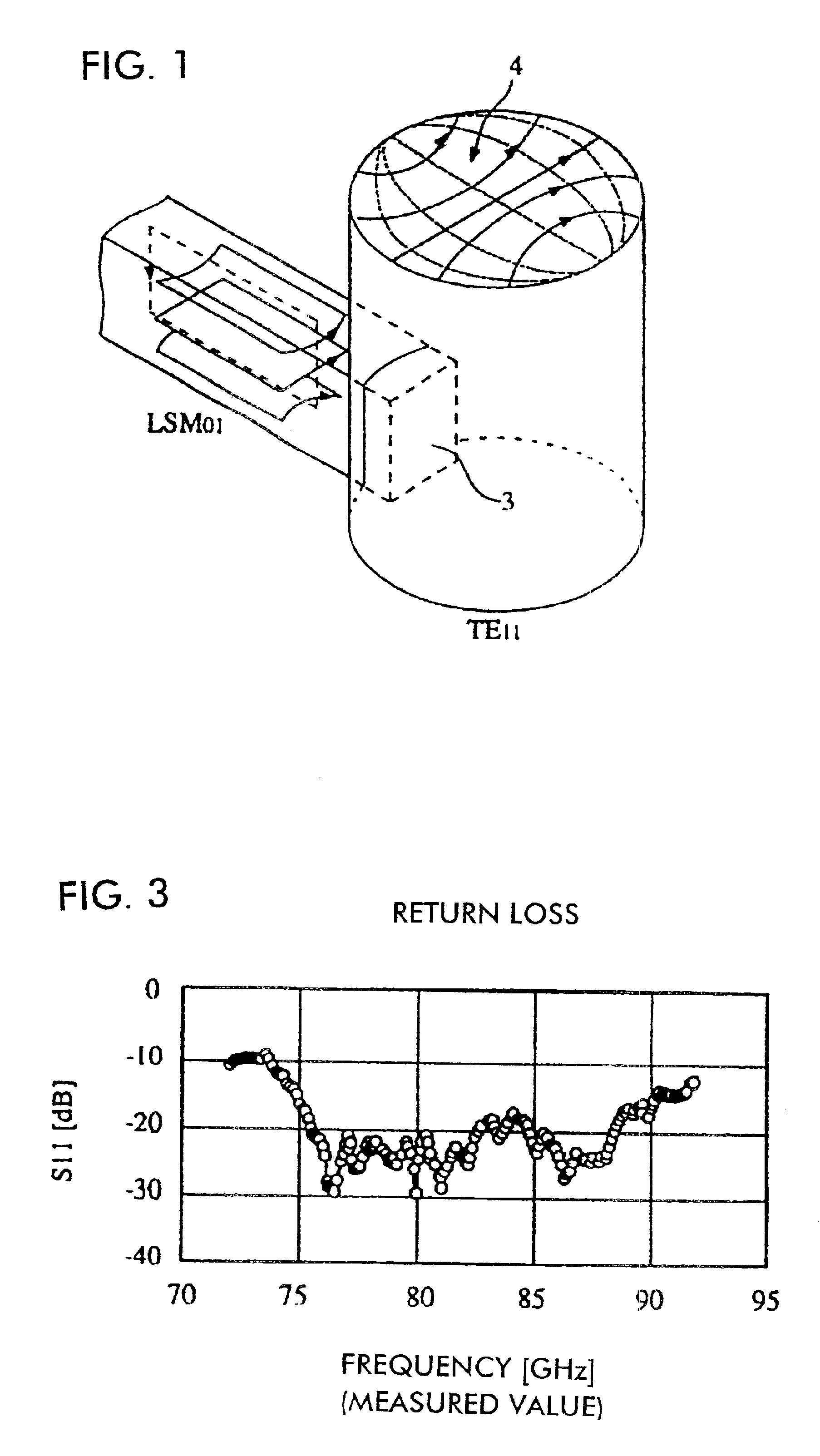
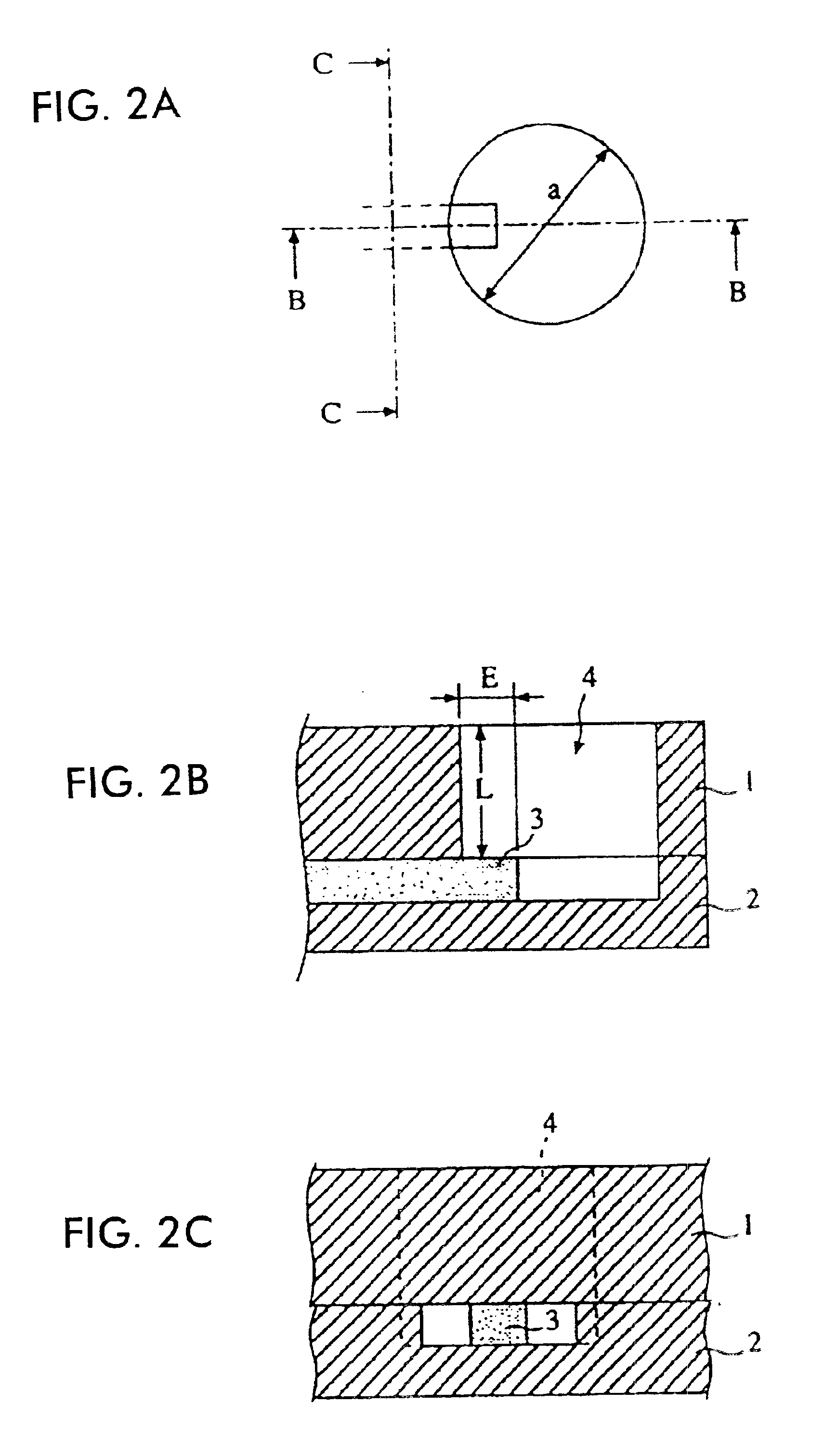
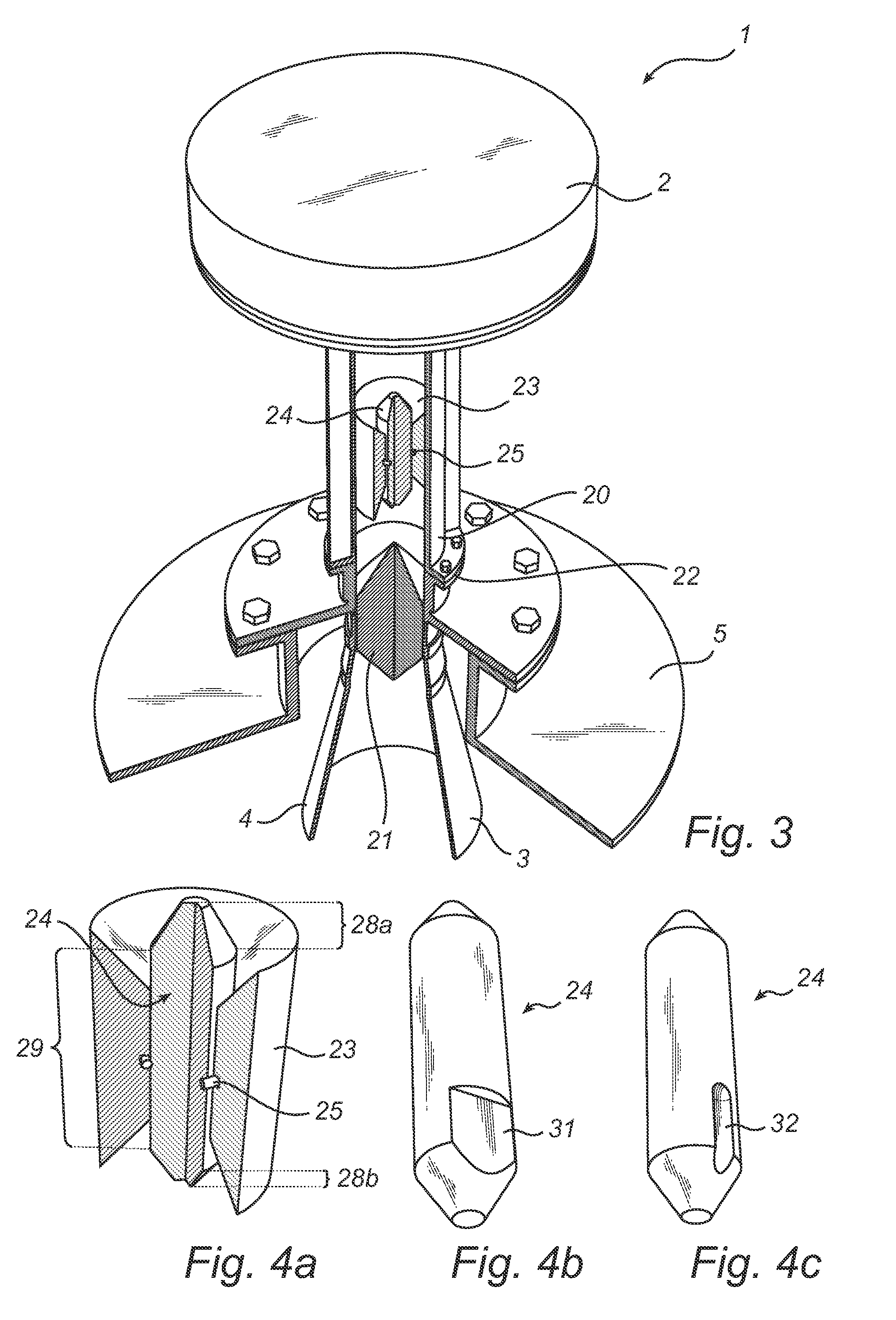
Horn antenna for a radar device
A horn antenna for a radar device comprising a metal body having a tubular hollow waveguide section opening into a hollow horn section, a dielectric filling body filling up the inner space of the horn section, and a dielectric cover, wherein the horn antenna is configured to protrude in a measurement environment, protected from highly aggressive process environments and is usable over a wide temperature range.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
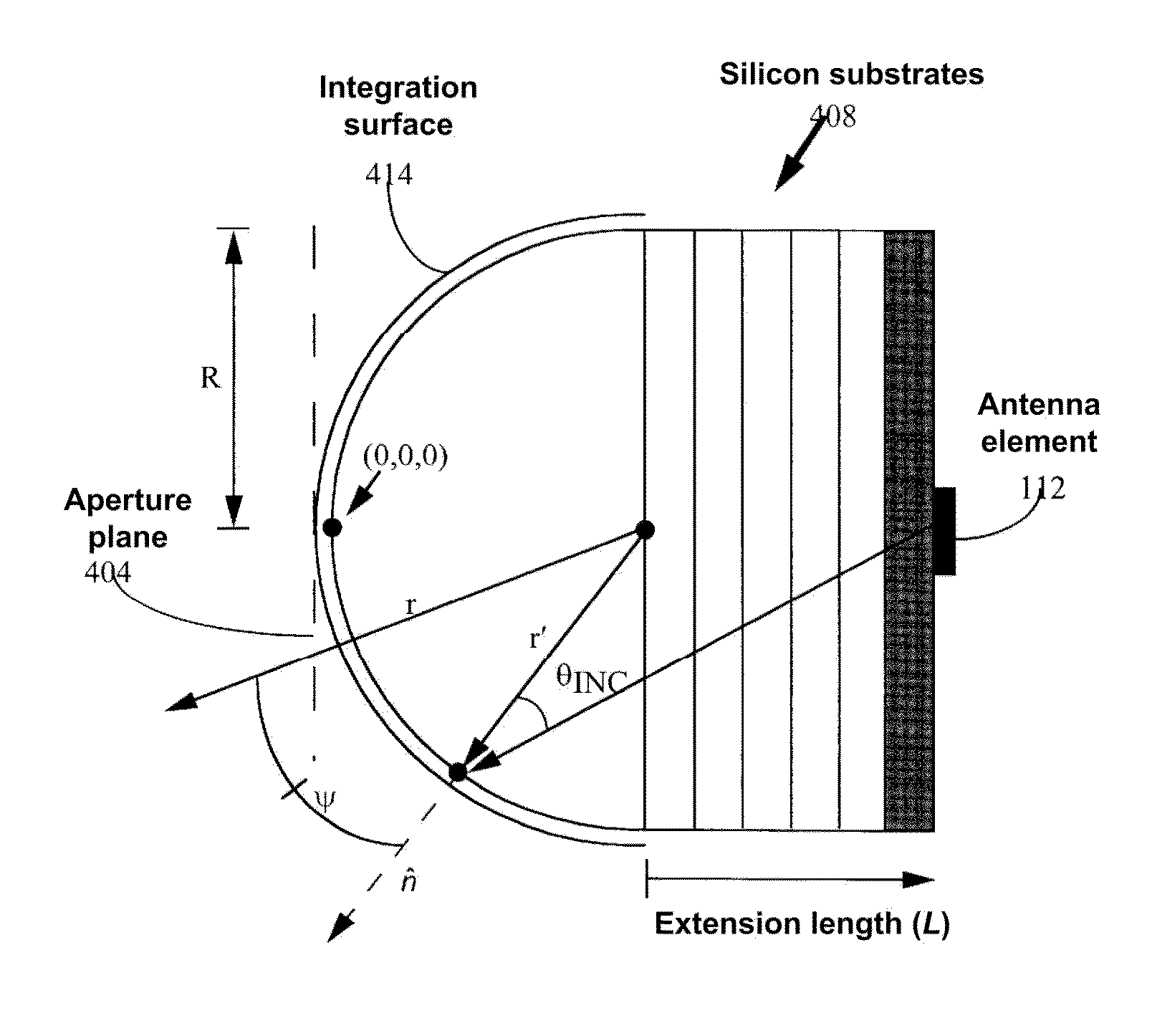
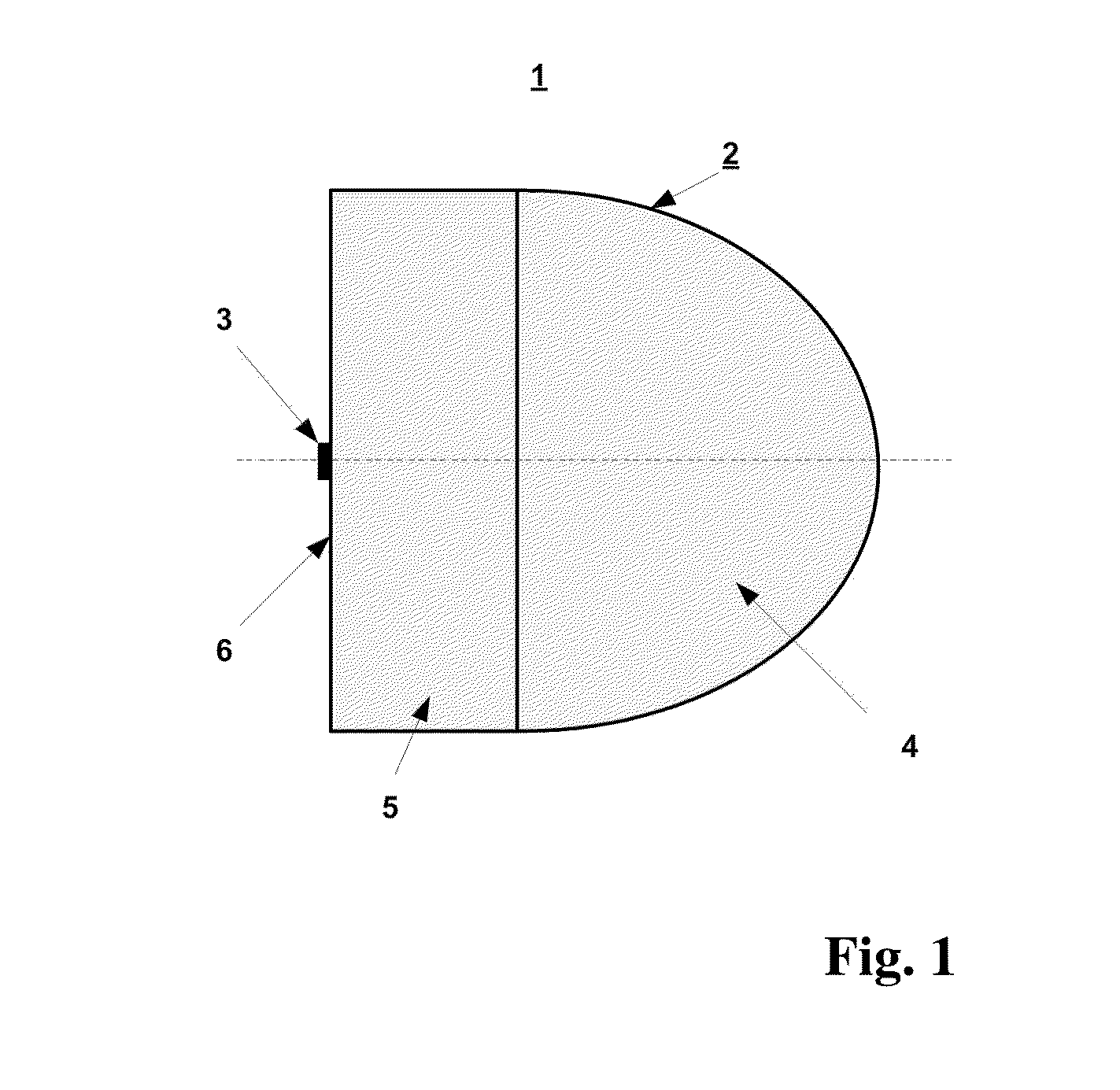
Lens antenna
ActiveUS20160087344A1Precise positioningDifferential interacting antenna combinationsRadio relayImpedance matching
Disclosed is a lens antenna comprising a dielectric lens consisting of a collimating part and an extension part, and an antenna element. The extension part of the lens comprises a substantially flat surface crossed by the axis of the collimating part, and the antenna element is rigidly fixed on the surface. The antenna element is formed by a hollow waveguide and comprises a dielectric insert with one end thereof adjacent to said surface; the size of the radiating opening of the waveguide is determined by the predefined width of the main beam and by side lobe levels of the radiation pattern of the lens antenna. The technical result of the invention is an increase in realized gain value due to the use of a waveguide antenna element with a dielectric insert, which provides impedance matching in a wide frequency bandwidth. The present invention can be used in radio-relay point-to-point communication systems, e.g. for forming backhaul networks of cellular mobile communication, in car radars and other radars, in microwave RF tags, in local and personal communication systems, in satellite and intersatellite communication systems, etc.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
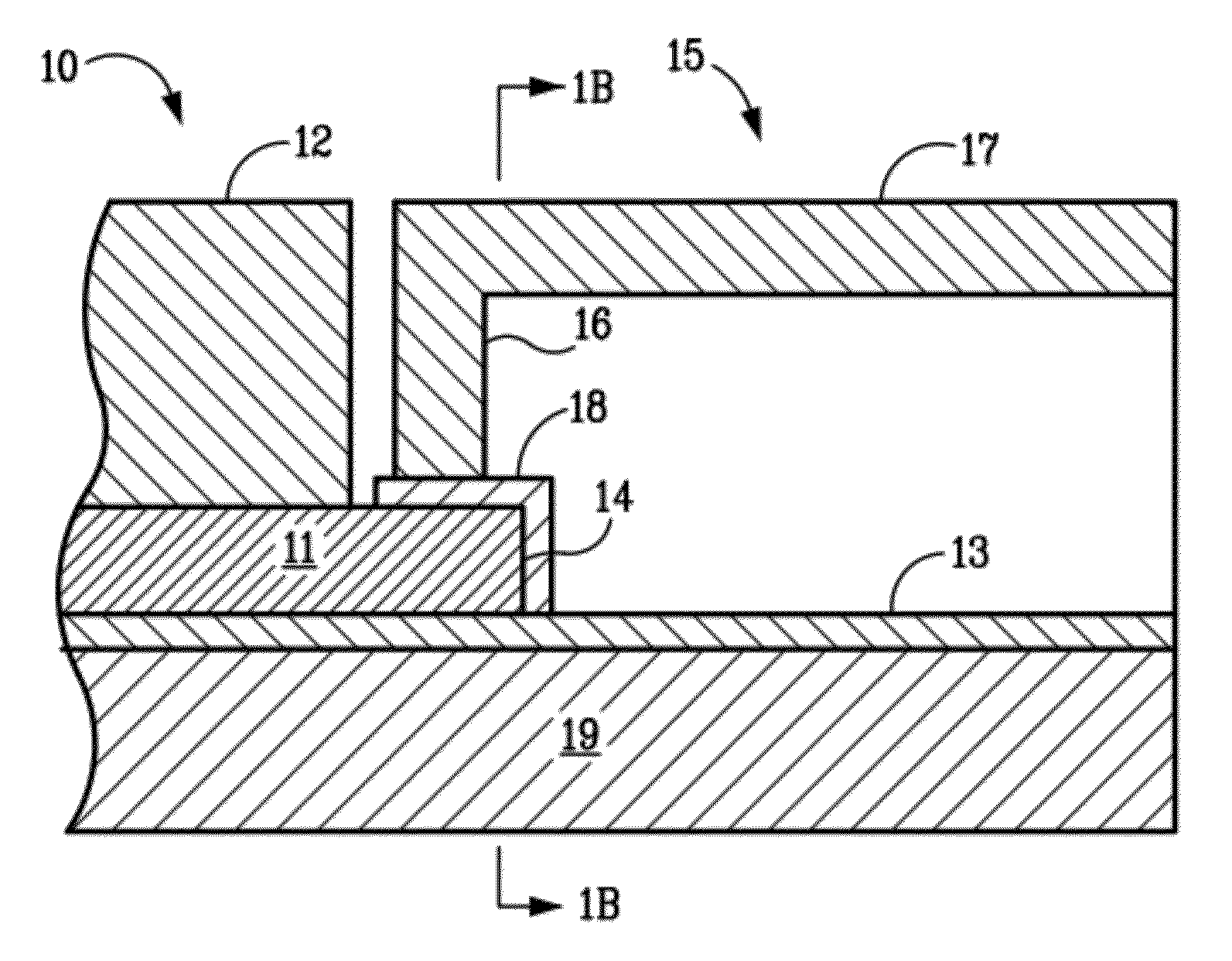
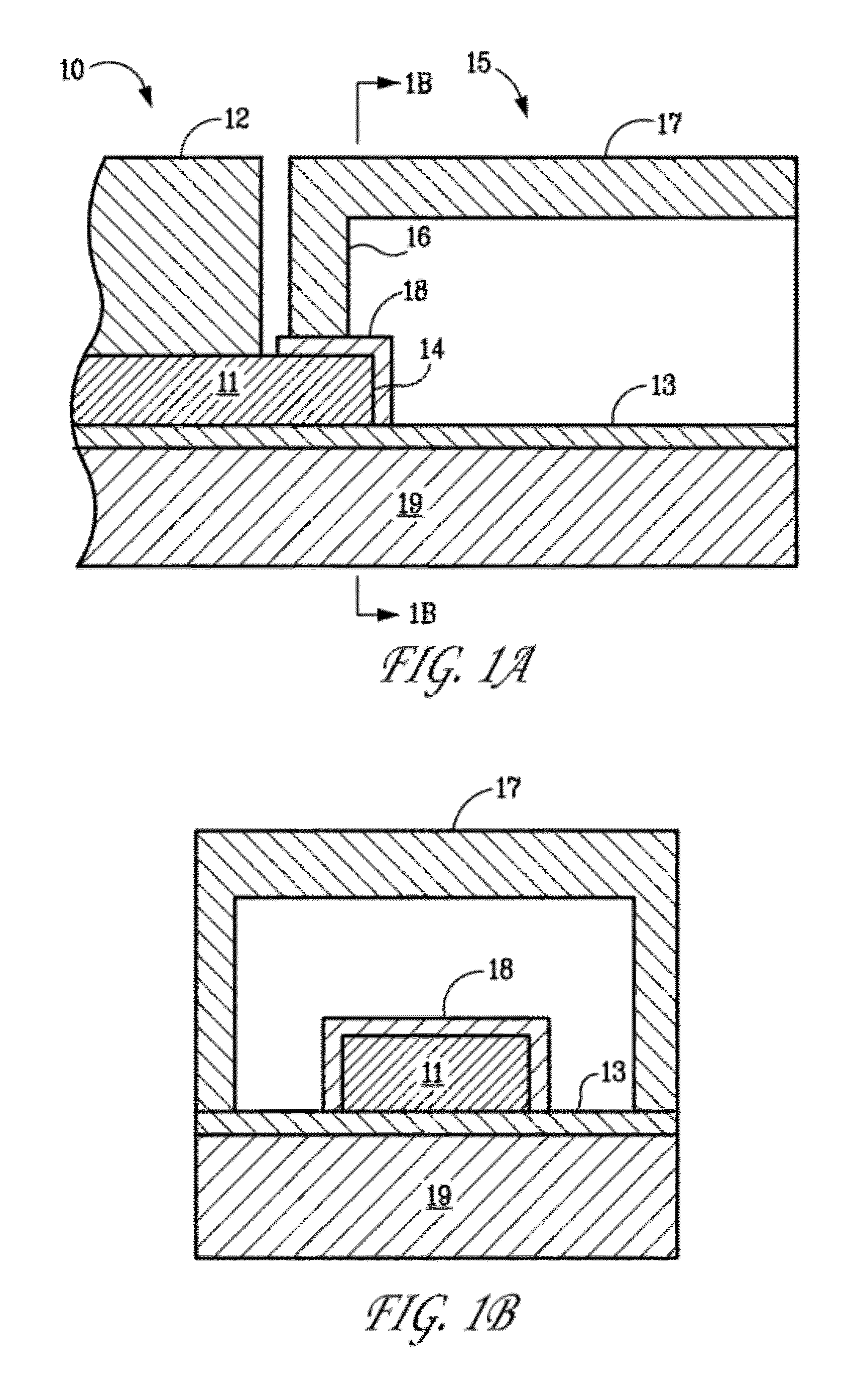
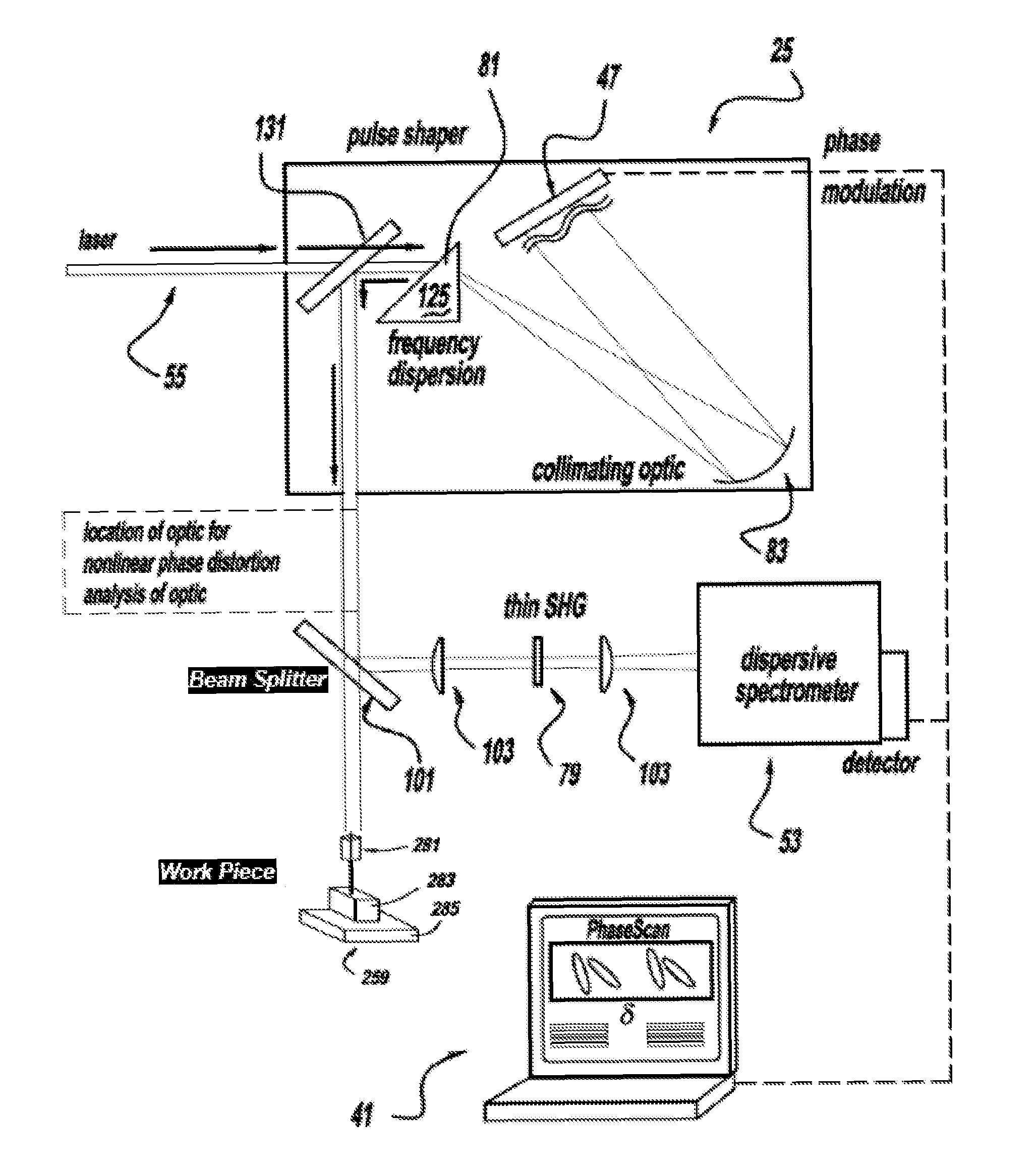
Laser Material Processing System
ActiveUS20090188901A1Wide bandwidthImprove laser pulse performanceLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamOptoelectronics
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Waveguide device, and antenna device including the waveguide device
InactiveUS20180351261A1Radiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysMicrowaveHollow waveguide
A waveguide device includes: a circuit board having a microstrip line thereon; a microwave IC connected to one end of the microstrip line; a first waffle-iron ridge waveguide; a second waffle-iron ridge waveguide; a first hollow waveguide which is at one end connected to another end of the microstrip line, and at another end connected to a first site of the first waffle-iron ridge waveguide; and a second hollow waveguide which is at one end connected to a second site of the first waffle-iron ridge waveguide, and at another end connected to a first site of the second waffle-iron ridge waveguide.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP +1
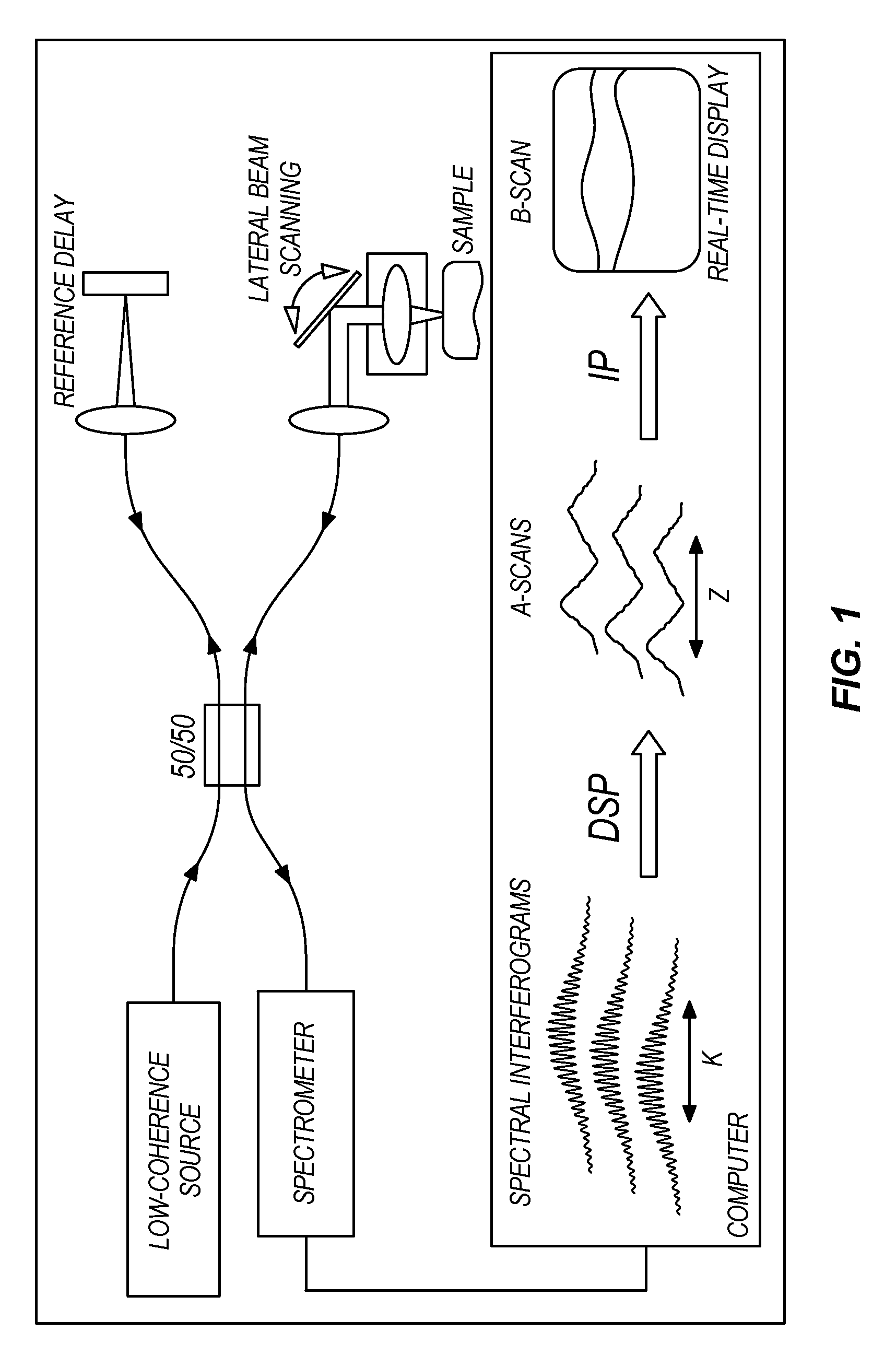
Apparatus and method for real-time imaging and monitoring of an electrosurgical procedure
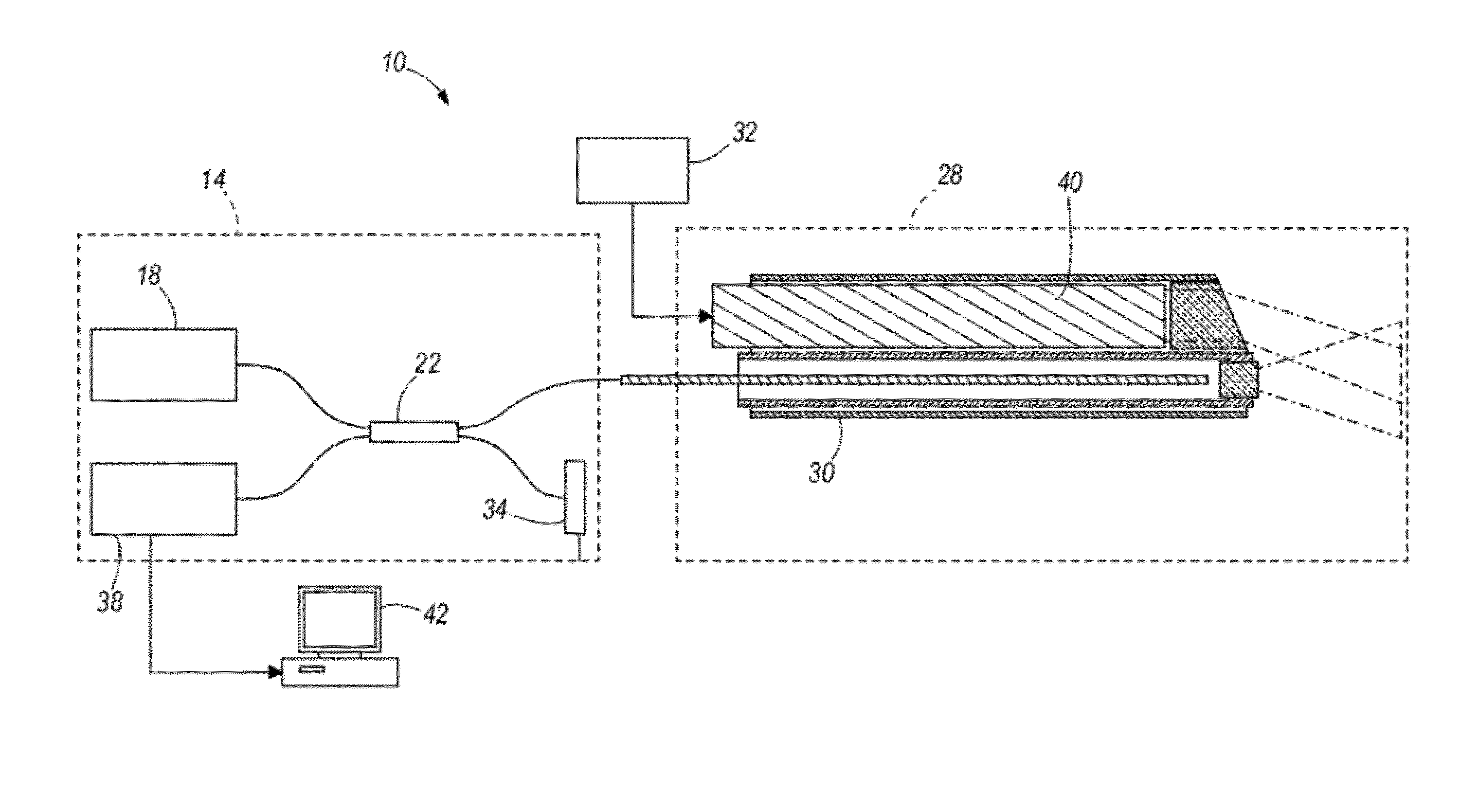
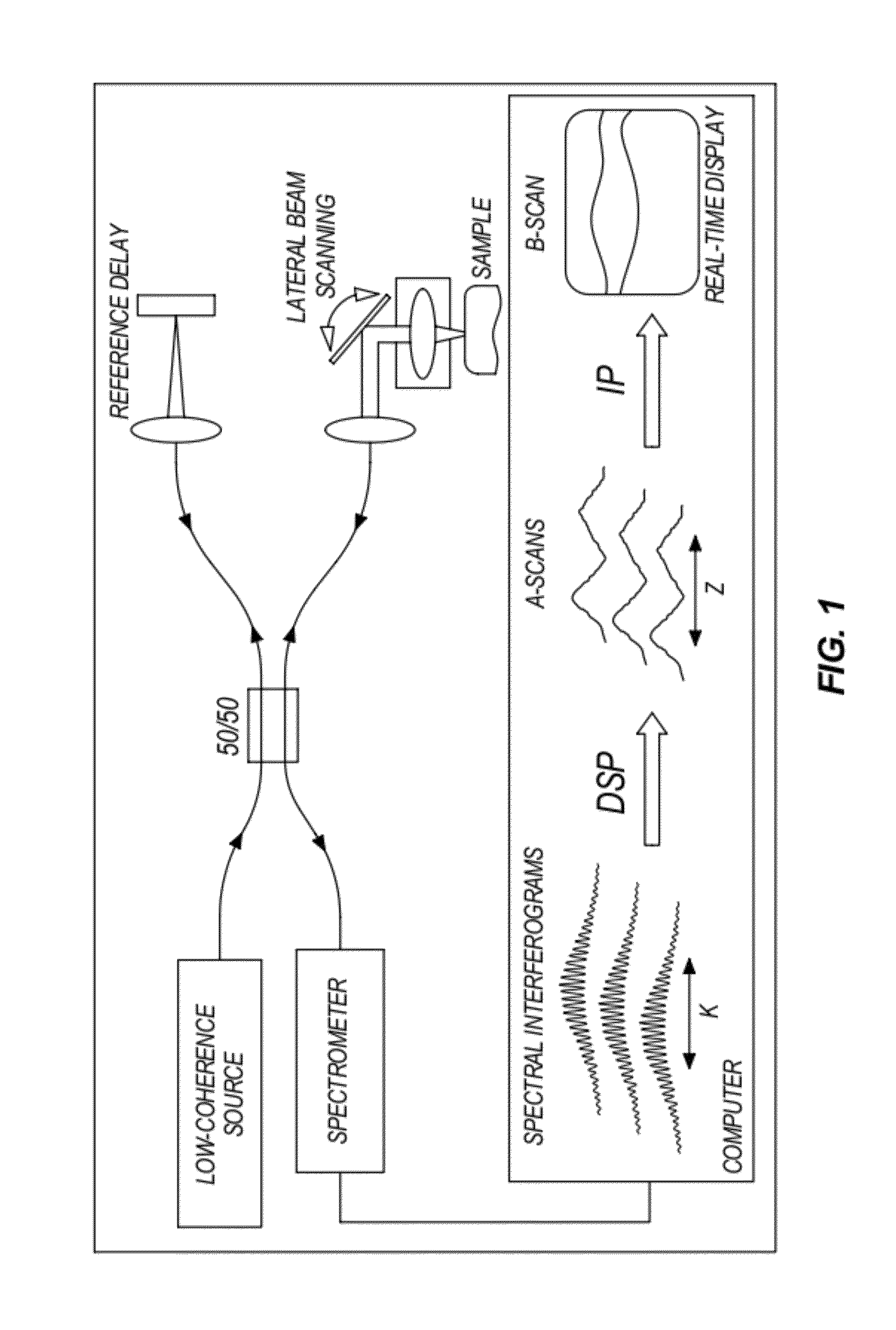
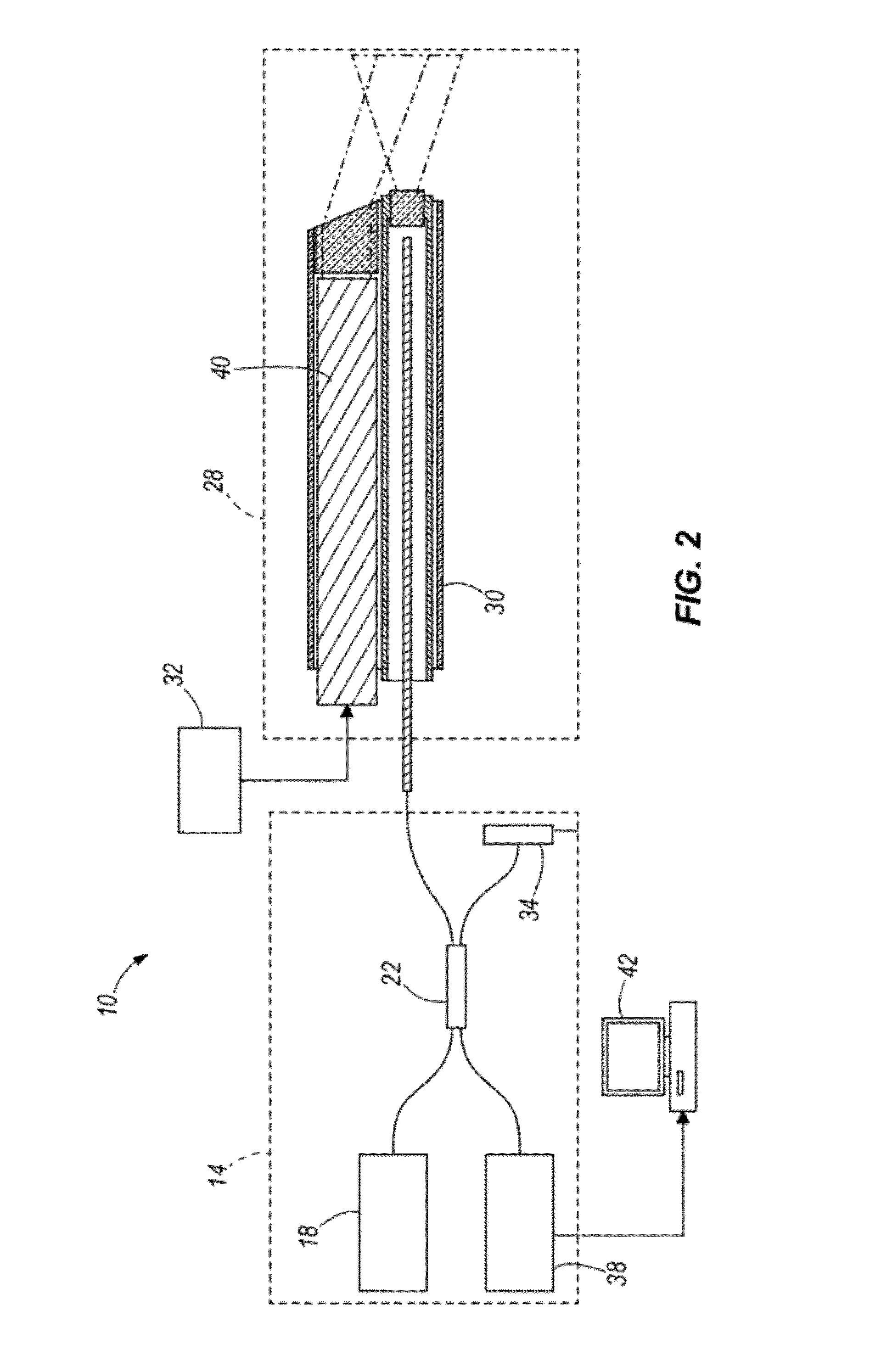
ActiveUS20120310042A1Profound effect upon ophthalmic imagingProfound diagnosisEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingElectrosurgeryEngineering
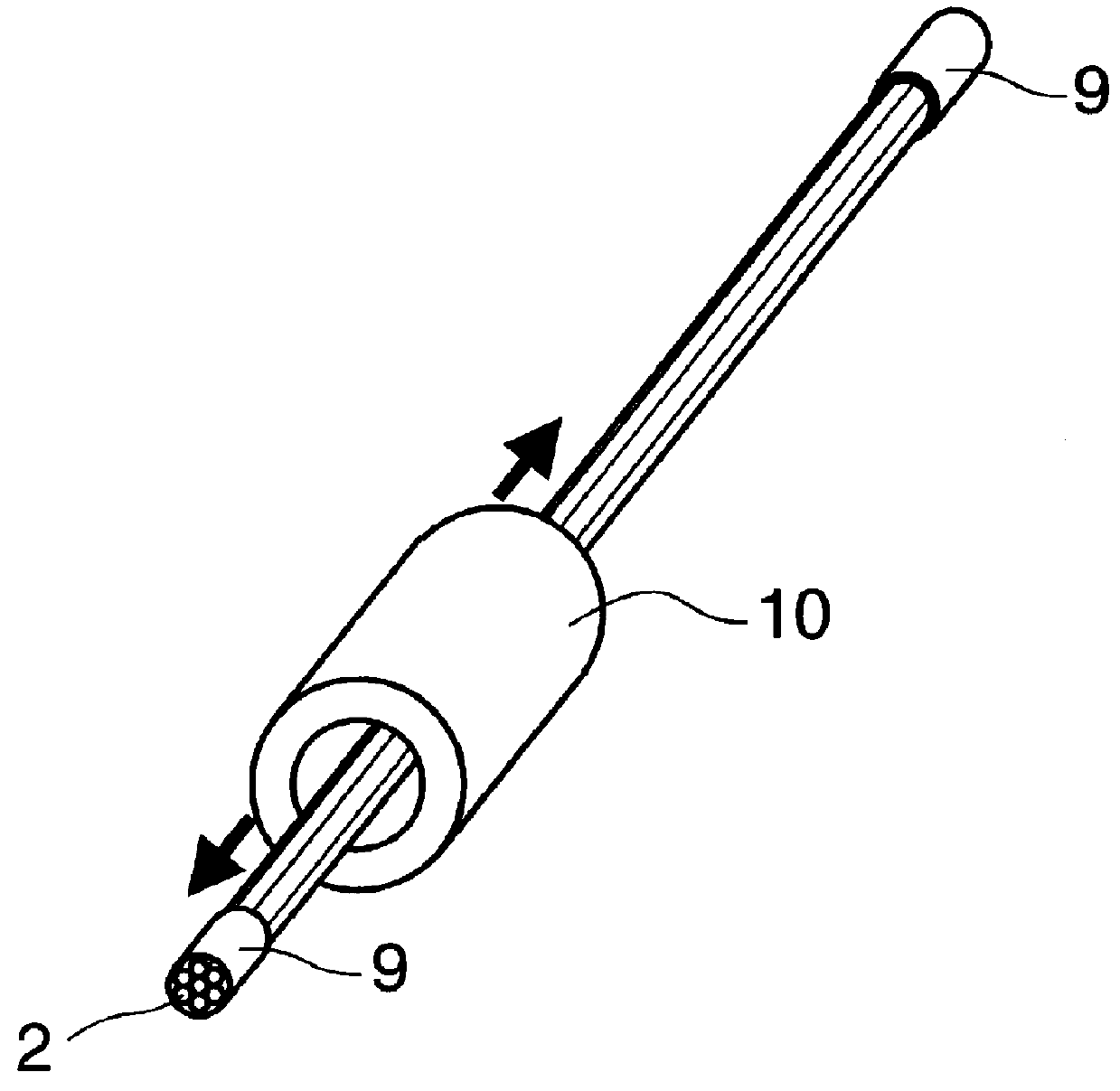
An optical coherence tomography probe and laser combination device configured for real-time z-directional guidance of the incisional depth of a surgical procedure. It can be used alone or placed within the working channel of an endoscope. The device includes an OCT single mode fiber, and a laser fiber or laser hollow waveguide or electrical surgical wire positioned adjacent to the OCT single mode fiber. The single mode fiber is configured to move laterally when activated by an actuator to scan light data reflected from a sample that is positioned in front of a distal end of the device. The light data can be processed to generate a B-scan image. The device can collect data in real-time during lasing, or immediately prior to and following the cutting. The surgical tool, when coupled to a processor, can deactivate when the B-scan image identifies that the incision is within a predefined tolerance.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
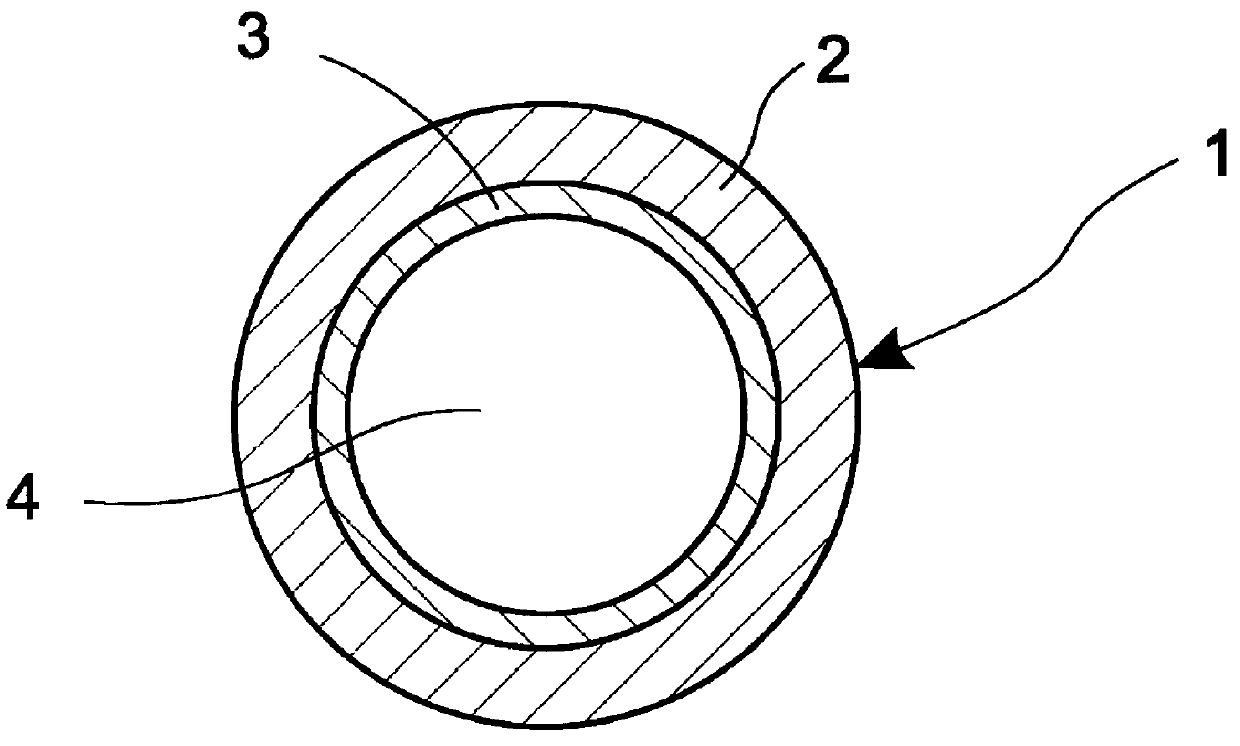
Substrate-Integrated Hollow Waveguide Sensors
ActiveUS20130081447A1Cladded optical fibreColor/spectral properties measurementsLight guideHollow waveguide
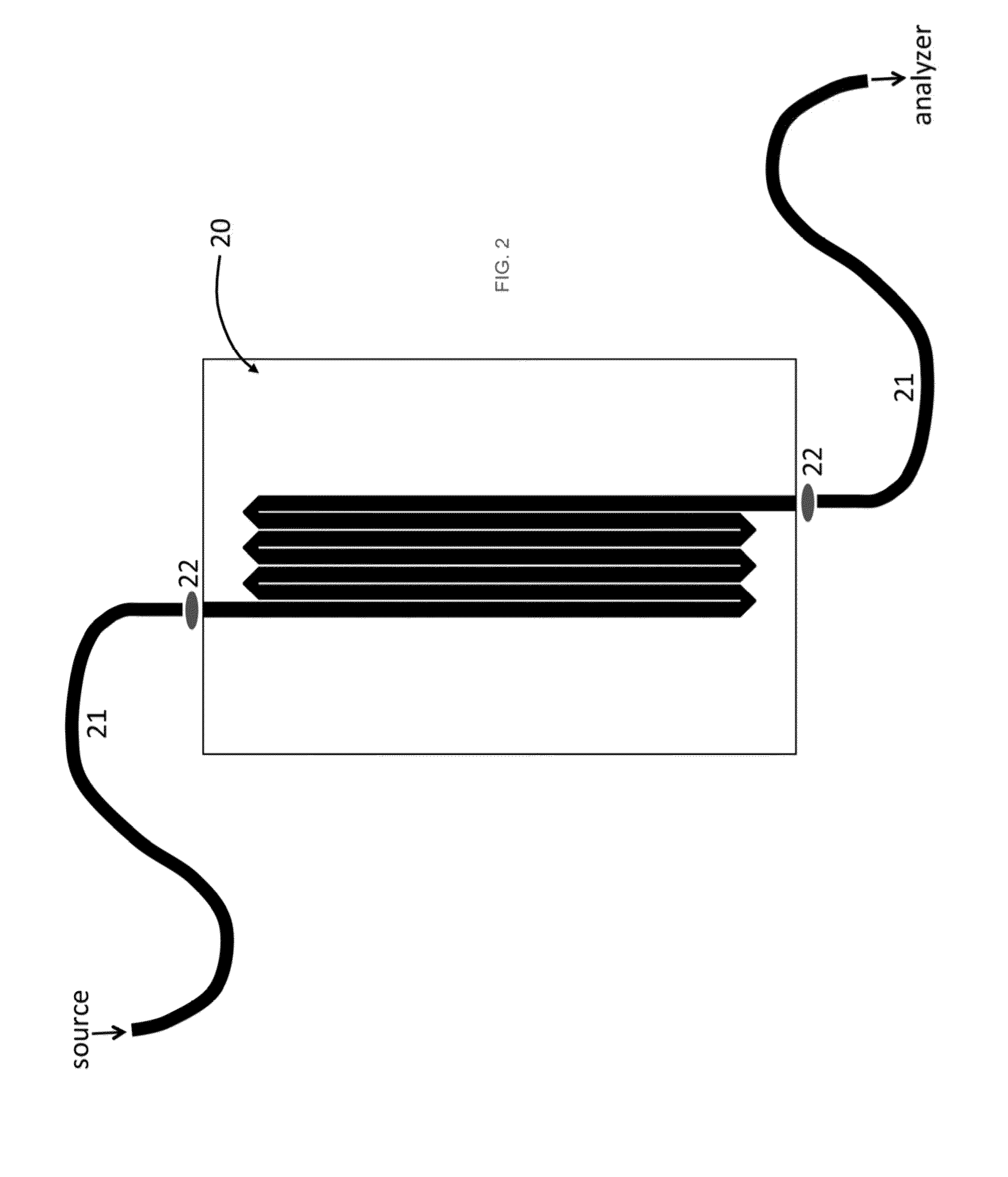
Methods and apparatuses are provided that greatly expand the utility of conventional hollow waveguide-based sensors via either straight, substrate-integrated channels or via meandering (e.g., circuitous, curved or folded optical paths) waveguide sensor designs. Full- or hybrid-integration of the meandering hollow waveguide with light source, detector, and light-guiding optics facilitates compact yet high-performance gas / vapor and / or liquid sensors of the substrate-integrated hollow waveguide sensor.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Radio Frequency (RF) Microwave Components and Subsystems Using Loaded Ridge Waveguide
InactiveUS20120092091A1Small component sizeImprove power performanceWaveguidesMicrowaveConductive materials
A waveguide having a non-conductive material with a high permeability (μ, μr for relative permeability) and / or a high permittivity (∈, ∈r for relative permittivity) positioned within a housing. When compared to a hollow waveguide, the waveguide of this invention, reduces waveguide dimensions by∝1μr*ɛr.The waveguide of this invention further includes ridges which further reduce the size and increases the usable frequency bandwidth.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Ultra-high sensitivity NDIR gas sensors
InactiveUS20080035848A1Inexpensively detectingRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsAngle of incidencePath length
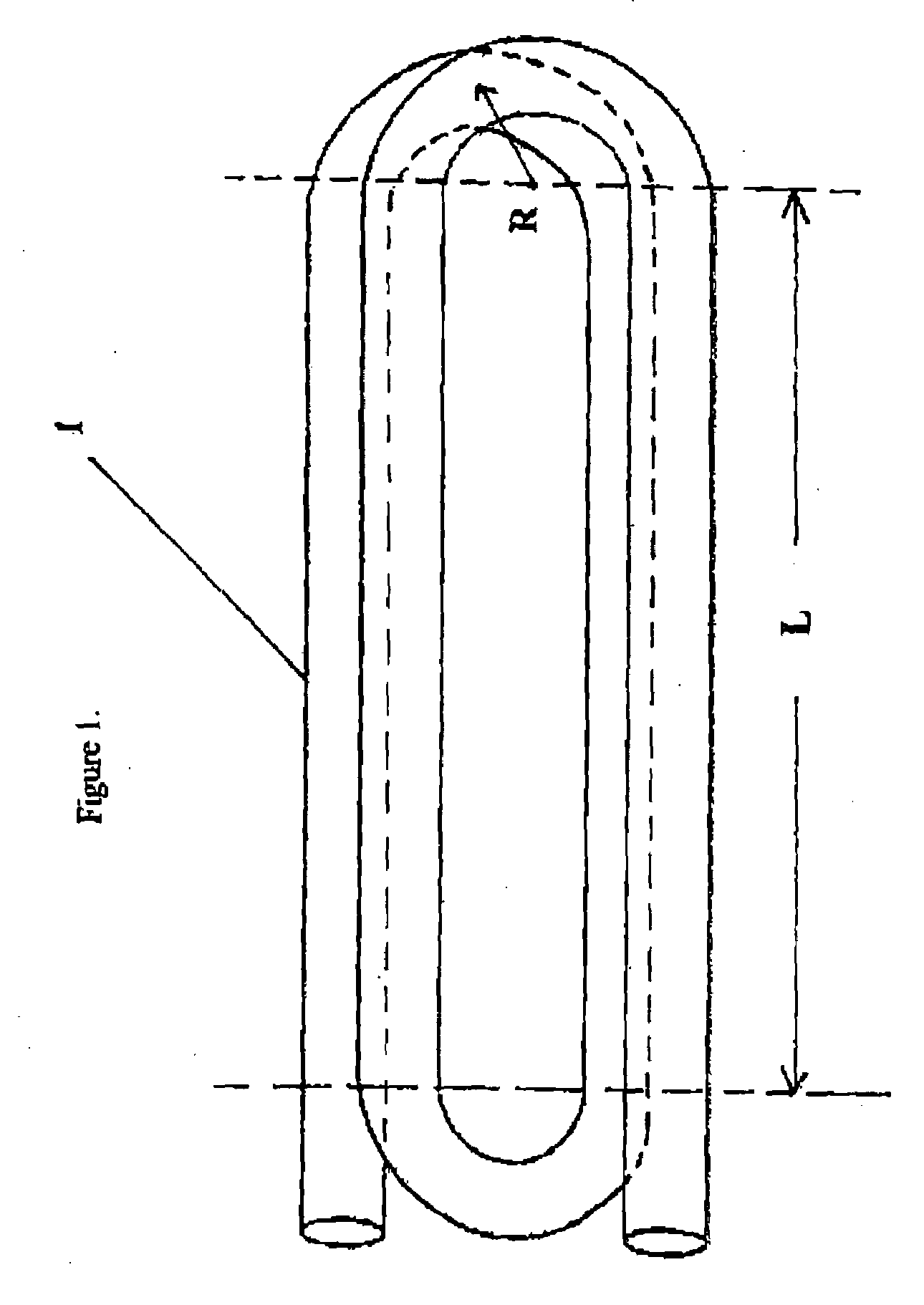
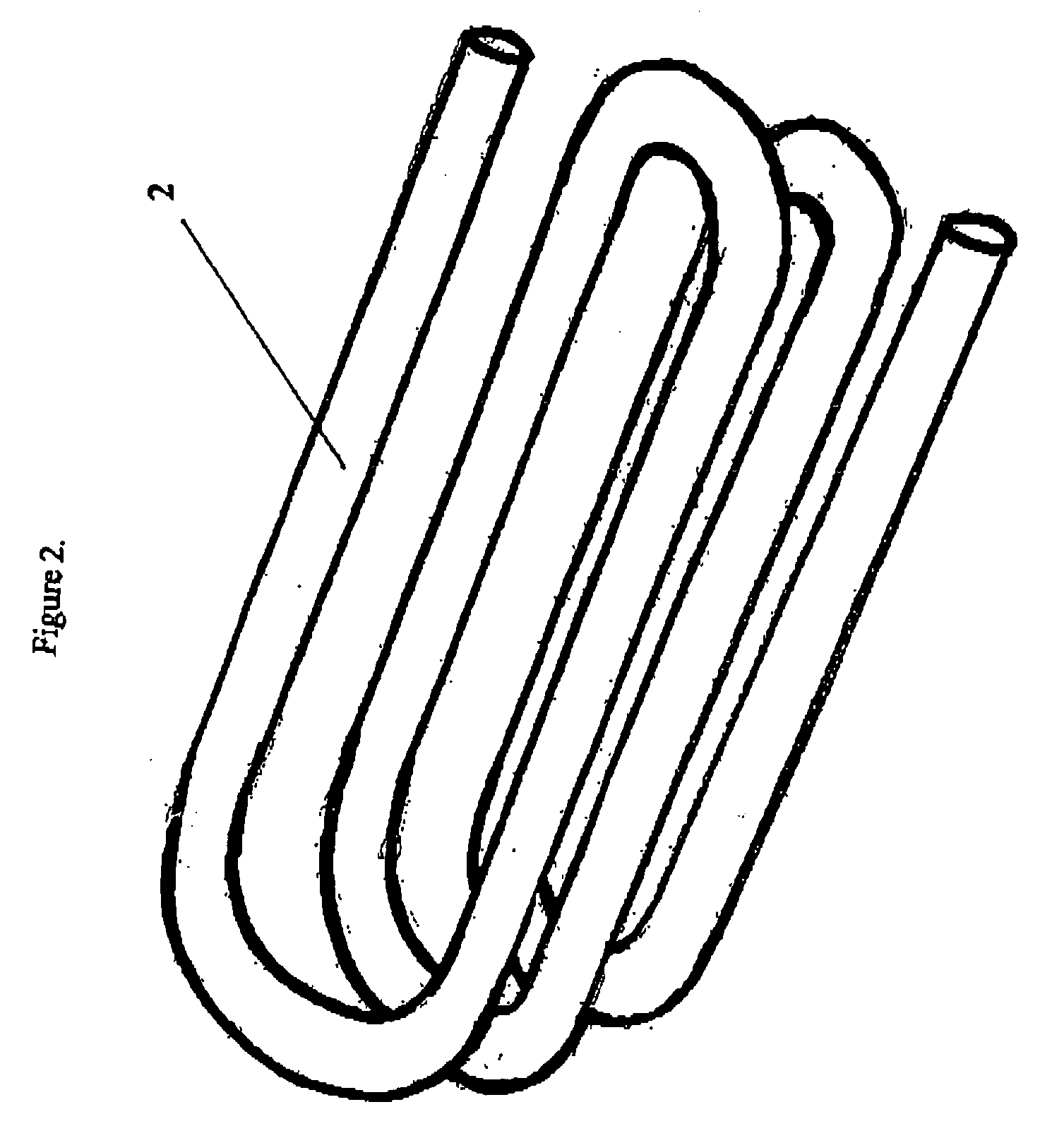
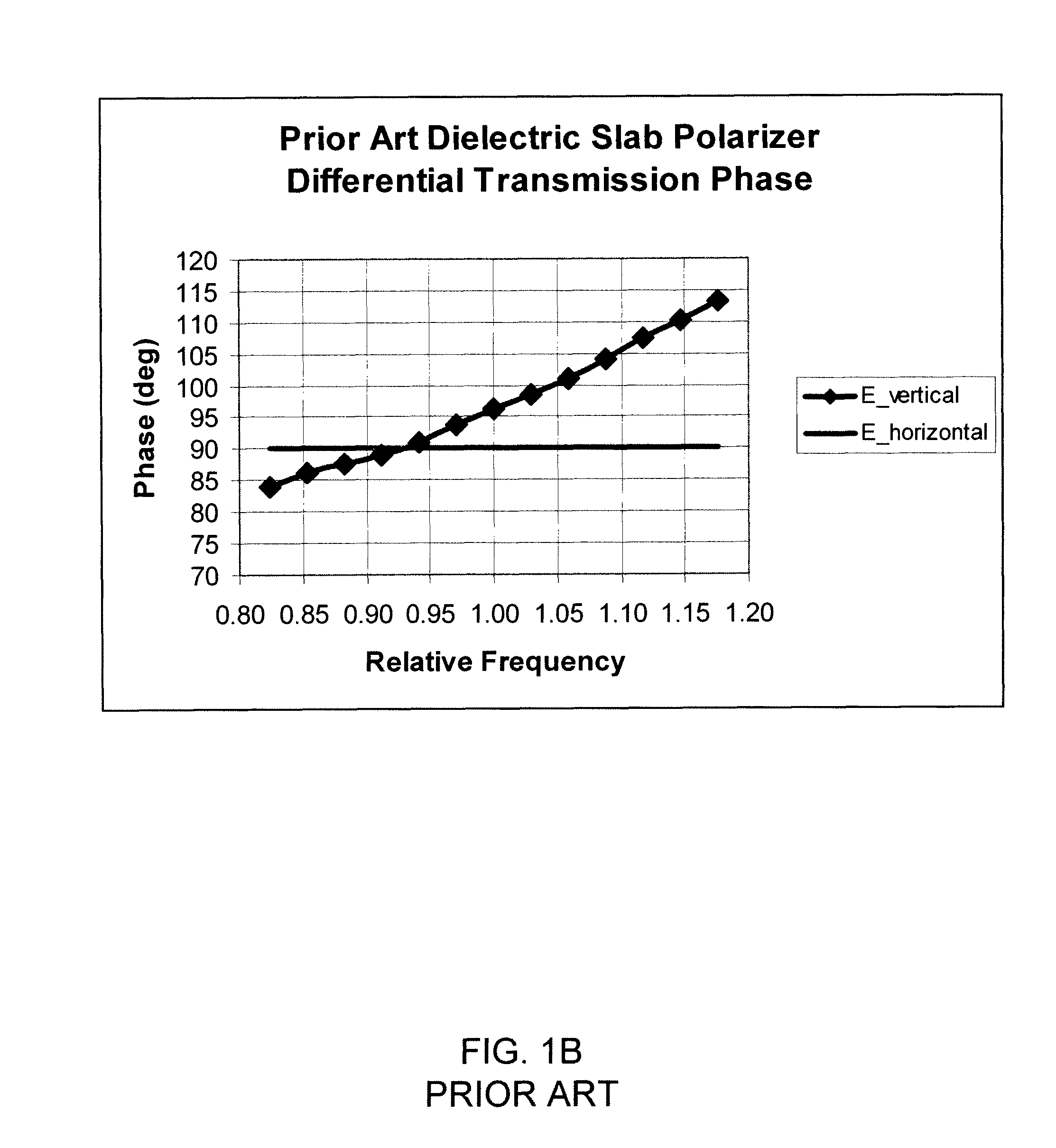
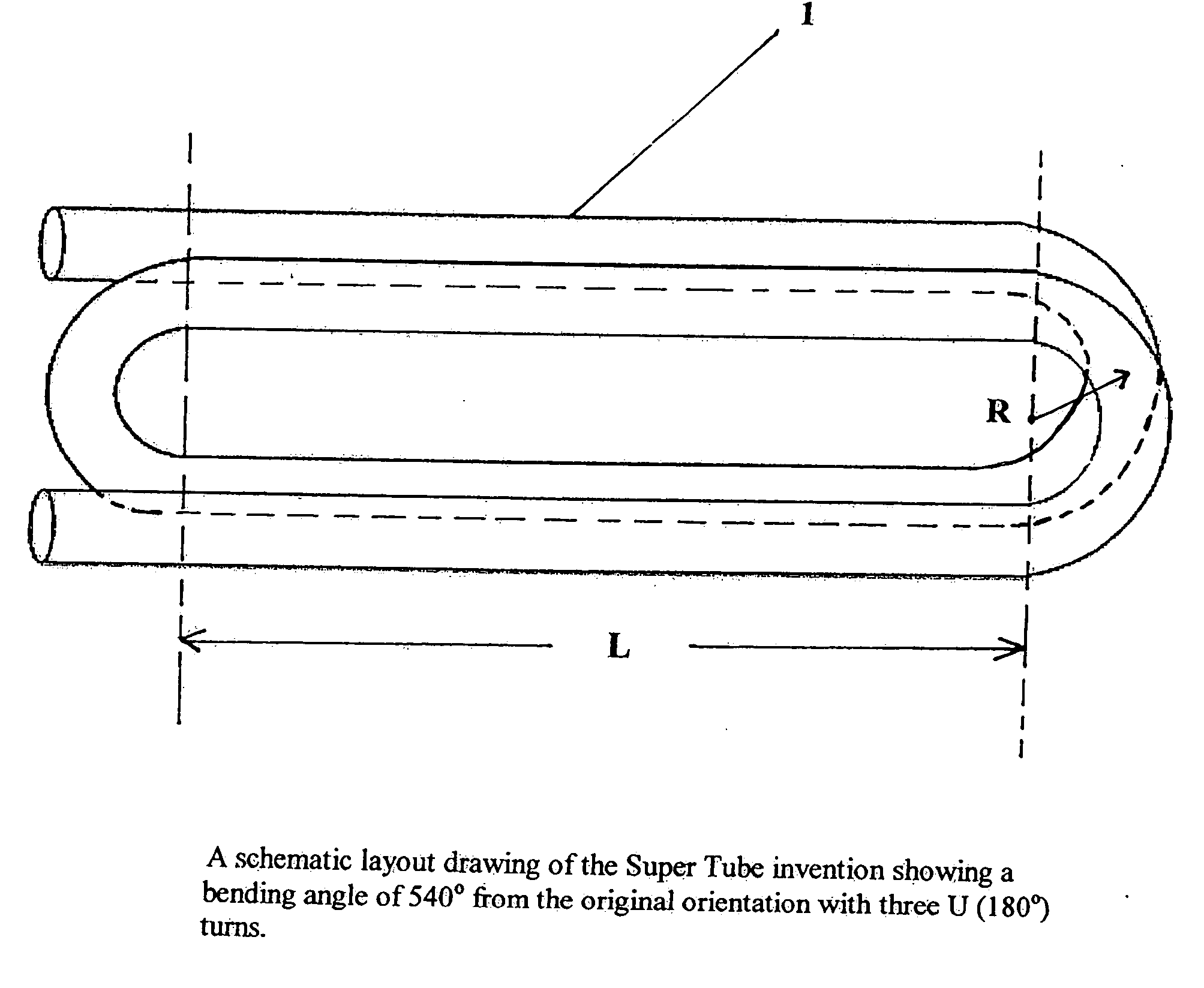
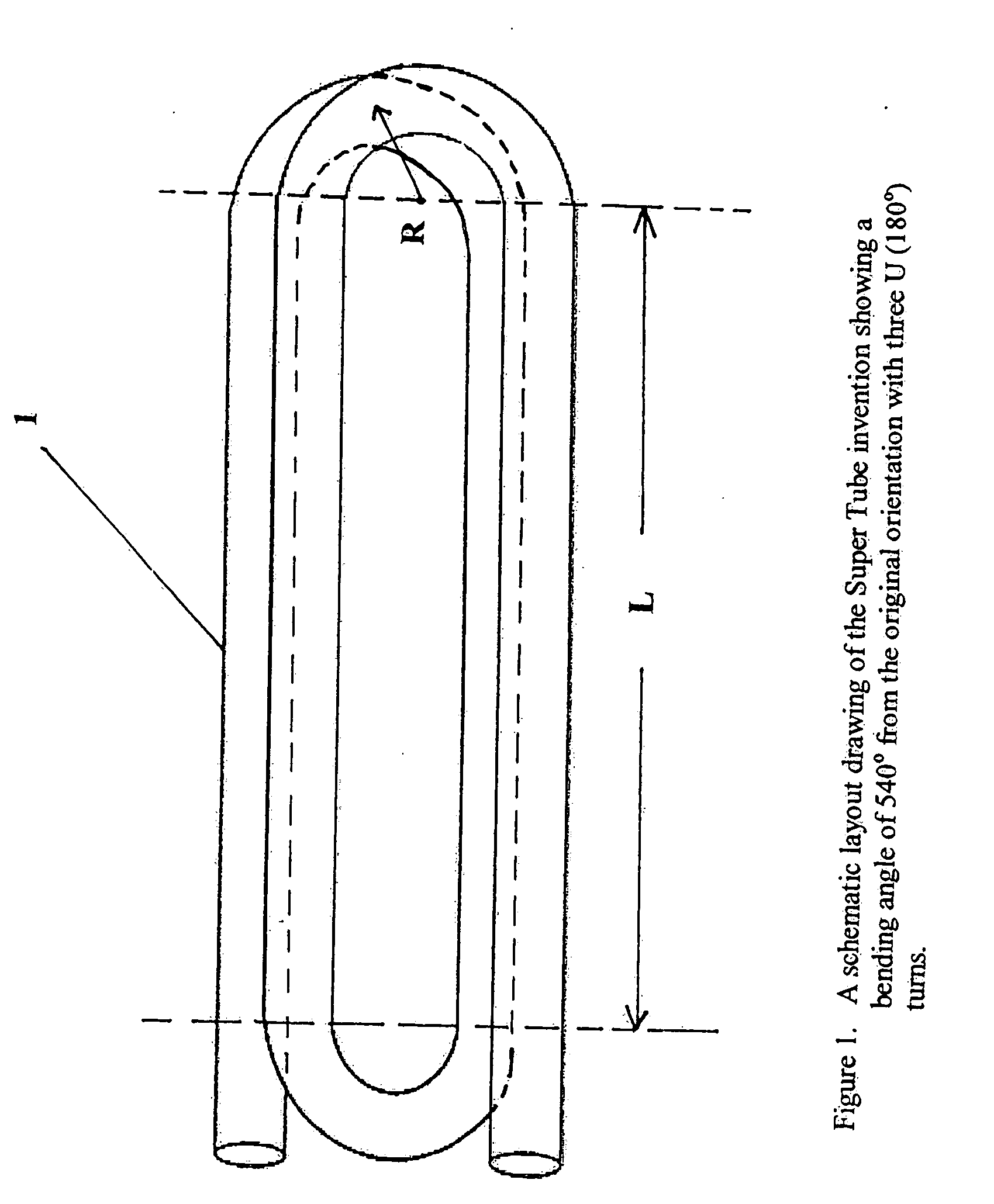
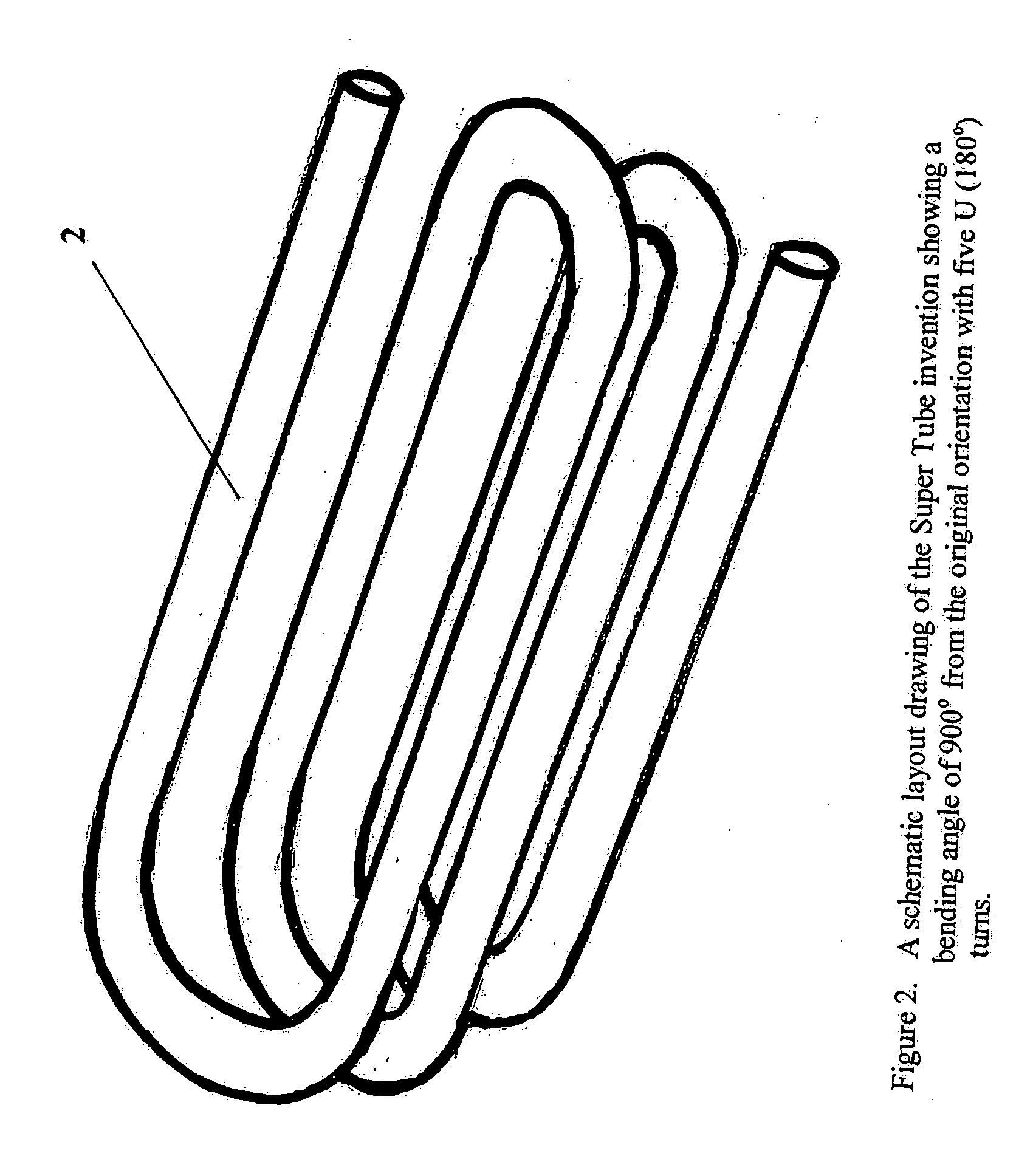
A compact and long path-length sample cell that is a hollow waveguide with a plurality of bends that are collectively greater than 180 degrees in three dimensions, a focusing device for quasi-focusing radiation into a beam with an angle of incidence between greater than approximately 0° and approximately 10° relative to a longitudinal axis of a first linear segment of the waveguide proximate a source of infrared radiation and a second focusing device for focusing infrared radiation after it has traveled through substantially all of the waveguide as it approaches a detector chamber. The sample cell can be used with two or more detectors to detect the concentrations of one or more gasses, to levels less than 100 ppm, after correction for water vapor.
Owner:WONG JACOB Y
Laser ablation apparatus useful for hard tissue removal
InactiveUS20070016177A1Increase speedMinimizes and removeControlling energy of instrumentDental toolsLight beamHard tissue
A laser ablation apparatus including a laser source for generating laser beams in a wavelength range suitable for ablating hard dental tissue, and a scanning device including a beam deflecting element that deflects and scans the laser beams over a surface such that the laser beams impinge on the surface with controllable overlapping (e.g., without overlapping each other). The scanning device and the laser source may be disposed in a hand piece. The scanning device may be coupled to the laser source without an optical fiber or hollow waveguide.
Owner:VAYNBERG BORIS +1
Horn Antenna for a Radar Device
A horn antenna for a radar device comprising a metal body having a tubular hollow waveguide section opening into a hollow horn section, a dielectric filling body filling up the inner space of the horn section, and a dielectric cover, wherein the horn antenna is configured to protrude in a measurement environment, protected from highly aggressive process environments and is usable over a wide temperature range.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Line transition device between dielectric waveguide and waveguide, and oscillator, and transmitter using the same
InactiveUS6489855B1Avoid radiationReduce lossResonatorsWaveguidesElectrical conductorHollow waveguide
A line transition device which intervenes between a non radiative dielectric waveguide and a hollow waveguide for example, includes a dielectric waveguide having a dielectric strip held by a pair of conductors which face each other, and a waveguide, wherein a part of the dielectric strip of the dielectric waveguide is adjacent to or inserted in the hollow waveguide.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Hollow waveguide for ultraviolet light and making the same
InactiveUS6141476ACladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationUltraviolet lights
A hollow waveguide that transmits ultraviolet light with low attenuation. The present invention comprises a small-diameter, thin-wall, glass tube and a thin aluminum film on the inner surface of the glass tube. The aluminum film is deposited by a chemical vapor deposition method using an organometallic of aluminum as a precursor. The deposition process produces high smoothness of the film surface.
Owner:MATSUURA YUJI +1
Device and method for delivery of long wavelength laser energy to a tissue site
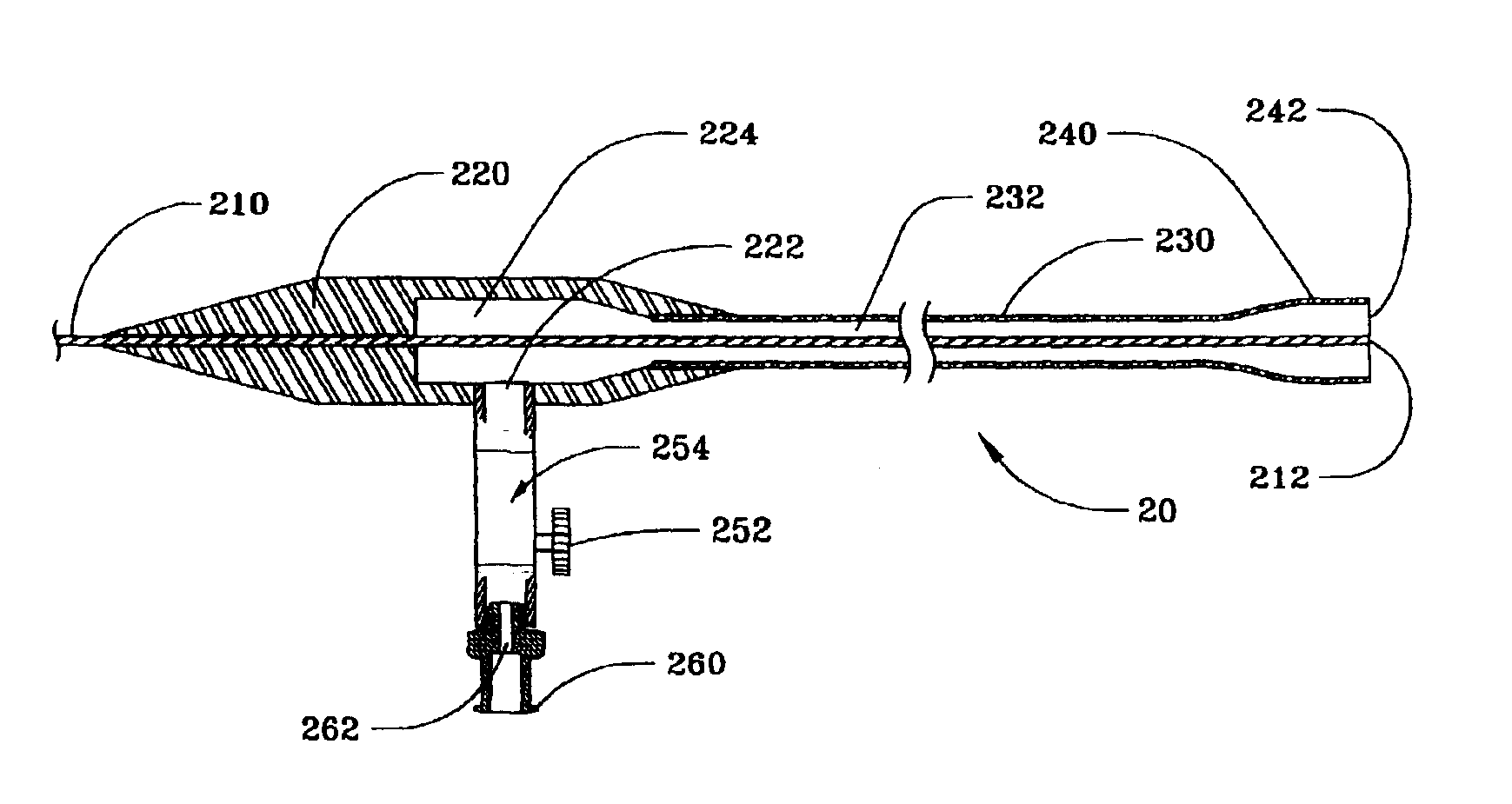
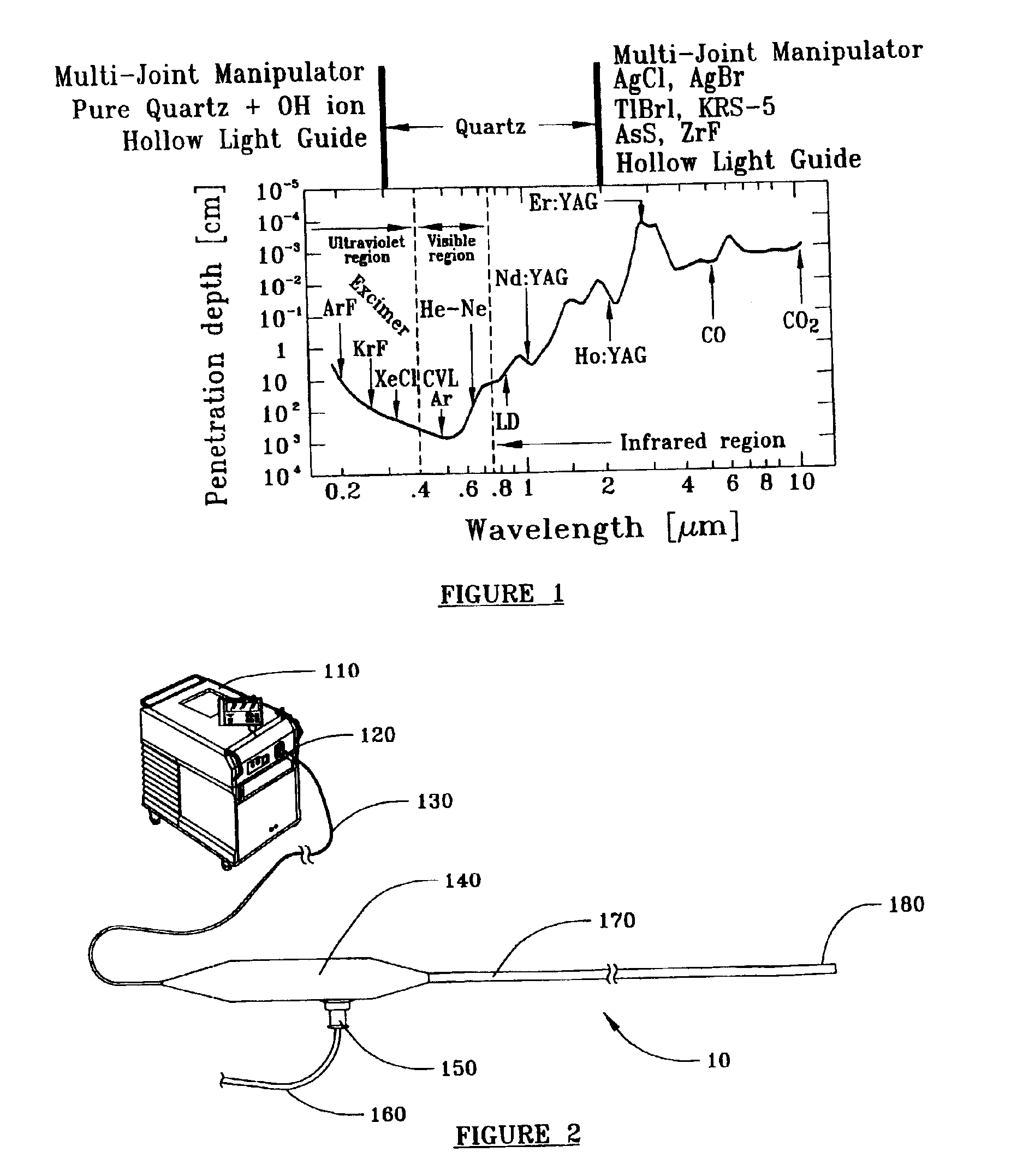
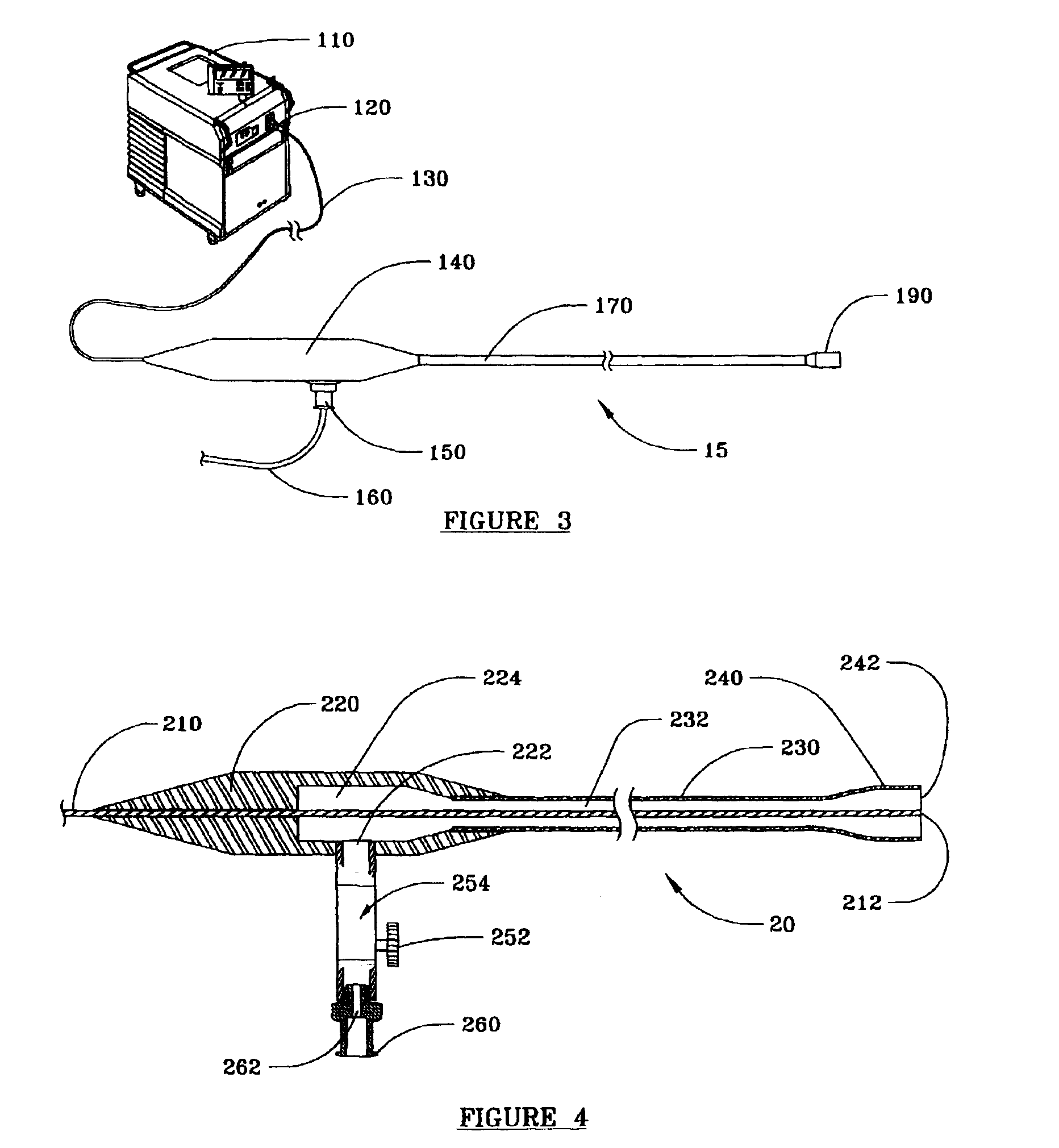
A laser energy delivery device and method are provided for irradiating a body tissue with relatively long wavelength laser energy in the presence of an aqueous liquid without significant absorption of the laser energy by the liquid. The device includes an elongate hollow sheath that is open at its distal end and closed at its proximal end, a laser energy conduit such as an optical fiber or hollow waveguide, within the sheath, the distal end of the conduit being disposed near the open distal end of the sheath, and the proximal end of the conduit being adapted for connection to a source of long wavelength laser energy. The sheath also includes an inlet port, spaced from the proximal end of the sheath, and adapted to receive and deliver a biologically compatible gas through the sheath to a body tissue site in contact with the open distal end of the sheath.
Owner:TRIMEDYNE
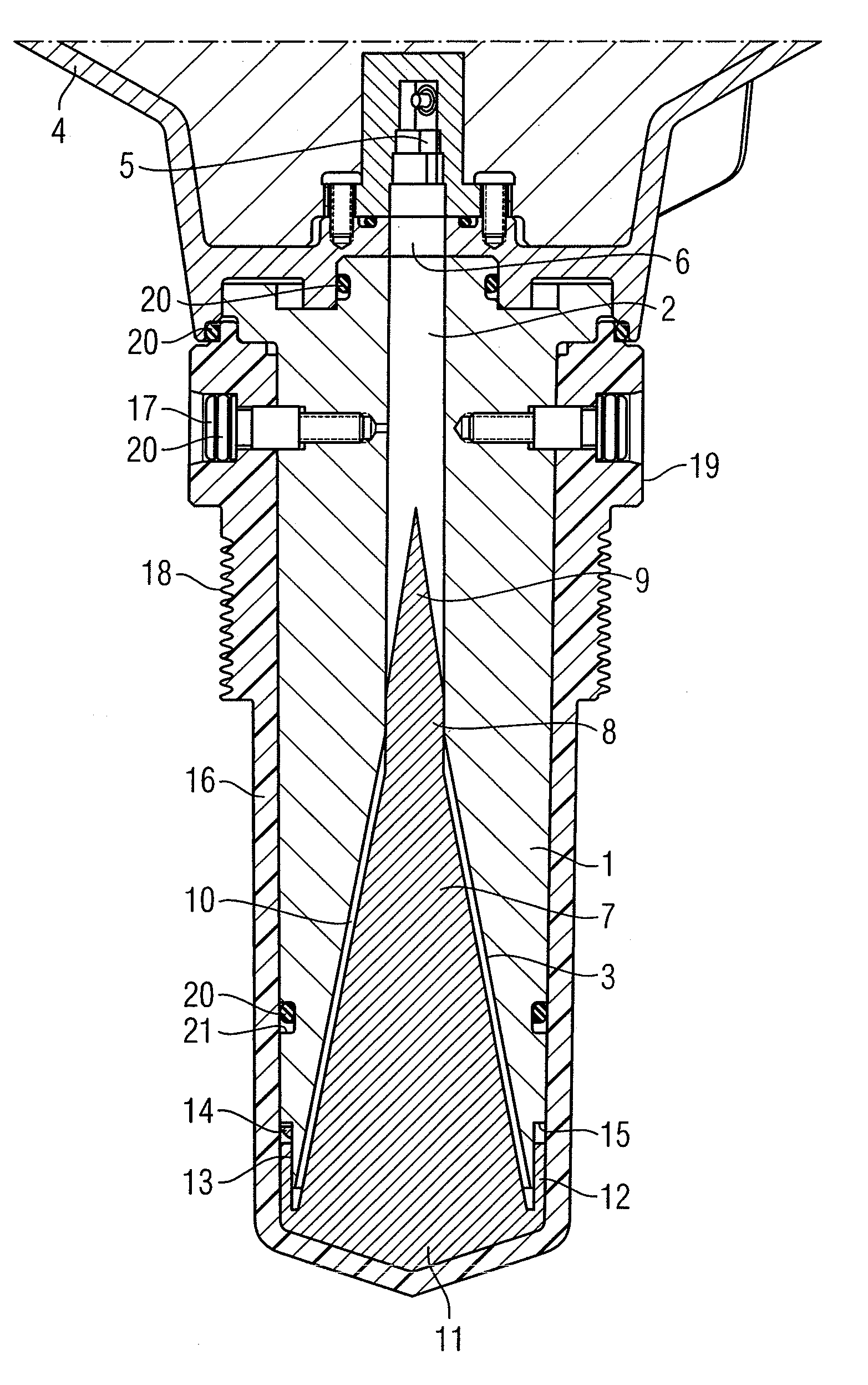
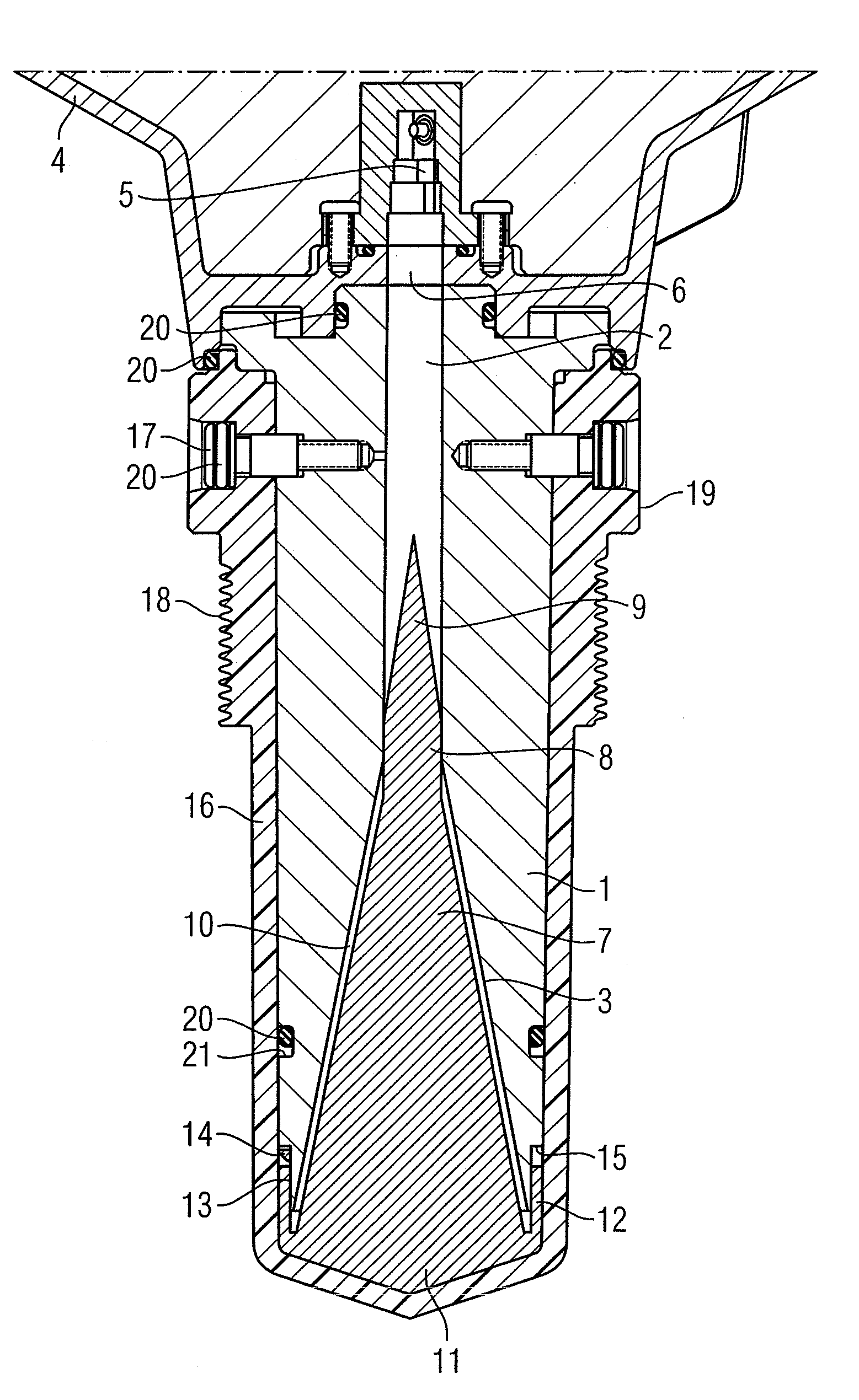
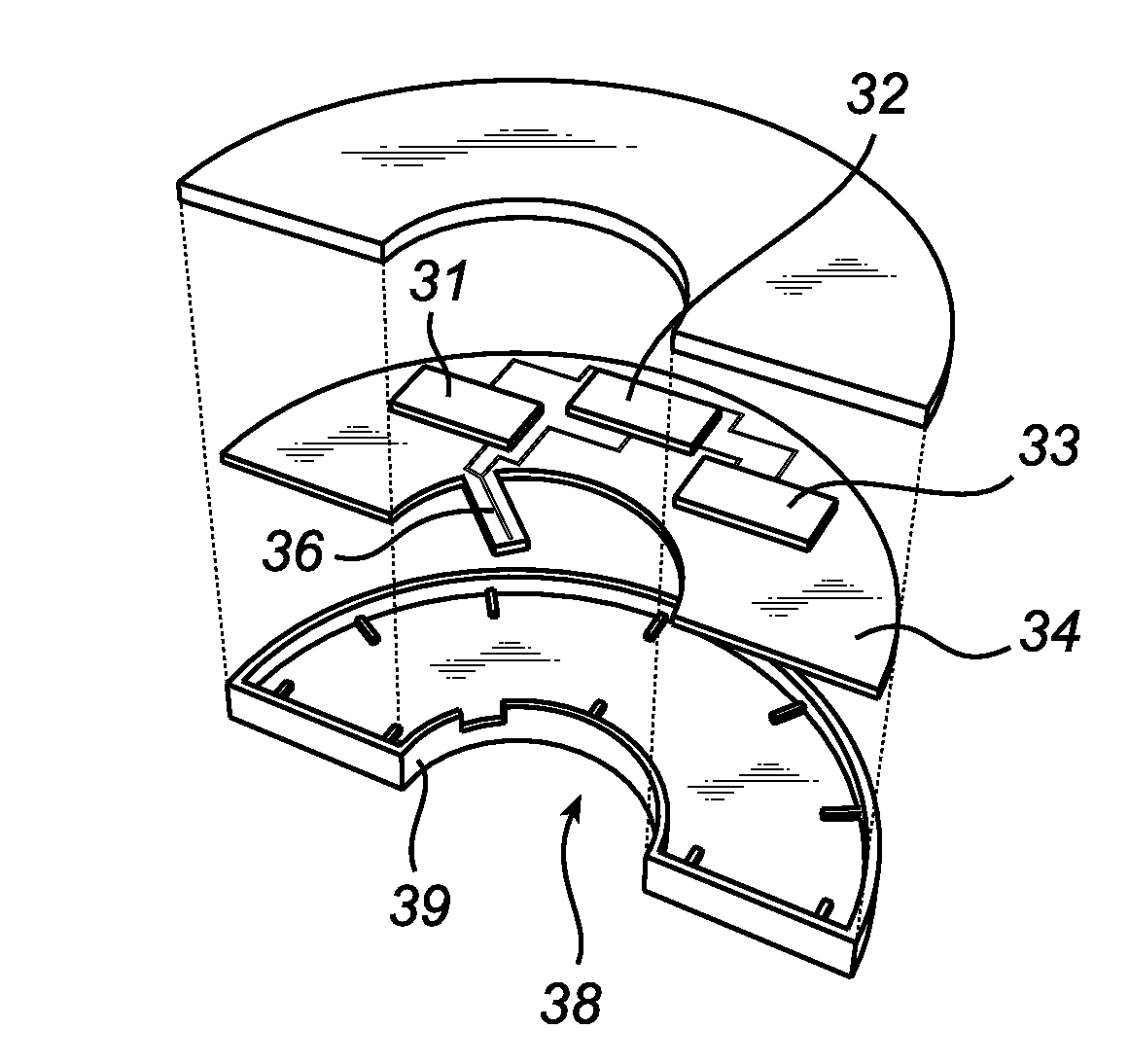
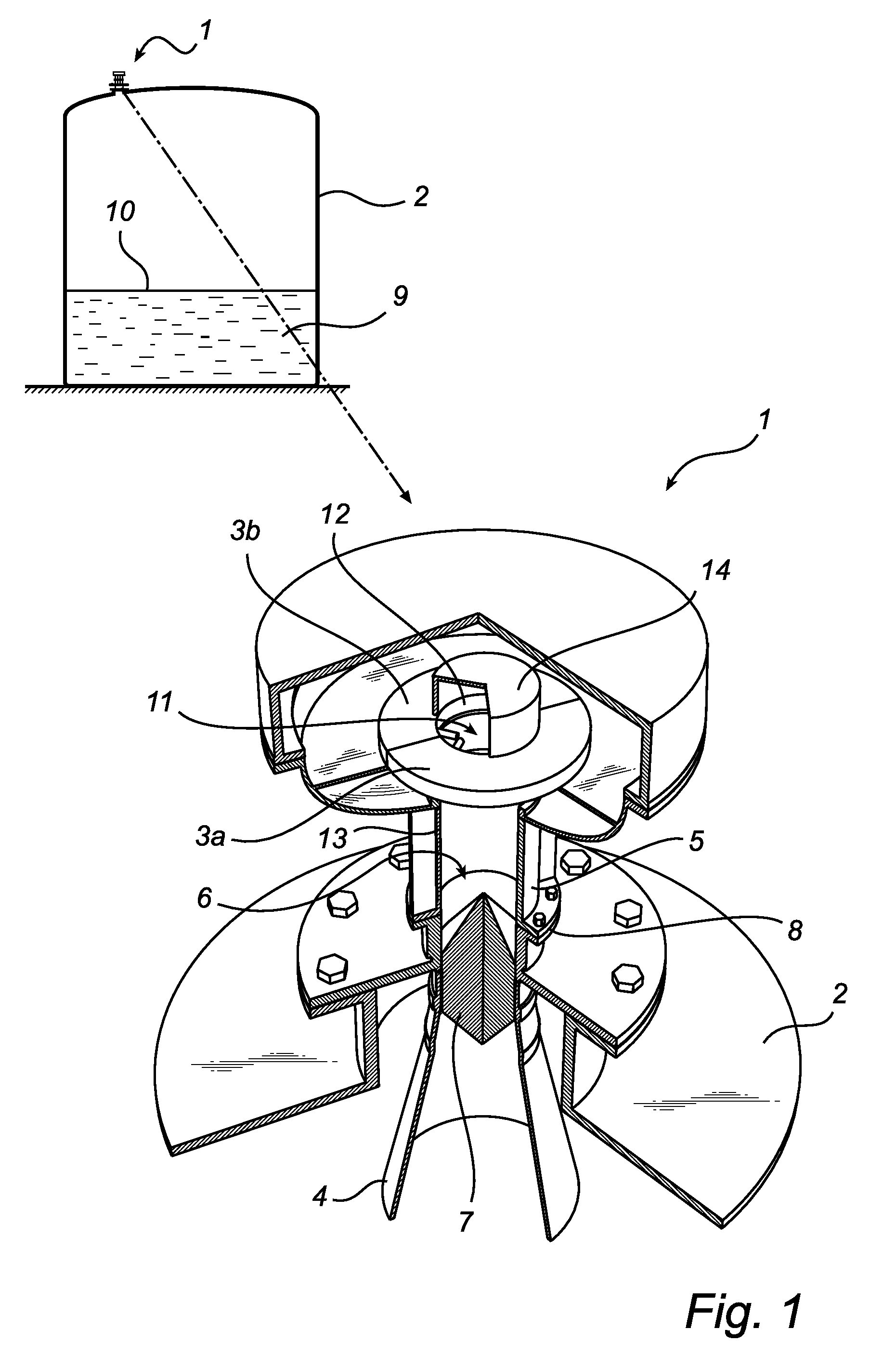
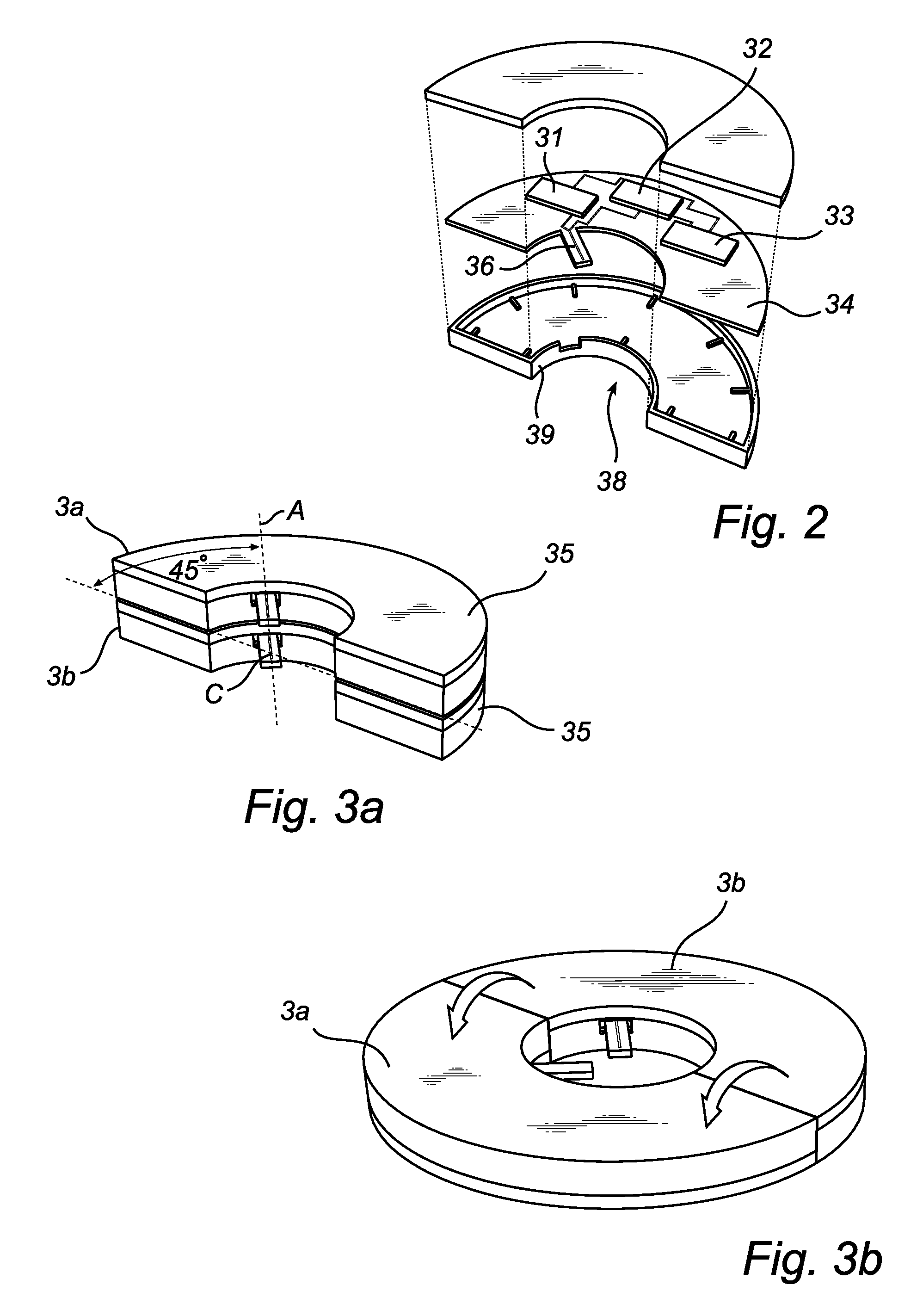
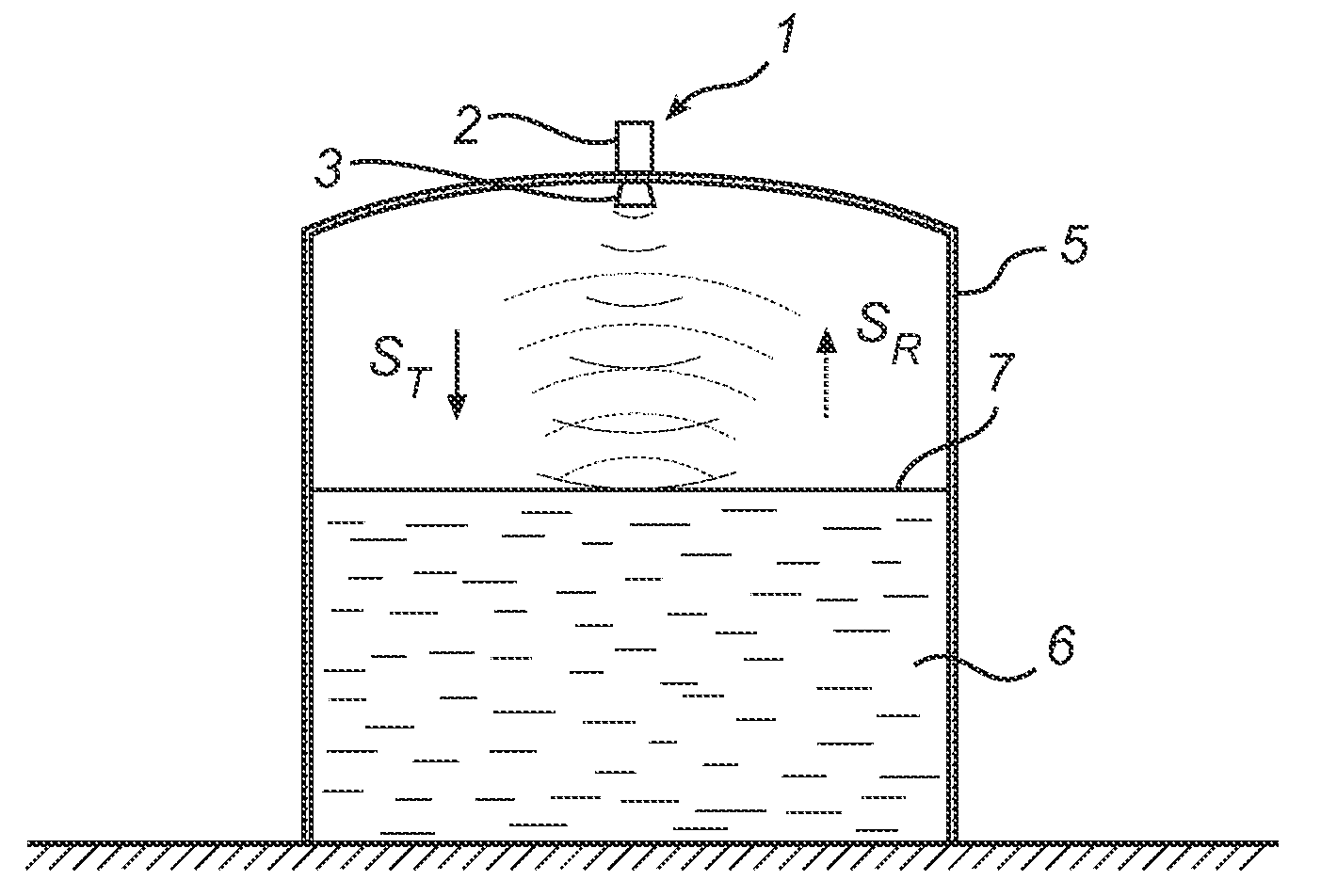
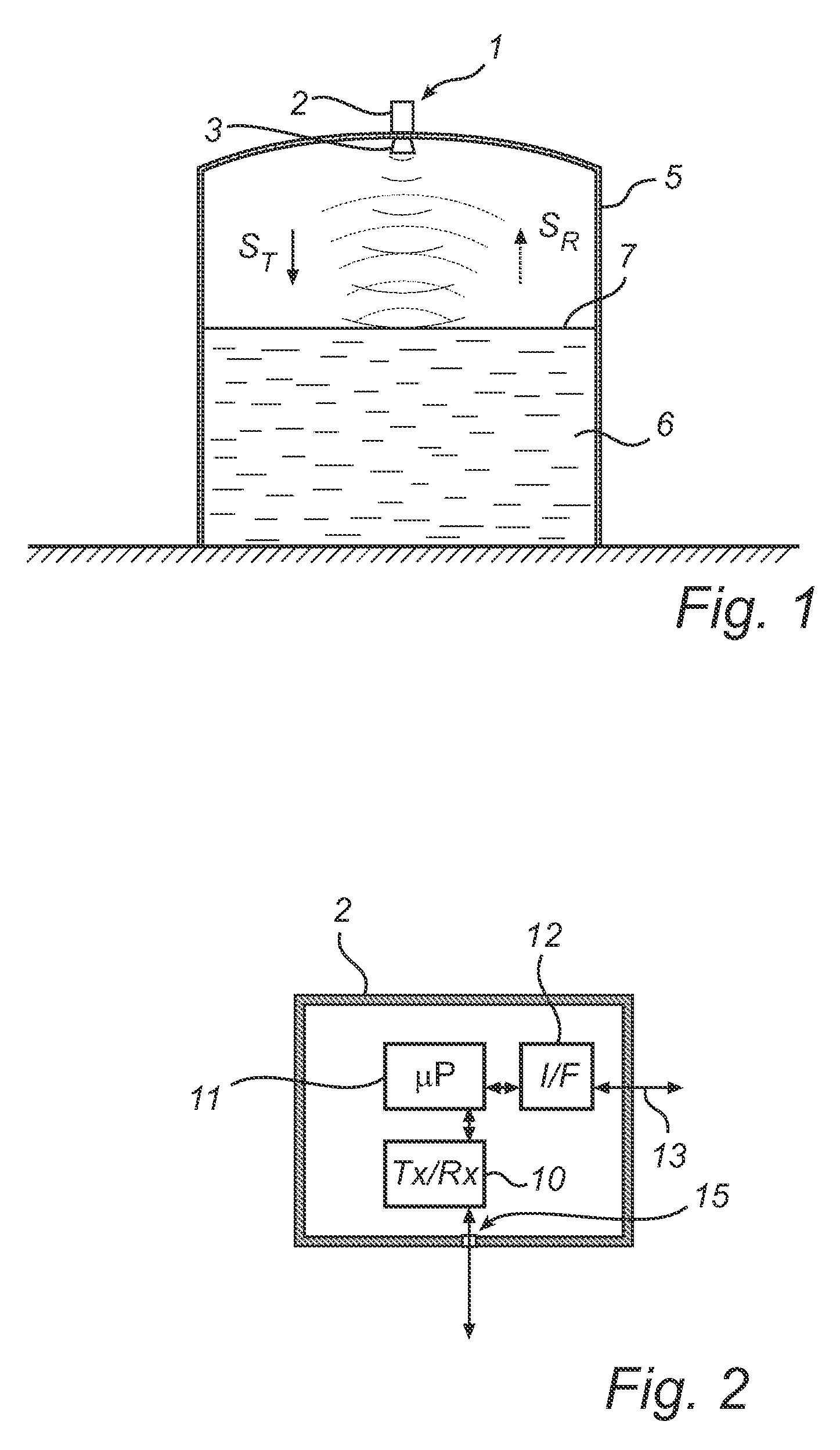
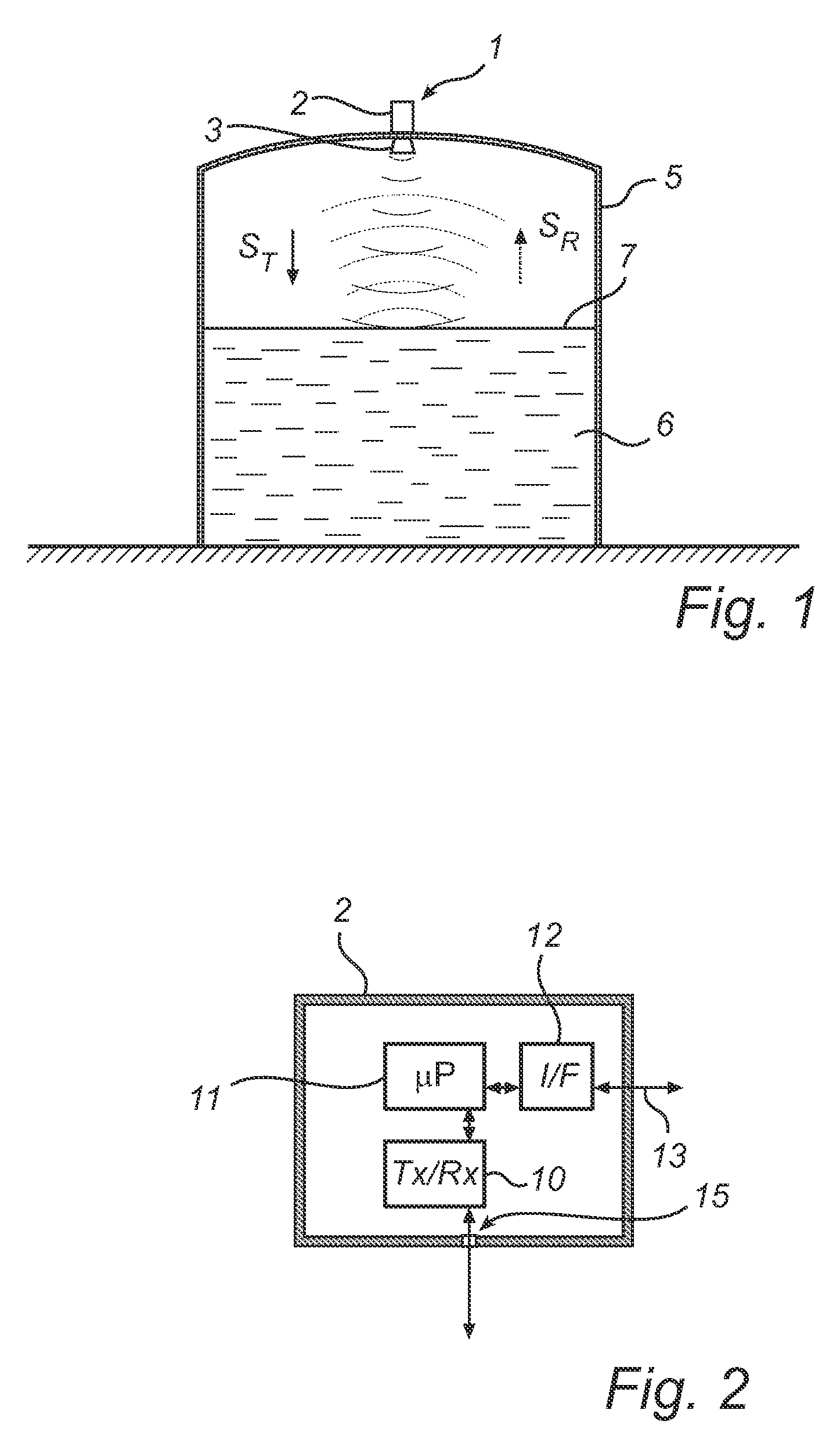
Multi-channel radar level gauge system
ActiveUS7701385B2Simple and cost-effective to produceImprove performanceLevel indicatorsAntenna detailsTransceiverRadar
A radar level gauging system for determining a filling level of a product contained in a tank by transmitting and receiving microwave signals over at least two functionally independent channels. Each channel has an electronics unit with transceiver circuitry arranged on a printed circuit board and processing circuitry connected to the transceiver circuitry for determining the filling level based on a relation between transmitted signals and received signals, and each electronics unit is electronically and galvanically separated from other electronics units. The system further comprises a single antenna for emitting microwave signals into the tank, and a hollow waveguide for guiding microwave signals between each transceiver circuitry and the antenna. Each electronics unit further comprises feeding circuitry arranged on the printed circuit board, the feeding circuitry comprising at least one feeding probe protruding into the waveguide for feeding the microwave signals into the waveguide.The present invention enables a very simple, cost-effective and reliable feeding for each channel.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Line transition device between dielectric waveguide and waveguide, and oscillator, and transmitter using the same
InactiveUS6867660B2Avoid radiationReduce lossResonatorsWaveguidesElectrical conductorHollow waveguide
A line transition device which intervenes between a non radiative dielectric waveguide and a hollow waveguide for example, includes a dielectric waveguide having a dielectric strip held by a pair of conductors which face each other, and a waveguide, wherein a part of the dielectric strip of the dielectric waveguide is adjacent to or inserted in the hollow waveguide.
Owner:KITURAMI BOILER
Waveguide device module and microwave module
InactiveUS20190140344A1Reduce lossesEasy to installSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesElectrical conductorMicrowave
A waveguide device module includes a waveguide device including a conductor with an electrically conductive surface, a waveguide extending alongside the electrically conductive surface and including an electrically-conductive waveguide surface, and a first artificial magnetic conductor extending on both sides of the waveguide, a coupler including a first surface having a groove, a second surface opposite to the first surface, and a through hole extending from the first surface through to the second surface. The groove is connected at one end to the through hole and defined by first and second metal side surfaces opposing each other and a metal bottom surface connecting between the first and second metal side surfaces. A second artificial magnetic conductor at least opposes the groove. The first and second metal side surfaces, and the metal bottom surface define a ½ rectangular hollow-waveguide. The ½ rectangular hollow-waveguide and the waveguide device are connected via the through hole.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP +1
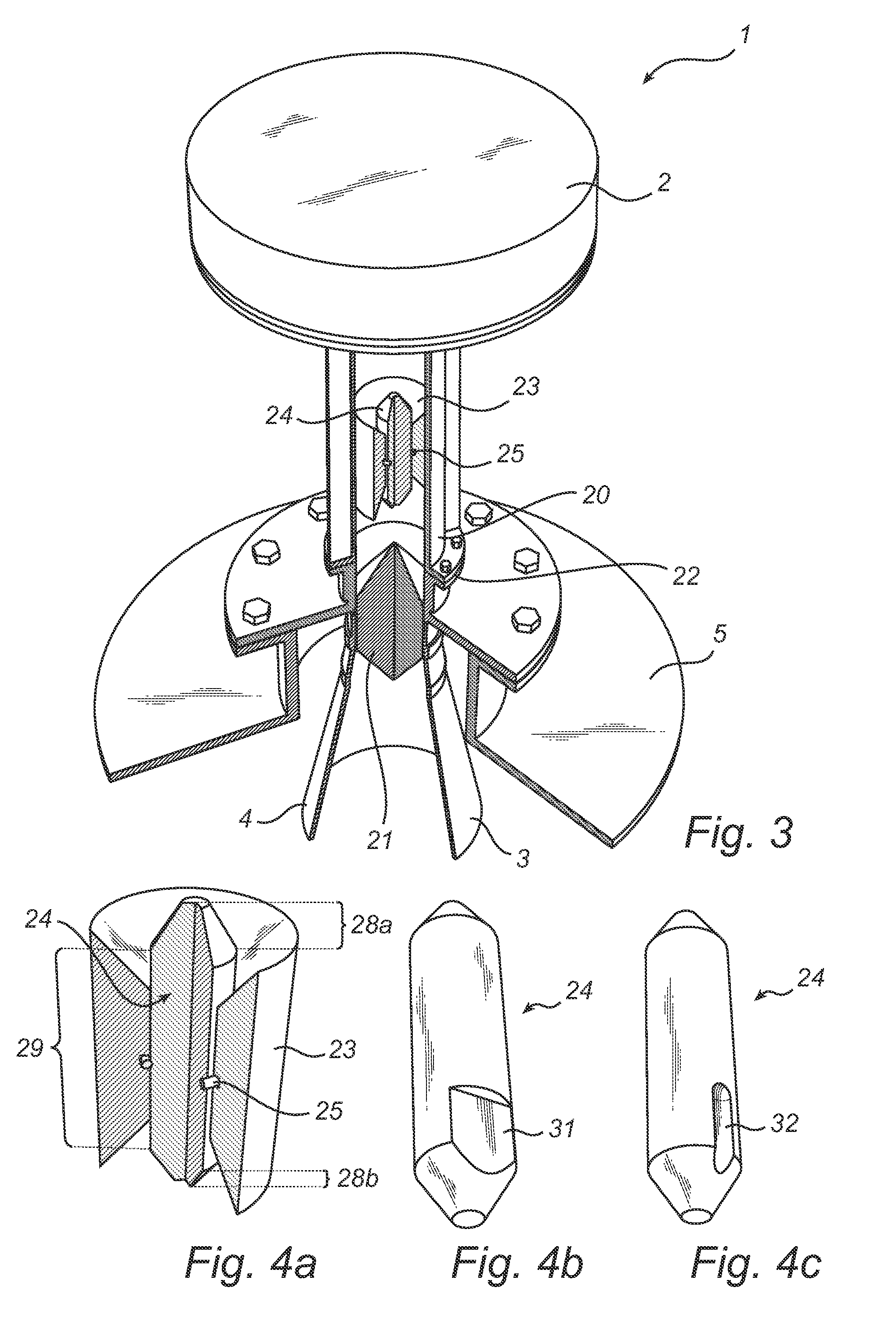
Radar level gauge system with leakage detection
InactiveUS20100231438A1Easily and conveniently changedImprove transmittanceDetection of fluid at leakage pointTesting/calibration apparatusMicrowave propagationTransceiver
A radar level gauge system, for determining a filling level of a product contained in a tank, comprising a transceiver for generating, transmitting and receiving electromagnetic signals; an antenna arranged to direct transmitted electromagnetic signals towards a surface of the product contained in the tank, and to return reflected electromagnetic signals resulting from reflections at impedance transitions encountered by the transmitted electromagnetic signals back to the transceiver; and a hollow waveguide connecting the transceiver and the antenna for guiding the electromagnetic signals therebetween. A sealing member is arranged to seal the waveguide to prevent fluid from passing into the waveguide from an interior of the tank; and the radar level gauge system further comprises processing circuitry connected to the transceiver and configured to determine the filling level based on the reflected electromagnetic signals. The radar level gauge system further comprises a leak indication member being movably arranged inside the hollow waveguide in such a way that a force resulting from leakage of the fluid at the sealing member causes a movement of the leak indication member when acting thereon; and the hollow waveguide is configured in such a way that the movement of the leak indication member causes a change in at least one microwave propagation characteristic of the hollow waveguide.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Integration of a terahertz quantum cascade laser with a hollow waveguide
ActiveUS8213476B1Improve efficiencyPower optimizationNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersAudio power amplifierCoupling
The present invention is directed to the integration of a quantum cascade laser with a hollow waveguide on a chip to improve both the beam pattern and manufacturability. By coupling the QCL output into a single-mode rectangular waveguide the radiation mode structure can be known and the propagation, manipulation, and broadcast of the QCL radiation can then be entirely controlled by well-established rectangular waveguide techniques. By controlling the impedance of the interface, enhanced functions, such as creating amplifiers, efficient coupling to external cavities, and increasing power output from metal-metal THz QCLs, are also enabled.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Laser material processing system
ActiveUS9018562B2Wide bandwidthImproving pulse performanceLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesOptoelectronicsMaterials processing
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Quasi-phase matching and quantum control of high harmonic generation in waveguides using counterpropagating beams
InactiveUS20080137696A1Enhance high-harmonic emissionSuppress emissionLaser using scattering effectsX-ray apparatusHigher order harmonicsLight beam
All-optical quasi-phase matching (QPM) uses a train of counterpropagating pulses to enhance high-order harmonic generation (HHG) in a hollow waveguide. A pump pulse enters one end of the waveguide, and causes HHG in the waveguide. The counterpropagation pulses enter the other end of the waveguide and interact with the pump pulses to cause QPM within the waveguide, enhancing the HHG.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Focusing multimodal optical microprobe devices
ActiveUS8554031B2Efficient couplingLittle lossNanoopticsSurgical instrument detailsHollow coreWavelength scale
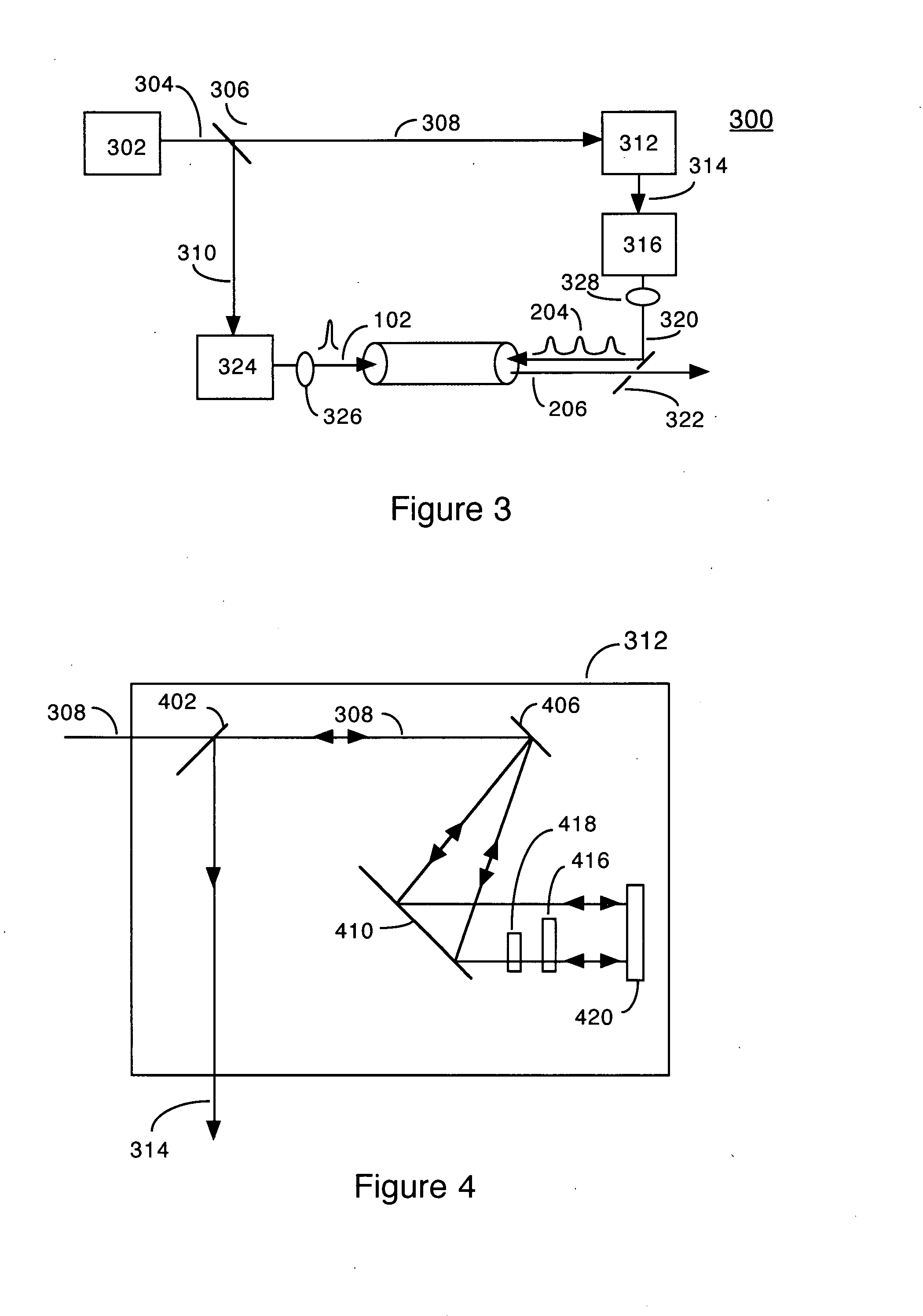
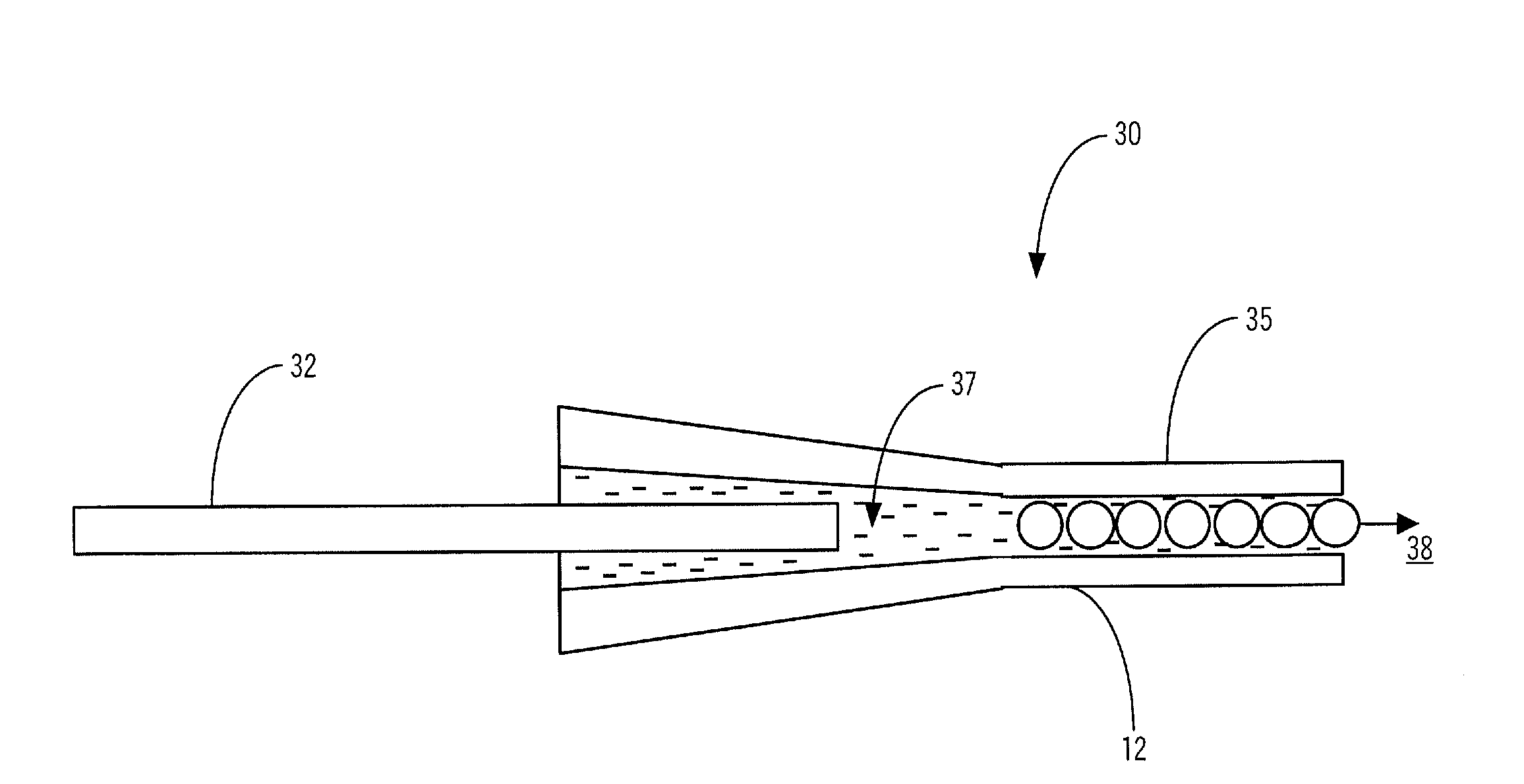
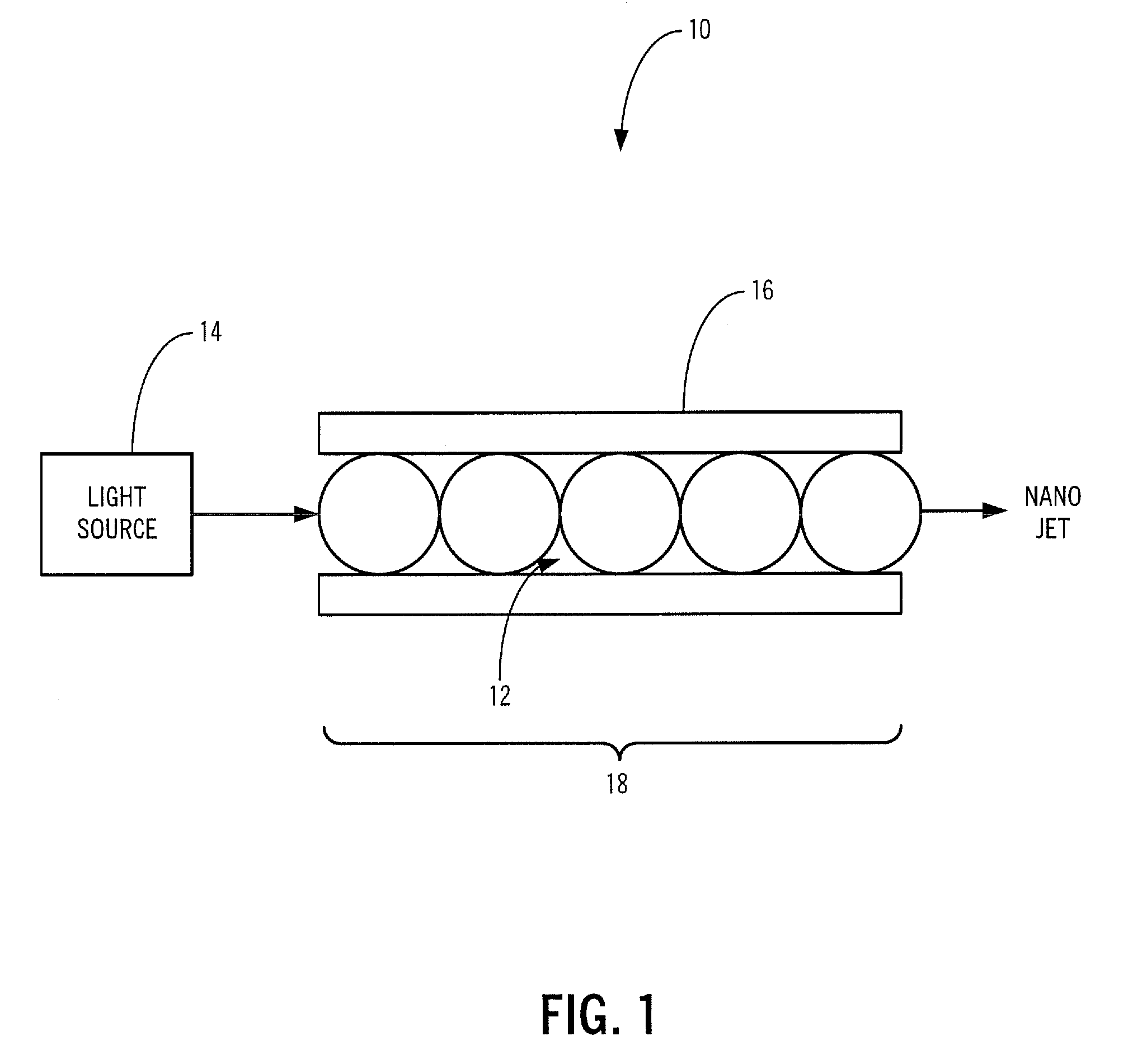
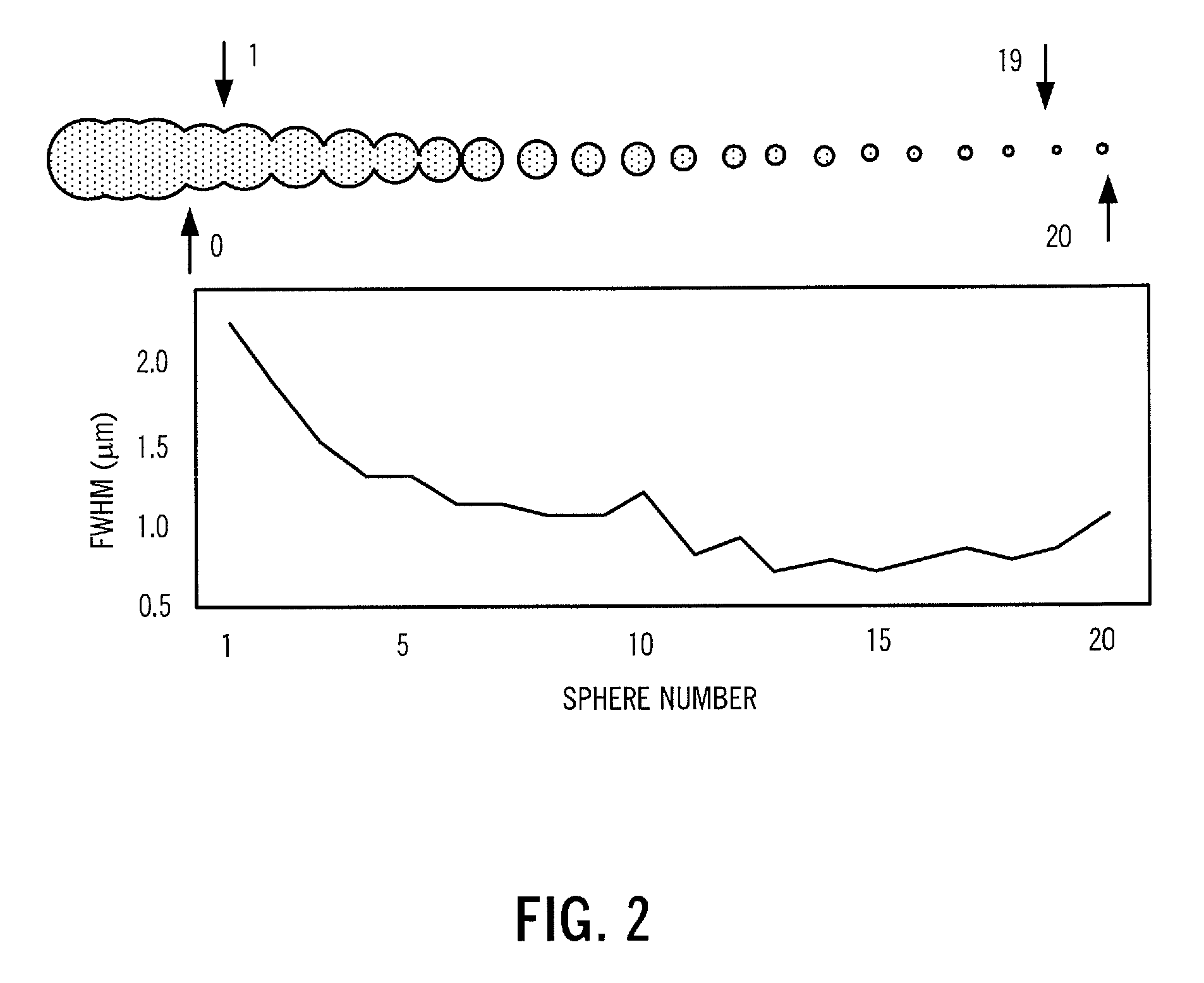
The present invention provides an optical microprobe device and method for focusing multimodal radiation with wavelength-scale spatial resolution and delivering the focused radiation to a specimen, including: a radiation source; and one or more of a plurality of optically transparent or semitransparent spheres and a plurality of optically transparent or semitransparent cylinders optically coupled to the radiation source; wherein the one or more of the plurality of optically transparent or semitransparent spheres and the plurality of optically transparent or semitransparent cylinders periodically focus radiation optically transmitted from the radiation source such that radiation ultimately transmitted to the specimen has predetermined characteristics. Preferably, the spheres or cylinders are assembled inside one of a hollow waveguide, a hollow-core photonic crystal fiber, a capillary tube, and integrated in a multimode fiber. Alternatively, the spheres or cylinders are assembled on a substrate. Optionally, the optical microprobe device also includes one or more of a waveguide, an optical fiber, a lens, and an optical structure disposed between the radiation source and the spheres or cylinders. Optionally, the spheres or cylinders are made from optically nonlinear or active materials that permit efficient nonlinear frequency generation and low-threshold lasing using the optical microprobe device.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
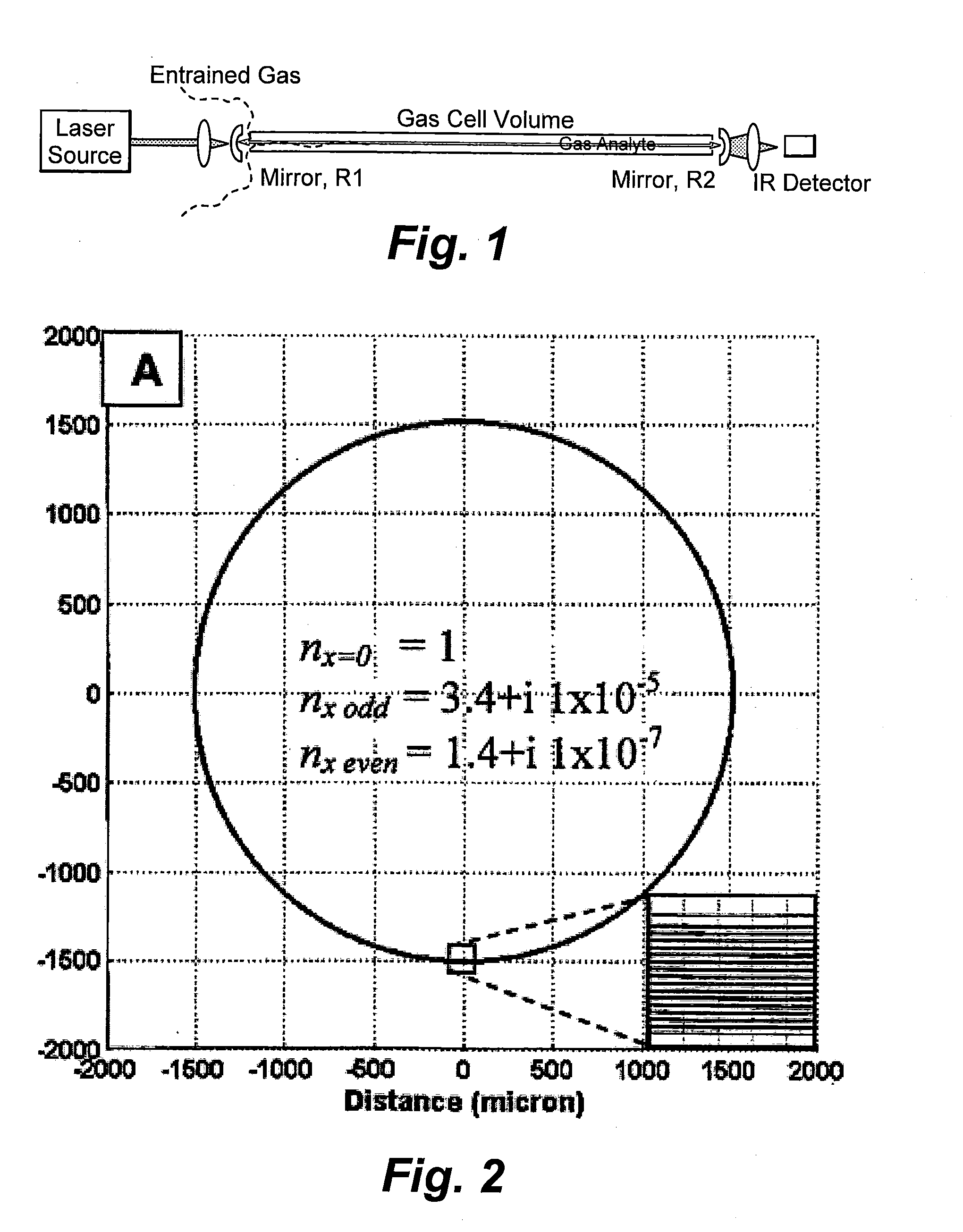
Hollow waveguide cavity ringdown spectroscopy
InactiveUS20090059234A1High energyEliminate requirementsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsLaser lightAbsorption spectroscopy
Laser light is confined in a hollow waveguide between two highly reflective mirrors. This waveguide cavity is used to conduct Cavity Ringdown Absorption Spectroscopy of loss mechanisms in the cavity including absorption or scattering by gases, liquid, solids, and / or optical elements.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
Optical switching system based on hollow waveguides
InactiveUS6839478B2Low insertion lossLow refractive indexCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesOptical communicationHollow waveguide
A hollow waveguide based optical switch, and novel hollow waveguide-based switch architectures for optical communications. The switch comprises a pair of hollow waveguides overlapping over a common section that includes a common opening, a first conductive flexible lever attached to one of the hollow waveguides, the first lever configured to assume upon actuation at least two switching positions within the pair of waveguides at the common opening, a second conductive flexible lever attached to the other of the hollow waveguides, the second lever configured to assume upon same the actuation same at least two switching positions within the pair of waveguides as the first lever while keeping a substantially parallel geometry with the first lever, and means to actuate the first and the second levers in order to achieve the at least two switching positions.
Owner:TERRAOP
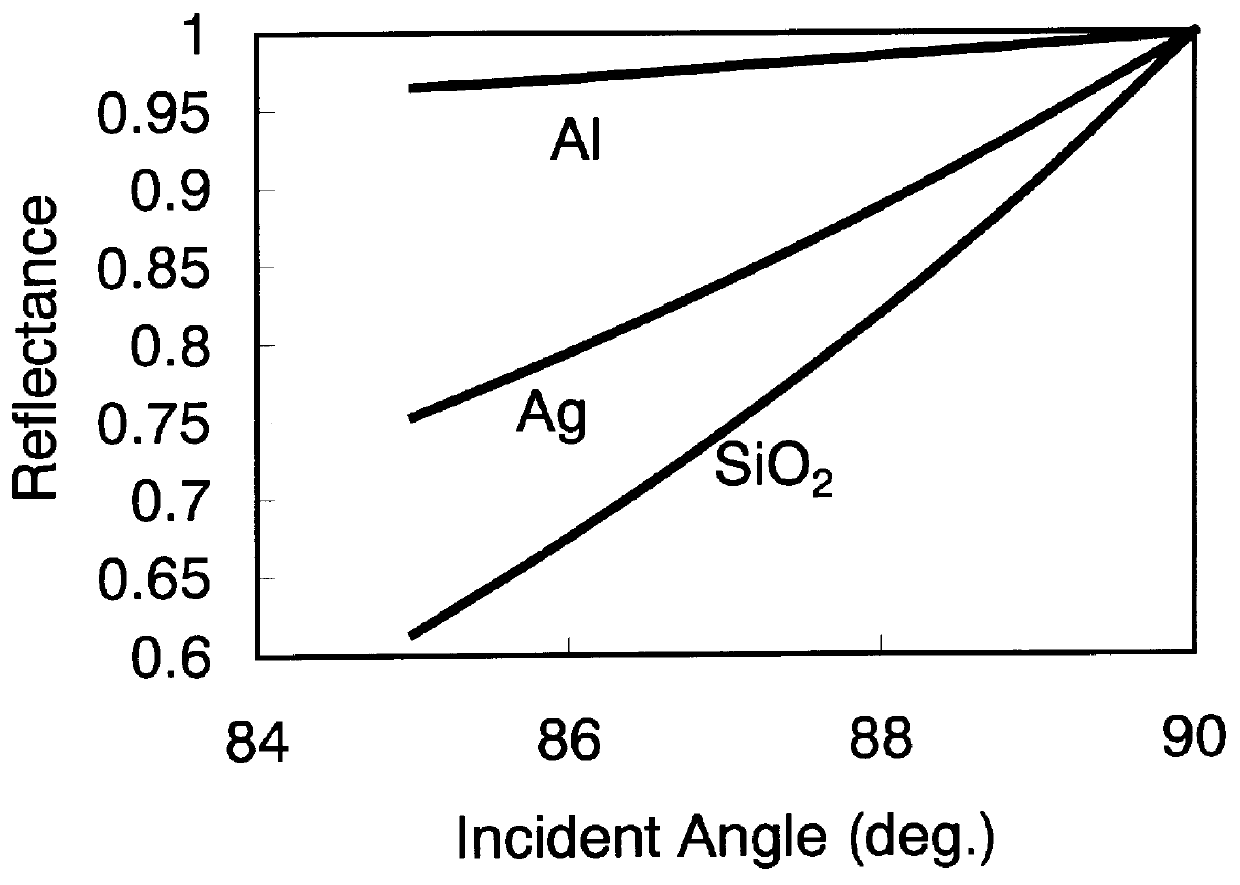
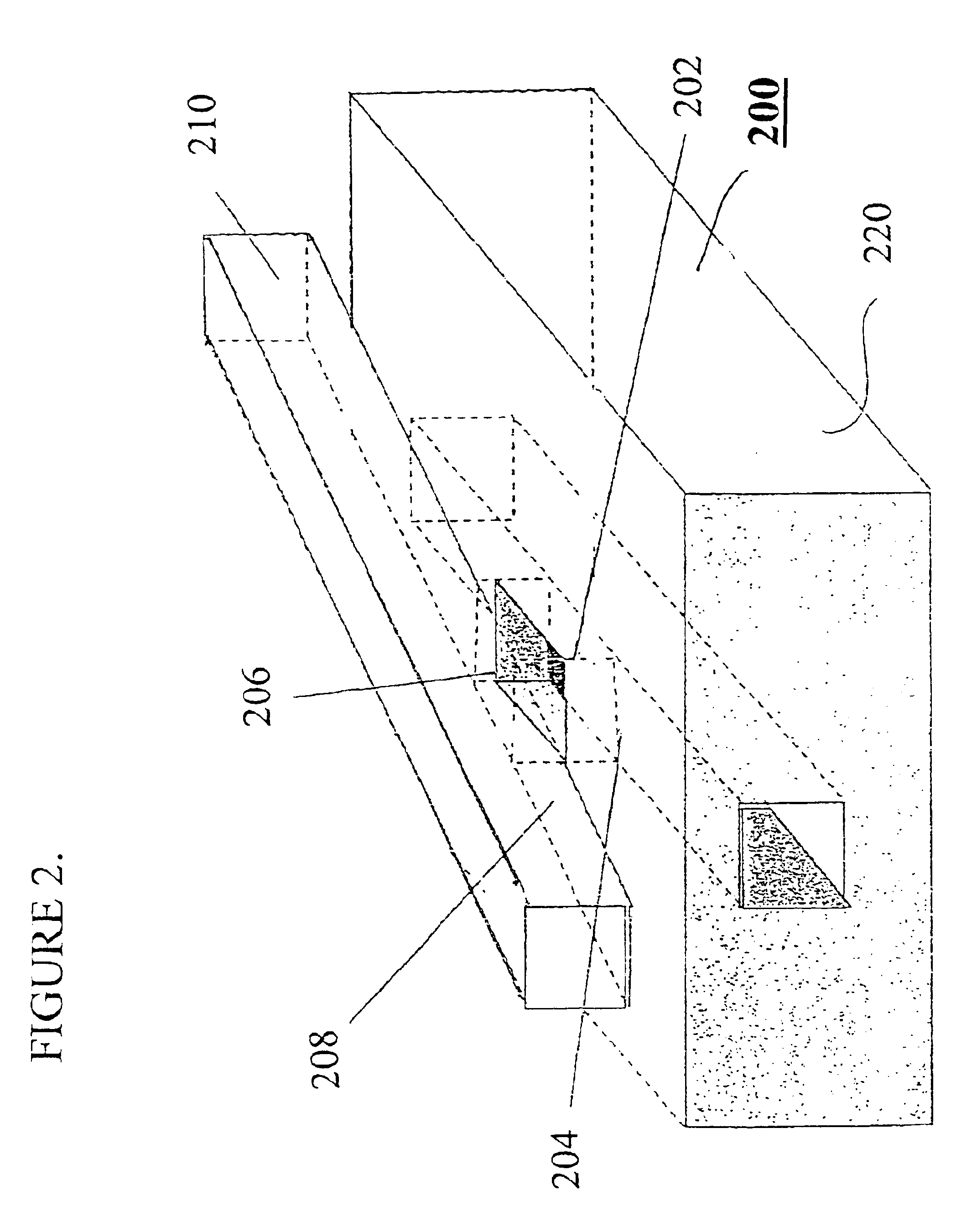
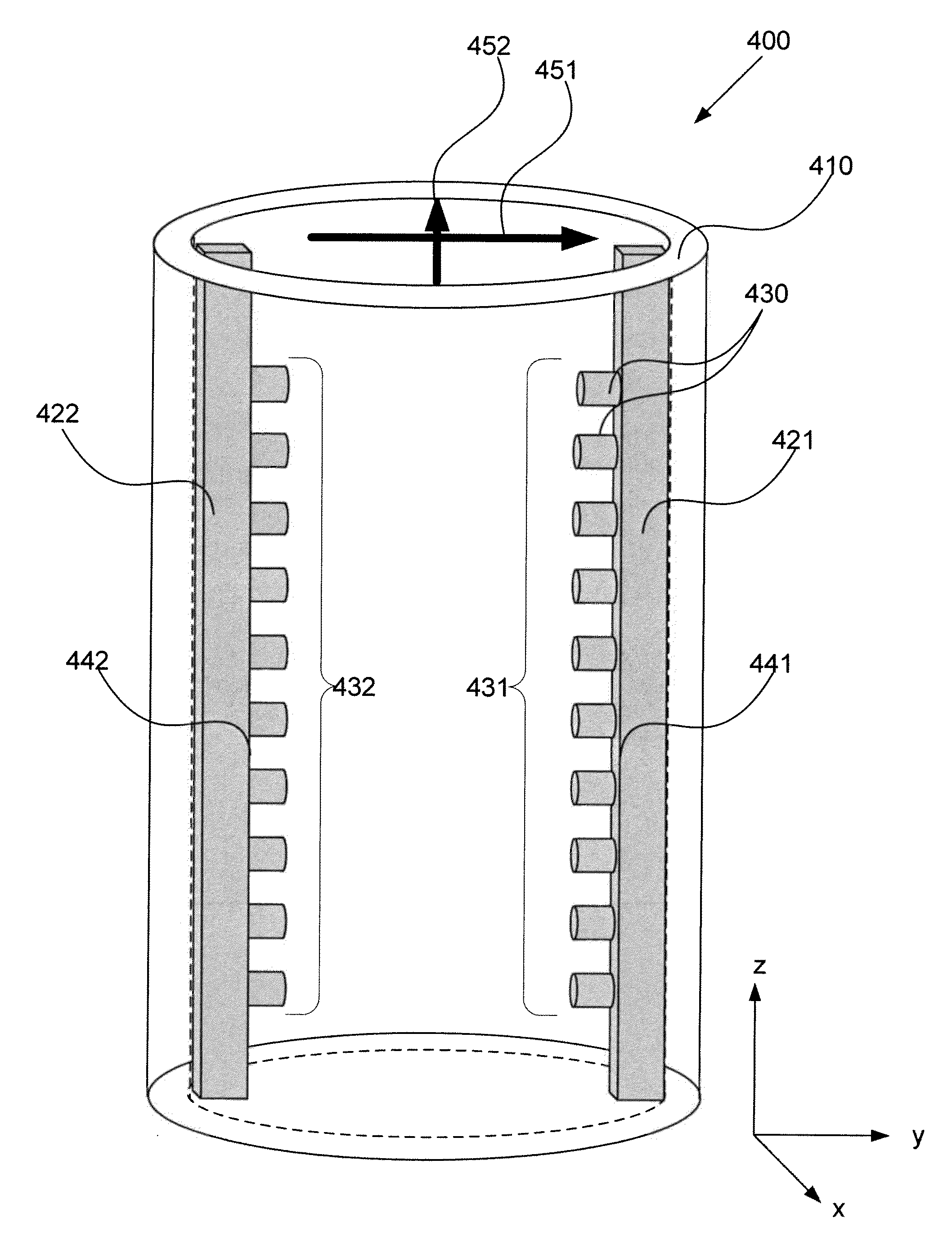
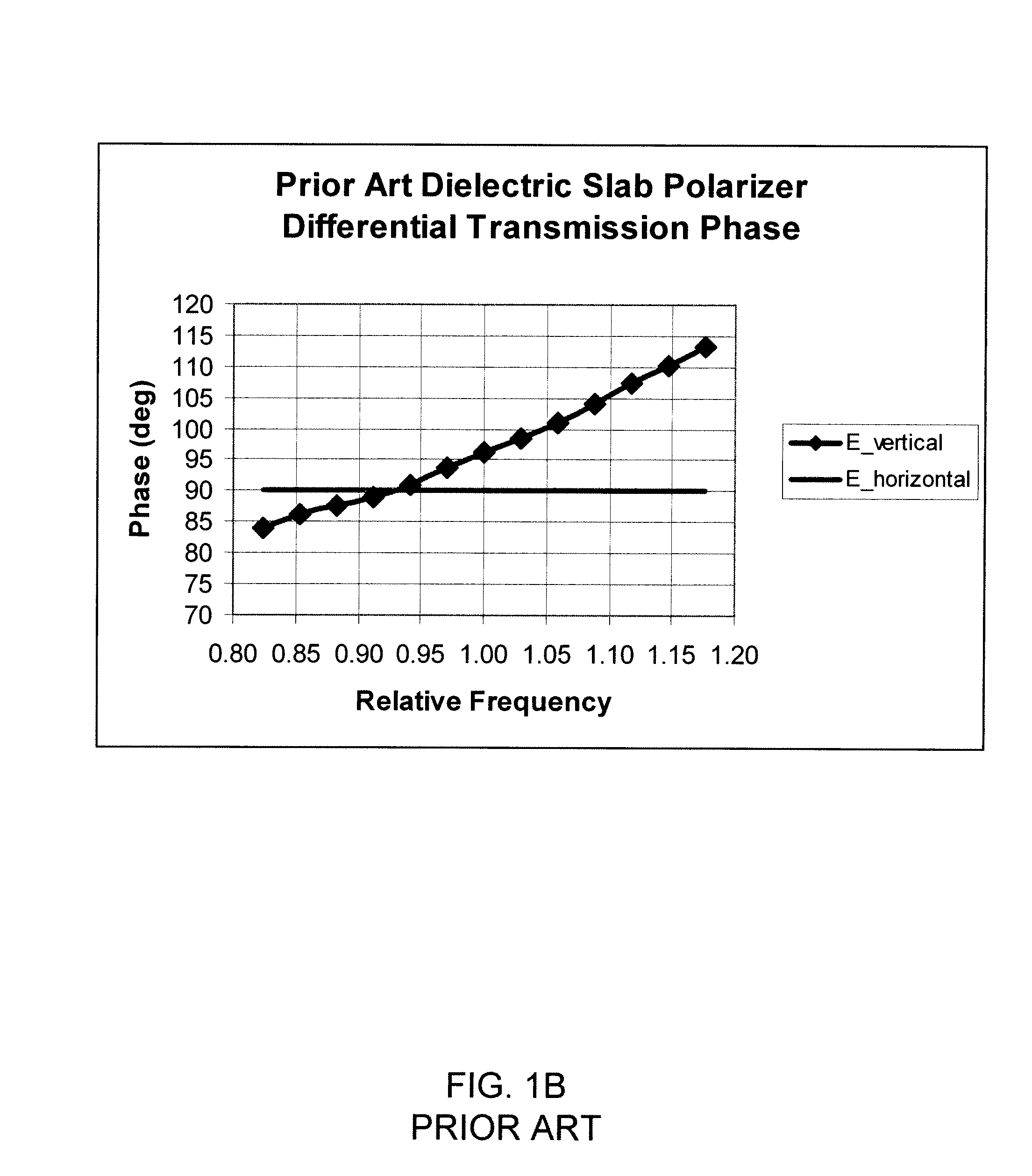
High Power Waveguide Polarizer With Broad Bandwidth and Low Loss, and Methods of Making and Using Same
ActiveUS20110133863A1Wide bandwidthOffset inductive loadingWaveguide type devicesPhase retardationElectrical conductor
Embodiments of the invention provide high power waveguide polarizers with broad bandwidth and low loss, and methods of making and using the same. Under one aspect of the present invention, a waveguide polarizer includes a hollow waveguide body having an interior surface; a first ridge disposed on the interior surface of the hollow waveguide body and having an inward-facing surface; and a first plurality of projections disposed on the inward-facing surface of the first ridge. The projections may have a width that is narrower than that of the ridge, and a length that is tunable. The length of the projections may be selected to induce about a 90-degree phase delay in a first mode propagating in a plane parallel to the first ridge relative to a second mode propagating in a plane perpendicular to the first ridge.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Apparatus and method for real-time imaging and monitoring of an electrosurgical procedure
ActiveUS8655431B2Profound effect upon ophthalmic imaging and diagnosisImprove resolutionEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrosurgeryEngineering
An optical coherence tomography probe and laser combination device configured for real-time z-directional guidance of the incisional depth of a surgical procedure. It can be used alone or placed within the working channel of an endoscope. The device includes an OCT single mode fiber, and a laser fiber or laser hollow waveguide or electrical surgical wire positioned adjacent to the OCT single mode fiber. The single mode fiber is configured to move laterally when activated by an actuator to scan light data reflected from a sample that is positioned in front of a distal end of the device. The light data can be processed to generate a B-scan image. The device can collect data in real-time during lasing, or immediately prior to and following the cutting. The surgical tool, when coupled to a processor, can deactivate when the B-scan image identifies that the incision is within a predefined tolerance.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Method and apparatus for delivery of x-ray irradiation
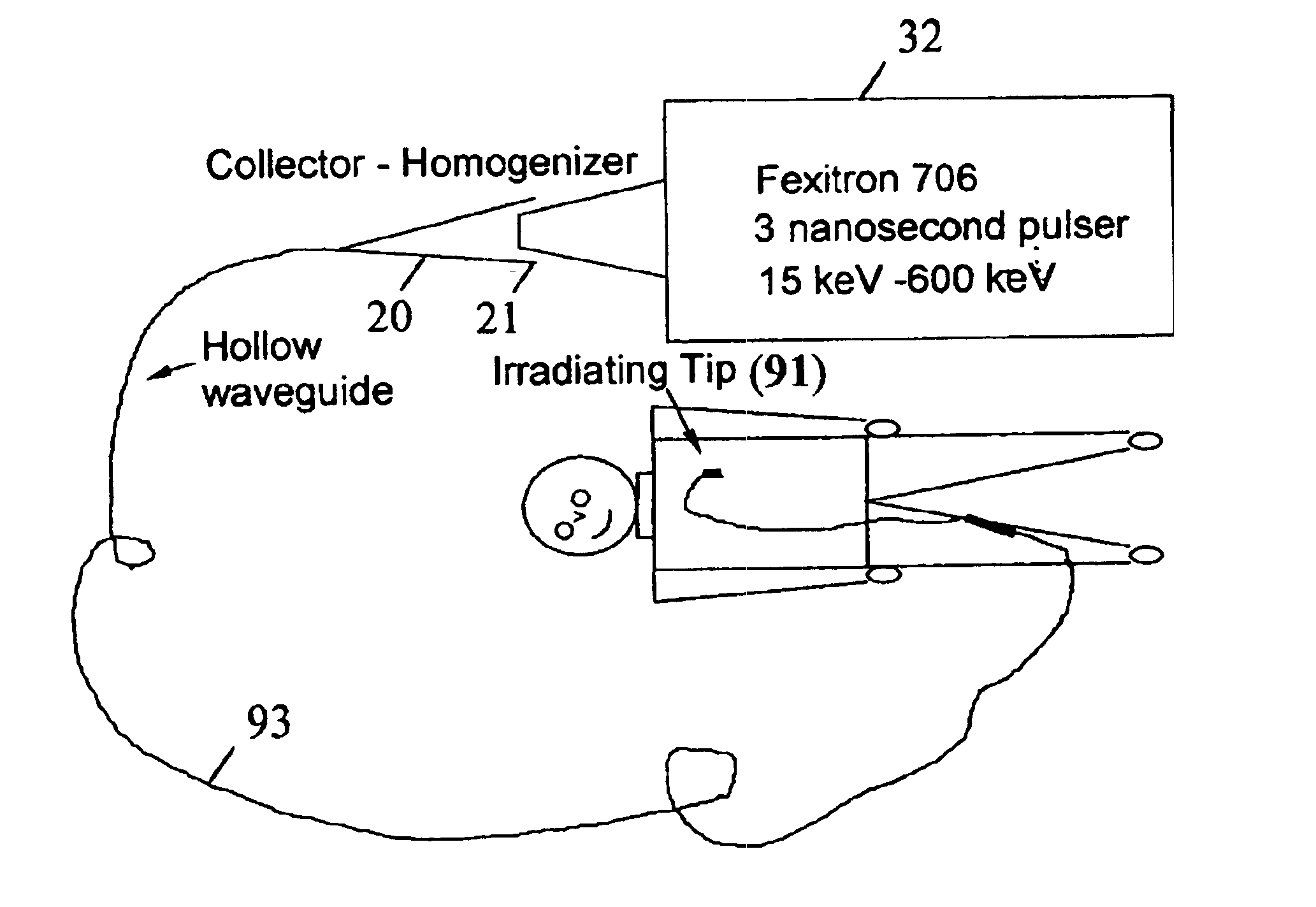
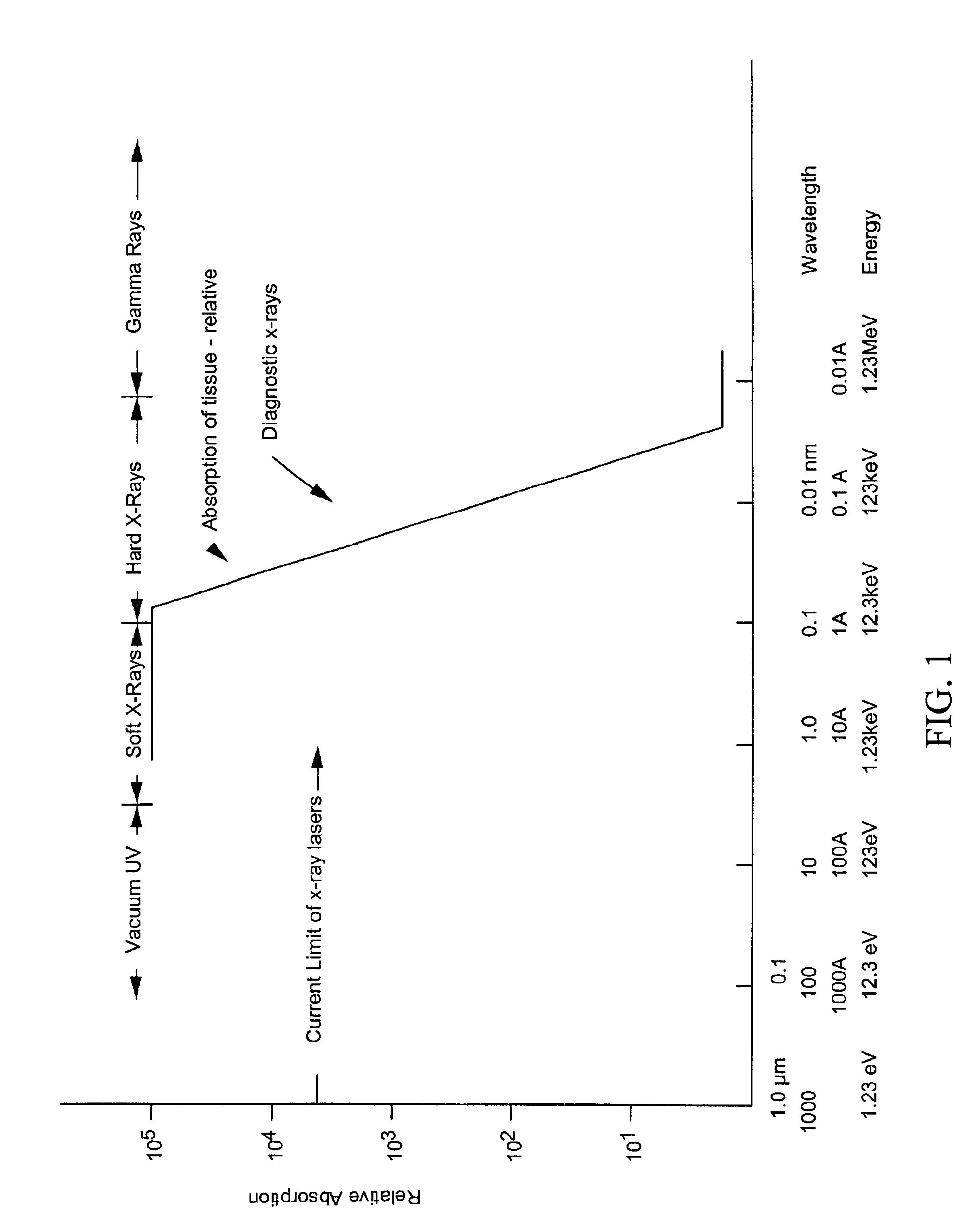
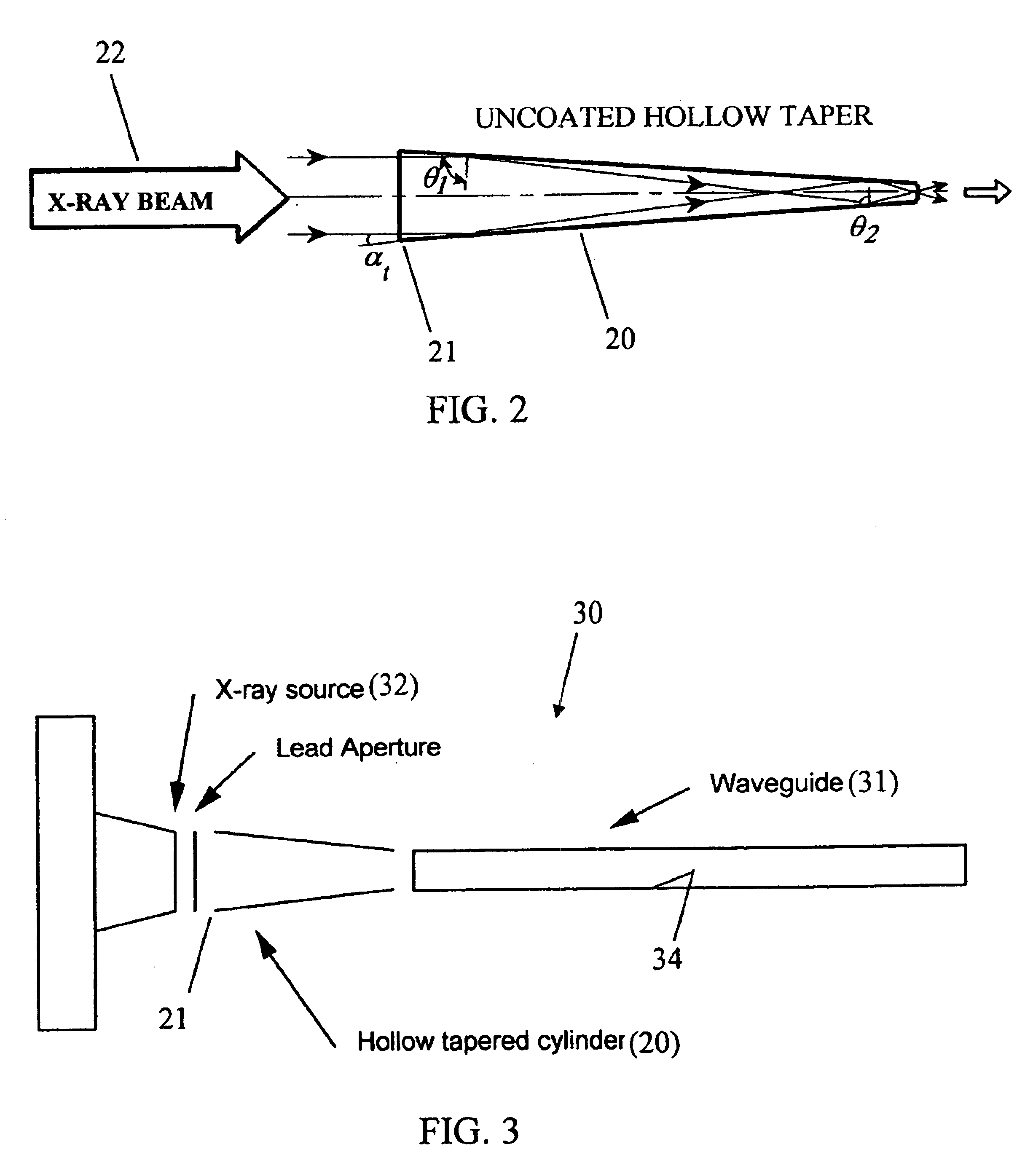
InactiveUS6847700B1Maximum effectivenessAvoid cloggingHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPercent Diameter StenosisX-ray
The subject invention pertains to a method and apparatus for generation and / or delivery of x-ray irradiation. The subject invention can be used to deliver x-ray irradiation to an artery in order to prevent restenosis in the artery. For example, a short pulse laser generated ionizing dose of x-ray irradiation can be effectively delivered to the arterial wall using hollow waveguides. The delivery of such a dose can help to prevent restenosis. The use of short pulse x-rays can allow energy to be precisely delivered, and can reduce diffusion of the energy to nearby normal tissue during the exposure. The arterial walls can be irradiated from a cylindrical or conical symmetric mirrored reflective end tip mounted on the end of a hollow waveguide. The subject invention also pertains to a method and apparatus for delivery of x-ray radiation with respect to medical therapies such as tumor necrosis.
Owner:FLORIDA INST OF TECH
High power waveguide polarizer with broad bandwidth and low loss, and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS8248178B2Wide bandwidthOffset inductive loadingCoupling devicesElectrical conductorPhase retardation
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Method for detecting a gas species using a super tube waveguide
InactiveUS20070145275A1Inexpensively detectingRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsAngle of incidenceWater vapor
A method for detecting the concentration of one or more gas species by using infrared radiation emitted from one or more sources into a sample cell which is a hollow waveguide with multiple bends collectively greater than 180 degrees in three dimensions, the infrared radiation being quasi-focused into a beam with an angle of incidence between greater than approximately 0° and approximately 10° relative to a longitudinal axis of a first linear segment of the sample cell proximate the source, then detecting two or more signals in which one of the signals is used to compensate for water vapor. The methods can detect gas concentrations down to 1 ppm or less.
Owner:AIRWARE INC
Two-dimensional surface normal slow-light photonic crystal waveguide optical phased array
ActiveUS8200055B2High thermo-optic coefficientPromote formationCladded optical fibreNanoopticsRefractive indexLaser light
Methods and devices for optical beam steering are disclosed including coupling a laser light into an apparatus comprising a first substrate; an array of air core photonic crystal waveguides; columnar members etched around each air core waveguide; a pair of metal electrodes around the columnar members; a trench around the pair of metal electrodes surrounding each air core photonic crystal waveguide; a second substrate coupled to the first substrate comprising electrical interconnection lines; and a holographic fanout array comprising a third substrate; a photopolymer film coated on the third substrate; a hologram written in the photopolymer film configured to couple the laser light into the third substrate; and an array of holograms recorded in the photopolymer film configured to couple a portion of the laser light into the waveguides; and passing a current through the electrodes to induce a refractive index change in the first substrate to control the phase of the portion of the laser light that passes through each waveguide. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Radar level gauge system with leakage detection
InactiveUS7855676B2Rapid and remote detectionMinimize damageDetection of fluid at leakage pointTesting/calibration apparatusMicrowave propagationTransceiver
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com