Patents
Literature
302 results about "Microprobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microprobe is an instrument that applies a stable and well-focused beam of charged particles (electrons or ions) to a sample.
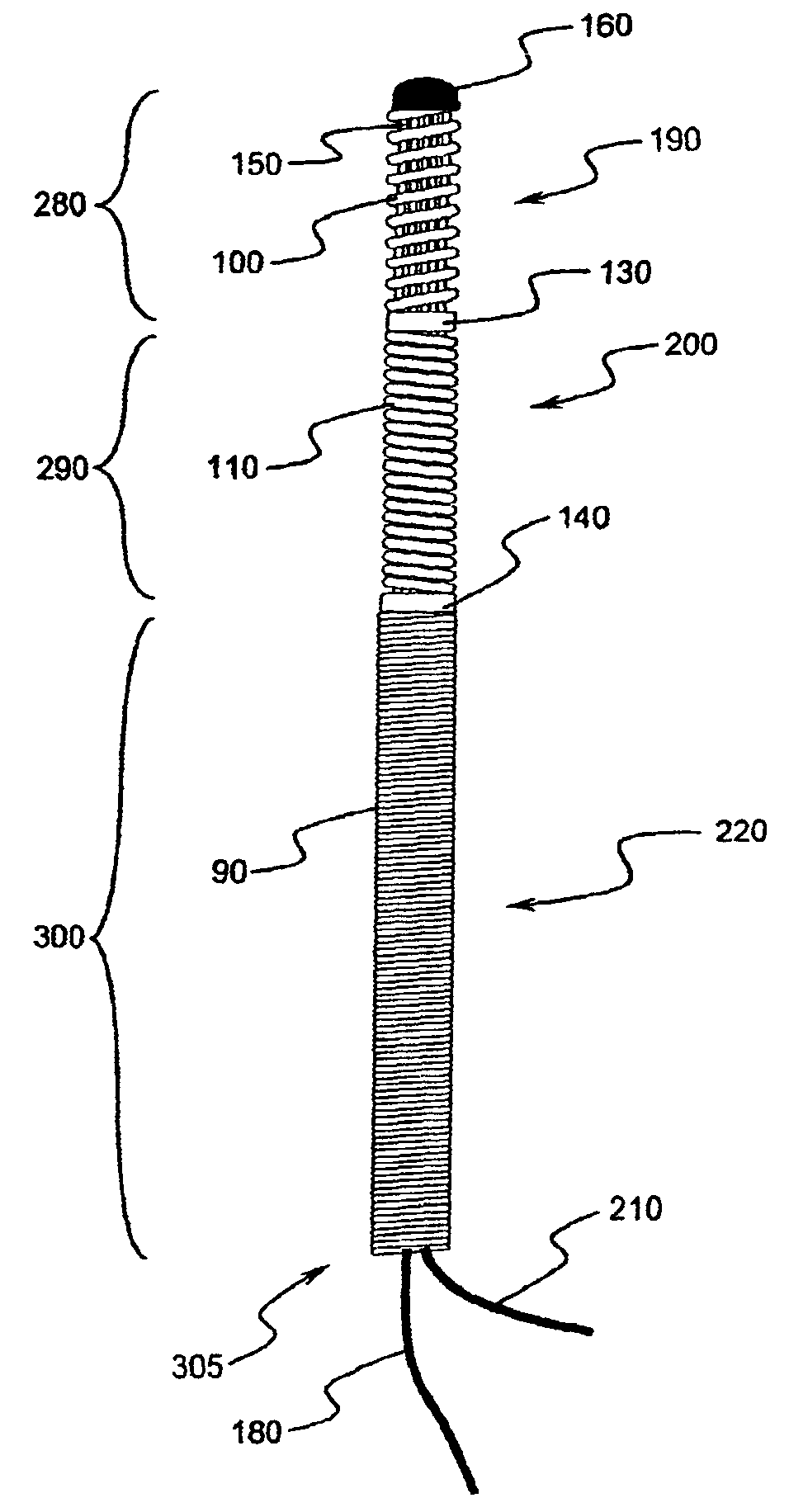
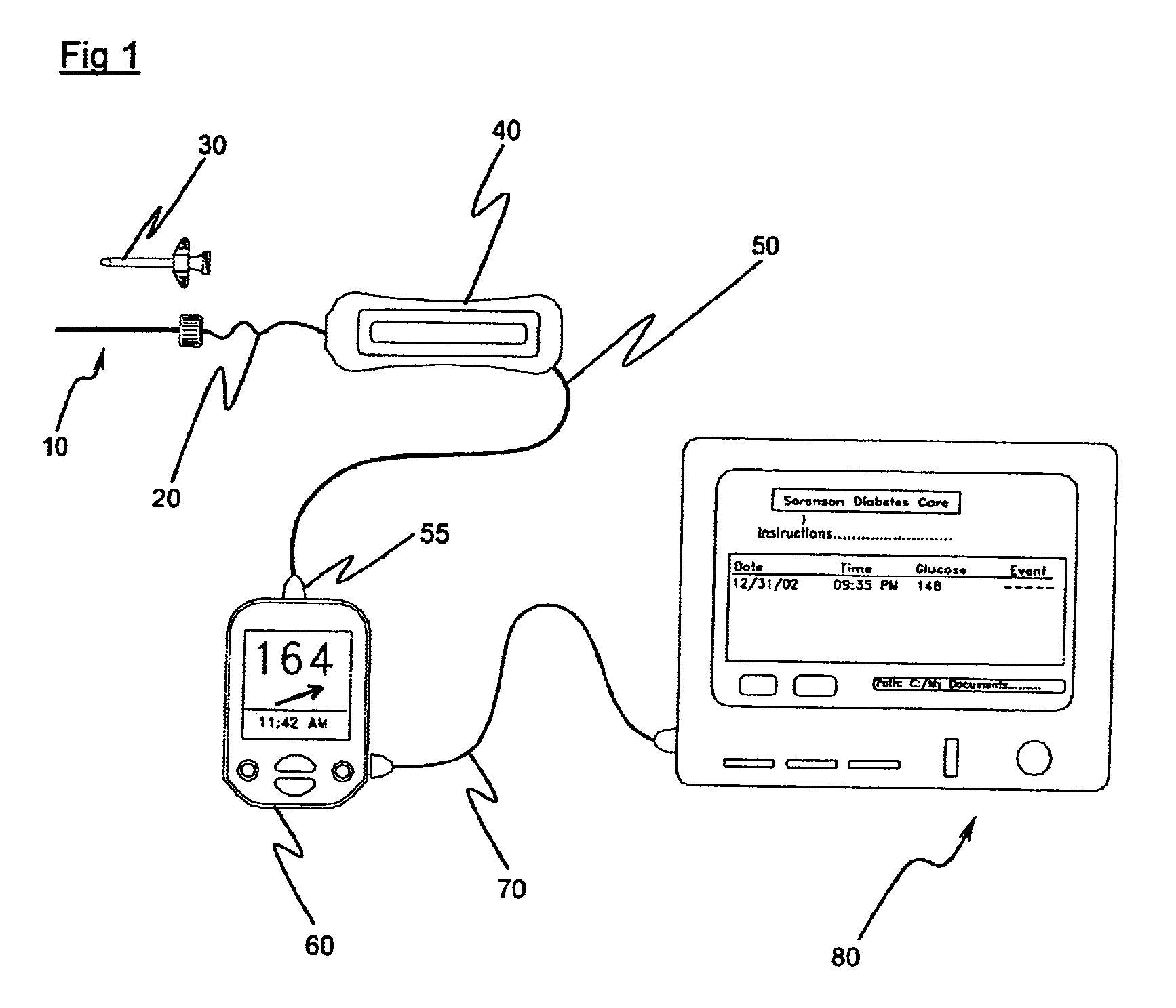
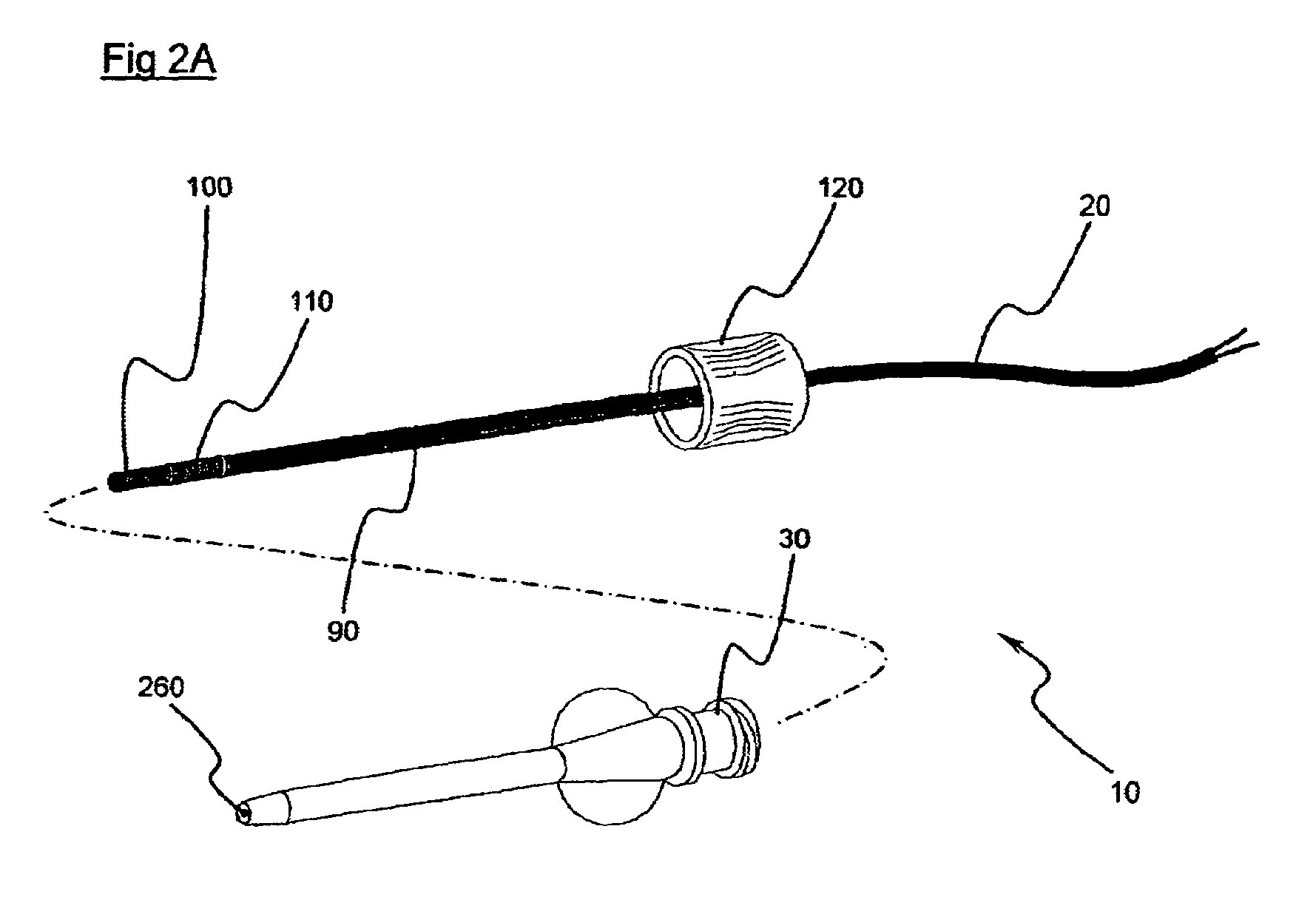
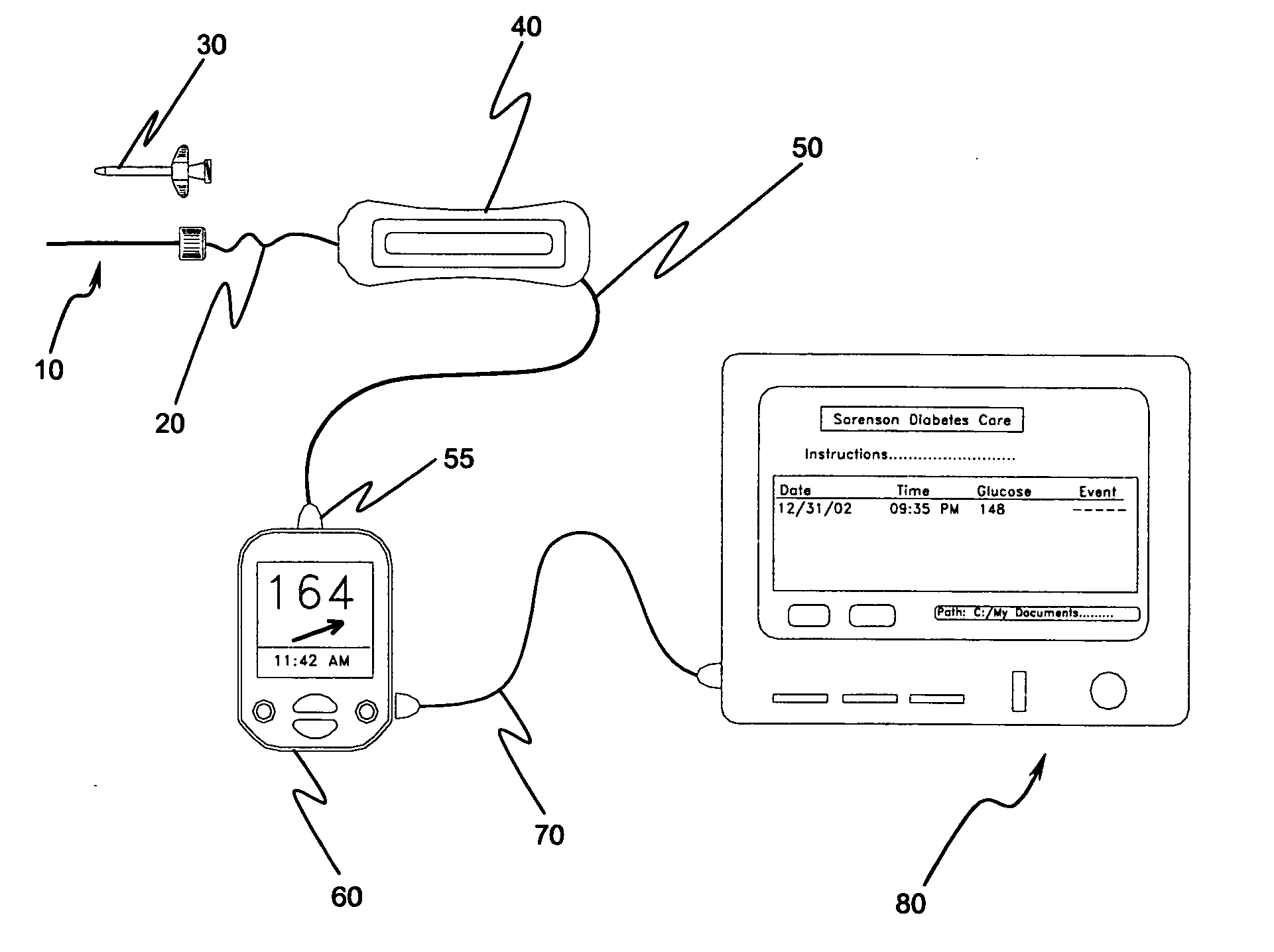
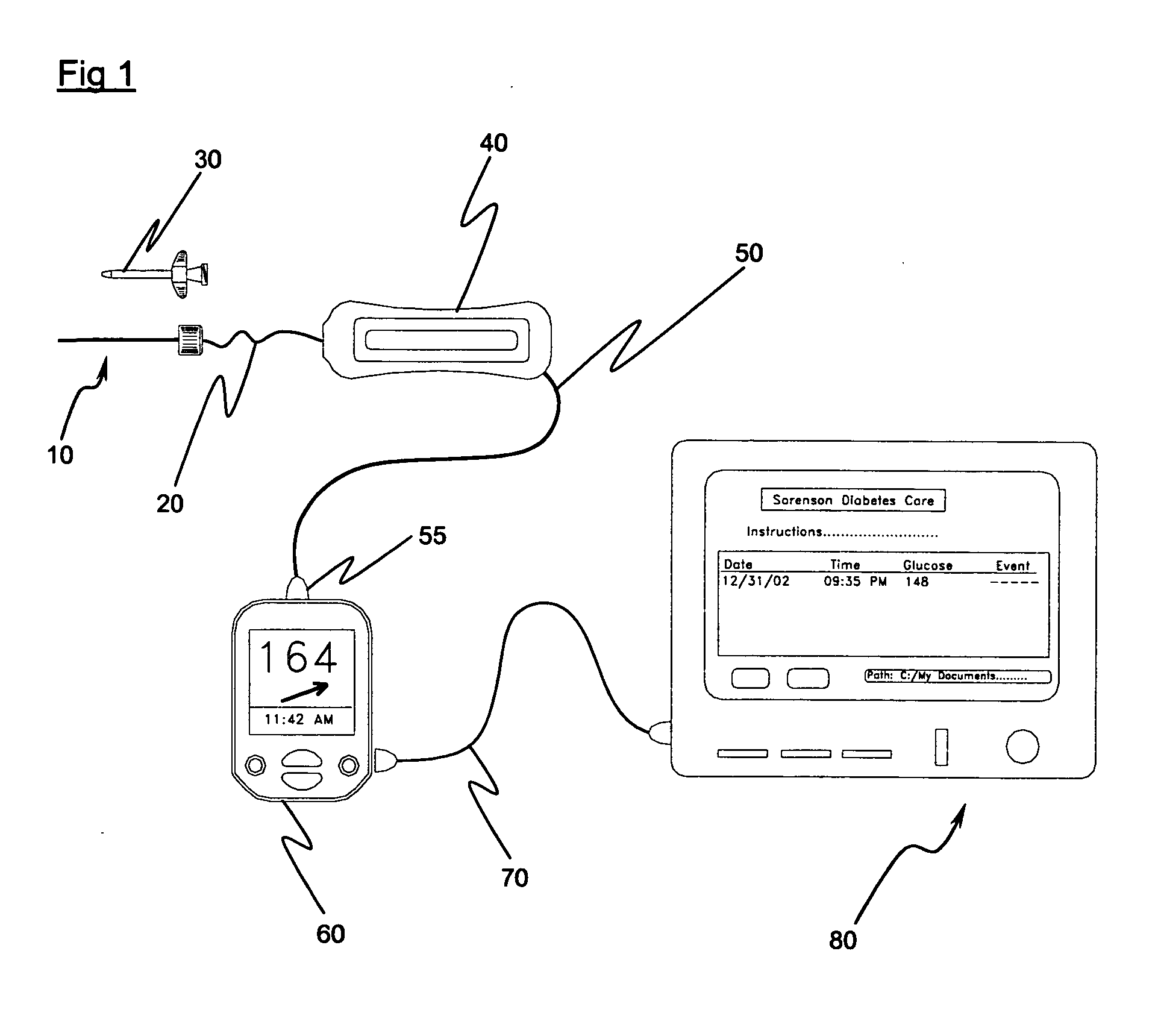
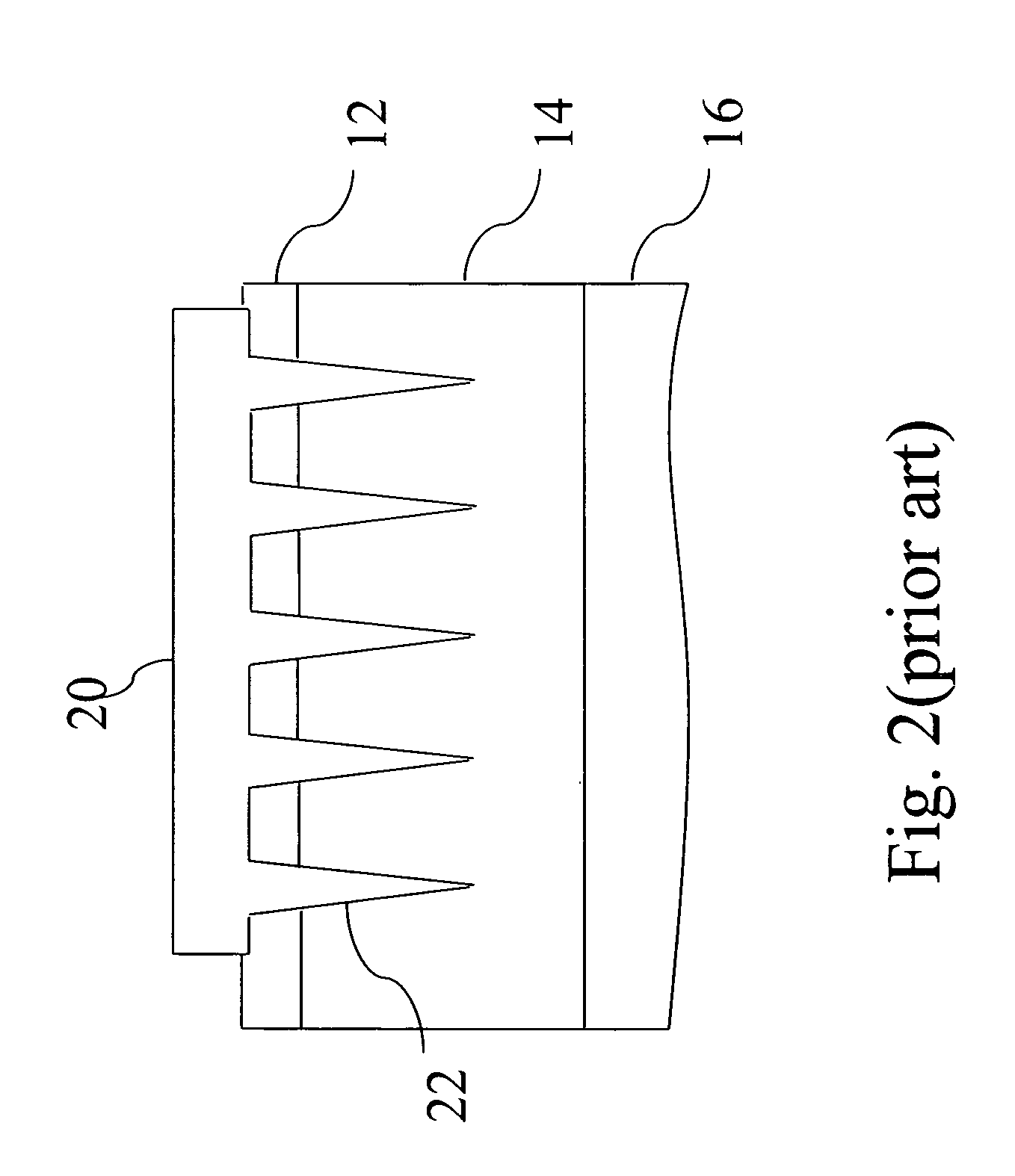
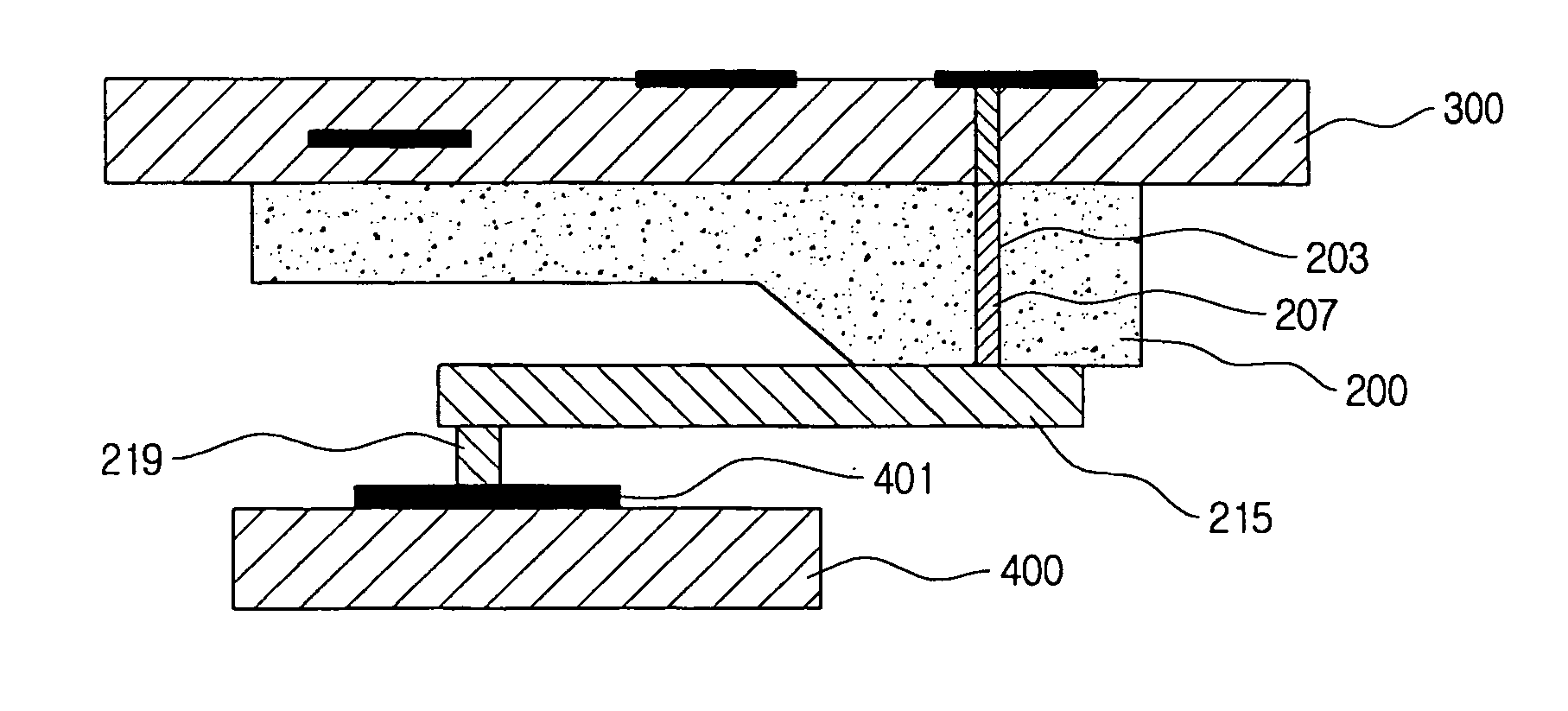
Implantable biosensor system, apparatus and method
InactiveUS6965791B1Good biocompatibilityIncrease volumeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsForeign matterInterstitial glucose
An implantable biosensor assembly and system includes an enzymatic sensor probe from which subcutaneous and interstitial glucose levels may be inferred. The assembly may be associated by direct percutaneous connection with electronics, such as for signal amplification, sensor polarization, and data download, manipulation, display, and storage. The biosensor comprises a miniature probe characterized by lateral flexibility and tensile strength and has large electrode surface area for increased sensitivity. Irritation of tissues surrounding the probe is minimized due to ease of flexibility and small cross section of the sensor. Foreign body reaction is diminished due to a microscopically rough porous probe surface.
Owner:SORENSON DEVMENT
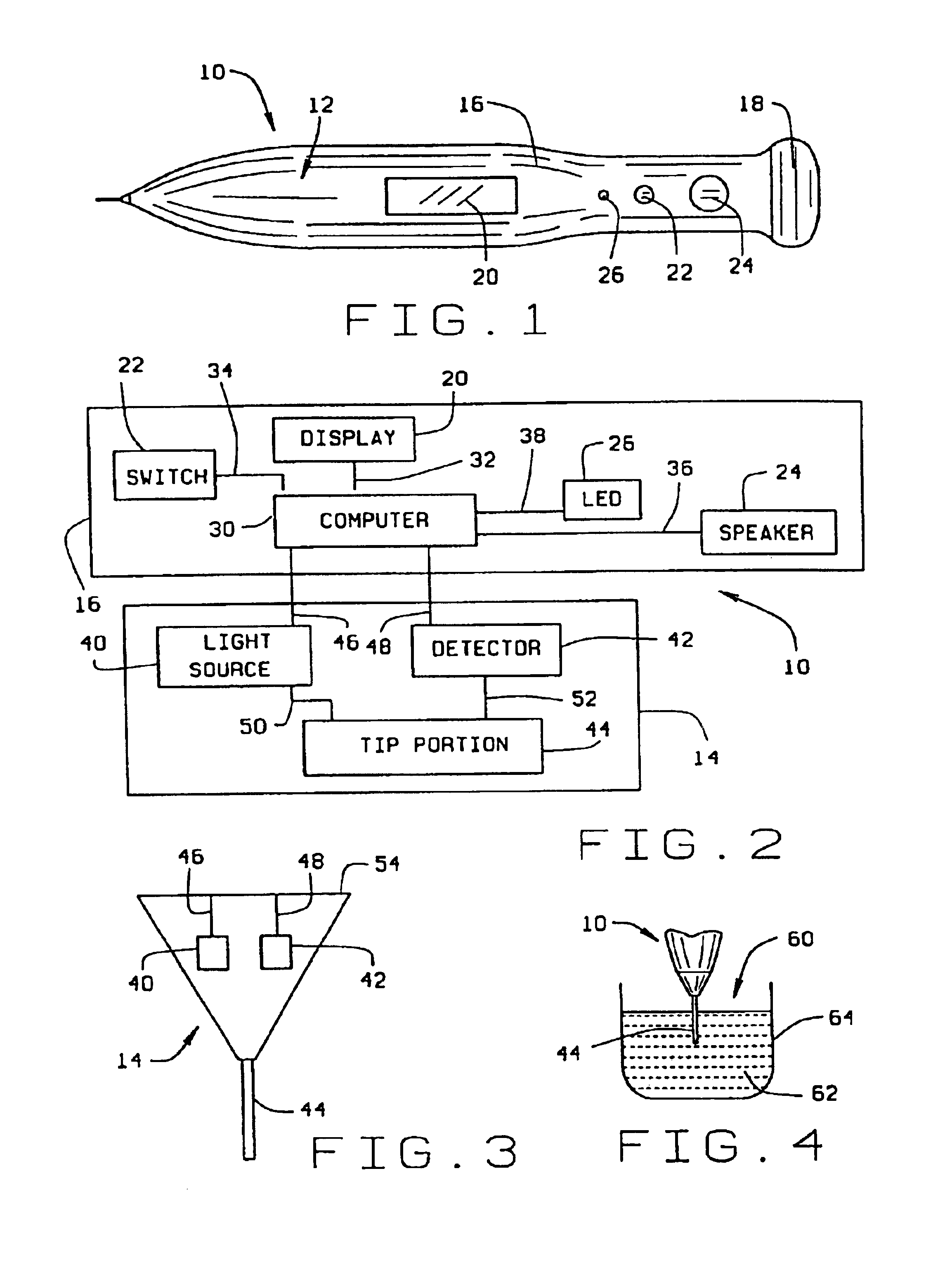
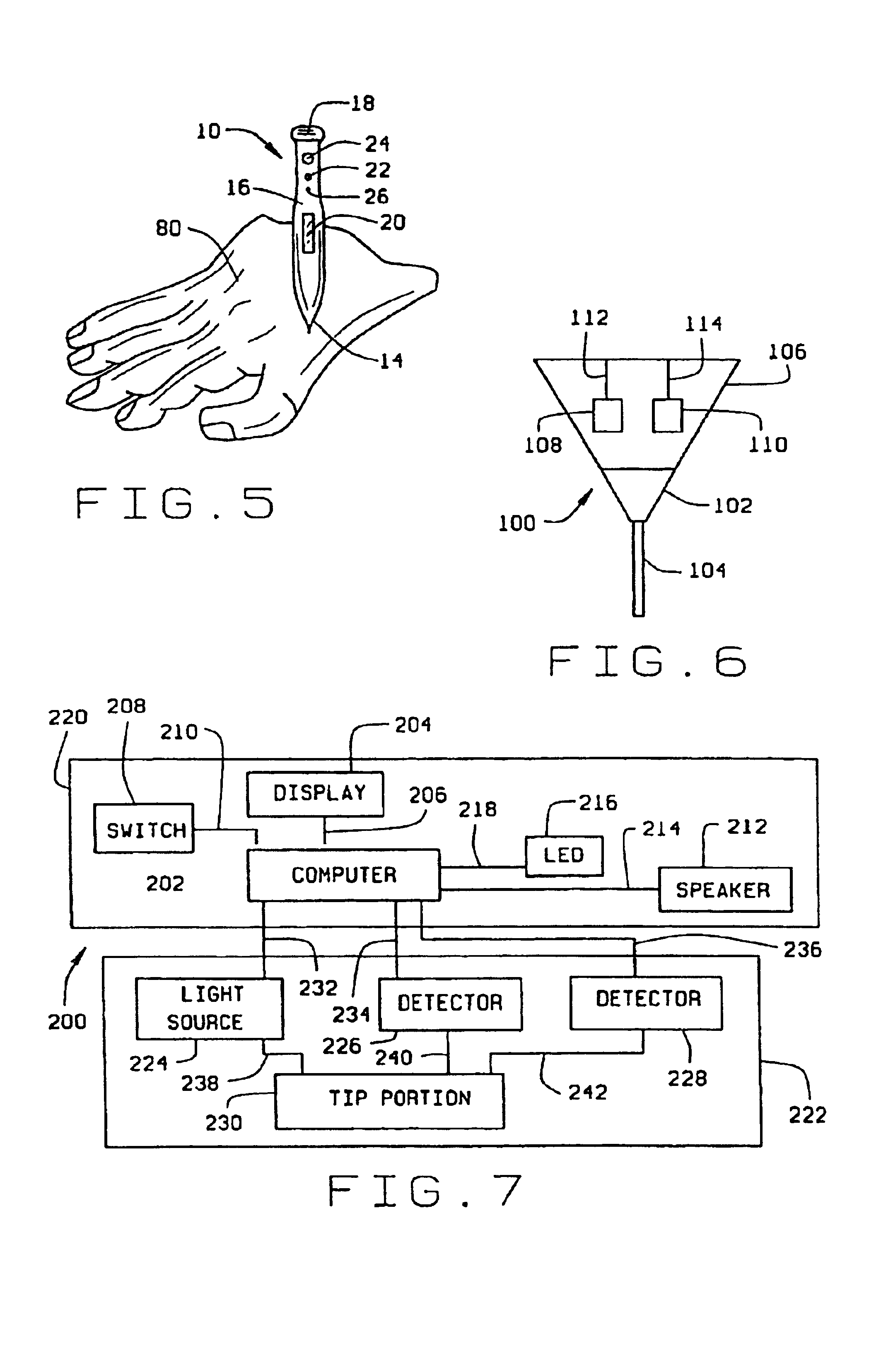
Micro-invasive method for painless detection of analytes in extracellular space
InactiveUS6904301B2Reduces and eliminates delay timeAvoid destructionAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgeryAnalyteStratum basale
A method of detecting at least one analyte in extra-cellular spaces includes the step of inserting a microprobe through the stratum corneum toward the stratum basale of the skin of a subject into extra-cellular spaces containing interstitial fluid having at least one analyte to be detected, said microprobe having a diameter at its tip no larger than approximately 10-50 microns. The method further includes optically testing for a predetermined analyte in the extra-cellular space adjacent the distal end of the microprobe without drawing a sample of the interstitial fluid. Preferably the microprobe body includes a sensor layer covering the distal optical tip of the microprobe body, the sensor layer being adapted to interact with a predetermined analyte to be detected in the interstitial fluid, and an optical detector responsive to interaction of the sensor layer with the predetermined analyte to signal detection of said predetermined analyte.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Implantable biosensor system, apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050183954A1Good biocompatibilityIncrease volumeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsForeign matterInterstitial glucose
An implantable biosensor assembly and system includes an enzymatic sensor probe from which subcutaneous and interstitial glucose levels may be inferred. The assembly may be associated by direct percutaneous connection with electronics, such as for signal amplification, sensor polarization, and data download, manipulation, display, and storage. The biosensor comprises a miniature probe characterized by lateral flexibility and tensile strength and has a large electrode surface area for increased sensitivity. Irritation of tissues surrounding the probe is minimized due to ease of flexibility and small cross section of the sensor. Foreign body reaction is diminished due to a microscopically rough porous probe surface.
Owner:SORENSON DEVMENT
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional spectrally encoded imaging
ActiveUS20050128488A1Point become highRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPhase sensitiveSingle mode fiber transmission
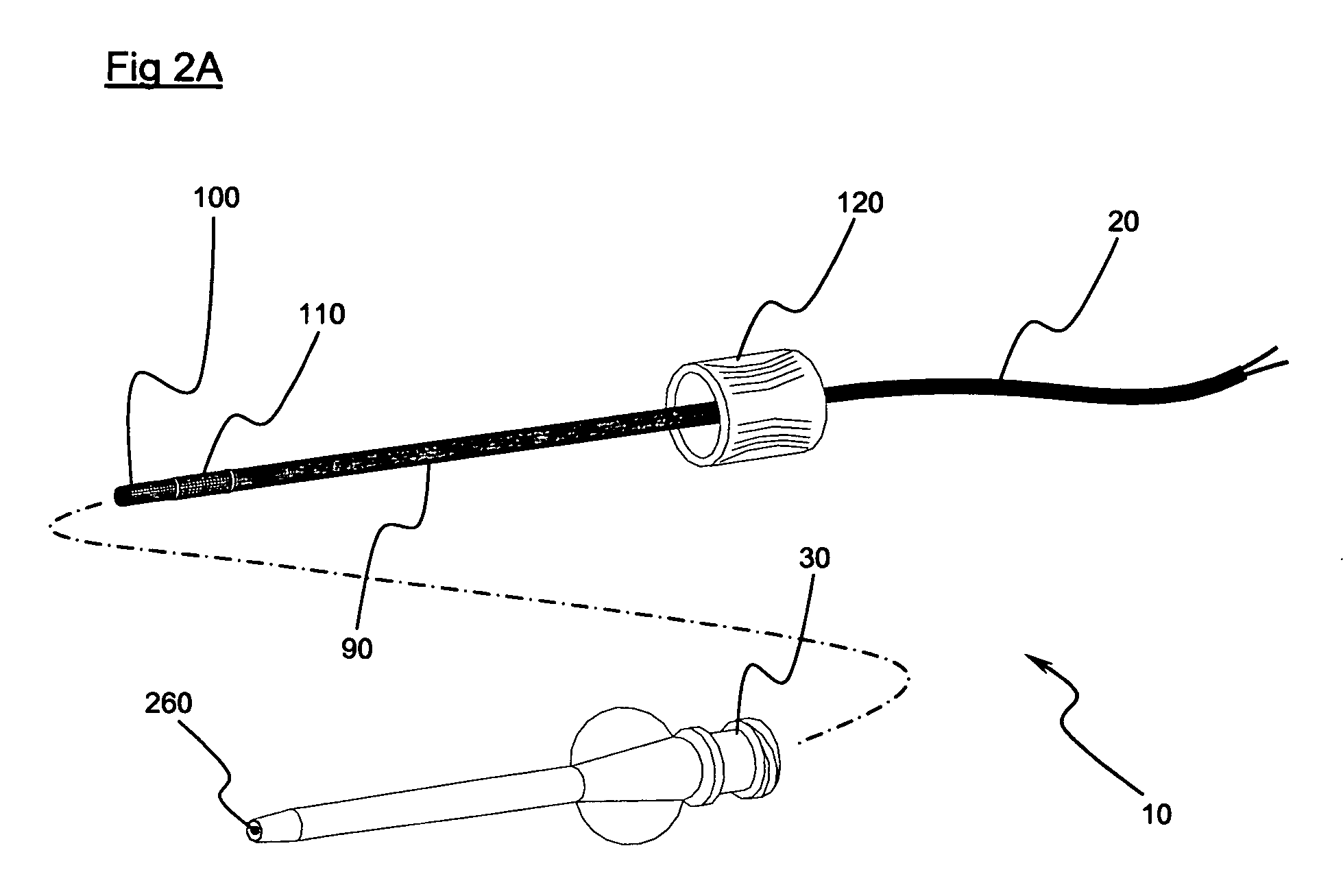
A method and apparatus for obtaining three-dimensional surface measurements using phase-sensitive spectrally encoded imaging is described. Both transverse and depth information is transmitted through a single-mode optical fiber, allowing this technique to be incorporated into a miniature probe.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Cantilever microprobes for contacting electronic components and methods for making such probes
ActiveUS20050179458A1Improve featuresElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingEngineeringElectronic component
Embodiments disclosed herein are directed to compliant probe structures for making temporary or permanent contact with electronic circuits and the like. In particular, embodiments are directed to various designs of cantilever-like probe structures. Some embodiments are directed to methods for fabricating such cantilever structures. In some embodiments, for example, cantilever probes have extended base structures, slide in mounting structures, multi-beam configurations, offset bonding locations to allow closer positioning of adjacent probes, compliant elements with tensional configurations, improved over travel, improved compliance, improved scrubbing capability, and / or the like.
Owner:MICROFAB
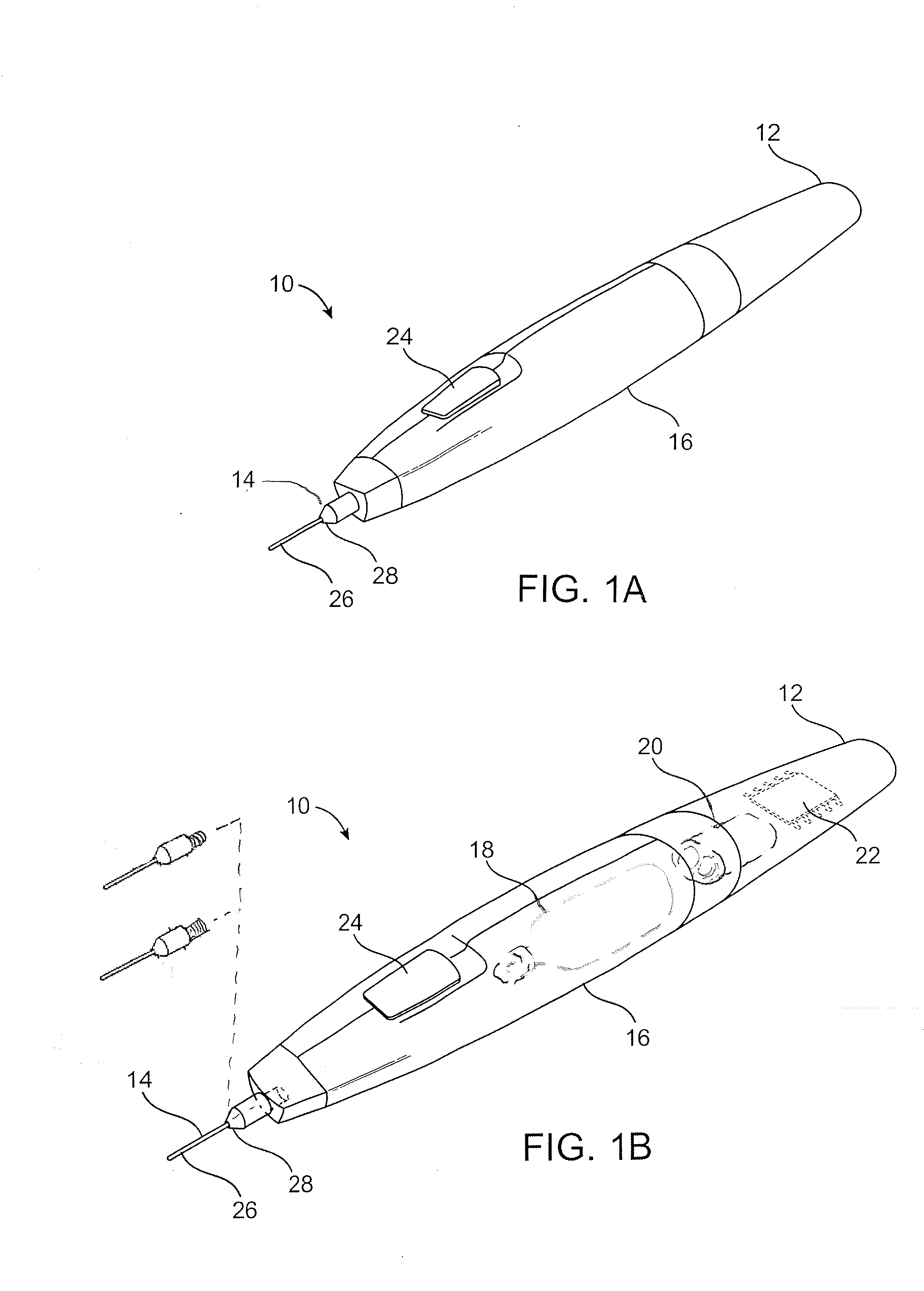
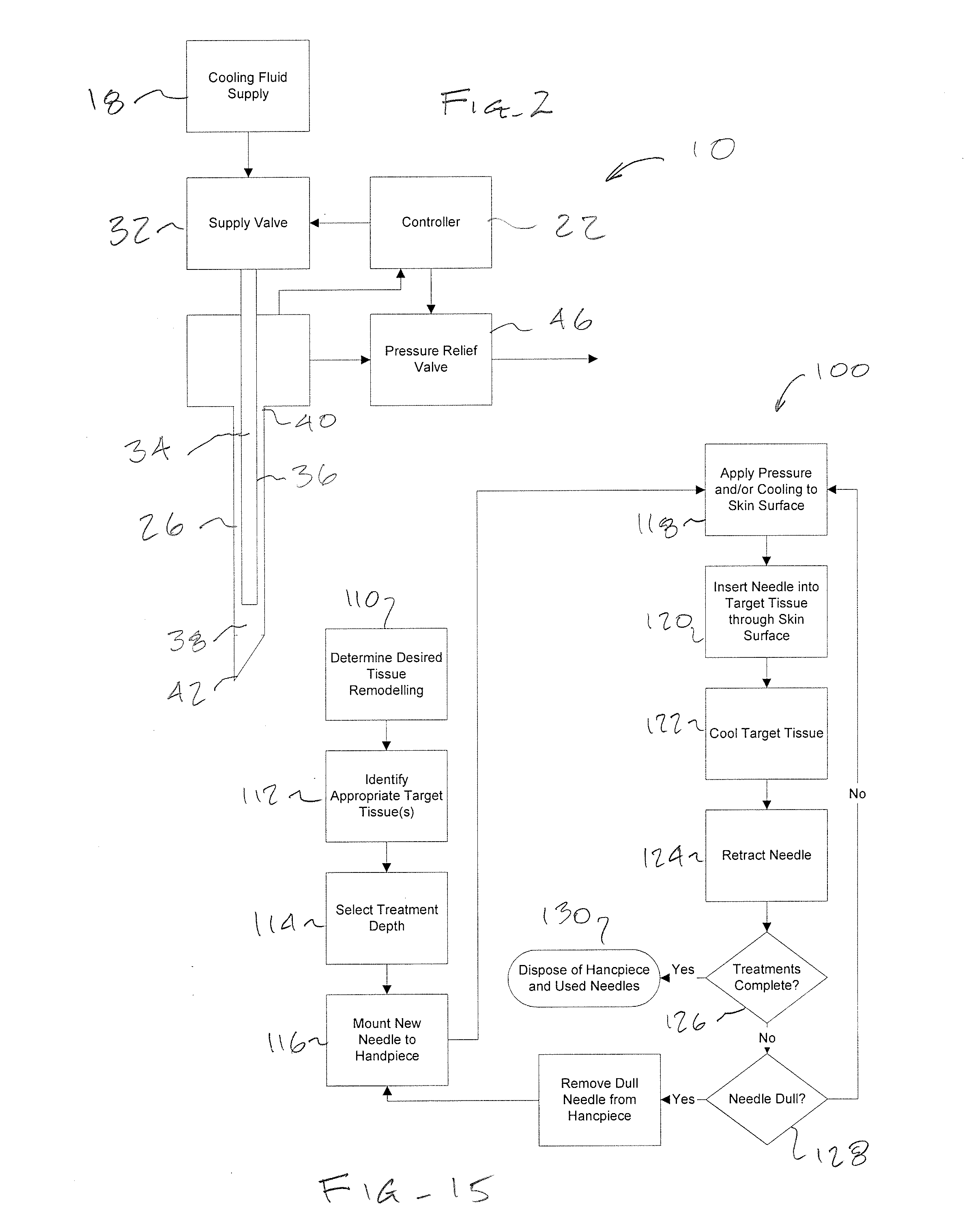
Dermal and Transdermal Cryogenic Microprobe Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20080154254A1Increase temperatureTime control be enhancedSurgical instruments for coolingTime controlMedical device
Medical devices, systems, and methods optionally treat dermatological and / or cosmetic defects, and / or a wide range of additional target tissues. Embodiments apply cooling with at least one small, tissue-penetrating probe, the probe often comprising a needle having a size suitable for inserting through an exposed surface of the skin of a patient without leaving a visible scar. Treatment may be applied along most or all of the insertable length of an elongate needle, optionally by introducing cryogenic cooling fluid into the needle lumen through a small, tightly-toleranced lumen of a fused silica fluid supply tube, with the supply tube lumen often metering the cooling fluid. Treatment temperature and / or time control may be enhanced using a simple pressure relief valve coupled to the needle lumen via a limited total exhaust volume space.
Owner:PACIRA CRYOTECH INC
Method and apparatus for specimen fabrication
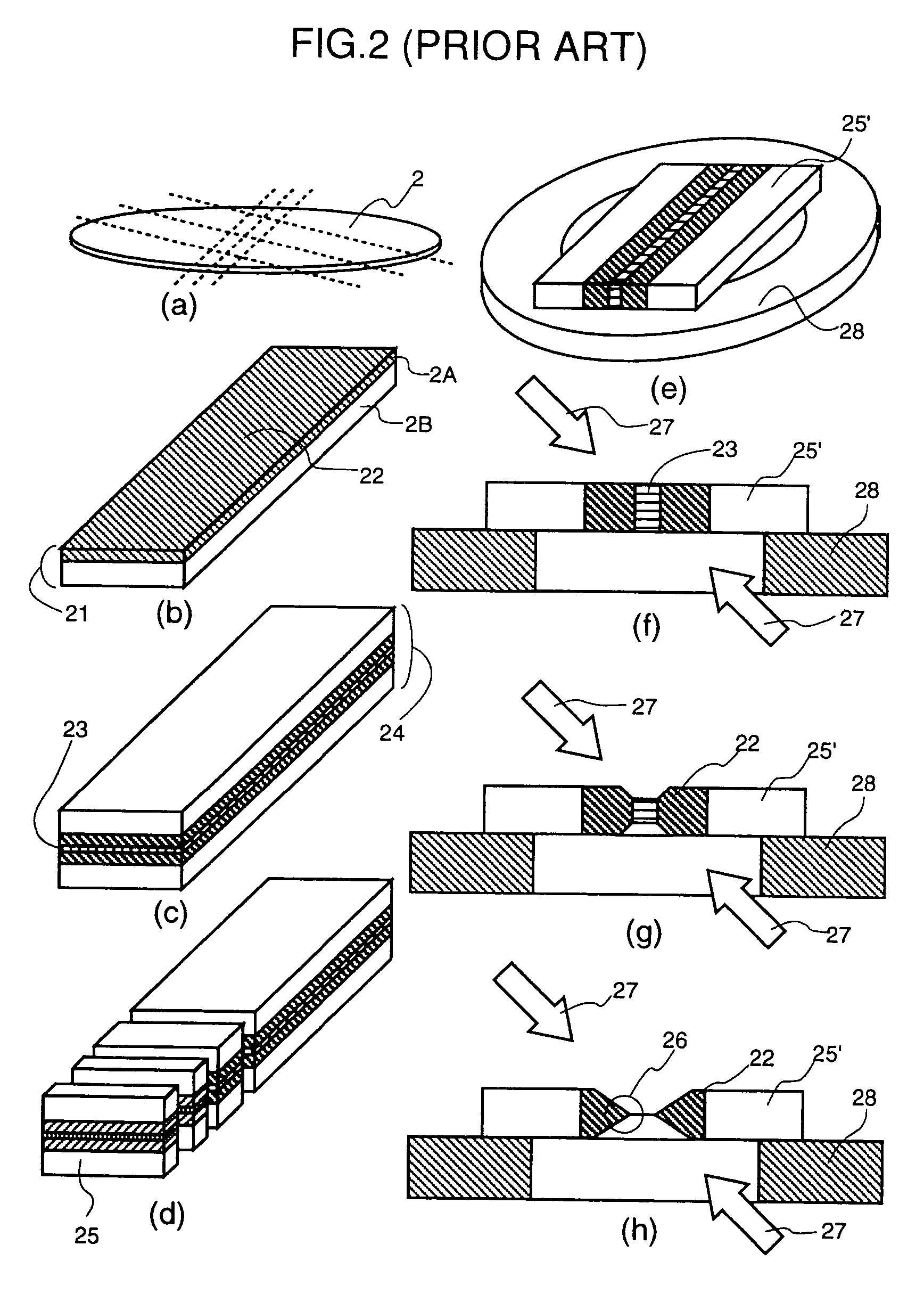
InactiveUS7071475B2Great fabricationSolve the quick positioningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMicroprobe
Owner:HITACHI LTD
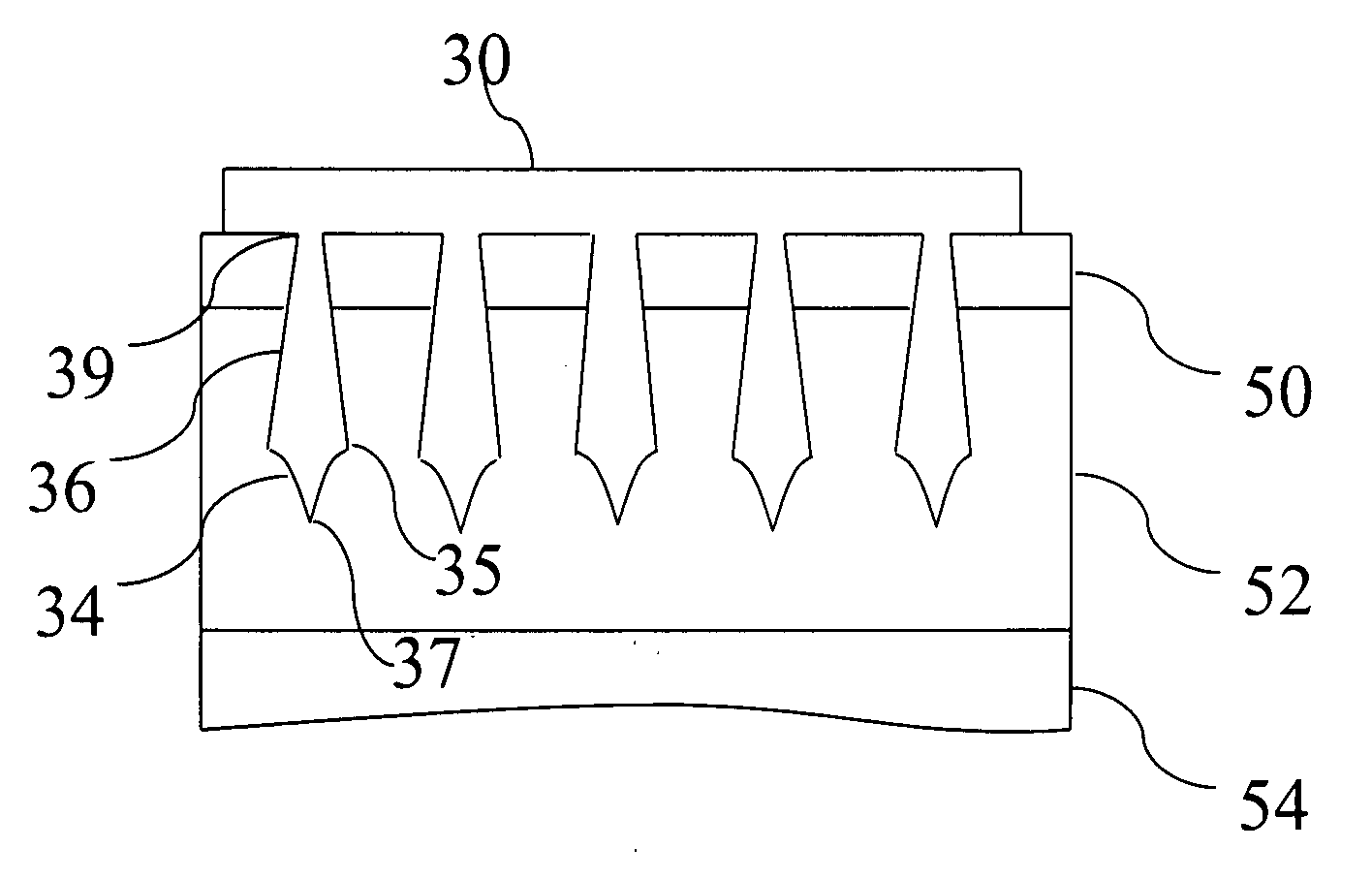
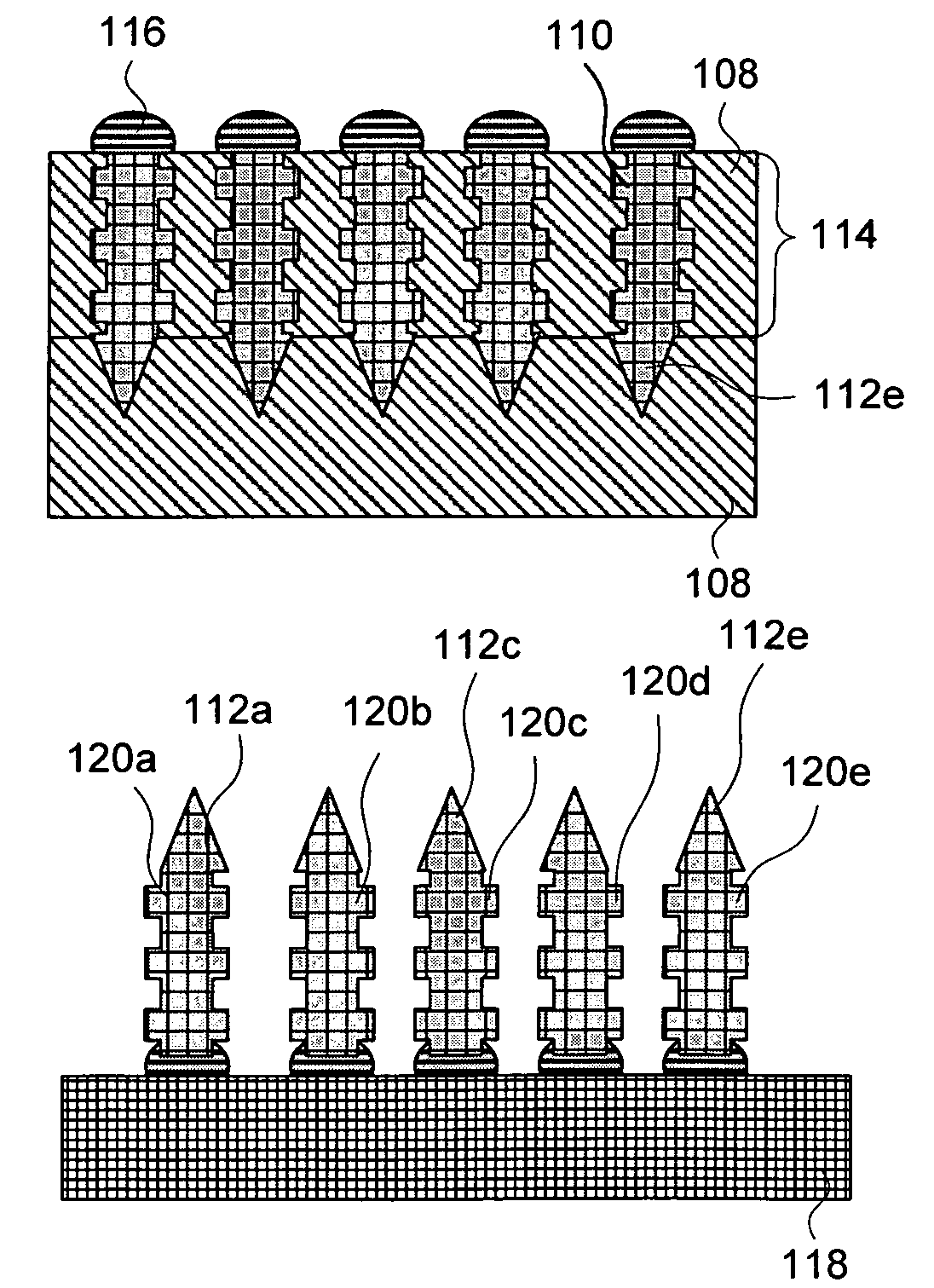
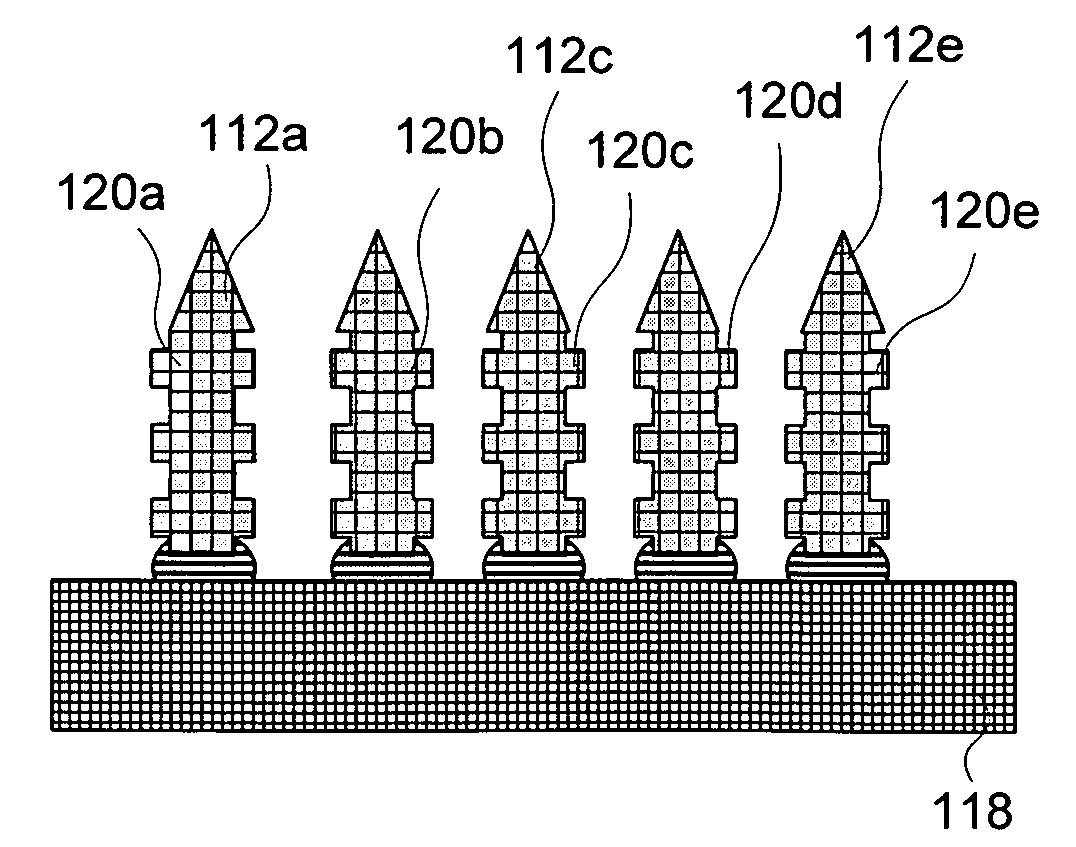
Microprobe array structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080009763A1Overcomes drawbackGood made and maintainedElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyEngineeringSelf-stabilization
A microprobe array structure with self-stabilization capability and a method for manufacturing the same are proposed. The microprobe array structure is used to sense various biopotential signals, and is characterized in that the etching parameters are controlled during etching to manufacture a microprobe structure with a reduced bottom cross section so that the microprobe can be firmly stabilized in the skin tissue. Moreover, a conducting layer is formed on the microprobe to sense signals. A design of electric isolation between microprobes is also proposed. The microprobe array can therefore be used for the measurement of various biopotential signals, and can also be used as a stimulus.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Electrochemically fabricated microprobes
InactiveUS20060006888A1Electrical measurement instrument detailsIndividual semiconductor device testingMulti materialEngineering
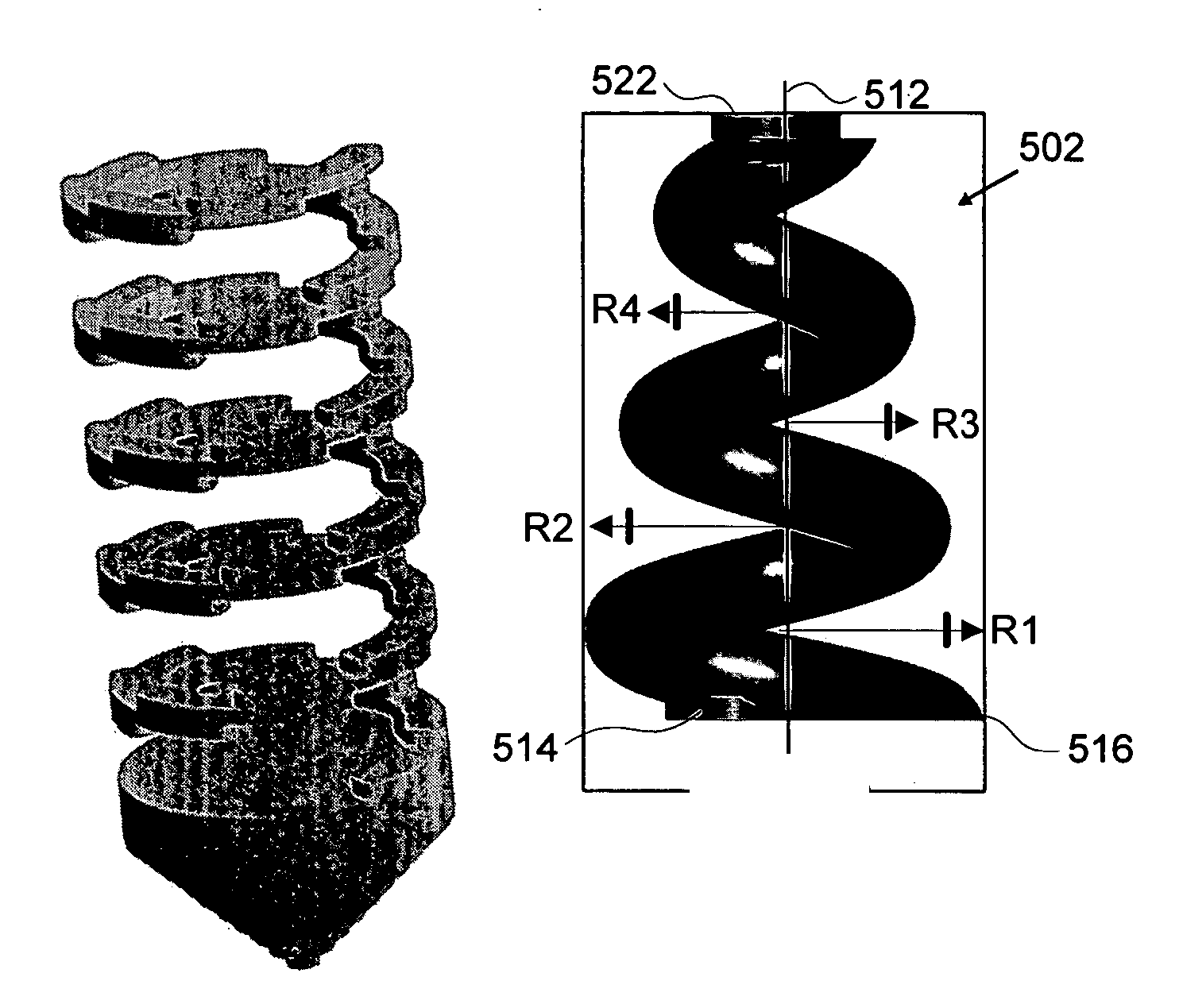
Multilayer probe structures for testing semiconductor die are electrochemically fabricated via depositions of one or more materials in a plurality of overlaying and adhered layers. In some embodiments the structures may include generally helical shaped configurations, helical shape configurations with narrowing radius as the probe extends outward from a substrate, bellows-like configurations, and the like. In some embodiments arrays of multiple probes are provided.
Owner:MICROFAB
Microsensor system and method for measuring data
InactiveUS7297113B1Guaranteed true stateAccurately identify viable and non-viable tissueLocal control/monitoringEndoradiosondesProximateEngineering
One embodiment is a microprobe. An example of the microprobe comprises a housing having an aperture. This example of the microprobe also comprises an ISFET attached to the housing. The ISFET may have a gate located proximate the aperture. This example of the microprobe further comprises a reference electrode attached to the housing proximate the aperture. Another embodiment is a microsensor system. Another embodiment is a method for measuring a characteristic of tissue. Yet another embodiment is a method for monitoring tissue pH.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Microprobe array structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7941201B2Overcomes drawbackGood made and maintainedElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyEngineeringSelf-stabilization
A microprobe array structure with self-stabilization capability and a method for manufacturing the same are proposed. The microprobe array structure is used to sense various biopotential signals, and is characterized in that the etching parameters are controlled during etching to manufacture a microprobe structure with a reduced bottom cross section so that the microprobe can be firmly stabilized in the skin tissue. Moreover, a conducting layer is formed on the microprobe to sense signals. A design of electric isolation between microprobes is also proposed. The microprobe array can therefore be used for the measurement of various biopotential signals, and can also be used as a stimulus.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Microprobe tips and methods for making
Owner:MICROFAB
Real-time multimode neurobiophysiology probe
Apparatus and methods in which very small volumes of material may be extracted, delivered, interrogated or stimulated via optical, electromagnetic or mechanical means, in vivo or in vitro, for site-specific detection, characterization, stimulation, diagnostics or therapy, comprising optical, fluidic, chemical, electromagnetic and biological techniques applied via a microprobe in a single intra-parenchymal tissue perforation procedure in the brain. The primary use of the device is in neuroscience research, clinical diagnostics and therapeutics applications in the brain, however, the device may also be beneficially applied to other organs and biological systems. Human clinical applications may include neurosurgical intra-operative monitoring, extra-operative chronic monitoring of devices introduced in an operation, and diagnostic monitoring combined with simultaneous neuroimaging.
Owner:BLUMENFELD WALTER +2
Optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and manufacturing method
The invention provides an optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and a manufacturing method. The probe has two optical channels which are coaxial, wherein an annular optical fiber core provides a Raman exciting light channel and a channel in the coaxial center is used for receiving Raman probe light; and by performing fine taper angle grinding on the fiber ends of coaxial dual waveguide channel optical fibers, a rotary symmetrical plane (or chambered surface) structure is formed. The structure can converge Raman exciting light transmitted by the annular core in a micron order, and on the one hand, the converged exciting light has an ability of capturing micron-order and nanoscale particles and on the other hand, the converged exciting light interacts with the particles, so that a back scattering Raman optical signal generated by the exciting light converged by the Raman scattering light can be collected and transmitted to a Raman spectrometer through an intermediate large-core fire cores. The microprobe provided by the invention can capture micro living matters of cell living bodies to effectively excite the Raman spectrum of the matters in cells and to obtain the Raman spectrum so as to achieve Raman measurement of micro liquids, single cells in living bodies and inner substances thereof.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
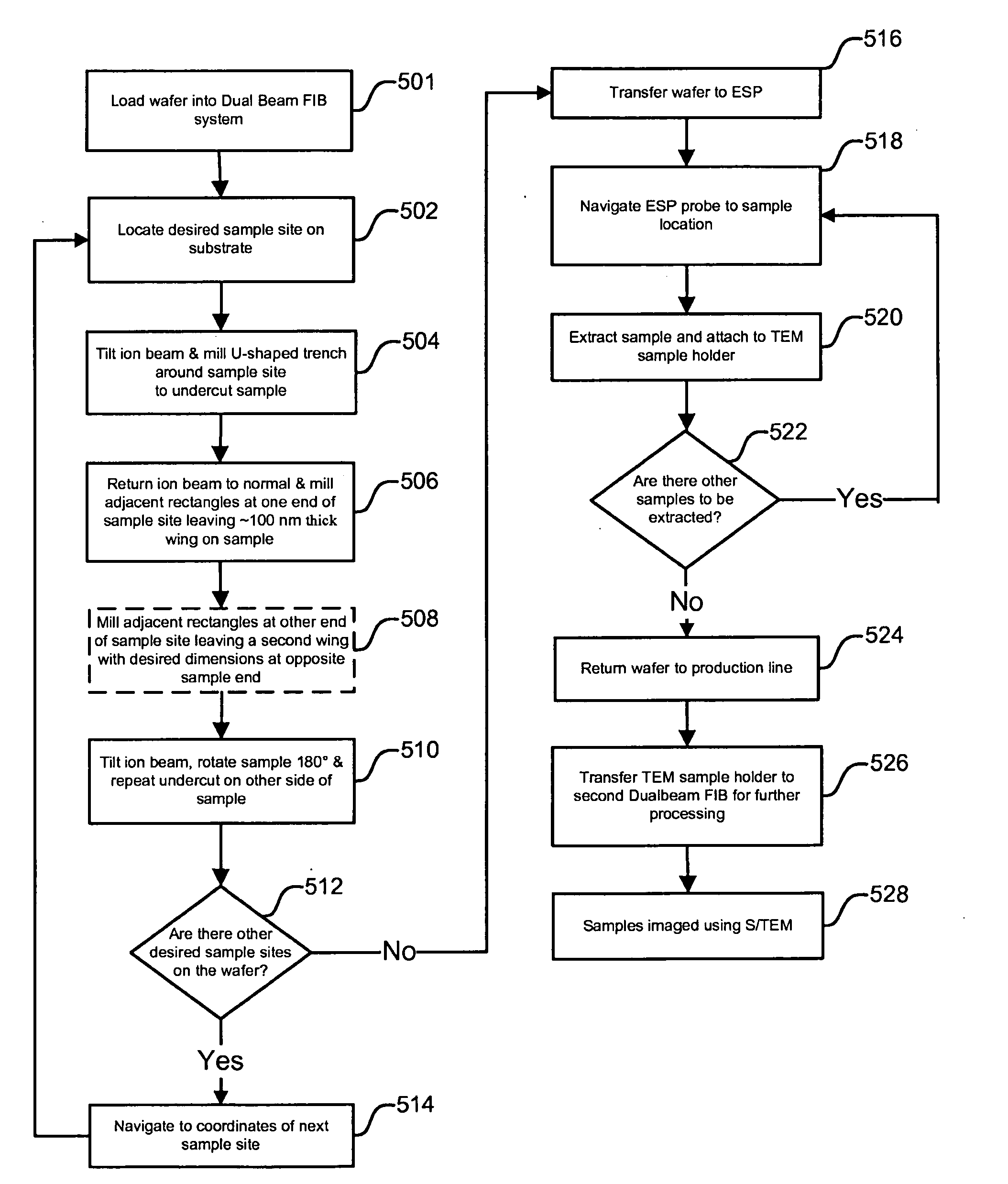
Method and apparatus for sample extraction and handling
ActiveUS20100305747A1Reduce labor intensityImprove throughputDigital data processing detailsElectrical testingVacuum pressureLong axis
An improved method and apparatus for extracting and handling samples for S / TEM analysis. Preferred embodiments of the present invention make use of a micromanipulator and a hollow microprobe probe using vacuum pressure to adhere the microprobe tip to the sample. By applying a small vacuum pressure to the lamella through the microprobe tip, the lamella can be held more securely and its placement controlled more accurately than by using electrostatic force alone. By using a probe having a beveled tip and which can also be rotated around its long axis, the extracted sample can be placed down flat on a sample holder. This allows sample placement and orientation to be precisely controlled, thus greatly increasing predictability of analysis and throughput
Owner:FEI CO
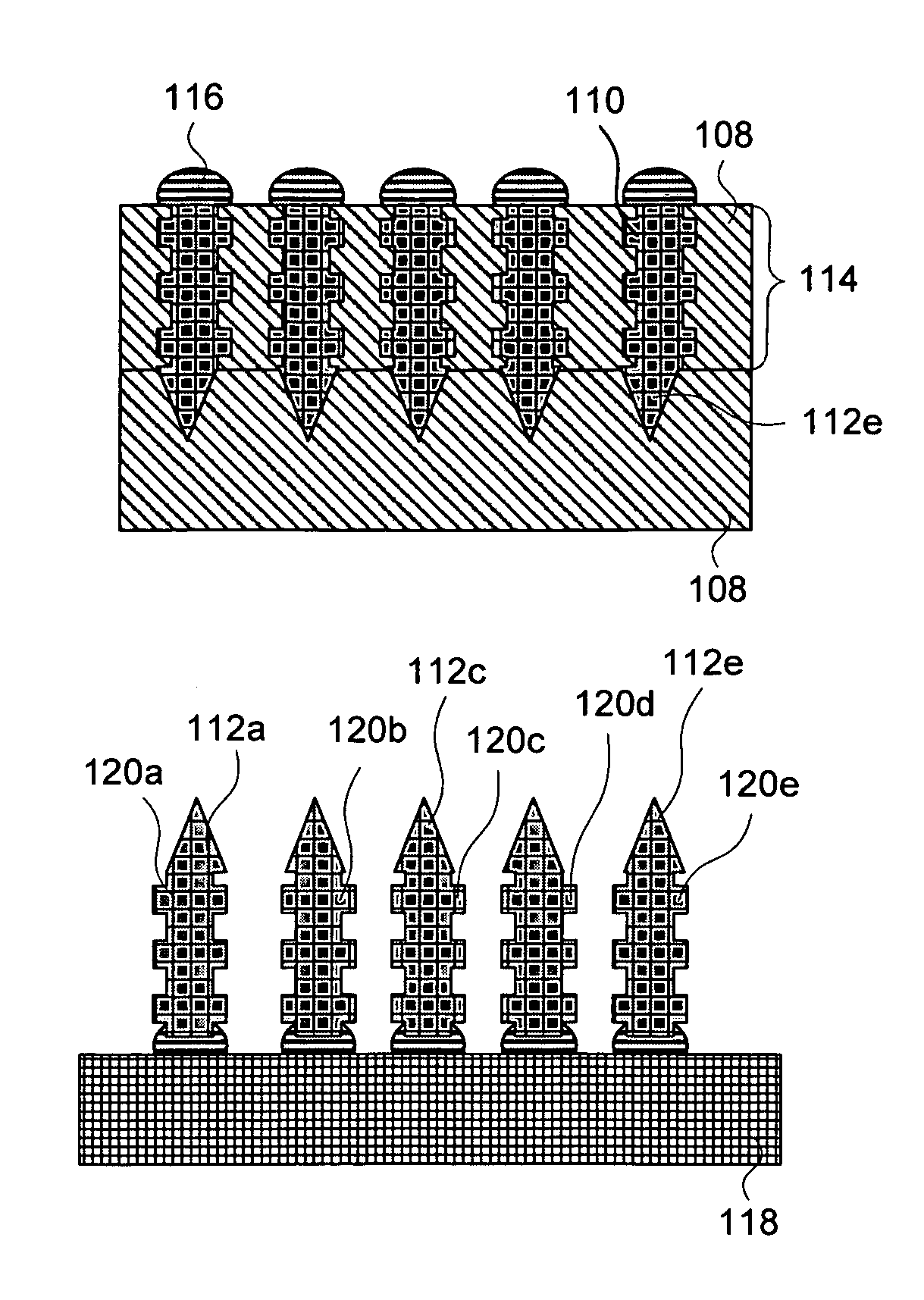
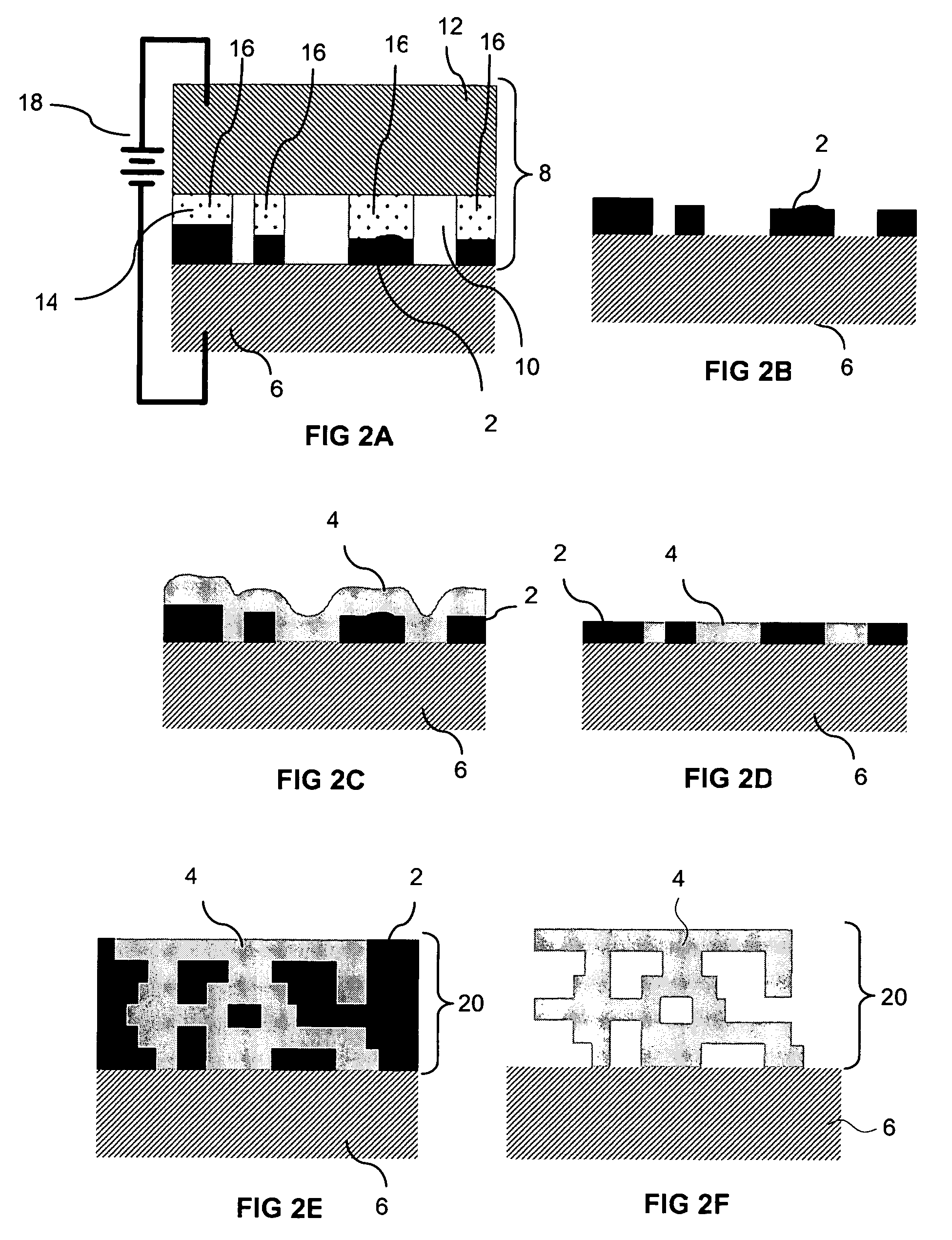
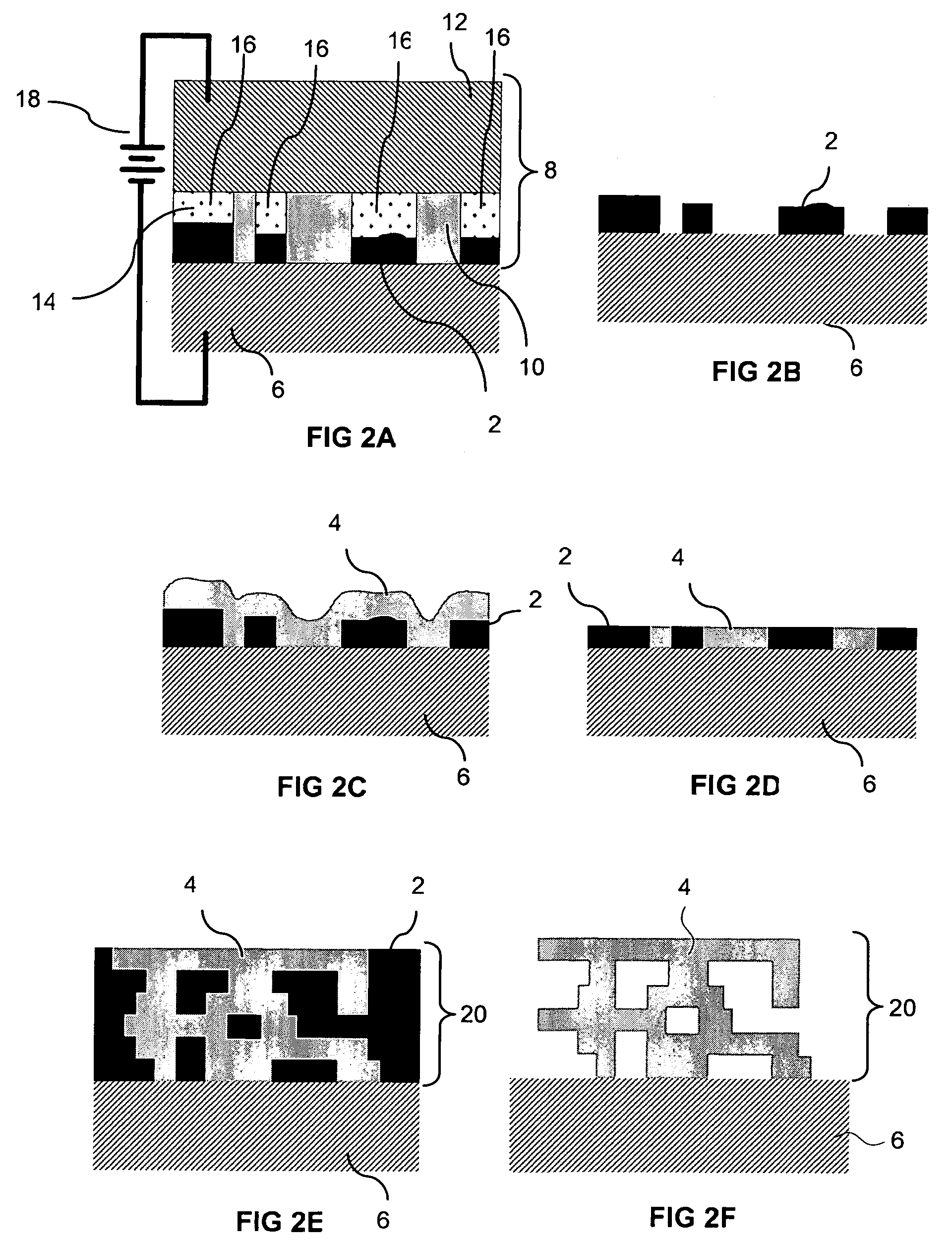
Electrochemical fabrication process for forming multilayer multimaterial microprobe structures
ActiveUS7531077B2Enhanced electrochemical processAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectrical measurement instrument detailsMulti materialInter layer
Some embodiments of the invention are directed to the electrochemical fabrication of microprobes which are formed from a core material and a material that partially coats the surface of the probe. Other embodiments are directed to the electrochemical fabrication of microprobes which are formed from a core material and a material that completely coats the surface of each layer from which the probe is formed including interlayer regions. These first two groups of embodiments incorporate both the core material and the coating material during the formation of each layer. Still other embodiments are directed to the electrochemical fabrication of microprobe arrays that are partially encapsulated by a dielectric material during a post layer formation coating process. In even further embodiments, the electrochemical fabrication of microprobes from two or more materials may occur by incorporating a coating material around each layer of the structure without locating the coating material in inter-layer regions.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
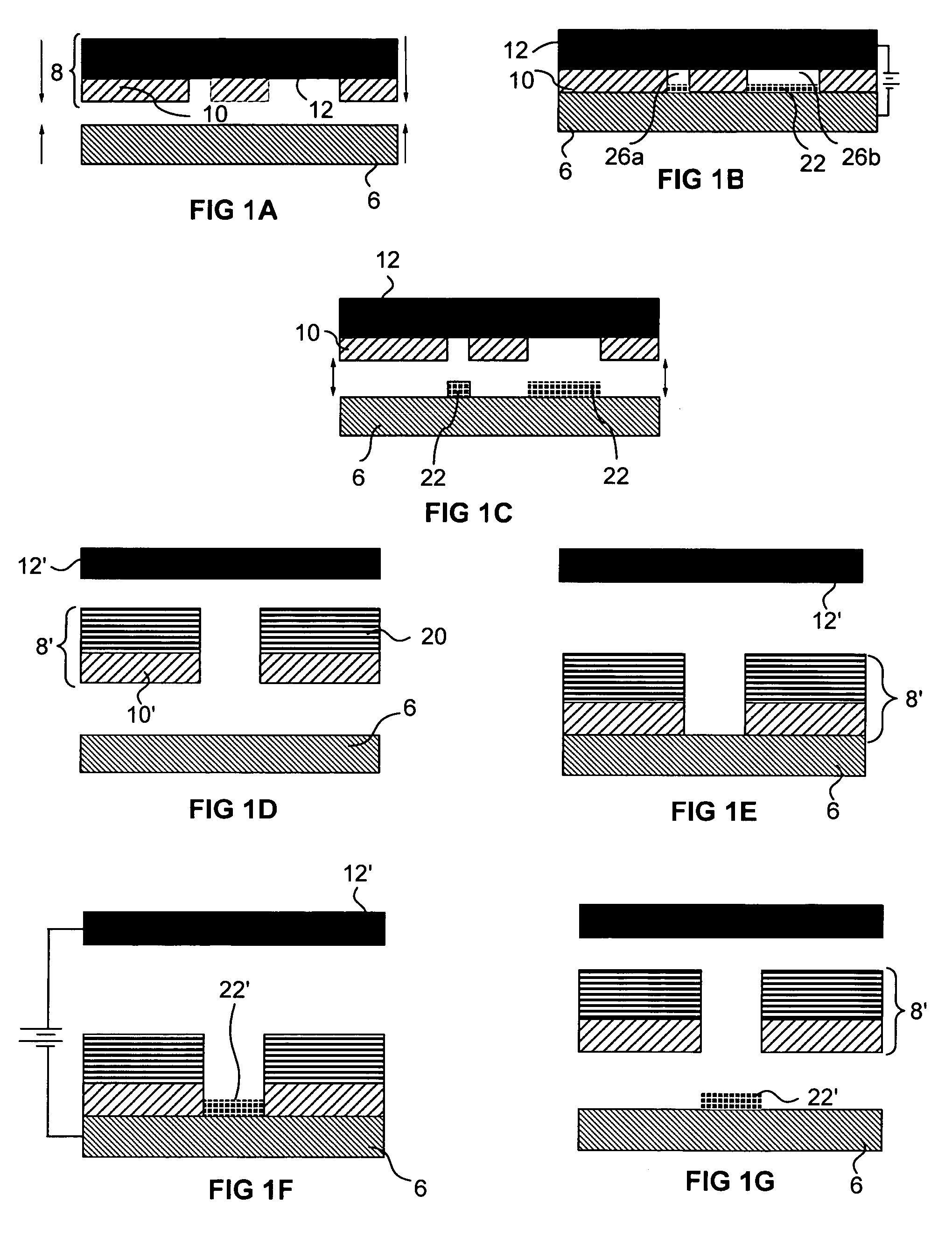
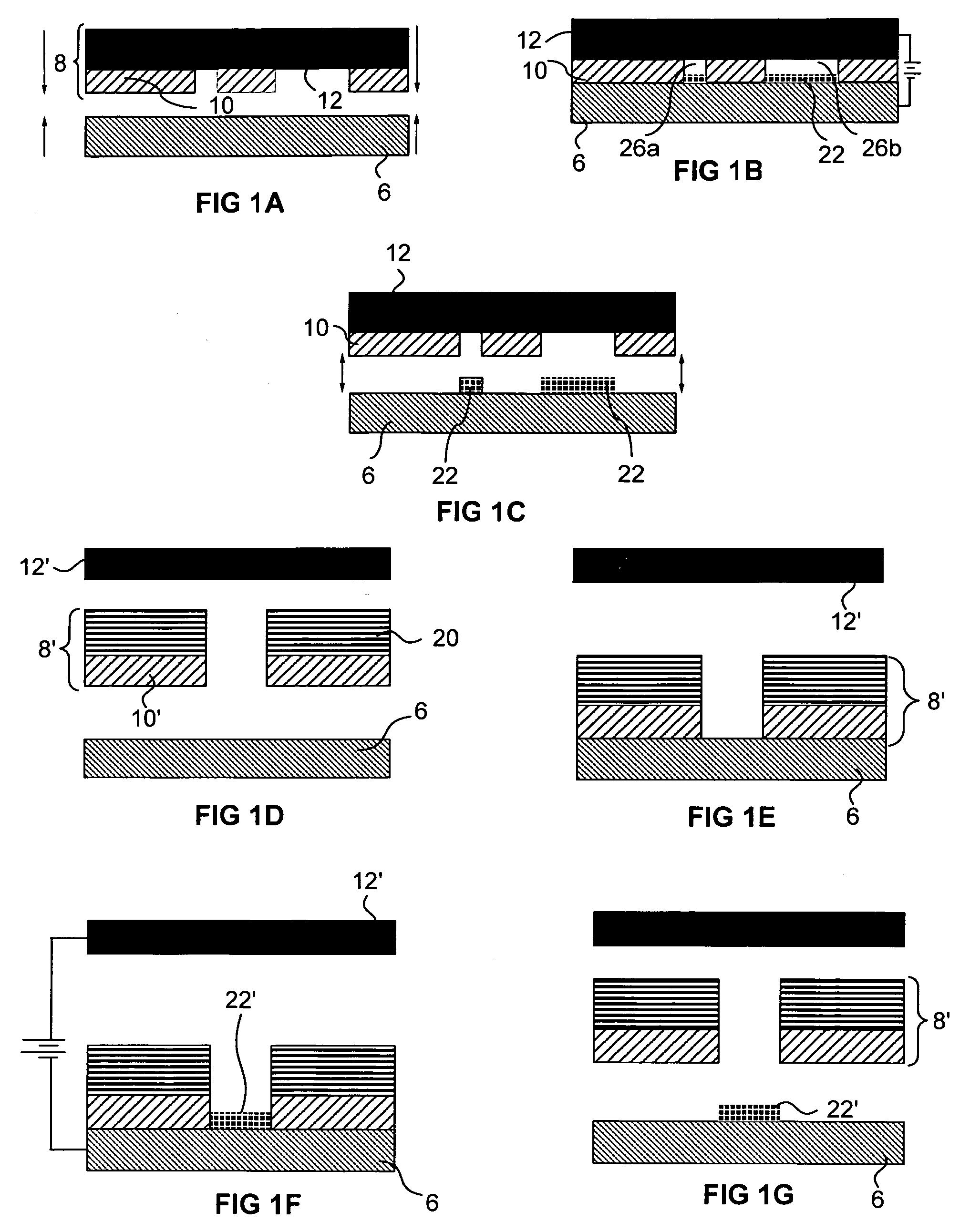
Method of making a contact
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to the formation of microprobe tips elements having a variety of configurations. In some embodiments tips are formed from the same building material as the probes themselves, while in other embodiments the tips may be formed from a different material and / or may include a coating material. In some embodiments, the tips are formed before the main portions of the probes and the tips are formed in proximity to or in contact with a temporary substrate. Probe tip patterning may occur in a variety of different ways, including, for example, via molding in patterned holes that have been isotropically or anisotropically etched silicon, via molding in voids formed in over exposed photoresist, via molding in voids in a sacrificial material that have formed as a result of the sacrificial material mushrooming over carefully sized and located regions of dielectric material, via isotropic etching of a the tip material around carefully sized placed etching shields, via hot pressing, and the like.
Owner:MICROFAB
Microprobe tips and methods for making
InactiveUS7273812B2Line/current collector detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to the formation of microprobe tips elements having a variety of configurations. In some embodiments tips are formed from the same building material as the probes themselves, while in other embodiments the tips may be formed from a different material and / or may include a coating material. In some embodiments, the tips are formed before the main portions of the probes and the tips are formed in proximity to or in contact with a temporary substrate. Probe tip patterning may occur in a variety of different ways, including, for example, via molding in patterned holes that have been isotropically or anisotropically etched silicon, via molding in voids formed in exposed photoresist, via molding in voids in a sacrificial material that have formed as a result of the sacrificial material mushrooming over carefully sized and located regions of dielectric material, via isotropic etching of the tip material around carefully sized and placed etching shields, via hot pressing, and the like.
Owner:MICROFAB
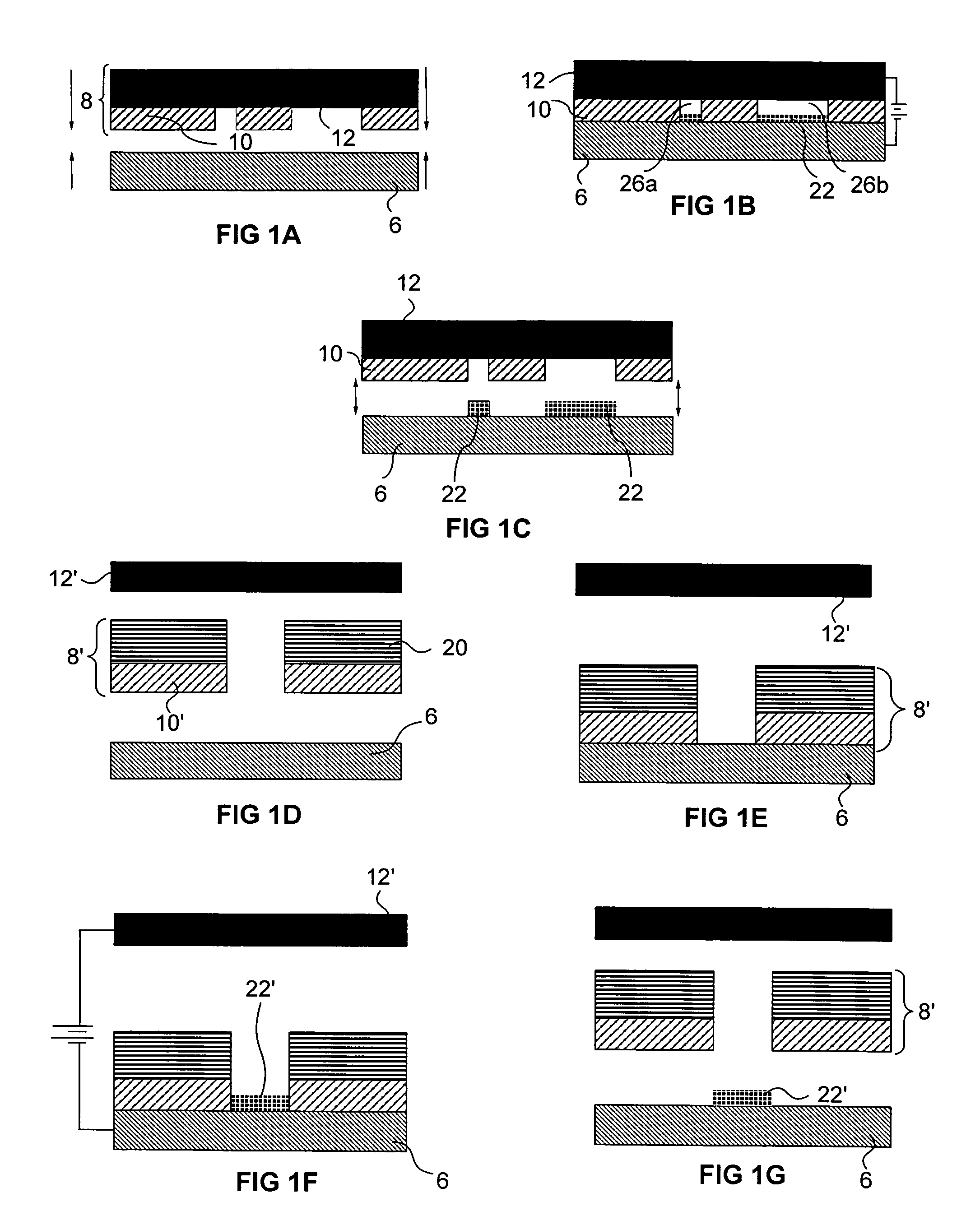
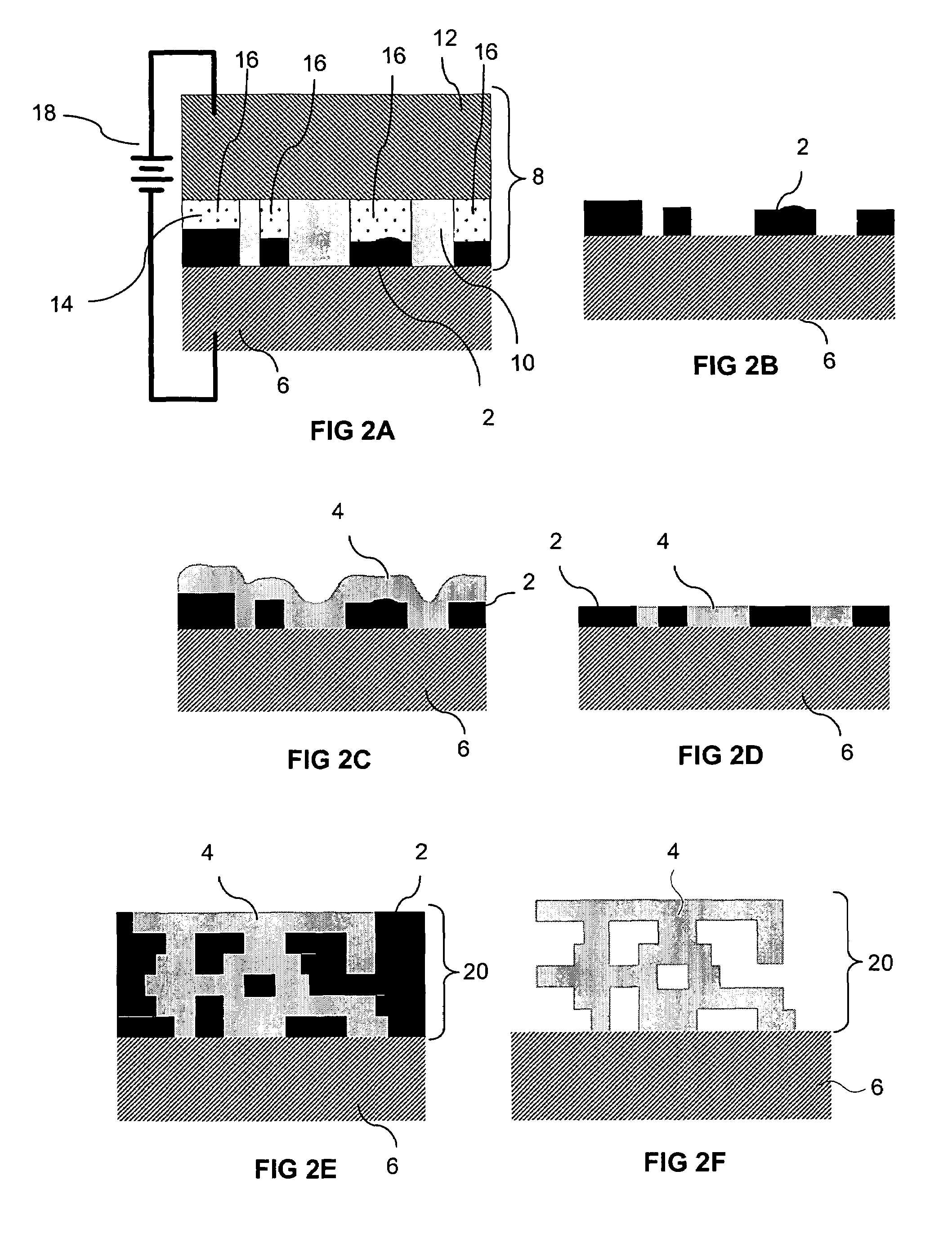
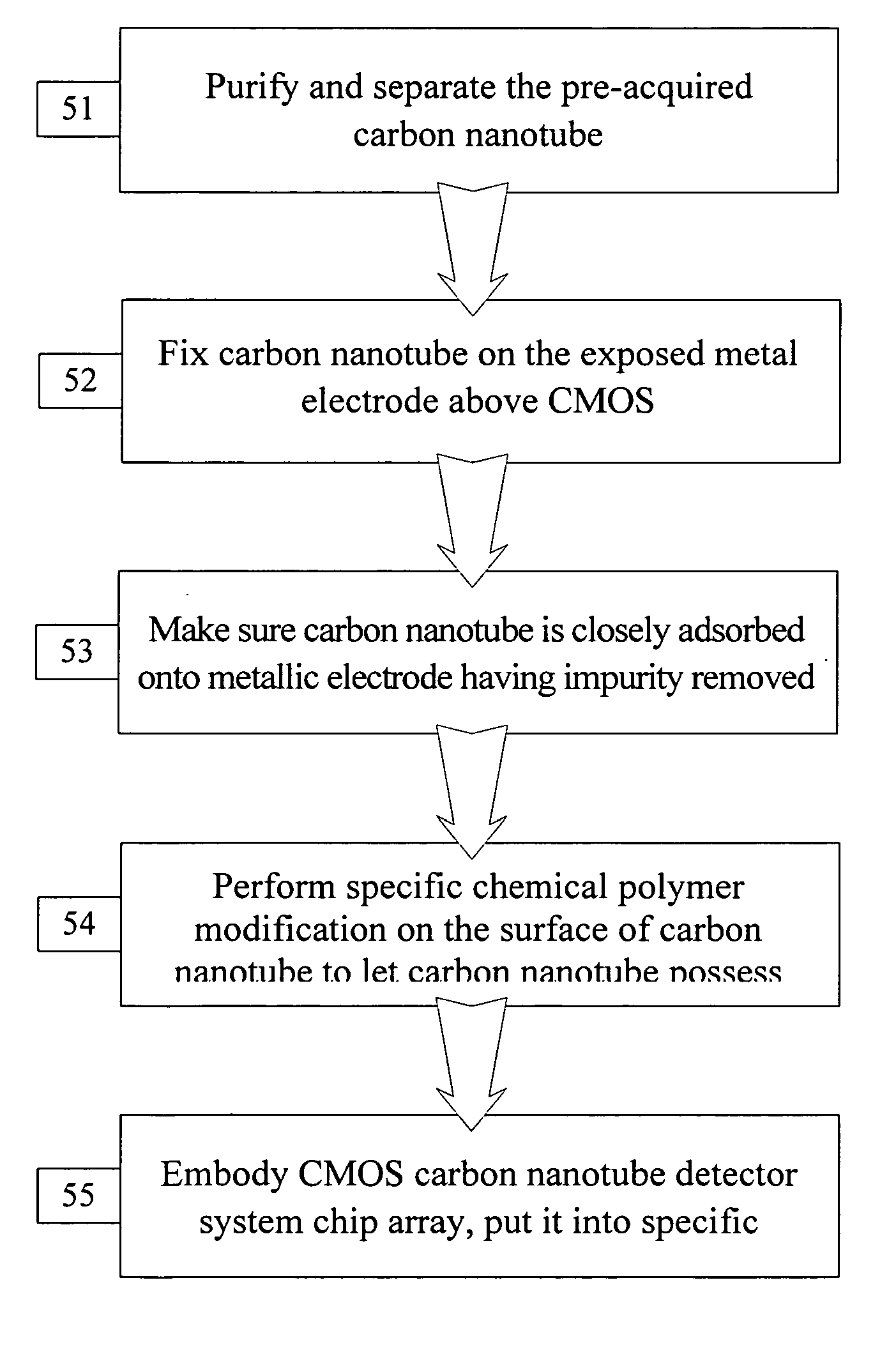
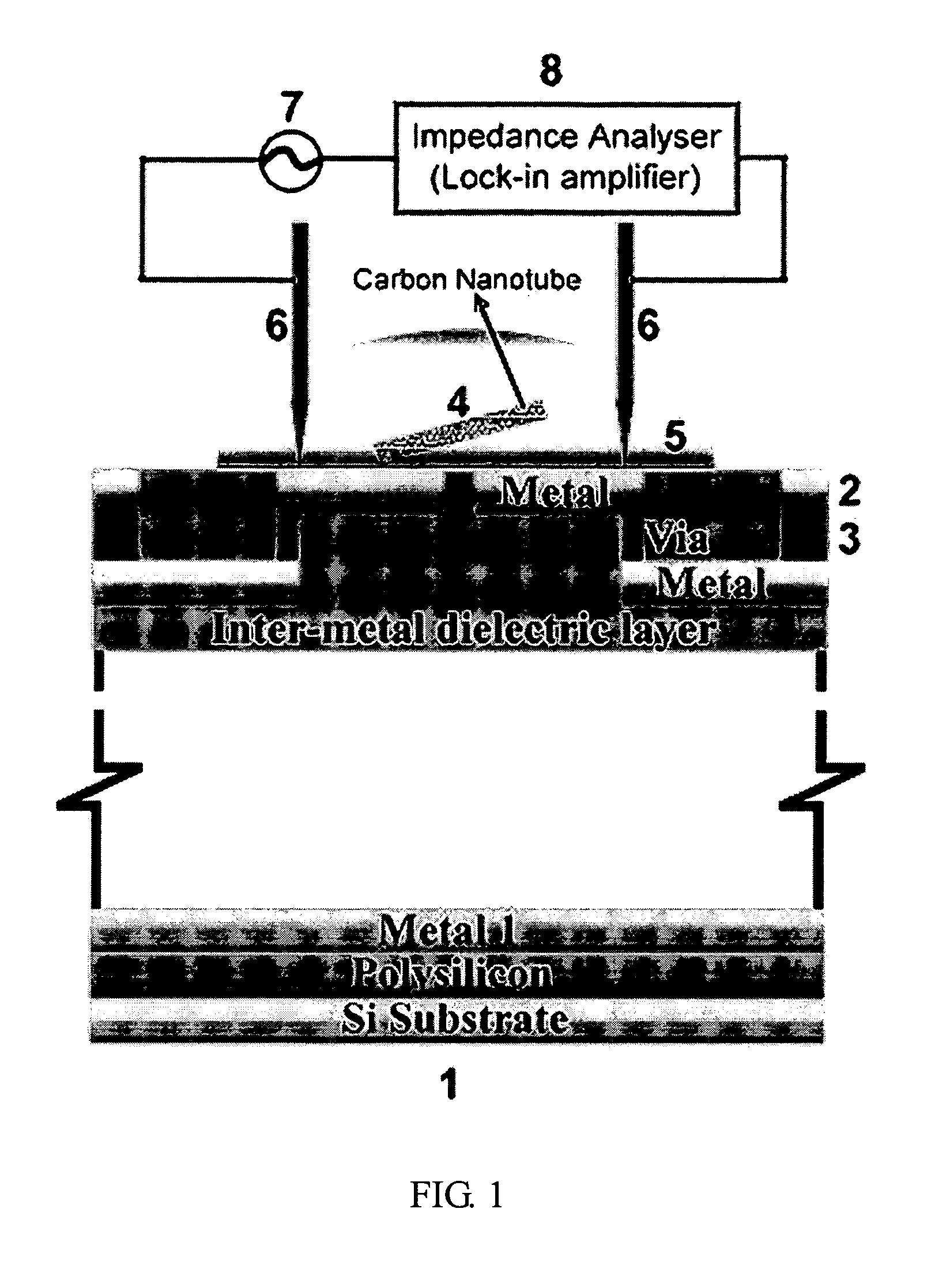
Method for integrating carbon nanotube with CMOS chip into array-type microsensor
InactiveUS20070134866A1Effectively and sequentially fixEfficient combinationNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesProbe cardManufacturing technology
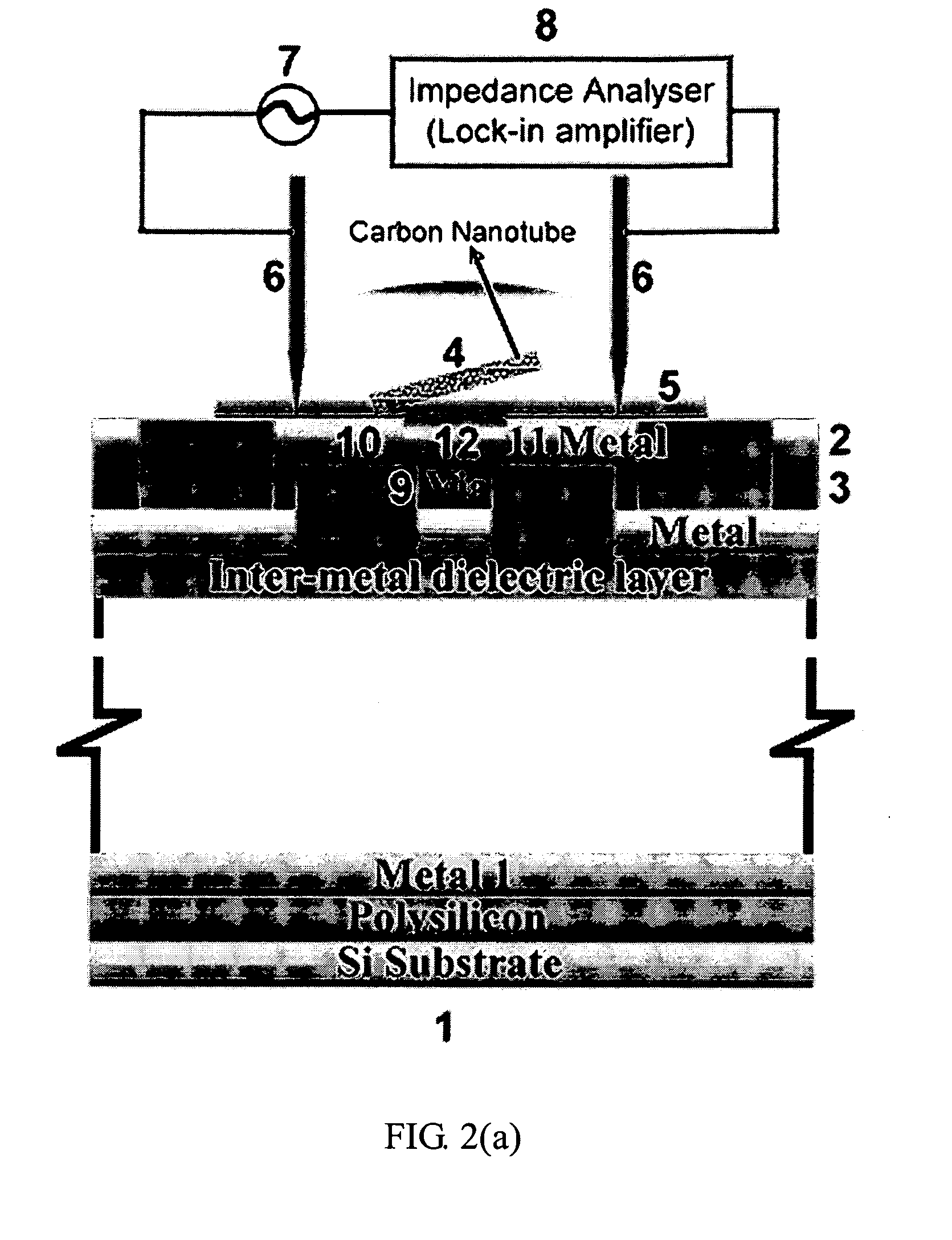
The invention disclosed a method for integrating CMOS circuit chips with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) into array-type sensors with signal processors enclosed. The method provides low-temperature and wafer-level fabrication processes including dripped a drop of dispersed CNTs solution on the top of CMOS chip, use micro probe card to contact with pairs of pads, with a function generator to generate dielectrophoresis (DEP) signal and with a lock-in amplifier to measure impedance value simultaneously. According to the impedance measurement it can detect the number of CNTs fixed on pair of pads. Only if the number of CNTs on the top of pair of pads were not expected, it would readjust the frequency of alternating current to the range of negative DEP force and repel CNTs from the top of pair of pads. Repeat positive DEP signal to attach CNTs until the number of CNTs as demand, then hold the DEP force until CNTs solution evaporated to make a well-contact between CNTs and pads. Furthermore, the surface of CNTs can be functionalized and let CNTs have high sensitivity to ambient molecules (Gas molecules, Bio molecules, et al.), then transfer the measured signal into signal processors of CMOS chips, the processors could be impedance measurement unit, current measurement unit, conductance measurement unit et. al., and it can measure, record and analyze the data of small varied signal directly.
Owner:HUANG JUNG TANG
Electrochemical fabrication method for fabricating space transformers or co-fabricating probes and space transformers
Embodiments of the invention provide electrochemical fabrication processes that may be used for the fabrication of space transformers or the co-fabrication of microprobe arrays along with one or more space transformers.
Owner:MICROFAB
Hydrothermal synthetic method for coating carbon nanometer tube with molybdenum sulphide
InactiveCN1613918AReduce usageLow reaction temperaturePigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsThioureaCarbon nanotube
Compound nano pipes coated by molybdenum sulphide are produced by water heating synthesis, including: first to put the molybdate and thiourea in the water and the mass percent of molybdate is 0.2%-1.5%, the thiourea is 0.2%-2.0%, then disperse the nano pipes of C in the solvent by the super sonic wave, and the mass percent of it is 0.1%-0.5%, the mixture is then put into the non-corrosive steel tank which is full of Teflon to react, at 200-250deg.C for 20-40h. The 2-6 phase of molybdenum sulphide obtained by the transmission electron microscopic and energy scattering analyze. They can be used to prepare high performance compound material of tribology, catalytic carrier, and microprobe. The process is simple, and it could avoid using the H2S.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microprobe for testing electronic device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050092709A1Improve flatnessImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectricityFine pitch
A microprobe is manufactured by forming via hole on one edge portion of the silicon substrate, filling the via hole with the conductive layer, forming the conductive spring unit on the silicon substrate so as to be electrically connected to the conductive layer in the via hole, forming the conductive tip portion on the leading end of the spring unit, removing the silicon substrate under the spring unit using isotropic etching, thereby supporting the spring unit only on the portion adjacent to the via hole. The spring unit and the tip portion are formed only in the window of a PR. The microprobe has benefits in that a separation of signal between tip portions is easy and mechanical and electrical properties of the probe tip are good, since the probe is formed on the silicon substrate by using micro-processing. Also, since the pitch between the tip portions can be reduced, a semiconductor device with fine pitch pad can be tested. Furthermore, the uniformity of flatness of the probe tip portion can be improved.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
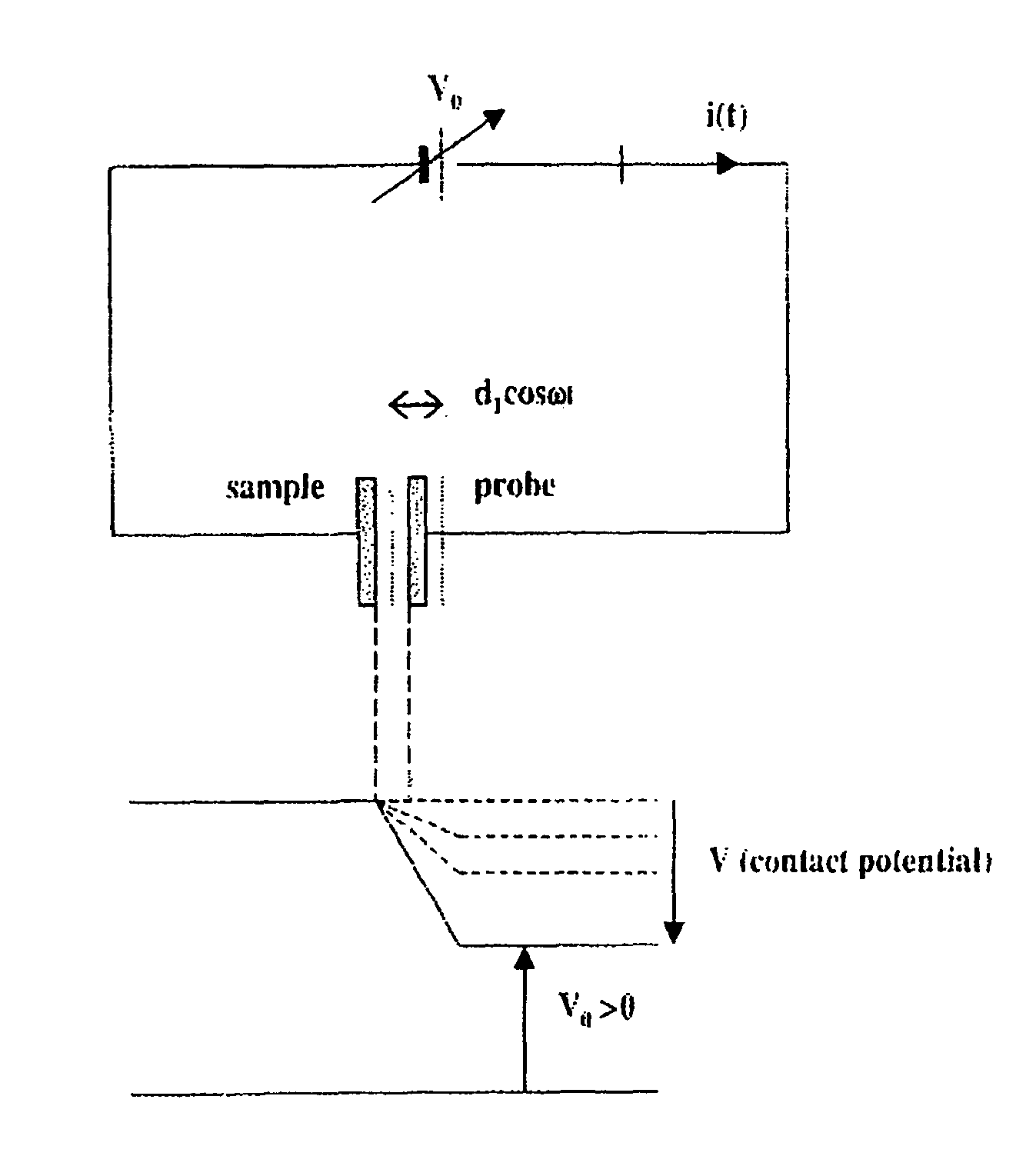
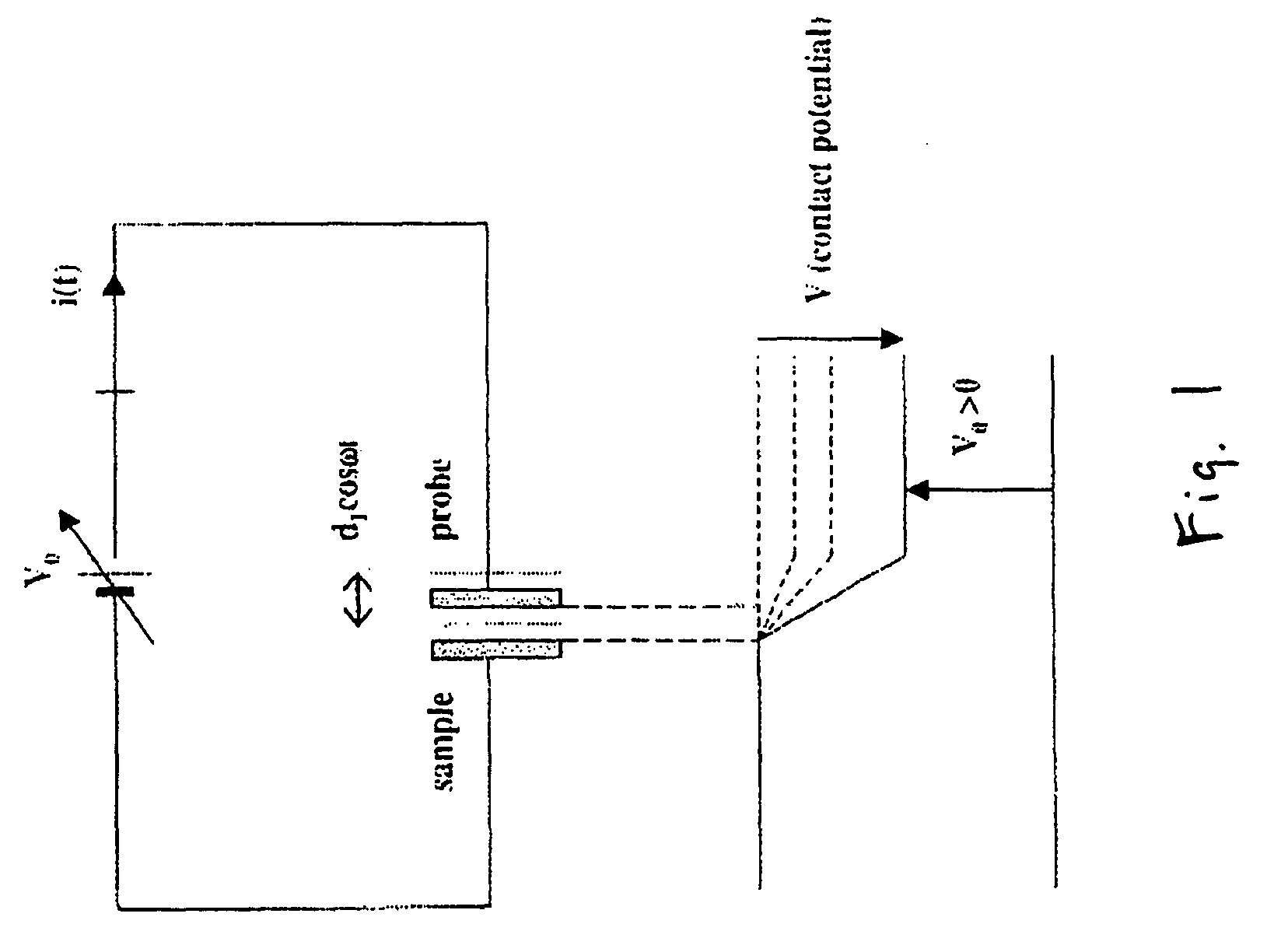
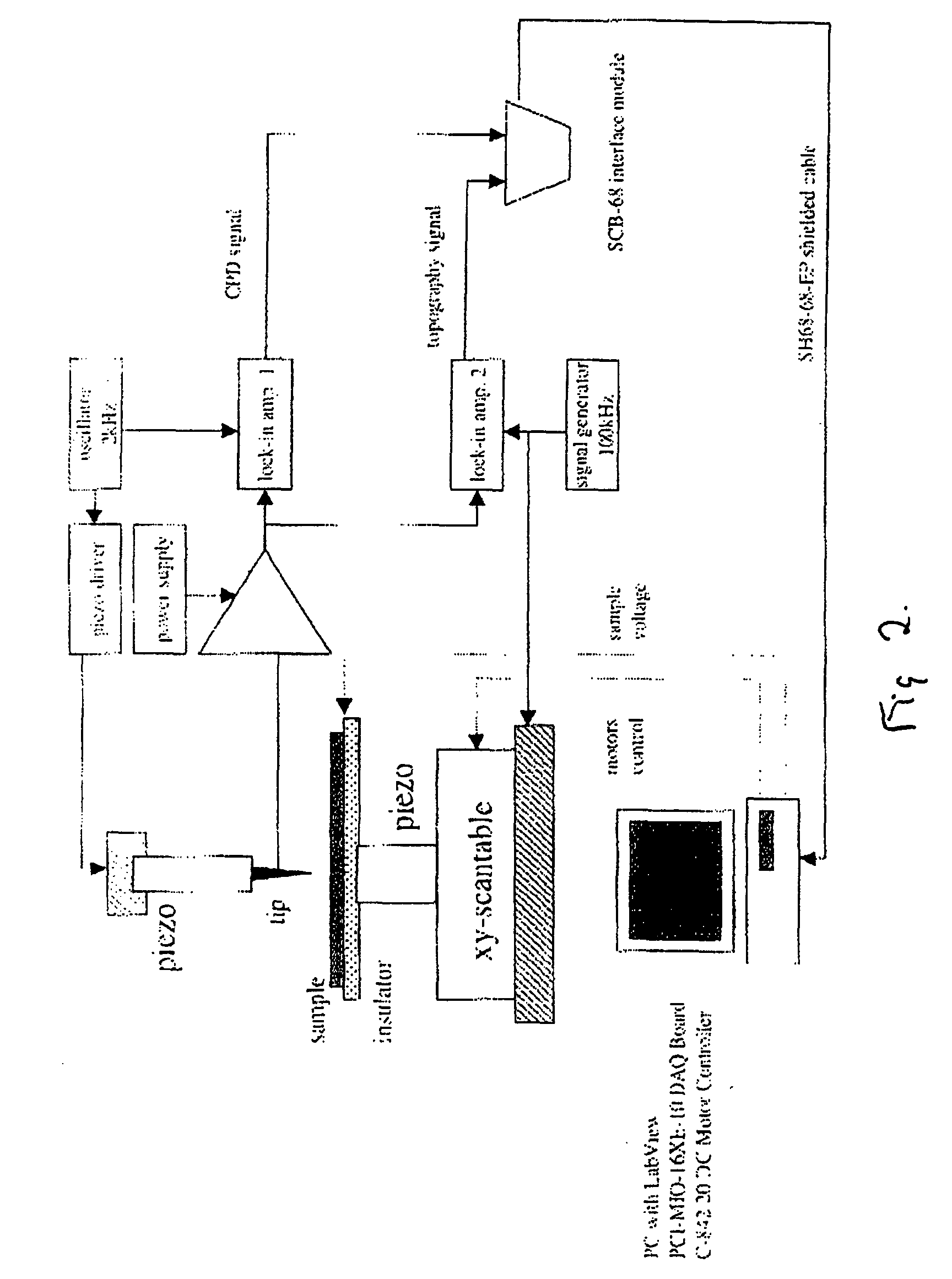
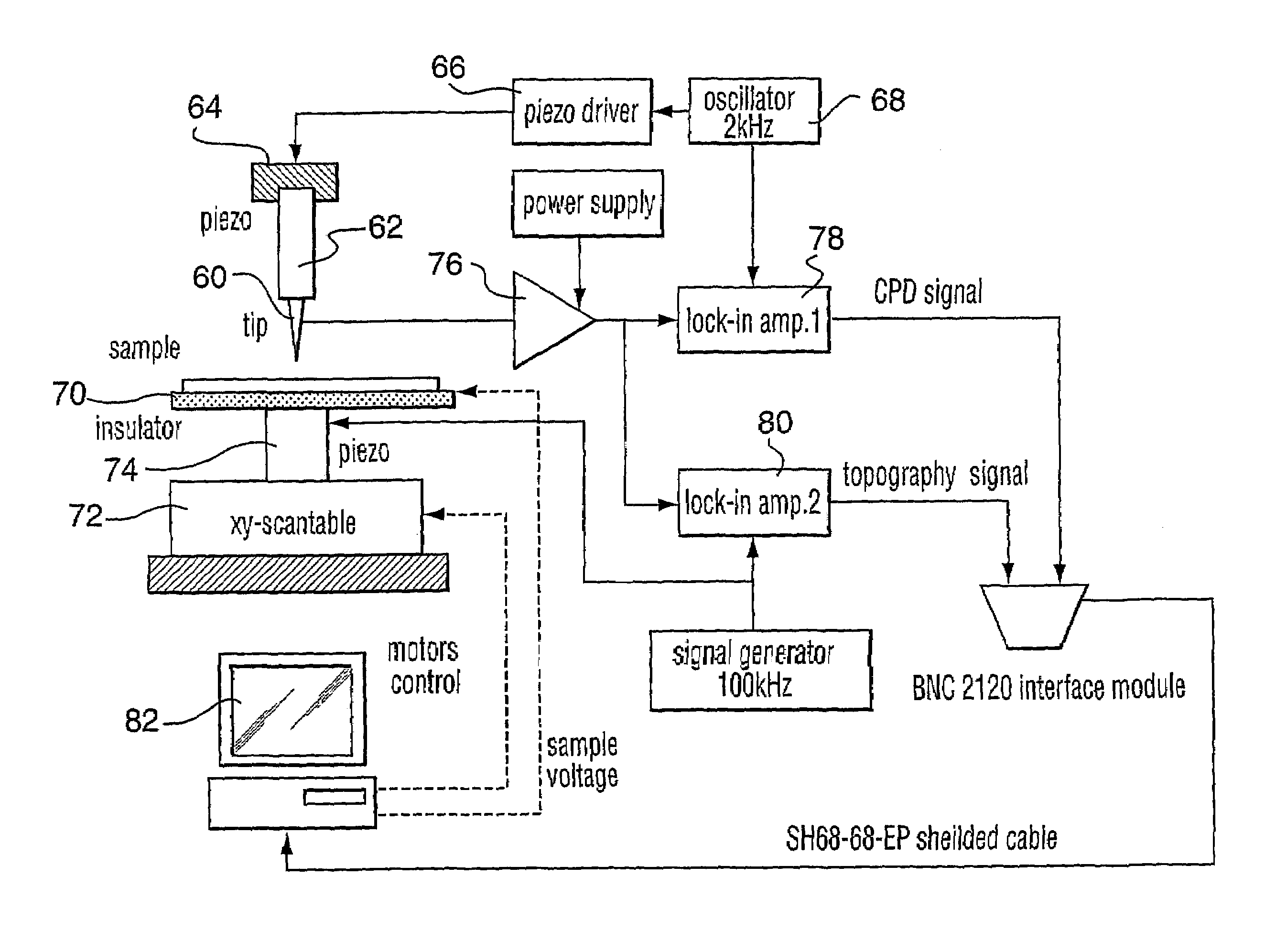
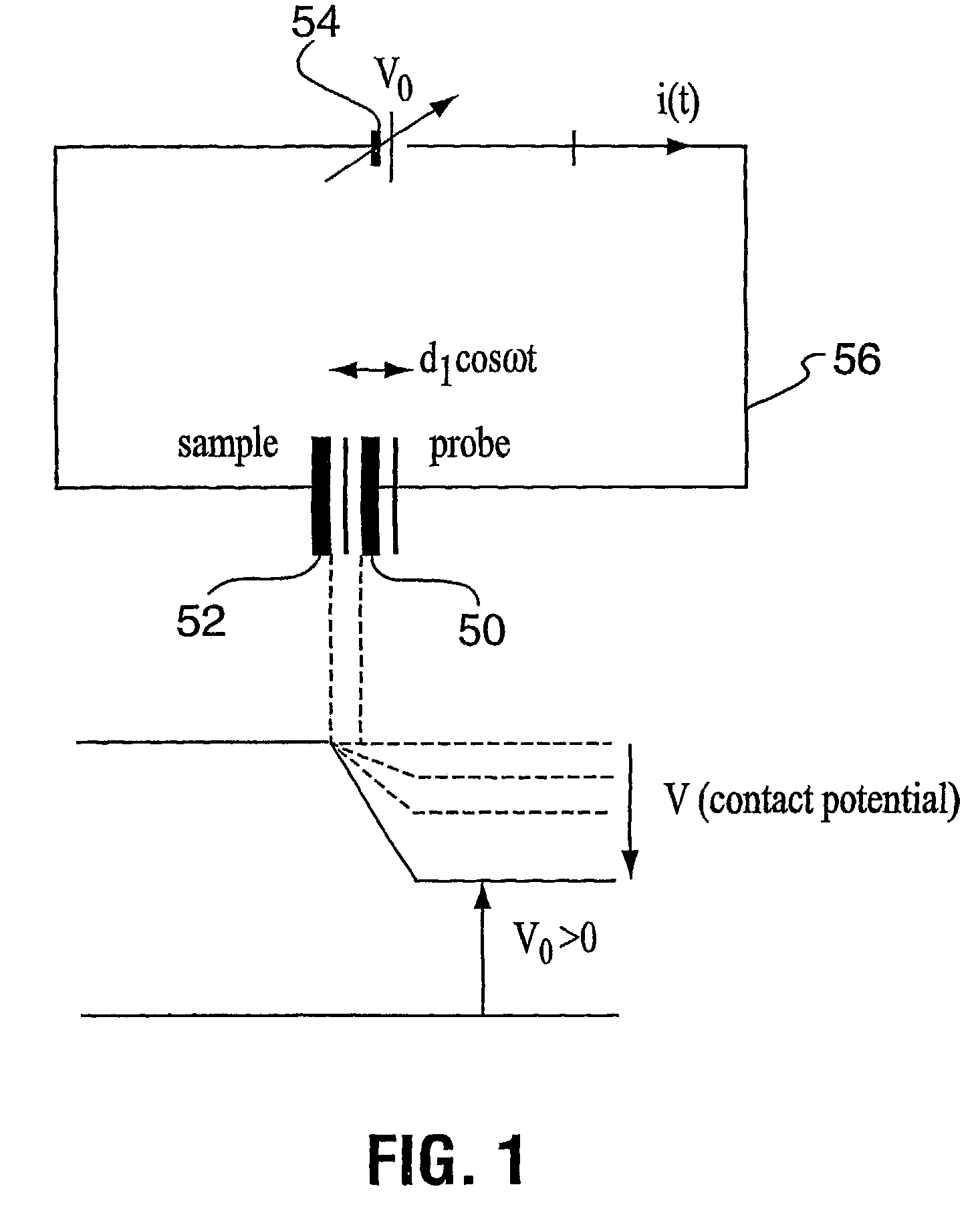
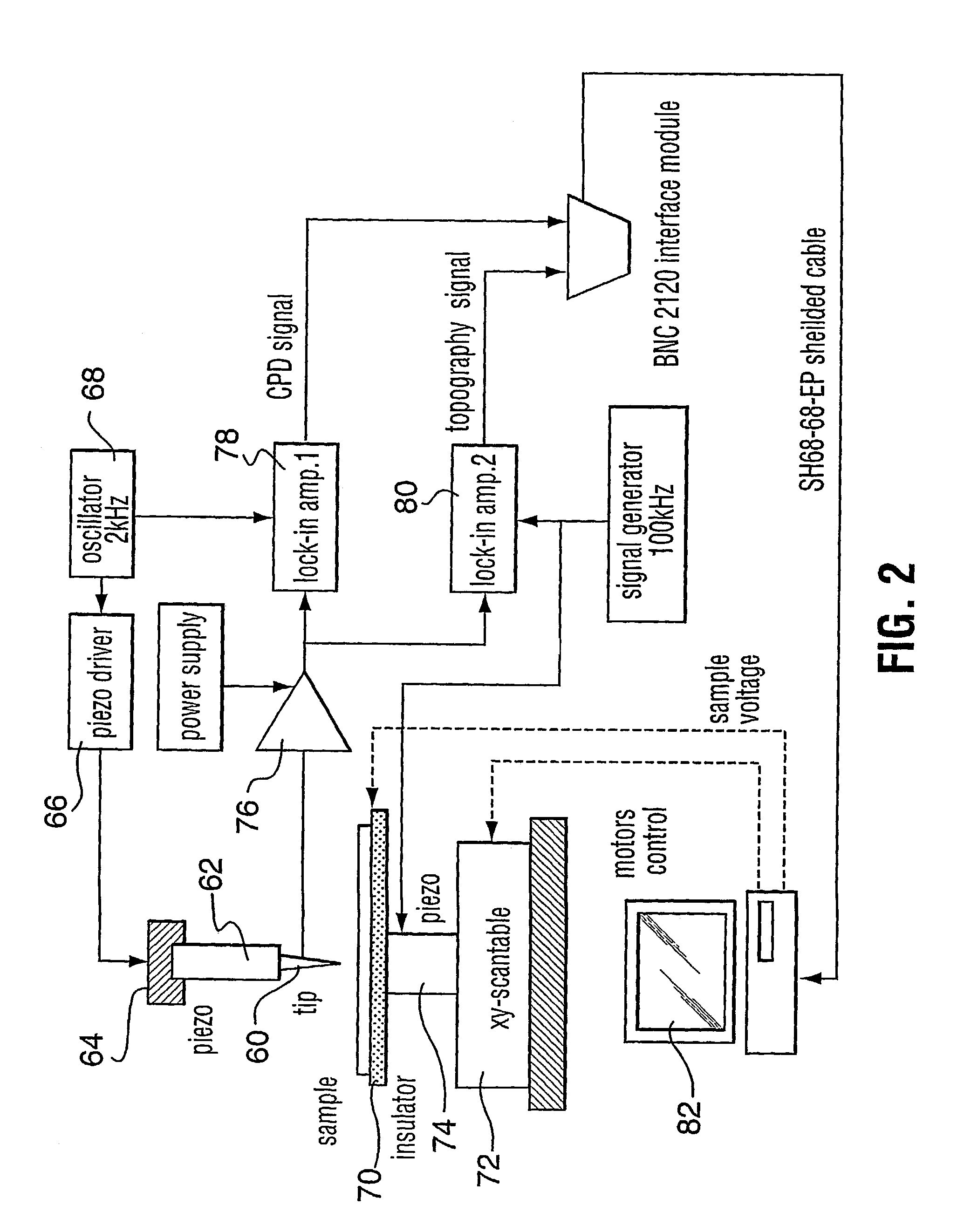
Scanning kelvinmicroprobe system and process for biomolecule microassay
InactiveUS20040029131A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPotential differenceAntibody antigen
There is provided a system and process for detecting biomolecular interaction on a substrate having a biomolecule immobilized on a surface of the substrate. The system and process incorporate a scanning Kelvin microprobe (SKM) capable of analyzing surface topography as well as a contact potential difference image signal. Also provided is the use of SKM in measuring and analyzing biochemical molecular interactions between a probe bound to the surface of the substrate, and a target suspected to be present in a liquid sample. One of the probe and target combination is a biomolecule such as a nucleic acid, a polypeptide, or a small molecule, and an antibody antigen combination may be used.
Owner:SENSORCHEM INT
Method and apparatus for sample extraction and handling
ActiveUS8357913B2Reduce labor intensityImprove throughputDigital data processing detailsElectrical testingVacuum pressurePredictability
Owner:FEI CO
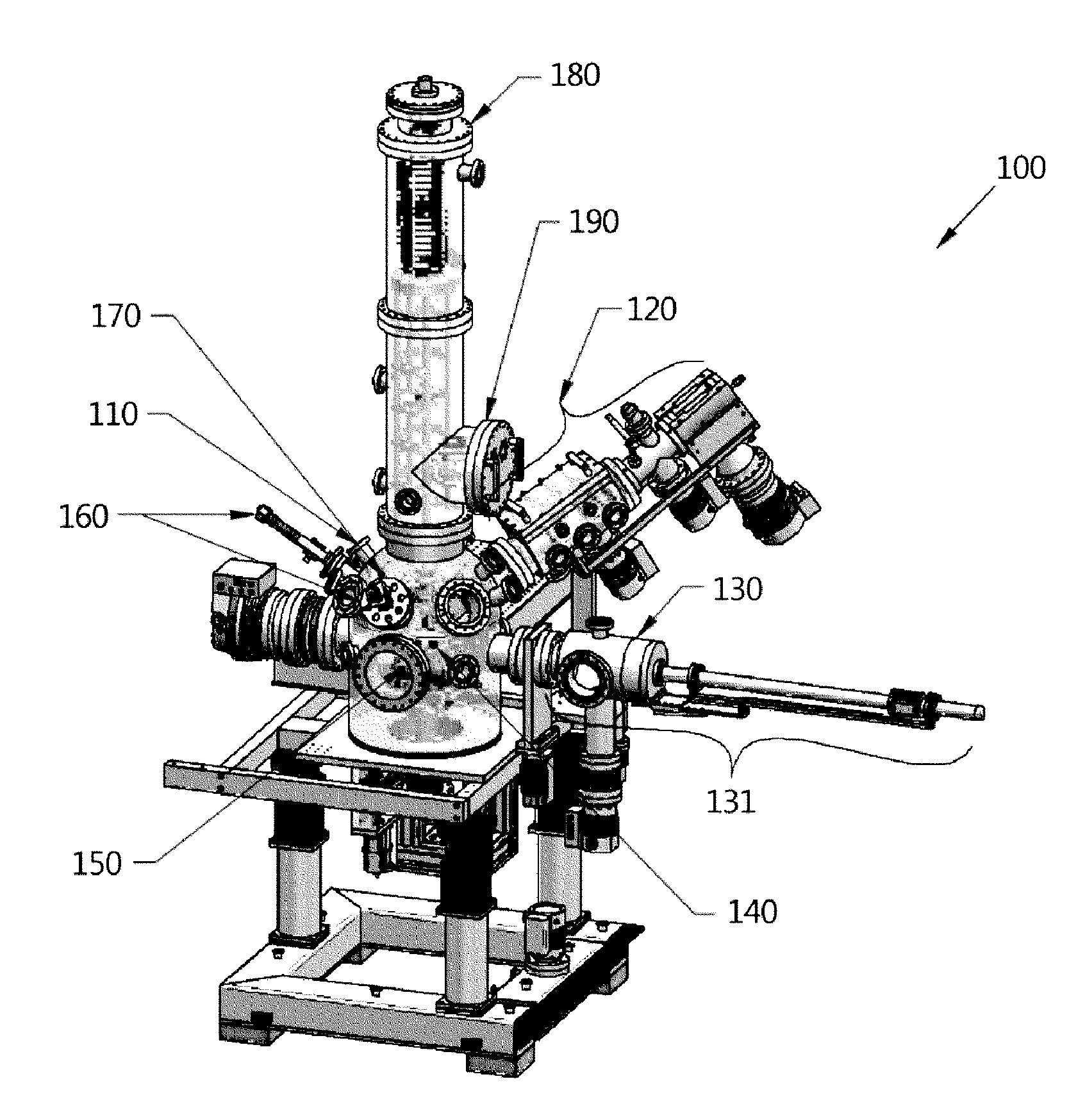
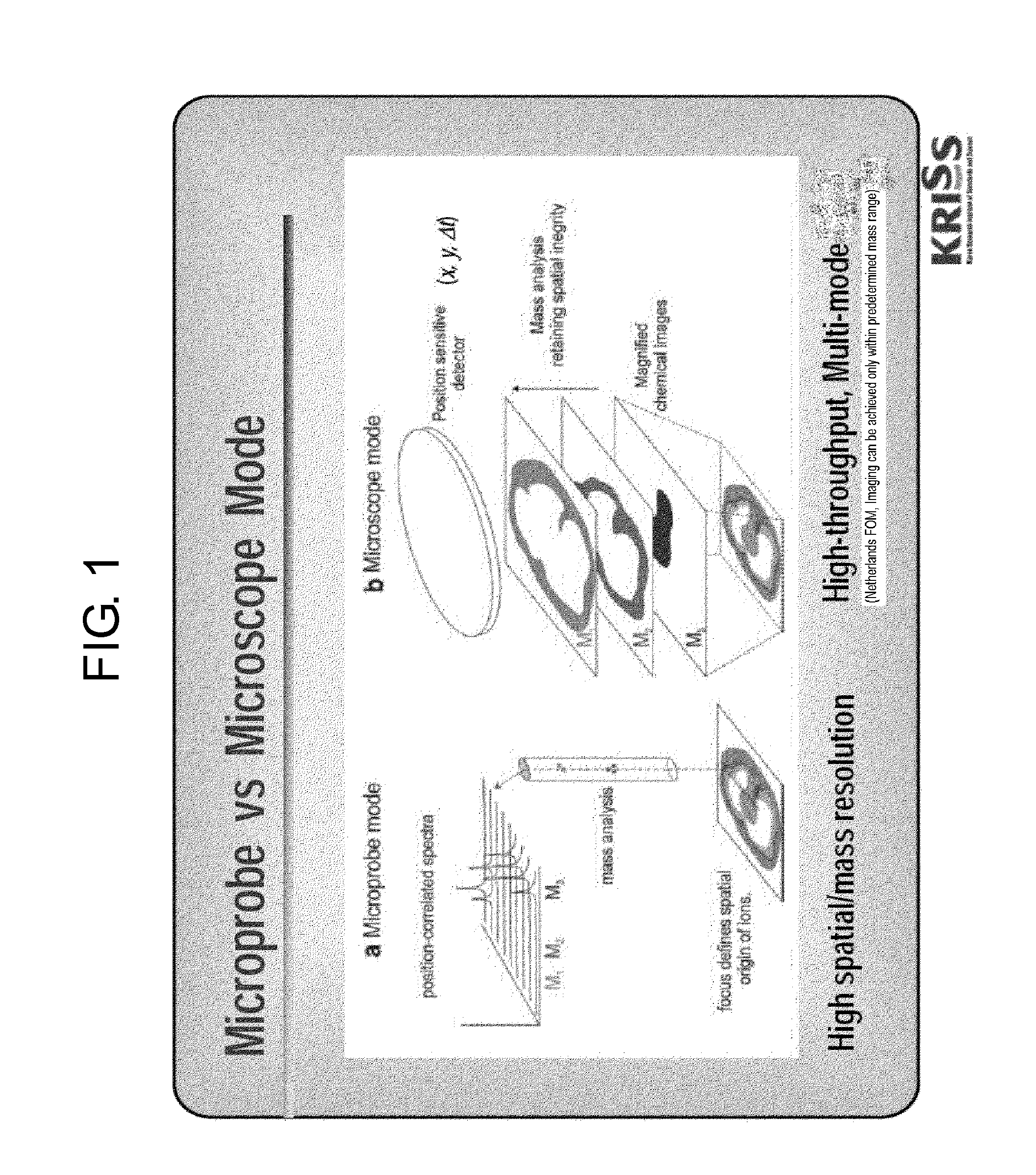
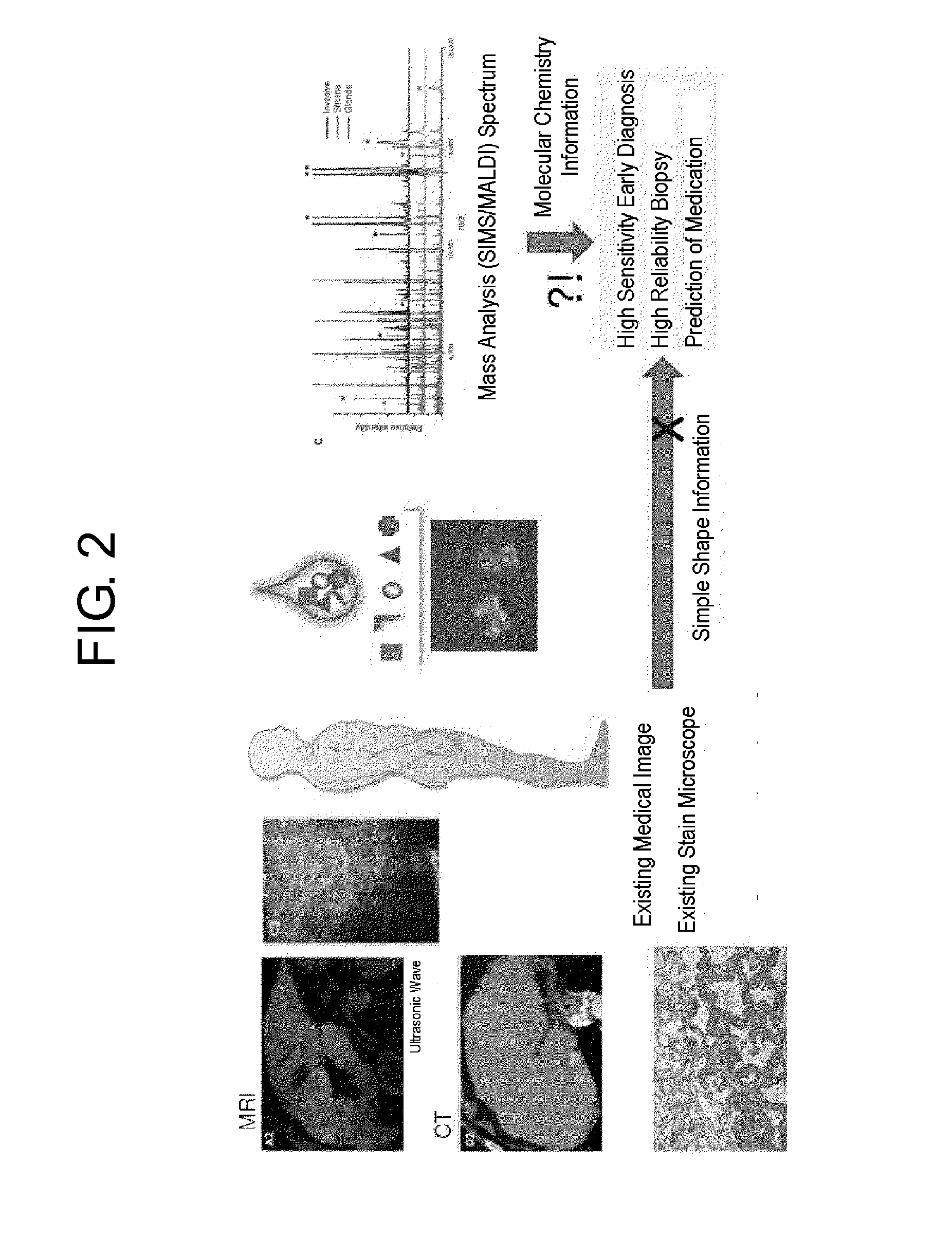
Flight time based mass microscope system for ultra high-speed multi mode mass analysis
ActiveUS20140183354A1Fast measurement speedIncreasing objectiveTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationHigh molecular massMetabolome
The present invention aims to provide a time-of-flight based mass microscope system for an ultra-high speed multi-mode mass analysis, for using a laser beam or an ion beam simultaneously to enable both a low molecular weight analysis such as for drugs / metabolome / lipids / peptides and a high molecular weight analysis such as for genes / proteins, without being limited by the molecular weight of the object being analyzed, and for significantly increasing the measuring speed by using a microscope method instead of a microprobe method.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
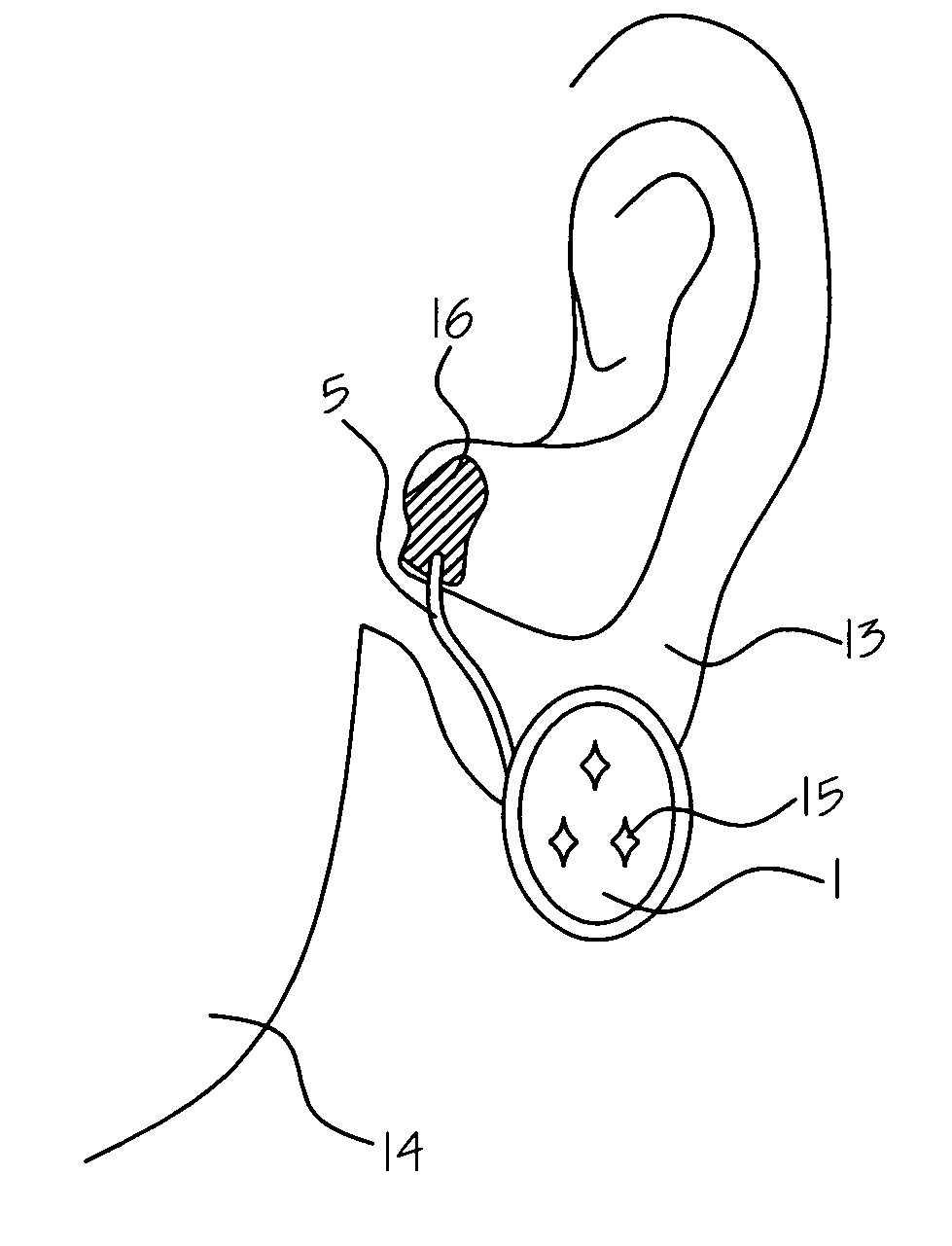
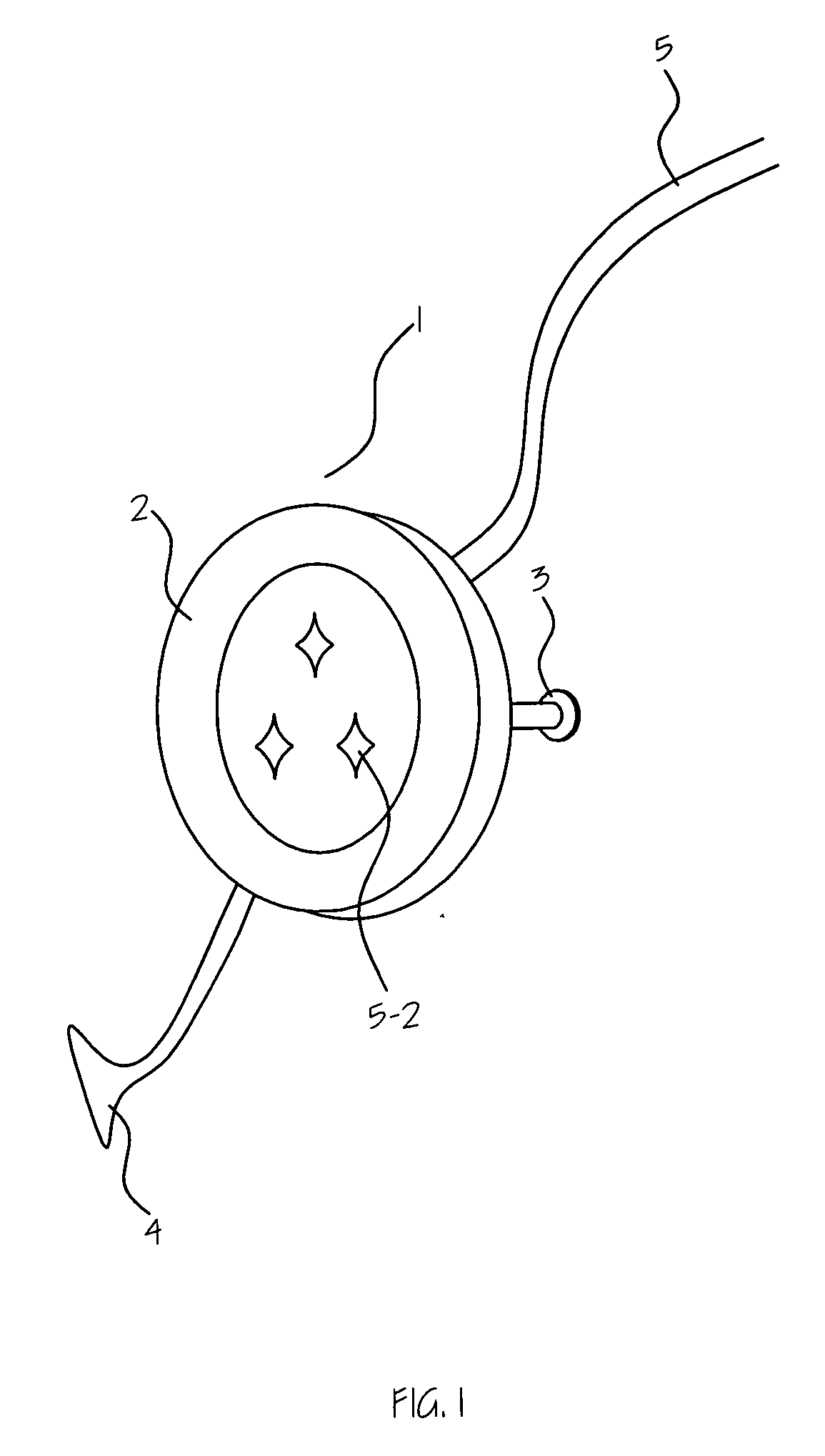
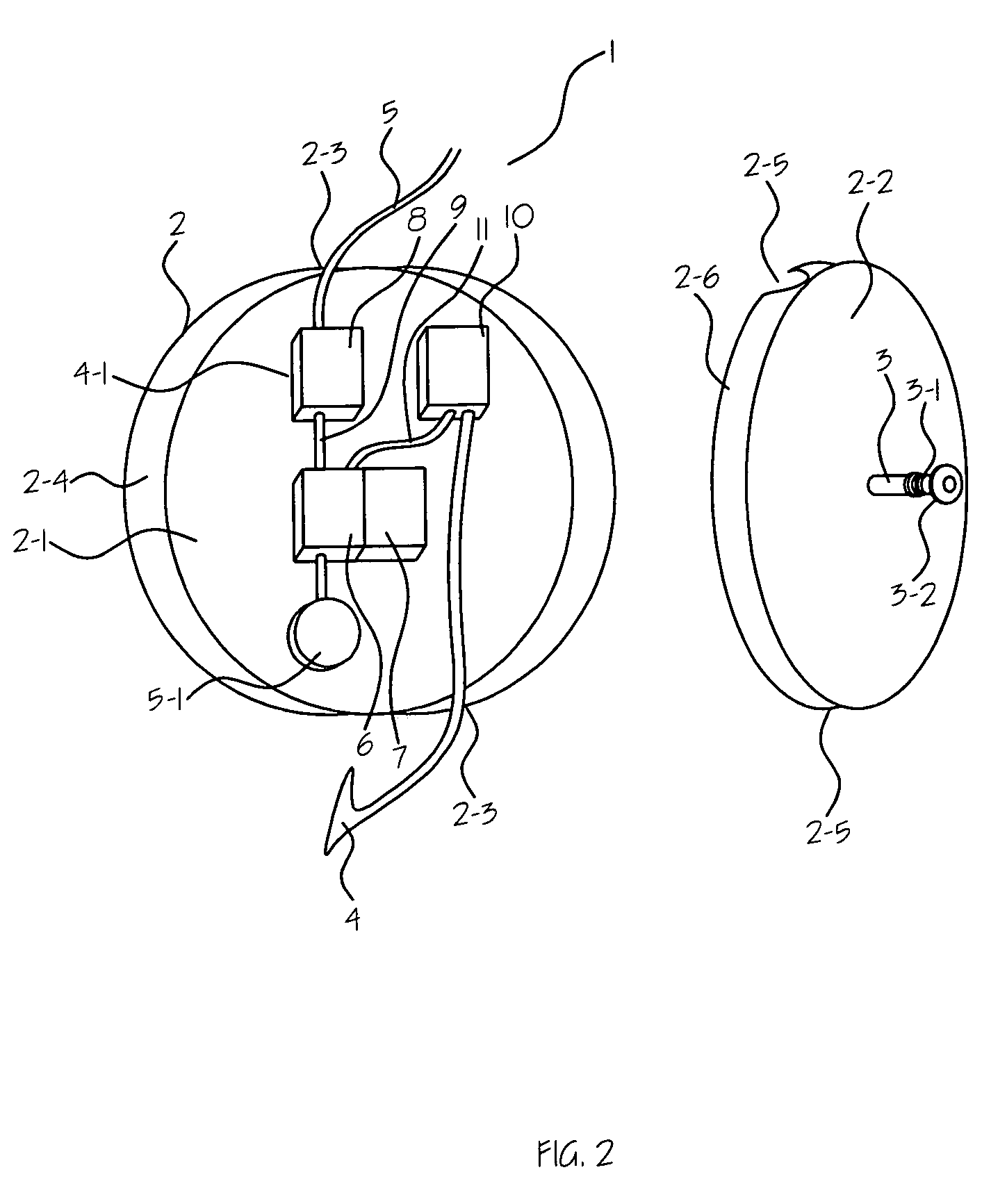
Ear ring type two way wireless mini-ear piece
A two-way communication earpiece, which is a small and comfortable. The ear-piece is comprised of a main body, a sound delivery probe, and a micro probe for sound pick up. The sound delivery probe, which is extended from main body, is configured to be inside of the external acoustic meatus of a user. The main body is attached to lobule of ear of the user like an ear ring. The sound delivery probe is coated with silicon for hygiene of the external acoustic meatus of the user. The micro probe for sound pick up is attached to a junction point of user's skin that locates behind the ear of the user, where rear surface of the antihelix, rear surface of the lobule, and neck skin of the user meets. At that point the microprobe picks up the voice of the user from the vibration of the skin.
Owner:RIE JIN
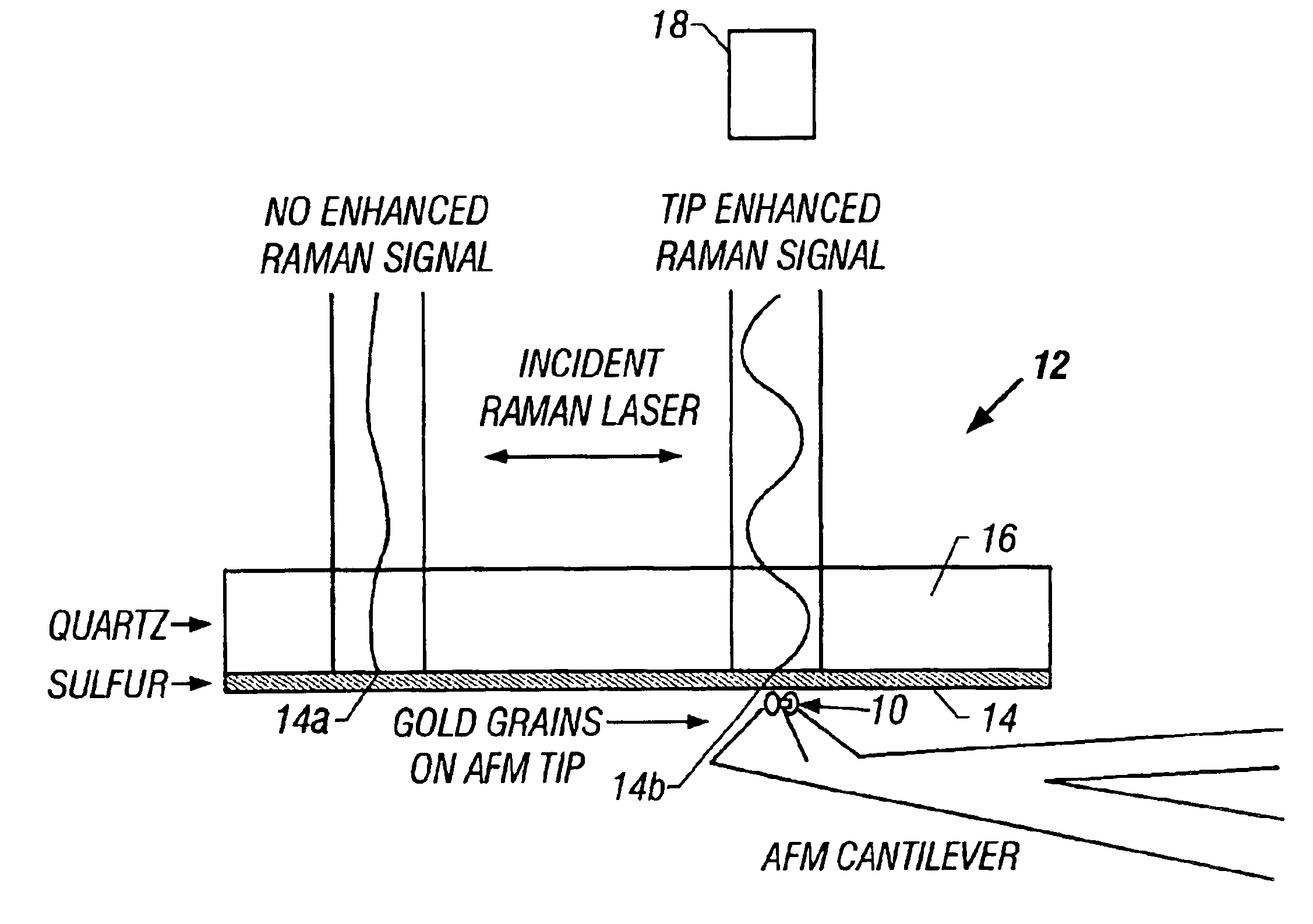
Locally enhanced raman spectroscopy with an atomic force microscope
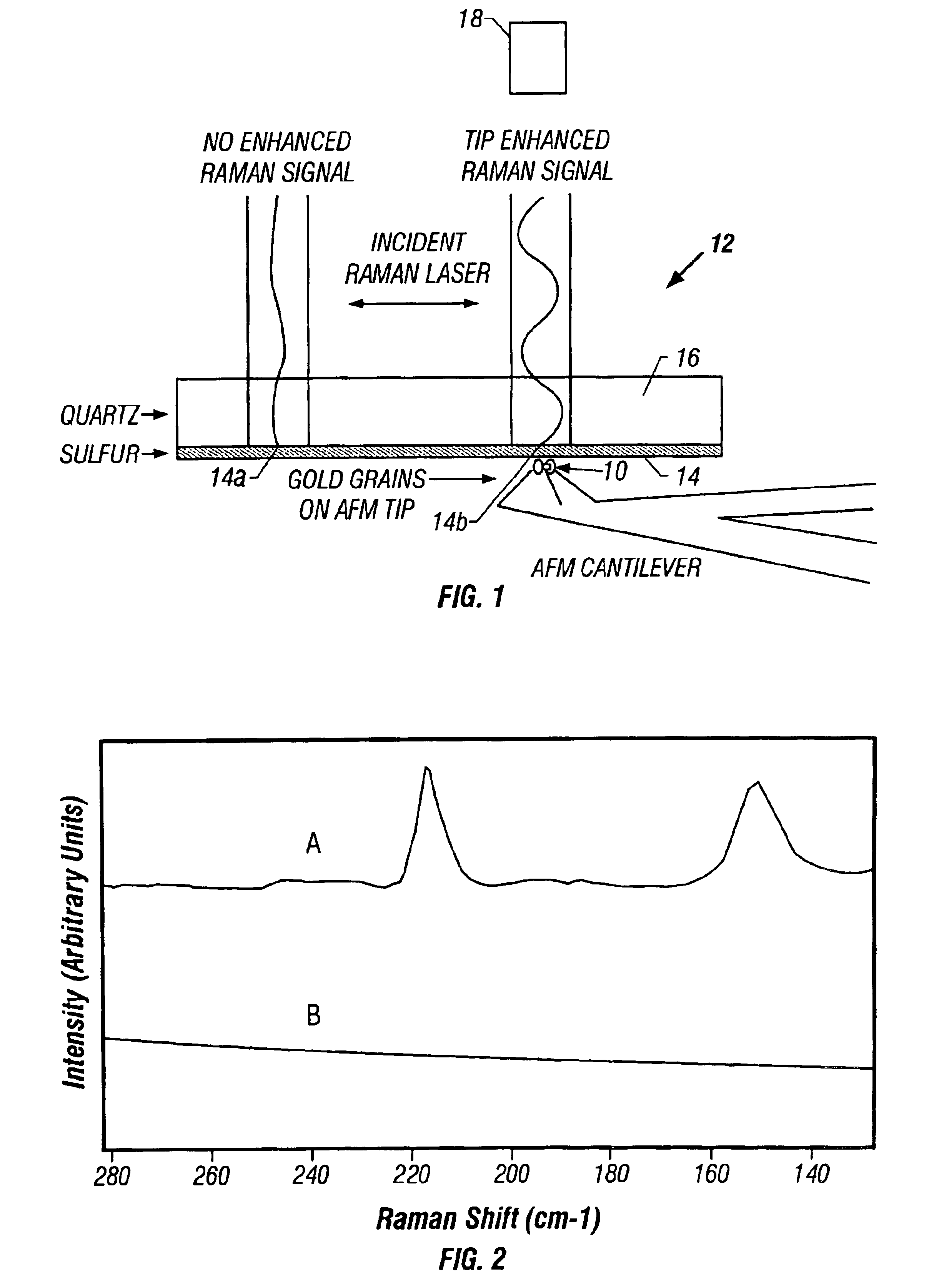
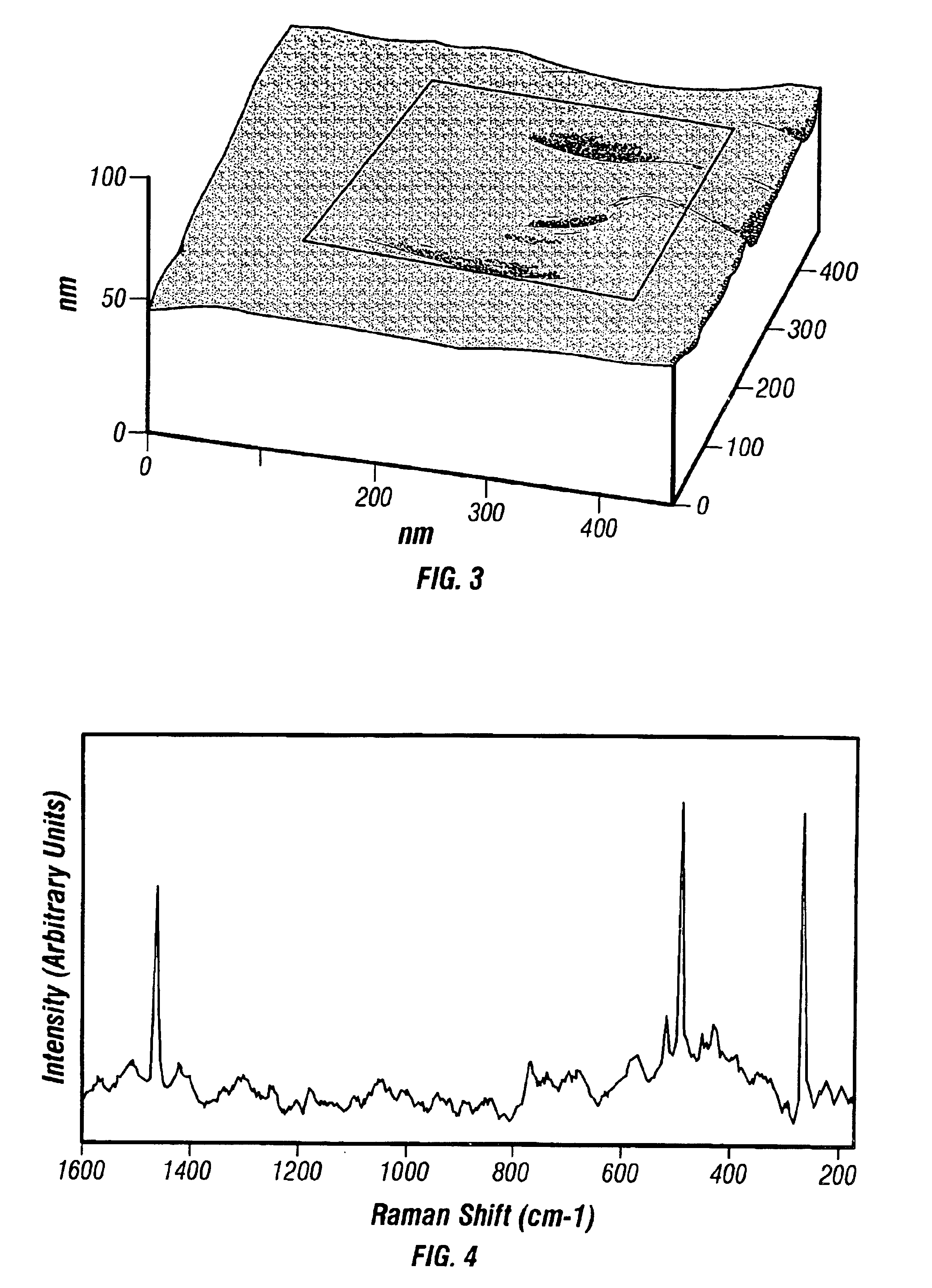
InactiveUS6850323B2Increase heightMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureMagnetic force microscopeAtomic force microscopy
An atomic force microscope (AFM) tip is used to selectively produce surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) for localized Raman spectroscopy. Spectra of thin films, undetectable with a Raman microprobe spectrometer alone, are readily acquired in contact with a suitably gold-coated AFM tip. Similarly, an AFM tip is used to remove sample layers at the nanometer scale and subsequently serve as a SERS substrate for ultra-trace analysis. This demonstrates the interface of an AFM with a Raman spectrometer that provides increases sensitivity, selectivity and spatial resolution over a conventional Raman microprobe. An AFM guiding the SERS effect has the potential for targeted single molecule spectroscopy.
Owner:NASA
Cantilever microprobes for contacting electronic components and methods for making such probes
InactiveUS20050189958A1Improve featuresElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingEngineeringElectronic component
Embodiments disclosed herein are directed to compliant probe structures for making temporary or permanent contact with electronic circuits and the like. In particular, embodiments are directed to various designs of cantilever-like probe structures. Some embodiments are directed to methods for fabricating such cantilever structures. In some embodiments, for example, cantilever probes have extended base structures, slide in mounting structures, multi-beam configurations, offset bonding locations to allow closer positioning of adjacent probes, compliant elements with tensional configurations, improved over travel, improved compliance, improved scrubbing capability, and / or the like.
Owner:MICROFAB
Scanning kelvin microprobe system and process for analyzing a surface
InactiveUS7084661B2Superior lateral resolutionThe process is stable and reliableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelf-assembled monolayerNano devices
A scanning Kelvin microprobe (SKM) system capable of measuring and analyzing surface characteristics of samples is provided. Also provided is a process of measuring and analyzing surface characteristics of samples. Further, there are provided uses of the SKM system in measuring and analyzing surface characteristics of conductors, semiconductors, insulators, chemicals, biochemicals, photochemicals, chemical sensors, biosensors, biochemical microarrays, microelectronic devices, electronic imaged devices, micromachined devices, nano-devices, corroded materials, stressed materials, coatings, adsorbed materials, contaminated materials, oxides, thin films, and self assembling monolayers.
Owner:SENSORCHEM INT
Integrated detector for micro-force micro-displacement measurement system
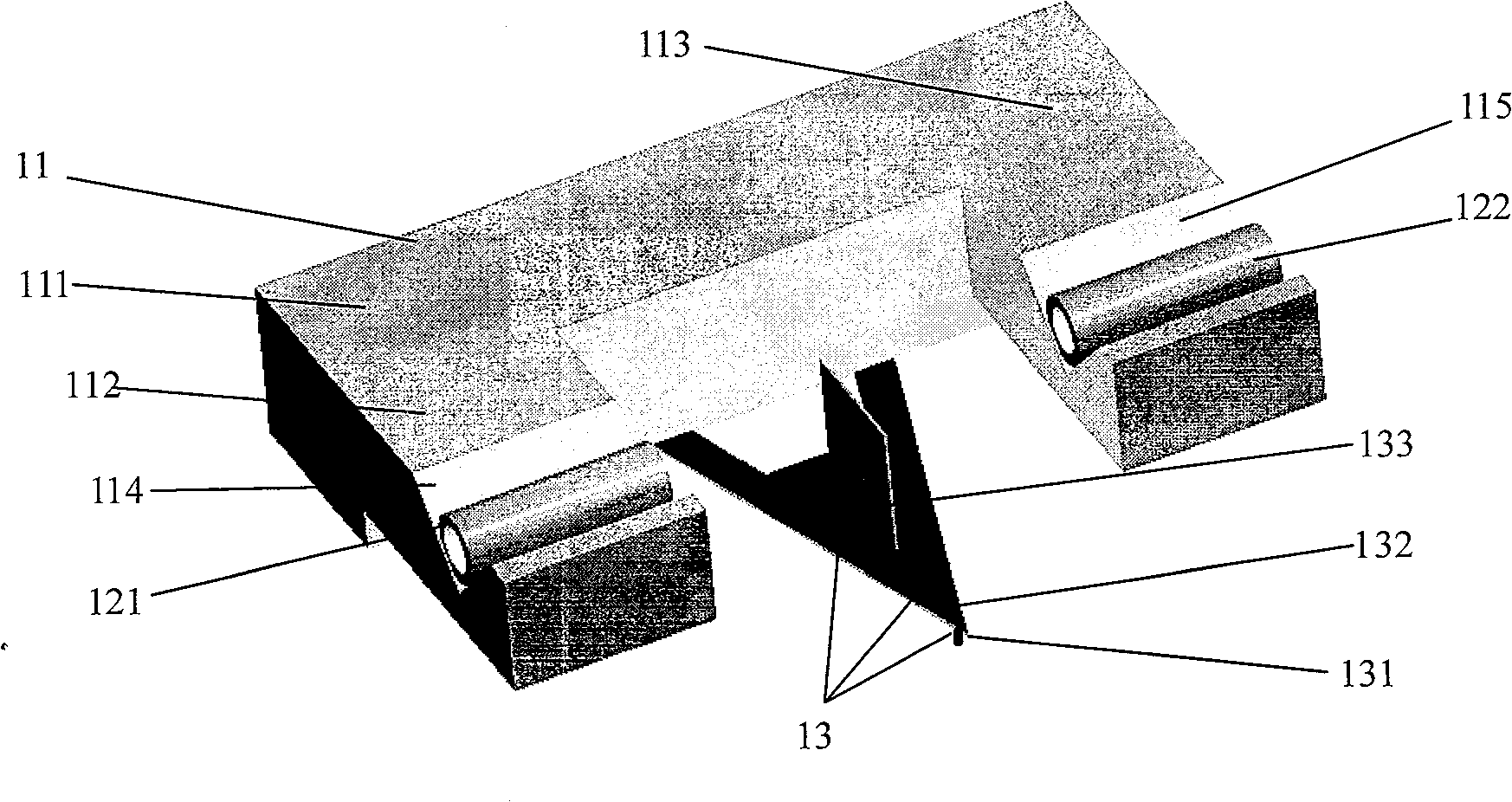
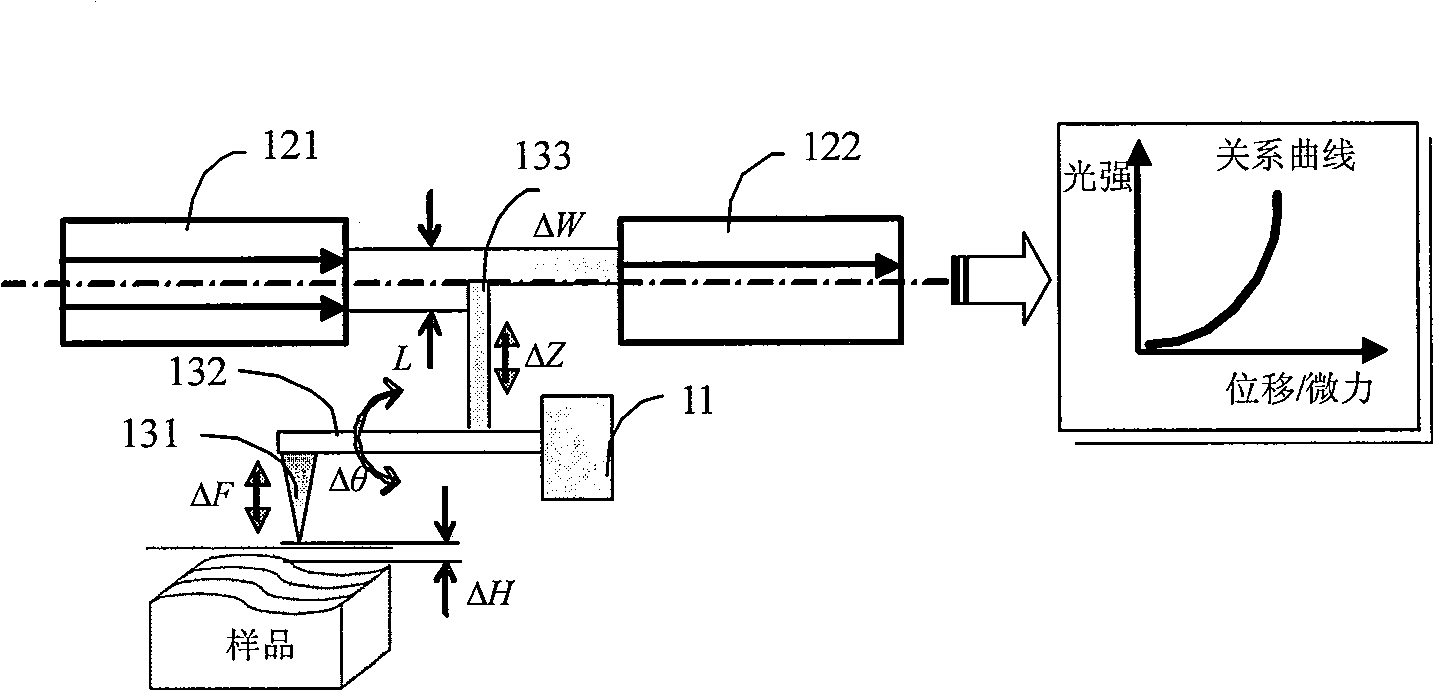
InactiveCN101957246AGood anti-interference performanceSimple structureDecorative surface effectsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationComputer moduleEngineering
The invention provides an integrated detector for a micro-force micro-displacement measurement system, which comprises a mounting bracket, an optical fiber sensing module and a micro-detection module, wherein the mounting bracket is U-shaped, and comprises a pedestal, a left arm and a right arm; the left arm is provided with a left V-shaped groove, while the right arm is provided with a right V-shaped groove; the optical fiber sensing module is used for detecting the variations of power of light incident to receiving optical fibers from emitting optical fibers; the emitting optical fibers are arranged in the left V-shaped groove of the mounting bracket, while the receiving optical fibers are arranged in the right V-shaped groove of the mounting bracket; the emitting optical fibers are coaxial with the receiving optical fibers; the micro-detection module comprises a microprobe, a micro-cantilever and a translational plate, and is used for changing the power of light incident to the receiving optical fibers in a way that the micro-cantilever drives the translational plate to produce vertical displacement according to the variations of the position of the microprobe on the surface of a sample; and the mounting bracket and the micro-detection module are machined into integrated firmware by using a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) process. The integrated detector provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple realization, relatively lower cost and relatively higher detection accuracy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com