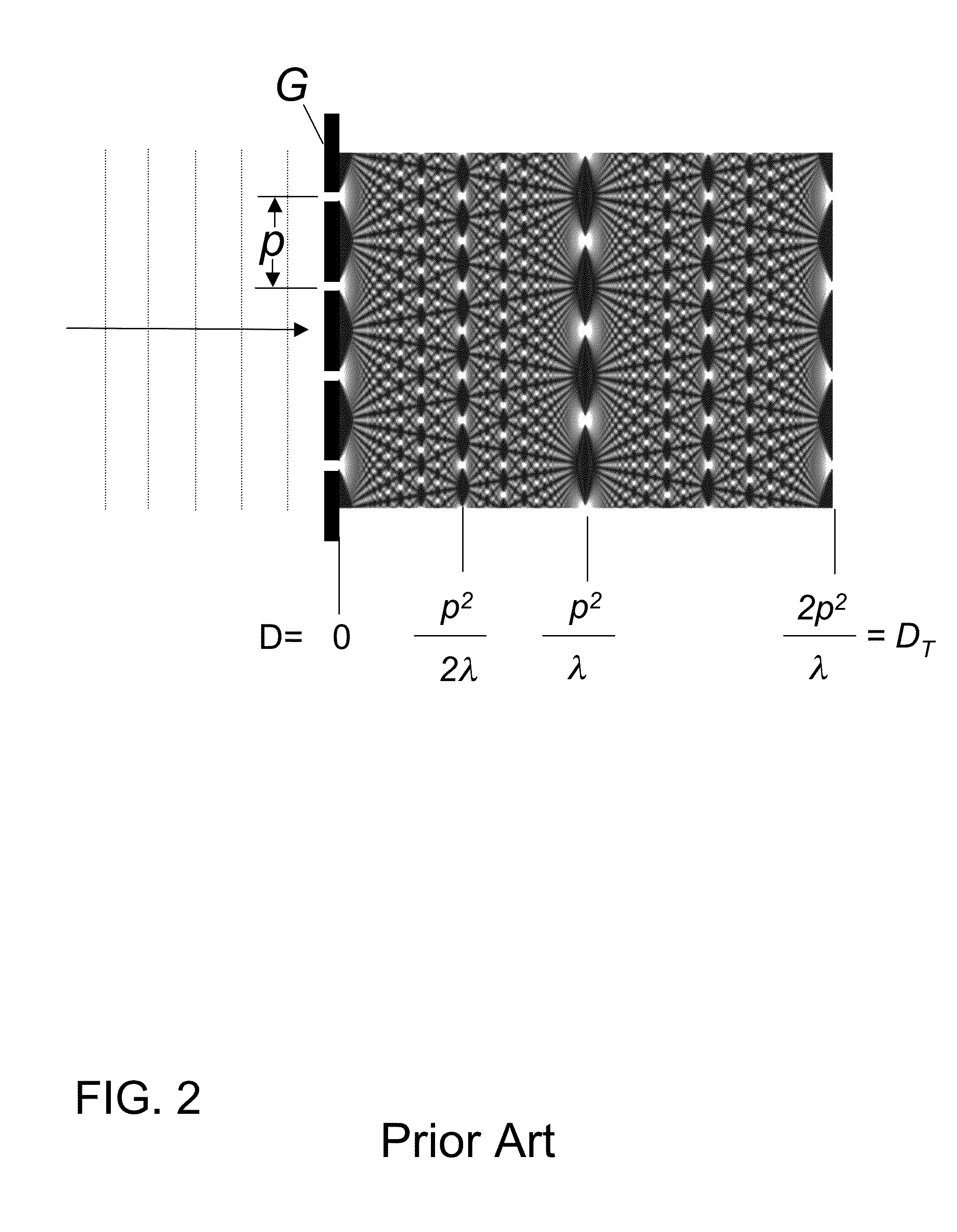
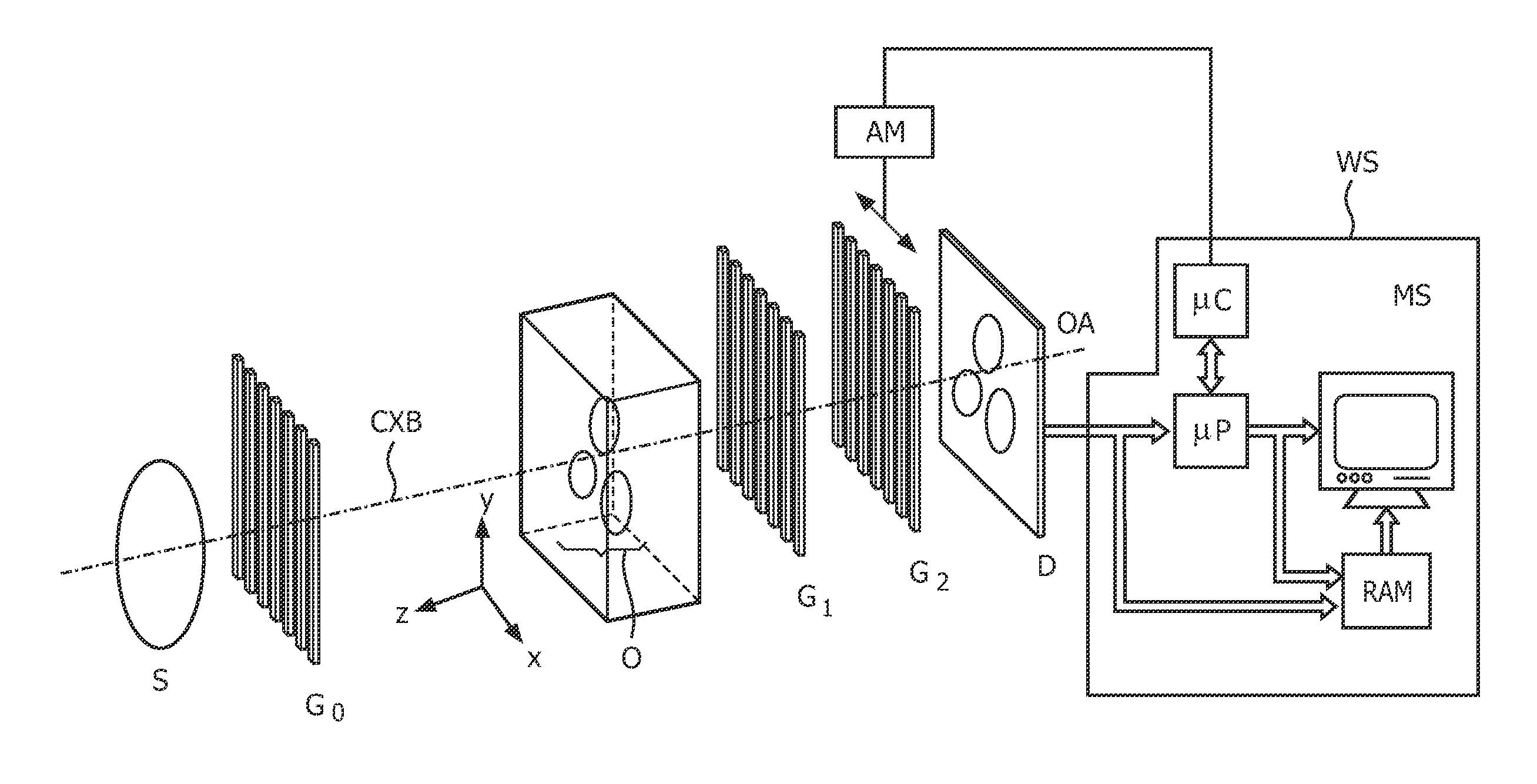
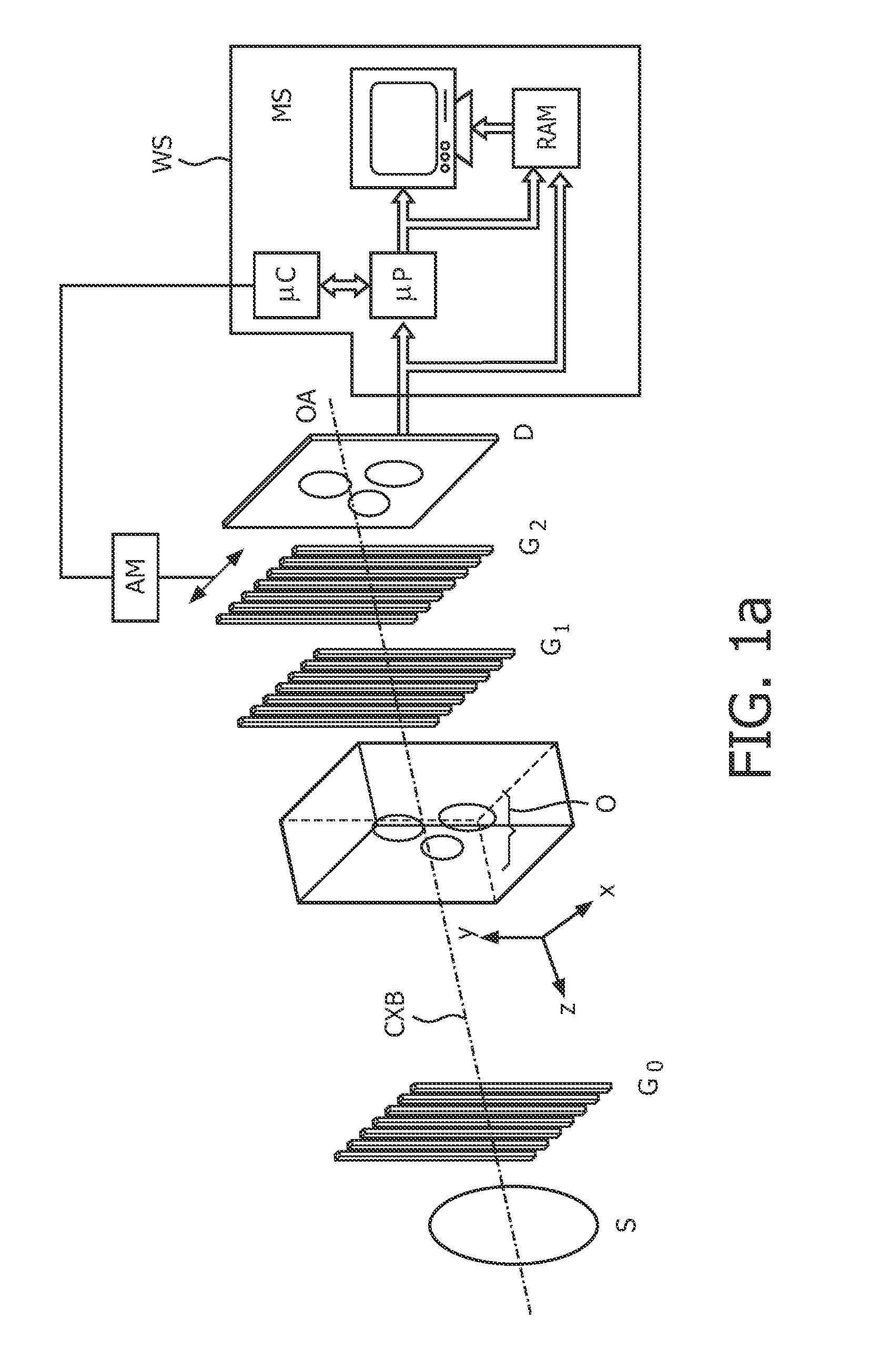
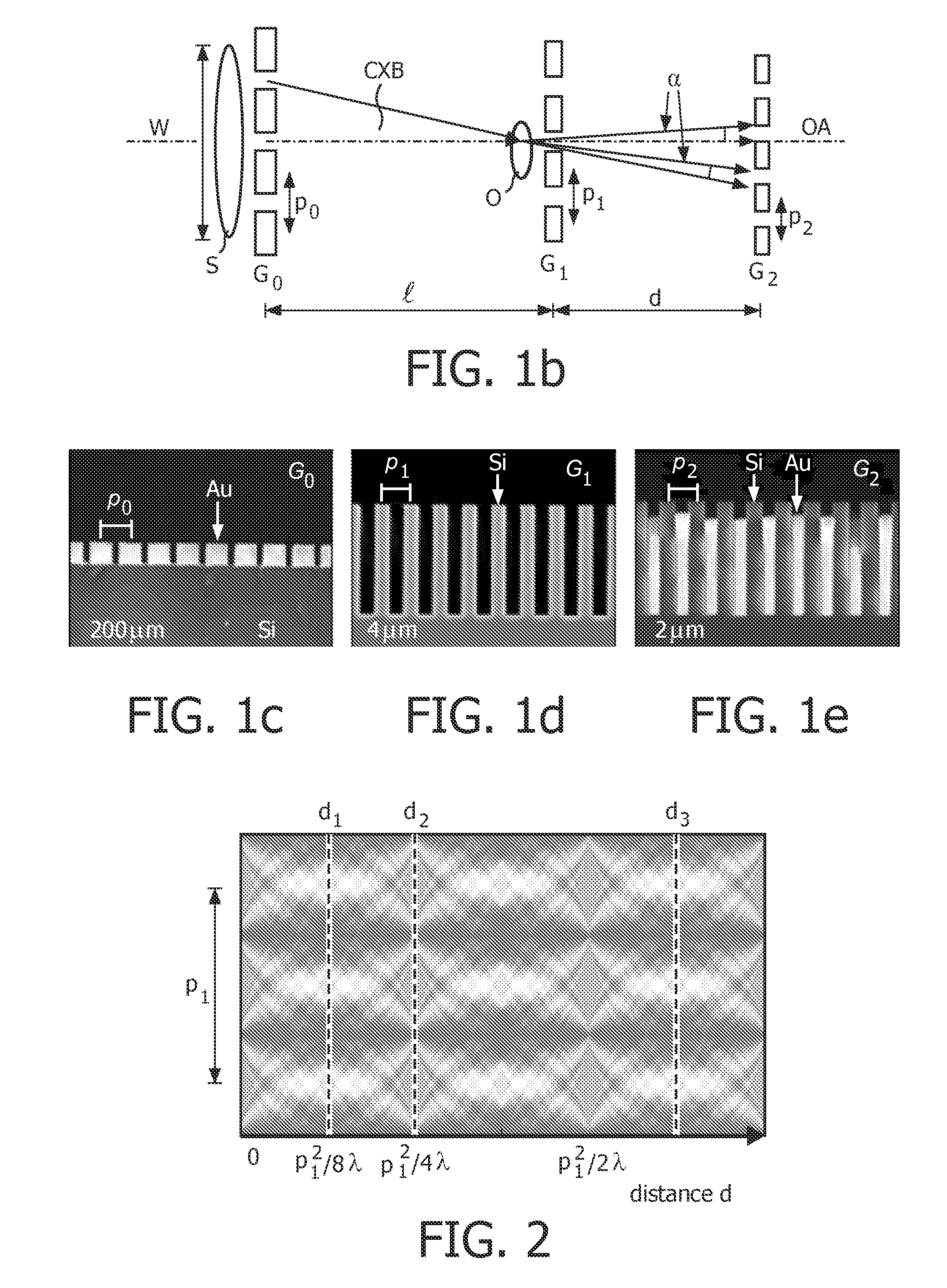
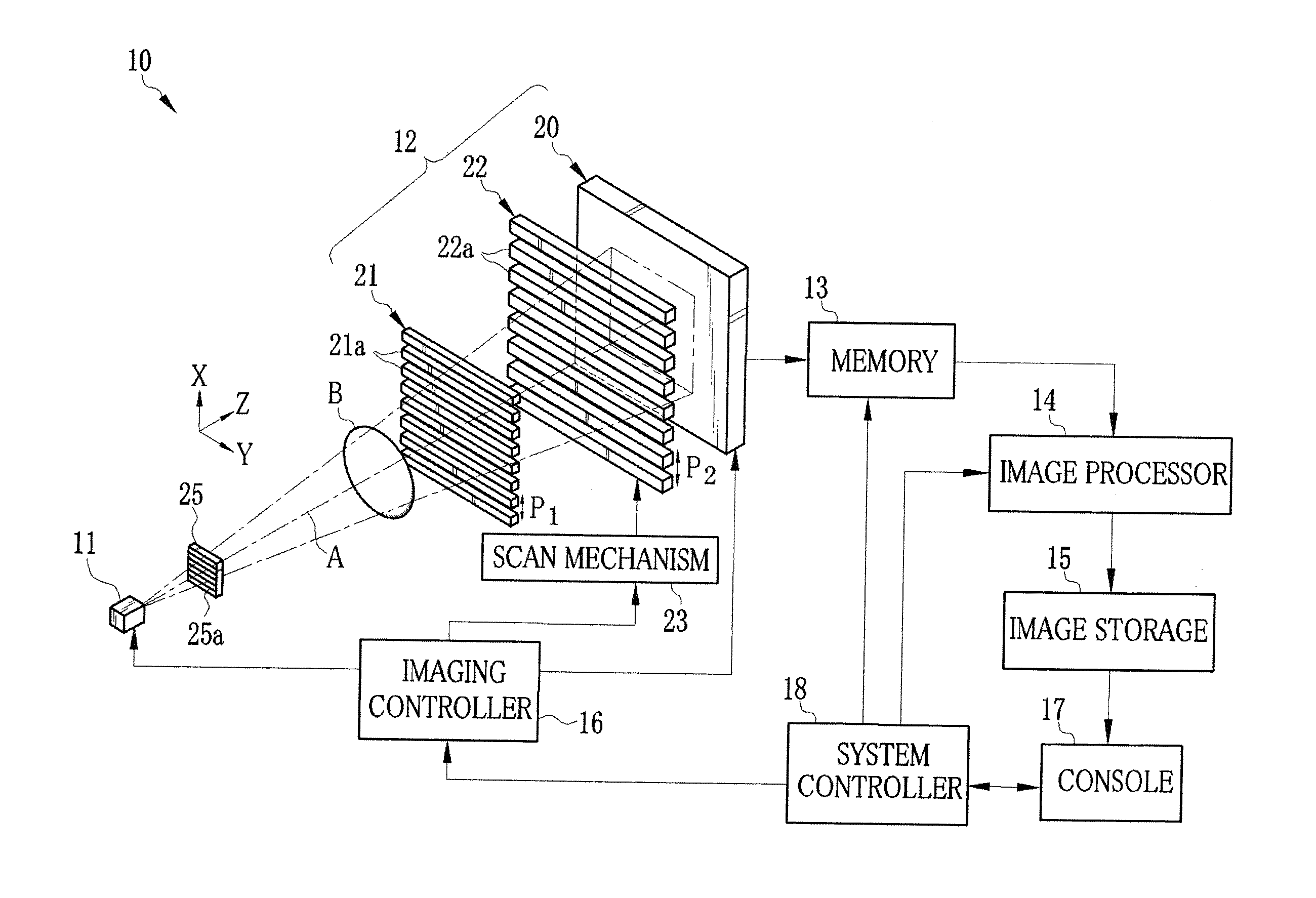
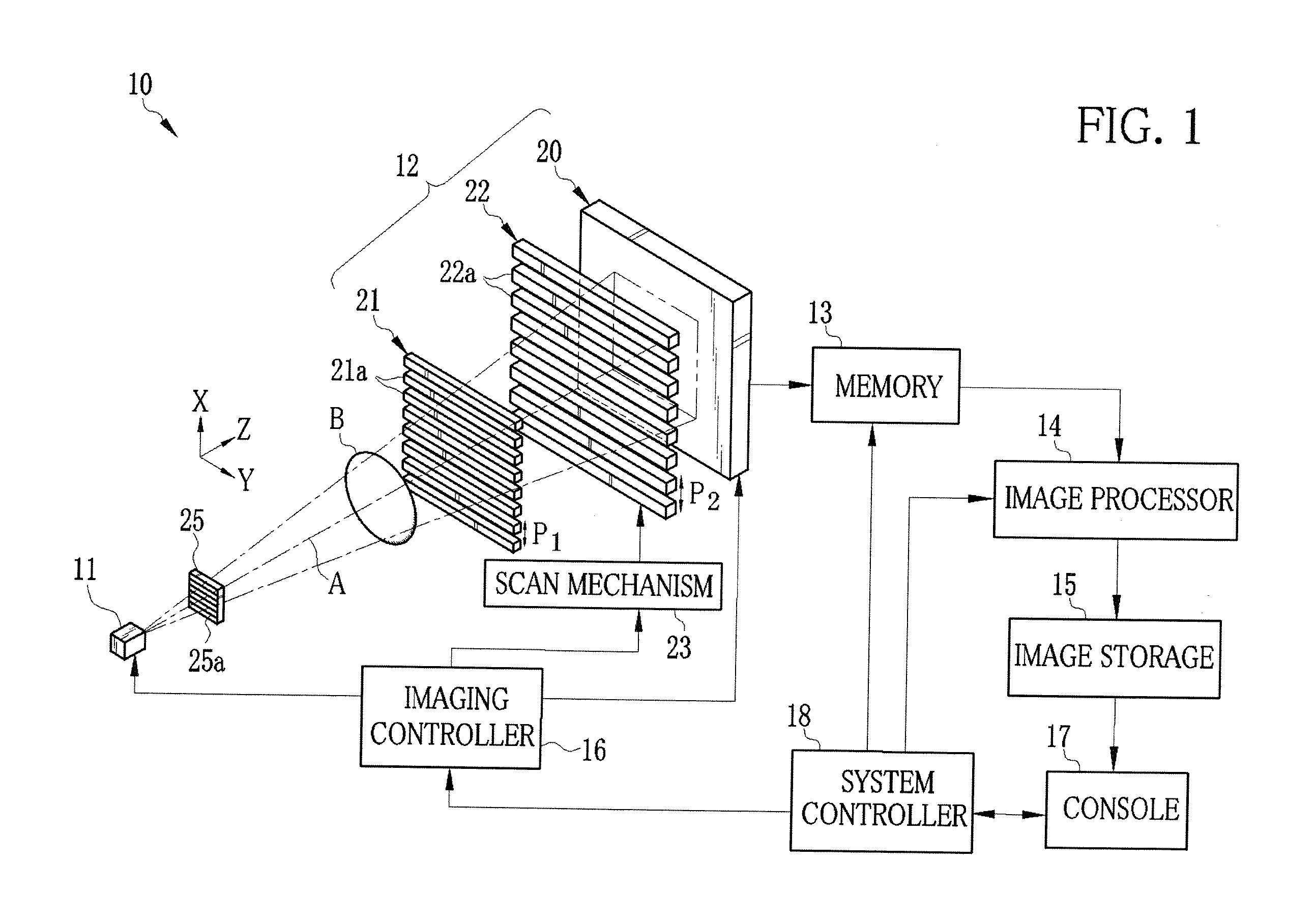
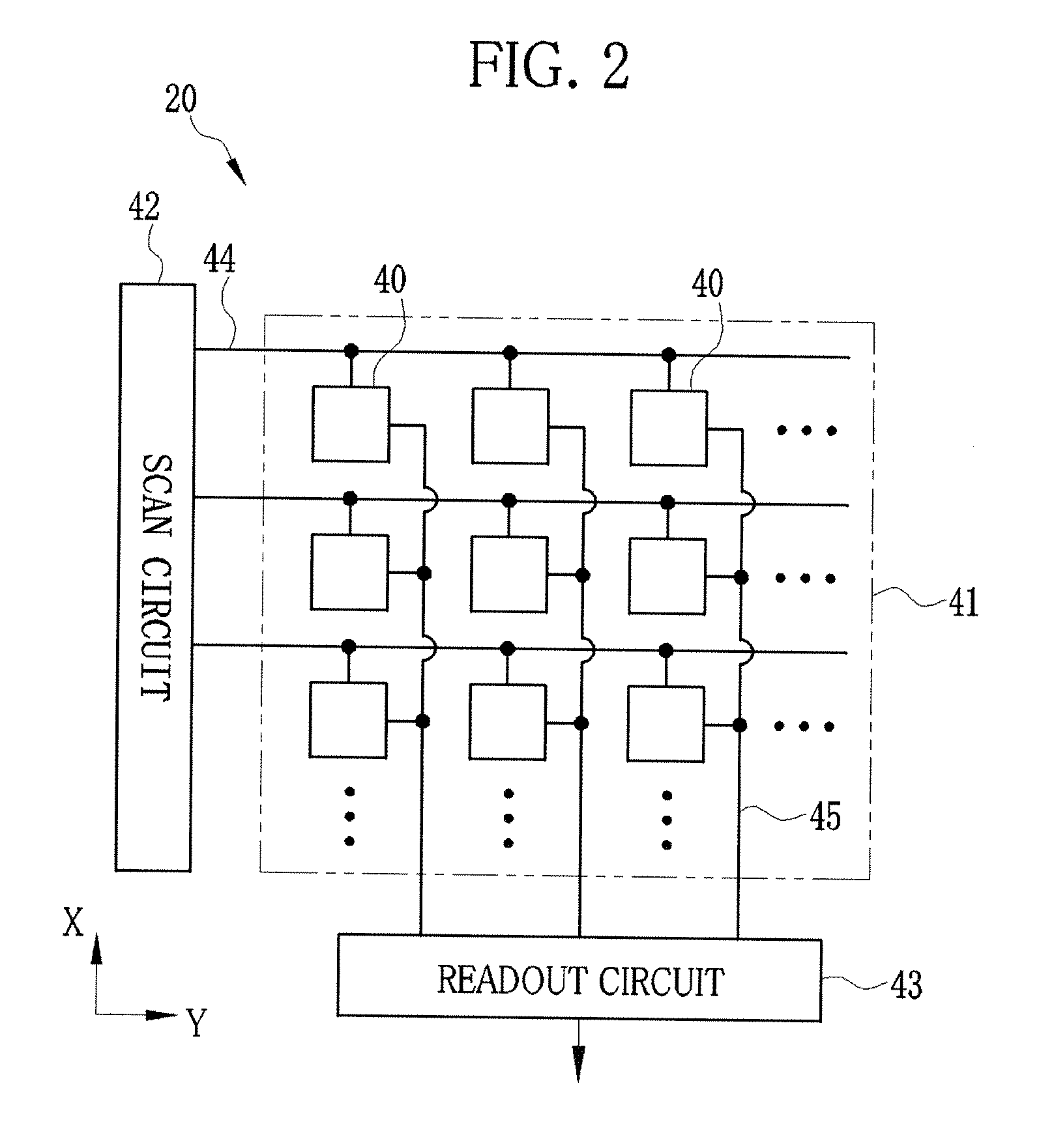
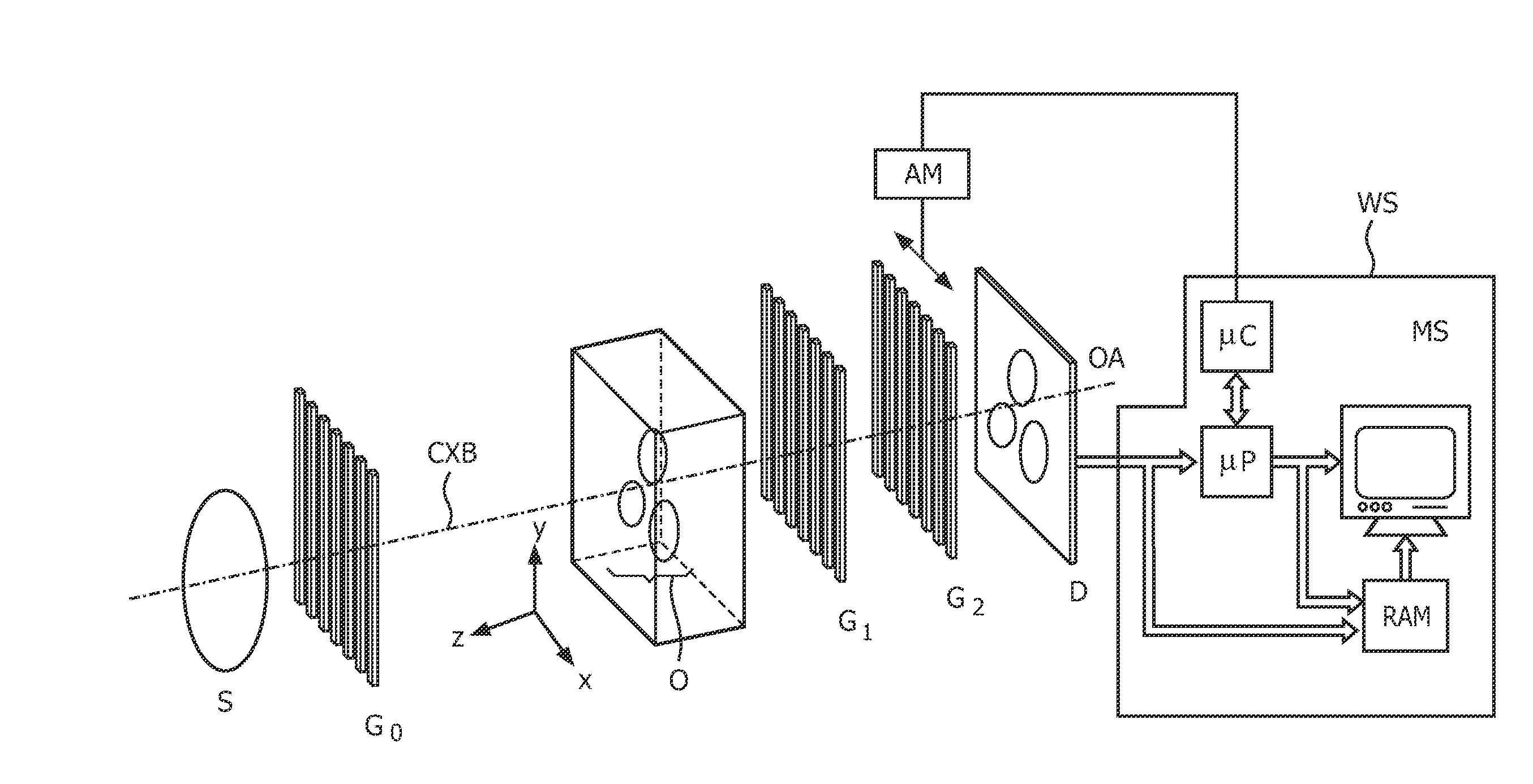
Patents
Literature
1357results about "Handling using diffraction/refraction/reflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
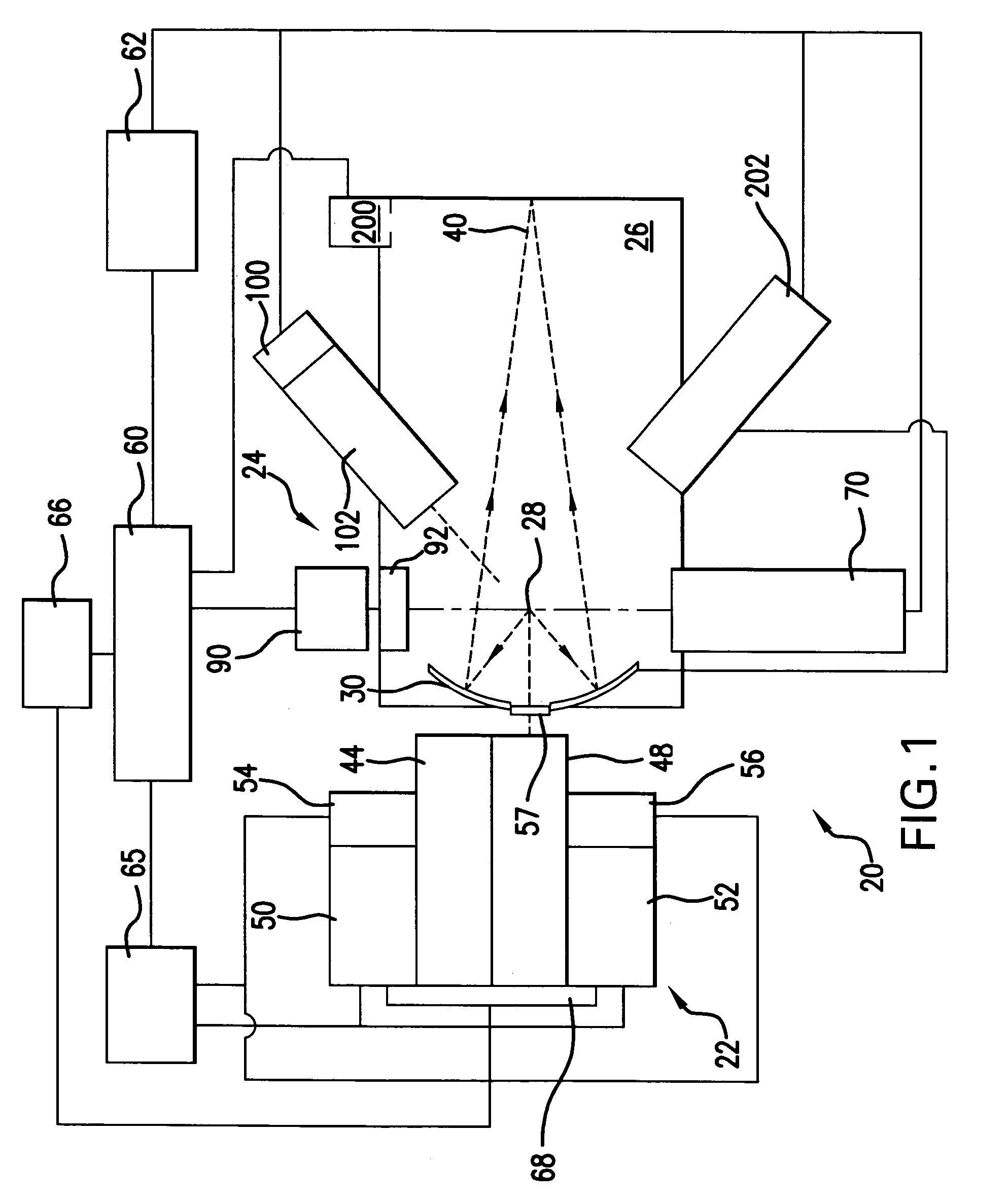
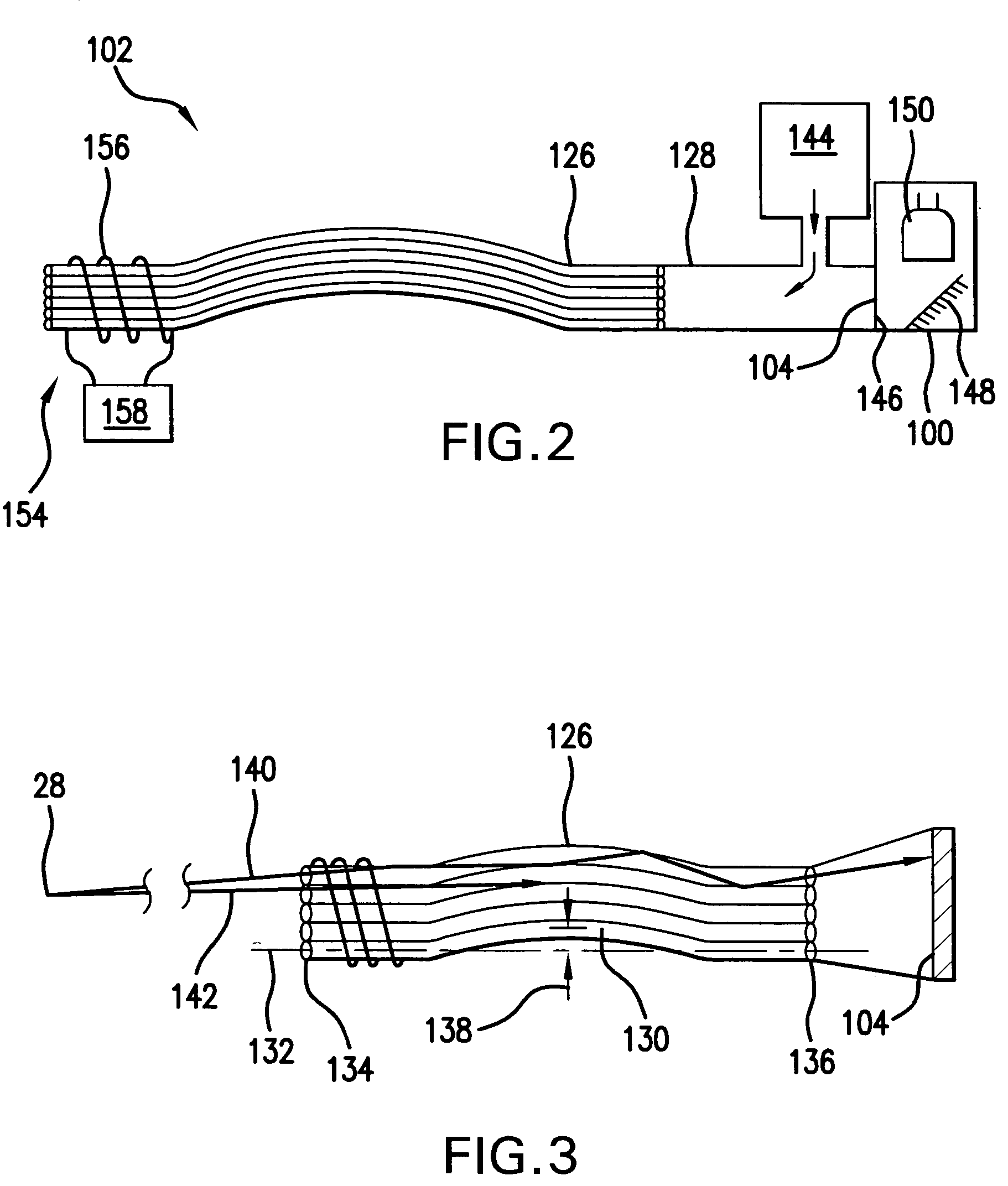
Illumination system with variable adjustment of the illumination
InactiveUS6658084B2Avoid lostSimple wayNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionGratingExit pupil
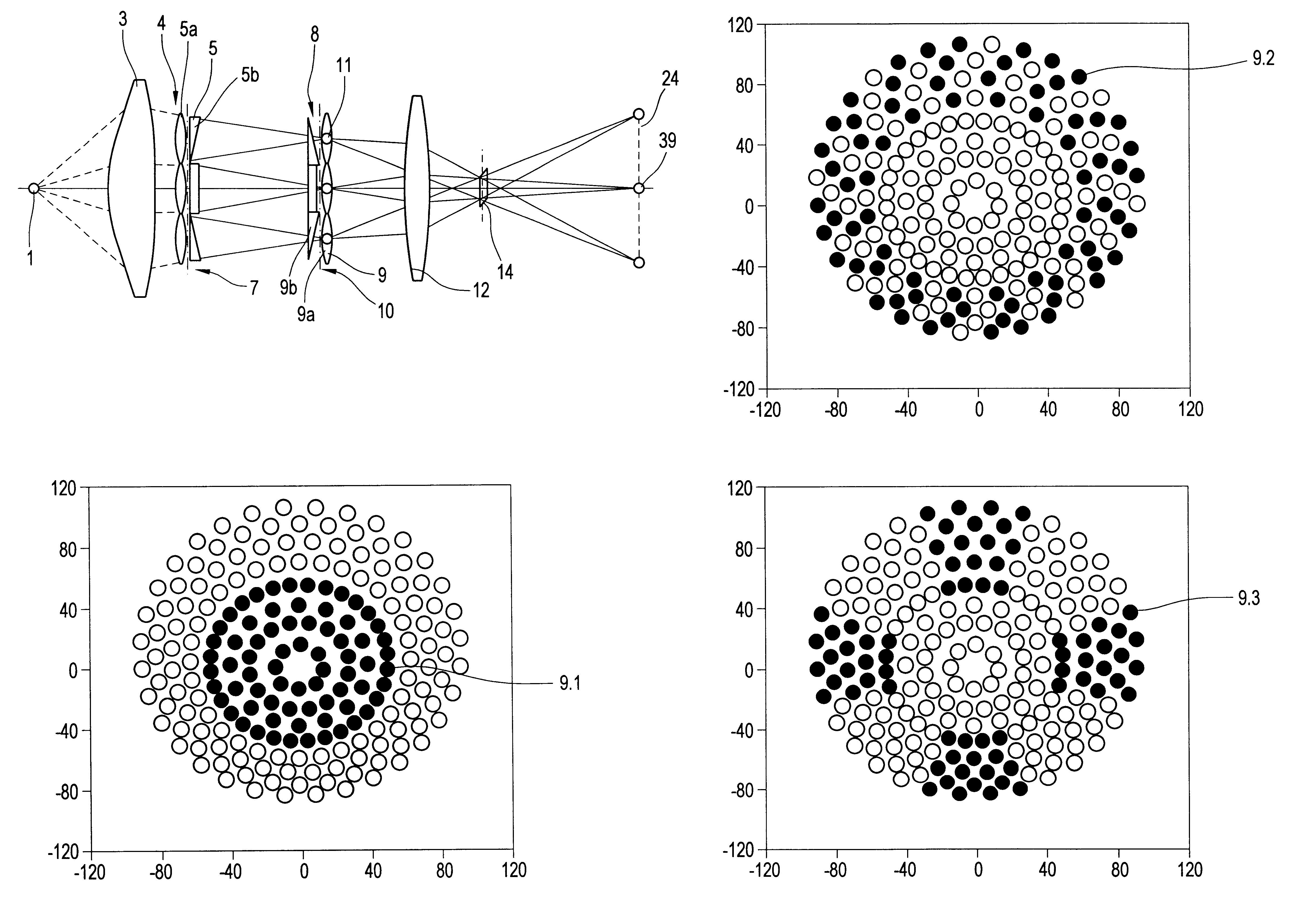
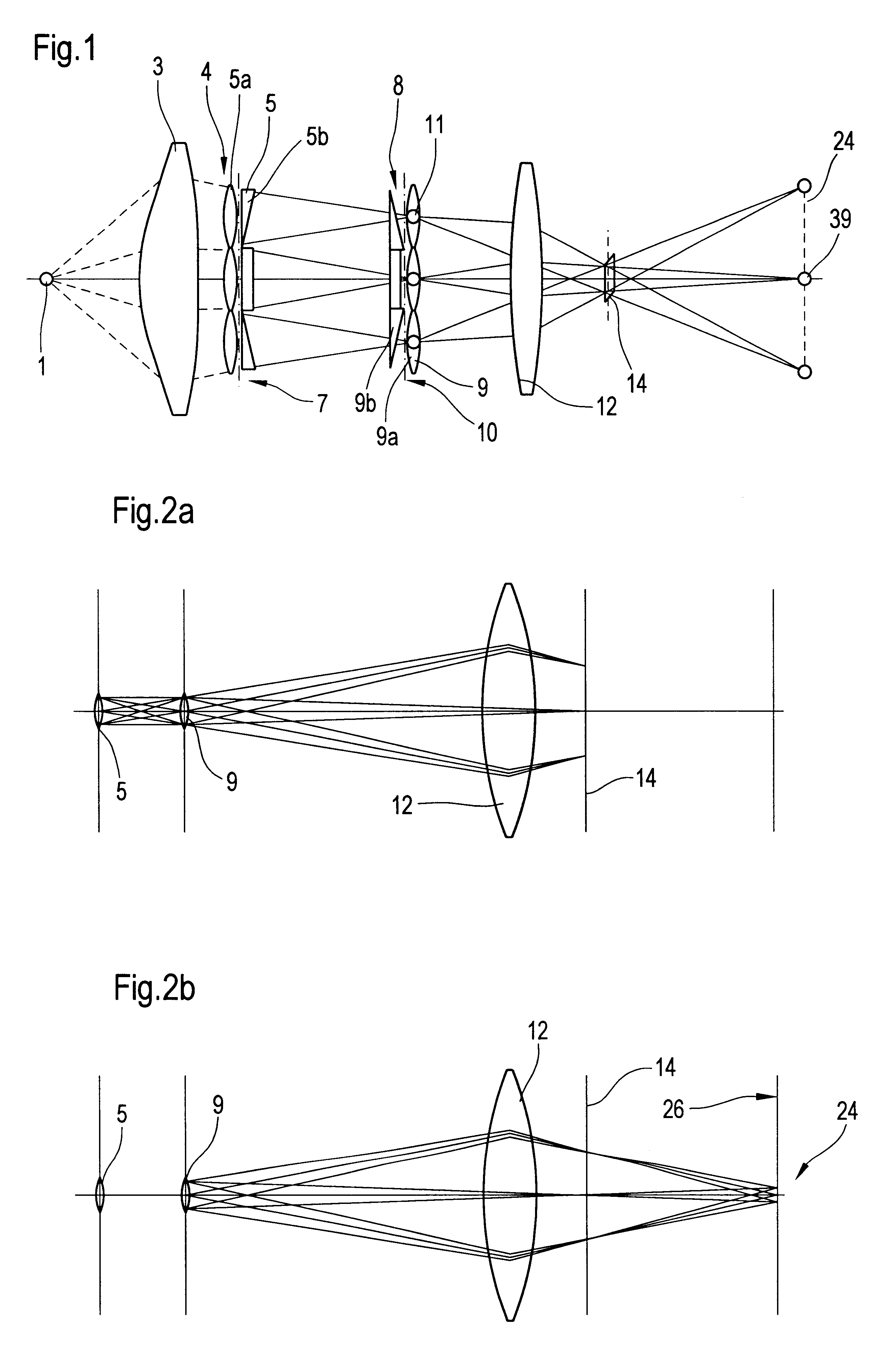
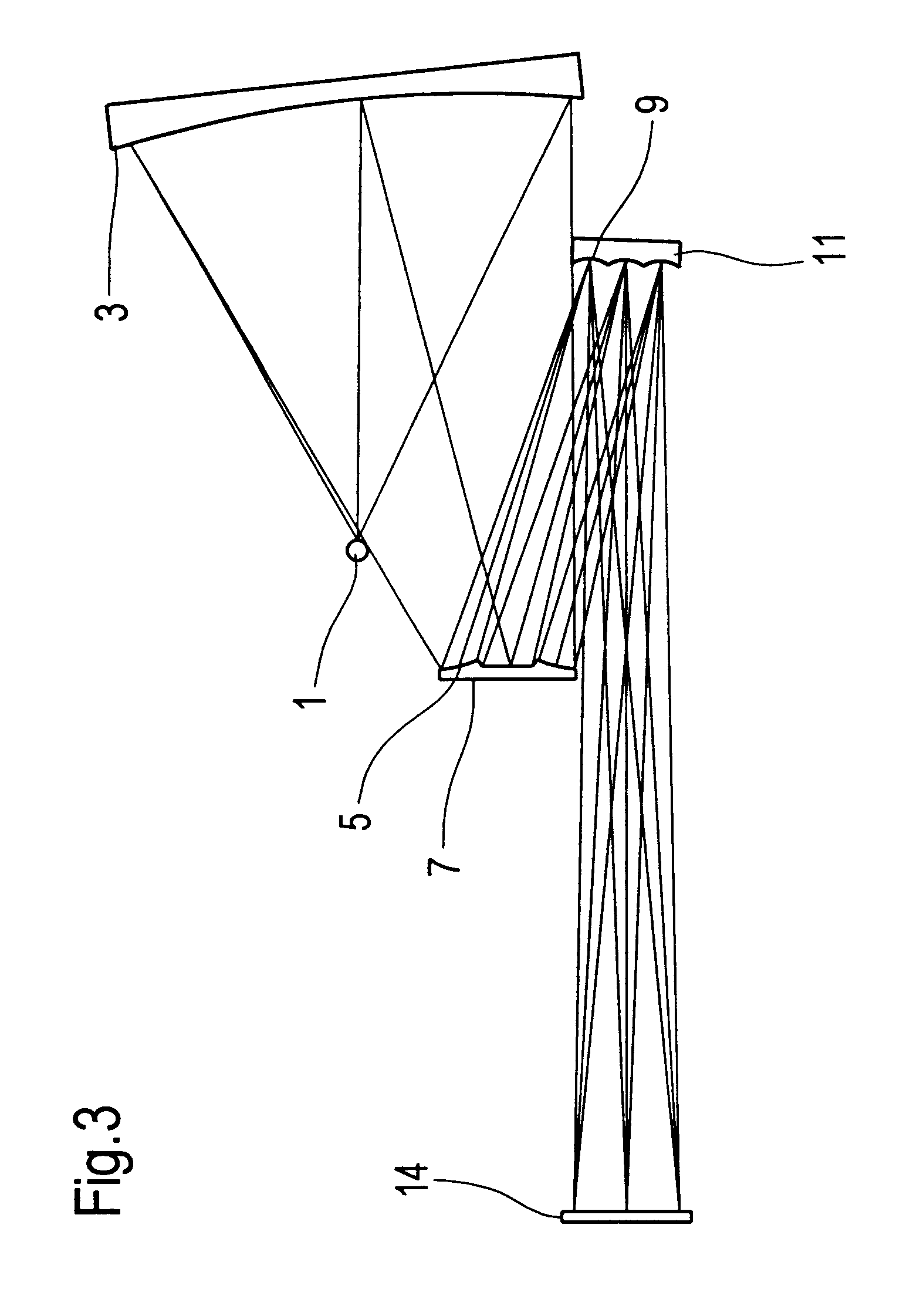
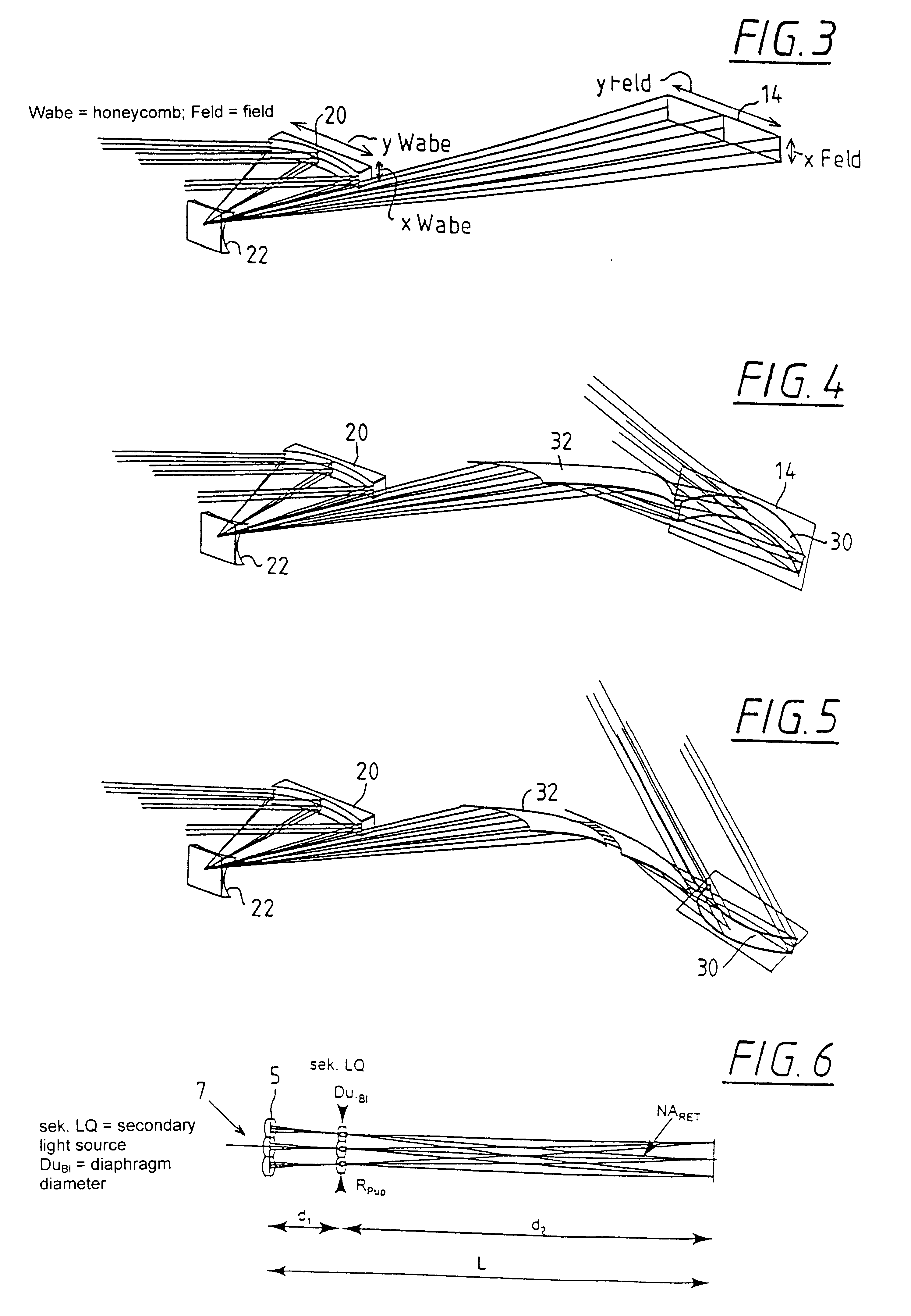
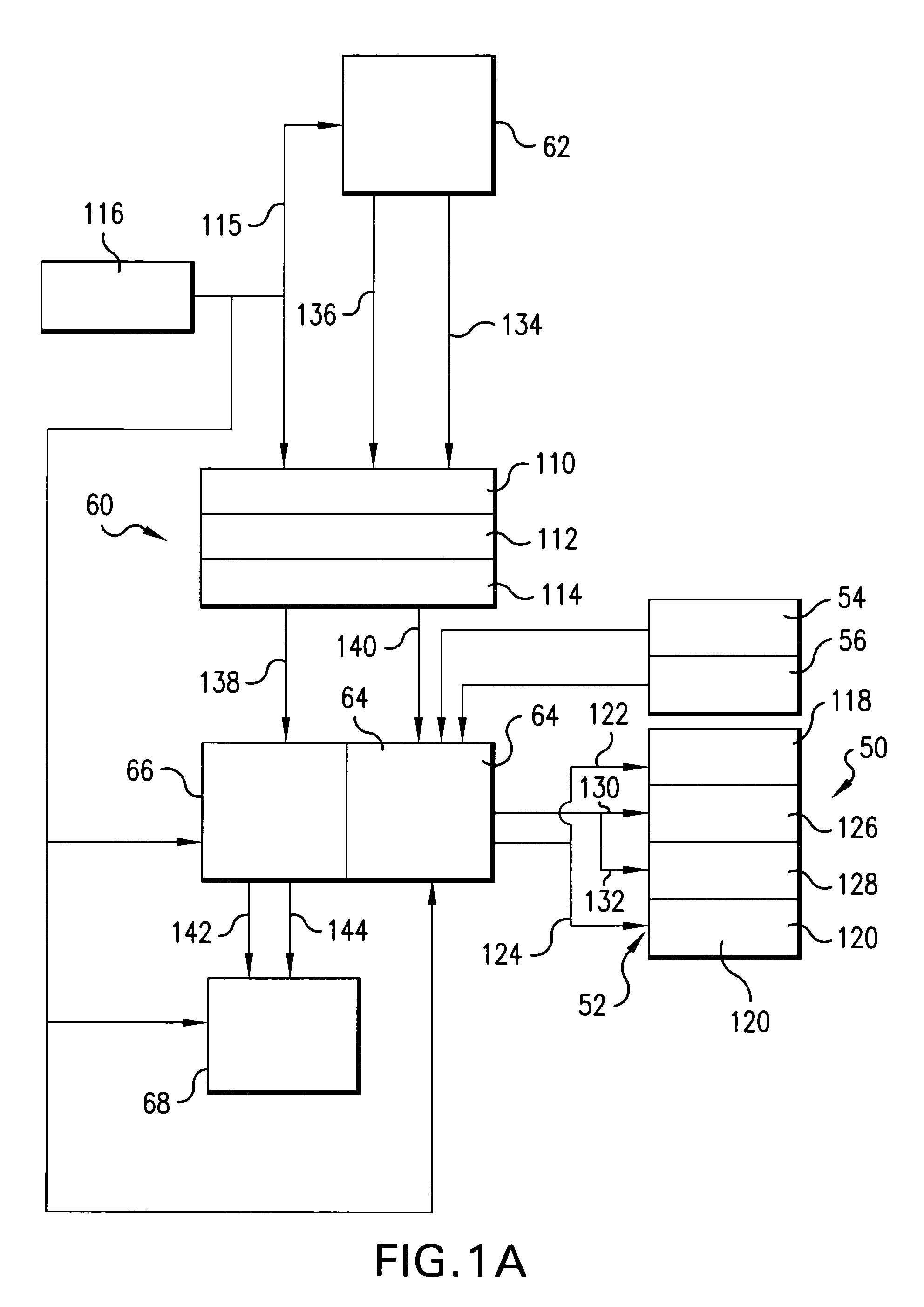
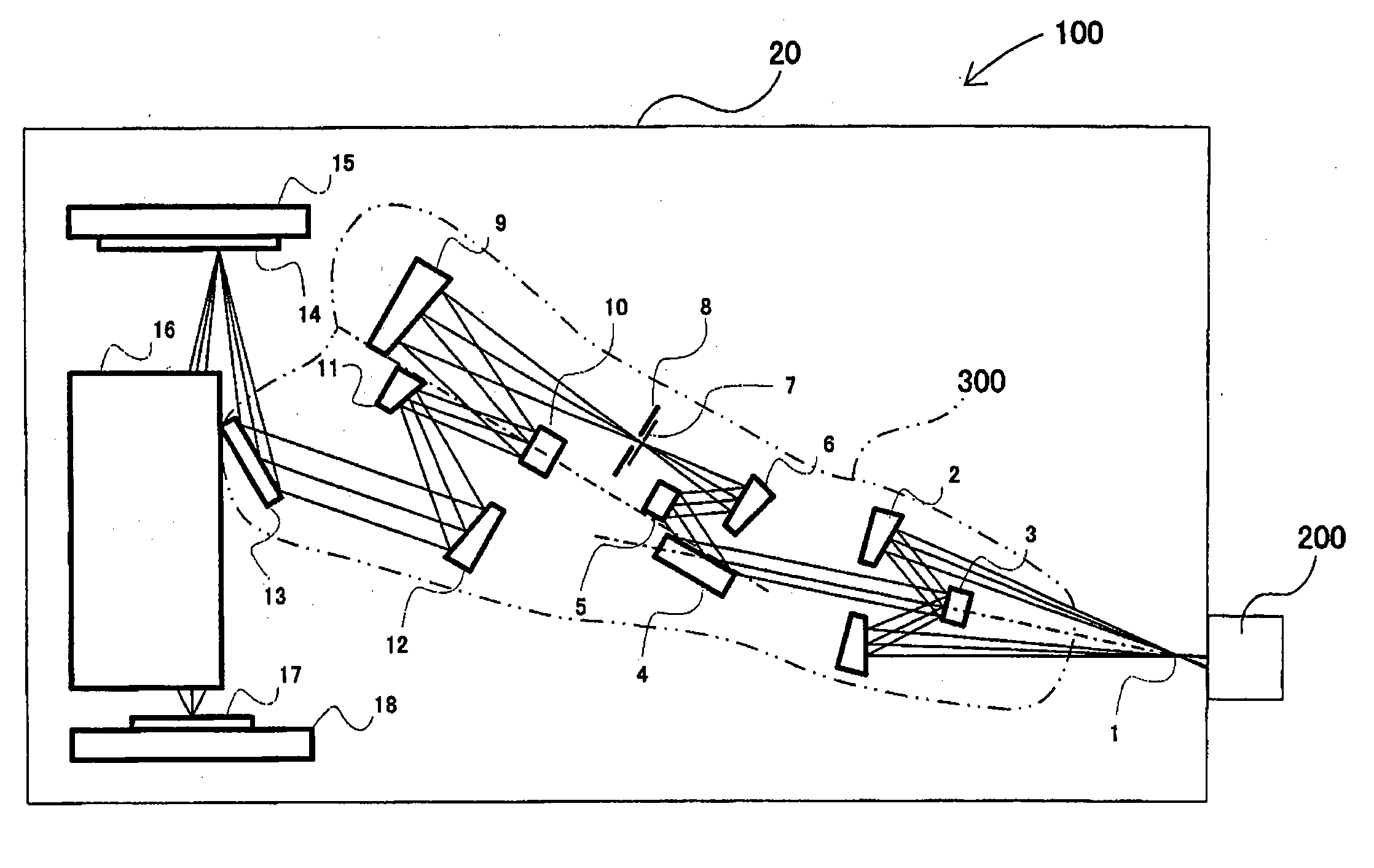
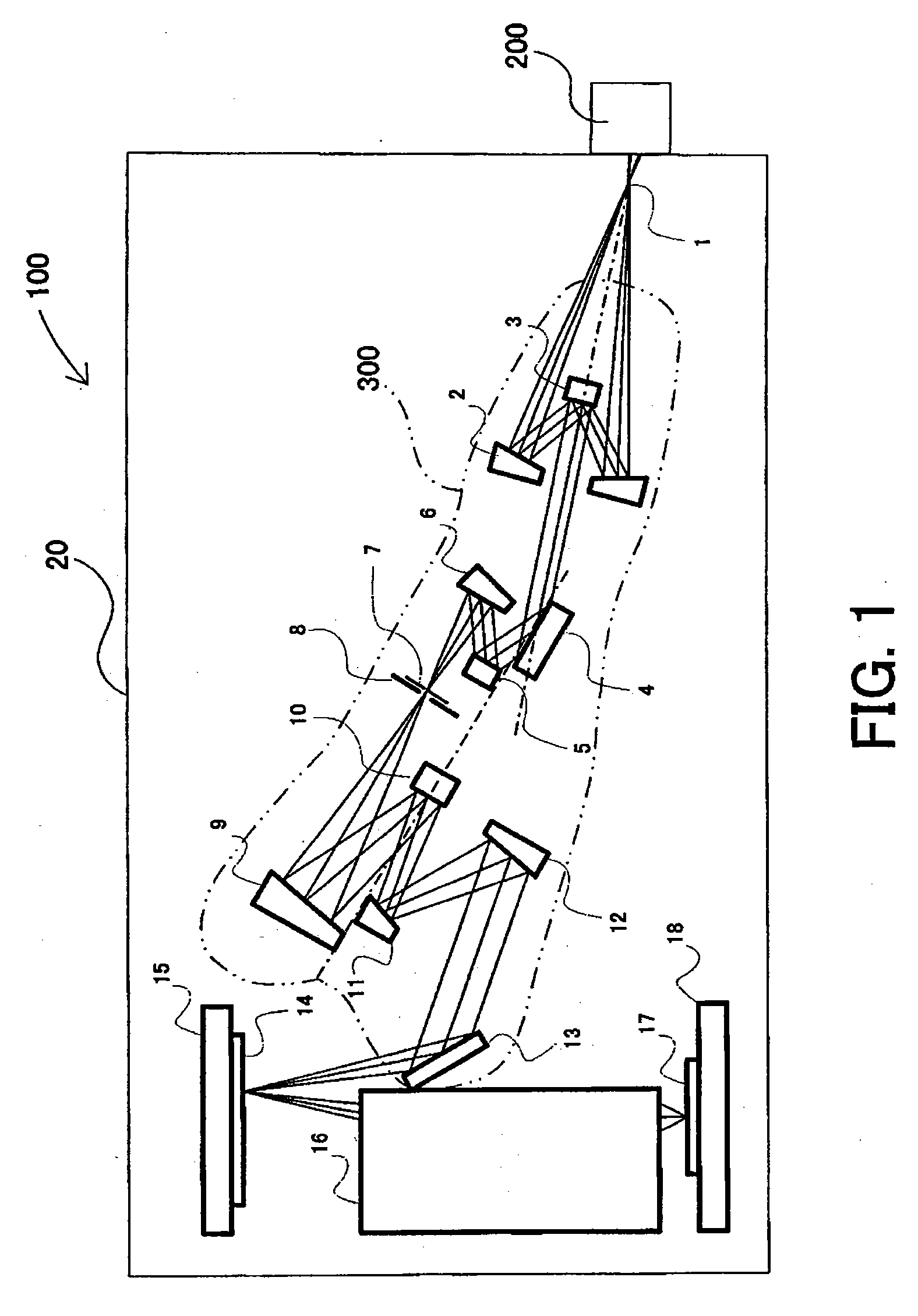
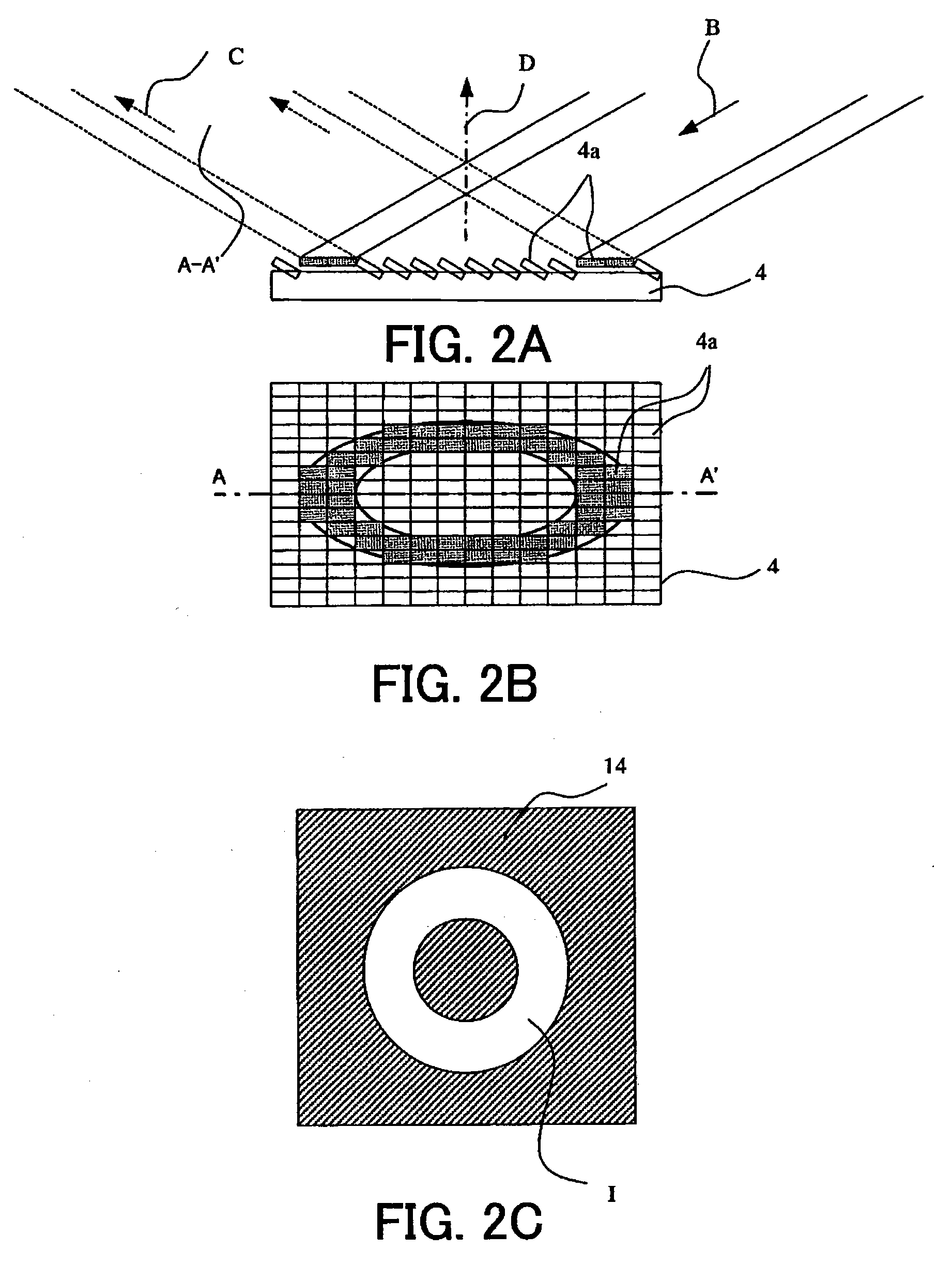
An illumination system comprises (a) a first optical element upon which a light beam impinges, where the first optical element has first raster elements that partition said light beam into light channels; (b) a second optical element that receives said light channels, where the second optical element has a second raster elements; (c) an object plane that receives said light channels via said second optical element; and (d) an exit pupil that is provided with an illumination via said object plane. The system is characterized by an assignment of a member of said first raster elements and a member of said second raster elements to each of said light channels to provide a continuous beam path from said first optical element to said object plane for each of said plurality of light channels. The assignment is changeable to provide an adjustment of said illumination in said exit pupil.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
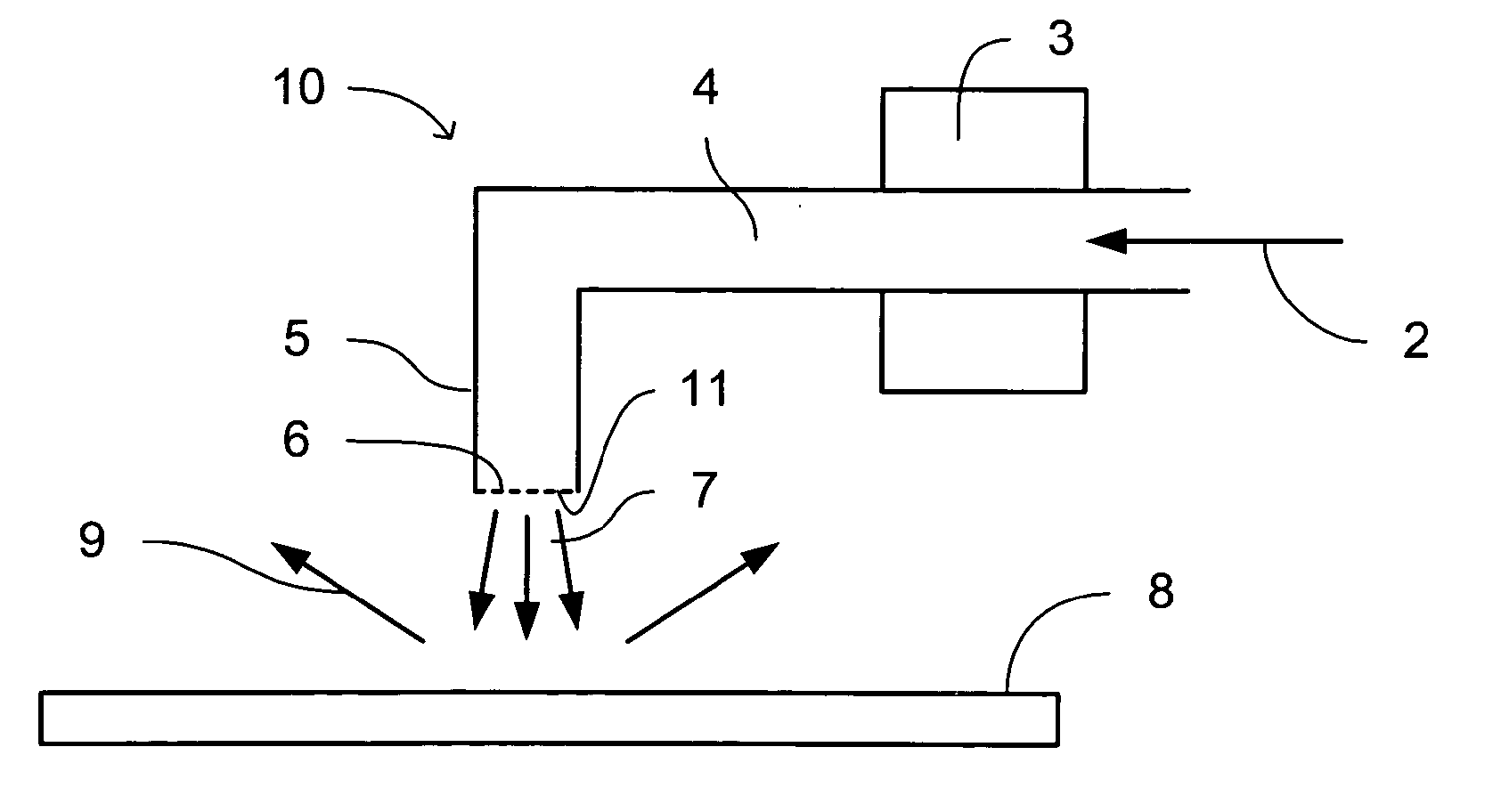
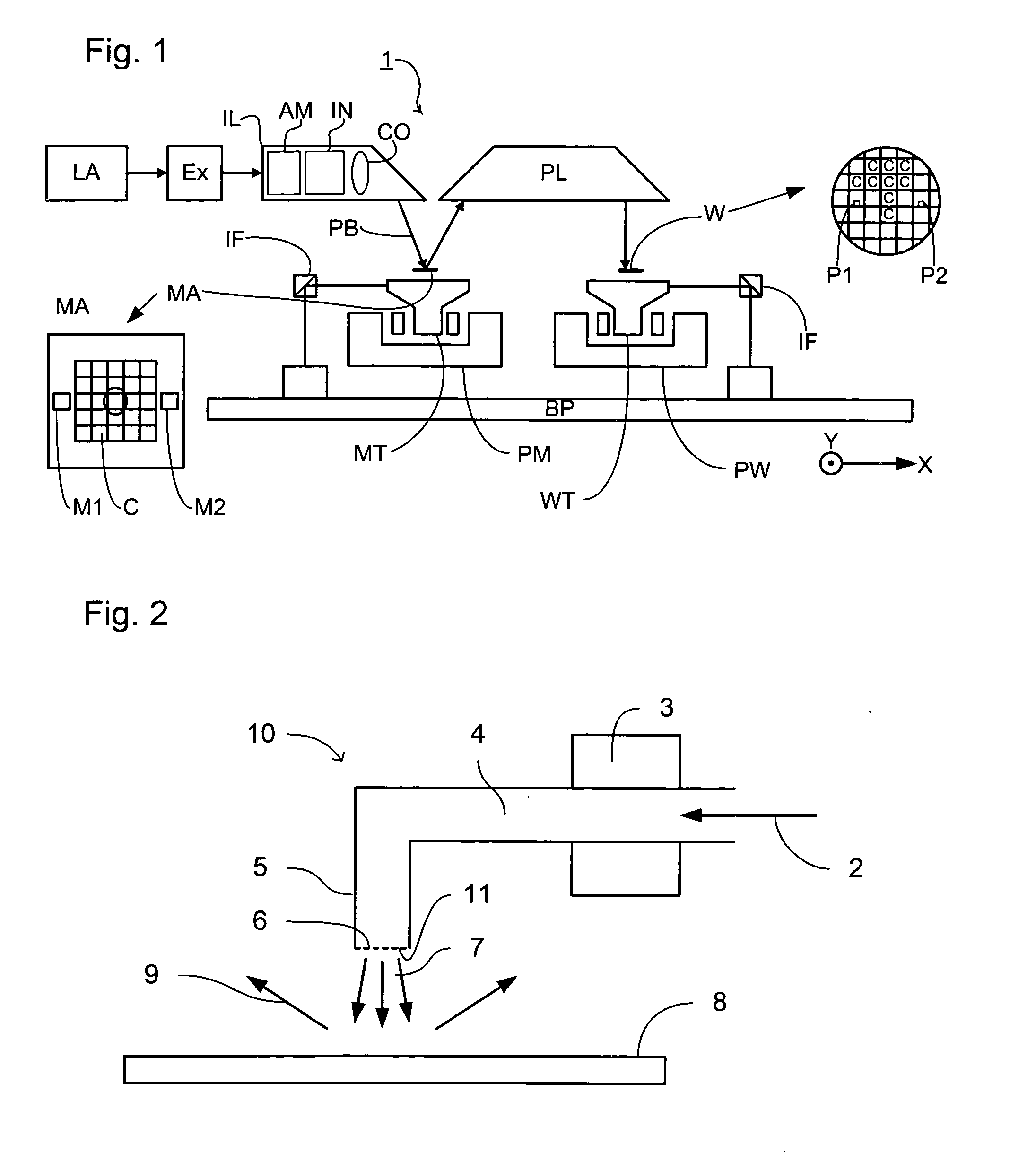
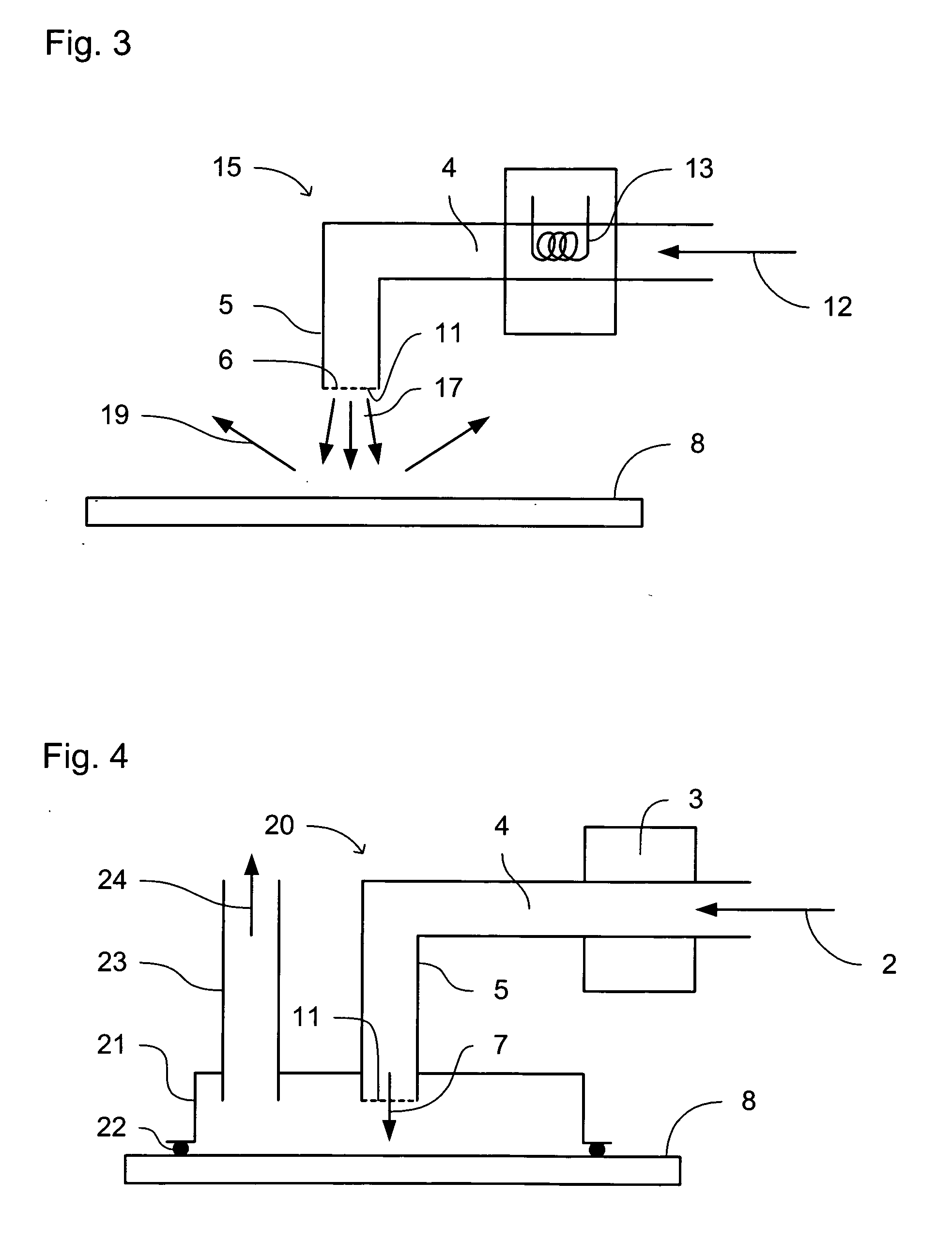
Systems and methods for reducing the influence of plasma-generated debris on the internal components of an EUV light source
ActiveUS7196342B2Prevented from reachingRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsSputteringHydrogen
Systems and methods are disclosed for reducing the influence of plasma generated debris on internal components of an EUV light source. In one aspect, an EUV meteorology monitor is provided which may have a heater to heat an internal multi-layer filtering mirror to a temperature sufficient to remove deposited debris from the mirror. In another aspect, a device is disclosed for removing plasma generated debris from an EUV light source collector mirror having a different debris deposition rate at different zones on the collector mirror. In a particular aspect, an EUV collector mirror system may comprise a source of hydrogen to combine with Li debris to create LiH on a collector surface; and a sputtering system to sputter LiH from the collector surface. In another aspect, an apparatus for etching debris from a surface of a EUV light source collector mirror with a controlled plasma etch rate is disclosed.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
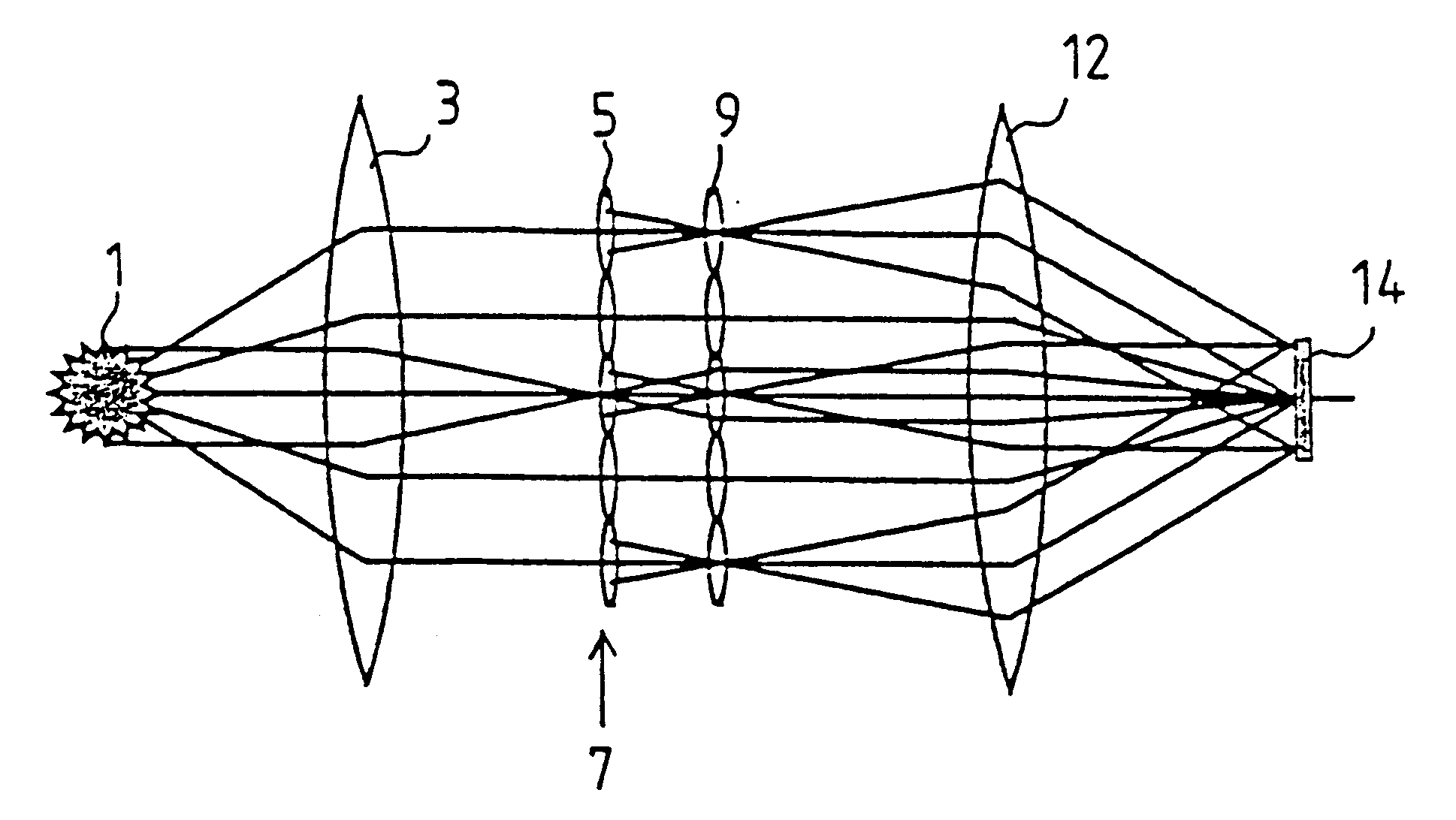
Illumination system particularly for EUV lithography
InactiveUS6198793B1Etendu can be effectively increasedAvoid blurringsNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionCamera lensGrating
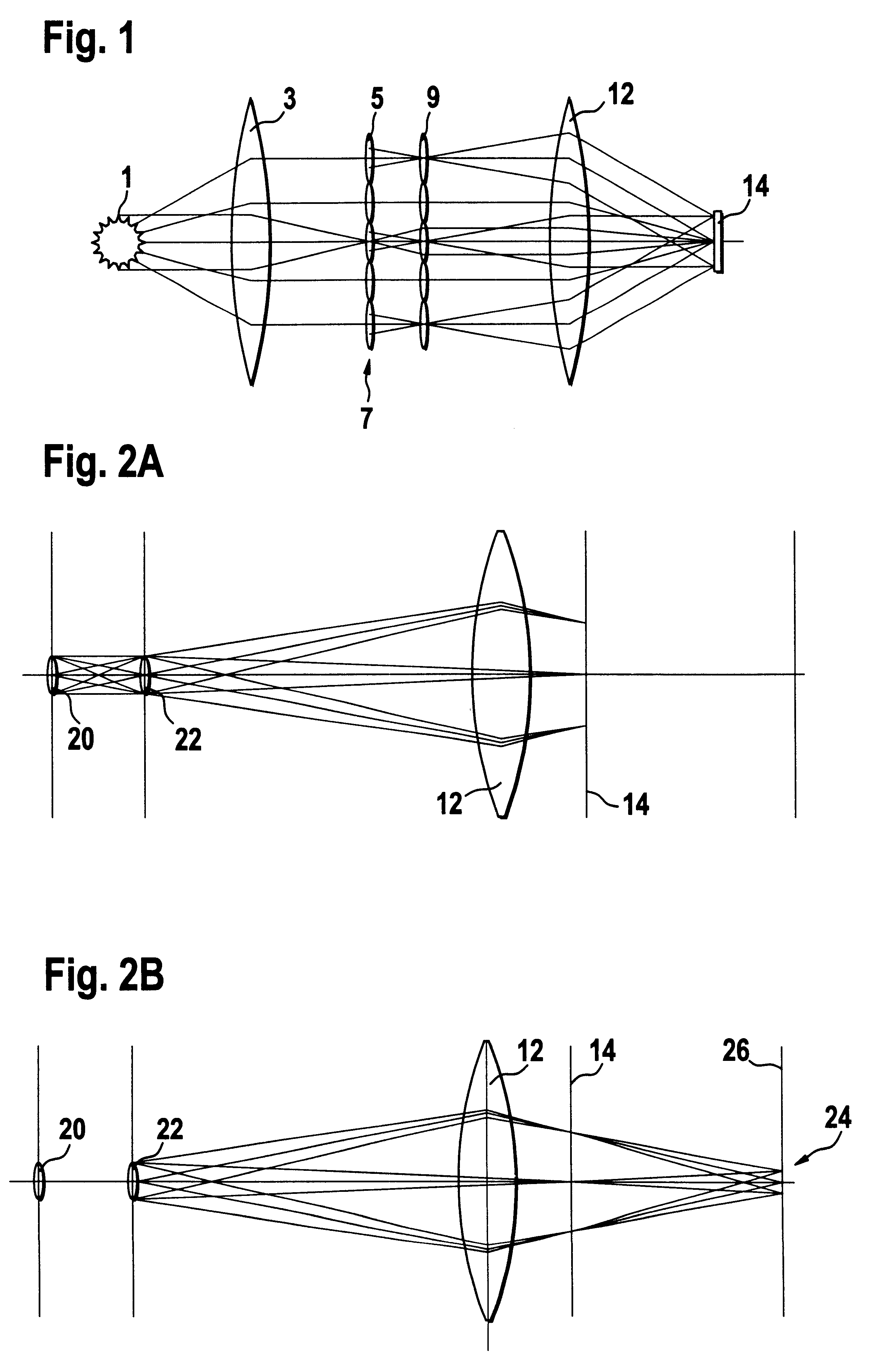
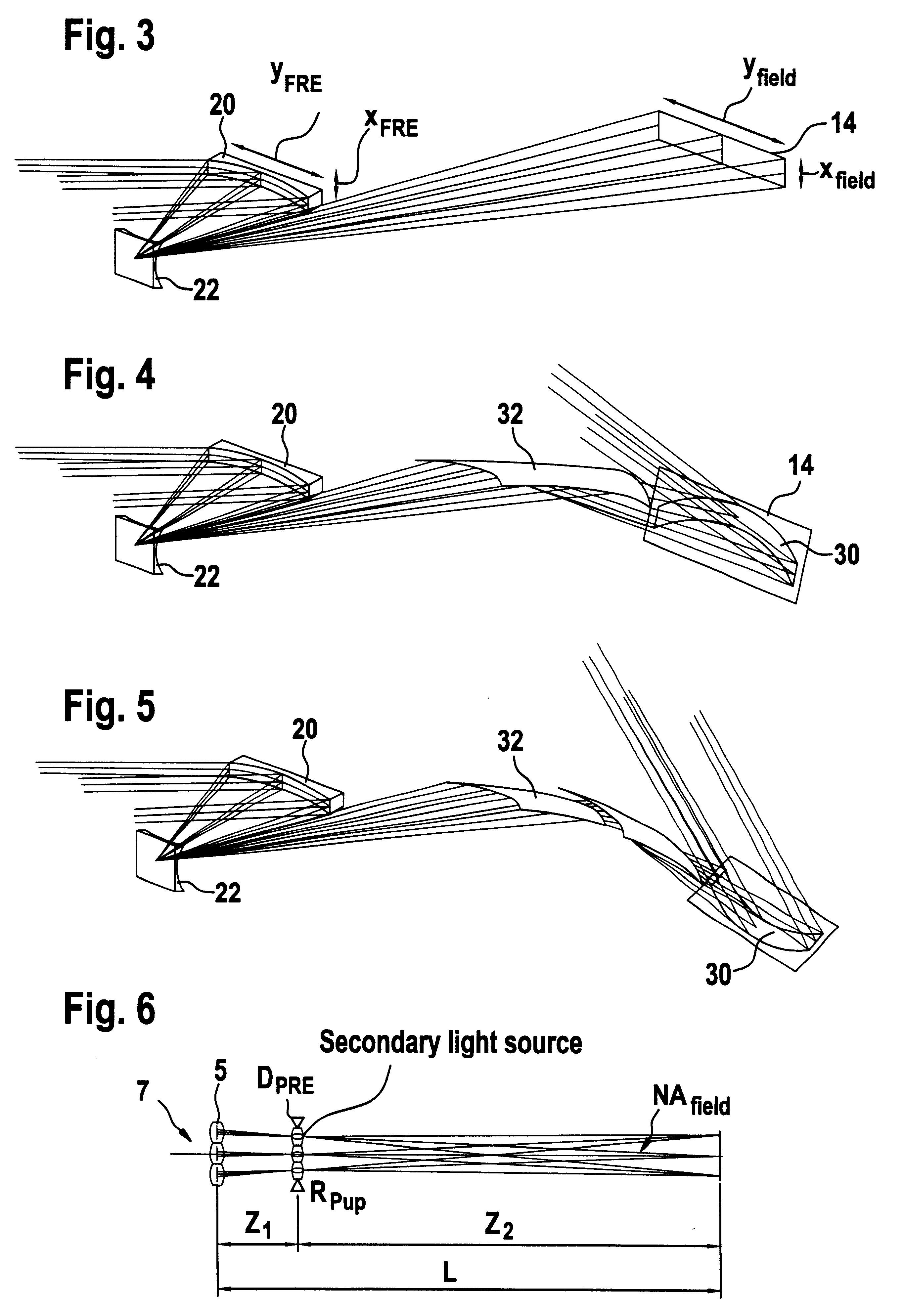
The invention concerns an illumination system for wavelengths <=193 nm, particularly for EUV lithography, with at least one light source, which has an illumination A in a predetermined surface; at least one device for producing secondary light sources; at least one mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements; one or more optical elements, which are arranged between the mirror or lens device comprising at least one mirror or one lens, which is or are organized into raster elements and the reticle plane, whereby the optical elements image the secondary light sources in the exit pupil of the illumination system.The illumination system is characterized by the fact that the raster elements of the one or more mirror or lenses are shaped and arranged in such a way that the images of the raster elements cover by means of the optical elements the major portion of the reticle plane and that the exit pupil defined by aperture and filling degree is illuminated.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
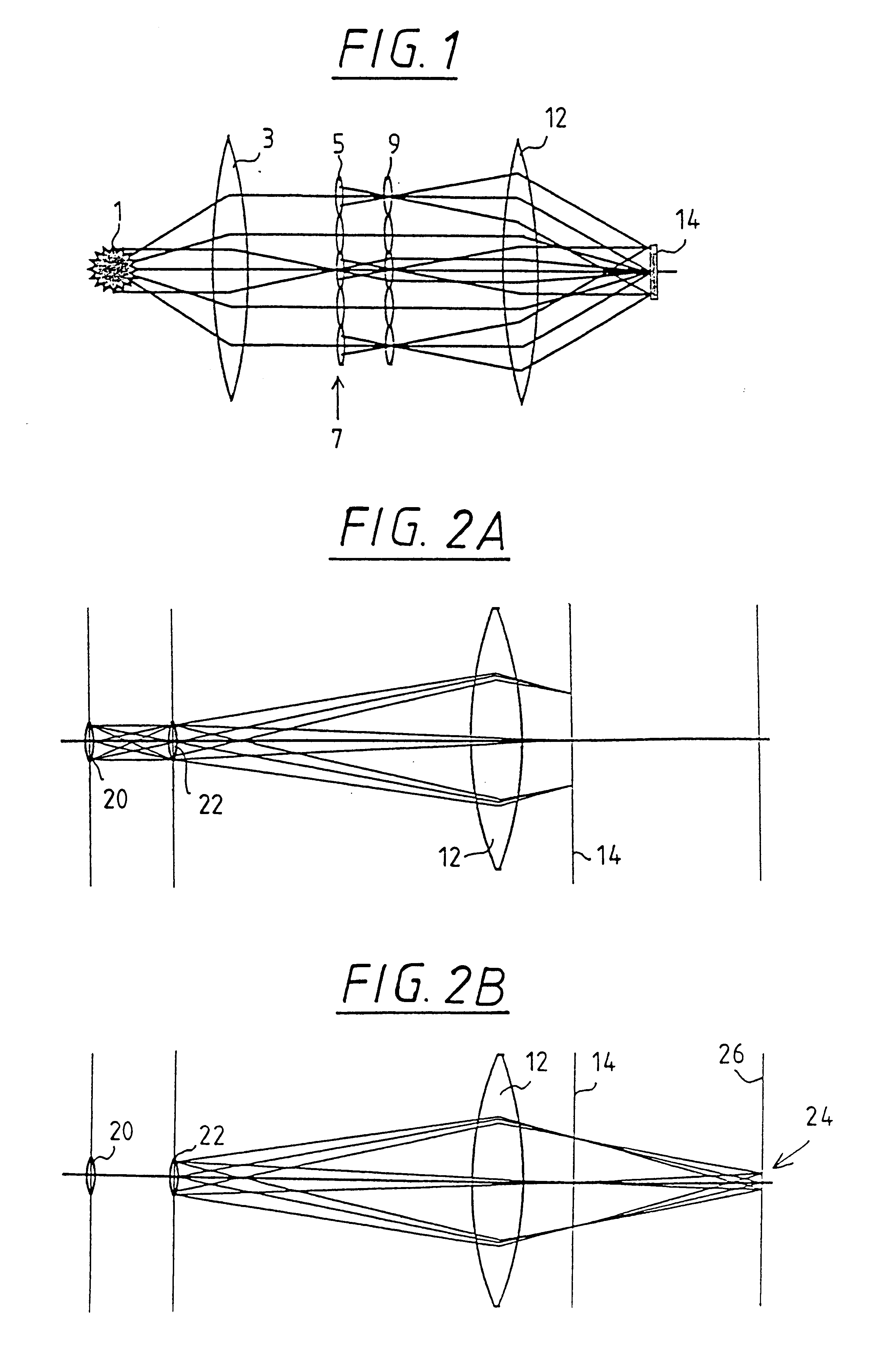
Illumination system particularly for microlithography
InactiveUS6438199B1Reduced beam diameterReduce the overall diameterNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionExit pupilGrating
The invention concerns an illumination system, particularly for microlithography with wavelengths <=193 nm, comprising a light source, a first optical component, a second optical component, an image plane and an exit pupil. The first optical component transforms the light source into a plurality of secondary light sources being imaged by the second optical component in said exit pupil. The first optical component comprises a first optical element having a plurality of first raster elements, which are imaged into said image plane producing a plurality of images being superimposed at least partially on a field in said image plane. The first raster elements deflect incoming ray bundles with first deflection angles, wherein at least two of the first deflection angles are different. The first raster elements are preferably rectangular, wherein the field is a segment of an annulus. To transform the rectangular images of the first raster elements into the segment of the annulus, the second optical component comprises a first field mirror for shaping the field to the segment of the annulus.
Owner:CARL-ZEISS-STIFTUNG TRADING AS CARL ZEISS
EUV light source
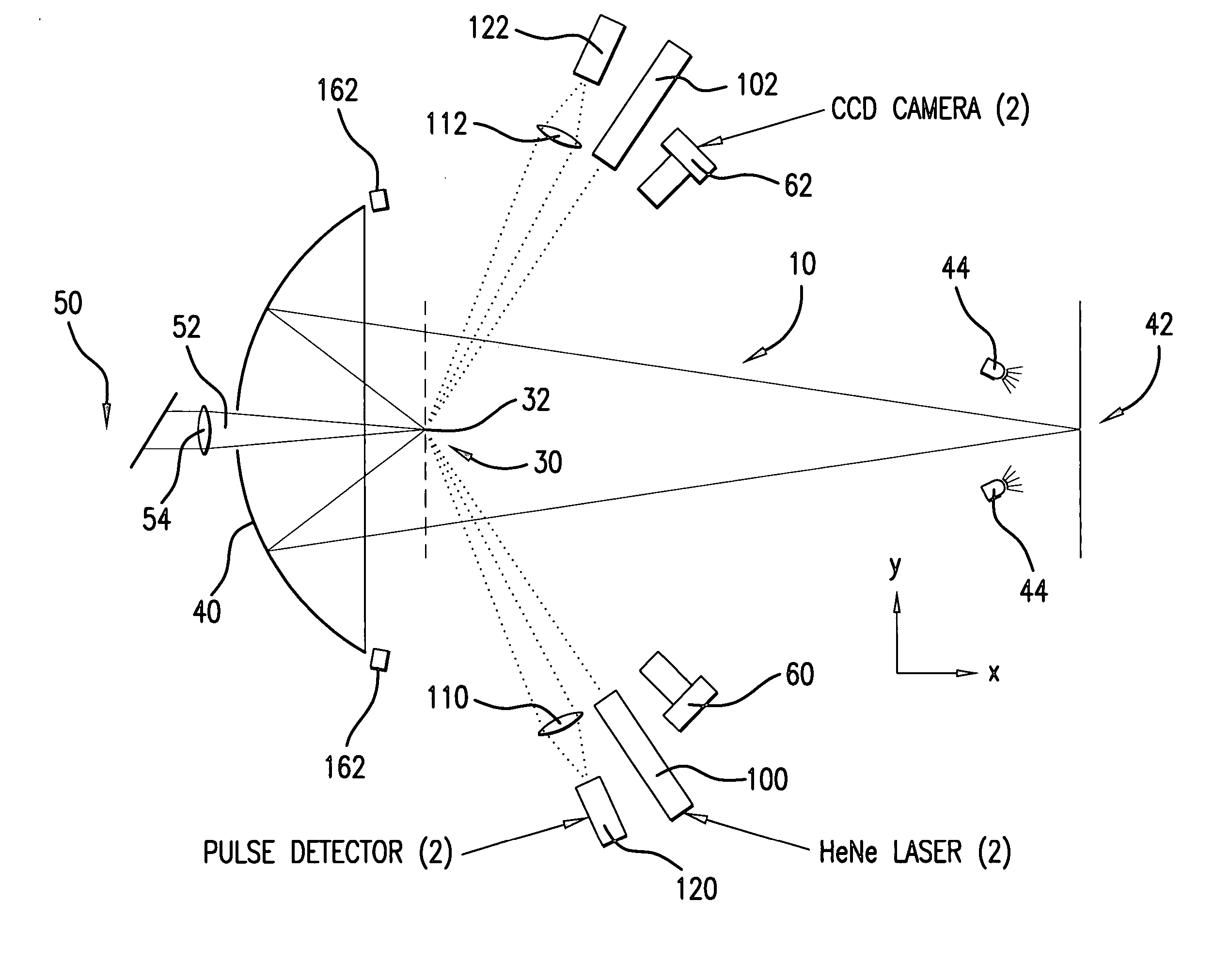
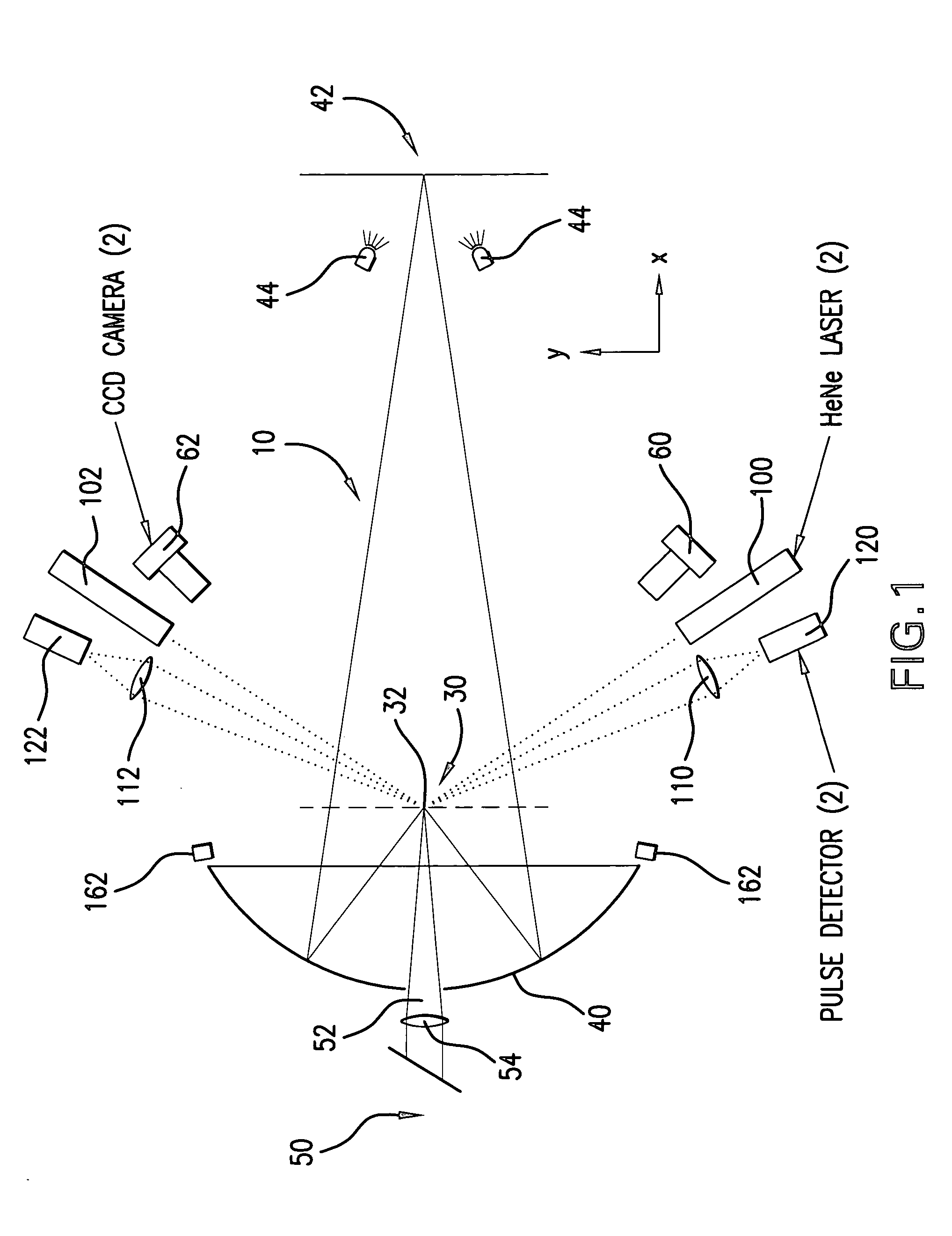
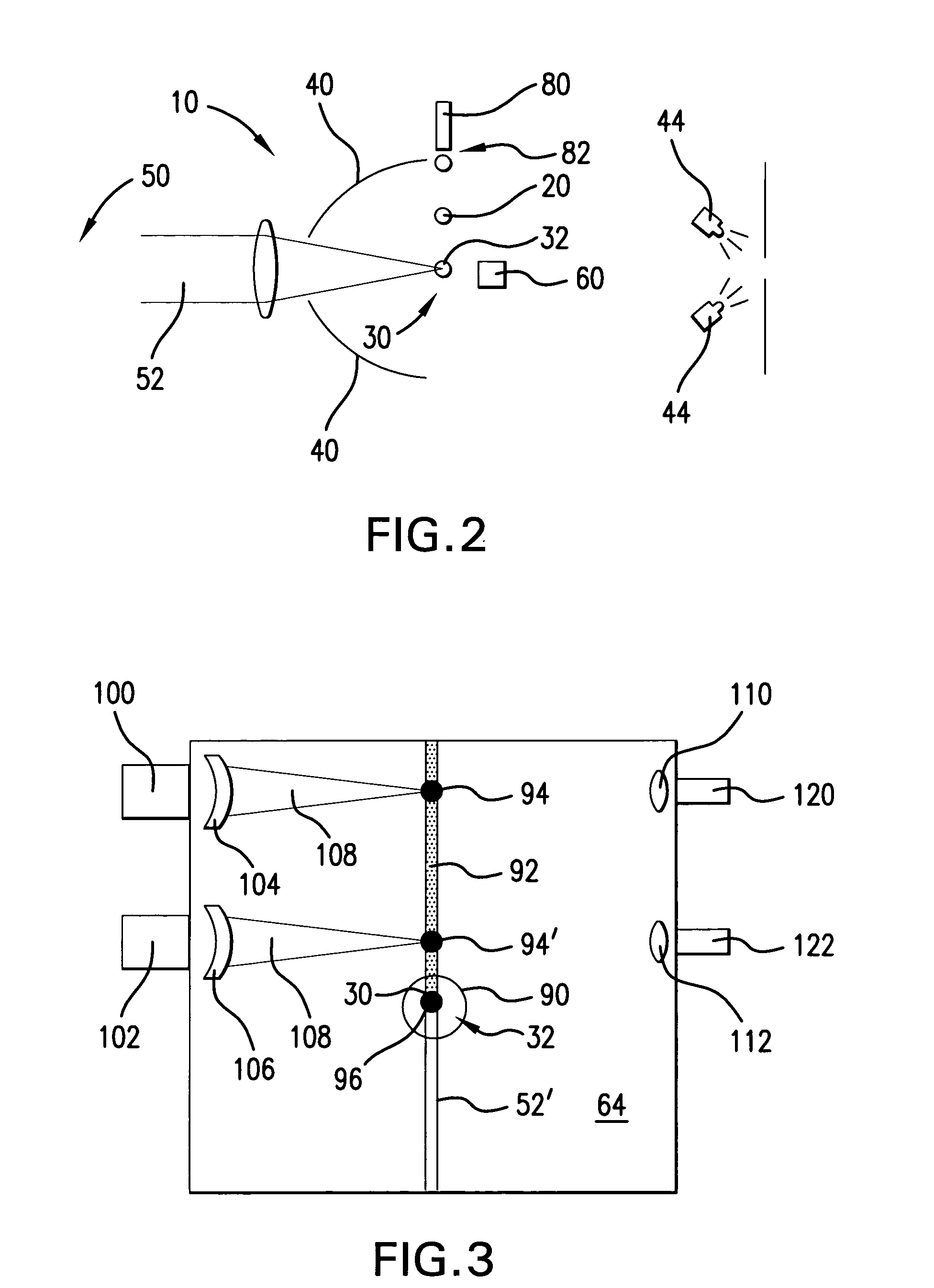
ActiveUS20050199829A1Sufficient sizeSufficient thermal massNanoinformaticsRadioactive sourcesControl systemDisplacement control
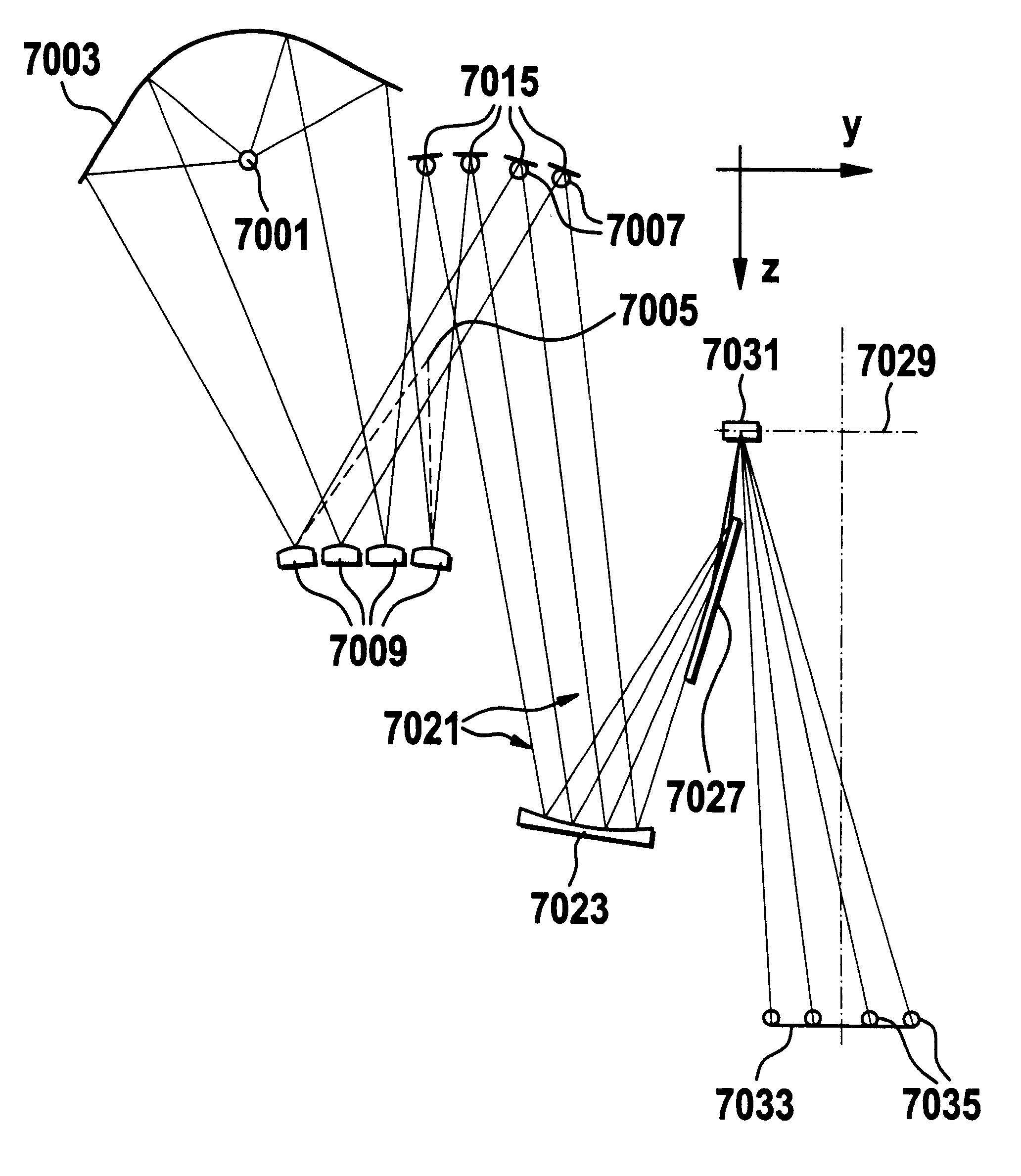
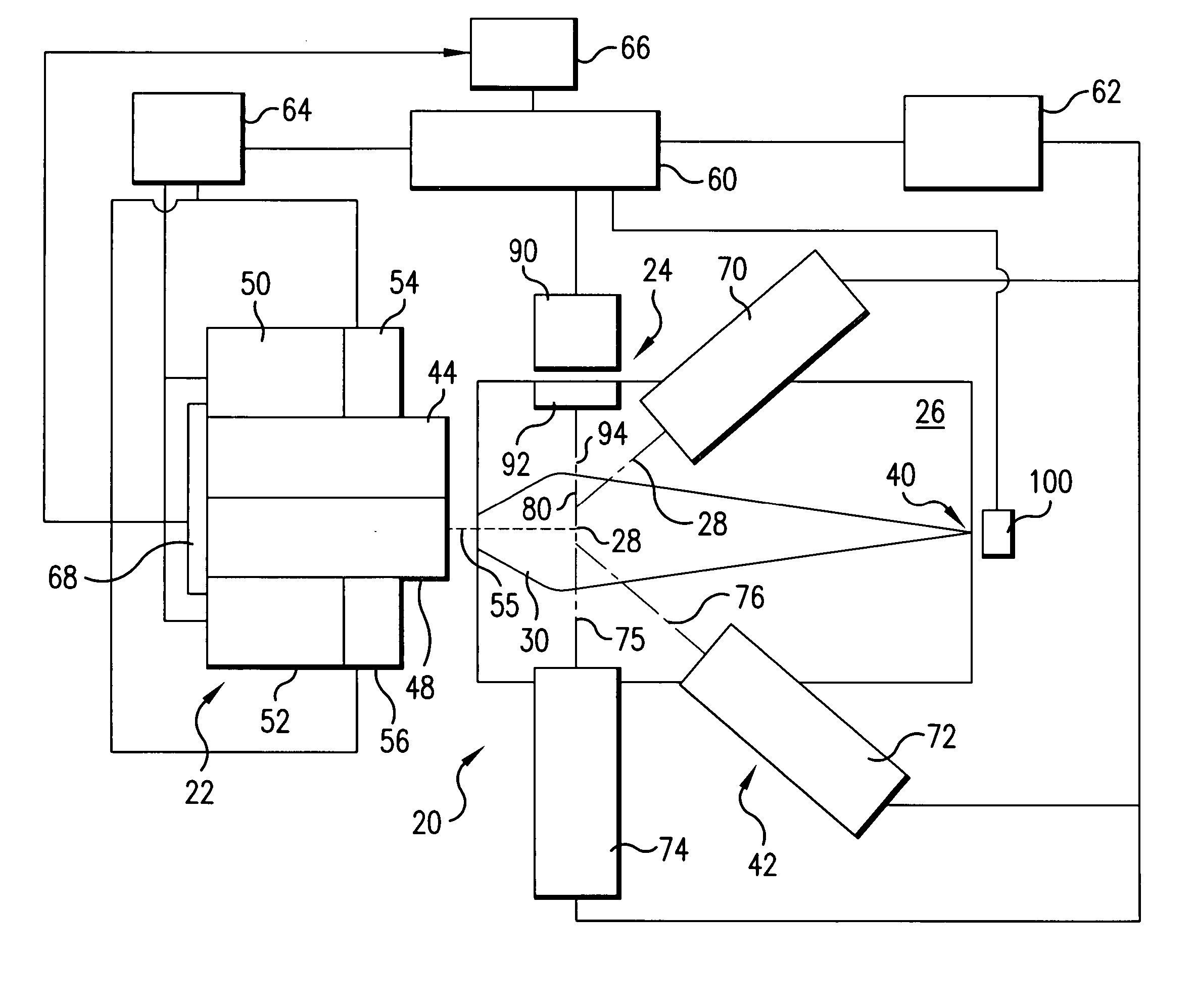
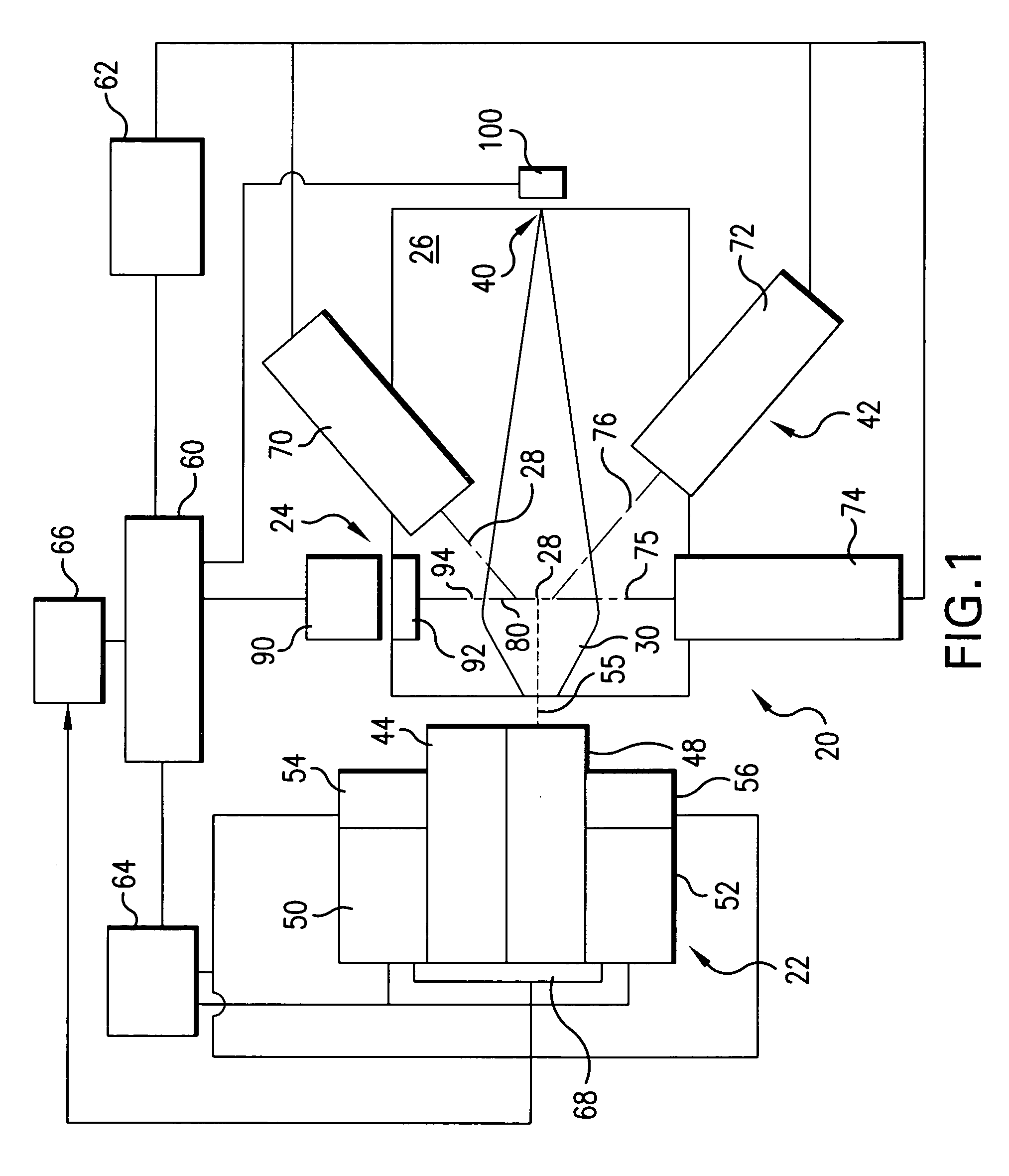
An apparatus and method for EUV light production is disclosed which may comprise a laser produced plasma (“LPP”) extreme ultraviolet (“EUV”) light source control system comprising a target delivery system adapted to deliver moving plasma initiation targets and an EUV light collection optic having a focus defining a desired plasma initiation site, comprising: a target tracking and feedback system comprising: at least one imaging device providing as an output an image of a target stream track, wherein the target stream track results from the imaging speed of the camera being too slow to image individual plasma formation targets forming the target stream imaged as the target stream track; a stream track error detector detecting an error in the position of the target stream track in at least one axis generally perpendicular to the target stream track from a desired stream track intersecting the desired plasma initiation site. At least one target crossing detector may be aimed at the target track and detecting the passage of a plasma formation target through a selected point in the target track. A drive laser triggering mechanism utilizing an output of the target crossing detector to determine the timing of a drive laser trigger in order for a drive laser output pulse to intersect the plasma initiation target at a selected plasma initiation site along the target track at generally its closest approach to the desired plasma initiation site. A plasma initiation detector may be aimed at the target track and detecting the location along the target track of a plasma initiation site for a respective target. An intermediate focus illuminator may illuminate an aperture formed at the intermediate focus to image the aperture in the at least one imaging device. The at least one imaging device may be at least two imaging devices each providing an error signal related to the separation of the target track from the vertical centerline axis of the image of the intermediate focus based upon an analysis of the image in the respective one of the at least two imaging devices. A target delivery feedback and control system may comprise a target delivery unit; a target delivery displacement control mechanism displacing the target delivery mechanism at least in an axis corresponding to a first displacement error signal derived from the analysis of the image in the first imaging device and at least in an axis corresponding to a second displacement error signal derived from the analysis of the image in the second imaging device.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
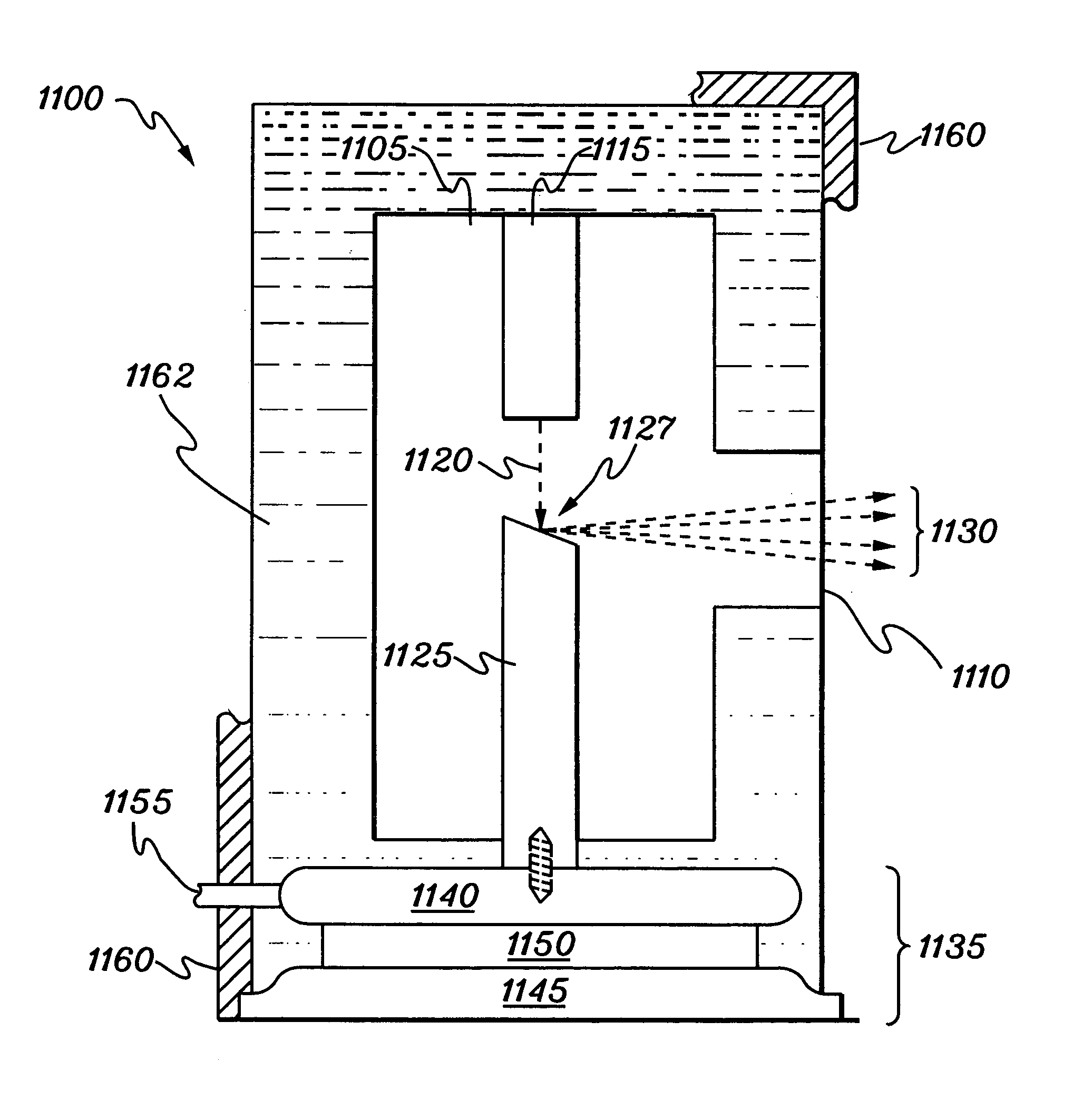
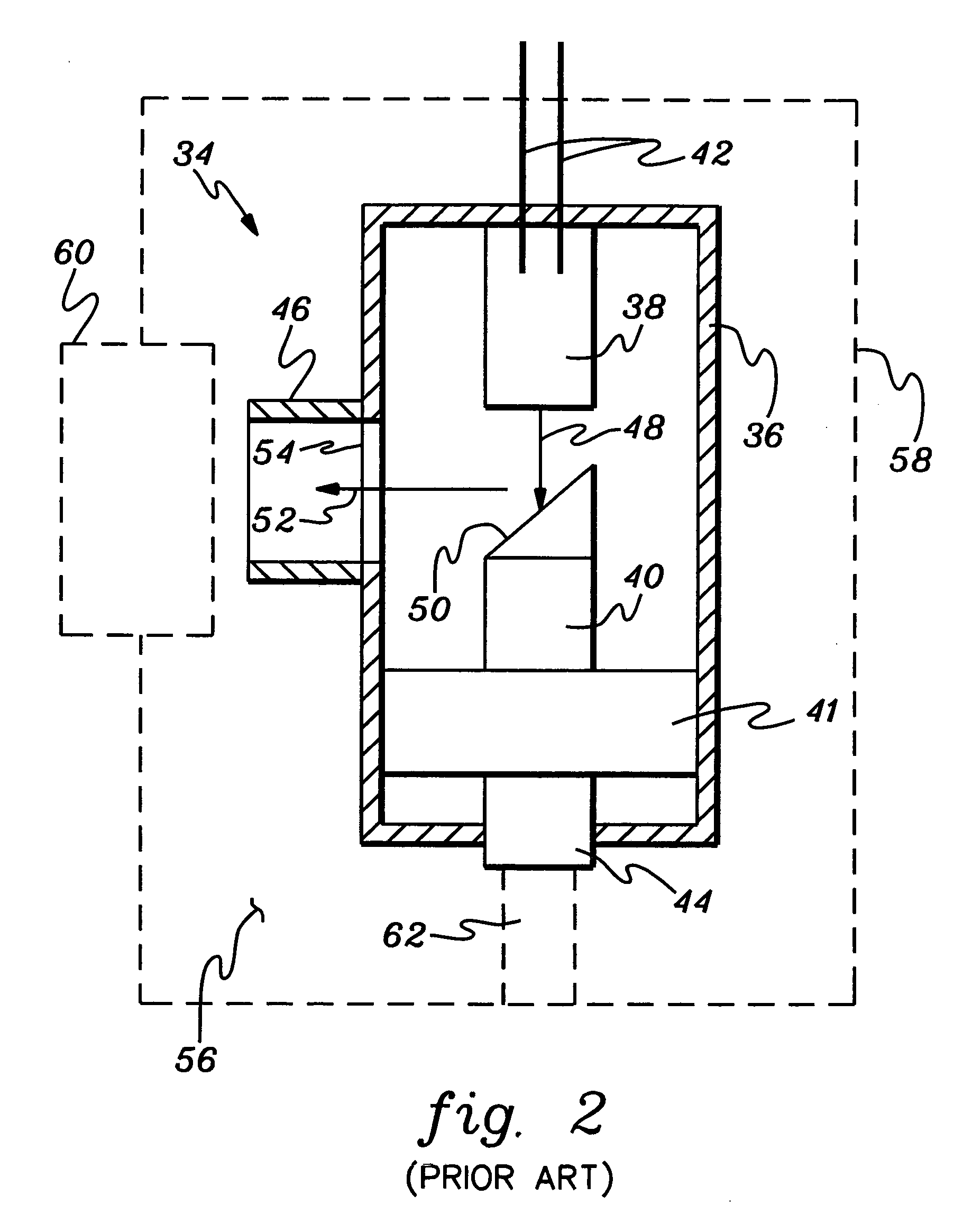
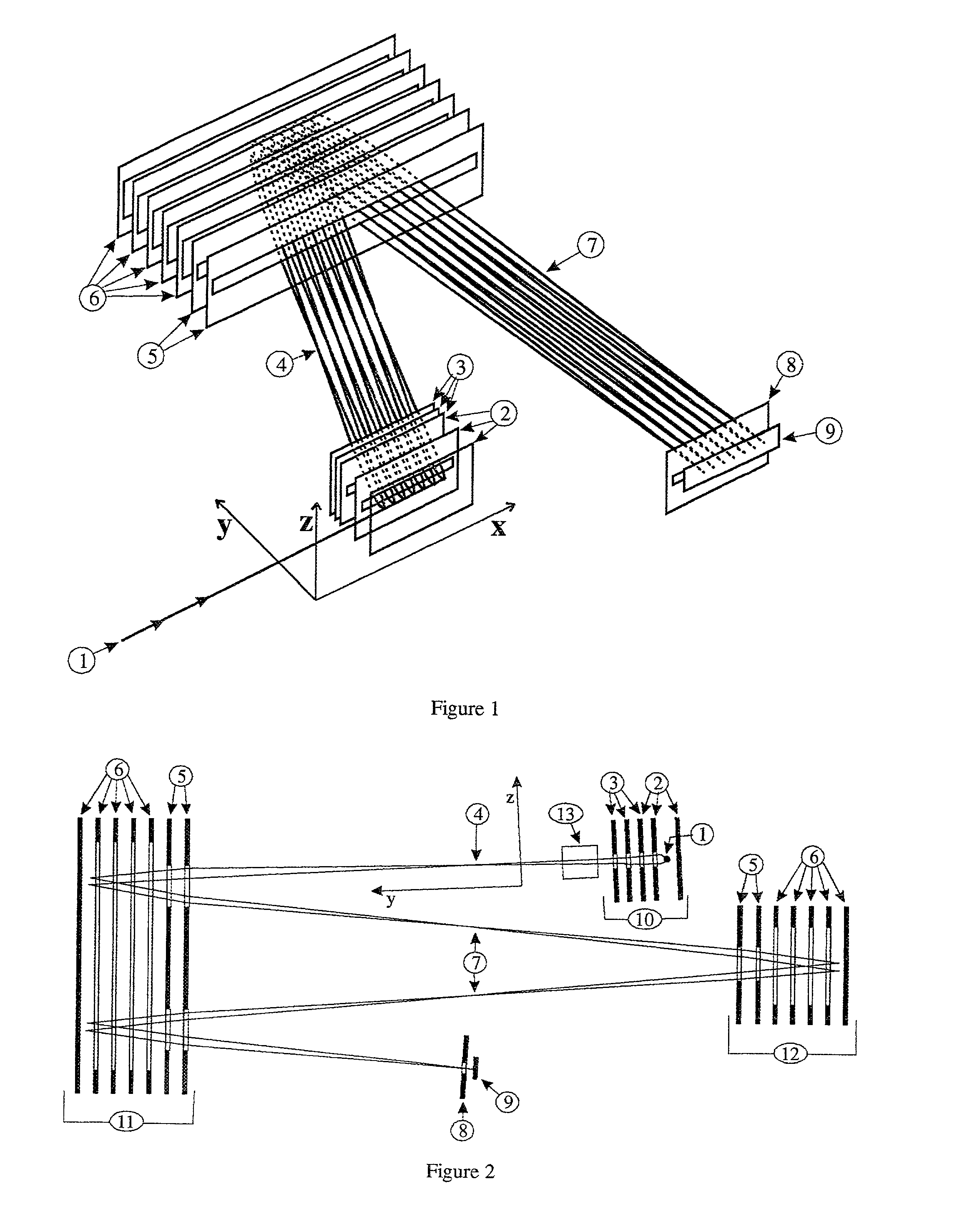
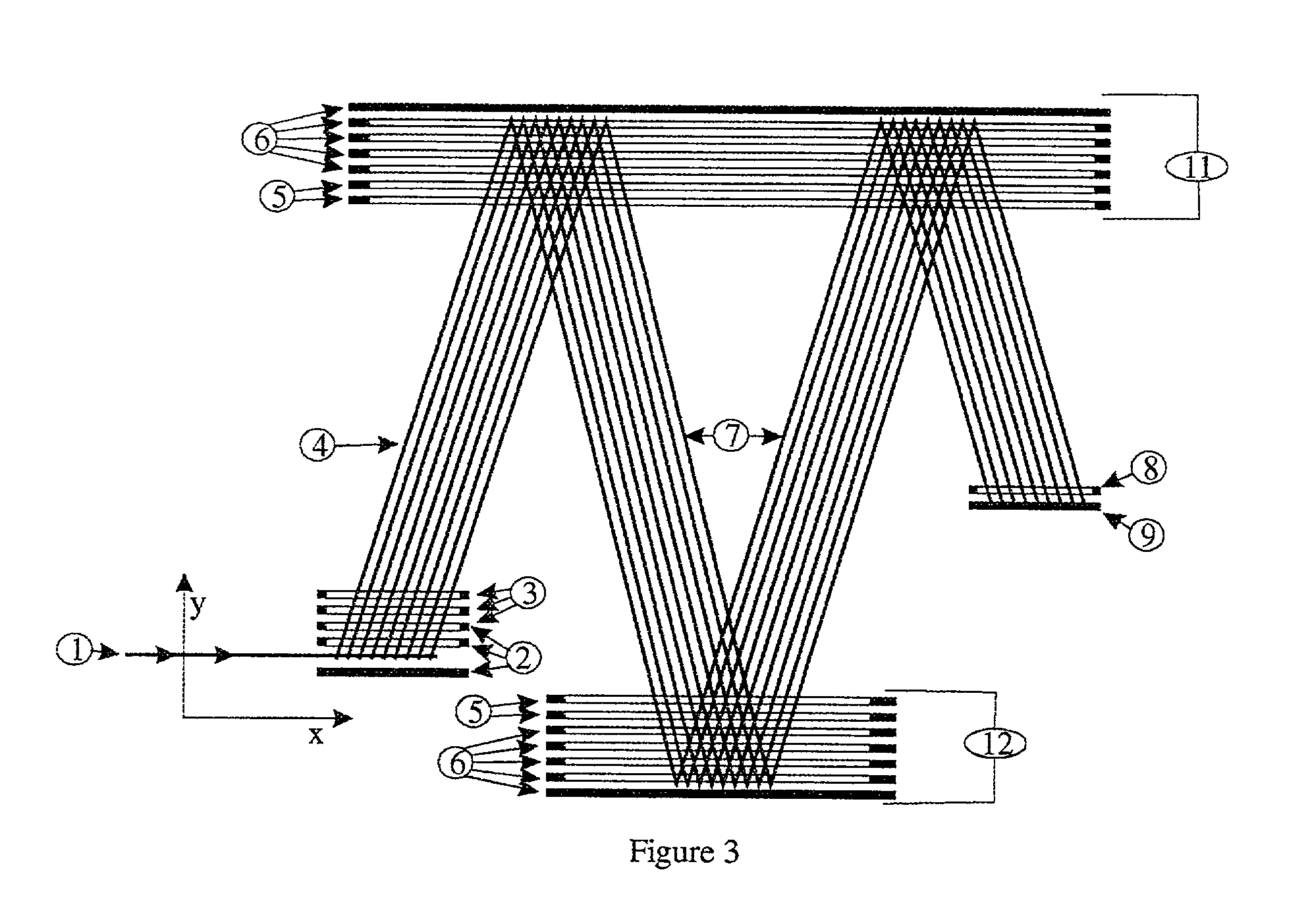
Method for obtaining a picture of the internal structure of an object using x-ray radiation and device for the implementation thereof
InactiveUS6754304B1Improve accuracyReduce usageX-ray spectral distribution measurementHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-rayX ray dose
Owner:KUMAKHOV MURADIN ABUBEKIROVICH
EUV light source
A laser produced plasma (“LPP”) extreme ultraviolet (“EUV”) light source control system comprises a target delivery system adapted to deliver moving plasma initiation targets and an EUV light collection optic having a focus defining a desired plasma initiation site, a target tracking and feedback system comprising: at least one imaging device providing as an output an image of a target stream track, and a stream track error detector detecting an error in the position of the target stream track in at least one axis generally perpendicular to the target stream track from a desired stream track intersecting the desired plasma initiation site.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
ActiveUS7180979B2Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionImage contrastImage detection
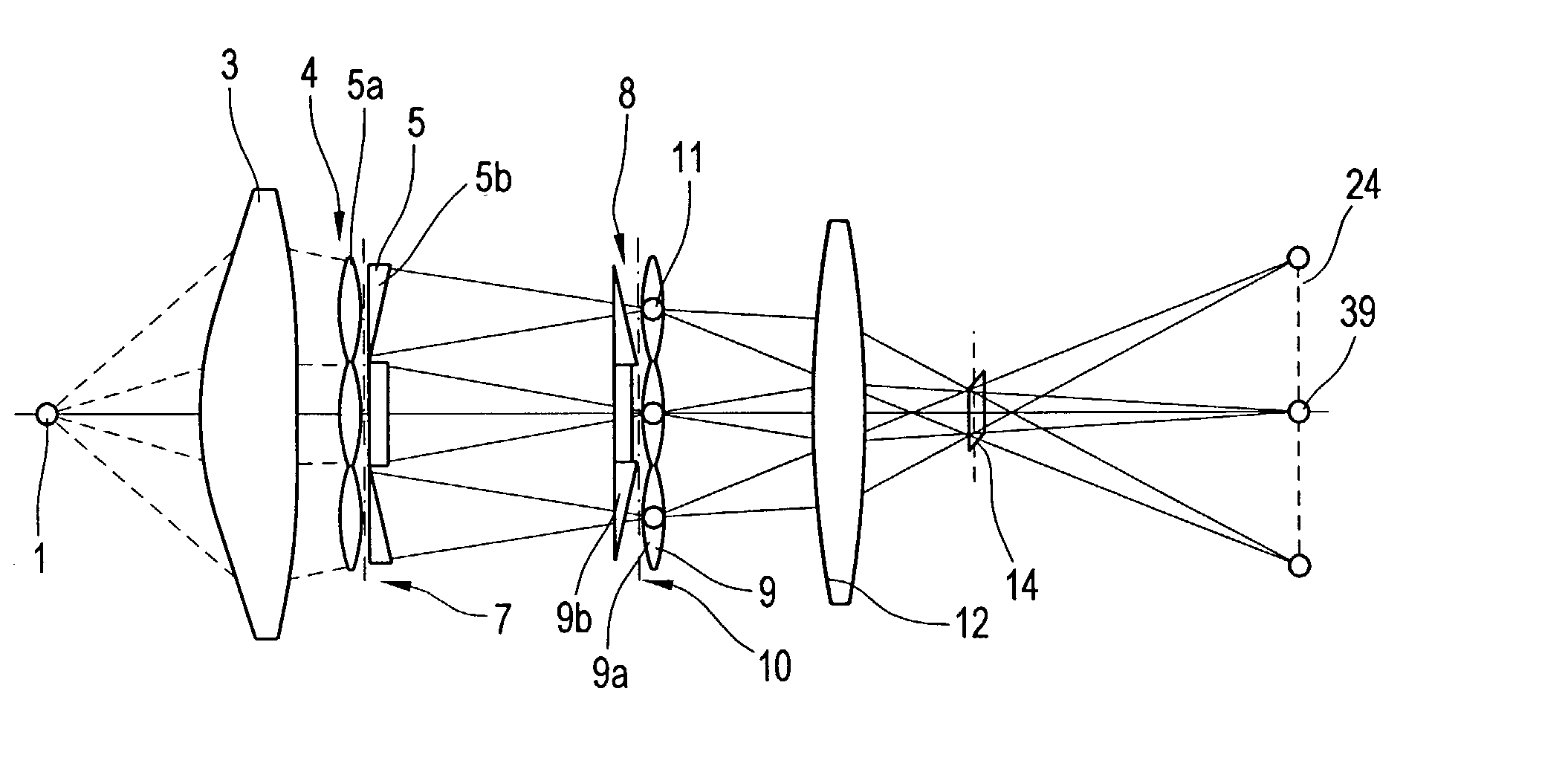
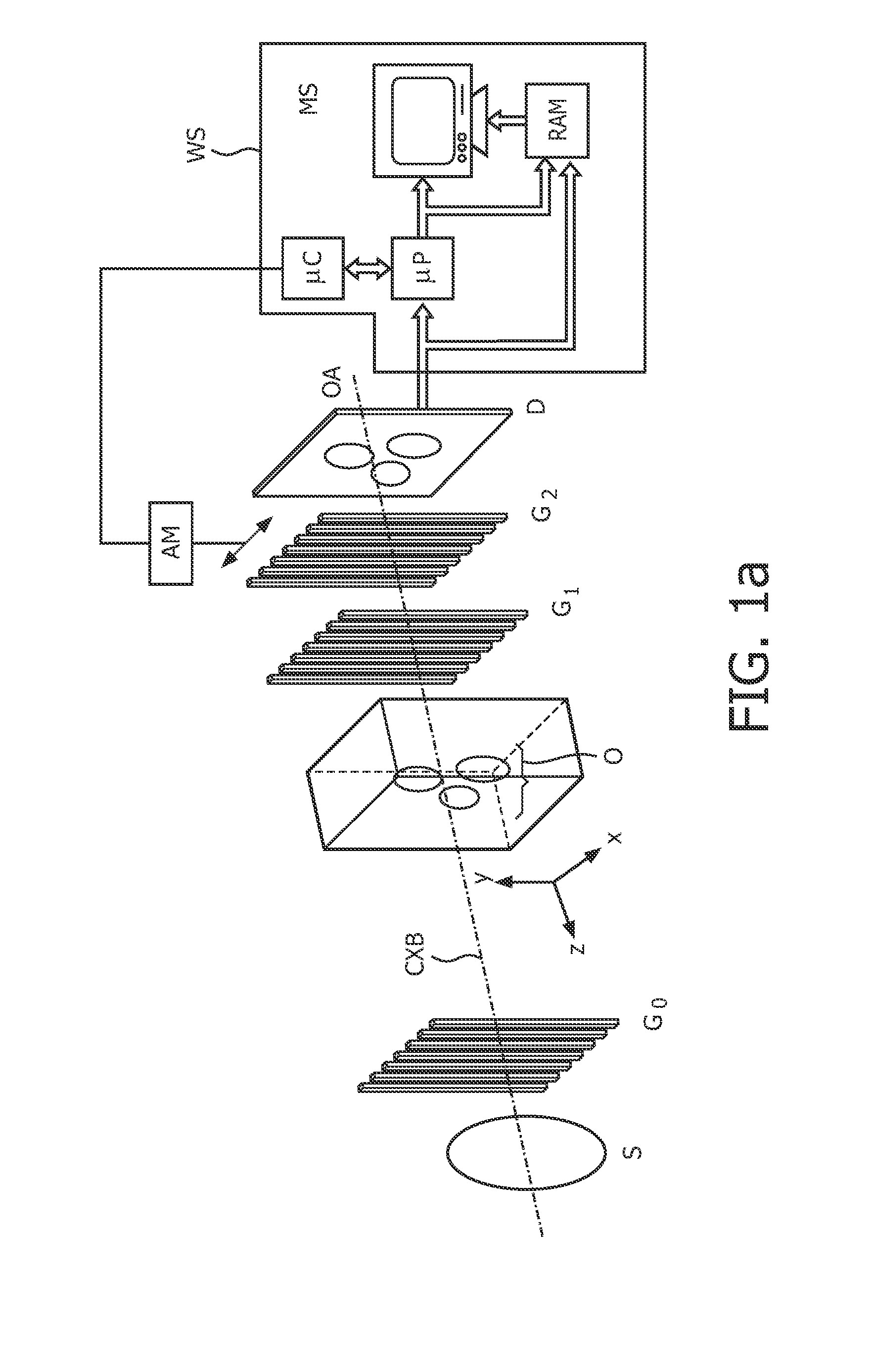
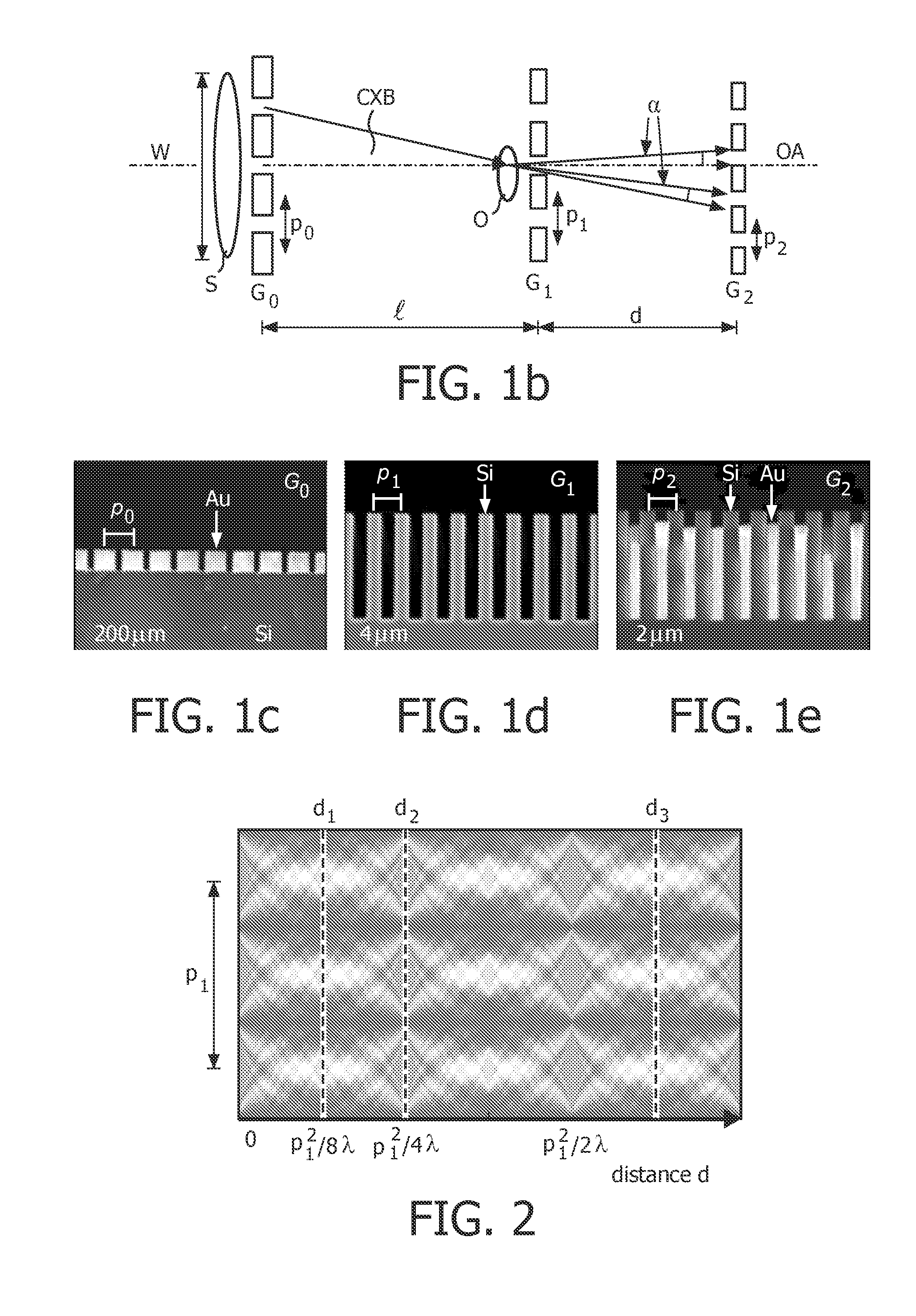
The present invention provides an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays. An X-ray imaging apparatus equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector are described. The first diffraction grating generates a Talbot effect and a second diffraction grating diffracts X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. An image detector is provided to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. In this manner, image contrasts caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to a subject arranged in front of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating can be achieved.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
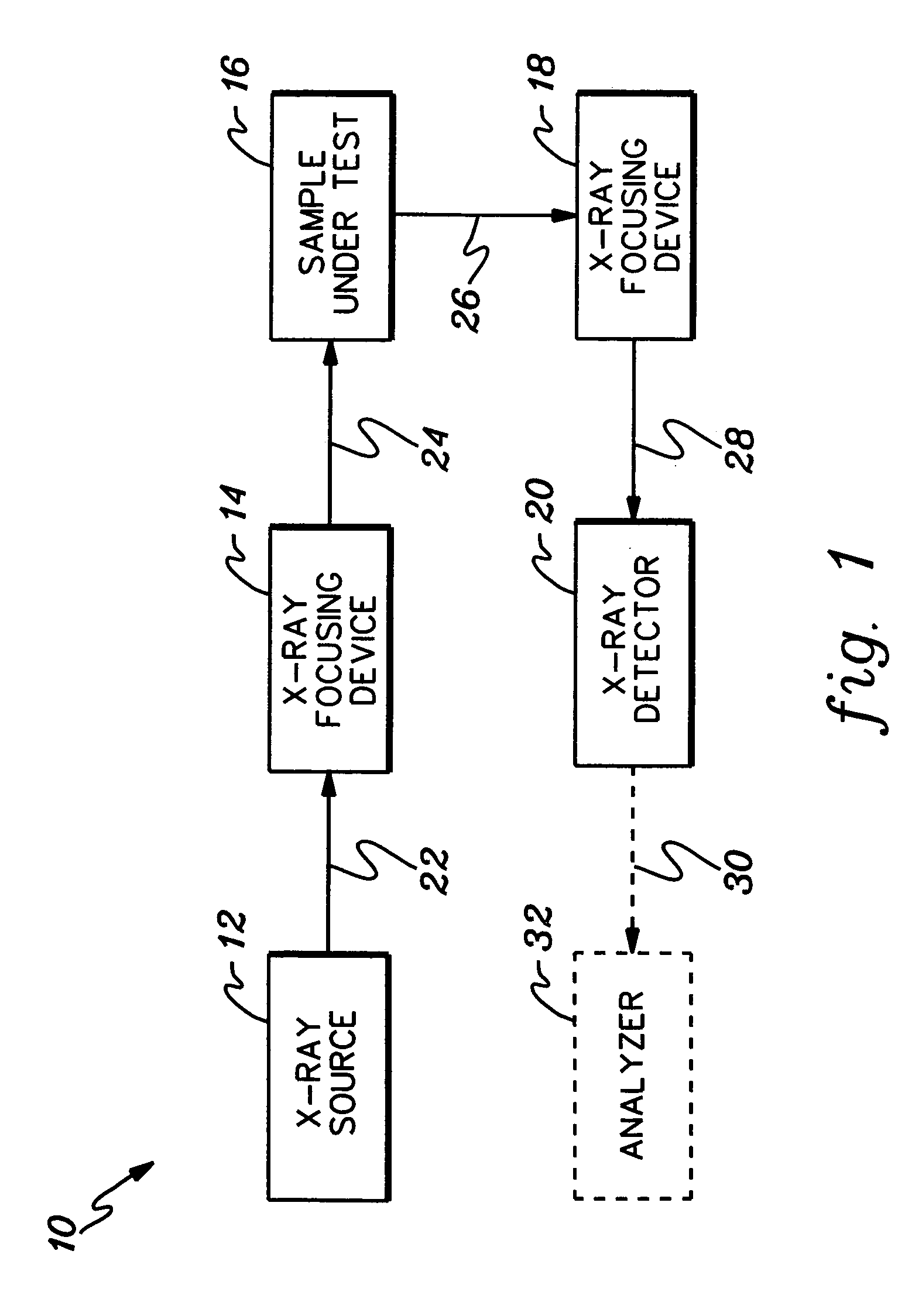
Wavelength dispersive XRF system using focusing optic for excitation and a focusing monochromator for collection
InactiveUS6934359B2Overcomes shortcomingX-ray/infra-red processesX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayAnalyte
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy systems and methods are provided. One system includes a source of x-ray radiation and an excitation optic disposed between the x-ray radiation source and the sample for collecting x-ray radiation from the source and focusing the x-ray radiation to a focal point on the sample to incite at least one analyte in the sample to fluoresce. The system further includes an x-ray fluorescence detector and a collection optic comprising a doubly curved diffracting optic disposed between the sample and the x-ray fluorescence detector for collecting x-ray fluorescence from the focal point on the sample and focusing the fluorescent x-rays towards the x-ray fluorescence detector.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
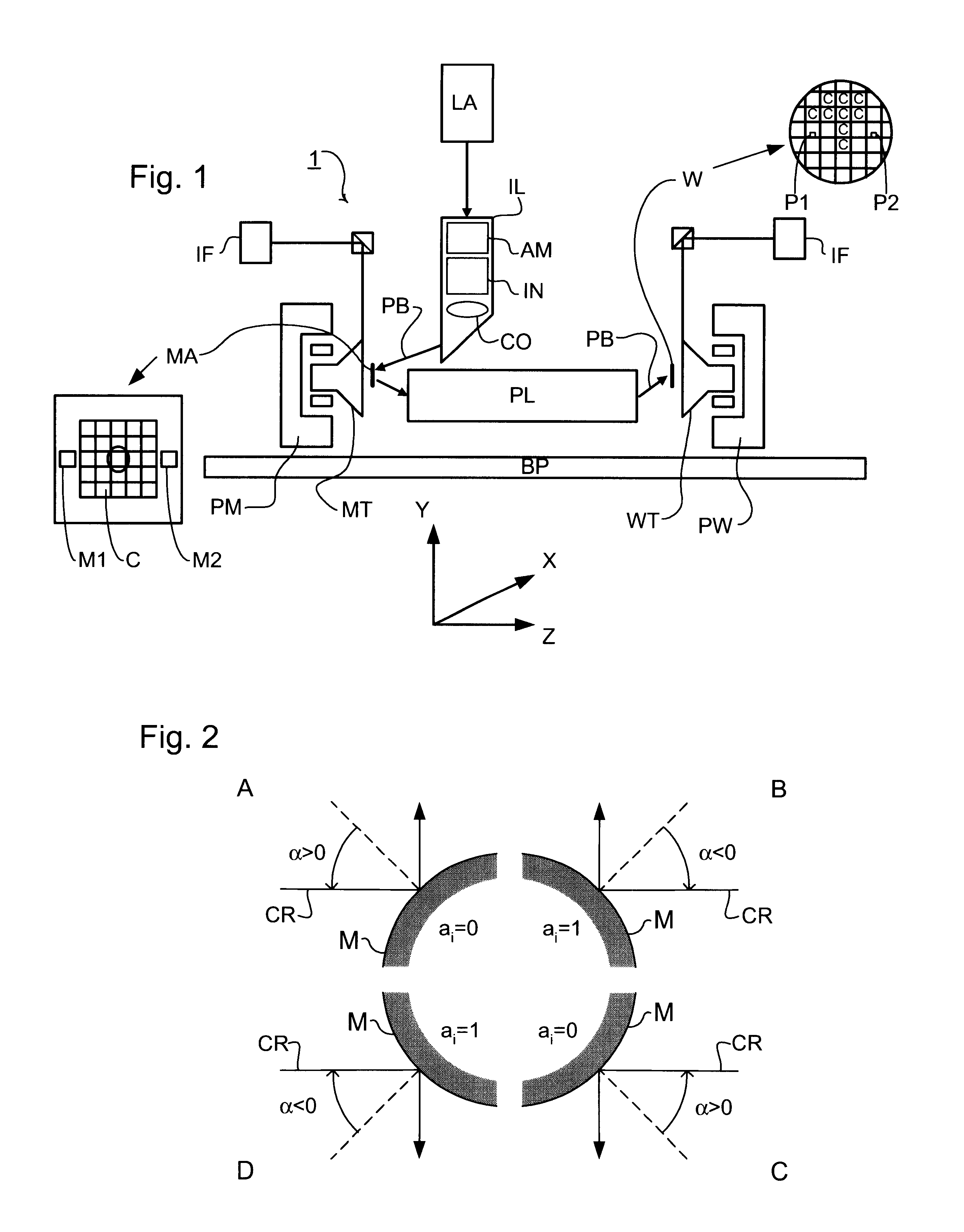
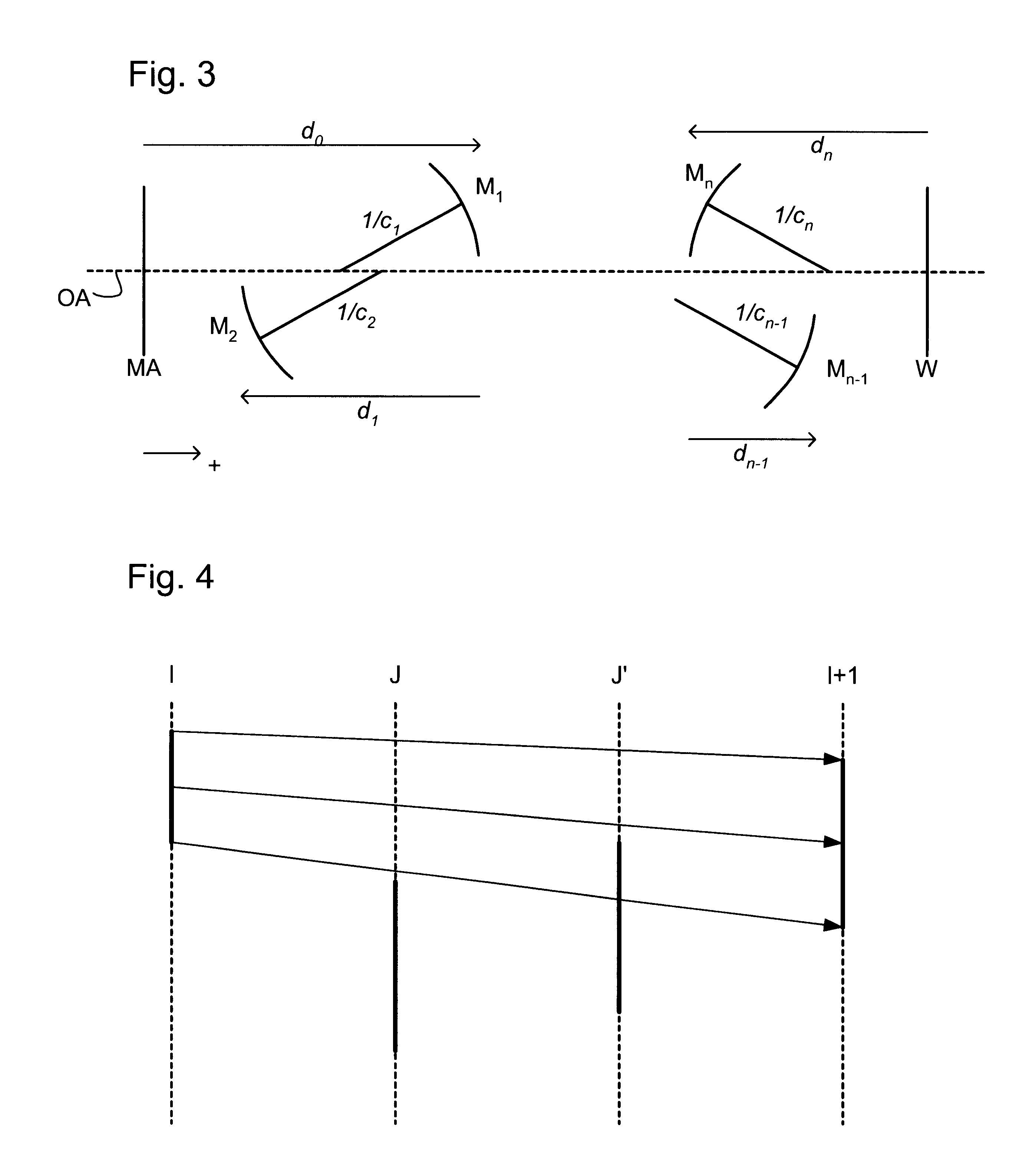
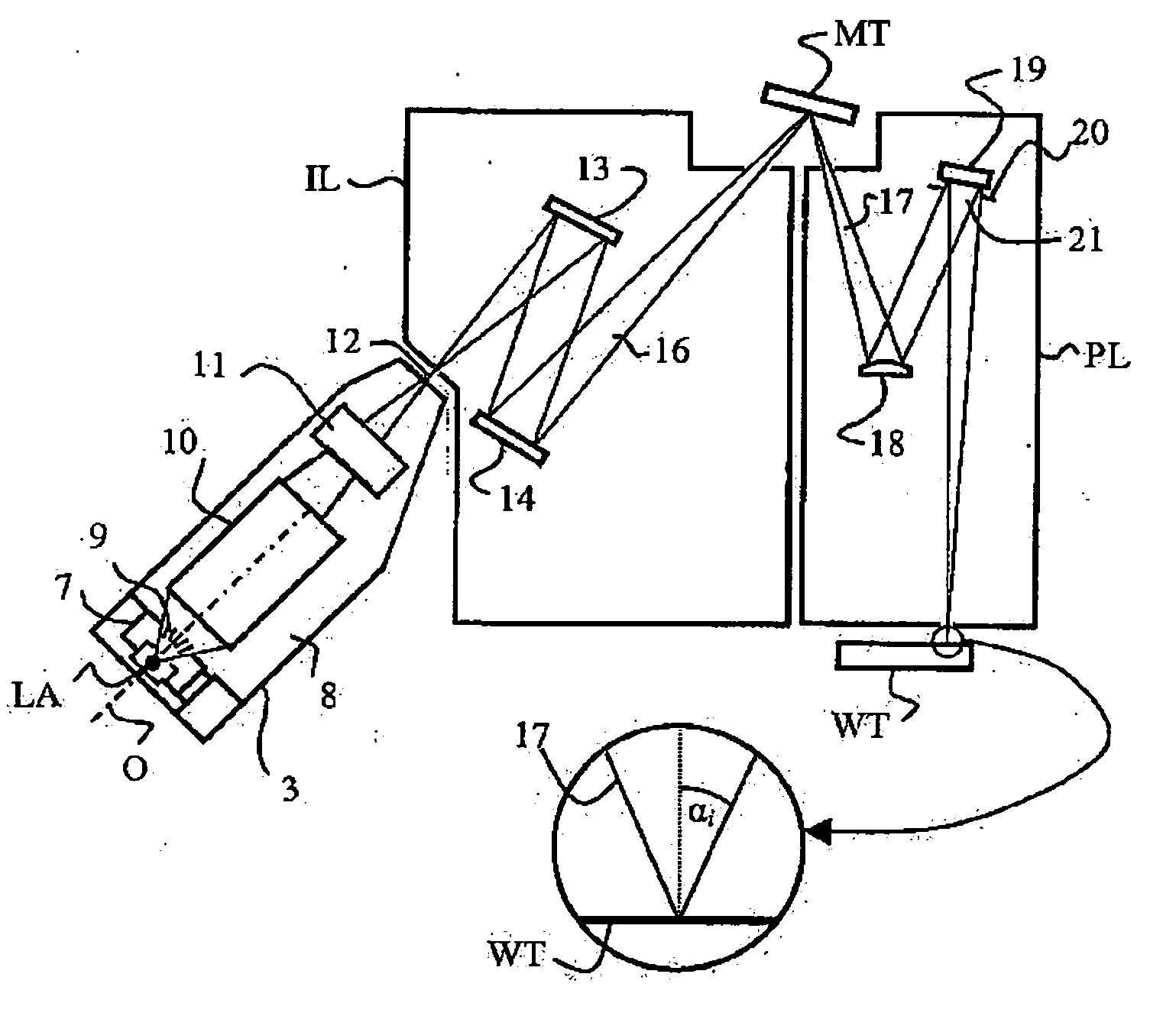
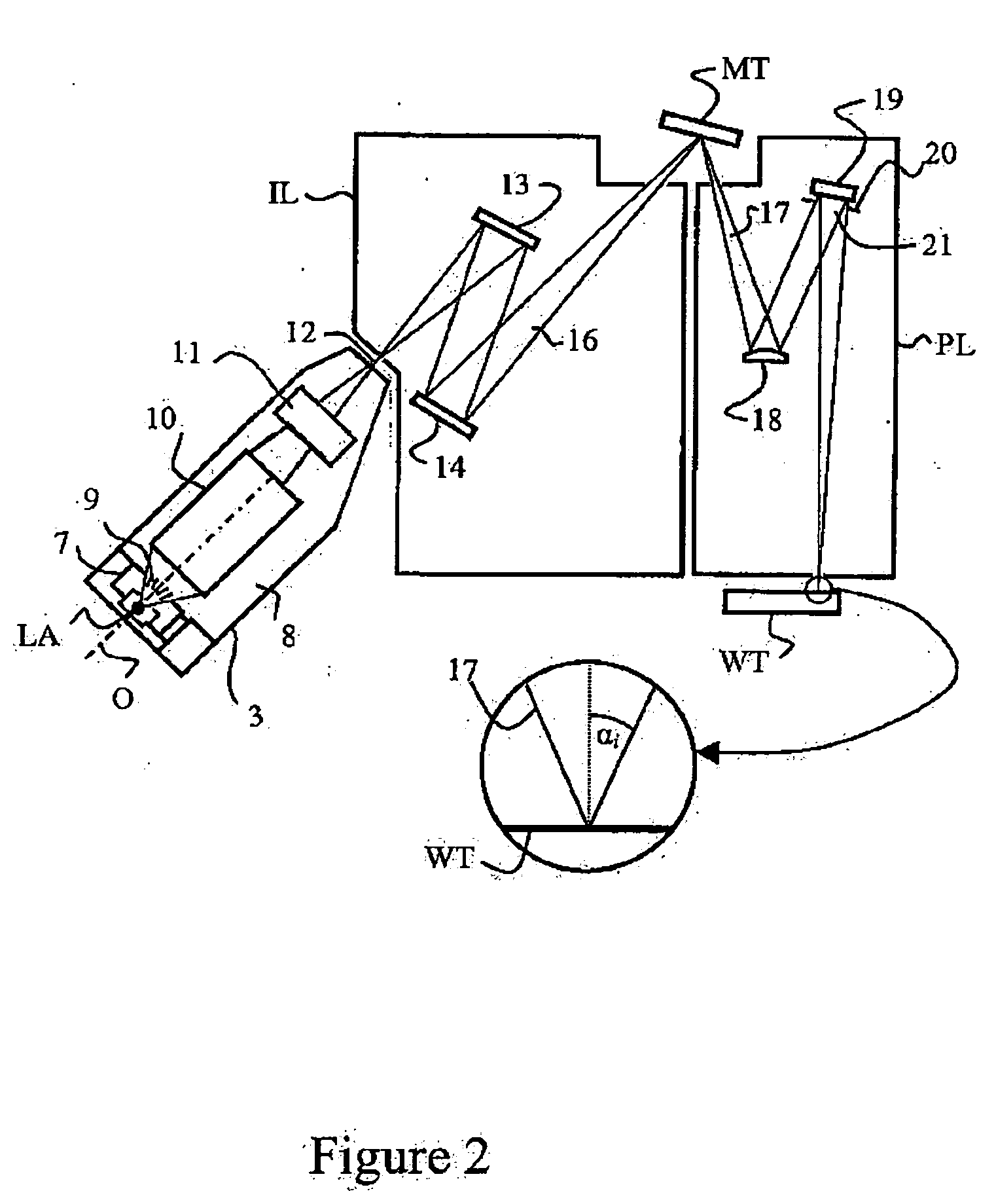
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
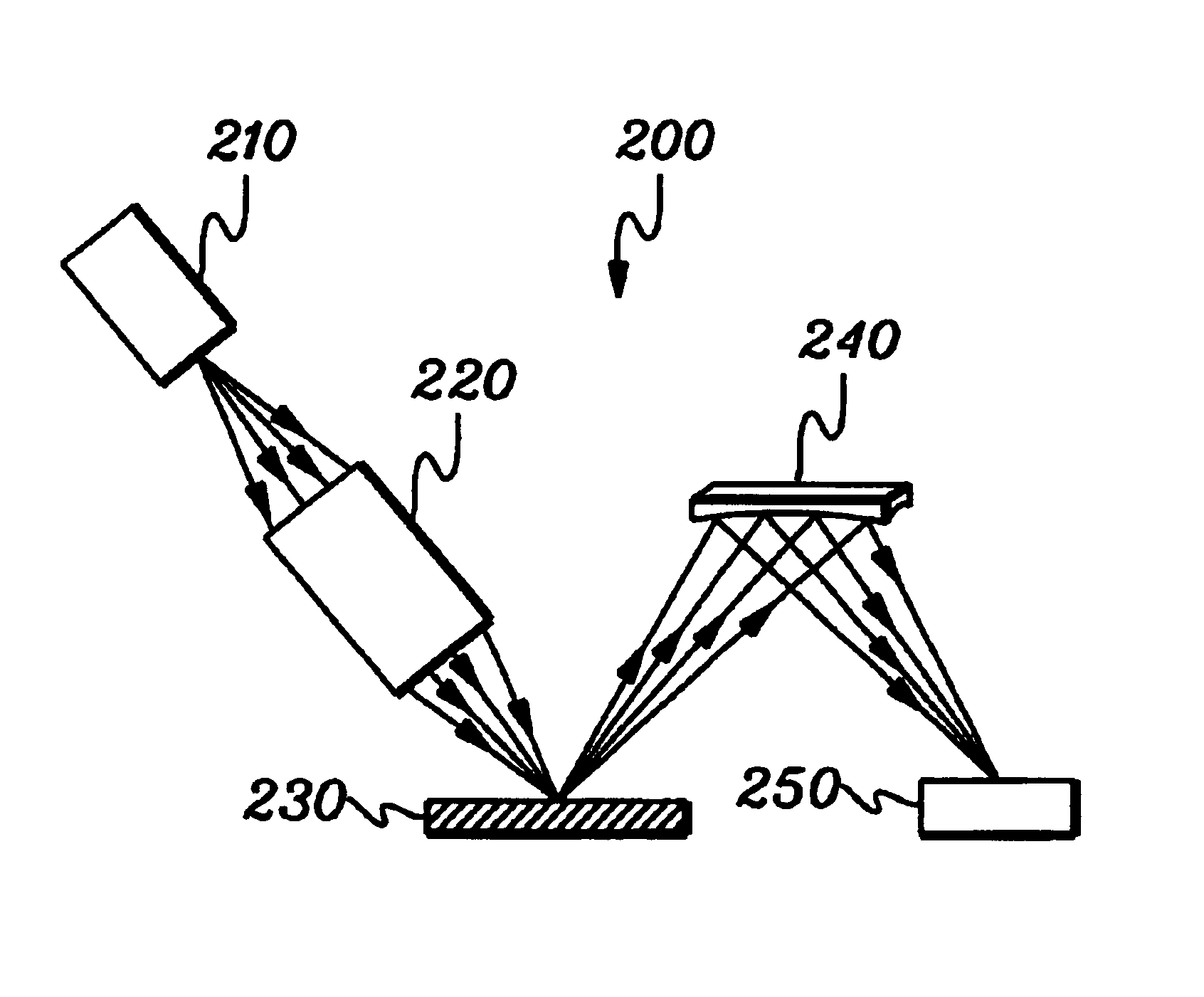
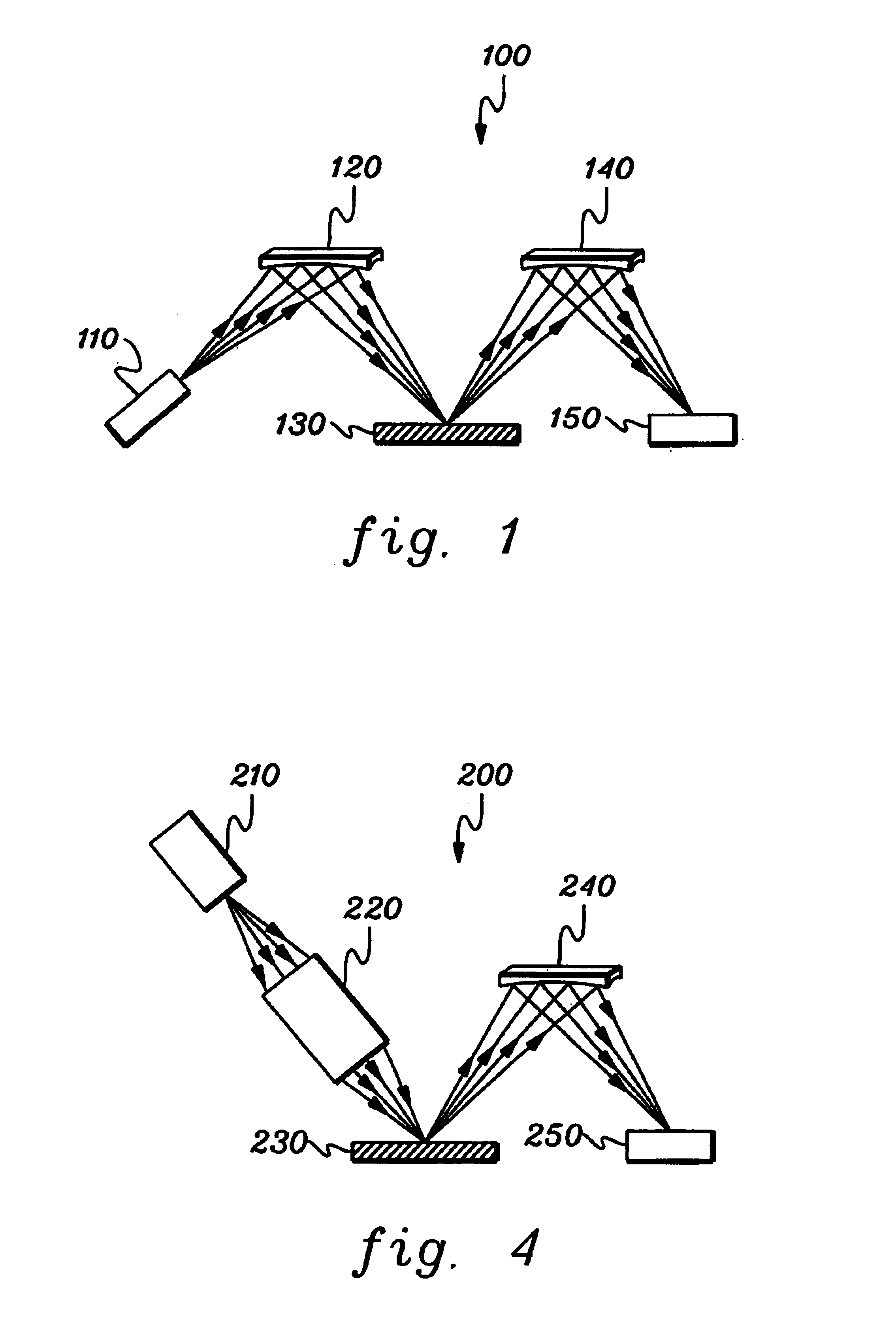
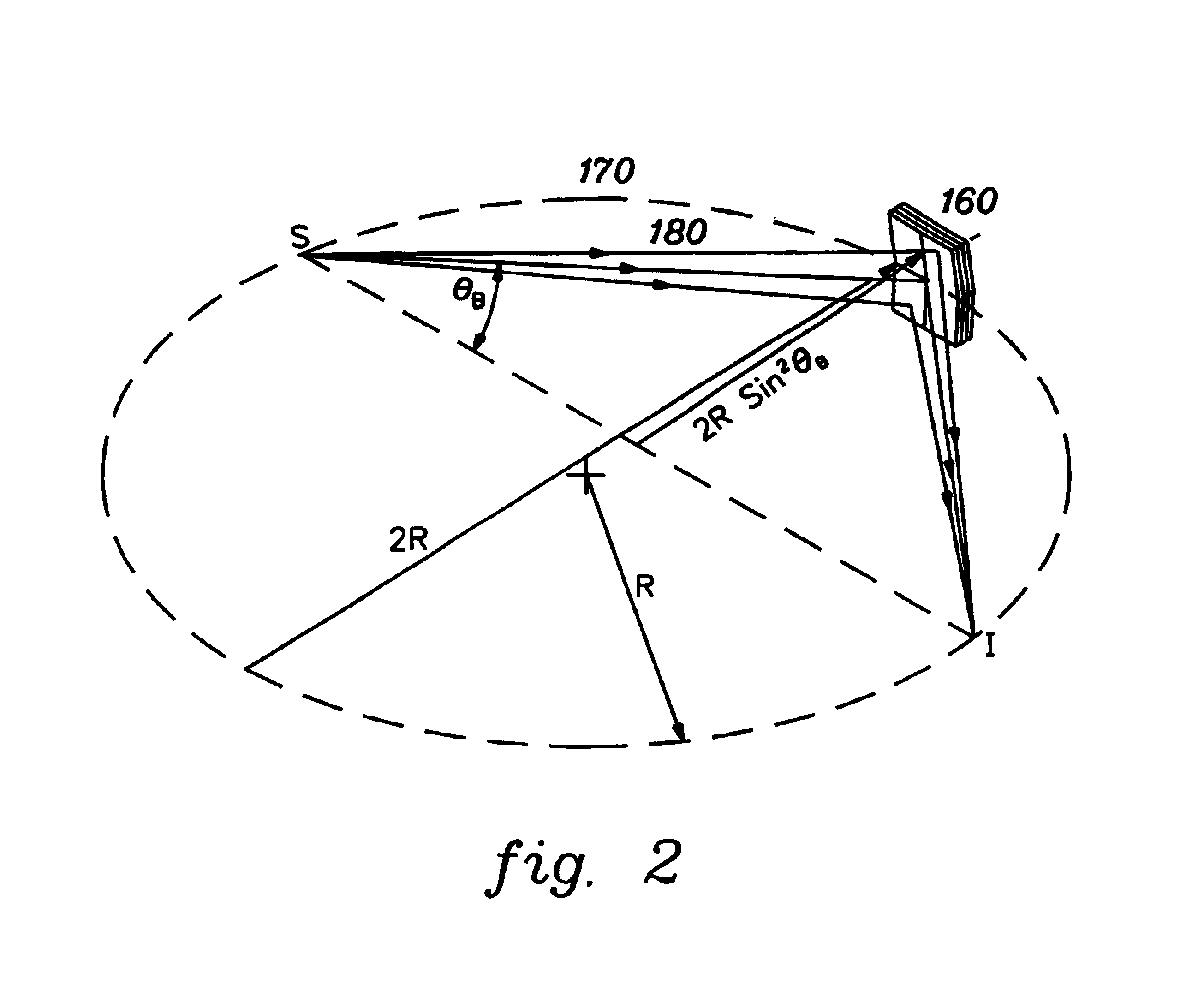
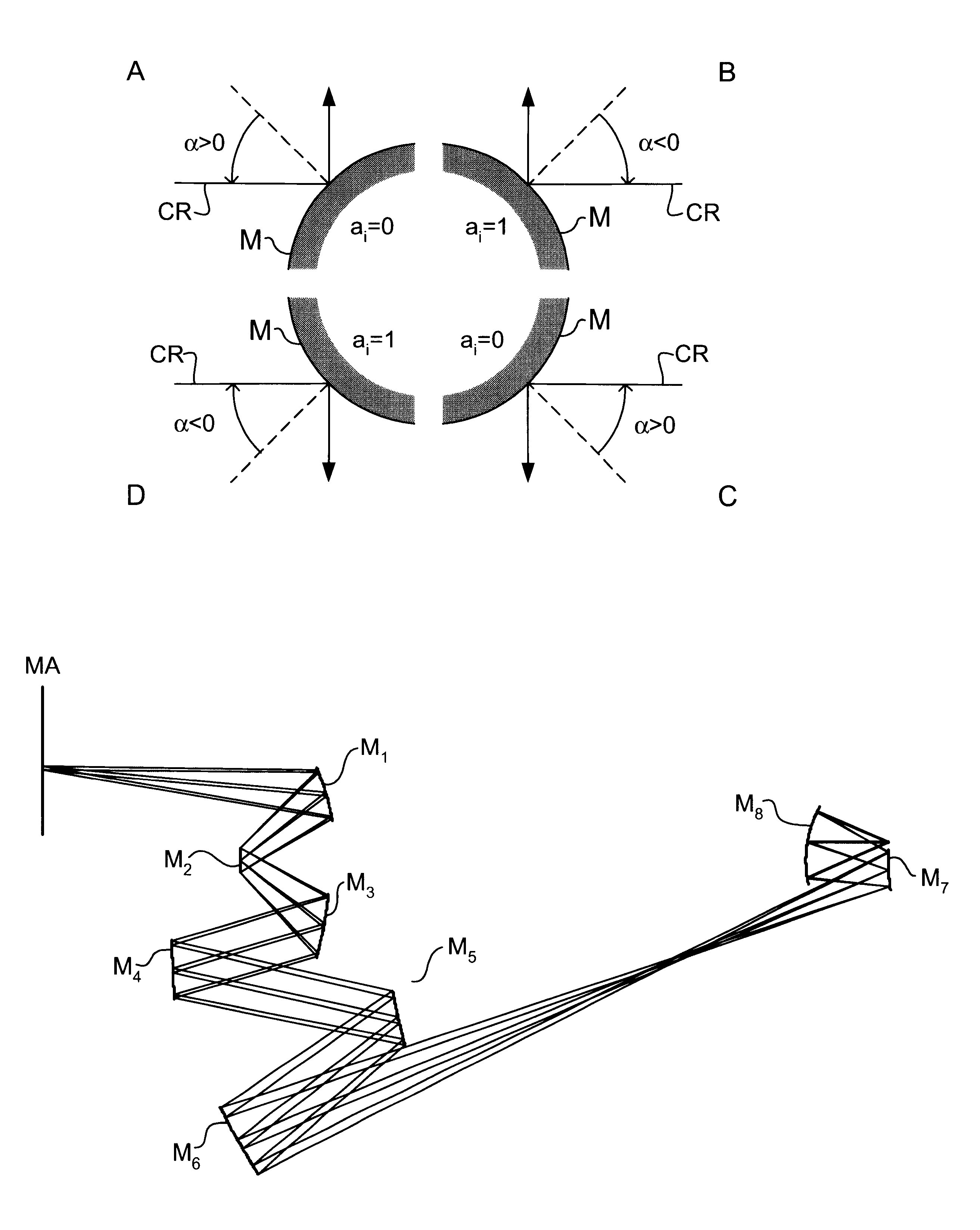
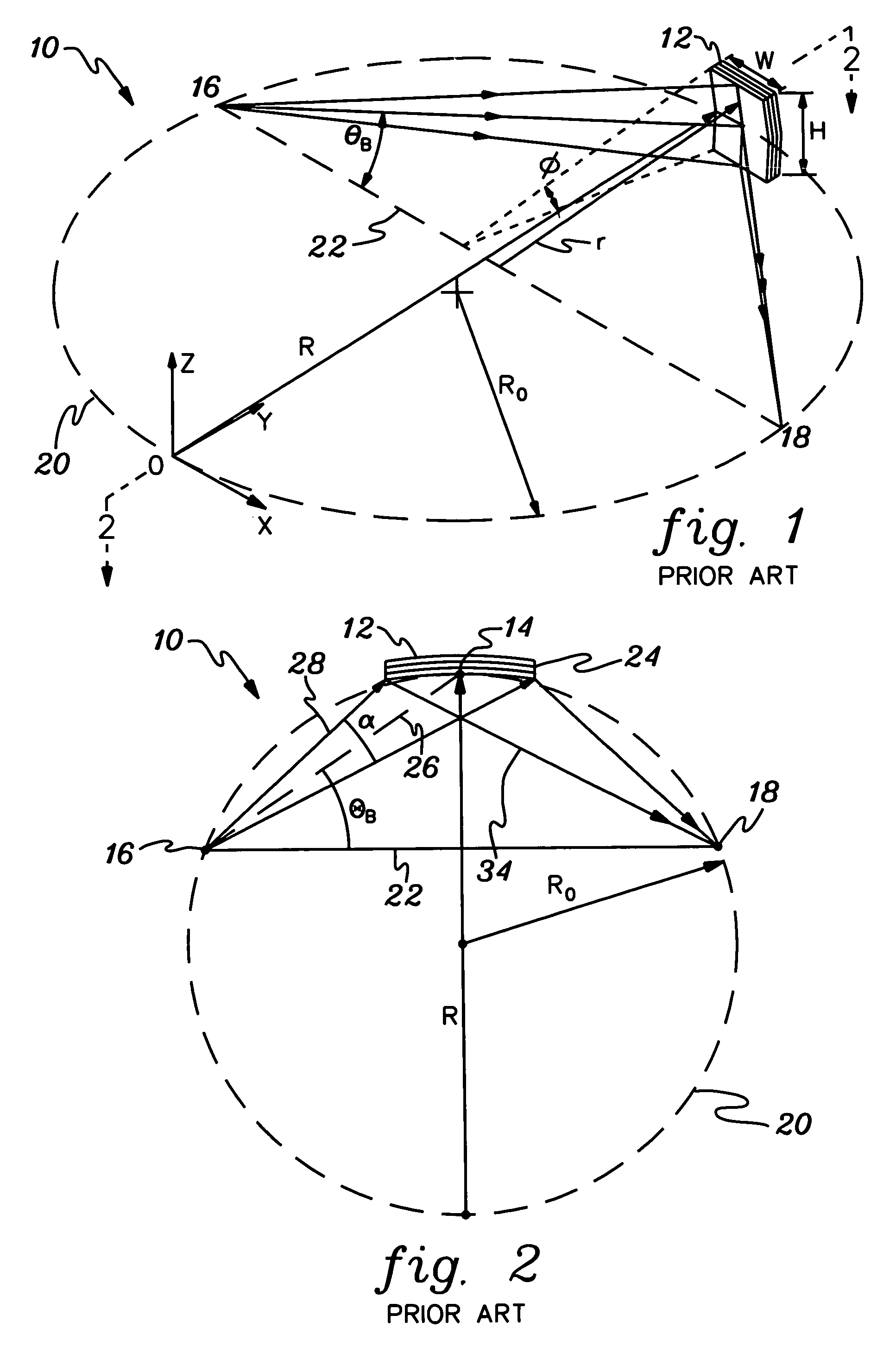
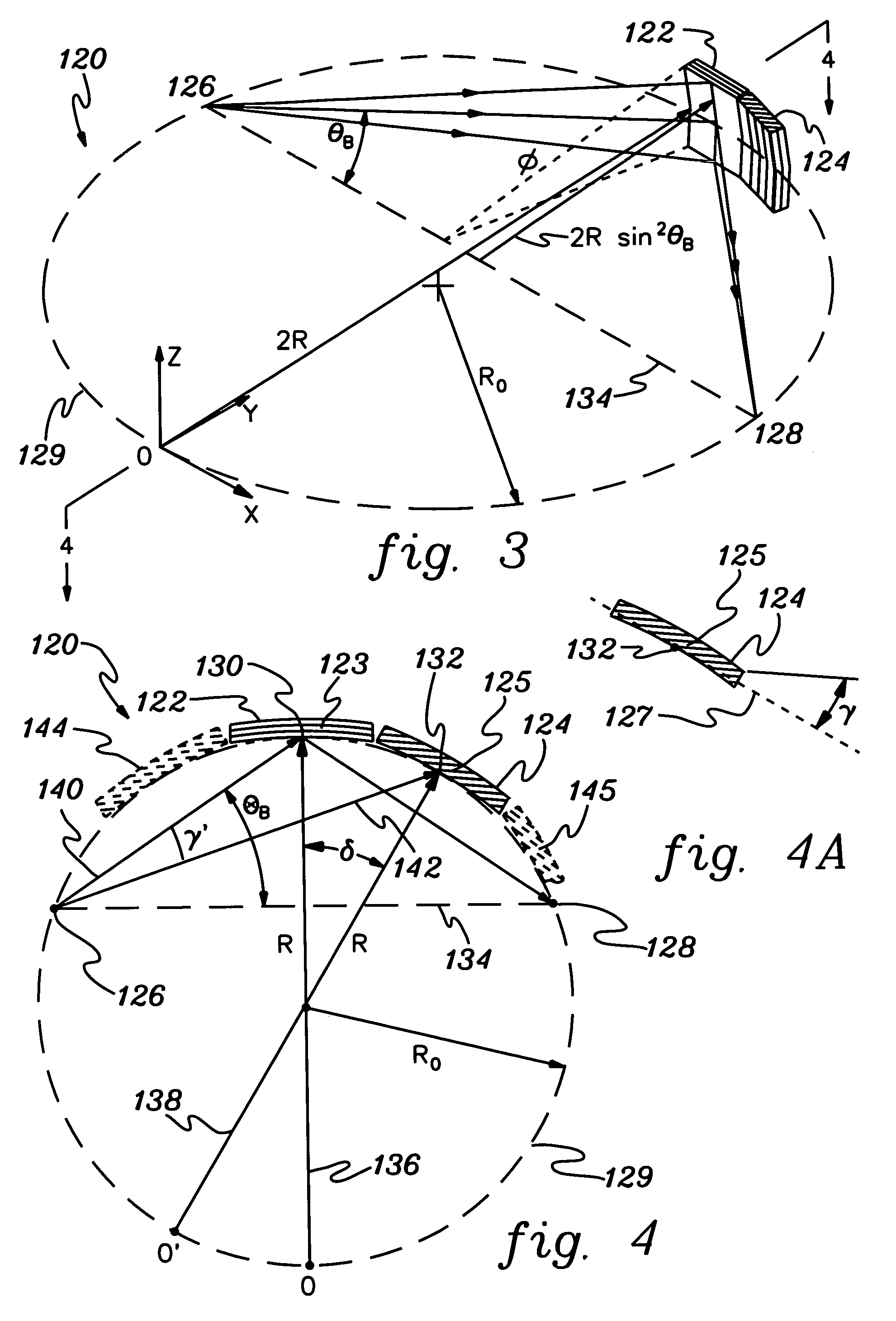
InactiveUS6556648B1MirrorsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionLithographic artistAngle of incidence
A classification system for systems of n mirrors, whereby systems of mirrors are classified by a number C, is defined as follows:where: ai=1 if the angle of incidence of the chief ray at mirror i is negative,ai=0 if the angle of incidence of the chief ray at mirror i is positive,M is the magnification of the projection system, andindex i numbers the mirrors of the system in series. Four mirror systems, six mirror systems and eight mirror systems in accordance with the present invention are useful in EUV lithography projection systems.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Collector for EUV light source
InactiveUS20060131515A1Increase probabilityReduce probabilityLaser detailsNanoinformaticsSputteringHigh probability
A method and apparatus for debris removal from a reflecting surface of an EUV collector in an EUV light source is disclosed which may comprise the reflecting surface comprises a first material and the debris comprises a second material and / or compounds of the second material, the system and method may comprise a controlled sputtering ion source which may comprise a gas comprising the atoms of the sputtering ion material; and a stimulating mechanism exciting the atoms of the sputtering ion material into an ionized state, the ionized state being selected to have a distribution around a selected energy peak that has a high probability of sputtering the second material and a very low probability of sputtering the first material. The stimulating mechanism may comprise an RF or microwave induction mechanism.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Illumination system with variable adjustment of the illumination
InactiveUS20020136351A1Avoid lostSimple wayNanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionGratingExit pupil
An illumination system comprises (a) a first optical element upon which a light beam impinges, where the first optical element has first raster elements that partition said light beam into light channels; (b) a second optical element that receives said light channels, where the second optical element has a second raster elements; (c) an object plane that receives said light channels via said second optical element; and (d) an exit pupil that is provided with an illumination via said object plane. The system is characterized by an assignment of a member of said first raster elements and a member of said second raster elements to each of said light channels to provide a continuous beam path from said first optical element to said object plane for each of said plurality of light channels. The assignment is changeable to provide an adjustment of said illumination in said exit pupil.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
X-ray imaging system and imaging method
ActiveUS20050286680A1Easy constructionImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayImage contrast
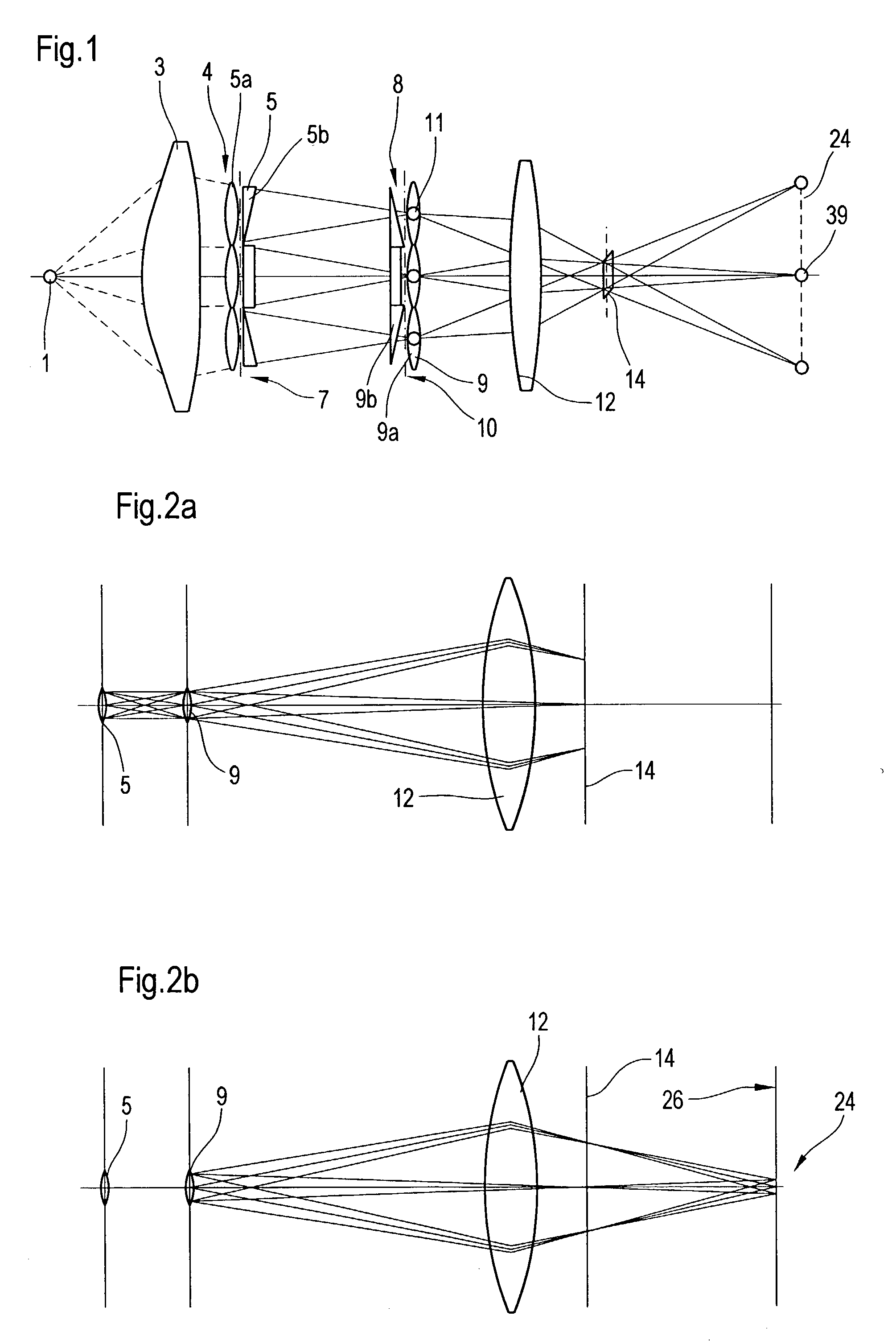
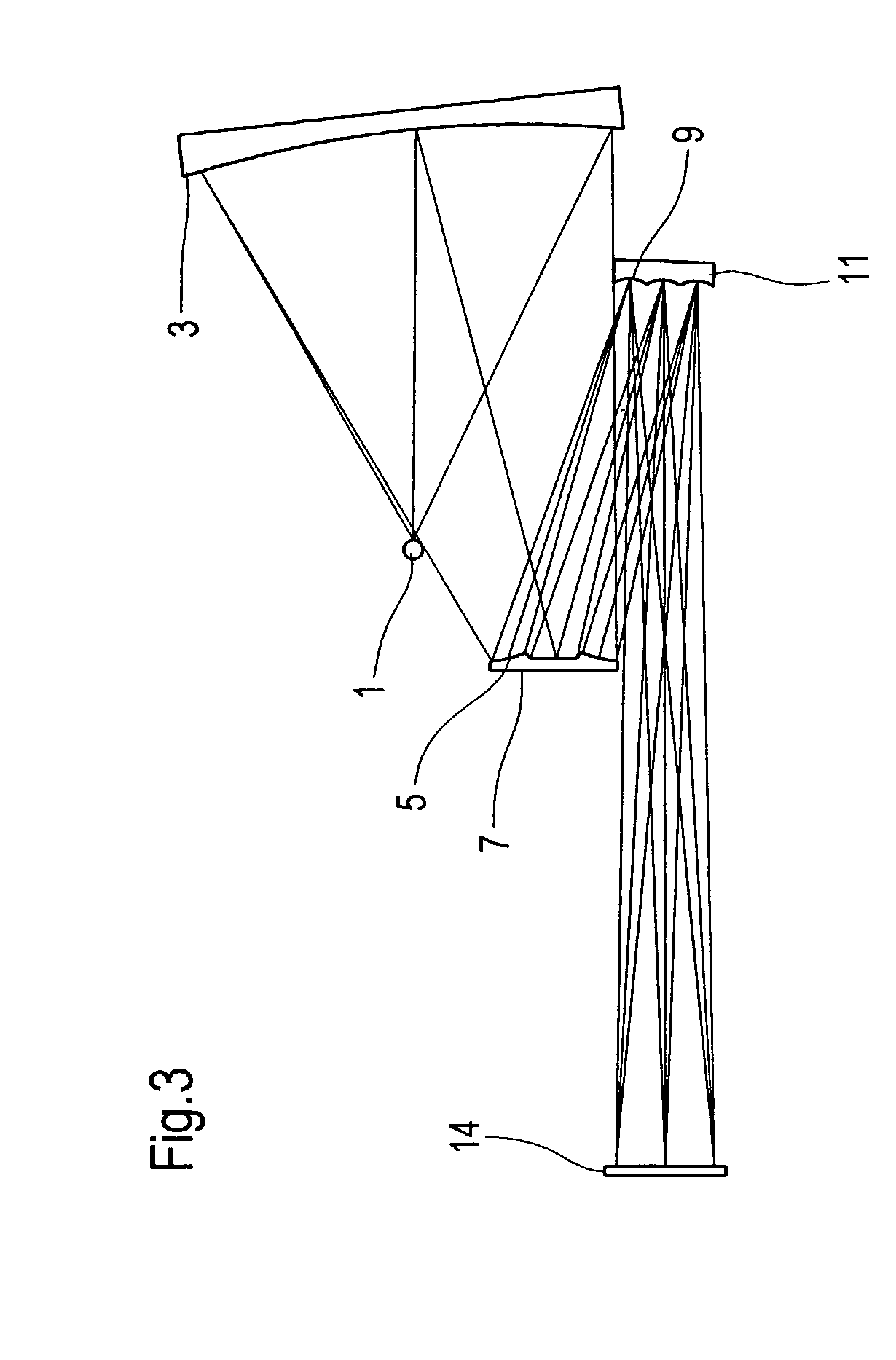
The object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus capable of X-ray imaging utilizing phase of X-rays with a simple construction. The X-ray imaging apparatus of the present invention is equipped with first and second diffraction gratings and an X-ray image detector. The first diffraction grating is constructed to generate the Talbot effect using X-rays irradiated at the first diffraction grating. The second diffraction grating is configured so as to diffract the X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is configured so as to detect the X-rays diffracted by the second diffraction grating. By diffracting X-rays diffracted by the first diffraction grating, the second diffraction grating is capable of forming image contrast caused by changes in phase of X-rays due to the subject arranged in front of the front surface of the first diffraction grating or between the first diffraction grating and the second diffraction grating. The X-ray image detector is capable of detecting X-rays creating image contrast.
Owner:MOMOSE ATSUSHI
Optical device for directing x-rays having a plurality of optical crystals
InactiveUS7035374B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayHigh energy
Devices for improving the capturing and utilization of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, for example, x-rays, gamma rays, and neutrons, for use in physical, medical, and industrial analysis and control applications are disclosed. The devices include optics having a plurality of optical crystals, for example, doubly-curved silicon or germanium crystals, arranged to optimize the capture and redirection of divergent radiation via Bragg diffraction. In one aspect, a plurality of optic crystals having varying atomic diffraction plane orientations are used to capture and focus divergent x-rays upon a target. In another aspect, a two- or three-dimensional matrix of crystals is positioned relative to an x-ray source to capture and focus divergent x-rays in three dimensions.
Owner:X-RAY OPTICAL SYSTEM INC
Illumination system for a wavelength of less than or equal to 193 nm, with sensors for determining an illumination
ActiveUS20050274897A1Avoid disadvantagesUniform lightHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMaterial analysis by optical meansLength waveLighting system
There is provided an illumination system that includes (a) a light source that emits light having a wavelength ≦193 nm, where the light provides a predetermined illumination in a plane distant from the light source and defines a used area in the plane, and (b) a sensor, situated in or near the plane, for detecting light outside the used area.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Spectral purity filter, lithographic apparatus including such a spectral purity filter, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS20060146413A1High spectral purityHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhotomechanical apparatusLength waveLight filter
A spectral purity filter includes an aperture, the aperture having a diameter, wherein the spectral purity filter is configured to enhance the spectral purity of a radiation beam by reflecting radiation of a first wavelength and allowing at least a portion of radiation of a second wavelength to transmit through the aperture, the first wavelength being larger than the second wavelength. The spectral purity filter may be used to improve the spectral purity of an Extreme Ultra-Violet (EUV) radiation beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and device for cooling and electrically insulating a high-voltage, heat-generating component such as an x-ray tube for analyzing fluid streams
InactiveUS7110506B2Minimise currentCurrent lossElectrically conductive connectionsX-ray tube electrodesX-rayHigh pressure
Owner:S RAY OPTICAL SYST
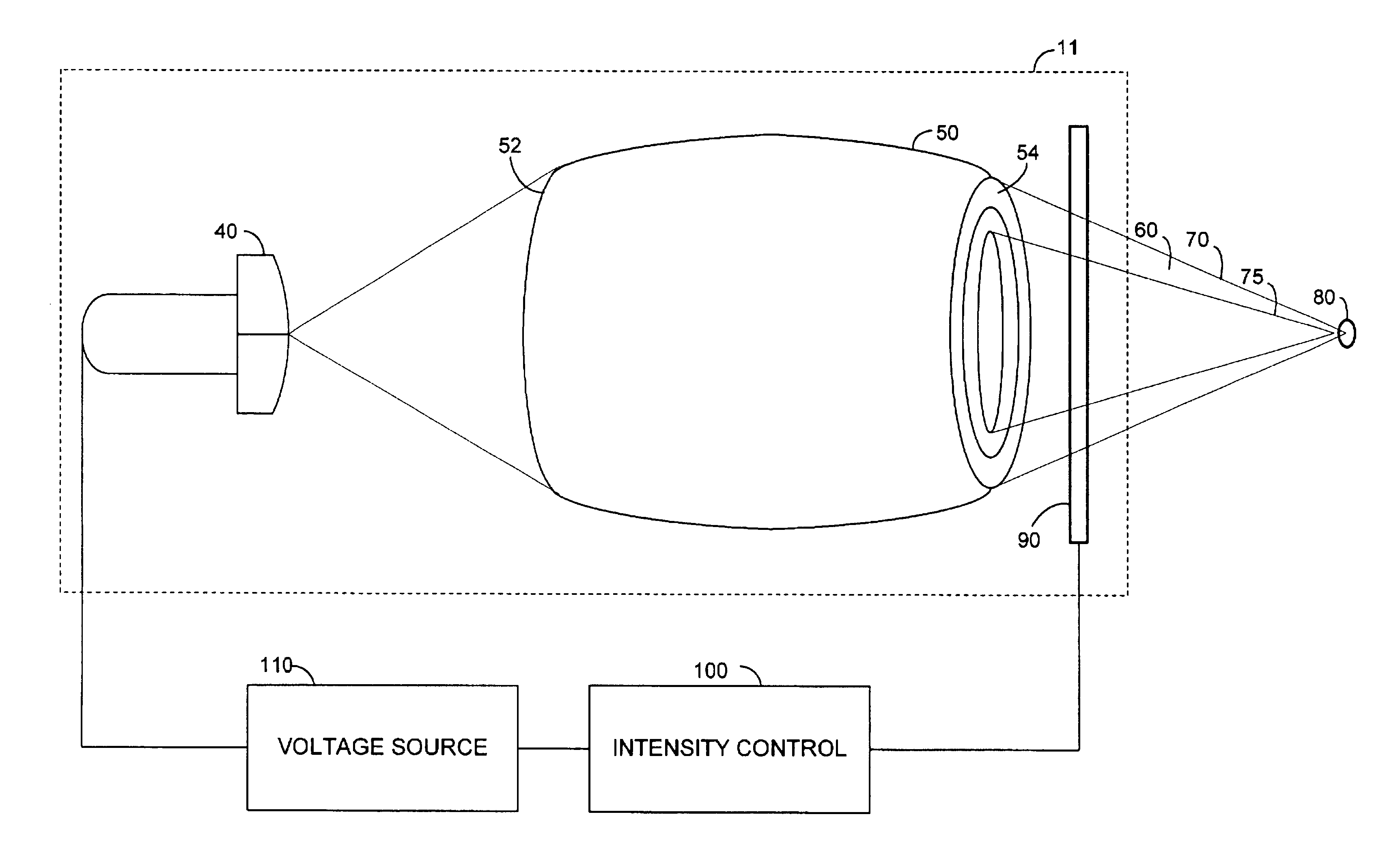
System providing multiple focused radiation beams
InactiveUS6853704B2Easy to adaptHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEngineeringVoltage source
A system includes a plurality of treatment heads, each of the plurality of treatment heads including a radiation source and a radiation-focusing lens. The system also includes a plurality of voltage sources, each of the plurality of voltage sources associated with a respective one of the plurality of treatment heads, and a control device to control an intensity of radiation emitted from each radiation-focusing lens of the plurality of treatment heads in accordance with a treatment plan.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Focus/detector system of an x-ray apparatus for generating phase contrast recordings
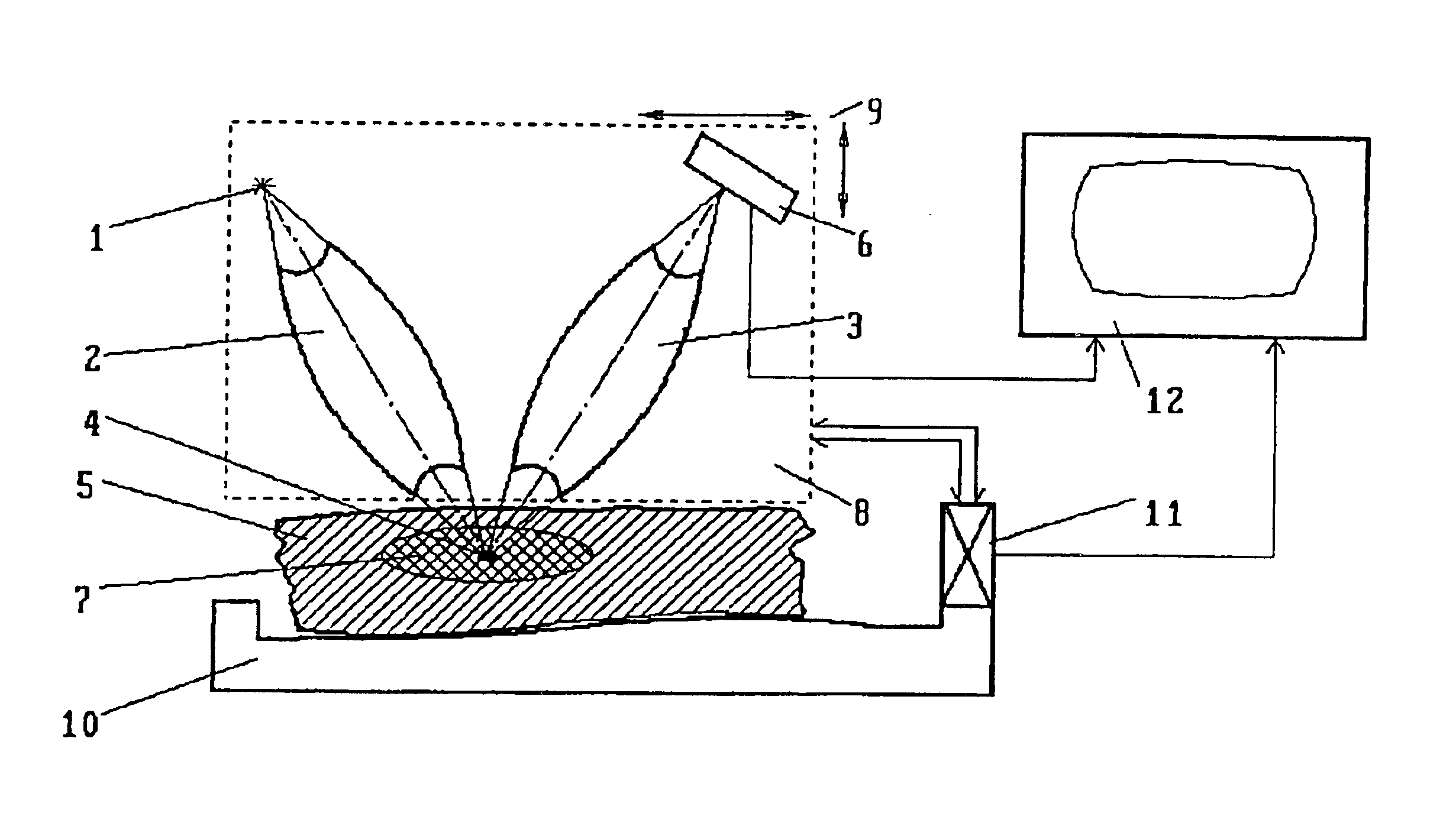
InactiveUS7492871B2Improve stabilitySimple structureImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhase gratingBeam source
A focus / detector system of an X-ray apparatus and a method for generating projective or tomographic phase contrast recordings, are disclosed. In an embodiment of the system, the system includes a beam source equipped with a focus and a focus-side source grating, arranged in the beam path and generates a field of ray-wise coherent X-rays, a grating / detector arrangement having a phase grating and grating lines arranged parallel to the source grating for generating an interference pattern, and a detector having a multiplicity of detector elements arranged flat for measuring the position-dependent radiation intensity behind the phase grating. Finally, the detector elements are formed by a multiplicity of elongate scintillation strips, which are aligned parallel to the grating lines of the phase grating and have a small period, whose integer multiple corresponds to the average large period of the interference pattern which is formed by the phase grating.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
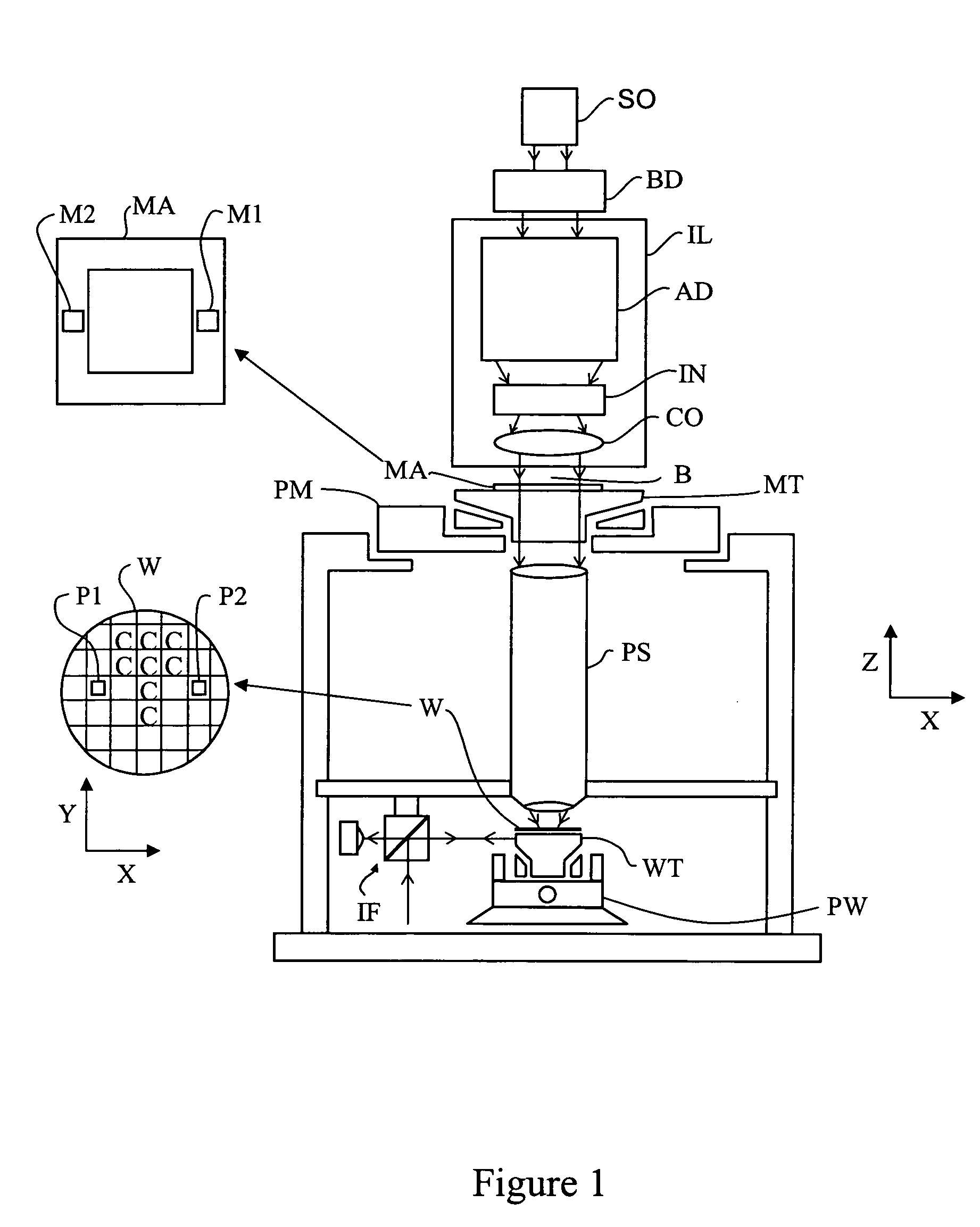
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20040165160A1Reduce component countMinimizes cost of apparatusHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight beamEngineering
A lithographic projection apparatus is disclosed. The apparatus includes a support structure constructed to support a patterning structure. The patterning structure is adapted to pattern a beam of radiation according to a desired pattern. The apparatus also includes a substrate holder that is constructed to hold a substrate, a projection system that is constructed and arranged to project the patterned beam onto a target portion of the substrate, and a downstream radical source that is connected to a gas supply and is configured to provide a beam of radicals onto a surface to be cleaned.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Gridless time-of-flight mass spectrometer for orthogonal ion injection
InactiveUS20010011703A1Reduce voltageFacilitates taskMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTime-of-flight spectrometersFlight directionFlat detector
The invention relates to a time-of-flight mass spectrometer for injection of the ions orthogonally to the time-resolving axis-of-flight component, with a pulser for acceleration of the ions of the beam in the axis-of-flight direction, preferredly with a velocity-focusing reflector for reflecting the ion beam and with a flat detector at the end of the flight section. The invention consists of using, both for acceleration in the pulser and for reflection in the reflectors, a gridless optical system made up of slit diaphragms which can spatially focus the ions onto the detector in the direction vertical to the directions of injection and flight axis, but which does not have any focusing or deflecting effect on the other directions. For some reflector geometries it is essential to use an additional cylindrical lens for focusing, and for other reflector geometries the use of such a lens may be advantageous.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
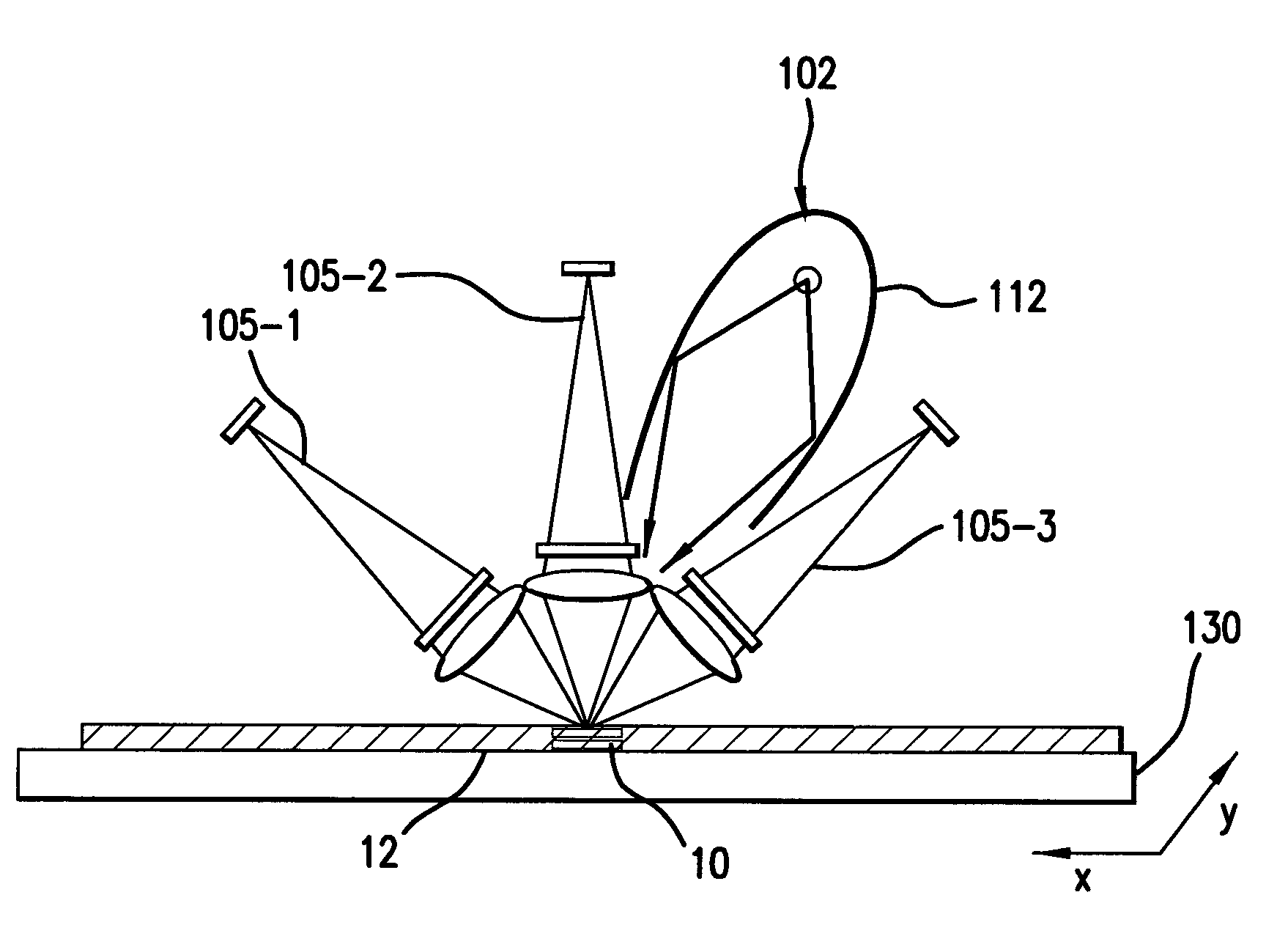
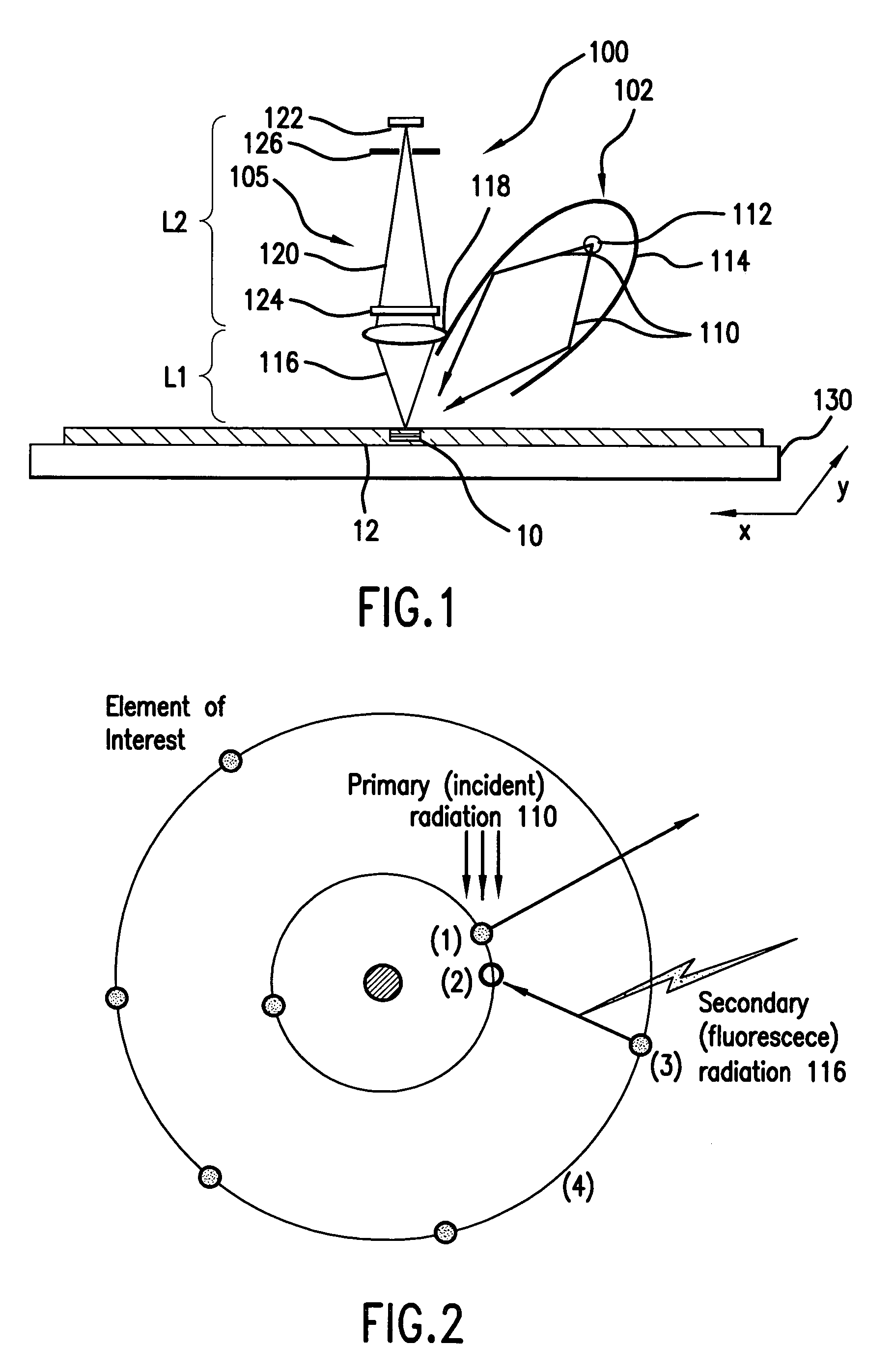
Element-specific X-ray fluorescence microscope and method of operation
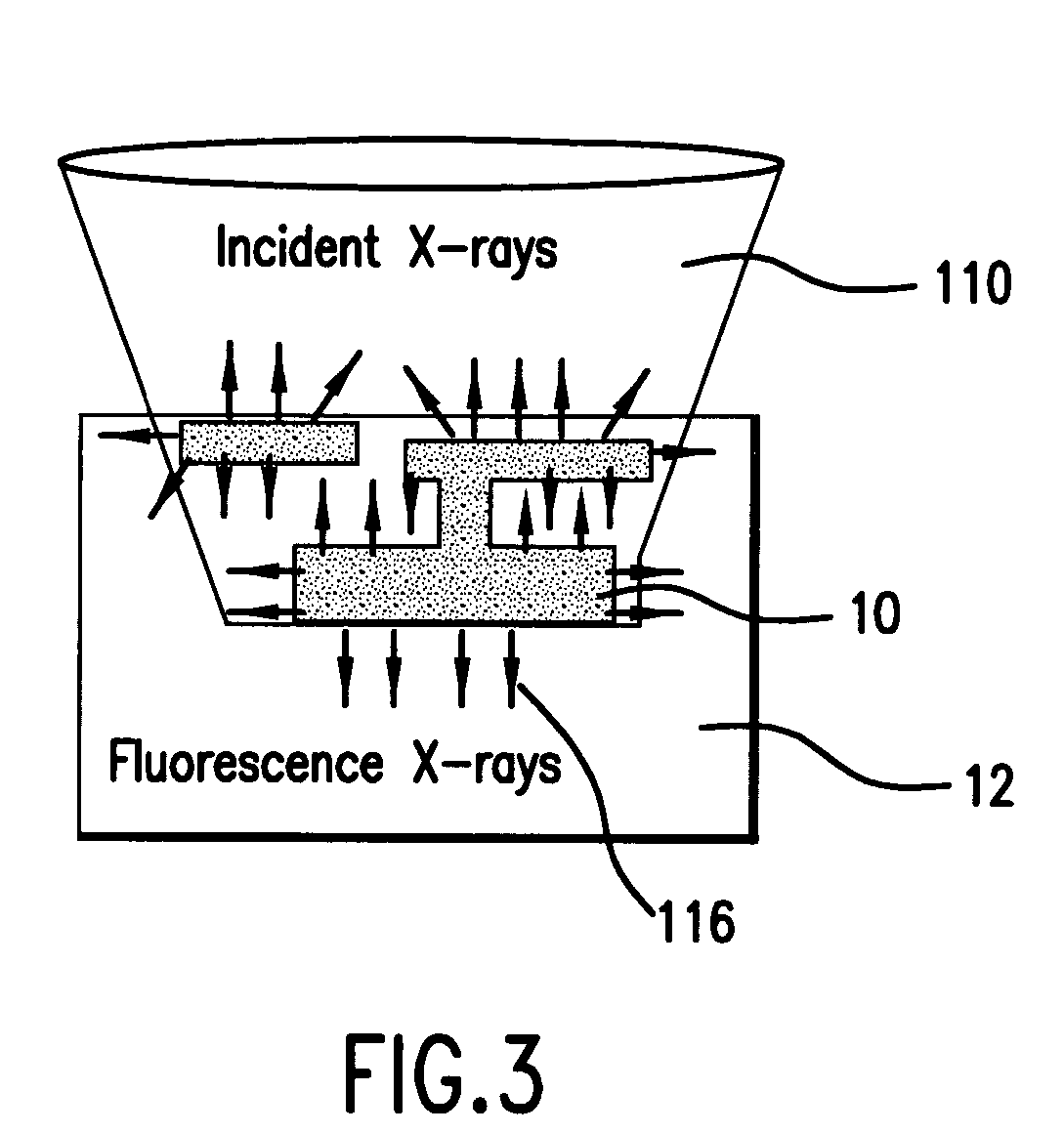
InactiveUS7183547B2Enhances preferential imagingEnhance the imageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesConfocalPeak value
An element-specific imaging technique utilizes the element-specific fluorescence X-rays that are induced by primary ionizing radiation. The fluorescence X-rays from an element of interest are then preferentially imaged onto a detector using an optical train. The preferential imaging of the optical train is achieved using a chromatic lens in a suitably configured imaging system. A zone plate is an example of such a chromatic lens; its focal length is inversely proportional to the X-ray wavelength. Enhancement of preferential imaging of a given element in the test sample can be obtained if the zone plate lens itself is made of a compound containing substantially the same element. For example, when imaging copper using the Cu La spectral line, a copper zone plate lens is used. This enhances the preferential imaging of the zone plate lens because its diffraction efficiency (percent of incident energy diffracted into the focus) changes rapidly near an absorption line and can be made to peak at the X-ray fluorescence line of the element from which it is fabricated. In another embodiment, a spectral filter, such as a multilayer optic or crystal, is used in the optical train to achieve preferential imaging in a fluorescence microscope employing either a chromatic or an achromatic lens.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Optimized x-ray energy for high resolution imaging of integrated circuits structures
ActiveUS7394890B1Increase contrastImprove throughputImaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementHigh resolution imagingX-ray
An x-ray imaging system uses particular emission lines that are optimized for imaging specific metallic structures in a semiconductor integrated circuit structures and optimized for the use with specific optical elements and scintillator materials. Such a system is distinguished from currently-existing x-ray imaging systems that primarily use the integral of all emission lines and the broad Bremstralung radiation. The disclosed system provides favorable imaging characteristics such as ability to enhance the contrast of certain materials in a sample, to use different contrast mechanisms in a single imaging system, and to increase the throughput of the system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Illumination optical system, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060175556A1Handling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhotomechanical apparatusPhysicsLight source
An illumination optical system for illuminating a target plane by using light from a light source includes plural displaceable mirrors that are two-dimensionally arranged at specific positions in said illumination optical system.
Owner:CANON KK
EUV light source optical elements
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for forming plasma generated EUV light source optical elements, e.g., reflectors comprising MLM stacks employing various binary layer materials and capping layer(s) including single and binary capping layers for utilization in plasma generated EUV light source chambers, particularly where the plasma source material is reactive with one or more of the MLM materials.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
X-ray interferometric imaging system
ActiveUS20150243397A1Increase brightnessLarge x-ray powerImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhysicsSoft x ray
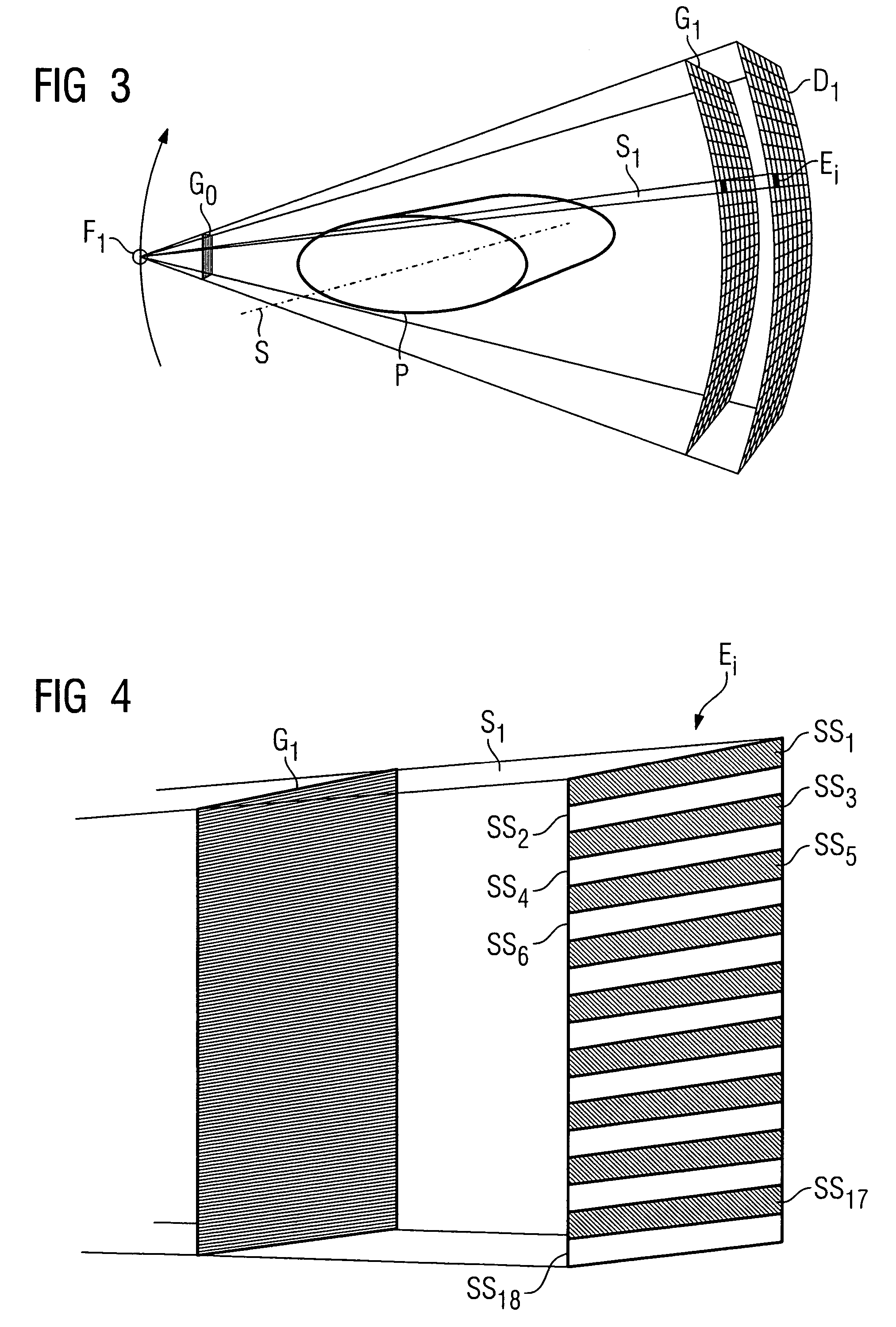
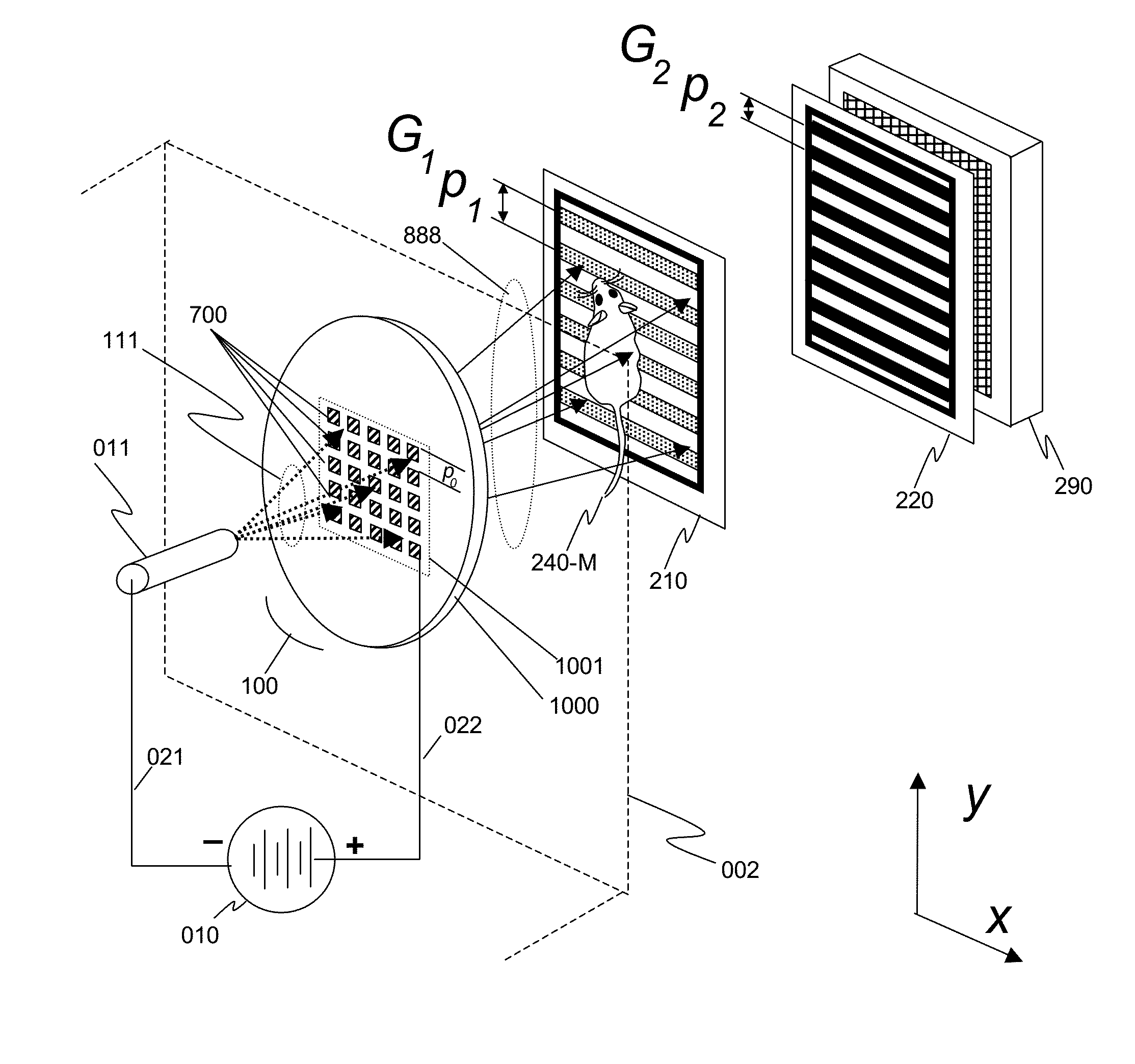
An x-ray interferometric imaging system in which the x-ray source comprises a target having a plurality of structured coherent sub-sources of x-rays embedded in a thermally conducting substrate. The system additionally comprises a beam-splitting grating G1 that establishes a Talbot interference pattern, which may be a π phase-shifting grating, and an x-ray detector to convert two-dimensional x-ray intensities into electronic signals. The system may also comprise a second analyzer grating G2 that may be placed in front of the detector to form additional interference fringes, a means to translate the second grating G2 relative to the detector. The system may additionally comprise an antiscattering grid to reduce signals from scattered x-rays. Various configurations of dark-field and bright-field detectors are also disclosed.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS8855265B2Reduce impactImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Diffraction grating and alignment method thereof, and radiation imaging system
InactiveUS20110243300A1Improve image qualityEasy to adjustImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionRadiation imagingX-ray
An X-ray imaging system includes first to third absorption gratings. Initially, the third absorption grating is disposed in a Z axis orthogonal to a detection surface of a FPD, and the position of the third absorption grating is adjusted in θx and θy directions based on a dose of X-rays having passed through the third absorption grating. Then, the first absorption grating is disposed in the Z axis so as to produce a moiré pattern. The position of the first absorption grating is adjusted in the θx and θy directions so that a frequency of the moiré pattern detected by the FPD becomes uniform. Then, the position of the first absorption grating is adjusted in a Z or θz direction so that the FPD loses the detection of the moiré pattern. After that, the second absorption grating is aligned in a like manner as the first absorption grating.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120099702A1Good estimateImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com