Patents
Literature
161 results about "Spectral purity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spectral purity is a term used in both optics and signal processing. In optics, it refers to the quantification of the monochromaticity of a given light sample. This is a particularly important parameter in areas like laser operation and time measurement. Spectral purity is easier to achieve in devices that generate visible and ultraviolet light, since higher frequency light results in greater spectral purity.
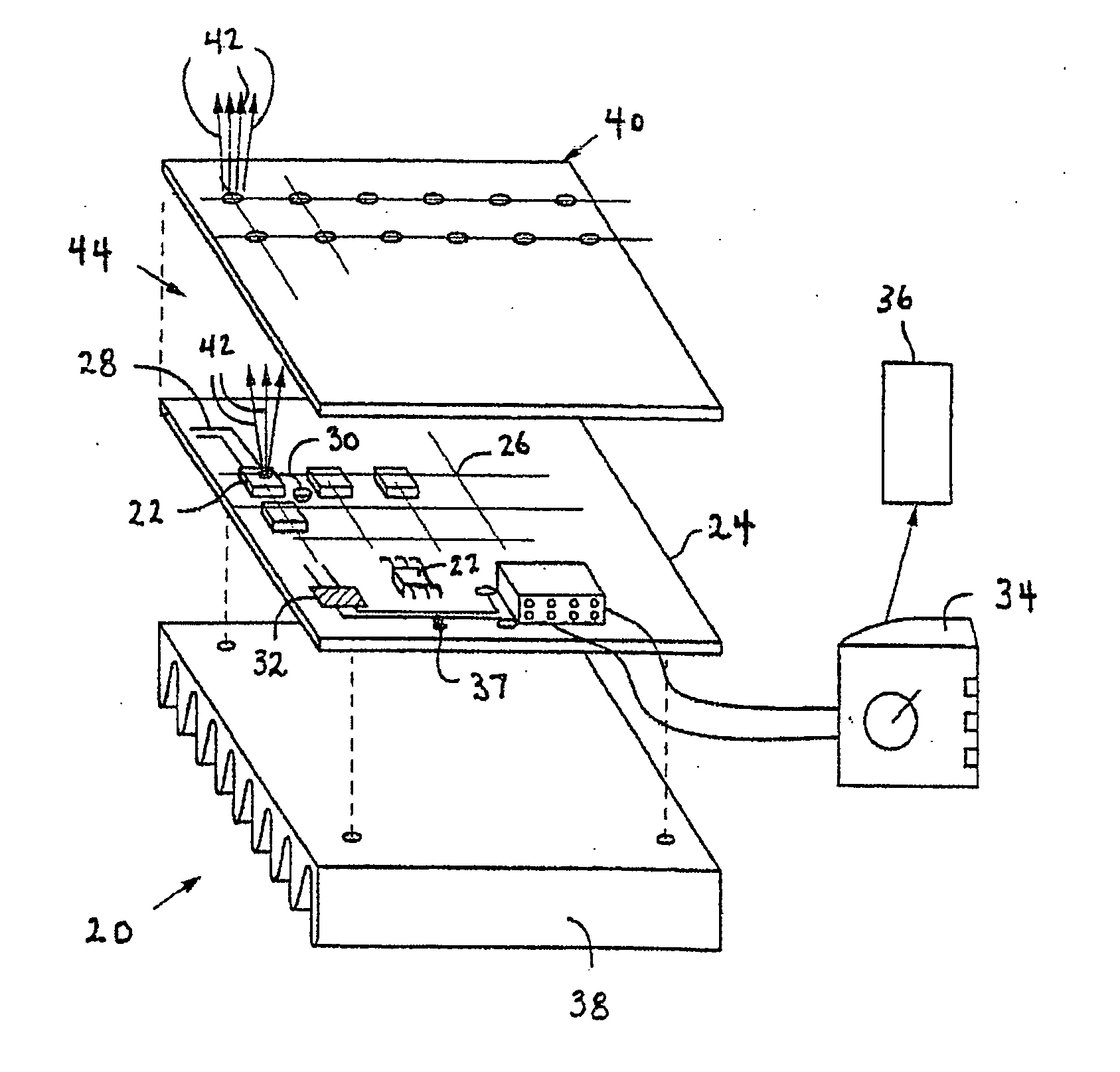
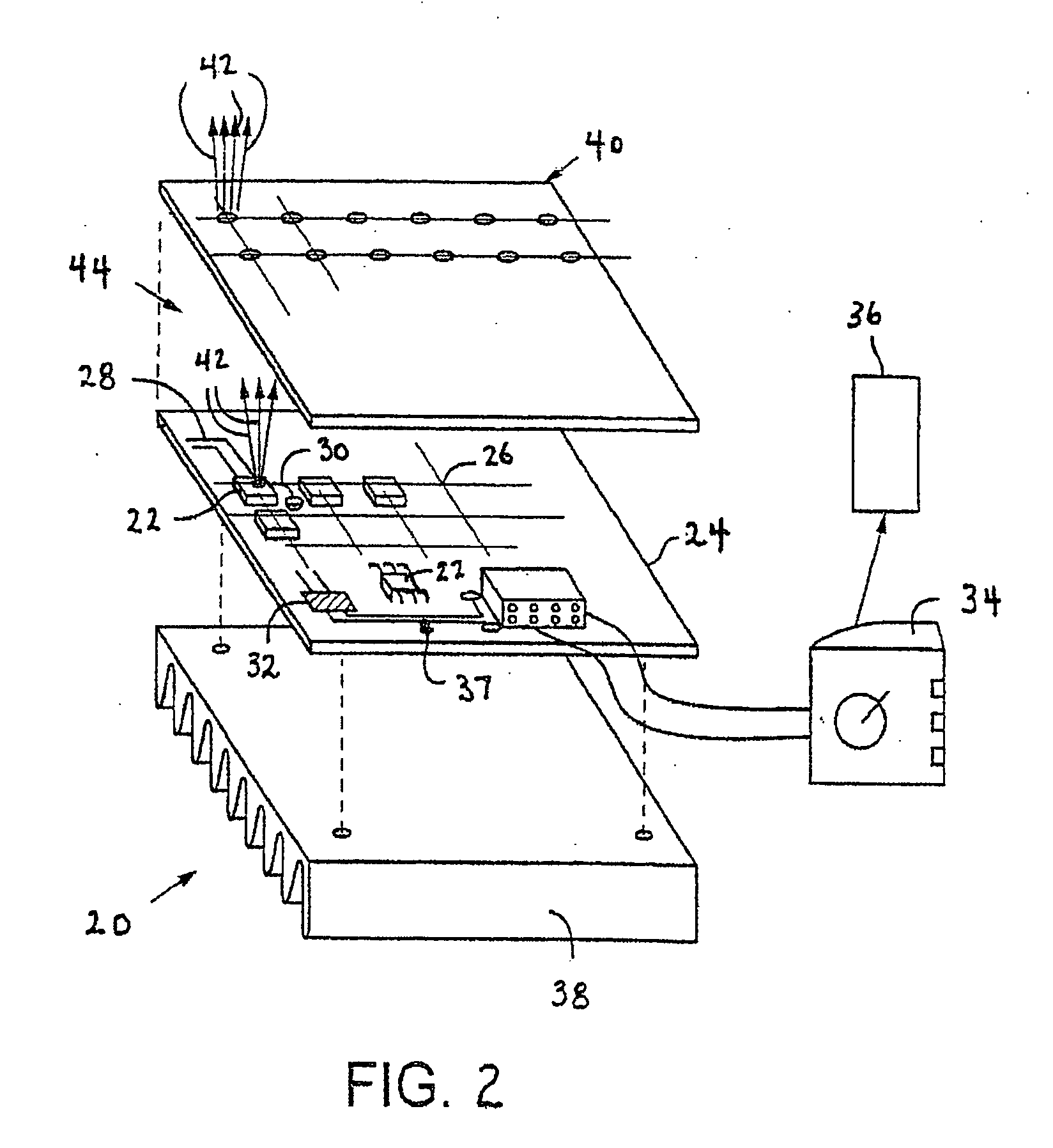
High efficiency solid-state light source and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS20050152146A1Eliminate needImprove light outputOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceDevice materialFluorescence
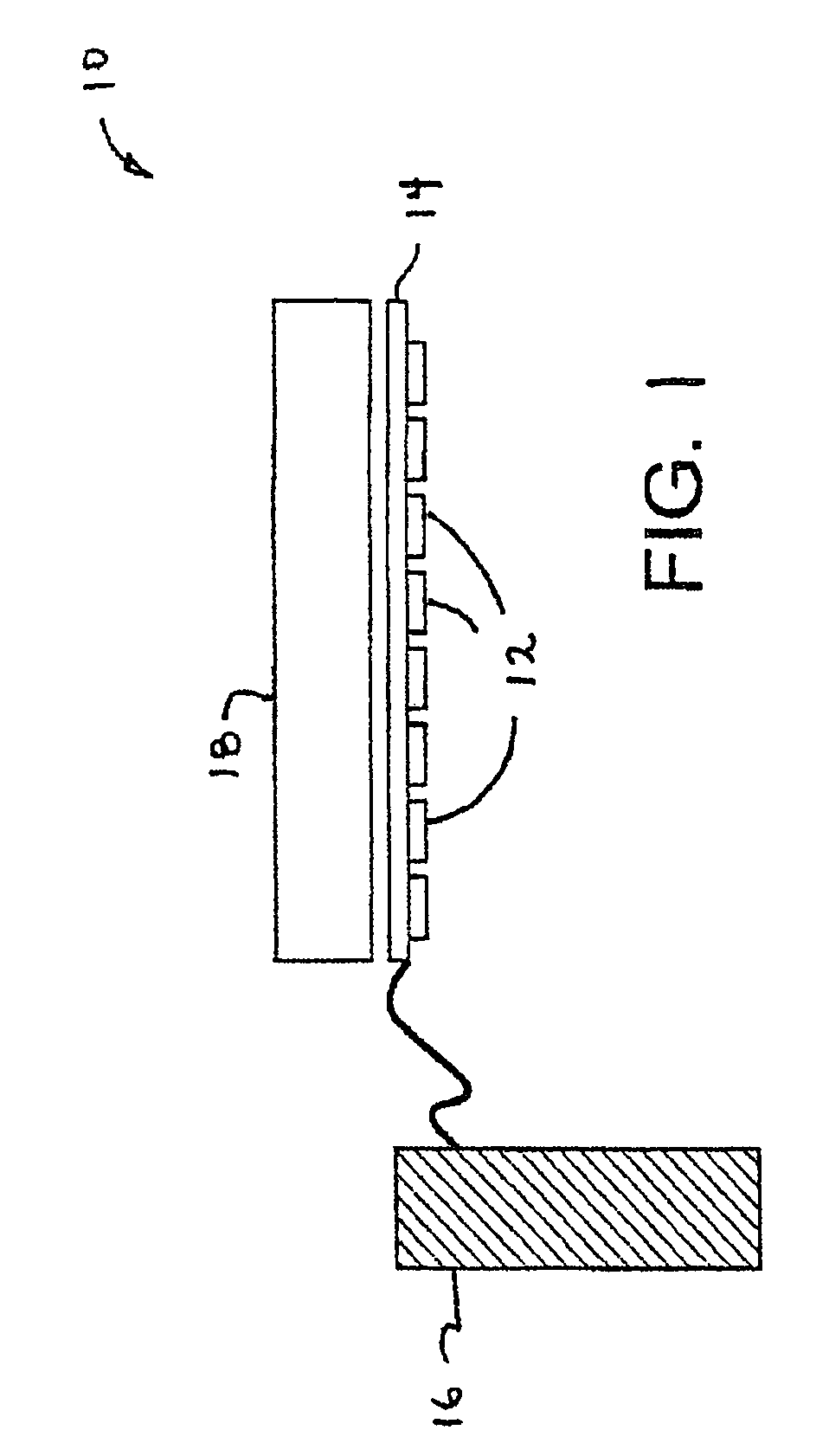
A high-intensity light source is formed by a micro array of a semiconductor light source such as a LEDs, laser diodes, or VCSEL placed densely on a liquid or gas cooled thermally conductive substrate. The semiconductor devices are typically attached by a joining process to electrically conductive patterns on the substrate, and driven by a microprocessor controlled power supply. An optic element is placed over the micro array to achieve improved directionality, intensity, and / or spectral purity of the output beam. The light module may be used for such processes as, for example, fluorescence, inspection and measurement, photopolymerzation, ionization, sterilization, debris removal, and other photochemical processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
High efficiency solid-state light source and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS8192053B2Improve efficiencyIncrease powerOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceHigh intensity light
A high-intensity light source is formed by a micro array of a semiconductor light source such as a LEDs, laser diodes, or VCSEL placed densely on a liquid or gas cooled thermally conductive substrate. The semiconductor devices are typically attached by a joining process to electrically conductive patterns on the substrate, and driven by a microprocessor controlled power supply. An optic element is placed over the micro array to achieve improved directionality, intensity, and / or spectral purity of the output beam. The light module may be used for such processes as, for example, fluorescence, inspection and measurement, photopolymerzation, ionization, sterilization, debris removal, and other photochemical processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
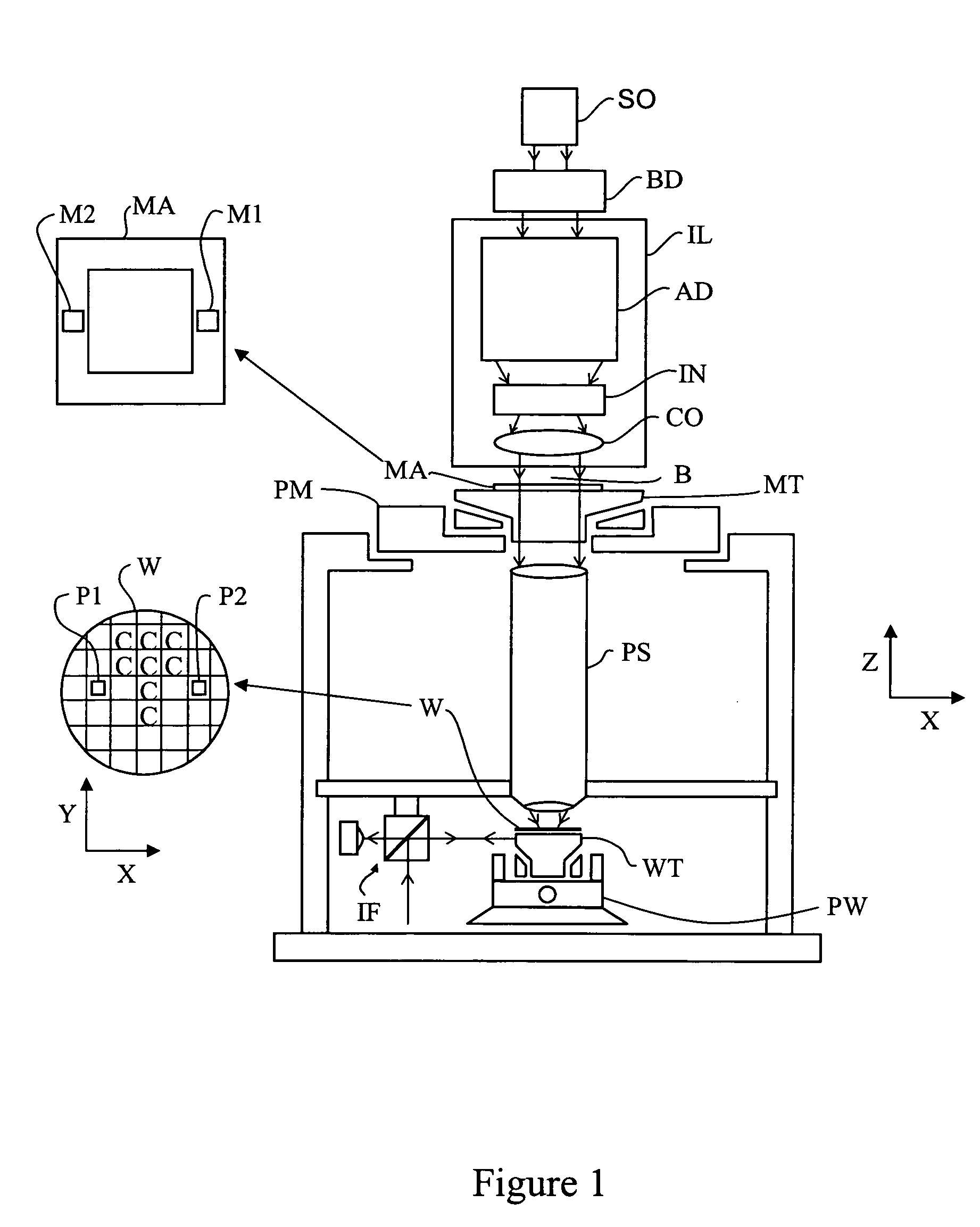
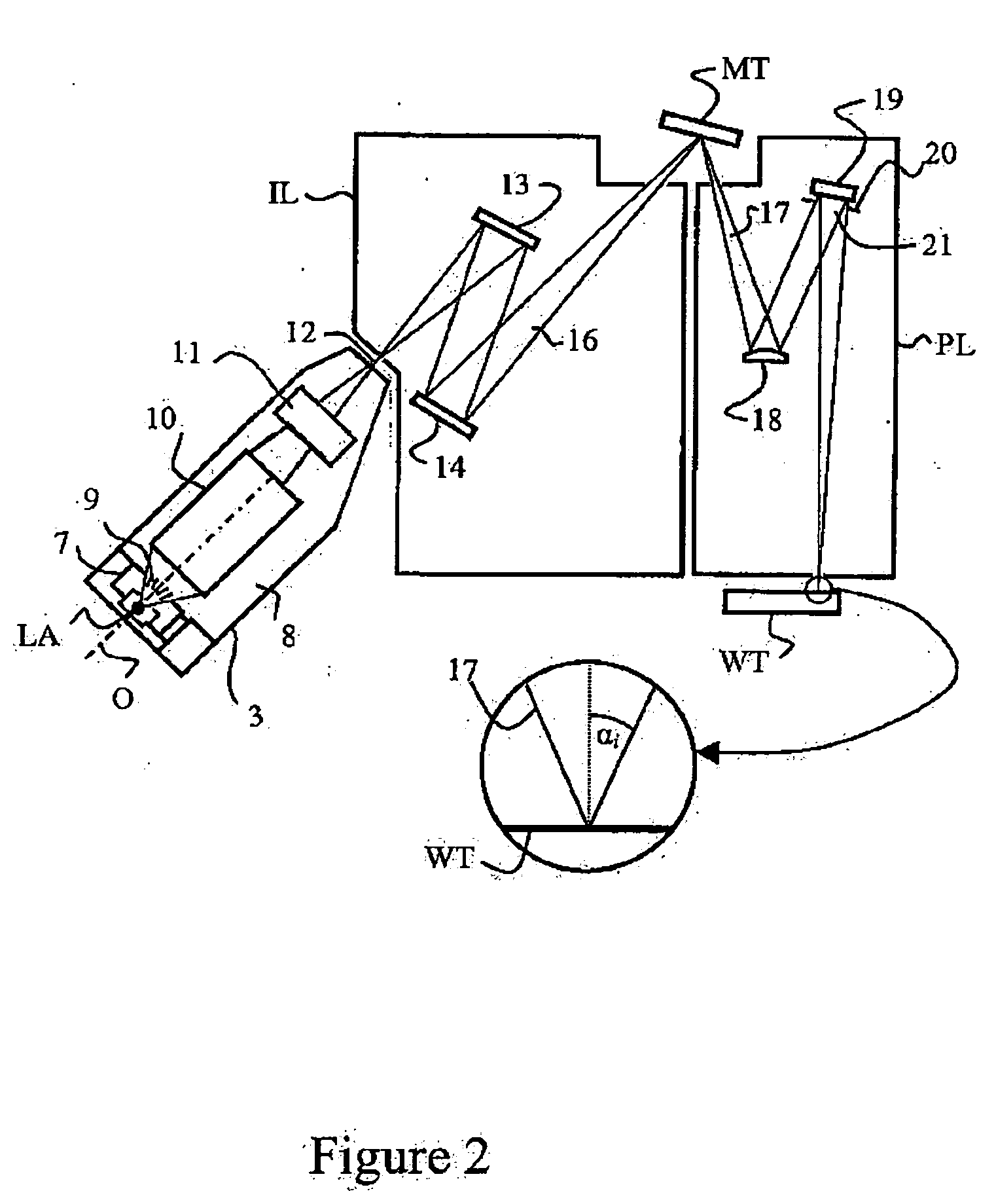
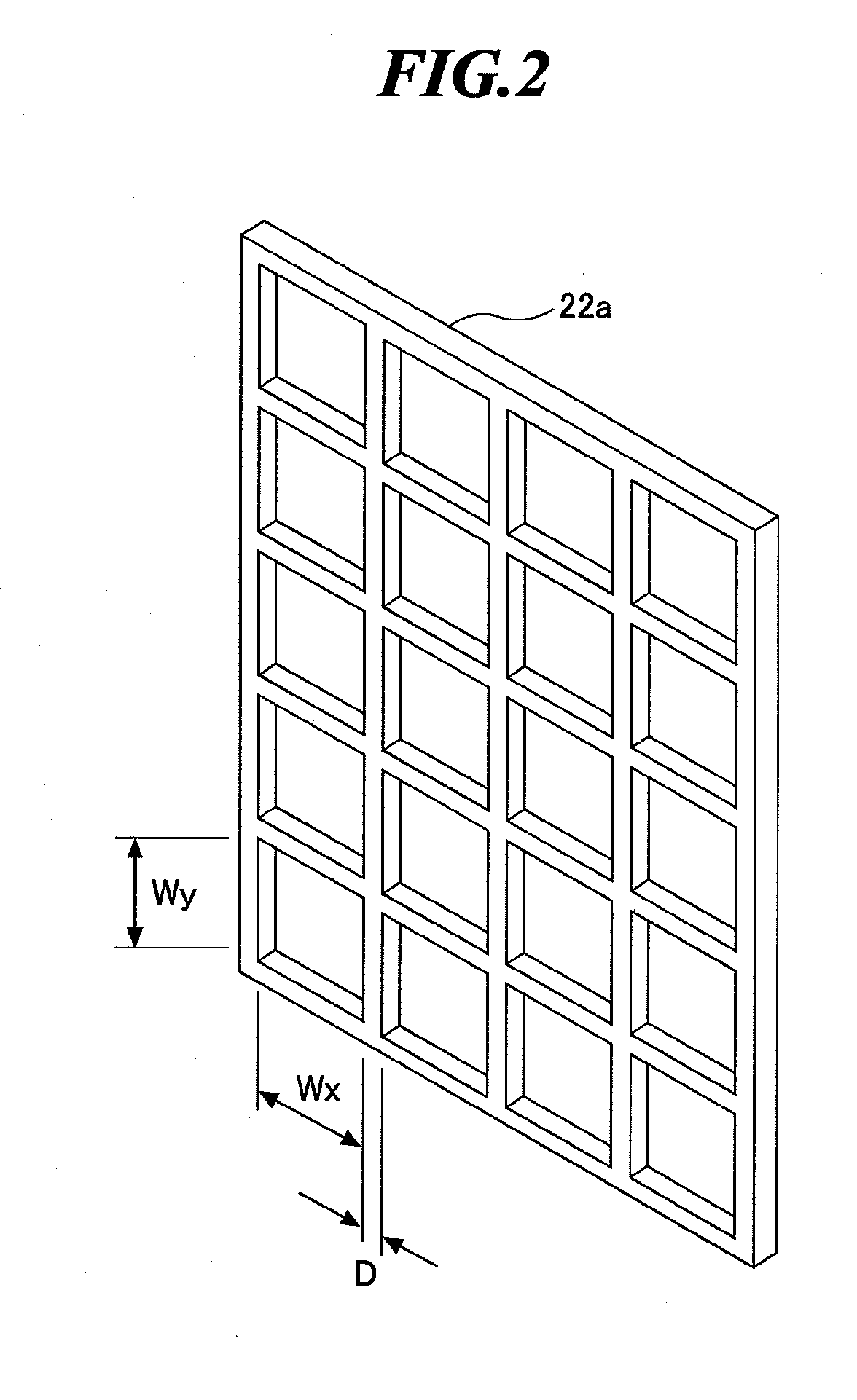
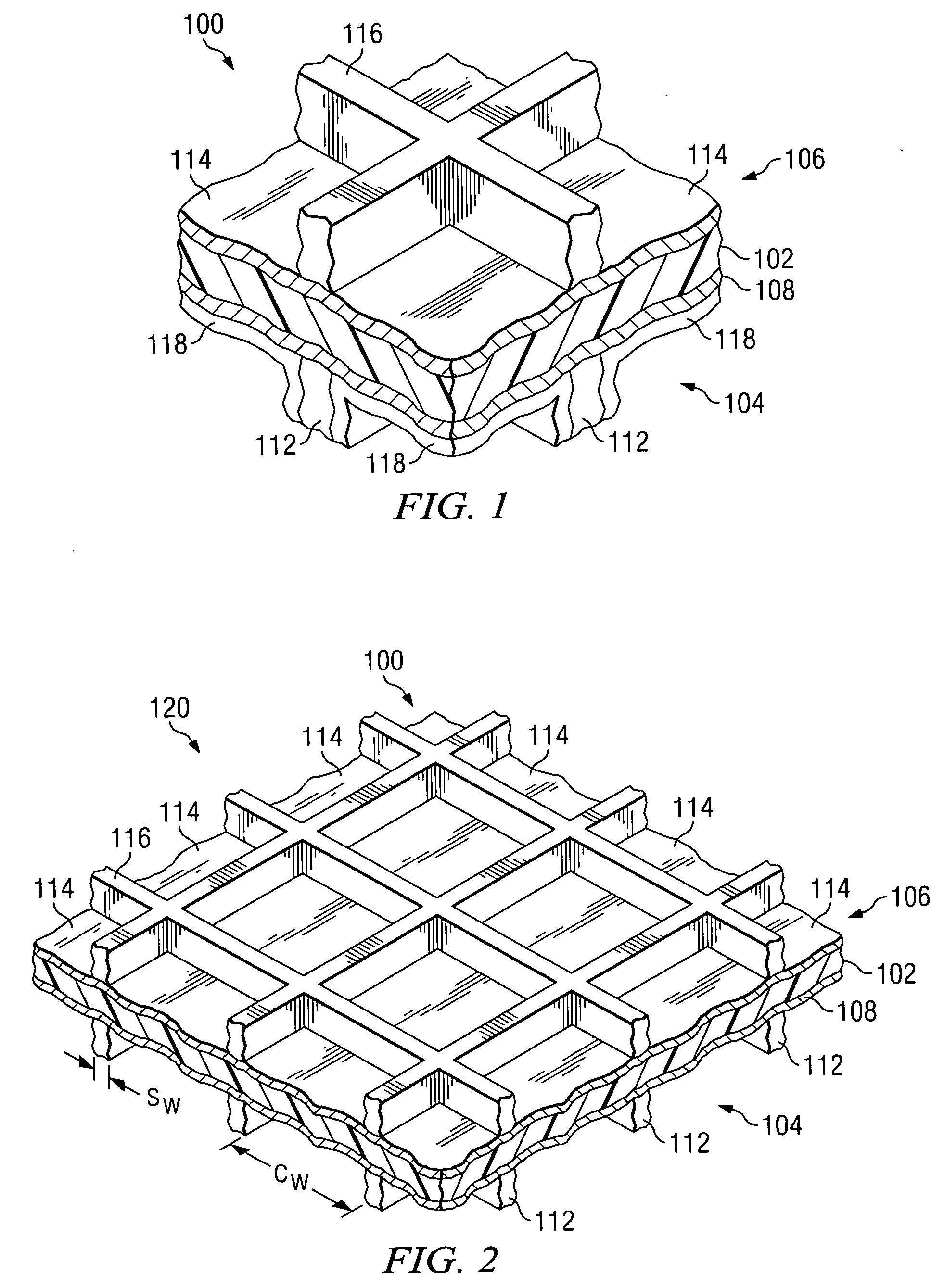
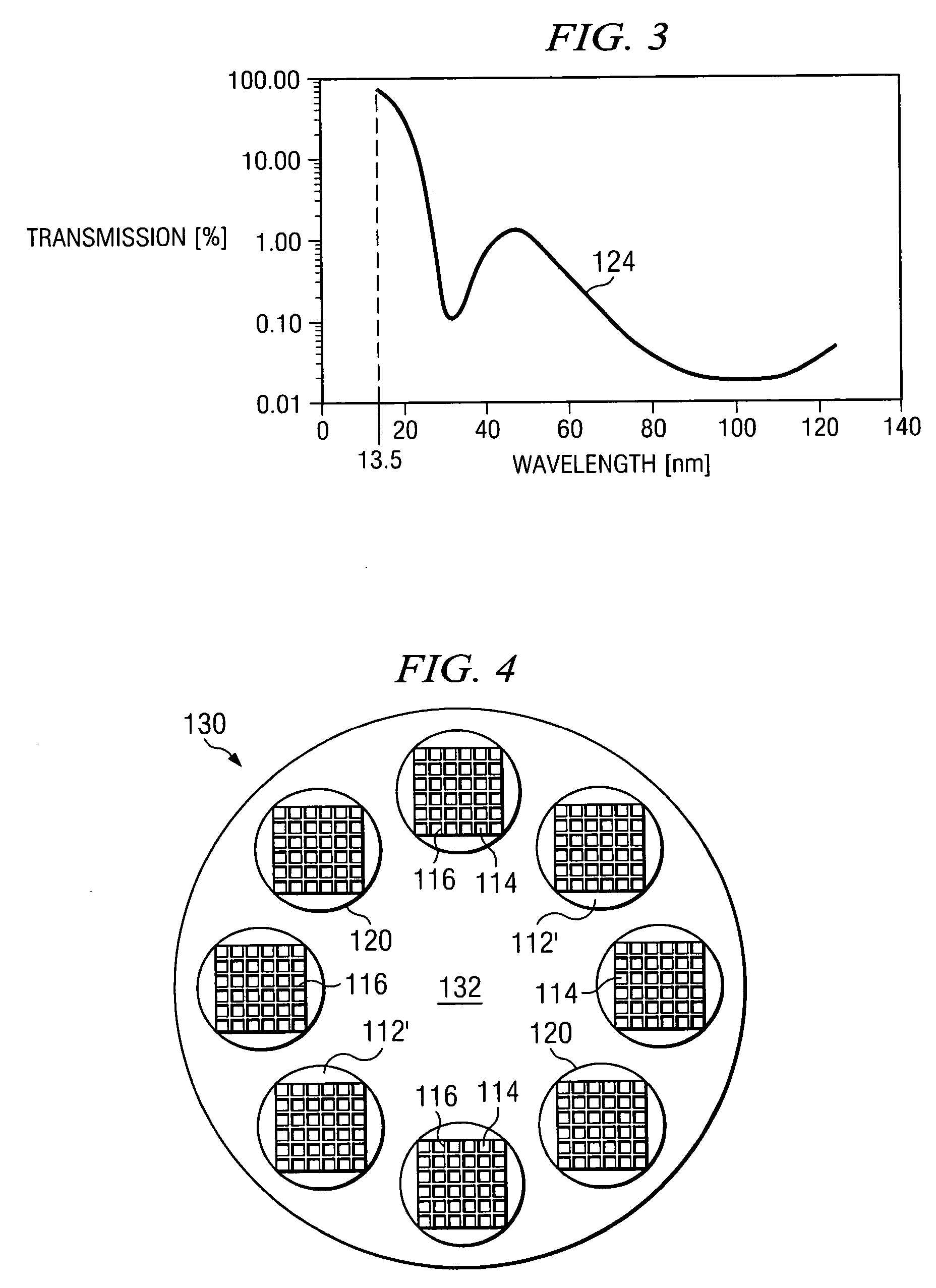
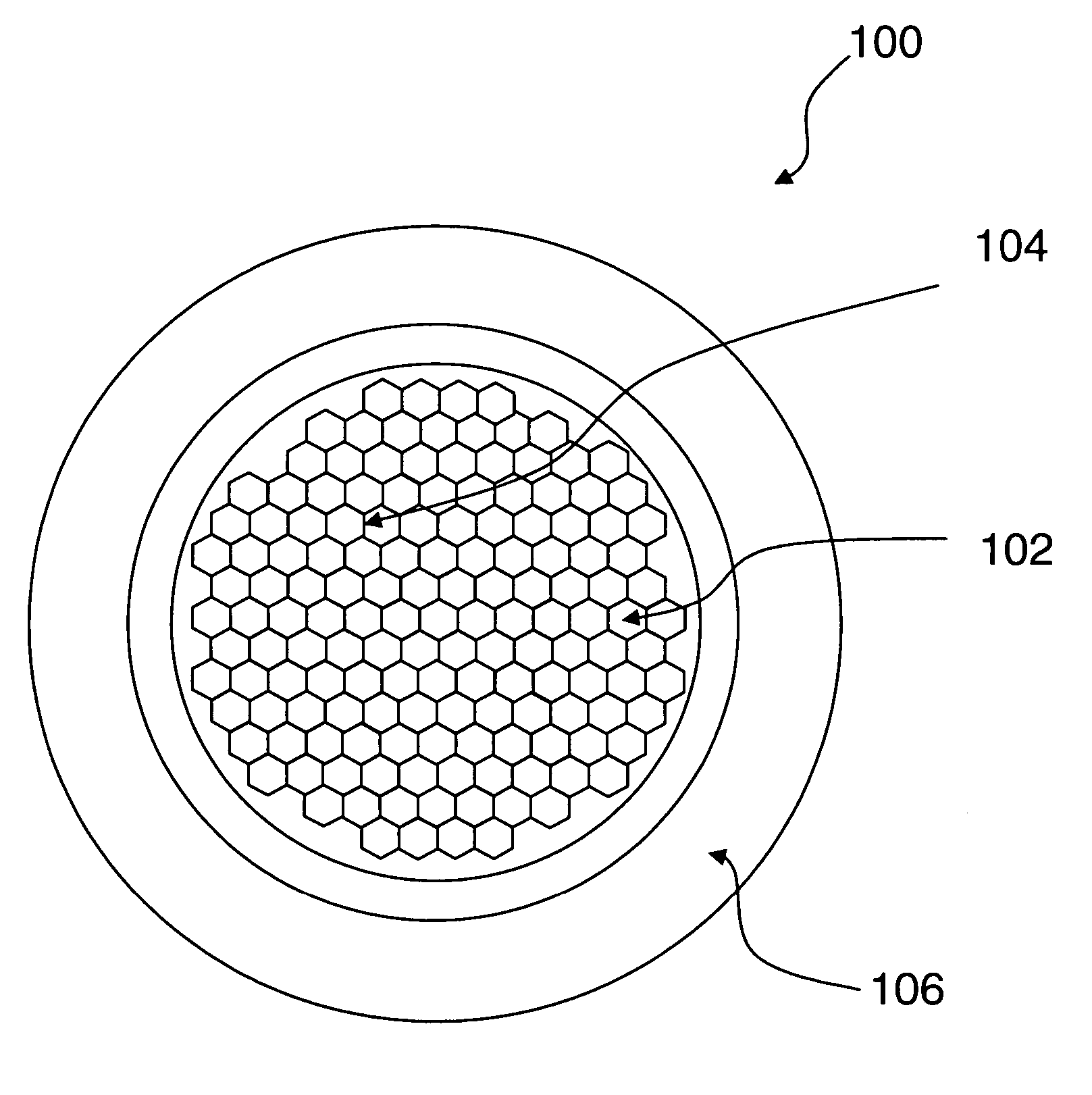
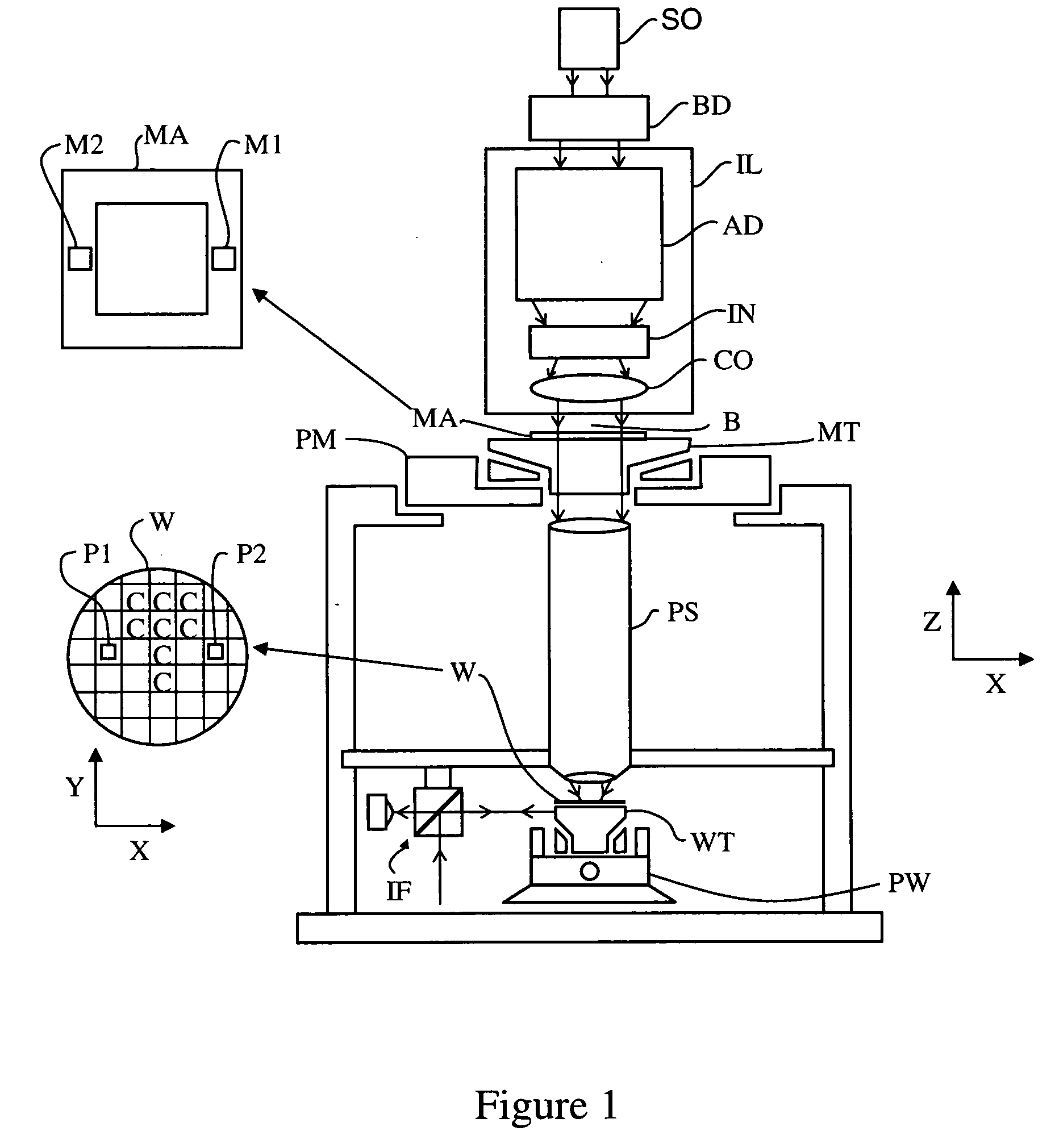
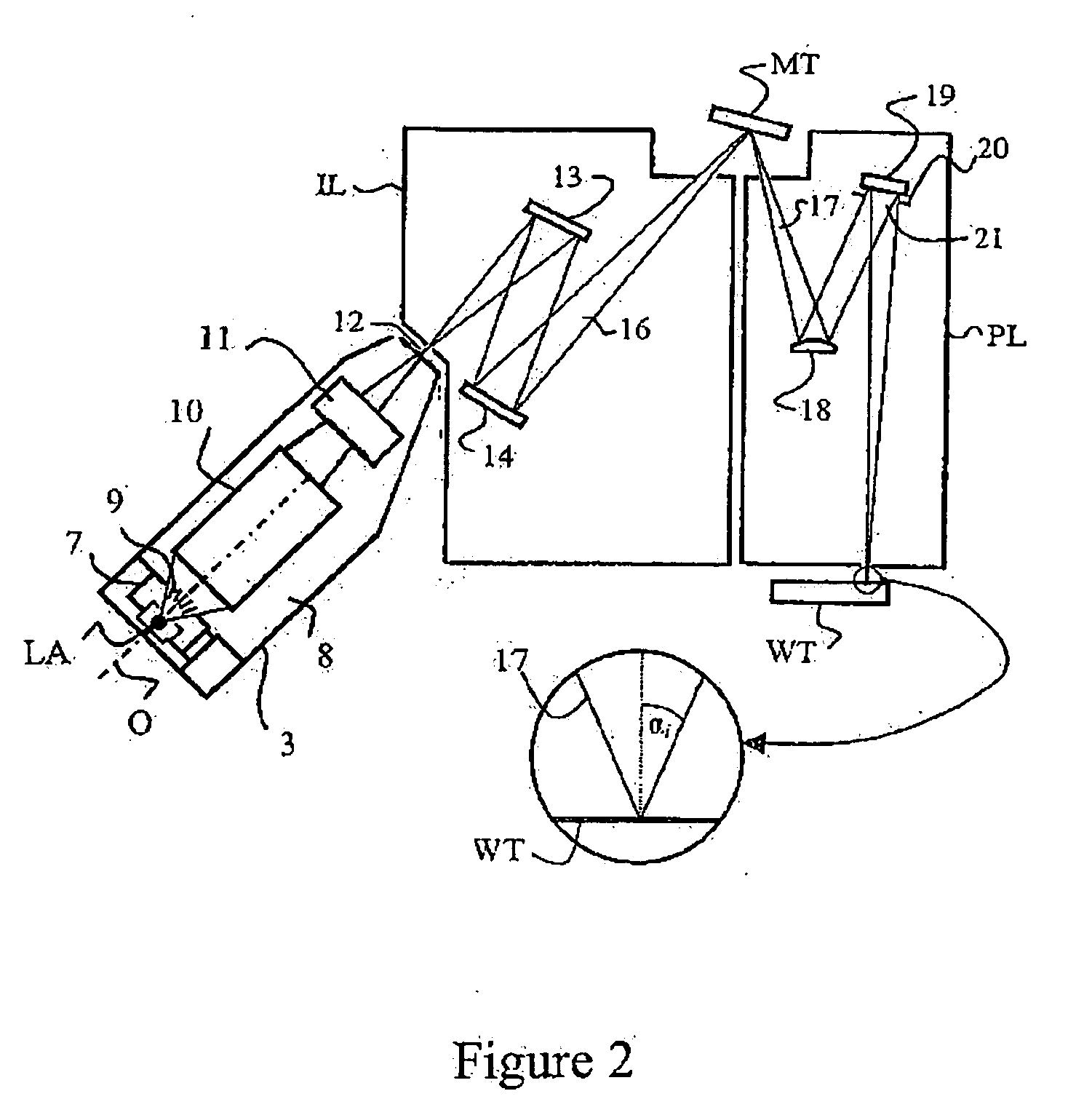
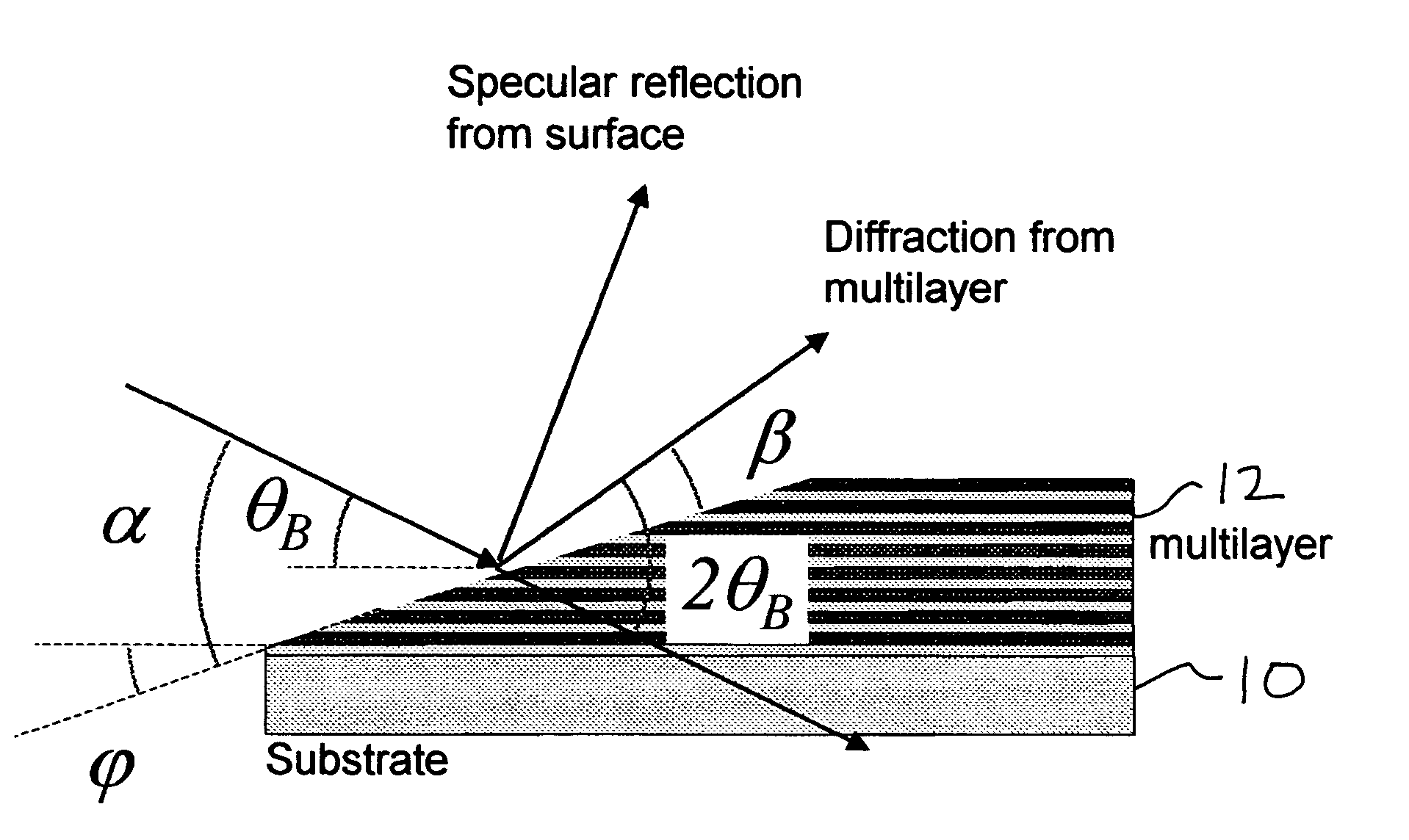
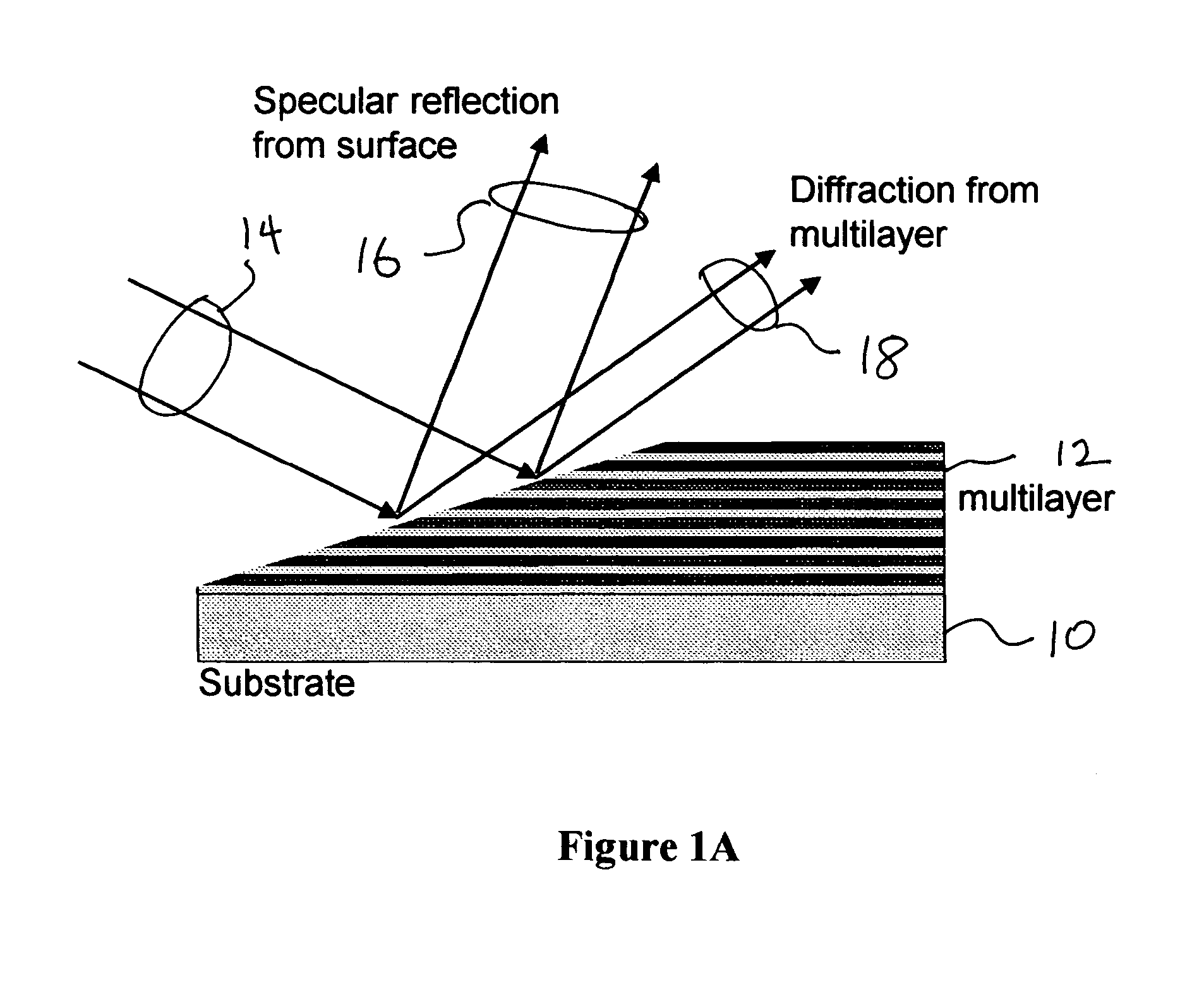
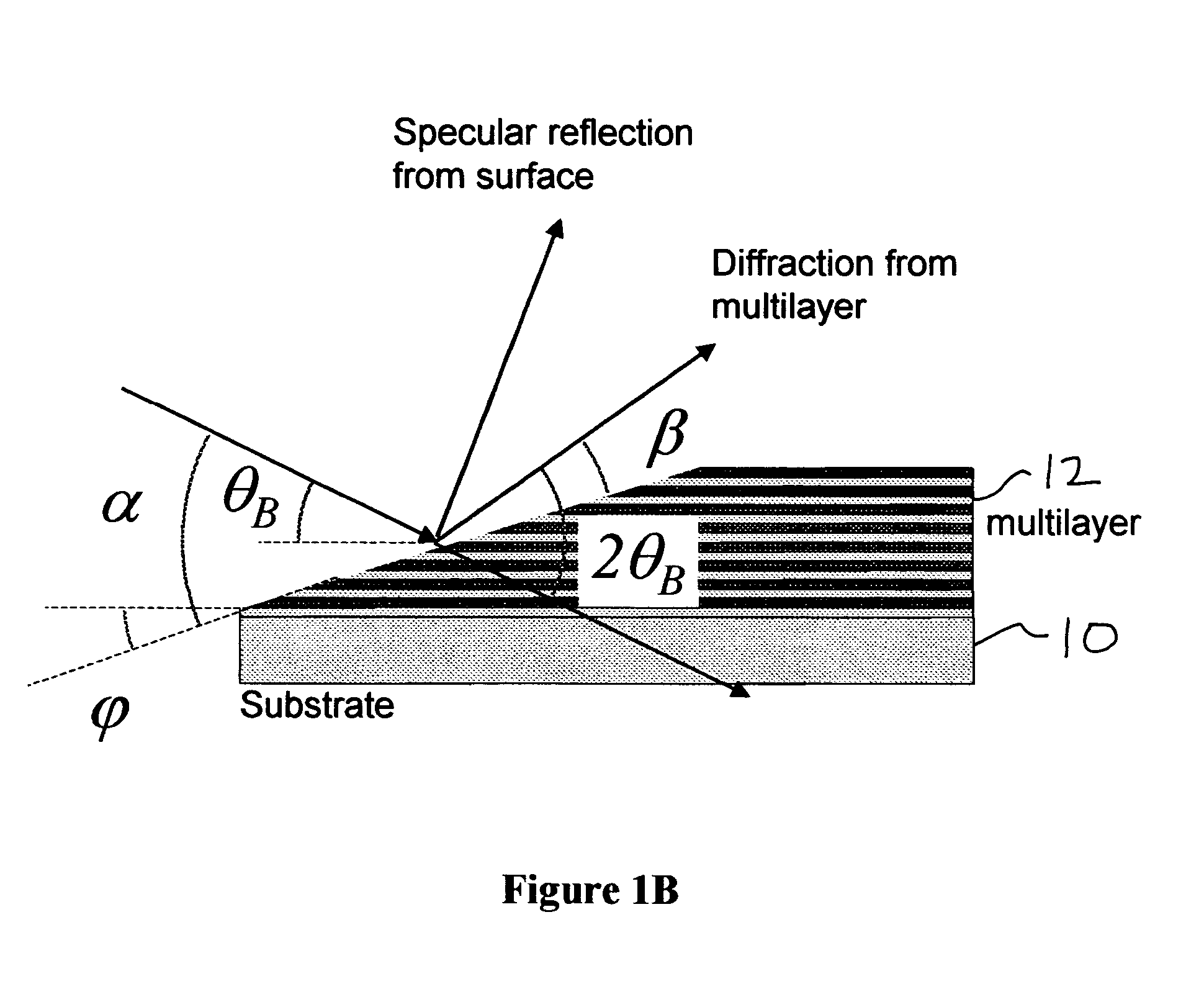
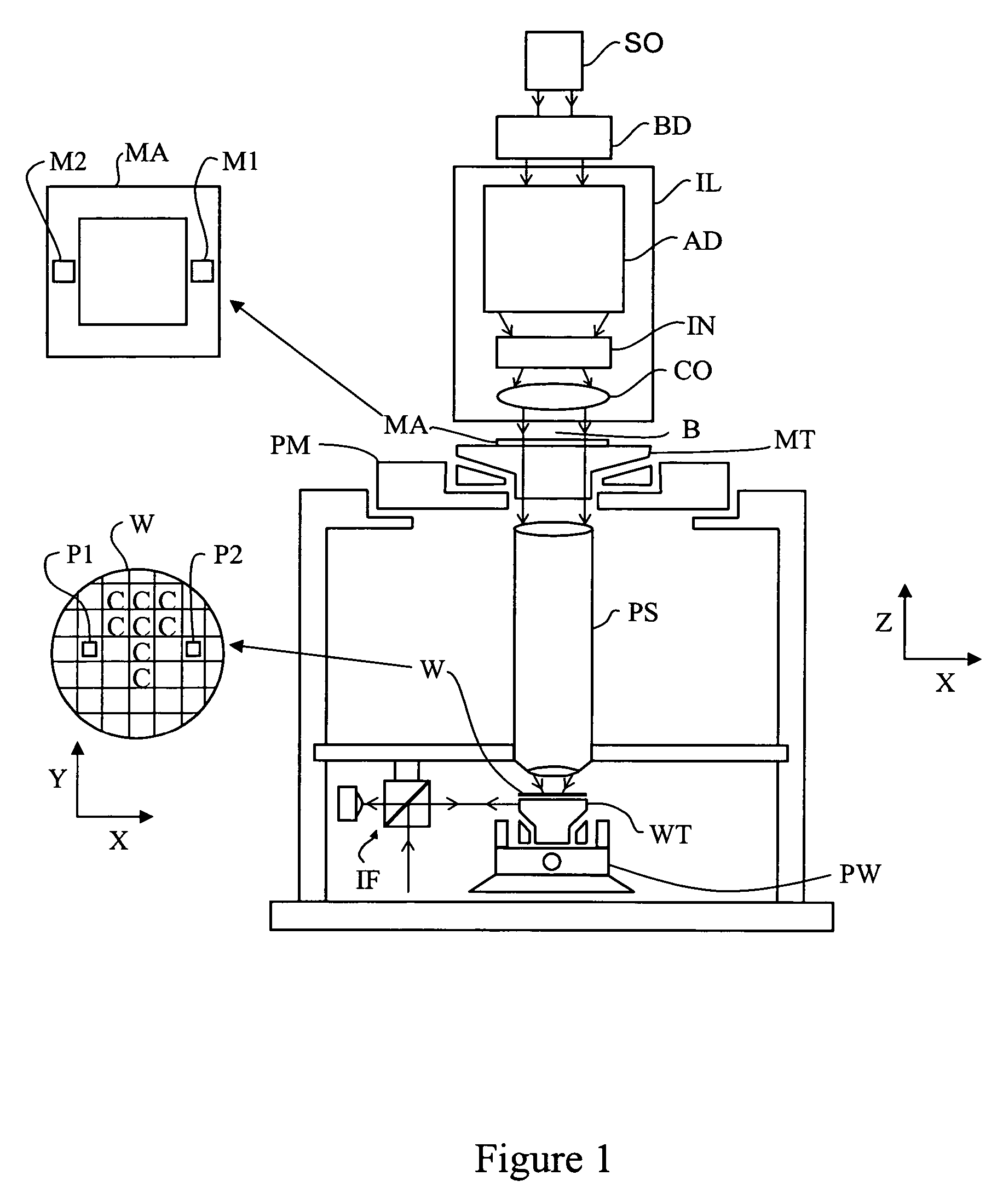
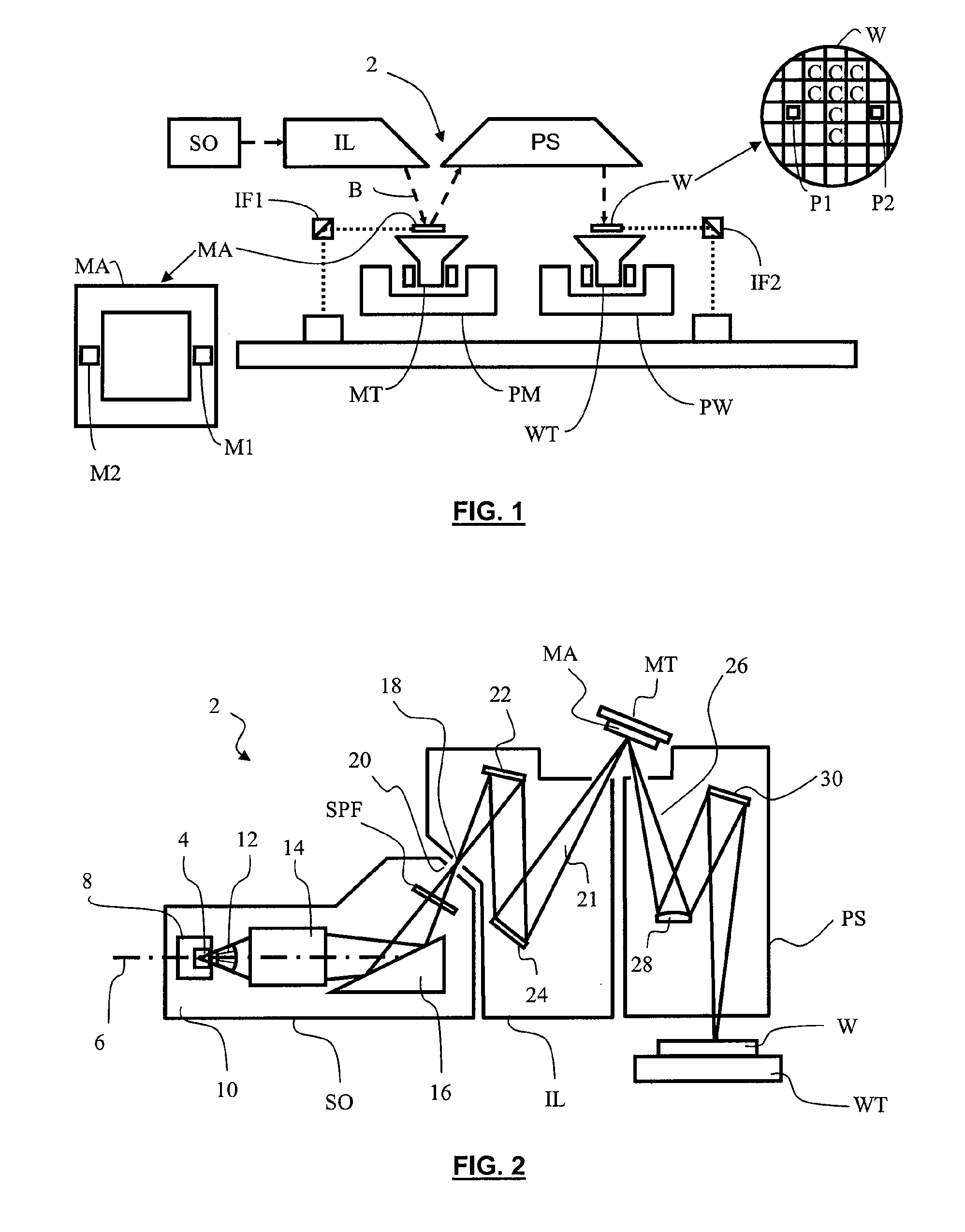
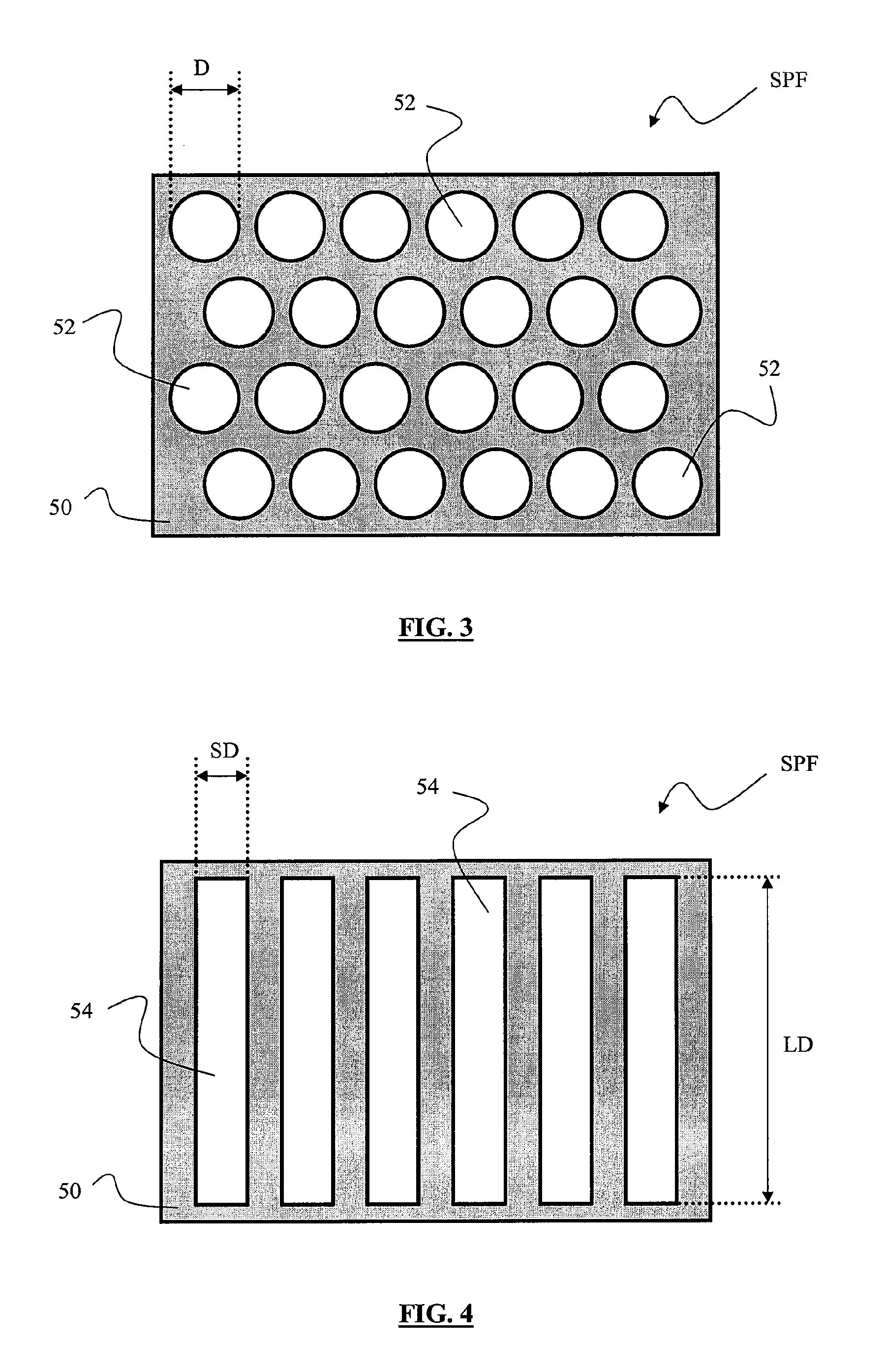
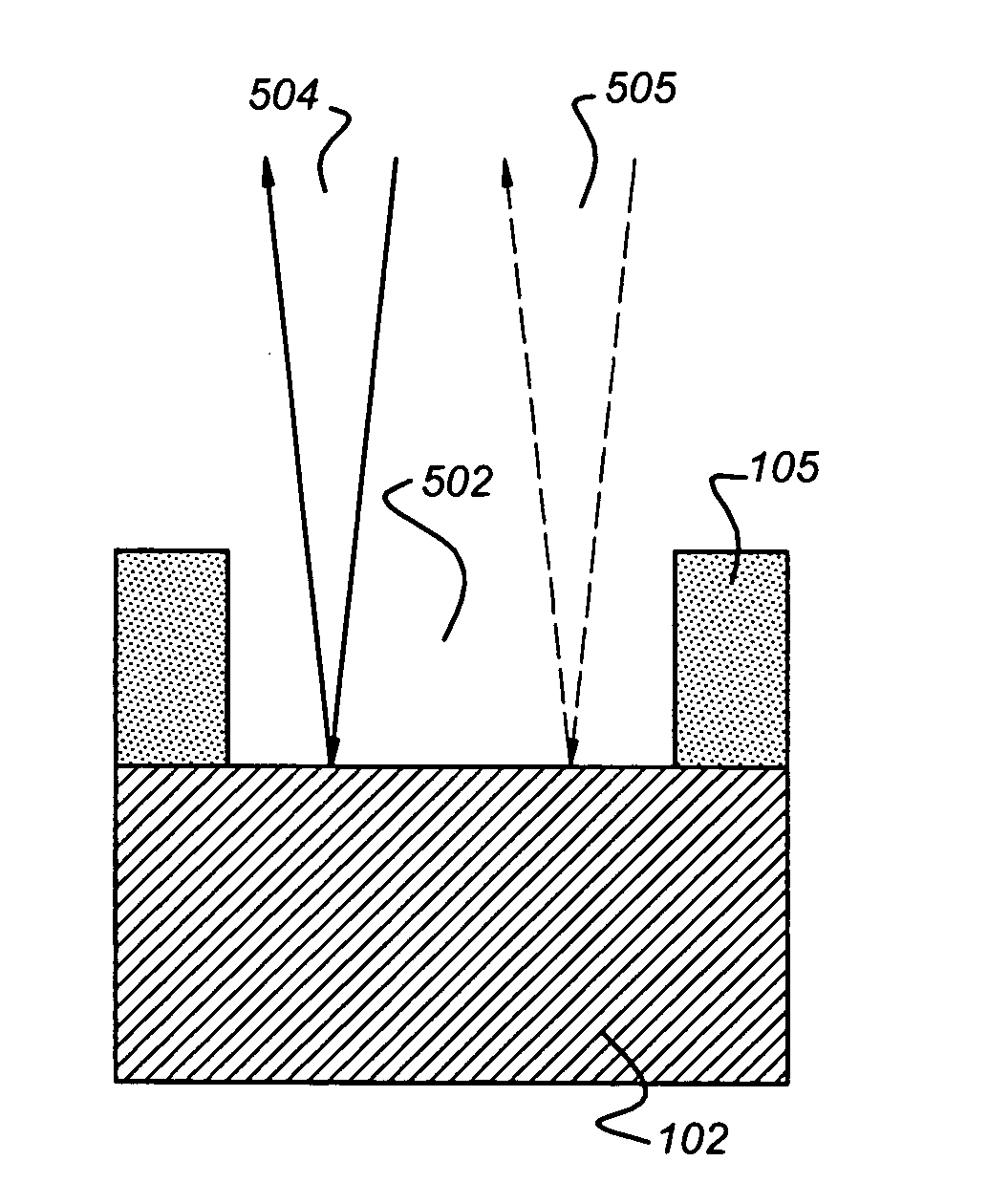
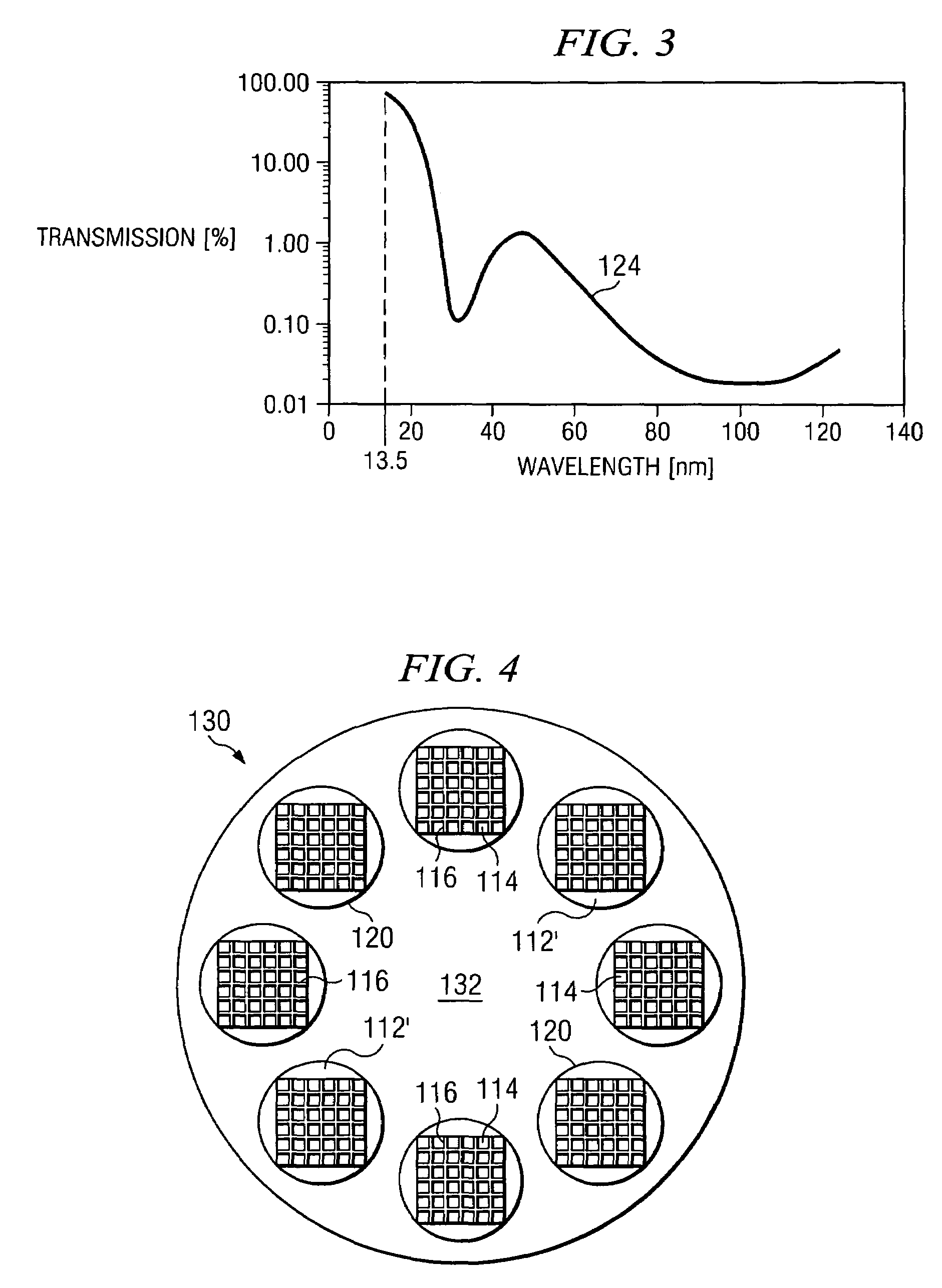
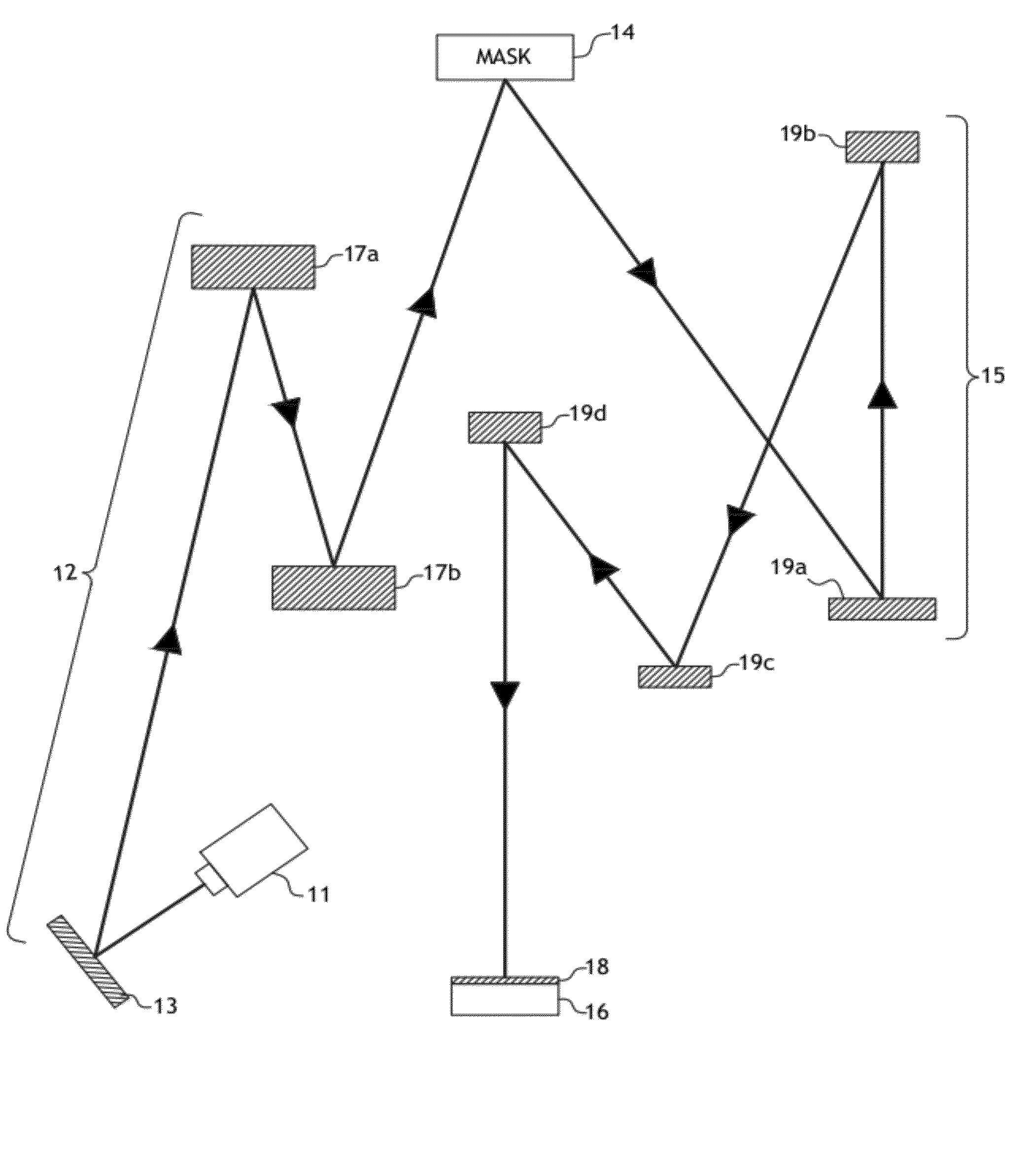
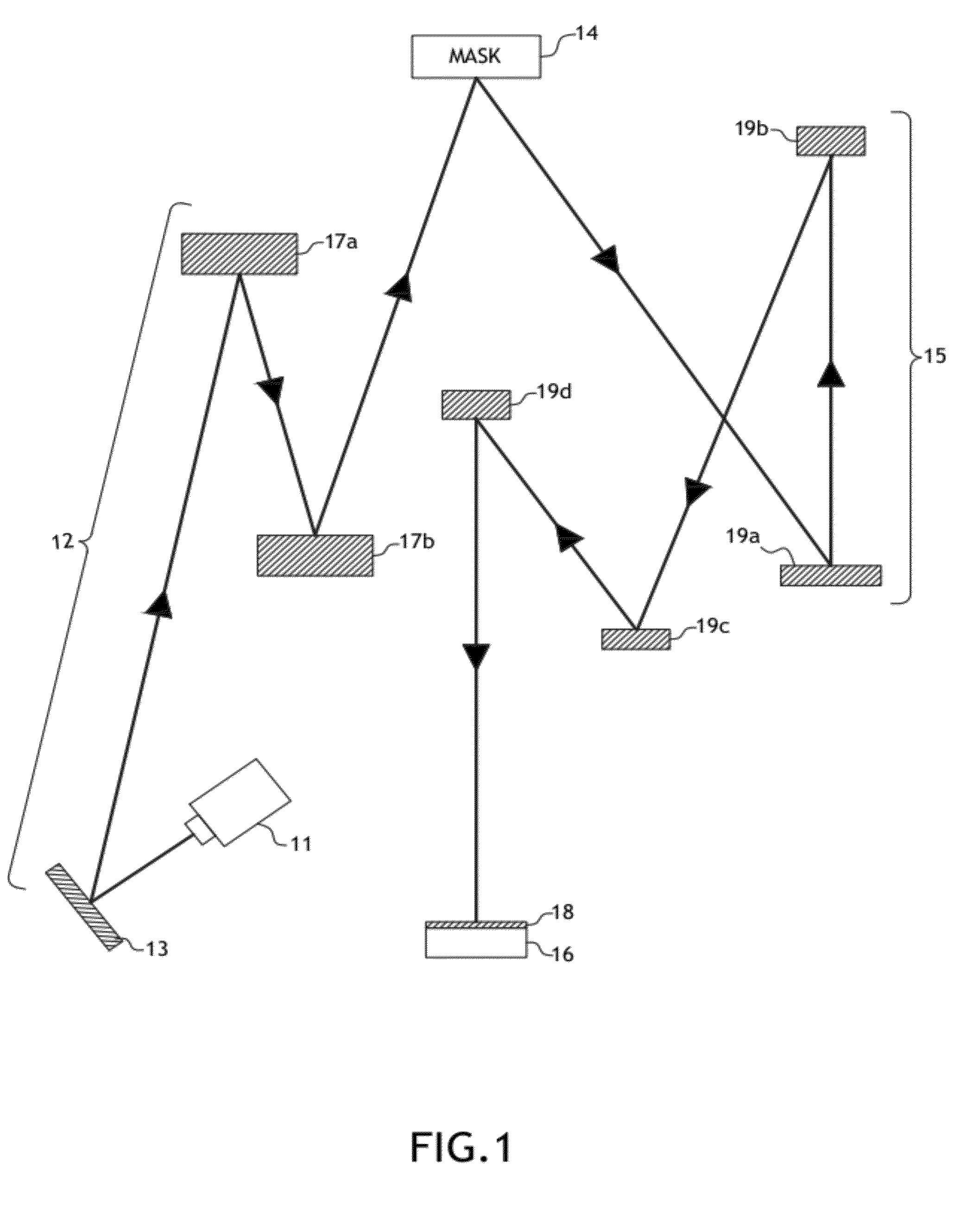
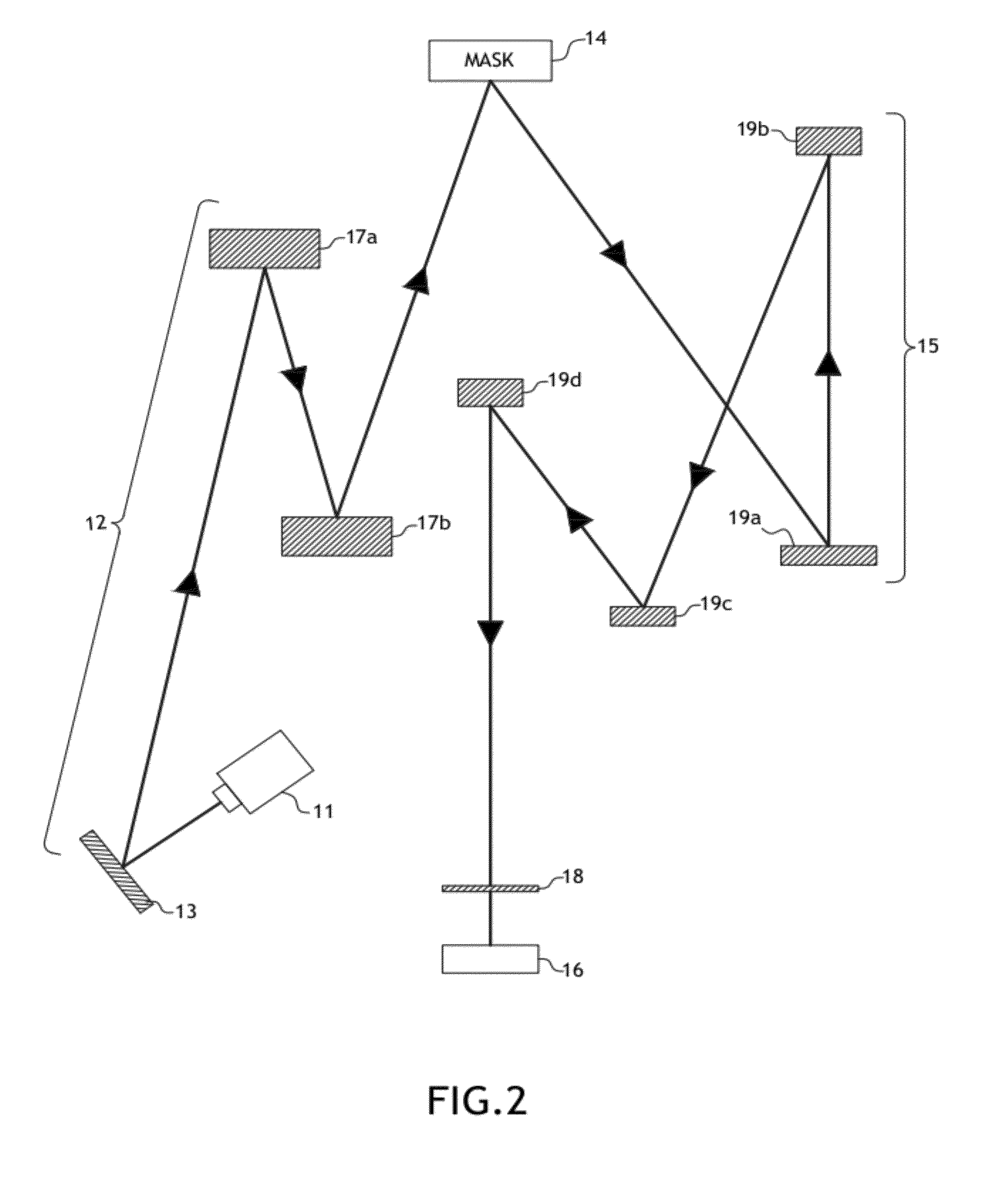
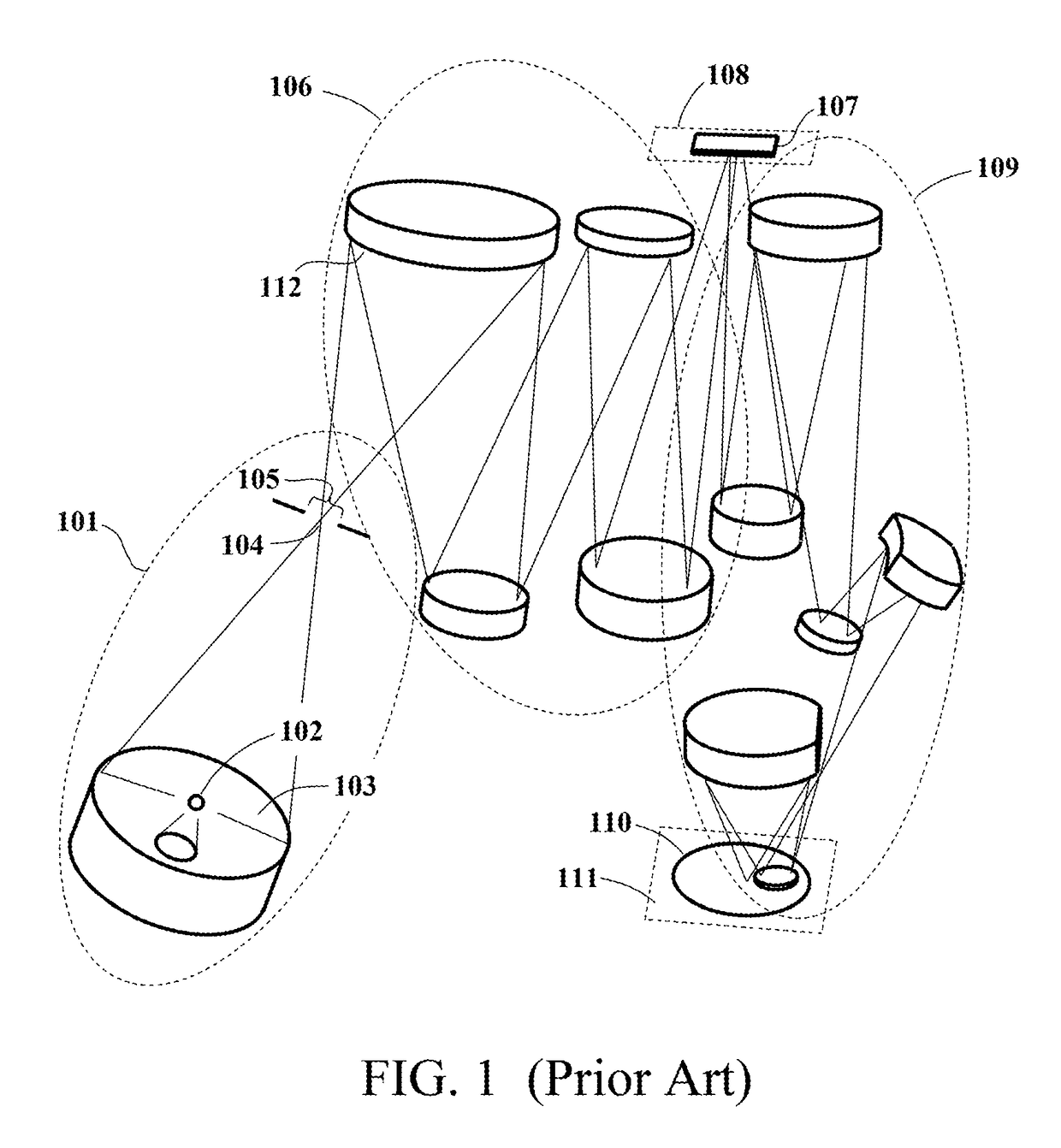
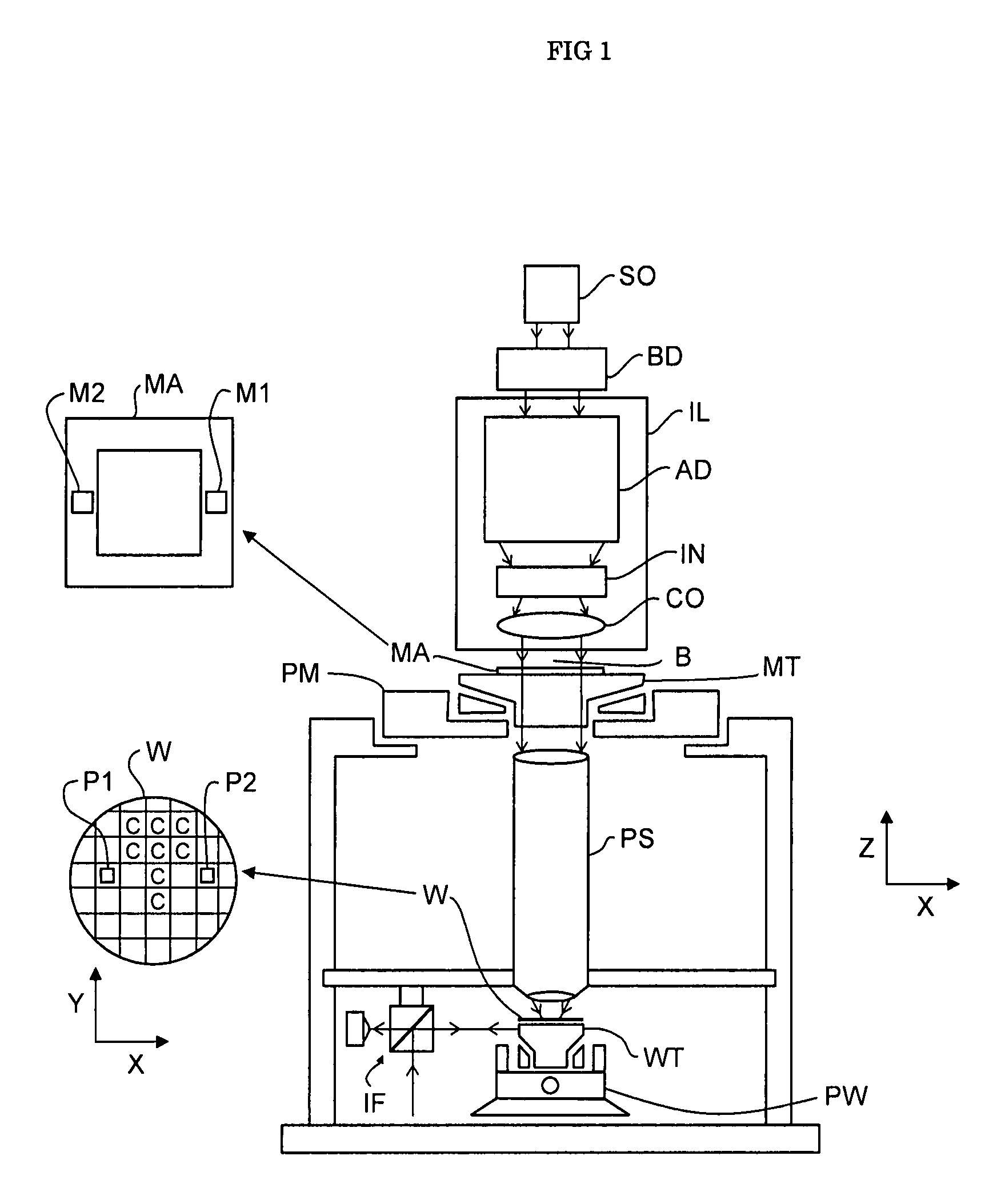
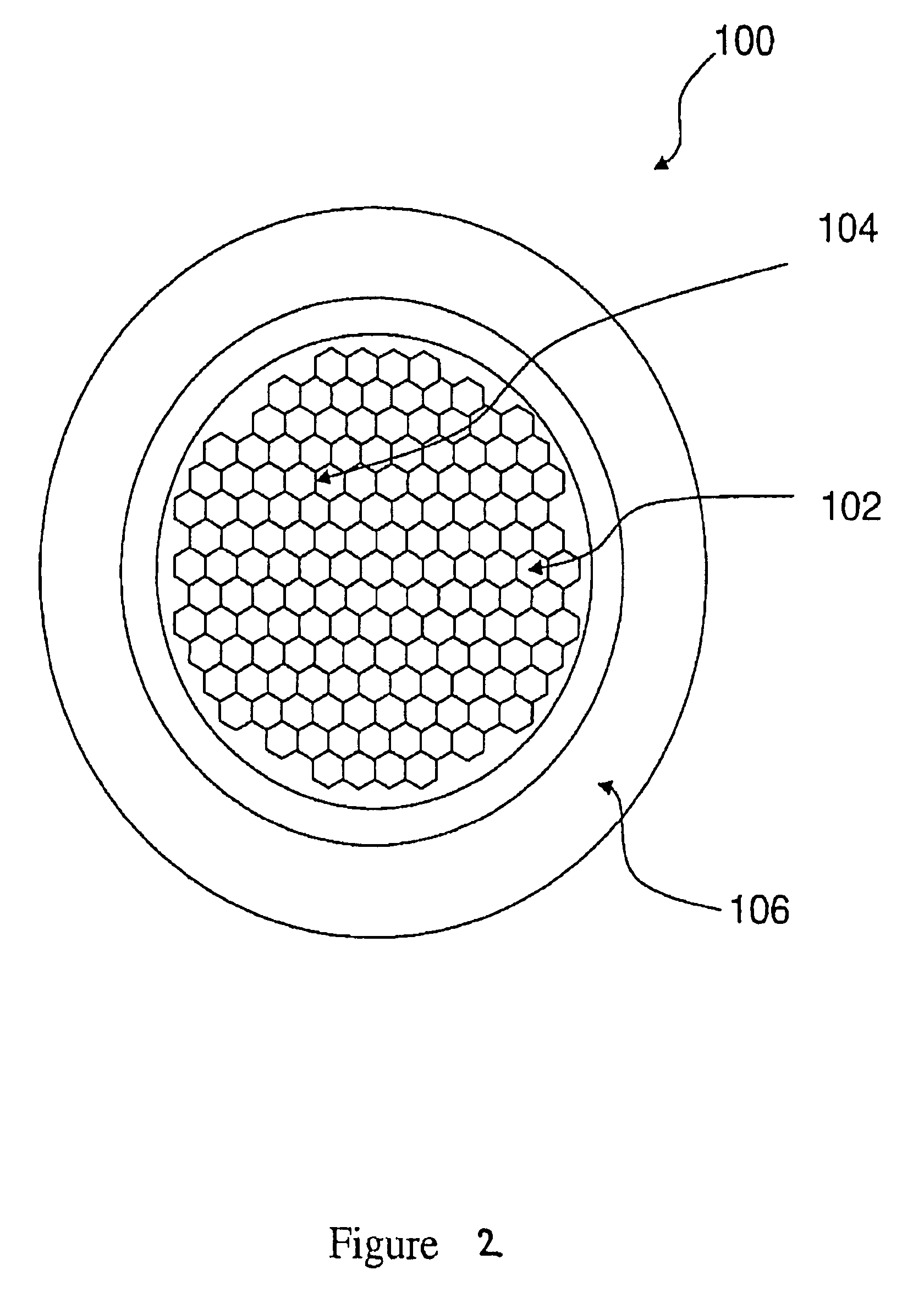
Spectral purity filter, lithographic apparatus including such a spectral purity filter, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS20060146413A1High spectral purityHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhotomechanical apparatusLength waveLight filter
A spectral purity filter includes an aperture, the aperture having a diameter, wherein the spectral purity filter is configured to enhance the spectral purity of a radiation beam by reflecting radiation of a first wavelength and allowing at least a portion of radiation of a second wavelength to transmit through the aperture, the first wavelength being larger than the second wavelength. The spectral purity filter may be used to improve the spectral purity of an Extreme Ultra-Violet (EUV) radiation beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
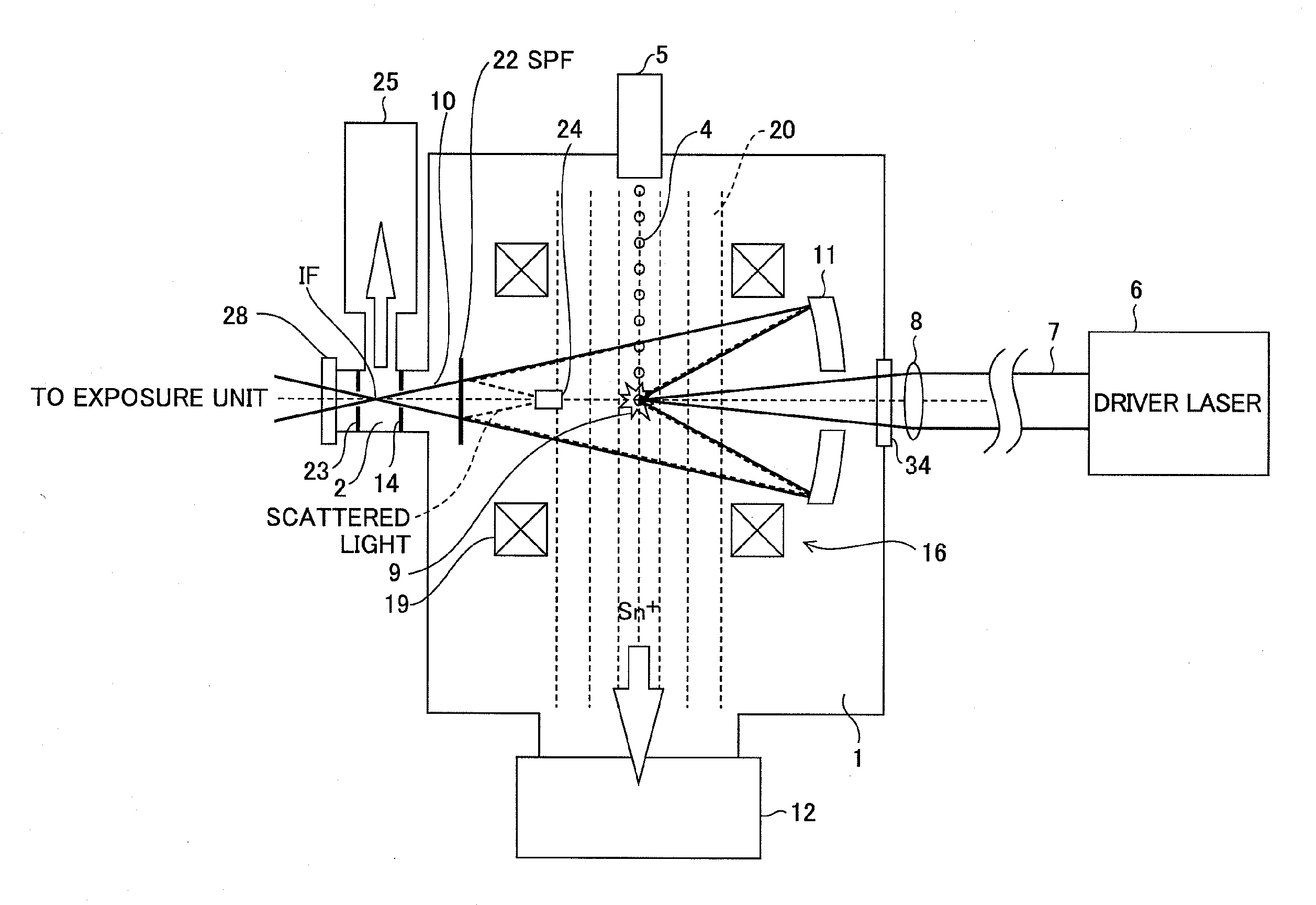
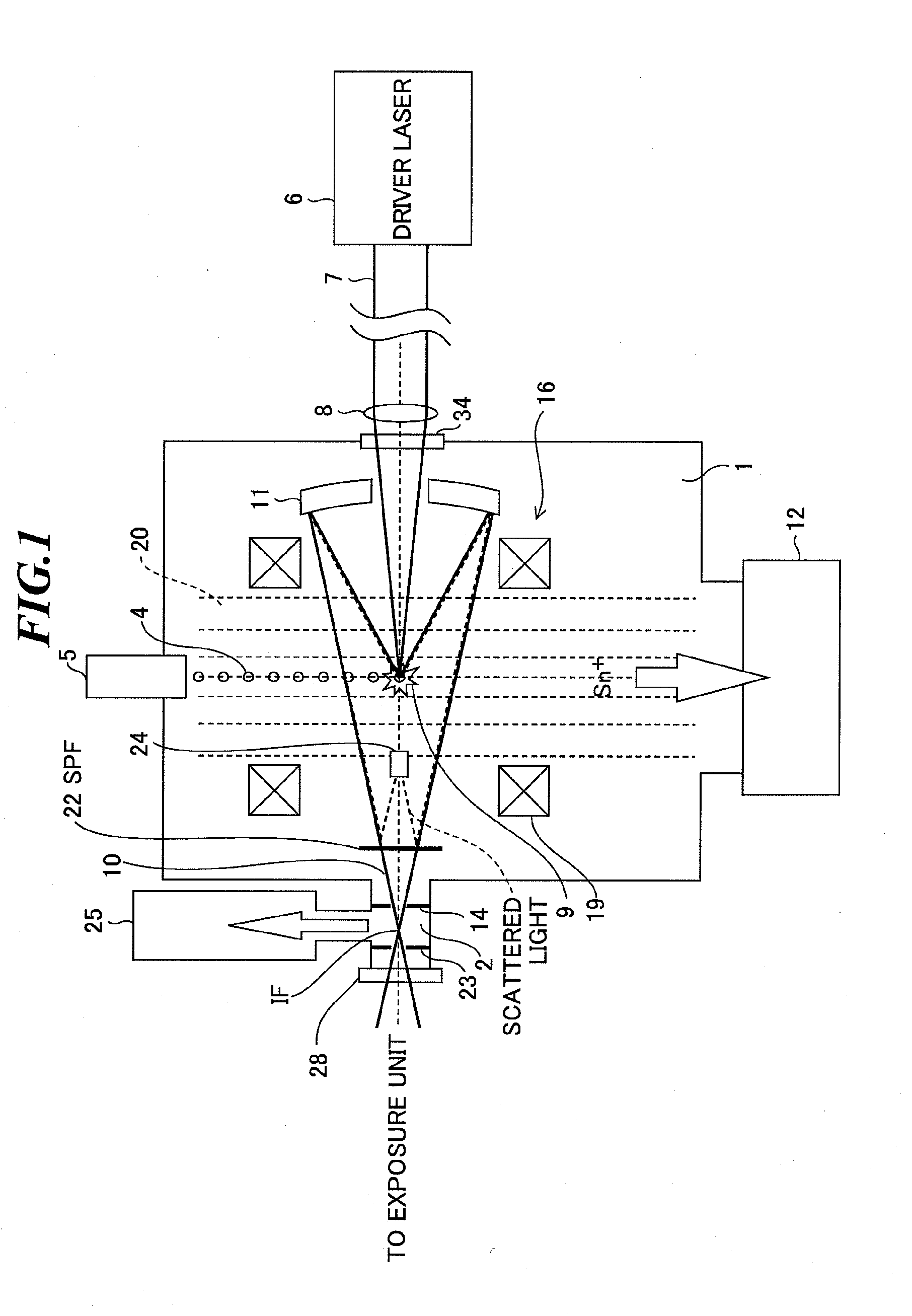
Extreme ultra violet light source apparatus
ActiveUS20090314967A1High spectral purityDifficult to absorbMirrorsOptical filtersLength waveExtreme ultraviolet
An extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus using a spectrum purity filter capable of obtaining EUV light with high spectrum purity. The apparatus includes a chamber; a target supply unit for supplying a target material; a driver laser using a laser gas containing a carbon dioxide gas as a laser medium, for applying a laser beam to the target material to generate plasma; a collector mirror for collecting and outputting the extreme ultraviolet light radiated from the plasma; and a spectrum purity filter provided in an optical path of the extreme ultraviolet light, for transmitting the extreme ultraviolet light and reflecting the laser beam, the spectrum purity filter including a mesh having electrical conductivity and formed with an arrangement of apertures having a pitch not larger than a half of a shortest wavelength of the laser beam applied by the driver laser.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
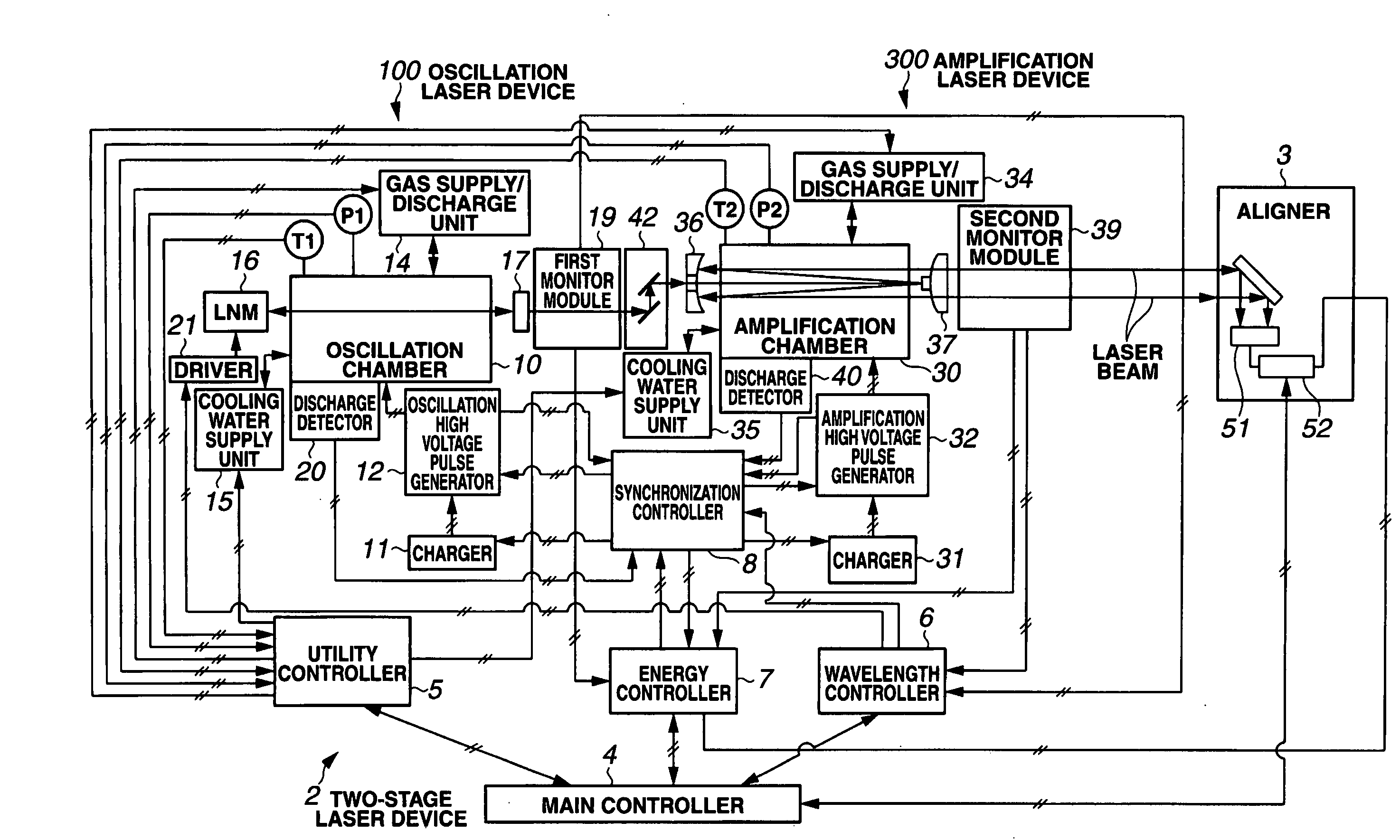
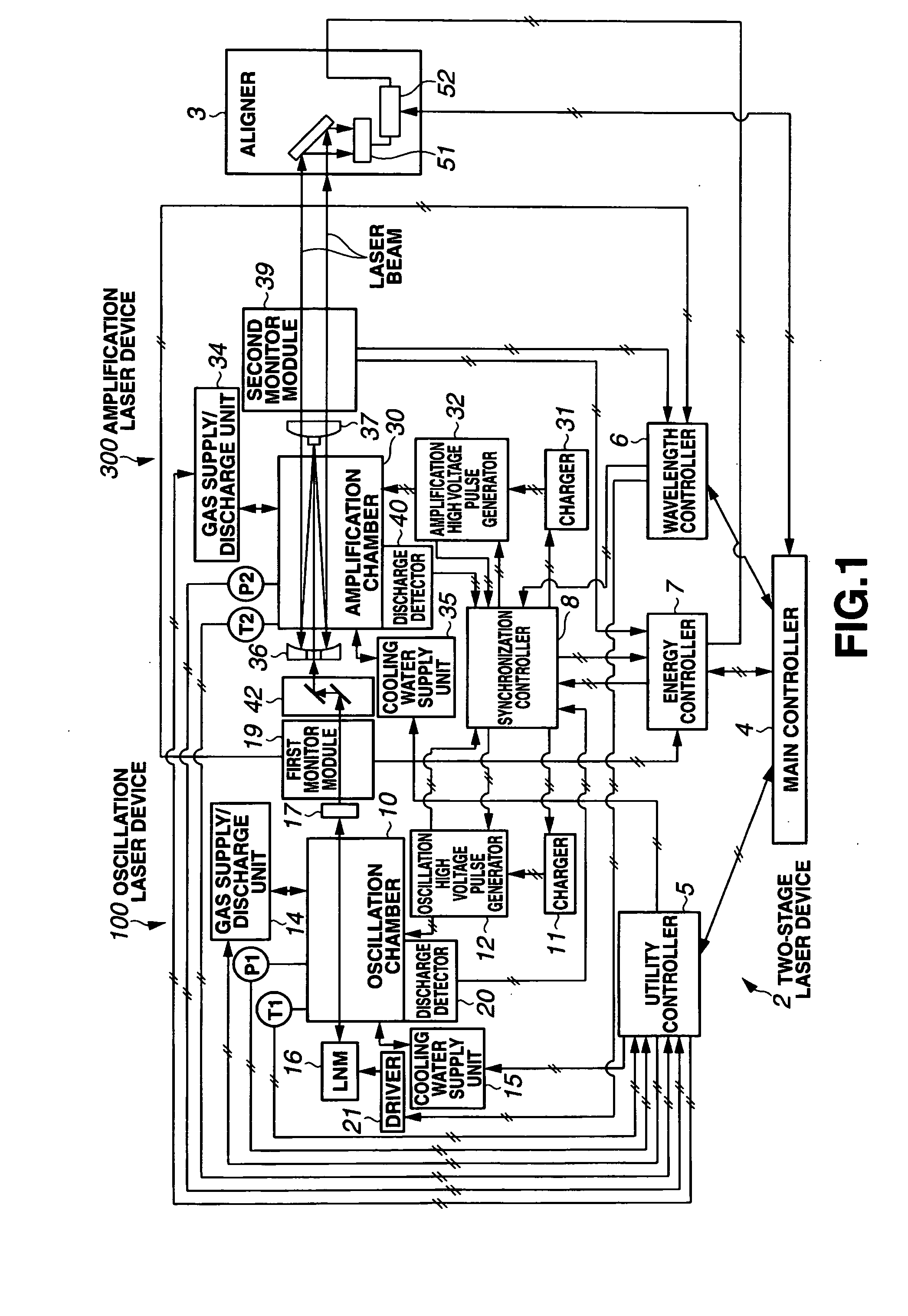
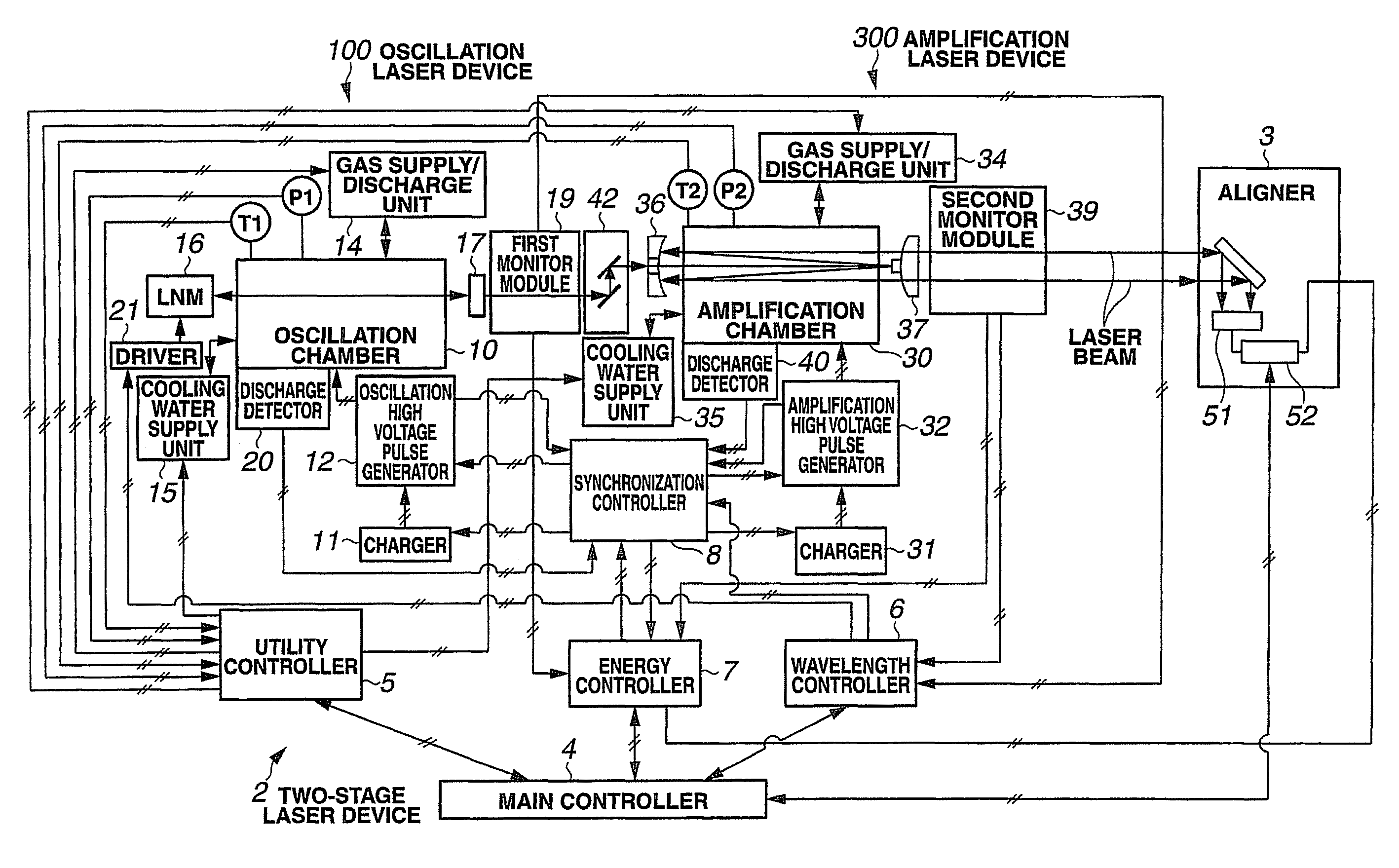
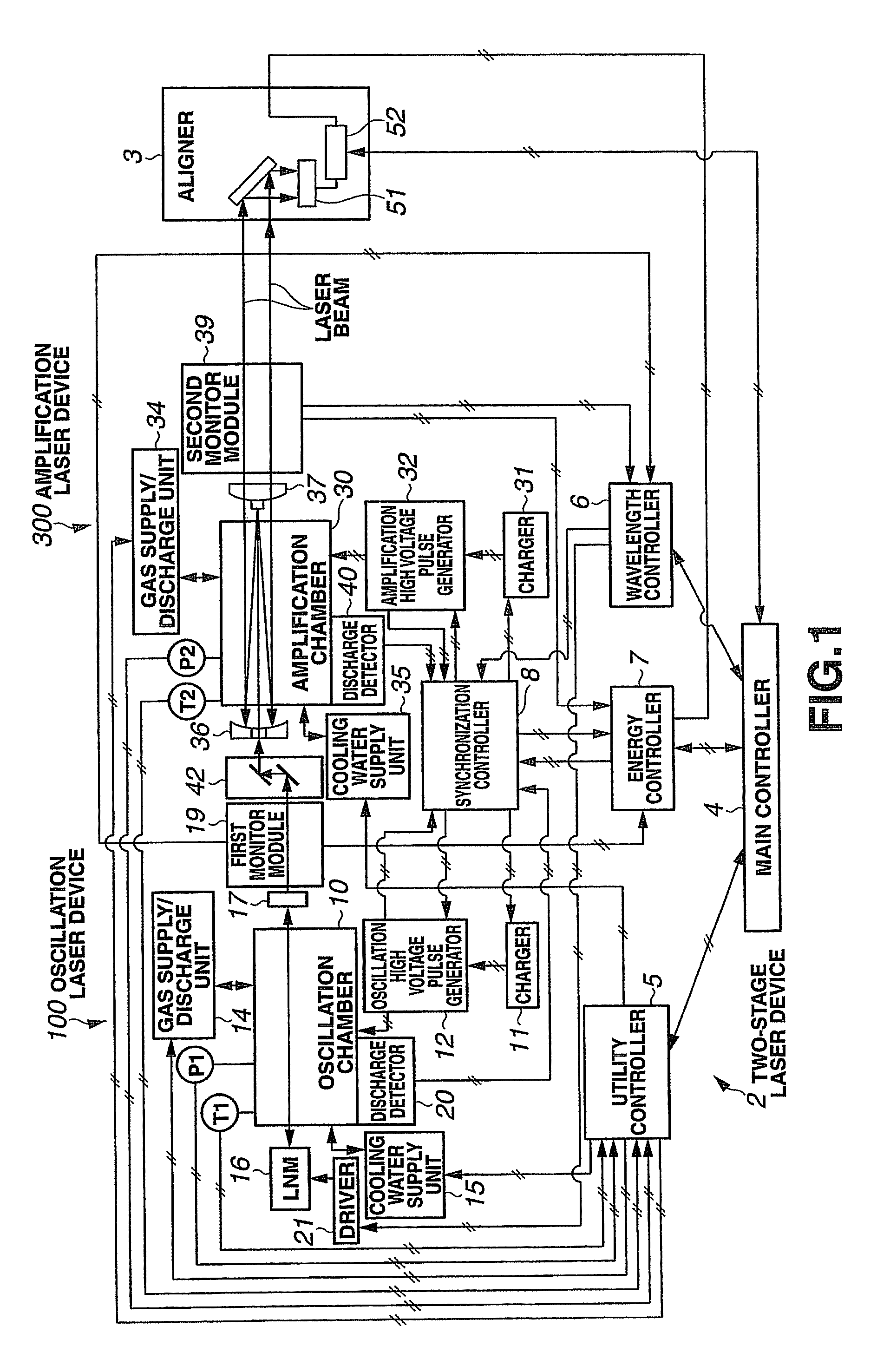
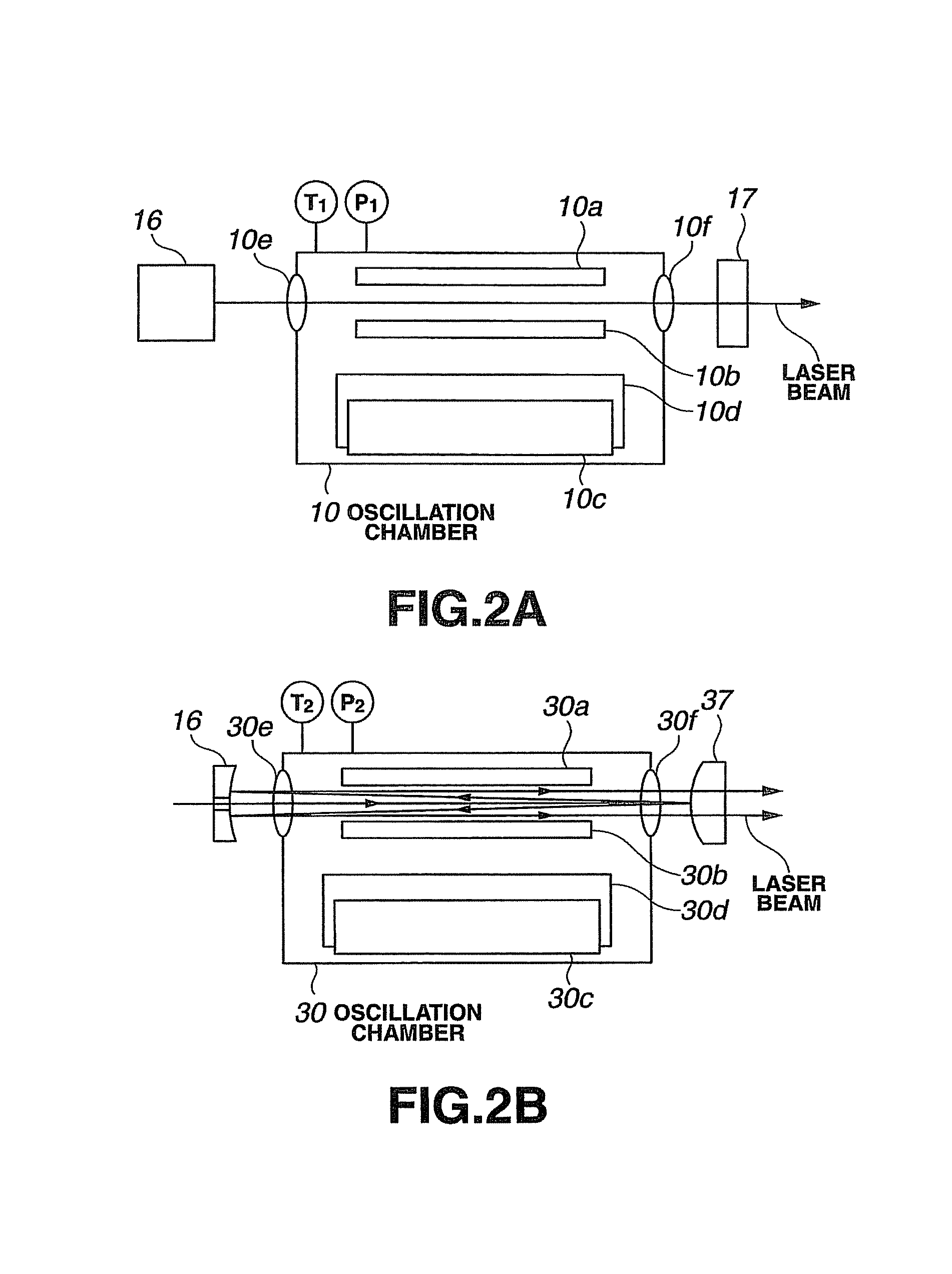
Narrow-Spectrum Laser Device
ActiveUS20080285602A1Improve controllabilityActive medium materialLaser cooling arrangementsOptoelectronicsLaser beams
A spectral purity range (E95) of a laser beam output from an amplifying laser device (300) is measured by spectral purity range measuring means. To have the measured spectral purity range (E95) within an allowable range E950±dE95 of a target spectral purity range (E950), discharge timing from a time when discharge is started by an oscillating laser device (100) to a time when discharge is started by the amplifying laser device (300) is controlled, and the spectral purity range (E95) is controlled to be stabilized.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
EUV lithography filter
InactiveUS20060160031A1Reduce the accumulation of debrisReduce harmRadiation/particle handlingPhotomechanical apparatusLithographic artistComputational physics
Filters for EUV lithography, methods of manufacture thereof, and methods of filtering in an EUV lithography system are disclosed. The filter comprises a nanotube material layer sandwiched by two thin material layers that are highly transmissive and provide structural support for the nanotube material layer. The filter is supported on at least one side by a patterned structural support. The filter mitigates debris, provides spectral purity filtering, or both.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Multi-layer spectral purity filter, lithographic apparatus including such a spectral purity filter, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS20060221440A1High spectral purityReduce fragmentationMirrorsOptical filtersLight filterRadiation beam
A multi-layered spectral purity filters improveS the spectral purity of an Extreme Ultra-Violet (EUV) radiation beam and also collect debris emitted from a radiation source.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus to enhance spectral purity of a light source
ActiveUS20170269279A1Good colorLight colorMechanical apparatusPhotovoltaicsBandpass filteringLength wave
A reflective filter serving as a multi-bandpass filter for a light source configured to emit light in a plurality of color primary wavelengths to improve color purity. The addition of a reflective / recirculation assembly reinforces and recirculates light not passed by the multi-bandpass filter back into a desired spectrum, which is subsequently passed by the multi-bandpass filter, or converts light not passed by the multi-bandpass into electrical energy for use by the system. The reflective filter, solely or along with the recirculation assembly, can be placed adjacent a conventional light source. Alternatively the multi-bandpass filter and the recirculation assembly can be placed in a modified light source, or placed in an optical stack along the path of light emission. Collimating structures that enforce the light into desired incident angle of attack onto the reflective filter can be included to enhance the efficiency of the reflective elements in the assembly.
Owner:PIXELDISPLAY INC
High-efficiency spectral purity filter for EUV lithography
InactiveUS7050237B2Simple and inexpensive wayImprove efficiencyMirrorsOptical filtersLithographic artistBlazed grating
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
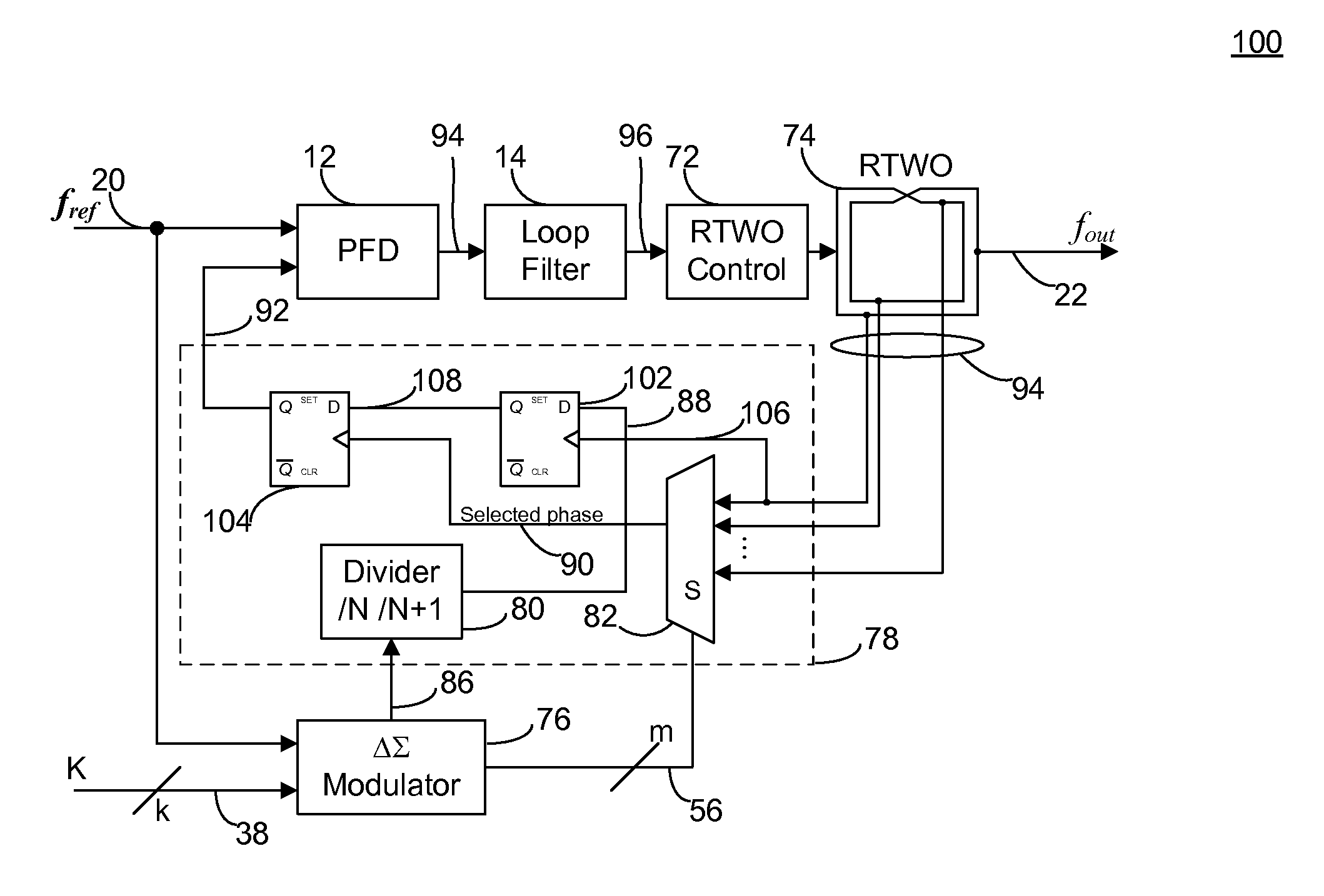
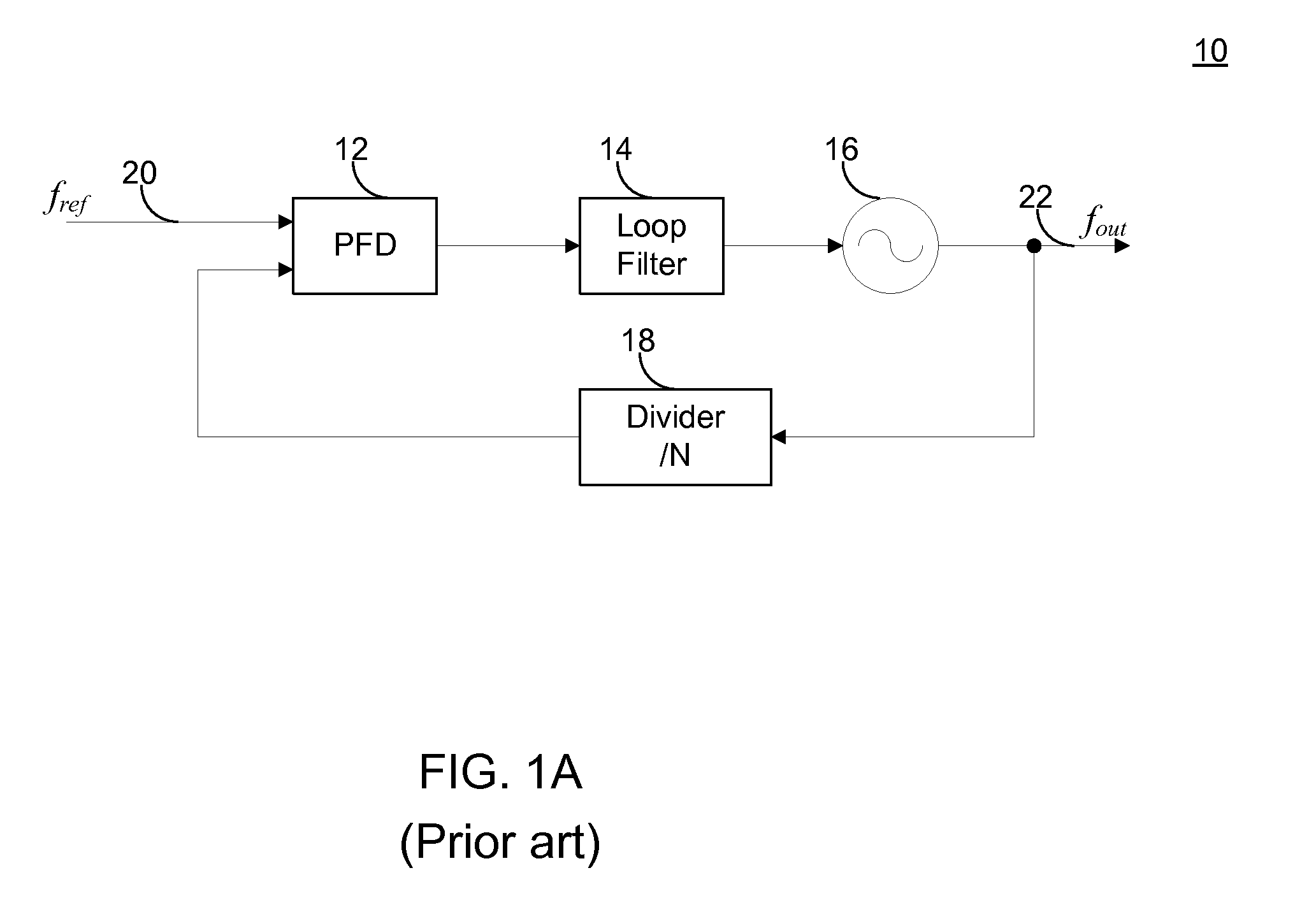
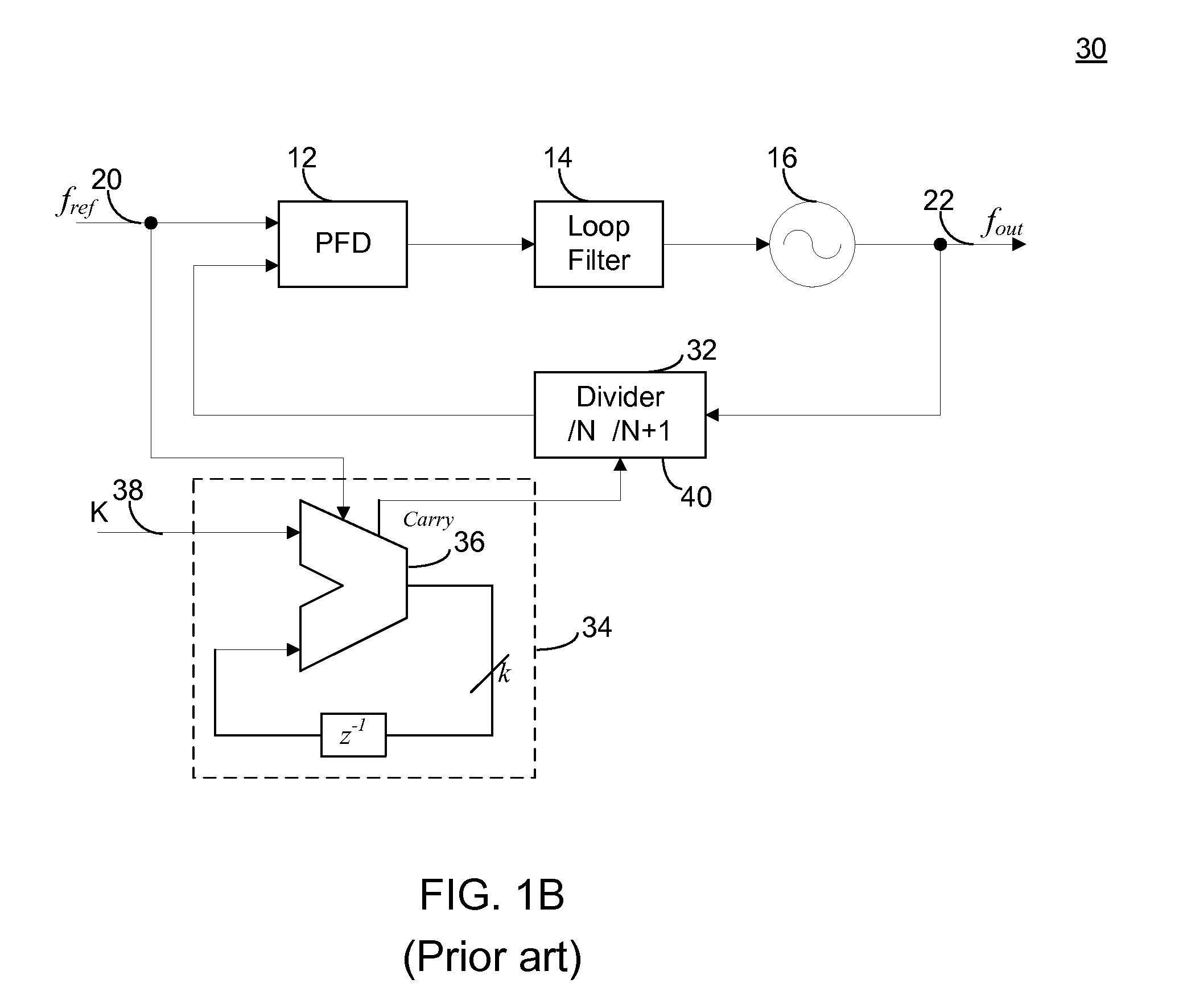
Low Noise Fractional Divider Using A Multiphase Oscillator
ActiveUS20110156773A1High purityAmenable to integrated circuit fabricationPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsLow noisePhase shifted
A frequency synthesis circuit is disclosed. The circuit includes a phase-locked loop and multi-phase oscillator such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator (RTWO). The oscillator provides a plurality of phases that are applied to a selection circuit. The selection circuit, in response to the output of a delta-sigma modulator, selects one of the phases of the multi-phase oscillator to minimize phase shift noise when the divider ratio in the loop changes, thereby eliminating a source of noise that contaminates the synthesized frequency. This permits the use of the frequency synthesis in applications requiring a high degree of spectral purity.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
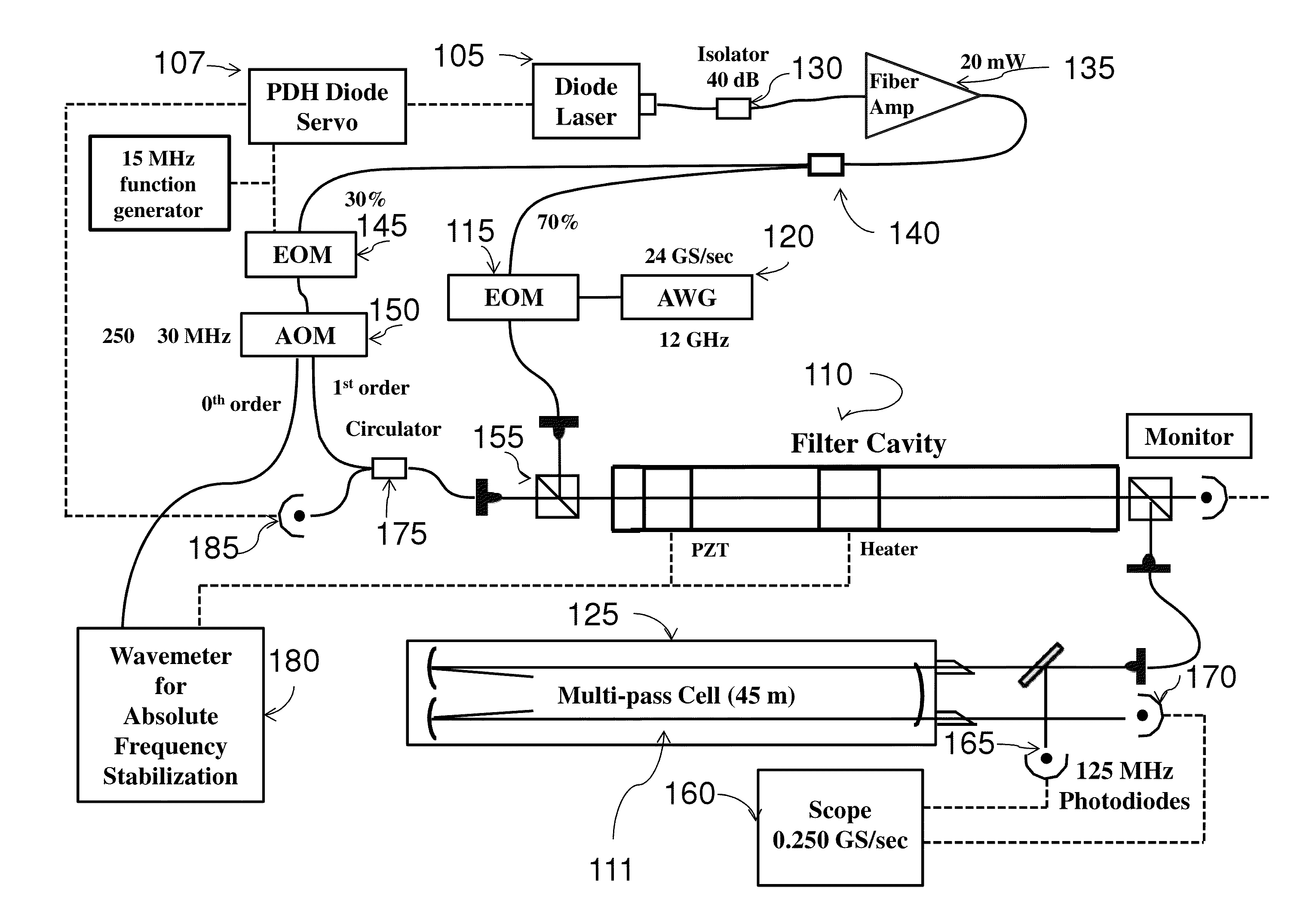
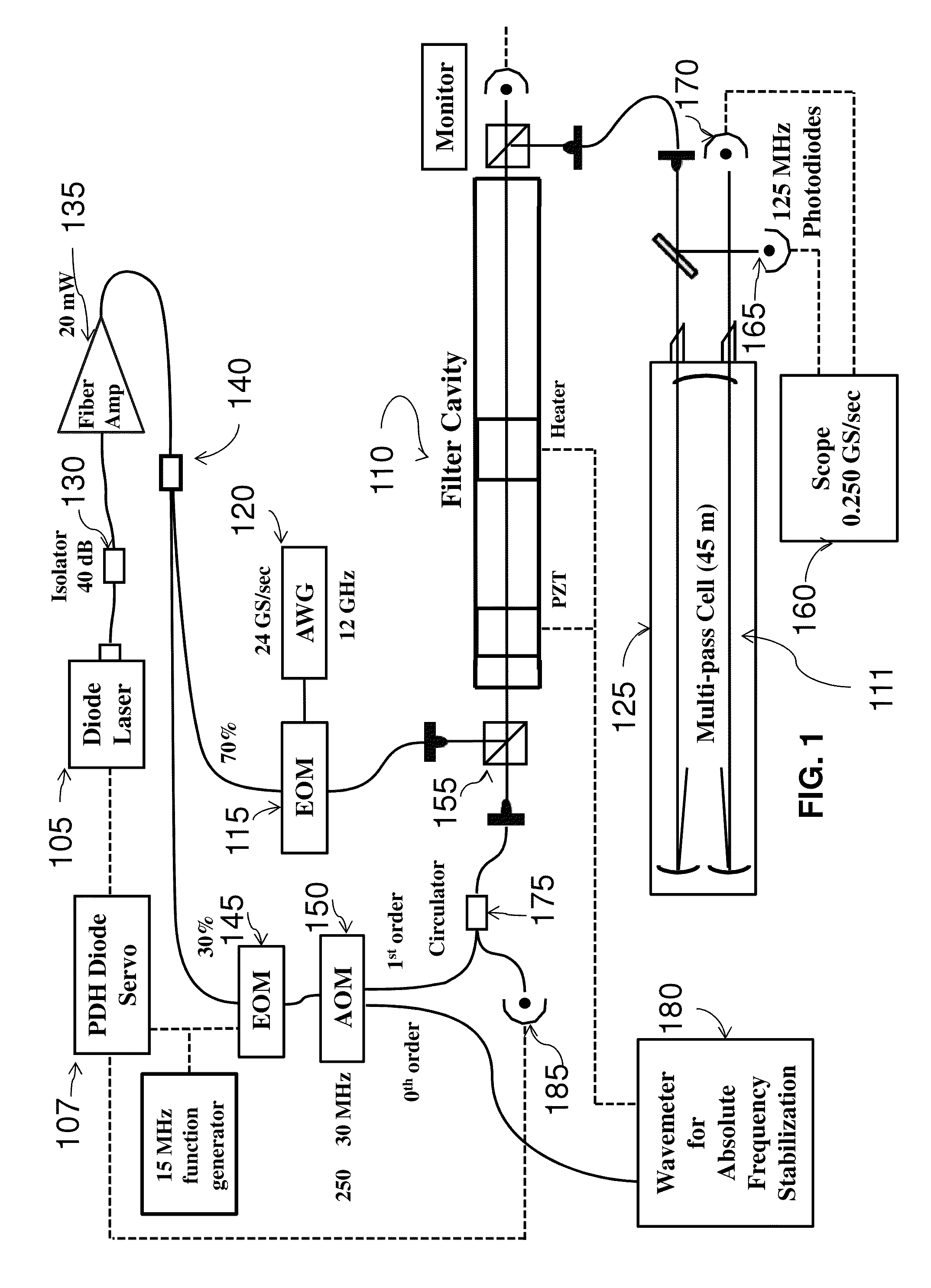
Fast Switching Arbitrary Frequency Light Source for Broadband Spectroscopic Applications
ActiveUS20130228688A1Enlarged cavityQuick switchRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using multiple reflectionSpectroscopySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
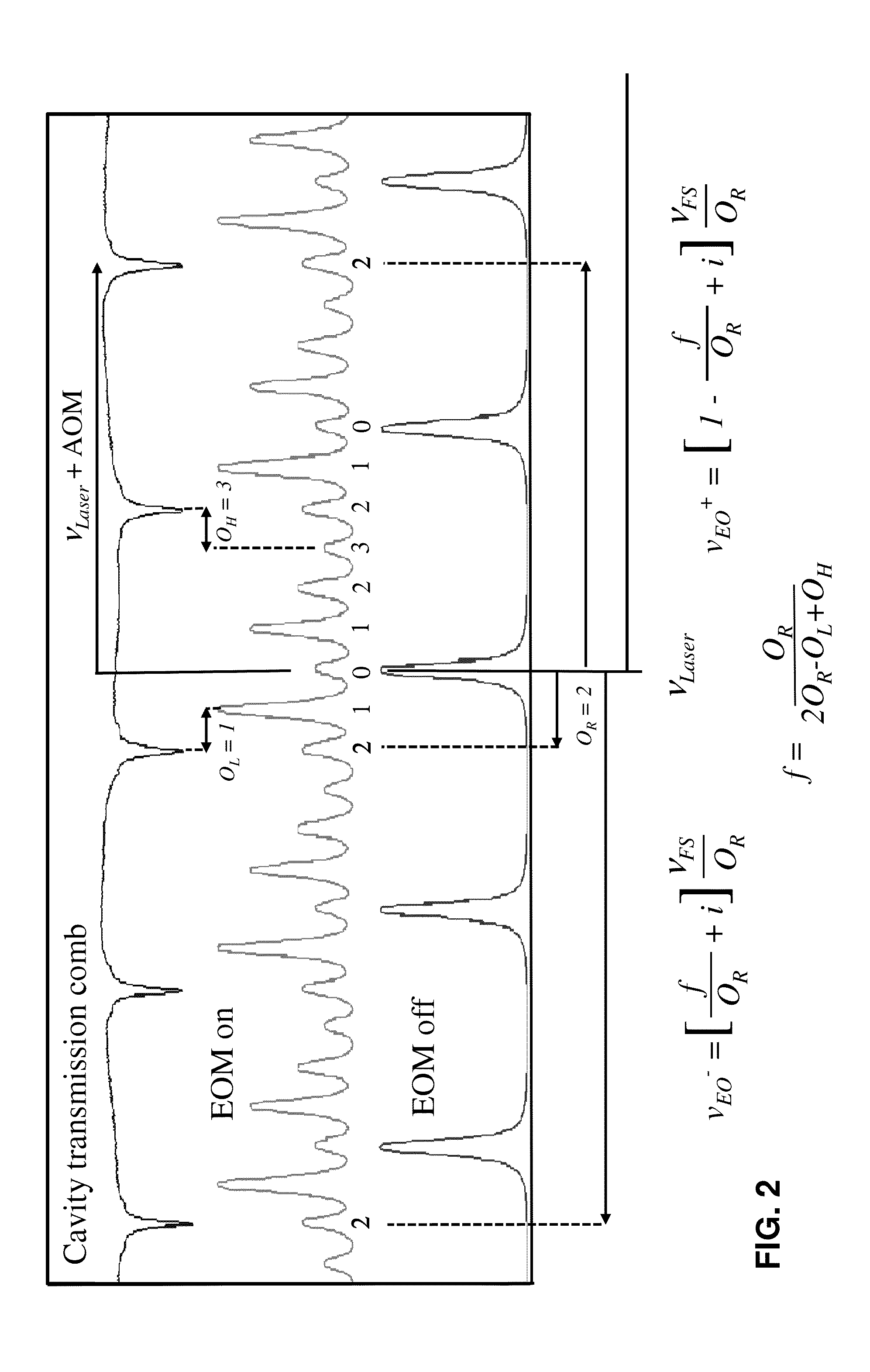
A fast switching arbitrary frequency light source for broadband spectroscopic applications. The light source may operate near 1.6 um based on sideband tuning using an electro-optic modulator driven by an arbitrary waveform generator. A Fabry-Perot filter cavity selects a single sideband of the light source. The finesse (FSR / ΔνFWHM) of the filter cavity may be chosen to enable rapid frequency switching at rates up to 5 MHz over a frequency range of 40 GHz (1.3 cm−1). The bandwidth, speed and spectral purity are high enough for spectroscopic applications where rapid and discrete frequency scans are needed. Significant signal-to-noise advantages may be realized using the rapid and broadband scanning features of this system in many areas of spectroscopy, e.g., process monitoring and control, reaction dynamics, and remote sensing (e.g., greenhouse gas monitoring, biological / chemical agent screening).
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY
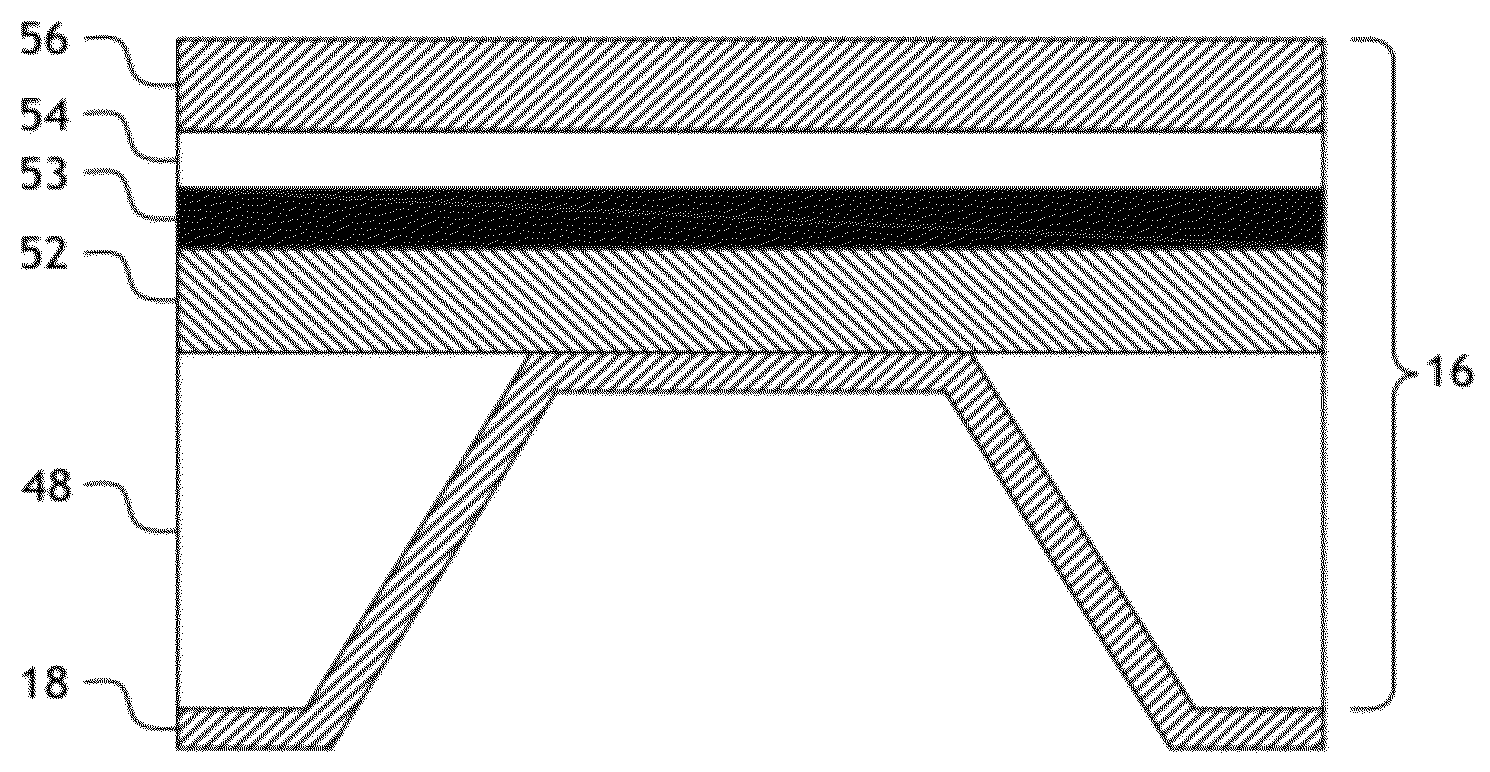
Spectral purity filter for a multi-layer mirror, lithographic apparatus including such multi-layer mirror, method for enlarging the ratio of desired radiation and undesired radiation, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060245058A1High spectral purityReduce radiationMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingInter layerOptoelectronics
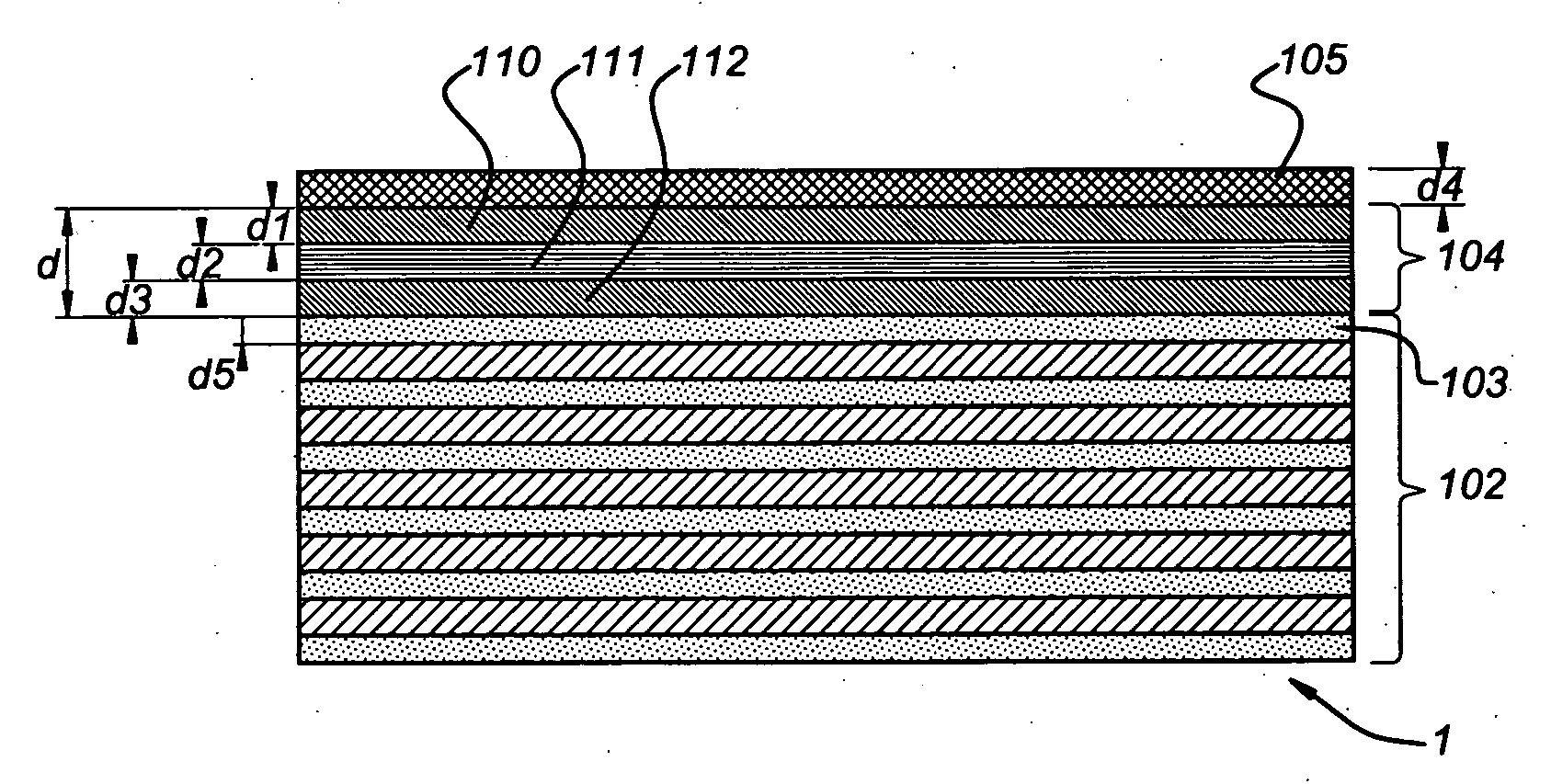
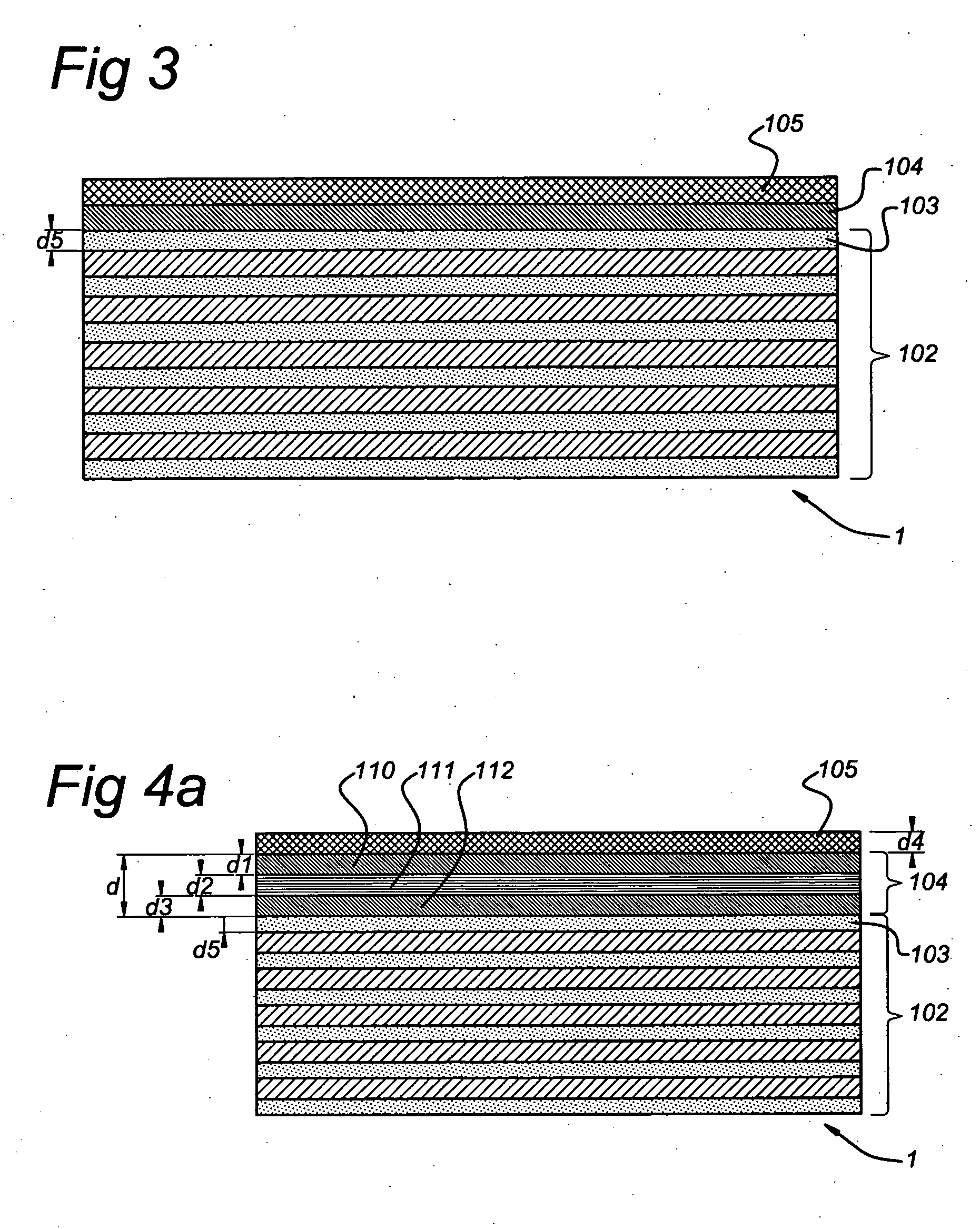
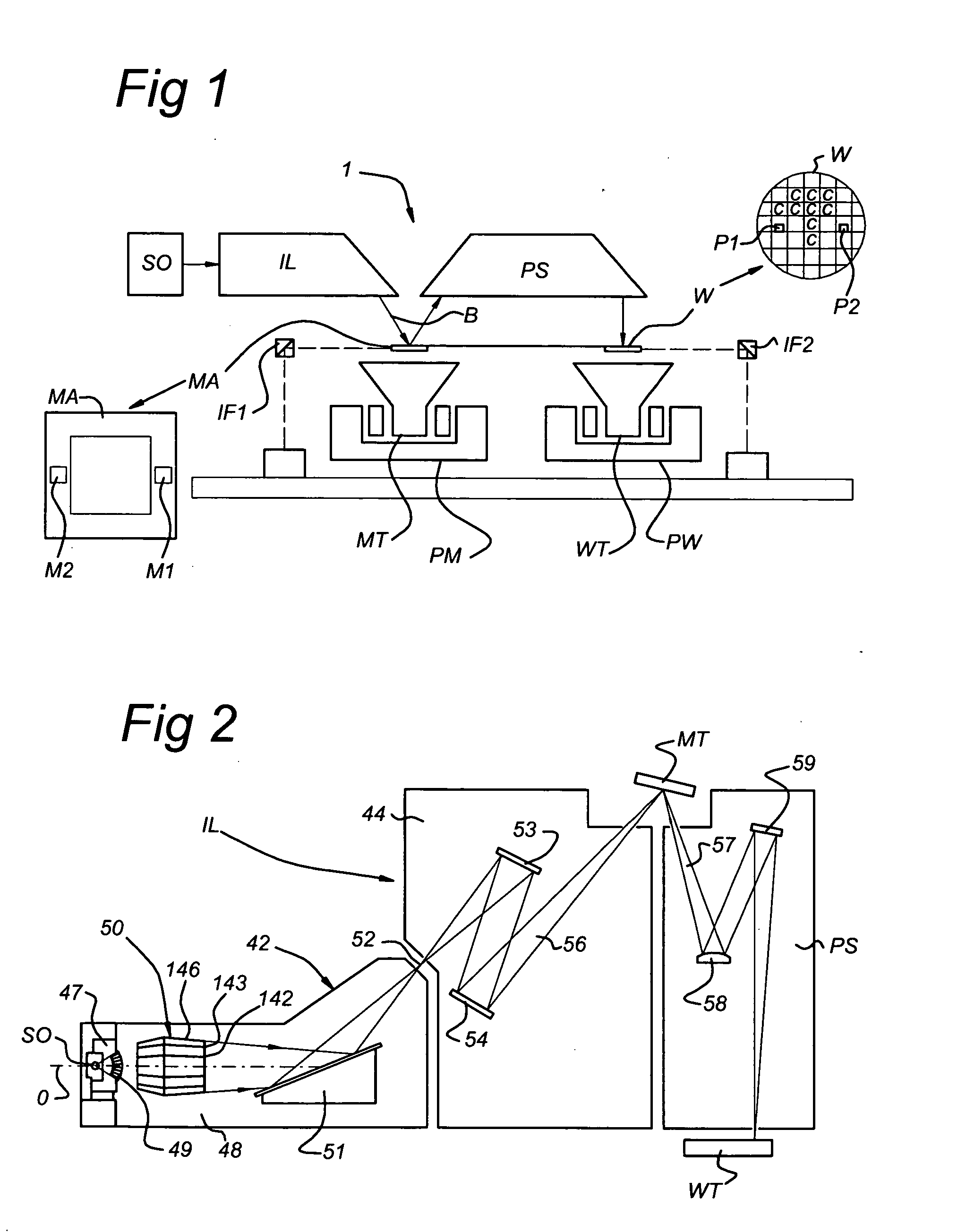
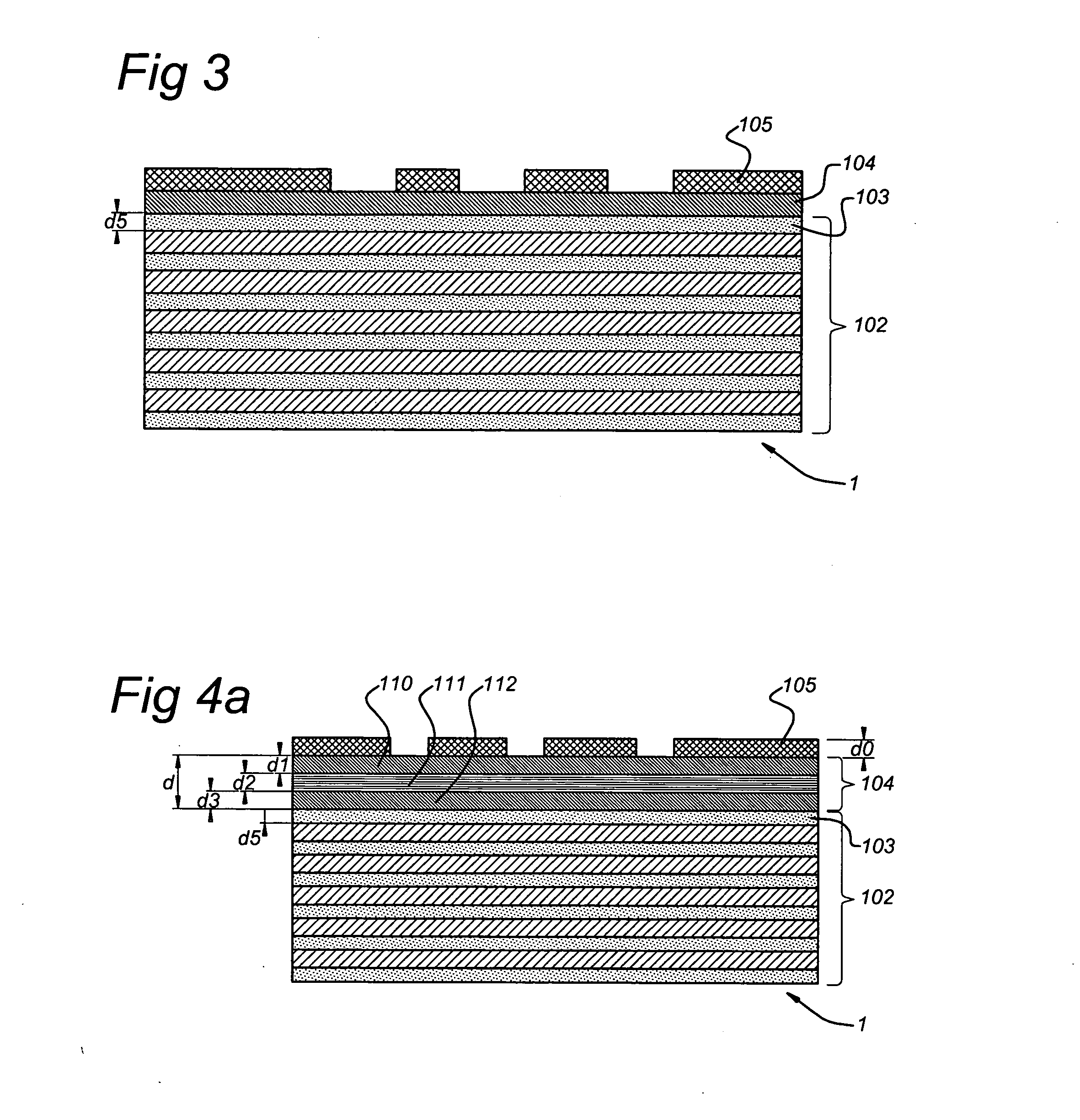
A multi-layer mirror includes on top of the multi-layer mirror a spectral purity enhancement layer, for example for application in an EUV lithographic apparatus. This spectral purity enhancement layer includes a first spectral purity enhancement layer, but between the multi-layer mirror and first spectral purity enhancement layer there may optionally be an intermediate layer or a second spectral purity enhancement layer and intermediate layer. Hence, multi-layer mirrors with the following configurations are possible: multi-layer mirror / first spectral purity enhancement layer; multi-layer mirror / intermediate layer / first spectral purity enhancement layer; and multi-layer mirror / second spectral purity enhancement layer / intermediate layer / first spectral purity enhancement layer. The spectral purity of normal incidence radiation may be enhanced, such that DUV radiation is diminished relatively stronger than EUV radiation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
High resolution synthesizer with improved signal purity
ActiveUS20050135524A1Increase sampling rateElectrical testingGenerating/distributing signalsCMOSData stream
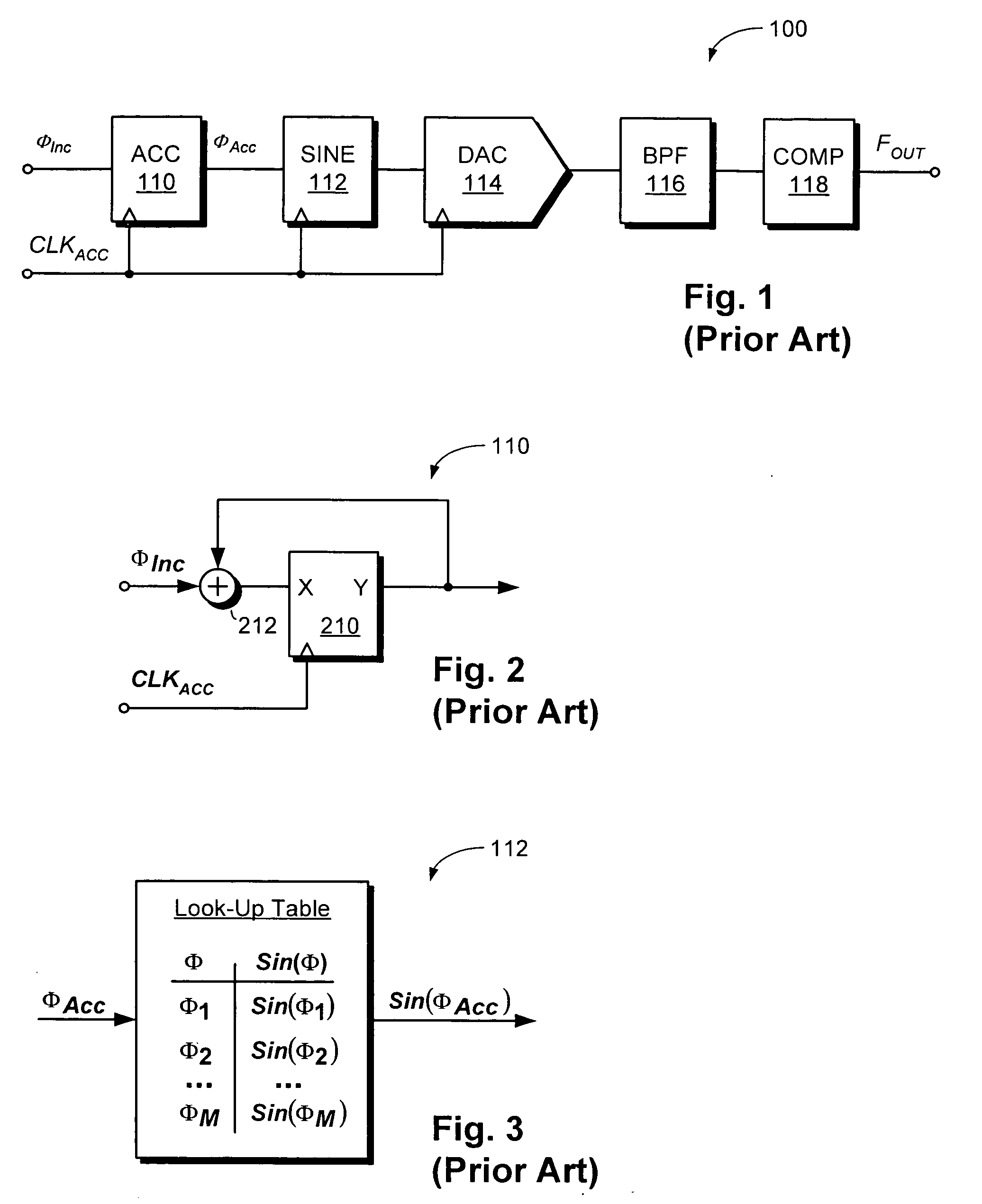
An automatic test system using a DDS signal generator to create a signal with high spectral purity or a low jitter digital clock. The low jitter clock has variable frequency and is programmed to control other test functions, such as the generation of arbitrary waveforms. The DDS uses a high resolution, high sampling rate DAC to generate a sine wave that is converted to a digital clock. The architecture of the DDS signal generator allows low cost CMOS circuitry to be used to generate the data stream that feeds the high sample rate DAC.
Owner:TERADYNE
Spectral purity filter, lithographic apparatus including such a spectral purity filter, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS7453645B2High spectral purityHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhotomechanical apparatusUltravioletWavelength
A spectral purity filter includes an aperture, the aperture having a diameter, wherein the spectral purity filter is configured to enhance the spectral purity of a radiation beam by reflecting radiation of a first wavelength and allowing at least a portion of radiation of a second wavelength to transmit through the aperture, the first wavelength being larger than the second wavelength. The spectral purity filter may be used to improve the spectral purity of an Extreme Ultra-Violet (EUV) radiation beam.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Spectral Purity Filters for Use in a Lithographic Apparatus
InactiveUS20100020304A1Promotes reflectionAvoid damageRadiation/particle handlingPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamLength wave
According to an aspect of the present invention, a spectral purity filter includes an aperture, the aperture being arranged to diffract a first wavelength of radiation and to allow at least a portion of a second wavelength of radiation to be transmitted through the aperture, the second wavelength of radiation being shorter than the first wavelength of radiation, wherein the aperture has a diameter greater than 20 μm.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Anti-reflection coating for an EUV mask
An EUV mask includes, on top of a multi-layer mirror, a spectral purity enhancement layer, for application in an EUV lithographic apparatus. On top of the spectral purity enhancement layer, a patterned absorber layer is provided. The spectral purity enhancement layer includes a first spectral purity enhancement layer, but between the multi-layer mirror and first spectral purity enhancement layer there may be an intermediate layer or a second spectral purity enhancement layer and intermediate layer. The patterned absorber layer may also itself function as an anti-reflection (AR) coating. The AR effect of this absorber layer is a function of the aperture sizes in the pattern. The spectral purity of a mask may be enhanced, such that DUV radiation is diminished relatively stronger than EUV radiation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multi-layer spectral purity filter, lithographic apparatus including such a spectral purity filter, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS7372623B2Reduce fragmentationHigh spectral purityMirrorsOptical filtersUltravioletLight filter
A multi-layered spectral purity filter improves the spectral purity of extreme ultra-violet (EUV) radiation and also collects debris emitted from a radiation source.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
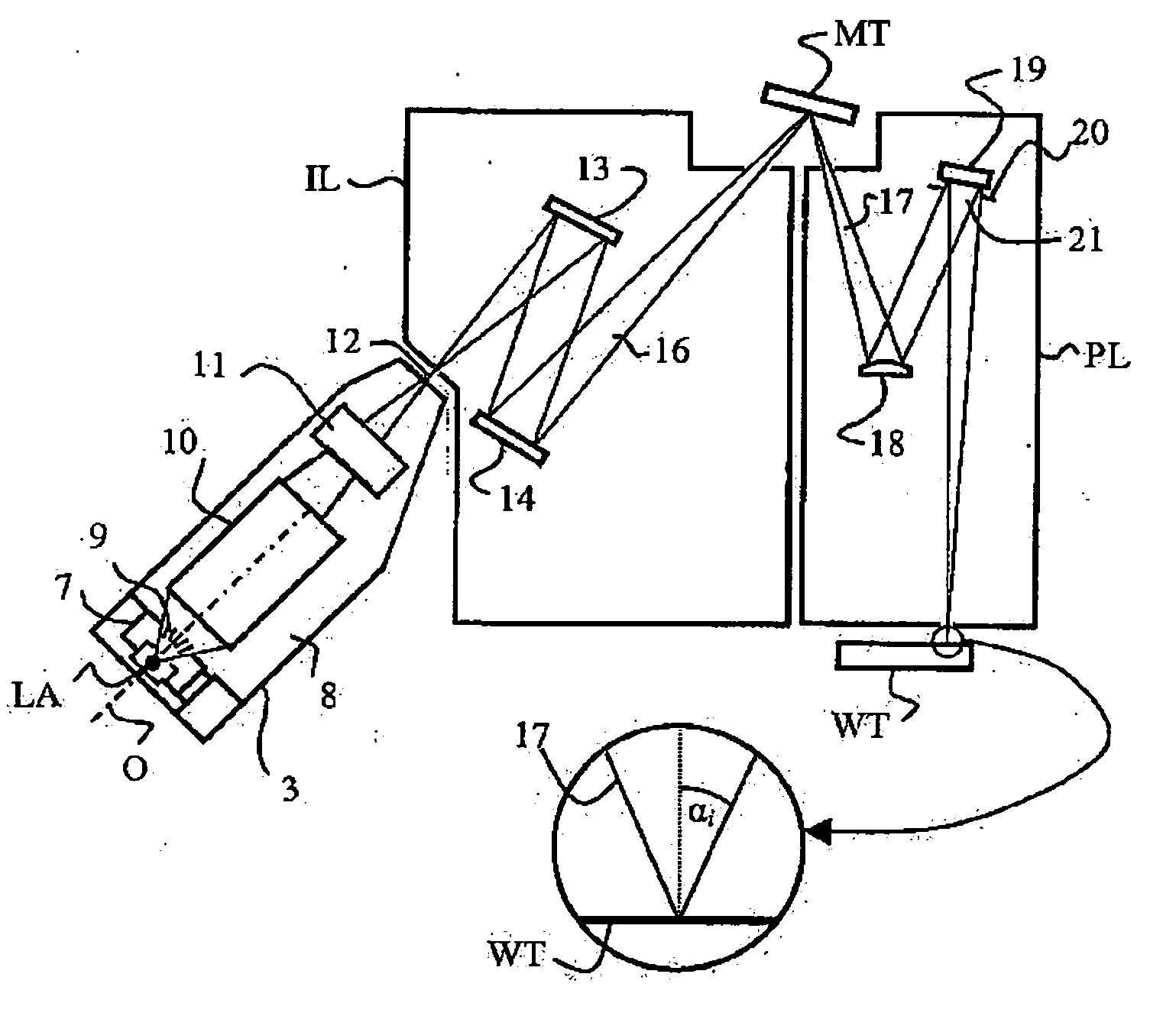
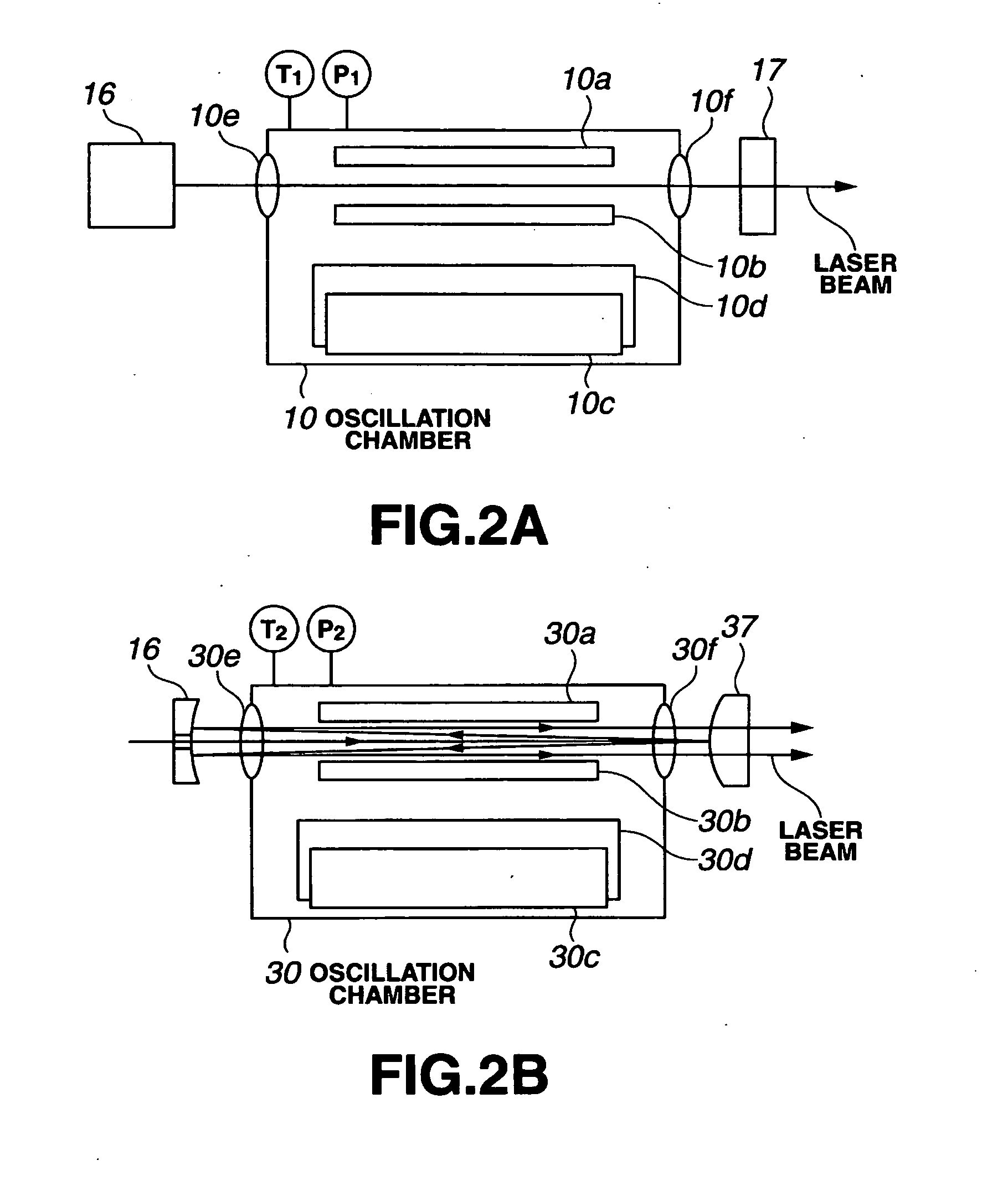
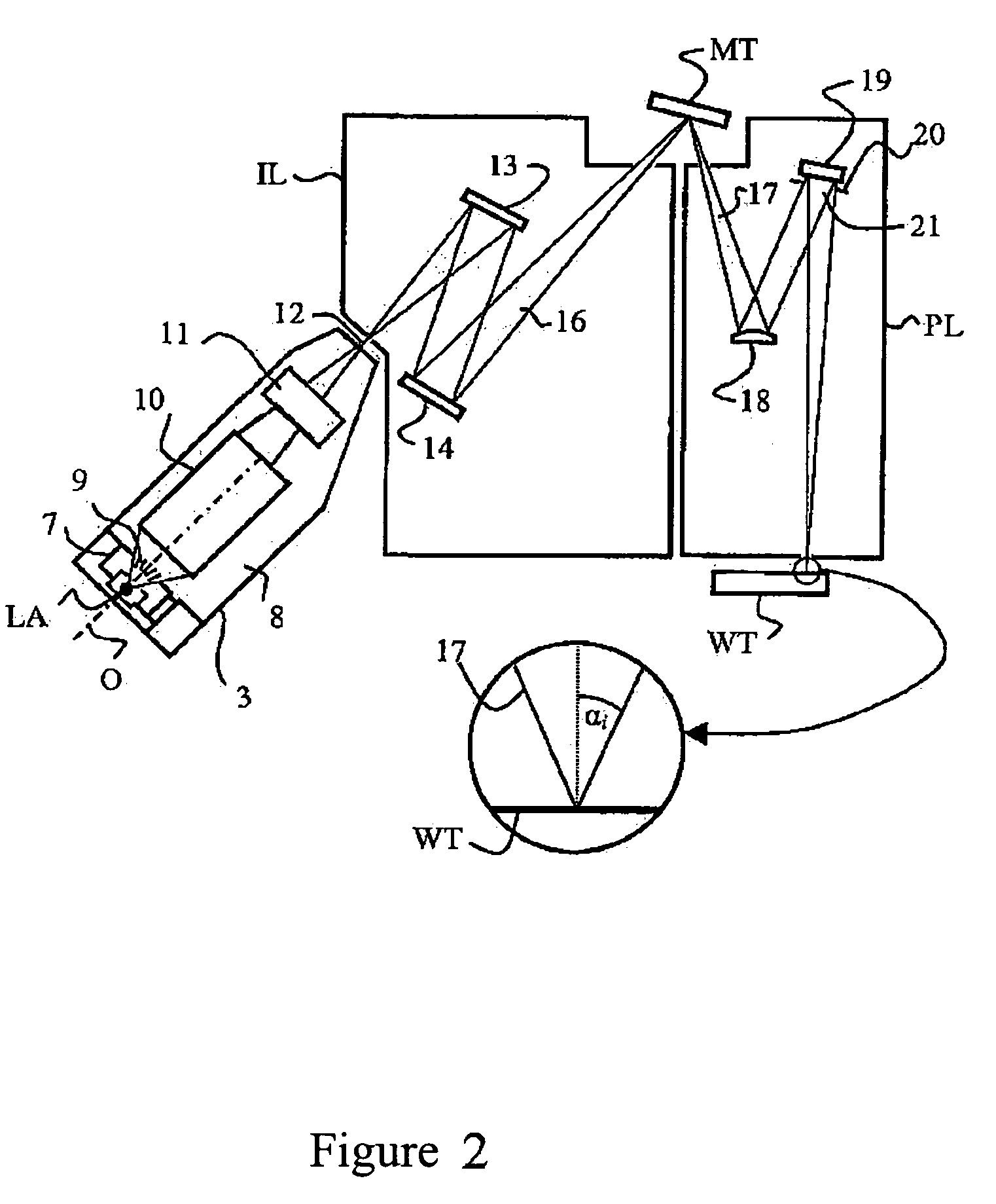
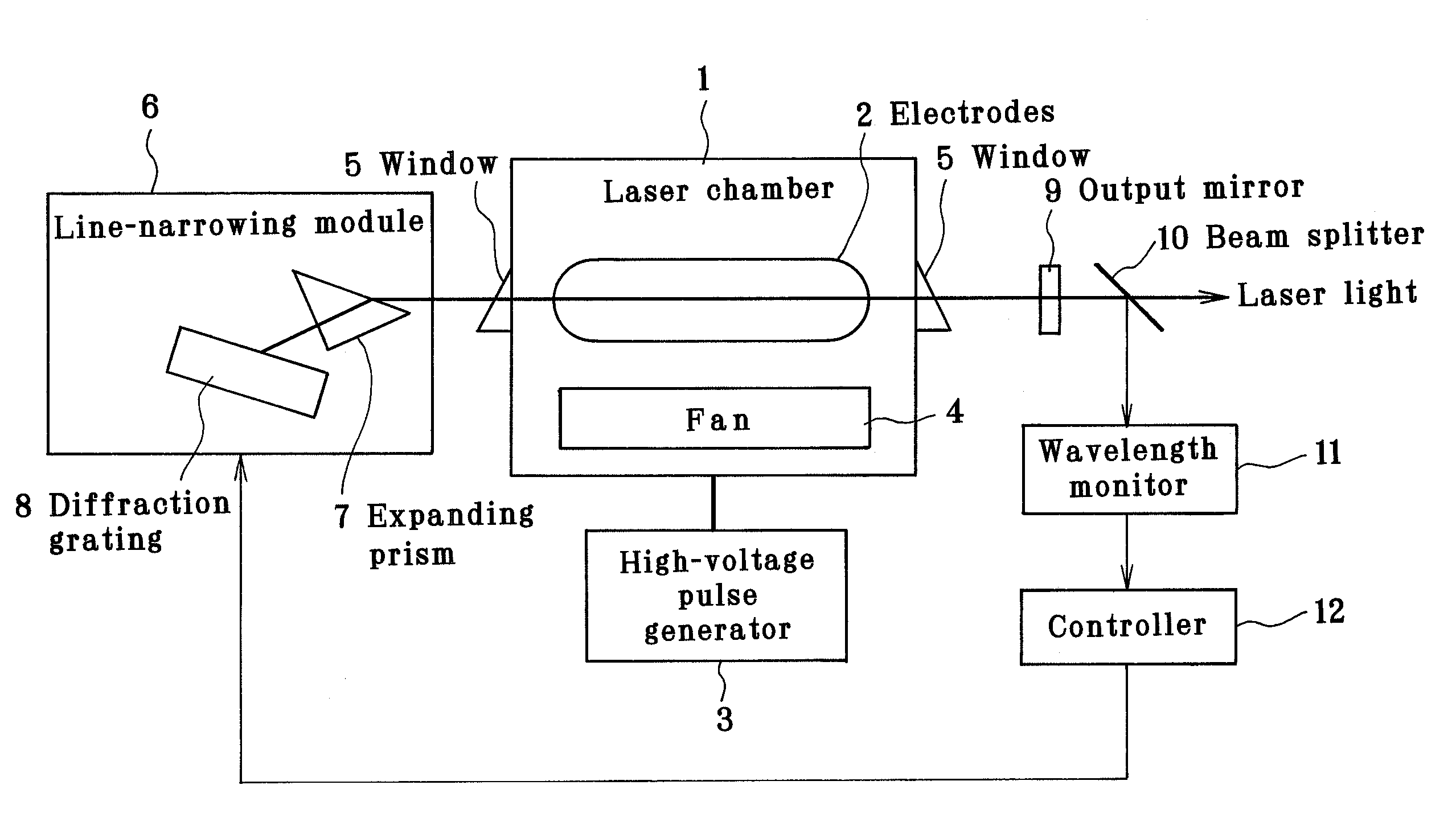
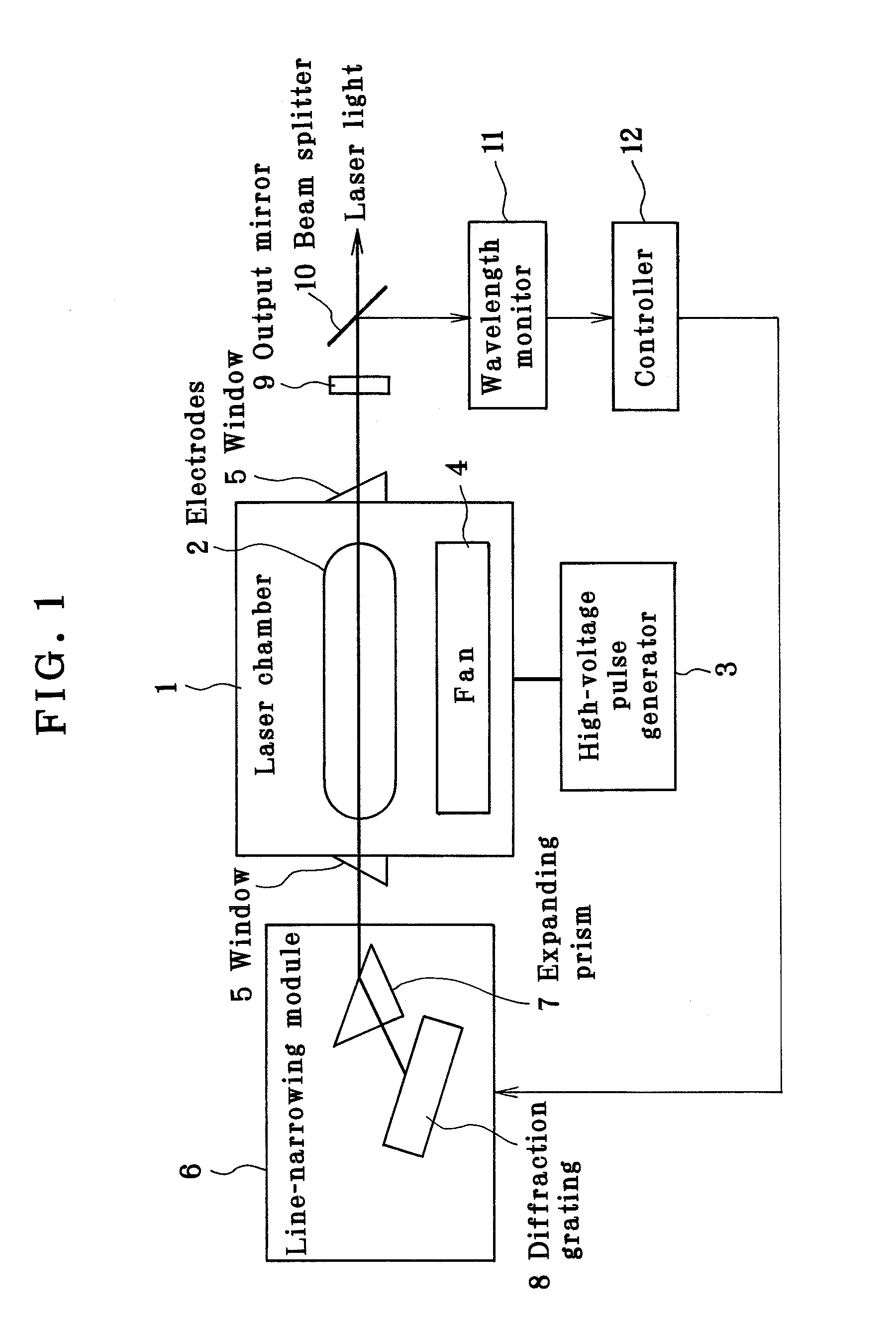
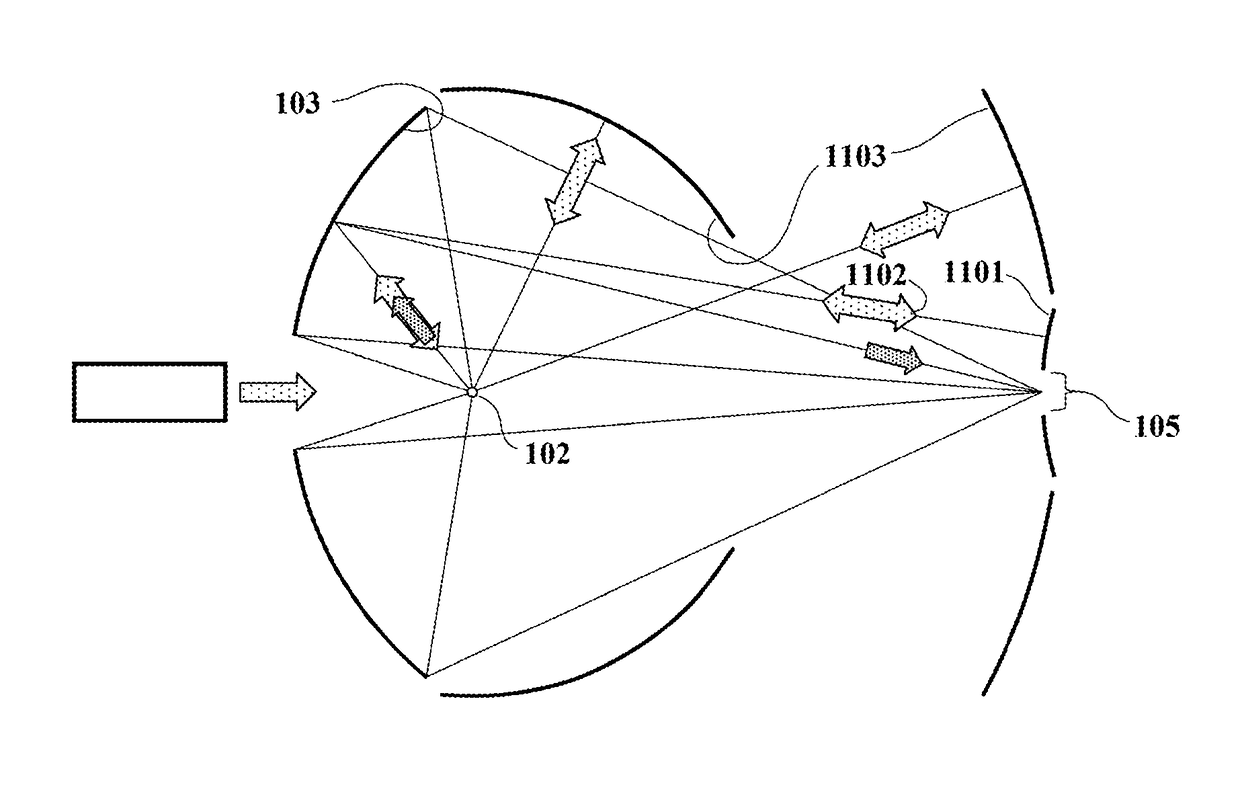
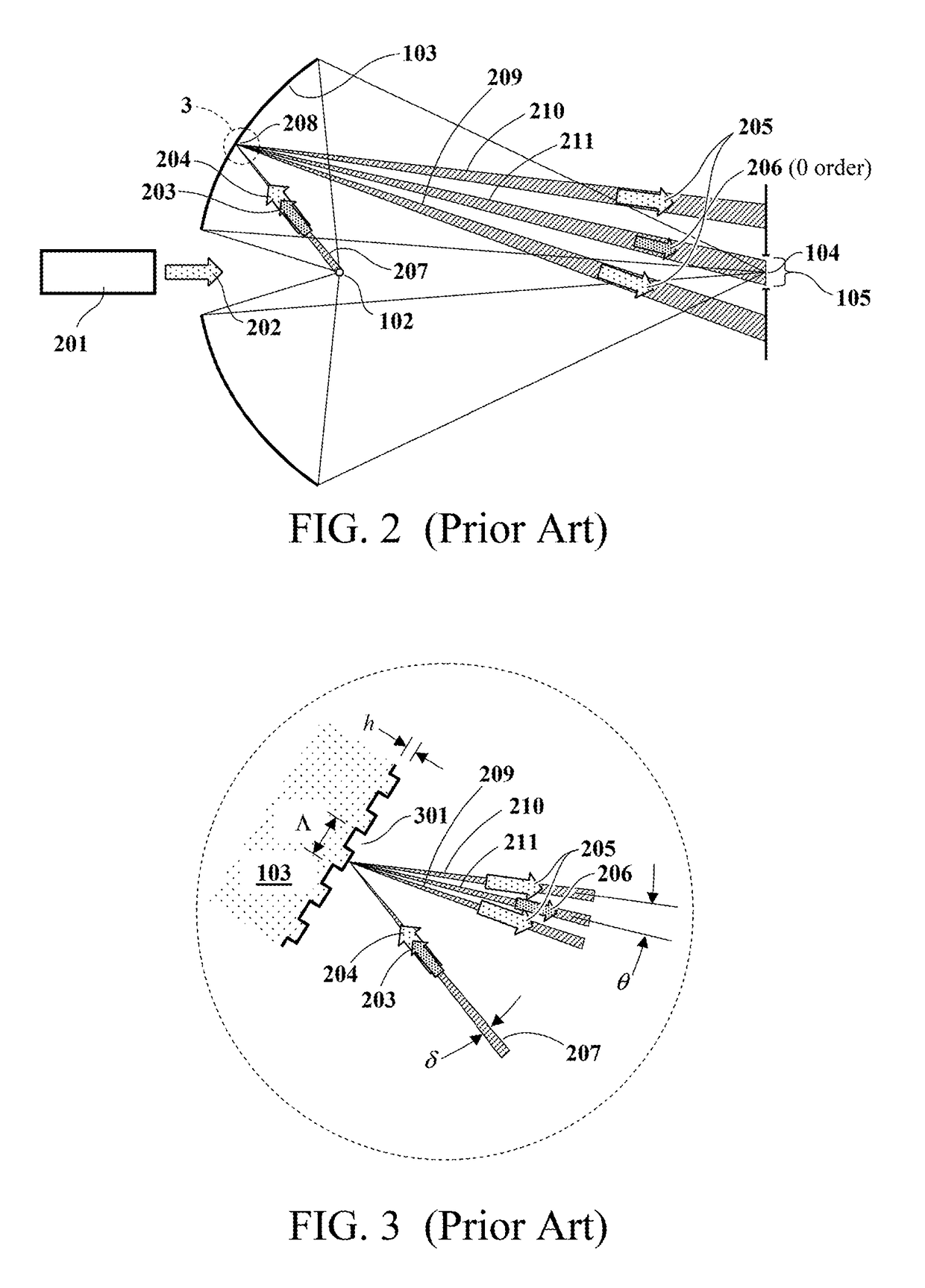
Line narrowed laser apparatus
ActiveUS20070014326A1Excitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionWavefrontOutput coupler
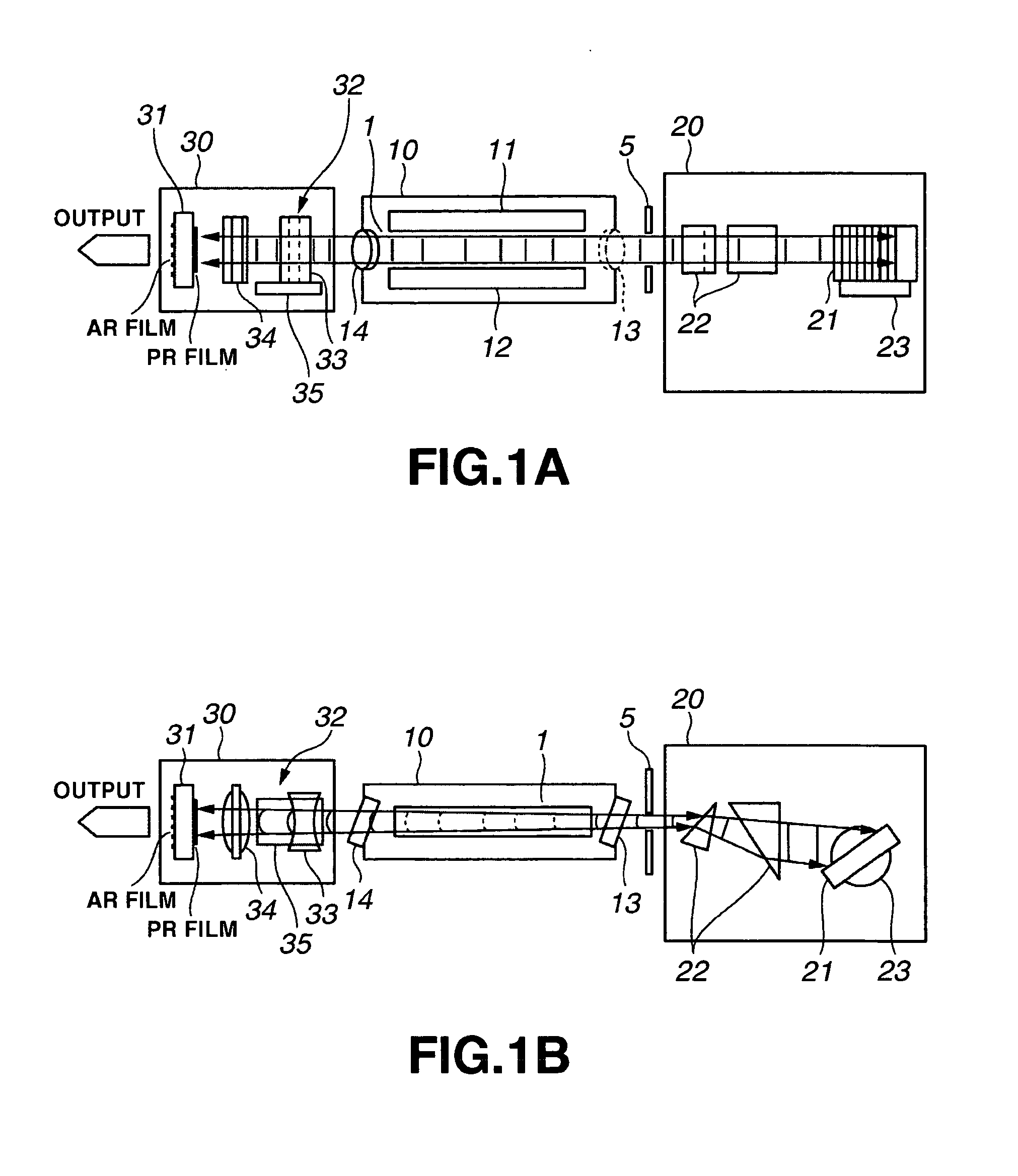
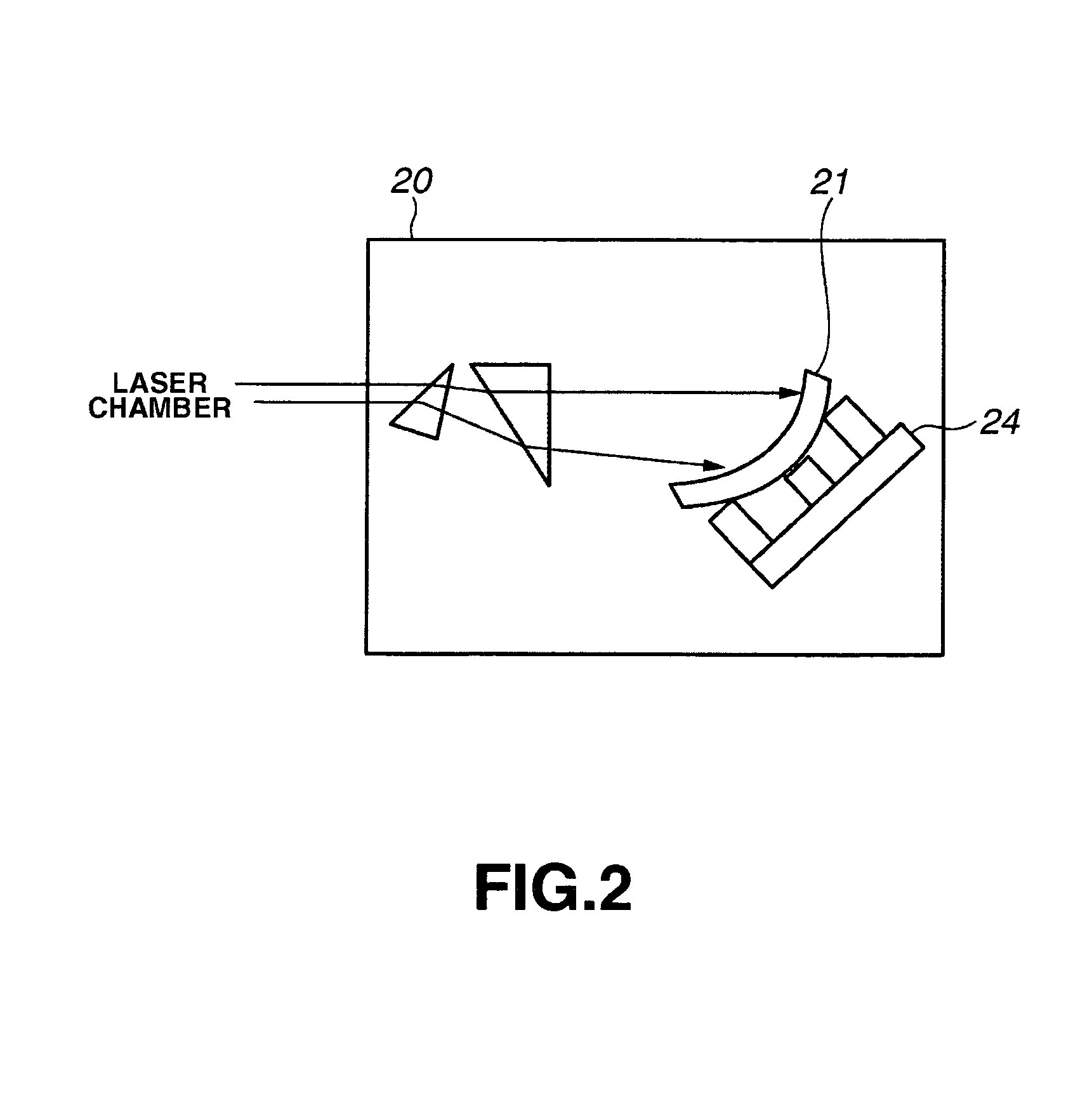
The control of the spectral purity width E95 is performed while imparting practically no effect to the control of a central wavelength, and the spectral purity width E95 is stabilized. A wavefront adjuster 32 is provided on an output side of the interior of an optical resonator, i.e., on an output coupler 31 side. Light generated in a laser chamber 10 is transmitted through the wavefront adjuster 32 from the laser chamber 10 side, and reaches the output coupler 31. In the wavefront adjuster 32, the distance between concave and convex lenses 33 and 34 is adjusted so that a desired spectral purity width E95 can be obtained. Then, when the light passes through the wavefront adjuster 32, the wavefront of the light is adjusted to a desired wavefront.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK +1
EUV lithography filter
InactiveUS7250620B2Reduce accumulationReduce harmPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansLithographic artistComputational physics
Filters for EUV lithography, methods of manufacture thereof, and methods of filtering in an EUV lithography system are disclosed. The filter comprises a nanotube material layer sandwiched by two thin material layers that are highly transmissive and provide structural support for the nanotube material layer. The filter is supported on at least one side by a patterned structural support. The filter mitigates debris, provides spectral purity filtering, or both.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
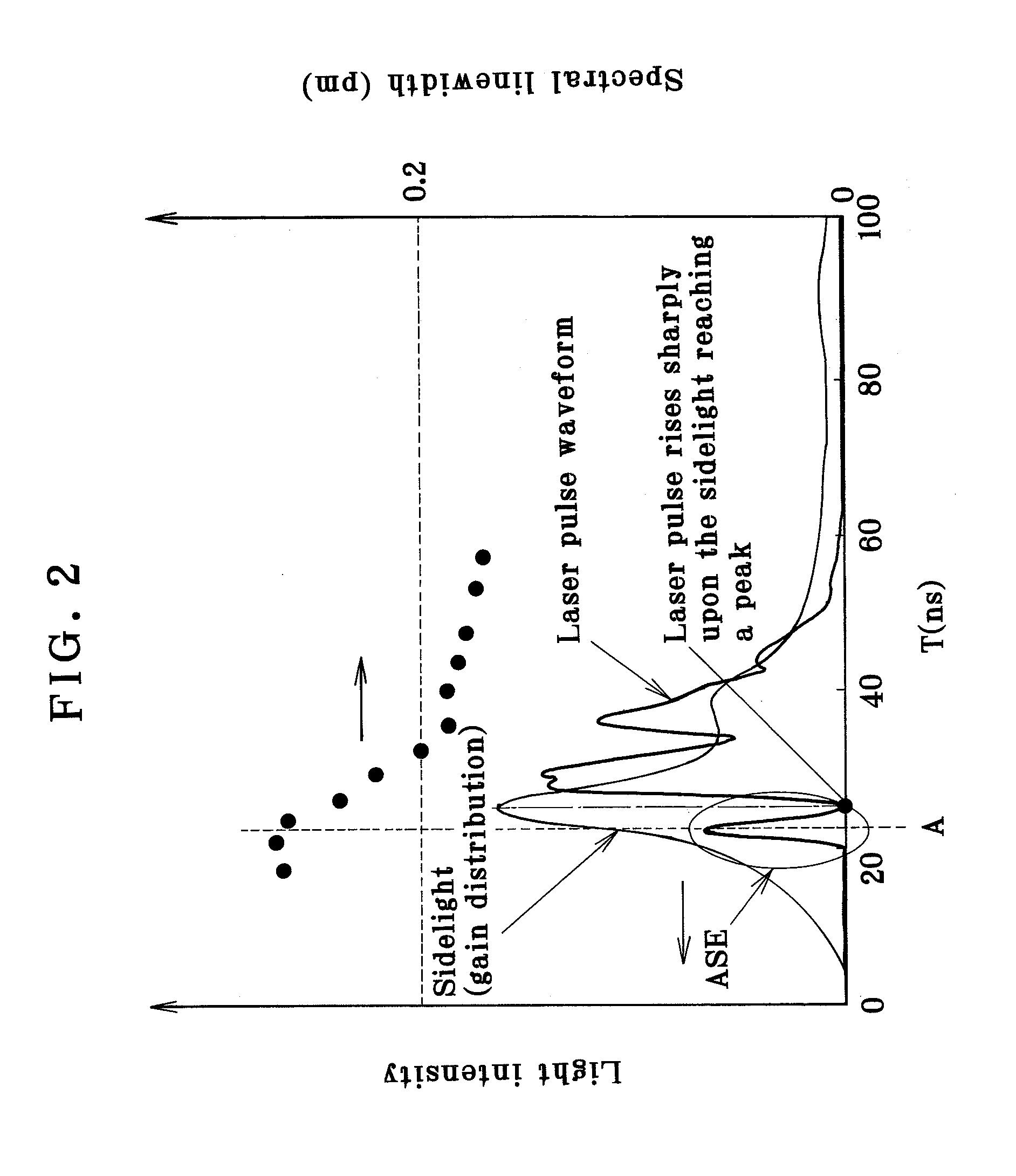
Line-narrowed gas laser system
ActiveUS7072375B2Improve abilitiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive medium materialLine widthPeak value
In a line-narrowed gas laser system such as a line-narrowed molecular fluorine laser system, ASE is cut off to obtain a spectral linewidth of 0.2 pm or lower and a spectral purity of 0.5 pm or lower. The laser system comprises a laser chamber filled with an F2-containing laser gas, discharge electrodes located in the laser chamber, a laser resonator and a line-narrowing module located in the laser resonator with a wavelength selection element, so that a line-narrowed laser beam emerges from the laser resonator. To cut off ASE from the laser beam emerging from the laser resonator, the duration from laser emission by discharge to generation of a laser beam is preset. Rise of the sidelight is made so gentle that the starting point of a laser pulse can exist after the time of the first sidelight peak.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
EUV actinic reticle inspection system using imaging sensor with thin film spectral purity filter coating
ActiveUS20120235049A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansExtreme ultravioletReticle
An extreme ultraviolet (EUV) actinic reticle imaging system suitable for discharge produced plasma (DPP) or laser produced plasma (LPP) reticle imaging systems using a thin film coating spectral purity filter (SPF) positioned on or proximate to the EUV imaging sensor; an EUV imaging sensor carrying this SPF; and methods for making and using the SPF for reticle inspection. The coating may be applied to the imaging sensor in any manner suitable for the particular coating selected. The coating may be composed of a single layer or multiple layers. Typical SPF coating materials include zirconium (Zr) and silicon-zirconium (Si / Zr) in a thickness between 10 nm and 100 nm.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
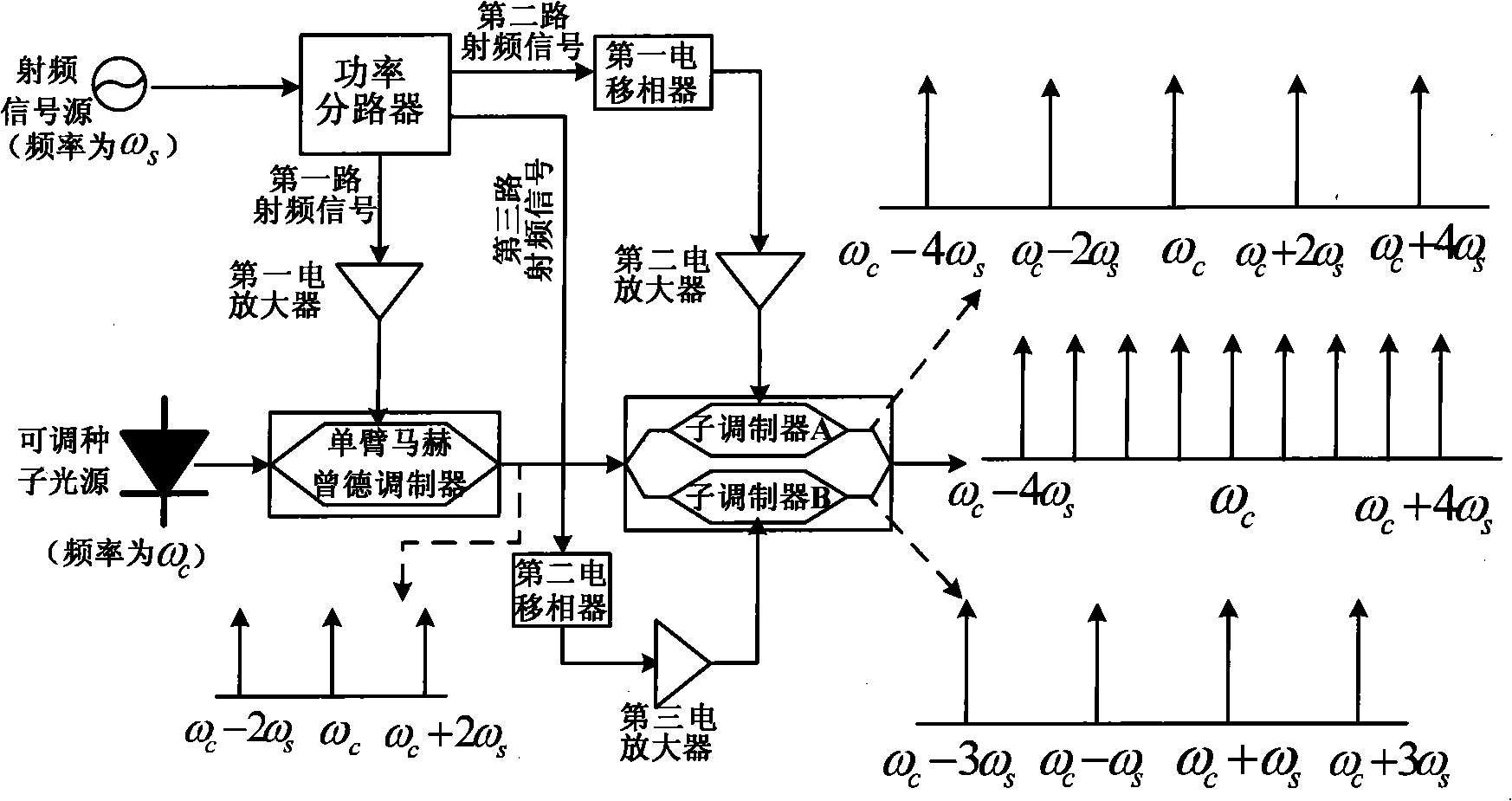
Multi-wavelength light source apparatus and method for generating accurate wavelength interval and high flatness
InactiveCN101321019AImprove flatnessElectromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumEngineering
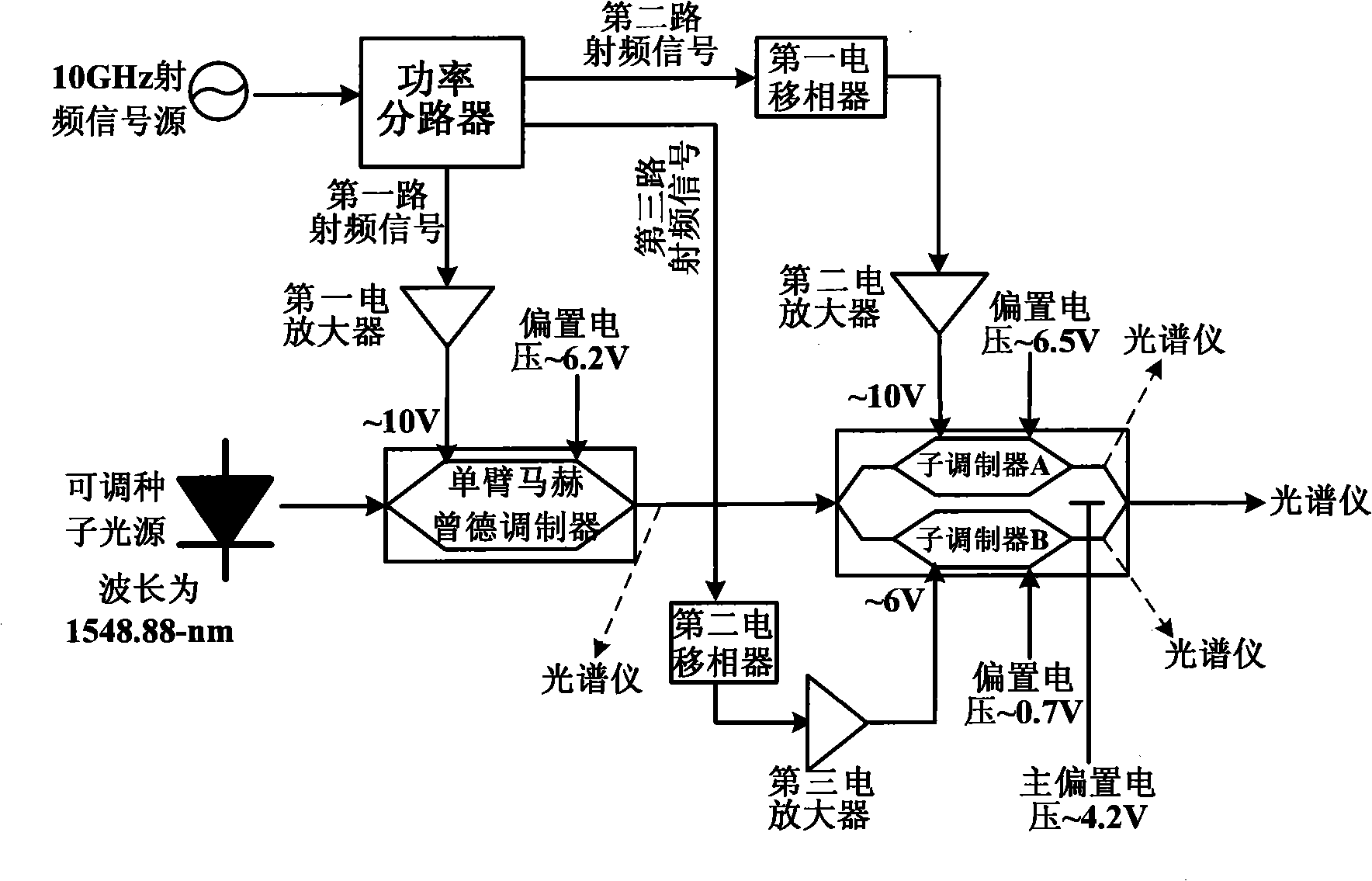
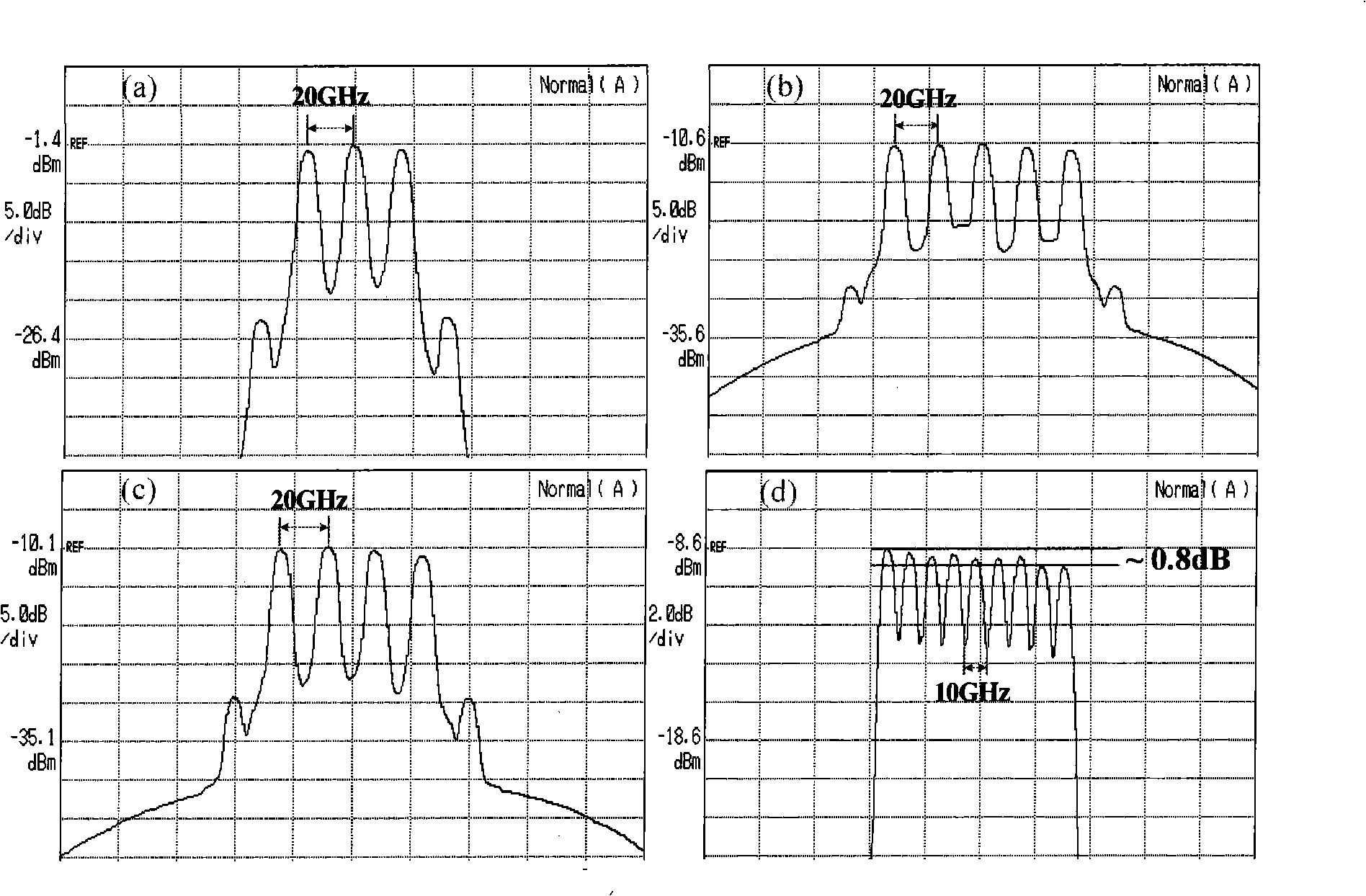
Disclosed is a device with precise channel spacing and multiple wavelength light source with high flatness and a method, belonging to the technical field of the optical communication, comprising an adjustable seed light source, a radio frequency signal source, a single arm mach tsend modulator, a double parallel mach tsend modulator, a power spliter, three electrical amplifiers and two electrical phase shifters. The method comprises: cascading the single arm mach tsend modulator and the double parallel mach tsend modulator, respectively driven by a low speed radio frequency signal, through selecting the bias points of the two modulators respectively as the highest point and the lowest point of the transmission curve, and simply control the amplitude and the phase of the radio frequency signal of the modulator, obtaining the wavelength light source including nine wavelengthes with the frequency interval equal to the frequency of the radio frequency signal. The wavelength light source of the invention has good spectral purity and phase coherence, high flatness, without expensive high power high frequency amplifier, thereby greatly reducing the arrangement cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
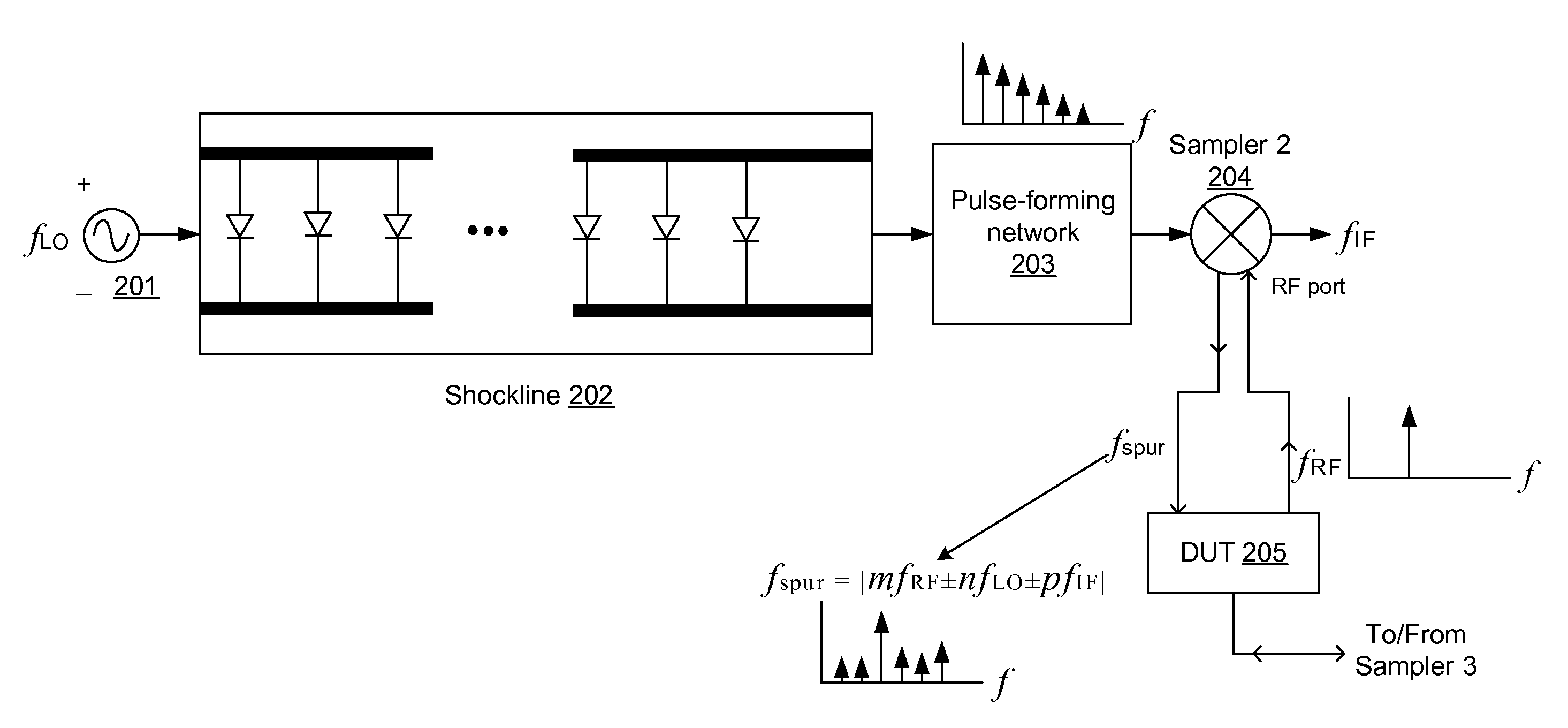
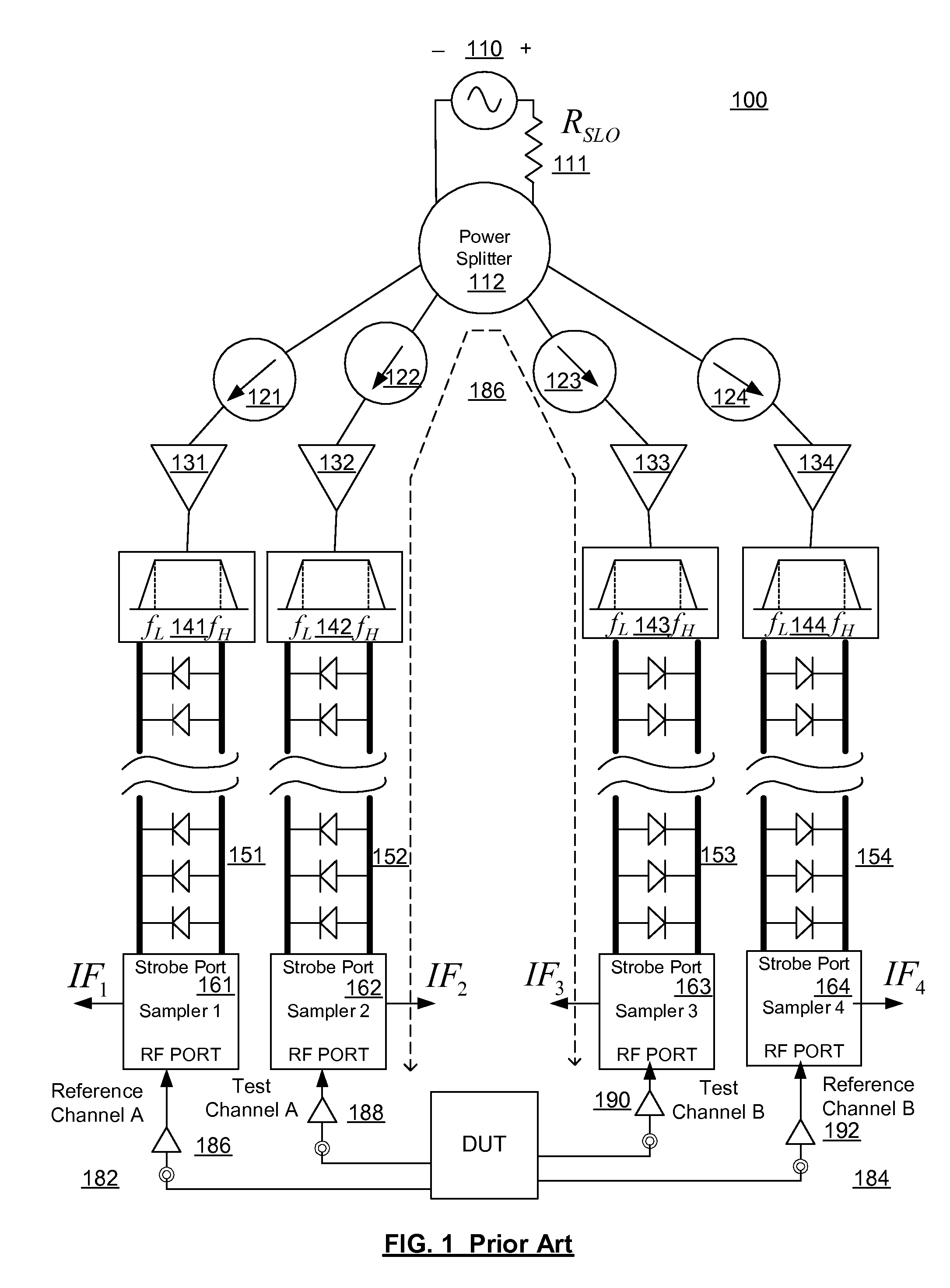
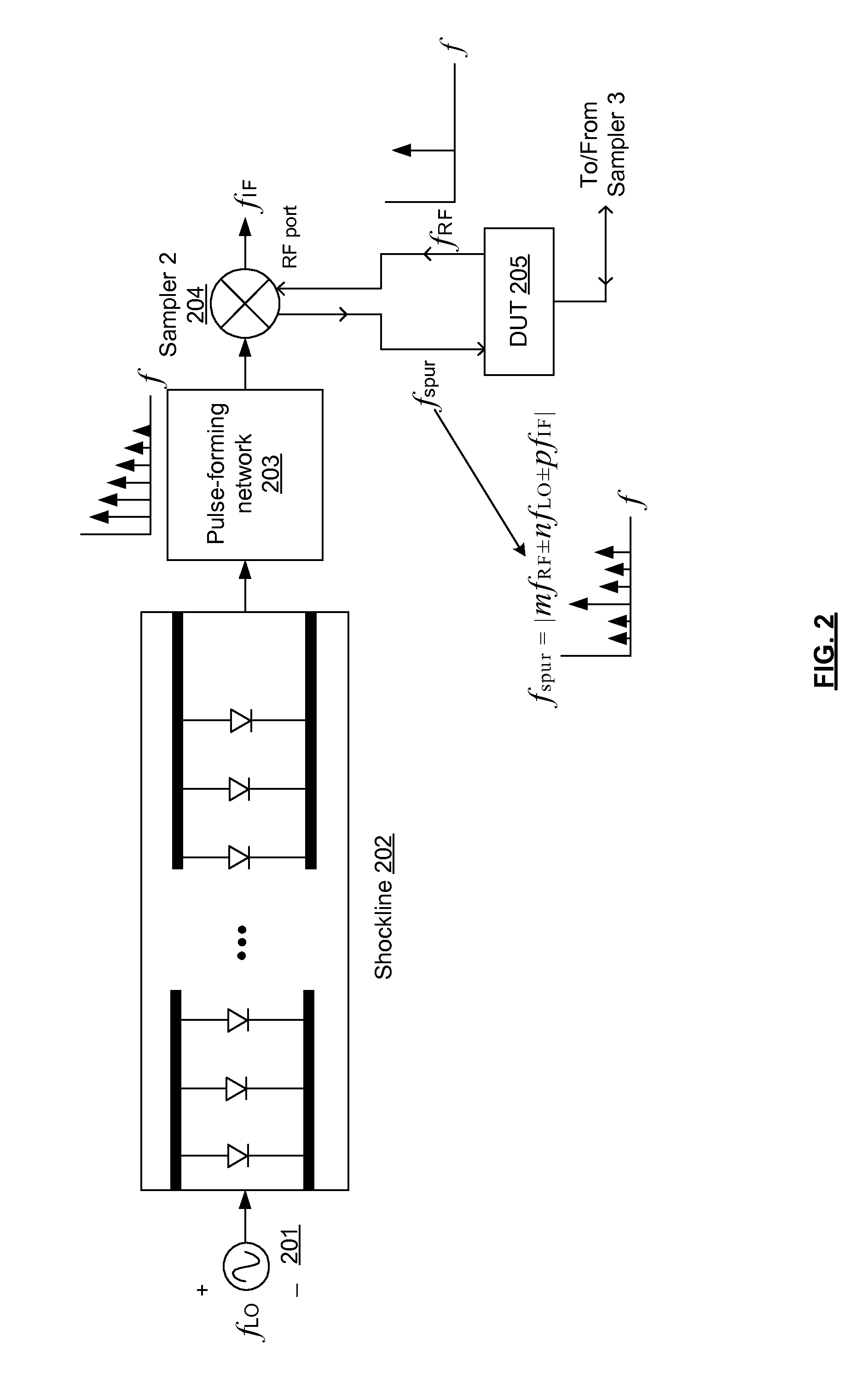
Apparatus for enhancing the dynamic range of shockline-based sampling receivers
ActiveUS8718586B2Improve dynamic rangeReduced isolationResistance/reactance/impedenceRadio transmissionHarmonicOperation mode
Shockline-based samplers of a vector-network analyzer (VNA) have enhanced dynamic range by using a dynamic bias network applied to the non-linear transmission lines (NLTLs) or shocklines. The bias voltage applied to the NLTL provides direct control over the falling-edge shockline compression, and thus the insertion loss and overall RF bandwidth of the sampler. Alternating between a forward bias voltage to turn off a shockline sampler when it is not needed and thereby reducing spurious generation and improving isolation can be alternatively applied with a reverse bias voltage to turn on the shockline sampler in a normal operation mode. By measuring the shockline output and providing feedback in the reverse-bias mode, the bias voltage can be dynamically adjusted to significantly increase the performance of the NLTL based sampler. In the presence of a strong positive bias voltage, the incoming LO and its harmonics experience large ohmic losses thus preventing gating pulses from forming in the shockline. The ohmic losses enable strong isolation between the LO sampling channels and will increase spectral purity at the VNA test ports.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Analytical multi-spectral optical detection system
InactiveCN101300478AHigh sensitivityMinimize the numberBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiberThroughput
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Narrow-spectrum laser device
ActiveUS7903700B2Improve controllabilityActive medium materialLaser cooling arrangementsMeasurement deviceOptoelectronics
Owner:GIGAPHOTON +1
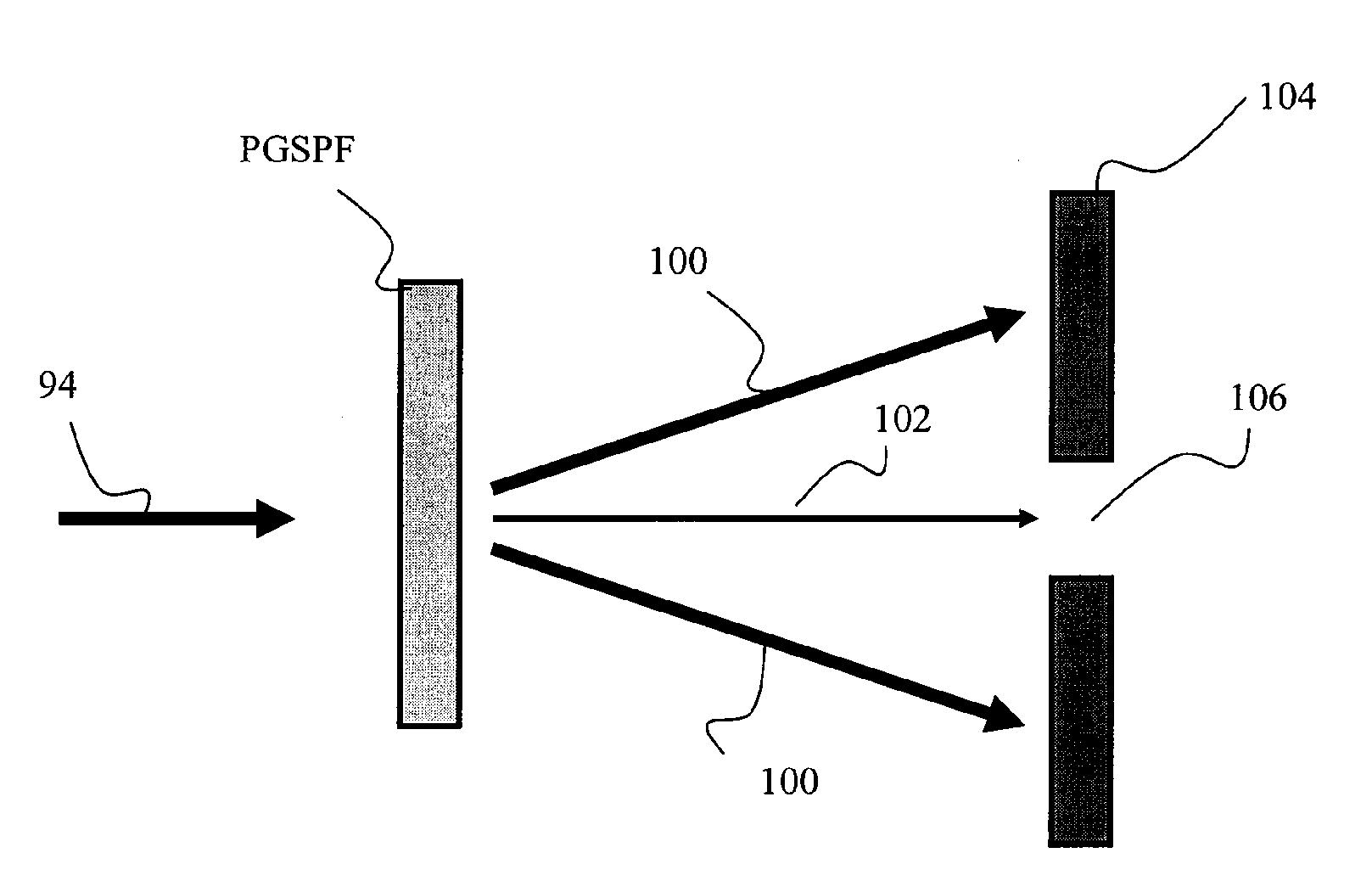
EUV light source with spectral purity filter and power recycling
InactiveUS9612370B1High diffraction efficiencyImprove efficiencyRadiation/particle handlingDiffraction gratingsOptoelectronicsOut of band radiation
A plasma-generated EUV light source uses an EUV-diffracting collection mirror to channel spectrally pure in-band radiation through an intermediate-focus aperture and through EUV illumination optics. Out-of-band radiation is either undiffracted by the collection mirror or is diffractively scattered away from the aperture. The undiffracted portion, plus plasma-emitted radiation that does not intercept the collection mirror, can be efficiently recycled back to the plasma via retroreflecting mirrors, cat's-eye reflectors, or corner-cube reflectors, to enhance generation of in-band EUV radiation by the plasma.
Owner:JOHNSON KENNETH C
Pellicle, lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
EUV actinic reticle inspection system using imaging sensor with thin film spectral purity filter coating
Owner:KLA CORP
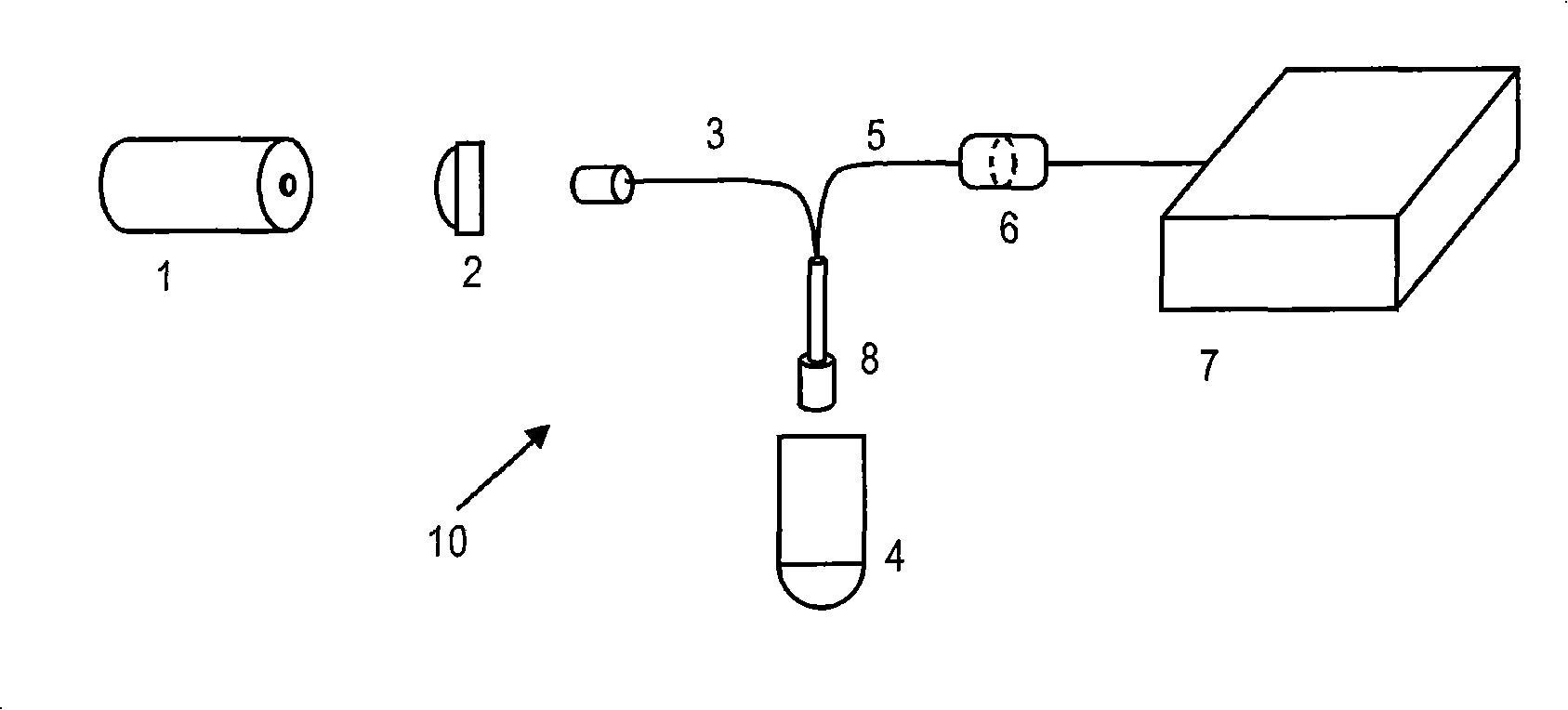
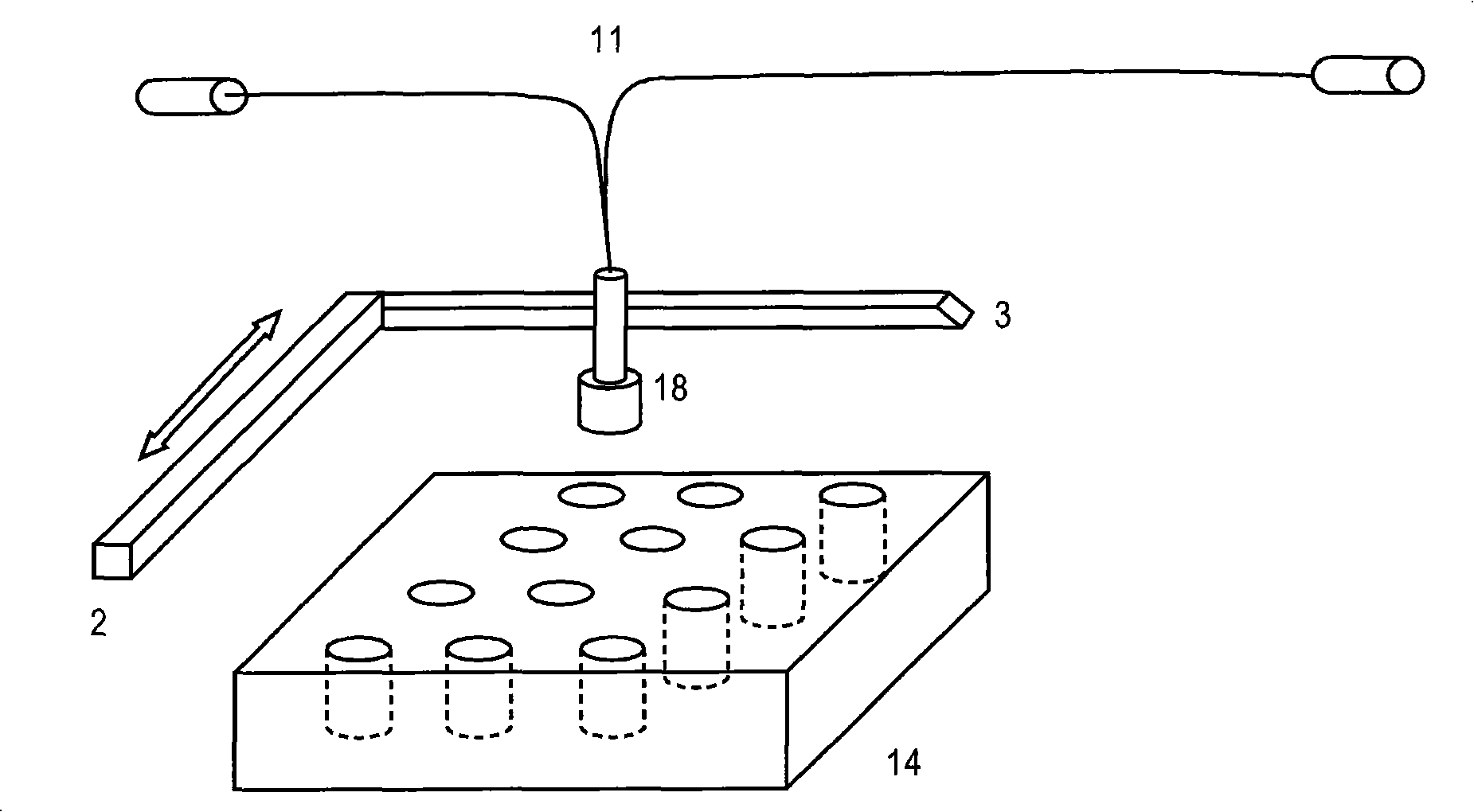
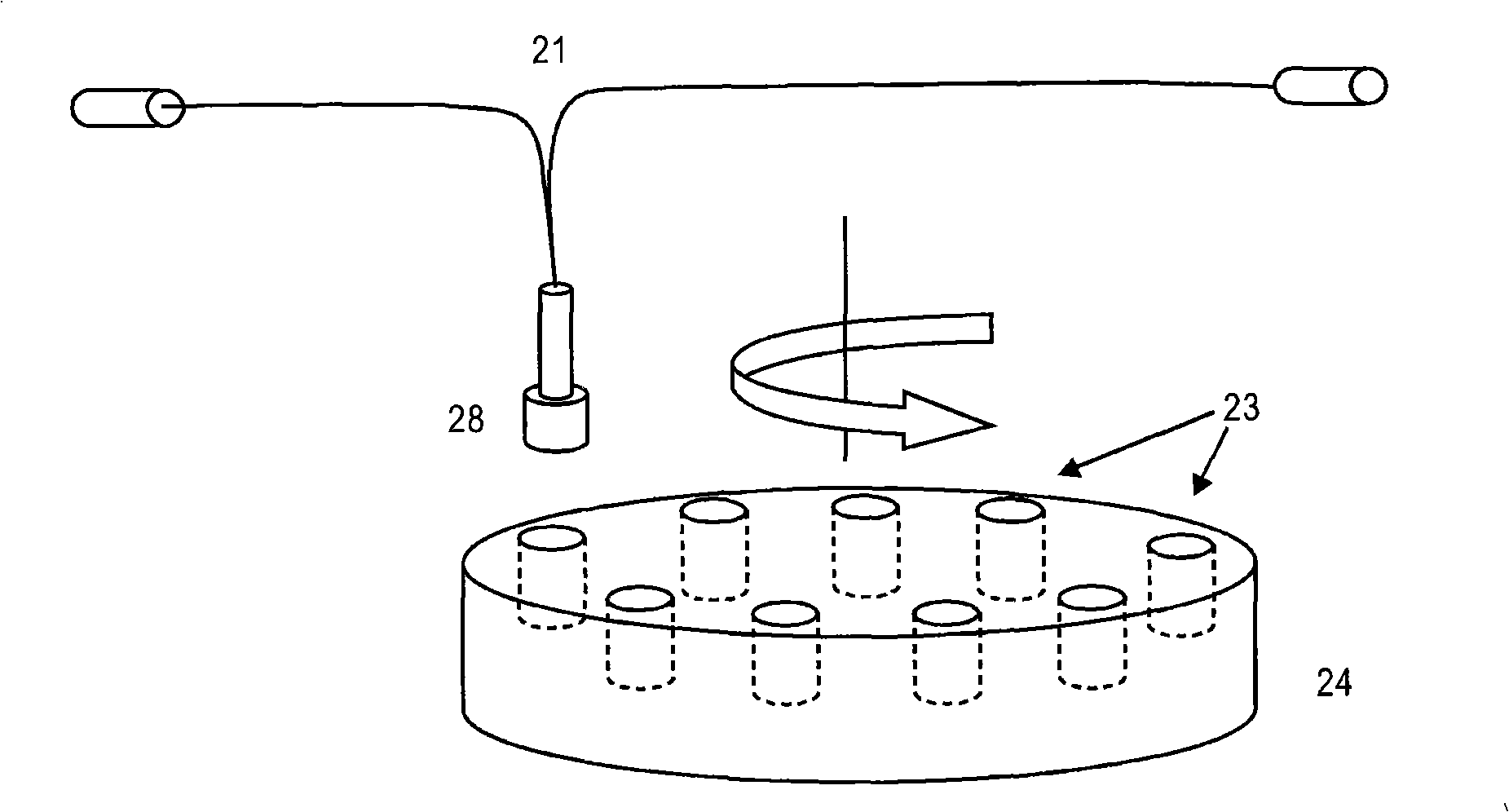
Apparatus and method for interleaving detection of fluorescence and luminescence
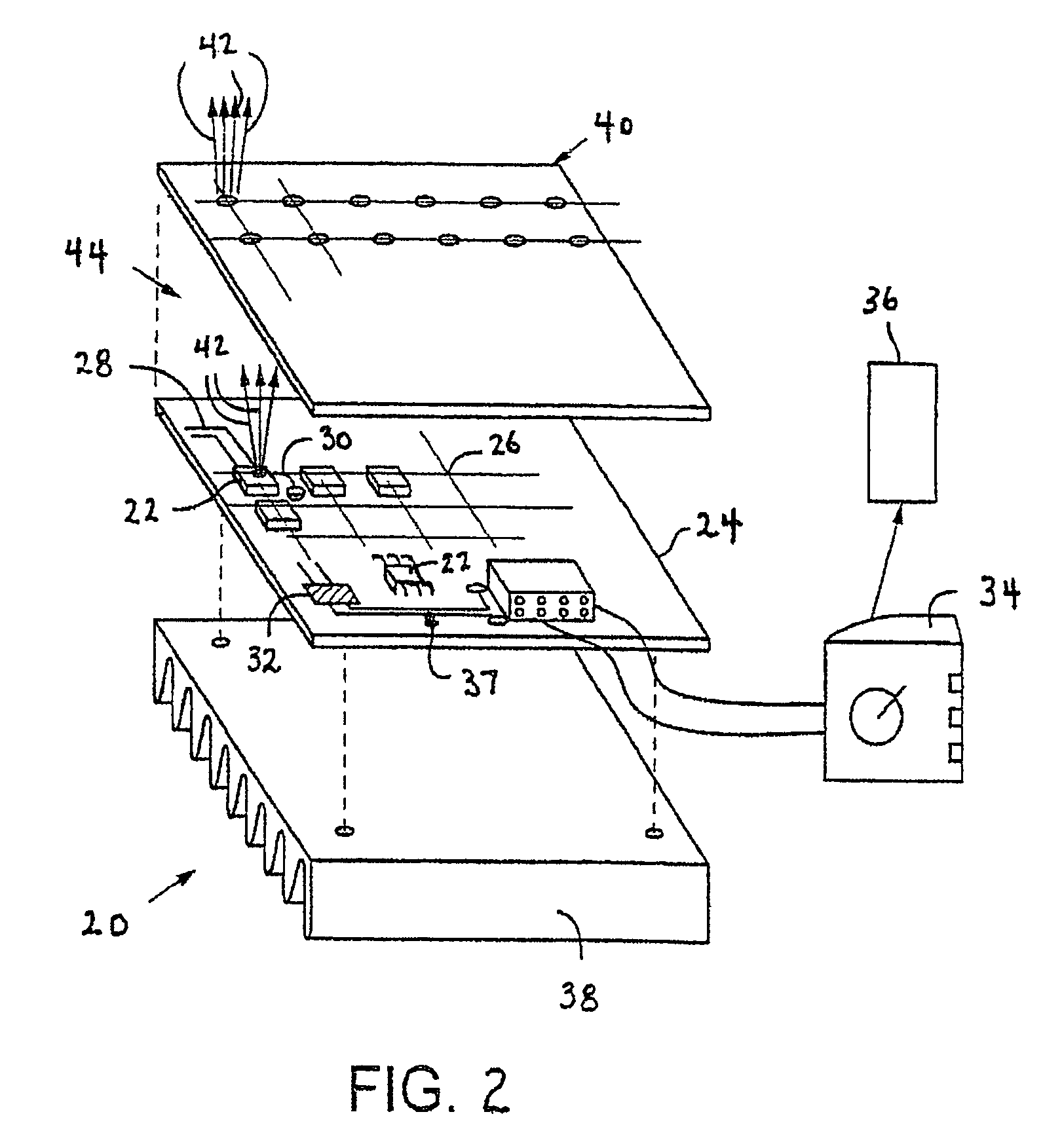
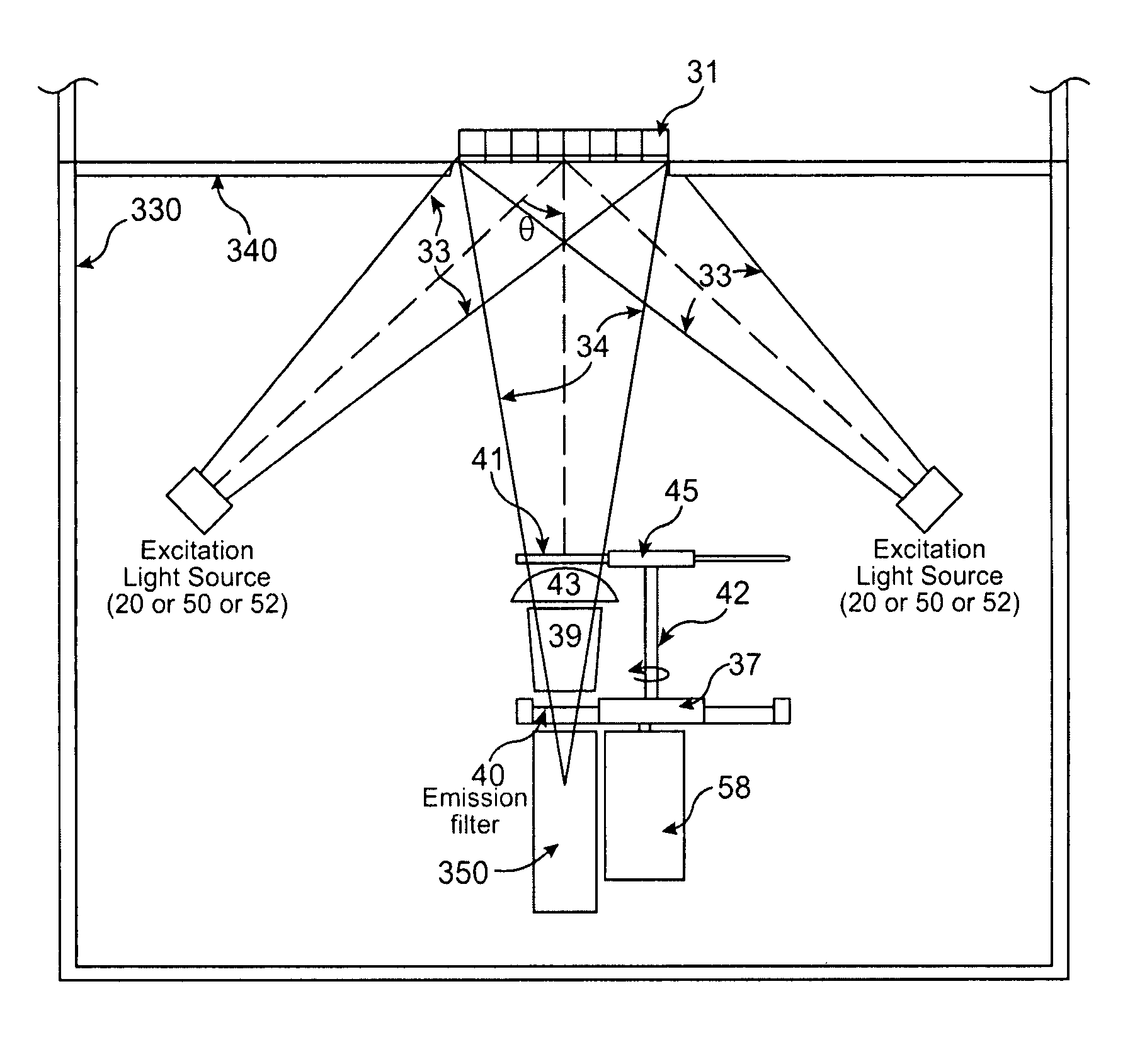
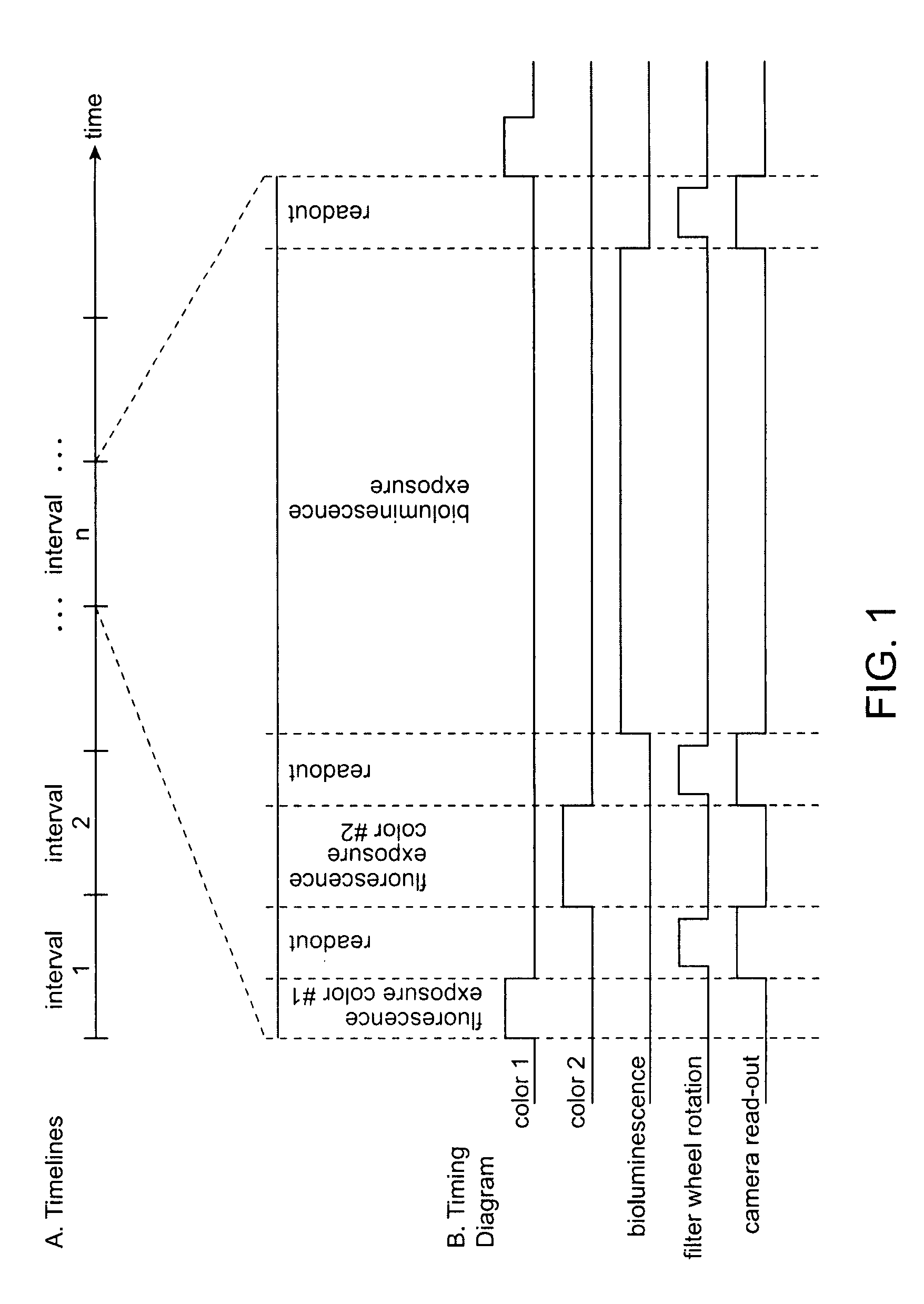
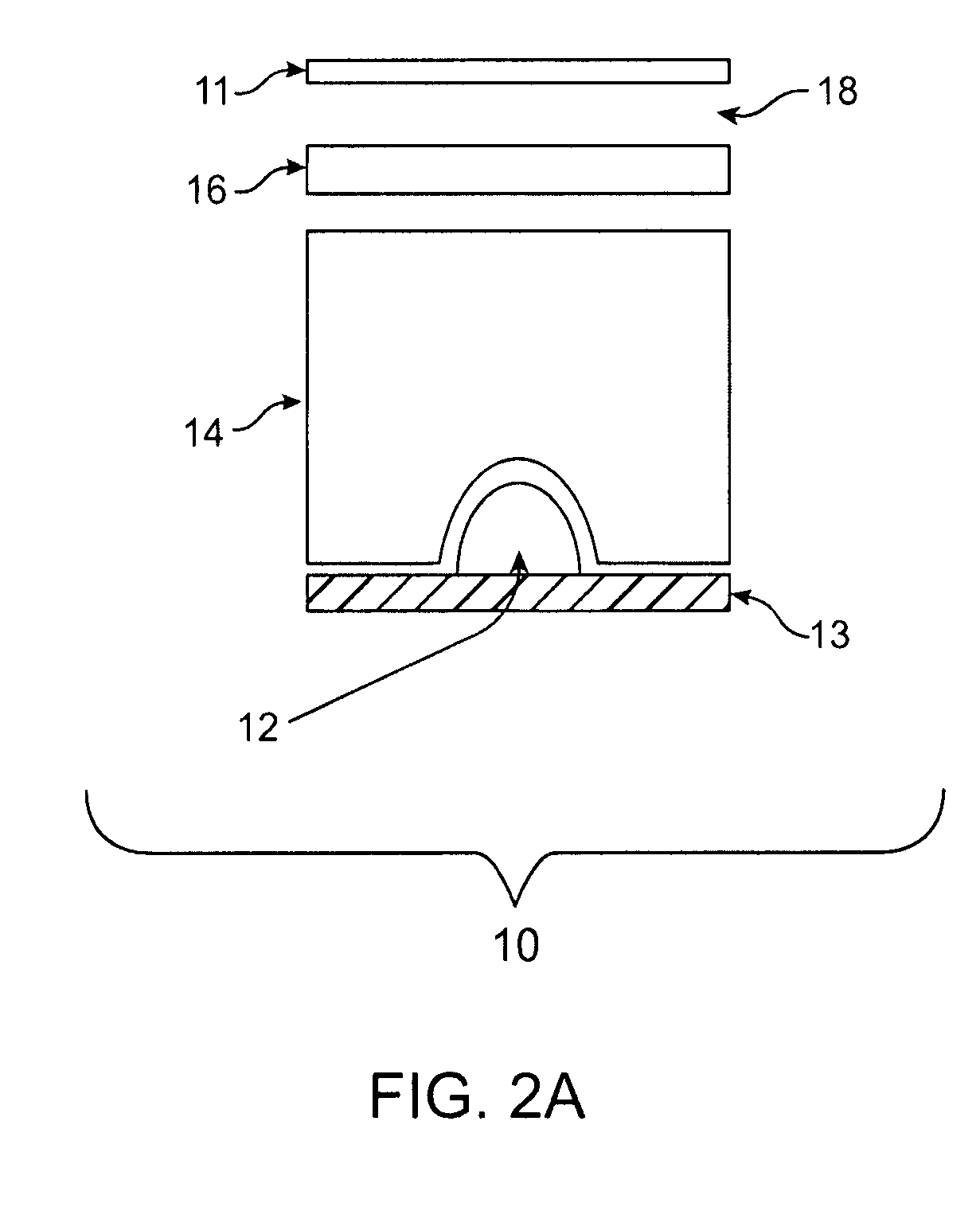
An apparatus is provided that is capable of interleaving detection of fluorescence and luminescence signals emitted from a plurality of samples. The apparatus is suitable for analysis of samples containing single cells or tissues up to and including living organisms. It contains an optical assembly or “sandwich” for producing a spectrally pure and spatially dispersed light source for illuminating the sample. The invention also provides a plurality of optical sandwiches that can be variously geometrically arranged and their intensities programmed to create spatially uniform illumination over a large sample. The invention further provides an apparatus having at least one of the optical sandwich and a detector system capable of interleaving detection of fluorescent and luminescent signals when a suitable sample is illuminated by the light source of the optical sandwich. Methods for preparing samples and using the sandwiches, arrays and apparatus, are further provided by this invention. A method for interleaving detection of fluorescent and luminescent signals emitted from a plurality of samples is disclosed.
Owner:ETALUMA
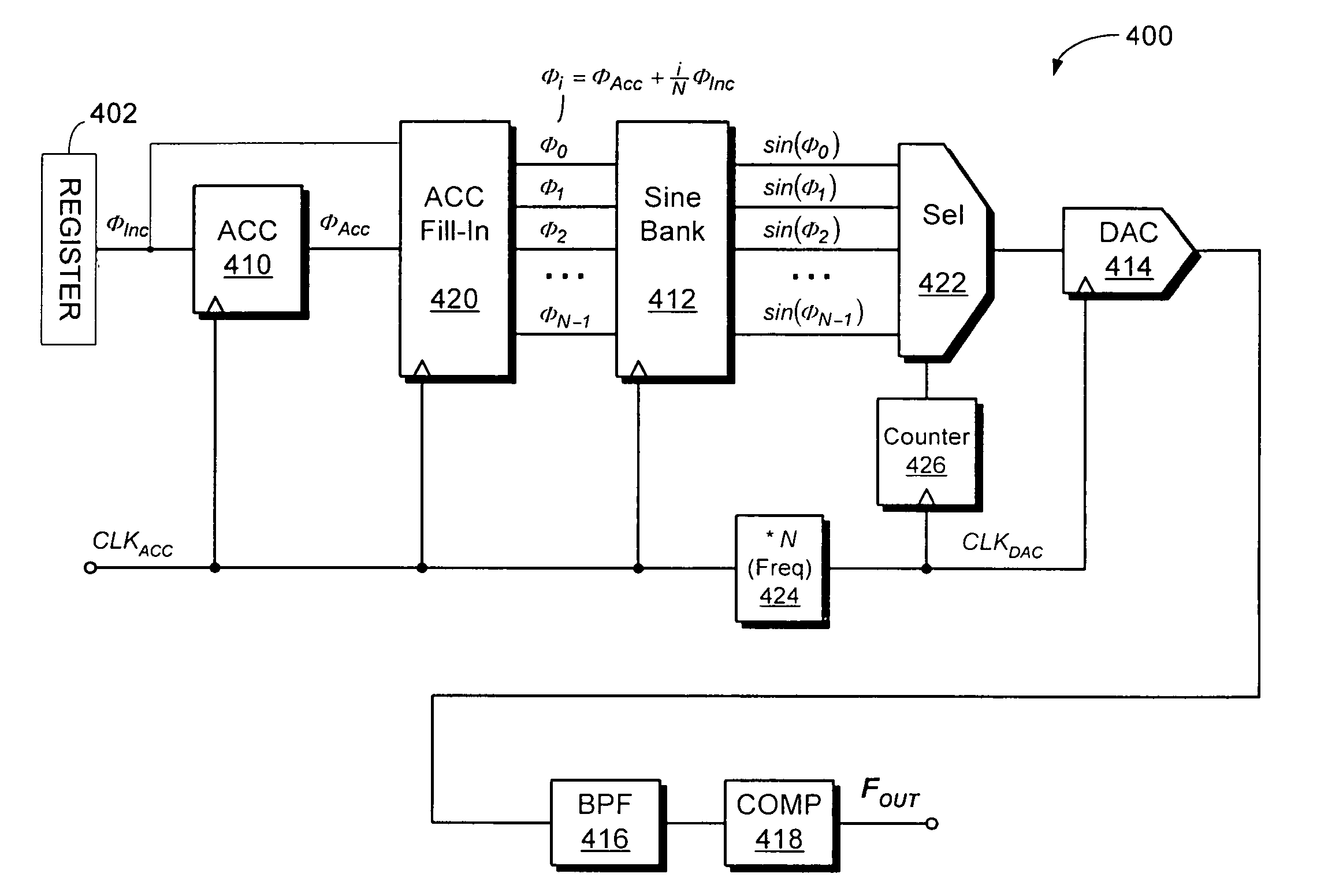
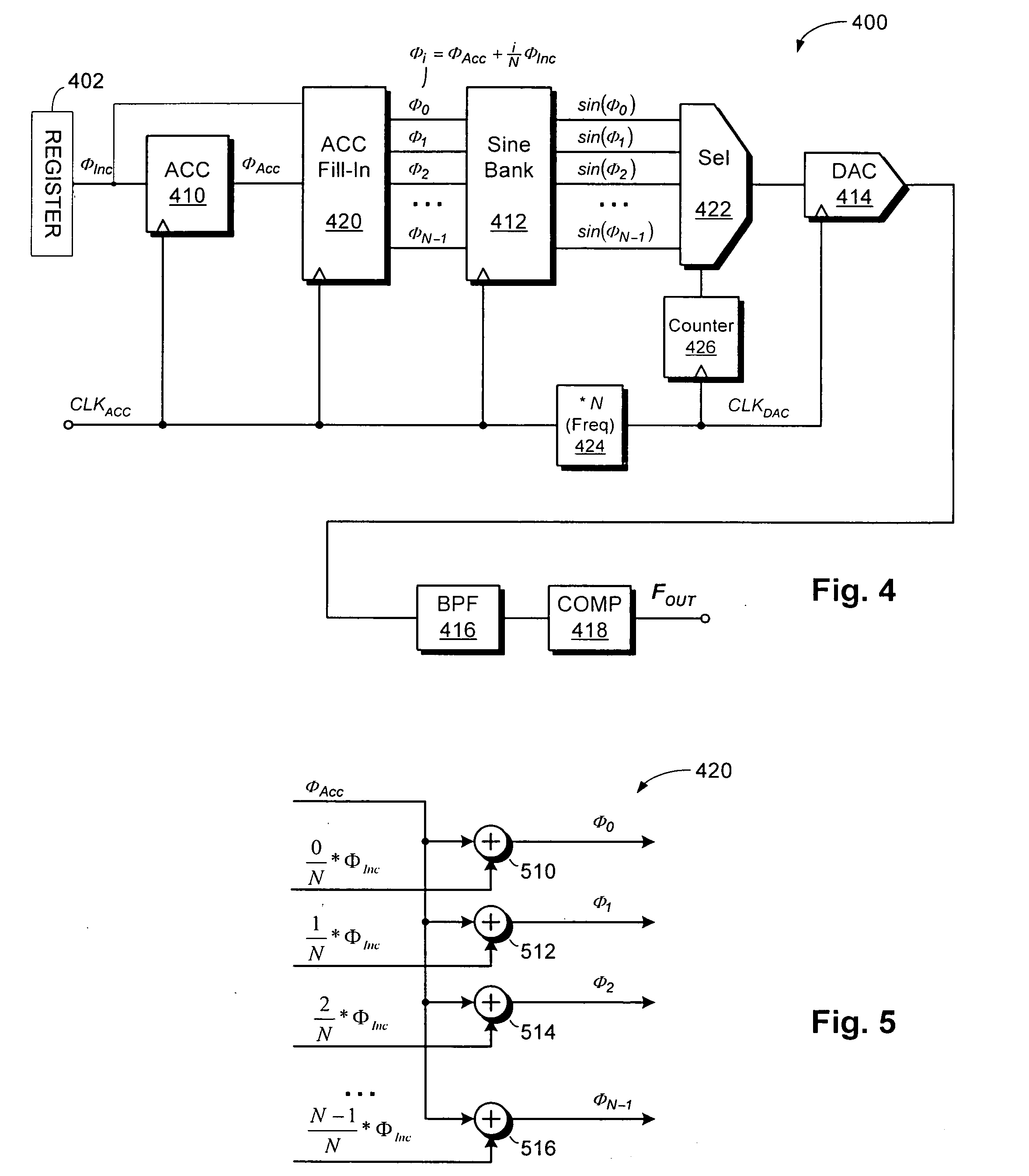
Phase to sine amplitude conversion system and method
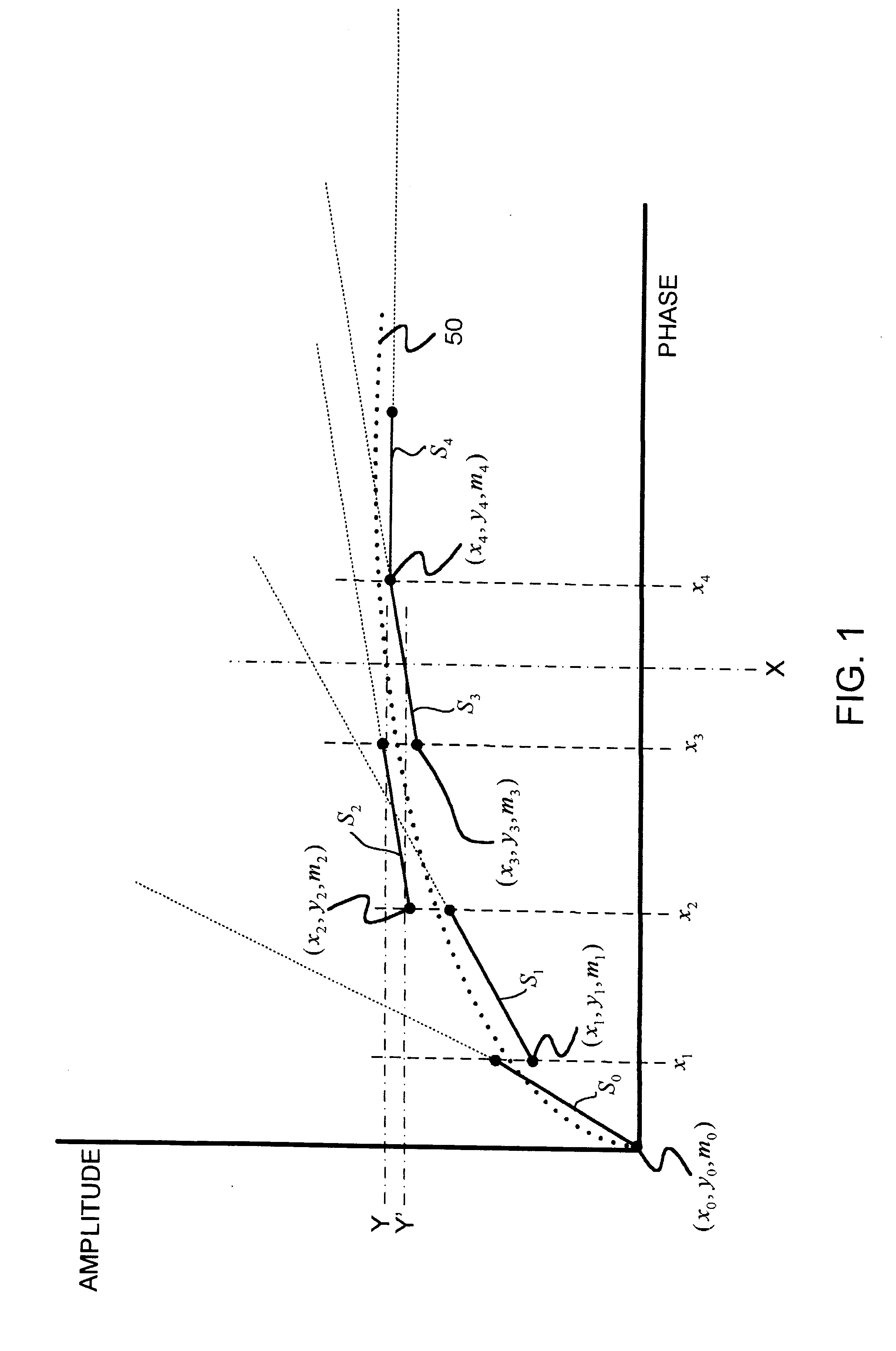
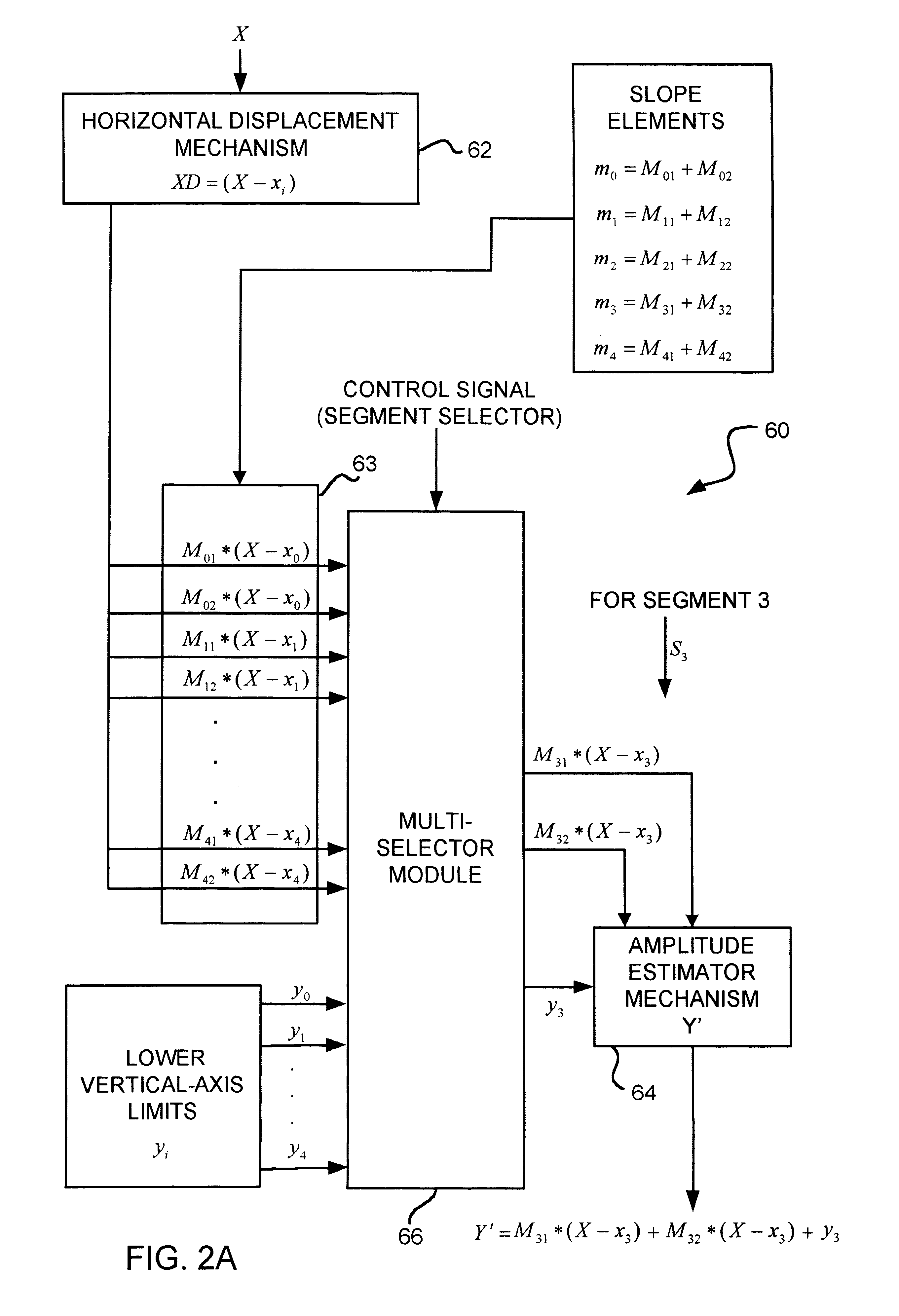
InactiveUS6657573B2Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlFrequency spectrumHorizontal axis
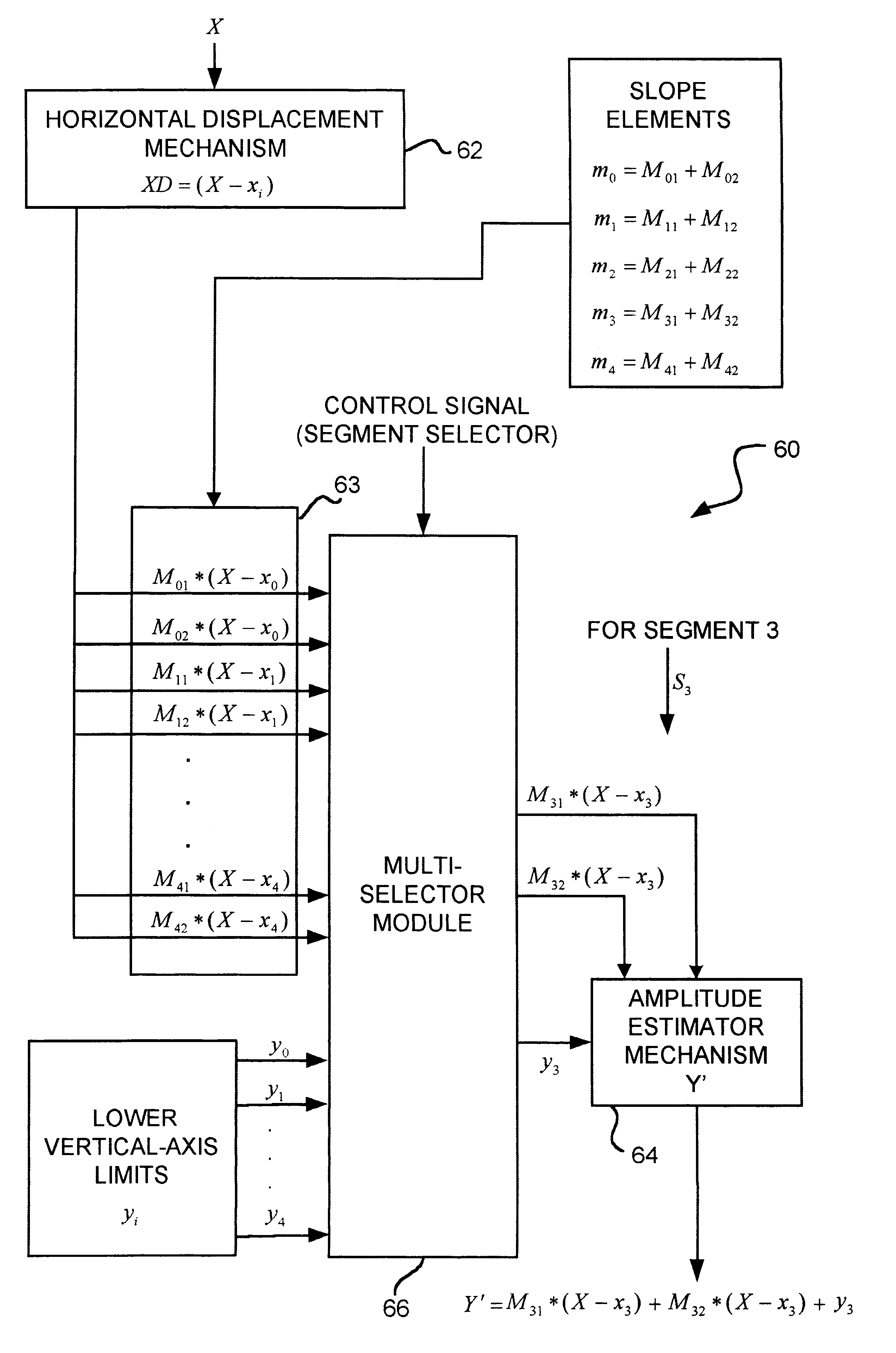
A phase-to-sinusoid-amplitude conversion system and method for use in, for example, direct digital frequency synthesizer applications. The system and method convert phase data to signal amplitude data using an approximation of the first quadrant of a sine function using a plurality of linear line segments of preferably equal length. Each segment is defined with a lower horizontal-axis bound; a lower vertical-axis bound; and a slope represented as a sum of a plurality of slope elements. Based on the approximation and for a given phase angle a set of values are evaluated, for each linear line segment, representing a product of (i) a horizontal displacement representing a difference between the prescribed phase angle and the lower horizontal-axis bound xi of a selected linear line segment where, for example, xi<X<Xi+1 and (ii) each one of the slope elements of the selected linear line segment. The approximation of the sinusoidal amplitude is then obtained by adding one of the sets of values determined above with the lower vertical-axis bound of the selected linear line segment. With appropriate selection of the number of line segments (e.g., integer power of two) and slopes elements (e.g., expressed as a sum of desired powers of two), the operations are computationally efficient and improve spectral purity and reduces implementation costs and power consumption of resulting circuitry.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com